Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
249 results about "Mid infrared laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
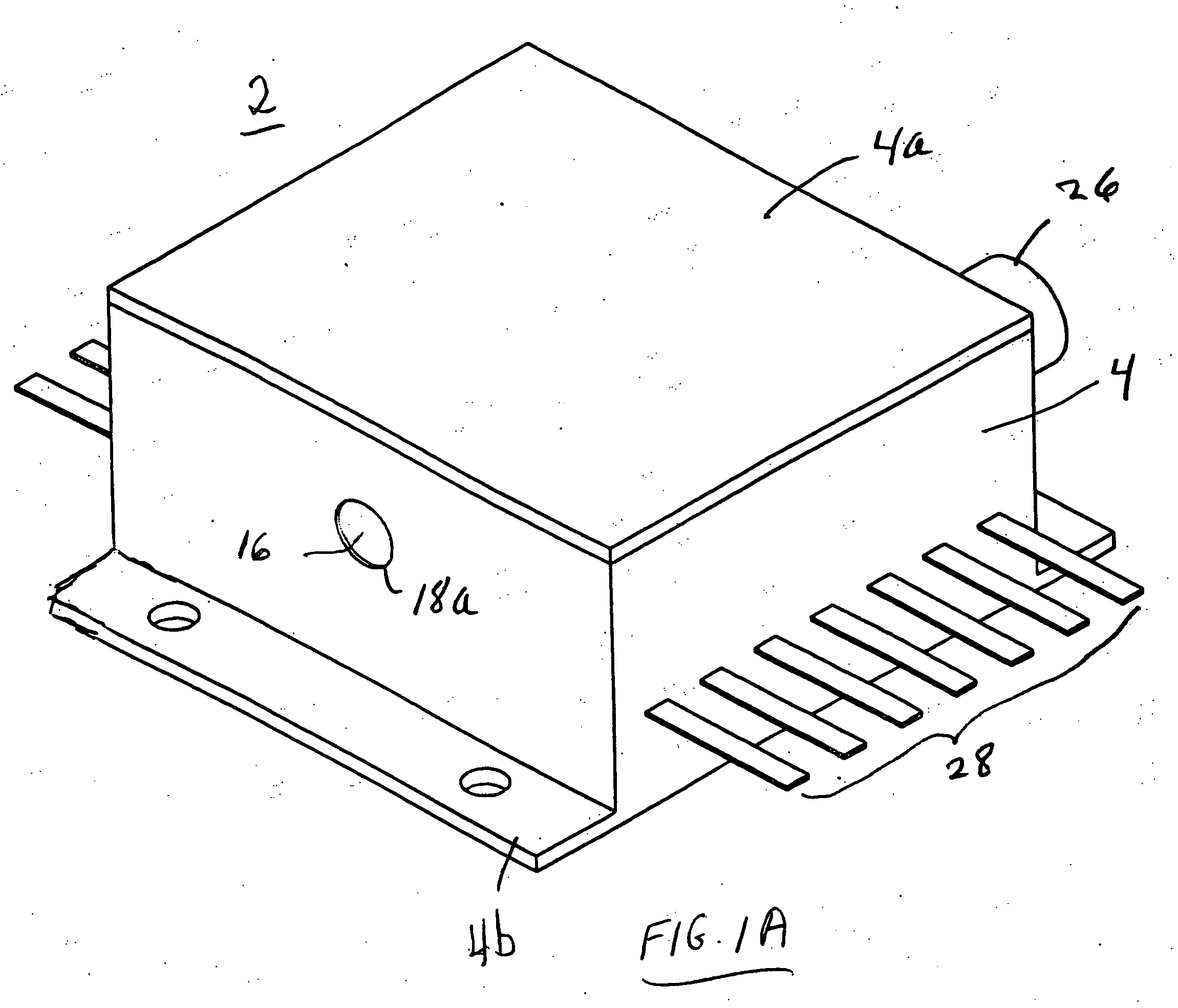
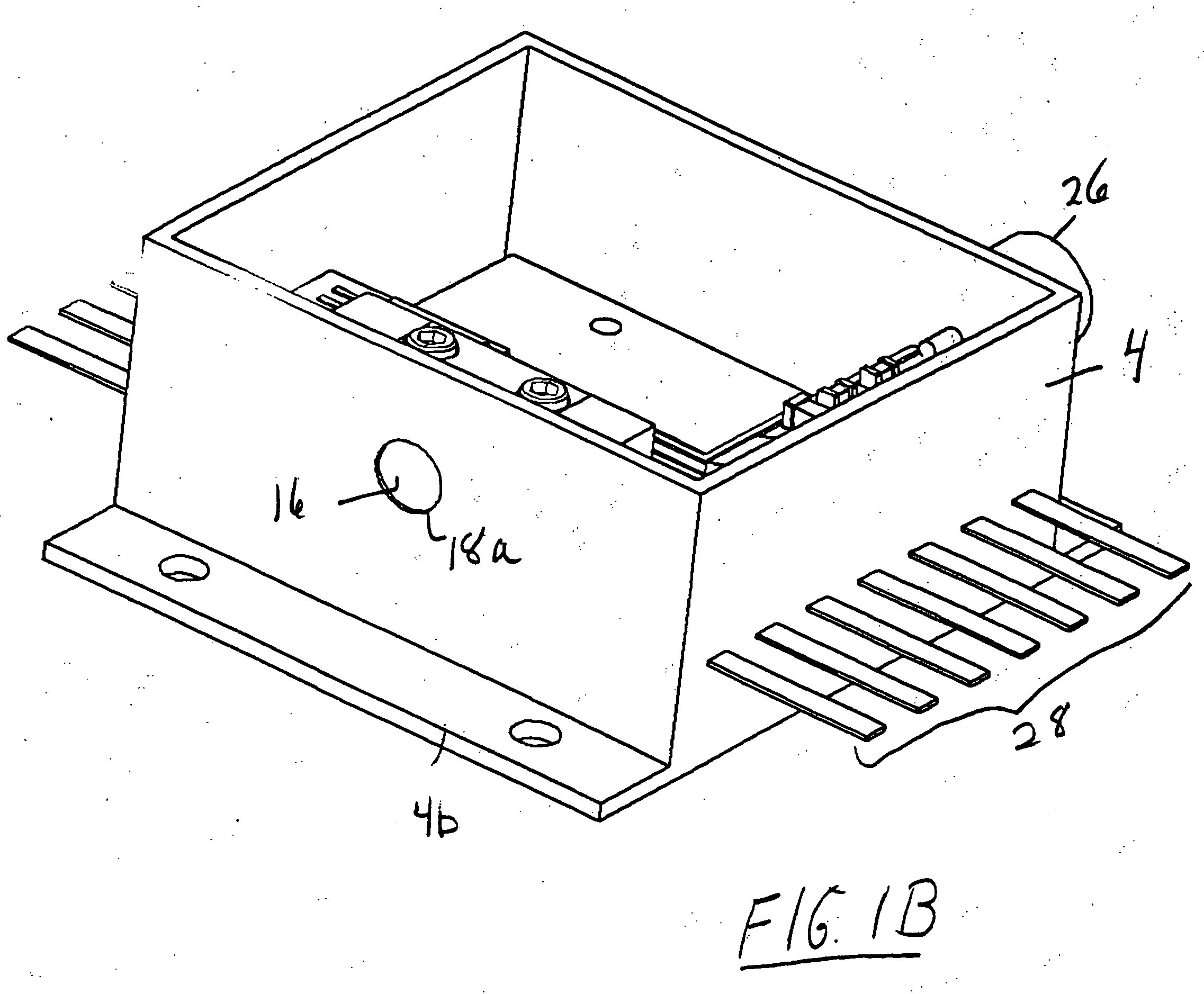
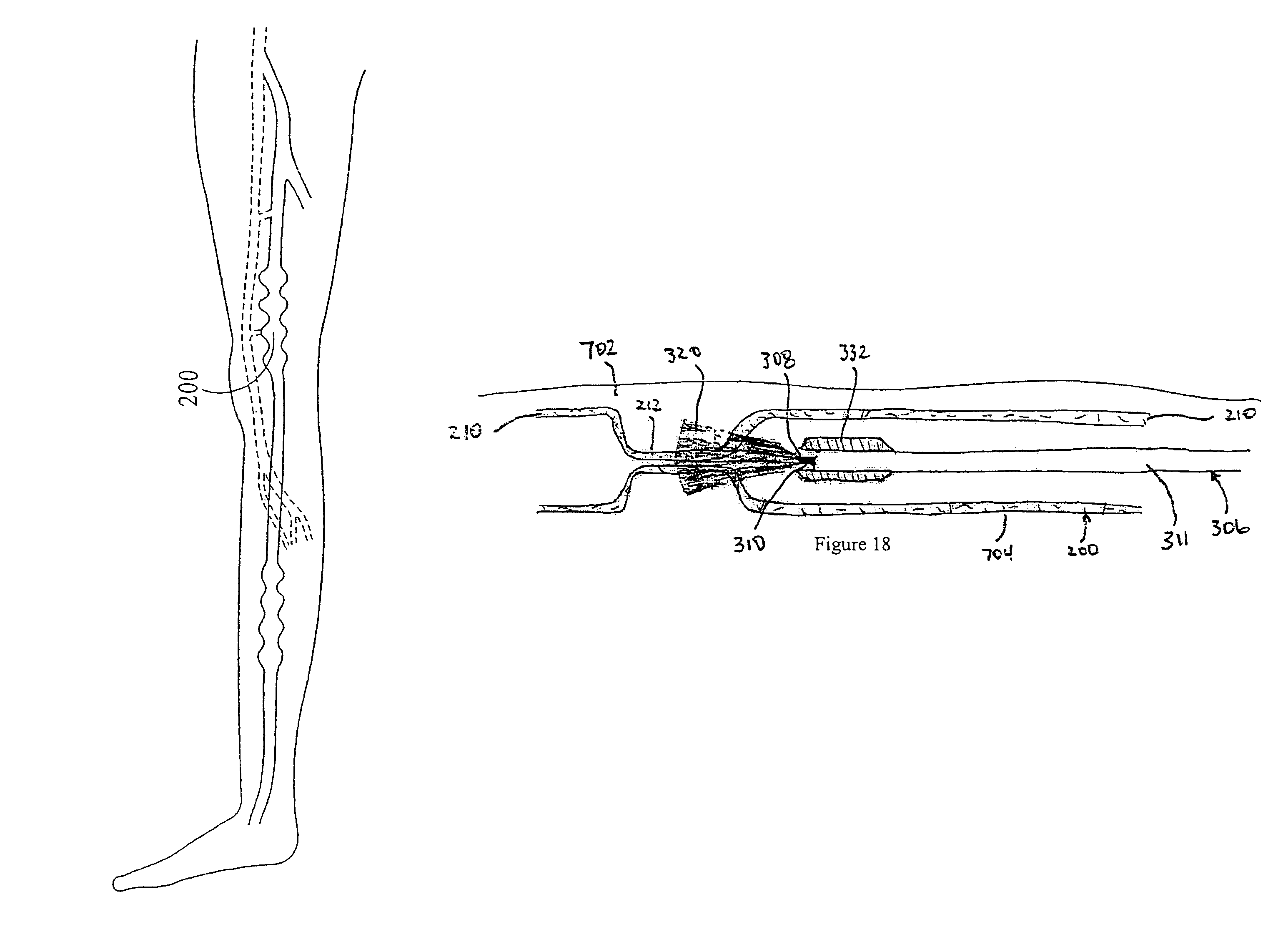
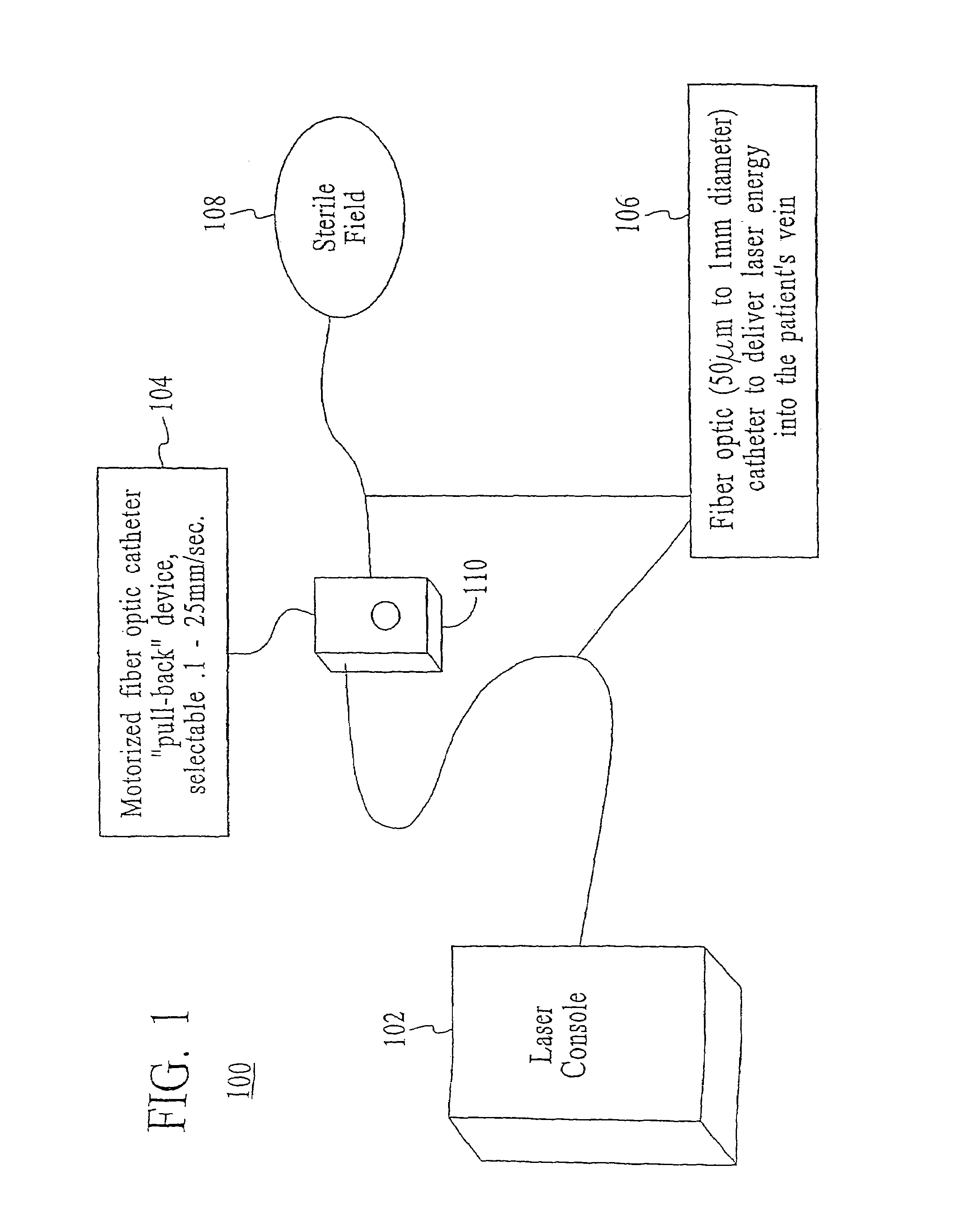
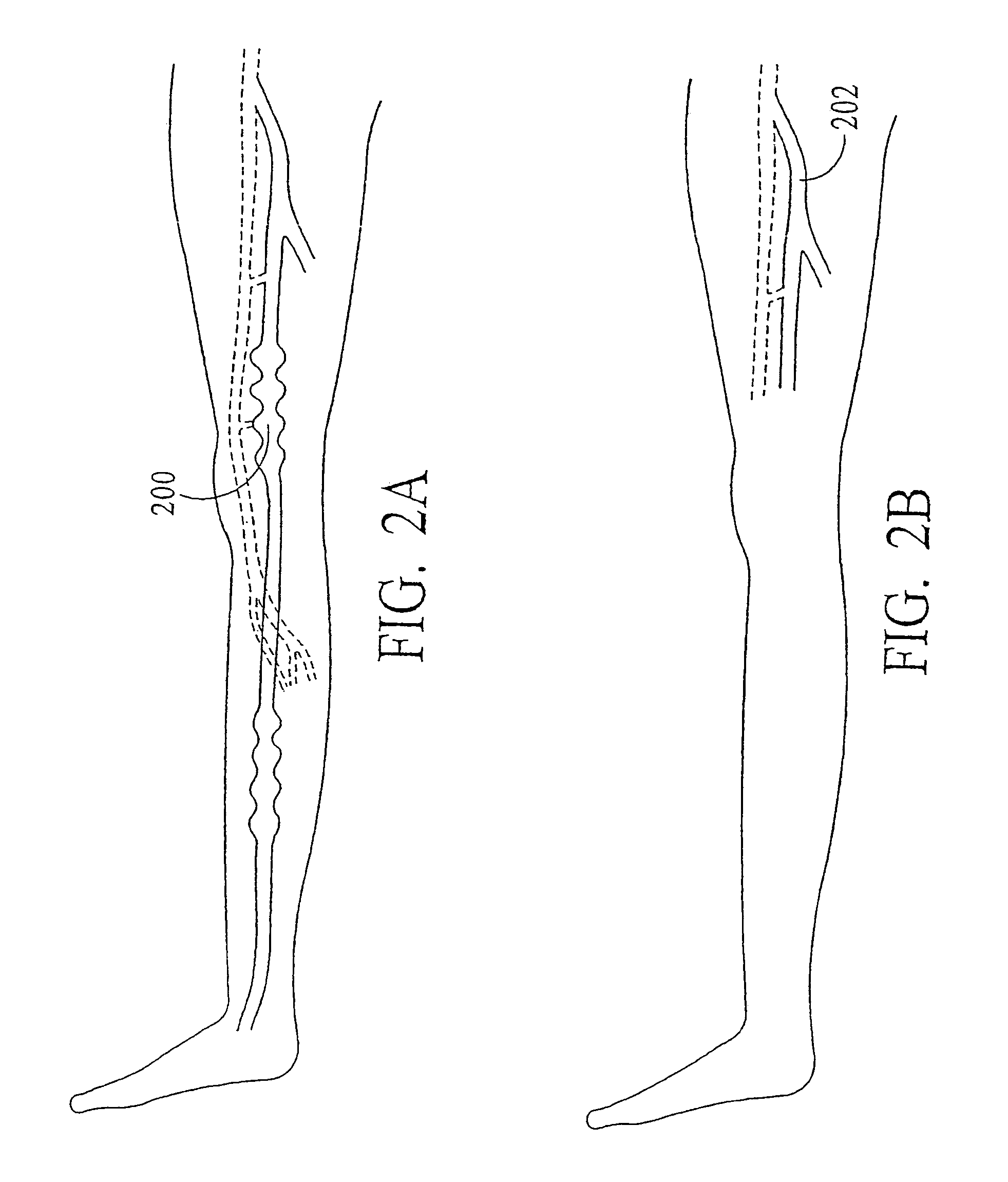
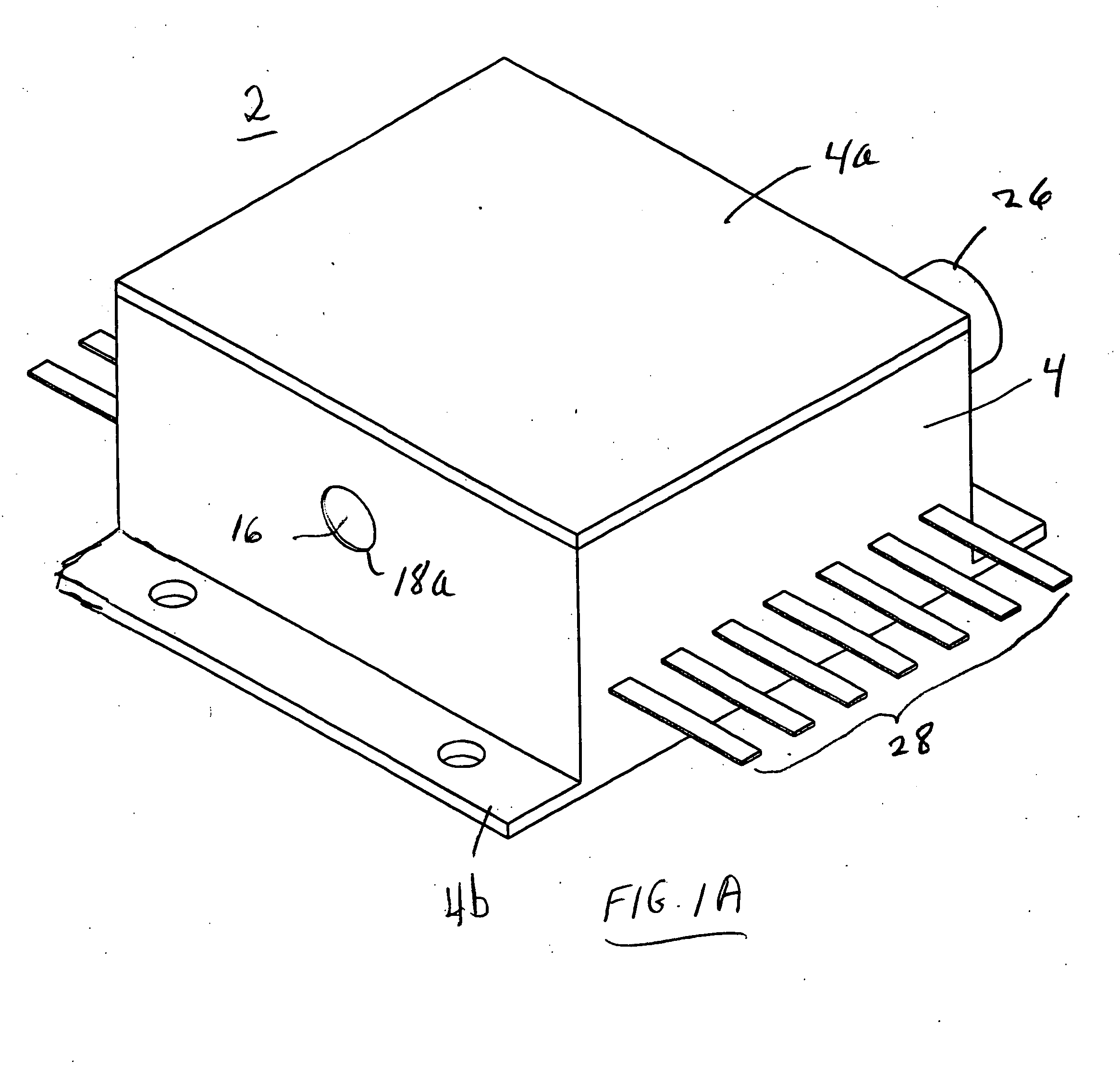
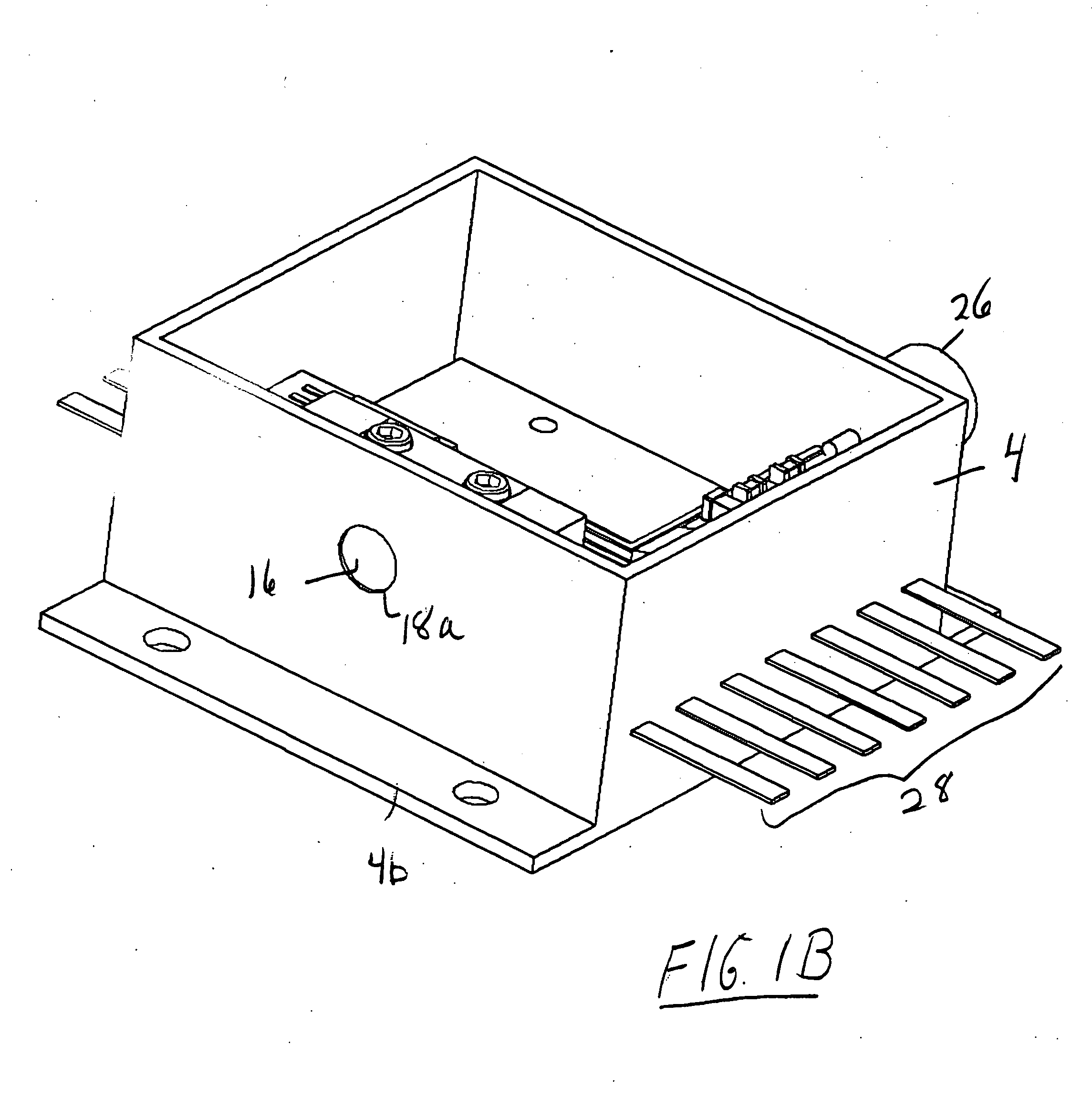
Endovenous closure of varicose veins with mid infrared laser
InactiveUS20050131400A1Less energyAvoid damageDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsProper treatmentMid infrared laser
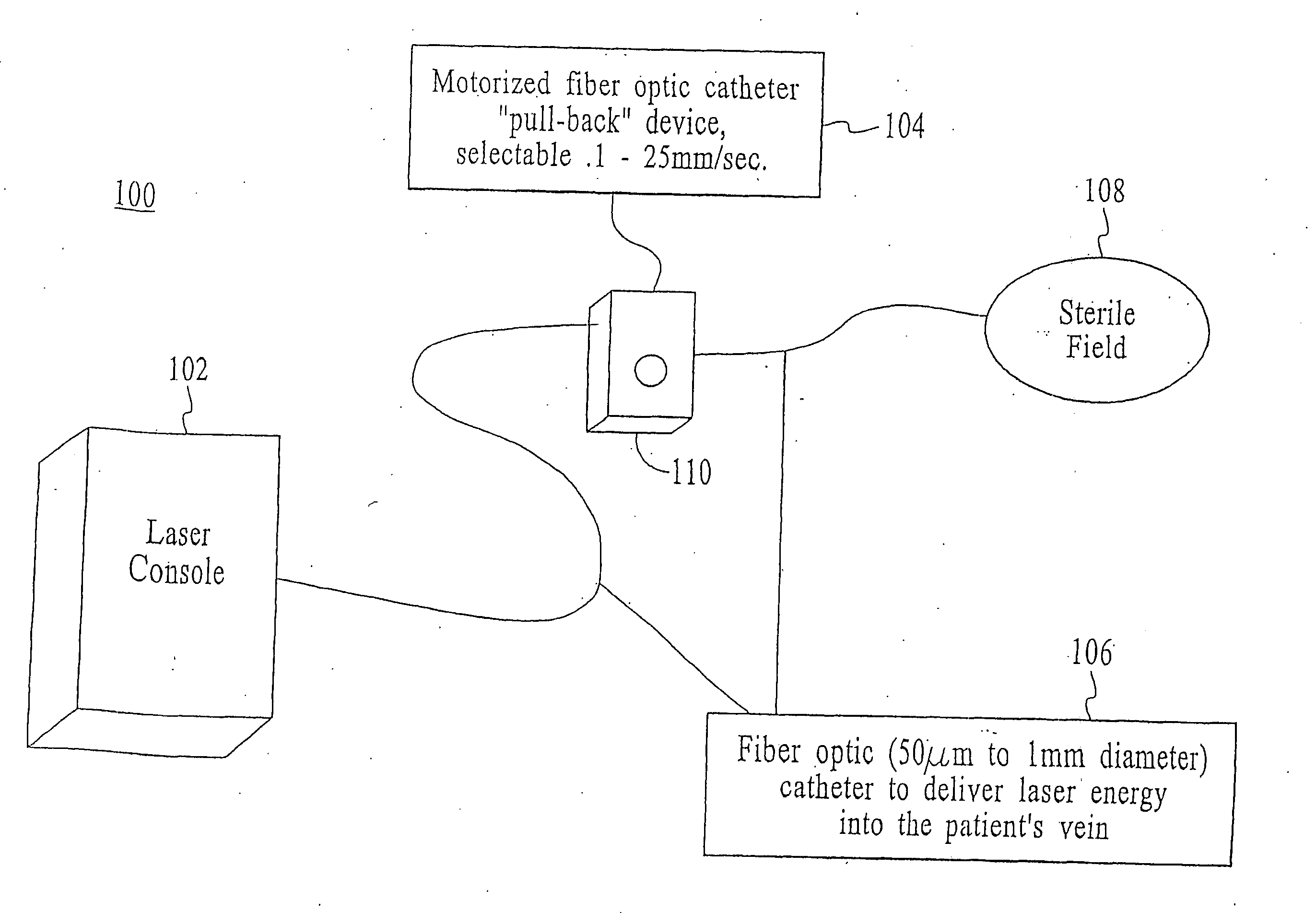
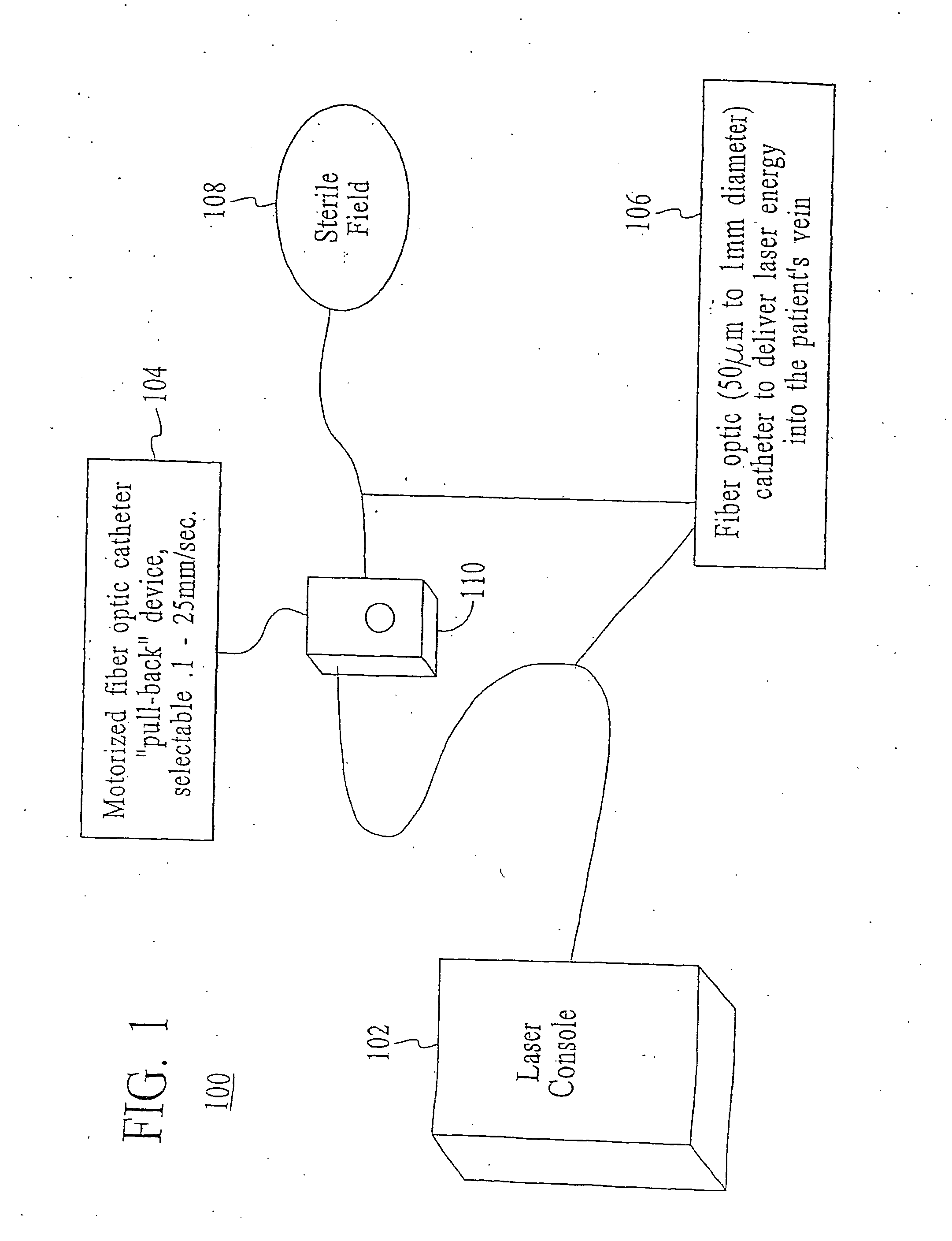
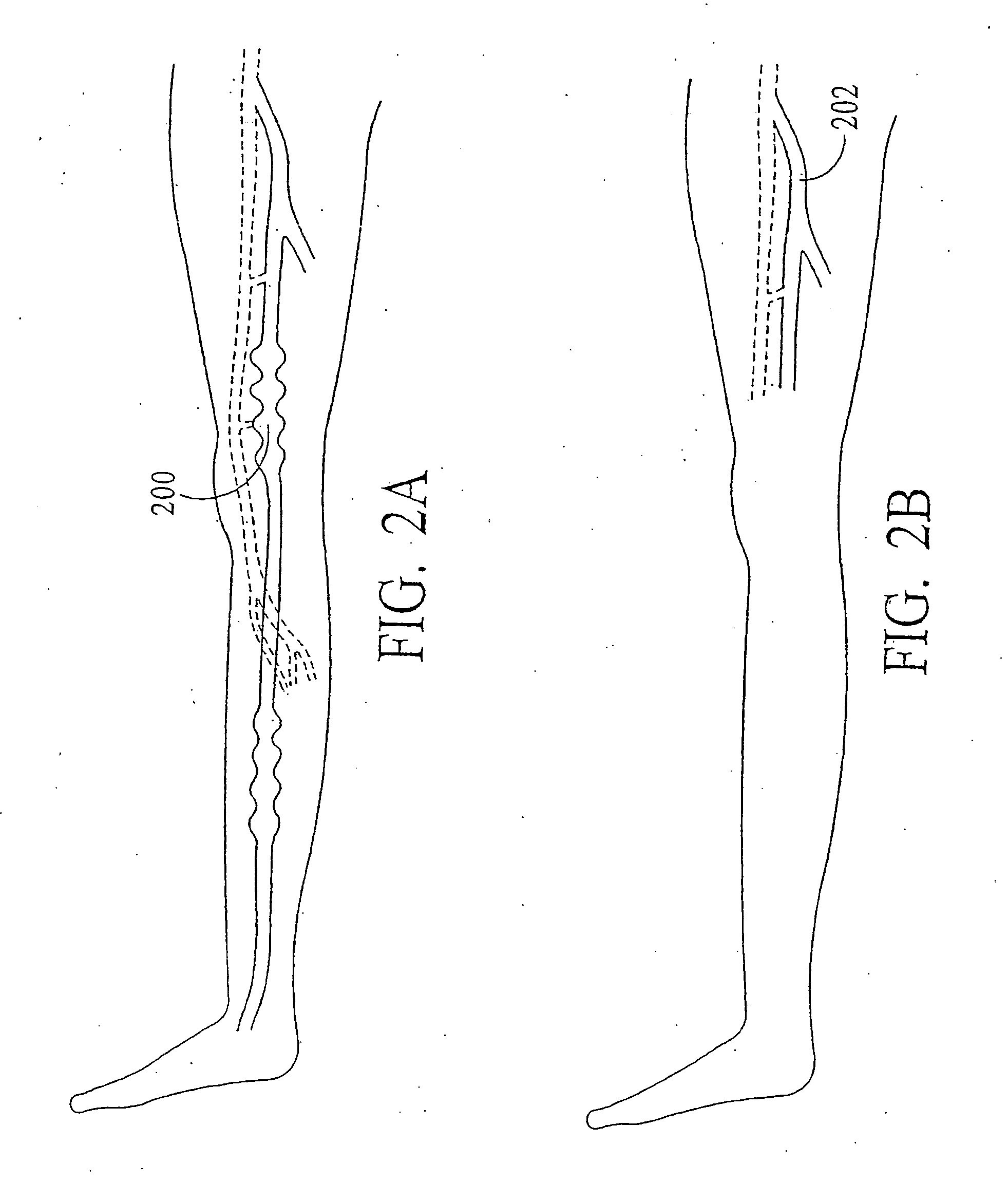
This invention is an improved method and device for treating varicose veins 200 or the greater saphenous vein 202. The method comprises the use of infrared laser radiation in the region of 1.2 to 2.2 um in a manner from inside the vessel 200 or 202 such that the endothelial cells of the vessel wall 704 are damaged and collagen fibers in the vessel wall 704 are heated to the point where they permanently contract, the vessel 200 or 202 is occluded and ultimately resorbed. The device includes a laser 102 delivered via a fiber optic catheter 300 that may have frosted or diffusing fiber tips 308, or that may be provided with a protective spacer. A motorized pull back device 104 may be used, and a thermal sensor 600 may be used to help control the power required to maintain the proper treatment temperature.
