Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
215625results about "Image analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
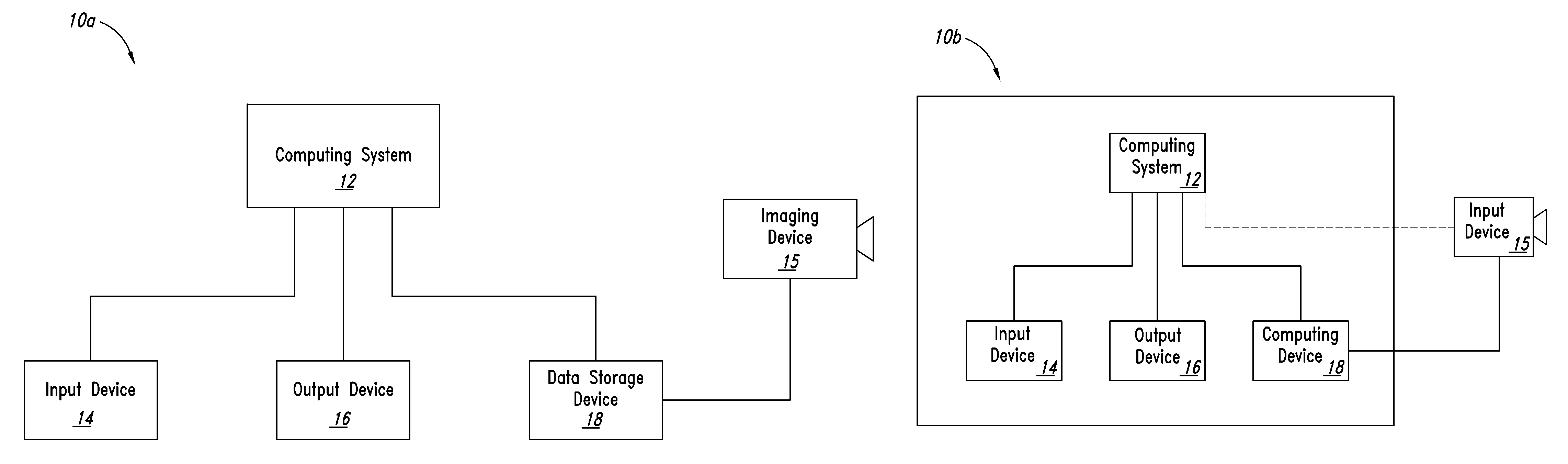
Method and apparatus for integrating manual input
InactiveUS6888536B2Simple methodEasy to learnInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisLow noiseBiomechanics
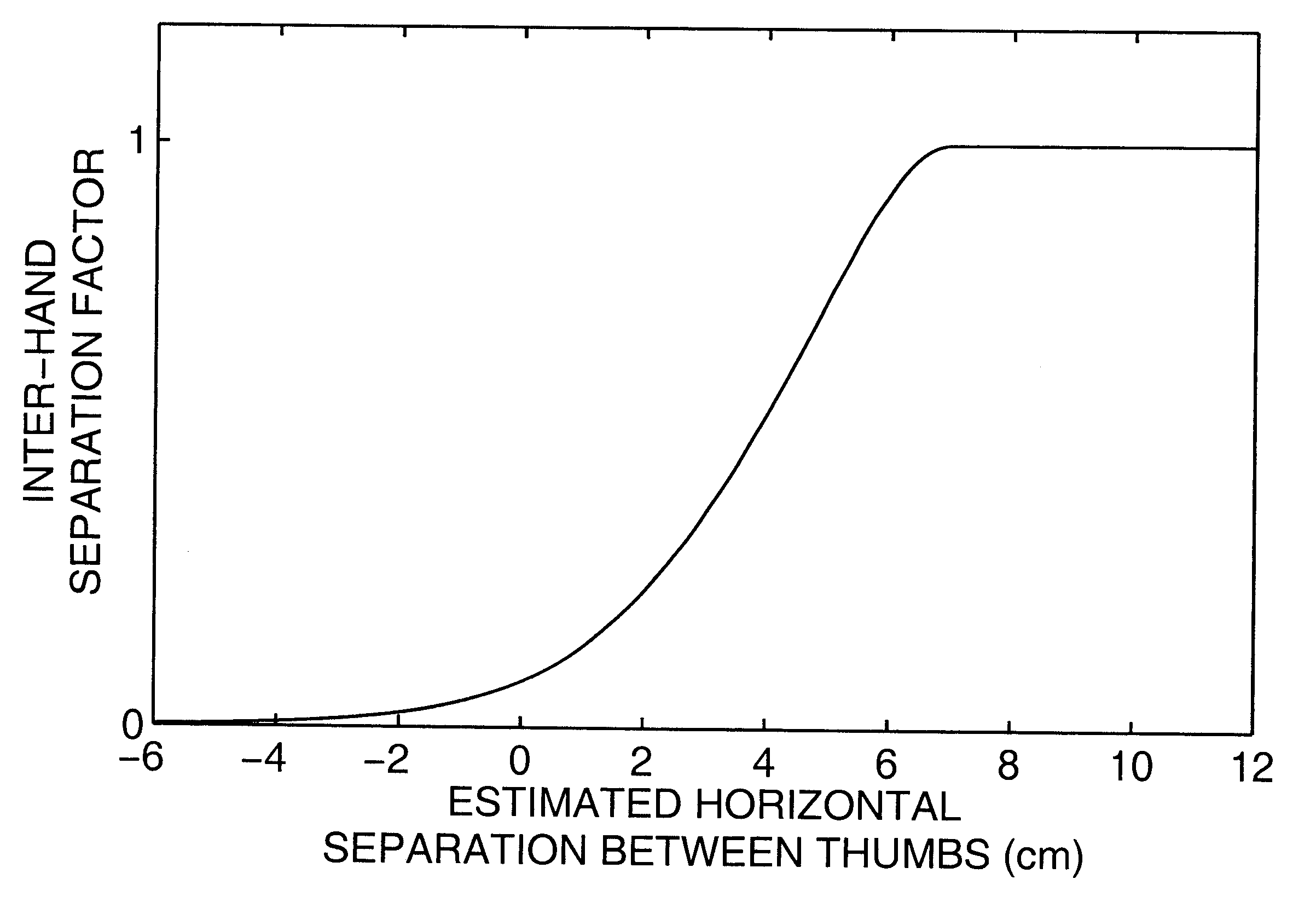
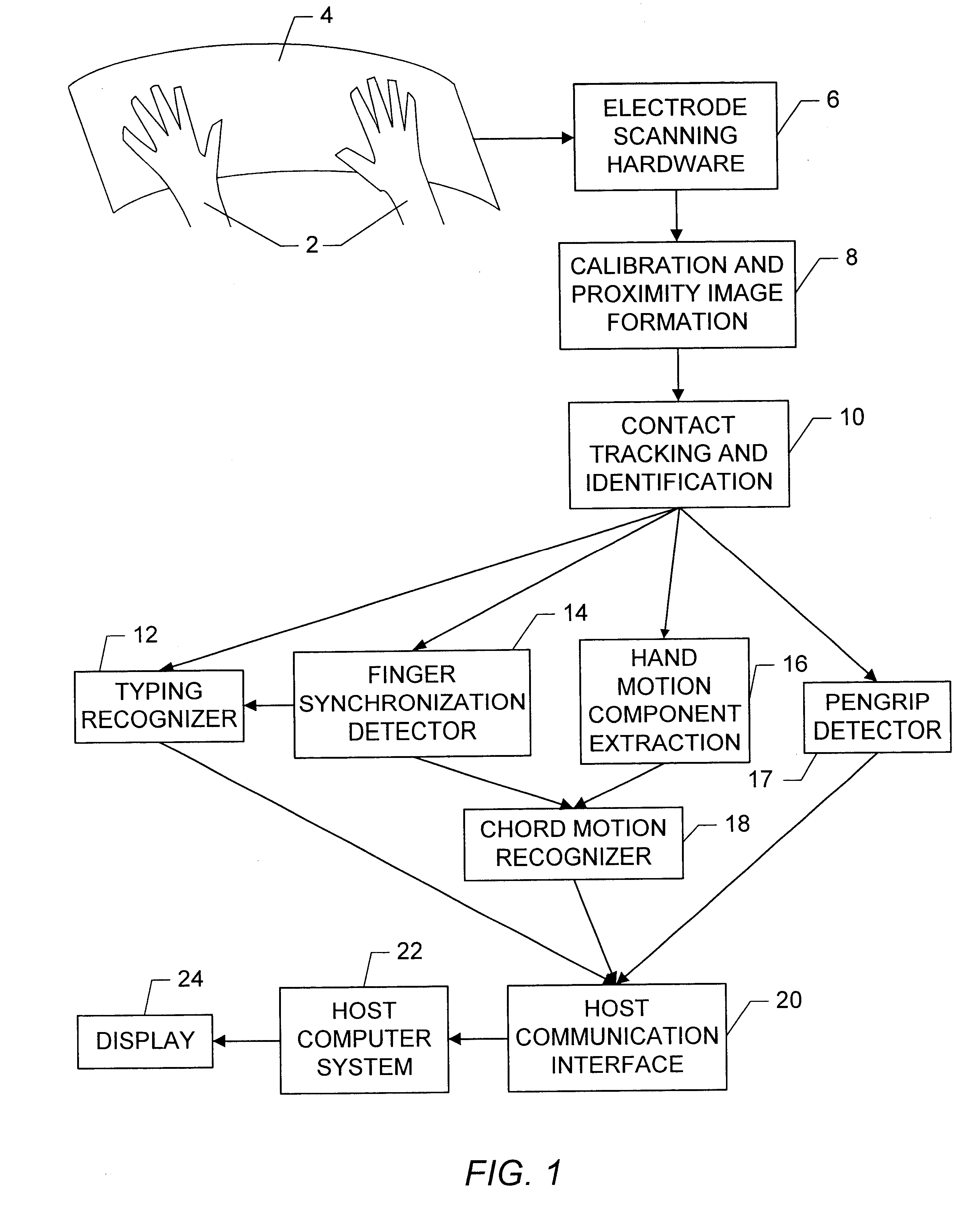
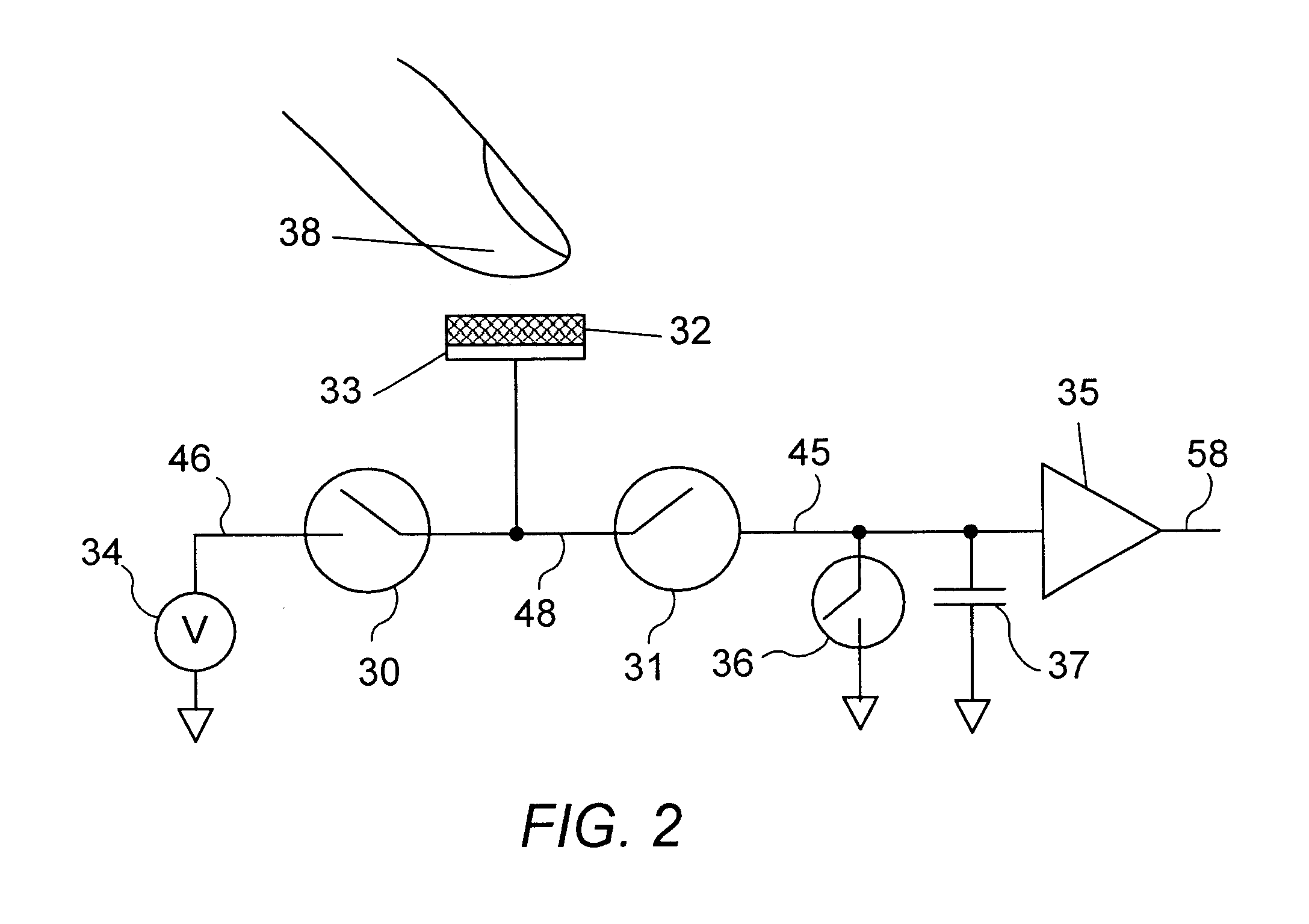
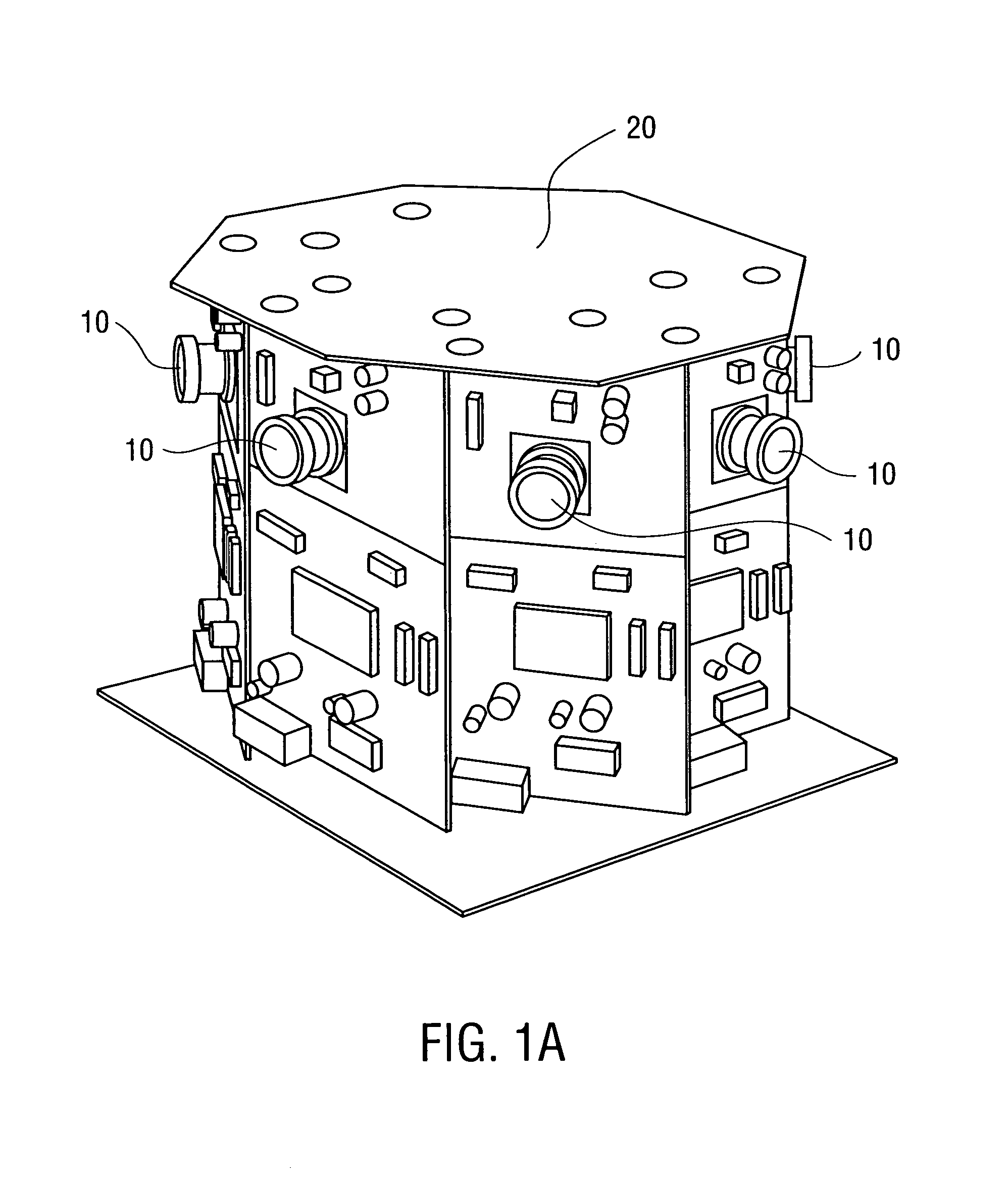
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for simultaneously tracking multiple finger and palm contacts as hands approach, touch, and slide across a proximity-sensing. compliant, and flexible multi-touch surface. The surface consists of compressible cushion, dielectric, electrode, and circuitry layers. A simple proximity transduction circuit is placed under each electrode to maximize signal-to-noise ratio and to reduce wiring complexity. Such distributed transduction circuitry is economical for large surfaces when implemented with thin-film transistor techniques. Scanning and signal offset removal on an electrode array produces low-noise proximity images. Segmentation processing of each proximity image constructs a group of electrodes corresponding to each distinguishable contact and extracts shape, position and surface proximity features for each group. Groups in successive images which correspond to the same hand contact are linked by a persistent path tracker which also detects individual contact touchdown and liftoff. Combinatorial optimization modules associate each contact's path with a particular fingertip, thumb, or palm of either hand on the basis of biomechanical constraints and contact features. Classification of intuitive hand configurations and motions enables unprecedented integration of typing, resting, pointing, scrolling, 3D manipulation, and handwriting into a versatile, ergonomic computer input device.
Owner:APPLE INC
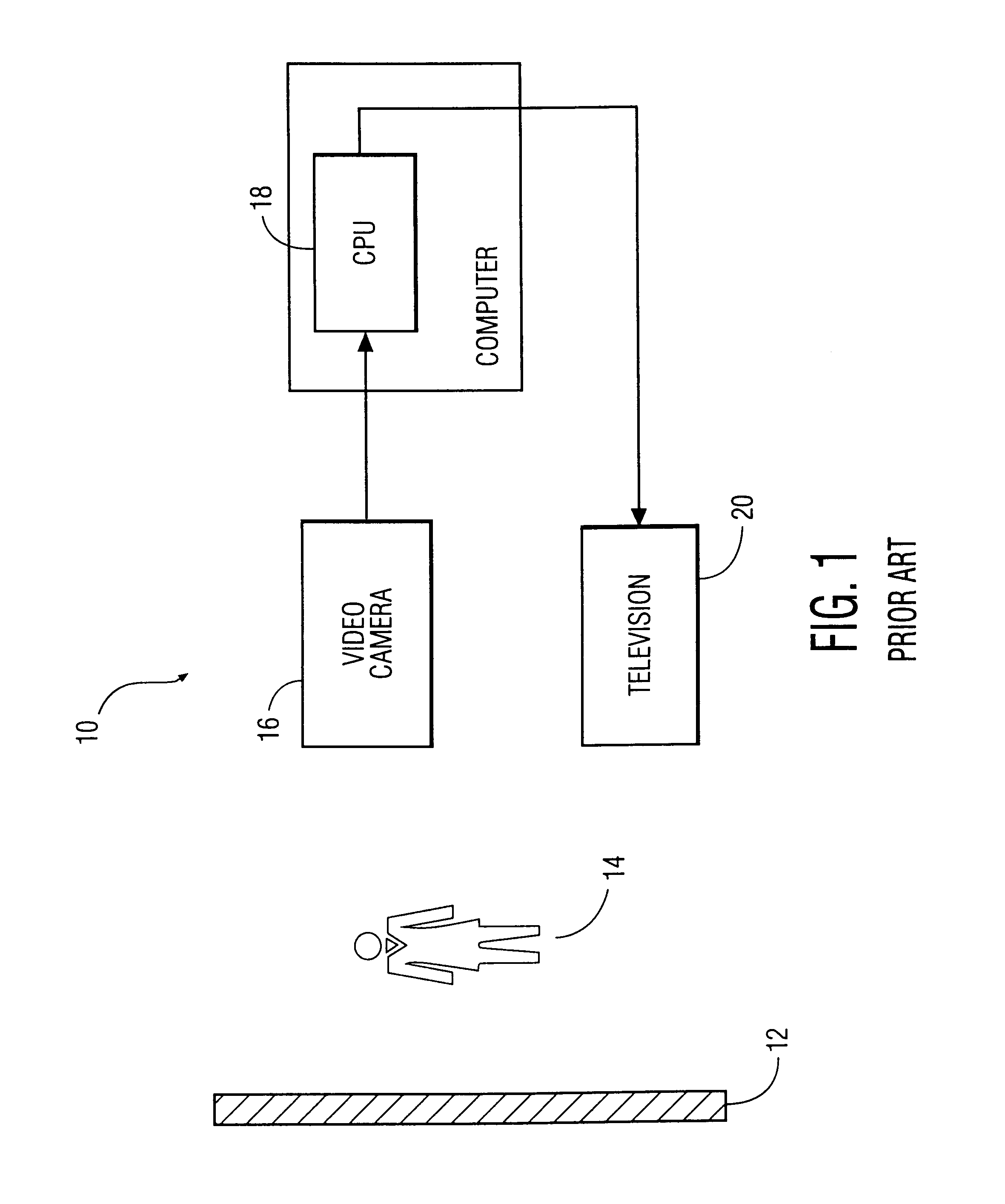
System and method for permitting three-dimensional navigation through a virtual reality environment using camera-based gesture inputs
InactiveUS6181343B1Input/output for user-computer interactionCosmonautic condition simulationsDisplay deviceThree dimensional graphics
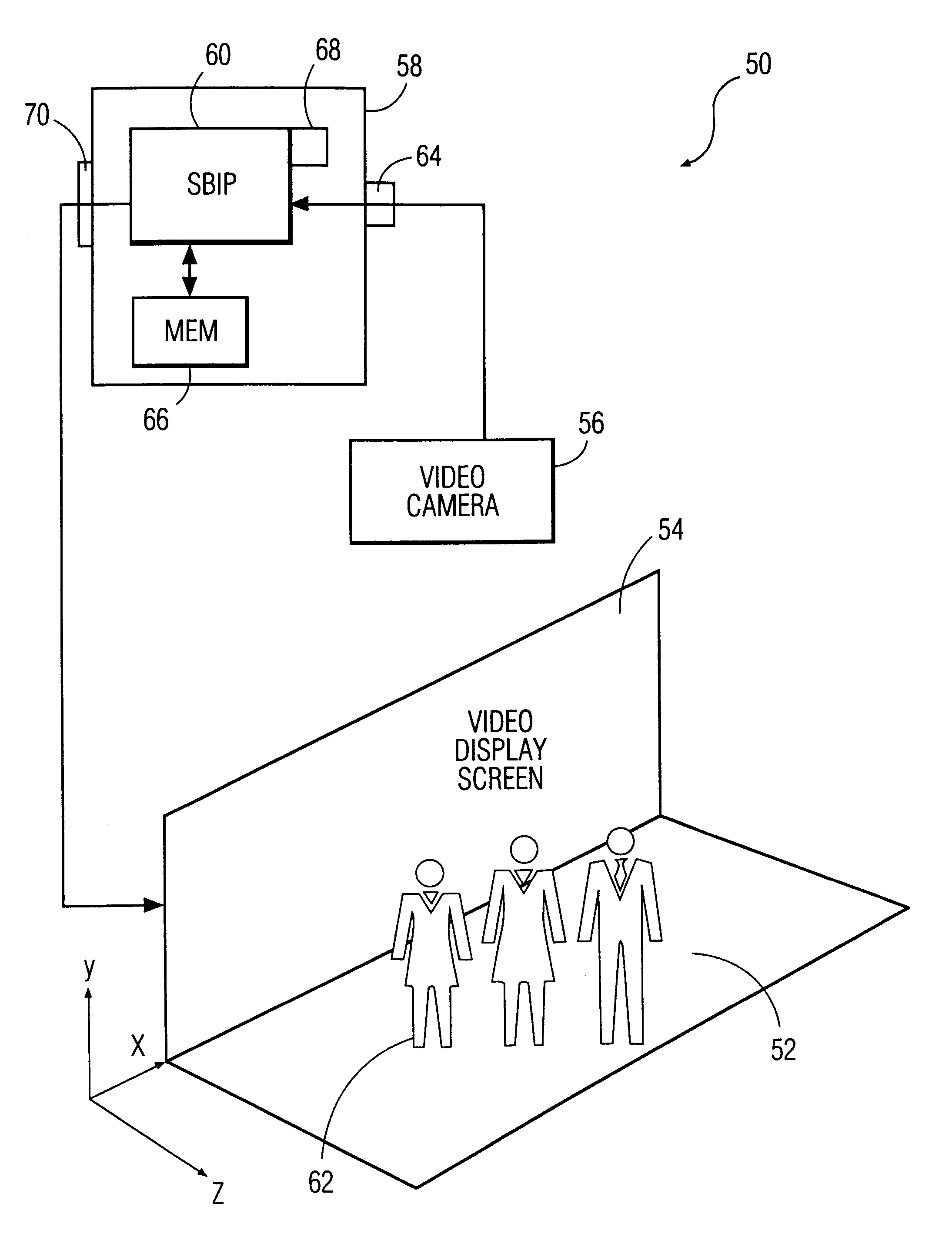
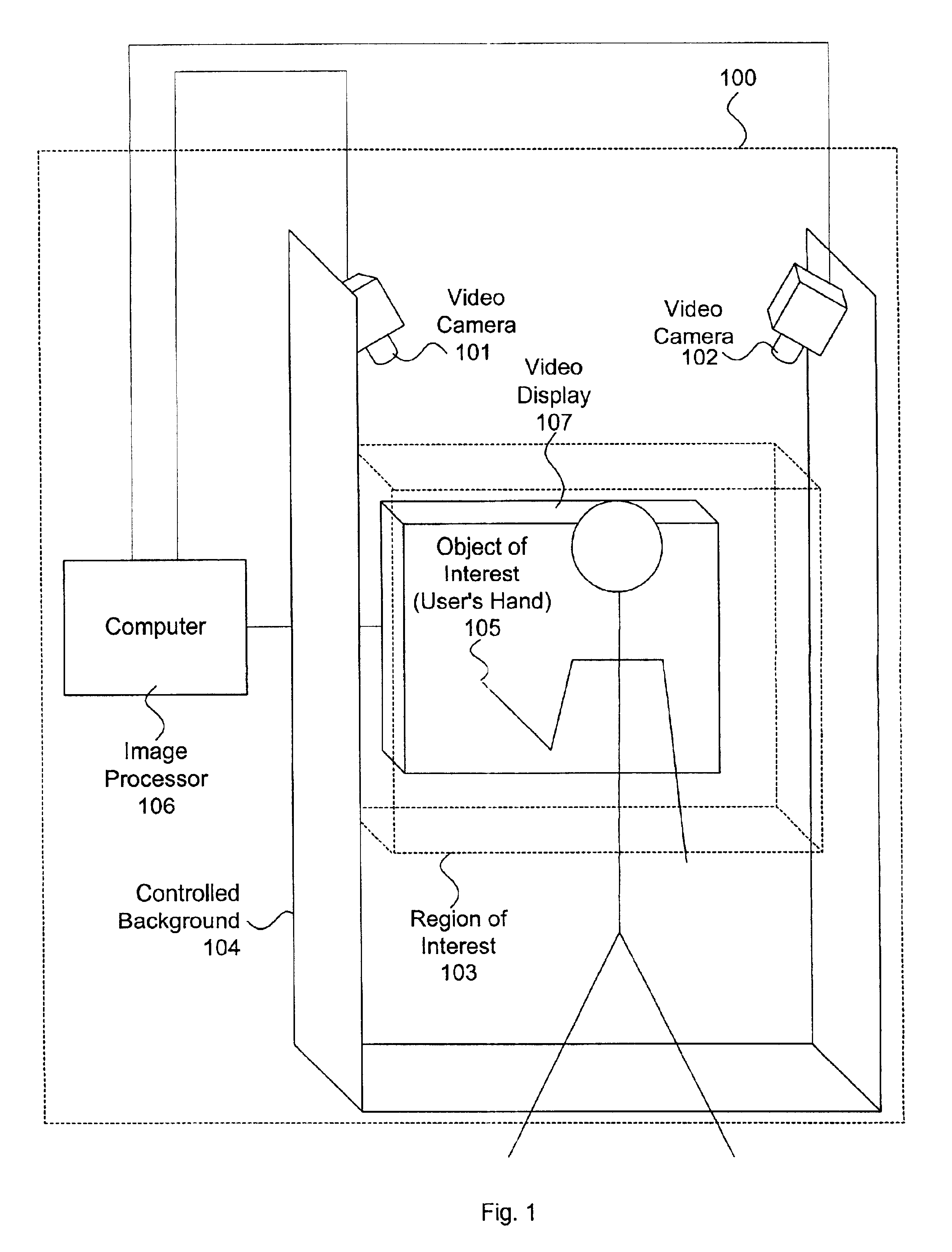
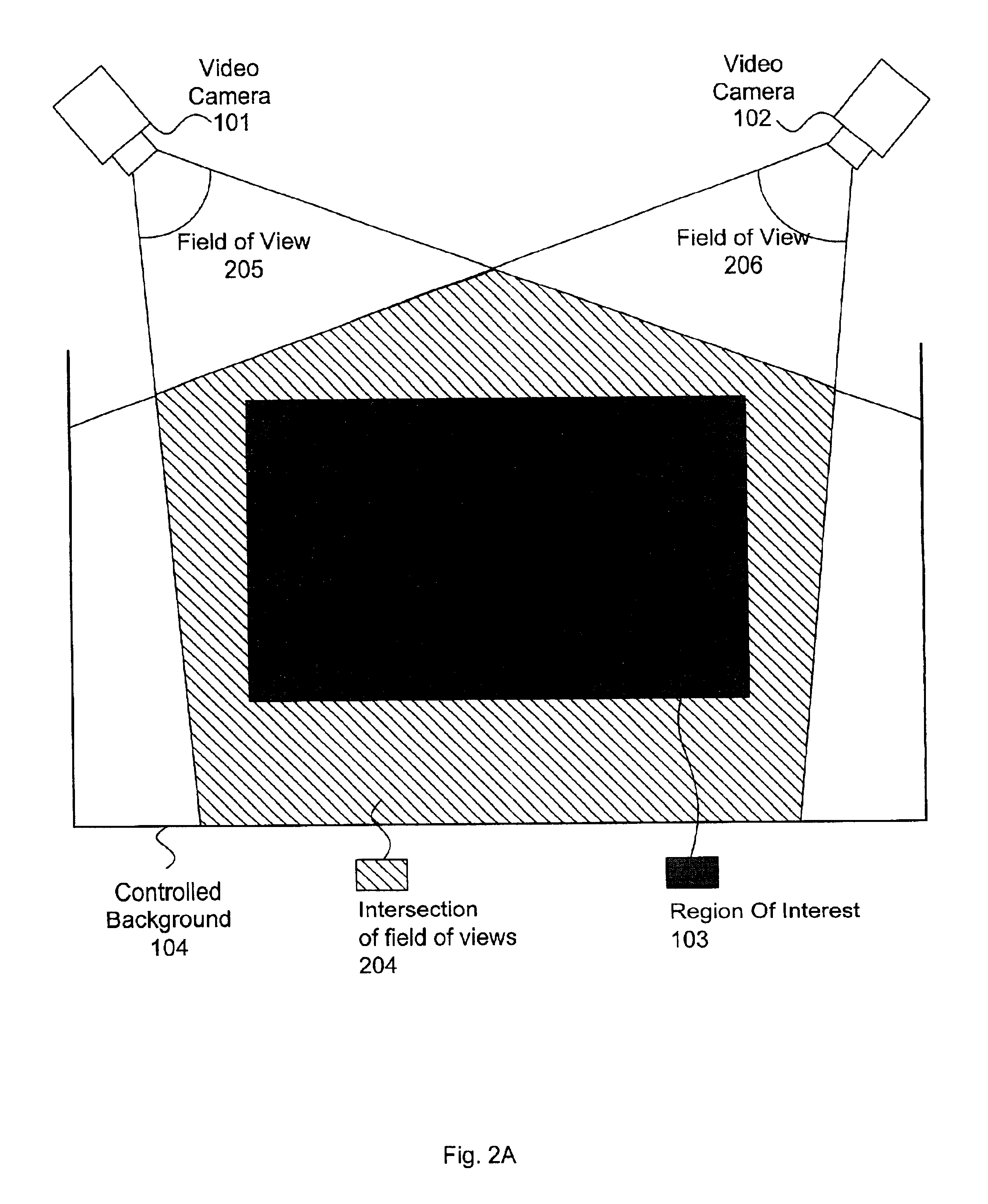
A system and method for permitting three-dimensional navigation through a virtual reality environment using camera-based gesture inputs of a system user. The system comprises a computer-readable memory, a video camera for generating video signals indicative of the gestures of the system user and an interaction area surrounding the system user, and a video image display. The video image display is positioned in front of the system user. The system further comprises a microprocessor for processing the video signals, in accordance with a program stored in the computer-readable memory, to determine the three-dimensional positions of the body and principle body parts of the system user. The microprocessor constructs three-dimensional images of the system user and interaction area on the video image display based upon the three-dimensional positions of the body and principle body parts of the system user. The video image display shows three-dimensional graphical objects within the virtual reality environment, and movement by the system user permits apparent movement of the three-dimensional objects displayed on the video image display so that the system user appears to move throughout the virtual reality environment.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
