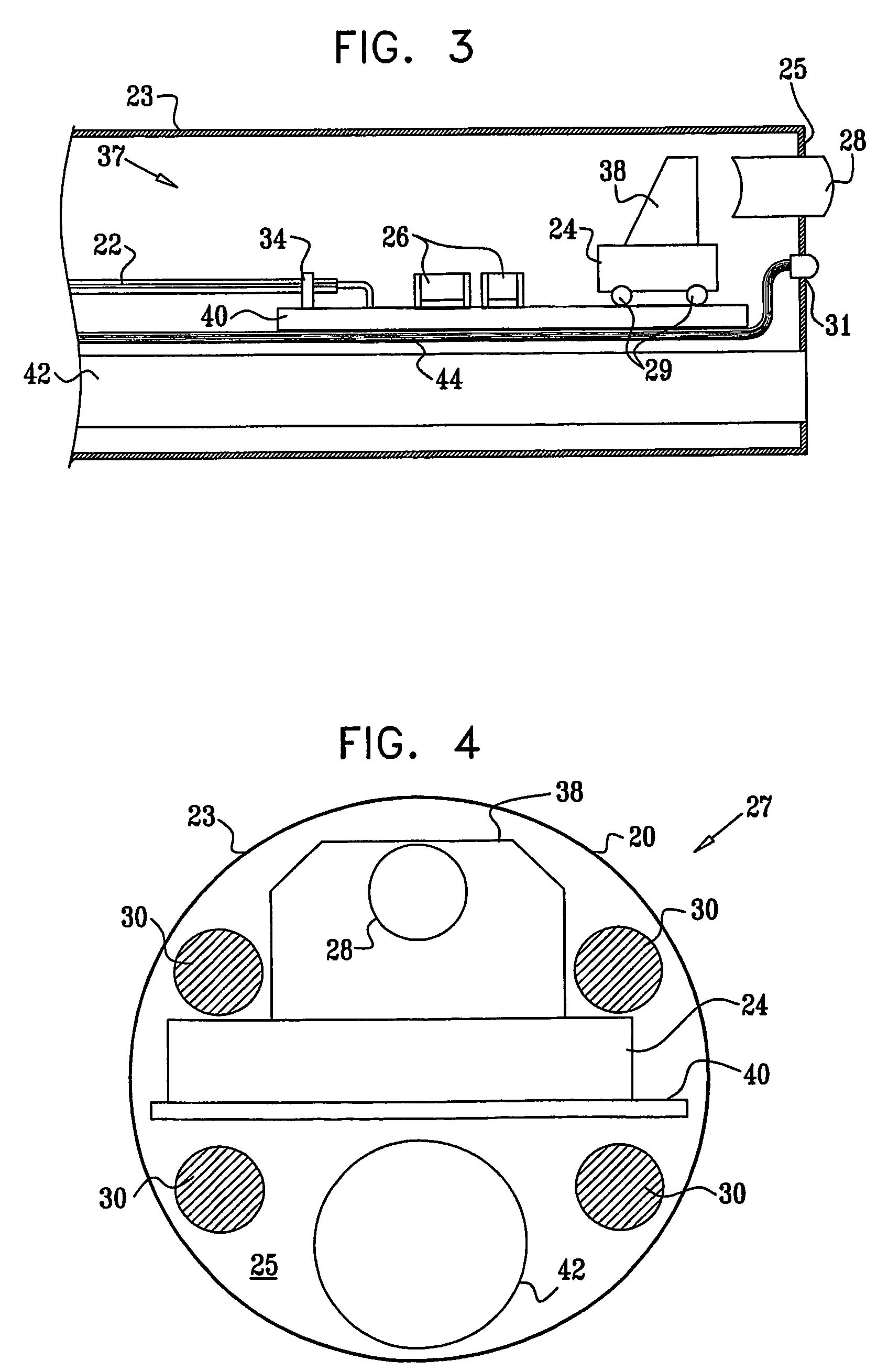
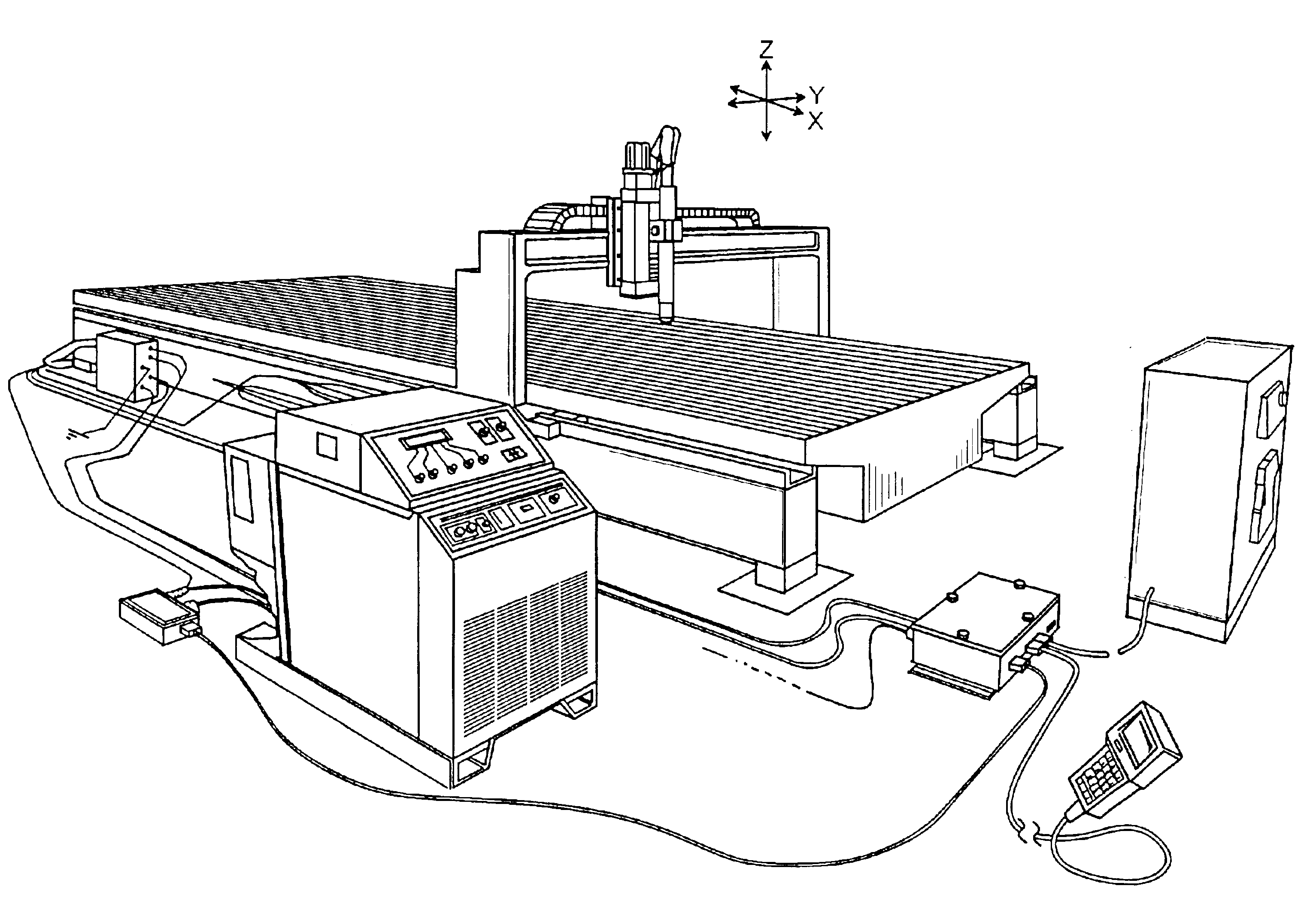
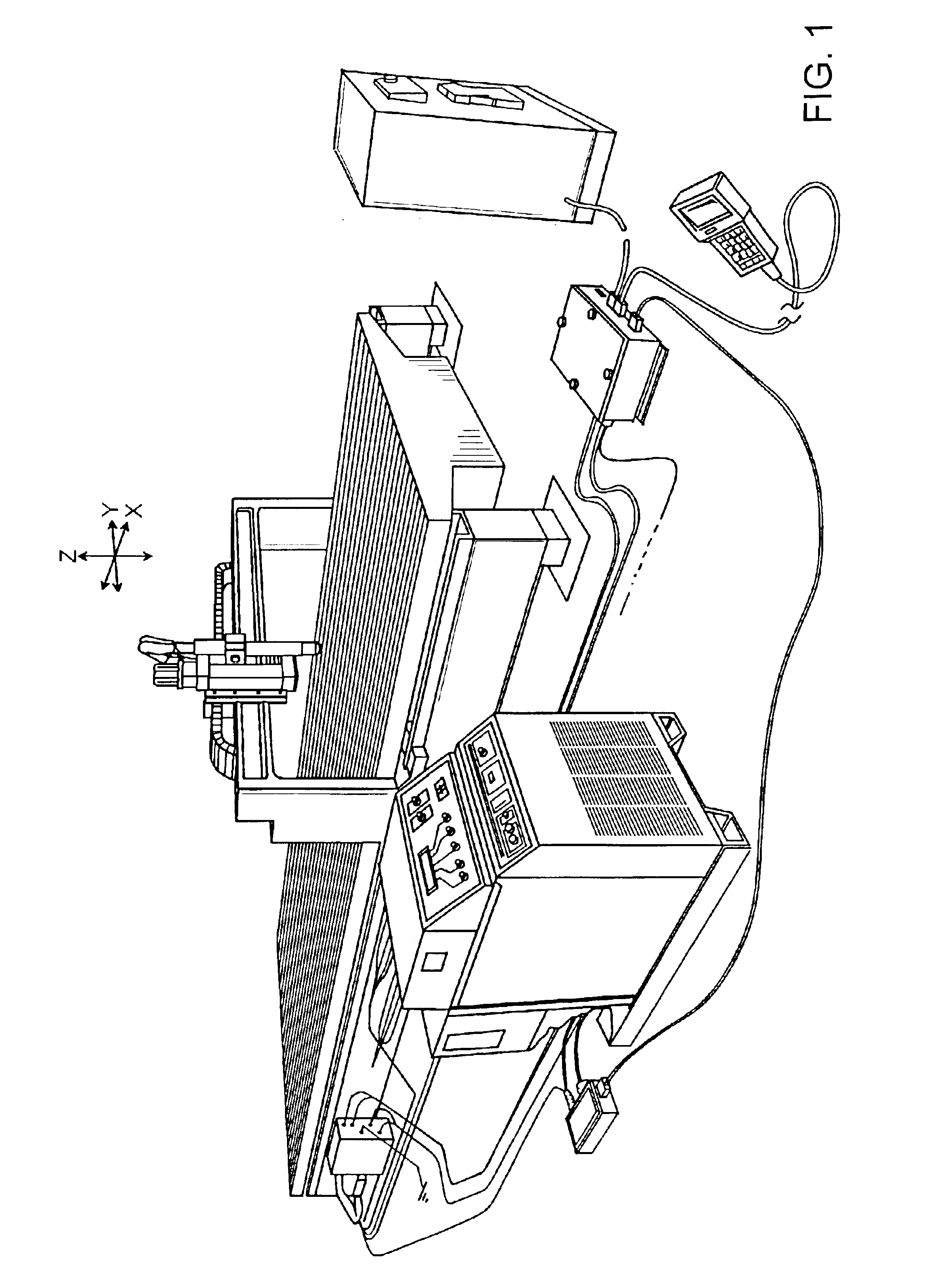
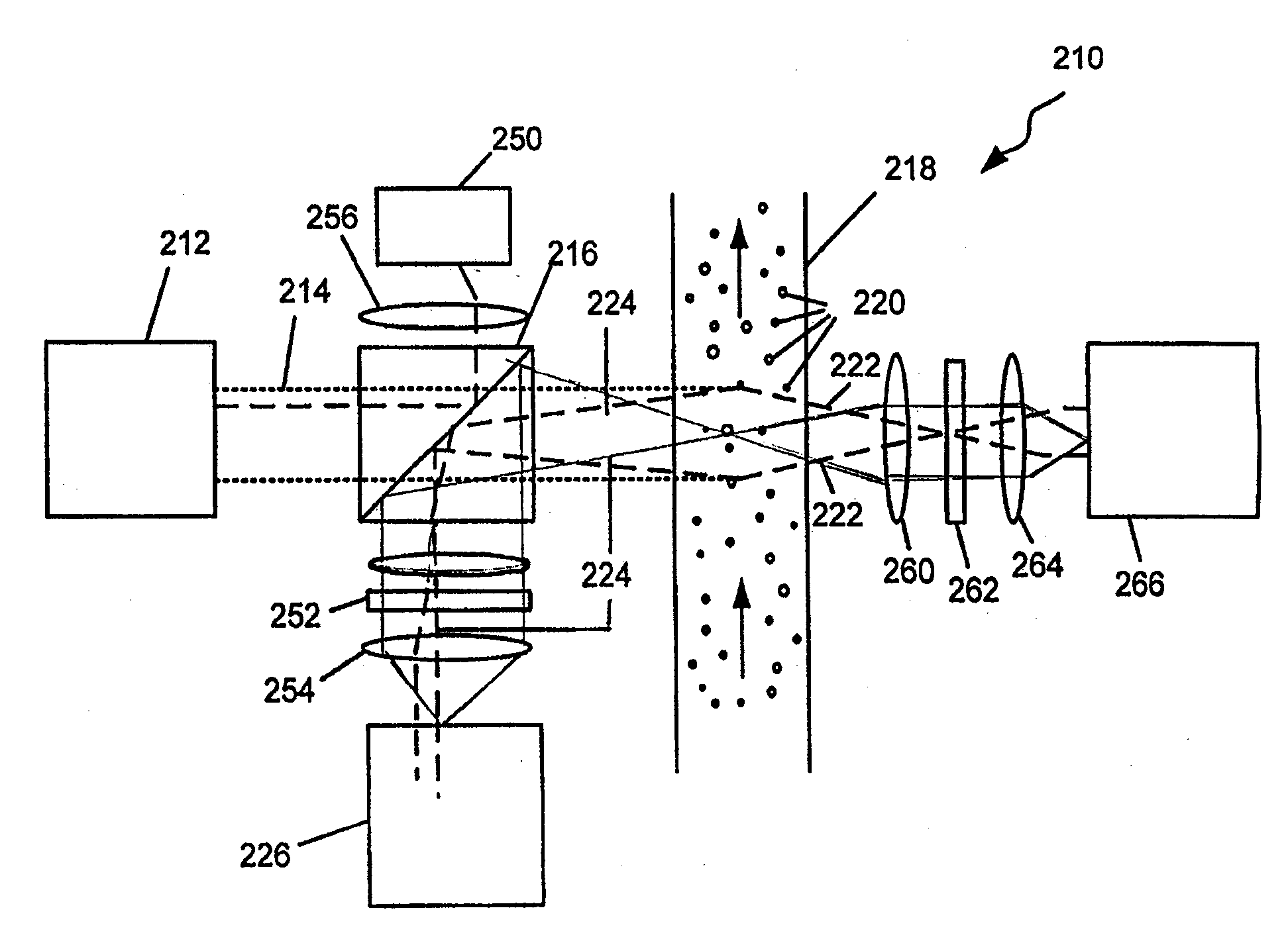
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
798 results about "Particle detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
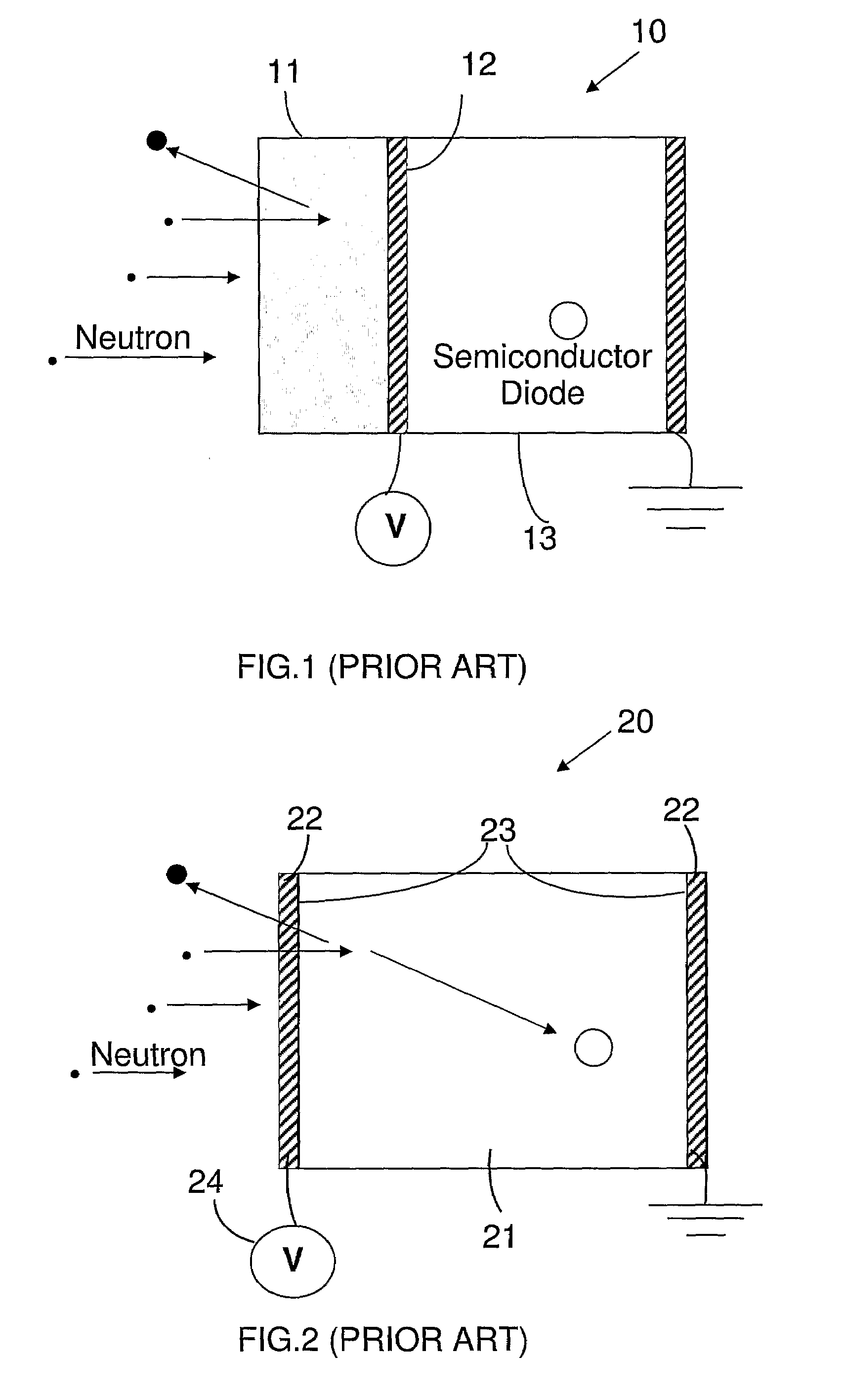
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle.