Owner:COOLTOUCH
External cavity tunable compact mid-IR laser
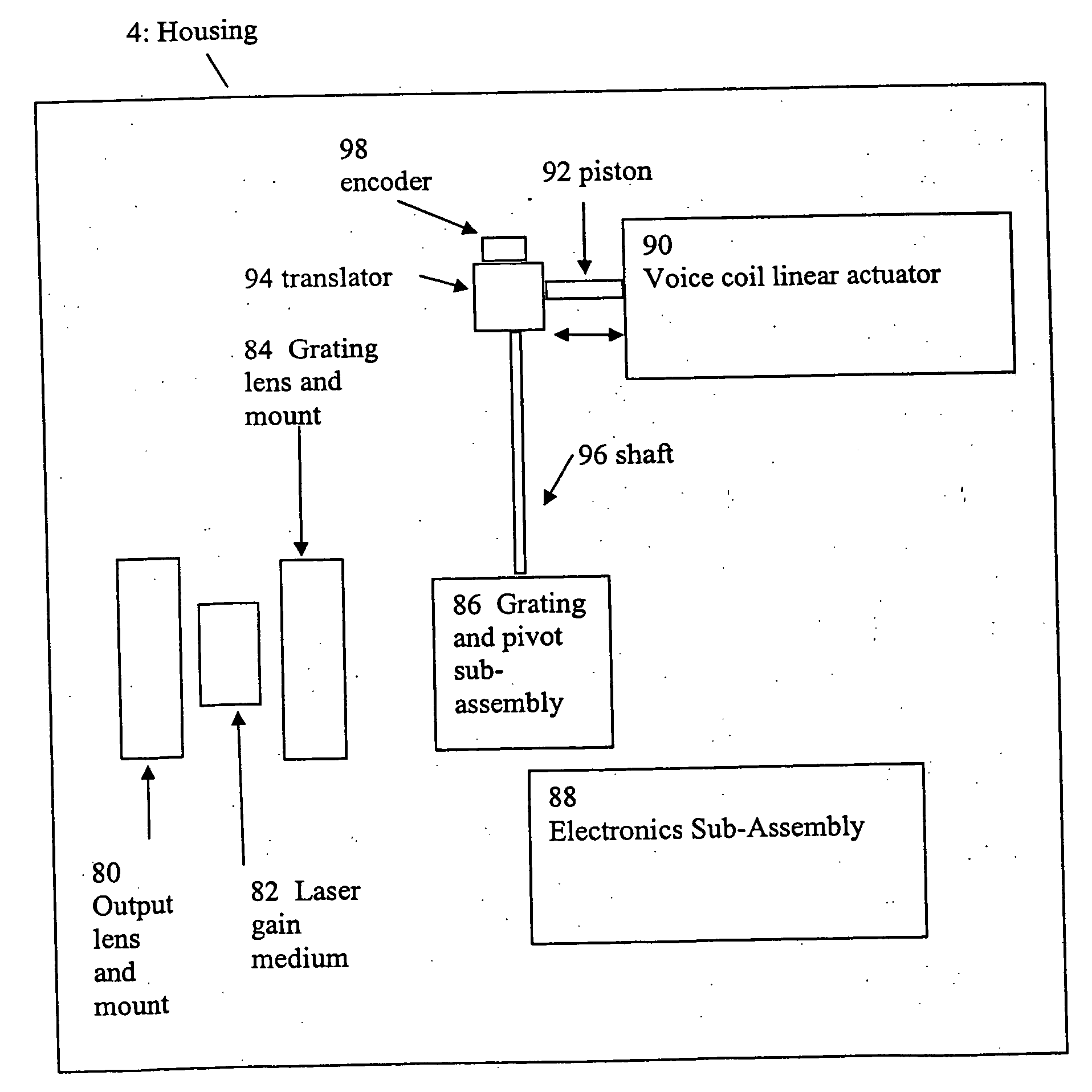
ActiveUS20070030865A1Reduce usageImprove cooling effectLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
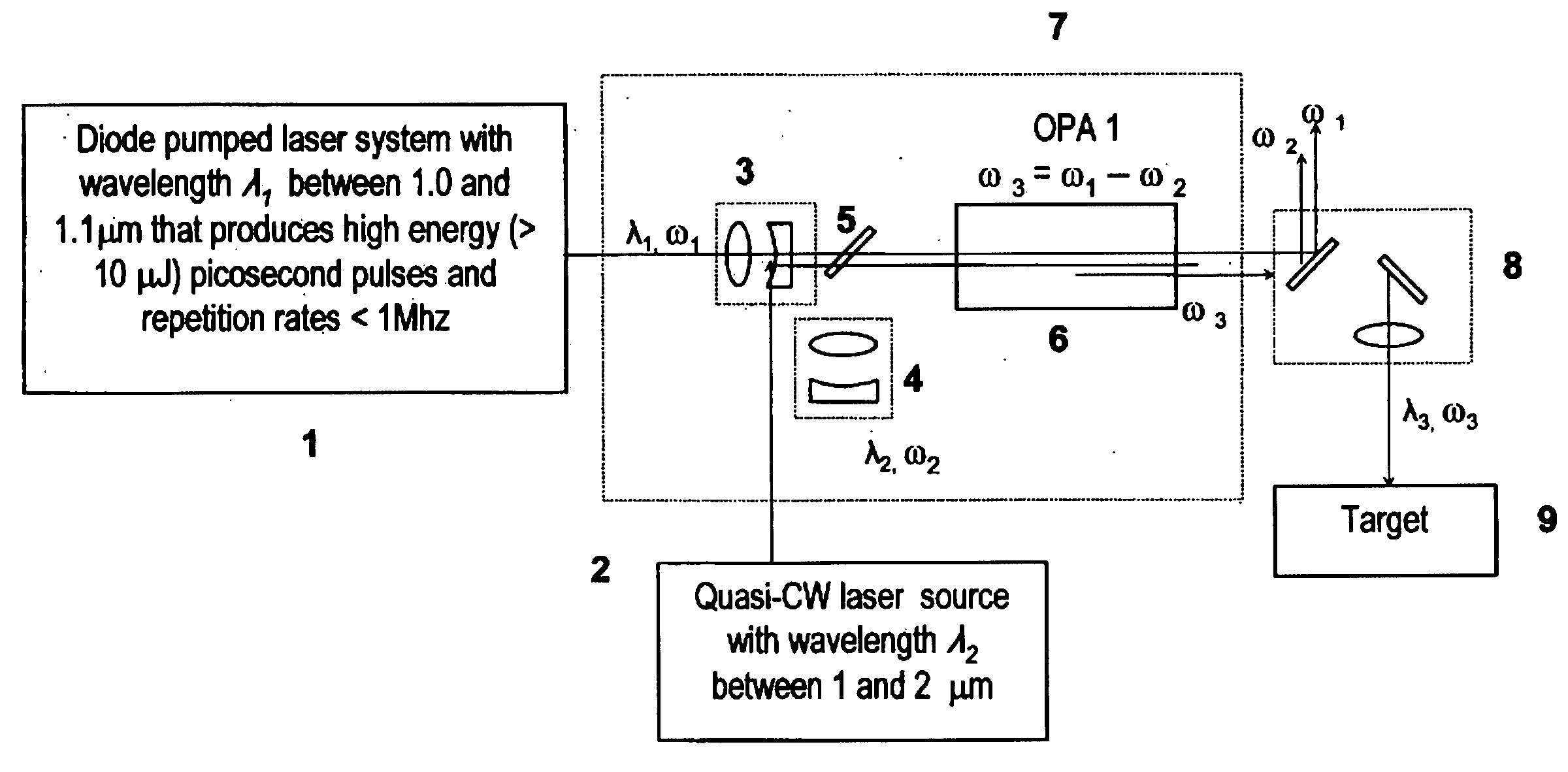
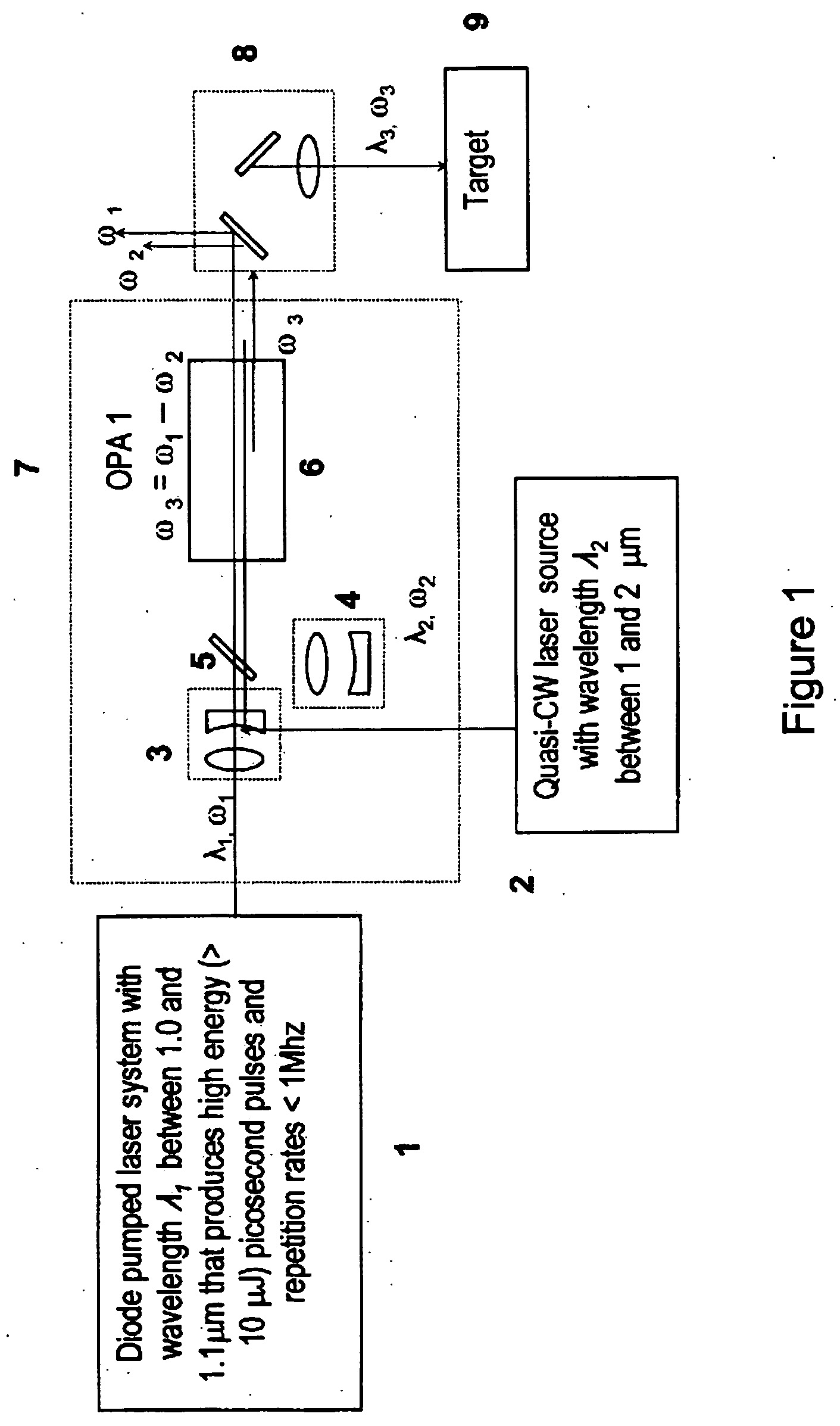
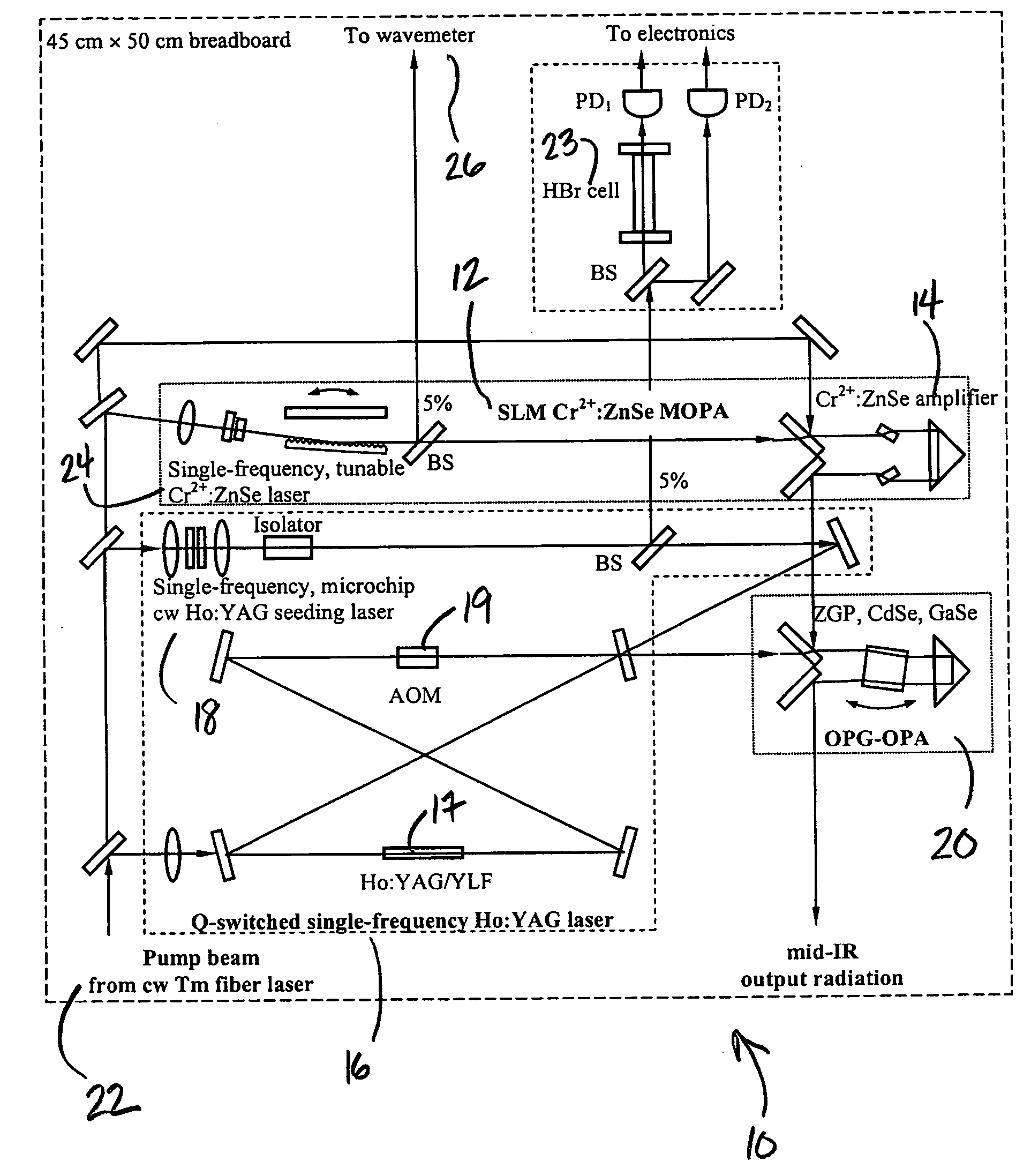
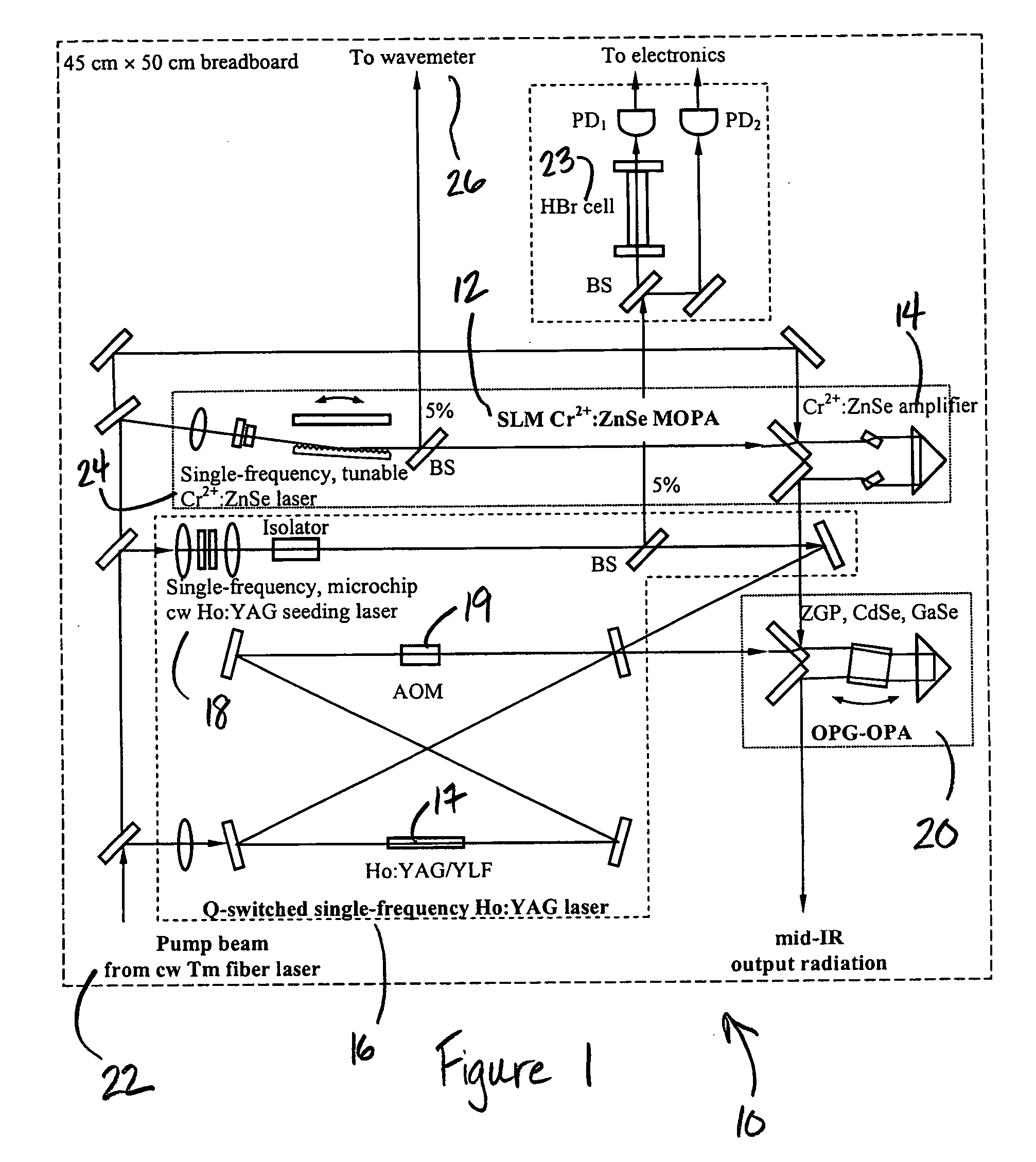
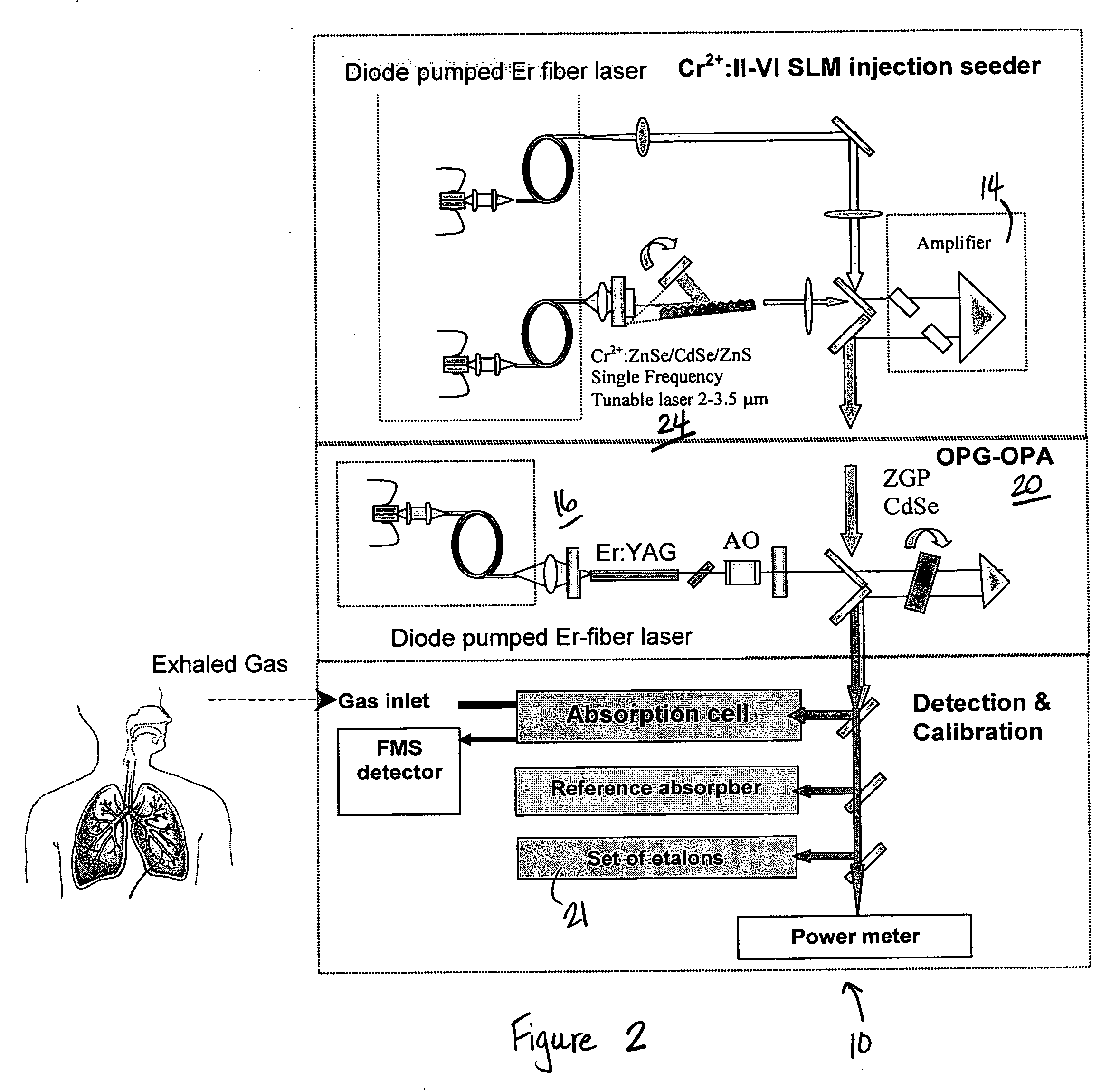
Laser system for generation of high-power sub-nanosecond pulses with controlable wavelengths in 2-15 mum region
ActiveUS20060153254A1Big spaceSubstantial temporal overlapLaser using scattering effectsSurgical instrument detailsSystems designHigh energy
A laser system capable of efficient production of high energy sub-nanosecond pulses in the 2-15 μm spectral region is disclosed. Diode pumped solid state lasers are used as pump sources. The system design is simple, reliable and compact allowing for easy integration. The laser system includes a combination of compact solid-state ˜1 micron laser sources, producing high power picosecond pulses, with optical parametric amplification and a quasi-continuous wave laser for seeding the amplification process that enables the efficient conversion of the high power ˜1 micron laser radiation to tuneable mid-infrared sub-ns pulses. New parametric processes are presented for achieving high gains in bulk nonlinear crystals. Furthermore, a method of exceeding the fundamental conversion efficiency limit of direct three wave mixing is presented. The compact and robust nature of this novel laser system opens up the use of high power and high peak power mid-infrared laser pulses to a wide variety of important medical and dental applications.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION
Method and apparatus for removing corneal tissue with infrared laser radiation and short pulse mid-infrared parametric generator for surgery
InactiveUS20050197655A1Reduce undesirable thermal damageMaximum flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser scalpelMid infrared laser
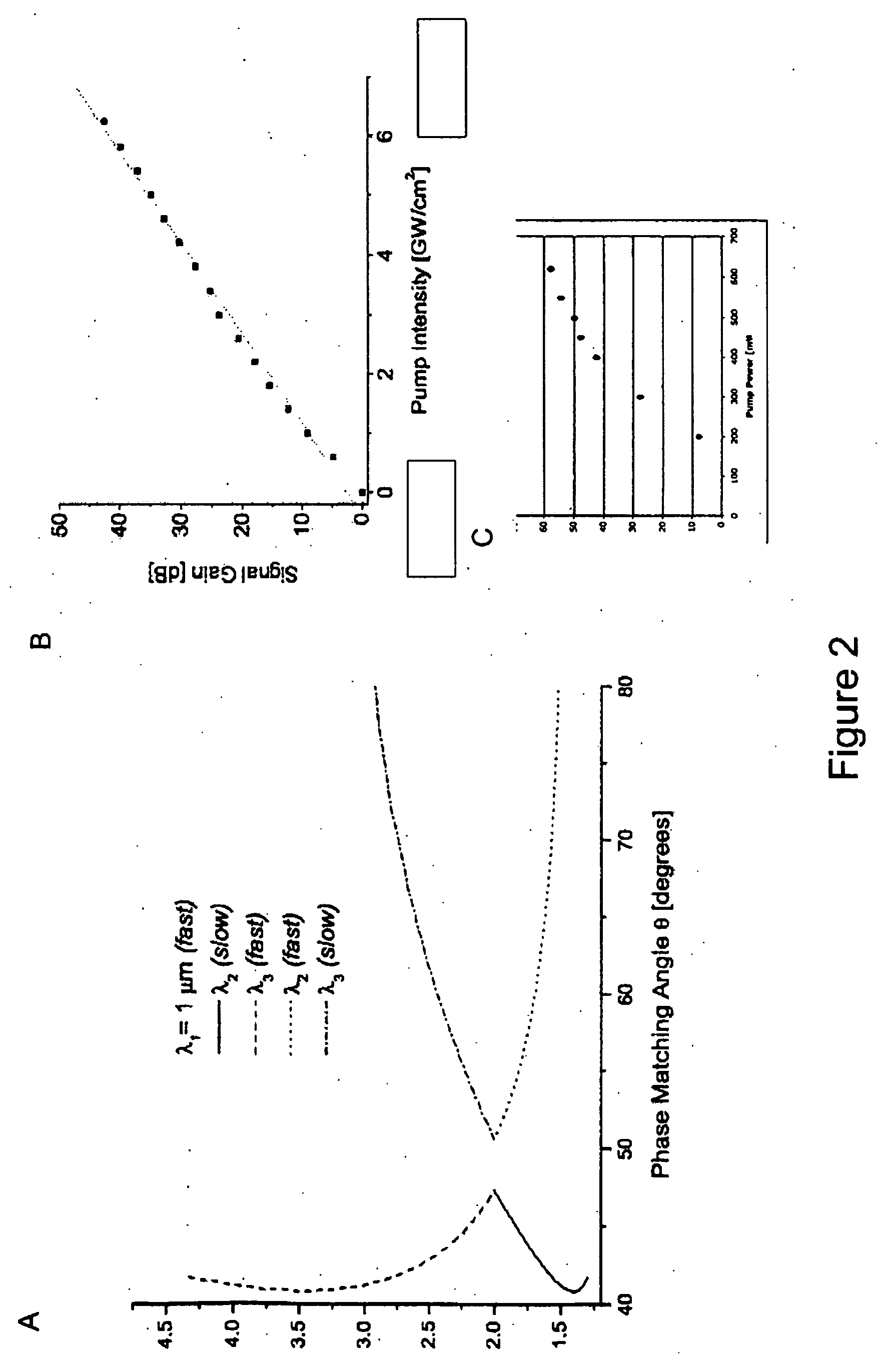
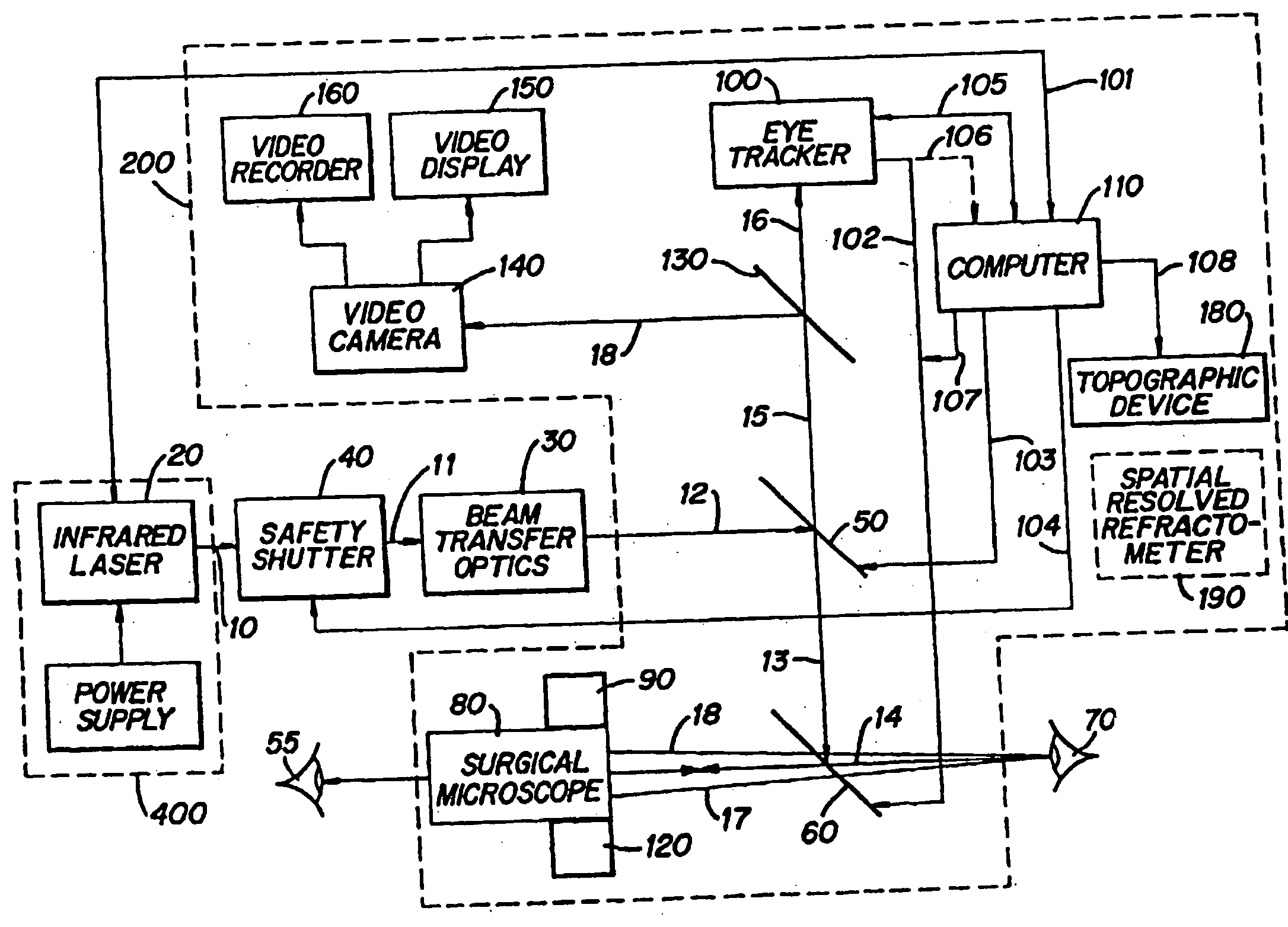
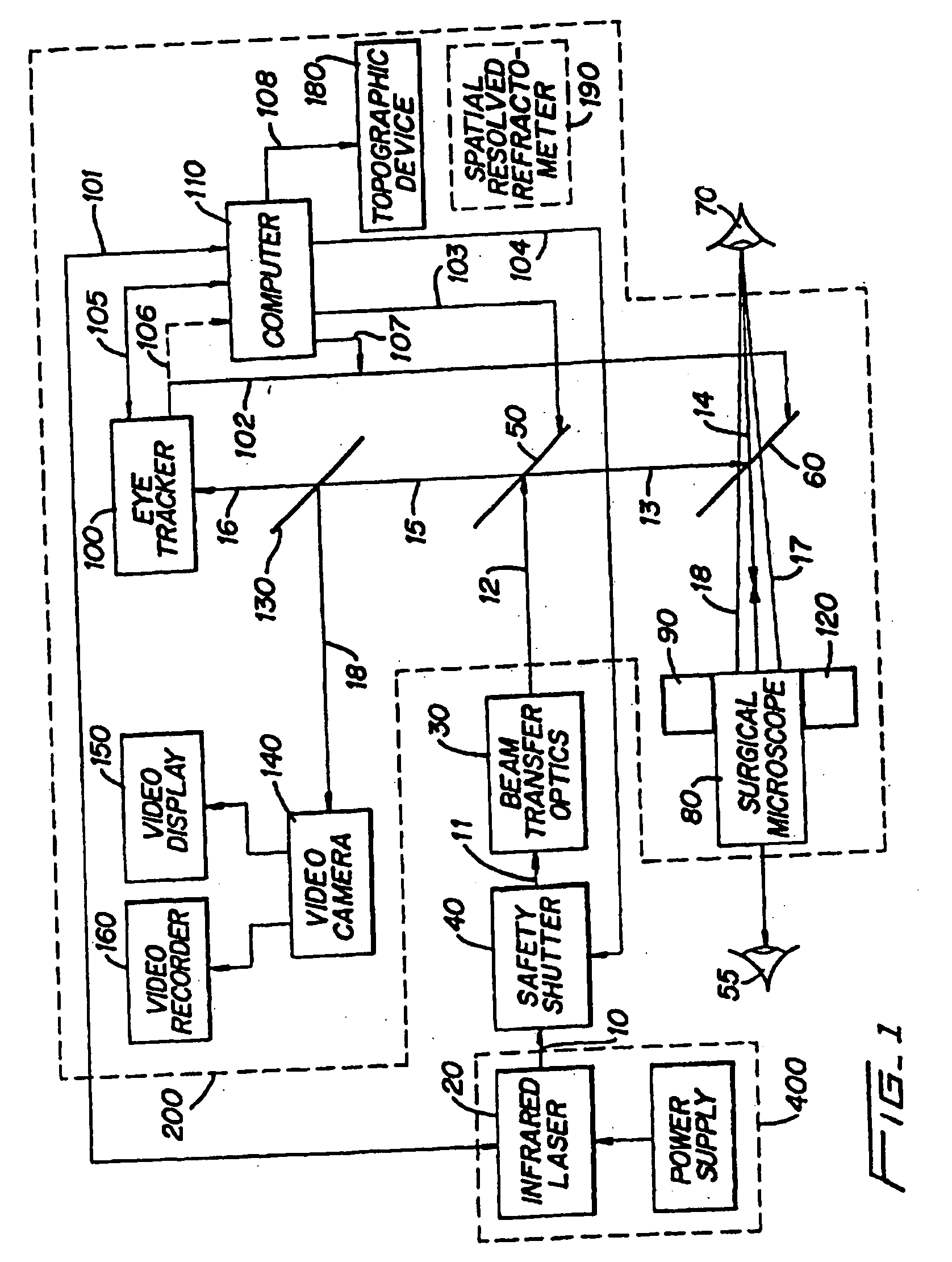
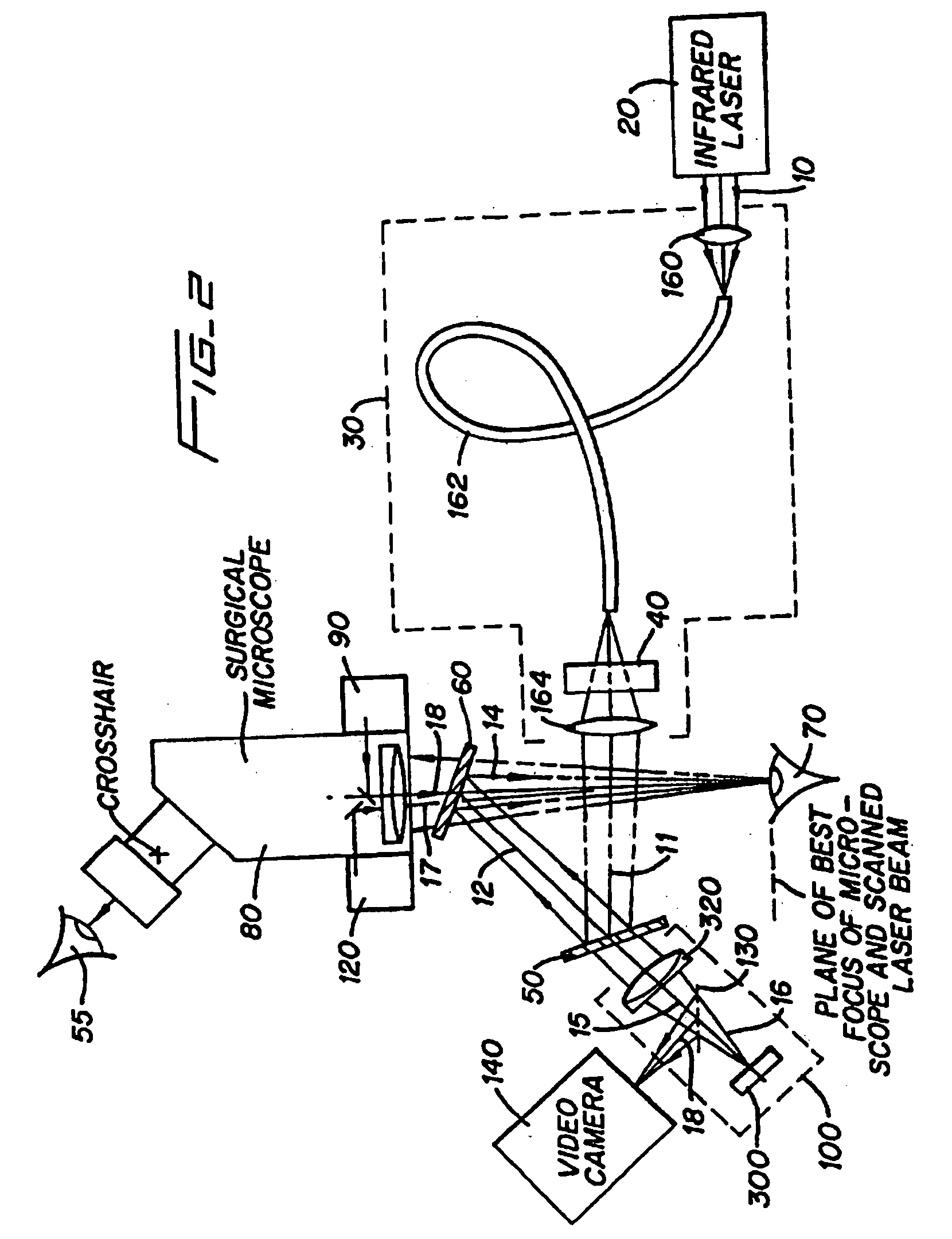
A surgical technique for removing corneal tissue with scanned infrared radiation is disclosed which utilizes short mid-infrared laser pulses to provide a tissue removal mechanism based on photospallation. Photospallation is a photomechanical ablation mechanism which results from the absorption of incident radiation by the corneal tissue. Since photospallation is a mechanical ablation process, very little heat is generated in the unablated adjacent tissue. The disclosed surgical system includes a scanning beam delivery system which allows