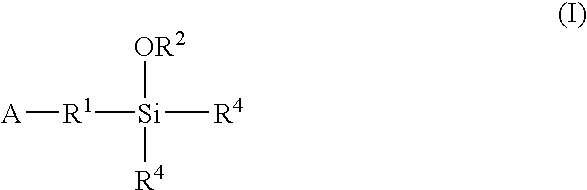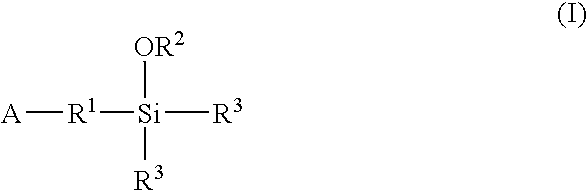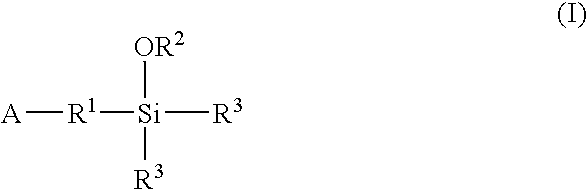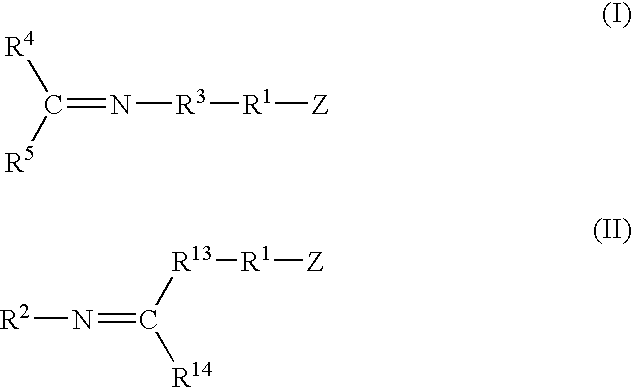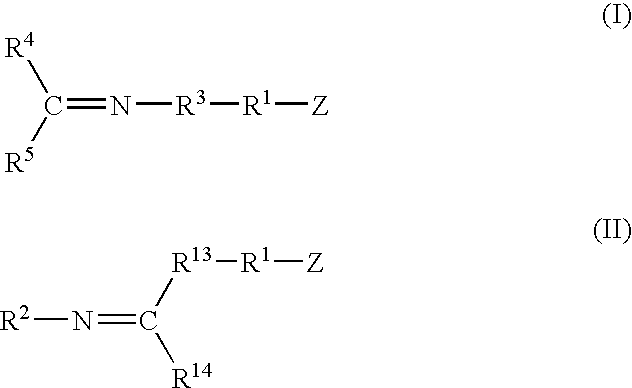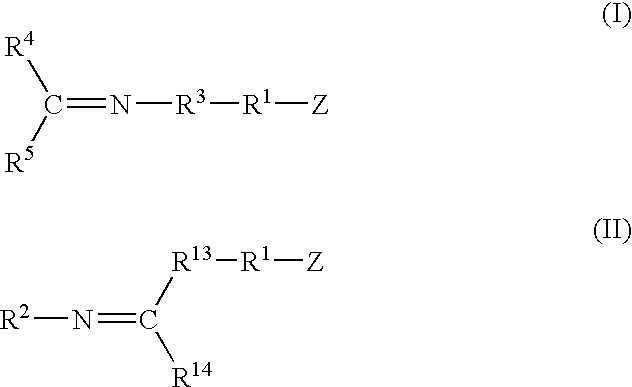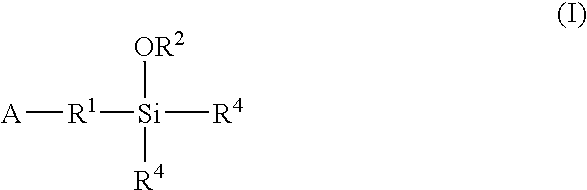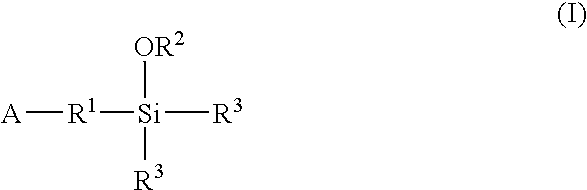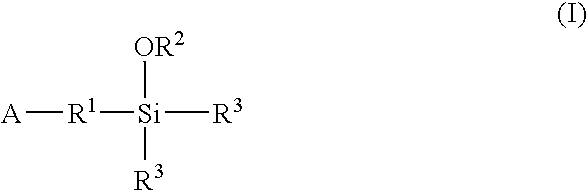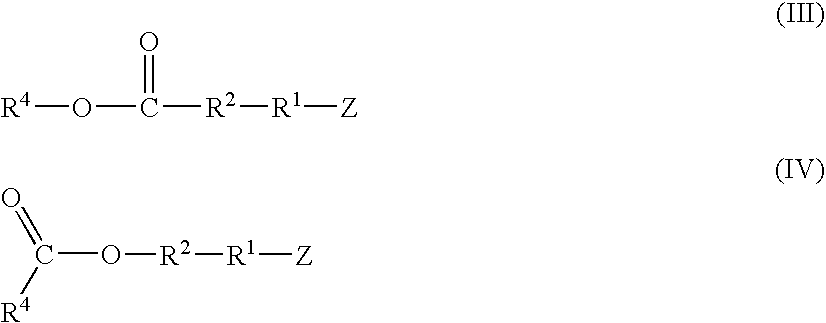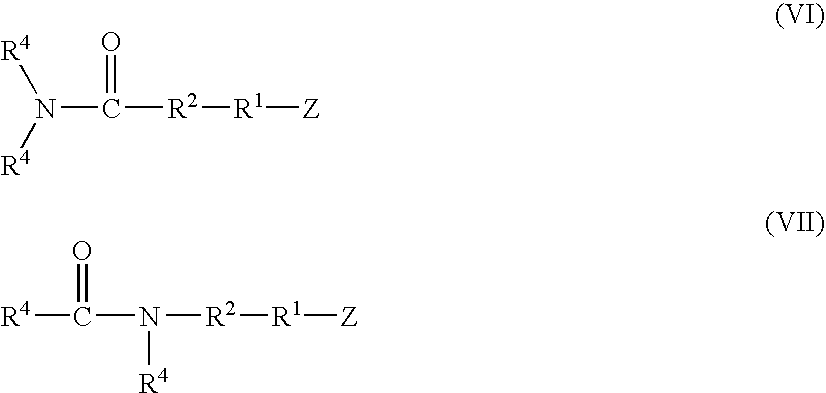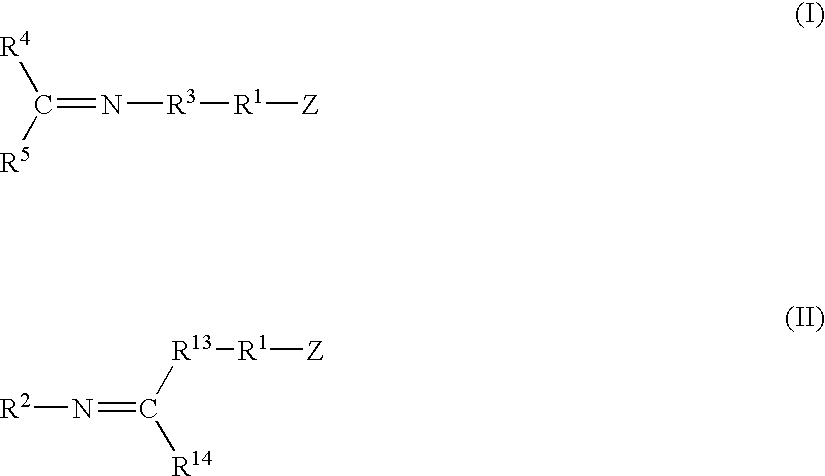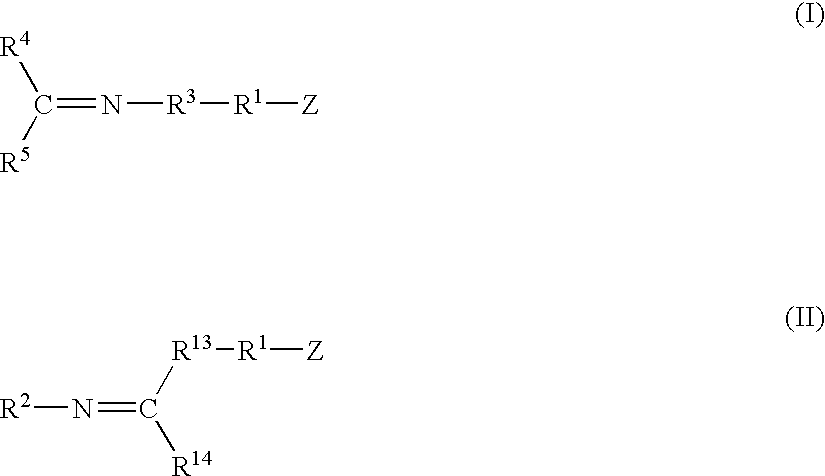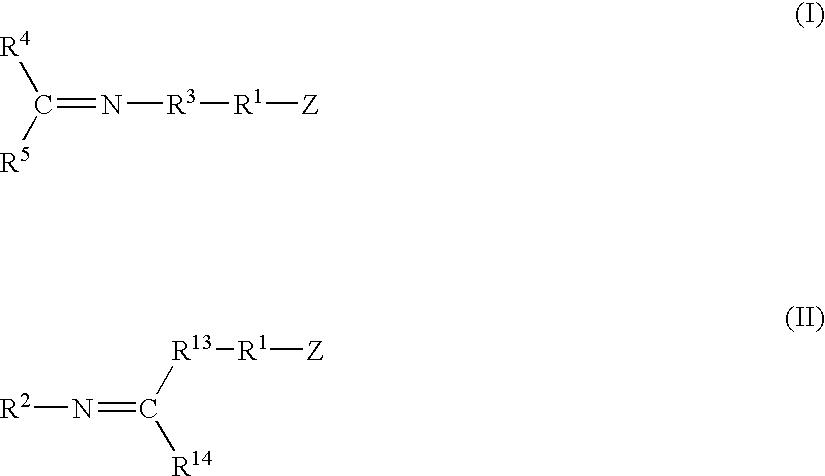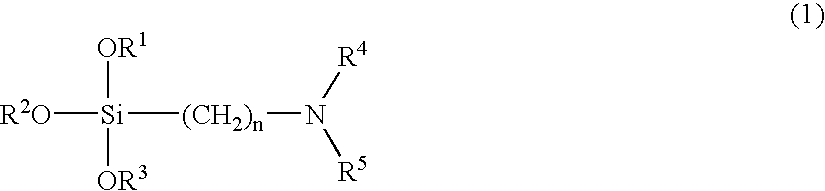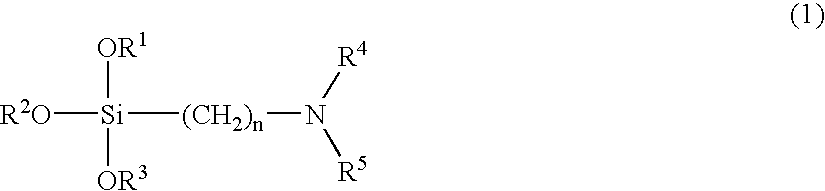Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
698 results about "Active polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
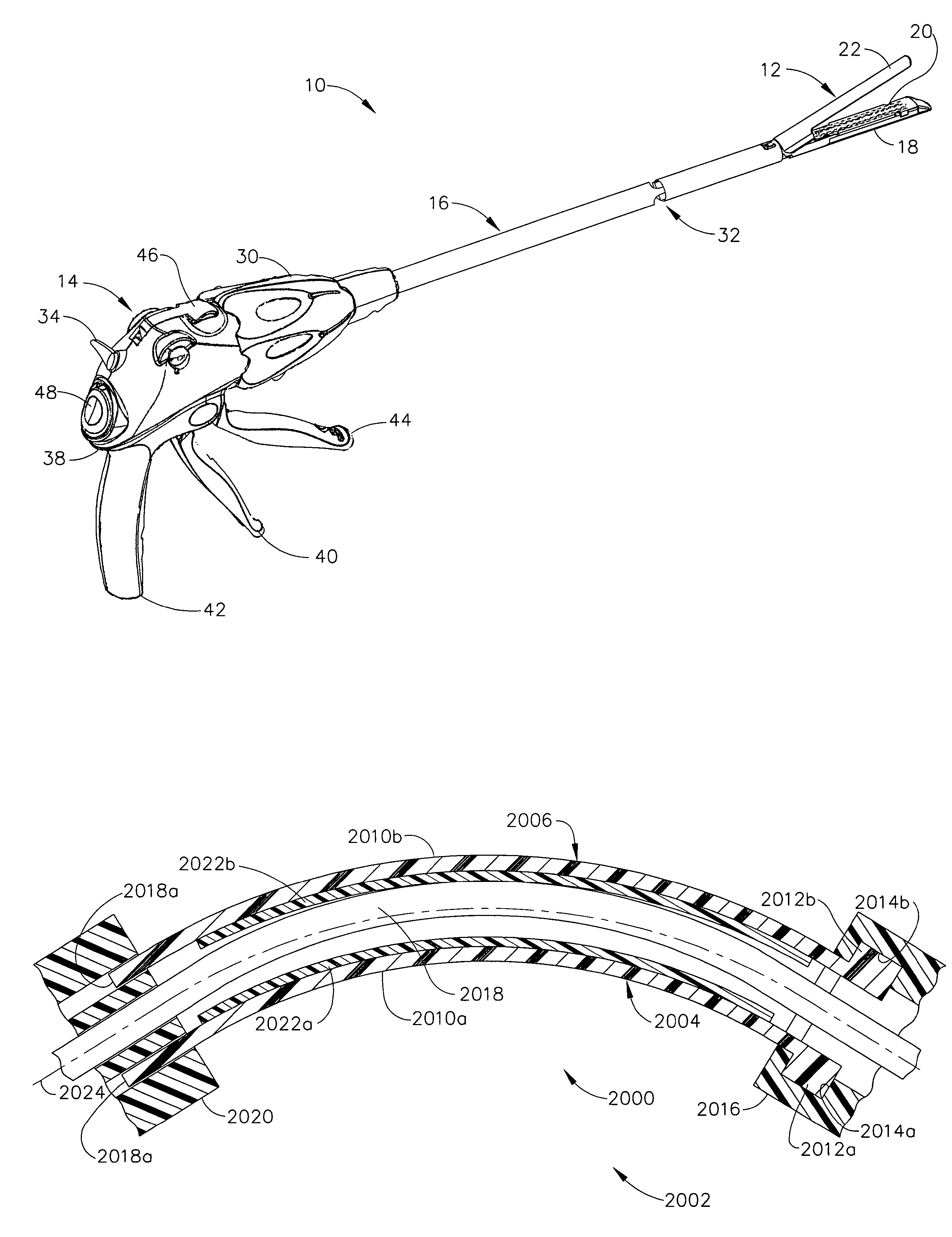
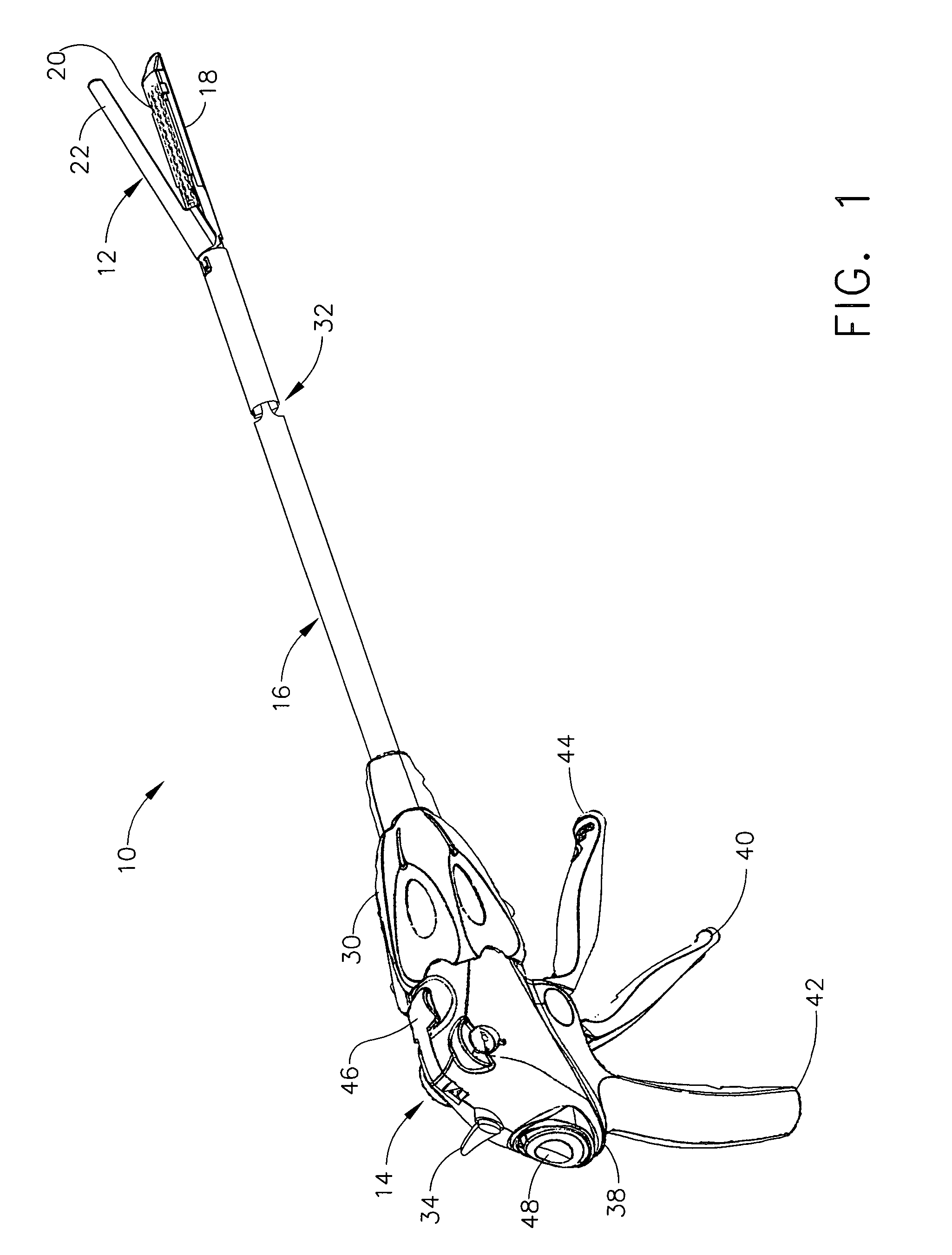
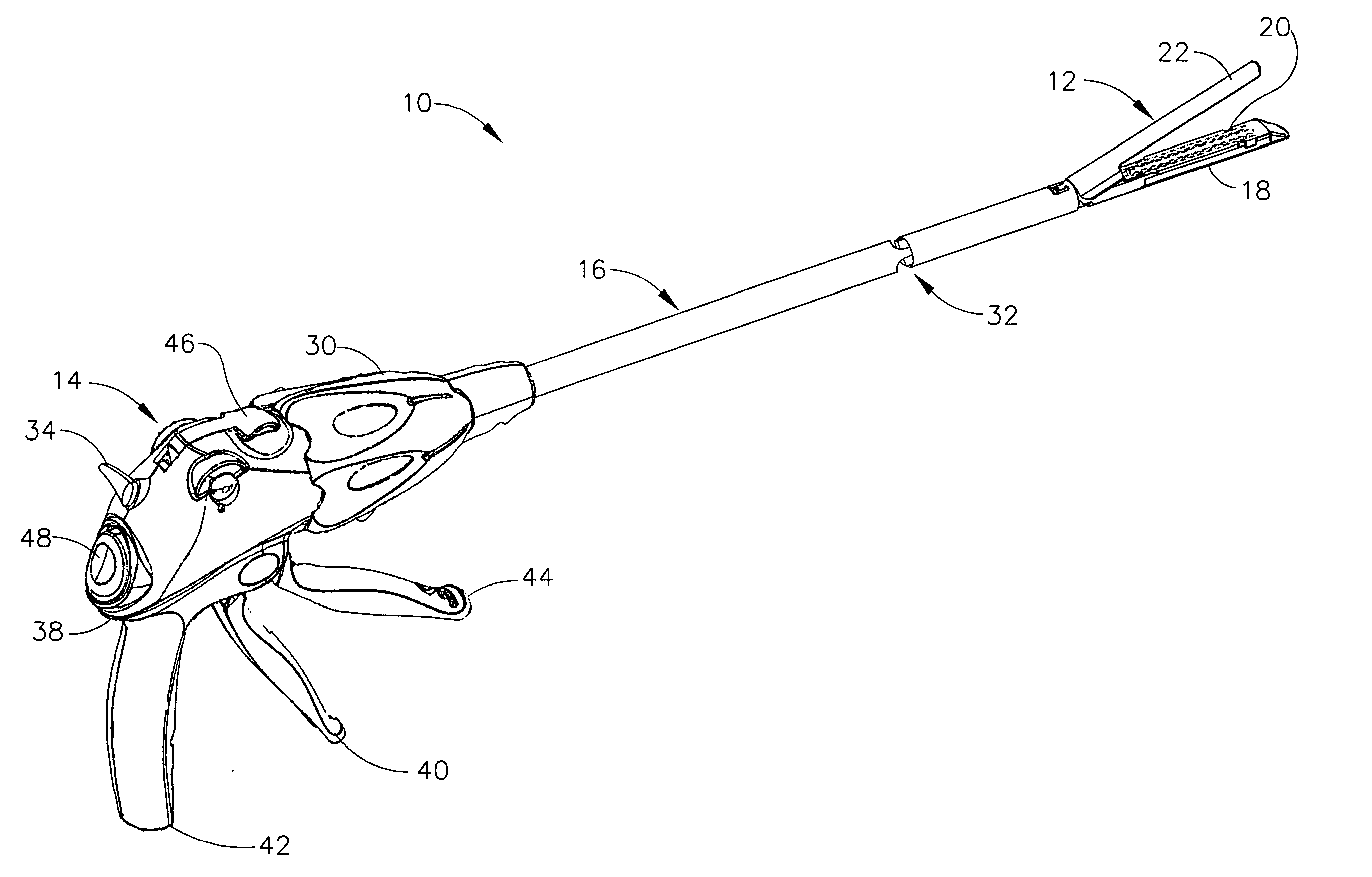
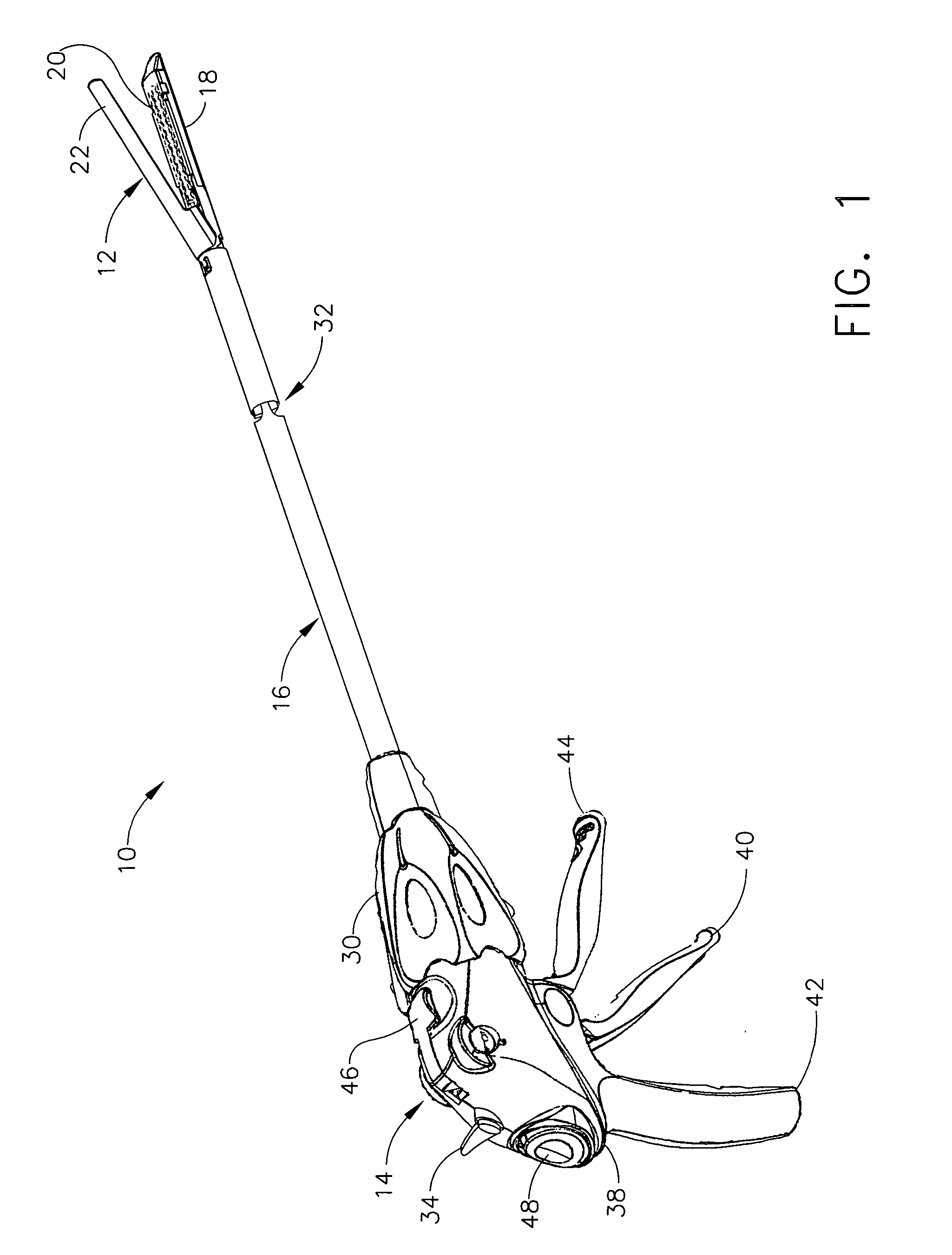
Surgical stapling instrument incorporating an electroactive polymer actuated firing bar track through an articulation joint
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument incorporating an electroactive polymer actuated firing bar track through an articulation joint
A surgical stapling instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use articulates an end effector (e.g., stapling and severing) that is actuated by a firing bar. An articulation mechanism in an elongate shaft incorporates electrically actuated polymer (EAP) actuators that laterally support the firing bar so that the firing bar is sufficiently constrained to avoid a blow-out, yet is guided without excessive friction and binding. Thereby, effective, consistent firing is accomplished without an undue increase in firing force required when the end effector is articulated.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Transducer for embedded bio-sensor using body energy as a power source
InactiveUS20050261563A1Improve accuracyAccurate measurementTelemedicineEndoradiosondesMuscle tissueVoltage pulse
Provided is a bio-sensor system which utilizes radio frequency identification technology and which includes a remote transponder in wireless communication with an implantable on-chip transponder. A power supply collects alternating current voltage pulses from an electro-active polymer generator embedded in muscle tissue for generating power for the on-chip transponder. The power supply is specifically adapted to provide a stable and precise sensor reference voltage to a sensor assembly to enhance the accuracy of measurements of a physiological parameter of a patient. The remote transponder receives data representative of the physiological parameter such as glucose concentration levels. The data is processed and transmitted to the remote transponder by the on-chip transponder. The precision and stability of the sensor reference voltage is enhanced by the specific circuit architecture of a glucose sensor to allow for relatively accurate measurement of glucose concentration levels without the use of a microprocessor.