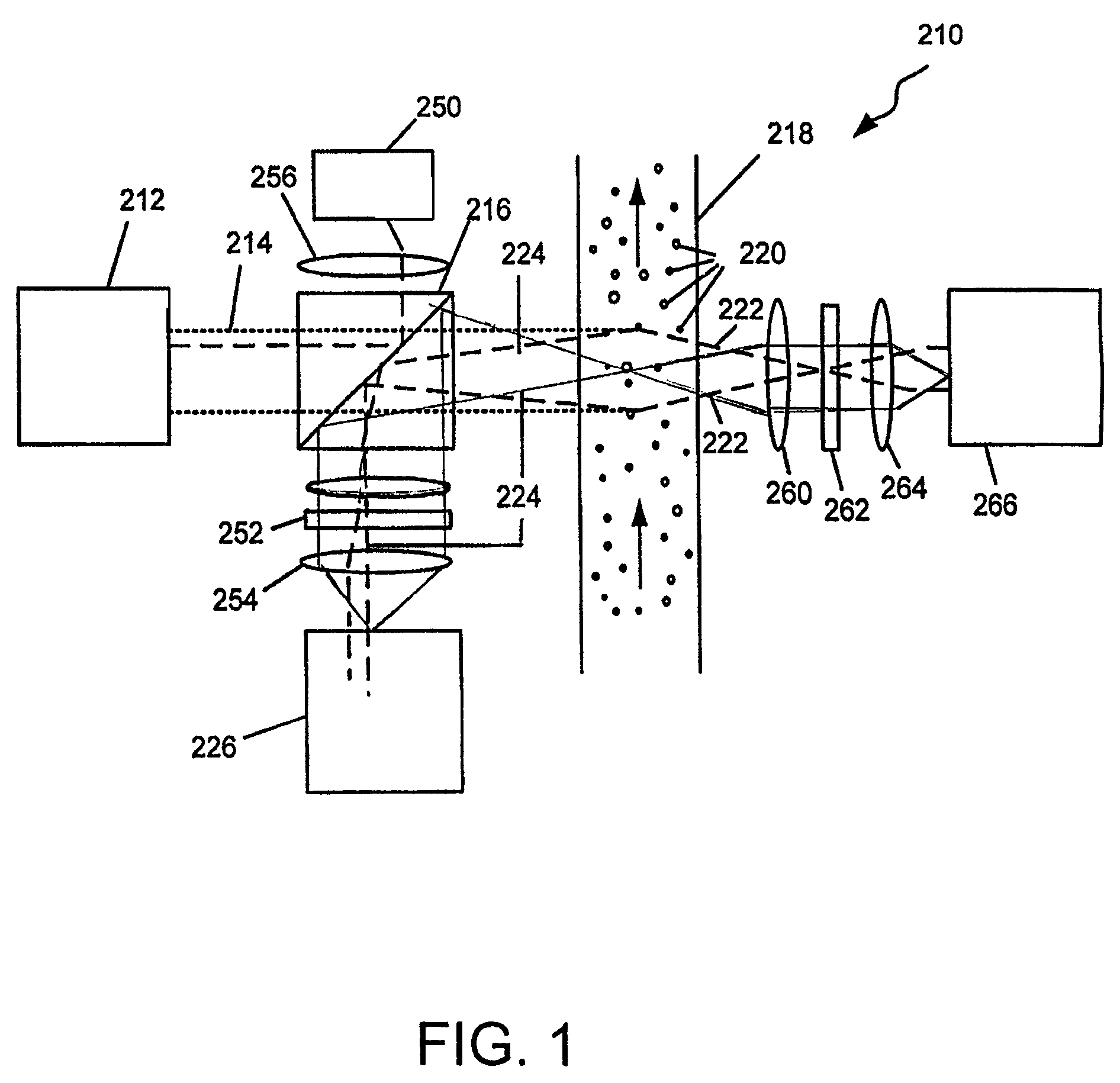
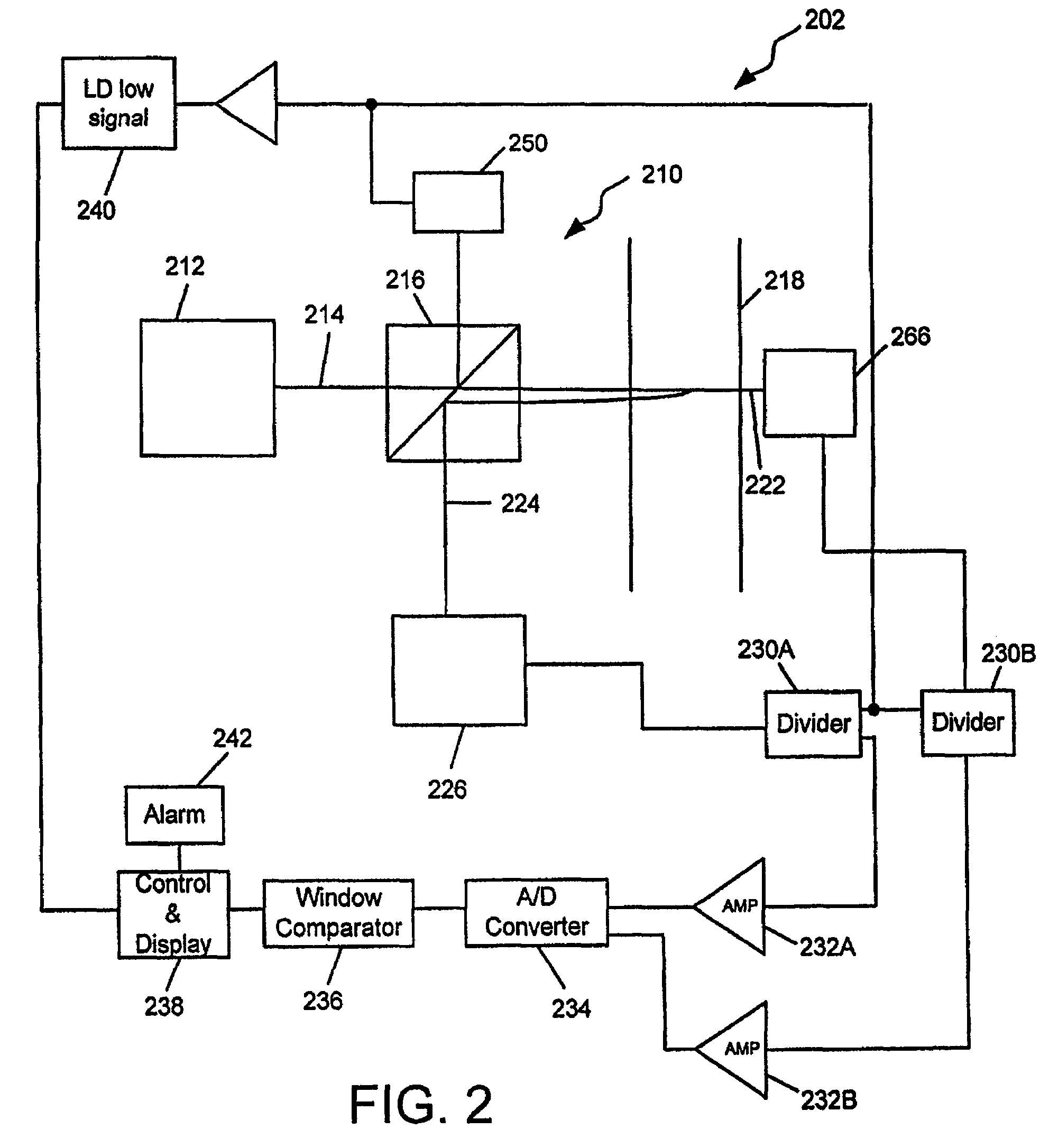
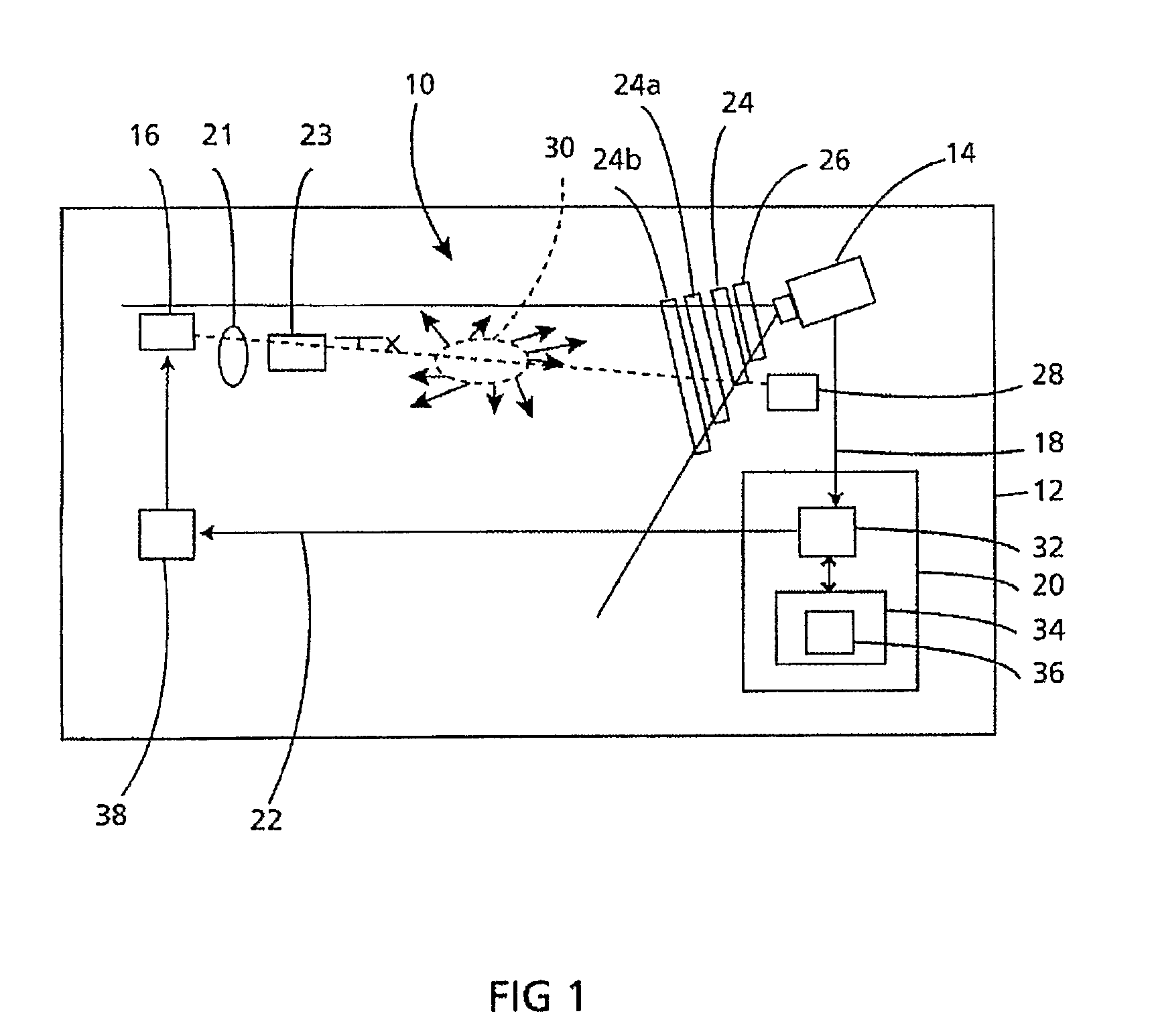
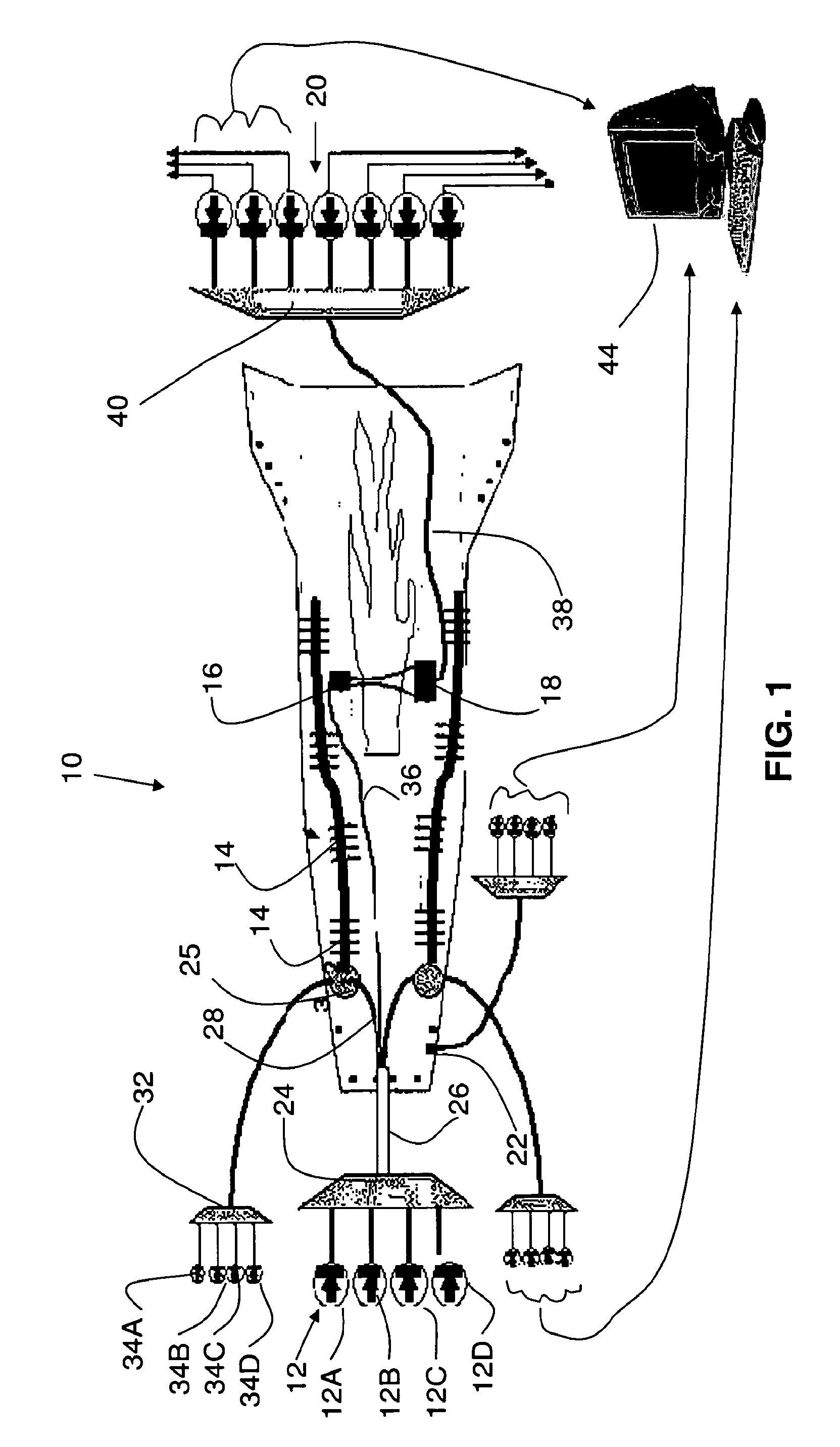
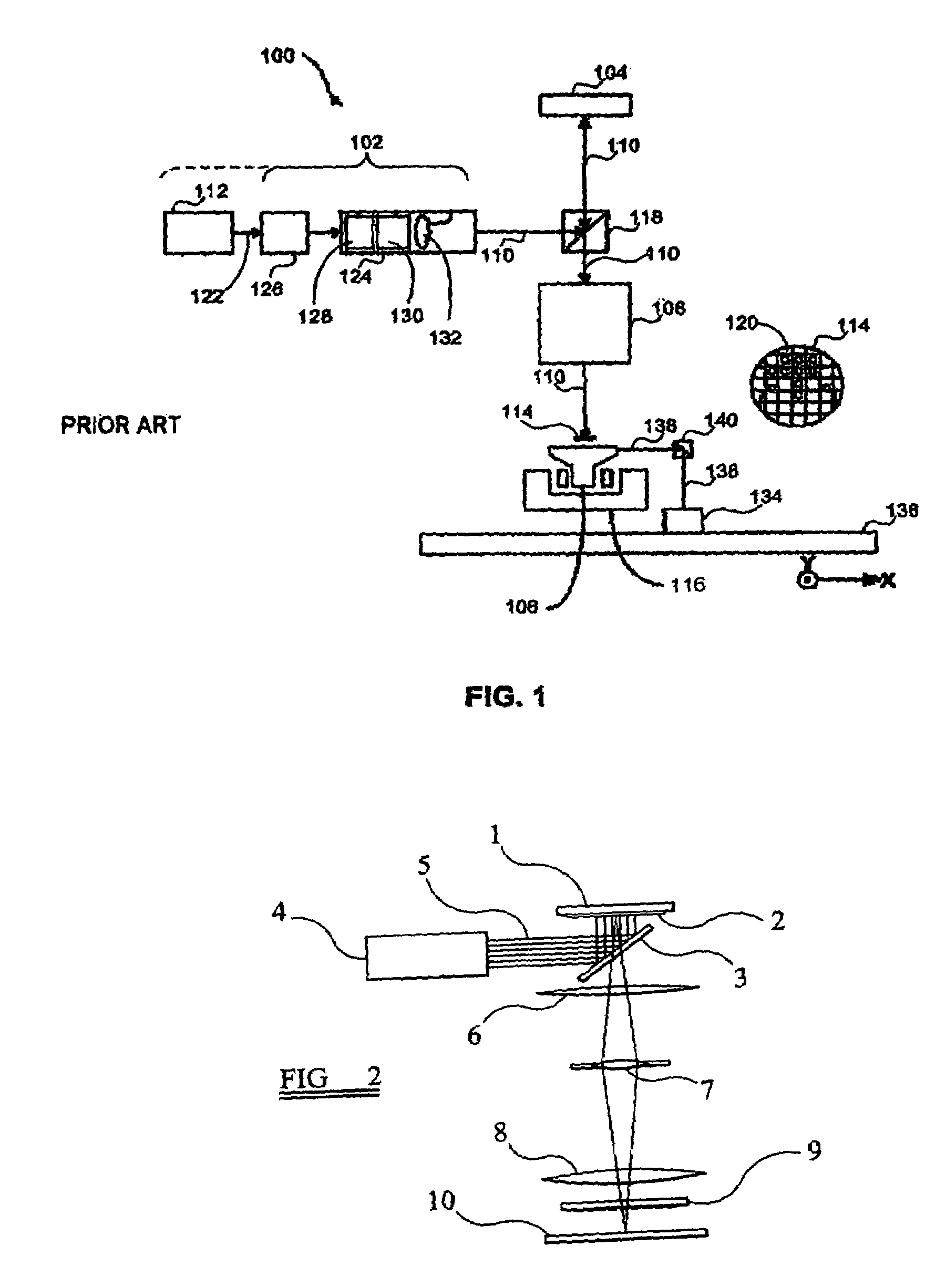
Particle Detector, System and Method
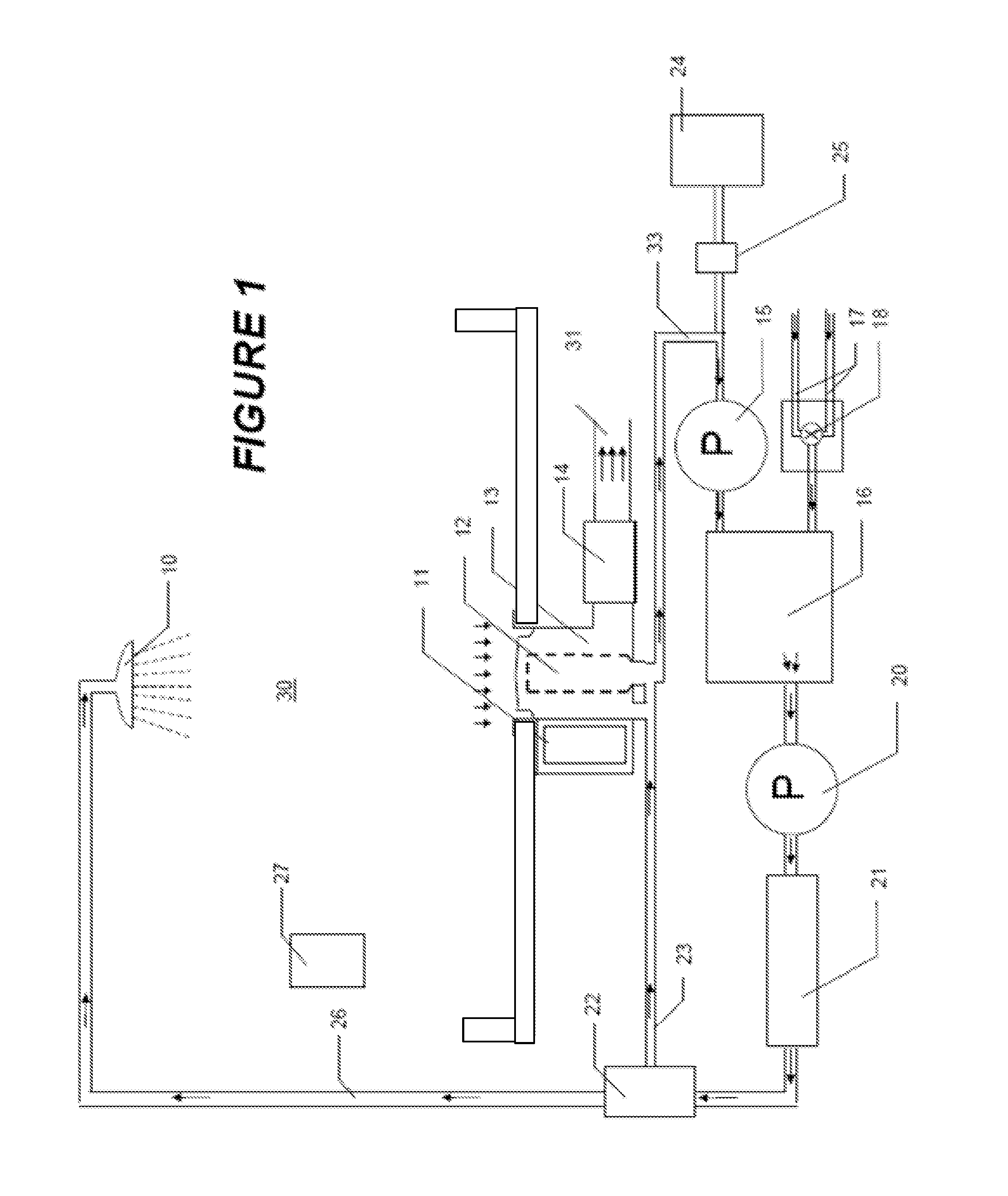
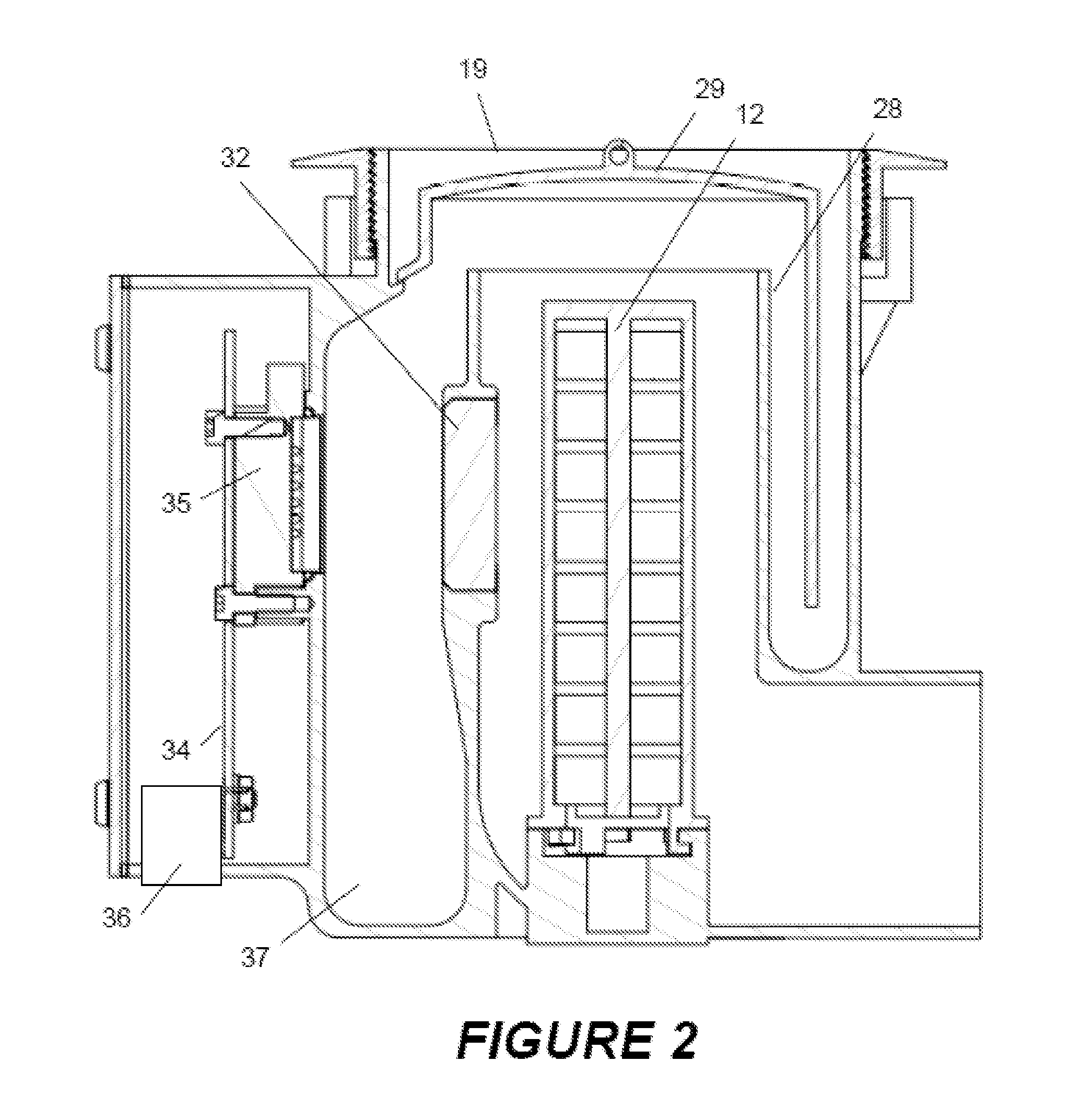
ActiveUS20080297360A1Easy to detectMethod using image detector and image signal processingScattering properties measurementsLaser beamsParticle detector
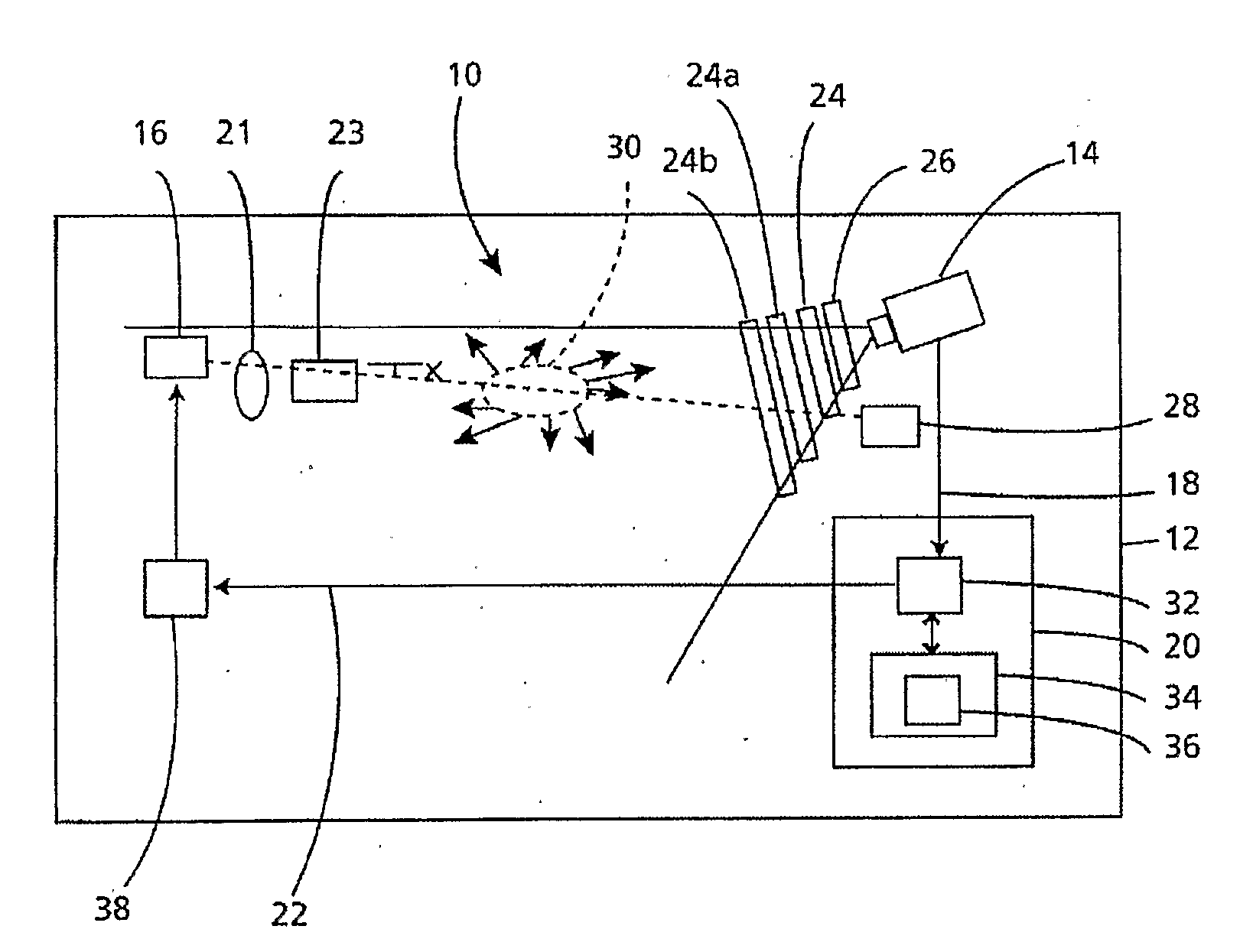
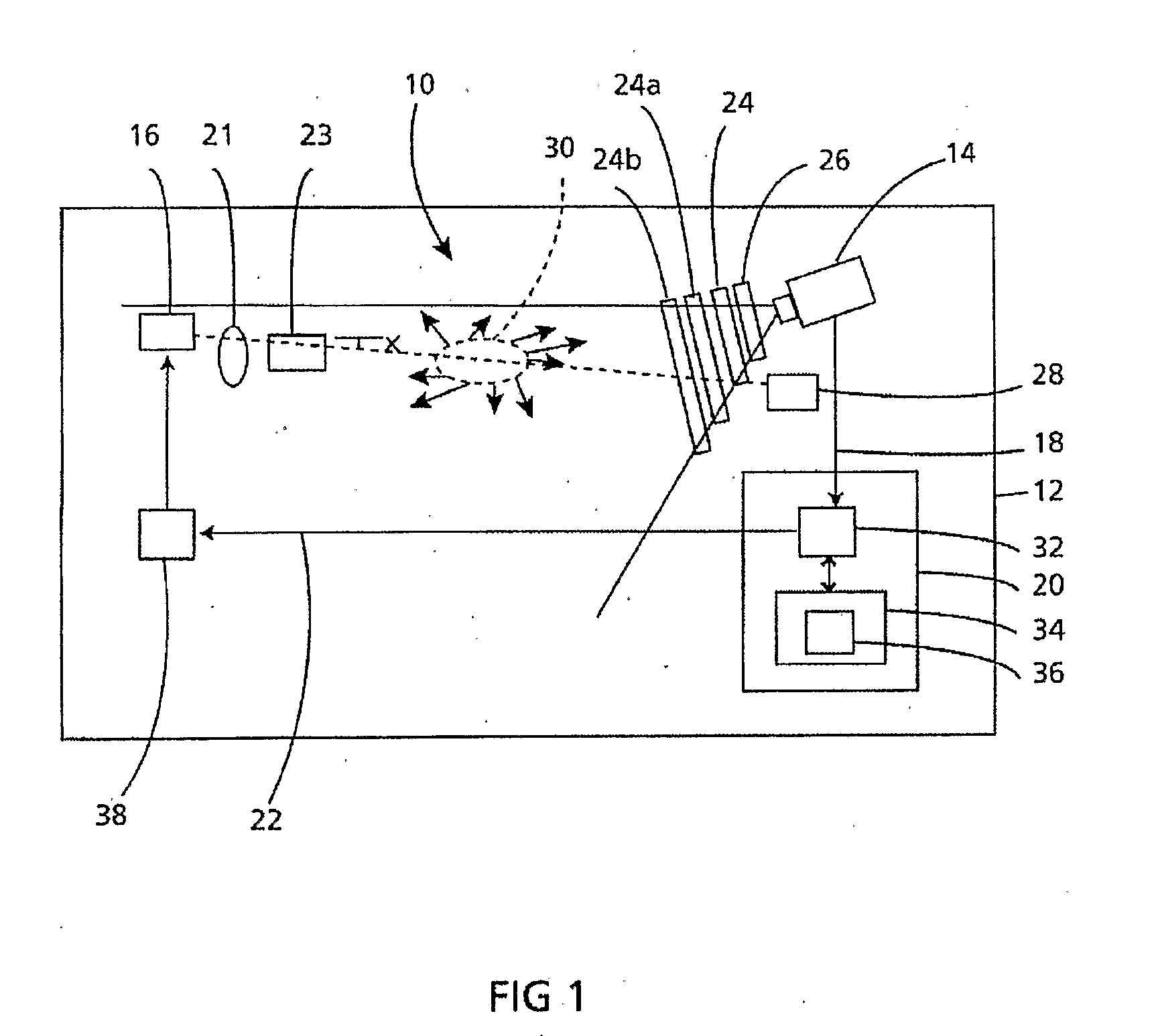
The invention provides use of one or more emitted beams of radiation (16), for example, laser beam(s), in combination with an image capturing means (14), for example, one or more video cameras and / or optical elements to detect particles (30), for example smoke particles, located in an open space (12).
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
Optical detector for a particle sorting system
ActiveUS7298478B2Accurate and Efficient MonitoringCost effectivelyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationData acquisitionMicrofluidic channel
An optical system for acquiring fast spectra from spatially channel arrays includes a light source for producing a light beam that passes through the microfluidic chip or the channel to be monitored, one or more lenses or optical fibers for capturing the light from the light source after interaction with the particles or chemicals in the microfluidic channels, and one or more detectors. The detectors, which may include light amplifying elements, detect each light signal and transducer the light signal into an electronic signal. The electronic signals, each representing the intensity of an optical signal, pass from each detector to an electronic data acquisition system for analysis. The light amplifying element or elements may comprise an array of phototubes, a multianode phototube, or a multichannel plate based image intensifier coupled to an array of photodiode detectors.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
Minimizing electrical outlet safety failures due to over temperature condition
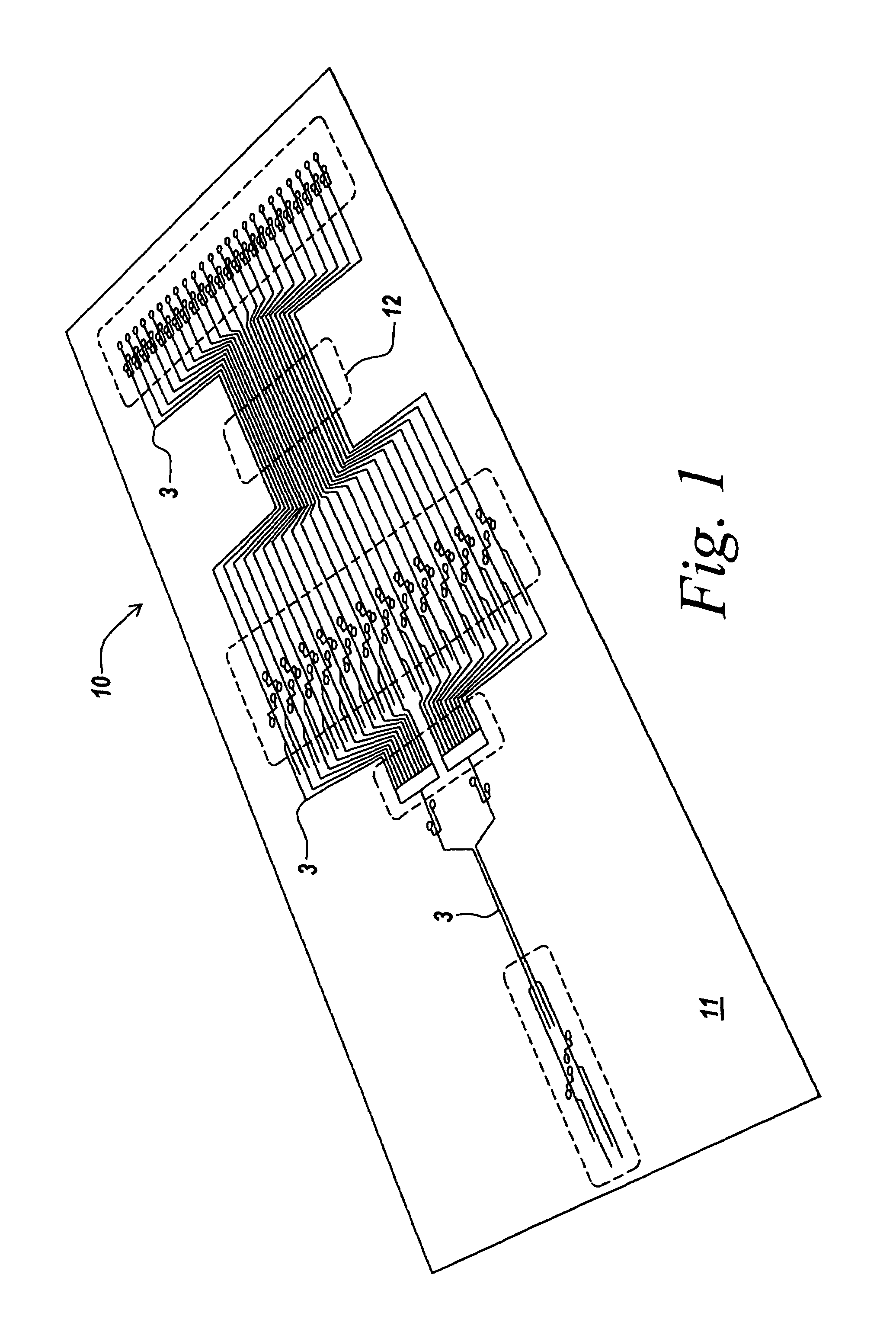
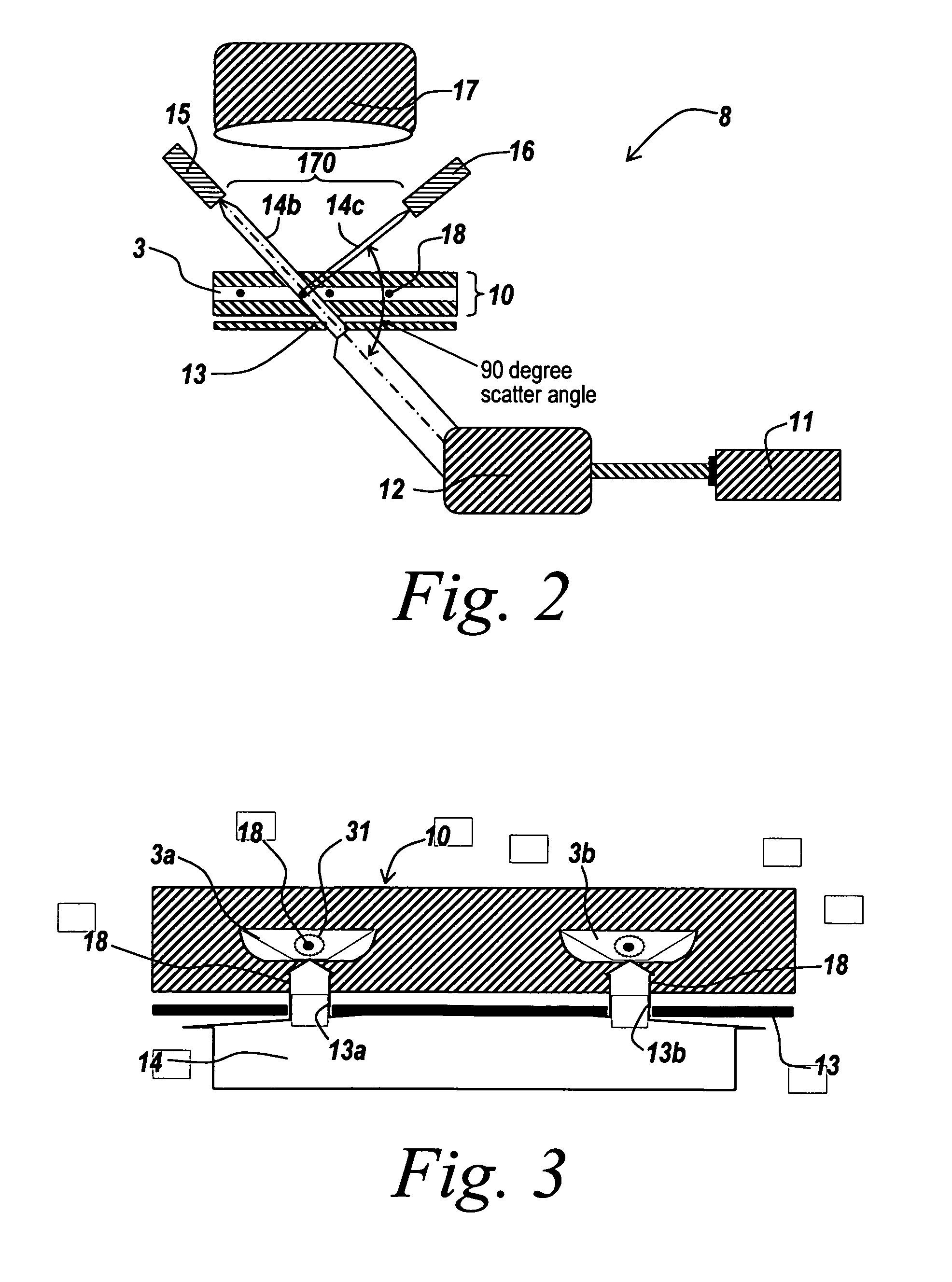
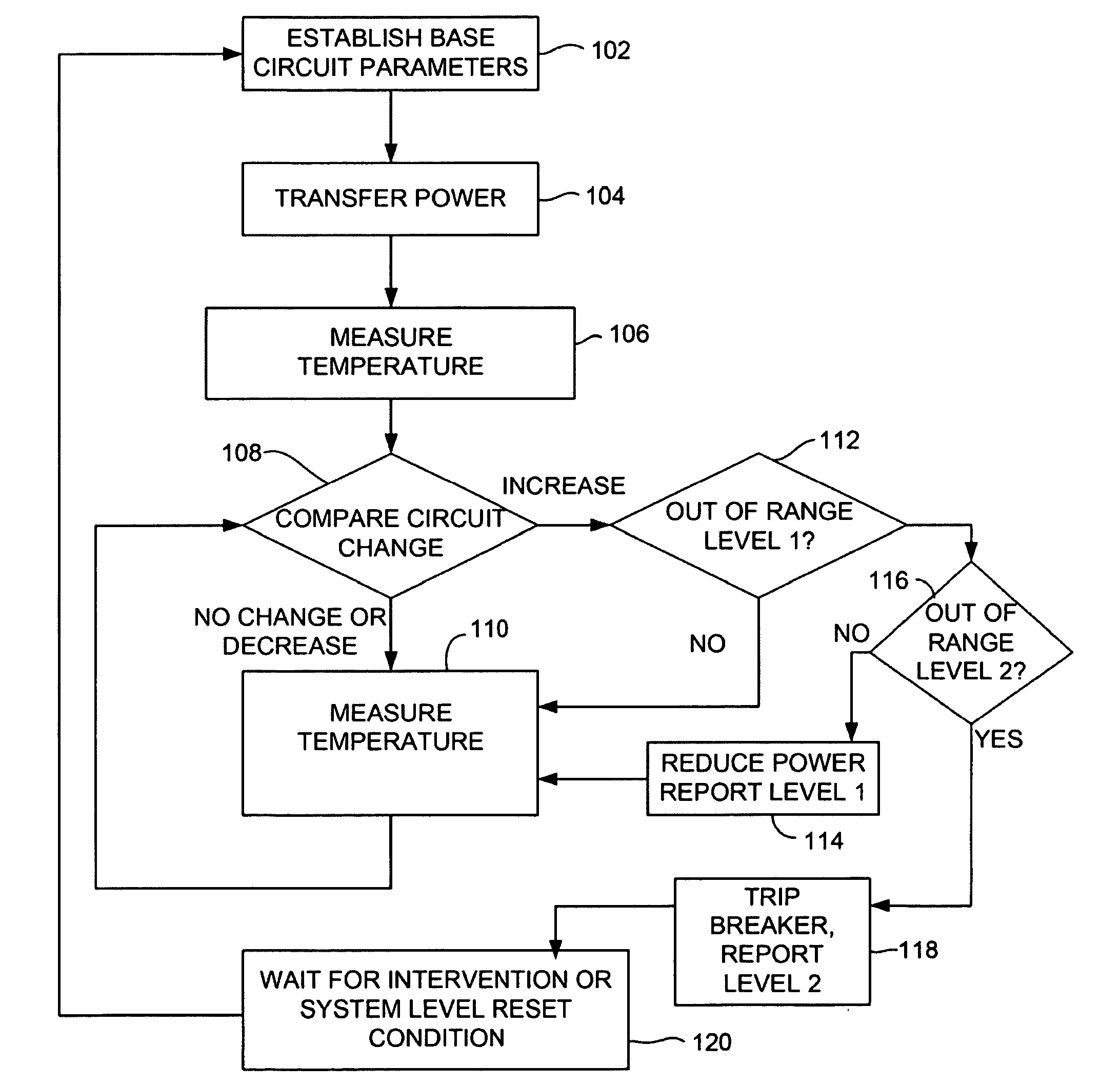
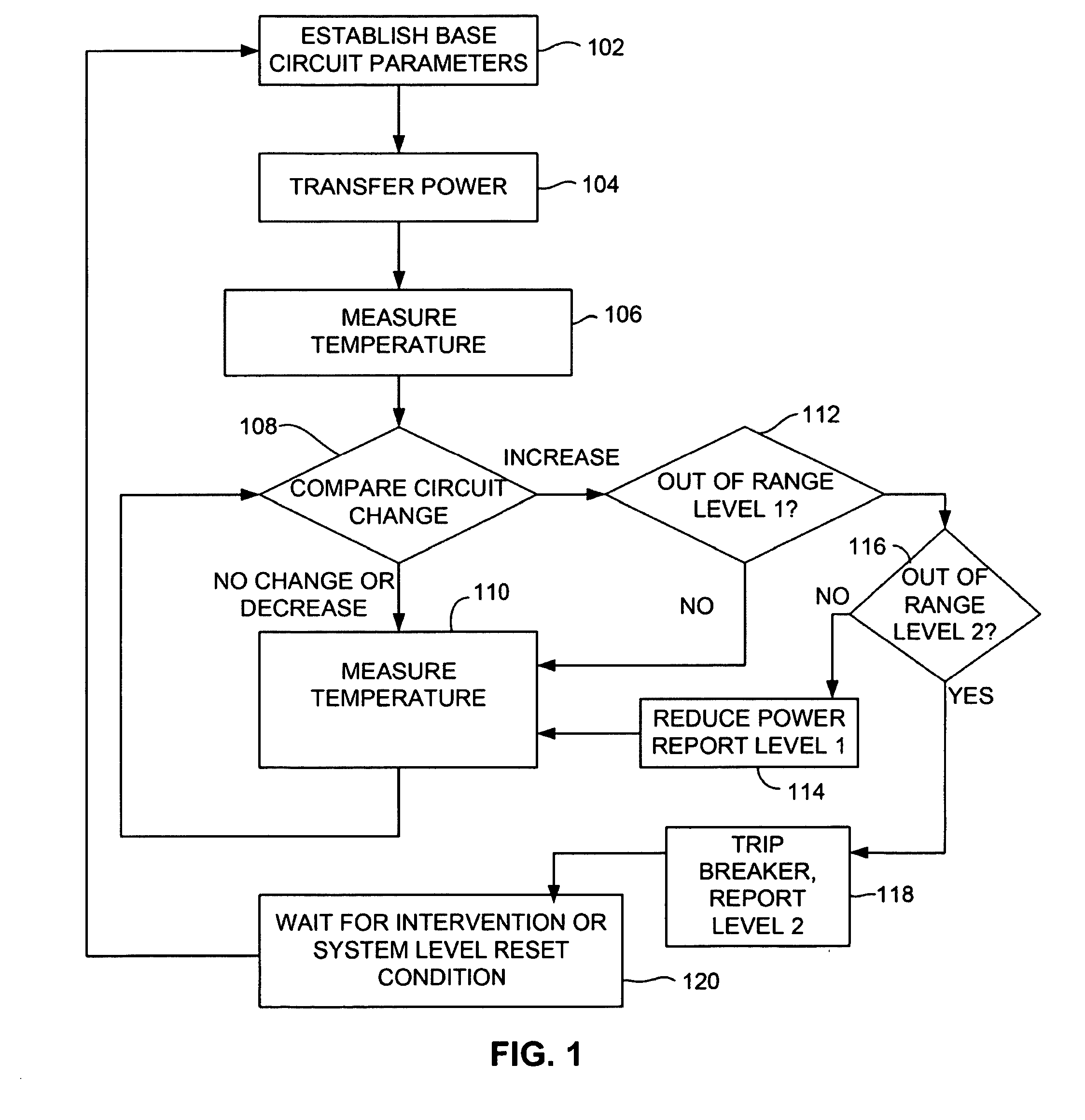