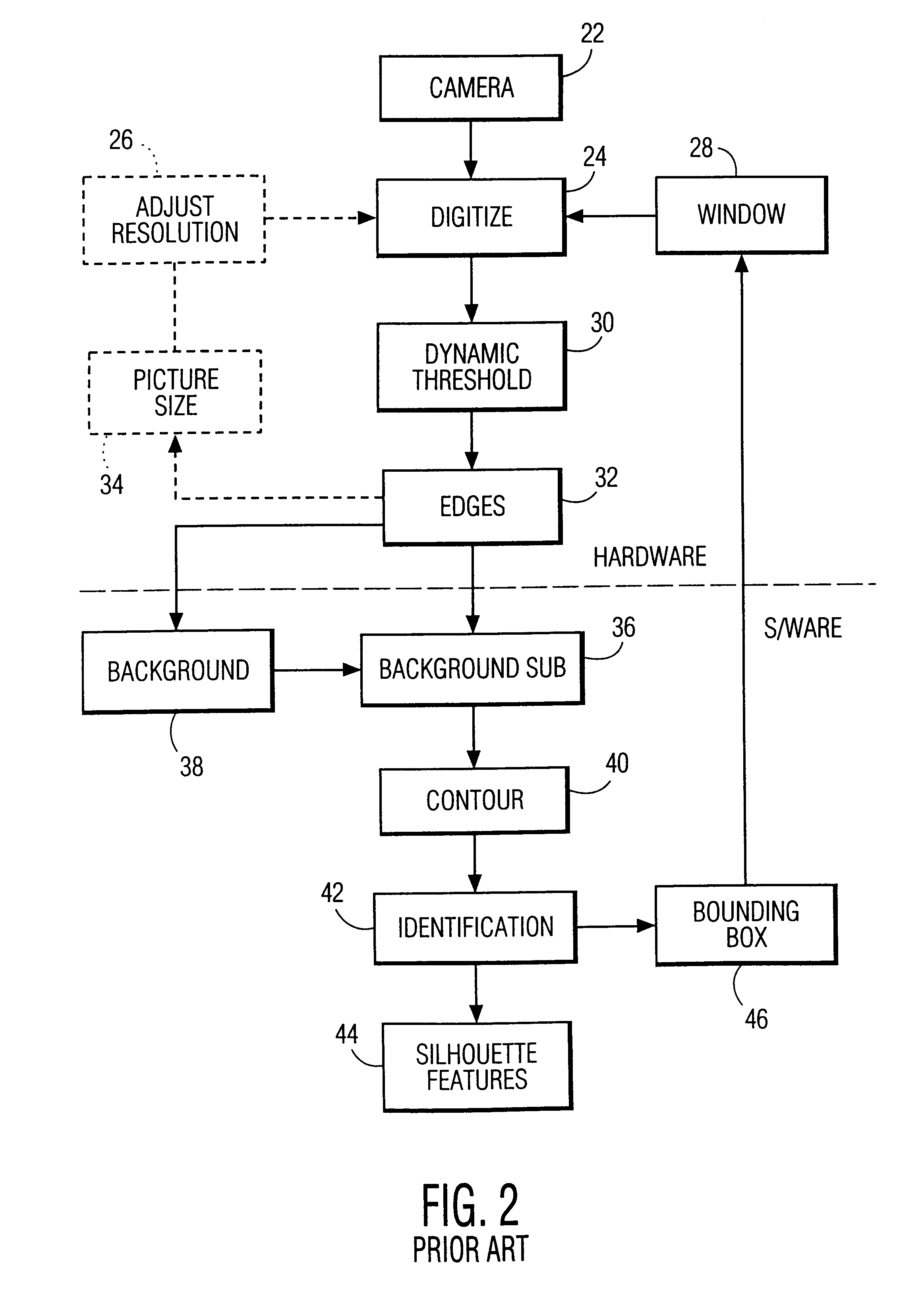
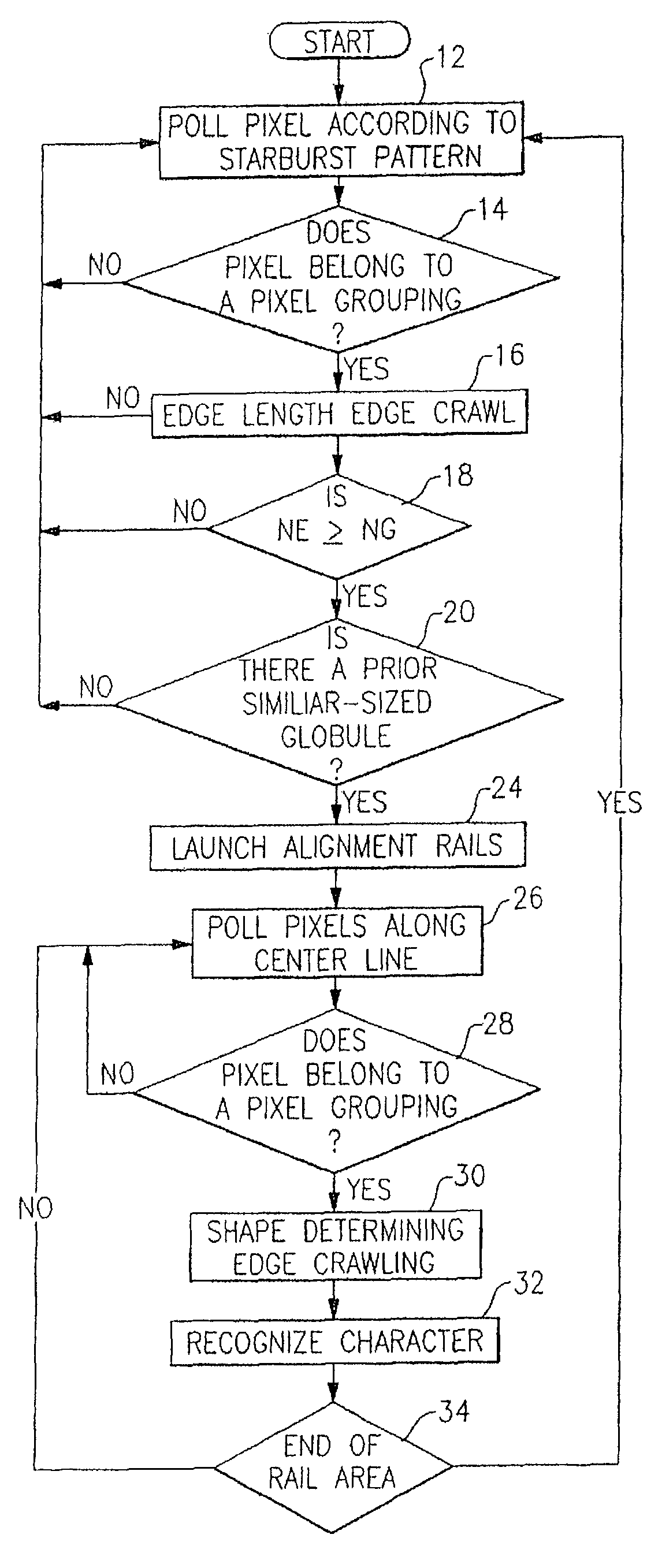
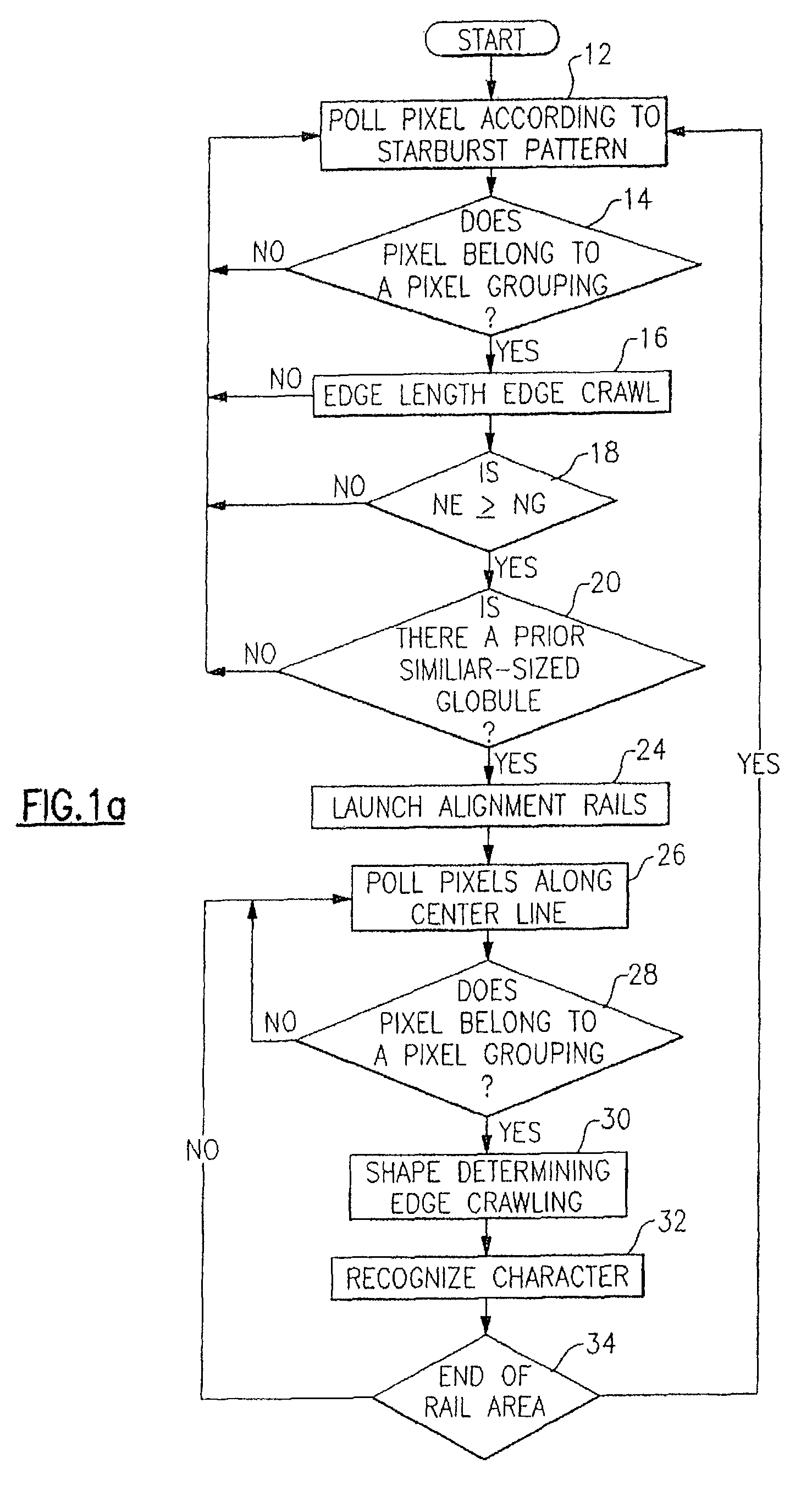
Method for omnidirectional processing of 2D images including recognizable characters
The invention is a method for omnidirectional recognition of recognizable characters in a captured two-dimensional image. An optical reader configured in accordance with the invention searches for pixel groupings in a starburst pattern, and subjects located pixel groupings to a preliminary edge crawling process which records the pixel position of the grouping's edge and records the count of edge pixels. If two similar-sized pixel groupings are located that are of sizes sufficient to potentially represent recognizable characters, then the reader launches “alignment rails” at pixel positions substantially parallel to a centerline connecting the center points of the two similarly sized groupings. A reader according to the invention searches for additional recognizable characters within the rail area, and subjects each located pixel grouping within the rail area to a shape-characterizing edge crawling process for developing data that characterizes the shape of a pixel grouping's edge. After adjusting the orientation representation of the shape-characterizing data the reader compares the developed shape-characterizing data to previously stored shape-characterizing data to determine the character represented by the grouping on the basis of the best fit data.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Data processing system and method
InactiveUS6215898B1Reduce overheadHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisStatic random-access memoryHigh memory
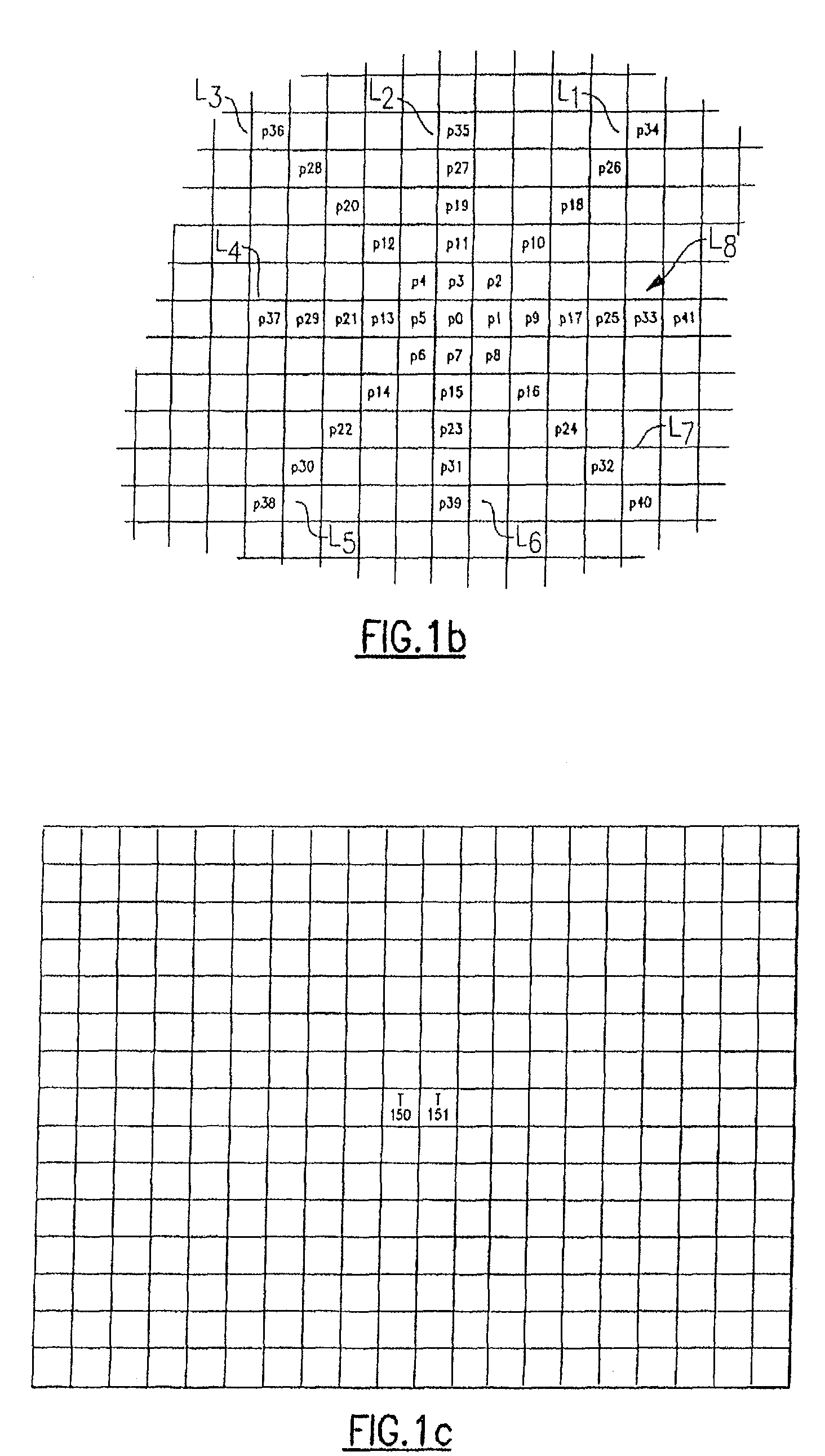
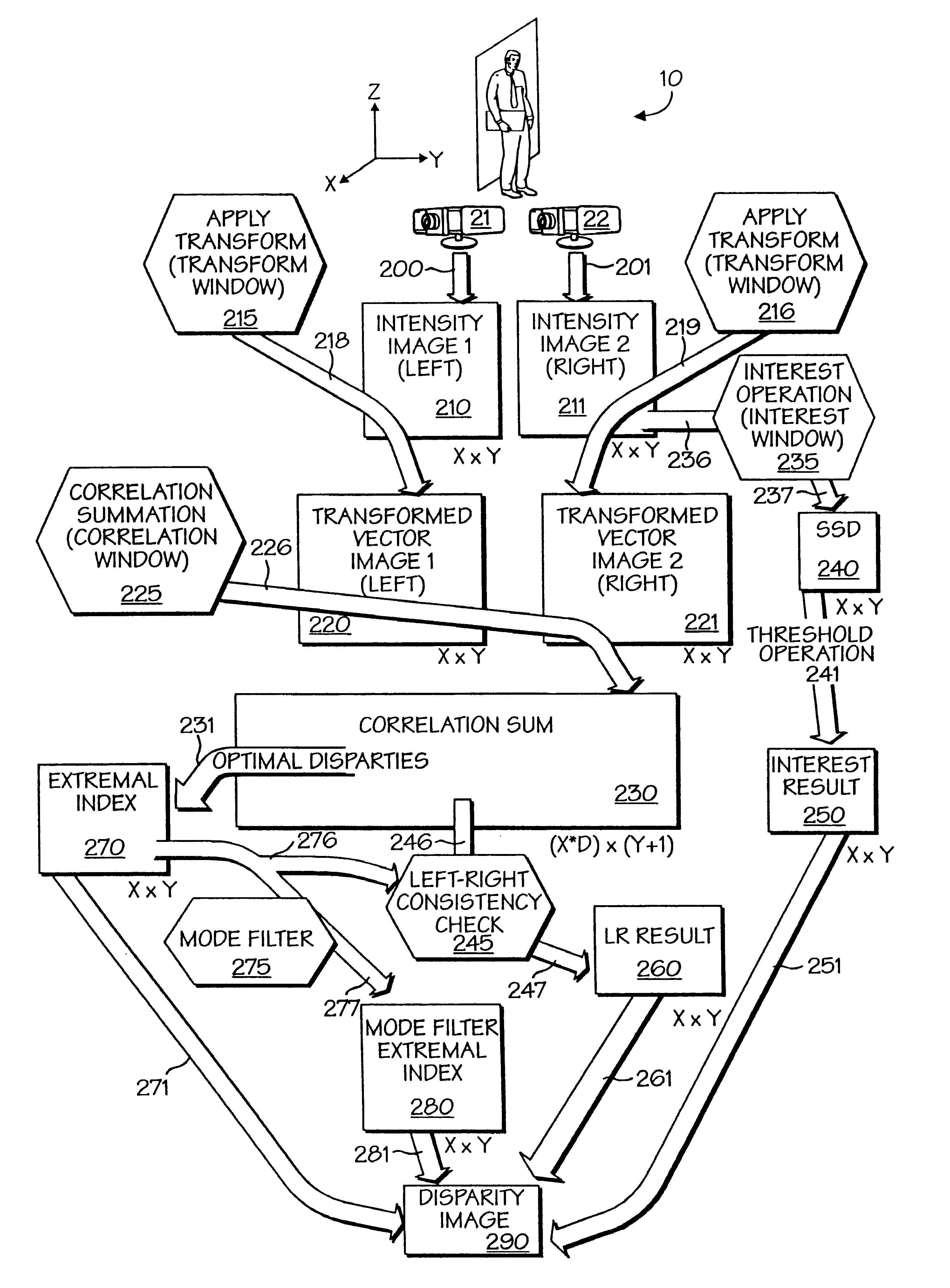
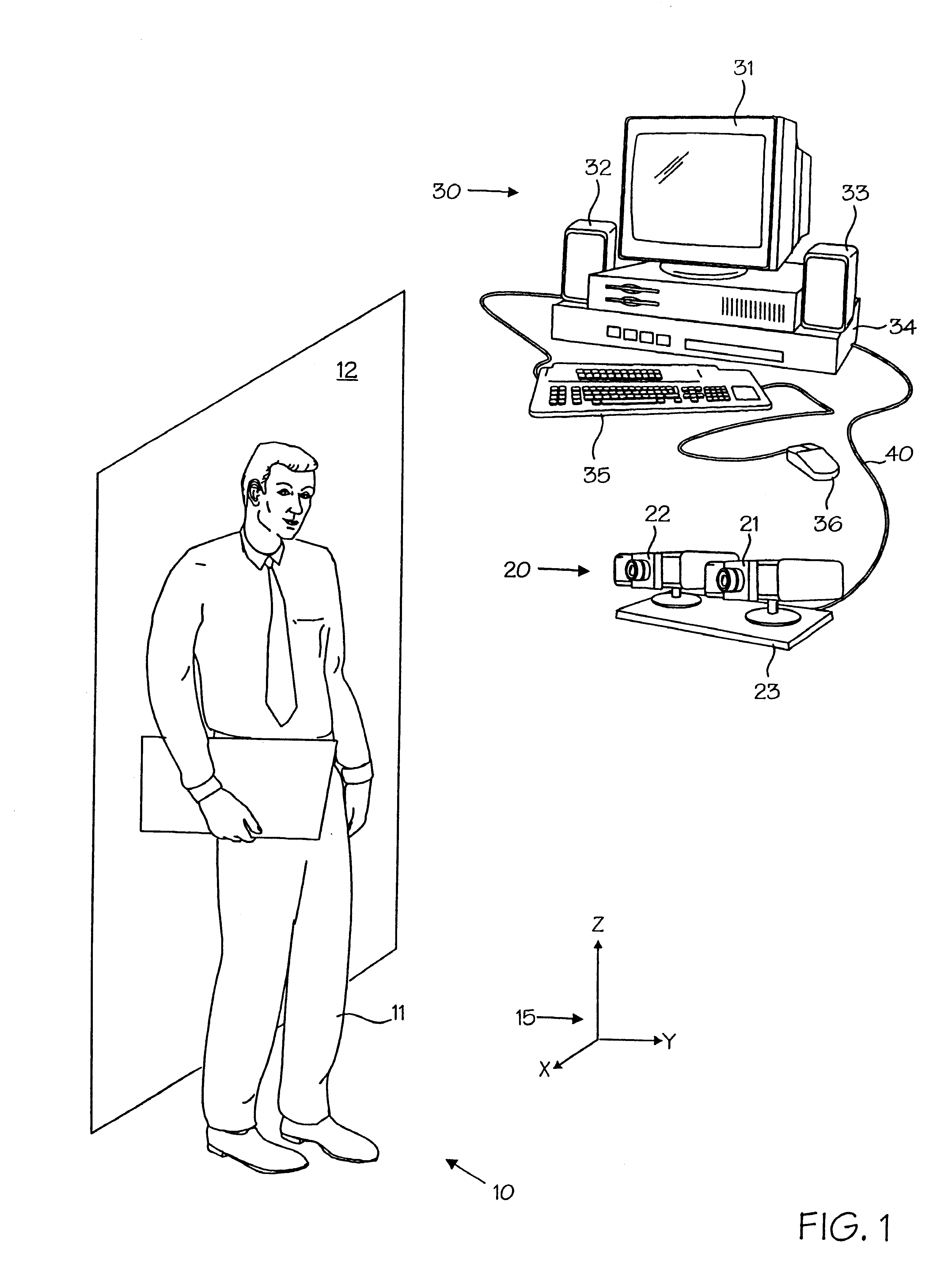
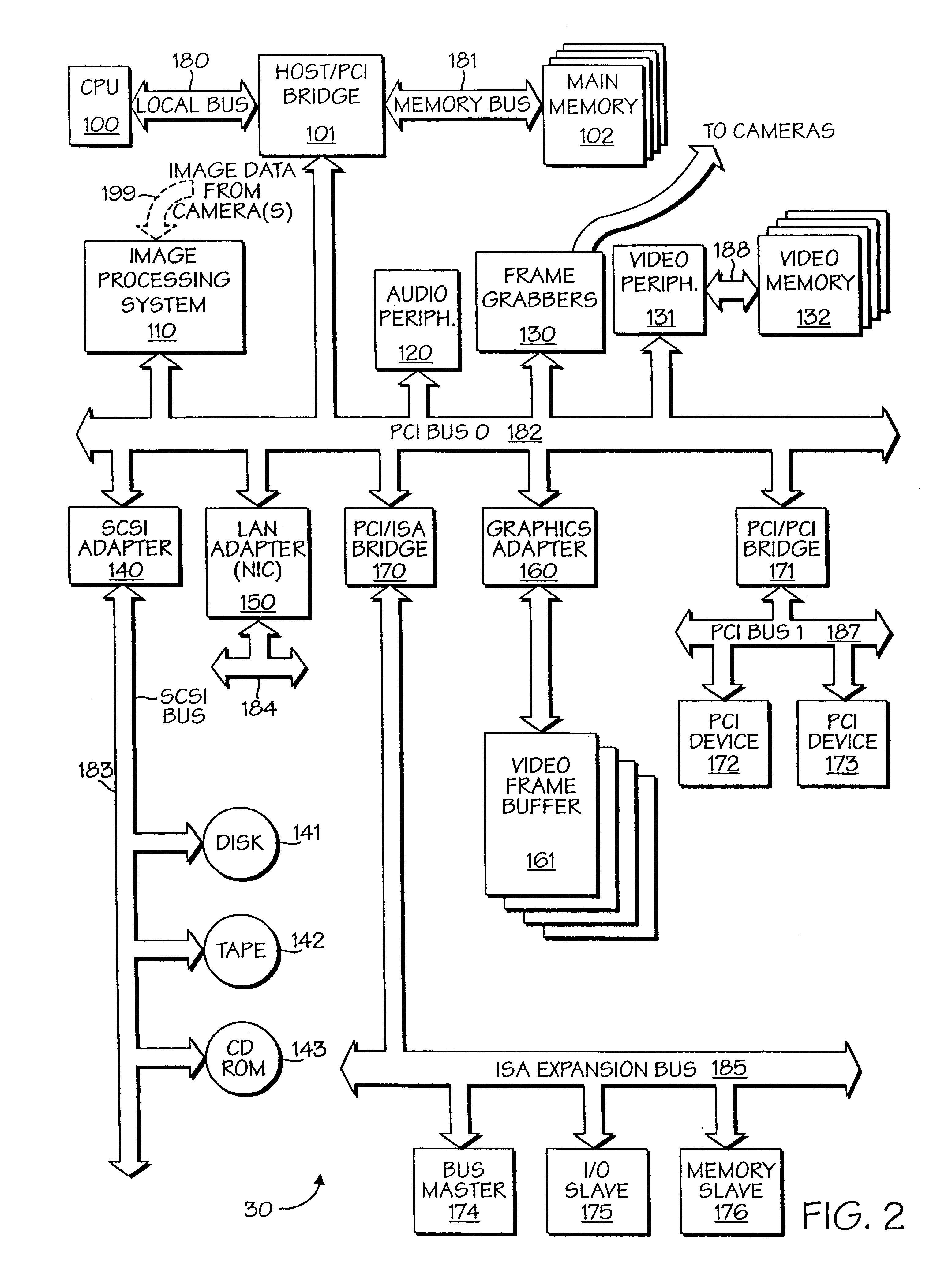
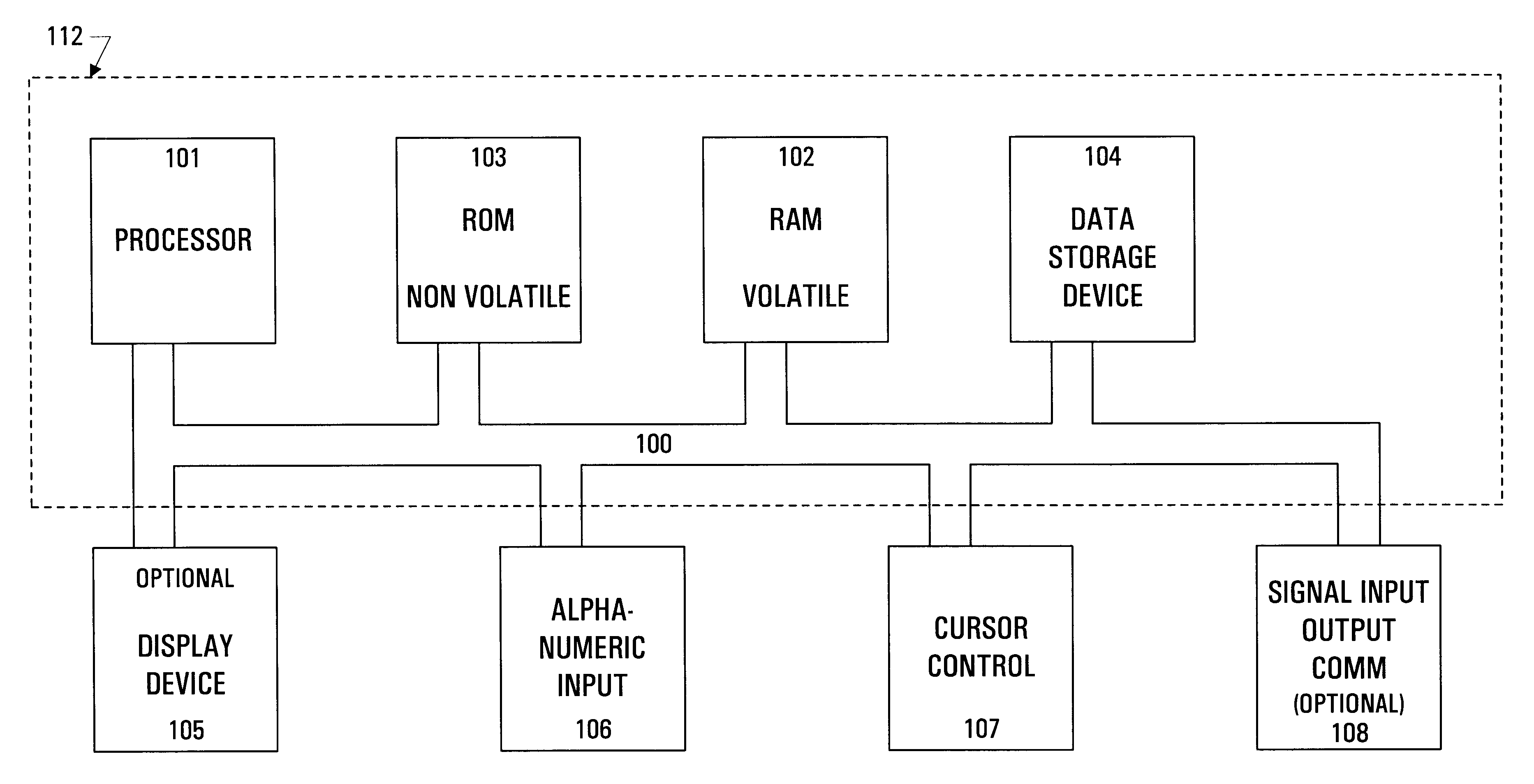
A powerful, scaleable, and reconfigurable image processing system and method of processing data therein is described. This general purpose, reconfigurable engine with toroidal topology, distributed memory, and wide bandwidth I / O are capable of solving real applications at real-time speeds. The reconfigurable image processing system can be optimized to efficiently perform specialized computations, such as real-time video and audio processing. This reconfigurable image processing system provides high performance via high computational density, high memory bandwidth, and high I / O bandwidth. Generally, the reconfigurable image processing system and its control structure include a homogeneous array of 16 field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) and 16 static random access memories (SRAM) arranged in a partial torus configuration. The reconfigurable image processing system also includes a PCI bus interface chip, a clock control chip, and a datapath chip. It can be implemented in a single board. It receives data from its external environment, computes correspondence, and uses the results of the correspondence computations for various post-processing industrial applications. The reconfigurable image processing system determines correspondence by using non-parametric local transforms followed by correlation. These non-parametric local transforms include the census and rank transforms. Other embodiments involve a combination of correspondence, rectification, a left-right consistency check, and the application of an interest operator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for estimating body shape
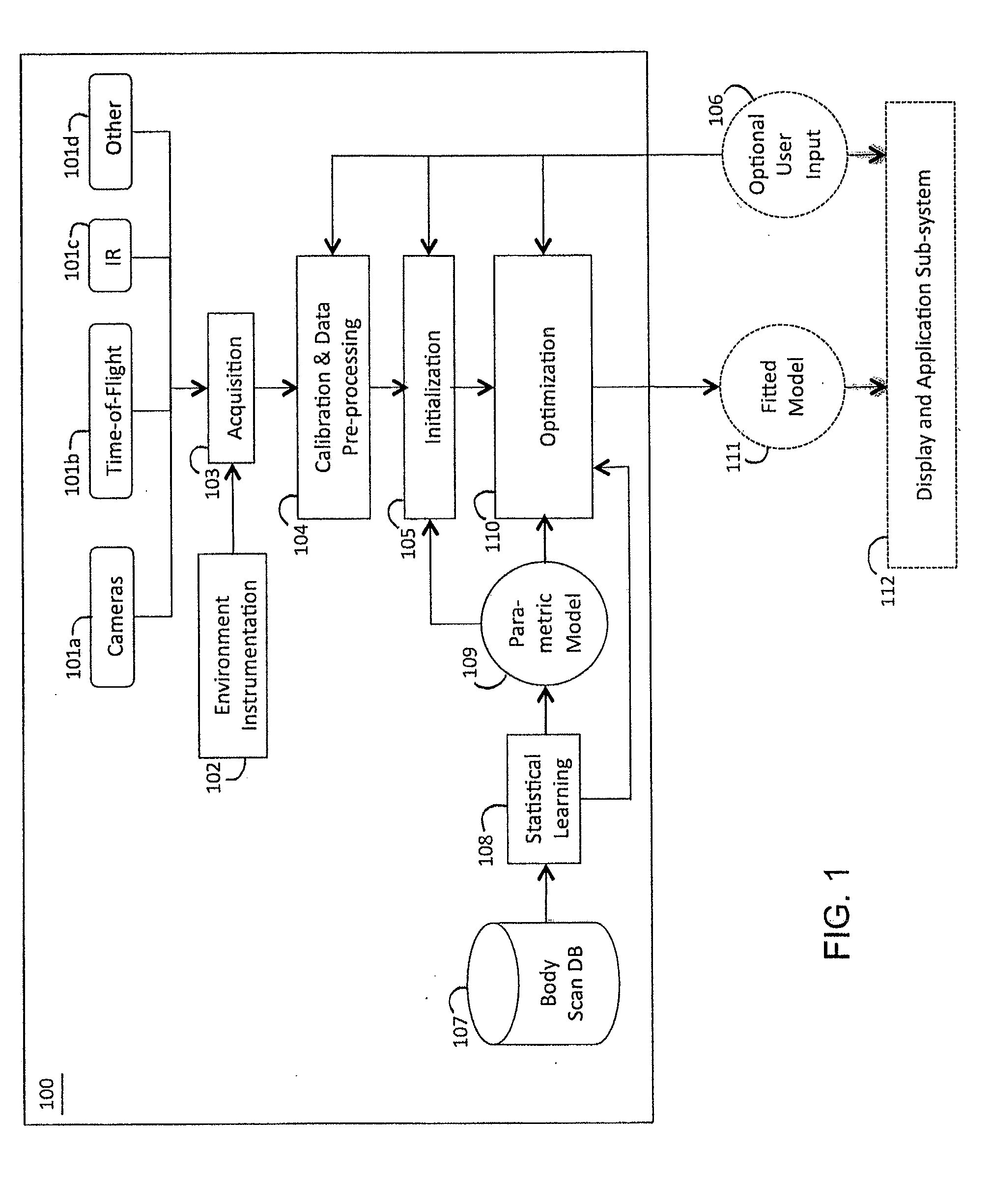
