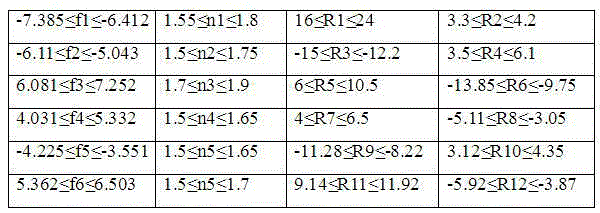
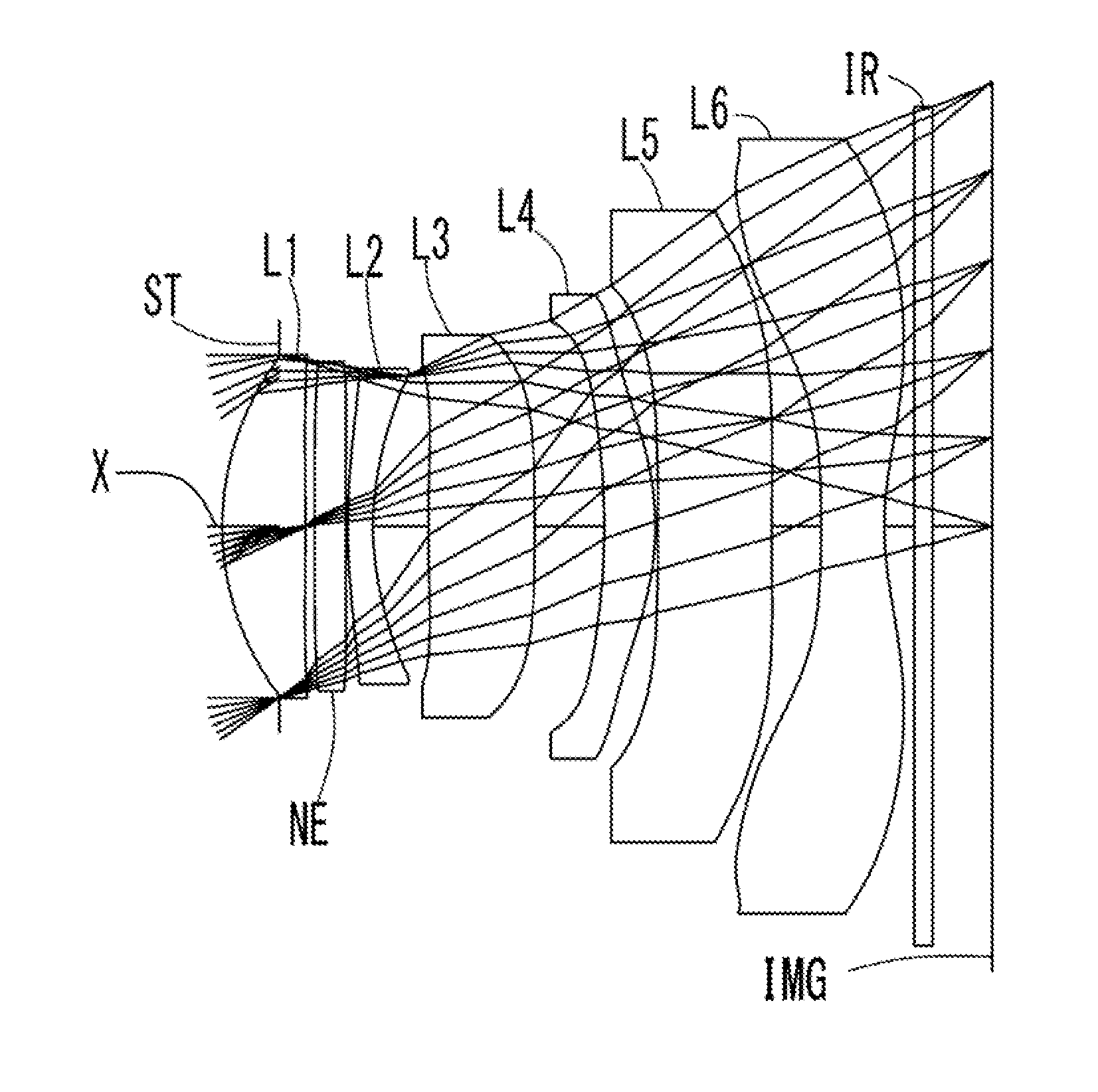
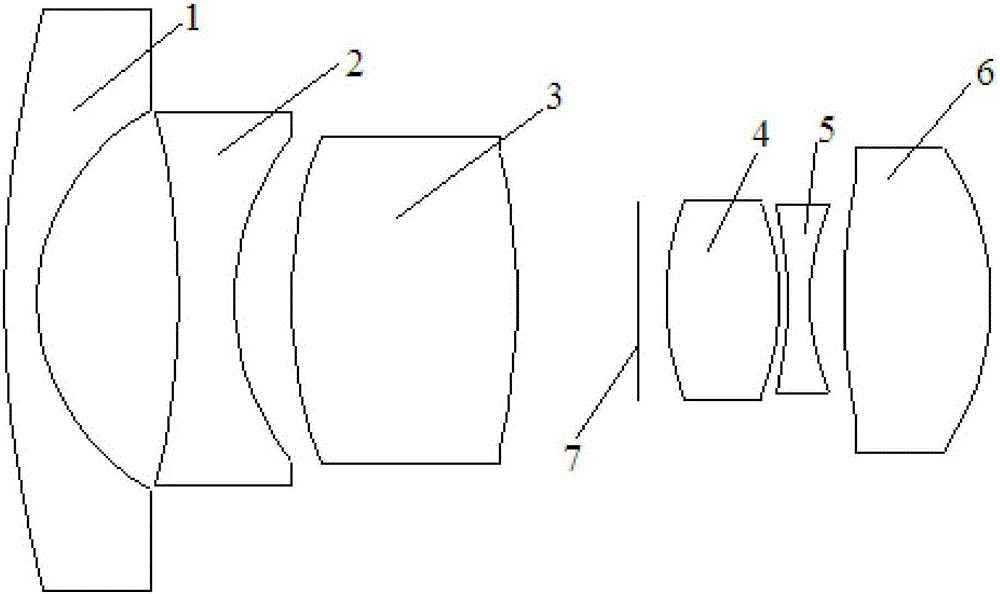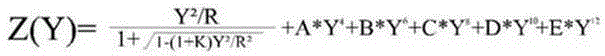Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1157 results about "Aspheric lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
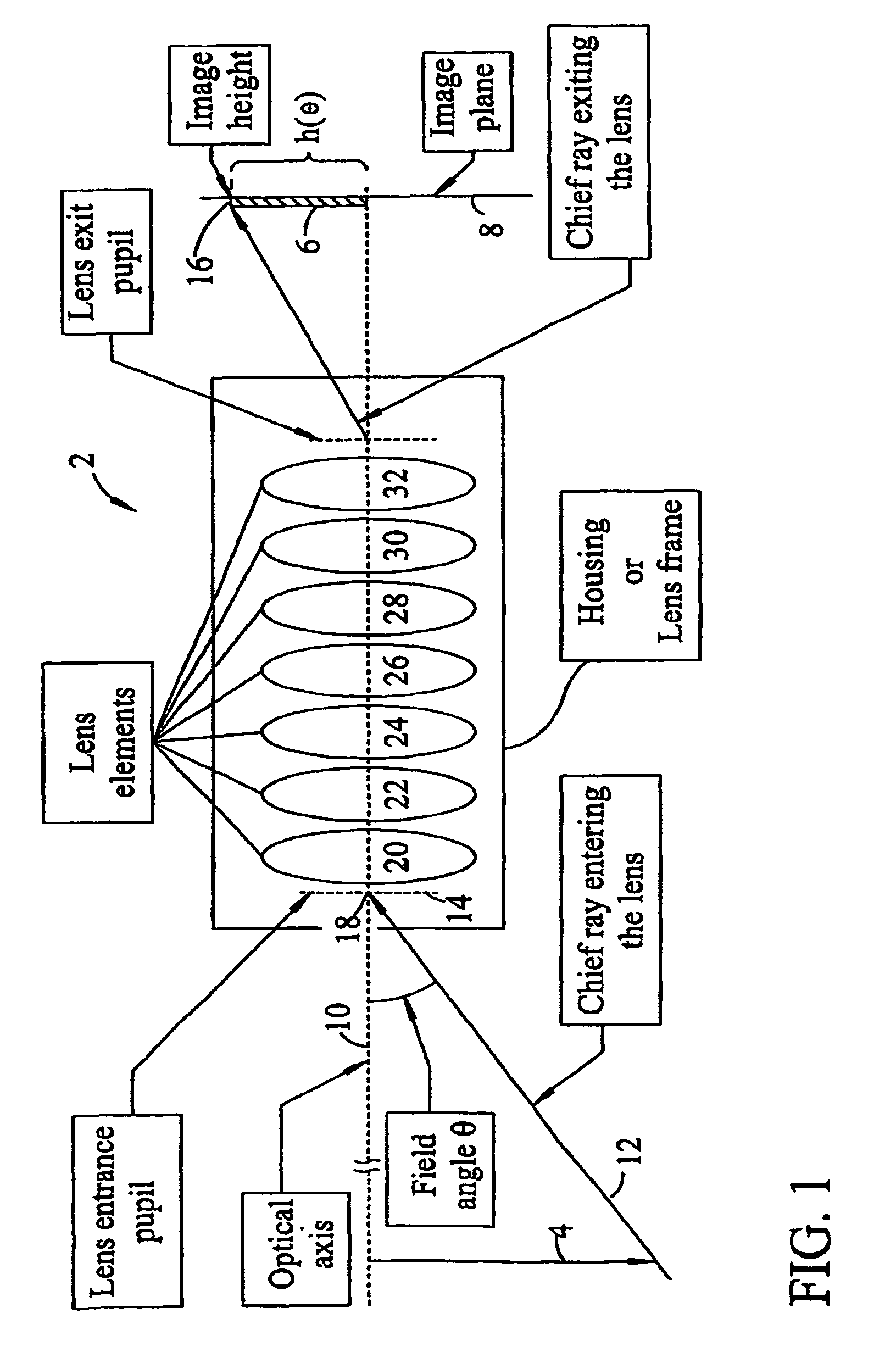
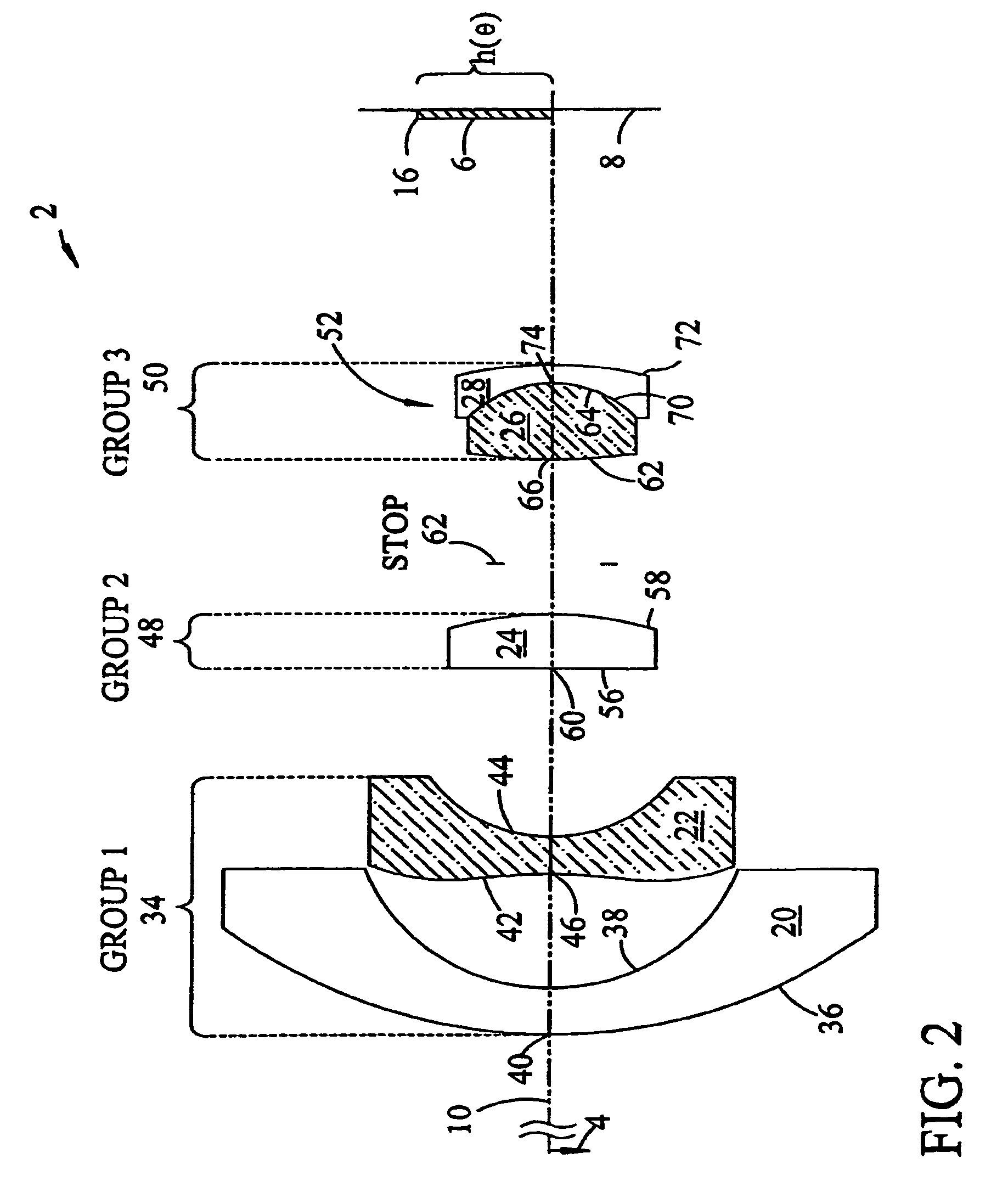
An aspheric lens or asphere (often labeled ASPH on eye pieces) is a lens whose surface profiles are not portions of a sphere or cylinder. In photography, a lens assembly that includes an aspheric element is often called an aspherical lens.
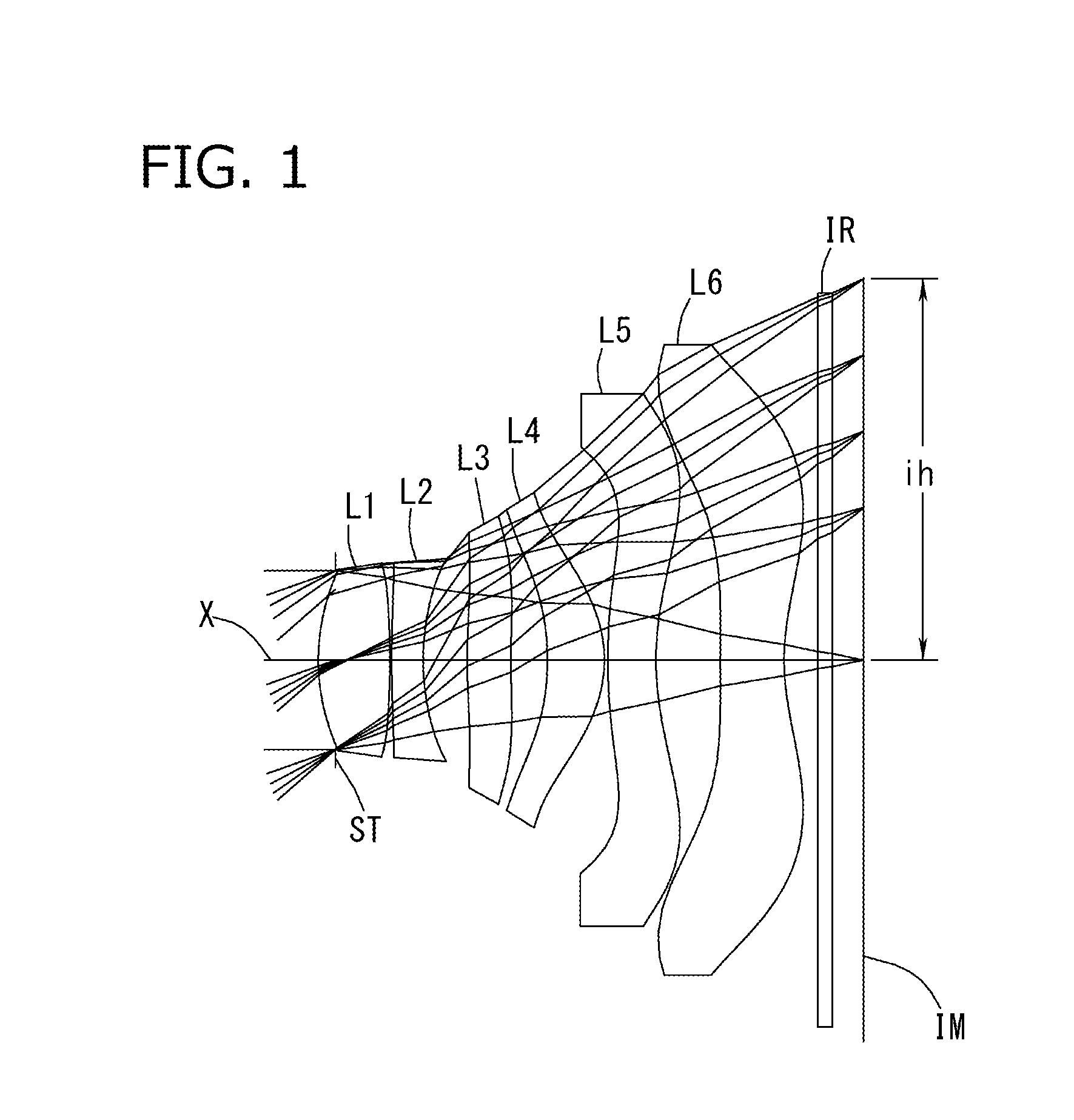
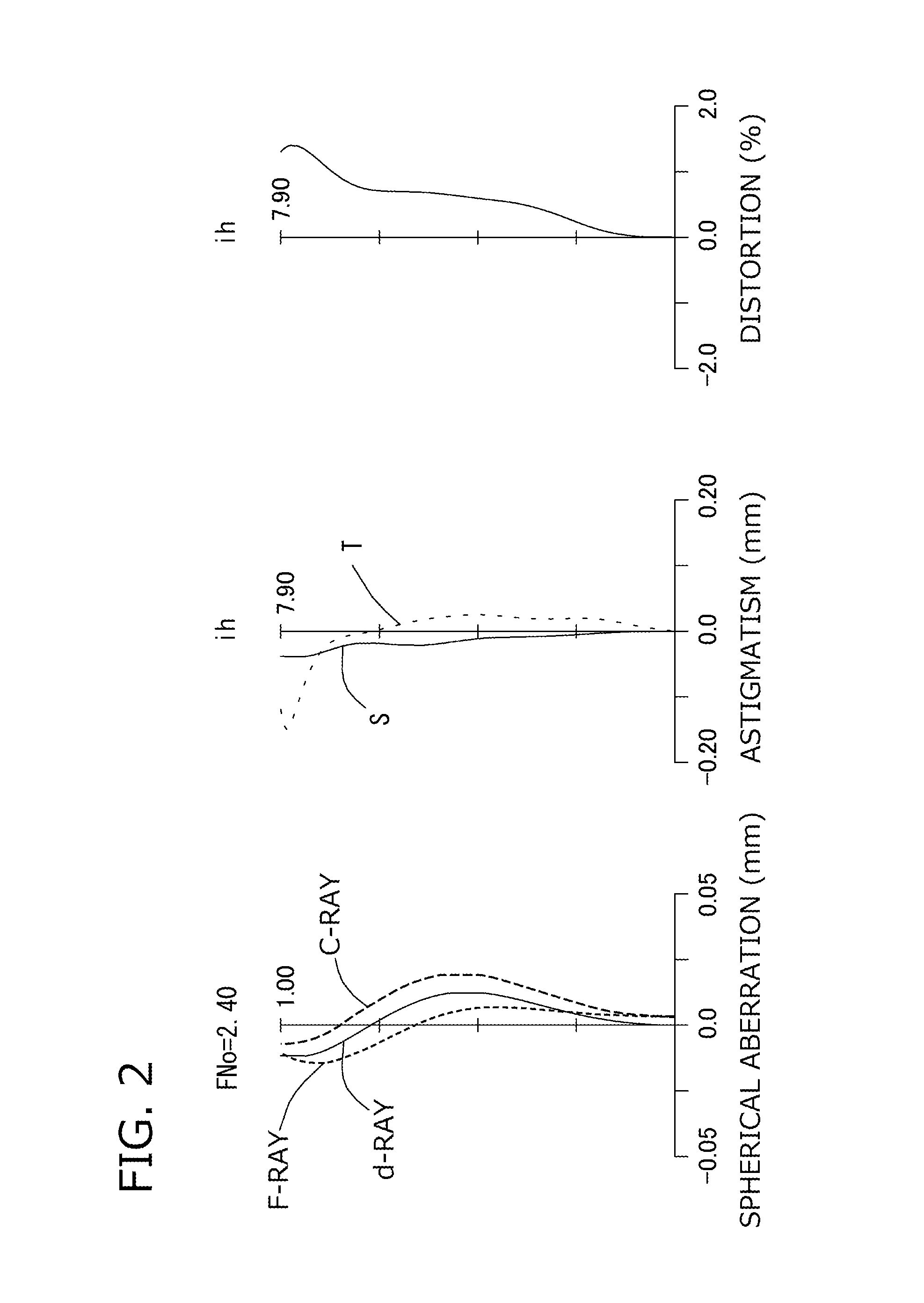
Imaging lens
ActiveUS20150070783A1Good optical performanceVarious aberrationImage enhancementStatic indicating devicesWide fieldAspheric lens
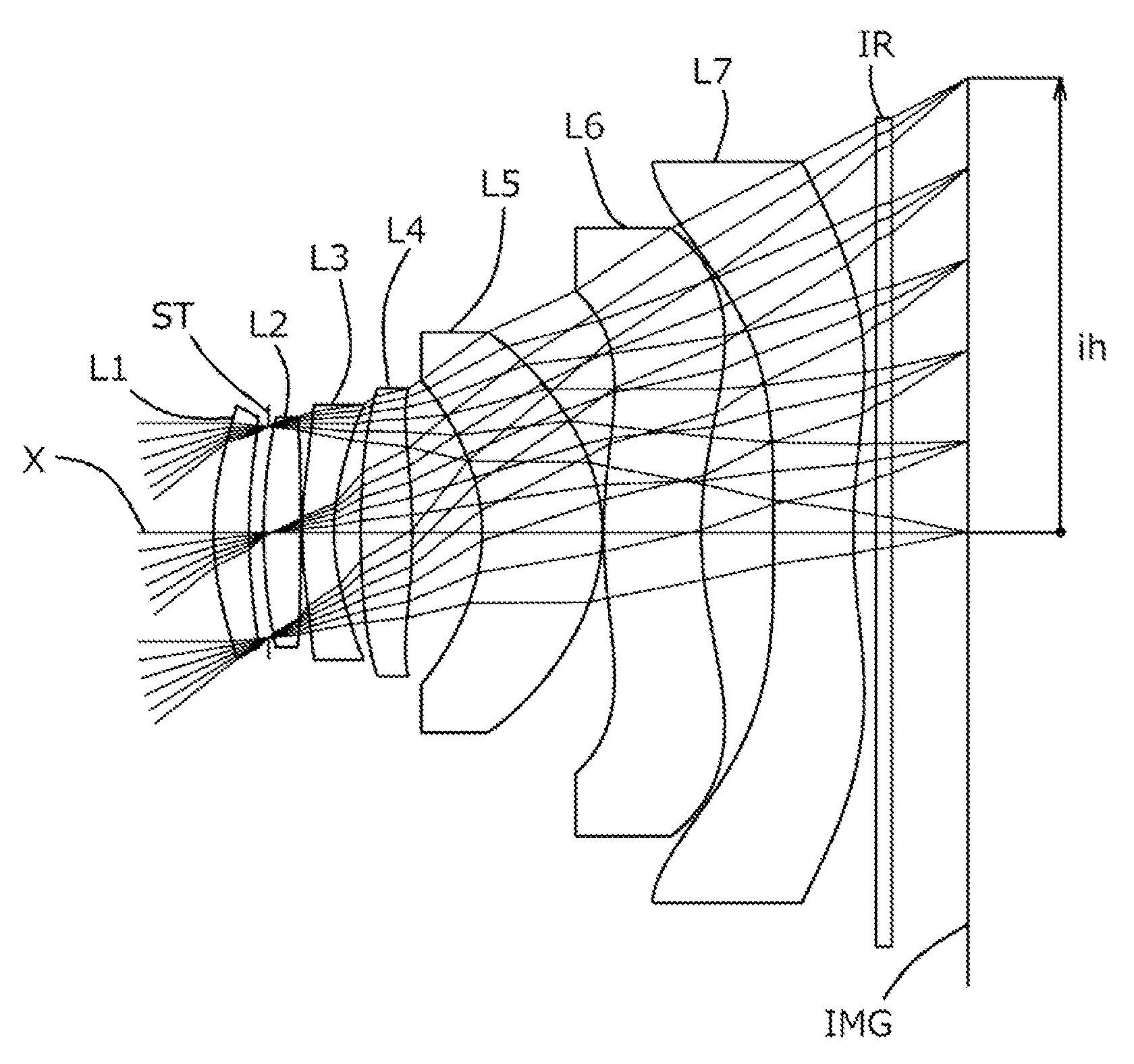
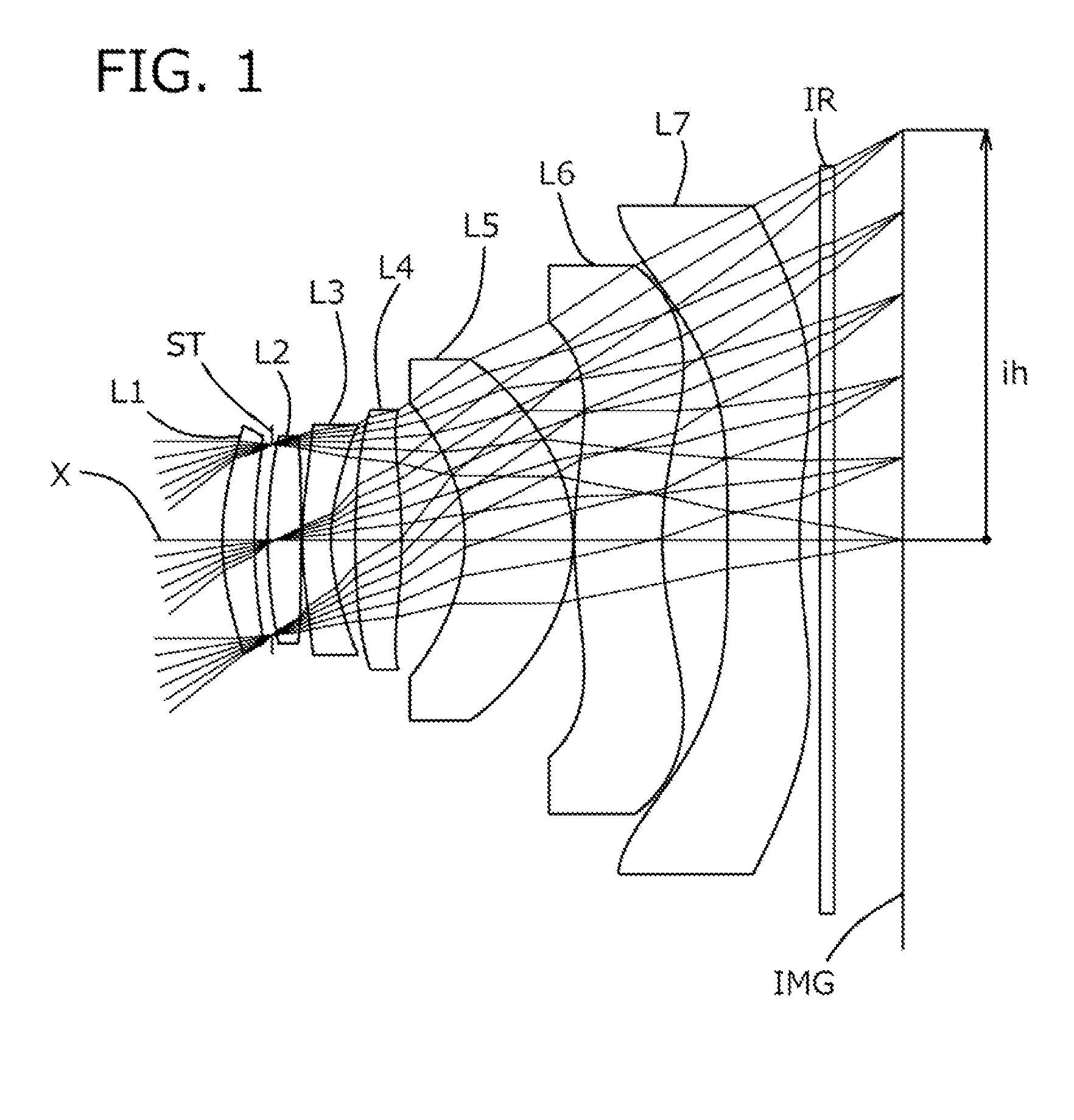
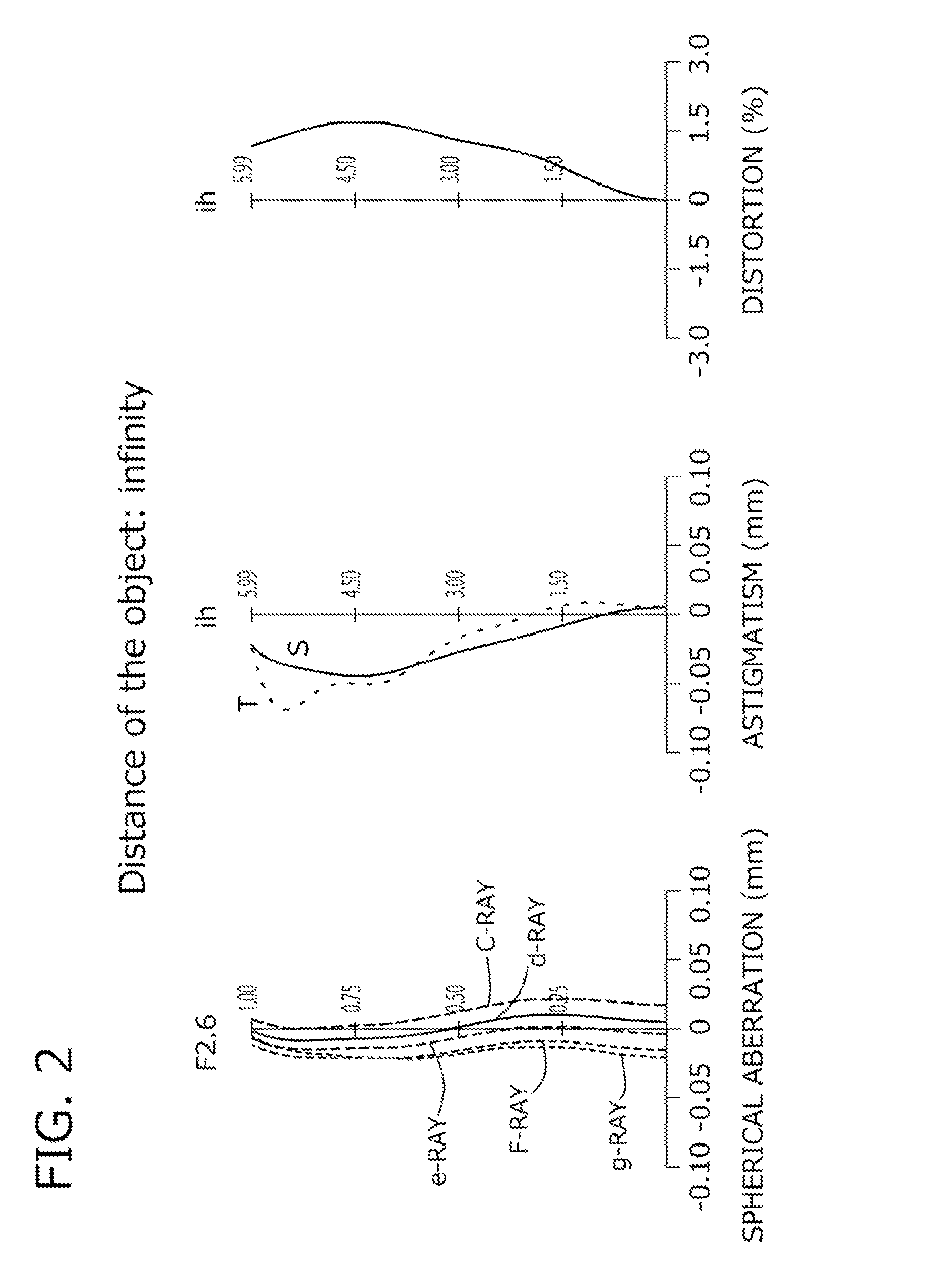
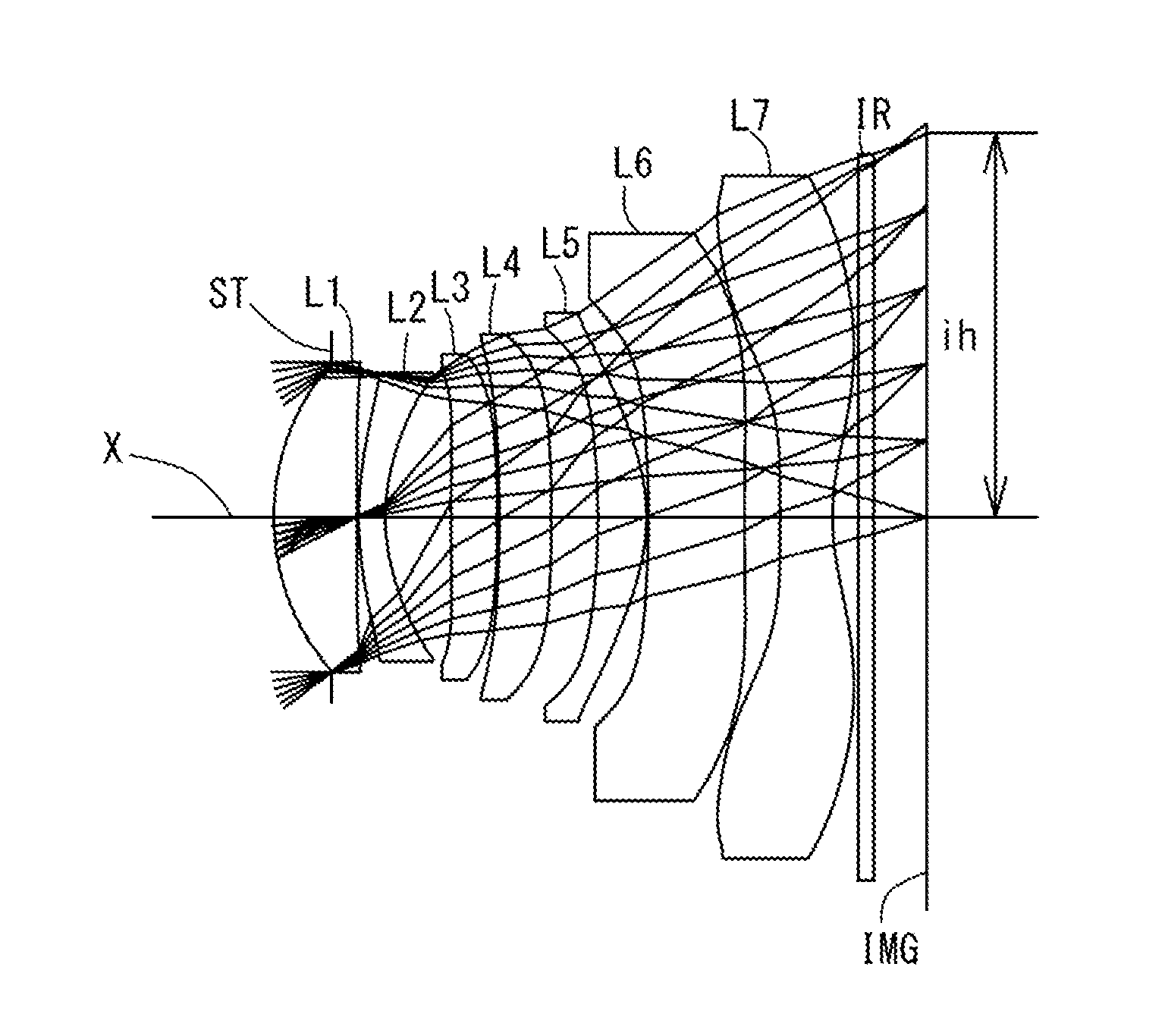
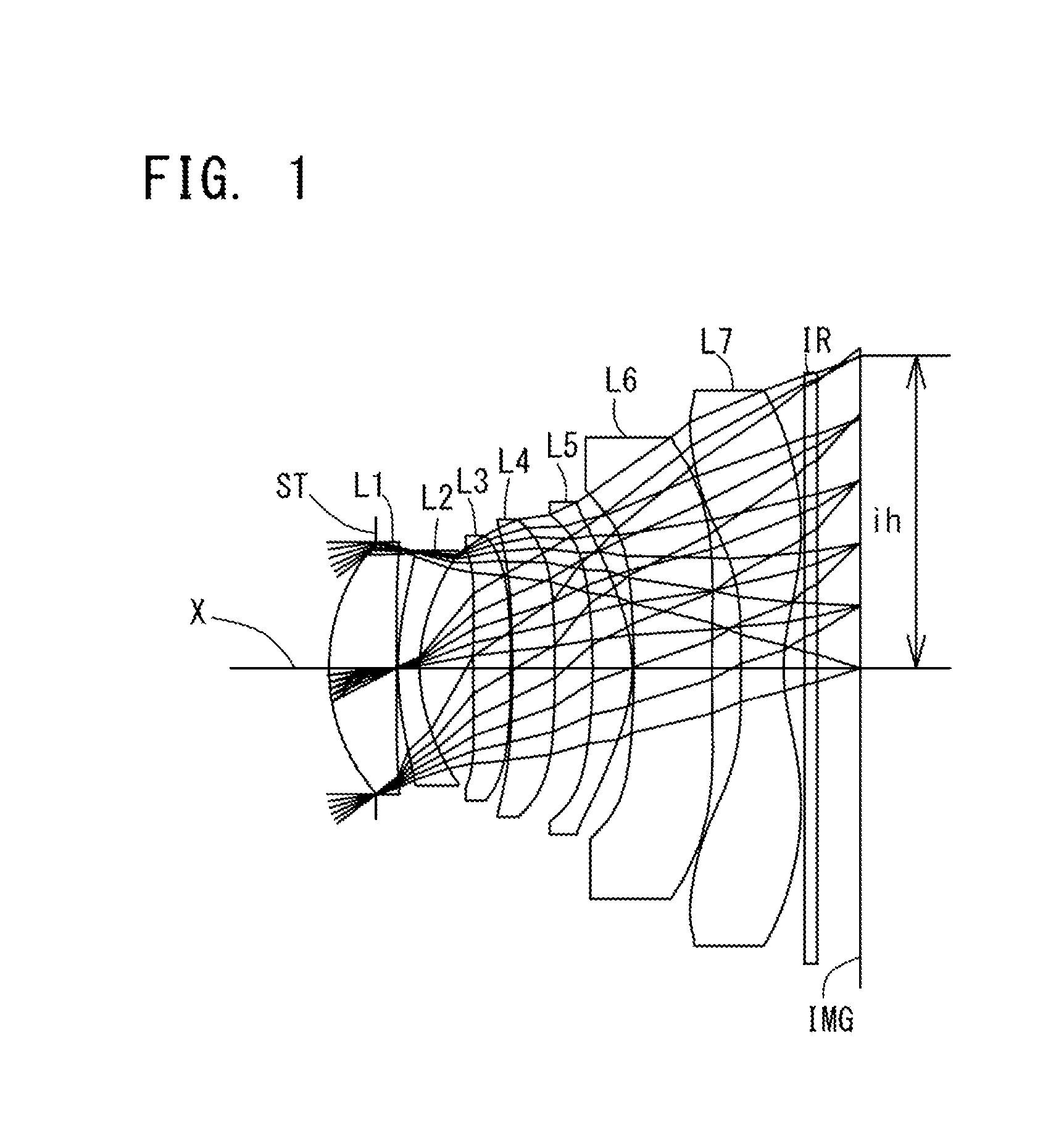
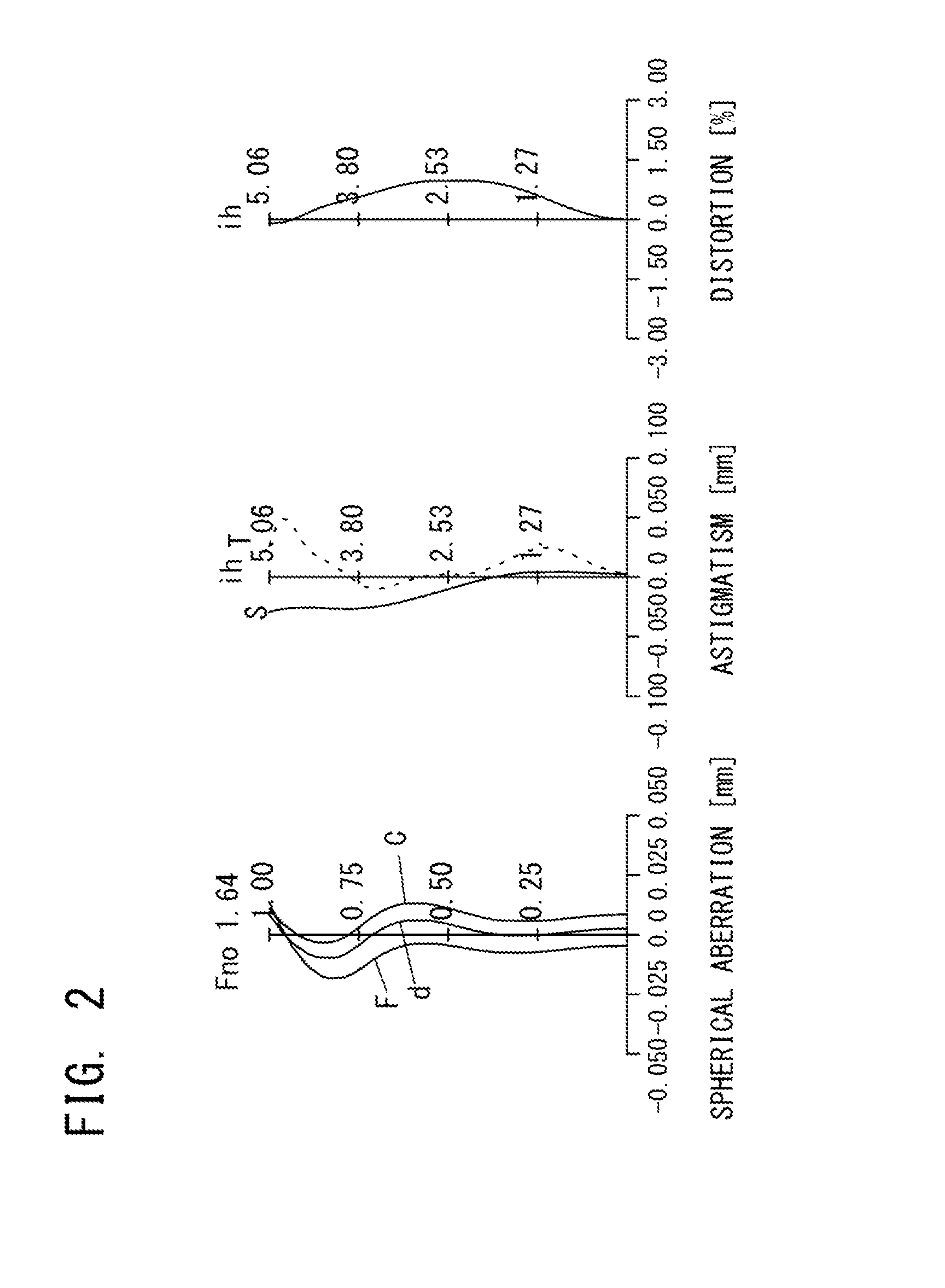
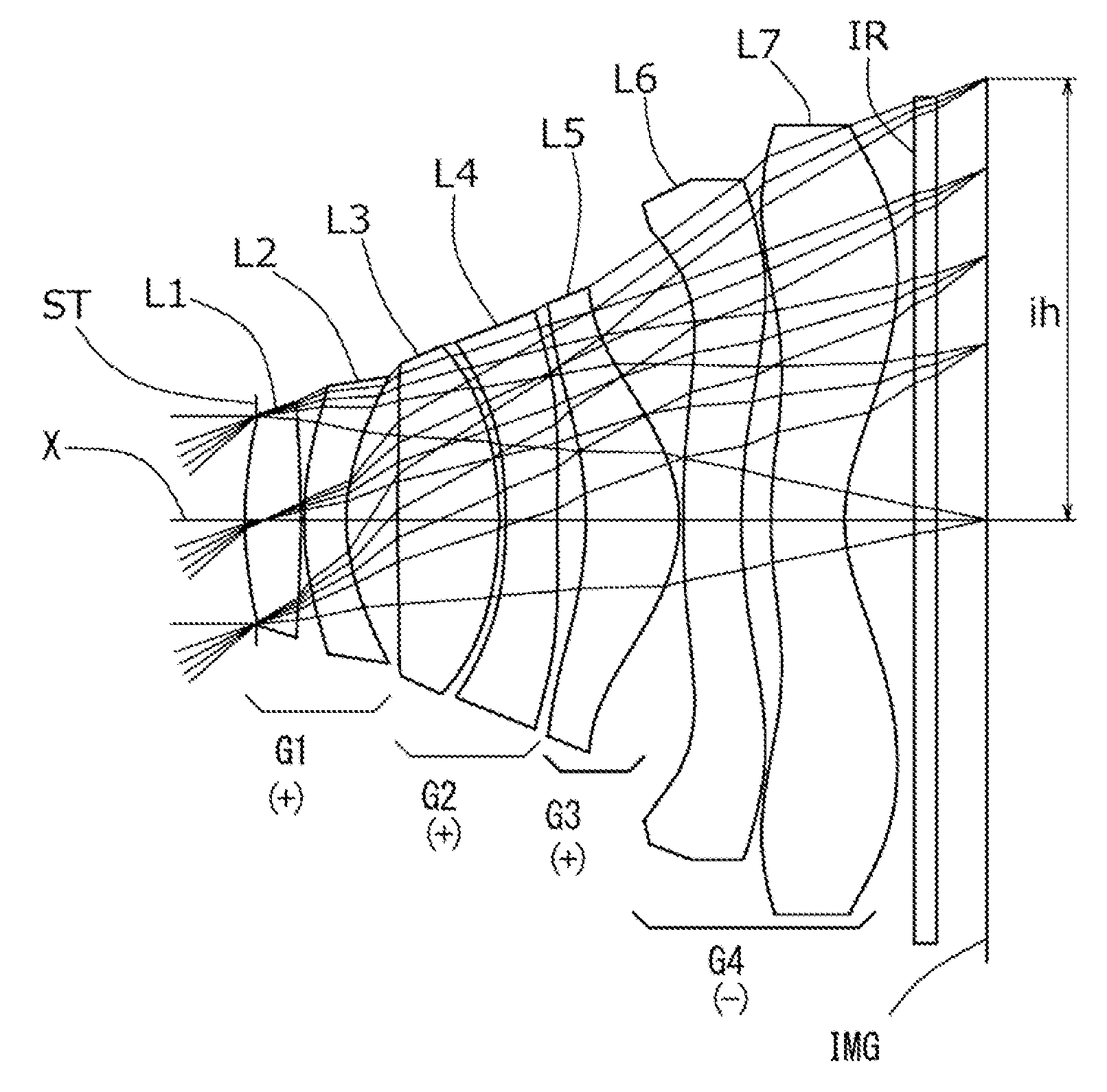
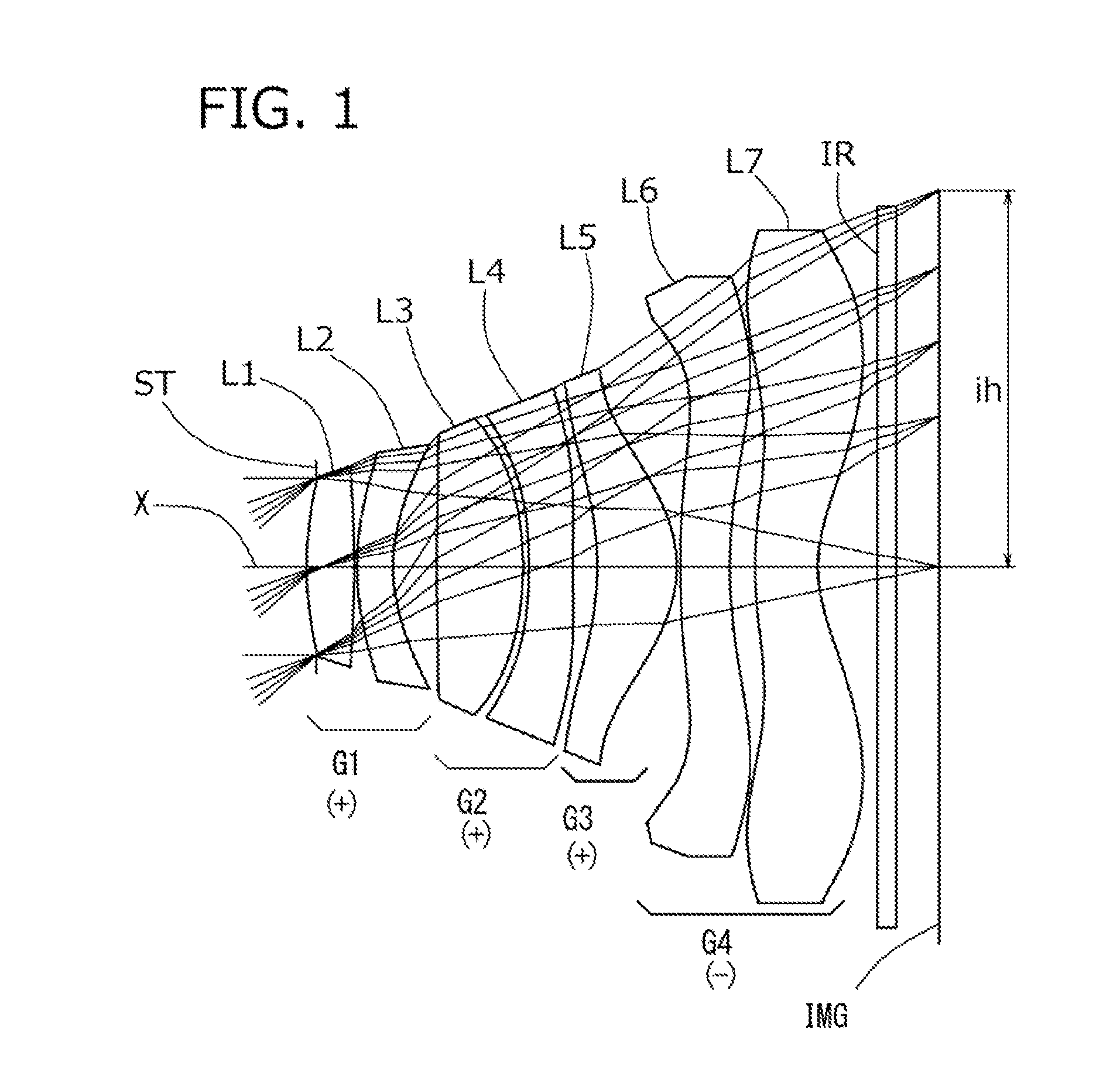
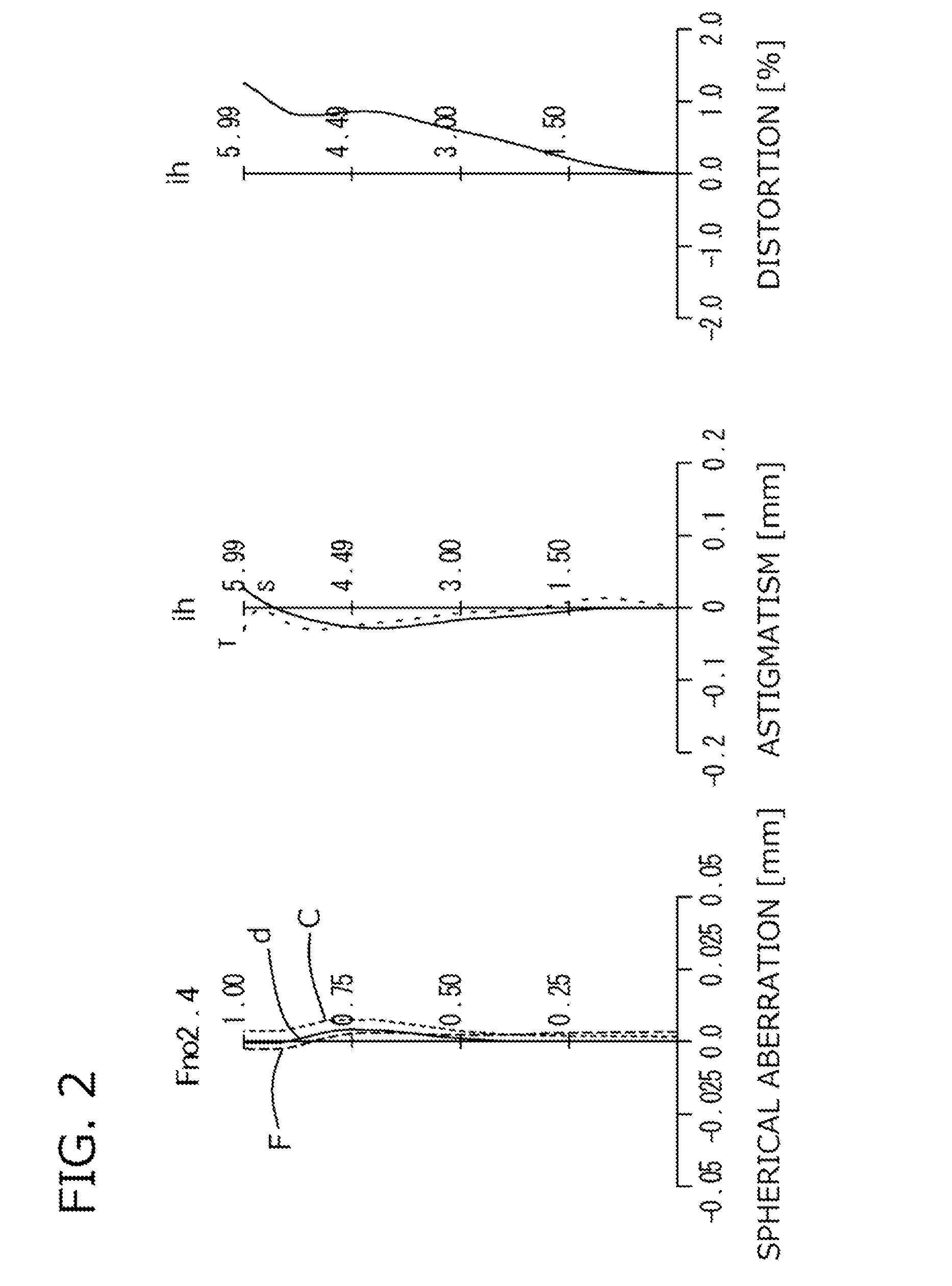
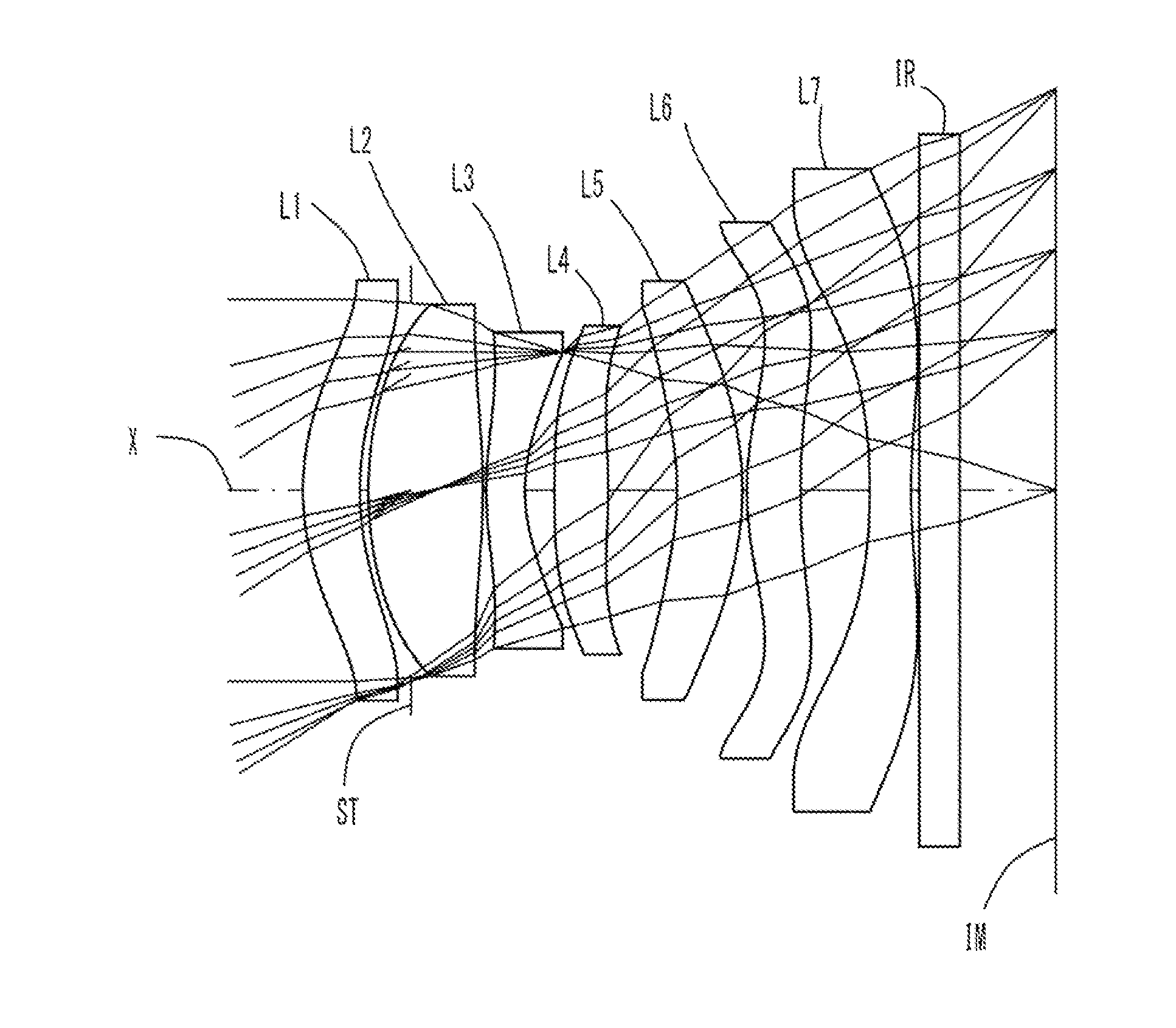
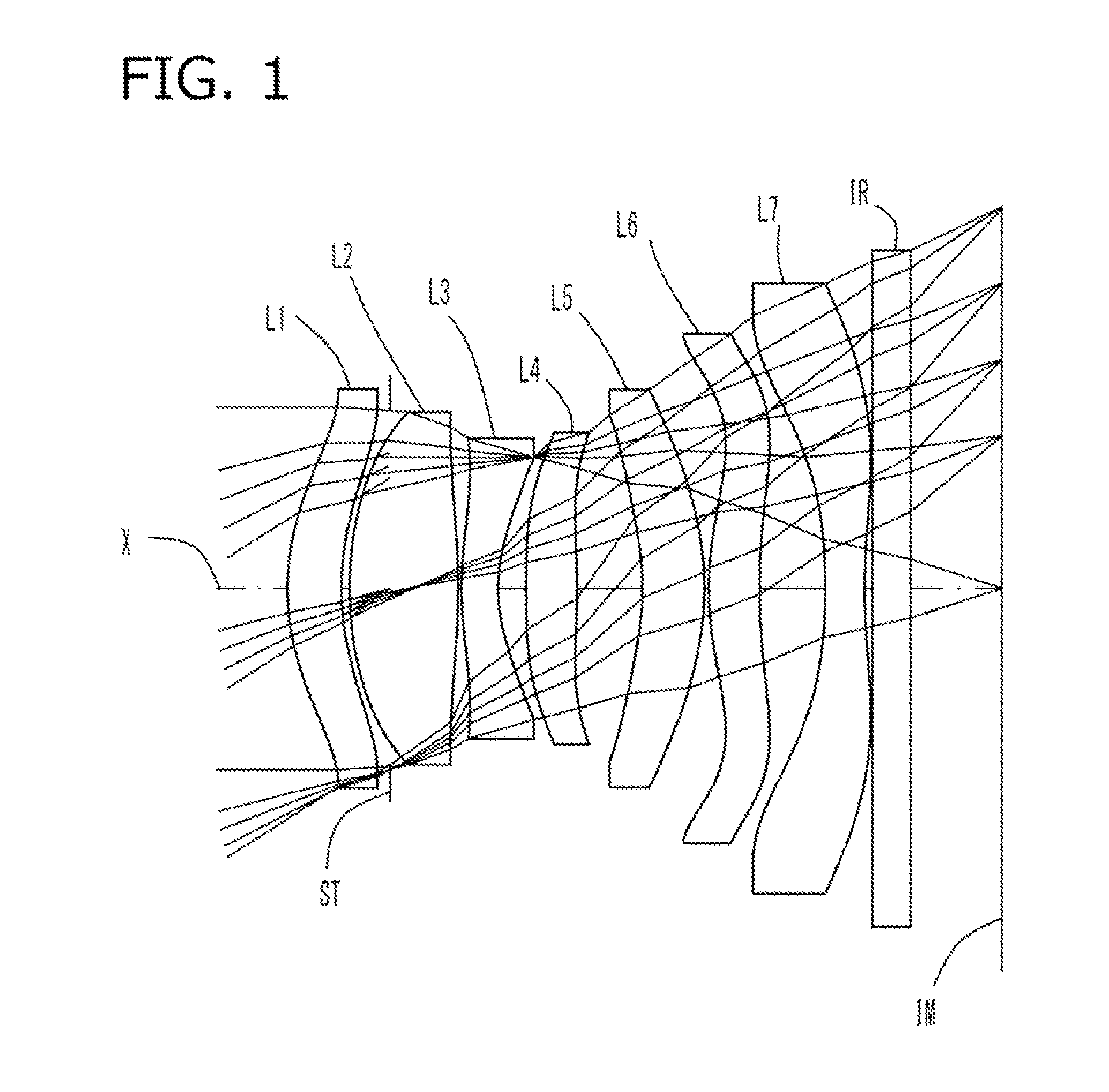
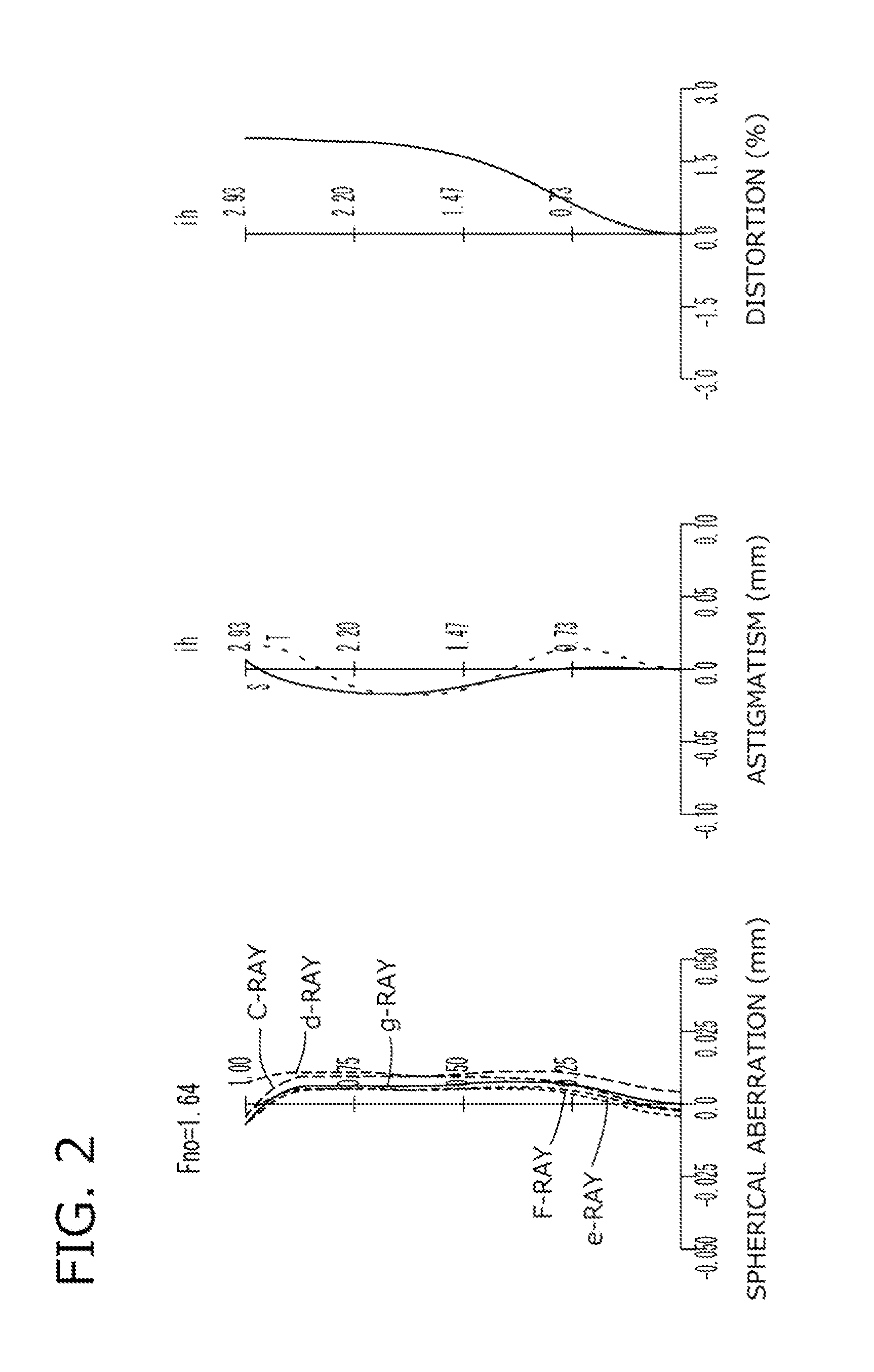
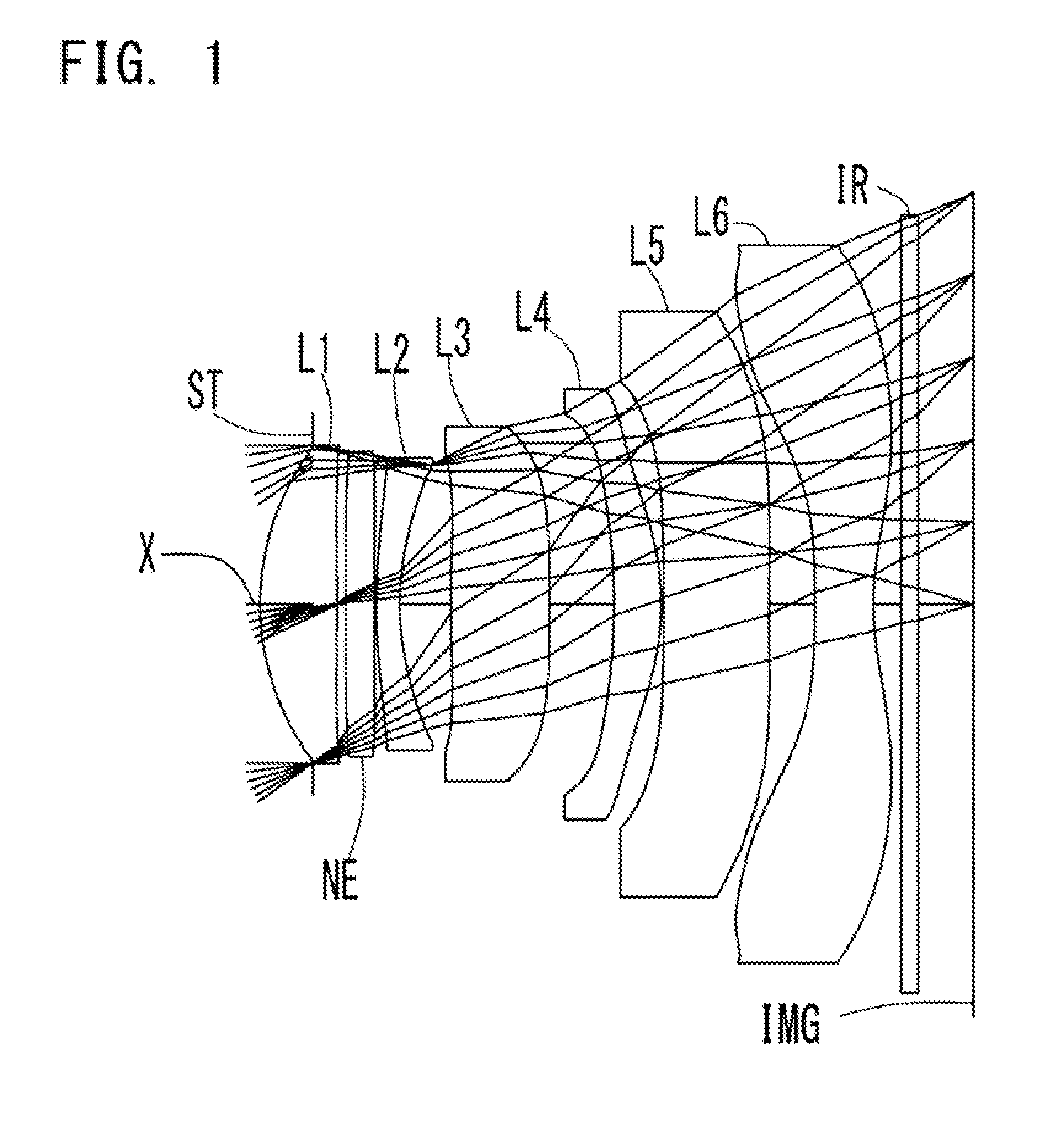
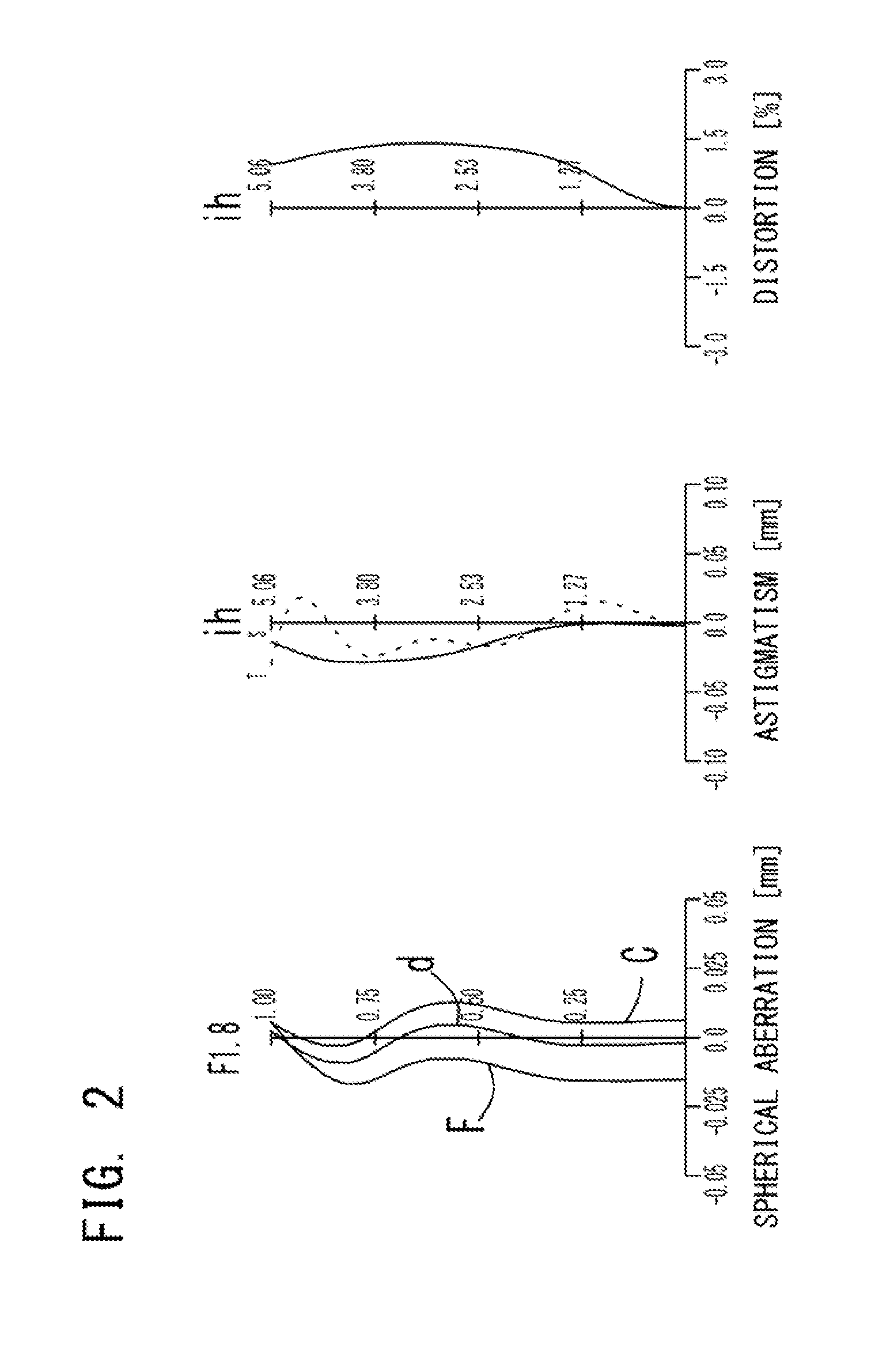
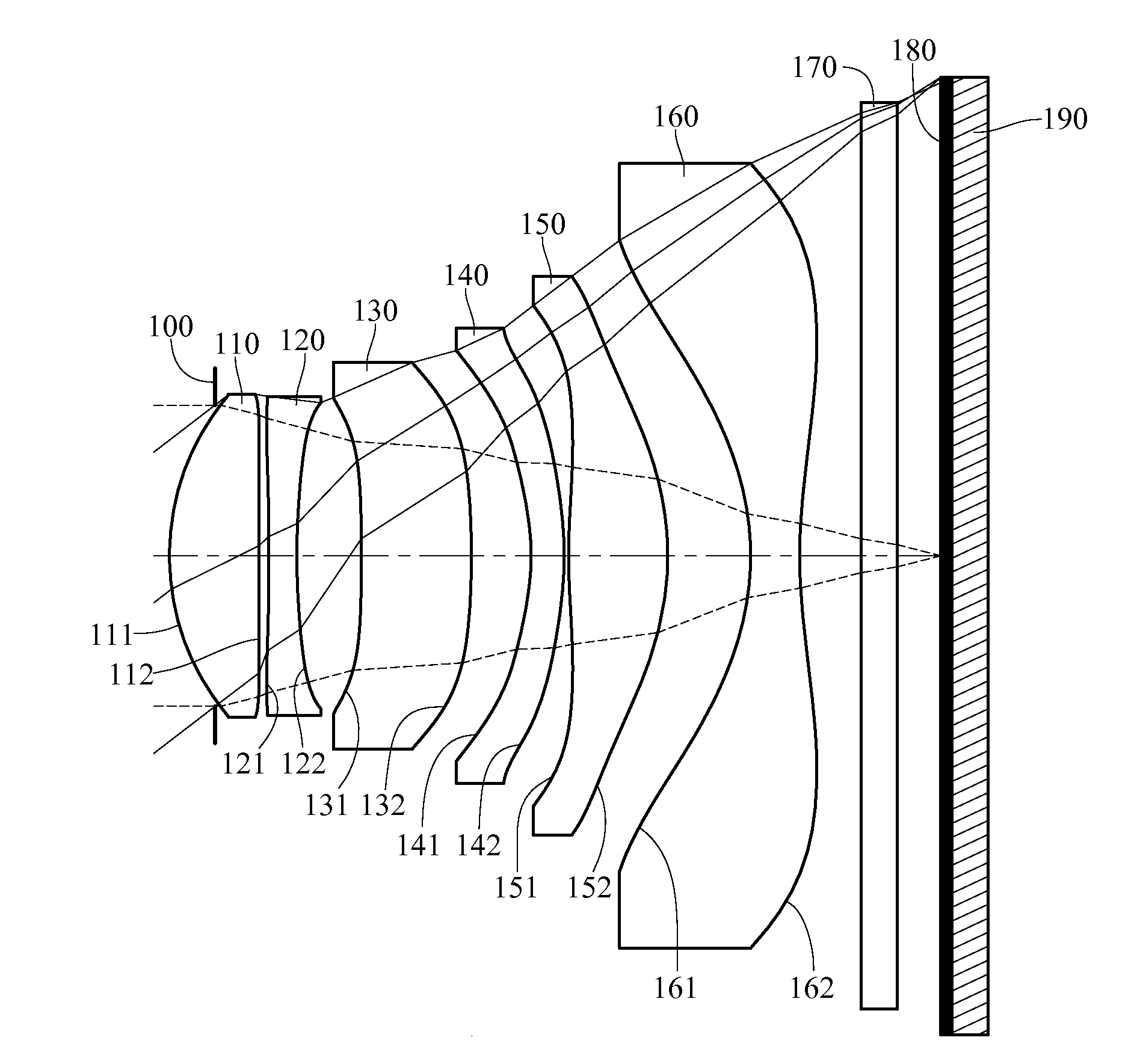
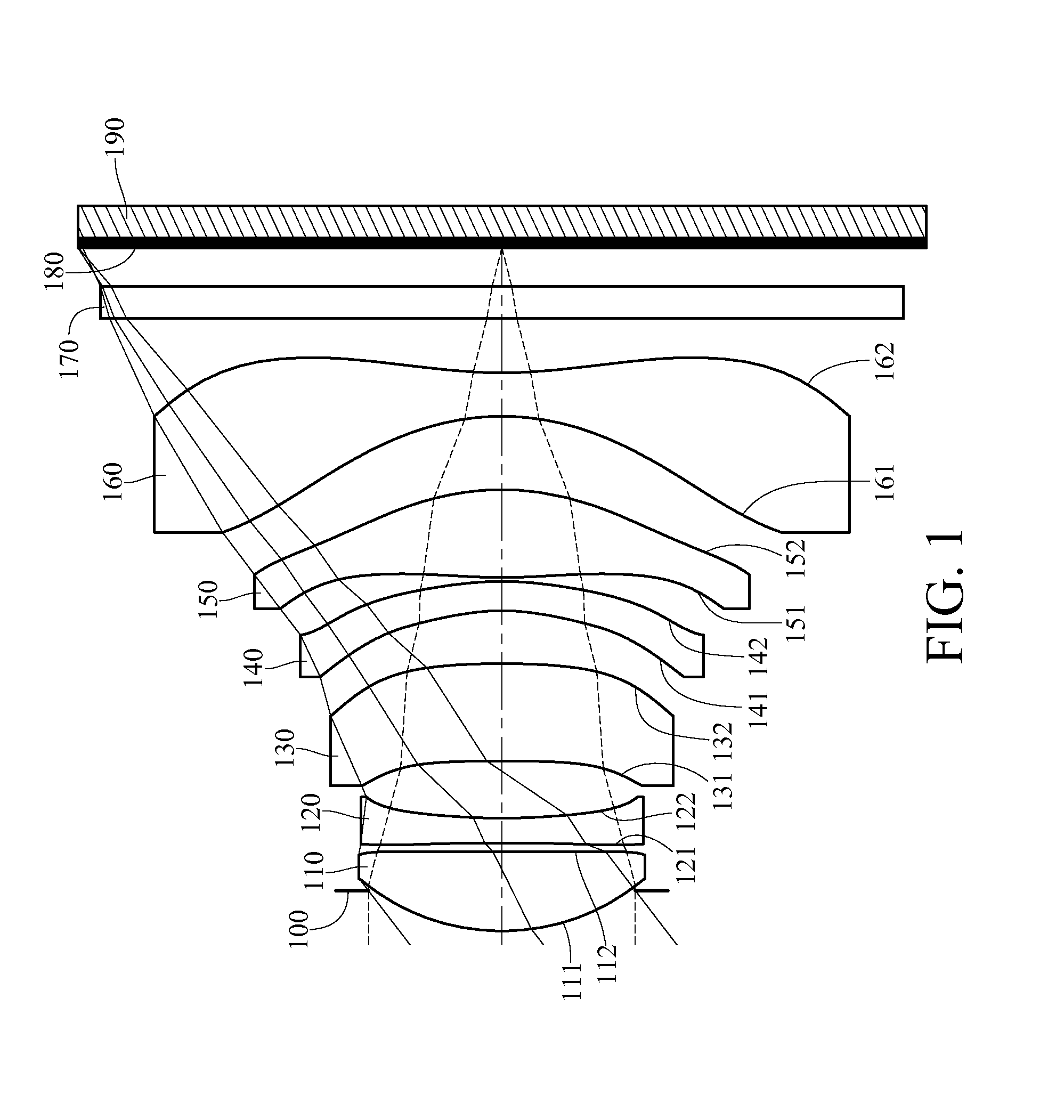
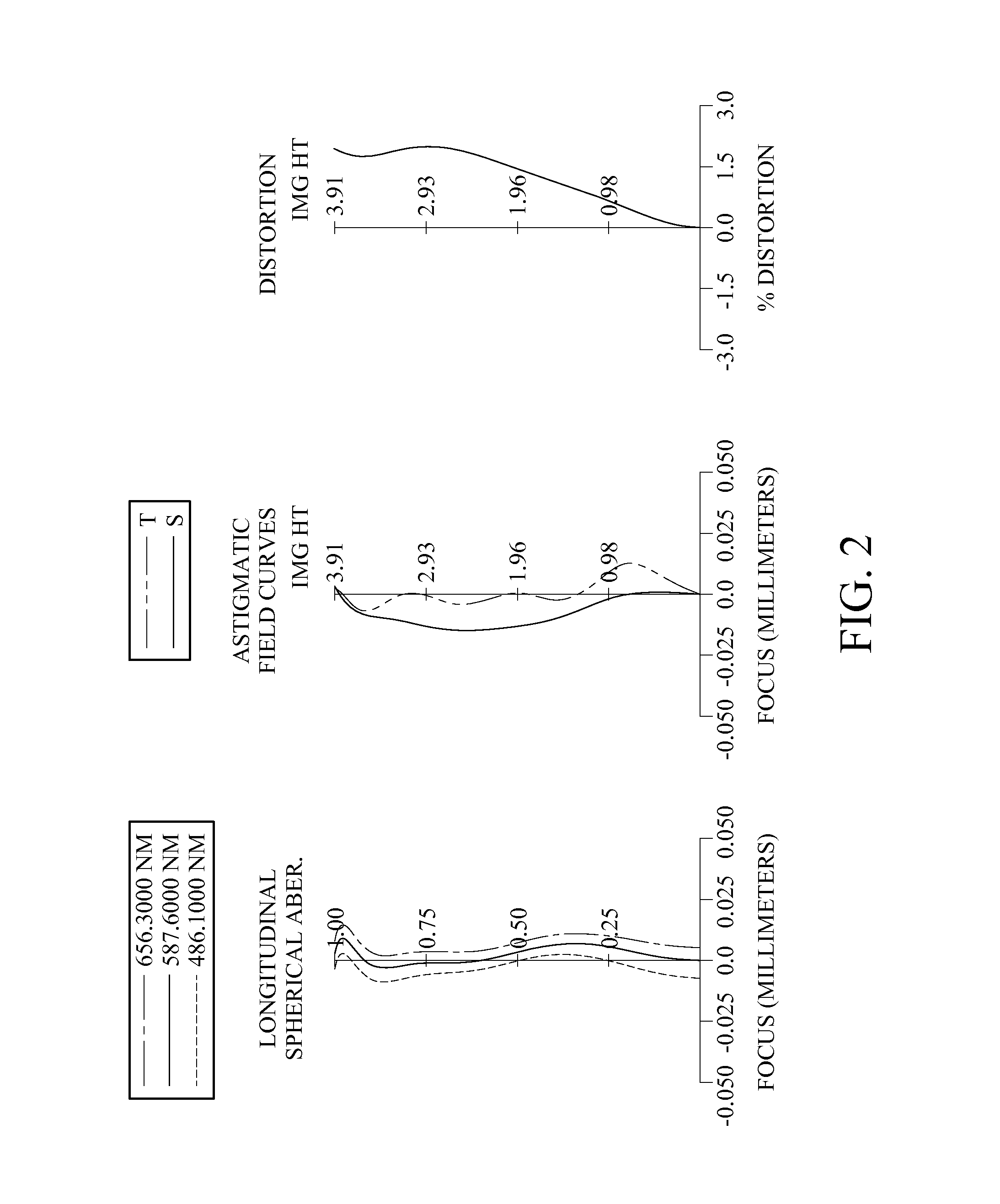
An imaging lens which uses a larger number of constituent lenses for higher performance and features compactness and a wide field of view. The imaging lens is composed of seven lenses to form an image of an object on a solid-state image sensor. The constituent lenses are arranged in the following order from an object side to an image side: a first lens with positive refractive power; a second lens with positive or negative refractive power; a third lens with negative refractive power; a fourth lens with positive or negative refractive power as a double-sided aspheric lens; a meniscus fifth lens having a convex surface on the image side; a sixth lens with positive or negative refractive power as a double-sided aspheric lens; and a seventh lens with negative refractive power, in which an air gap is provided between lenses.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Imaging lens
