Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6679 results about "Laser source" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Laser Source, LLC. utilizes the latest in laser marking technology to provide customers from various industries with precise and accurate laser etch or laser engraving.
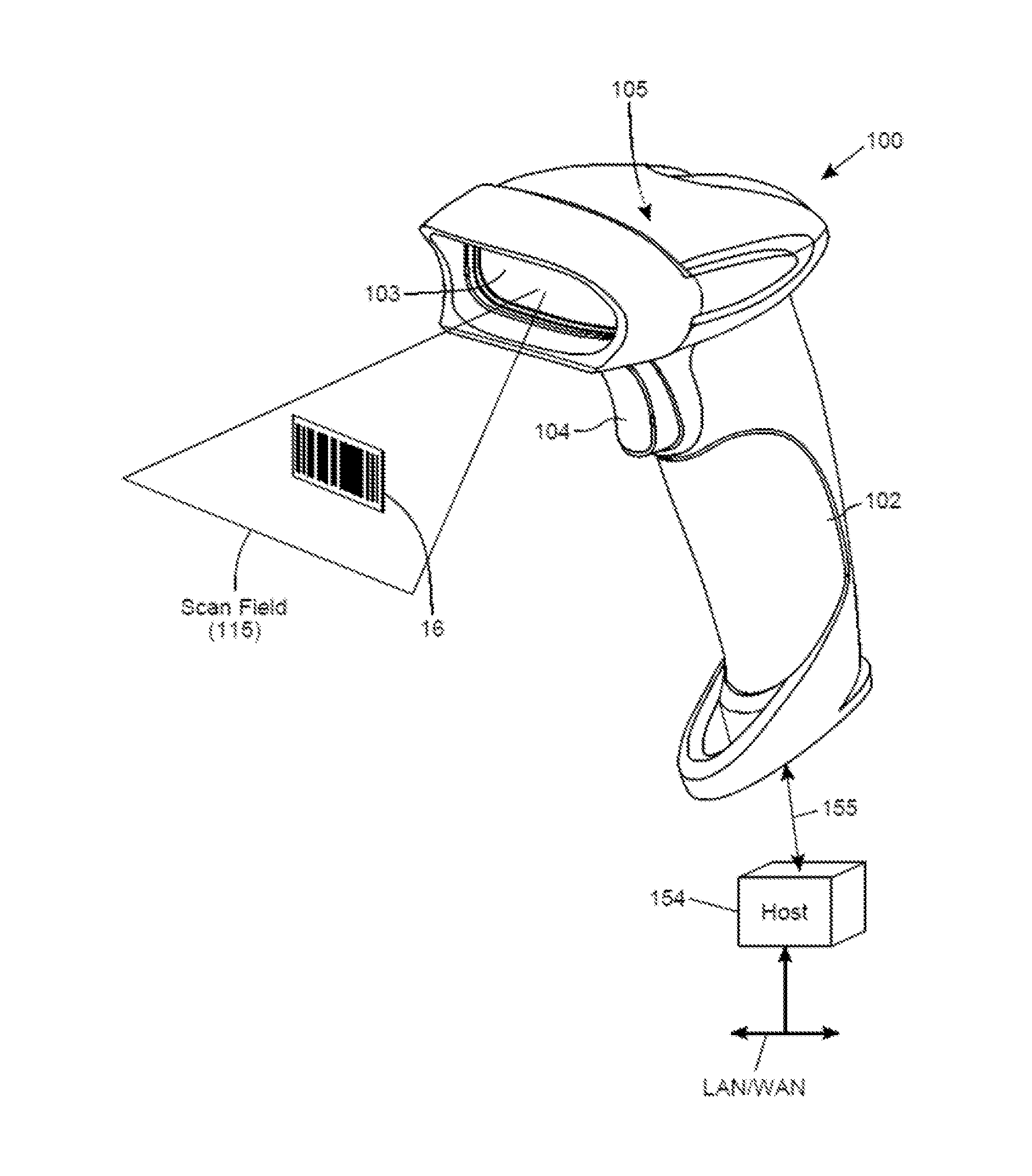
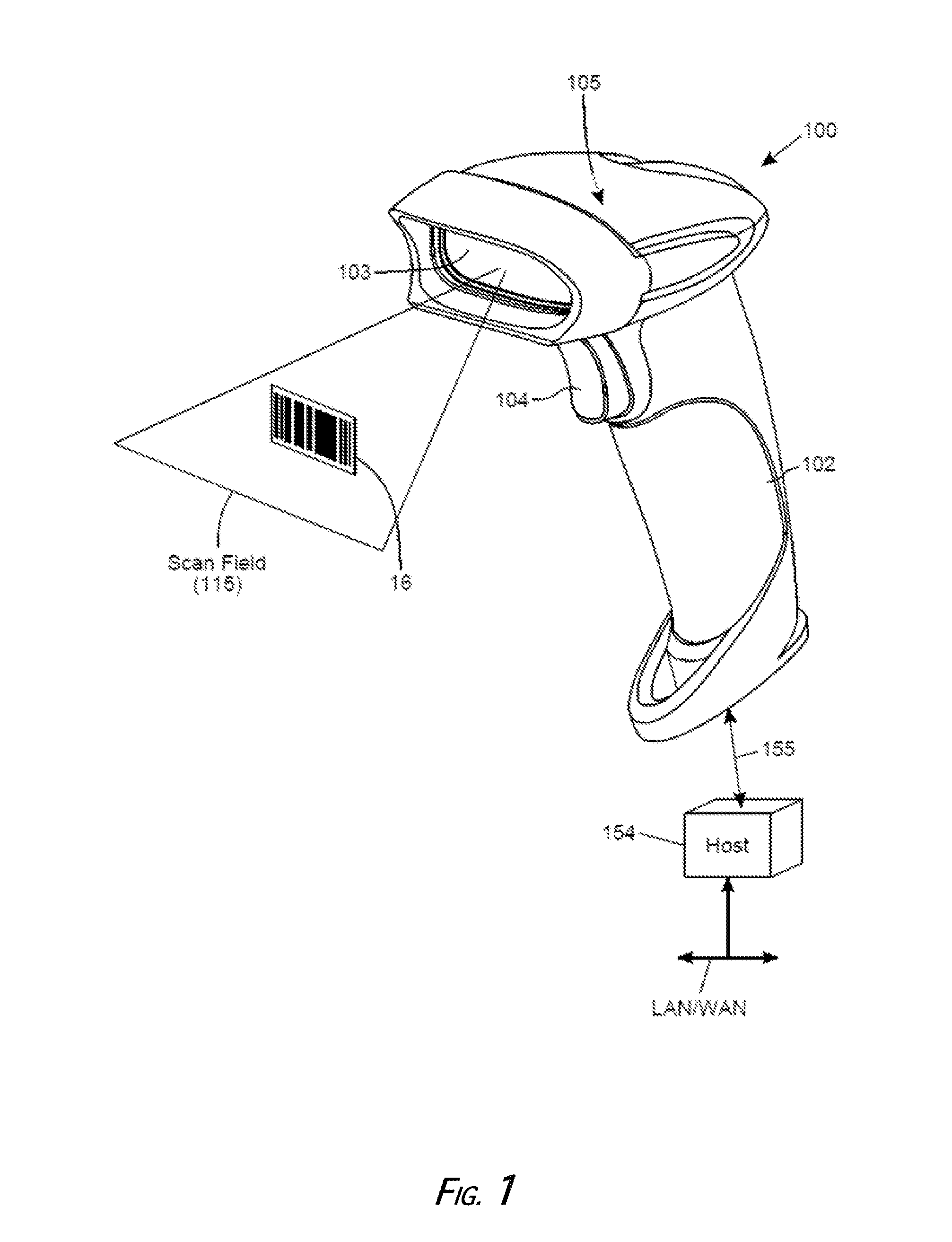
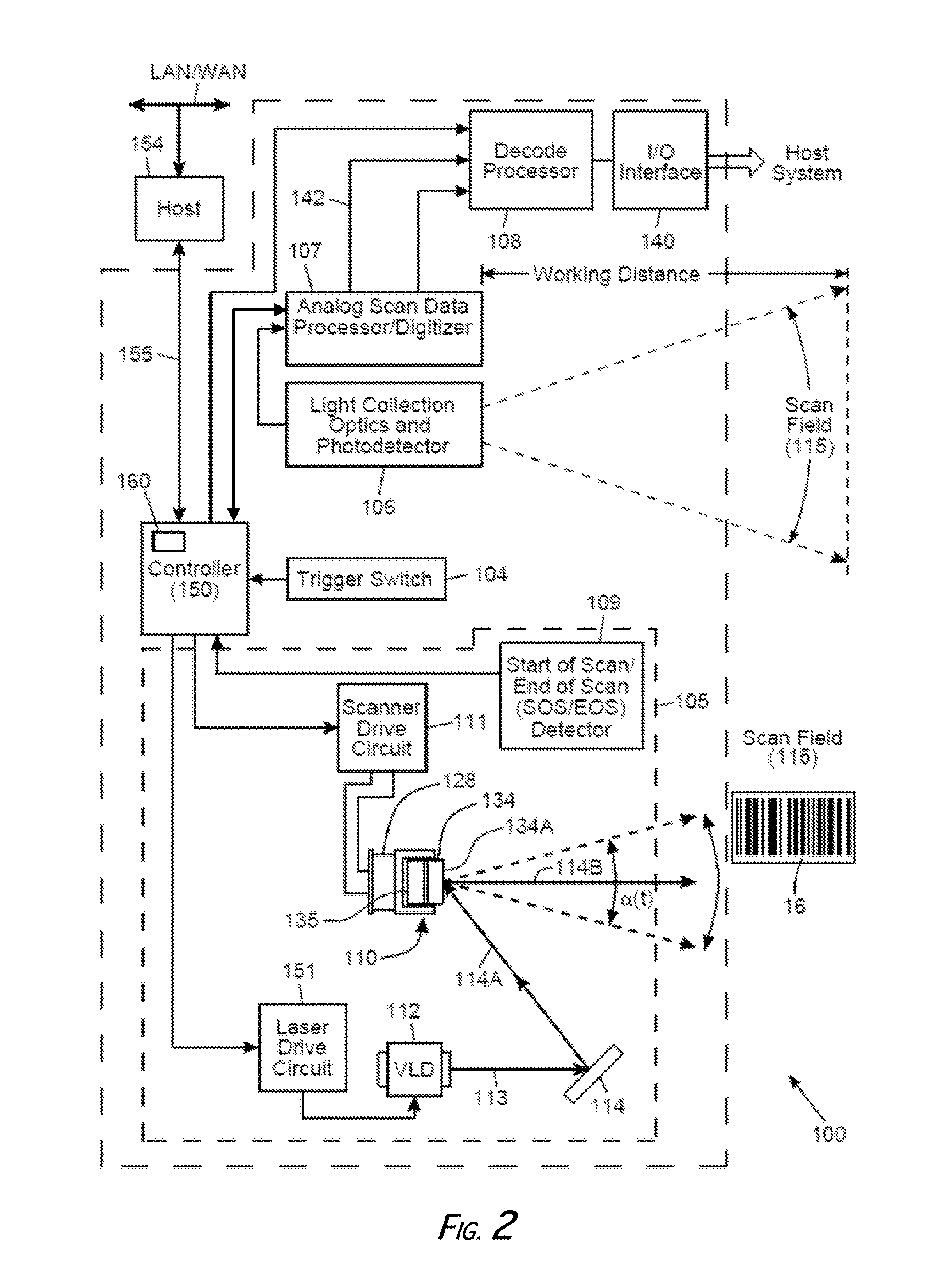
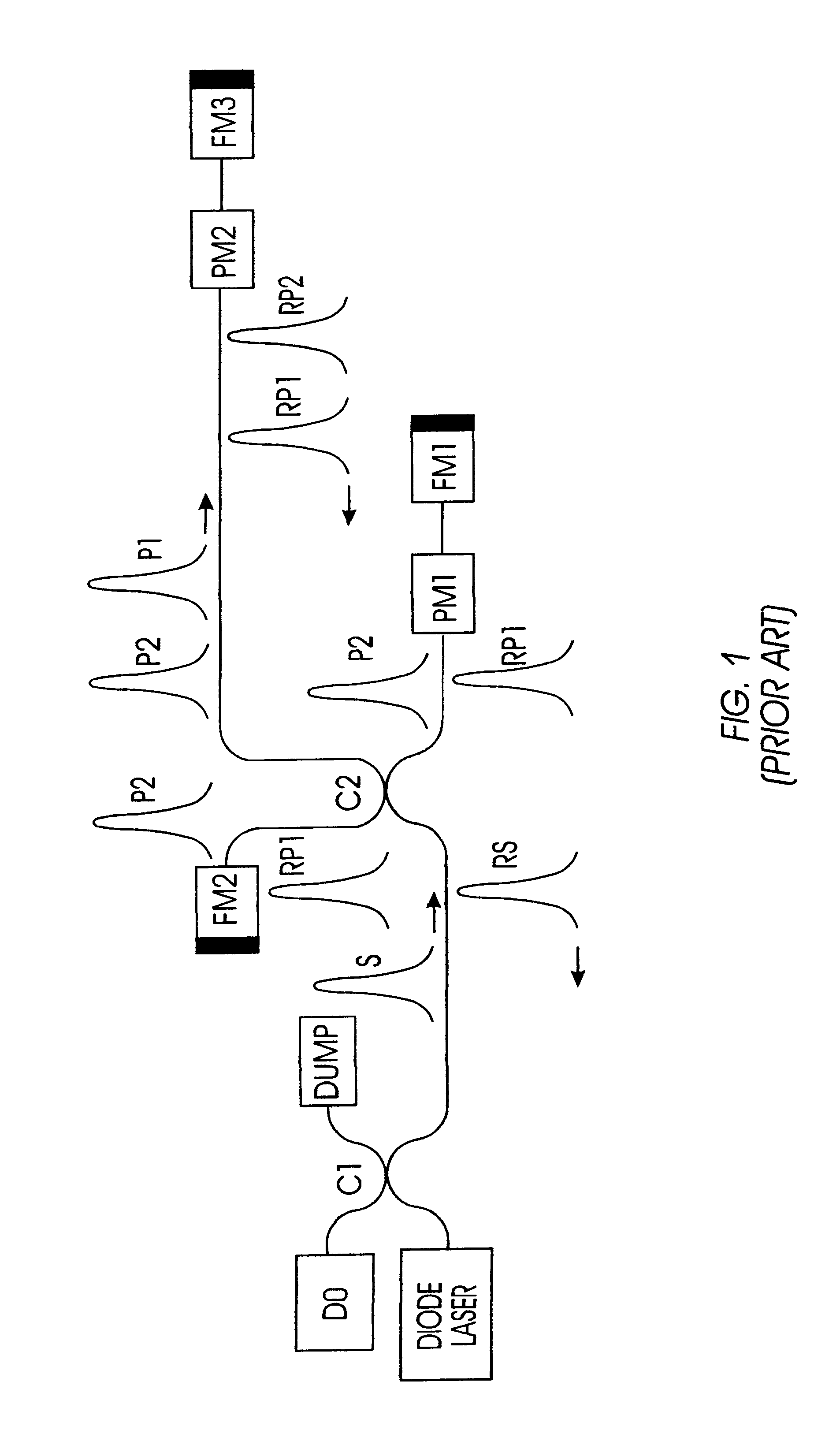
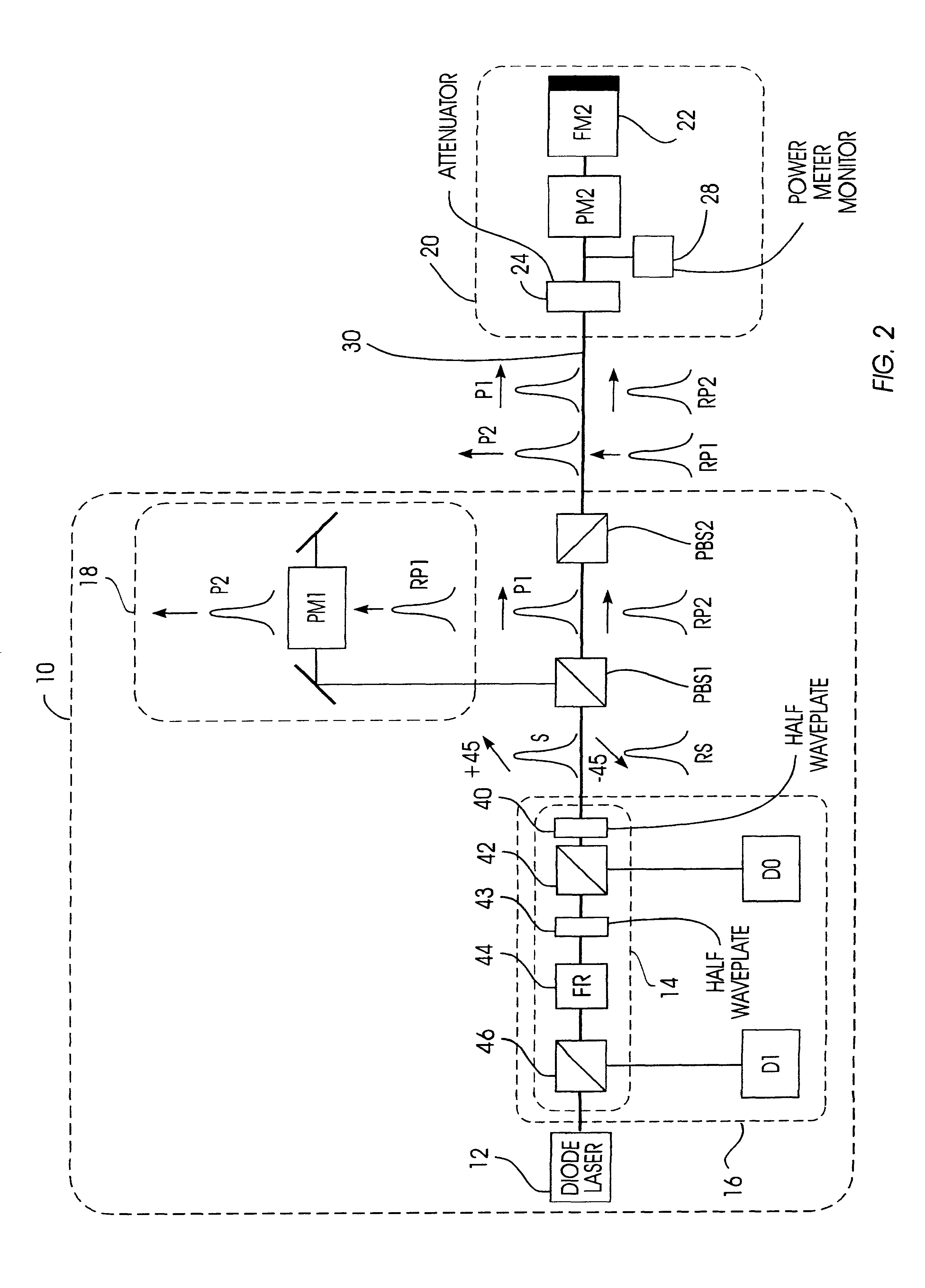
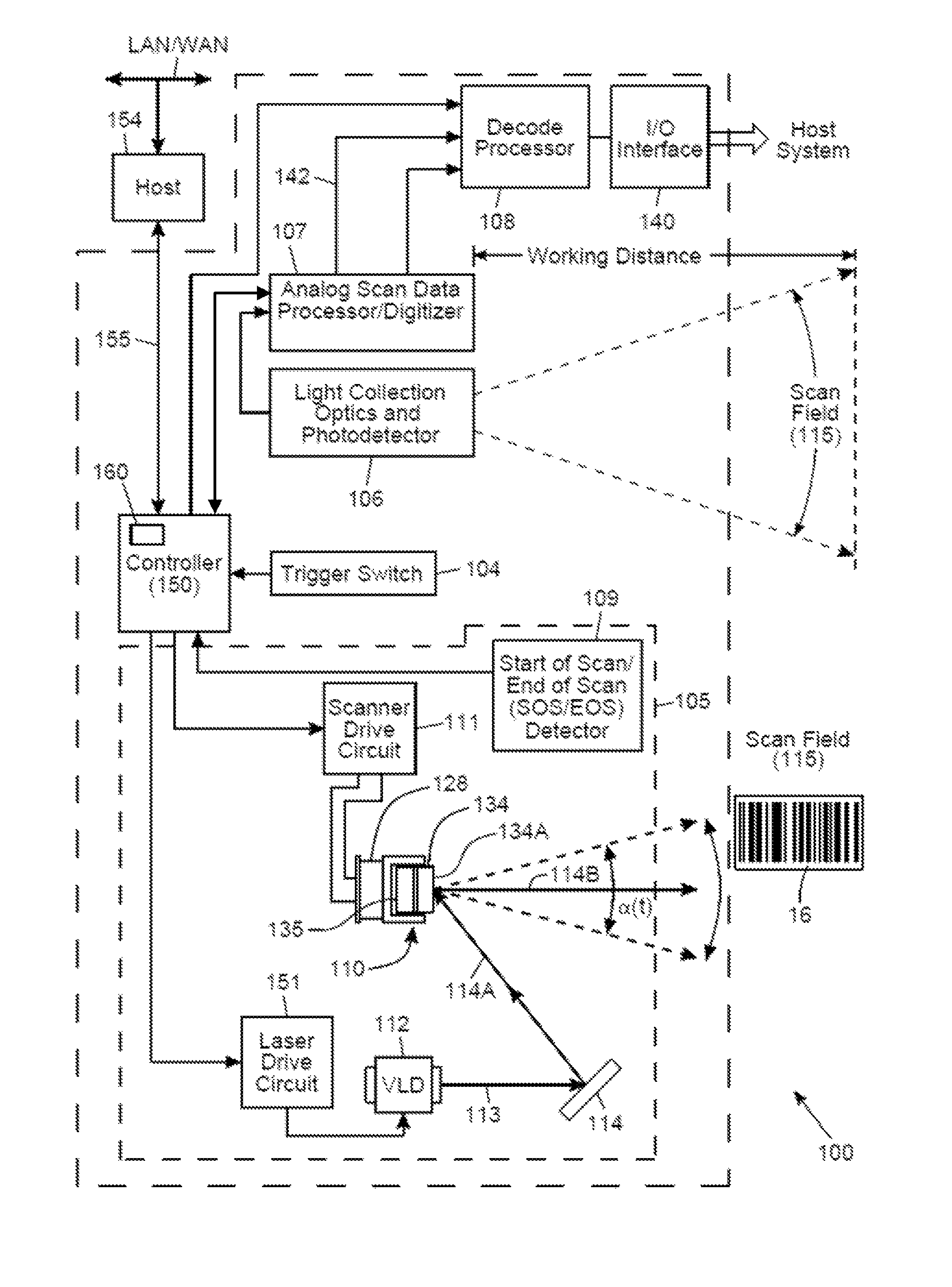
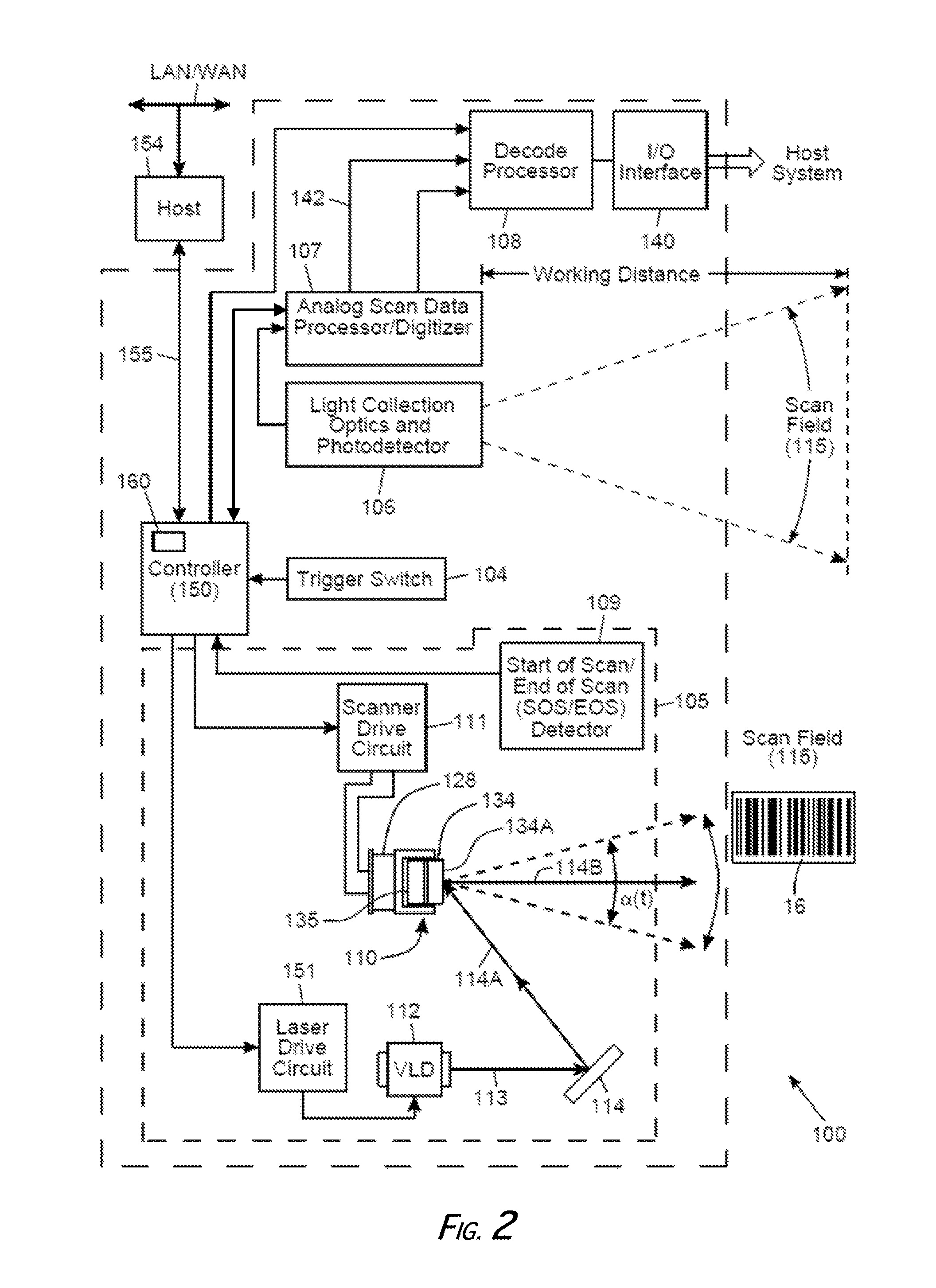
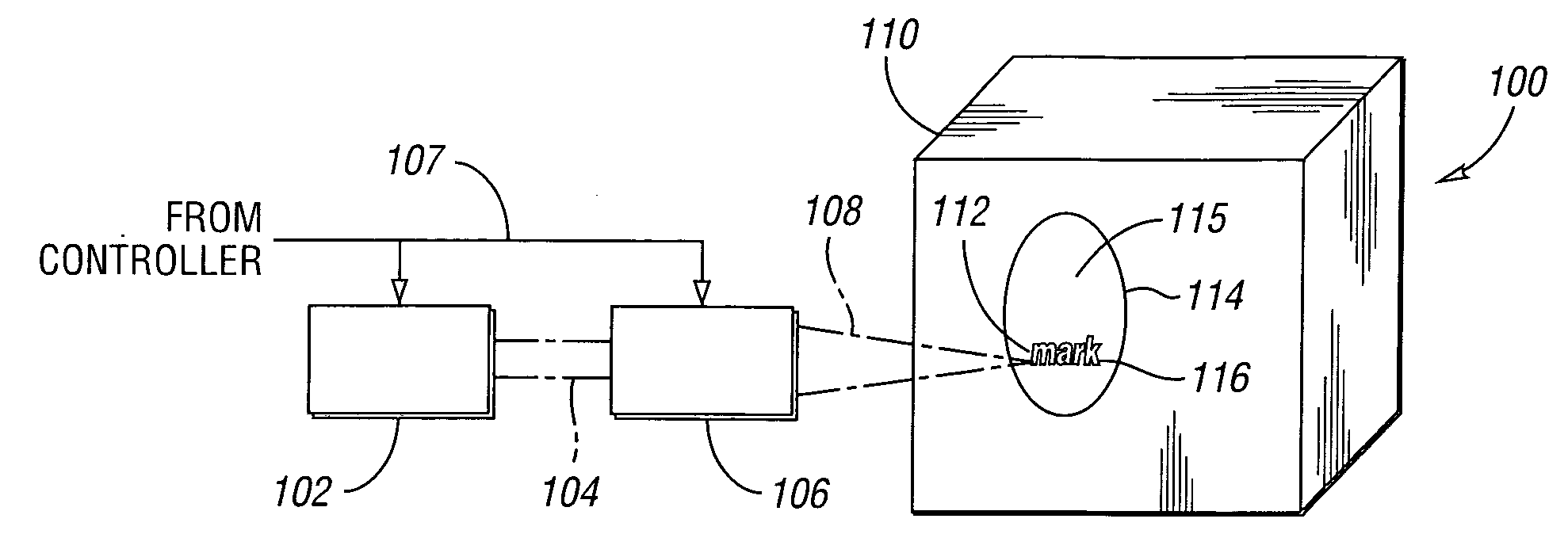
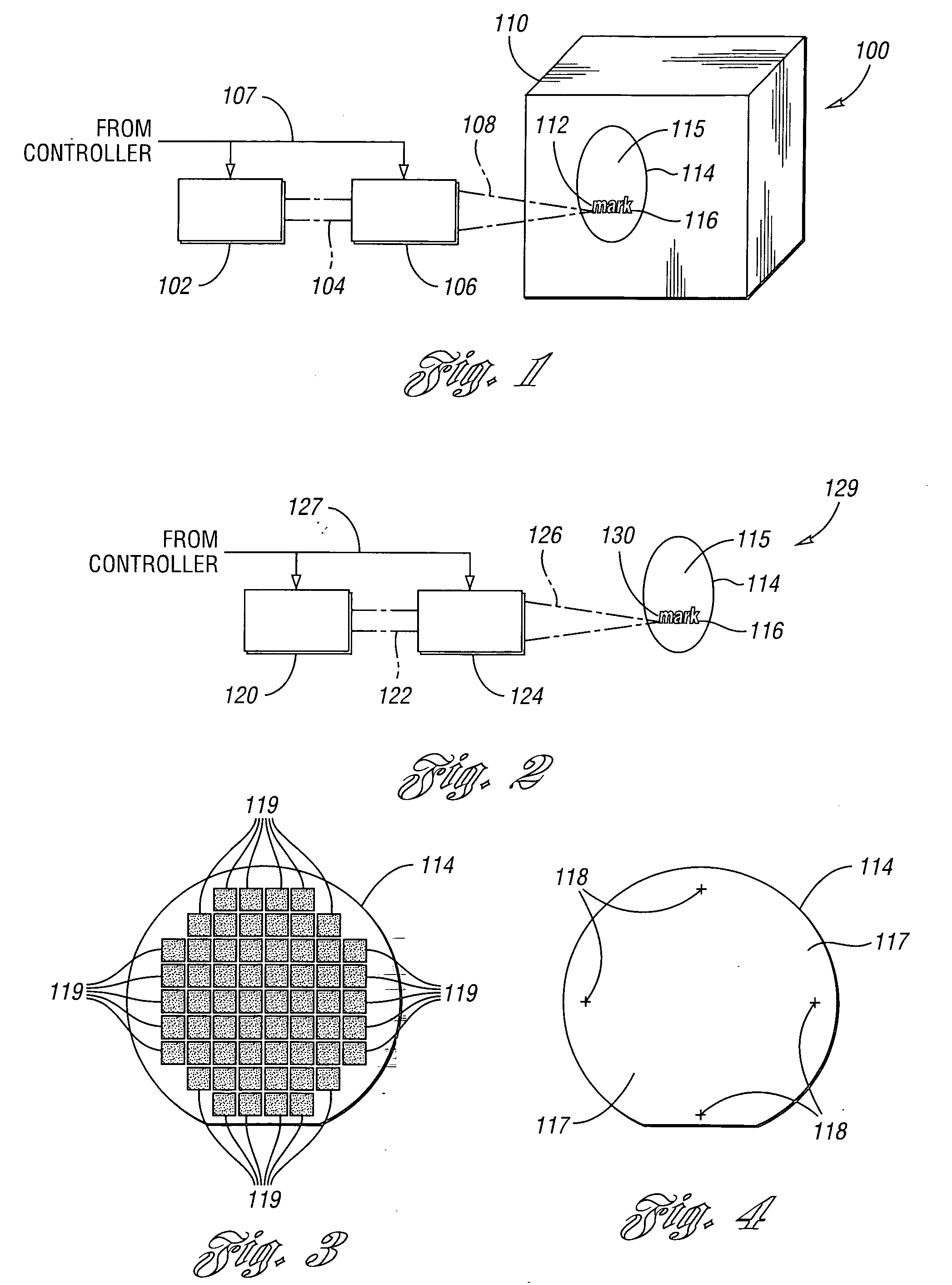
System and Method for Reading Code Symbols at Long Range Using Source Power Control
A system and method are presented for improving the performance of code scanners in the extended and far ranges. At these distances, the intensity of the laser beam reflected off the code symbol can be markedly decreased, thereby decreasing the likelihood of a successful reading of the code symbol by the code scanner. The system provides for dynamic power increases to the laser source to generate a greater dynamic range.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
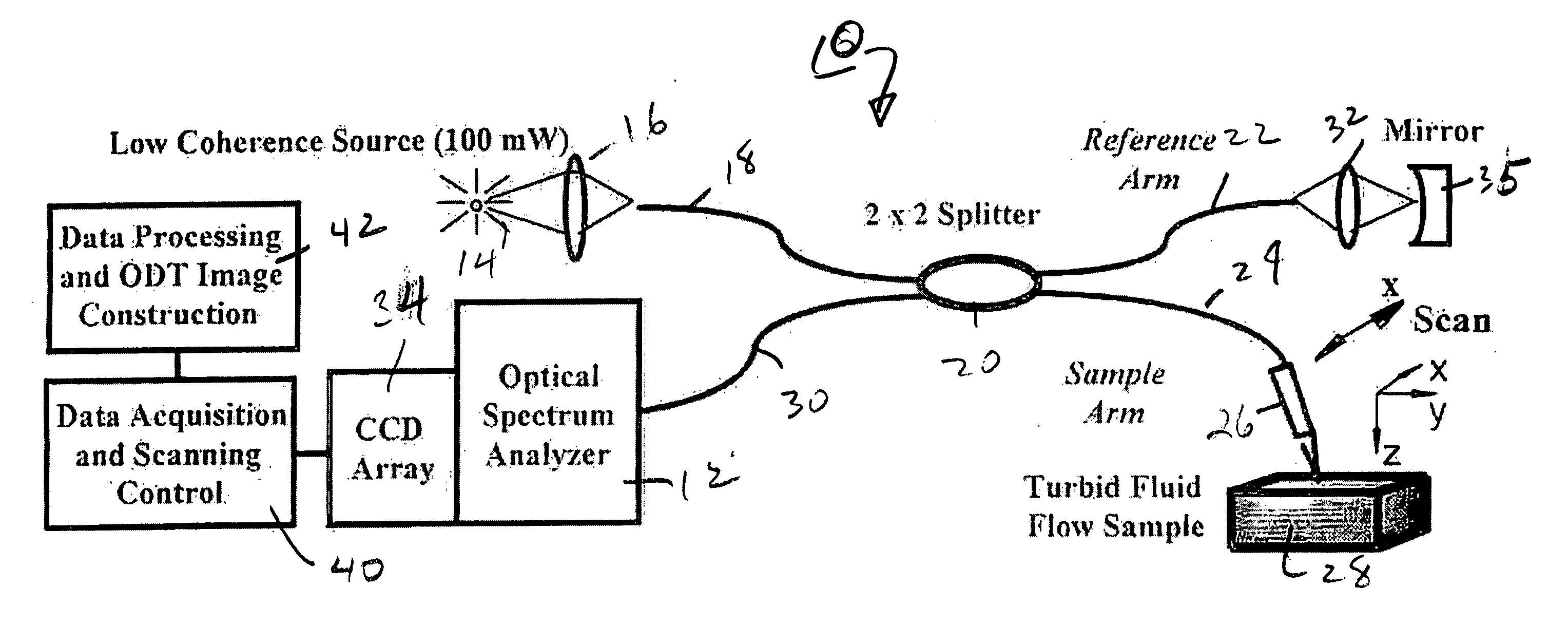
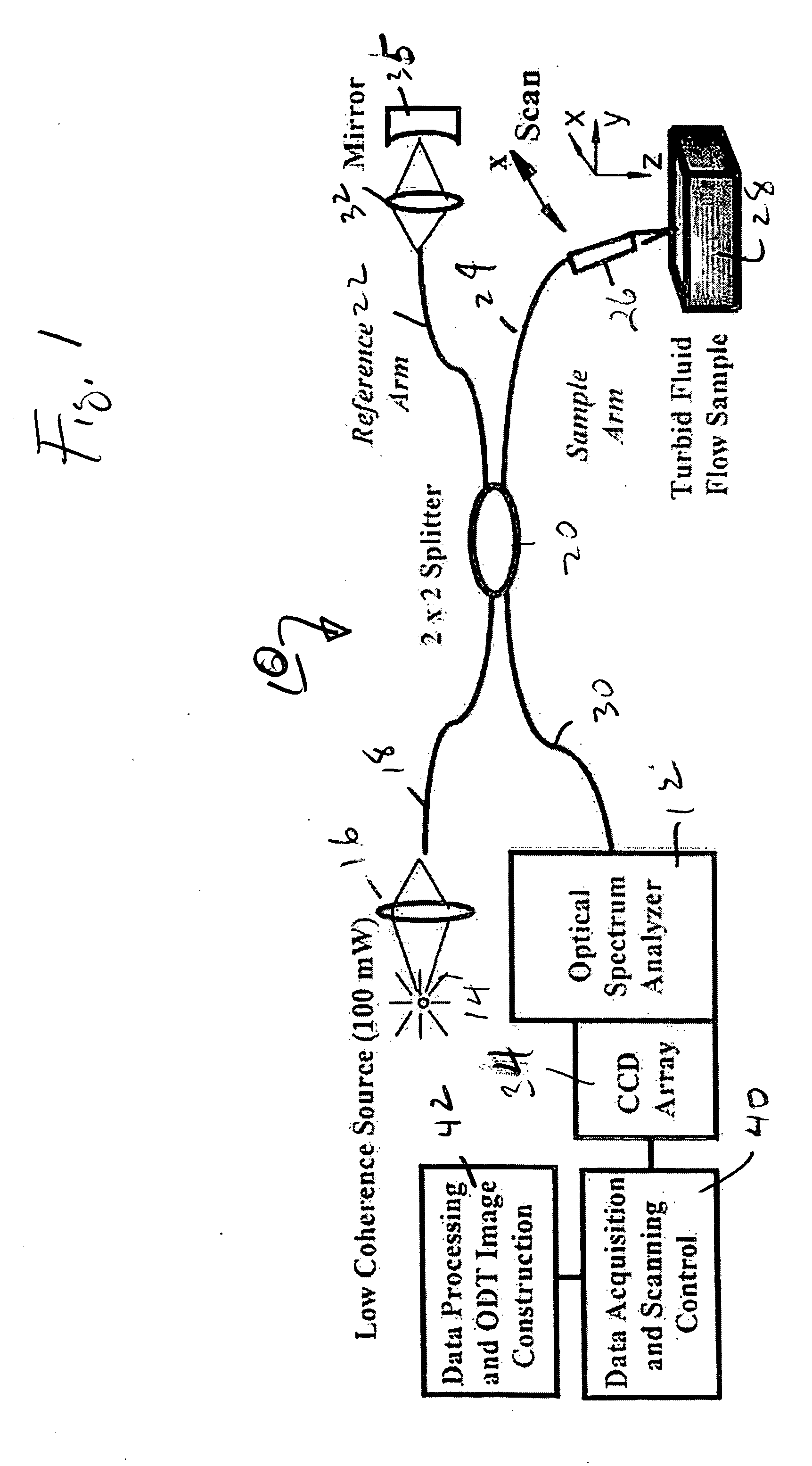
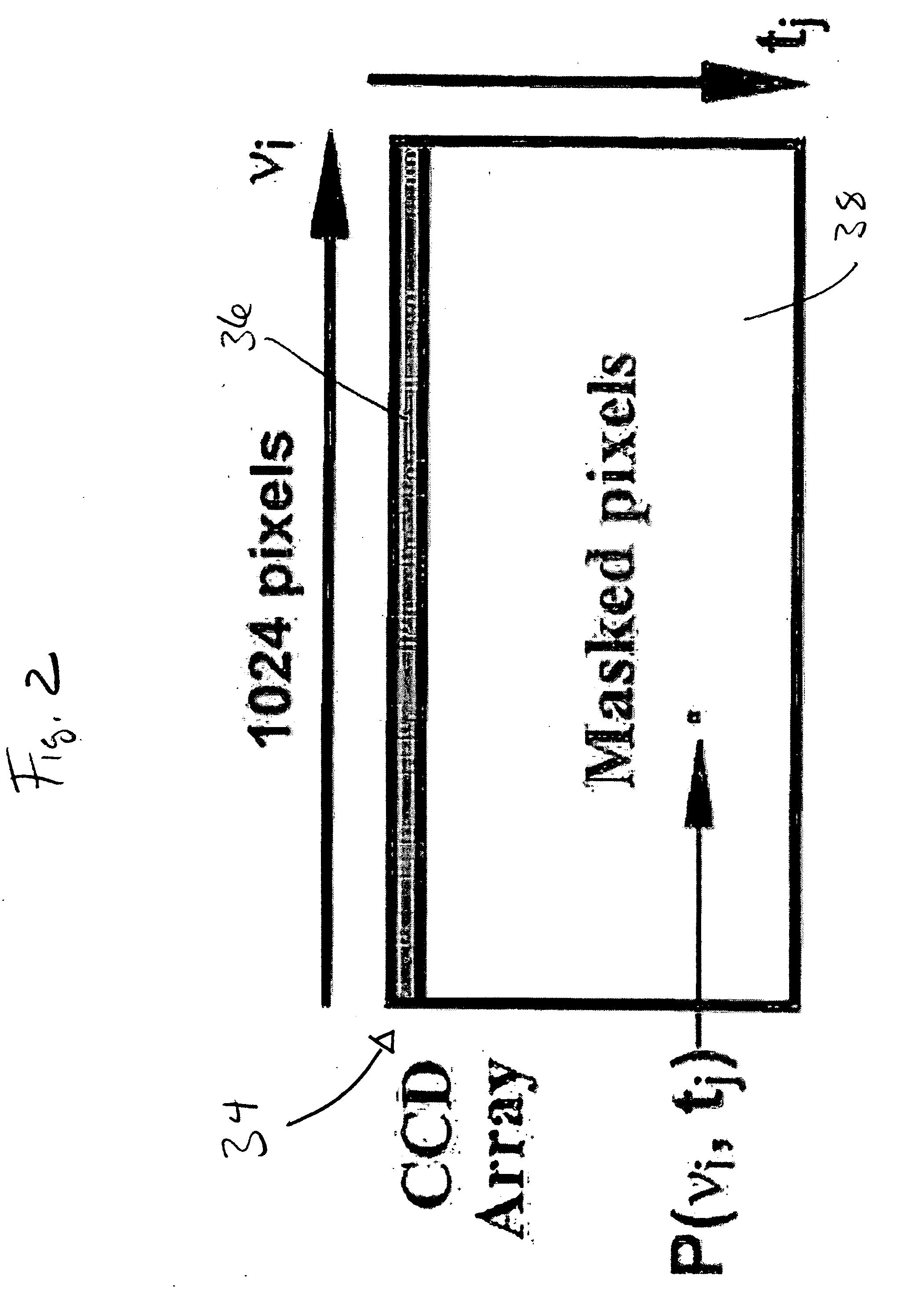
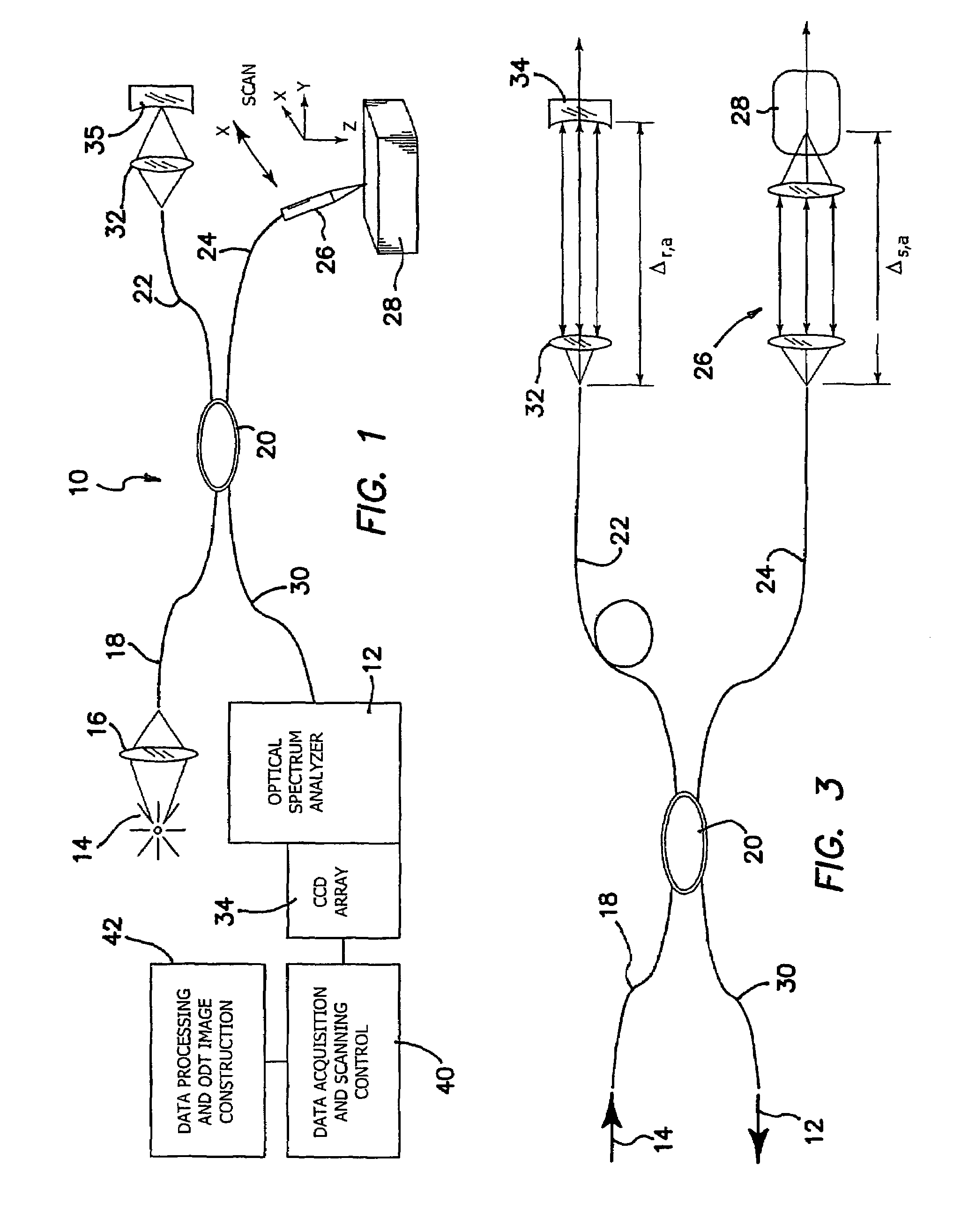
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
ActiveUS20050171438A1Accurate settingImprove system sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBlood flowIn vivo