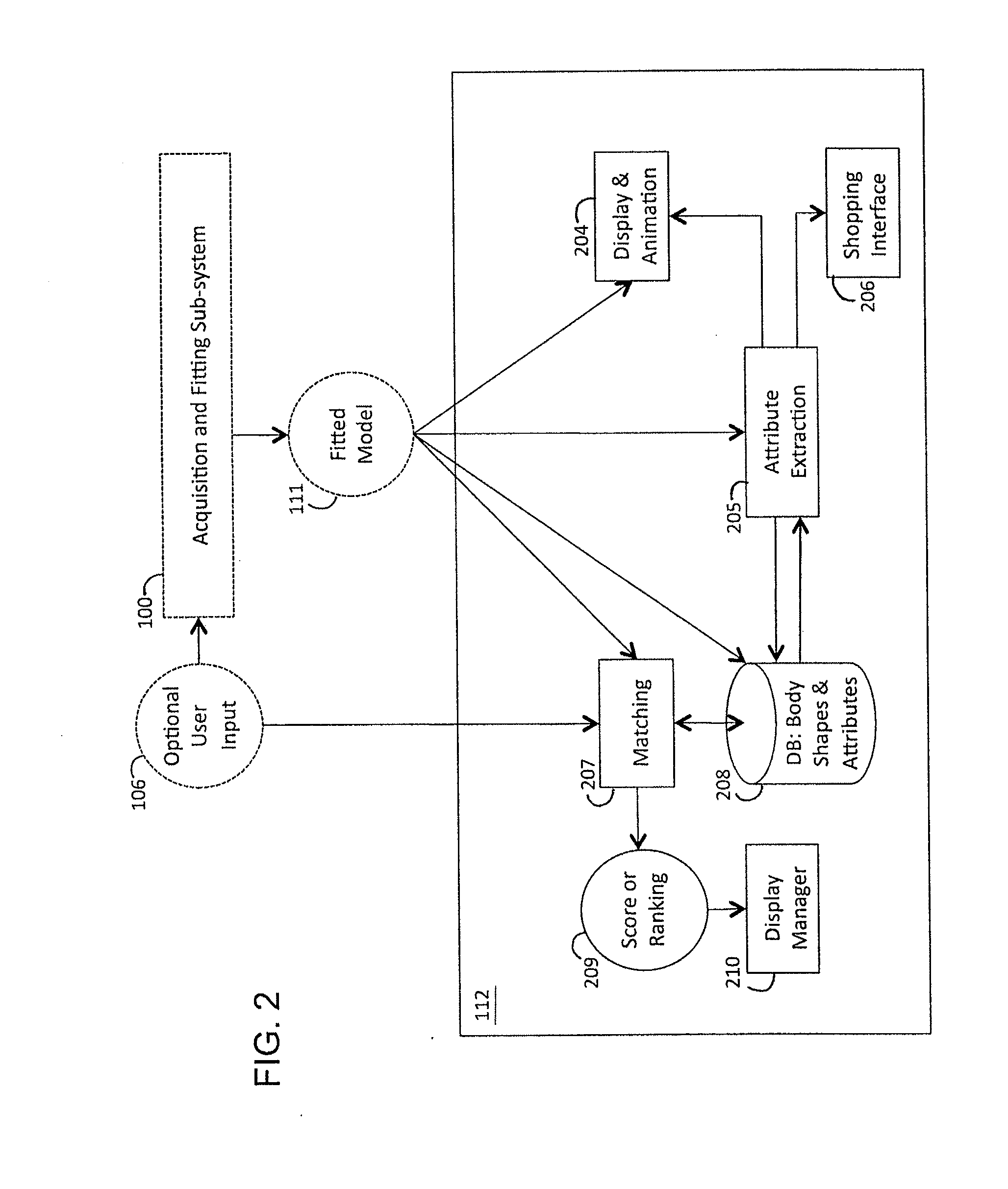
ActiveUS20100111370A1Less-accurate measurementAccurate captureImage enhancementImage analysisBody shapeThe Internet
A system and method of estimating the body shape of an individual from input data such as images or range maps. The body may appear in one or more poses captured at different times and a consistent body shape is computed for all poses. The body may appear in minimal tight-fitting clothing or in normal clothing wherein the described method produces an estimate of the body shape under the clothing. Clothed or bare regions of the body are detected via image classification and the fitting method is adapted to treat each region differently. Body shapes are represented parametrically and are matched to other bodies based on shape similarity and other features. Standard measurements are extracted using parametric or non-parametric functions of body shape. The system components support many applications in body scanning, advertising, social networking, collaborative filtering and Internet clothing shopping.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
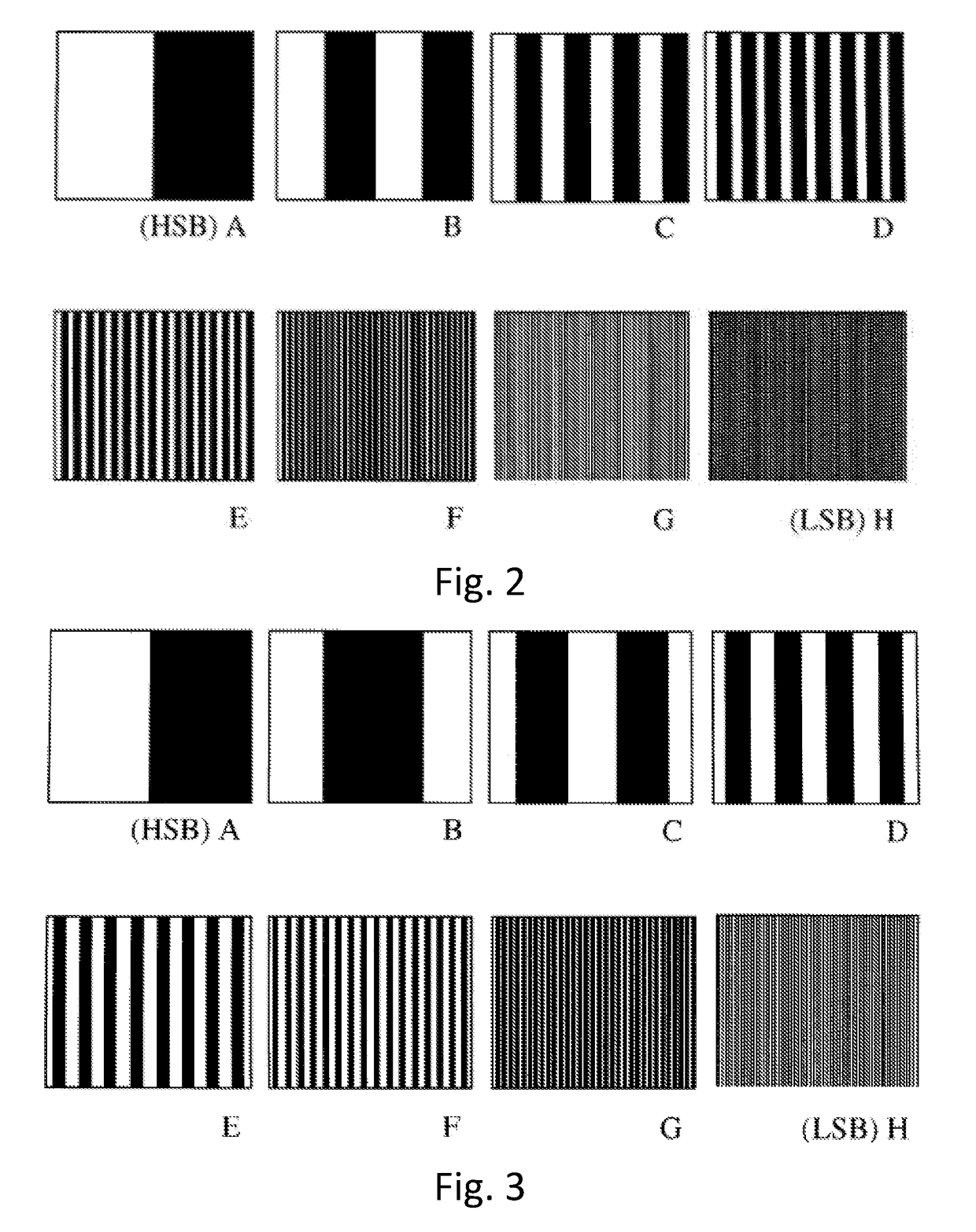
Method and system operative to process monochrome image data
A method and system operative to process monochrome image data are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method can comprise the steps of receiving monochrome image data, segmenting the input pixel values into pixel value ranges, assigning pixel positions in the lowest pixel value range an output pixel value of a first binary value, assigning pixel positions in the highest pixel value range an output pixel value of a second binary value, wherein the first and second binary values are different, and assigning pixel positions in intermediate pixel value ranges output pixel values that correspond to a spatial binary pattern. The resulting binary image data can be written to a file for subsequent storage, transmission, processing, or retrieval and rendering. In further embodiments, a system can be made operative to accomplish the same.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
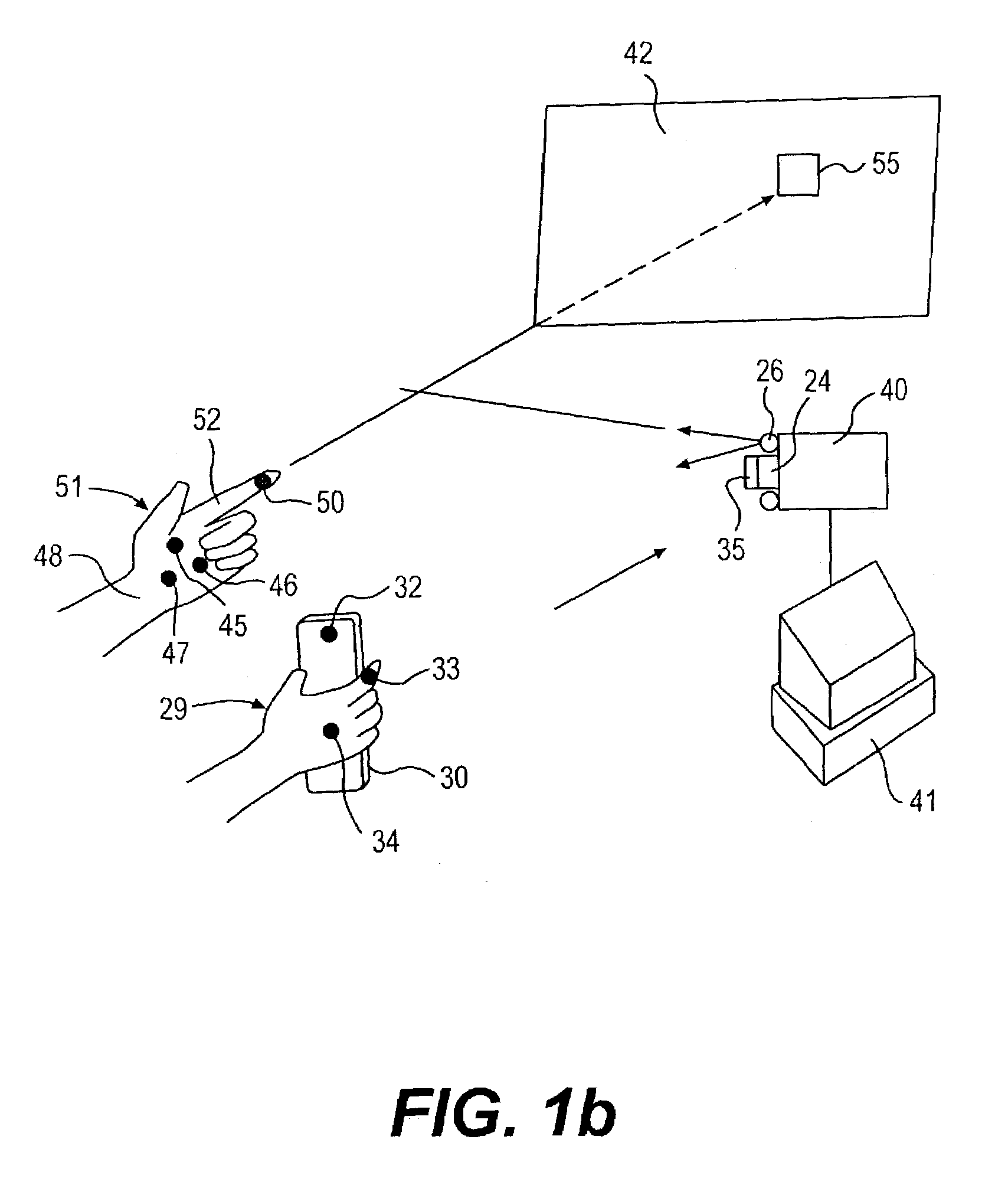
Man machine interfaces and applications
InactiveUS7042440B2Avoid carpal tunnel syndromeImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrophonic musical instrumentsComputer Aided DesignHuman–machine interface
Affordable methods and apparatus are disclosed for inputting position, attitude (orientation) or other object characteristic data to computers for the purpose of Computer Aided Design, Painting, Medicine, Teaching, Gaming, Toys, Simulations, Aids to the disabled, and internet or other experiences. Preferred embodiments of the invention utilize electro-optical sensors, and particularly TV Cameras, providing optically inputted data from specialized datum's on objects and / or natural features of objects. Objects can be both static and in motion, from which individual datum positions and movements can be derived, also with respect to other objects both fixed and moving. Real-time photogrammetry is preferably used to determine relationships of portions of one or more datums with respect to a plurality of cameras or a single camera processed by a conventional PC.
Owner:PRYOR TIMOTHY R +1
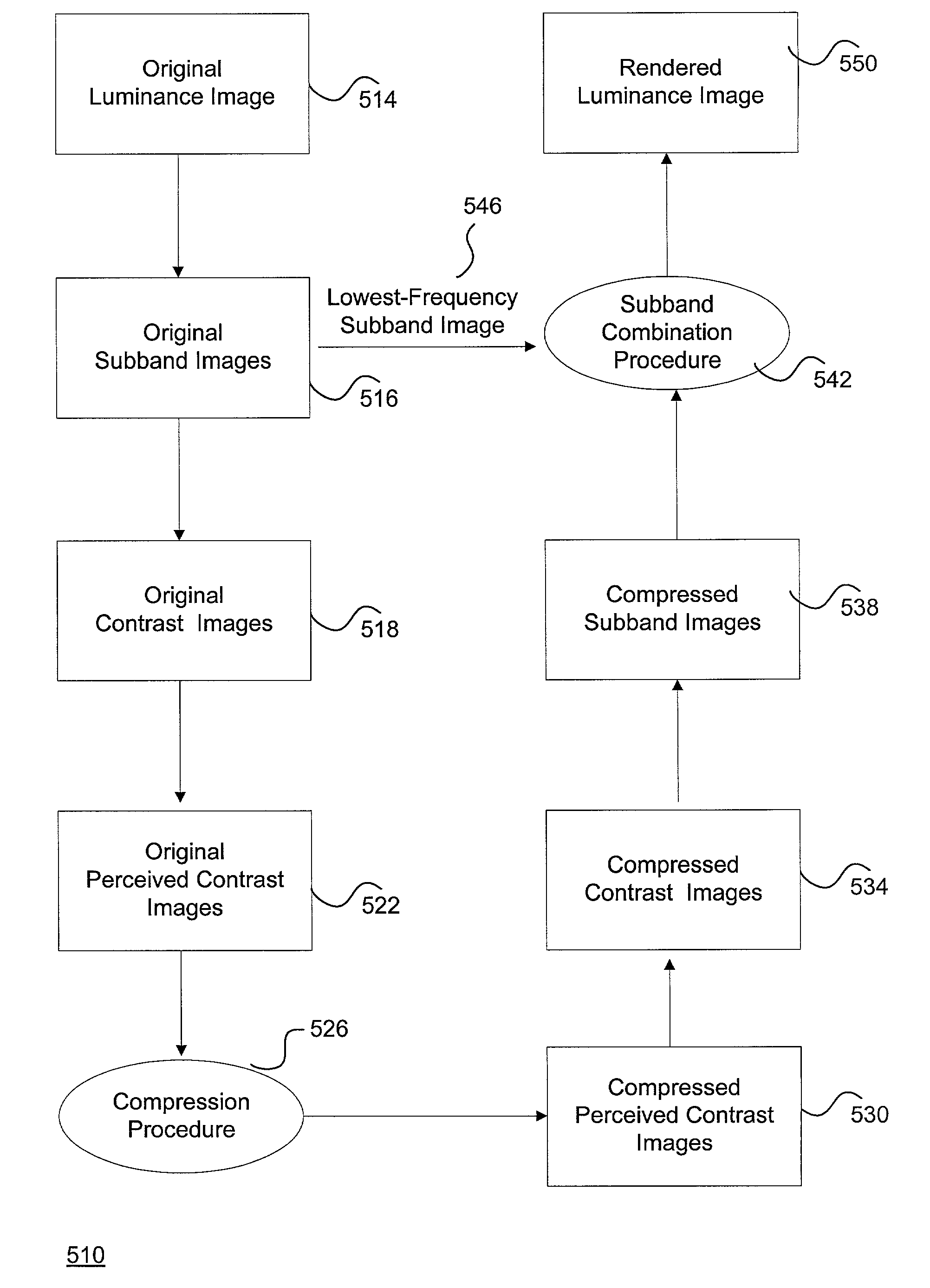
System and method for effectively rendering high dynamic range images
InactiveUS6993200B2High imagingEffectively renderingImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image conversion