A compact low-profile low-cost imaging lens with a small F-value which offers a wide field of view and corrects aberrations properly. Its elements are spaced from each other and arranged from an object side to an image side as follows: a first positive lens having a convex object-side surface; a second negative lens; a third positive or negative lens; a fourth positive or negative lens; a fifth positive or negative lens; a sixth positive or negative lens; and a seventh lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface. The third to sixth lenses each have at least one aspheric surface. The aspheric image-side surface of the seventh lens has a pole-change point off an optical axis. The imaging lens satisfies a conditional expression −1.0<f1 / f2<−0.15, where f1 denotes focal length of the first lens, and f2 denotes focal length of the second lens.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Imaging lens
An imaging lens which uses a larger number of constituent lenses for higher performance and features a low F-value, low-profile design and a wide field of view. Designed for a solid-state image sensor, the imaging lens includes constituent lenses arranged in order from an object side to an image side: a first positive refractive power lens having a convex object-side surface; a second negative refractive power lens having a concave image-side surface; a third positive refractive power lens having a convex image-side surface; a fourth negative refractive power lens having a concave image-side surface; a fifth positive refractive power lens as a meniscus lens having a convex image-side surface; a sixth lens as a meniscus double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near an optical axis; and a seventh negative refractive power lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Imaging lens
