Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
18879results about "Material analysis using wave/particle radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
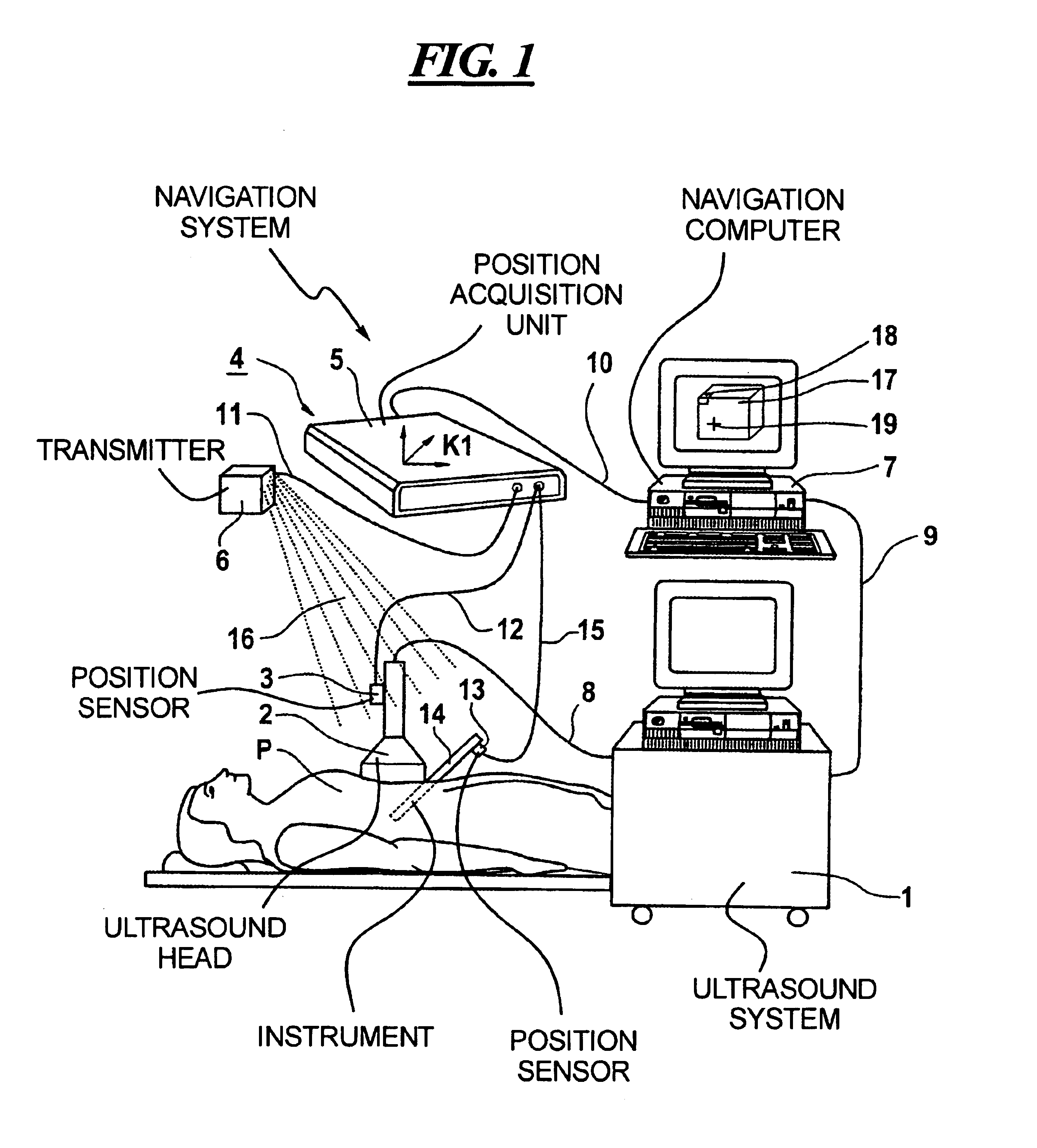
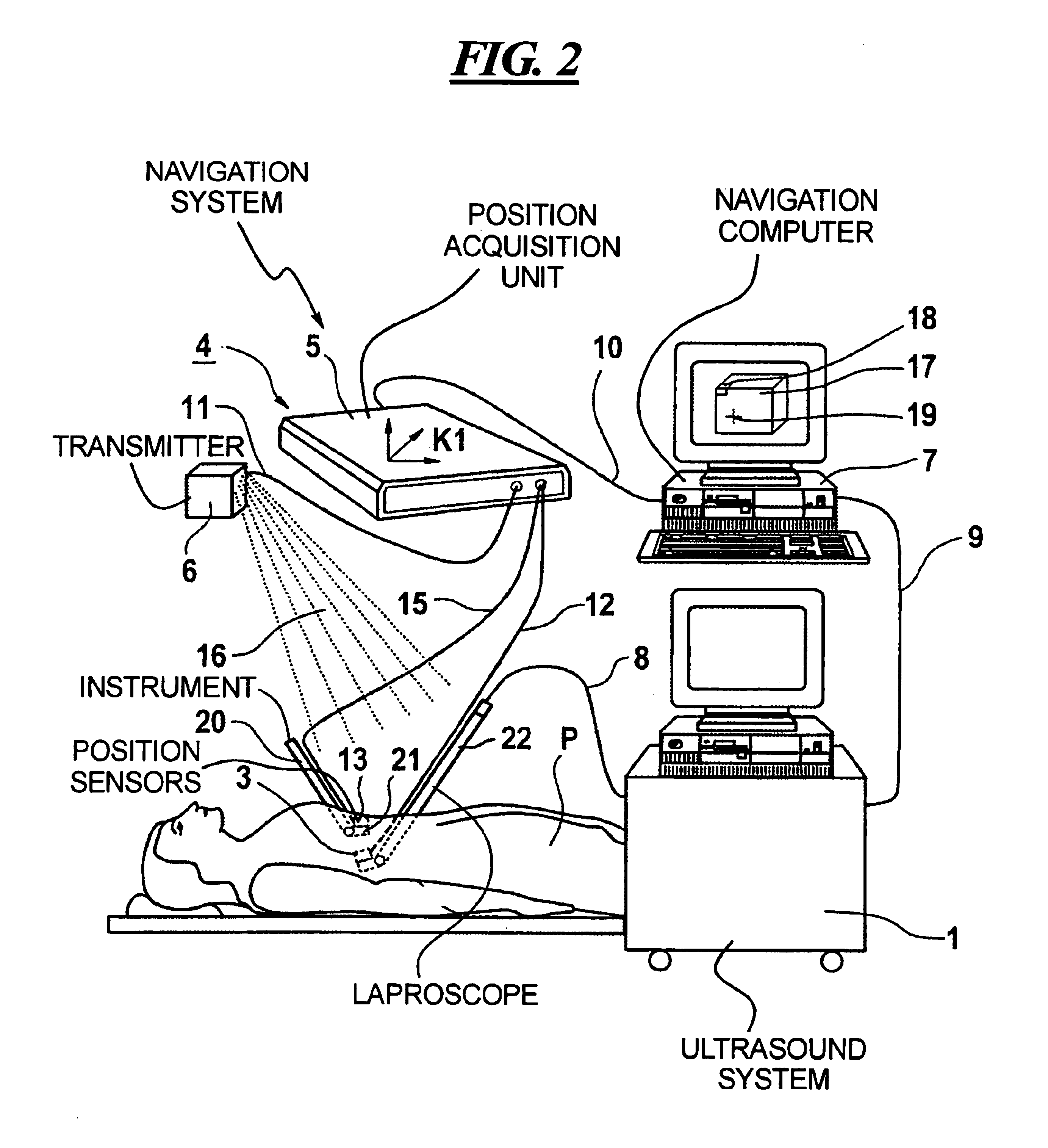
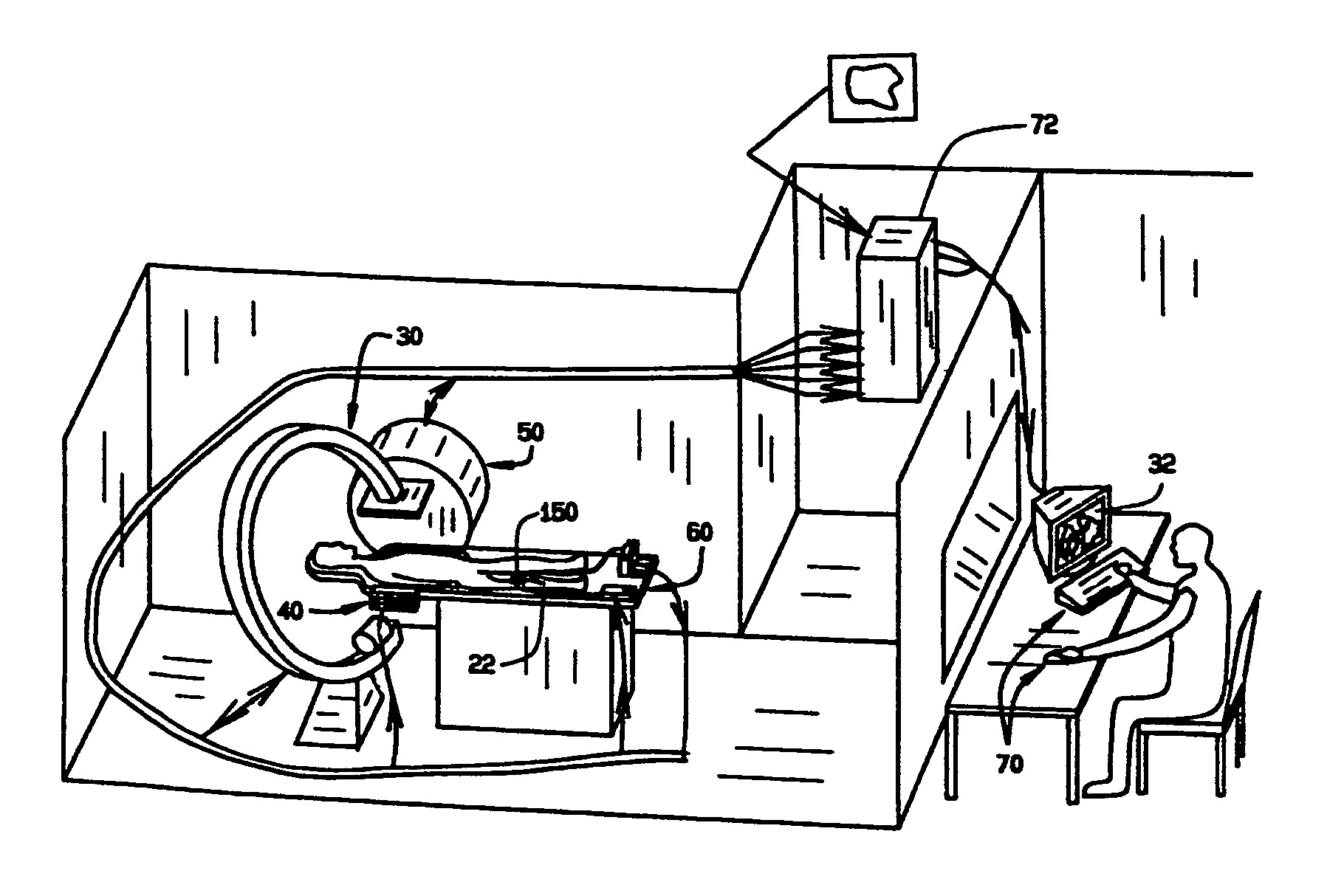
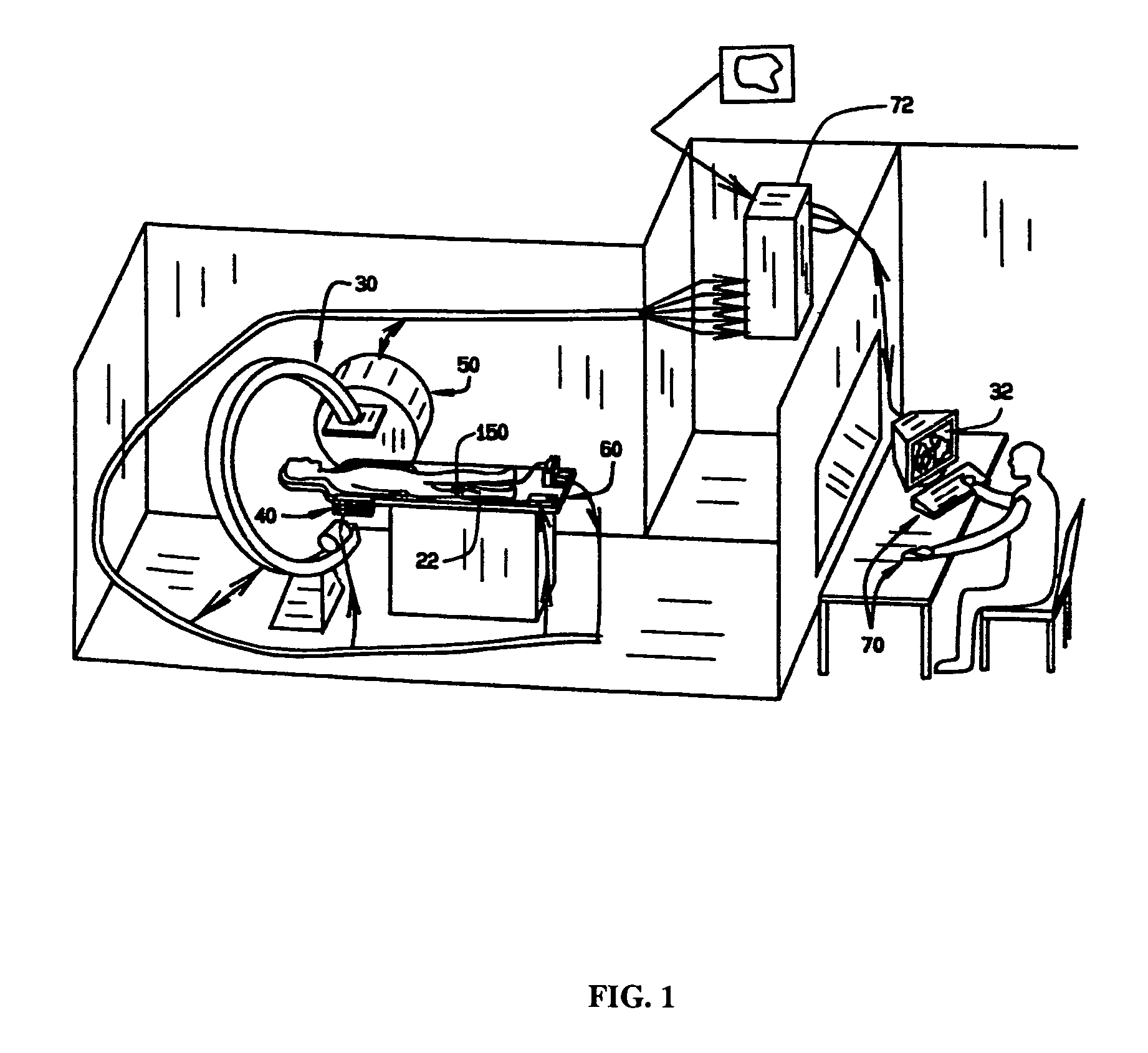
Virtual operating room integration
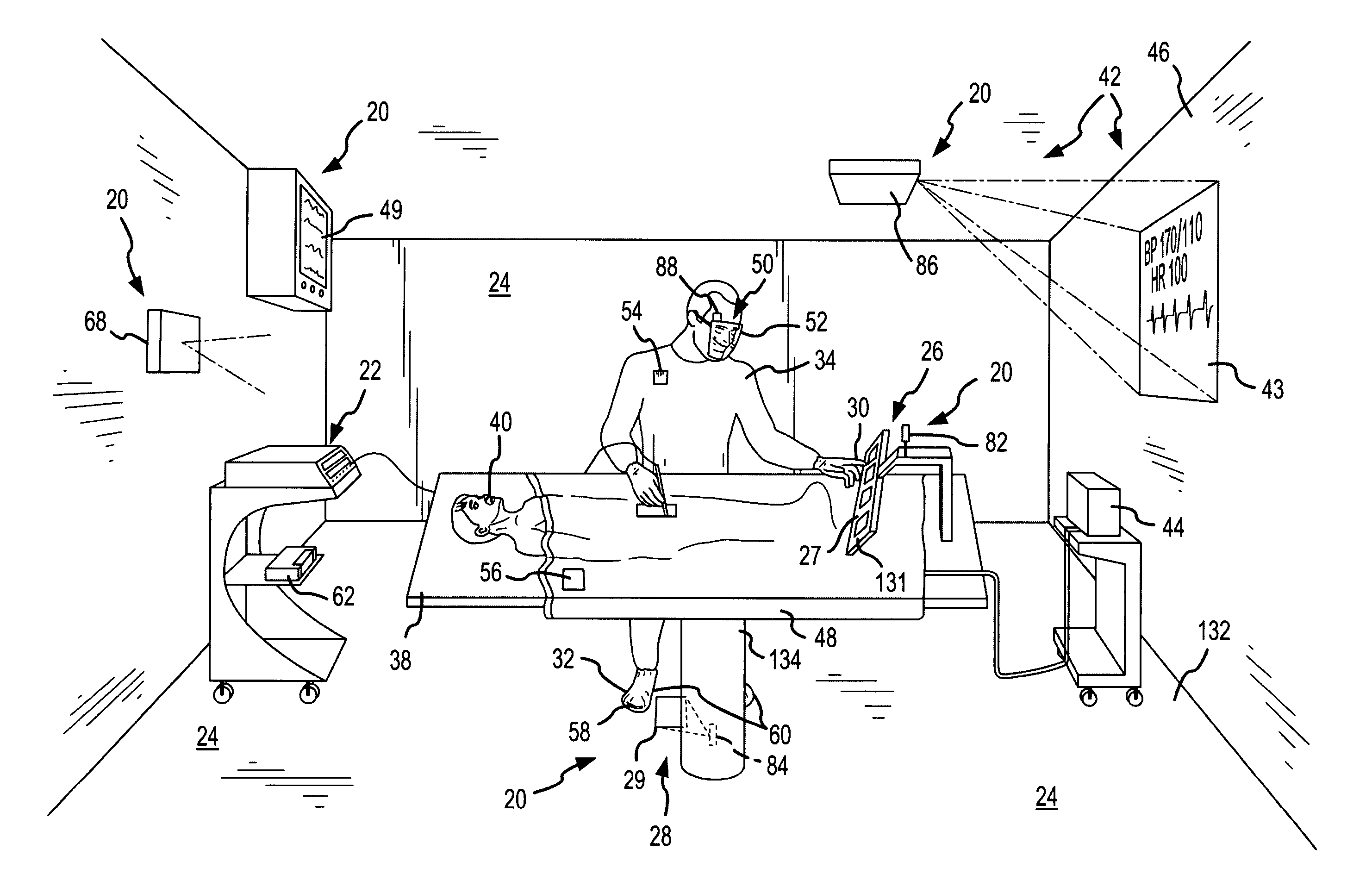
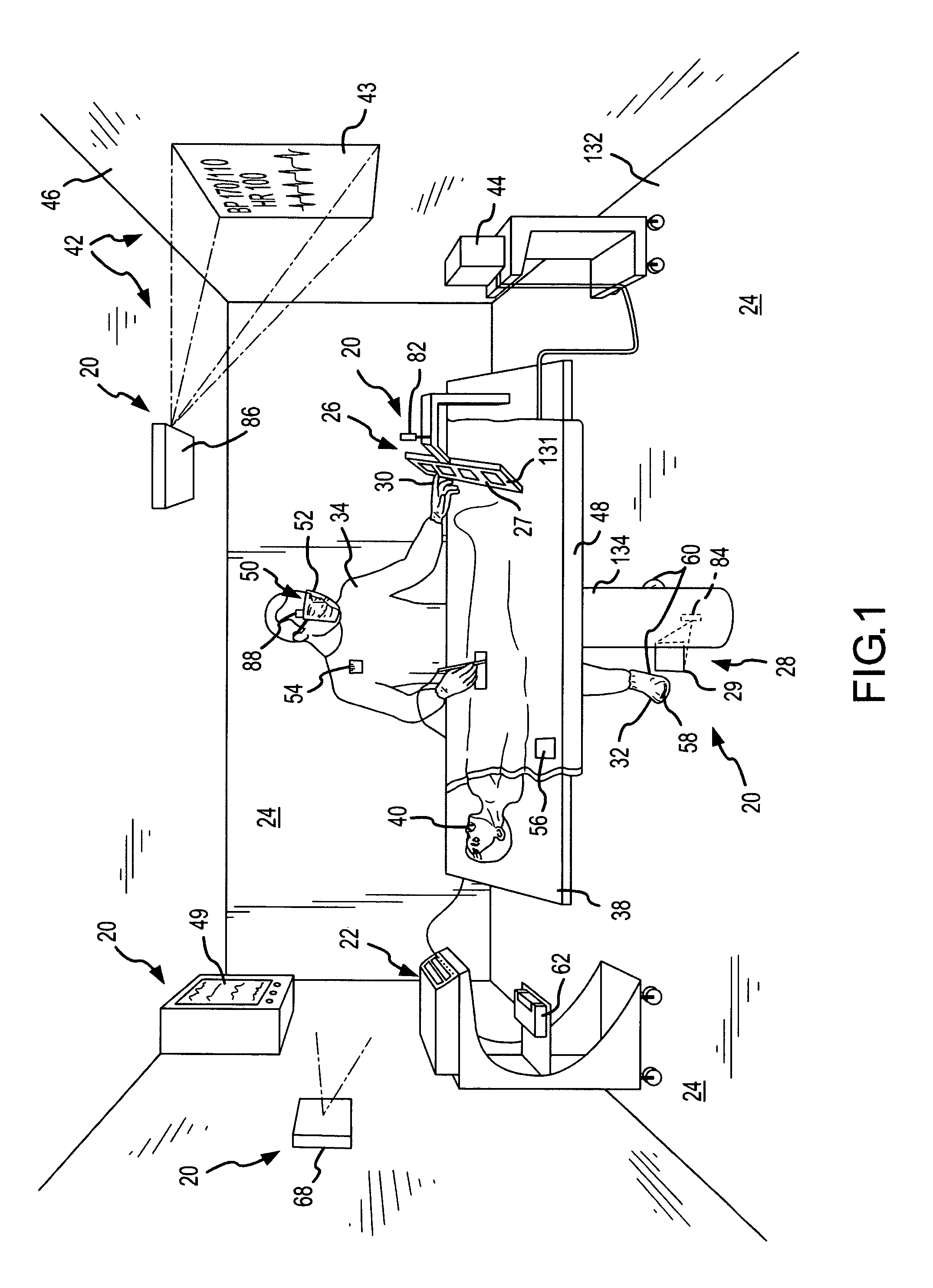
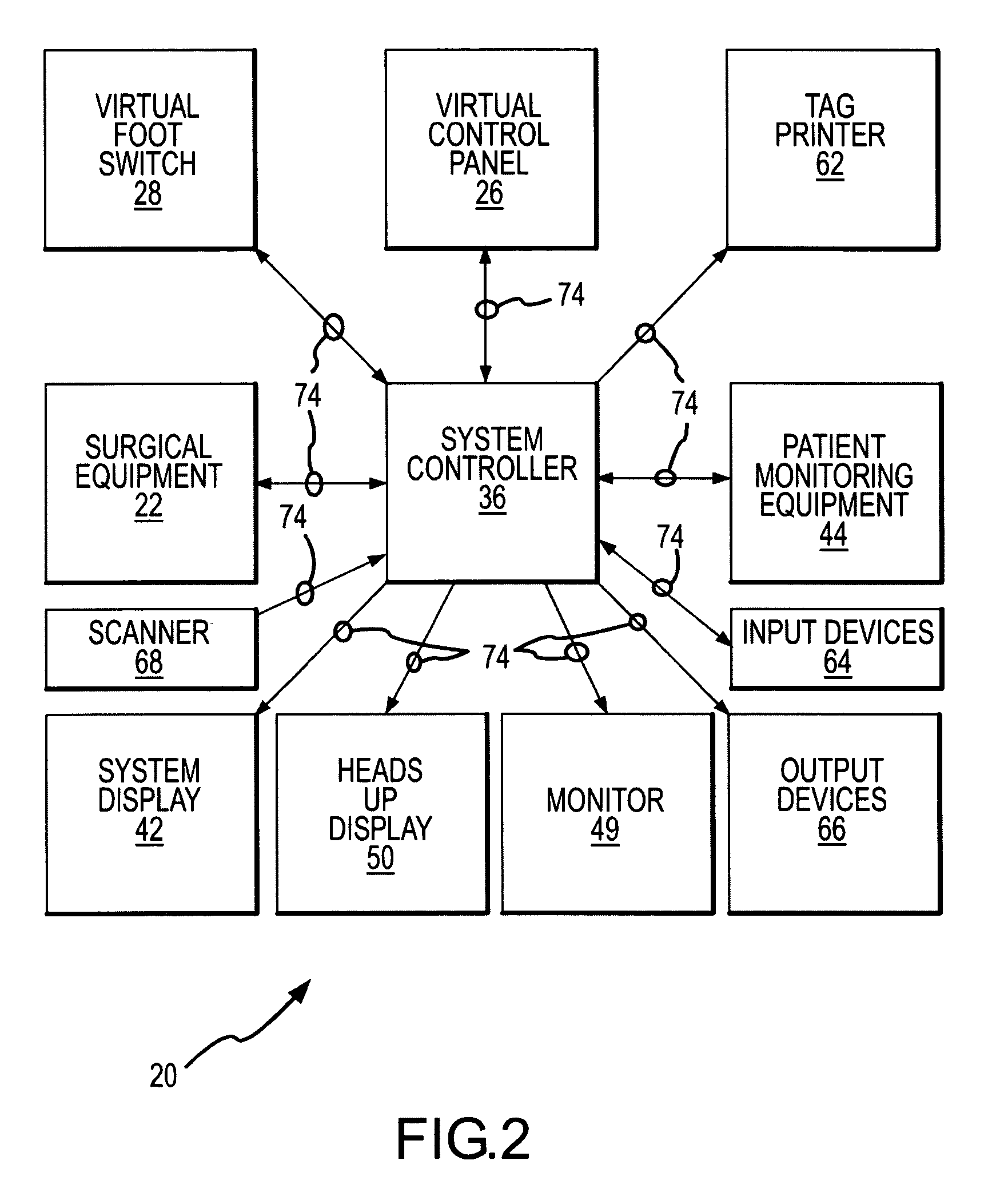
InactiveUS7317955B2Direct and accurate controlEliminating clutter and risk of trippingElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical operationSTERILE FIELD
A virtual control system for an operating room establishes virtual control devices to control surgical equipment and patient monitoring equipment and to display control, status and functionality information concerning the surgical equipment and condition information of the patient. The virtual control devices permit direct interaction by the surgeon while maintaining a sterile field, and avoid the use of actual physical devices and electrical cables connecting them to the surgical equipment.
