Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38697results about How to "Accurate measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
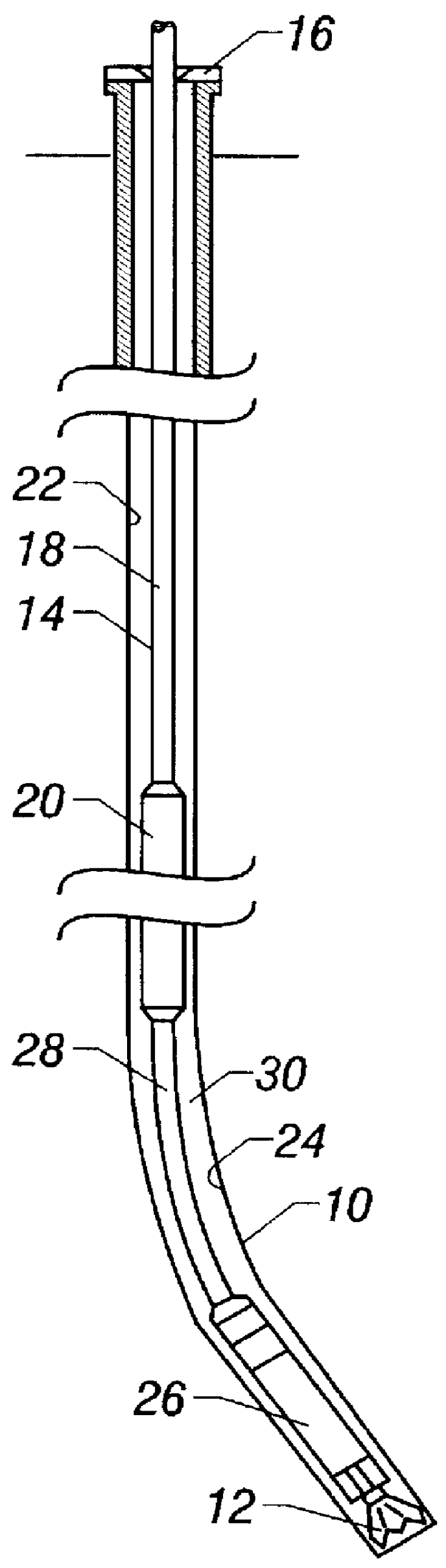
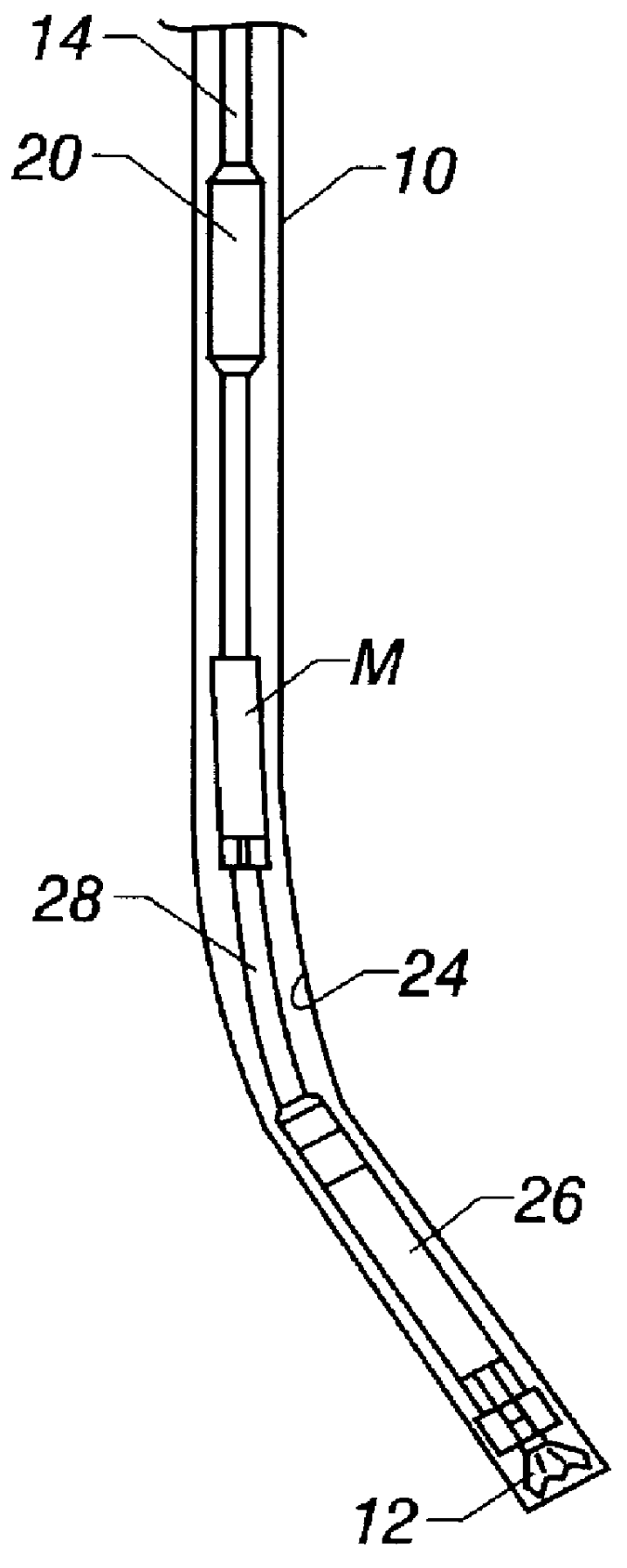
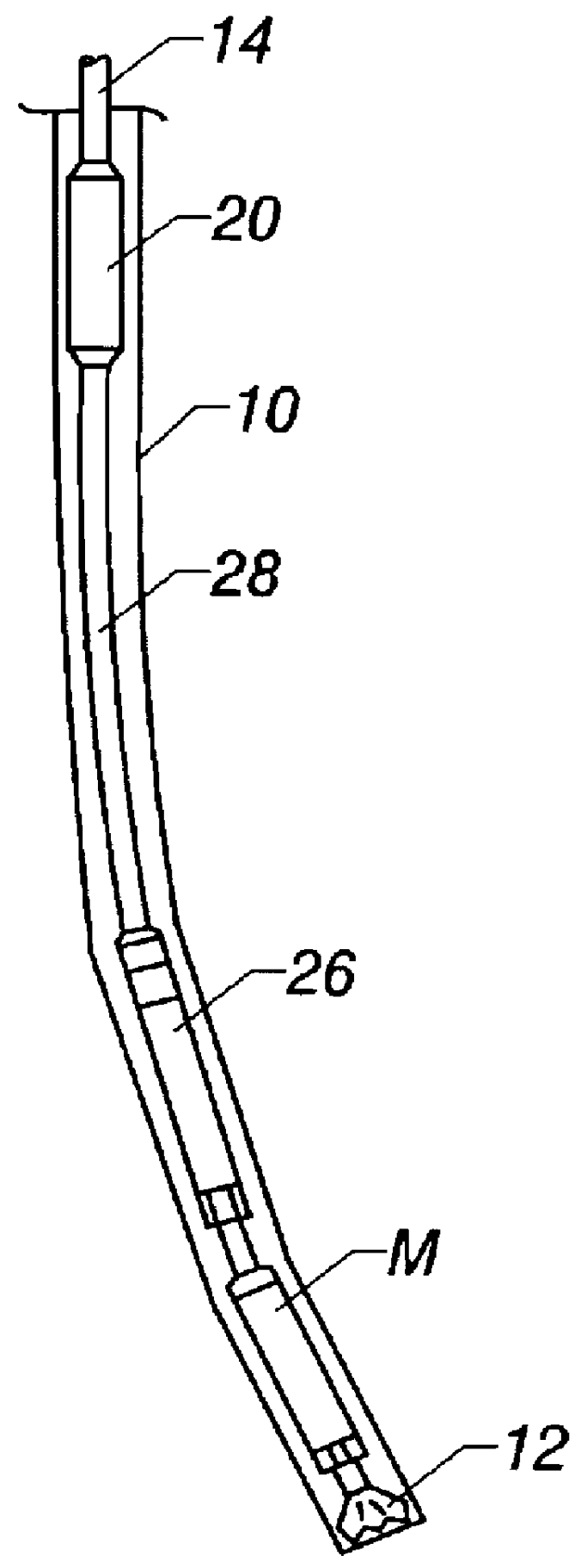
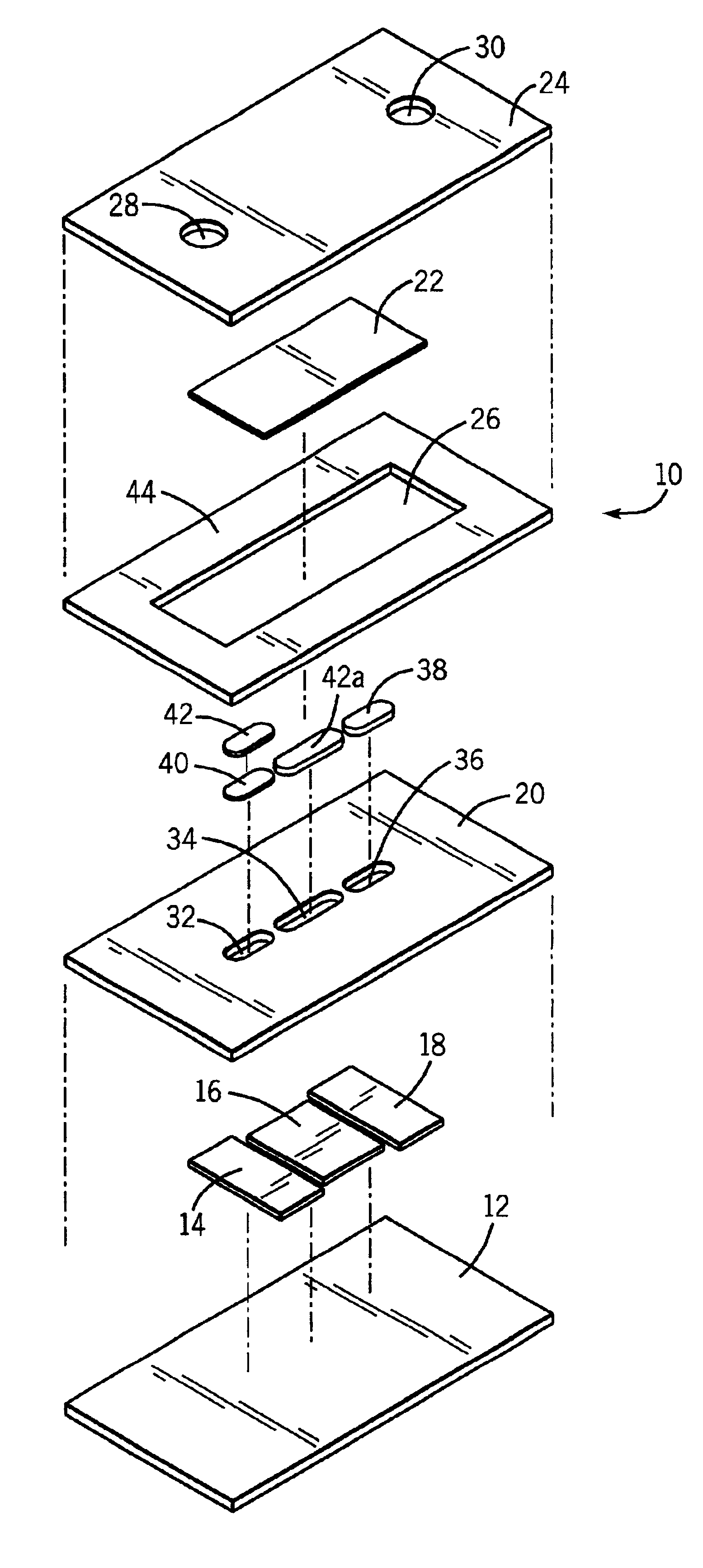
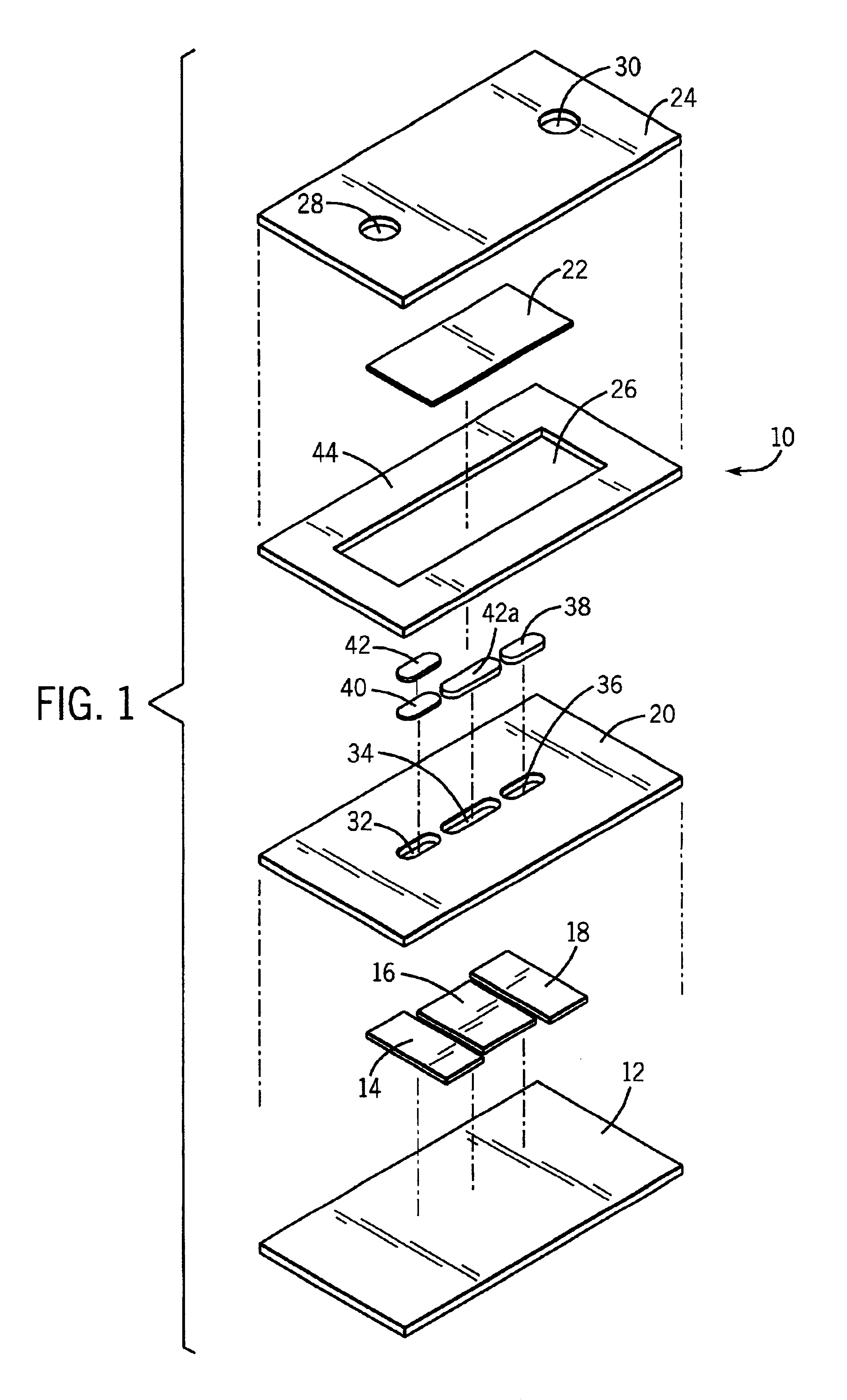
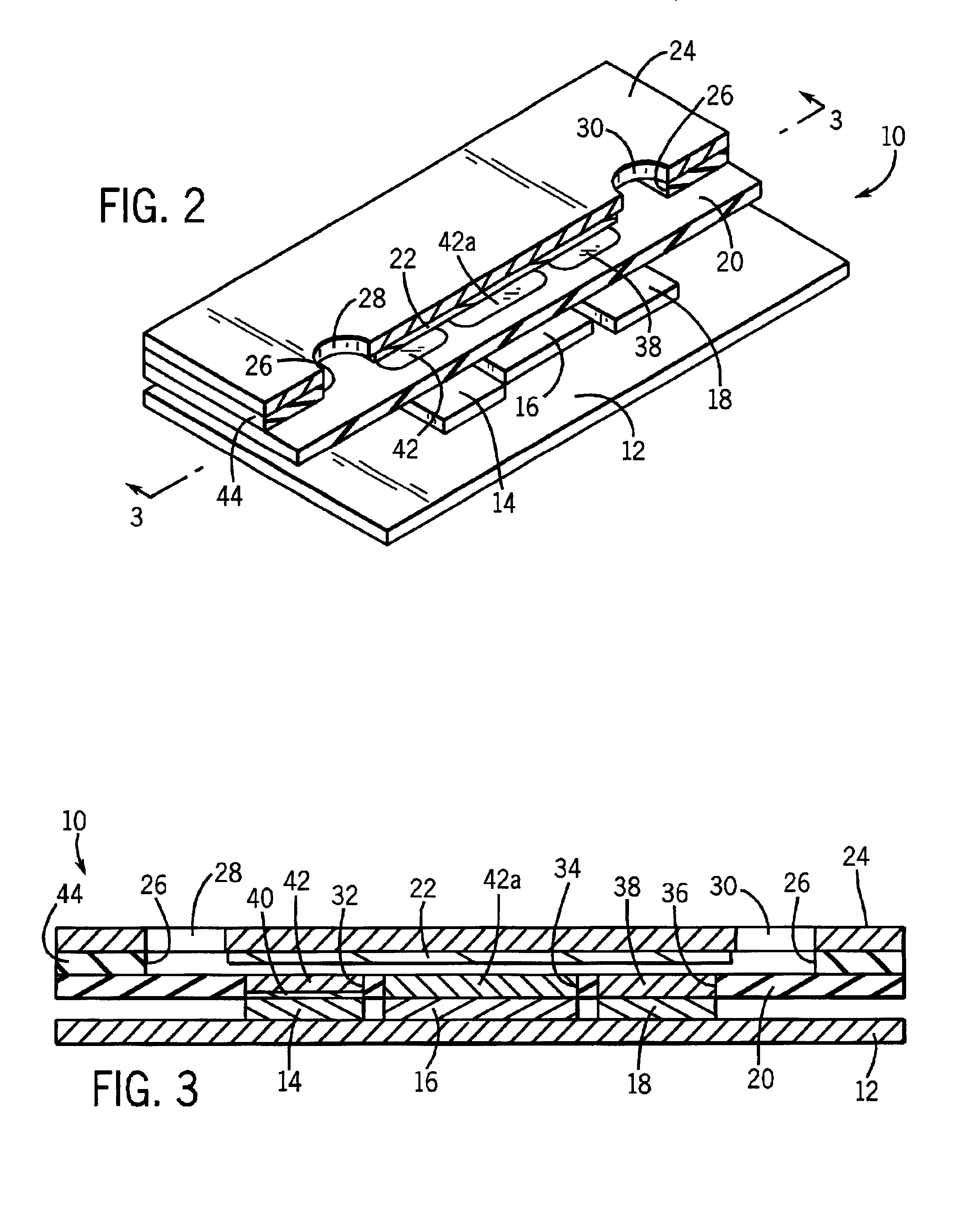
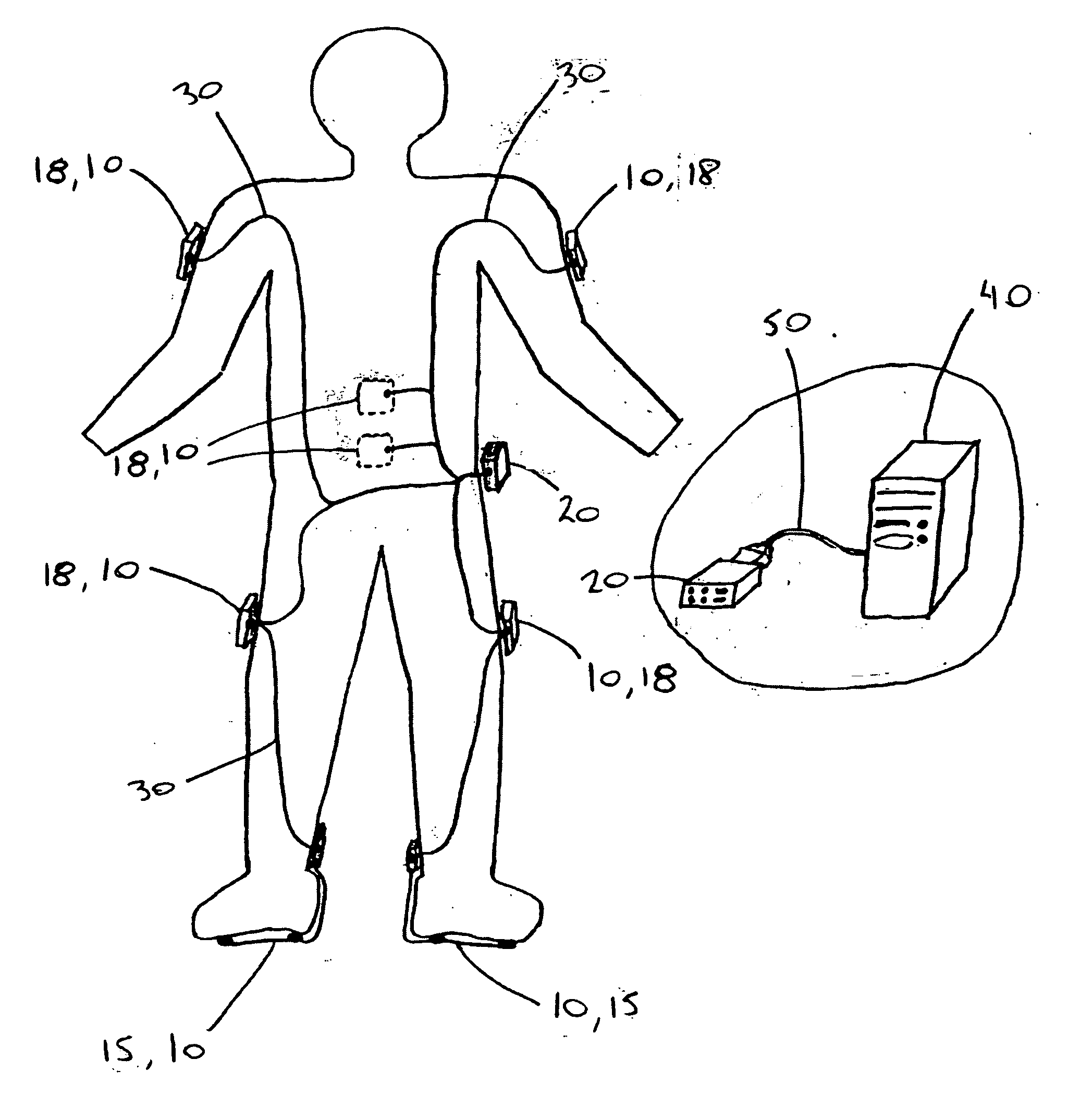
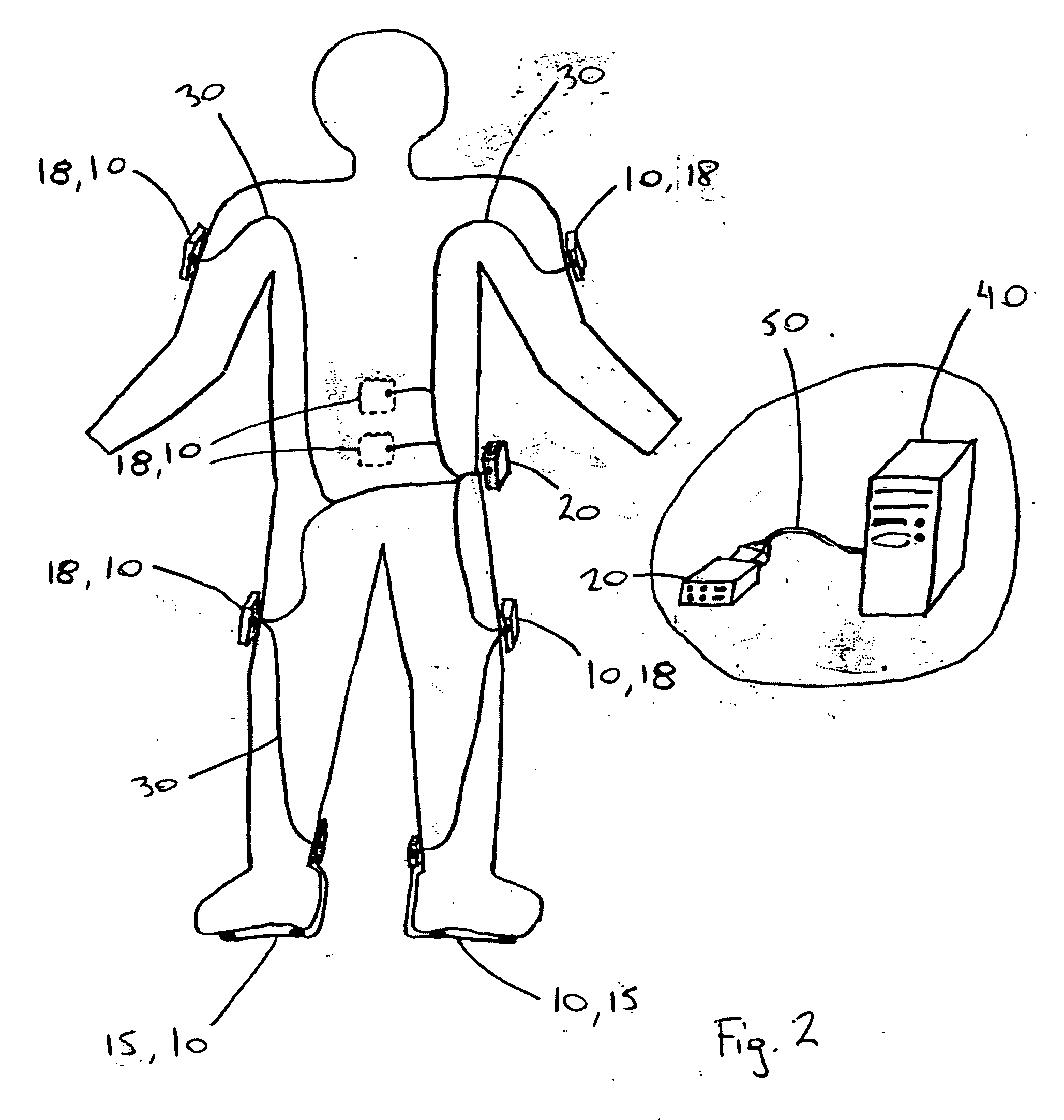
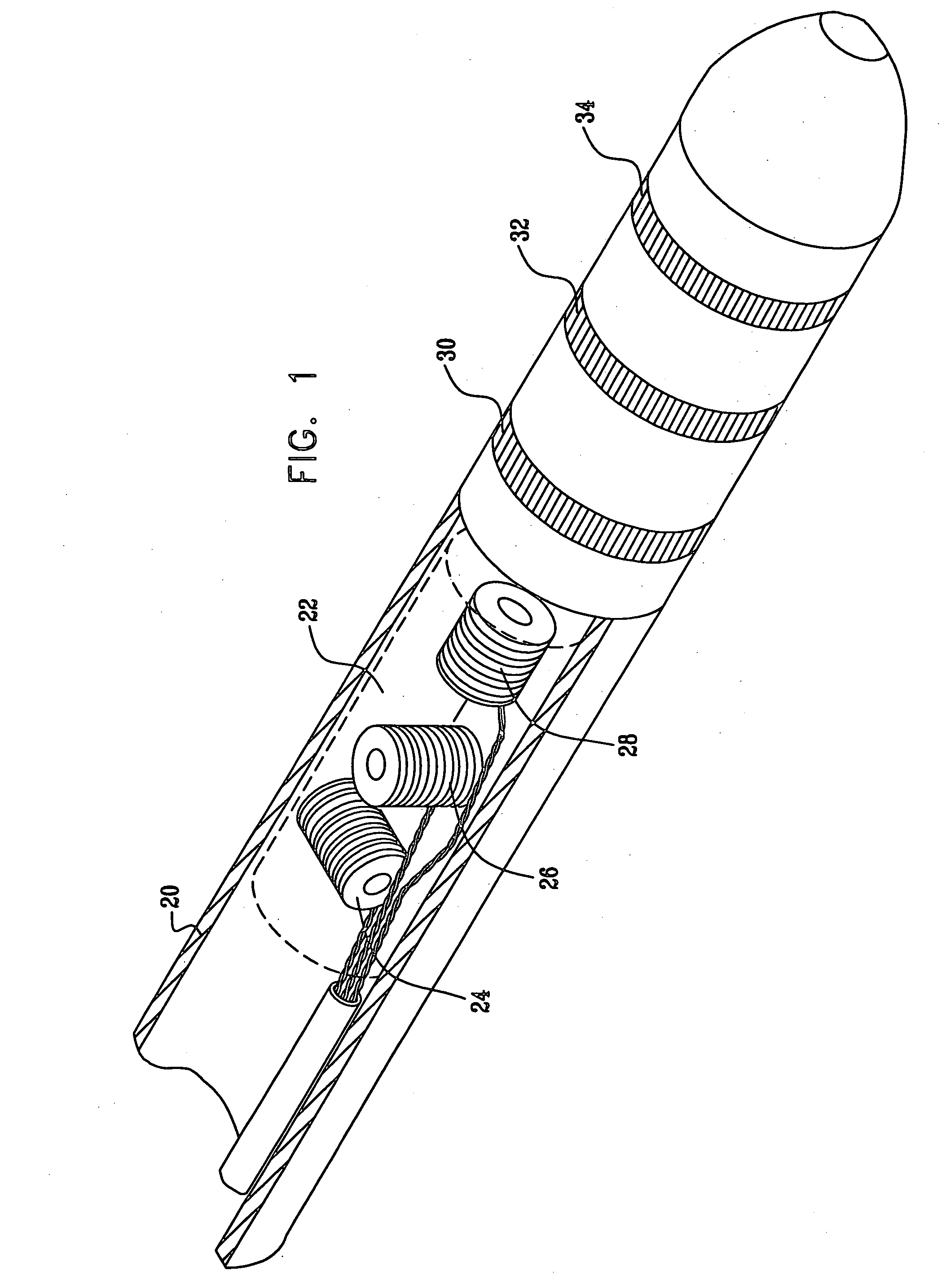
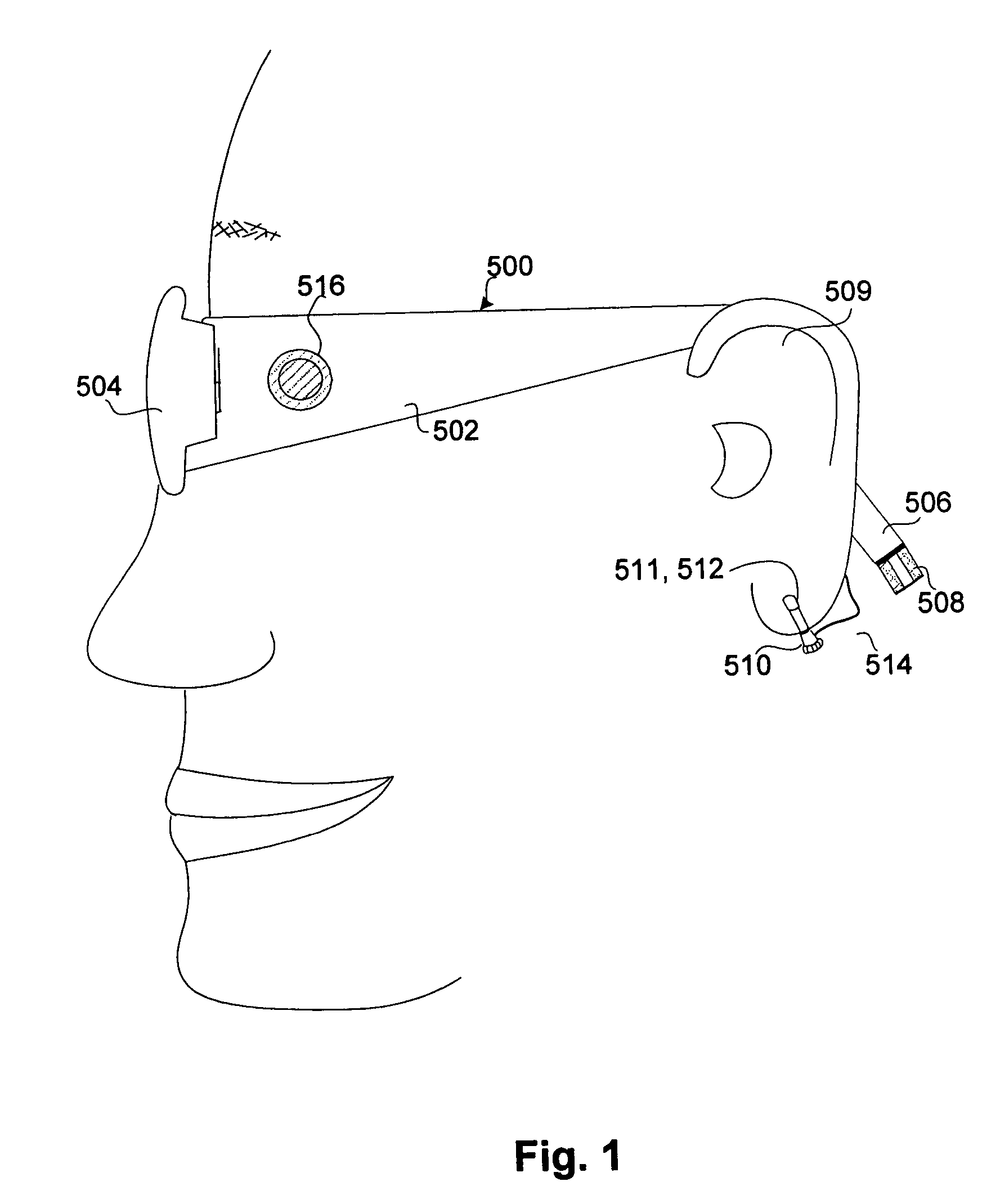
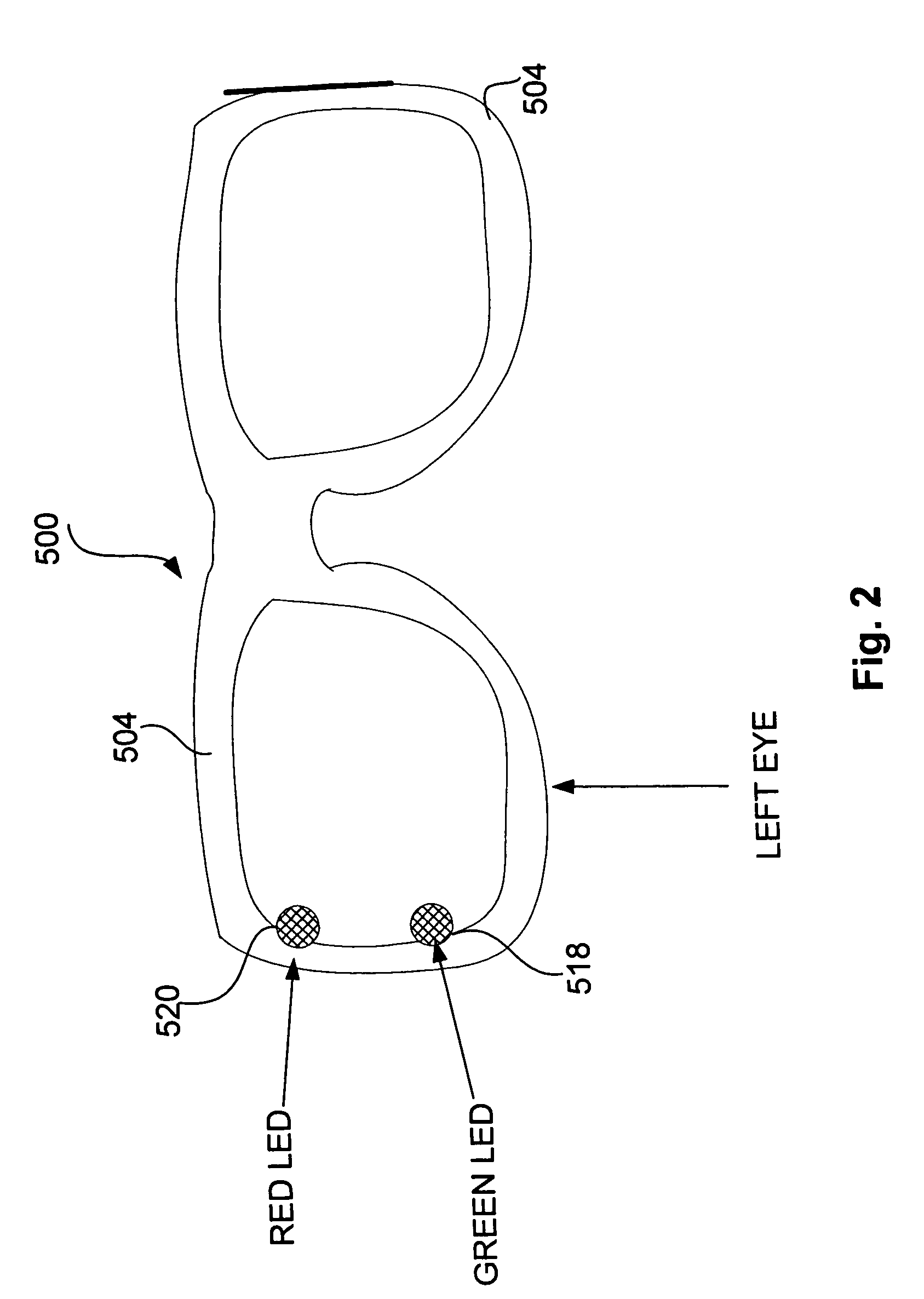
Atraumatic insertion of a subcutaneous device
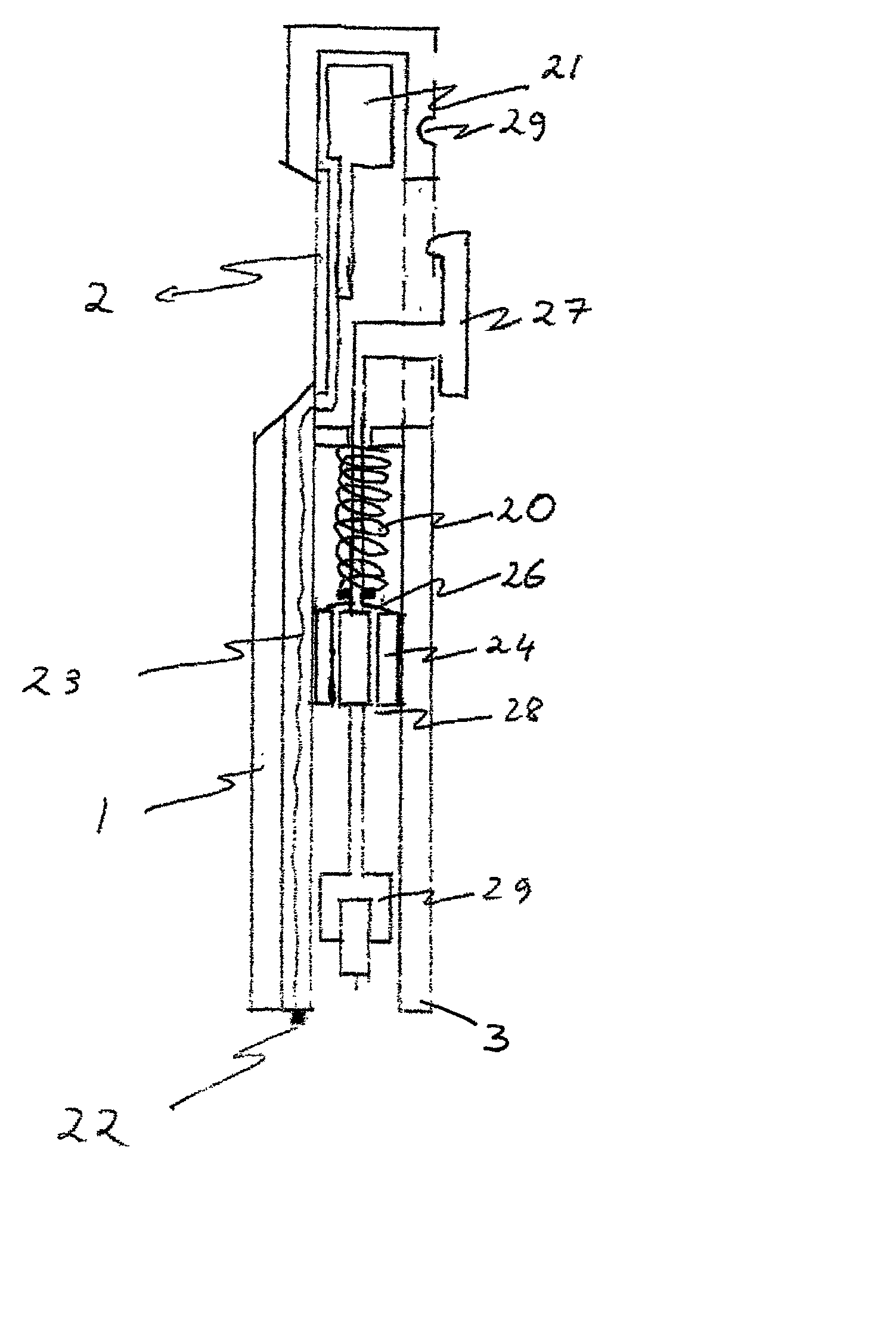
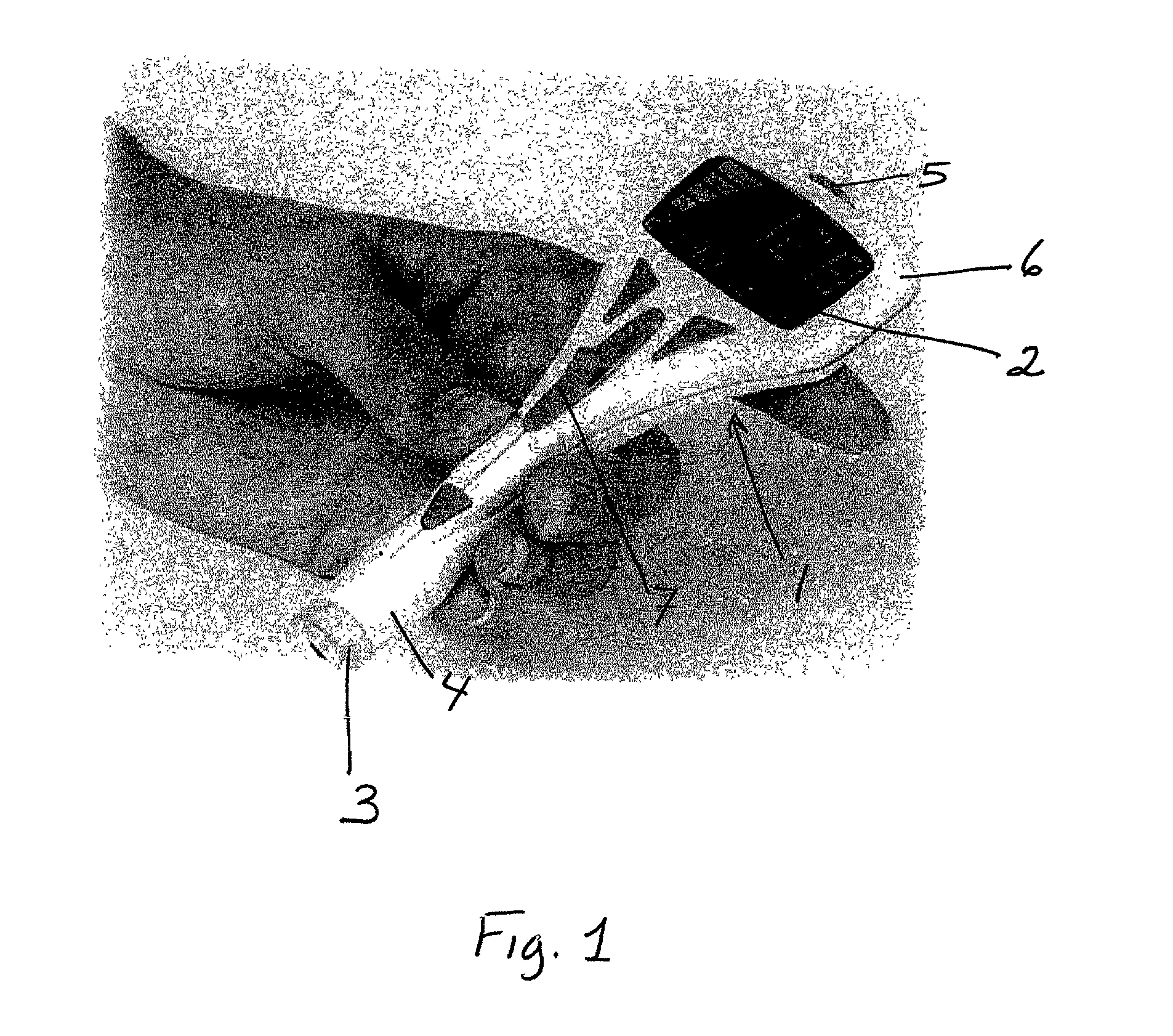
The invention relates to a concept for placing a subcutaneous device such as a sensor at a selected site within the body of a patient, e.g. to obtain blood glucose readings. In a first aspect, an insertion needle comprises an oblong needle body and a distal end portion, the distal end portion having a pointed distal tip allowing the needle to be introduced subcutaneously and a distally facing generally smooth surface, the body comprising along a portion thereof a longitudinal groove adapted to at least partially accommodate the subcutaneous device. In a second aspect, a combination of an insertion needle and a subcutaneous device form an oblong body portion and a distal end portion formed by either of the members or in combination by the two members, the distal end portion having a pointed distal tip and a distally facing generally smooth surface. By the above configuration, a concept is provided reducing the severity of the body response following transcutaneous placement of a device as well as reducing the pain associated with the insertion.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
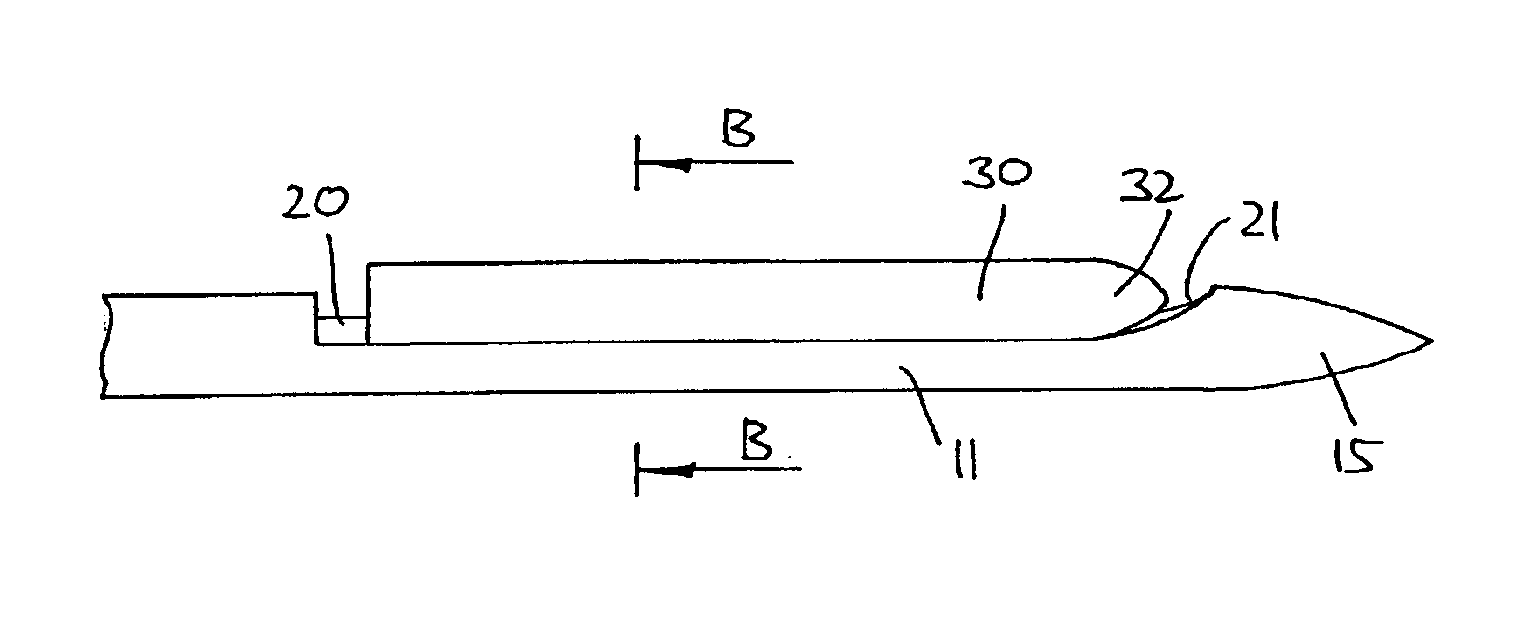
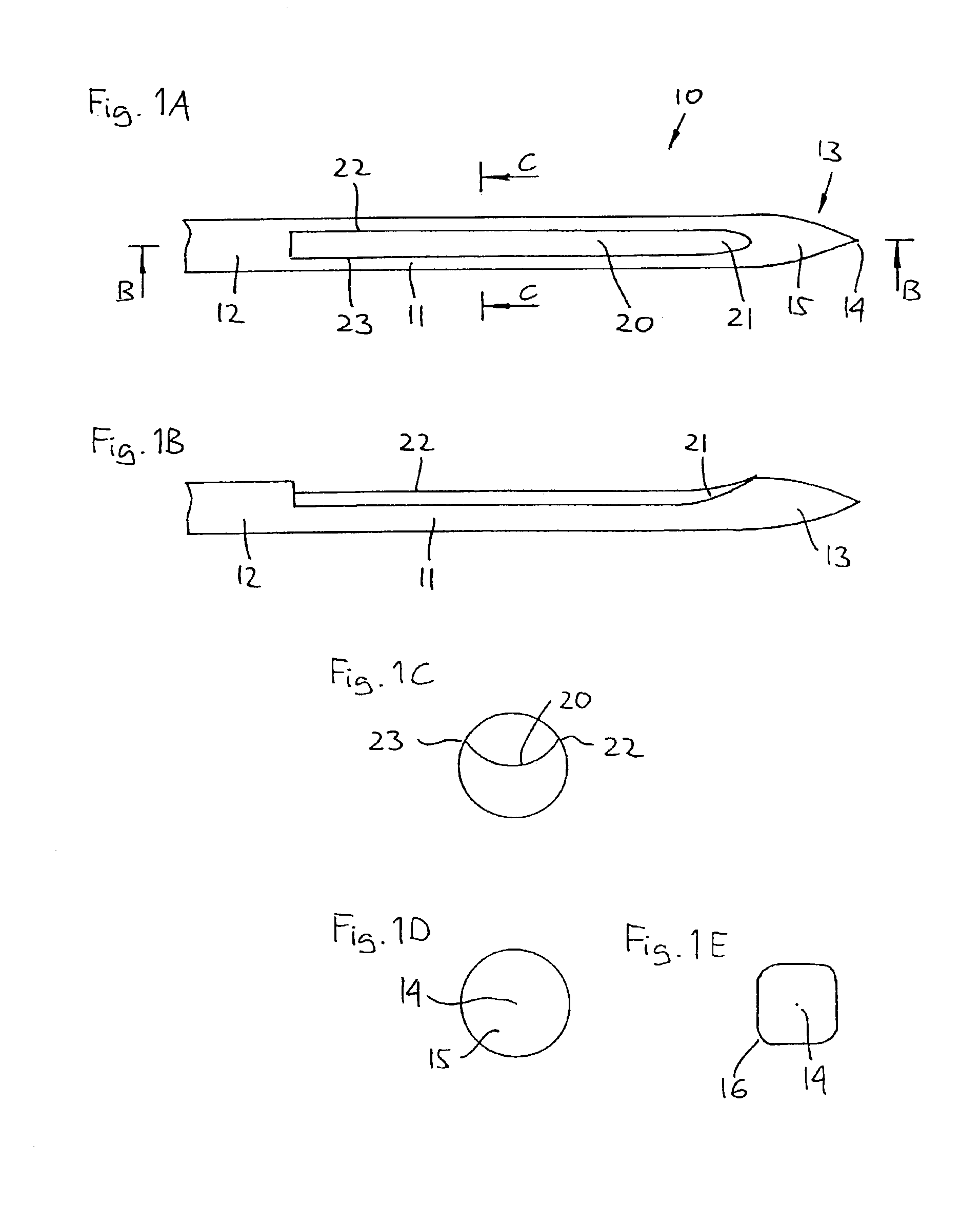
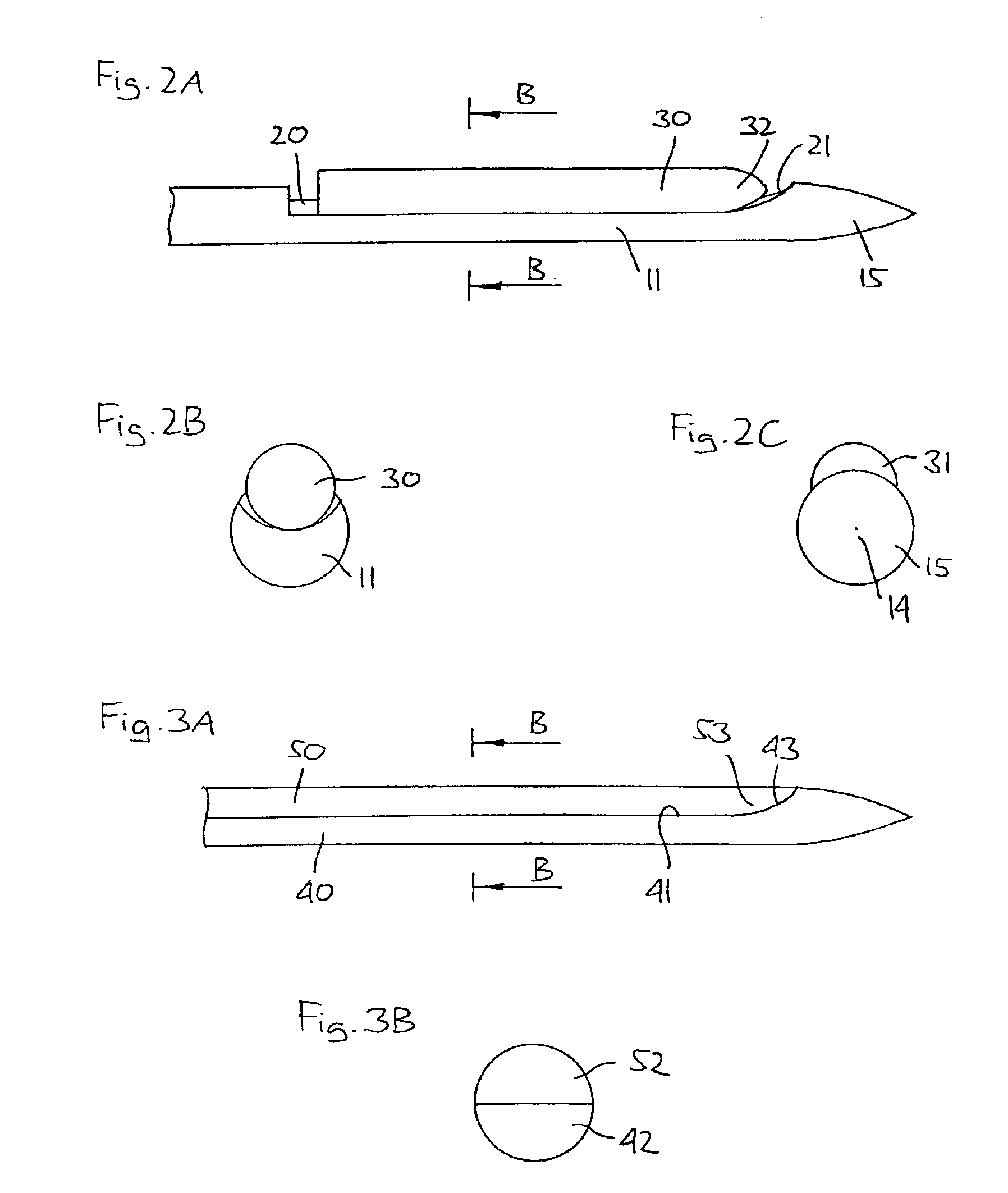
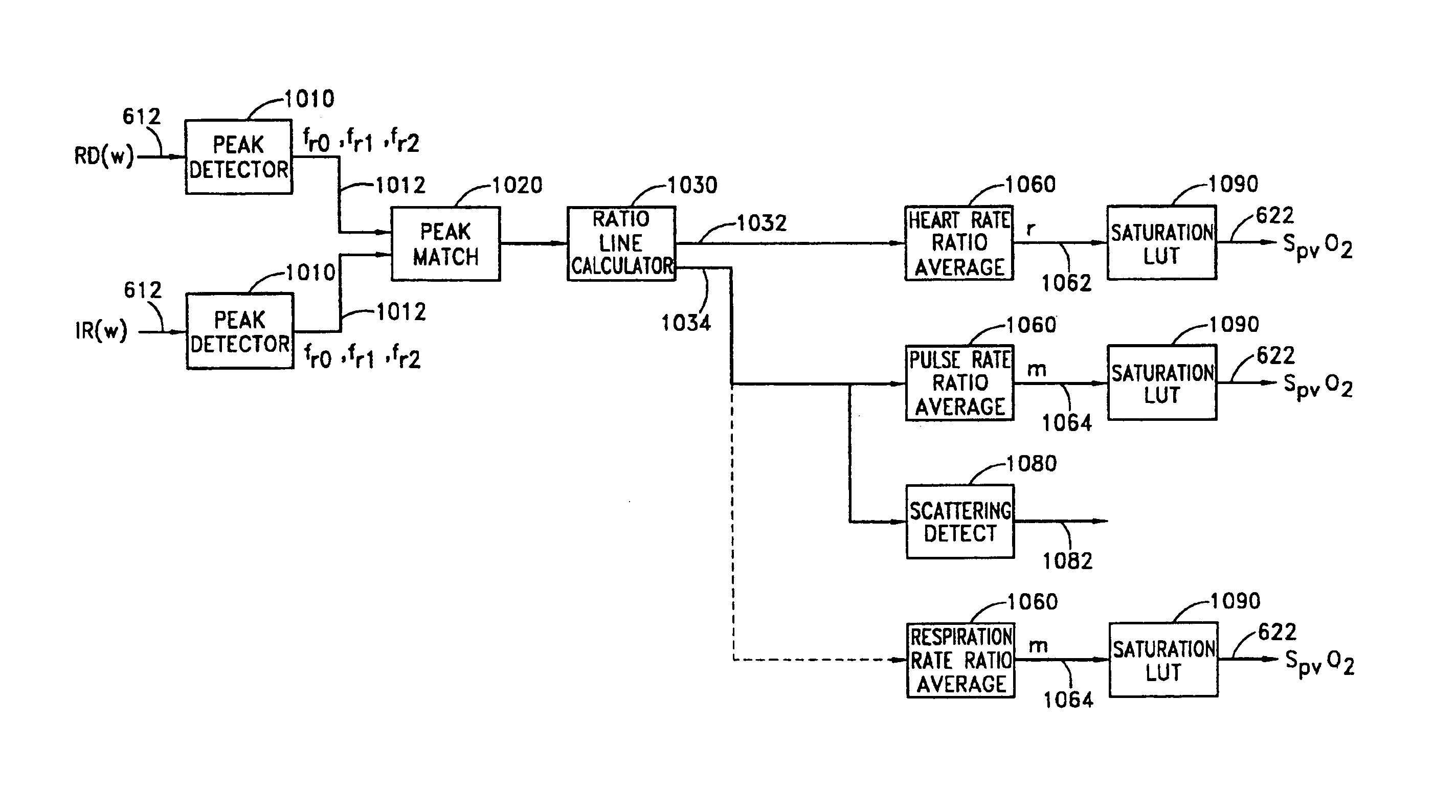
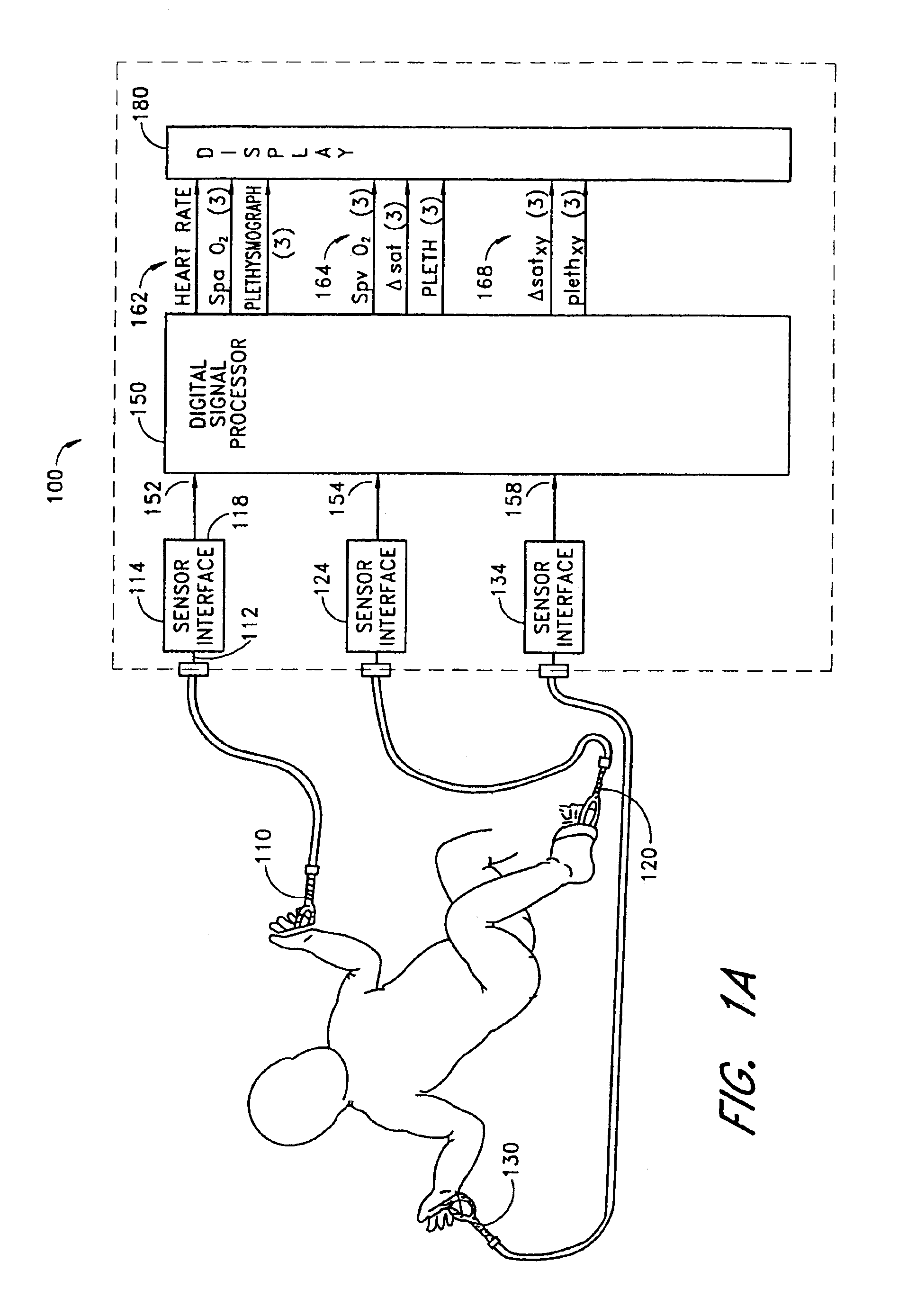
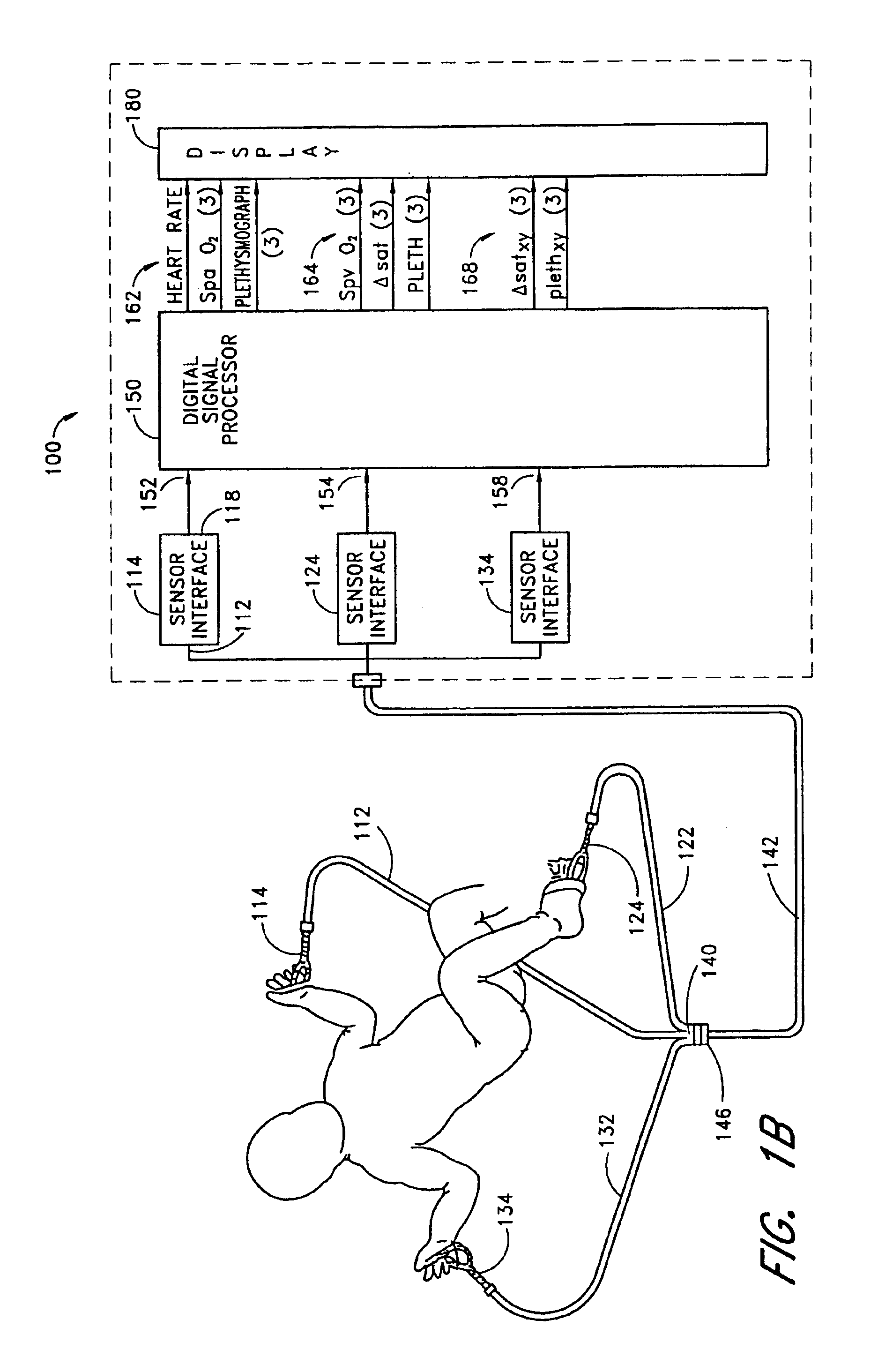
Stereo pulse oximeter
InactiveUS6898452B2Exact reproductionAccurate measurementRespiratorsMedical devicesVenous blood specimenVenous blood
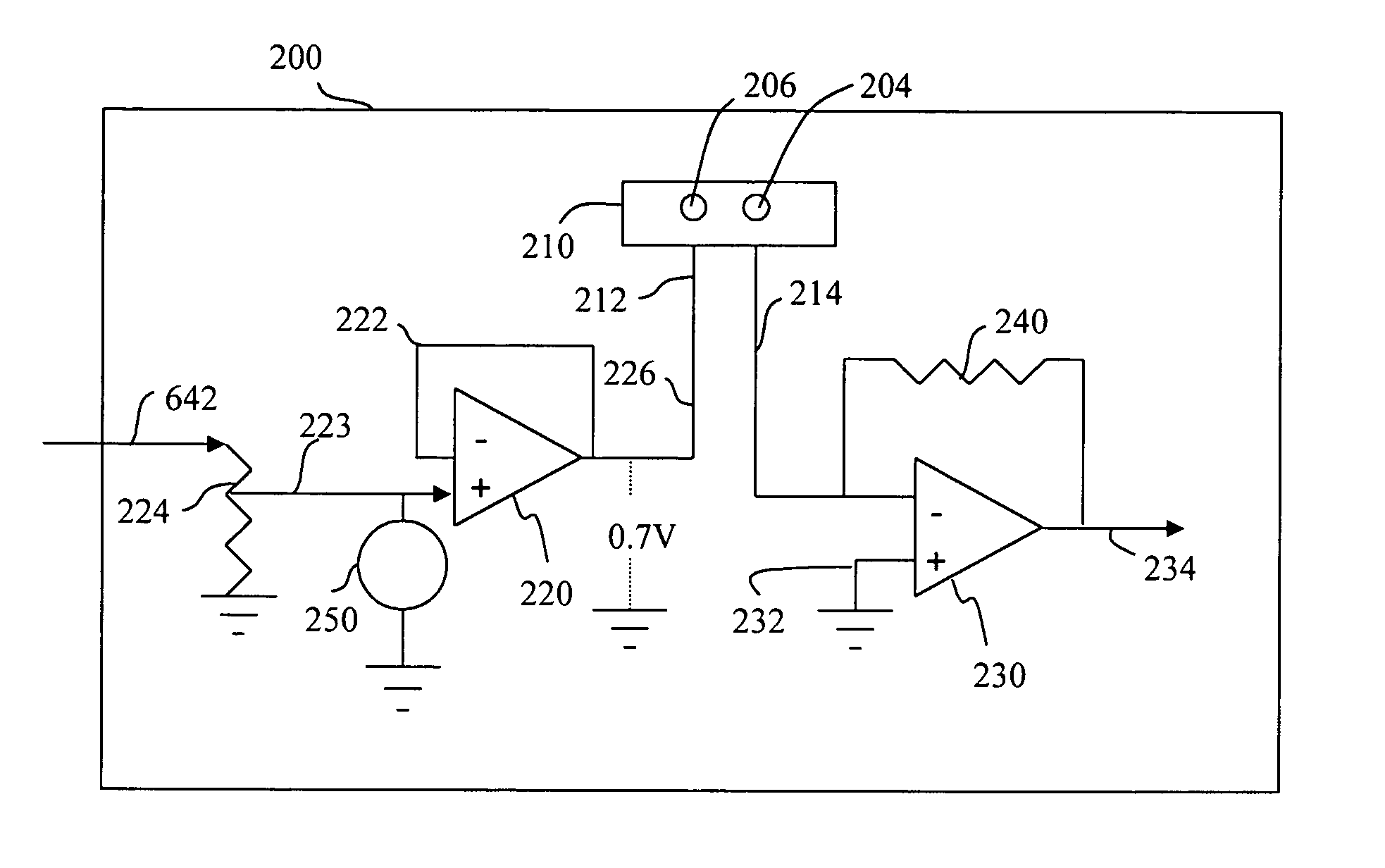
An improved pulse oximeter provides for simultaneous, noninvasive oxygen status and photoplethysmograph measurements at both single and multiple sites. In particular, this multiple-site, multiple-parameter pulse oximeter, or “stereo pulse oximeter” simultaneously measures both arterial and venous oxygen saturation at any specific site and generates a corresponding plethysmograph waveform. A corresponding computation of arterial minus venous oxygen saturation is particularly advantageous for oxygen therapy management. An active pulse-inducing mechanism having a scattering-limited drive generates a consistent pulsatile venous signal utilized for the venous blood measurements. The stereo pulse oximeter also measures arterial oxygen saturation and plethysmograph shape parameters across multiple sites. A corresponding calculation of delta arterial saturation and comparison of plethysmograph shape parameters between multiple sites is particularly advantageous for the detection and management of persistent pulmonary hypertension in neonates (PPHN), a patent ductus arteriosis (PDA), and aortic coarctation.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