A low-cost imaging lens which corrects aberrations properly with a small F-value, ensures high performance with a larger number of constituent lenses and has a more low-profile design than before. The constituent lenses are arranged in the following order from an object side to an image side: a positive (refractive power) first lens having a convex object-side surface near an optical axis; a positive second lens having convex object-side and image-side surfaces near the optical axis; a negative third lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis; a fourth lens having at least one aspheric surface; a meniscus fifth lens having a concave object-side surface near the optical axis; a sixth lens as a double-sided aspheric lens; and a negative seventh lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis. These constituent lenses are not joined to each other.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
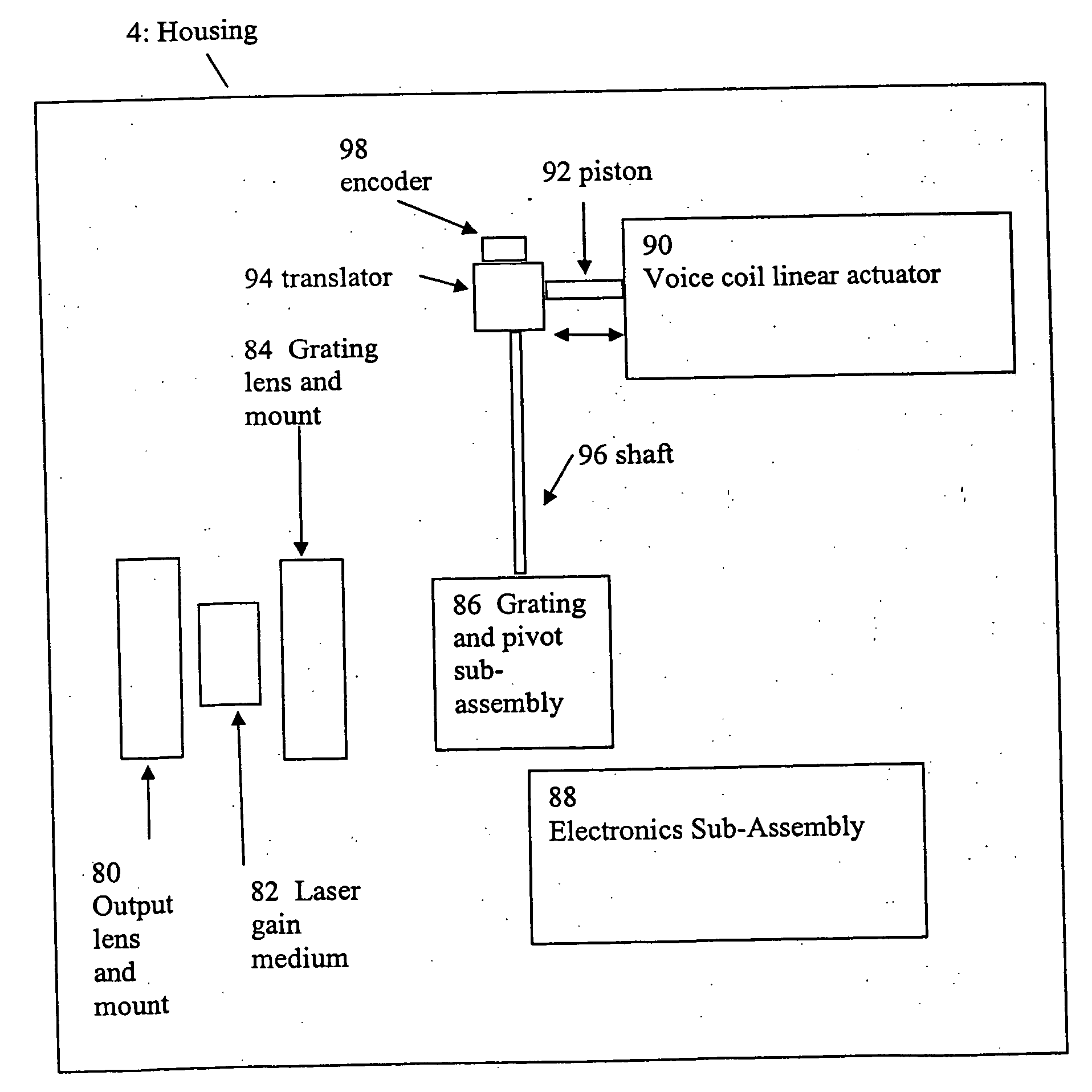
External cavity tunable compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070030865A1Reduce usageImprove cooling effectLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Vision catheter system including movable scanning plate
InactiveUS7273452B2Facilitates diagnosis and treatmentReduce and eliminate dependenceSurgeryEndoscopesColor imageGrating
A disposable imaging catheter that produces high resolution, color images comparable to those obtained from an endoscope. The device may also be made to function as a guidewire. The device may also include a sheath which slides over the catheter body for stiffening and which may include a working channel for accepting interventional devices, as well as LEDs to illuminate the field of view. The vision catheter system includes a detector assembly, scanning mechanism, and distal objective lens. In one embodiment, a photodetector is mated to a lens / pinhole assembly that allows the detector to read light from a small discrete point. This assembly is then scanned in raster or spiral patterns via electric wire coils that actuate a magnetic scan plate to read the area of interest. By adding a fixed objective lens, such as an aspheric lens that is attached to the distal tip of the catheter body, the field of view or acceptance angle of the system is magnified, yielding a wide angle image similar to that commonly obtained from an endoscope.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Irradiance-redistribution lens and its applications to LED downlights