Owner:CONMED CORP
Moving lens for immersion optical lithography
InactiveUS20050145803A1Reduce turbulenceReduces air bubbleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotometryLithographic artistImage resolution
An apparatus for immersion optical lithography having a lens capable of relative movement in synchrony with a horizontal motion of a semiconductor wafer in a liquid environment where the synchronous motion of the lens apparatus and semiconductor wafer advantageously reduces the turbulence and air bubbles associated with a liquid environment. The relative motions of the lens and semiconductor wafer are substantially the same as the scanning process occurs resulting in optimal image resolution with minimal air bubbles, turbulence, and disruption of the liquid environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
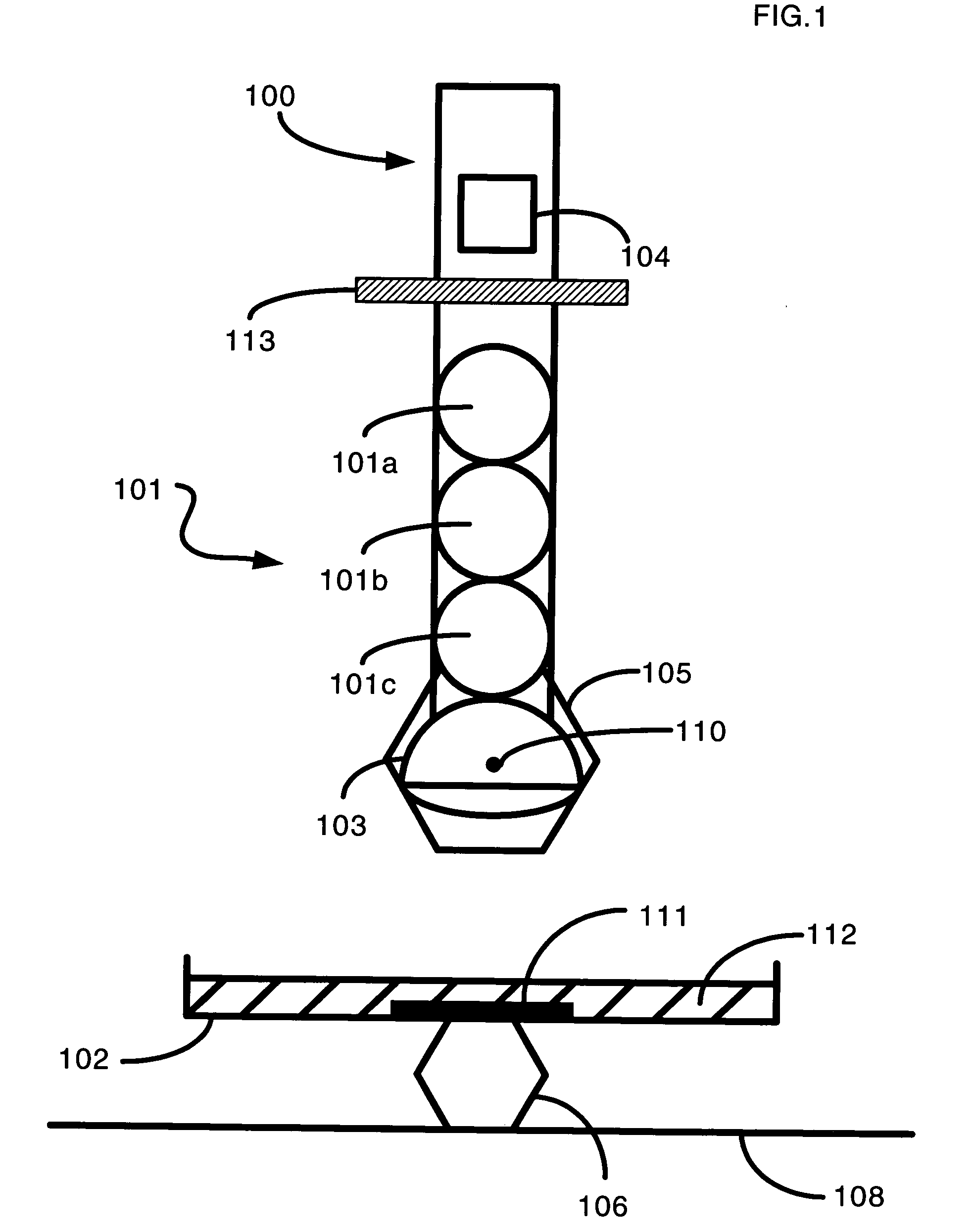
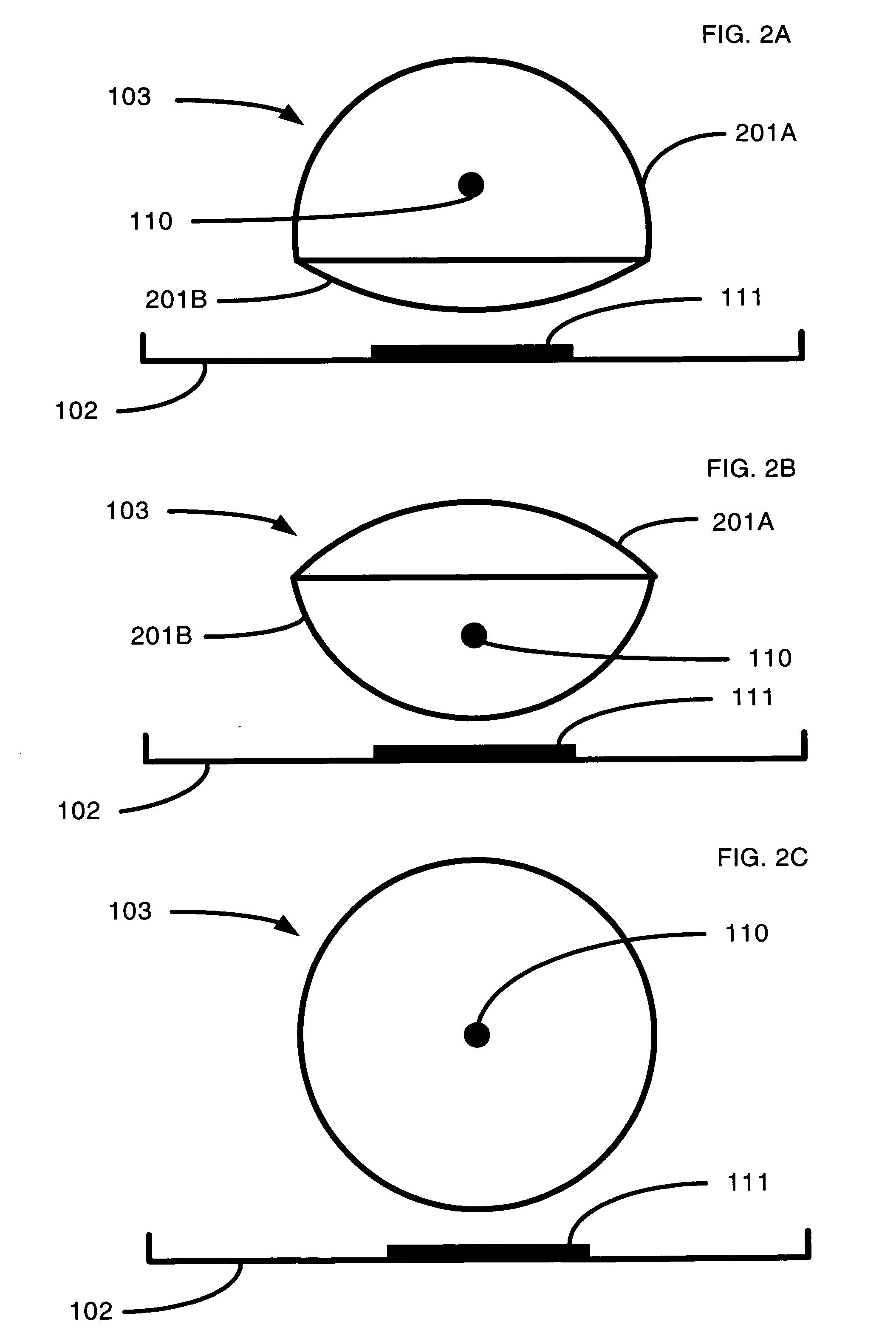
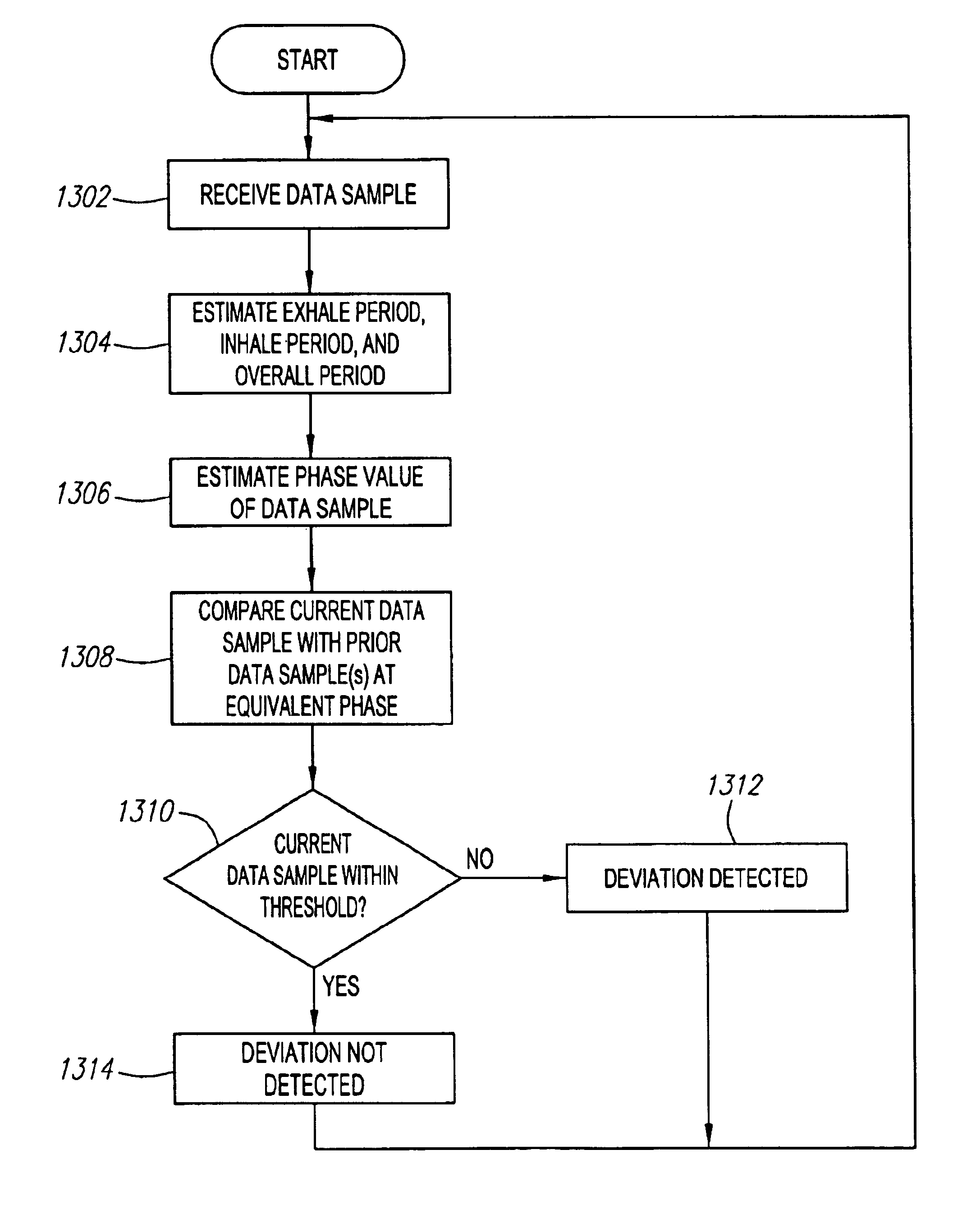
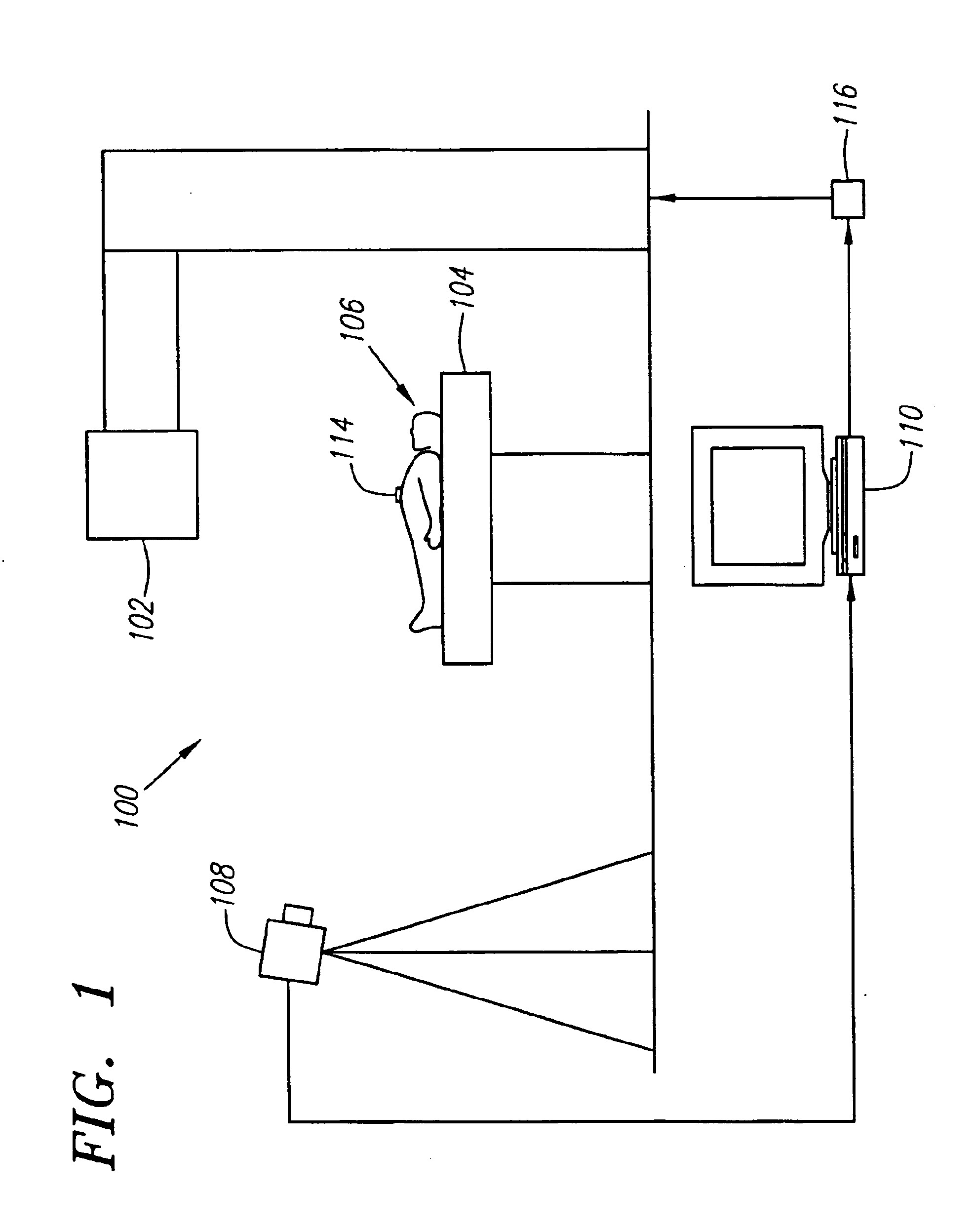
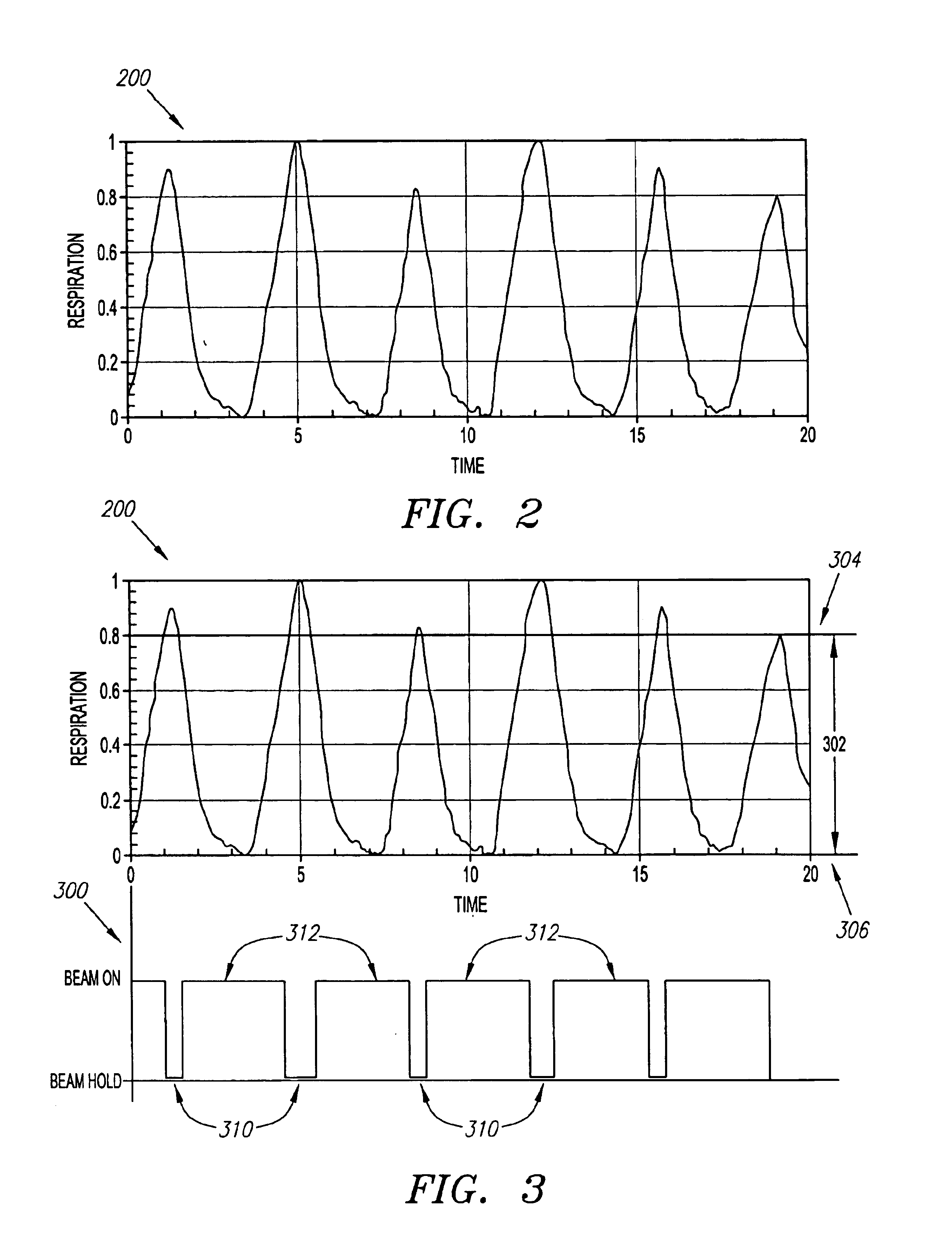
Method and system for predictive physiological gating
InactiveUS6937696B1Consistent positionEasy to FeedbackSurgeryDiagnostic markersComputed tomographyEngineering
A method and system for physiological gating is disclosed. A method and system for detecting and predictably estimating regular cycles of physiological activity or movements is disclosed. Another disclosed aspect of the invention is directed to predictive actuation of gating system components. Yet another disclosed aspect of the invention is directed to physiological gating of radiation treatment based upon the phase of the physiological activity. Gating can be performed, either prospectively or retrospectively, to any type of procedure, including radiation therapy or imaging, or other types of medical devices and procedures such as PET, MRI, SPECT, and CT scans.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
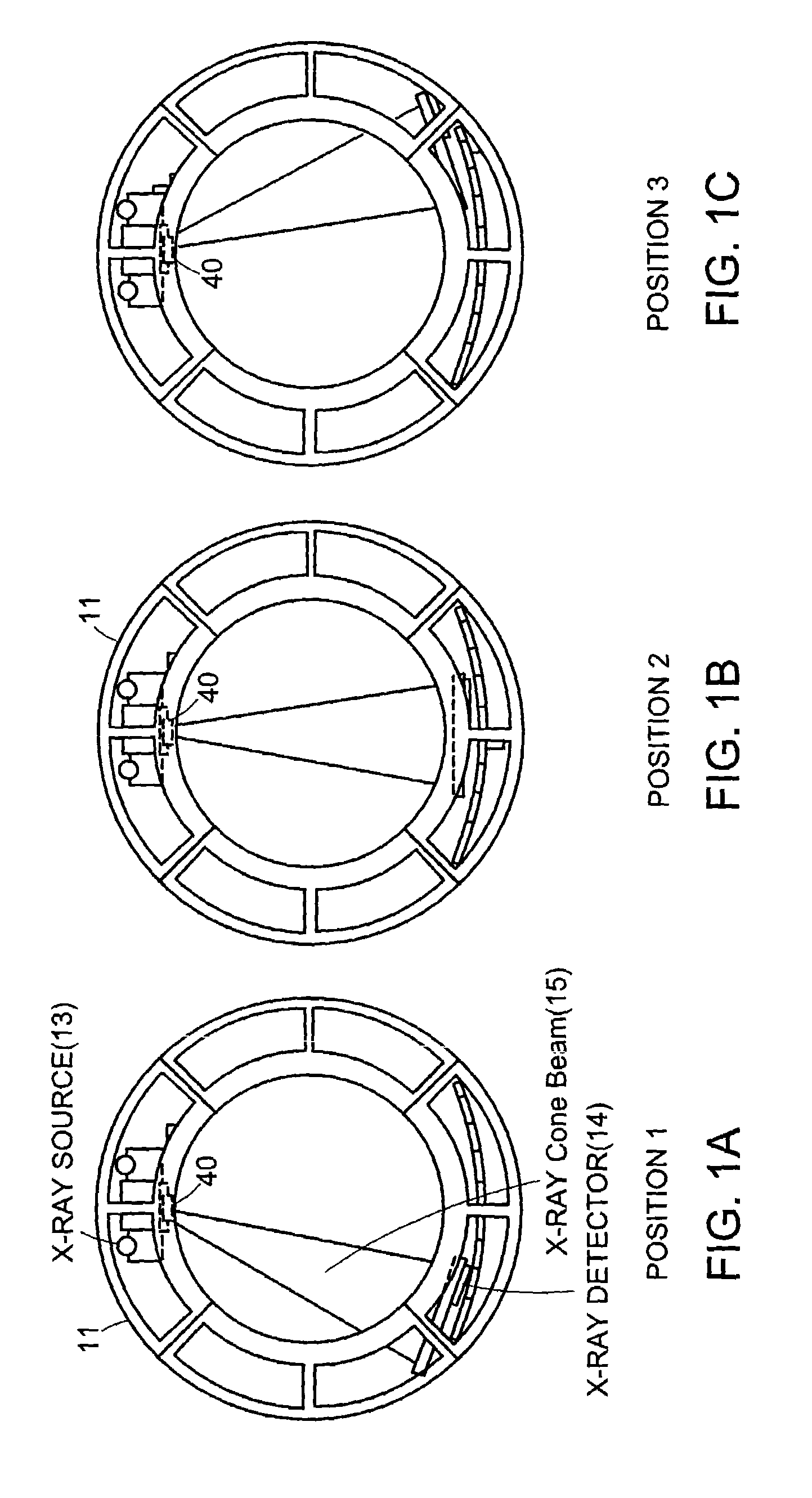
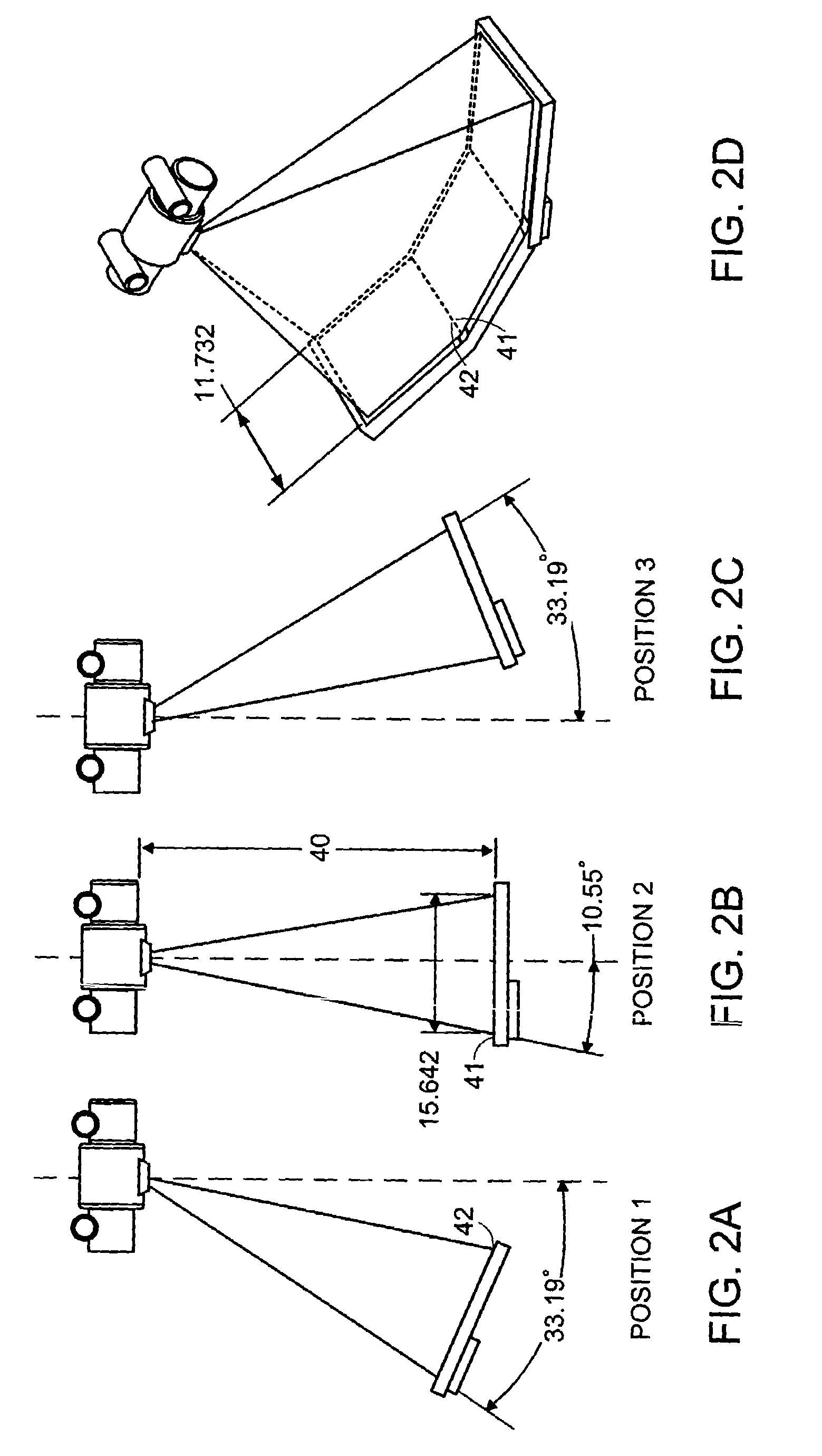
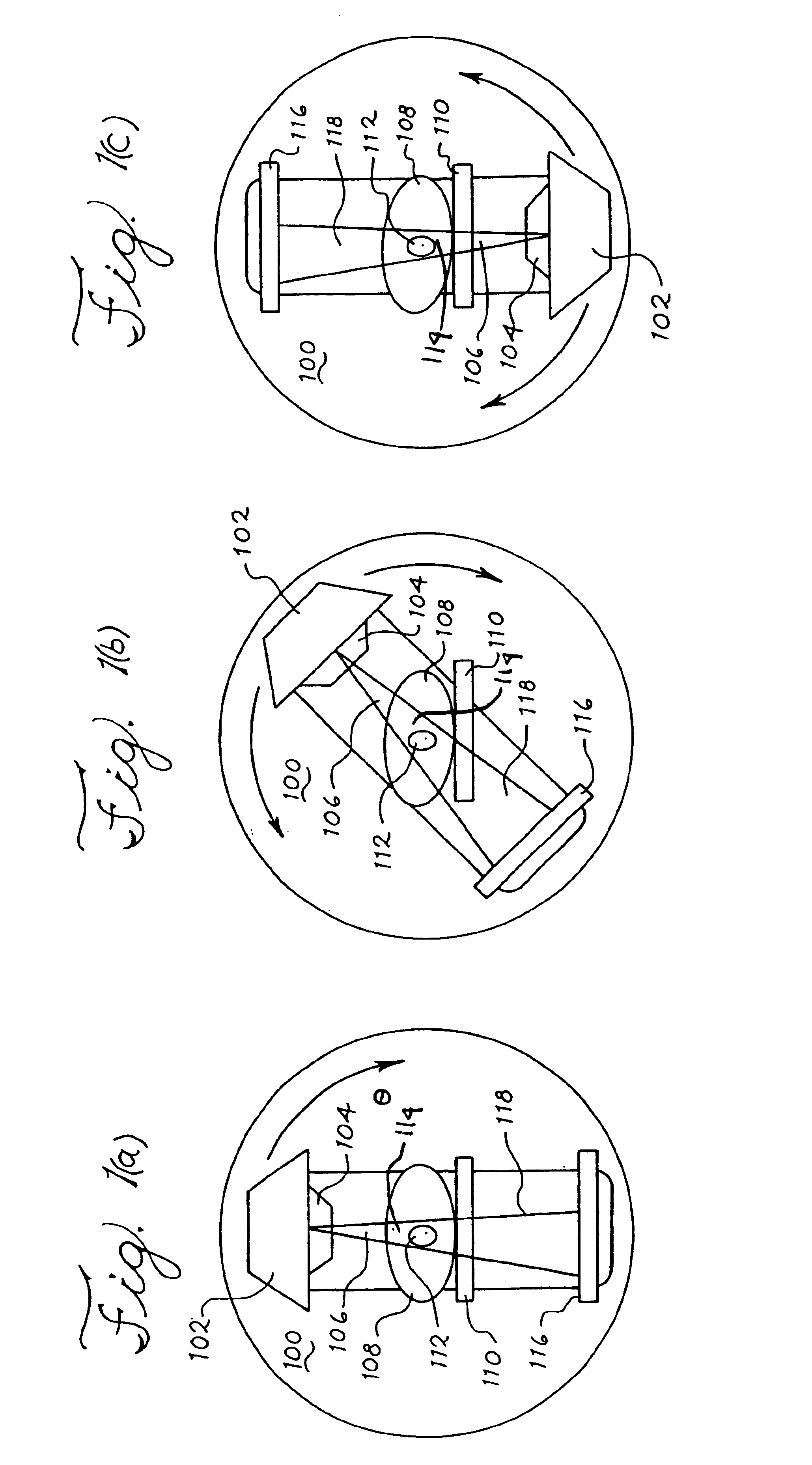
Systems and methods for imaging large field-of-view objects
InactiveUS7108421B2Quantity minimizationAvoiding corrupted and resulting artifacts in image reconstructionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingBeam sourceX-ray
An imaging apparatus and related method comprising a source that projects a beam of radiation in a first trajectory; a detector located a distance from the source and positioned to receive the beam of radiation in the first trajectory; an imaging area between the source and the detector, the radiation beam from the source passing through a portion of the imaging area before it is received at the detector; a detector positioner that translates the detector to a second position in a first direction that is substantially normal to the first trajectory; and a beam positioner that alters the trajectory of the radiation beam to direct the beam onto the detector located at the second position. The radiation source can be an x-ray cone-beam source, and the detector can be a two-dimensional flat-panel detector array. The invention can be used to image objects larger than the field-of-view of the detector by translating the detector array to multiple positions, and obtaining images at each position, resulting in an effectively large field-of-view using only a single detector array having a relatively small size. A beam positioner permits the trajectory of the beam to follow the path of the translating detector, which permits safer and more efficient dose utilization, as generally only the region of the target object that is within the field-of-view of the detector at any given time will be exposed to potentially harmful radiation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
Cone beam computed tomography with a flat panel imager
InactiveUS6842502B2Adequate visualizationReduce errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayAmorphous silicon
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
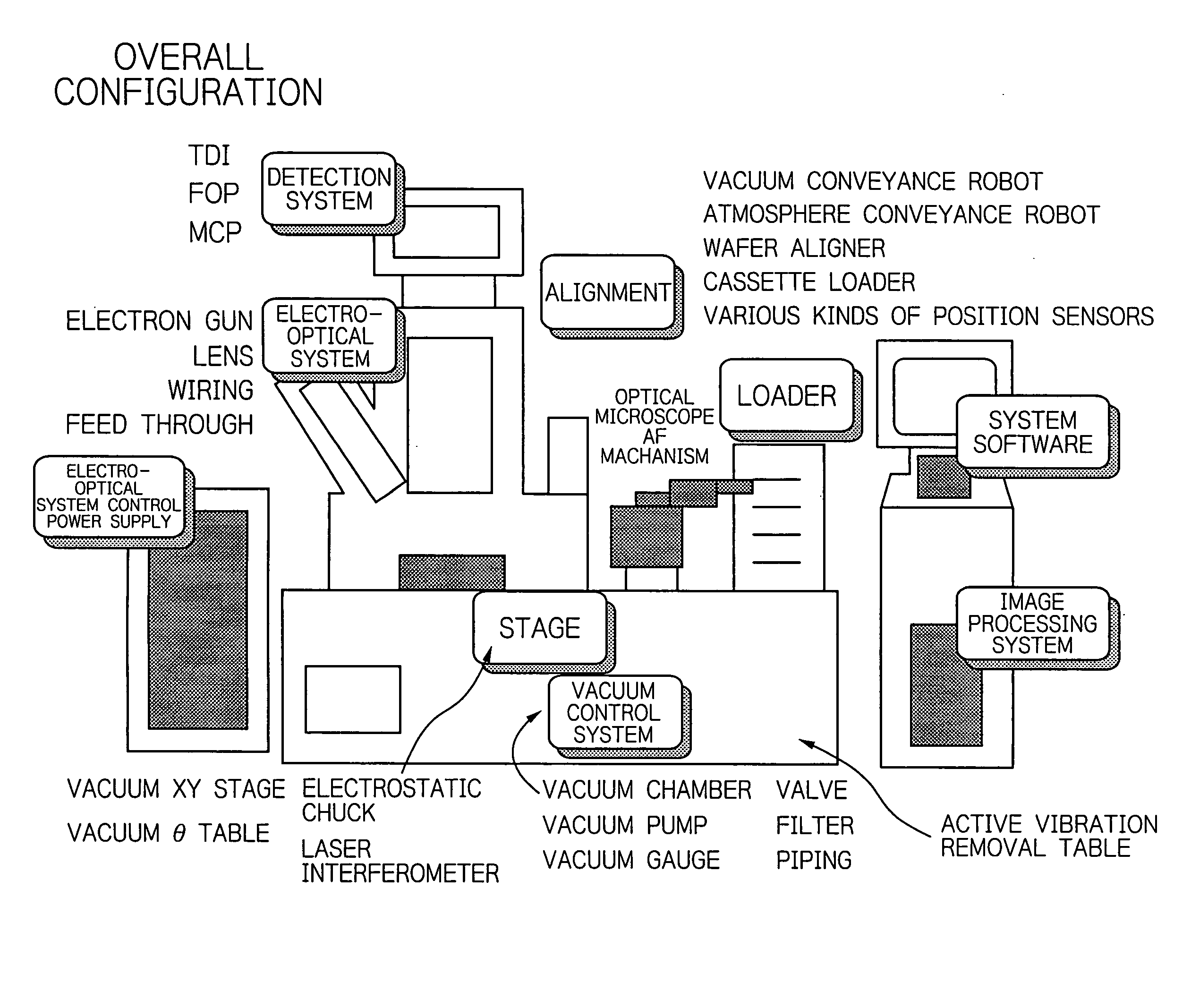
Testing apparatus using charged particles and device manufacturing method using the testing apparatus
ActiveUS20050045821A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAtomic physicsPhysics
A system for further enhancing speed, i.e. improving throughput in a SEM-type inspection apparatus is provided. An inspection apparatus for inspecting a surface of a substrate produces a crossover from electrons emitted from an electron beam source 25••1, then forms an image under a desired magnification in the direction of a sample W to produce a crossover. When the crossover is passed, electrons as noises are removed from the crossover with an aperture, an adjustment is made so that the crossover becomes a parallel electron beam to irradiate the substrate in a desired sectional form. The electron beam is produced such that the unevenness of illuminance is 10% or less. Electrons emitted from the sample W are detected by a detector 25•11.
