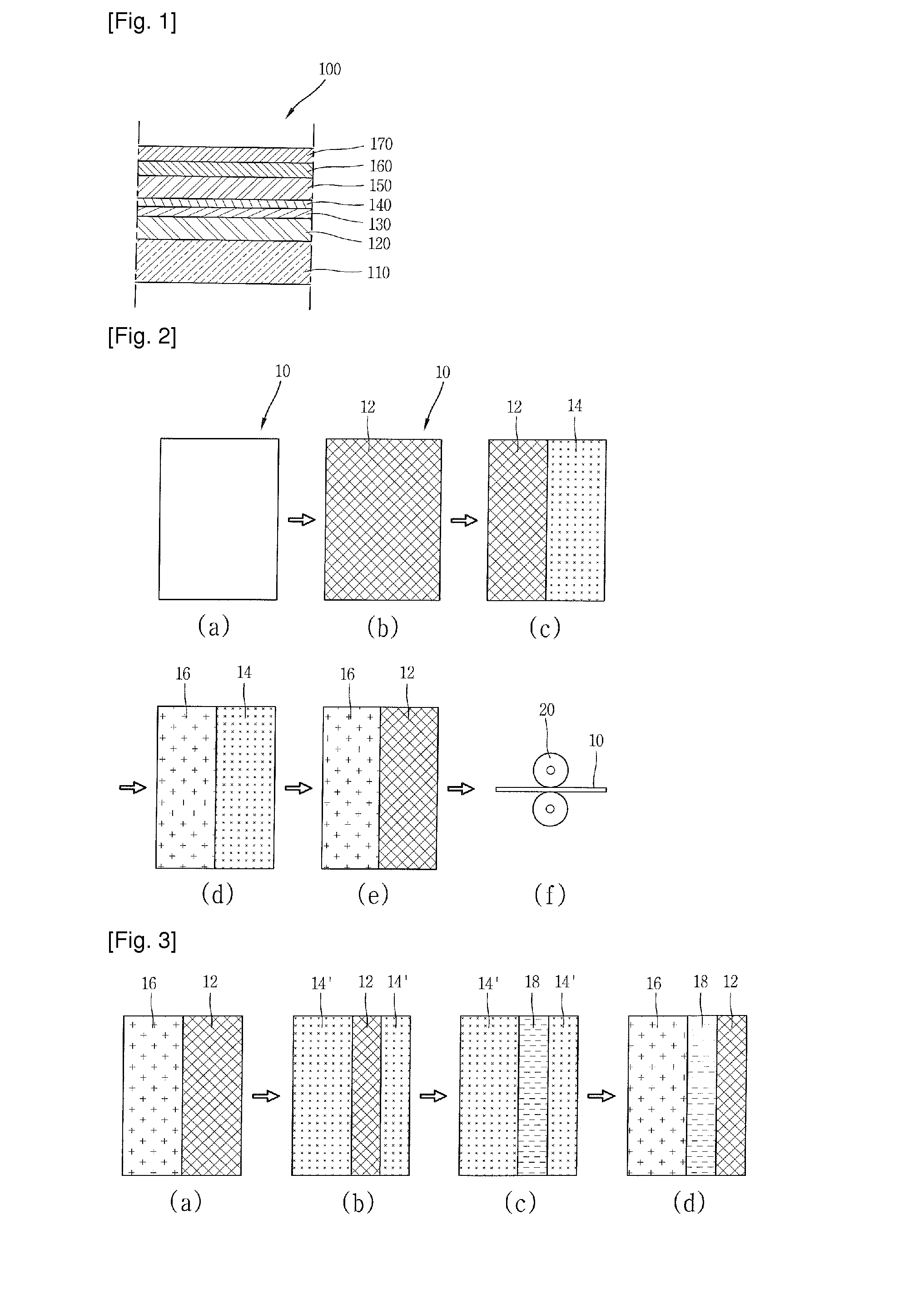
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Aluminum deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
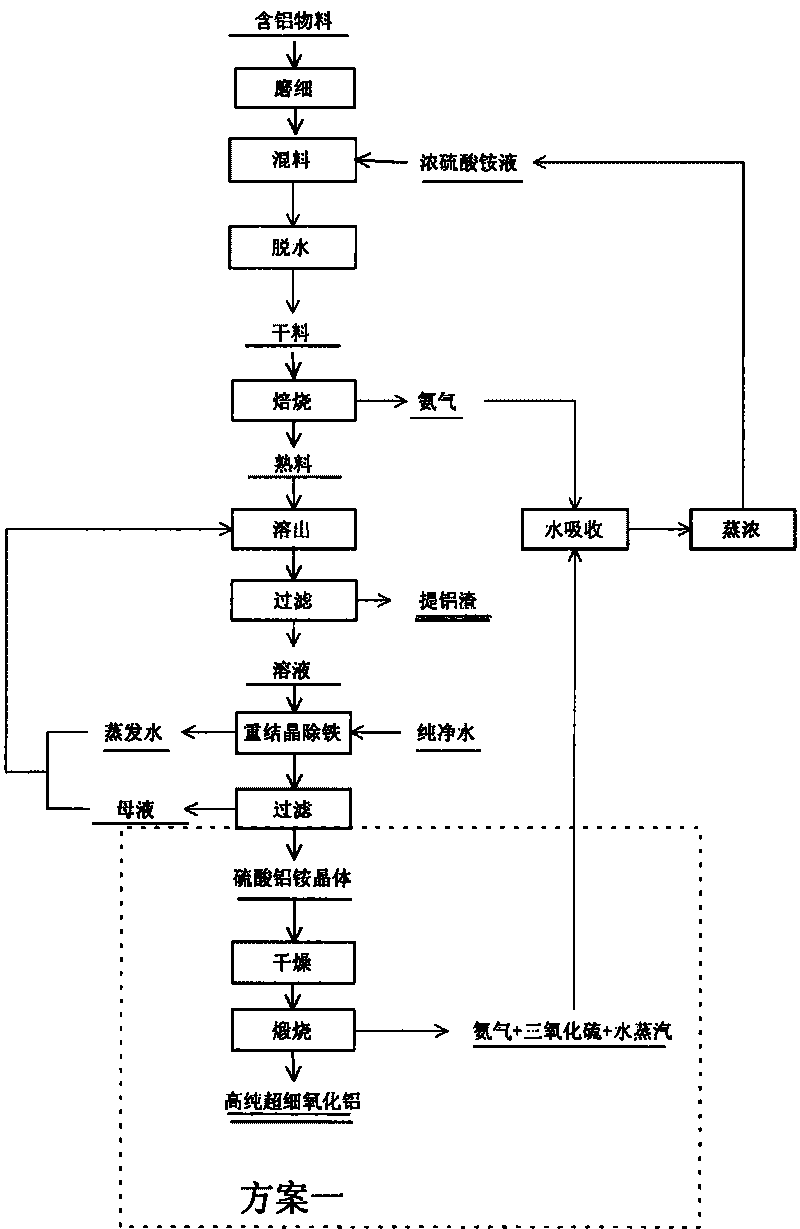
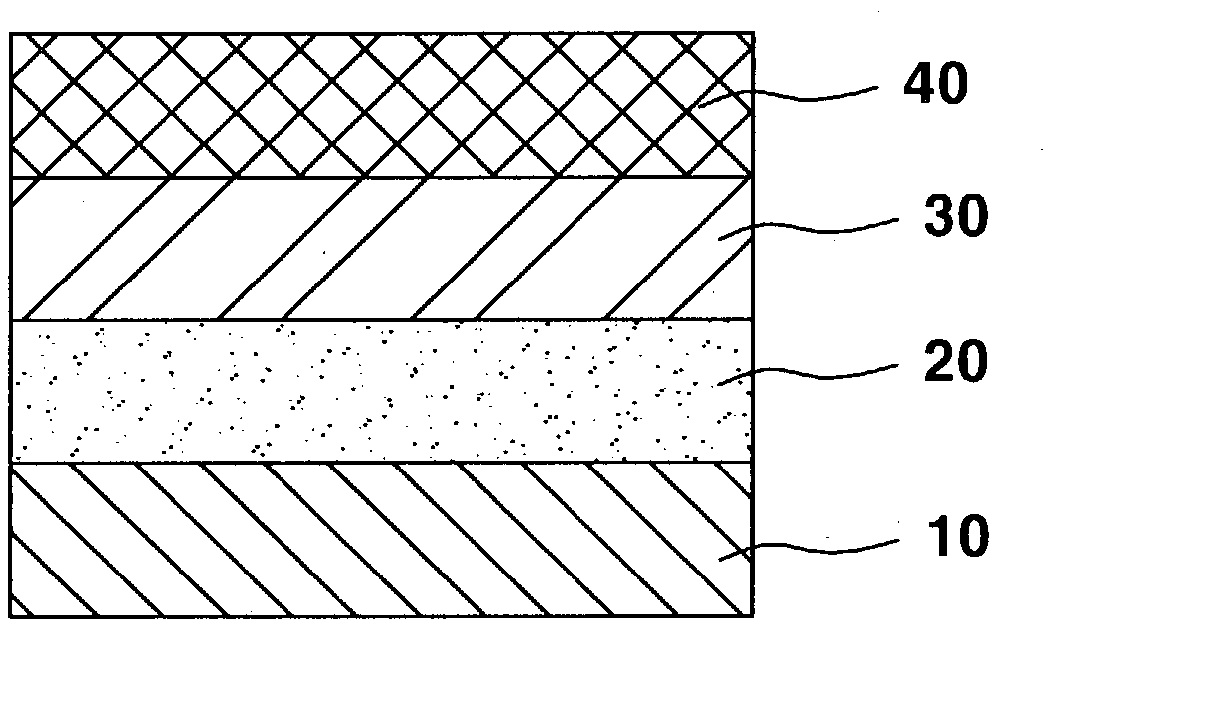
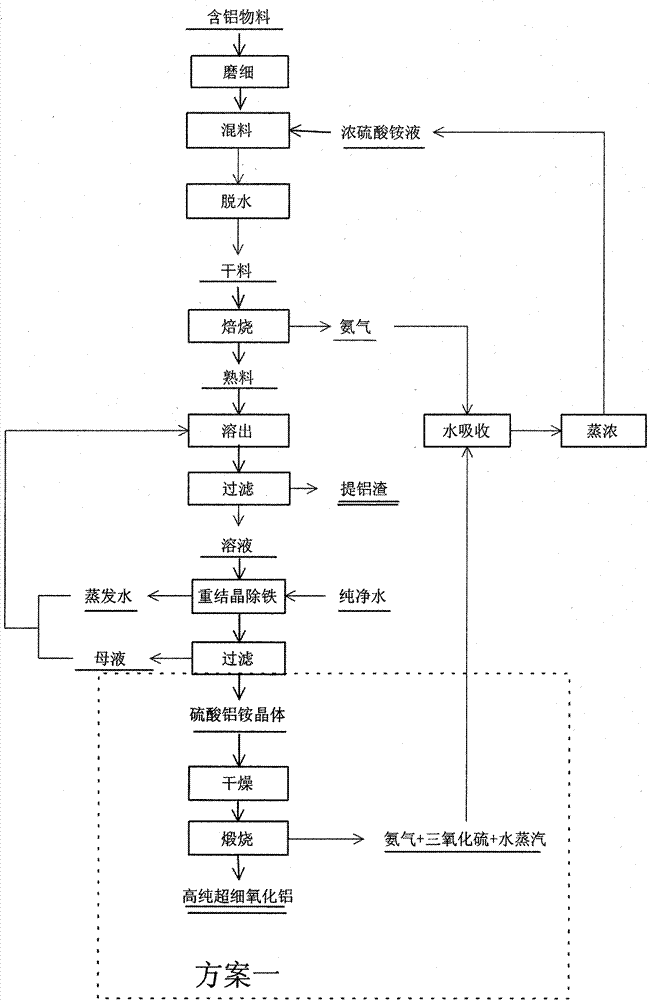
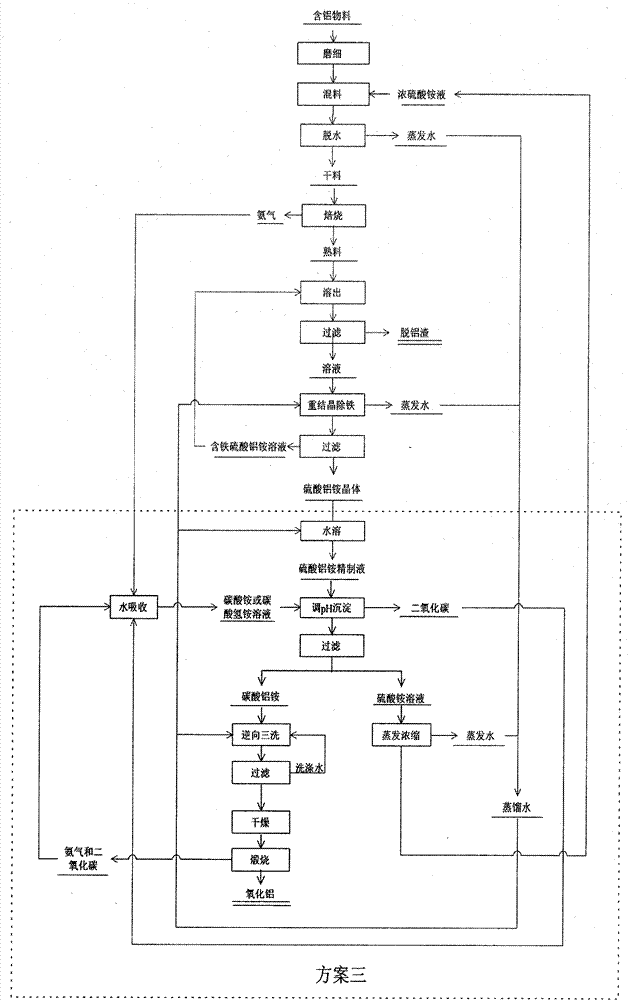
Method for preparing aluminum oxide from aluminiferous material
InactiveCN101734698AHigh value-added comprehensive utilizationCause secondary pollutionAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium hydroxide preparationAluminum ammonium sulfateAlunite
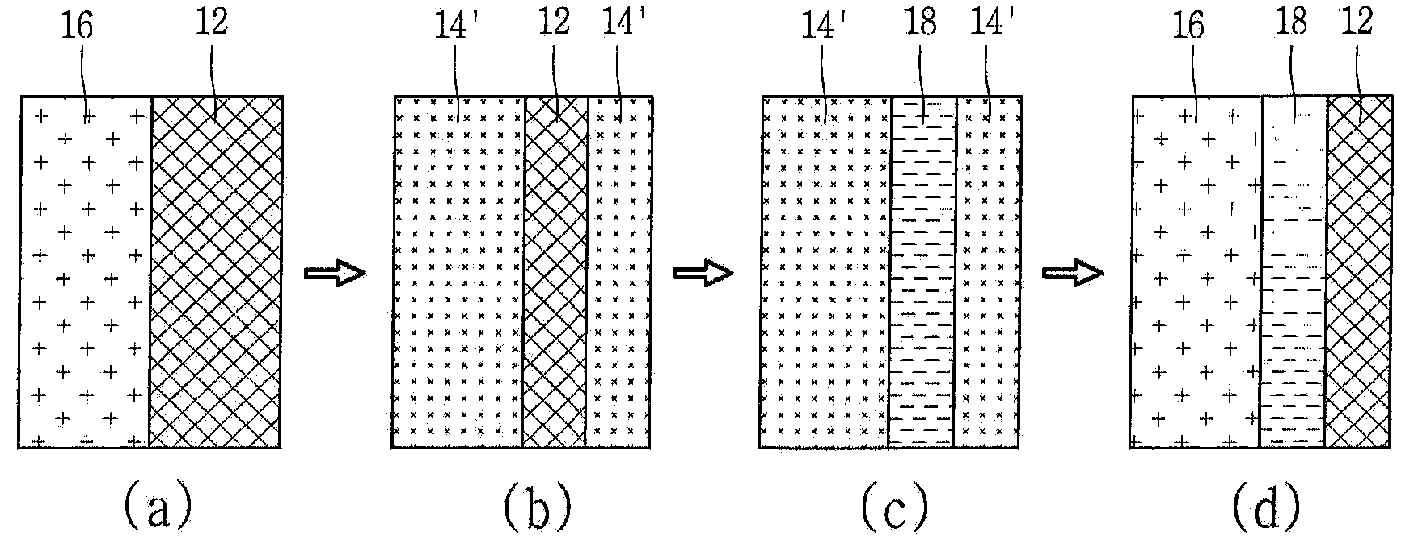
The invention provides a method for preparing aluminum oxide and other products from aluminiferous materials such as bauxite, high iron bauxite, alunite, kaoline, alumina, fly ash, coal gangue, aluminum ash, nepheline, clay and the like. The method comprises the following steps: (1) crushing, grinding and mixing the aluminiferous materials with ammonium sulfate and then roasting; (2) dissolving the roasted product (clinker aggregate) in water, and filtering to obtain aluminum ammonium sulfate solution and filter residues; (3) carrying out deferrization, aluminum deposition or recrystallization on the aluminium ammonum sulfate solution with ammonia to prepare aluminum oxide, and meanwhile, recycling the ammonium sulfate; (4) preparing silicon dioxide from the filter residues, and taking the remaining residues containing ferrum as the raw material for ironmaking. The method is suitable for treating various aluminiferous materials, has the advantages of simple technical process, simple equipment, no emission of solid, liquid and gas wastes, and no secondary pollution, and realizes the high-added-value green complex utilization of the aluminiferous materials such as bauxite, high ironbauxite, alunite, kaoline, alumina, fly ash, coal gangue, aluminum ash, nepheline, clay and the like.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Production method for reducing and fining the high-carbon chromium bearing steel D-type impurity
ActiveCN1621538AGood workmanshipMeet production needsProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceAlkalinityHigh carbon
The production process with reduced and fined type-D inclusion in high-carbon chromium bearing steel features the four-step metallurgical process including initial smelting of steel liquid in electric furnace, refining in bottom blowing Ar LF ladle furnace, deairing in VD vacuum furnace, and die casting or continuous casting. By means of the comprehensive deoxidation process including pre-deoxidation of aluminum deposition of the steel from electric furnace, deoxidation with Fe-Si powder diffusion slag in LF site and vacuum carbon deoxidation in VD site; and the new refining process including high alkalinity slag desulfurization in LF site, adoption of low alkalinity slag in the VD site and reducing free CaO inside slag, the present invention reaches the aims of reducing and fining type-D inclusion.