An illumination-redistribution lens comprising a thick aspheric lens collecting a high proportion of the luminous output of a compact LED with a quasi-hemispheric pattern. After receiving the highly nonuniform illuminance from the nearby LED, the lower surface refractively deflects these rays into a less diverging angular pattern that results in uniform illuminance on the upper surface of the lens, which itself is shaped so its distribution of slope angles refractively deflects the uniform illuminance distribution into an exiting beam that will produce uniform illuminance on a distant target, such as a table below a ceiling-mounted unit. When square-cut sections of such lenses are laterally arrayed to form a downlight, a uniform rectangular spot will be produced on the target.
Owner:SINOTECHNIX LLC
Fisheye lens unit
InactiveUS20070139793A1Improve performanceSmall spherical aberrationOptical elementsFisheye lensAspheric lens
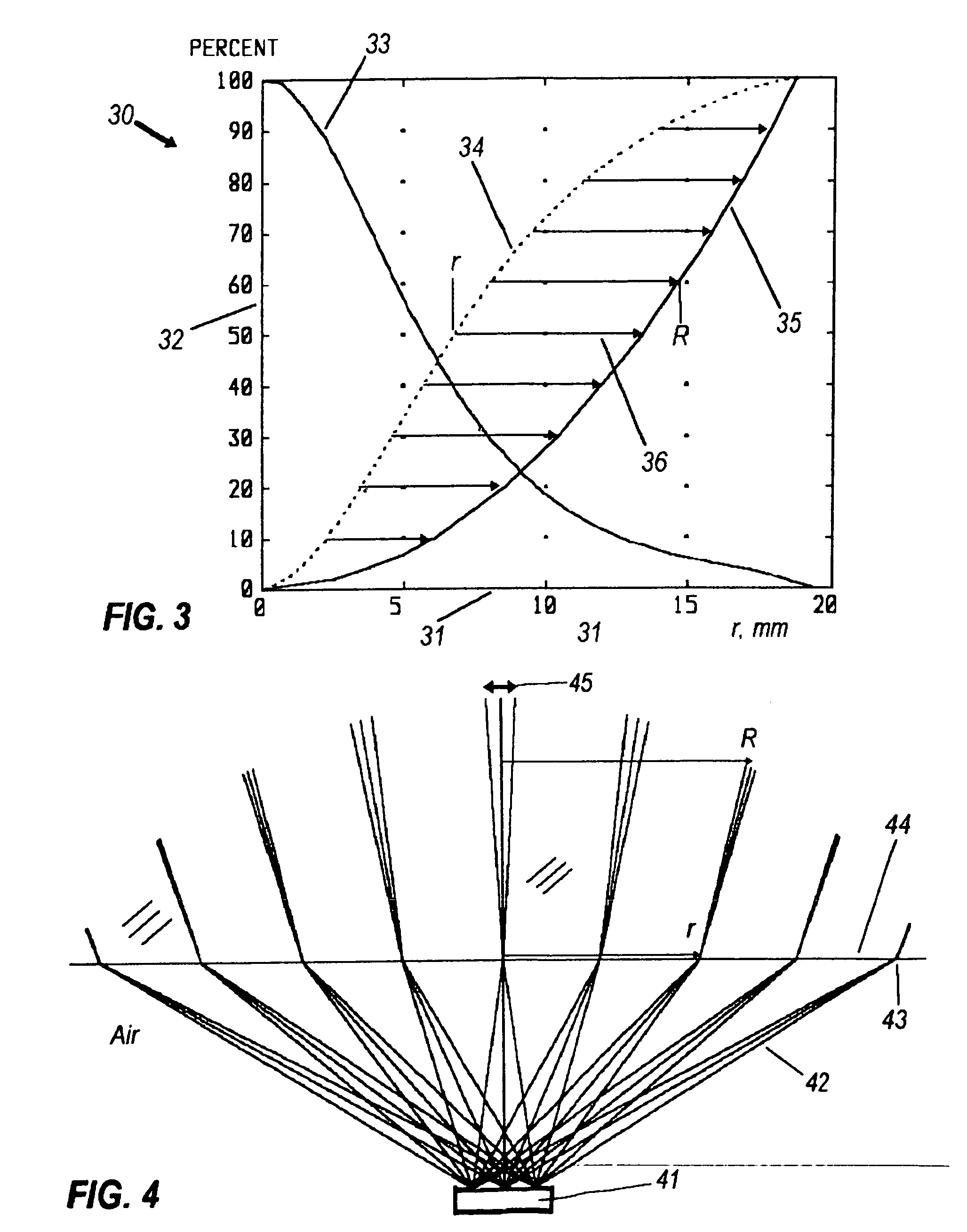
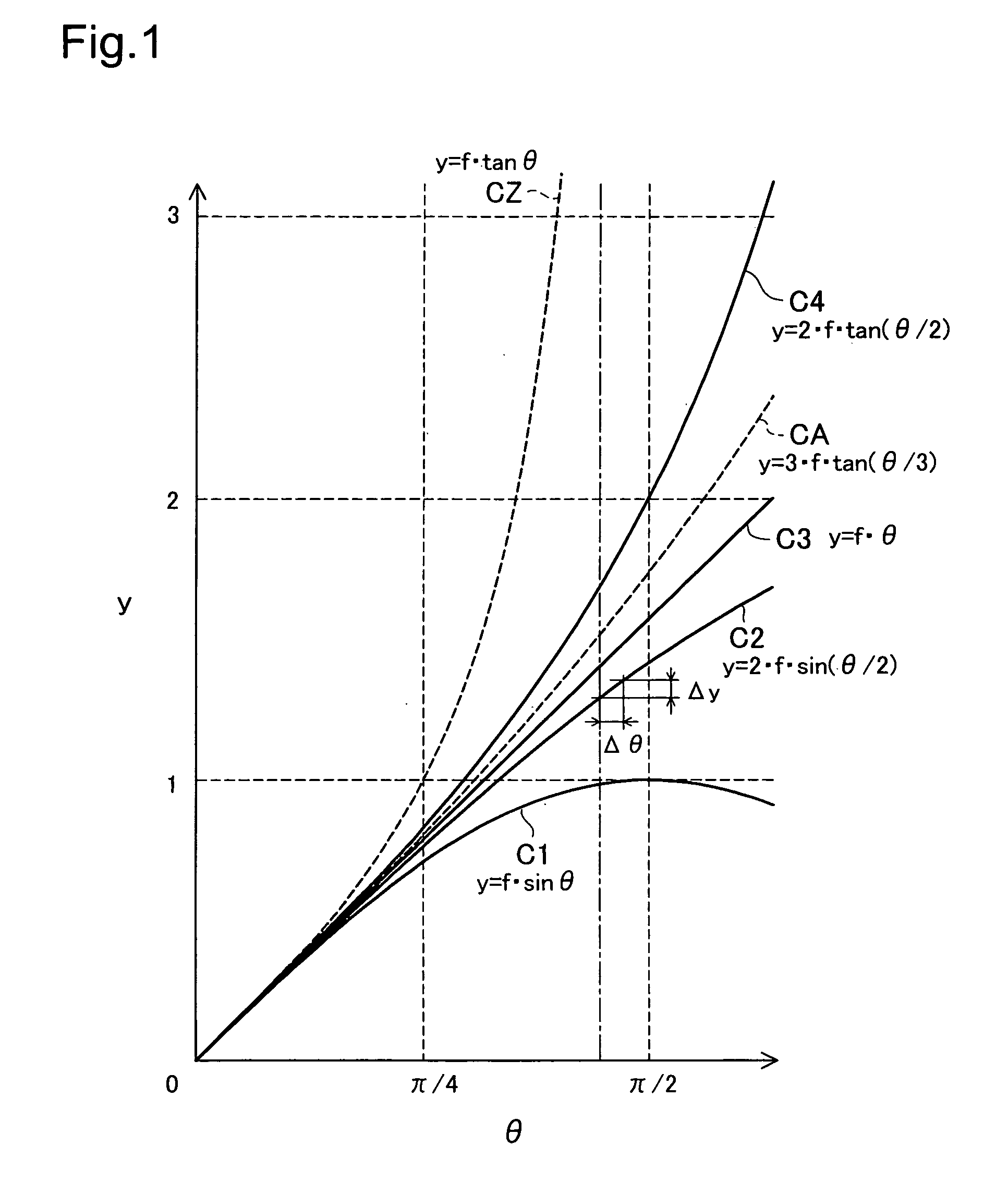
To provide a technique to constitute a fisheye lens unit with a small number of lenses. A fisheye lens unit uses a predetermined projection method, wherein a variation for the predetermined projection method is not less than the variation for an equidistant projection method, the variation being expressed by an increment of an image height in relation to an increment of an incident angle at a predetermined incident angle. The fisheye lens unit includes: a first lens group provided on an object side; a second lens group provided on an image side; and an aperture stop provided between the first lens group and the second lens group. The first lens group consists of three or four lenses, the second lens group consists of two or three lenses including a final lens provided on the furthest image side of the second lens group, and the final lens is an aspheric lens that has an aspheric shape on at least one of two surfaces of the aspheric lens.