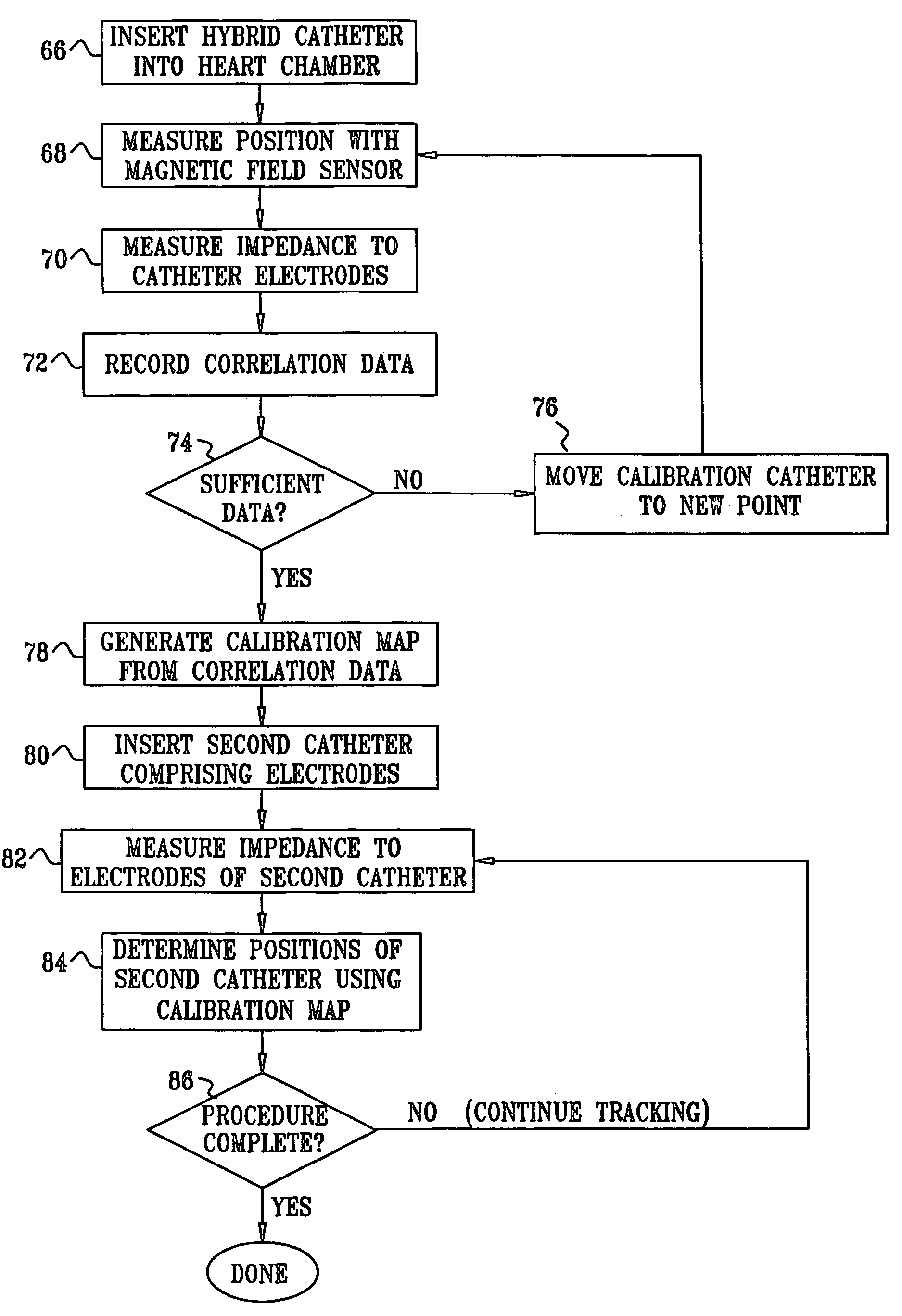
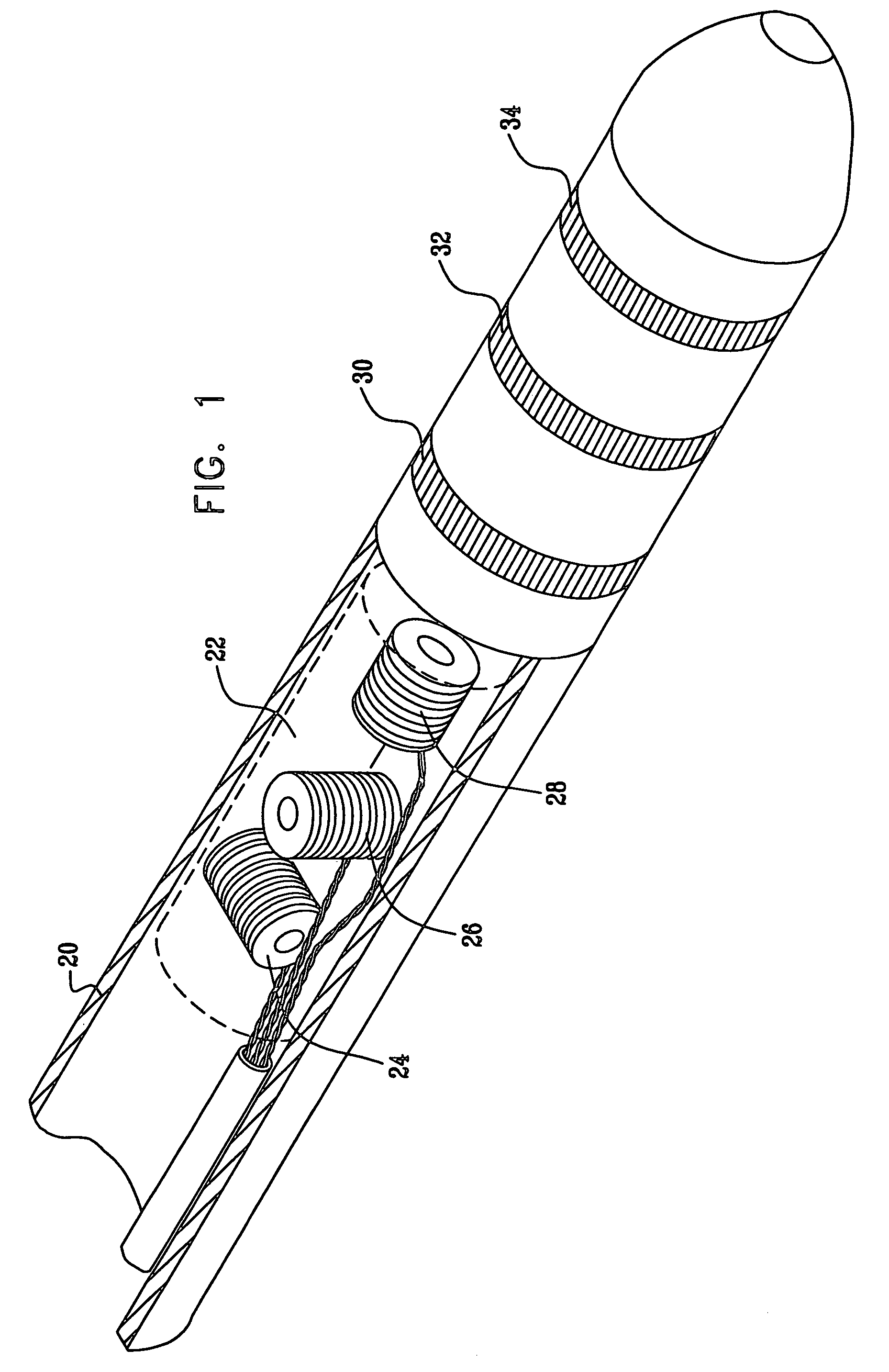
Hybrid magnetic-based and impedance-based position sensing
ActiveUS7536218B2Improve accuracyLow costCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTransducerBody surface
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
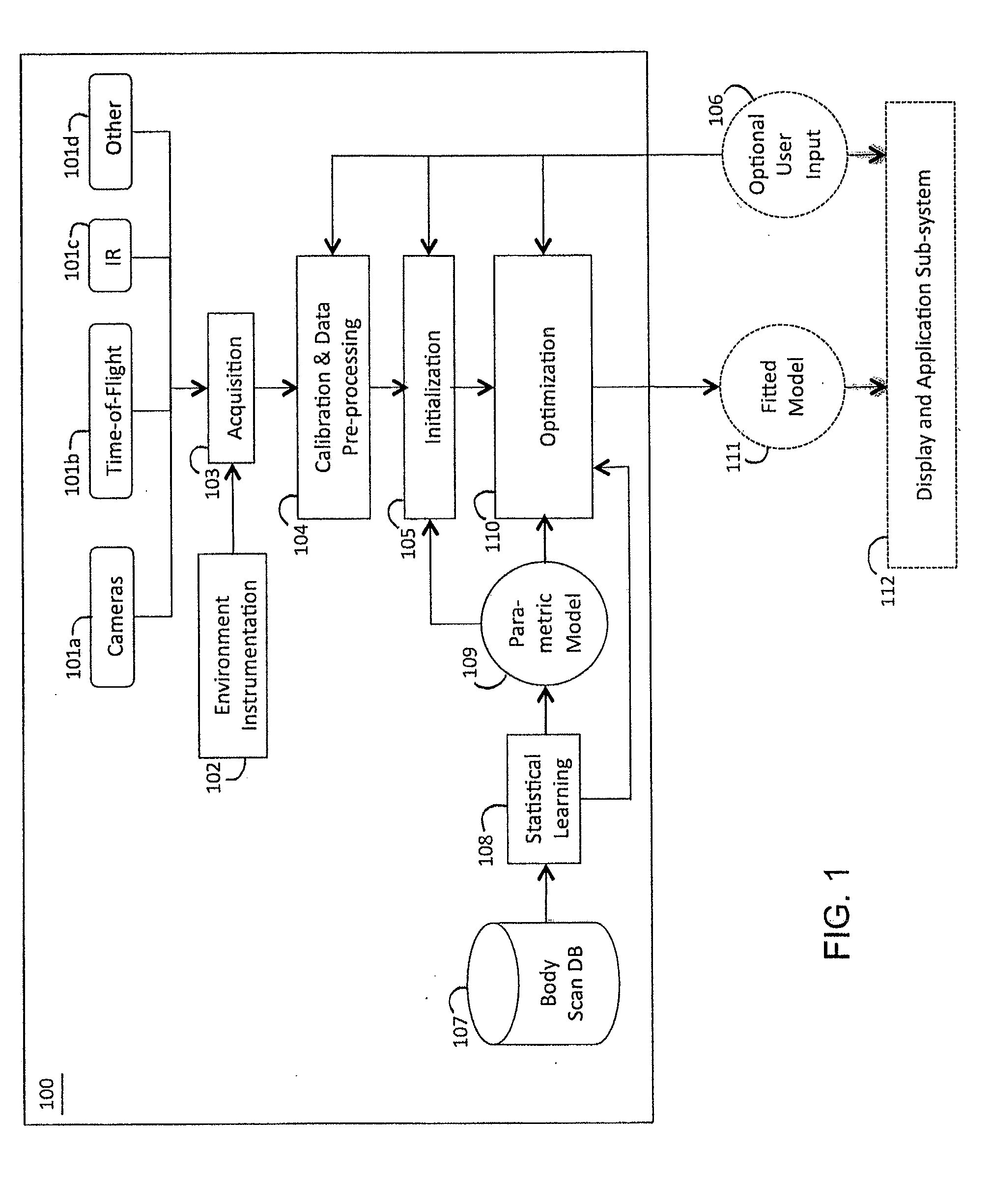
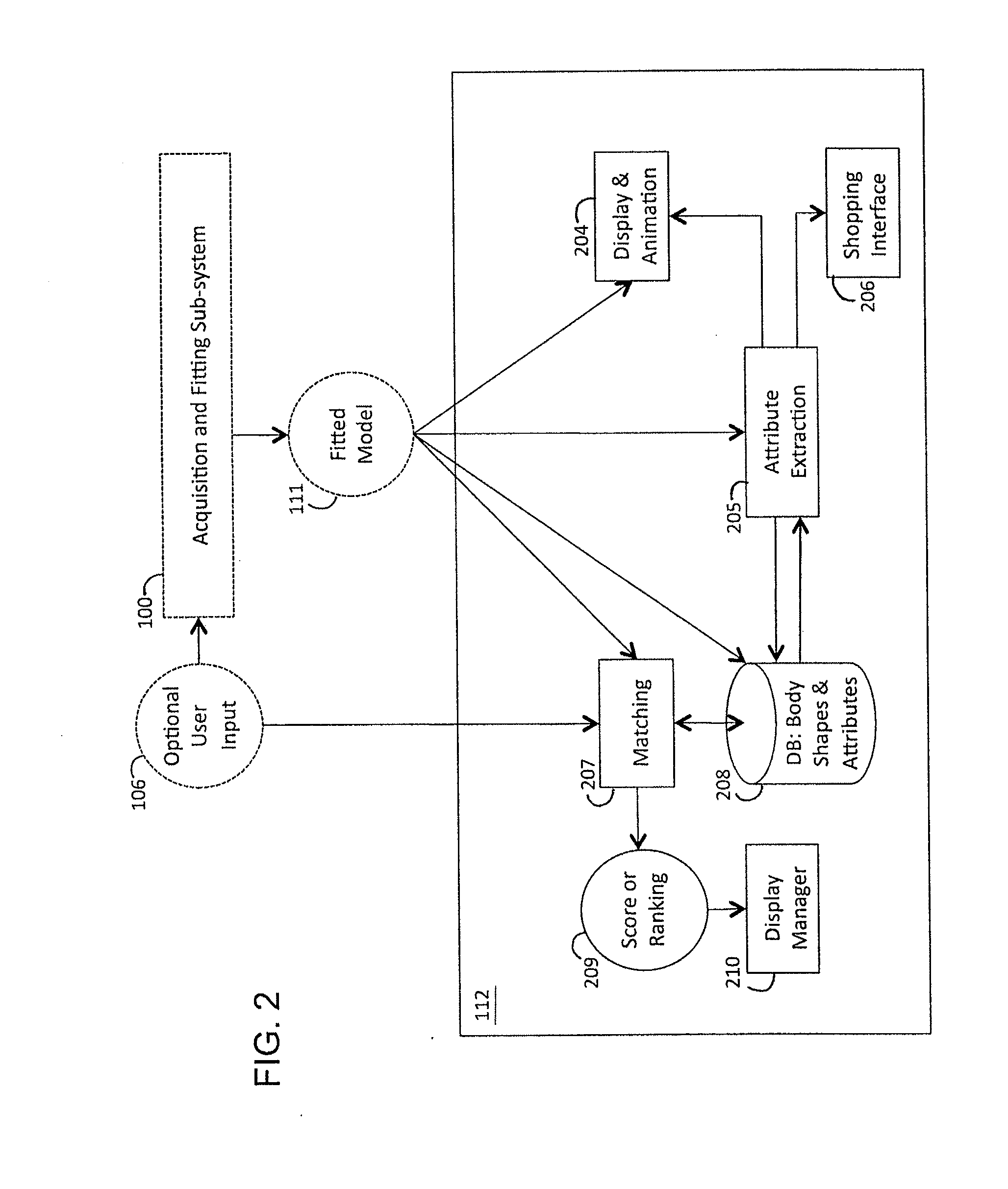
Method and apparatus for estimating body shape
ActiveUS20100111370A1Less-accurate measurementAccurate captureImage enhancementImage analysisBody shapeThe Internet
A system and method of estimating the body shape of an individual from input data such as images or range maps. The body may appear in one or more poses captured at different times and a consistent body shape is computed for all poses. The body may appear in minimal tight-fitting clothing or in normal clothing wherein the described method produces an estimate of the body shape under the clothing. Clothed or bare regions of the body are detected via image classification and the fitting method is adapted to treat each region differently. Body shapes are represented parametrically and are matched to other bodies based on shape similarity and other features. Standard measurements are extracted using parametric or non-parametric functions of body shape. The system components support many applications in body scanning, advertising, social networking, collaborative filtering and Internet clothing shopping.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Actively controlled rotary steerable system and method for drilling wells
InactiveUS6092610AEfficient rotary speedPromote productionDrilling rodsConstructionsAccelerometerDirectional drilling
An actively controlled rotary steerable drilling system for directional drilling of wells having a tool collar rotated by a drill string during well drilling. A bit shaft has an upper portion within the tool collar and a lower end extending from the collar and supporting a drill bit. The bit shaft is omni-directionally pivotally supported intermediate its upper and lower ends by a universal joint within the collar and is rotatably driven by the collar. To achieve controlled steering of the rotating drill bit, orientation of the bit shaft relative to the tool collar is sensed and the bit shaft is maintained geostationary and selectively axially inclined relative to the tool collar during drill string rotation by rotating it about the universal joint by an offsetting mandrel that is rotated counter to collar rotation and at the same frequency of rotation. An electric motor provides rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and is servo-controlled by signal input from position sensing elements such as magnetometers, gyroscopic sensors, and accelerometers which provide real time position signals to the motor control. In addition, when necessary, a brake is used to maintain the offsetting mandrel and the bit shaft axis geostationary. Alternatively, a turbine is connected to the offsetting mandrel to provide rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and a brake is used to servo-control the turbine by signal input from position sensors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method of determining analyte level using subcutaneous electrode