Owner:宝武特种冶金有限公司
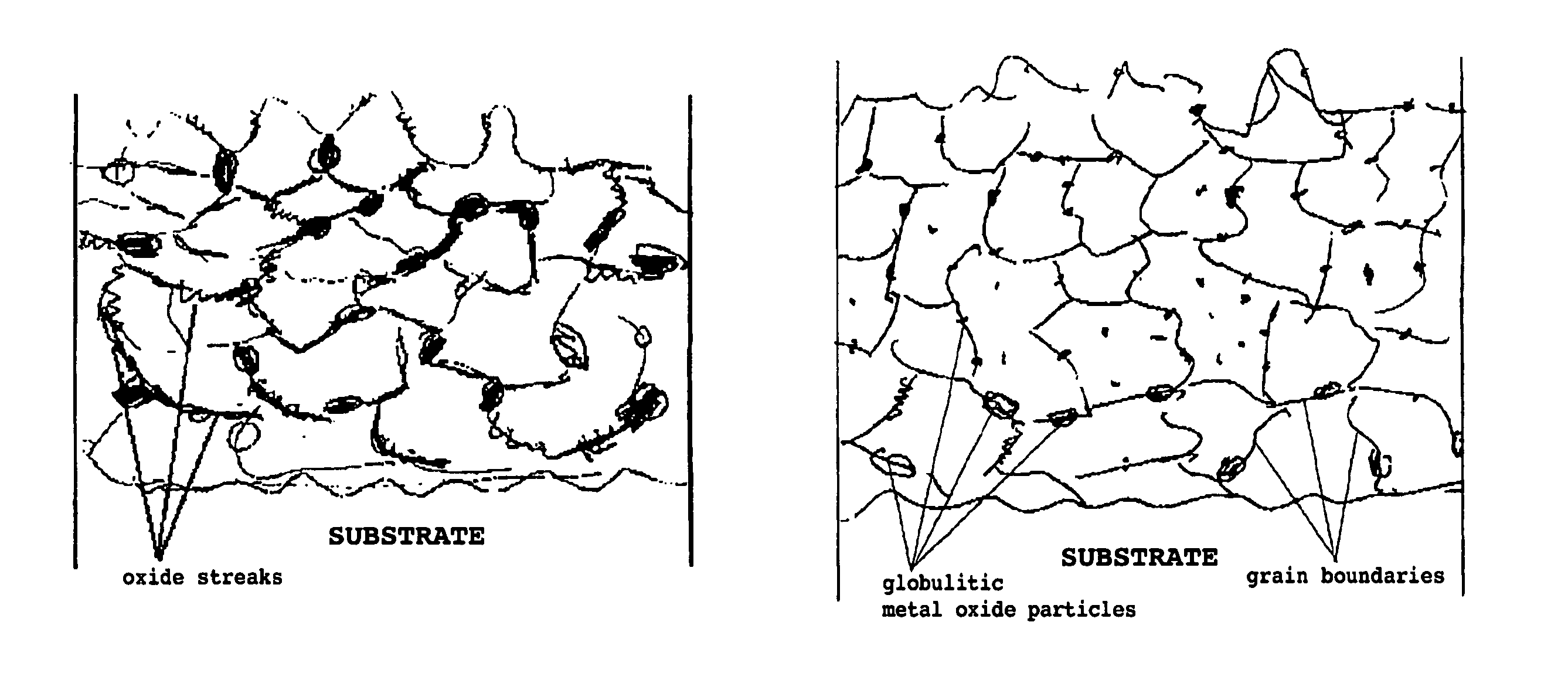
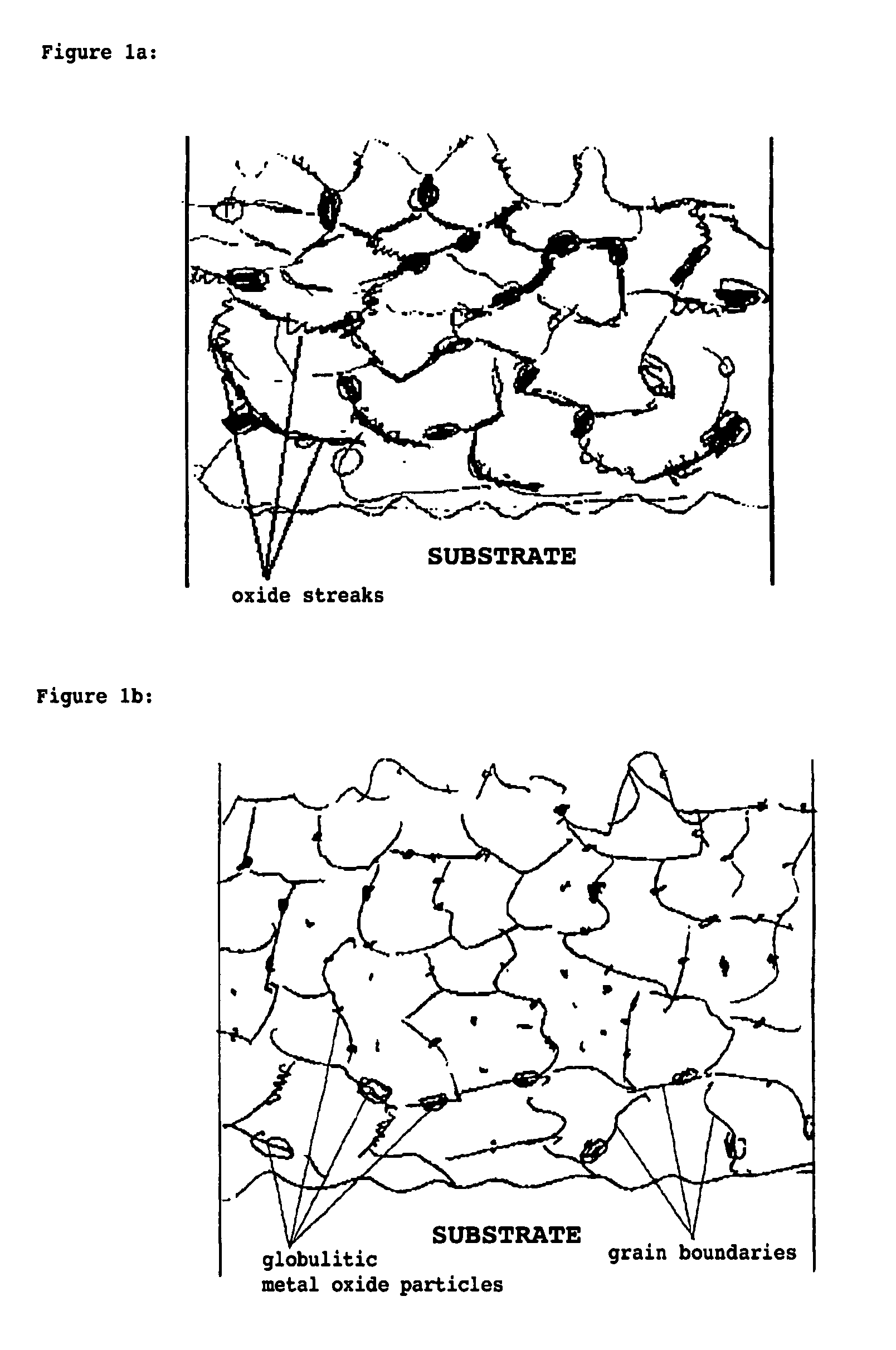
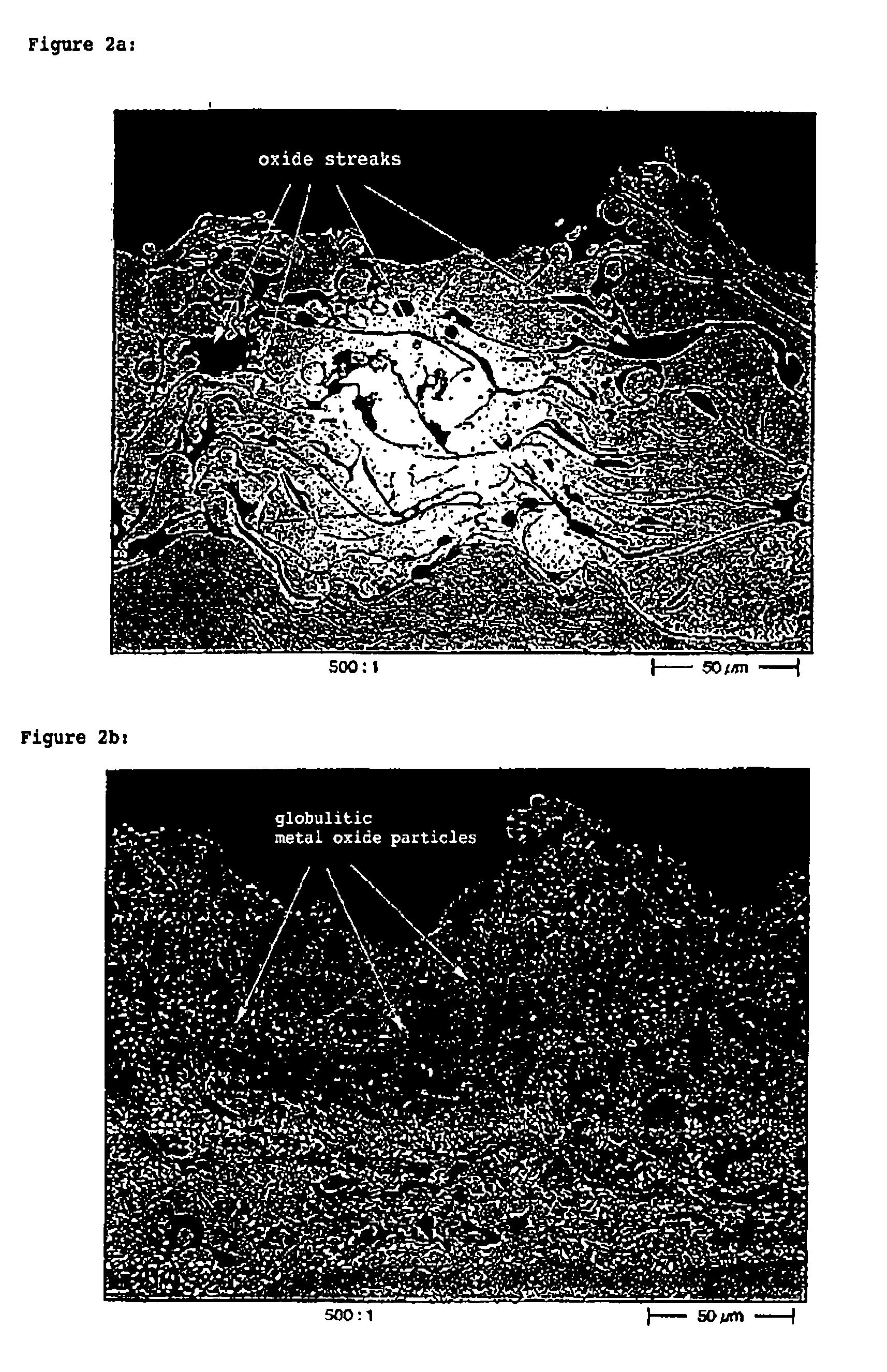
Protective coating for application to a substrate and method for manufacturing a protective coating
InactiveUS20060292390A1High heat and corrosion resistanceCost-effective manufacturingMolten spray coatingPretreated surfacesMetallic materialsSpray coating
A refractory, oxidation-resistant, and corrosion-resistant protective coating for application to a substrate, in particular for application to parts of turbines or aircraft propulsion engines, is described, including a spray coating made of a thermally sprayed, primarily metallic material, the coating being at least partially subjected to a thermochemical aluminum (Cr, Si) deposition process having a specifically high aluminum deposition activity after the application of the protective coating to the substrate, in such a way that the protective coating has alloy gradients of Al (Cr, Si) which increase from the substrate surface to the coating surface and isolated globulitic metal oxide particles. Furthermore, a method for manufacturing this protective coating and its use are described.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
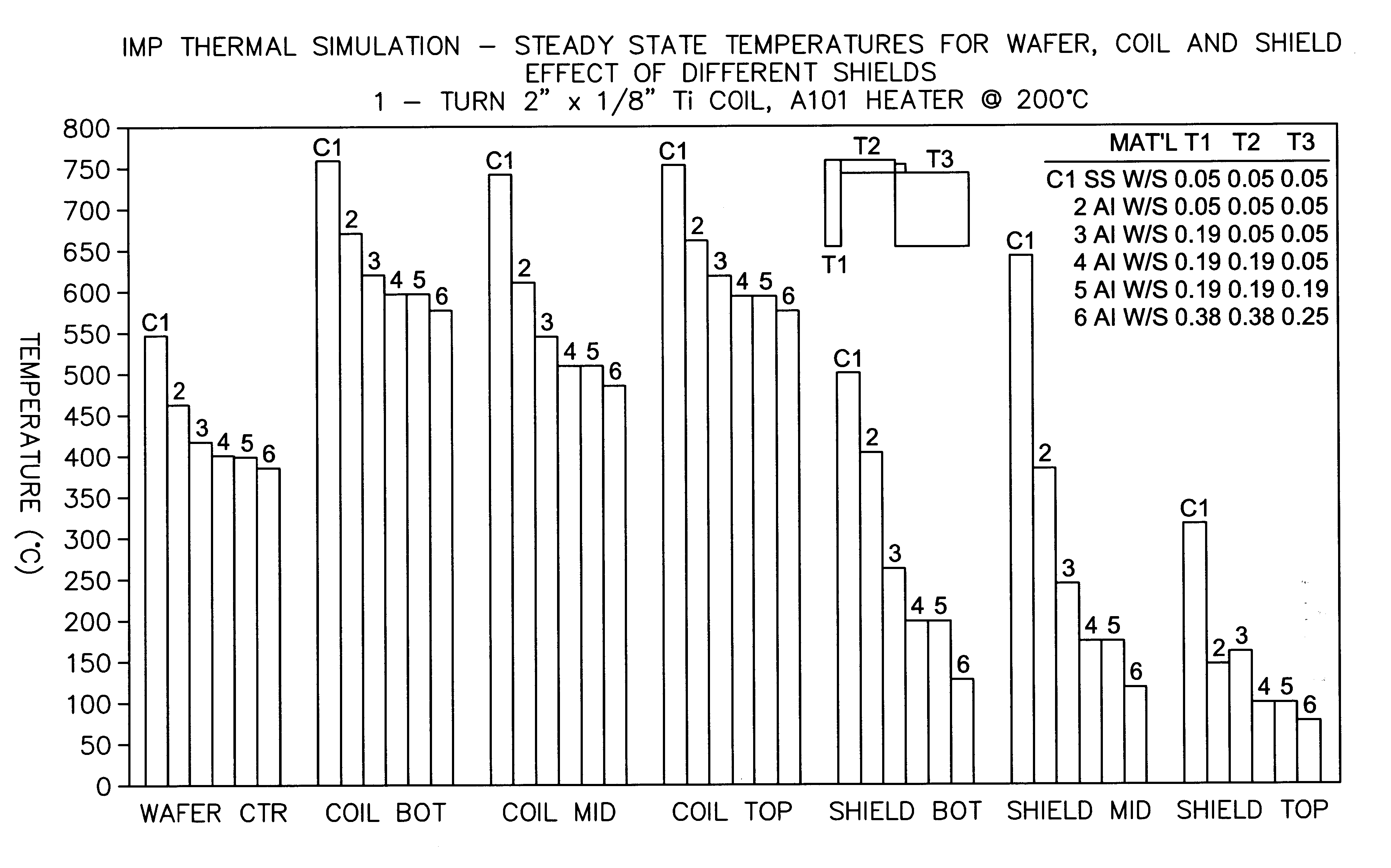
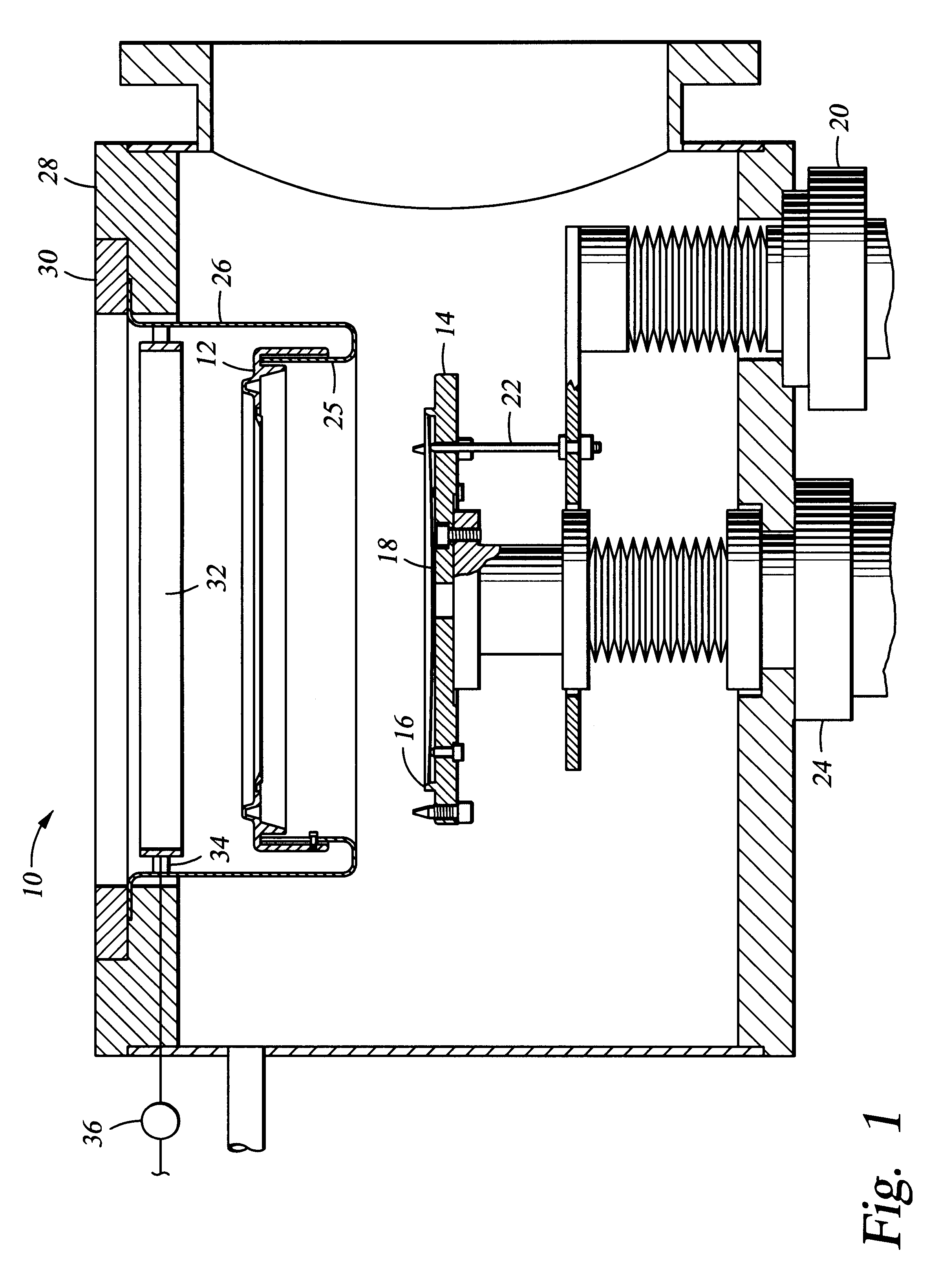
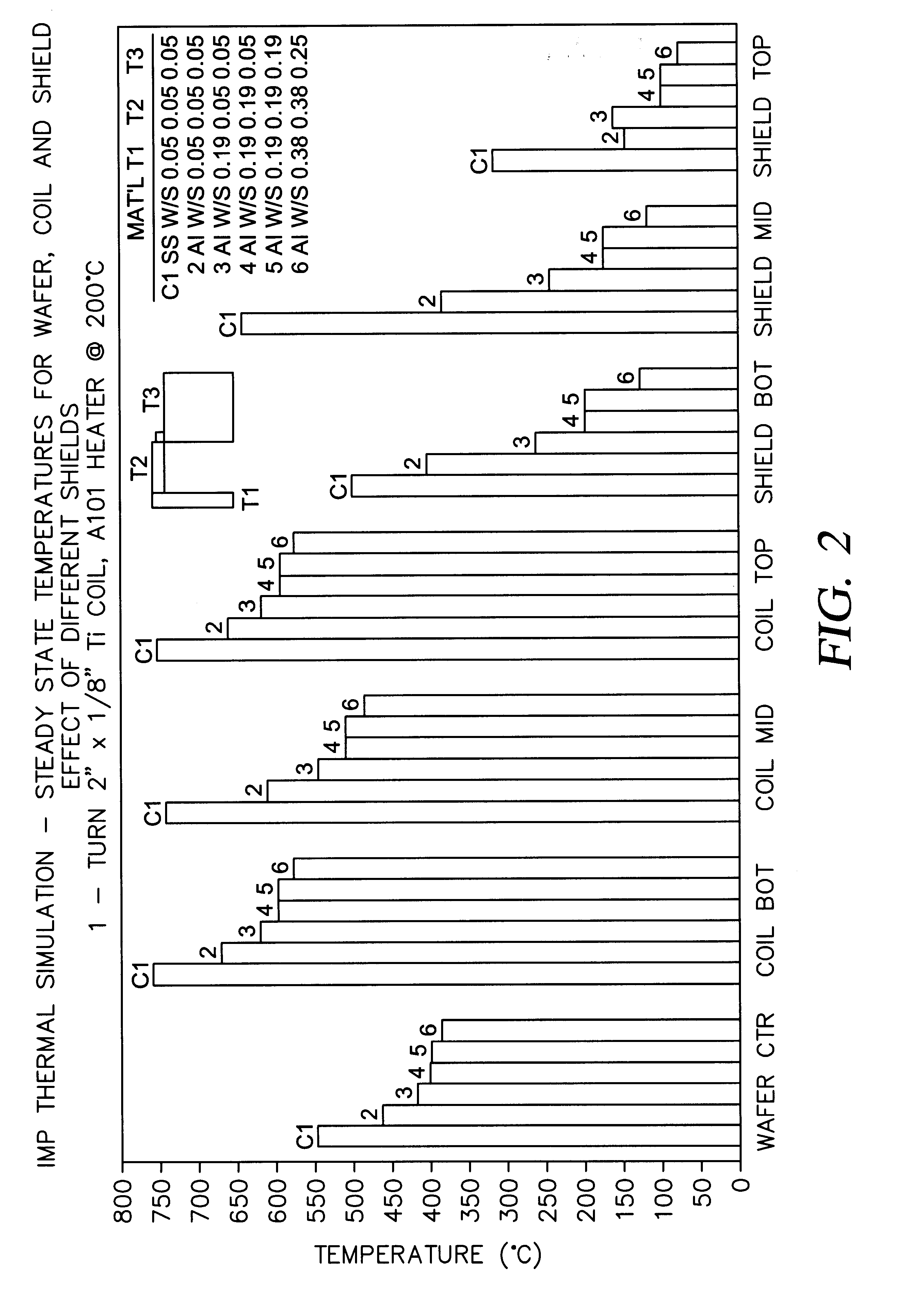
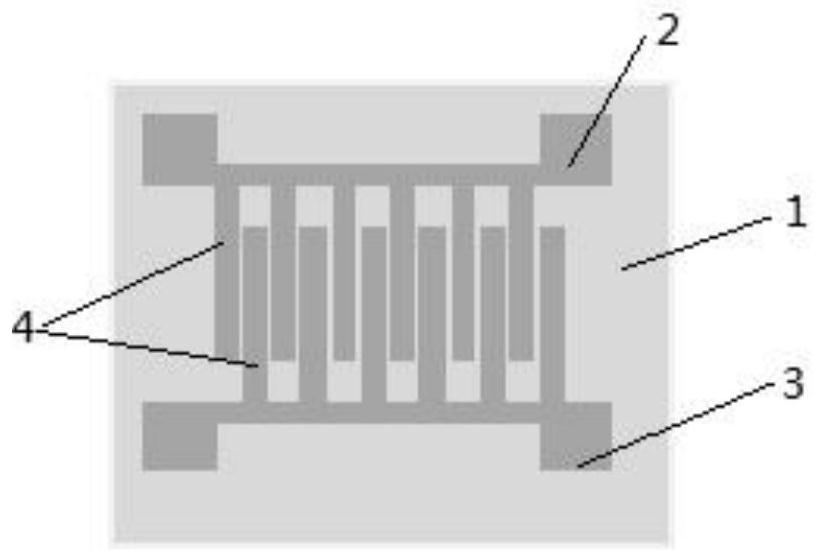
Aluminum deposition shield
An aluminum deposition shield substantially improves transfer of radiated heat from within the vacuum chamber, in comparison to a stainless steel deposition shield. The aluminum deposition shield remains cooler during wafer processing and assists in cooling the chamber components.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
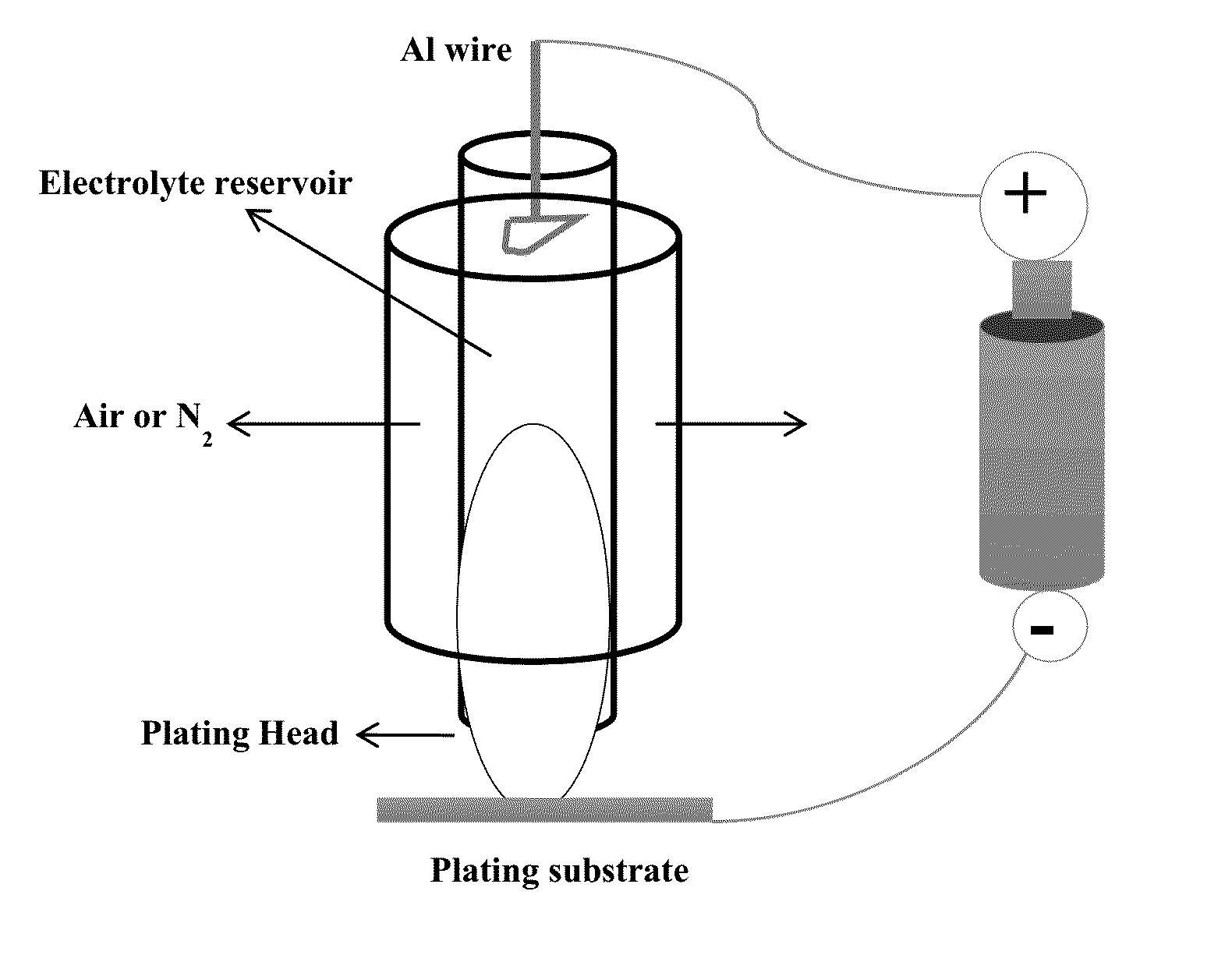
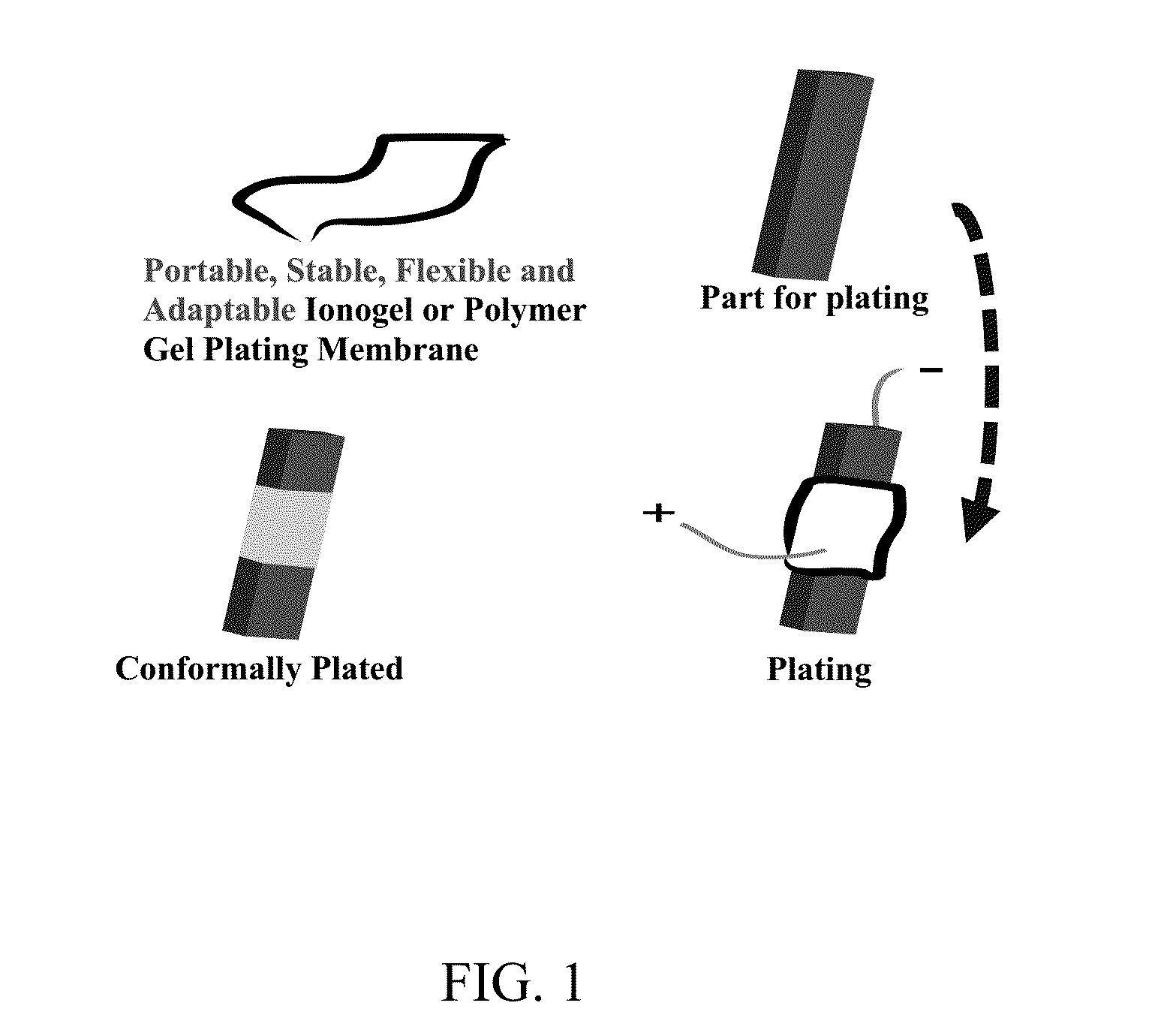
Aluminum deposition devices and their use in spot electroplating of aluminum