uniform irradiation of the treatment region and utilizes low energy outputs to achieve controlled tissue removal. A real-time servo-controlled dynamic eye tracker, based on a multiple-detector arrangement, is also disclosed which senses the motion of the eye and provides signals that are proportional to the errors in the lateral alignment of the eye relative to the axis of the laser beam. Temporal and frequency discrimination are preferably utilized to distinguish the tracking illumination from the ambient illumination and the surgical laser beam. A laser parametric generator for surgical applications is disclosed which utilizes short-pulse, mid-infrared radiation. The mid-infrared radiation may be produced by a pump laser source, such as a neodymium-doped laser, which is parametrically down converted in a suitable nonlinear crystal to the desired mid-infrared range. The short pulses reduce unwanted thermal effects and changes in adjacent tissue to potentially submicron-levels. The parametrically converted radiation source preferably produces pulse durations shorter than 25 ns at or near 3.0 microns but preferably close to the water absorption maximum associated with the tissue. The down-conversion to the desired mid-infrared wavelength is preferably produced by a nonlinear crystal such as KTP or its isomorphs. In one embodiment, a non-critically phased-matched crystal is utilized to shift the wavelength from a near-infrared laser source emitting at or around 880 to 900 nm to the desired 2.9-3.0 microns wavelength range. A fiber, fiber bundle or another waveguide means utilized to separate the pump laser from the optical parametric oscillation (OPO) cavity is also included as part of the invention.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Endovenous closure of varicose veins with mid infrared laser
InactiveUS7524316B2More controllableMore predictableDiagnosticsCatheterProper treatmentMid infrared laser
This invention is an improved method and device for treating varicose veins 200 or the greater saphenous vein 202. The method comprises the use of infrared laser radiation in the region of 1.2 to 2.2 um in a manner from inside the vessel 200 or 202 such that the endothelial cells of the vessel wall 704 are damaged and collagen fibers in the vessel wall 704 are heated to the point where they permanently contract, the vessel 200 or 202 is occluded and ultimately resorbed. The device includes a laser 102 delivered via a fiber optic catheter 300 that may have frosted or diffusing fiber tips 308, or that may be provided with a protective spacer. A motorized pull back device 104 may be used, and a thermal sensor 600 may be used to help control the power required to maintain the proper treatment temperature.