Owner:ELMO CO LTD
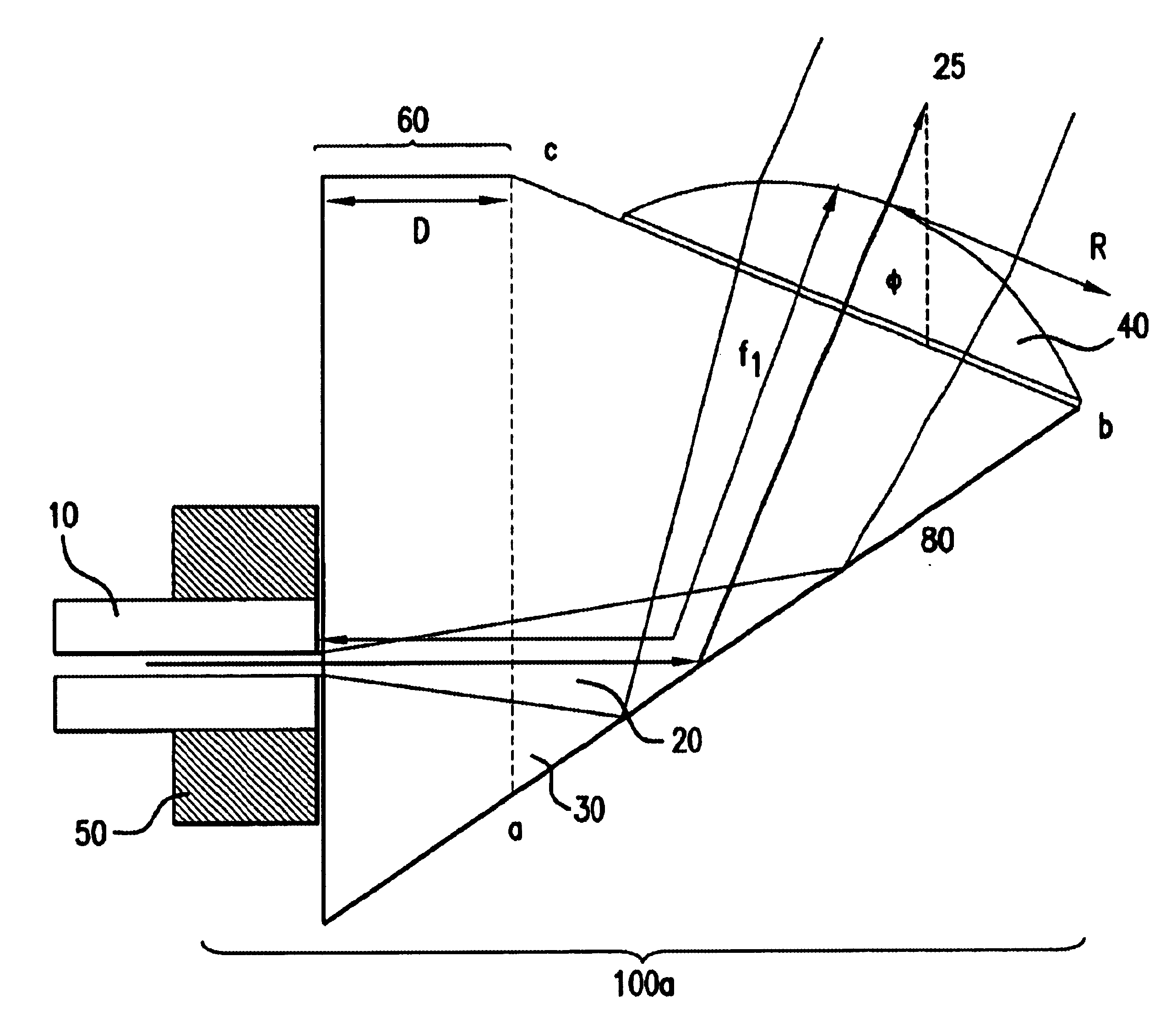
System and method for collimating and redirecting beams in a fiber optic system
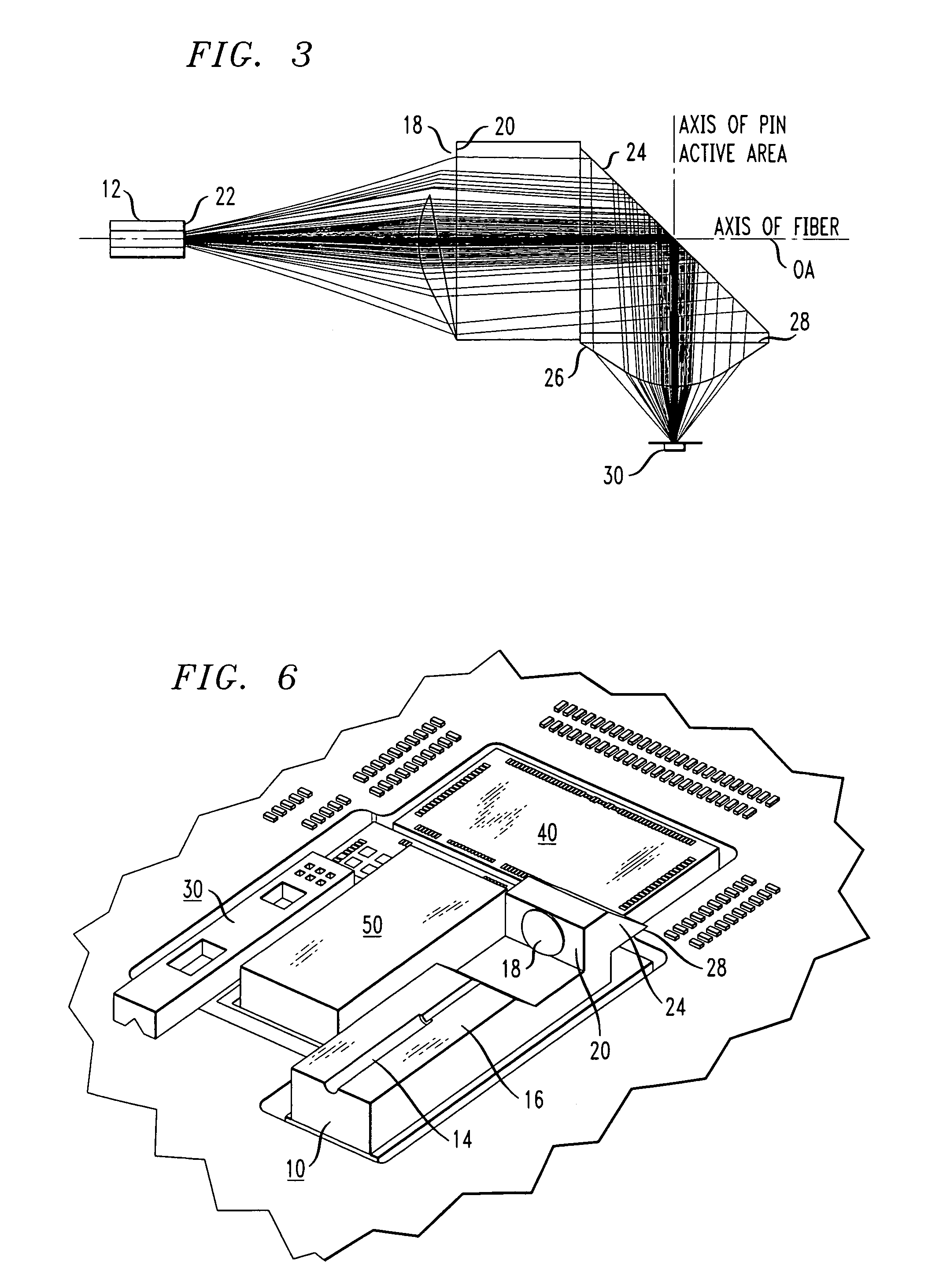
A connector to an optical fiber comprises a prism, a ferrule and an aspheric lens. The prism includes a triangular wedge element having a first surface, a second surface and a base. The ferrule guides the optical fiber so as to contact the optical fiber with the first surface of the prism. The aspheric lens is integrated on the second surface, the integrated aspheric lens being positioned so that the prism serves to redirect a light beam at an angle relative to an axis of the optical source input through total internal reflection by utilizing the base of the triangle wedge element. The aspheric lens serves to collimate the redirected light beam or focus the light beam before being redirected. This arrangement may, for example, be used within a WDM system to multiplex and de-multiplex several wavelengths of light, using a "zig-zag" optical path configuration and thin film filters to separate the wavelengths.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070291804A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser optical deviceThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
System and method for collimating and redirecting beams in a fiber optic system
A connector to an optical fiber comprises a prism, a ferrule and an aspheric lens. The prism includes a triangular wedge element having a first surface, a second surface and a base. The ferrule guides the optical fiber so as to contact the optical fiber with the first surface of the prism. The aspheric lens is integrated on the second surface, the integrated aspheric lens being positioned so that the prism serves to redirect a light beam at an angle relative to an axis of the optical source input through total internal reflection by utilizing the base of the triangle wedge element. The aspheric lens serves to collimate the redirected light beam or focus the light beam before being redirected. This arrangement may, for example, be used within a WDM system to multiplex and de-multiplex several wavelengths of light, using a “zig-zag” optical path configuration and thin film filters to separate the wavelengths.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Optical lens
InactiveCN104297906AEffectively corrects aberrationsLow costOptical elementsCamera lensMiniaturization
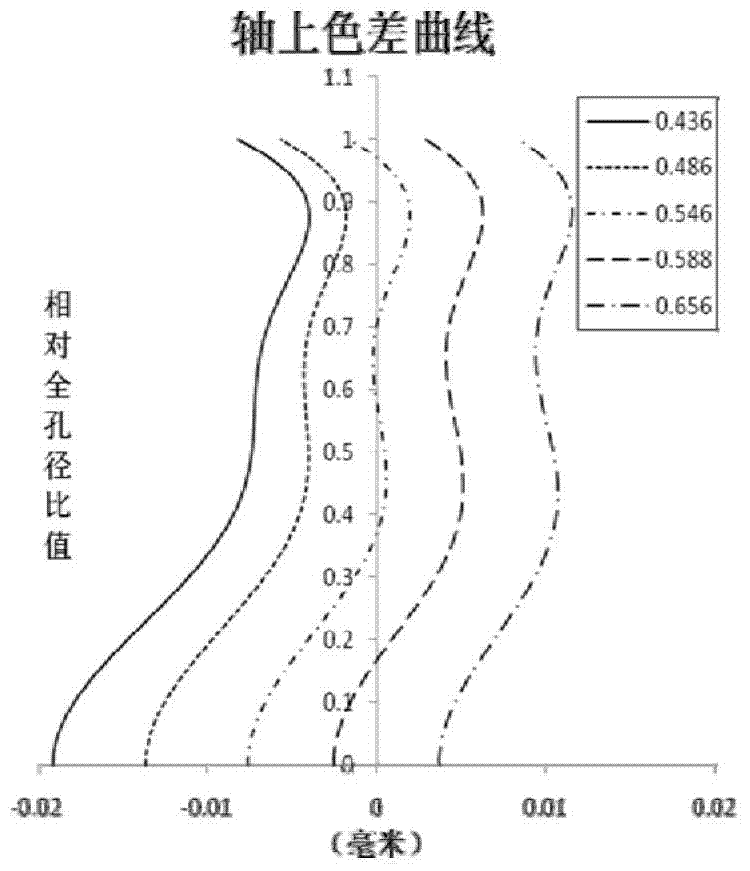
The invention relates to an optical lens which sequentially comprises a front lens group with positive focal power, a diaphragm element and a rear lens group with positive focal power from the object space to the image space. The front lens group sequentially comprises a first lens and a second lens from the object space to the image space. The first lens is a biconcave lens with negative focal power. The second lens is a biconvex lens with positive focal power. The rear lens group sequentially comprises a third lens, a fourth lens and a fifth lens from the object space to the image space. A gluing lens is formed by the third lens and the fourth lens. The fifth lens is an aspheric surface lens with positive focal power, and two concave faces of the fifth lens are in the same-direction crescent shape. According to the optical lens, high pixels, small deformation and large apertures can be achieved under the condition that the requirements for low cost and miniaturization are met, a perfect image can still be kept within the temperature range of -40 DEG C to 85 DEG C, and the optical lens is particularly suitable for monitors and vehicle-mounted camera systems which work in the day and at night or under a poor illumination condition.
Owner:NINGBO SUNNY AUTOMOTIVE OPTECH
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7492806B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Imaging lens
ActiveUS20140355134A1Increase in total track length is preventedTelephoto ability is enhancedElectrical componentsLensCamera lensWide field
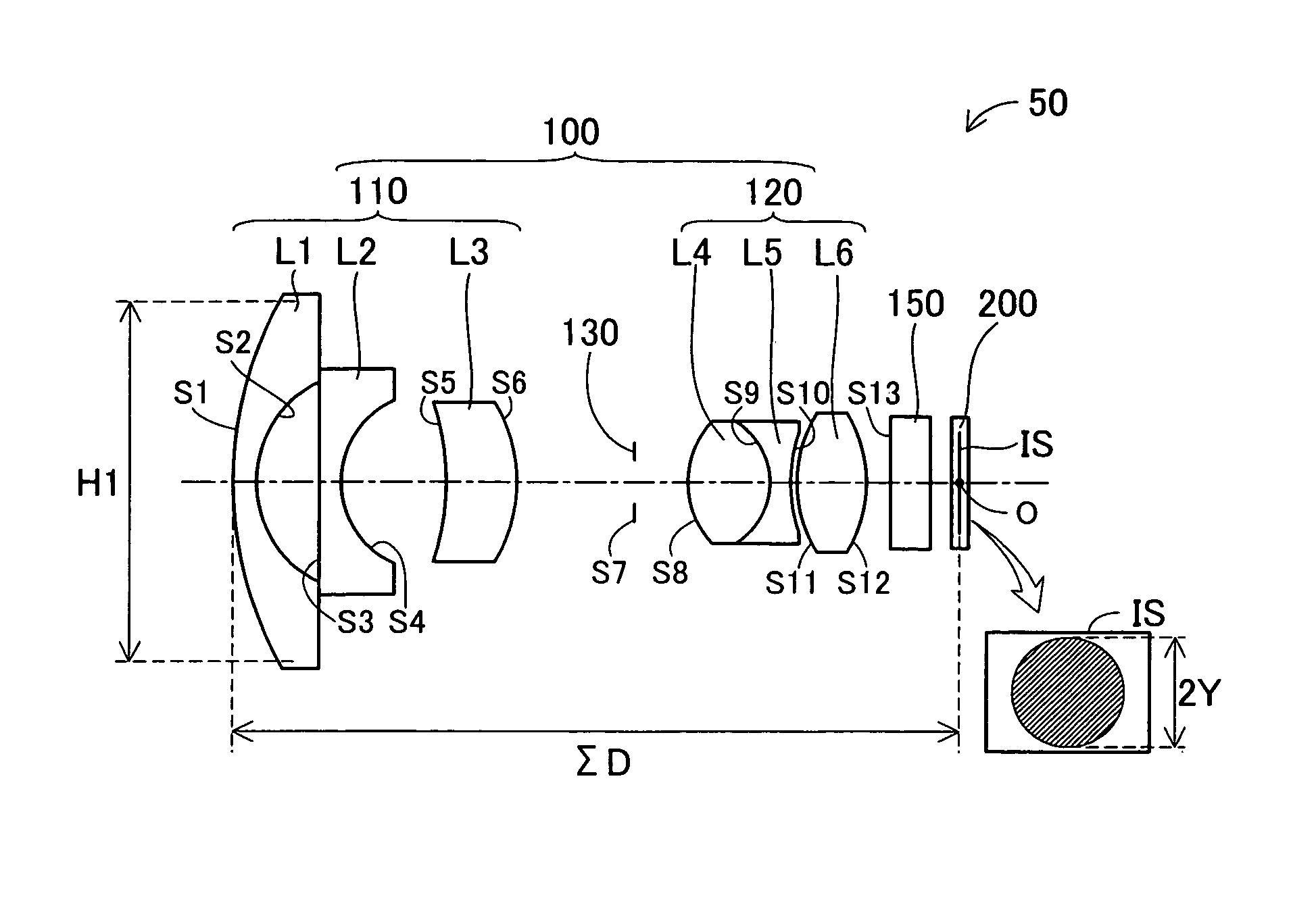
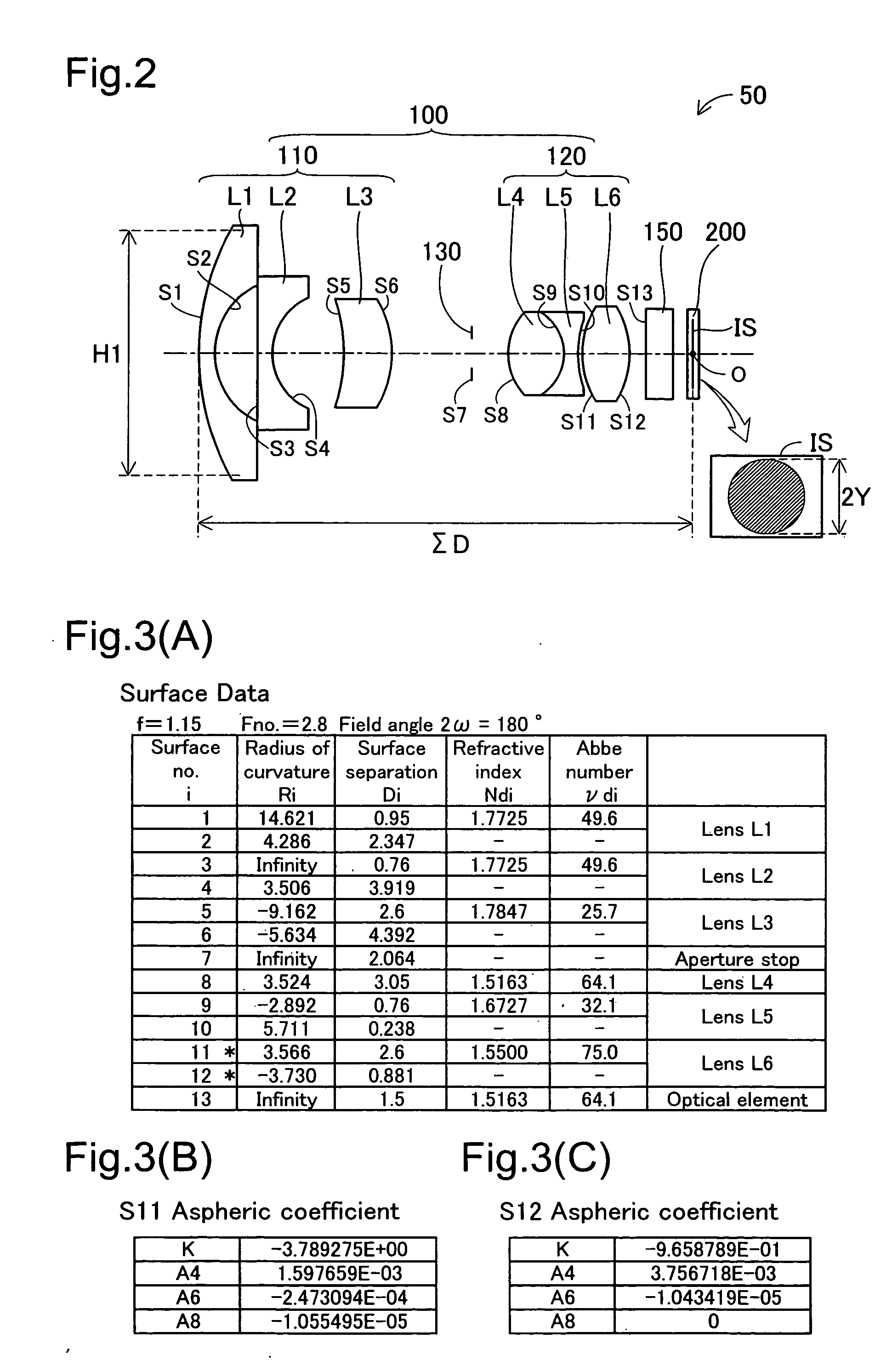
A compact high-resolution imaging lens which provides a wide field of view of 80 degrees or more and corrects various aberrations properly. Designed for a solid-state image sensor, the imaging lens includes constituent lenses arranged in the following order from an object side to an image side: a first positive (refractive power) lens having a convex object-side surface; a second negative lens having a concave image-side surface; a third positive lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a convex object-side surface; a fourth positive lens having a convex image-side surface; a fifth lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface; and a sixth negative lens having a concave image-side surface. The image-side surface of the sixth lens has an aspheric shape with a pole-change point in a position off an optical axis.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
