Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
205 results about "Group velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall envelope shape of the wave's amplitudes—known as the modulation or envelope of the wave—propagates through space. For example, if a stone is thrown into the middle of a very still pond, a circular pattern of waves with a quiescent center appears in the water, also known as a capillary wave. The expanding ring of waves is the wave group, within which one can discern individual wavelets of differing wavelengths traveling at different speeds. The shorter waves travel faster than the group as a whole, but their amplitudes diminish as they approach the leading edge of the group. The longer waves travel more slowly, and their amplitudes diminish as they emerge from the trailing boundary of the group.
Smith-Purcell free electron laser and method of operating same
A free electron laser for generating a Smith-Purcell radiation. In one embodiment, the free electron laser includes a grating having a grating surface, an electron emitter for generating a beam of electrons, and a guiding member positioned therebetween the electron emitter and the grating for directing the beam of electrons along a path extending over the grating surface of the grating with a focal point so that in operation a Smith-Purcell radiation and an evanescent wave are generated by interaction of the beam of electrons with the grating. In operation, the beam current of the beam of electrons is equal to or greater than a threshold current and the group velocity of the evanescent wave is substantially close to zero or negative so that the evanescent wave travels backward to allow electrons in the beam of electrons are bunched by interaction with the evanescent wave to substantially enhance the Smith-Purcell radiation over the range of wavelengths.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
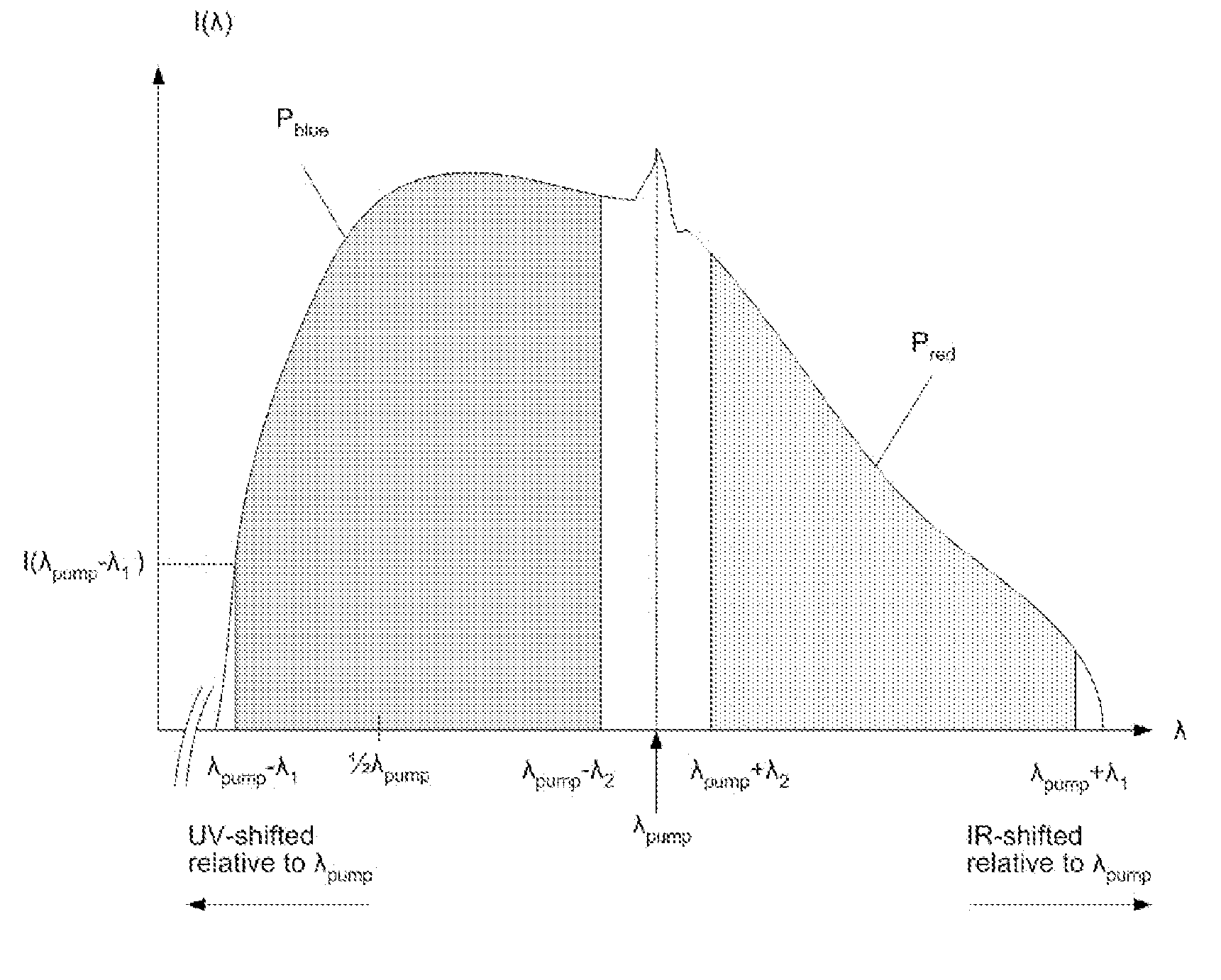
Blue extended super continuum light source
InactiveUS7800818B2Increase powerLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInstabilityRefractive index