A device and system for monitoring the condition of an electrical outlet such as a 110 volt or 220 volt outlet to alert a user to a dangerous situation and to interrupt power to the circuit in the event of the dangerous condition. The device monitors the circuit for degradation to the electrical outlet. The system can include a temperature sensor voltage meter or particle detector (smoke detector) connected with a power outlet. When a parameter of a circuit exceed a predetermined level (indicating the outlet has degraded to an unsafe level) a warning can be reported and if necessary power to the device can be adjusted or interrupted.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Nanoscale scanning sensors
ActiveUS20150253355A1High sensitivityReduce data collection timeMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesRelative motionFluorescent light
A sensing probe may be formed of a diamond material comprising one or more spin defects that are configured to emit fluorescent light and are located no more than 50 nm from a sensing surface of the sensing probe. The sensing probe may include an optical outcoupling structure formed by the diamond material and configured to optically guide the fluorescent light toward an output end of the optical outcoupling structure. An optical detector may detect the fluorescent light that is emitted from the spin defects and that exits through the output end of the optical outcoupling structure after being optically guided therethrough. A mounting system may hold the sensing probe and control a distance between the sensing surface of the sensing probe and a surface of a sample while permitting relative motion between the sensing surface and the sample surface.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Domestic water recycling apparatus and fluid contamination detection system therefor
ActiveUS20110146800A1Avoid turbulenceReduce presenceGeneral water supply conservationBathsUser inputWastewater
A domestic water recycling system using a combination of an optical detector to detect certain smaller sized (non-filtered) contaminants and a filter to remove larger sized (filtered) contaminants provides an efficient wastewater recycling system. Optical detection of contaminants determines whether water is discharged or filtered and recycled. The optical detection system can use several discrete optical wavelengths that are passed through the fluid, and can determine a relative presence of the contaminants based on the resulting wavelength response. A recycling shower using optical detection, an electronically actuated directional device and pump and a controller allows for automatic recycling or discharging of water without requiring user input. The system may include a turbulence reduction baffle in a collection chamber, and a disinfection unit for the recycled water.
