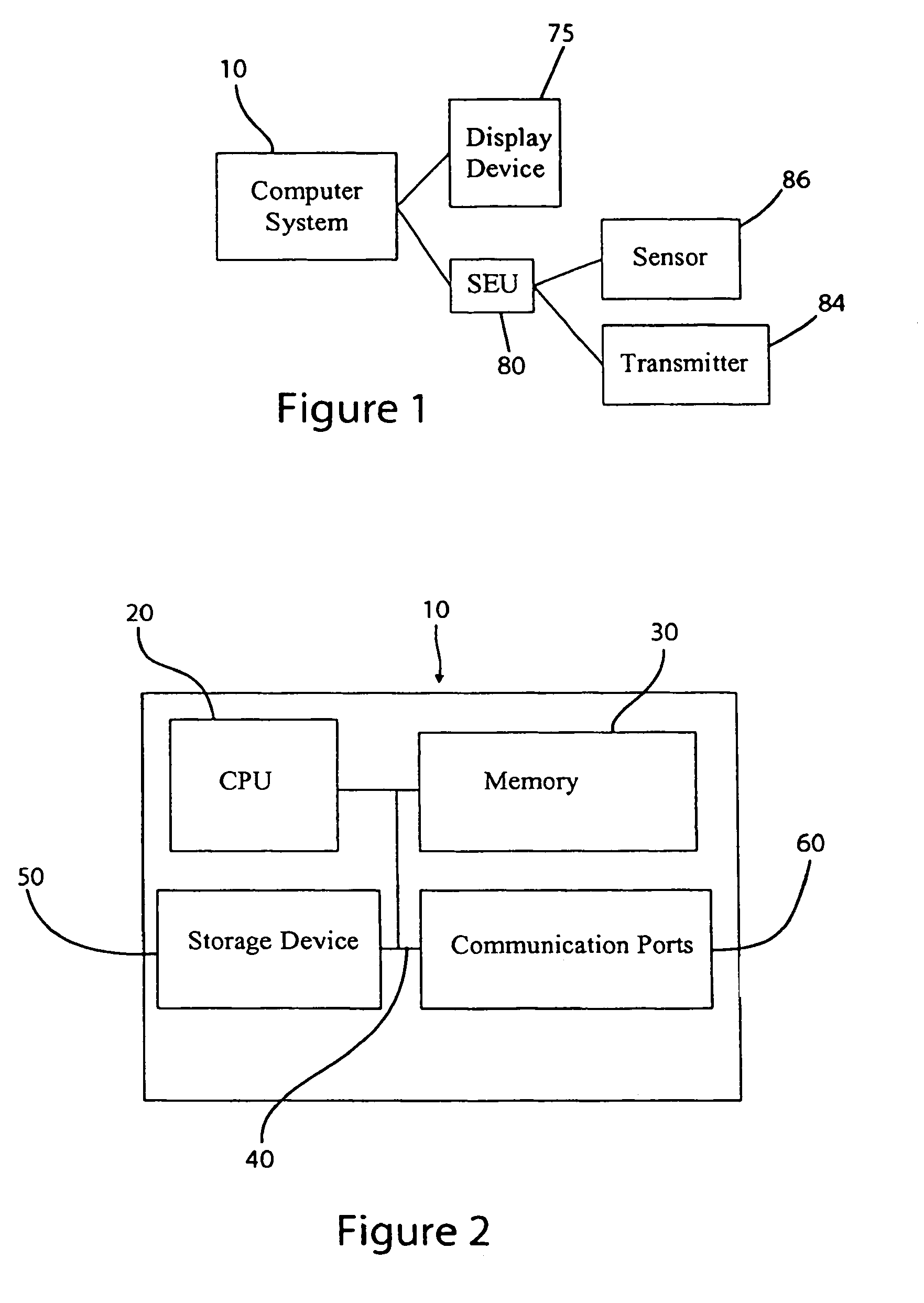
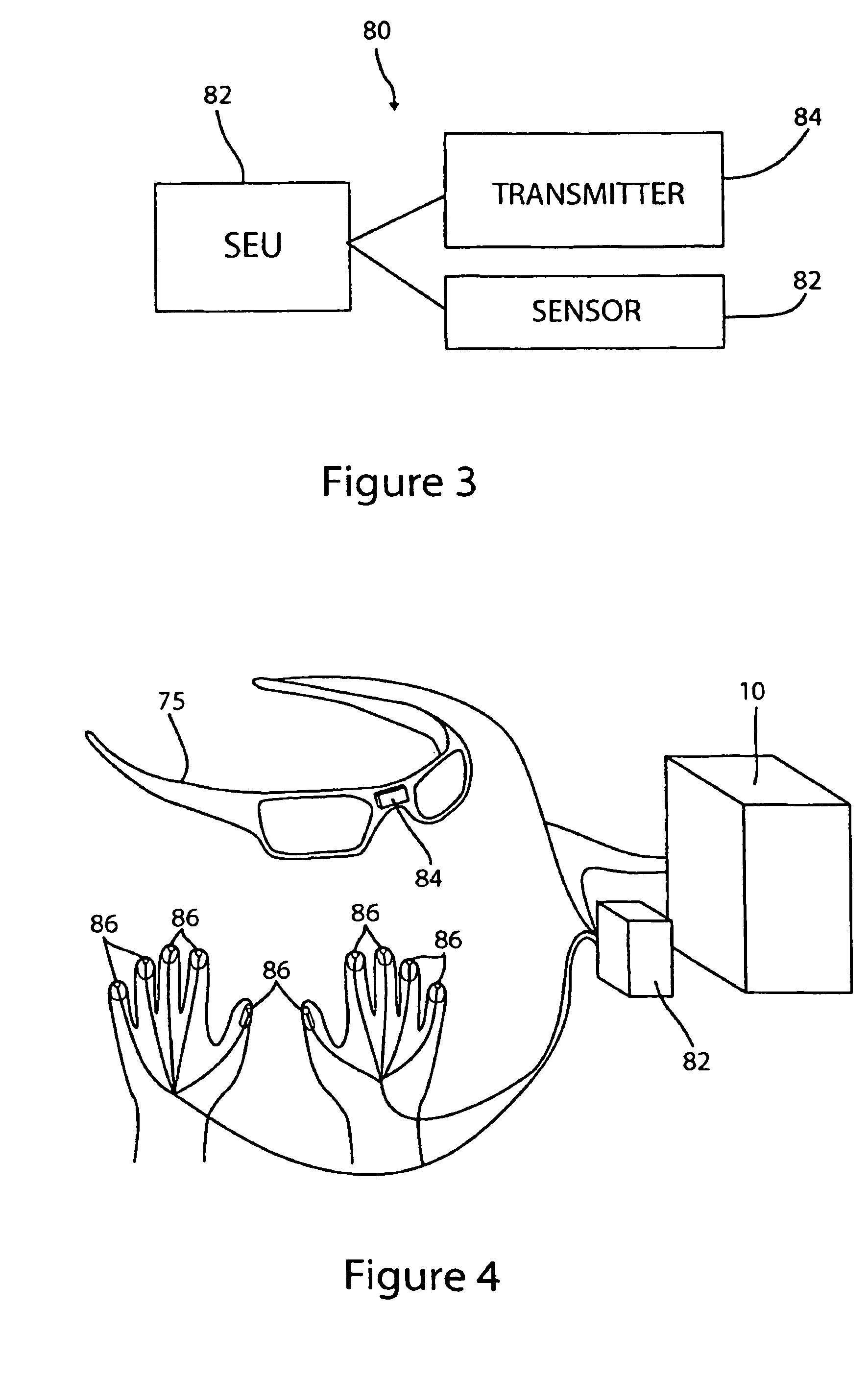
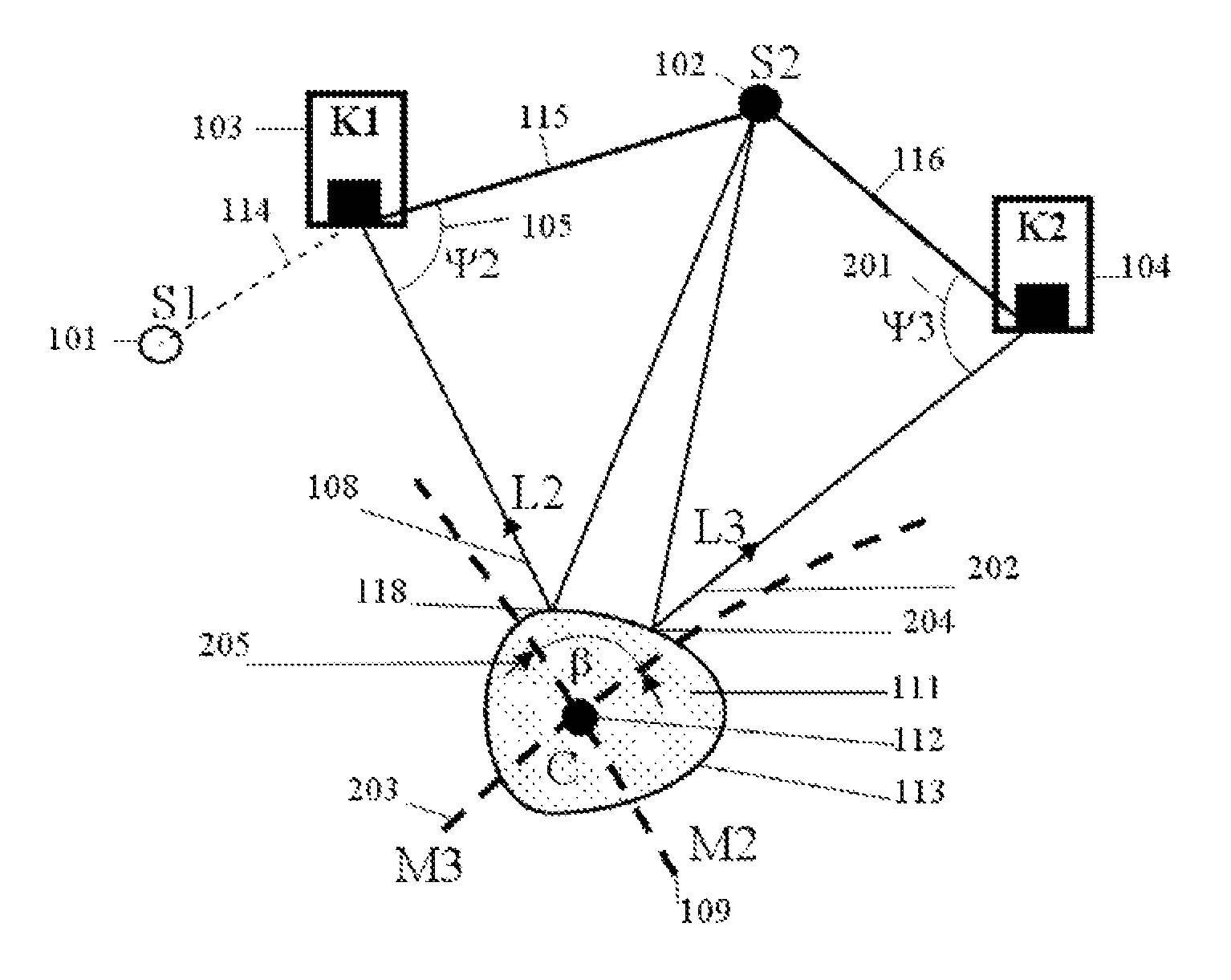
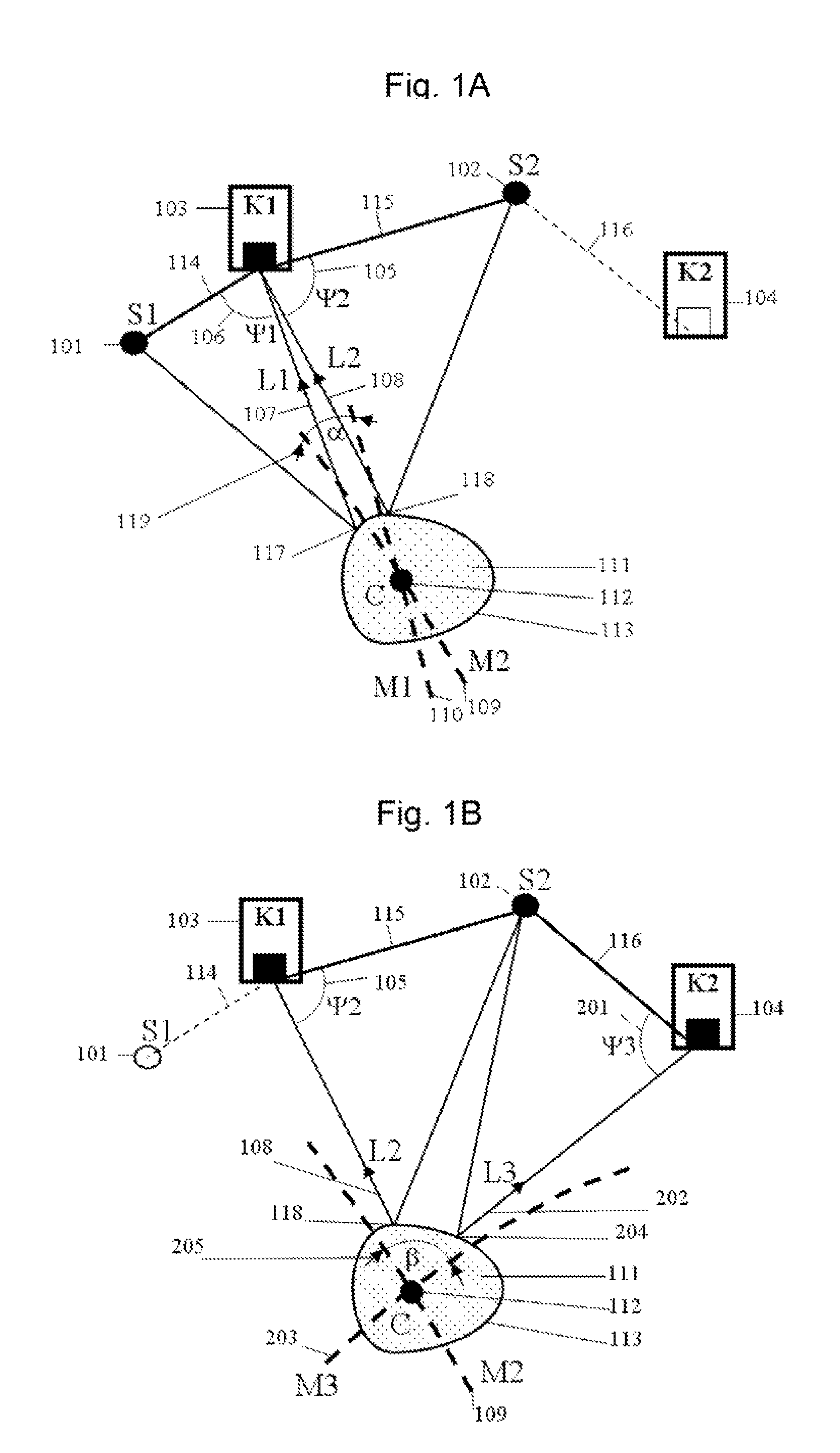
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1478 results about "Single camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
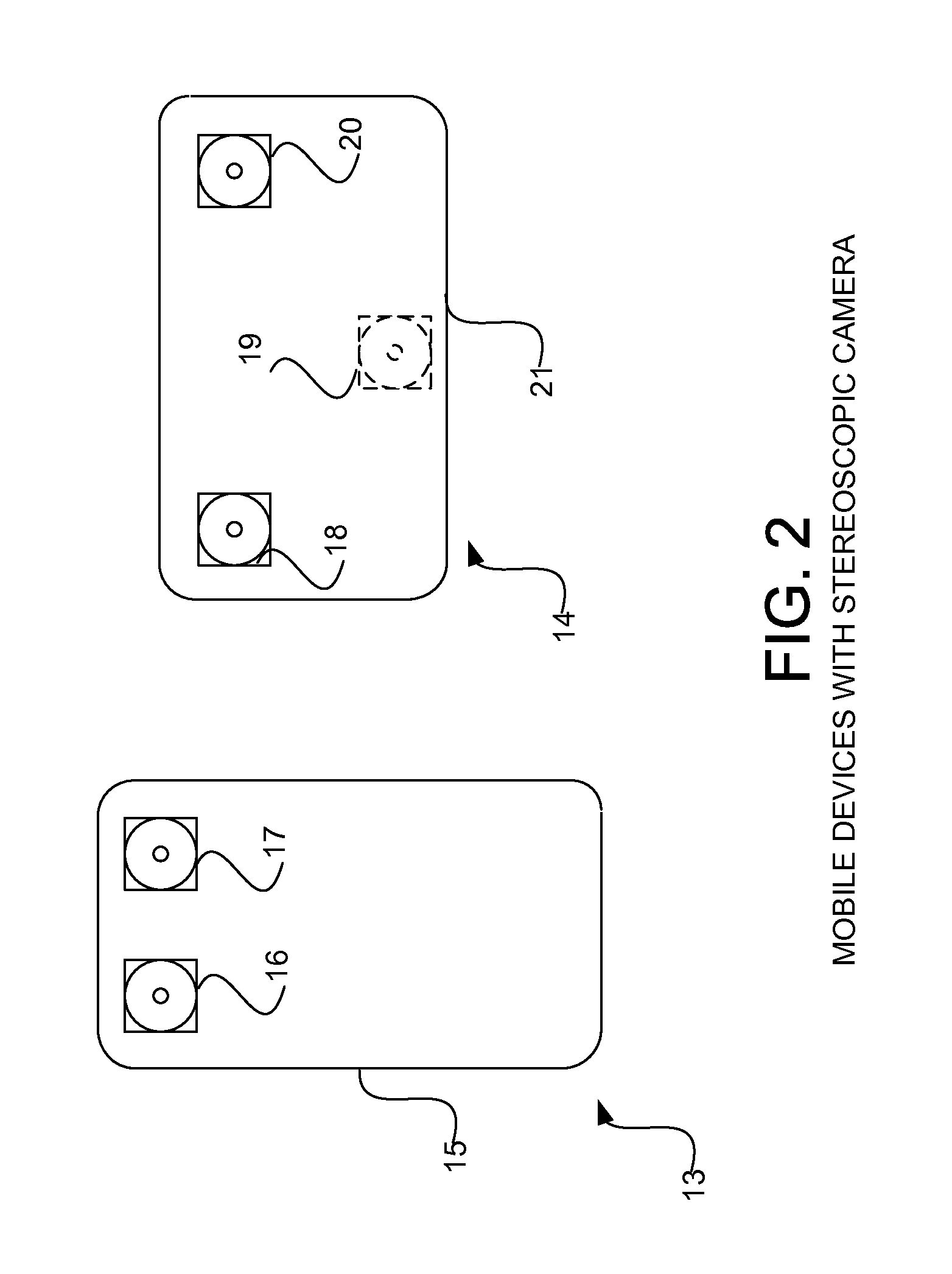
The single-camera setup, or single-camera mode of production, also known as Portable Single Camera, is a method of filmmaking and video production.
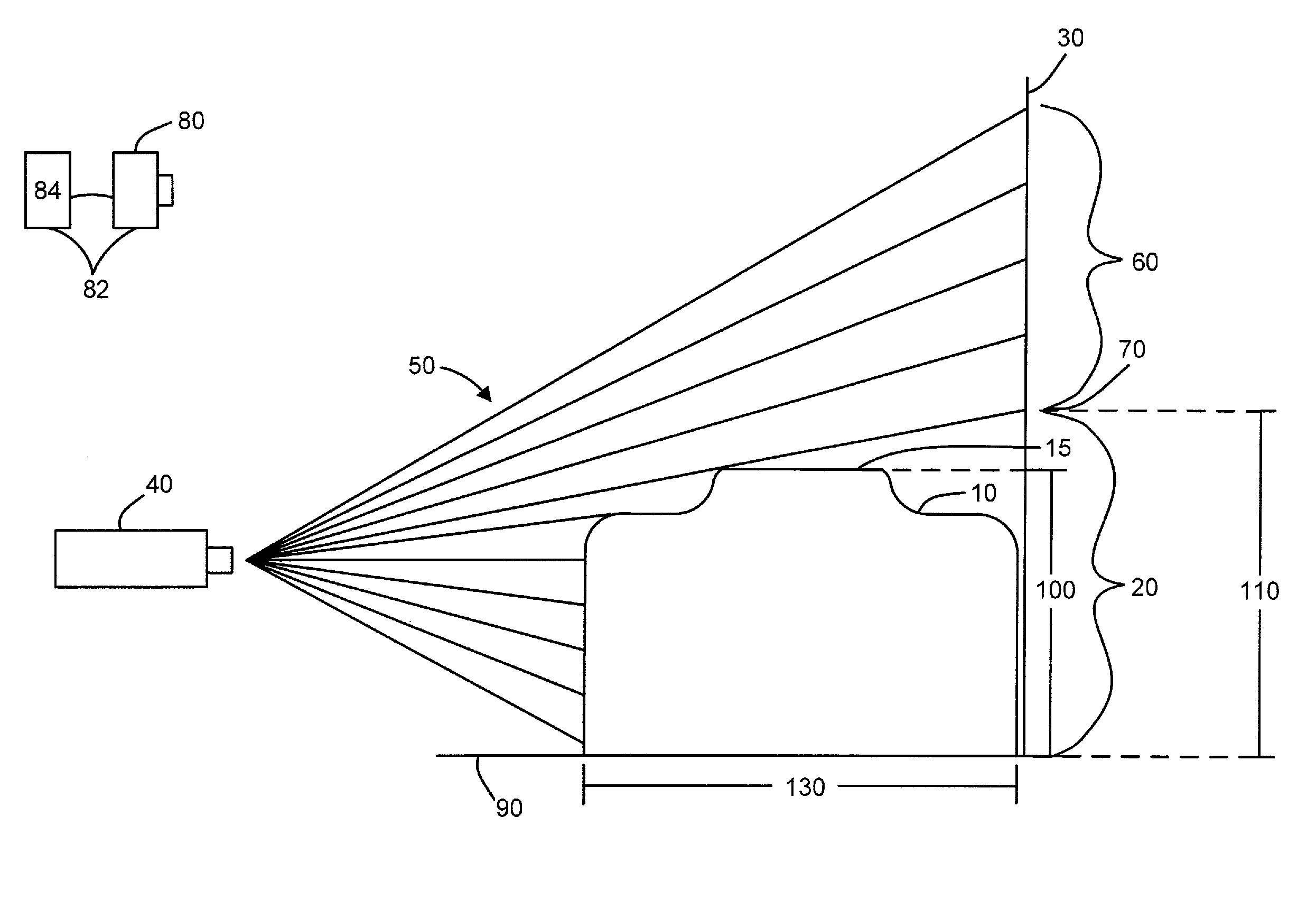
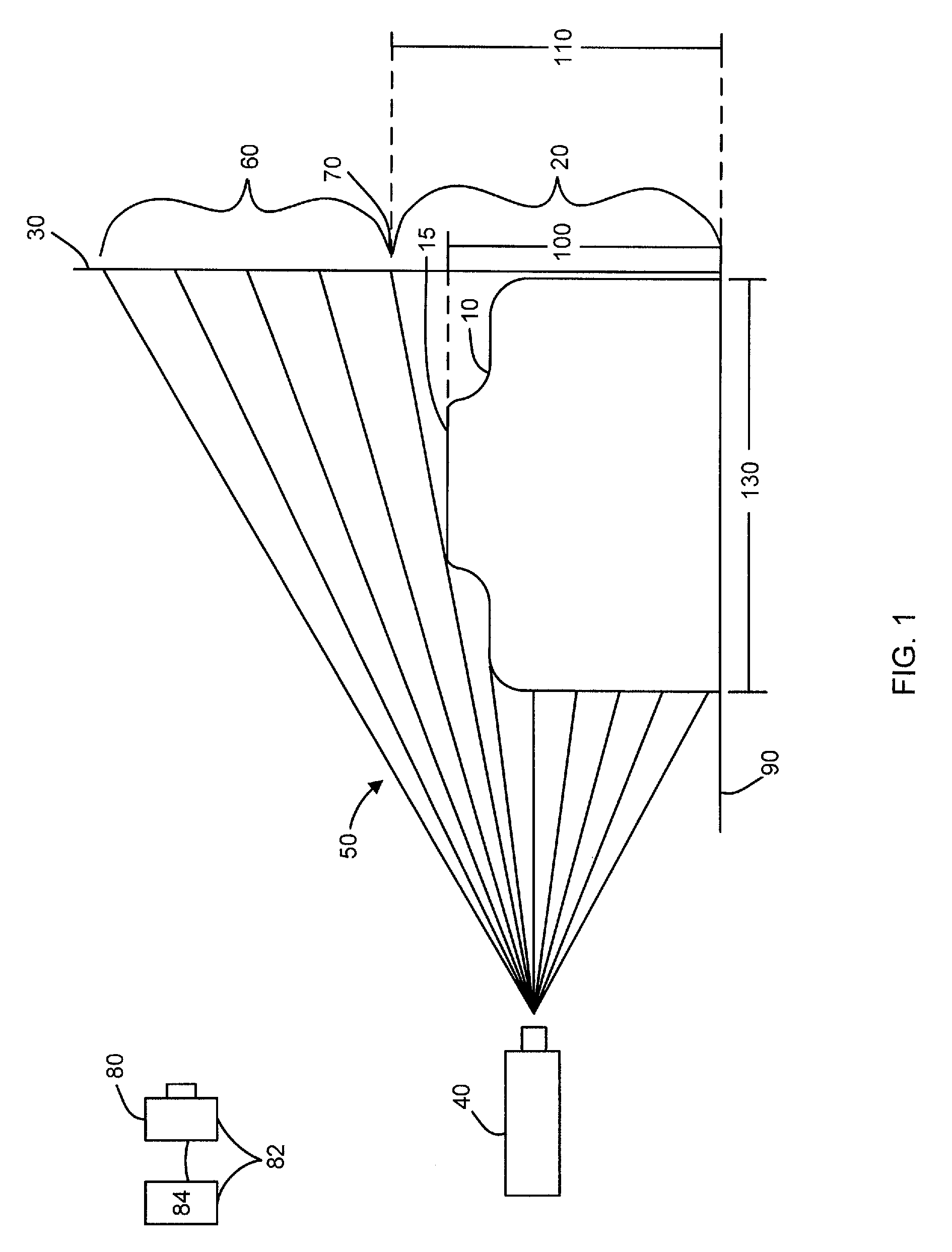
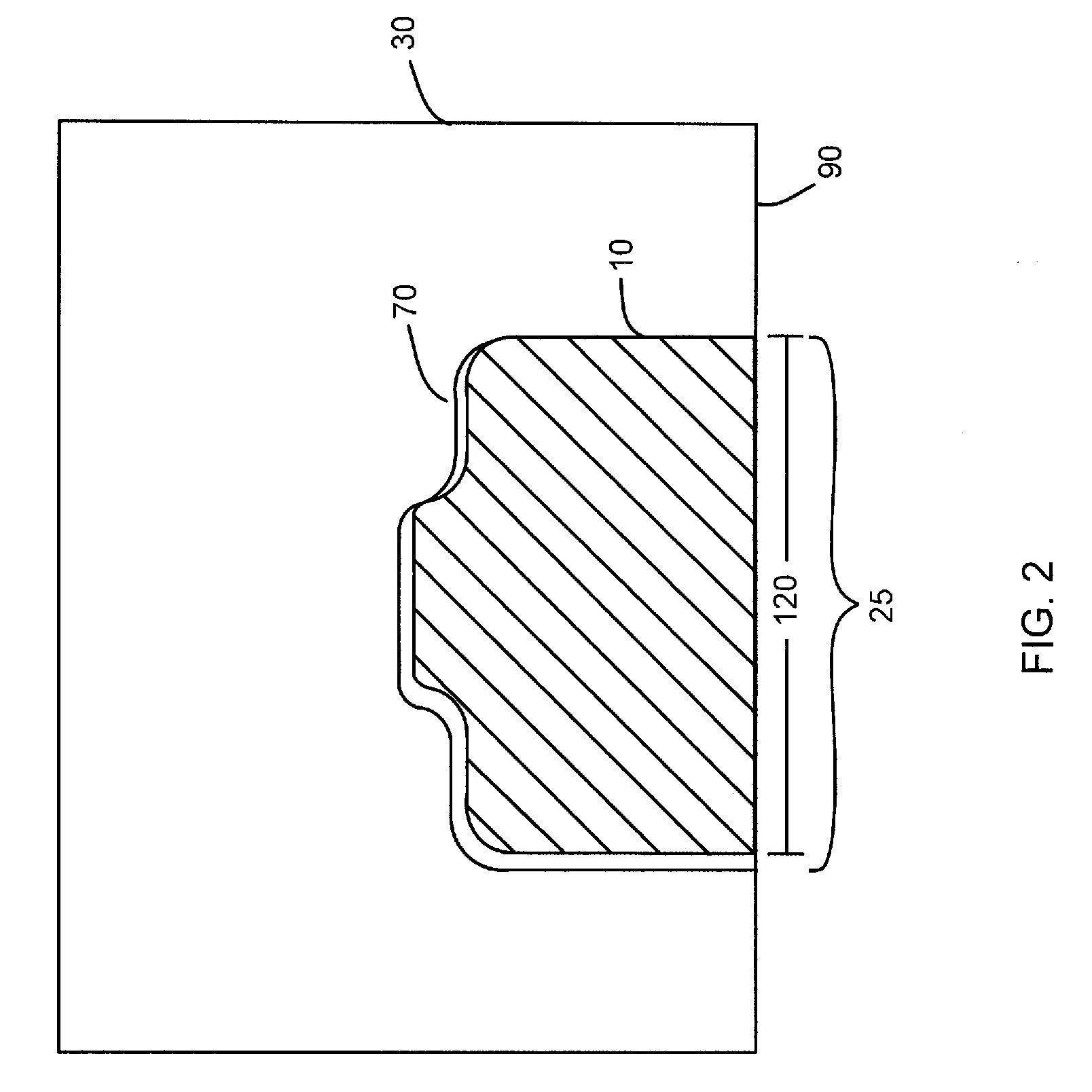
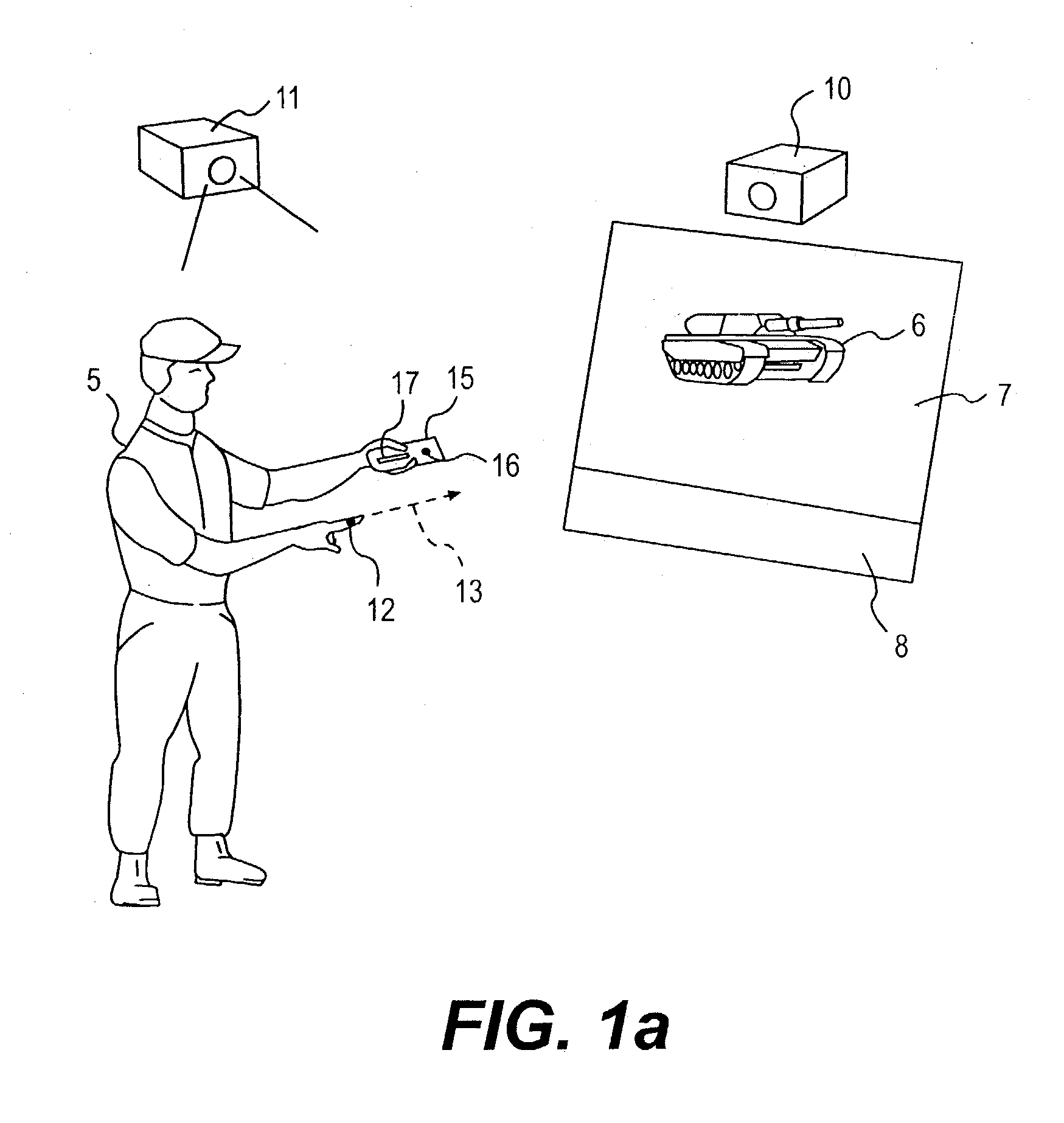
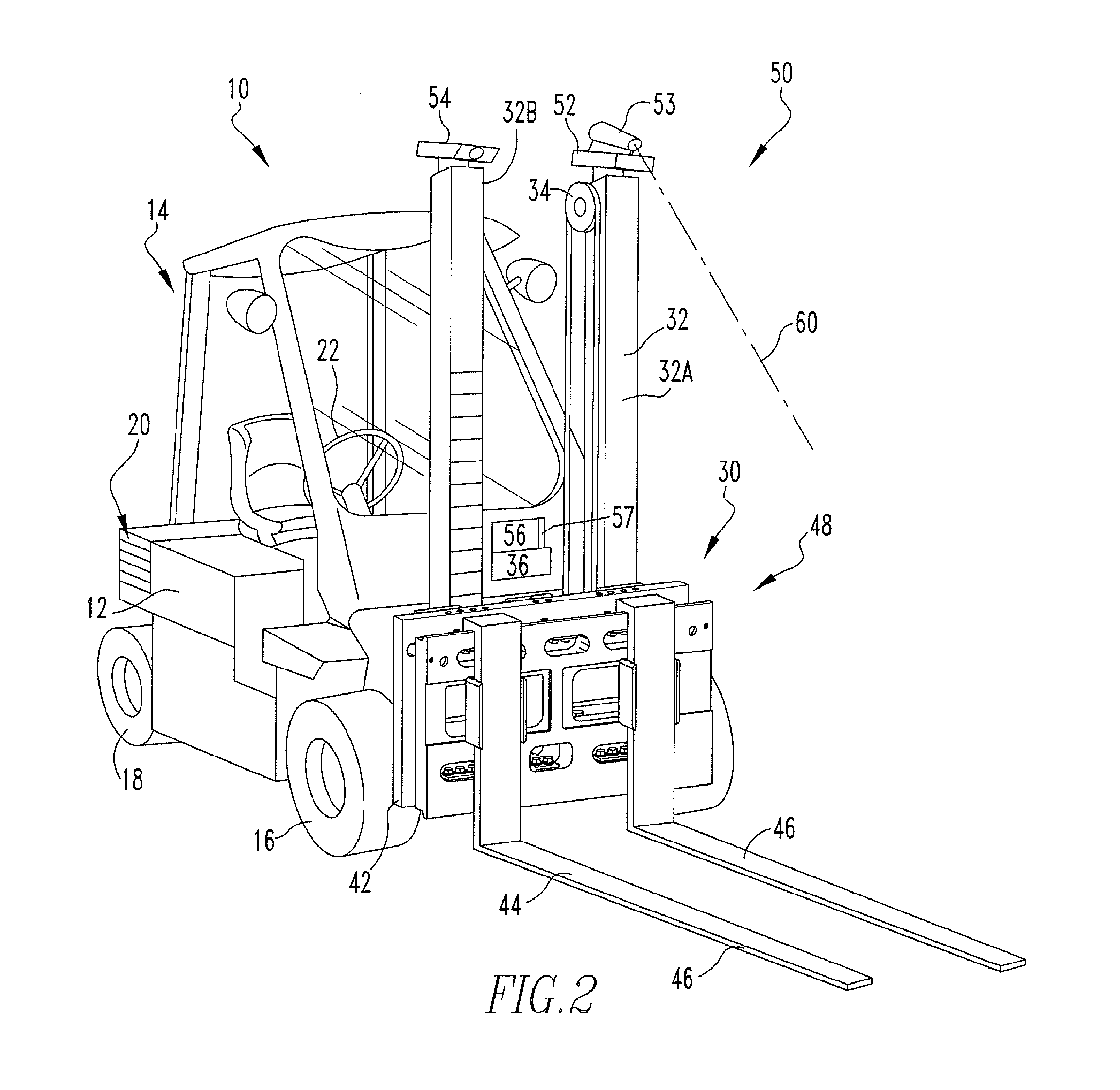
System and method for measuring irregular objects with a single camera
ActiveUS8643717B2Rapid and efficient mannerAccurate chargesCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsFresnel lensSize measurement
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
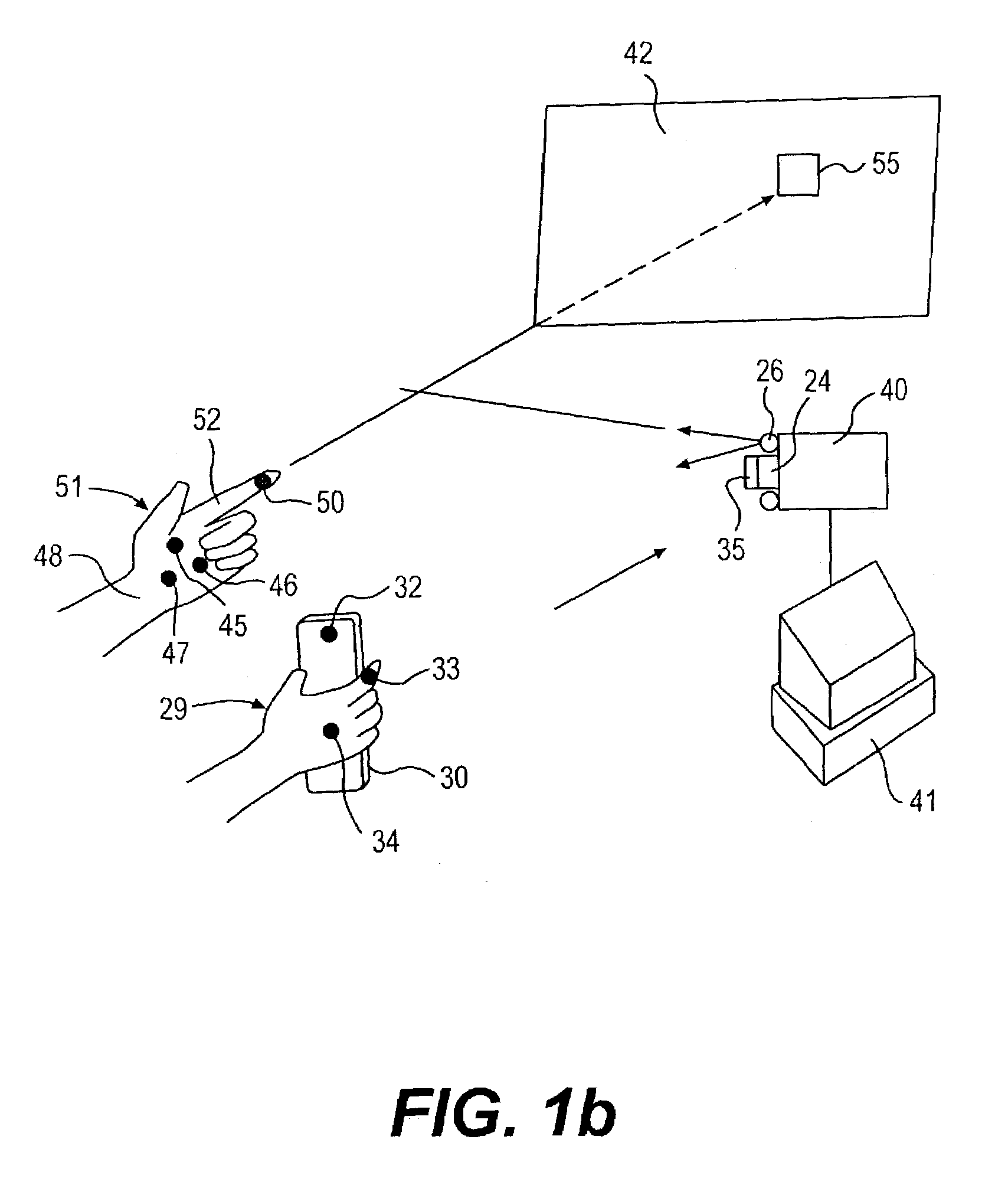
Man machine interfaces and applications
InactiveUS7042440B2Avoid carpal tunnel syndromeImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrophonic musical instrumentsComputer Aided DesignHuman–machine interface
Affordable methods and apparatus are disclosed for inputting position, attitude (orientation) or other object characteristic data to computers for the purpose of Computer Aided Design, Painting, Medicine, Teaching, Gaming, Toys, Simulations, Aids to the disabled, and internet or other experiences. Preferred embodiments of the invention utilize electro-optical sensors, and particularly TV Cameras, providing optically inputted data from specialized datum's on objects and / or natural features of objects. Objects can be both static and in motion, from which individual datum positions and movements can be derived, also with respect to other objects both fixed and moving. Real-time photogrammetry is preferably used to determine relationships of portions of one or more datums with respect to a plurality of cameras or a single camera processed by a conventional PC.
Owner:PRYOR TIMOTHY R +1
Automatic Scene Modeling for the 3D Camera and 3D Video
InactiveUS20080246759A1Reduce video bandwidthIncrease frame rateTelevision system detailsImage enhancementAutomatic controlViewpoints
Single-camera image processing methods are disclosed for 3D navigation within ordinary moving video. Along with color and brightness, XYZ coordinates can be defined for every pixel. The resulting geometric models can be used to obtain measurements from digital images, as an alternative to on-site surveying and equipment such as laser range-finders. Motion parallax is used to separate foreground objects from the background. This provides a convenient method for placing video elements within different backgrounds, for product placement, and for merging video elements with computer-aided design (CAD) models and point clouds from other sources. If home users can save video fly-throughs or specific 3D elements from video, this method provides an opportunity for proactive, branded media sharing. When this image processing is used with a videoconferencing camera, the user's movements can automatically control the viewpoint, creating 3D hologram effects on ordinary televisions and computer screens.
