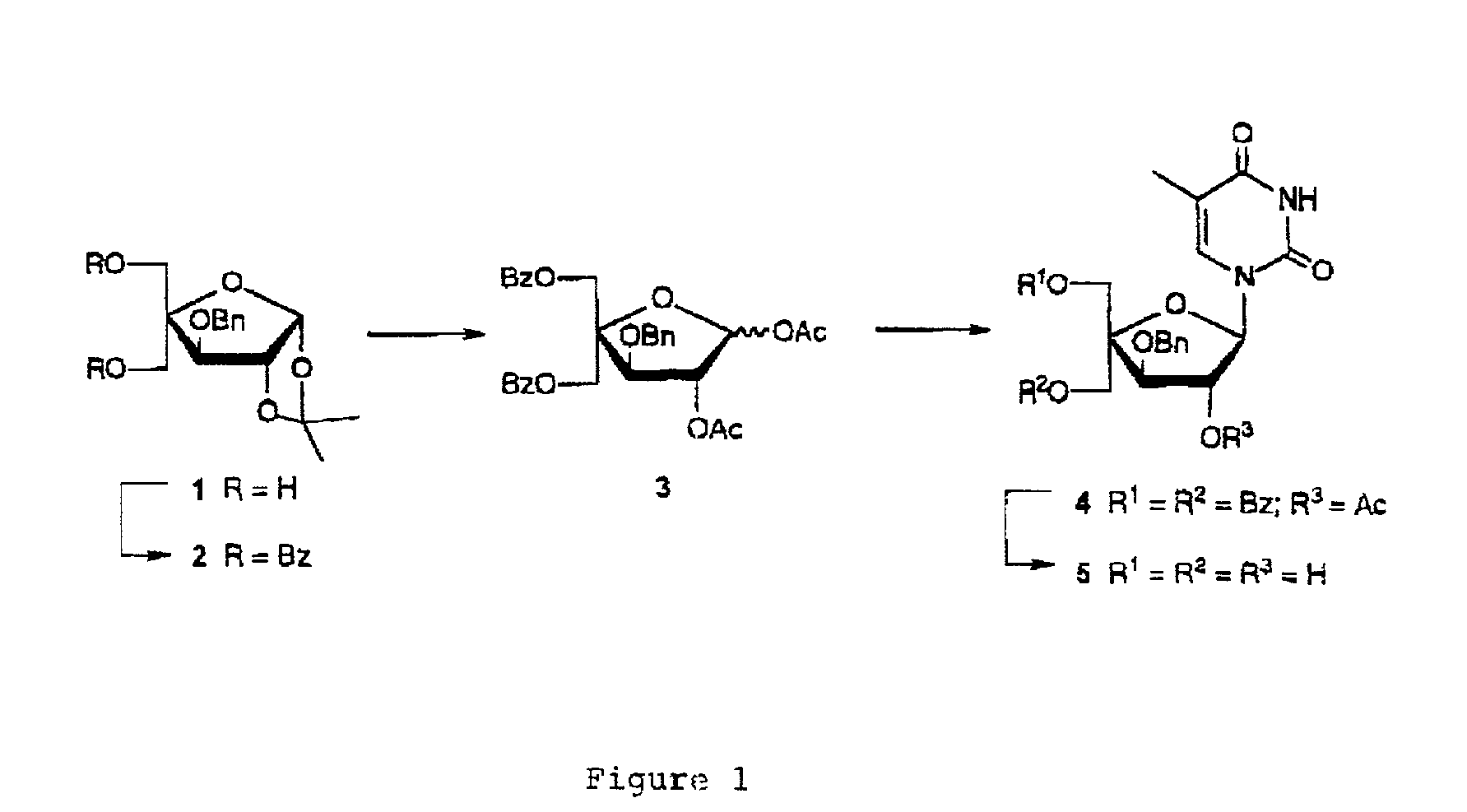
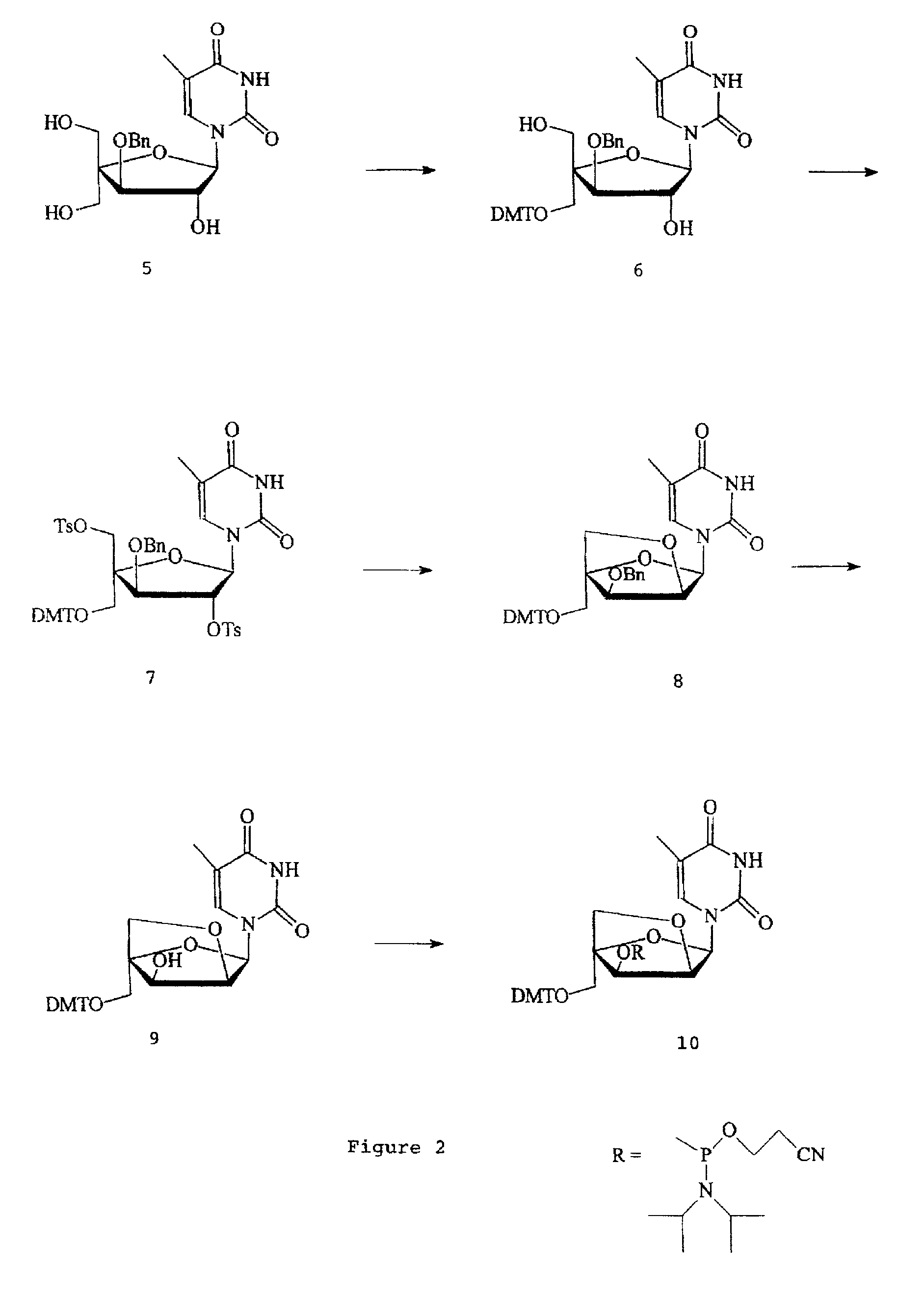
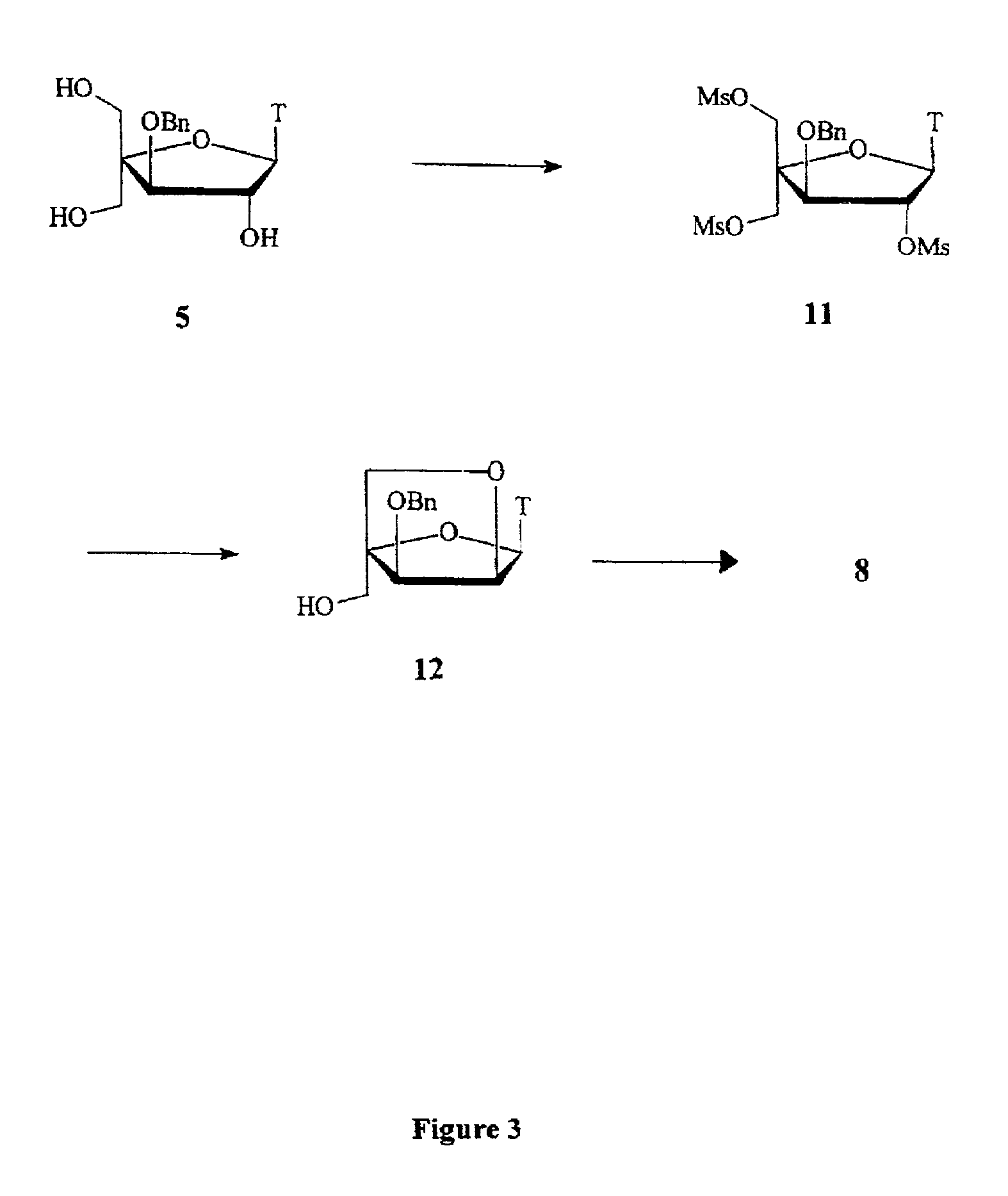
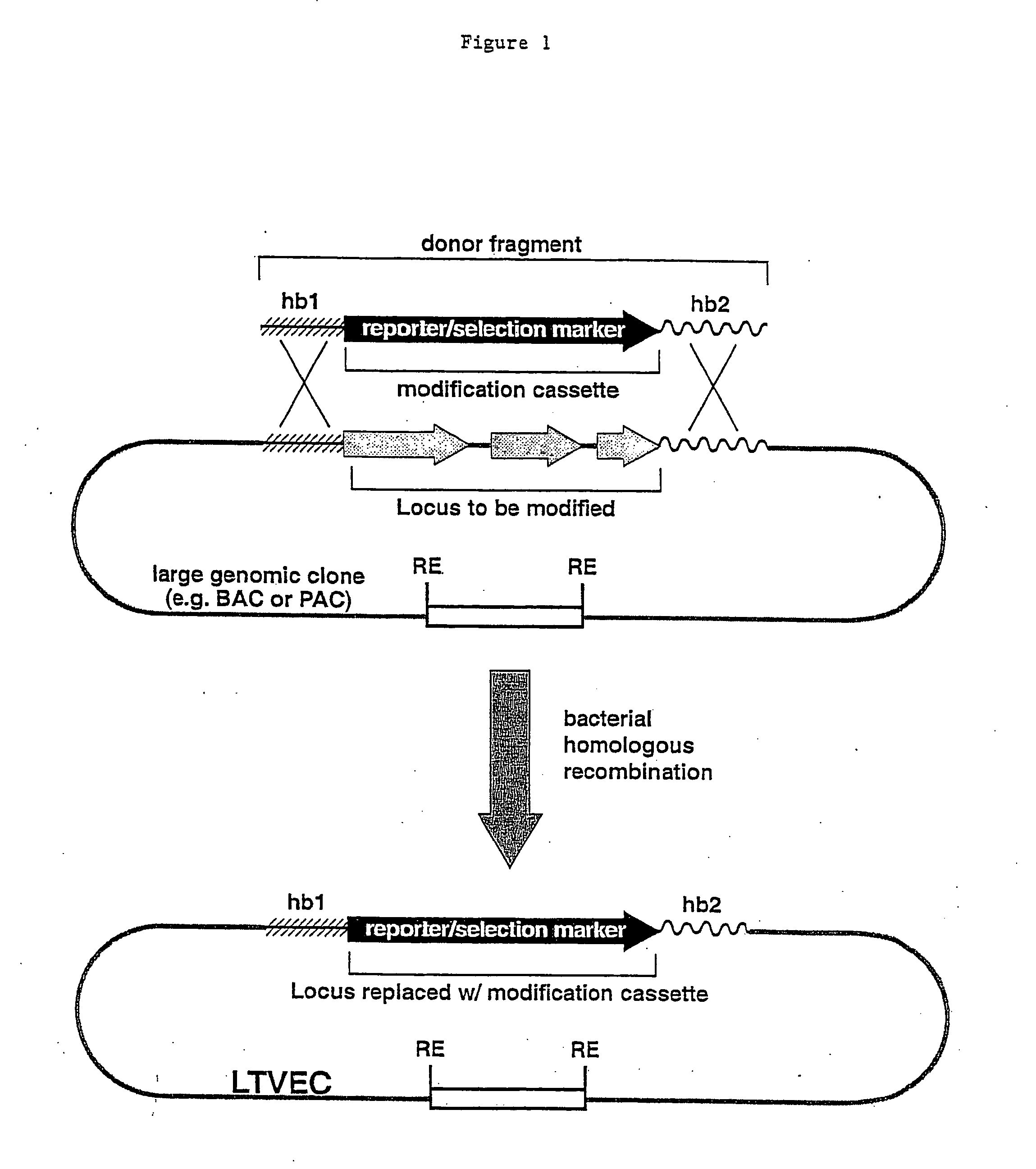
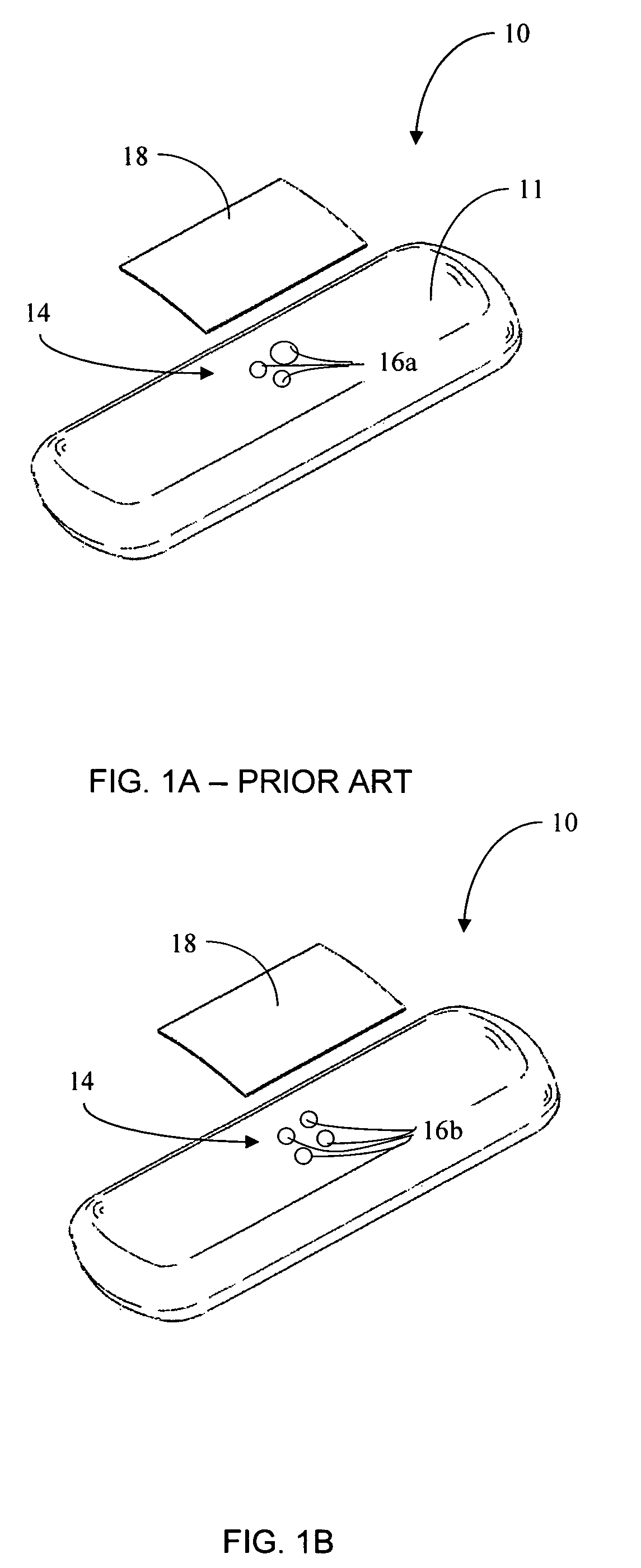
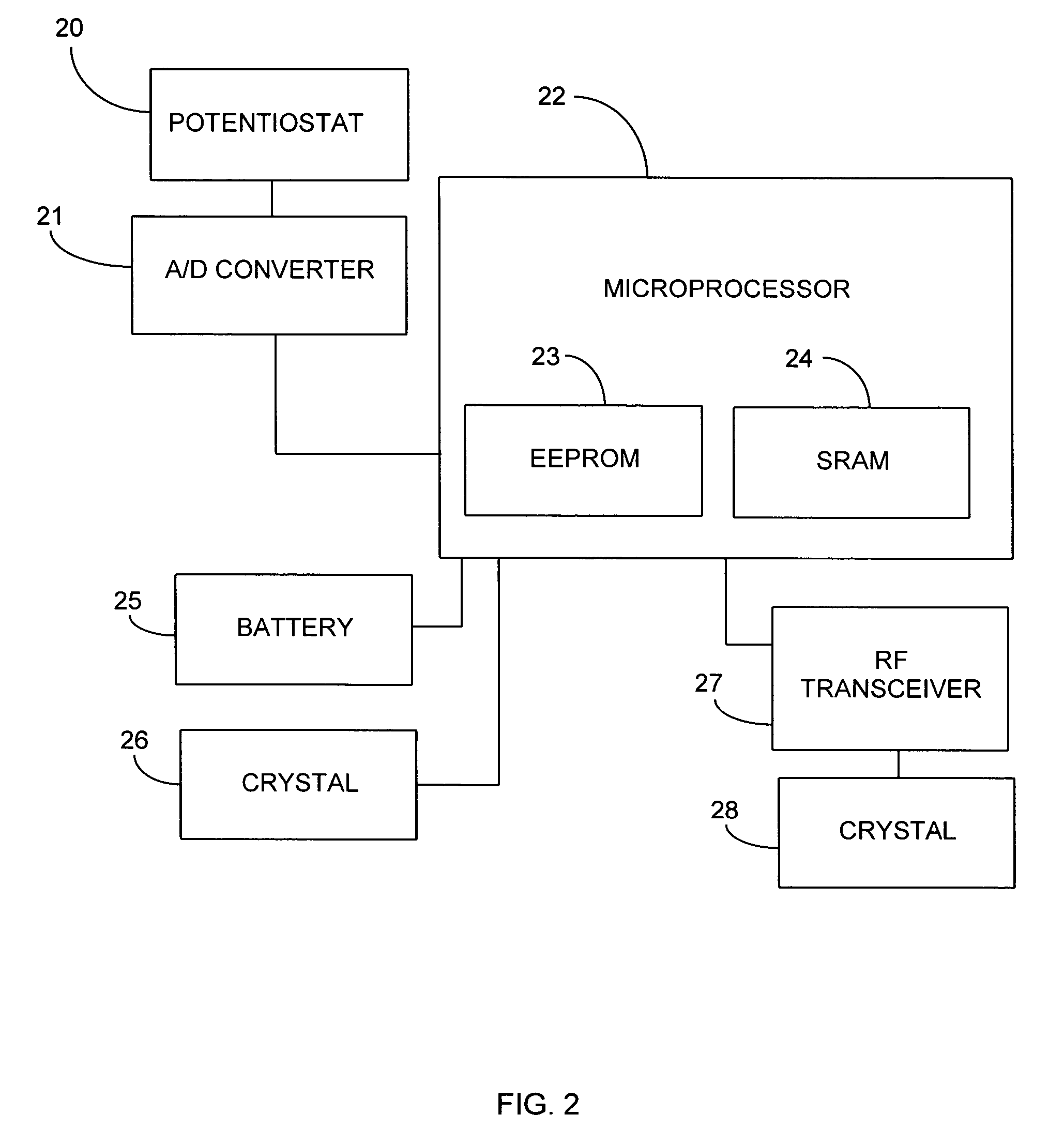
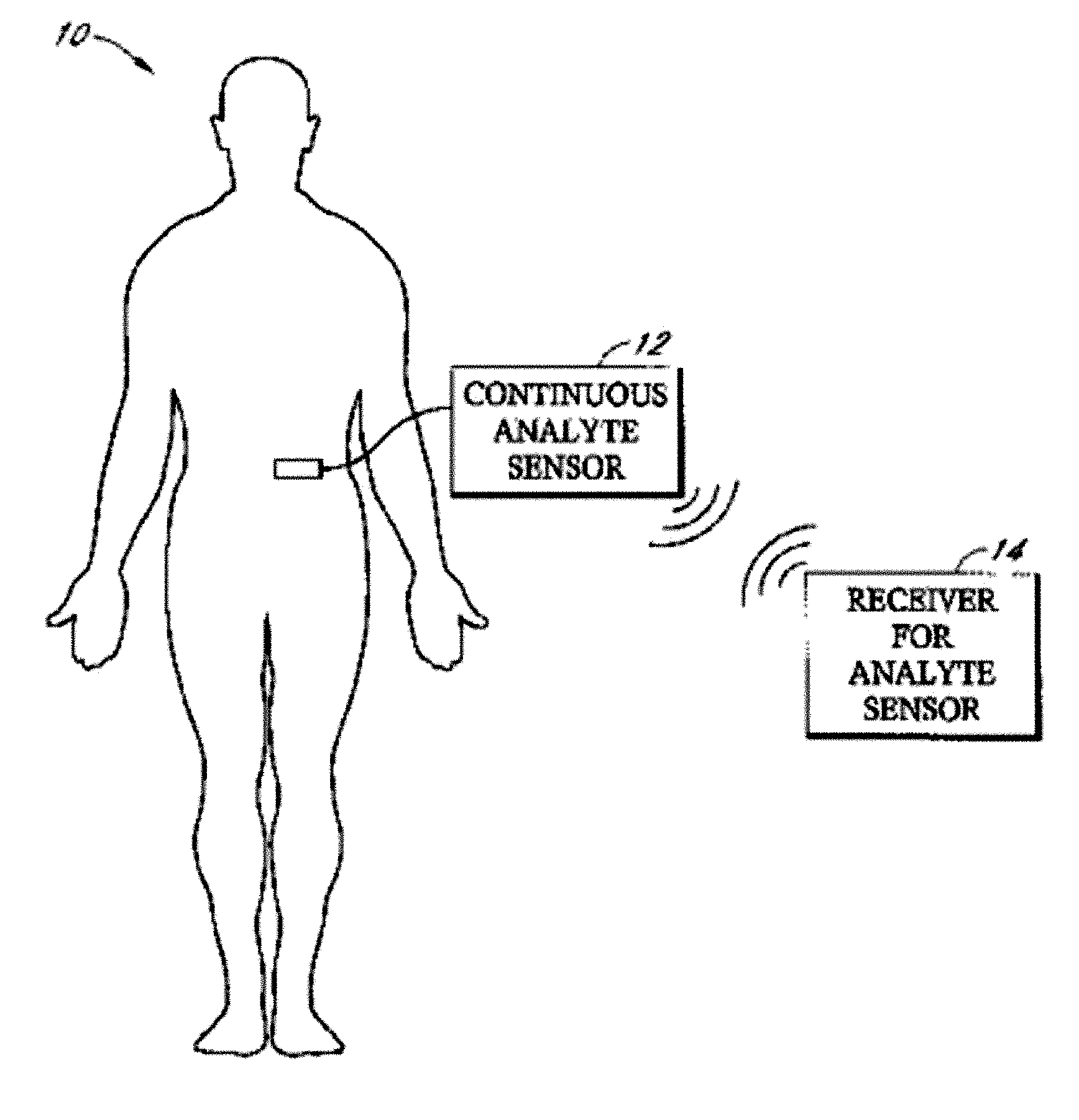
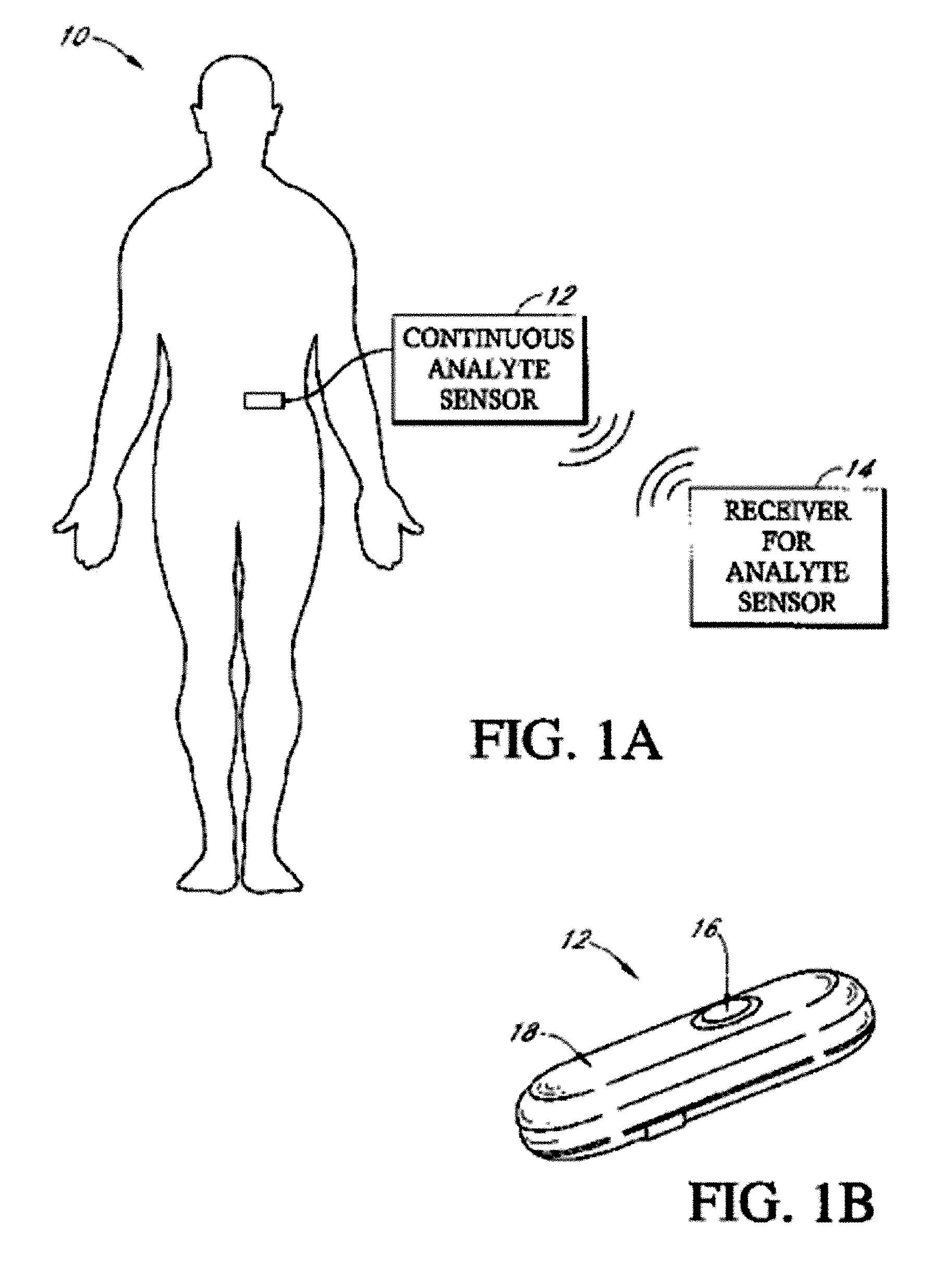
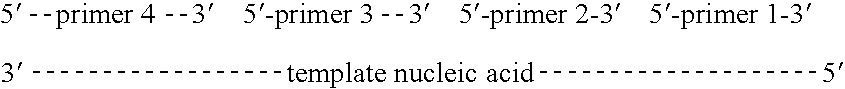Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
165036results about "Microbiological testing/measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
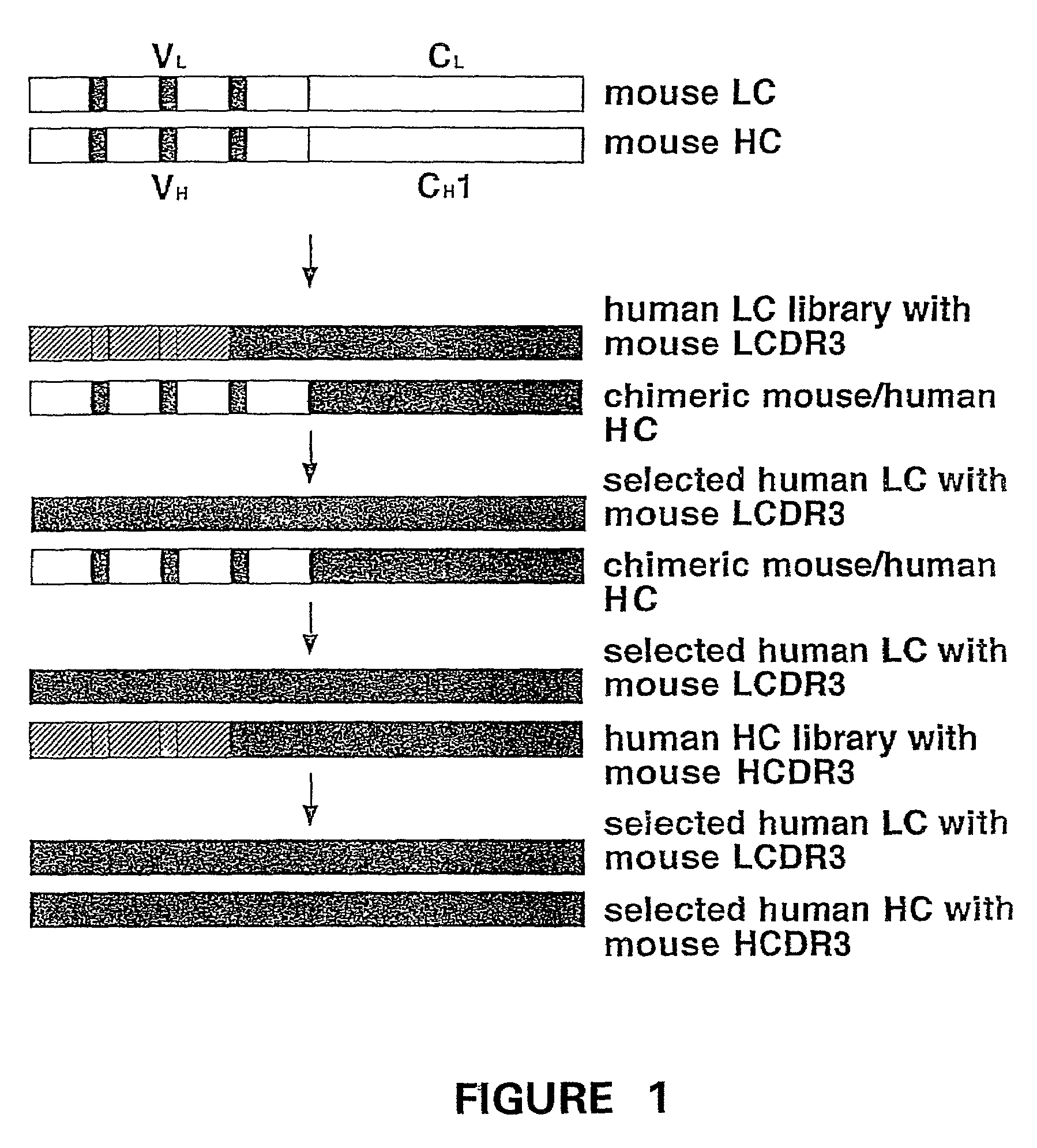
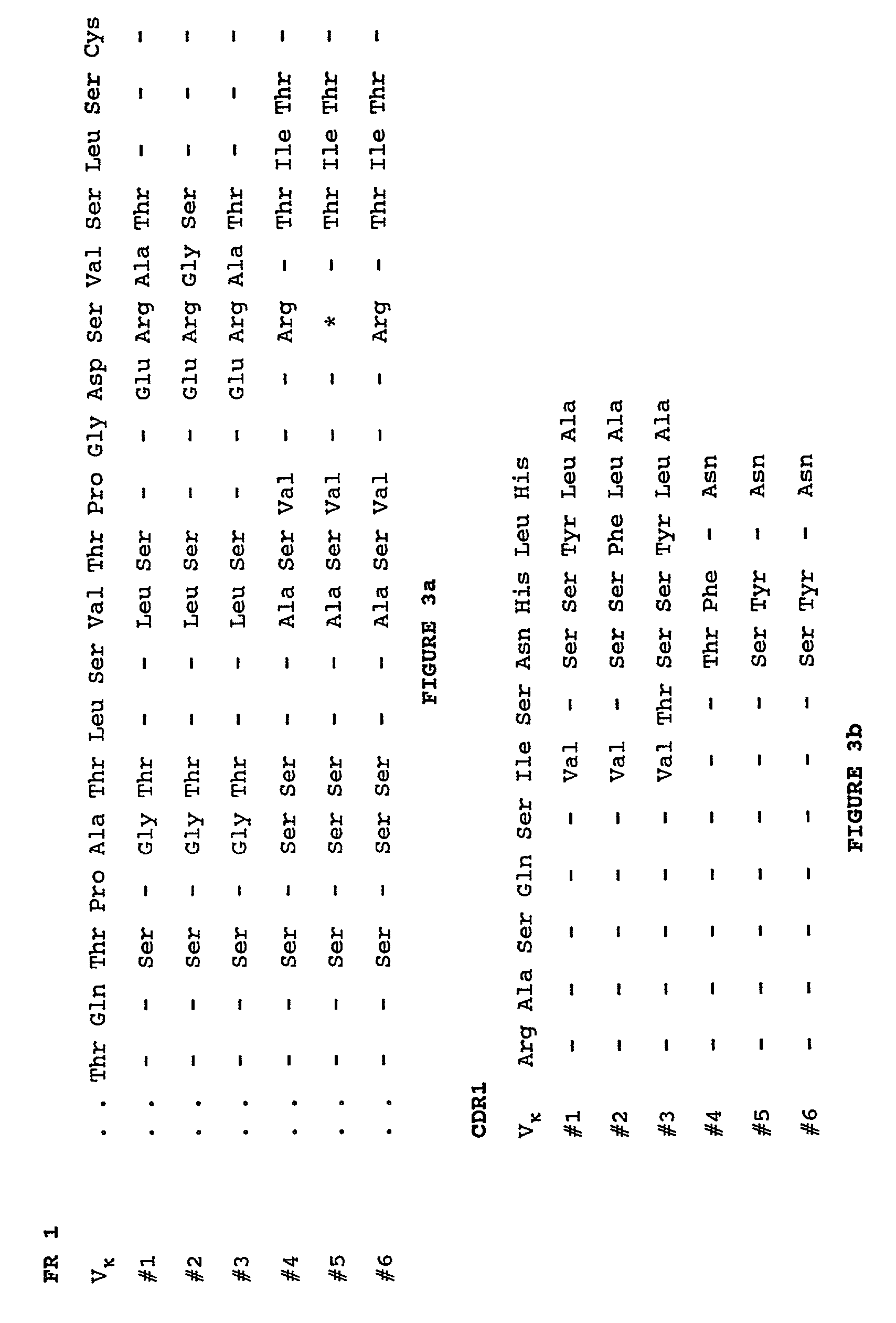