Owner:JAMM TECH INC
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) where A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, R1 is a divalent organic group, R2 is a monovalent organic group, and each R4, which may be the same or different, is a monovalent organic group or a substituent defined by —OR5 where R5 is a monovalent organic group, with the proviso that A, R1, R2, R4, and R5 are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer. Also, the functionalized polymer and a vulcanizable composition containing the polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
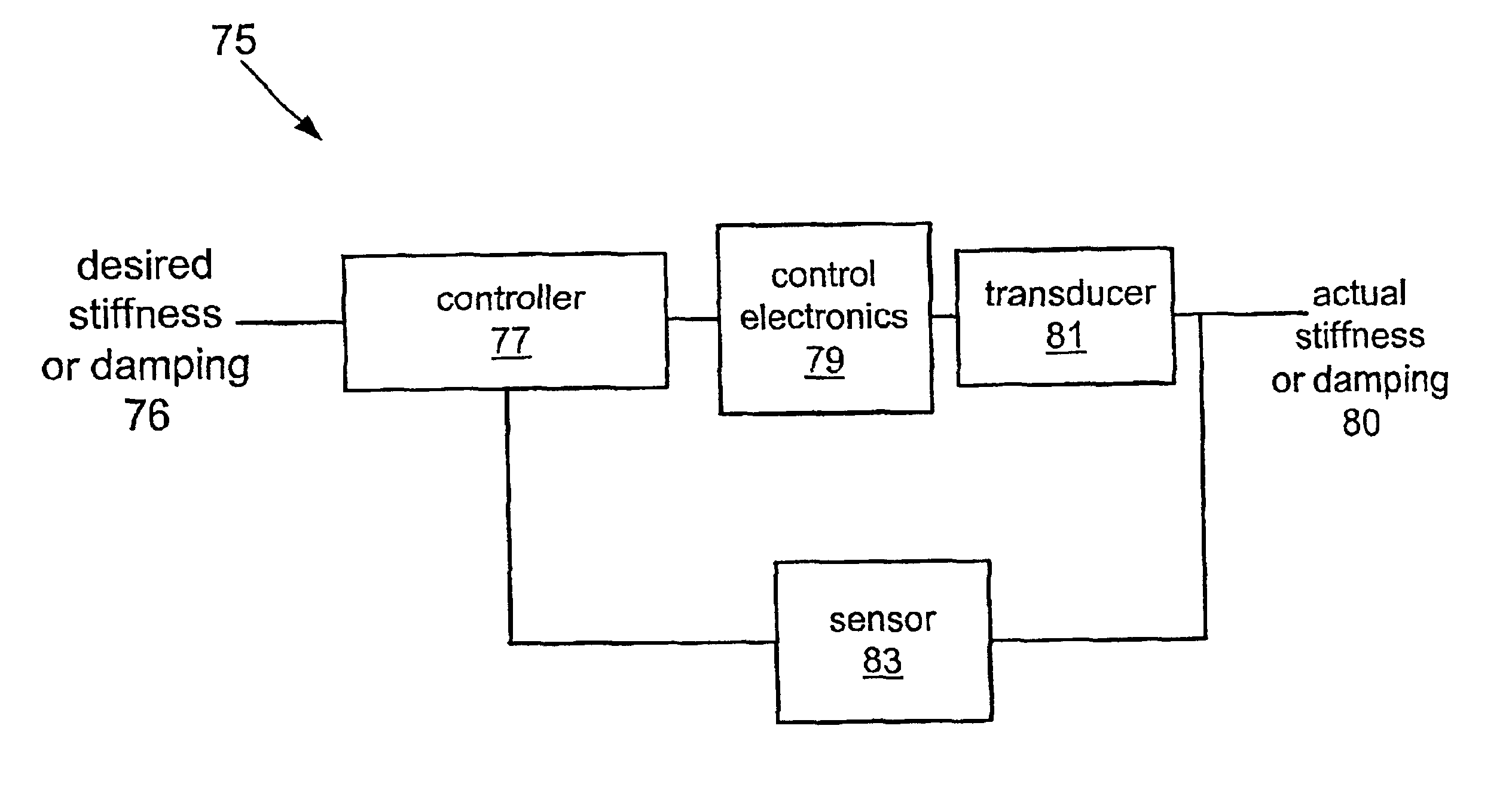
Variable stiffness electroactive polymer systems
InactiveUS6882086B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesResilient suspensionsActive polymerPolymer science
The invention relates to systems that provide variable stiffness and / or variable damping using an electroactive polymer transducer. Systems described herein offer several techniques that provide variable and controlled stiffness and / or damping. A transducer may be implemented using open loop control, thereby providing simple systems that inactively deliver a desired stiffness and / or damping performance. Alternately, closed loop control techniques permit electroactive polymer transducer designs that actively adapt the stiffness and / or damping performance of a system. Further, transducers may be implemented in a device whose stiffness changes with deflection of the polymer.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, where said pseudo-living polymer is characterized by having greater than about 85 percent of the polymer in the cis microstructure and less than about 3 percent of the polymer is in the 1,2- or 3,4-microstructure, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) or (II) where Z is a substituent that will react or interact with organic or inorganic fillers; R1 is a single bond or a divalent organic group; R2 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R13 or R14; R3 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R4 or R5; R13 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R14; R4 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R5; R14 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R13; and R5 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R4; with the proviso that each group attached to the imino carbon is attached via a carbon atom and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R13, R14 and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Electroactive polymer generators
InactiveUS7034432B1Speed up the conversion processImprove responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPre strainActive polymer
The present invention relates to transducers, their use and fabrication. The transducers convert between mechanical and electrical energy. Some transducers of the present invention include a pre-strained polymer. The pre-strain improves the conversion between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention also relates to devices including an electroactive polymer to convert between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention further relates to compliant electrodes that conform to the shape of a polymer included in a transducer. The present invention provides methods for fabricating electromechanical devices including one or more electroactive polymers.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
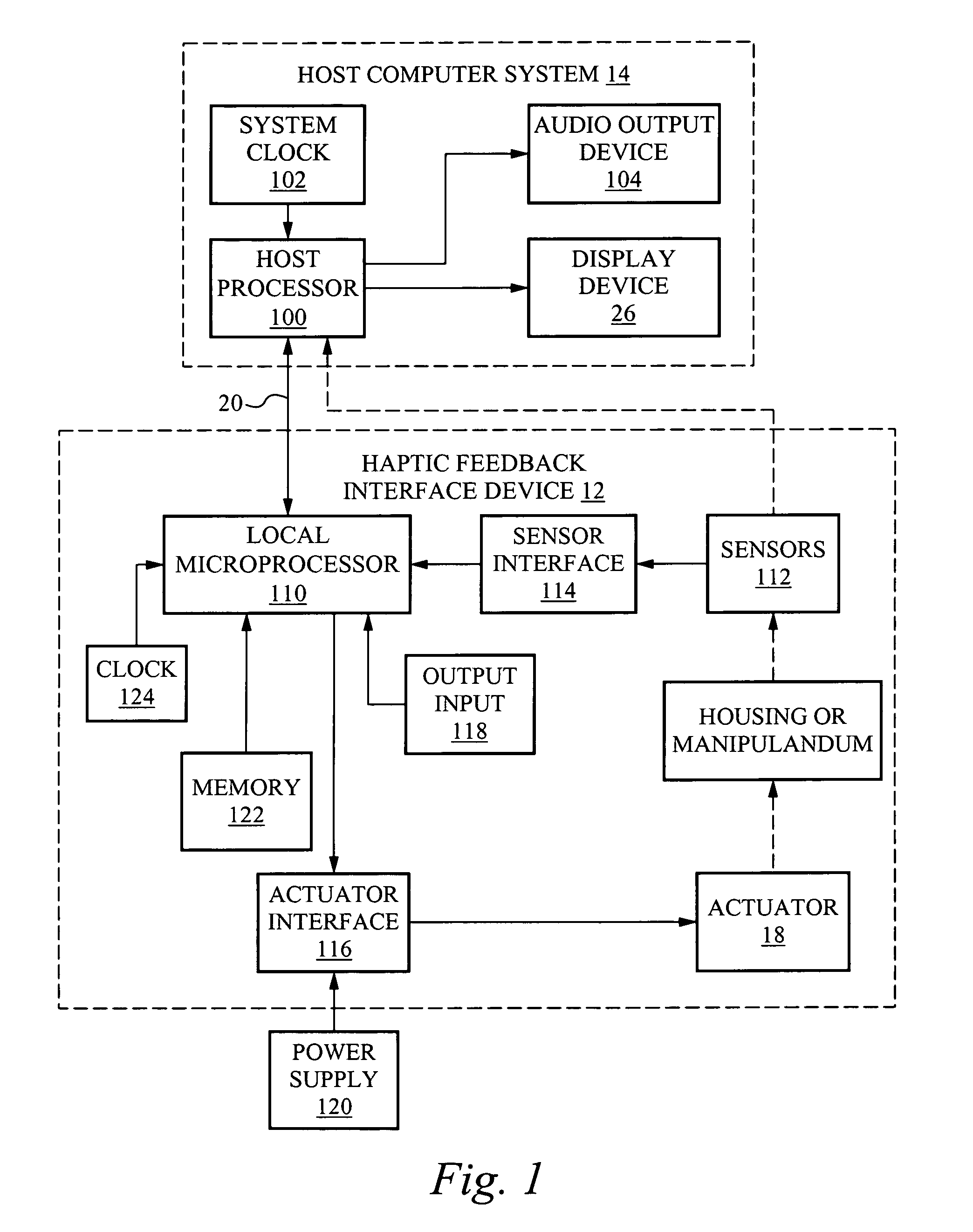
Haptic button and haptic device using the same
InactiveUS20070152974A1Easy to operateInput/output for user-computer interactionSingle unit pavingsActive polymerEngineering
A haptic button providing various stimulations to a user according to a current application and a haptic device using the same are provided. The haptic button includes an electro-active polymer having a flat shape, a pair of electrodes contacting two sides of the electro-active polymer, an electric circuit applying a predetermined voltage to the pair of electrodes, and a sensor sensing a button input from a user, wherein stimulation provided from the electro-active polymer to the user is changed by changing a waveform of the voltage according to a current application status.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
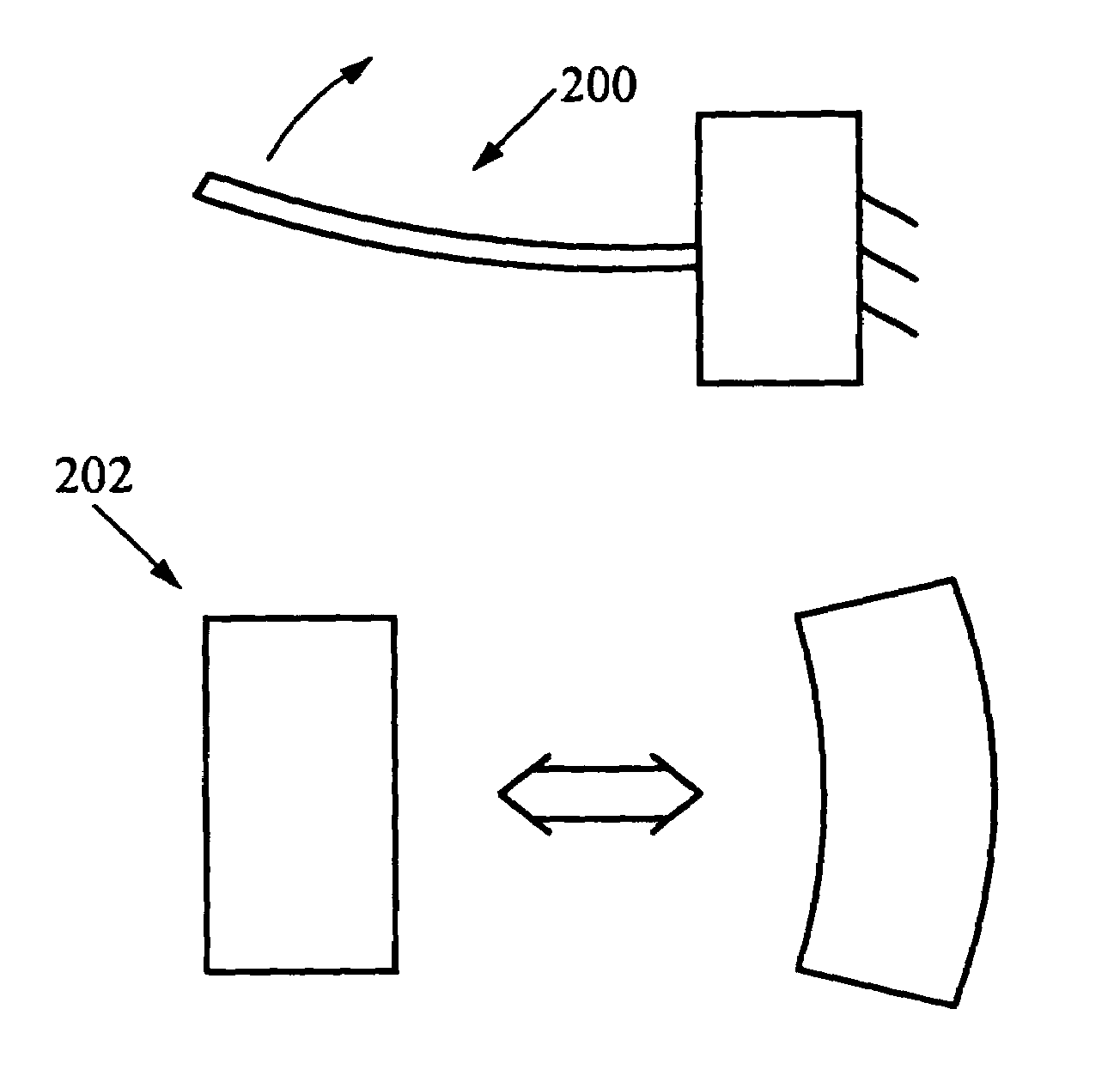
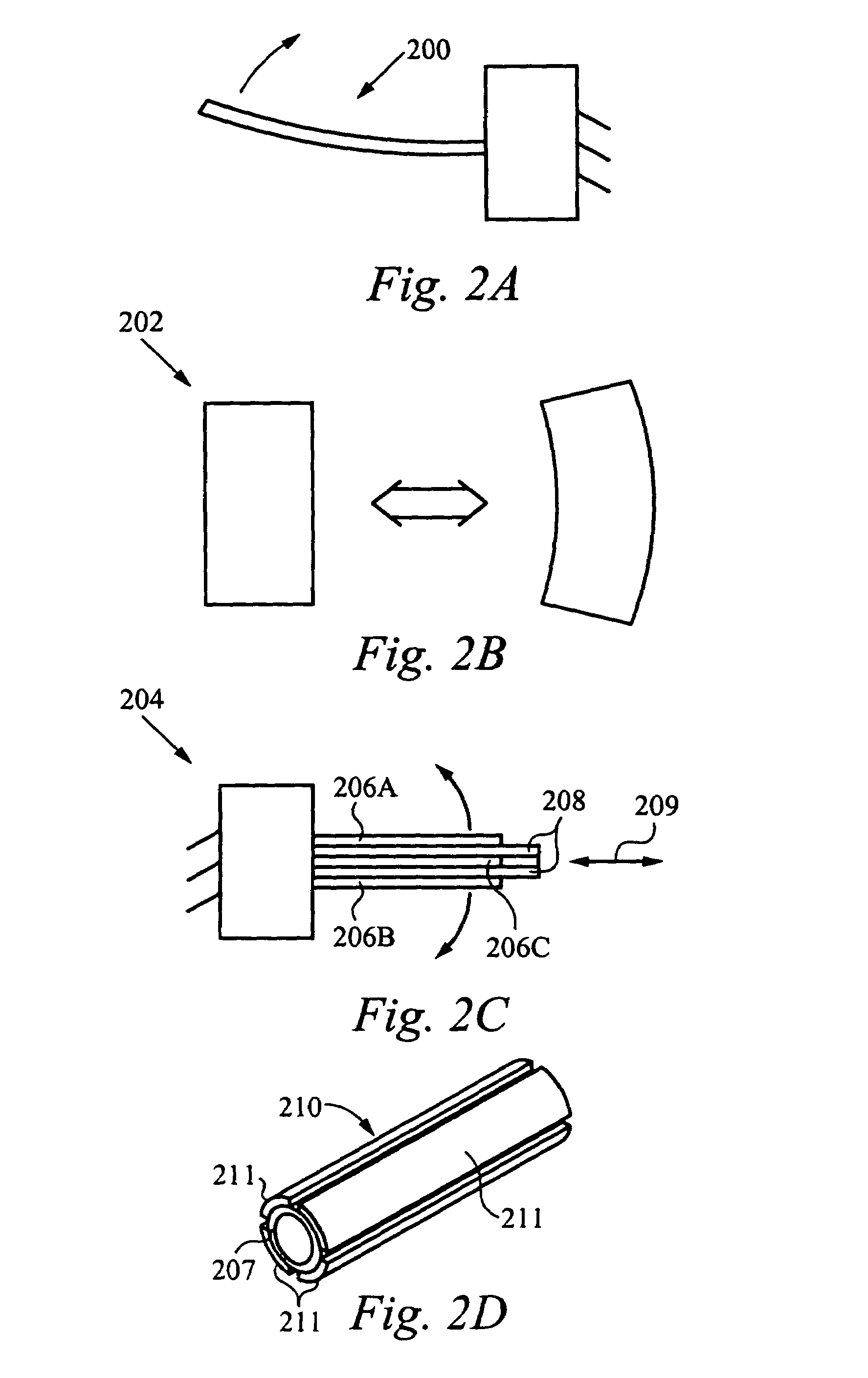
Haptic devices using electroactive polymers
ActiveUS7196688B2Low costEfficiently provideInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersActive polymerHaptic sensing