Owner:COOLTOUCH
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070291804A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser optical deviceThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
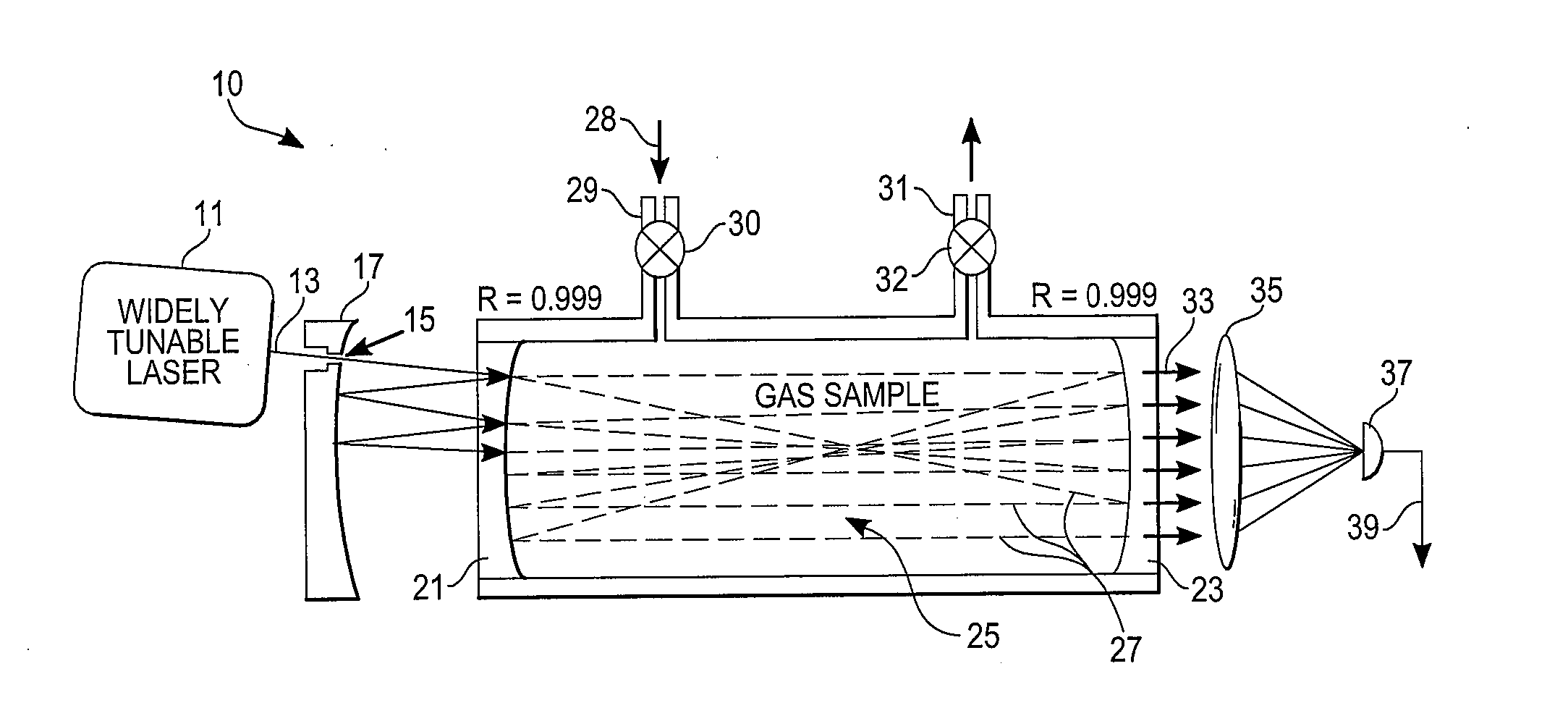
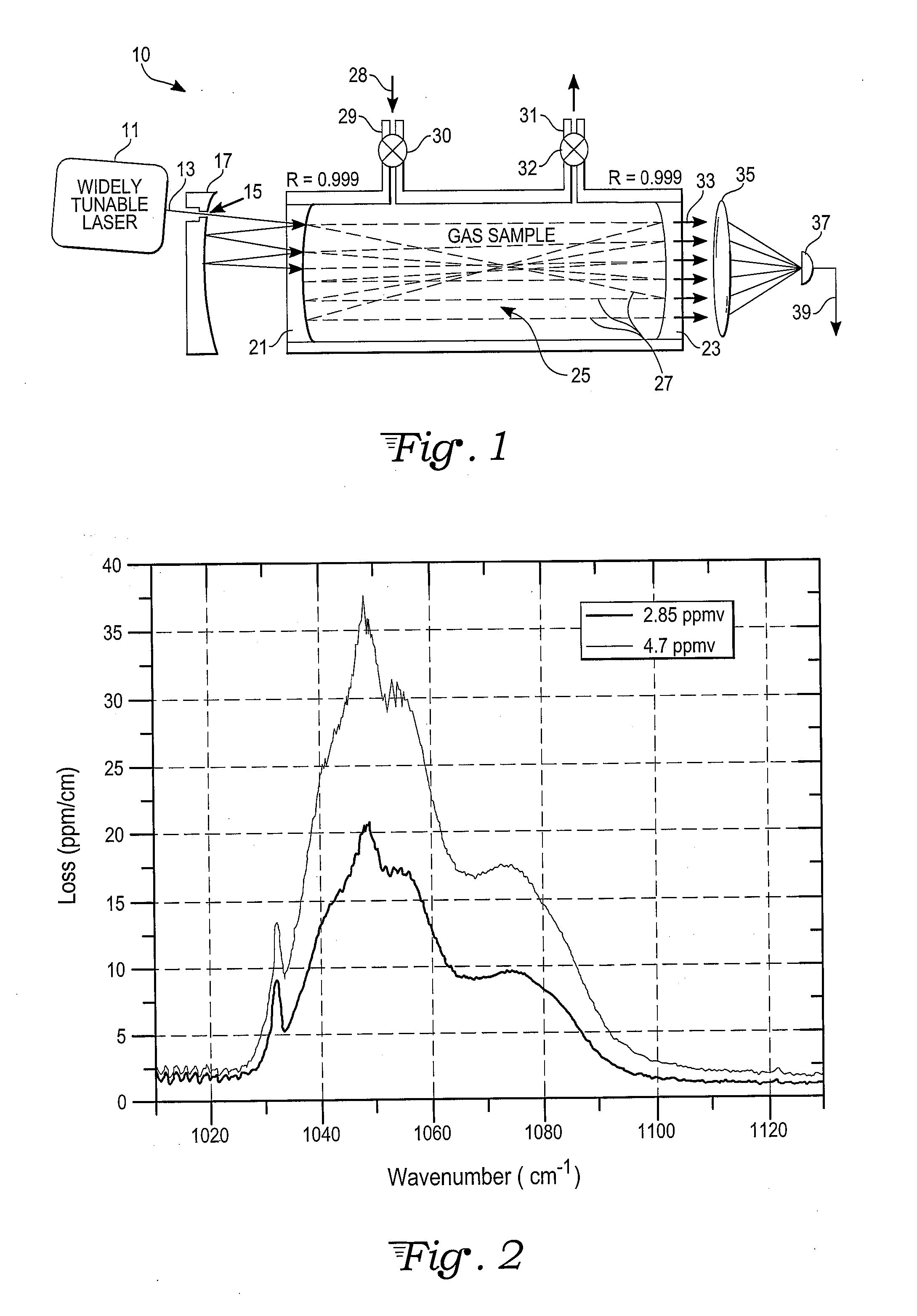
Mid-IR laser instrument for analyzing a gaseous sample and method for using the same
InactiveUS20070064748A1Wide tunabilityRapidly tuned SLM idlerPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingNoseMicrometer
An optical nose for detecting the presence of molecular contaminants in gaseous samples utilizes a tunable seed laser output in conjunction with a pulsed reference laser output to generate a mid-range IR laser output in the 2 to 20 micrometer range for use as a discriminating light source in a photo-acoustic gas analyzer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
External cavity tunable compact Mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7535936B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
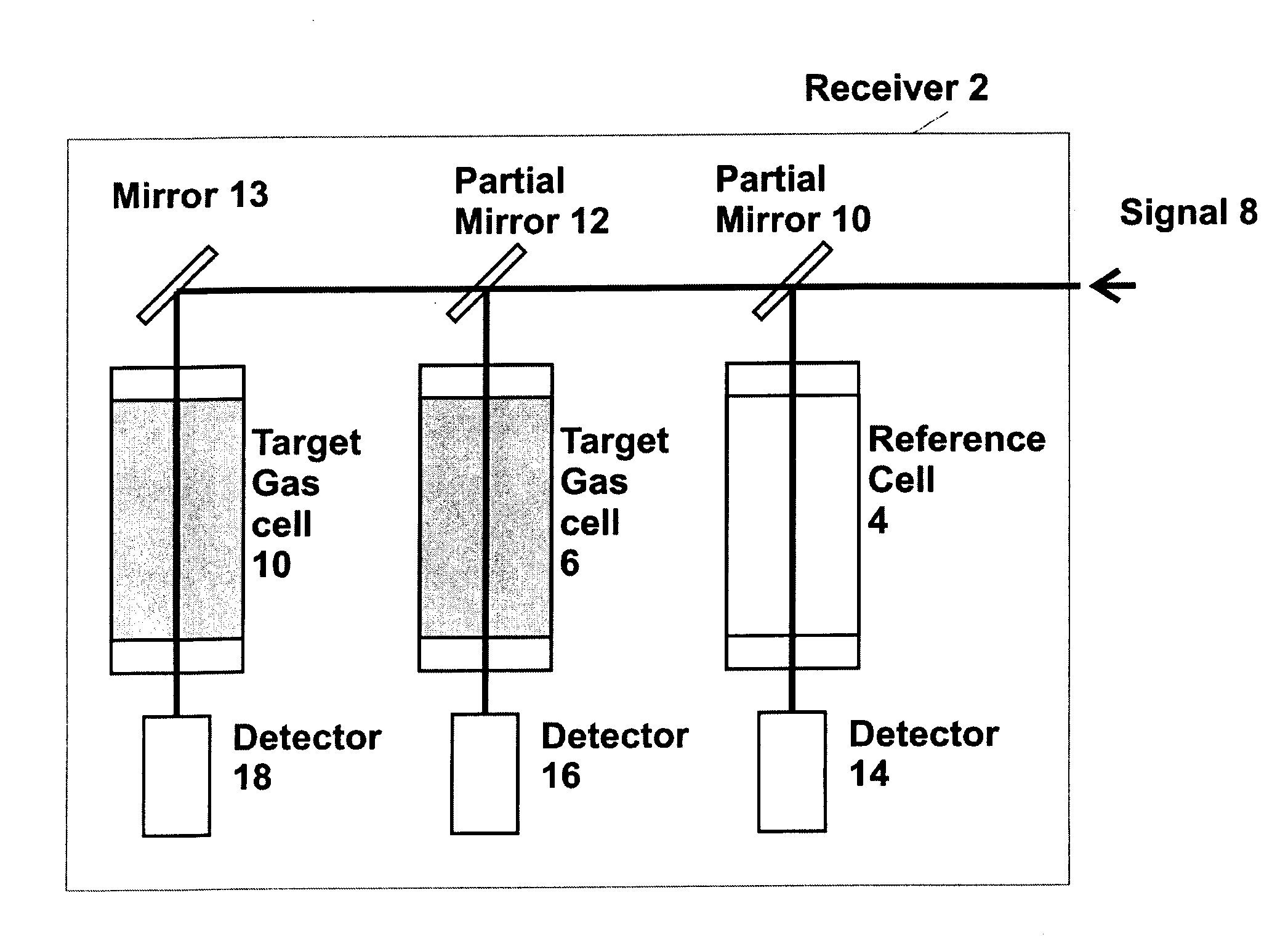
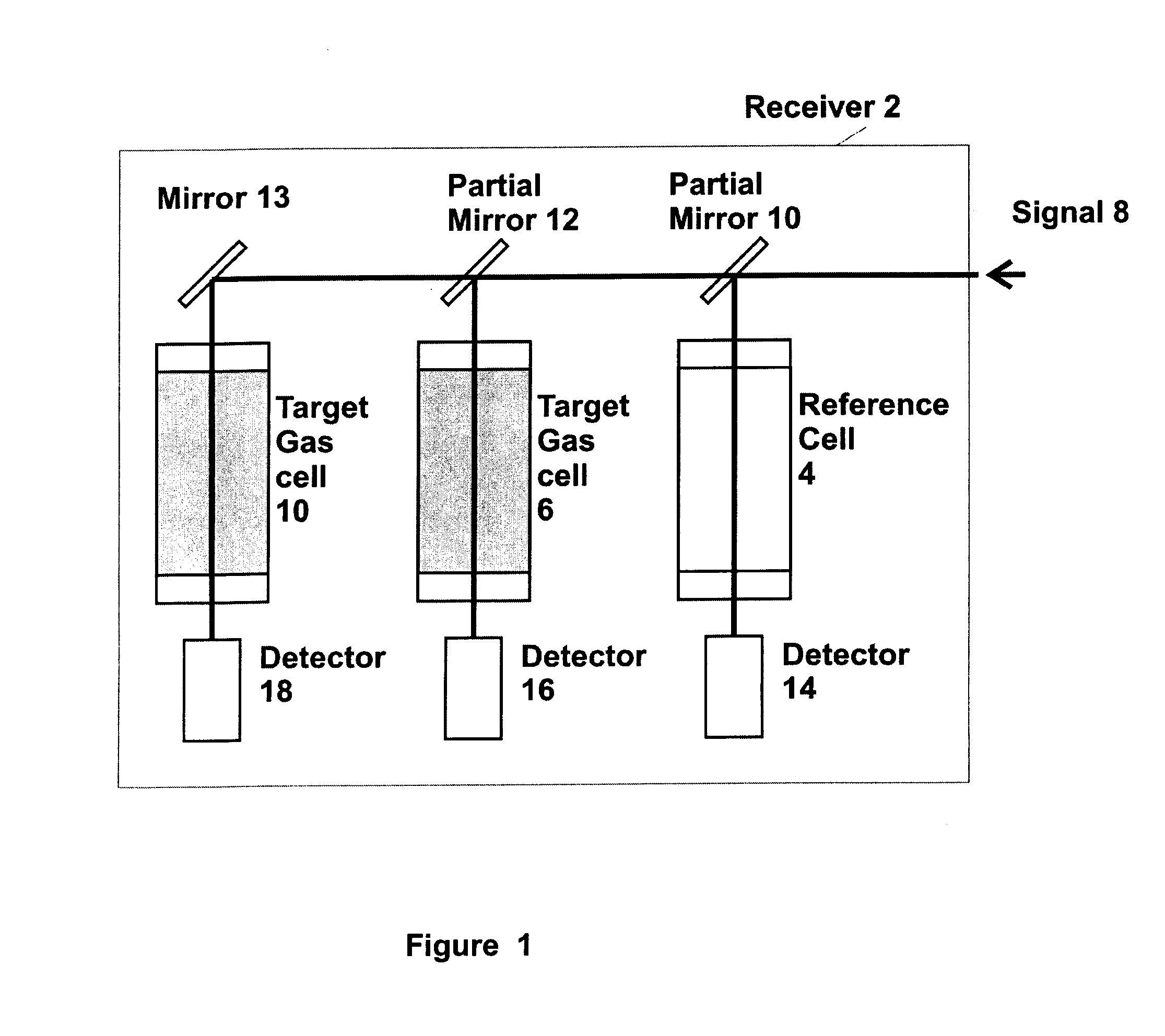
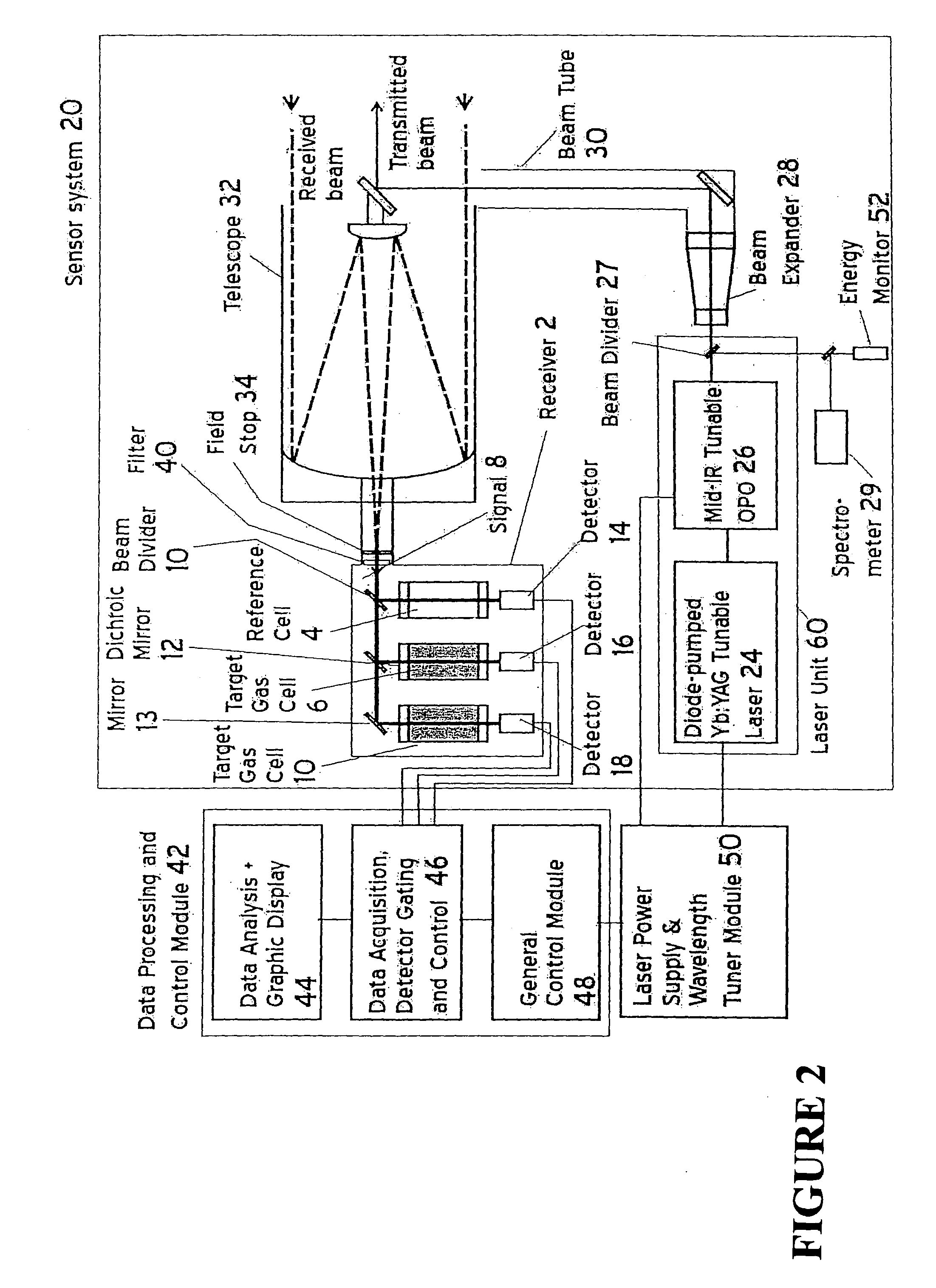
Airborne tunable mid-ir laser gas-correlation sensor
InactiveUS20080259340A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMid infrared laserGas concentration
A method and apparatus for measuring target gas concentrations in an atmosphere. The method and apparatus emit in the atmosphere a laser beam tuned to a molecular absorption line of a target gas, receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, divide and direct the received signal into a first optical path and a second optical path including in one of the paths a correlation gas cell filled with a predetermined concentration of the target gas, detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path, and calculate a target gas concentration by comparing a first signal transmitted through the first optical path to a second signal transmitted through the second optical path. The apparatus includes a laser source tunable to a specific molecular absorption line of a target gas and configured to emit in the atmosphere a laser beam having a spectral bandwidth greater than a full width of the molecular absorption line of the target gas, a receiver configured to receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, and at least one detector configured to detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
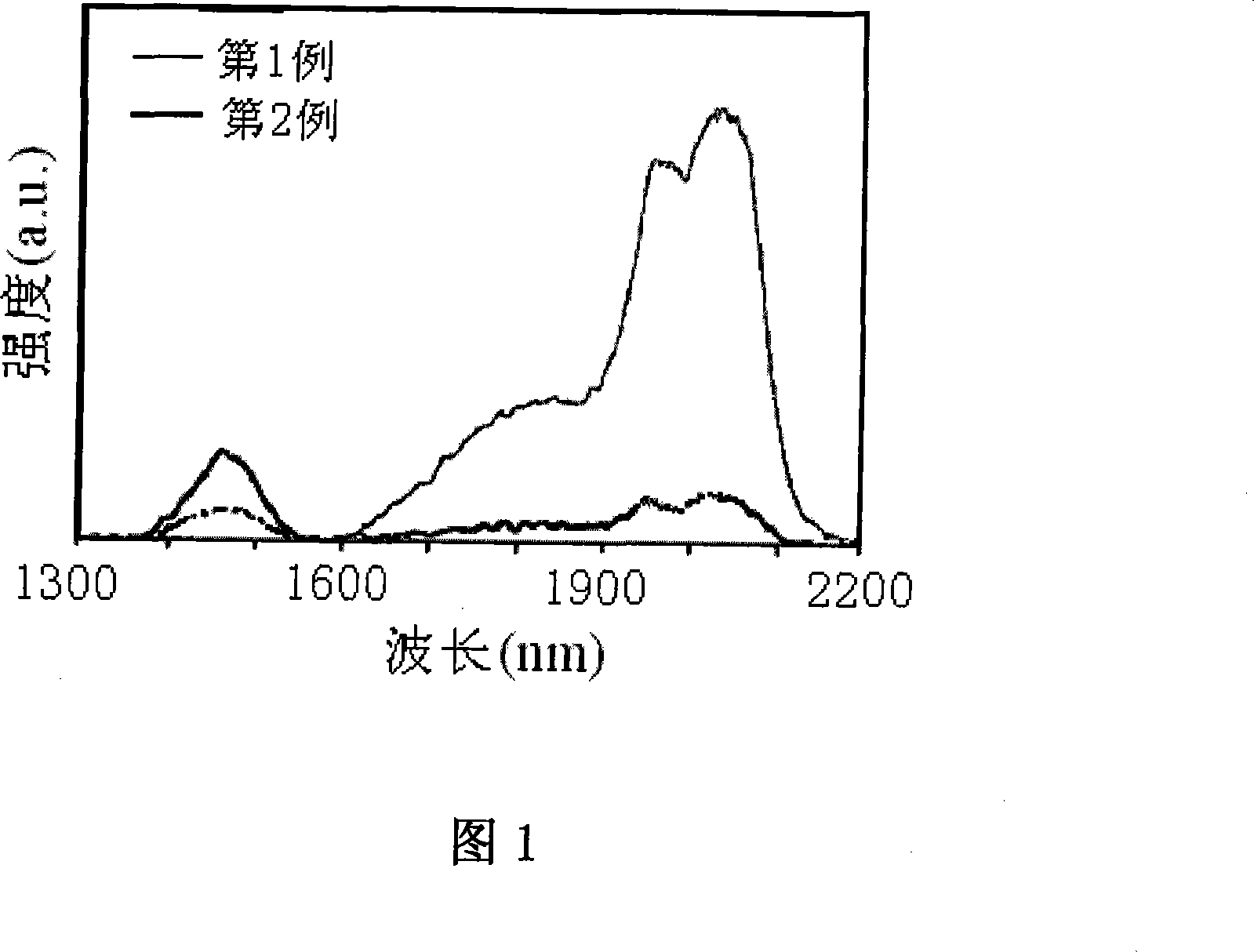
2ª–m band light-emitting oxyhalide tellurite glasses
The invention relates to a piece of luminous oxyhalide tellurate glass with 2 Mum wave band, the glass compositions and mole percentages are as follows: TeO2: 40-85, PbO: 0-15; PbF2 plus ZnF2: 5-30; ZnO: 0-15; GeO2: 0-10; Nb2O5: 0-10; WO3: 0-10; Li2O plus Na2O plus K2O: 3-10; Tm2O3 plus Ho2O3 plus Er2O3 plus Yb2O3: 2-7, wherein, at least one of the Tm2O3 and the Ho2O3 is not equal to zero. The glass is prepared through a common melting method. The oxyhalide tellurate glass of the invention has the advantages of high infrared transmittance, transparence, no crystallization, no bubbles and stripes, excellent pinhole test, high luminous efficiency at the 2 Mum wave band, etc. The preparation technique is simple, can be operated easily and has lower cost. The materials of the invention are applicable to infrared laser optical lenses at the 2 Mum wave band or infrared special fiber matrix materials at the 2 Mum wave band.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High sensitivity gas pollution detection laser radar system
PendingCN106970392AReduce difficultyHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsLine width
The invention discloses a high sensitivity gas pollution detection laser radar system comprising an intermediate infrared tunable narrow linewidth high energy laser device, a wavelength and power monitoring module, an optical transmit-receive module, an aiming module and a data processing module that are integrated; the intermediate infrared tunable narrow linewidth high energy laser device is used for emitting intermediate infrared laser, one part of the intermediate infrared laser is subjected to wavelength monitoring and power monitoring via the wavelength and power monitoring module, the other part is emitted out to a detection object via the optical transmit-receive module, the detection object is aimed at via the aiming module, echo signals in the detection object are reflected back via the intermediate infrared laser are received via the optical transmit-receive module, then the echo signals are transmitted to the data processing module and are subjected to processing and analyzing operation, and a polluted gas concentration value is obtained. The high sensitivity gas pollution detection laser radar system can be used for conducting real time monitoring and data analyzing operation on main atmosphere pollutant concentration indexes.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ADVANCED LASER TECH
Fixed wavelength mid infrared laser source with an external cavity
InactiveUS20090028197A1Large amount of adjustmentImprove production yieldLaser detailsNanoopticsLight beamLasing wavelength
A MIR laser source that produces a fixed frequency output beam that is within the MIR range includes a QC gain media, and a wavelength dependent (“WD') feedback assembly that is spaced apart from the QC gain media and that cooperates with the QC gain media to form an external cavity. The WD feedback assembly may be used to precisely tune and control a lasing wavelength of the external cavity, and the position of the WD feedback assembly relative to the QC gain media may be fixed to maintain the precise lasing wavelength of the external cavity. With this design, each MIR laser source can be individually tuned to achieve the desired fixed frequency output beam that is within the MIR range.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Optical fiber type mid-IR laser source generated by 3-5micrometre continuous wave differential frequency and its implementing method
InactiveCN101504507ASatisfy the broadband phase matching conditionRealize infrared outputNon-linear opticsFiber couplerS-wave
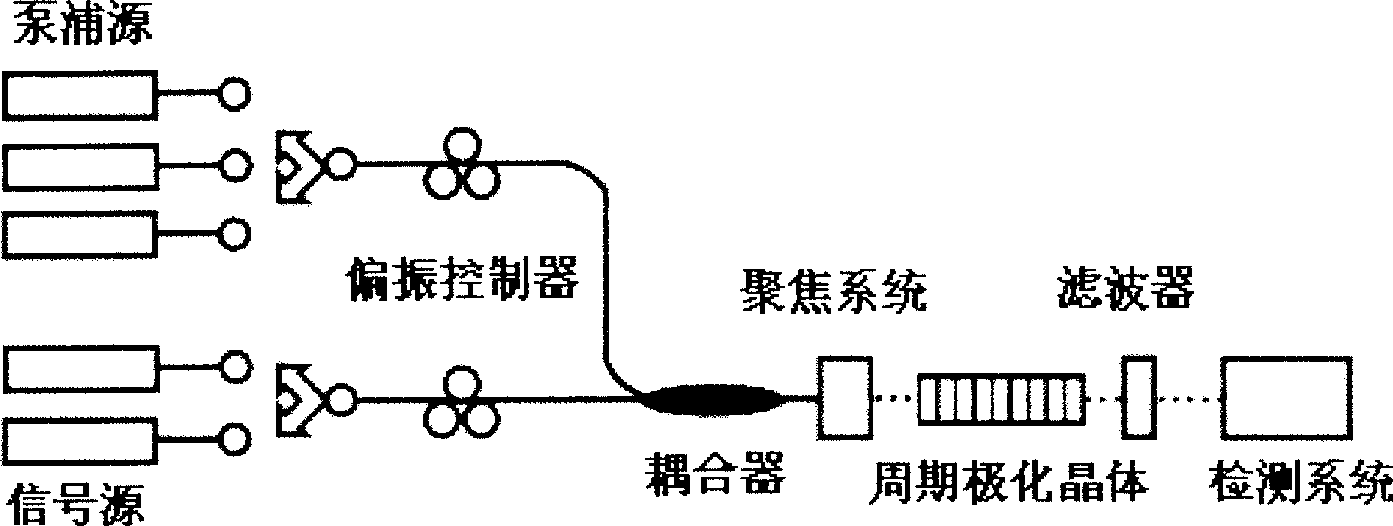
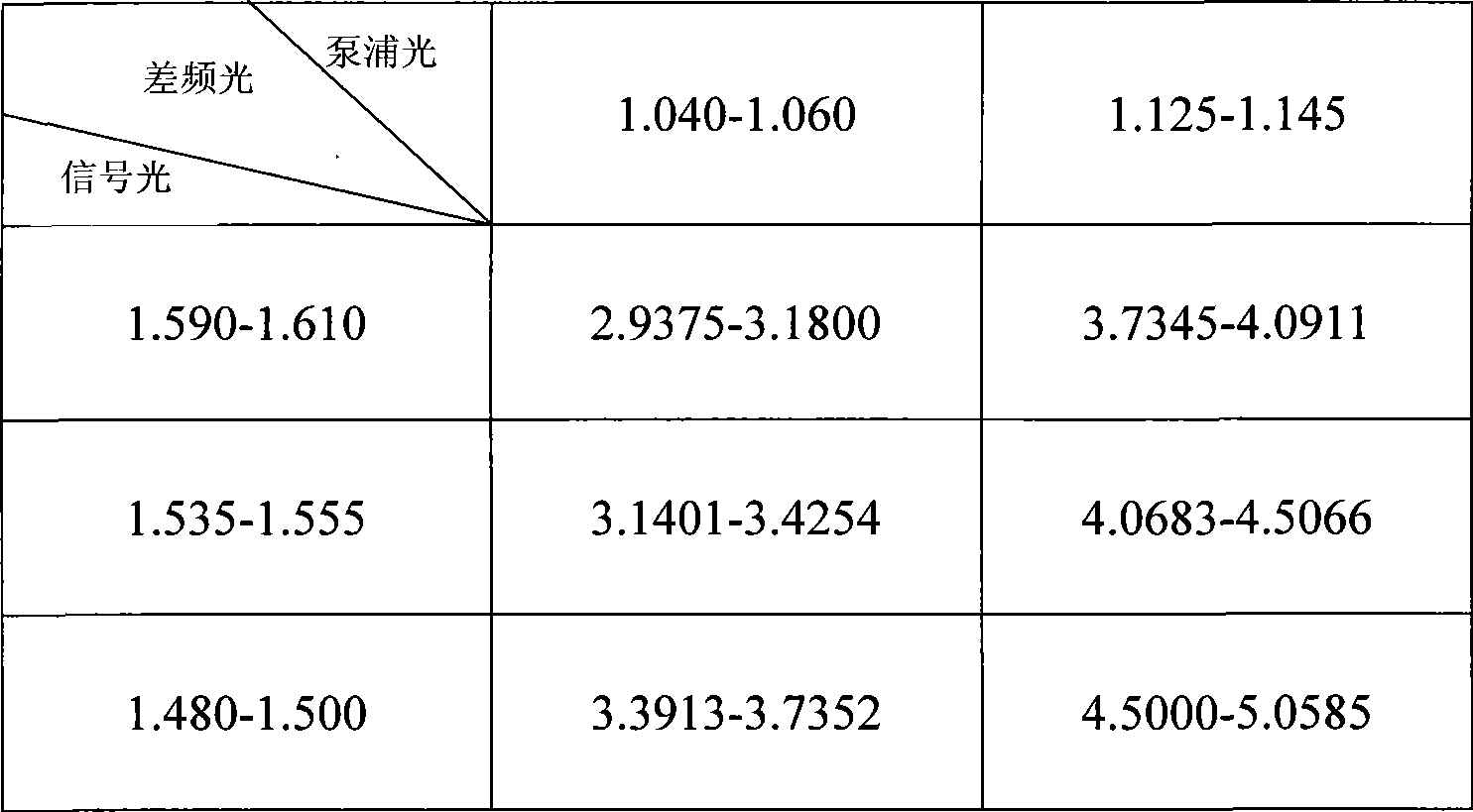
The invention discloses an iraser light source in the generation of an optical fiber type 3-5-micron continuous wave difference frequency and a method for achieving the same, wherein a pump light and a signal light adopt a wavelength sectional combining plan, a rare-earth-doped fiber laser with suitable wavelength is selected, a pump source adopts a ytterbium-doped fiber laser with a wave band of 1,060 nm and wave bands of over 1,100 nm, and the wave bands can be exchanged with each other. The signal light adopts an erbium-doped fiber laser with an S wave band, a C wave band and an L wave band, and the wave bands can be exchanged with each other. The ytterbium-doped fiber laser and the erbium-doped fiber laser emit the pump light and the signal light respectively, the pump light and the signal light are adjusted to be parallel with an optical axis of a crystal by a polarization controller respectively and are combined together by a fiber coupler, then a lens focusing system focuses the two light beams into a periodical polarization lithium niobate crystal; and by adjusting the length of the polarization cycle and the crystal temperature of the periodical polarization lithium niobate crystal, the pump light, the signal light and the difference frequency light meet a phase matching condition to finally achieve the infrared output in the generation of the difference frequency.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mid-infrared laser measurement system and method for engine combustion process monitoring