Humanization of murine antibody
InactiveUS7087409B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesComplementarity determining regionHeavy chain
A humanized murine antibody is provided. The amino acid sequences of a light chain complementarity determining region from a mouse antibody are grafted onto a human light chain, and a heavy chain complementarity determining region from a mouse antibody are grafted onto a human antibody heavy chain to produce libraries from which a humanized murine antibody having the desired specificity is selected.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
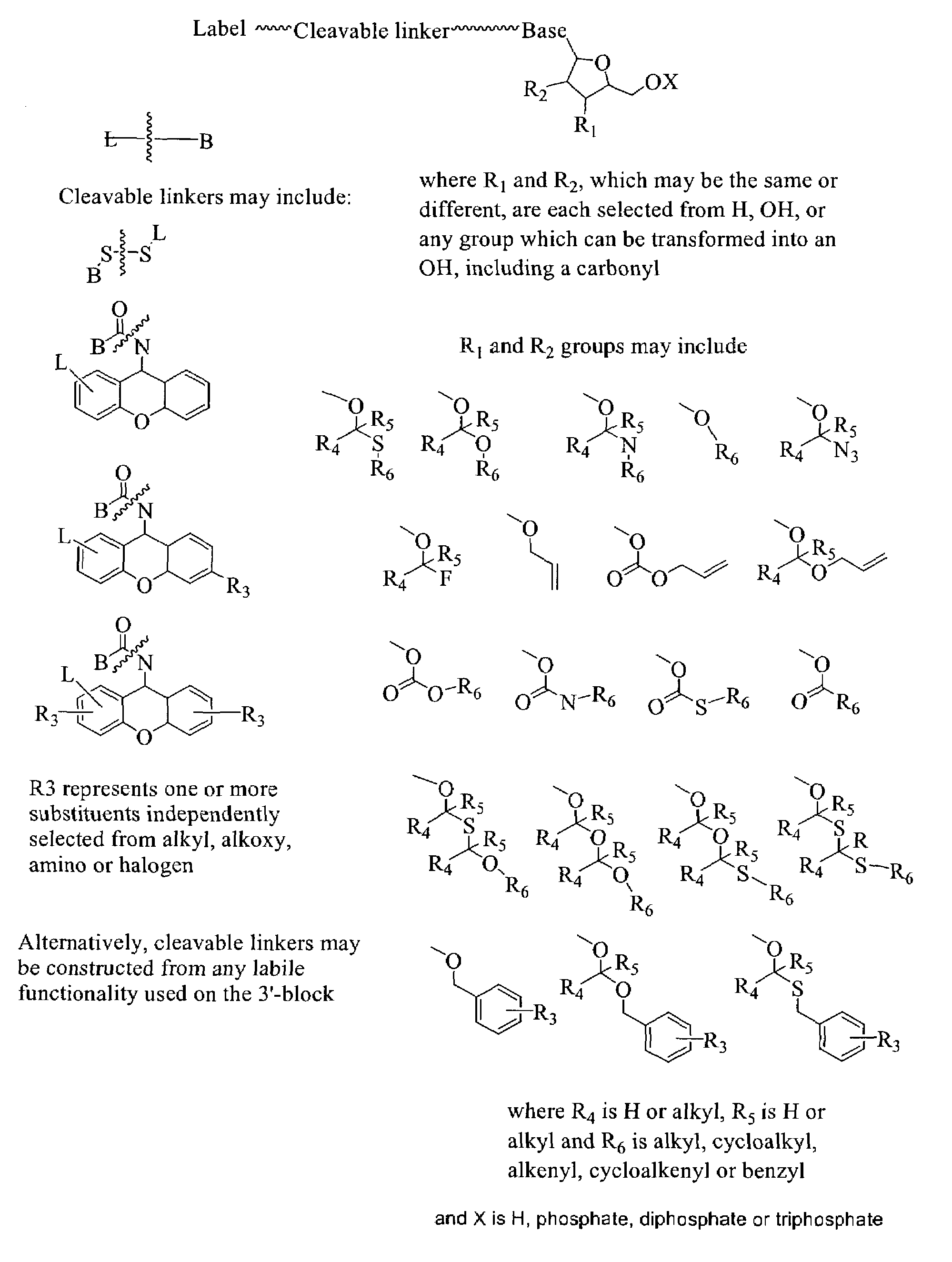
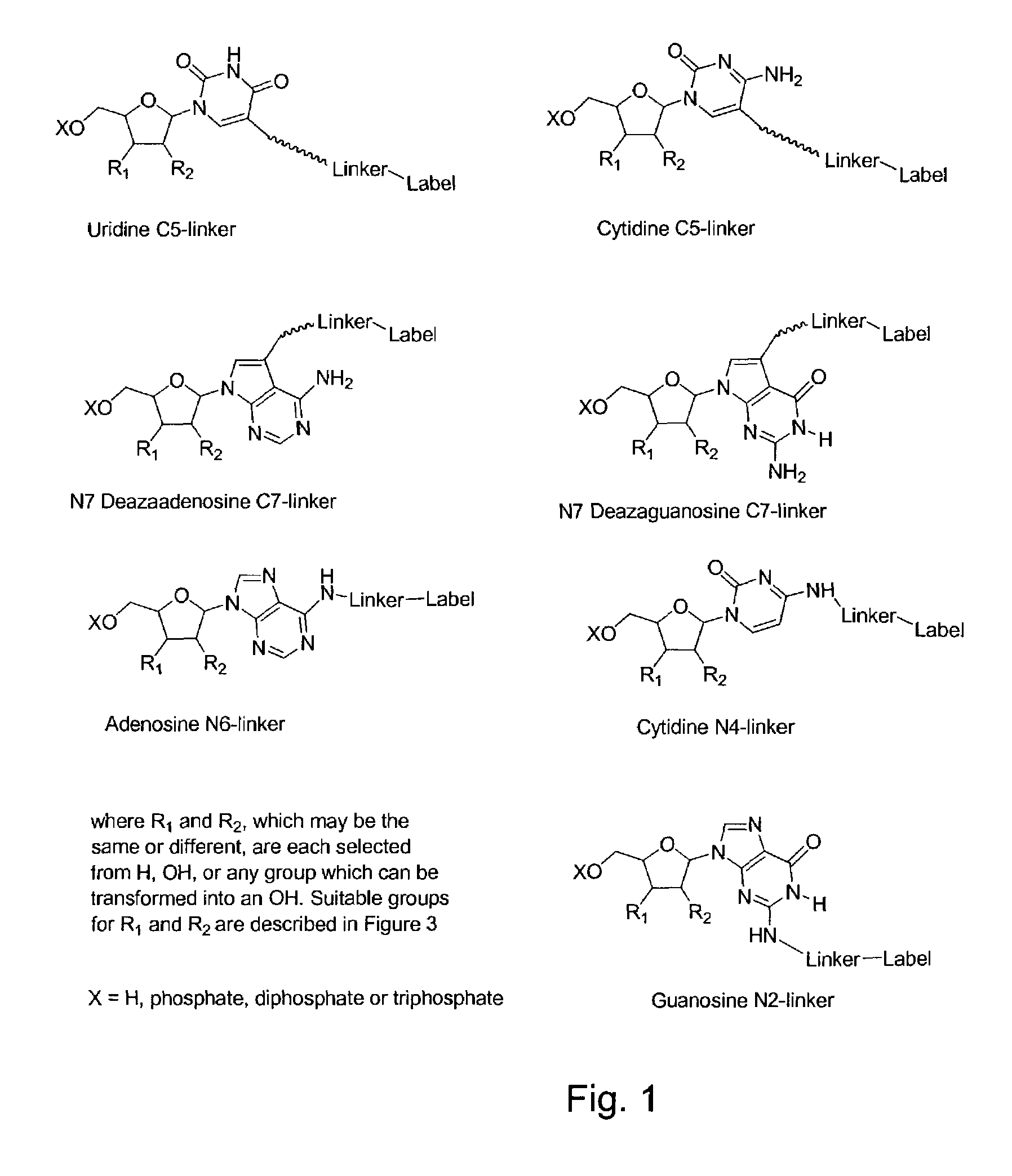
Labelled nucleotides
InactiveUS7057026B2Use of techniqueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOrganic chemistryNucleoside
Nucleosides and nucleotides are disclosed that are linked to detectable labels via a cleavable linker group.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
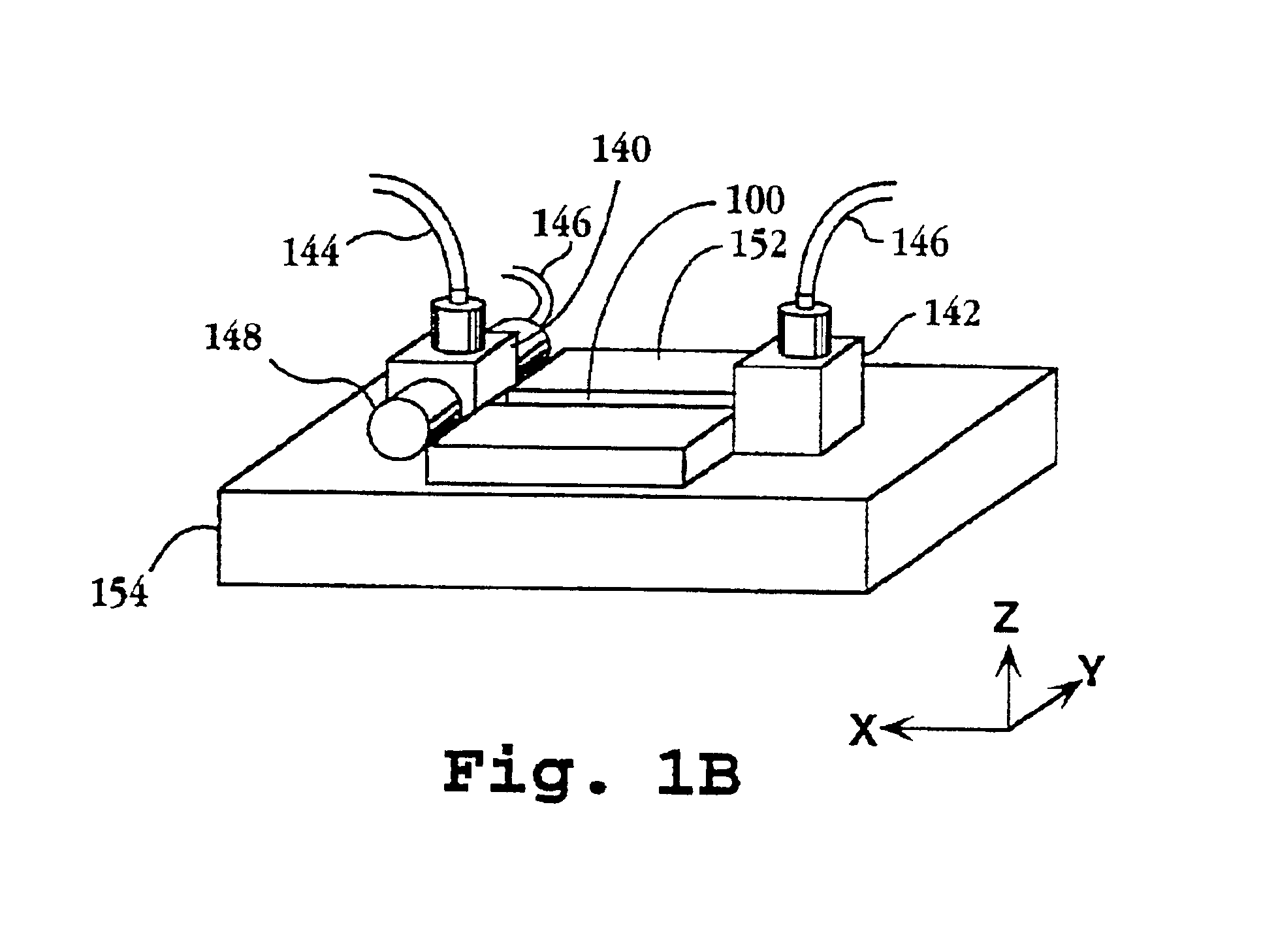
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS6484046B1Avoid and reduce corrosionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteElectrolysis
An electrochemical analyte sensor having conductive traces on a substrate is used to determine a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
L-ribo-LNA analogues
Provided are L-ribo bicyclic nucleotide compounds as well as syntheses of such compounds. The nucleoside compounds of the invention are useful in forming oligonucleotides that can produce nucleobase specific duplexes with complementary single stranded and double stranded nucleic acids.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
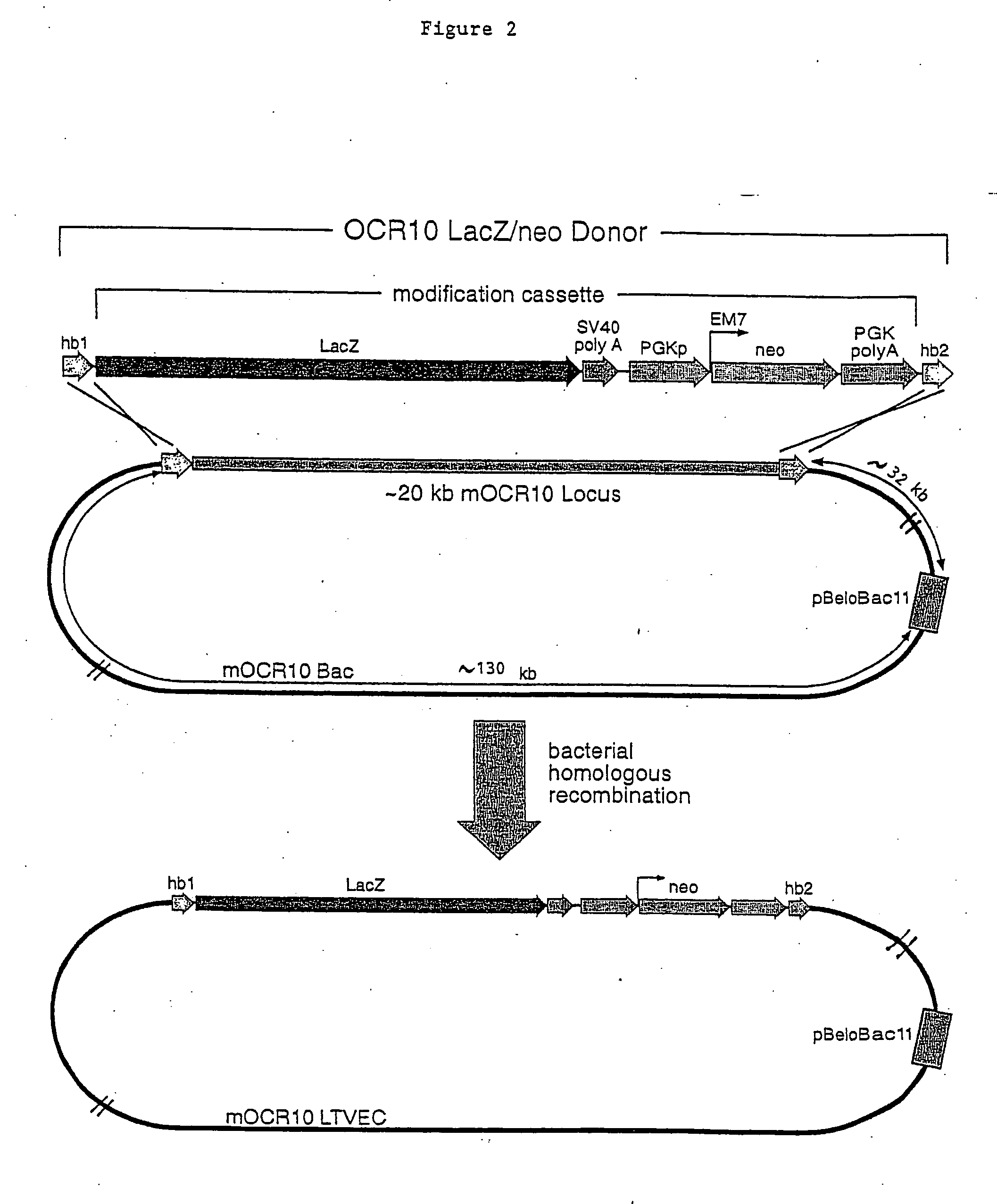
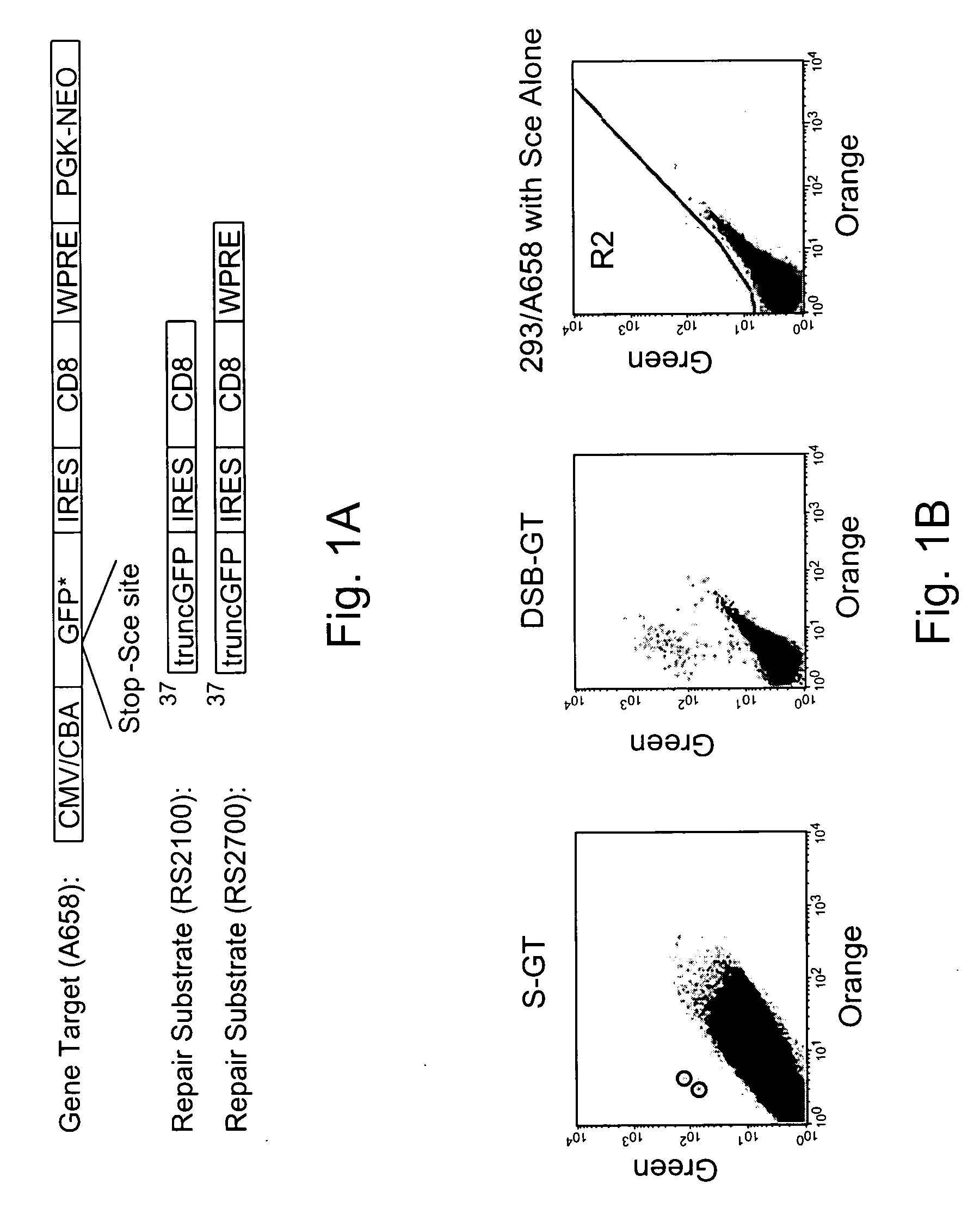