In a blue extended super continuum light source, when pulses of partly coherent monochromatic “pump” radiation of essentially constant amplitude are propagating through a microstructure fiber medium within a region of anomalous dispersion of the medium, then, provided the medium has a finite nonlinear coefficient of the index of refraction, the pump pulse is subject to a modulation instability. This results in formation of a train of narrow pulses with Tera Hertz repetition rate. Phase match between red shifted Raman solitons generated by the pump pulse and energy shed by the pump pulse at all frequencies with a group velocity below the pump pulse group velocity may lead to the formation of Cherenkov radiation. The solitons may seed Cherenkov radiation at different wavelengths depending on the actual fiber parameters. This allows extension of generated super continuum light beyond the four wave mixing limit when applying picosecond or nanosecond pump pulses.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
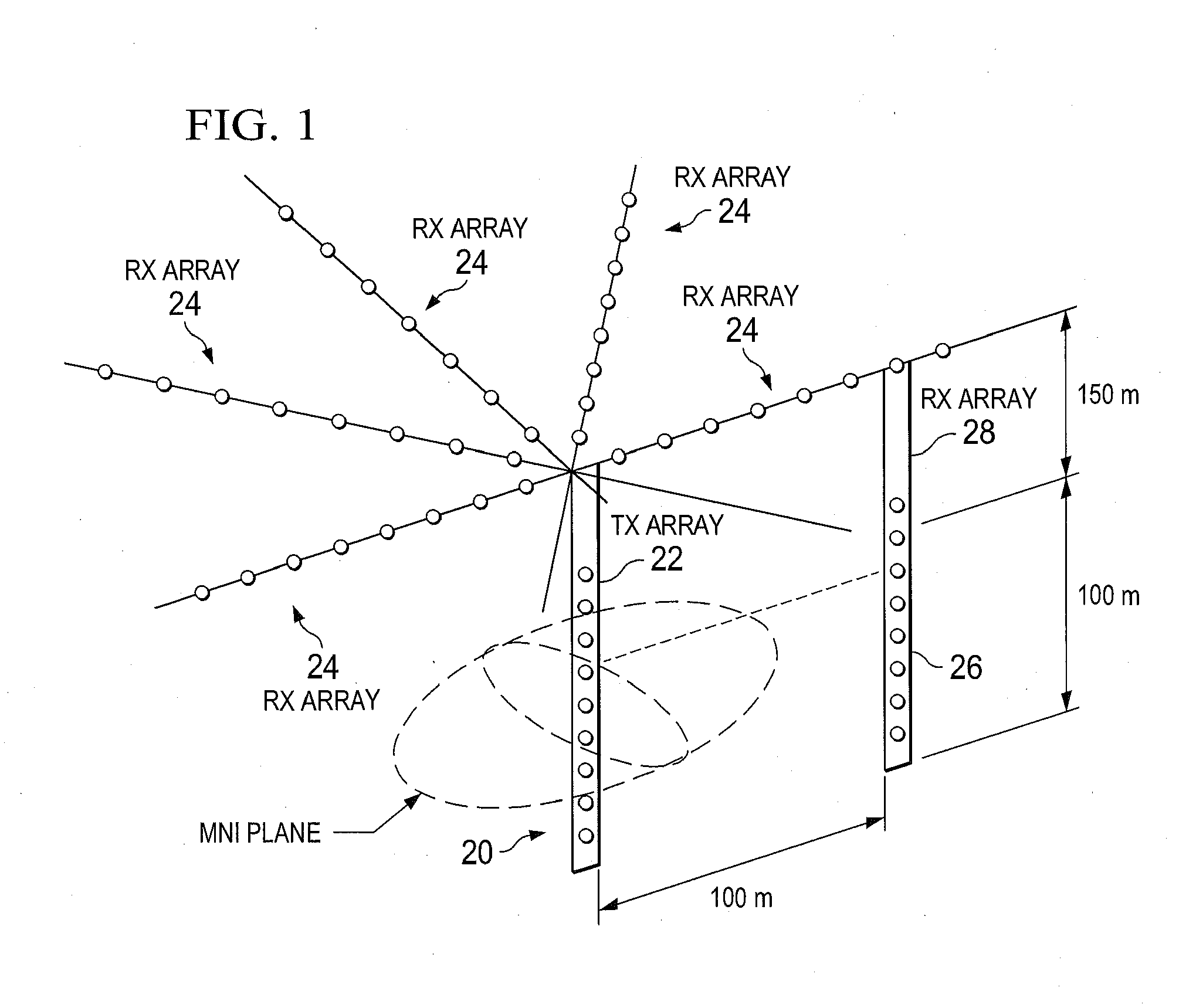
Long-range acoustical positioning system on continental shelf regions
ActiveUS20120092964A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationVocal tractArrival time
Methods and systems for determining a geophysical position of an object in an underwater channel are provided. Acoustic signals from at least two sources are received by a receiver of the object. The acoustic signals have a frequency corresponding to at least one waveguide mode associated with the underwater channel, where the acoustic signals are transmitted at predetermined transmission times. An arrival time for the at least one waveguide mode is determined from the received signals, based on the predetermined transmission times. The geophysical position is determined based on the arrival time and a modal group velocity for the at least one waveguide mode.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
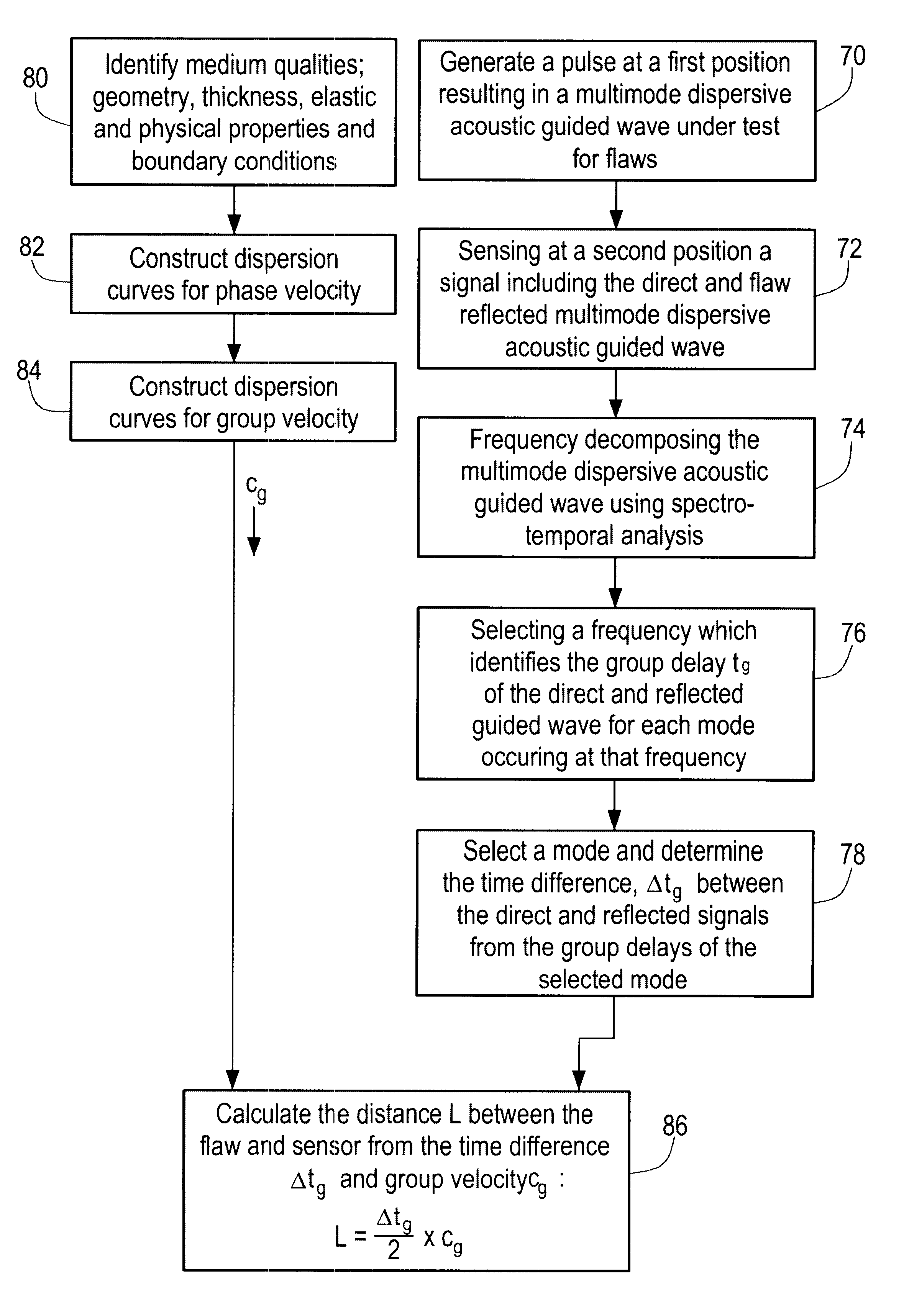
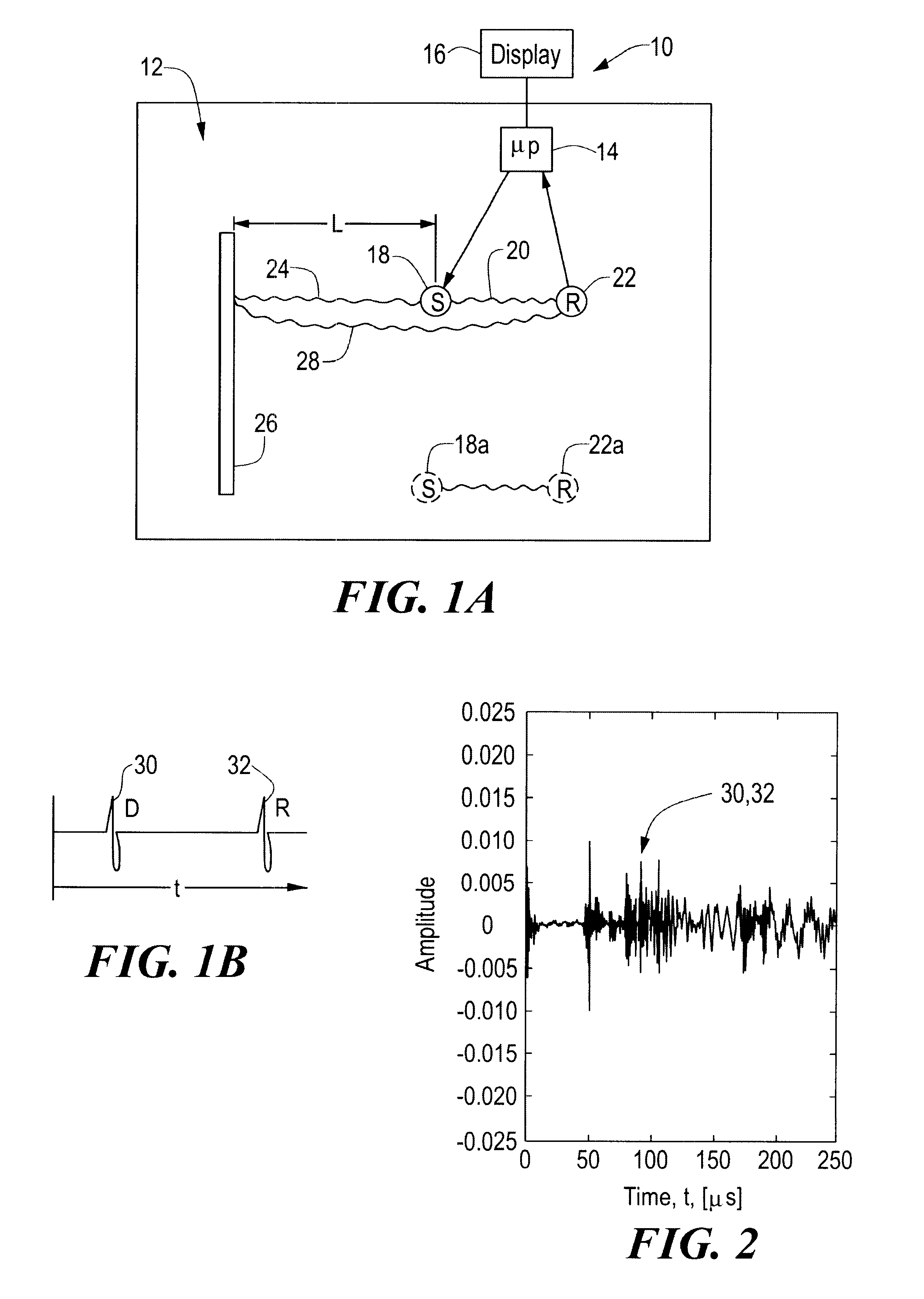
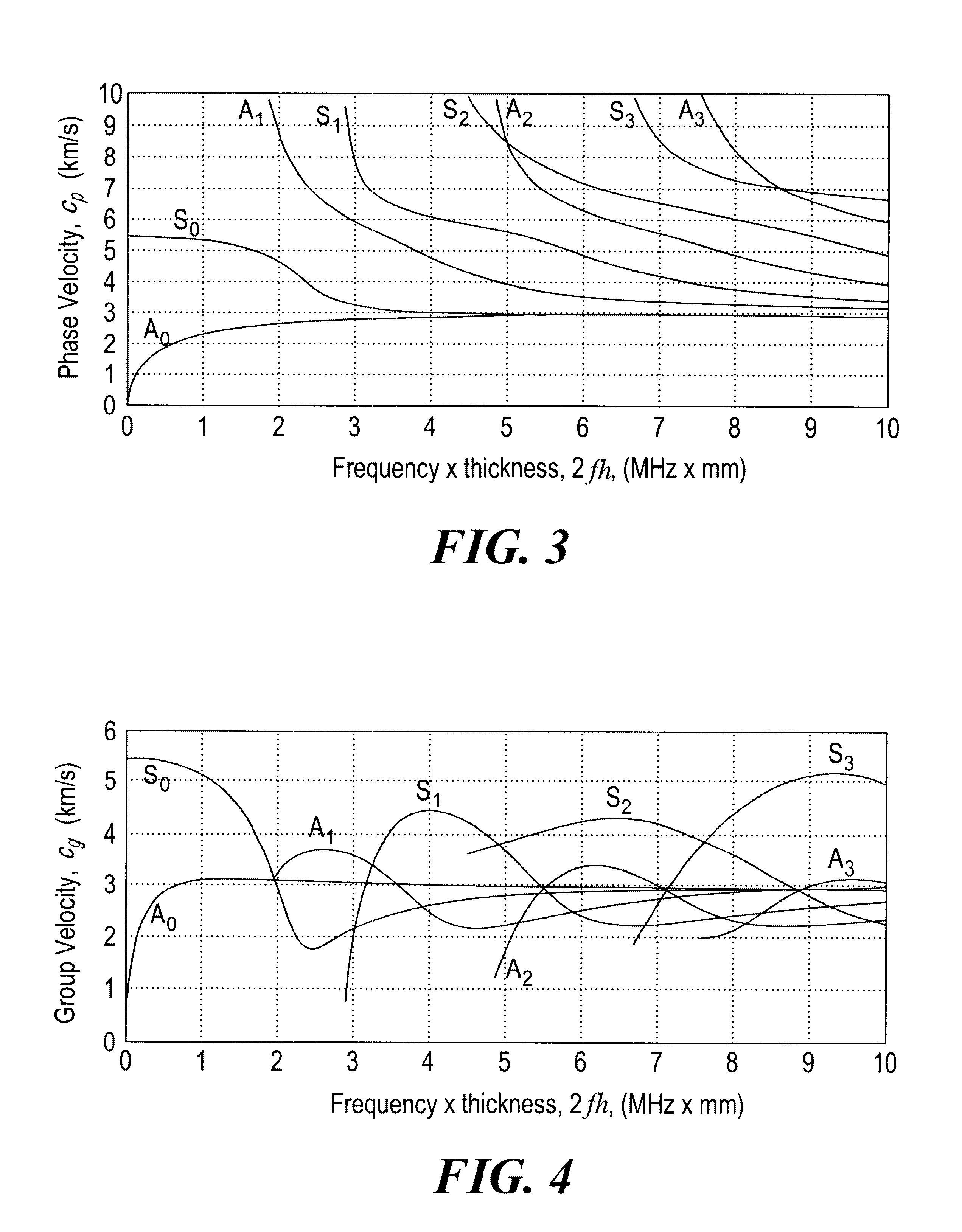
Method and system for interpreting and utilizing multimode dispersive acoustic guided waves
InactiveUS6360609B1Easy to measureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionDispersion curveUnknown Source
A method and system of locating discontinuities, measuring distances, locating unknown sources, and measuring the thickness of multimode dispersive medium includes sensing a multimode dispersive acoustic guided wave and frequency decomposing that wave using spectral temporal analysis; selecting a frequency which identifies a group delay of the guided wave for each mode occurring at that frequency; selecting a mode from the group delays of the selected mode, determining the group velocity from the dispersion curves and computing the desired parameter.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Apparatus and method for radar-based level gauging