Owner:EBARA CORP
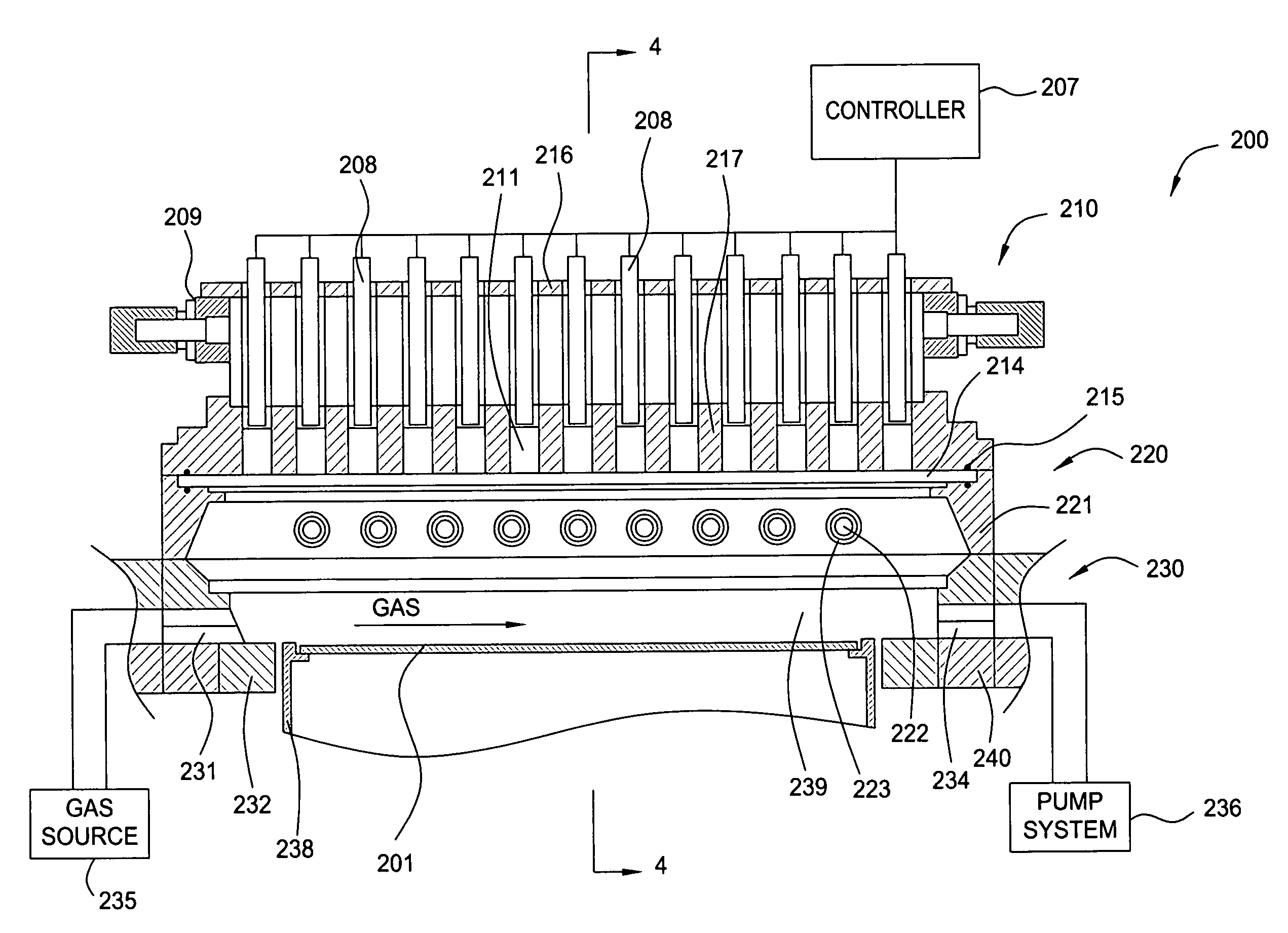
Method for supplying gas with flow rate gradient over substrate
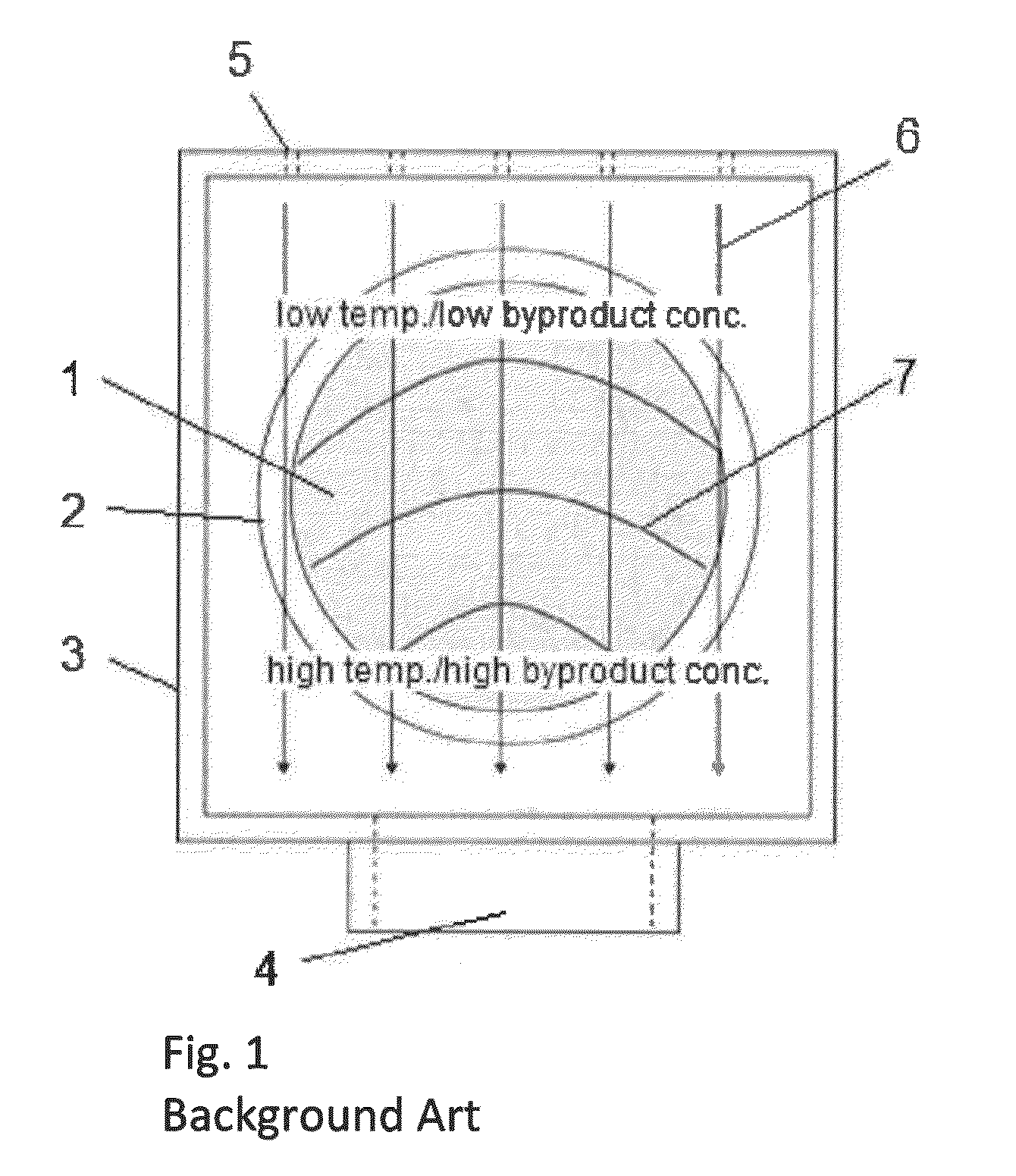
ActiveUS8664627B1Reduce gradientIncrease concentrationMaterial analysis by optical meansPipeline systemsReaction chamberChemistry
A method for supplying gas over a substrate in a reaction chamber wherein a substrate is placed on a pedestal, includes: supplying a first gas from a first side of the reaction chamber to a second side of the reaction chamber opposite to the first side; and adding a second gas to the first gas from sides of the reaction chamber other than the first side of the reaction chamber so that the second gas travels from sides of the substrate other than the first side in a downstream direction.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
UV assisted thermal processing
InactiveUS7547633B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesThermodynamicsThermal treatment
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for performing thermal processes to a semiconductor substrate. Thermal processing chambers of the present invention comprise two different energy sources, such as an infrared radiation source and a UV radiation source. The UV radiation source and the infrared radiation source may be used alone or in combination to supply heat, activate electronic, or create active species inside the thermal processing chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
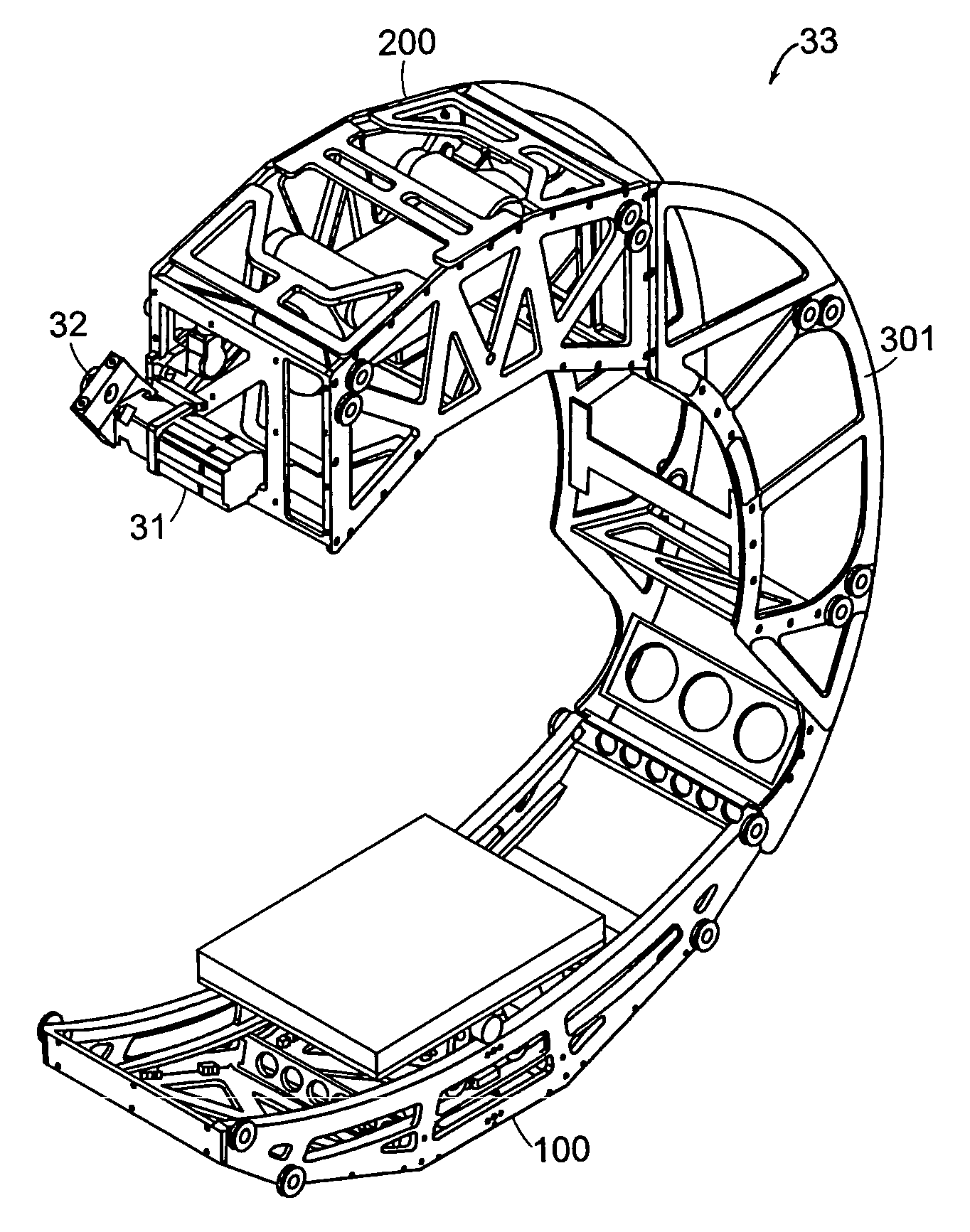
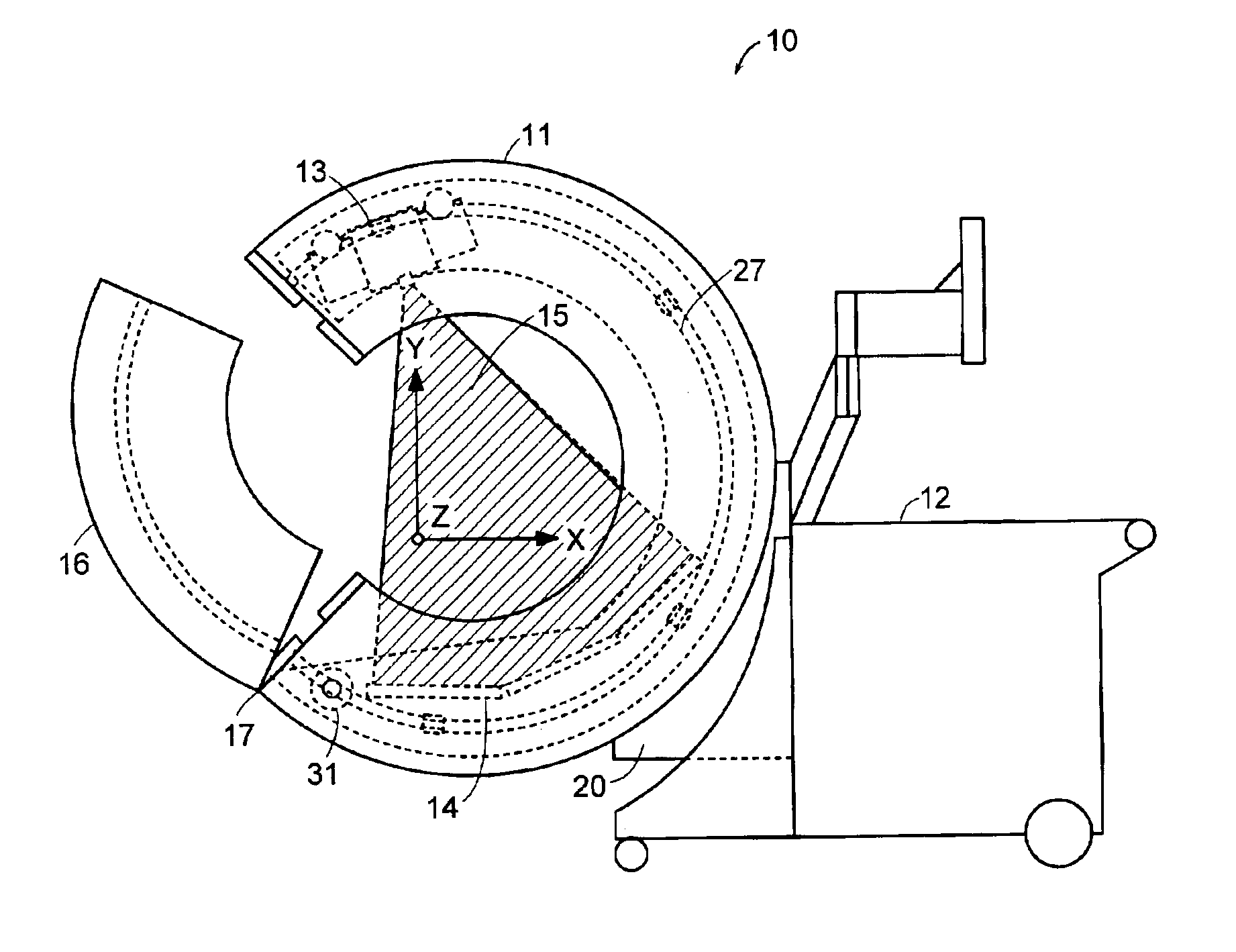
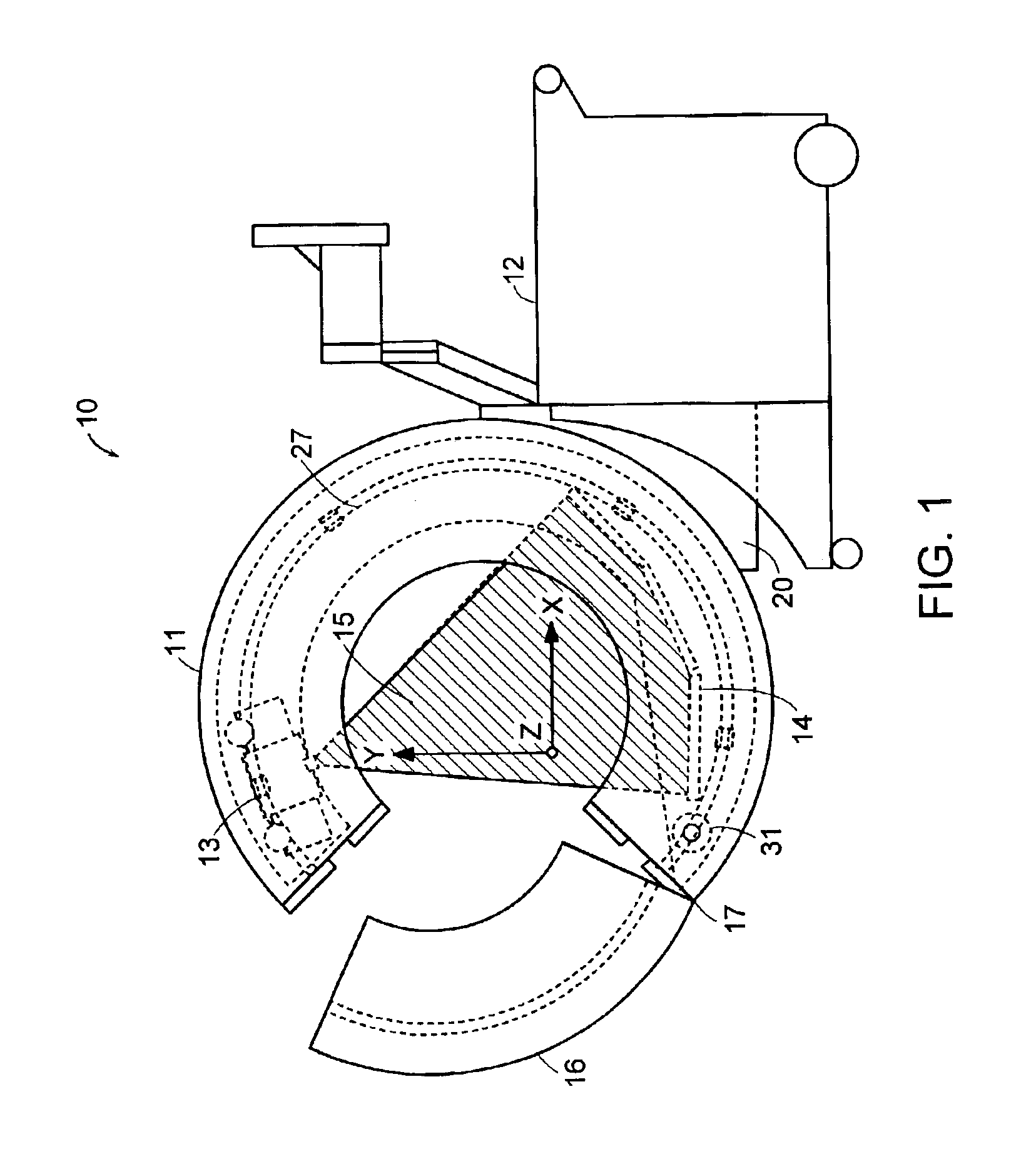
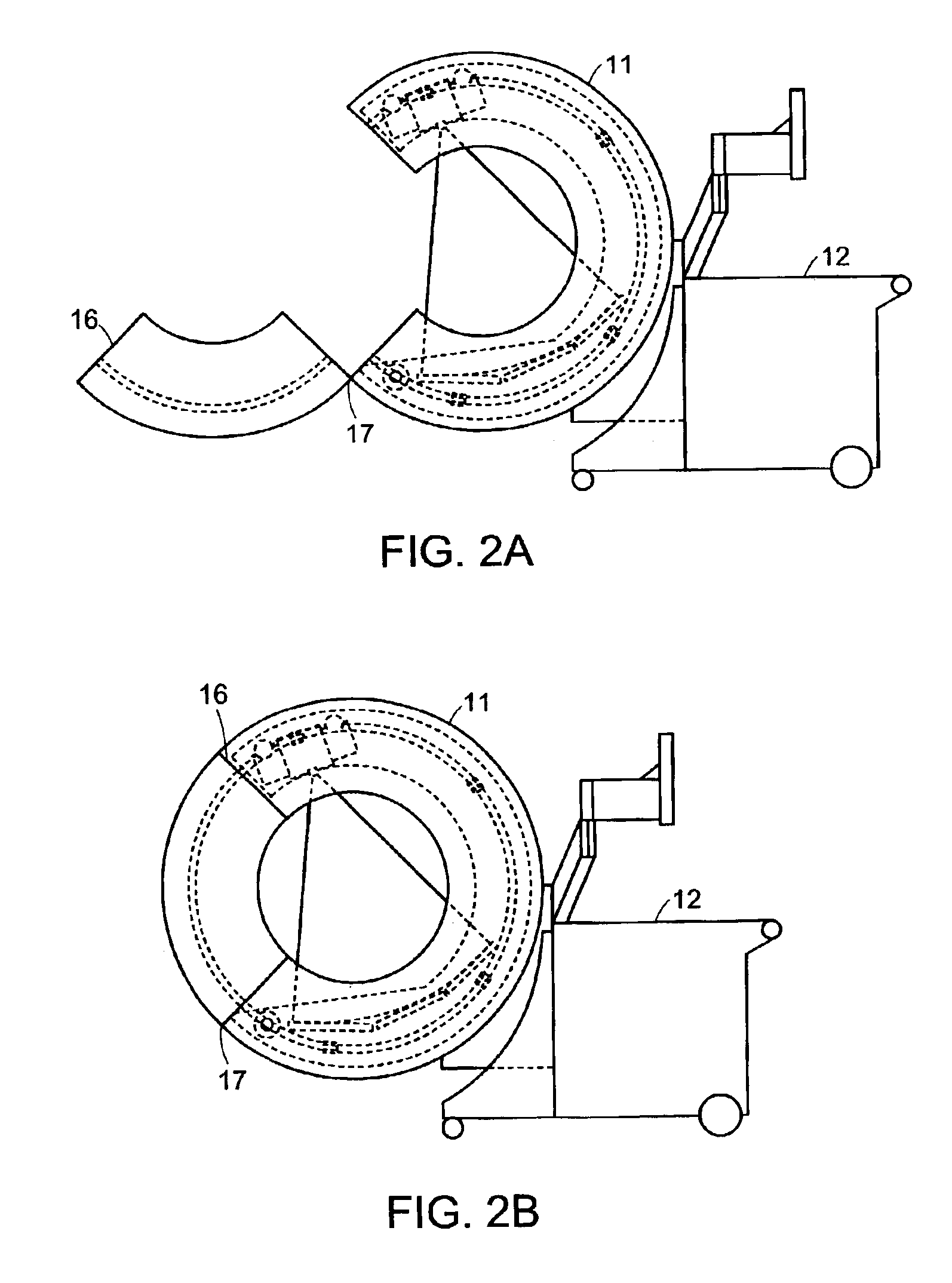
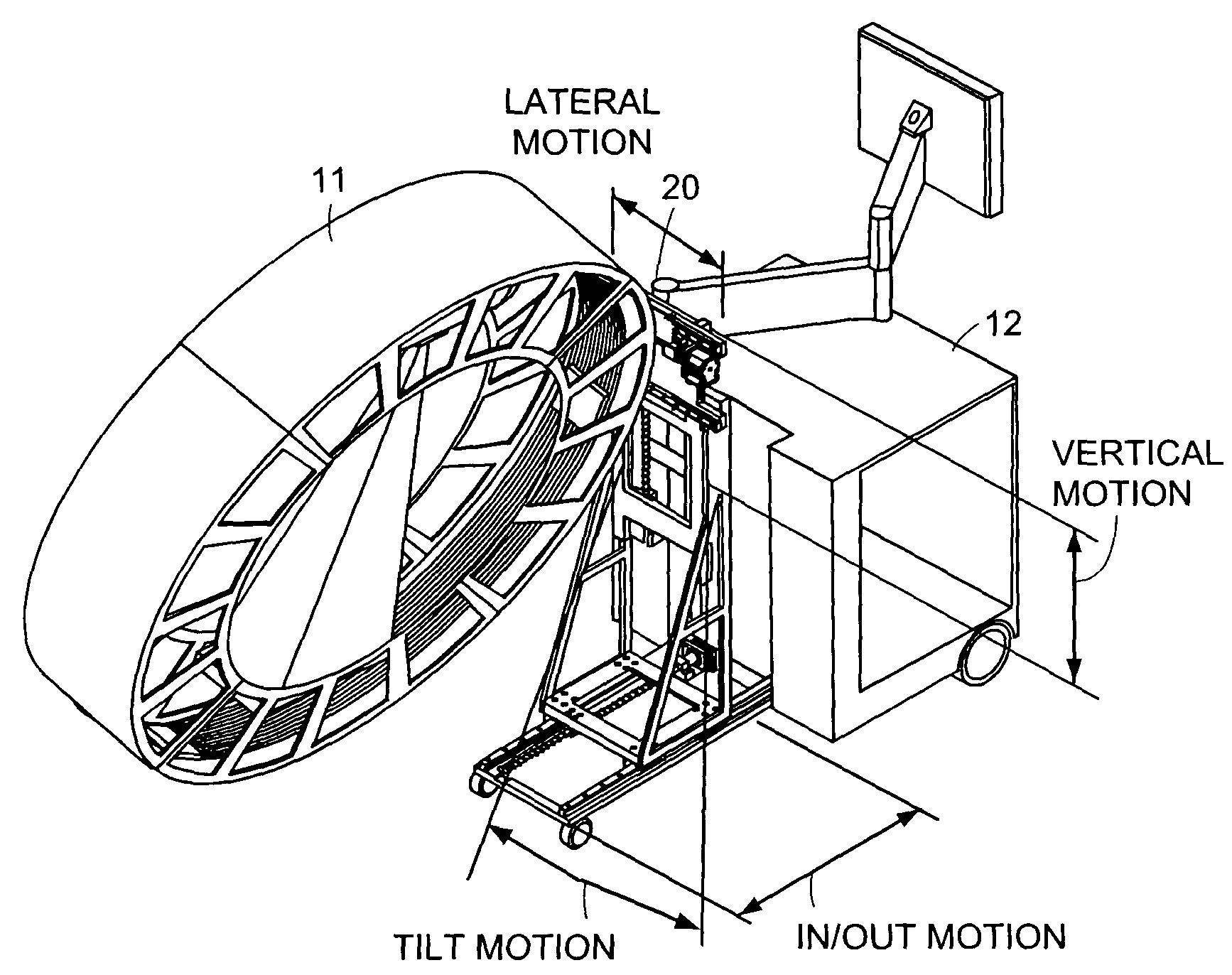
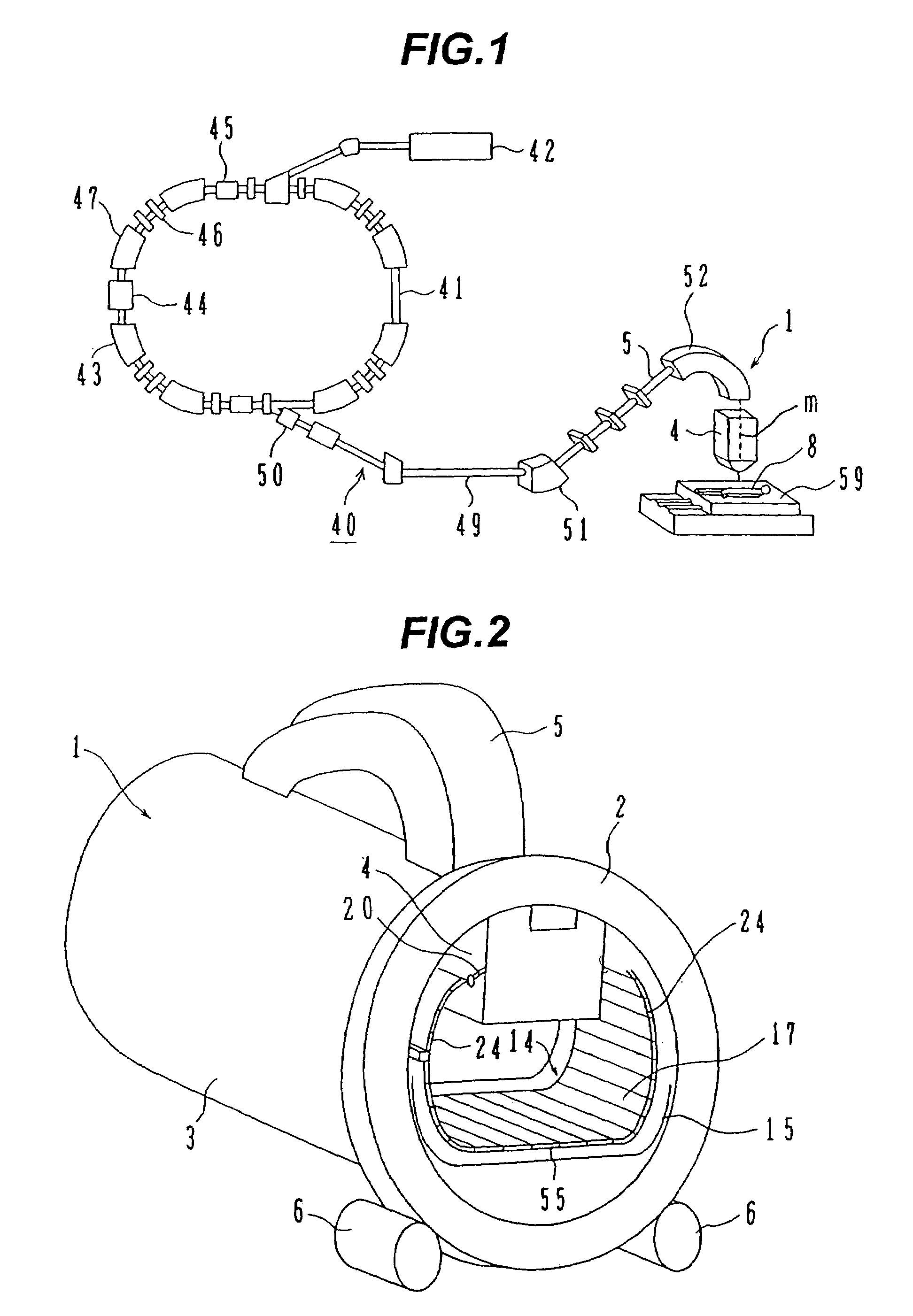
Breakable gantry apparatus for multidimensional x-ray based imaging
InactiveUS6940941B2Easily approach patientHigh quality imagingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayComputed tomography
An x-ray scanning imaging apparatus with a generally O-shaped gantry ring, which has a segment that fully or partially detaches (or “breaks”) from the ring to provide an opening through which the object to be imaged may enter interior of the ring in a radial direction. The segment can then be re-attached to enclose the object within the gantry. Once closed, the circular gantry housing remains orbitally fixed and carries an x-ray image-scanning device that can be rotated inside the gantry 360 degrees around the patient either continuously or in a step-wise fashion. The x-ray device is particularly useful for two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) imaging applications.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
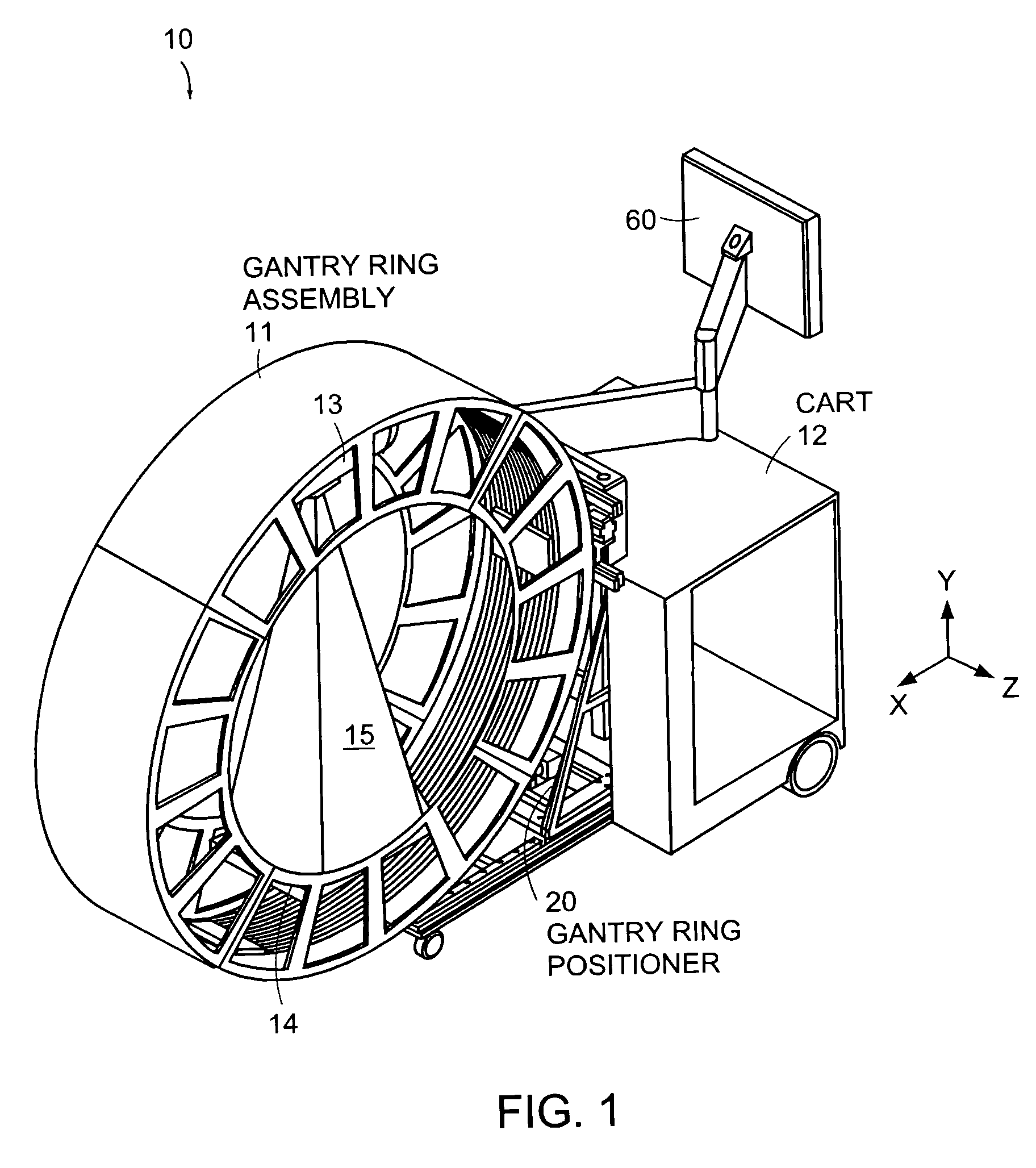
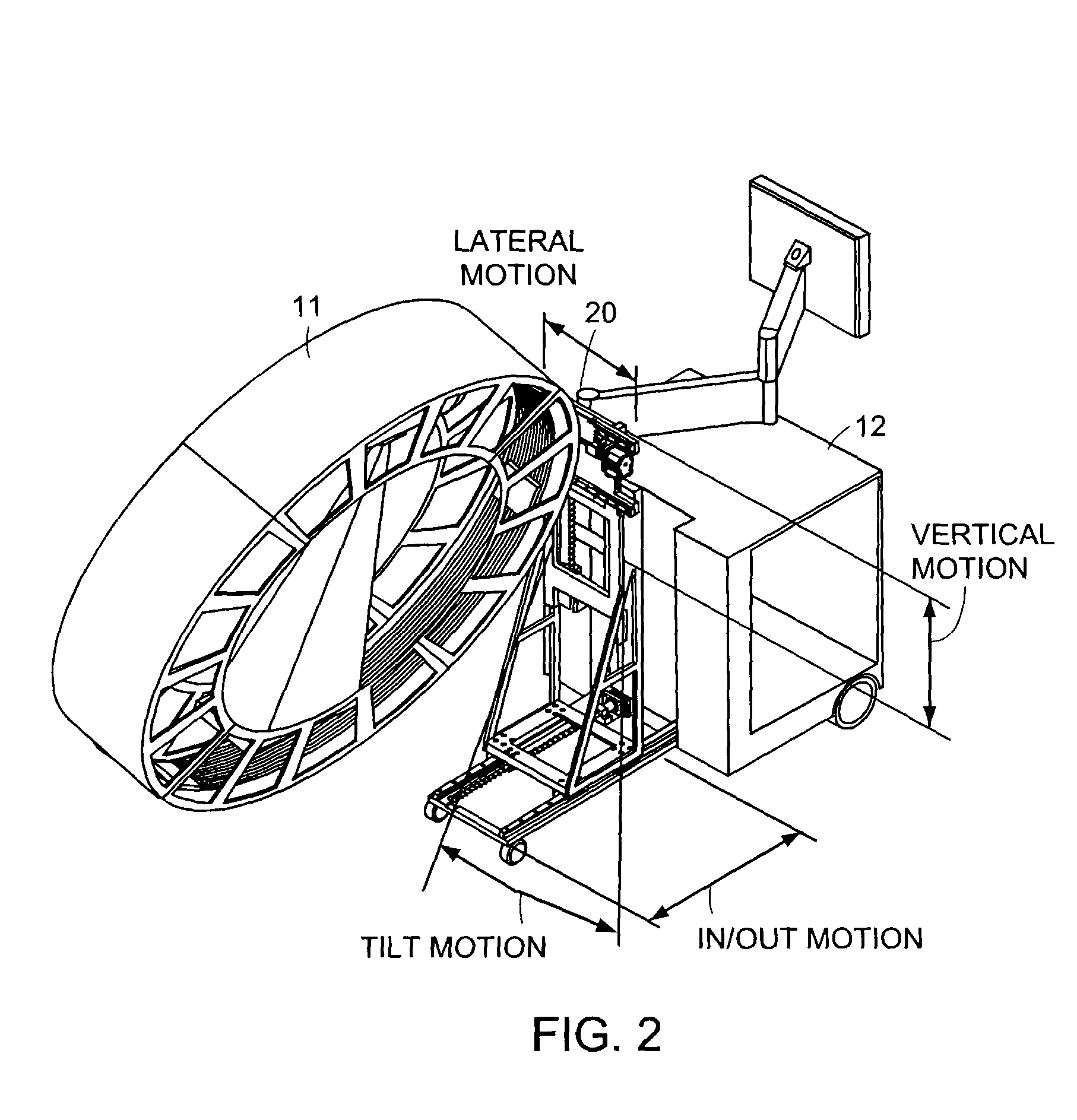
Cantilevered gantry apparatus for x-ray imaging
An x-ray scanning imaging apparatus with a rotatably fixed generally O-shaped gantry ring, which is connected on one end of the ring to support structure, such as a mobile cart, ceiling, floor, wall, or patient table, in a cantilevered fashion. The circular gantry housing remains rotatably fixed and carries an x-ray image-scanning device that can be rotated inside the gantry around the object being imaged either continuously or in a step-wise fashion. The ring can be connected rigidly to the support, or can be connected to the support via a ring positioning unit that is able to translate or tilt the gantry relative to the support on one or more axes. Multiple other embodiments exist in which the gantry housing is connected on one end only to the floor, wall, or ceiling. The x-ray device is particularly useful for two-dimensional multi-planar x-ray imaging and / or three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) imaging applications
