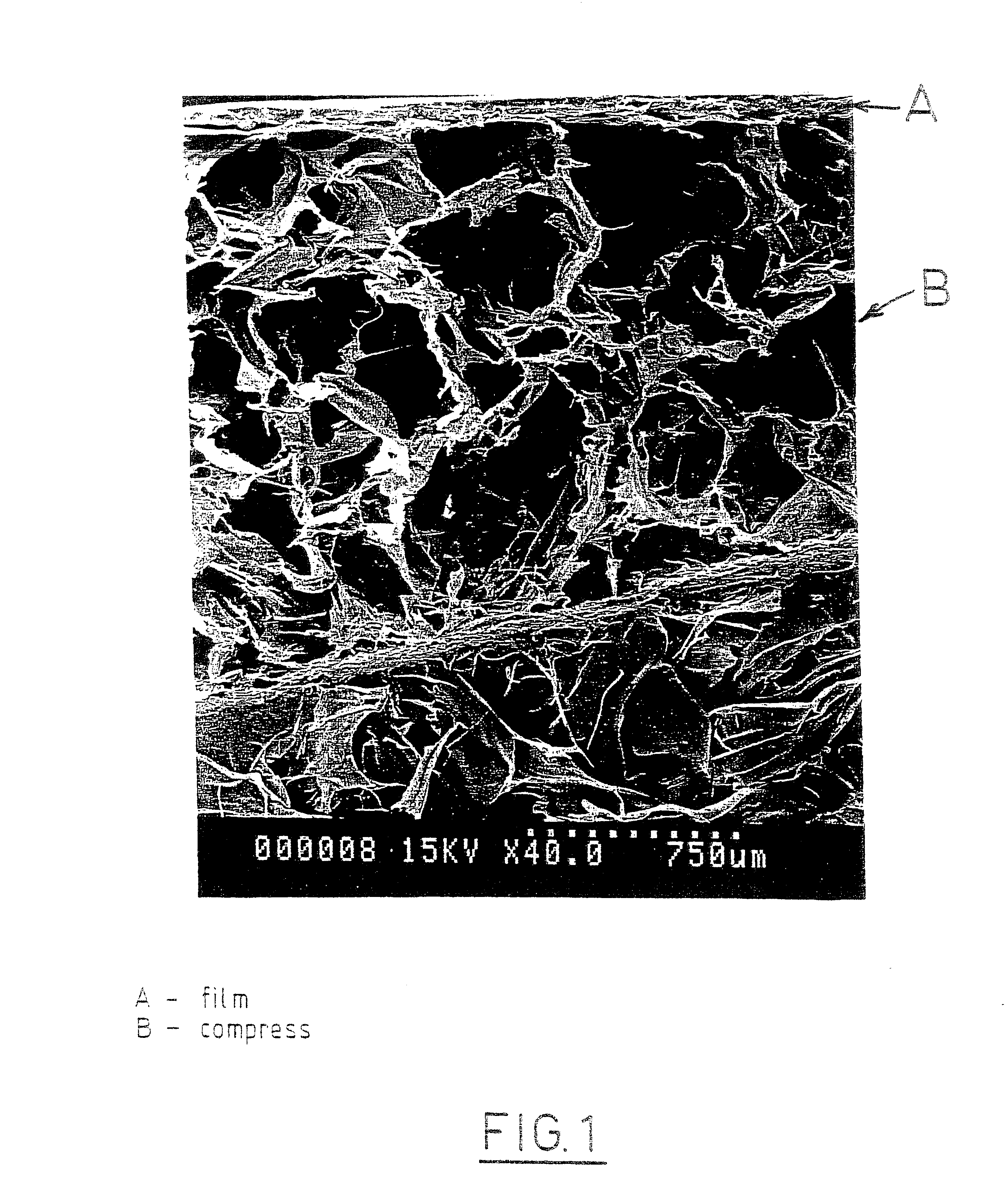
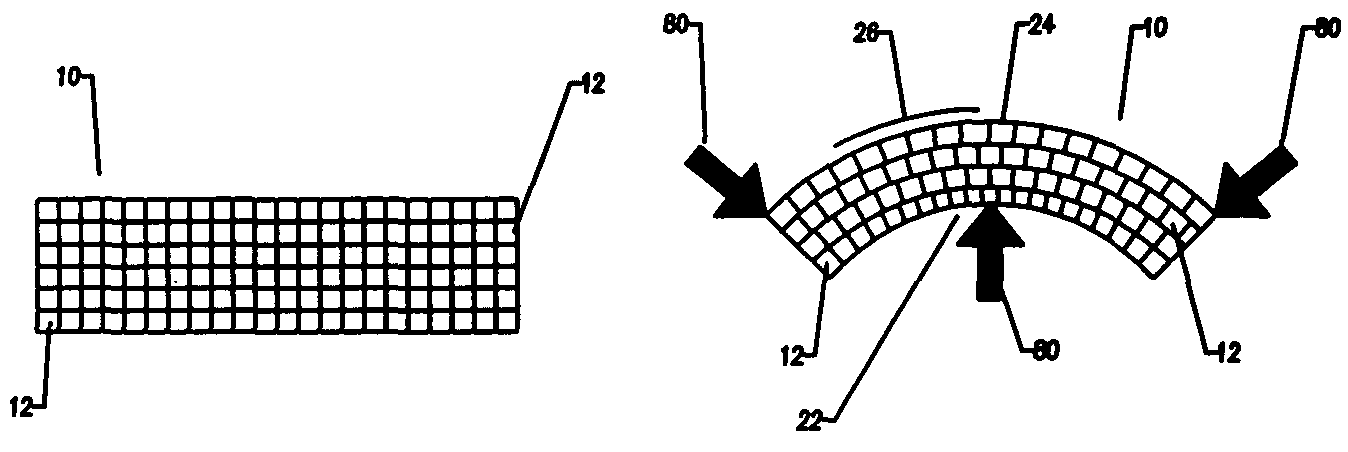
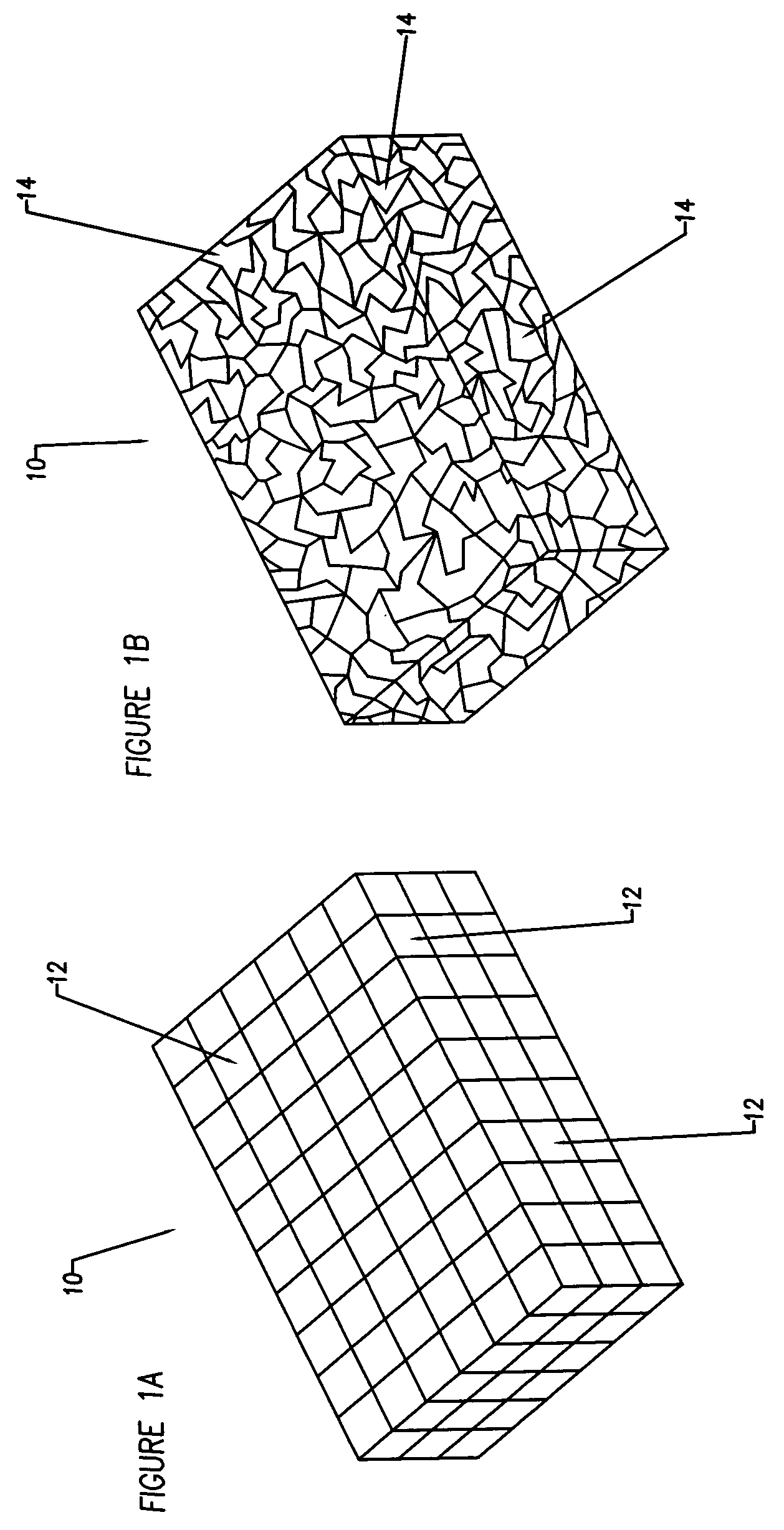
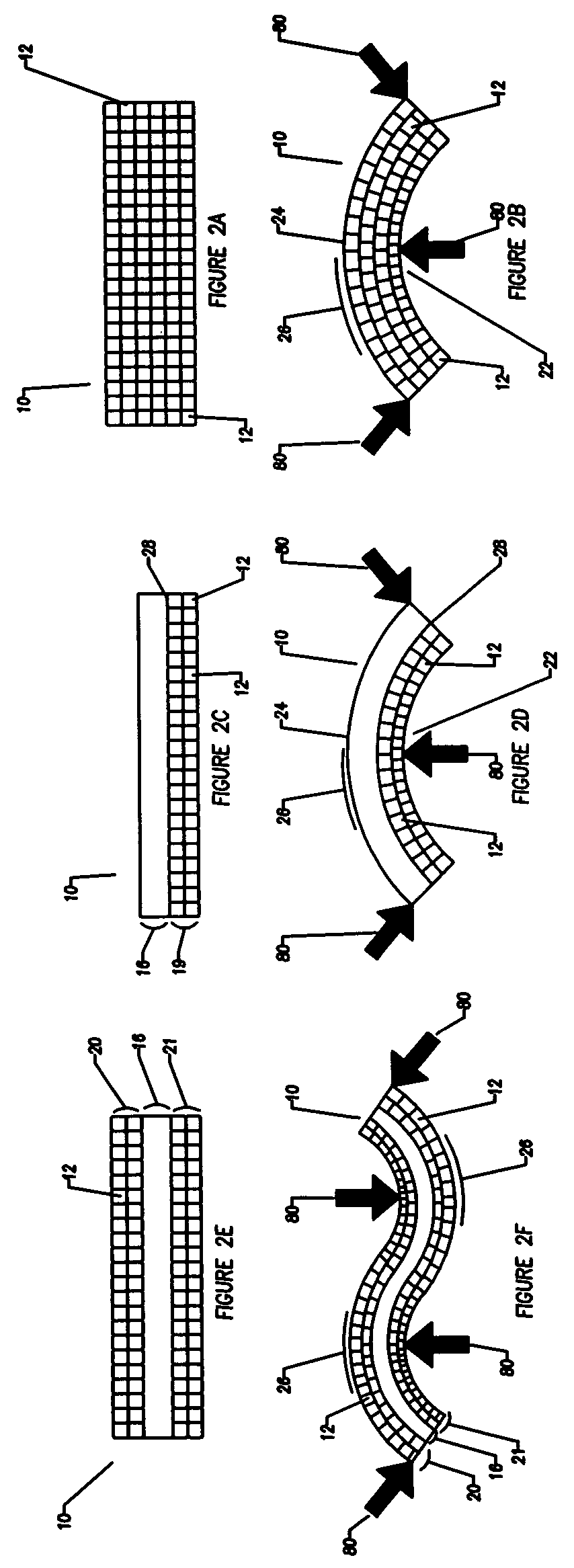
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
133100 results about "Polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A polymer (/ˈpɒlɪmər/; Greek poly-, "many" + -mer, "part") is a large molecule, or macromolecule, composed of many repeated subunits. Due to their broad range of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form glasses and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The terms polymer and resin are often synonymous with plastic.
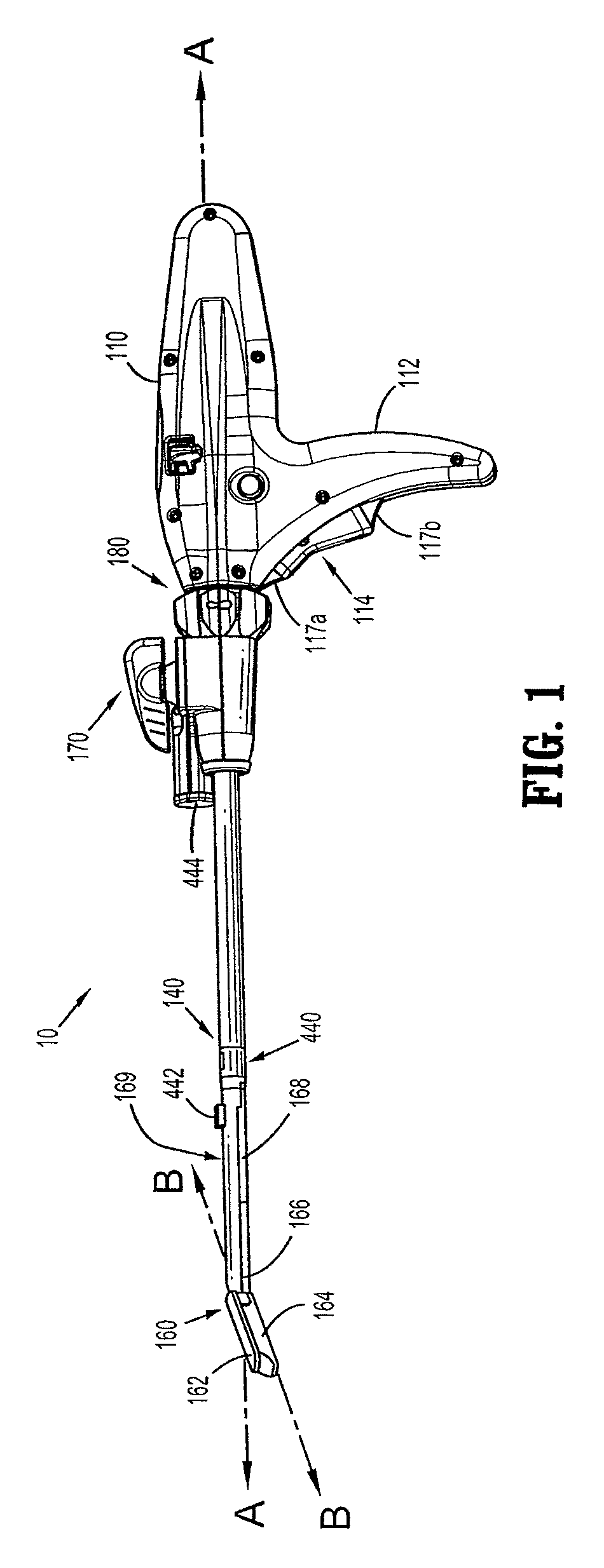
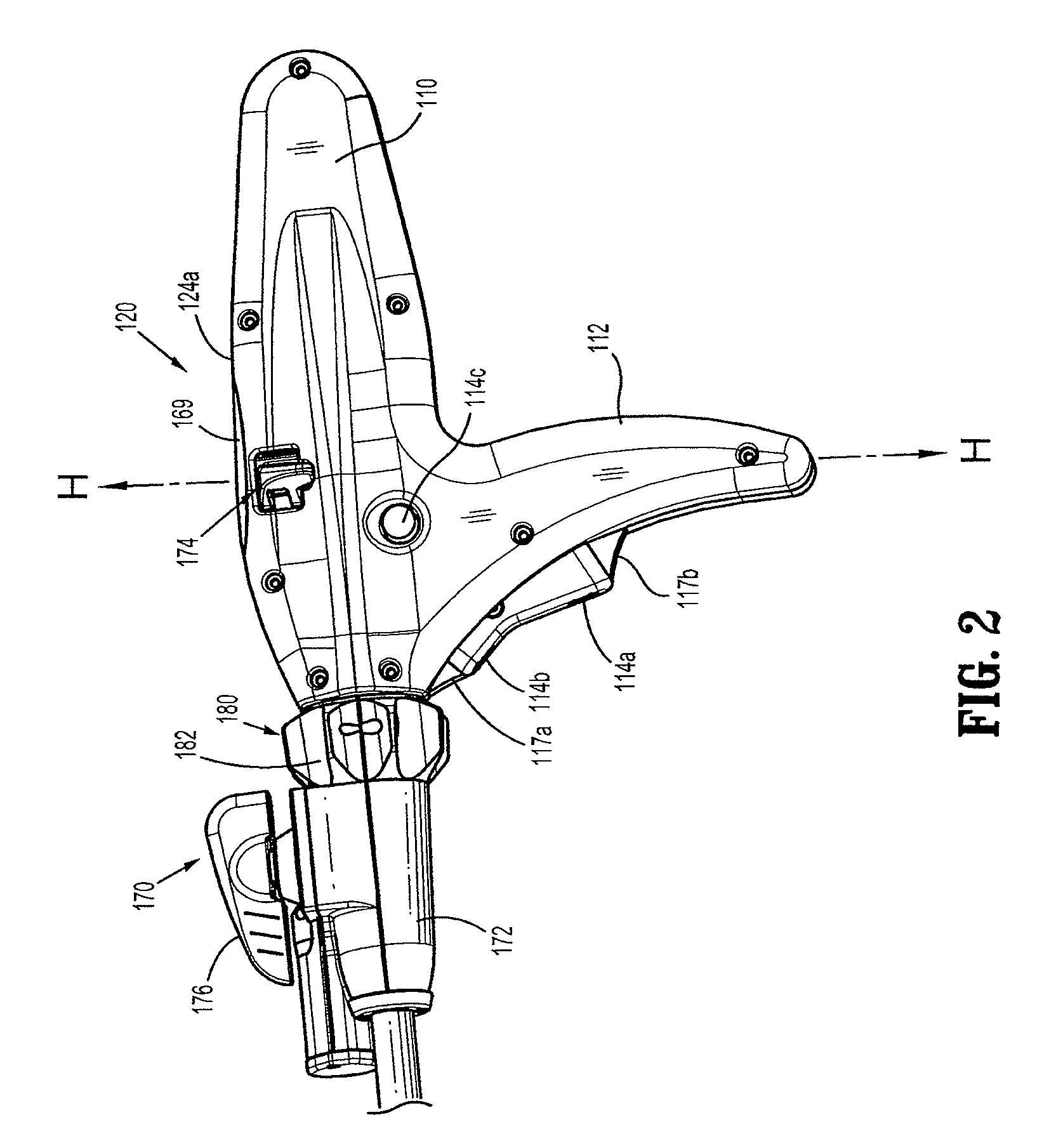
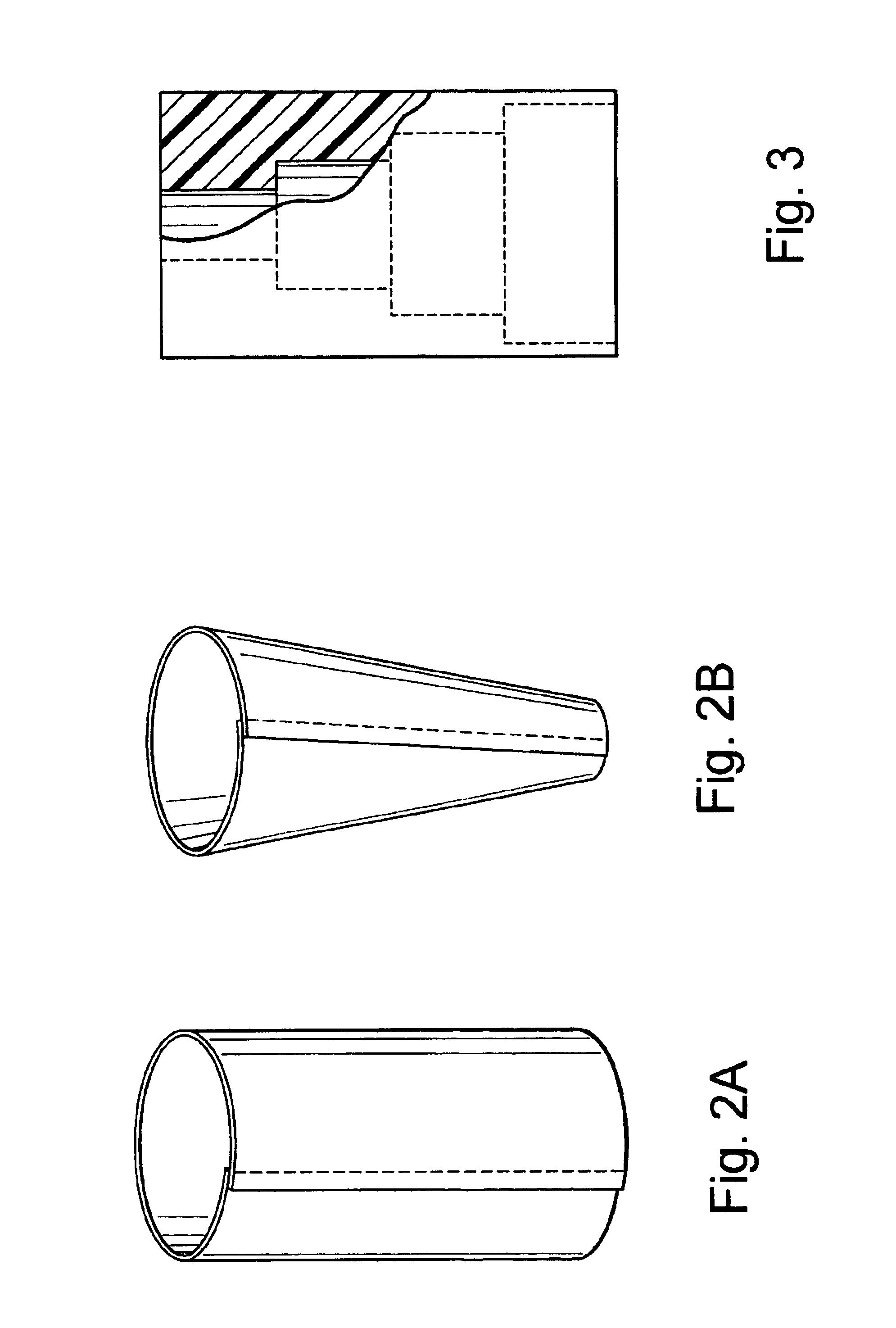
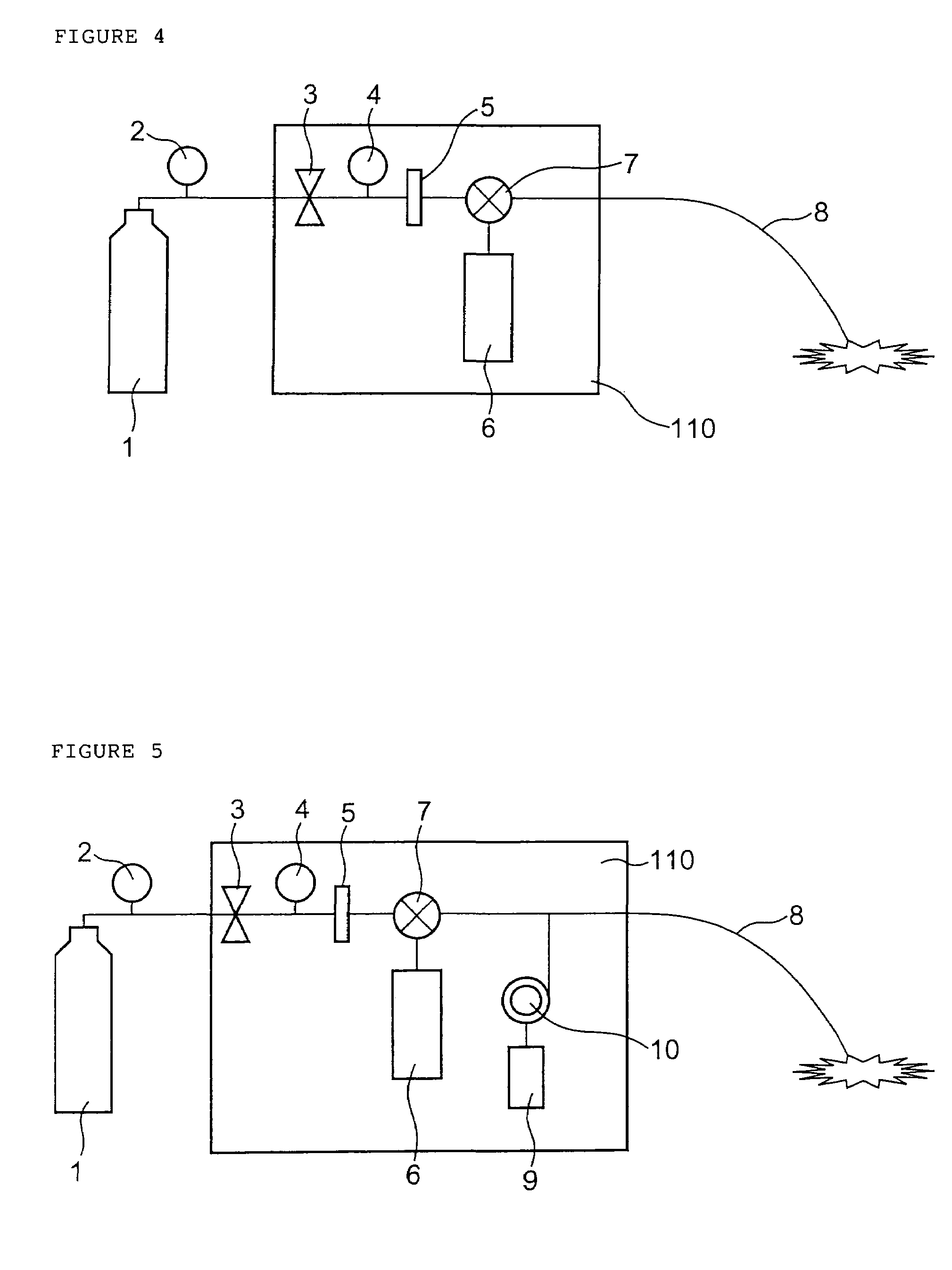
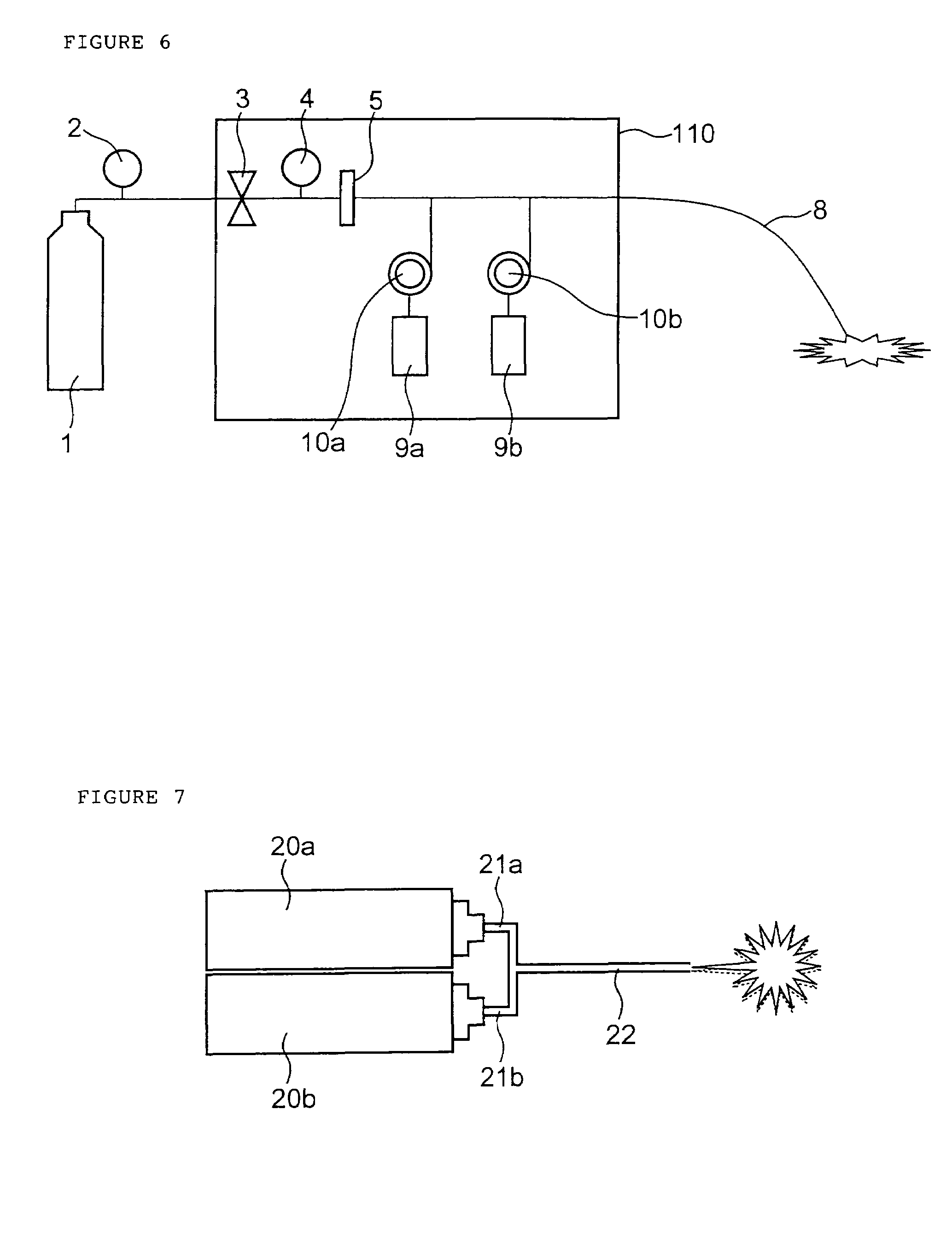
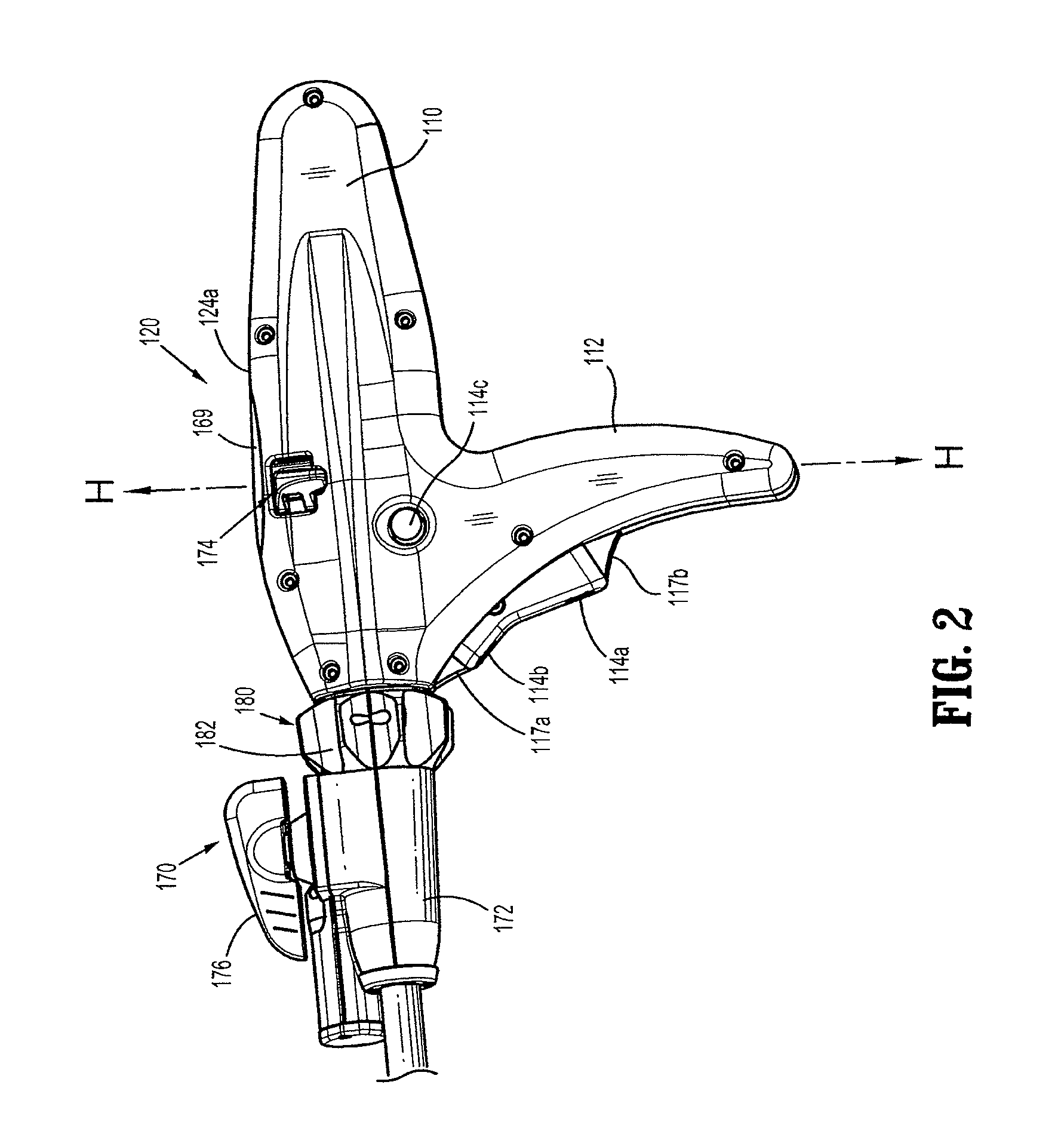
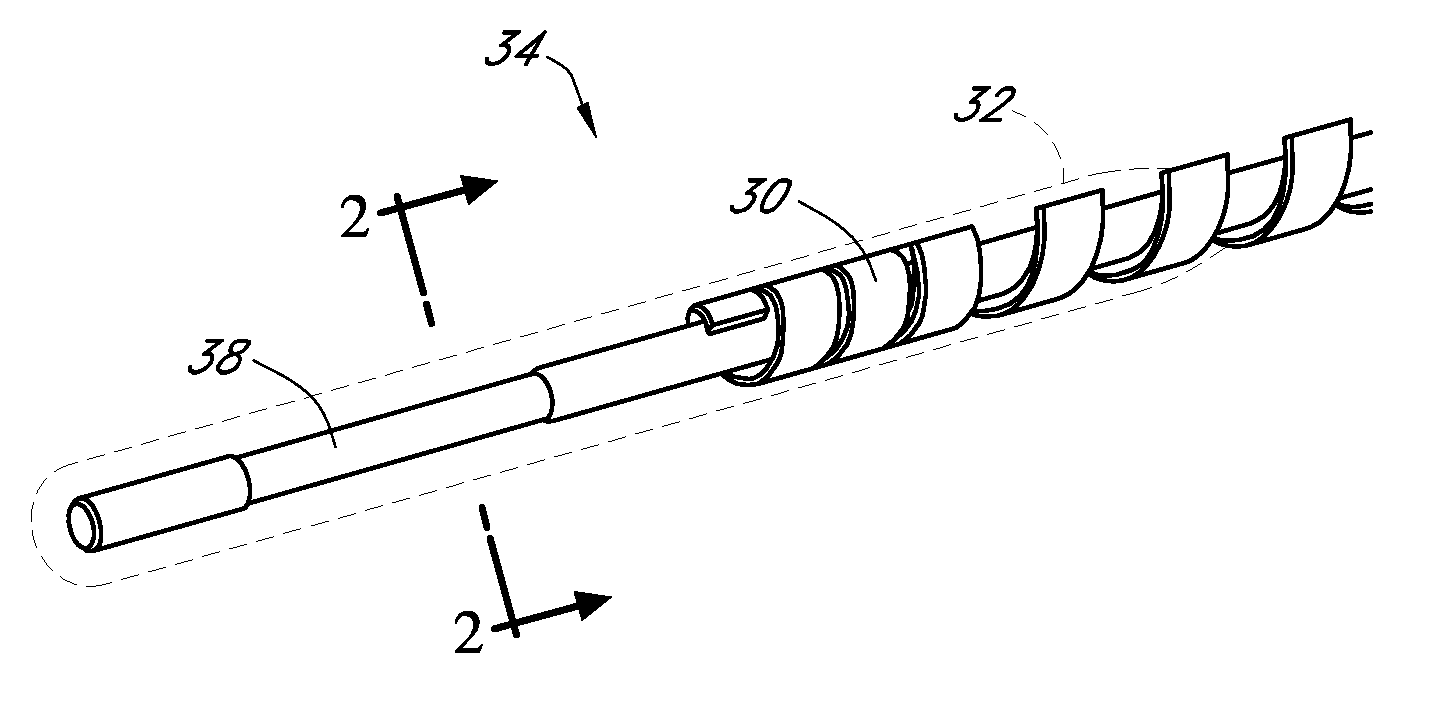
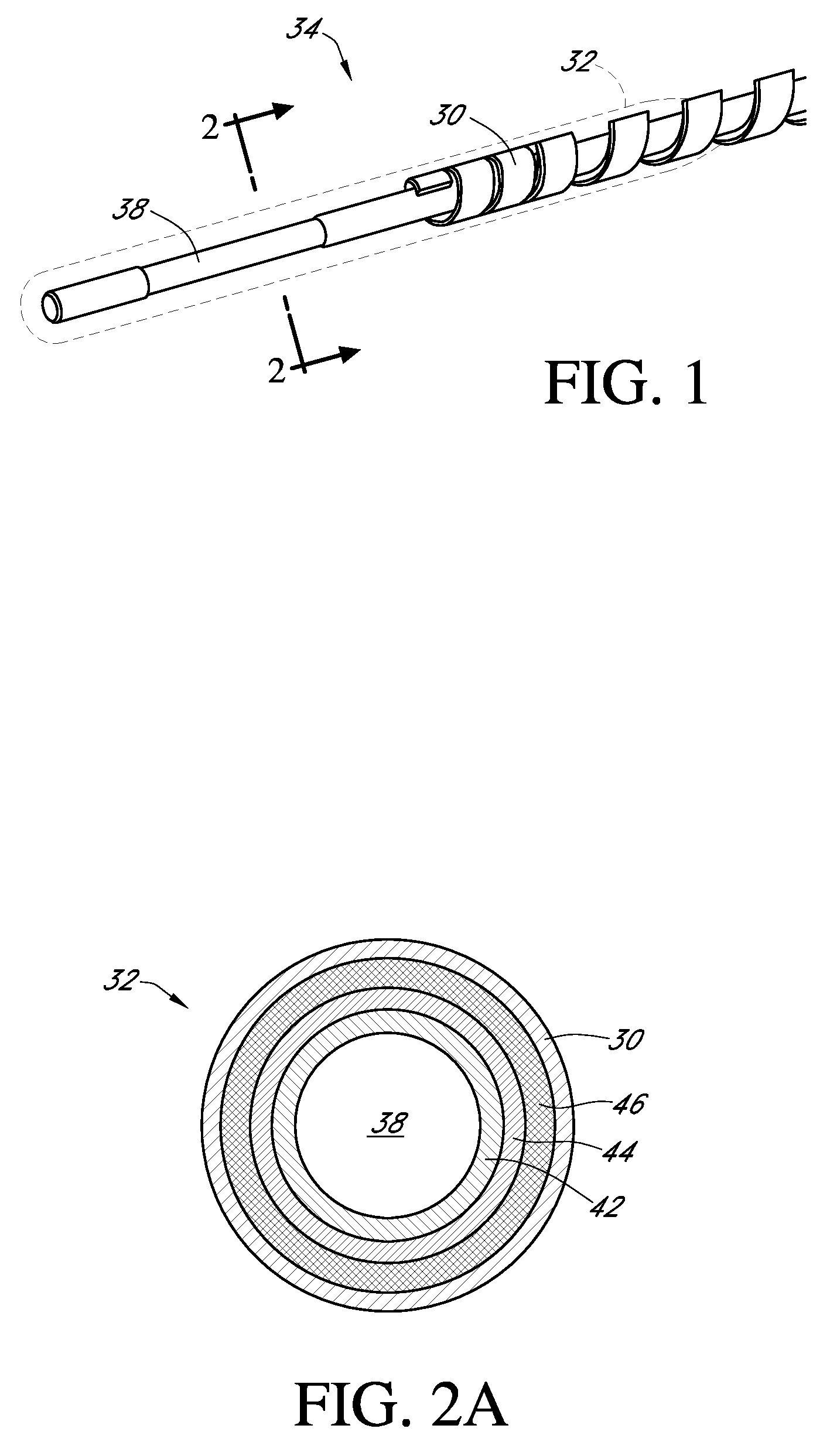
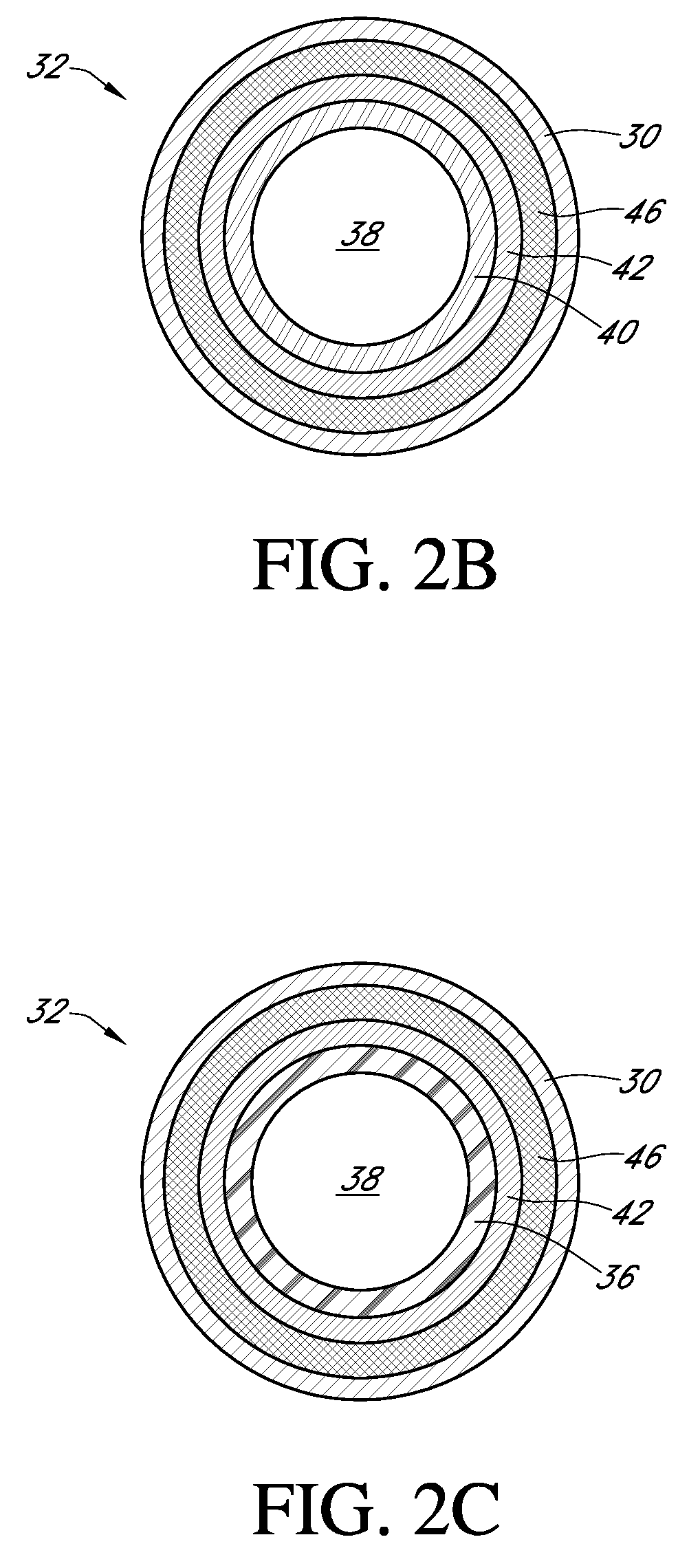
Activated polymer articulated instruments and methods of insertion
An electro-polymeric articulated endoscope and method of insertion are described herein. A steerable endoscope having a segmented, elongated body with a manually or selectively steerable distal portion and an automatically controlled proximal portion can be articulated by