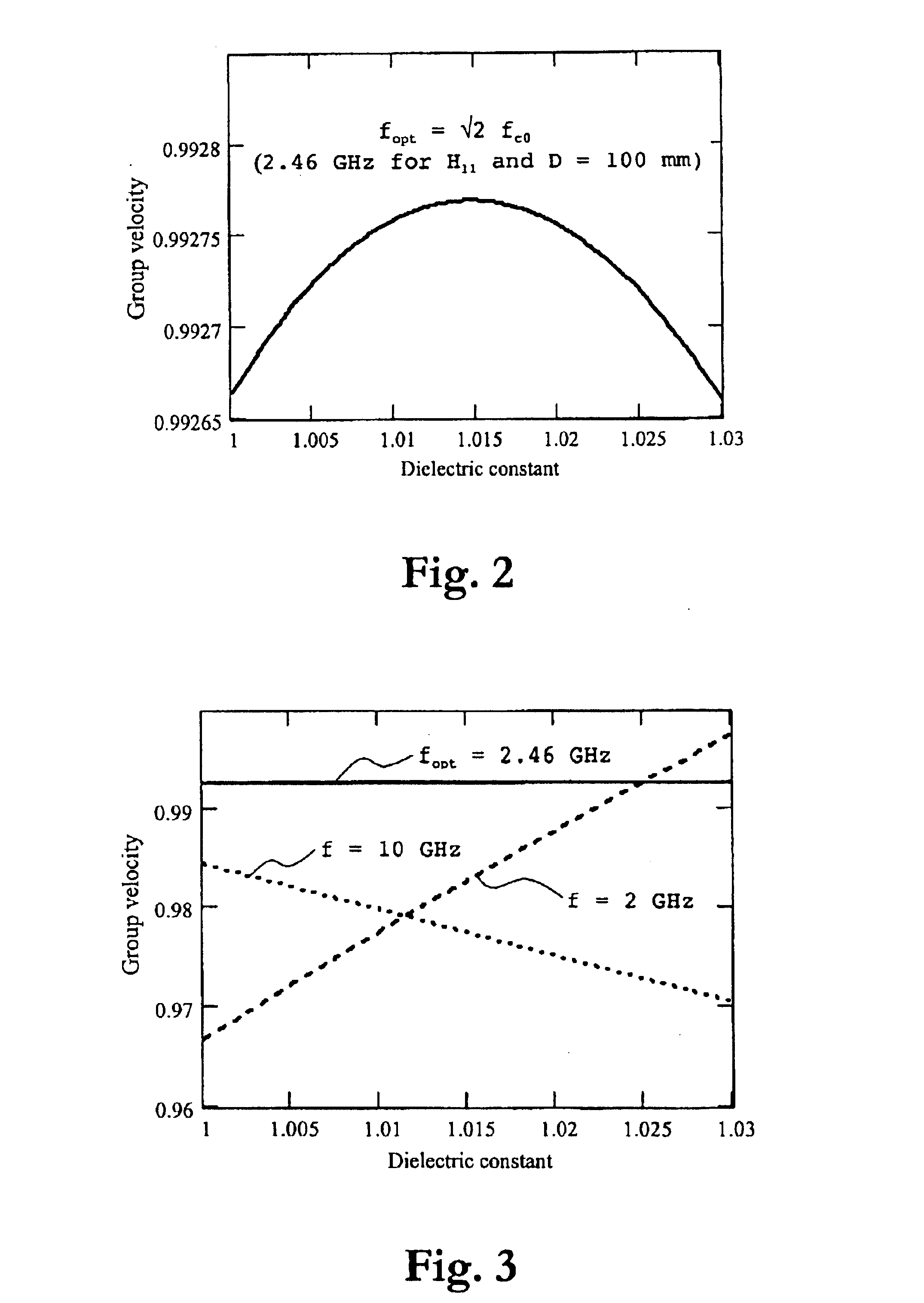
InactiveUS20040099058A1Accurate measurementReduce errorsWaveguide hornsResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricPropagation time
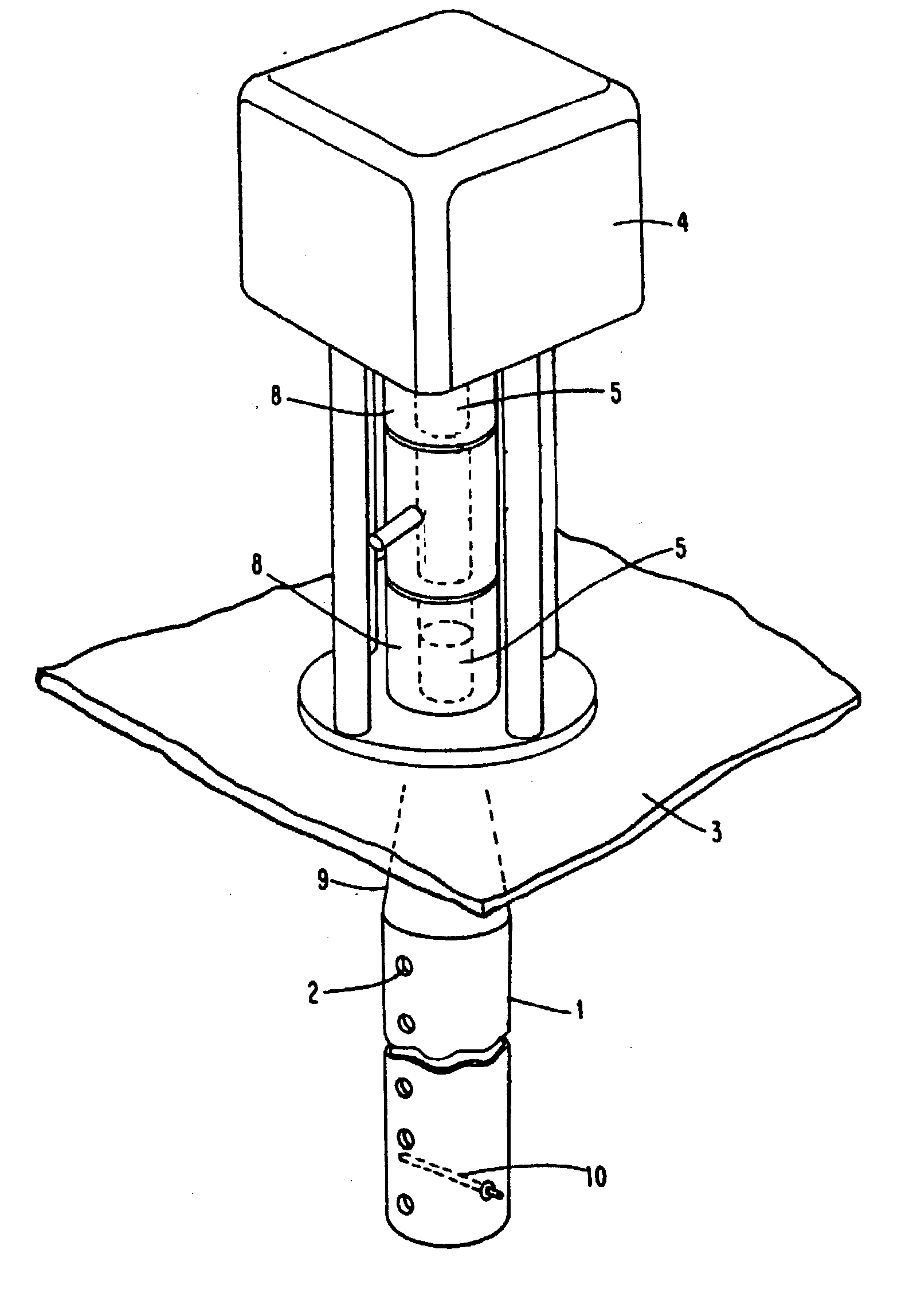
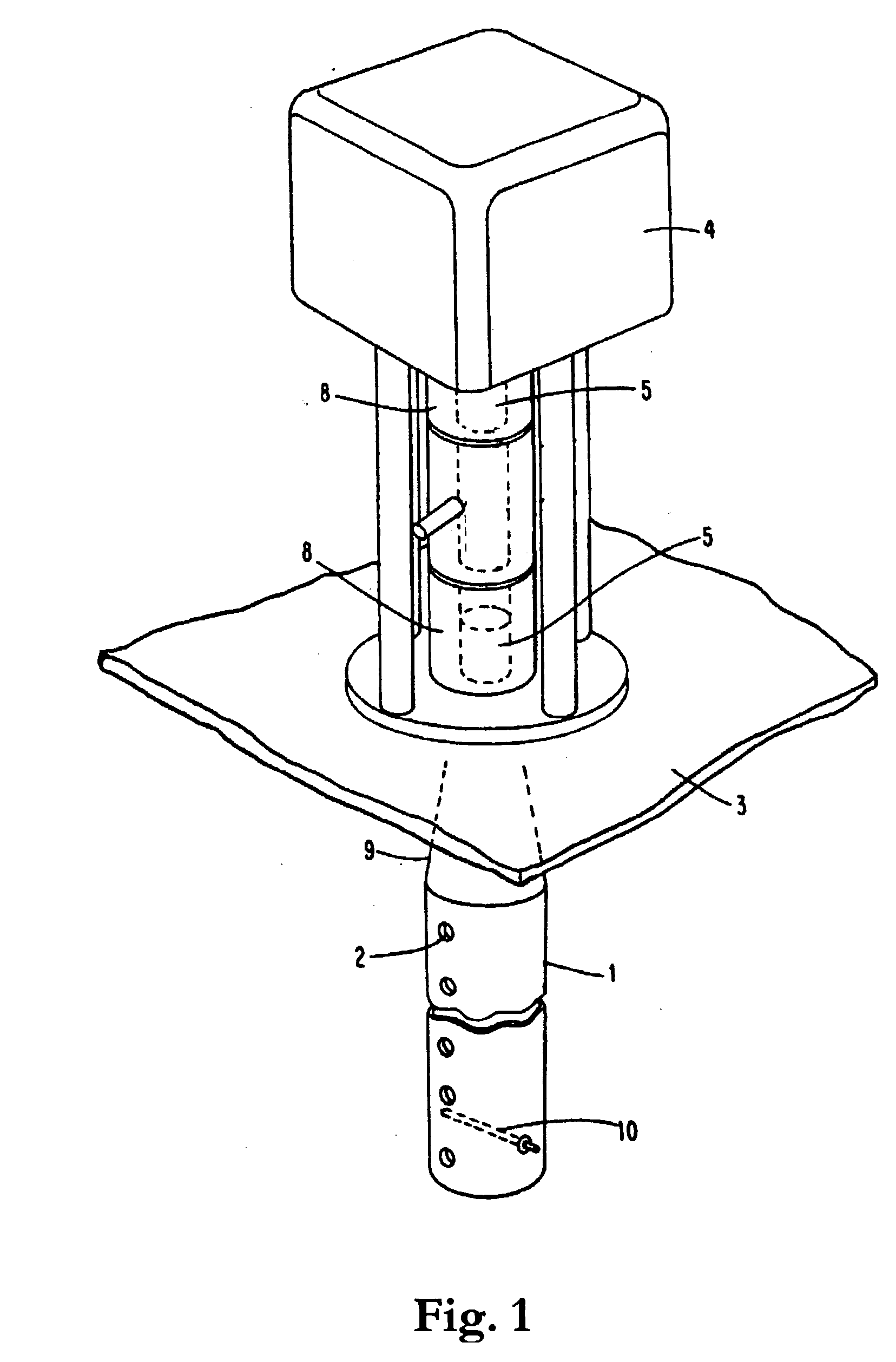
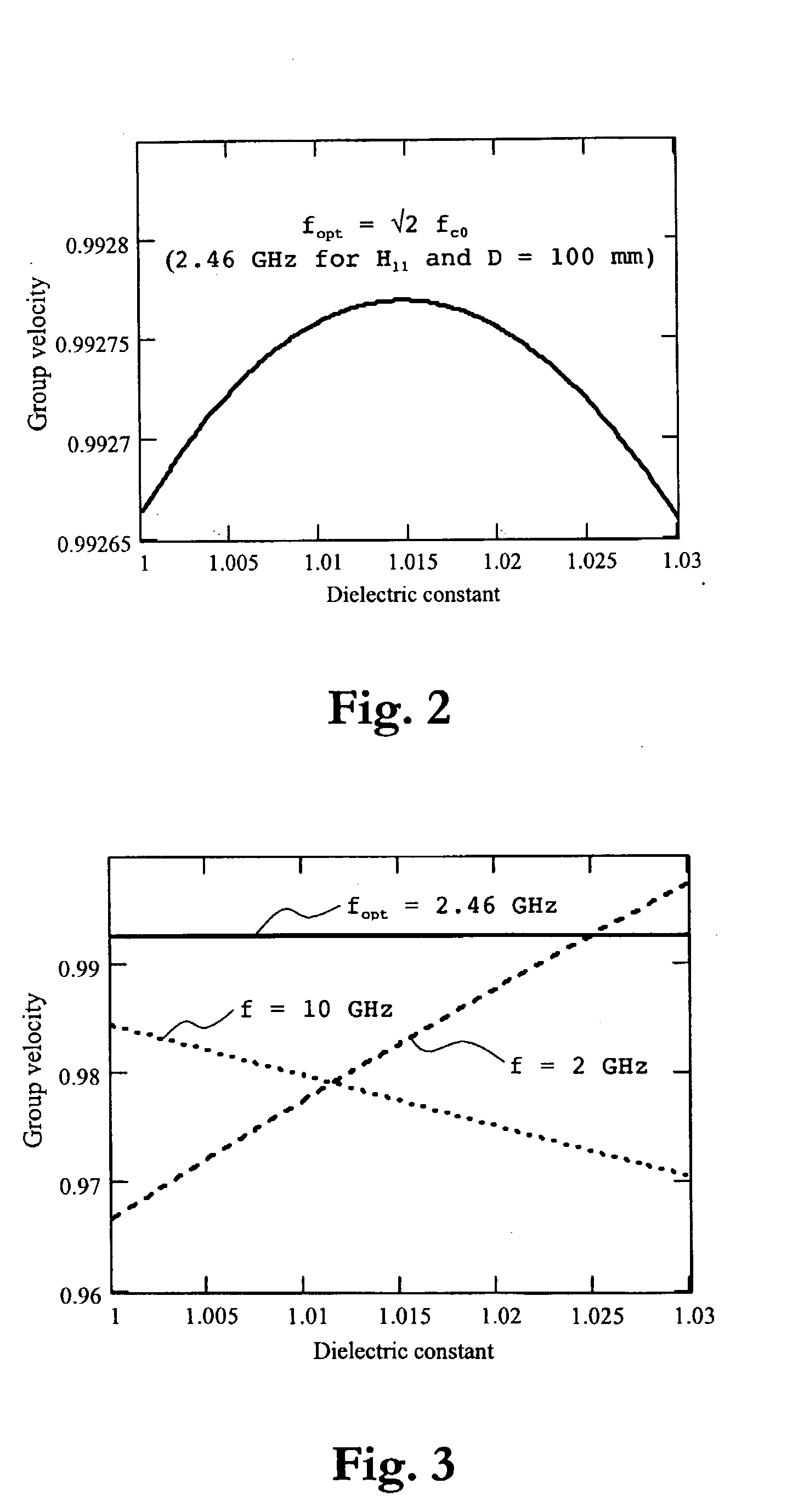
An apparatus for gauging the level of a liquid, above which a gas having a dielectric constant within a predetermined dielectric constant range exists, comprises a transmitter for transmitting a microwave signal in a propagation mode in a tube through the gas towards the liquid surface; a receiver for receiving the microwave signal reflected against the liquid surface and propagating back through the tube; and a processing device for calculating from the propagation time of the transmitted and reflected microwave signal the level of the liquid. In order to essentially avoid the influence on the calculated level by the dielectric constant of the gas above the liquid, the transmitter is adapted to transmit the microwave signal in a frequency band, at which the group velocity of the microwave signal in the propagation mode in the tube is, within the predetermined dielectric constant range, essentially independent of the dielectric constant.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
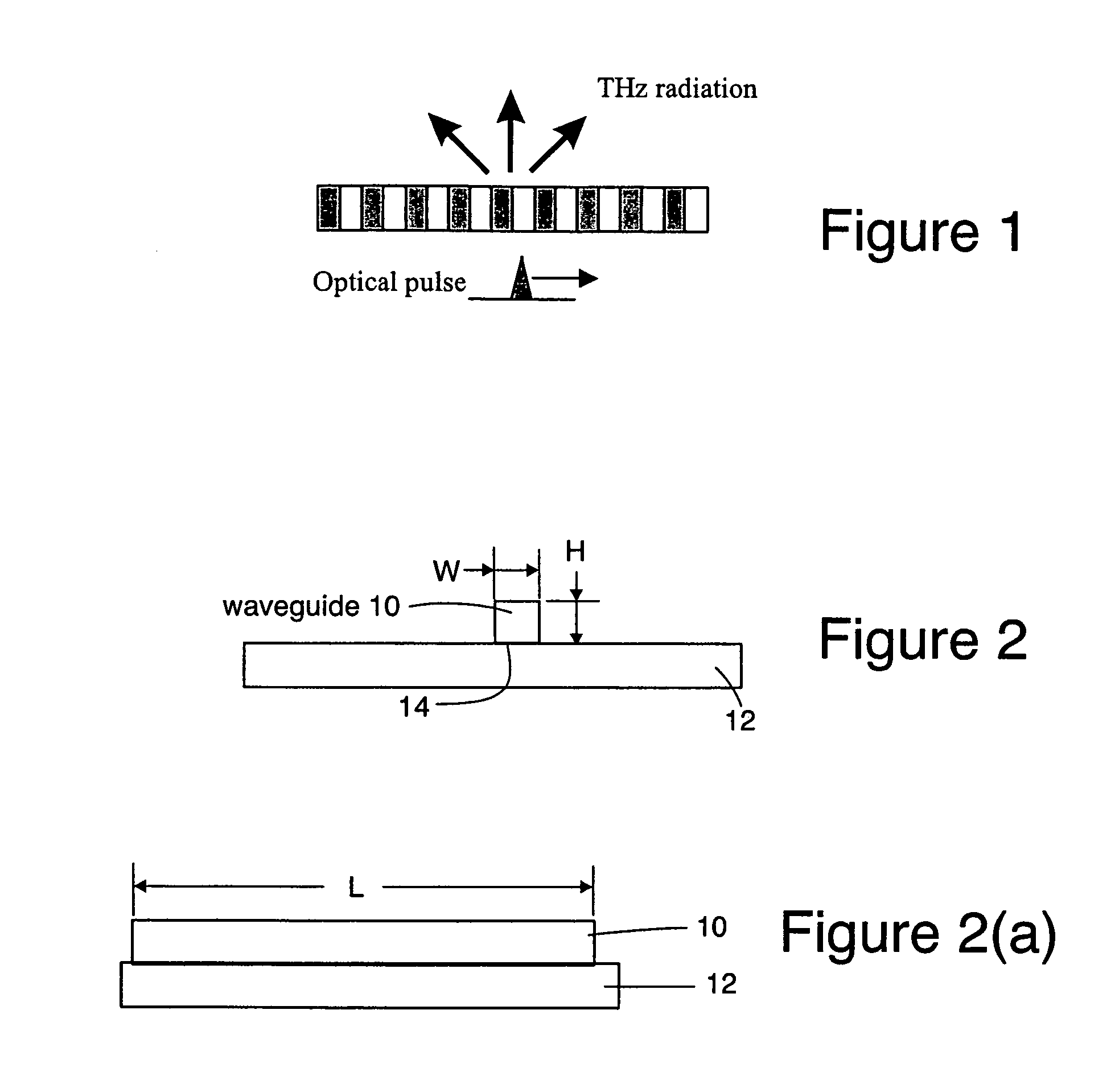
Highly efficient waveguide pulsed THz electromagnetic radiation source and group-matched waveguide THz electromagnetic radiation source
InactiveUS7272158B1Reduce impactReduce travel requirementsCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsNonlinear waveguideOptical power
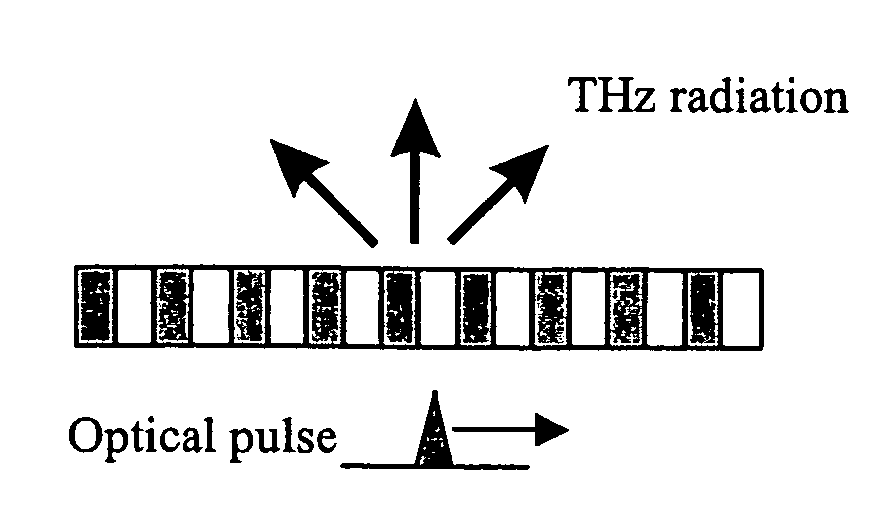
Electromagnetic radiation sources operating in the Terahertz (THz) region capable of overcoming the Manley-Rowe limits of known optical schemes by achieving phase matching between a THz wave and optical pulse in a nonlinear waveguide, or by achieving both phase and group velocity matching between a THz wave and optical pulse in a nonlinear waveguide to yield even higher efficiencies in converting optical power to the THz region.