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
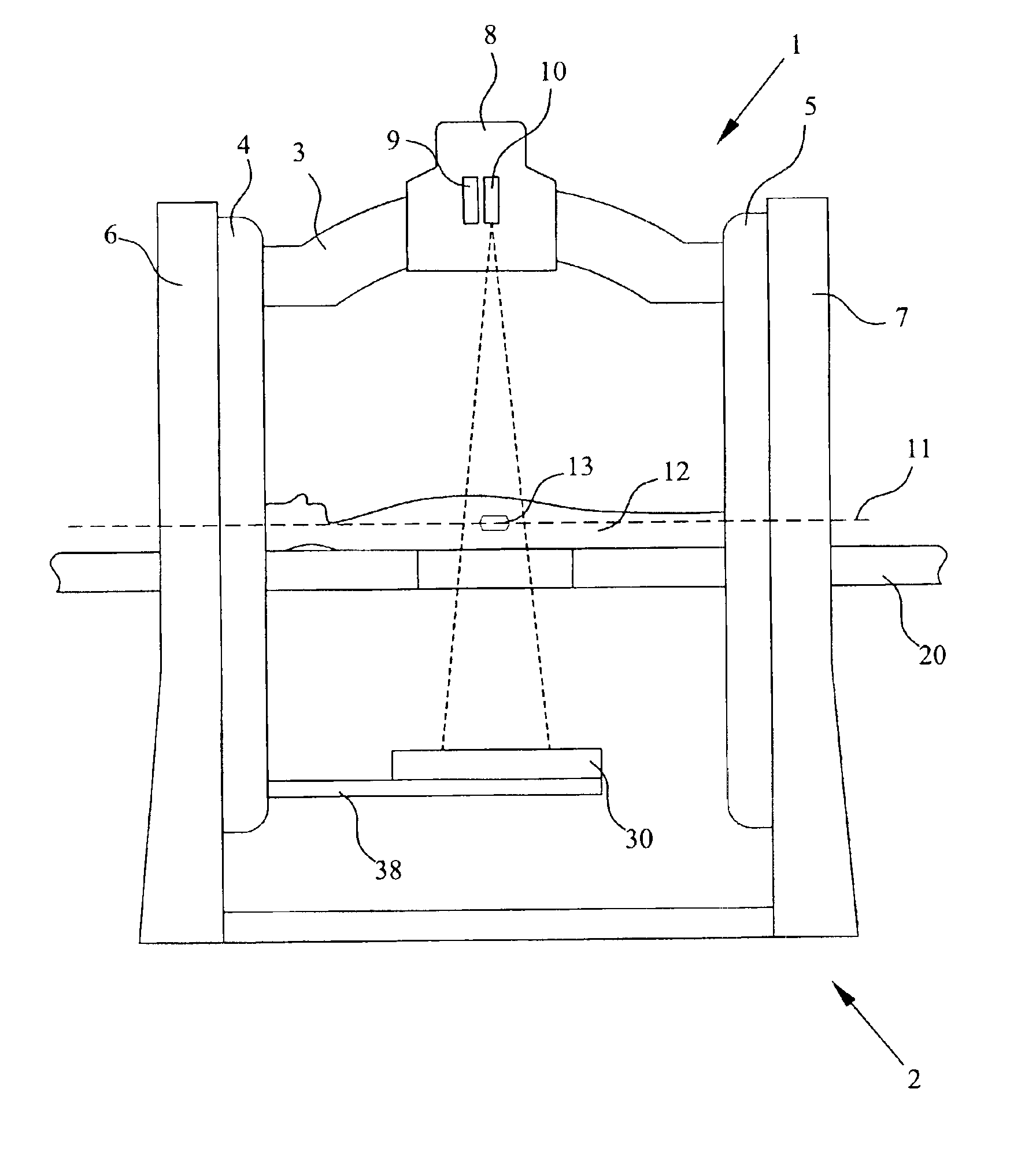
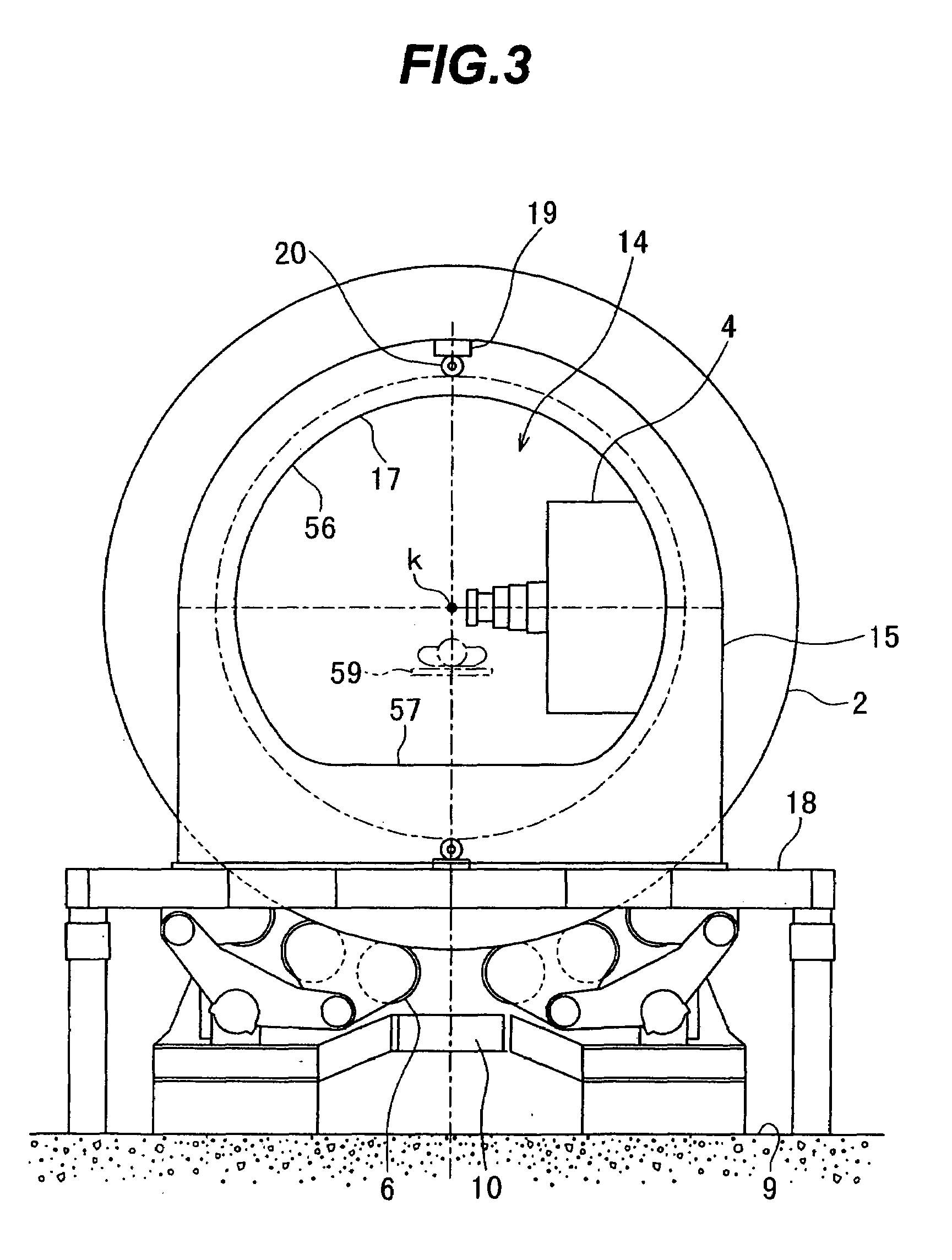
Radiation system with inner and outer gantry parts
InactiveUS6865254B2Increase speedImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHigh resolution imagingRotation velocity
A radiation machine incorporating a diagnostic imaging system is disclosed. The invention provides a very stable design of the machine by supporting an inner gantry part, including a treatment and diagnostic radiation source and detector, by an outer gantry part at two support locations situated at opposite sides of a treatment volume in a patient to be irradiated. This stable gantry design provides a high rotation speed of the inner gantry part relative the outer gantry part around the target volume, which speed is adapted for the high resolution imaging system. Based on the obtained images, changes and developments in tumor tissue and misplacement of patient may be detected. The images may be compared to a reference image to detect any anatomical or spatial difference therebetween. Based on this comparison the settings of the radiation machine may be adapted accordingly.
Owner:C-RAD INNOVATION AB
Technique for low-temperature ion implantation
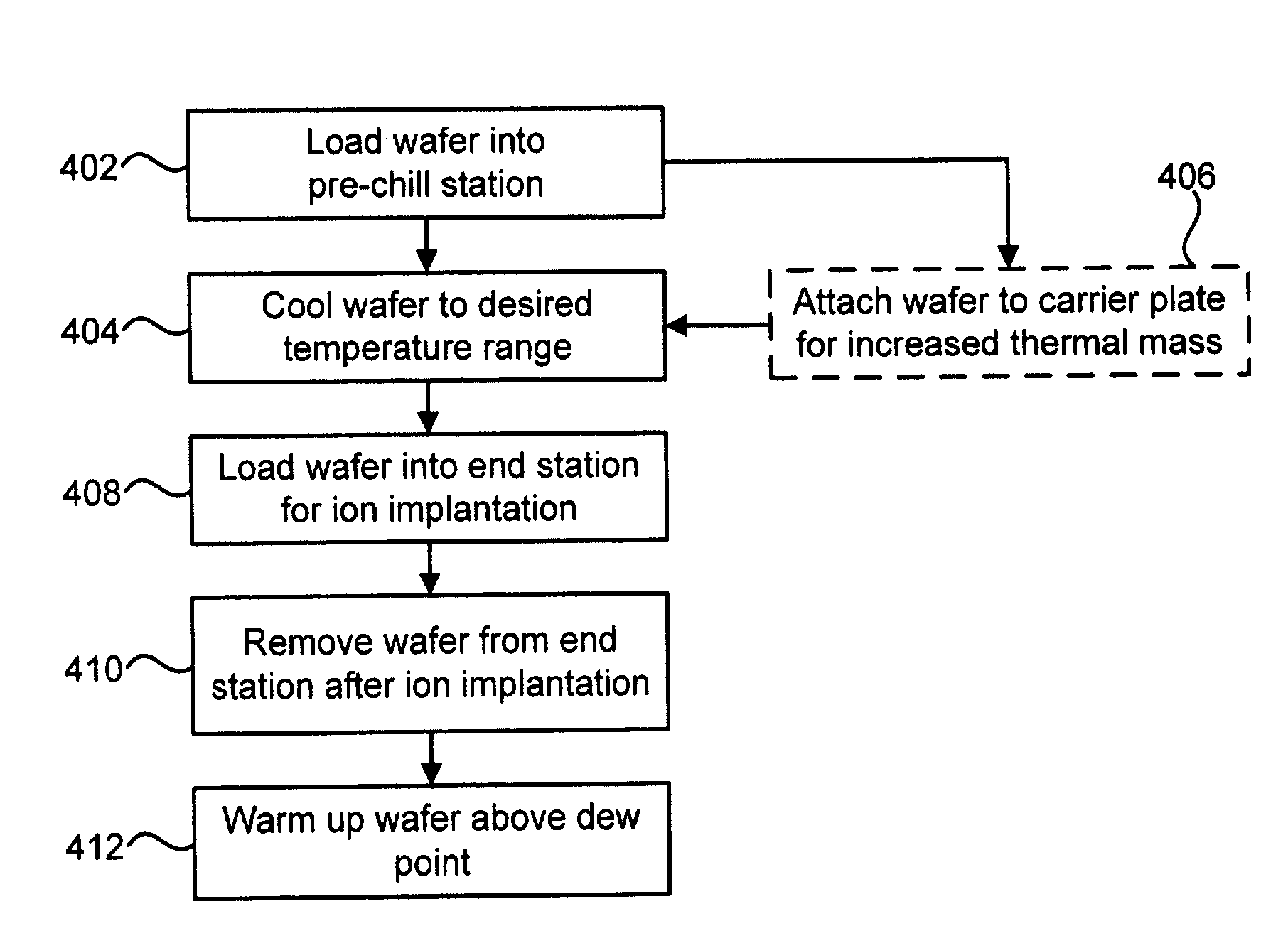
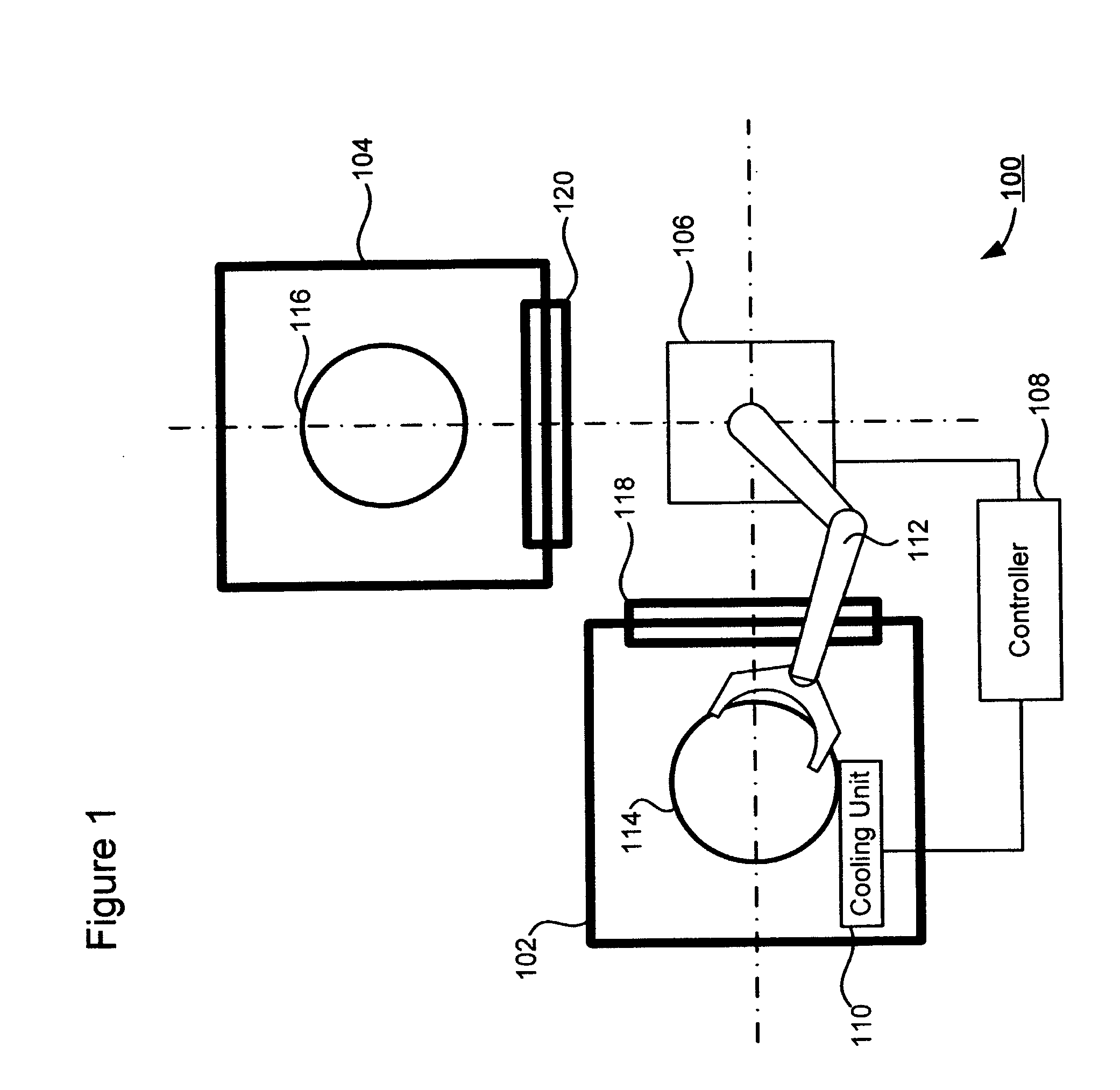
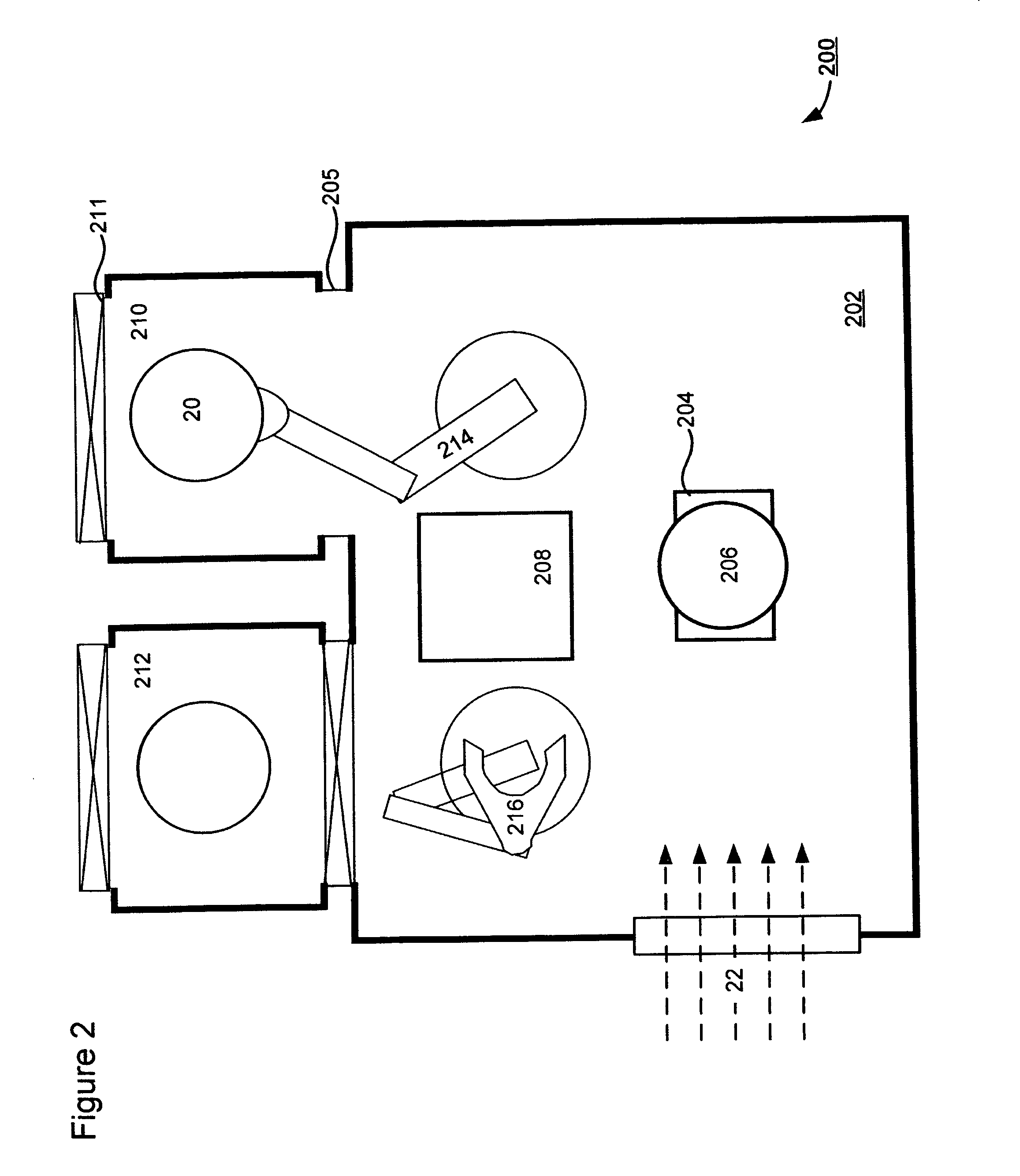
ActiveUS20080044938A1Avoid overall overheatingFacilitate tilting and rotationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesEngineeringIon implantation
A technique for low-temperature ion implantation is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as an apparatus for low-temperature ion implantation. The apparatus may comprise a pre-chill station located in proximity to an end station in an ion implanter. The apparatus may also comprise a cooling mechanism within the pre-chill station. The apparatus may further comprise a loading assembly coupled to the pre-chill station and the end station. The apparatus may additionally comprise a controller in communication with the loading assembly and the cooling mechanism to coordinate loading a wafer into the pre-chill station, cooling the wafer down to a predetermined temperature range, and loading the cooled wafer into the end station where the cooled wafer undergoes an ion implantation process.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
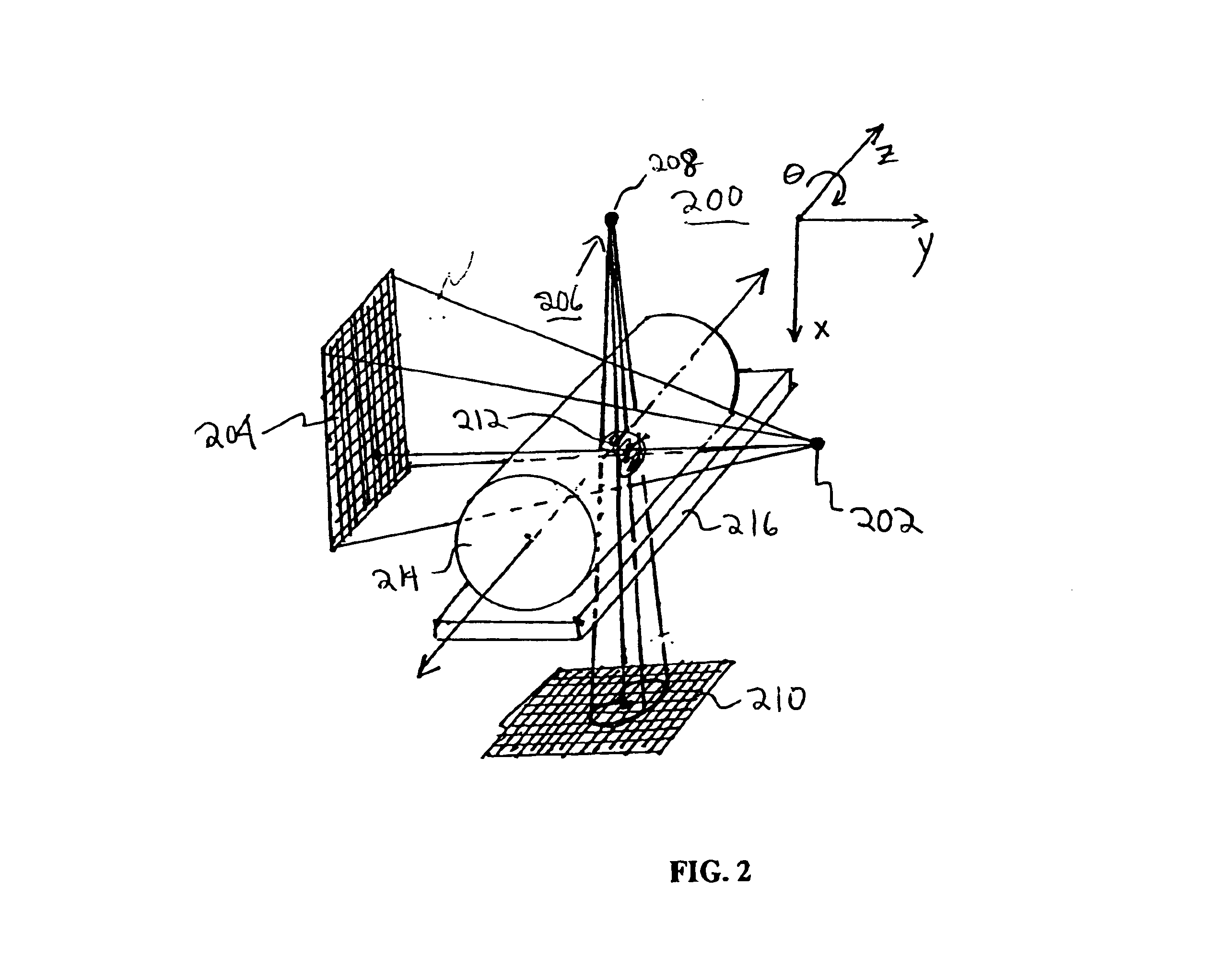
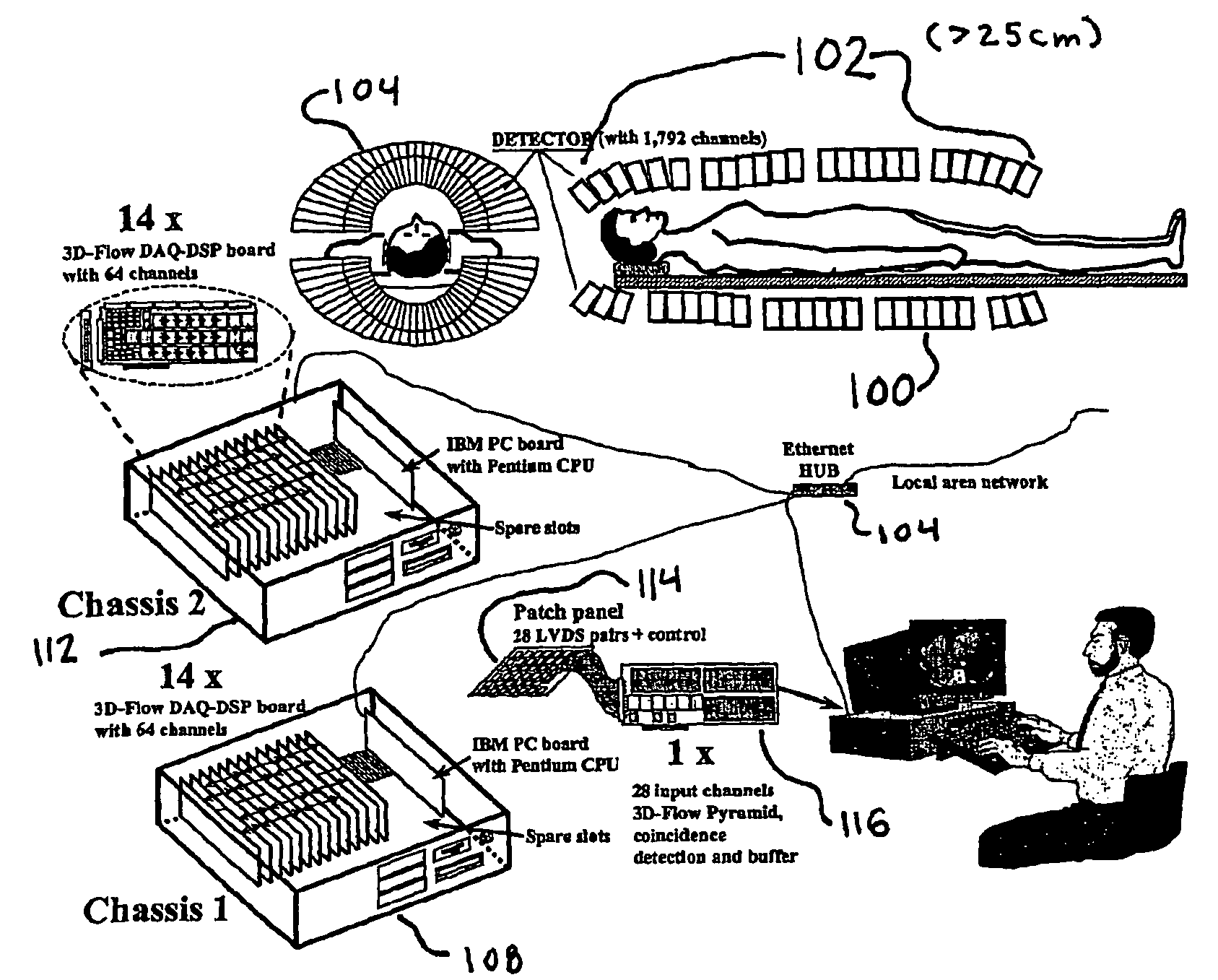
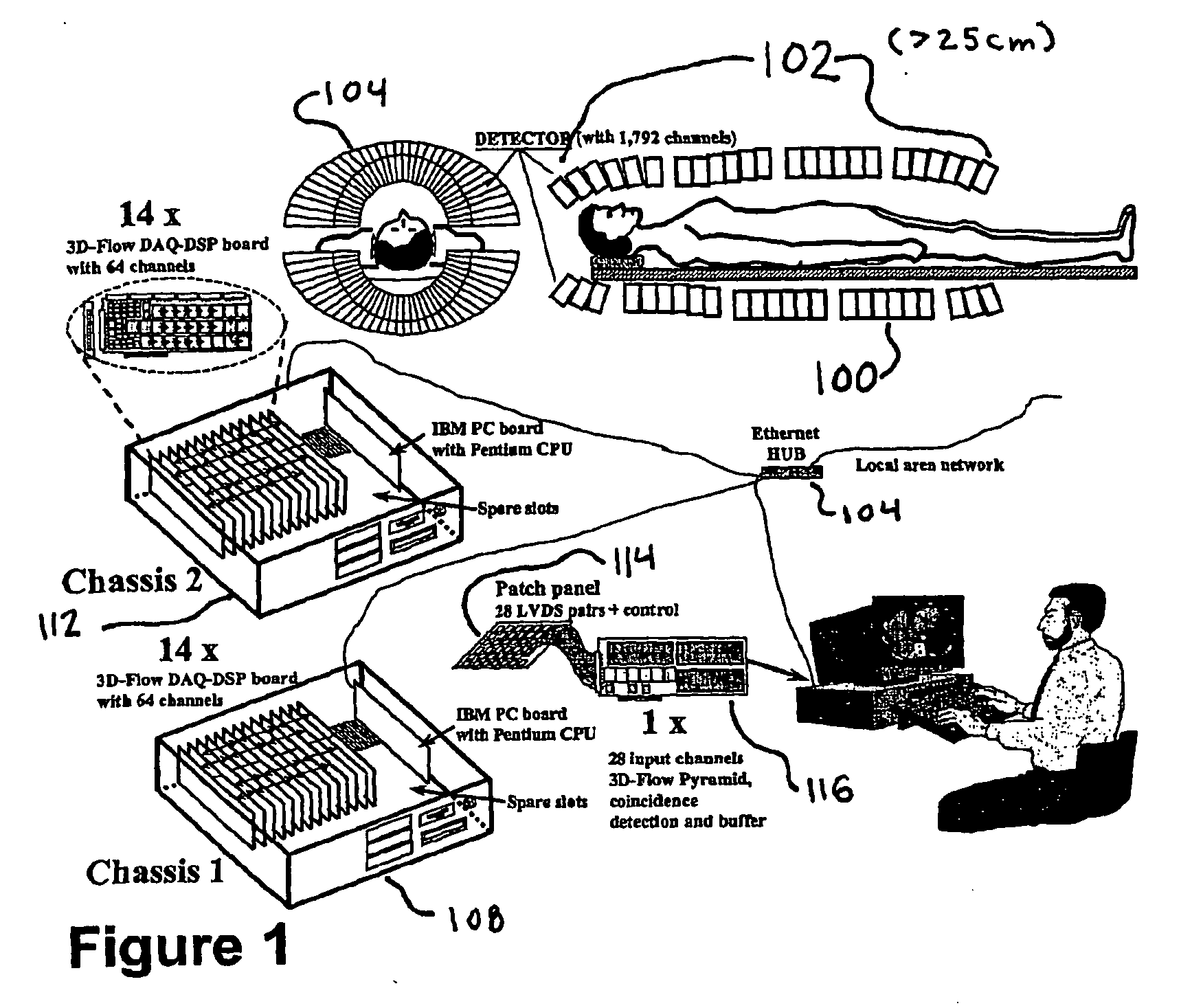
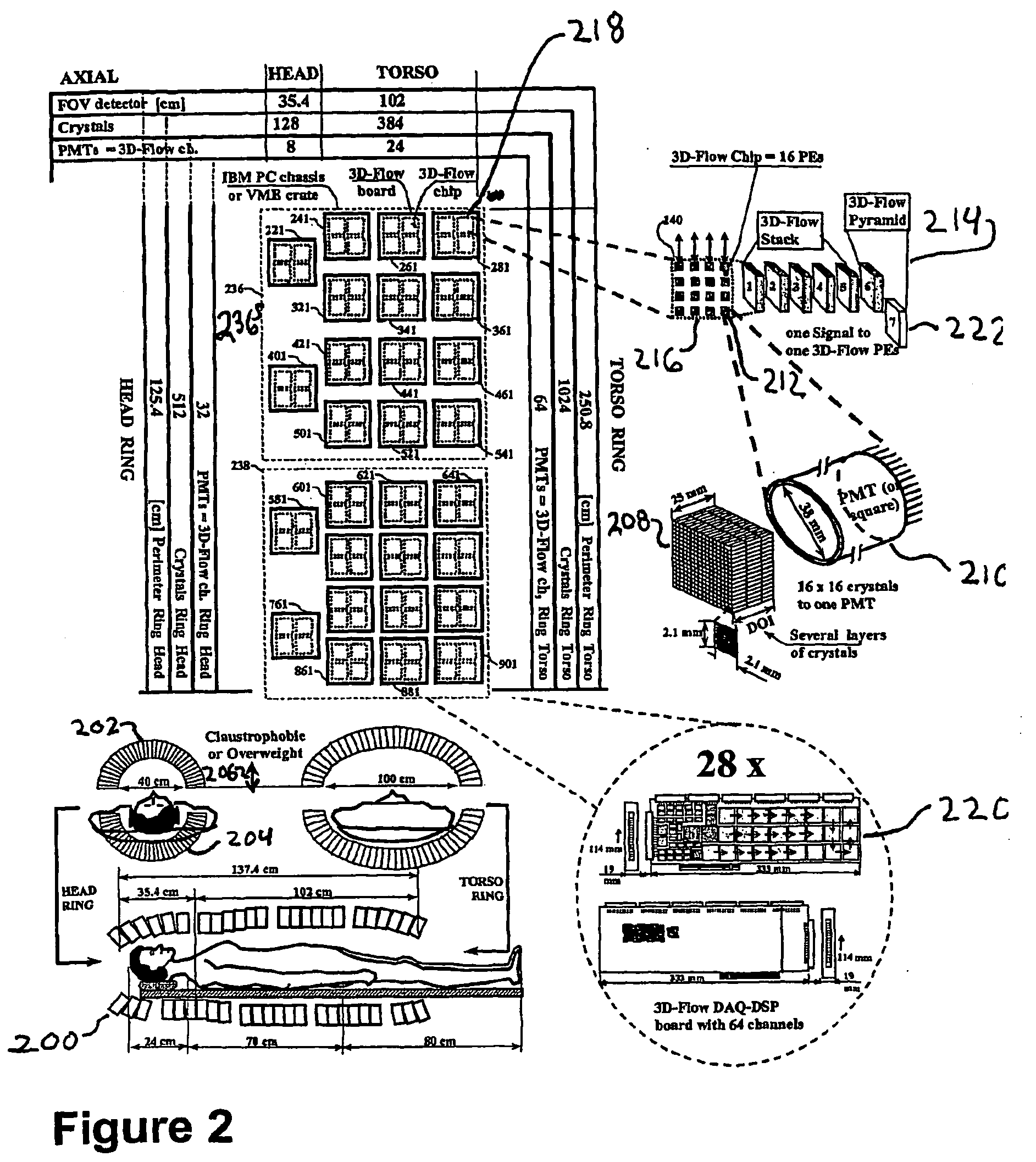
Method and apparatus for anatomical and functional medical imaging
InactiveUS20040195512A1Increase the lengthDistance minimizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMedical imagingFunctional imaging
A body scanning system includes a CT transmitter and a PET configured to radiate along a significant portion of the body and a plurality of sensors (202, 204) configured to detect photons along the same portion of the body. In order to facilitate the efficient collection of photons and to process the data on a real time basis, the body scanning system includes a new data processing pipeline that includes a sequentially implemented parallel processor (212) that is operable to create images in real time not withstanding the significant amounts of data generated by the CT and PET radiating devices.