A method for spot electroplating aluminum onto a metallic substrate without submersion or dipping of the metallic substrate in an electroplating bath, the method comprising: (i) spot coating said metallic substrate with an aluminum ion-containing electrolyte contained within a protective structure possessing at least one aperture, and releasing said electrolyte from said at least one aperture onto said metallic substrate to form a coating of said electrolyte thereon, wherein said electrolyte is in contact with an anode; and (ii) applying a voltage potential between the anode and metallic substrate polarized as cathode when the aluminum ion-containing electrolyte is released from said aperture and forms a coating on the metallic substrate, to produce a coating of aluminum on the substrate. Devices, such as brush and ball pen plating devices, for achieving the above-described method are also described.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Multi-functional micro electromechanical devices and method of bulk manufacturing same
InactiveUS6706549B1Avoid destructionDoubling the fabrication cost for makingAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsResistPhosphoric acid
A method of bulk manufacturing SiC sensors is disclosed and claimed. Materials other than SiC may be used as the substrate material. Sensors requiring that the SiC substrate be pierced are also disclosed and claimed. A process flow reversal is employed whereby the metallization is applied first before the recesses are etched into or through the wafer. Aluminum is deposited on the entire planar surface of the metallization. Photoresist is spun onto the substantially planar surface of the Aluminum which is subsequently masked (and developed and removed). Unwanted Aluminum is etched with aqueous TMAH and subsequently the metallization is dry etched. Photoresist is spun onto the still substantially planar surface of Aluminum and oxide and then masked (and developed and removed) leaving the unimidized photoresist behind. Next, ITO is applied over the still substantially planar surface of Aluminum, oxide and unimidized photoresist. Unimidized and exposed photoresist and ITO directly above it are removed with Acetone. Next, deep reactive ion etching attacks exposed oxide not protected by ITO. Finally, hot phosphoric acid removes the Al and ITO enabling wires to connect with the metallization. The back side of the SiC wafer may be also be etched.