Owner:SUMMERS
Digital security multimedia sensor
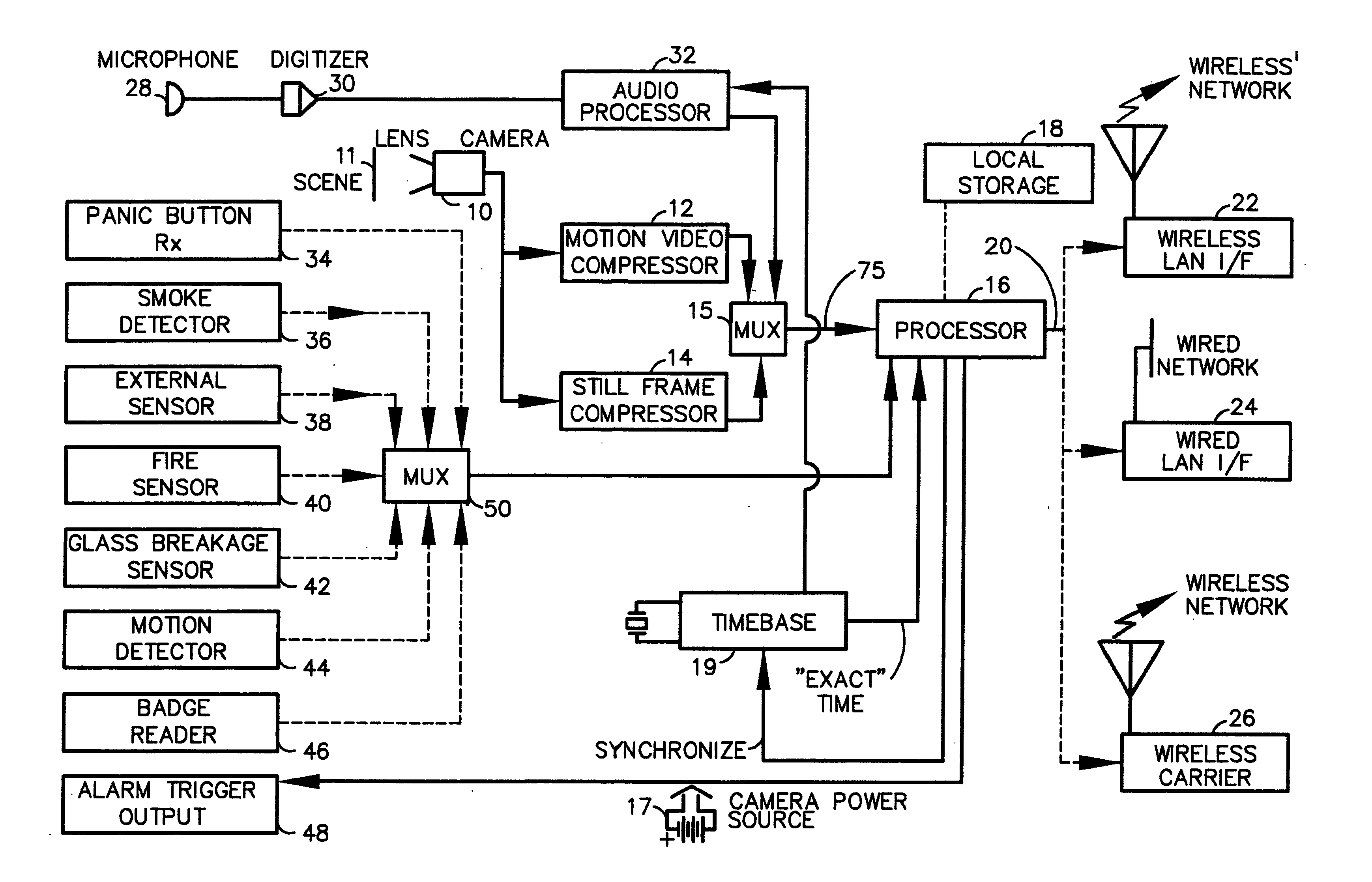
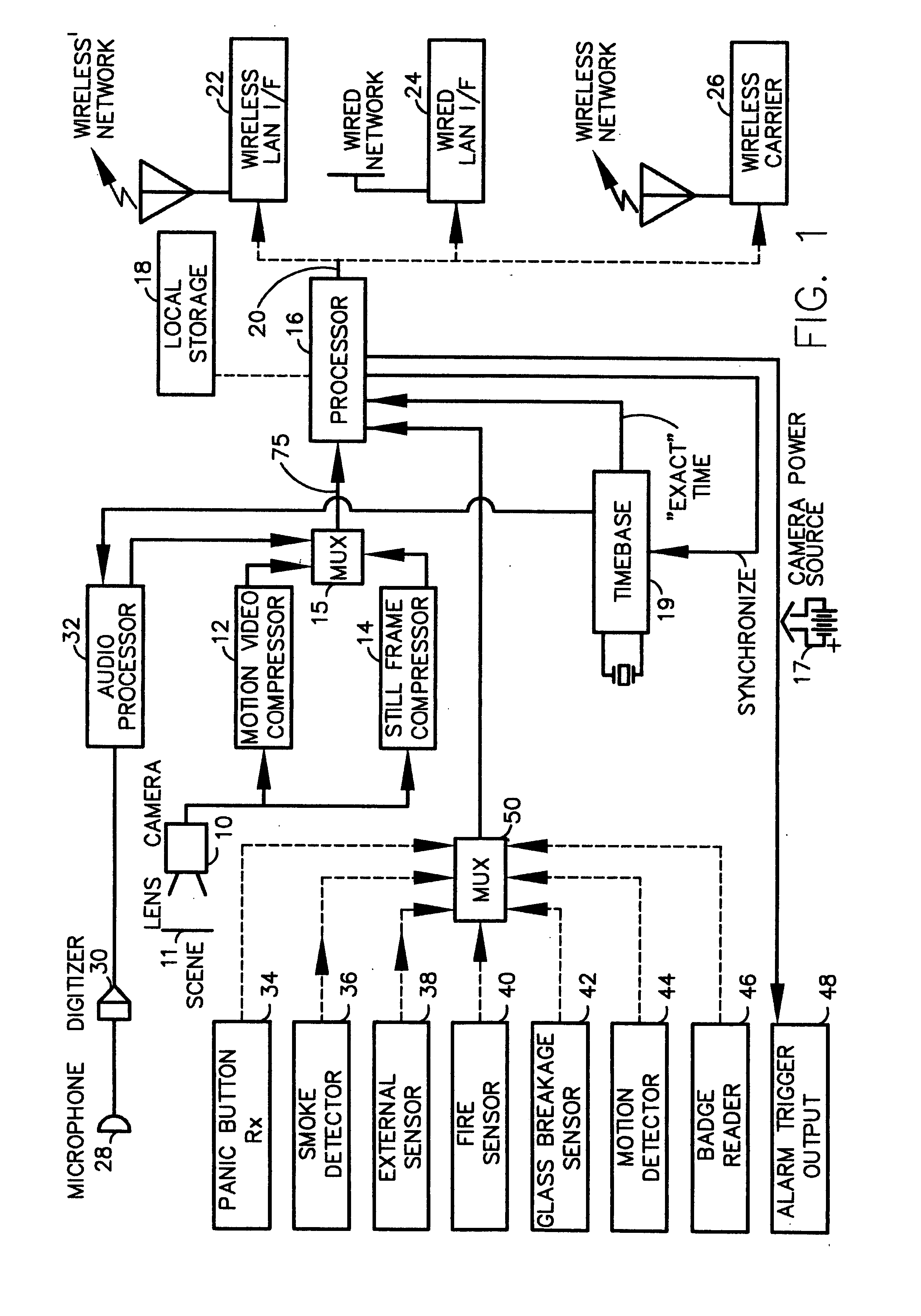
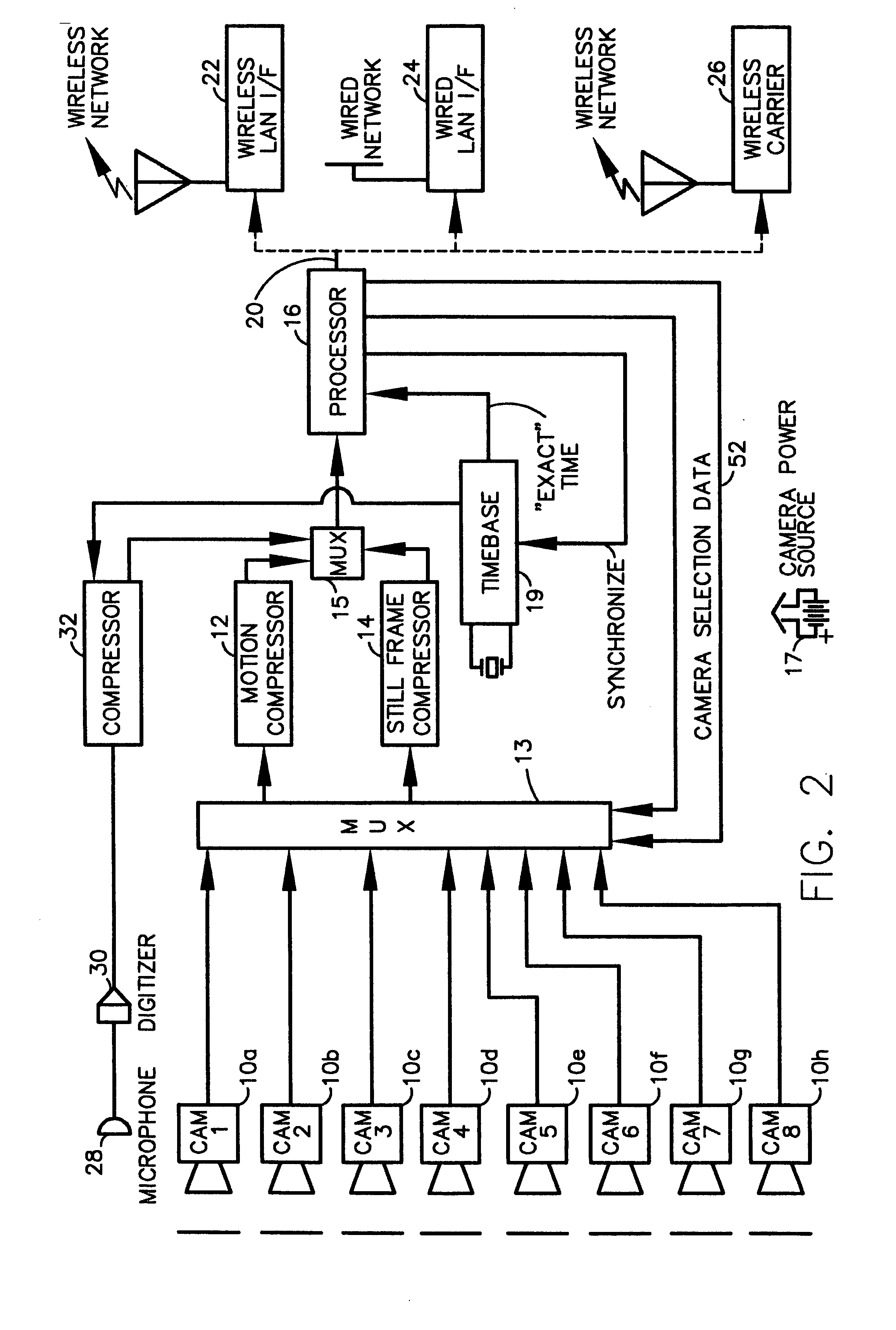
InactiveUS7023913B1Quality improvementImprove accuracyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage transferBiological activation
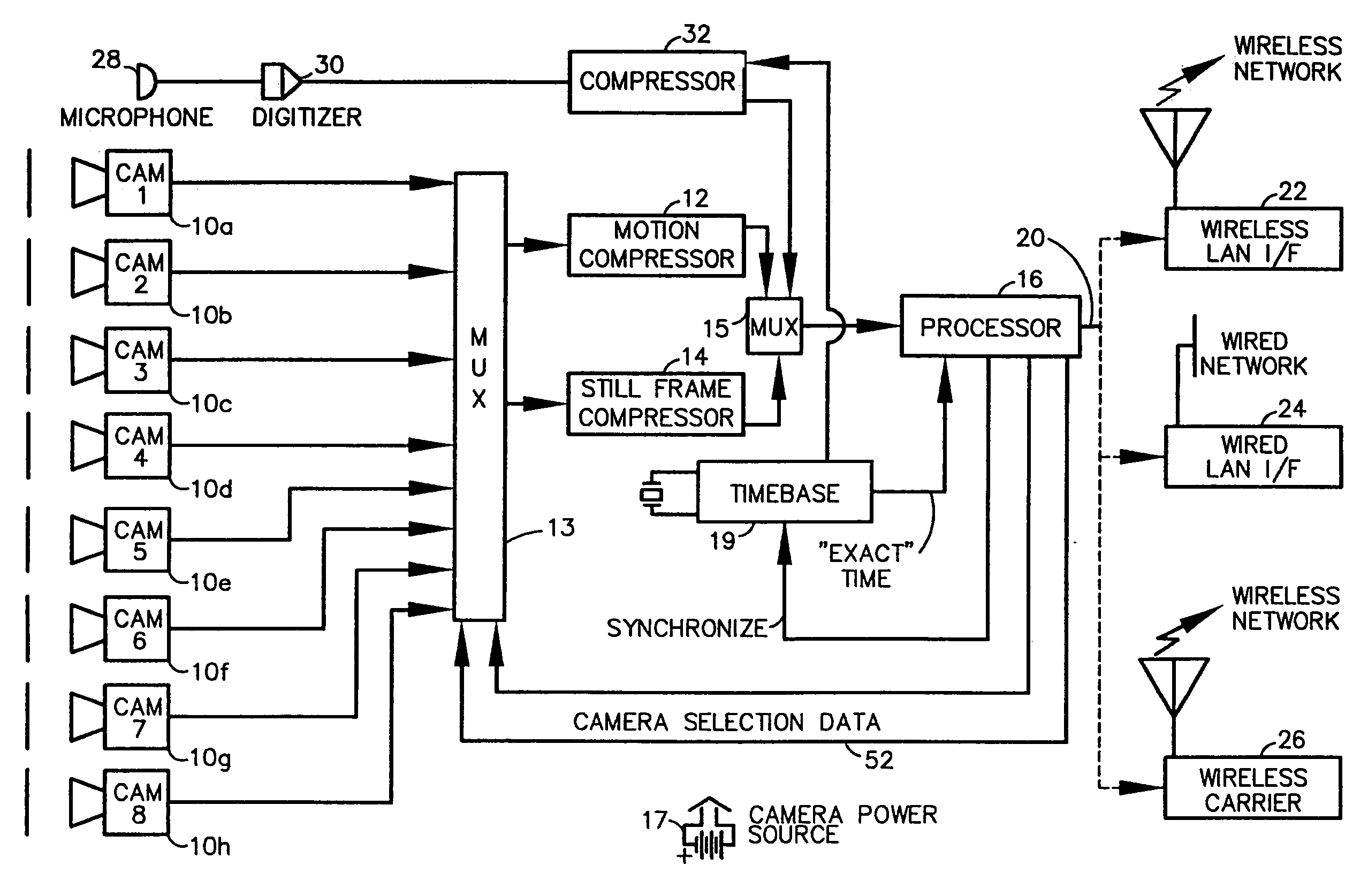
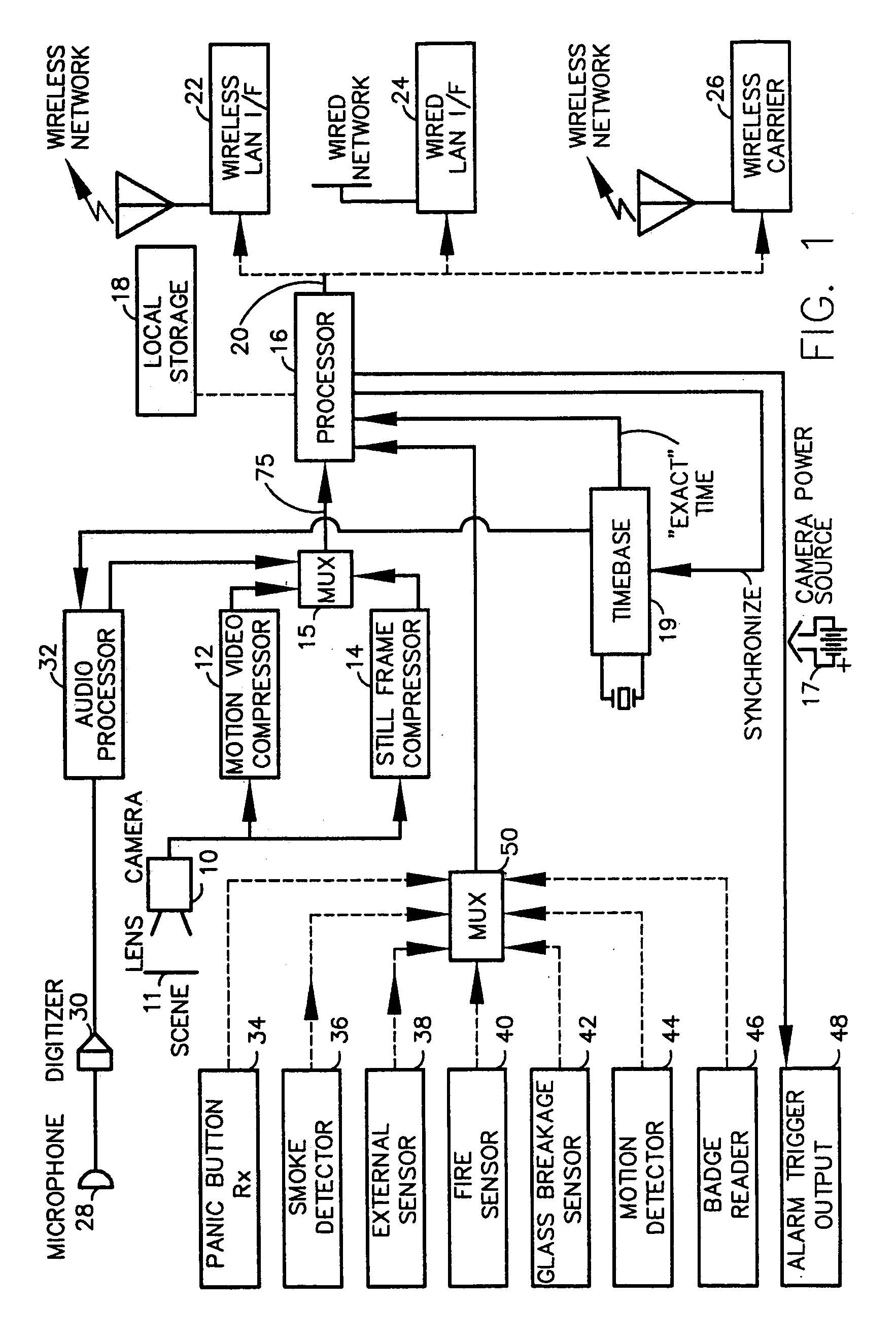
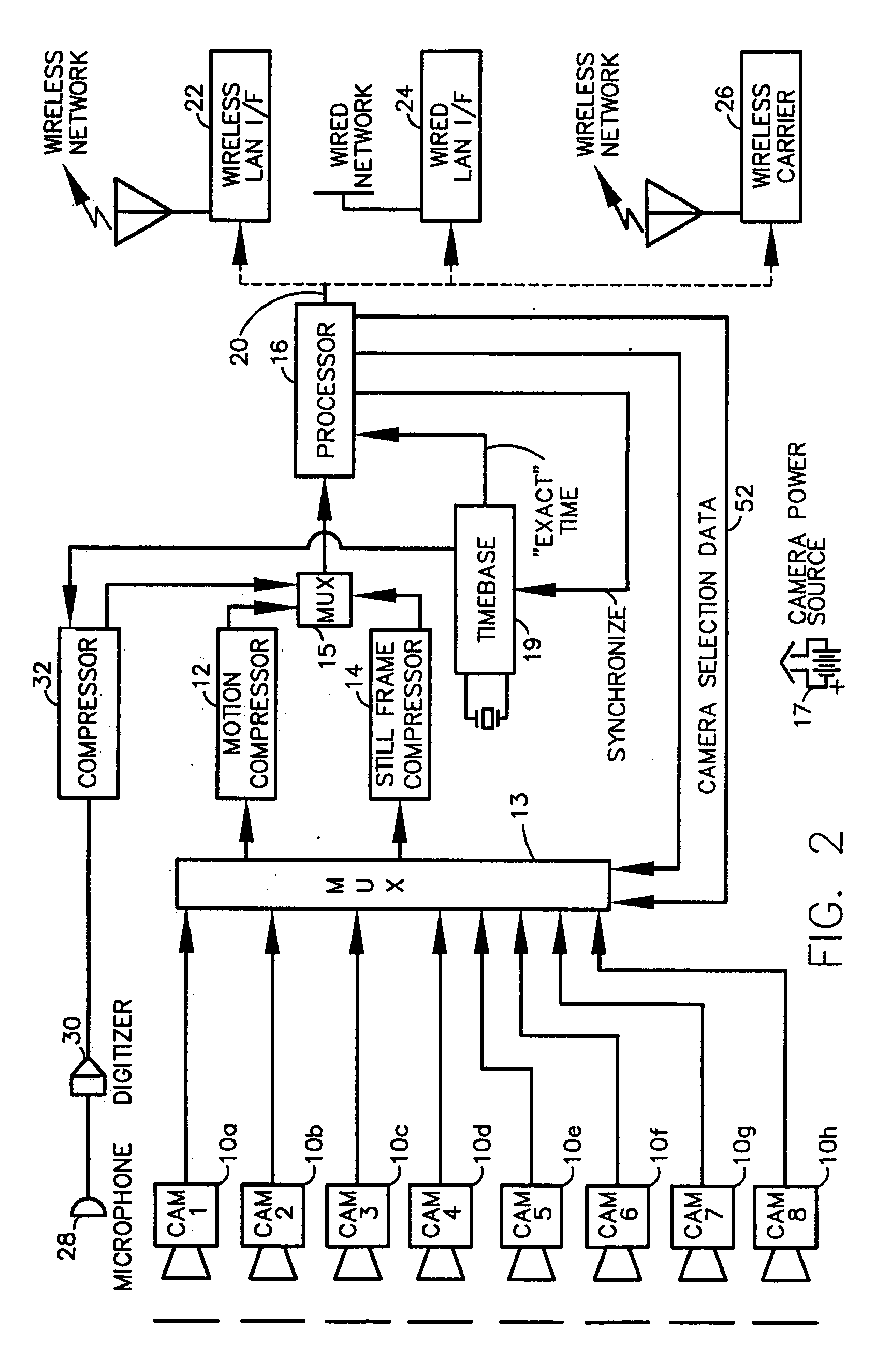
A fully digital camera system provides high-resolution still image and streaming video signals via a network to a centralized, server supported security and surveillance system. The digital camera for collects an image from one or more image transducers, compressing the image and sending the compressed digital image signal to a receiving station over a digital network. A plurality of image transducers or sensors may be included in a single camera unit, providing array imaging such as full 360 degree panoramic imaging, universal or spherical imaging and field imaging by stacking or arranging the sensors in an array. The multiple images are then compressed and merged at the camera in the desired format to permit transmission of the least amount of data to accomplish the desired image transmission. The camera also employs, or connects to, a variety of sensors other than the traditional image sensor. Sensors for fire, smoke, sound, glass breakage, motion, panic buttons, and the like, may be embedded in or connected to the camera. Data captured by these sensors may be digitized, compressed, and networked to detect notable conditions. An internal microphone and associated signal processing system may be equipped with suitable signal processing algorithms for the purpose of detecting suitable acoustic events and their location. In addition, the camera is equipped with a pair of externally accessible terminals where an external sensor may be connected. In addition, the camera may be equipped with a short-range receiver that may detect the activation of a wireless ‘panic button’ carried by facility personnel. This ‘panic button’ may employ infrared, radio frequency (RF), ultrasonic, or other suitable methods to activate the camera's receiver.
Owner:PR NEWSWIRE
Digital security multimedia sensor
InactiveUS20050207487A1Ensure effective disseminationEfficient routingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage compressionBiological activation
A fully digital camera system provides high-resolution still image and streaming video signals via a network to a centralized, server supported security and surveillance system. The digital camera for collects an image from one or more image transducers, compressing the image and sending the compressed digital image signal to a receiving station over a digital network. A plurality of image transducers or sensors may be included in a single camera unit, providing array imaging such as