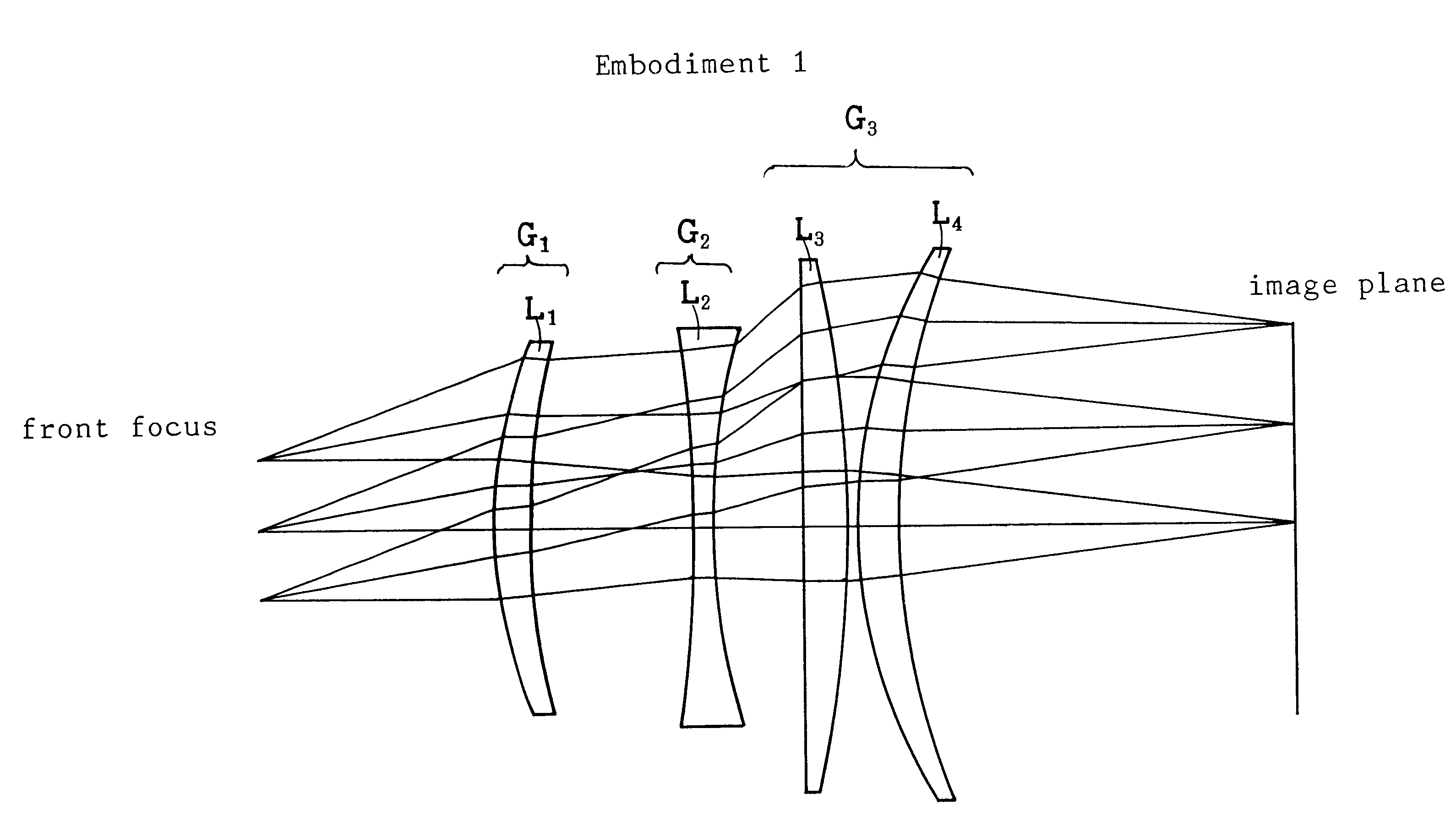
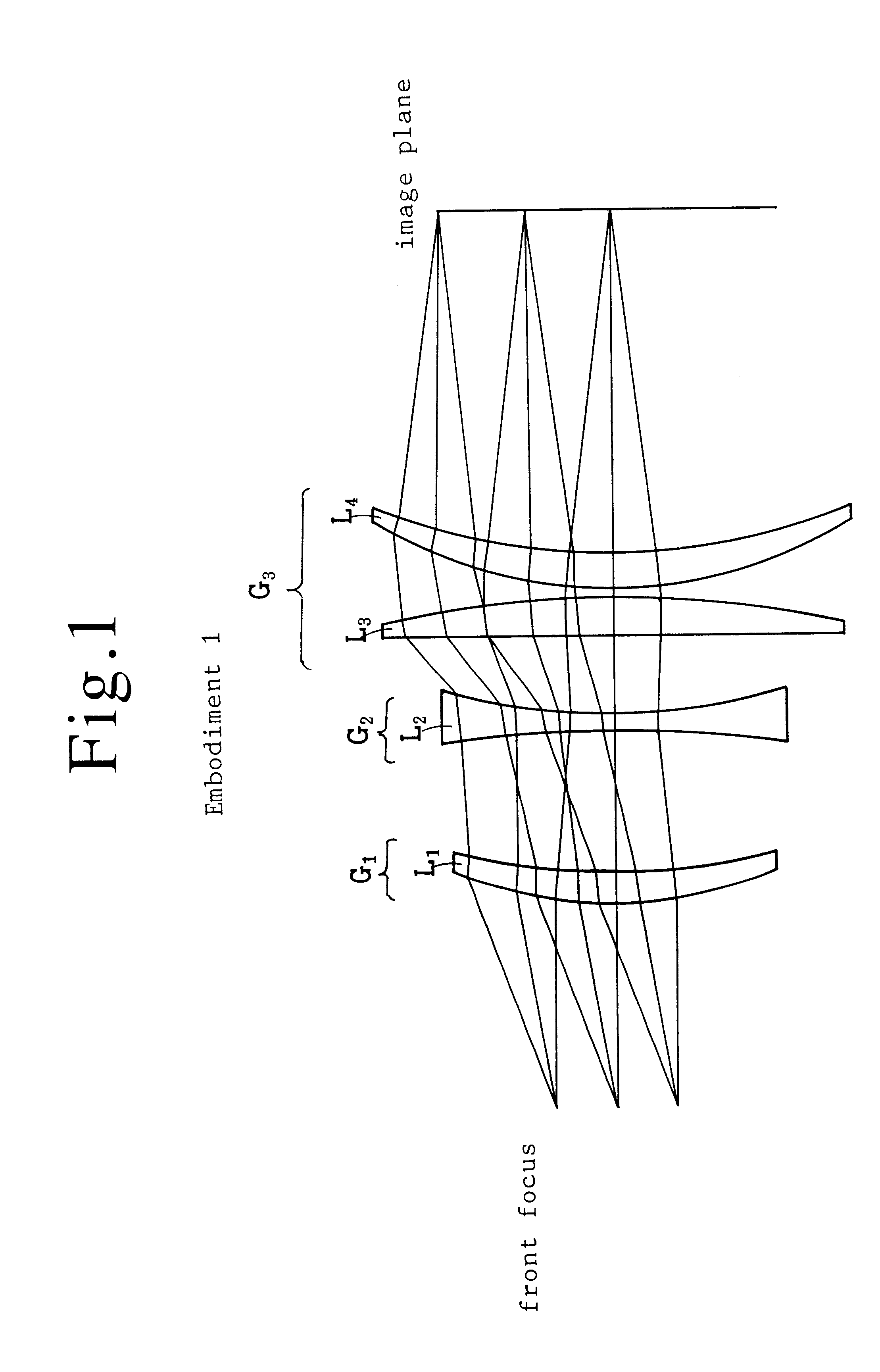
Ftheta lens
InactiveUS6324015B1Easy to manufactureLow costWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusCamera lensZinc selenide
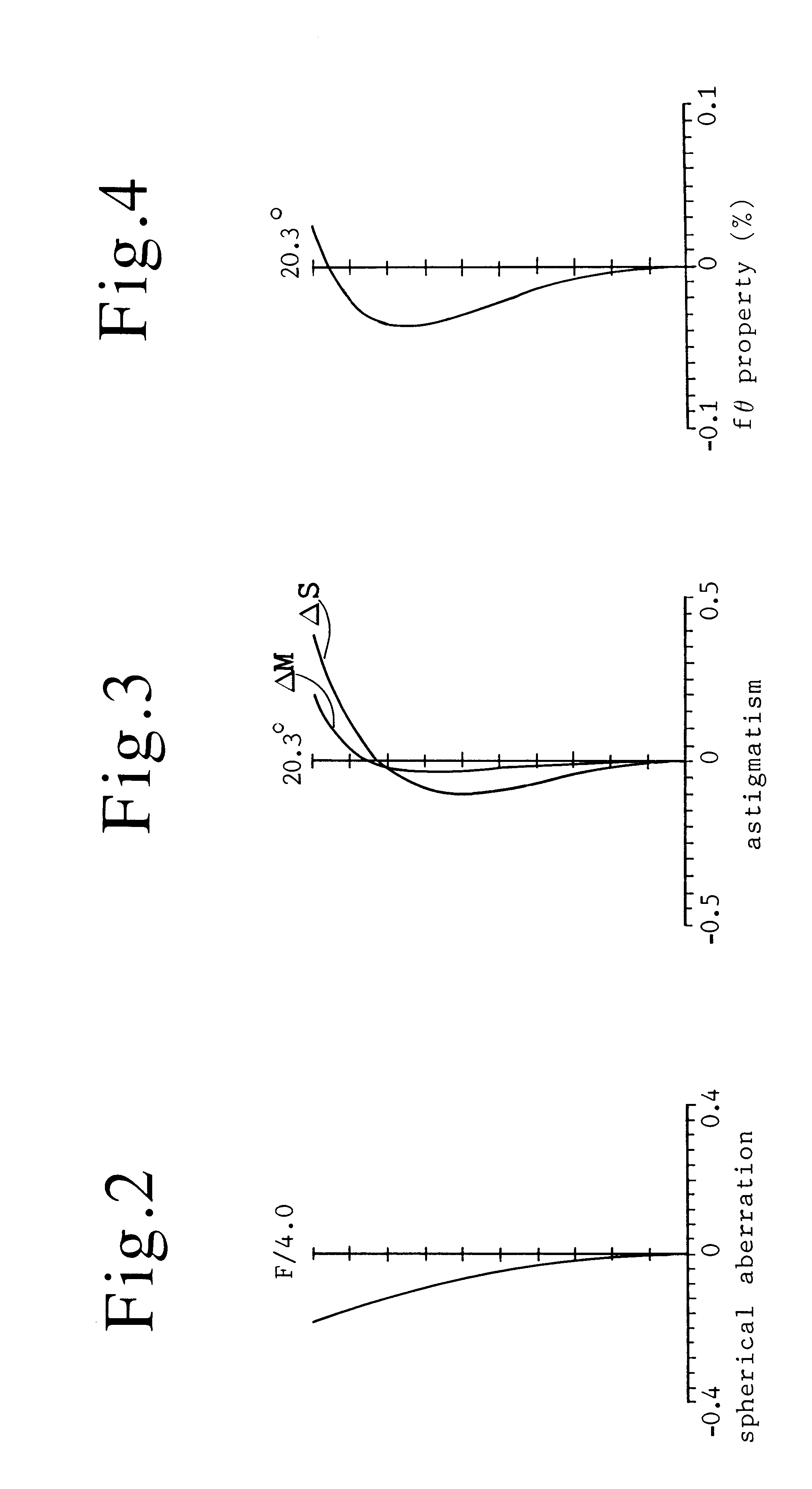
An ftheta lens containing a first lens group having an object-side convex positive lens, a second lens group having an object-side concave negative lens, a third lens group having a positive refractive power, the third lens group being a single positive lens, an assembly of a positive lens and a negative lens or another assembly of a positive lens and another positive lens. The lens components satisfy the conditions (a) to (c);where f2 is the focal length of the second lens group, f3 is the focal length of the third lens group, f is the focal length of the whole lens system and d is the distance from the front focus to the image plane. The material of the lens is zinc selenide (ZnSe) or germanium (Ge). Adoption of an aspherical lens facilitates the design of the ftheta lens.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
External cavity tunable compact Mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7535936B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Imaging lens
A compact imaging lens which addresses low-profile and low F value, and corrects aberrations. An imaging lens includes a first lens having positive refractive power and a convex surface on an object side near an optical axis, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens, a seventh lens and a eighth lens having a concave surface on an image side near the optical axis as double-sided aspheric lens, wherein the second to seventh lenses each have at least one aspheric surface, and the eighth lens has pole points off an optical axis on the aspheric image-side surface.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Optimized intraocular lens
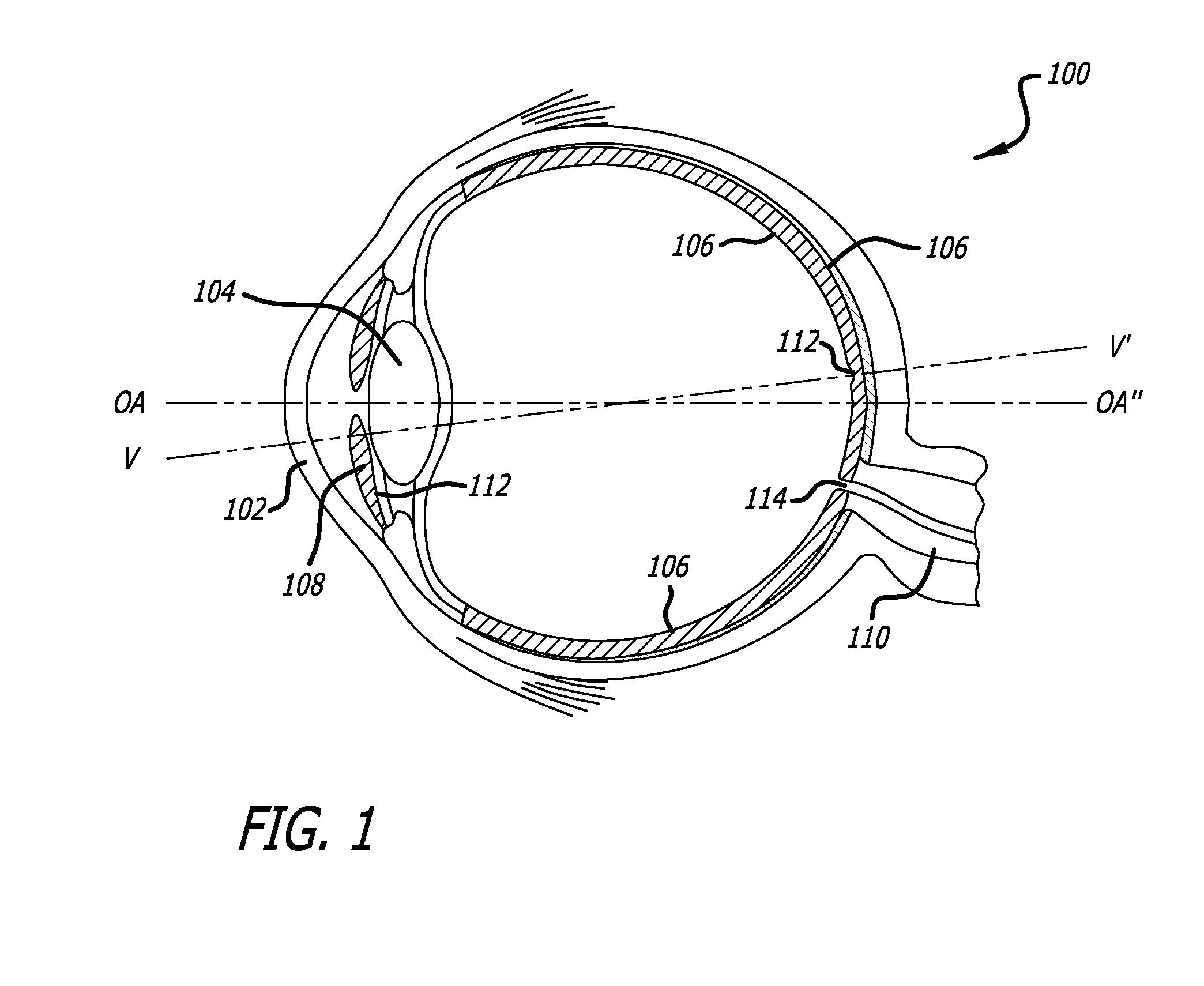
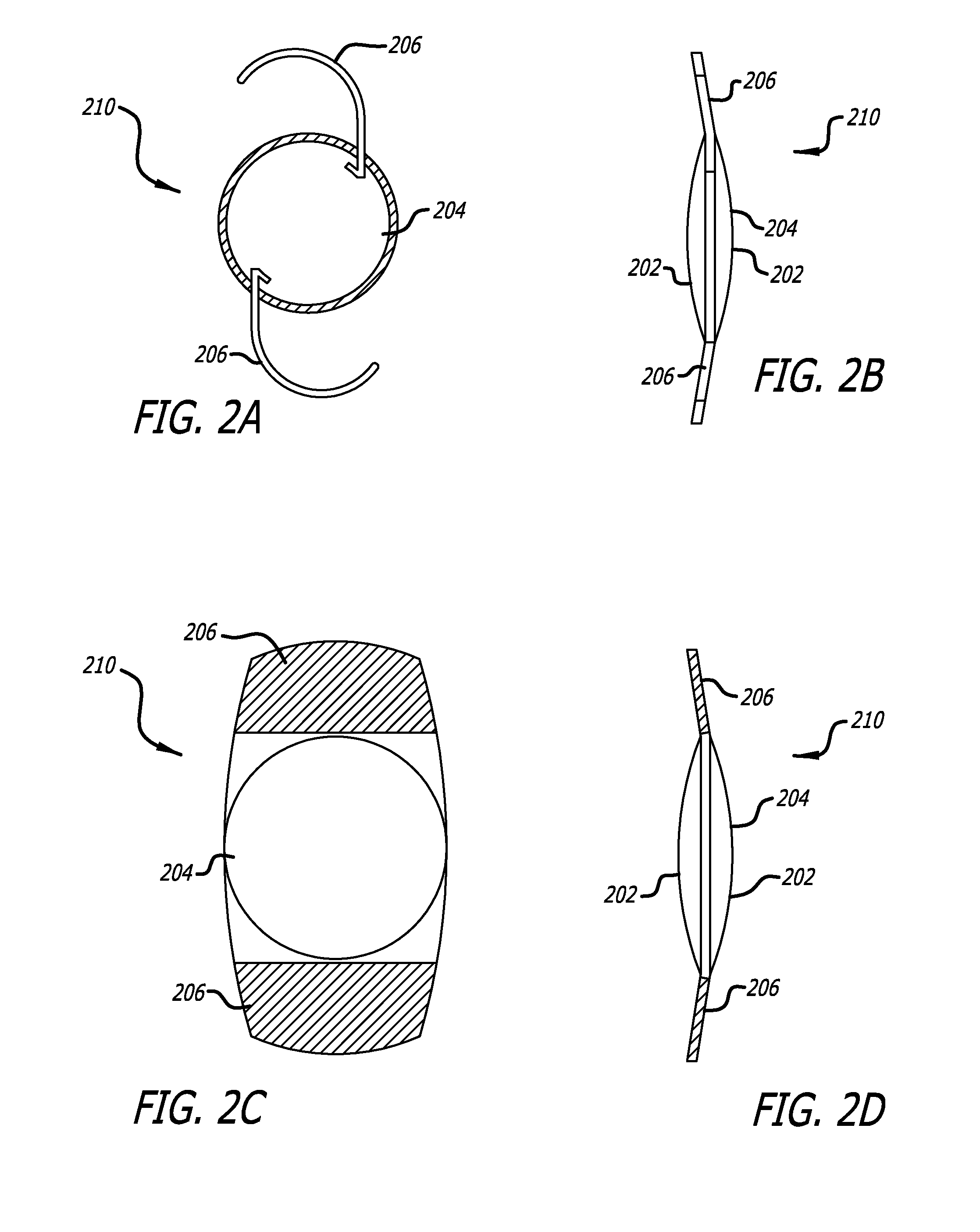
InactiveUS20090292354A1Improve visual acuityImproved peripheral visionSurgeryEye diagnosticsCamera lensIntraocular lens
An optimized aspheric lens has improved optics when implanted into a patient having a curved retina. Light entering the optimized aspheric lens on-axis or at an angle to the optical axis is properly focused by the lens, reducing aberrations and producing a much smaller spot size of light on the retina. A method of selecting the optimized values for variables of the lens design, such as base radii of the front and back surface of the lens, conic constants of the front and back surfaces, and / or center thickness of the lens, among other possible parameters is provided. The method includes calculating changes in a merit function while changing the various values for the variables and selecting an optimized merit function.
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
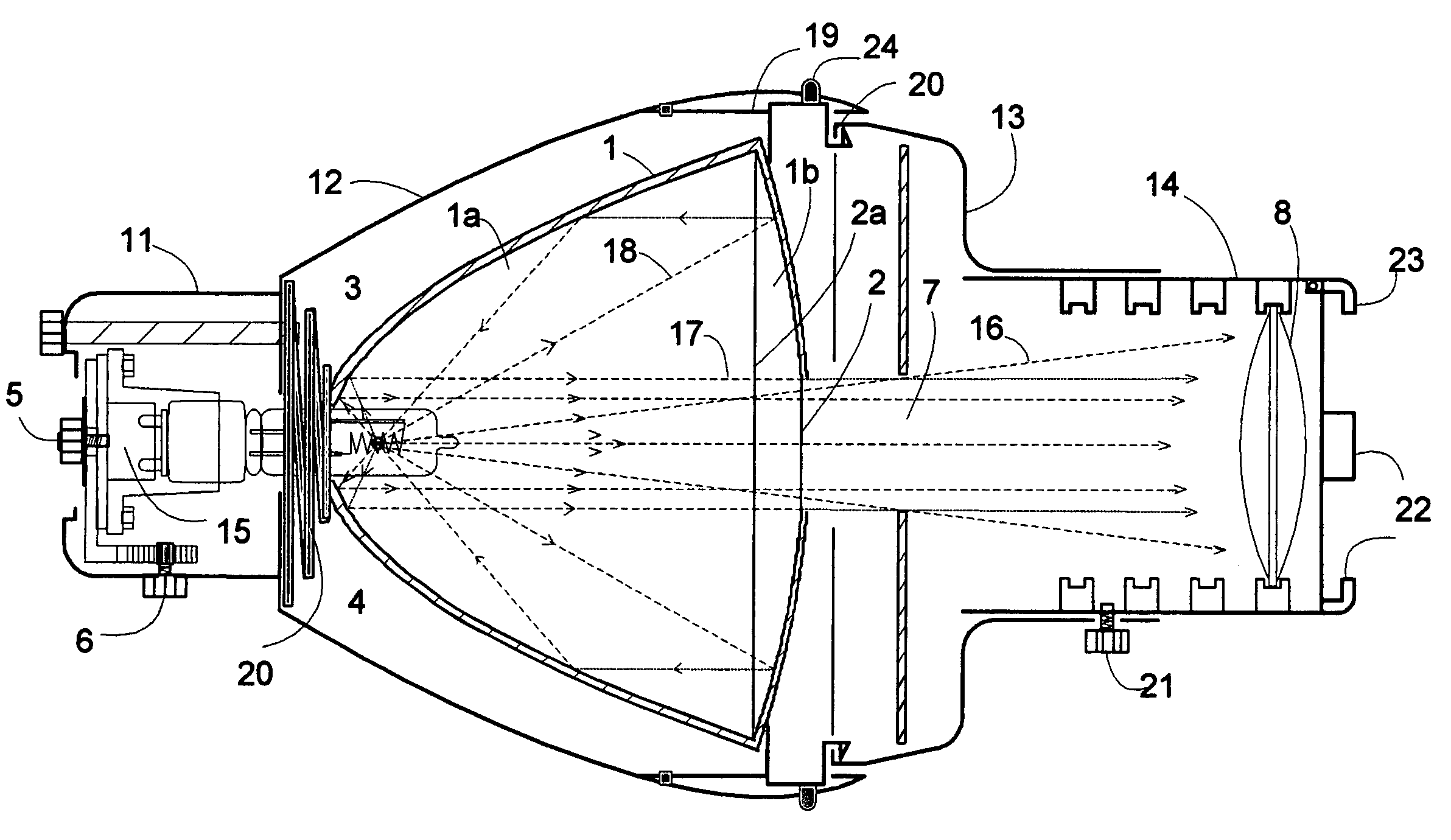
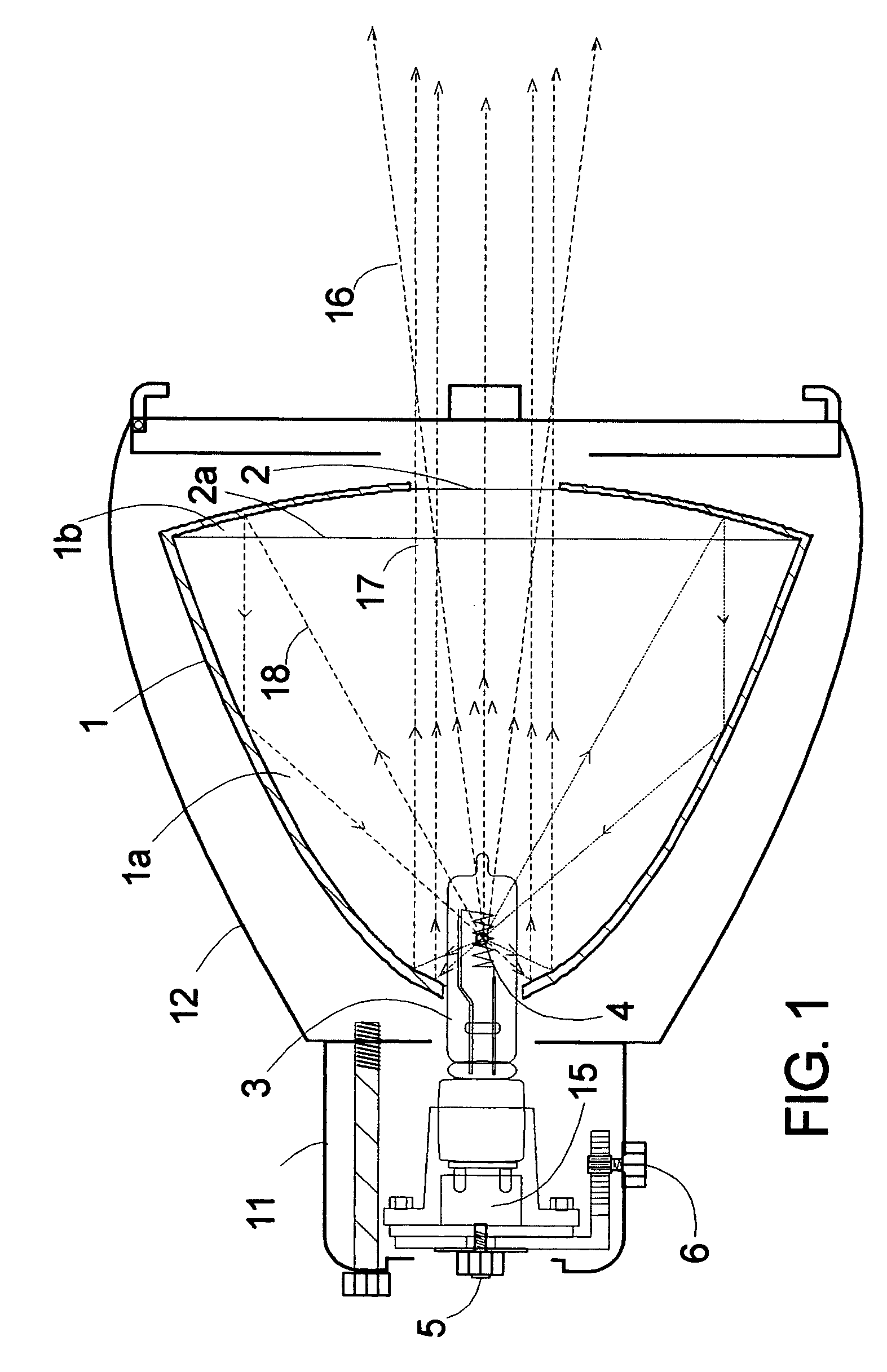
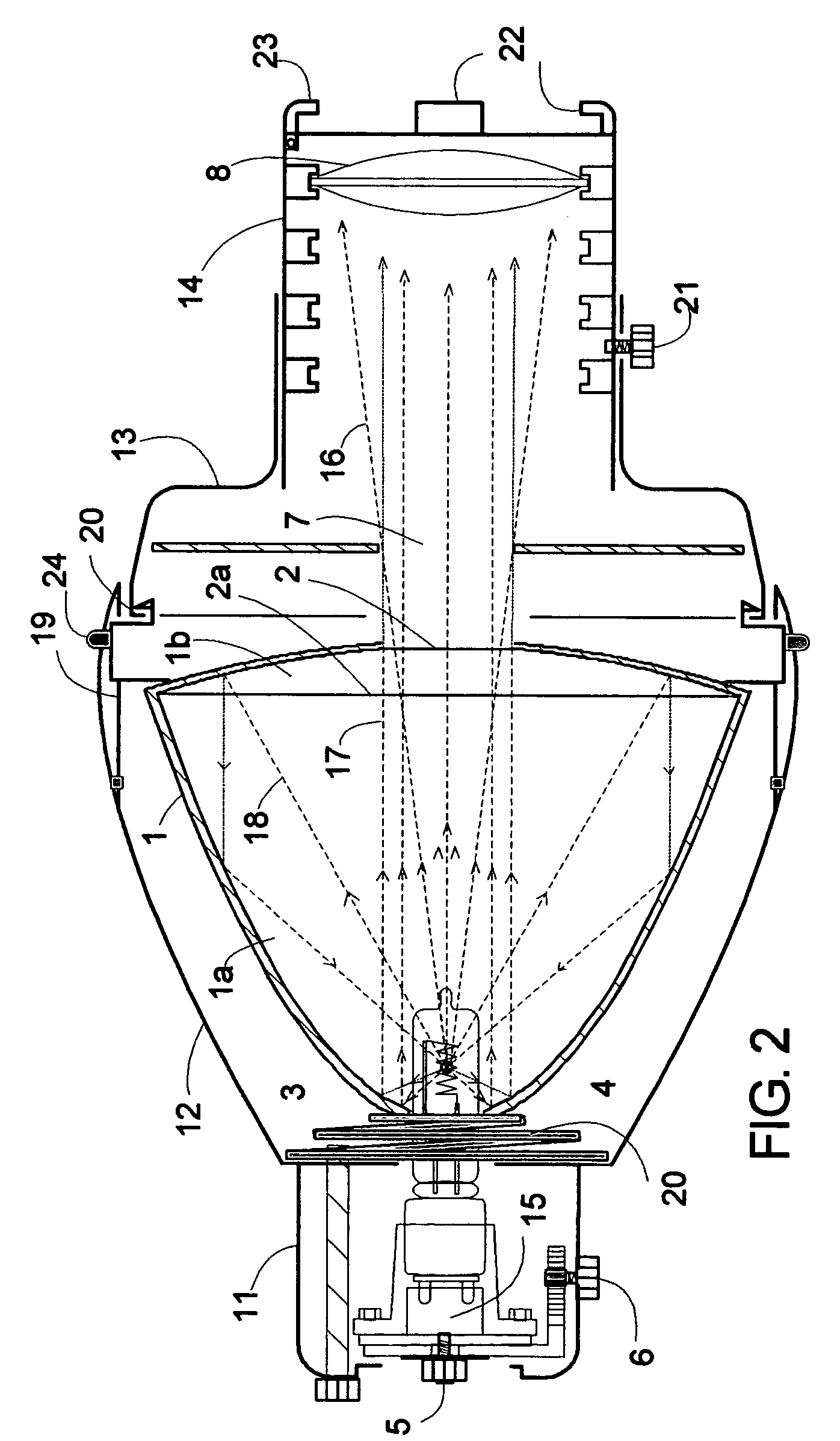
Par² lighting fixture
InactiveUS20080137345A1Easy to shapeReduce heat radiationLighting applicationsMechanical apparatusLocking mechanismAspheric lens
An improved lighting fixture is disclosed for imaging a high-intensity beam of light at a distant location. A specially-made duel parabolic reflector system cooperates with a gate aperture and a single aspheric lens to produce a beam that incorporates a very high proportion of emitted visible light. Alternatively, said fixture has two lenses in a positioning mechanism mounted in the housing, and includes a rack and pinion gear device that adjusts the distance between the front and rear lenses in response to the rotation of an actuator. The actuator is configured to slide along a slot in the housing, controlling the translation of the first and second lenses with respect to the gate aperture. A shielding baffle covers the slot. The actuator is further configured with a locking mechanism that constrains the actuator from being moved with respect to the housing when the locking mechanism is in position. Additionally the rear parabolic reflector part has a dichroich coating that reflects only a low proportion of infrared light. The projected beam thereby has a relatively low energy density, such that the front portion of the fixture can be reduced substantially in size, be made of light weight materials with lower temperature resistance, and utilize lenses made of plastic. The gate is selectively rotatable relative to the fixture's rear housing.