Owner:ORBITAL SYST
Improved signal processing for optical computing system
ActiveUS20100149537A1High speed machiningIncrease speedScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsMonitoring systemSubject matter
The present subject matter relates to methods of high-speed analysis of product samples during production of the product. Light is directed to a portion of a product under analysis and reflected from or transmitted through the product toward optical detectors. Signals from the optical detectors are compared to determine characteristics of the product under analysis. Temperature within the monitoring system may be monitored in order to provide compensation for the signals produced by the optical detectors. The products under analysis may be stationary, moved by an inspection point by conveyor or other means, or may be contained within a container, the container including a window portion through which the product illuminating light may pass.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Vehicle collision warning system based on optical communication
InactiveCN102013174ASimple methodReliable methodAnti-collision systemsFree-space transmissionEngineeringOptical communication
The invention relates to a vehicle collision warning system based on optical communication, which comprises optical indicators and optical detectors and is used for the safety monitoring and the information interaction among running vehicles. The optical indicators are distributed around or on the top of a vehicle and can transmit modulated optical signals in different directions, wherein the optical signals carry the angle indication information, mounting position information and other information of the vehicle which are corresponding to the optical signals, thereby forming optical antennae. The optical detectors mounted on another vehicle can detect optical pulse signals transmitted by a certain light emitting diode (LED) of the optical indicators and then extract the carried indication angle information, mounting position information and the like; and a processing unit of the optical detector analyzes and processes the information, estimates whether an abnormal running state exists based on the change rate of light indication angle, the change rate of light intensity and the like, and outputs the result to other systems of the vehicle by a controller.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Solid-state neutron and alpha particles detector and methods for manufacturing and use thereof
InactiveUS20090302226A1Optimize detection resultsMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesParticulatesSemiconductor materials
A solid-state detector for detection of neutron and alpha particles detector and methods for manufacturing and use thereof are described. The detector has an active region formed of a polycrystalline semiconductor compound comprising a particulate semiconductor material sensitive to neutron and alpha particles radiation imbedded in a binder. The particulate semiconductor material contains at least one element sensitive to neutron and alpha particles radiation, selected from a group including 10Boron, 6Lithium, 113Cadmium, 157Gadolinium and 199Mercury. The semiconductor compound is sandwiched between an electrode assembly configured to detect the neutron and alpha particles interacting with the bulk of the active region. The binder can be either an organic polymer binder or inorganic binder. The organic polymer binder comprises at least one polymer that can be selected from the group comprising polystyrene, polypropylene, Humiseal™ and Nylon-6. The inorganic binder can be selected from B2O3, PbO / B2O3 / , Bi2O3 / PbO, Borax glass, Bismuth Borate glass and Boron Oxide based glass.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Miniature camera head
ActiveUS8194121B2Reduce the overall diameterReduce the overall heightTelevision system detailsSurgeryOptical radiationOptical axis
An electronic imaging device (27) includes an optical objective (28) for collecting optical radiation from an object, the objective having an optical axis, and an image sensor (24), including a matrix of optical detectors arranged in a plane that is substantially non-perpendicular to the optical axis, the image sensor having a lateral dimension in the plane. A turning mirror (38) has an optical surface that is positioned so as to reflect the radiation collected by the objective in order to form a focused image in the plane of the image sensor, while a maximum distance from the optical surface to the plane of the image sensor is substantially less than the lateral dimension of the image sensor.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Centralized control architecture for a laser materials processing system
InactiveUS6947802B2Welding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusHandling systemMaterials processing
Apparatus, systems, and methods for monitoring the processing of a workpiece that includes directing an incident laser beam onto the workpiece and using an optical detector for measuring a signal emitted from the workpiece as a result of the incident laser beam. The detector generates at least two signals based upon the optical signal. The method also involves use of a light source monitor in determining workpiece processing quality based upon the quotient of the two outputs as well as a magnitude of one of the two quotients.
Owner:HYPERTHERM INC
Pathogen and particle detector system and method
InactiveUS20100108910A1Backward-enhanced fluorescencePhotometryScattering properties measurementsForward scatterLength wave
The system includes an excitation source for providing a beam of electromagnetic radiation having a source wavelength. A first wavelength selective device is positioned to be impinged by the beam of electromagnetic radiation. The first wavelength selective device is constructed to transmit at least a portion of any radiation having the source wavelength and to reflect radiation of other wavelengths. A medium containing particles is positioned to be impinged by the beam of electromagnetic radiation. At least a portion of the beam of electromagnetic radiation becomes scattered within the medium, the scattered electromagnetic radiation including forward scattered electromagnetic radiation and backward scattered electromagnetic radiation. An optical detector is positioned to receive backward and / or forward scattered electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:BIOVIGILANT SYST
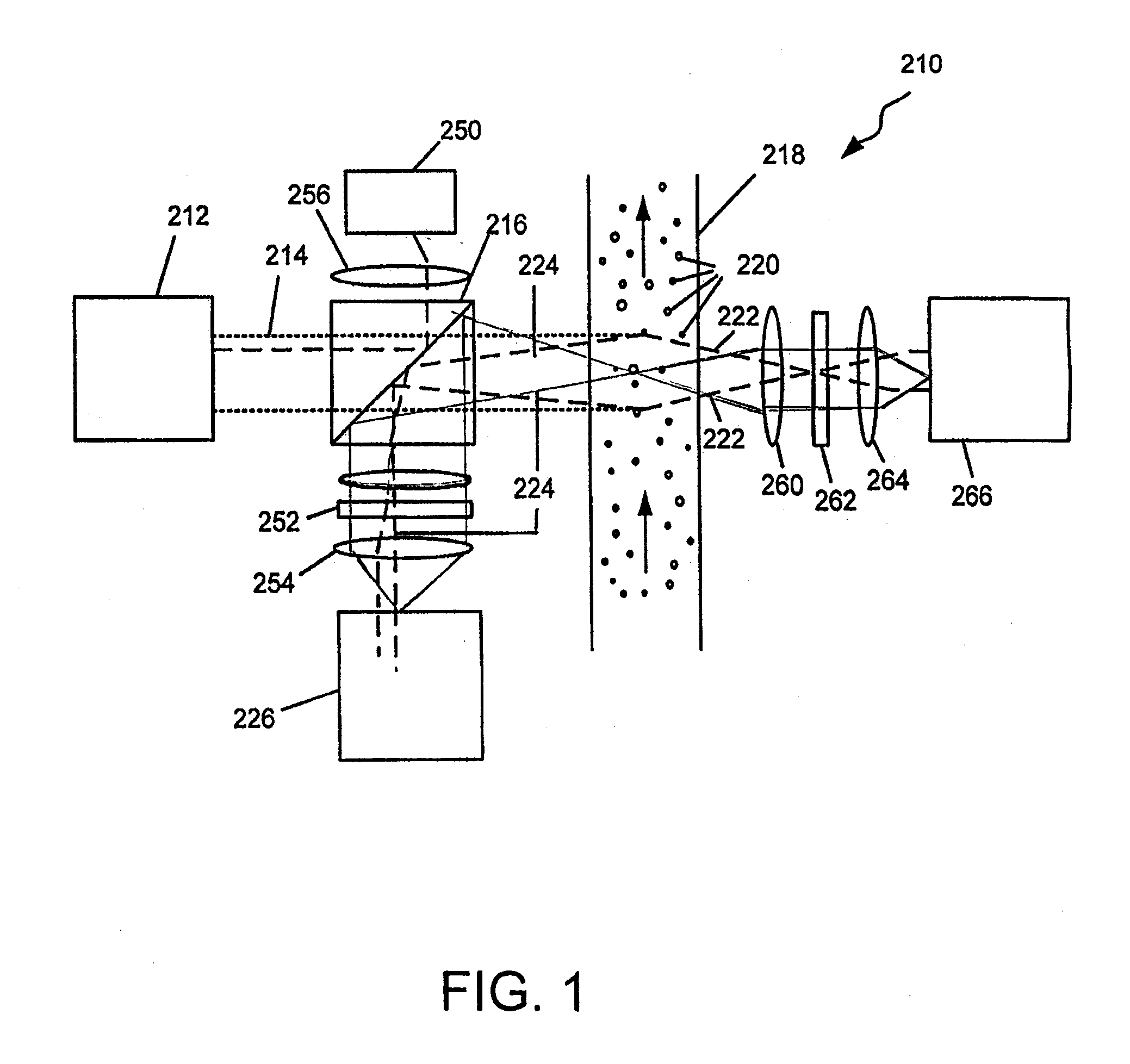
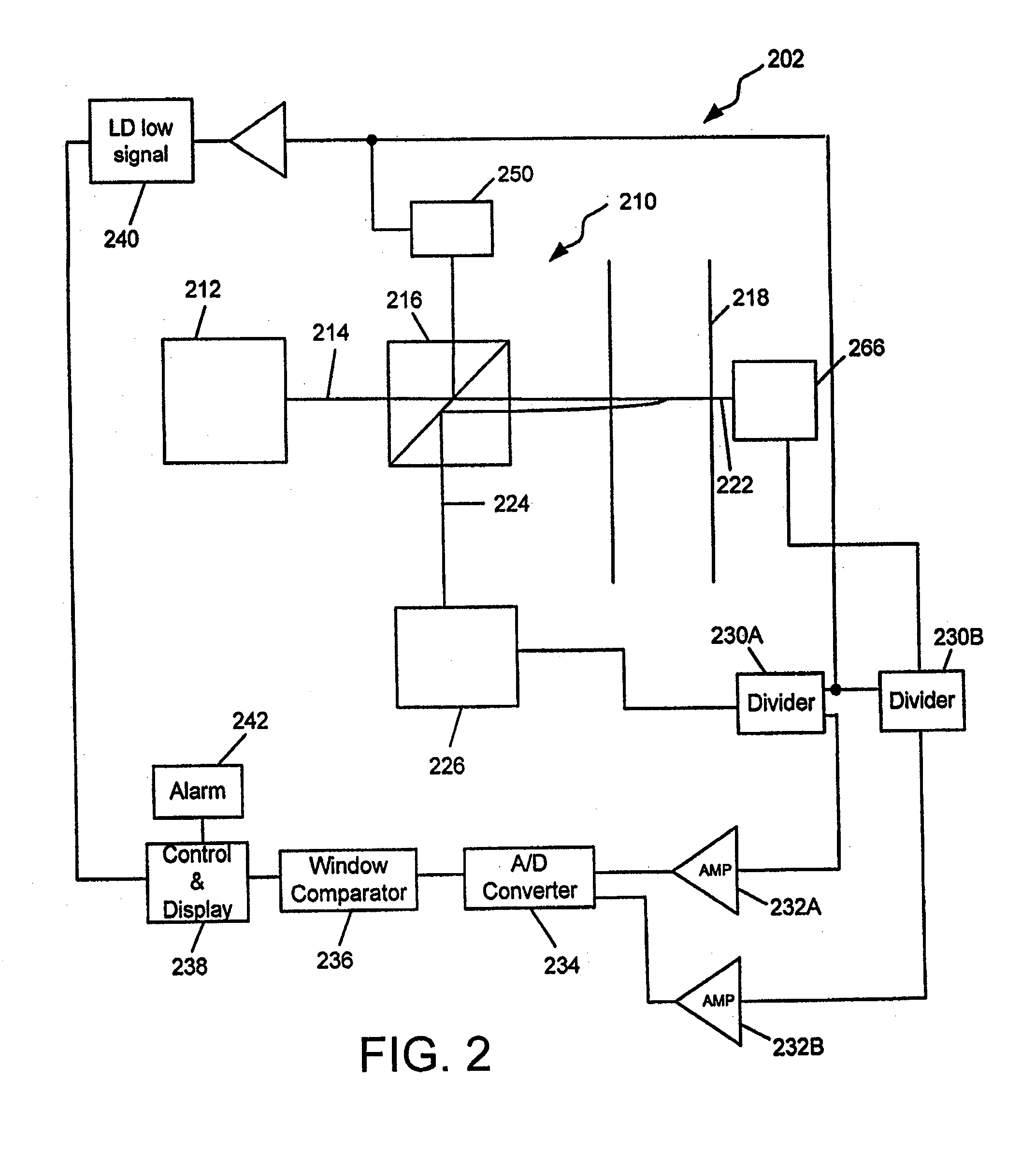
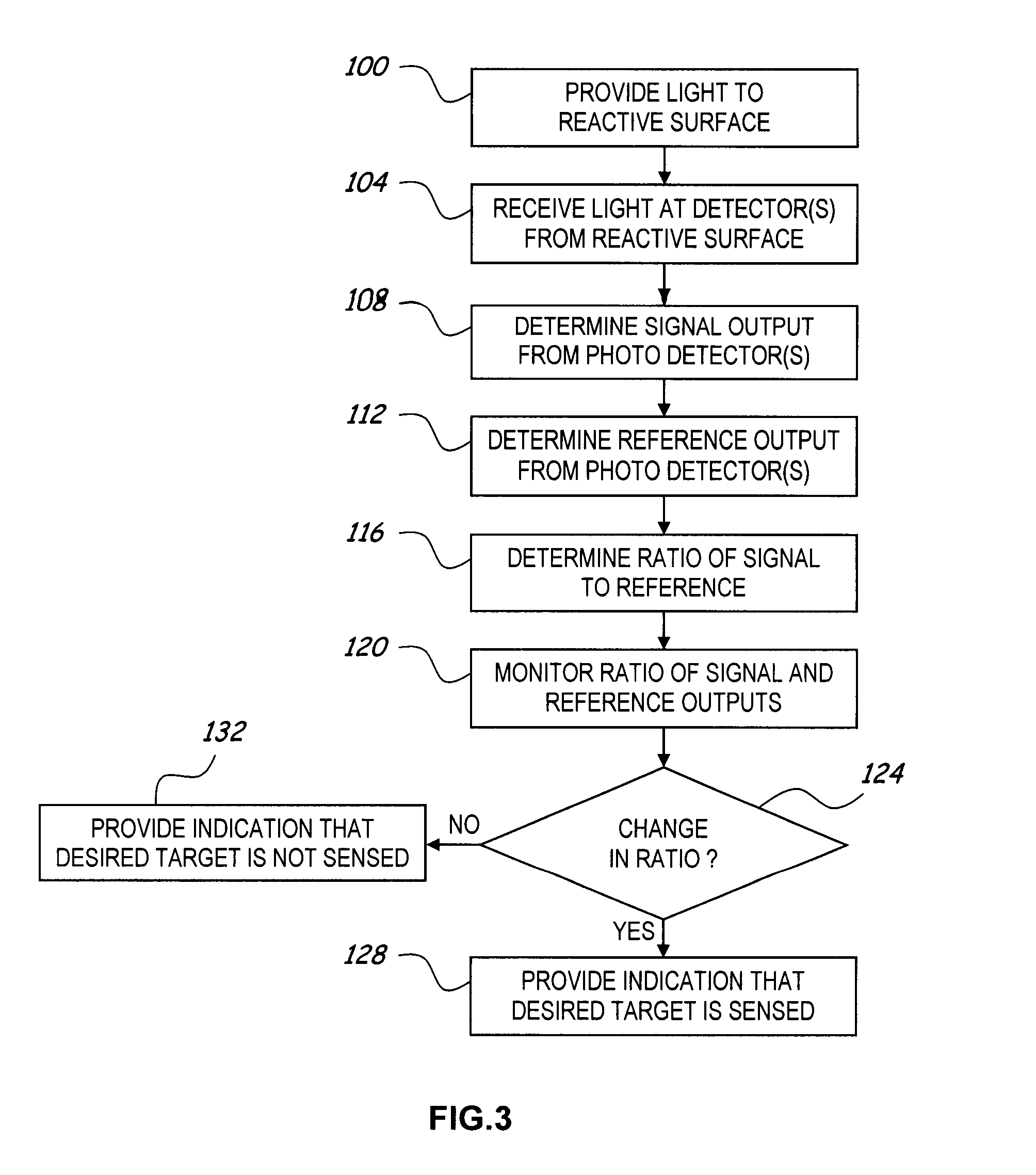
Optical sensor with chemically reactive surface
ActiveUS7652767B2Emission spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsChemical reactionOptical property
An improved optical sensor and methods for measuring the presence of various materials or constituents in a fluid sample uses reactive material(s) in a fluid environment. The reactive materials have optical properties that change in the presence of a target material that may be present in the environment. An optical emitter generates light that is directed to the reactive materials, and one or more optical detectors receive reflected light from one or more interfaces in the optical path between the emitter and the detector(s), one or more of the interfaces having a reactive material. The reactive material(s), emitter(s), and detector(s) are selected based on the desired target material to be sensed.
Owner:SPORIAN MICROSYST
Optical detector based on two-dimensional stratiform atomic crystal materials
InactiveCN103219403AStrong light absorption propertiesAdjust and control the detection spectrum rangeSemiconductor devicesSpectral responsivityGraphene
The invention discloses an optical detector based on two-dimensional stratiform atomic crystal materials. The optical detector comprises a silicon substrate coated with silica, a first graphene conducting layer, a two-dimensional stratiform atomic crystal semiconductor material layer and a second graphene conducting layer are sequentially coated on the silicon substrate coated with the silica in a superposition mode, and the first graphene conducting layer and the second graphene conducting layer respectively form heterogeneous structures with the two-dimensional stratiform atomic crystal semiconductor material layer. One end of the first graphene conducting layer and one end of the second graphene conducting layer are provided with a first electrode layer and a second electrode layer respectively, and the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer have no any overlapping, and the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer are arranged outside an overlapping area of the first graphene conducting layer, the second graphene conducting layer and the two-dimensional stratiform atomic crystal semiconductor material layer at the same time. A passivation layer is respectively arranged above each layer. The optical detector based on the two-dimensional stratiform atomic crystal materials utilizes the two-dimensional stratiform atomic crystal materials, has the operating characteristics that detection spectrum range is wide, response speed is fast and cut-off frequency is high, and has the characteristics that spectral responsivity of a device is high and extraction of a photon-generated carrier is simple.
Owner:深圳激子科技有限公司
In-Line Smoke Attenuator
ActiveUS20090002182A1Constant ratioReduce concentrationDispersed particle filtrationWithdrawing sample devicesSmoke EmissionEngineering
In one form the present invention provides an apparatus in an airflow path before a particle detector, wherein the apparatus removes a substantially constant proportion of all sizes of airborne particles from the airflow over time. In an example the apparatus includes a flow splitting arrangement configured to divide a fluid flow into a plurality of sub-flows, the splitting arrangement 10 including means for defining a plurality of substantially identically dimensioned flow apertures configured to direct a portion of the fluid into a respective sub-flow.