A method for tomographic imaging comprises the steps of providing a source of at least partially coherent radiation and a frequency-swept laser source through an interferometer; phase modulating the radiation in the interferometer at a modulation frequency for elimination of DC and autocorrelation noises as well as the mirror image; detecting interference fringes of the radiation backscattered from the sample into the interferometer to obtain a spectral signal; transforming the spectral signal of the detected backscattered interference fringes to obtain a time and location dependent signal, including the Doppler shift and variance, at each pixel location in a data window; and generating a tomographic image of the fluid flow in the data window and of the structure of the scanned fluid flow sample in the data window from the time and location dependent signal. The apparatus comprises a system for tomographic imaging operating according to the above method.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Scanning device for coded data
InactiveUS7128270B2Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A scanning device for scanning coded data indicative of a plurality of locations disposed on a surface is provided. The device generates interaction data based on the sensed coded data. The scanning device comprises a laser source for exposing a coded data portion, a photodetector, an analog to digital converter, a framestore, an image processor and a host processor.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
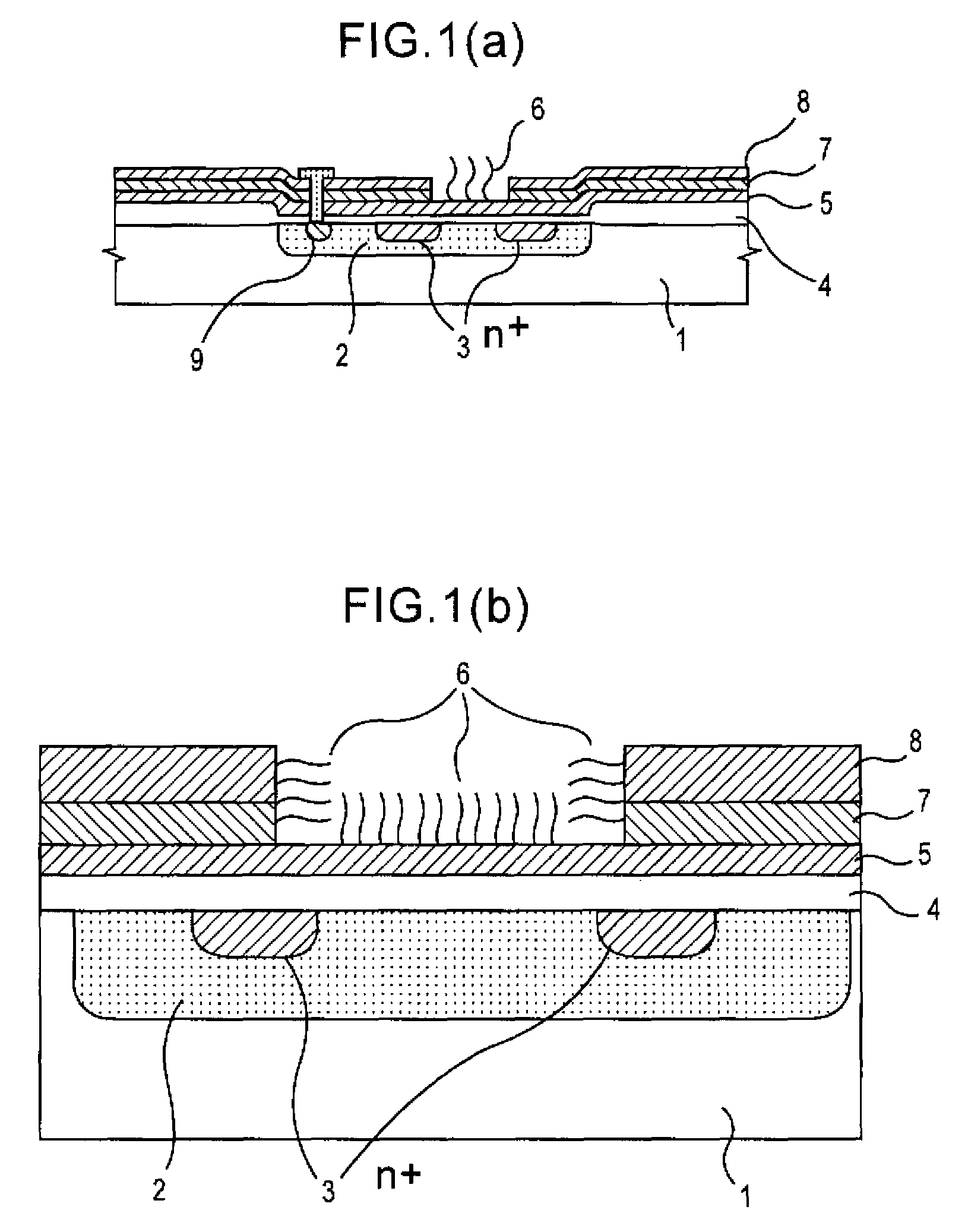