Owner:WIMBERLY RANDAL LEE
Pick-up lens
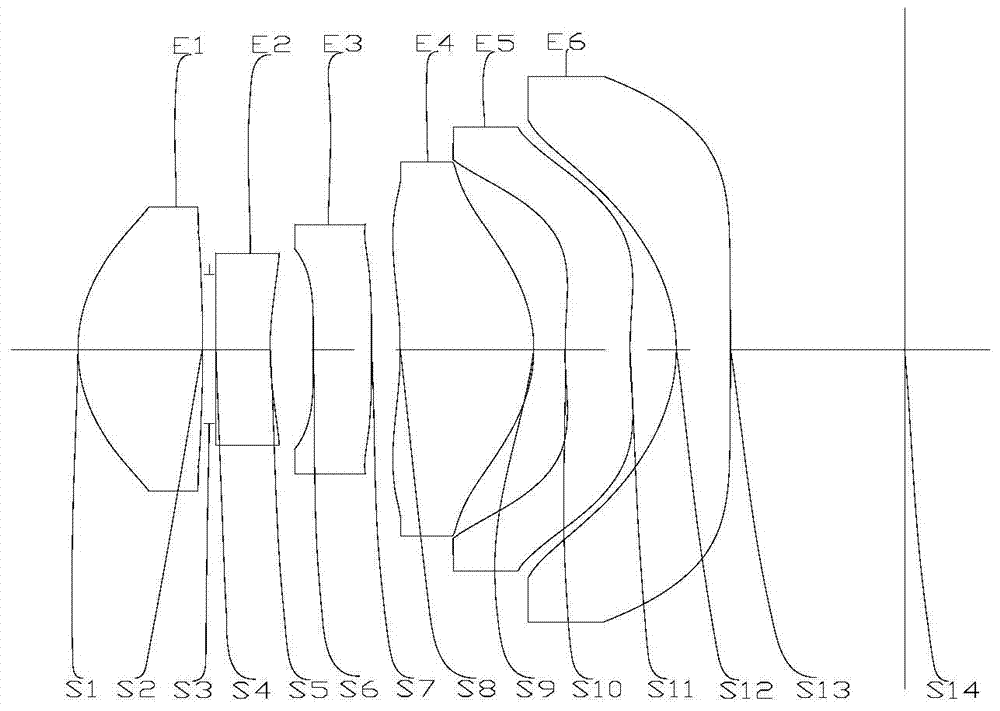
The invention provides a pick-up lens. The pick-up lens comprises a first lens set and a second lens set, wherein the first lens set and the second lens set are arranged in sequence from an object side to an image side; the first lens set comprises a first lens, a second lens and a third lens in sequence from the object side to the image side, the first lens has positive focal power and the object side surface of the first lens is a convex surface, and the second lens has negative focal power and the object side surface of the second lens is a convex surface; the second lens set comprises a fourth lens, a fifth lens and a sixth lens in sequence from the object side to the image side, the fifth lens has negative focal power and the image side surface of the fifth lens is a convex surface, and the sixth lens has negative focal power and the object side surface of the sixth lens is a concave surface. According to the pick-up lens, the six plastic aspherical lenses are adopted, and the defects in the prior art are overcome through distribution of different kinds of focal power. The pick-up lens has the advantages that the resolution is high, the imaging quality is high, the overall length of the pick-up lens is quite small, the pick-up lens is convenient to carry, and a novel solution is provided to meet current specification requirements and performance requirements.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Projection lens and projection device
A projection lens provided is for projecting an image beam. The projection lens is disposed on a transmission path of the image beam and includes a first group of lenses and a second group of lenses. The first group of lenses includes a first spherical lens and a first aspheric lens. After the image beam passes through the first group of lenses, an intermediate image is formed between the first group of lenses and the second group of lenses, in which the first aspheric lens is the lens in the first group of lenses closest to the second group of lenses. A projection device using the projection lens is also provided. The projection device further includes a planar reflector on the transmission path of the image beam.
Owner:YOUNG OPTICS
Ultra-wide angle objective lens
Owner:NING ALEX
Pick-up lens
The invention provides a pick-up lens which sequentially comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens and a sixth lens from object space to image space. The first lens has positive focal power, and the object side surface of the first lens is a convex surface; the second lens has negative focal power, and the image side surface of the second lens is a concave surface; the fourth lens has positive focal power, and the image side surface of the fourth lens is a convex surface; the image side surface of the fifth lens is a concave surface, and at least one point of inflexion is formed in the surface of the object side of the fifth lens or the surface of the image side of the fifth lens; the object side surface of the sixth lens is a concave surface, and the image side surface of the sixth lens is a convex surface. According to the pick-up lens, the six plastic aspherical lenses are adopted, so that the defects in the prior art are overcome through different types of focal power distribution; the pick-up lens has the advantages that the resolution is high, imaging quality is good, the total length of the pick-up lens is small, and the pick-up lens is convenient to carry; the pick-up lens provides a novel solution to meet current specification requirements and performance requirements.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Imaging lens
A low-cost, compact and low-profile imaging lens with relatively high brightness, which provides a wide angle of view of about 90 degrees and corrects various aberrations properly. It is designed for use in a solid-state image sensor and includes the following elements arranged in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens as a positive or negative double-sided aspheric lens having a convex object-side surface near an optical axis; an aperture stop; a positive second lens having a convex image-side surface; a negative third lens having a concave image-side surface; a positive fourth lens having a convex image-side surface; and a fifth lens as a negative meniscus lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis. It satisfies a conditional expression (1) below:0.9<ih / f<1.1 (1)wheref: focal length of the overall optical system of the imaging lensih: maximum image height
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
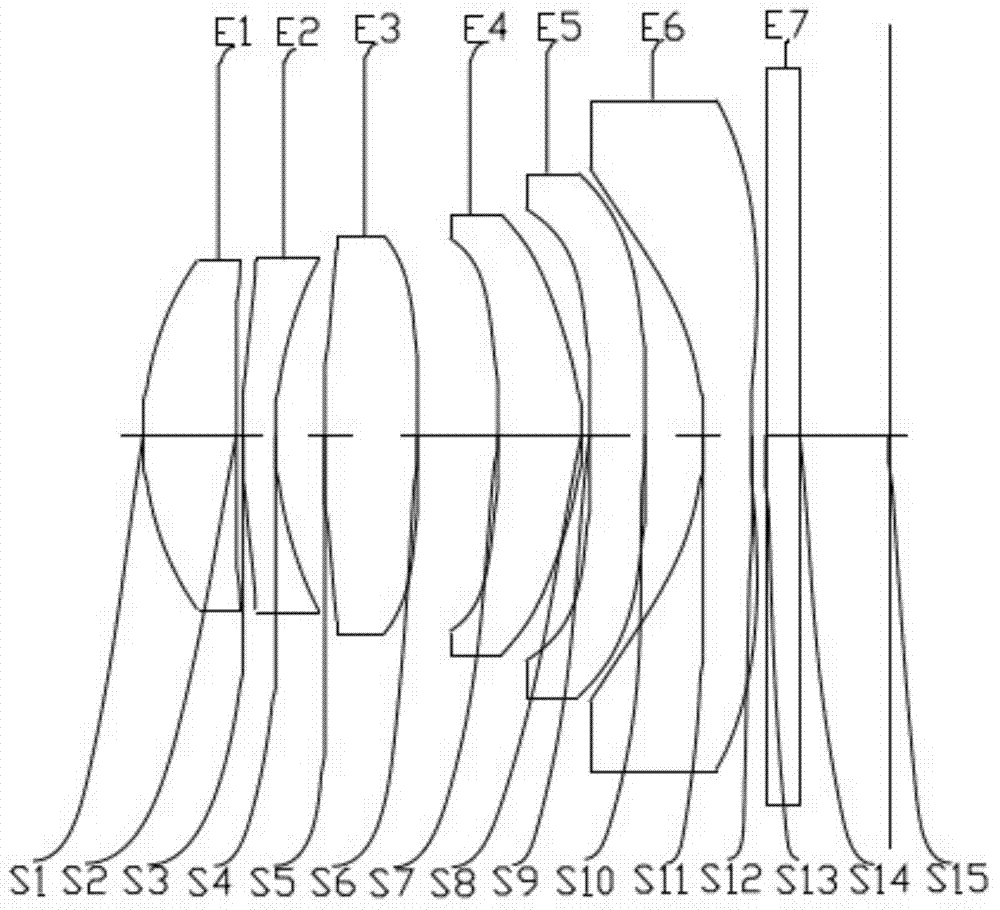
High-definition super wide angle prime lens
The invention belongs to the technical field of lenses, particularly to a high-definition super wide angle prime lens which comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens and a sixth lens which are sequentially arranged from the object space to the image space, wherein the fourth lens and the fifth lens adopt plastic aspherical lenses; the first lens, the second lens, the third lens and the sixth lens are glass spherical lenses; the first lens is a convex-concave negative focal power lens; the second lens is a bi-concave negative focal power lens; the third lens is a bi-convex positive focal power lens; the fourth lens is a bi-convex positive focal power lens; the fifth lens is a bi-concave negative focal power lens; the sixth lens is a bi-convex positive focal power lens. According to the high-definition super wide angle prime lens, glass lenses and plastic lenses are reasonably combined, so that a large aperture is realized, the imaging quality is good, 4 megapixel can be realized under the precondition that infrared does not focus again, and clear and bright monitoring pictures can be realized even at night with a low illumination level; the lens has a temperature compensation function, and can be used at the temperature of minus 30 DEG C-80 DEG C without being out of focus.