Owner:NASA
Panel with Anti-fingerprint property and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20140030488A1Improve propertiesReduce manufacturing costLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsPassivationFinger print
The present disclosure relates to a film-attached panel having an anti-fingerprint property and a manufacturing method thereof. The film-attached panel includes a base material, a base layer attached on a surface of the base material, an aluminum deposition layer attached on the base layer, the aluminum deposition layer being processed to have hairlines, a passivation layer disposed on the aluminum deposition layer, and a glossy coating layer formed on the passivation layer, wherein a depth of the hairline processed on the aluminum deposition layer is in the range of 0.25 to 0.35 microns.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
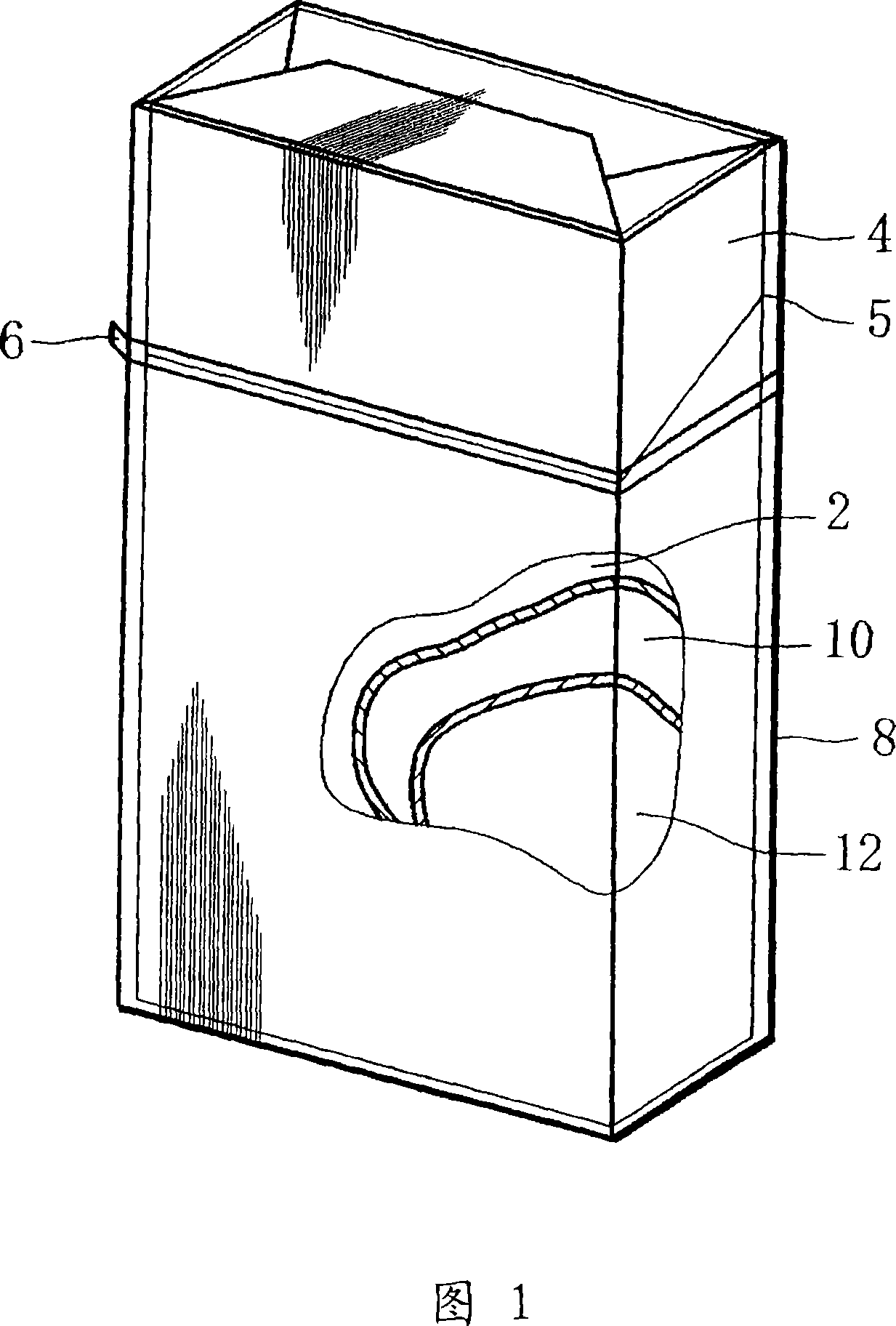
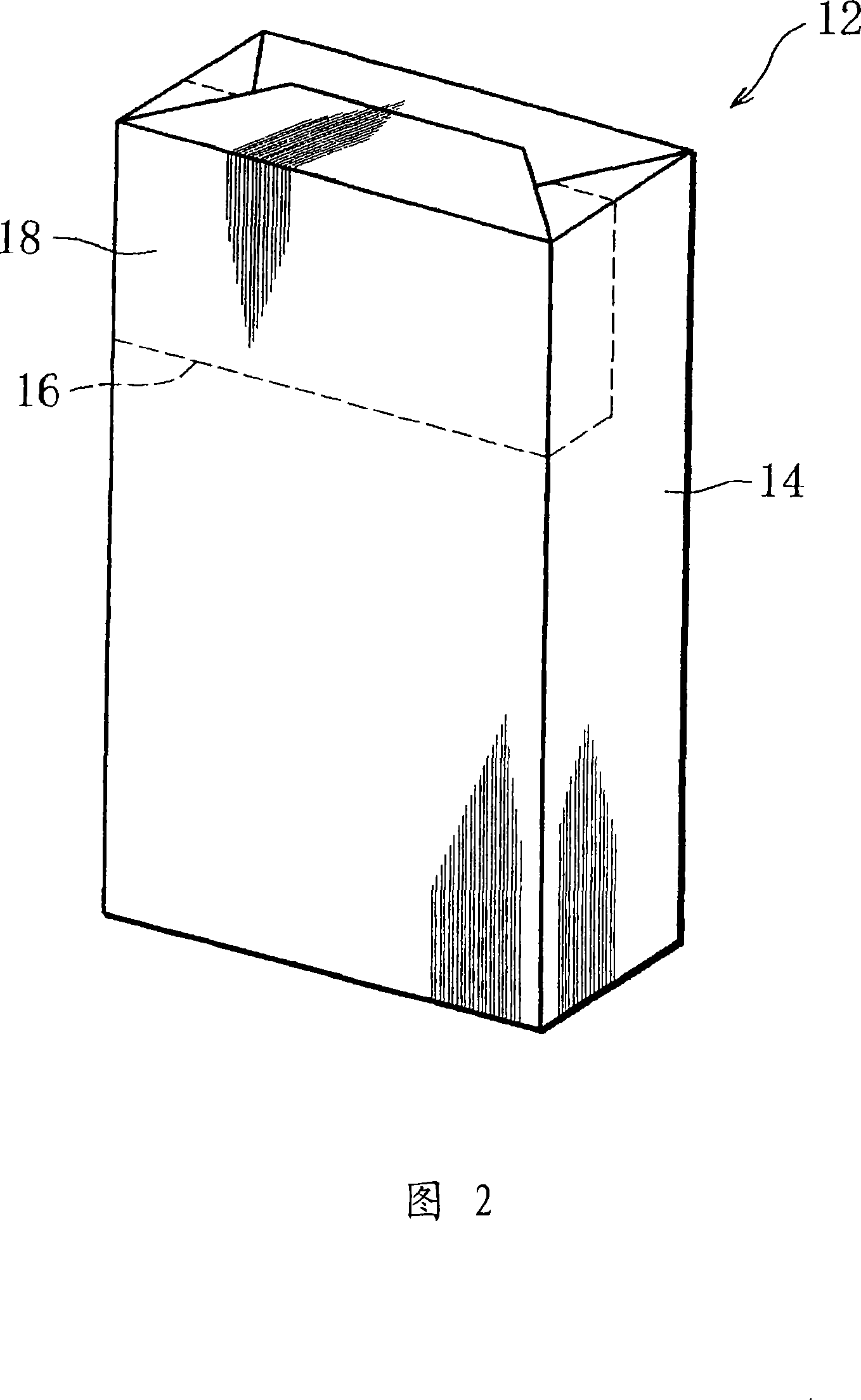
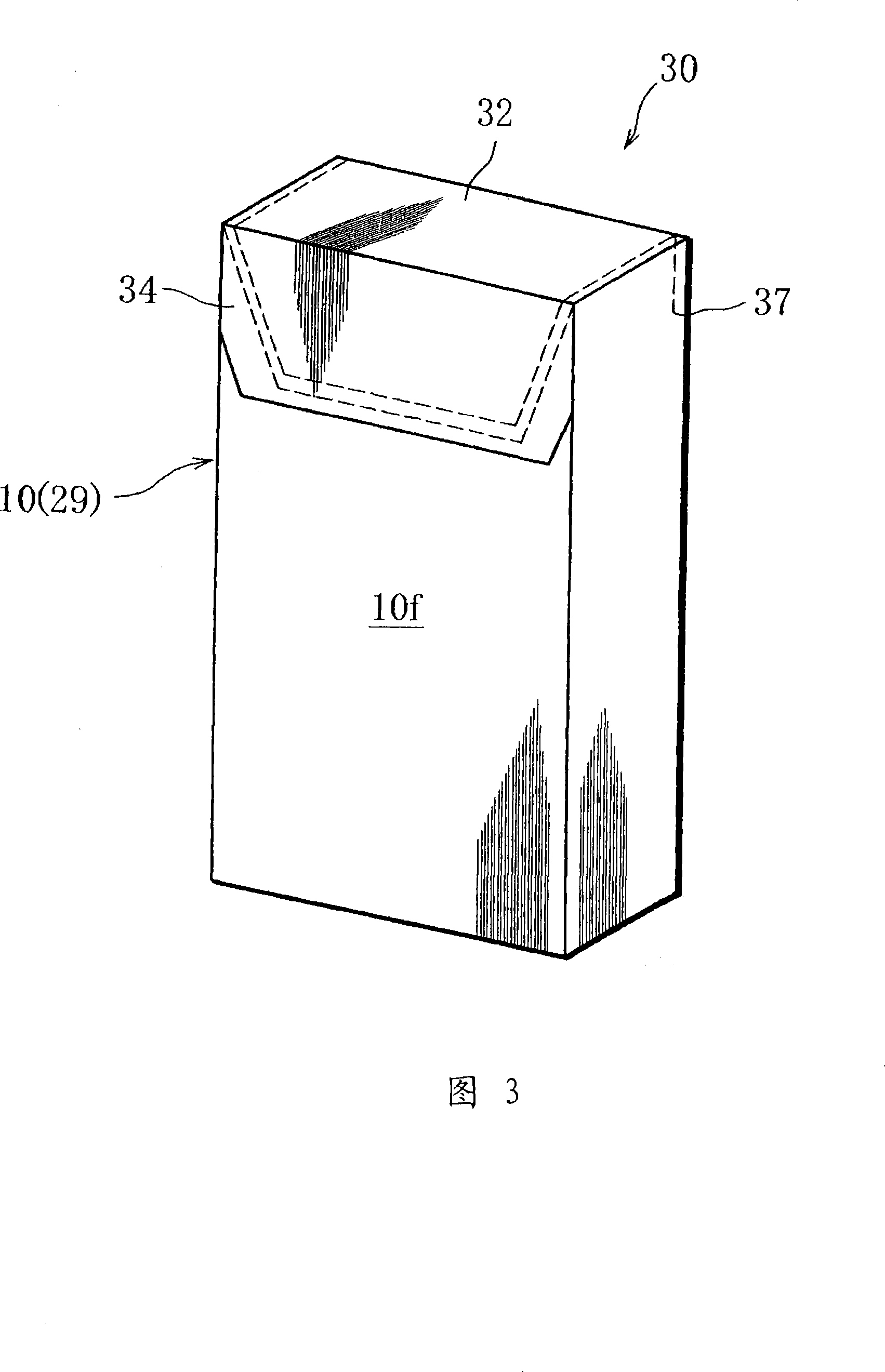
Cigarette package and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveCN101065301AEasy to manufactureKeep the flavorContainers for flexible articlesPackaging cigaretteEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cigarette package and a method of manufacturing the cigarette package. The cigarette package comprises an inner pack (12) formed by wrapping a bundle of cigarettes by an aluminum-deposition paper (inner wrapper), a tongue lid type inner box (10) sealingly storing the inner pack (12), and a hinge lid type outer box (2) storing the inner box (10). The inner box (10) is formed by folding an inner blank around the inner pack (12), and the inner blank is formed in a laminated structure in which the resin layers of polyethylene are formed on both surfaces of an aluminum layer.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
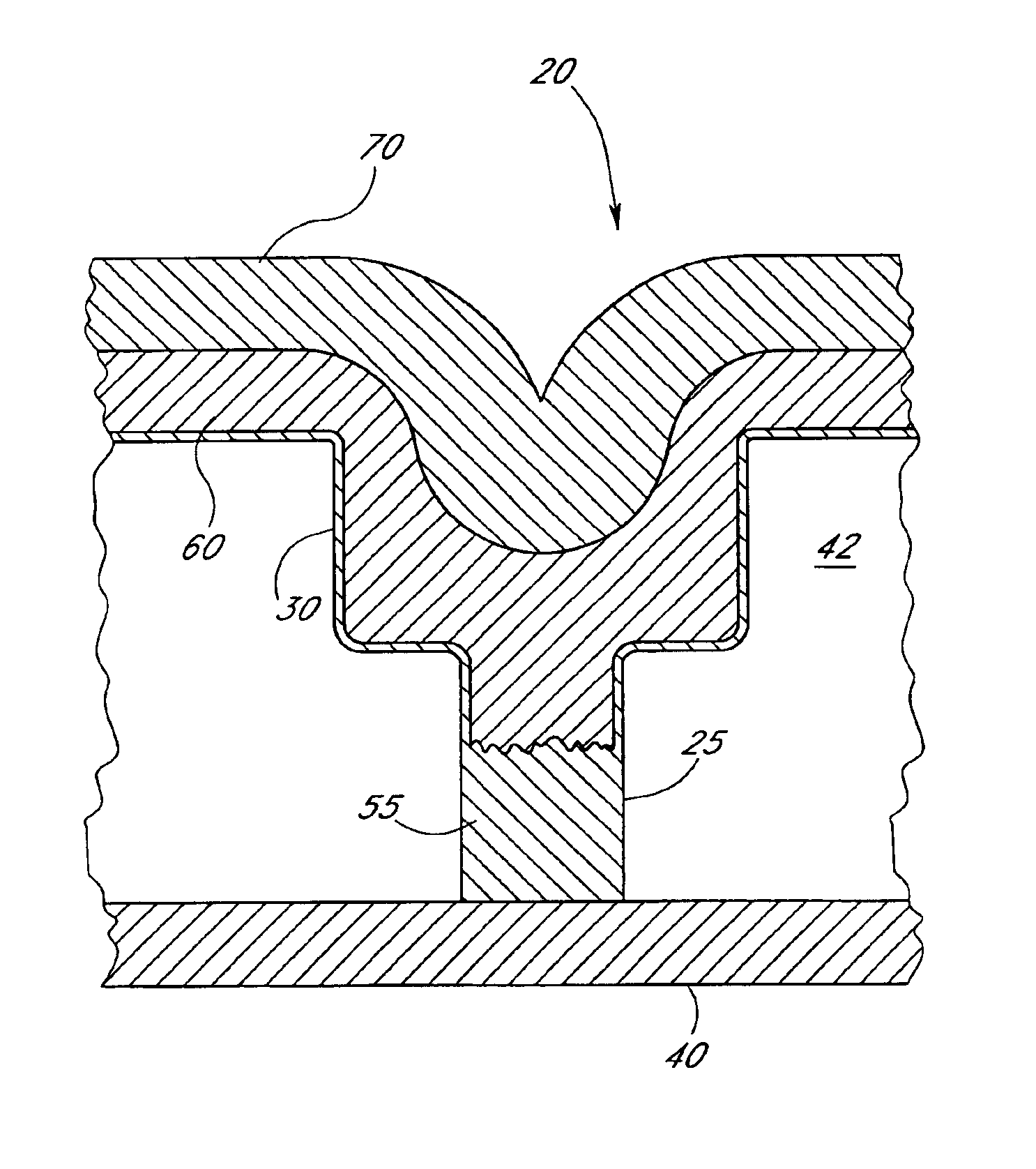
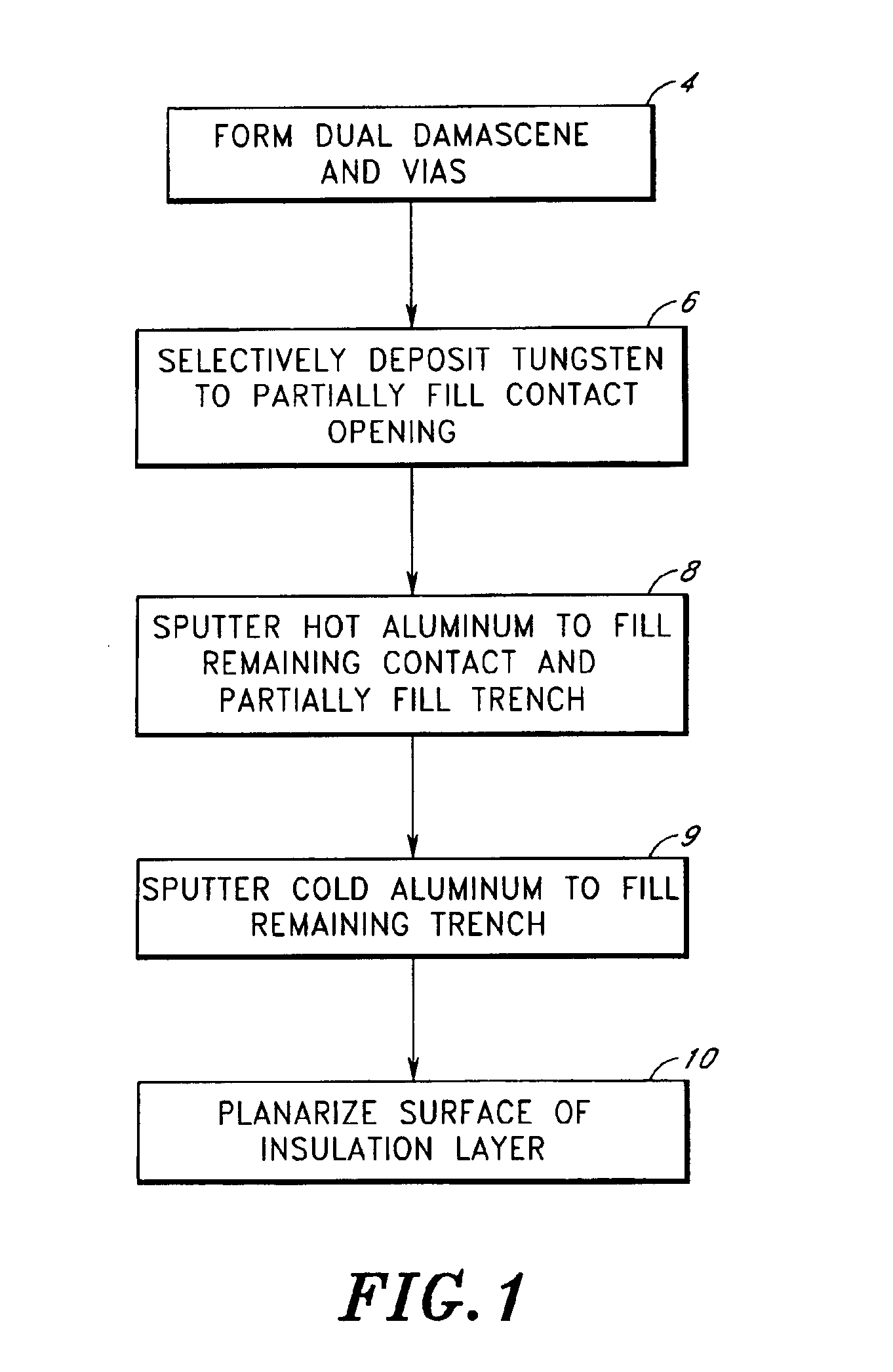
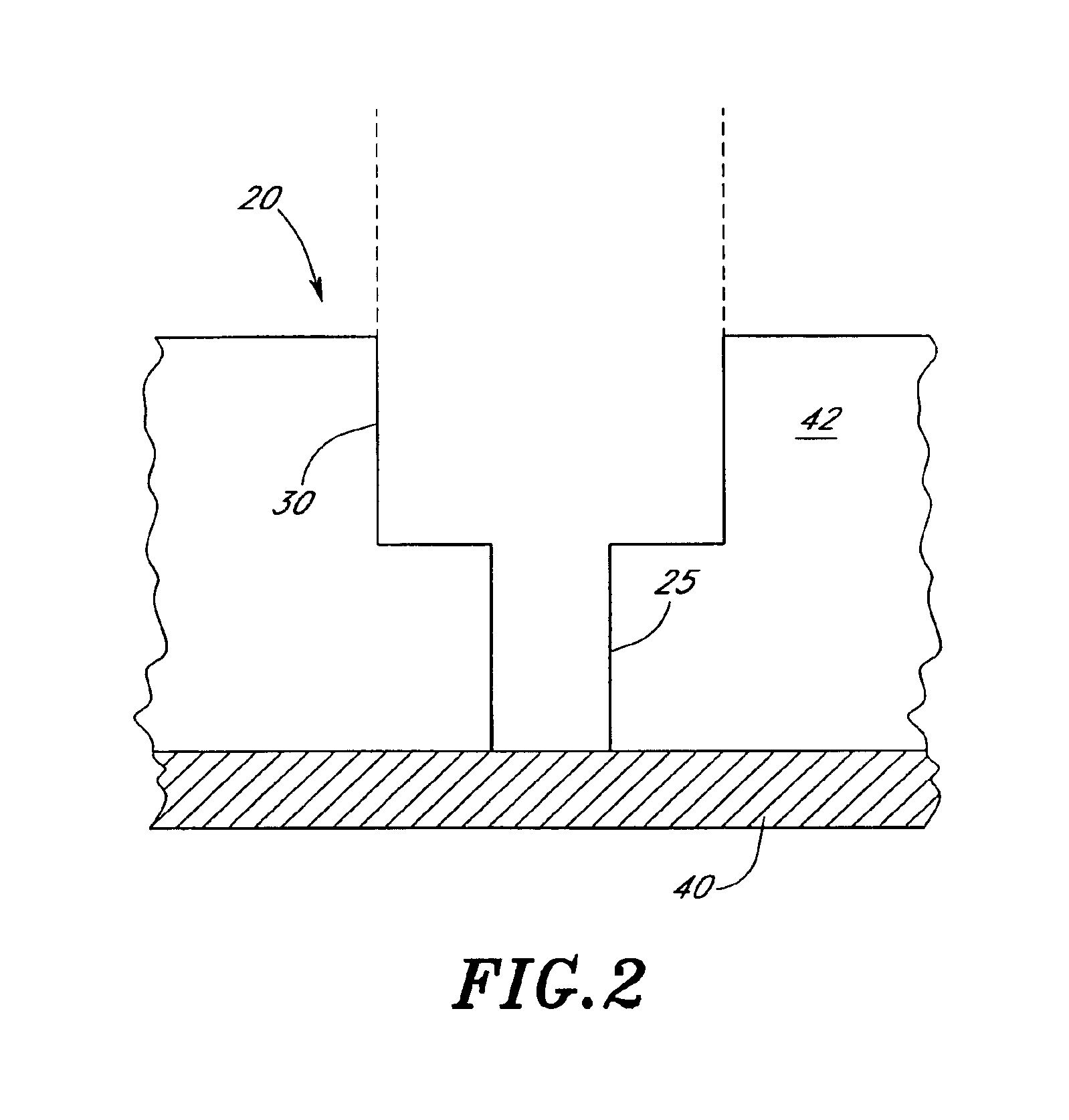
Method of forming a dual damascene interconnect by selective metal deposition
InactiveUS6893957B2Satisfies needSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConductive materialsEngineering
A dual damascene process is disclosed, in which a contact via and trench pattern is etched into insulating layer(s). The via is first partially filled by selective metal (e.g., tungsten) deposition, thereby forming a partial plug that raises the floor and reduces the effective aspect ratio of the trench and via structure. The remaining portion of the contact via is then filled with a more conductive material (e.g., aluminum). This deposition also at least partially fills the overlying trench to form metal runners. In the illustrated embodiment, hot aluminum deposition fills the portion of the contact via left unoccupied by the selective deposition and overfills into the trench. A further, cold aluminum deposition then follows, topping off the trench prior to planarization. The dual damascene structure thus exhibits a raised floor relative to conventional dual damascene metallization, while still retaining the conduction benefits of aluminum through a significant portion of the contact and the metal runner formed in the trench.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Single step process for blanket-selective CVD aluminum deposition
InactiveUS6077781ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingMetal interconnectSelective deposition
The present invention relates generally to an improved apparatus and process for providing uniform step coverage on a substrate and planarization of metal layers to form continuous, void-free contacts or vias in sub-half micron aperture width applications. In one aspect of the invention, a dielectric layer is formed over a conducting member. A thin nucleation layer is then deposited onto the dielectric layer prior to etching high aspect ratio apertures through the nucleation and dielectric layers to expose the underlying conducting member on the aperture floor. A CVD metal layer is then deposited onto the structure to achieve selective deposition within the apertures, while preferably also forming a blanket layer on the field. The present apparatus and process reduce the number of steps necessary to fabricate CVD metal interconnects and layers that are substantially void-free and planarized. The metallization process is preferably carried out in an integrated processing system that includes both a PVD and CVD processing chamber so that once the substrate is introduced into a vacuum environment, the metallization of the apertures to form vias and contacts occurs without the formation of oxides between the layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Composite metallization process for filling high aspect ratio contact holes
InactiveUS20010045661A1Enhanced barrier functionImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveTitanium
A process has been developed in which high aspect ratio contact holes can be successfully filled, without voids, using a composite metallization layer. After adhesive and barrier layers are deposited, an additional titanium adhesive layer is deposited, for purposes of improving the adhesion of subsequent, overlying metallizations to underlying device structures. A two step aluminum deposition process is then employed, using an initial cold deposition followed by a hot aluminum deposition. The hot aluminum deposition process results in complete filling of the high aspect ratio contact hole, and also allows the formation of a titanium-aluminum intermetallic layer at the interface of the titanium adhesive layer and the initial, cold aluminum deposition layer.