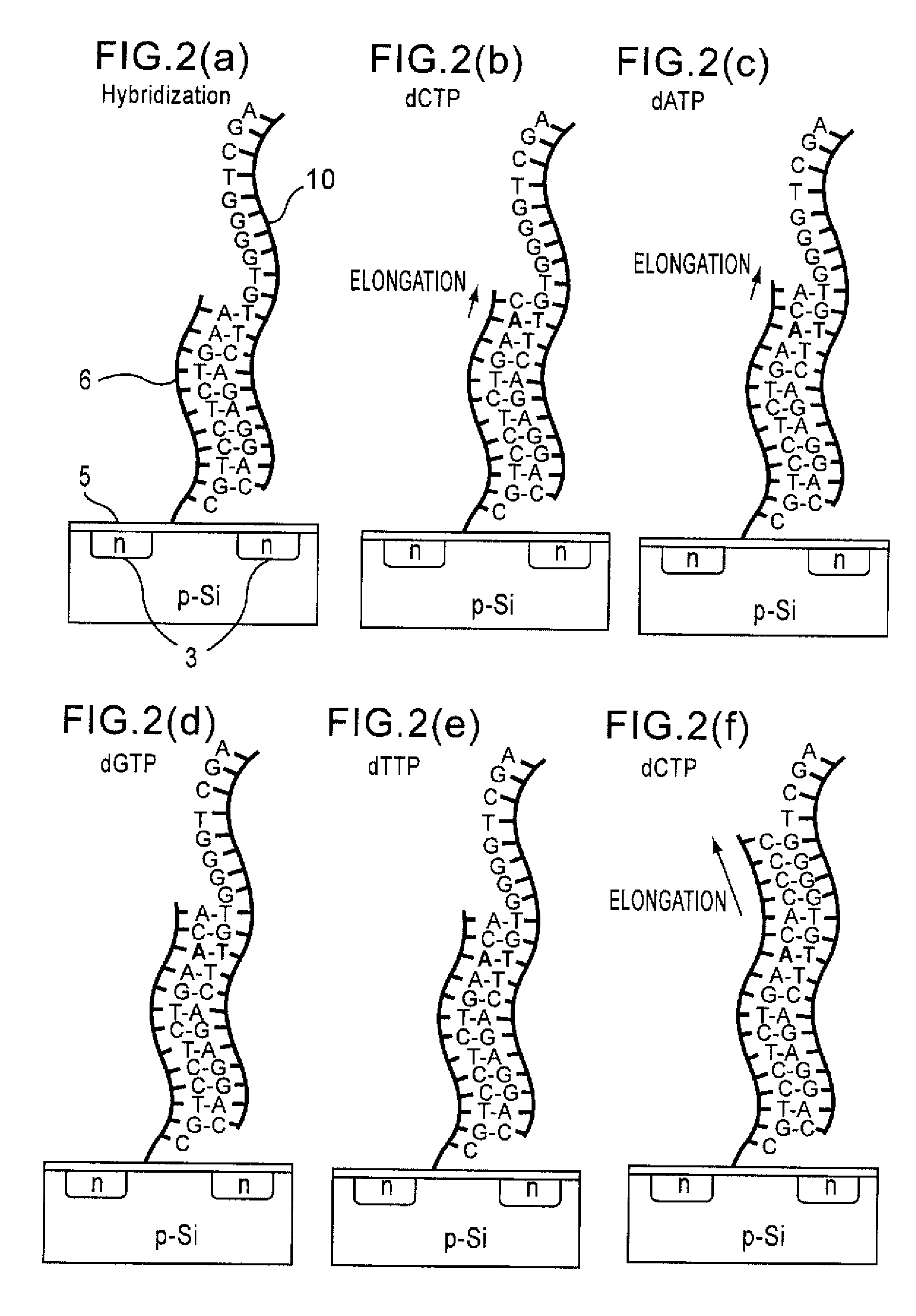
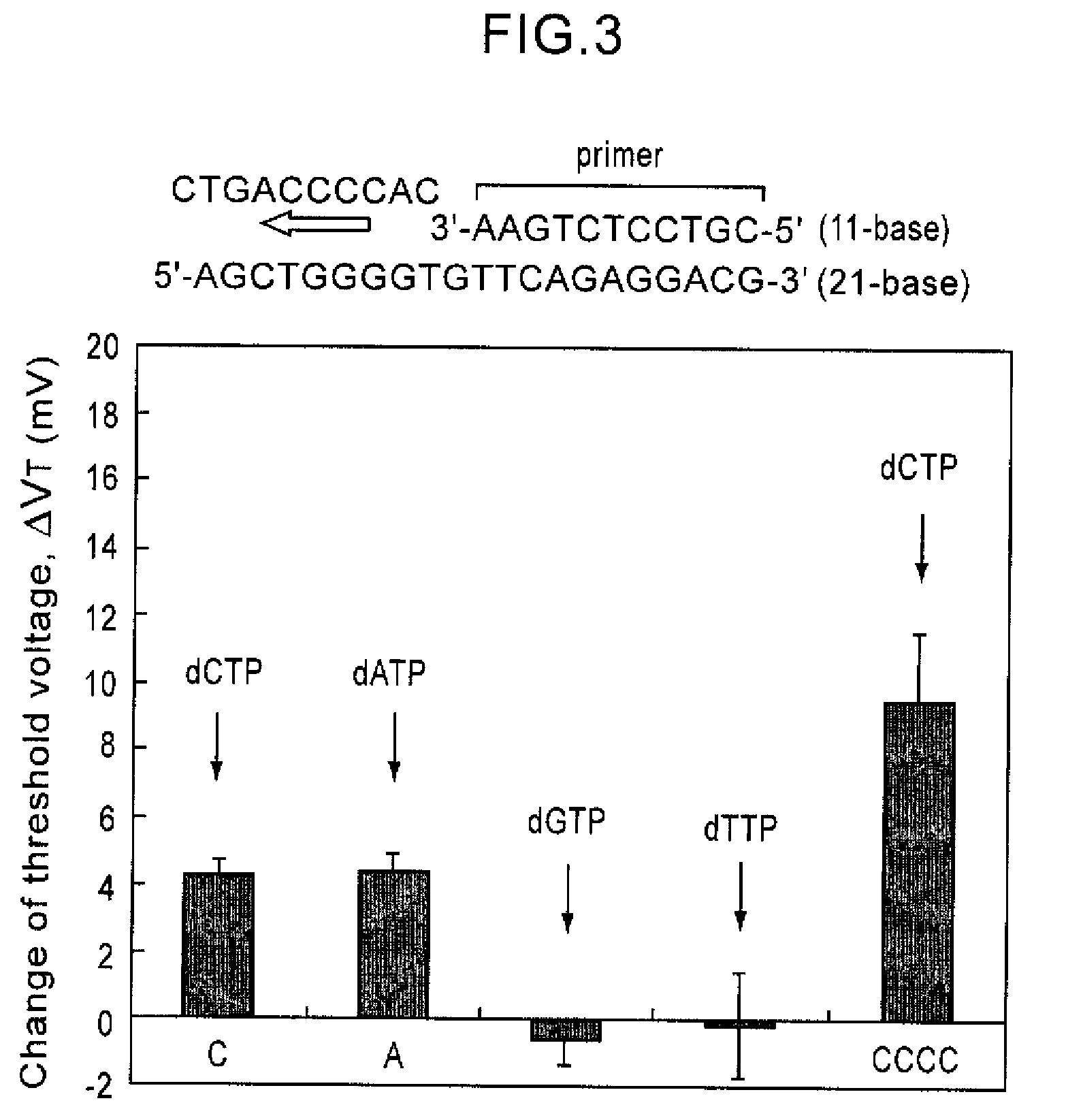
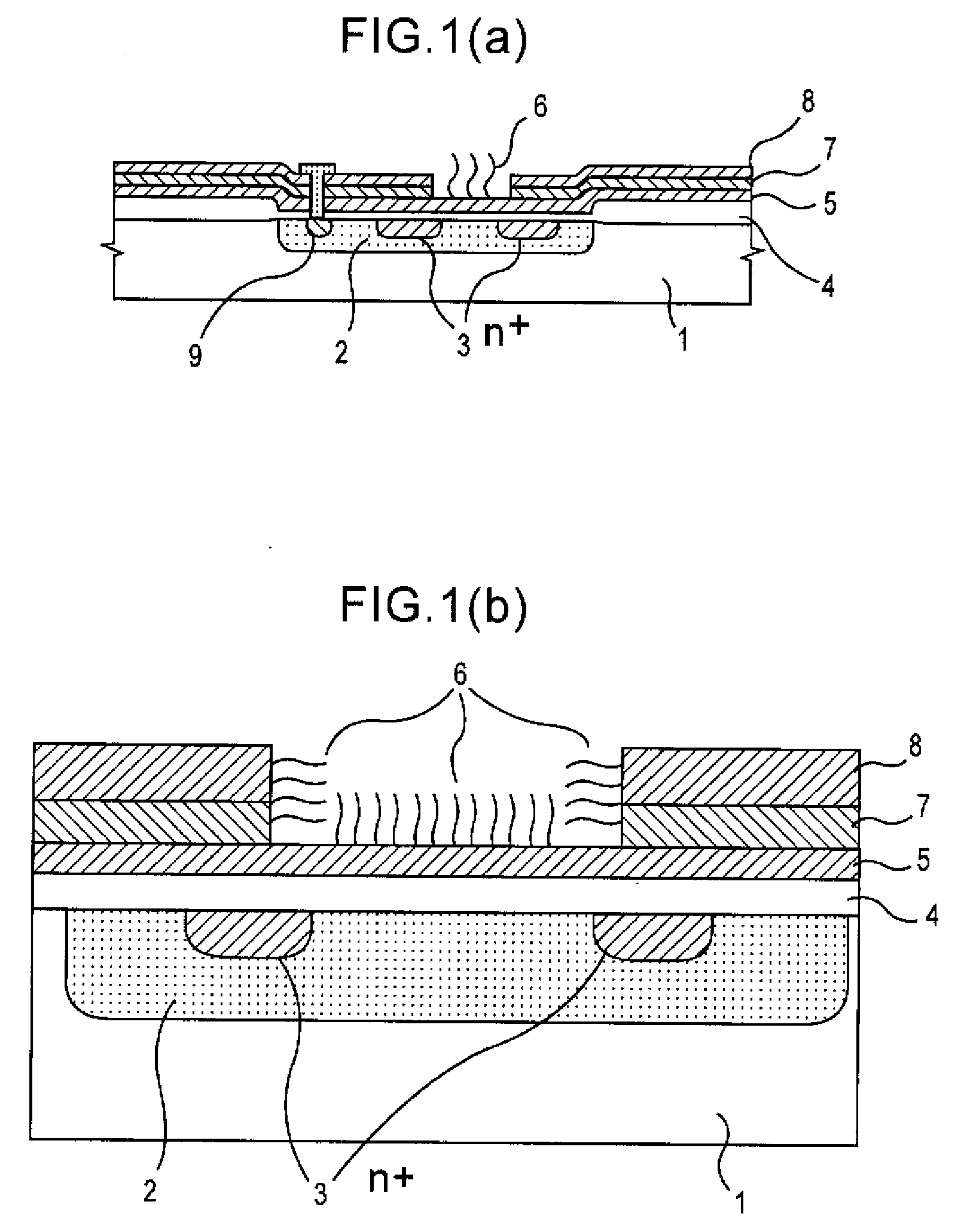
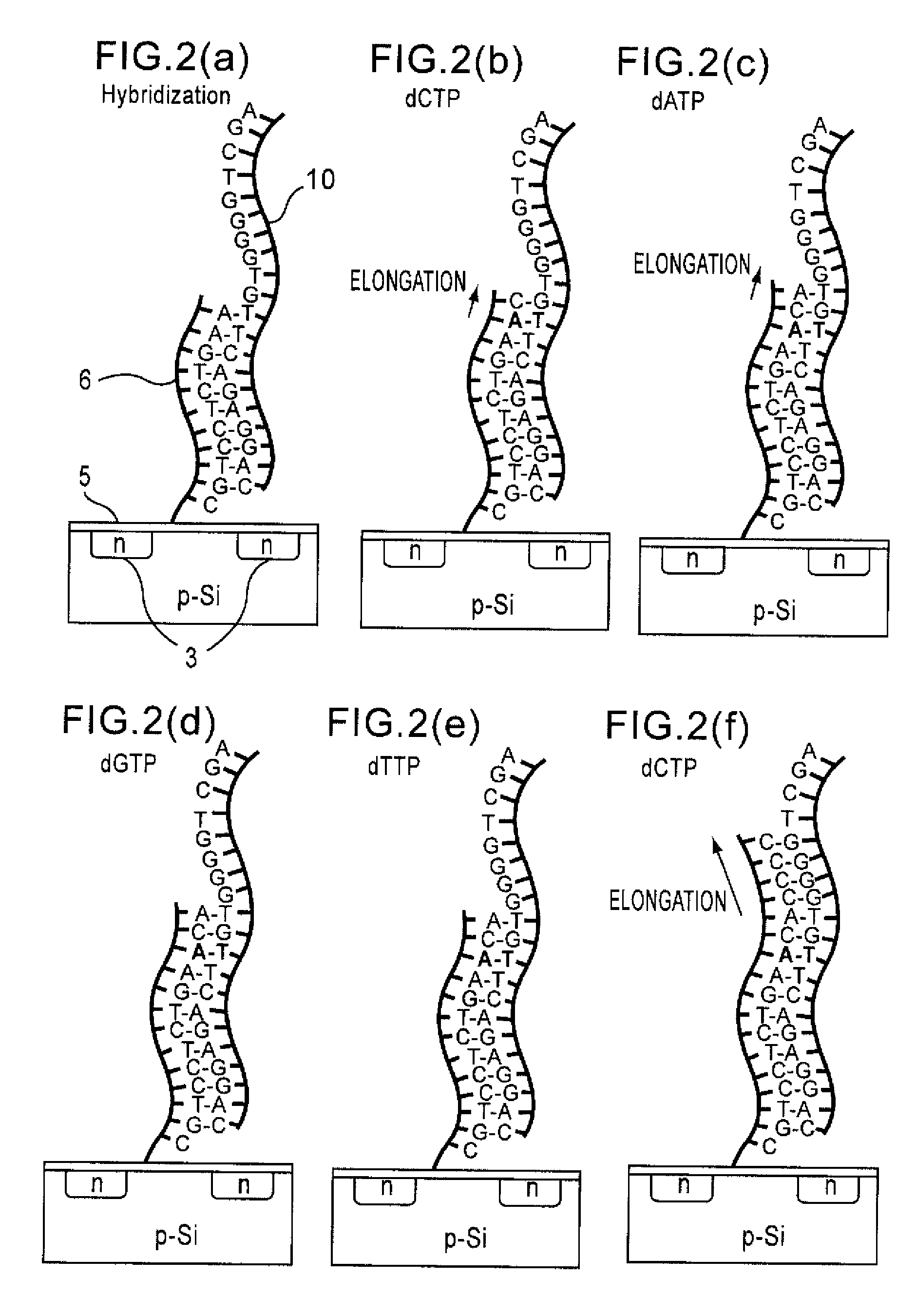
Method of analyzing DNA sequence using field-effect device, and base sequence analyzer
ActiveUS7888013B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
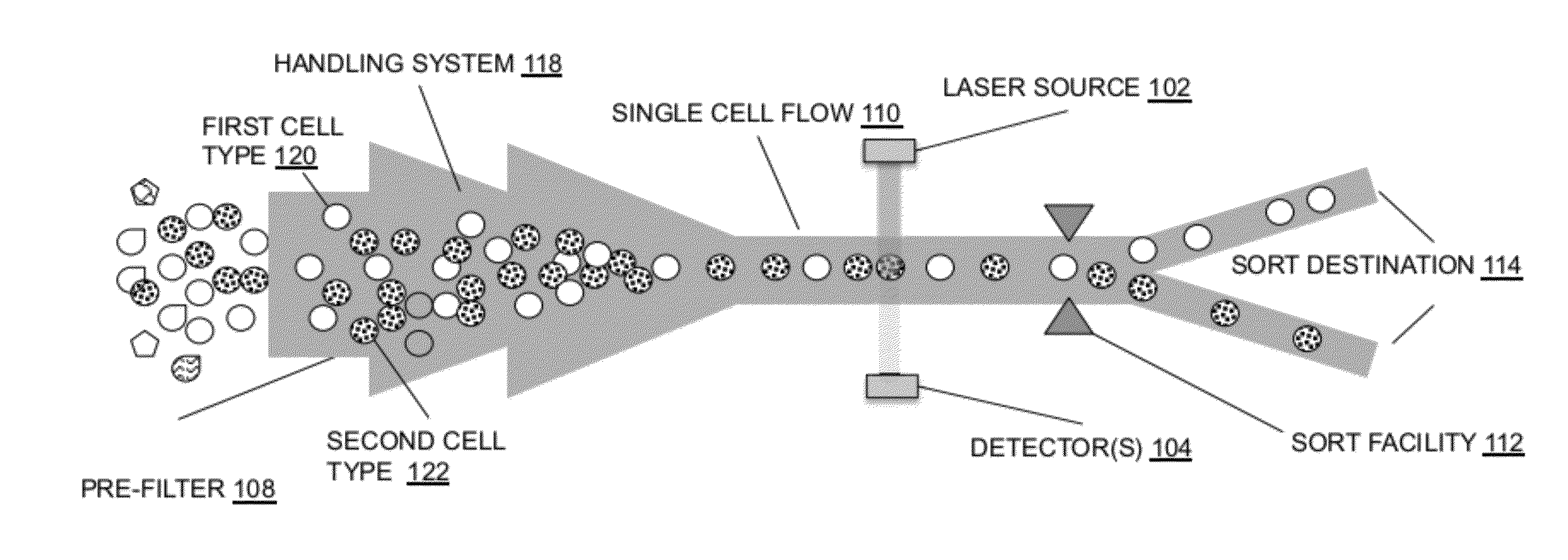
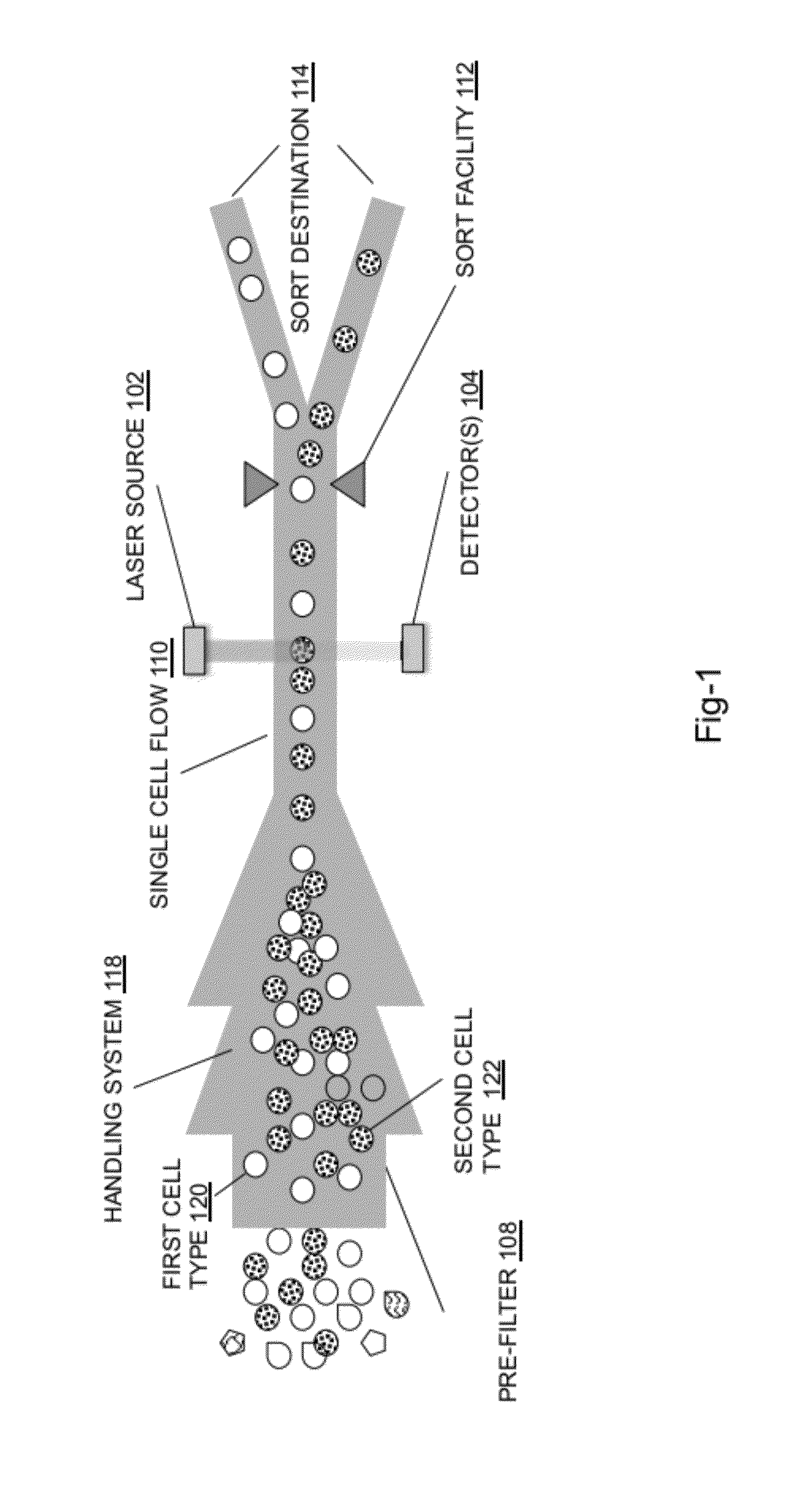
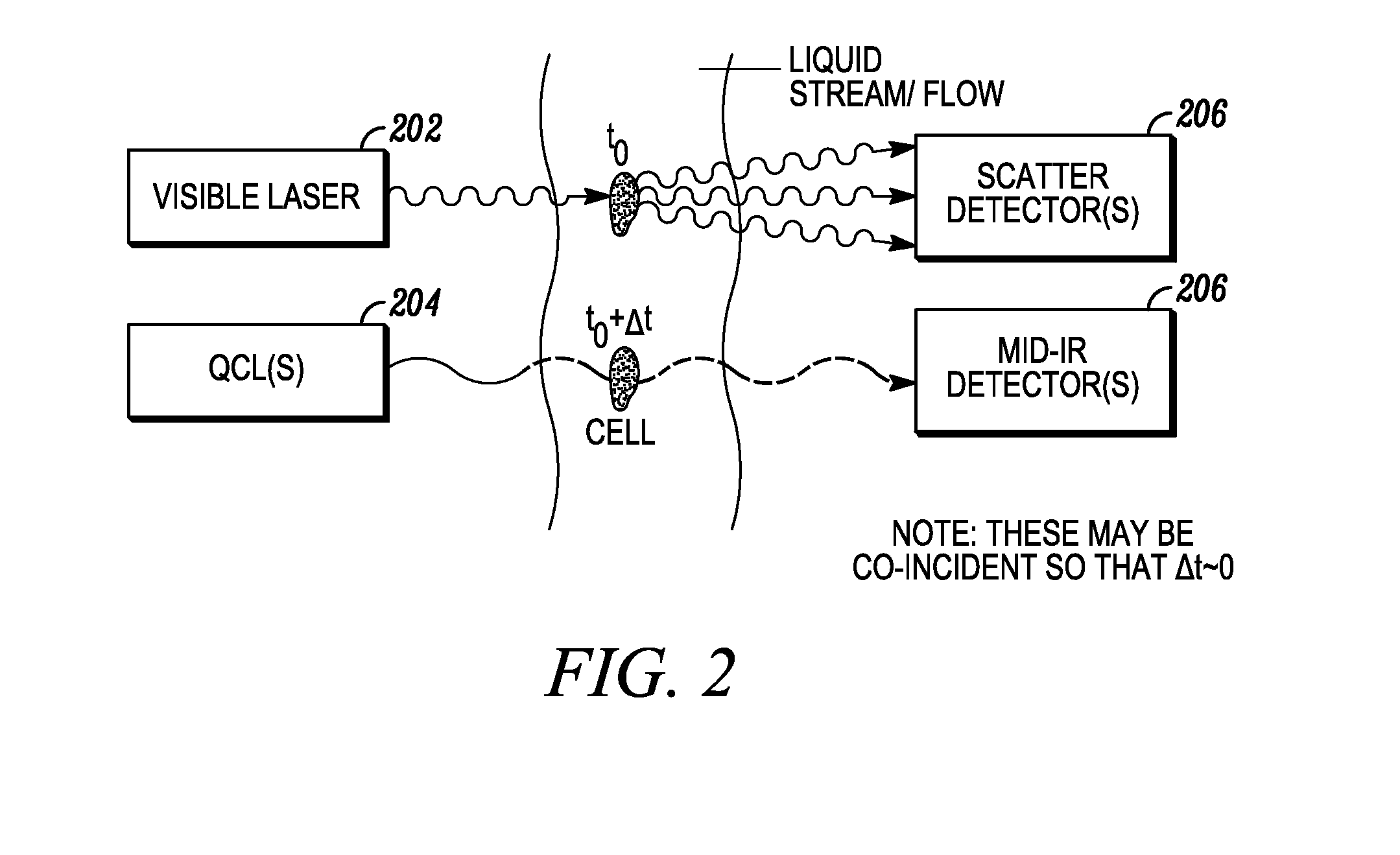
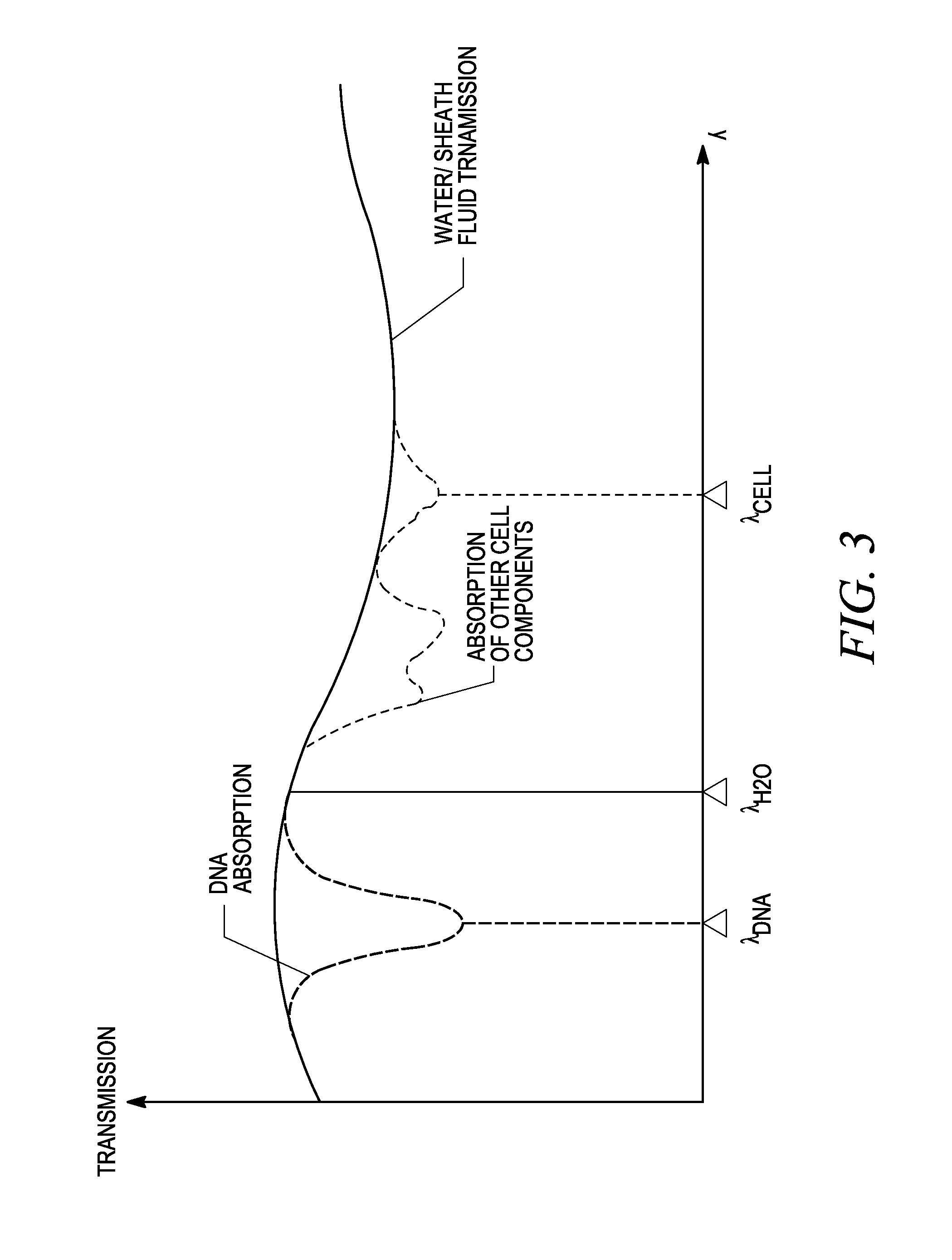
System for identifying and sorting living cells
ActiveUS20120122084A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow cellIr absorption
In embodiments of the present invention, a system and method of cytometry may include presenting a single sperm cell to at least one laser source configured to deliver light to the sperm cell in order to induce bond vibrations in the sperm cell DNA, and detecting the signature of the bond vibrations. The bond vibration signature is used to calculate a DNA content carried by the sperm cell which is used to identify the sperm cell as carrying an X-chromosome or Y-chromosome. Another system and method may include flowing cells past at least one QCL source one-by-one using a fluid handling system, delivering QCL light to a single cell to induce resonant mid-IR absorption by one or more analytes of the cell, and detecting, using a mid-infrared detection facility, the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light, wherein the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light is used to identify a cell characteristic.