Owner:CROSETTO DARIO B
Medical workstation, imaging system, and method for mixing two images
InactiveUS6895268B1Well mixedEffective supportGeometric image transformationSurgeryWorkstationComputer science
In a system, method and workstation, images of a first subject are acquired with an image signal acquisition unit, the position of the image signal acquisition unit is determined, the position of a second subject is determined and the position of the second subject relative to the image signal acquisition unit is also determined and an image of the second subject is mixed into an image of the first subject acquired with the image signal acquisition unit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
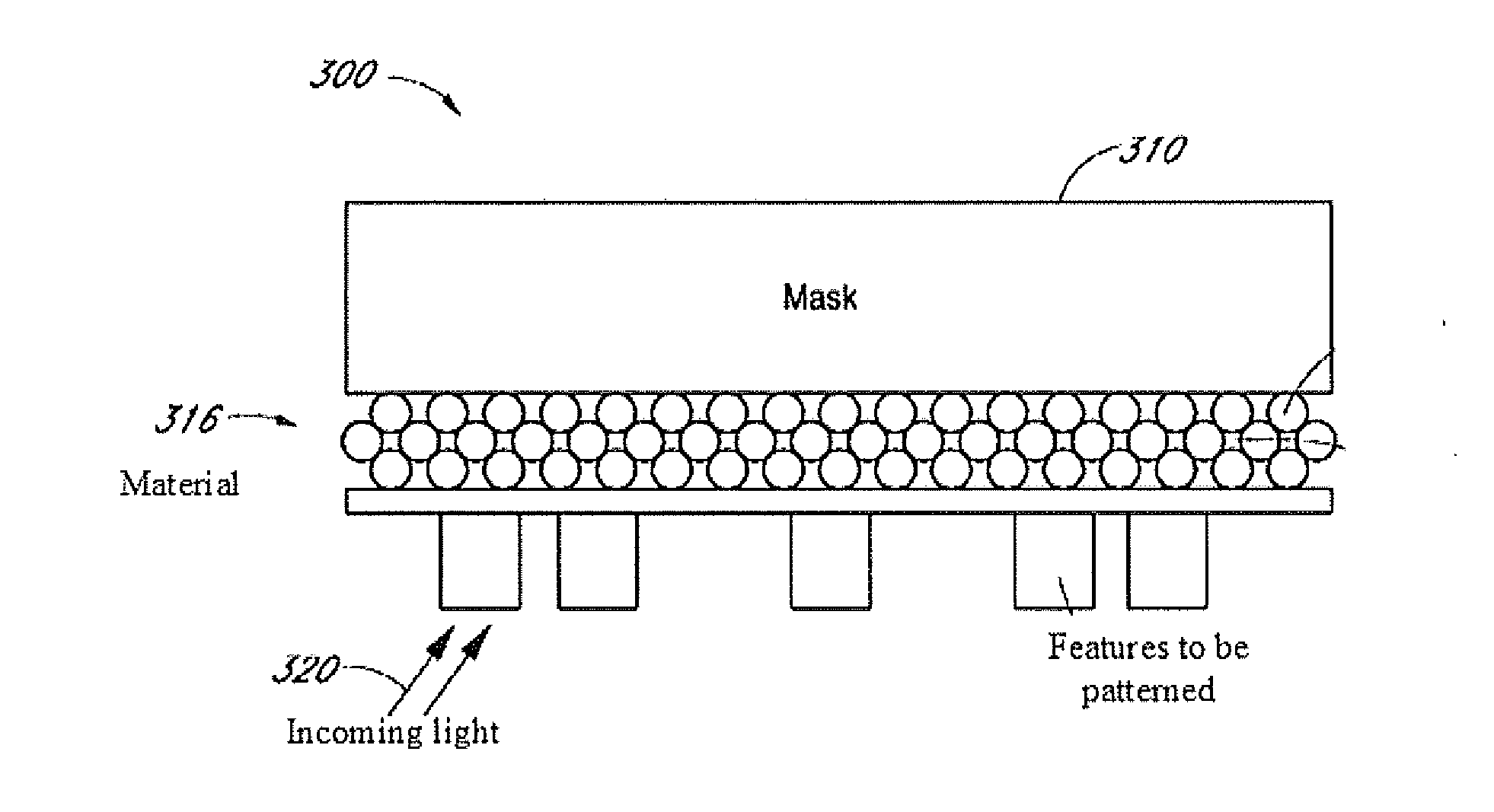
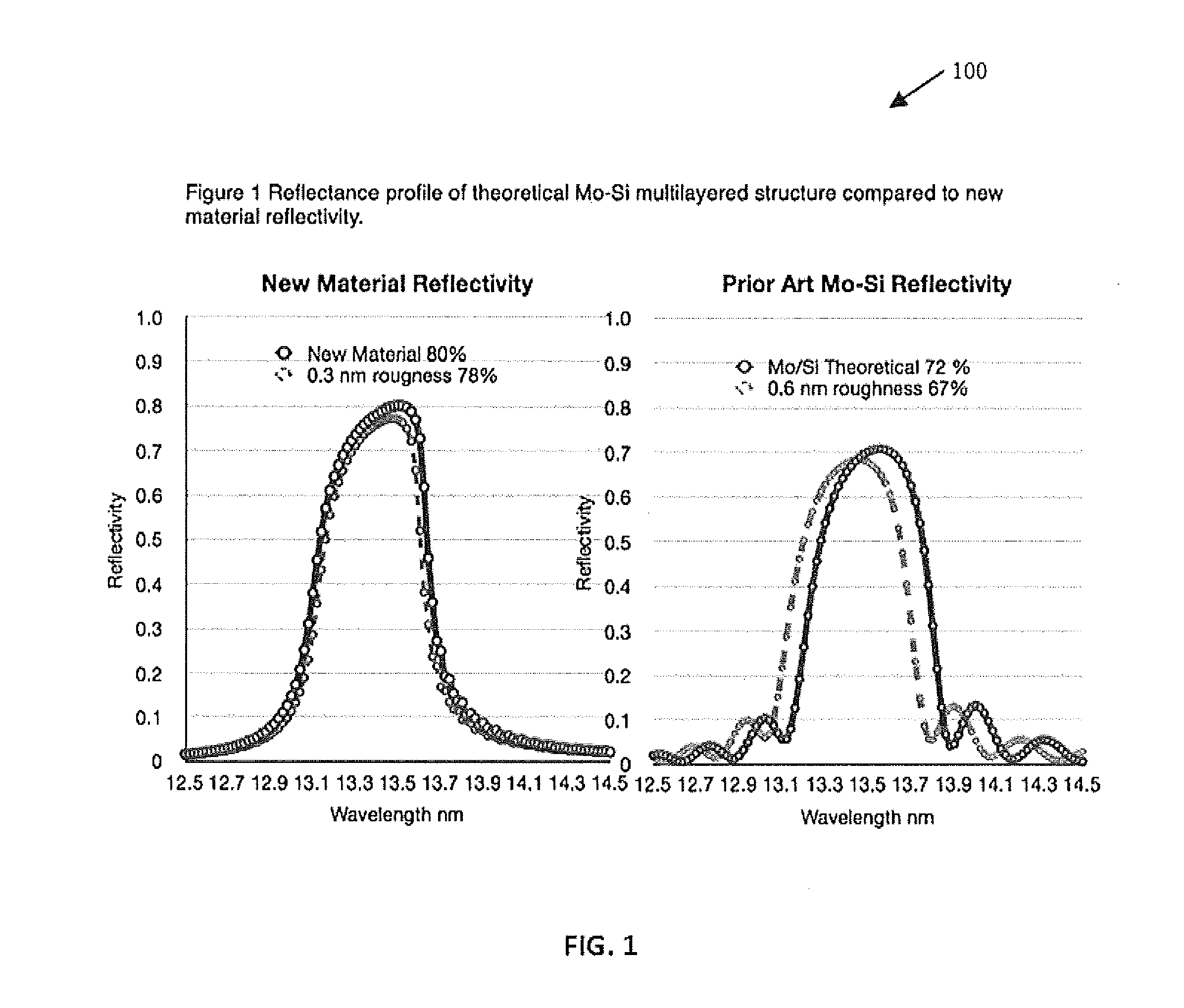
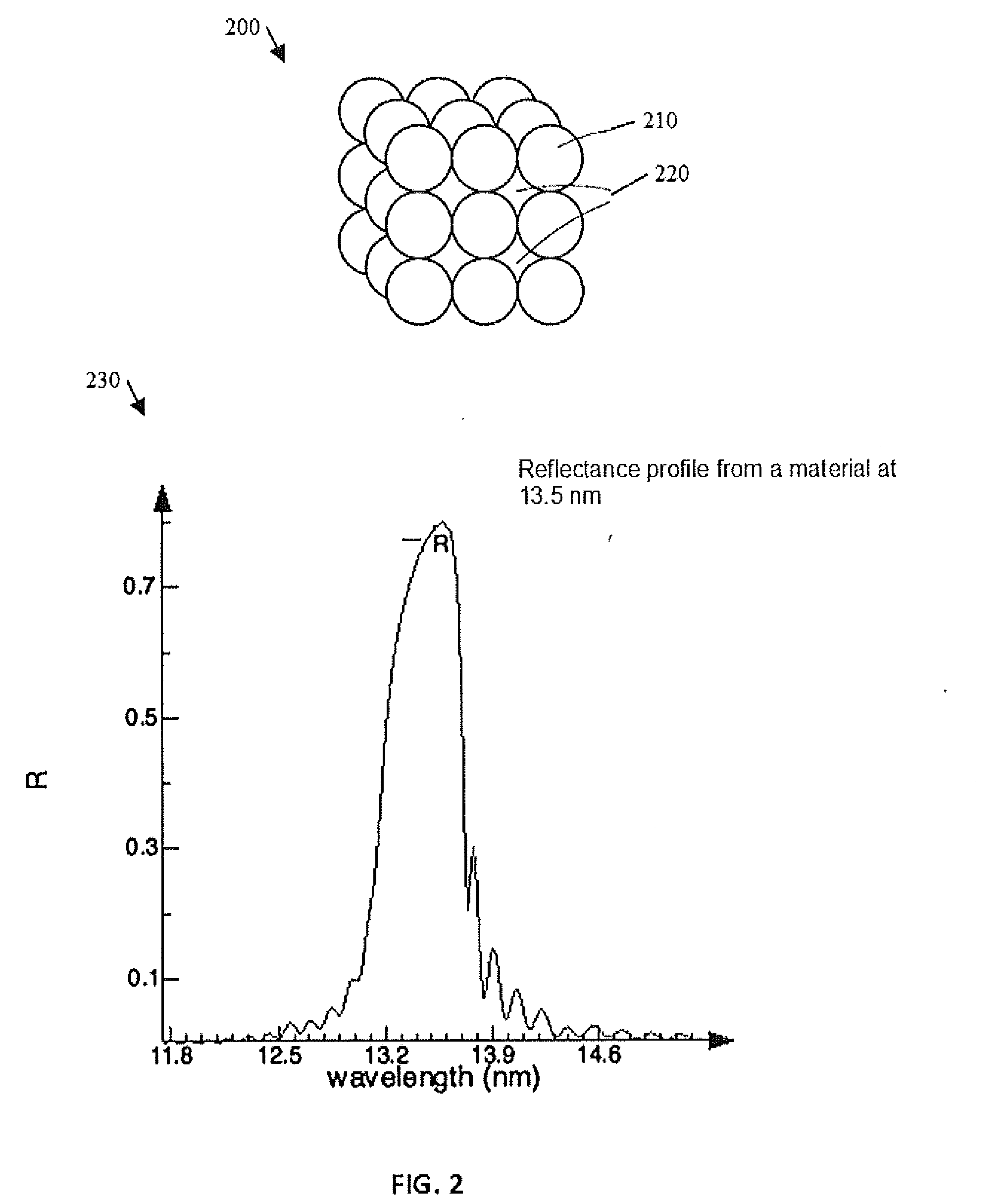
Materials, components, and methods for use with extreme ultraviolet radiation in lithography and other applications
ActiveUS20160085003A1Improve reflectivitySpread the wordMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhotonicsUltraviolet
Nanostructured photonic materials, and associated components for use in devices and systems operating at ultraviolet (UV), extreme ultraviolet (EUV), and / or soft Xray wavelengths are described. Such a material may be fabricated with nanoscale features tailored for a selected wavelength range, such as at particular UV, EUV, or soft Xray wavelengths or wavelength ranges. Such a material may be used to make components such as mirrors, lenses or other optics, panels, lightsources, masks, photoresists, or other components for use in applications such as lithography, wafer patterning, astronomical and space applications, biomedical applications, biotech or other applications.
Owner:JAISWAL SUPRIYA
Cone-beam computerized tomography with a flat-panel imager
InactiveUS20030007601A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAmorphous siliconX-ray
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Apparatus and method for registering two medical images
ActiveUS8620055B2Time requiredShorten the timeImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGeometric modelingOrgan surface
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
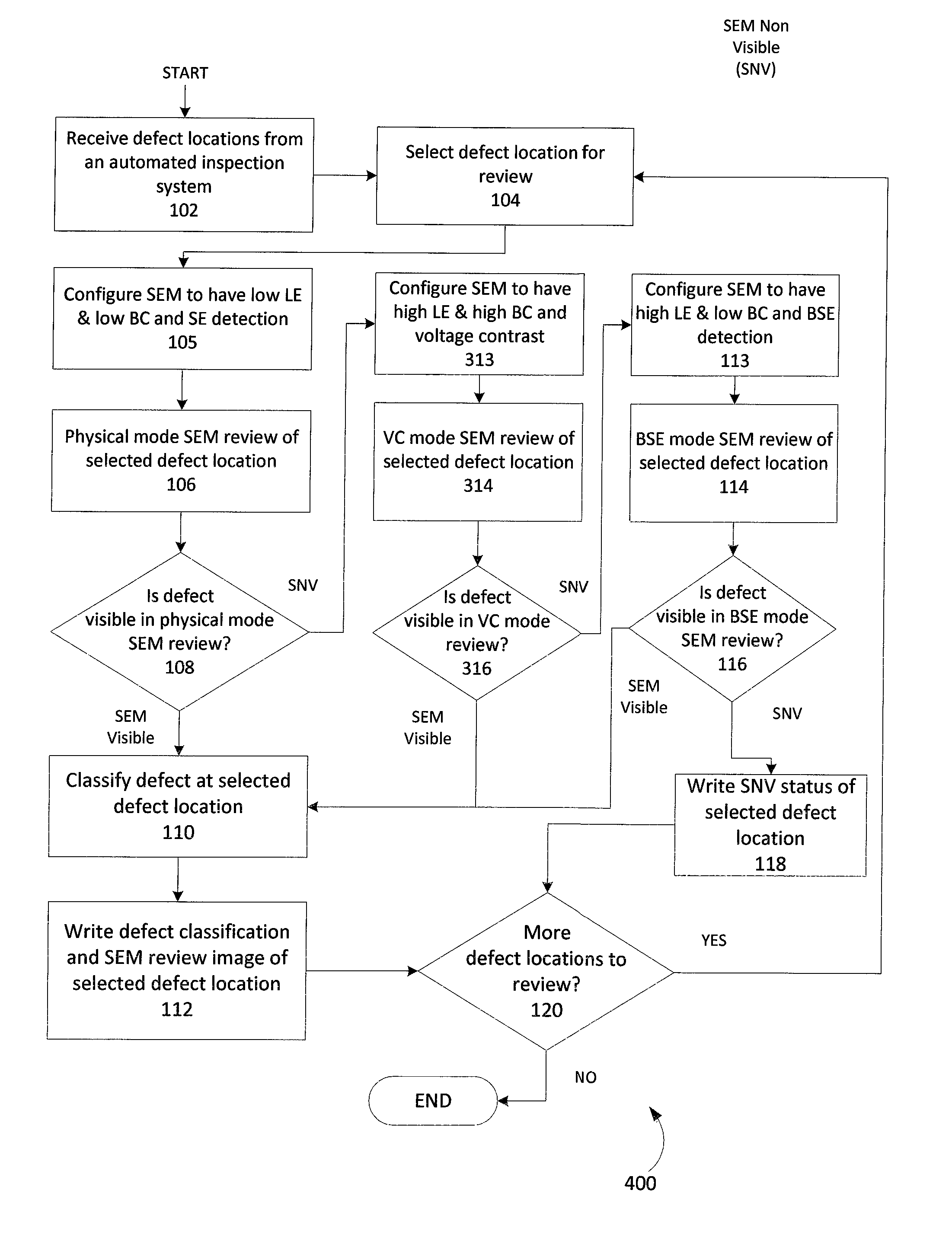
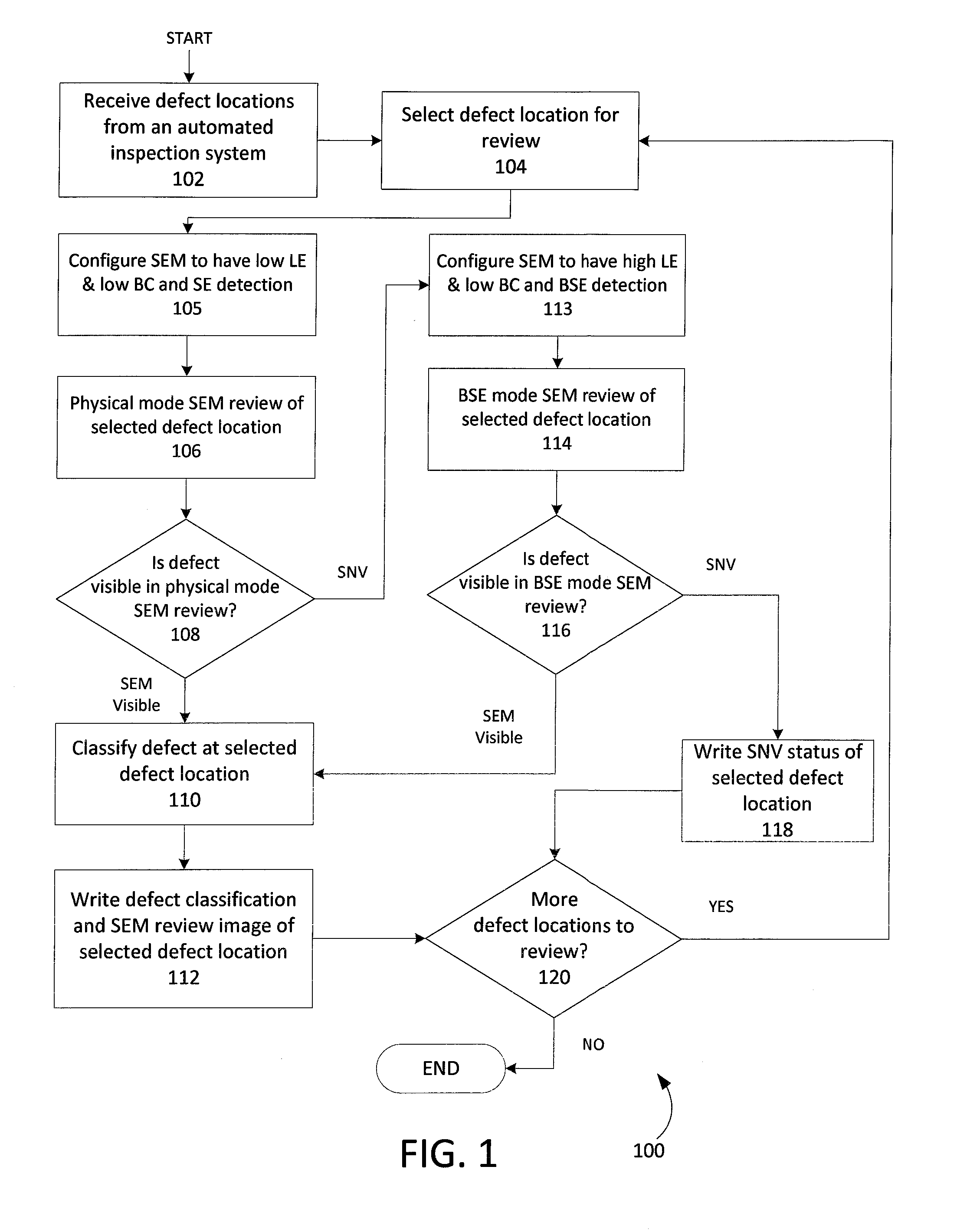
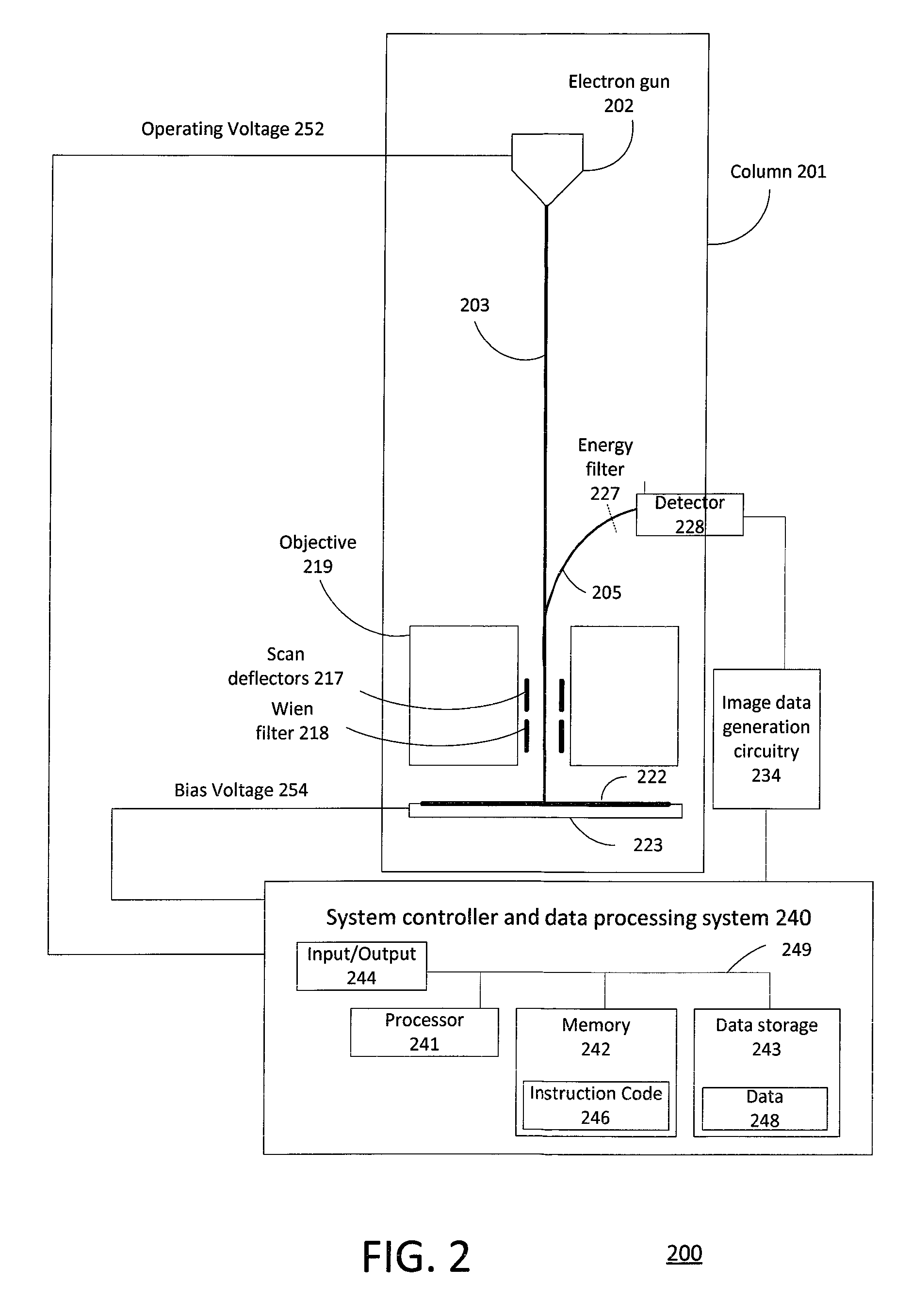
Methods and apparatus to review defects using scanning electron microscope with multiple electron beam configurations
ActiveUS8716662B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesScanning tunneling microscopeElectron
One embodiment relates to a method of reviewing defects using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). A defect location having a defect for review is selected, and the SEM is configured to be in a first imaging configuration. The selected defect location is imaged using the SEM to generate a first SEM image of the selected defect location. A determination is made as to whether the defect is visible or non-visible in the first SEM image. If the defect is non-visible in the first SEM image, then the SEM is configured to be into a second imaging configuration, the selected defect location is imaged using the SEM to generate a second SEM image of the selected defect location, and a further determination is made as to whether the defect is visible or non-visible in the second SEM image. Other embodiments, aspects and features are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
System and method of measuring disease severity of a patient before, during and after treatment
ActiveUS20050065421A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisData setImaging data
A system and method of obtaining serial biochemical, anatomical or physiological in vivo measurements of disease from one or more medical images of a patient before, during and after treatment, and measuring extent and severity of the disease is provided. First anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a first co-registered composite image data set. At least a volume of interest (ROI) within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. The first co-registered composite image data set including the ROI is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine extent and severity of the disease. Second anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a second co-registered composite image data set. A global, rigid registration is performed on the first and second anatomical image data sets, such that the first and second functional image data sets are also globally registered. At least a ROI within the globally registered image data set using the identified ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. A local, non-rigid registration is performed on the ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set and the ROI within the globally registered image data set, thereby producing a first co-registered serial image data set. The first co-registered serial image data set including the ROIs is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine severity of the disease and / or response to treatment of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Overlay alignment measurement of wafers
InactiveUS6079256AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementControl systemEngineering
The present invention is a method and apparatus that uses a microscopic height variation positioned relative to a semiconductor device to scan a target on the device to produce an electrical signal representative of height variations of first and second periodic structures of the target in a selected path across the device, and a computing and control system to provide translation between the microscopic height variation detector and the target on the device in a selected path, and to calculate any offset between the first periodic structure and the second periodic structure of the target from the electrical signals from the microscopic height variation detector. The first periodic structure of the target is on a first layer of the device, and the second periodic structure, that complements the first periodic structure, is on a second layer of the device at a location that is adjacent the first periodic structure.
