Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3621 results about "Gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In laser physics, gain or amplification is a process where the medium transfers part of its energy to the emitted electromagnetic radiation, resulting in an increase in optical power. This is the basic principle of all lasers. Quantitatively, gain is a measure of the ability of a laser medium to increase optical power.
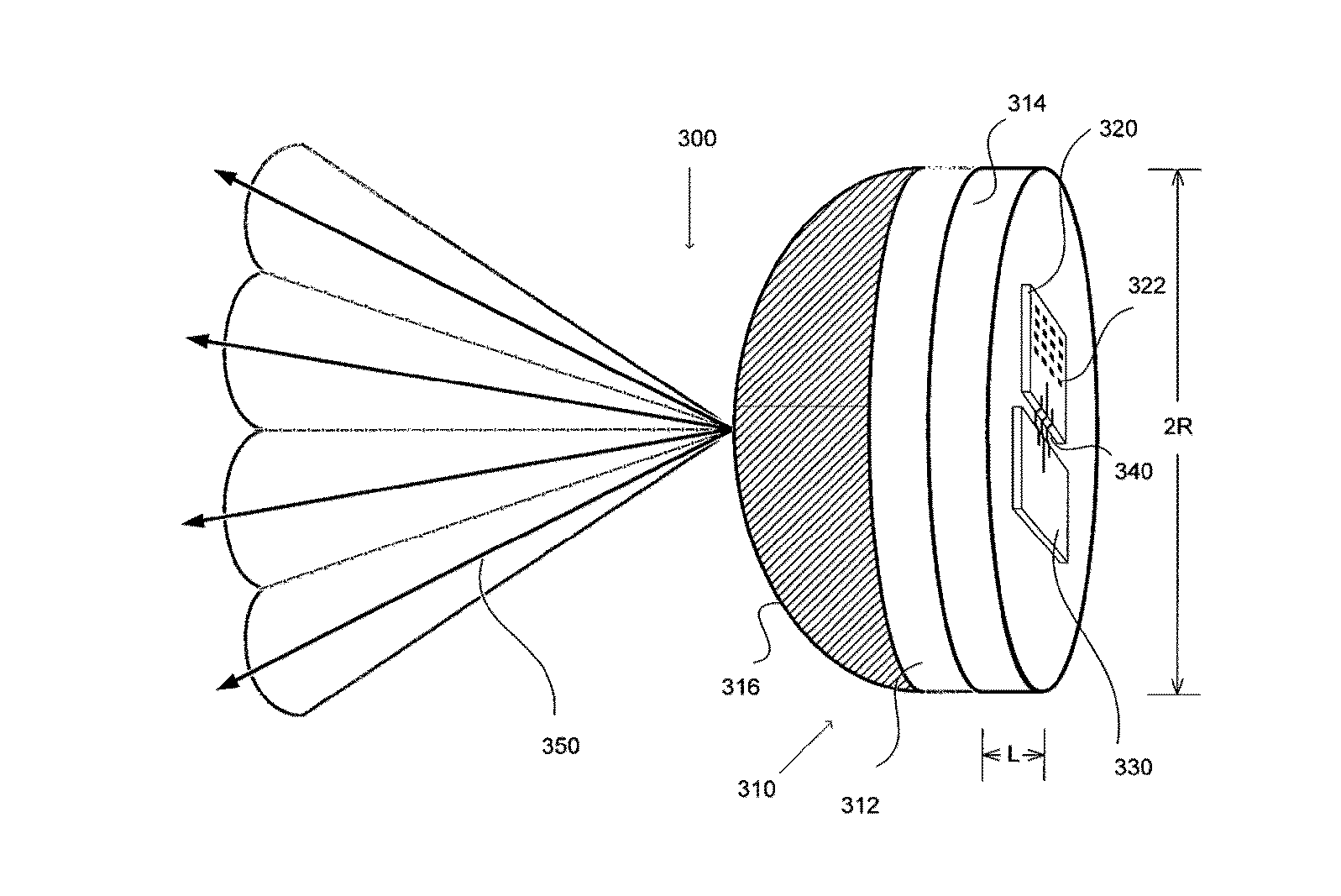
Lens antenna with electronic beam steering capabilities
InactiveUS20150116154A1Improve directivityImprove radiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntenna gainRadio relay
The invention discloses a lens antenna with high directivity intended for use in radio-relay communication systems, said antenna providing the capability of electronic steering of the main radiation pattern beam by switching between horn antenna elements placed on a plane focal surface of the lens. Electronic beam steering allows antenna to automatically adjust the beam direction during initial alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and in case of small antenna orientation changes observed due to the influence of different reasons (wind, vibrations, compression and / or extension of portions of the supporting structures with the temperature changes, etc.). The technical result of the invention is the increase of the antenna directivity with simultaneously provided capability of scanning the beam in a continuous angle range and also the increase of the antenna radiation efficiency and, consequently, the increase of the lens antenna gain. This result is achieved by the implementation of horn antenna elements with optimized geometry.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
Optoelectronic shutter, method of operating the same and optical apparatus including the optoelectronic shutter
InactiveUS20100308211A1Electroluminescent light sourcesPhase-affecting property measurementsShutterGain
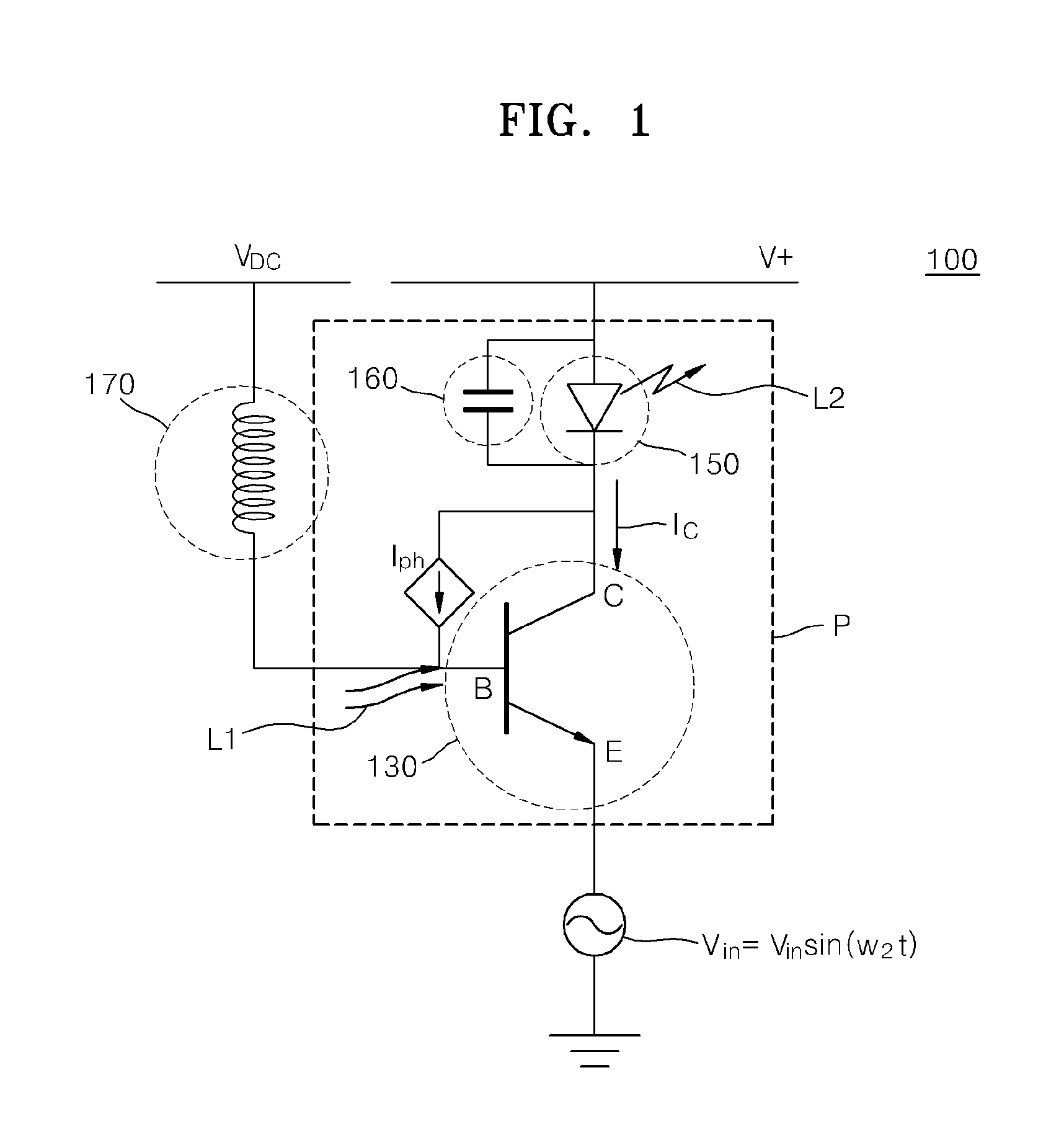
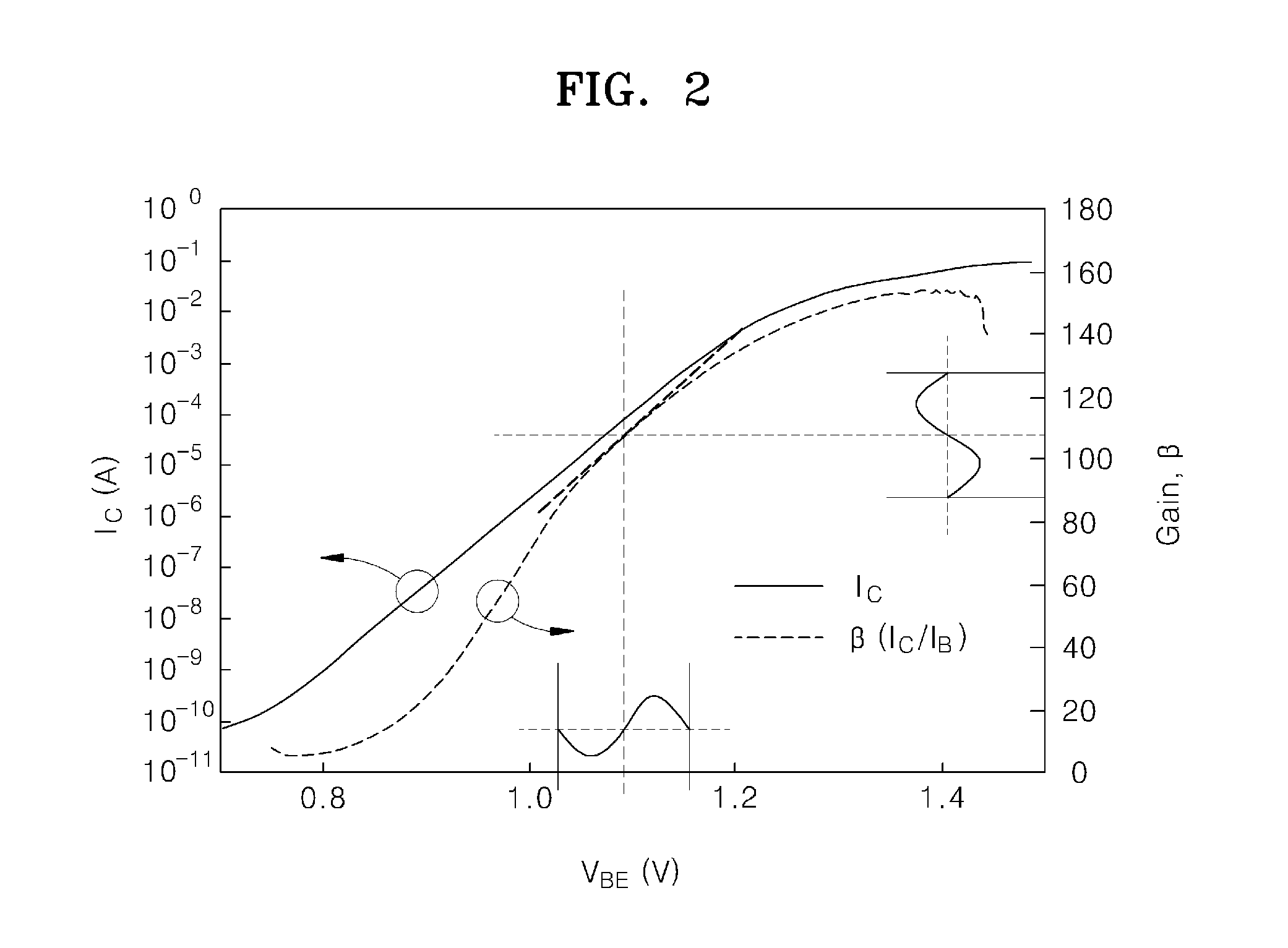
An optoelectronic shutter, a method of operating the same, and an optical apparatus including the optoelectronic shutter are provided. The optoelectronic shutter includes a phototransistor which generates an output signal from incident input light and a light emitting diode serially connected to the phototransistor. The light emitting diode outputs output light according to the output signal, and the output signal is gain-modulated according to a modulation of a current gain of the phototransistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and system to enhance dynamic range conversion useable with CMOS three-dimensional imaging
InactiveUS6678039B2Low noiseLarge dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSContinuous measurement
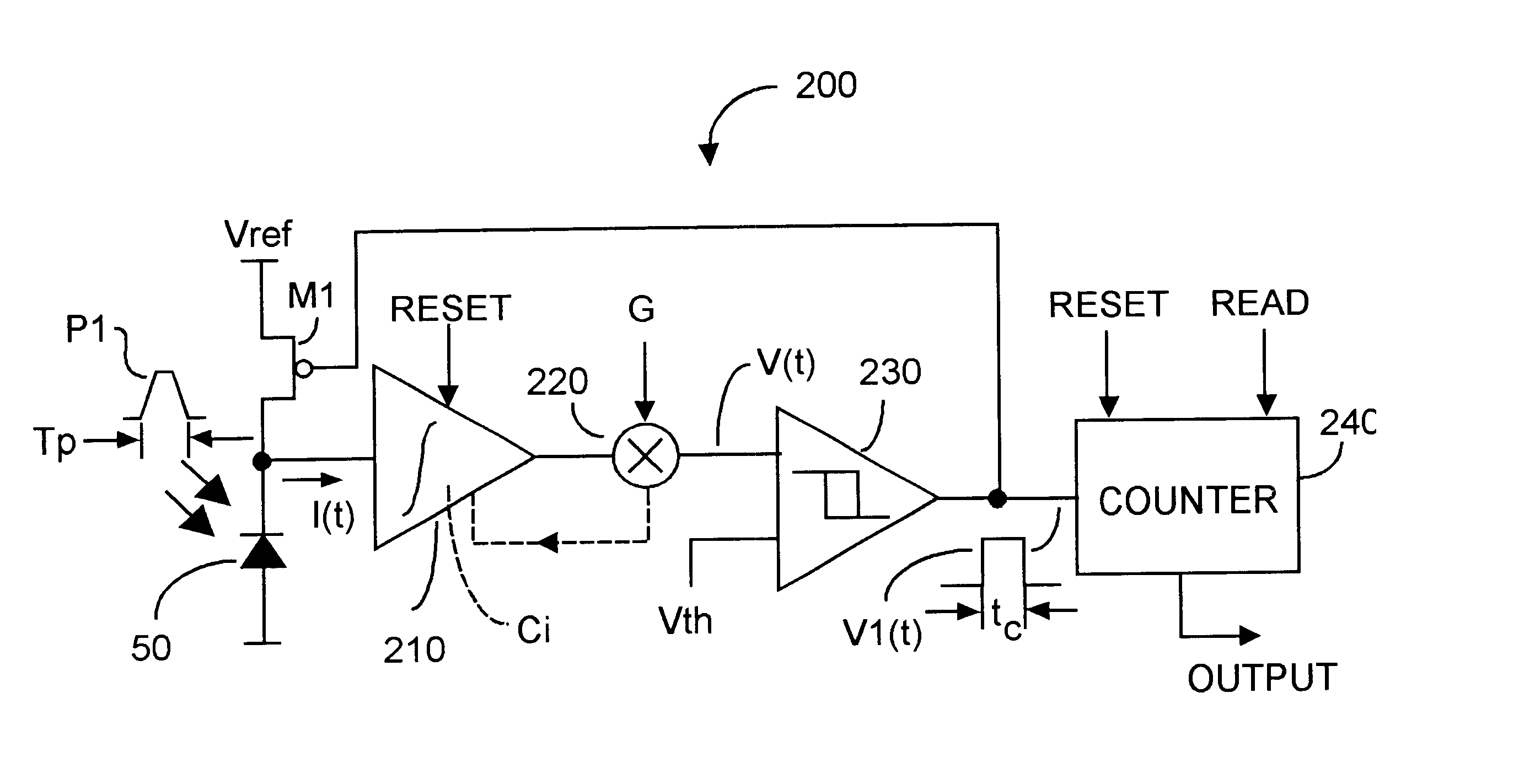
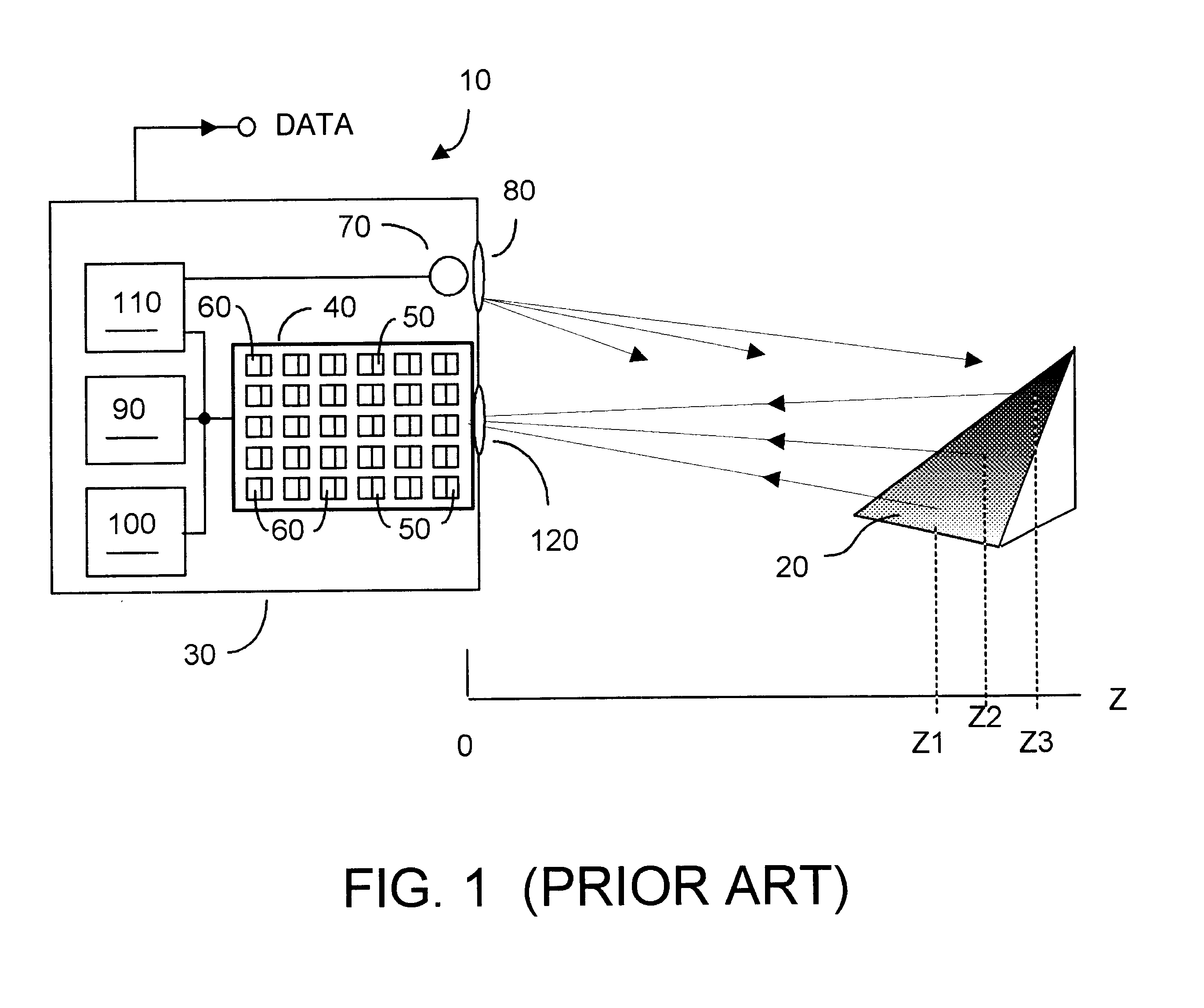
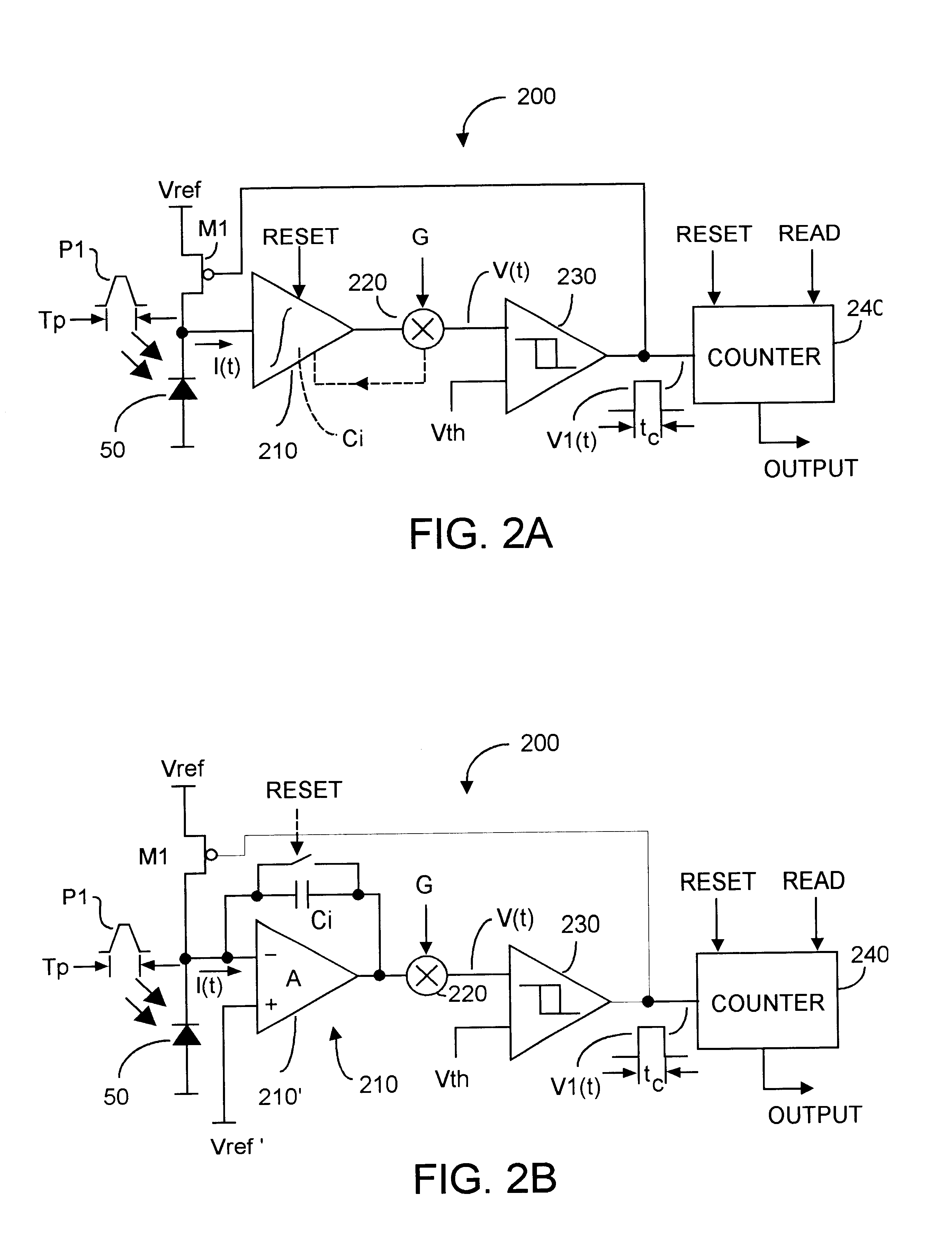
High dynamic range brightness information is acquired by inputting detection current to a high (adjustable) gain resettable integrator whose output V(t) is compared to a Vth threshold by a comparator whose output is counted by a reset counter as V(t).gtoreq.Vth. When a desired count is attained, data acquisition ends, the counter is read, and the entire circuit is reset. A TOF data acquisition circuit includes first and second sequences of series-coupled delay units, and a like number of latch units coupled between respective delay units. A phase discriminator compares output from each chain and feedback a signal to one of the chains and to a comparator and can equalize delay through each chain. A control voltage is coupled to the remaining chain to affect through-propagation delay time. The latch units can capture the precise time when V(t).gtoreq.Vth. Successive measurement approximation can enhance TOF resolution.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for averaged luminance and uniformity correction in an amoled display