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
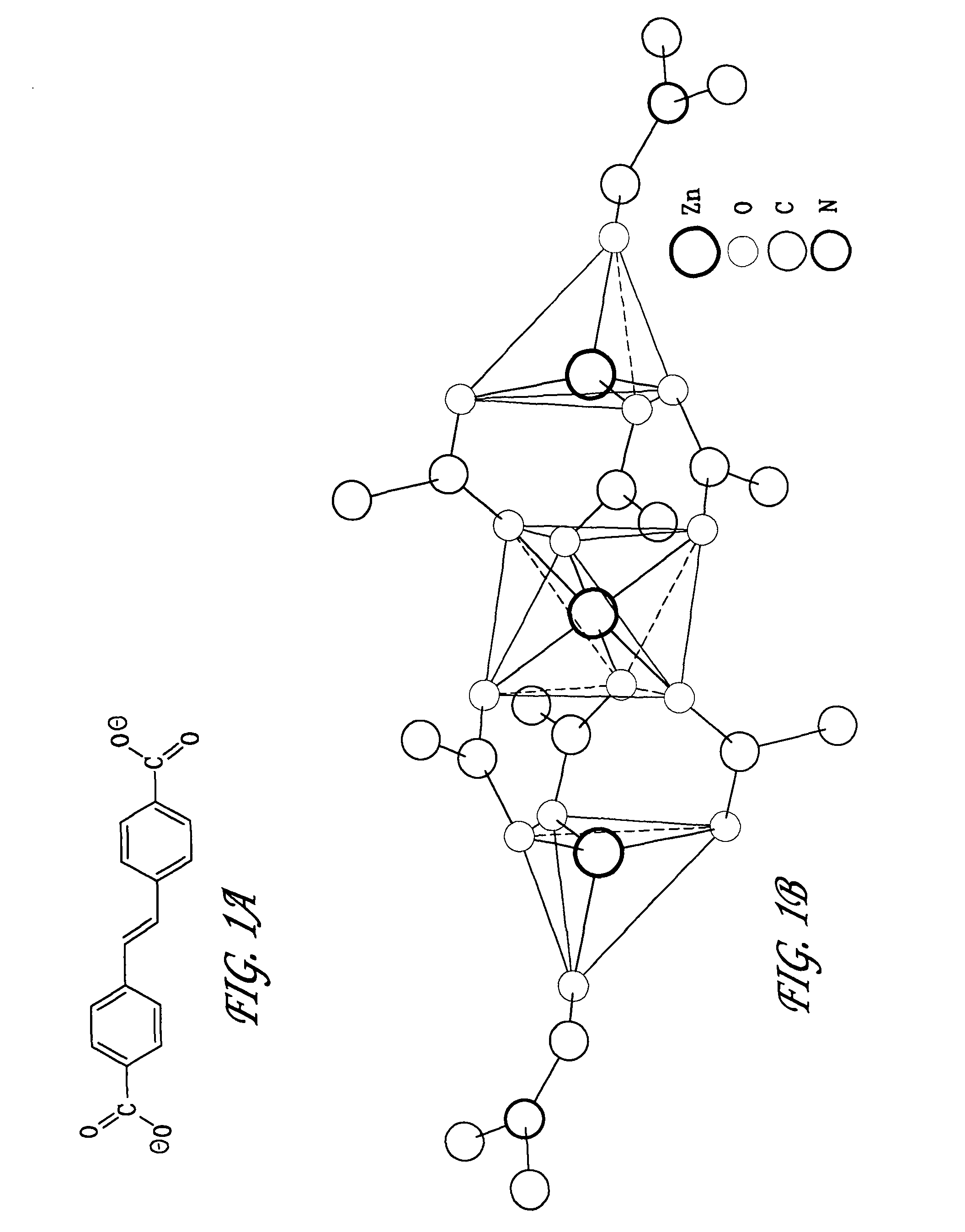
Hybrid metal organic scintillator materials system and particle detector
ActiveUS7985868B1Minimized quenching effectMinimize quenching effectPolycrystalline material growthOrganic chemistryOctahedronZinc nitrate
We describe the preparation and characterization of two zinc hybrid luminescent structures based on the flexible and emissive linker molecule, trans-(4-R,4′-R′) stilbene, where R and R′ are mono- or poly-coordinating groups, which retain their luminescence within these solid materials. For example, reaction of trans-4,4′-stilbenedicarboxylic acid and zinc nitrate in the solvent dimethylformamide (DMF) yielded a dense 2-D network featuring zinc in both octahedral and tetrahedral coordination environments connected by trans-stilbene links. Similar reaction in diethylformamide (DEF) at higher temperatures resulted in a porous, 3-D framework structure consisting of two interpenetrating cubic lattices, each featuring basic to zinc carboxylate vertices joined by trans-stilbene, analogous to the isoreticular MOF (IRMOF) series. We demonstrate that the optical properties of both embodiments correlate directly with the local ligand environments observed in the crystal structures. We further demonstrate that these materials produce high luminescent response to proton radiation and high radiation tolerance relative to prior scintillators. These features can be used to create sophisticated scintillating detection sensors.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
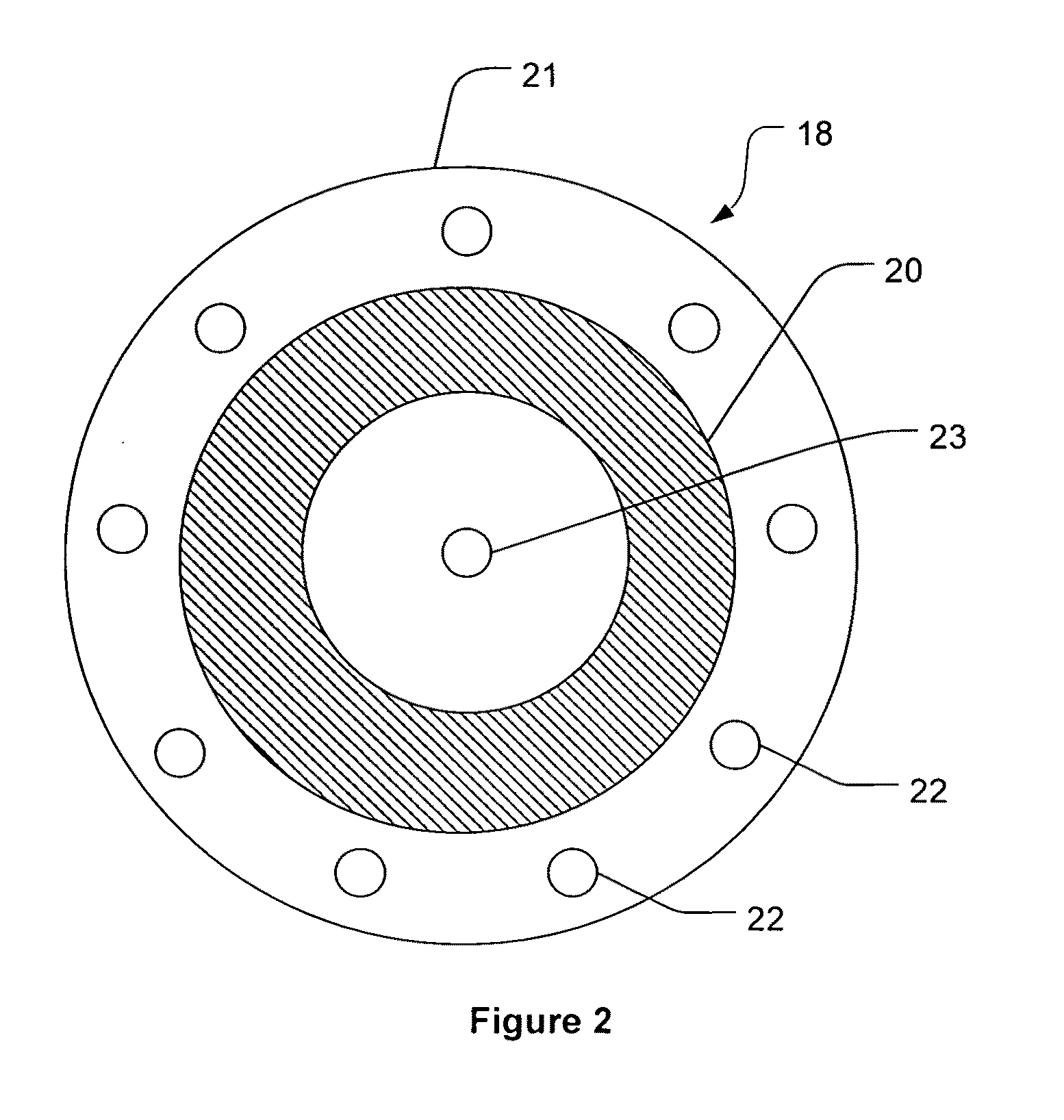
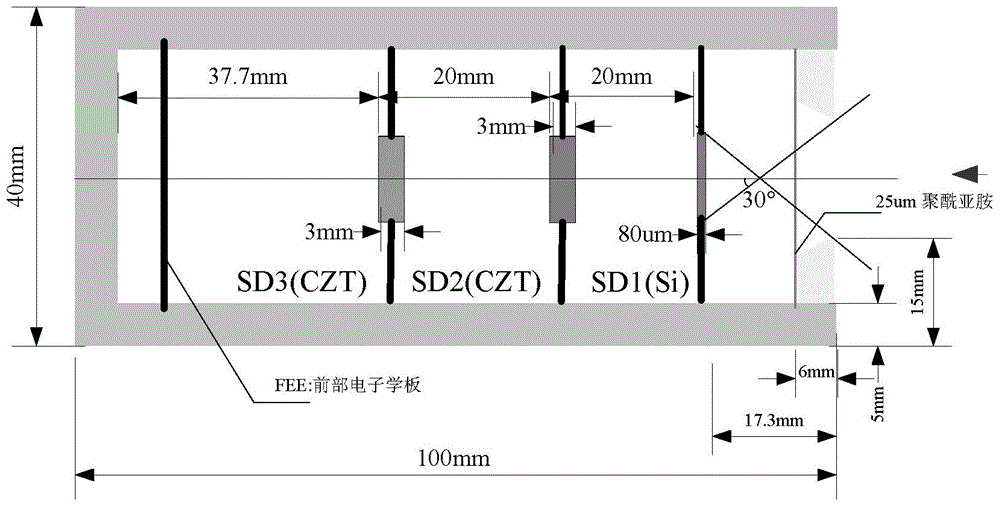
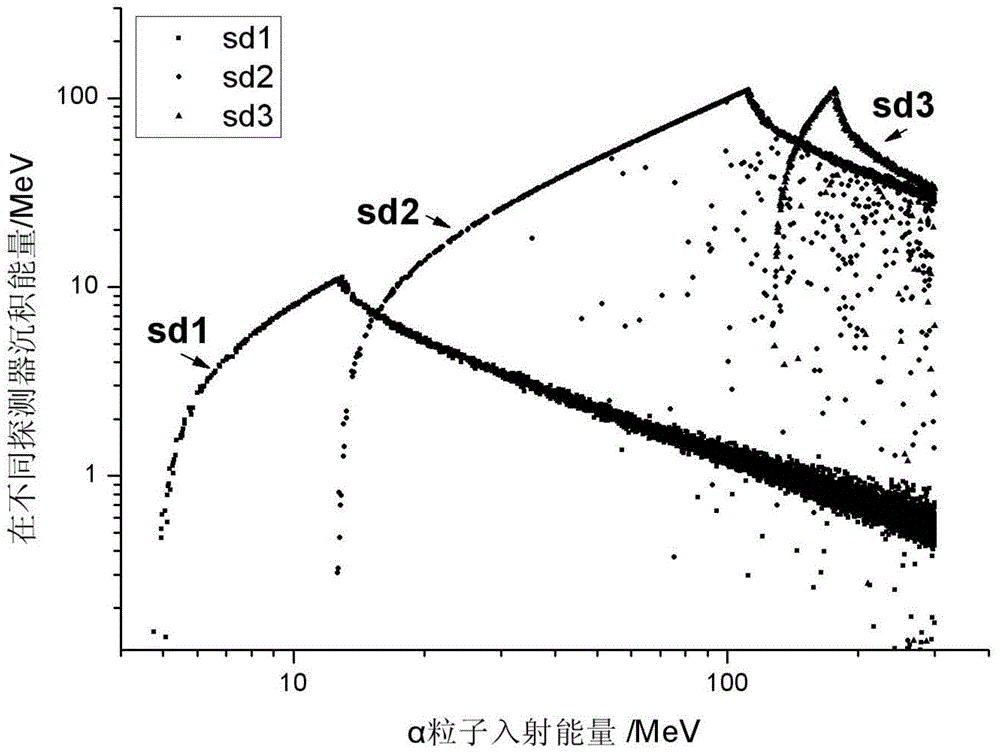
Space particle detector and data collecting and processing method thereof
ActiveCN103954988AReduce areaReduce power consumptionRadiation intensity measurementIncident energyData collecting
The invention discloses a space particle detector and a data collecting and processing method thereof. The space particle detector comprises a semi-closed structure with an incidence window. A part energy detection unit SD1, an energy detection unit SD2 and an anticoincidence detection unit SD3 are sequentially arranged in the semi-closed structure along the incidence window inwards. The part energy detection unit SD1, the energy detection unit SD2 and the anticoincidence detection unit SD3 are arranged in parallel, and the center of the part energy detection unit SD1, the center of the energy detection unit SD2 and the center of the anticoincidence detection unit SD3 are located on the same axis. The signal output end of the part energy detection unit SD1, the signal output end of the energy detection unit SD2 and the signal output end of the anticoincidence detection unit SD3 are connected with a data processing unit. The data processing unit is used for judging particle varieties and energy ranges according to input signals. The detector is suitable for space particle detection and low in energy consumption; charged particles and uncharged particles can be detected, the different particles are distinguished, the incident energy ranges of the particles are judged, and the data of the detector are processed in real time and downloaded in real time.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Enhanced resolution imaging systems for digital radiography
ActiveUS20130028379A1Enhanced advantageAdvantage is lostSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFluorescenceCompanion animal
The invention provides methods and apparatus for enhanced PCI and dual-use radiation imaging systems. In one implementation high resolution storage phosphor plate radiation detector (an area detector) is employed for conventional attenuation radiation imaging and / or PCI (including conventional PCI and coded aperture PCI). Slit and slot scan implementations for dual-use systems are introduced. Dedicated single and dual-use slit and slot scan system for conventional attenuation imaging and PCI are described that employ face-on or edge-on detectors. Slit and slot scan systems that employ area detectors are described. Edge-on, structured cell detector designs are described. Applications of edge-on structured cell detectors for CT, Nuclear Medicine, PET, and probe detectors are described.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Dual beam system
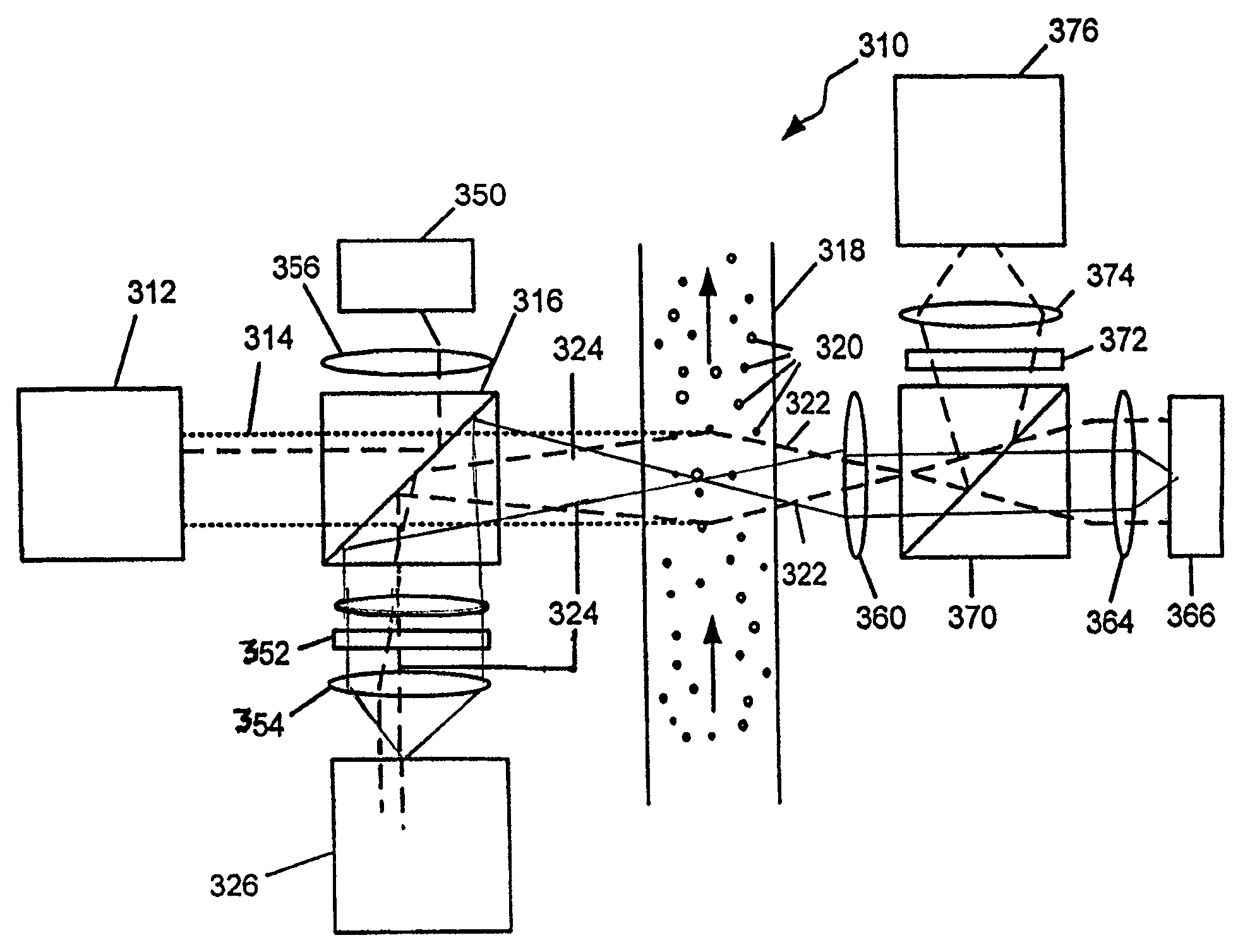
ActiveUS20050035291A1Remove blurEasy to collectThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDual beamScanning tunneling microscope
A dual beam system includes an ion beam system and a scanning electron microscope with a magnetic objective lens. The ion beam system is adapted to operate optimally in the presence of the magnetic field from the SEM objective lens, so that the objective lens is not turned off during operation of the ion beam. An optional secondary particle detector and an optional charge neutralization flood gun are adapted to operate in the presence of the magnetic field. The magnetic objective lens is designed to have a constant heat signature, regardless of the strength of magnetic field being produced, so that the system does not need time to stabilize when the magnetic field is changed.
Owner:FEI CO
Optical touch apparatus and optical touch display apparatus
InactiveUS20110122094A1Improve accuracyUniform brightnessOptical light guidesInput/output processes for data processingLight guideLight beam
An optical touch apparatus includes a light source, light guide unit, and optical detector. The light source next to the display area emits a beam. The light guide unit next to the display area and in the transmission path of the beam includes a light guide body and a Lambertian scattering structure. The light guide body has first, second, third, fourth, and light incident surfaces. The beam enters the light guide body through the light incident surface and is transmitted from the first surface to a sensing space in front of the display area. The Lambertian scattering structure is disposed on at least one of the second, third, and fourth surfaces for scattering the beam to the first surface. The optical detector next to the display area senses a change in light intensity of the beam in the sensing space. An optical touch display apparatus is also provided.