Owner:KLA INSTR
Model building and analysis engine for combined x-ray and optical metrology
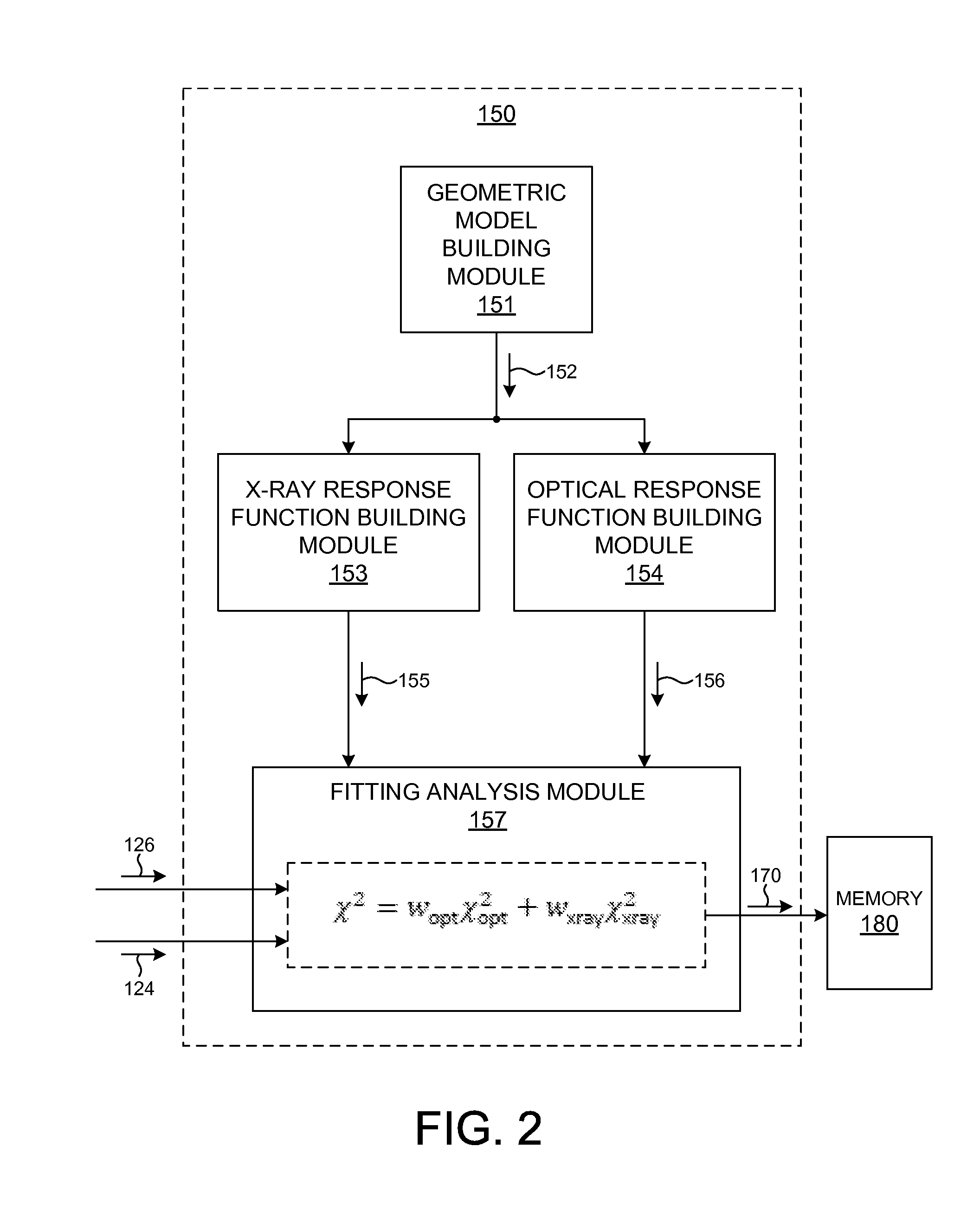
ActiveUS20140019097A1Reduce in quantityReduce correlationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotomechanical apparatusX-rayGeometric modeling
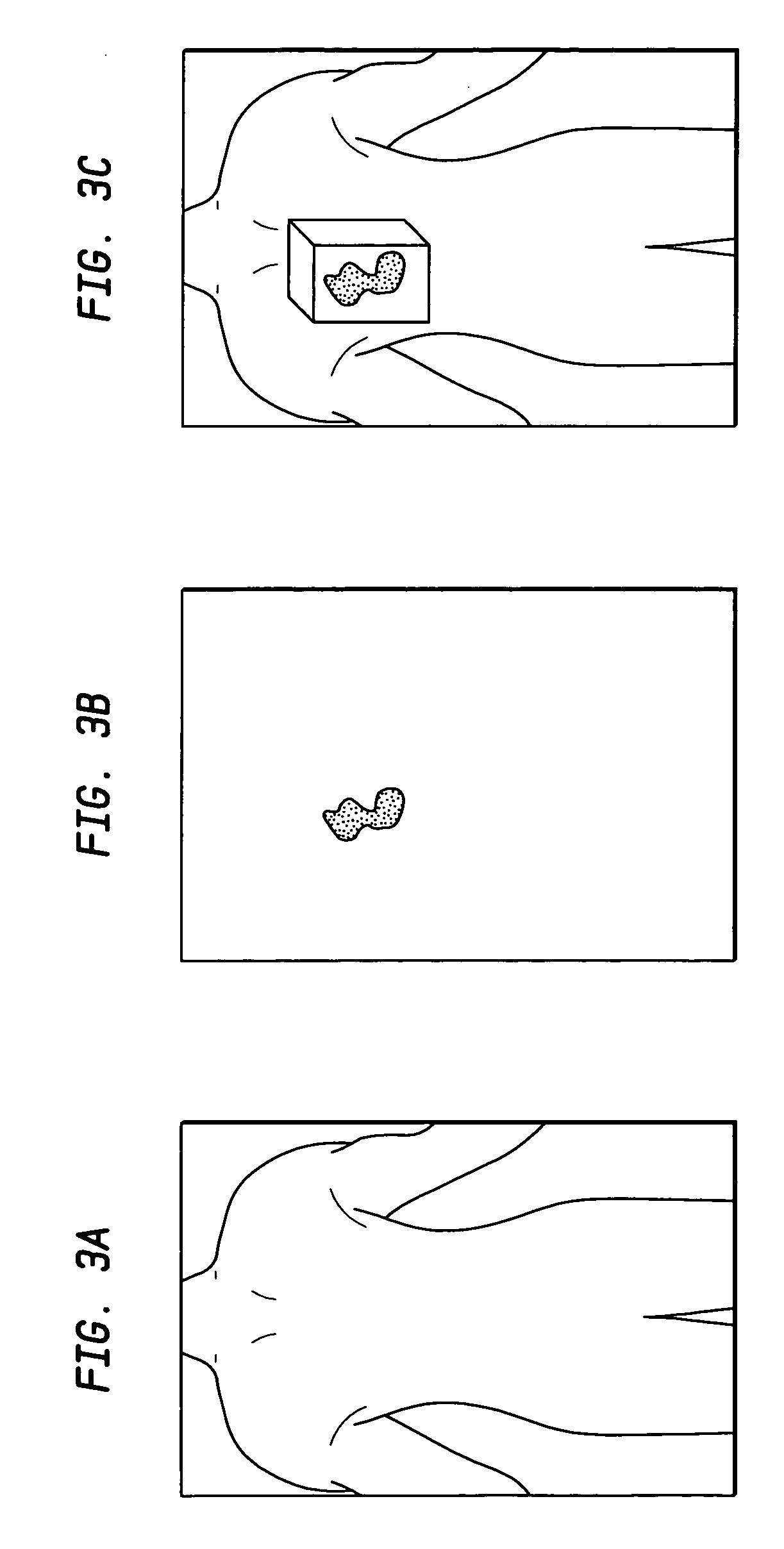
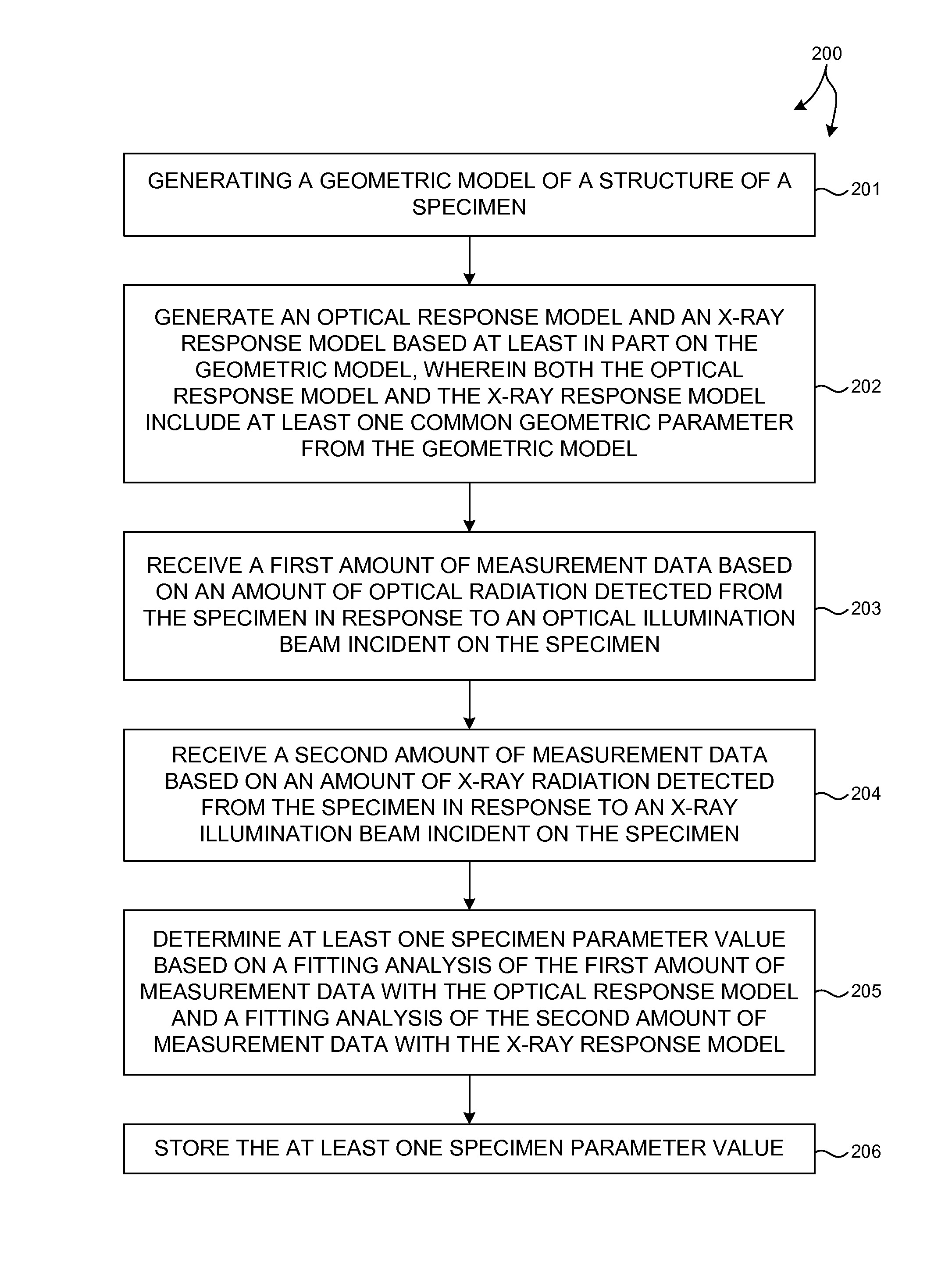
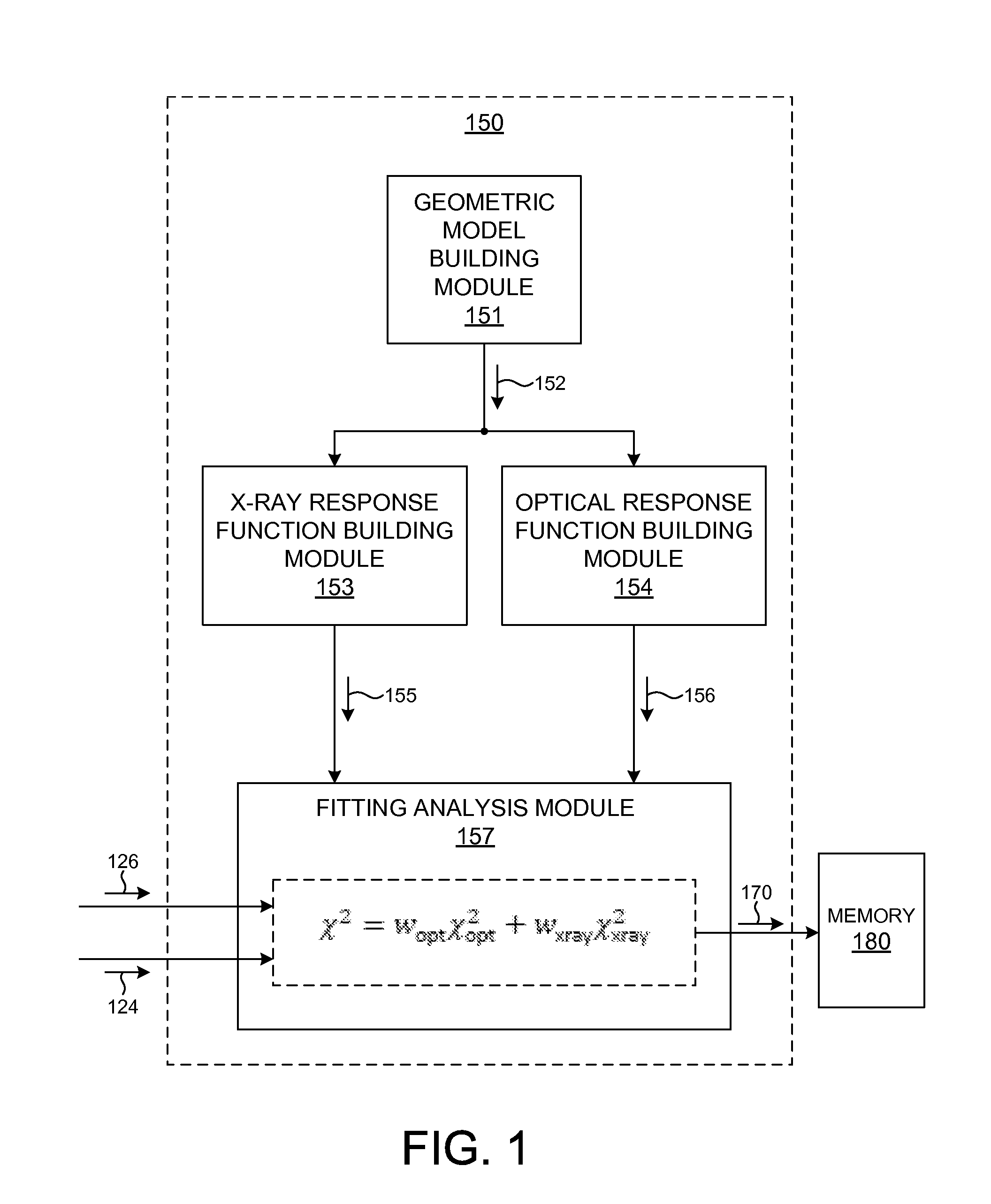
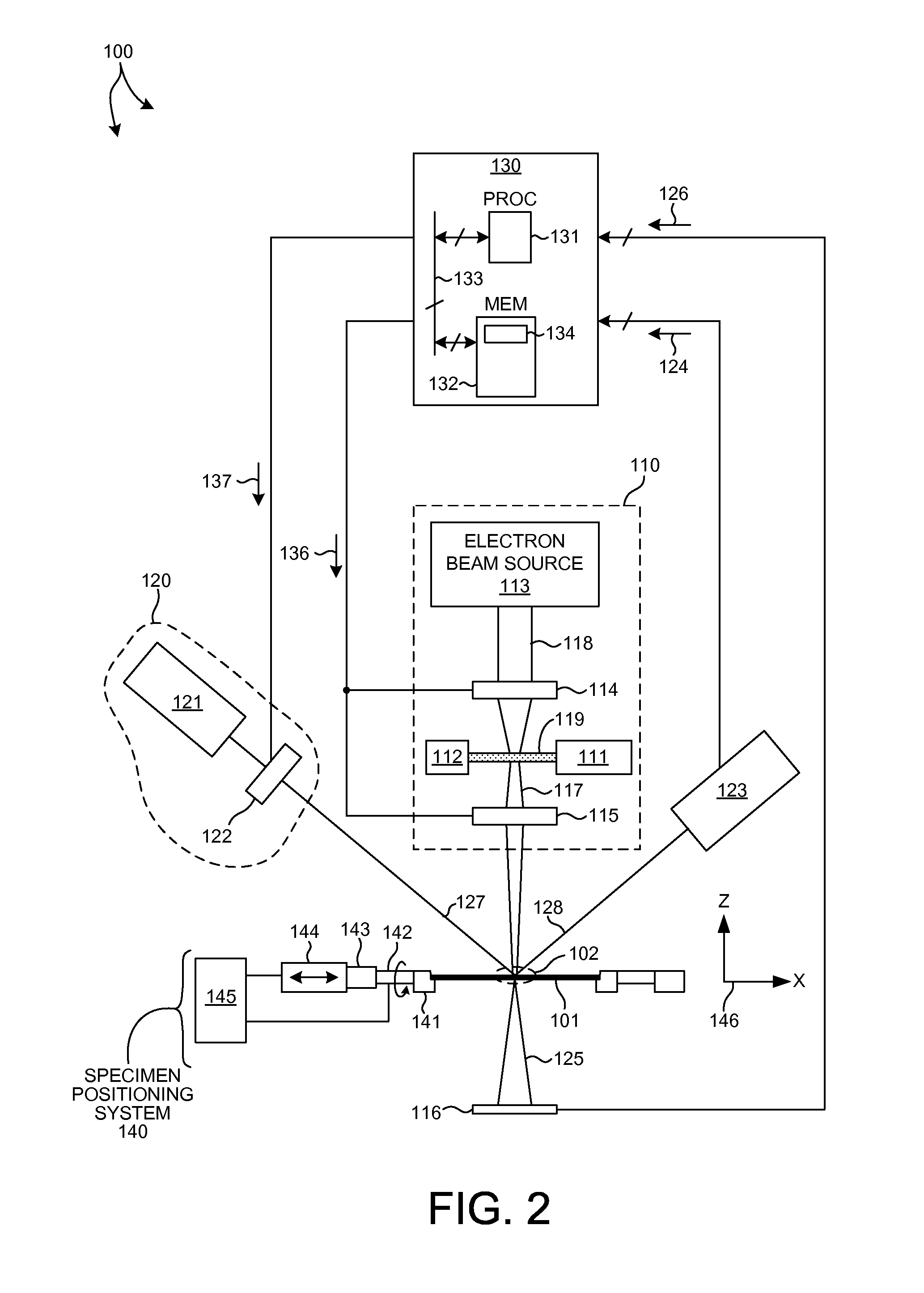
Structural parameters of a specimen are determined by fitting models of the response of the specimen to measurements collected by different measurement techniques in a combined analysis. Models of the response of the specimen to at least two different measurement technologies share at least one common geometric parameter. In some embodiments, a model building and analysis engine performs x-ray and optical analyses wherein at least one common parameter is coupled during the analysis. The fitting of the response models to measured data can be done sequentially, in parallel, or by a combination of sequential and parallel analyses. In a further aspect, the structure of the response models is altered based on the quality of the fit between the models and the corresponding measurement data. For example, a geometric model of the specimen is restructured based on the fit between the response models and corresponding measurement data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for reconstruction of volumetric images in a divergent scanning computed tomography system
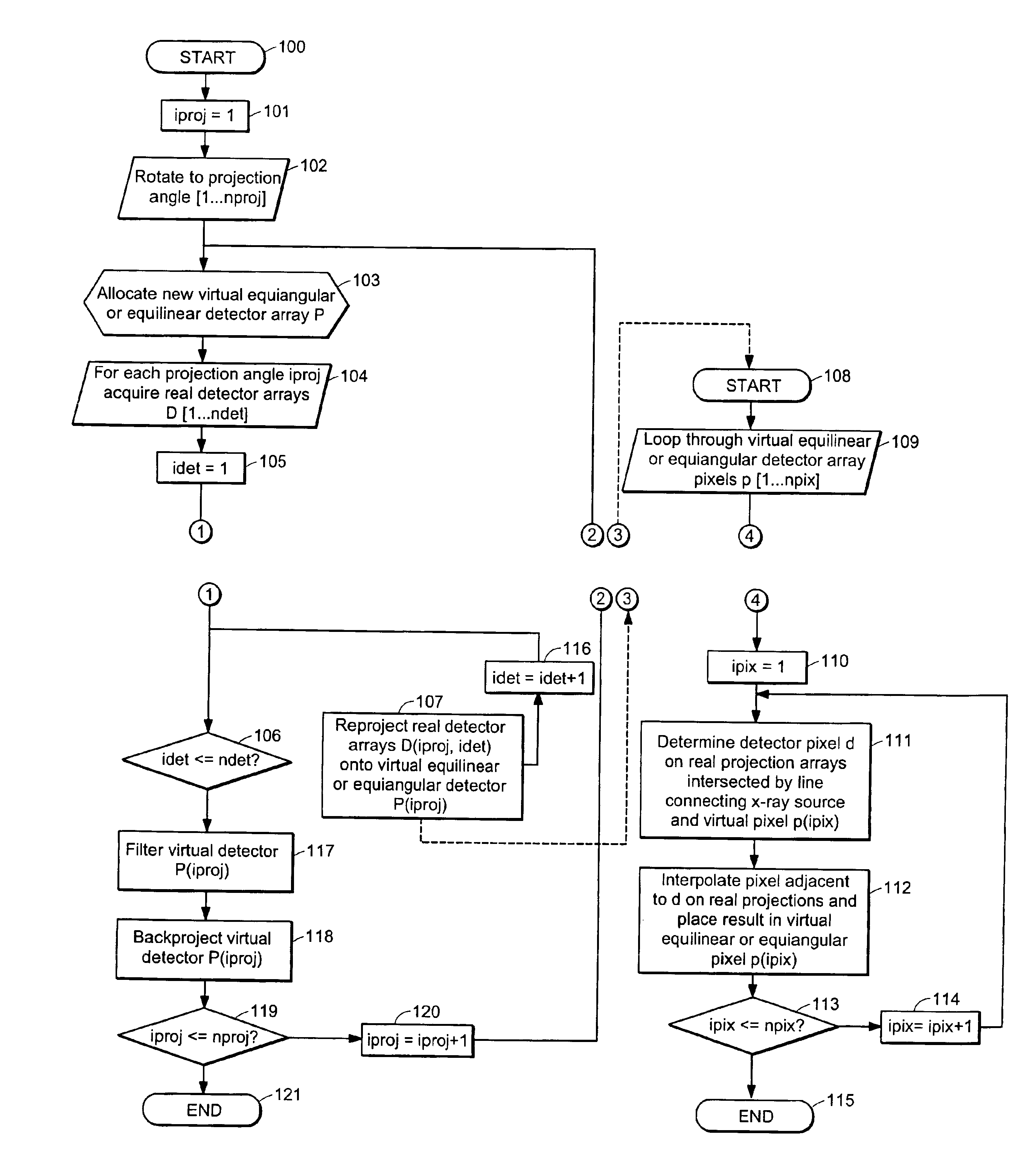
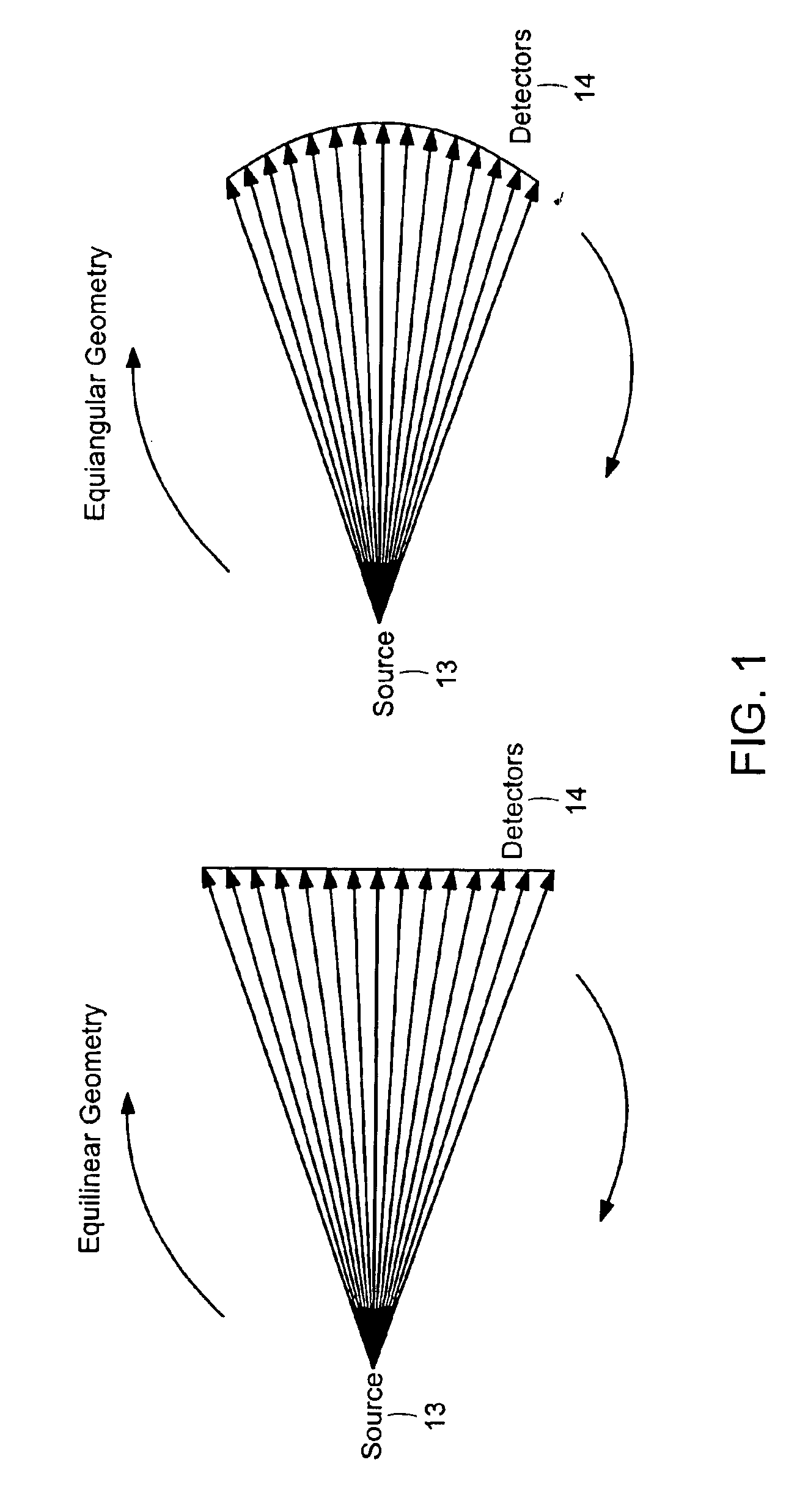
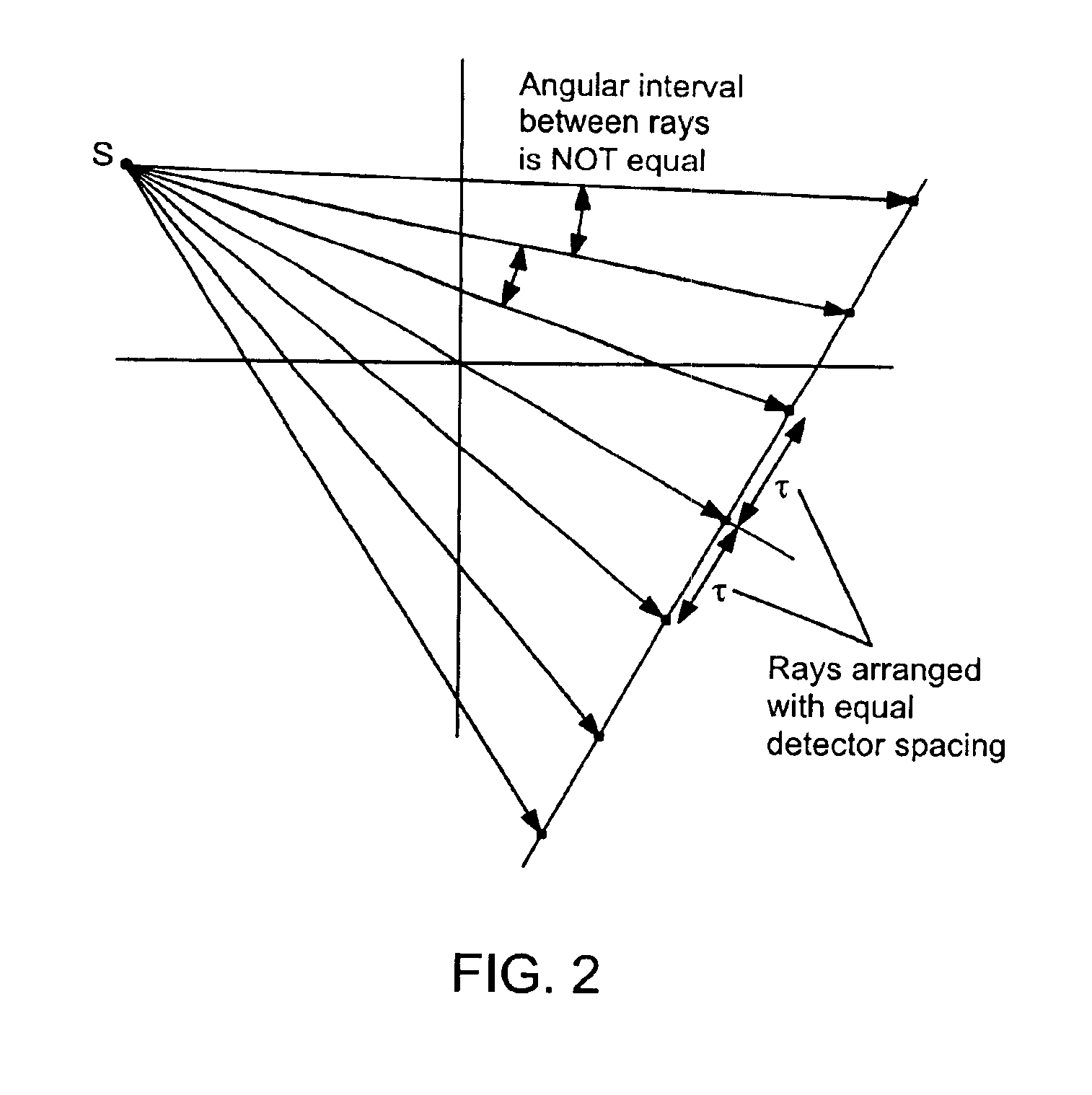
ActiveUS7106825B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDetector arrayComputing tomography
An apparatus and method for reconstructing image data for a region are described. A radiation source and multiple one-dimensional linear or two-dimensional planar area detector arrays located on opposed sides of a region angled generally along a circle centered at the radiation source are used to generate scan data for the region from a plurality of diverging radiation beams, i.e., a fan beam or cone beam. Individual pixels on the discreet detector arrays from the scan data for the region are reprojected onto a new single virtual detector array along a continuous equiangular arc or cylinder or equilinear line or plane prior to filtering and backprojecting to reconstruct the image data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
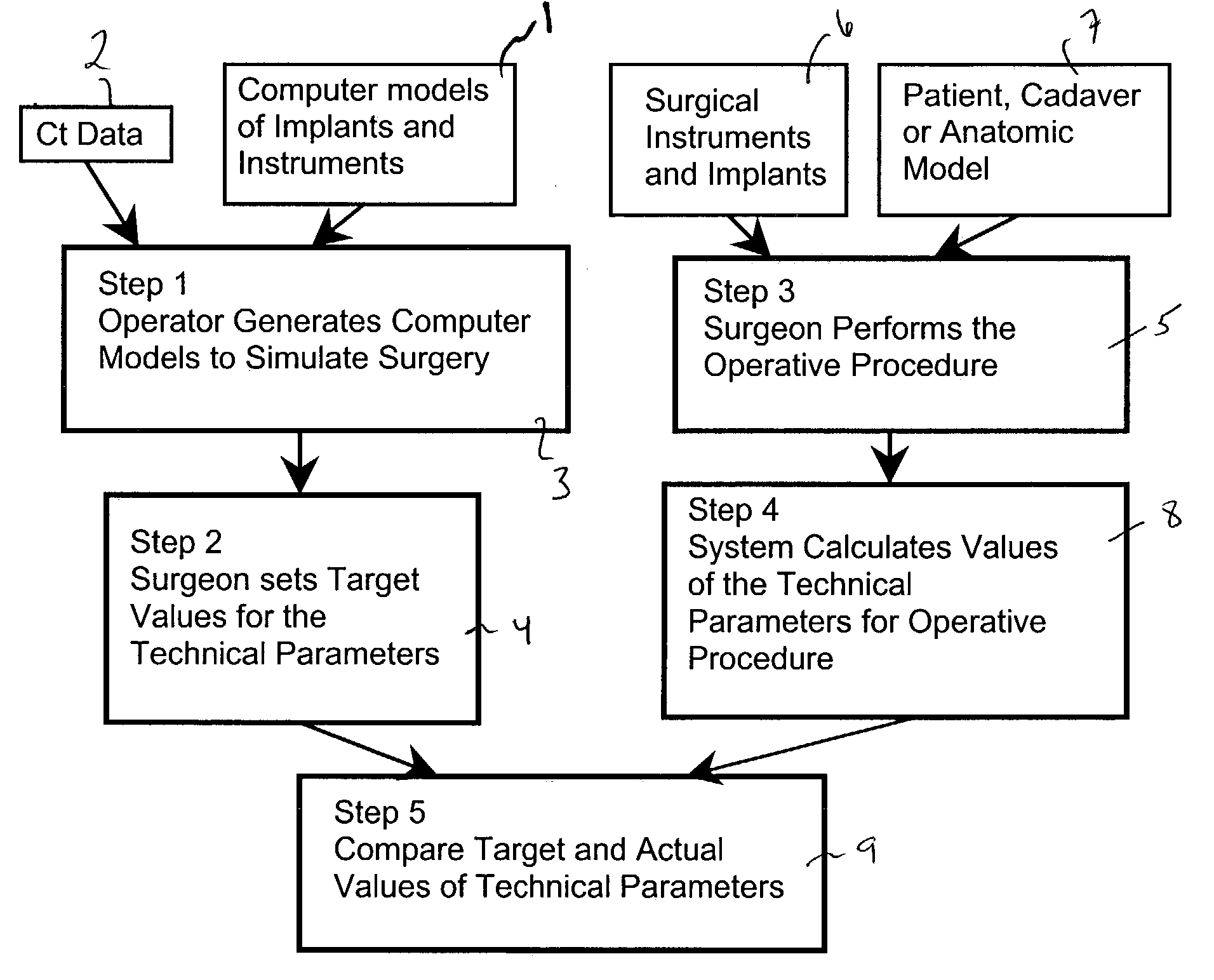
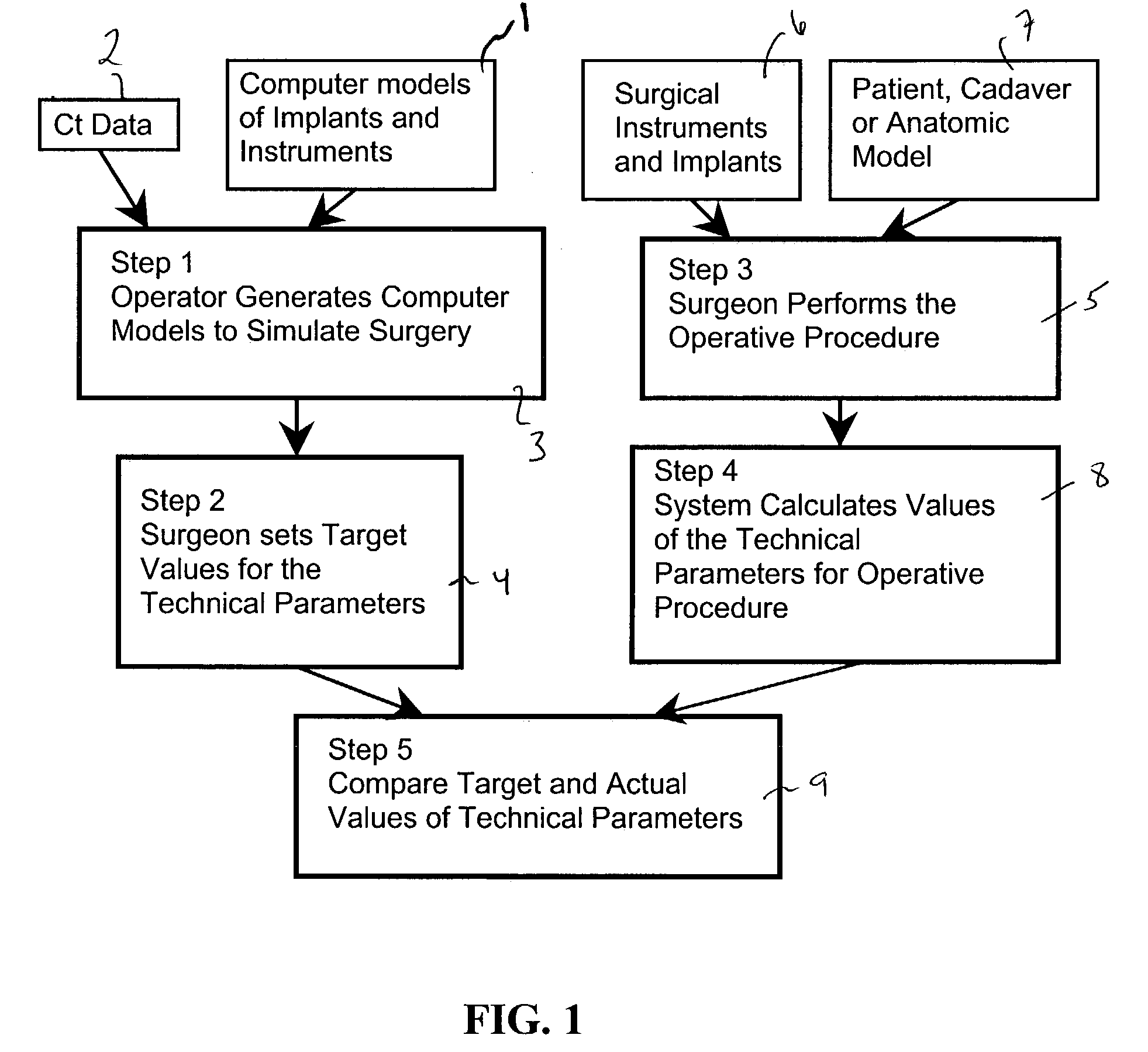
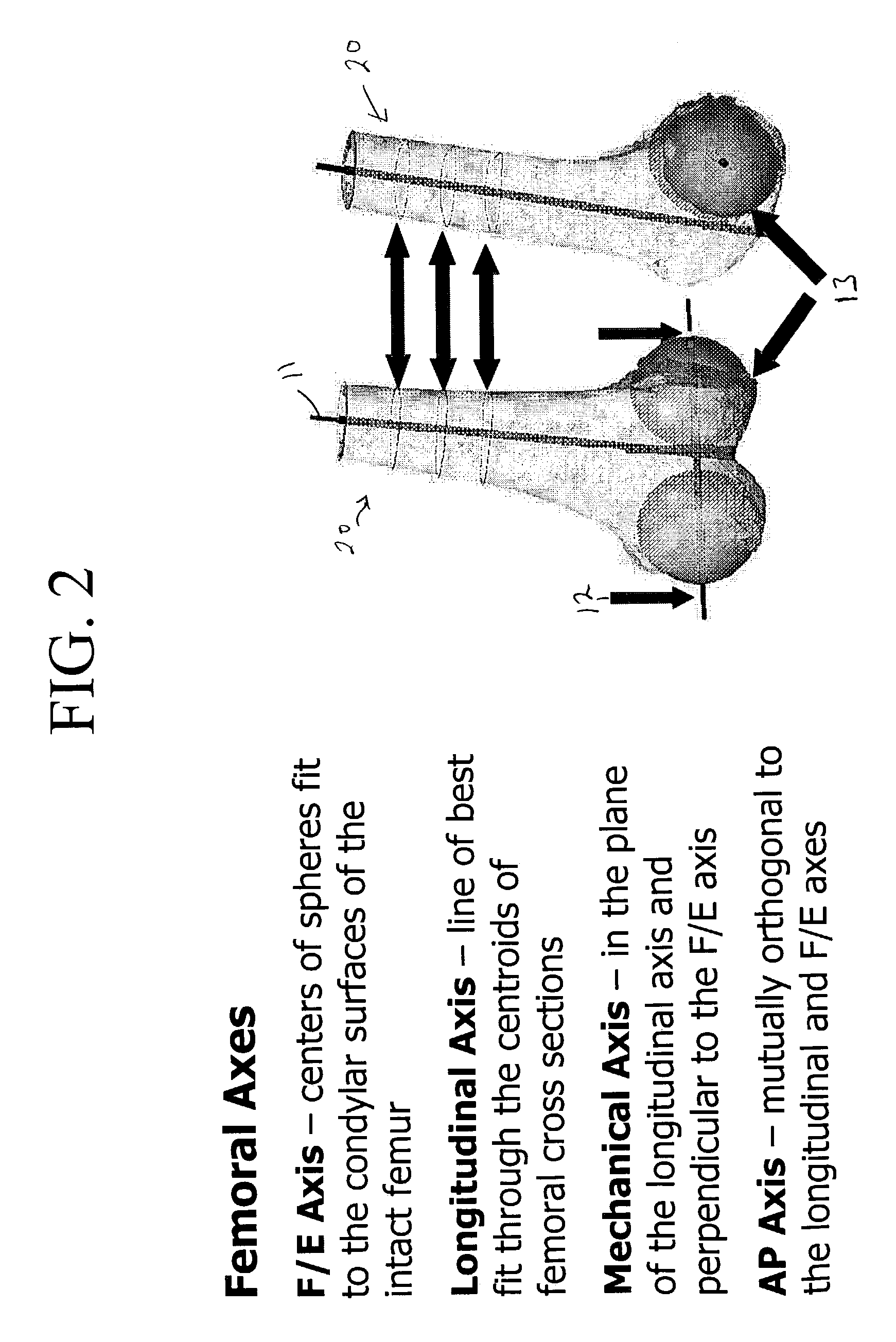
Computer-based training methods for surgical procedures
ActiveUS7427200B2Without expenseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSystems analysisTechnical success
A method is disclosed for analyzing surgical techniques using a computer system for gathering and analyzing surgical data acquired during a surgical procedure on a body portion and comparing that data to pre-selected target values for the particular surgical procedure. The inventive method allows the surgeon, for example, to measure the technical success of a surgical procedure in terms of quantifiable geometric, spatial, kinematic or kinetic parameters. The method comprises calculation of these parameters from data collected during a surgical procedure and then comparing these results with values of the same parameters derived from target values defined by the surgeon, surgical convention, or computer simulation of the same procedure prior to the operation itself.