InactiveUS20050287620A1Reduce transportationAccurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansConcentrations glucosePeroxidase
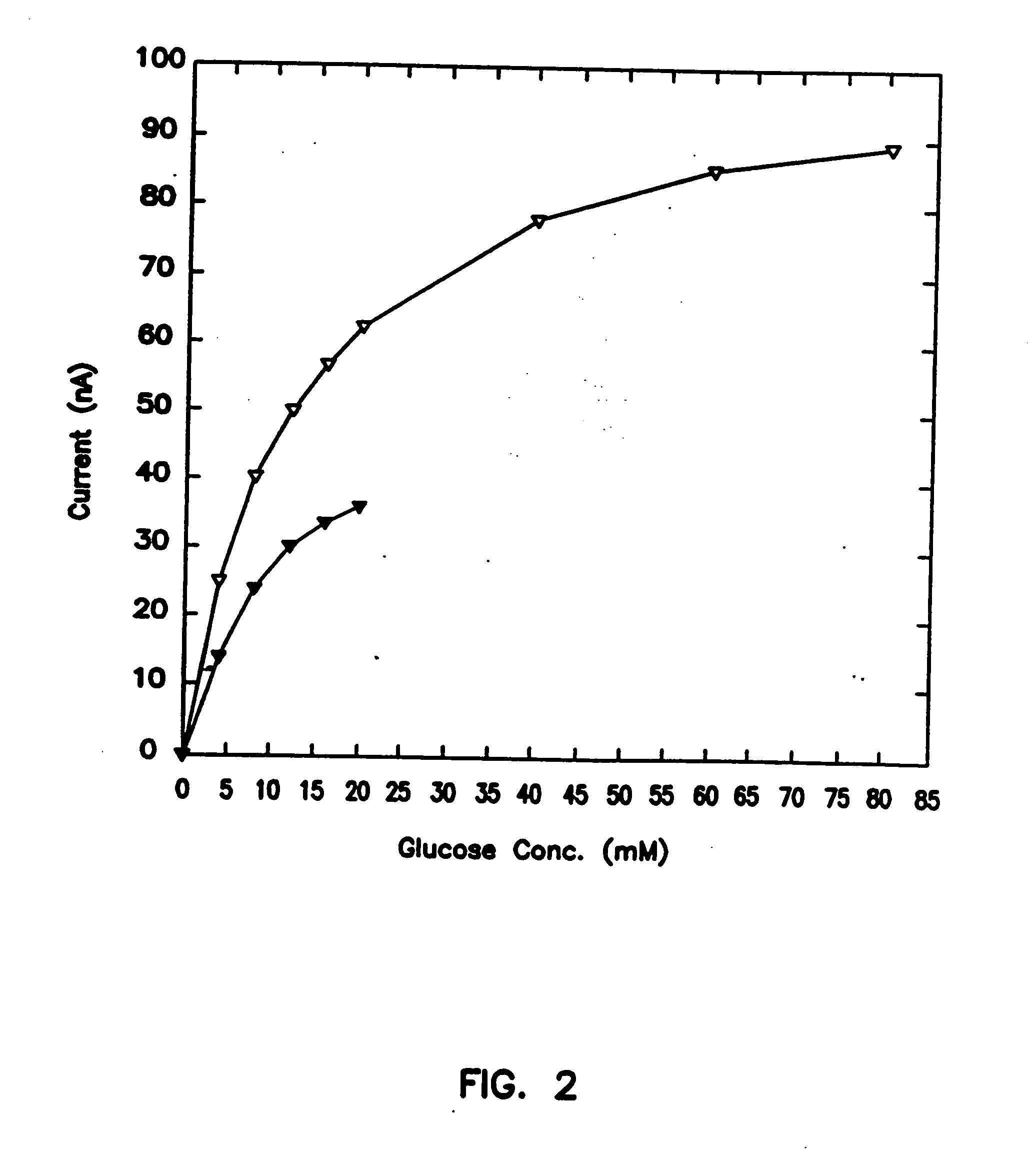
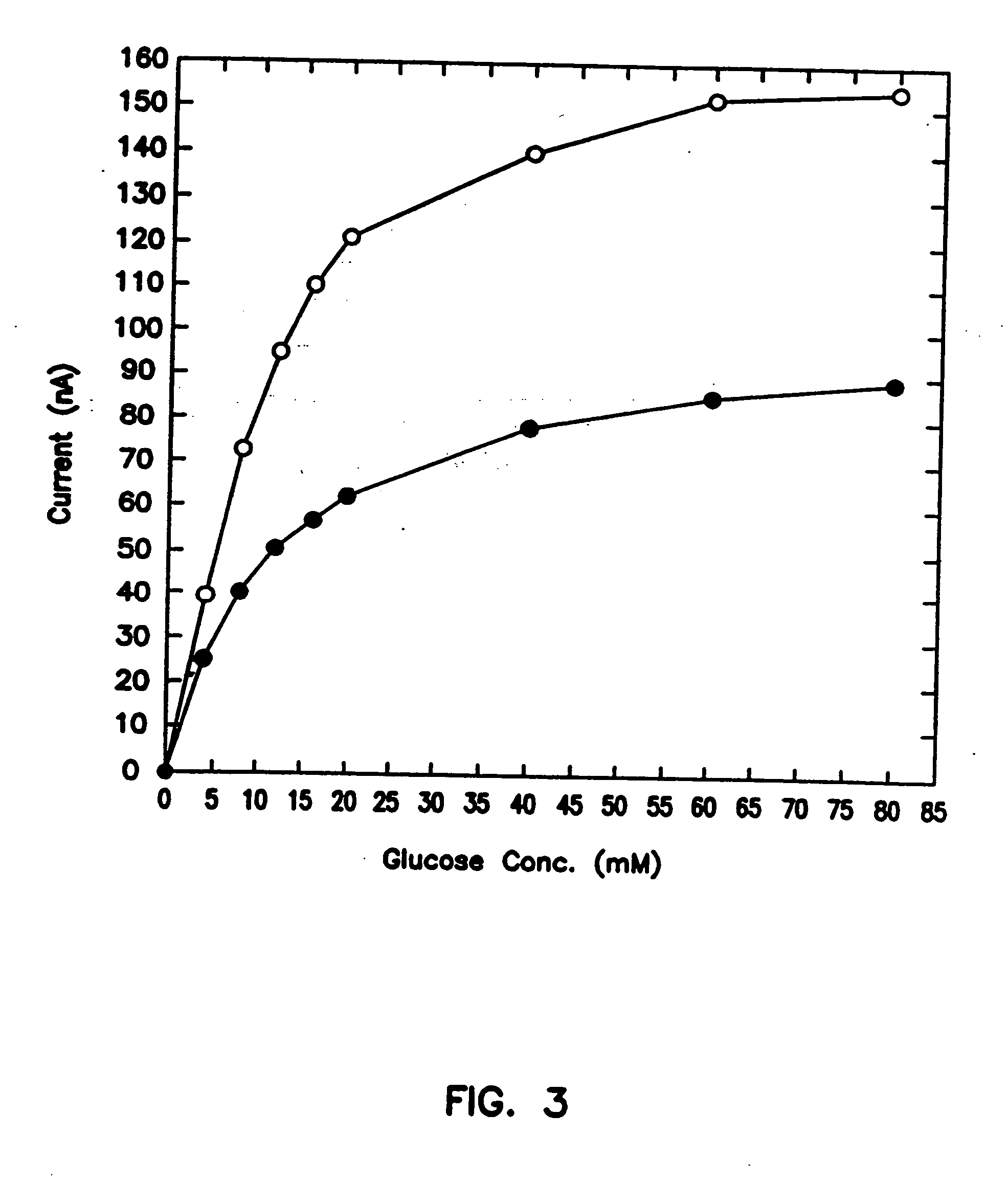
A small diameter flexible electrode designed for subcutaneous in vivo amperometric monitoring of glucose is described. The electrode is designed to allow “one-point” in vivo calibration, i.e., to have zero output current at zero glucose concentration, even in the presence of other electroreactive species of serum or blood. The electrode is preferably three or four-layered, with the layers serially deposited within a recess upon the tip of a polyamide insulated gold wire. A first glucose concentration-to-current transducing layer is overcoated with an electrically insulating and glucose flux limiting layer (second layer) on which, optionally, an immobilized interference-eliminating horseradish peroxidase based film is deposited (third layer). An outer (fourth) layer is biocompatible.
Owner:THERASENSE
Combined lancet and electrochemical analyte-testing apparatus
InactiveUS20020130042A1Easy to takeReduces and eliminates disposal issueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteDisplay device
An apparatus for detection and quantitation of an electrochemically-detect- able analyte, such as glucose, in blood or interstitial fluid includes a meter unit, a lancet and an electrochemical sensor. Of these components, the meter is preferably reusable, while the lancet and the electrochemical sensor are preferably incorporated in assemblies intended for single-use. The meter unit has a housing, within which a lancet is engaged with a mechanism for moving then lancet; a connector disposed within the housing for engaging an electrochemical sensor specific for the analyte and transmitting a signal indicative of the amount of analyte, and a display operatively-associated with a connector for displaying the amount of the analyte to user. The electrochemical sensor is adapted for detection of a particular analyte. In addition, the electrochemical sensor has an absorptive member for uptake of a sample of blood or interstitial fluid. In one version, the lancet moves from a initial position to a piercing position in which skin of the user is pierced and optionally back to a retracted position. The electrochemical sensor is disposed such that the absorptive member takes up a sample from the pierced skin of the user when it is pierced by the lancet without movement of the apparatus. In an alternative version, the lancet is a hollow cannula through which blood or interstitial fluid is transported from the puncture site to an absorbent portion of the electrochemical sensor. In either version, the apparatus provides single-step operation in which sample acquisition and analysis occur as a result of the single action of pressing the apparatus against the users skin.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