electro-polymeric materials. These materials are configured to mechanically contract or expand in the presence of a stimulus, such as an electrical field. Adjacent segments of the endoscope can be articulated using the electro-polymeric material by inducing relative differences in size or length of the material when placed near or around the outer periphery along a portion of the endoscope.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
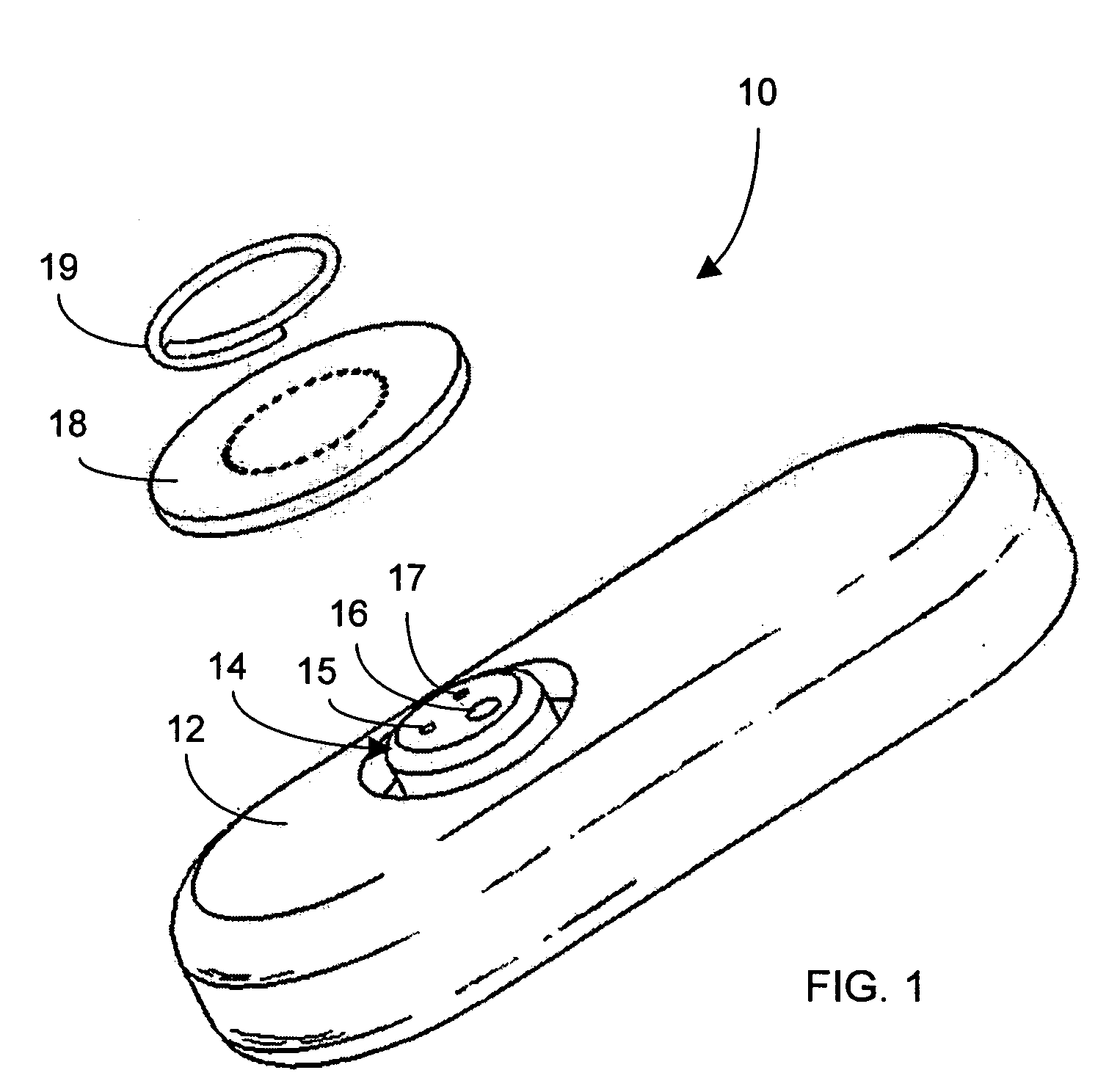
Internal backbone structural chassis for a surgical device
ActiveUS9113880B2Reduce Medical WasteAccurate configurationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsOperating pointEmbedded system
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional biopolymeric materials and methods
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional cross-linked proteinaceous biopolymeric materials that may be implanted in vivo, and methods of making such materials are disclosed. The biopolymeric materials most preferably include reinforcing media, such as biocompatible fibrous or particulate materials. In use, the preformed, shaped biopolymeric materials may be applied to tissue in need of repair and then sealed around its edges with a liquid bioadhesive. In such a manner, repaired tissue which is capable of withstanding physiological pressures may be provided.