ActiveCN107576505AAvoid interferenceAvoid intensityChemical analysis using combustionEngine testingBeam splitterData acquisition
The invention discloses a mid-infrared laser measurement system and method for engine combustion process monitoring. The measurement system comprises a laser device and detectors, the laser device cantransmit mid-infrared laser within a specific wavelength range, and the mid-infrared laser is absorbed by engine combustion flames. Particularly, the laser transmitted by the laser device is dividedinto two beams by a beam splitter, one beam of laser passes a laser calibration device and is measured by the first detector and used for calibrating wavelengths generated by the laser device, the other beam of laser is absorbed by carbon dioxide gas generated by combustion, measured by the second detector and acquired by a data acquisition system, and concentration information of carbon dioxide can be acquired by processing, so that the combustion efficiency of an engine is acquired. According to the system, background absorption interference of the carbon dioxide in an environment is omittedwithin the selected laser wavelength range, the carbon dioxide is obviously absorbed in the high-temperature environment, interference of other combustion products such as water molecules and intermediates is omitted, and high measurement accuracy of the combustion efficiency of the engine can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
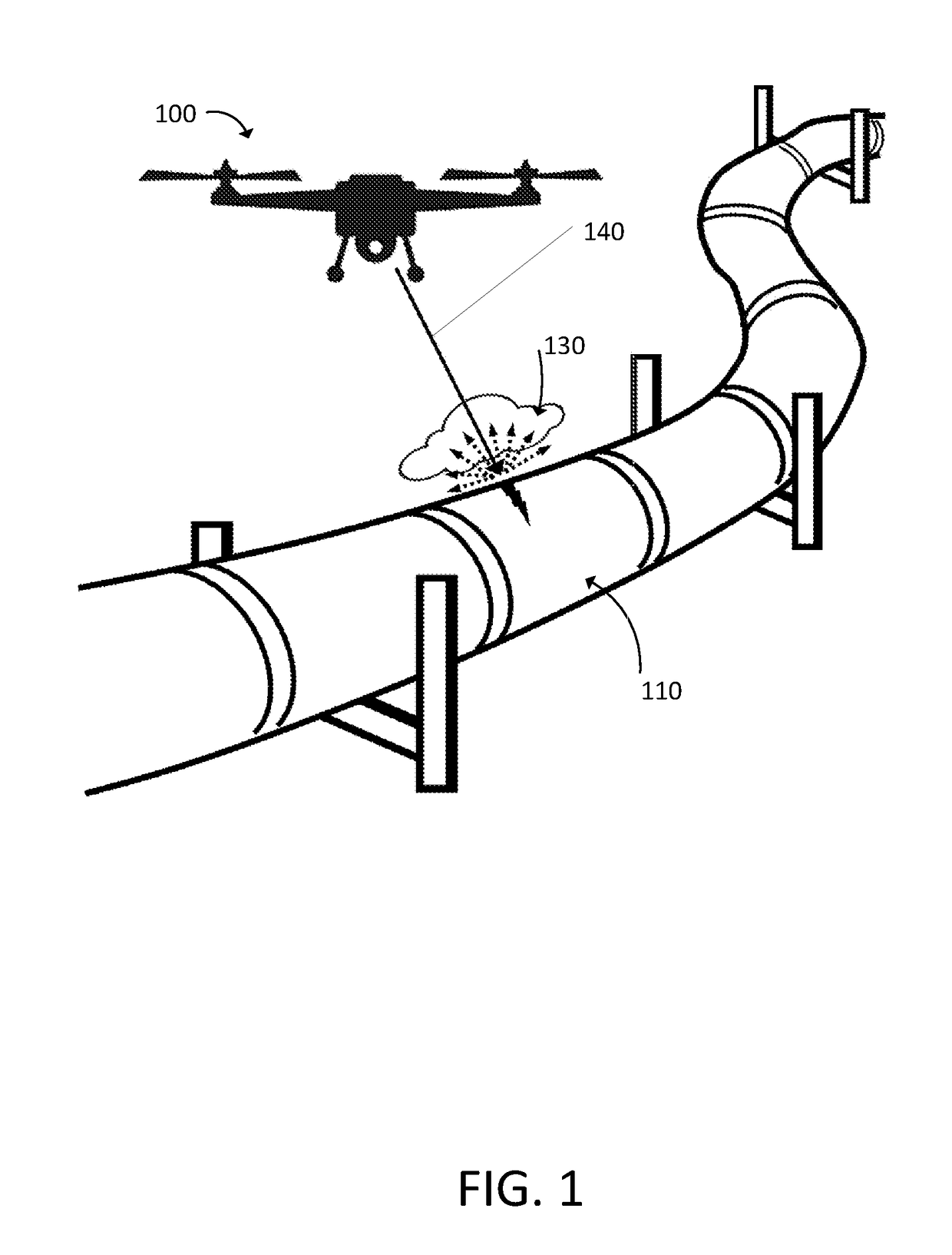
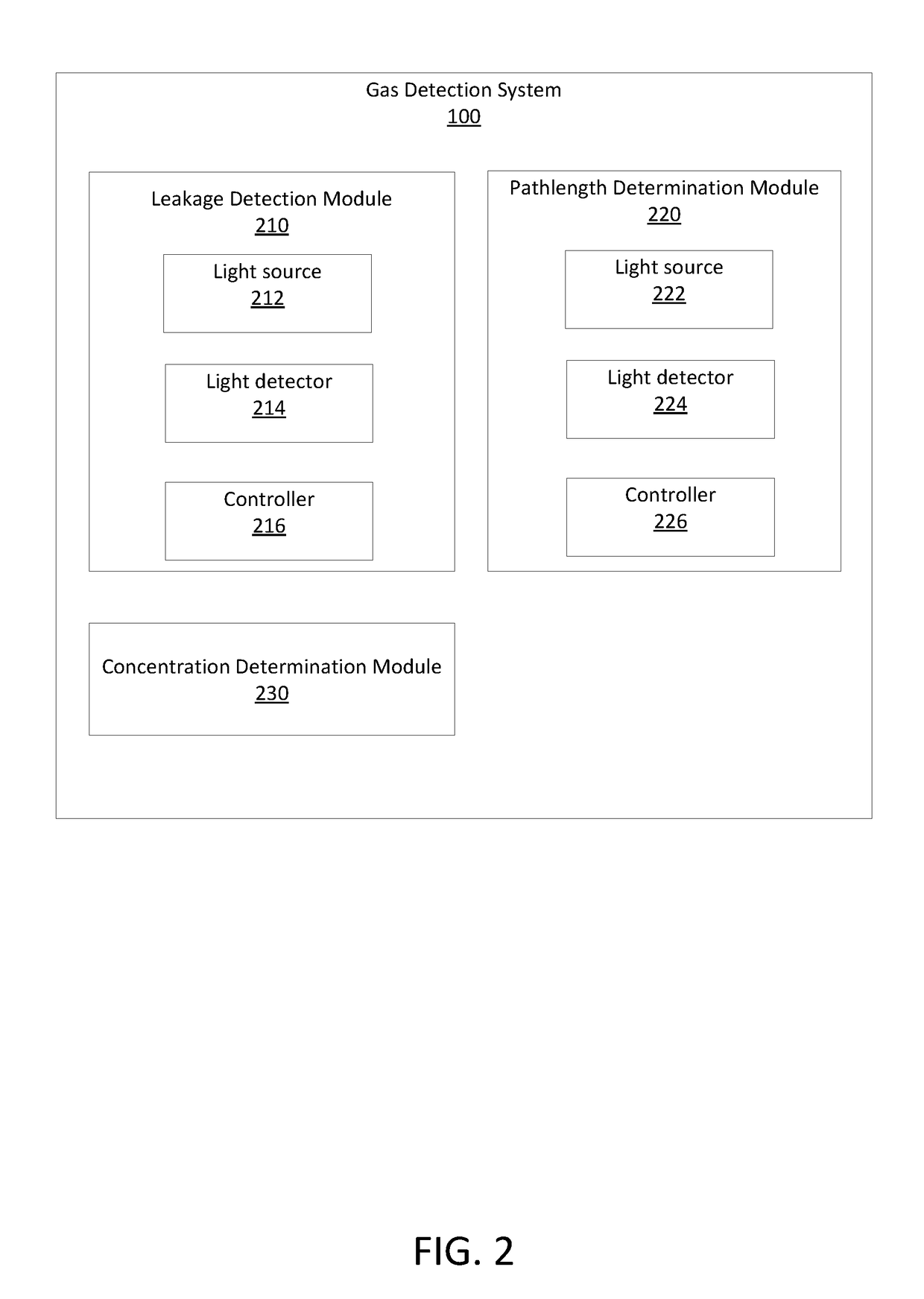
Remote gas leakage detection systems using mid-infrared laser
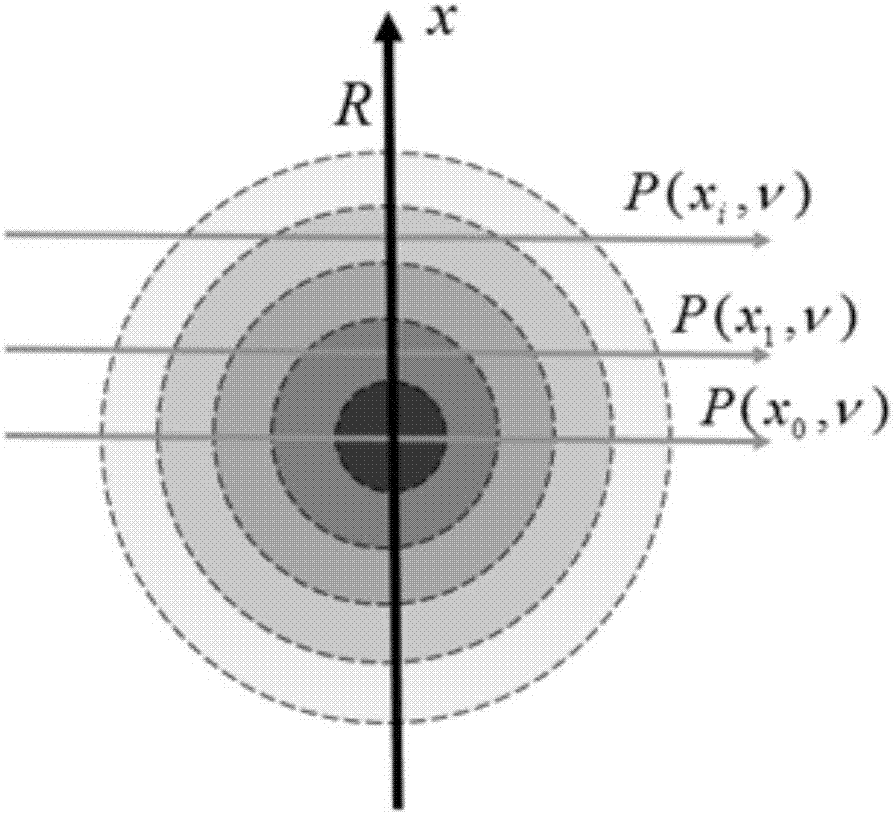
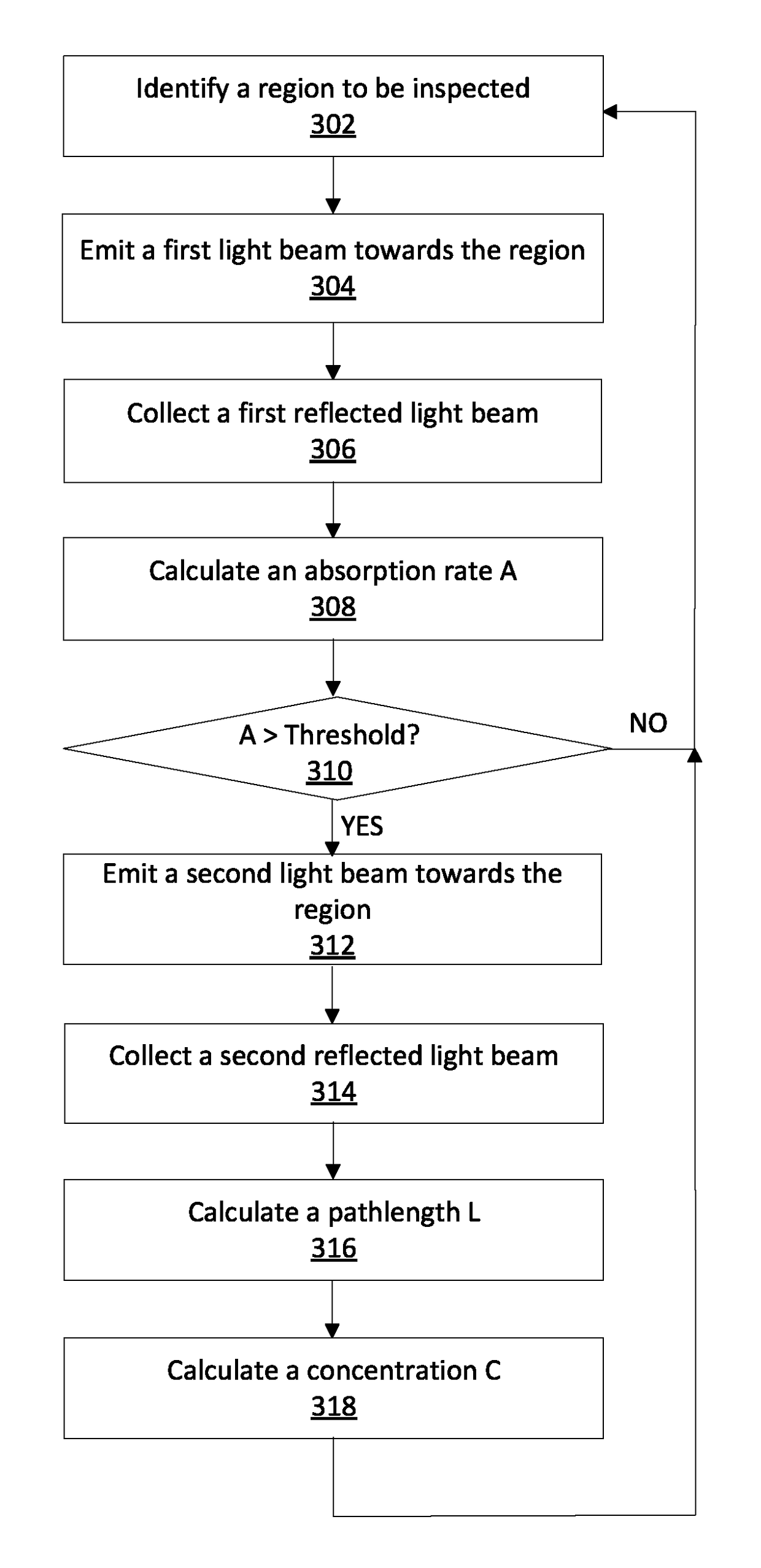
A system remotely detects a gas leakage from a target in an area. The gas detection system includes two light sources: a mid-infrared (mid-IR) laser for detecting absorbance of the gas in the area, and a visible laser for detecting a pathlength of the mid-IR laser. The absorption is determined based on the relative amplitude difference of the emitted and reflected mid-IR light beams. The mid-IR laser may use wavelength modulation techniques to improve the absorption determination. The pathlength is determined by comparing a phase between the emitted visible light beam and the measured visible light beam. The gas detection system calculates a concentration of the gas in the area using the determined absorption and pathlength. The gas detection system may be attached to an unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:AURORA INNOVATIVE TECH LLC
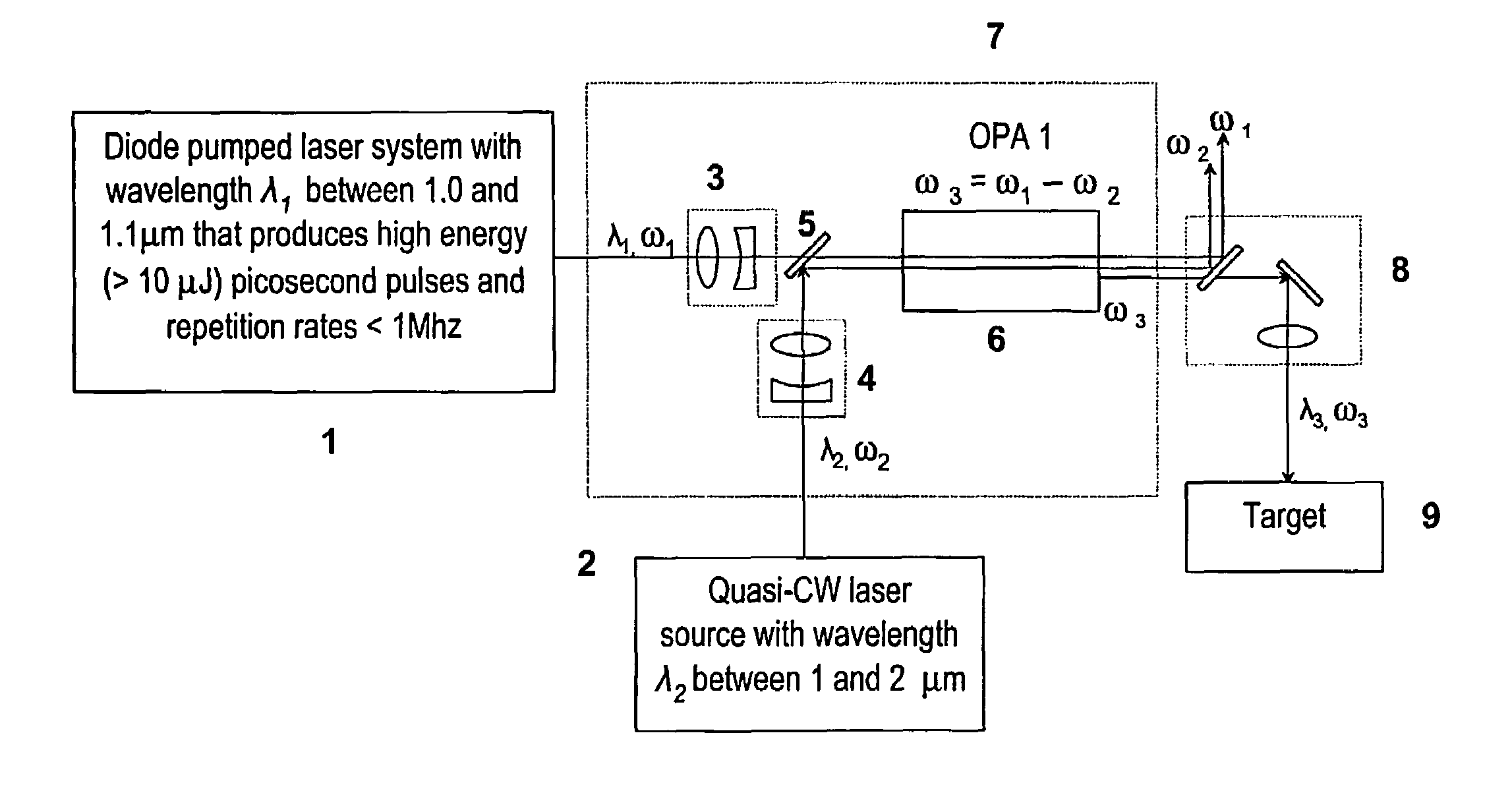
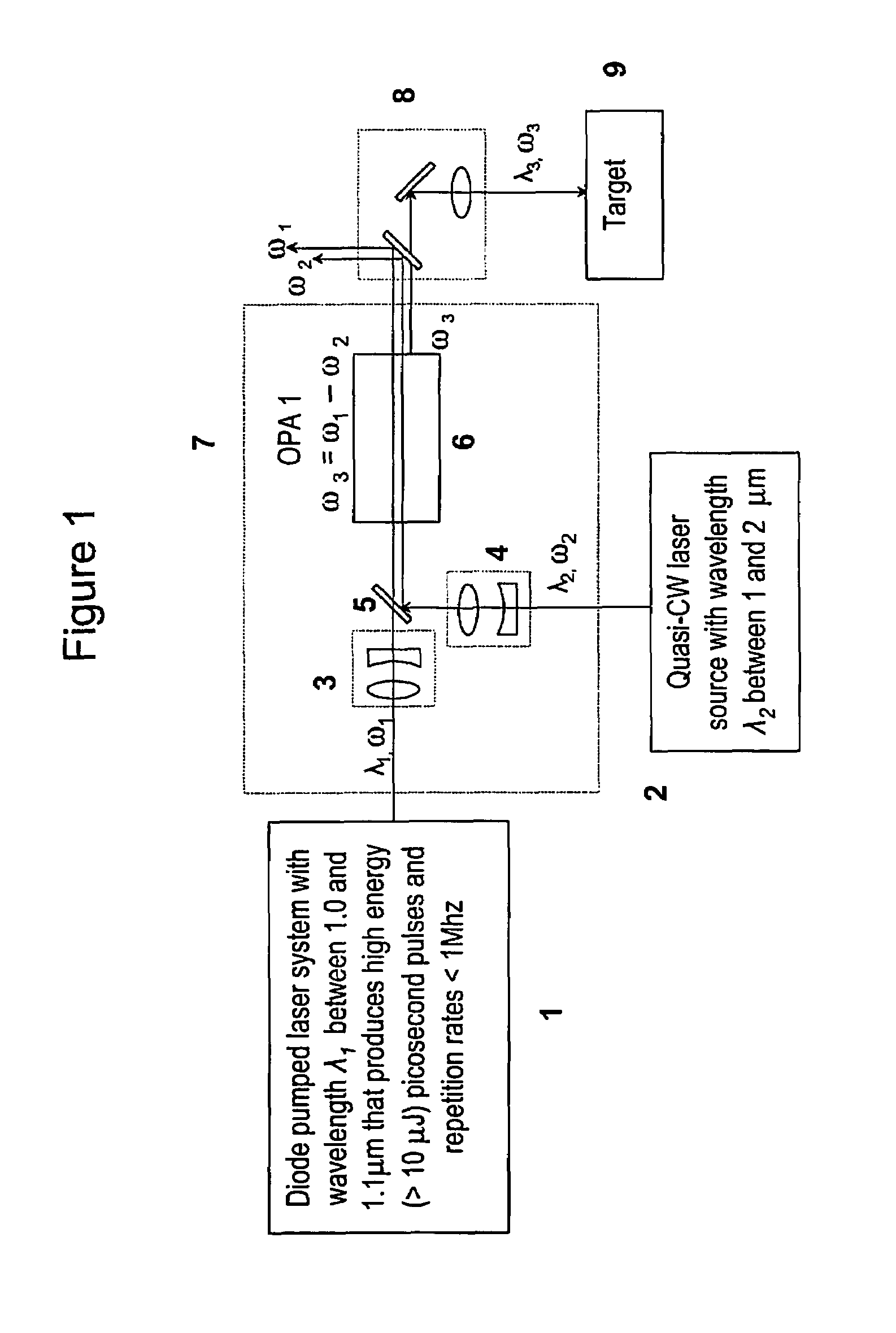
Laser system for generation of high-power sub-nanosecond pulses with controllable wavelength in 2-15 mum region
A laser system capable of efficient production of high energy sub-nanosecond pulses in the 2-15 μm spectral region is disclosed. Diode pumped solid state lasers are used as pump sources. The system design is simple, reliable and compact allowing for easy integration. The laser system includes a combination of compact solid-state ˜1 micron laser sources, producing high power picosecond pulses, with optical parametric amplification and a quasi-continuous wave laser for seeding the amplification process that enables the efficient conversion of the high power ˜1 micron laser radiation to tuneable mid-infrared sub-ns pulses. New parametric processes are presented for achieving high gains in bulk nonlinear crystals. Furthermore, a method of exceeding the fundamental conversion efficiency limit of direct three wave mixing is presented. The compact and robust nature of this novel laser system opens up the use of high power and high peak power mid-infrared laser pulses to a wide variety of important medical and dental applications.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION INC
Mid-infrared cascade Raman fiber lasers
InactiveCN101582559AAvoid craft difficultiesAvoiding the difficulties of high-efficiency lasersLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionGratingMid infrared laser
The invention discloses a mid-infrared cascade Raman fiber lasers, which is characterized by comprising a doubly coated ZBLAN fluoride fiber that comprises the following components: 53mol. % of ZrF4, 20mol. % of BaF2, 4mol. % of LaF3, 4mol. % of AlF3 and 20mol. % of NaF. One end of the doubly coated ZBLAN fluoride fiber is connected with a high power fiber-doped pump laser, and a cavity resonator of Raman lasers is formed by a plurality of fiber Bragg grating pairs inscribed on two ends of the ZBLAN fiber. By using the stimulated Raman effect of ZBLAN fiber, the Stokes light in all phases generated by Raman frequency shift of pump light form resonance in the fiber Bragg grating pairs to finally realize output of mid-infrared laser. The invention has the advantages of simple and compact structure, high beam quality, high conversation rate, solves the problem that the traditional fiber laser is difficult to generate laser in mid-infrared section, and can be widely used in various fields such as military, medical treatment, environmental monitoring and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
End-pumped mid-infrared KTA parametric oscillator
InactiveCN101673917ALower the thresholdImprove efficiencyOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialSignal lightLaser light
The invention belongs to the technical field of parametric oscillators and relates to an end-pumped mid-infrared KTA parametric oscillator. The end-pumped mid-infrared KTA parametric oscillator comprises a pumping source, a coupling lens set, an Nd:YVO4 laser and an intracavity optical parametric oscillator arranged in the Nd:YVO4 laser, wherein the pumping source adopts a semiconductor laser withoutput wavelength of 808 nm and outputs a laser crystal passing through a laser crystal Nd:YVO4 pumped at the rear end of the coupling lens set; the Nd:YVO4 laser is a flat-concave cavity for generating linearly polarized 1064 nm laser light, and a laser crystal Nd:YVO4, an acousto-optic Q-switch and the intracavity optical parametric oscillator are arranged in the Nd:YVO4 laser in sequence; an anti-reflection film with 808 nm and an anti-reflection film with 1064 nm are coated at both ends of the Nd:YVO4 laser crystal; a 1064 nm high anti-reflective film and a 1.5-1.6 mum highly reflective film are coated on an input mirror for the intracavity optical parametric oscillator, a KTA crystal is arranged in the cavity mirror, and dielectric films for performing anti reflection to base frequency light 1064 nm, signal light 1.5-1.6 mum and idle light 3.5 mum are coated at the both ends of the cavity mirror. The mid-infrared laser output with low threshold value, high efficiency and high-repetition frequency can be obtained in the invention.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Airborne tunable mid-ir laser gas-correlation sensor
InactiveUS20100163733A1Radiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsMid infrared laserGas concentration