full 360 degree panoramic imaging, universal or spherical imaging and field imaging by stacking or arranging the sensors in an array. The multiple images are then compressed and merged at the camera in the desired format to permit transmission of the least amount of data to accomplish the desired image transmission. The camera also employs, or connects to, a variety of sensors other than the traditional image sensor. Sensors for fire, smoke, sound, glass breakage, motion, panic buttons, and the like, may be embedded in or connected to the camera. Data captured by these sensors may be digitized, compressed, and networked to detect notable conditions. An internal microphone and associated signal processing system may be equipped with suitable signal processing algorithms for the purpose of detecting suitable acoustic events and their location. In addition, the camera is equipped with a pair of externally accessible terminals where an external sensor may be connected. In addition, the camera may be equipped with a short-range receiver that may detect the activation of a wireless ‘panic button’ carried by facility personnel. This ‘panic button’ may employ infrared, radio frequency (RF), ultrasonic, or other suitable methods to activate the camera's receiver.
Owner:PR NEWSWIRE
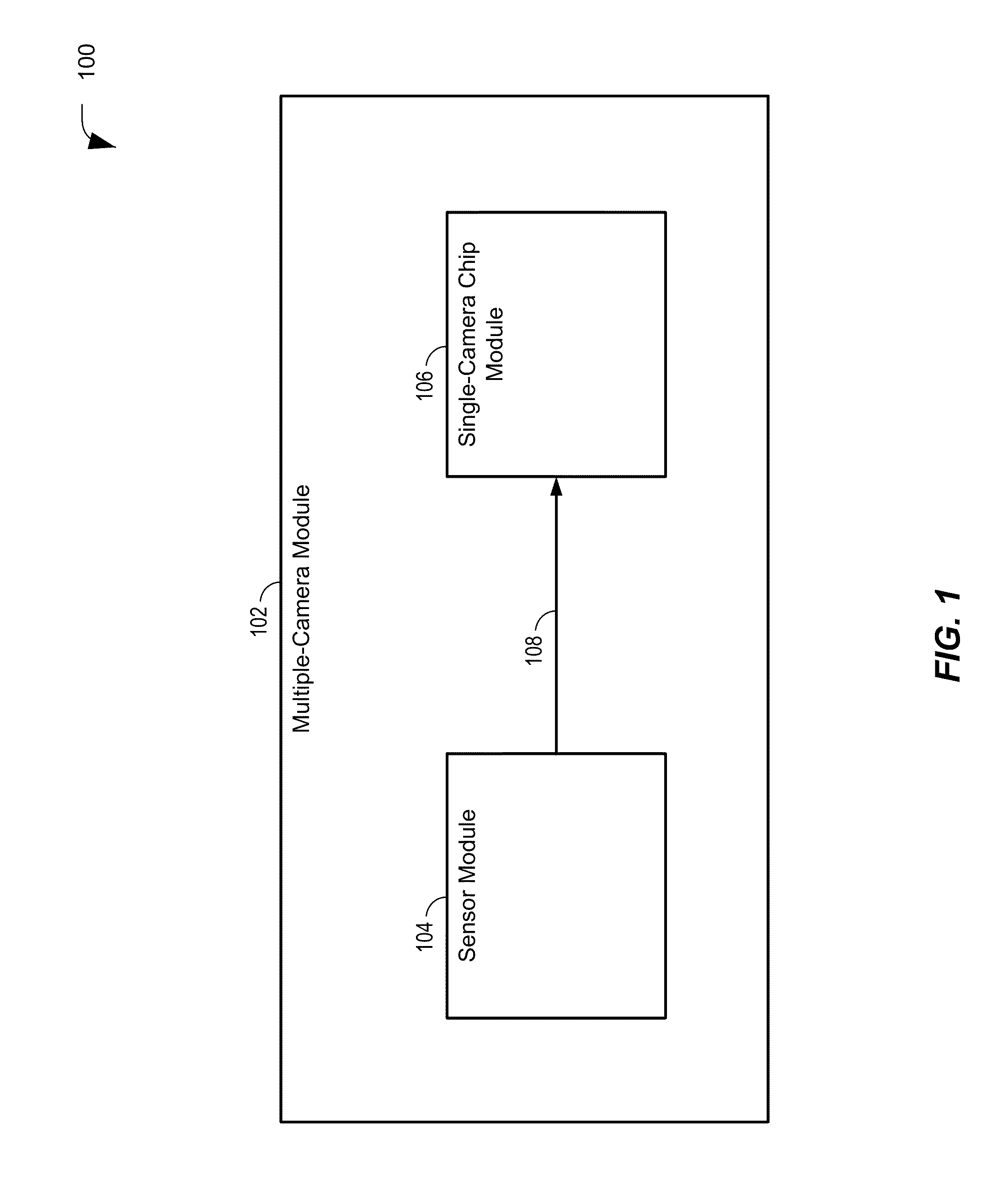
Combining data from multiple image sensors
InactiveUS20110242355A1Avoid pollutionTelevision system detailsSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Control signal
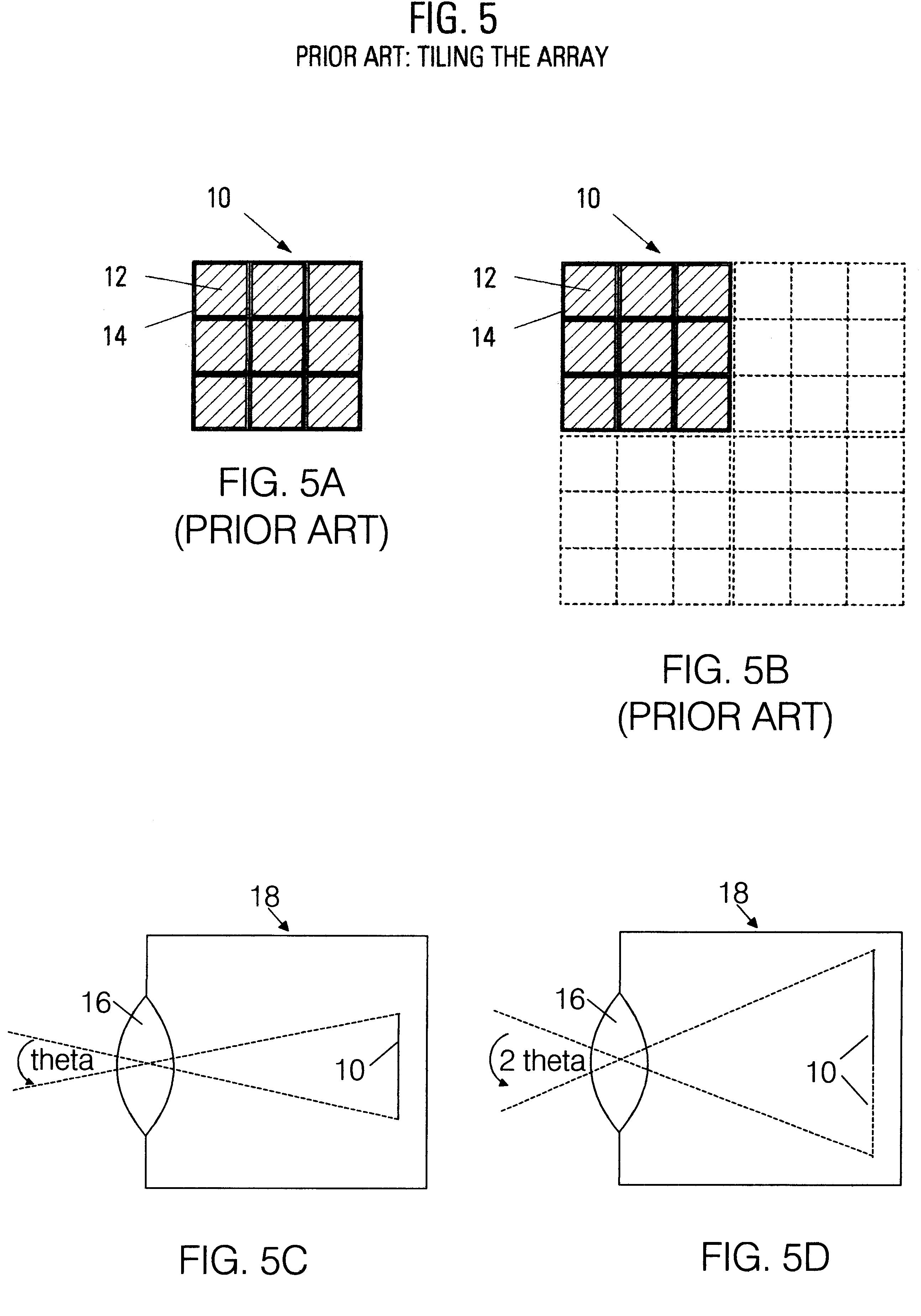
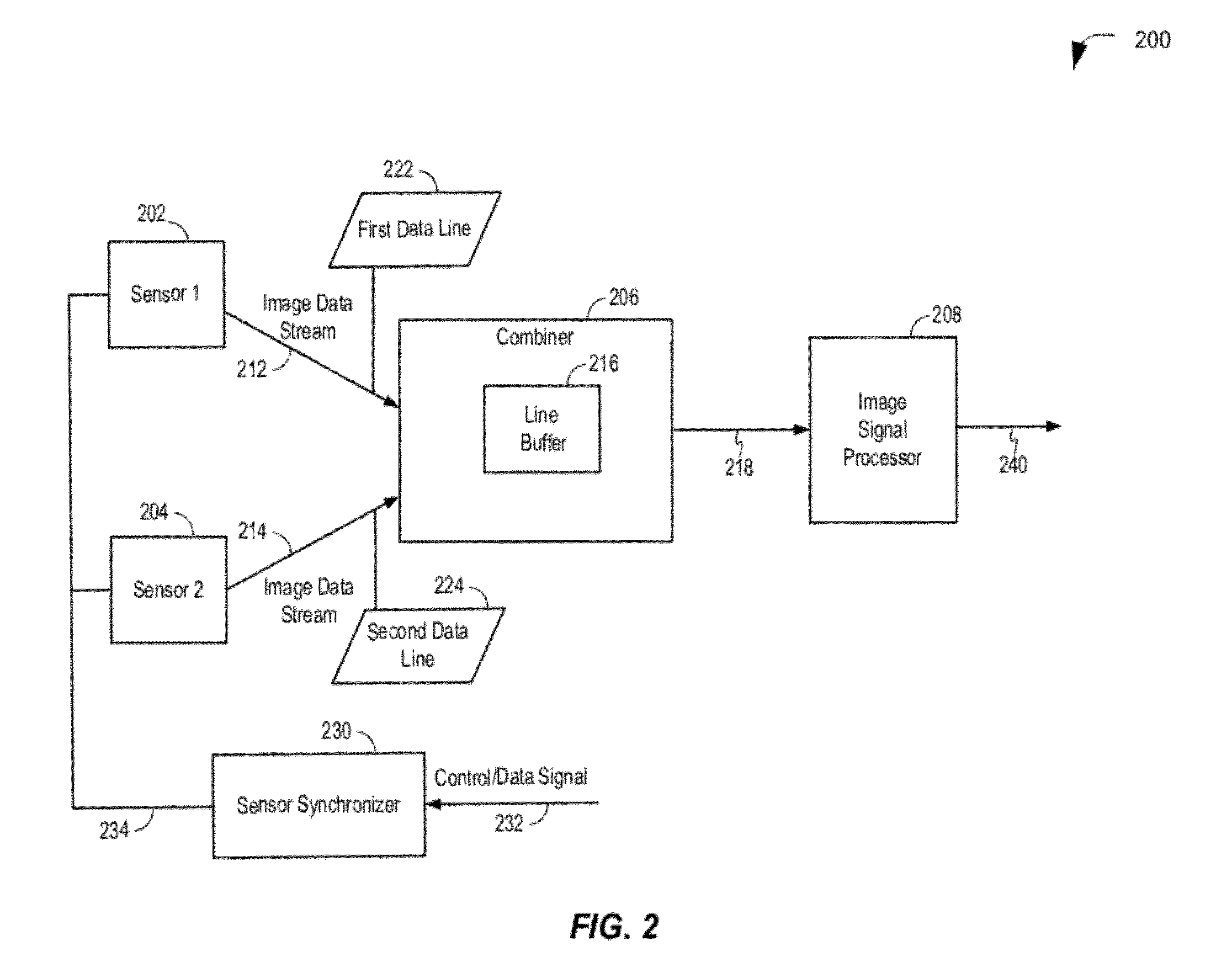
A method of combining data from multiple sensors is disclosed. The method includes providing a common control signal to multiple image sensors. Each of the multiple image sensors is responsive to the common control signal to generate image data. The method also includes receiving synchronized data output from each of the multiple image sensors, combining the synchronized data output from each of the multiple image sensors to generate a synchronized data line, and providing the synchronized data line to an image processor via a single camera input of the image processor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method of stereoscopic 3D image capture using a mobile device, cradle or dongle
InactiveUS20100194860A1Accurate image captureImprove image captureTelevision system detailsSubstation equipmentComputer graphics (images)3d image
A system, apparatus, method, and computer-readable media are provided for the capture of stereoscopic three dimensional (3D) images using multiple cameras or a single camera manipulated to deduce stereoscopic data. According to one method, a dongle or cradle is added to a mobile phone or other device to capture stereoscopic images. According to another method, the images are captured from cameras with oblique orientation such that the images may need to be rotated, cropped, or both to determine the appropriate stereoscopic 3D regions of interest. According to another method, a single camera is manipulated such that stereoscopic 3D information is deduced.