Owner:YANG CHI CHENG +1
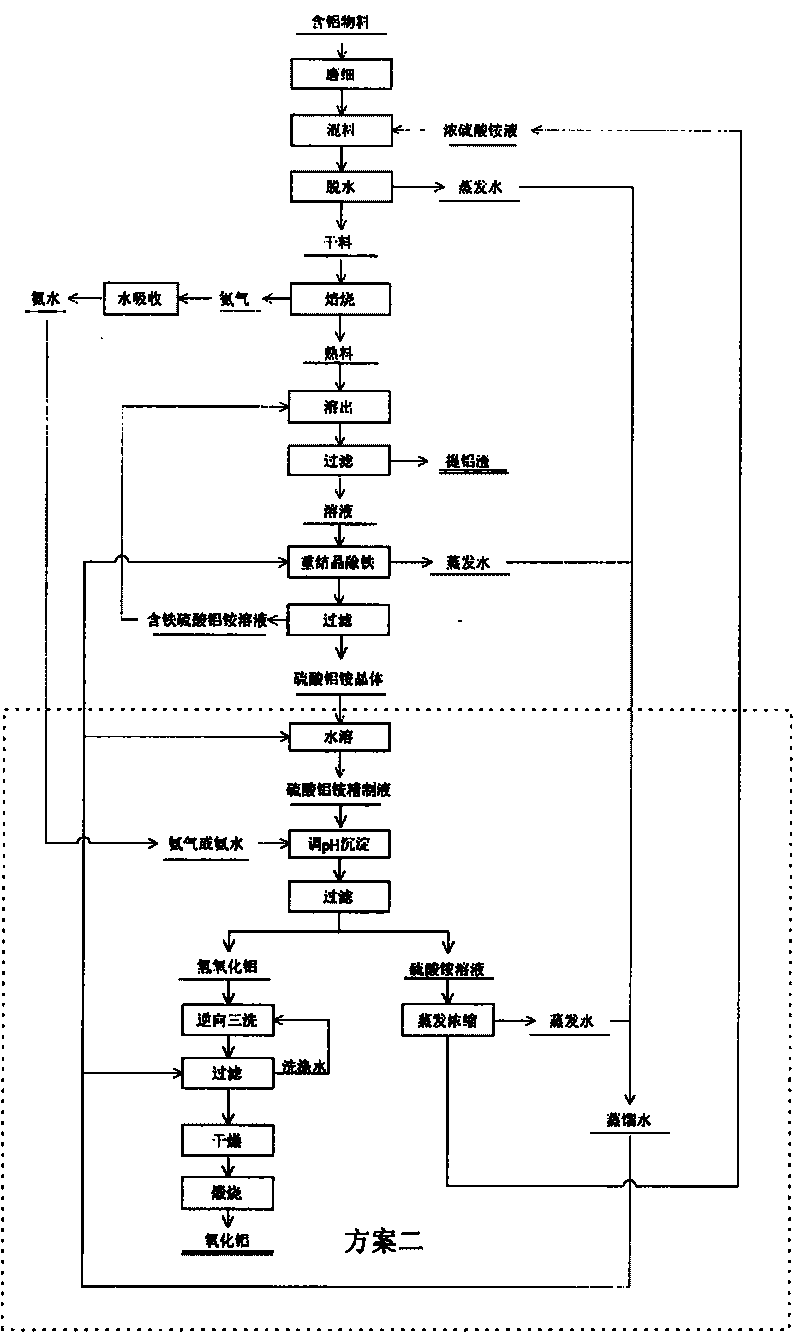
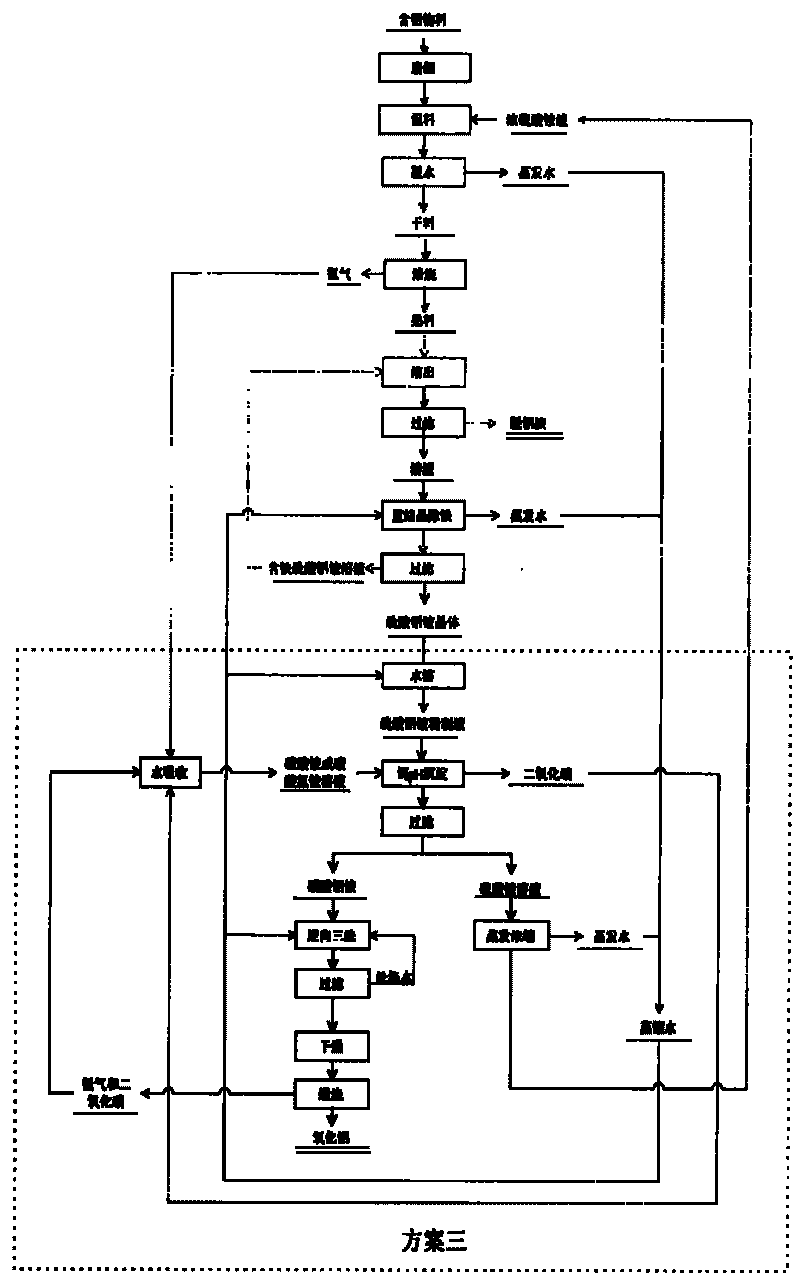
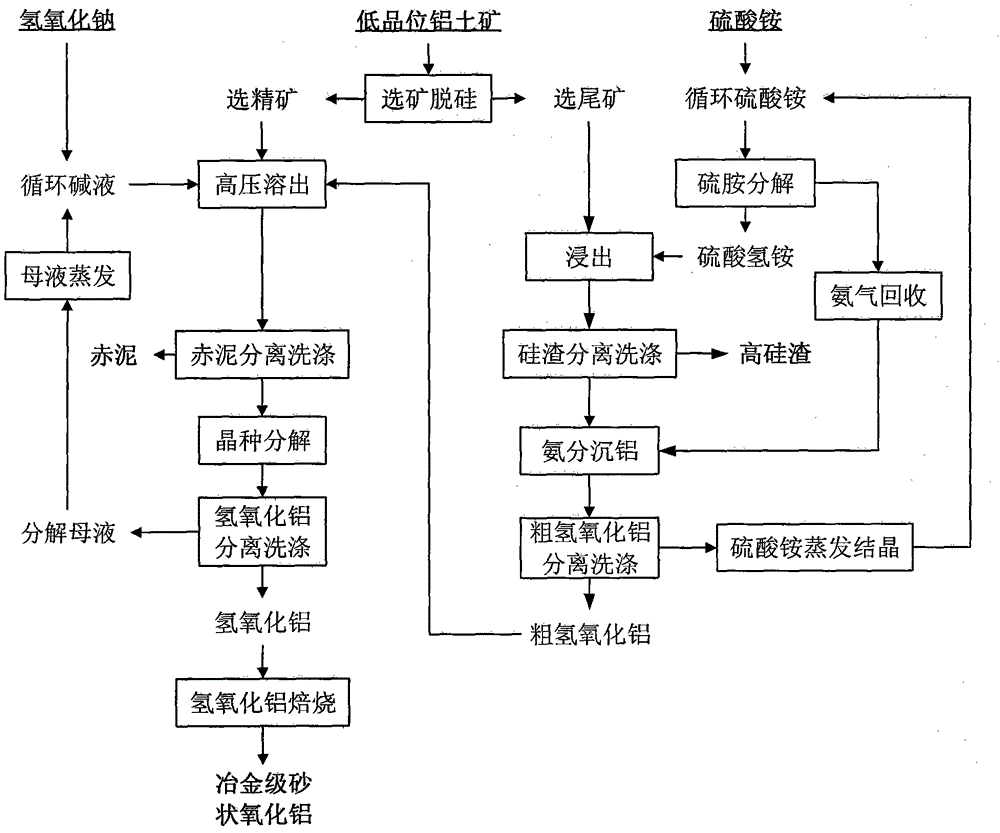
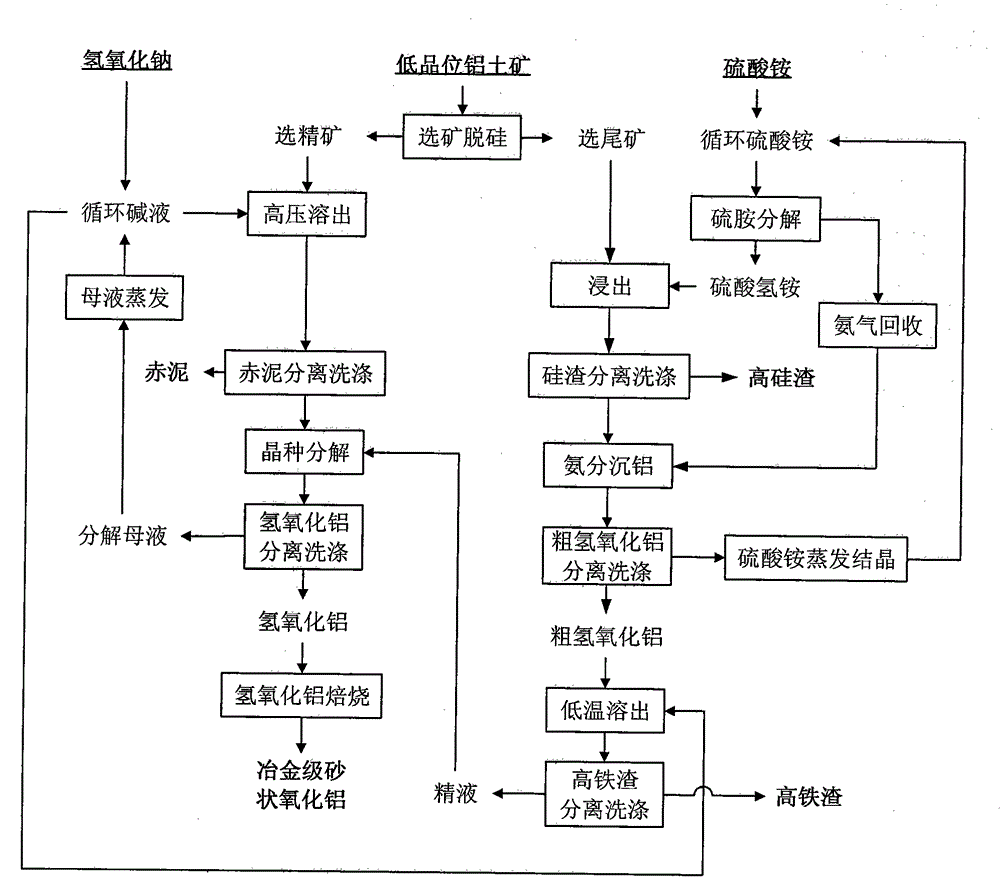
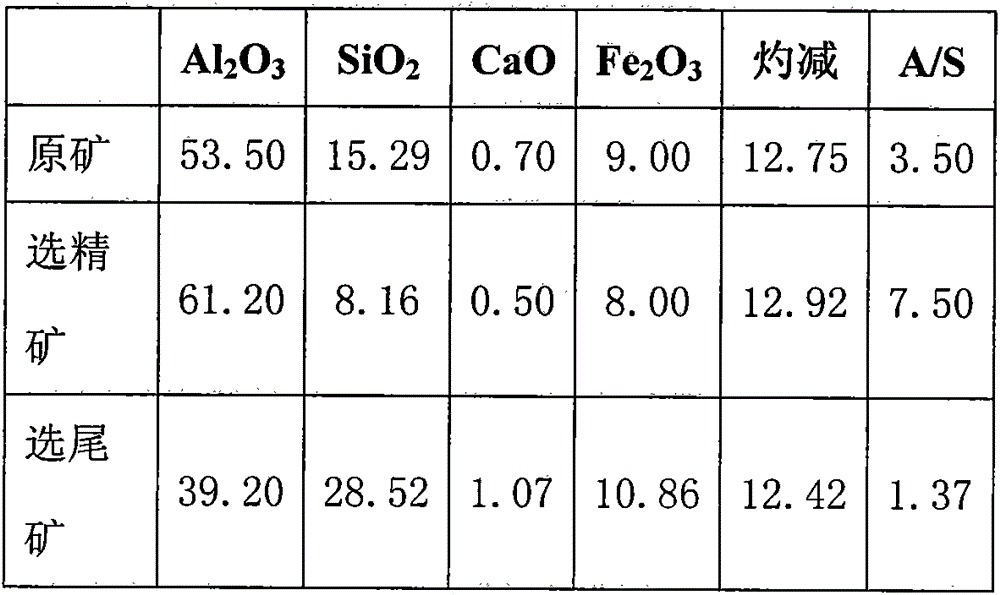
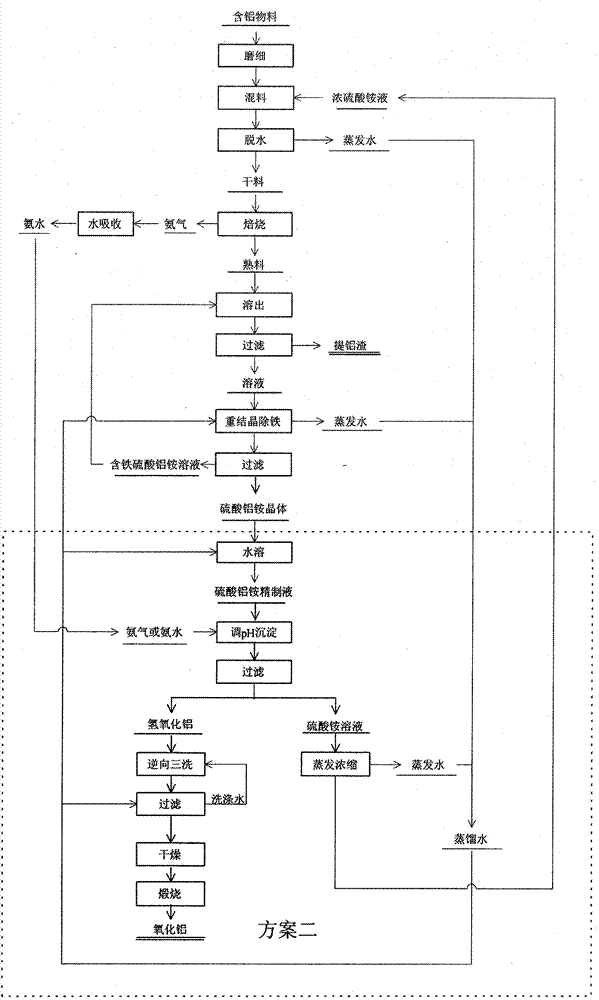
Method for producing aluminum oxide by treating low-grade bauxite with ammonia-alkali combination method
InactiveCN104528786AIncrease Al-Si RatioComprehensive utilization of resources is highAluminium oxides/hydroxidesHydrogen SulfateDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for producing aluminum oxide by treating low-grade bauxite with an ammonia-alkali combination method. The method comprises the following main steps: performing mineral dressing and silicon removal on the low-grade bauxite; selecting concentrates, performing processes of high-pressure dissolution, red mud separation and washing, crystal seed decomposition, aluminum hydroxide separation and washing, aluminum hydroxide calcination and the like on the selected concentrates to produce metallurgical-grade sand-shaped aluminum oxide, and recycling a seed precipitation solution after evaporation and allocation; and selecting tailings, performing low-temperature leaching by adopting an ammonium hydrogen sulfate solution, and performing silicon residue separation and washing, ammonia separation aluminum deposition and coarse aluminum hydroxide separation and washing to obtain coarse aluminum hydroxide. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the organic combination of a mineral dressing and silicon removing process, a high-temperature Bayer method process for selecting concentrates and an ammonium hydrogen sulfate solution low-temperature leaching process for selecting tailings is achieved, the advantages of each process are brought into full play, and the utilization ratio of a low-grade bauxite resource is maximized while high-quality metallurgical-grade sand-shaped aluminum oxide is produced.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Single step process for blanket-selective cvd aluminum deposition
InactiveUS20020068427A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectSelective deposition
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Panel with anti-fingerprint property and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103648767AImprove anti-fingerprint characteristicsReduce qualitySynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingFingerprintCoating
The present disclosure relates to a film-attached panel having an anti-fingerprint property and a manufacturing method thereof. The film-attached panel includes a base material, a base layer attached on a surface of the base material, an aluminum deposition layer attached on the base layer, the aluminum deposition layer being processed to have hairlines, a passivation layer disposed on the aluminum deposition layer, and a glossy coating layer formed on the passivation layer, wherein a depth of the hairline processed on the aluminum deposition layer is in the range of 0.25 to 0.35 micron.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for reducing defects on aluminum gasket surface
ActiveCN103165483AIncrease kinetic energyIncreased DC powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAluminum IonReaction temperature
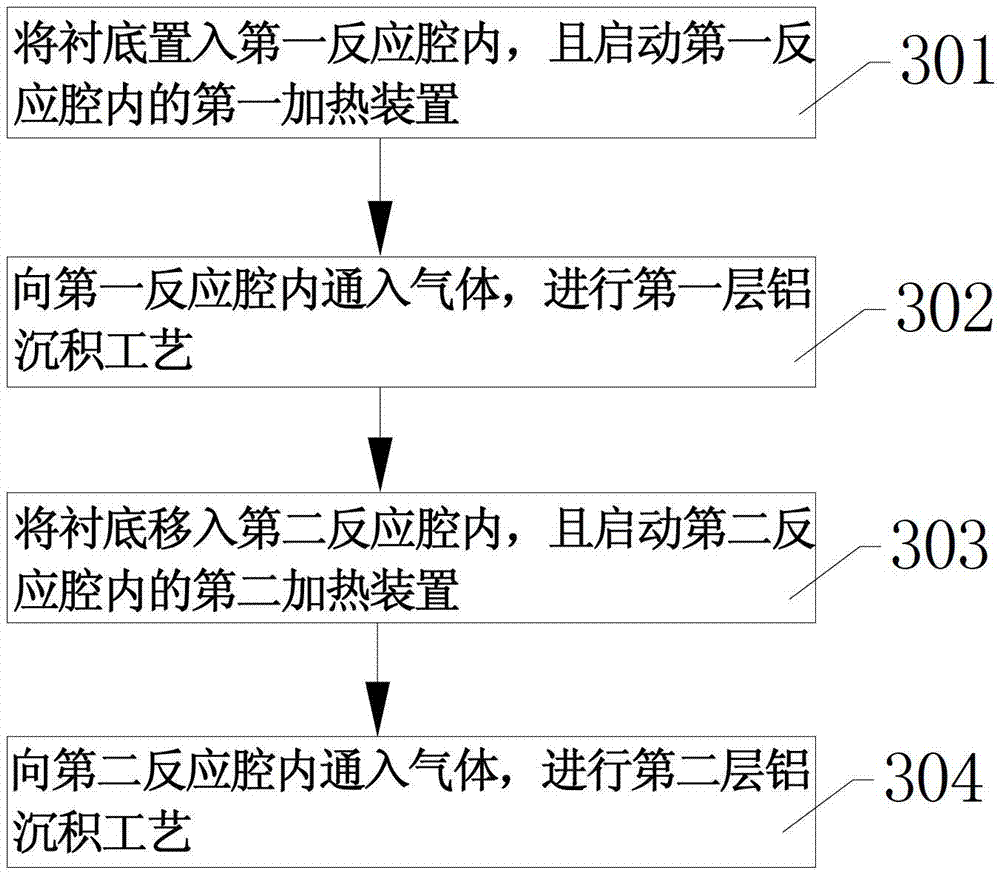
The invention discloses a method for reducing defects on an aluminum gasket surface. According to the method for reducing the defects on the aluminum gasket surface, an aluminum gasket is divided into two layers and the two layers are respectively deposited. According to first layer aluminum deposition, a thin aluminum layer grows at a low temperature through the method of magnifying target direct current power. Second layer aluminum deposition grows at a high temperature. Due to low reaction temperature, a first aluminum layer is small in grains and smooth in surface, a surface medium layer is effectively controlled, the surface medium layer is easily etched and removed during a follow-up forming process of a metal wire graph, meanwhile, the direct current power is magnified when the aluminum layer grows at the lower temperature, sputtered aluminum ions have large motion energy, and therefore good passivation layer step covering capacity is achieved. When the second aluminum layer grows at high-temperature environment, due to cooling buffering time, temperature of wafer surfaces drops, and due to the fact that the first aluminum layer at the lower layer of the second aluminum layer is smooth in surface, stress can be released easily, and beard-shaped defects are reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
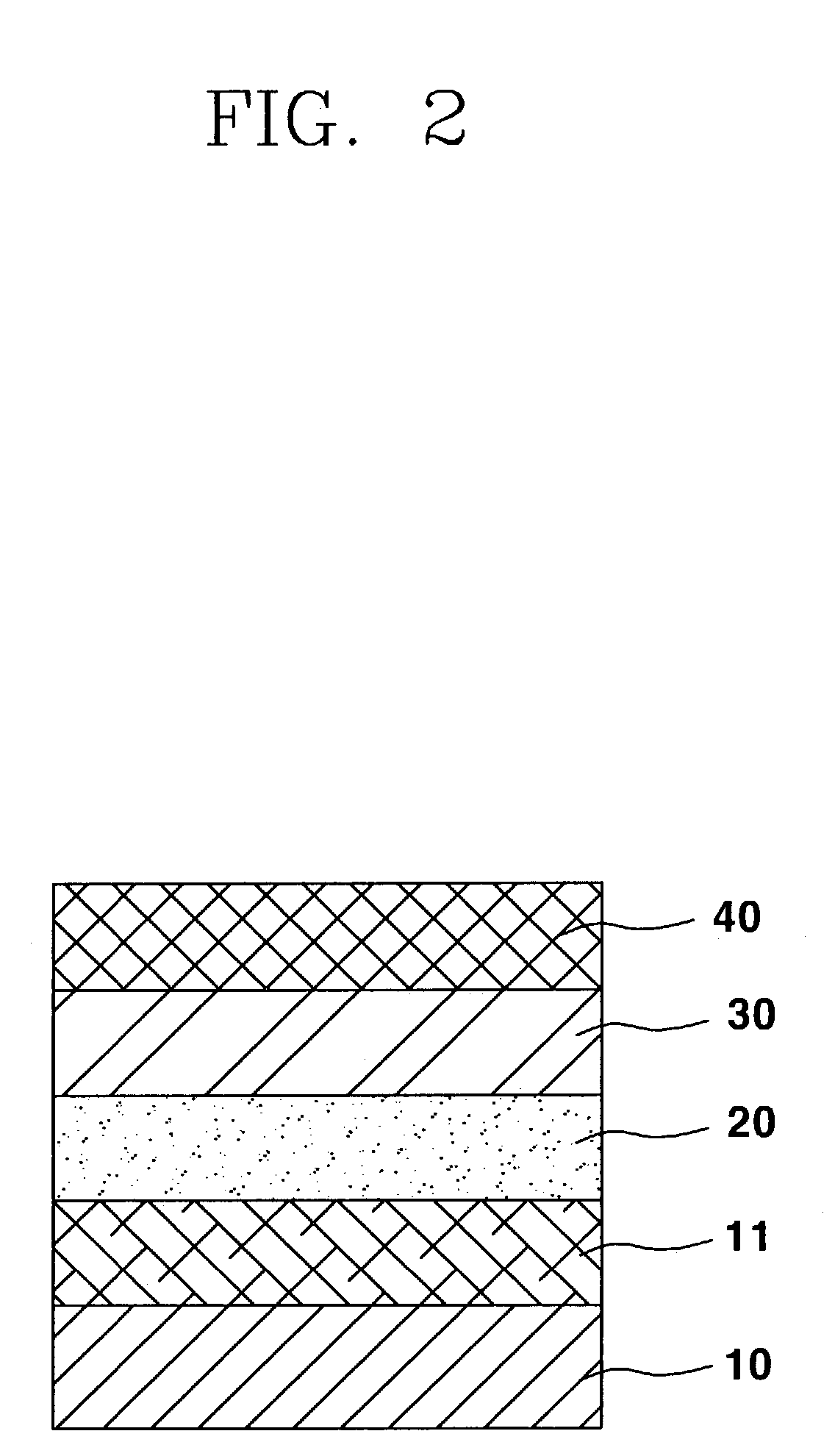
Transfer paper by heat able to dissolve a metal layer partially and the preparation method thereof