InactiveUS20070290958A1Improve uniformityImproved lifetimeStatic indicating devicesActive matrixDisplay device
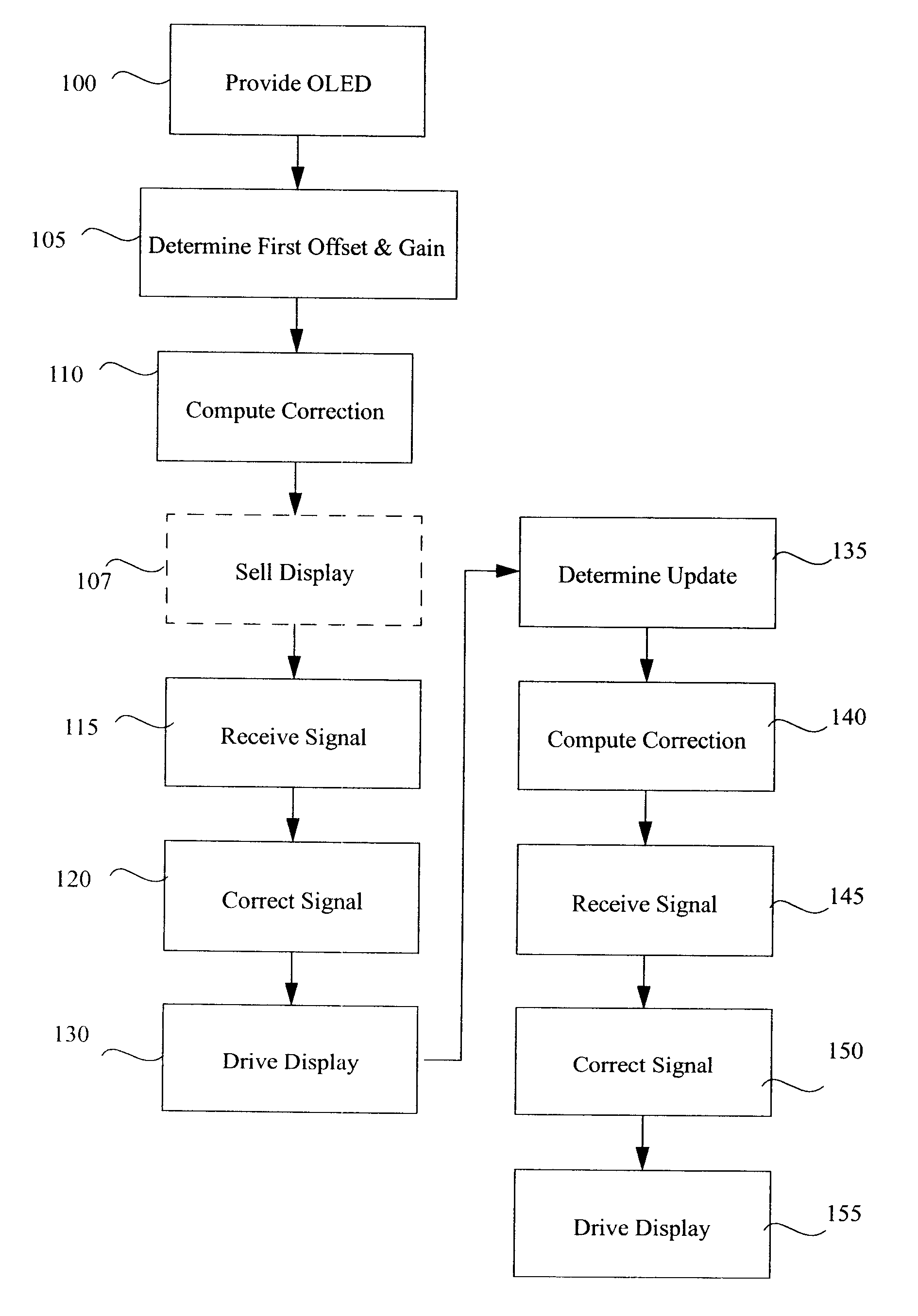
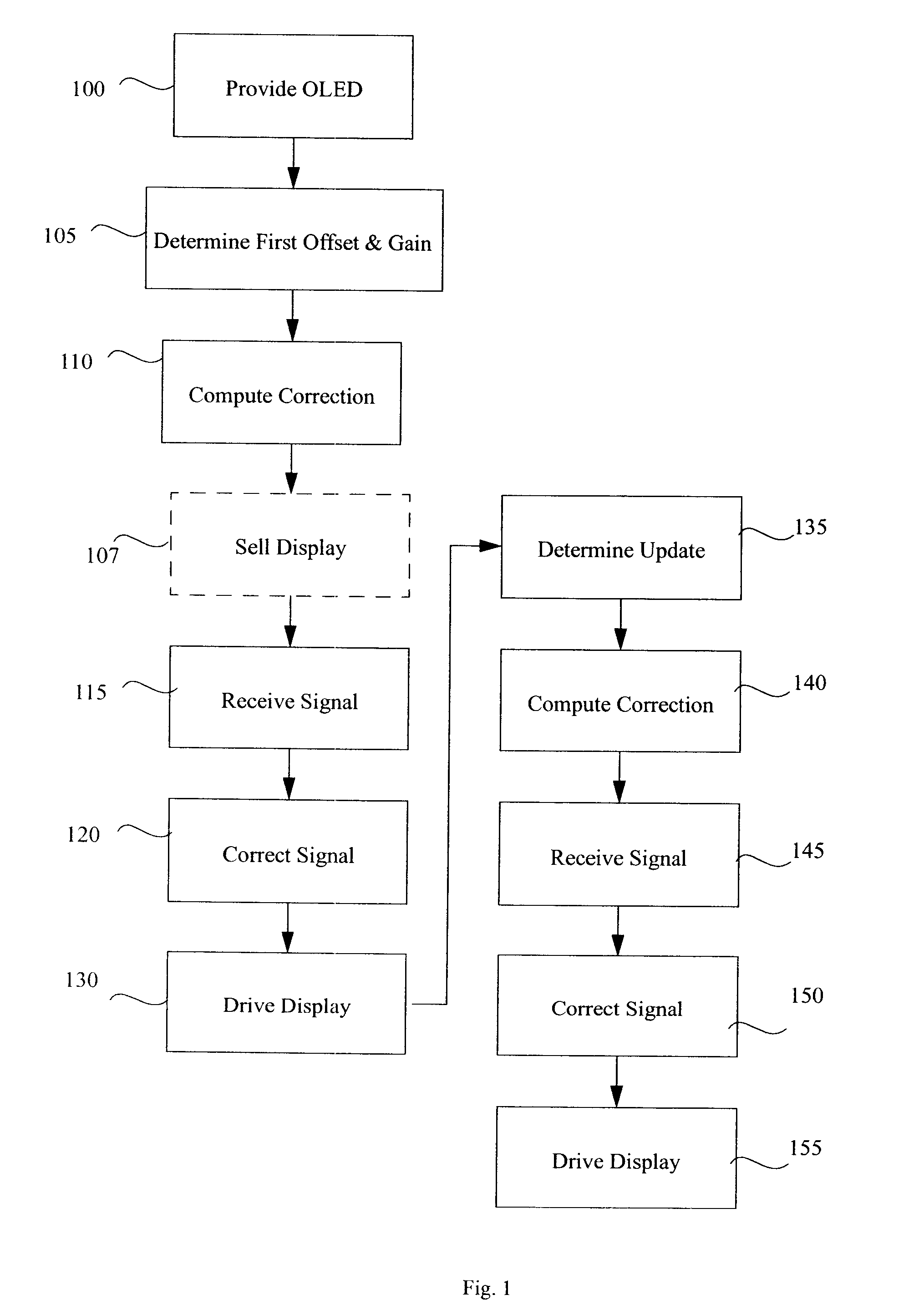
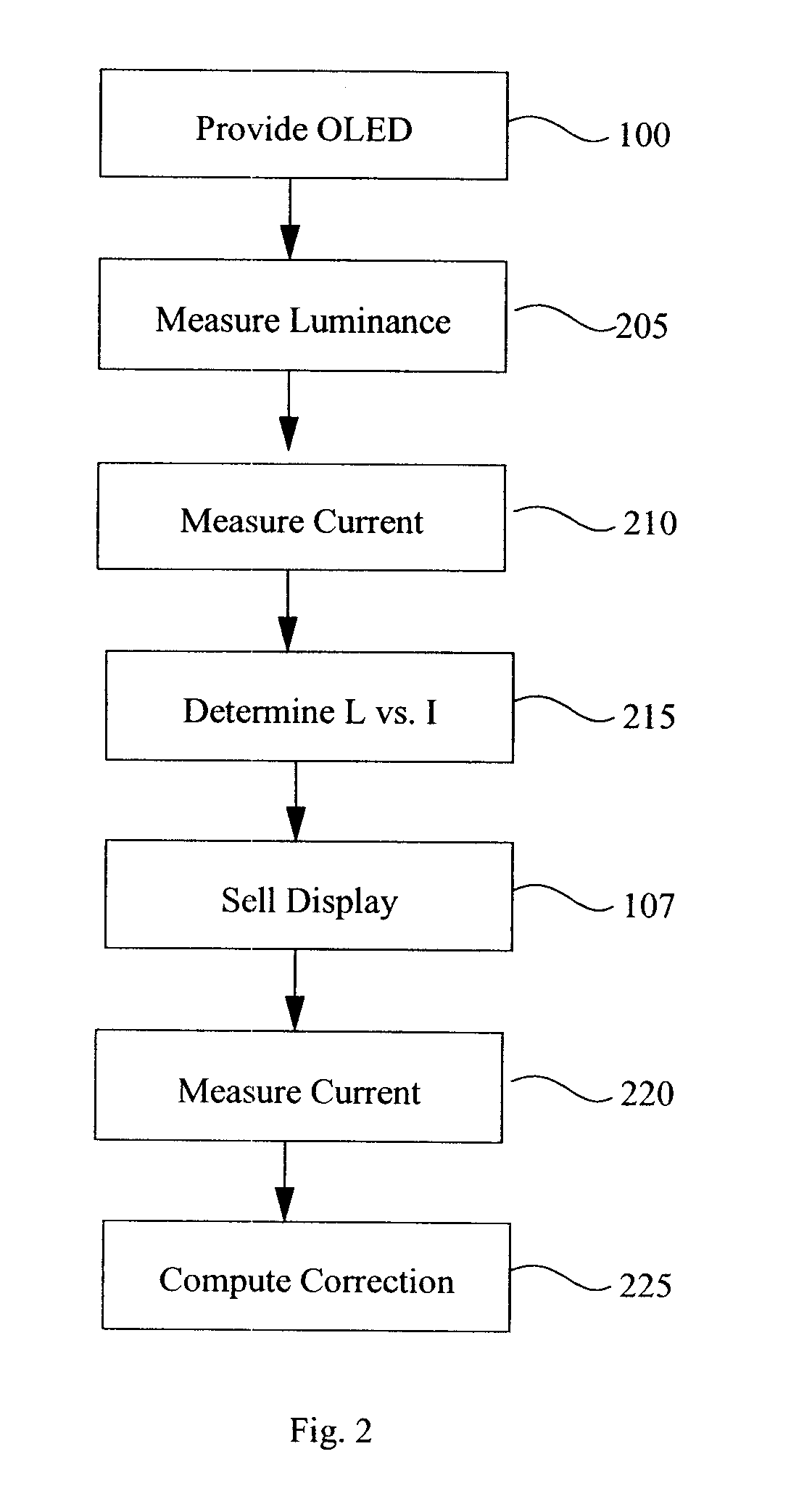
A method for the correction of average luminance or luminance uniformity variations in an active-matrix OLED display, comprising:a) providing an active-matrix OLED display;b) determining at a first time a first offset voltage and a first gain relationship between the voltage and the current passing through one or more light-emitting elements;c) receiving a signal for driving the light-emitting elements after step b), correcting the signal by employing the first offset voltage and gain relationship values to compute a linear correction for the light-emitting elements to form a corrected signal, and driving the display with the corrected signal;d) determining at a time after the first time an updated offset voltage and an updated gain relationship between the voltage and the current passing through the light-emitting elements; ande) receiving a signal for driving the one or more light-emitting elements after step d), correcting the signal by employing the updated offset voltage and gain relationship values to compute a linear correction for the light-emitting elements to form an updated corrected signal, and driving the display with the updated corrected signal.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
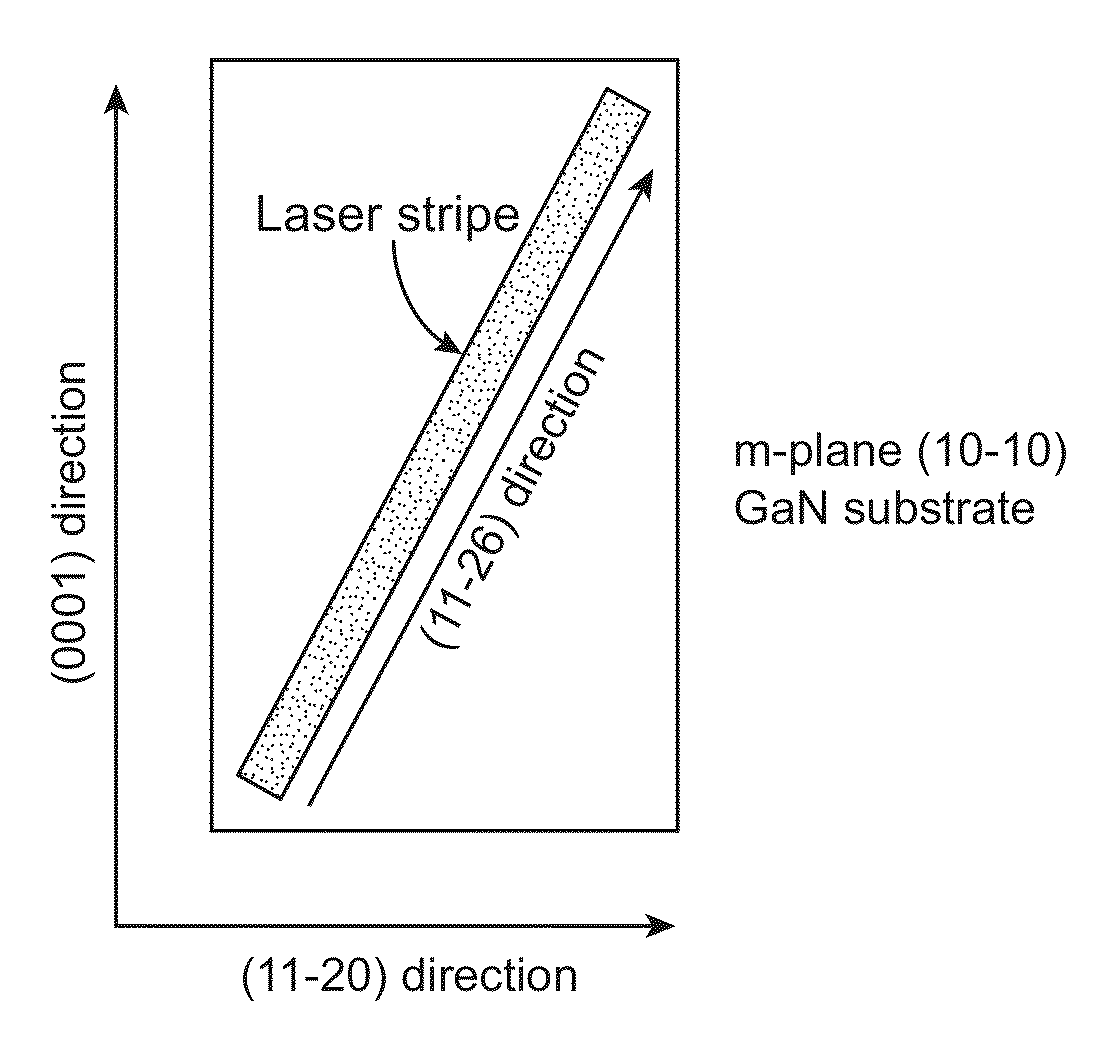
Solid State Laser Device Using a Selected Crystal Orientation in Non-Polar or Semi-Polar GaN Containing Materials and Methods
ActiveUS20130064261A1Facilitates parallel facetsReduce surface roughnessLaser detailsLaser active region structureHigh current densitySolid-state laser device
An edge emitting solid state laser and method. The laser comprises at least one AlInGaN active layer on a bulk GaN substrate with a non-polar or semi-polar orientation. The edges of the laser comprise {1 1−2±6} facets. The laser has high gain, low threshold currents, capability for extended operation at high current densities, and can be manufactured with improved yield. The laser is useful for optical data storage, projection displays, and as a source for general illumination.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC +1
Portable fluorescence detection system and microassay cartridge
InactiveUS20150346097A1Avoiding complexity and expenseLow heat resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusLow noiseOn board
Disclosed is a compact, microprocessor-controlled instrument for fluorometric assays in liquid samples, the instrument having a floating stage with docking bay for receiving a microfluidic cartridge and a scanning detector head with on-board embedded microprocessor operated under control of a ODAP daemon resident in the detector head for controlling source LEDs, emission signal amplification and filtering in an isolated, low noise, high-gain environment within the detector head. Multiple optical channels may be incorporated in the scanning head. In a preferred configuration, the assay is validated using dual channel optics for monitoring a first fluorophore associated with a target analyte and a second fluorophore associated with a control. Applications include molecular biological assays based on PCR amplification of target nucleic acids and fluorometric assays in general, many of which require temperature control during detection.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
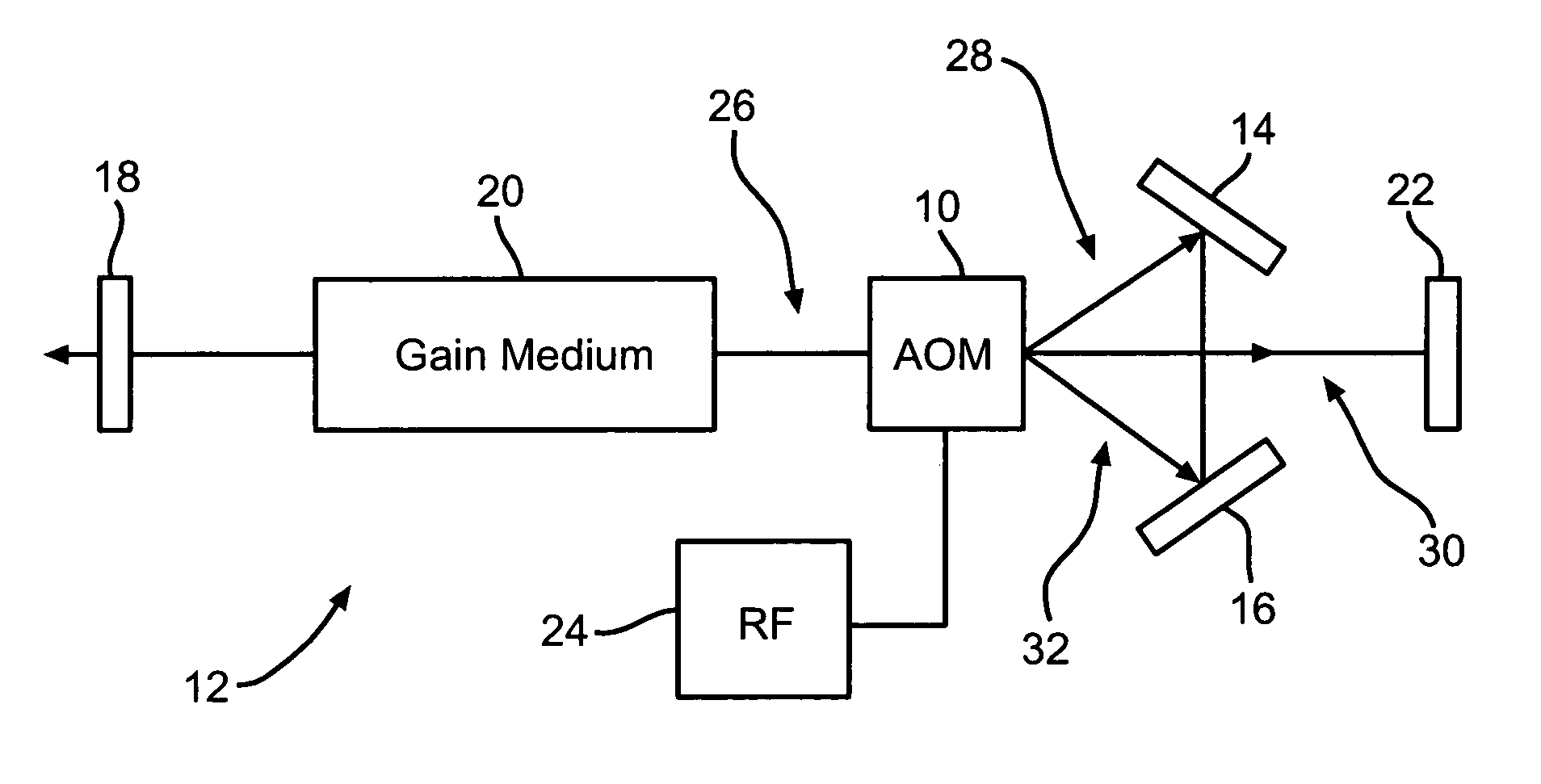
Laser cutting of stents and other medical devices