Owner:BIT CAULDRON CORP
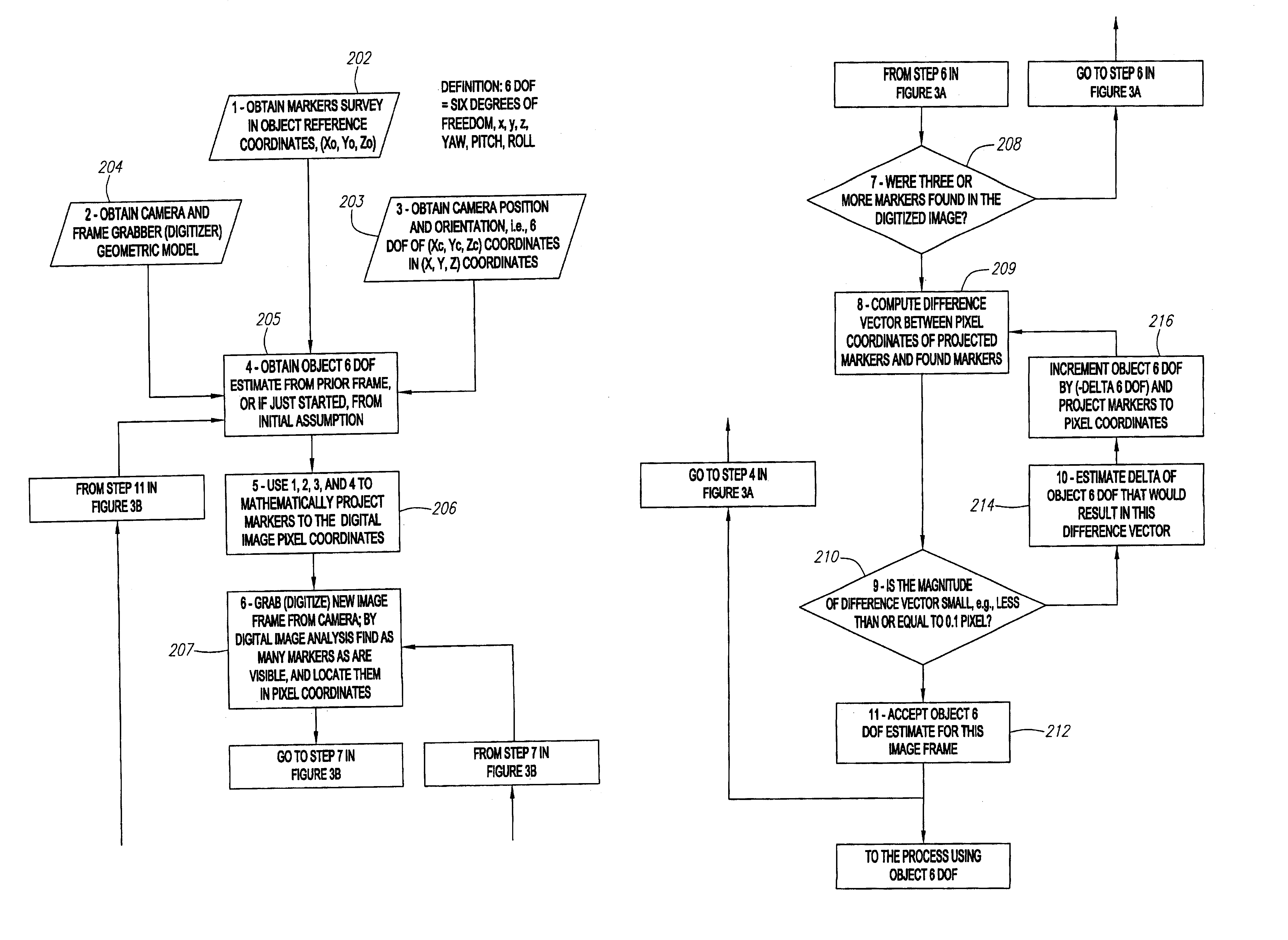
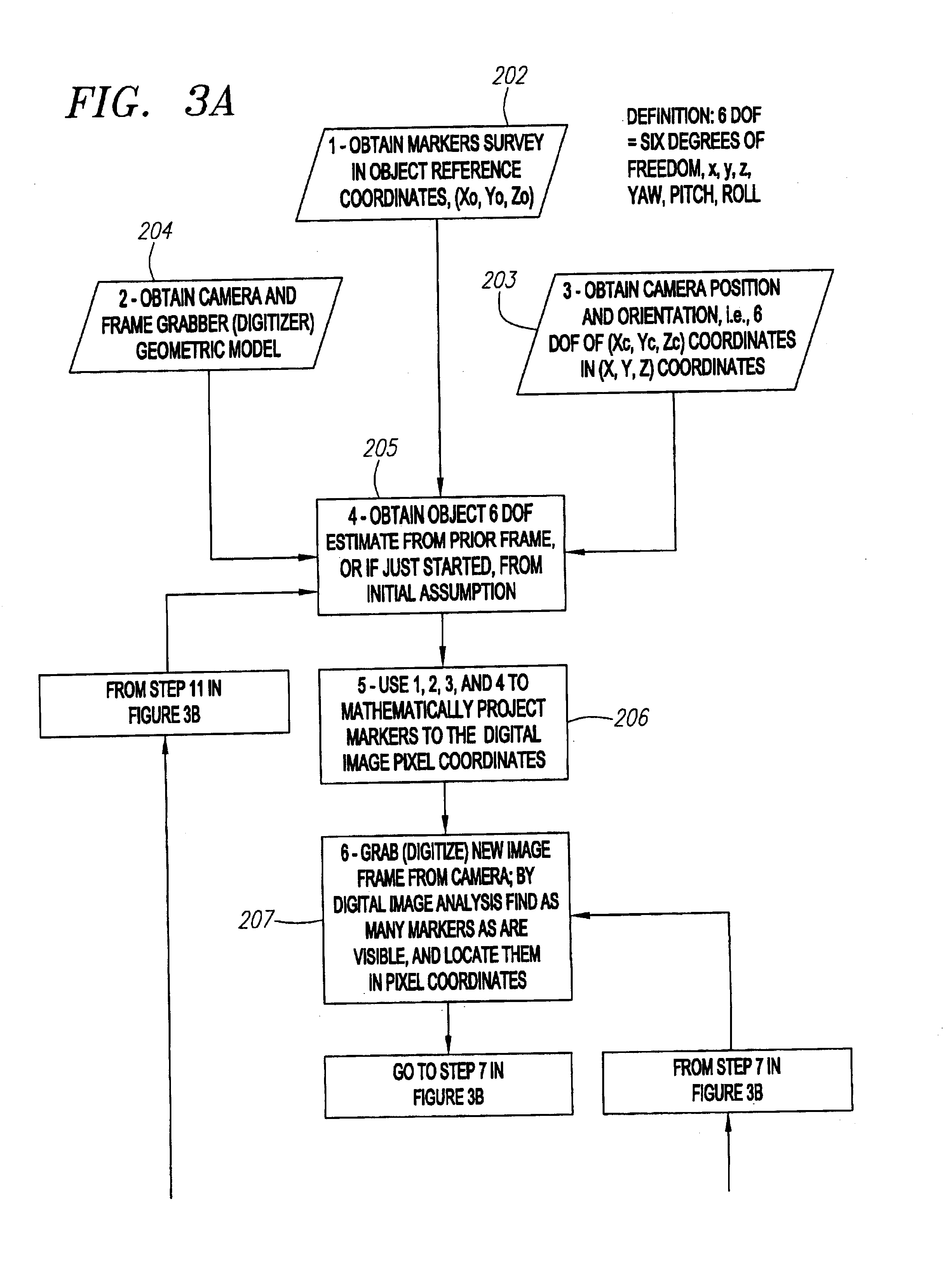
Single-camera tracking of an object
InactiveUS6973202B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementOptical trackingVideo camera
A method and system for determining the position and orientation of an object is disclosed. A set of markers attached or associated with the object is optically tracked and geometric translation is performed to use the coordinates of the set of markers to determine the location and orientation of their associated object.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
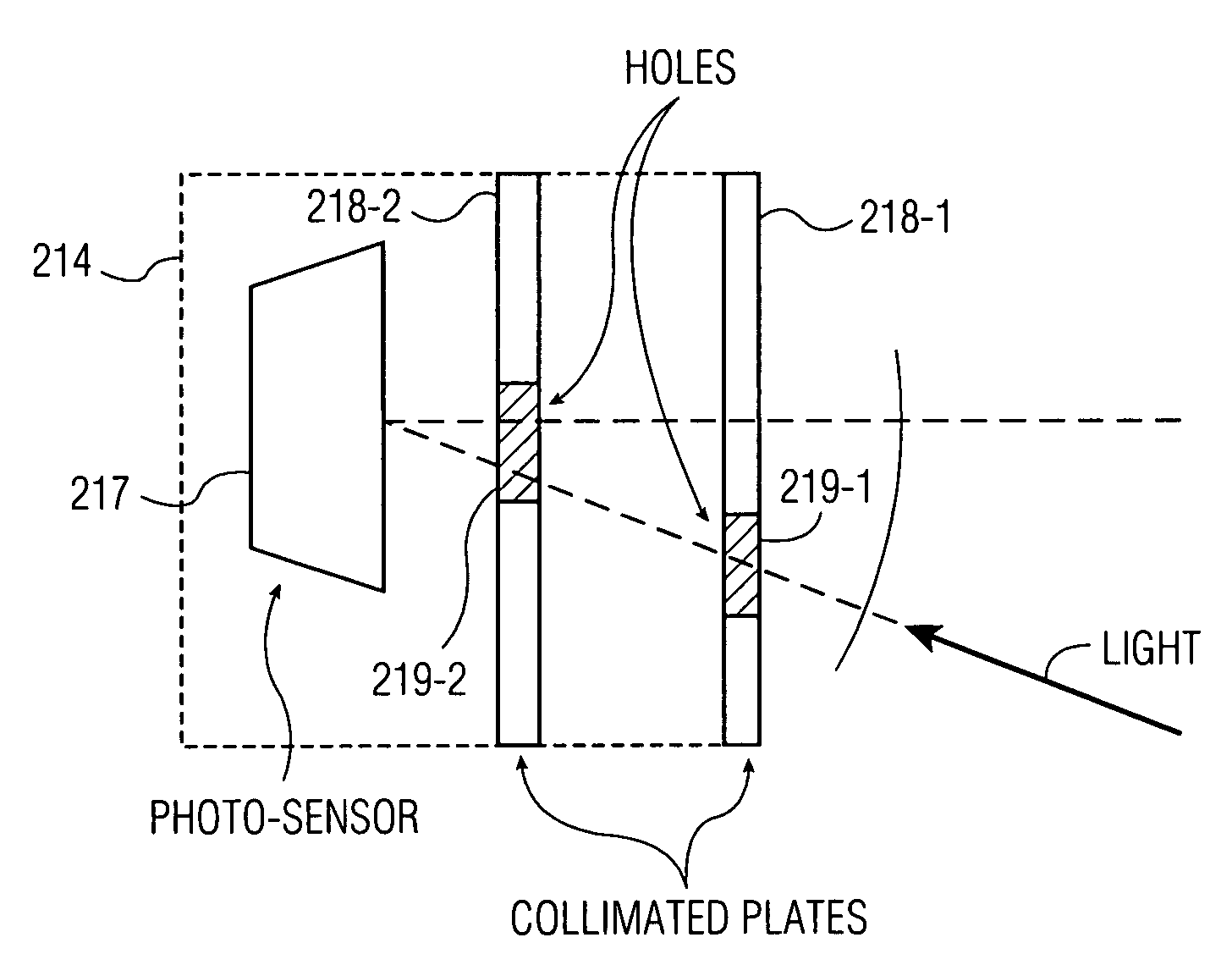
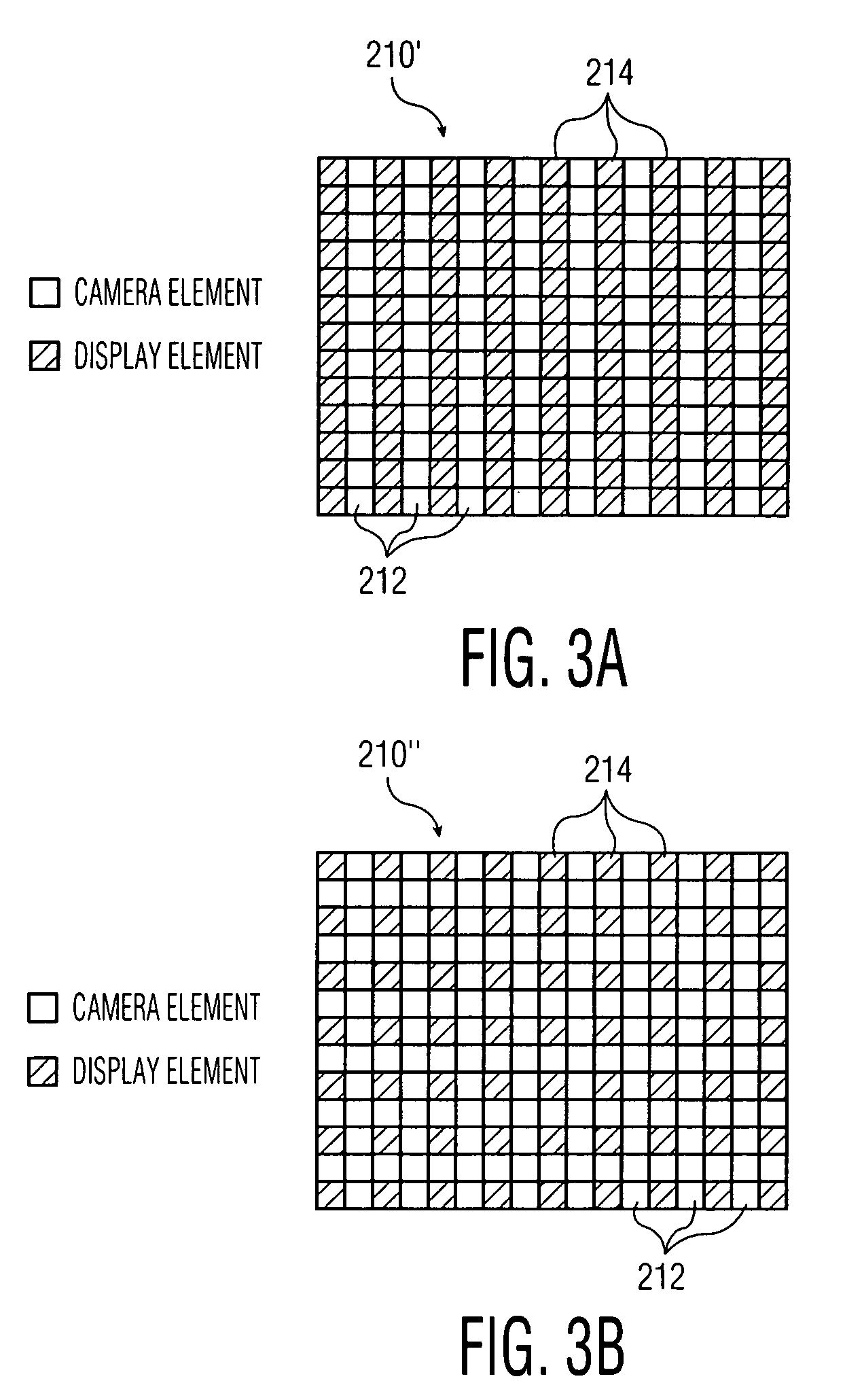
Combined display-camera for an image processing system
InactiveUS7034866B1Hinder its implementationSuitable for useTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensPinhole camera
An image processing system includes a combined display-camera having an array of interspersed display elements and camera elements, arranged substantially in a common plane of a flat panel or other display. Each of at least a subset of the camera elements has one or more imaging angles associated therewith, with the one or more imaging angles being selected to provide a desired imaging operation for the combined display-camera. The imaging angles of the camera elements can be selected to provide an imaging operation which approximates that of a lens-based single-camera system, a pin-hole camera system or other type of system. Each of the camera elements may include multiple image sensors, such that different imaging angles can be set for the different image sensors of a given camera element, and different perspectives of a scene can be generated in the image processing system.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
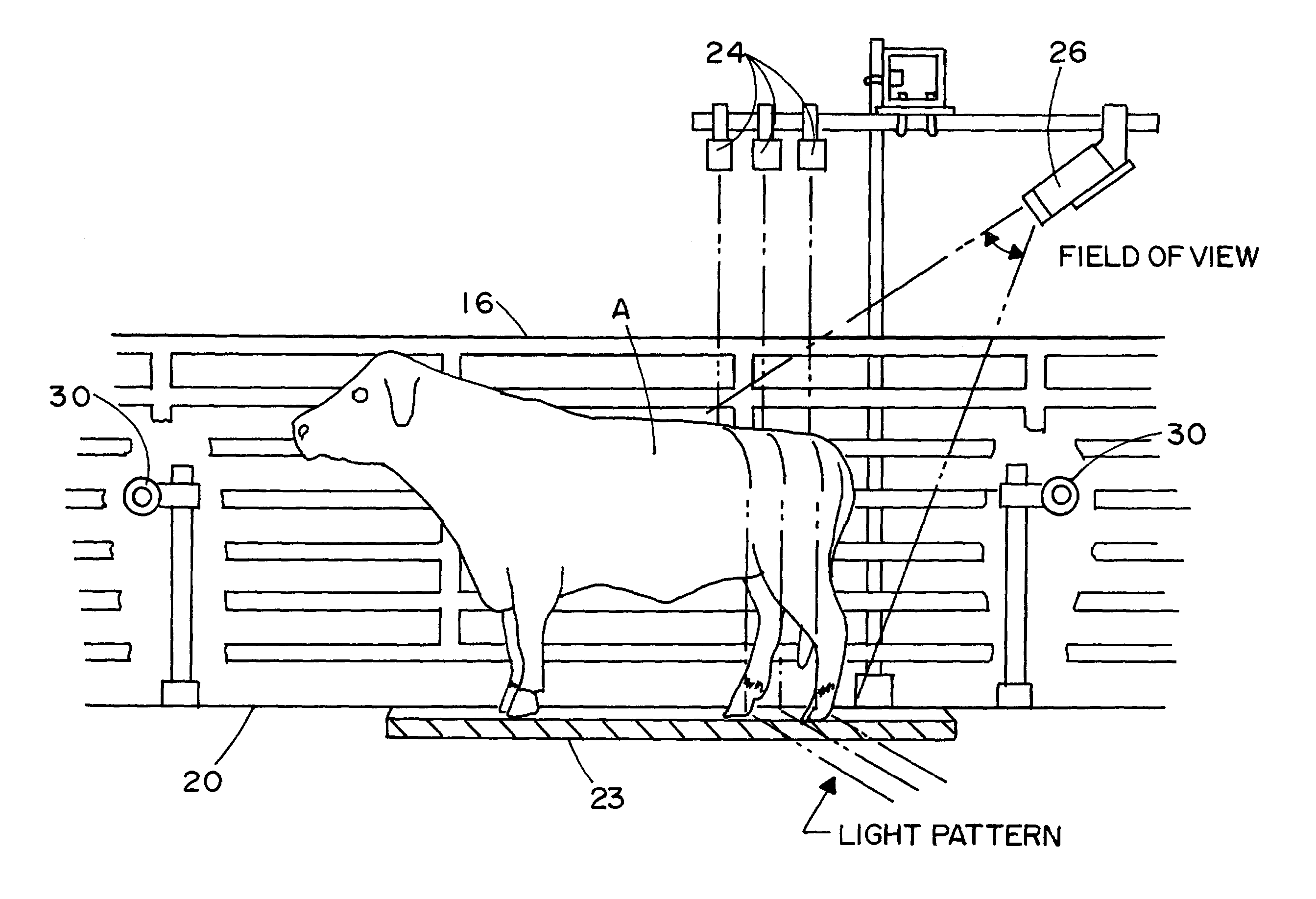
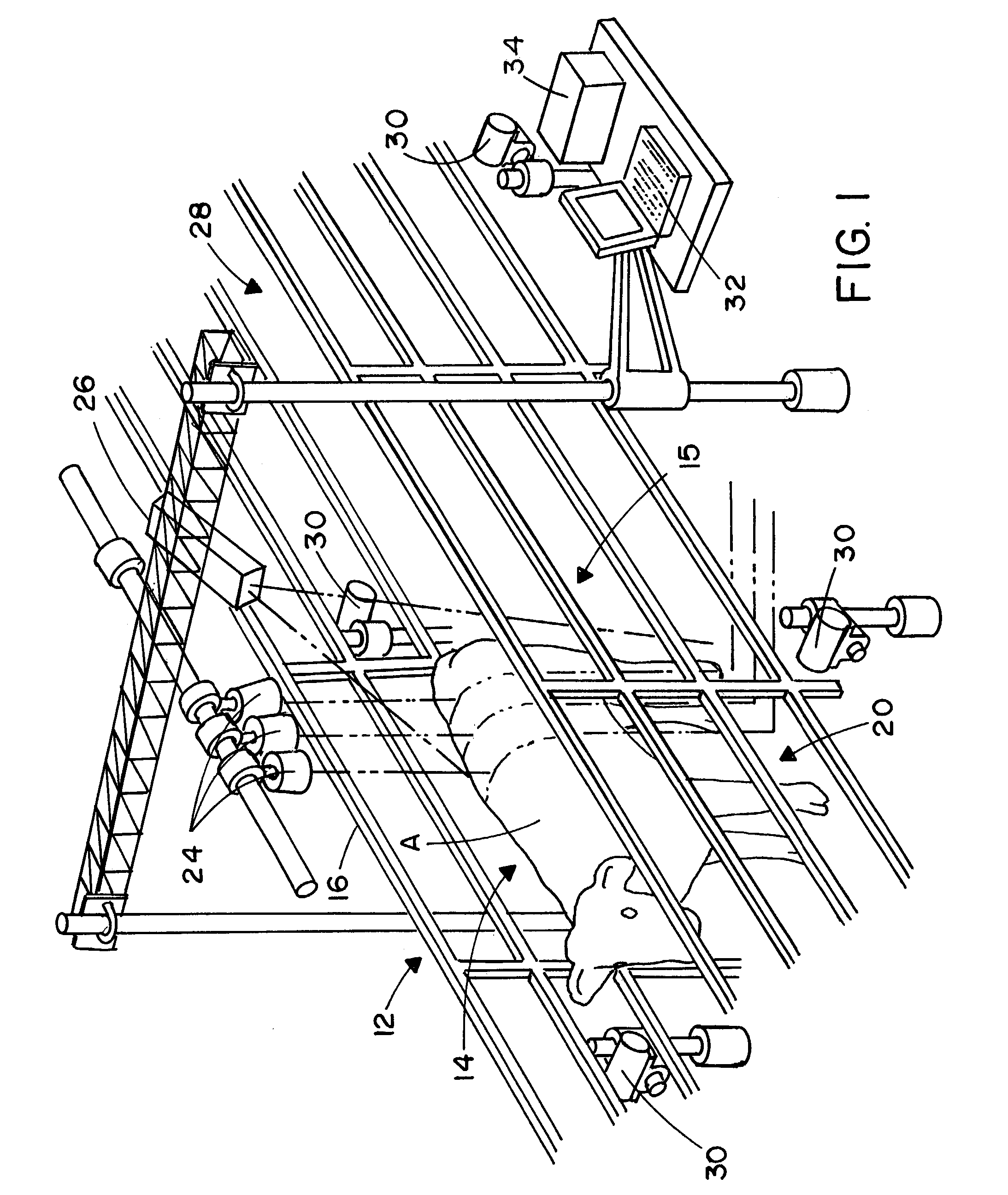
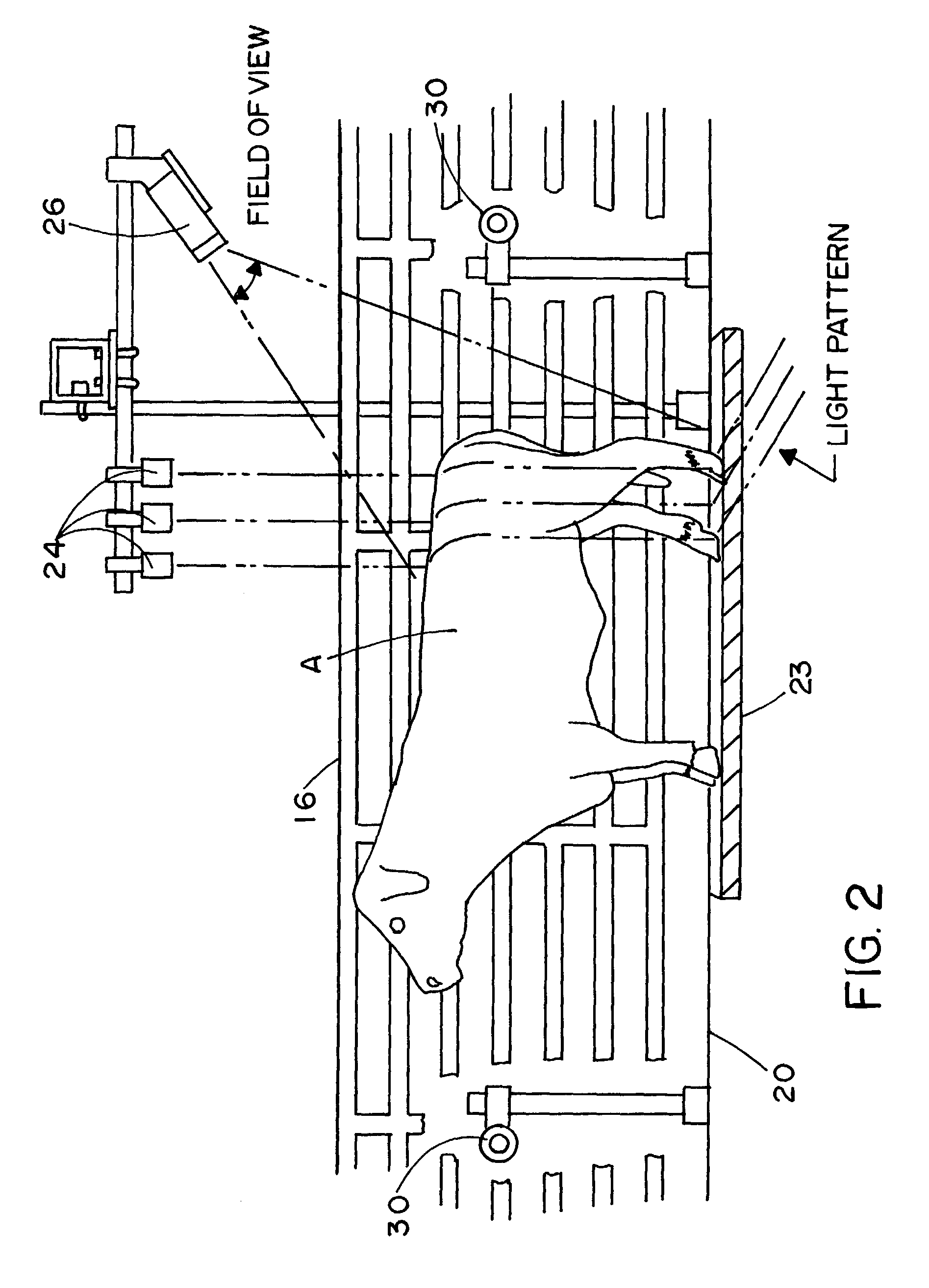
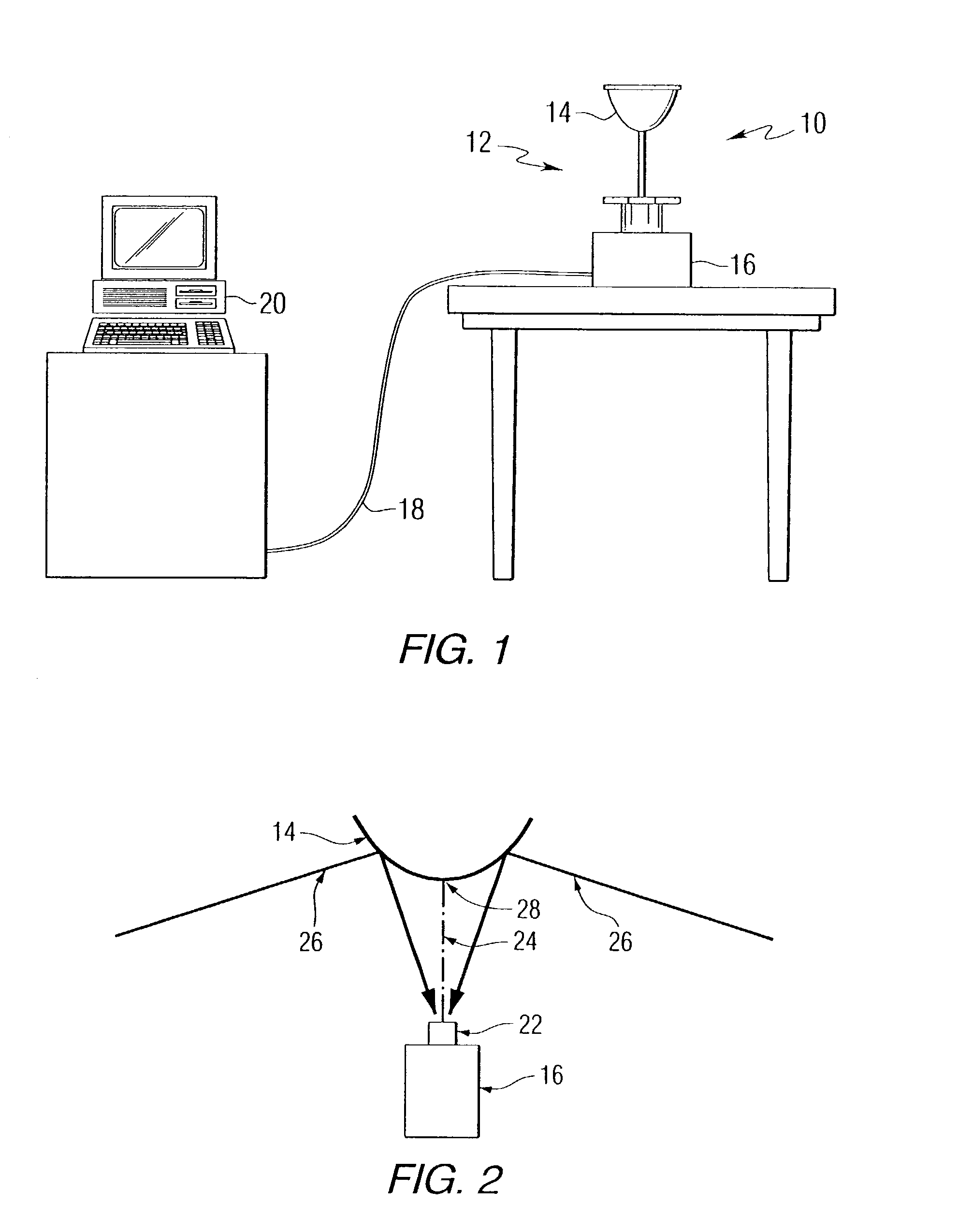
Methods and apparatus for the dimensional measurement of livestock using a single camera
ActiveUS7039220B2Increase speedImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansBiologyLivestock
A method and apparatus for measuring target animals, including livestock animals and full carcasses, and more specifically livestock animals such as cattle and hogs using a single camera system. More particularly, the method of the invention is directed toward obtaining key measurements of the target animal, such as animal weight, animal hip height and animal hip width.