Owner:HRL LAB
Apparatus and method for radar-based level gauging
InactiveUS6915689B2Level gaugingImprove accuracyWaveguide hornsResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricPropagation time
An apparatus for gauging the level of a liquid, above which a gas having a dielectric constant within a predetermined dielectric constant range exists, comprises a transmitter for transmitting a microwave signal in a propagation mode in a tube through the gas towards the liquid surface; a receiver for receiving the microwave signal reflected against the liquid surface and propagating back through the tube; and a processing device for calculating from the propagation time of the transmitted and reflected microwave signal the level of the liquid. In order to essentially avoid the influence on the calculated level by the dielectric constant of the gas above the liquid, the transmitter is adapted to transmit the microwave signal in a frequency band, at which the group velocity of the microwave signal in the propagation mode in the tube is, within the predetermined dielectric constant range, essentially independent of the dielectric constant.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Ultra-slow down and storage of light pulses, and altering of pulse spectrum
Light pulses can be stopped and stored coherently, with an all-optical process that involves an adiabatic and reversible pulse bandwidth compression occurring entirely in the optical domain. Such a process overcomes the fundamental bandwidth-delay constraint in optics, and can generate arbitrarily small group velocities for light pulses with a given bandwidth, without the use of any coherent or resonant light-matter interactions. This is accomplished only by small refractive index modulations performed at moderate speeds and has applications ranging from quantum communications and computing to coherent all-optical memory devices. A complete time reversal and / or temporal / spectral compression and expansion operation on any electromagnetic field is accomplished using only small refractive index modulations and linear optical elements. This process does not require any nonlinear multi-photon processes such as four-wave mixing and thus can be implemented using on-chip tunable microcavity complexes in photonic crystals. The tuning process requires only small refractive index modulations, and moderate modulation speeds without requiring any high-speed electronic sampling.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
CMOS-compatible light emitting aperiodic photonic structures
A fabrication method and materials produce high quality aperiodic photonic structures. Light emission can be activated by thermal annealing post growth treatments when thin film layers of SiO2 and SiNx or Si-rich oxide are used. From these aperiodic structures, that can be obtained in different vertical and planar device geometries, the presence of aperiodic order in a photonic device provides strong group velocity reduction (slow photons), enhanced light-matter interaction, light emission enhancement, gain enhancement, and / or nonlinear optical properties enhancement.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Casing Thickness Evaluation Method
ActiveUS20100263449A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesClassical mechanicsLength wave
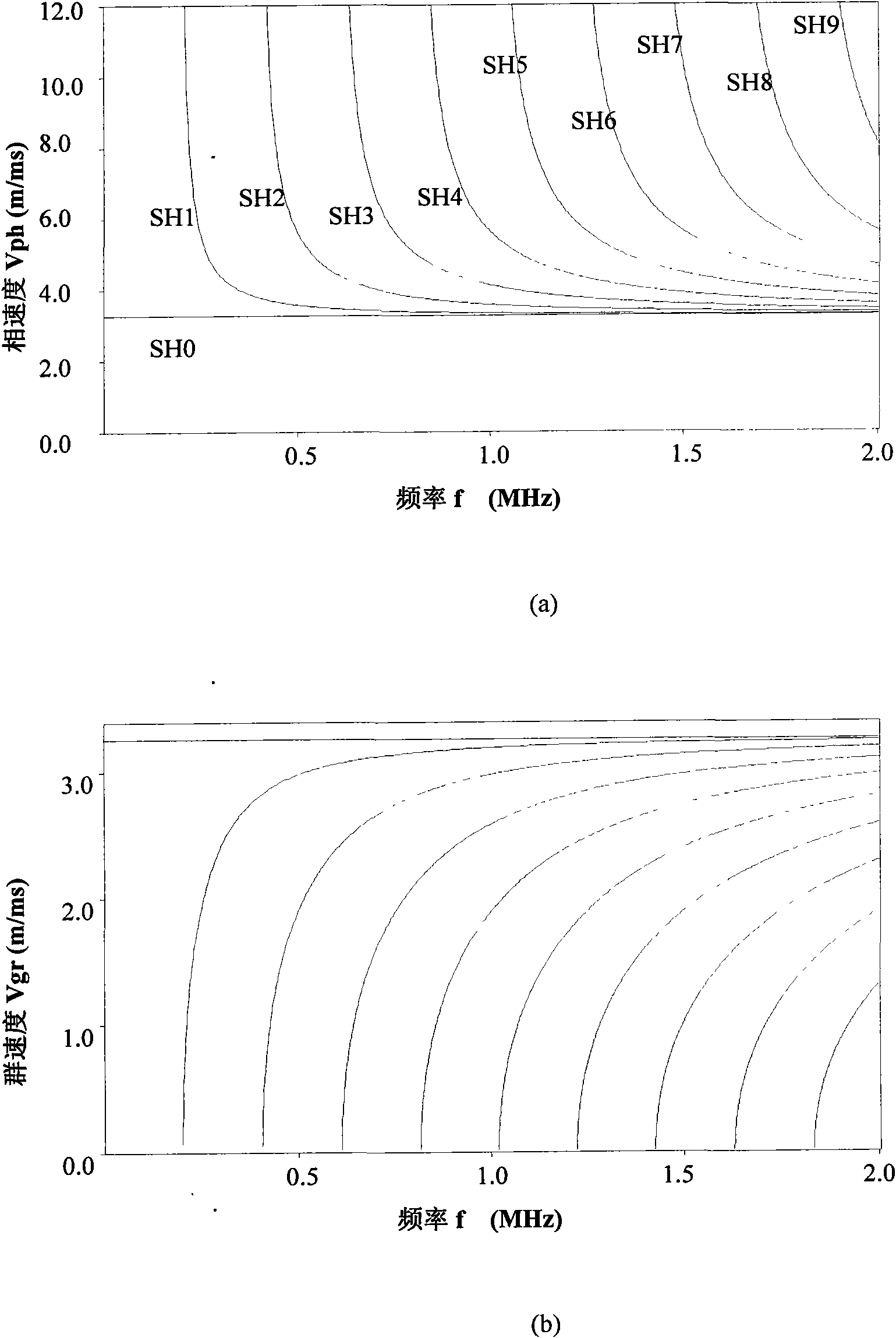
Evaluating casing thickness by inducing SH0 and SH1 modes of a shear wave in the casing. The SH0 group velocity and SH1 mode group velocity (Vg) are measured and the measured SH0 mode group velocity is assigned as the tubular material shear velocity (Vs). A shear wave wavelength λ from the ratio of SH0 mode frequency (fo) and the measured SH0 group velocity is estimated. The tubular thickness (d) is estimated from the estimated shear wave wavelength λ The transmitter can be calibrated to operate at an optimum frequency.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for guiding an electromagnetic radiation, in particular in an integrated optical device
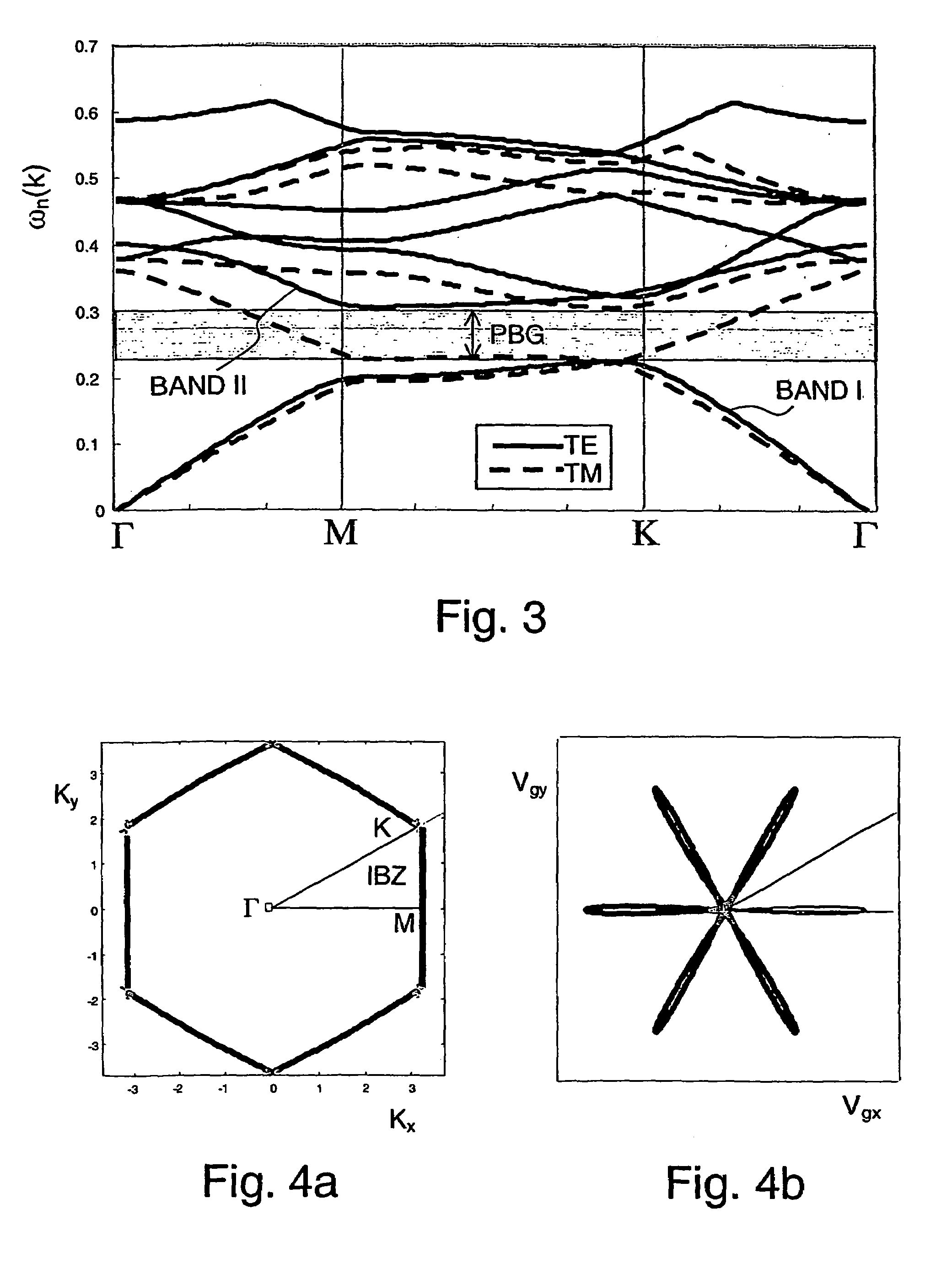
A method for guiding electromagnetic radiation by providing a photonic crystal made of a bulk material with a predetermined refractive index and having a periodic array of holes with predetermined radius, and feeding to that region an electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength in the fundamental photonic band and so related to the refractive index of the bulk material, to the radius of the holes and to the period of the array that, starting from an isotropic distribution of the wave vectors within a first angular range that is twice the angular extension of the first irreducible Brillouin zone of the photonic crystal, the corresponding group velocity vectors are rearranged as concerns direction and module so that at least 50% of them become directed within a second angular range that is about one-third of the first angular range and the width at half-maximum of the distribution of the modules of the vectors is lower than about two-thirds of the second angular range.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Nanophononic metamaterials
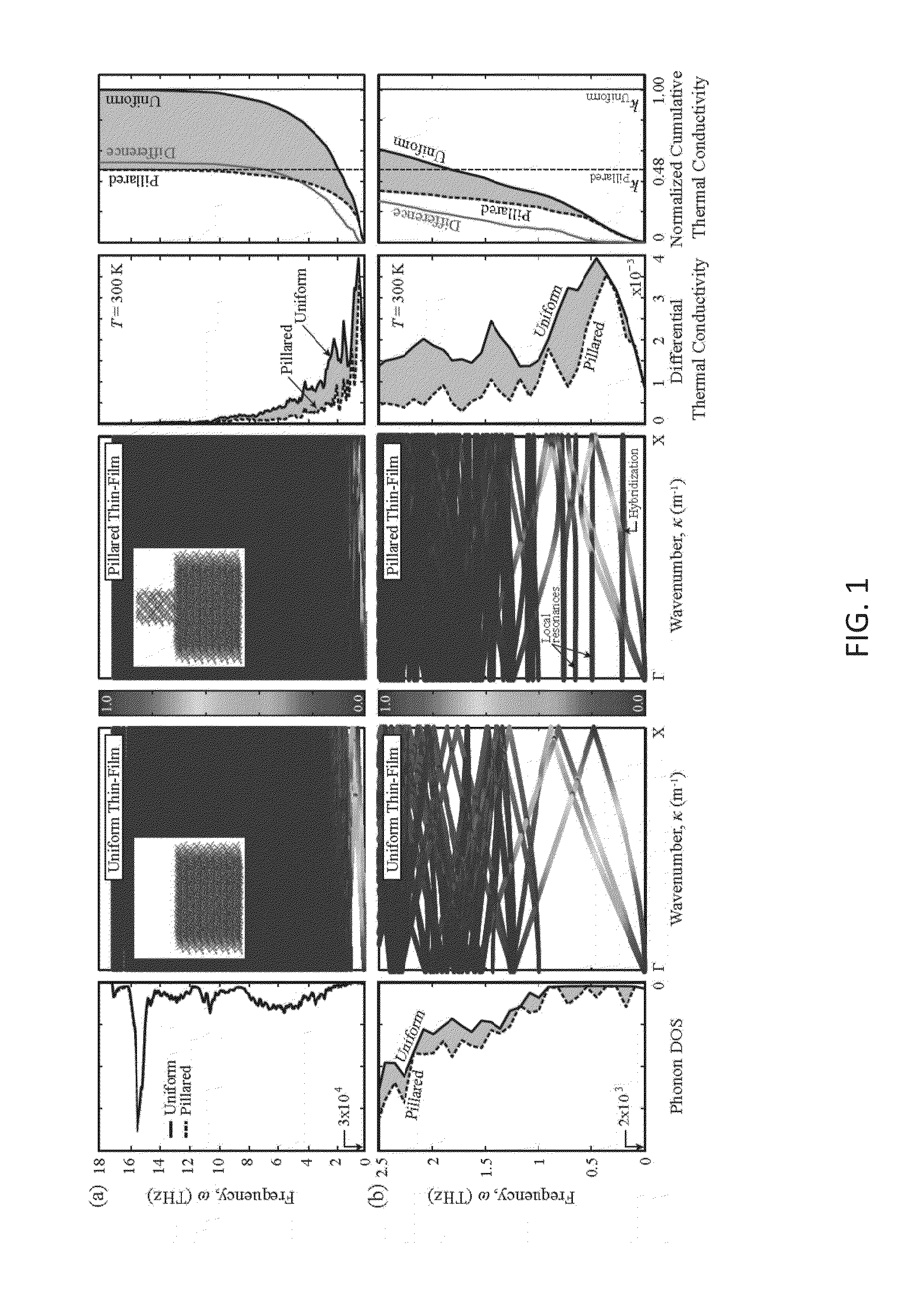
ActiveUS20150015930A1Low thermal conductivityImprove energy conversionMaterial nanotechnologyImpedence networksPhotonic metamaterialGroup velocity
Nanophononic metamaterials and methods for reducing thermal conductivity in at least partially crystalline base material are provided, such as for thermoelectric energy conversion. In one implementation, a method for reducing thermal conductivity through an at least partially crystalline base material is provided. In another implementation, a nanophononic metamaterial structure is provided. The nanophononic metamaterial structure in this implementation includes: an at least partially crystalline base material configured to allow a plurality of phonons to move to provide thermal conduction through the base material; and at least one nanoscale locally resonant oscillator coupled to the at least partially crystalline base material. The at least one nanoscale locally resonant oscillator is configured to generate at least one vibration mode to interact with the plurality of phonons moving within the base material and slowing group velocities of at least a portion of the interacting phonons and reduce thermal conductivity through the base material.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Super-resolution formation fluid imaging with contrast fluids
ActiveUS20140347055A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electromagnetic wavesLow noiseTime domain
Cross-well electromagnetic (EM) imaging is performed using high-power pulsed magnetic field sources, time-domain signal acquisition, low-noise magnetic field sensors, spatial oversampling and super-resolution image enhancement and injected contrast fluids. The contrast fluids increase the electromagnetic character of the formation and fluids, either the magnetic permeability or the dielectric permittivity. The acquired signals are processed and inter-well images are generated mapping electromagnetic (EM) signal speed (group velocity) rather than conductivity maps. EM velocity maps with improved resolution for both native and injected fluids are provided.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Super-Resolution Formation Fluid Imaging
ActiveUS20130146756A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electromagnetic wavesLow noiseOversampling
Cross-well electromagnetic (EM) imaging is performed using high-power pulsed magnetic field sources, time-domain signal acquisition, low-noise magnetic field sensors, spatial oversampling and super-resolution image enhancement and injected magnetic nanofluids. Inter-well images are generated mapping electromagnetic (EM) signal speed (group velocity) rather than conductivity maps. EM velocity maps with improved resolution for both native and injected fluids are provided.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Group sound velocity real-time adjustable ultrasound diagnostic equipment and wave beam synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN101664321AFine adjustment of sound velocityAppropriate speed of soundUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging qualitySynthesis methods
The invention discloses a group sound velocity real-time adjustable ultrasound diagnostic equipment and a wave beam synthesis method thereof, which relates to the technical field of medicinal ultrasound diagnostic equipment. The equipment uses changeable group sound velocity to accurately calculate wave beam synthesis, and through the combination between the equipment and a pre-value storage device, a doctor can select examination positions to automatically load the most matched group sound velocity for imaging and to permit the real-time adjustment and imaging of the group sound velocity. Theinvention changes the traditional wave beam synthesis method so as to improve the imaging quality of the ultrasound diagnostic equipment, reduce imaging error caused by using fixed group sound velocity and increase the accuracy of measuring results simultaneously.