A method and apparatus for measuring target gas concentrations in an atmosphere. The method and apparatus emit in the atmosphere a laser beam tuned to a molecular absorption line of a target gas, receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, divide and direct the received signal into a first optical path and a second optical path including in one of the paths a correlation gas cell filled with a predetermined concentration of the target gas, detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path, and calculate a target gas concentration by comparing a first signal transmitted through the first optical path to a second signal transmitted through the second optical path. The apparatus includes a laser source tunable to a specific molecular absorption line of a target gas and configured to emit in the atmosphere a laser beam having a spectral bandwidth greater than a full width of the molecular absorption line of the target gas, a receiver configured to receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, and at least one detector configured to detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
All-fiber intermediate infrared high-energy passively Q-switched fiber laser
ActiveCN104934843ASolving low energySolve efficiency problemsActive medium shape and constructionGratingHigh energy
The present invention relates to the technical field of intermediate infrared laser, and solves the technical problems that when an intermediate infrared passively Q-switched fiber laser in the prior art outputs an intermediate infrared laser light source at a 3[mu]m wave band, the outputted laser light source is low in energy and low in output efficiency. An all-fiber intermediate infrared high-energy passively Q-switched fiber laser comprises a random laser pumping source, a double-cladding Ho3+-doped ZBLAN optical fiber, and a single-cladding Dy3+-doped ZBLAN optical fiber which are connected in order, wherein a first fluoride fiber grating is etched at the front end of the double-cladding Ho3+-doped ZBLAN optical fiber, a second fluoride fiber grating is etched at the tail end of the single-cladding Dy3+-doped ZBLAN optical fiber, a resonant cavity is formed between the first fluoride fiber grating and the second fluoride fiber grating, thereby achieving the technical effect of outputting high-energy and high-efficiency intermediate infrared laser at the 3[mu]m wave band.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
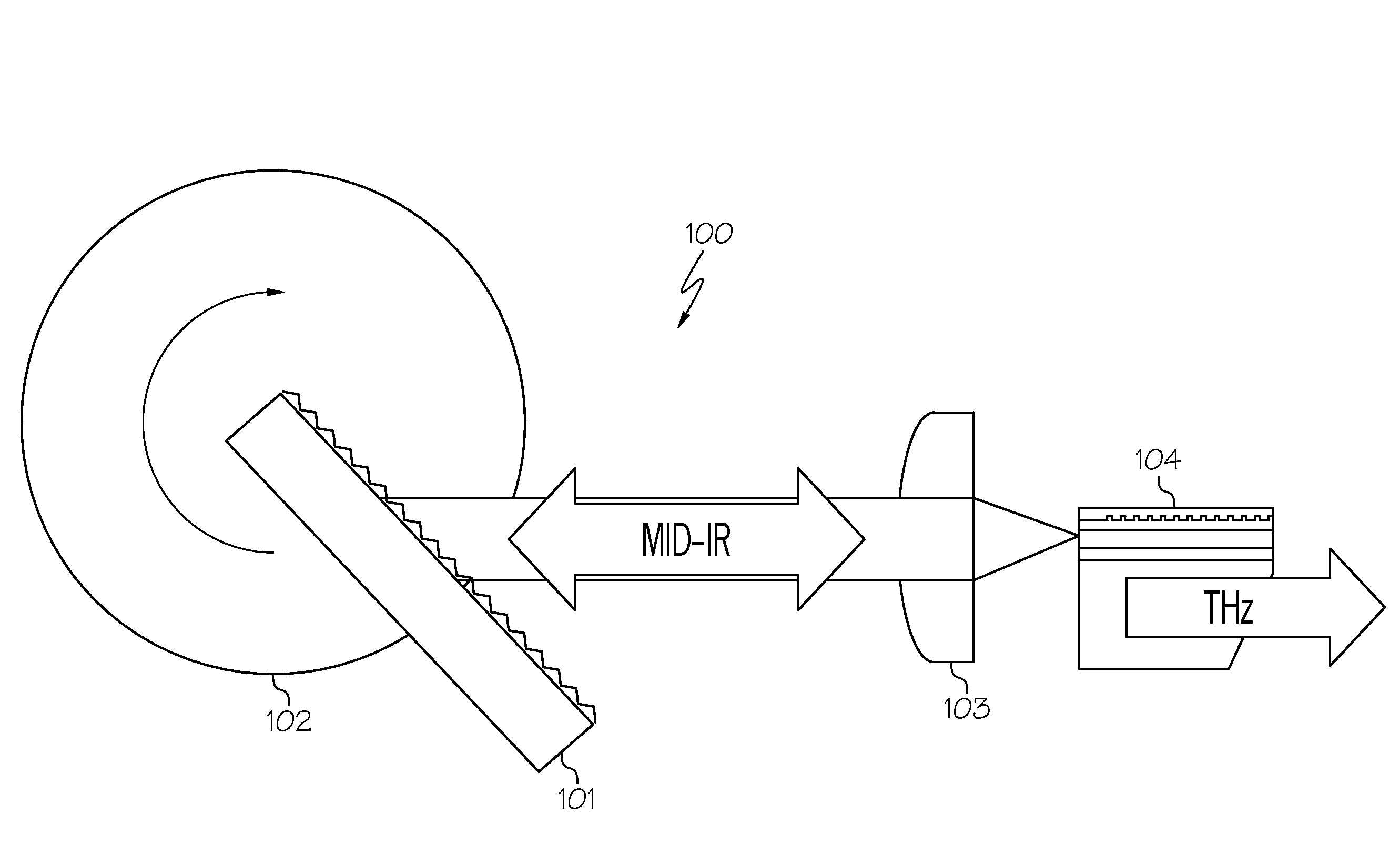
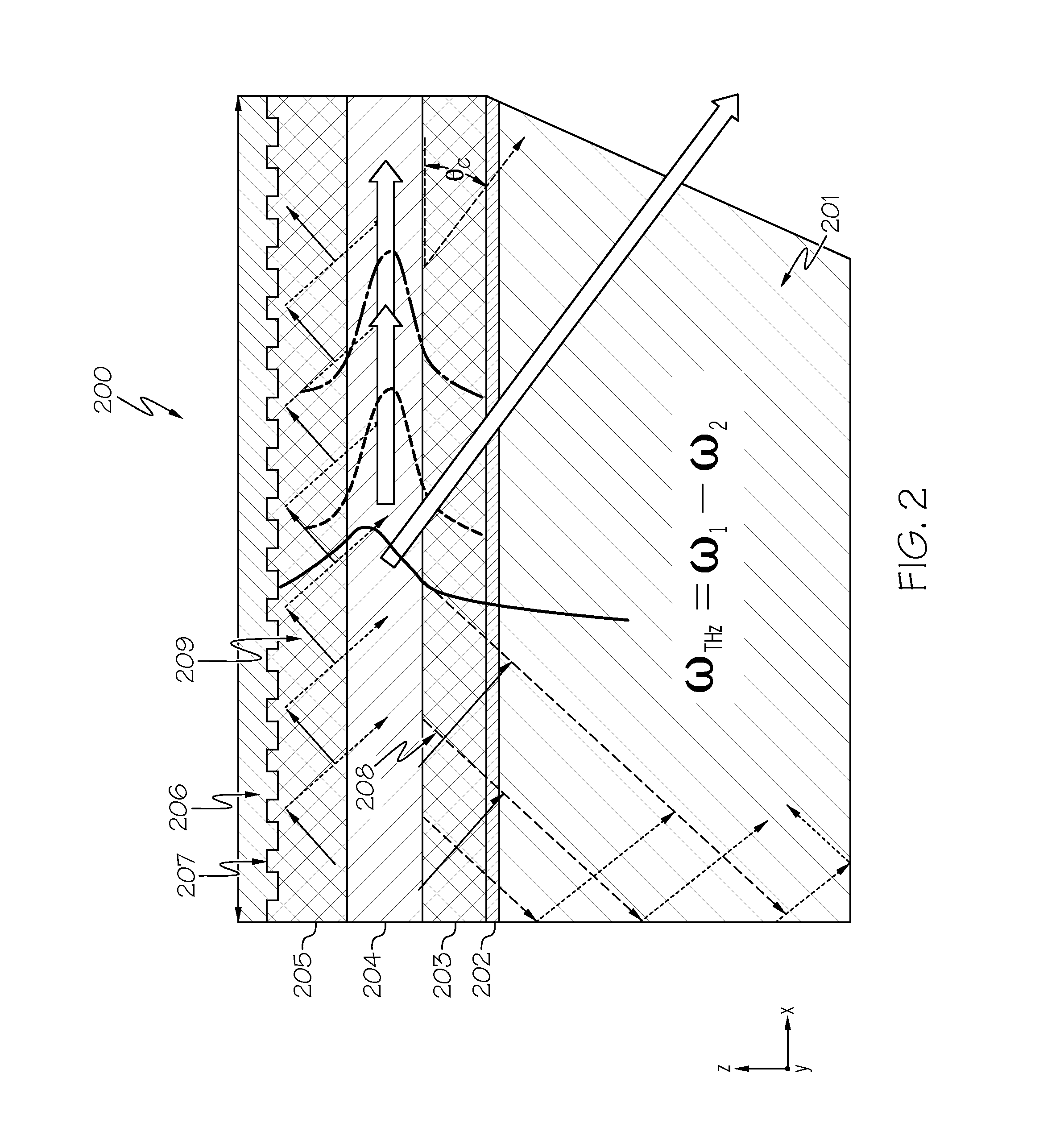
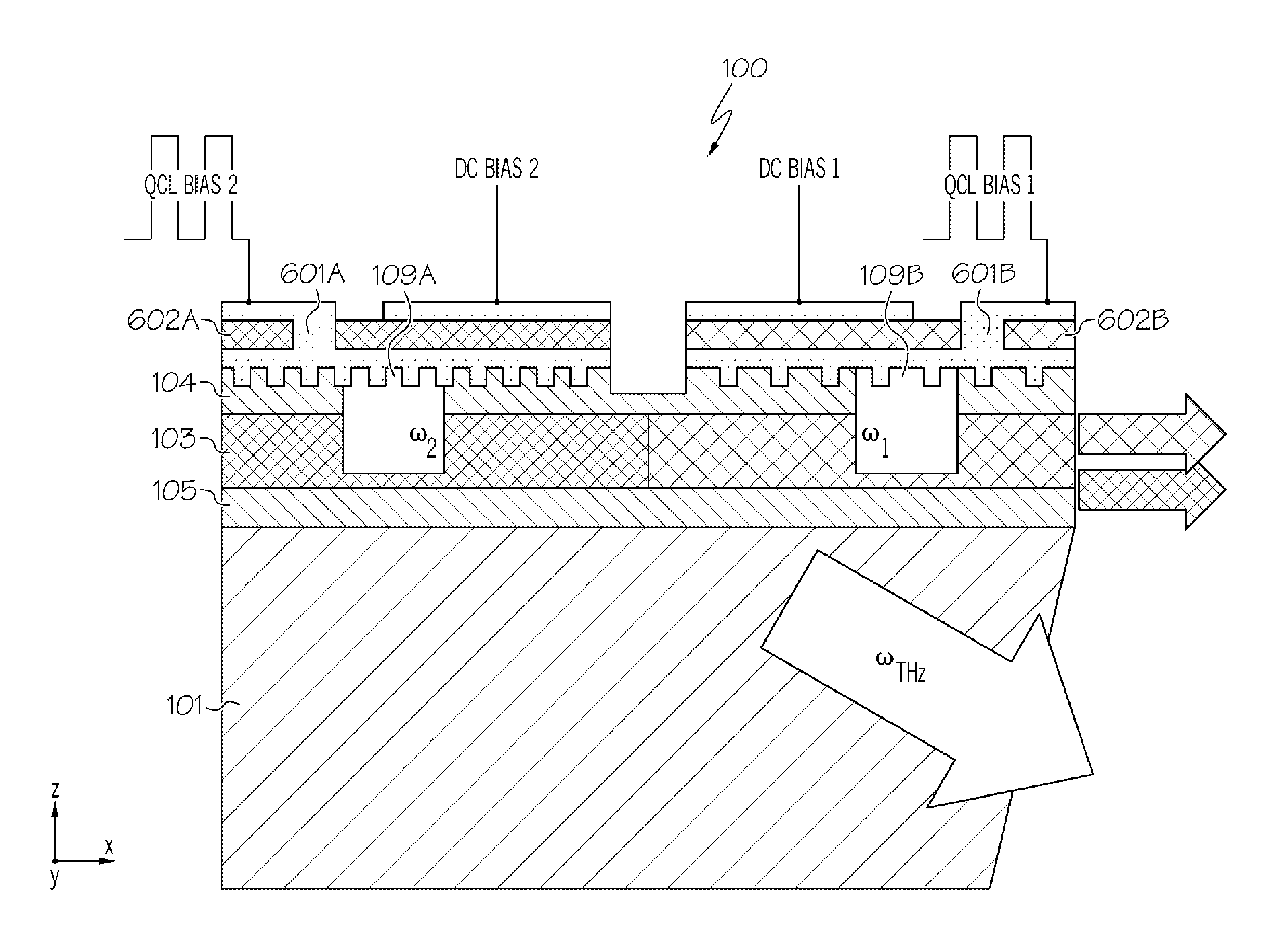
External cavity system generating broadly tunable terahertz radiation in mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers
InactiveUS20150311665A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionMid infraredFrequency generation
A broadly tunable terahertz source constructed as an external cavity system using a difference-frequency generation quantum cascade laser source. The external cavity system includes an external diffraction grating configured to tune and reflect mid-infrared emission at a first wavelength. The laser includes a mid-infrared feedback grating defined in the laser waveguide of the laser to fix mid-infrared lasing at a second wavelength. Alternatively, two external diffraction gratings may be configured to tune and reflect mid-infrared emission at a first wavelength and a second wavelength. Tunable terahertz radiation is then generated at frequency ωTHz=|ω1−ω2|, where ω1 and ω2 are the frequencies of the first and second mid-infrared lasing wavelengths.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a construction method of an infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice. By utilizing the optic superlattice of the structure, the structure of the optic superlattice provides two reciprocal lattice vectors simultaneously, wherein one reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in an OPO (optical parametric oscillation) process from near infrared to intermediate infrared, and the other reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in a signal light pump OPA (optical parametric amplification) from the OPO process, in the process, the intermediate infrared laser which is generated in the OPO process can be amplified further, thus more efficient intermediate infrared laser output of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained; and a commensurability ratio double periodic structure is adopted for the optic superlattice, thus the more efficient intermediate infrared laser of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ADVANCED LASER TECH
Intermediate/far infrared super-continuum spectrum fiber laser
InactiveCN102856783AIncrease powerLow costActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionInfraredChalcogenide glass
The invention discloses an intermediate / far infrared super-continuum spectrum fiber laser which relates to the field of laser photoelectrons. The intermediate / far infrared super-continuum spectrum fiber laser comprises a pulse fiber laser, a quartz photonic crystal fiber, a passive intermediate infrared chalcogenide glass fiber, a passive intermediate / far infrared chalcogenide glass fiber, a filter, an excitation source and a rare earth ion doped chalcogenide glass fiber, wherein a super-continuum spectrum laser is generated by the pulse laser emitted by the pulse fiber laser through the quartz photonic crystal fiber to excite the passive intermediate infrared chalcogenide glass fiber so as to generate an intermediate infrared super-continuum spectrum laser; the intermediate infrared super-continuum spectrum laser is filtered by the filter; the filtered intermediate infrared super-continuum spectrum laser is used as a seed resource laser and amplified through the rare earth ion doped chalcogenide glass fiber; and the amplified intermediate laser is used for exciting the passive intermediate / far infrared chalcogenide glass fiber so as to generate an intermediate / far infrared super-continuum spectrum laser with a wavelength of 5-14 micrometers. According to the intermediate / far infrared super-continuum spectrum fiber laser, the shortage of light sources of intermediate / far infrared lasers is solved and the output of the intermediate / far infrared super-continuum spectrum laser is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Long-path infrared spectrometer
ActiveUS20140319352A1Improve accuracyLong effective optical path lengthRadiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsGratingGas composition
A tunable mid-infrared laser operated in a pulsed mode is coupled off-axis into a high-finesse optical cavity to produce a long-path spectrometer. The cavity receives a gas sample. Laser pulses may be wavelength-scanned by stepping an external grating, allowing the grating to mechanically settle, then measuring the ring-down with a set of laser pulses, before moving on the next wavelength. A detector receiving infrared light exiting the cavity supplies a cavity ring-down trace representative of sample absorption of the infrared pulses. A processor determines an absolute absorption spectrum of the gas sample from the ring-down trace and analyzes sample gas composition and trace concentration from that spectrum. The absorption baseline is highly reproducible and stable, improving the accuracy of multivariate fits, and the spectral resolution can be better than 0.001 cm−1 (contingent upon the laser source), allowing for high-resolution measurements of sharp absorption features.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Natural gas leakage telemetering laser radar