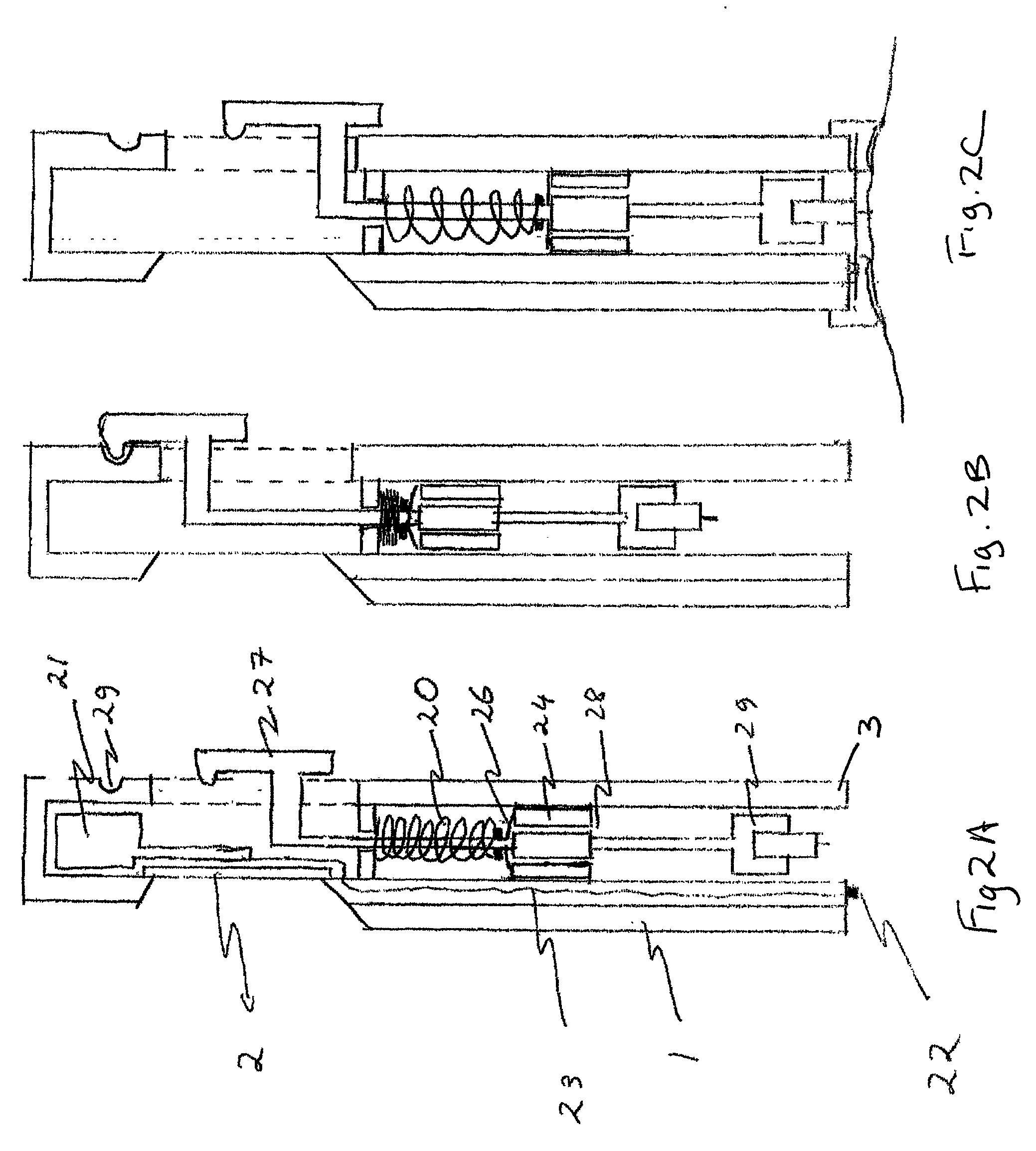
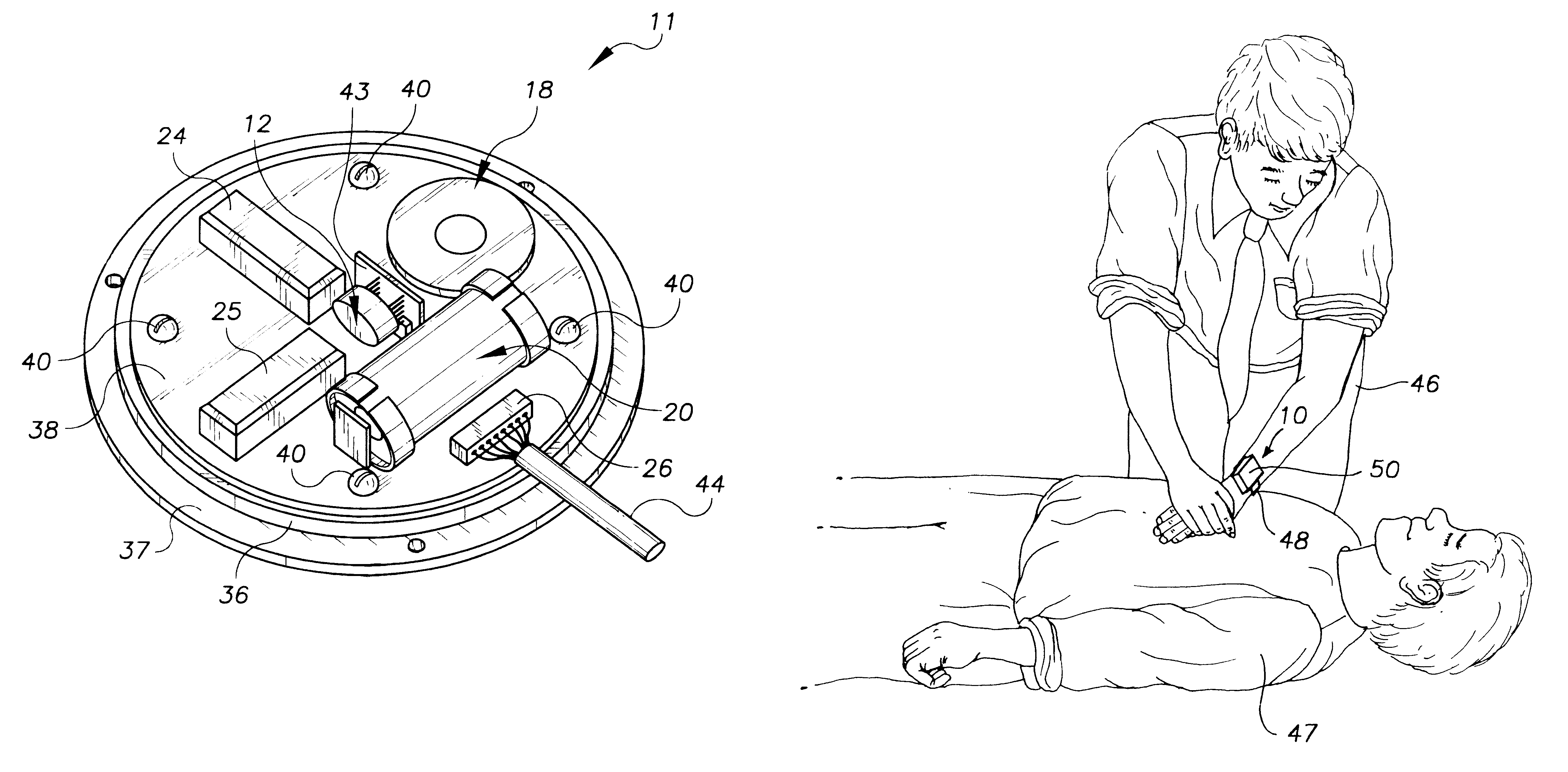
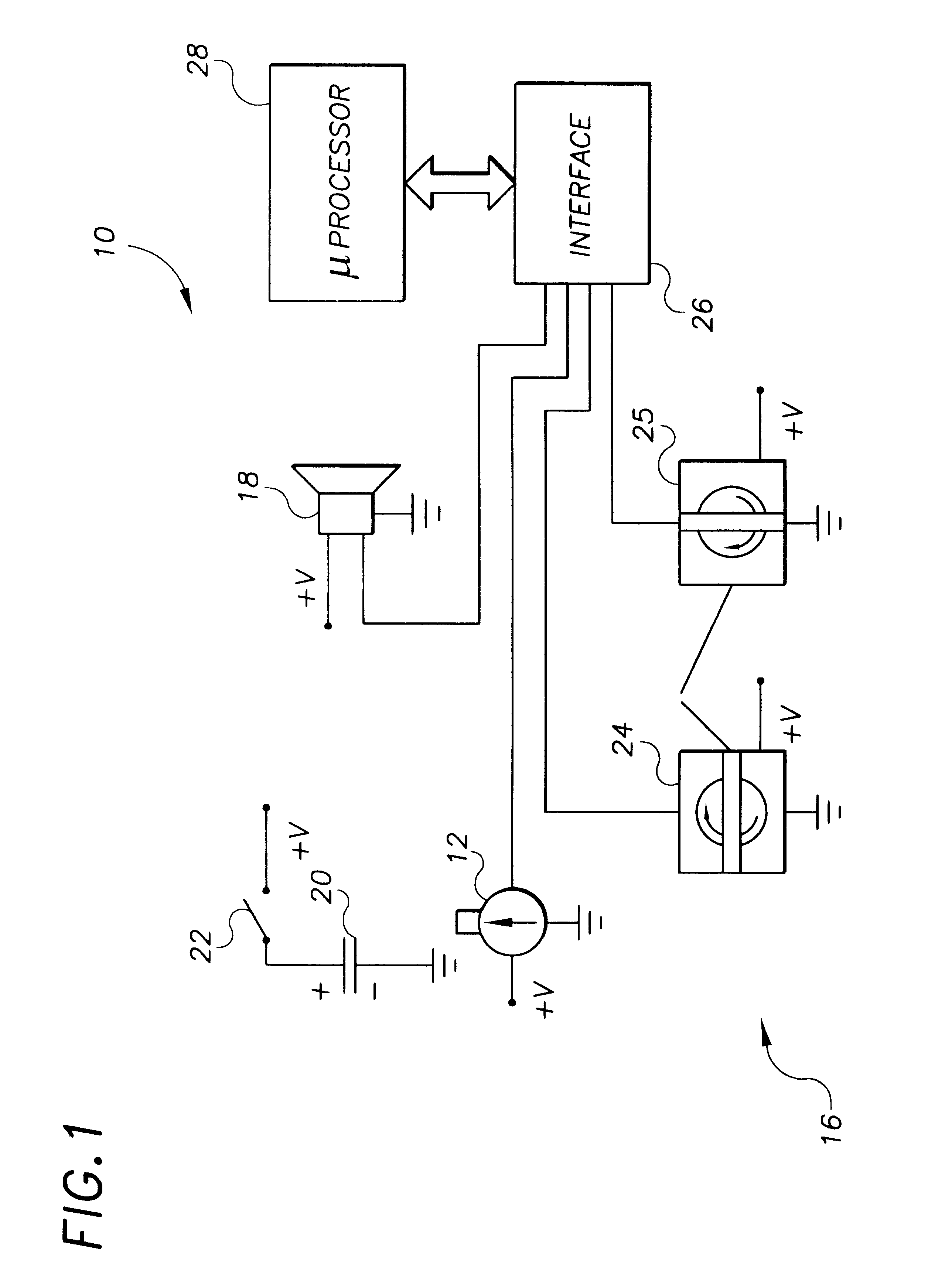
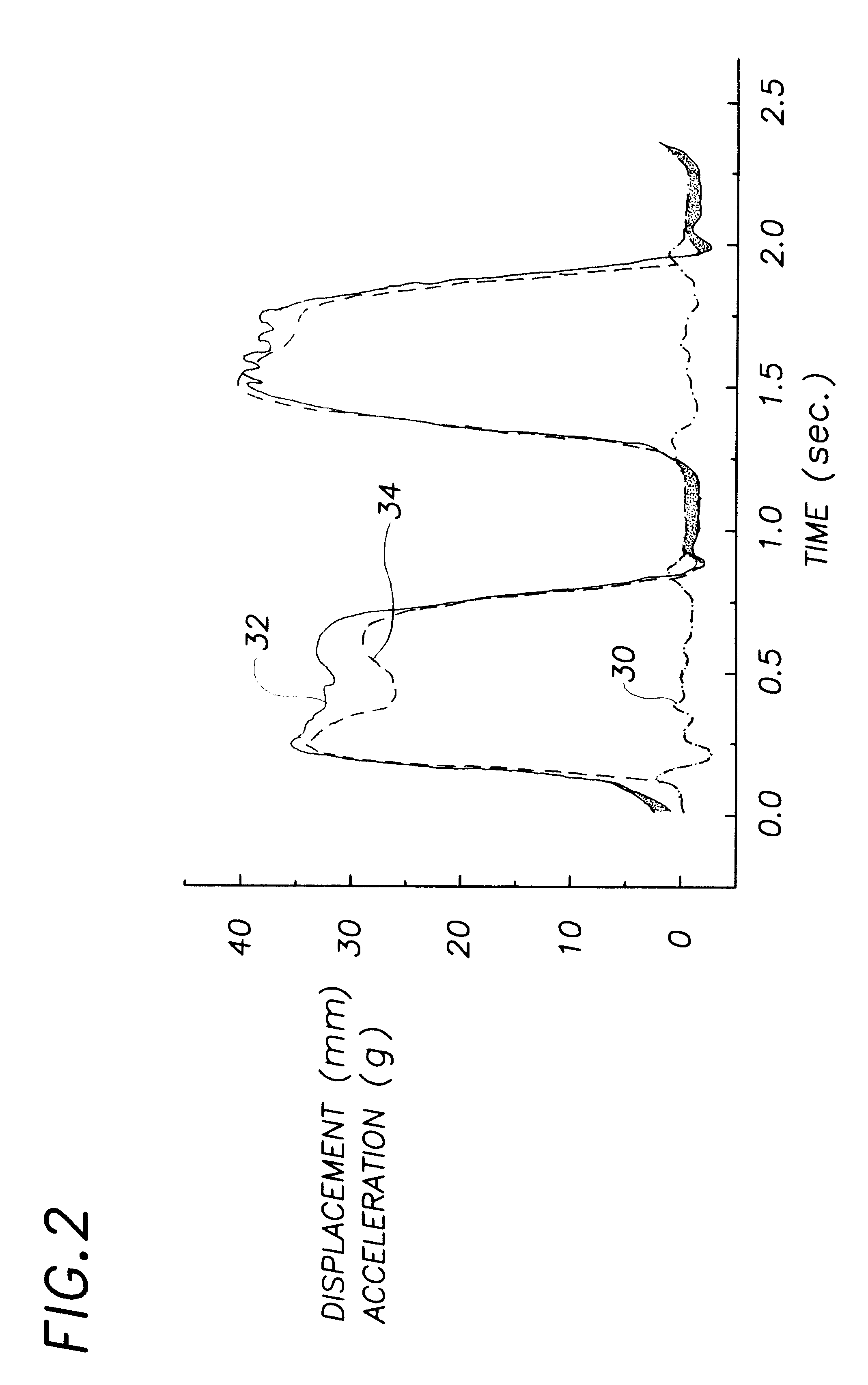
CPR chest compression monitor
InactiveUS6390996B1Accurate measurementSmall sizeHeart defibrillatorsInertial sensorsEcg signalEmergency medicine
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
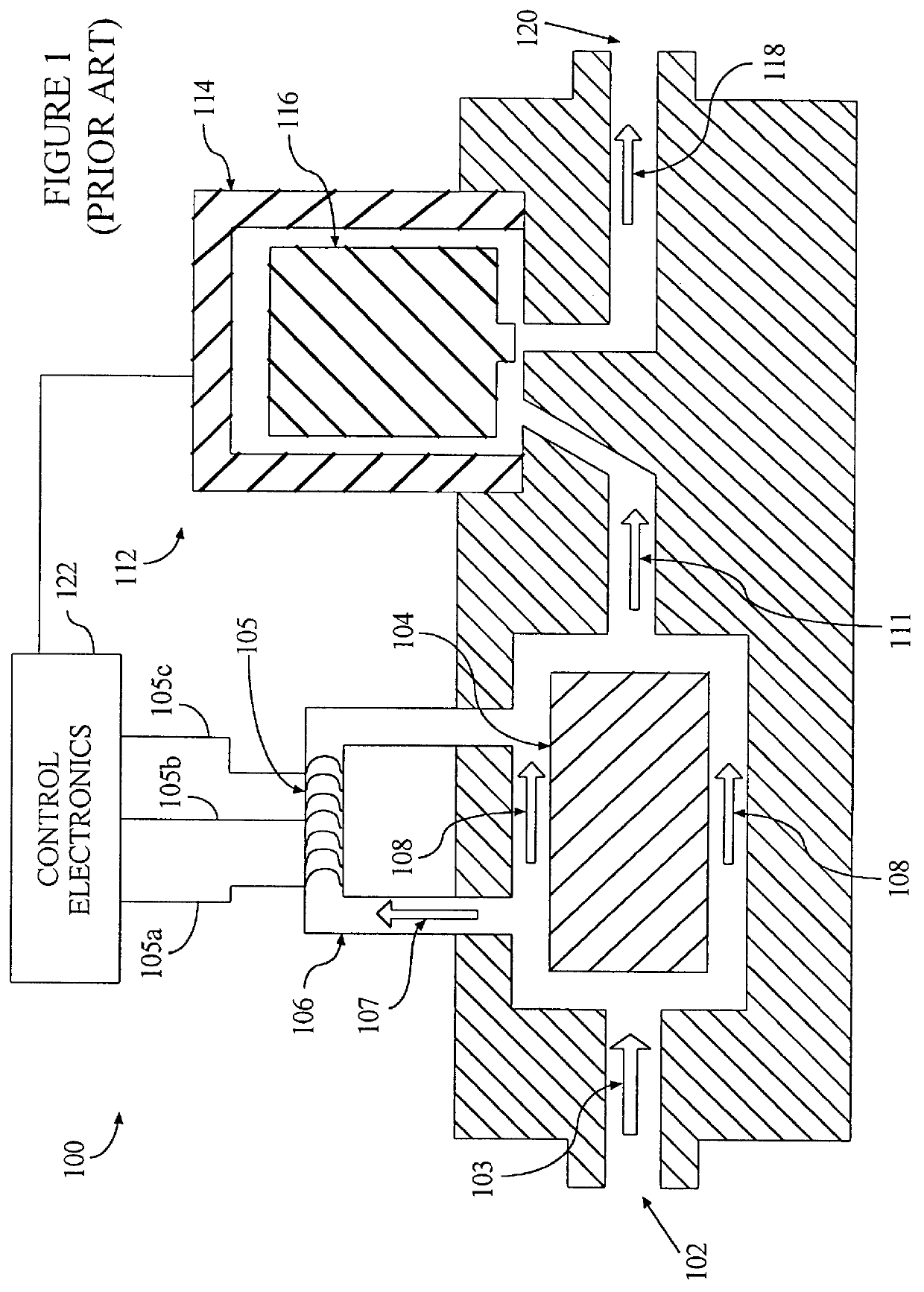
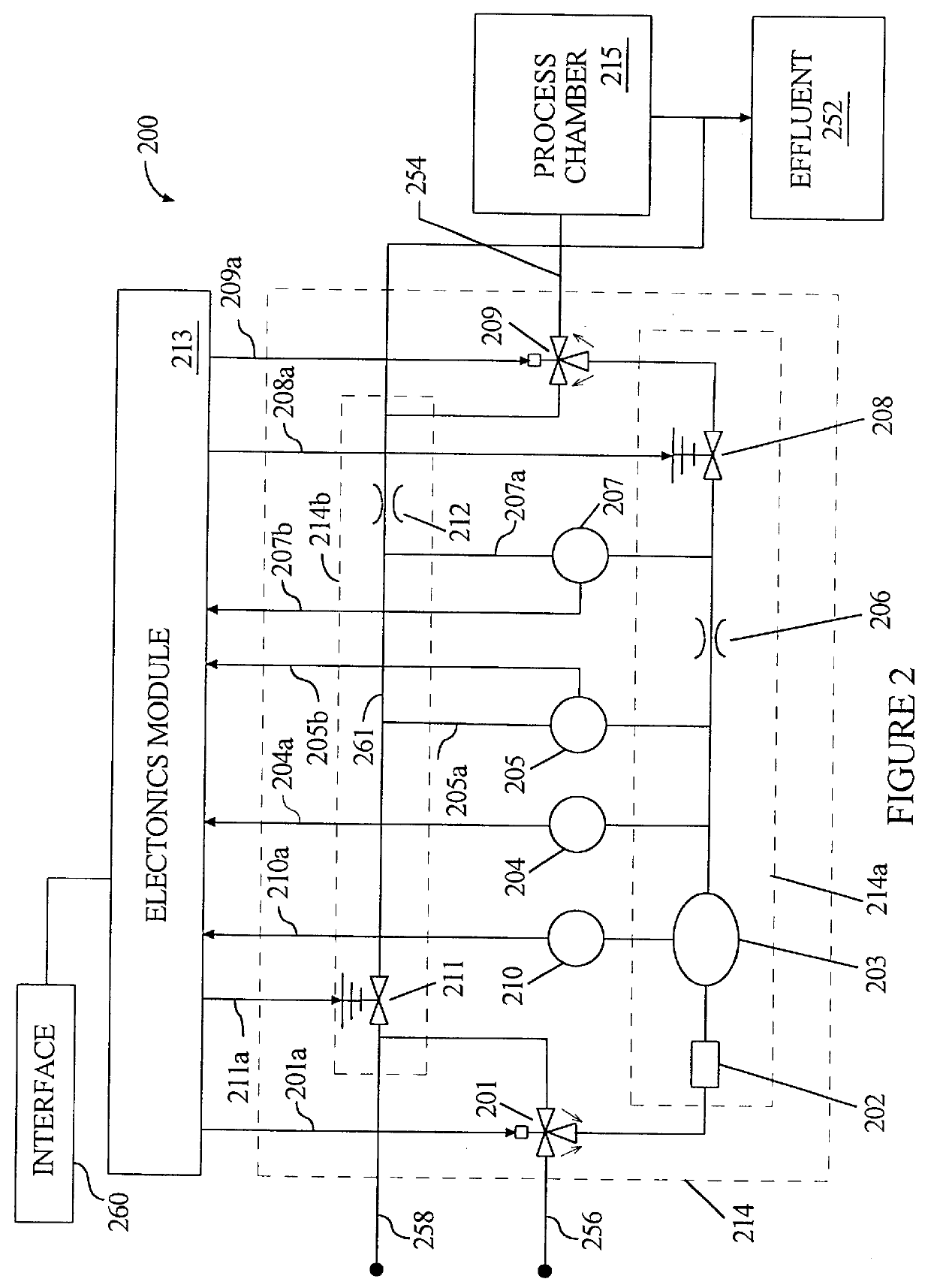
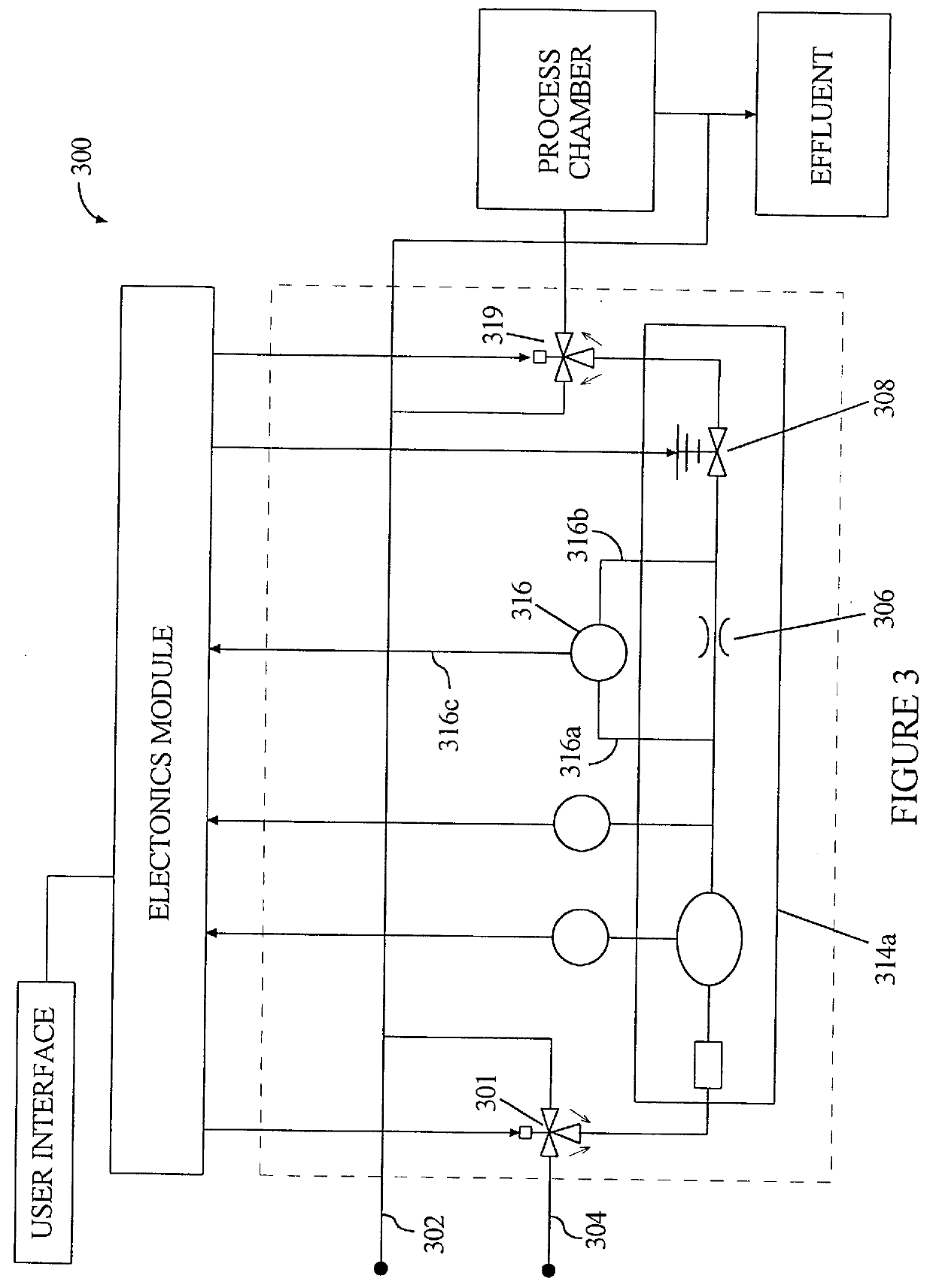
Method for wide range gas flow system with real time flow measurement and correction
InactiveUS6119710AAccurate measurementAccurate flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsDifferential pressureInlet valve
A gas delivery system accurately measures and optionally regulates mass flow rate in real time. A fluid conduit connects an inlet valve, calibration volume, flow restrictor, and outlet valve in series. Pressure and temperature sensors are coupled to the calibration volume. One or more pressure sensors may be attached across the flow restrictor. Alternatively, an absolute pressure sensor may be attached upstream of the flow restrictor. One embodiment of differential pressure sensors comprises a floating reference differential pressure sensor, including a first transducer attached to the fluid conduit upstream of the flow restrictor and a second transducer attached to the conduit downstream of the flow restrictor. In this embodiment, each transducer receives a reference pressure from a reference source, and optionally, after the calibration volume is charged, the floating reference differential pressure transducers are calibrated. When gas flow is initiated, differential and / or absolute pressure measurements are repeatedly taken, and a measured mass flow rate calculated thereon. Gas flow is adjusted until the measured mass flow rate reaches a target mass flow. Using the temperature / pressure sensors at the calibration volume, repeated calculations of actual flow rate are made to uncover any discrepancy between actual and measured mass flow rates. Whenever a discrepancy is found, the manner of calculating measured mass flow is conditioned to account for the discrepancy; thus, the measured mass flow rate more accurately represents the actual mass flow rate thereby providing an actual mass flow rate more accurately achieving the target mass flow rate.
Owner:CYBER INSTR TECH LLC AN ARIZONA LIMITED LIABILITY +1
Sensor having electrode for determining the rate of flow of a fluid
InactiveUS6801041B2Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsTarget analysisAnalyte
Sensors that are capable measuring the rate of flow of a fluid that passes over the electrodes of the sensor. In these sensors, an electrode, designated the flow rate-determining electrode, is used in conjunction with the conventional electrodes, e.g., the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, to determine the rate of flow of the fluid. In one aspect, this invention provides a sensor for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid when the sample flows continuously over the electrodes of the sensor, especially when the rate of flow of the sample is relatively low. In another aspect, this invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid, wherein the rate of flow of the sample varies during the period of time that the sensor is in place. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor employs four electrodes, namely, a working electrode, a reference electrode, a counter electrode, and a flow rate-determining electrode. Alternatively, a single electrode that performs both the function of the reference electrode and the function of the counter electrode can replace the reference electrode and the counter electrode. In addition, a dummy electrode or a blank electrode can be used to compensate for interference from electrochemically active species. The reagent(s) specific to the analyte of interest is required to be deposited on the working electrode.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Non-invasive method and apparatus for determining a physiological parameter
InactiveUS20050192488A1Accurate resultAccurately measureElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyLinear algorithmNon invasive
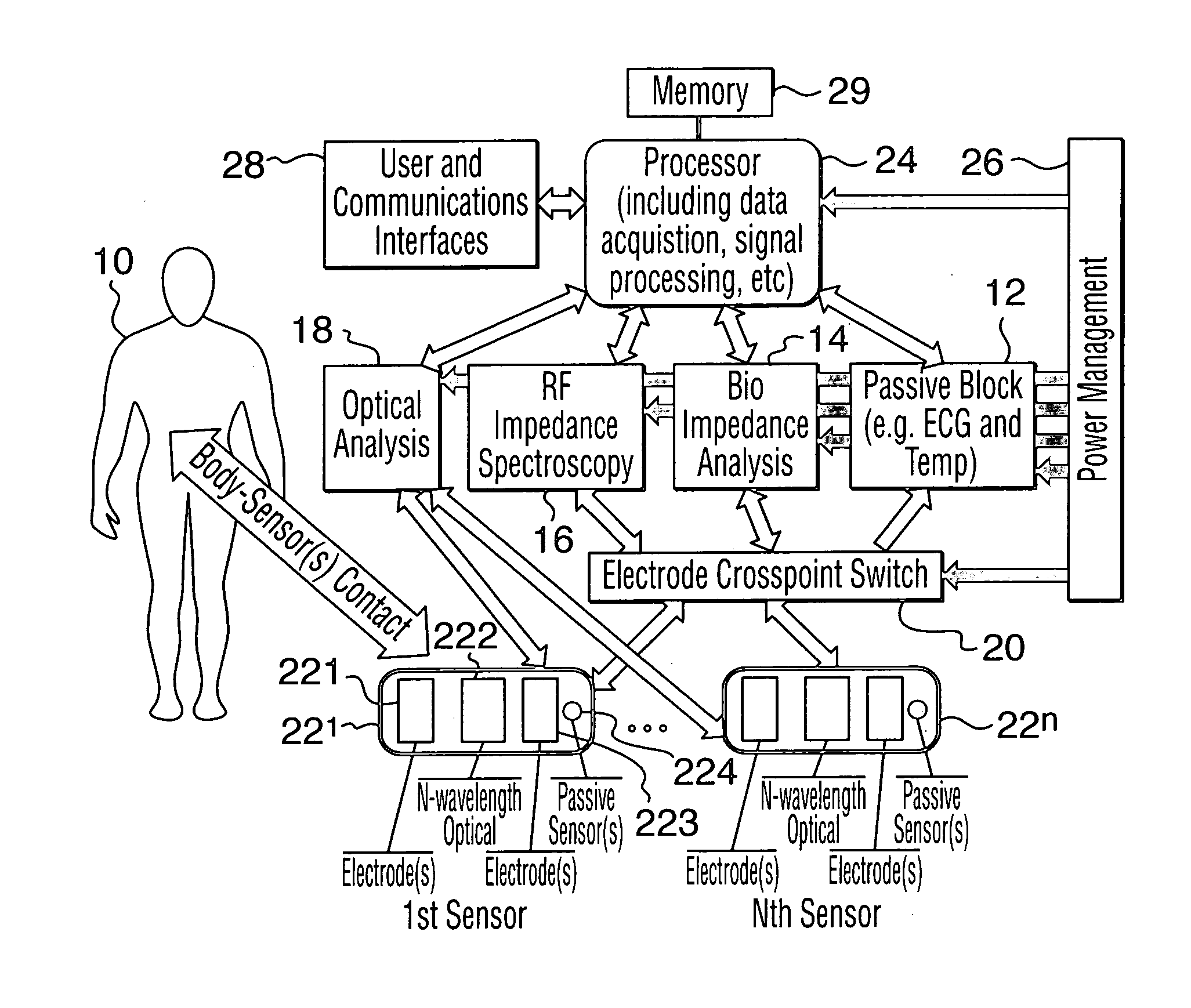
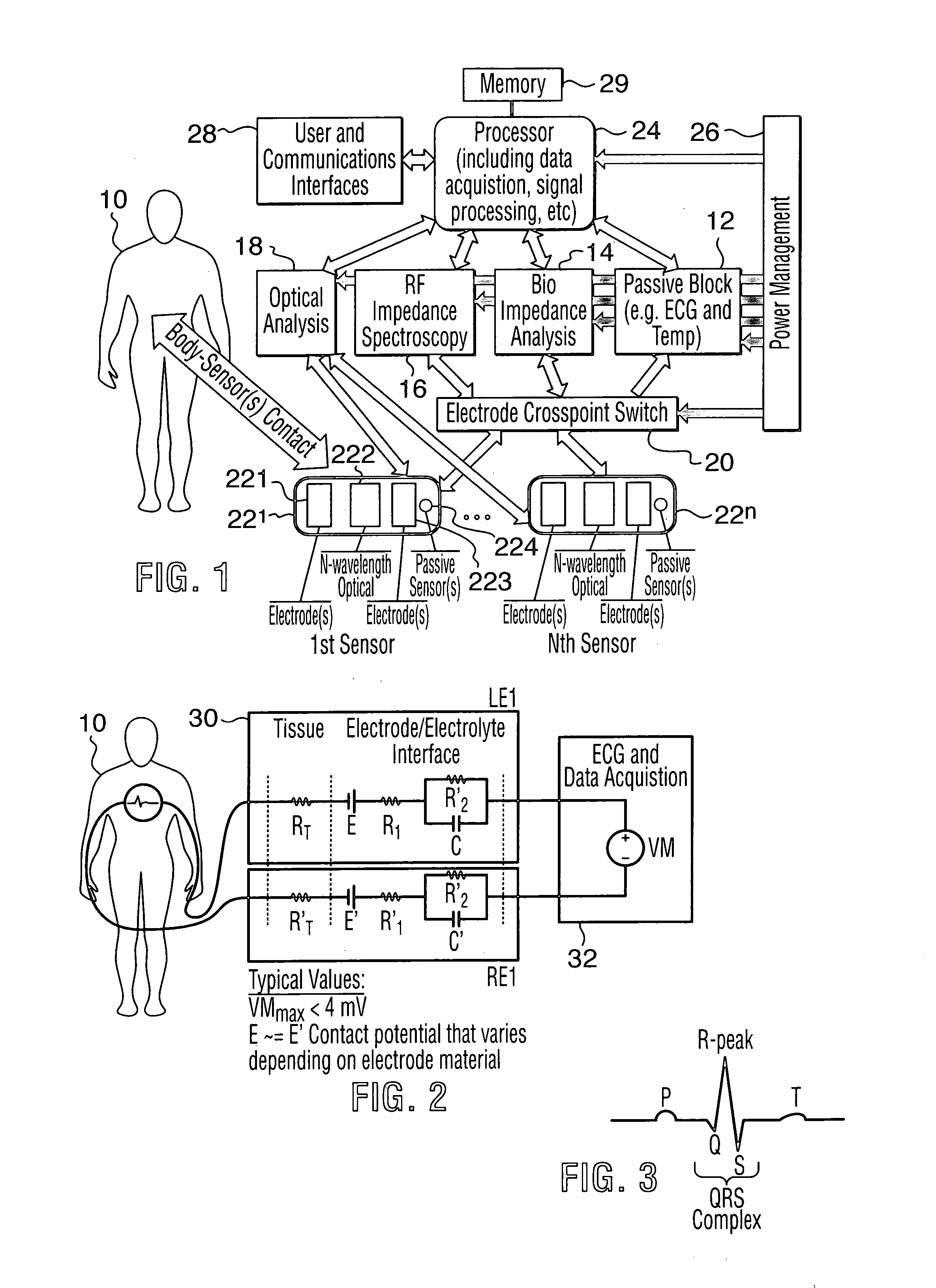
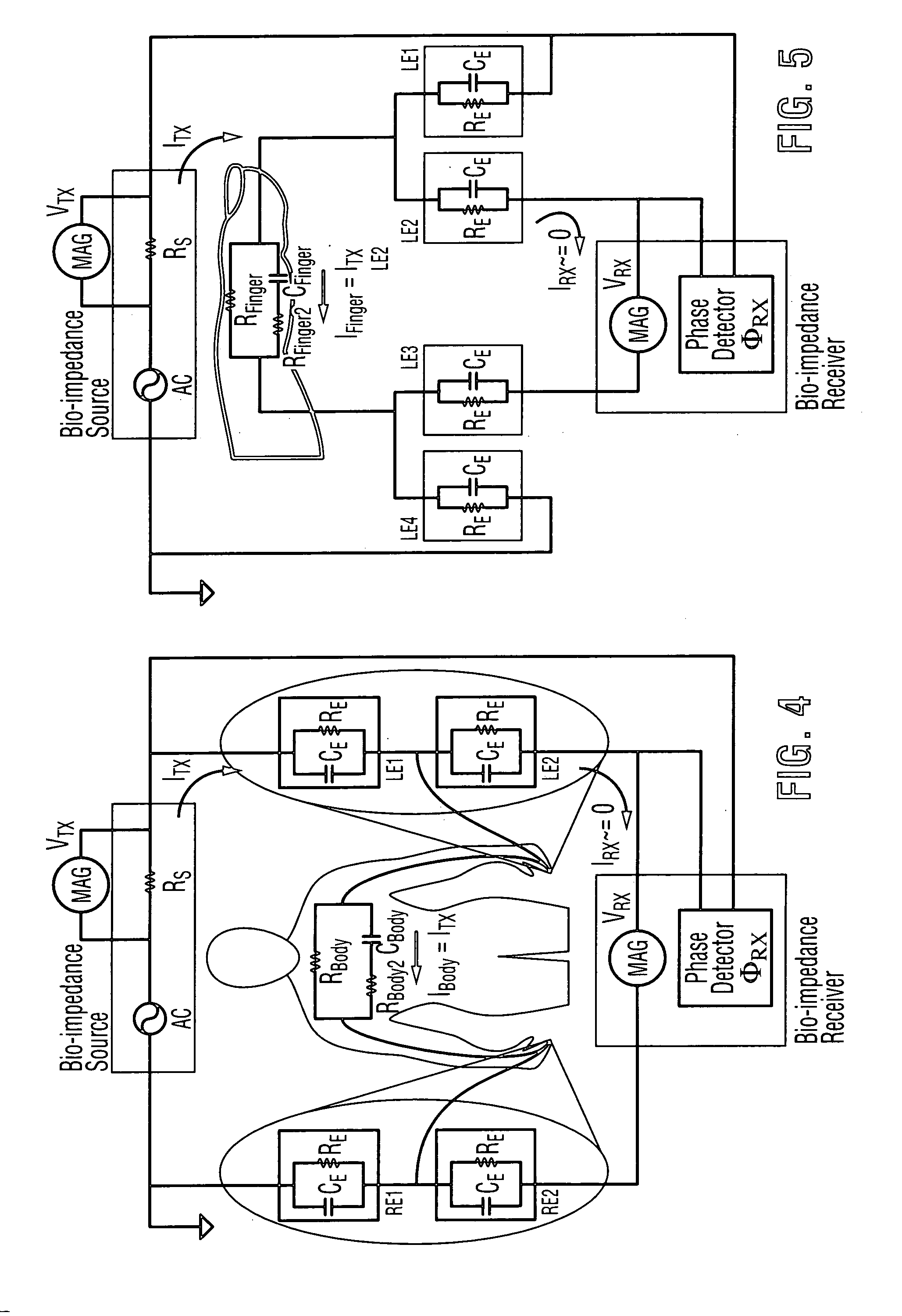
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for the non-invasive analysis of physiological attributes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, cardiac output, respiratory response, body composition, and blood chemistry analytes including glucose, lactate, hemoglobin, and oxygen saturation. Using a combination of multi-functioning disparate sensors, such as optical and electrical, improvements are made over existing physiological measurement devices and techniques. The special configuration of one or more multi-functional sensors is used to non-invasively measure multi-wavelength optical plus one or more of ECG, Bio-impedance, and RF-impedance spectroscopic data. This information is used to develop self-consistent, non-linear algorithm in order to derive the physiological attributes while compensating for various forms of interfering effects including motion artifacts, sensor attachment variability, device component variability, subject physical and physiology variability, and various interfering physiological attributes.
Owner:BIOPEAK CORP
Monitoring system for determining and communicating a cost of insurance
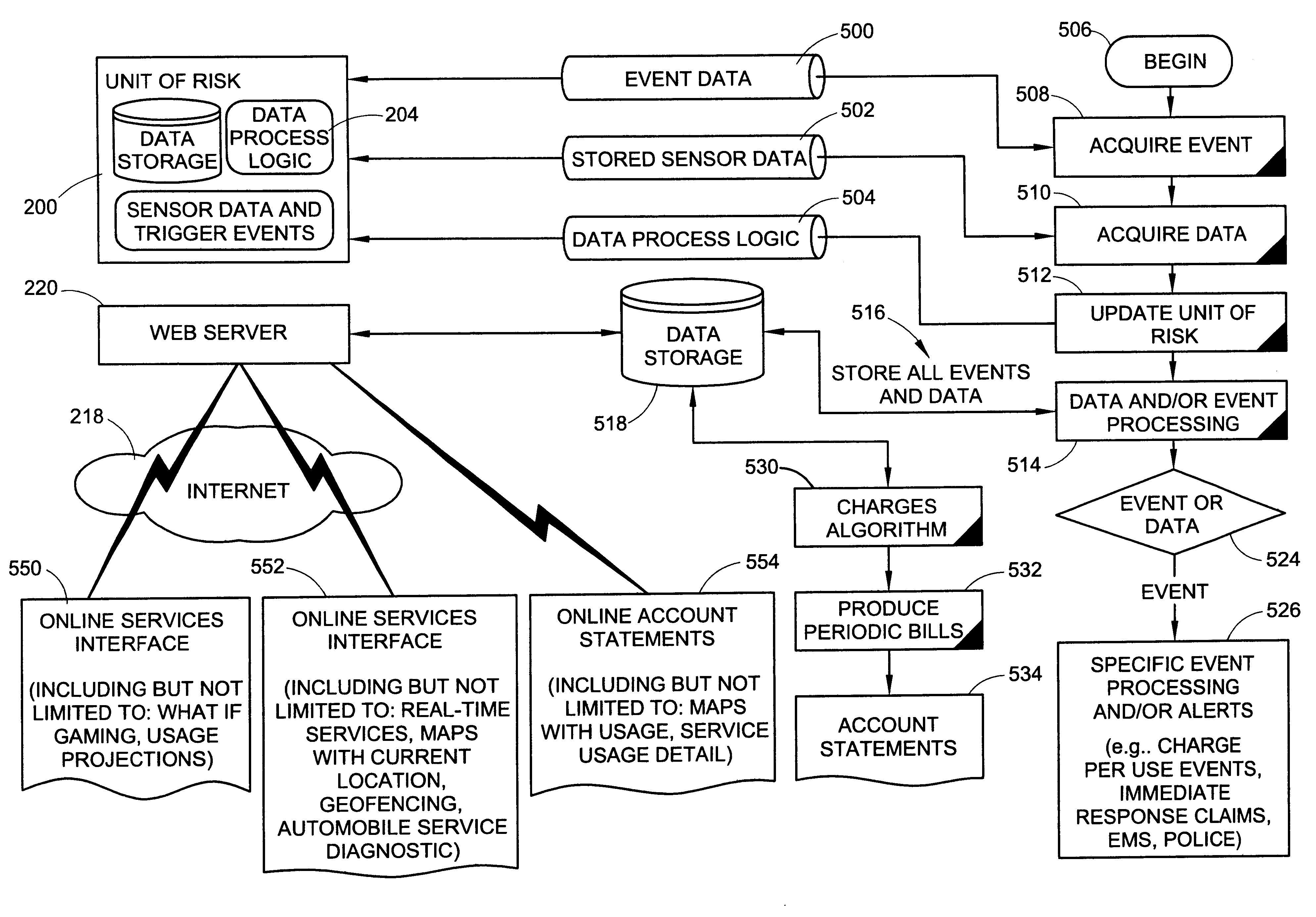
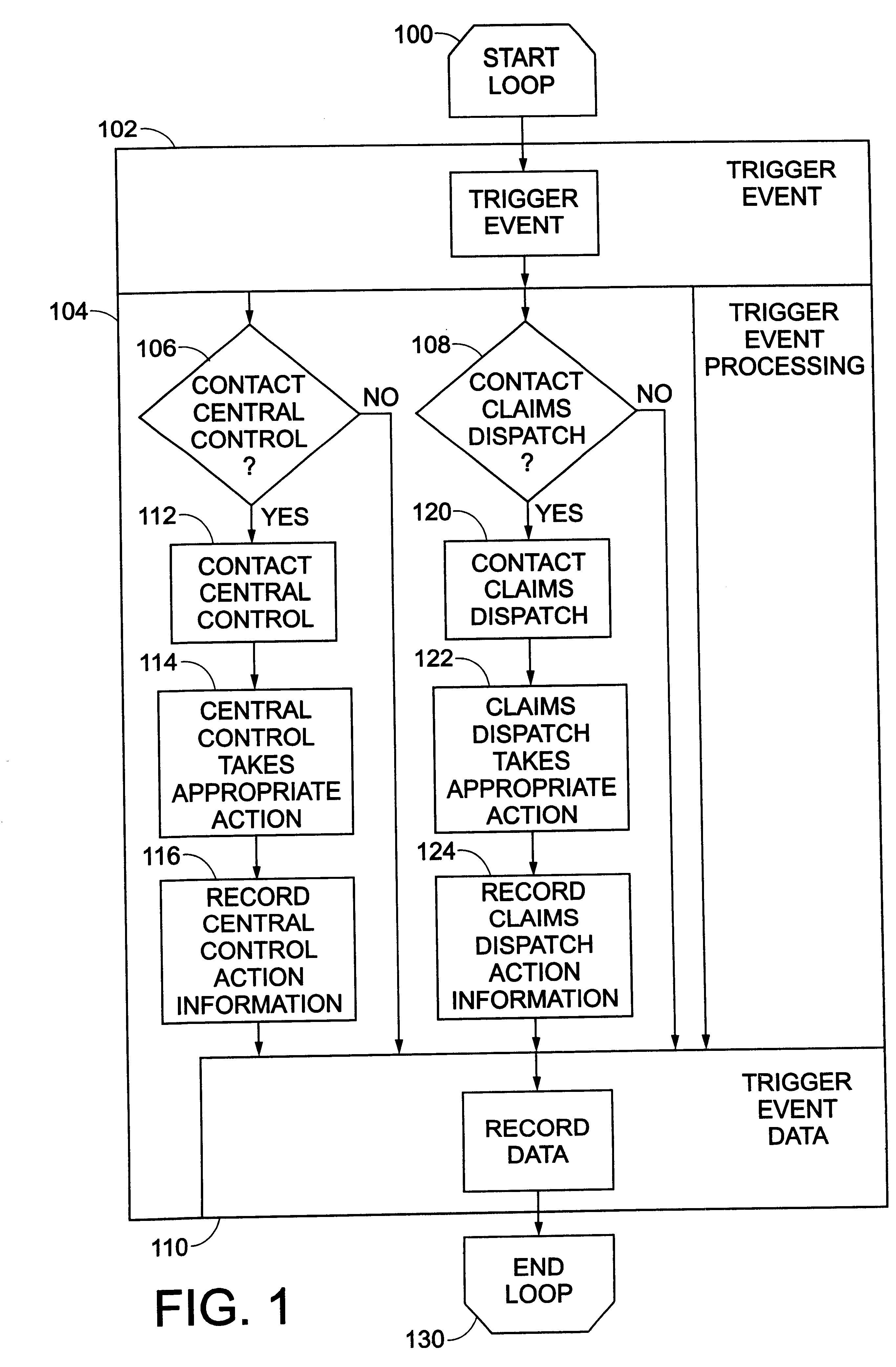
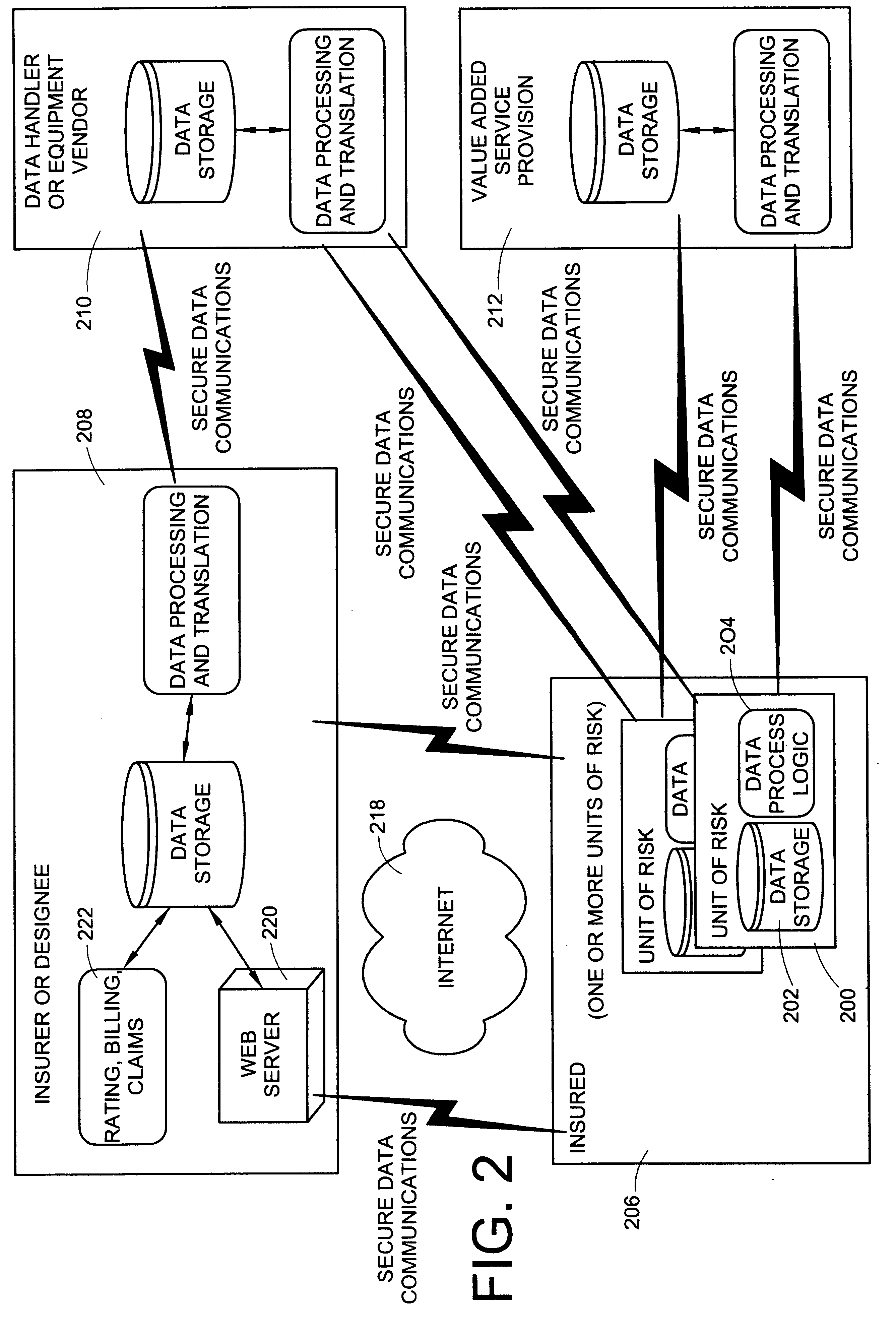
InactiveUS6868386B1Accurate measurementError rateElectric signal transmission systemsFinanceInternet communicationMonitoring system
A method and system for communicating insurance related services between an insured and an insurer through an Internet communication scheme includes a processing system for processing acquired event and sensored data to compute the cost of insurance for the same period as the data is acquired. An enhanced Internet communication scheme provides an insured access to the acquired data and its processing through enhanced presentation systems (e.g., maps with usage, service or special event processing or even automobile service diagnostics.) In addition, communication packages can provide estimates based upon user-supplied information identifying projected usages.