Owner:1087 SYST
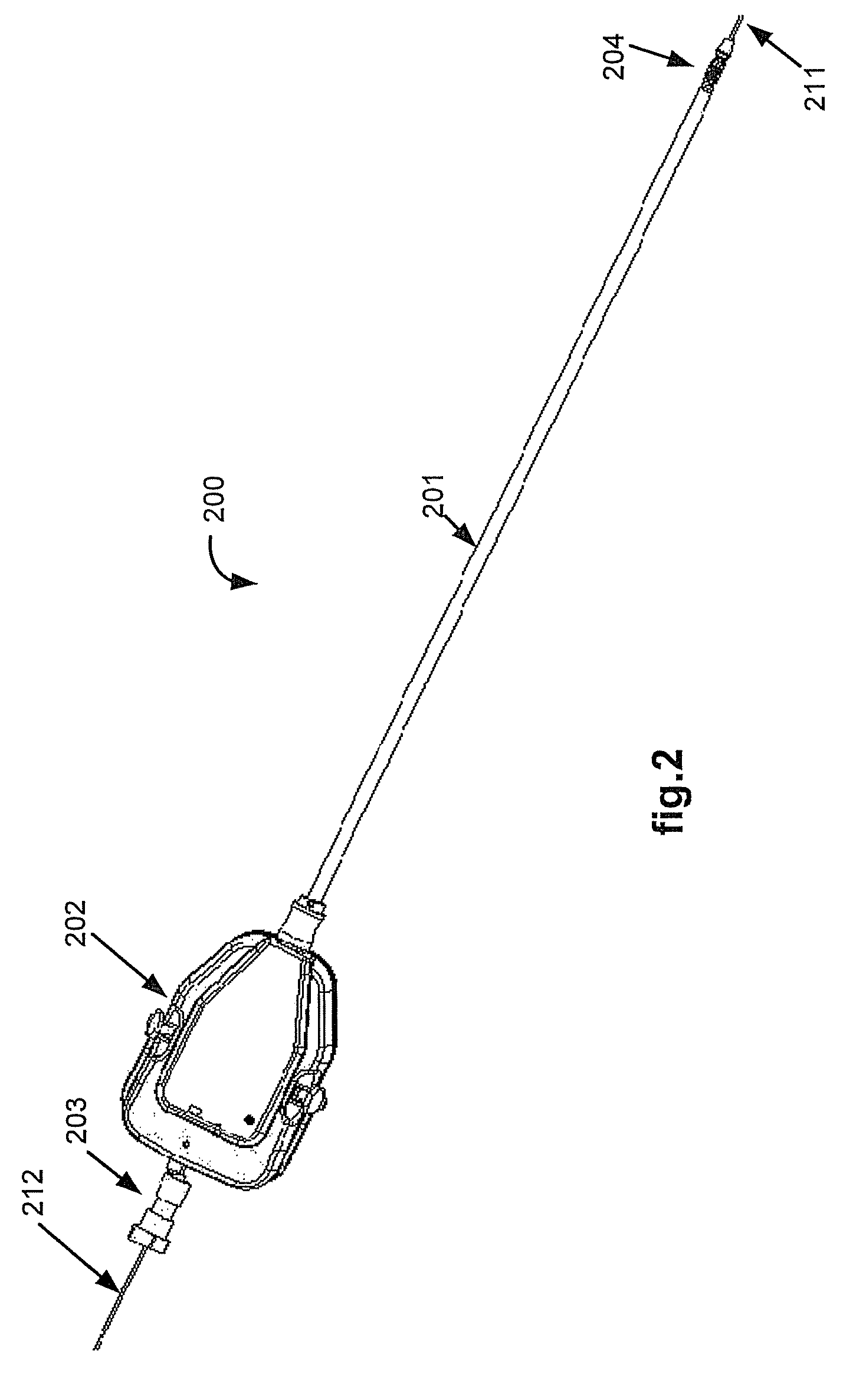
Medical device with orientable tip for robotically directed laser cutting and biomaterial application
A medical device used in a medical robotic system has a conduit and an orientable tip. An optical fiber coupled to a laser source and / or a catheter coupled to one or more biomaterial sources extends through the conduit and tip so that the tip of the medical device may be robotically directed towards a target tissue for laser and / or biomaterial application as part of a medical procedure performed at a surgical site within a patient. A protective sheath covers the fiber as it extends through the conduit and tip. A first coupler adjustably secures at least the sheath to the medical device and a second coupler adjustably secures the fiber to at least the sheath. A similar dual coupler mechanism may be used to secure the sheathed catheter to the medical device.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
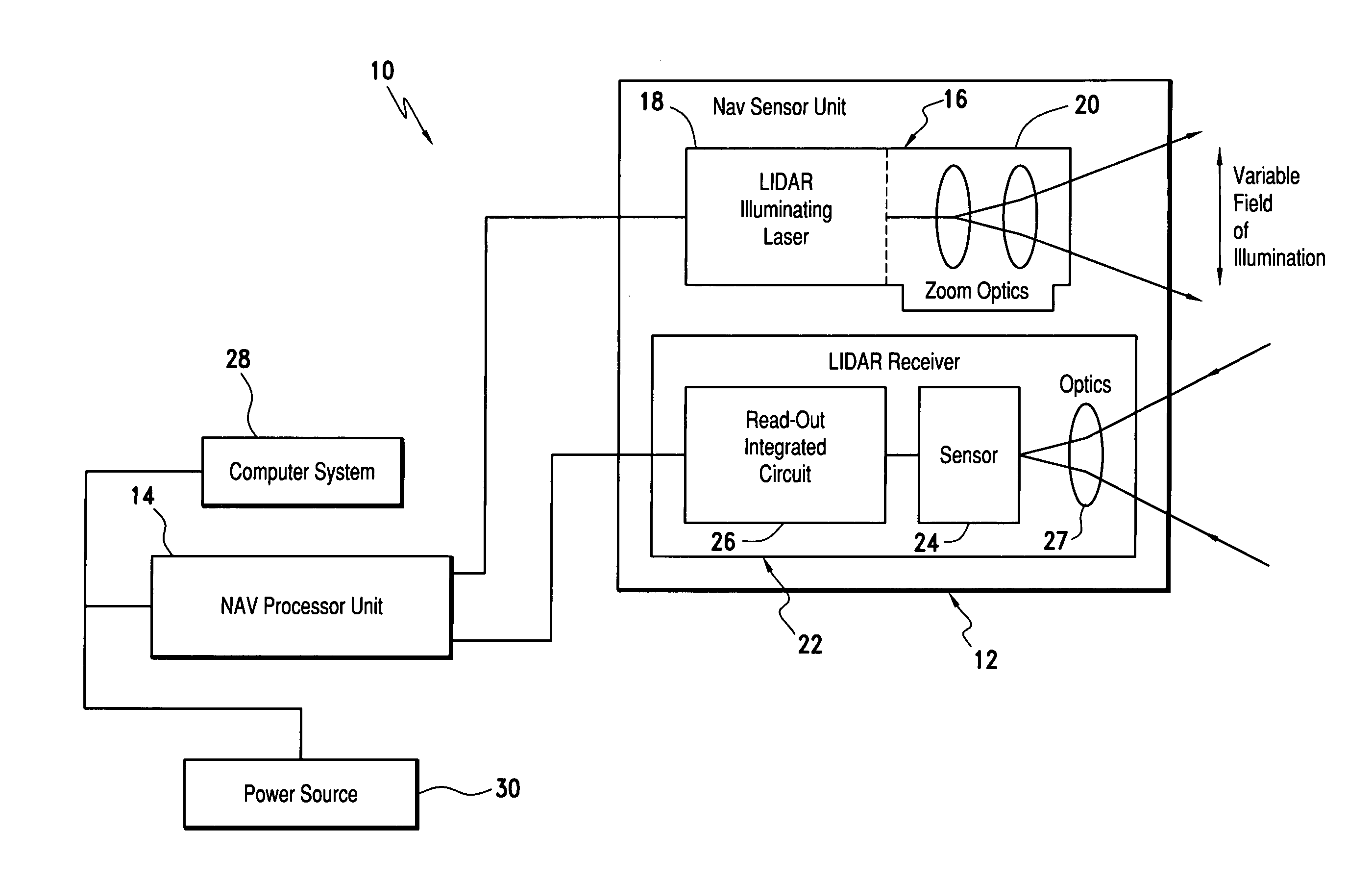
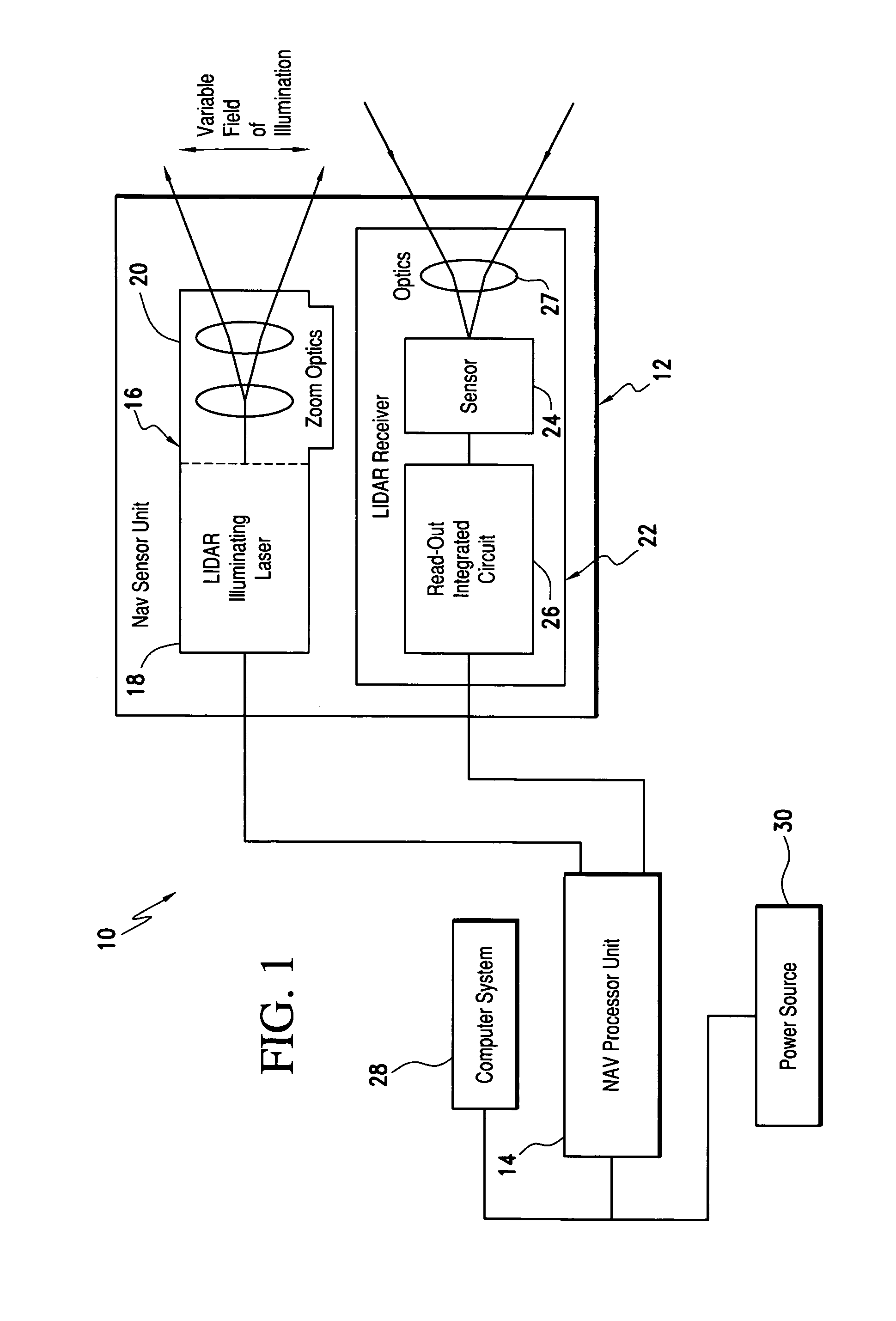
Laser range finding system using variable field of illumination flash lidar
ActiveUS8072581B1Reduce areaReduce resolutionOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingImage resolution
The laser range finding system includes a light detection and ranging (LIDAR) sensor unit (SU) and a LIDAR processor unit (PU). The LIDAR SU is for transmitting light pulses and receiving resulting input light signals reflected from objects within the field of view of the SU. The LIDAR SU includes a flash LIDAR illuminating laser source for transmitting light pulses. The LIDAR illuminating laser source includes an illuminating laser and zoom optics operatively associated with the laser. A LIDAR receiver receives resulting input light signals reflected from the objects. The LIDAR receiver includes a sensor; and, a flash readout integrated circuit (IC). The flash readout IC measures the transit time of the light pulses. The LIDAR processor unit (PU) is operatively associated with the LIDAR SU and it utilizes flash LIDAR ranging. A power source is operatively coupled to the LIDAR PU. Zooming of the transmitted light pulses results in the received resulting input light signals illuminating a relatively reduced area of the frame. Thus, a flash LIDAR image of relatively reduced resolution but enhanced range is provided by utilization of the transit time measurements.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Optical imaging of blood circulation velocities
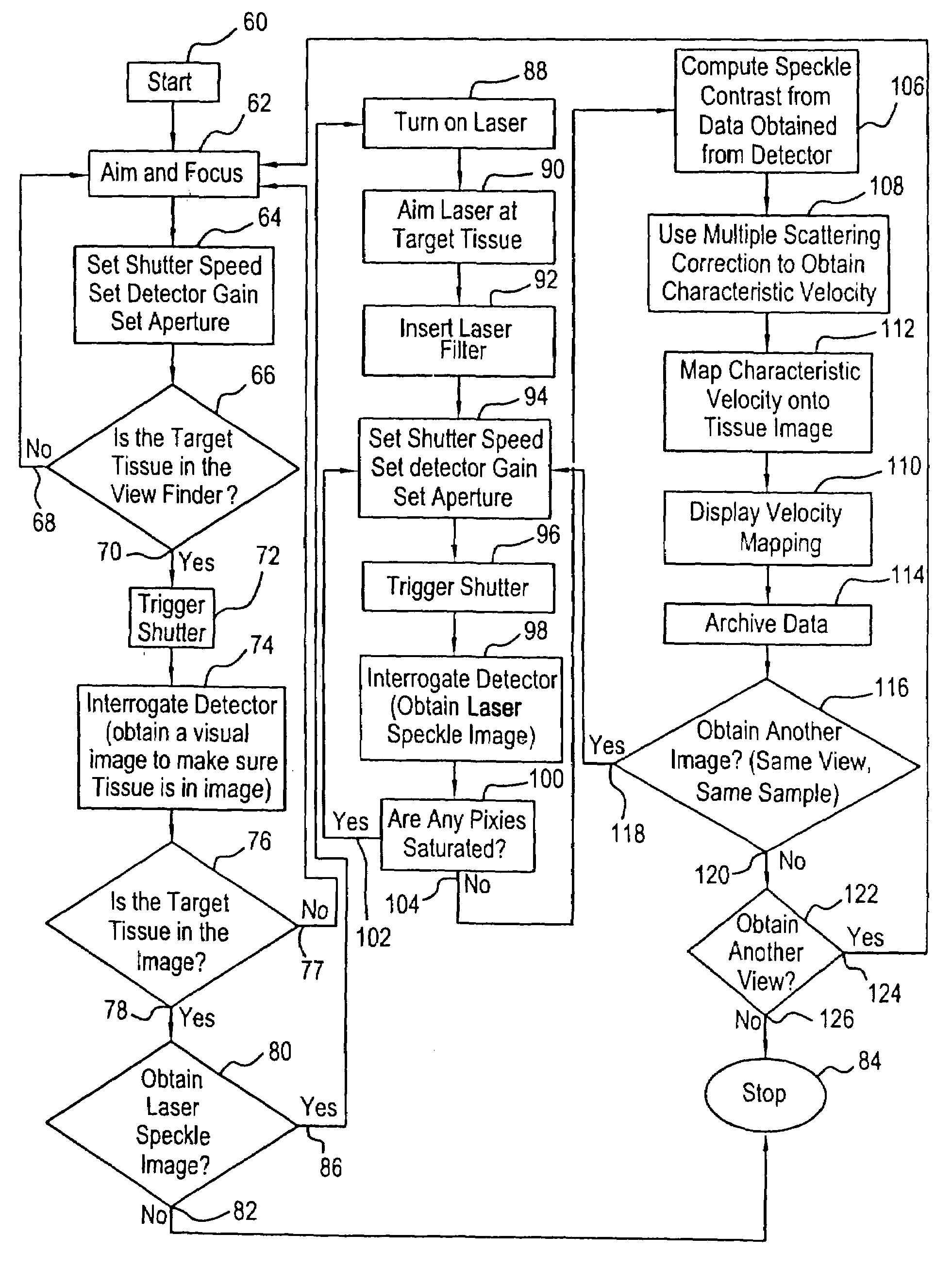
InactiveUS7113817B1Reduce the impactImprove accuracyTesting eggsDiagnostics using lightDigital imagingDetector array
New devices and methods are provided for noninvasive and noncontact real-time measurements of tissue blood velocity. The invention uses a digital imaging device such as a detector array that allows independent intensity measurements at each pixel to capture images of laser speckle patterns on any surfaces, such as tissue surfaces. The laser speckle is generated by illuminating the surface of interest with an expanded beam from a laser source such as a laser diode or a HeNe laser as long as the detector can detect that particular laser radiation. Digitized speckle images are analyzed using new algorithms for tissue optics and blood optics employing multiple scattering analysis and laser Doppler velocimetry analysis. The resultant two-dimensional images can be displayed on a color monitor and superimposed on images of the tissues.
Owner:WINTEC LLC
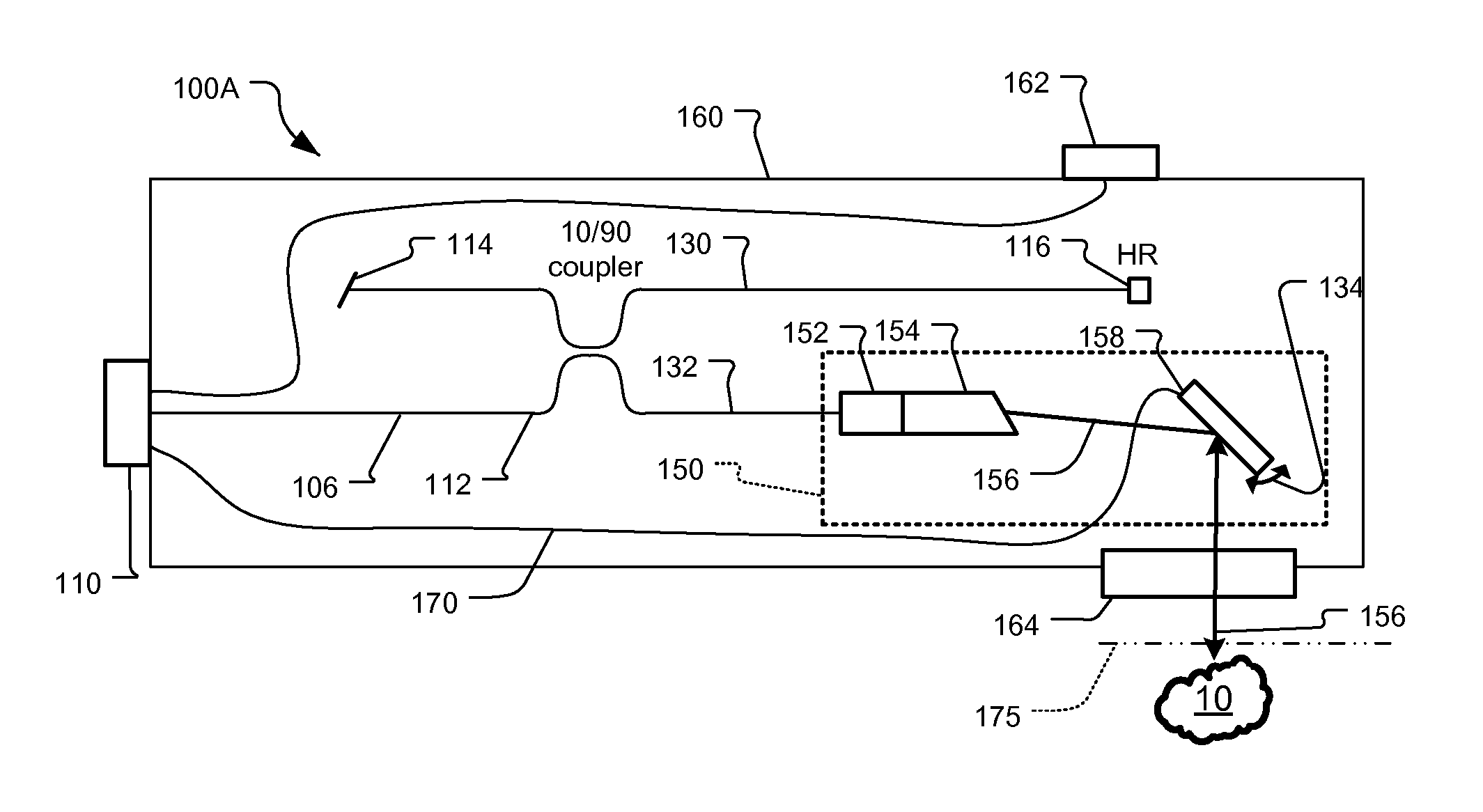
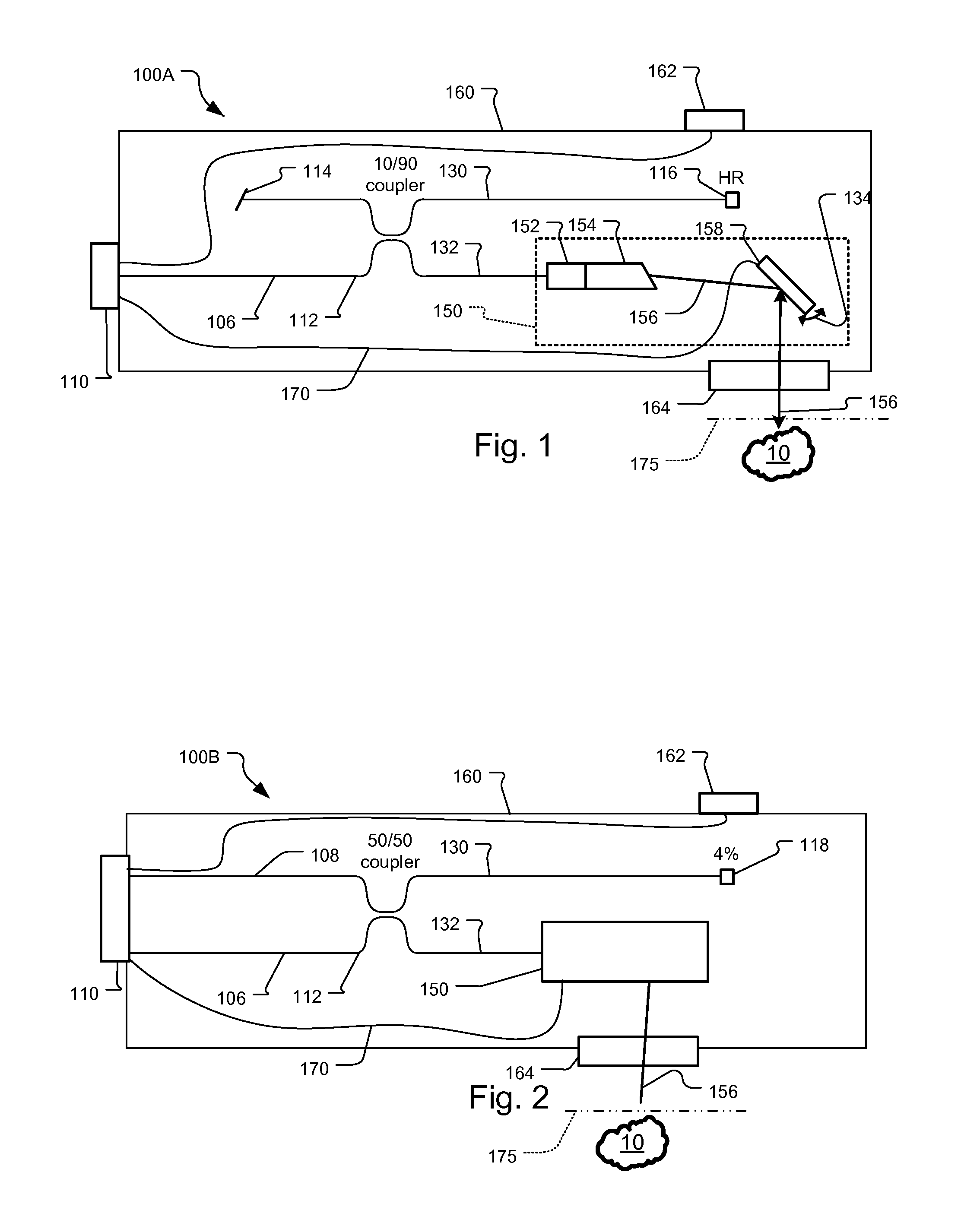
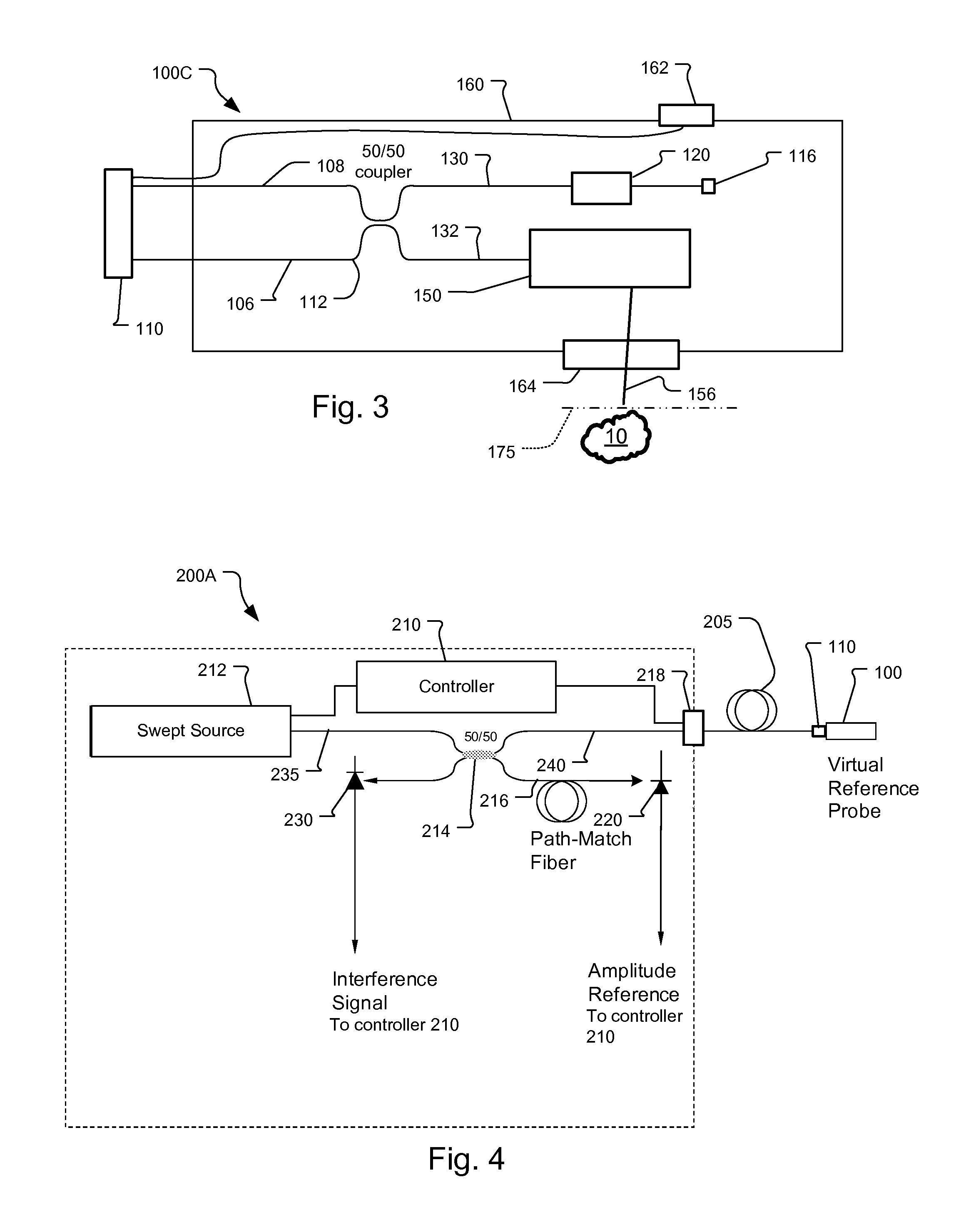
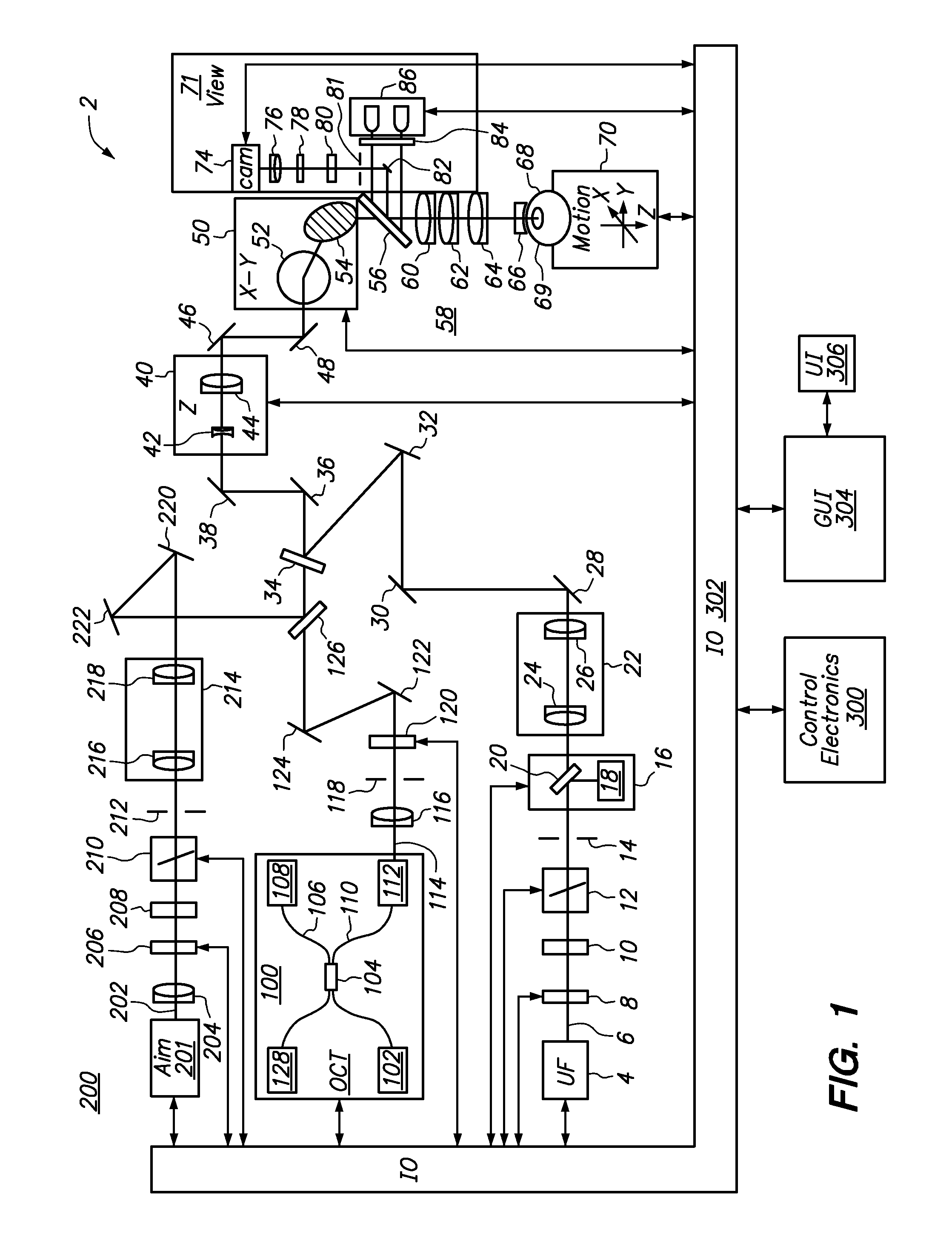
OCT Combining Probes and Integrated Systems
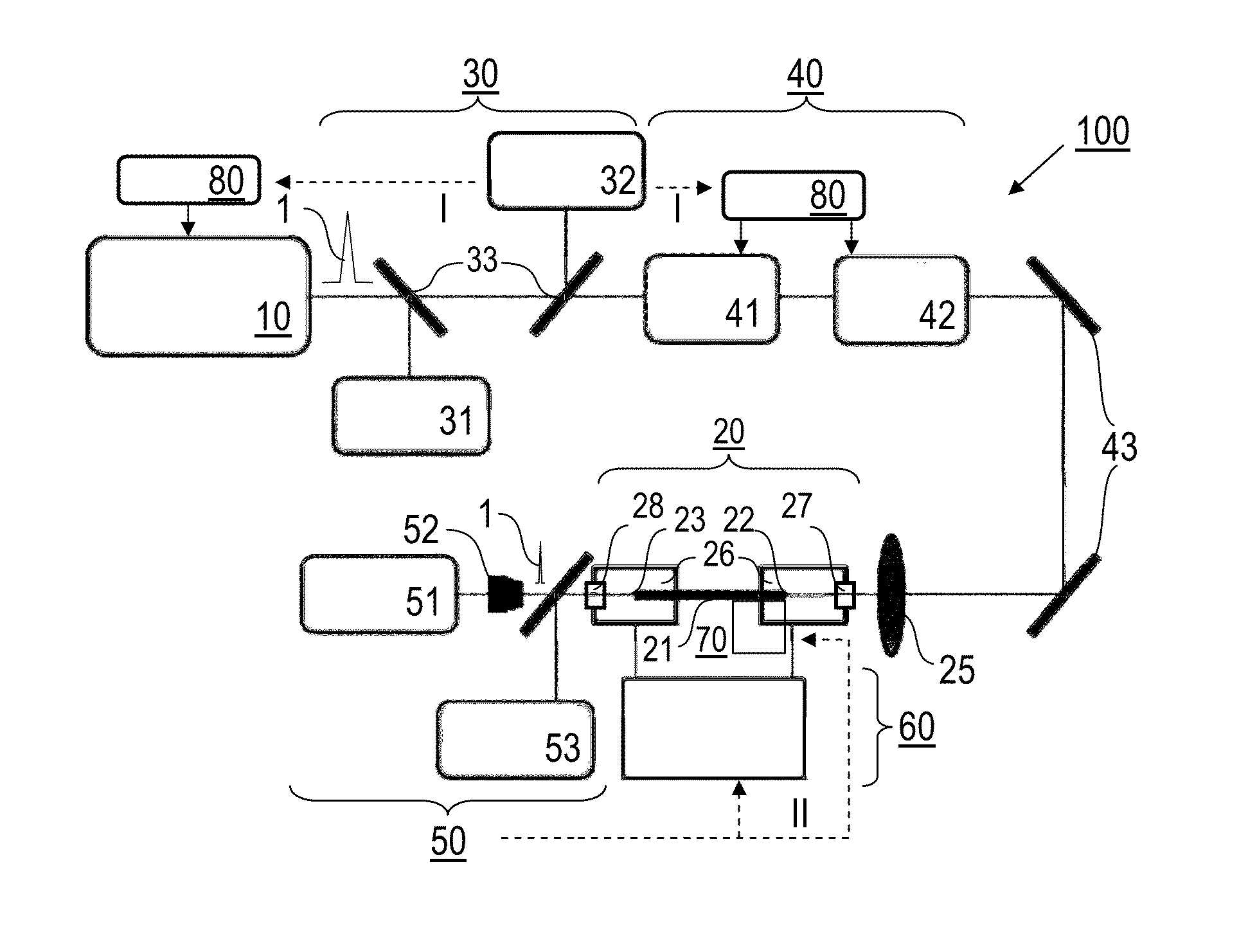
ActiveUS20090284749A1Noise minimizationInterference minimizationInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansSystems designLaser source
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) probe and system designs are disclosed that minimize the effects of mechanical movement and strain to the probe to the OCT analysis. It also concerns optical designs that are robust against noise from the OCT laser source. Also integrated OCT system-probes are included that yield compact and robust electro-opto-mechanical systems along with polarization sensitive OCT systems.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
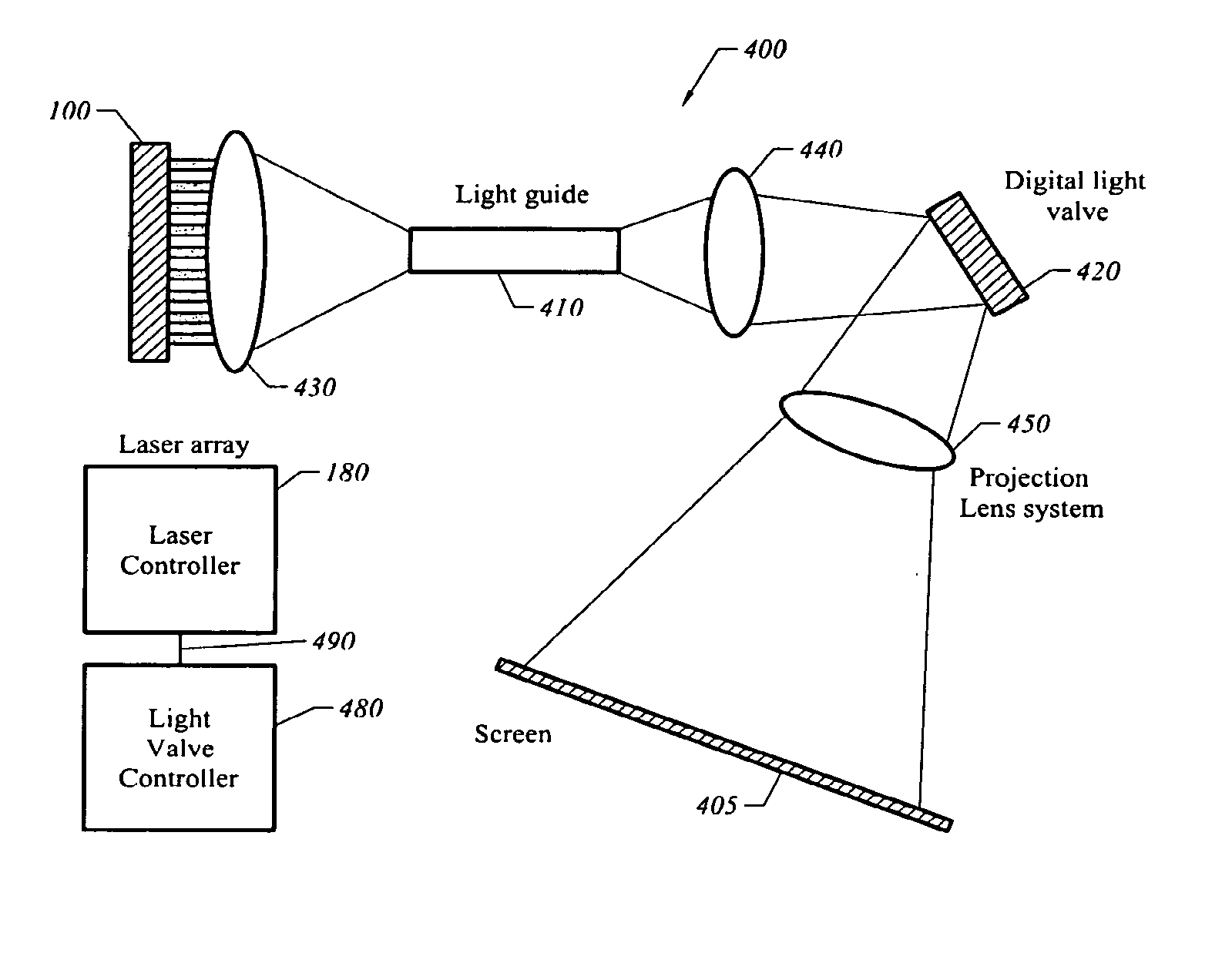
System and method for driving semiconductor laser sources for displays
InactiveUS20060268241A1Television system detailsLaser using scattering effectsDisplay deviceSemiconductor
A light engine includes a multi-color laser source having a set of semiconductor lasers. A controller synchronizes the operation of the laser source to operate in a color sequential order with a spatial modulator.