Owner:CORETRONIC
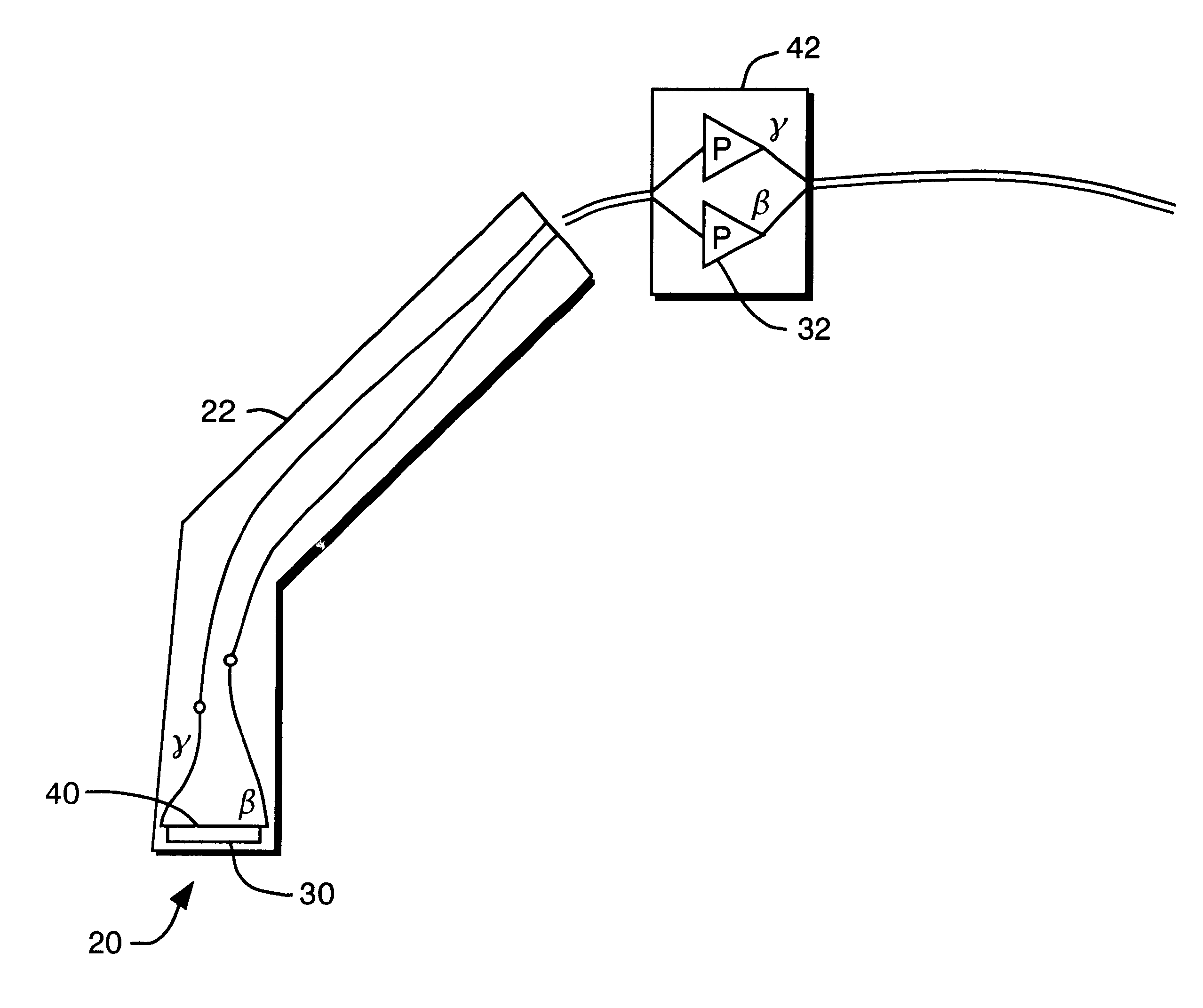
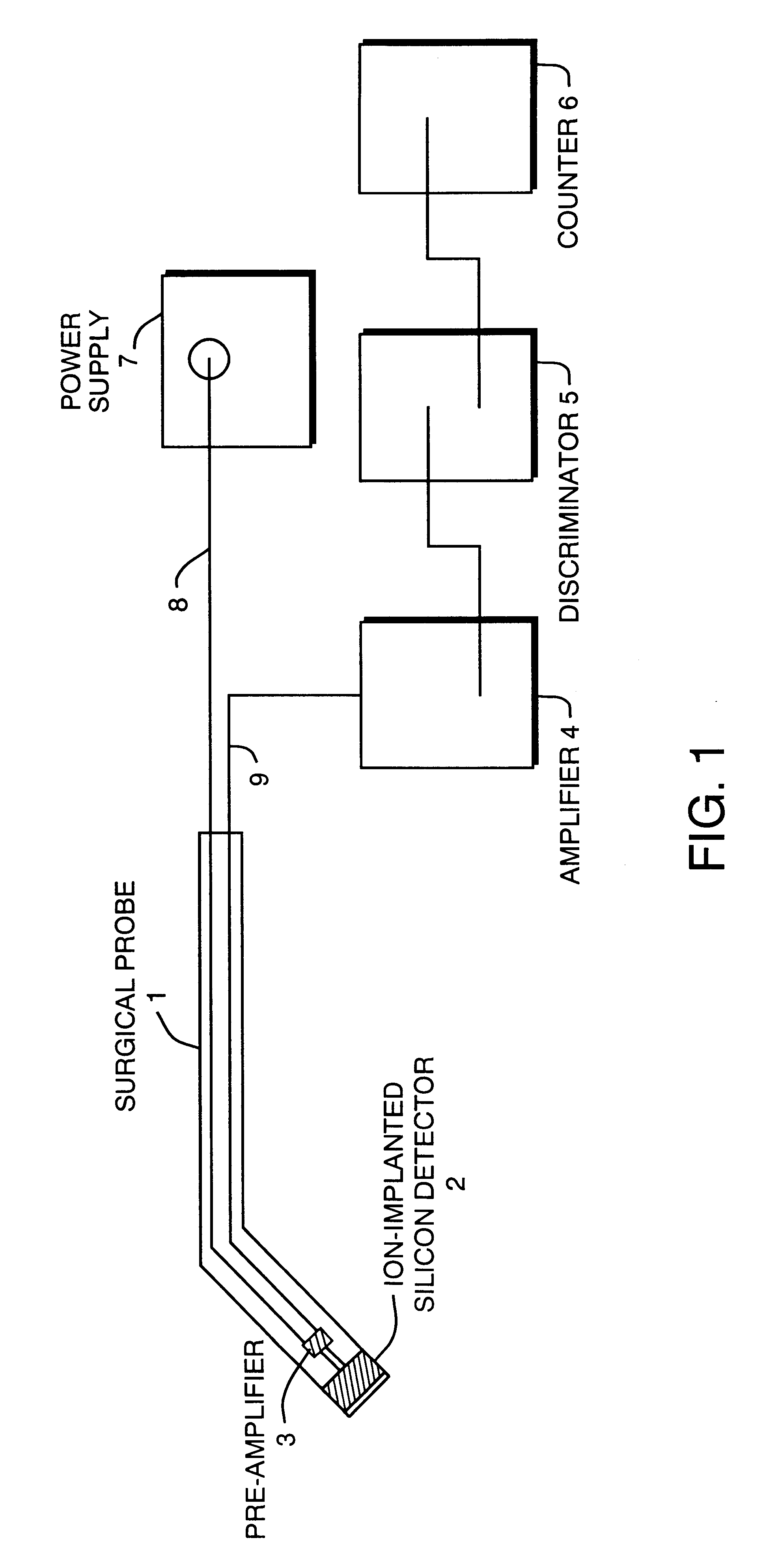
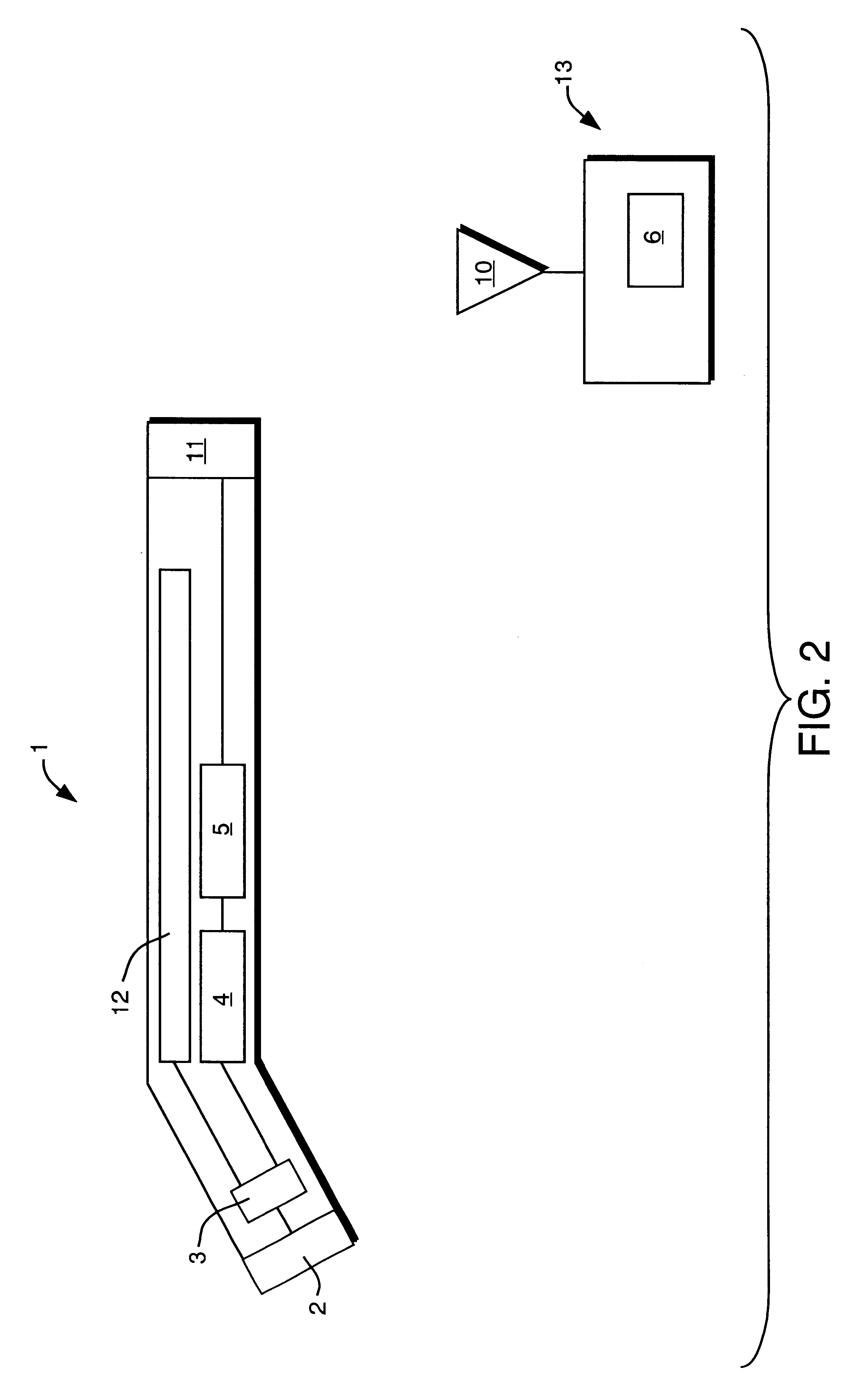
Solid state beta-sensitive surgical probe
InactiveUS6456869B1Sensitive highMinimizing requisite sizeSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredAudio power amplifier
An intraoperative probe system for preferentially detecting beta radiation over gamma radiation emitted from a radiopharmaceutical is described. In one embodiment, the probe system of the present invention is a probe having an ion-implanted silicon charged-particle detector for generating an electrical signal in response to received beta particles. In such an embodiment, a preamplifier may be located in close proximity to the detector filters and amplifies the electrical signal. Furthermore, a wire may be used to couple the probe to a processing unit for amplifying and filtering the electrical signal, and a counter may be utilized to analyze the resulting electrical signal to determine the number of beta particles being received by the detector. Alternatively, the wire can be replaced with an infrared or radio transmitter and receiver for wireless operation of the probe.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Pathogen and particle detector system and method
InactiveUS7738099B2PhotometryScattering properties measurementsForward scatterElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:BIOVIGILANT SYST
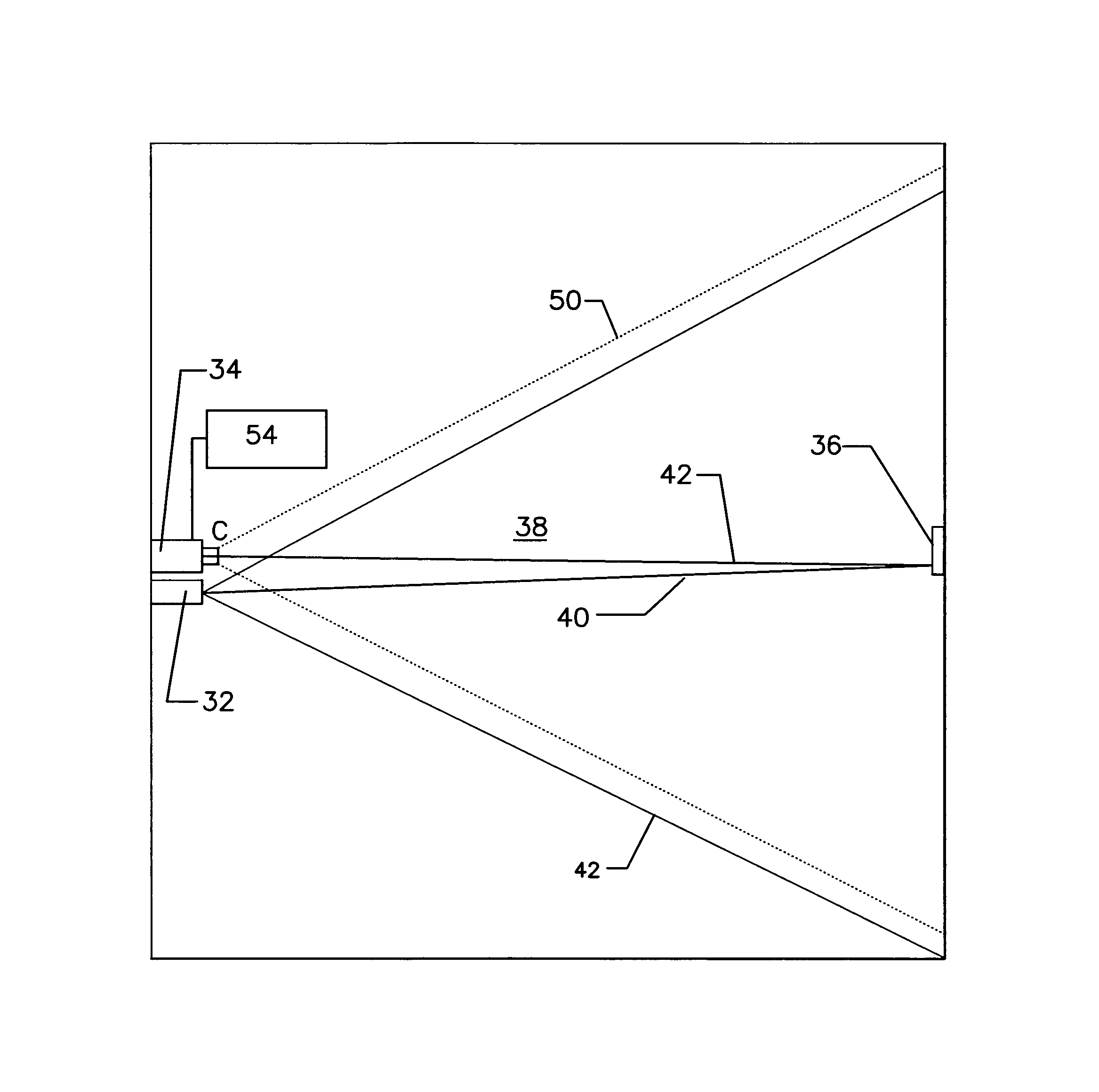
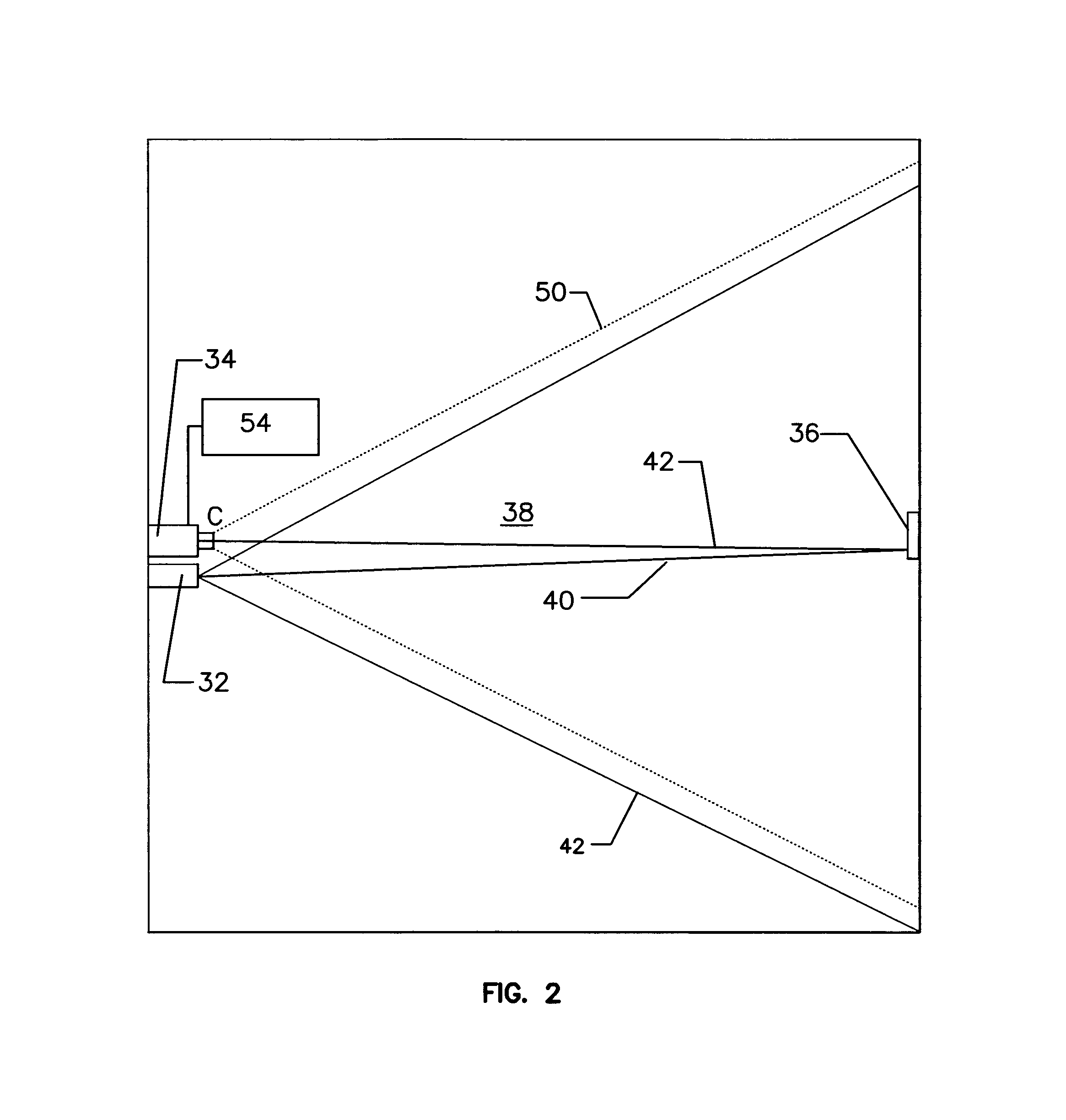
Particle detectors
ActiveUS8797531B2Sensitive to lightTransistorScattering properties measurementsLight beamField of view
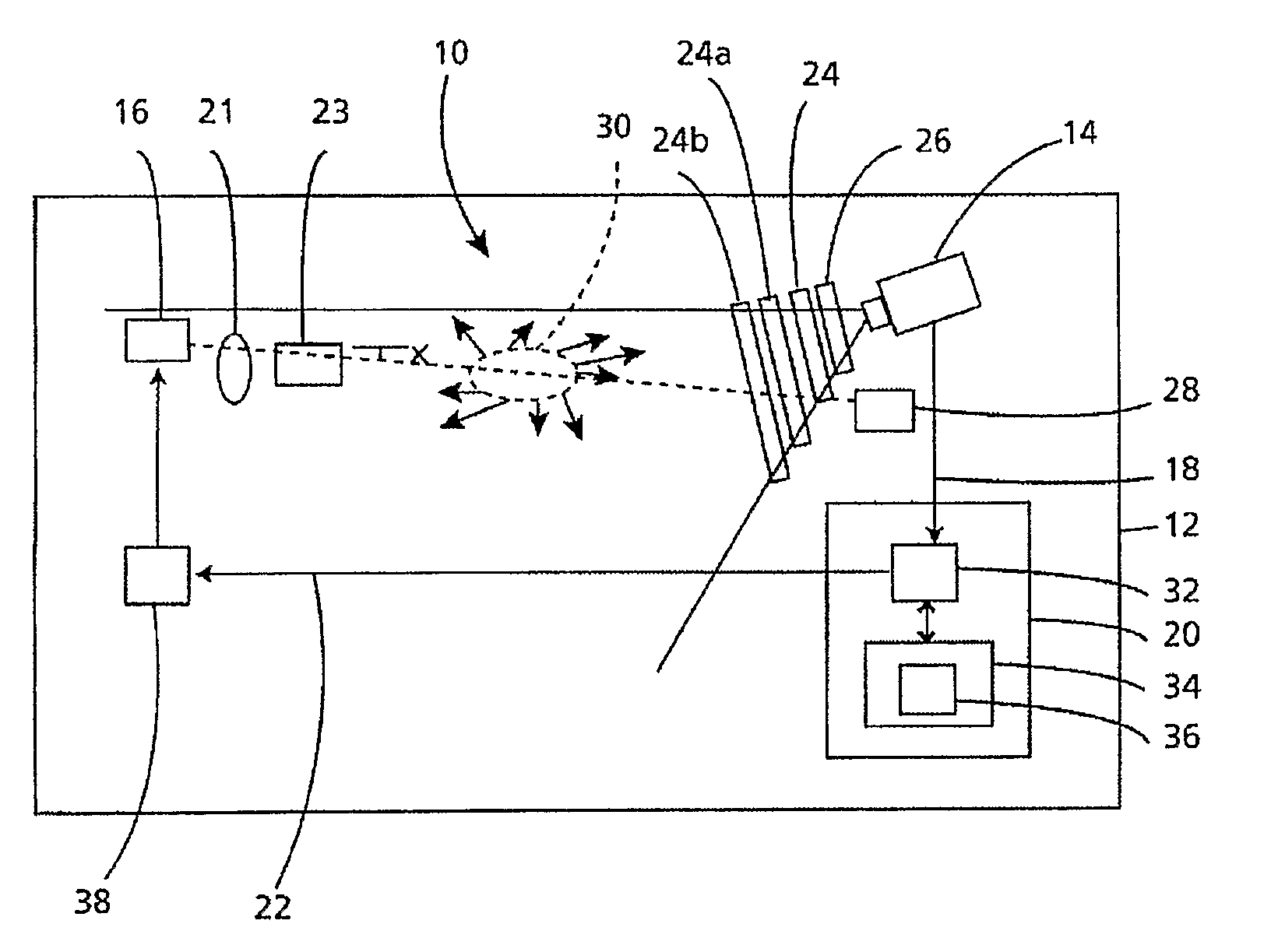
A beam detector (10) including a light source (32), a receiver (34), and a target (36), acting in co-operation to detect particles in a monitored area (38). The target (36), reflects incident light (40), resulting in reflected light (32) being returned to receiver (34). The receiver (34) is a receiver is capable of recording and reporting light intensity at a plurality of points across its field of view. In the preferred form the detector (10) emits a first light beam (3614) in a first wavelength band; a second light beam (3618) in a second wavelength band; and a third light beam (3616) in a third wavelength band, wherein the first and second wavelengths bands are substantially equal and are different to the third wavelength band.