A desired pattern may be cut into a stent preform by impinging a laser beam onto the stent preform. The laser beam is formed using a laser system comprising a resonator cavity for resonating laser radiation, a gain medium contained in the resonator cavity, a pump for periodically pumping the gain medium and an electro-optical modulator in communication with the resonator cavity. The laser system produces a radiation pulse for each pump period. Each radiation pulse is conditioned by suppressing at least a portion of the pulse. The pulse may also be modulated with an electro-optical modulator to produce a pulse train of ordered pulses of radiation. Each pulse train is output from the optical cavity as an output laser beam which is directed at the stent preform to cut a desired pattern in the stent preform.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Composition for optical waveguide article and method for making continuous clad filament
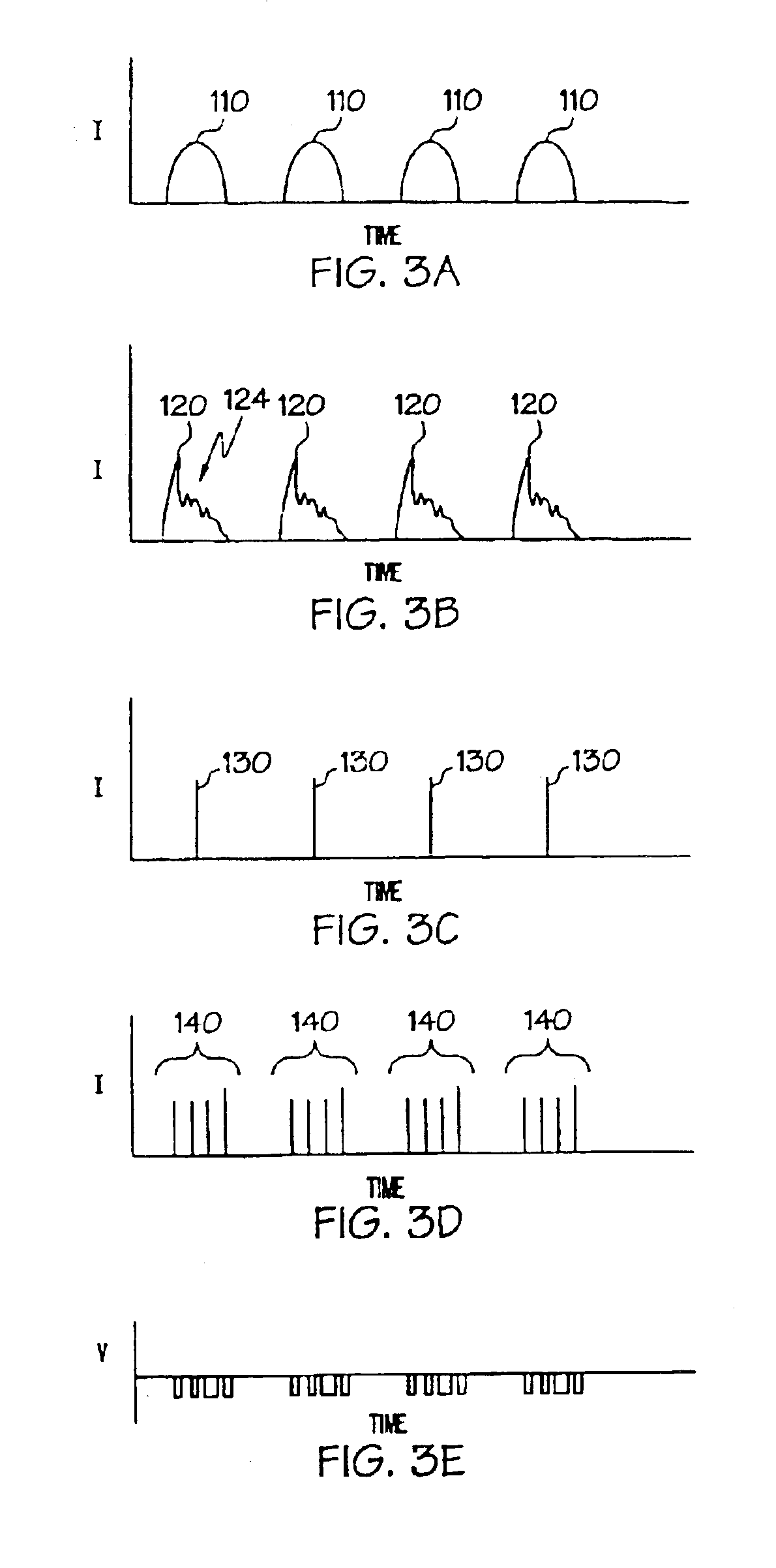
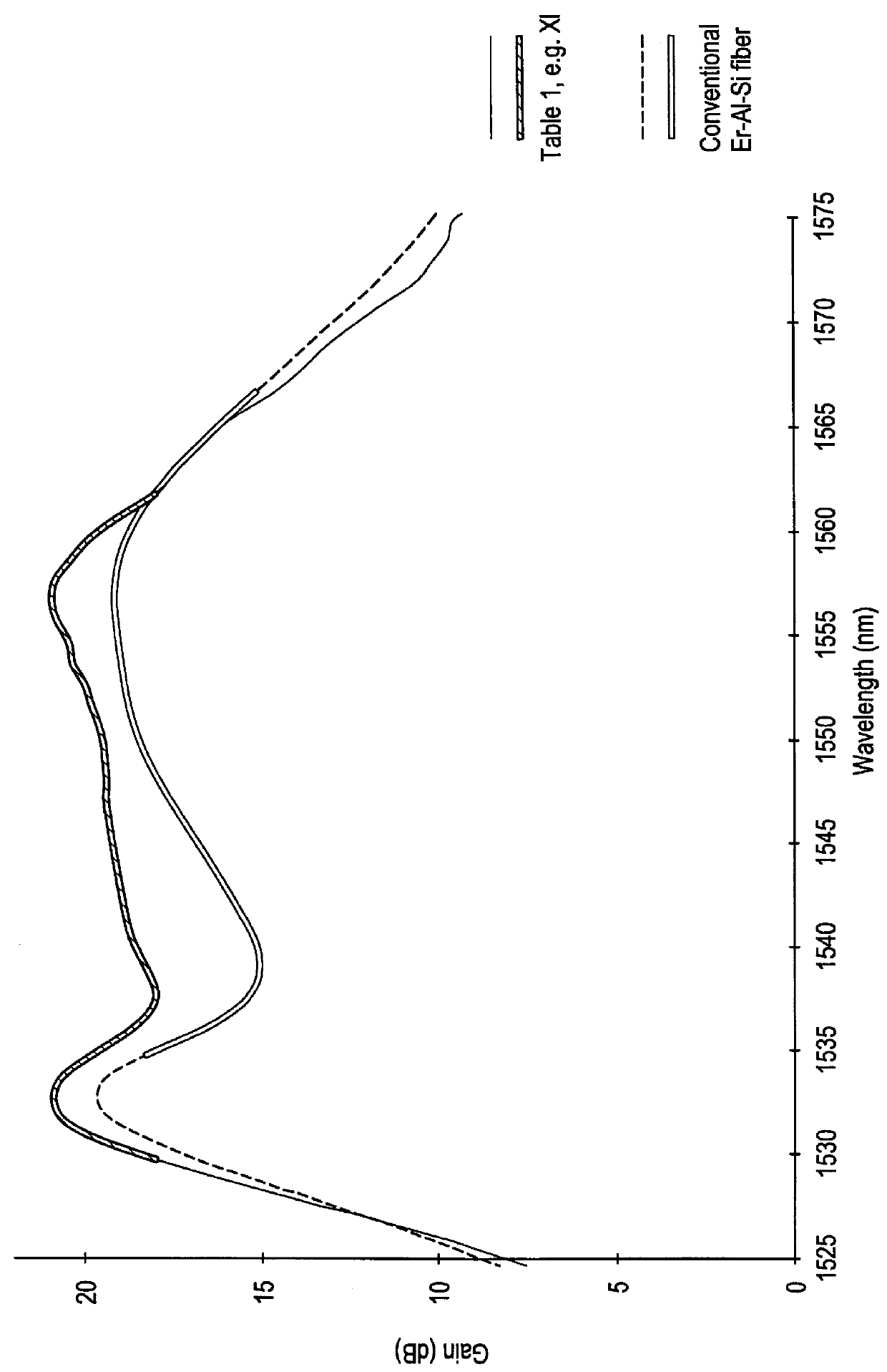
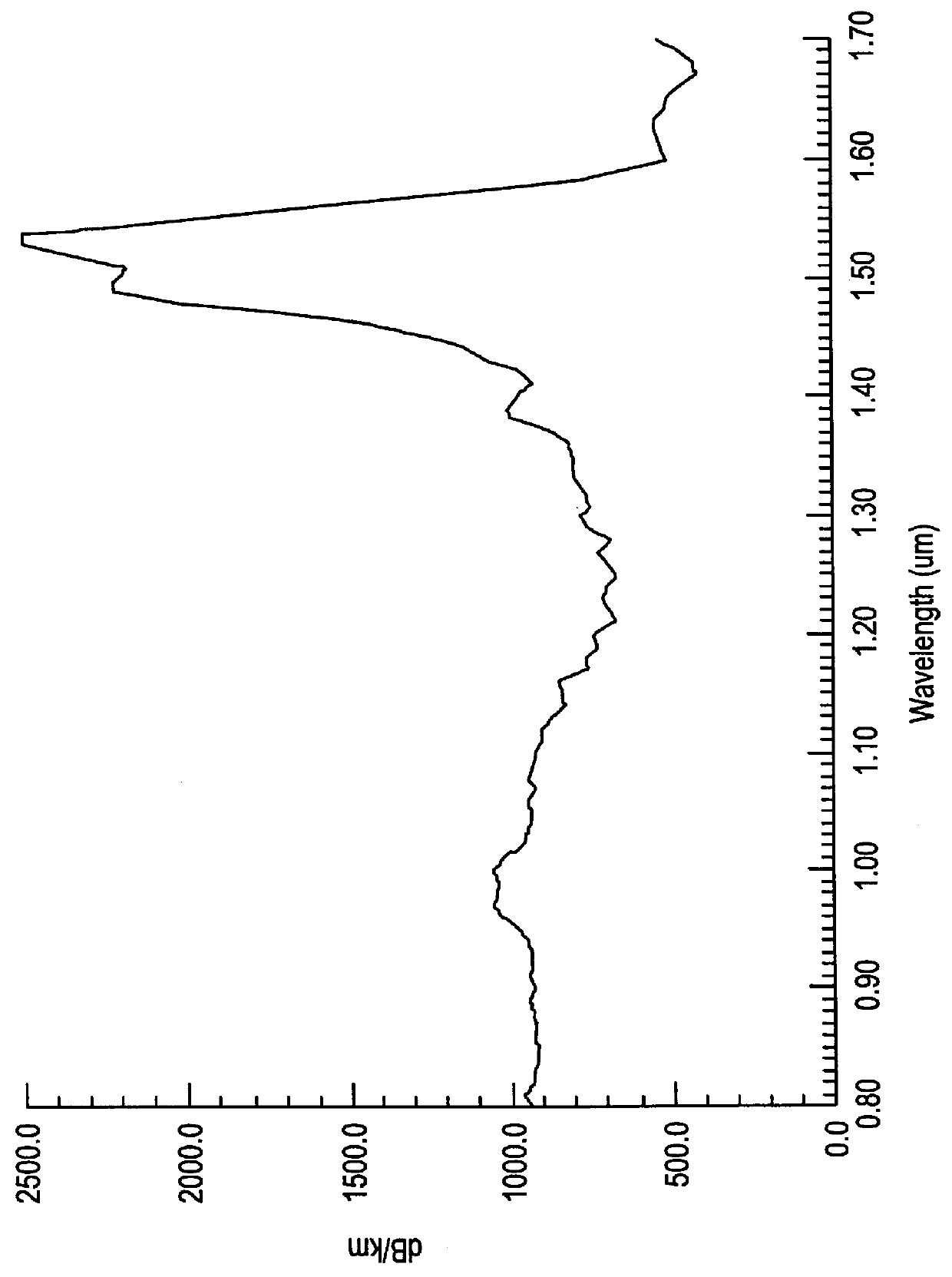
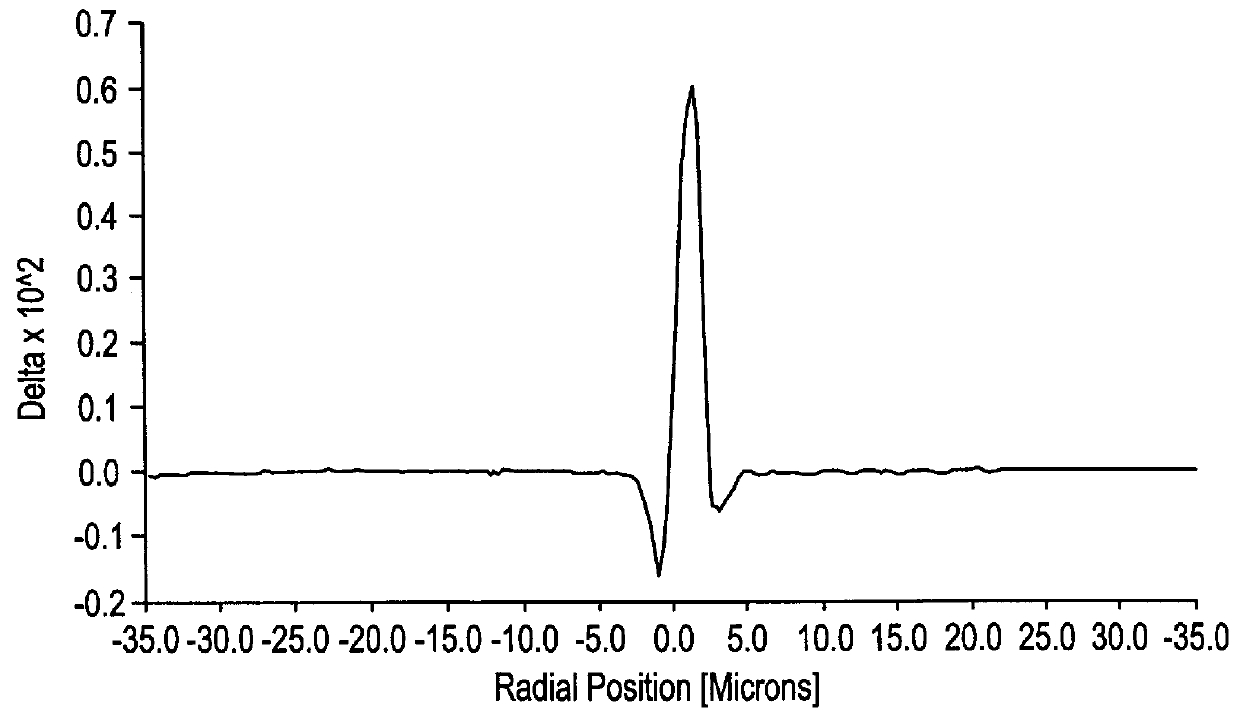
An optical article having a rare earth doped, fluorinated aluminosilicate glass core composition consisting essentially, in mole %, of: - SiO2 0-90 - GeO2 0-90 - Na2O 0-25 - Li2O 0-10 - K2O 0-25 - Rb2O 0-25 - Cs2O 0-25 - Al2O3 5-40 - Ga2O3 5-40 - RE2(1)O3 0-40 - RE2(2)O3 0-1 - Er2O3 0.001-5 - Yb2O3 0-5 - PbO 0-15 - RO 0-20 - ZnO 0-10 - ZrO2 0-2 - TiO2 0-2 - Nb2O5 0-10 - Ta2O5 0-10 - P2O5 0-5 - B2O3 0-15 - As2O3 0-10 - Sb2O3 0-20 - Na2Cl2 0-10 - Bi2O3 0-5, and - up to 15 weight % fluorine in the form of at least one of a fluorinated component of the glass composition and a batch constituent selected from a group consisting of at least one of AlF3, REF3, NH5F2, NaF, Na2SiF6, Na3AlF6, where RE(1) is at least one of Y, La, Gd, and Lu; RE(2) is at least one of Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Tb, Dy, Ho, and Tm; R is at least one of Ba, Ca, Mg, and Sr; (SiO2+GeO2) is in the range (40-90); and (Al2O3+Ga2O3)>(RO+"alk"2O+RE2O3) where "alk" is at least one of Li, Na, K, Cs, and Rb. A cullet-in-tube method for making continuous clad filament is also described. The invention provides for an optical waveguiding article having relatively high gain, a relatively flat gain spectrum, compatibility with conventional silica fiber, good durability and ease of manufacture.
Owner:CORNING INC
Silk optical particles and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130243693A1Good lookingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFood additiveOptical property
Disclosed herein are methods of preparing silk particles having at least one optical property, e.g., reflectivity, diffraction, refraction, absorption, optical-gain, fluorescence, and light scattering, and compositions resulted therefrom. The compositions and methods of the invention can be utilized in various applications, e.g., medical applications, cosmetics, sunscreen and food additives.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV
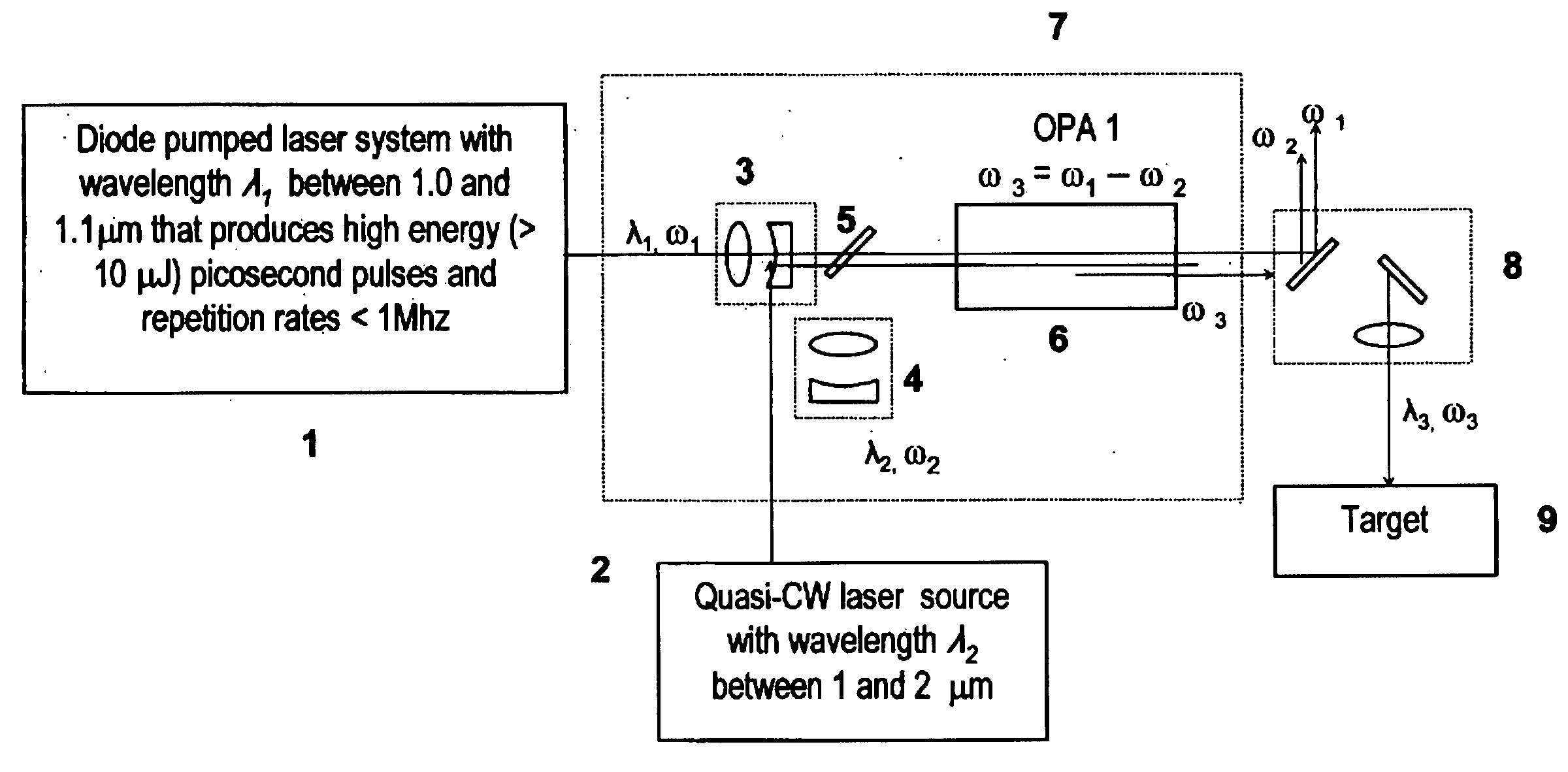
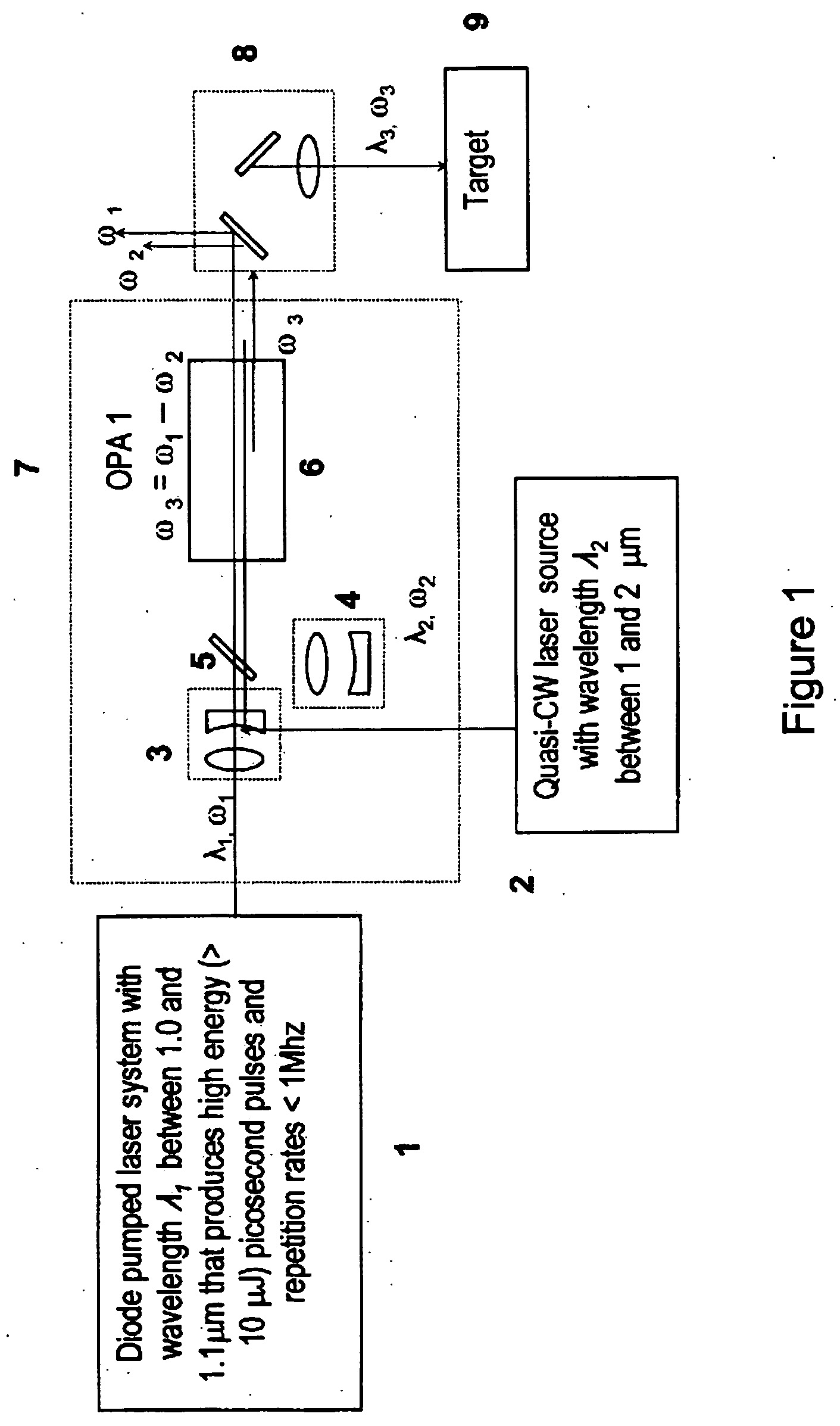
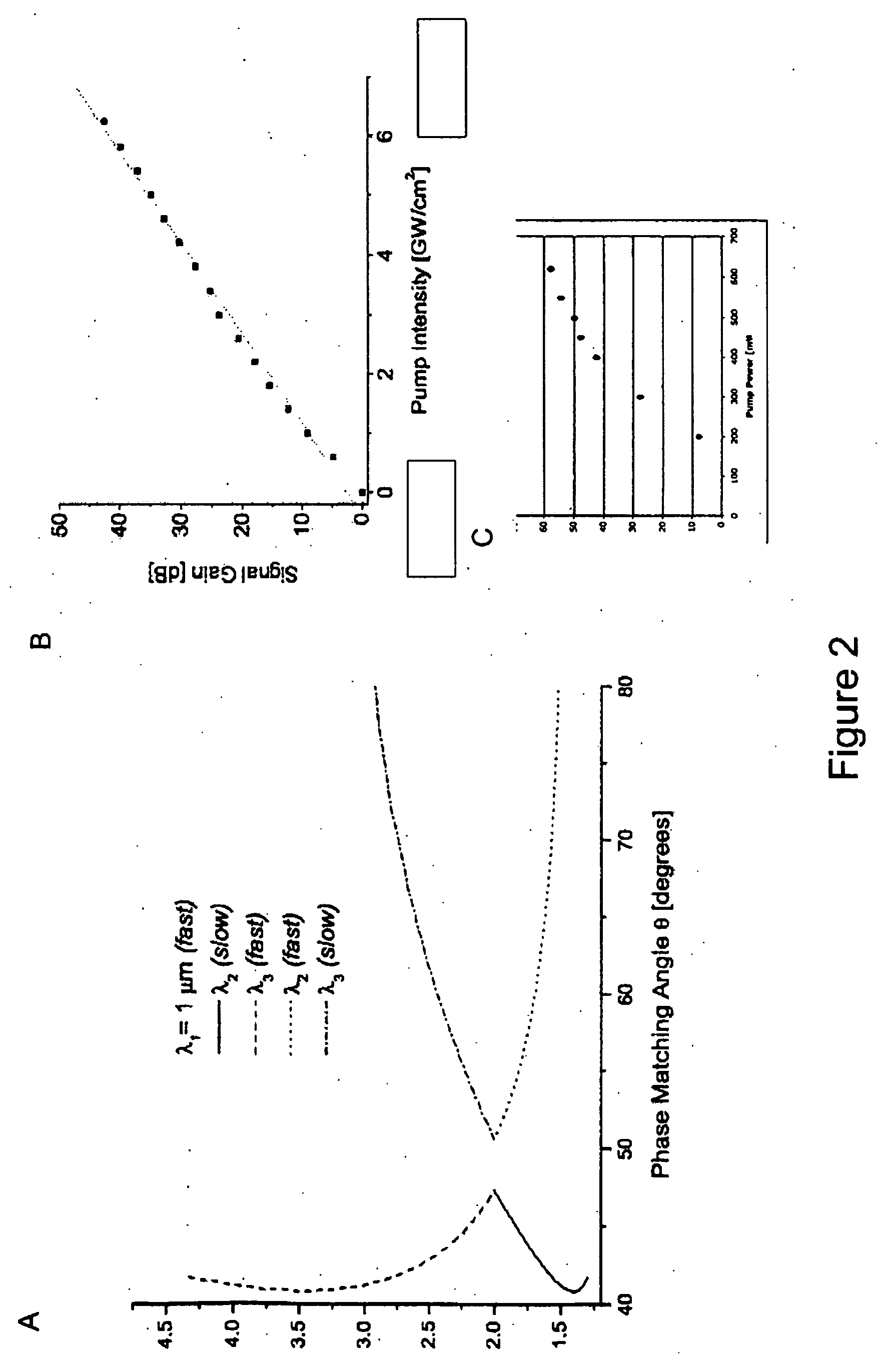
Laser system for generation of high-power sub-nanosecond pulses with controlable wavelengths in 2-15 mum region
ActiveUS20060153254A1Big spaceSubstantial temporal overlapLaser using scattering effectsSurgical instrument detailsSystems designHigh energy
A laser system capable of efficient production of high energy sub-nanosecond pulses in the 2-15 μm spectral region is disclosed. Diode pumped solid state lasers are used as pump sources. The system design is simple, reliable and compact allowing for easy integration. The laser system includes a combination of compact solid-state ˜1 micron laser sources, producing high power picosecond pulses, with optical parametric amplification and a quasi-continuous wave laser for seeding the amplification process that enables the efficient conversion of the high power ˜1 micron laser radiation to tuneable mid-infrared sub-ns pulses. New parametric processes are presented for achieving high gains in bulk nonlinear crystals. Furthermore, a method of exceeding the fundamental conversion efficiency limit of direct three wave mixing is presented. The compact and robust nature of this novel laser system opens up the use of high power and high peak power mid-infrared laser pulses to a wide variety of important medical and dental applications.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION
Portable high gain fluorescence detection system
ActiveUS20120115214A1Improve manufacturabilityHigh amplification gainBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalyteFluorophore
An instrument for fluorometric assays in liquid samples is disclosed. The instrument may include multiple optical channels for monitoring a first fluorophore associated with a target analyte and a second fluorophore associated with a control. The disclosed instrument finds utility in any number of applications, including microfluidic molecular biological assays based on PCR amplification of target nucleic acids and fluorometric assays in general.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Tunable optical filter
InactiveUS7035484B2Reliable and compact and inexpensiveReliable, compact, and inexpensive tunable spectral filteringCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsMultiplexerChannel blocker
A tunable optical filter is provided that includes an array of independently tunable filter elements. Each of the elements is located along a different optical path that extends between an input and an output port. Optical assemblies for receiving an incident optical signal for providing a filtered optical signal are also provided. In one embodiment, polarization independent spectral filtering can be achieved. Wavelength selectable add / drop multiplexers and demultiplexers, dynamic gain equalizers and attenuators, optical channel blockers and branch filters, switches, and modulators are also provided. Furthermore, methods for constructing and operating filters consistent with this invention are also provided.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
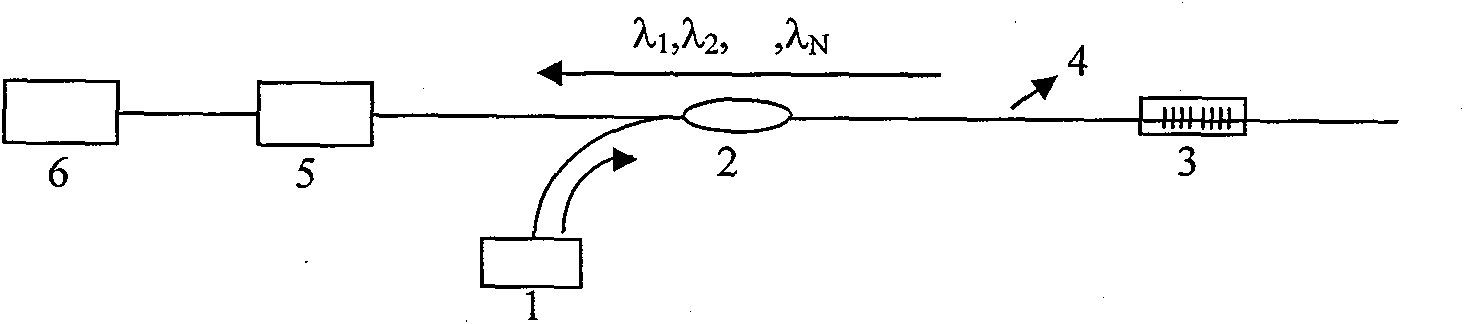
Full-distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor based on coherent heterodyne detection
InactiveCN102168953AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce false negative rateSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansContinuous lightPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention relates to a full-distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor based on coherent heterodyne detection, which comprises a laser (1), a coupler, a pulse modulation module, a programming gain amplifier (4), an optical amplifier, a circulator (6), a sensing fiber (7), a polarization-preserving fiber (8), the coupler, a balancing photoelectric detector (10), a reversal switch, a mixer, a microwave source, a band-pass filter, and a signal processing unit, wherein the continuous light output by the laser (1) is divided into two paths after passing through the coupler (2); an output end of the balancing photoelectric detector is connected to the reversal switch; the reversal switch is switched to a channel 1 and a channel 2; when the channel 1 is switched on, the system utilizes the Brillouin optical fiber time domain reflection to measure; and when the programming gain amplifier (4) is closed and the channel 2 is switched on, the system utilizes the polarization optical time-domain reflection to measure. By using the full-distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor provided by the invention, the full-distributed measurement for strain as well as the weak vibration and the full-distributed measurement for vibration can be performed on a single optical fiber.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Double-sided turning film