Disclosed is a thermal transfer paper comprising a metal layer and capable of partially dissolving the metal layer, which comprises a dissolving function formed of at least one resin selected from the group consisting emulsion resins, water-soluble acryl resins, water-soluble polybutyral resins, alcohol-soluble polybutyral resins, water-soluble vinyl resins and alcohol-soluble vinyl resins, water or an alcohol solvent, and sodium hydroxide or an acid on the metal layer. The thermal transfer paper according to the present invention is provided with a dissolving function layer 30 able to dissolve a part of a metal layer 20, preferably an aluminum deposition layer 21 to form a dissolved part according to a desired design or pattern. Therefore, it is possible to produce unique color and texture, unlike a metal layer pattern formed by oxidation of a part on the metal layer. Specially, when a different color is transferred on a transfer object by an ink layer formed on the transfer paper, it is harmonized with a background color of the transfer object to produce a partial metal-like effect. Thus, according to the present invention, a design with superior texture and color can be readily formed in various patterns, thereby accomplishing a speedy, simple and thereby efficient working process for production and cost saving effect.
Owner:KOREA CHEM CO LTD
Neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet surface protection method
InactiveCN105803408AImprove bindingImprove anti-corrosion performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputter depositionProtection layer
The invention provides a neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet surface protection method. The method comprises 1, material polishing: carrying out conventional polishing on a permanent magnetism material, 2, degreasing oil removal: adding an alkaline solution into the polished permanent magnetism material and carrying out conventional degreasing oil removal, 3, conventional rust removal utilizing wet method sandblasting, 4, vacuum magnetron sputtering aluminum deposition and 5, vacuum plating of an aluminum trioxide protection layer. Through vacuum magnetron sputtering aluminum and aluminum trioxide plating, a neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet vacuum aluminum plating binding force is improved and corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN SANHUAN LUCKY NEW MATERIAL CO LTD +1
Graphite sheet and metal layer composed thermally conductive sheet and its composing method
PendingCN106328614AGood thickness controllabilityIncrease heating capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDiffusion methodsGraphite
The invention provides a graphite sheet and metal layer composed thermally conductive sheet and its composing method. According to one embodiment of the invention, through a PVD aluminum deposition layer, the composition of a graphite sheet and other metal layers becomes possible so as to solve the difficulty with increasing the thickness of graphite sheet and thermally-conductive sheet and the problem of low thermal conductivity in the thickness direction. Based on these ideas, the invention aims to improve the overall heat capacity of the thermally conductive sheet and the comprehensive thermal conductivity in the thickness direction. The thermally conductive sheet of the invention can replace the product structure characterized by the adhesion of adhesive layers among multiple graphite sheet layers or between a graphite sheet and metal. Based on the prior art, the present invention combines the PVD aluminum plating technique and the metal hot-press diffusion method. Compared with the pure use of CVD or liquid plating method, the method of the invention is more efficient to obtain a composite metal layer with the same thickness. In addition, the once hard-to-obtain composite thickness and composite structure in the prior art can be more likely to be achieved. The composing method resolves the problem of how to accumulate composite metal layers with designated thicknesses and avoids the inherent defects of CVD and the liquid plating method.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINHENGKUN TECH
Anode composite material, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106571458AImprove thermal conductivityImprove conductivityCell electrodesConcentration polarizationDendrite
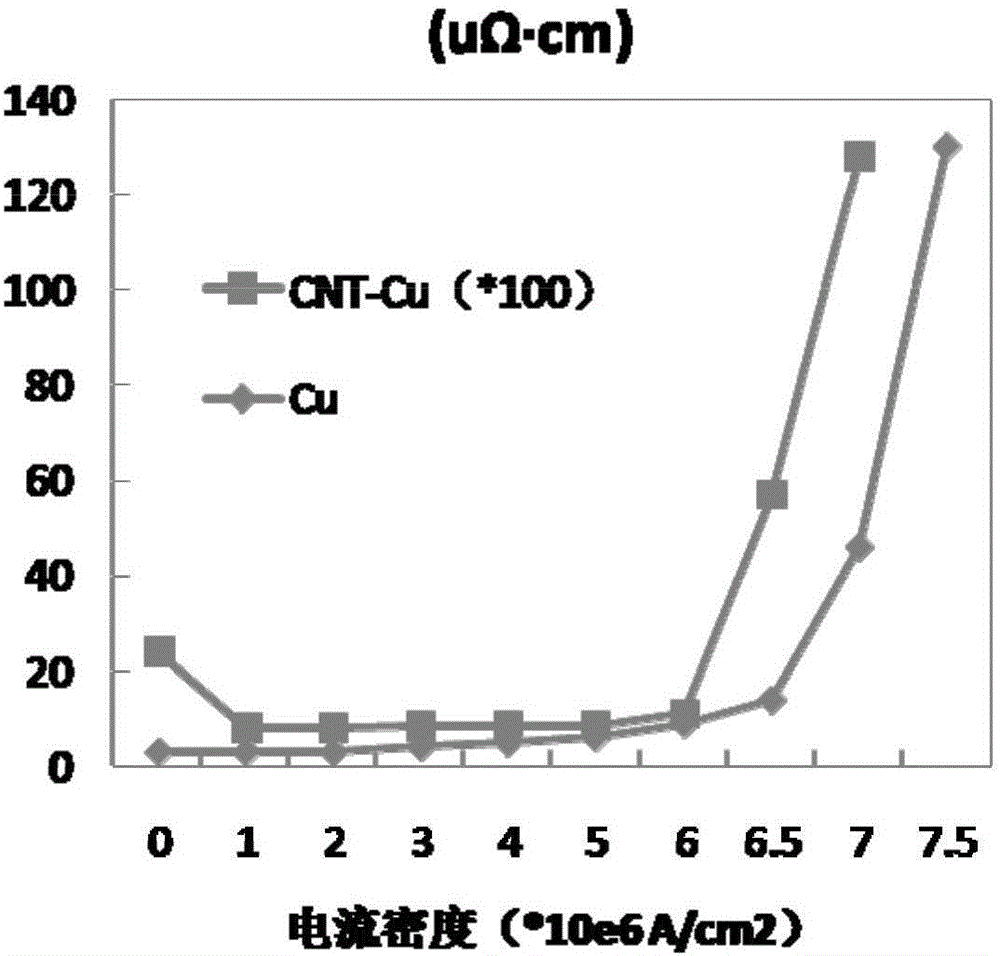
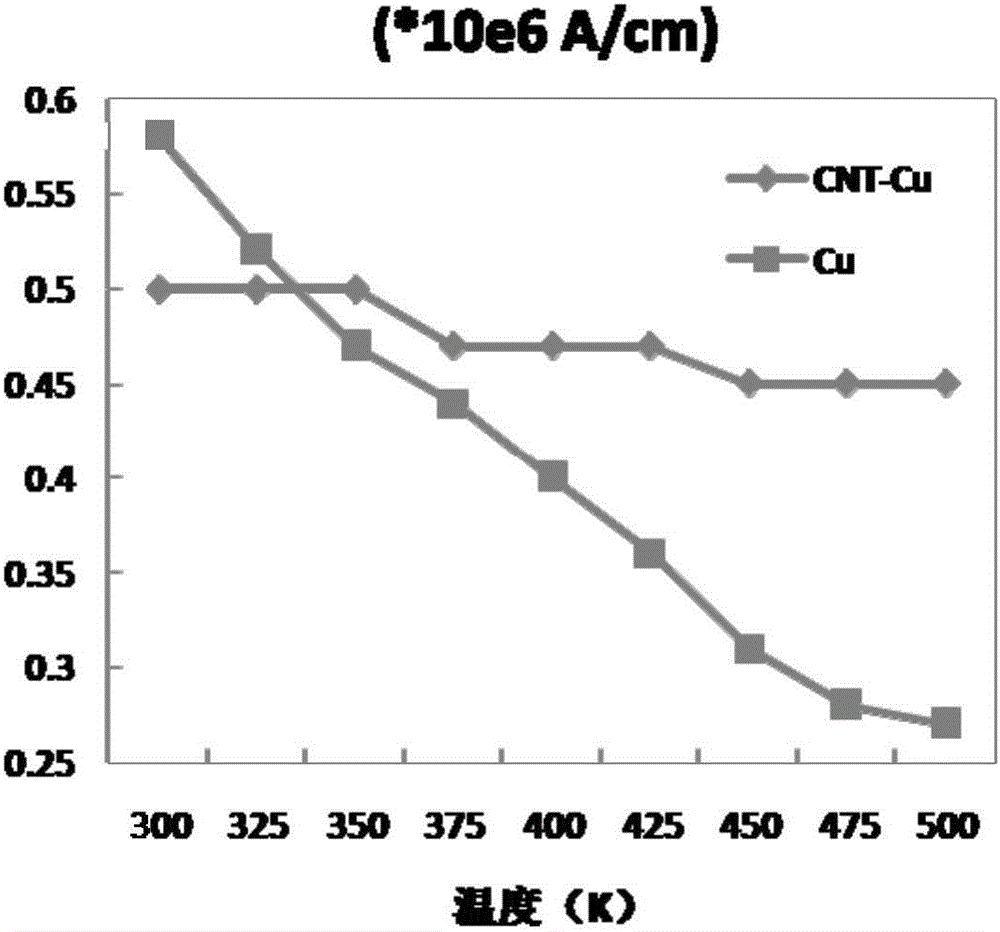
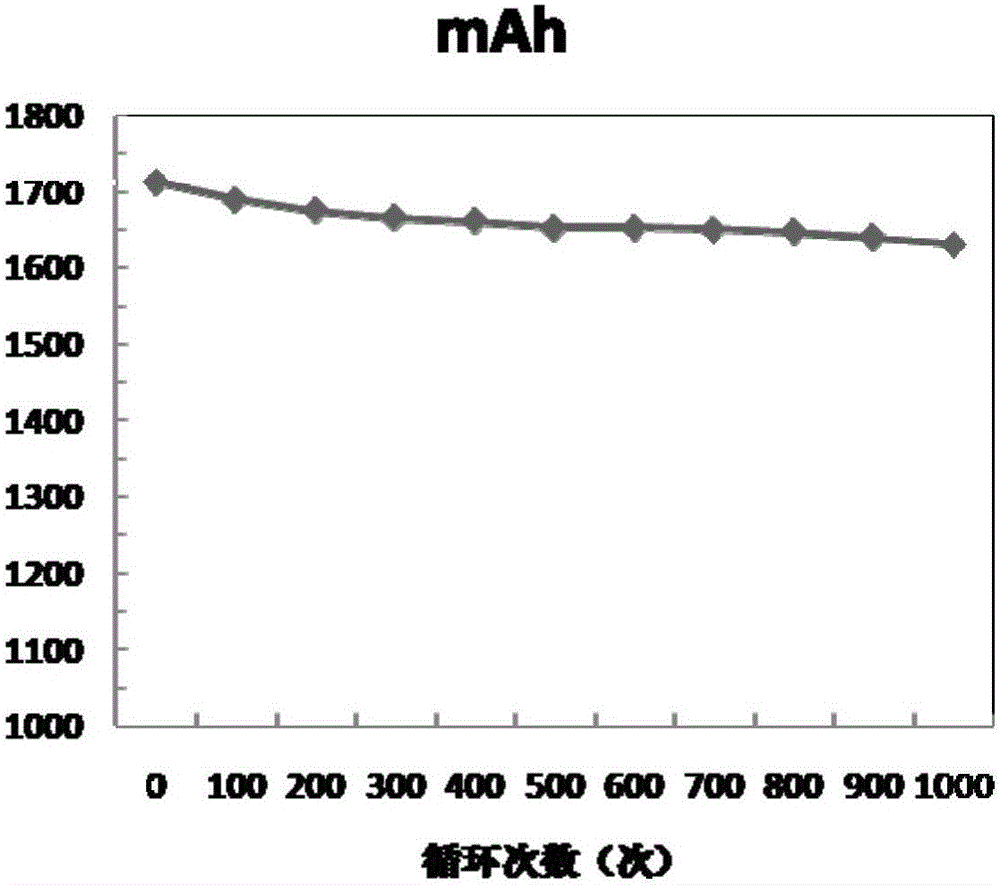
The invention discloses an anode composite material, and a preparation method thereof. The anode composite material is prepared via combination of a C-Cu composite current collector, and metal M (M=Li, Na, Mg, or Al), and possesses a C-Cu-CuM-M laminated structure. According to the preparation method, nanocarbon-copper is taken as the current collector, and metal lithium (or sodium, magnesium, and aluminium) is deposited onto the surface of the current collector, so as to prepare a combined electrode with high heat conduction performance, electric conduction performance, and mechanical strength; and in addition, utilization of the excellent liquid absorbing capacity of nanocarbon is adopted to reduce concentration polarization, improve ion conductive ability of the combined electrode, avoide generation of metallic dendrite effectively, and improve the safety and reliability of corresponding secondary batteries effectively.