Owner:KALLINA
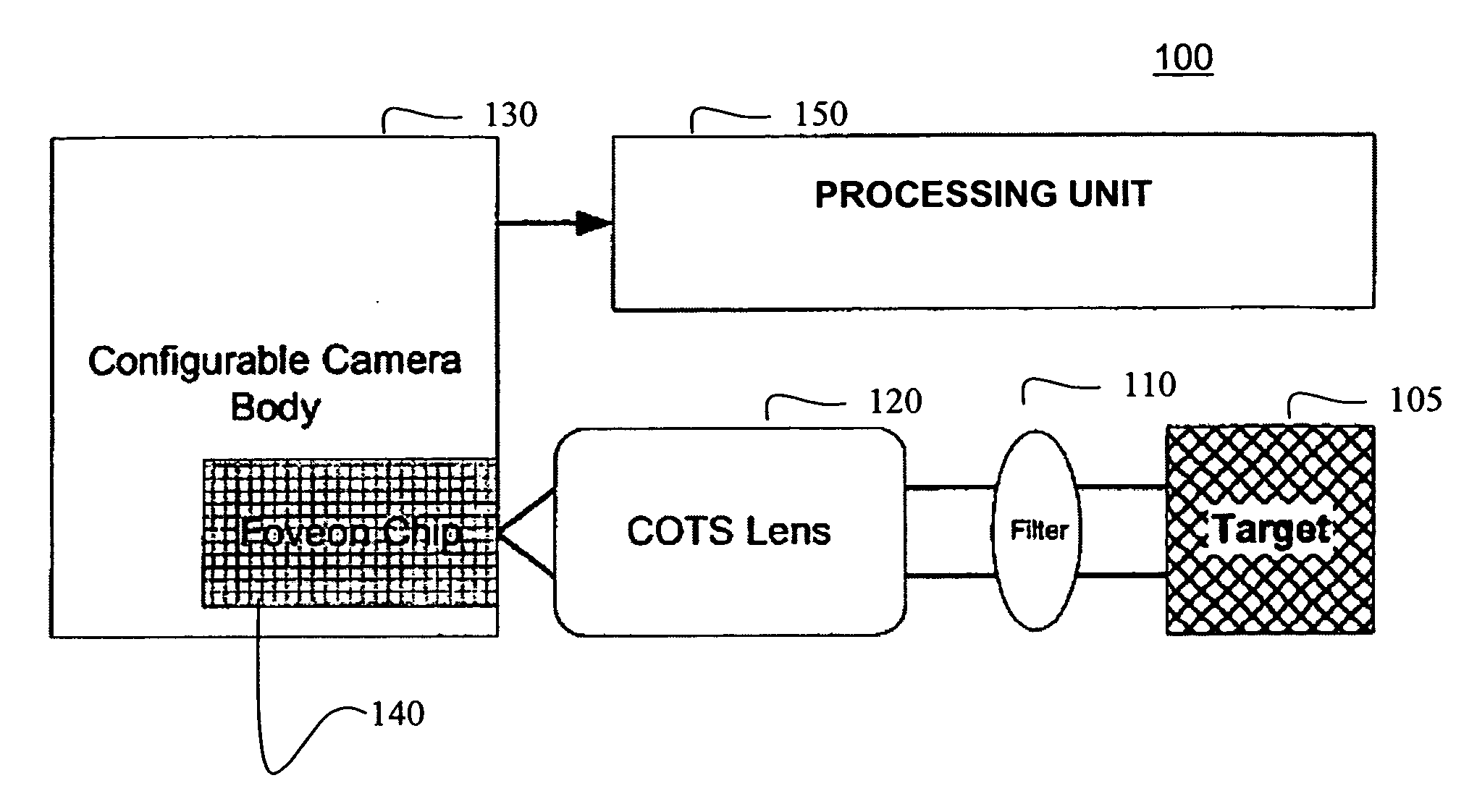
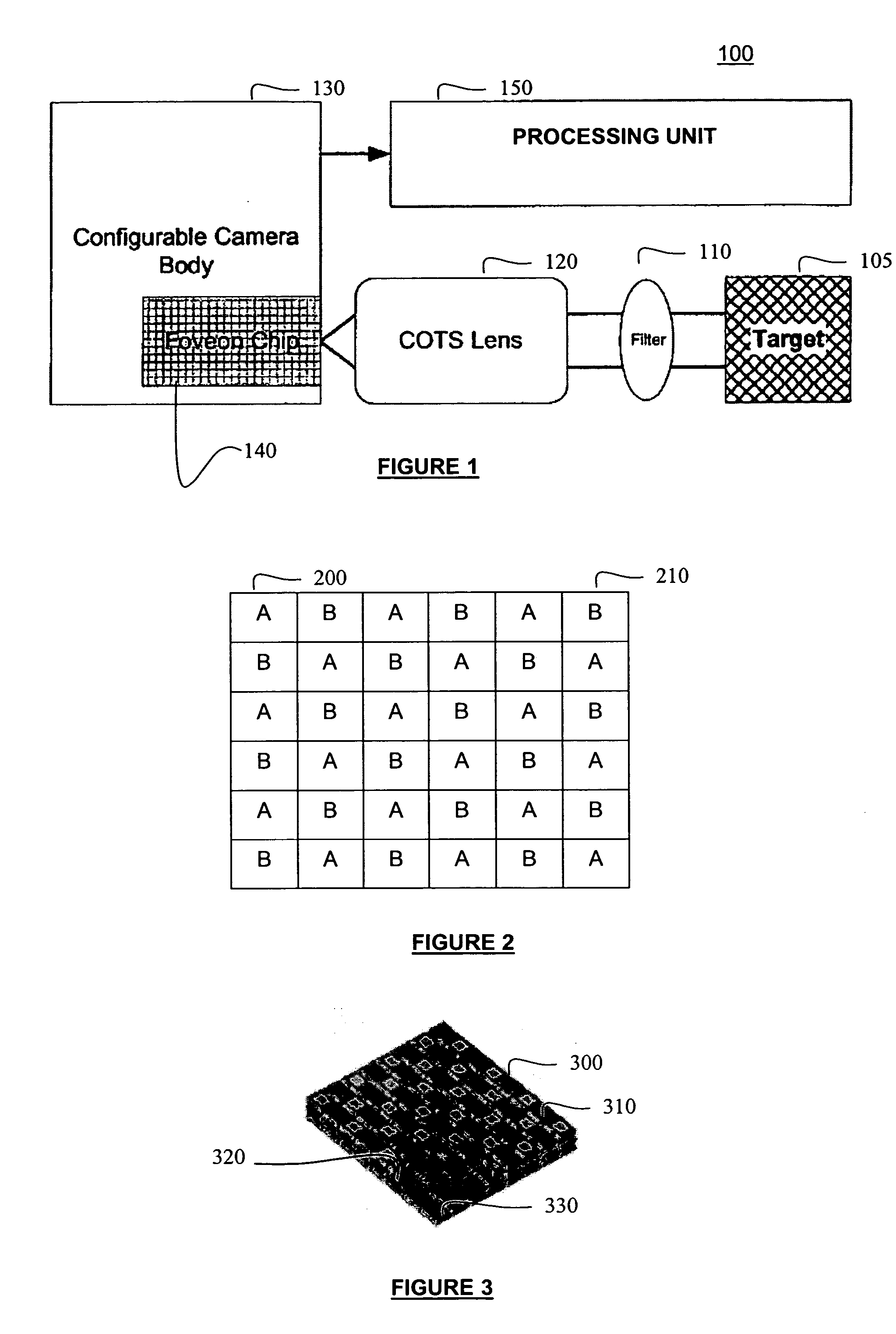
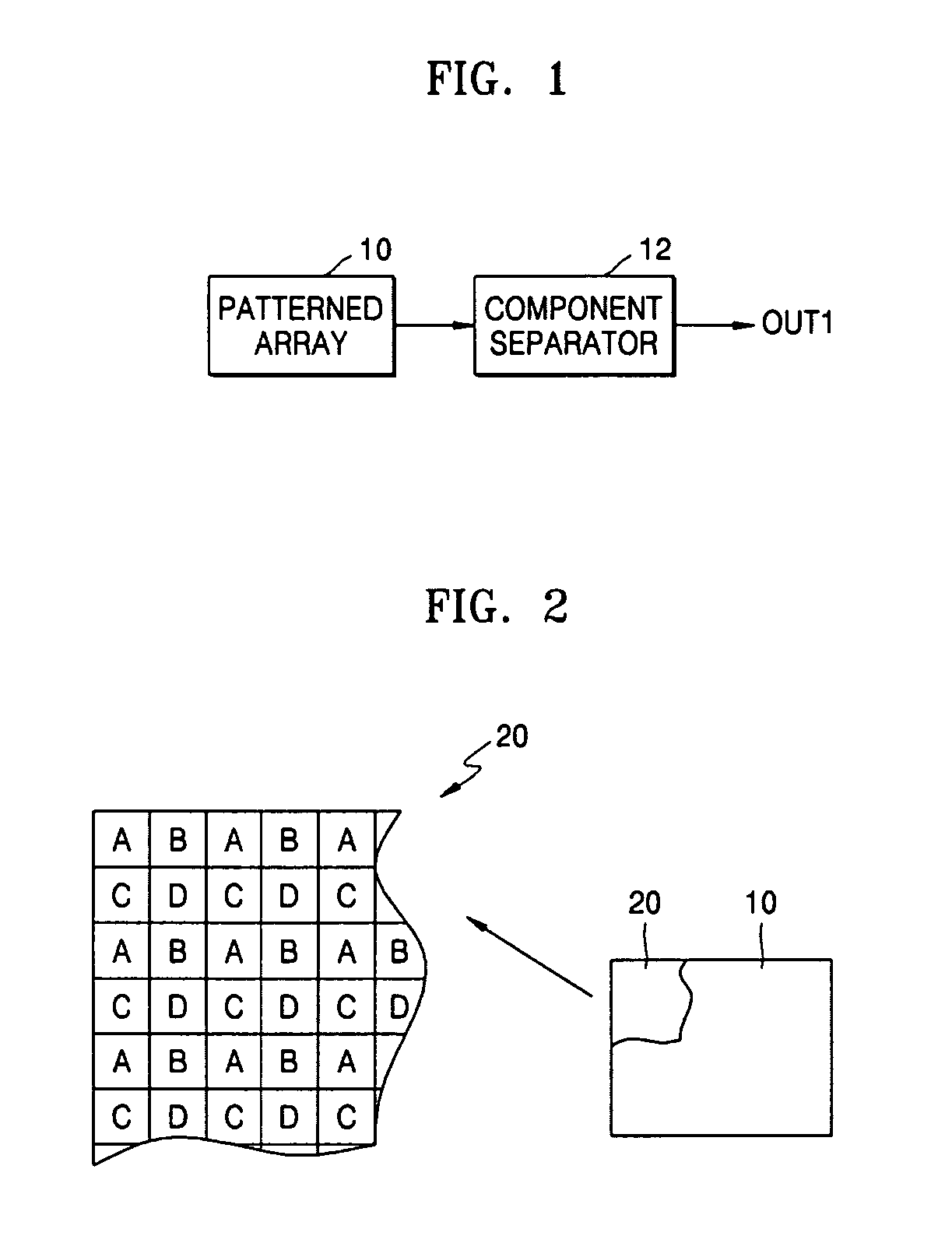
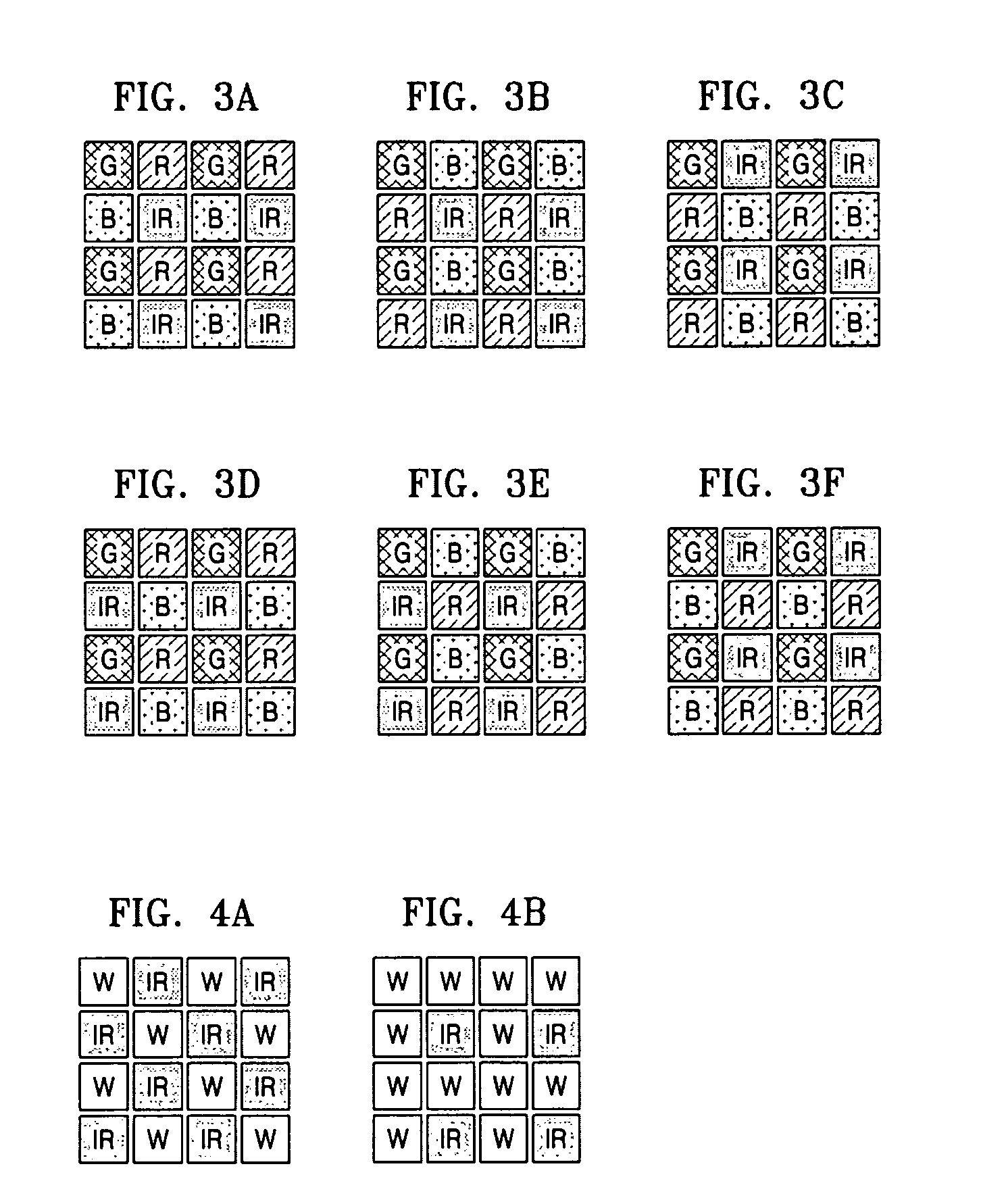
Single camera multi-spectral imager
ActiveUS20070159541A1Improve discriminationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMulti bandSpectral bands
An imaging system has a single focal plane array that does not require the precise alignment of multiple cameras relative to one another. It incorporates a multi-band, band pass filter that includes filter elements corresponding to pixel regions of a detector within a camera. The imaging system may further incorporate a detector that vertically discriminates among radiation in different spectral bands incident on an image plane of the detector. In this manner, spectral content may be determined in each spatial region without the need for beam splitting or multiple cameras. The filter itself may further comprise different filter elements, for example, filter elements A and B arranged in a checkerboard pattern, where filter element A passes different spectral bands than filter element B. In this manner, multi-spectral, high resolution images may be generated using a single camera that significantly improves upon image discrimination as compared to, for example, the Bayer color filter array pattern. The single camera implementation is well suited for incorporation into marine, land and air vehicles.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
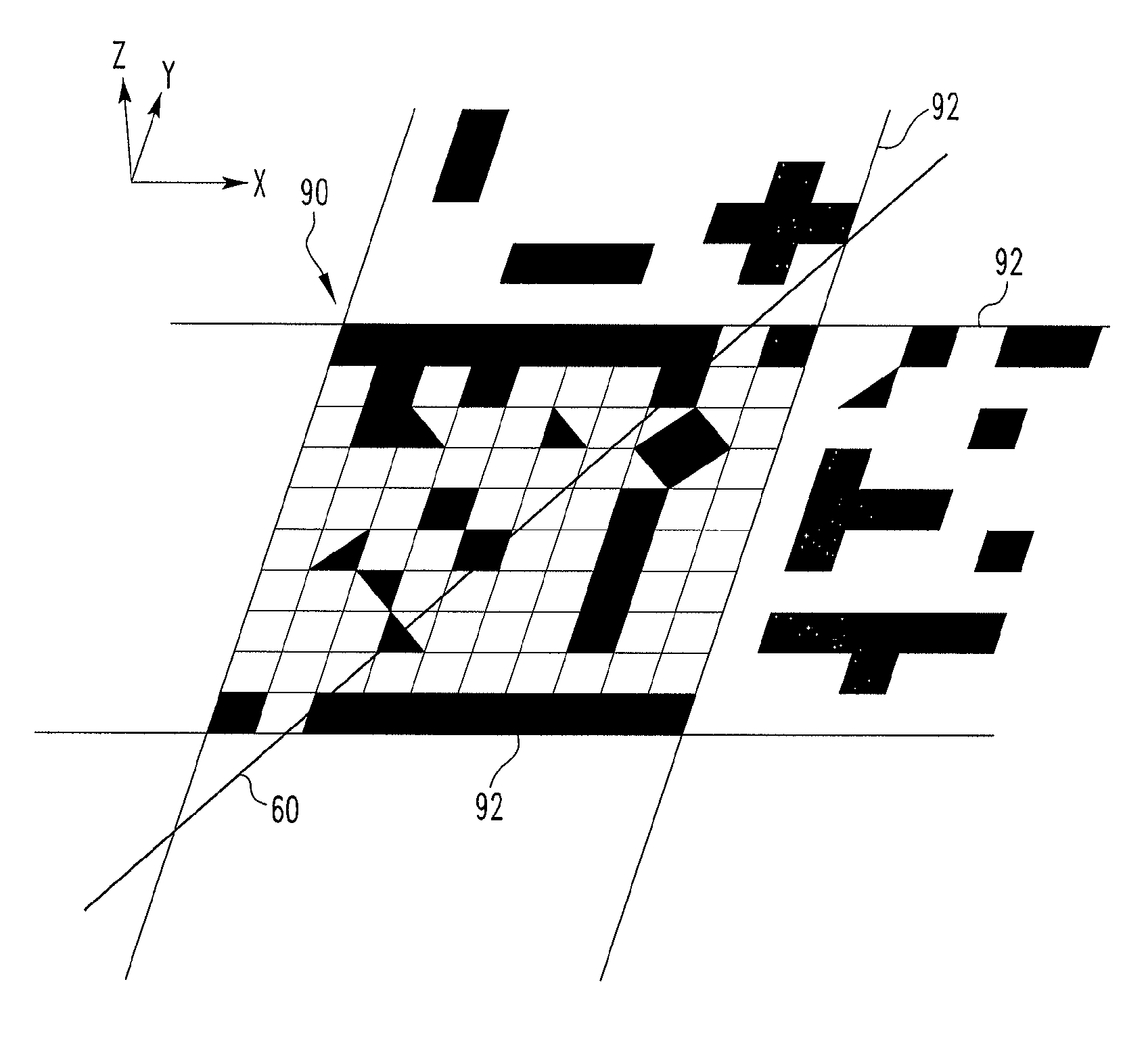
High aspect stereoscopic mode camera and method
InactiveUS6747686B1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsFlight directionComputer graphics (images)
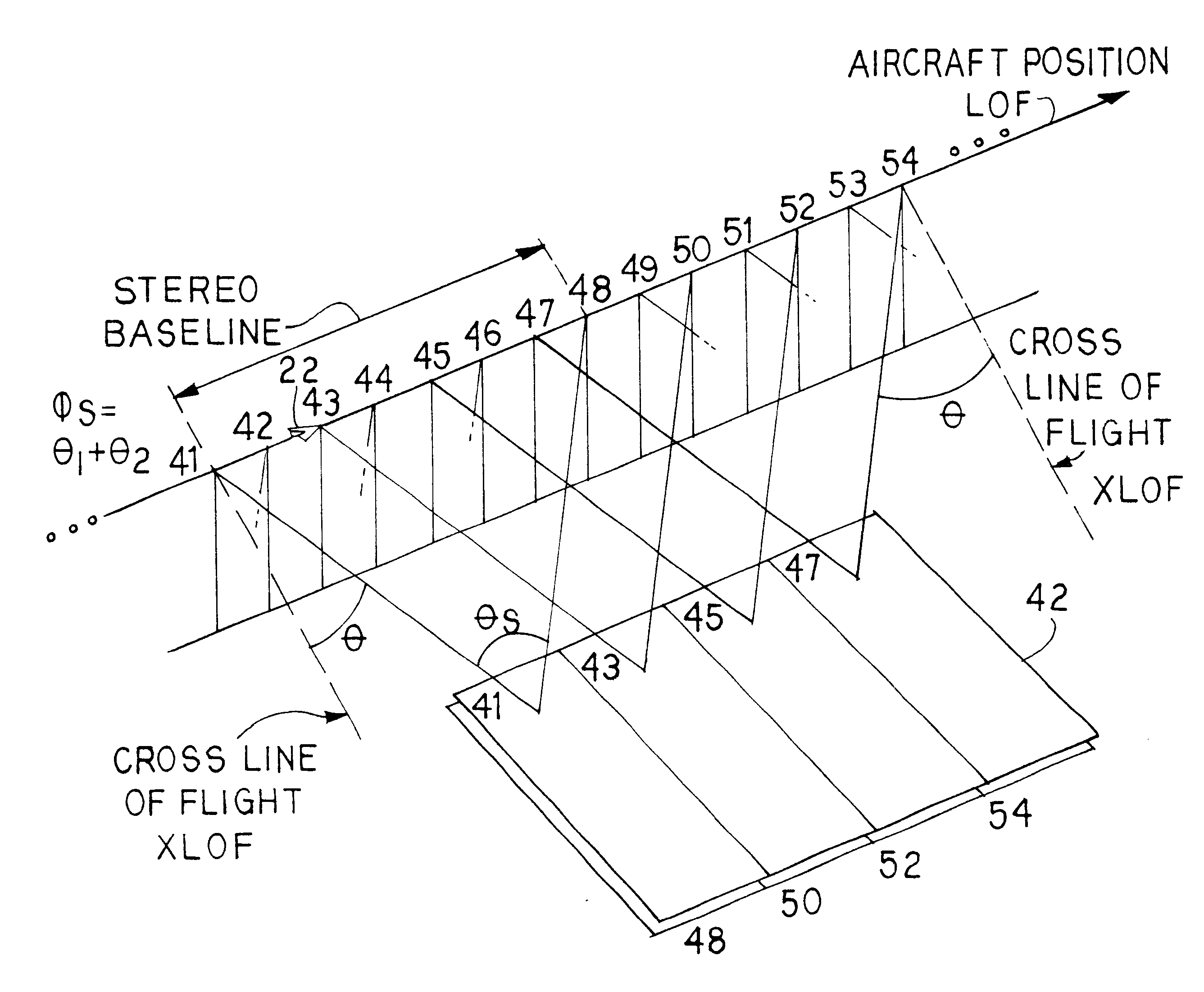
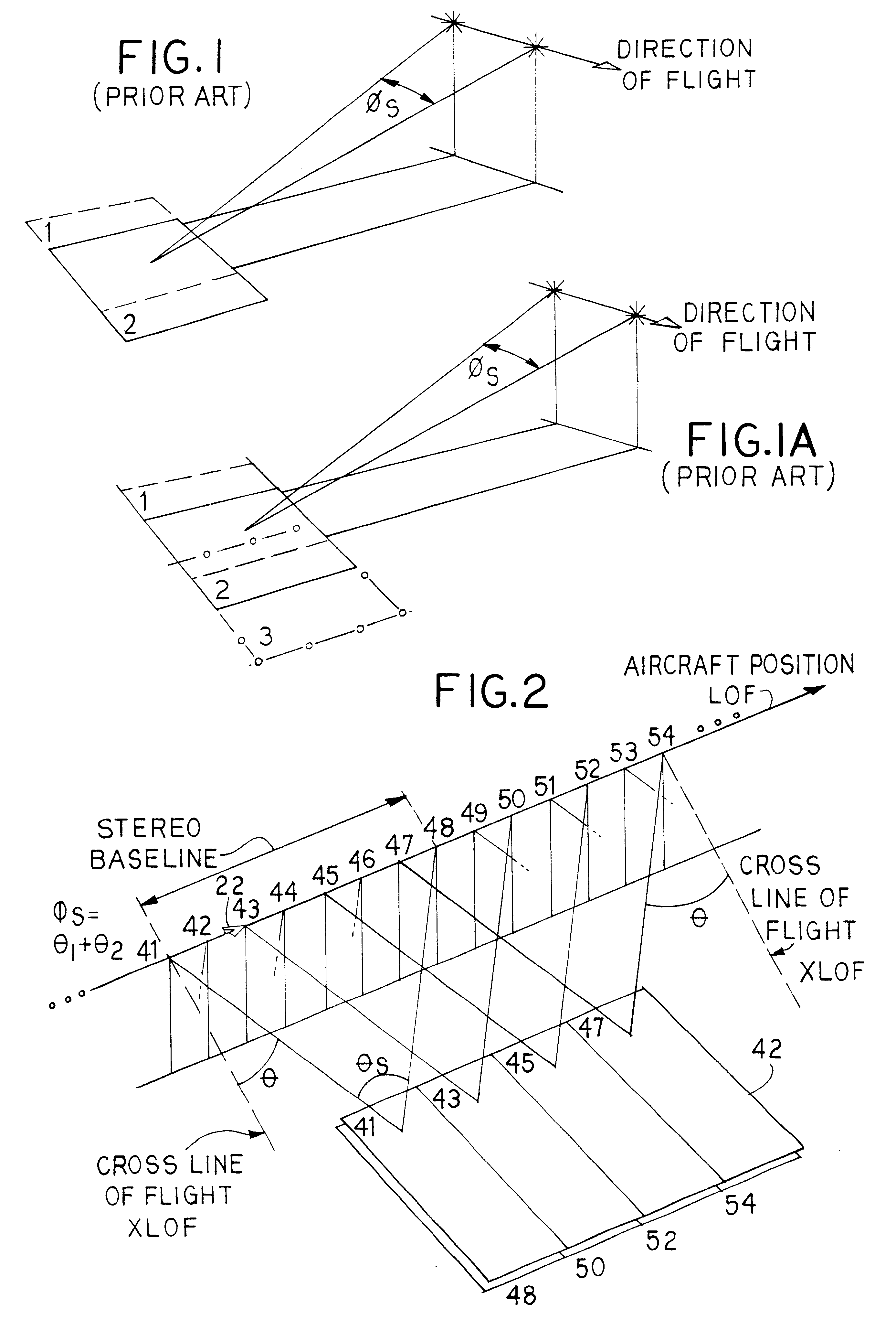
An aerial reconnaissance camera and method provides for generating a first image of the terrain of interest with the camera pointing angle oriented or rotated about an azimuthal axis some angular amount (theta1) to a first, typically forward orientation, i.e., forward of a cross-line of flight direction. An image is obtained of the ground at this orientation. Then the camera is rotated about the azimuthal axis to new angular value (theta2), which will typically be aft of the cross line of flight direction. An image is generated at this value. The camera is then rotated back to the value of theta1, and a second image in the forward orientation is generated. The camera is then rotated again to the value of theta2 and another image in the aft orientation is generated. This process of rotating the camera about the azimuthal axis and generating images in forward and aft orientations continues over and over. Eventually, as the aircraft flies past the terrain of interest, any given location in the terrain of interest will have been imaged from two different perspectives-forward and aft. The motion of the aircraft during the interim in combination with the values of theta1 and theta2 provide the high baseline for the stereo image pairs. By selection of suitable values for the angular separation of theta1 and theta2 (such as theta1=+10 degrees and theta2=-10 degrees) the result will be pairs of images of the terrain of interest having a large baseline, producing truly high aspect stereo images from a single camera. The method also works in a similar fashion by rotation back and forth about the pitch axis and imaging the terrain in forward oblique and aft oblique orientations.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Self-calibrating, digital, large format camera with single or mulitiple detector arrays and single or multiple optical systems
InactiveUS20020163582A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationDigital signal processingAccelerometer
Large format, digital camera systems (10, 100, 150, 250, 310) expose single detector arrays 20 with multiple lens systems (12, 14, 16, 18) or multiple detector arrays (104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 152, 162, 172, 182, 252, 262, 272, 282, 322, 324) with one or more single lens systems (156, 166, 176, 186) to acquire sub-images of overlapping sub-areas of large area objects. The sub-images are stitched together to form a large format, digital, macro-image (80, 230'', 236'', 238'', 240''), which can be colored. Dampened camera carrier (400) and accelerometer (404) signals with double-rate digital signal processing (306, 308) are used.