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
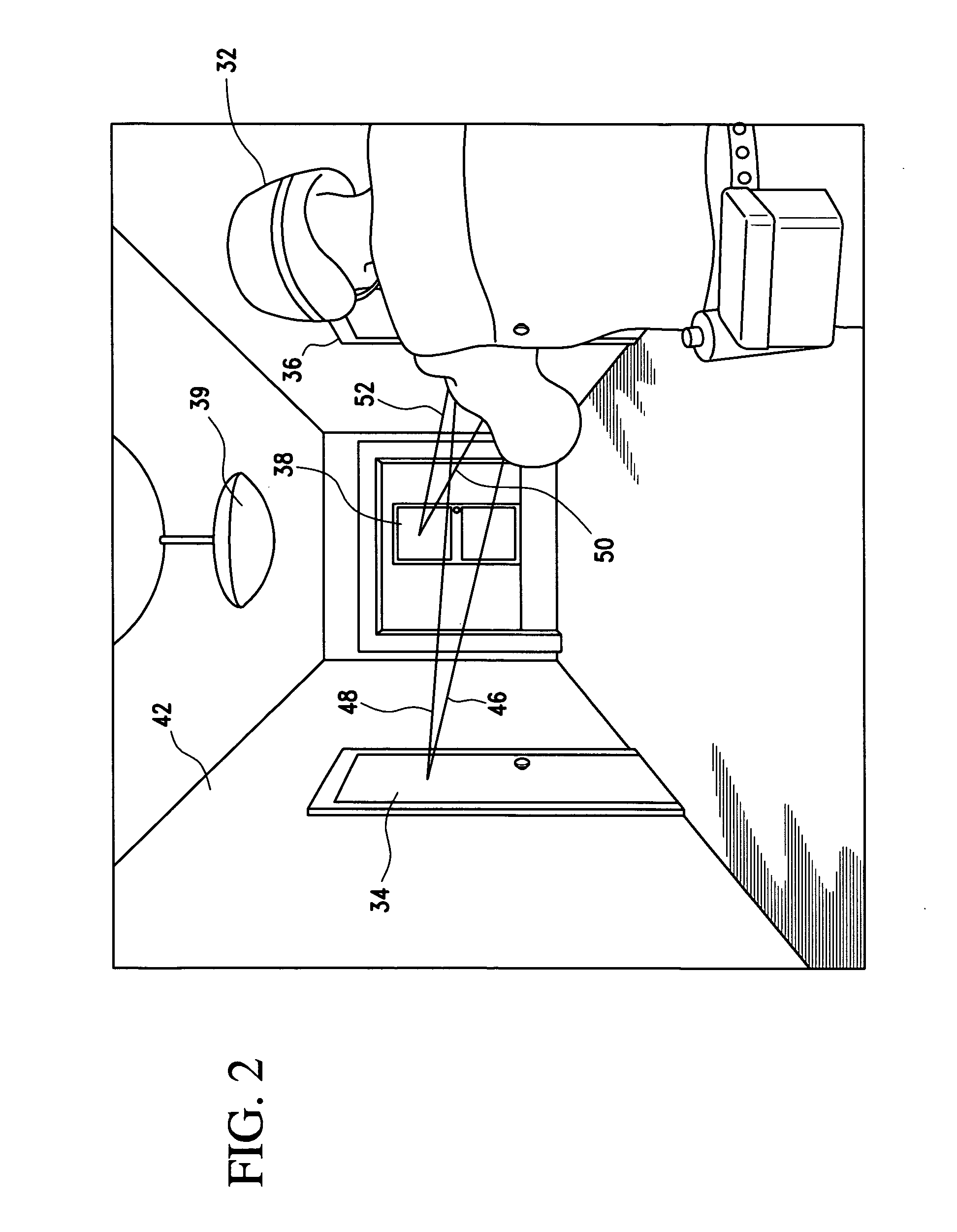
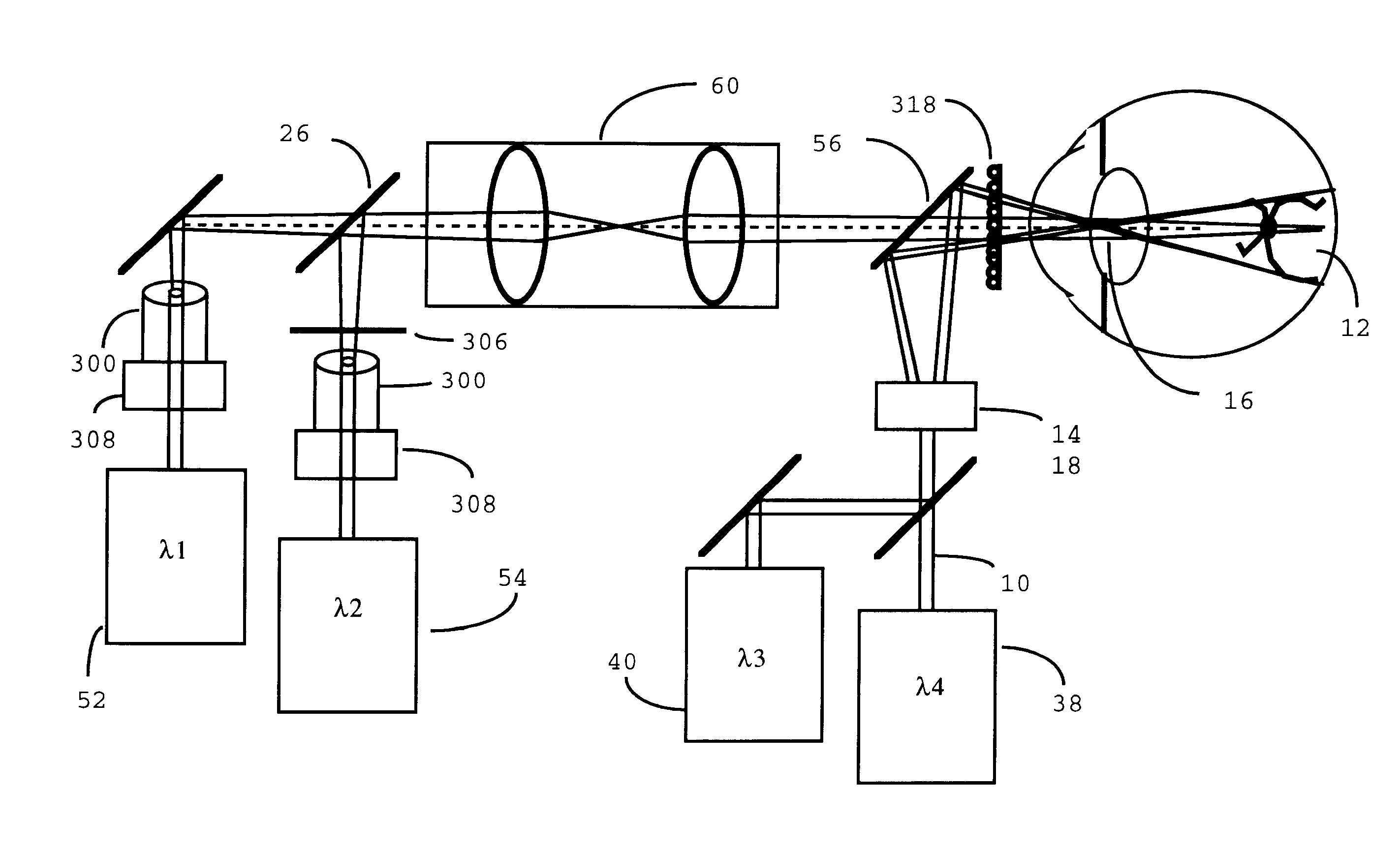
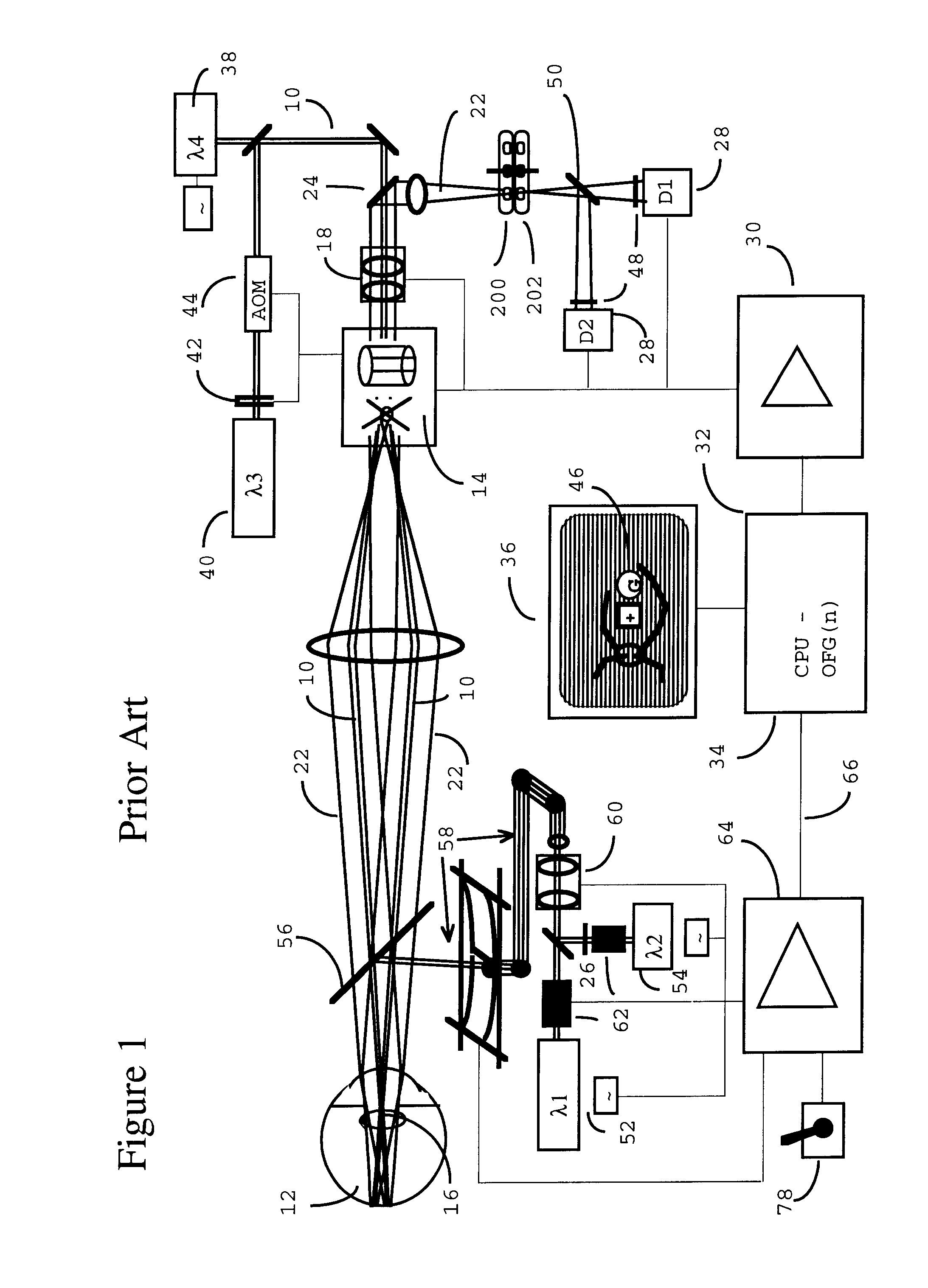
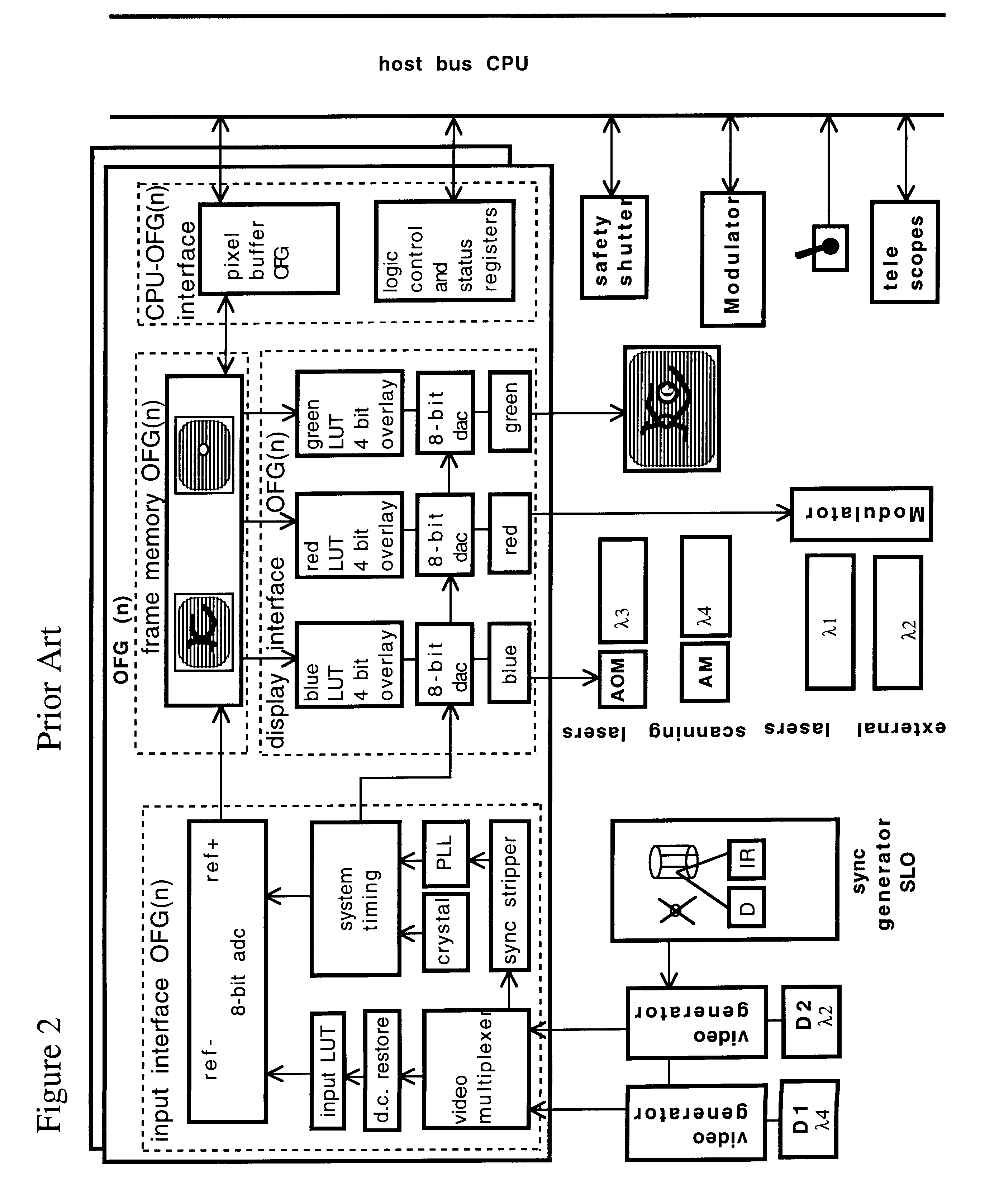
Scanning laser ophthalmoscope for selective therapeutic laser
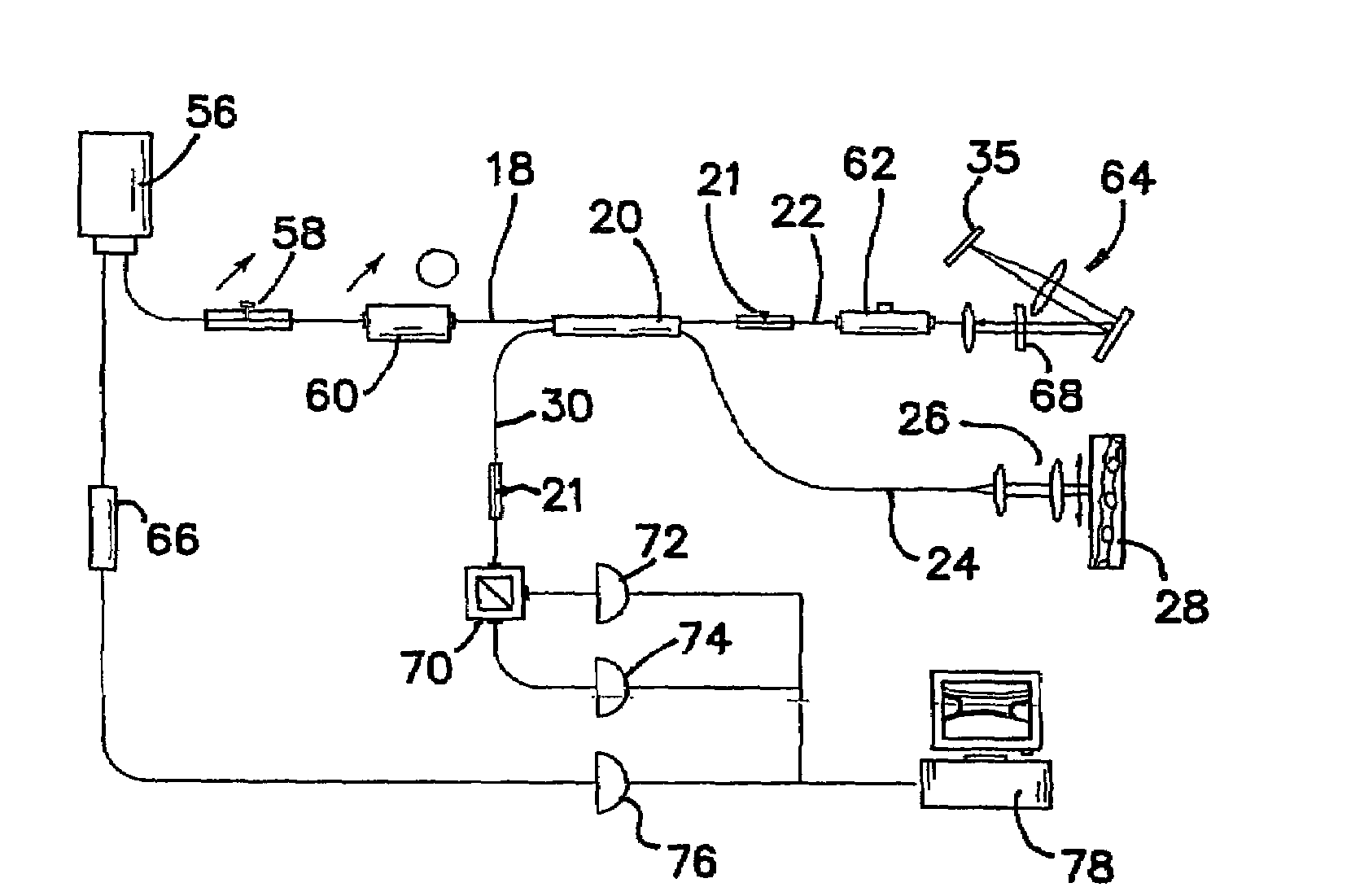
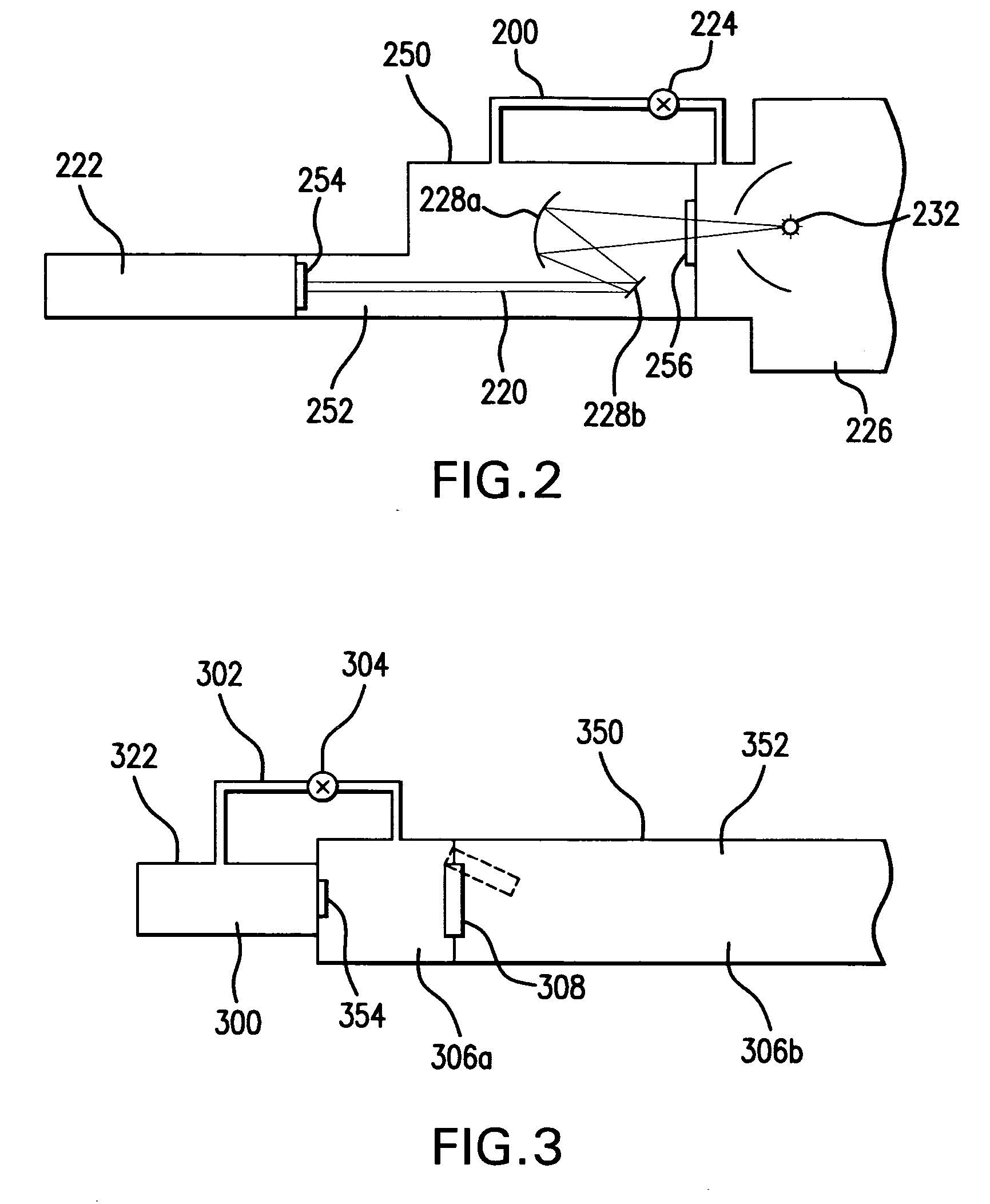
A combination of a scanning laser ophthalmoscope and external laser sources (52) is used for microphotocoagulation and photodynamic therapy, two examples of selective therapeutic laser. A linkage device incorporating a beamsplitter (56) and collimator-telescope (60) is adjusted to align the pivot point (16) of the scanning lasers (38, 40) and external laser source (52). A similar pivot point minimizes wavefront aberrations, enables precise focusing and registration of the therapeutic laser beam (52) on the retina without the risk of vignetting. One confocal detection pathway of the scanning laser ophthalmoscope images the retina. A second and synchronized detection pathway with a different barrier filter (48) is needed to draw the position and extent of the therapeutic laser spot on the retinal image, as an overlay (64). Advanced spatial modulation increases the selectivity of the therapeutic laser. In microphotocoagulation, an adaptive optics lens (318) is attached to the scanning laser ophthalmoscope, in proximity of the eye. It corrects the higher order optical aberrations of the eye optics, resulting in smaller and better focused applications. In photodynamic therapy, a spatial modulator (420) is placed within the collimator-telescope (60) of the therapeutic laser beam (52), customizing its shape as needed. A similar effect can be obtained by modulating a scanning laser source (38) of appropriate wavelength for photodynamic therapy.