InactiveUS7530721B2Many solutionsImprove the level ofPrismsDiffusing elementsLight guideDisplay device
A backlight device for a display comprising (1) a side-lit light source, (2) a light guide plate and (3) a turning film comprising a light entry and a light exit surface comprising lenticular elements on the exit surface and prismatic structures on the entry surface, wherein the average values of the parameters of the features and the thickness of the film are selected to provide a peak output angle of ±10° from normal to the light exit surface of the light guide plate and an optical gain of at least 1.25. Also disclosed are methods of making the turning film and a display incorporating the backlight.
Owner:SKC HAAS DISPLAY FILMS CO LTD
Device for generating or detecting electromagnetic radiation, and fabrication method of the same
InactiveUS20060214176A1Easily reducedEasy to fallSolid masersSolid-state devicesMolecular physicsElectromagnetic radiation
A device for generating or detecting electromagnetic radiation includes a substrate, a gain medium provided on the substrate, a plurality of reflectors for confining electromagnetic radiation at a predetermined frequency range and substantially perpendicular to a face of the substrate, and spacer means for spacing the reflectors from each other at a predetermined distance, with the gain medium being sandwiched between the reflectors. The gain medium has a quantum well structure formed of a semiconductor material, and gives a gain to electromagnetic radiation by transitioning between subbands created in at least a quantum well in the quantum well structure. The spacer means is formed of a material different from a material of the gain medium.
Owner:CANON KK
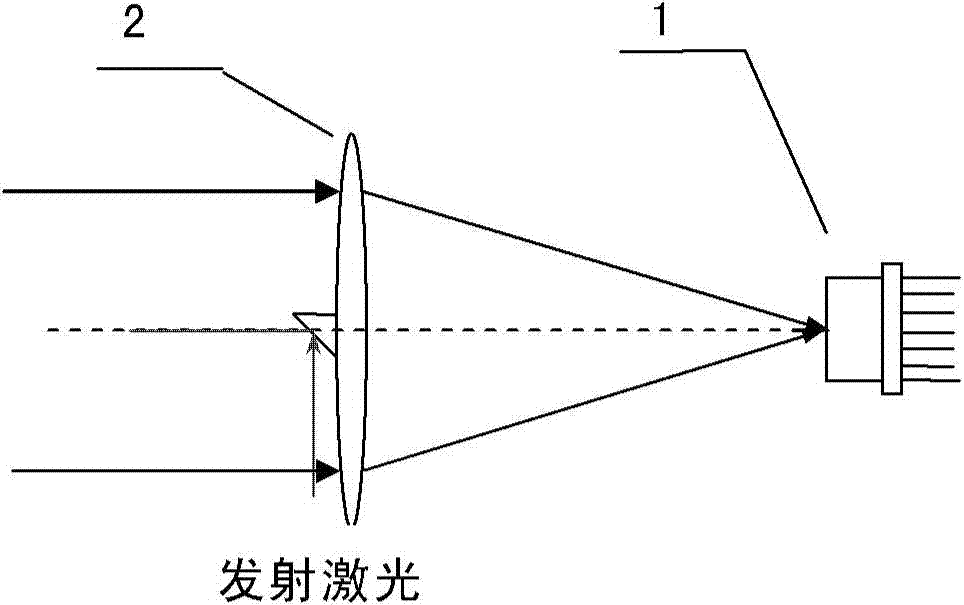
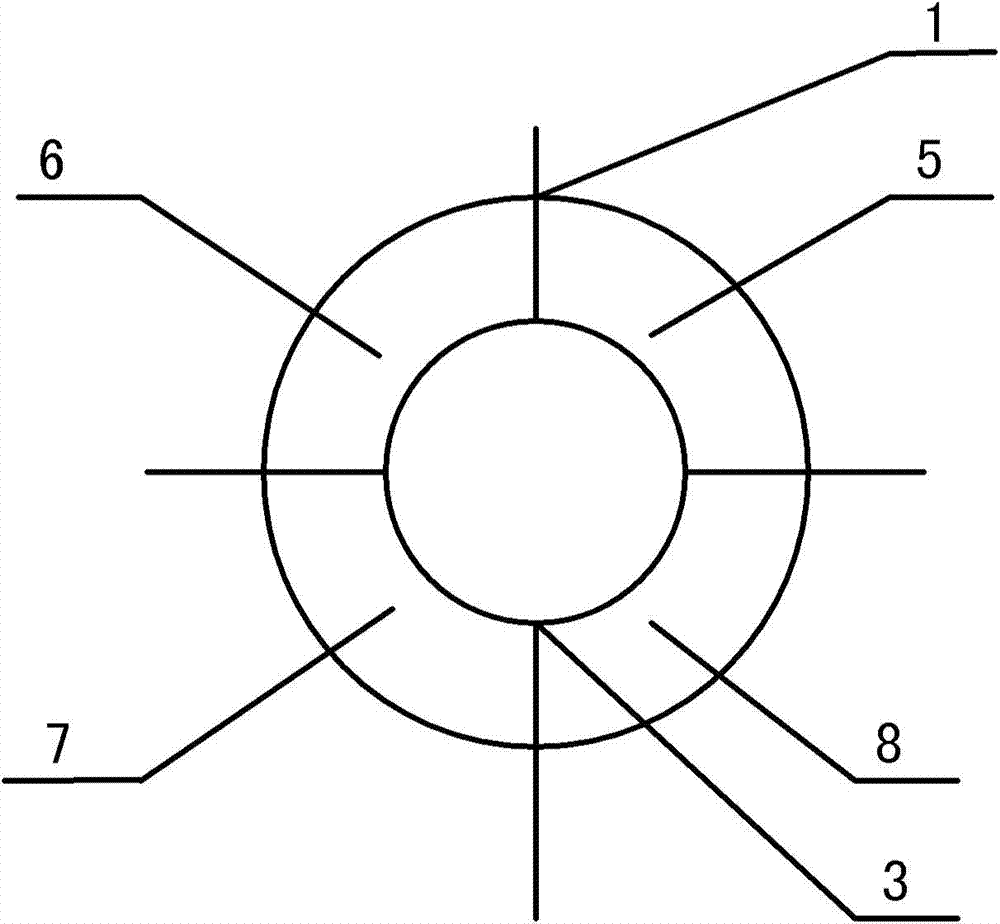
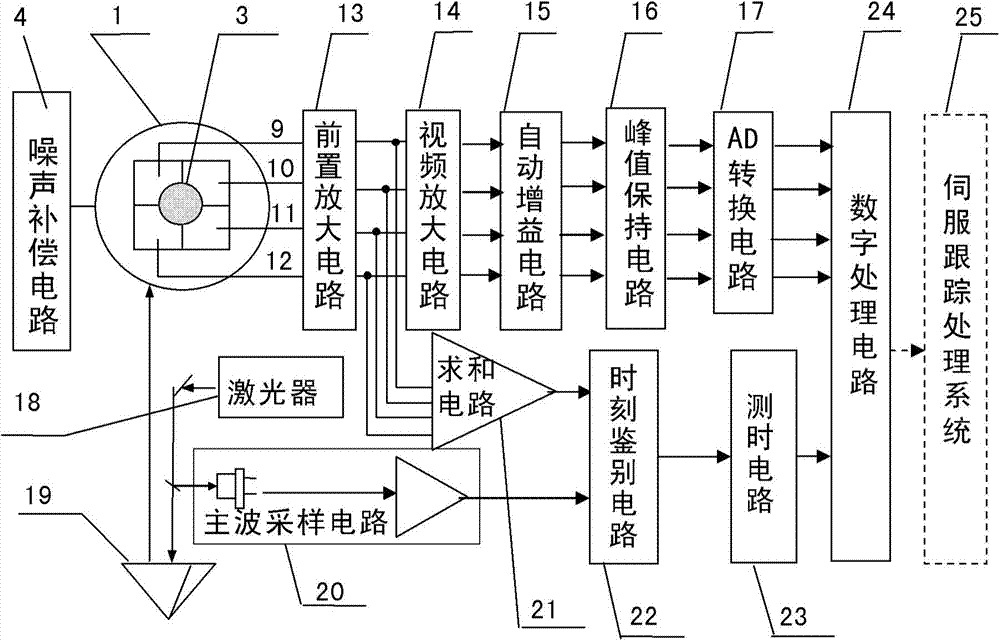
Measuring device and method for target line-of-sight angel offset and distance
ActiveCN103499819AHigh sensitivityEnsuring Gain StabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationMeasurement devicePhotodetector
The invention provides a measuring device and method for the target line-of-sight angel offset and distance. The device is composed of a four-quadrant avalanche photodetector, a receiving and sending optical unit, a noise compensation circuit, a four-circuit front amplification circuit, a video amplification circuit, an automatic gain amplification circuit, a peak keeping circuit, an AD conversion circuit, a laser, a dominant wave sampling circuit, a summing circuit, a time identifying circuit, a time test circuit and a digital processing circuit, wherein the receiving and sending optical unit enables narrow pulse laser rays emitted by the laser to be converged on the photoelectric detector to form echo light spots after target reflection, photovoltaic conversion of the four-quadrant avalanche photodetector, front amplification, video amplification and automatic gain amplification are conducted, narrow-pulse peak keeping is conducted, transmission of the AD conversion circuit is conducted, and the digital processing circuit extracts the digital line-of-sight angel offset; summing is conducted on the four-circuit front amplification circuit, the dominant wave sampling circuit is combined, the time identifying circuit determines laser emitting and echo coming and returning time, the time is transmitted to the time identifying circuit to be measured, and the digital processing circuit decodes the corresponding distance.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sensing method of optical-fiber Bragg grating laser device