Haptic feedback interface devices using electroactive polymer (EAP) actuators to provide haptic sensations and / or sensing capabilities. A haptic feedback interface device is in communication with a host computer and includes a sensor device that detects the manipulation of the interface device by the user and an electroactive polymer actuator responsive to input signals and operative to output a force to the user caused by motion of the actuator. The output force provides a haptic sensation to the user. Various embodiments of interface devices employing EAP actuators are described, including embodiments providing direct forces, inertial forces, and braking forces.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
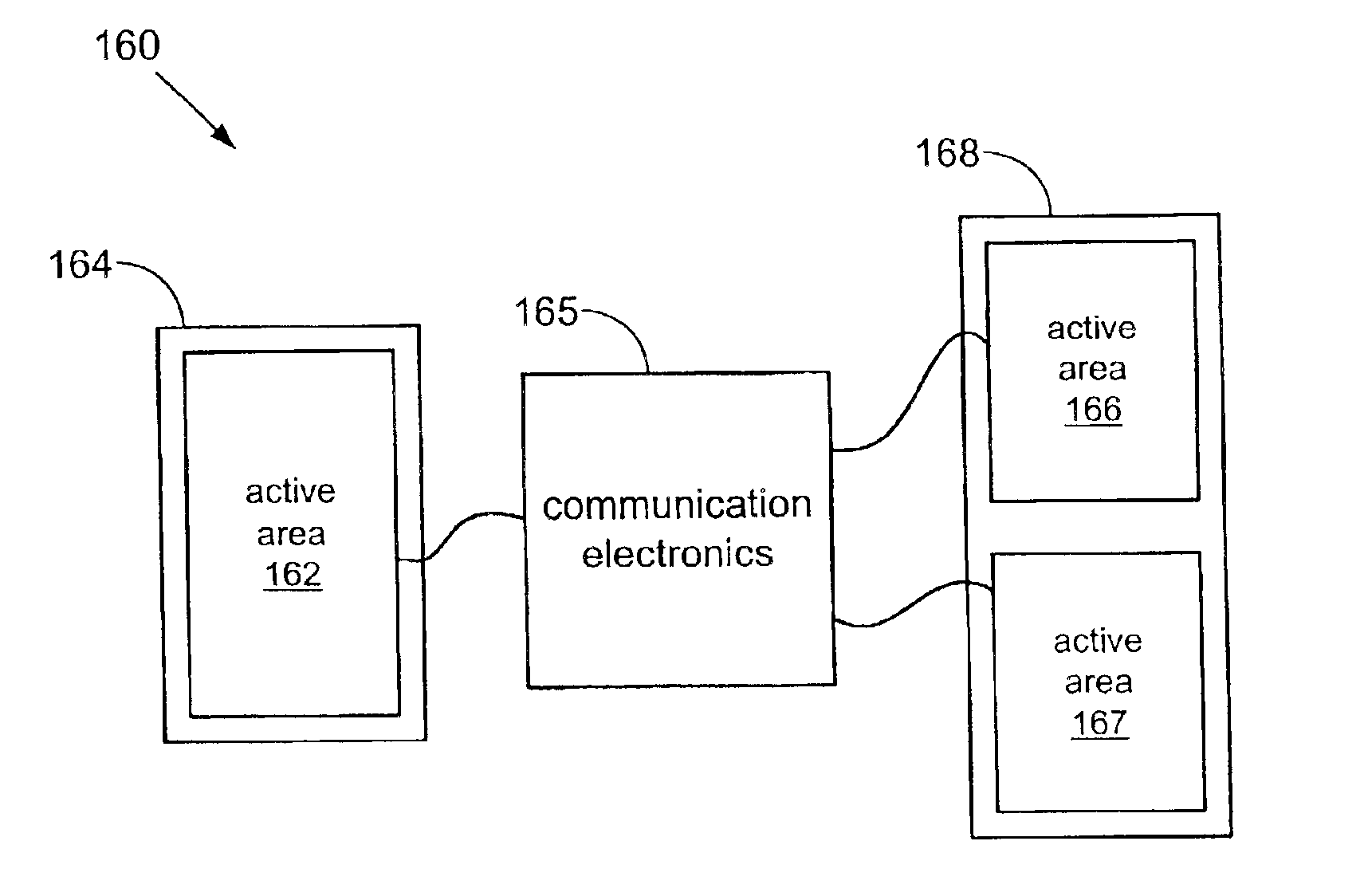
Master/slave electroactive polymer systems
InactiveUS6876135B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionActive polymerTransducer
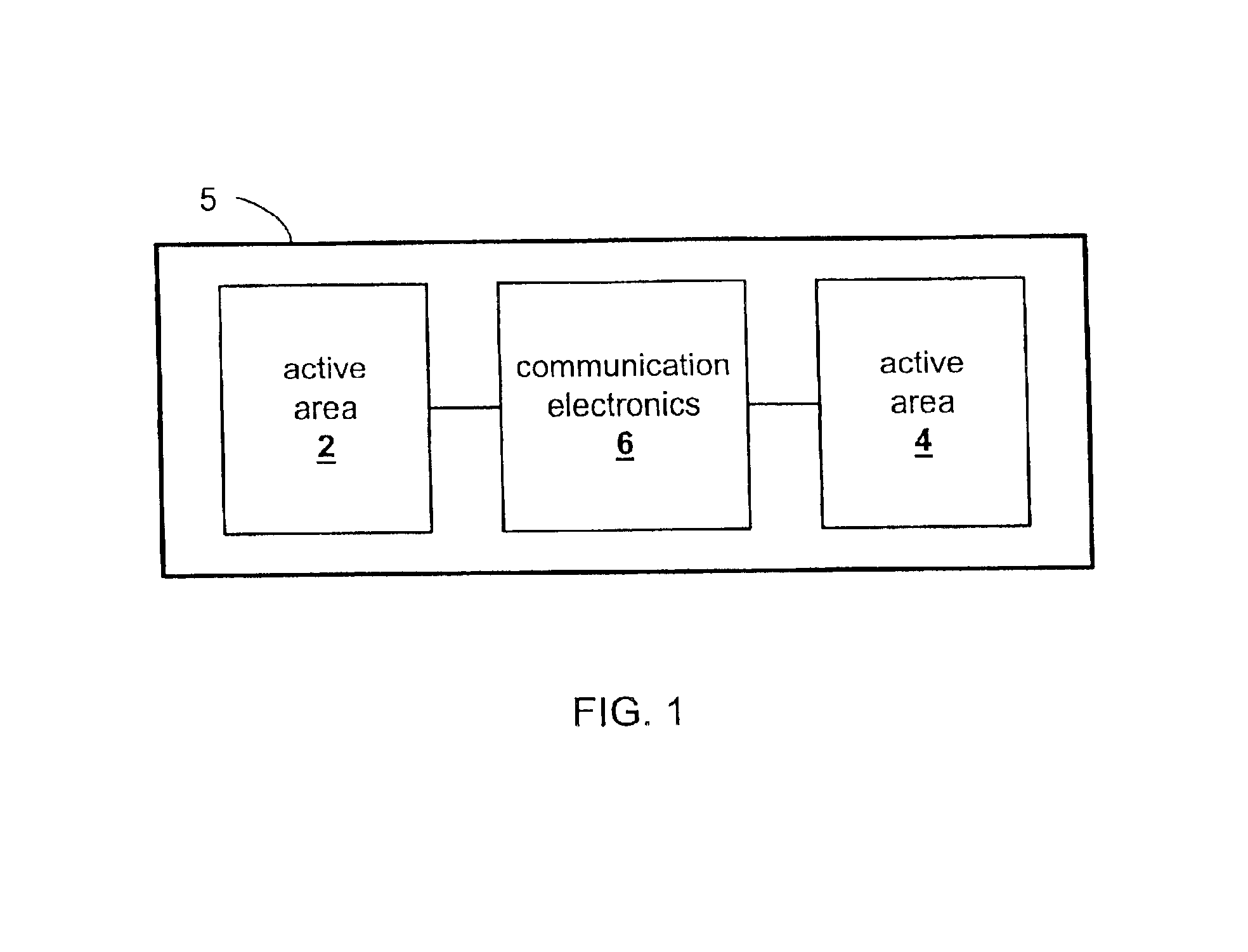
The present invention relates to improved devices, systems and methods that convert between electrical and mechanical energy. An electroactive polymer transducer converts between electrical and mechanical energy. An active area is a portion of an electroactive polymer transducer. The active area comprises a portion of an electroactive polymer and at least two electrodes that provide or receive electrical energy to or from the portion. The present invention relates to transducers and devices comprising multiple active areas that are in electrically communication. More specifically, the present invention relates to master / slave arrangements for multiple active areas disposed on one or more electroactive polymers. In a master / slave arrangement, a first active area deflects (a ‘master’), and a second active area reacts (a ‘slave’). Communication electronics in electrical communication with electrodes for the first active area and in electrical communication with electrodes for the second active area transfer electrical energy between the two active areas.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) where A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, R1 is a divalent organic group, R2 is a monovalent organic group, and each R4, which may be the same or different, is a monovalent organic group or a substituent defined by —OR5 where R5 is a monovalent organic group, with the proviso that A, R1, R2, R4, and R5 are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer. Also, the functionalized polymer and a vulcanizable composition containing the polymer.
Owner:ENEOS MATERIALS CORP
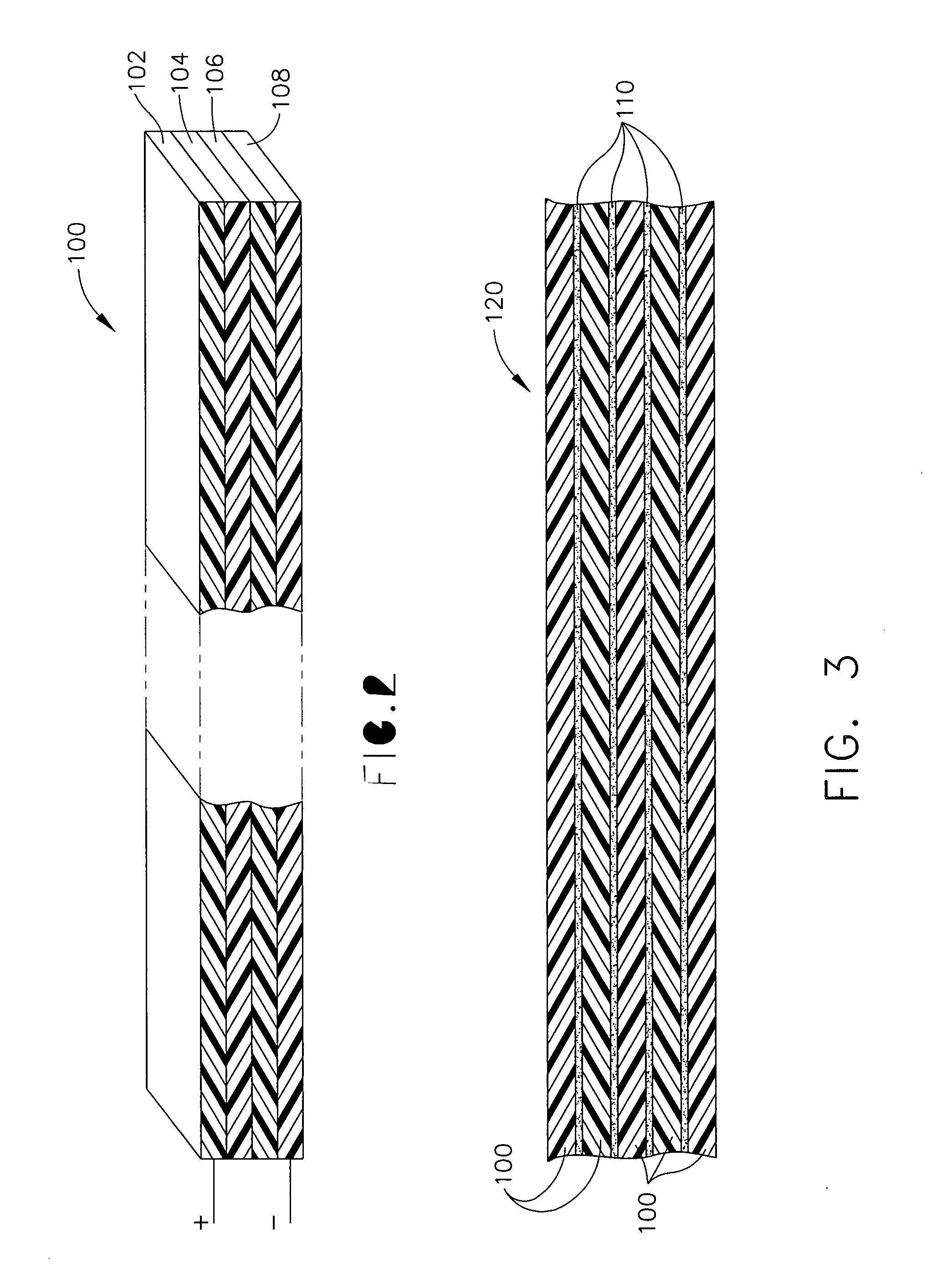
Energy efficient electroactive polymers and electroactive polymer devices
InactiveUS6911764B2Increase deflectionImprove energy conversion efficiencyTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesActive polymerMechanical energy
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Functionalized high cis-1,4-polybutadiene prepared using novel functionalizing agents
InactiveUS20060004131A1High ci microstructureLower glass transition temperatureInksActive polymerPolymer science
A functionalized polymer prepared by a process comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with a functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) A-R1-Z (I) where R1 is a divalent bond or divalent organic group comprising from 0 to about 20 carbon atoms, A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, and Z is a substituent that will react or interact with silica or carbon black reinforcing fillers, with the proviso that A, R1, and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, where said pseudo-living polymer is characterized by having greater than about 85 percent of the polymer in the cis microstructure and less than about 3 percent of the polymer is in the 1,2- or 3,4-microstructure, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) or (II) where Z is a substituent that will react or interact with organic or inorganic fillers; R1 is a single bond or a divalent organic group; R2 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R13 or R14; R3 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R4 or R5; R13 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R14; R4 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R5; R14 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R13; and R5 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R4; with the proviso that each group attached to the imino carbon is attached via a carbon atom and R1, R2 R3, R4, R5, R13, R14 and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Cross-linkable, photoactive polymer materials
InactiveUS6107427AAvoid problemsReverse twist can beLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryActive polymerAryl
The invention is concerned with novel cross-linkable, photoactive polymer materials with 3-aryl-acrylic acid esters and amides as well as their use as orienting layers for liquid crystals and for the production of non-structured or structured optical elements and multi-layer systems.