Owner:VAN DE VELDE JOZEK F
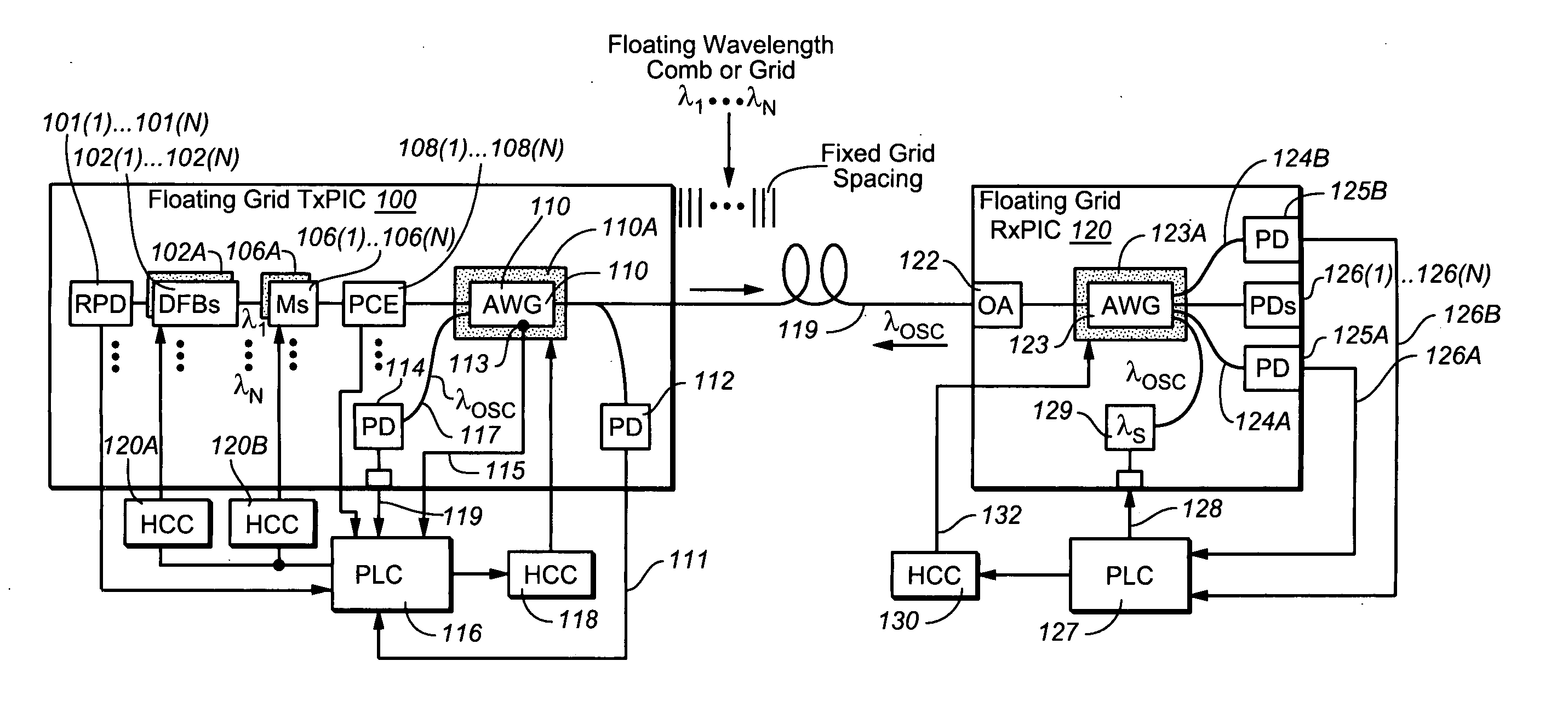
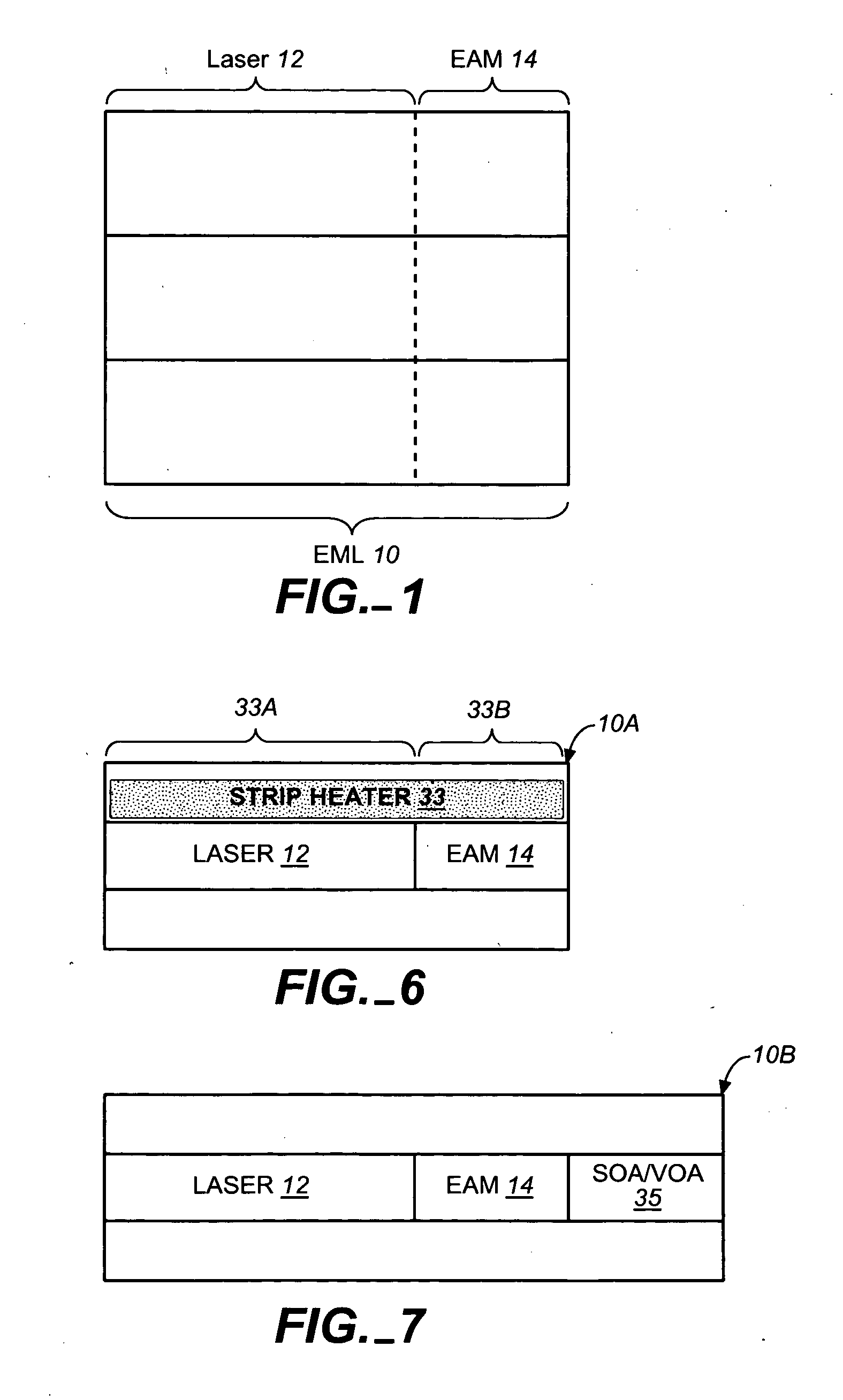
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Scanning device for coded data
InactiveUS20050254106A9Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsGratingPhotodetector
A scanning device for: scanning coded data disposed on a surface; and generating interaction data based on the sensed coded data, the interaction data being indicative of interaction of the scanning device with the surface; the coded data including, at a plurality of locations on the interface surface, a corresponding plurality of coded data portions, the scanning device comprising: (a) a laser source and scan optics configured to emit a scanning beam through an aperture in a housing of the scanning device, the scanning beam being directed in first and second orthogonal directions to thereby generate a raster scan pattern over a scanning patch, the scanning patch being positioned to cause the exposure of the at least one coded data portion when the surface and the sensing device are positioned operatively with respect to each other; (b) a photodetector for detecting reflection of the scanning beam from the surface, thereby to capture sample information; (c) at least one analog to digital converter for converting the captured sample information into sample data; (d) a first framestore for storing successive sample data as image data; (e) an image processor for processing the image data to generate processed image data; (e) a host processor for generating the interaction data based at least partially on the processed image data.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
Micro-projector
InactiveUS20110037953A1Increase brightnessQuality improvementTelevision system detailsPrismsDisplay deviceLaser source
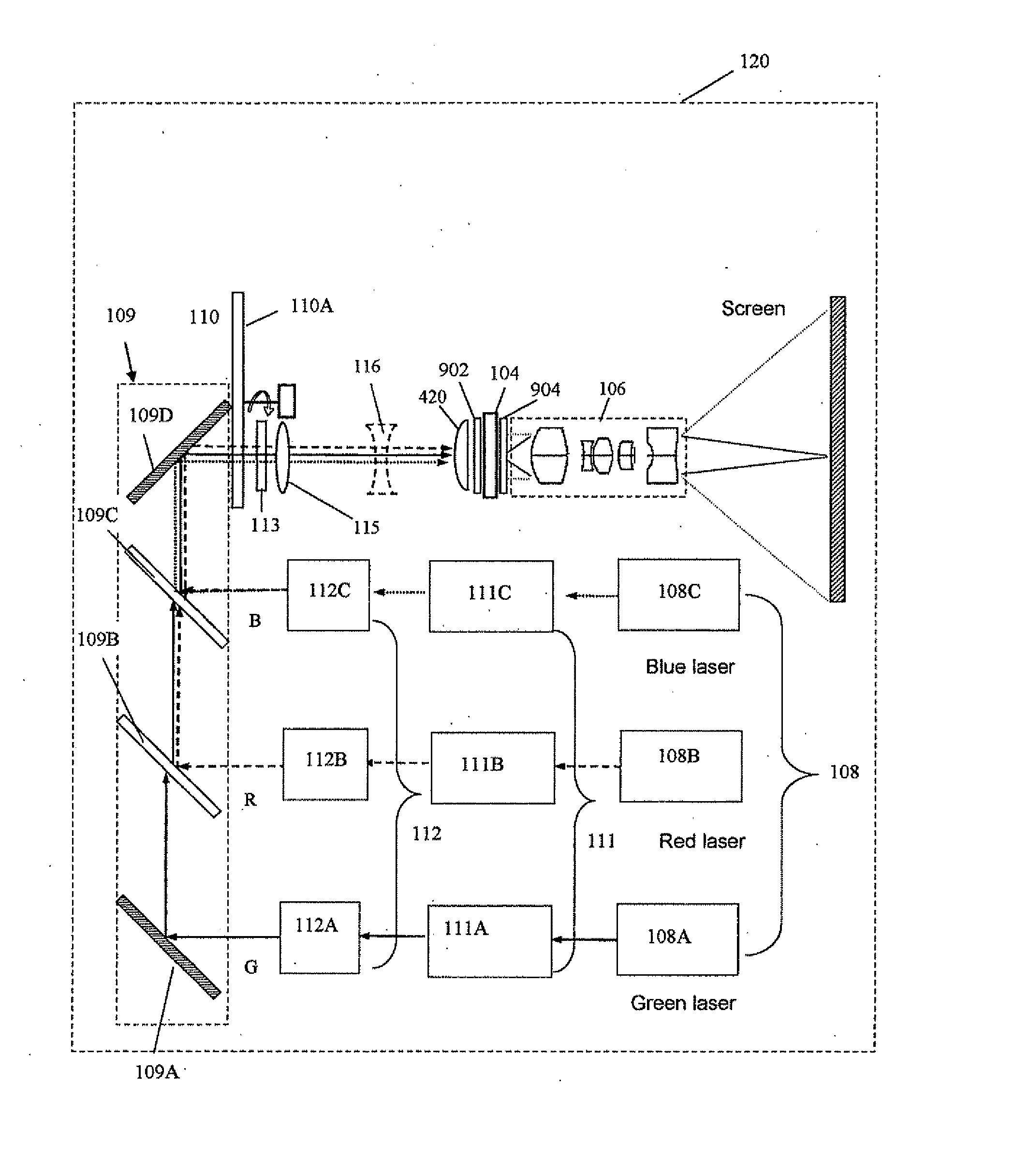
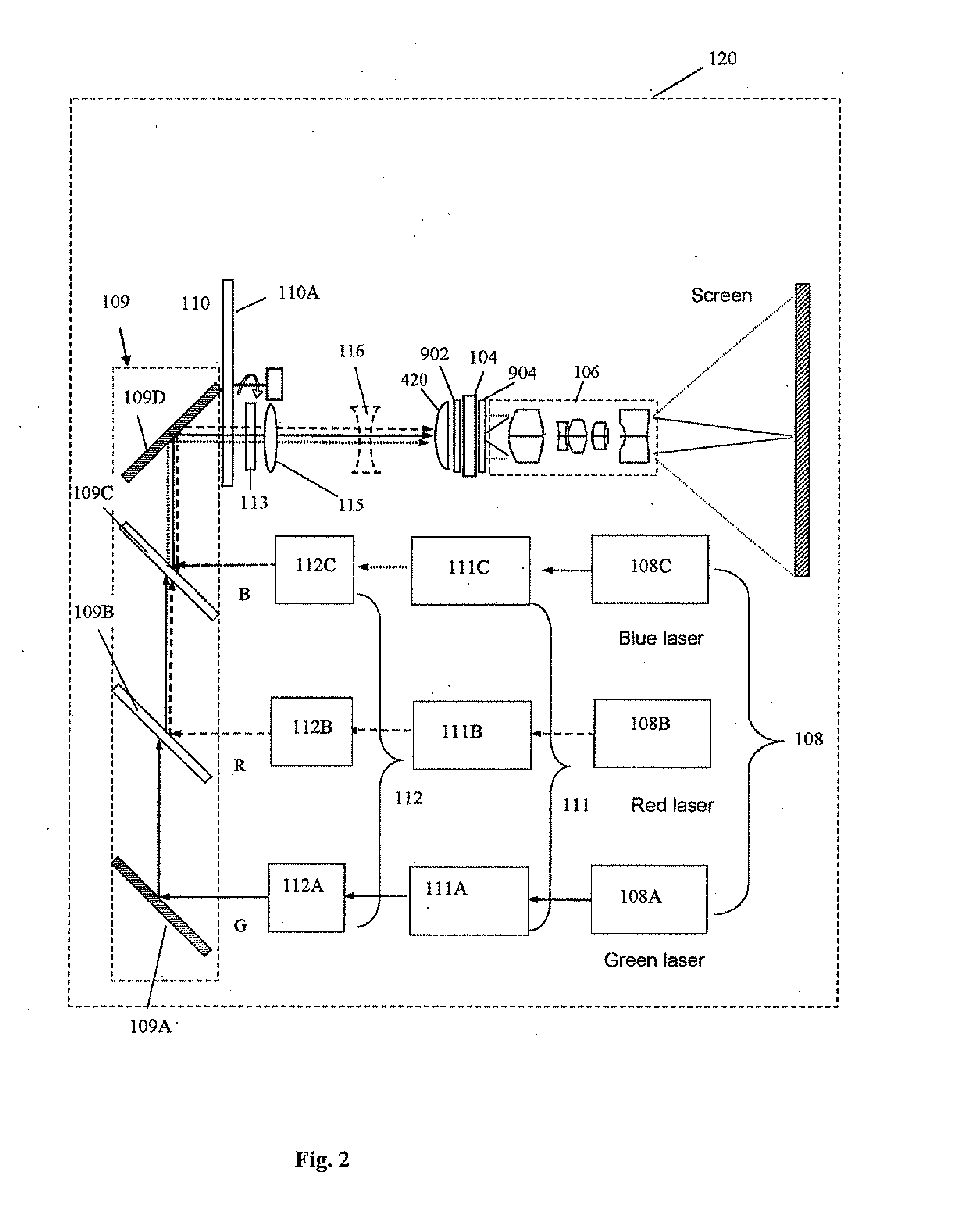
The present invention provides a projection display comprising an illumination system comprising at least one laser source unit and configured and operable for producing one or more light beams; a spatial light modulating (SLM) system accommodated at output of the illumination system and comprising one or more SLM units for modulating light incident thereon in accordance with image data; and a light projection optics for imaging modulated light onto a projection surface. The illumination system comprises at least one beam shaping unit comprising a Dual Micro-lens Array (DMLA) arrangement formed by front and rear micro-lens arrays (MLA) located in front and rear parallel planes spaced-apart along an optical path of light propagating towards the SLM unit, the DMLA arrangement being configured such that each lenslet of the DMLA directs light incident thereon onto the entire active surface of the SLM unit, each lenslet having a geometrical aspect ratio corresponding to an aspect ratio of said active surface of the SLM unit.
Owner:EXPLAY
Autocompensating quantum cryptographic key distribution system based on polarization splitting of light
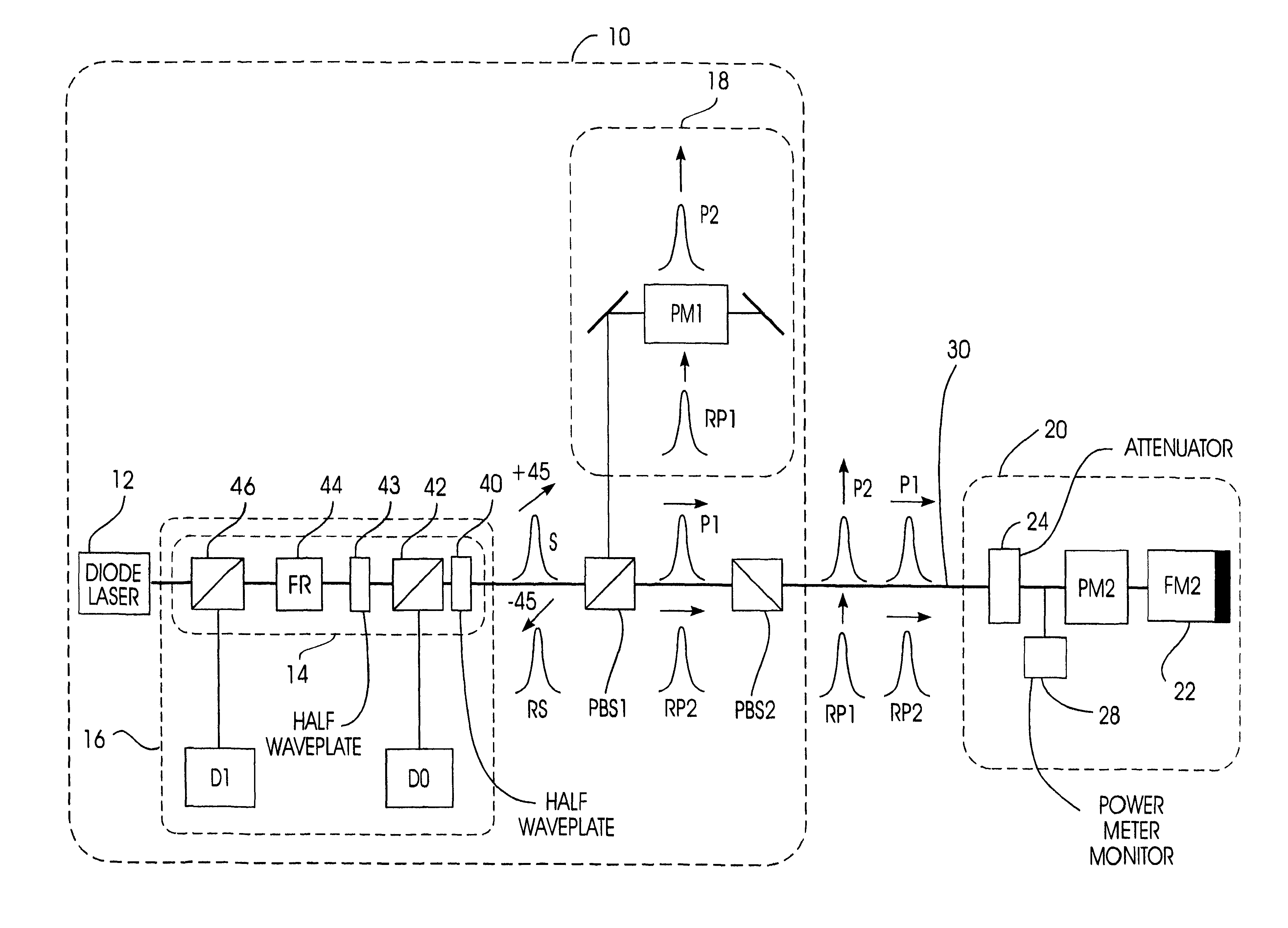
A quantum cryptographic key distribution (QKD) system splits discrete light signals from a laser source into a pair of light pulses that are orthogonally polarized with respect to each other, imparts a phase shift to one or both of these separate pulses during their round trip from the sender to the receiver and back, assures that the return pulses from the receiver are attenuated to single-photon pulses, recombines the phase-shifted pulses at the sender, and then detects from the recombined signal its polarization state, which is representative of the net phase shift imparted by the sender and receiver. The phase modulator at the receiver transmits only one polarization (e.g., vertical), but is used in a manner that permits it to equally modulate both polarization components of an arriving pulse. In this arrangement, when both components of a pulse reach the phase modulator at the receiver, they are both entirely vertically polarized and a phase shift is imparted at that time. This has the advantage that the effect of any time variation or phase errors in the phase modulator will be the same on both components. The key information is decoded at a detection stage at the sender that uses two detectors, one of which detects a first polarization state corresponding to the phase difference between the two phase shifts being 0 and the other of which detects a second polarization state corresponding to the phase difference between the two phase shifts being pi.