A system and method for rendering high dynamic range images includes a rendering manager that divides an original luminance image into a plurality of original subband images. The rendering manager converts the original subband images into original contrast images which are converted into original perceived contrast images. The rendering manager performs a compression procedure upon the original perceived contrast images to produce compressed perceived contrast images. The rendering manager converts the compressed perceived contrast images into compressed contrast images which are converted into compressed subband images. The rendering manager performs a subband combination procedure for combining the compressed subband images together with a lowest-frequency subband image to generate a rendered luminance image. The rendering manager may combines the rendered luminance image with corresponding chrominance information to generate a rendered composite image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
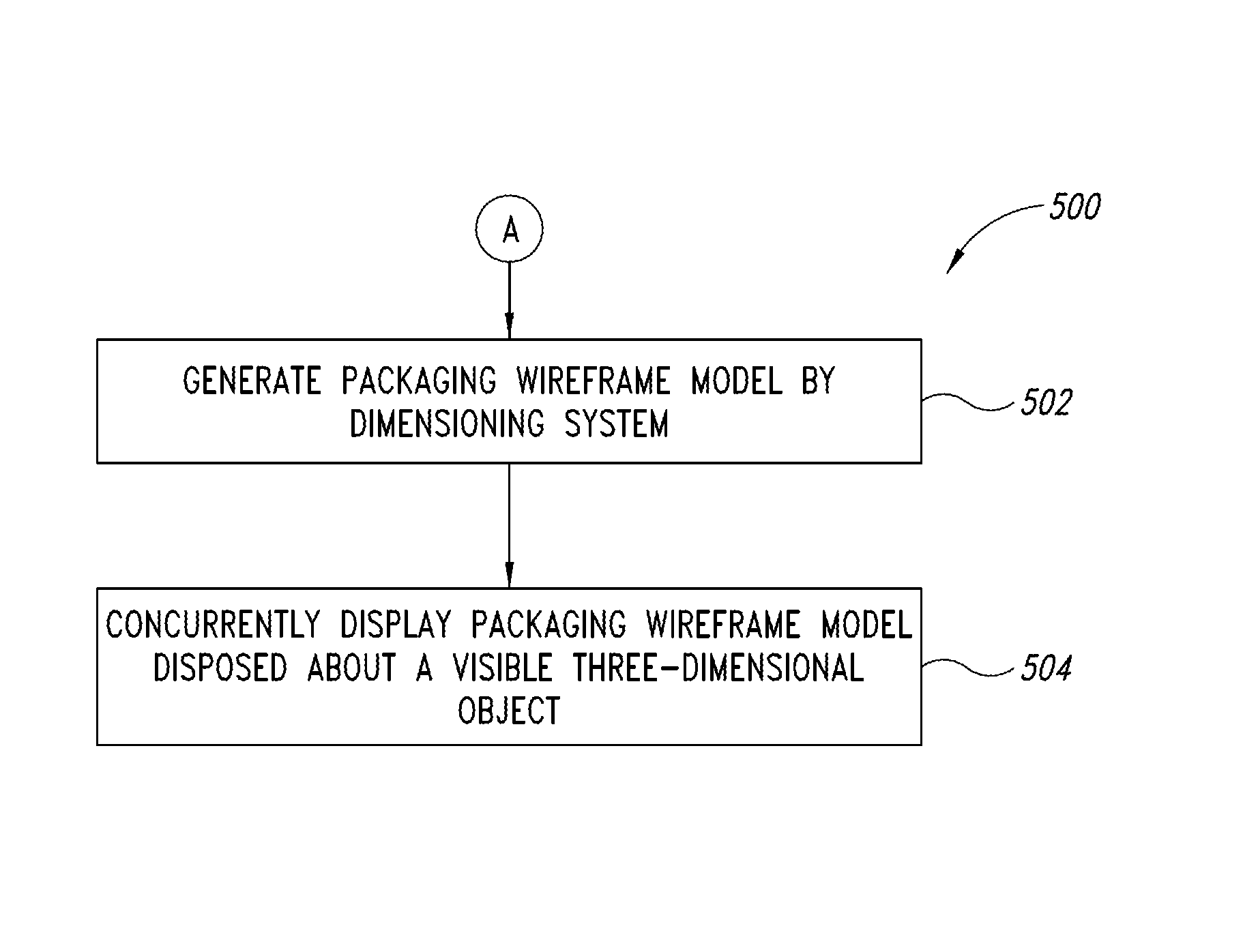
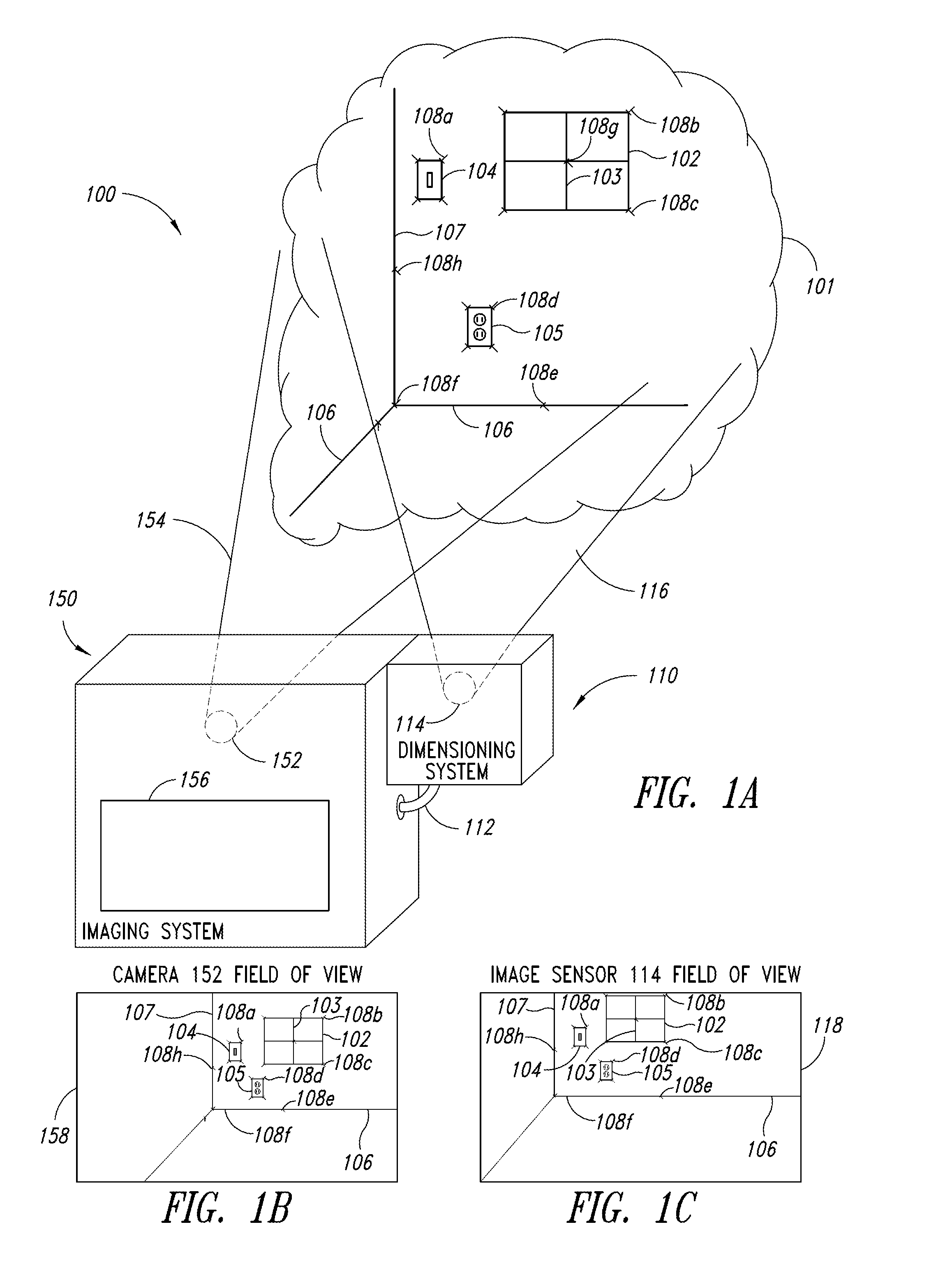
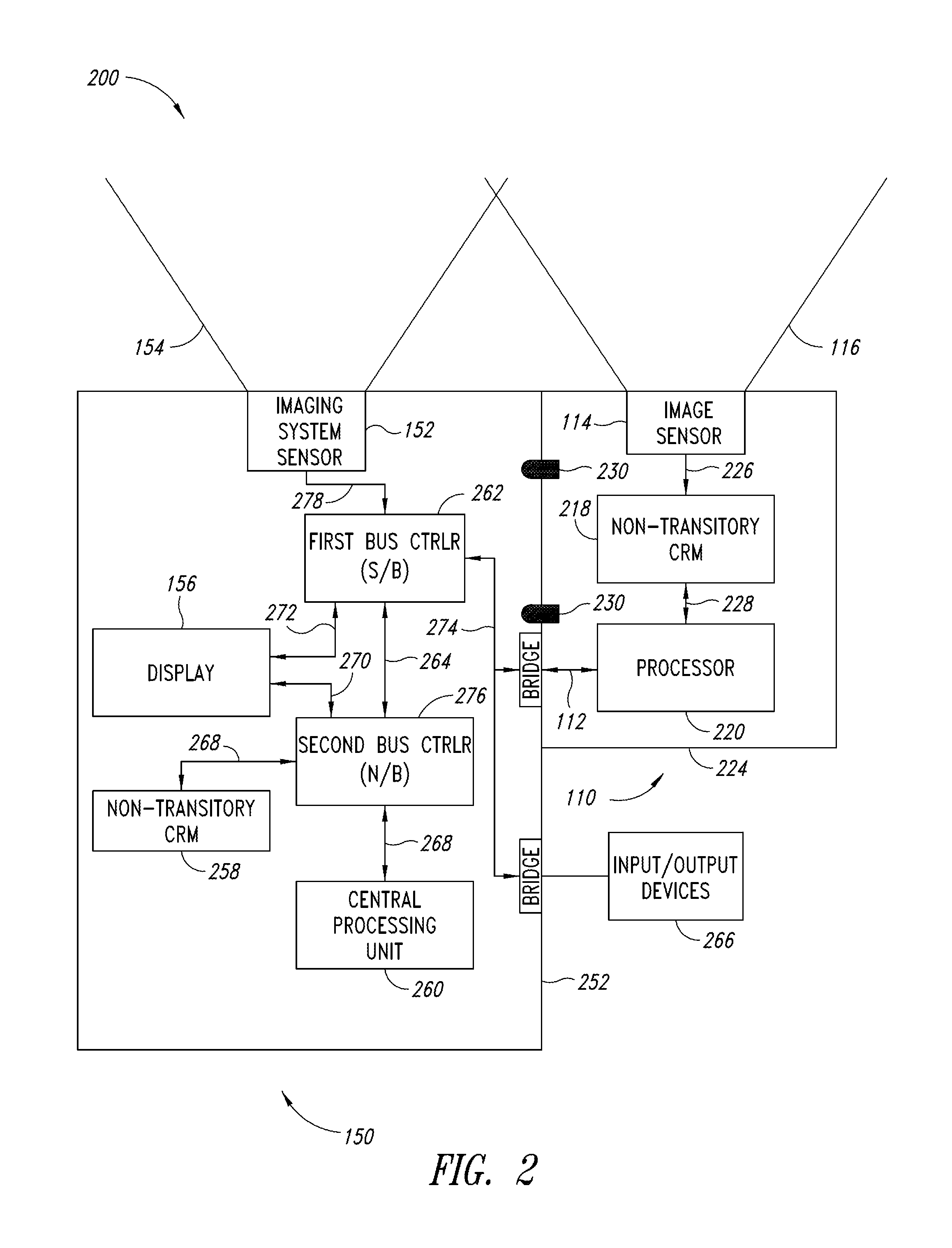
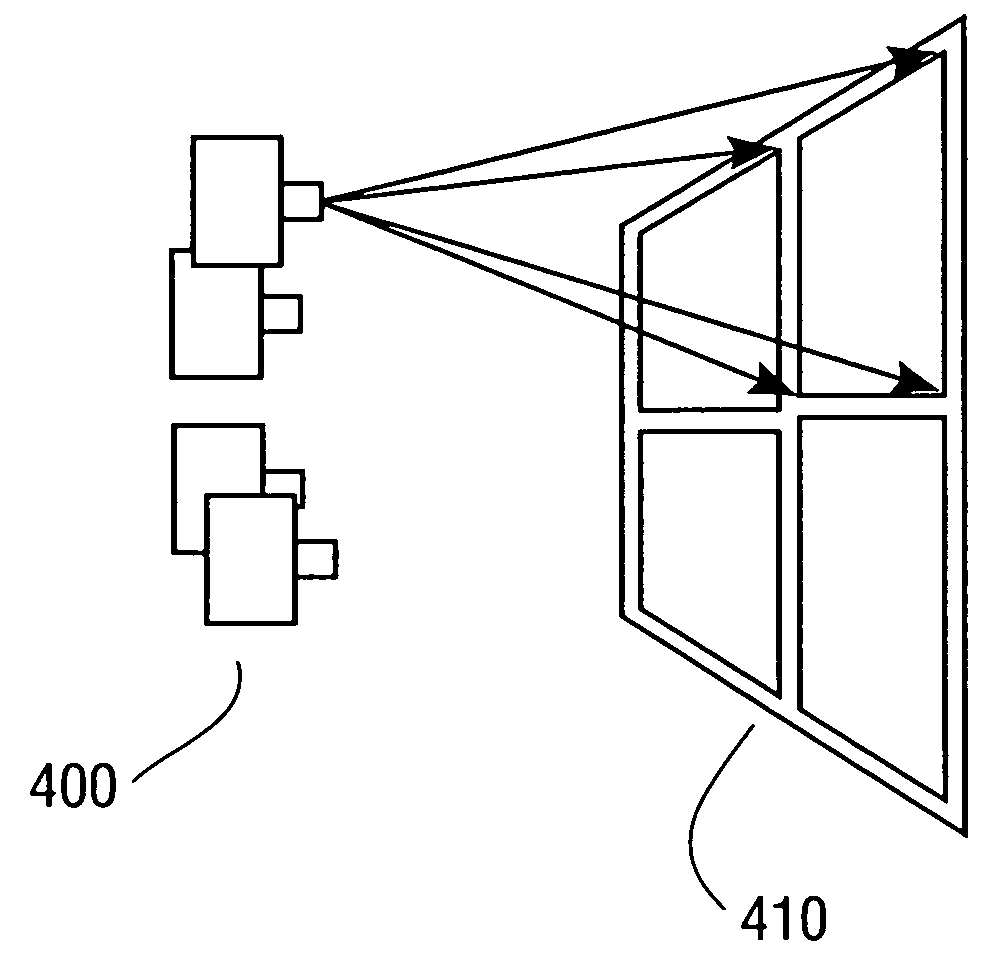
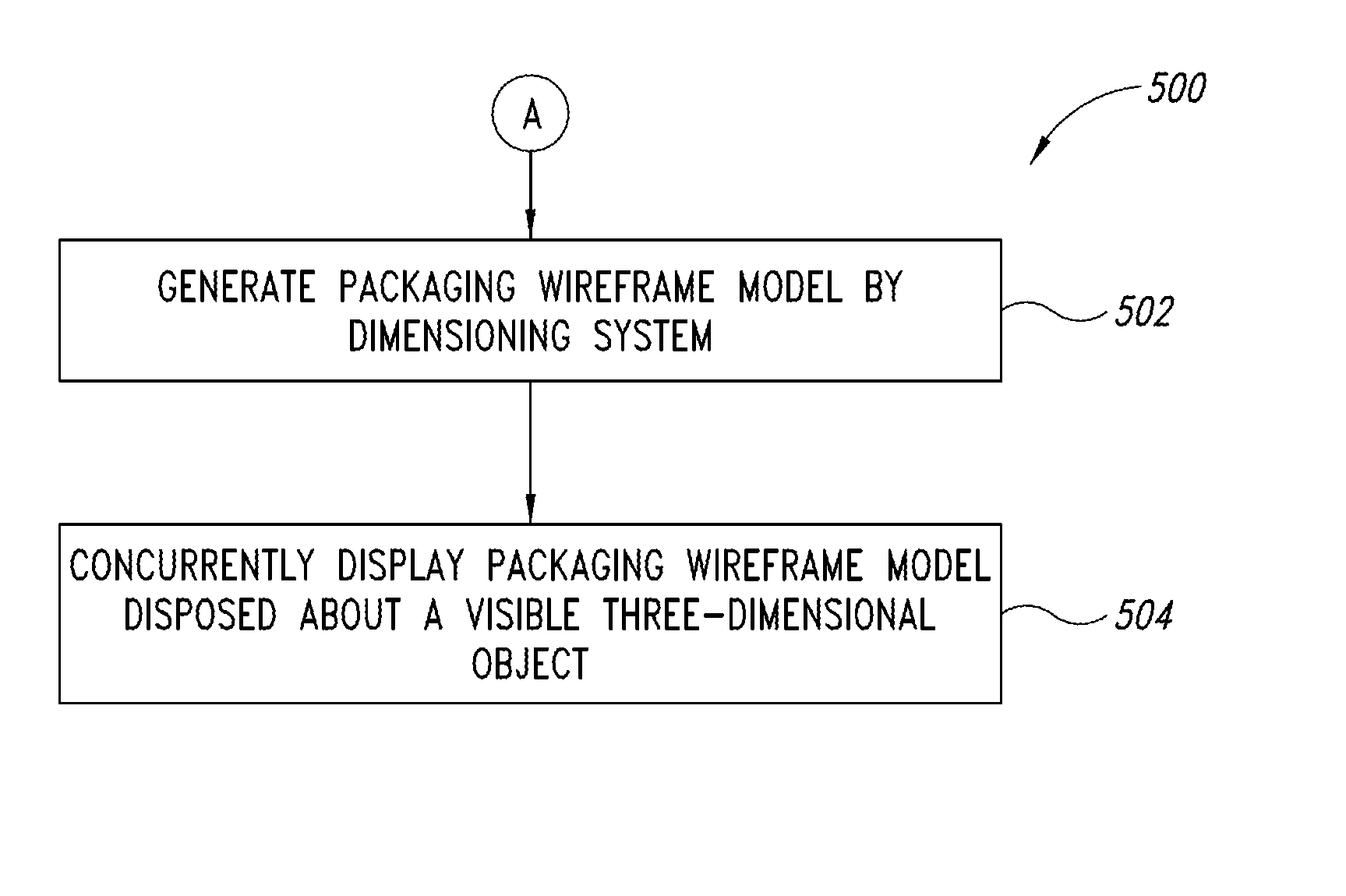
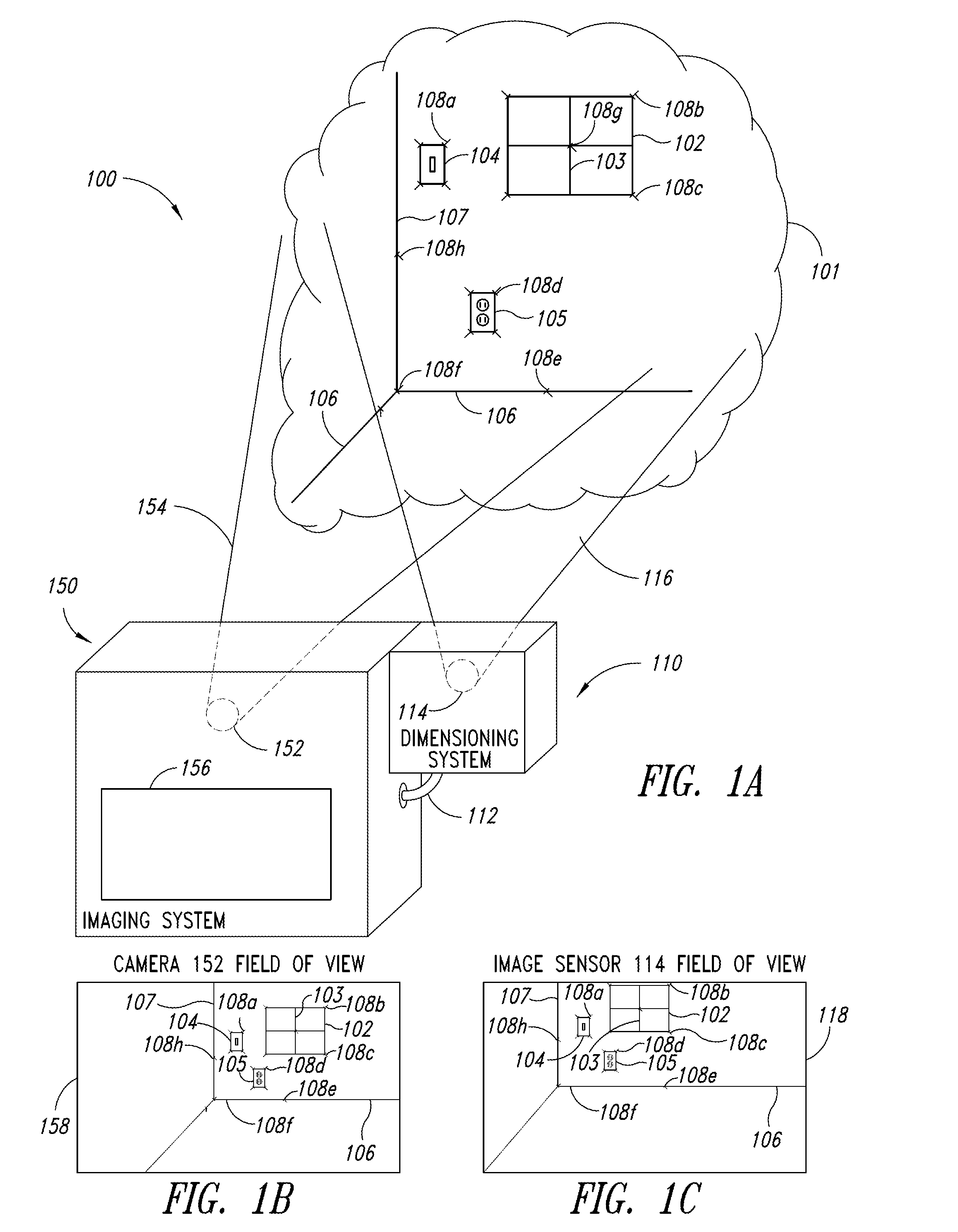
Dimensioning system calibration systems and methods
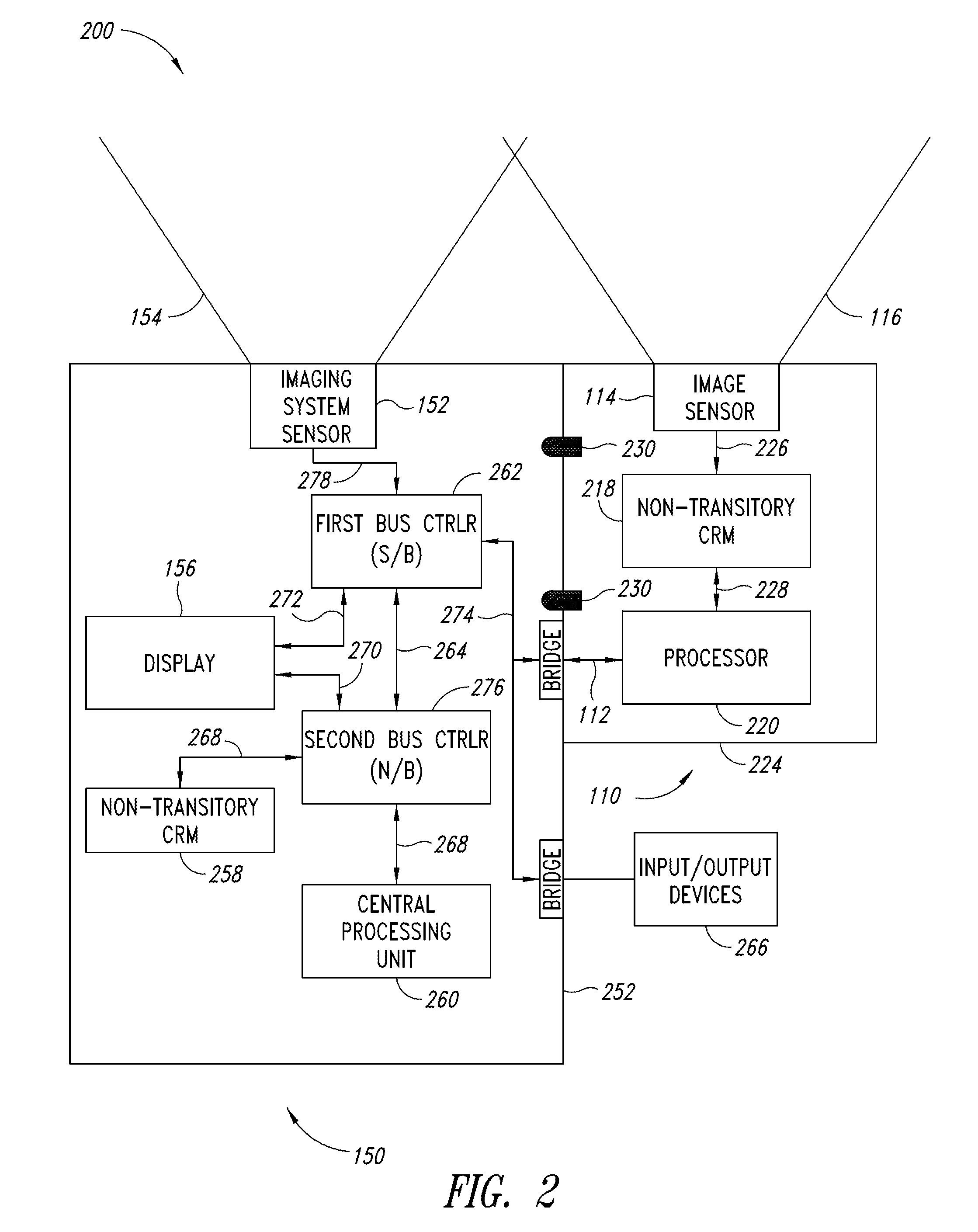
Systems and methods of determining the volume and dimensions of a three-dimensional object using a dimensioning system are provided. The dimensioning system can include an image sensor, a non-transitory, machine-readable, storage, and a processor. The dimensioning system can select and fit a three-dimensional packaging wireframe model about each three-dimensional object located within a first point of view of the image sensor. Calibration is performed to calibrate between image sensors of the dimensioning system and those of the imaging system. Calibration may occur pre-run time, in a calibration mode or period. Calibration may occur during a routine. Calibration may be automatically triggered on detection of a coupling between the dimensioning and the imaging systems.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
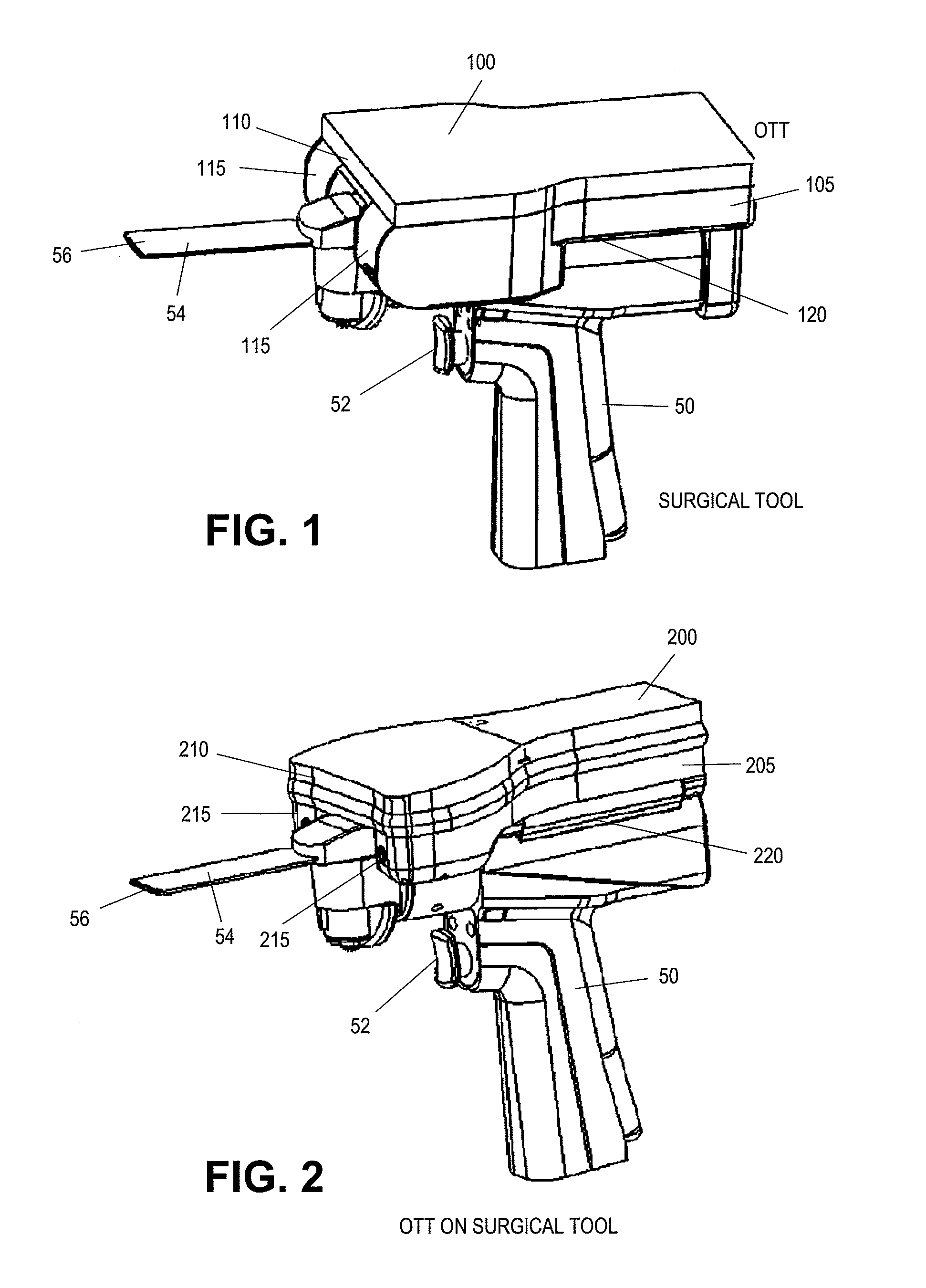
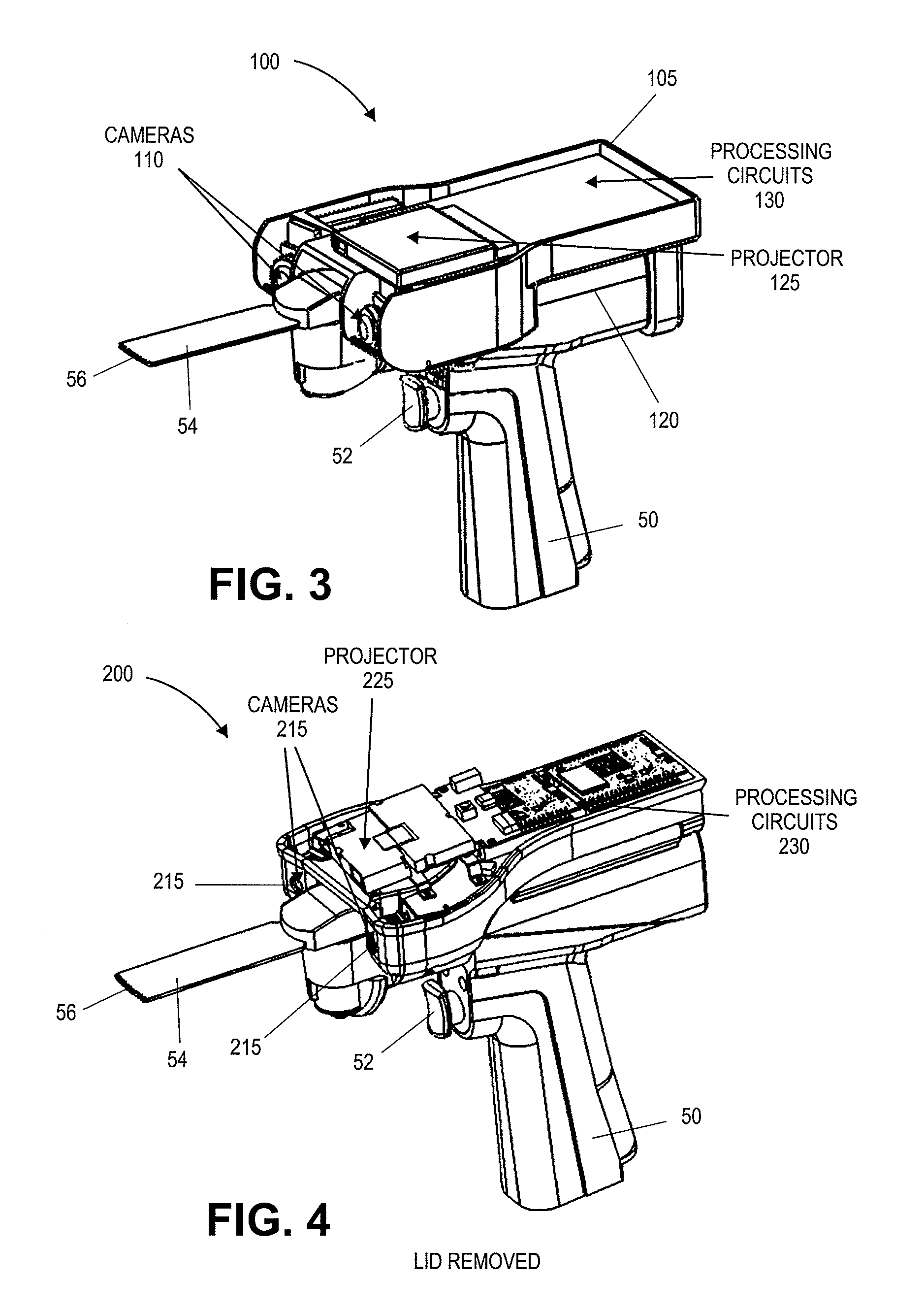
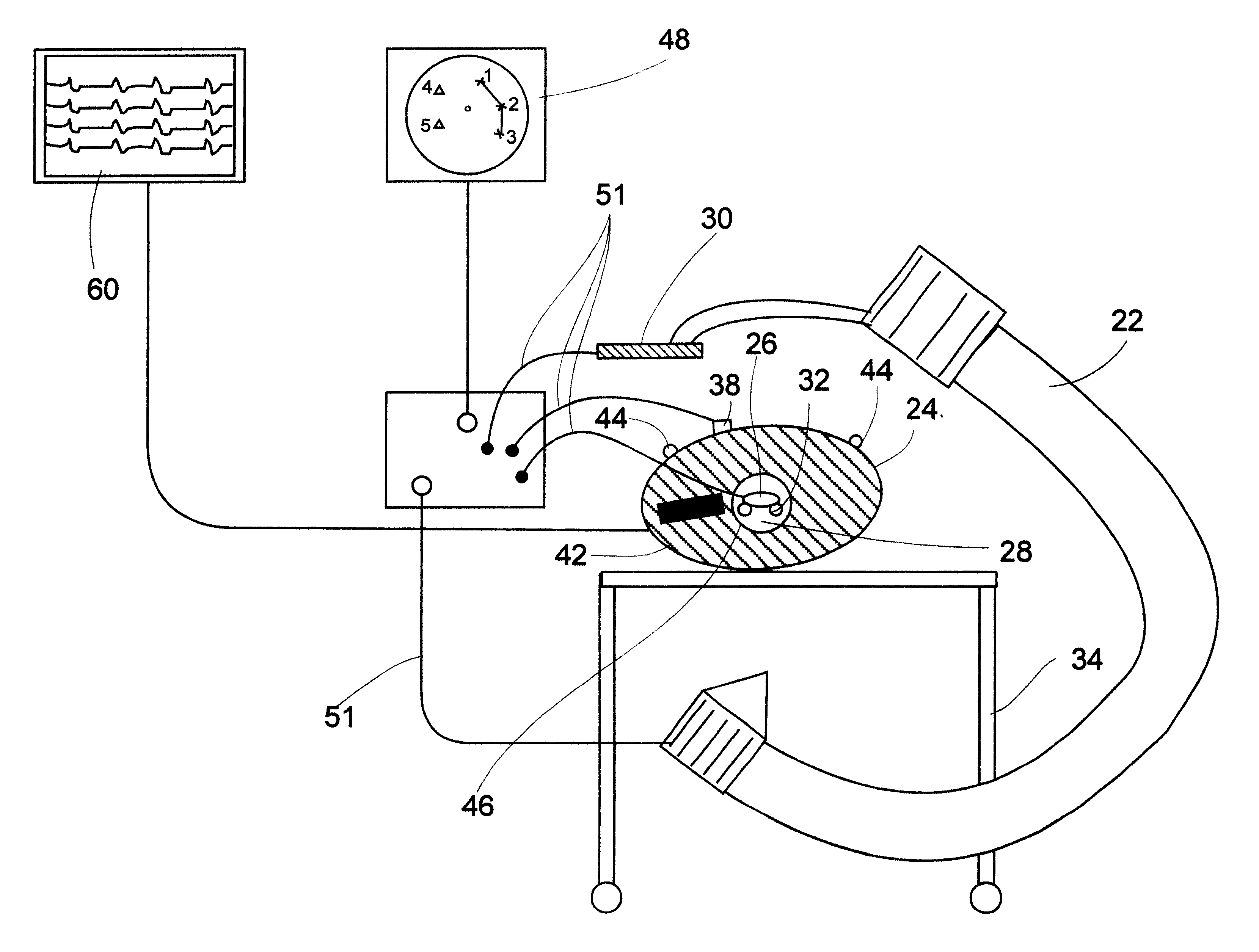
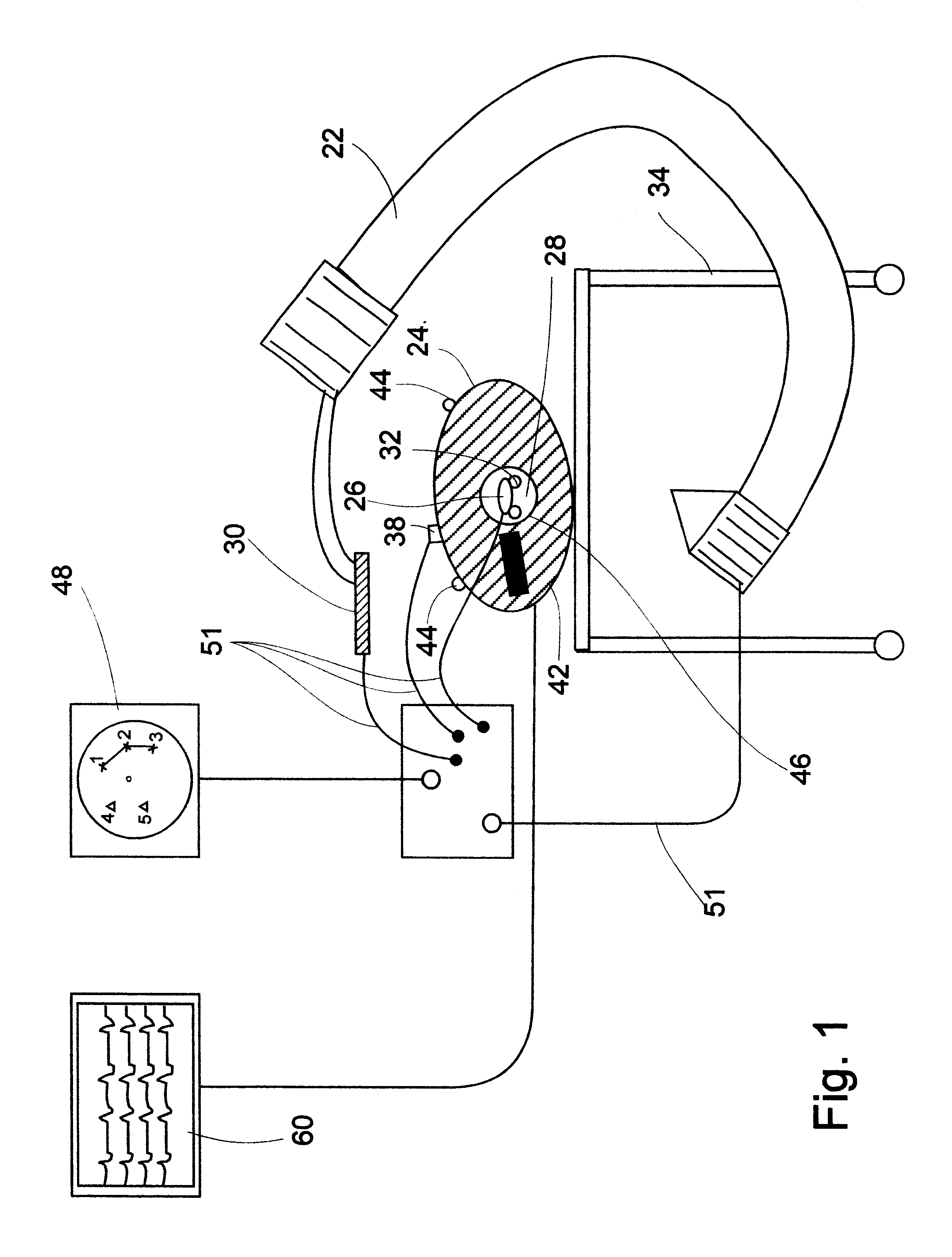
On-board tool tracking system and methods of computer assisted surgery
A number of improvements are provided relating to computer aided surgery utilizing an on tool tracking system. The various improvements relate generally to both the methods used during computer aided surgery and the devices used during such procedures. Other improvements relate to the structure of the tools used during a procedure and how the tools can be controlled using the OTT device. Still other improvements relate to methods of providing feedback during a procedure to improve either the efficiency or quality, or both, for a procedure including the rate of and type of data processed depending upon a CAS mode.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
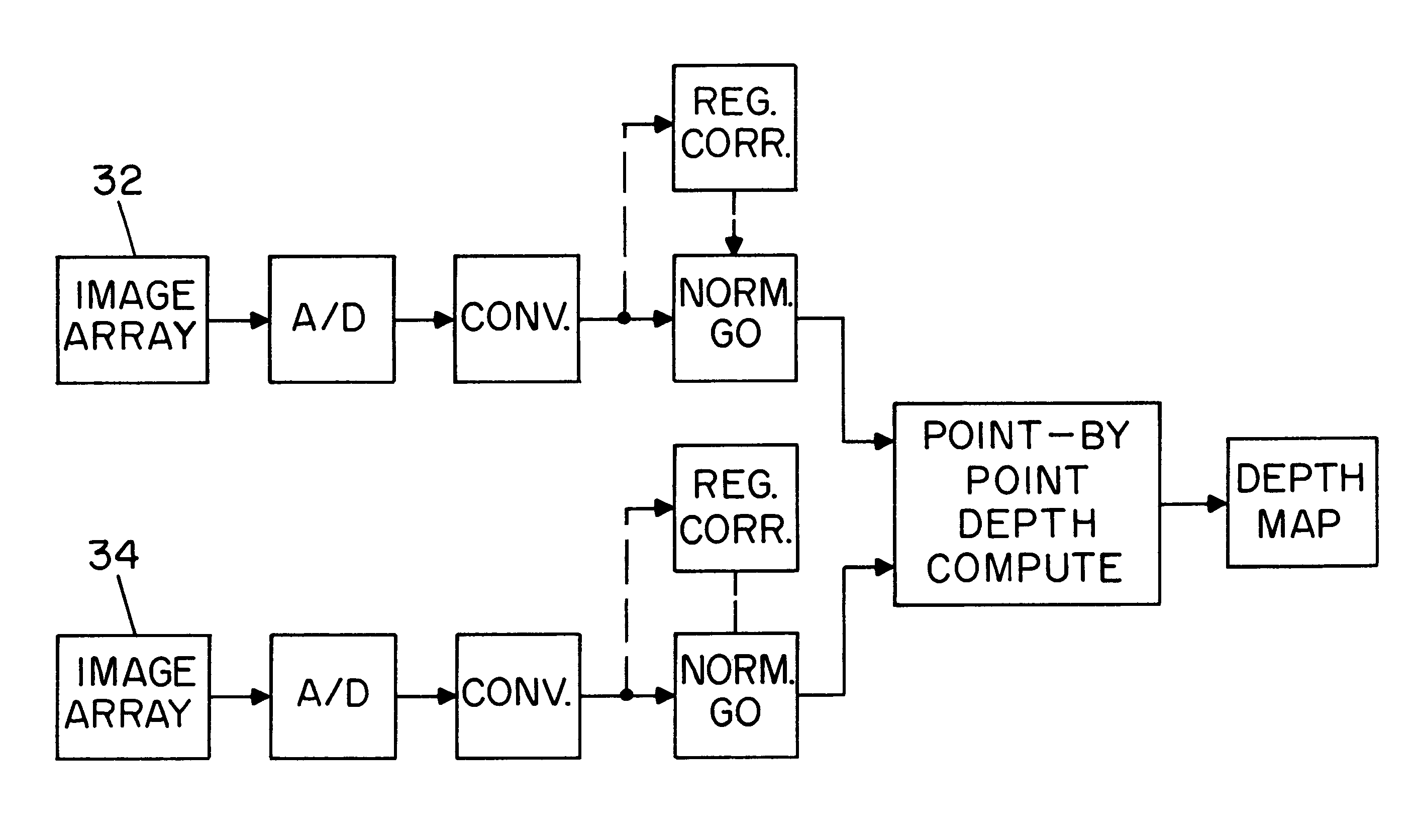
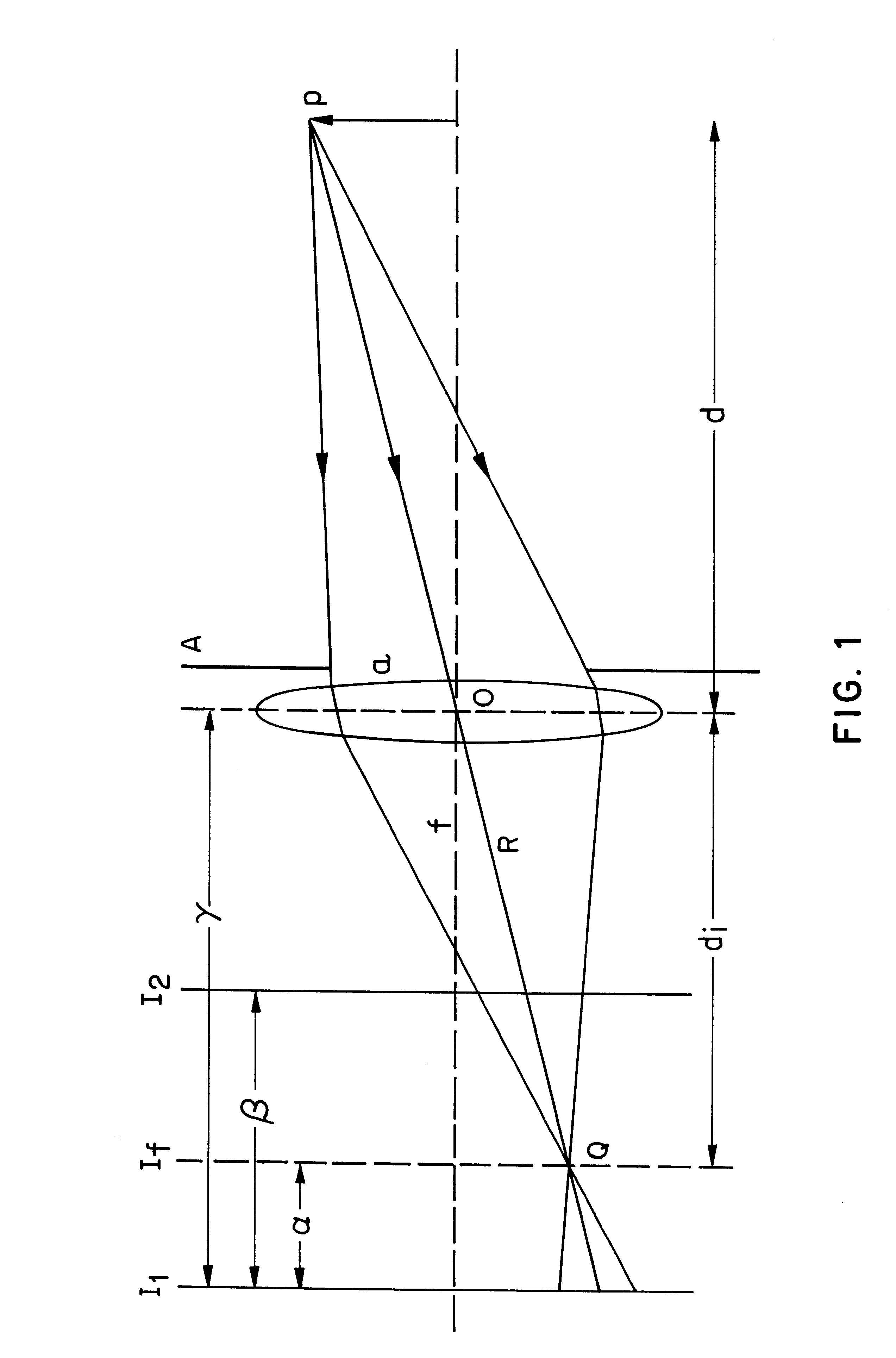
Apparatus and methods for determining the three-dimensional shape of an object using active illumination and relative blurring in two images due to defocus
A method and apparatus for mapping depth of an object (22) in a preferred arrangement uses a projected light pattern to provide a selected texture to the object (22) along the optical axis (24) of observation. An imaging system senses (32, 34) first and second images of the object (22) with the projected light pattern and compares the defocused of the projected pattern in the images to determine relative depth of elemental portions of the object (22).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