Owner:CHISON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Photonic crystal element
A waveguide stub is connected to a pillar-type square-lattice photonic crystal waveguide. Within the waveguide stub, the diameter of a defect is made larger than that of the original photonic crystal waveguide thereby reducing the group velocity of a guided light. The original waveguide and the waveguide stub are smoothly connected via a taper waveguide. Because of low group velocity of light in the waveguide stub, free spectral range (FSR) decreases thereby allowing the size of the waveguide stub to be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
Compensating for polarisation mode dispersion in optical transmission fibers
InactiveUS6707957B1Easy to controlWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingPhotonic crystal
Compensating for polarization mode dispersion in a birefringent optical transmission fibre is achieved by controlling the birefringence of the fibre. The difference in group velocity of the orthogonal polarization states of an optical signal transmitted over the fibre is monitored to generate an error signal representing the difference. The birefringence of the fibre is adjusted accordingly to minimize the difference and thereby provide dynamic compensation. Birefringence control may be achieved by a non-linear fibre grating written into the fibre to impose a differential time delay. The fibre may be a side hole fibre (SHF), a holey fibre (HF), a photonic crystal fibre (PCF), or any other suitable microstructure fibre. The fibre may have stressing rods, may be tapered along its length and may be controlled electrically, mechanically, acoustically or thermally by spaced heating elements.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
High-order longitudinal wave guide measuring method of steel strand prestress
ActiveCN101441199AQuick measurementEfficient measurementAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructivePre stress
The invention relates to high-order longitudinal guided-wave measurement method for steel strand prestress, belonging to non-destructive test field. High-order longitudinal mode of which group velocity is maximum at a frequency is selected for measuring the prestress loaded by the steel strand. At the frequency, the group velocity of the high-order longitudinal mode monotonically increases or reduces along with the tensile stress in the elastic deformation range of steel strand, and when the steel strand bears different prestress in the elastic deformation range of steel strand, the deviation value between the frequency value on the maximum value of high-order longitudinal mode group velocity and the initial frequency value of the longitudinal mode in free state is not more than 1%, and the error between the prestress value measured by the high-order longitudinal guided-wave and the actual value is not more than 1%. The invention solves the problems that the prestress applied to the steel strand can not be rapidly, precisely, and online measured.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