Owner:CRYOLIFE
Silicone composition for biocompatible membrane
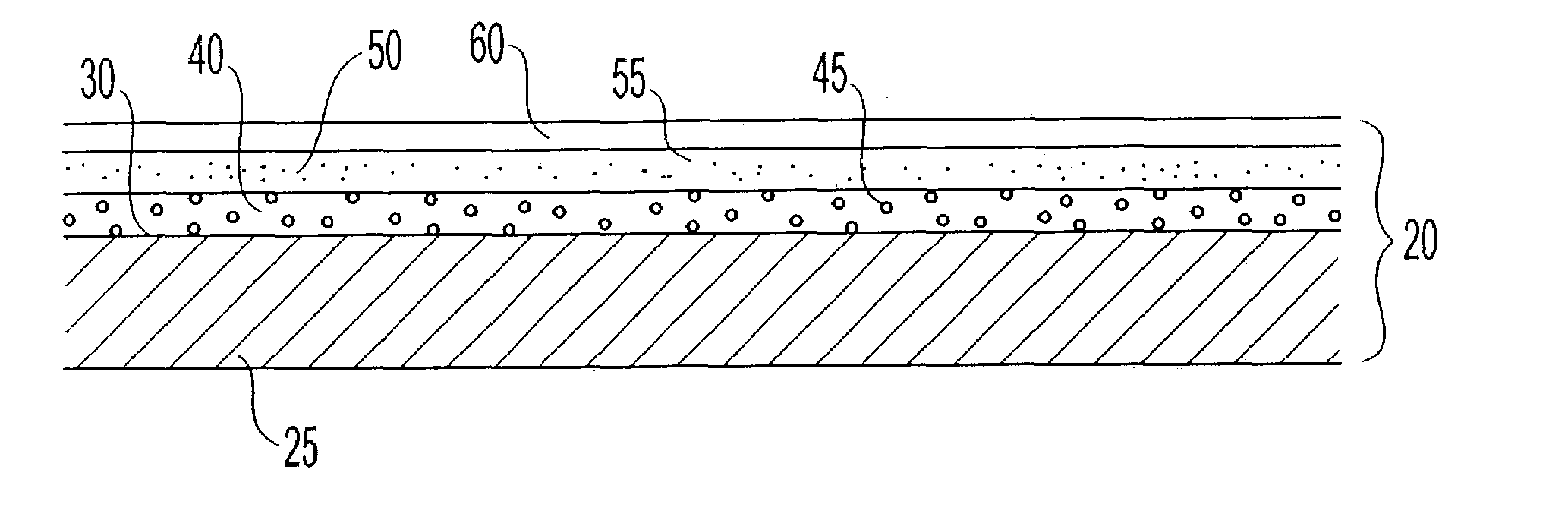
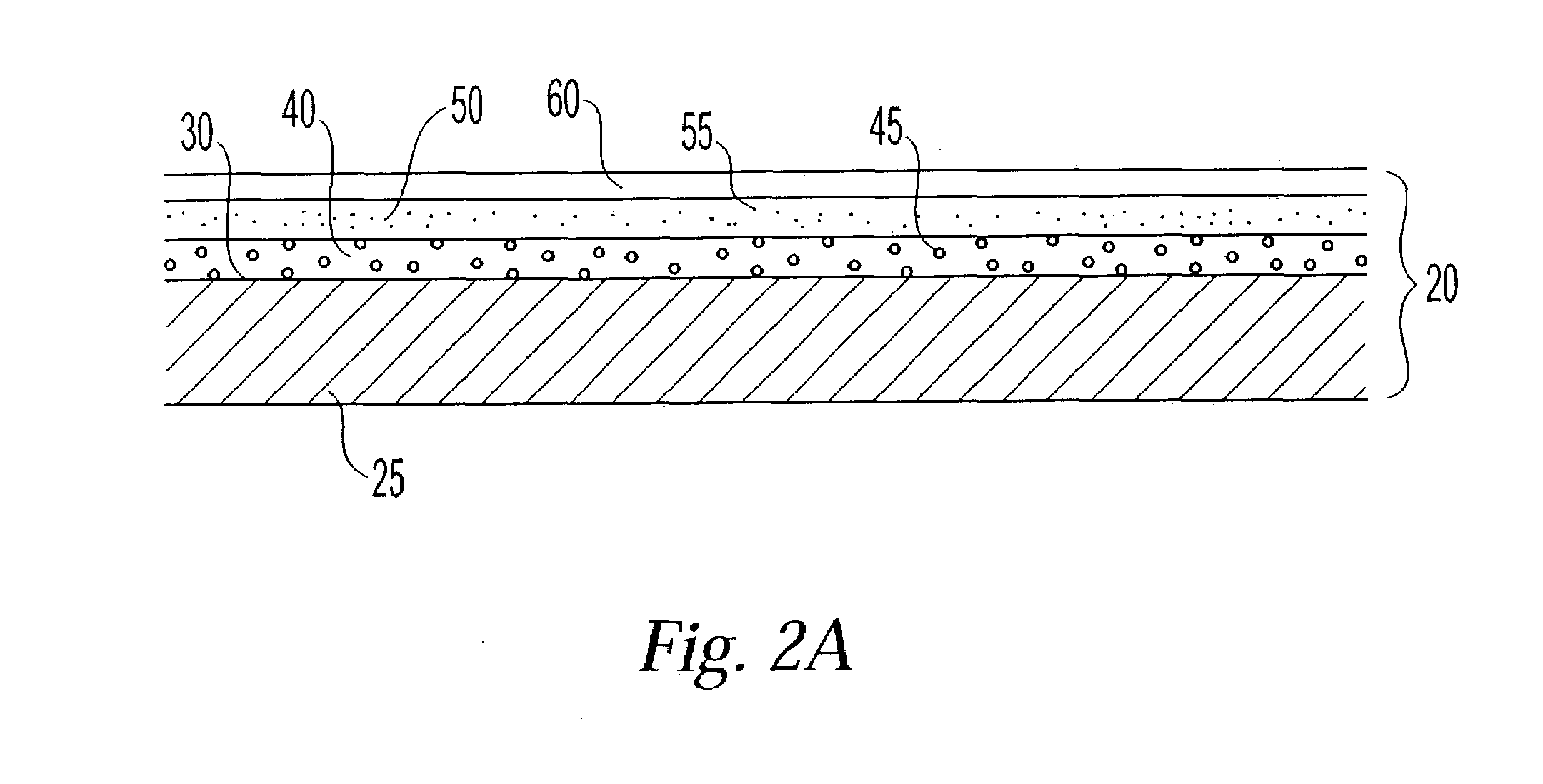
InactiveUS20050090607A1Microbiological testing/measurementSynthetic resin layered productsSensor materialsPolymer
Owner:DECOM
Method for preparing two-layer bicomposite collagen material for preventing post-operative adhesions
InactiveUS6596304B1Improve propertiesAvoid stickingPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgerySurgical operationPost operative
A bicomposite material based on collagen is prepared which has two closely bound layers and is biocompatible, non-toxic, hemostatic and biodegradable in less than a month, and can be used in surgery to achieve hemostasis and prevent post-surgical adhesion. To prepare the material, a solution of collagen or gelatin, which may contain glycerine and a hydrophilic additive such as polyethylene glycol or a polysaccharide, is poured onto an inert support to form a layer 30 .mu.m to less than 100 .mu.m thick. Then a polymeric porous fibrous layer is applied during gelling of the collagen or gelatin, and the resultant material is dried. The polymeric porous fibrous layer may be made of collagen or a polysaccharide, and have a density of not more than 75 mg / cm.sup.2, a pore size from 30 .mu.m to 300 .mu.m and a thickness of 0.2 cm to 1.5 cm.
Owner:IMEDEX BIOMATERIAUX CHAPONOST
Compliant osteosynthesis fixation plate
ActiveUS7931695B2Maintaining structural rigidityBending stabilityBone implantBone platesMedicineLiving body
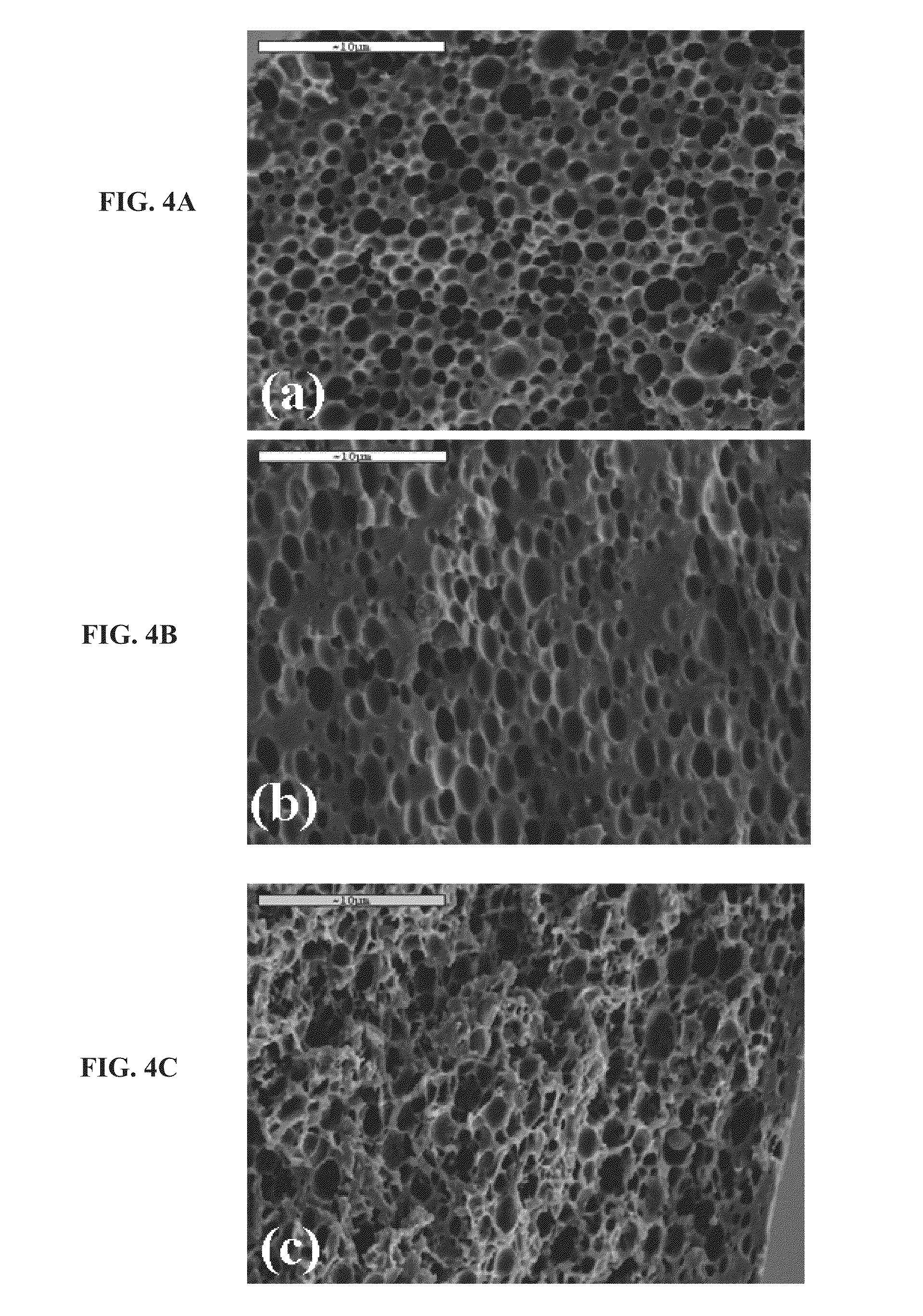
A bendable polymer tissue fixation device suitable to be implanted into a living body, comprising a highly porous body, the porous body comprising a polymer, the porous body comprising a plurality of pores, the porous body being capable of being smoothly bent, wherein the bending collapses a portion of the pores to form a radius curve, the polymer fixation device being rigid enough to protect a tissue from shifting. In a preferred embodiment the polymer fixation device may be capable of being gradually resorbed by said living body. In one embodiment, the polymer fixation device comprises a plurality of layers distinguishable by various characteristics, such as structural or chemical properties. In another embodiment, the polymer fixation device may comprise additional materials; the additional materials serving to reinforce or otherwise alter the structure or physical characteristics of the device, or alternatively as a method of delivering therapy or other agents to the system of a living being.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
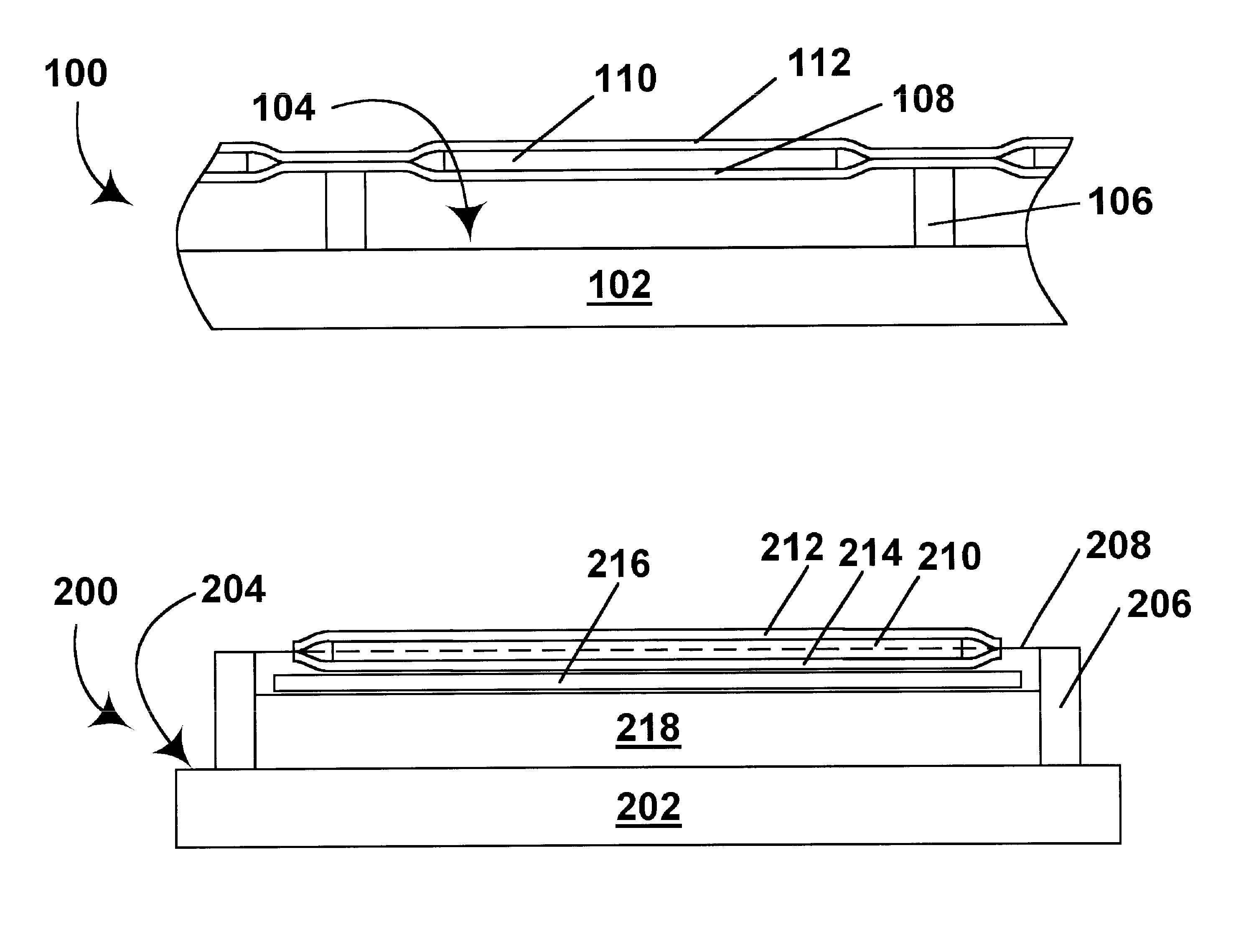
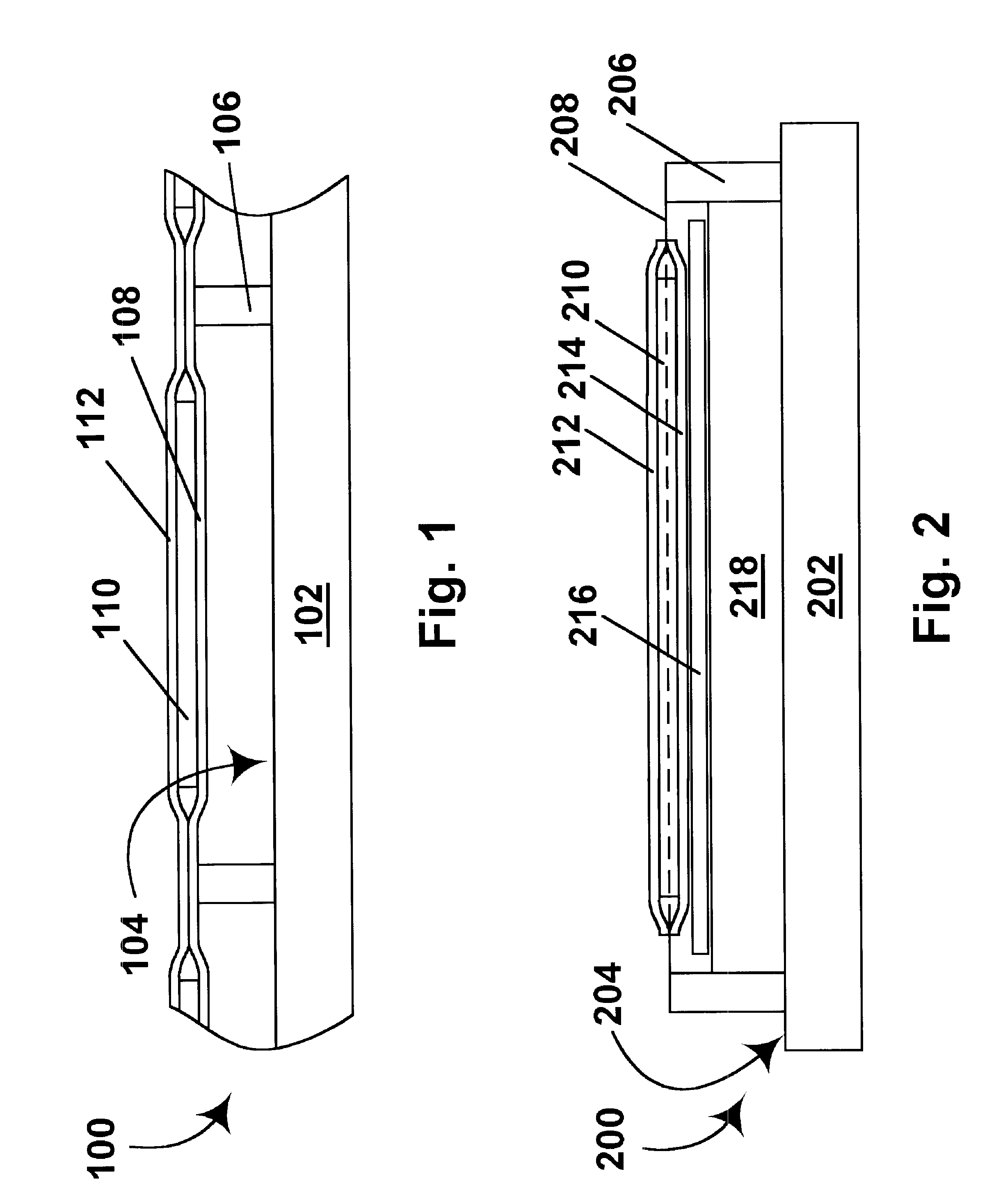
Controlling the dissolution of dissolvable polymer components in plural component fibers
The dissolution of dissolvable components in plural component polymer fibers is achieved by providing a polymer fiber including at least two sections, where at least one fiber section includes a dissolvable component. The rate at which at least part of the fiber dissolves is controlled by at least one of a fiber section having a non-round cross-sectional geometry, and at least two fiber sections including two different dissolvable components. In an exemplary embodiment, island-in-the-sea fibers are formed with non-round and elongated cross-sectional geometries. In another embodiment, sheath-core fibers are formed in which the sheath and core include different dissolvable components.