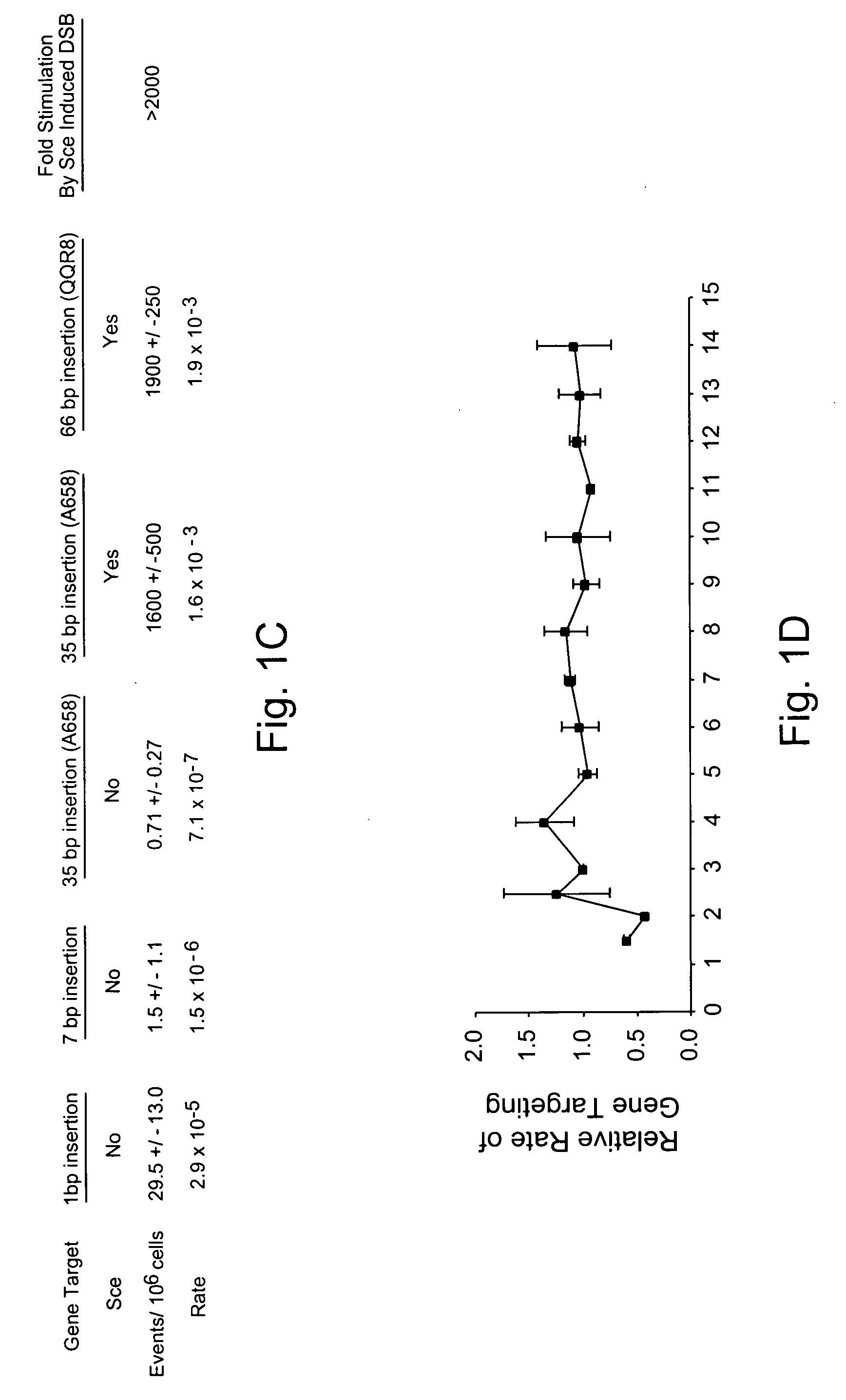
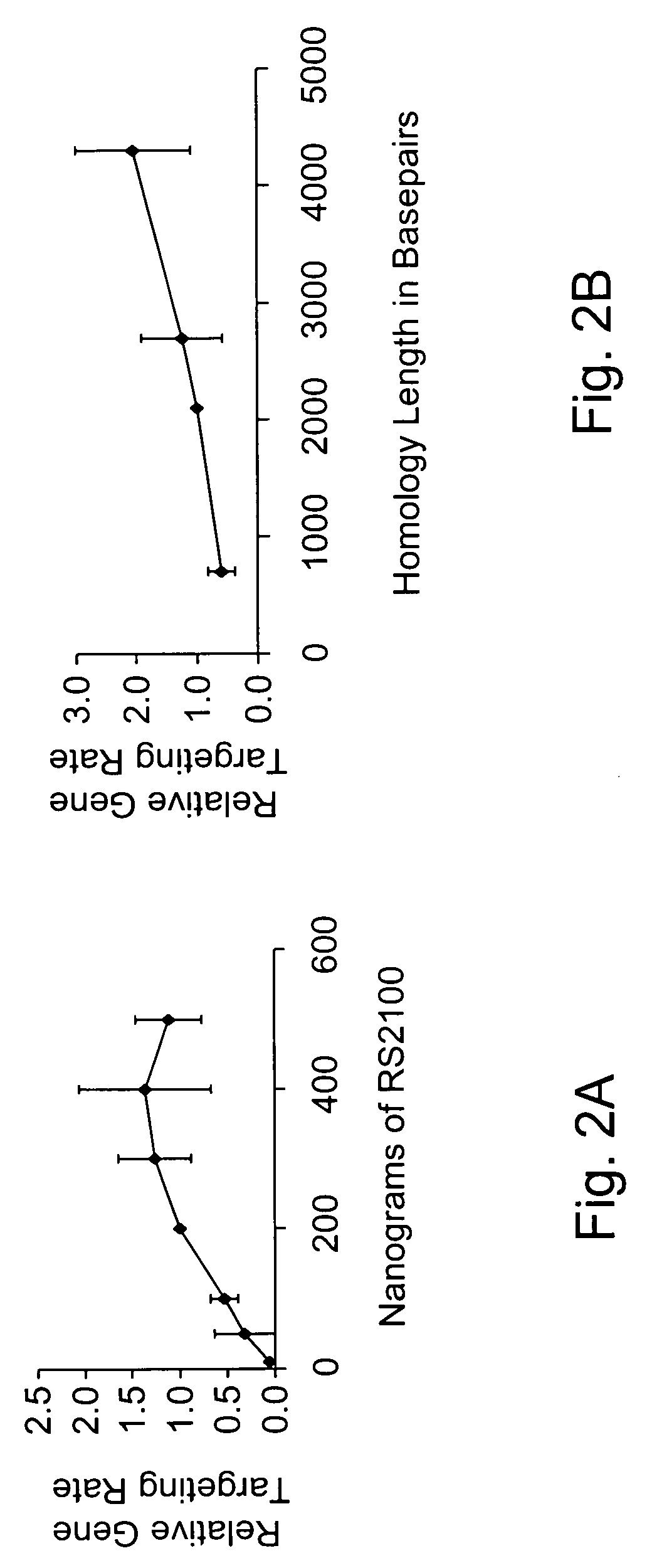
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
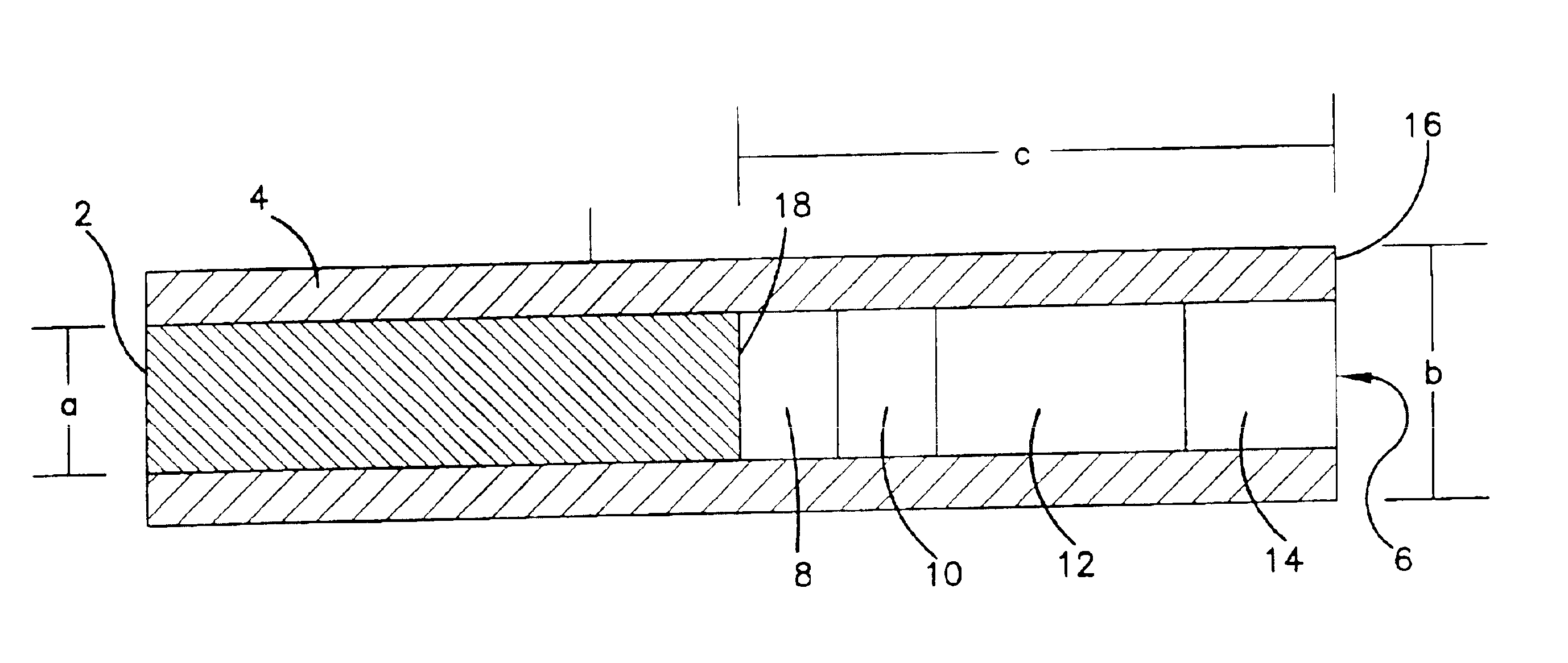
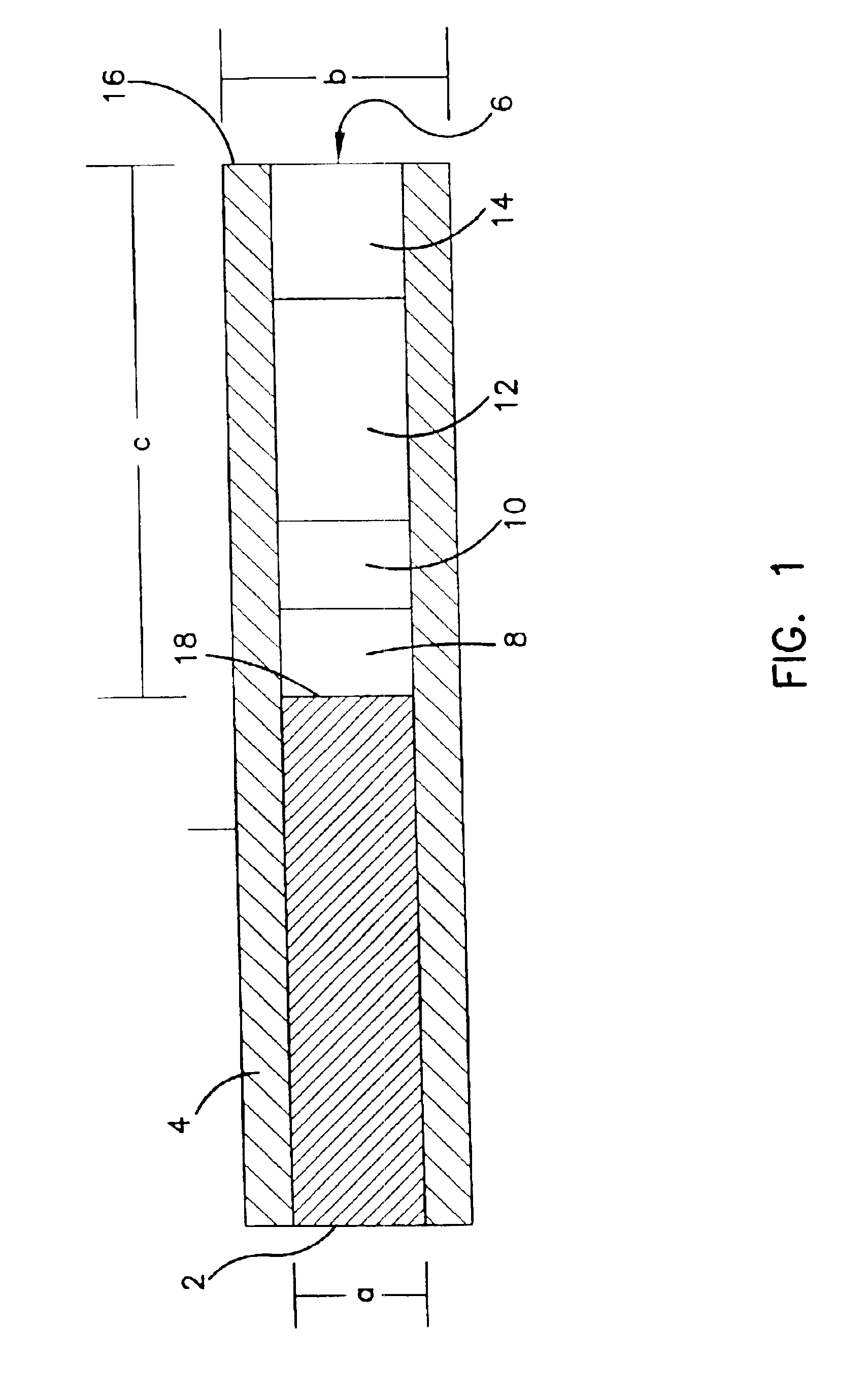
Subcutaneous glucose electrode
InactiveUS6881551B2Reduce transportationAccurate measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConcentrations glucosePolyamide
A small diameter flexible electrode designed for subcutaneous in vivo amperometric monitoring of glucose is described. The electrode is designed to allow “one-point” in vivo calibration, i.e., to have zero output current at zero glucose concentration, even in the presence of other electroreactive species of serum or blood. The electrode is preferably three or four-layered, with the layers serially deposited within a recess upon the tip of a polyamide insulated gold wire. A first glucose concentration-to-current transducing layer is overcoated with an electrically insulating and glucose flux limiting layer (second layer) on which, optionally, an immobilized interference-eliminating horseradish peroxidase based film is deposited (third layer). An outer (fourth) layer is biocompatible.