Owner:PROGRESSIVE CASUALTY INSURANCE
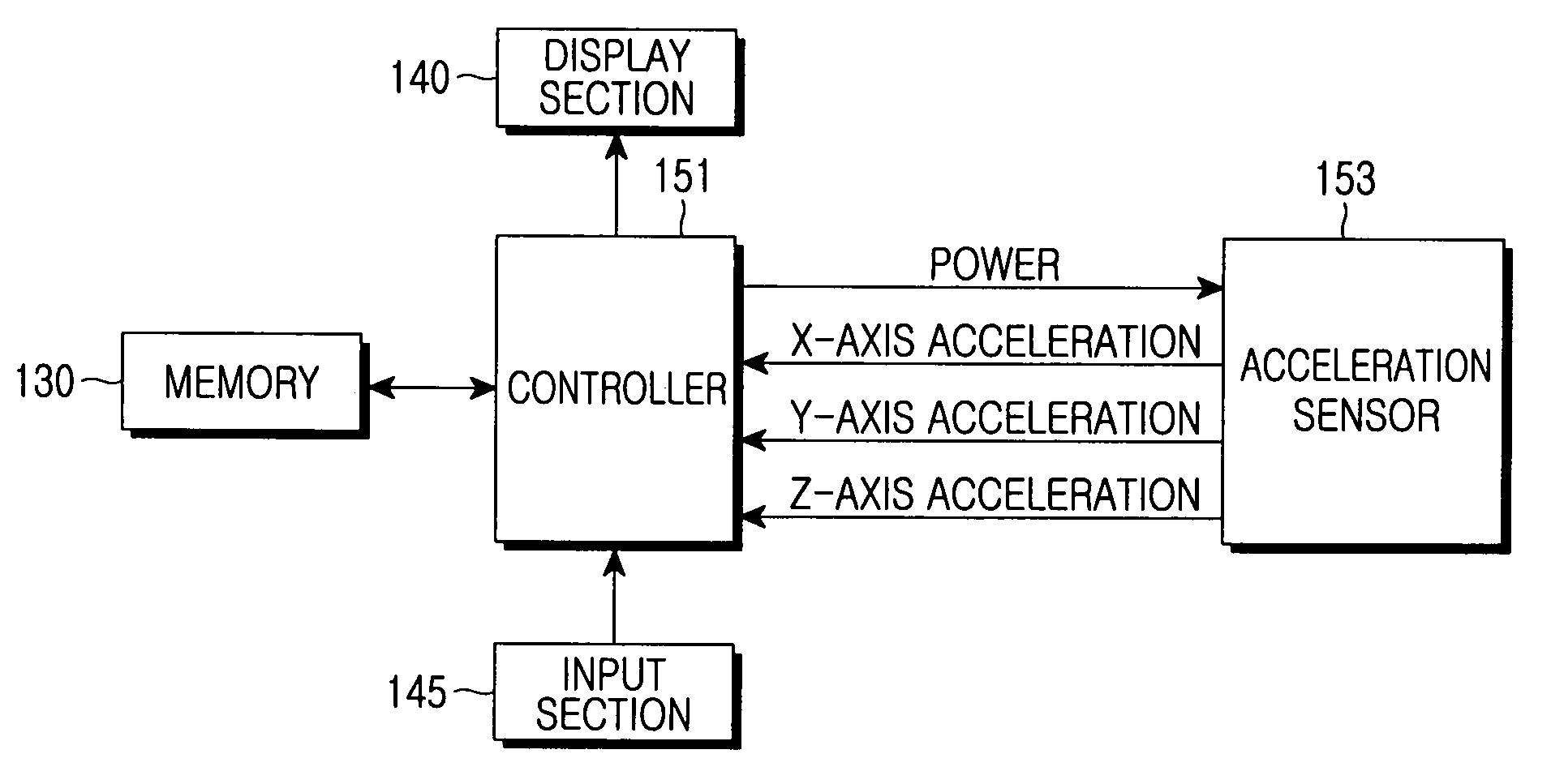
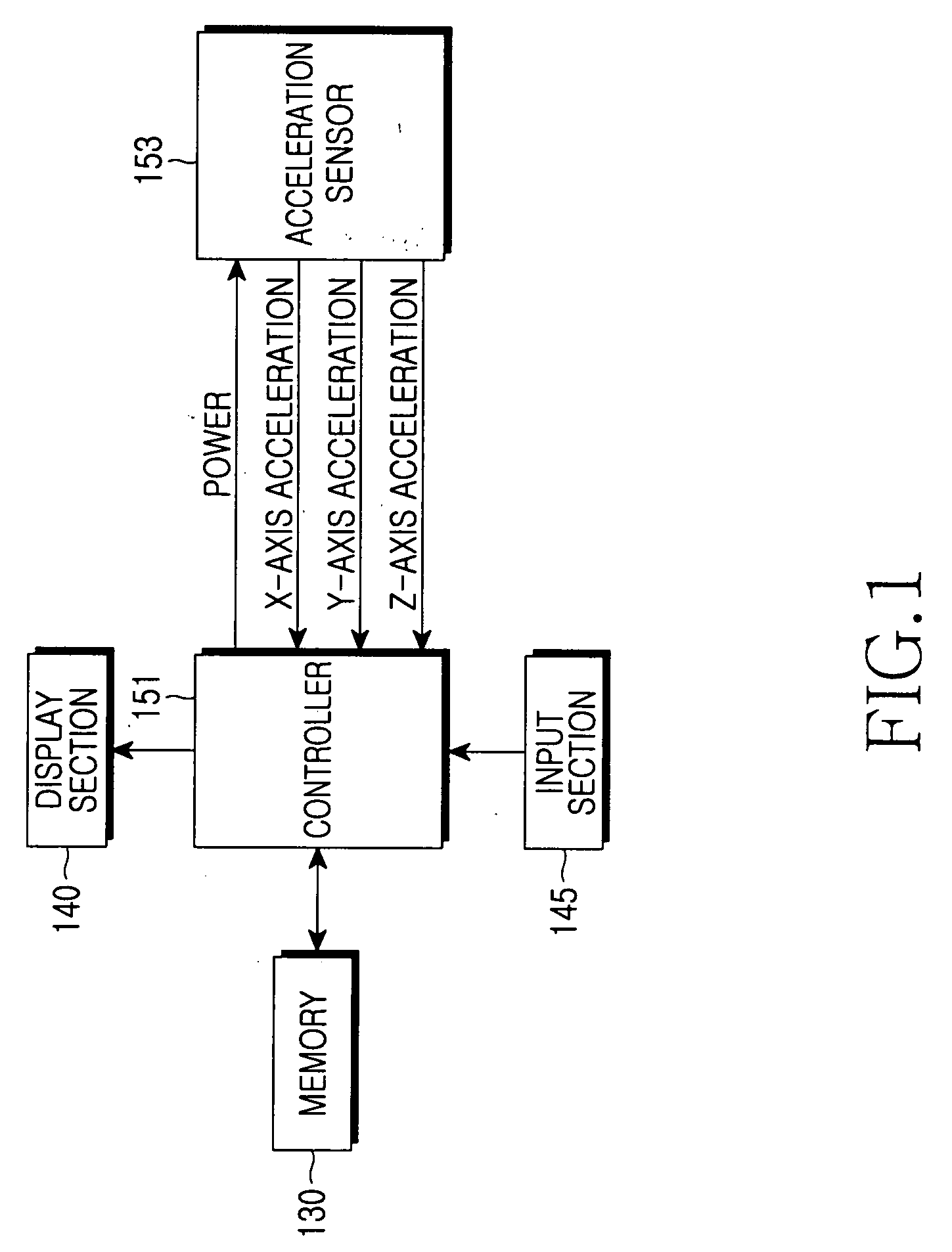
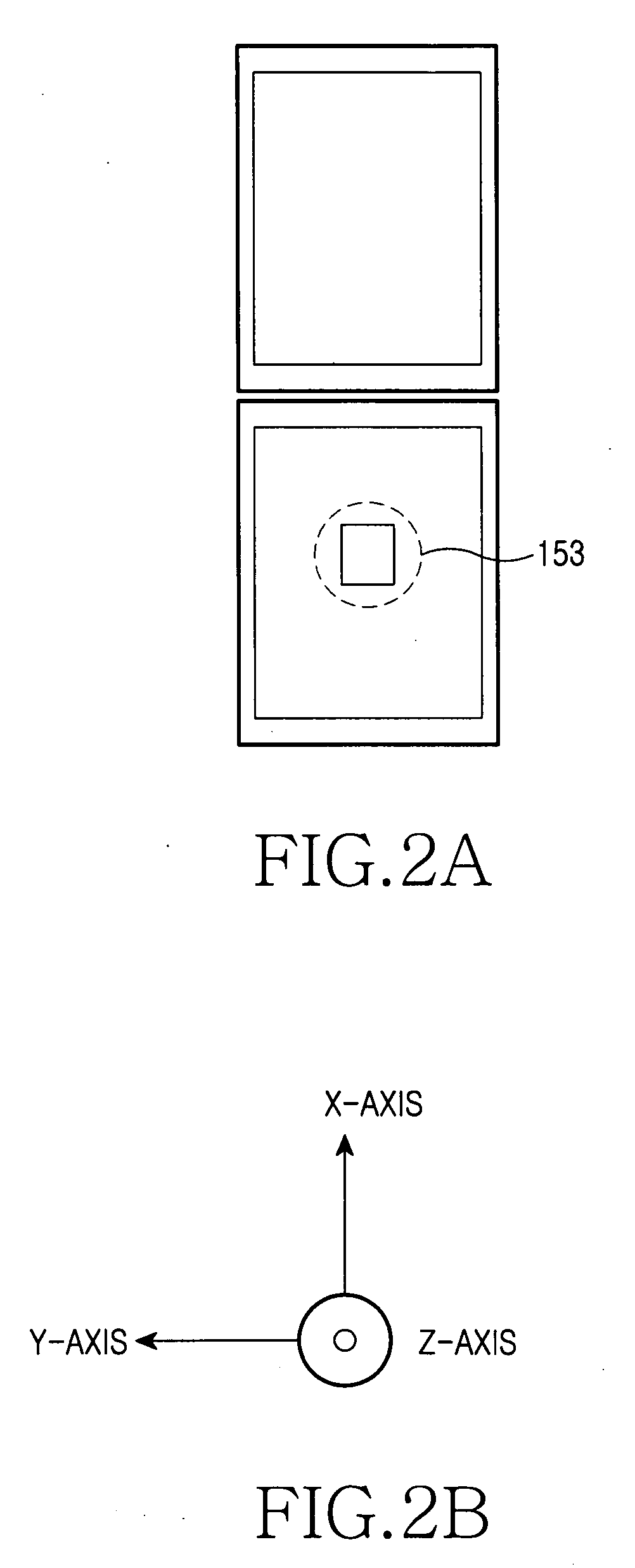
Apparatus and method for measuring quantity of physical exercise using acceleration sensor
ActiveUS20060020177A1Eliminating exercise informationReduce power consumptionGymnastic exercisingPerson identificationEngineeringElectric power
Disclosed are a method for measuring quantity of exercise and an apparatus comprising an acceleration sensor for generating acceleration information by measuring the quantity of exercise according to user movement, sensor control unit for supplying power to the acceleration sensor and sampling the acceleration information generated from the acceleration sensor, a dynamic energy measurement unit for converting the sampled acceleration information into dynamic energy, comparing a local maximum value with a predetermined threshold value if an ascending gradient of the dynamic energy has the local maximum value exceeding a predetermined value and determining a user step if the local maximum value exceeds the predetermined threshold value, a calorie consumption measurement unit for calculating calorie consumption by analyzing an energy level of dynamic energy determined as a user step, a memory for storing information, and a display section for displaying information related to the number of steps and calorie consumption.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
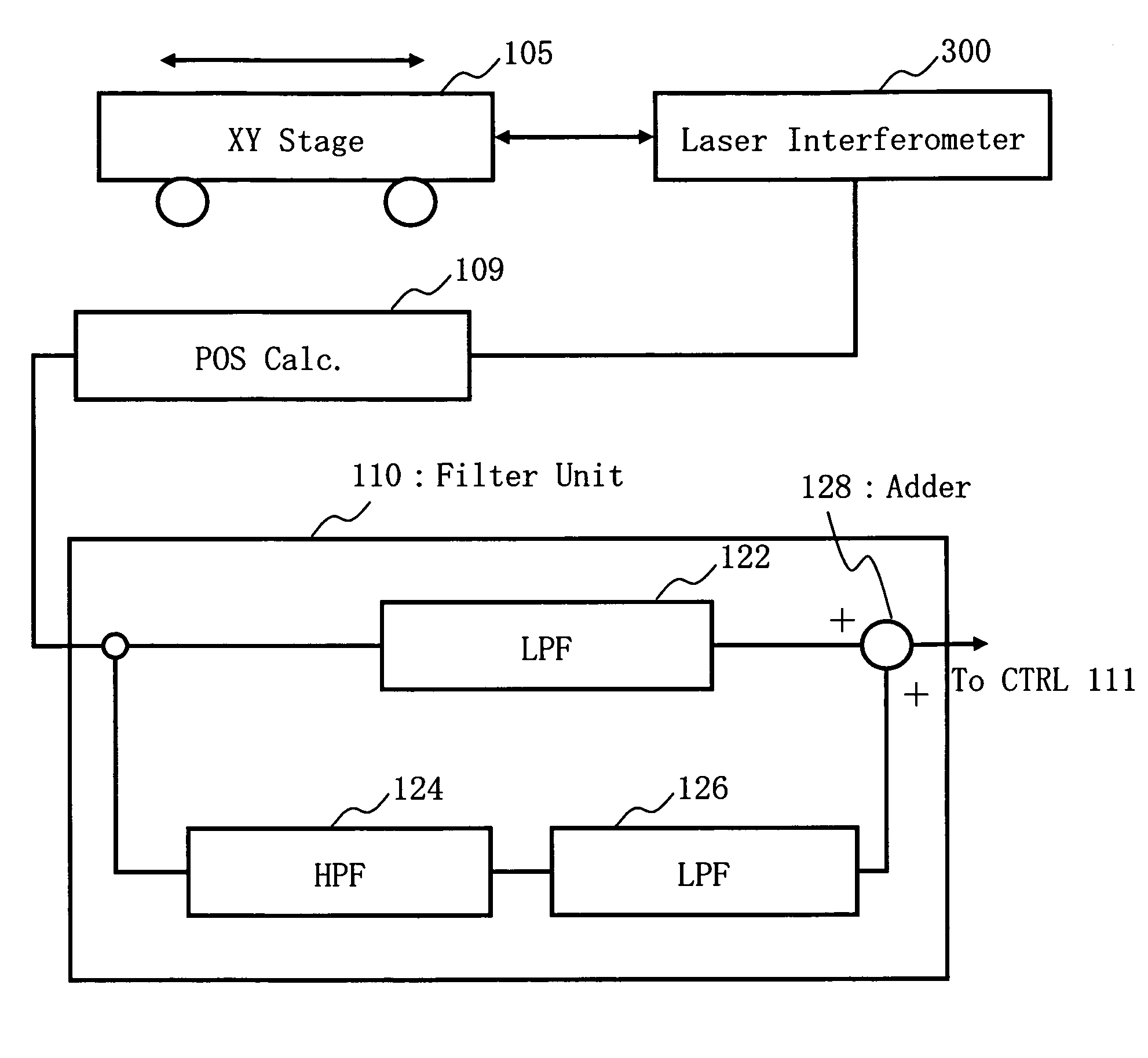
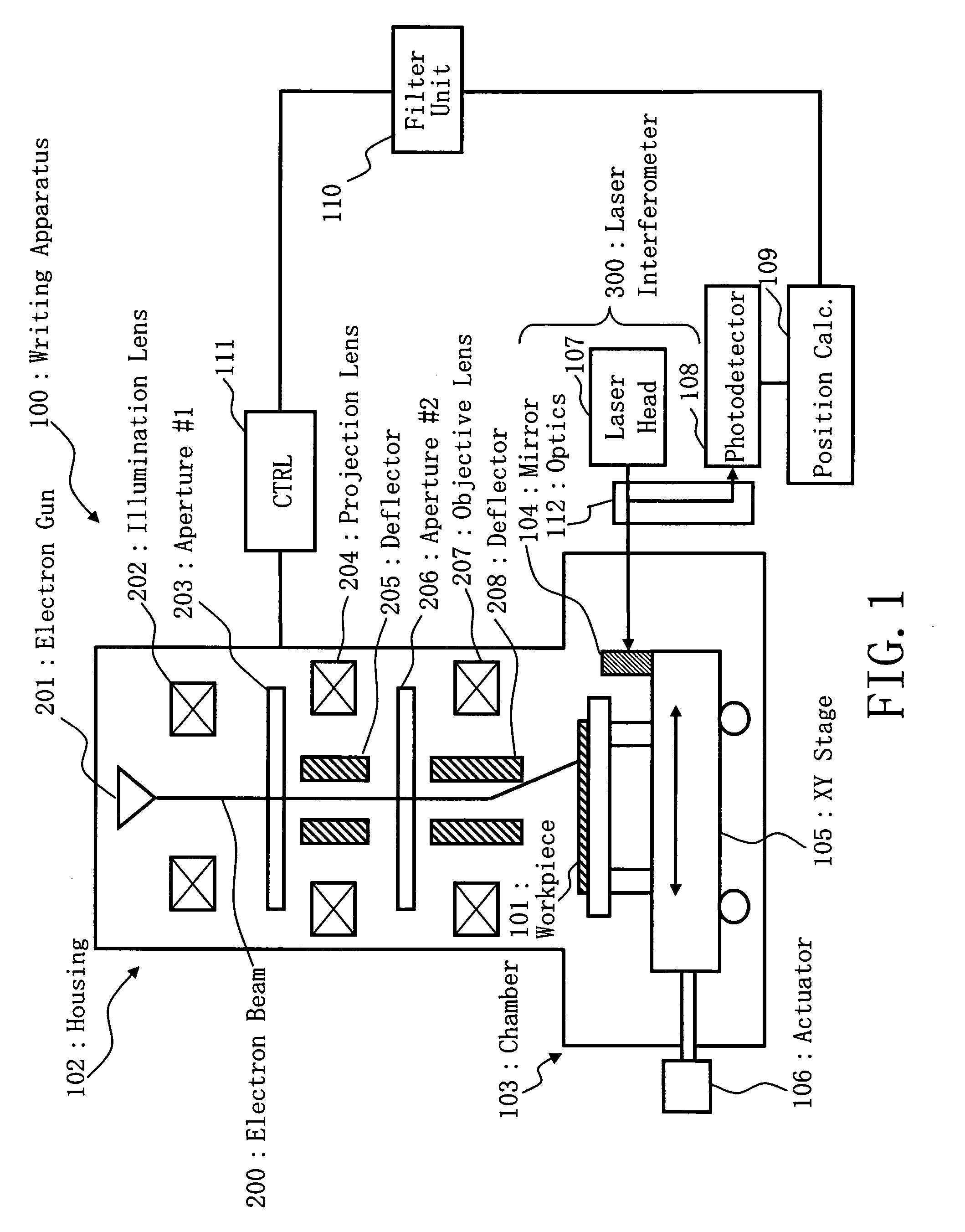
Position measurement apparatus and method and pattern forming apparatus and writing method
ActiveUS7640142B2Accurate measurementAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceElectric discharge tubesLaserElectrical and Electronics engineering
A position measurement apparatus includes a movable stage structure, a measurement unit using a laser to measure a moved position of the stage and to output a corresponding measured value, a first filter configured to attenuate a first component of a certain frequency region of the measured value outputted by the measurement unit, a second filter connected in parallel with the first filter configured to attenuate a second component other than the certain frequency region of the measured value outputted by the measurement unit, a third filter connected in series to the second filter with the series connection of the second and third filters connected in parallel with the first filter, configured to attenuate the first component of the certain frequency region of the measured value outputted by the measurement unit, and a processing unit configured to combine an output of the first filter and an output of the series connection of the second and third filters and to thereby output a first combined value.
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
Wafer holder, heater unit used for wafer prober having the wafer holder, and wafer prober having the heater unit
InactiveUS20090050621A1Improve thermal uniformityAvoid measuringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHot plates heating arrangementsEngineeringSilicon
A wafer holder that prevents positional deviation of the wafer mounted on the wafer-mounting surface of a chuck top and enables better thermal uniformity of the wafer, as well as a heater unit including the wafer holder and a wafer prober mounting these are provided. The wafer holder has a chuck top mounting and fixing the wafer and a supporter supporting the chuck top, and the chuck top has water absorption of at least 0.01% and preferably at least 0.1%. Preferable material of the chuck top is a composite of metal and ceramics, and particularly, a composite of aluminum and silicon carbide, or a composite of silicon and silicon carbide.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Systems and methods for ion species analysis with enhanced condition control and data interpretation
ActiveUS20050253061A1Reduces spectral peak overlapHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSystems approachesComputer science
The invention relates generally to ion mobility based systems, methods and devices for analyzing samples and, more particularly, to sample detection using enhanced condition control and data interpretation.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
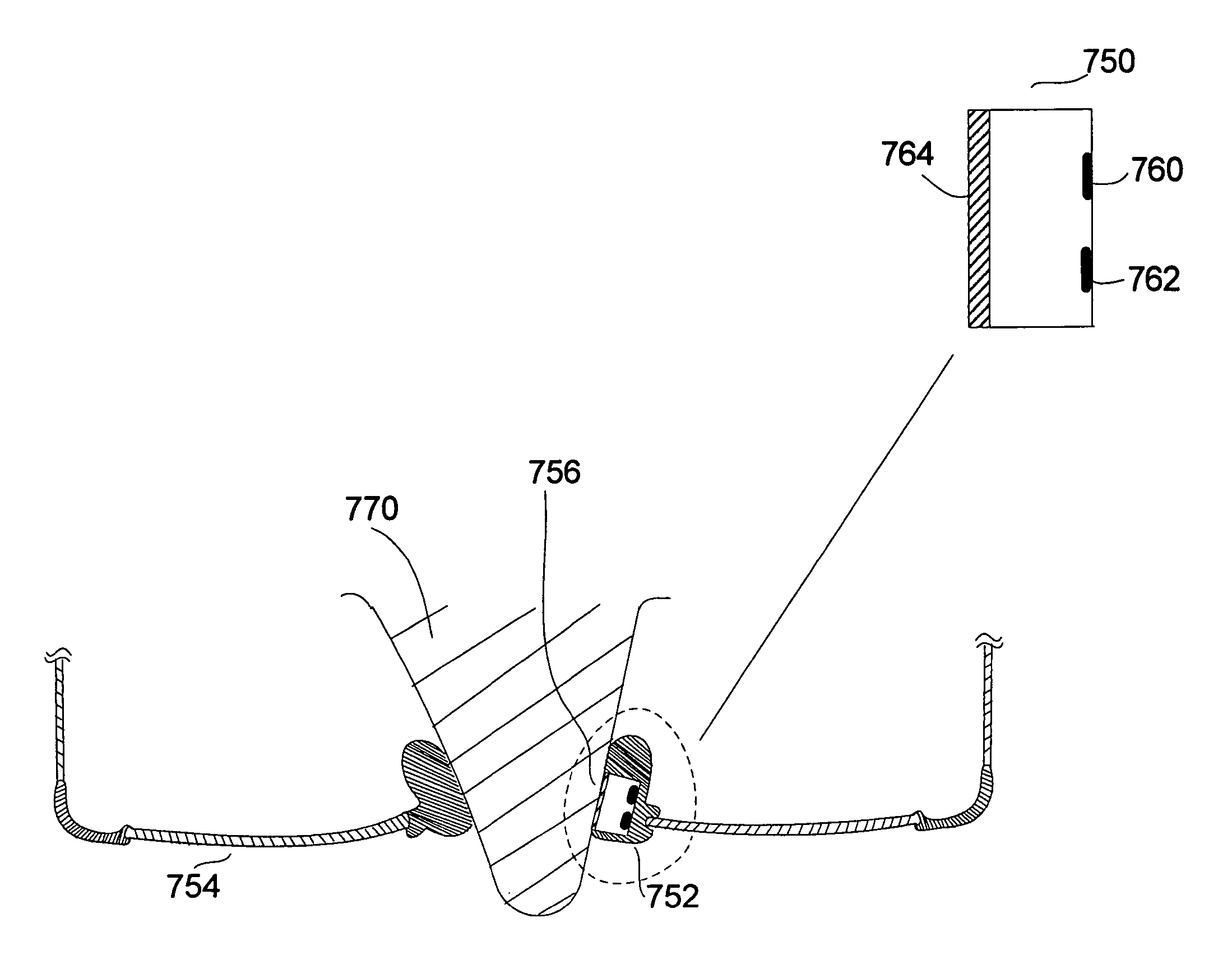
Embedded bio-sensor system
InactiveUS7125382B2Improve accuracyAccurate measurementTelemedicineEndoradiosondesGlucose sensorsConcentrations glucose
Provided is a bio-sensor system which utilizes radio frequency identification technology and which includes a remote transponder in wireless communication with an implantable passively-powered on-chip transponder. The bio-sensor system is specifically adapted to provide a substantially stable and precise sensor reference voltage to a sensor assembly that is included with the on-chip transponder. The remote transponder is also configured to remotely receive data representative of a physiological parameter of the patient as well as identification data and may enable readout of one or more of the physiological parameters that are measured, processed and transmitted by the on-chip transponder upon request by the remote transponder. The precision and stability of the sensor reference voltage is enhanced by the specific circuit architecture of the glucose sensor to allow for relatively accurate measurement of the physiological parameter such as measurement of glucose concentration by a glucose sensor without the use of a microprocessor.