Owner:赛福纳米科技(徐州)有限公司
Preparation technology for bacterial-resistant stainless steel
InactiveCN106216212AAchieve preparationImprove antibacterial propertiesPretreated surfacesCoatingsColloidSteam room
The invention discloses a preparation technology for bacterial-resistant stainless steel. The preparation technology comprises steps of (1) conducting alkali-cleaning, chemical oxidization, aluminum deposition and acid-cleaning for stainless steel orderly to achieve a primary work piece, and (2) spraying silver glue body on the surface of the primary work piece and then sintering the primary work piece for 30 to 35 mins at the temperature of 300 to 500 DEG C. The chemical oxidization process is that the stainless steel work piece is placed in a steaming chamber; the steam chamber is filled with water steam; the chemical oxidization time is one to two hours; then the stainless steel work piece is taken out of the steam chamber and then immersed into thick sulfuric acid solution for 5 mins; the aluminum deposition process is that the aluminum glue body is sprayed on the surface of the stainless steel work piece and sintered at the temperature of 200 DEG C; and during the spraying, the primary work piece is at a vibrating state with vibration frequency of 100 to 150 times / min. By the use of the preparation technology, bacterial-resistant stainless steel can be prepared.
Owner:王虹
Antistatic composition for electrochemical aluminum coloring layer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110591488AEliminate static electricitySimple preparation processPolyamide coatingsElectrically-conductive paintsHot stampingAcrylic resin
The invention provides an antistatic composition for an electrochemical aluminum coloring layer and a preparation method thereof. A BOPET film layer, which is used as the carrier of various coatings of electrochemical aluminum, is an insulator. Continuous friction in the production process makes it easy to accumulate and enrich static electricity, which causes certain harm to subsequent processing. The antistatic composition is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-50 parts of acrylic resin, 1-10 parts of cellulose acetate butyrate, 5-10 parts of aluminum powder, 0.1-1 part of aluminate coupling agent, 0.1-1 part of polyamide wax slurry, 10-40 parts of butanone, 10-40 parts of ethyl acetate, 1-10 parts of n-propyl acetate. The antistatic composition has the advantages of simple and easy control preparation process, stable performance, no aluminum deposition phenomenon, convenient and quick use, excellent compatibility with most polymer resins, obvious antistatic effect, no influence on glossiness and hot stamping performance of electrochemical aluminum, and greatly improving appearance quality and yield of electrochemical aluminum.
Owner:云南玉溪东魅包装材料有限公司
Alignment marking method in DMOS (Double-diffusion Metal Oxide Semiconductor) process flow
ActiveCN102543733AGuaranteed alignmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOrganic filmDouble diffusion
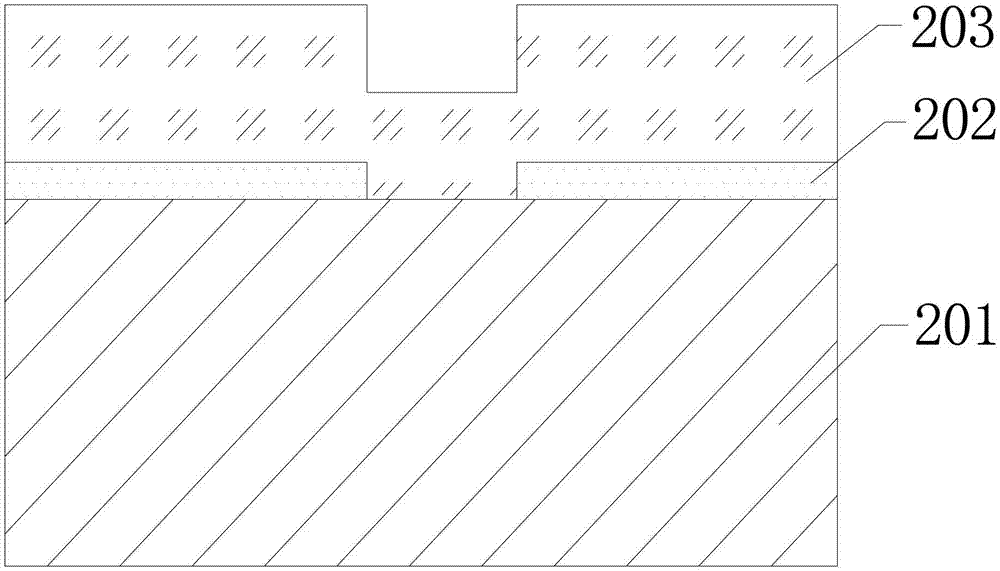
The invention discloses an alignment marking method which comprises the steps of: providing a wafer substrate provided with an inorganic film structure, carrying out groove etching on the inorganic film structure to form a groove and first alignment marks; carrying out polysilicon filling by depending on the first alignment marks, covering the organic film structure and filling partial groove by polysilicon, then removing partial polysilicon in the groove through photoetching and forming second alignment marks; carrying out hole medium filling by depending on the second alignment marks, filling a hole medium layer in the second alignment marks and covering the upper surface of the polysilicon, then removing partial hole medium between the second alignment marks through etching to form third alignment marks; carrying out tungsten deposition by depending on the third alignment marks, covering the upper surface of the hole medium layer and filling partial third alignment marks by tungsten to form fourth alignment marks, then removing tungsten on the surface of the hole medium layer by adopting a chemical mechanical polishing manner; and carrying out aluminum deposition by depending on the fourth alignment marks, and filling the fourth alignment marks and covering the upper surface of the hole medium layer by aluminum.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Transfer paper by heat able to dissolve a metal layer partially and the preparation method thereof
Disclosed is a thermal transfer paper comprising a metal layer and capable of partially dissolving the metal layer, which comprises a dissolving function formed of at least one resin selected from the group consisting emulsion resins, water-soluble acryl resins, water-soluble polybutyral resins, alcohol-soluble polybutyral resins, water-soluble vinyl resins and alcohol-soluble vinyl resins, water or an alcohol solvent, and sodium hydroxide or an acid on the metal layer. The thermal transfer paper according to the present invention is provided with a dissolving function layer 30 able to dissolve a part of a metal layer 20, preferably an aluminum deposition layer 21 to form a dissolved part according to a desired design or pattern. Therefore, it is possible to produce unique color and texture, unlike a metal layer pattern formed by oxidation of a part on the metal layer. Specially, when a different color is transferred on a transfer object by an ink layer formed on the transfer paper, it is harmonized with a background color of the transfer object to produce a partial metal-like effect. Thus, according to the present invention, a design with superior texture and color can be readily formed in various patterns, thereby accomplishing a speedy, simple and thereby efficient working process for production and cost saving effect.
Owner:KOREA CHEM CO LTD
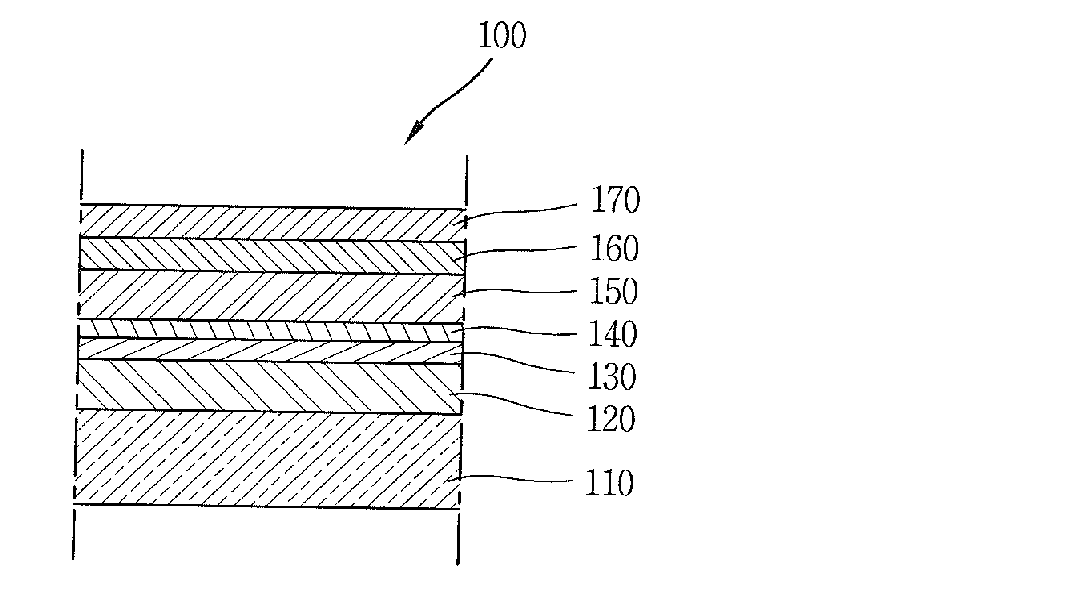
Three layer aluminum deposition process for high aspect ratio CL contacts
InactiveUS6794282B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorMetallurgy
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Porous aluminum macroscopic body and manufacturing system and method thereof
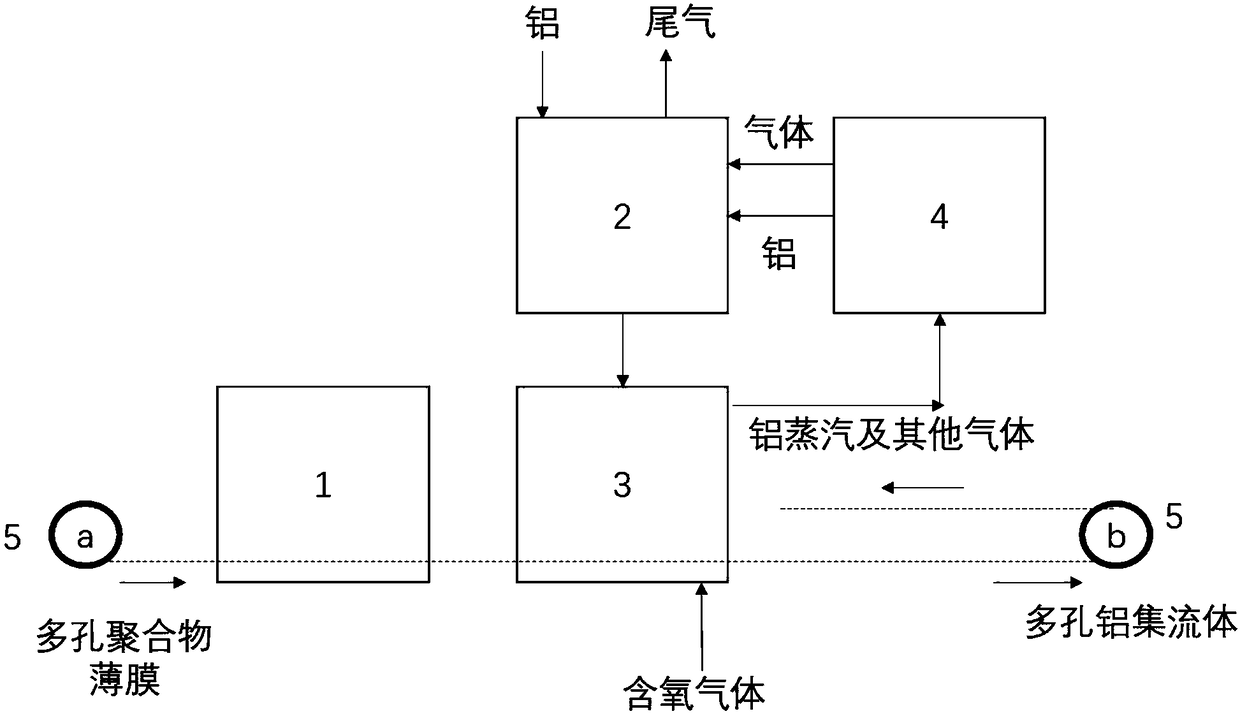
ActiveCN108520833AHigh speedLow costHybrid capacitor electrodesElectrode carriers/collectorsCompressive resistancePolymer thin films
The invention discloses a porous aluminum macroscopic body and a manufacturing system and method thereof. The porous aluminum macroscopic body is a three-dimensional all-through hole structure formedby connecting hollow aluminum wires; the hollow aluminum wires have a wall thickness of 7-100 micrometers; and the overall porosity of the porous aluminum macroscopic body is 85-99%, the tensile strength is 0.4-2MPa, and the compressive strength is 1-3.5Mpa. The manufacturing system includes a magnetron sputtering subsystem, a high temperature aluminum vapor subsystem, a low temperature aluminum deposition subsystem, an aluminum vapor recovery subsystem, and a porous polymer film conveying subsystem. The manufacturing method comprises: rapidly sputtering an aluminum layer having the thicknessof 1-500 nm on a porous polymer film by using the magnetron sputtering method; placing the aluminum layer in a low-pressure physical vapor deposition apparatus; and continuously depositing the aluminum layer, and decomposing the polymer film in situ to obtain the porous aluminum macroscopic body when the thickness of the aluminum layer is 7-100 micrometers. The porous aluminum macroscopic body hasthe advantages of flexible void ratio adjustment and high strength; and the manufacturing method is short in manufacturing time, the requirement for the porous polymer film is low, pretreatment can be avoided, continuous operation can be achieved, and the cost is low.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN SUPERCAPACITOR TECH CO LTD +2
Diamond particle detector electrode structure and preparation method thereof
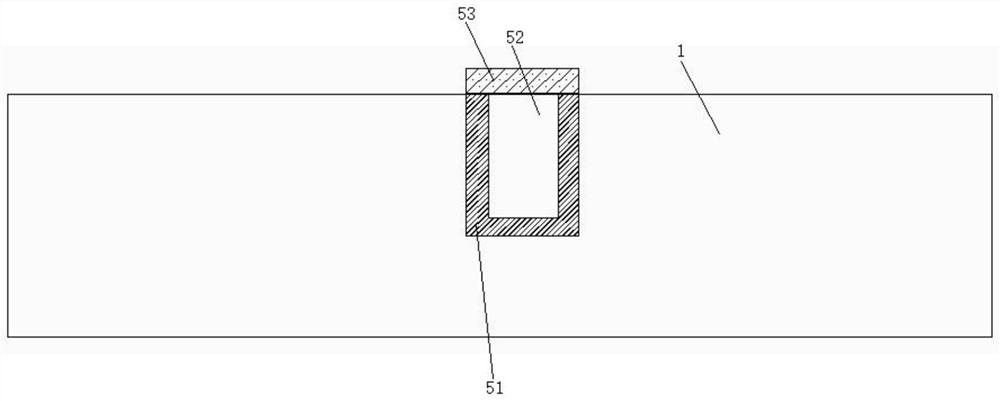
PendingCN114335238AImprove responsivenessHigh sensitivitySemiconductor devicesSingle crystalInterdigitated electrode
The invention relates to a method for preparing an electrode structure of a diamond particle detector, which comprises the following steps of: S1, manufacturing a periodic groove structure on a monocrystal diamond, and enabling all grooves to be correspondingly parallel; s2, the prepared single crystal diamond is cleaned; s3, depositing aluminum on the four sides and the bottom of the inner wall of the groove, depositing gold in the groove which is not filled with the aluminum, and finally covering the upper surfaces of the aluminum and the gold with chromium to obtain a planar electrode; and S4, an interdigitated electrode, a positive metal electrode and a negative metal electrode are deposited on the monocrystal diamond, and the planar electrode is connected with the positive metal electrode and the negative metal electrode through the interdigitated electrode. According to the invention, the planar electrode is introduced into the single crystal diamond wafer, so that efficient and rapid collection of ionized electron-hole pairs in the diamond is realized, and the responsivity and sensitivity of the detector are improved; two layers of metal, namely aluminum and gold, are adopted as electrodes, a good ohmic contact effect is achieved, the upper chromium can prevent the metal electrodes from being oxidized, and the service life of the device is prolonged.