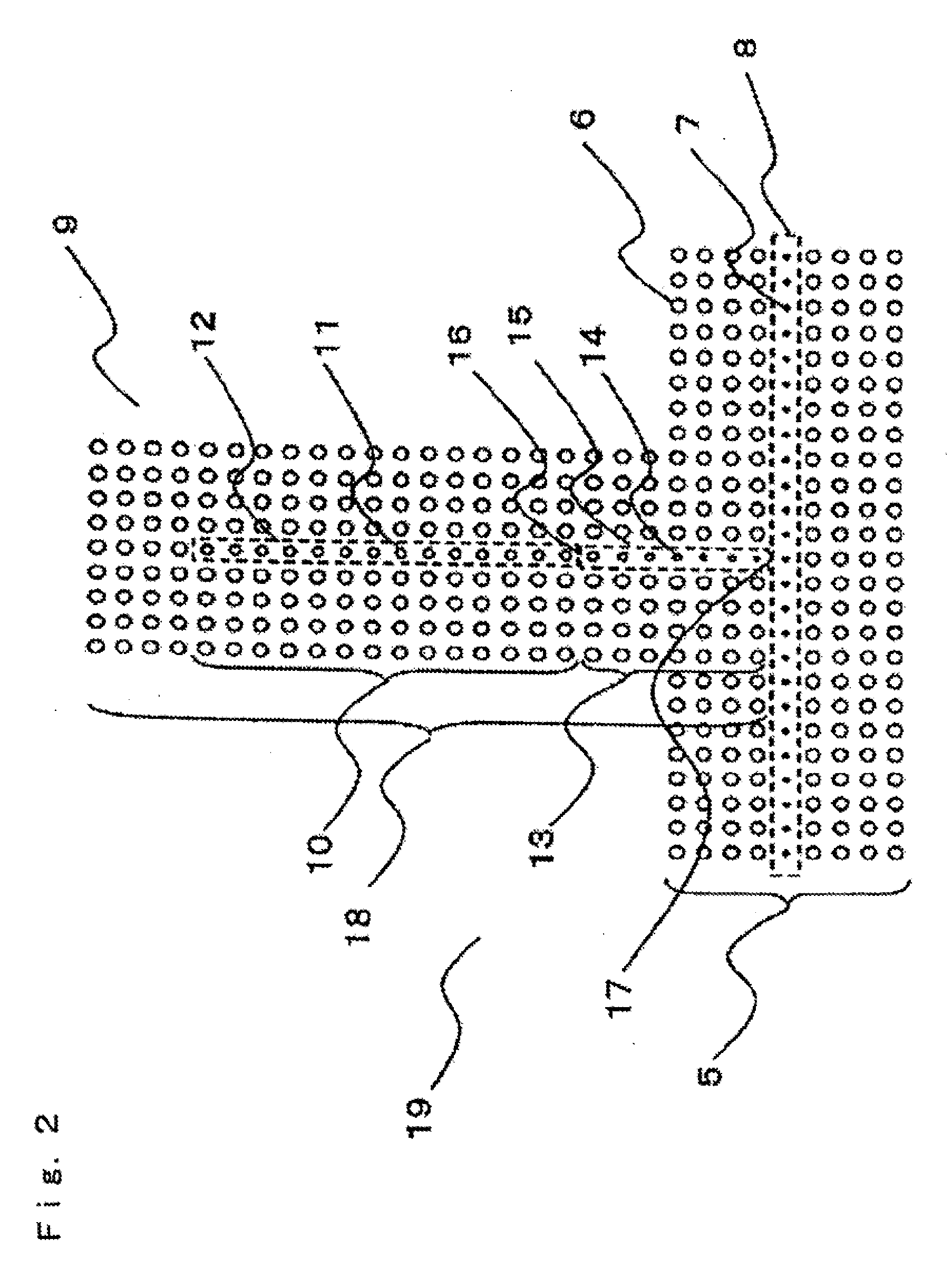
Ultrasonic Lamb wave-based butt weld nondestructive testing method
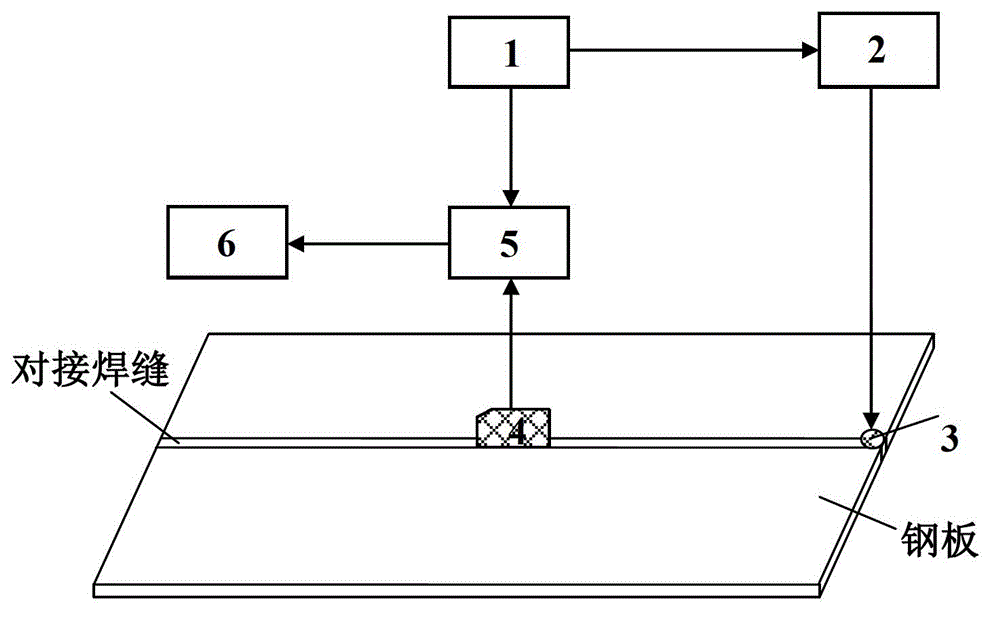
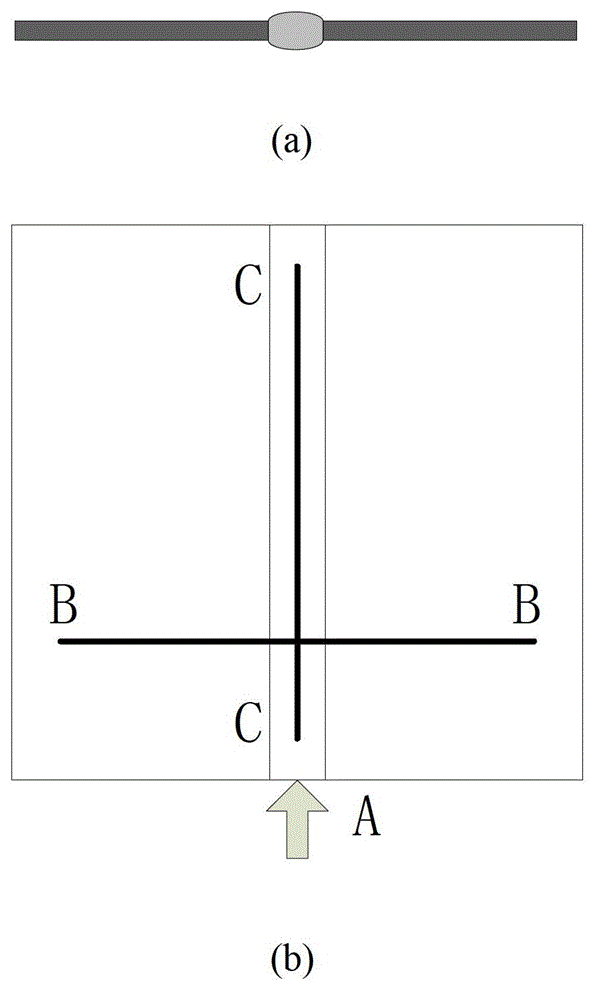
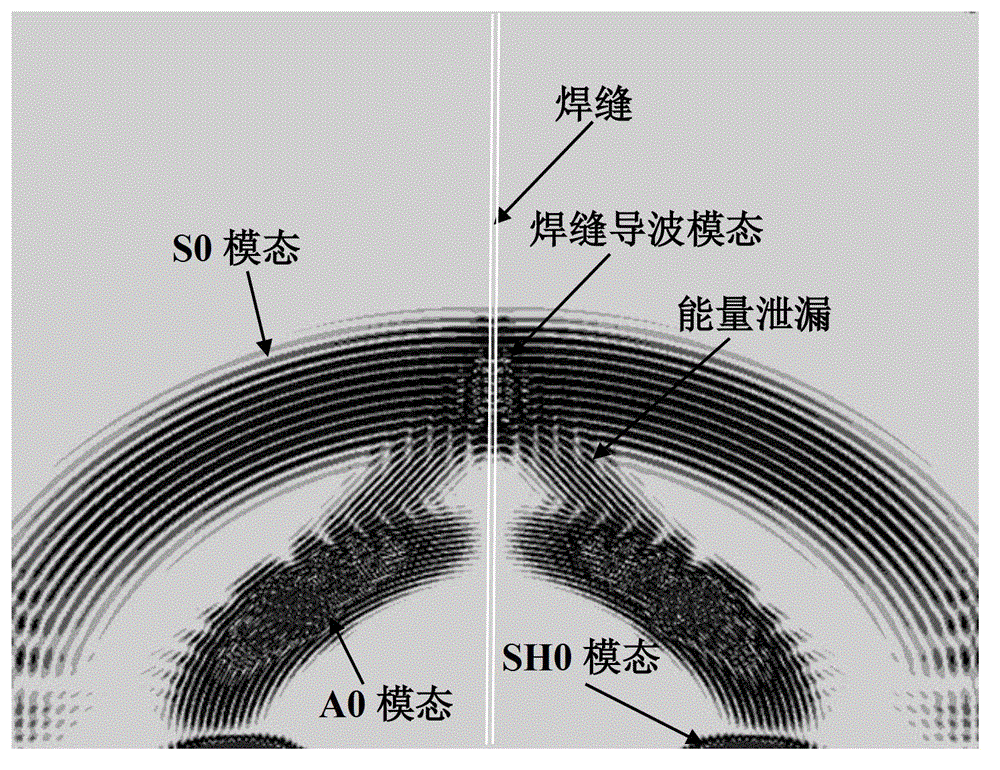
ActiveCN103336054AHigh energyEasy to detectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalHigh energyFunction generator
The invention concretely relates to an ultrasonic Lamb wave-based butt weld nondestructive testing method and belongs to the ultrasonic guided-wave nondestructive testing field. An excitation source is loaded at the end of a weld joint. Two piezoelectric patches are pasted on the upper surface and the lower surface of a plate symmetrically and excited. The generated weld joint guided-wave mode propagating along the weld joint has high energy and slow attenuation, and the long-distance testing problem can be solved. The testing system is shown in the figure, and composed of a function generator (1), a power amplifier (2), piezoelectric patches (3), an oblique incidence-type piezoelectric ultrasonic sensor (4), an oscilloscope (5) and a computer (6). By utilizing the testing system, when the ultrasonic Lamb wave encounters flaws of the weld joint, flaw echoes are generated. According to the time difference between the excitation waveforms and the waveforms of flaw echoes and the group velocity of the weld joint guided-wave mode, the distance from the flaws to the excitation source can be obtained, and therefore the effective locating of weld joint flaws can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
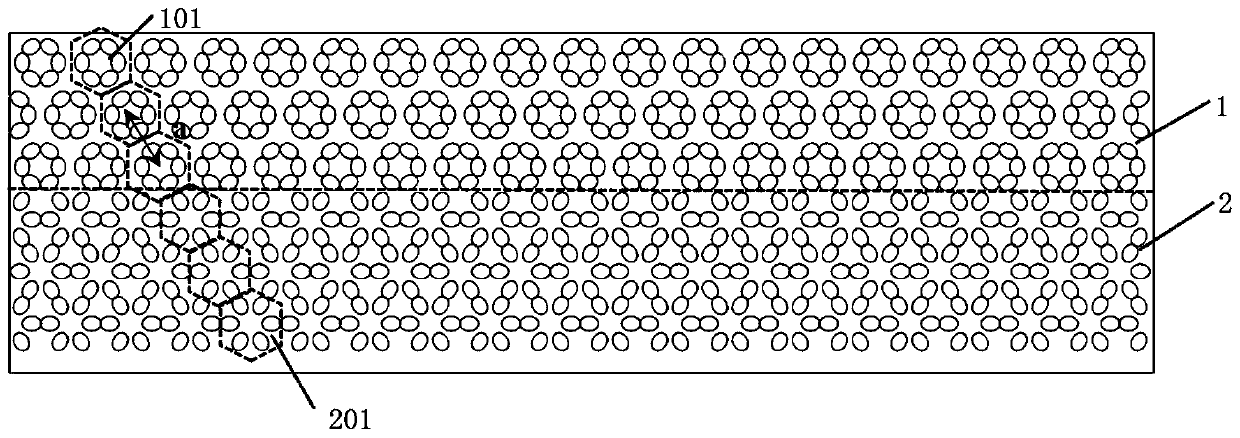
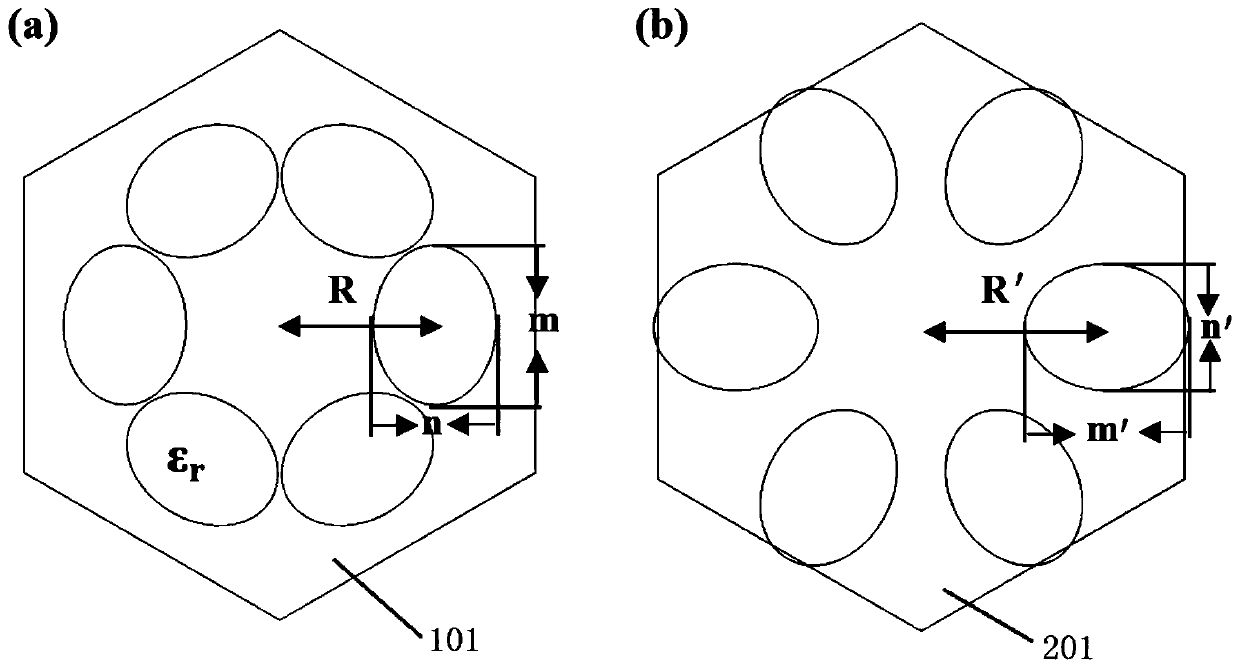
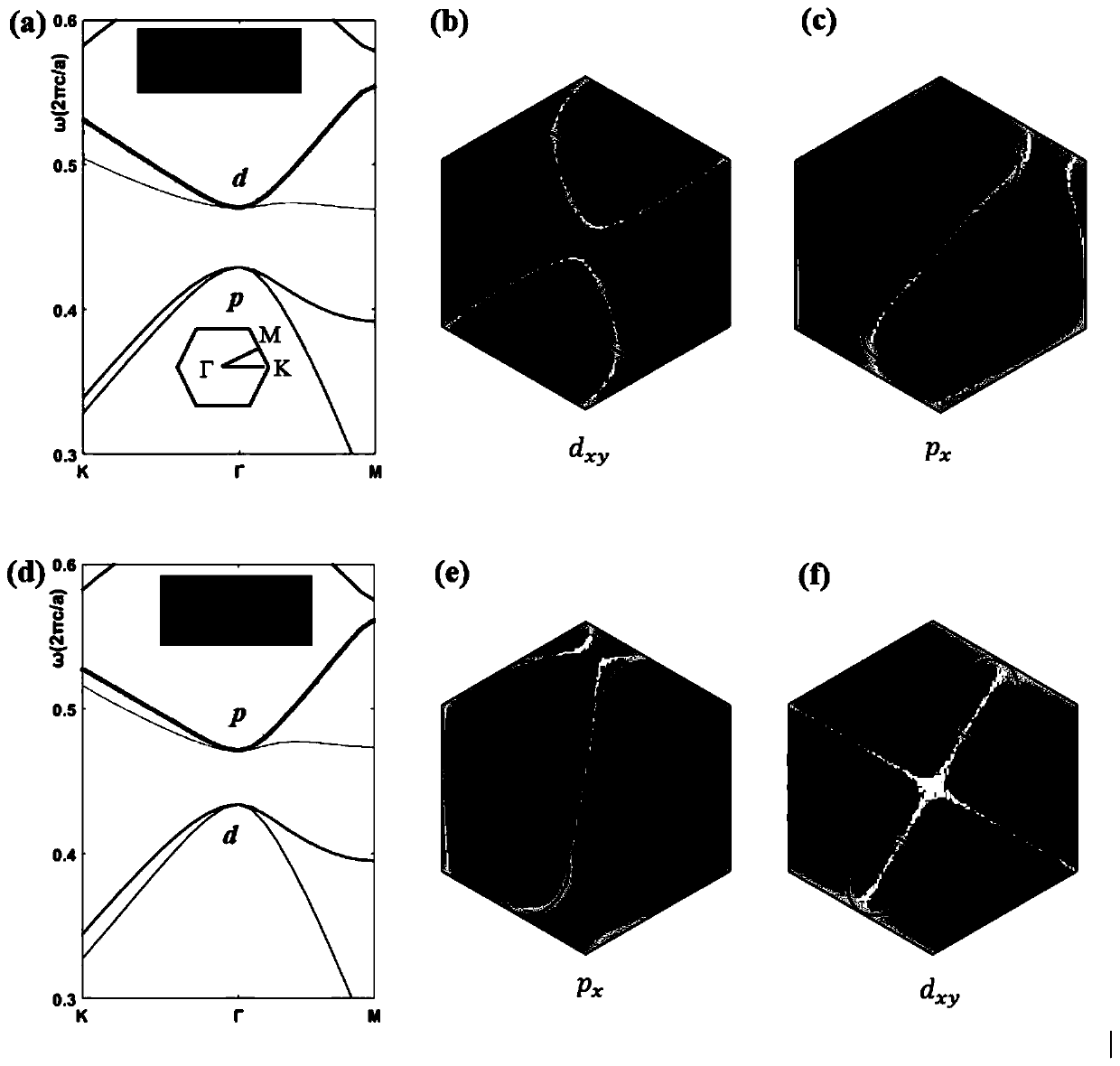
Photonic crystal slow light waveguide based on honeycomb structure
ActiveCN110161621AReduce manufacturing costRealize slow light transmissionCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideDielectric cylinderSlow light
The invention provides a photonic crystal slow light waveguide based on a honeycomb structure. The photonic crystal slow light waveguide based on the honeycomb structure comprises a topology mediocrestructure and a topology non-mediocre structure, and the other part is composed of crystal cells which are arranged and have topology non-mediocre property. A relatively mild energy band appears in afirst Brillouin zone in an energy band structure, and transmission group velocity of light at the frequency is close to 0, so that slow light transmission is realized. An elliptical dielectric cylinder is made from a common dielectric material silicon, and production cost is low.