Owner:JAMM TECH INC
Overlay alignment metrology using diffraction gratings
InactiveUS6819426B2Accurate measurementLimited space availableSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetrologyAngle of incidence
Alignment accuracy between two or more patterned layers is measured using a metrology target comprising substantially overlapping diffraction gratings formed in a test area of the layers being tested. An optical instrument illuminates all or part of the target area and measures the optical response. The instrument can measure transmission, reflectance, and / or ellipsometric parameters as a function of wavelength, polar angle of incidence, azimuthal angle of incidence, and / or polarization of the illumination and detected light. Overlay error or offset between those layers containing the test gratings is determined by a processor programmed to calculate an optical response for a set of parameters that include overlay error, using a model that accounts for diffraction by the gratings and interaction of the gratings with each others' diffracted field. The model parameters might also take account of manufactured asymmetries. The calculation may involve interpolation of pre-computed entries from a database accessible to the processor. The calculated and measured responses are iteratively compared and the model parameters changed to minimize the difference.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
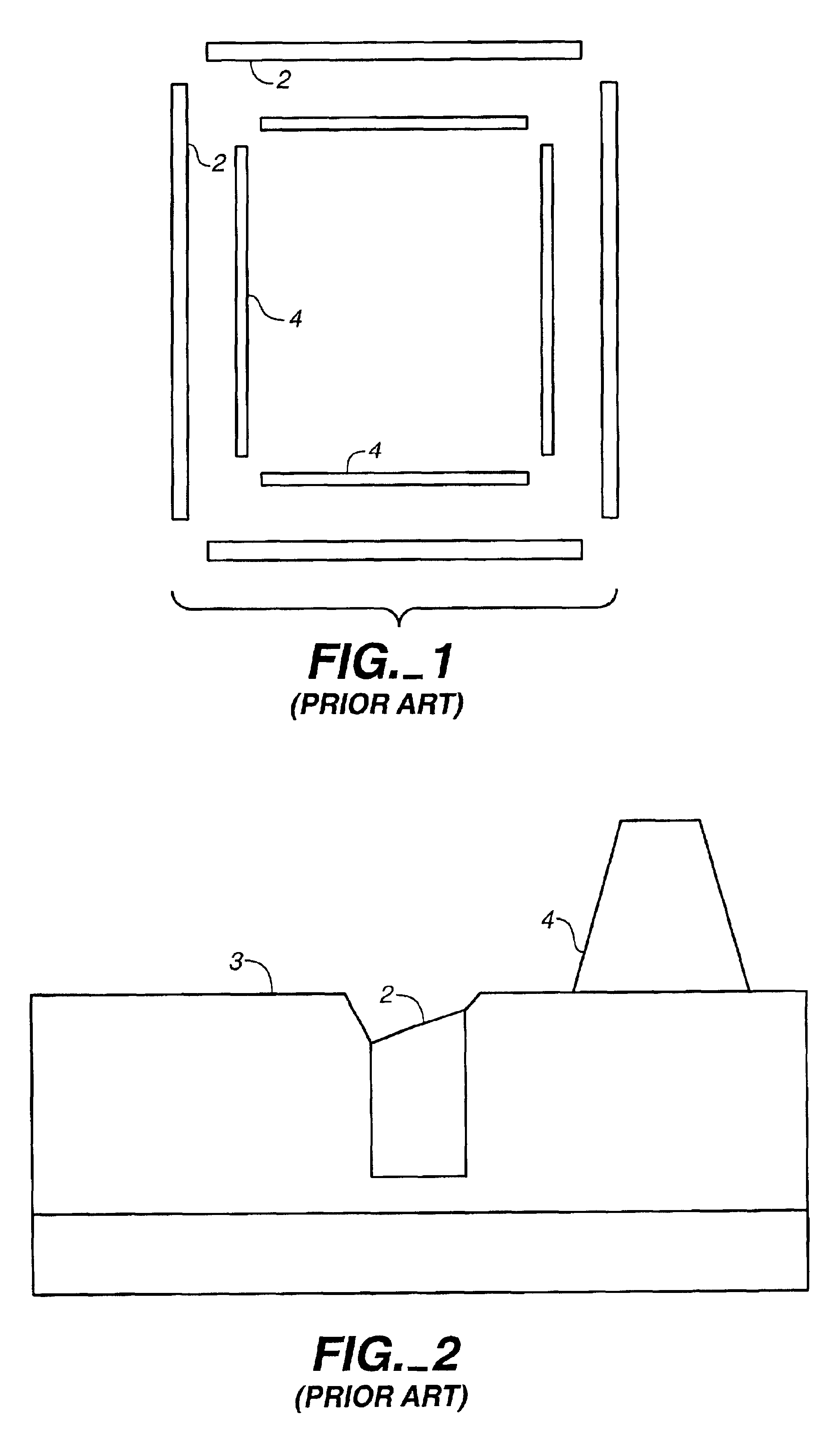
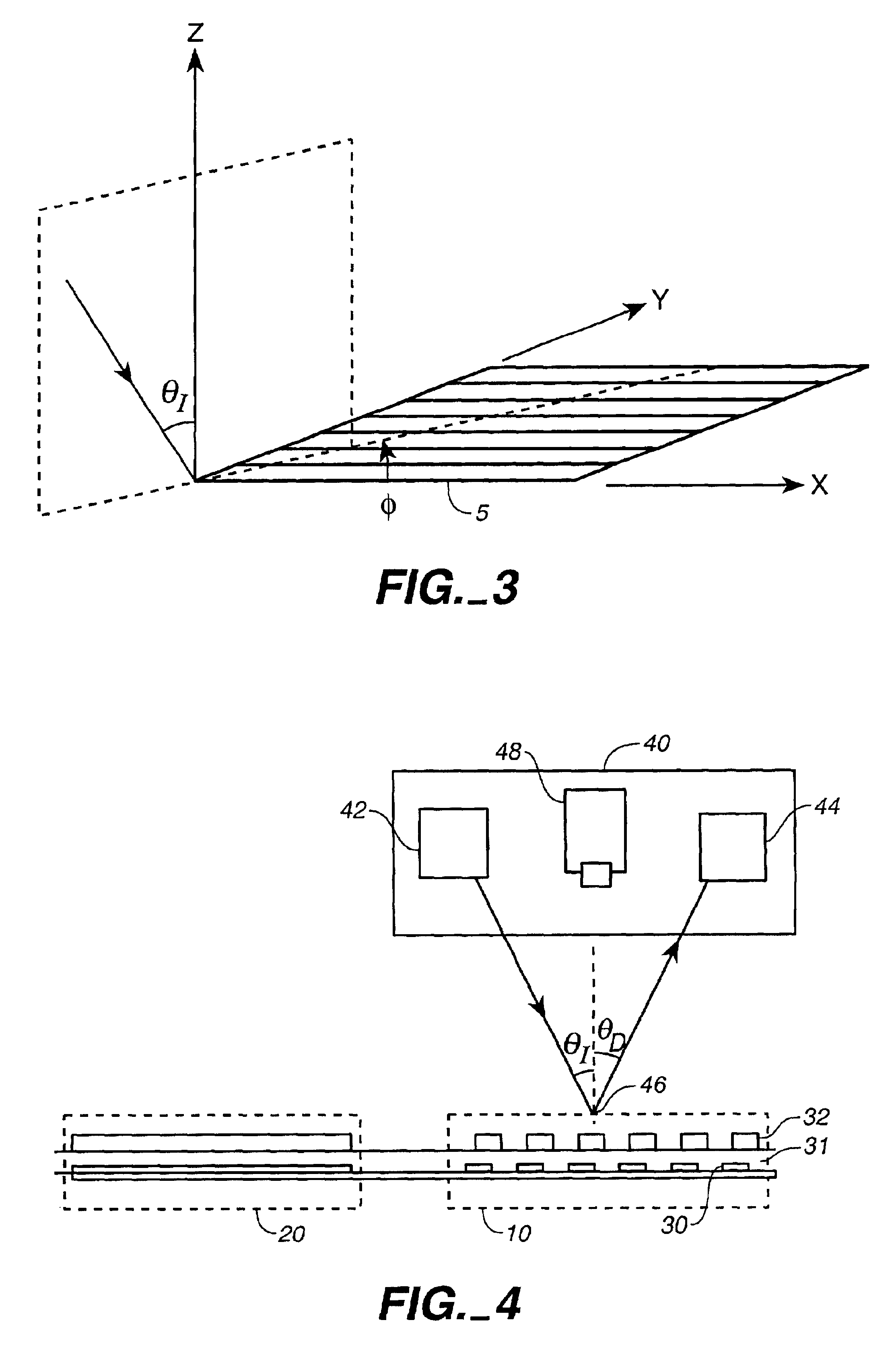
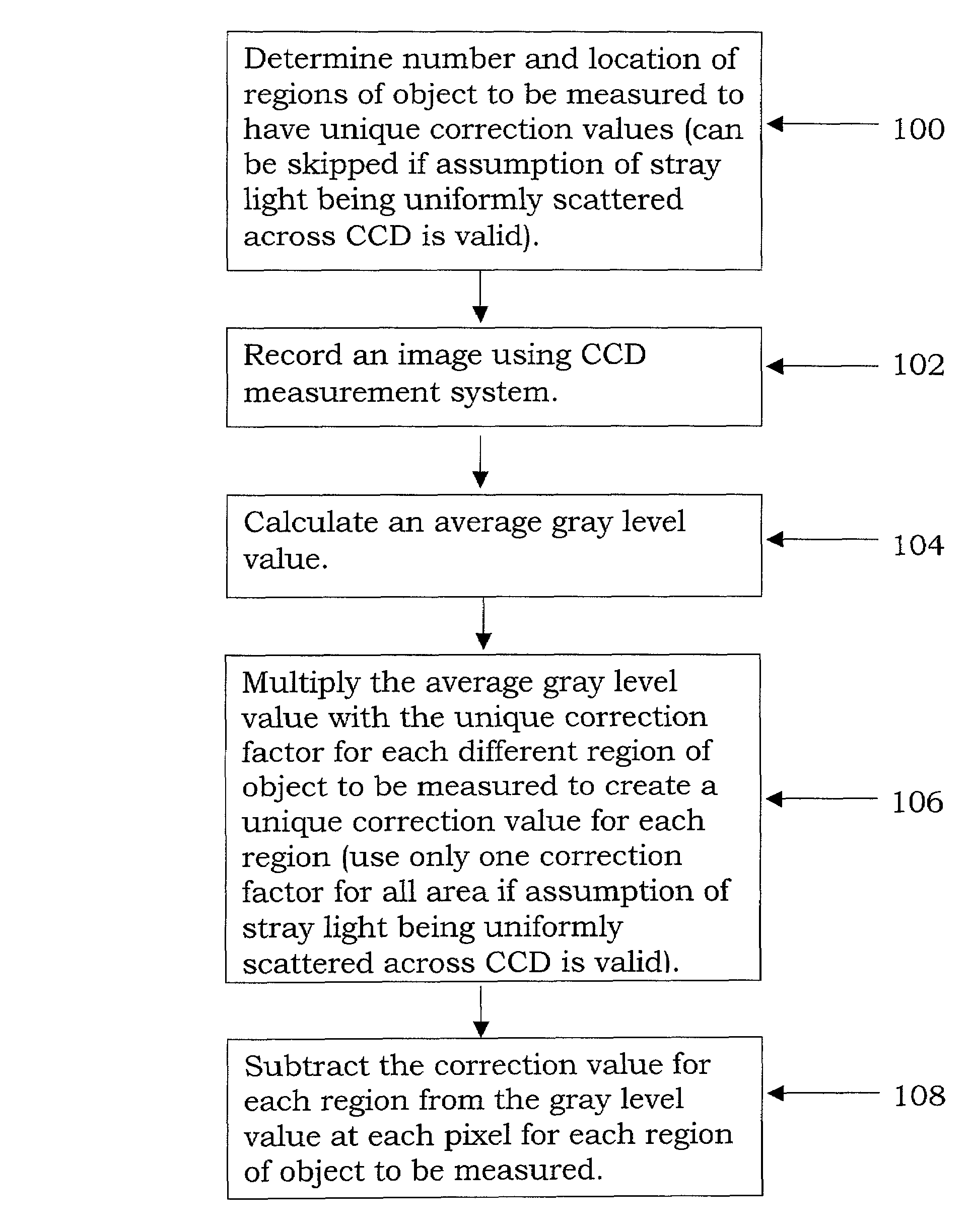
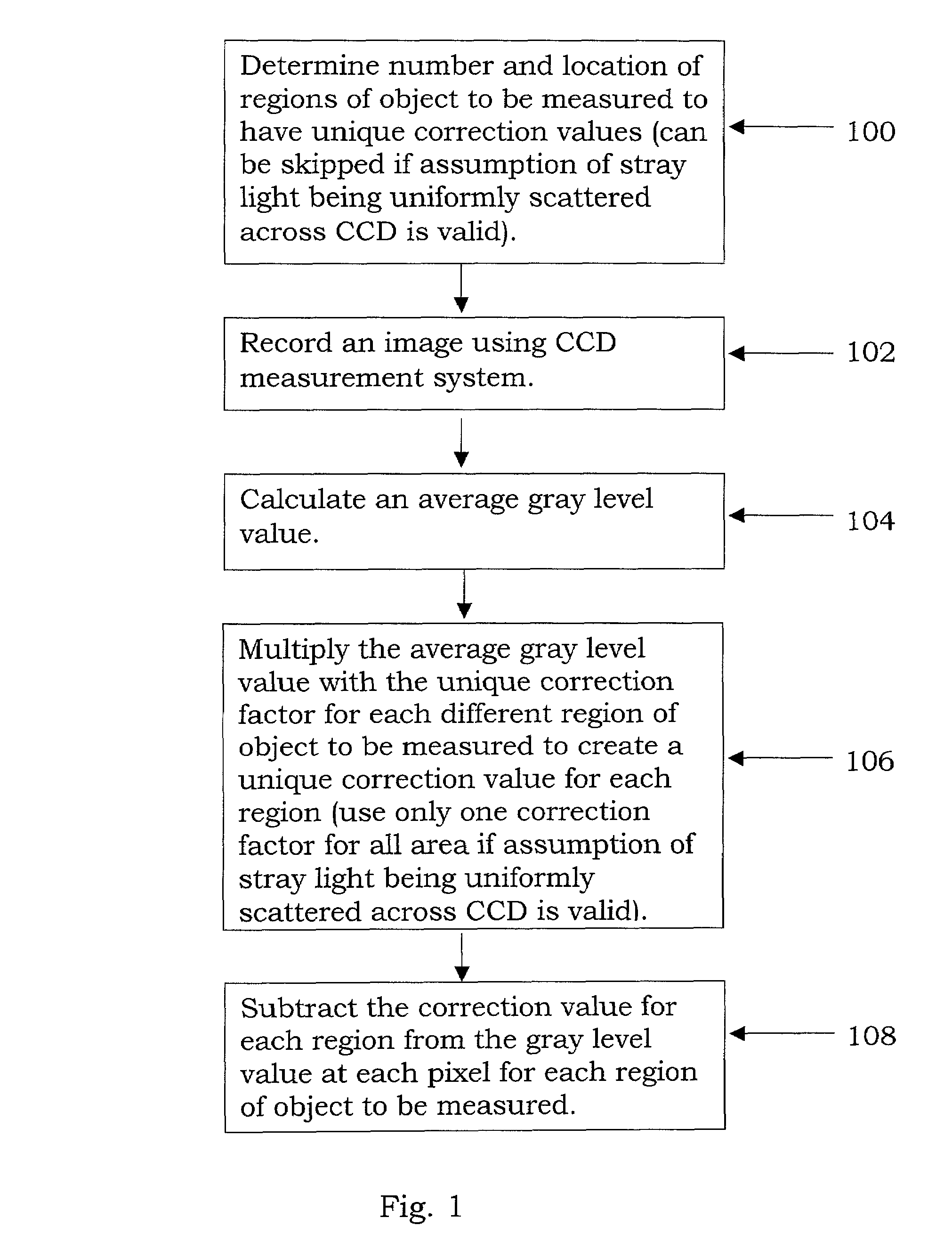
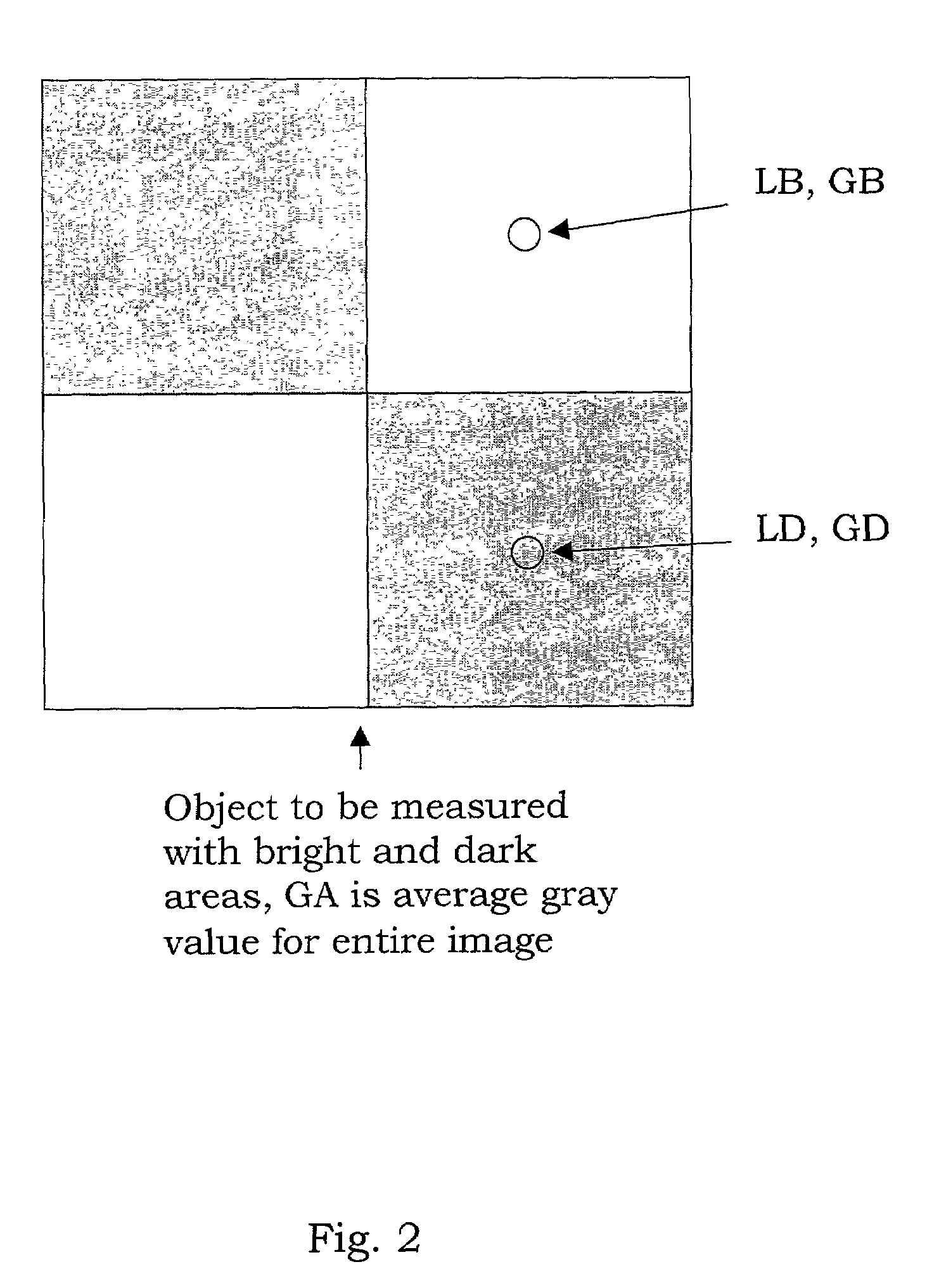
Stray light correction method for imaging light and color measurement system
ActiveUS6975775B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease grayscaleTelevision system detailsImage enhancementGray levelOptoelectronics
A stray light correction method for image light and color measurement system, uses a solid-state light detector array such as a charge-coupled device to record an image, so that a gray level value for each pixel of the solid-state light detector array is obtained. An average gray level value of the solid-state light detector array is calculated based on the gray level value for each pixel. The average gray level value is further multiplied with a stray light factor to obtain a correction value. The gray level value of each pixel is then subtracted with the correction value, such that the stray light effect can be eliminated.
Owner:RADIANT ZEMAX
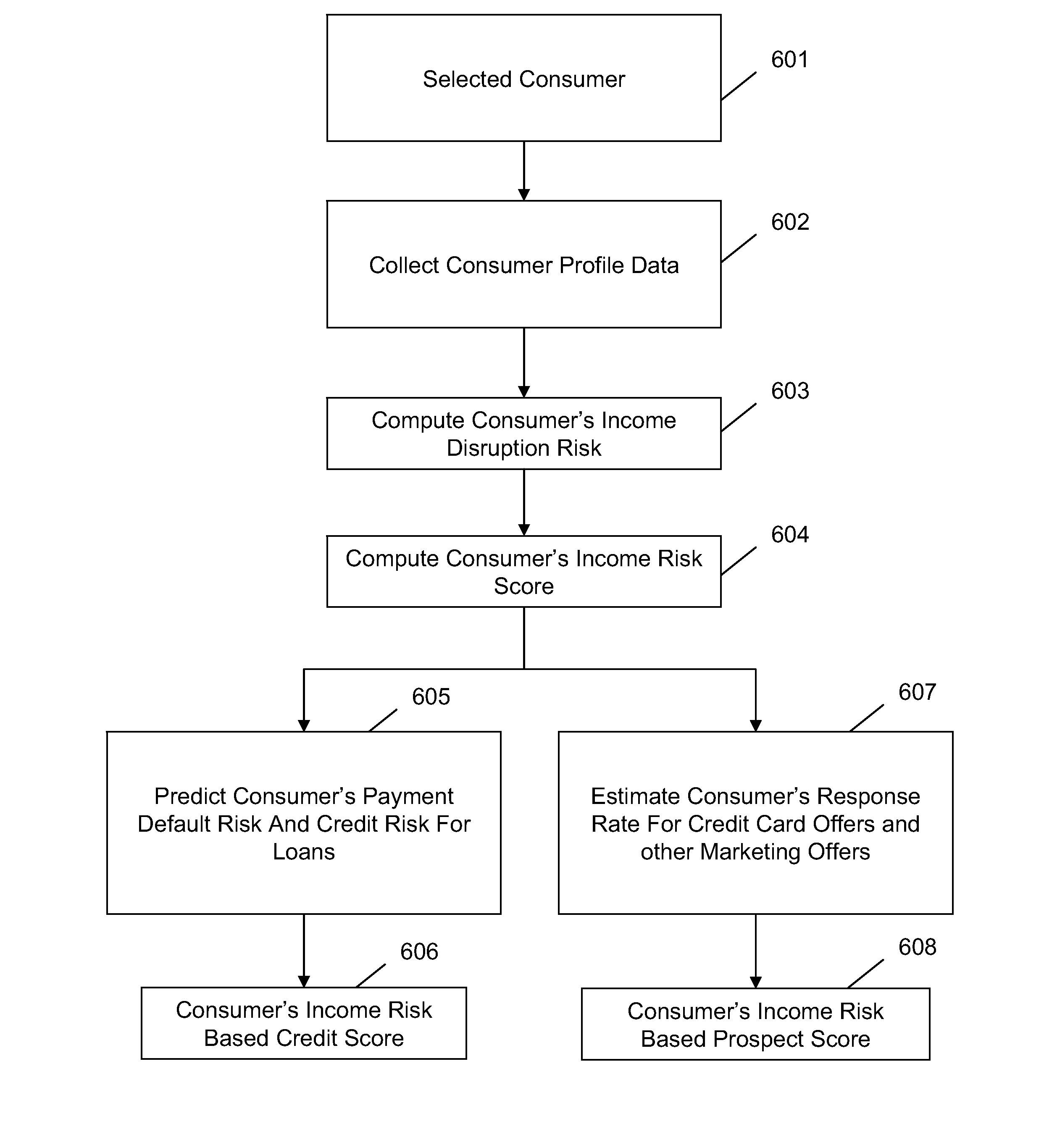
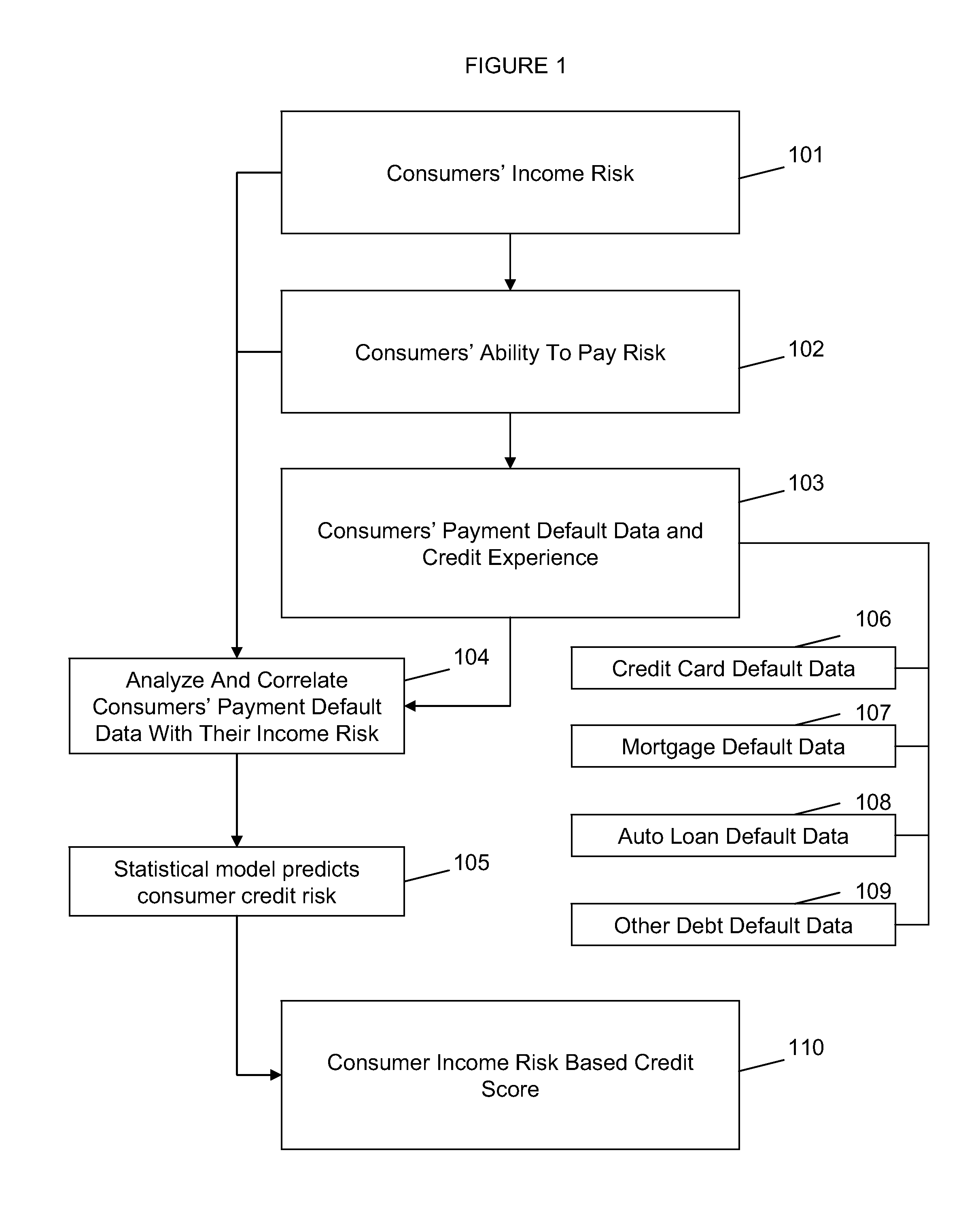
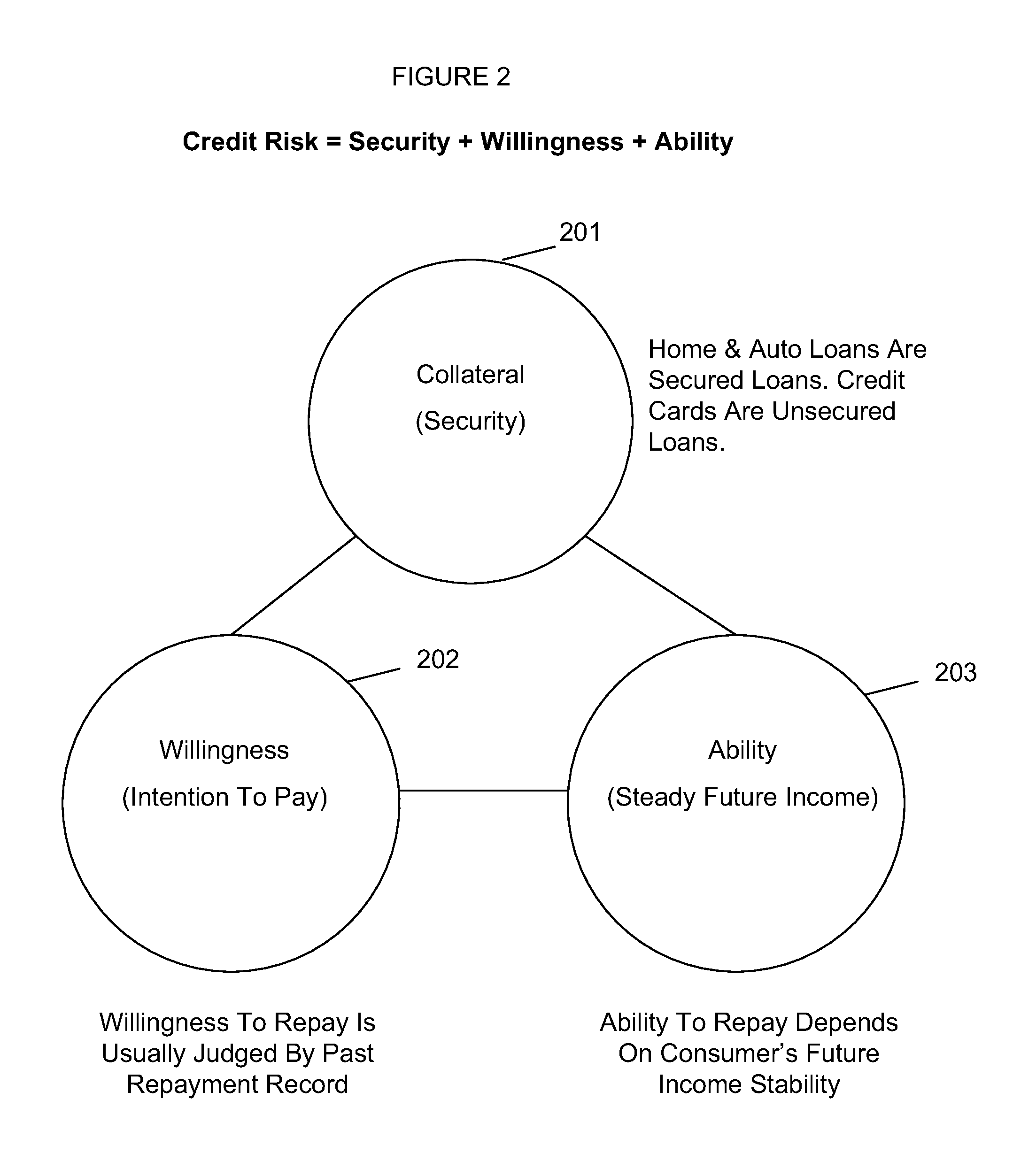
System and method for predicting consumer credit risk using income risk based credit score
InactiveUS20110078073A1Accurate assessmentImprove acquisitionFinanceIncome lossProspective evaluation
Systems and methods are described for scoring consumers' credit risk by determining consumers' income risk and future ability to pay. Methods are provided for measuring consumers' income risk by analyzing consumers' income loss risk, income reduction risk, probability of continuance of income, and economy's impact on consumers' income. In one embodiment, a method is provided to evaluate an individual's creditworthiness using income risk based credit score thereby providing creditors, lenders, marketers, and companies with deeper, new insights into consumer's credit risk and repayment potential. By predicting consumers' income risk and the associated creditworthiness the present invention increases the accuracy and reliability of consumers' credit risk assessments, results in more predictive and precise consumer credit scoring, and offers a new method of rendering a forward-looking appraisal of an individual's ability to repay a debt or the ability to pay for products and services.