InactiveCN101793570AReduced spectral rangeHigh precisionThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansGratingFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a sensing method with an optical-fiber Bragg grating laser device. An optical-fiber Bragg grating is used as a reflector of the resonant cavity, an active optical fiber capable of generating sufficient gains is added, and a double wavelength / multiple wavelength optical-fiber Bragg grating laser device is formed under the action of a pump light source and used as a sensor. When the outside strain, temperature and other physical quantities act on the sensing system, the beat signal frequency among the double wavelength or multiple wavelength laser can shift, and counter stress, temperature and other physical parameters can be measured precisely by detecting the beat signal frequency information. The invention has the advantages of simple manufacture, stable and reliable operation, stable measurement result and high precision, and is free from the interference of light intensity, polarization and other optical information quantities. The multipoint distribution sensing measurement can be realized in a frequency-division multiplexing mode. An electrooptical modulator is added before the spectrum analyzer starts detection so as to randomly adjust the beat signal frequency, thereby greatly reducing the spectral range of the spectrum analyzer and reducing the detection cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
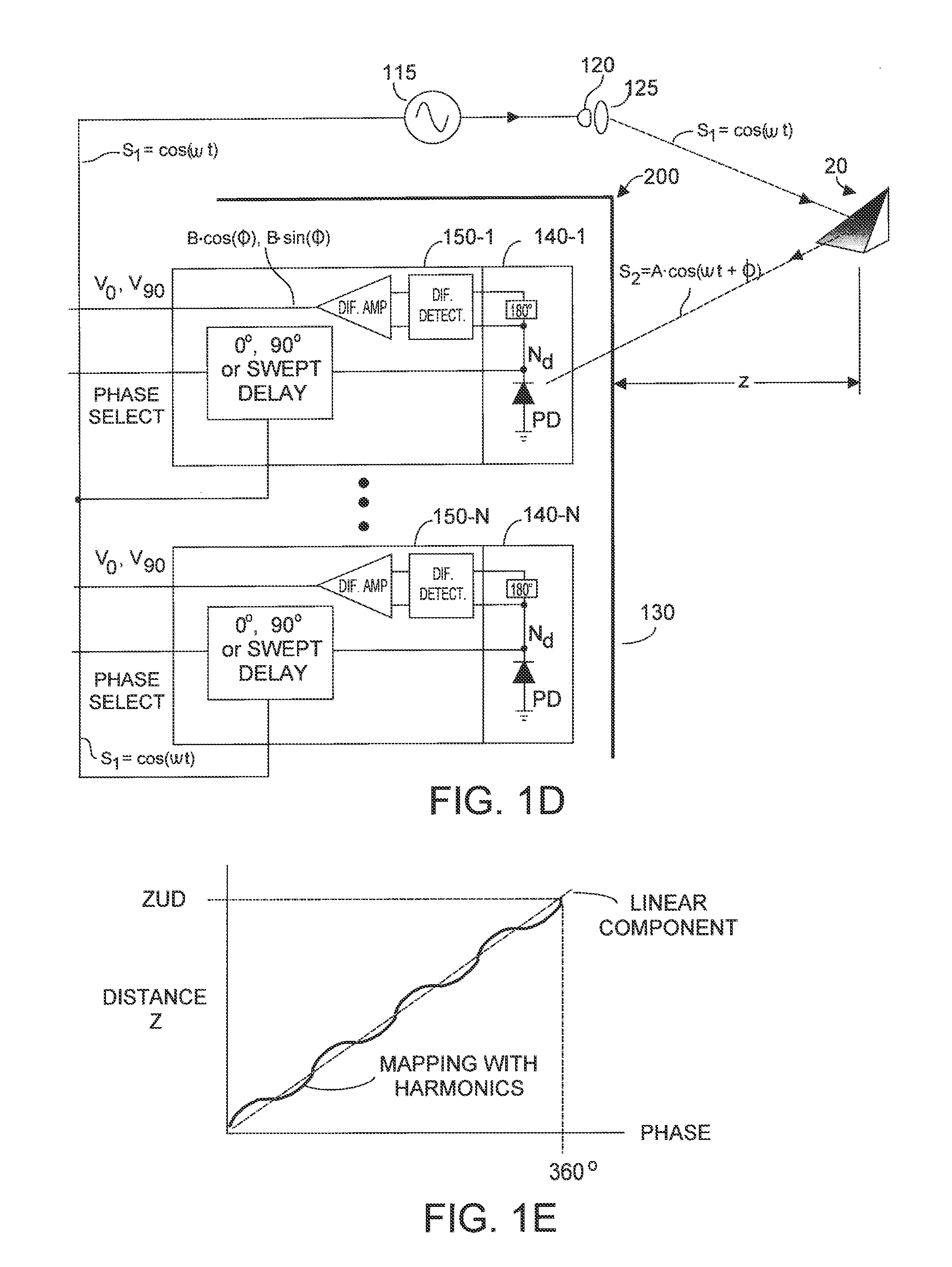
Method and system for multi-phase dynamic calibration of three-dimensional (3D) sensors in a time-of-flight system
ActiveUS20120013887A1Reduces bias errorMaximize modulation contrastOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationAudio power amplifierFall time
A phase-based TOF system preferably generates an optical waveform with fast rise and fall times, to enhance modulation contrast, notwithstanding there will be many high order harmonics. The system is preferably operated with an odd number of phases, to reduce system bias error due to the higher order harmonics, while maintaining good modulation contrast, without unduly increasing system memory requirements. Preferably the system can dynamically calibrate (and compensate for) higher order harmonics in the TOF generated optical energy waveform, over time and temperature. Within the optical energy transmission channel, or within the optical energy detection channel, detection amplifier gain may be modified, and / or detector signal integration time may be varied, and / or digital values may be employed to implement calibration and error reduction The resultant TOF system can operate with improved phase-vs-distance characteristics, with reduced calibration requirements.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
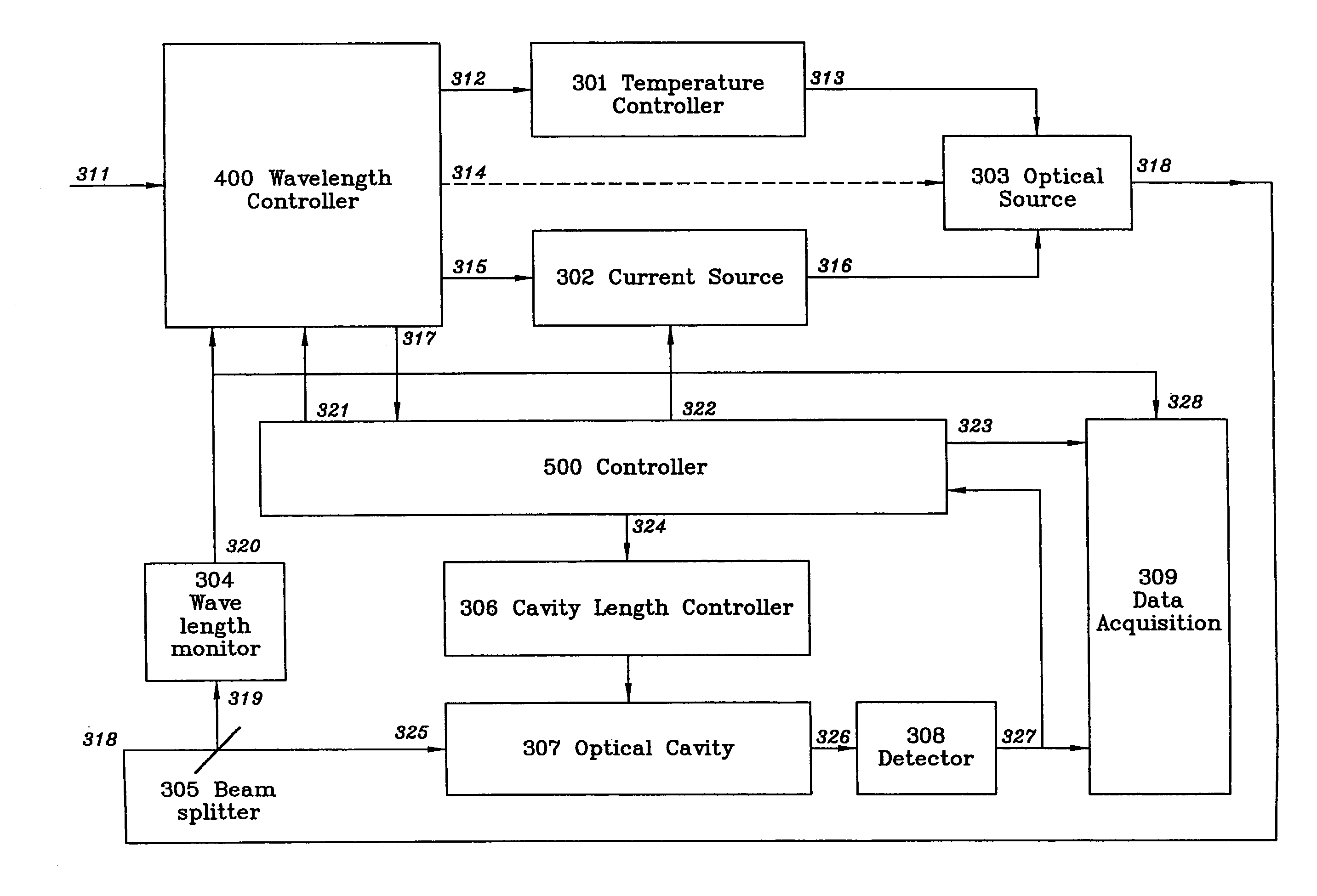
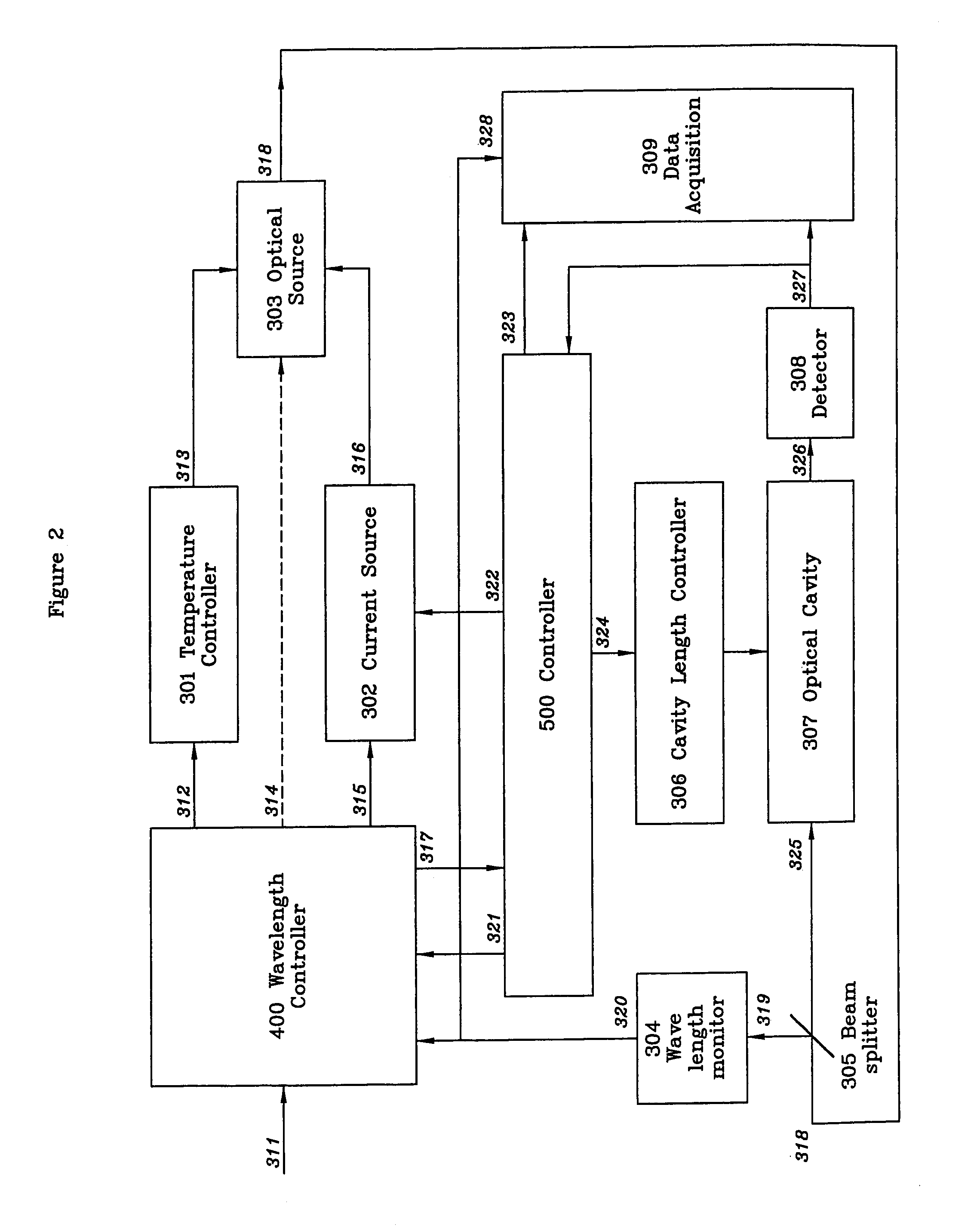
System and method for controlling the light source of a cavity ringdown spectrometer
InactiveUS20050254056A1Reduce repetition rateEasy to controlRadiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsHigh reflectivitySpectrometer
A system and method for controlling the light source of a cavity ring-down spectrometer (CRDS). The system comprises a resonant optical cavity having at least two high reflectivity mirrors; a source for providing a continuous wave optical signal into the optical cavity, the source comprising an electrically pumped semiconductor gain medium; and a SOA interposed between the optical signal source and the optical cavity. The SOA receives the optical signal and transmits it to the resonant optical cavity. The system also includes a first detector for monitoring the intensity of radiation emitted from said cavity and generating a first detection signal based thereon; and at least a first controller for deactivating the optical signal based on a comparison of the first detection signal and a predetermined threshold and for thereafter reactivating the optical signal after a delay period in excess of the ring-down time of the optical cavity, the deactivating and reactivating being achieved by respectively turning off and then turning on electrical current to the SOA.