Owner:IBM CORP
Processing multilayer semiconductors with multiple heat sources
ActiveUS20060018639A1Muffle furnacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDistribution systemEngineering
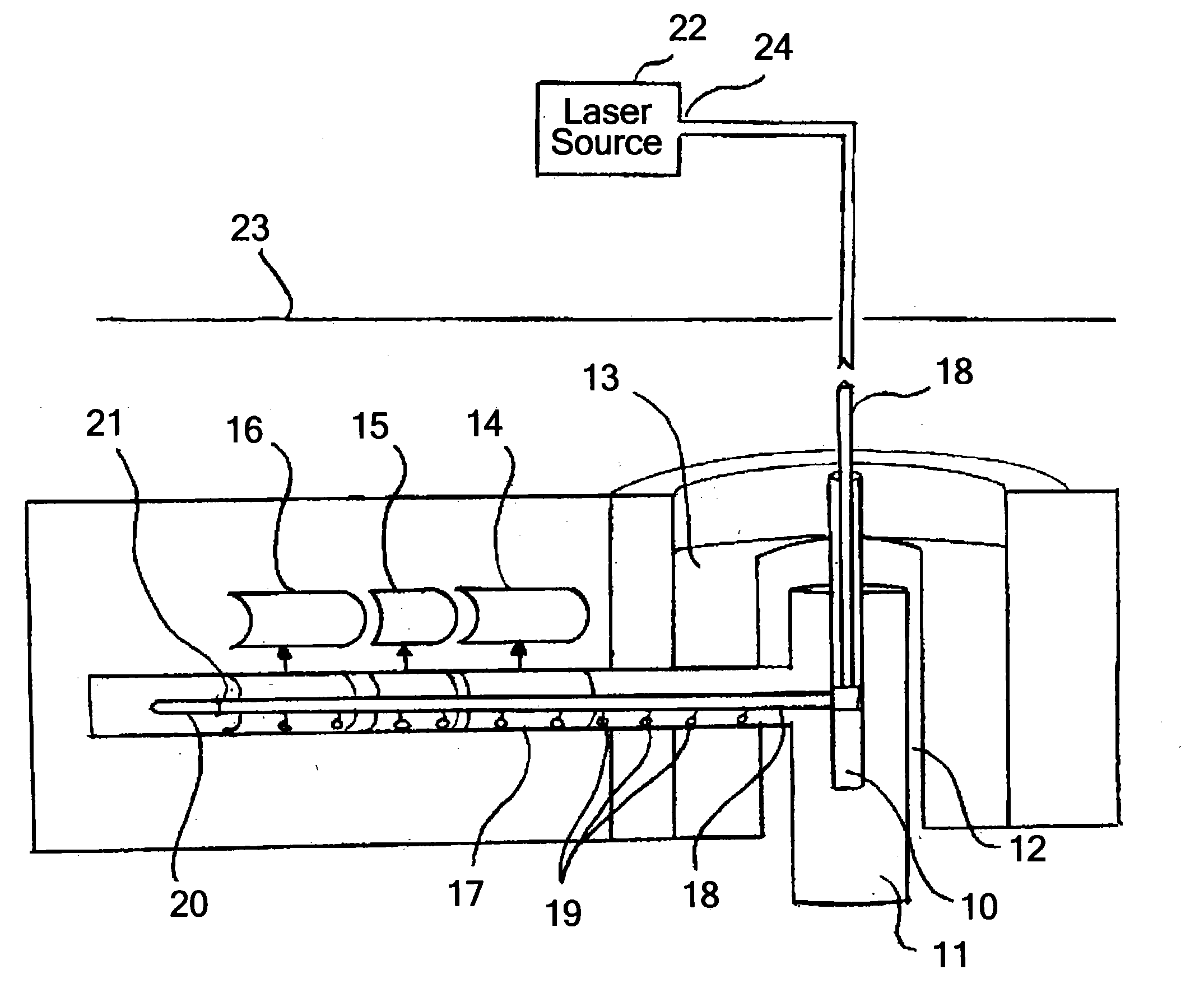
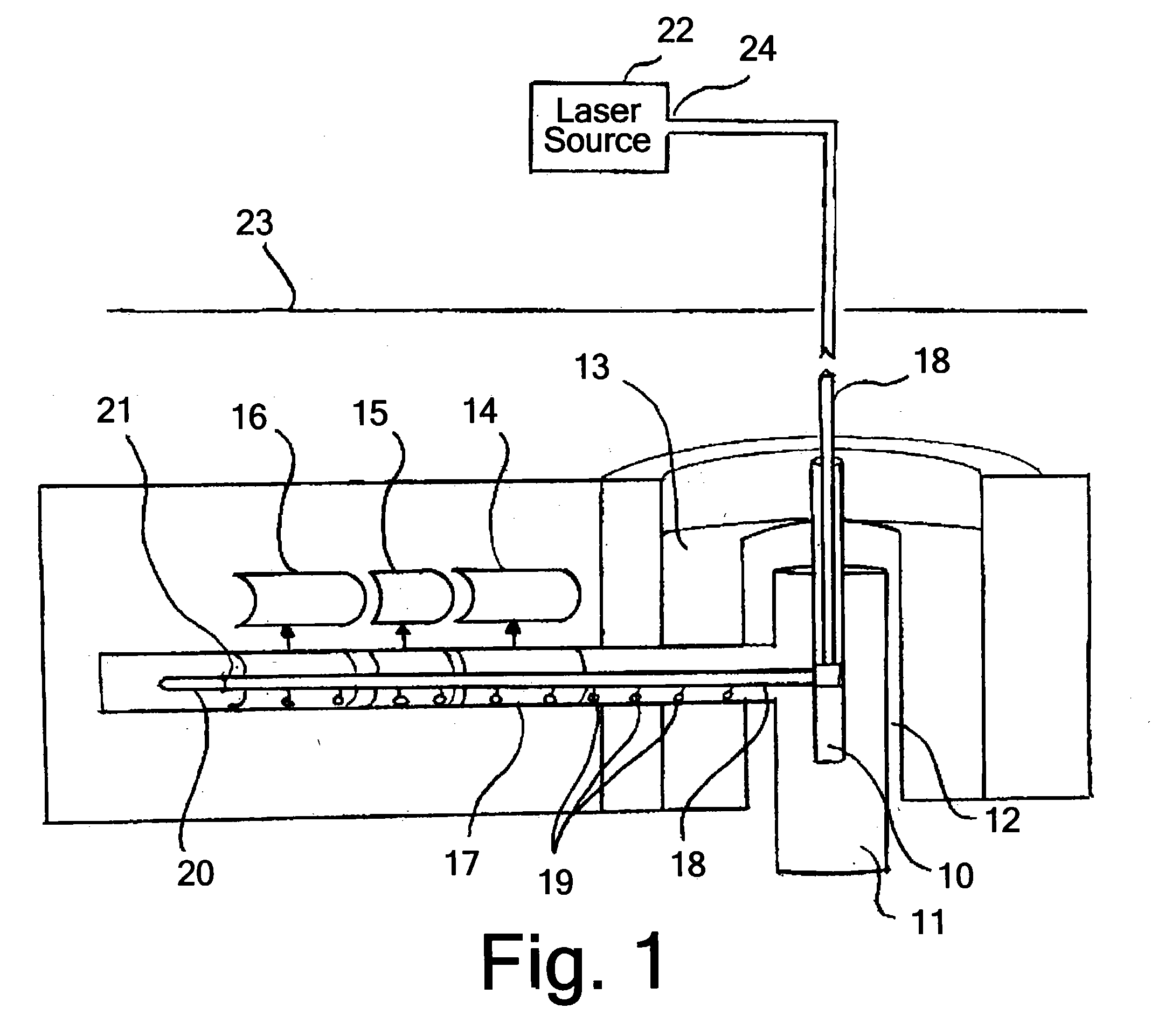
A method and apparatus for rapid thermal annealing comprising a plurality of lamps affixed to a lid of the chamber that provide at least one wavelength of light, a laser source extending into the chamber, a substrate support positioned within a base of the chamber, an edge ring affixed to the substrate support, and a gas distribution assembly in communication with the lid and the base of the chamber. A method and apparatus for rapid thermal annealing comprising a plurality of lamps comprising regional control of the lamps and a cooling gas distribution system affixed to a lid of the chamber, a heated substrate support with magnetic levitation extending through a base of the chamber, an edge ring affixed to the substrate support, and a gas distribution assembly in communication with the lid and the base of the chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Enhanced portable digital lidar system
InactiveUS20060231771A1Easy to set upEasy maintenancePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral bandsFluorescence
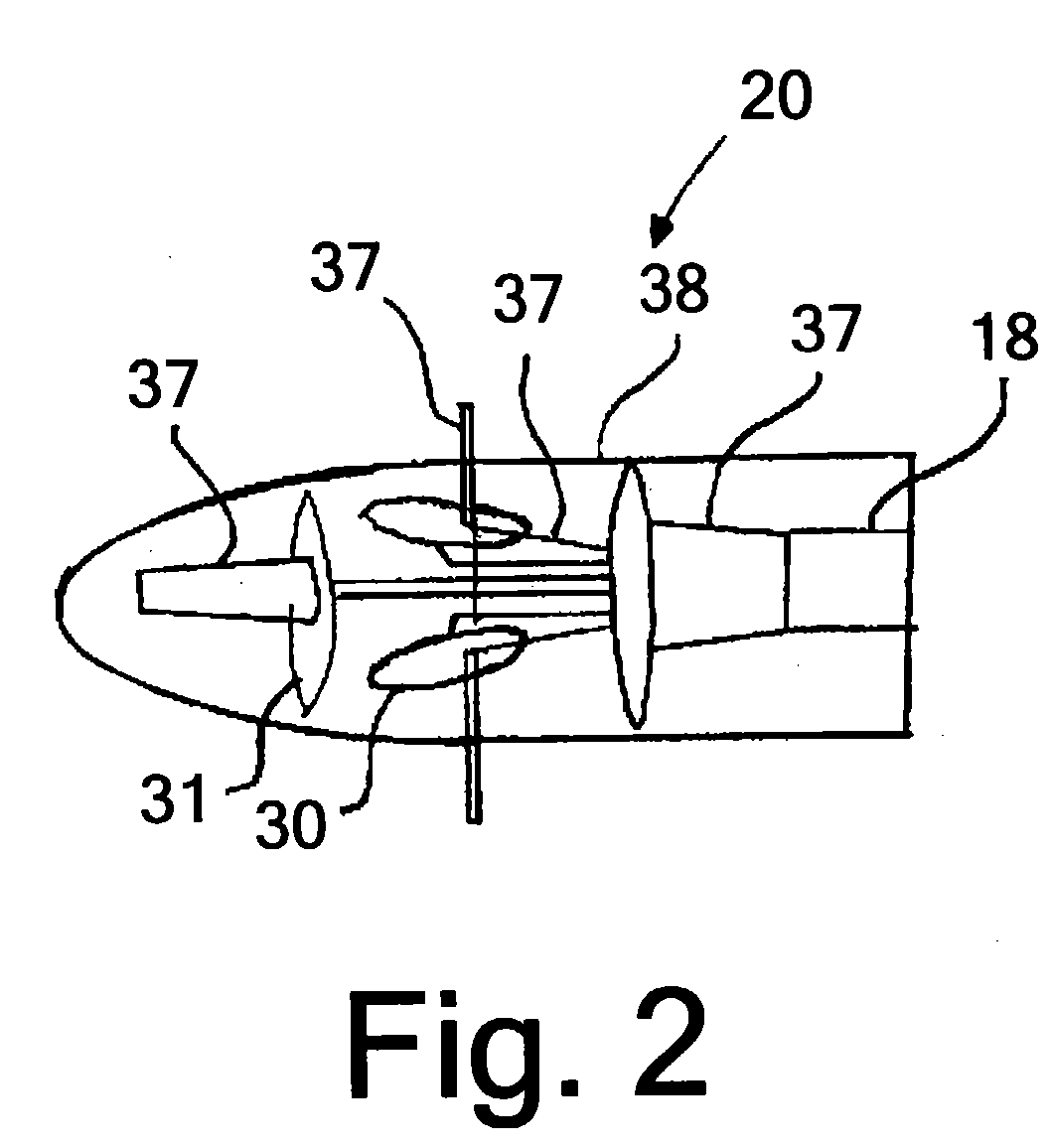
A system for detecting airborne agents. The system can include a laser source that provides laser pulses of at least two wavelengths, a transmitter that transmits the laser pulses, and a coupling mechanism configured to remotely couple the laser pulses between the laser source and the transmitter. The system can include a receiver receives both elastically backscattered signals from airborne agents and fluorescence signals from the airborne agents. The system can include a telescope both transmits a collimated laser beam of the laser pulse from the transmitter to a far field and receives the elastically backscattered signals and the fluorescence signals from the far field. The system can include a detection system having at least one of a backscatter optical detector that detects the elastically backscattered signals and one or more fluorescence optical detectors that detect the fluorescence signals in selected spectral band(s) from the airborne agents.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
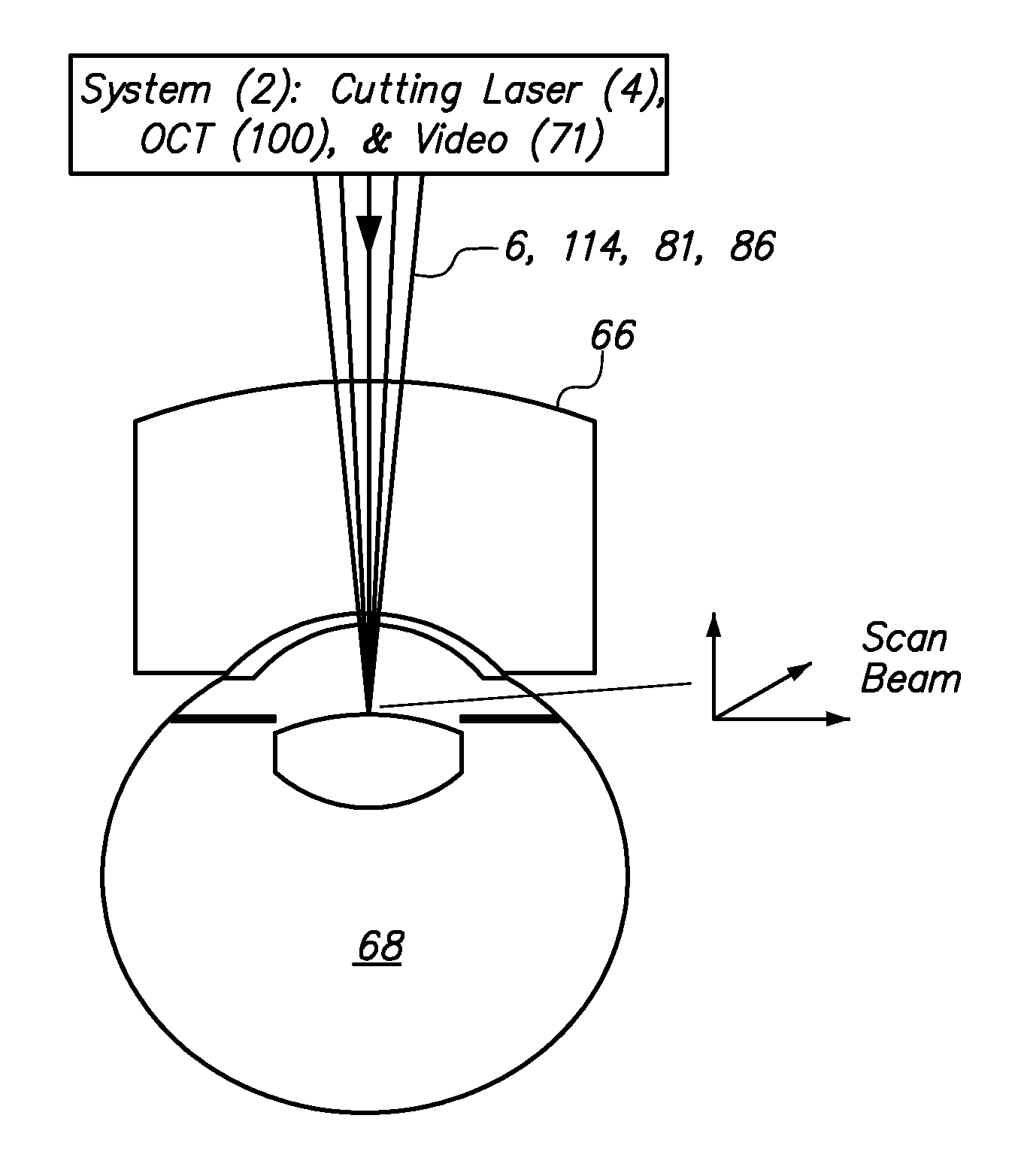
Method and apparatus for automated placement of scanned laser capsulorhexis incisions
ActiveUS20110202046A1Easy to implantLaser surgeryImage enhancementAnatomical structuresRobust least squares
Systems and methods are described for cataract intervention. In one embodiment a system comprises a laser source configured to produce a treatment beam comprising a plurality of laser pulses; an integrated optical system comprising an imaging assembly operatively coupled to a treatment laser delivery assembly such that they share at least one common optical element, the integrated optical system being configured to acquire image information pertinent to one or more targeted tissue structures and direct the treatment beam in a 3-dimensional pattern to cause breakdown in at least one of the targeted tissue structures; and a controller operatively coupled to the laser source and integrated optical system, and configured to adjust the laser beam and treatment pattern based upon the image information, and distinguish two or more anatomical structures of the eye based at least in part upon a robust least squares fit analysis of the image information.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Method of Analyzing Dna Sequence Using Field-Effect Device, and Base Sequence Analyzer
ActiveUS20080286767A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
System and method for reading code symbols at long range using source power control
A system and method are presented for improving the performance of code scanners in the extended and far ranges. At these distances, the intensity of the laser beam reflected off the code symbol can be markedly decreased, thereby decreasing the likelihood of a successful reading of the code symbol by the code scanner. The system provides for dynamic power increases to the laser source to generate a greater dynamic range.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Fiber optics laser perforation tool
InactiveUS6888097B2Eliminate damageReduce productionDisloding machinesThermal drillingFiberOptoelectronics
Owner:GAS TECH INST
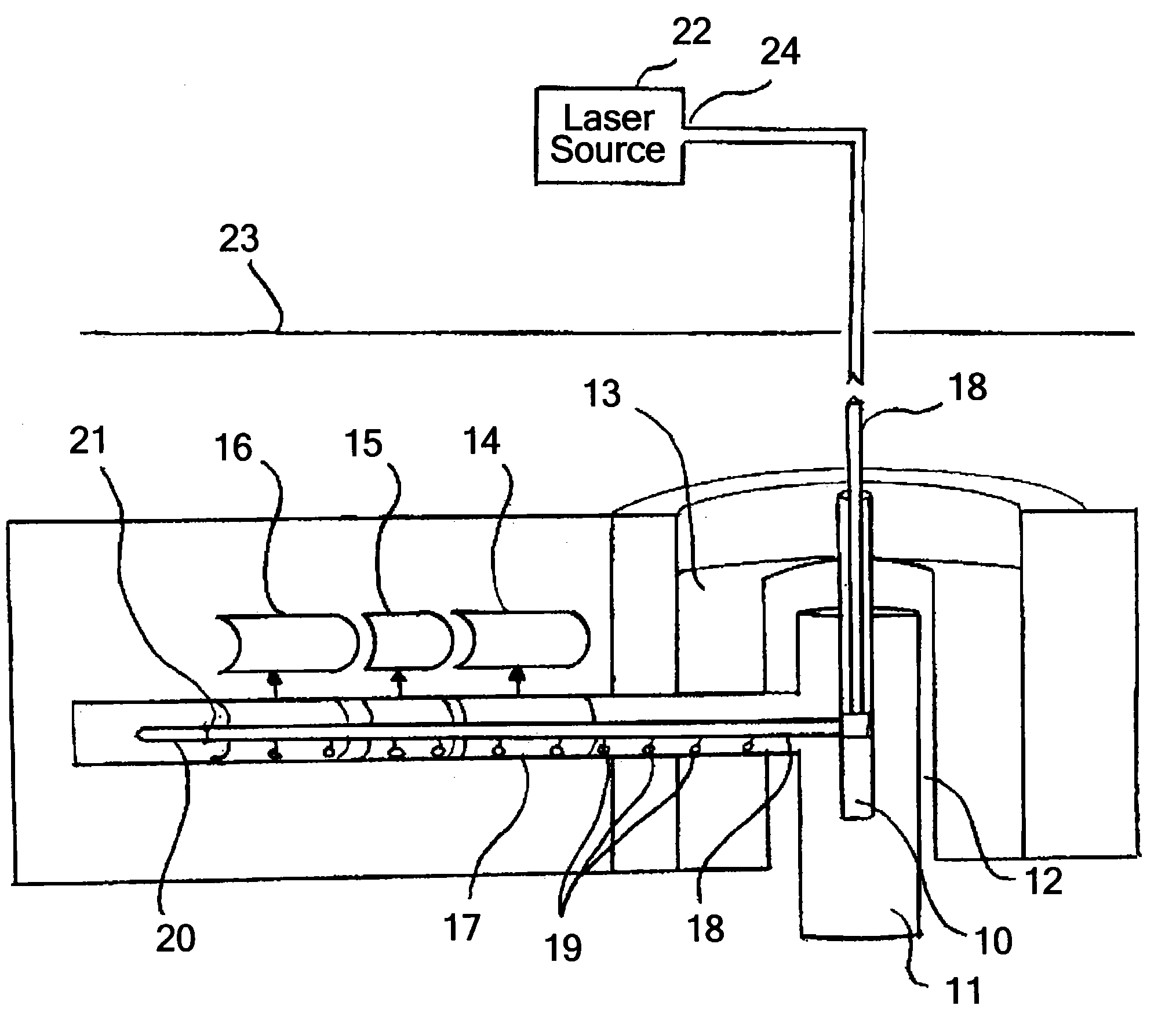
Laser-based method and system for processing targeted surface material and article produced thereby
InactiveUS20060000814A1Prevent unwanted changesSufficient total fluenceAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTarget surfaceSlag
A laser-based method and system for processing targeted surface material and article produced thereby are provided. The system processes the targeted surface material within a region of a workpiece while avoiding undesirable changes to adjacent non-targeted material. The system includes a primary laser subsystem including a primary laser source for generating a pulsed laser output including at least one pulse having a wavelength and a pulse width less than 1 ns. A delivery subsystem irradiates the targeted surface material of the workpiece with the pulsed laser output including the at least one pulse to texture the targeted surface material. The pulsed laser output has sufficient total fluence to initiate ablation within at least a portion of the targeted surface material and the pulse width is short enough such that the region and the non-targeted material surrounding the material are substantially free of slag.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method and device for creating supercontinuum light pulses
ActiveUS9160137B1Simple controllabilityRemissionLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsGroup velocity dispersionOptoelectronics
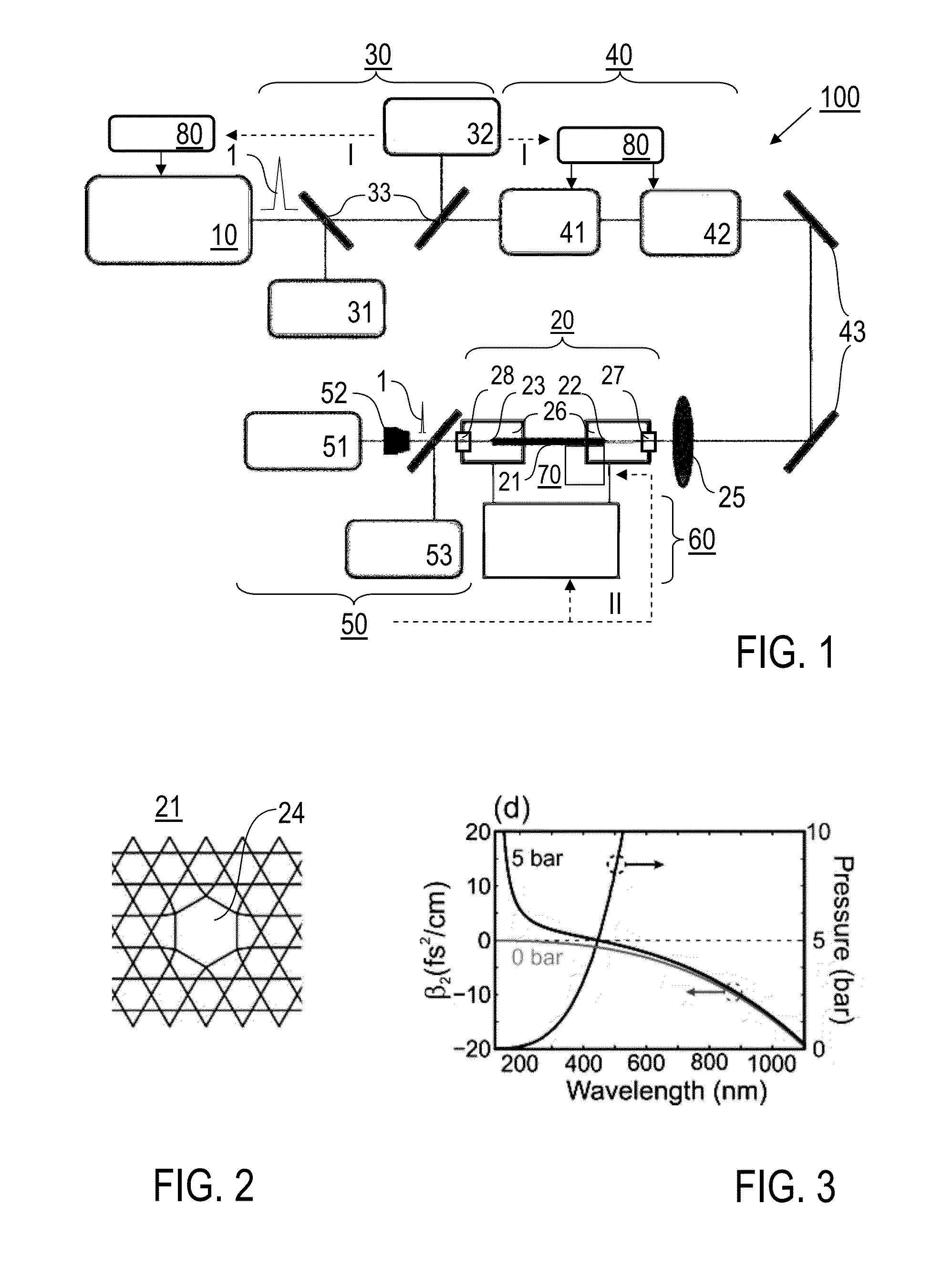
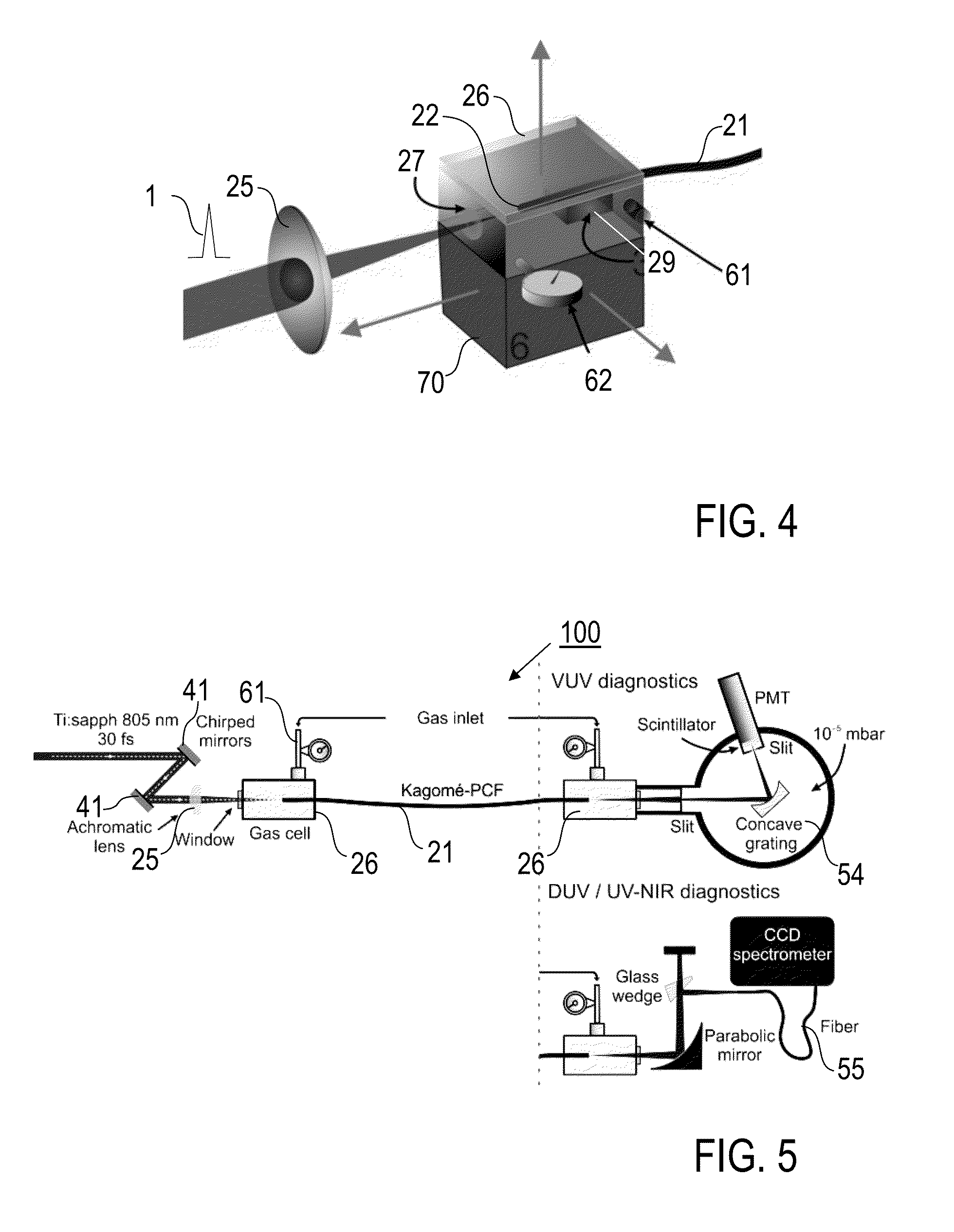