Owner:HILLS CO
Drug administration method
InactiveUS7427607B2Reduce weightPrevention of the adhesion of an organBiocidePowder deliveryBiopolymerDrug administration
A method of administering a drug whereby a fine drug powder can be accurately administered to a target site (in particular, a target site in the body cavity) via fluidization and spraying with a gas by using a micro tube. Concerning the administration mode, in particular, the drug alone or a biopolymer is administered or the biopolymer is employed as a carrier in the above method. More specifically speaking, a method of administering a fine drug powder which comprises finely milling one or more types fine particles of the drug and / or the biopolymer, blending them each other, fluidizing the blend with a gas, then transporting the fluidized matter in a micro tube by the gas stream and spraying the fine drug powder from the tip of the micro tube toward the target site. Further, an administration method which comprises concentrically providing a capillary tube in the micro tube, supplying an aqueous solution of the drug and / or the biopolymer from the capillary tube into the gas stream and then mixing it with other fine particles of the drug and / or the biopolymer under transportation by the gas.
Owner:NEXT21 KK
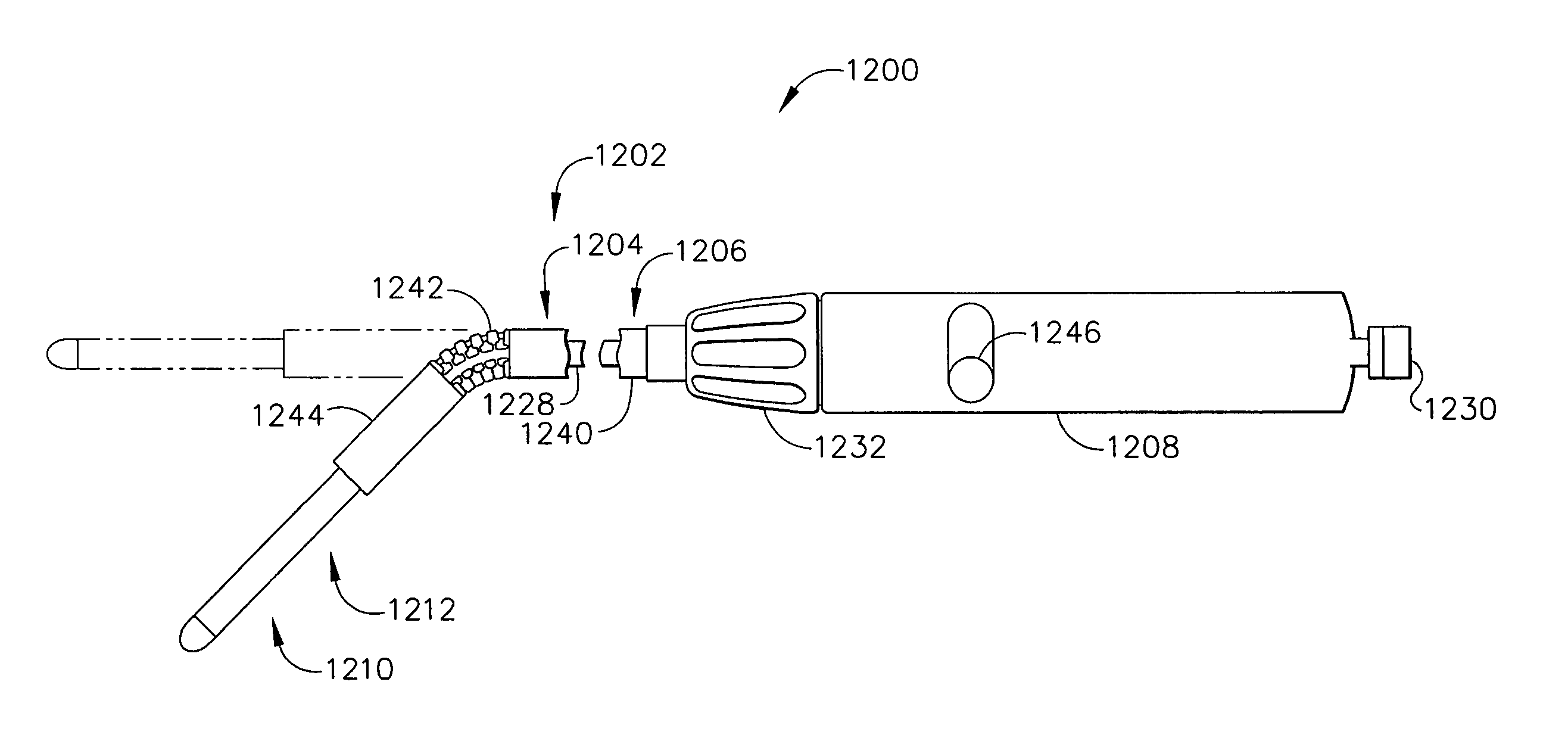
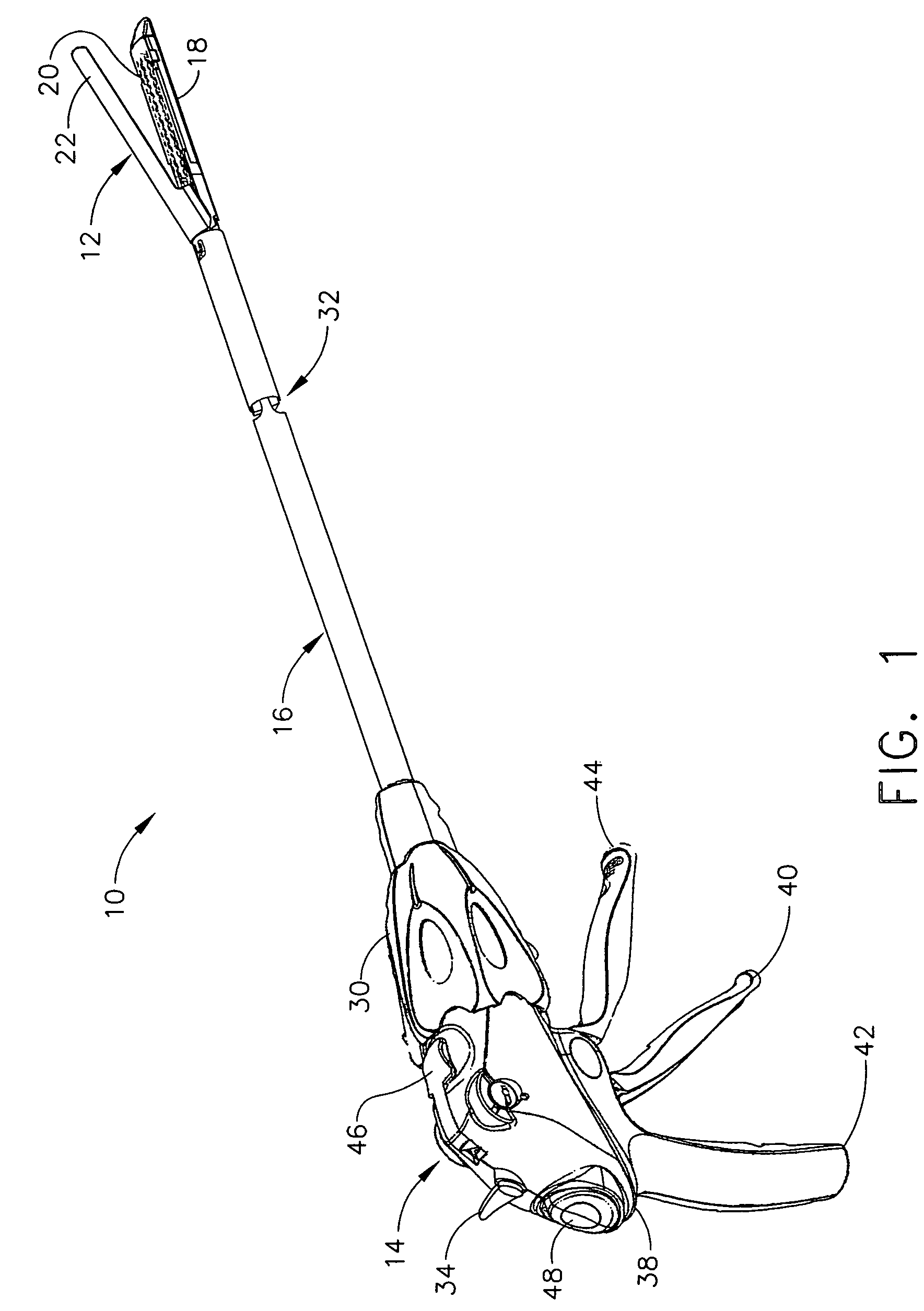
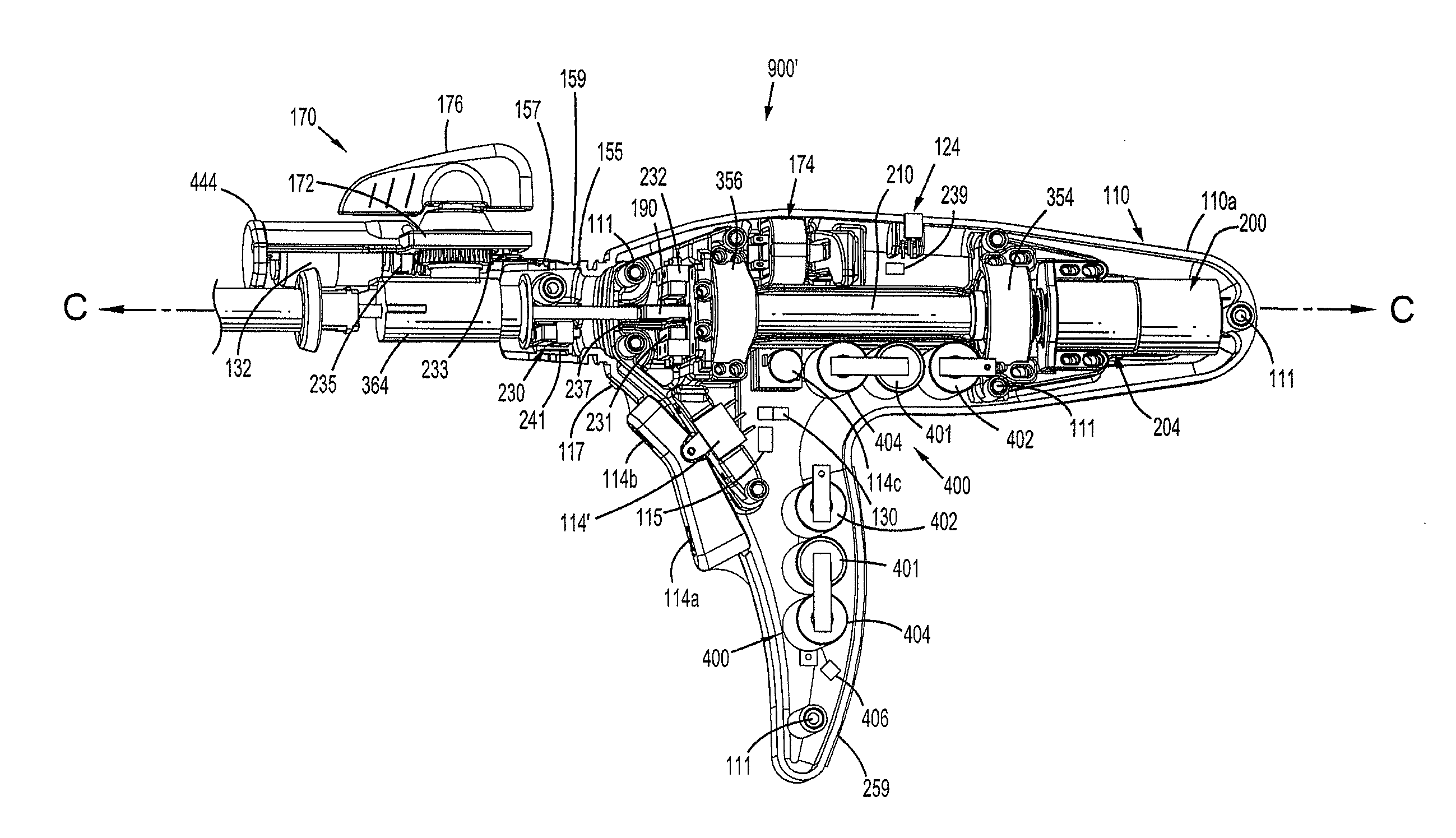
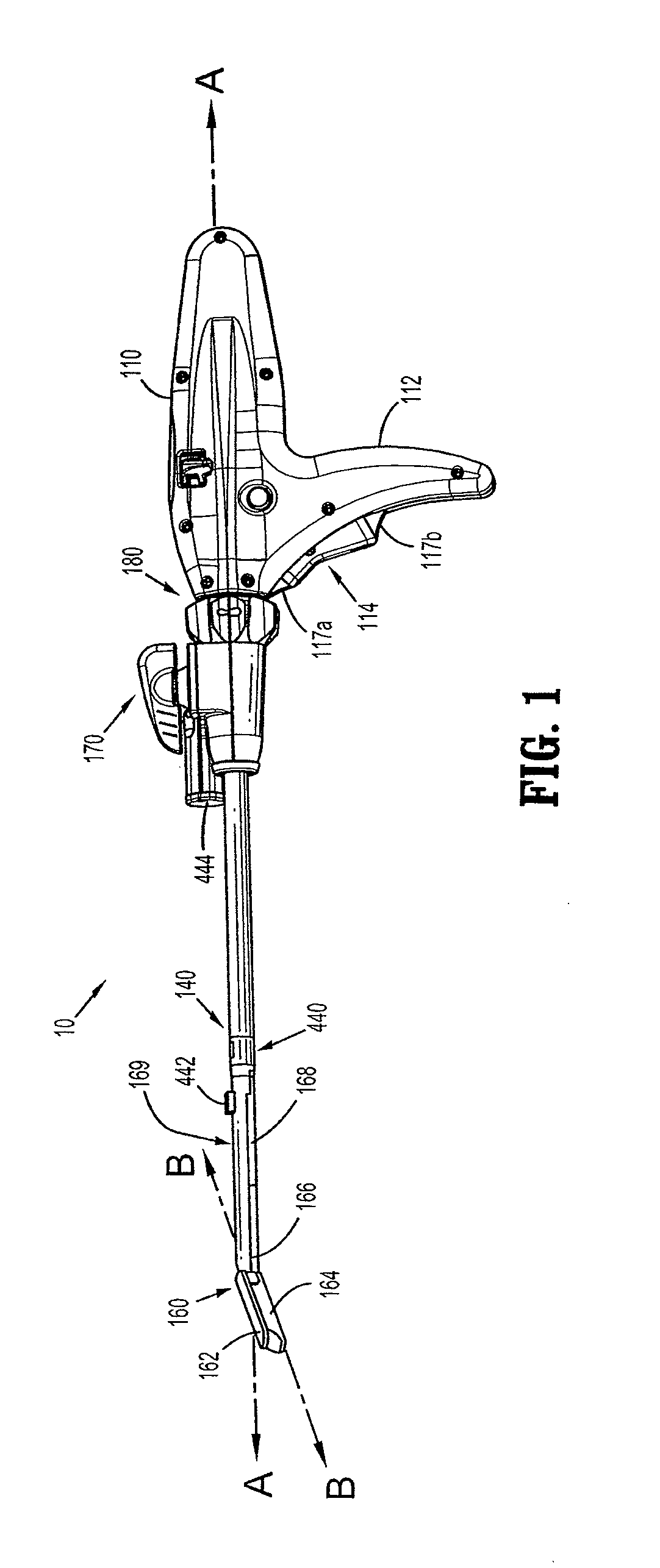
Surgical instrument incorporating an electrically actuated articulation locking mechanism
A surgical instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use articulates an end effector by including an articulation mechanism in an elongate shaft that incorporates an electrically actuated polymer (EAP) articulation locking mechanism actuator. Thereby, additional options for articulation become feasible, especially those that are actively powered and would otherwise dissipate heat and power if required to maintain position. Alternatively, a mechanically actuated articulation mechanism may be designed with reduced strength, and thus size, since the EAP articulation lock mechanism assists in preventing back driving after articulation. Versions of a. EAP articulation locking mechanism lock a pivoting articulation joint and others lock a flexible neck articulation joint.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
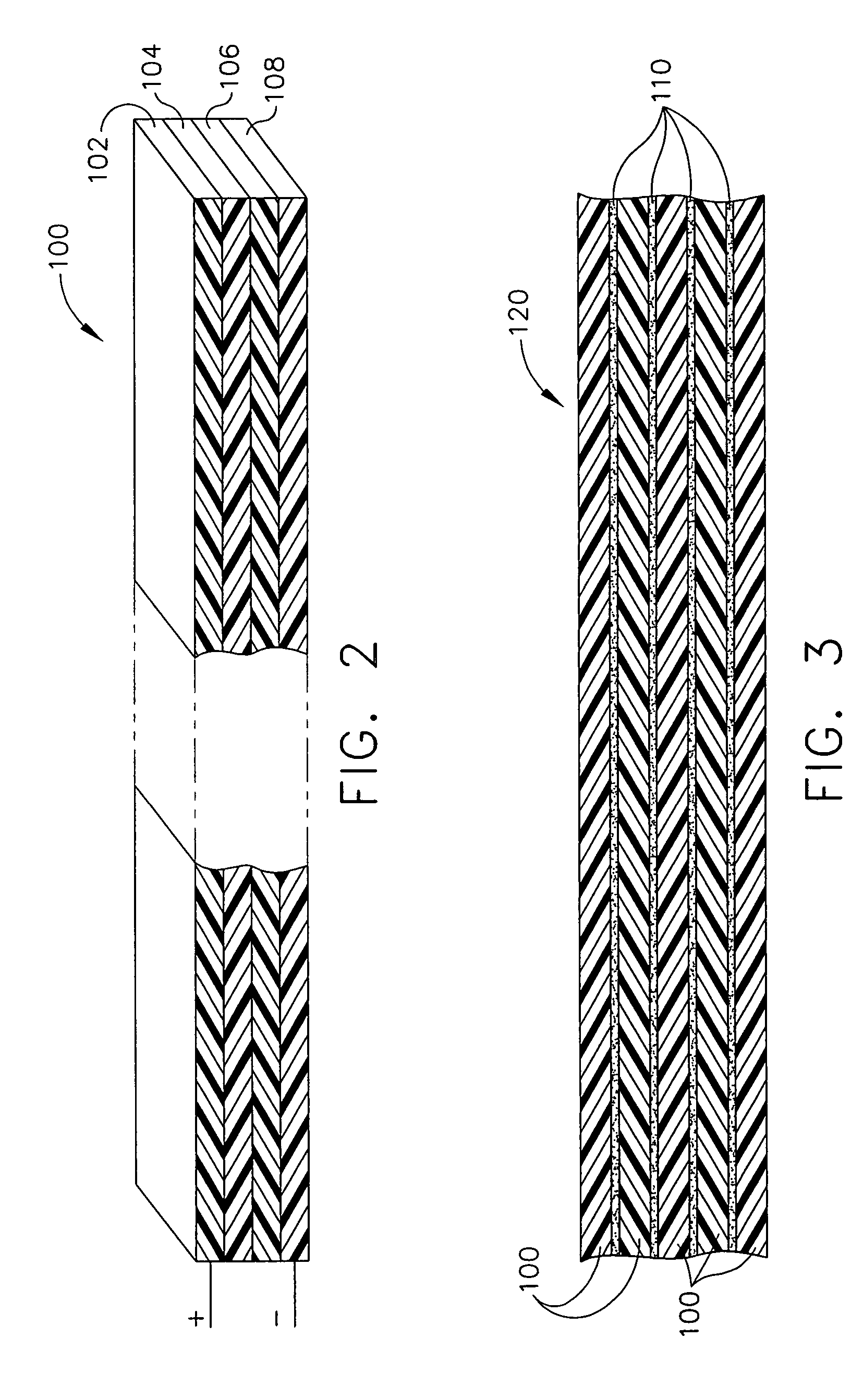
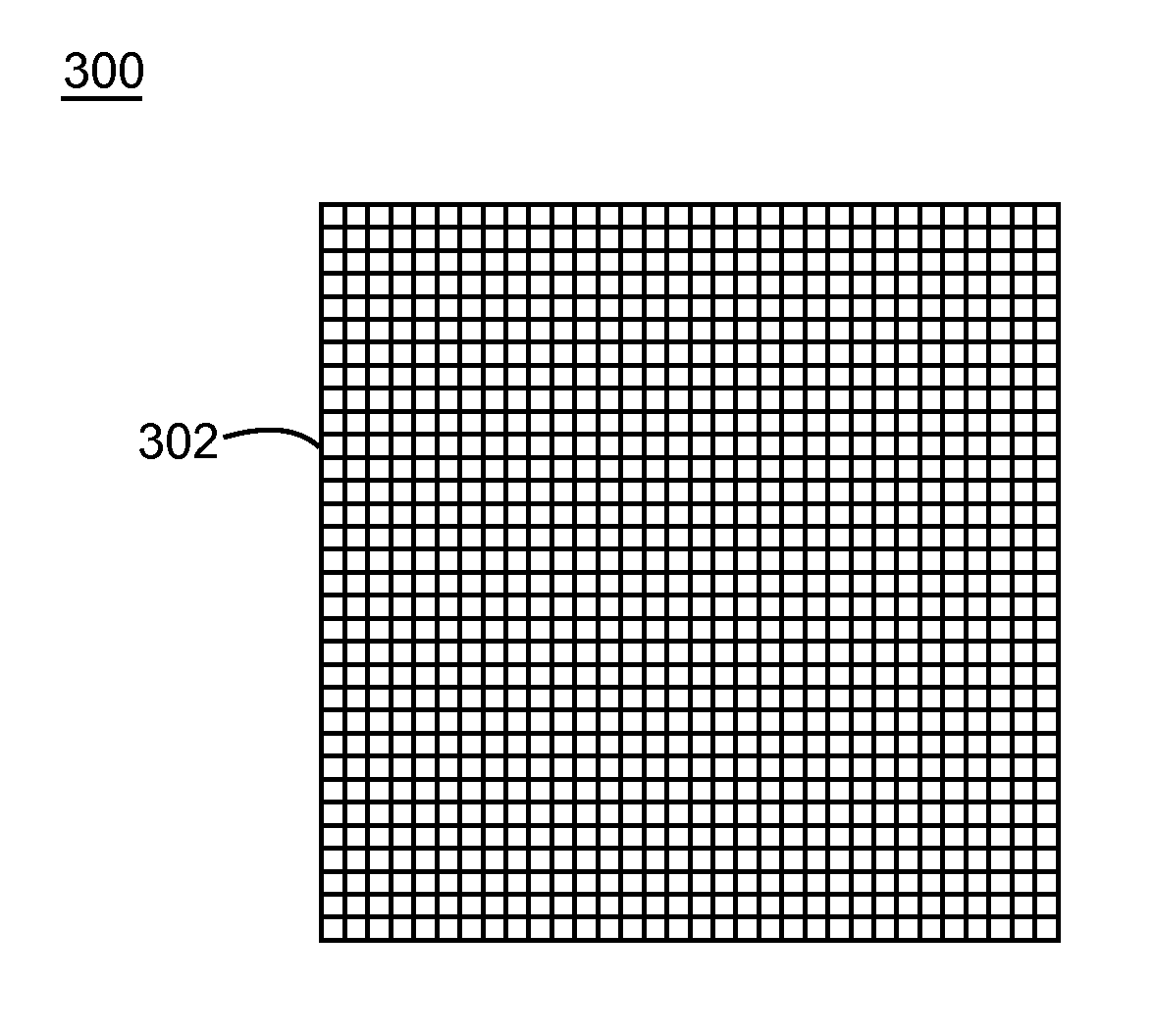
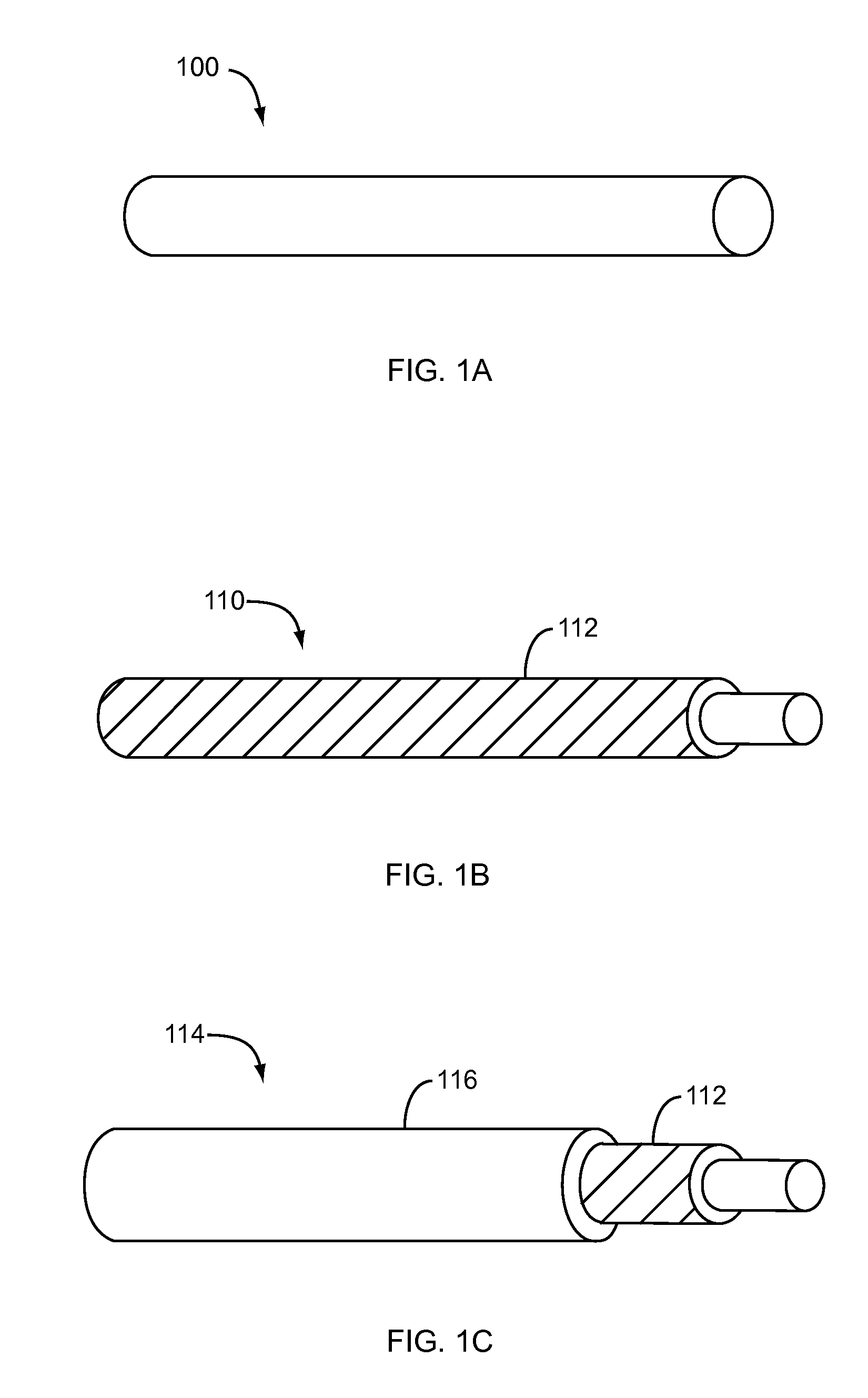
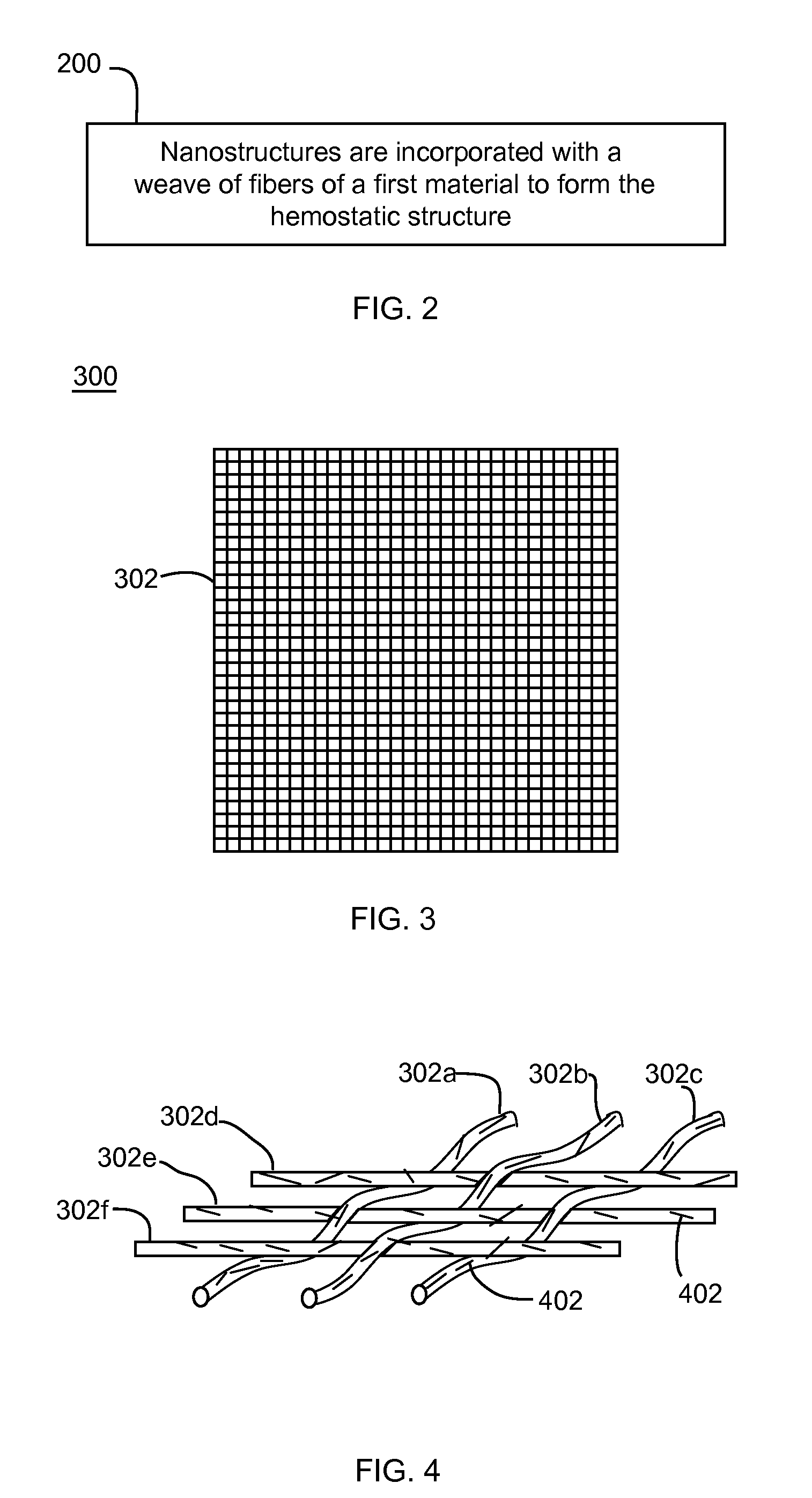
Nanostructure-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic structures
InactiveUS8319002B2Enhancing overall rate and strengthInduce platelet binding and efficient hemostasisBiocideSurgical adhesivesPlateletNanofiber
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for nanomaterial-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic medical devices are provided. Hemostatic materials and structures are provided that induce platelet binding, including platelet binding and the coagulation of blood at a wound / opening caused by trauma, a surgical procedure, ulceration, or other cause. Example embodiments include platelet binding devices, hemostatic bandages, hemostatic plugs, and hemostatic formulations. The hemostatic materials and structures may incorporate nanostructures and / or further hemostatic elements such as polymers, silicon nanofibers, silicon dioxide nanofibers, and / or glass beads into a highly absorbent, gelling scaffold. The hemostatic materials and structures may be resorbable.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Scaffold for connective tissue repair