Owner:THERASENSE
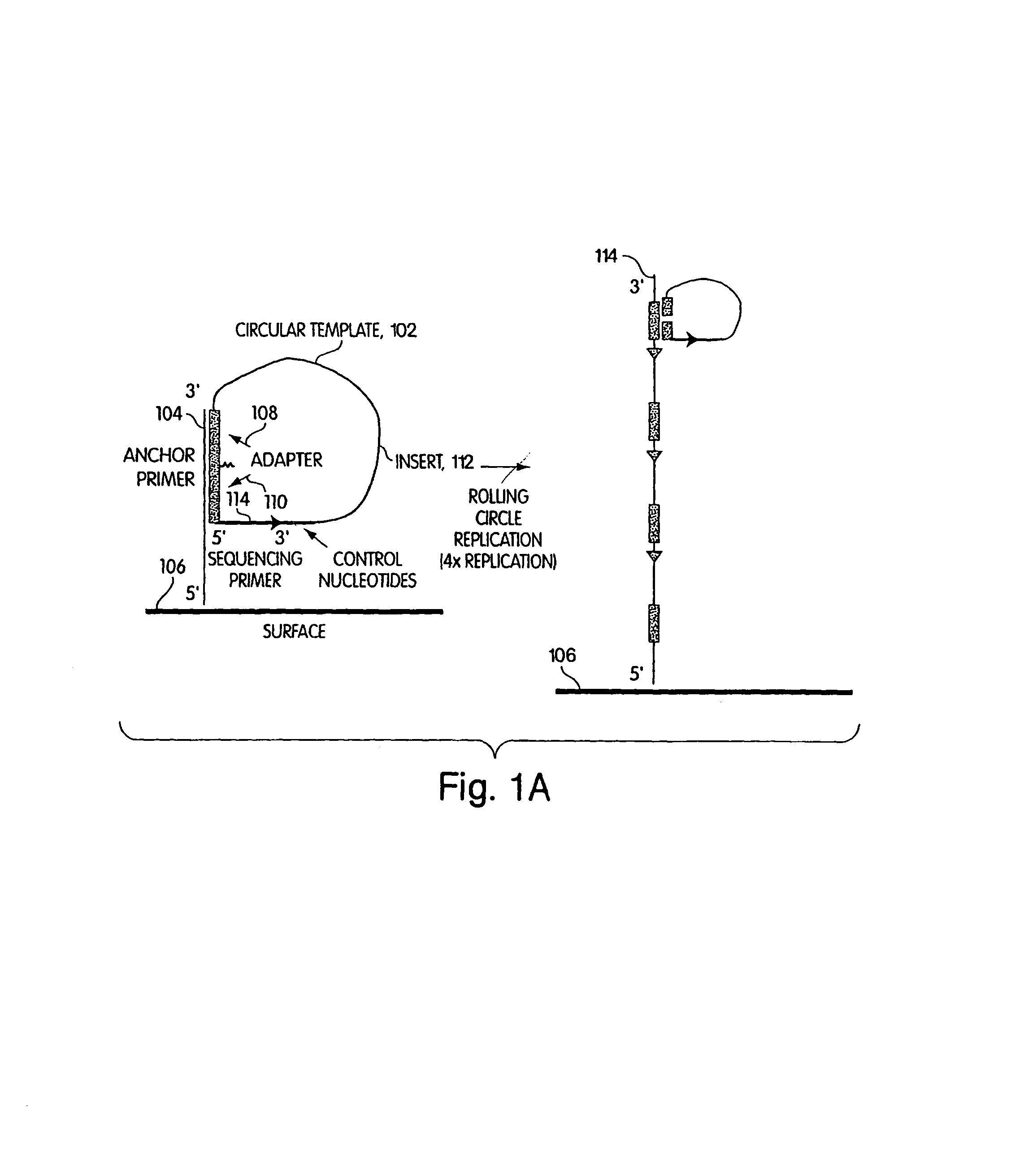
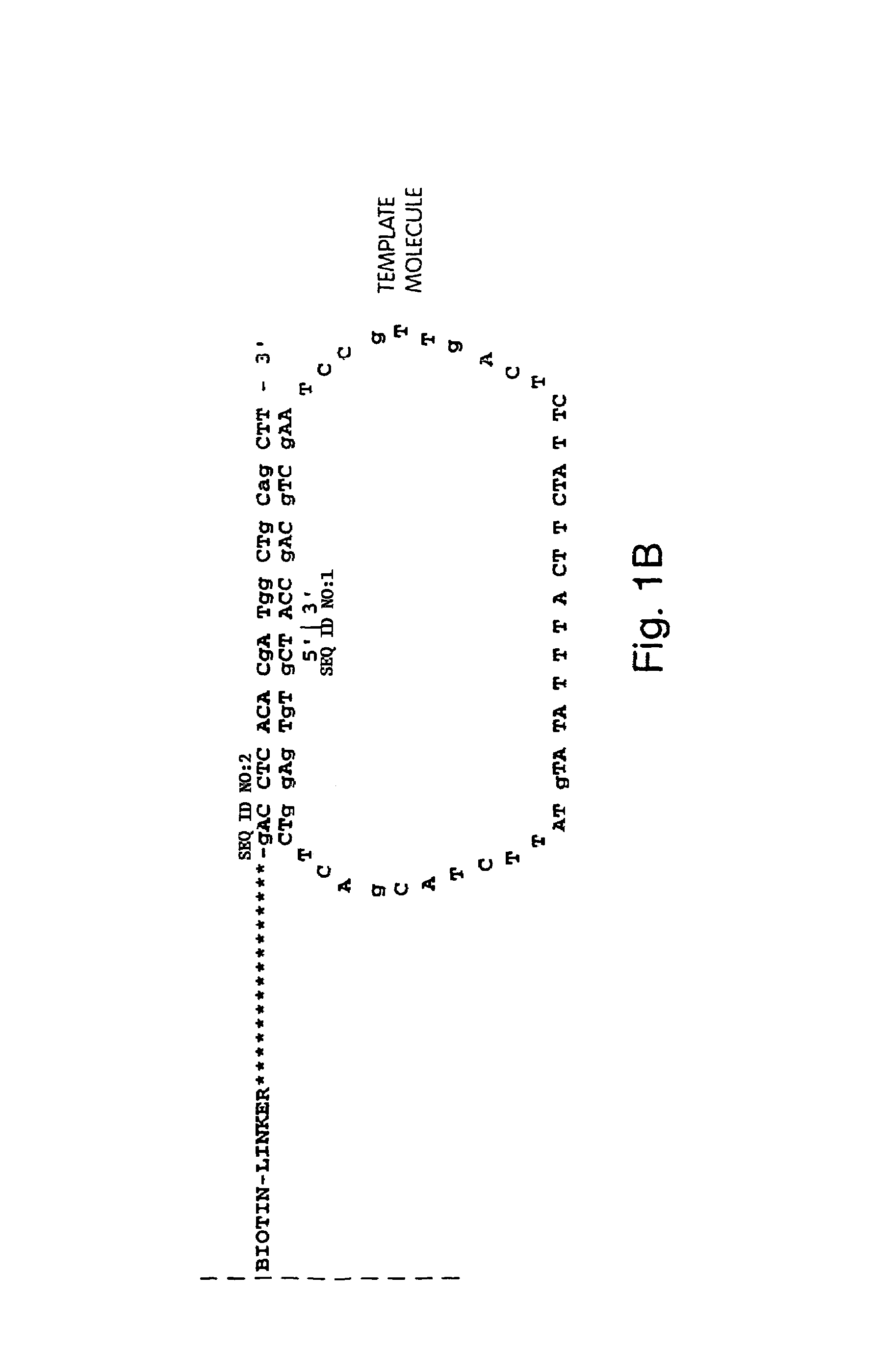
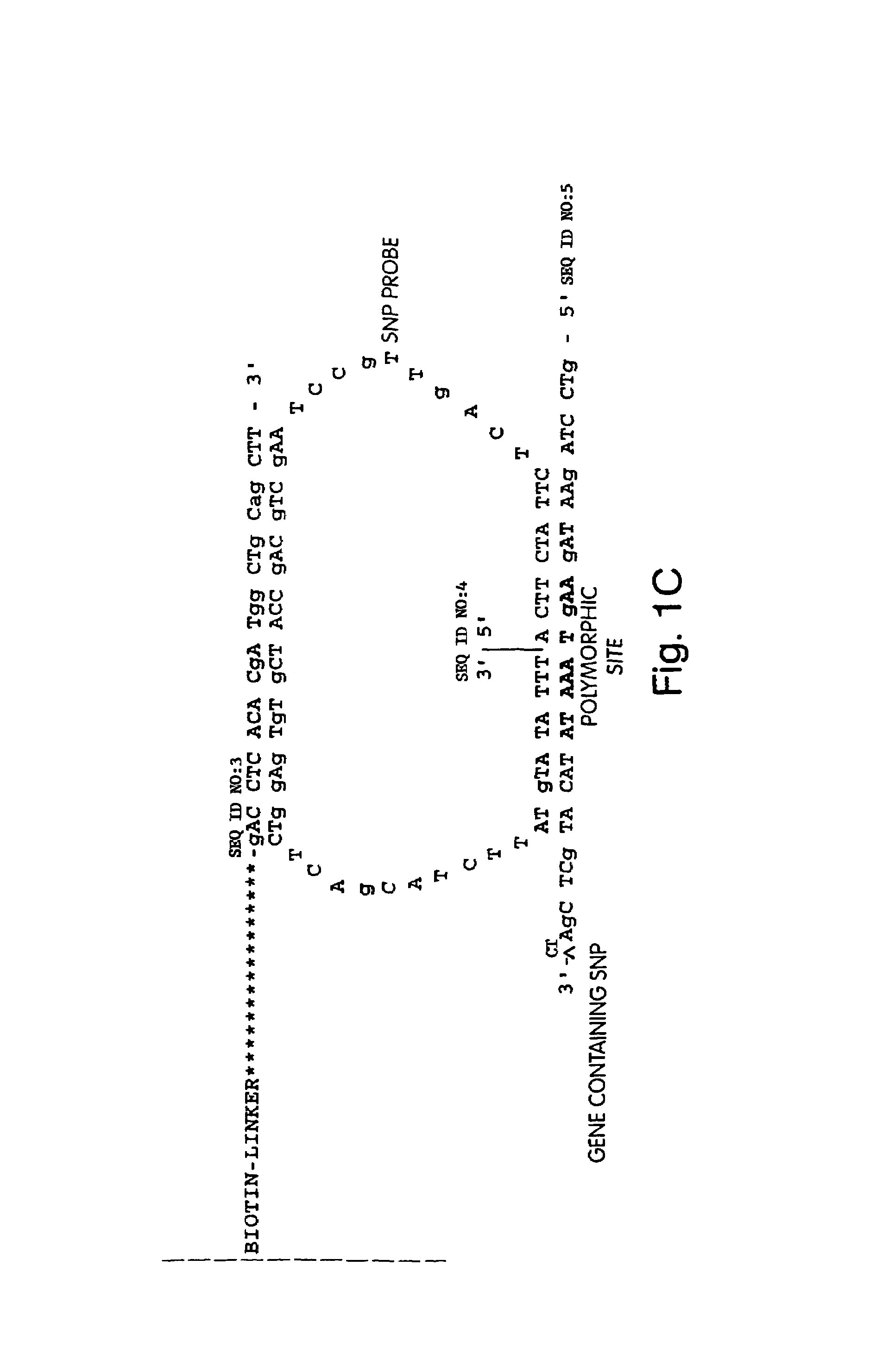
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
Biointerface membranes incorporating bioactive agents
InactiveUS20050031689A1Improve performancePowder deliveryAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiointerfaceActive agent
A biointerface membrane for an implantable device including a nonresorbable solid portion with a plurality of interconnected cavities therein adapted to support tissue ingrowth in vivo, and a bioactive agent incorporated into the biointerface membrane and adapted to modify the tissue response is provided. The bioactive agents can be chosen to induce vascularization and / or prevent barrier cell layer formation in vivo, and are advantageous when used with implantable devices wherein solutes are transported across the device-tissue interface.