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
Two-dimensional ionising particle detector
InactiveUS7238951B2Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberMean free path
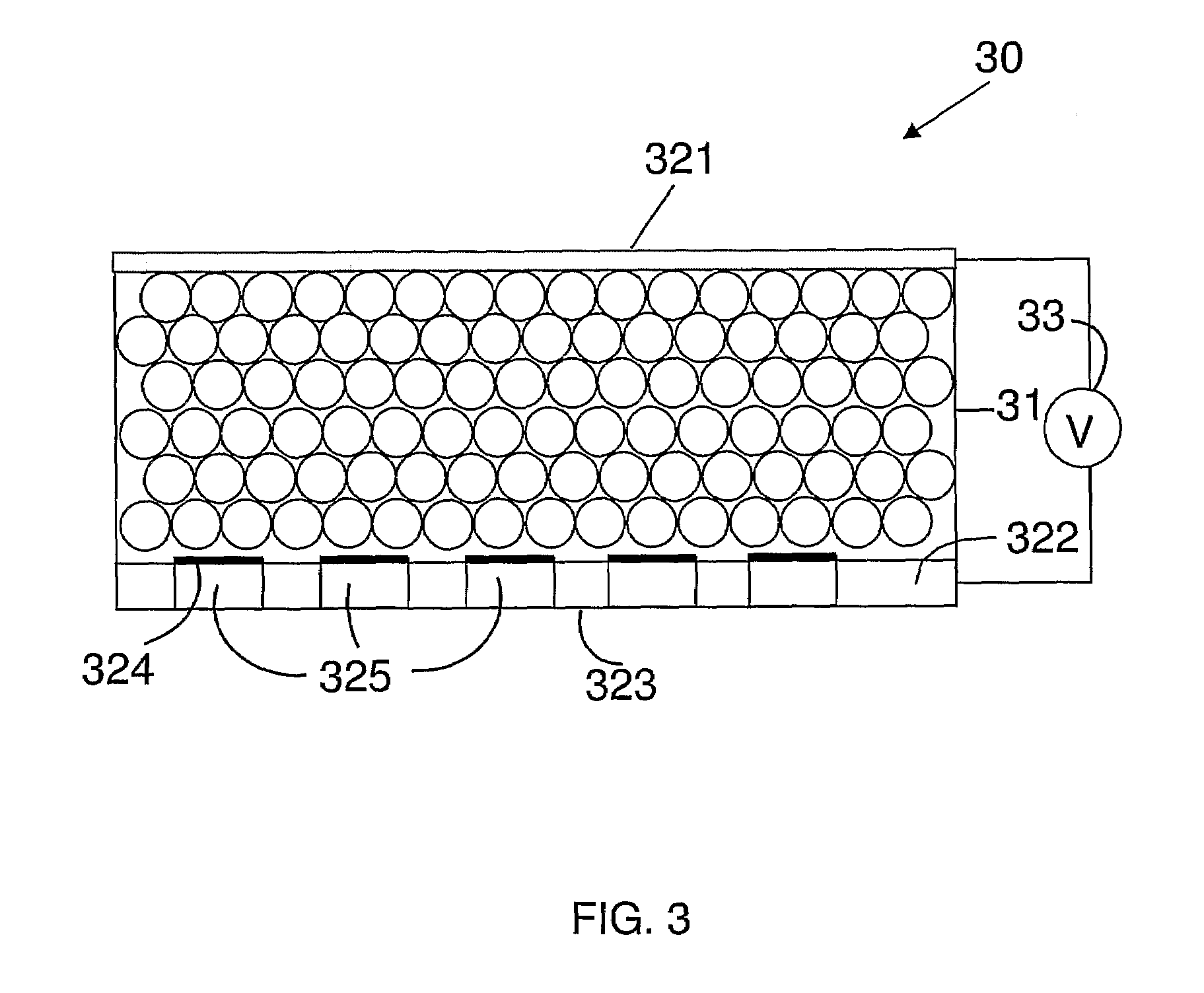
A two-dimensional ionising particle detector including a matrix of detecting fibers, each detecting fiber forming a pixel of the detector. Each detecting fiber is composed of a glass capillary filled with a liquid scintillator for which the chemical composition is chosen such that an average free path of primary scintillation photons is negligible compared with a diameter of the capillary. The detector is applicable, for example, to high resolution particle imagery.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Quantum random number generator
InactiveUS20060010182A1Maximizing numberRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationTime segmentNumber generator
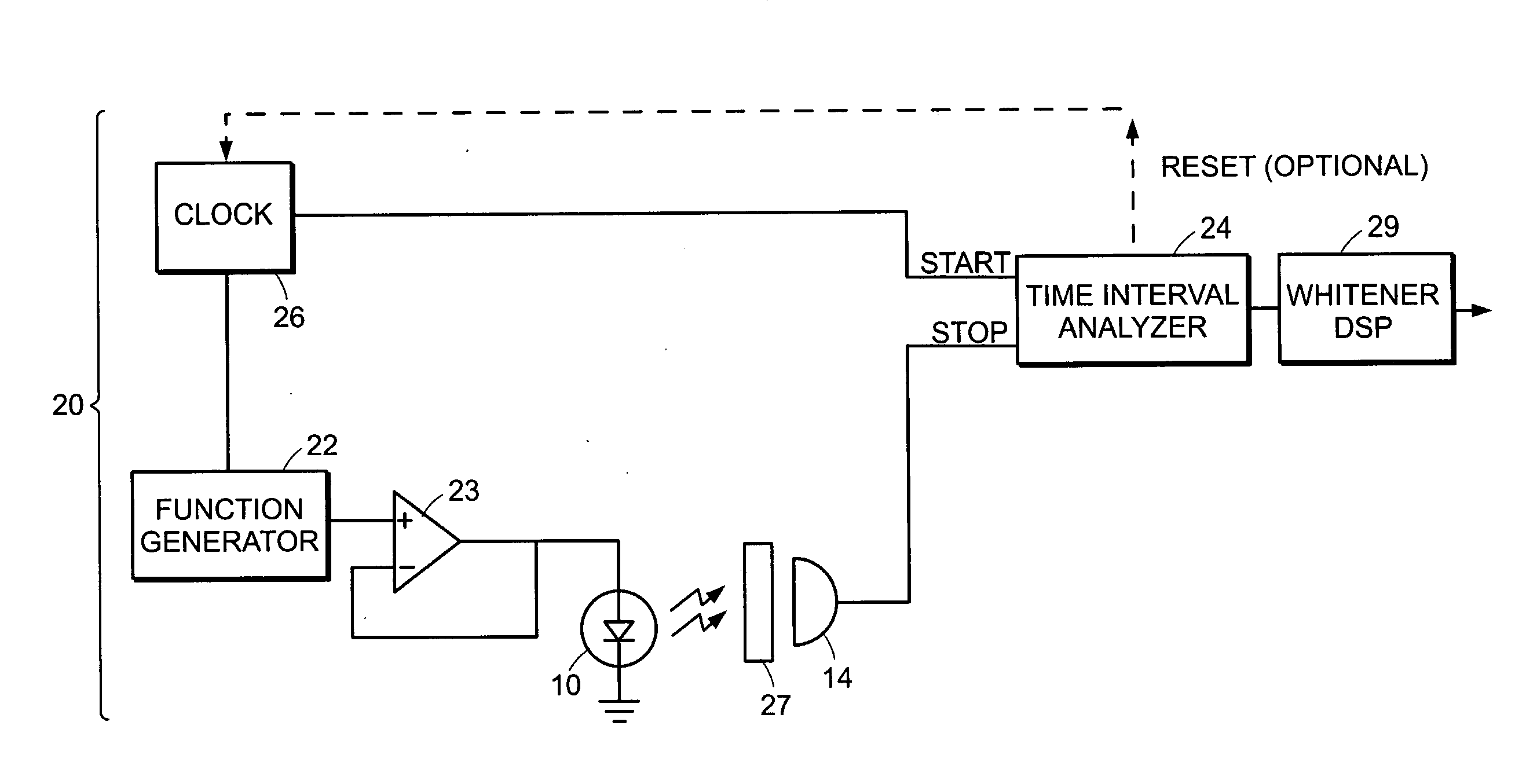
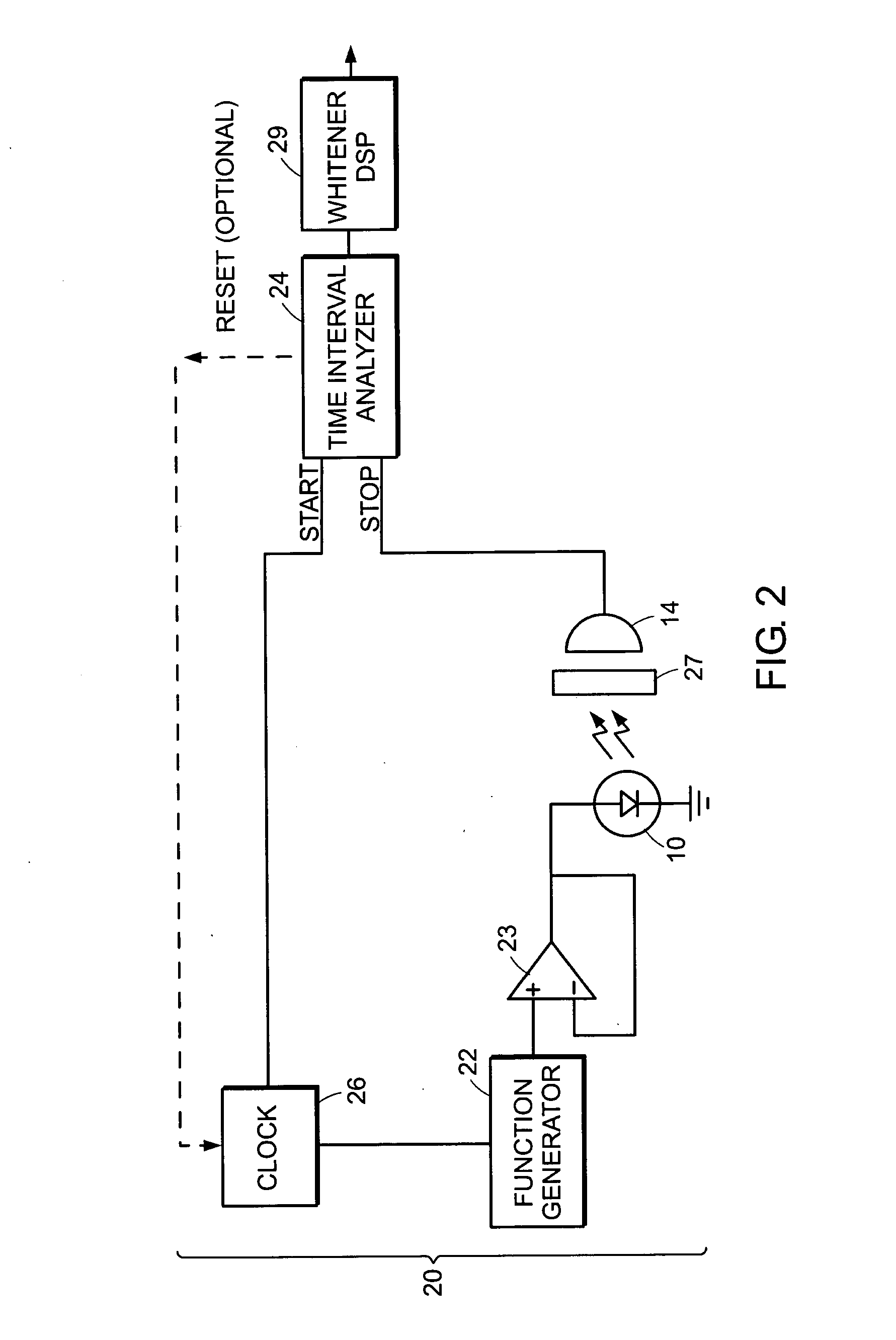
A method and apparatus for generating random numbers. Events characteristic of a random process are registered, and a particular time segment, from among a set of time segments, is identified based upon registration of an event within that time segment, and a value is associated based on the identified time segment. The events may be detections of a particle by a particle detector such as a photon detector. A random number is outputted based at least upon the associated value. Outputting of the random numbers may be followed by a whitening process. The source of particles may be driven to provided various specified probability distributions of values.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
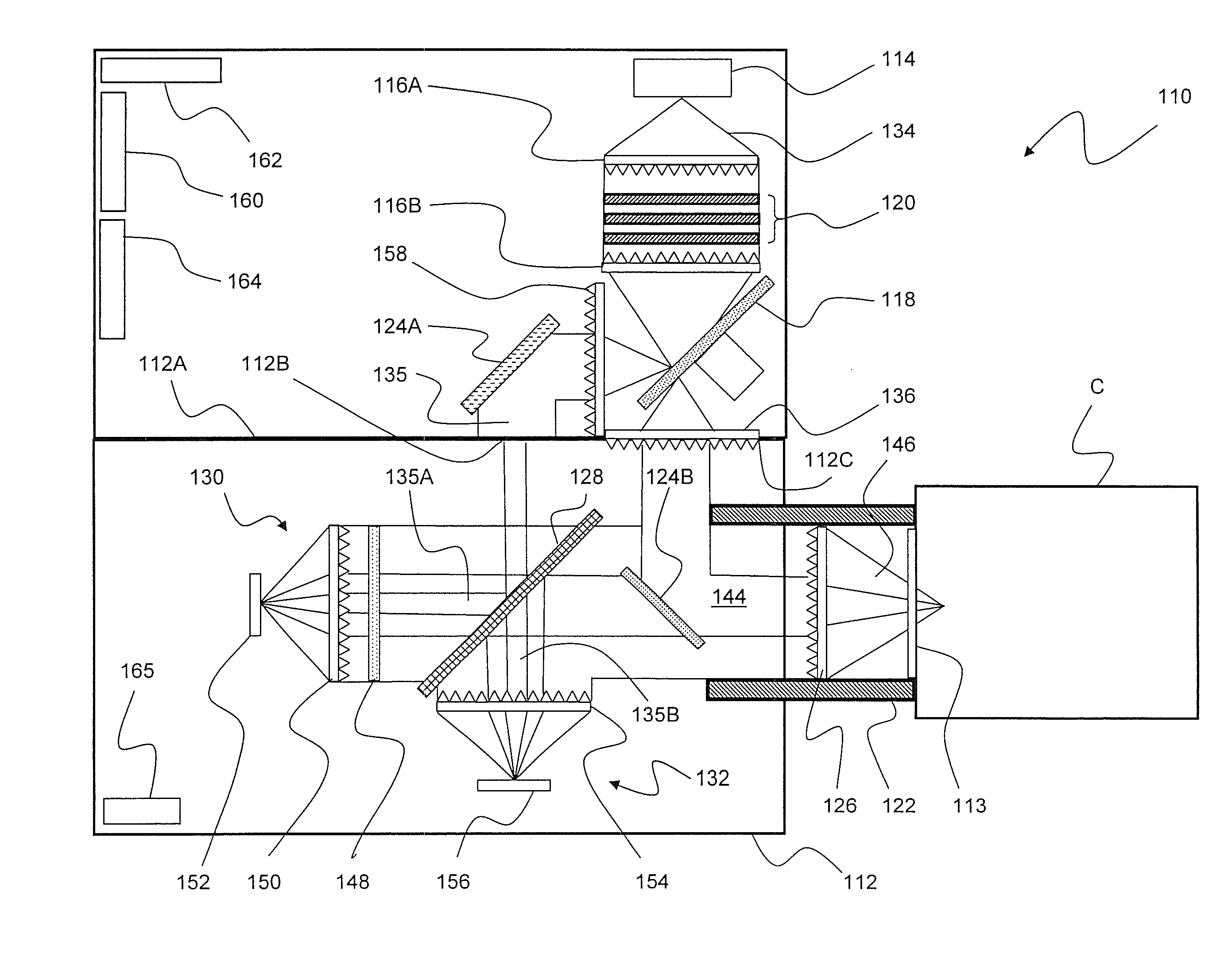
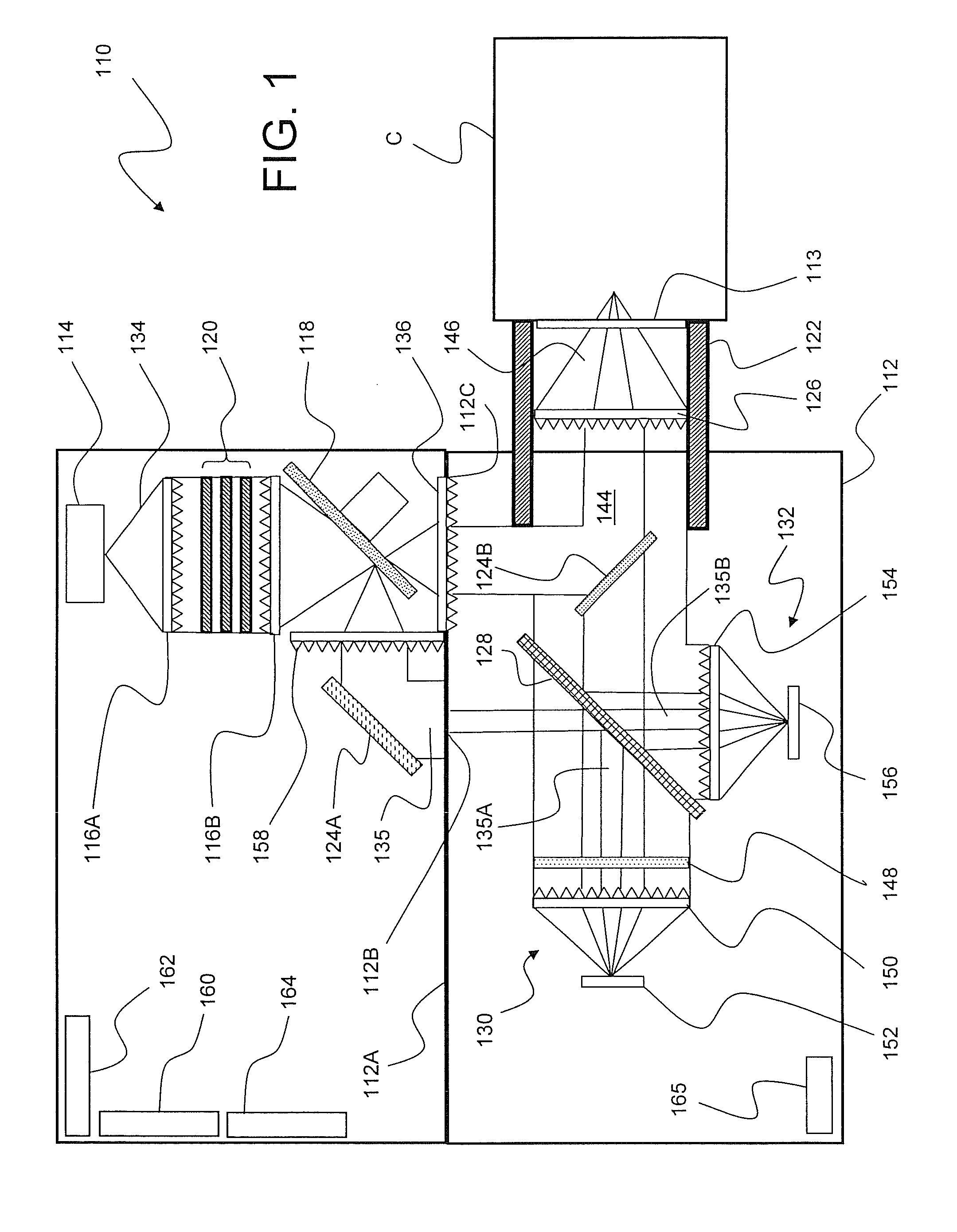
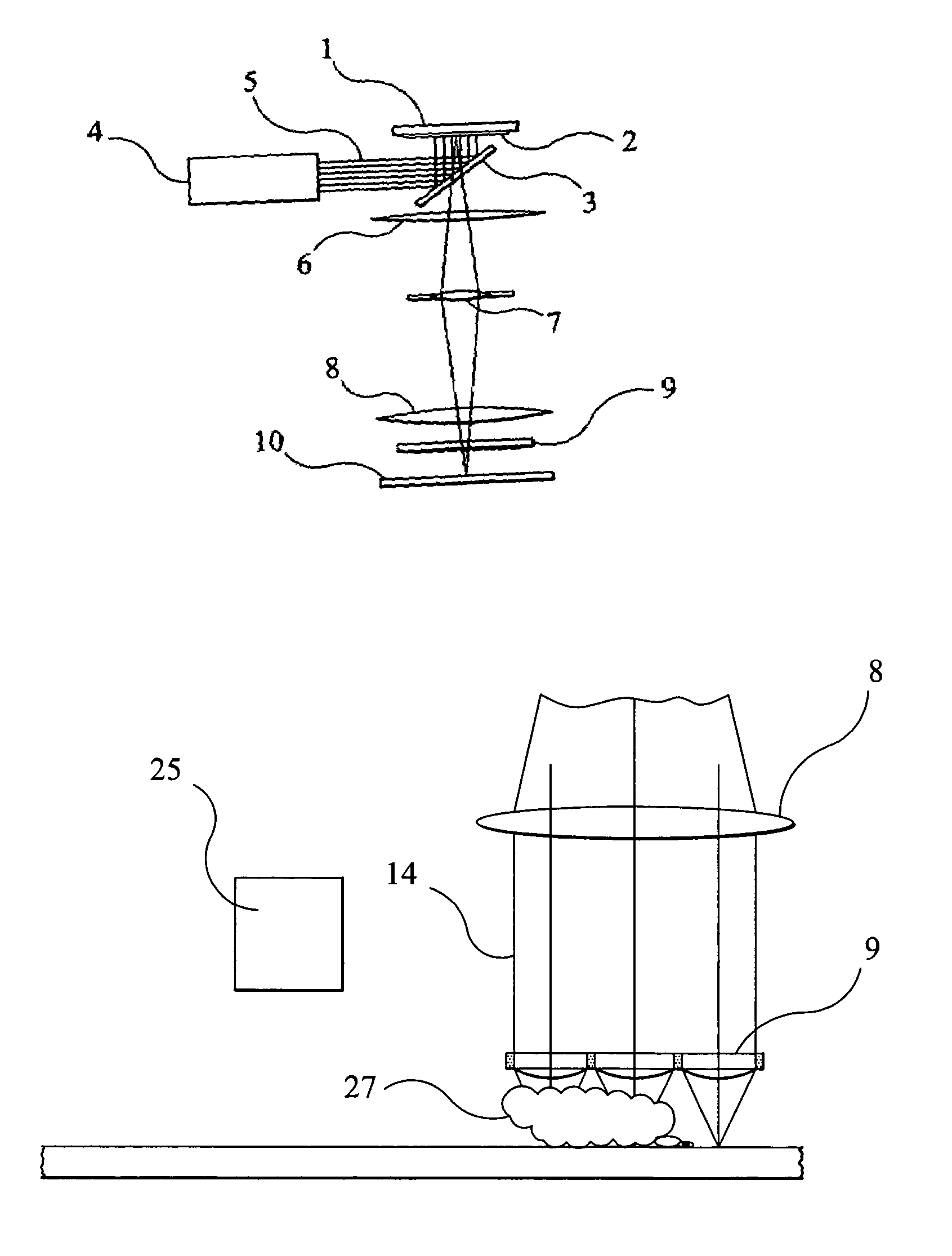
Particle detector, system and method
ActiveUS8508376B2Easy to detectMethod using image detector and image signal processingScattering properties measurementsLaser beamsParticle detector
The invention provides use of one or more emitted beams of radiation (16), for example, laser beam(s), in combination with an image capturing means (14), for example, one or more video cameras and / or optical elements to detect particles (30), for example smoke particles, located in an open space (12).
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
Multidirectional high energy particle detector
InactiveCN102183779AAchieve integrationAchieve directional fluxX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementAudio power amplifierHigh energy
The invention relates to a multidirectional high energy particle detector. The detector includes a direction sensor which includes semiconductor detectors, the semiconductor detectors are staggeredly arranged in four rows on a side cylinder of a cylindrical pedestal which has a semi-circular cross section, and the semiconductor detectors are positioned with an interval angle of 11.25 degrees; a high energy electron spectrum sensor which includes three different conductor detectors; a high energy particle spectrum sensor which includes three different semiconductor detectors; main amplifiers; peak value retainers; ADC collection circuits; an FPGA processing chip; wherein the output terminals of preposing amplifiers are connected with the corresponding output terminals of the main amplifiers respectively via forming circuits, the output terminals of main discharge circuits are connected with the corresponding output terminals of the peak value retainers respectively, the output terminals of the peak value retainers are connected with the corresponding output terminals of the ADC collection circuits respectively, and the output terminals of the ADC collection circuits are connected with the output terminal of the FPGA processing chip after the analog-digital conversion. The detector detects the flux of the high energy particle along a 180 degrees sector direction, and also detects the power spectrum of the high energy particle along a vertical sector direction.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
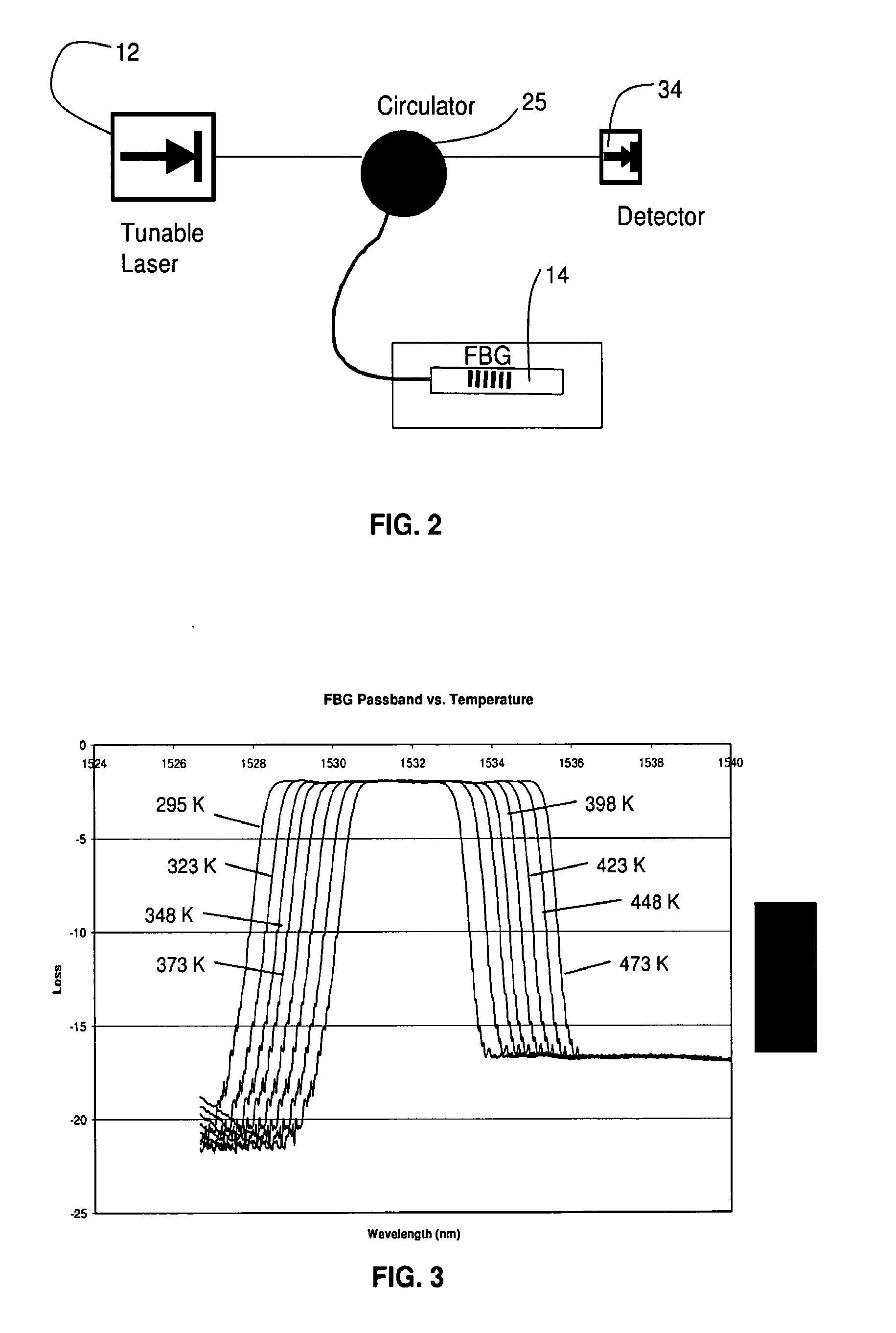
All-Fiber Architecture for an Embedded Flight Sensor for Aeropropulsion Applications
InactiveUS20080285916A1Sensing radiation from gases/flamesThermometers using physical/chemical changesAviationGrating
An embedded flight sensor system having a laser and one or more flight sensors in optical communication with the laser plus a data processing device in optical communication with the flight sensors. The flight sensors may be laser based optical components such as a fiber Bragg grating in combination with an optical detector, a spectroscopy grating and detector or an optical detector associated with catch optics. The parameters sensed by the flight sensors may be used to determine any flight parameter. Representative flight parameters include but are not limited to an airframe or external surface temperature, airstream velocity, combustion zone temperature, engine inlet temperature, a gas concentration or a shock front position.