Owner:DONGGUAN YUTONG OPTICAL TECH
Imaging lens composed of seven optical elements
A compact low-profile imaging lens which offers a wide field of view and corrects aberrations properly. It includes: a first positive (refractive power) lens having a convex object-side surface as a first optical element; a second negative meniscus lens having a concave image-side surface as a second optical element; a third lens having at least one aspheric surface as a third optical element; a fourth lens having at least one aspheric surface as a fourth optical element; a fifth lens having at least one aspheric surface as a fifth optical element; and a sixth double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface as a sixth optical element. The aspheric image-side surface of the sixth lens has pole-change points off an optical axis. As a seventh optical element, one double-sided aspheric aberration correction optical element with virtually no refractive power is located between the first lens and an image plane.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Dual-lensed unitary optical receiver assembly
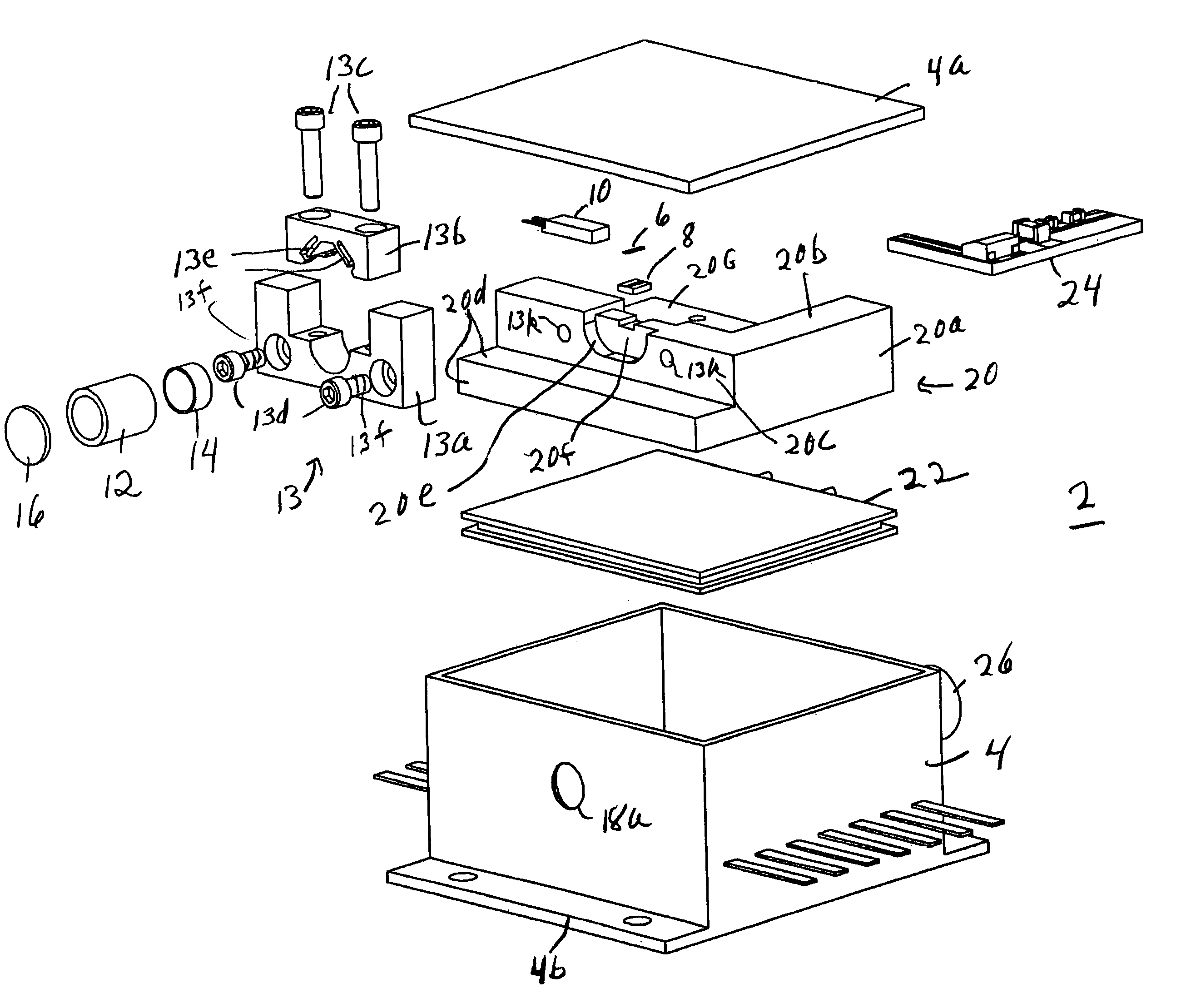
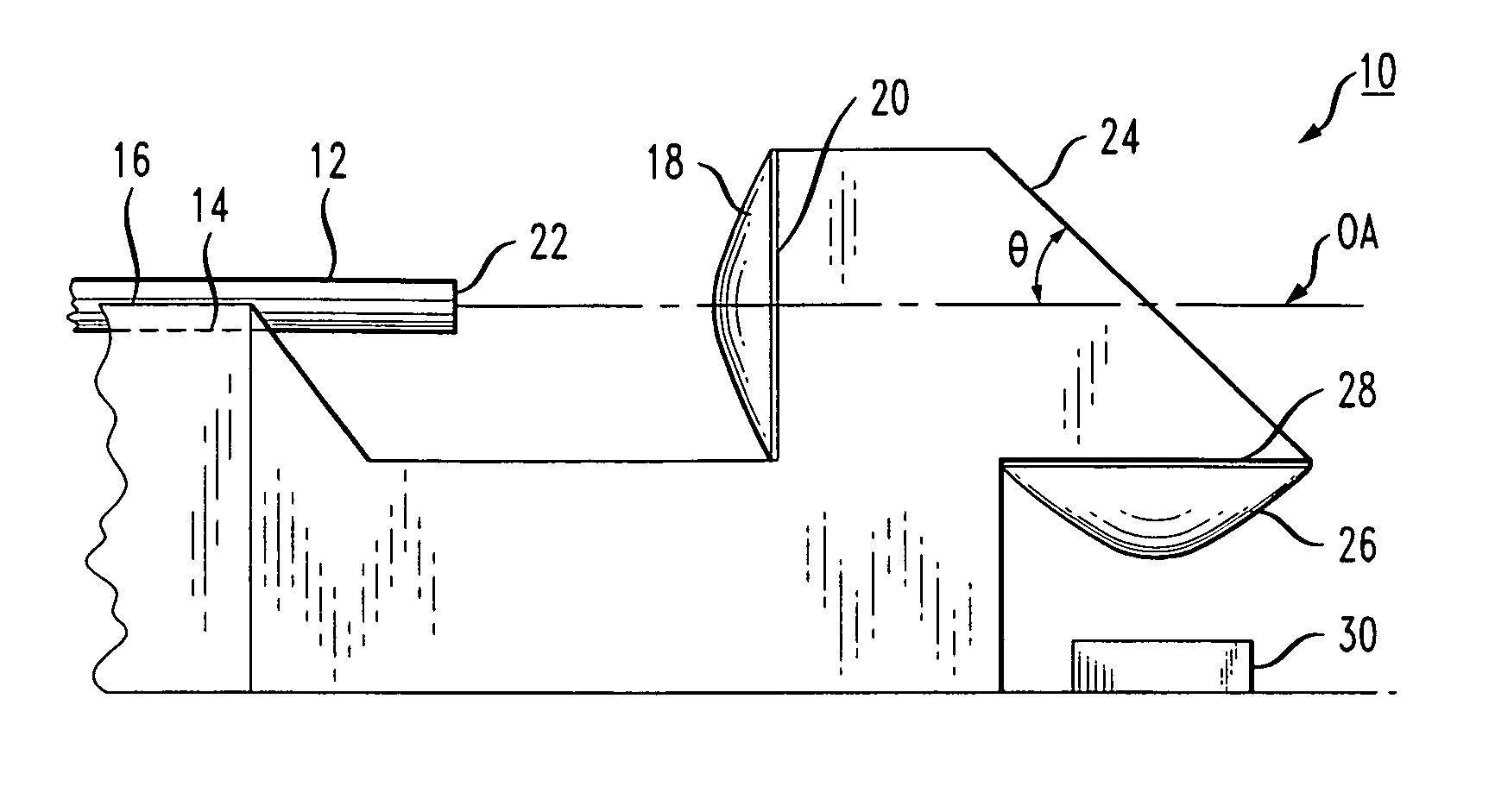
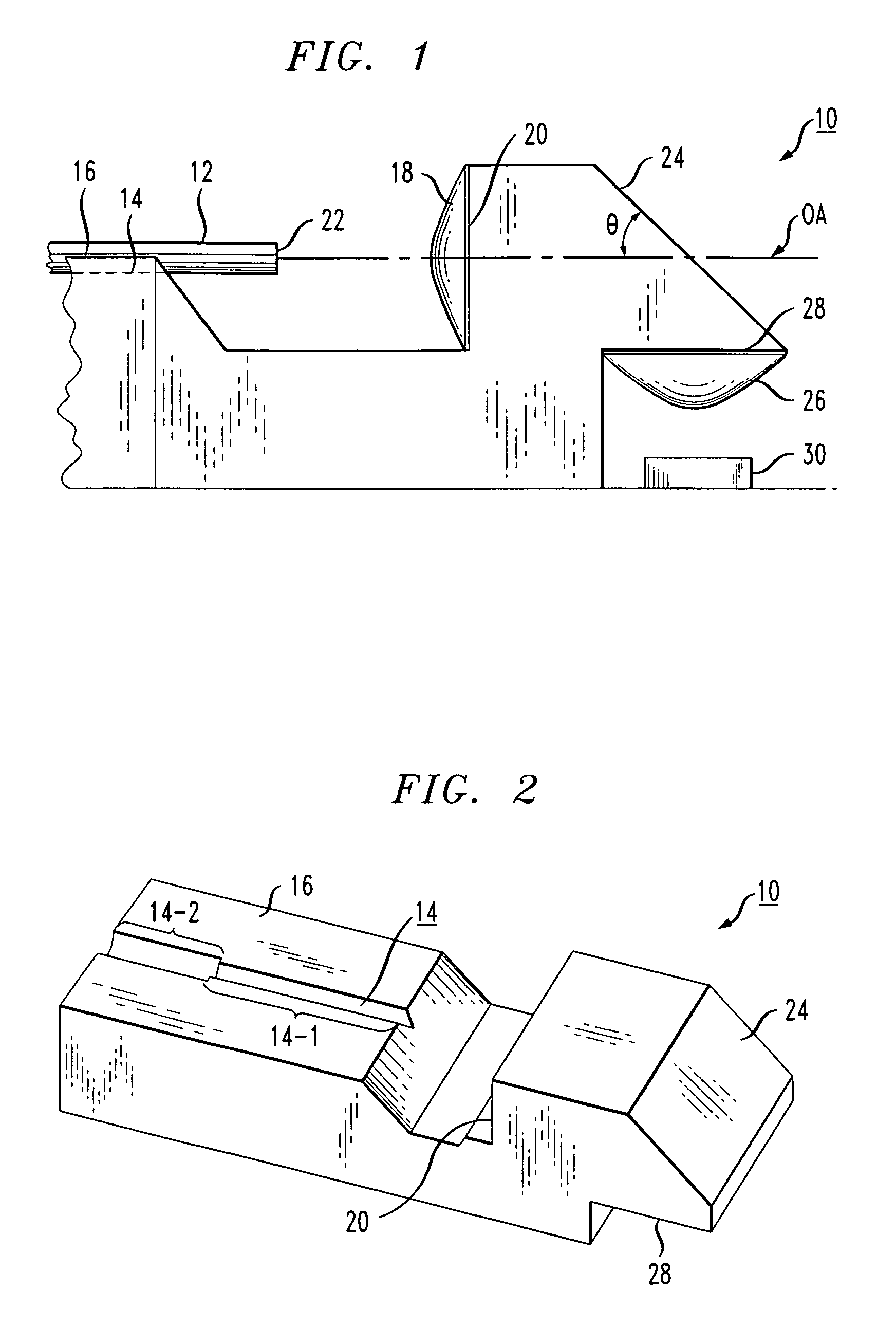
InactiveUS7556440B2Efficient couplingReducing cost and complexityCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic receiversAspheric lensPhysics
A unitary optical receiver assembly is formed to include a V-groove passively aligned with a first aspheric lens (the lens formed along a surface perpendicular to the V-groove). An optical fiber is disposed along the V-groove and is used to bring the received optical signal into the unitary assembly. Upon passing through the first aspheric lens, the received optical signal will intercept a 45° turning mirror wall that directs the signal downward, through a second aspheric lens (also molded in the unitary assembly), and then into a photosensitive device. Advantageously, the photosensitive device is disposed in passive alignment with the second aspheric lens, allowing for a received signal to be coupled from an incoming optical fiber to a photosensitive device without needing any type of active alignment therebetween.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optical imaging lens assembly and optical imaging device
ActiveUS20150054994A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAspheric lensPhysics
An optical imaging lens assembly includes, in order from the object side to the image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element, a fifth lens element and a sixth lens element. The first lens element with positive refractive power has a convex object-side surface in a paraxial region. The fourth lens element with negative refractive power has a concave object-side surface in a paraxial region. The fifth lens element with positive refractive power has a convex image-side surface in a paraxial region. The sixth lens element with negative refractive power has a concave object-side surface in a paraxial region, a concave image-side surface in a paraxial region and at least one convex shape in the off-axial region of the image-side surface of the sixth lens element. The fifth lens element and the sixth lens element are aspheric lens elements.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
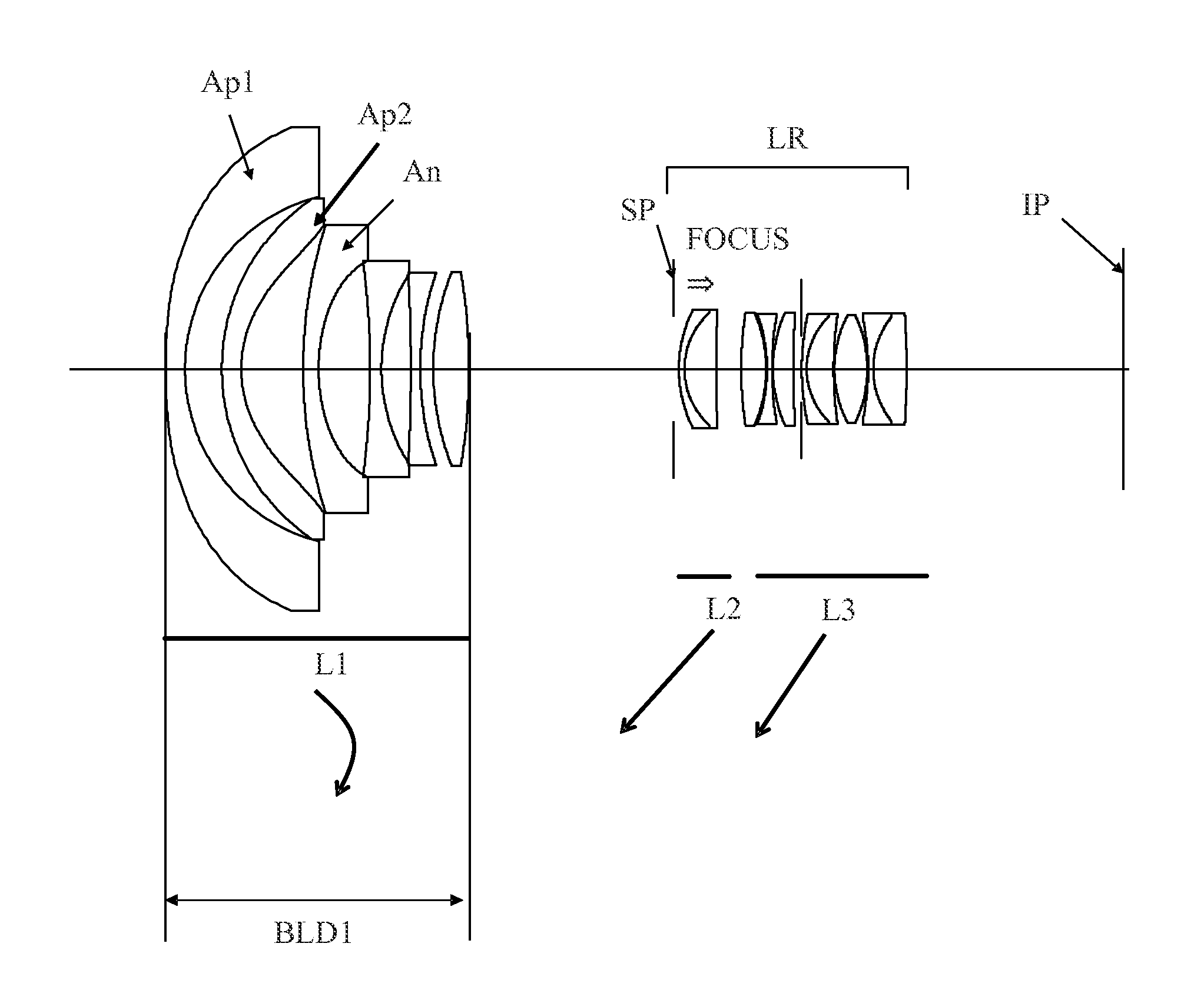
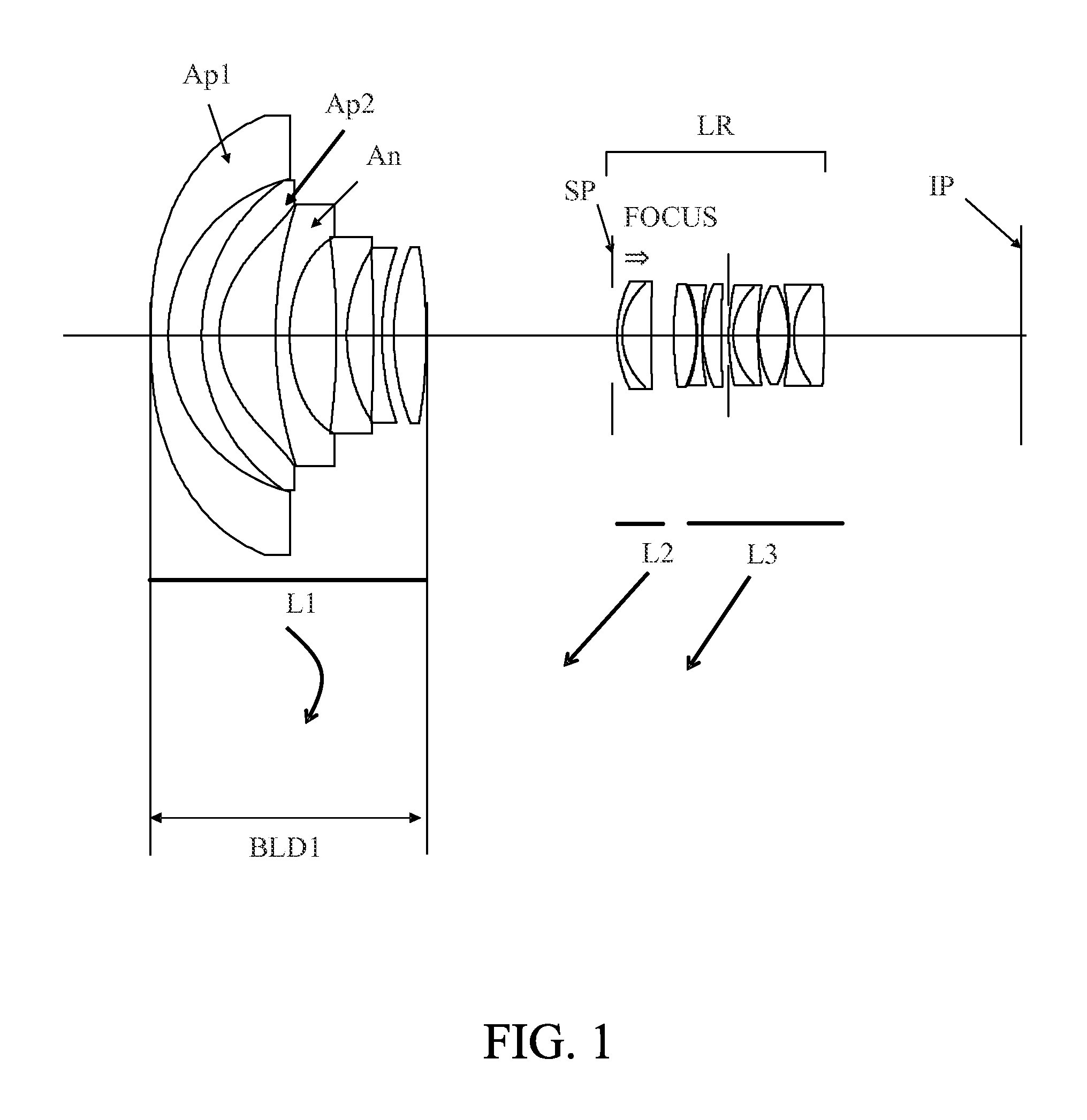
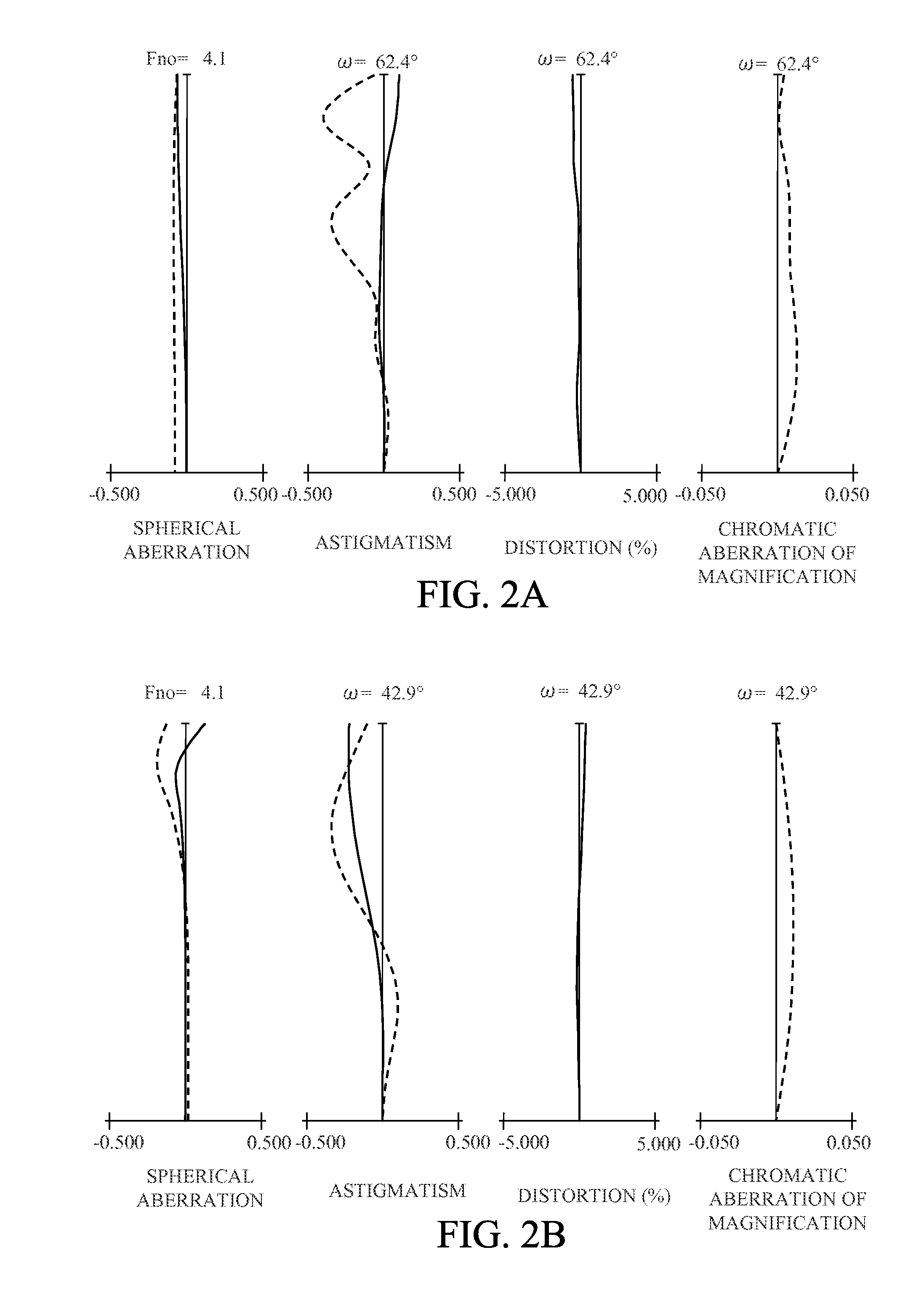
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus including same
ActiveUS20140125858A1Good optical performanceWide viewing angleTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAspheric lensRefractive index
The zoom lens includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit having a negative refractive power, and a rear lens group including one or more lens units and having as a whole a positive refractive power. The first and rear lens group are moved during zooming so that a distance therebetween decreases at a telephoto end as compared with at a wide-angle end. The first lens unit includes an image side aspheric lens having a negative aspheric amount and one or more object side aspheric lenses disposed on the object side further than the image side aspheric lens. A condition of 0.060<ΣAspi×Ndi / BLD1<0.200 is satisfied where Aspi represents an aspheric amount of an i-th object side aspheric lens, Ndi represents a refractive index of the i-th object side aspheric lens, BLD1 represents a length of the first lens unit.
Owner:CANON KK
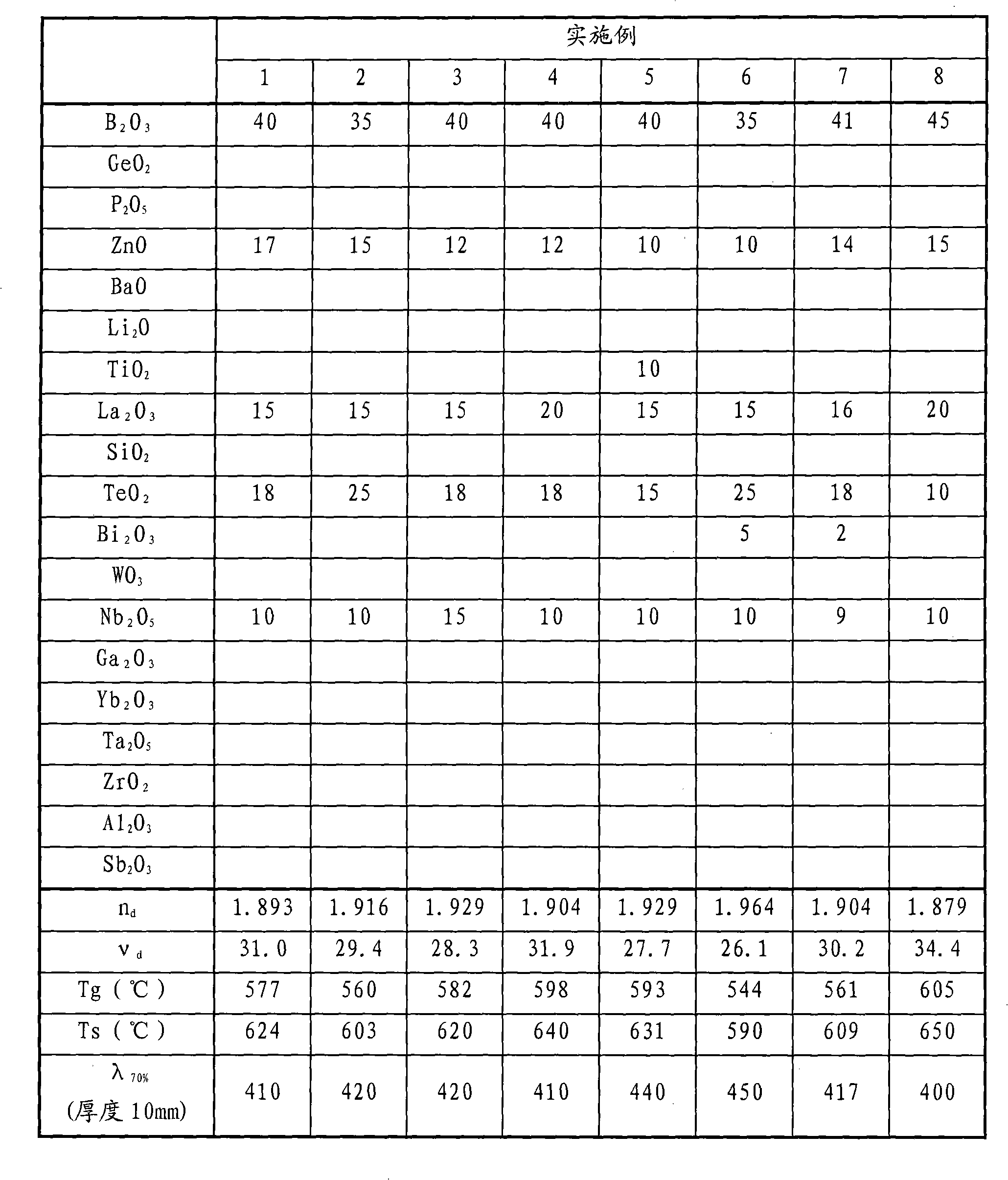
Optical glass
InactiveCN101279816ALower glass transition temperatureExcellent devitrification resistanceGlass pressing apparatusOptical elementsCompression moldingResist
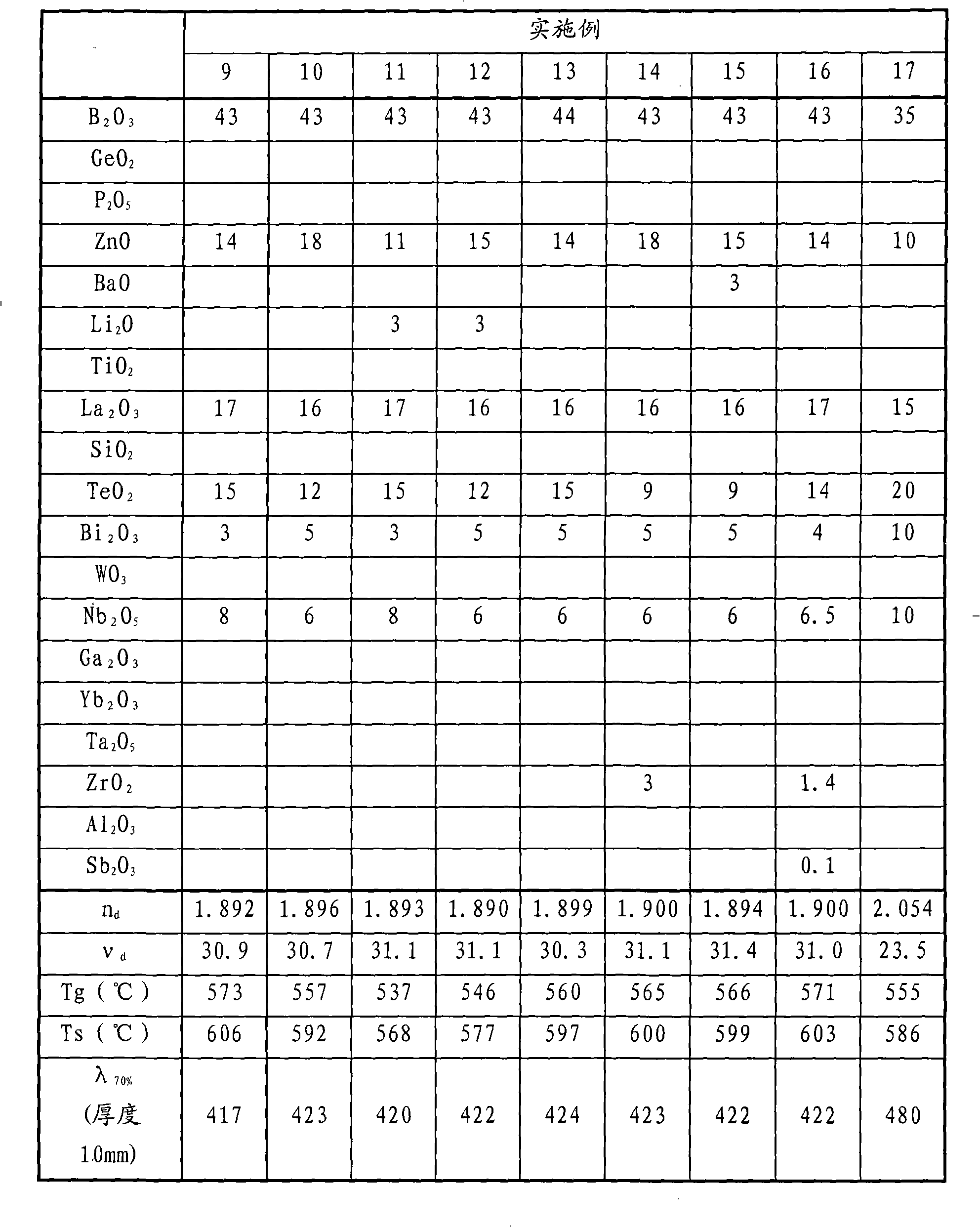
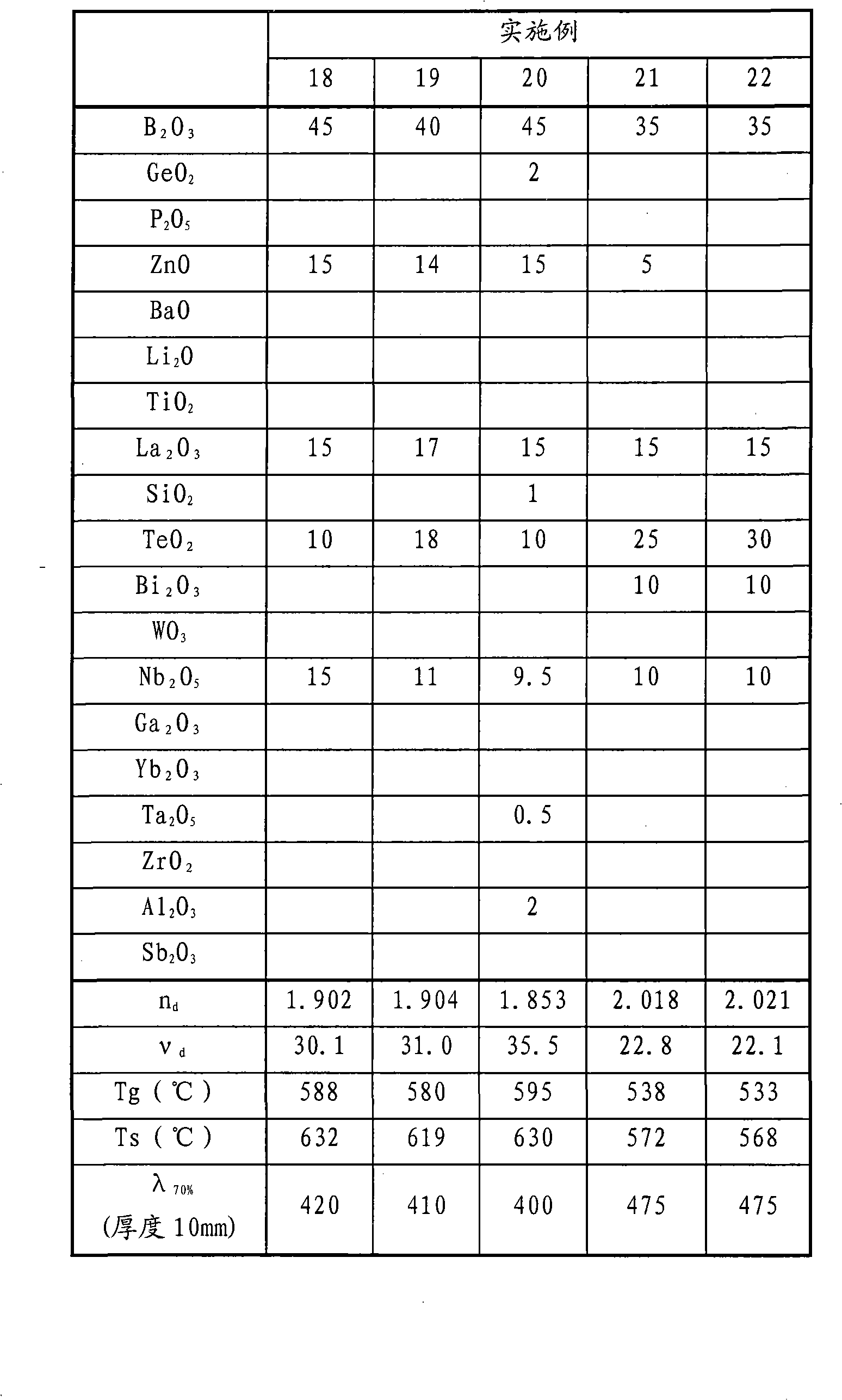
The present invention provides a novel optical glass, which is B2O3-TeO2-La2O3 composed of glass with good resist-losing of transparency at the same time, having optical constant (refractive index, abbe number and so on) required by aspheric lens and so on, having low glass transition temperature, and being suitable for accurate compression molding.The optical glass is characterized in that: mole percentage (Mol%) based on oxide, having 5-60% B2O3, and having 0.2-60% TeO2.In addition, refractive index (nd) being 1.80-2.20, abbe number (Gammad) being 16-40 optical constant, and glass transition temperature (Tg) below 680 EDG C.
Owner:OHARA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com