A connective tissue scaffold including opposed first and second anchoring segments formed from a plurality of bioresorbable polymeric fibers oriented in a direction substantially parallel to a longitudinal axis of the scaffold and a plurality of bioresorbable polymeric fibers oriented in a direction substantially transverse to a longitudinal axis of the scaffold. A central segment joins the first and second anchoring segments and includes a plurality of bioresorbable polymeric fibers oriented in a direction substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the scaffold. The scaffold can also a tissue particle and / or biological component.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Electronically activated capture device
InactiveUS7063671B2Great driving forceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsControl signalElectroactive polymer actuators
A novel capture device apparatus comprising: (a) a capture device portion, at least a part of which is adaptable for insertion into a patient and (b) a control unit. The capture device portion comprises one or more apertures and one or more electroactive polymer actuators that open and close the one or more apertures based on control signals sent from the control unit. In another aspect of the present invention, a method of capturing a specimen within a patient's body of provided. The method comprises (a) providing a capture device apparatus like that above, (b) inserting at least a portion of the capture device portion of the apparatus into the patient such that the capture device portion is adjacent the specimen; and (c) closing the one or more apertures using the control unit, thereby capturing the specimen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Extraction of solvents from drug containing polymer reservoirs
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Reinforced foam implants with enhanced integrity for soft tissue repair and regeneration
InactiveUS6852330B2Sufficient structural integritySufficient propertyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairSoft tissue repair
A biocompatible tissue repair stimulating implant or “scaffold” device, and methods for making and using such a device, are provided. The implant includes one or more layers of a bioabsorbable polymeric foam having pores with an open cell pore structure. A reinforcement component is also present within the implant to contribute enhanced mechanical and handling properties. The implant houses a biological component that may be released to tissue adjacent the location in which the implant is implanted to faciliate and / or expedite the healing of tissue. This biological component resides primarily within the foam component of the implant, being incorporated within pores formed within the foam.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
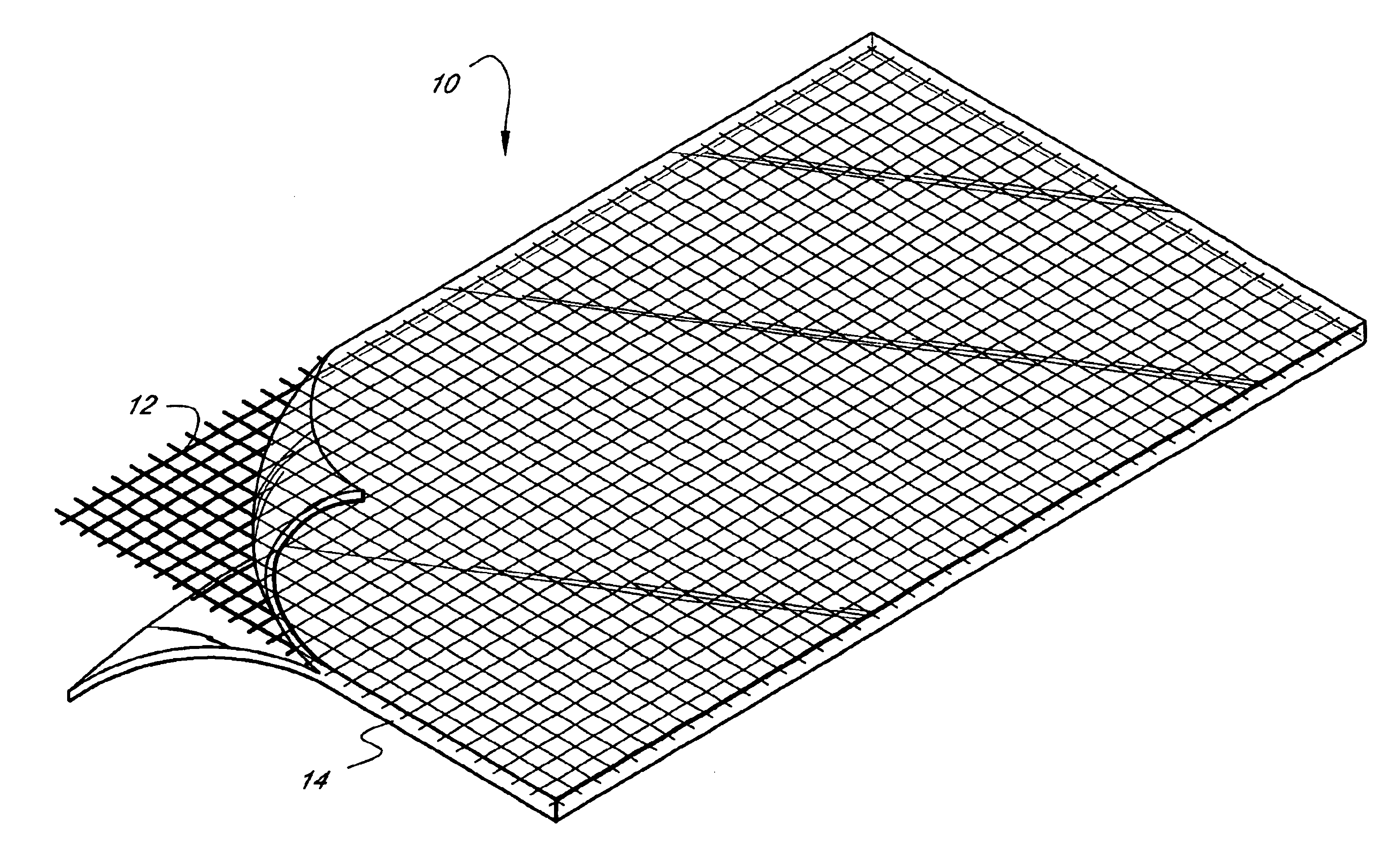
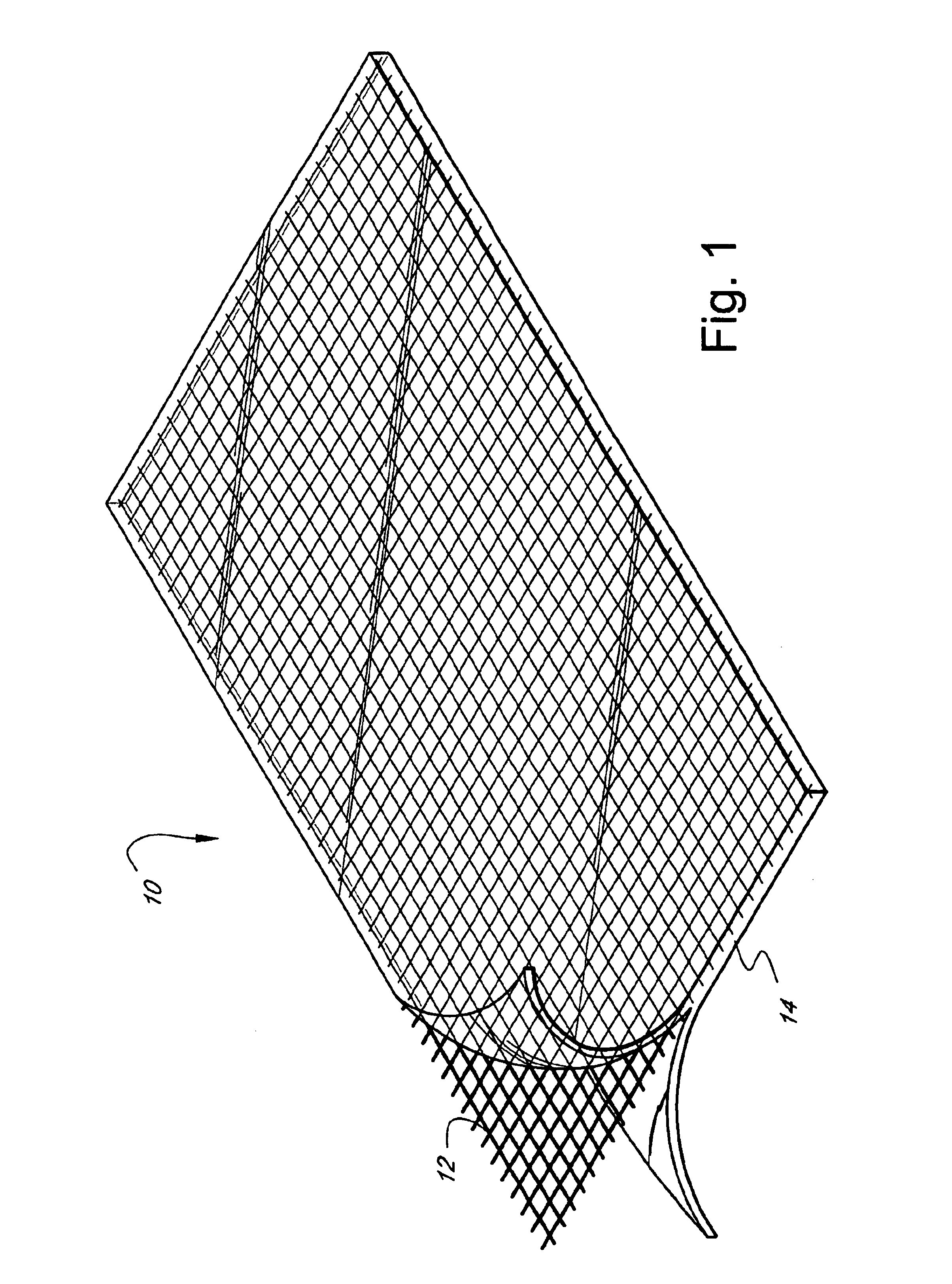
Wound closure material
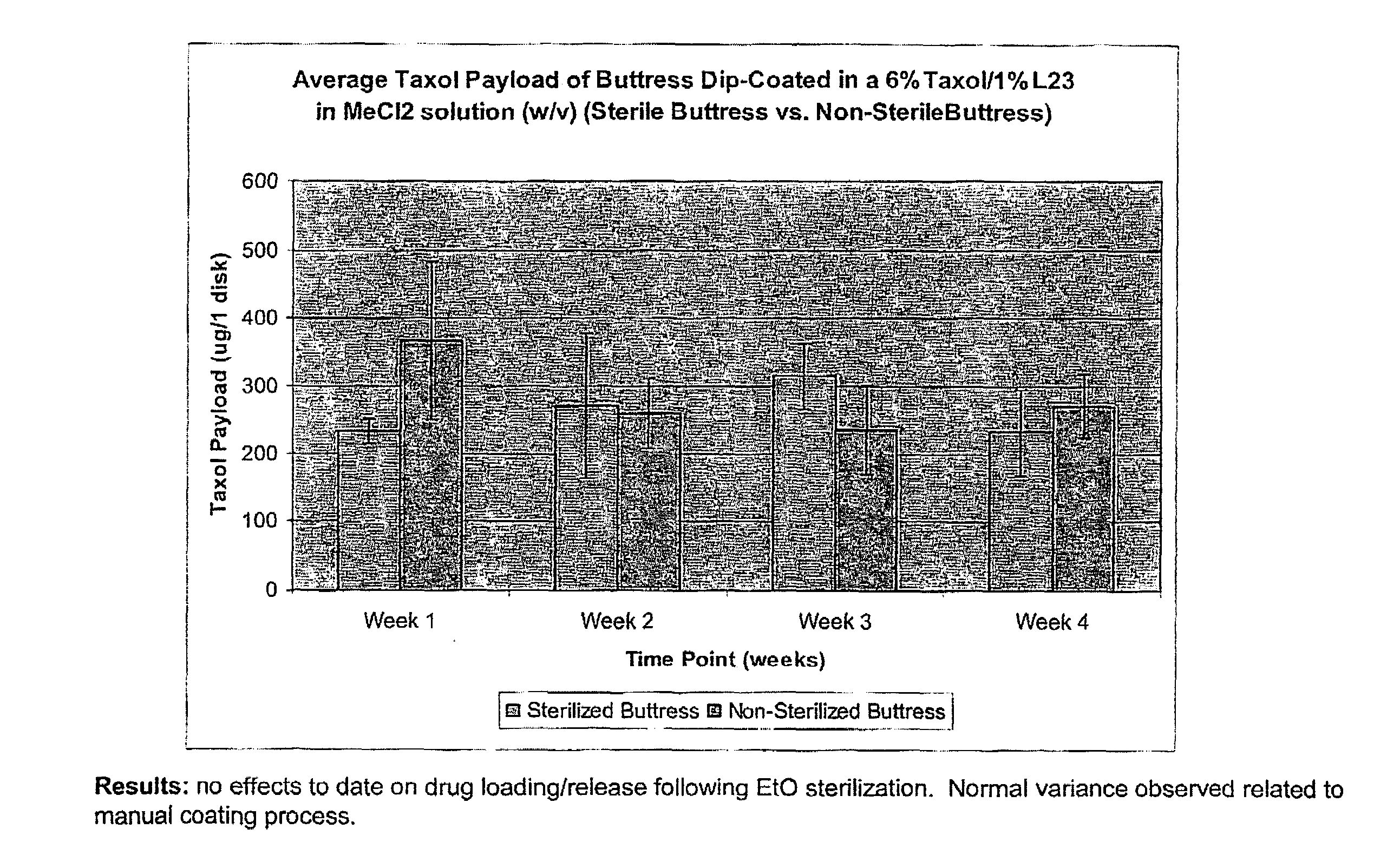
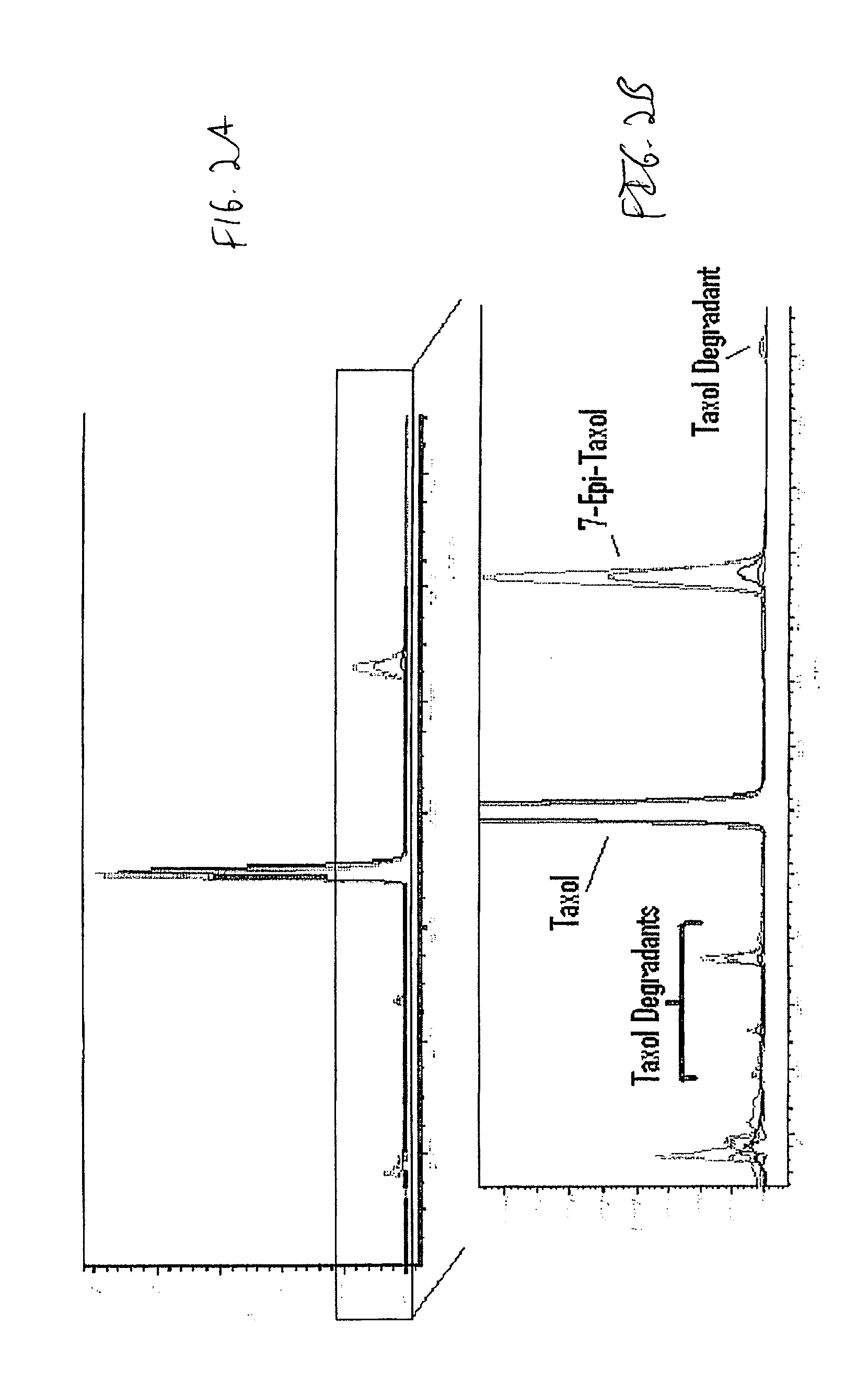
InactiveUS20100076489A1Prevent leakageSuture equipmentsHeavy metal active ingredientsButtressBiomedical engineering