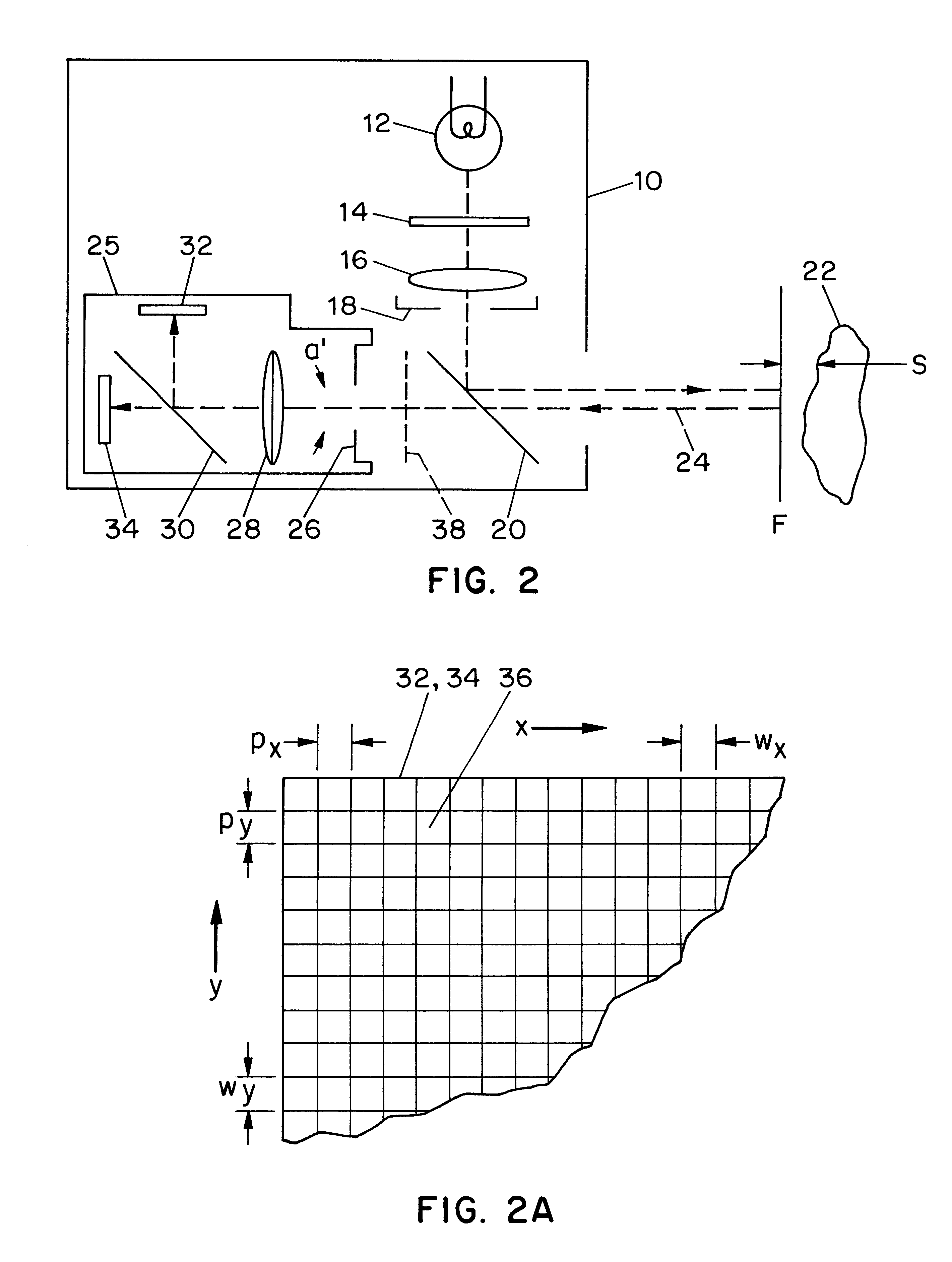
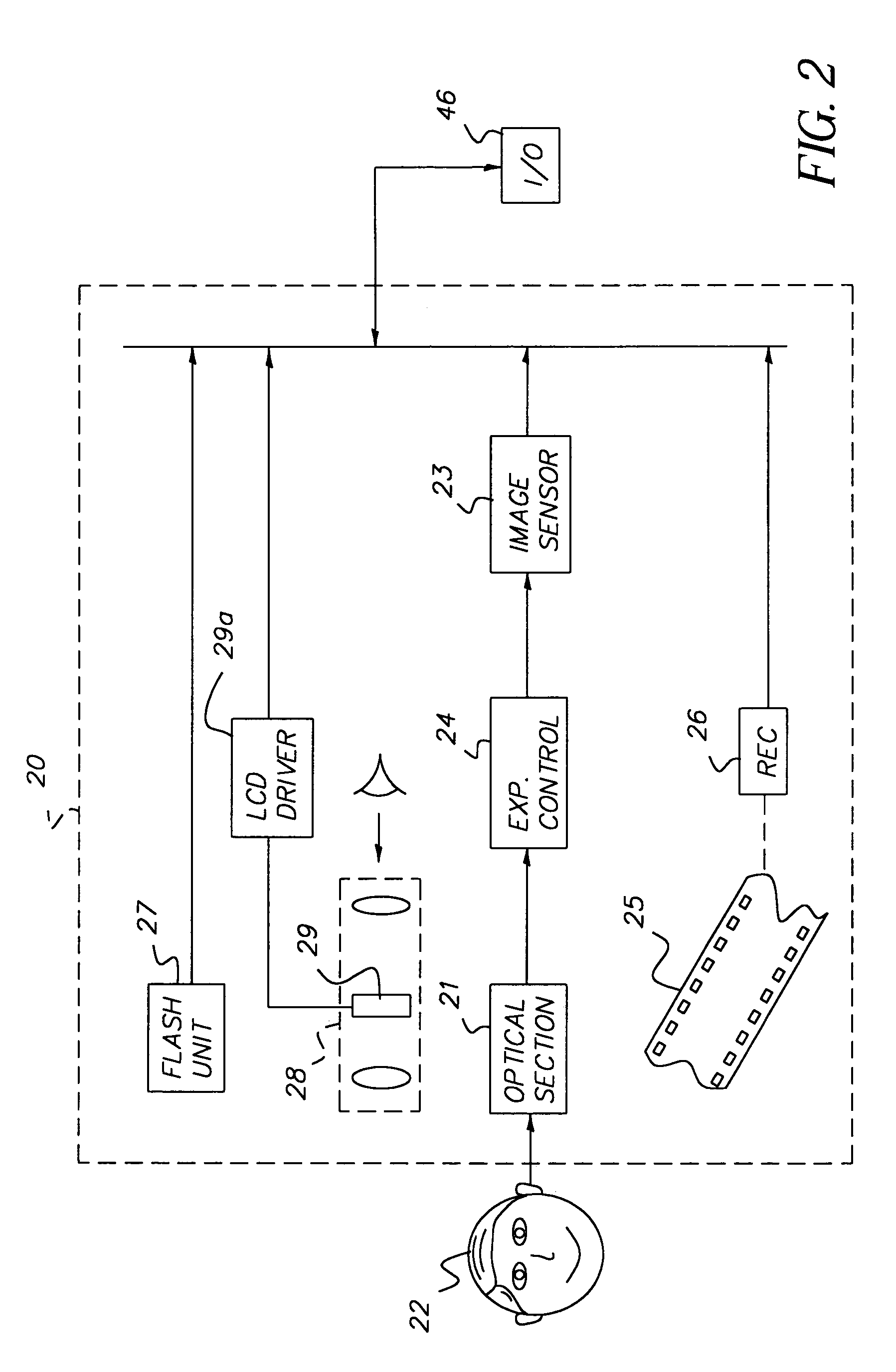
Face detecting camera and method
InactiveUS6940545B1Improve photo experienceGood and more pleasing photographTelevision system detailsImage analysisFace detectionPattern recognition
A method for determining the presence of a face from image data includes a face detection algorithm having two separate algorithmic steps: a first step of prescreening image data with a first component of the algorithm to find one or more face candidate regions of the image based on a comparison between facial shape models and facial probabilities assigned to image pixels within the region; and a second step of operating on the face candidate regions with a second component of the algorithm using a pattern matching technique to examine each face candidate region of the image and thereby confirm a facial presence in the region, whereby the combination of these components provides higher performance in terms of detection levels than either component individually. In a camera implementation, a digital camera includes an algorithm memory for storing an algorithm comprised of the aforementioned first and second components and an electronic processing section for processing the image data together with the algorithm for determining the presence of one or more faces in the scene. Facial data indicating the presence of faces may be used to control, e.g., exposure parameters of the capture of an image, or to produce processed image data that relates, e.g., color balance, to the presence of faces in the image, or the facial data may be stored together with the image data on a storage medium.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
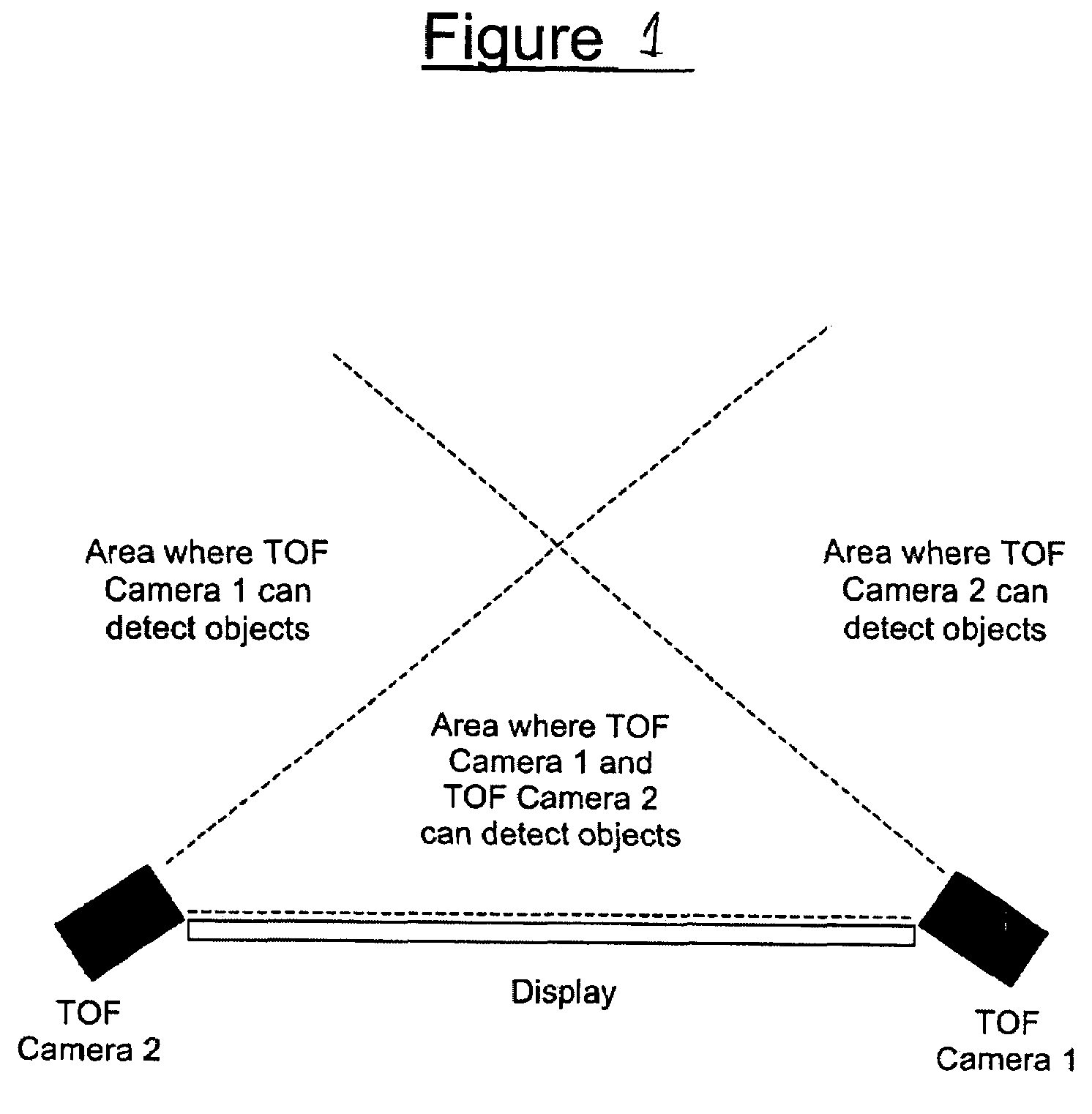
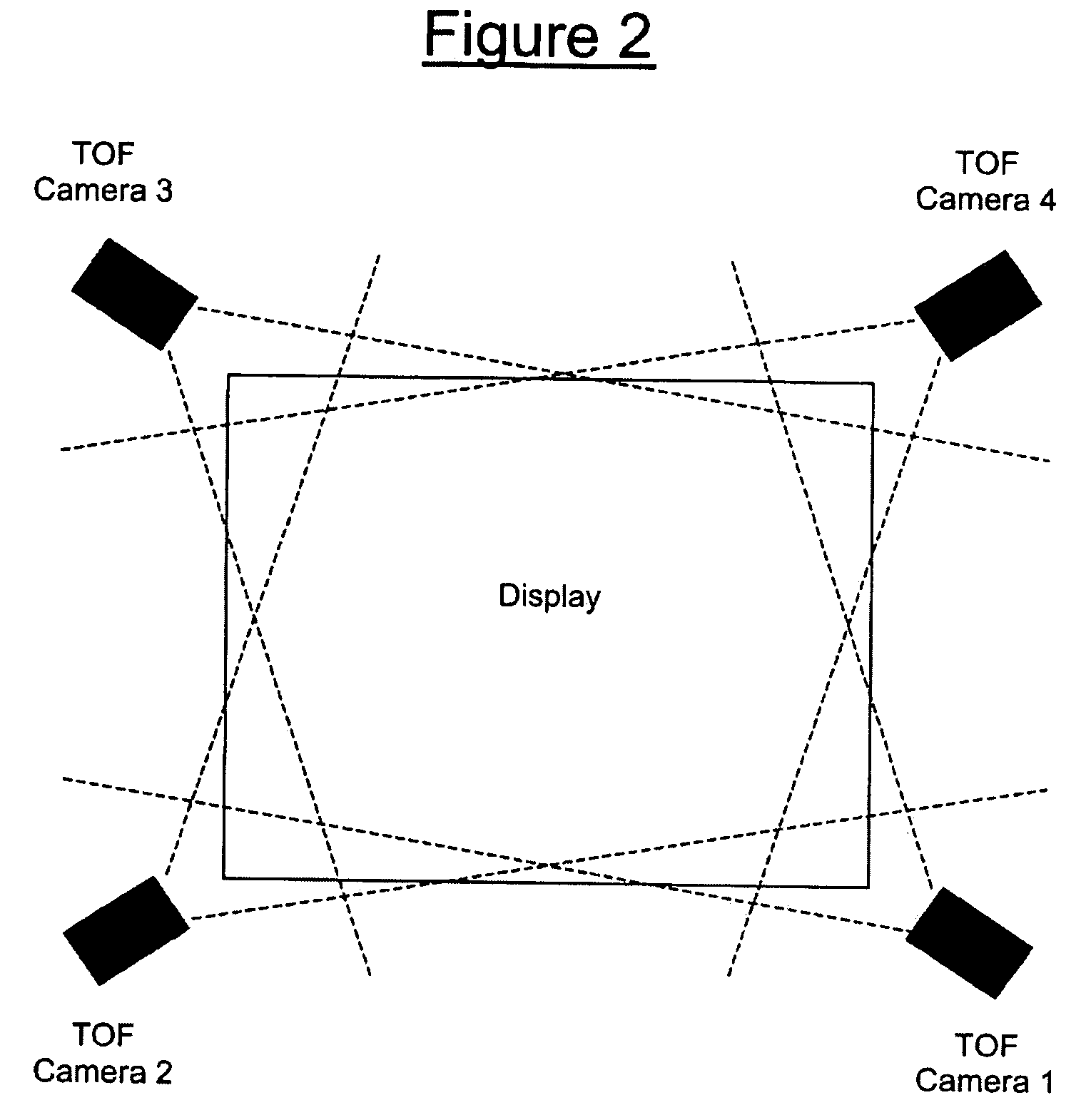
Multiple camera control system
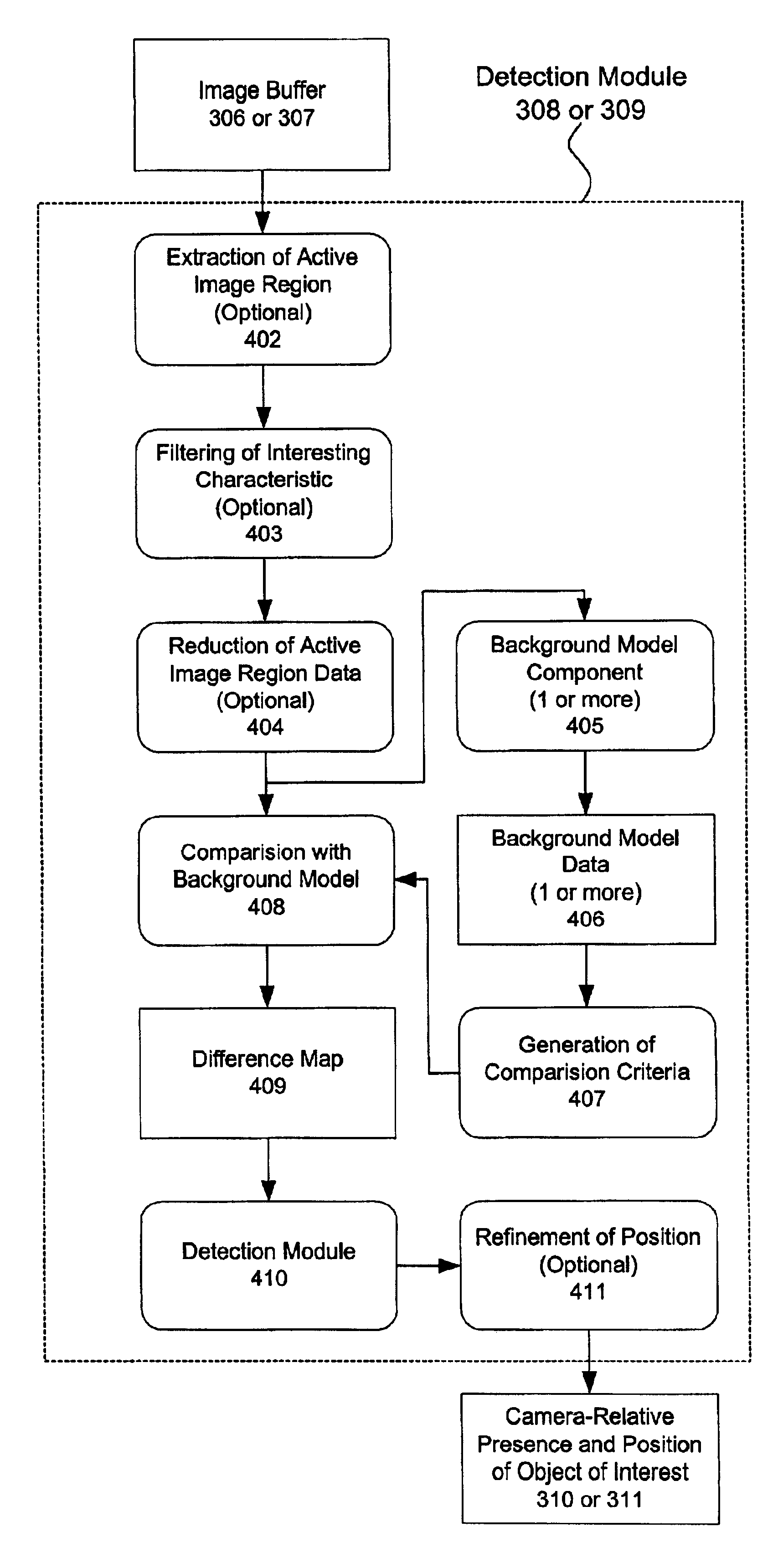
A multiple camera tracking system for interfacing with an application program running on a computer is provided. The tracking system includes two or more video cameras arranged to provide different viewpoints of a region of interest, and are operable to produce a series of video images. A processor is operable to receive the series of video images and detect objects appearing in the region of interest. The processor executes a process to generate a background data set from the video images, generate an image data set for each received video image, compare each image data set to the background data set to produce a difference map for each image data set, detect a relative position of an object of interest within each difference map, and produce an absolute position of the object of interest from the relative positions of the object of interest and map the absolute position to a position indicator associated with the application program.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
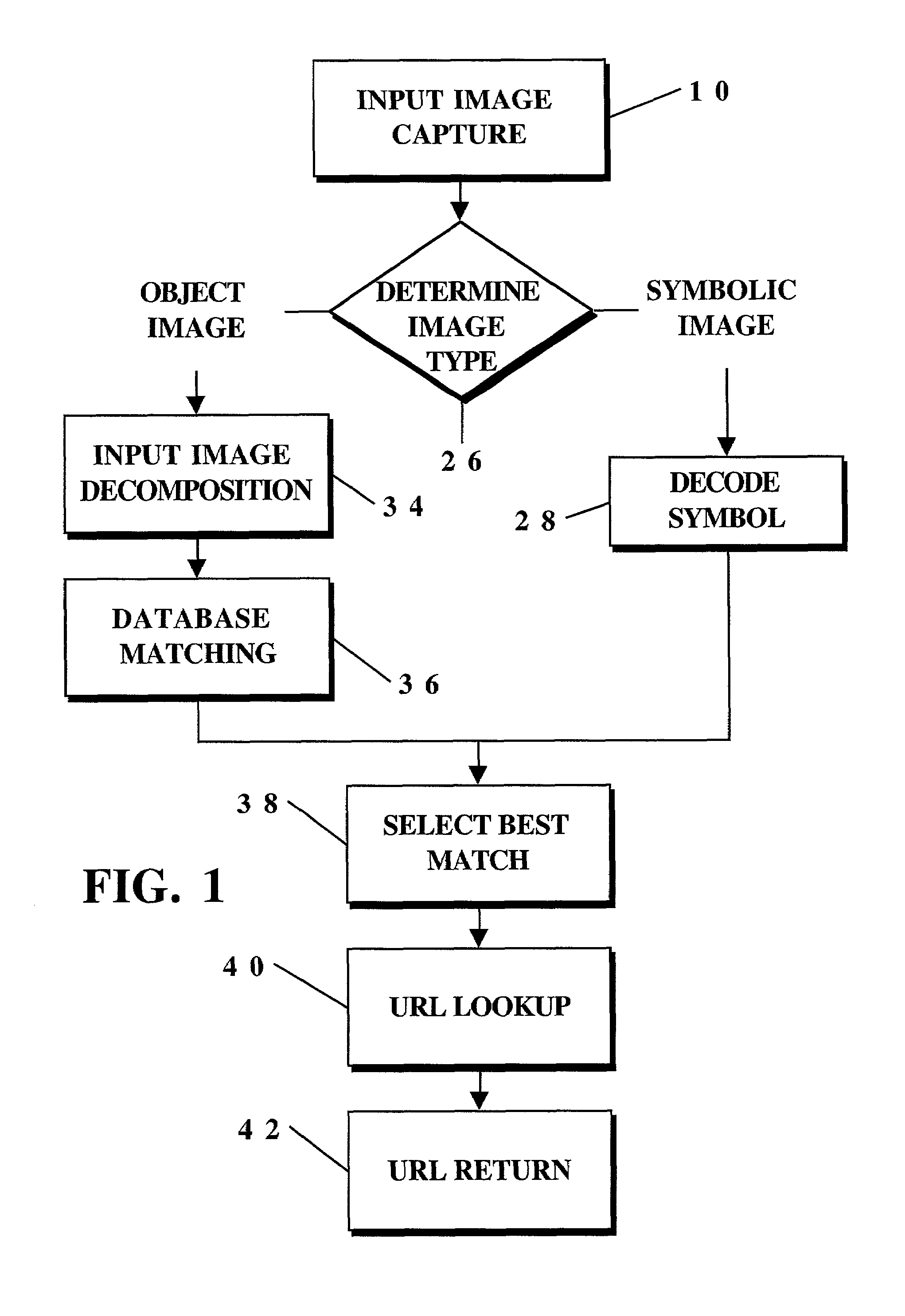
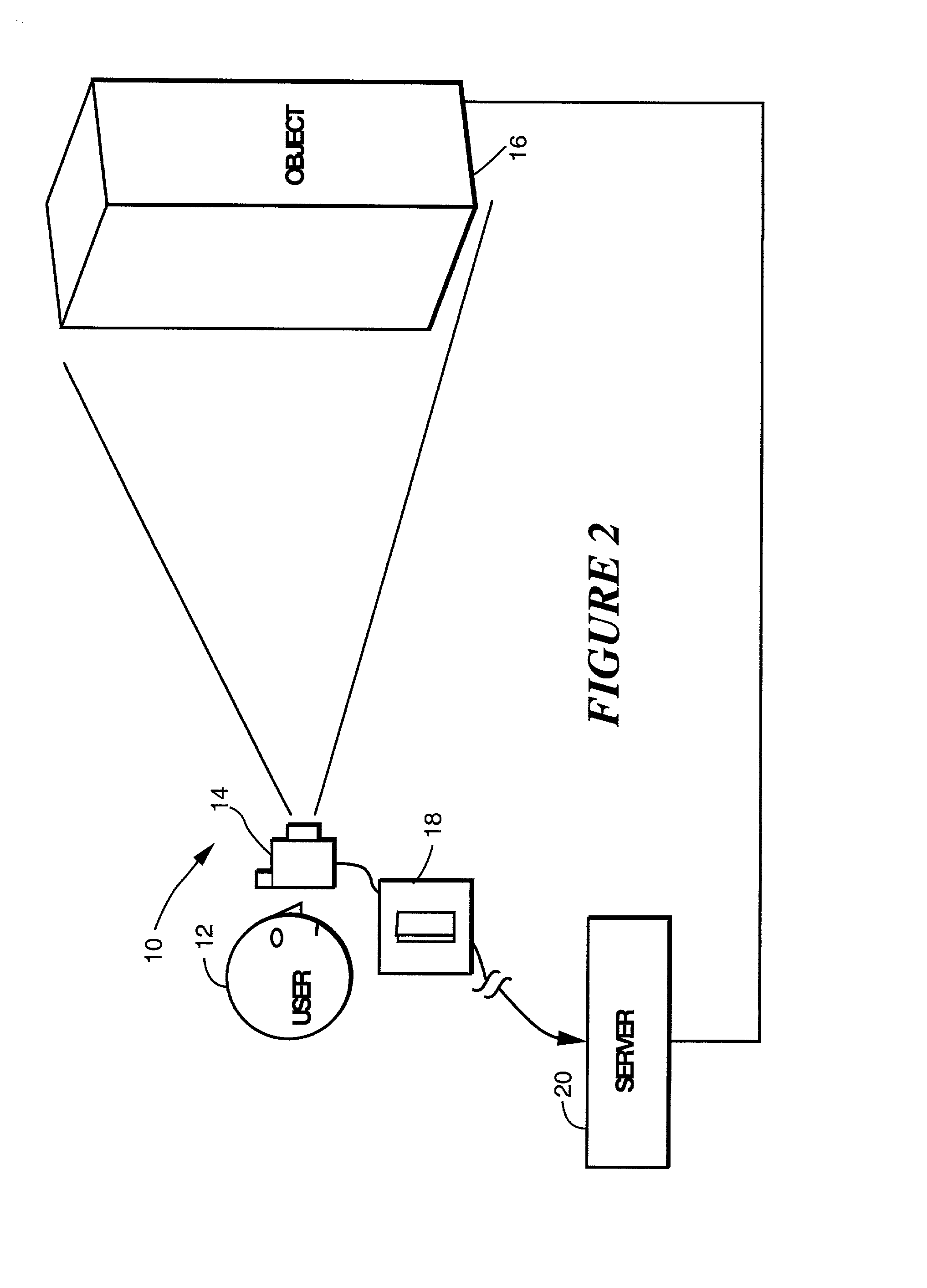
Image capture and identification system and process
InactiveUS7016532B2Fast and reliable detection and recognitionReduce sizeDigital data information retrievalImage analysisDigital imageImage capture
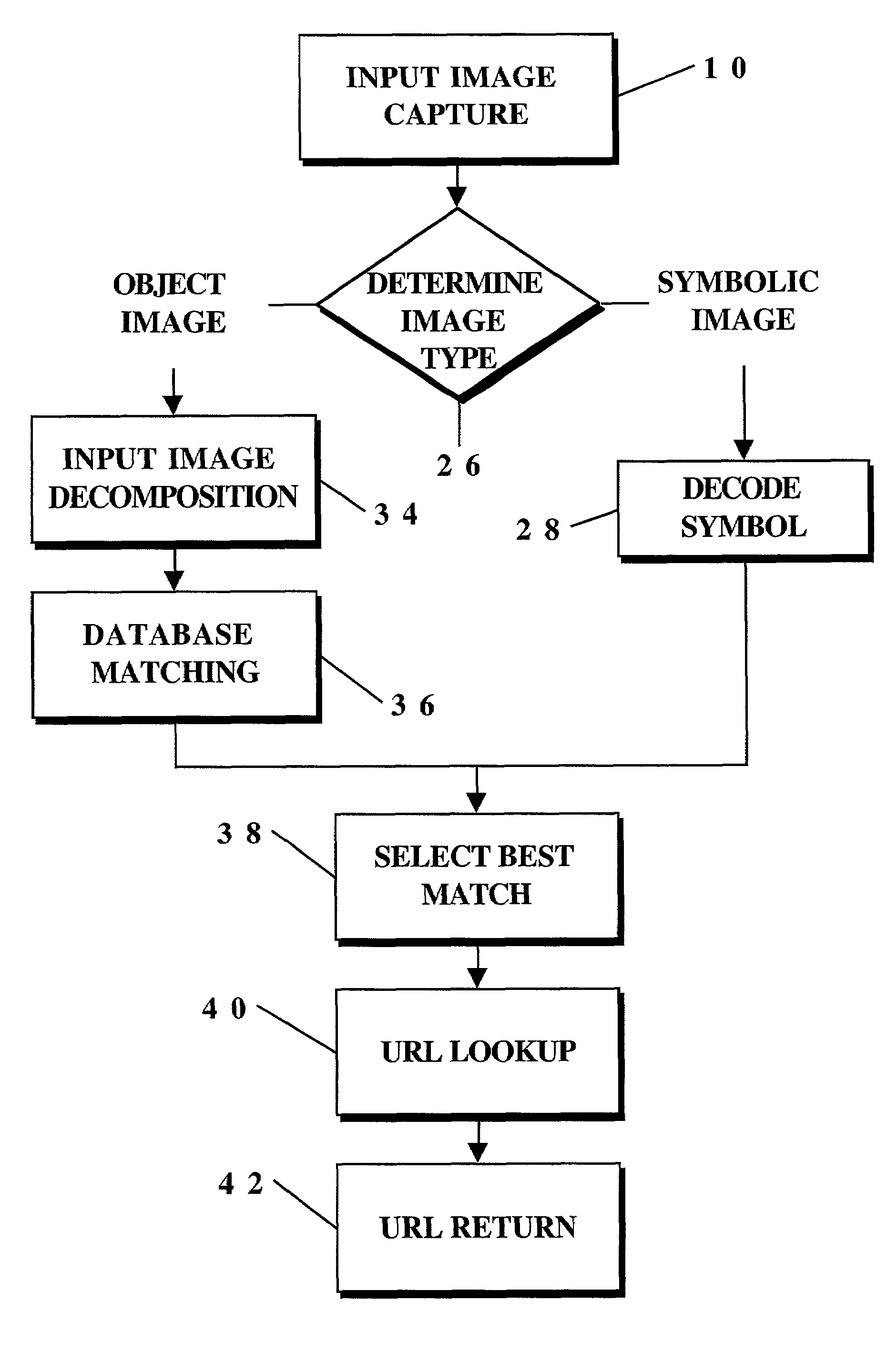
An identification method and process for objects from digitally captured images thereof that uses image characteristics to identify an object from a plurality of objects in a database. The image is broken down into parameters such as a Shape Comparison, Grayscale Comparison, Wavelet Comparison, and Color Cube Comparison with object data in one or more databases to identify the actual object of a digital image.