Owner:ROLIC AG
Variable stiffness catheter assembly
InactiveUS20070250036A1Variable stiffnessIncrease thrustStentsMulti-lumen catheterVariable stiffnessActive polymer
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Electroactive polymers transducers and actuators
InactiveUS6940211B2Speed up the conversion processImprove mechanical responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPre strainActive polymer
The present invention relates to electroactive polymers that are pre-strained to improve conversion from electrical to mechanical energy. When a voltage is applied to electrodes contacting a pre-strained polymer, the polymer deflects. This deflection may be used to do mechanical work. The pre-strain improves the mechanical response of an electroactive polymer. The present invention also relates to actuators including an electroactive polymer and mechanical coupling to convert deflection of the polymer into mechanical work. The present invention further relates to compliant electrodes that conform to the shape of a polymer. The present invention provides methods for fabricating electromechanical devices including one or more electroactive polymers.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Electroactive polymer rotary clutch motors
ActiveUS7166953B2Increased torsional stiffnessPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesActive polymerMechanical energy
The present invention relates to mechanical-electrical power conversion systems. The systems comprise one or more electroactive polymers that convert between electrical and mechanical energy. When a voltage is applied to electrodes contacting an electroactive polymer, the polymer deflects. This deflection may be converted into rotation of a power shaft included in a motor. Repeated deflection of the polymer may then produce continuous rotation of the power shaft.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
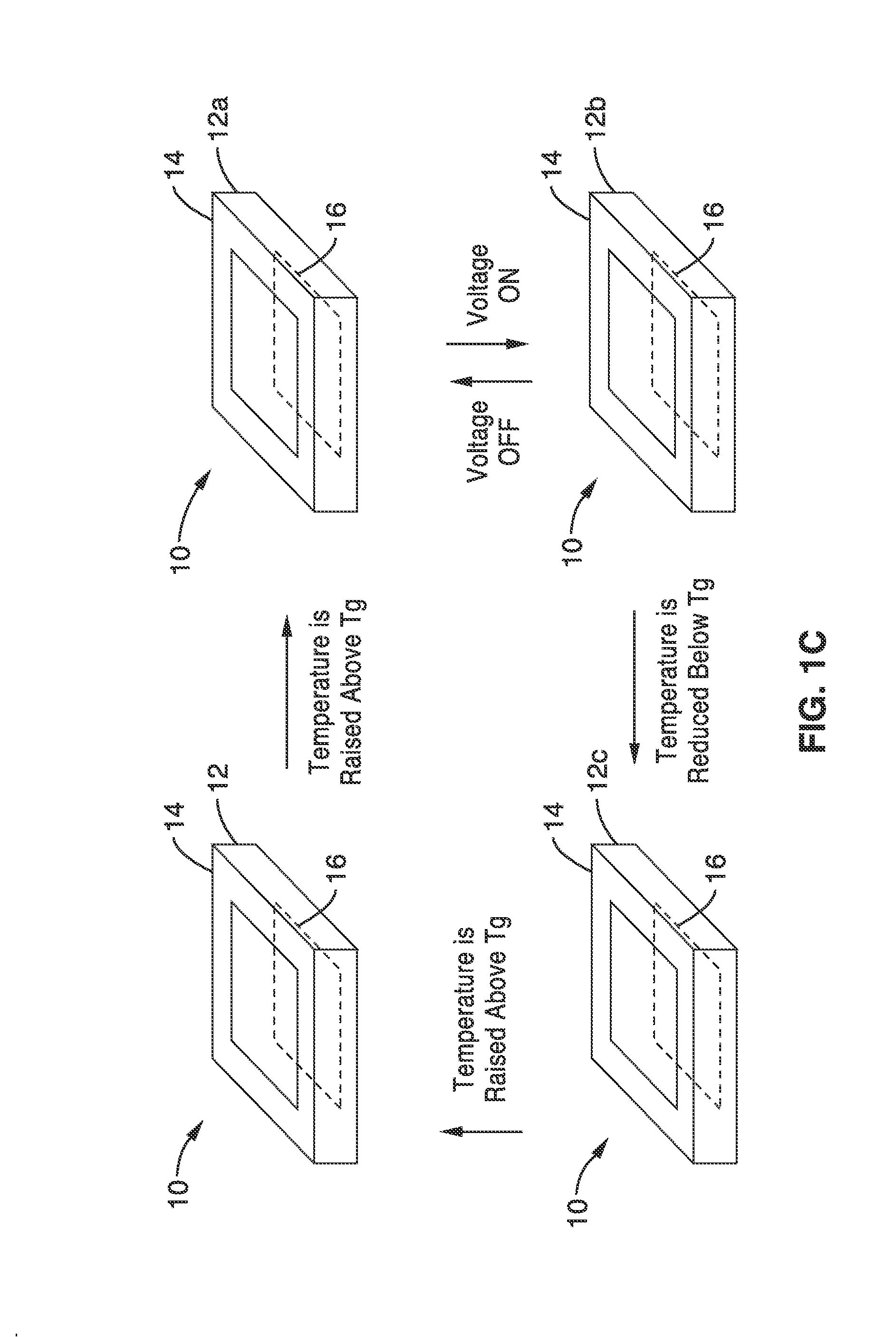
Bistable electroactive polymers
ActiveUS20100171393A1Improve mechanical energySpeed up the conversion processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionHigh energyShock resistance
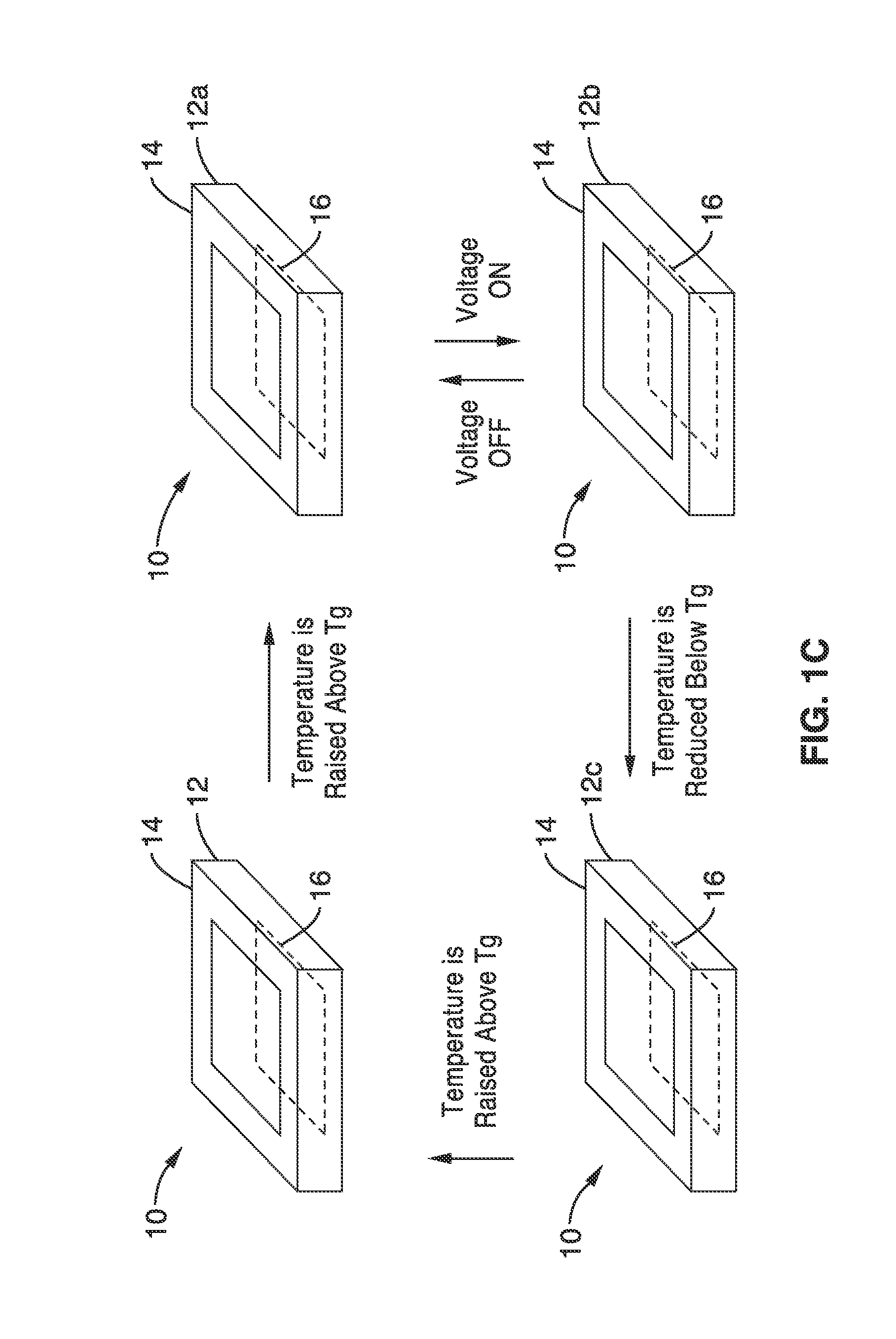
A bistable electroactive polymer transducer is provided for electrically actuated deformation of rigid electroactive polymer members. The polymers have glass transition temperatures (Tg) above ambient conditions and turn into rubbery elastomers above Tg and have high dielectric breakdown strength in the rubbery state. They can be electrically deformed to various rigid shapes with maximum strain greater than 100% and as high as 400%. The actuation is made bistable by cooling below Tg to preserve the deformation. The dielectric actuation mechanism includes a pair of compliant electrodes in contact with a dielectric elastomer which deforms when a voltage bias is applied between the pair of electrodes. In some of the transducers of the present invention, the dielectric elastomer is also a shape memory polymer. The deformations of such bistable electroactive polymers can be repeated rapidly for numerous cycles. The polymer transducers have such advantages as high energy and power densities, quietness, mechanical compliancy (for shock resistance and impedance matching), high efficiency, lightweight, and low cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for producing modified diene polymer rubber