Owner:PICARRO
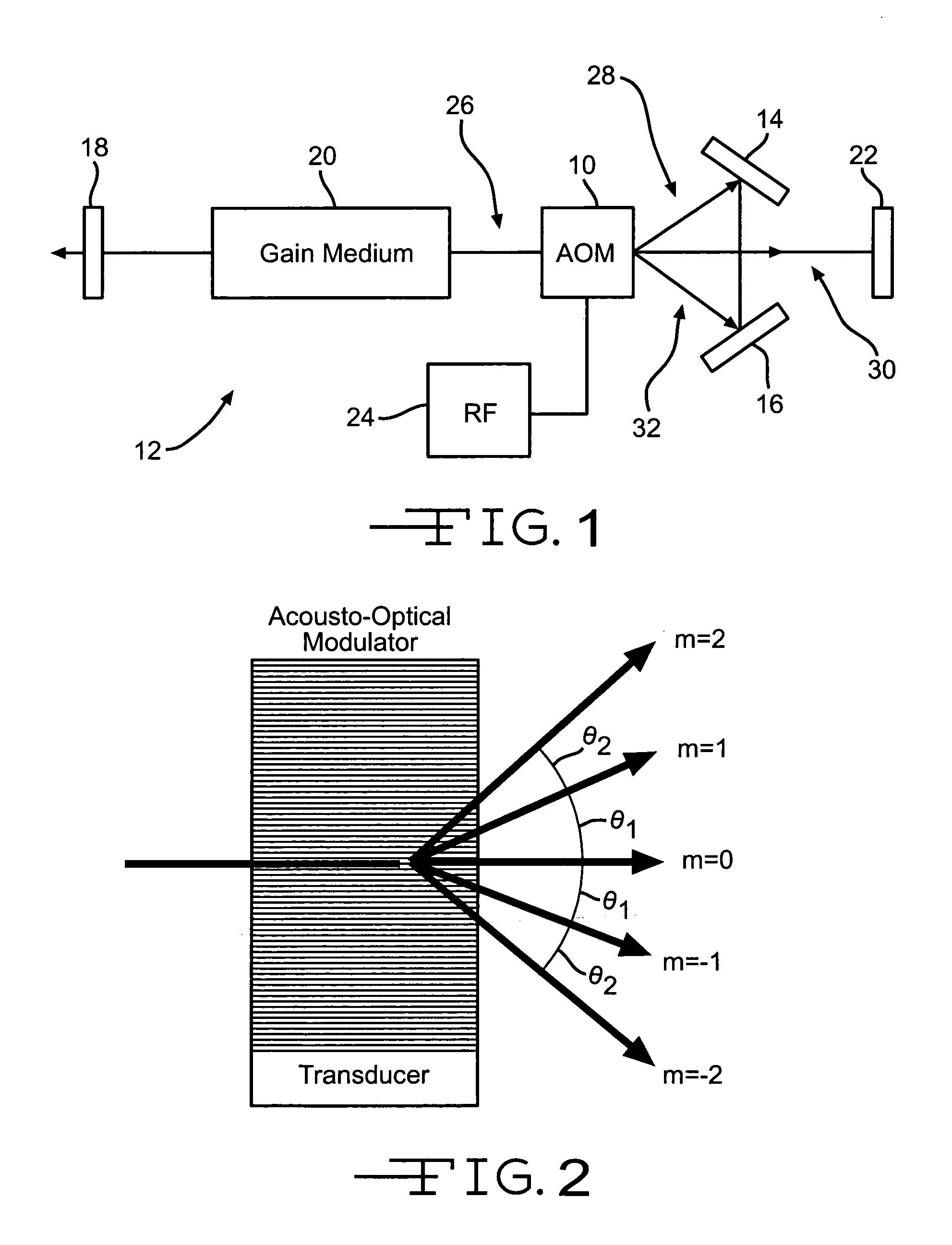
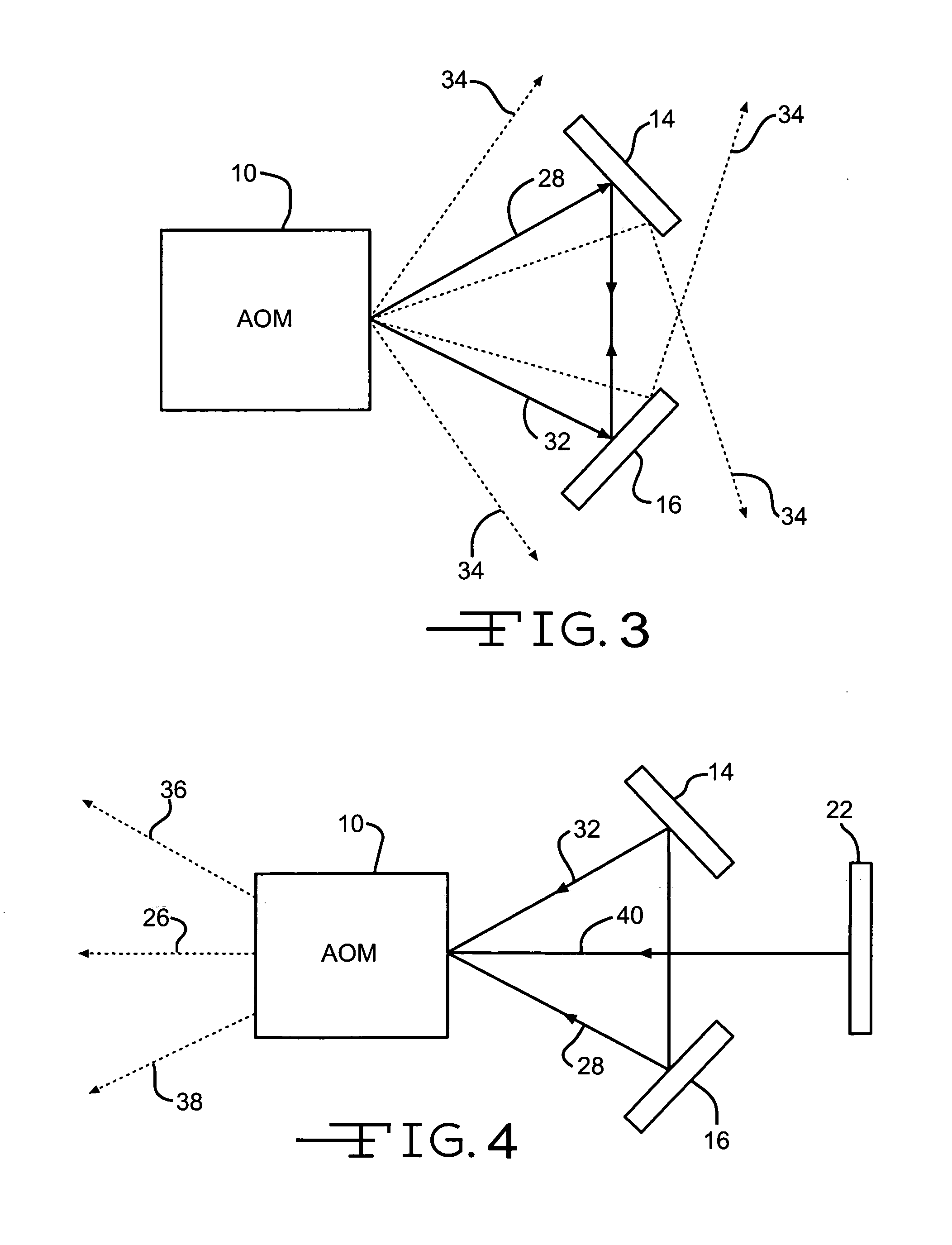
Laser intra-cavity electronic wavelength tuner
An apparatus for adjusting the wavelength of a laser capable of lasing at multiple wavelengths by using a single acousto-optical modulator and a pair of optical reflectors inside a laser cavity. By adjusting the frequency and amplitude of the radio-frequency source to the acousto-optical modulator, undesired wavelengths are suppressed in the laser cavity, leaving appreciable gain only at the desired wavelength.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
External cavity laser array system and WDM optical system including same
ActiveUS20130223844A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser transmitterExternal cavity laser
An external cavity laser array system may be used in a WDM optical system, such as a WDM-PON, for transmitting optical signals at multiple channel wavelengths. The system generally includes a plurality of laser emitters (e.g., gain chips) optically coupled to and separated from respective exit reflectors (e.g., tunable narrow-band reflectors), thereby forming an array of external cavity lasers with extended lasing cavities. The exit reflectors may be distributed Bragg reflectors (DBRs) located in the waveguides in an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG). The laser emitters emit a range of wavelengths including multiple channel wavelengths and the DBRs reflect a subset of channel wavelengths including at least a channel wavelength associated with the laser emitter such that lasing occurs at the subset of channel wavelengths. The AWG then filters the emitted laser light at the associated channel wavelengths.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Apparatus for differentiating blood cells using back-scatter
InactiveUS6869569B2Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotodetectorRed blood cell
Blood cells of interest are readily distinguishable from other blood cells and look-a-like particles found in a blood sample by their back-scatter signature. A preferred method for differentiating platelets in a blood sample is to irradiate the cells and particles, one at a time, with a beam of radiation, and to detect back-scattered (reflected) radiation using a plurality of optical fibers to transmit the back-scattered radiation to a high-gain photodetector, e.g. a photomultiplier tube. Preferably, the back-scatter signal so obtained is combined with a second signal representing, for example, either the level of forward-scatter within a prescribed, relatively narrow angular range, or the level of side-scattered radiation, or the level of attenuation of the cell-irradiating beam caused by the presence of the irradiated cell or particle in the beam, or the electrical impedance of the irradiated cell or particle, to differentiate the cells of interest. The method and apparatus of the invention are particularly useful in differentiating platelets and basophils in a blood sample.
Owner:COULTER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
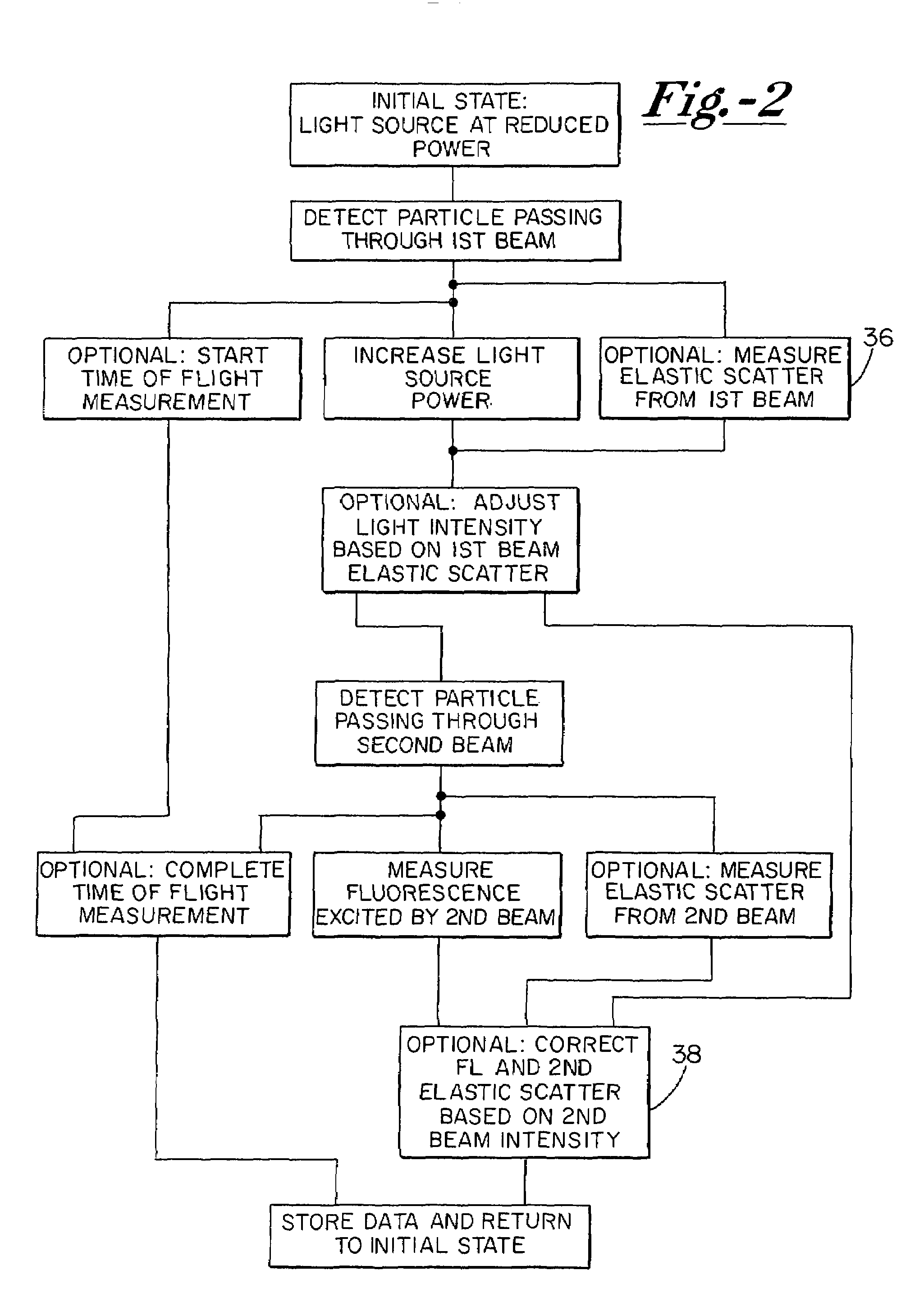
Analysis systems detecting particle size and fluorescence
ActiveUS7057712B2Systems can be simplifiedImprove efficiencyTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrum investigationFluorescent radiationMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Particle analyzing systems with fluorescence detection are disclosed, primarily in connection with particle sizing based on scattered light intensity or time-of-flight measurement. In one system, emission of fluorescence is used as a threshold for selecting particles for further analysis, e.g. mass spectrometry. In another embodiment, laser beams arranged sequentially along an aerosol path are selectively switched on and off, to increase the useful life of components, and diminish the potential for interference among several signals. Other embodiments advantageously employ color discrimination in aerodynamic particle sizing, single detectors positioned to sense both scattered and emitted fluorescent radiation, and laser beam amplitude or gain control to enhance the range of fluorescence detection.
Owner:TSI INC
Wavelength control for cavity ringdown spectrometer
ActiveUS7106763B2Easy to controlShort response timeLaser detailsTransmissivity measurementsTarget analysisRing down
A cavity ring-down spectrometer includes:a) multiple detectors for monitoring the intensity of the radiation emitted from the cavity and the wavelength of the radiation injected into the cavity;b) controllers which turn off the radiation into the cavity and precisely adjust the temperature of, and current to, the laser gain medium; andc) means for adjusting the beam path length of the optical cavit to bring the cavity into resonance with the injected radiation. Additionally, disclosed is a method for using the spectrometer to detect a target analyte.
Owner:PICARRO
Sensor dark pixel offset estimation
InactiveUS20130271628A1Easy CalibrationEfficient executionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsGainComputer science
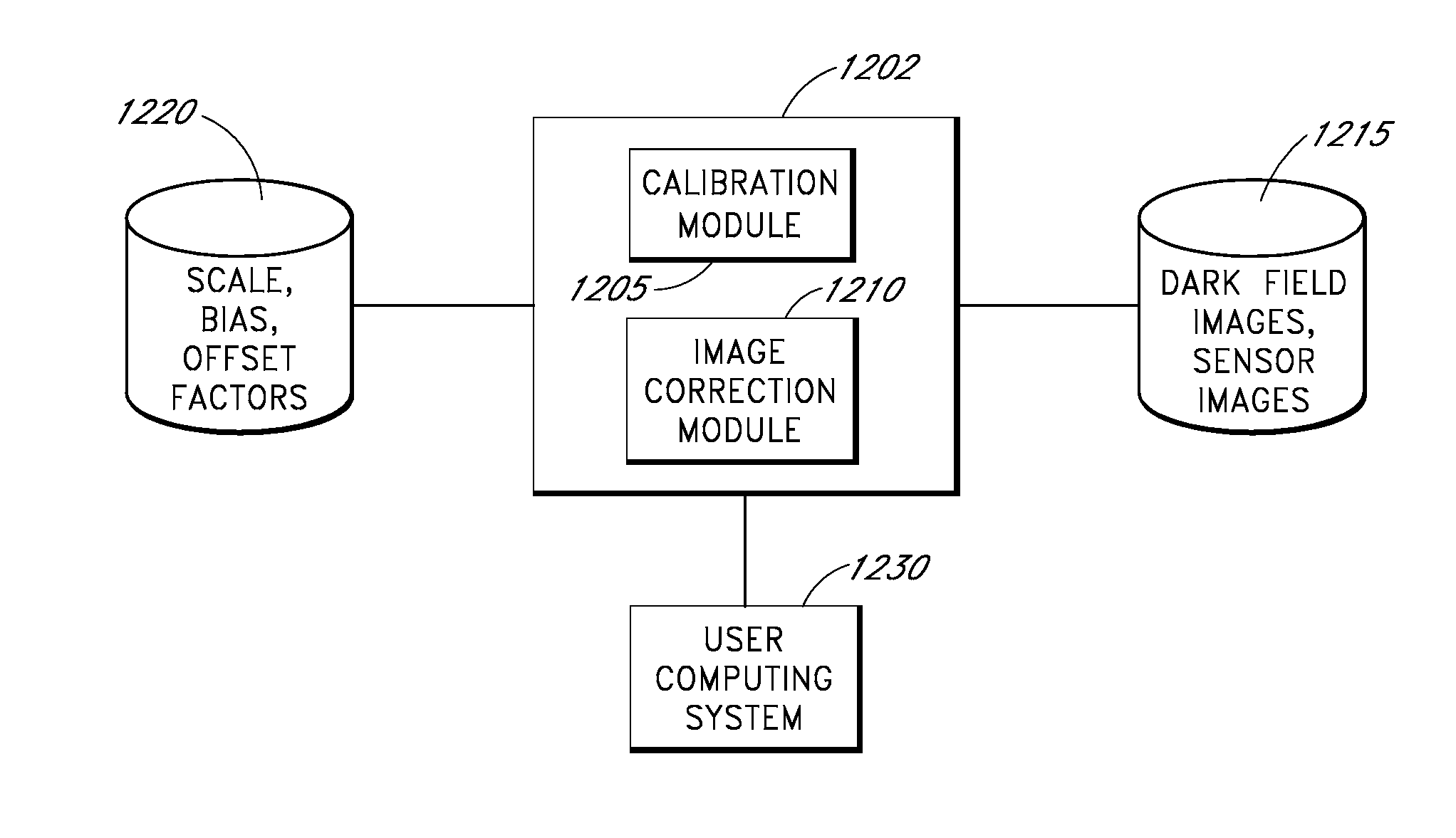
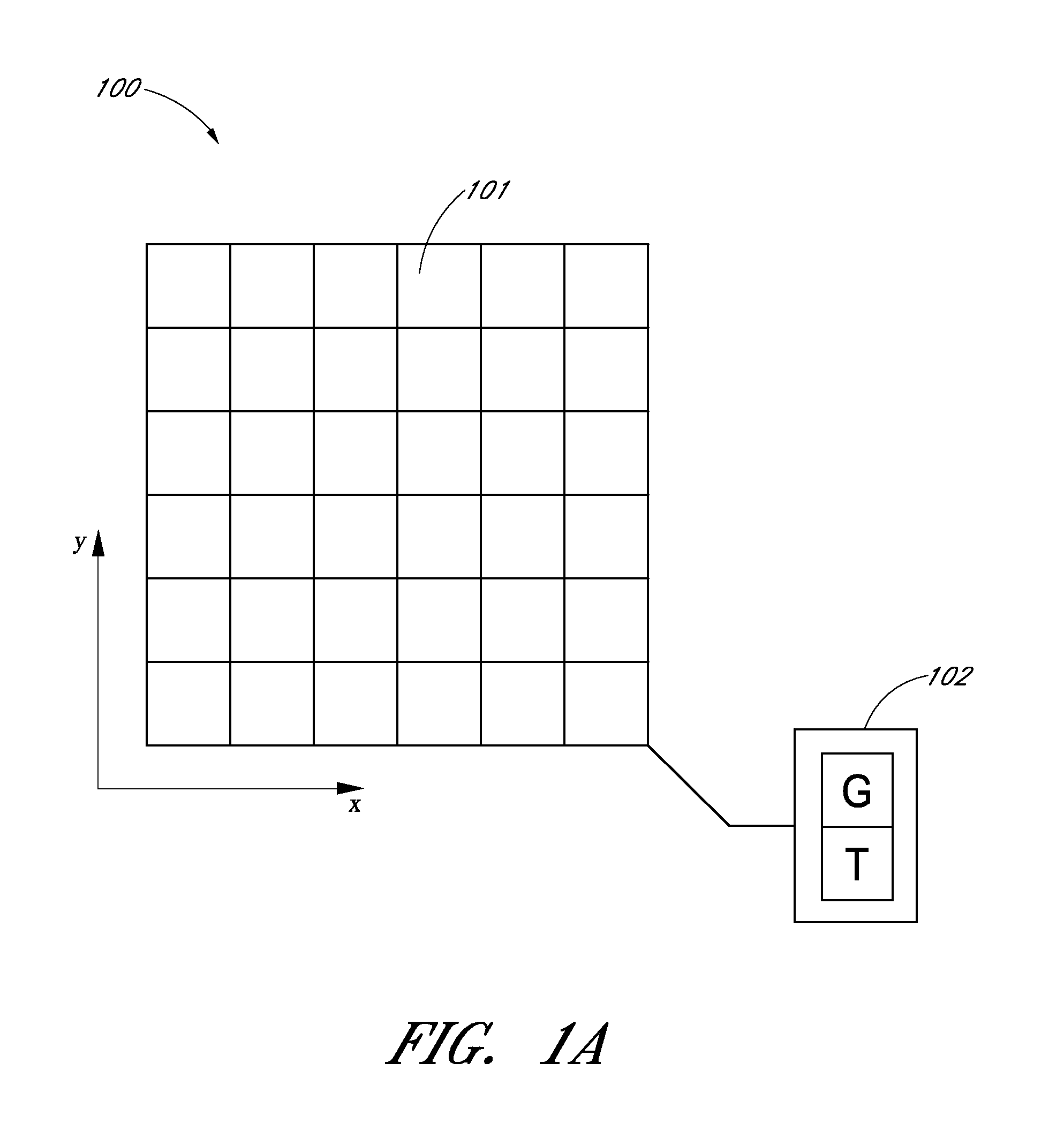
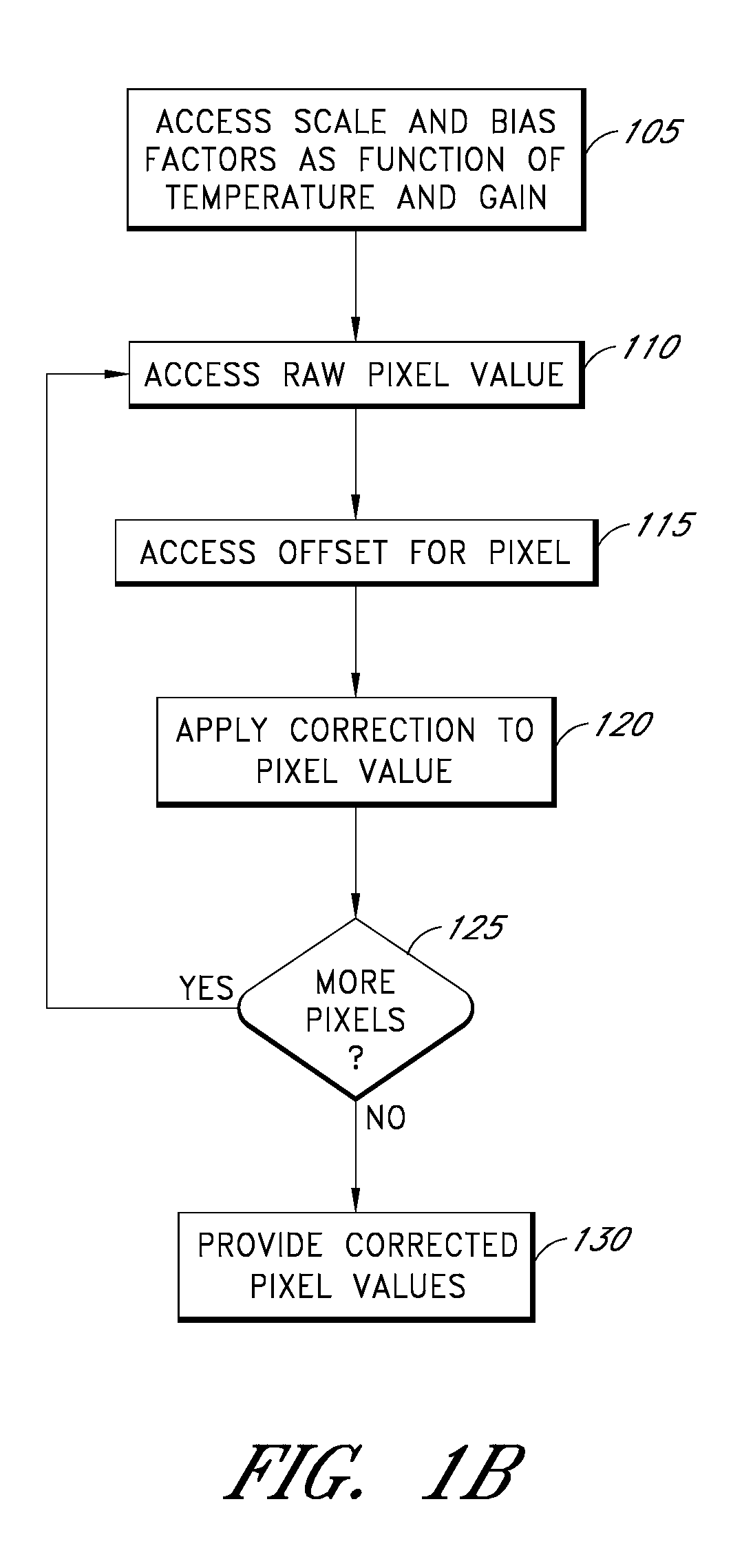