Owner:NANT HLDG IP LLC
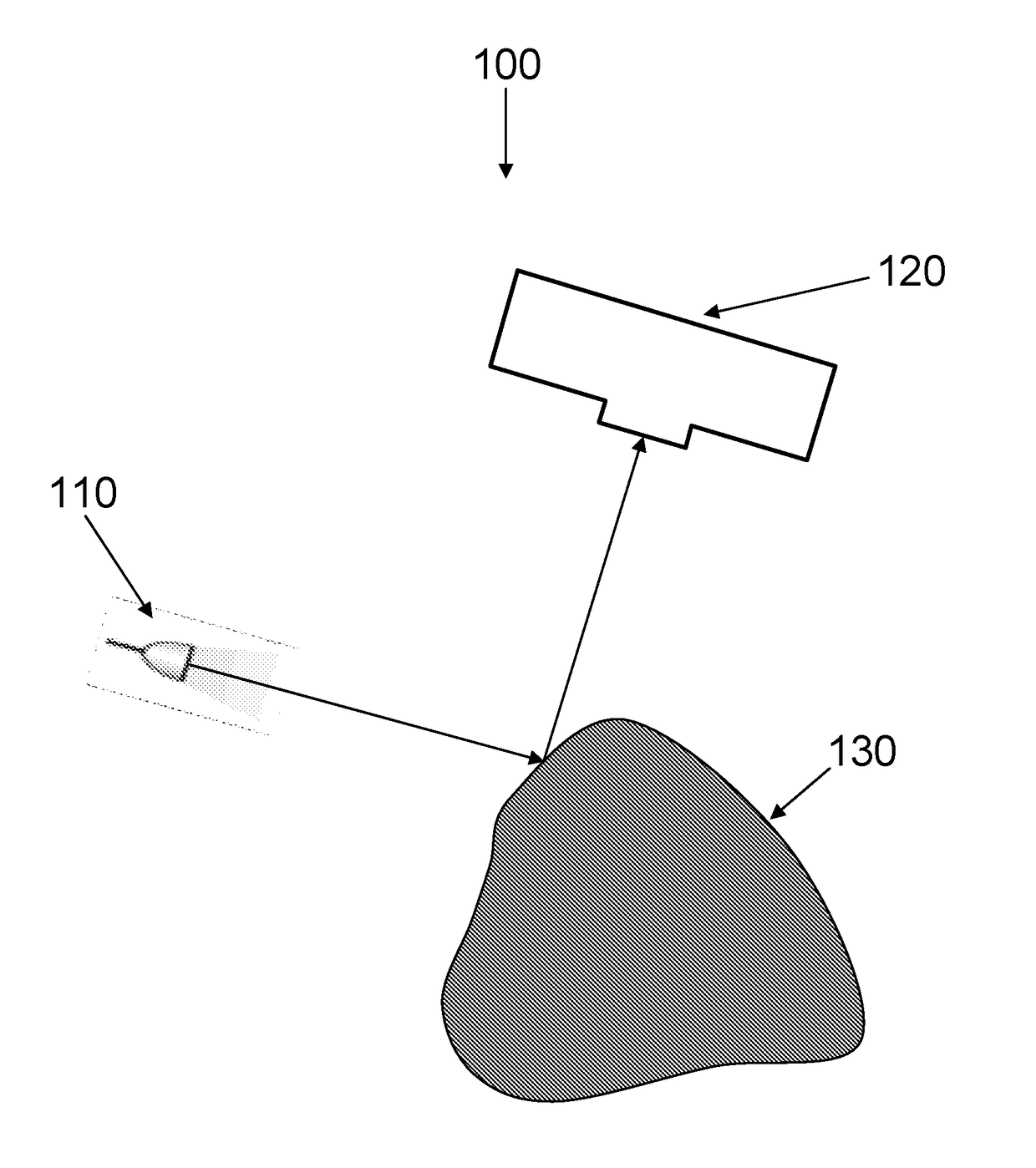
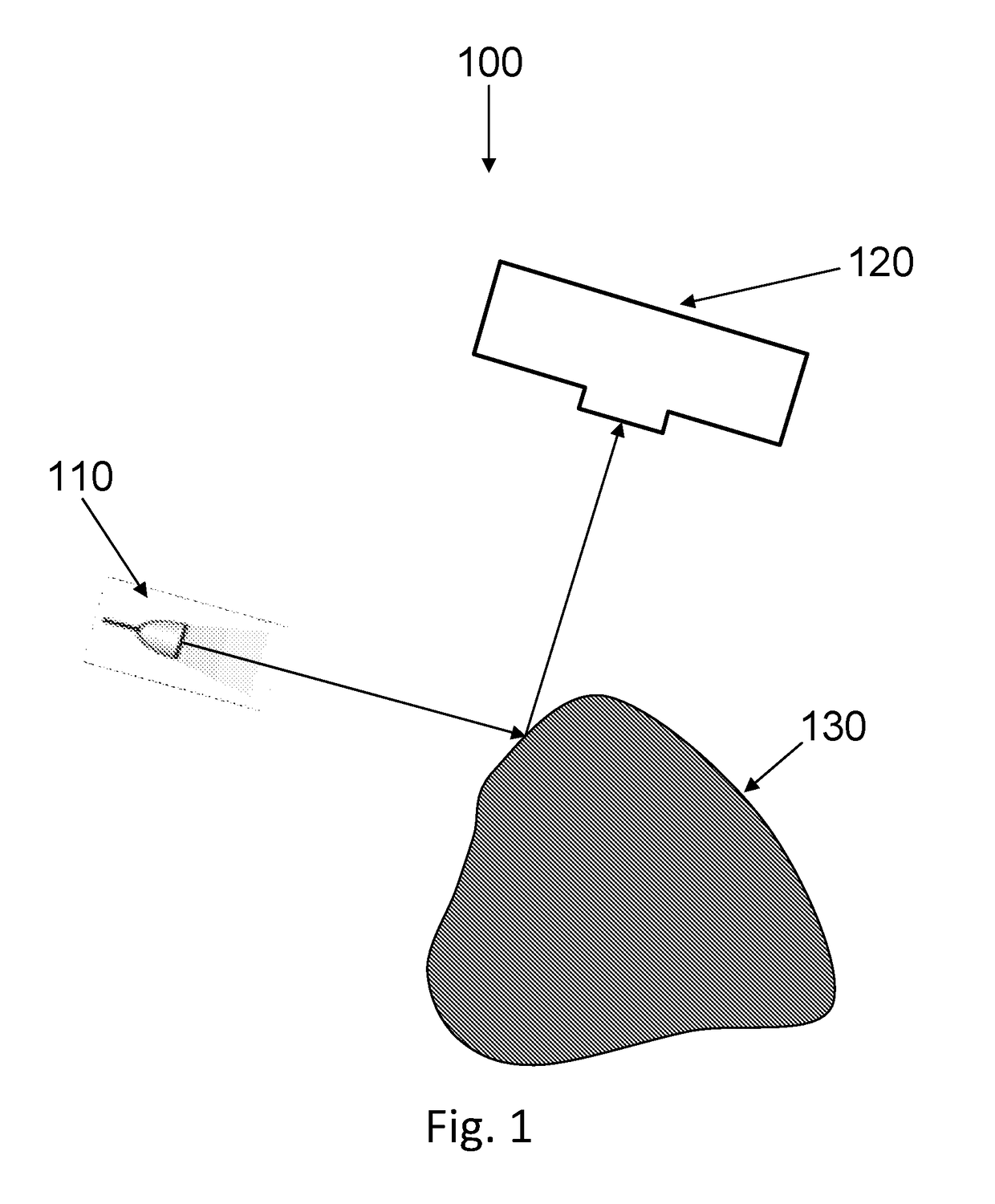
System and method for determining the location of a catheter during an intra-body medical procedure
A system and method of displaying at least one point-of-interest of a body during an intra-body medical procedure. The method is effected by (a) establishing a location of the body; (b) establishing a location of an imaging instrument being for imaging at least a portion of the body; (c) defining at least one projection plane being in relation to a projection plane of the imaging instrument; (d) acquiring at least one point-of-interest of the body; and (c) projection said at least one point-of-interest on said at least one projection plane; such that, in course of the procedure, the locations of the body and the imaging instrument are known, thereby the at least one point-of-interest is projectable on the at least one projection plane even in cases whereby a relative location of the body and the imaging instrument are changed.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Image processing method and apparatus
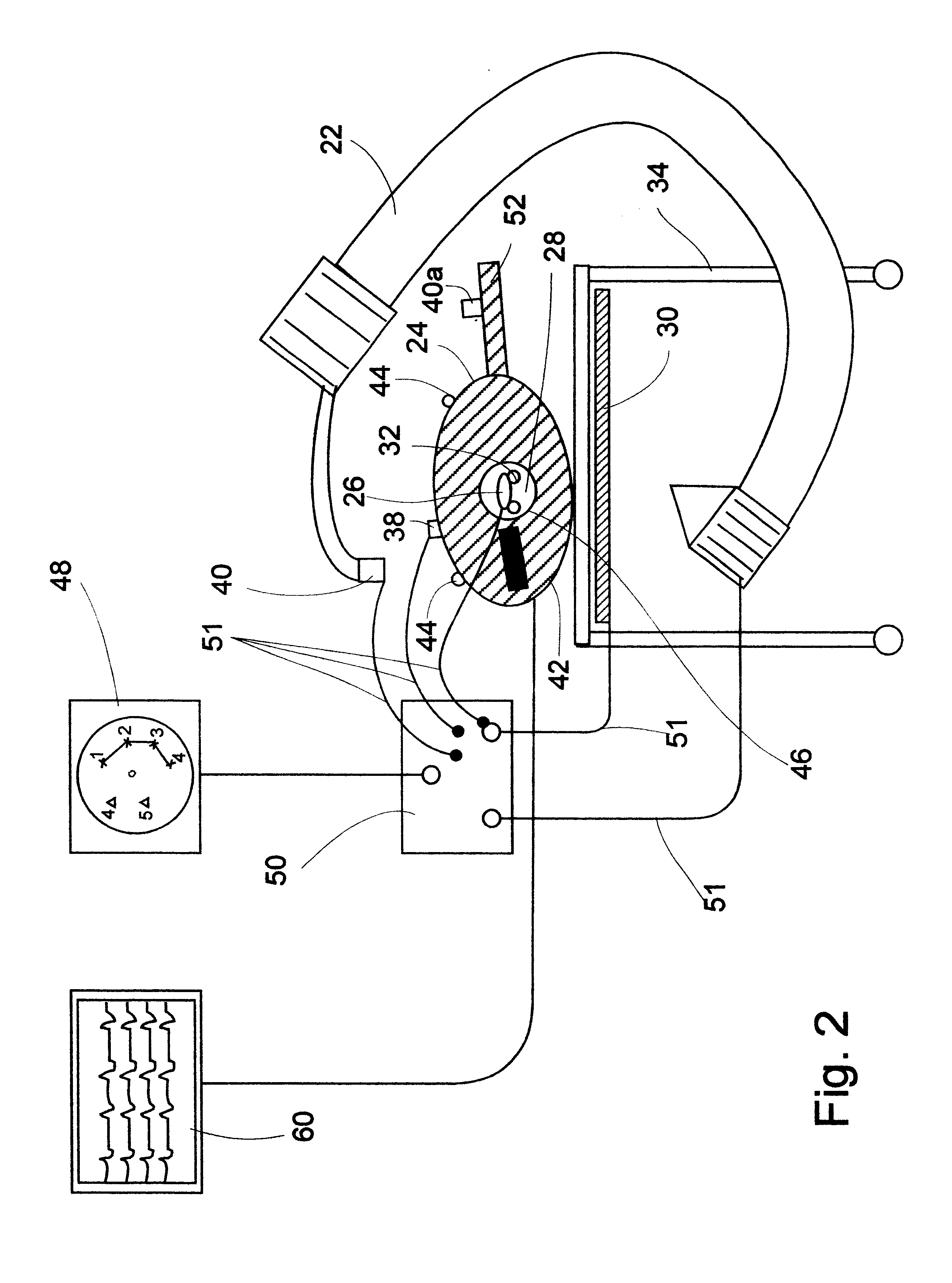
InactiveUS6496598B1Improve the three-dimensional effectImproving stereoscopic image pairImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage transfer
An image conversion system for converting monoscopic images for viewing in three dimensions including: an input means adapted to receive the monoscopic images; a preliminary analysis means to determine if there is any continuity between a first image and a second image of the monoscopic image sequence; a secondary analysis means for receiving monoscopic images which have a continuity, and analyzing the images to determine the speed and direction of motion, and the depth, size and position of objects; a first processing means for processing the monoscopic images based on data received from the preliminary analysis means or the secondary analysis means; a second processing means capable of further processing images received from the first processing means; a transmission means capable of transferring the processed images to a stereoscopic display system.
Owner:DYNAMIC DIGITAL DEPTH RES
Automatic video system using multiple cameras
InactiveUS7015954B1Reduce manufacturing costCombine accuratelyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDynamic equationCombined use
A camera array captures plural component images which are combined into a single scene from which “panning” and “zooming” within the scene are performed. In one embodiment, each camera of the array is a fixed digital camera. The images from each camera are warped and blended such that the combined image is seamless with respect to each of the component images. Warping of the digital images is performed via pre-calculated non-dynamic equations that are calculated based on a registration of the camera array. The process of registering each camera in the arrays is performed either manually, by selecting corresponding points or sets of points in two or more images, or automatically, by presenting a source object (laser light source, for example) into a scene being captured by the camera array and registering positions of the source object as it appears in each of the images. The warping equations are calculated based on the registration data and each scene captured by the camera array is warped and combined using the same equations determined therefrom. A scene captured by the camera array is zoomed, or selectively steered to an area of interest. This zooming- or steering, being done in the digital domain is performed nearly instantaneously when compared to cameras with mechanical zoom and steering functions.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
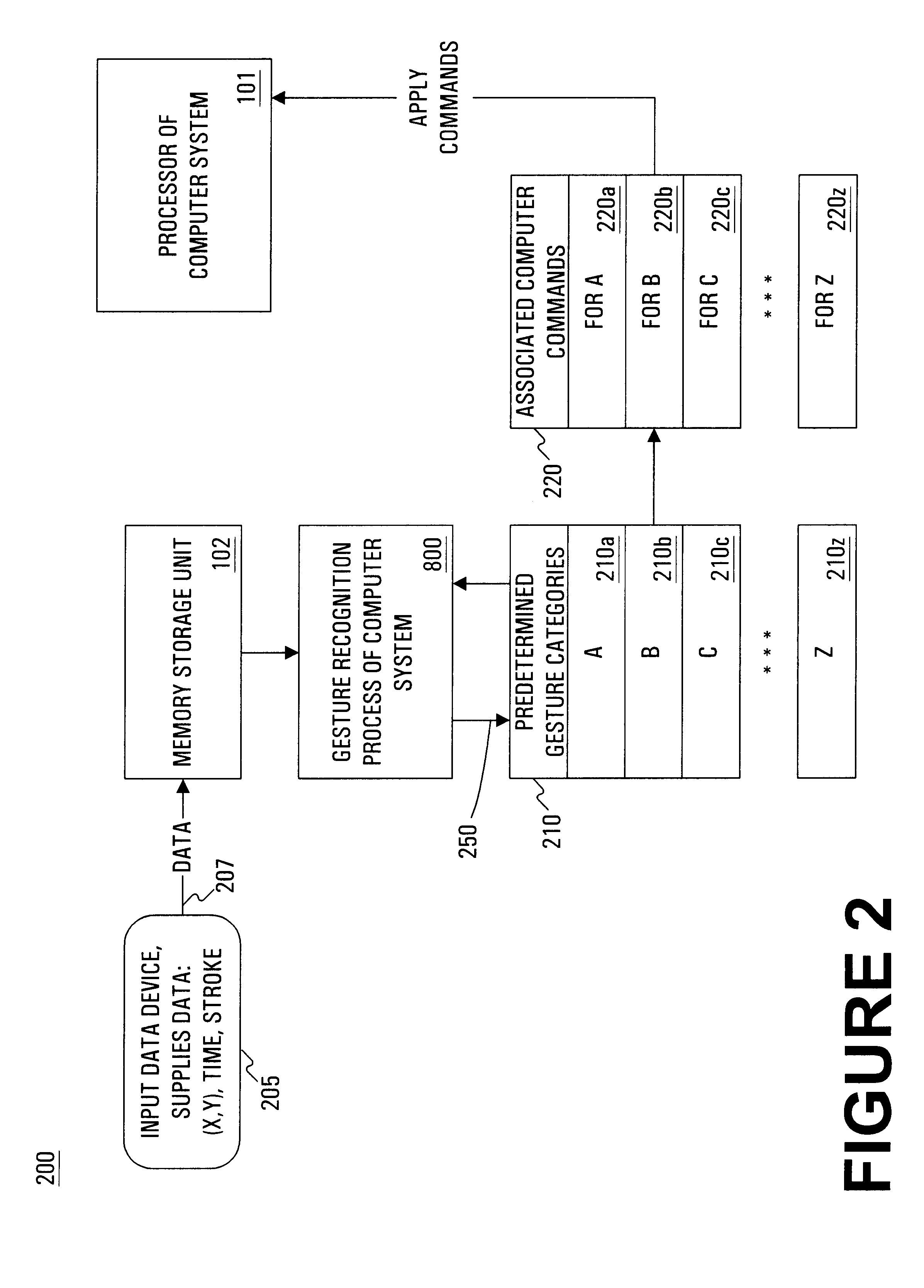
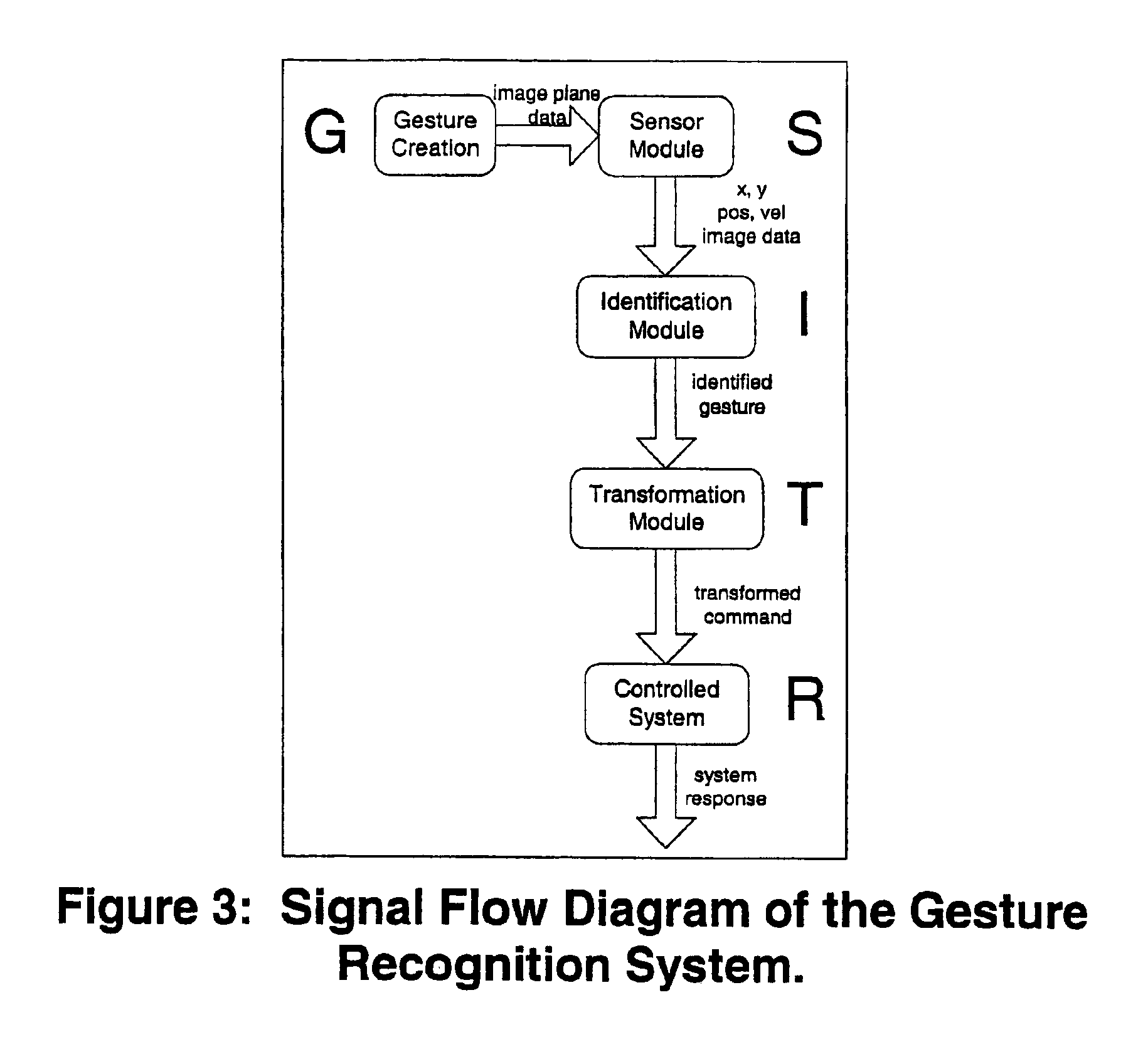
Method and system for gesture category recognition and training using a feature vector
InactiveUS6249606B1Image analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsCategory recognitionApplication software
A computer implemented method and system for gesture category recognition and training. Generally, a gesture is a hand or body initiated movement of a cursor directing device to outline a particular pattern in particular directions done in particular periods of time. The present invention allows a computer system to accept input data, originating from a user, in the form gesture data that are made using the cursor directing device. In one embodiment, a mouse device is used, but the present invention is equally well suited for use with other cursor directing devices (e.g., a track ball, a finger pad, an electronic stylus, etc.). In one embodiment, gesture data is accepted by pressing a key on the keyboard and then moving the mouse (with mouse button pressed) to trace out the gesture. Mouse position information and time stamps are recorded. The present invention then determines a multi-dimensional feature vector based on the gesture data. The feature vector is then passed through a gesture category recognition engine that, in one implementation, uses a radial basis function neural network to associate the feature vector to a pre-existing gesture category. Once identified, a set of user commands that are associated with the gesture category are applied to the computer system. The user commands can originate from an automatic process that extracts commands that are associated with the menu items of a particular application program. The present invention also allows user training so that user-defined gestures, and the computer commands associated therewith, can be programmed into the computer system.