There is provided a process for producing a modified diene polymer rubber comprising the steps of: (1) polymerizing a conjugated diene monomer or a combination thereof with an aromatic vinyl monomer in a hydrocarbon solvent, in the presence of an alkali metal catalyst, to form an alkali metal end-carrying active polymer, and (2) reacting the alkali metal end-carrying active polymer with a silane compound defined by a specific formula.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
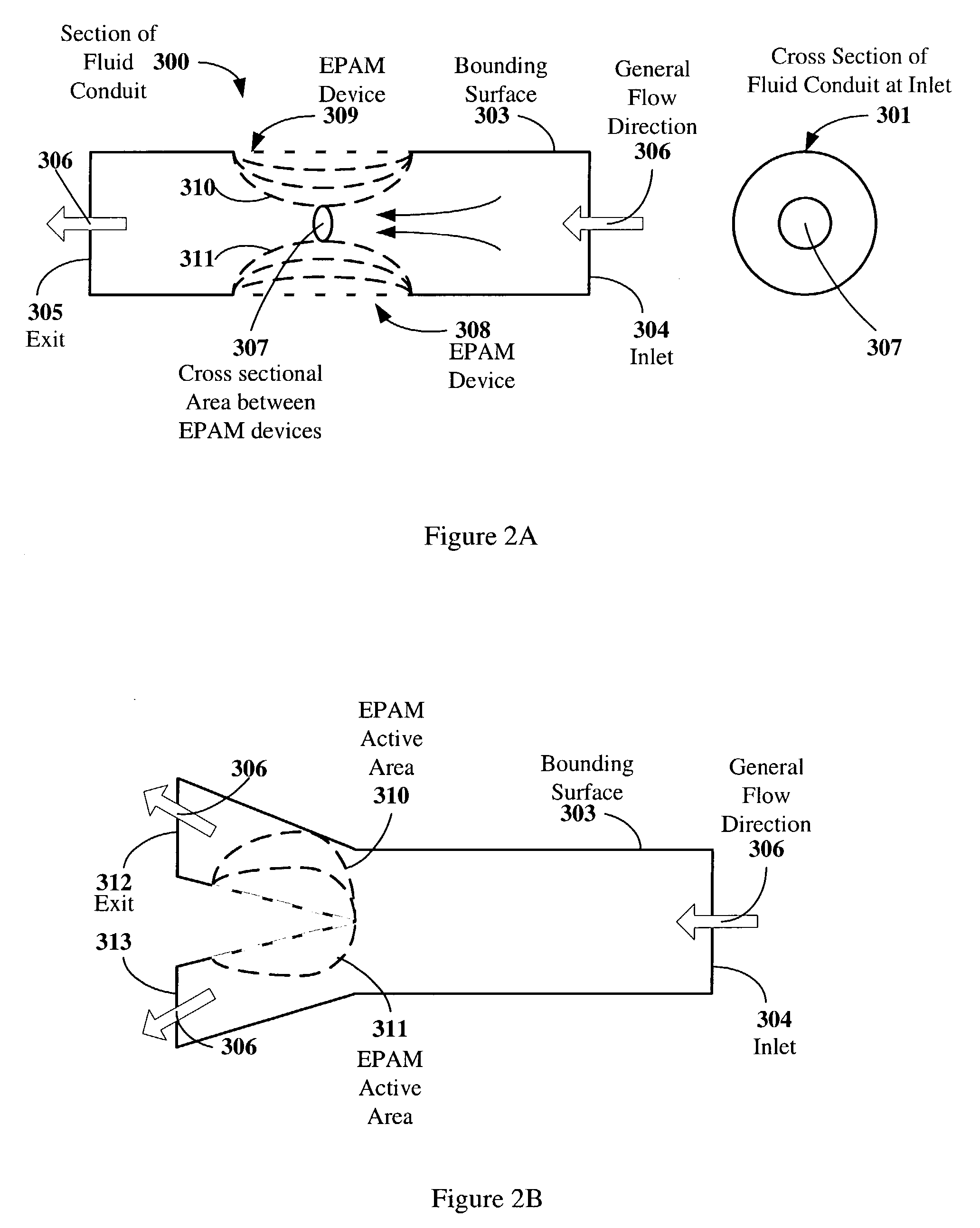
Electroactive polymer devices for controlling fluid flow
InactiveUS7320457B2Improve mechanical responseImprove responsePiezoelectric/electrostrictive gramophone pickupsTransducer detailsMomentumTransducer
The invention describes devices for controlling fluid flow, such as valves. The devices may include one or more electroactive polymer transducers with an electroactive polymer that deflects in response to an application of an electric field. The electroactive polymer may be in contact with a fluid where the deflection of the electroactive polymer may be used to change a characteristic of the fluid. Some of the characteristic of the fluid that may be changed include but are not limited to 1) a flow rate, 2) a flow direction, 3) a flow vorticity, 4) a flow momentum, 5) a flow mixing rate, 6) a flow turbulence rate, 7) a flow energy, 8) a flow thermodynamic property. The electroactive polymer may be a portion of a surface of a structure that is immersed in an external fluid flow, such as the surface of an airplane wing or the electroactive polymer may be a portion of a surface of a structure used in an internal flow, such as a bounding surface of a fluid conduit.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Compliant electroactive polymer transducers for sonic applications
InactiveUS20070200467A1Avoid excessive elastic modulusPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersActive polymerTransducer
Described herein are compliant electroactive polymer transducers for use in acoustic applications. A compliant electroactive polymer transducer includes a compliant electroactive polymer at least two electrodes. For sound production, circuitry in electrical communication with the transducer electrodes is configured to apply a driving signal that causes the electroactive polymer to deflect in the acoustic range.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Electrospun electroactive polymers
InactiveUS20060057377A1Easy to set upFast and easy to runMaterial nanotechnologyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPolyesterFiber
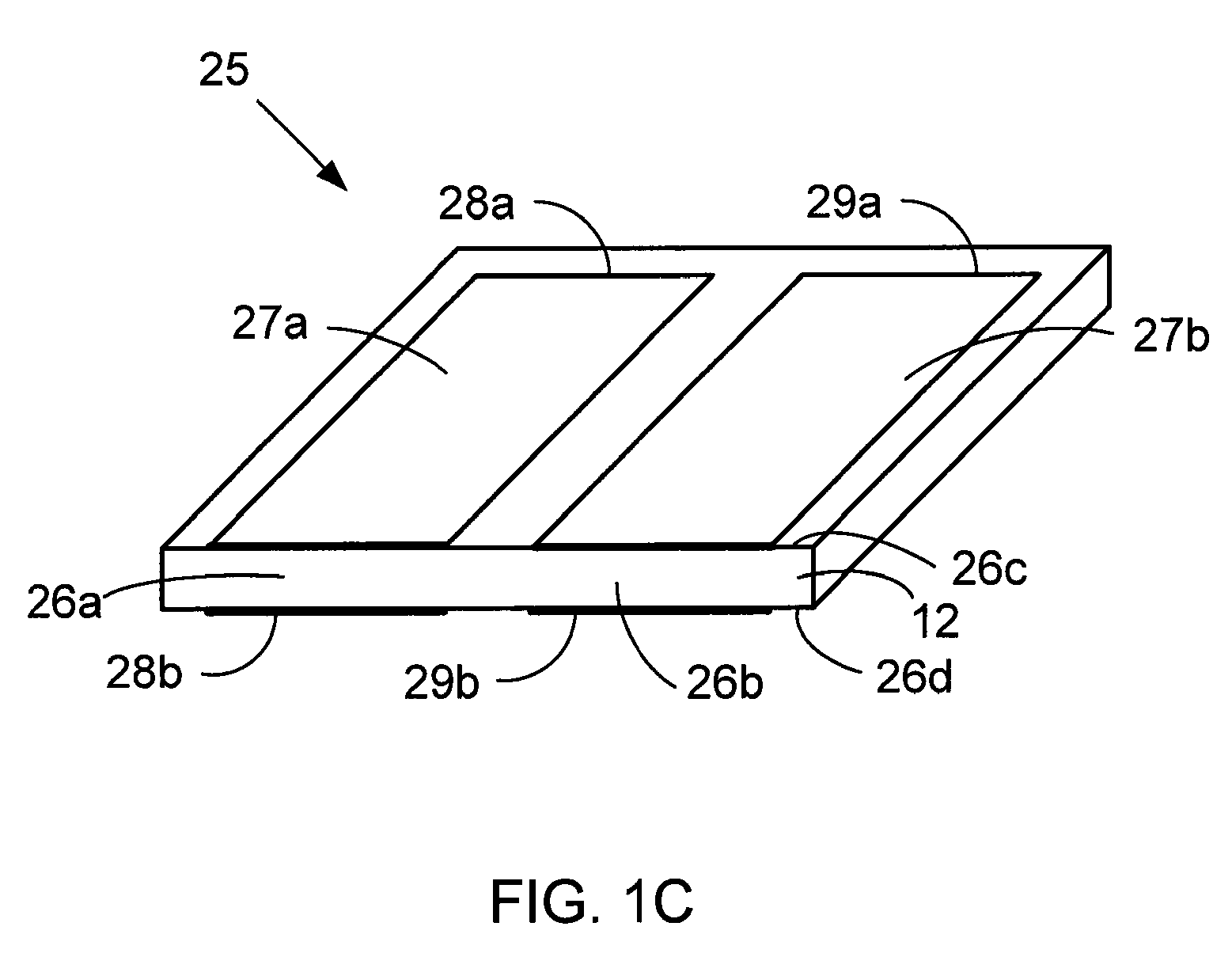
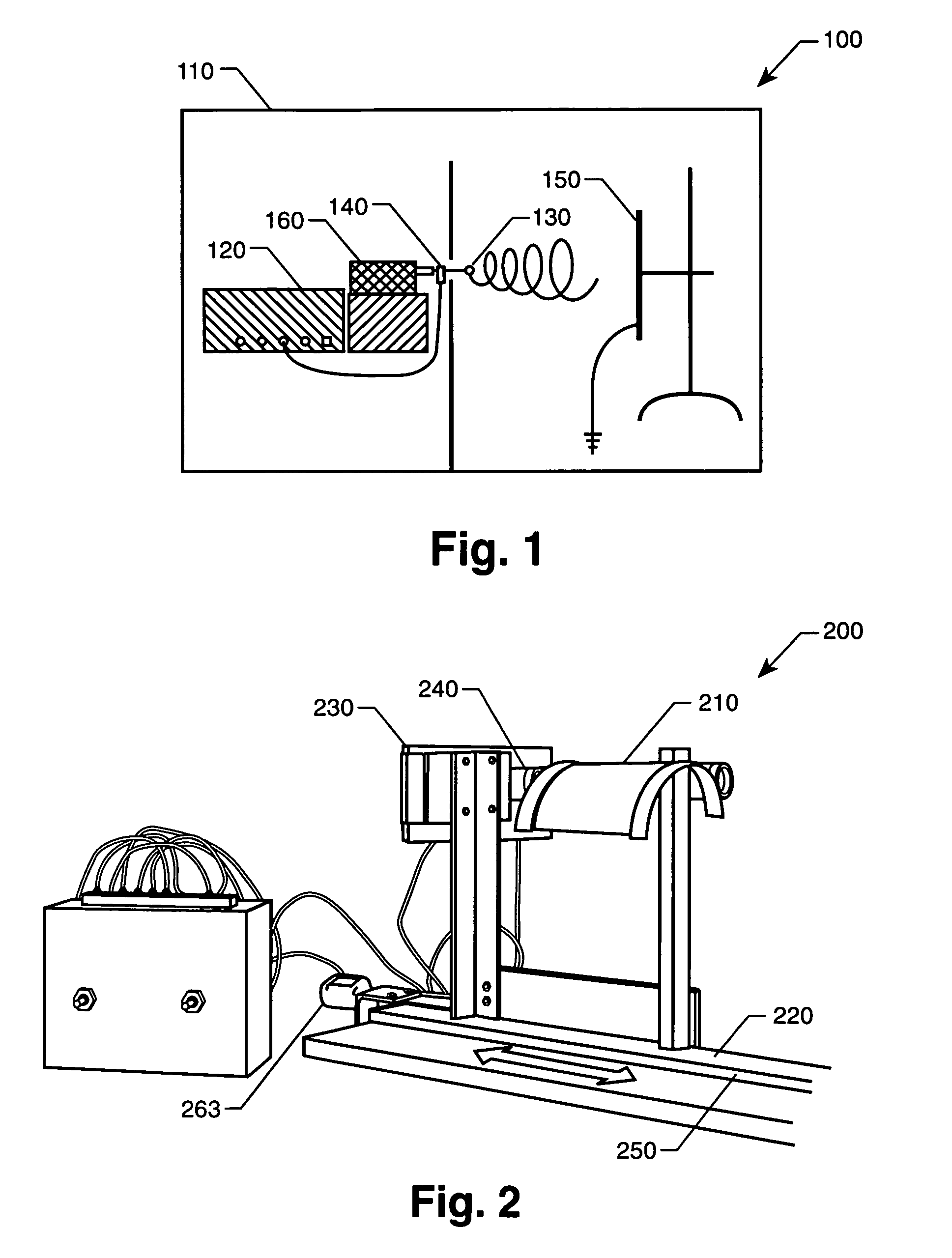
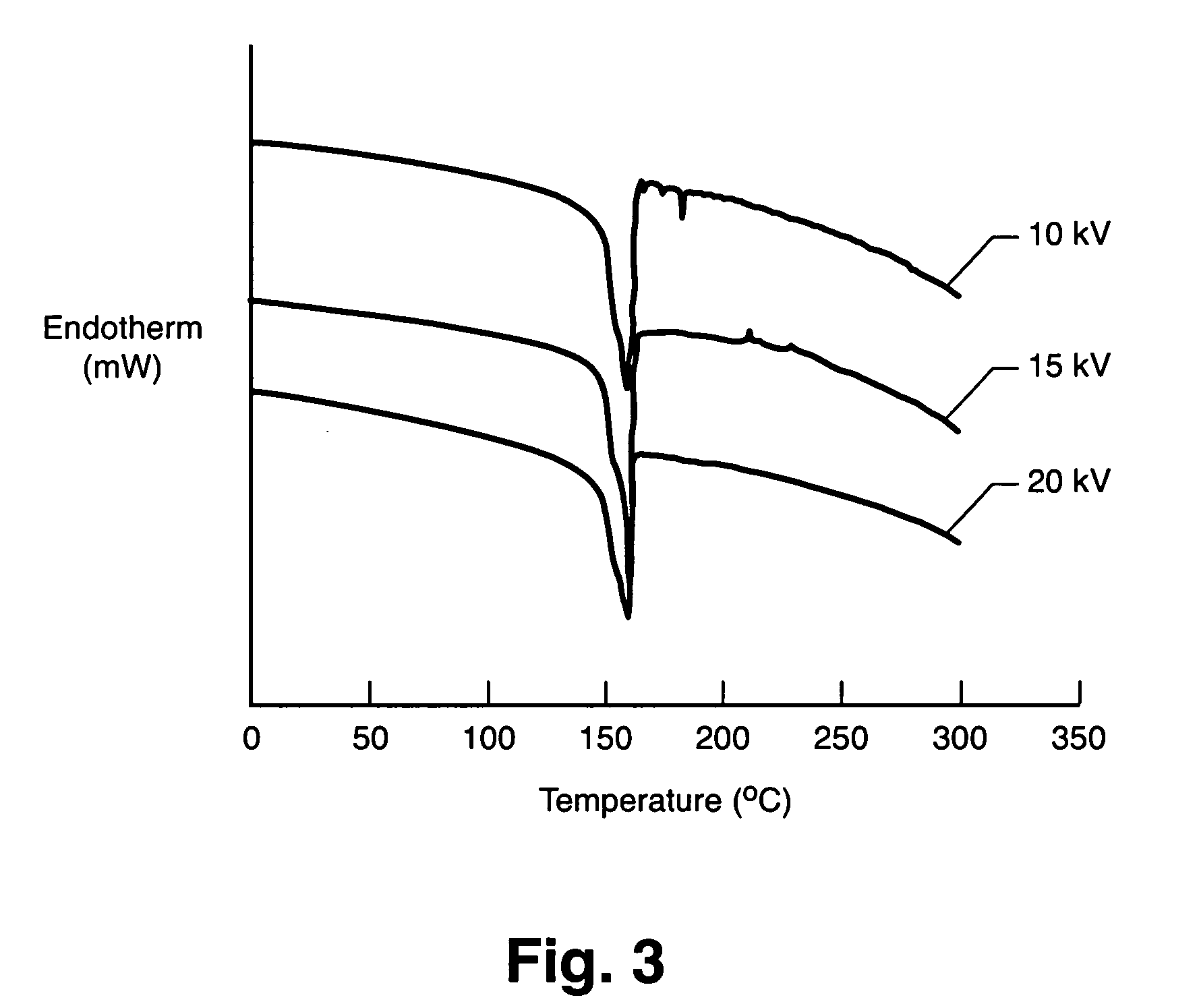
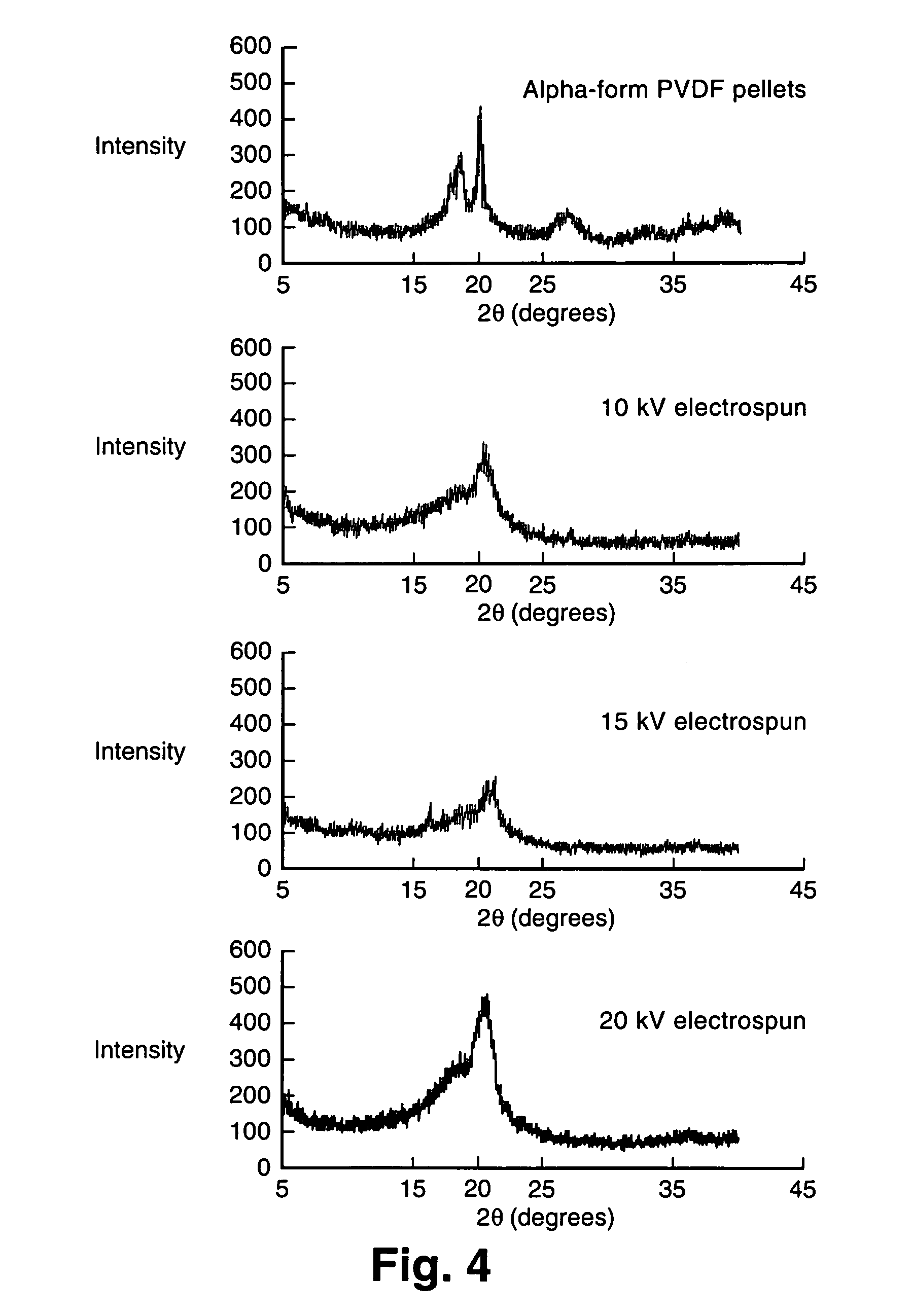
Electroactive polymers are produced via electrospinning. The induction of electroactivity via electrospinning can be utilized with one or more soluble polymers with polarizable moieties. Suitable polymer classes include but are not limited to polyimides, polyamides, vinyl polymers, polyurethanes, polyureas, polythioureas, polyacrylates, polyesters, and biopolymers. Any one or more solvents sufficient to dissolve the one or more polymers of interest and make a spinnable solution can be utilized. The polymer can be electrospun into fiber and fibrous nonwoven mat. The electroactive polymer can be doped with inclusions, such as nanotubes, nanofibers, and piezoceramic powders for dielectric enhancement The availability of electroactive polymer fibers and fibrous nonwoven mat will enable many new applications for electroactive polymers.