Owner:VEXCEL IMAGING US INC
Dimensional Detection System and Associated Method
InactiveUS20110286007A1Clear visionSafety devices for lifting equipmentsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setLight beam
An improved dimensional detection system is portable and can be used to characterize a workpiece. The dimensional detection system employs as few as a single focused light source and as few as a single camera along with a calibration data set to convert the illuminated pixels of an image of a beam on the workpiece into a cloud of real world points in space on an outer surface of the workpiece. The cloud of points can be processed to characterize the workpiece, such as by determining the right hexahedron that would encompass all of the real world points in space and which could be used to determine a dimensional weight of the workpiece.
Owner:LTS SCALE CO LLC
Imaging apparatus, medium, and method using infrared rays with image discrimination
InactiveUS20060097172A1Easy to identifyTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryColor imageInfrared
An imaging apparatus, medium, and apparatus using infrared rays with image discrimination. The imaging apparatus may includes an image sensor optically together sensing a visible light component and an infrared component of an image, and an image processor to recognize an object component of the image. Accordingly, an infrared component cell can be far more easily implemented than conventionally. Also, an object component can be more accurately identified while being less affected by ambient illumination of the object component because an infrared component is used. Furthermore, both iris identification and color image acquisition can be achieved using a single camera by employing the image sensor, which senses the infrared component and the visible light component together. Thus, both the iris identification and the color image acquisition can be incorporated and executed by a single camera. Therefore, the imaging apparatus can be made compact.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Novel man machine interfaces and applications
InactiveUS20060202953A1Good adhesionIncrease brightnessInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrophonic musical instrumentsComputer Aided DesignHuman–machine interface
Affordable methods and apparatus are disclosed for inputting position, attitude (orientation) or other object characteristic data to computers for the purpose of Computer Aided Design, Painting, Medicine, Teaching, Gaming, Toys, Simulations, Aids to the disabled, and internet or other experiences. Preferred embodiments of the invention utilize electro-optical sensors, and particularly TV Cameras, providing optically inputted data from specialized datum's on objects and / or natural features of objects. Objects can be both static and in motion, from which individual datum positions and movements can be derived, also with respect to other objects both fixed and moving. Real-time photogrammetry is preferably used to determine relationships of portions of one or more datums with respect to a plurality of cameras or a single camera processed by a conventional PC.
Owner:MOTION GAMES
Occupant sensing system
InactiveUS7415126B2Improve comfortAvoid accidentsVehicle seatsBelt retractorsCMOSClassification methods
Optical classification method for classifying an occupant in a vehicle by acquiring images of the occupant from a single camera and analyzing the images acquired from the single camera to determine a classification of the occupant. The single camera may be a digital CMOS camera, a high-power near-infrared LED, and the LED control circuit. It is possible to detect brightness of the images and control illumination of an LED in conjunction with the acquisition of images by the single camera. The illumination of the LED may be periodic to enable a comparison of resulting images with the LED on and the LED off so as to determine whether a daytime condition or a nighttime condition is present. The position of the occupant can be monitored when the occupant is classified as a child, an adult or a forward-facing child restraint.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
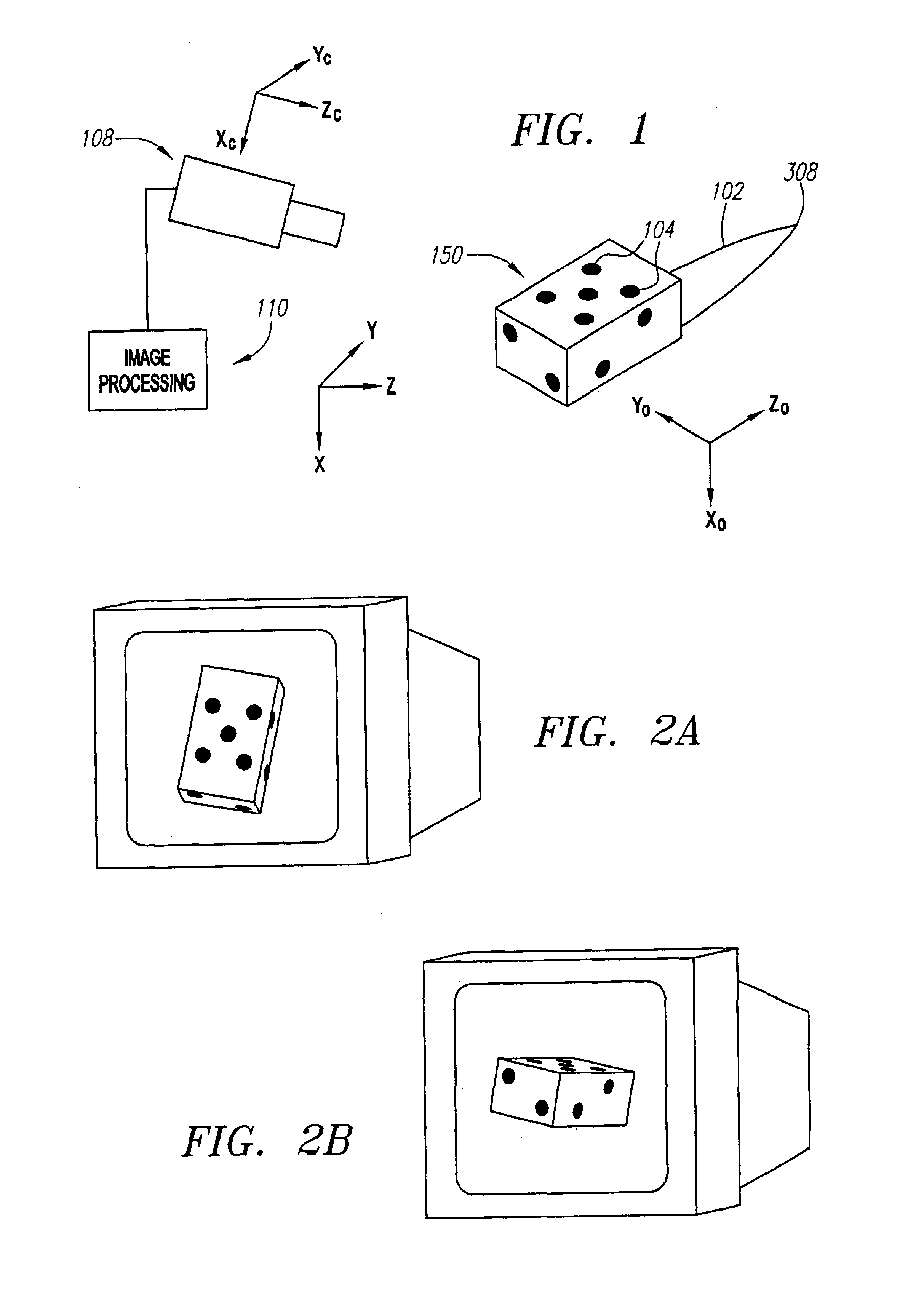
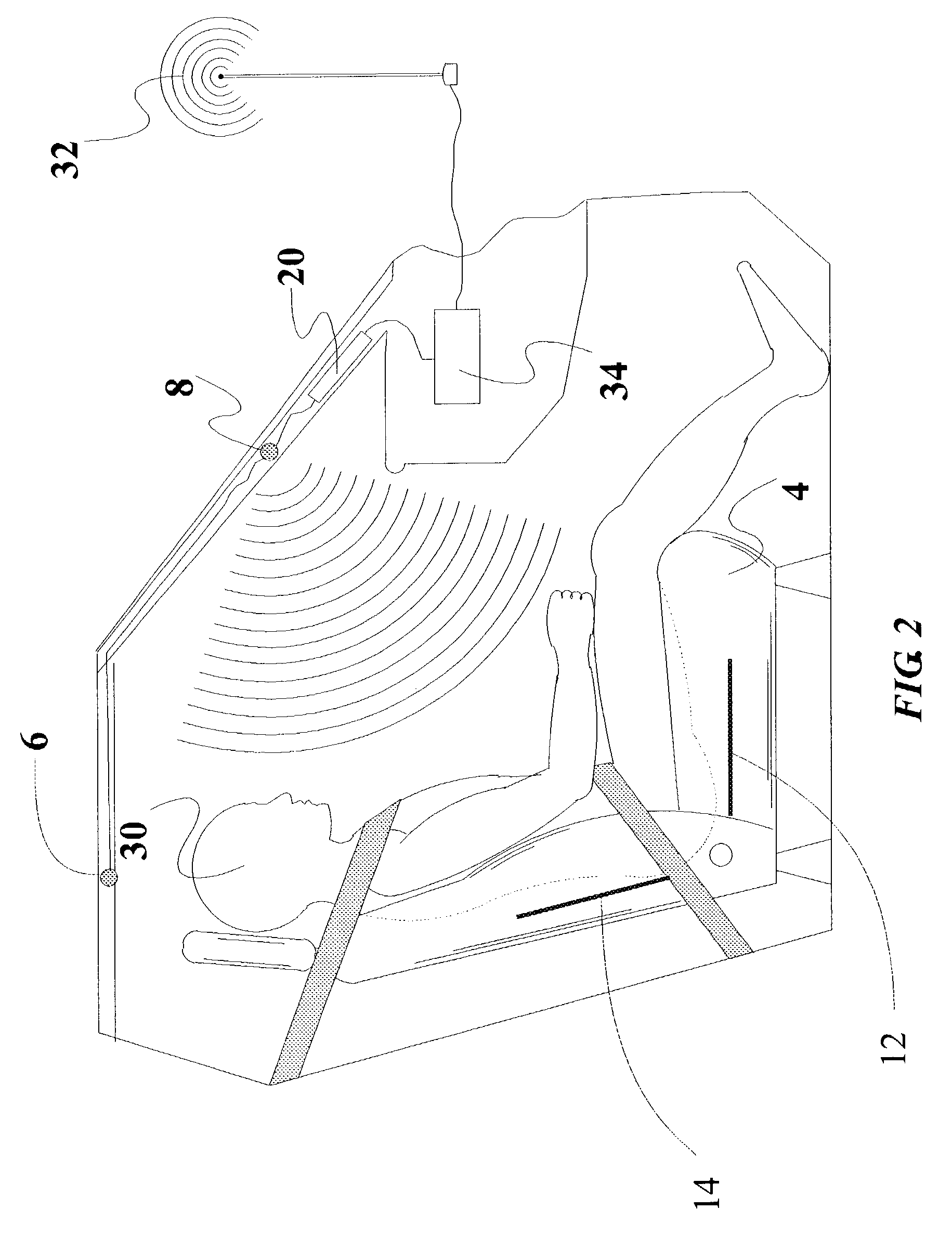
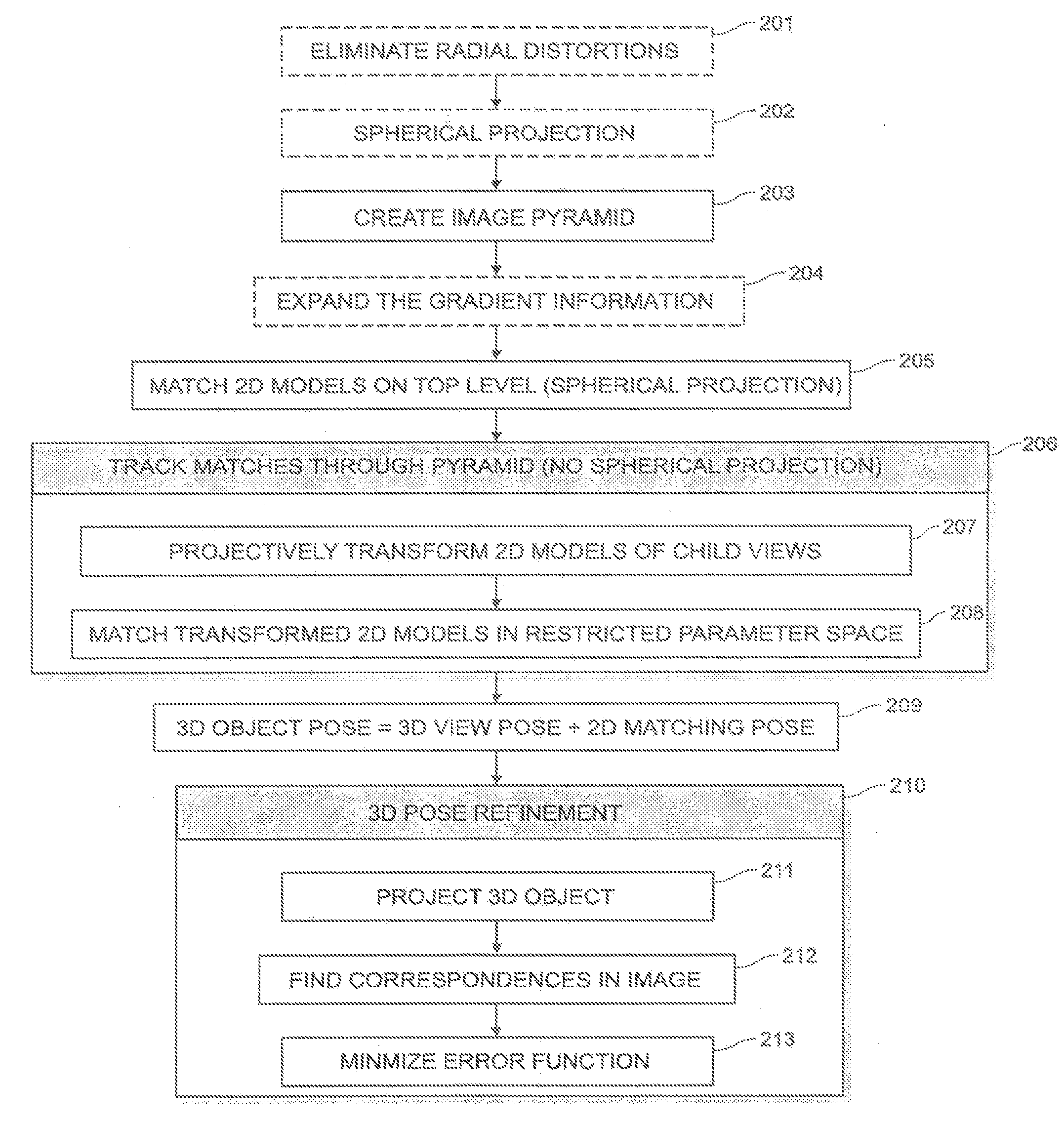
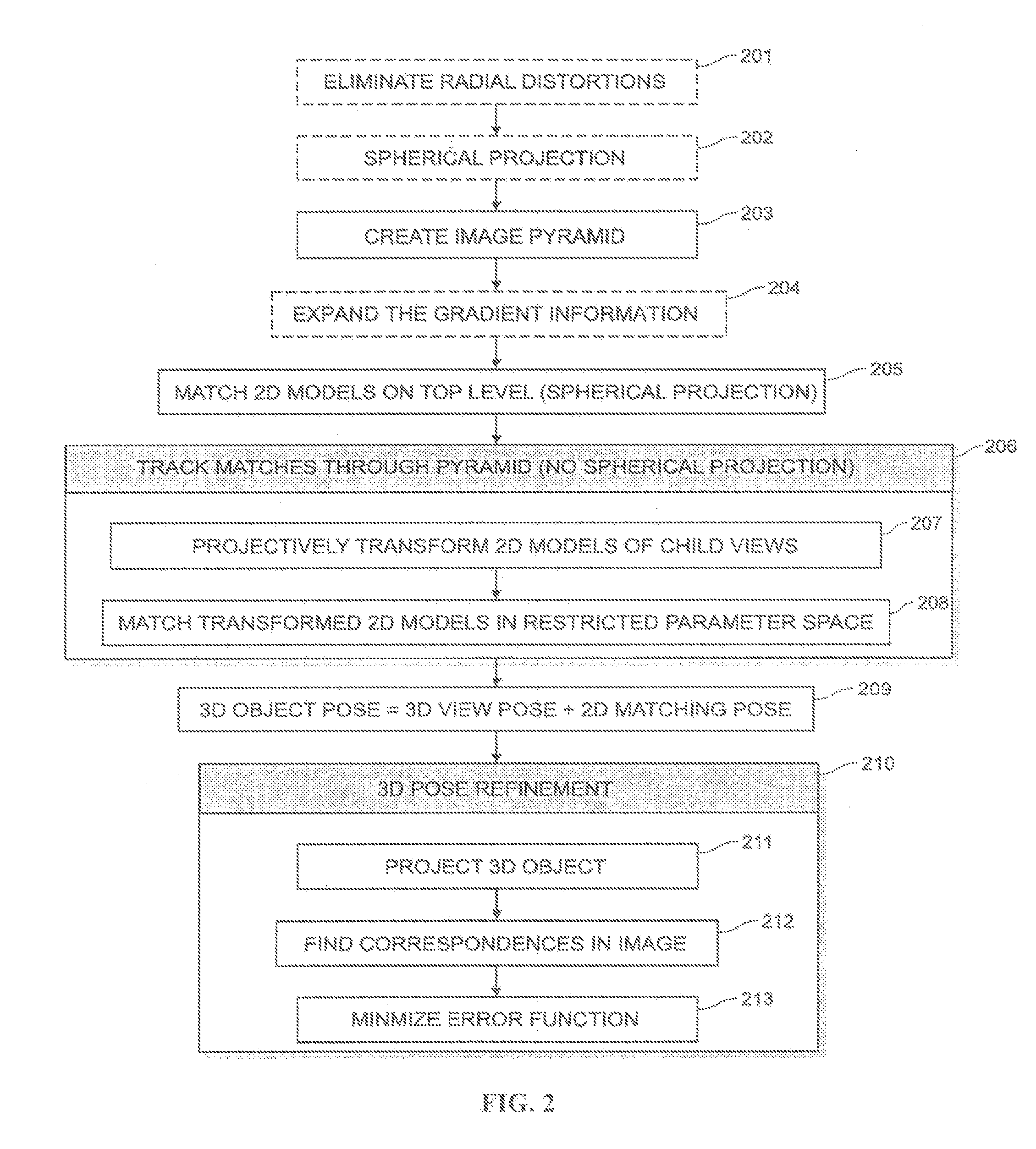
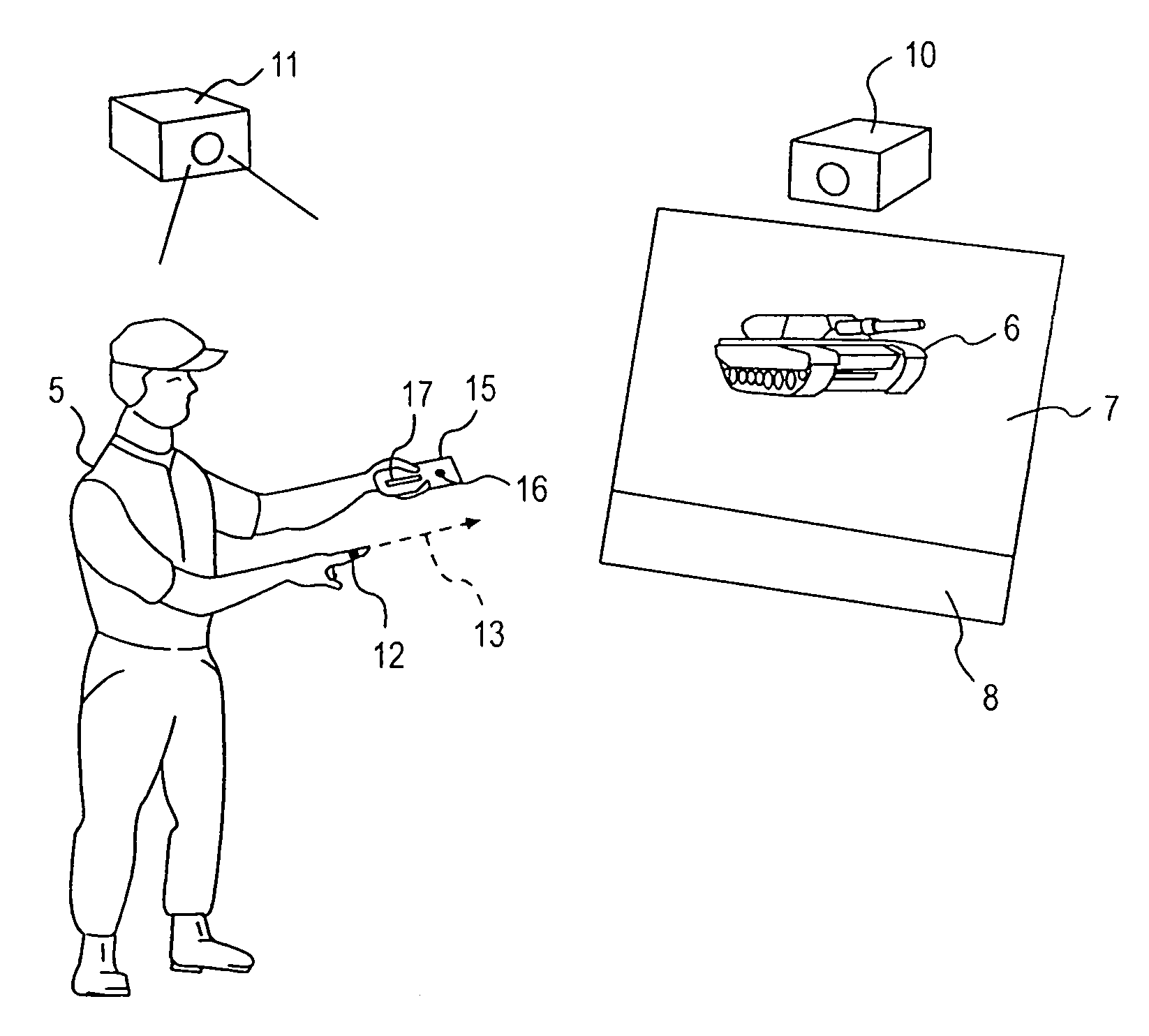
System and method for 3D object recognition
ActiveUS20090096790A1Significant distortionReduce the impactProgramme-controlled manipulator3D-image renderingPresent methodView based
The present invention provides a system and method for recognizing a 3D object in a single camera image and for determining the 3D pose of the object with respect to the camera coordinate system. In one typical application, the 3D pose is used to make a robot pick up the object. A view-based approach is presented that does not show the drawbacks of previous methods because it is robust to image noise, object occlusions, clutter, and contrast changes. Furthermore, the 3D pose is determined with a high accuracy. Finally, the presented method allows the recognition of the 3D object as well as the determination of its 3D pose in a very short computation time, making it also suitable for real-time applications. These improvements are achieved by the methods disclosed herein.