Owner:CHANGSHA ADVANCED MATERIALS IND RES INST CO LTD
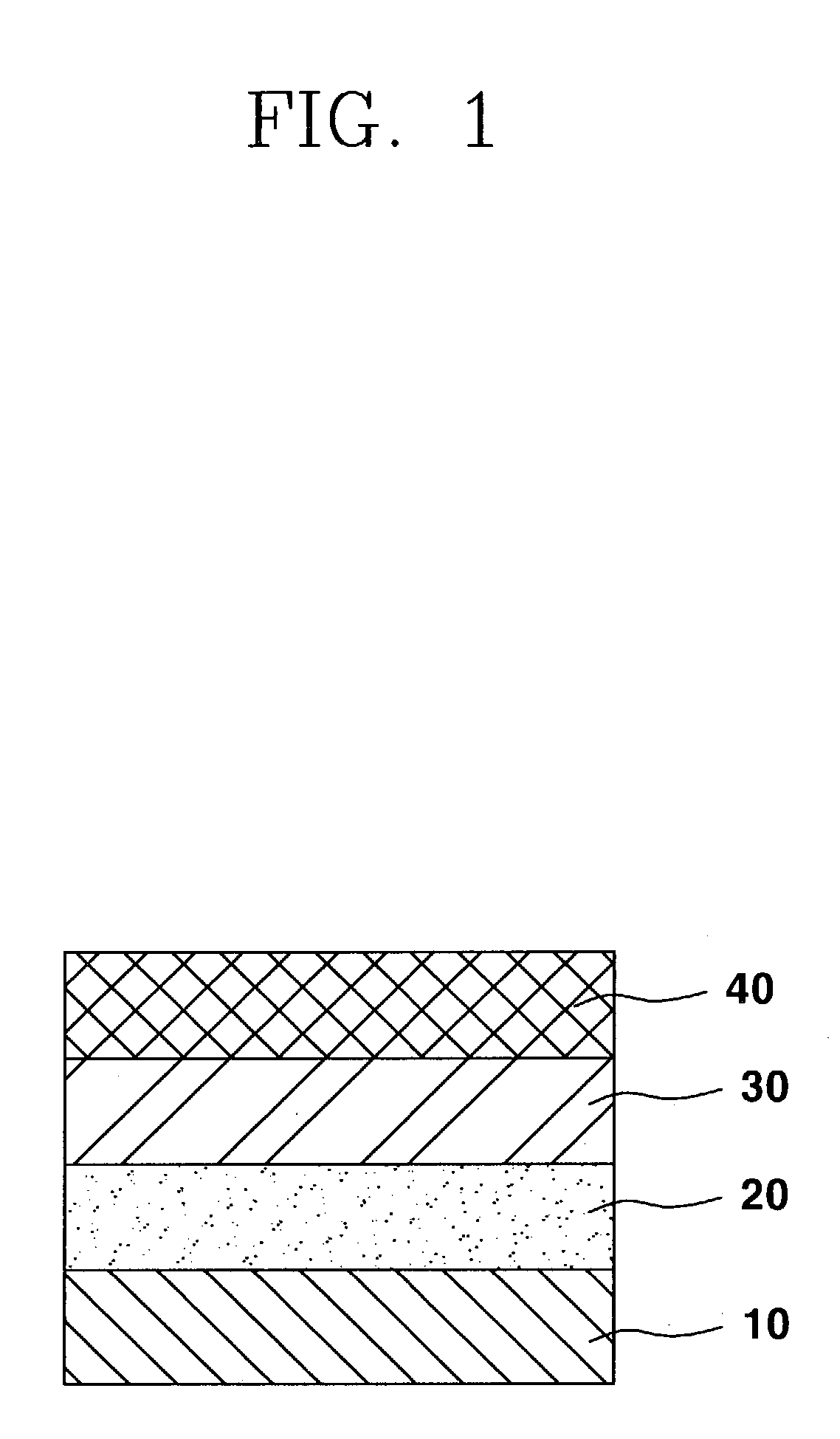
Method for preparing aluminum oxide from aluminiferous material
InactiveCN101734698BAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium hydroxide preparationAluminum ammonium sulfateKaolin clay
The invention provides a method for preparing aluminum oxide and other products from aluminiferous materials such as bauxite, high iron bauxite, alunite, kaoline, alumina, fly ash, coal gangue, aluminum ash, nepheline, clay and the like. The method comprises the following steps: (1) crushing, grinding and mixing the aluminiferous materials with ammonium sulfate and then roasting; (2) dissolving the roasted product (clinker aggregate) in water, and filtering to obtain aluminum ammonium sulfate solution and filter residues; (3) carrying out deferrization, aluminum deposition or recrystallization on the aluminium ammonum sulfate solution with ammonia to prepare aluminum oxide, and meanwhile, recycling the ammonium sulfate; (4) preparing silicon dioxide from the filter residues, and taking the remaining residues containing ferrum as the raw material for ironmaking. The method is suitable for treating various aluminiferous materials, has the advantages of simple technical process, simple equipment, no emission of solid, liquid and gas wastes, and no secondary pollution, and realizes the high-added-value green complex utilization of the aluminiferous materials such as bauxite, high ironbauxite, alunite, kaoline, alumina, fly ash, coal gangue, aluminum ash, nepheline, clay and the like.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
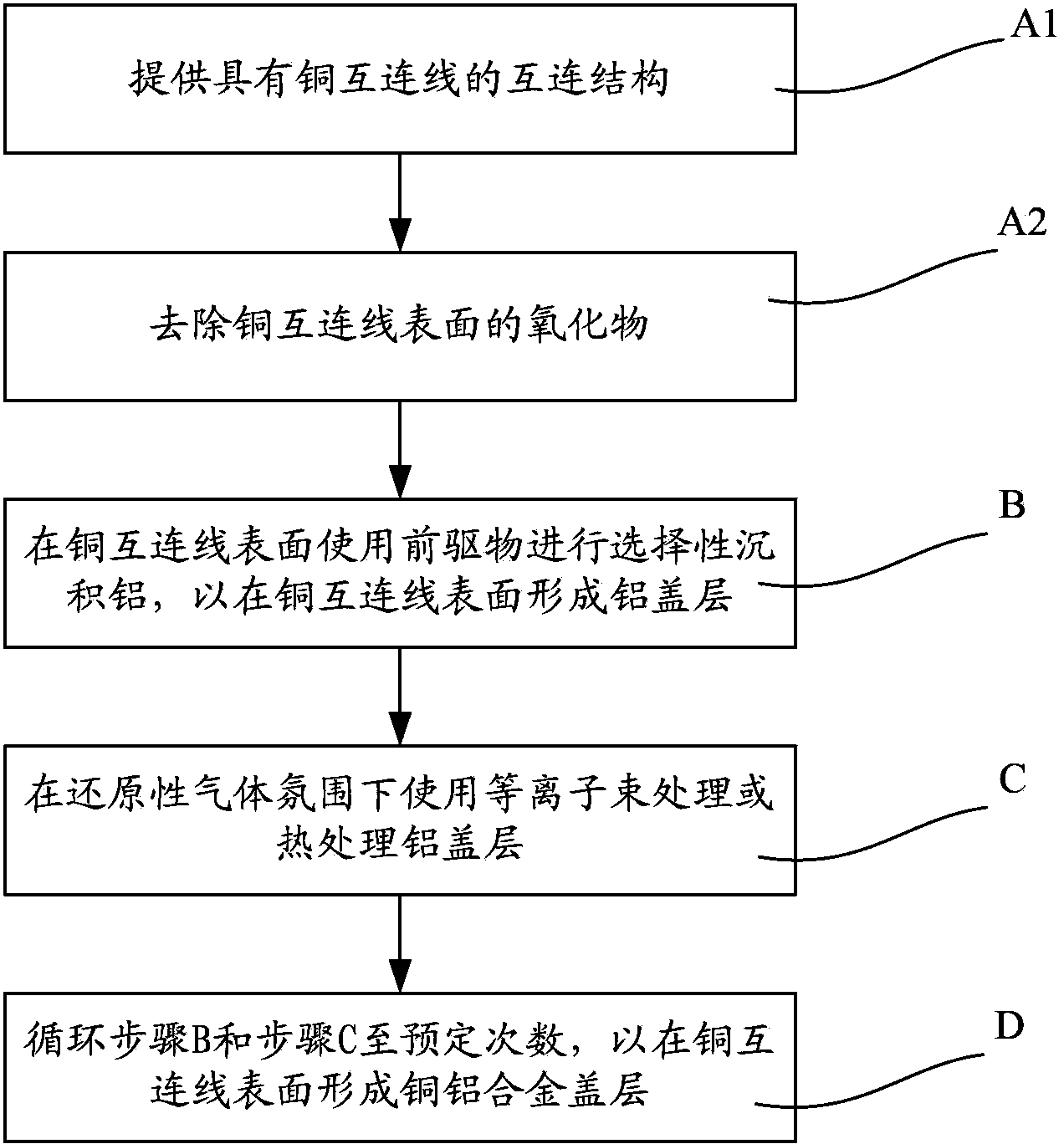
Method for processing copper surface of interconnected wire
InactiveCN103779269APrevent proliferationAvoid failureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopper interconnectAlloy
The invention discloses a method for processing the copper surface of an interconnected wire. A step of forming an aluminum cover layer on the surface of a copper interconnected wire by using selective aluminum deposition and a step of processing the aluminum cover layer by using a plasma beam in reductive gas atmosphere are executed cyclically. Aluminum atoms are gradually dissolved into the surface of the copper interconnected wire in order to form a copper aluminum alloy cover layer on the surface of the copper interconnected wire. The mobility of the copper aluminum alloy cover layer is less than that of the aluminum cover layer, so a problem of semiconductor device failure caused by electro mobility of the interconnected wire is suppressed while copper atoms are prevented from diffusing.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Method for producing polyvinyl alcohol laminated paper, polyvinyl alcohol laminated paper and cosmetic box
Provided is a method for producing a polyvinyl alcohol laminated paper, which is free of wrinkles and concave curls, whereby an aluminum vapor-deposited layer obtained by vacuum deposition of aluminum is disposed on the surface of a polyvinyl alcohol film, a water-based adhesive having a concentration of 40 to 60%, a viscosity of 500 to 4,000 mPa.s and a coverage of 3 to 5 g / m2 is applied to the reverse surface of the polyvinyl alcohol film, said polyvinyl alcohol film is laminated to a base paper, and a printed layer is formed by printing on the polyvinyl alcohol laminated paper. Alternatively, the water-based adhesive having a concentration of 40 to 60%, a viscosity of 500 to 4,000 mPa.s and a coverage of 3 to 5 g / m2 is applied to the reverse surface of the polyvinyl alcohol film, said polyvinyl alcohol film is laminated to a base paper, an aluminum deposition layer of a transfer foil obtained by vacuum deposition of aluminum is transferred to the polyvinyl alcohol film, and a printed layer is formed by printing on the polyvinyl alcohol laminated paper.
Owner:GOJO PAPER MFG CO LTD
Molten alkali metal-aluminum secondary battery
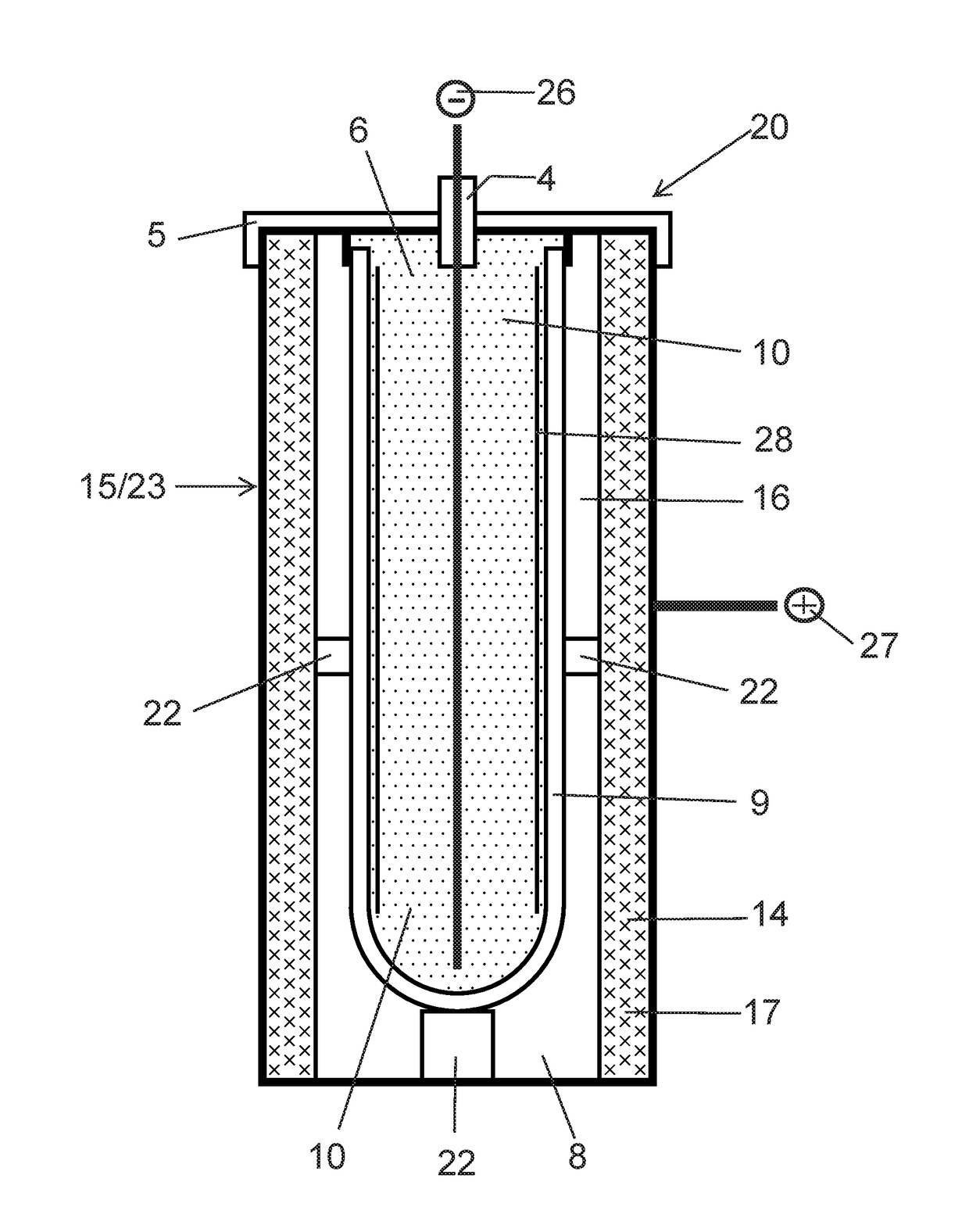
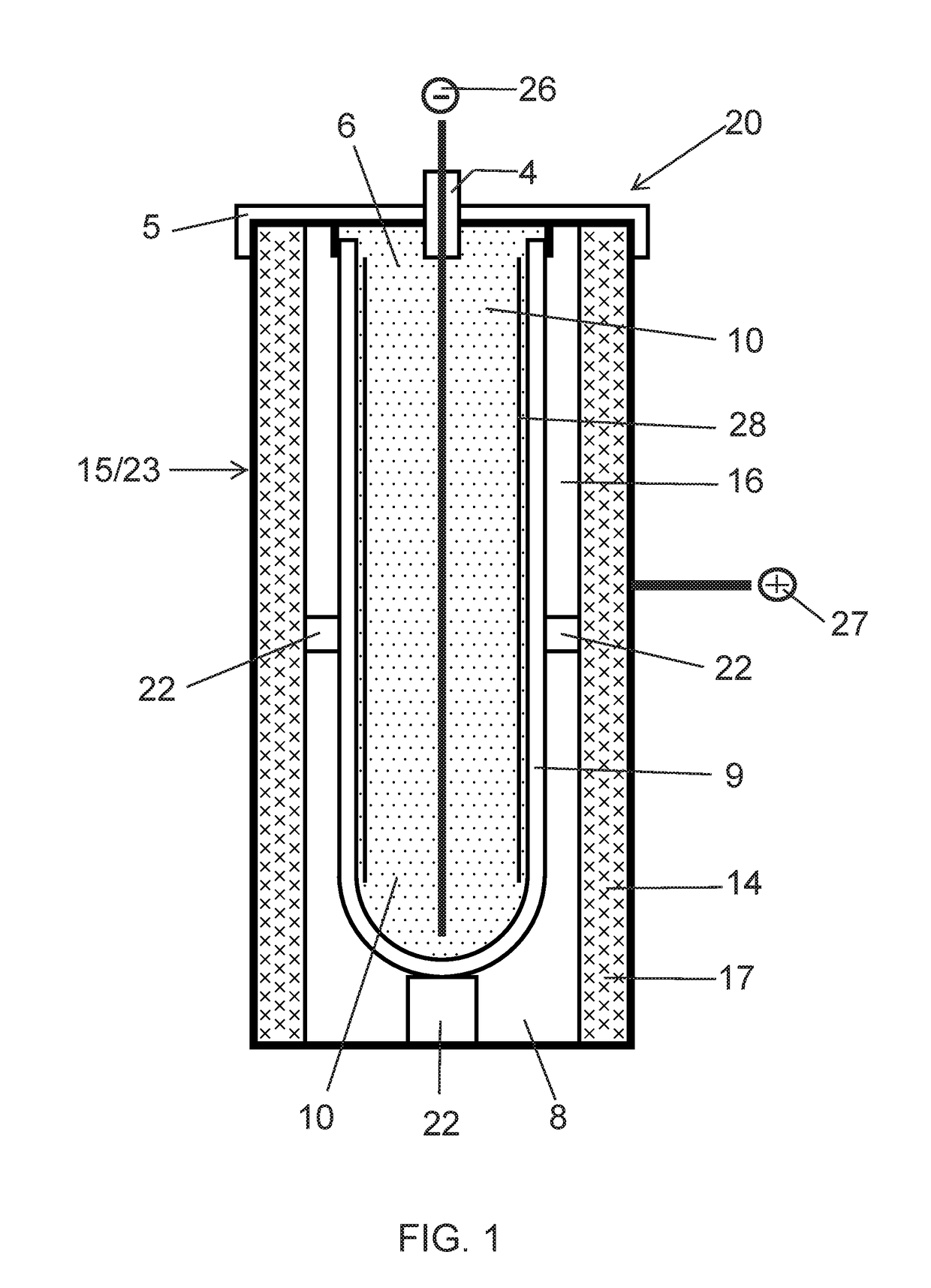
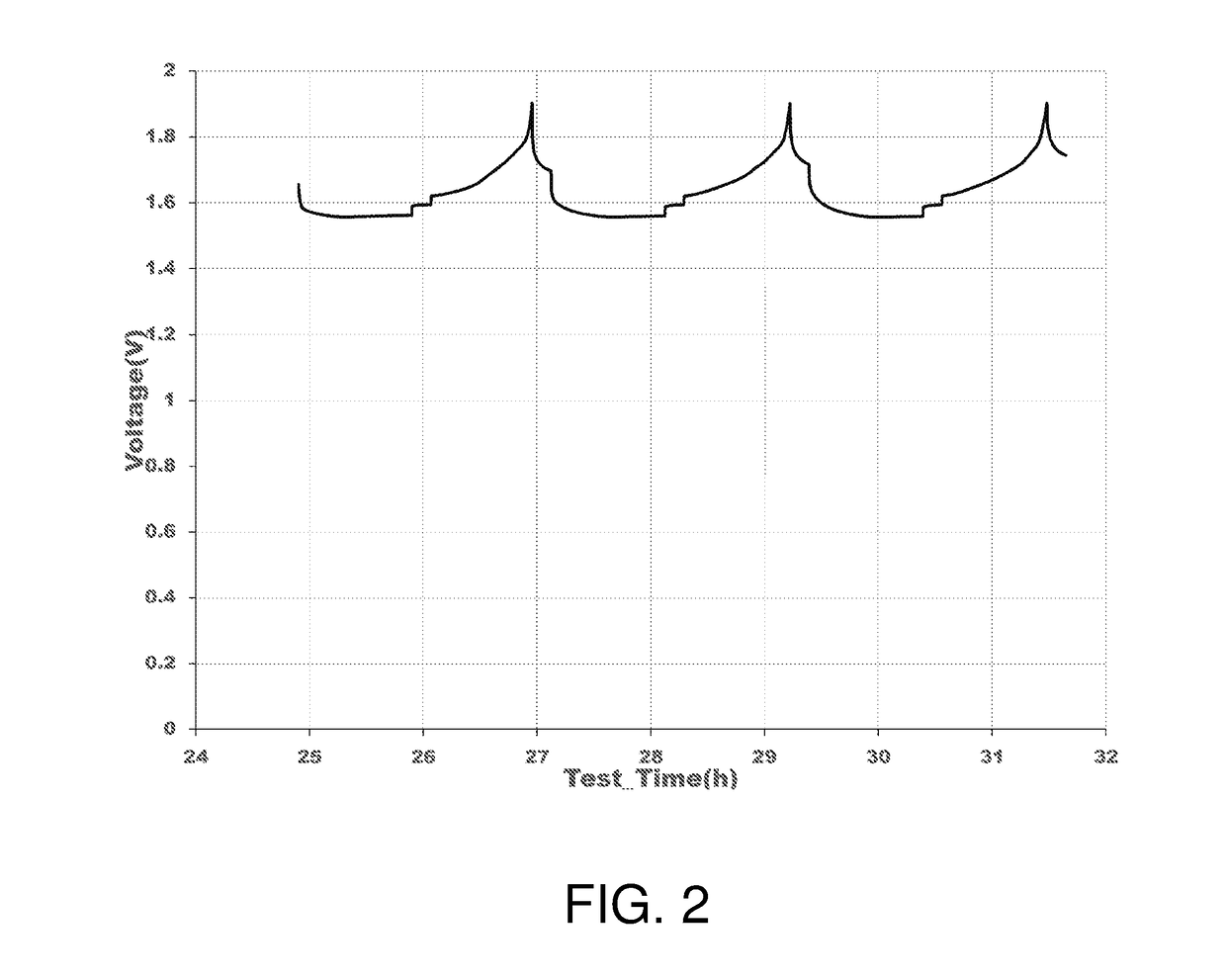
ActiveUS20170294685A1Electrode carriers/collectorsSecondary cells charging/dischargingPorous substrateAluminum metal
An aluminum-based cathode (positive electrode) for storage cells formed by deposition of a layer of aluminum metal on a porous conductive substrate. Storage cells and batteries having the cathode. The porous conducting substrate can be metal, conductive carbon or a refractory material, such as a metal boride or metal carbide. The aluminum-deposited porous substrate is in electrical contact with a cathode current collector and a suitable liquid catholyte. The cathode is, for example, combined with a molten alkali metal anode to form a storage cell. The alkali metal and the catholyte are molten or liquid at operating temperatures of the cell. Methods of storing energy and generating energy using cell having the aluminum-based cathode are provided.
Owner:DYNANTIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com