Owner:NASA +2
Electroactive polymers
InactiveUS20060113878A1Speed up the conversion processImprove responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPre strainActive polymer
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Surface deformation electroactive polymer transducers
InactiveUS20080289952A1Augments out-of-plane deflectionsIncrease awarenessPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEfficient propulsion technologiesPolymeric surfaceVisibility
The present invention provides electroactive polymer transducers that produce out-of-plane deflections. The transducers form a set of surface features based on deflection of an electroactive polymer. The set of surface features may include elevated polymer surface features and / or depressed electrode surface features. Actuation of an active area may produce the polymer deflection that creates one or more surface features. A passive layer may operably connect to a polymer. The passive layer may comprise a thicker and softer material to amplify polymer thickness changes and increase surface feature visibility.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Electroactive polymer based artificial sphincters and artificial muscle patches
InactiveUS6921360B2Lower esophageal sphincter dysfunctionAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryLower esophagusElectroactive polymer actuators
Provided are artificial muscle patches, which are adapted to be implanted adjacent a patient's heart, and artificial sphincter cuffs, which are adapted to be implanted around a body lumen, such as the urethra, the anal canal, or the lower esophagus. The devices of the present invention comprise: (a) one or more electroactive polymer actuators; and (b) a control unit for electrically controlling the one or more electroactive polymer actuators to expand or contract the devices.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
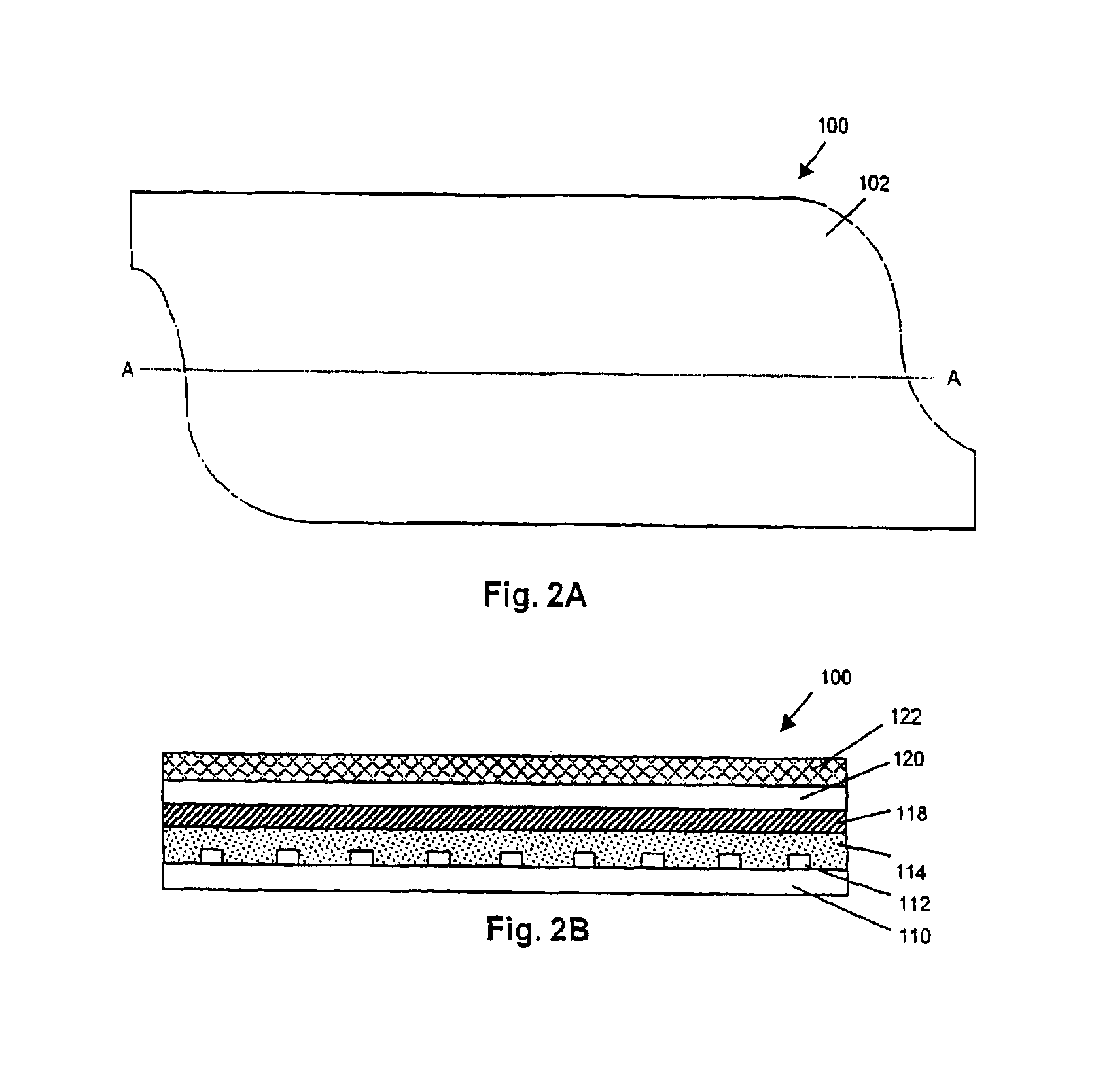
Polymer Delivery in Well Treatment Applications
InactiveUS20090023614A1Reduce solubilityEasy to pumpTransportation and packagingFluid removalActive polymerEmulsion
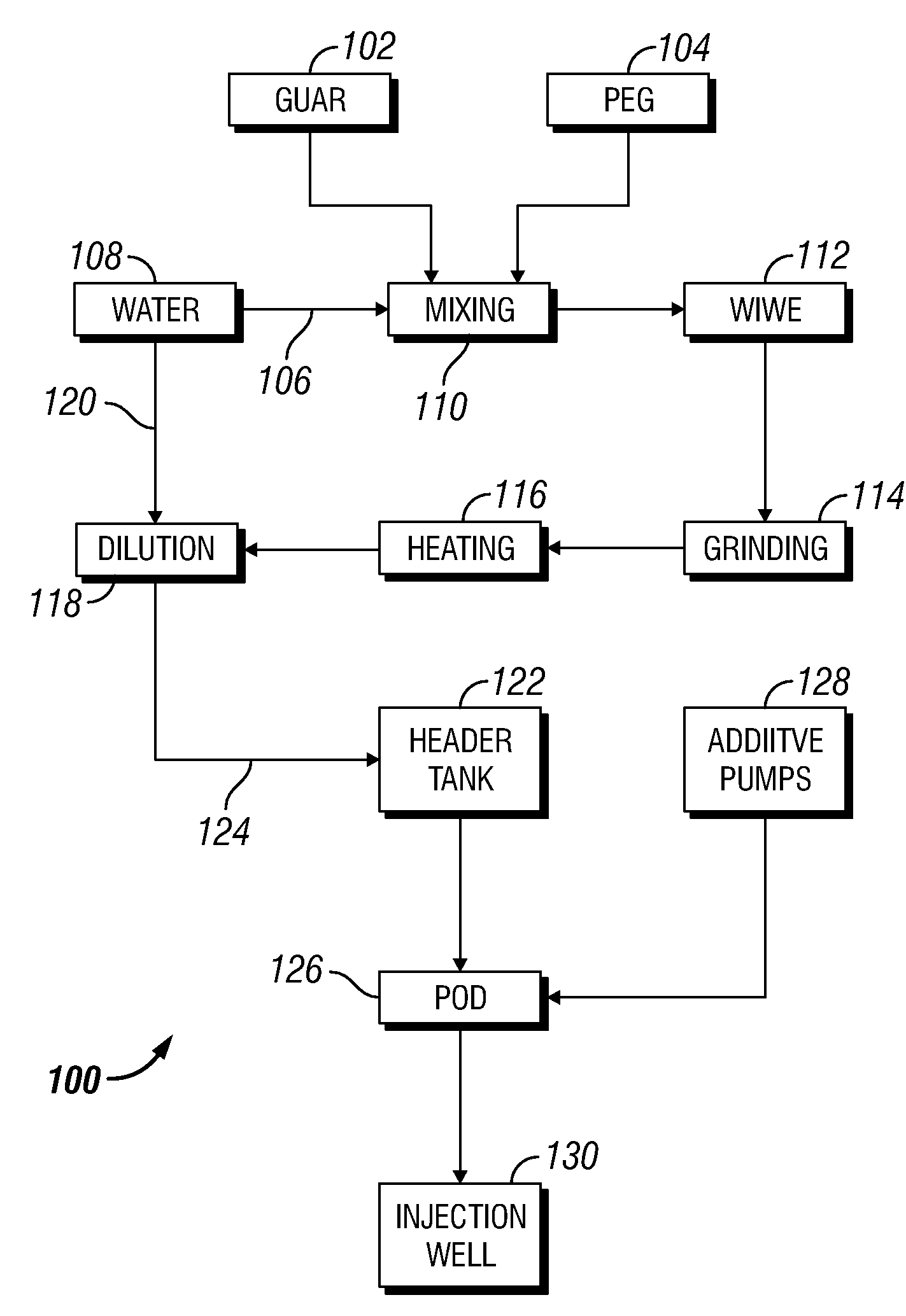
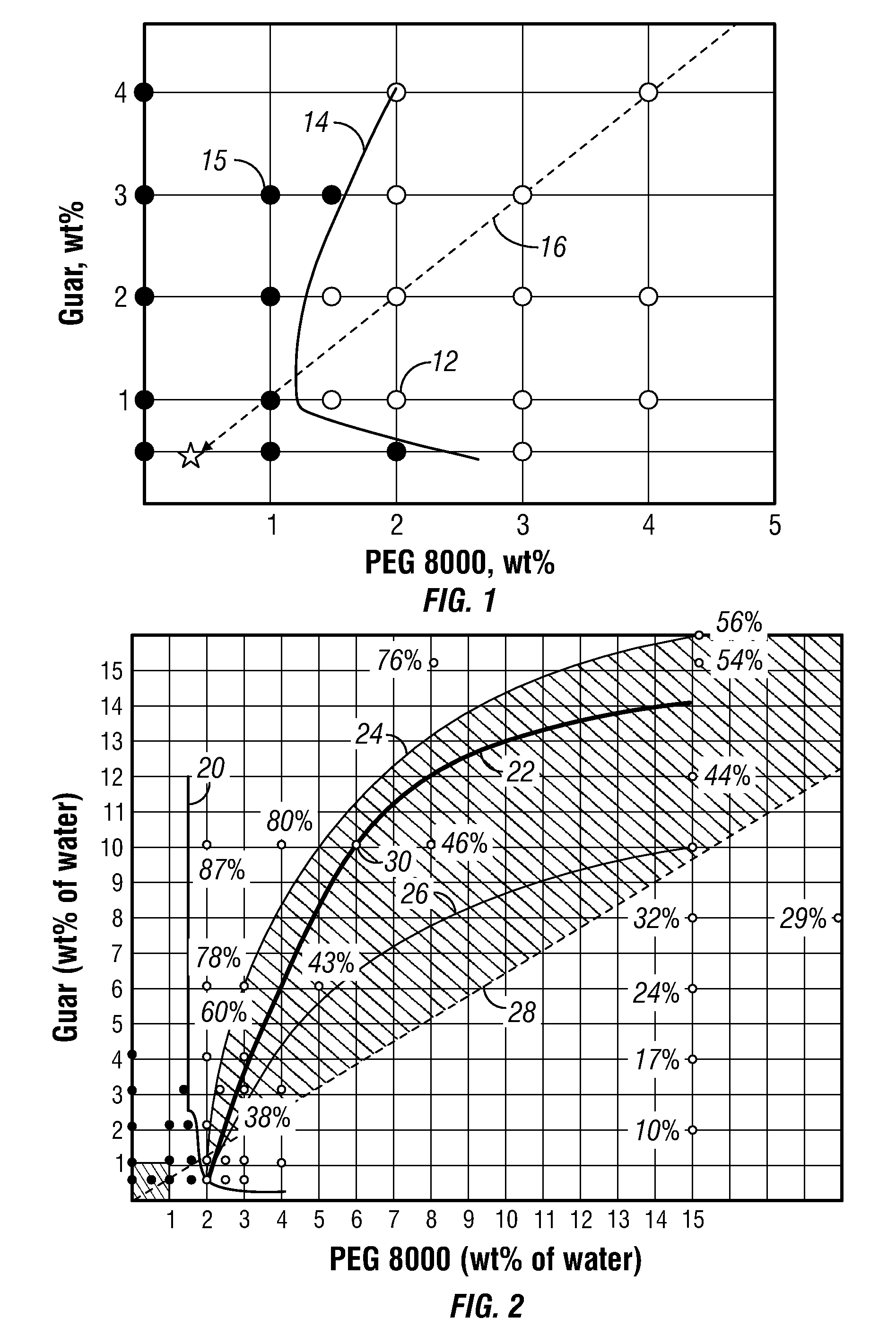
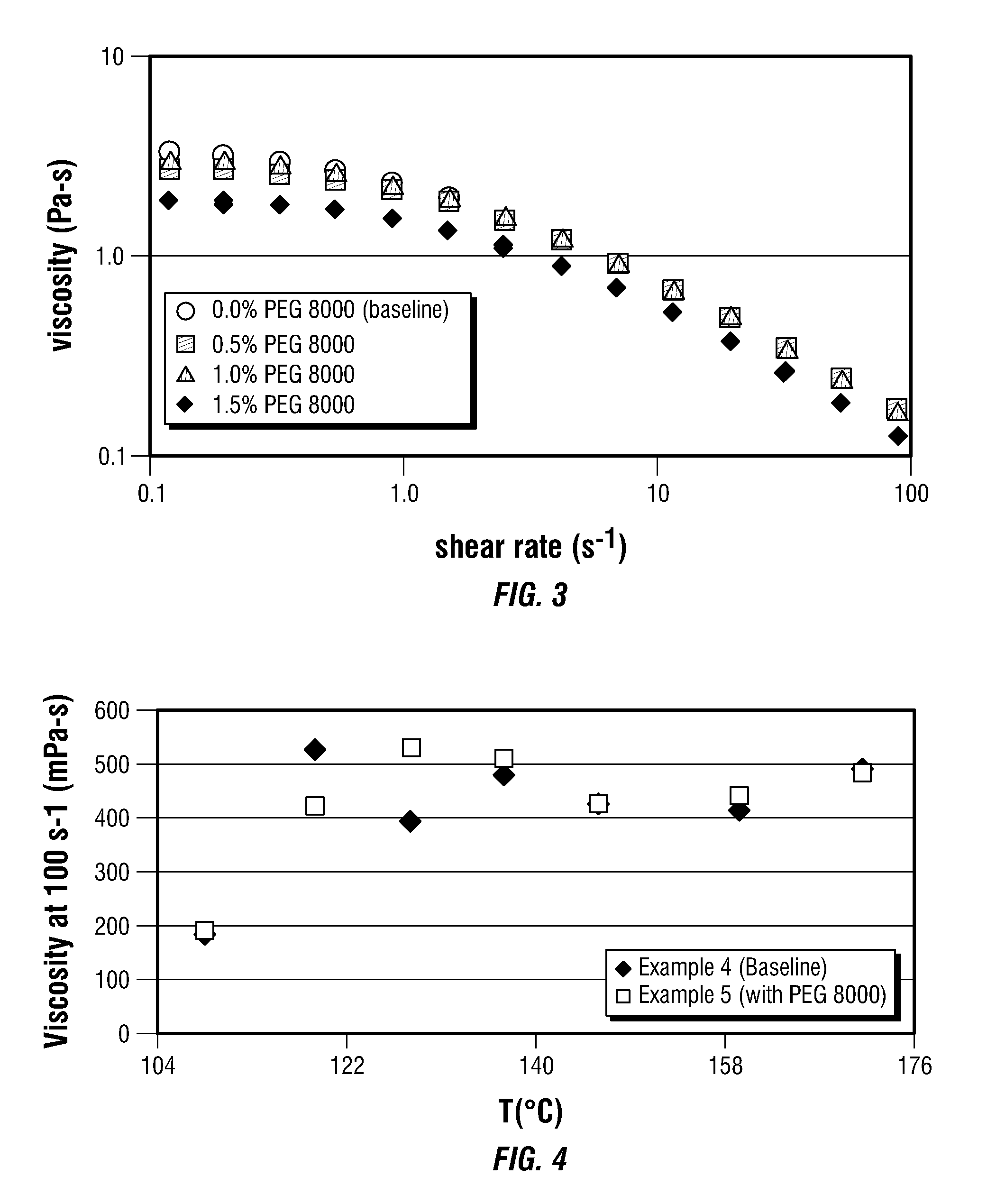
This invention relates to compositions and methods for treating subterranean formations, in particular, oilfield stimulation compositions and methods using water-in-water polymer emulsions to uniformly dissolve a rheologically active polymer, such as a thickener or friction reducer, in the treatment fluid. The emulsions have a low viscosity and are easily pumped for mixing into a treatment fluid, where upon dilution with an aqueous medium, the polymer is easily hydrated without forming fish-eyes. The partitioning agent in the water-in-water emulsion does not generally affect the rheology of the treatment fluid. The invention also relates to further processing of the emulsion by wet grinding, high shear mixing and / or heating to enhance the hydration rate in the preparation of the well treatment fluid.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Bistable electroactive polymers