Owner:MVTEC SOFTWARE
Interactive video based games using objects sensed by TV cameras
InactiveUS7843429B2Good adhesionIncrease brightnessInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionInteractive videoStereo cameras
A method and apparatus for interactive TV camera based games in which position or orientation of points on a player or of an object held by a player are determined and used to control a video display. Both single camera and stereo camera pair based embodiments are disclosed, preferably using stereo photogrammetry where multi-degree of freedom information is desired. Large video displays, preferably life-size may be used where utmost realism of the game experience is desired.
Owner:MOTION GAMES
Resolution-enhancement method for digital imaging
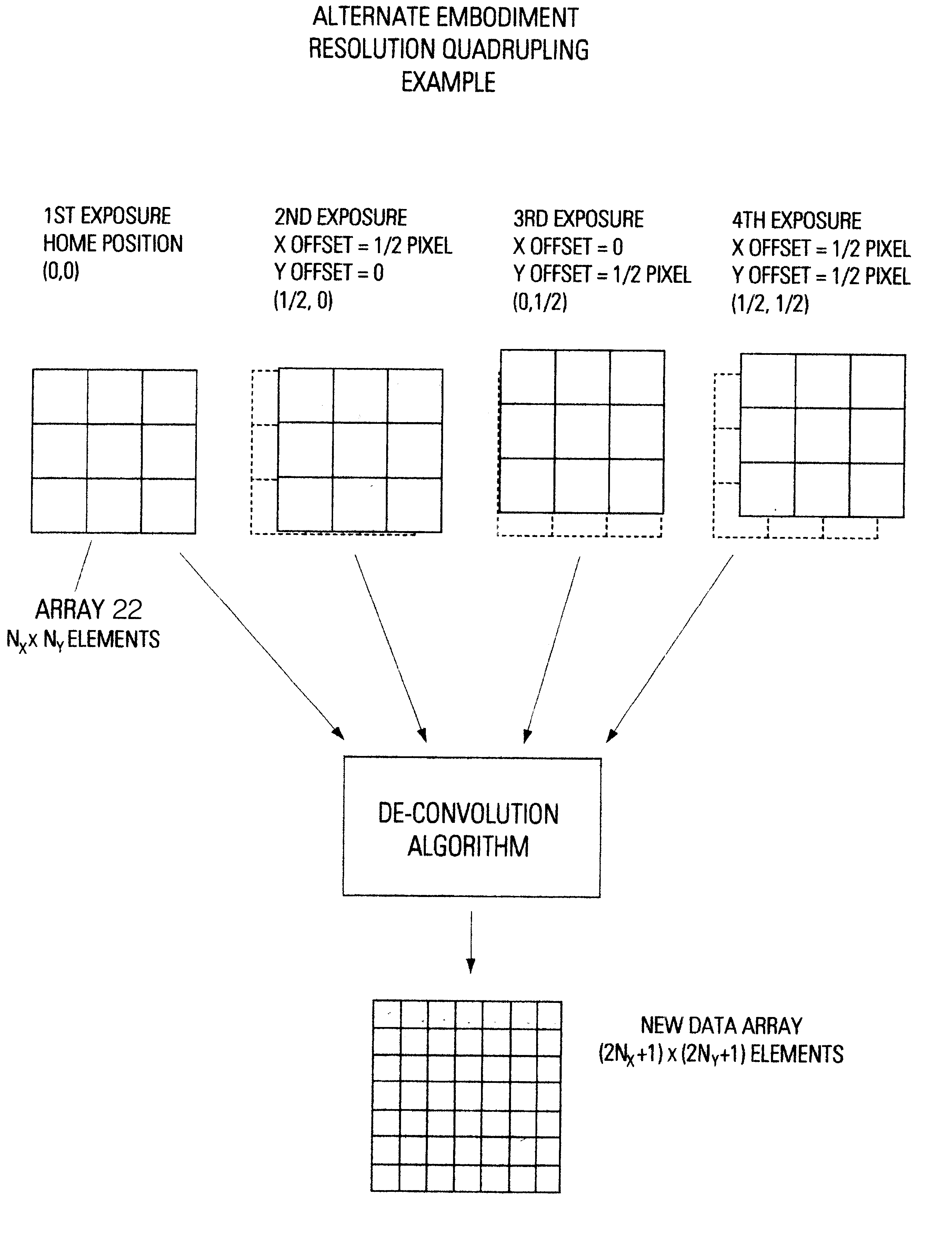
InactiveUS6570613B1High resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital imagingImage resolution
A method for resolution enhancement of a still-image made by a digital imaging device. The method allows the use of high-aperture-ratio sensing arrays that produce resolution-enhancement, independent of the angle of view. Resolution-enhancement is achieved using a multiple-exposure technique of a sub-pixel overtap in conjunction with a whole-pixel shift. The method suppresses color-aliasing in a multiple-exposure native-resolution mode and enables the use of a single camera for single-exposure and multiple-exposure modes.
Owner:HOWELL
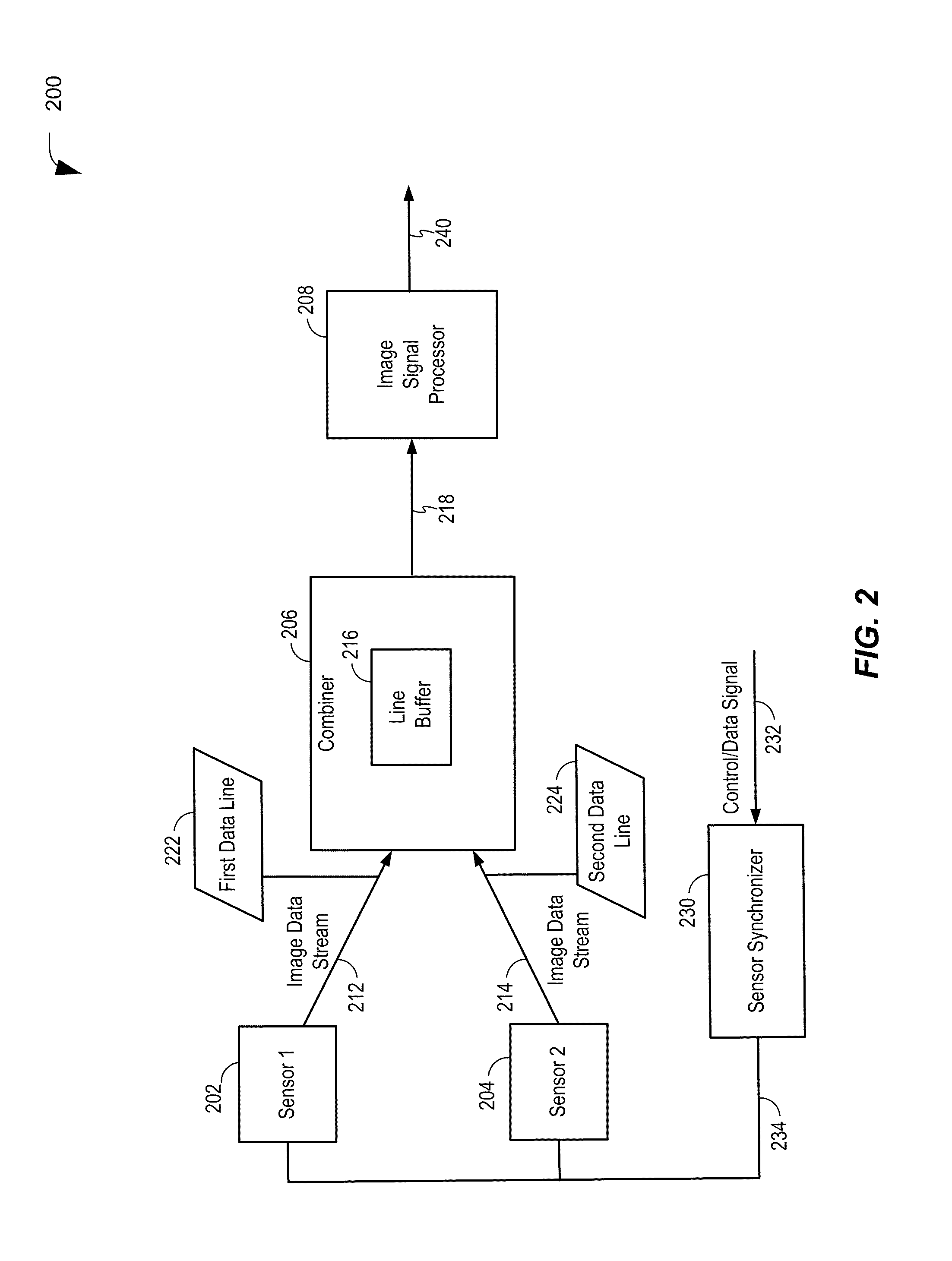
Combining data from multiple image sensors
ActiveUS20120081519A1Avoid pollutionTelevision system detailsSteroscopic systemsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A method of combining data from multiple sensors is disclosed. The method includes receiving lines of image data at an image processor having an input for a single camera. Each line of the image data includes first line data from a first image captured by a first camera and second line data from a second image captured by a second camera. The method also includes generating an output frame having a first section corresponding to line data of the first image and having a second section corresponding to line data of the second image. The first section and the second section are configured to be used to generate a three-dimensional (3D) image format or a 3D video format.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Dimensional detection system and associated method
InactiveUS8134717B2Clear visionSafety devices for lifting equipmentsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setLight beam
An improved dimensional detection system is portable and can be used to characterize a workpiece. The dimensional detection system employs as few as a single focused light source and as few as a single camera along with a calibration data set to convert the illuminated pixels of an image of a beam on the workpiece into a cloud of real world points in space on an outer surface of the workpiece. The cloud of points can be processed to characterize the workpiece, such as by determining the right hexahedron that would encompass all of the real world points in space and which could be used to determine a dimensional weight of the workpiece.
Owner:LTS SCALE CO LLC
Audio-visual three-dimensional input/output
InactiveUS7774075B2Input/output for user-computer interactionComputer controlThird generationMobile device
Methods and apparatus for determining an object's three-dimensional location (i.e. real world coordinates) using the audio-video infrastructure of a 3G cellular phone or a 3C (Computer, Communications, Consumer) electronic device. A first detection device (e.g. a camera) is used to capture images of the objects. The captured image data is used to compute location data of the object in a first two-dimensional plane. A second detection device (e.g. microphone or infrared detector) may be used to collect additional location data in a second plane, which when combined with image data from the captured images allows the determination of the real world coordinates (x, y, z) of the object. The real-world coordinate data may be used in various applications. If the size of an object of interest is known or can be calculated, and the size of the projected image does not vary due to rotation of the object, a single camera (e.g. the camera in a 3G or 3C mobile device) may be used to obtain three-dimensional coordinate data for the applications.
Owner:LIN JULIUS J Y
Optical tracking apparatus using six degrees of freedom
InactiveUS8077914B1Improve robustnessAccurate trackingAcquiring/recognising eyesEye diagnosticsAngular degreesLight-emitting diode
This invention discloses an optical object tracking method and system with to up to six degrees of freedom: three translational and three angular coordinates. In the preferred embodiment, the system includes two near-infra-red light sources (e.g., light emitting diode), two cameras, and a digital signal processor. The system performs to tasks: object locking and tracking. For object locking and tracking, a single camera and two off-axis light sources are engaged. For more precise object tracking, two spatially-separate cameras and a single diode are used. In another embodiment, a third camera may be used to separate the locking and tracking tasks. The light sources may have different light wavelengths and may operate in a sequential mode. The cameras may be sensitive over different spectral ranges and may also differ in terms of field-of-view and resolution. The invention describes a method based on capturing images of light reflections at the camera focal plane and analyzing them, through mathematical mapping, for known locations of light sources and cameras. Invention can be adopted for the tracking of an eyeball. The related method determines an object location and orientation or a gaze vector and a point-of-regard.
Owner:KAPLAN ARKADY
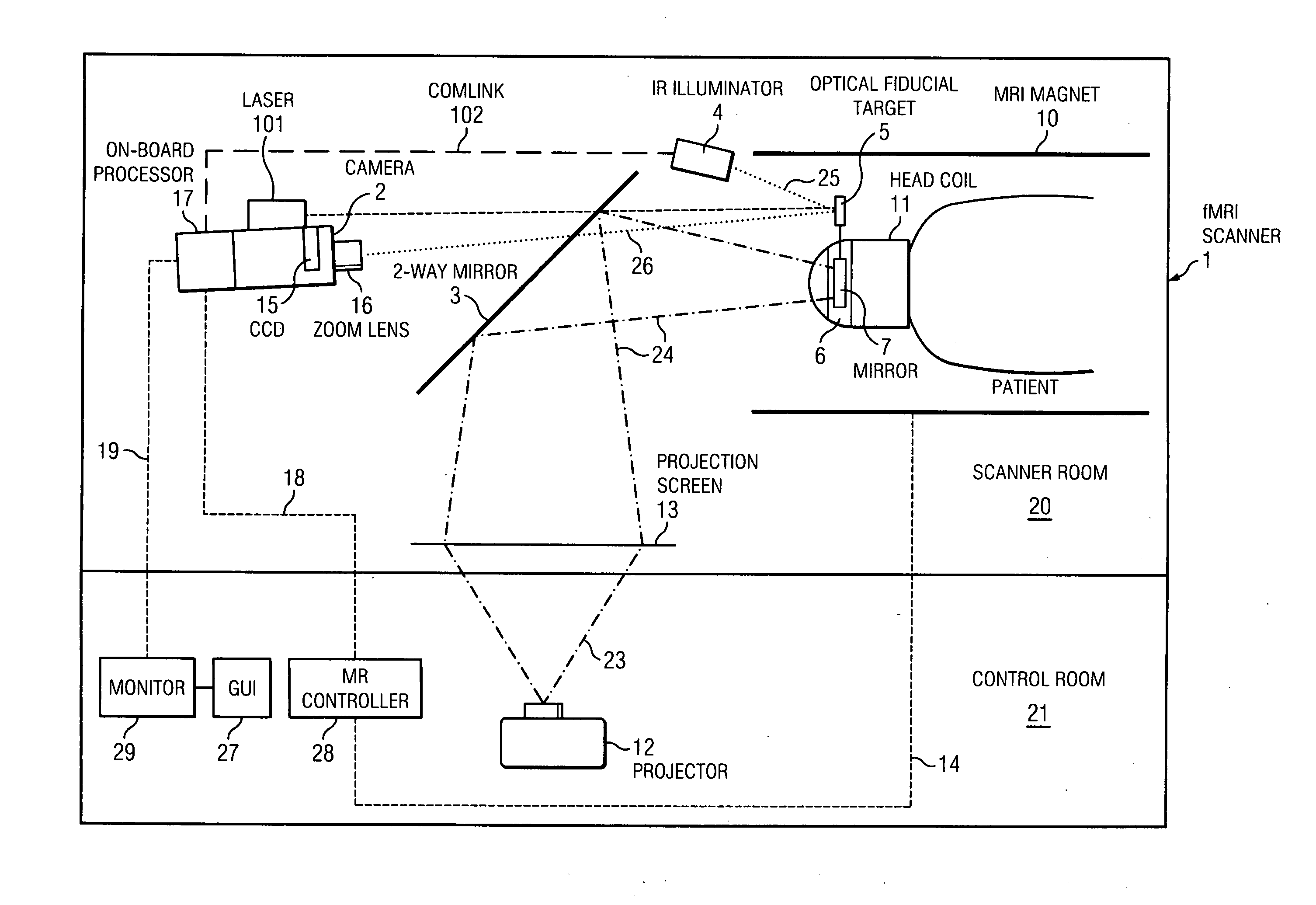
Single camera motion measurement and monitoring for magnetic resonance applications
InactiveUS20110230755A1Improves imaging timeImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisOn boardResonance
An optically-based rigid-body 6-DOF motion tracking system optimized for prospective (real-time) motion correction in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) applications using a single camera with an on-board image processor, an IR illuminator and optical fiducial targets affixed to a patient. An angle extraction algorithm operated by the on-board image processor utilizes successive approximation to solve the 3-point pose problem for angles close to the origin to achieve convergence to sub-microradian levels. A motion alarm is enabled by a monitor and GUI application in communication with the motion tracking system. A motion correction is enabled for MR scan images taken while operating the motion tracking system wherein an MRI controller is in communication with the motion tracking system.