Owner:NOBLE PHILIP C +1
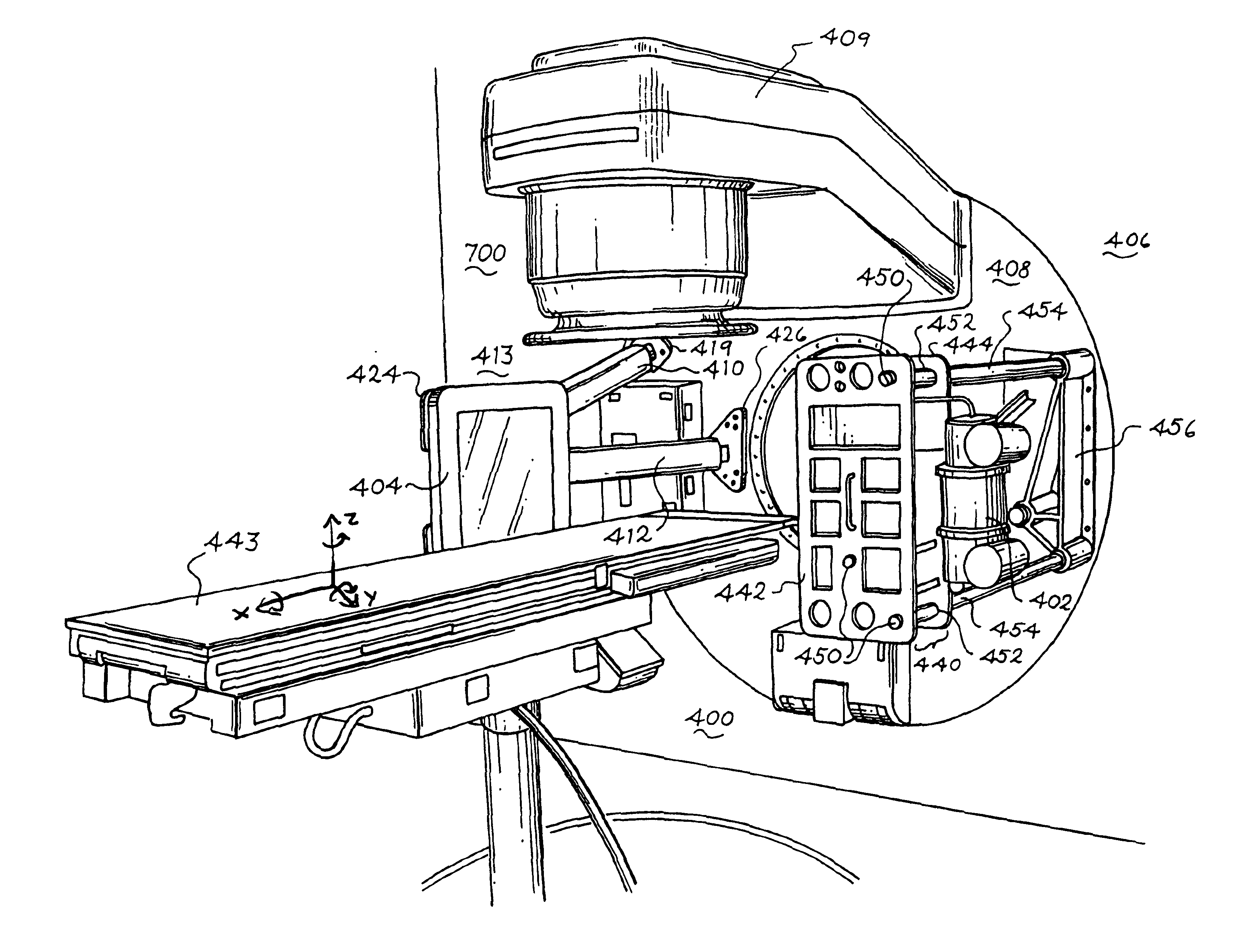
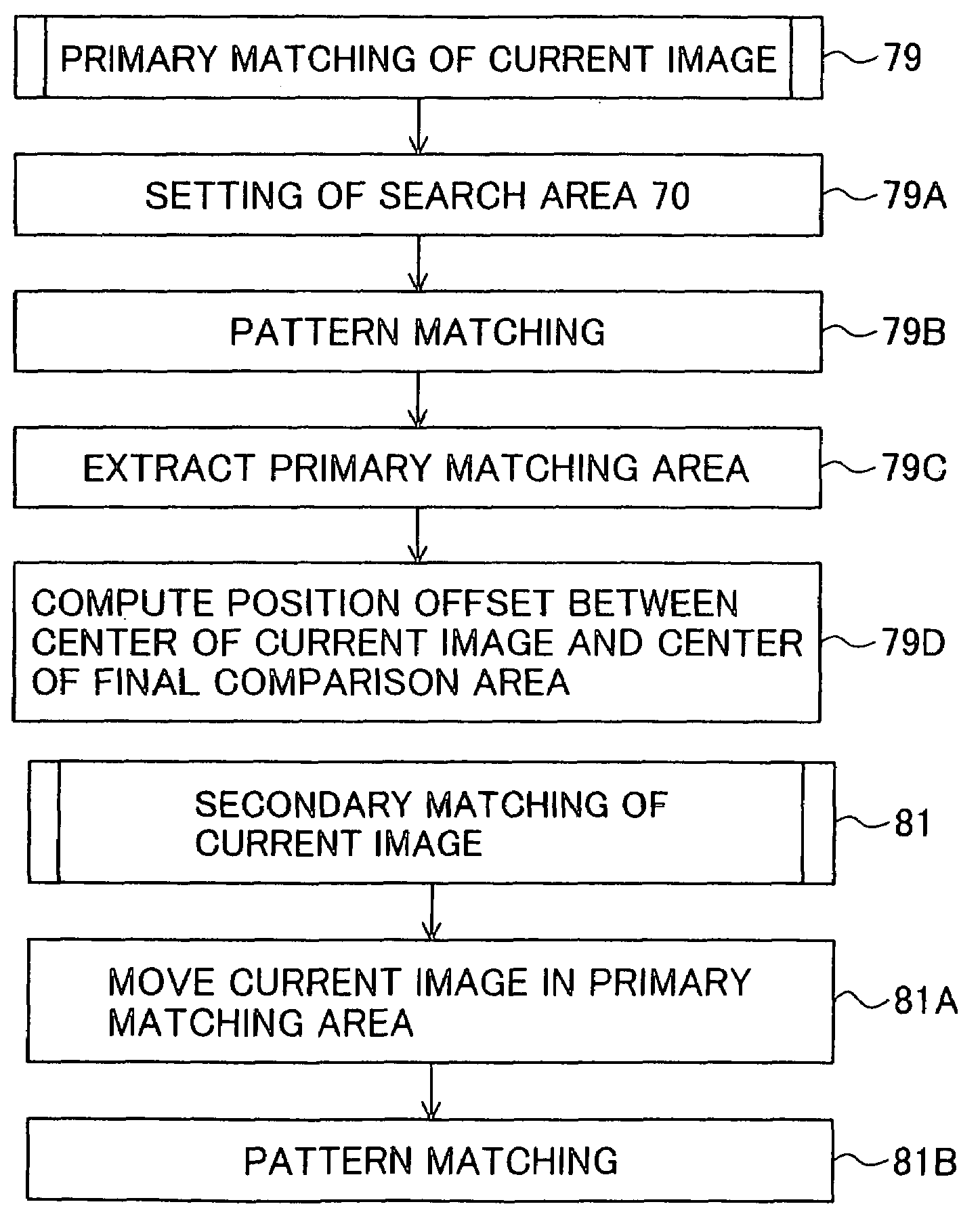
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
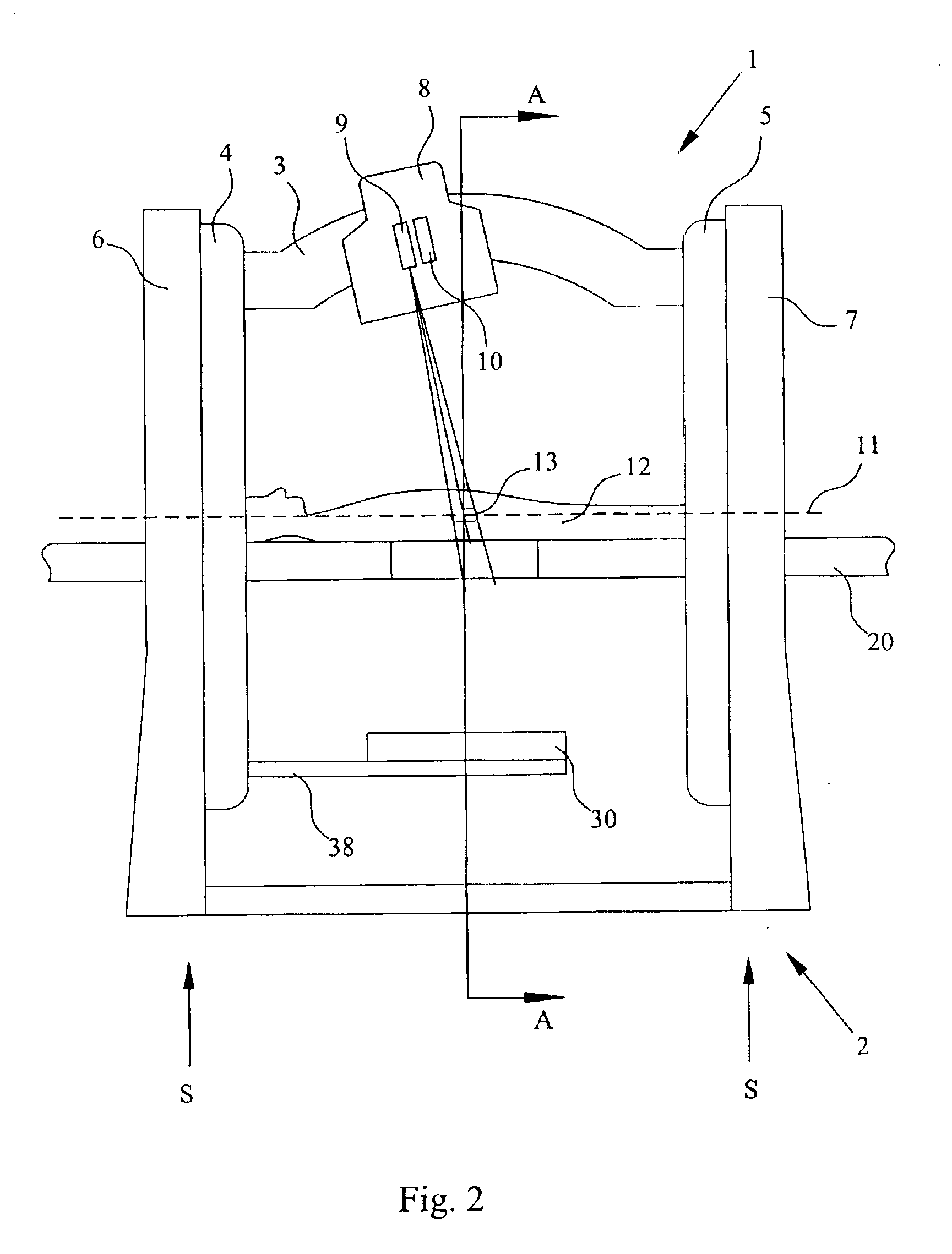
InactiveUS7212609B2Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPattern matchingX-ray
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
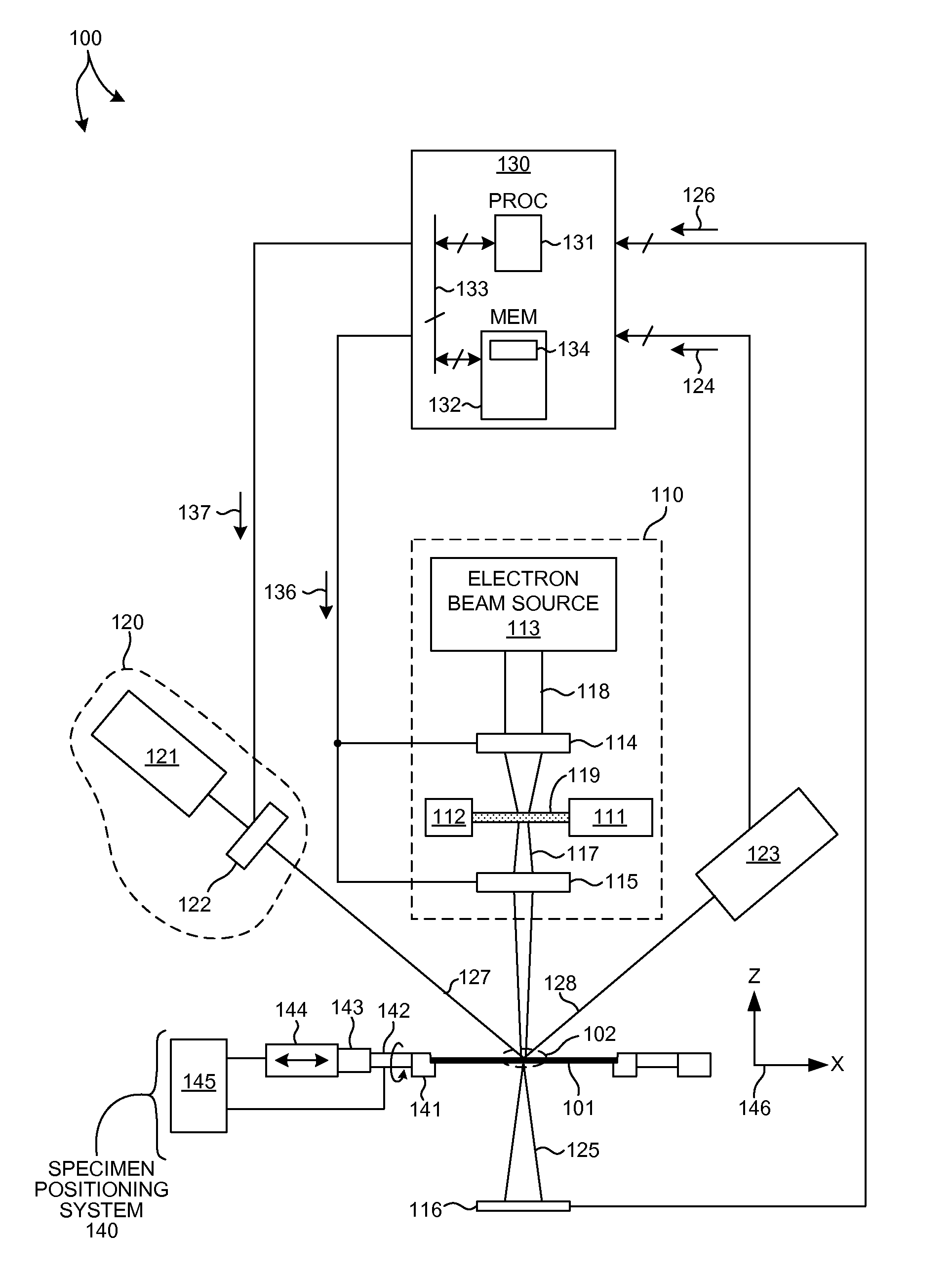
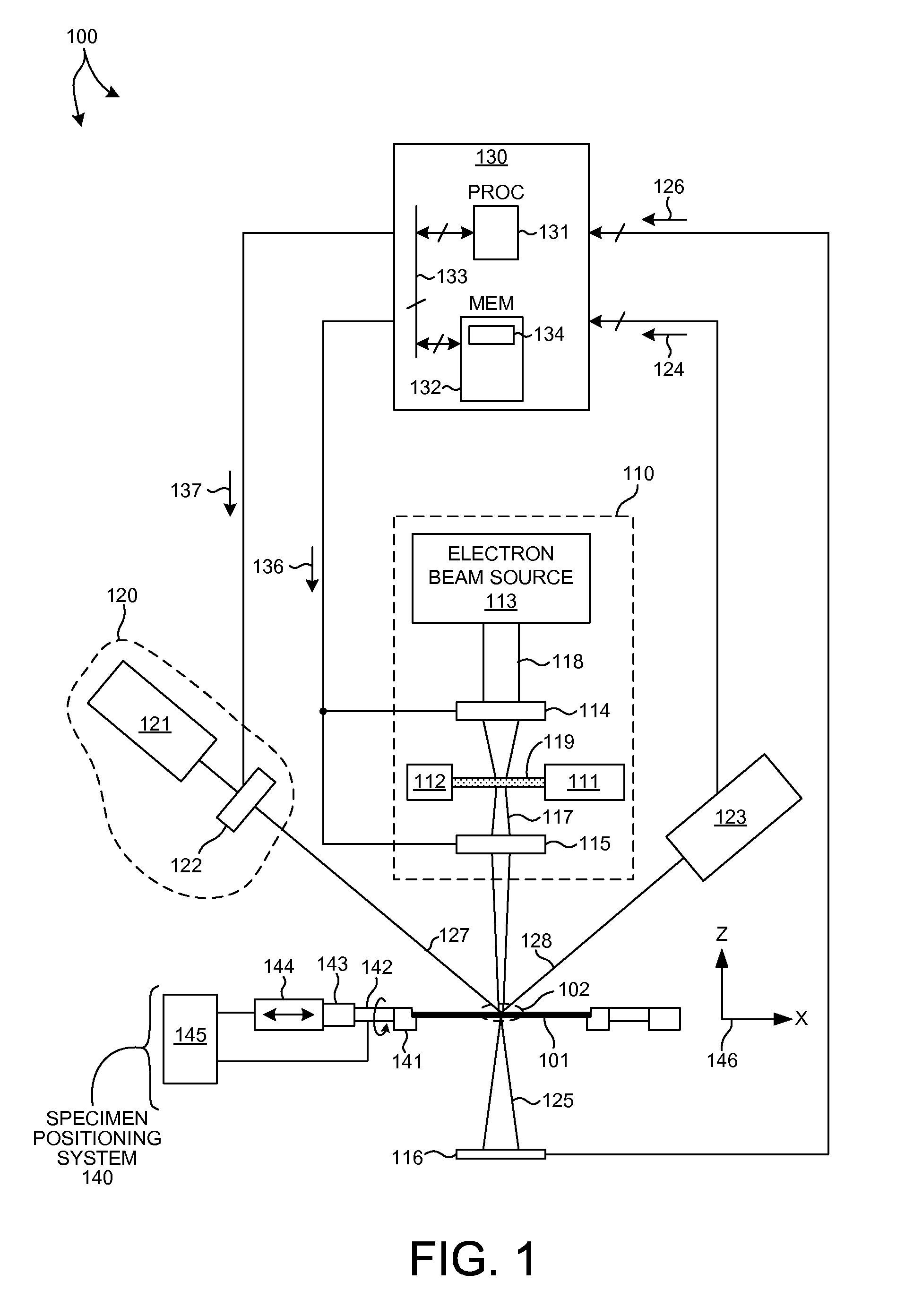
Charged particle beam apparatus and method for operating the same
ActiveUS7045781B2Less spaceLow costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLight beamParallel imaging
A charged particle beam apparatus is provided which comprises a charged particle source for producing a primary beam of charged particles, aperture means for collimating said primary beam of charged particles, wherein said aperture means is adapted to switch between a collimation of said primary beam to a width appropriate for serial imaging of a sample as well as a collimation of said primary beam to a width appropriate for parallel imaging of said sample, a condenser lens for condensing said primary beam of charged particles, scanning means for deflecting said primary beam of charged particles, an objective lens for focusing said condensed primary beam, a sectorized detector for detecting a secondary charged particles. Also, several different operation modes of the beam apparatus are described allowing for serial imaging as well as parallel imaging.