Examples of systems and methods to provide estimates of dark current for pixels of a photosensor as a function of the temperature of the sensor and the gain applied to the photosensor are described. In various implementations, the dark current estimated for each pixel can depend at least partly on a global scale factor and a global bias that depend on temperature and gain and a temperature-independent and gain-independent offset value for each pixel. The scale, bias, and offsets may be determined from multiple dark field images taken by the sensor over a range of operating temperatures. In some cases, the scale and bias can be determined using a subset of less than all the image pixels. Scale and bias derived for a particular sensor can be used in the calibration of different sensors.
Owner:PLANET LABS PBC
Double-sided turning film
InactiveUS20080259634A1Many solutionsImprove the level ofPrismsMechanical apparatusLight guideDisplay device
A backlight device for a display comprising (1) a side-lit light source, (2) a light guide plate and (3) a turning film comprising a light entry and a light exit surface comprising lenticular elements on the exit surface and prismatic structures on the entry surface, wherein the average values of the parameters of the features and the thickness of the film are selected to provide a peak output angle of ±10° from normal to the light exit surface of the light guide plate and an optical gain of at least 1.25. Also disclosed are methods of making the turning film and a display incorporating the backlight.
Owner:SKC HAAS DISPLAY FILMS CO LTD
External cavity tunable compact Mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7535936B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Beam-forming apparatus and method using a spatial interpolation based on regular spatial sampling
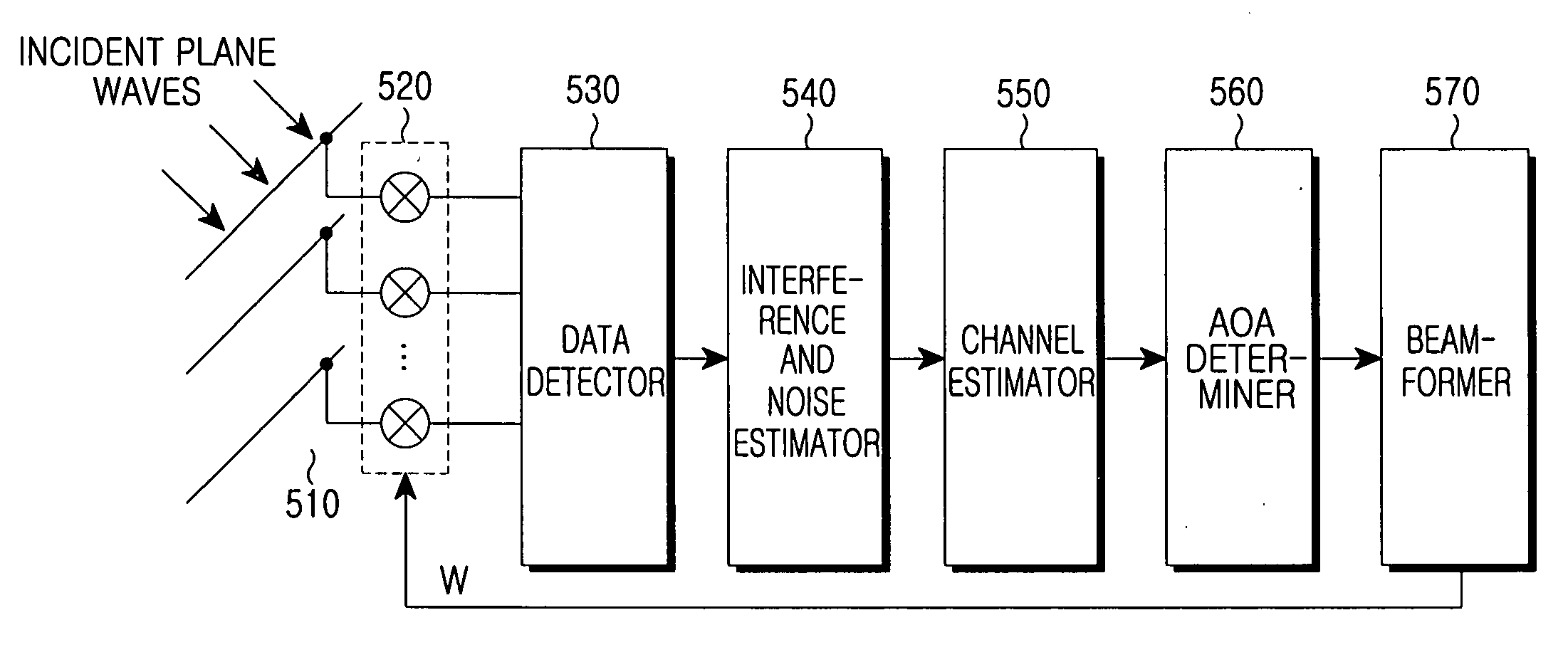
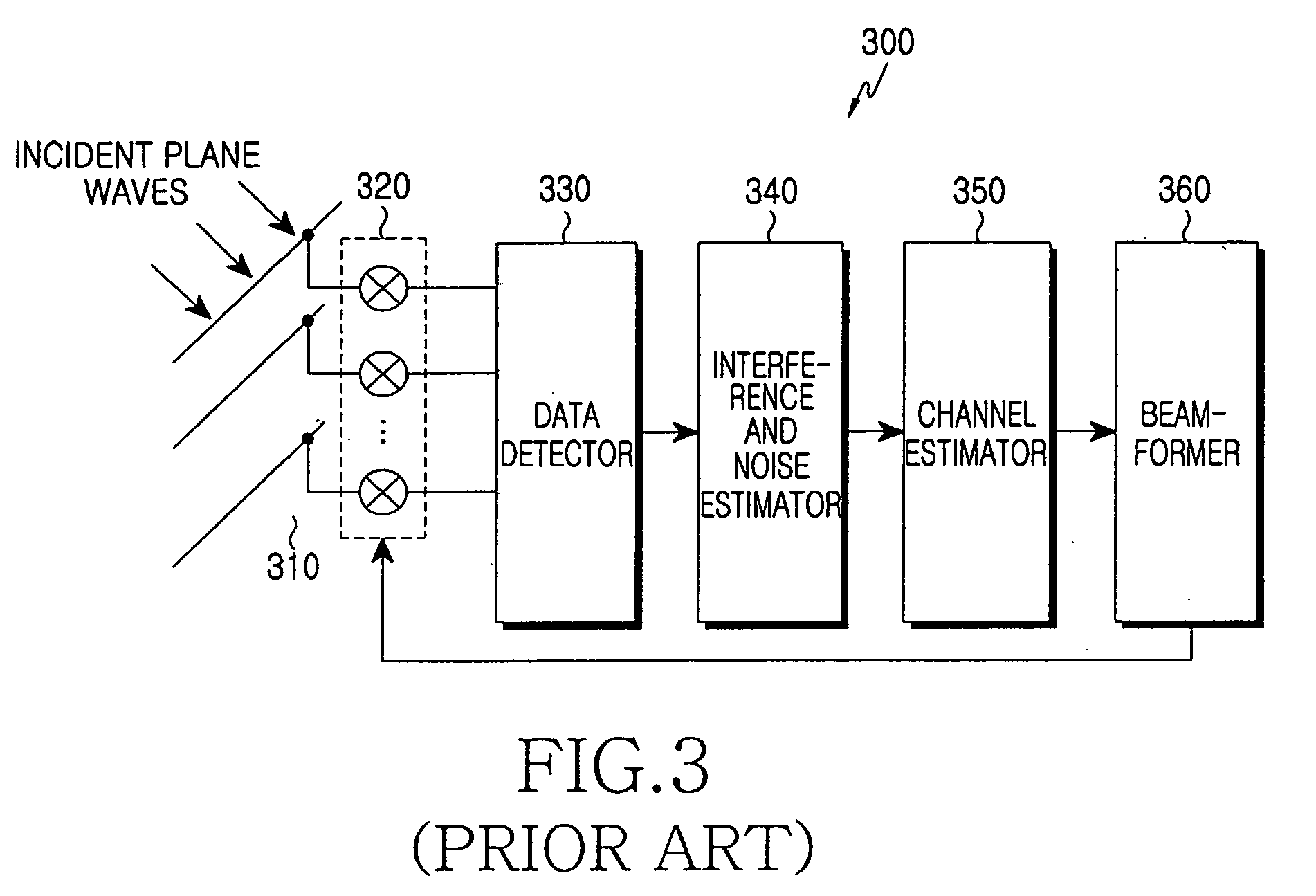
ActiveUS20060244660A1Reduce complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeam angleInterference ratio
A beam-forming apparatus and method for improving system performance using a spatial interpolation and at least one Angle of Arrival (AoA) in a system based on regular spatial sampling is provided. The AoA is estimated using a carrier-to-interference ratio. Beam-forming angles are distributed and steered in a predefined scheme such that an identical process is applied in all directions. According to this steering, a linear system model is computed based on regular spatial sampling using regular spatial separation at beam angles. Beam-forming performance is improved by compensating for a difference between adaptive and sector-type arrays. Only the steps of computing a spatial interpolation and determining an angle range for beam-forming using at least one AoA are added. The precision of estimating an AoA and the precision of beam-forming increase without an additional antenna. Because the system is simpler than that of an adaptive beam-forming system, significant gain is obtained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical phase conjugation laser diode
A phase-conjugating resonator that includes a semiconductor laser diode apparatus that comprises a phase-conjugating array of retro-reflecting hexagon apertured hexahedral shaped corner-cube prisms, an electrically and / or optically pumped gain-region, a distributed bragg reflecting mirror-stack, a gaussian mode providing hemispherical shaped laser-emission-output metalized mirror. Wherein, optical phase conjugation is used to neutralize the phase perturbating contribution of spontaneous-emission, acoustic phonons, quantum-noise, gain-saturation, diffraction, and other intracavity aberrations and distortions that typically destabilize any stimulated-emission made to undergo amplifying oscillation within the inventions phase-conjugating resonator. Resulting in stablized high-power laser-emission-output into a single low-order fundamental transverse cavity mode and reversal of intra-cavity chirp that provides for high-speed internal modulation capable of transmitting data at around 20-Gigabits / ps.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
Method for defect detection and surface measurement of silicon wafer
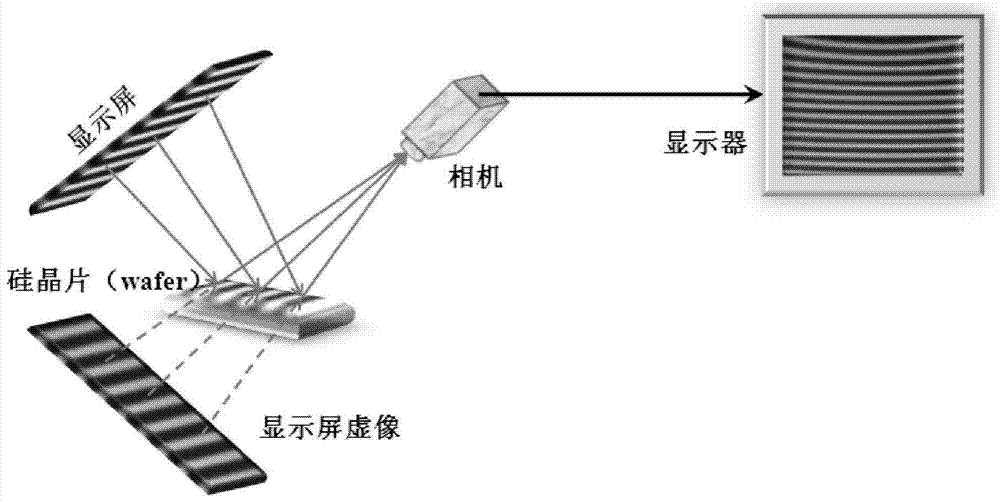
ActiveCN103487441ASensitive highHigh precisionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansWaferingGain
The invention provides a method for defect detection and surface measurement of a silicon wafer. According to the method, the phase-measuring deflectometry(PMD) is used for surface measurement of a silicon wafer. The PMD-based mirror object three-dimensional surface measurement method is a highly-sensitive, high-precision, quick and incoherent optical full-field measurement technology, and an experimental device is simple and mainly comprises a computer, a digital camera and a display screen. When the PMD is used for surface measurement of the silicon wafer, the surface gradient distribution of the silicon wafer can be directly obtained, the surface curvature distribution of the silicon wafer can be obtained so long as gradient derivation is performed, defects are detected through curvature distribution, the surface height data of the silicon wafer can be obtained through gradient integration, and accordingly, the three-dimensional shape can be observed. The invention has the main gain that the high-precision and quick full-field measurement technology is provided to realize surface defect detection and surface measurement of the silicon wafer.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com