InactiveCN104237898ALong detection distanceFar SensitivityPipeline systemsColor/spectral properties measurementsMicrometerRadar
The invention relates to a natural gas leakage telemetering laser radar used for remote laser telemetering. The natural gas leakage telemetering laser radar can timely find pipeline leakage points and diffusion range and reduce loss caused by leakage. The technical scheme includes that a specially-designed wide-spectrum mid-infrared laser device is mounted on a radar platform, and range of spectra emitted by the laser device is 3.2-3.4 micrometers; laser spectra are measured by adopting a mid-infrared spectrograph before laser is emitted through an emitting antenna, the laser going through the emitting antenna goes through leaking gas cloud cluster and then is reflected by pipelines, soil or seawater, reflected laser is received by a receiving antenna, the mid-infrared spectrograph measures spectra of the received laser, and leakage condition of methane gas is judged by comparing absorbing condition of the spectra, of the laser before being emitted and after being received, at a position with the spectrum of 3.31 micrometer. Compared with a methane gas detecting device adopting continuous laser of 1.65 micrometer, the natural gas leakage telemetering laser radar has the advantages of longer detecting distance, higher system sensitivity and capability of being used for patrolling natural gas pipelines and submarine natural gas leakage.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
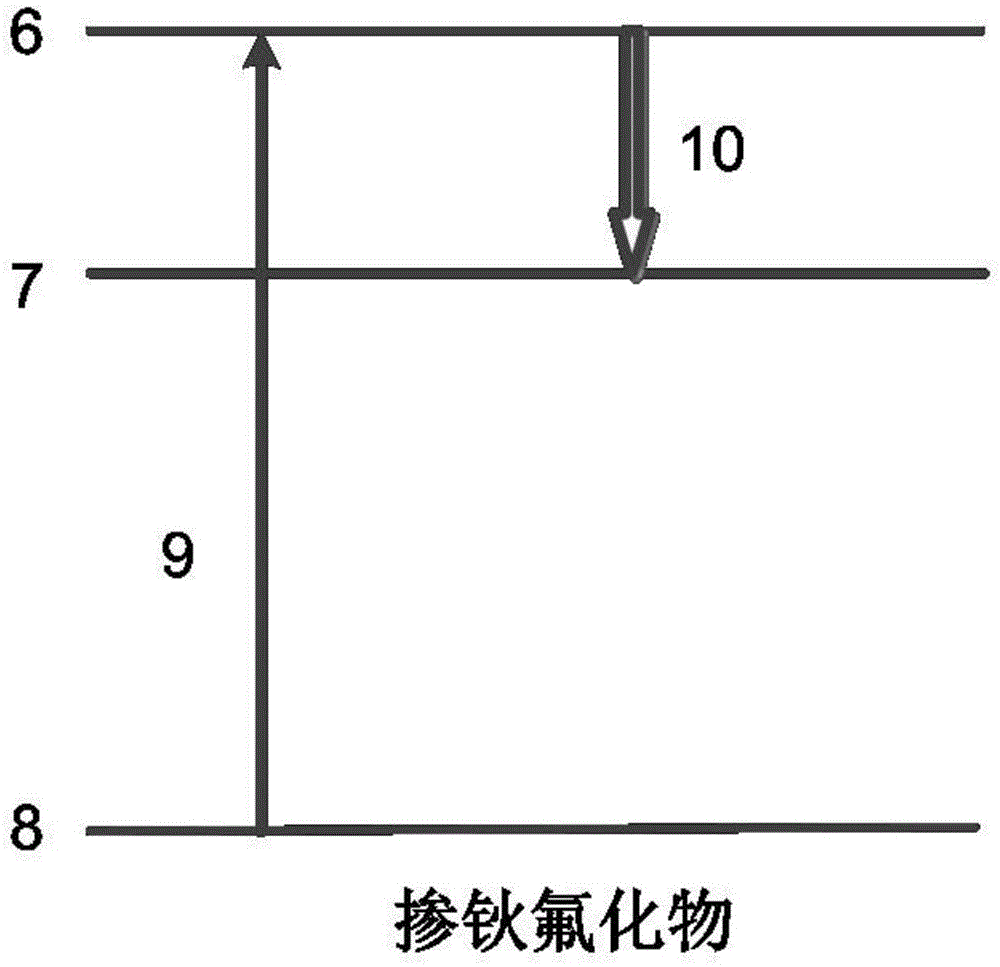
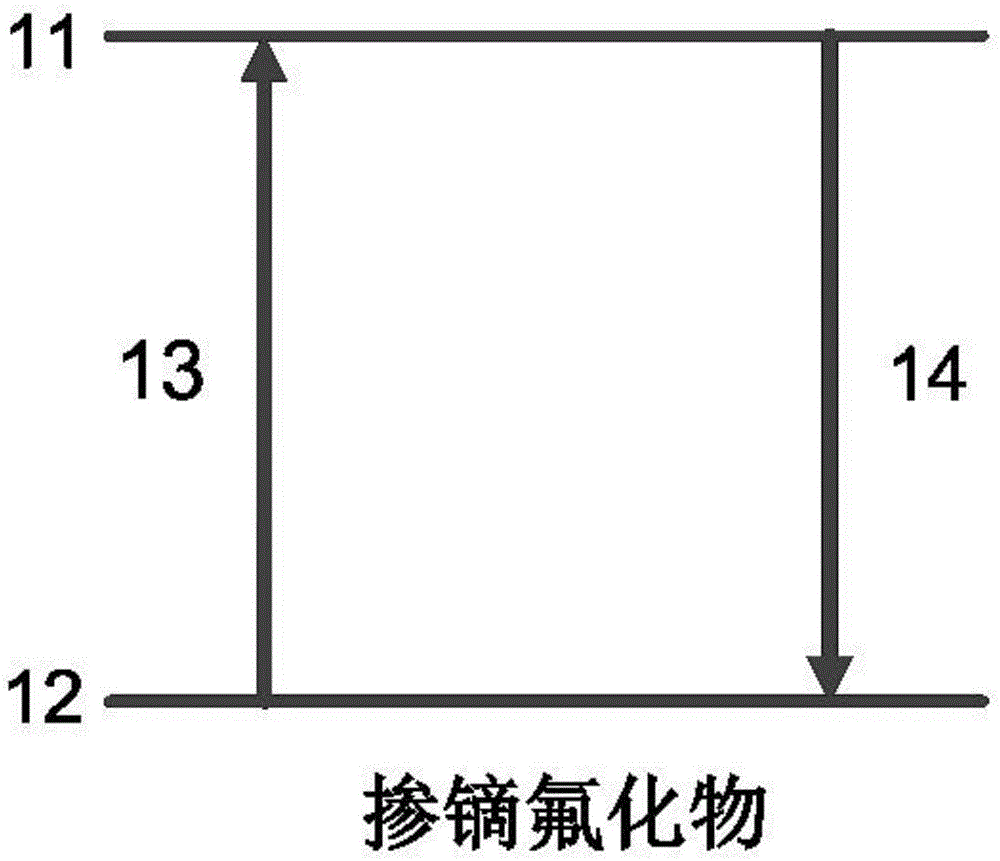
Lutecium lithium fluoride intermediate infrared laser crystal of dysprosium activated
In this invention, LiLuF4 is used as laser raw host material, Dy3+ is used as active ions, to produce LiLuF4: Dy3+ laser crystal. And also LiLuF4 is used as laser raw hast material, Dy3+ as active ions, Yb3+ as used as sensitizing ions to produce the invented product LiLuF4: Dy3+: Yb3+ laser crystal. Said crystals are used for realization of tunable output of middle infrared laser at 3.0-5.0 micron wave band.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
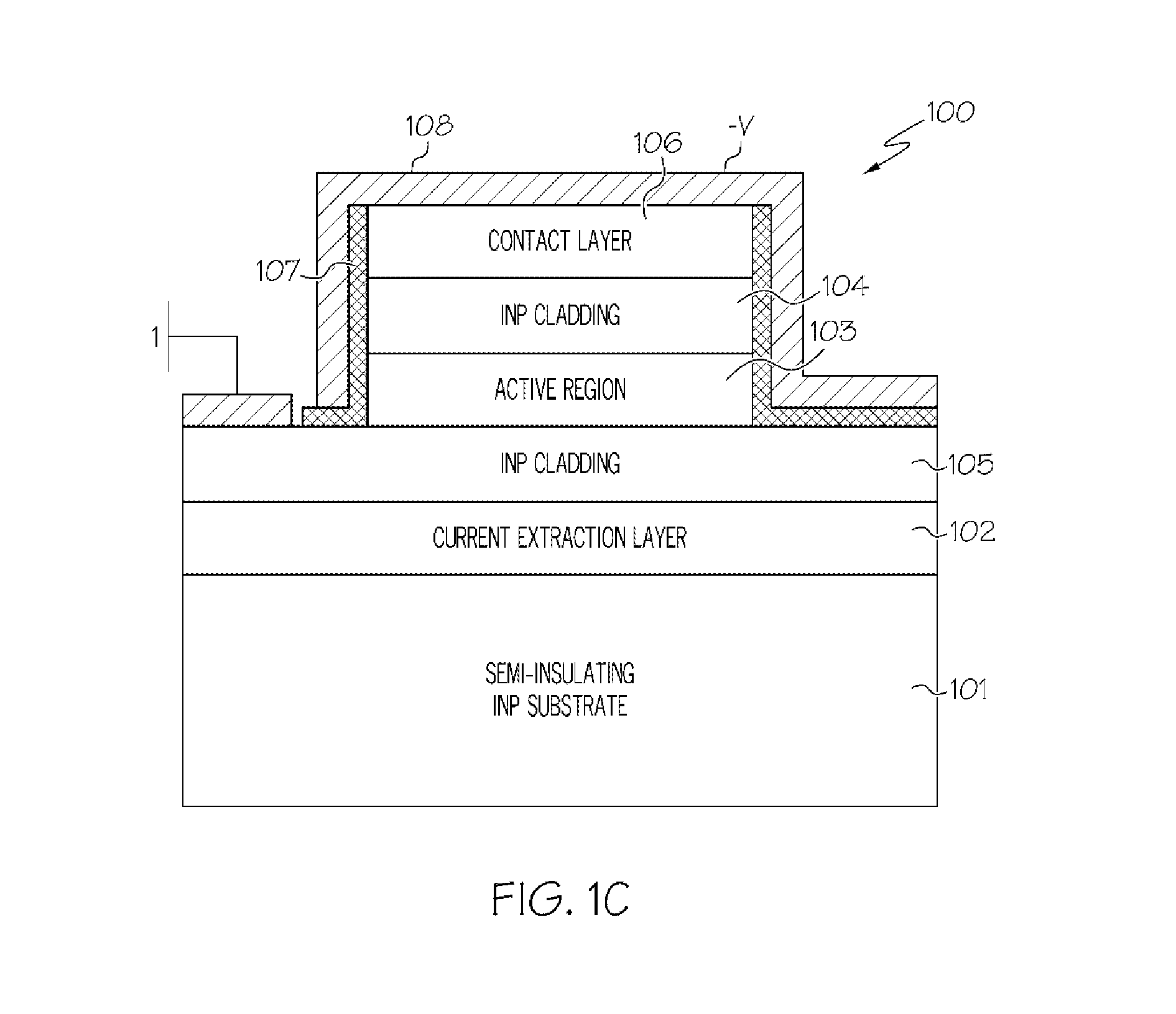
Monolithic tunable terahertz radiation source using nonlinear frequency mixing in quantum cascade lasers
A terahertz difference-frequency generation quantum cascade laser source that provides monolithic, electrically-controlled tunable terahertz emission. The quantum cascade laser includes a substrate, a lower cladding layer positioned above the substrate and an active region layer with optical nonlinearity positioned on the lower cladding layer. The active region layer is arranged as a multiple quantum well structure. One or more feedback gratings are etched into spatially separated sections of the cladding layer positioned on either side of the active region. The periodicity of each grating section determines the mid-infrared lasing frequencies. The grating sections are electrically isolated from one another and biased independently. Tuning is achieved by changing a refractive index of one or all of the grating sections via a DC current bias thereby causing a shift in the mid-infrared lasing frequency. In this manner, a monolithic, electrically-pumped, tunable THz source is achieved.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Medium-infrared thulium doped optical fiber laser amplifier
InactiveCN101340053AGood heat dissipationIncrease powerActive medium shape and constructionFiber couplerMiddle infrared
The invention discloses a middle-infrared thulium-doped fiber laser amplifier which is composed of a seed light source, an optical isolator, a focusing lens, a pumping light source, a multi-path fiber coupler, double clad thulium-doped fiber, a collimating lens and a beam splitting plate. The position relationships of the components are as follows: the optical isolator, the focusing lens, the multi-path fiber coupler, the double clad thulium-doped fiber, the collimating lens and the beam splitting plate are sequentially arranged along the laser output direction of the seed light source, an input end of the seed optical fiber of the multi-path fiber coupler is positioned at the focus of the collimating lens, an output end of the seed optical fiber is welded with the double clad thulium-doped fiber, the other end of the double clad thulium-doped fiber is positioned at a front focus of the collimating lens, and the beam splitting plate and the output light beam of the collimating lens are arranged at an angle of 45 degrees. The laser amplifier has good heat dissipation characteristic, improves the pumping power and can obtain high-power mid-infrared laser output.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mid-infrared parameter oscillator
ActiveCN101614928ALow cost performanceLower requirementLaser detailsNon-linear opticsResonant cavityOptical cavity
The invention relates to a mid-infrared parameter oscillator, belonging to the technical field of laser. The invention comprises a 1.06mu m laser and a two-level optical parameter oscillator and a light focusing cavity; a laser resonant cavity of the 1.06mu m laser and a first level optical parameter oscillator use a same resonant cavity mirror, the first level optical parameter oscillator and a second level optical parameter oscillator use a same resonant cavity mirror. The two-level optical parameter oscillator of the invention is an inner cavity type non-critical phase matching optical parameter oscillator and the optical parameter conversion receiving angle is large, a walk-off angle is small. The invention can fully use optical power density in a pump optical cavity and optical parameter conversion polarization matched condition to derivate various structures, reduce the technical requirement on pump light of optical parameter oscillator, therefore, the optical parameter conversion efficiency is high and high power mid-infrared laser can be obtained; the structure of the laser is simpler, volume is small, cost is low and overall cost performance is high.
Owner:NO 717 INST CHINA MARINE HEAVY IND GRP
Optical fiber gas cascaded Raman laser capable of realizing 3-5-micron band tuning
ActiveCN106300002ADevelop a compact and stable structureReduce lossLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionFiberMid infrared laser
The invention provides an optical fiber gas cascaded Raman laser capable of realizing 3-5-micron band tuning. The laser comprises a 1-micron band tunable Raman pump source, a first level gas Raman laser generation device and a second level gas Raman laser generation device, the first level gas Raman laser generation device converts 1-micron pump laser generated by the 1-micron band tunable Raman pump source into first level Raman scattering laser, and the first level Raman scattering laser is laser of 1.5-micron band or 2-micron band; and the second level gas Raman laser generation device converts the first level Raman scattering laser into second level Raman scattering laser, and the second level Raman scattering laser is 3-5-micron band tunable mid-infrared laser. According to the optical fiber gas cascaded Raman laser provided by the invention, the output of 3-5-micron band tunable mid-infrared laser is realized in an anti-resonant hollow fiber with a negative curvature by employing a gas Raman cascading manner for the first time.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com