Owner:ASSOCIATIVE COMPUTING +1
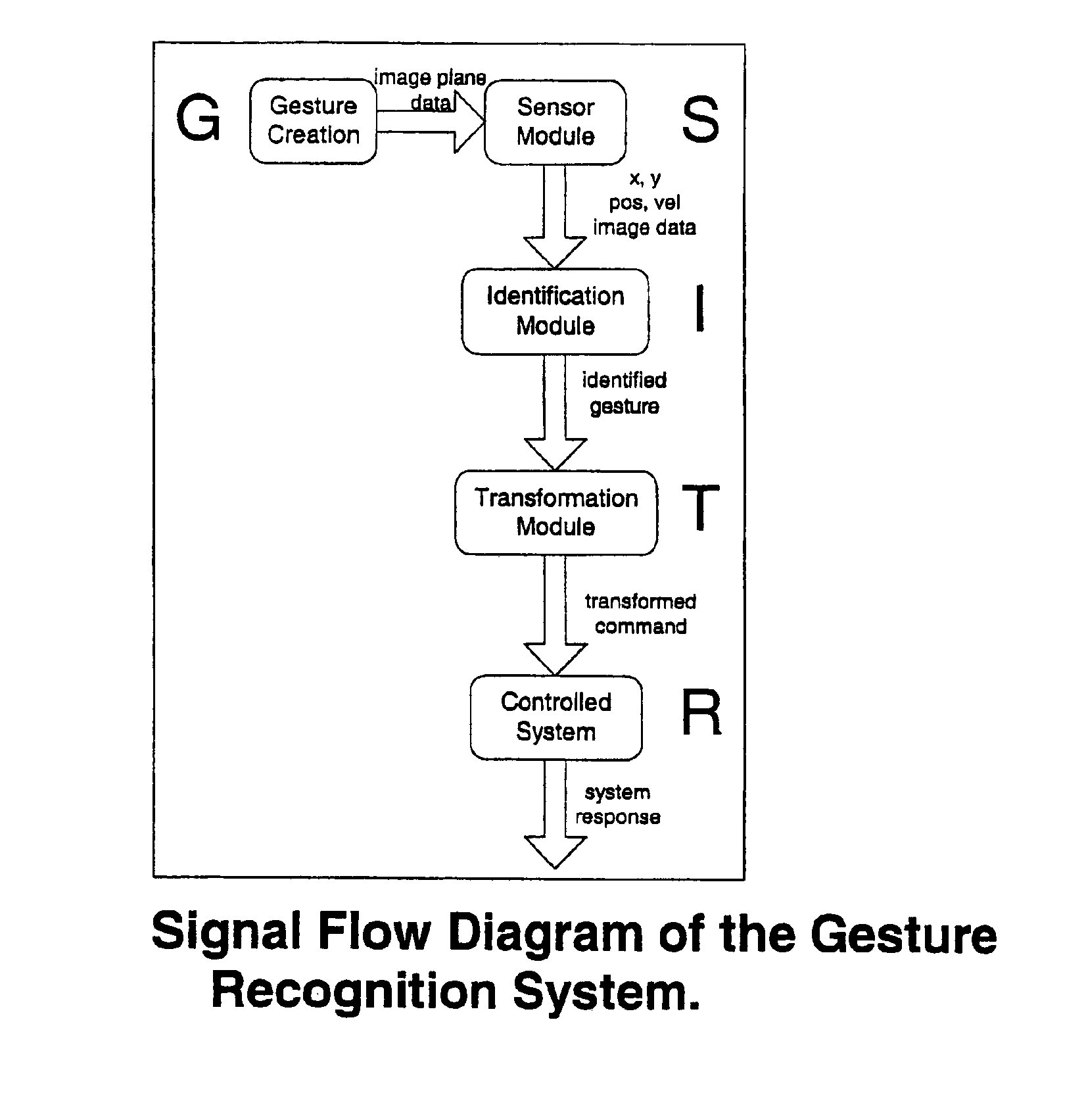
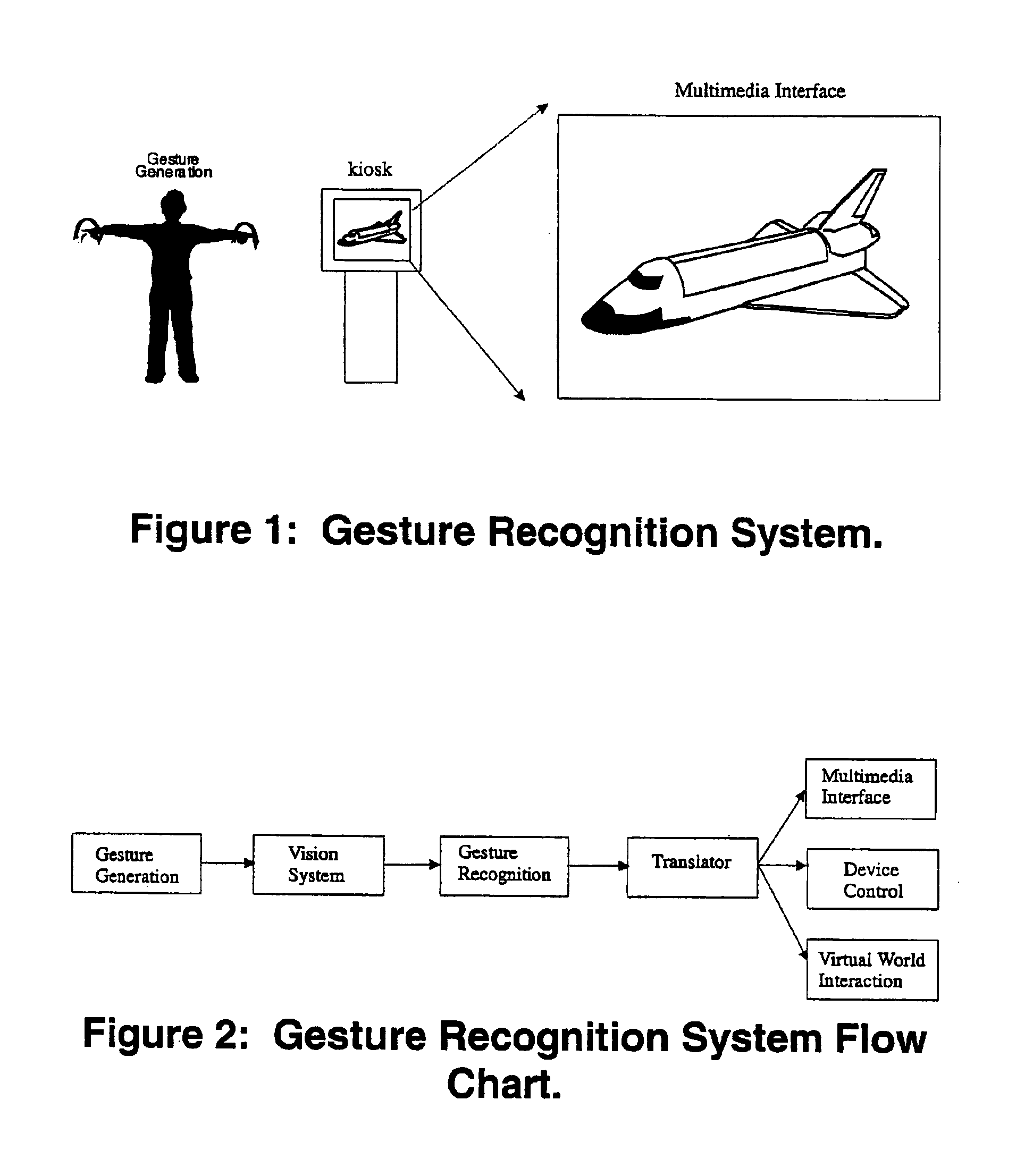
Gesture-controlled interfaces for self-service machines and other applications
InactiveUS6950534B2Input/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisApplication softwareHuman–computer interaction
A gesture recognition interface for use in controlling self-service machines and other devices is disclosed. A gesture is defined as motions and kinematic poses generated by humans, animals, or machines. Specific body features are tracked, and static and motion gestures are interpreted. Motion gestures are defined as a family of parametrically delimited oscillatory motions, modeled as a linear-in-parameters dynamic system with added geometric constraints to allow for real-time recognition using a small amount of memory and processing time. A linear least squares method is preferably used to determine the parameters which represent each gesture. Feature position measure is used in conjunction with a bank of predictor bins seeded with the gesture parameters, and the system determines which bin best fits the observed motion. Recognizing static pose gestures is preferably performed by localizing the body / object from the rest of the image, describing that object, and identifying that description. The disclosure details methods for gesture recognition, as well as the overall architecture for using gesture recognition to control of devices, including self-service machines.
Owner:JOLLY SEVEN SERIES 70 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
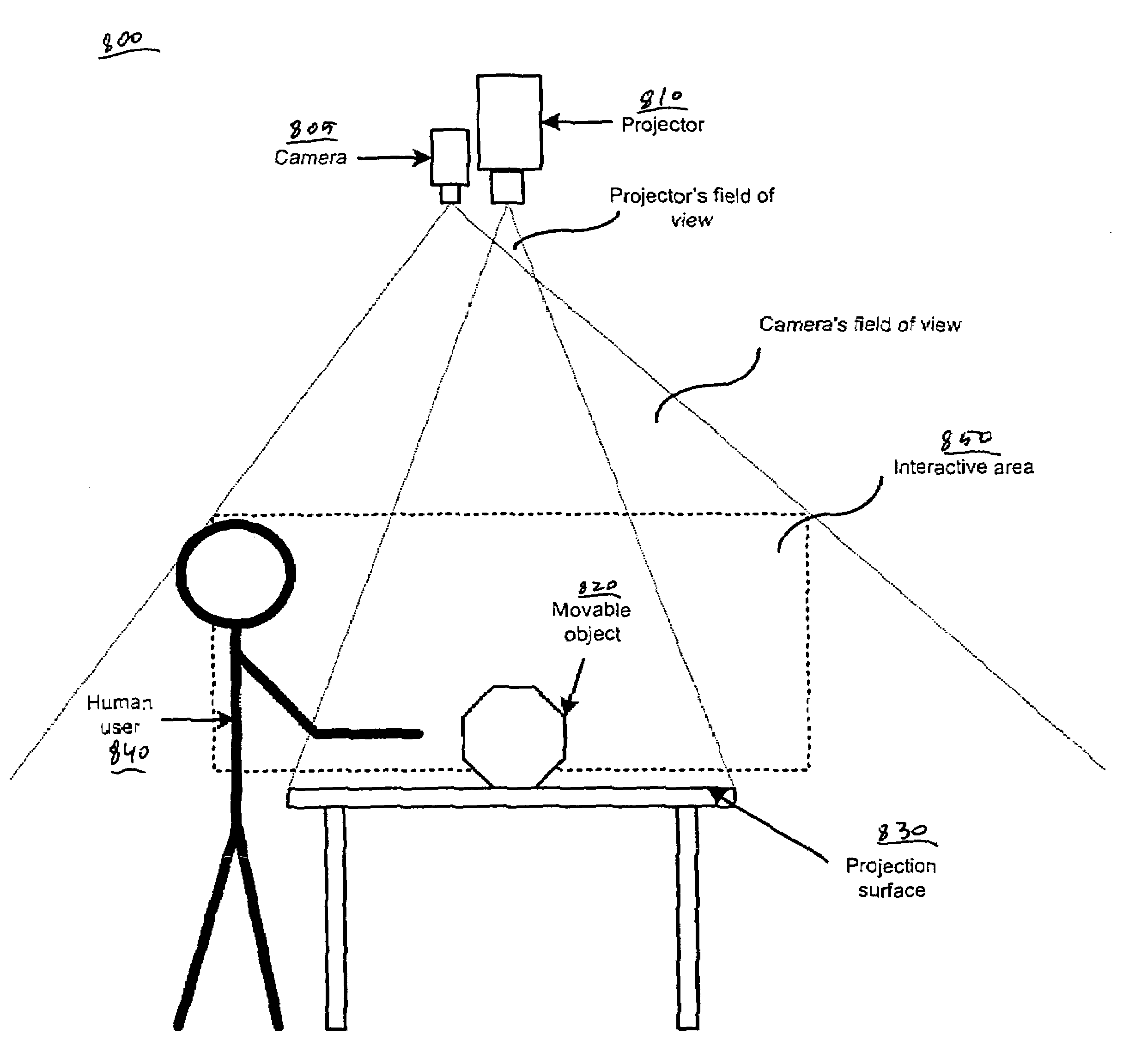
Interactive video display system
InactiveUS7348963B2Quality improvementHigh-quality informationImage enhancementImage analysisInteractive videoComputer graphics (images)
An interactive video display system. A display screen is for displaying a visual image for presentation to a user. A camera is for detecting an object in an interactive area located in front of the display screen, the camera operable to capture three-dimensional information about the object. A computer system is for directing the display screen to change the visual image in response to the object.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
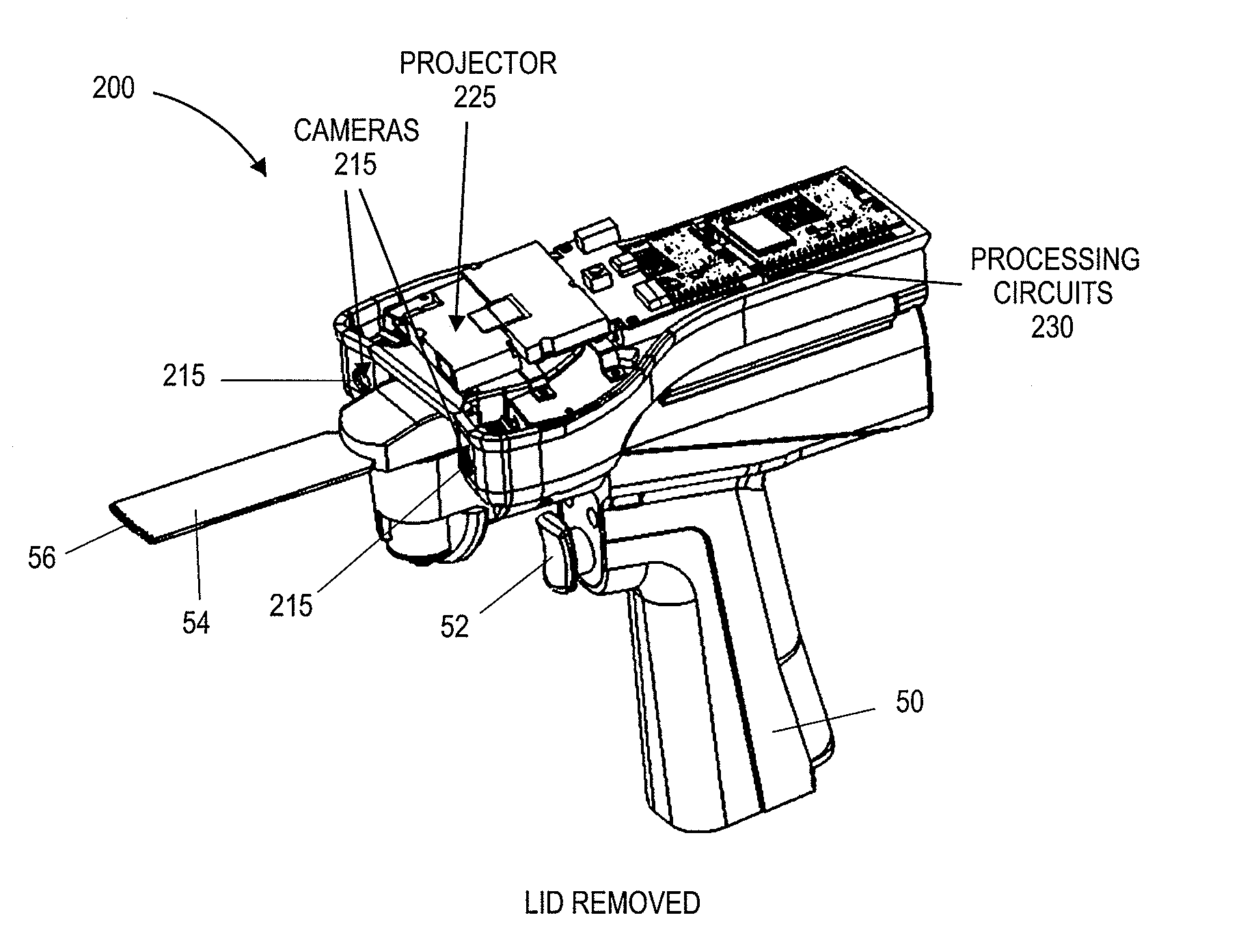
Semi-automatic dimensioning with imager on a portable device
A method of operating a dimensioning system to determine dimensional information for objects is disclosed. A number of images are acquired. Objects in at least one of the acquired images are computationally identified. One object represented in the at least one of the acquired images is computationally initially selected as a candidate for processing. An indication of the initially selected object is provided to a user. At least one user input indicative of an object selected for processing is received. Dimensional data for the object indicated by the received user input is computationally determined.
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
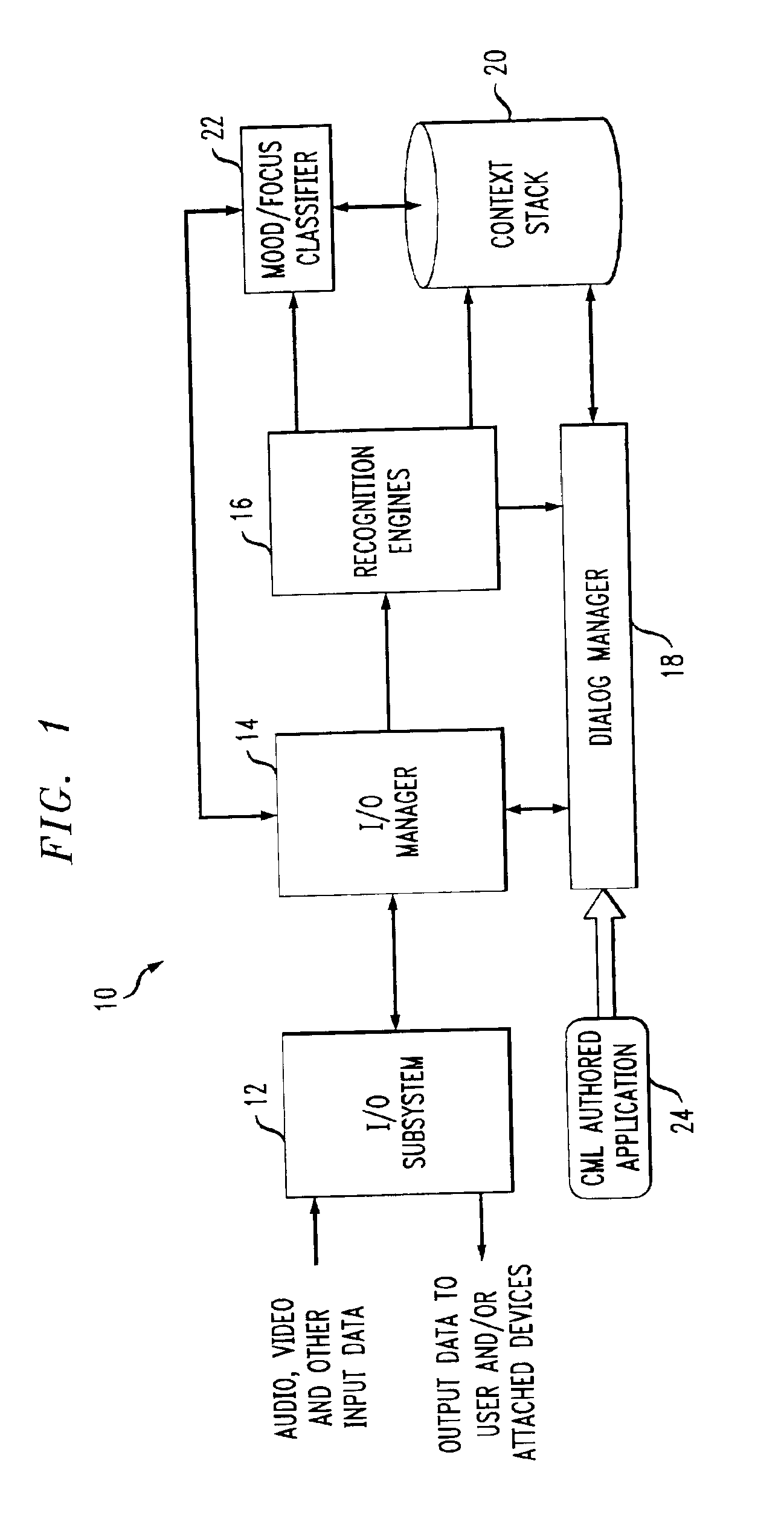
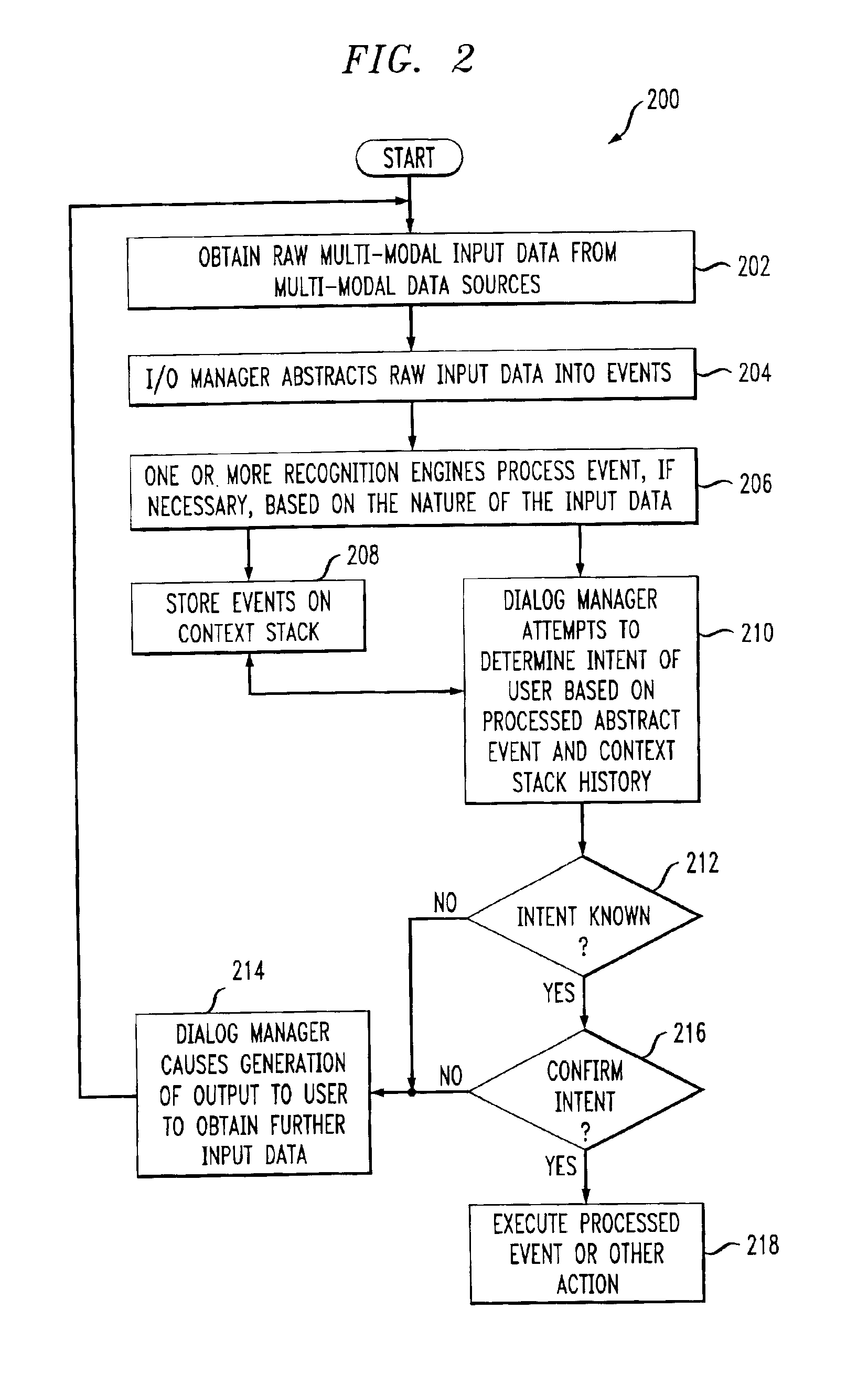
System and method for multi-modal focus detection, referential ambiguity resolution and mood classification using multi-modal input
InactiveUS6964023B2Effective conversational computing environmentInput/output for user-computer interactionData processing applicationsOperant conditioningComputer science
Owner:IBM CORP
Dimensioning system calibration systems and methods
Systems and methods of determining the volume and dimensions of a three-dimensional object using a dimensioning system are provided. The dimensioning system can include an image sensor, a non-transitory, machine-readable, storage, and a processor. The dimensioning system can select and fit a three-dimensional packaging wireframe model about each three-dimensional object located within a first point of view of the image sensor. Calibration is performed to calibrate between image sensors of the dimensioning system and those of the imaging system. Calibration may occur pre-run time, in a calibration mode or period. Calibration may occur during a routine. Calibration may be automatically triggered on detection of a coupling between the dimensioning and the imaging systems.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
Patient selectable joint arthroplasty devices and surgical tools facilitating increased accuracy, speed and simplicity in performing total and partial joint arthroplasty
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
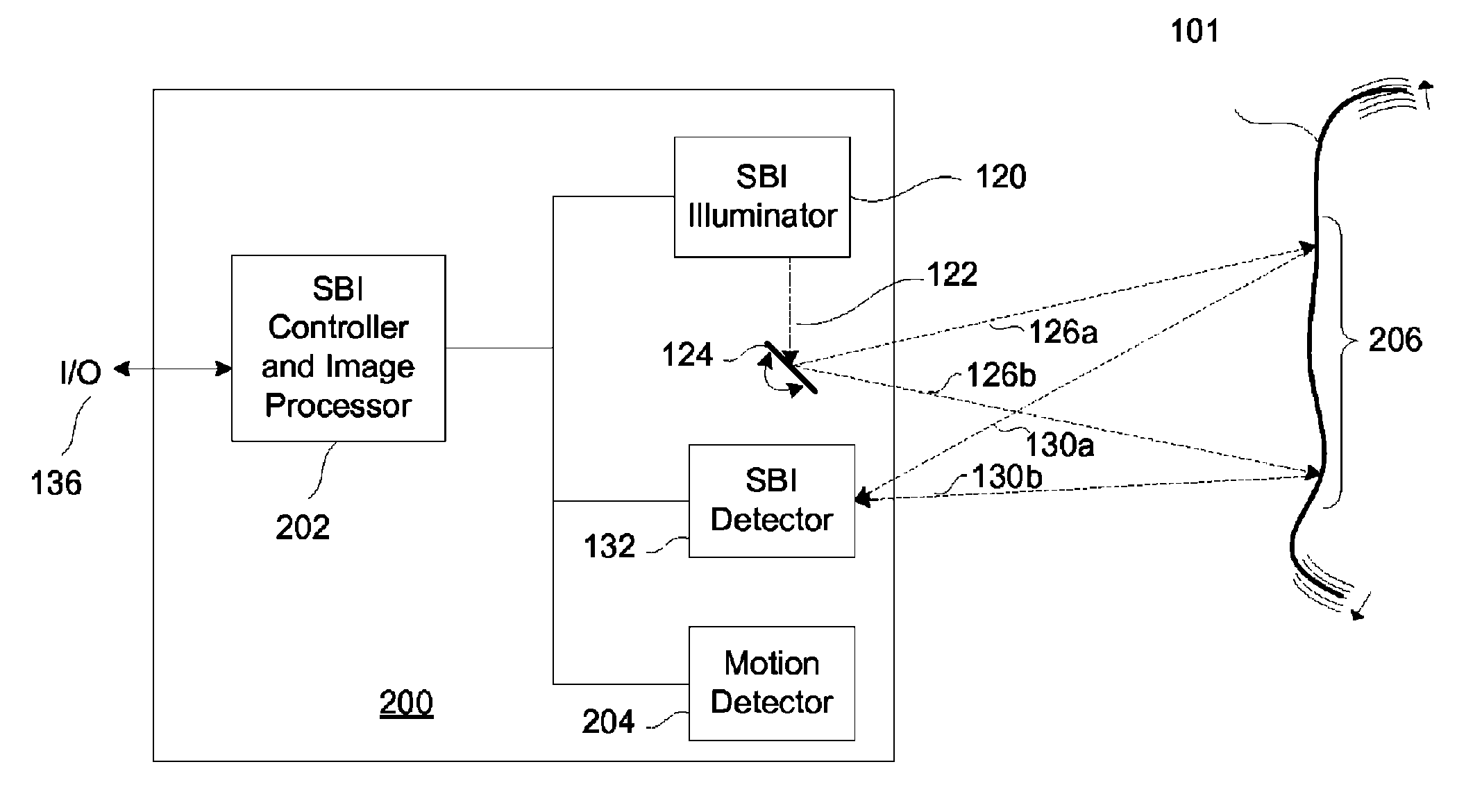
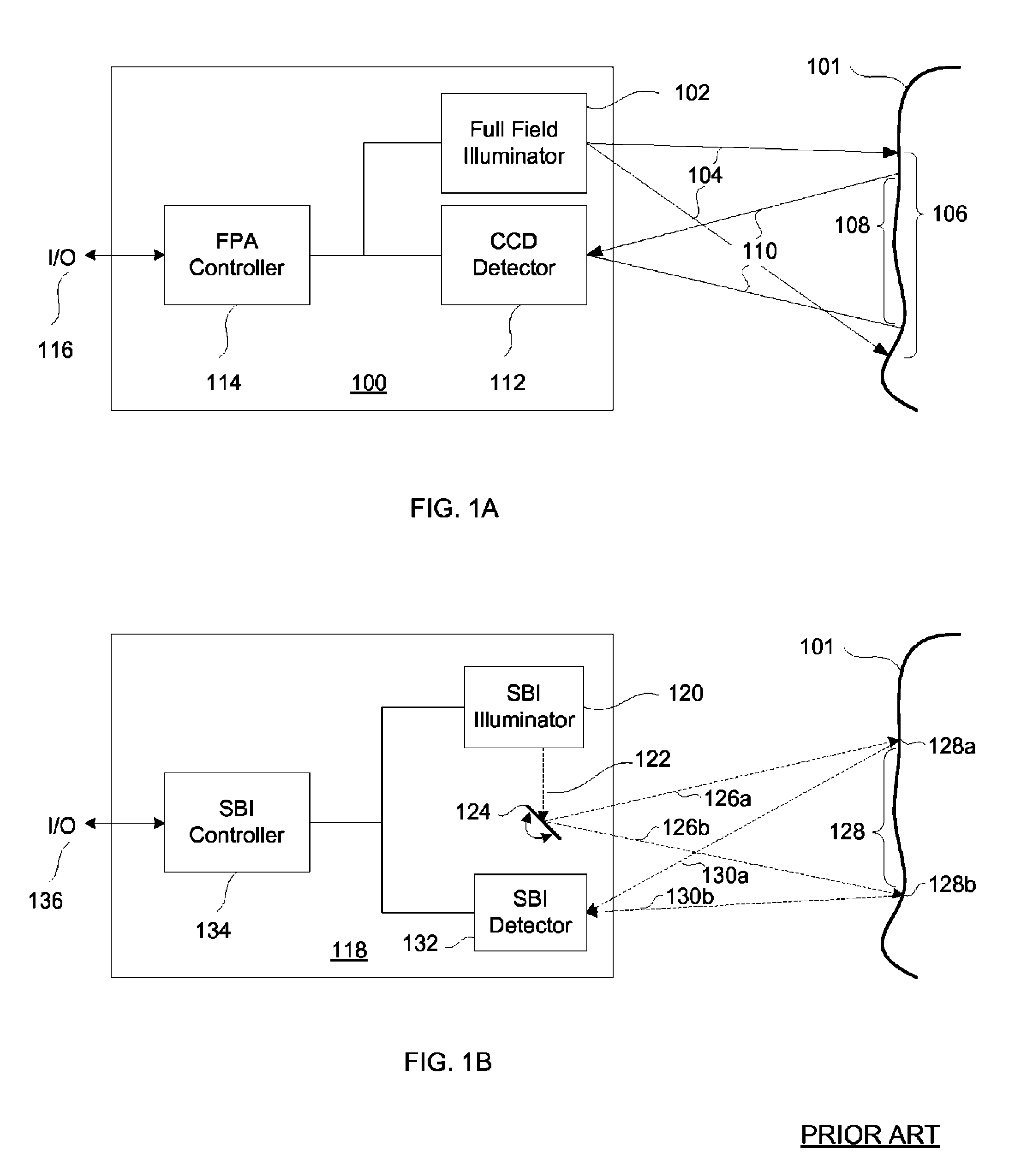
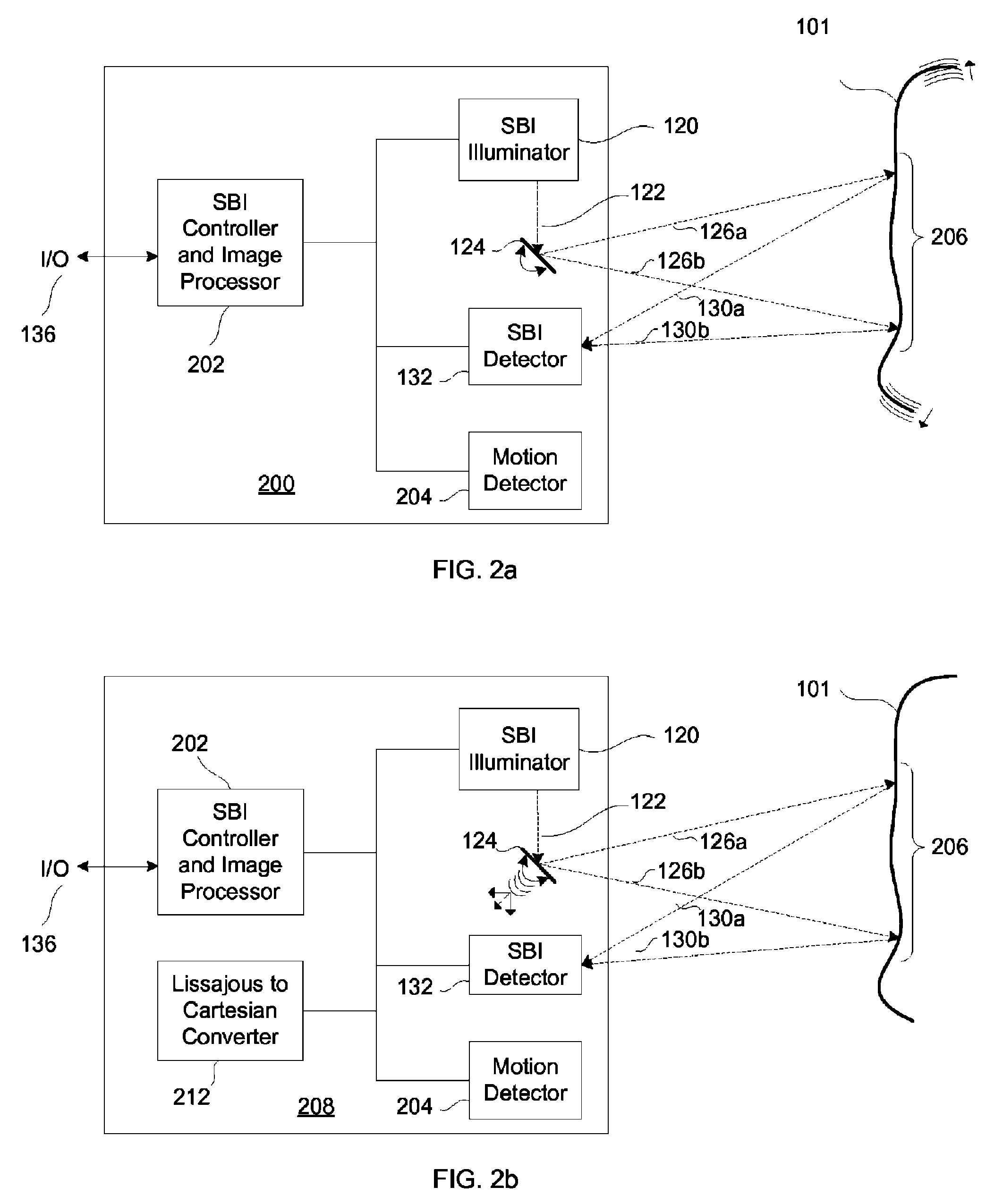
SBI motion artifact removal apparatus and method
InactiveUS7982776B2Reduce generationReduce image resolutionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage resolutionSubject matter
A system, method and apparatus for eliminating image tearing effects and other visual artifacts perceived when scanning moving subject matter with a scanned beam imaging device. The system, method and apparatus uses a motion detection means in conjunction with an image processor to alter the native image to one without image tearing or other visual artifacts. The image processor monitors the motion detection means and reduces the image resolution or translates portions of the imaged subject matter in response to the detected motion.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