Owner:ZOLO TECHNOLOGIES INC
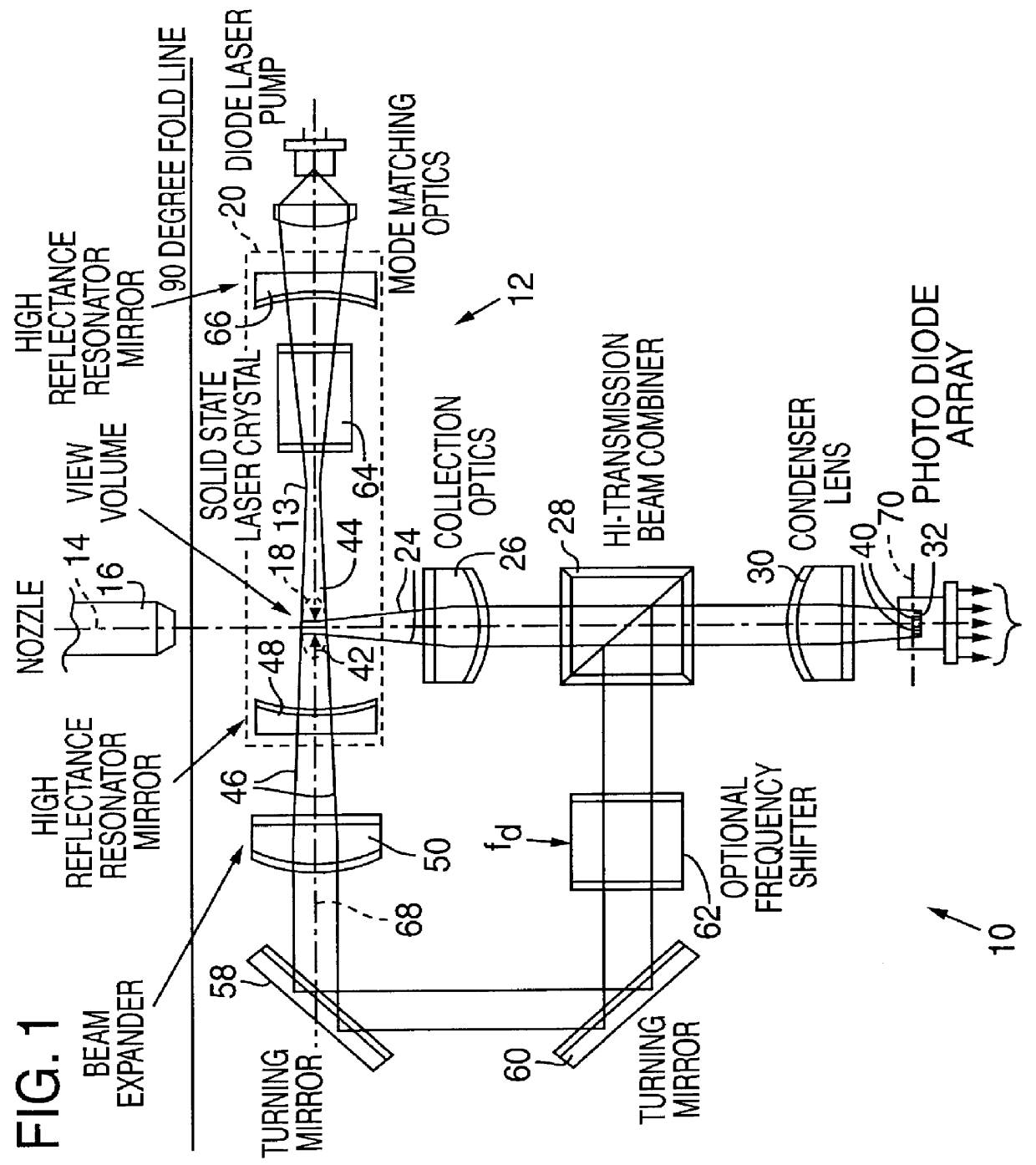
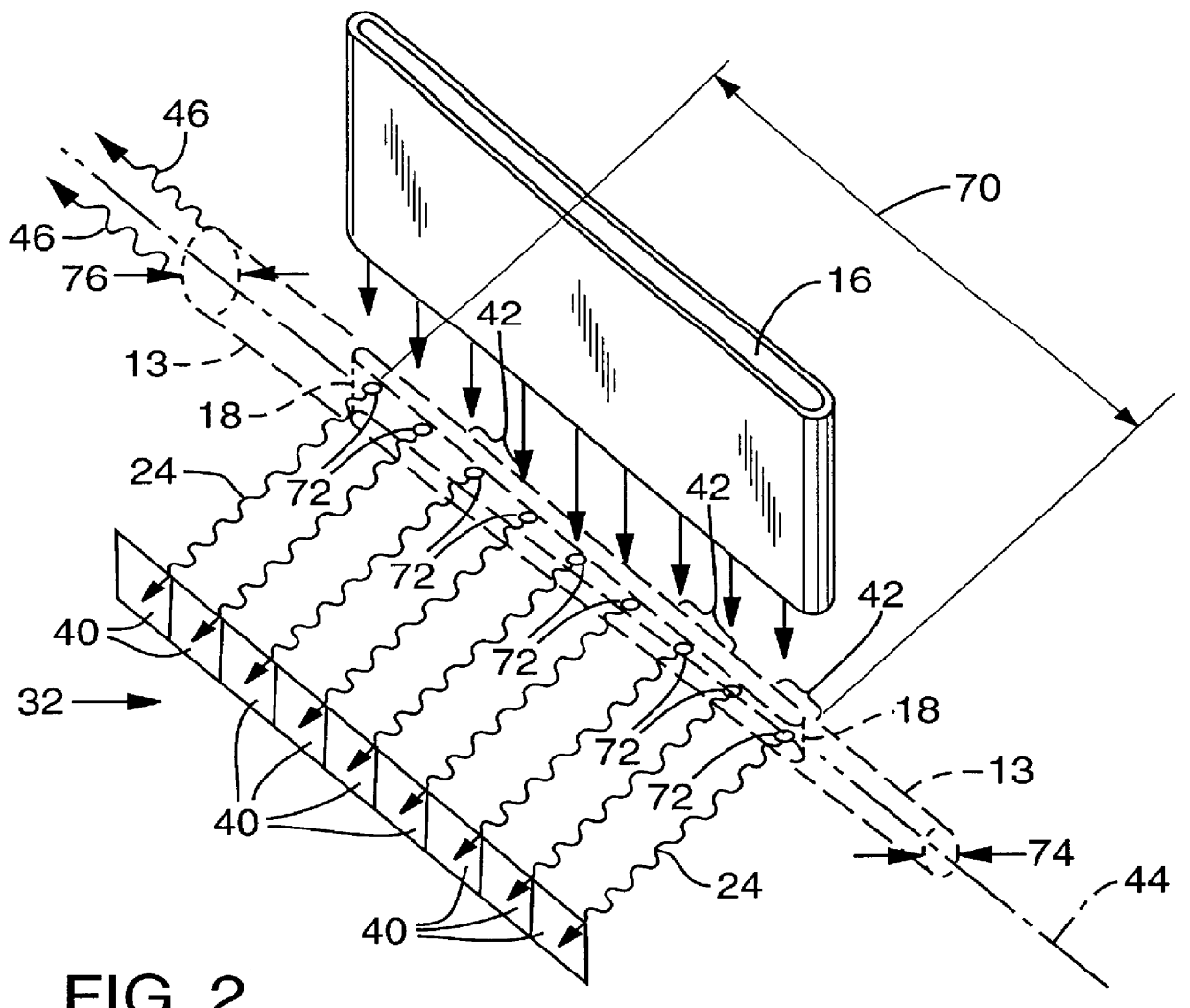
Flow apertured intracavity laser particle detector
InactiveUS6111642AHigh submicron particle detection sensitivityAccurate particle size determinationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsLaser lightLaser beams
A particle counter (10) passes a sample stream of a carrier gas or fluid containing particles (72) through an elongated, flattened nozzle (16) and into a view volume (18) formed by an intersection of the sample stream and a laser beam (13). Particles entrained in the sample stream scatter light rays while passing through the view volume. The scattered light is collected by an optical system (26) and focused on to a detector (40). The magnitude of signal coming from the detector is indicative of the particle size. To correct for variances in particle velocity and light beam intensity across the view volume, flow aperturing is used. Flow aperture modeling (Eqs. 1-7) provides a format for designing the nozzle such that the lateral velocity profile matches the laser beam lateral intensity profile, thereby providing uniform detection sensitivity to laser light scattered from monodisperse particles distributed laterally across the view volume. Uniform detection sensitivity of monodisperse particles provides accurate particle sizing resolution.
Owner:HACH CO
Spectrometer incorporating signal matched filtering
ActiveUS7154599B2Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryDigital signal processingOptical processing
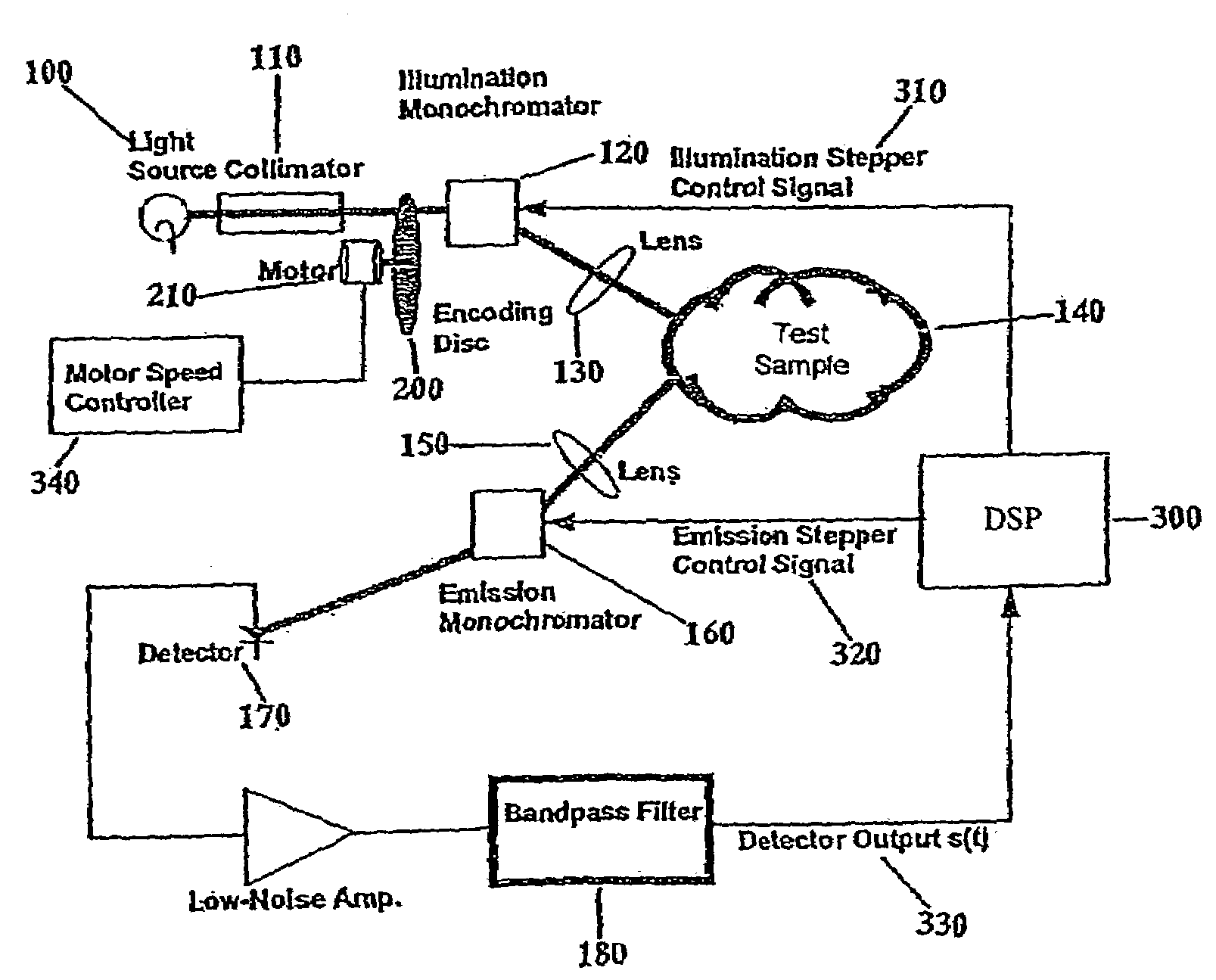
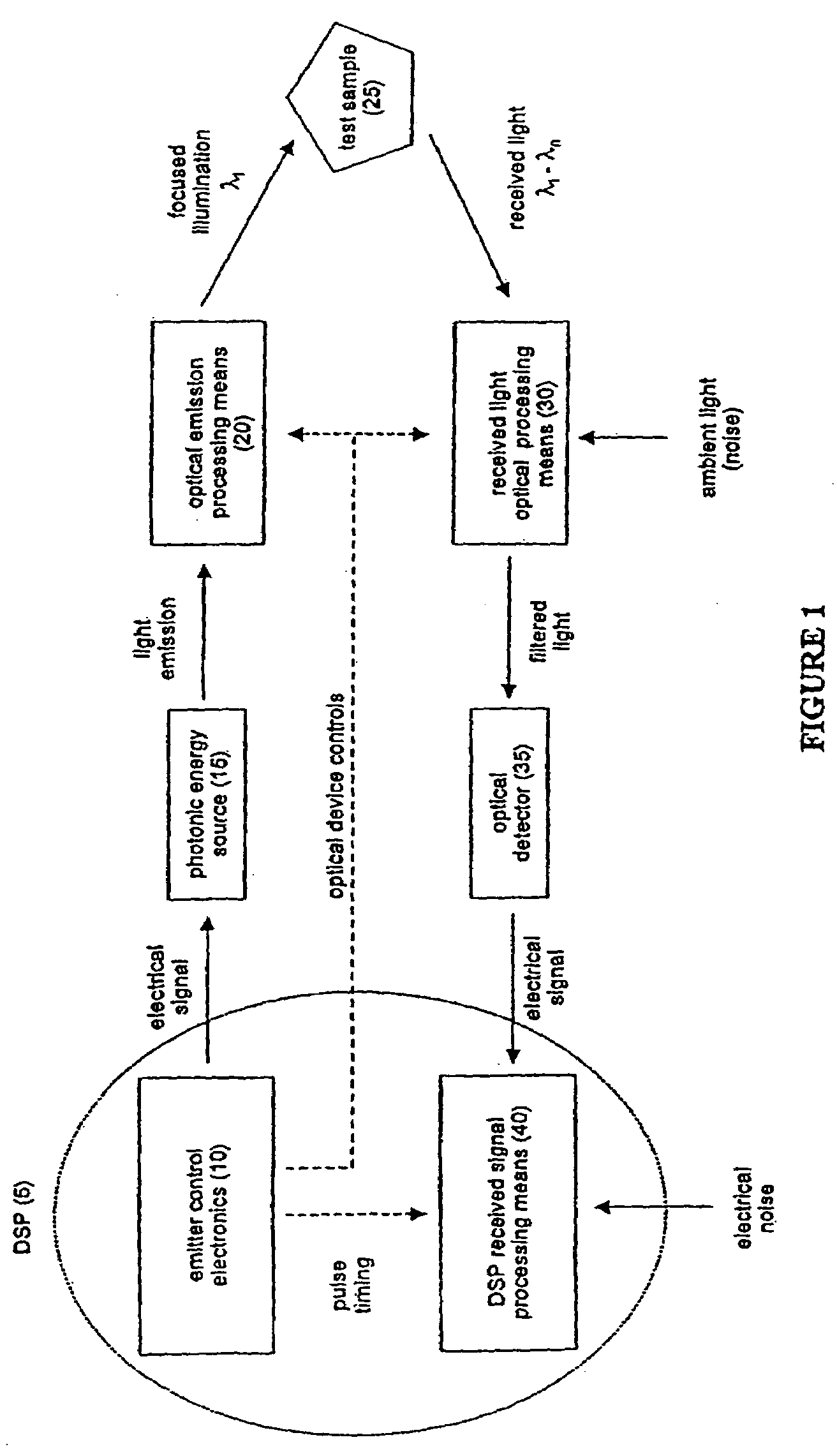
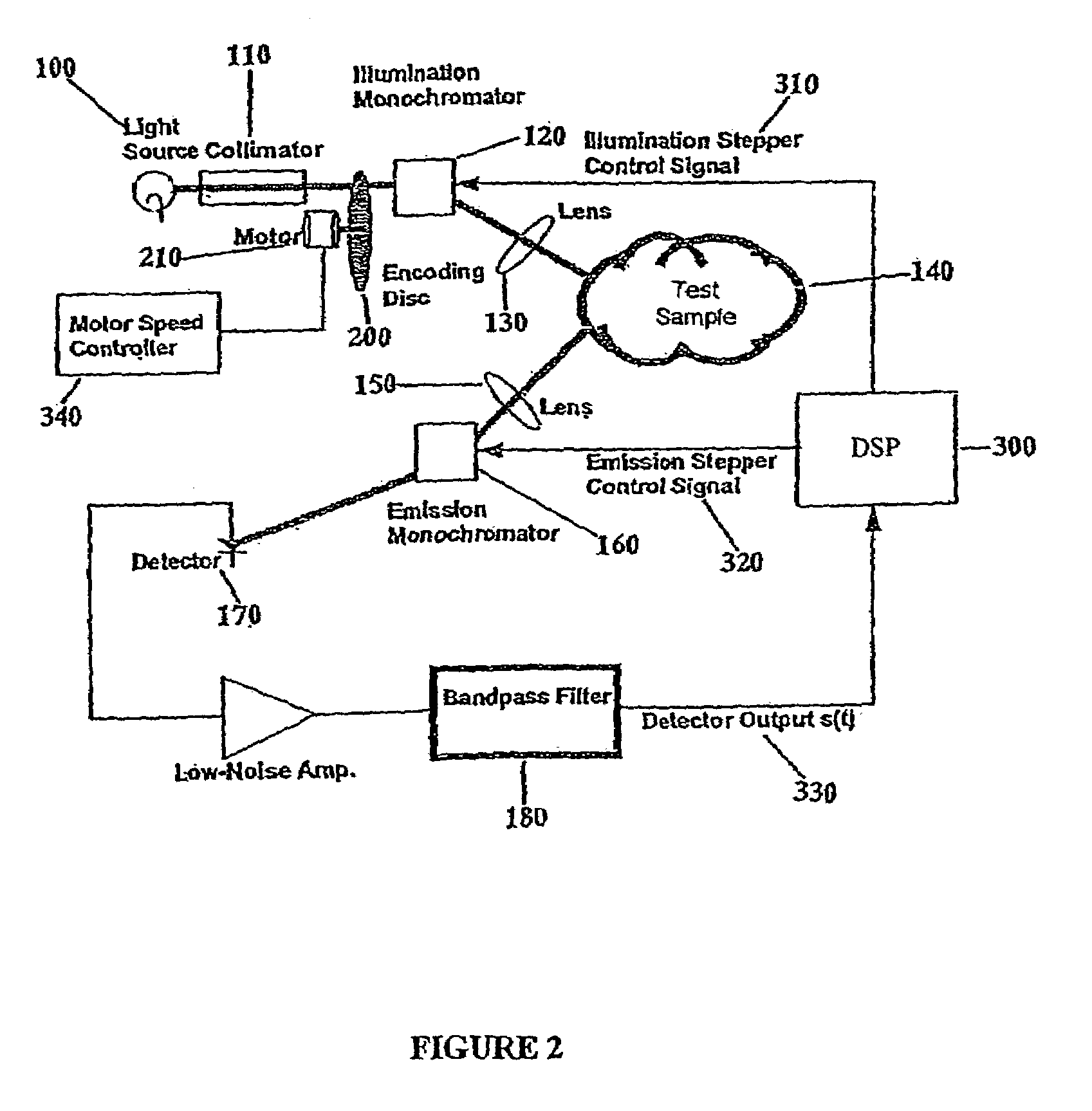
An optical system for performing a spectral analysis of test samples is provided. The optical system comprises a photonic energy source, an optical emission processing system, a received light optical processing system, an optical detector and a digital signal processing system. The optical emission processing system transmits one or more illumination wavelengths to a test sample. The received light optical processing system collects and isolates one or more wavelengths received from the test sample and transmits them to an optical detector. The optical detector converts the isolated one or more wavelengths of received electromagnetic radiation into an electrical signal which is transmitted to the digital signal processing system. The digital signal processing system performs matched filtering of the electrical signal received from the optical detector and additionally controls the functionality of the photonic energy source, the optical emission processing system and the received light optical processing system.
Owner:ADAMS BRUCE WILLIAM MR
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS7158208B2Avoid damageReduce contaminationPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingControl systemLight beam
A lithographic apparatus and method in which an illumination system supplies a projection beam, a patterning system imparts to the beam a pattern in its cross section, and a projection system projects the patterned beam onto a target portion of a substrate. The projection system comprises an array of lenses spaced from the substrate such that each lens in the array focuses part of the patterned beam onto the substrate. A displacement system causes displacement between the lens array and the substrate. A particle detector detects particles on the substrate which are approaching the lens array. A free working distance control system increases the spacing between the lens array and the substrate in response to detection of a particle. The lens array is moved away from the substrate as the detected particle passes the lens array. Thus damage to the lens array can be avoided.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com