Articles are provided having no orientation or a multi-directional orientation. Such articles may be in the form of films, ribbons, sheets, and / or tapes and may be utilized as buttresses with a surgical stapling apparatus or as reinforcing means for suture lines. The articles may be produced with a polymeric material having an agent, such as a chemotherapeutic agent or a radiotherapeutic agent, incorporated therein or applied as a coating thereon.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electrophoretic medium and display with improved image stability
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of particles suspended in a suspending fluid, the particles being capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium, the fluid having dissolved or dispersed therein a polymer having a number average molecular weight in excess of about 20,000, the polymer being essentially non-absorbing on the particles. The polymer improves the bistability of the display (i.e., the period for which a written image persist without the display being refreshed) but does not greatly increase the viscosity of the suspending fluid, thus keeping the switching time of the display within reasonable limits. The medium may be encapsulated, or may be in the form a polymer-dispersed electrophoretic medium.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Energetically-controlled delivery of biologically active material from an implanted medical device
InactiveUS7101394B2Facilitated releaseReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
A medical device and system capable of providing on-demand delivery of biologically active material to a body lumen patient, and a method of making such medical device. A first coating layer comprising a biologically active material and optionally a polymeric material is disposed on the surface of the medical device. A second coating layer comprising magnetic particles and a polymeric material is disposed on the first coating layer. The second coating layer, which is substantially free of a biologically active material, protects the biologically active material prior to delivery. The system includes the medical device and a source of energy, such as an electromagnetic or mechanical vibrational energy. When the patient is exposed to the energy source, the magnetic particles move out of the second coating layer and create channels therein through which the biologically active material can be released.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
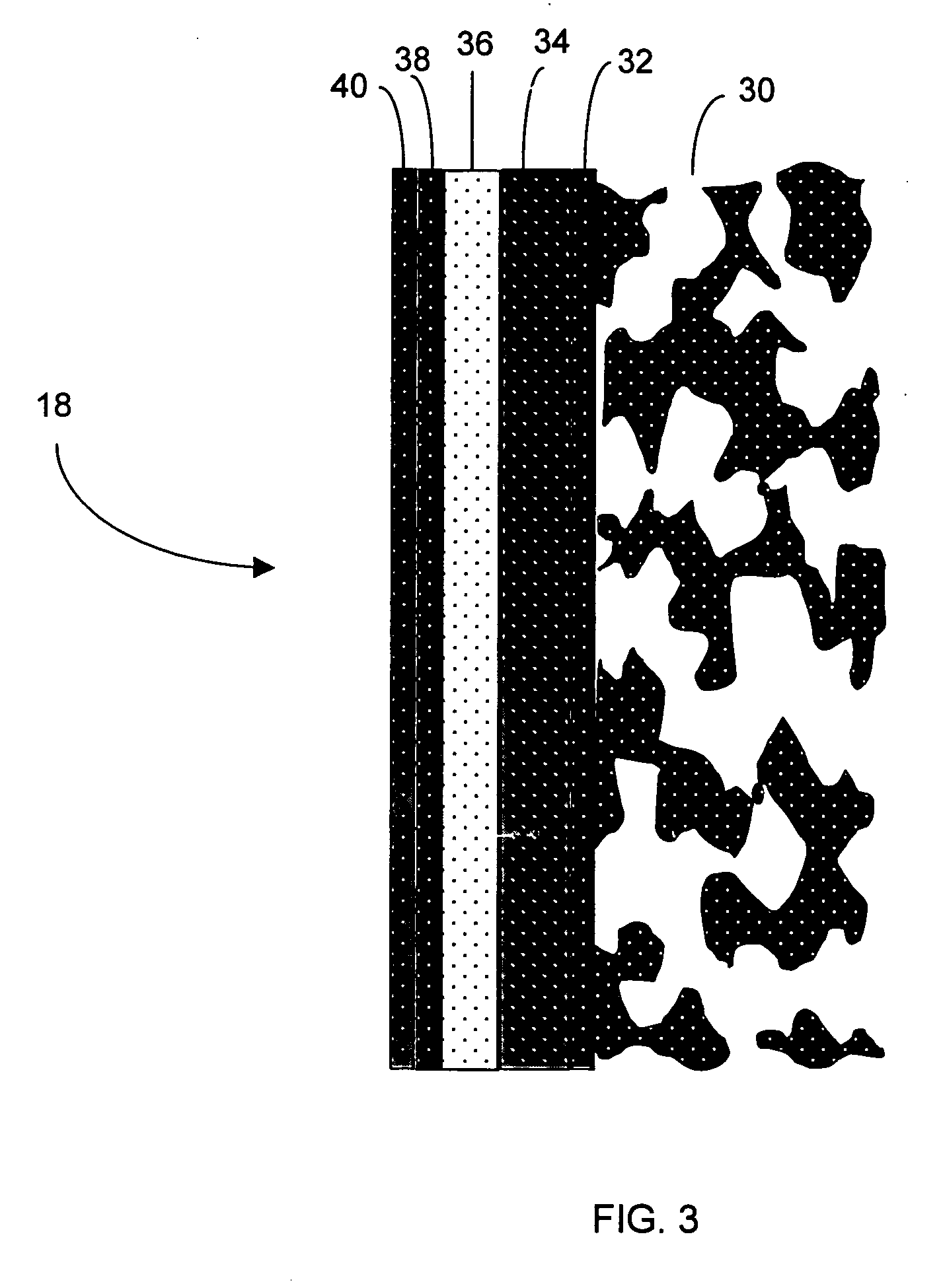
Silicone composition for biocompatible membrane
InactiveUS20080045824A1Prevent penetrationMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic resin layered productsSensor materialsBiosensor
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Method of preparation of bioabsorbable porous reinforced tissue implants and implants thereof
A biocompatible tissue implant. The tissue implant may be bioabsorbable, consists of a biocompatible polymeric foam. The tissue implant also includes a biocompatible reinforcement member. The polymeric foam and the reinforcement member are soluble in a lyophilizing solvent. The reinforcement may be annealed and / or coated.
Owner:DEPUY MITEK INC
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
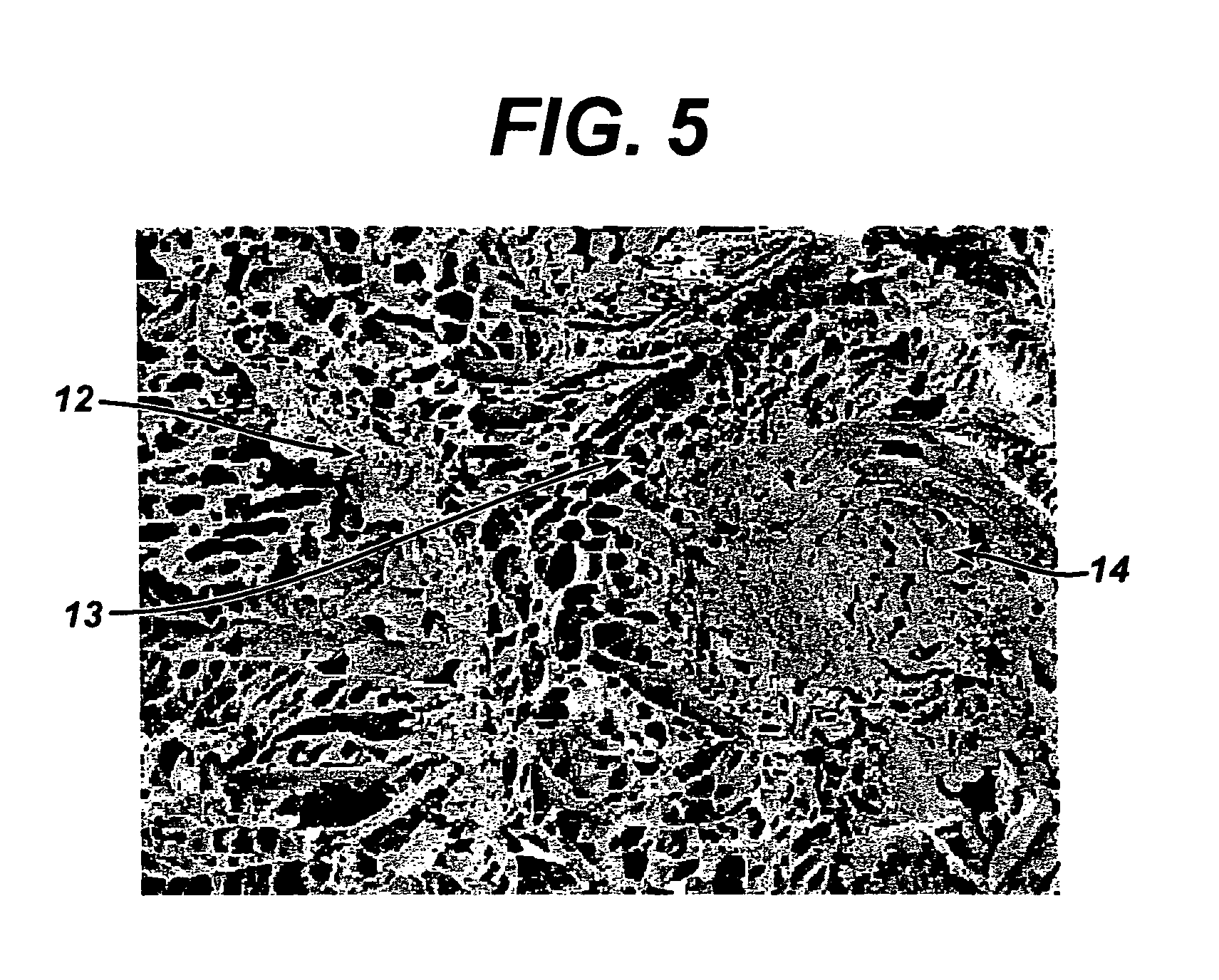
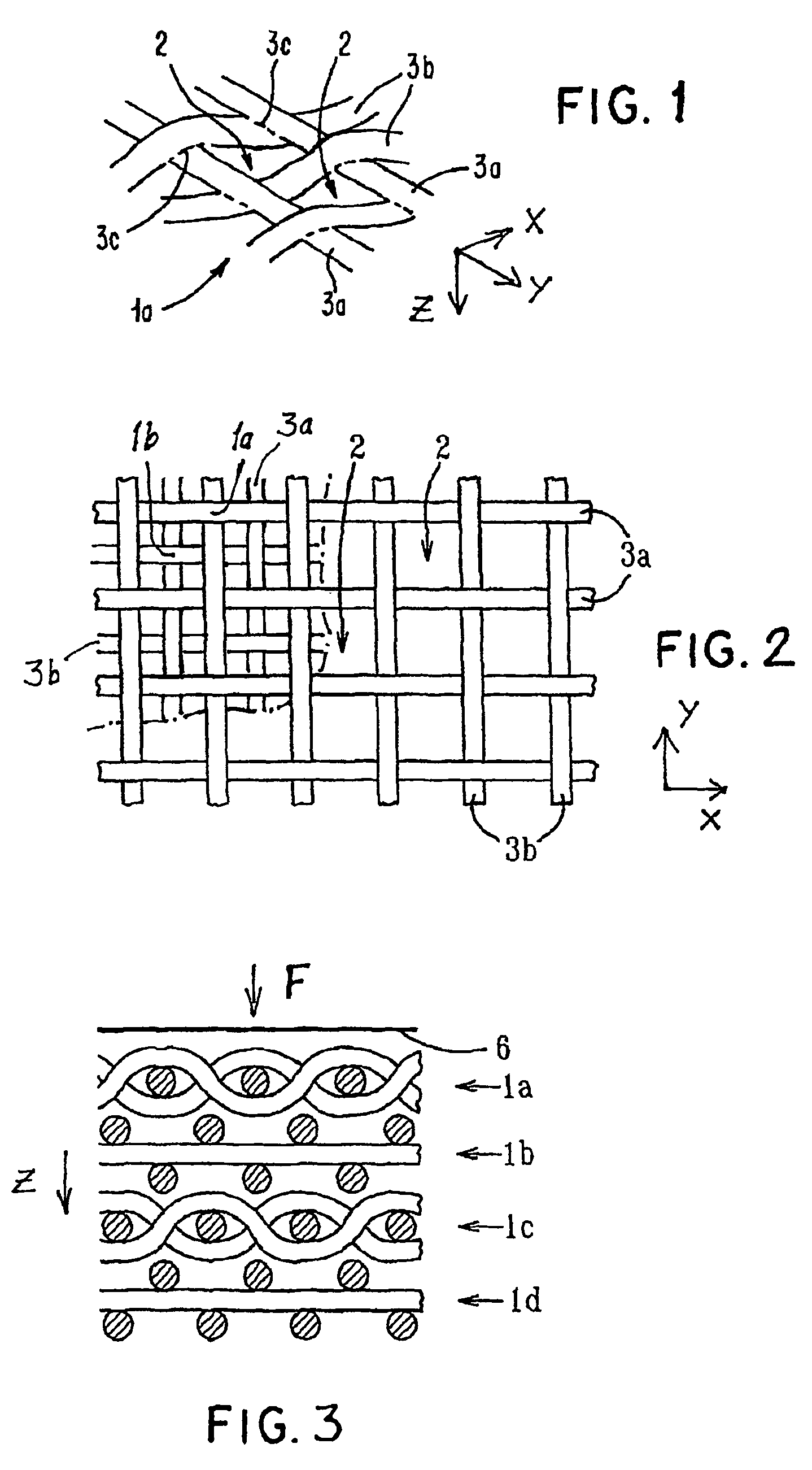
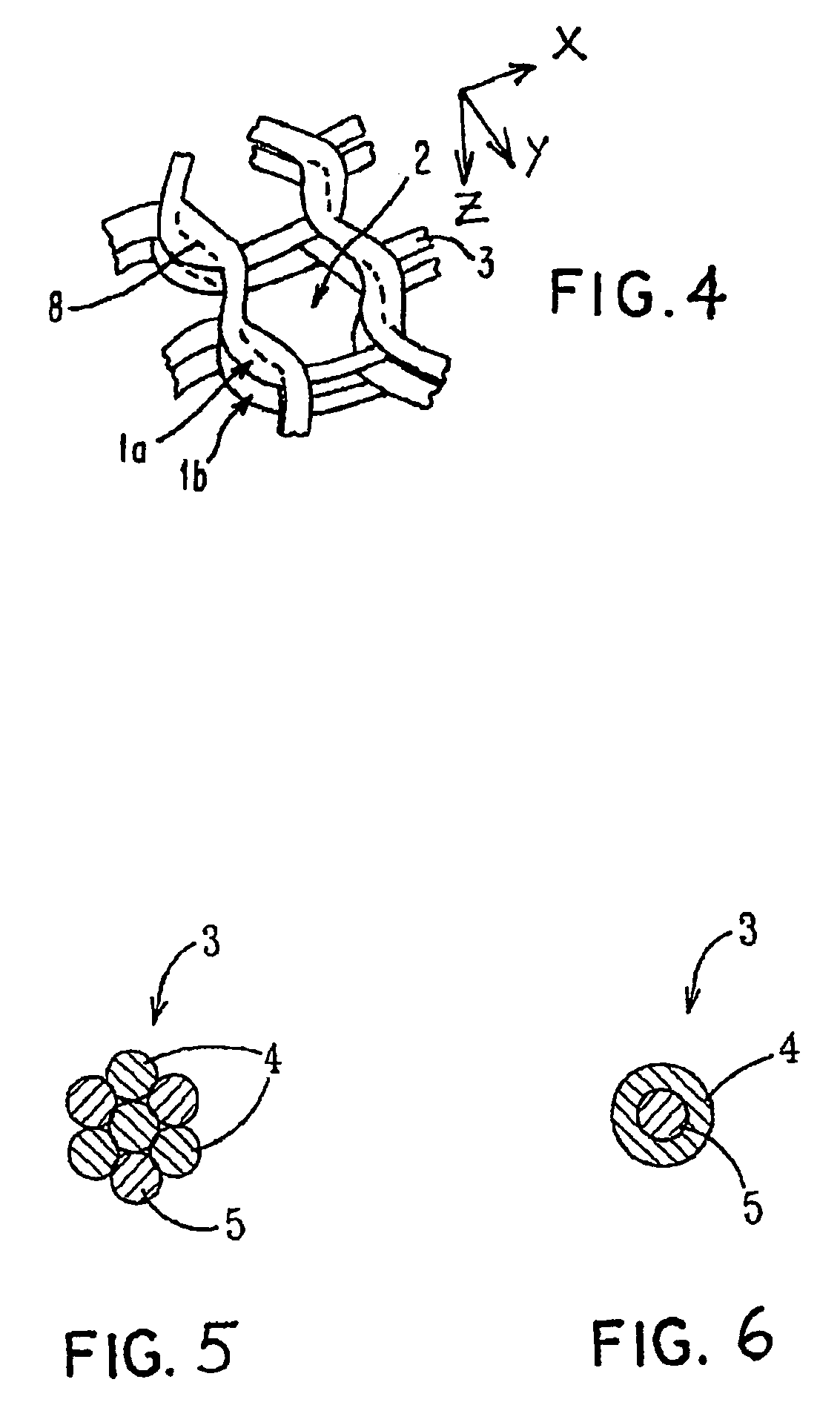