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
Ultraviolet ray generator, ultraviolet ray irradiation processing apparatus, and semiconductor manufacturing system
InactiveUS20050263719A1High dielectric constantReduce transmission intensityFurnace componentsLiving organism packagingUltravioletNitrogen gas
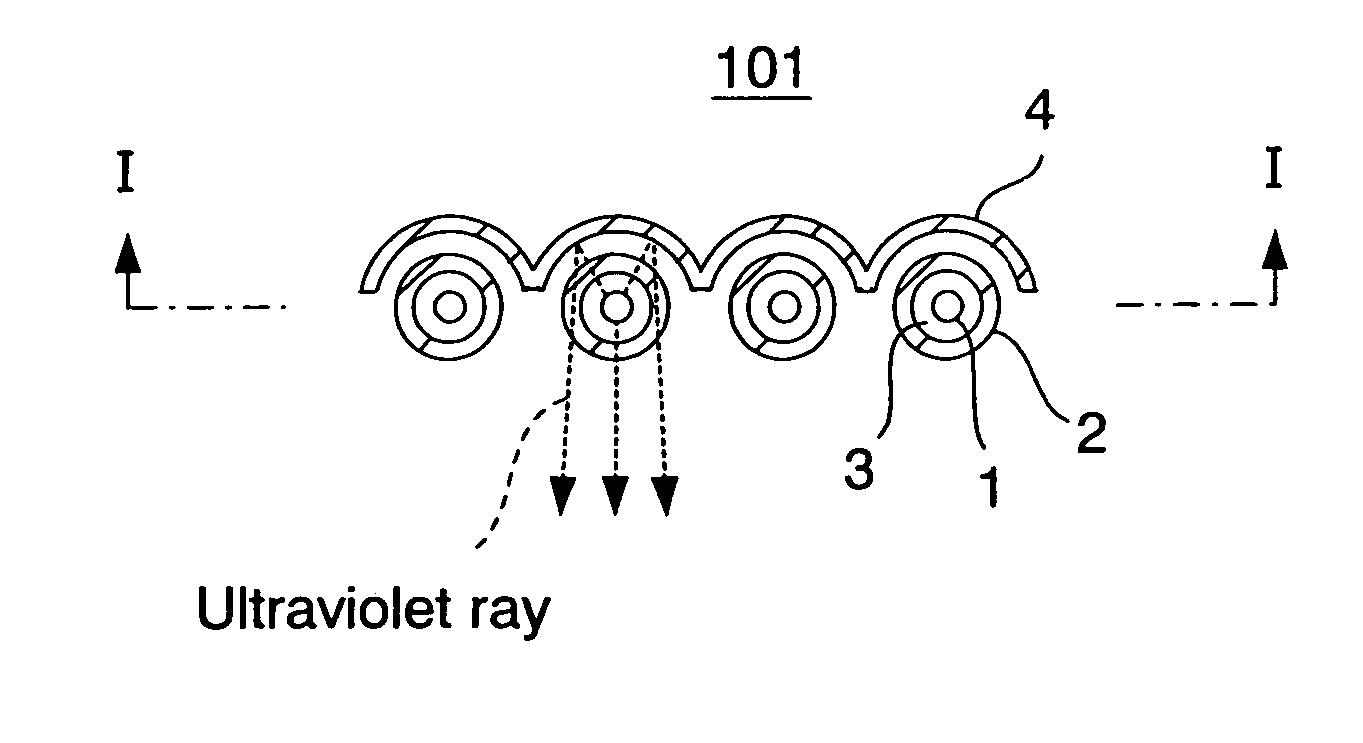
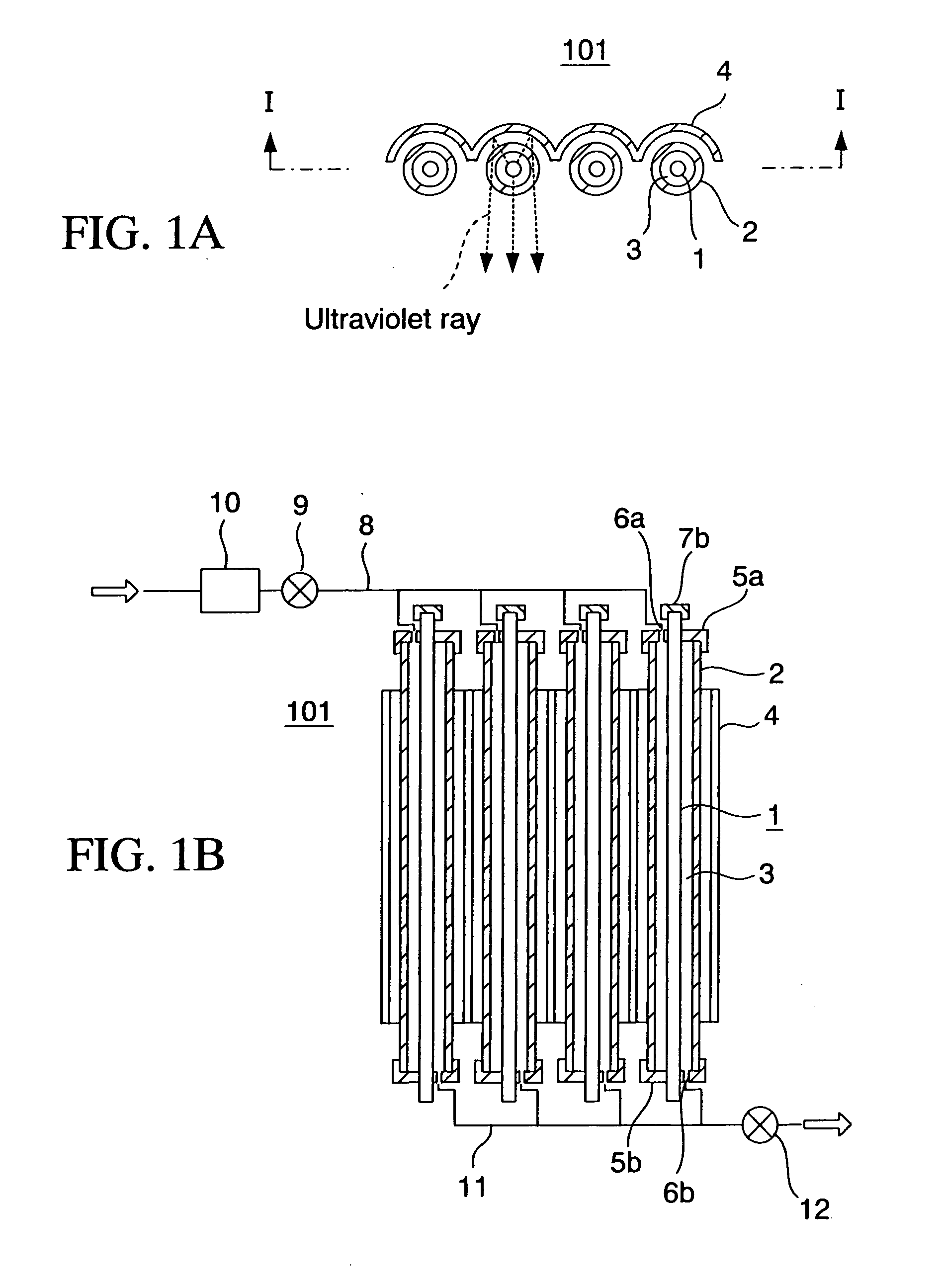
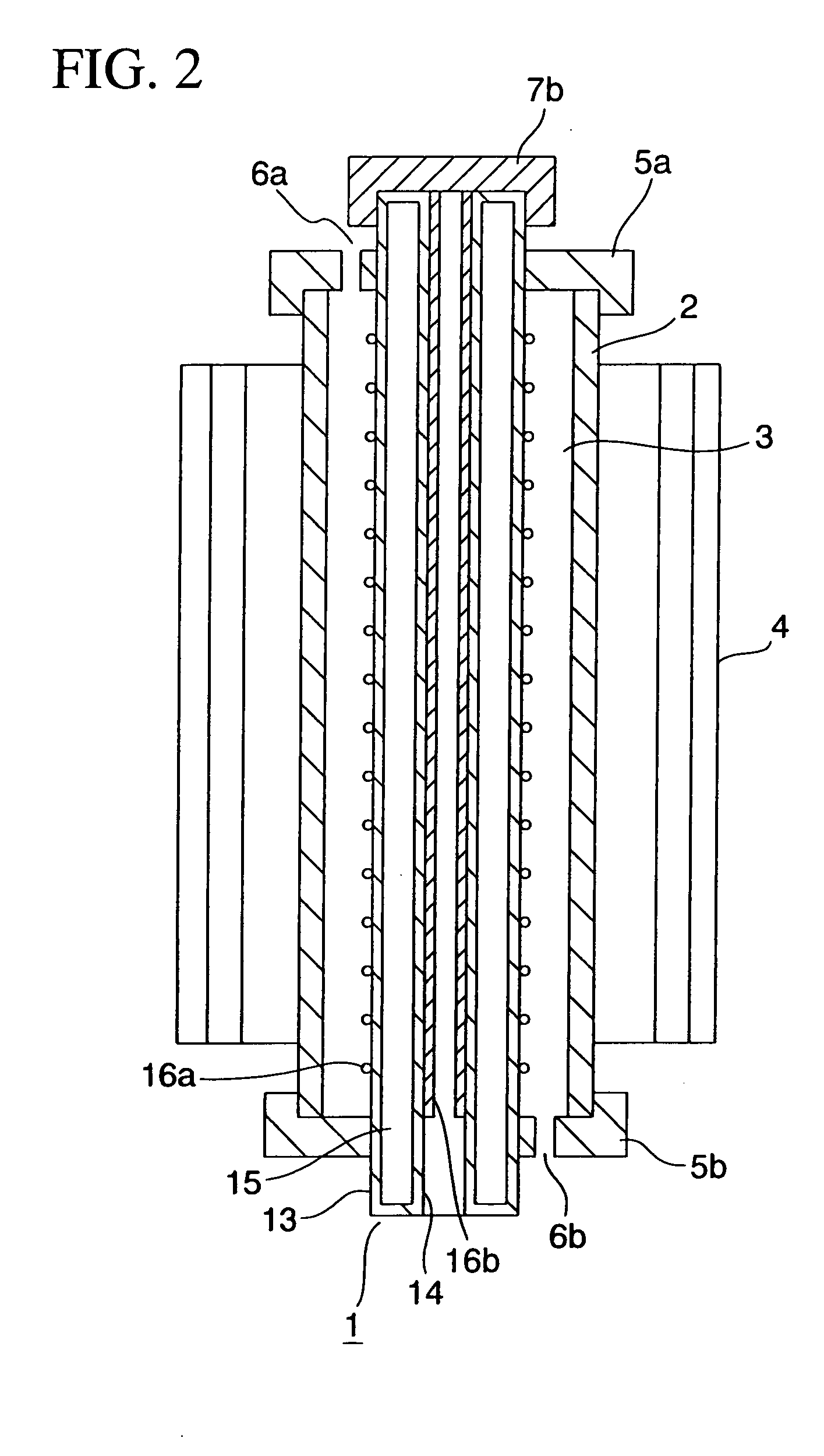
The present invention relates to an ultraviolet ray generator 101, and the generator 101 has an ultraviolet ray lamp 1, a protective tube 2 being made of a material which is transparent with respect to ultraviolet ray and housing the ultraviolet ray lamp 1, and gas introduction port 6a introducing nitrogen gas or inert gas into the protective tube 2.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
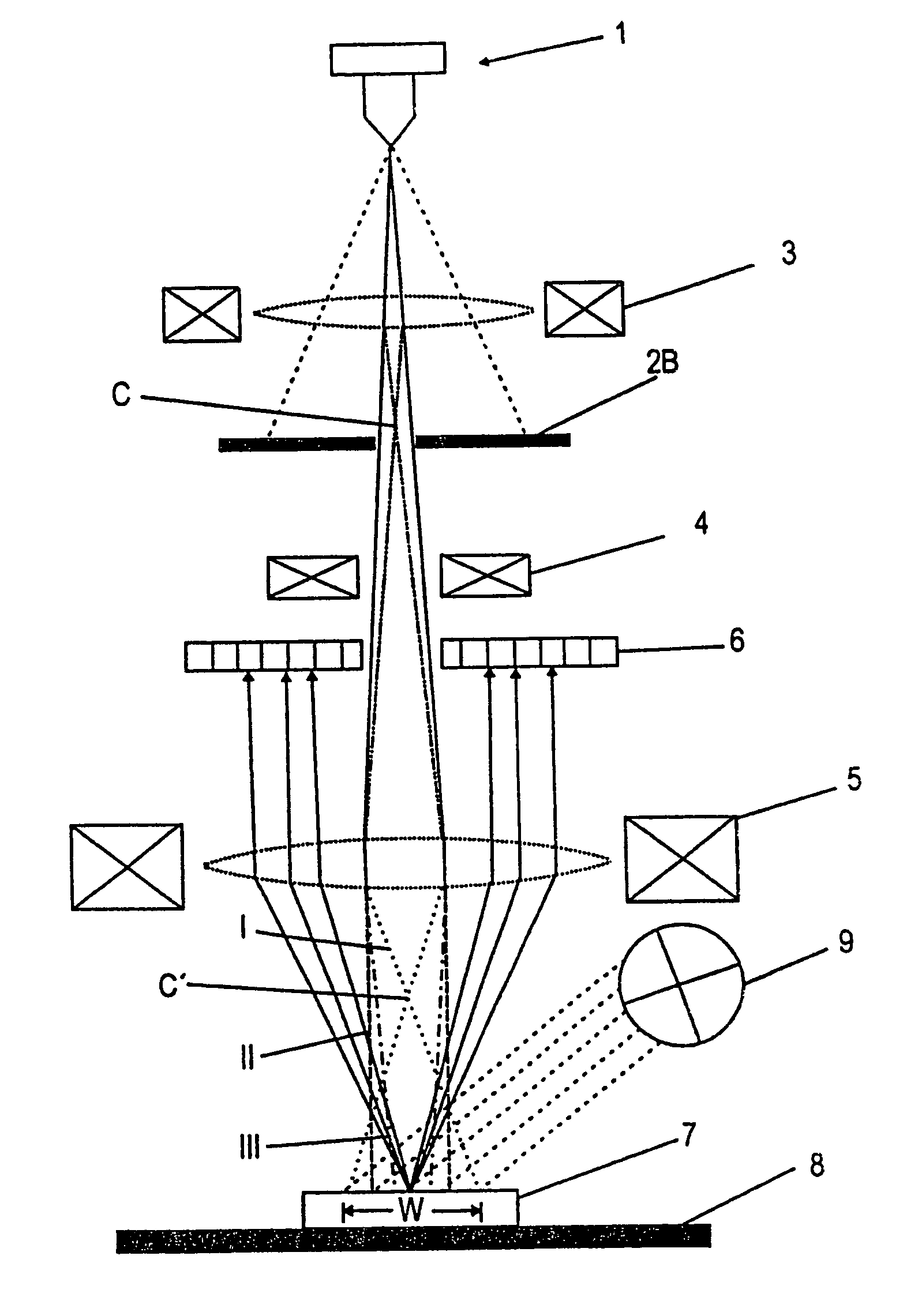
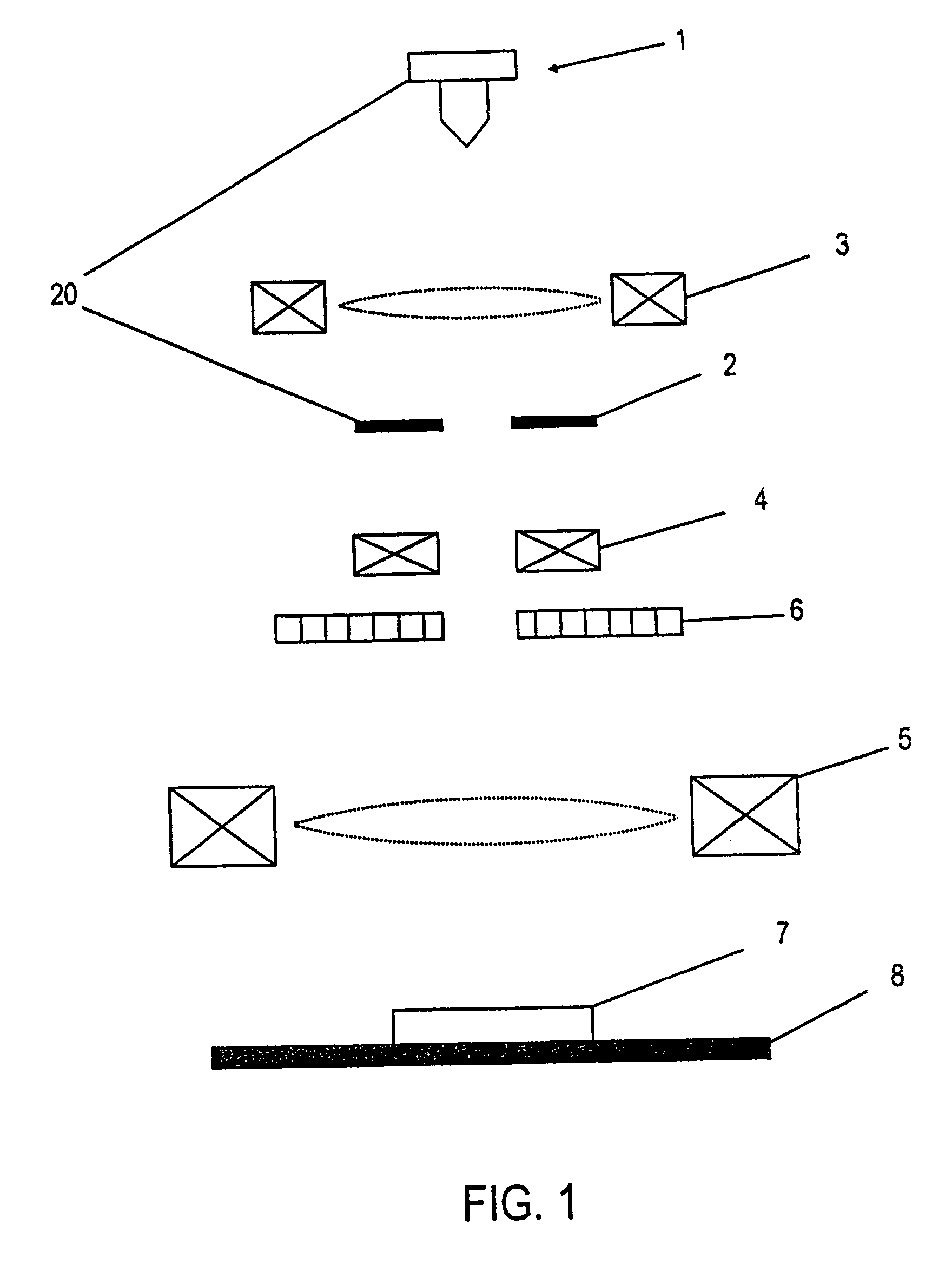
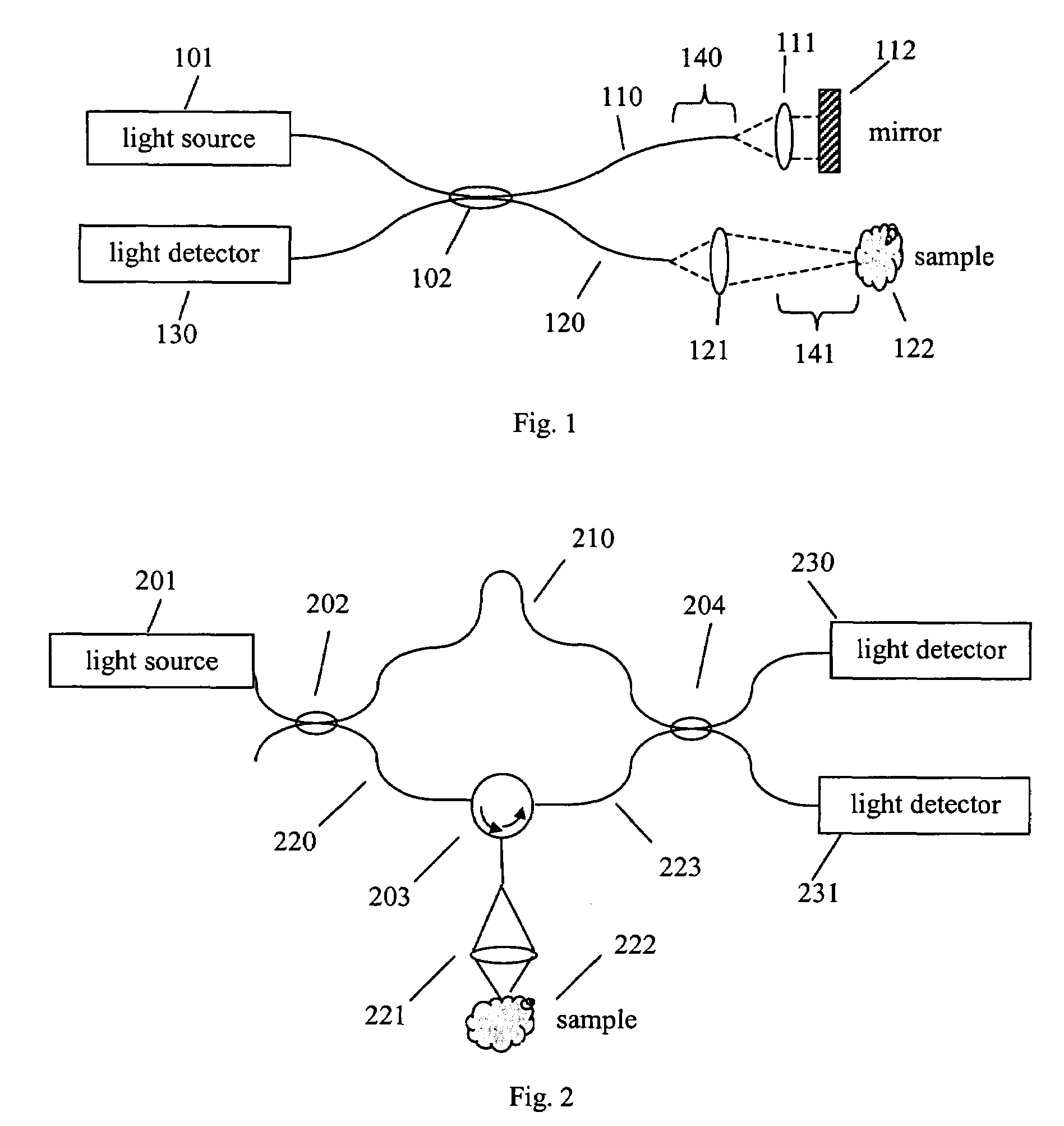
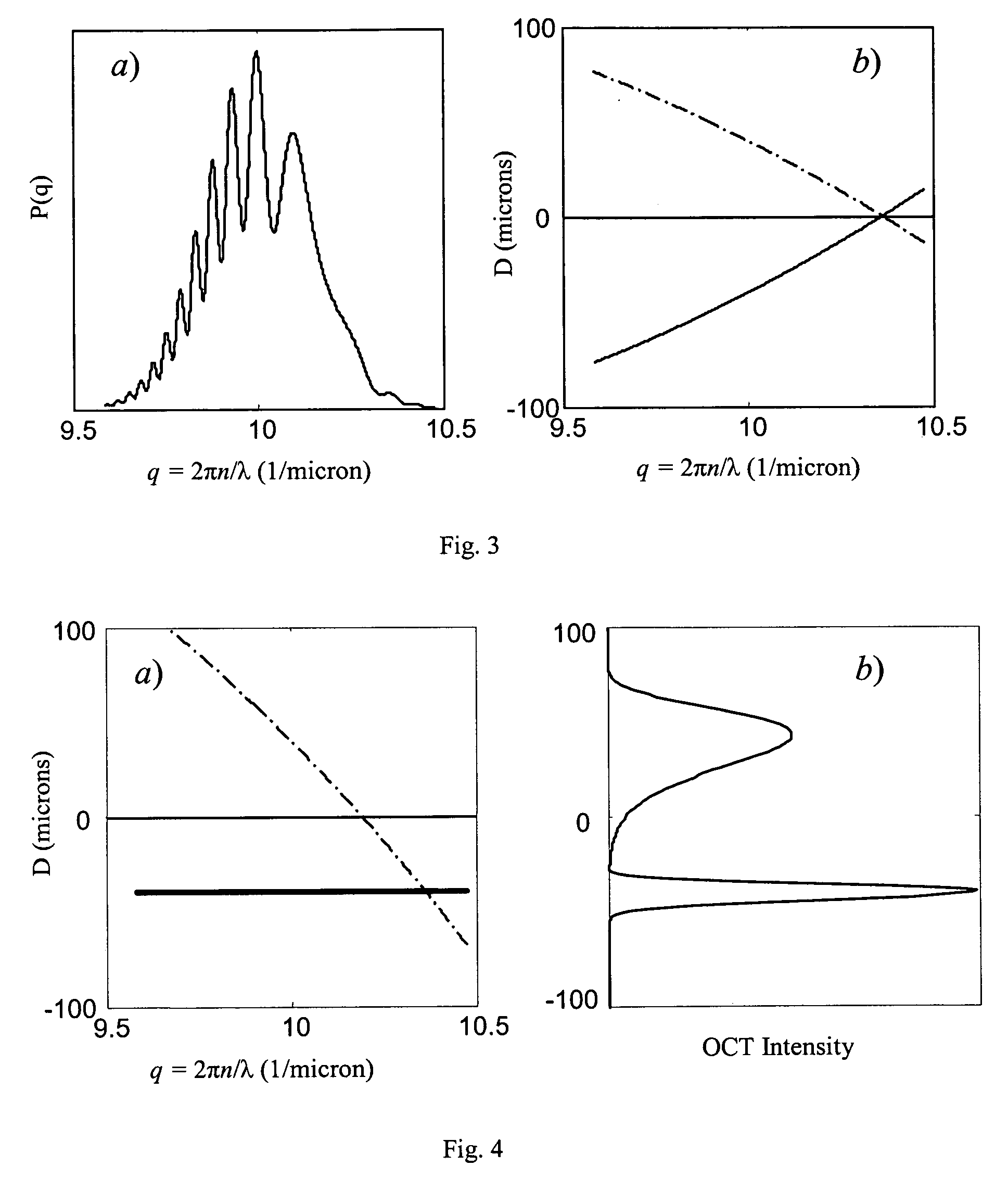
Method to suppress artifacts in frequency-domain optical coherence tomography
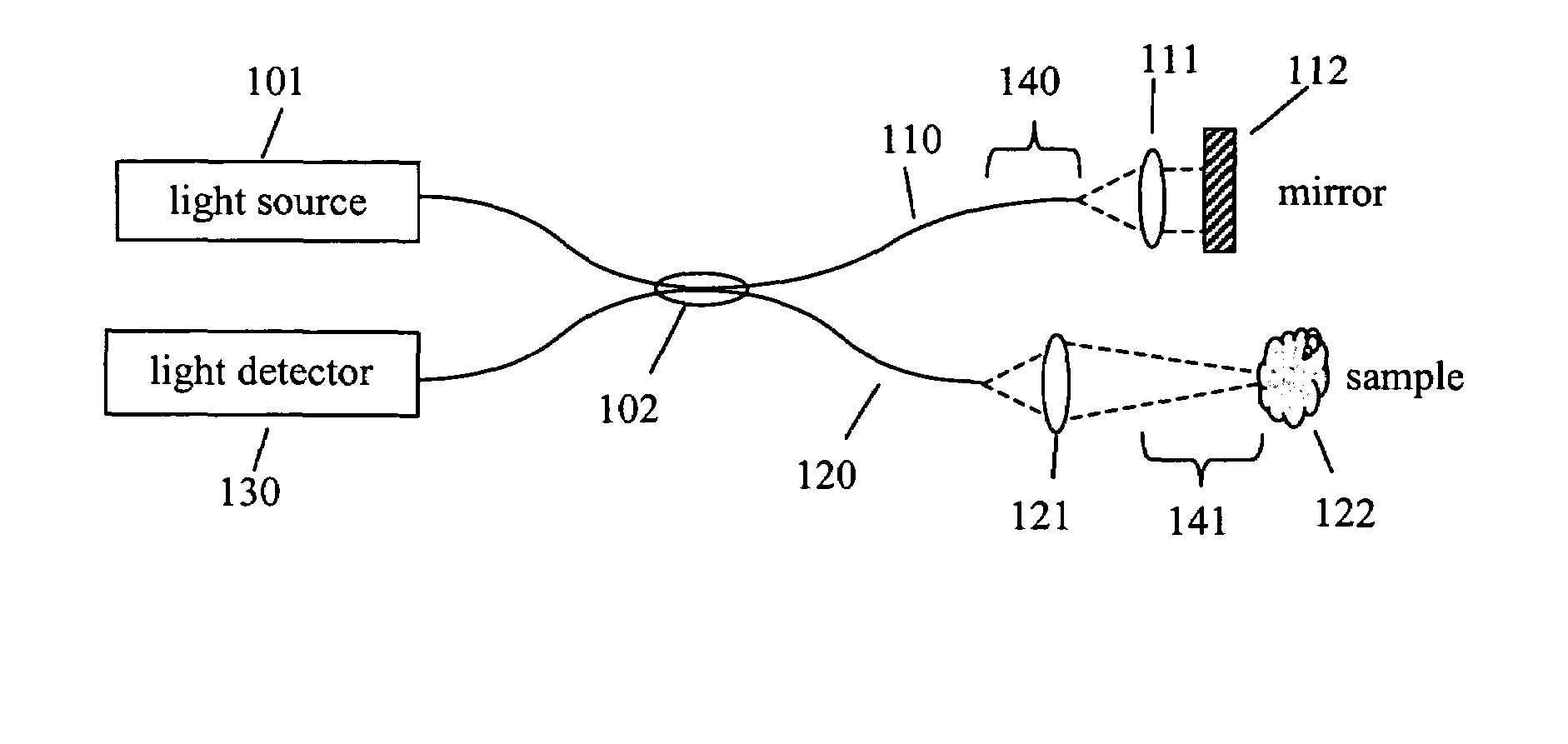
ActiveUS7330270B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFrequency domain optical coherence tomographySignificant difference
One embodiment of the present invention is a method for suppressing artifacts in frequency-domain OCT images, which method includes (a) providing sample and reference paths with a significant difference in their chromatic dispersion (b) correcting for the effects of the mismatch in chromatic dispersion, for the purpose of making artifacts in the OCT image readily distinguishable from the desired image.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Metrology Tool With Combined X-Ray And Optical Scatterometers
ActiveUS20130304424A1Reduce correlationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData setMetrology
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous optical scattering and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements over a desired inspection area of a specimen are presented. SAXS measurements combined with optical scatterometry measurements enables a high throughput metrology tool with increased measurement capabilities. The high energy nature of x-ray radiation penetrates optically opaque thin films, buried structures, high aspect ratio structures, and devices including many thin film layers. SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements of a particular location of a planar specimen are performed at a number of different out of plane orientations. This increases measurement sensitivity, reduces correlations among parameters, and improves measurement accuracy. In addition, specimen parameter values are resolved with greater accuracy by fitting data sets derived from both SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements based on models that share at least one geometric parameter. The fitting can be performed sequentially or in parallel.
Owner:KLA CORP
Targeting method, targeting device, computer readable medium and program element
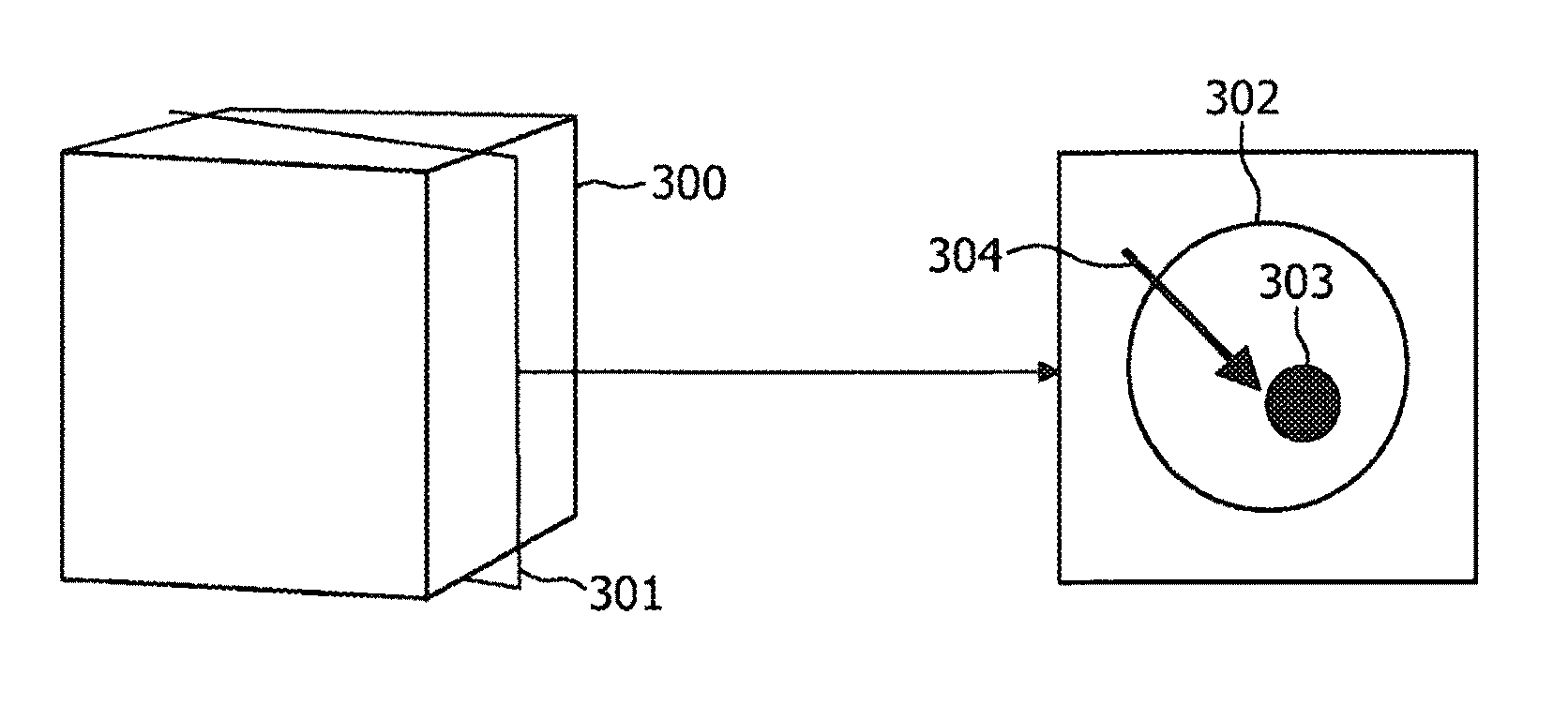
ActiveUS8208708B2Efficient methodReduce doseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFluoroscopic imageEntry point
According to an exemplary embodiment a targeting method for targeting a first object from an entry point to a target point in an object (110) under examination is provided, wherein the method comprises selecting a two-dimensional image (301) of the object under examination depicting the entry point (305) and the target point (303) and determining a planned path (304) from the entry point to the target point, wherein the planned path has a first direction. Furthermore, the method comprises recording data representing a fluoroscopic image of the object under examination, wherein the fluoroscopic image is recorded under a second direction so that a normal of the image coincide with the first direction and determining whether the first object is on the determined planned path based on shape and / or position of the projection of the first object in the fluoroscopic image.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
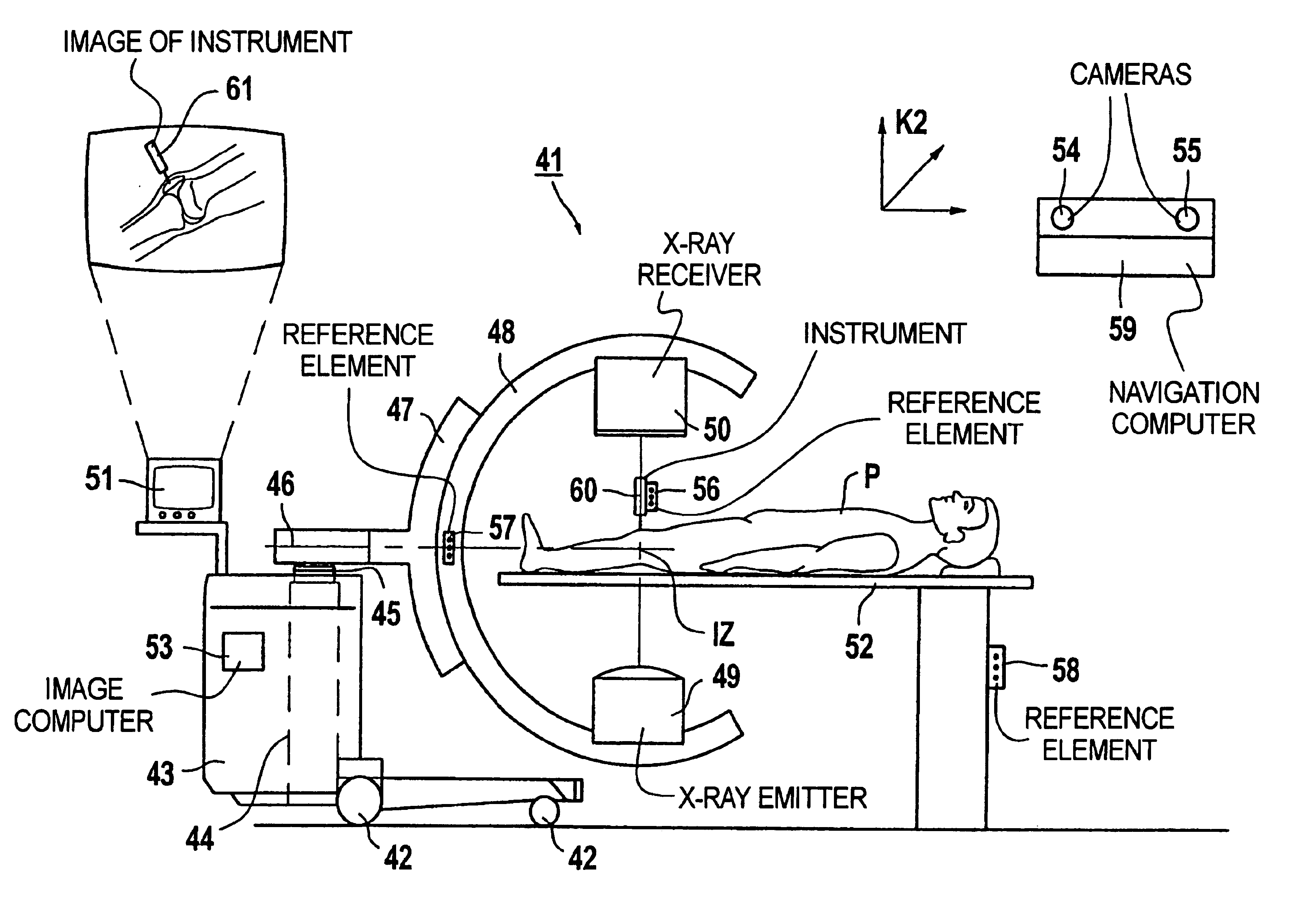
System and method of surgical imagining with anatomical overlay for navigation of surgical devices
ActiveUS7831294B2Improve the display effectPrecise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDisplay device
A system and method are provided for control of a navigation system for deploying a medical device within a subject, and for enhancement of a display image of anatomical features for viewing the projected location and movement of medical devices, and projected locations of a variety of anatomical features and other spatial markers in the operating region. The display of the X-ray imaging system information is augmented in a manner such that a physician can more easily become oriented in three dimensions with the use of a single-plane X-ray display. The projection of points and geometrical shapes within the subject body onto a known imaging plane can be obtained using associated imaging parameters and projective geometry.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com