Owner:南通宁竞信息科技有限公司
Coupled waveguide photo detector
An embodiment of the invention provides a coupled waveguide photo detector device. Optically, the device includes an input waveguide. An output waveguide is coupled to the input waveguide with a nonuniform coupling coefficient in a coupling section. An absorber is included in the coupling section to convert an absorbed portion of optical radiation into photo current. The location of absorber and the optical radiation intensity pattern in the coupling section are set to control the maximum intensity of output power absorbed by the output waveguide to be within a predetermined limit that avoids saturation. The absorber is also part of a transmission line collector which has a phase and group velocity to match those of the optical wave in the coupling section such that currents collected by the transmission line collector add in phase as the optical wave propagates in the output waveguide.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical modulator and communications system
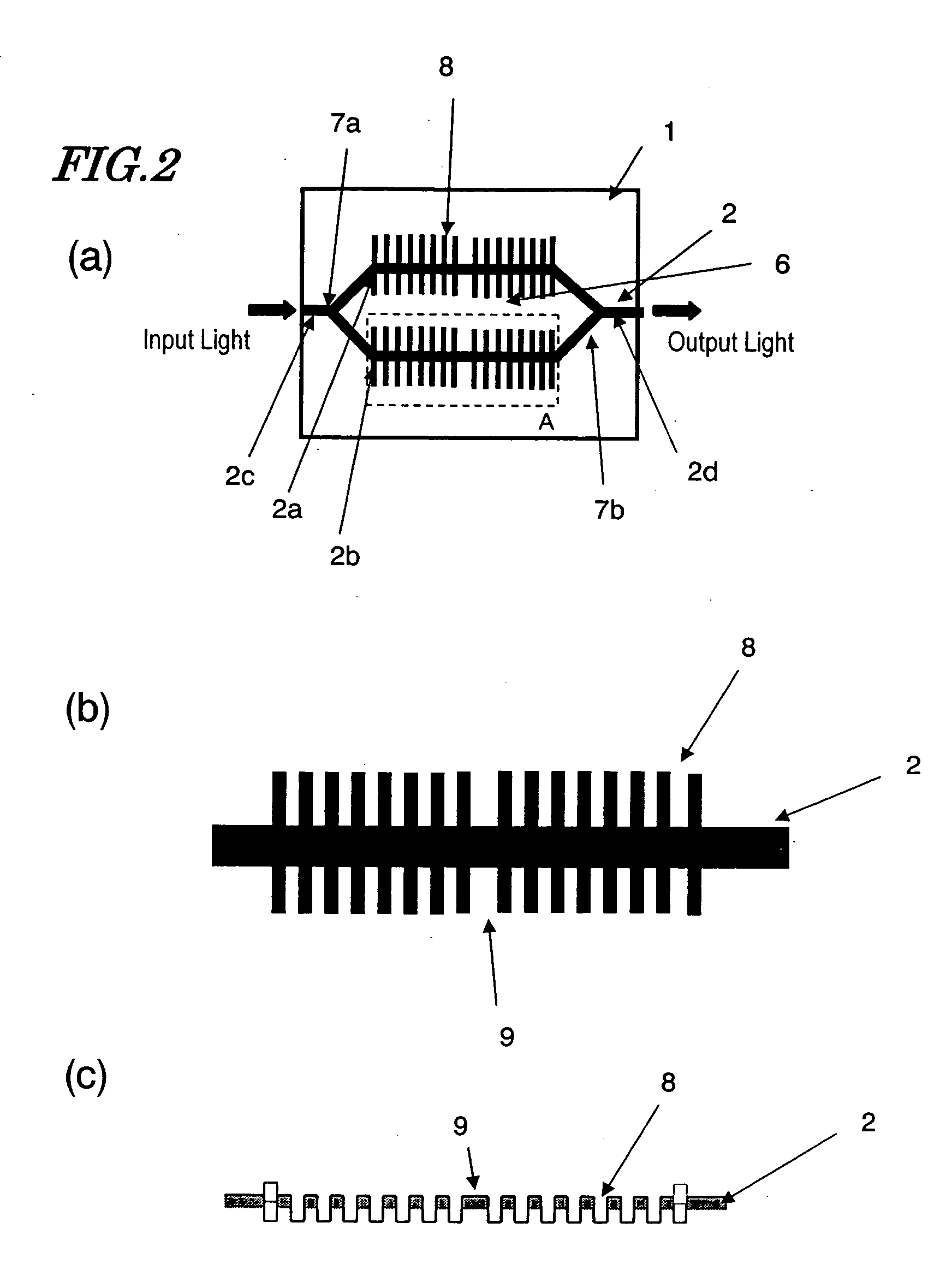
InactiveUS20050196092A1Improve modulation efficiencyEasy to useCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsCommunications systemRefractive index
An optical modulator according to the present invention includes an optical waveguide 2a to 2d made of a material with an electro-optic effect and a modulating electrode 3 for applying a modulating electric signal to light propagating through the optical waveguide 2a to 2d. The modulator further includes a periodic structure, of which the equivalent refractive index changes periodically in a light propagation direction and which can reduce the group velocity of the light propagating through the optical waveguide 2a, 2b.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
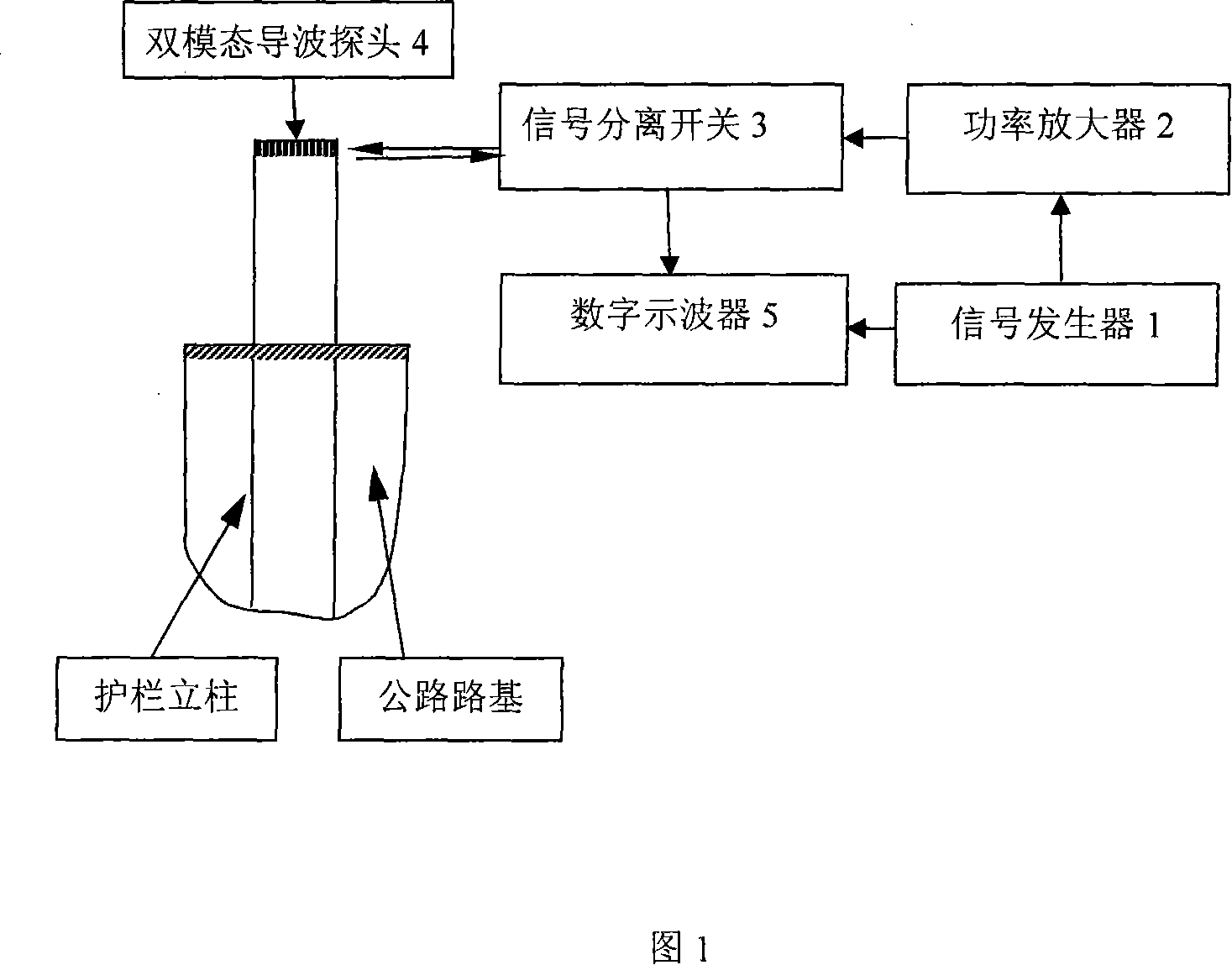
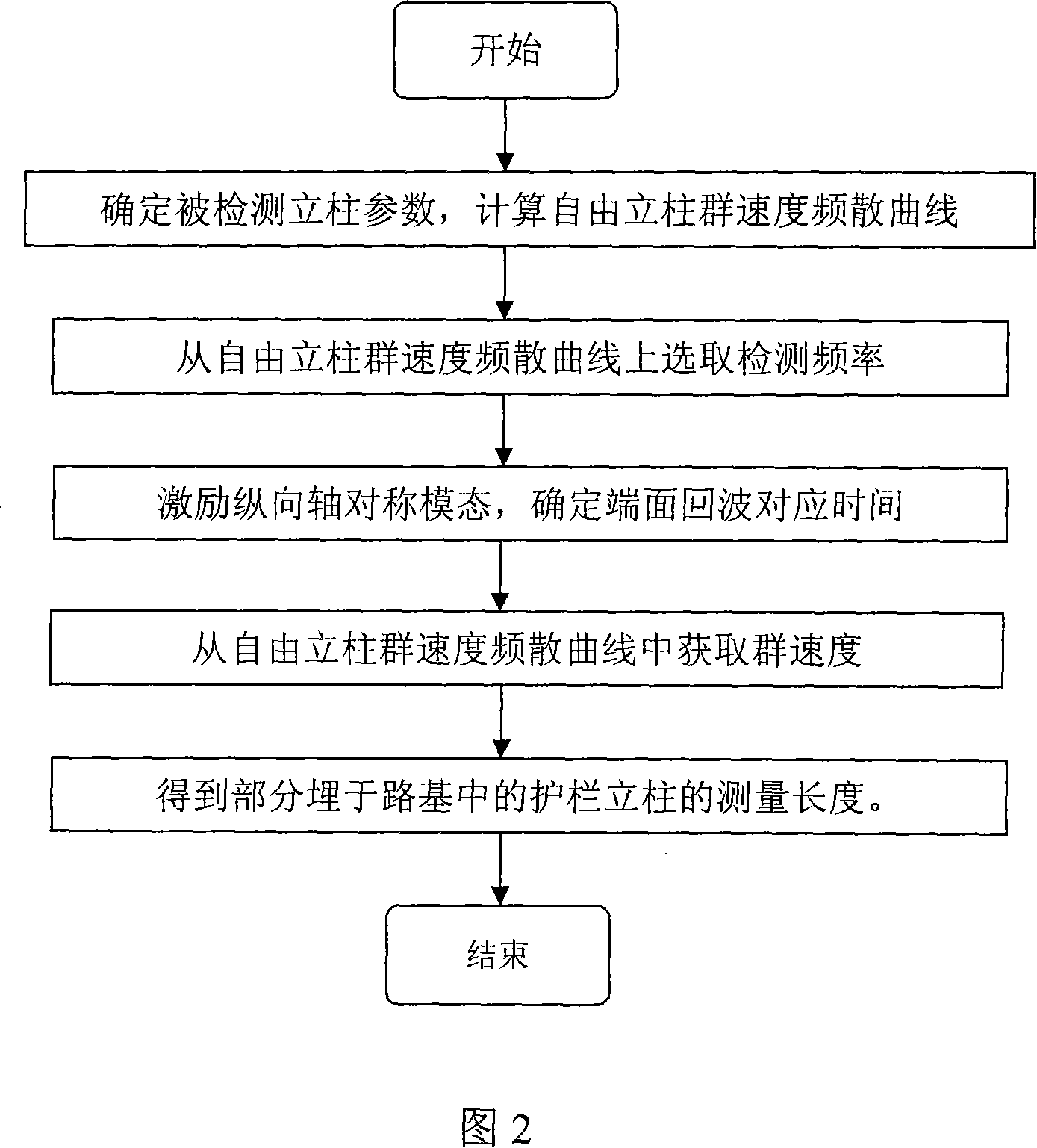
Method for nondestructive detecting length of high speed highway guardrail upright post by ultrasonic guided wave
InactiveCN101131319AFree from destructionNot affected by working conditionsUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansAcoustic wave reradiationTransceiverSonification
A method of using ultrasonic guided wave to detect the length of grate column of half buried under different highway roadbed, belongs to nondestructive testing field. The method is to determine parameters of grate column before buried calculate group velocity dispersion curve of grate column before buried; select detection frequency from the curve and input the arbitrary function generator to form a single audio signal through the power amplifier module, switch modules, guided wave transceiver components, stimulate the vertical axisymmetric guided wave mode in the vertical column; the guided wave modal generate end echo when encounter the end of the column, the end echo is sent to oscilloscope through guided wave transceiver components and switch modules, determine the corresponding time of end echo, obtain the group velocity from the group velocity dispersion curve, multiple the group velocity with the echo time, divided by 2 to obtain the length of column. The present invention has the advantages of do not need to consider surrounding medium of column, high detection accuracy and of low cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
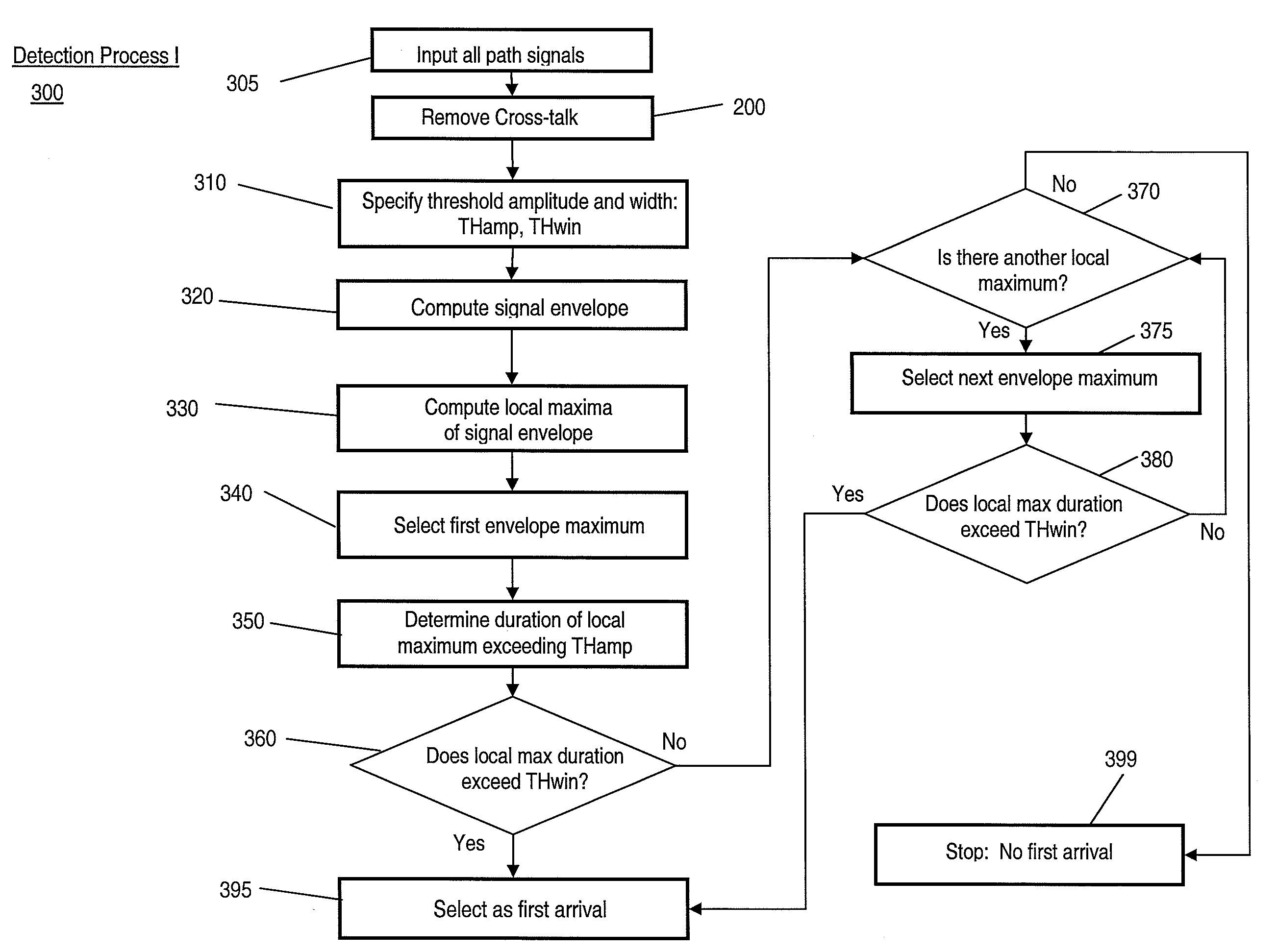
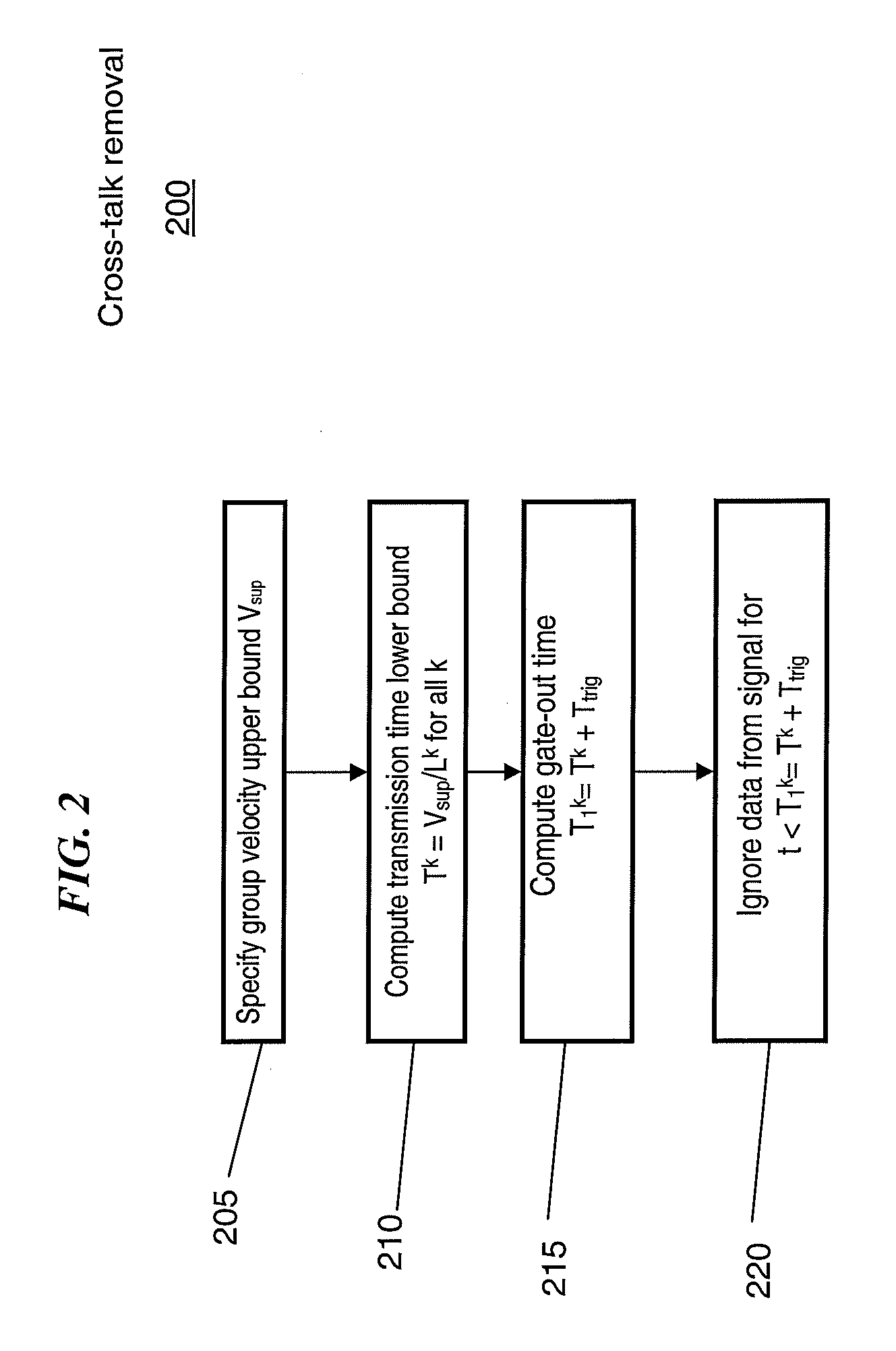
Methods and apparatus for extracting first arrival wave packets in a structural health monitoring system
ActiveUS20080253229A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesStructural health monitoringPropagation time
Methods and apparatus for extracting the first arrival wave packet of an acoustic signal in a structural health monitoring (SHM) system include receiving an acoustic signal transmitted between two transducers thereof. Electromagnetic cross-talk is removed from the signal. Signal amplitude threshold values used for picking out the first arrival wave packet are chosen based on signal characteristics or chosen adaptively as the value that leads to the minimum variance of the group velocity estimates of all the actuation-sensing transducer pairs. The group velocity is estimated as the known actuator-sensor distance divided by the propagation time of the first wave packet of which the envelope exceeds a candidate threshold value. The first arrival wave packet is determined as the signal segment where the signal envelope first exceeds the chosen amplitude threshold and the segment length exceeds a specified threshold of time width.
Owner:ACELLENT TECH
Methods and apparatus of entangled photon generation using four-wave mixing
A non-linear optical device is provided. The device comprises an optical disk or ring microresonator fabricated from a material that exhibits an optical nonlinearity able to produce degenerate four-wave mixing (FWM) in response to a pump beam having a pump frequency in a specified effective range. The microresonator is conformed to exhibit an angular group velocity minimum at a pump frequency within the specified effective range such that there is zero angular group velocity dispersion at the pump frequency. We refer to such a pump frequency as the “zero dispersion frequency”. In embodiments, excitation of the resonator by a pump beam of sufficient intensity at the zero-dispersion frequency causes the resonator to emit a frequency comb of entangled photon pairs wherein the respective frequencies in each pair are symmetrically placed about the zero-dispersion frequency.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
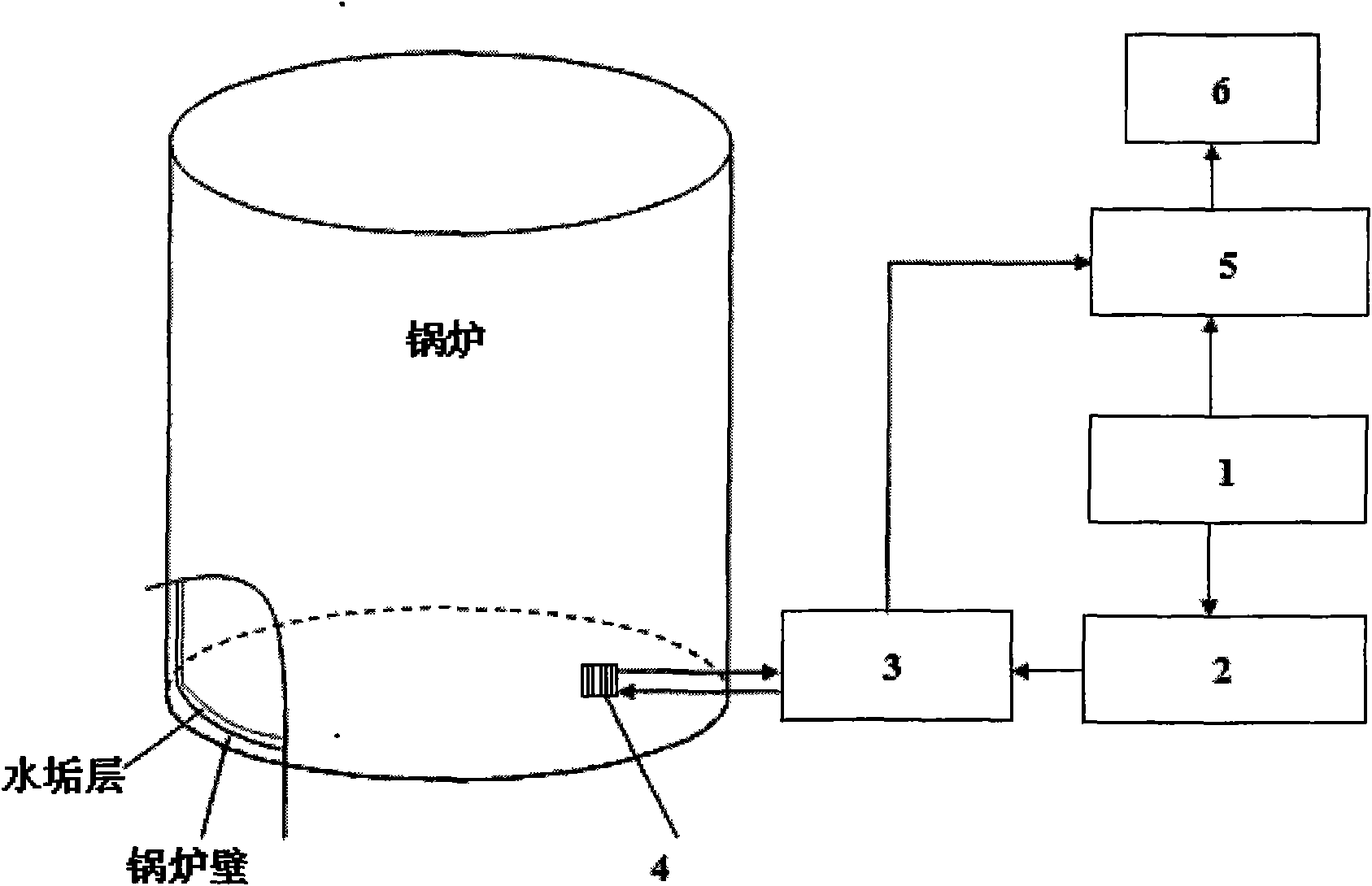
System and method for detecting thickness of industrial boiler scale based on SH (Shear) wave
InactiveCN101819032AHigh measurement accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansDispersion curveUltrasonic guided wave