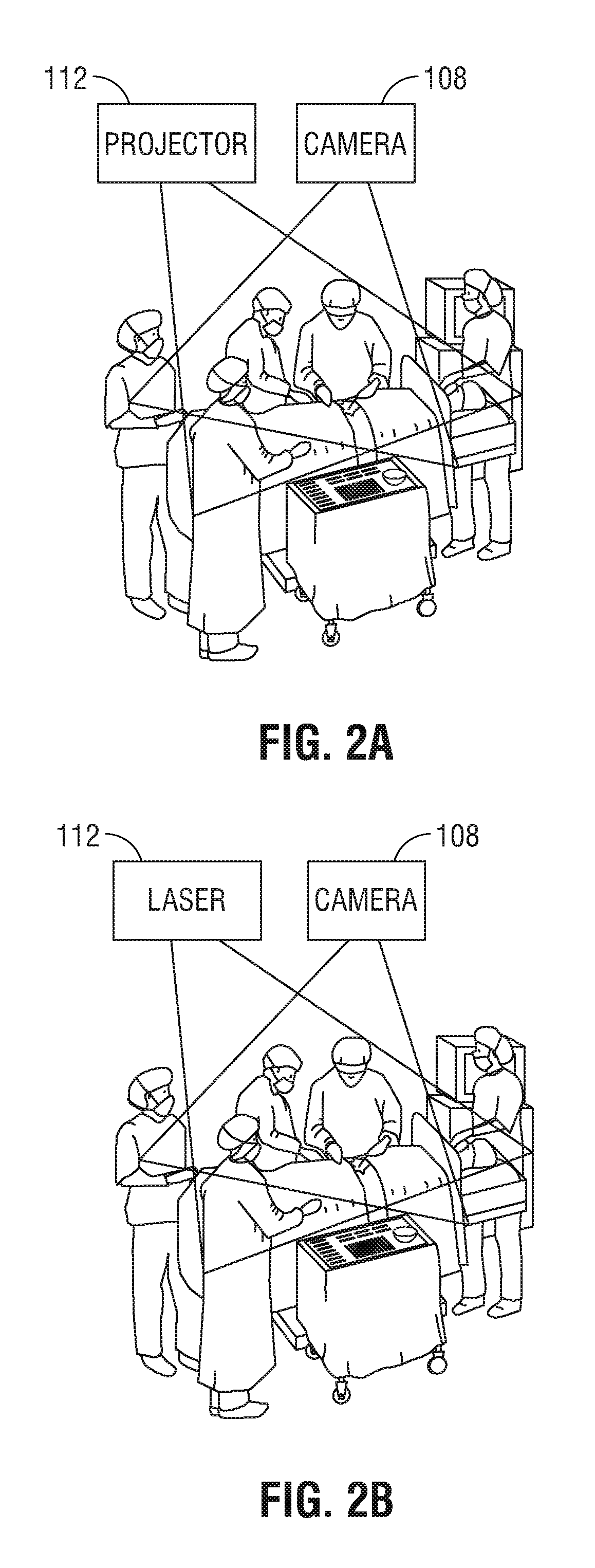
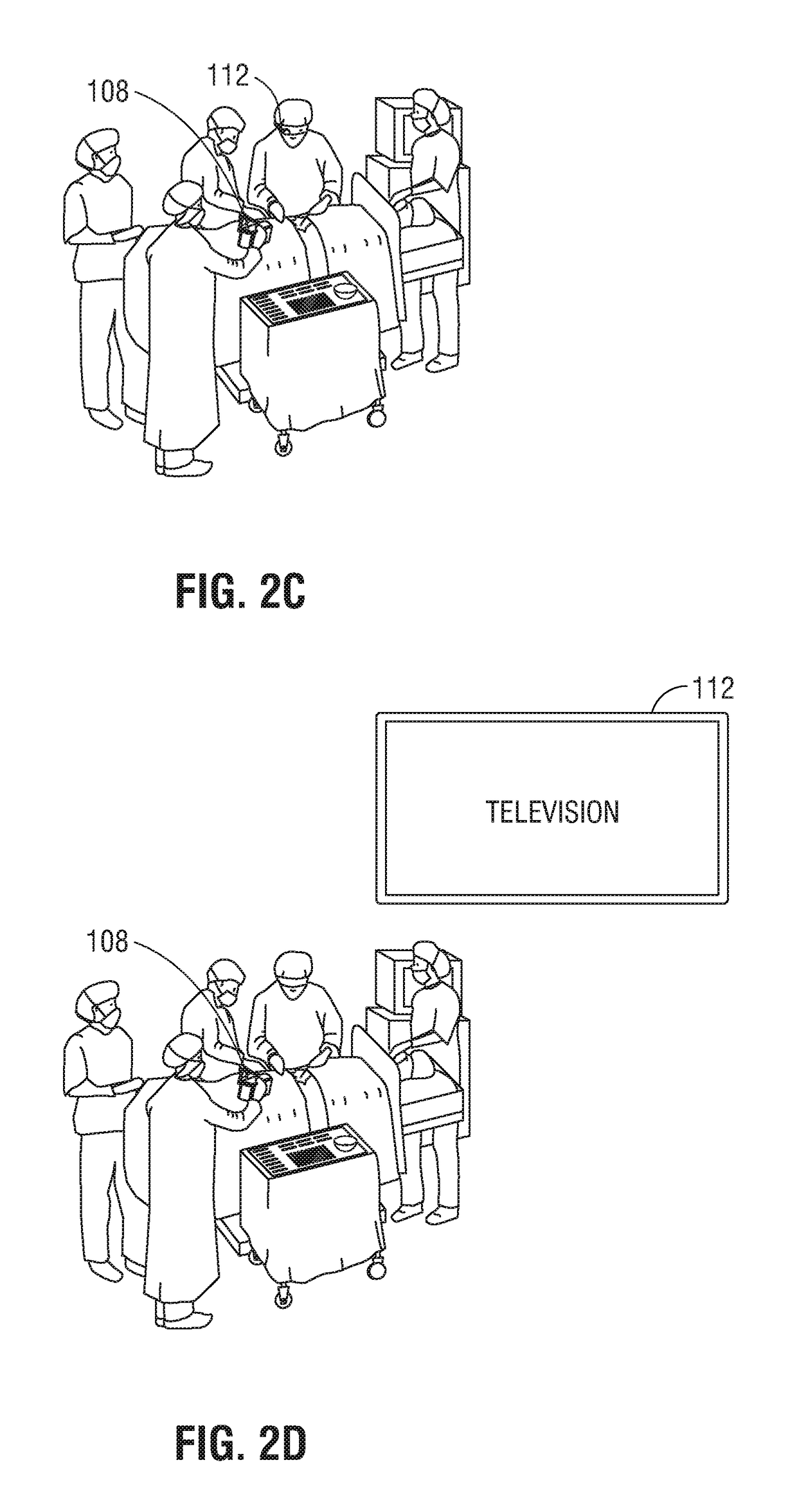
Augmented surgical reality environment
The present disclosure is directed to an augmented reality surgical system for viewing an augmented image of a region of interest during a surgical procedure. The system includes an image capture device that captures an image of the region of interest. A controller receives the image and applies at least one image processing filter to the image. The image processing filter includes a spatial decomposition filter that decomposes the image into spatial frequency bands. A temporal filter is applied to the spatial frequency bands to generate temporally filtered bands. An adder adds each band spatial frequency band to a corresponding temporally filtered band to generate augmented bands. A reconstruction filter generates an augmented image by collapsing the augmented bands. A display displays the augmented image to a user.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
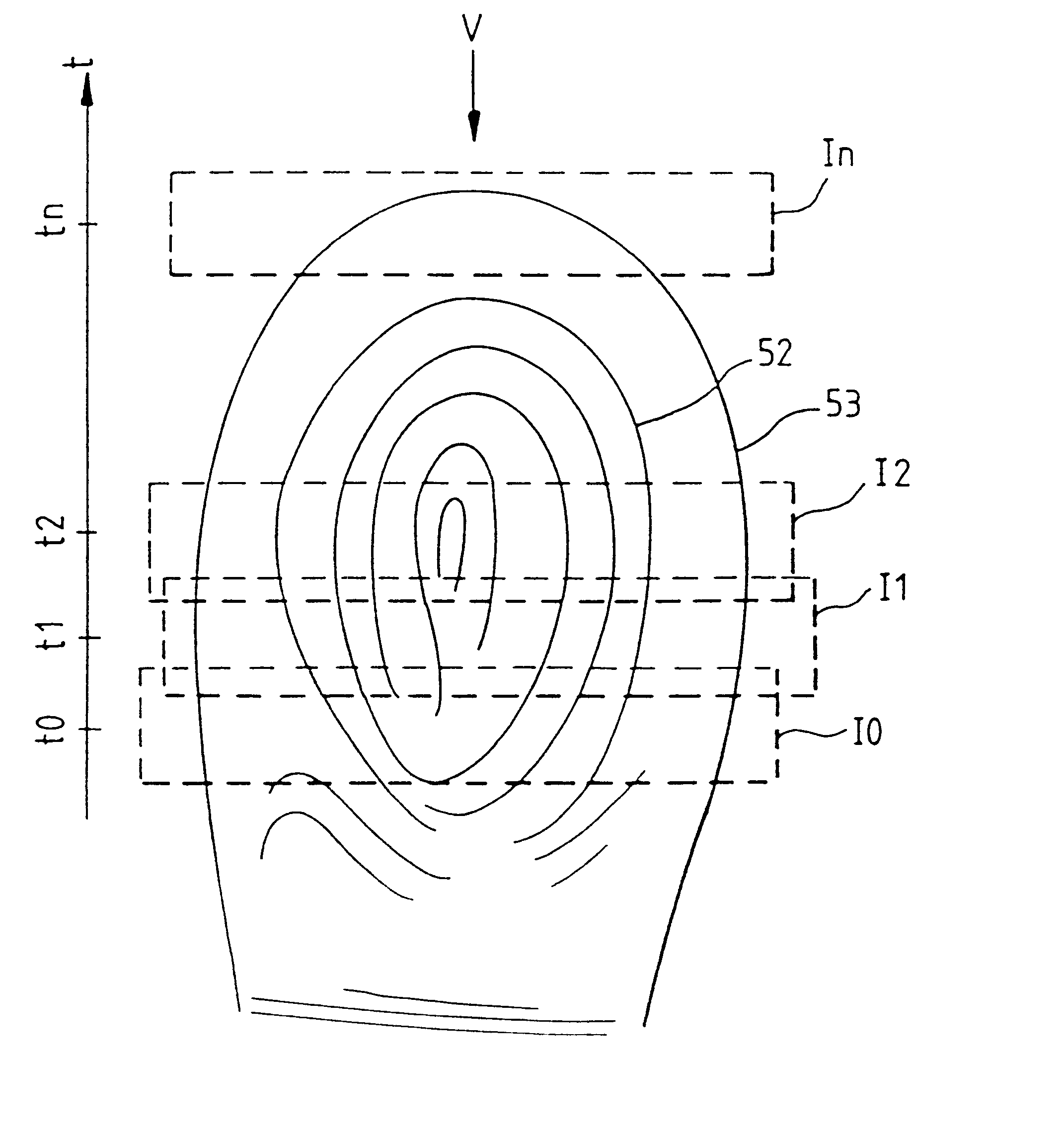
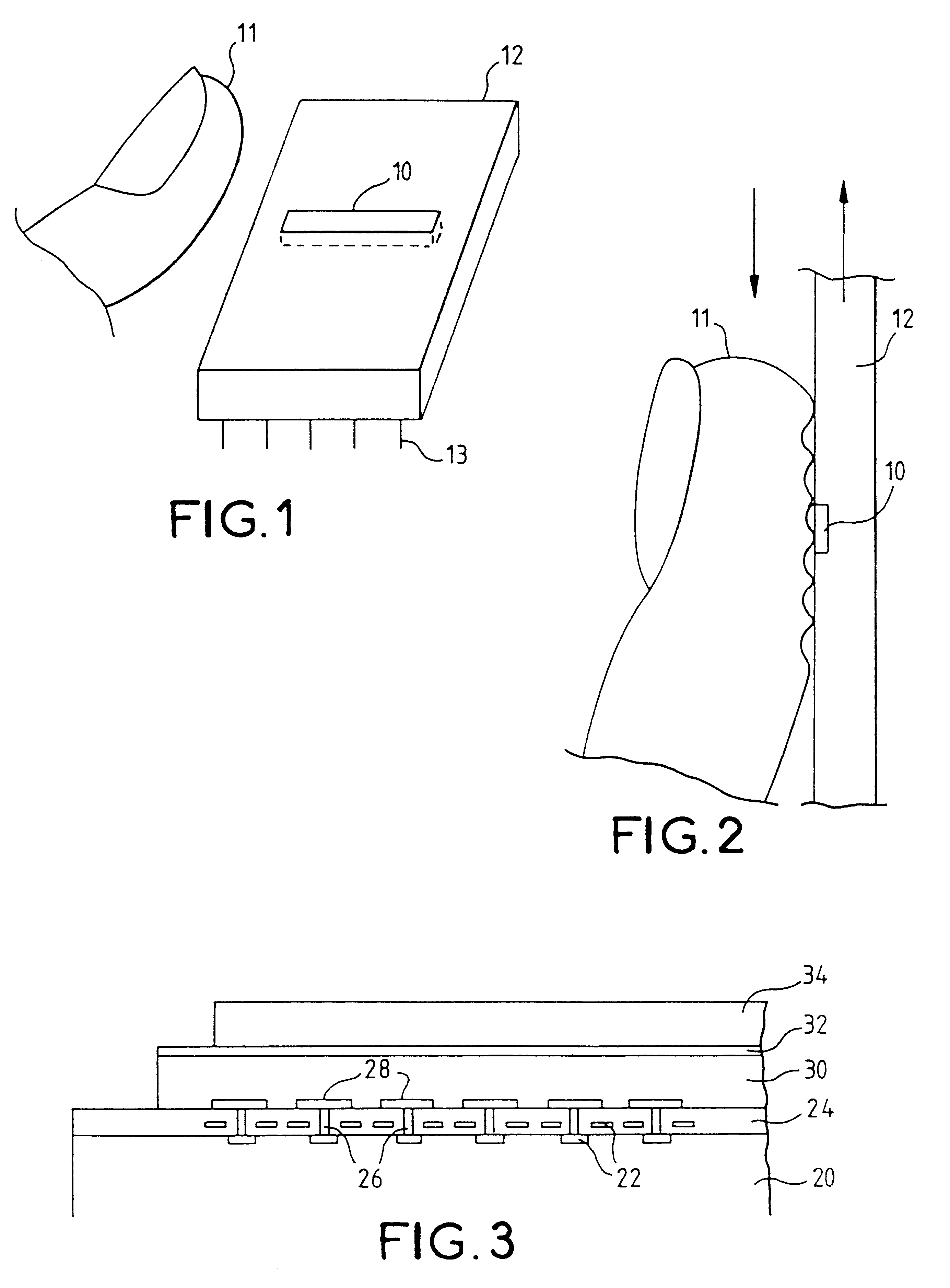
Fingerprint-reading system
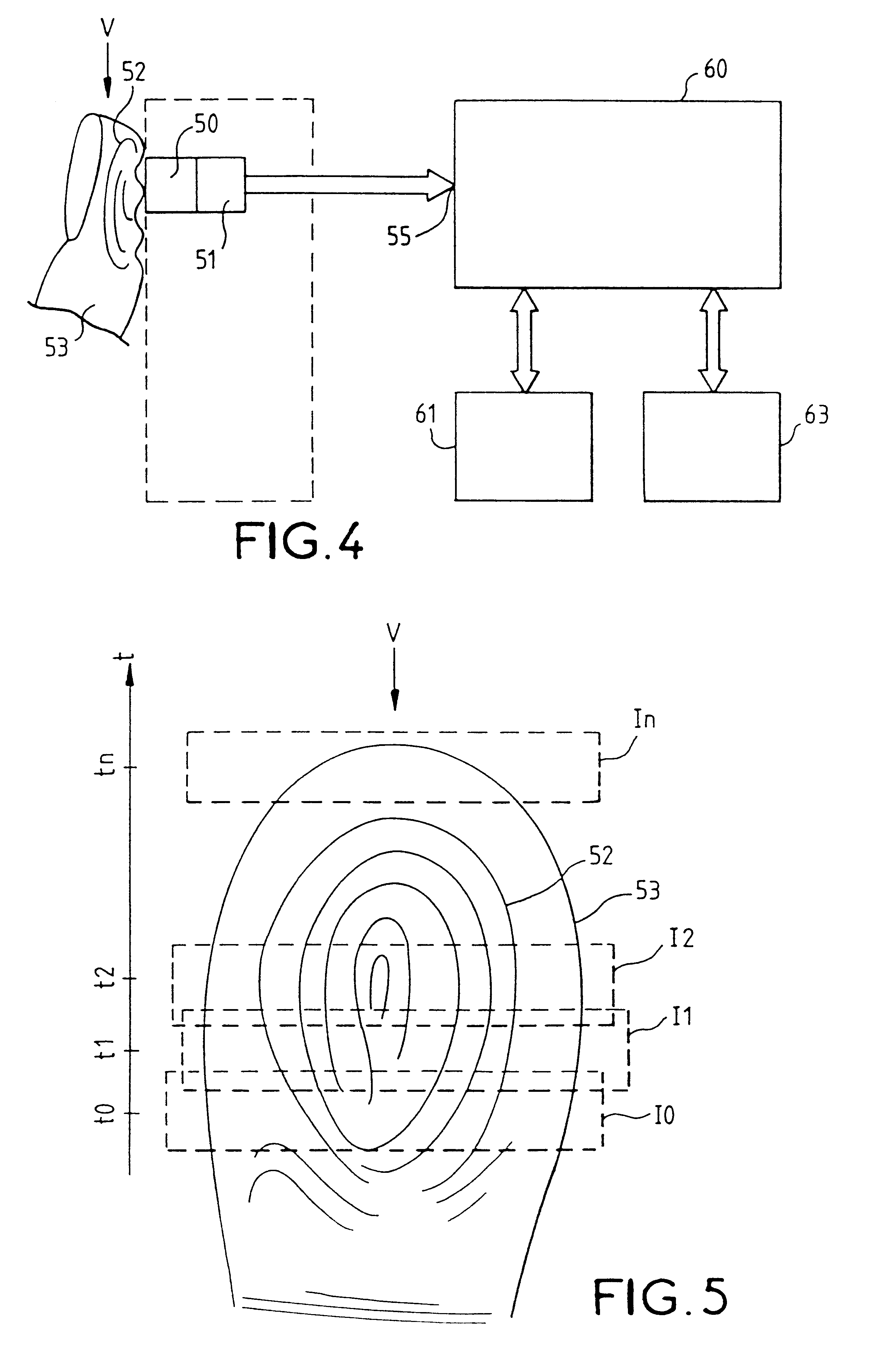
InactiveUS6289114B1Image analysisElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsEffective surfaceRelative motion
A fingerprint-reading system includes a fingerprint sensor having an active surface sensitive to the pressure and temperature of a finger. The surface area of this sensor is far smaller than the surface area of the fingerprint to be read. The reading is done when the sensor and the finger are in contact and in a relative motion of sliding of the sensor and the finger with respect to each other. The system reconstitutes a complete image of the fingerprint from the partial images given by the sensor during this motion.
Owner:APPLE INC
Object matching for tracking, indexing, and search
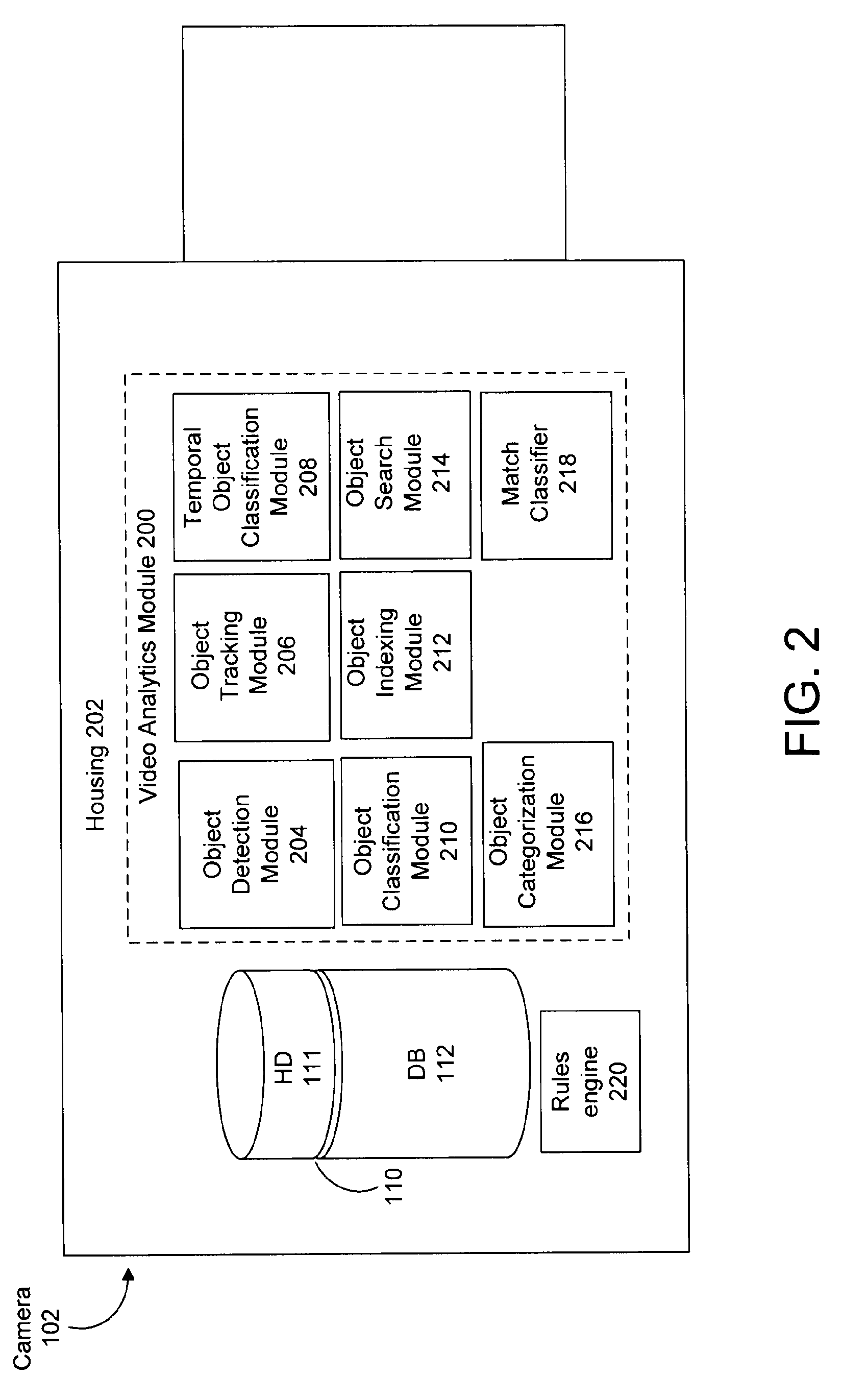
A camera system comprises an image capturing device, object detection module, object tracking module, and match classifier. The object detection module receives image data and detects objects appearing in one or more of the images. The object tracking module temporally associates instances of a first object detected in a first group of the images. The first object has a first signature representing features of the first object. The match classifier matches object instances by analyzing data derived from the first signature of the first object and a second signature of a second object detected in a second image. The second signature represents features of the second object derived from the second image. The match classifier determine whether the second signature matches the first signature. A training process automatically configures the match classifier using a set of possible object features.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
An articulated structured light based-laparoscope
The present invention provides a structured-light based system for providing a 3D image of at least one object within a field of view within a body cavity, comprising: a. An endoscope; b. at least one camera located in the endoscope's proximal end, configured to real-time provide at least one 2D image of at least a portion of said field of view by means of said at least one lens; c. a light source, configured to real-time illuminate at least a portion of said at least one object within at least a portion of said field of view with at least one time and space varying predetermined light pattern; and, d. a sensor configured to detect light reflected from said field of view; e. a computer program which, when executed by data processing apparatus, is configured to generate a 3D image of said field of view.
Owner:TRANSENTERIX EURO SARL
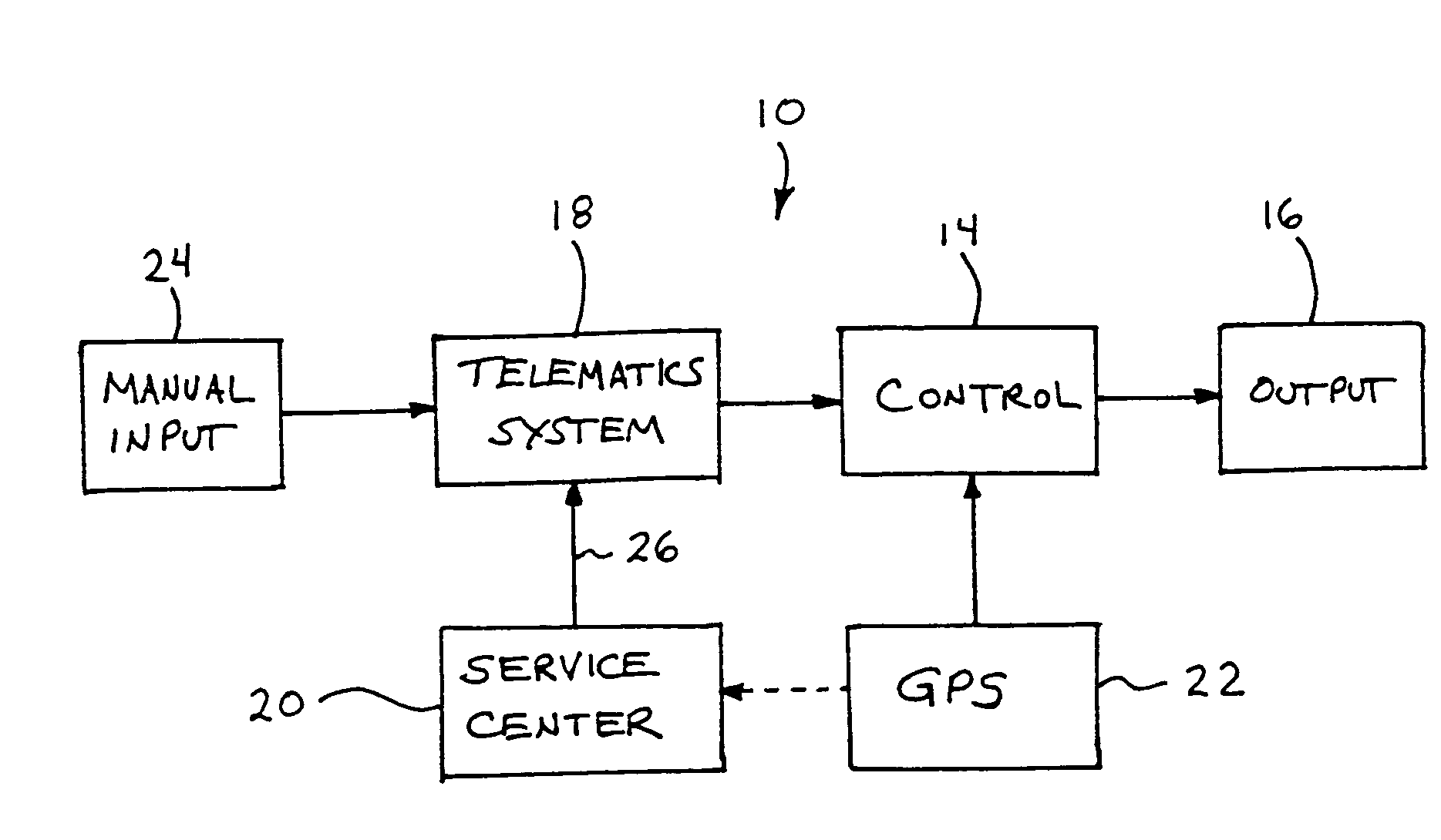
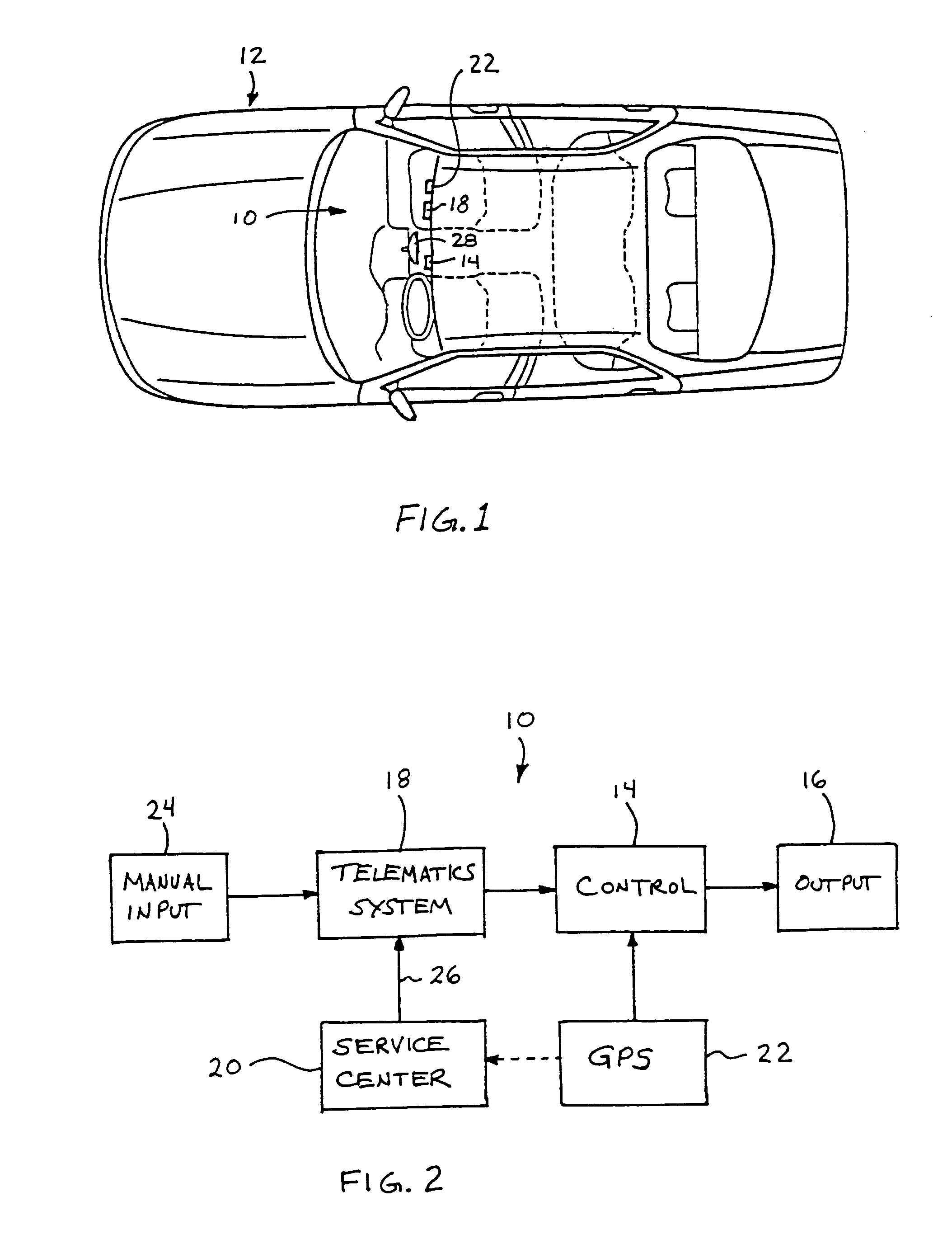
Vehicle navigation system for use with a telematics system
InactiveUS7167796B2Low costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDriver/operatorService provision
A navigation system for a vehicle includes a vehicle-based telematics system, a vehicle-based global positioning system and a control. The telematics system is operable to receive a user input from a driver of the vehicle and to download directional information from an external service provider to the control in response to the user input and an initial geographic position of the vehicle. The directional information comprises at least two instructions with each of the instructions being coded or associated with or linked to a respective geographic location. The control is operable to provide an output corresponding to each of the instructions in response to a current actual geographic position of the vehicle. The control is operable to provide each instruction only when the then current actual geographic position of the vehicle at least generally corresponds to the particular geographic location associated with the instruction.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com