A method of spectrally broadening light pulses includes the steps of providing the light pulses with a laser source, said light pulses having a pulse duration below 1 ps, in-coupling the light pulses into a hollow optical waveguide device, and spectrally broadening the light pulses propagating along the pulse guiding medium by subjecting them to a Raman nonlinearity via excitation of a Raman polarization having a first Raman period, wherein the optical waveguide device subjects the light pulses to anomalous group velocity dispersion which combines with the spectral broadening of the light pulses to result in a Raman-enhanced self-compression of the light pulses, and the light pulses further propagate along the optical waveguide device such that the Raman-enhanced self compression results in a further excitation of a Raman polarization having a second Raman period which is faster than the first Raman period.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Laser produced plasma EUV light source
ActiveUS20060219957A1Increase the rate of chemical reactionsRadiation pyrometryNanoinformaticsLine tubingLight beam
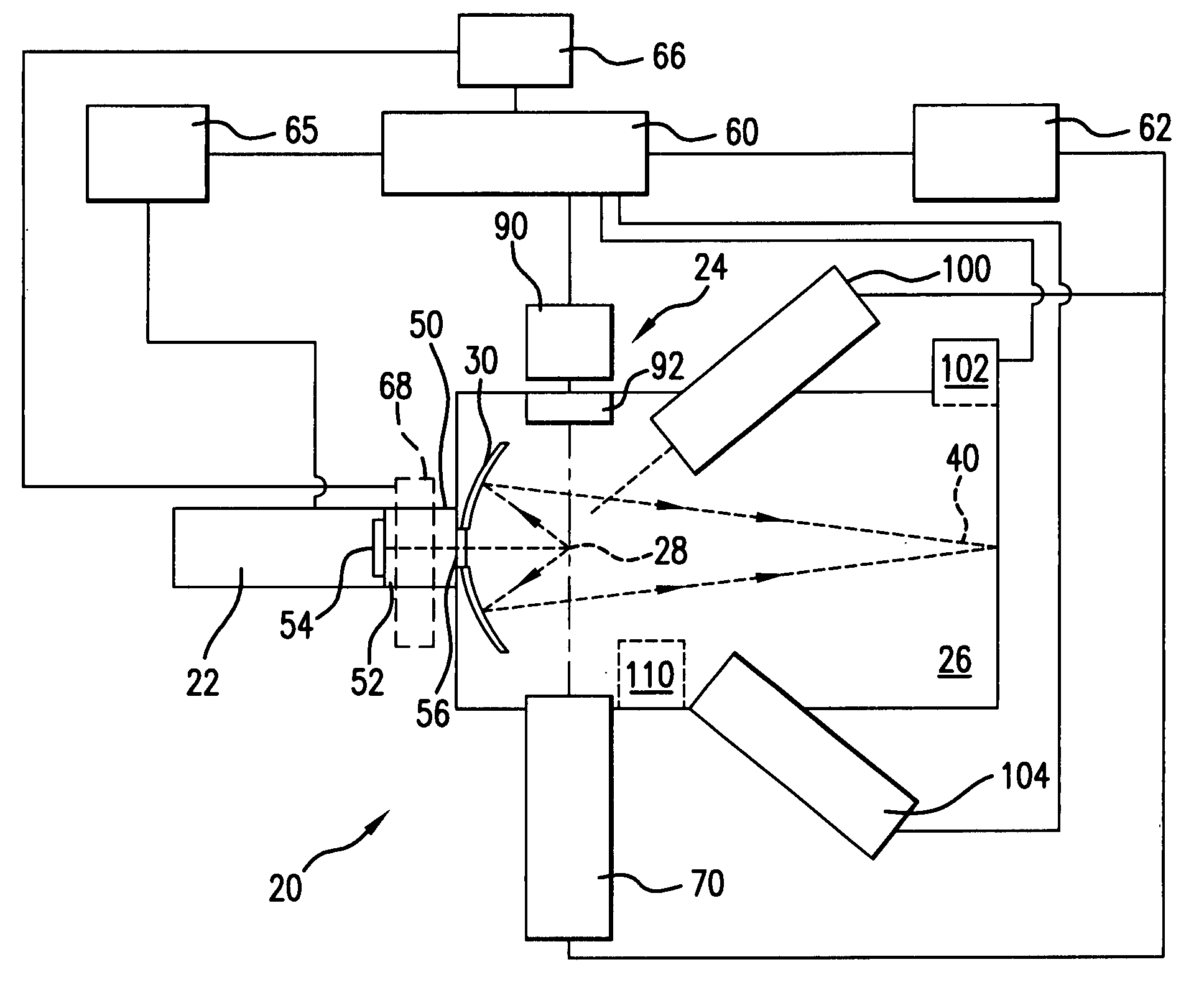
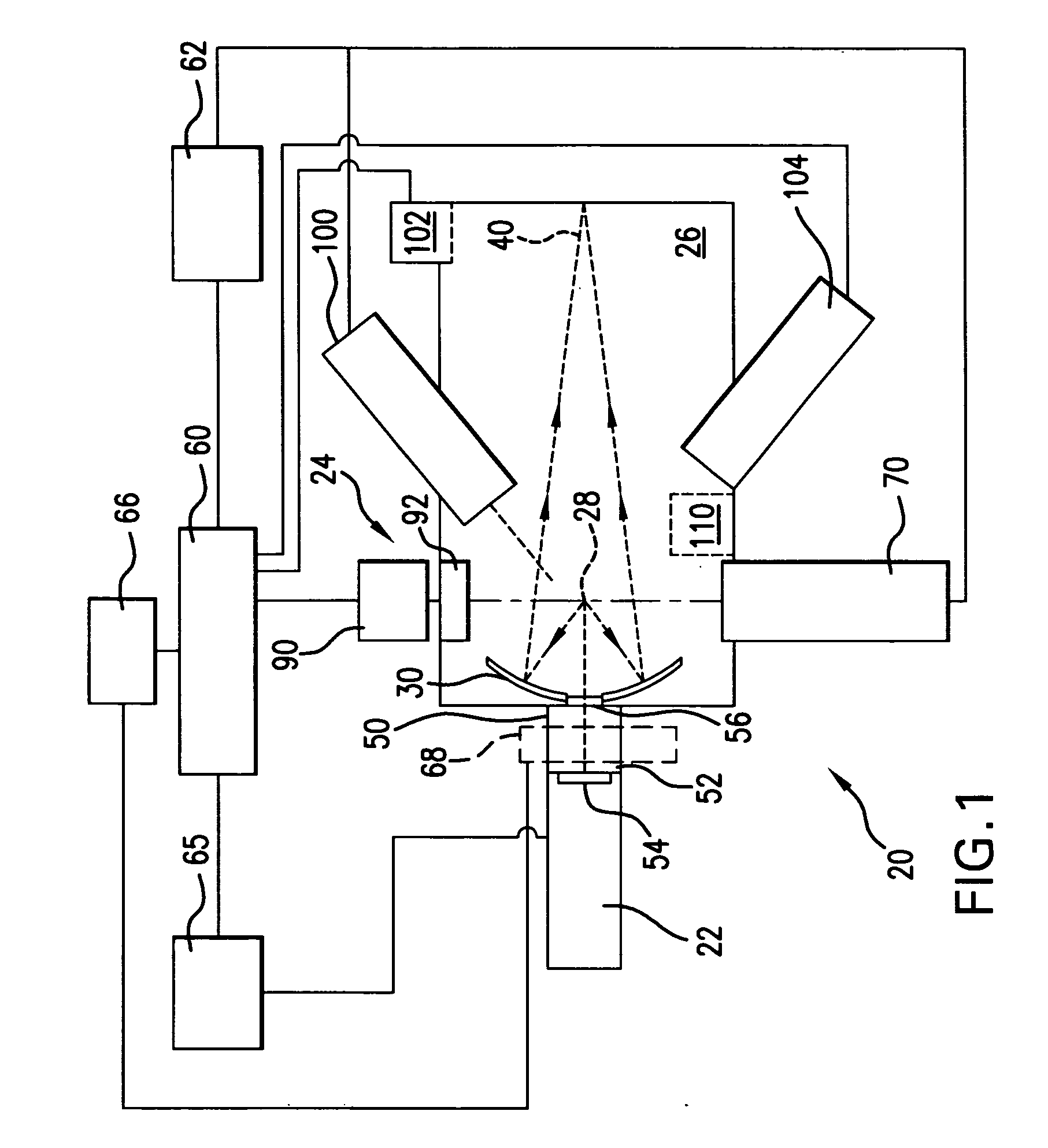
An EUV light source is disclosed that may include a laser source, e.g. CO2 laser, a plasma chamber, and a beam delivery system for passing a laser beam from the laser source into the plasma chamber. Embodiments are disclosed which may include one or more of the following; a bypass line may be provided to establish fluid communication between the plasma chamber and the auxiliary chamber, a focusing optic, e.g. mirror, for focusing the laser beam to a focal spot in the plasma chamber, a steering optic for steering the laser beam focal spot in the plasma chamber, and an optical arrangement for adjusting focal power.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Fiber optics laser perforation tool
InactiveUS20040256103A1Eliminate damageReduce productionDisloding machinesThermal drillingFiberOptoelectronics
An apparatus for perforation of wellbore walls, which apparatus includes a fiber optic cable having a laser input end and a laser output end. A laser source is operably connected to the laser input end and a laser head is connected to the laser output end. The laser head includes a laser control components for controlling at least one laser beam characteristic. Laser head control elements for controlling the motion and location of the laser head are operably connected to the fiber optic cable. The laser head is enclosed in a protective housing, which protects the fiber optic cable and elements, such as reflectors and lenses for controlling the laser beam emitted by the fiber optic cable disposed therein, from the harsh environments encountered in downhole operations.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Power source for a dispersion compensation fiber optic system
InactiveUS6963685B2Minimize signalingIncrease bitrateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency modulationDispersion compensation
Owner:OPTICAL HORIZONS CORP +1
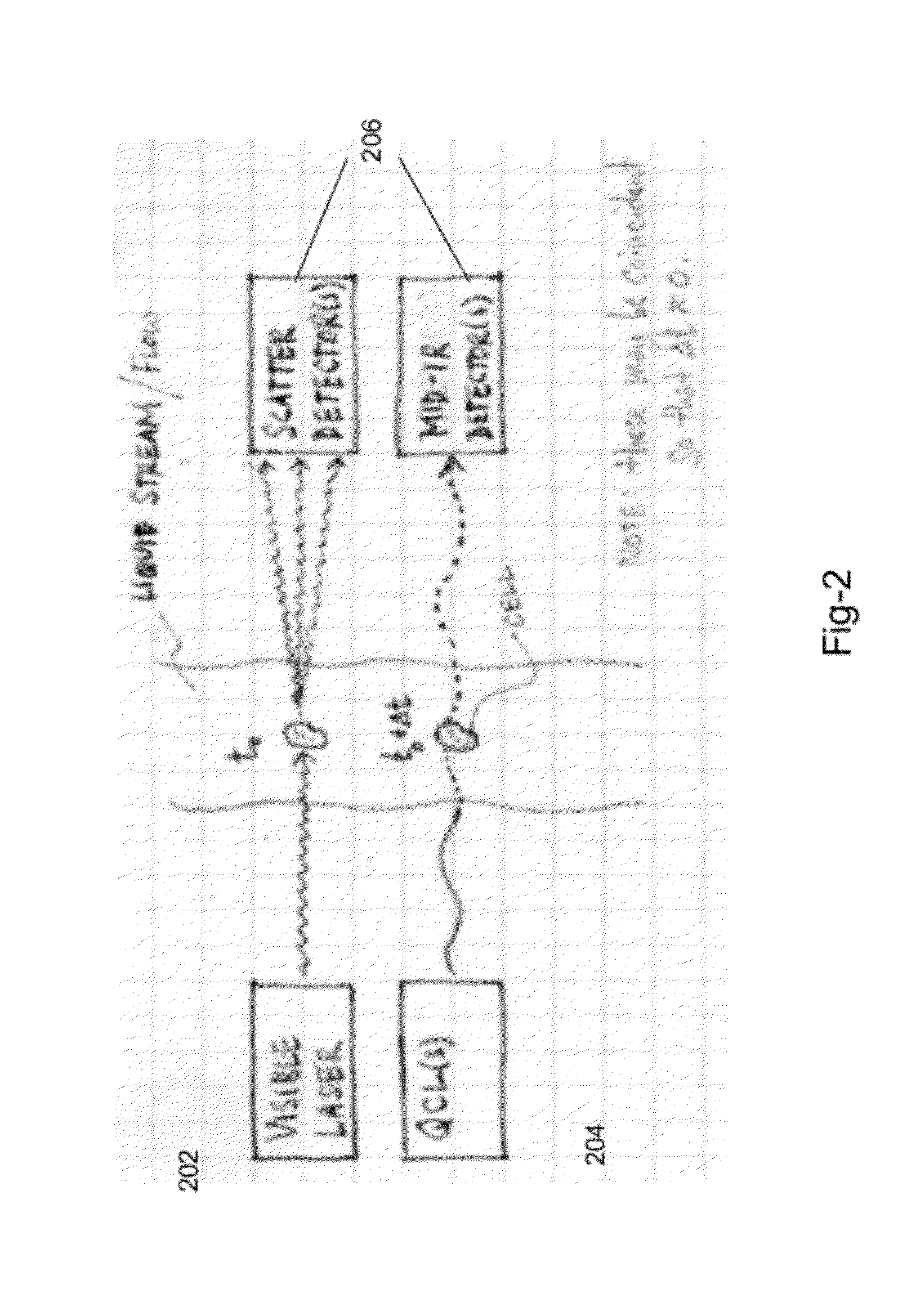
Cytometry system with quantum cascade laser source, acoustic detector, and micro-fluidic cell handling system configured for inspection of individual cells
InactiveUS20120225475A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteCell handling
This disclosure concerns a cytometry system including a handling system that presents single cells to at least one quantum cascade laser (QCL) source. The QCL laser source is configured to deliver light to a cell within the cells in order to induce resonant mid-IR vibrational absorption by one or more analytes, leading to local heating that results in thermal expansion and an associated shockwave. An acoustic detection facility that detects the shockwave emitted by the single cell.
Owner:1087 SYST
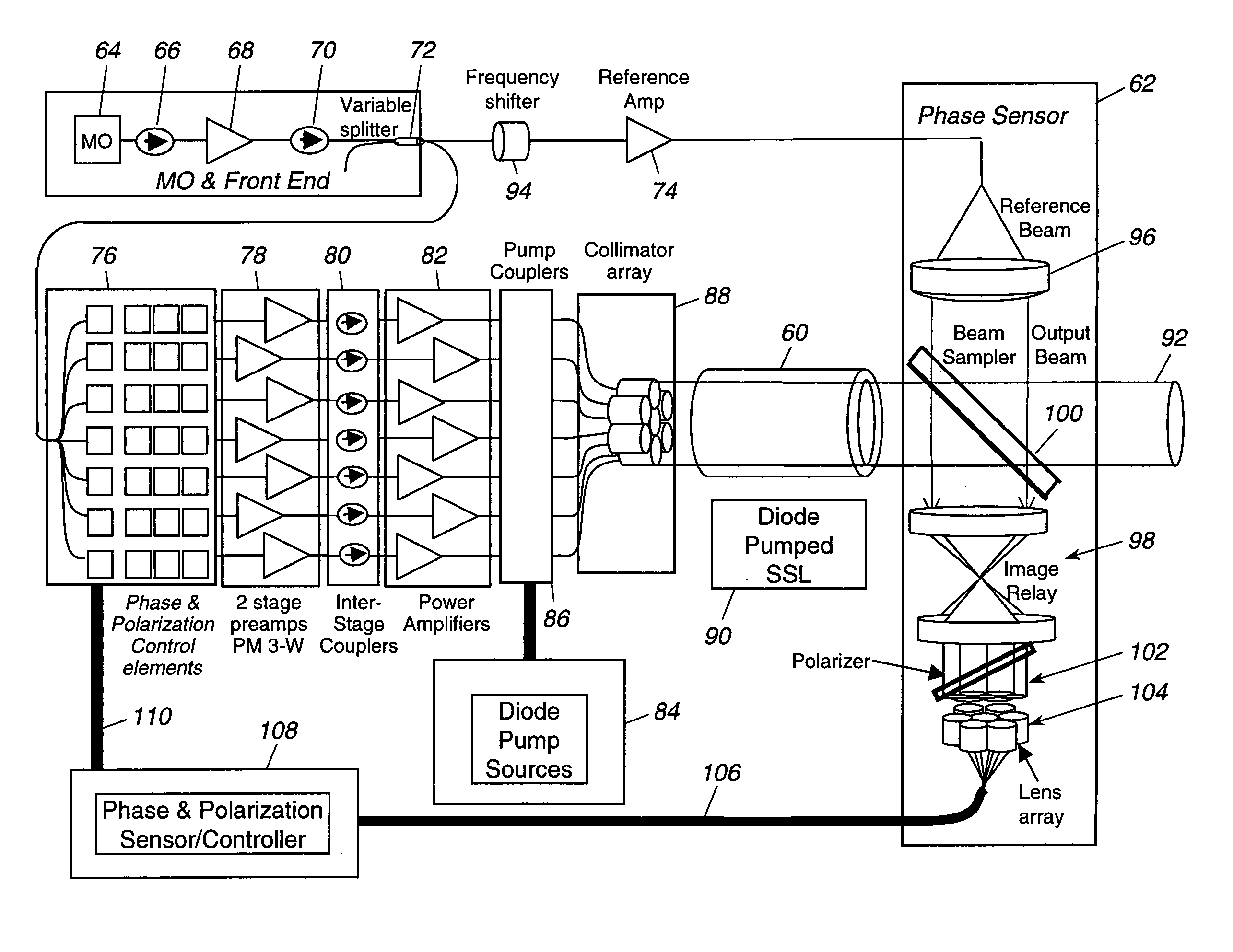
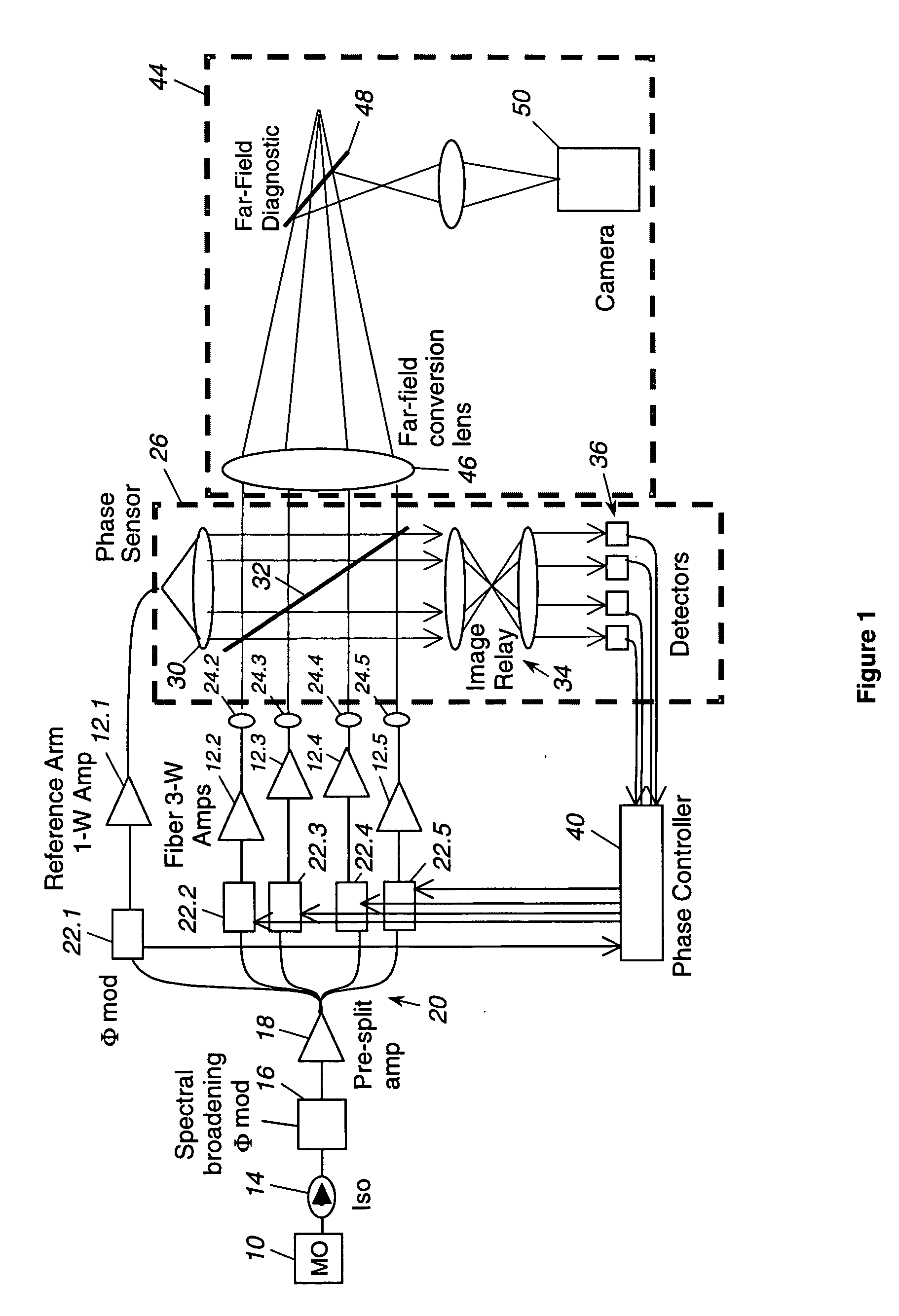
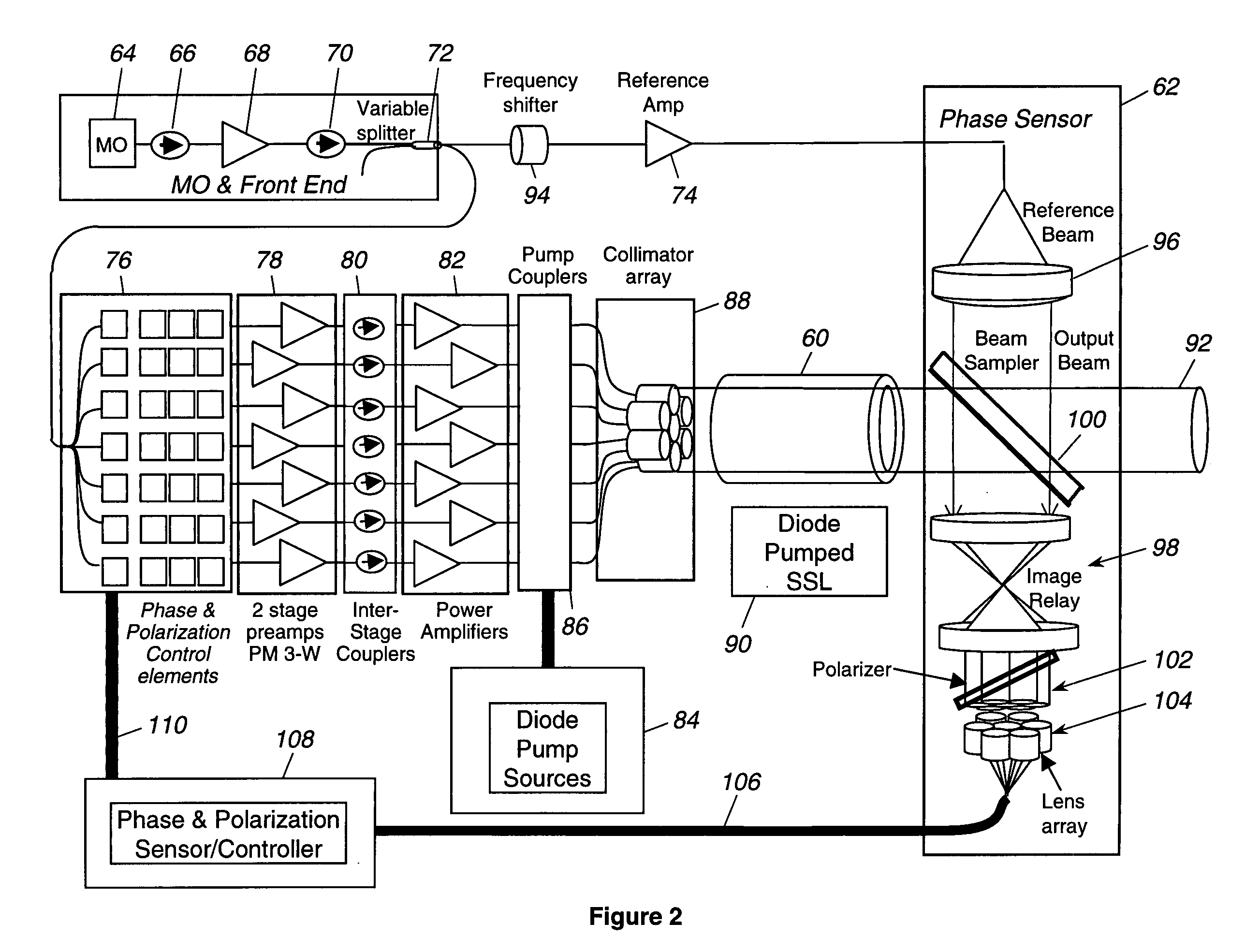
Laser source comprising amplifier and adaptive wavefront/polarization driver
ActiveUS20050201429A1Compensation DistortionOptical measurementsLaser using scattering effectsWavefrontAudio power amplifier
A hybrid laser source including a solid state laser driven by an array of fiber laser amplifiers, the inputs of which are controllable in phase and polarization, to compensate for distortions that arise in the solid state laser, or to achieve desired output beam properties relating to direction or focus. The output beam is sampled and compared with a reference beam to obtain phase and polarization difference signals across the output beam cross section, at spatial positions corresponding with the positions of the fiber laser amplifiers providing input to the solid state laser. Therefore, phase and polarization properties of the output beam may be independently controlled by predistortion of these properties in the fiber laser amplifier inputs.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
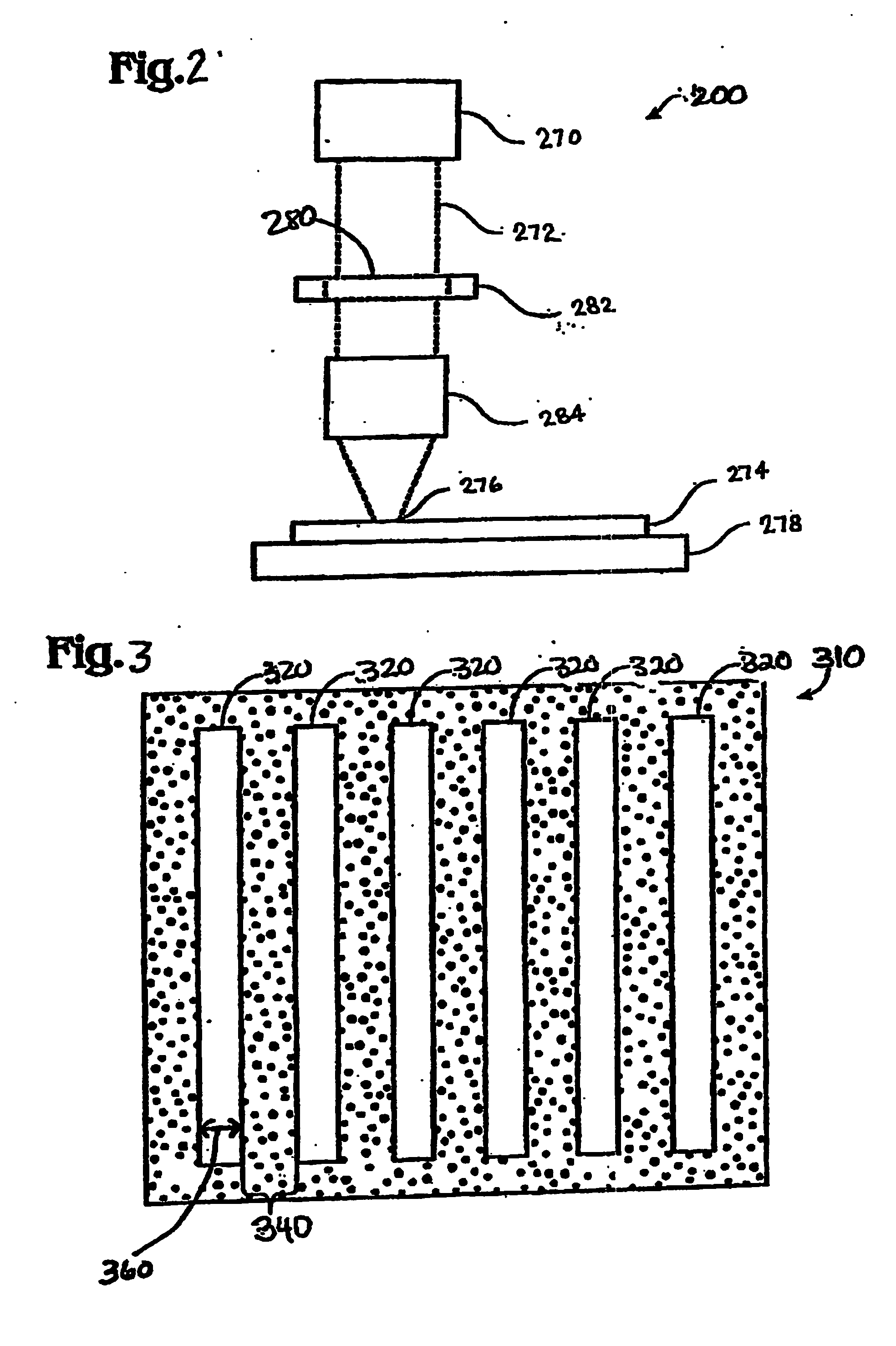
Systems and methods for processing thin films
InactiveUS20050059265A1Utilizing energyReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntegratorIrradiation
The present disclosure is directed to methods and systems for processing a thin film samples. In an exemplary method, semiconductor thin films are loaded onto two different loading fixtures, laser beam pulses generated by a laser source system are split into first laser beam pulses and second laser beam pulses, the thin film loaded on one loading fixture is irradiated with the first laser beam pulses to induce crystallization while the thin film loaded on the other loading fixture is irradiated with the second laser beam pulses. In a preferred embodiment, at least a portion of the thin film that is loaded on the first loading fixture is irradiated while at least a portion of the thin film that is loaded on the second loading fixture is also being irradiated. In an exemplary embodiment, the laser source system includes first and second laser sources and an integrator that combines the laser beam pulses generated by the first and second laser sources to form combined laser beam pulses. In certain exemplary embodiments, the methods and system further utilize additional loading fixtures for processing additional thin film samples. In such methods and systems, the irradiation of thin film samples loaded on some of the loading fixtures can be performed while thin film samples are being loaded onto the remaining loading fixtures. In certain exemplary methods and systems, the crystallization processing of the semiconductor thin film samples can consist of a sequential lateral solidification (SLS) process.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com