Owner:MACFARLANE DUNCAN +1
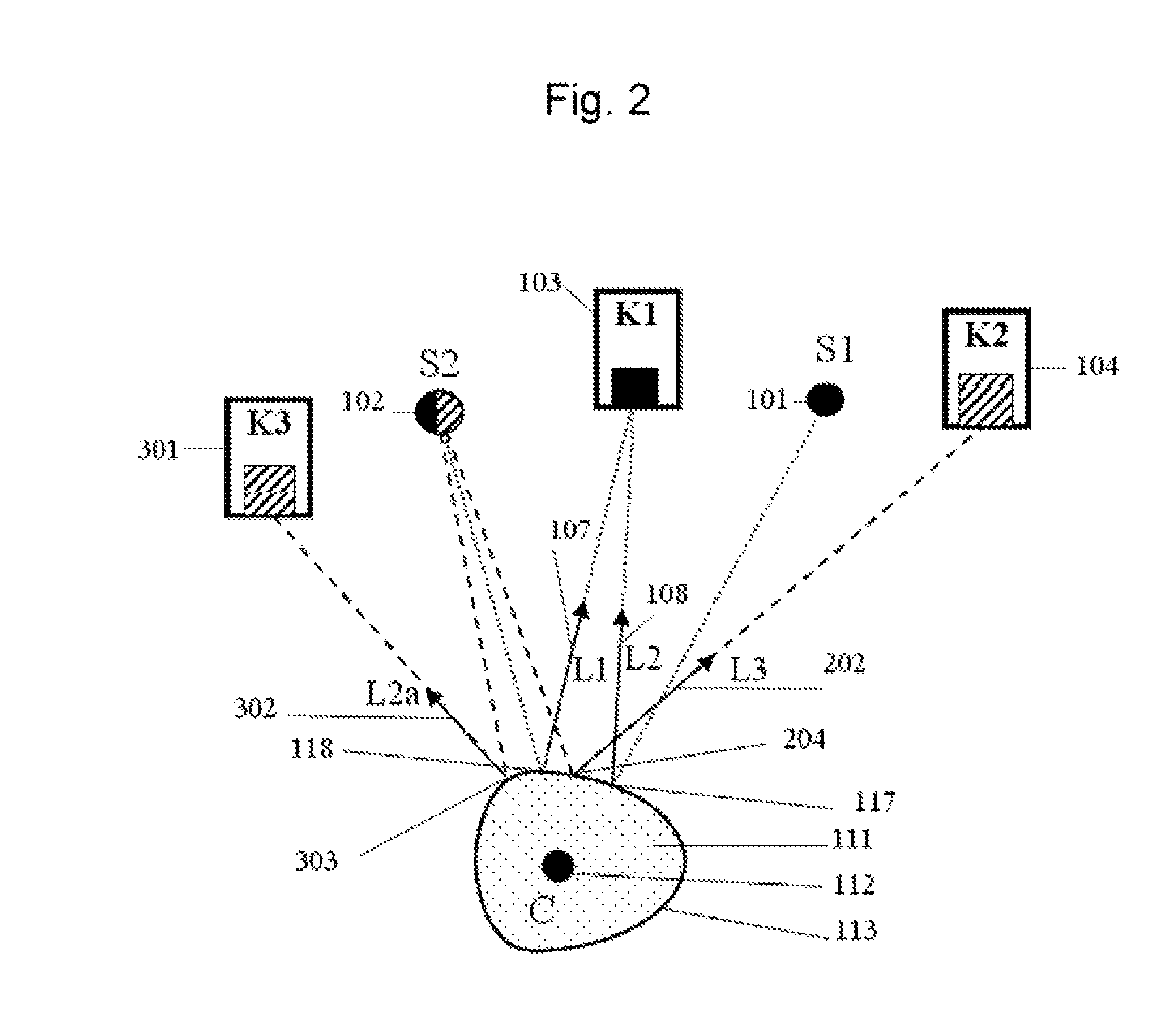
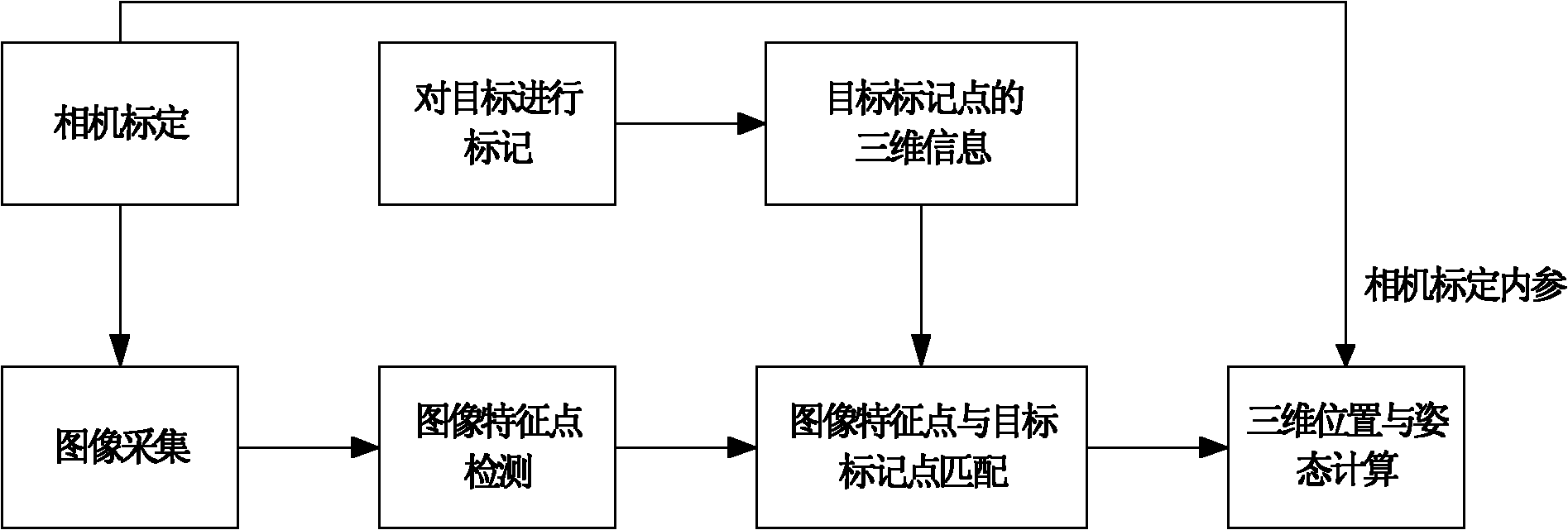
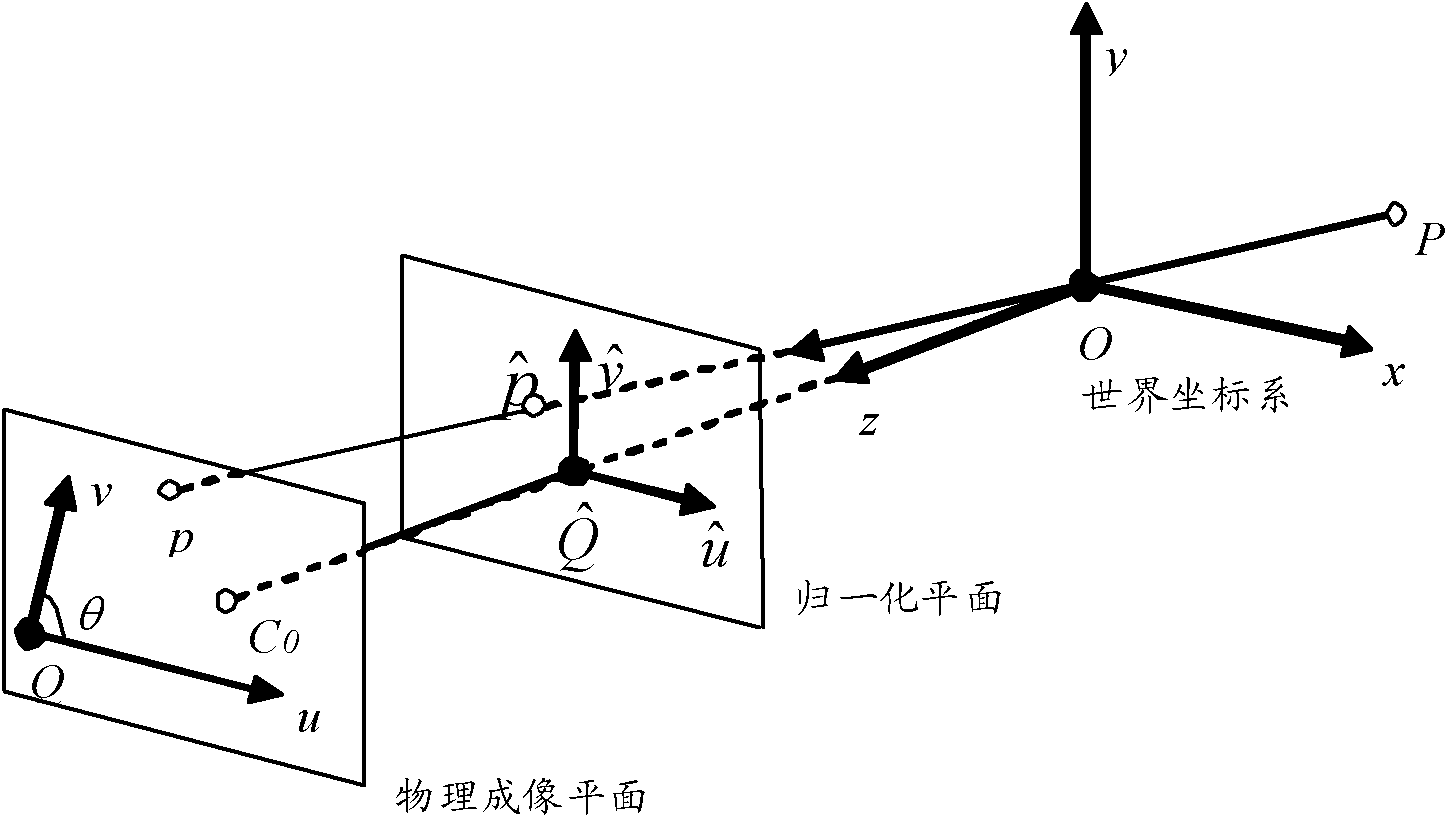
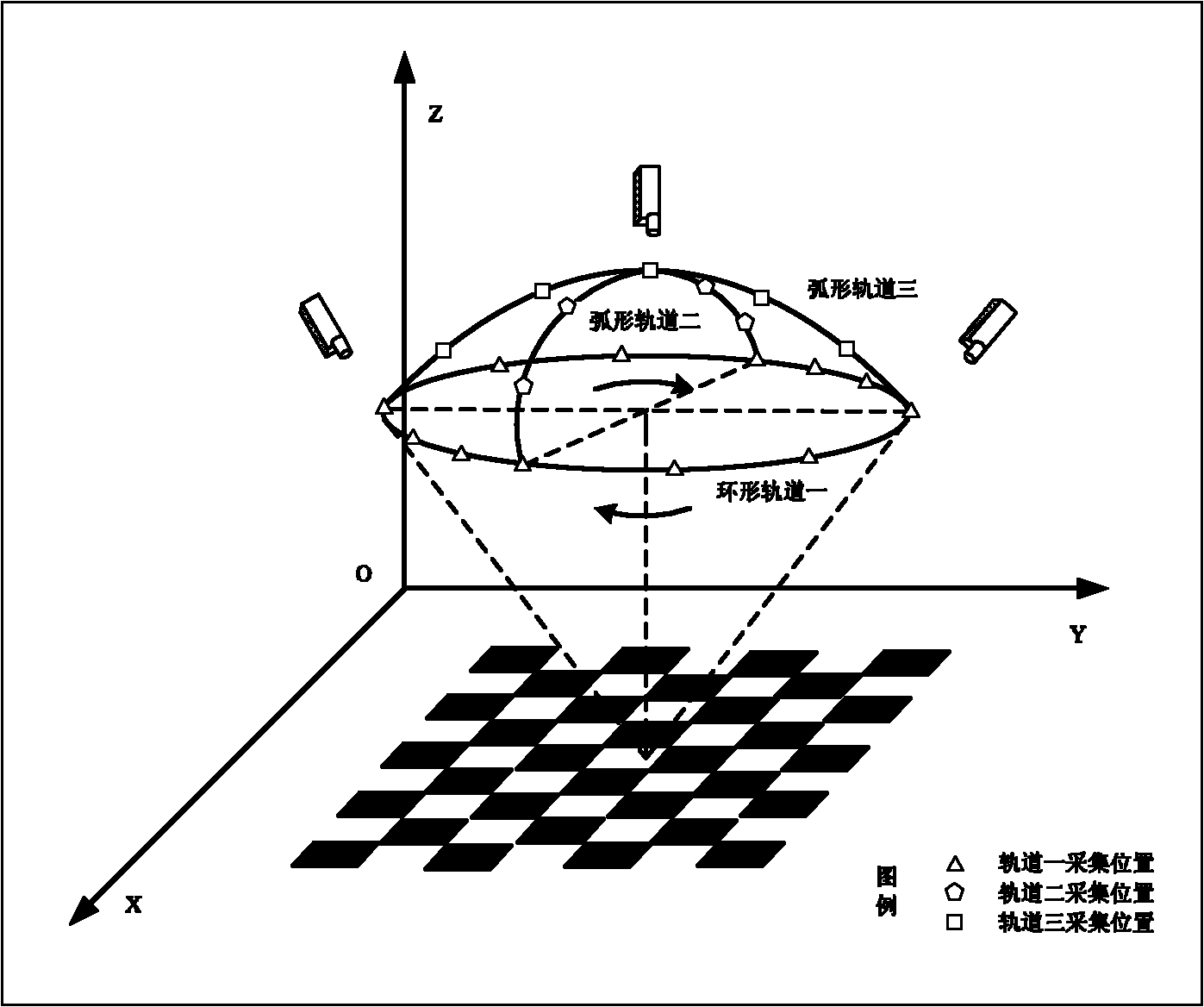
Method for measuring three-dimensional position and stance of object with single camera
InactiveCN101839692AReduce cost of measurementReduce volumeUsing optical meansPicture interpretationThree-dimensional spaceMeasurement point
The invention discloses a method for measuring the three-dimensional position and the stance of an object with a single camera. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring an image of a target to be measured by utilizing a single camera; confirming the real-time three-dimensional position and stance information of the target to be measured by accurately identifying marking points on the target to be measured; selecting a suitable camera according to a detection scene and a range and calibrating the camera to acquire inner and outer parameters of the camera; designing target marking points according to the target to be measured and reasonably arranging the marking points; then, detecting the target, identifying characteristic points according to the image shot by the camera, and matching the detected characteristic points with the marking points; and finally, solving the three-dimensional position and stance information of the target to be measured according to the corresponding relation between the measuring points and the object marking points. Whether a non-rigid object is deformed or not can also be detected by using the method. In the invention, the single camera is adopted to realize three-dimensional measurement, acquire the information of the target in a three-dimensional space, such as space geometrical parameters, position, stance, and the like, decrease the measuring cost and the size of a measuring system, and facilitate the operation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
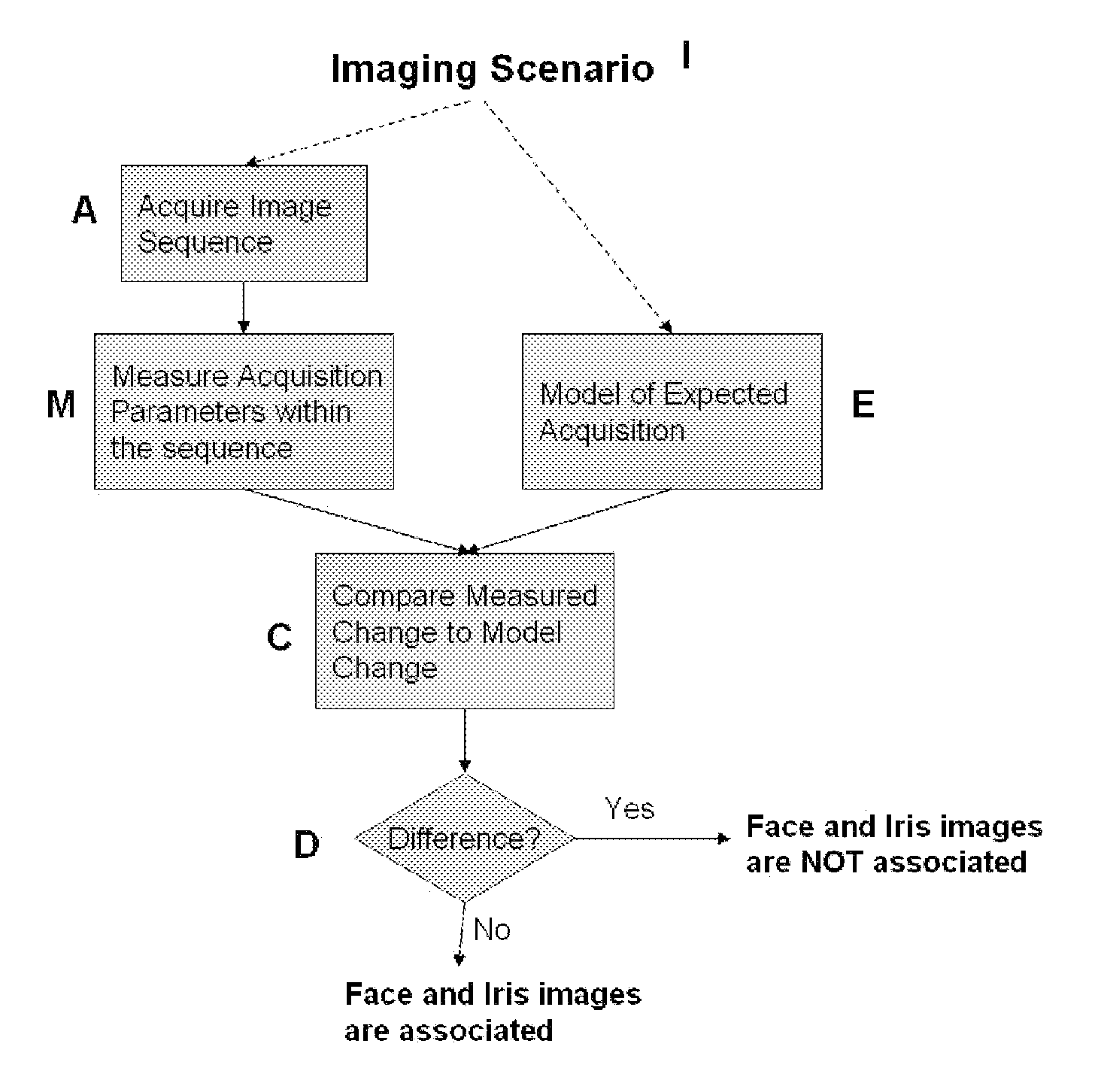
Methods for performing biometric recognition of a human eye and corroboration of same
A method of biometric recognition is provided. Multiple images of the face or other non-iris image and iris of an individual are acquired. If the multiple images are determined to form an expected sequence of images, the face and iris images are associated together. A single camera preferably acquires both the iris and face images by changing at least one of the zoom, position, or dynamic range of the camera. The dynamic range can be adjusted by at least one of adjusting the gain settings of the camera, adjusting the exposure time, and / or adjusting the illuminator brightness. The expected sequence determination can be made by determining if the accumulated motion vectors of the multiple images is consistent with an expected set of motion vectors and / or ensuring that the iris remains in the field of view of all of the multiple images.
Owner:EYELOCK
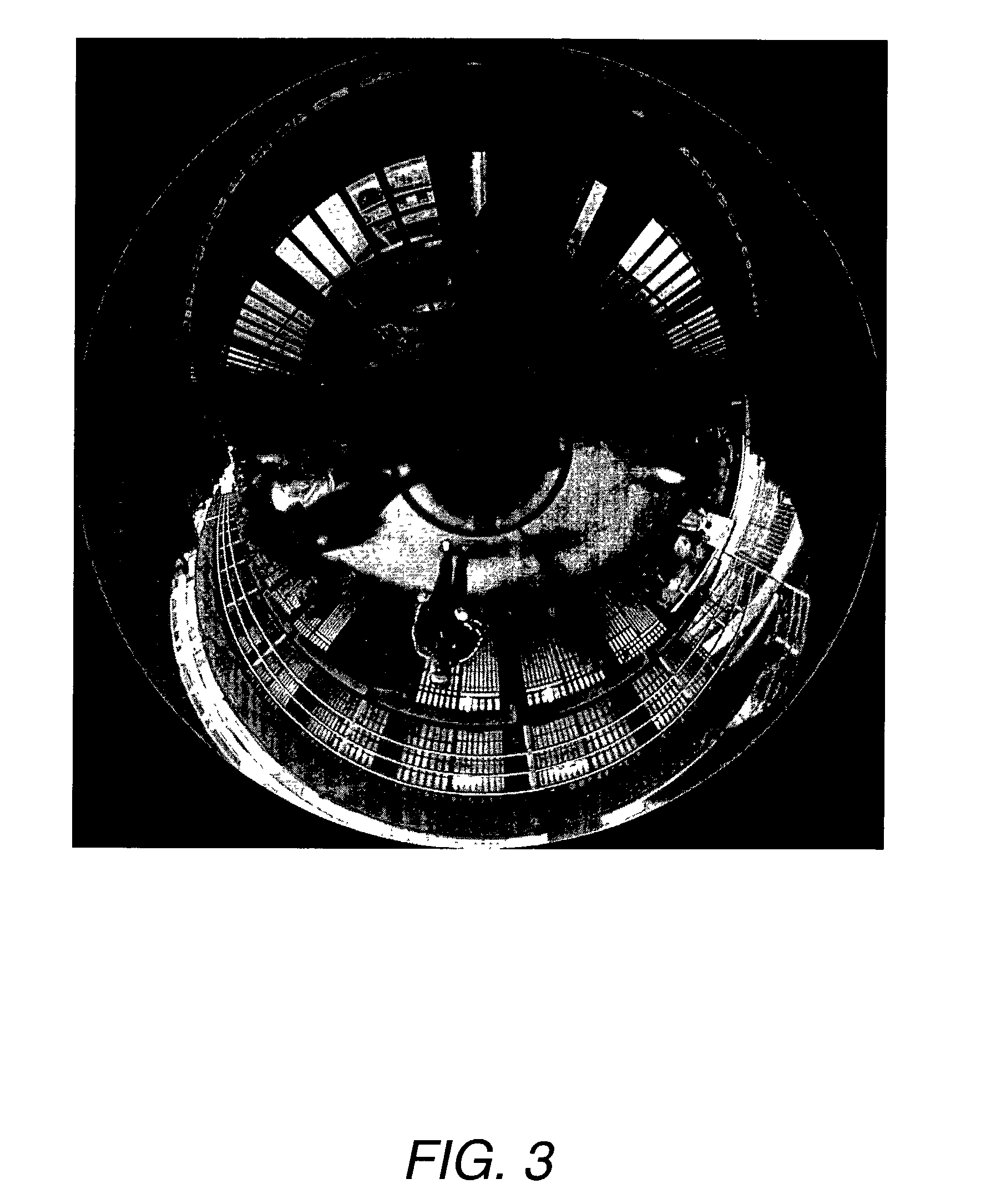
System and method for panoramic imaging
InactiveUS7058239B2High-resolution imageQuickly present the userGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImage capturePixel image
The present invention provides a system for processing panoramic photographic images. The system includes a mirror for reflecting an image of a scene, a mounting assembly for mounting the mirror on an axis, a first camera for capturing the image reflected by the mirror, at least one secondary camera for capturing a portion of the scene, means for mapping pixel data of the image captured by the first camera into a viewable image, and means for cooperatively displaying the viewable image and the portion of the scene captured by the at least one of the secondary cameras. The mirror may include a convex reflective surface defined by rotating around the axis: an equi-angular shape or a compensated equi-angular shape. The secondary camera may also capture a portion of the image reflected by the mirror. Alternatively, the system may include a single camera including an active-pixel image sensor for capturing at least a portion of the image reflected by the mirror. Methods for processing images in accordance with the system are also provided.
Owner:360AI SOLUTIONS LLC
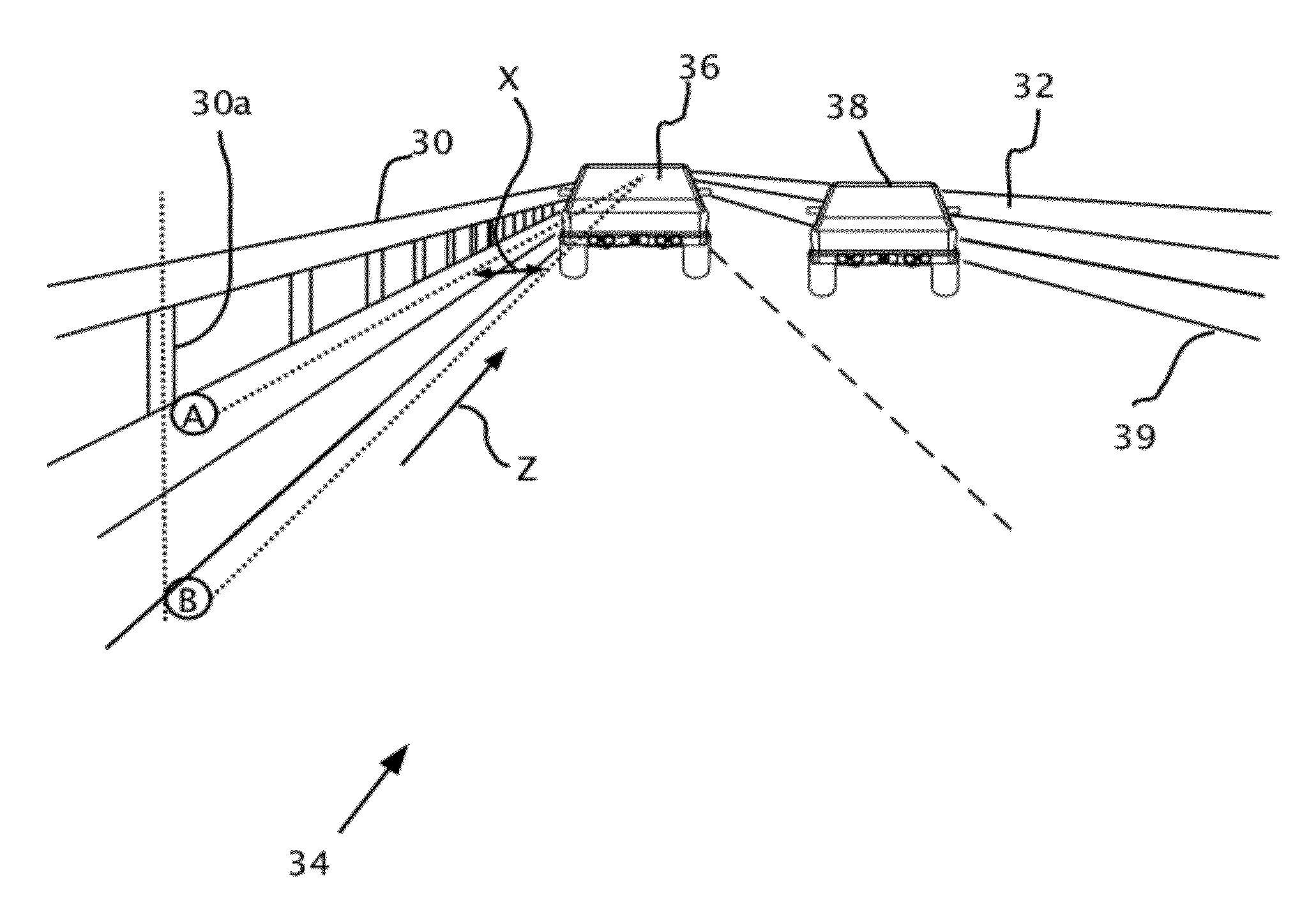
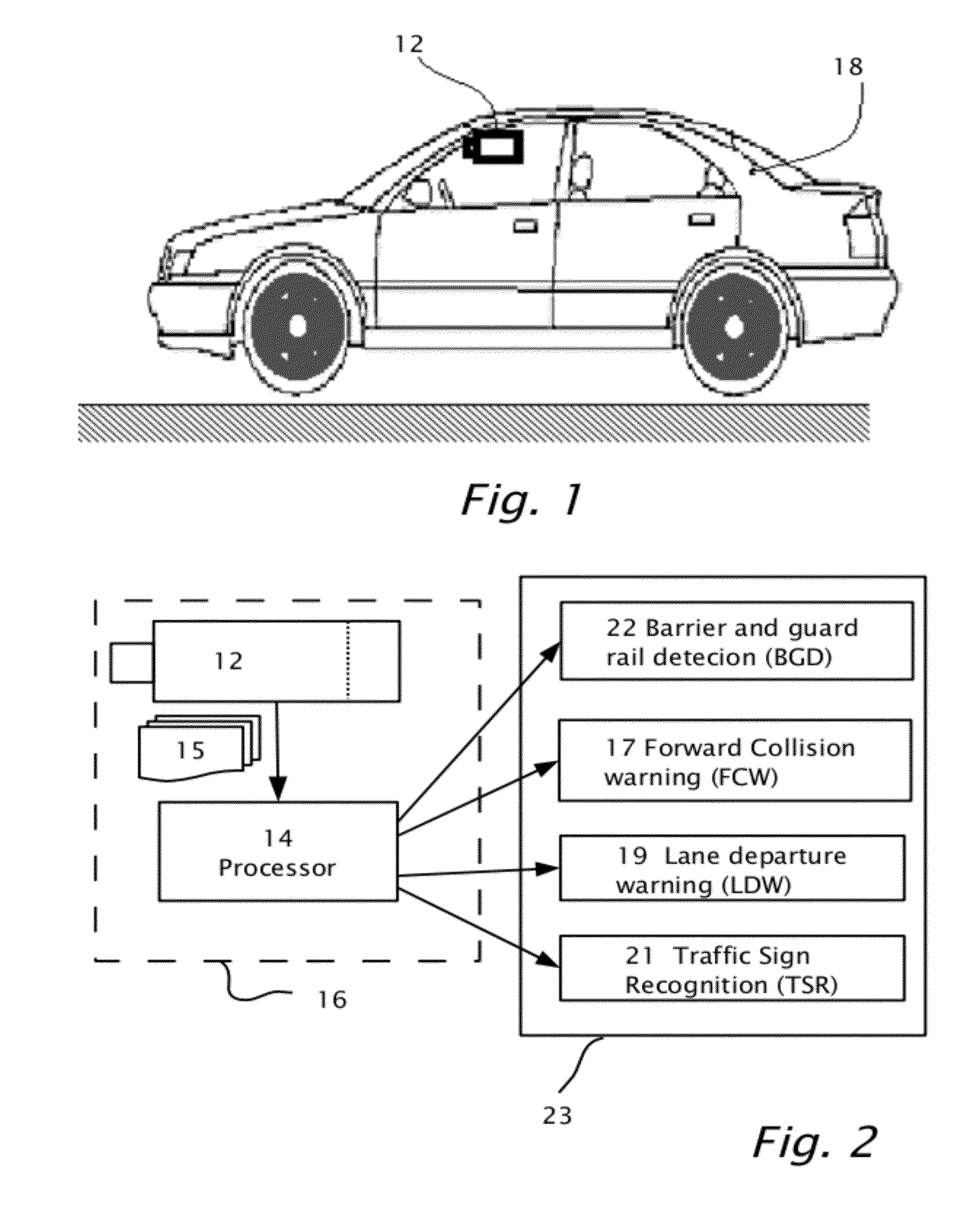
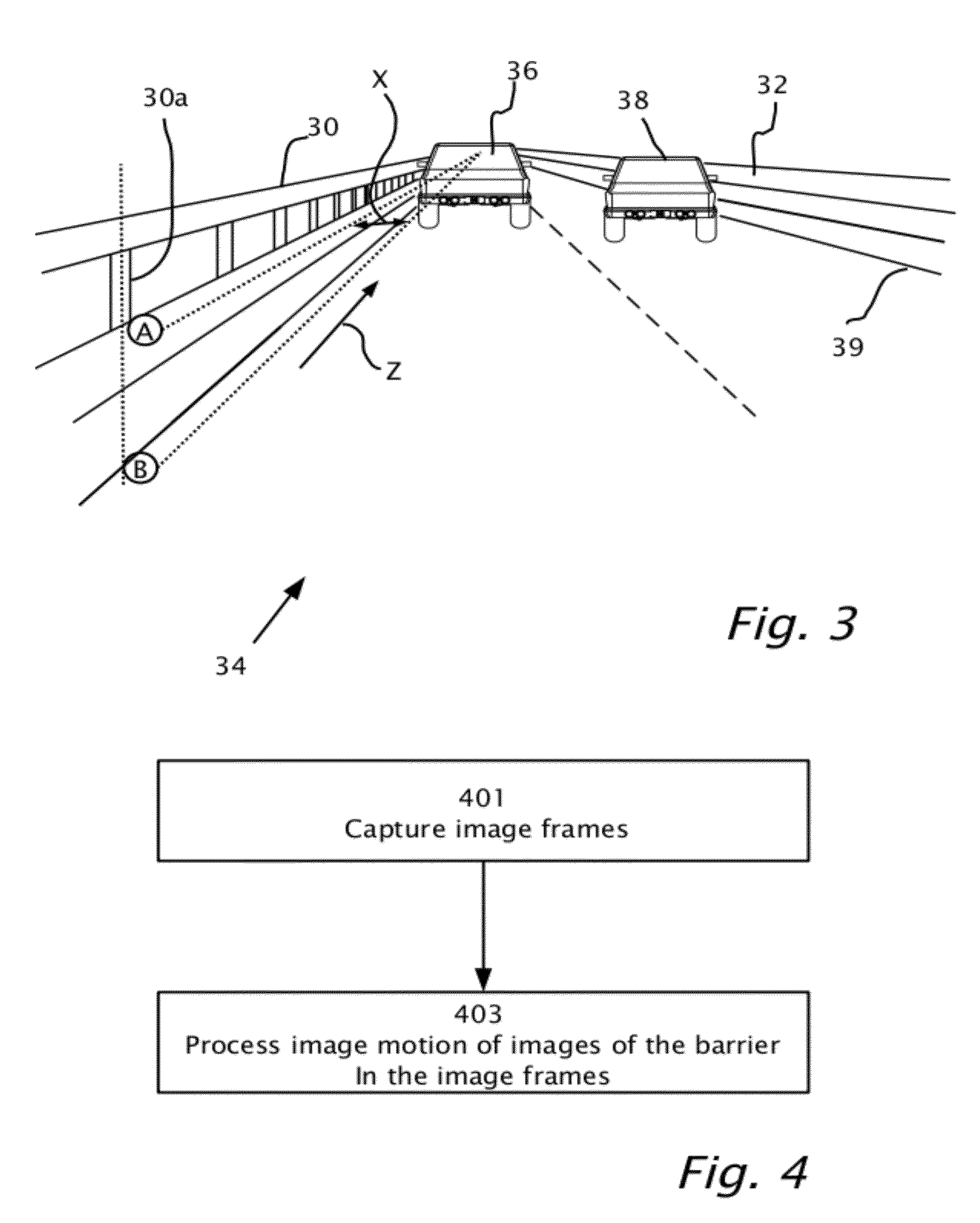
Barrier and guardrail detection using a single camera
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Digital eye camera
InactiveUS6361167B1High resolutionIncrease contrastLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEyepieceRetina
A digital camera that combines the functions of the retinal camera and corneal camera into one, single, small, easy to use instrument. The single camera can acquire digital images of a retinal region of an eye, and digital images of a corneal region of the eye. The camera includes a first combination of optical elements for making said retinal digital images, and a second combination of optical elements for making said corneal digital images. A portion of these elements are shared elements including a first objective element of an objective lens combination, a digital image sensor and at least one eyepiece for viewing either the retina or the cornea. The retinal combination also includes a first changeable element of said objective lens system for focusing, in combination with said first objective element, portions or all of said retinal region at or approximately at a common image plane. The retinal combination also includes a retinal illuminating light source, an aperture within said frame and positioned within said first combination to form an effective retinal aperture located at or approximately at the lens of the eye defining an effective retinal aperture position, an infrared camera for determining eye position, and an aperture adjustment mechanism for adjusting the effective retinal aperture based on position signals from said infrared camera. The cornea combination of elements includes a second changeable element of said objective lens system for focusing, in combination with said first objective element, portions or all of said cornea region at or approximately at a common image plane.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com