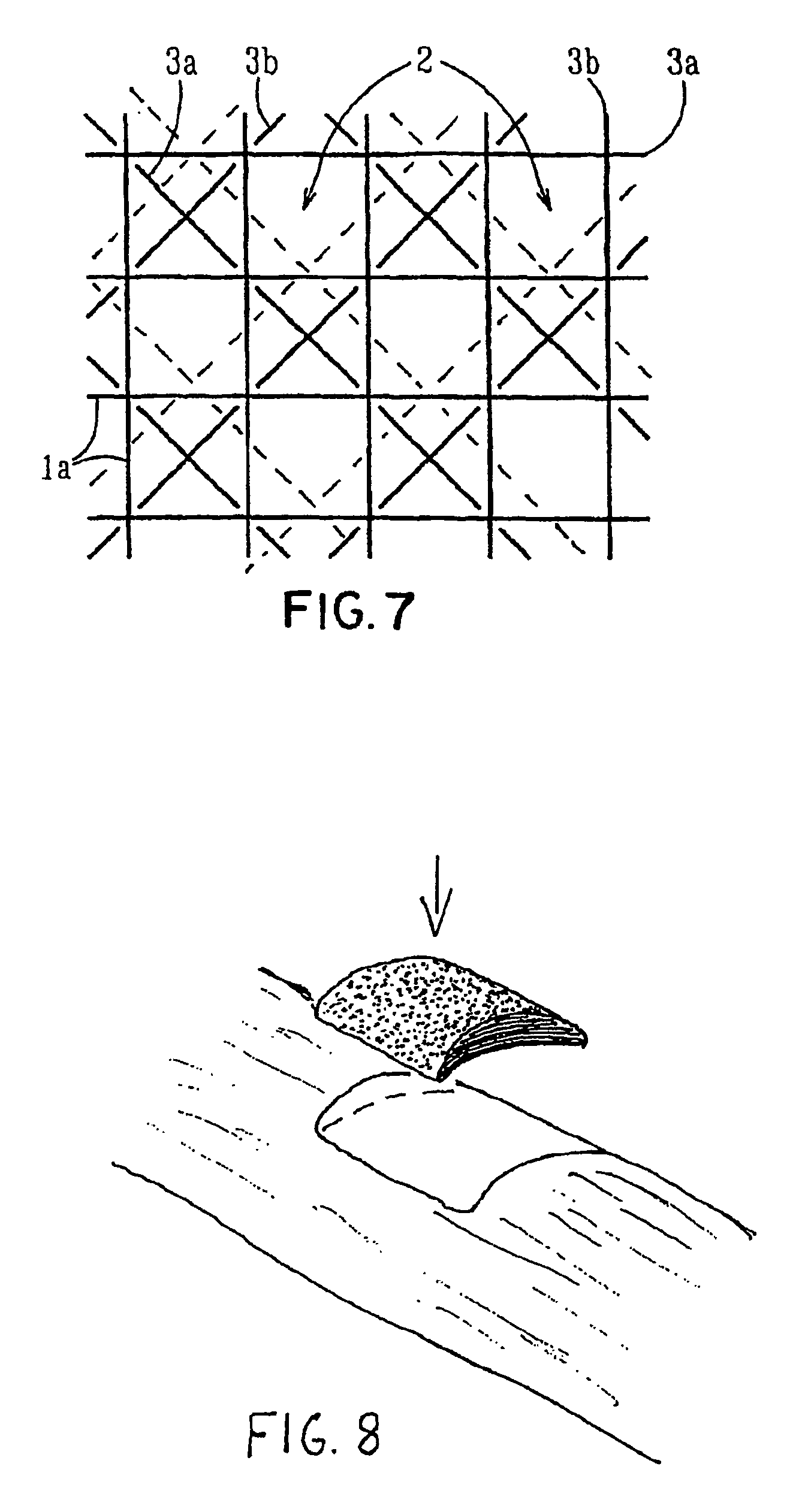
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Bioabsorbable Polymer, Bioabsorbable Composite Stents
InactiveUS20080249608A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureVarying of ductilityStentsSurgeryMetallic materialsMedical device
Biocompatible materials may be configured into any number of implantable medical devices including intraluminal stents. The biocompatible material may comprise metallic and non-metallic materials in hybrid structures. In one such structure, a device may be fabricated with one or more elements having an inner metallic core that is biodegradable with an outer shell formed from a polymeric material that is biodegradable. Additionally, therapeutic agents may be incorporated into the microstructure or the bulk material.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
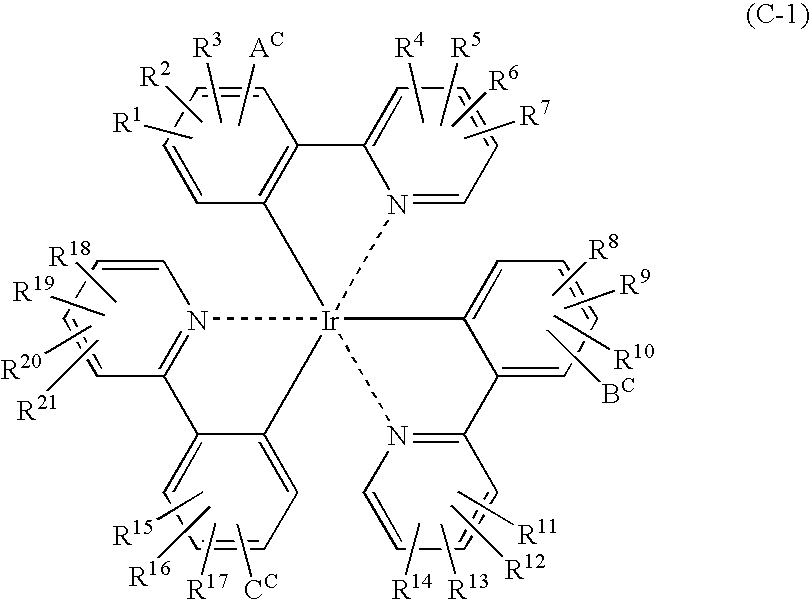
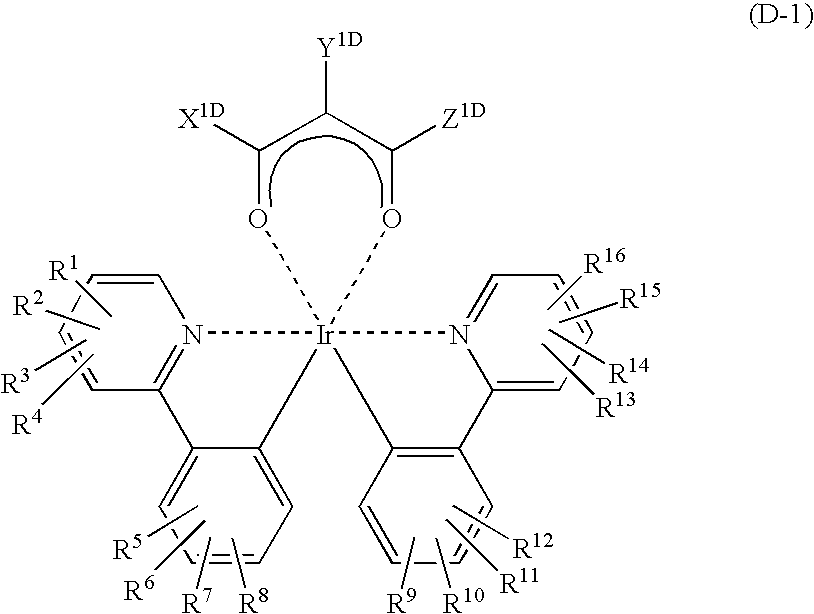
Light emitting material and organic light-emitting device
InactiveUS7396598B2High efficiency of light emissionKeep energy smallDischarge tube luminescnet screensGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsFluorescenceTriplet state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Internal backbone structural chassis for a surgical device
ActiveUS20110017801A1Reduce decreaseAccurate configurationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsInterior spaceSurgical device
A chassis for mounting a set of operating components of a power head of a surgical instrument is disclosed. The power head has a housing enabling access to an interior volume of the power head encompassed by the housing. The set of operating components have a proper configuration for alignment when mounted within the interior volume encompassed by the housing. The chassis is configured to provide the proper configuration for alignment of either an original or replacement set of operating components mounted on the chassis if the chassis and set of operating components are mounted within the interior volume of the housing. The chassis may be formed from metal and the housing formed from a polymer. The chassis may be configured to ground at least one electrical component.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Flexible electro-optic displays
An encapsulated electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of capsules dispersed in a polymeric binder, each of the capsules comprising a capsule wall, a suspending fluid contained within the capsule wall, and a plurality of electrically charged particles suspended in the suspending fluid and capable of moving therethrough upon application of an electric field to the medium, the polymeric binder having a shear modulus of at least about 10 mPa at 20° C., and preferably over the range of 10-50° C.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
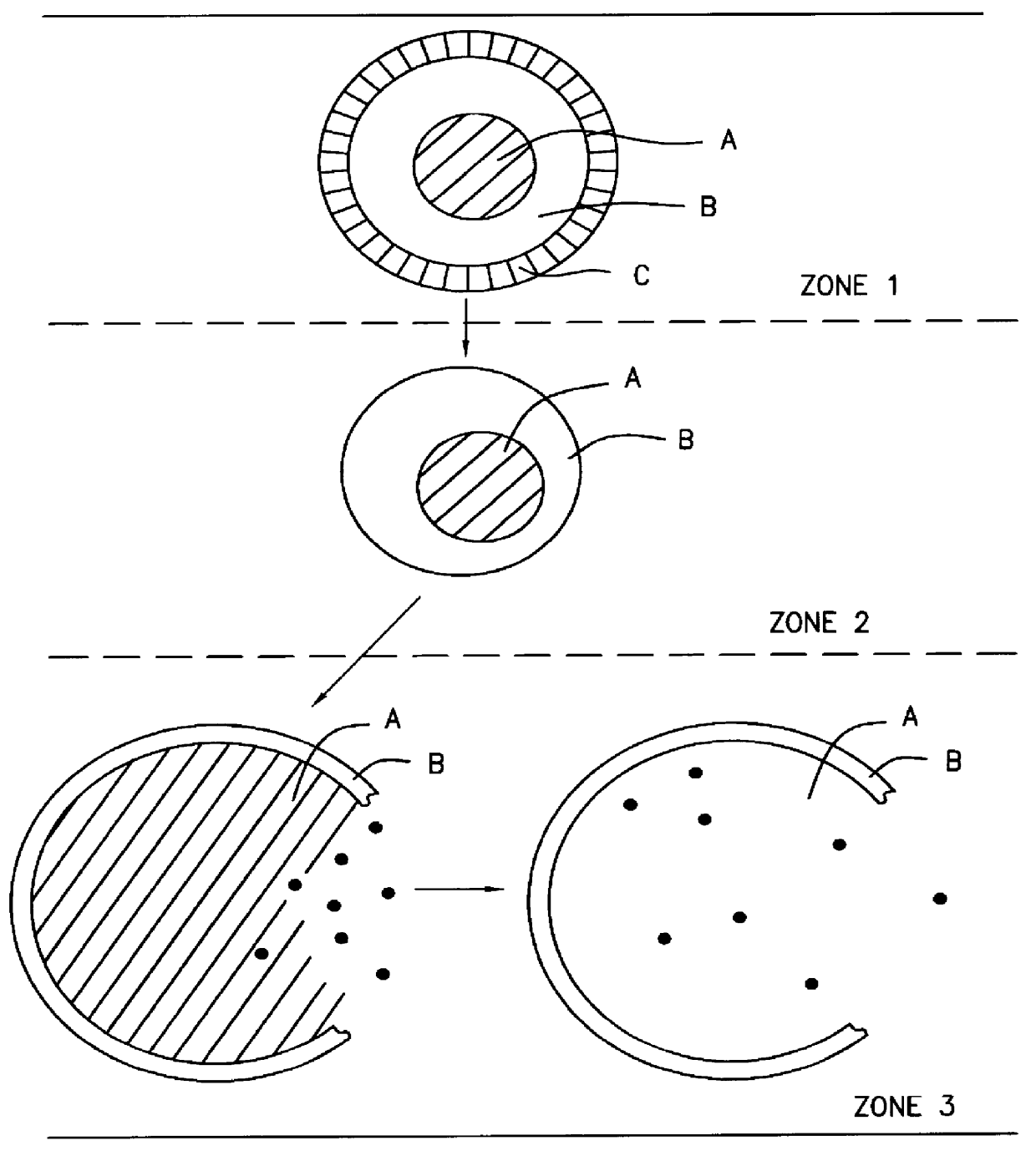
Colon targeted delivery system
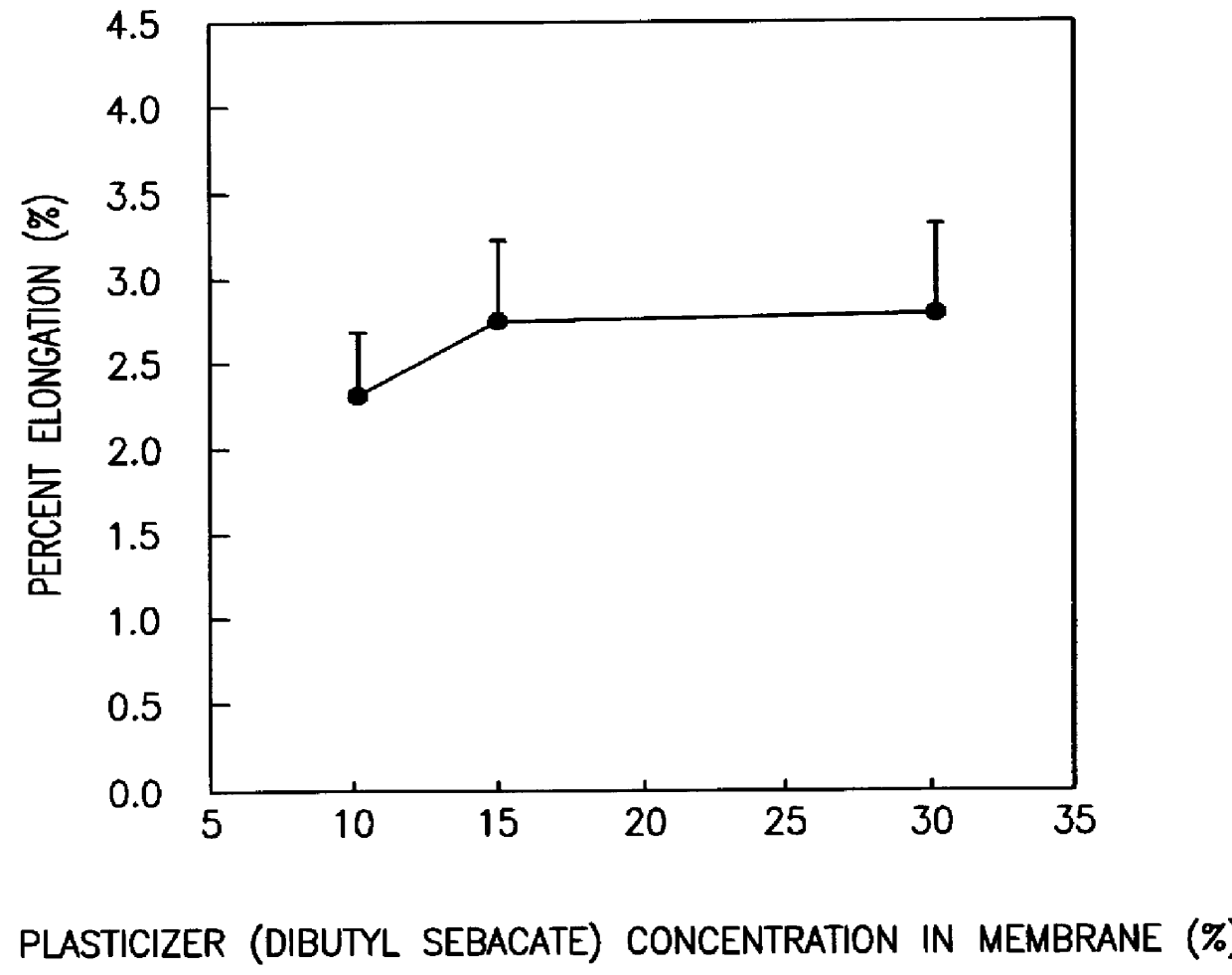
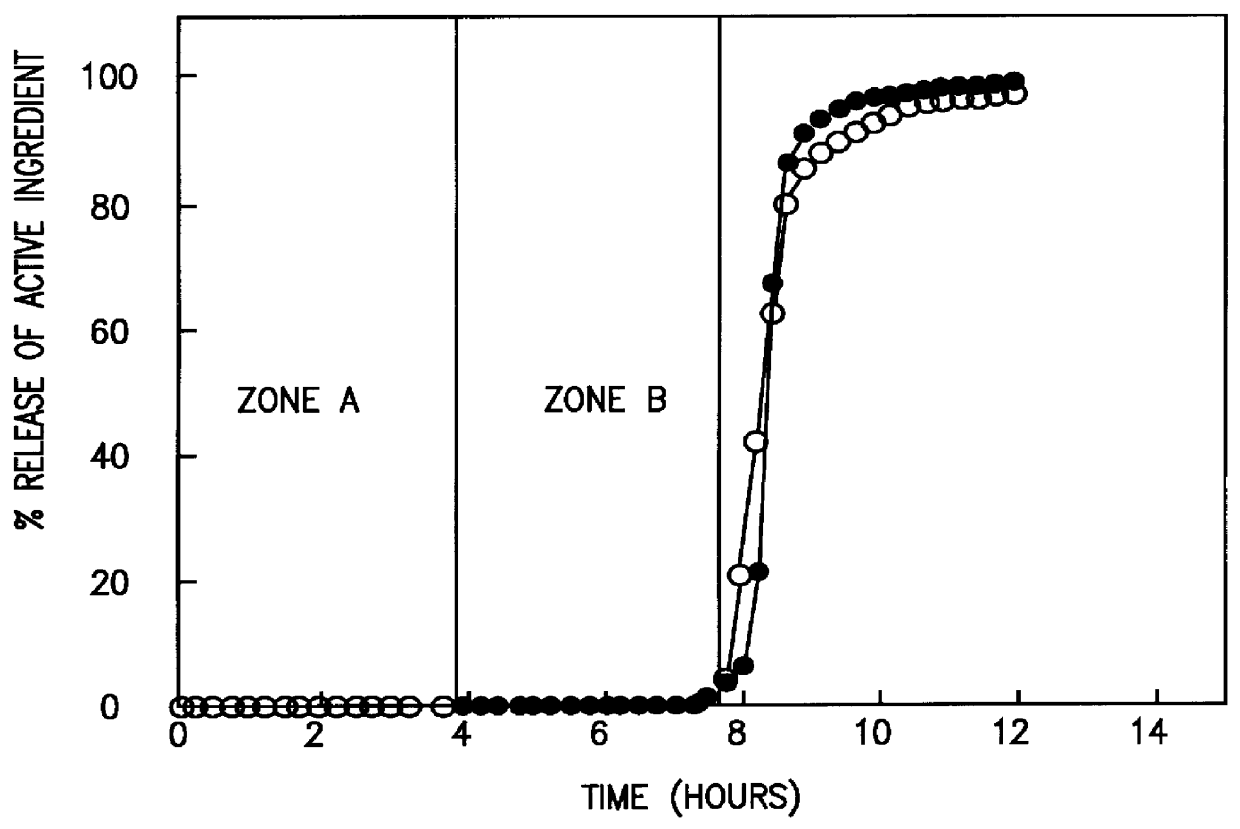
A novel delivery system for targeting drugs to the colon is herein described. The system is a tablet comprised of three parts: 1) an outer enteric coating, 2) an inner semi-permeable polymer membrane containing a plasticizer and 3) a central core comprising swelling excipients and an active ingredient. The novel dosage form described herein will release the drug consistently in the colon by a time-dependent explosion mechanism. This delivery system is particularly suitable for delivering viral protease inhibitors to the colon.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Medical devices having electrodes mounted thereon and methods of manufacturing therefor