ActiveUS8237324B2Improve mechanical energySpeed up the conversion processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesVitrificationActive polymer
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
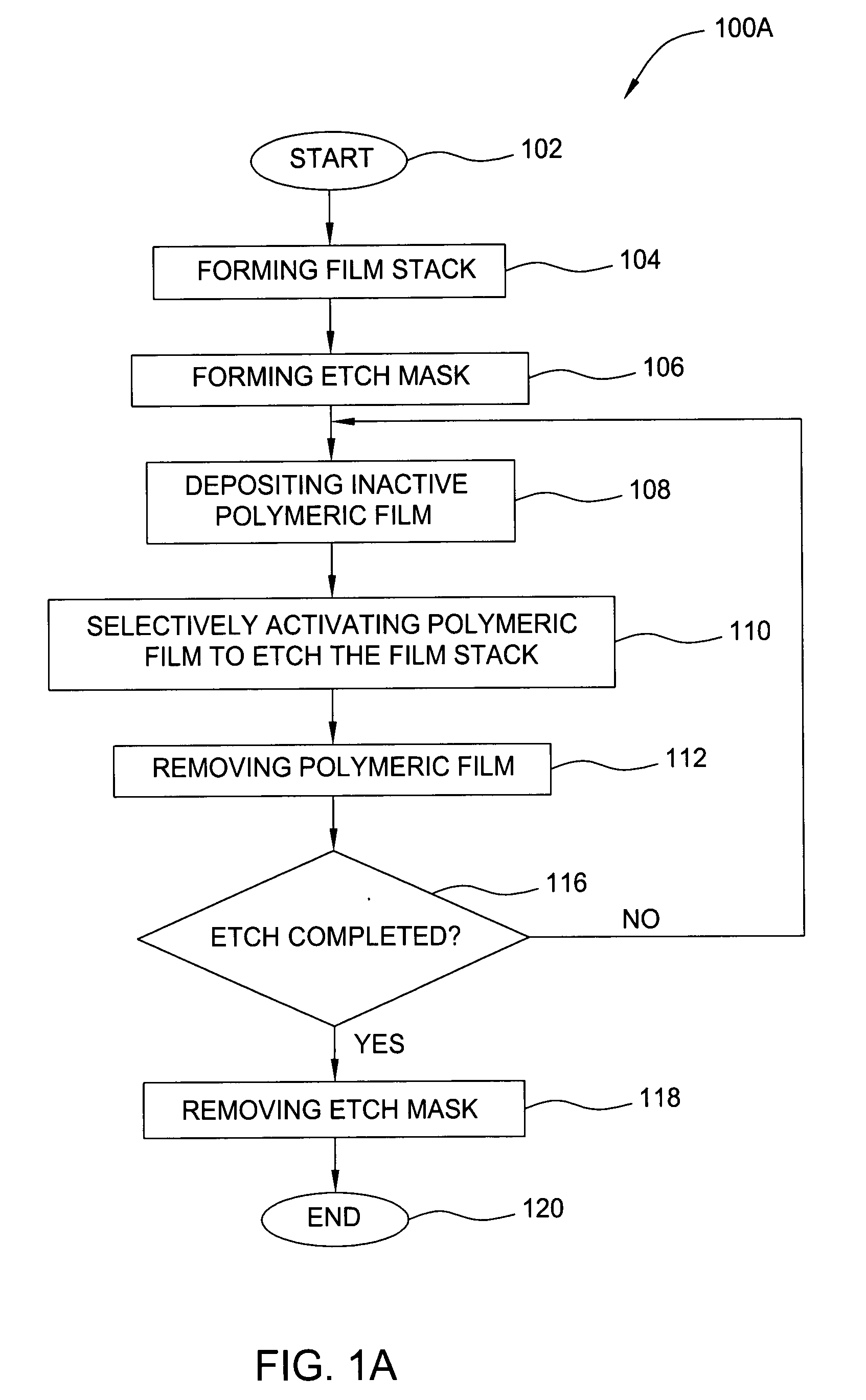
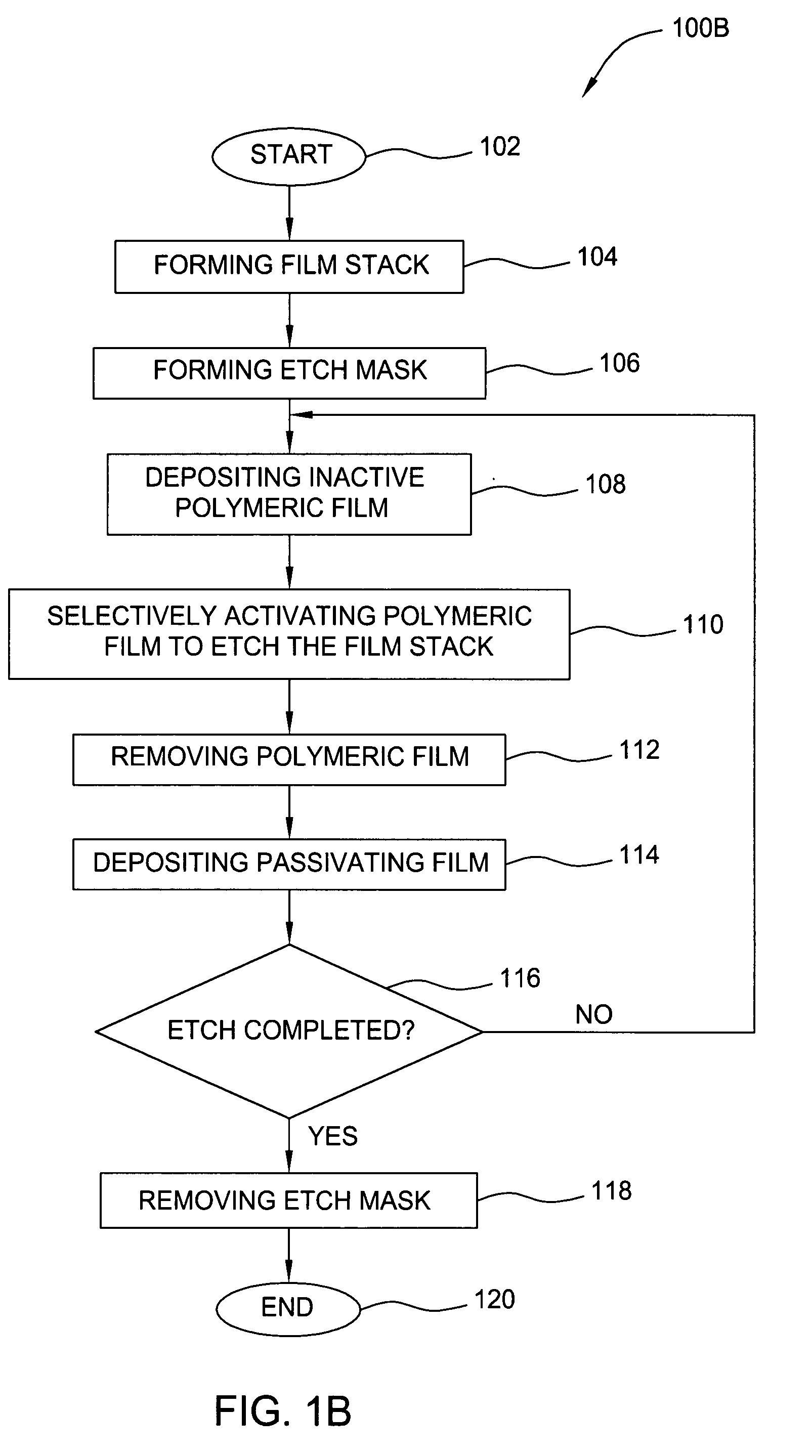
Method for plasma etching a dielectric layer
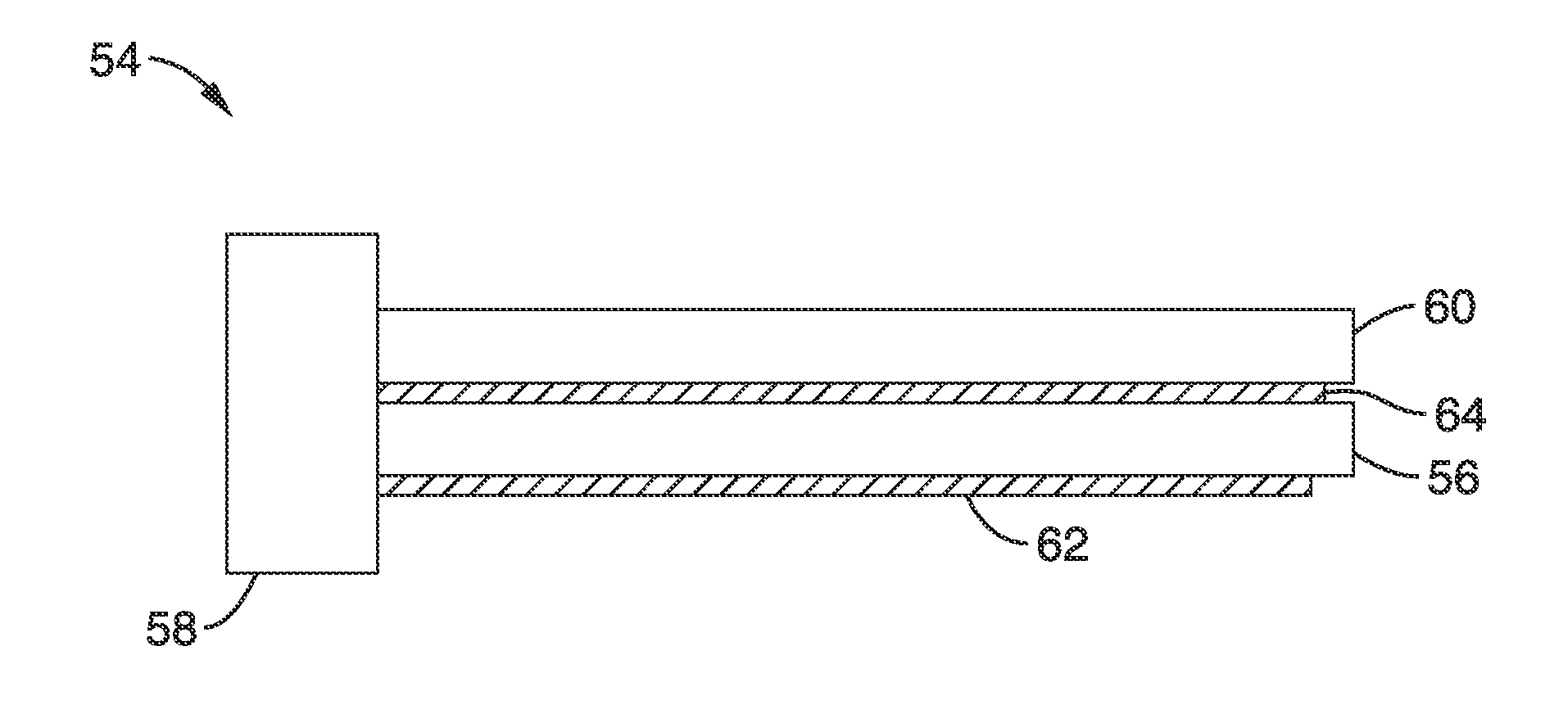
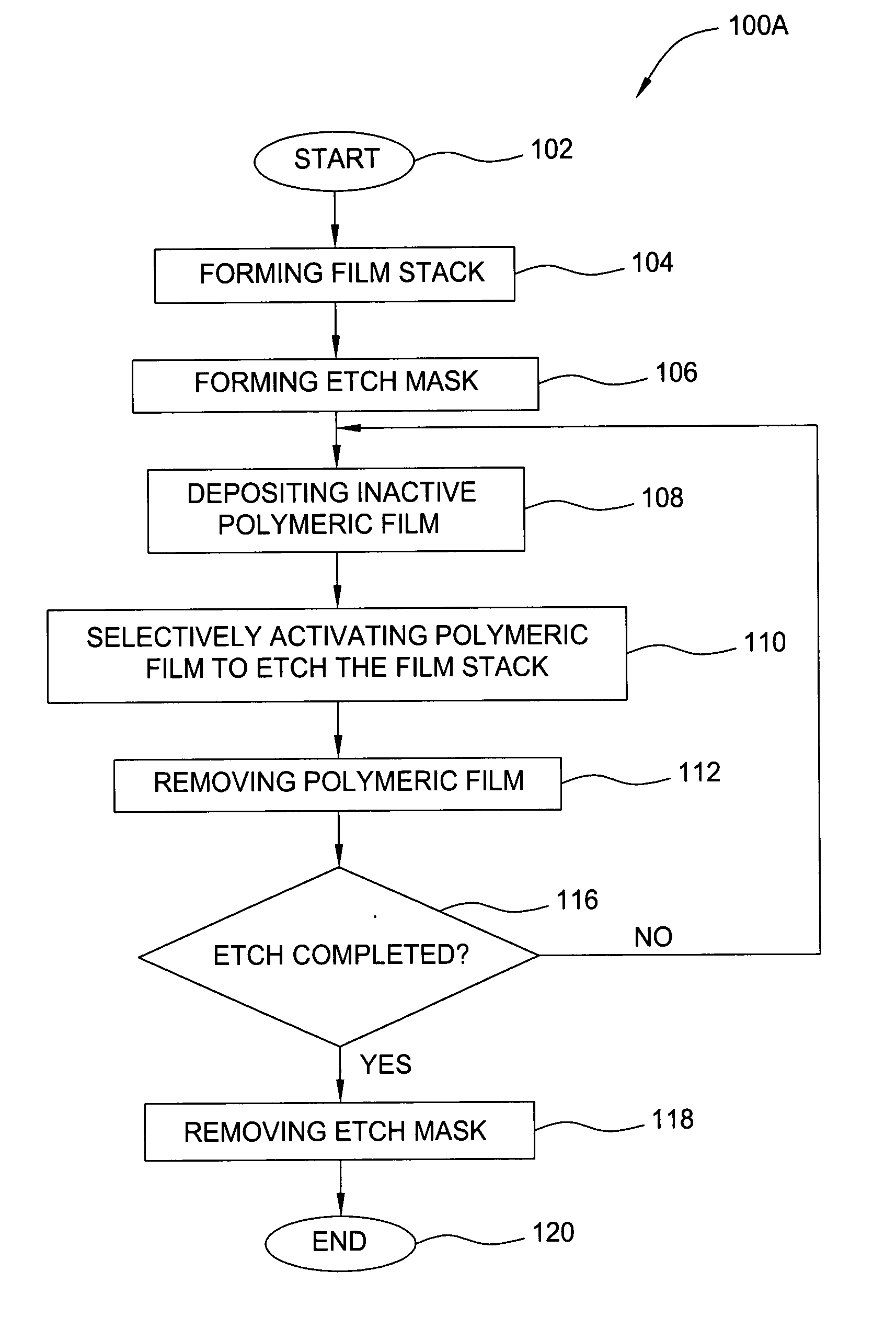
A method of etching a dielectric layer formed on a substrate including a sequence of processing cycles, wherein each cycle comprises steps of depositing an inactive polymeric film, activating the film to etch the structure, and removing the film is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method uses a fluorocarbon gas to form the polymeric film and a substrate bias to activate such film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for mesoscale deposition of biological materials and biomaterials
InactiveUS20060280866A1Wide viscosity rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical containersDielectricEngineering
Methods and apparatus for the direct deposition or patterning of biological materials and compatible biomaterials. The method is capable of depositing biological materials and biomaterials in a computer defined pattern, and uses aerodynamic focusing of an aerosol stream to deposit mesoscale patterns onto planar or non-planar targets without the use of masks or modified environments. The aerosolized compositions may be processed before deposition (pre-processing) or after deposition on the target (post-processing). Depositable materials include, not are not limited to conductive metal precursors, nanoparticle metal inks, dielectric and resistor pastes, biocompatible polymers, and a range of biomolecules including peptides, viruses, proteinaceous enzymes, extra-cellular matrix biomolecules, as well as whole bacterial, yeast, and mammalian cell suspensions. The targets may be planar or non-planar, and are optionally biocompatible. Applications include biosensor rapid prototyping and microfabrication, lab-on-chip manufacturing, biocompatible electroactive polymer development (ambient temperature bio-production of electronic circuitry), and various additive biomaterial processes for hybrid BioMEMS, Bio-Optics, and microfabrication of biomedical devices.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com