The invention relates to a method for detecting the thickness of industrial boiler scale by utilizing an SH (Shear) wave which is sensitive to an attachment on the surface of a plate layer, belonging to the field of nondestructive inspection of ultrasonic guided waves. In the method, firstly, a dispersion curve with different scale thicknesses is drawn by utilizing a dispersion equation for SH wave propagation in a double-layer structure to obtain a variation curve of SH0 modal group velocity changing along with the increase of the thickness of the scale, and then a high detection frequency and a low detection frequency respectively corresponding to thinner scales and thicker scales are further obtained. A detection system is shown as the drawing and comprises a function generator (1), a power amplifier (2), a change-over switch (3), an EMAT (Electromagnetic-Acoustic Transducer) sensor (4), an oscillometer (5) and a computer (6). The group velocity of an SH0 modal in a structure formed by a boiler and scales can be measured by the system, and the thickness of the scale can be obtained according to the corresponding curve of the group velocity and the scale thickness by the calculation, thereby the online and nondestructive testing on the thickness of the industrial boiler scale is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Bunting position and energy measurement method based on wave propagation time and energy function
ActiveCN103019446AReduce weightReduce complexityInput/output processes for data processingCapacitancePattern perception
The invention relates to a bunting position and energy measurement method based on a wave propagation time and energy function. According to the method, a plurality of sensors are arranged below a touch equipment perception panel so as to response a blast wave signal generated by bunting; blast wave signal energy and arrival time therefore are detected; according to a principle that the blast wave group velocity is similarly equal in each direction on the aspects of isotropic or quasi-isotropic structure, the bunting position is analyzed and calculated; and according to the relationship that the bunting dynamics and the blast wave signal energy are in direct proportion, the blunting energy is analyzed and calculated. According to the bunting position and energy measurement method based on the wave propagation time and energy function, which is disclosed by the invention, the method in the prior art that a group sensor, such as an array sensor, needs to be arranged to sense the bunting dynamics is changed, and the amount of required sensors is reduced so as to reduce the total weight, the complexity and the energy consumption of the touch equipment, and the cost is greatly lowered. The bunting position and energy measurement method based on the wave propagation time and energy function can be used for electronic equipment with a propagation panel, such as a touch screen, a game control panel and a shooting target, and performs the functions of assisting or replacing the traditional positioning method based on the technology, such as resistance and capacitance.
Owner:BEIJING TAIFANG TECH CO LTD
Dielectric waveguide with transverse index variation that support a zero group velocity mode at a non-zero longitudinal wavevector
InactiveUS20020126713A1Avoiding the optical losses associatedEasy to manufactureLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingRefractive indexGroup velocity
Optical components including a laser based on a dielectric waveguide extending along a waveguide axis and having a refractive index cross-section perpendicular to the waveguide axis, the refractive index cross-section supporting an electromagnetic mode having a zero group velocity for a non-zero wavevector along the waveguide axis.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
High-sensitivity resonance type optical fiber peg-top based on slow light group velocity
InactiveCN101126642AHigh sensitivityLow costSagnac effect gyrometersCoupling light guidesBeam splitterRefractive index
The utility model relates to a resonator fiber optic gyro with high sensitivity, belonging to the technical field of a fiber optic gyro, which aims at overcoming the problems that low sensibility (0.1 degree / hour) exists upon prior resonator fiber optic gyro and can not meet attitude tracking of short range / midrange missiles and commercial aircrafts, more particularly can not meet areas such as space positioning and submarine navigation with high requirement for sensibility. The utility model is characterized in that a laser output end of a frequency conversion laser (1) is connected with a dispersion fiber ring resonator (11) through a group speed control system (2), a fiber beam splitter (3), a first lithium niobate phase modulator (4), a second lithium niobate phase modulator (5), a first optical fiber coupler (6), a second optical fiber coupler (7) and a third optical fiber coupler (10). The utility model has the advantages of high sensibility up to ng times (The ng is group speed refractive index), low production cost, simple structure and small size.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Short light pulse generation device, terahertz wave generation device, camera, imaging device, and measurement device
InactiveUS20140240509A1Positive group velocity dispersion characteristicPositive group velocity dispersion characteristicsTelevision system detailsLaser using scattering effectsPath lengthMeasurement device
A short light pulse generation device includes: a light pulse generation portion that has a quantum well structure and generates a light pulse; a frequency chirping portion that has a quantum well structure and chirps a frequency of the light pulse; a light branching portion that branches a chirped light pulse; and a group velocity dispersion portion that has a plurality of optical waveguides, on which each of a plurality of the light pulses branched in the light branching portion is incident, and produces a group velocity difference depending on a wavelength with respect to a plurality of branched light pulses, wherein light path lengths of the light pulses in a plurality of light paths before the light pulse is branched in the light branching portion and then incident on the plurality of optical waveguides of the group velocity dispersion portion are equal to each other.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com