InactiveUS20120130217A1For automatic positioningContact member manufacturingElectrocardiographyMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
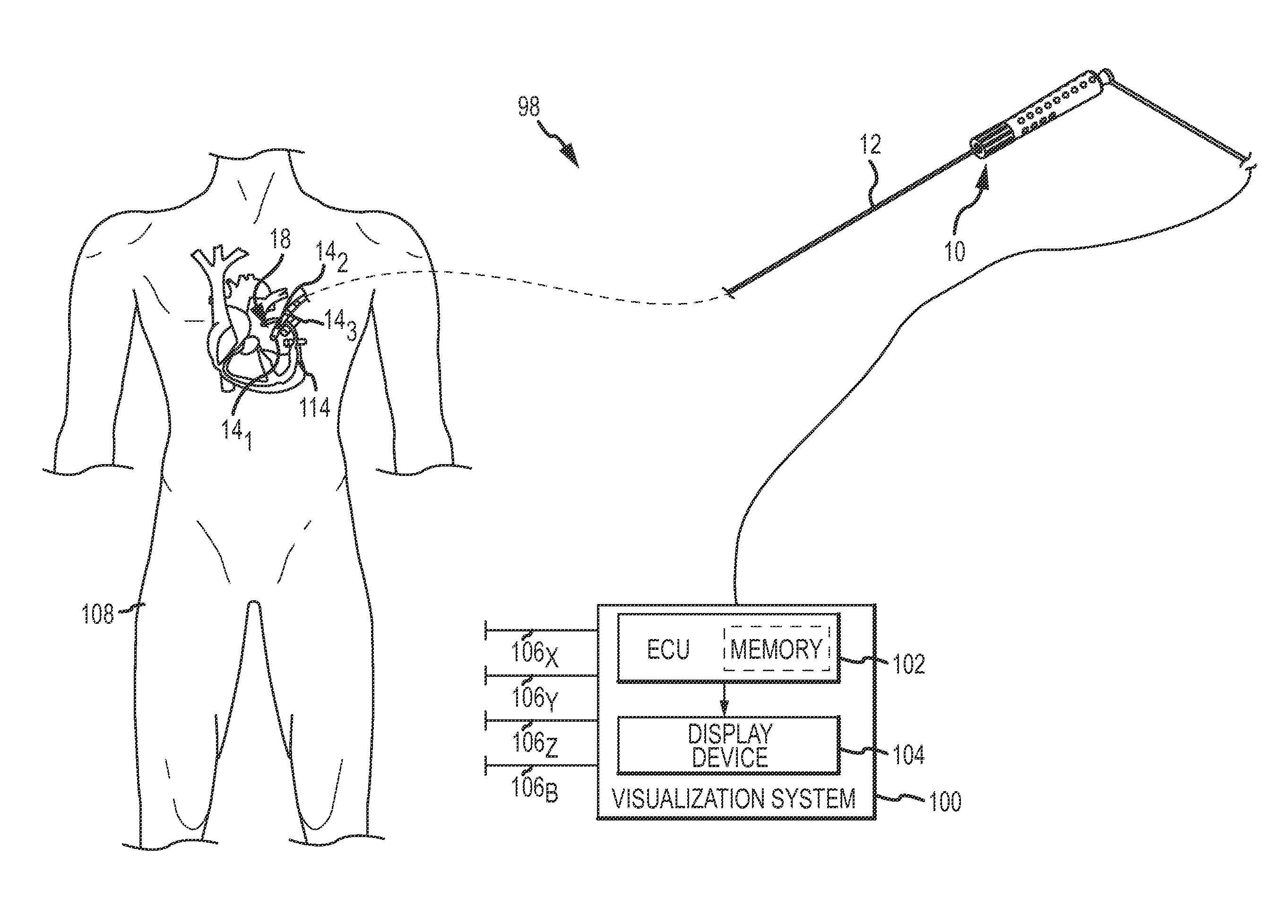
Medical devices, methods of manufacturing medical devices, and systems comprising medical devices are provided. The device comprises a shaft having a major lumen sized to receive a second medical device and an electrode mounted thereon. The shaft includes an inner liner and outer layer. The method of manufacture includes forming a shaft by forming an inner liner and an outer layer by covering the inner liner with a polymeric material. The method further includes mounting an electrode onto the shaft of the device, and then heating and cooling the shaft. The system comprises a medical device having a shaft and an electrode mounted thereon. The shaft has a major lumen sized to receive another device. The system further comprises an electronic control unit configured to receive signals from the electrode and to determine a position of the electrode and / or monitor electrophysiological data.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Prosthesis for reinforcement of tissue structures
The present invention relates to a composite prosthesis for reinforcement of a tissue structure, including a porous textile support which includes an arrangement of threads each composed of at least one filament of nonabsorbable polymer material, said textile support defining a microporous texture including the interstices located between at least two threads at the sites of contact of one thread with at least one other thread, wherein, in at least one protected zone of the textile support, a hydrophilic absorbable material coats the textile support, forming a film enveloping and penetrating into the arrangement of threads, occluding at least the microporous texture, but without forming a plane layer covering at least one face of the textile support.It also relates to a process for preparing such a composite reinforcement prosthesis.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
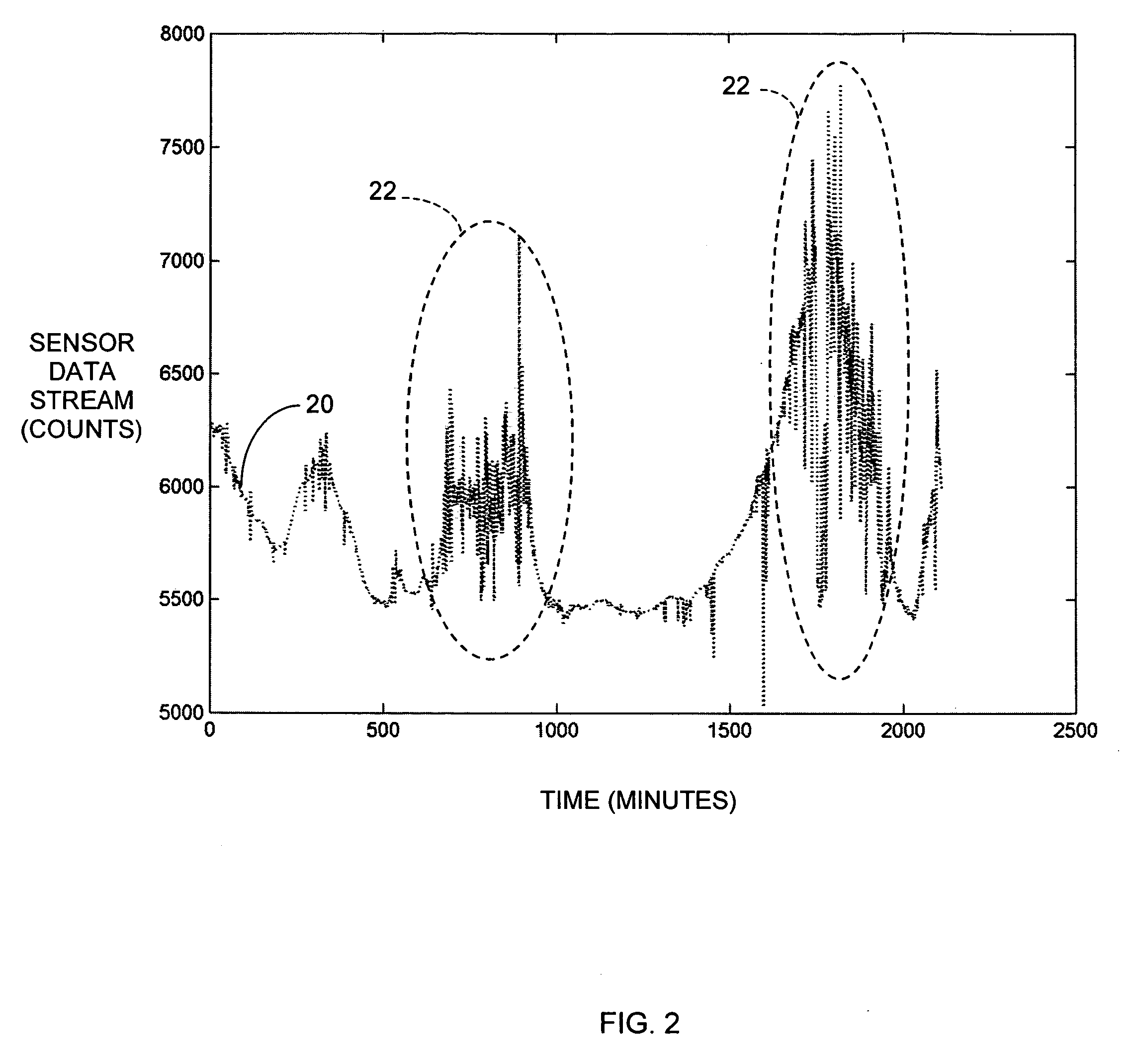
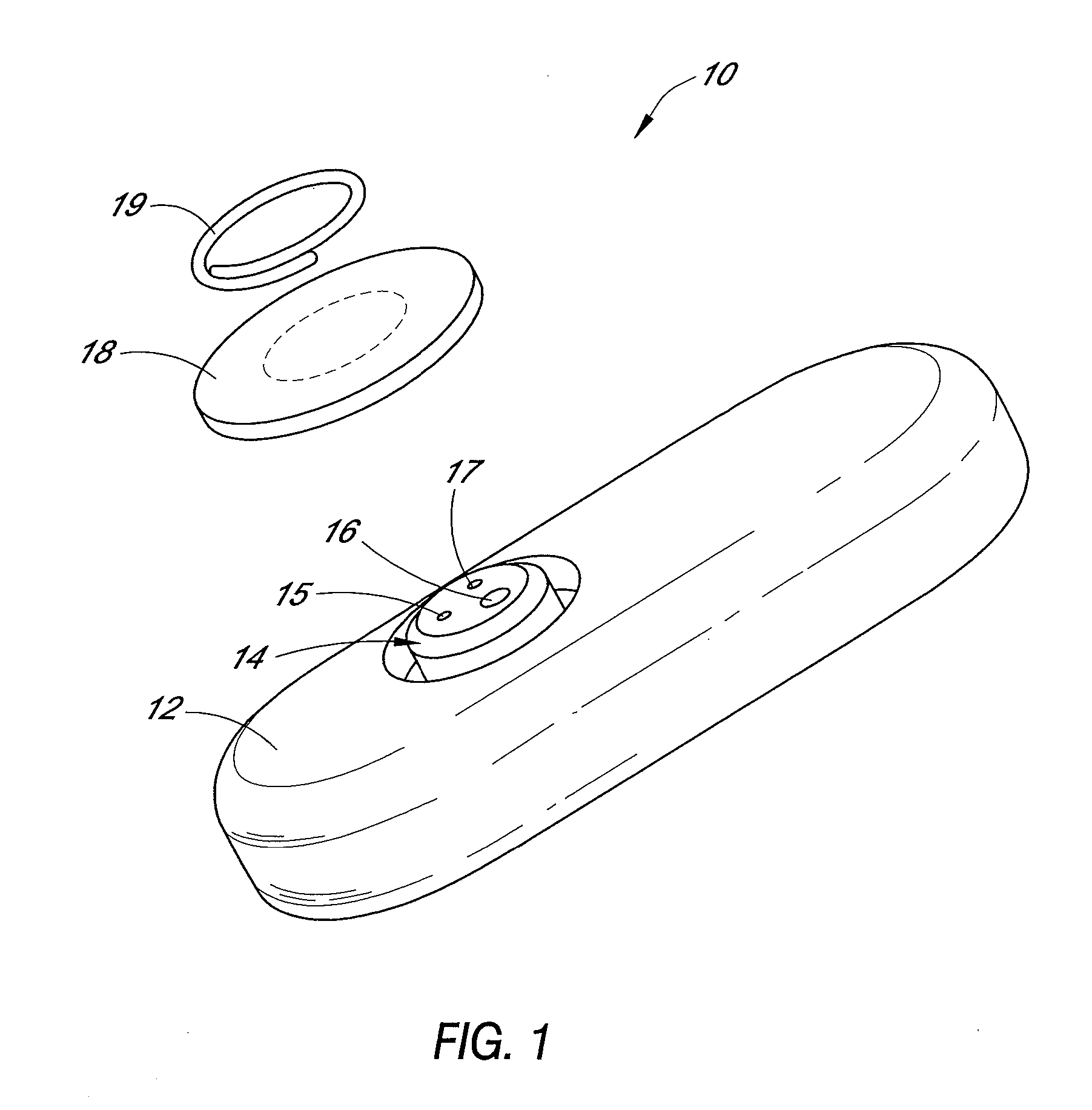
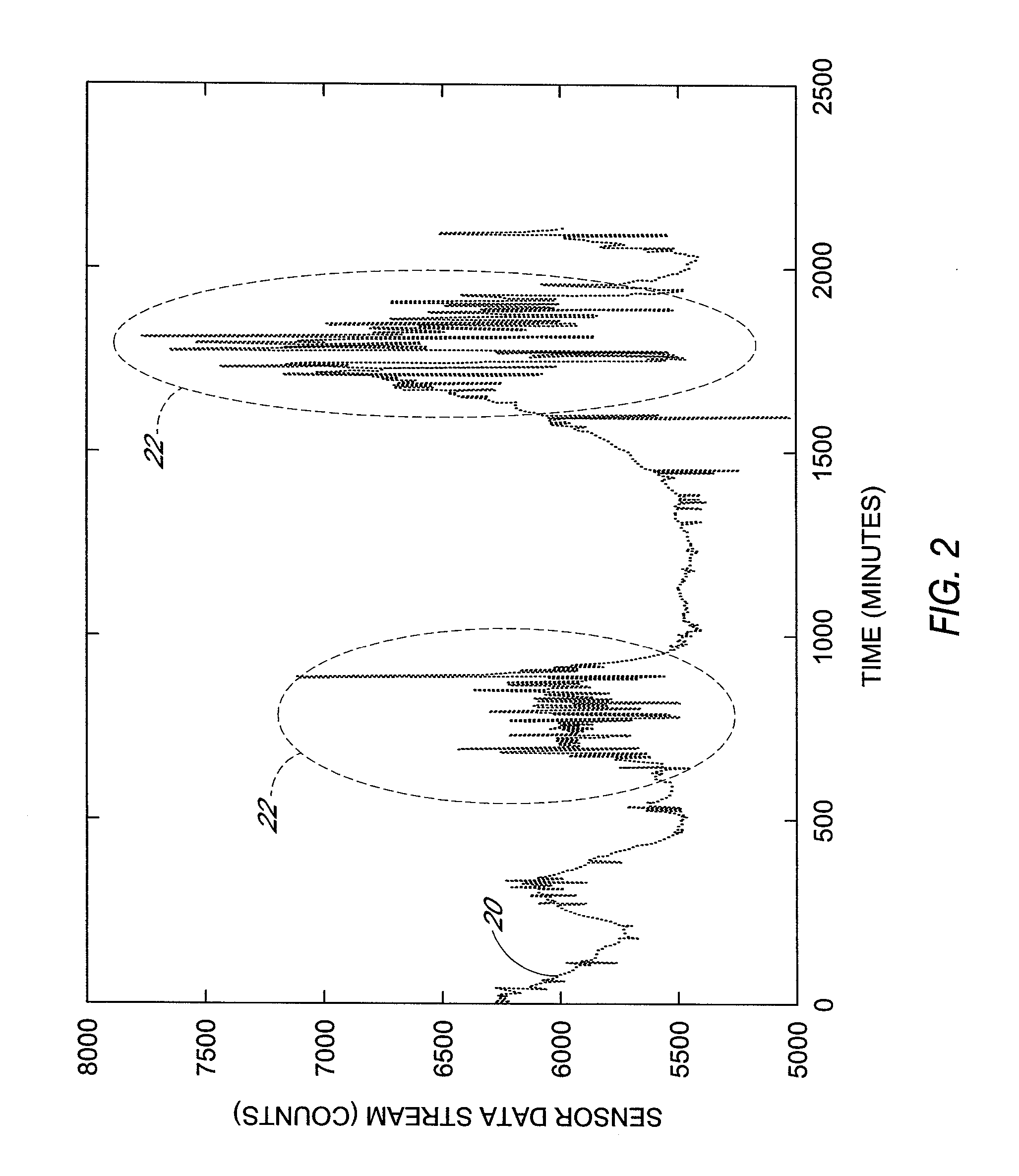
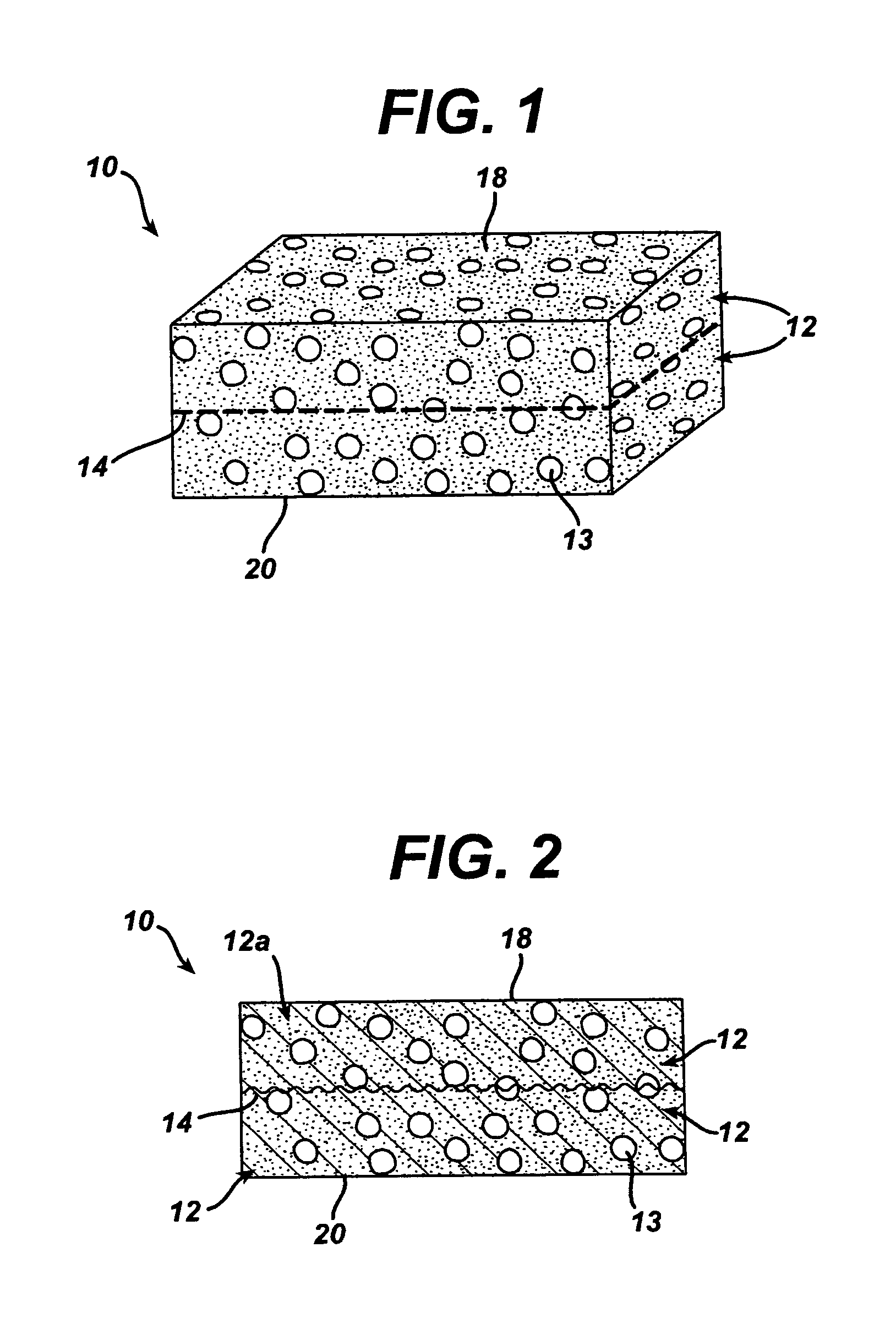
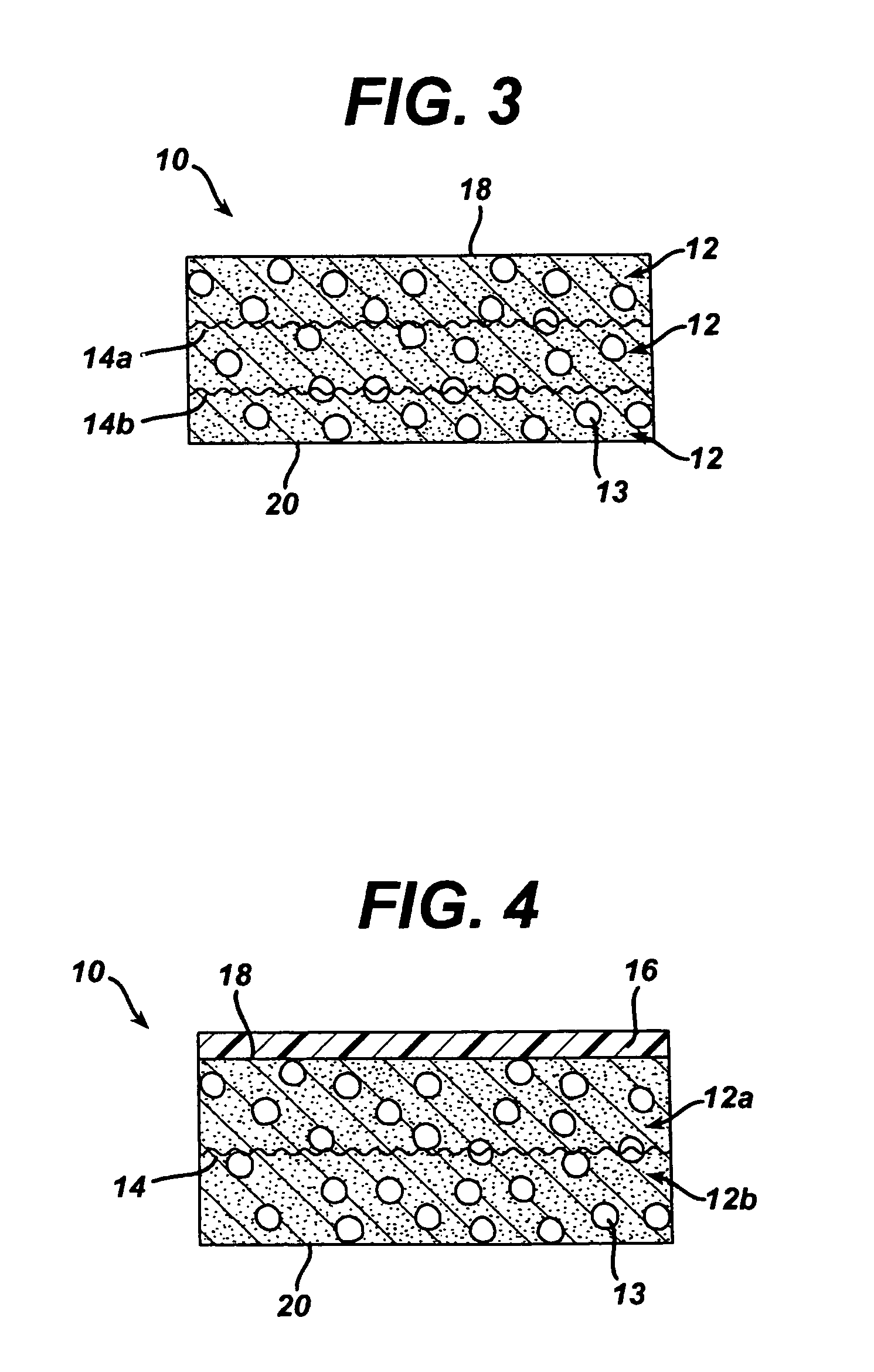
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Drug-eluting medical devices
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
Internal fixation devices
InactiveUS20100318085A1Sufficient expansionImprove fullySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBiomedical engineeringPolymer
The present disclosure relates to an internal fixation device including an interface portion, a polymer material coupled to the interface portion, wherein the polymer material includes at least one feature on a surface of the polymer material, and means for allowing adequate expansion of the polymer material on each side of the bone fracture site. A method of fixating the internal fixation device to a bone and other internal fixation devices and methods for fixating are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com