Owner:SCORELOGIX
System for detecting and analyzing body motion
InactiveUS20070032748A1Performed efficiently and accuratelyAccurate measurementPerson identificationInertial sensorsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
A portable sensor system that uses acceleration-insensitive, three-dimensional angle sensors located at various points on the patient's body, and collects data on the frequency and nature of the movements over extended periods of time.
Owner:608442 BC
System and method to provide routing control of information over data networks
InactiveUS7222190B2Cost-effective useAccurate measurementError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityData traffic
A system and a method for controlling routing of data over multiple networks. Accordingly, network users can define specific flow polices to ensure that a particular flow of data traffic maintains an acceptable level of performance, such as in terms of latency, loss, jitter, or an acceptable level usage that includes cost and bandwidth management across multiple networks.
Owner:INTERNAP HLDG LLC
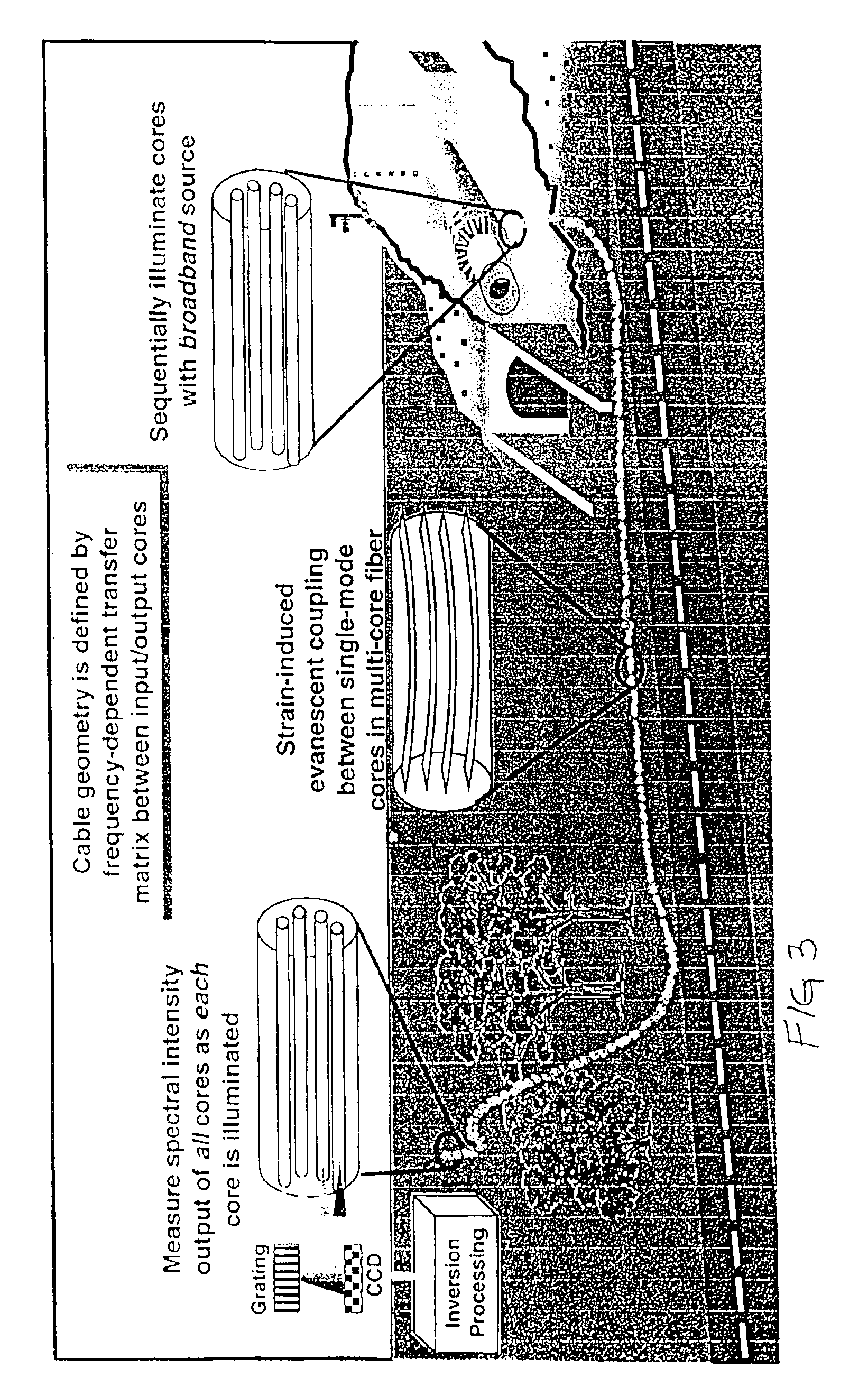
Fiber optic sensor for precision 3-D position measurement
InactiveUS6888623B2Accurate measurementForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringFiber optic sensor
The central system component of the present invention is a flexible “smart cable” which enables accurate measurement of local curvature and torsion along its length. These quantities are then used to infer the position and attitude of one end of the cable relative to the other. Sufficiently accurate measurements of the local curvature and torsion along the cable allow reconstruction of the entire cable shape, including the relative position and orientation of the end points. The smart cable for making these measurements comprises a multicore optical fiber, with individual fiber cores constructed to operate in the single mode regime, but positioned close enough to cause cross-talk (mode coupling) between cores over the length of the fiber. This cross-talk is very sensitive to the distribution of strains (curvature and torsion) along the cable.
Owner:DYNAMICS TECH
Method and system for analysis of intended meaning of natural language
InactiveUS7526466B2Flexible and efficient natural language interfaceAccurate measurementSemantic analysisChaos modelsData treatmentHand held devices
A computer implemented data processor system automatically disambiguates a contextual meaning of natural language symbols to enable precise meanings to be stored for later retrieval from a natural language database, so that natural language database design is automatic, to enable flexible and efficient natural language interfaces to computers, household appliances and hand-held devices.
Owner:DATACLOUD TECH LLC
Transducer for embedded bio-sensor using body energy as a power source
InactiveUS20050261563A1Improve accuracyAccurate measurementTelemedicineEndoradiosondesMuscle tissueVoltage pulse
Provided is a bio-sensor system which utilizes radio frequency identification technology and which includes a remote transponder in wireless communication with an implantable on-chip transponder. A power supply collects alternating current voltage pulses from an electro-active polymer generator embedded in muscle tissue for generating power for the on-chip transponder. The power supply is specifically adapted to provide a stable and precise sensor reference voltage to a sensor assembly to enhance the accuracy of measurements of a physiological parameter of a patient. The remote transponder receives data representative of the physiological parameter such as glucose concentration levels. The data is processed and transmitted to the remote transponder by the on-chip transponder. The precision and stability of the sensor reference voltage is enhanced by the specific circuit architecture of a glucose sensor to allow for relatively accurate measurement of glucose concentration levels without the use of a microprocessor.
Owner:JAMM TECH INC
Hybrid magnetic-based and impedance-based position sensing
ActiveUS20070016007A1Improve accuracyLow costCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTransducerBody surface
A position sensing system includes a probe adapted to be introduced into a body cavity of a subject. The probe includes a magnetic field transducer and at least one probe electrodes. A control unit is configured to measure position coordinates of the probe using the magnetic field transducer. The control unit also measures an impedance between the at least one probe electrodes and one or more points on a body surface of the subject. Using the measured position coordinates, the control unit calibrates the measured impedance.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Method and apparatus for measuring stream availability, quality and performance
InactiveUS7010598B2Improve accuracyAccurate measurementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsApplication programming interfaceService provision
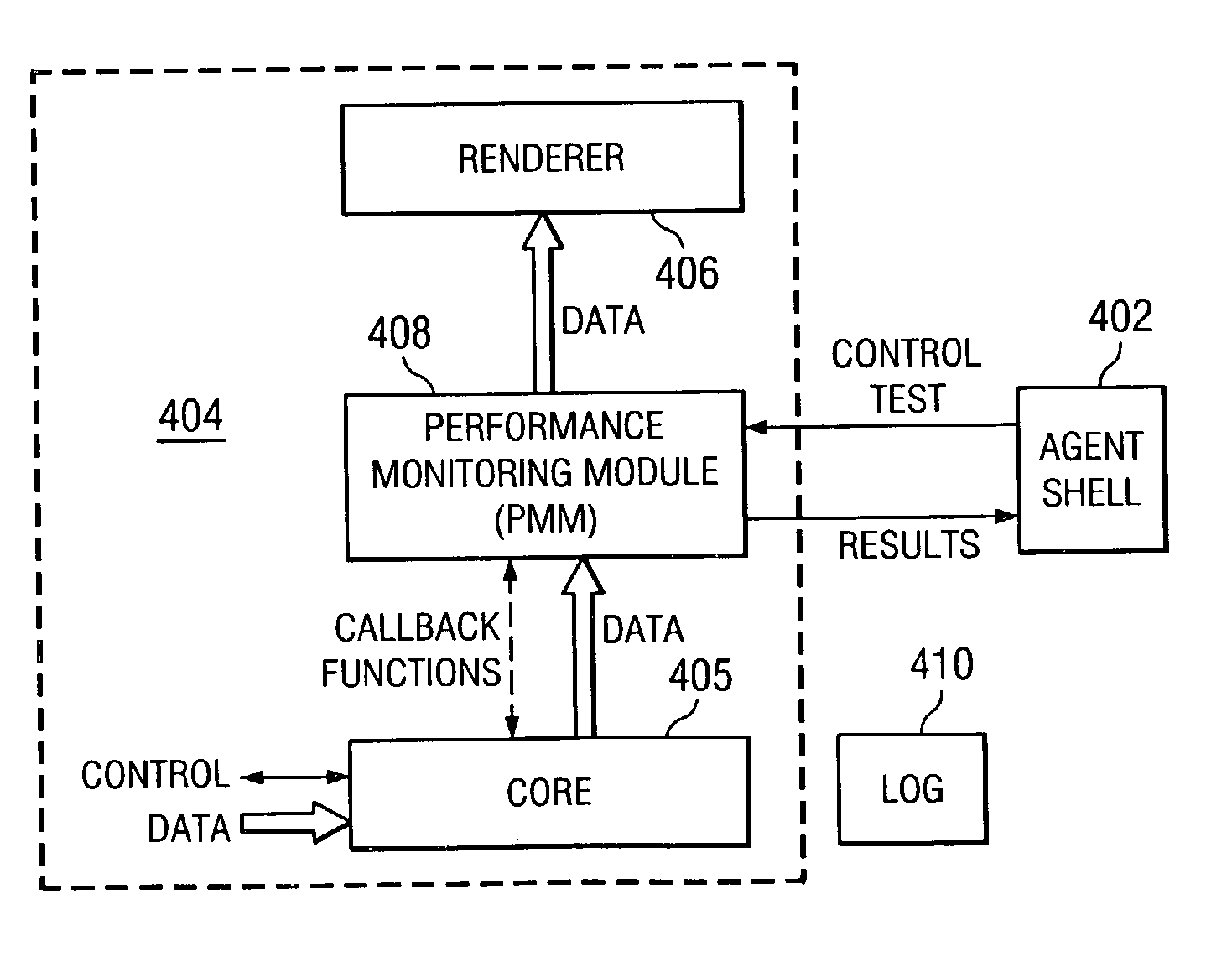
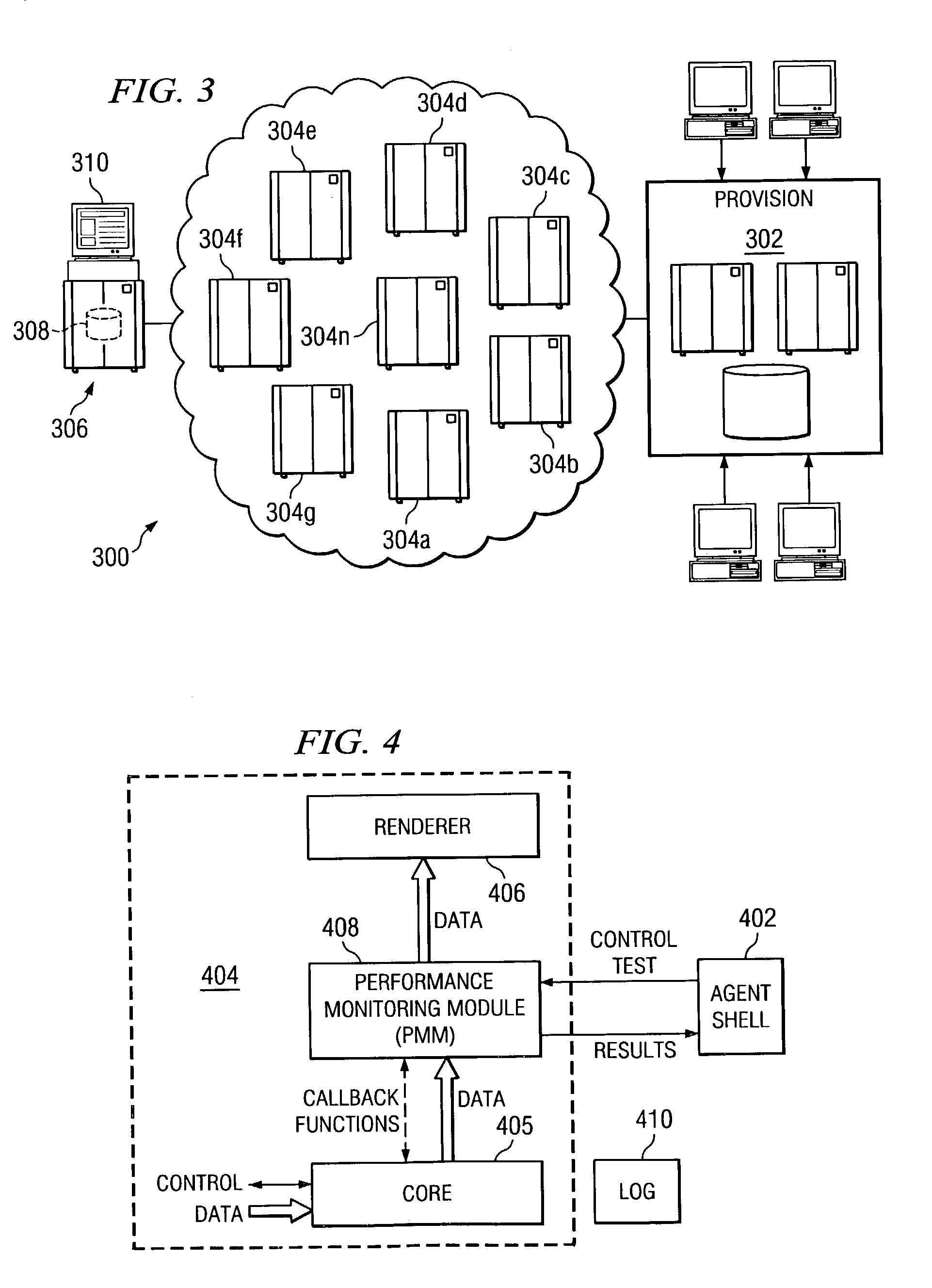
A streaming measurement agent designed to experience, measure, and report on a media stream as an actual end user would experience the stream. Preferably, agent resides transparently within a streaming media player itself so that it can monitor stream packet flows within the player as the measured streams are being played. In an illustrative embodiment, the agent comprises a performance monitoring module (PMM), which is software that resides in an interface between an existing core module and a renderer of a media player. The agent PMM intercepts each useful packet as it goes from the core to the renderer and, as a result, it is able to compute quality metrics about the playback. The agent functions “transparently” to the media player by presenting the core with an application programming interface (API) that emulates the API that the renderer normally presents to the core. Thus, when the core believes it is calling the renderer, it is actually calling the agent PMM, which can then receive all the packets from the core and process them. After computing relevant performance metrics using the packets it receives, the agent PMM calls the renderer. A set of performance agents can be managed by a service provider to enable a content provider to determine how a stream is perceived by end users.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Measurement methods and apparatus
InactiveUS20050057745A1Precise positioningImprove viewing effectAngle measurementActive open surveying meansMeasurement deviceLocation determination
A measurement device is provided that allows for determining distance, range and bearing of a target of interest. The distance, range and bearing to the target of interest are determined relative to the position of the measurement device and are stored in memory. The device is further operative to translate these relative positions of the target to an absolute position at the time of measurement, or, when the position of the measurement device becomes known. The absolute position of the measurement device may be determined utilizing GPS technologies or through the measurement of geophysical reference points. Measurement of the relative location of target(s) of interest is performed utilizing an electronic range finding device and elevation and heading sensors. The resulting information is stored in memory for conversions to vector information that may be utilized to generate, for instance, topographical images.
Owner:GEOSCAN TECH
Single unit surgical fastener and method
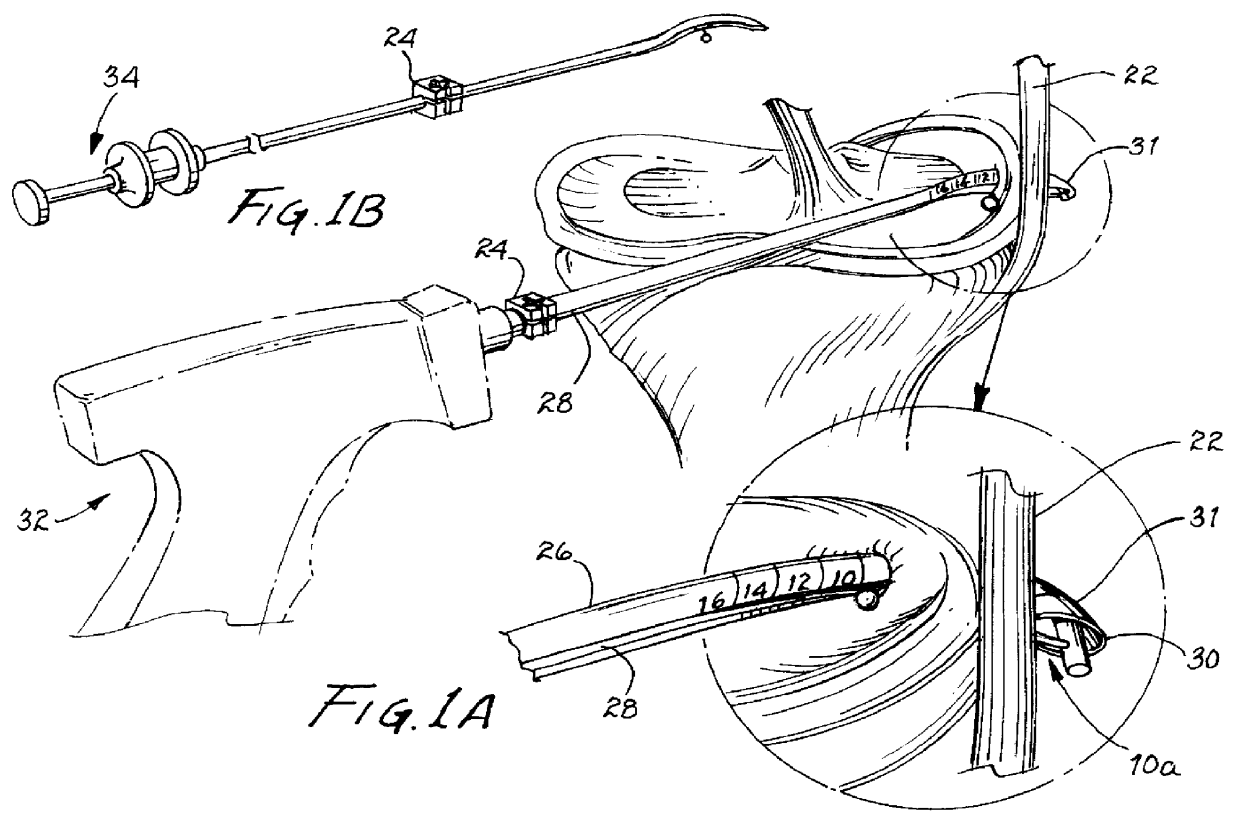
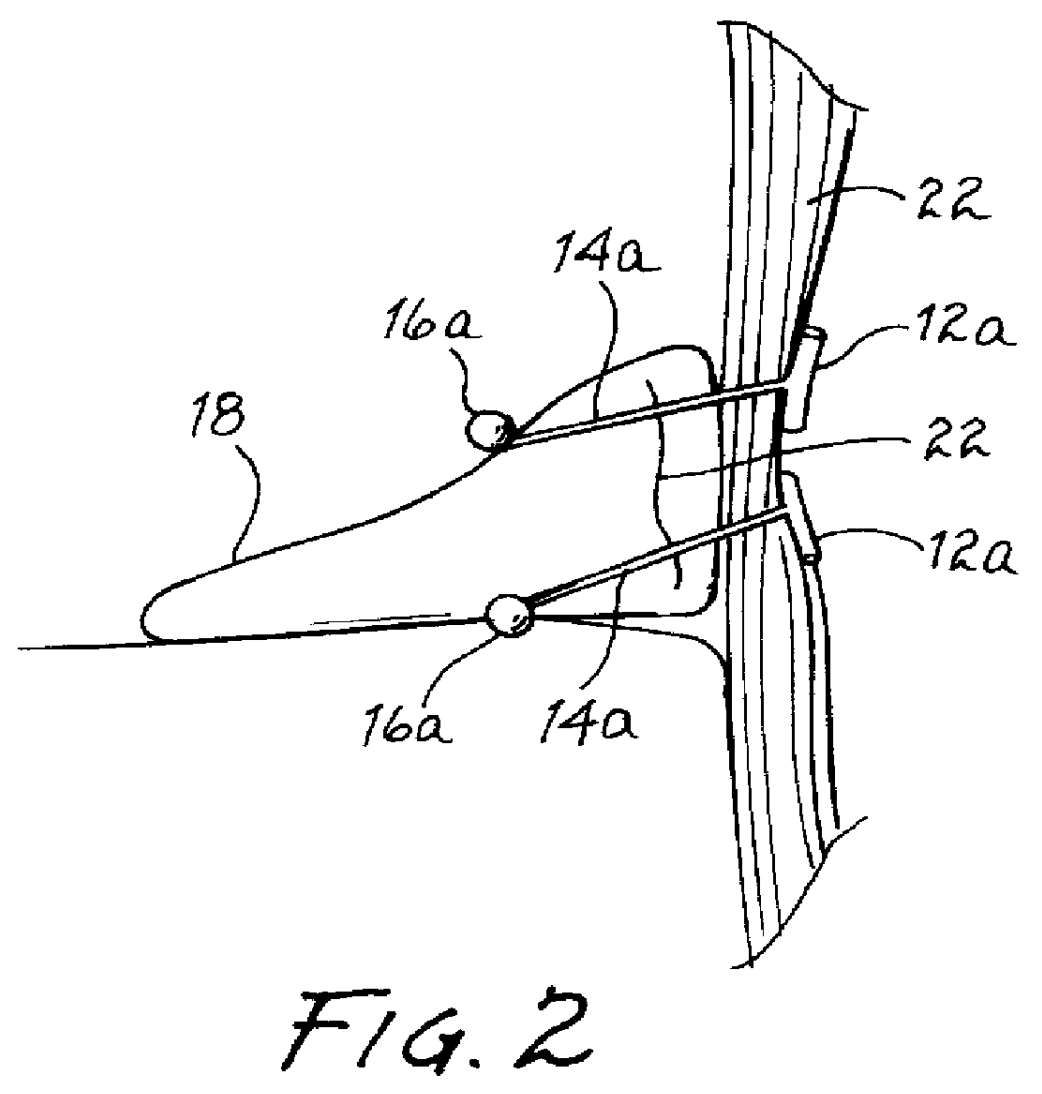
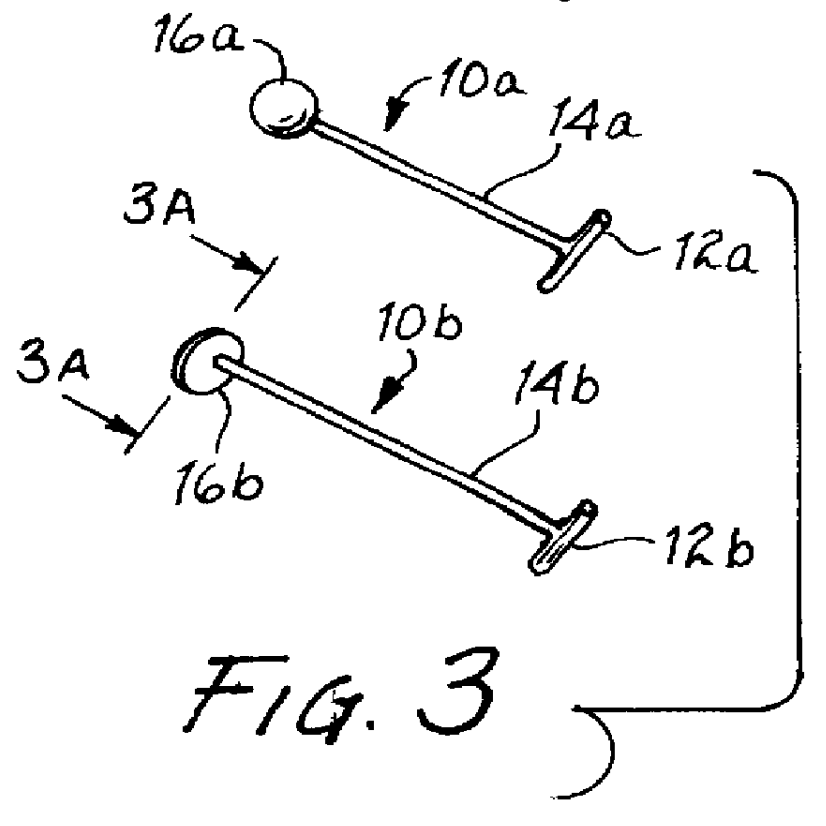
InactiveUS6039753AReduce riskAccurate measurementSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsMeniscal tissueEngineering
A single unit surgical fastener and system and method for repairing torn meniscus tissue in an arthroscopic, all-inside procedure. The desired length of the single unit surgical fastener is first determined by measuring the distance from the interior of the meniscus across the tear and across the joint capsule, and then a single unit surgical fastener of desired length is then inserted across the tear in one or more places through a curved, slotted cannula.
Owner:MEISLIN ROBERT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com