Owner:DEXCOM
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS6862465B2Reduce in quantityControl volumeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteImplanted device
Devices and methods for determining analyte levels are described. The devices and methods allow for the implantation of analyte-monitoring devices, such as glucose monitoring devices that result in the delivery of a dependable flow of blood to deliver sample to the implanted device. The devices include unique architectural arrangement in the sensor region that allows accurate data to be obtained over long periods of time.
Owner:DEXCOM
Silicone composition for biocompatible membrane
InactiveUS20050090607A1Microbiological testing/measurementSynthetic resin layered productsSensor materialsPolymer
Owner:DECOM
Electrode systems for electrochemical sensors
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for improved electrochemical measurement of analytes. The preferred embodiments employ electrode systems including an analyte-measuring electrode for measuring the analyte or the product of an enzyme reaction with the analyte and an auxiliary electrode configured to generate oxygen and / or reduce electrochemical interferants. Oxygen generation by the auxiliary electrode advantageously improves oxygen availability to the enzyme and / or counter electrode; thereby enabling the electrochemical sensors of the preferred embodiments to function even during ischemic conditions. Interferant modification by the auxiliary electrode advantageously renders them substantially non-reactive at the analyte-measuring electrode, thereby reducing or eliminating inaccuracies in the analyte signal due to electrochemical interferants.
Owner:DEXCOM
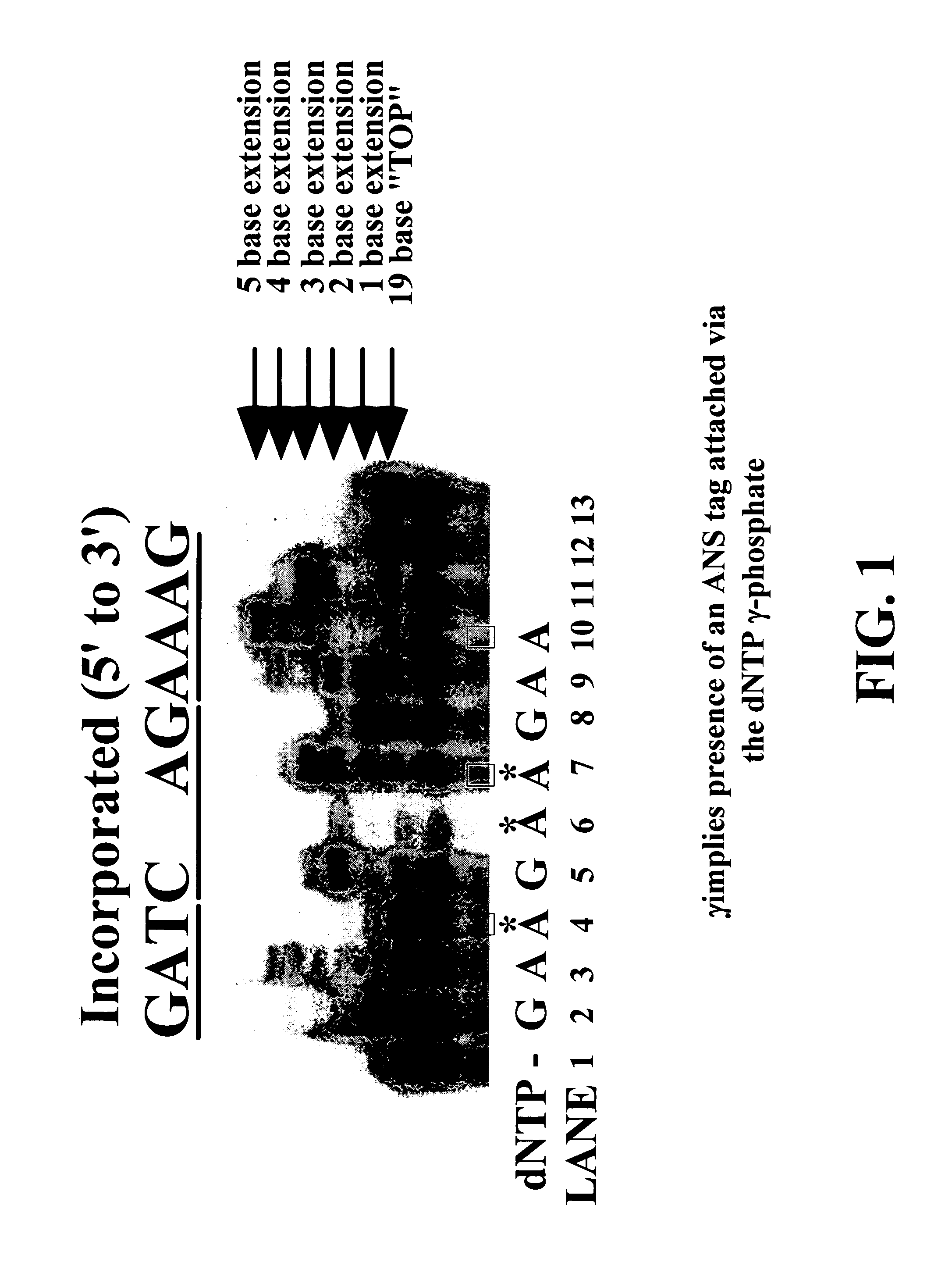
Enzymatic nucleic acid synthesis: compositions and methods for altering monomer incorporation fidelity
InactiveUS7211414B2Extent of pyrophosphorolysis of a primer extension product is reducedImprove fidelityBiocideSugar derivativesPhosphatePhosphoric acid
Nucleotide triphosphate probes containing a molecular and / or atomic tag on a a γ and / or β phosphate group and / or a base moiety having a detectable property are disclosed, and kits and method for using the tagged nucleotides in sequencing reactions and various assay. Also, phosphate and polyphosphate molecular fidelity altering agents are disclosed.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
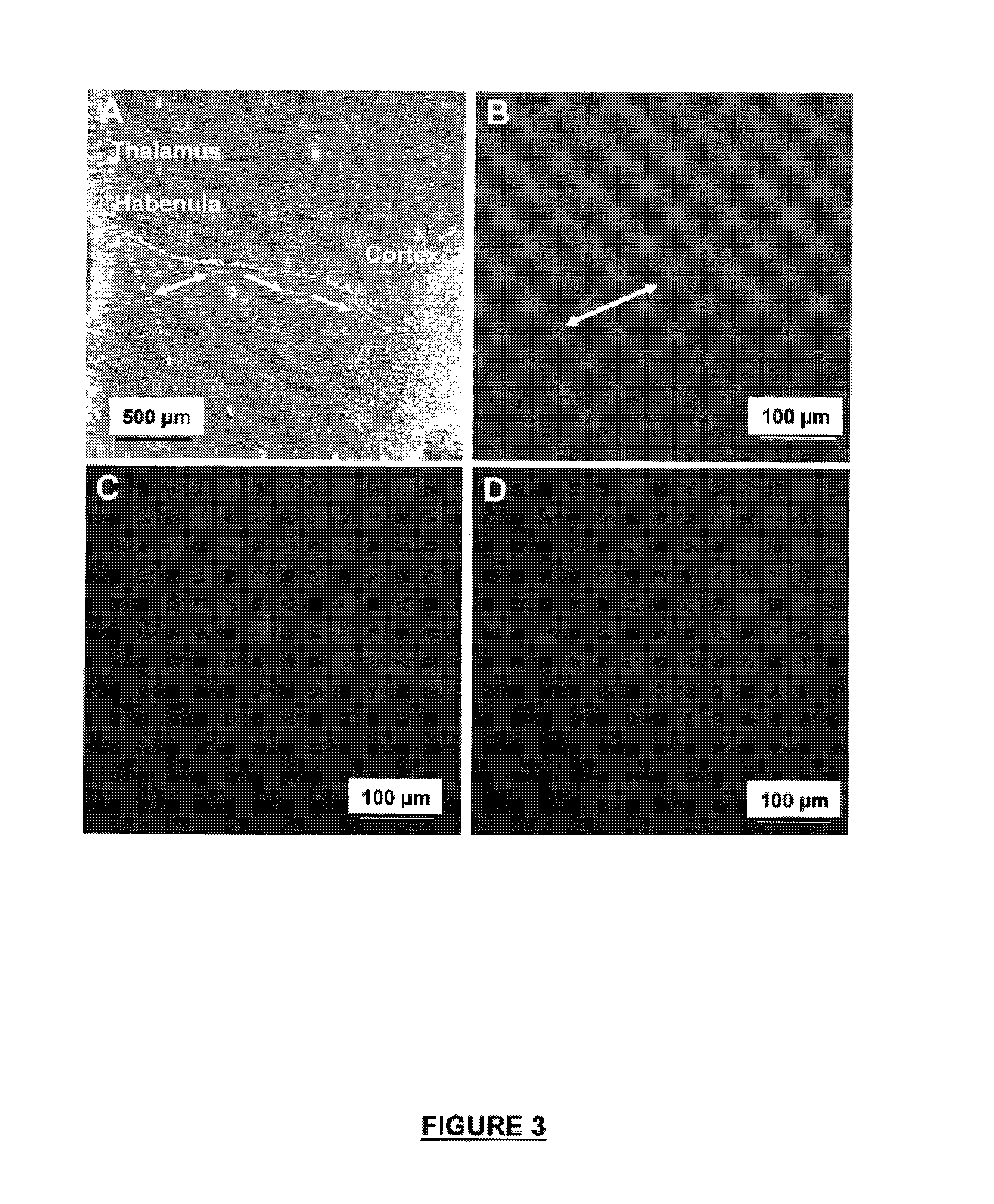
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use in treatment of brain damage
InactiveUS7563862B2High expressionEasy SurvivalPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNervous systemInjury brain
The invention discloses a family of peptides termed NRP compounds or NRPs that can promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation and / or neuronal survival, and provides compositions and methods for the use of NRPs in the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. NRP compounds can induce neurons and neuroblasts to proliferate and migrate into areas of damage caused by acute brain injury or chronic neurodegenerative disease, such as exposure to toxins, stroke, trauma, nervous system infections, demyelinating diseases, dementias, and metabolic disorders. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly, and directly into the nervous system of a patient. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dose forms for therapeutic use. Methods for detecting neural regeneration, neural proliferation, neural differentiation, neurite outgrowth and neural survival can be used to develop other neurally active agents.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
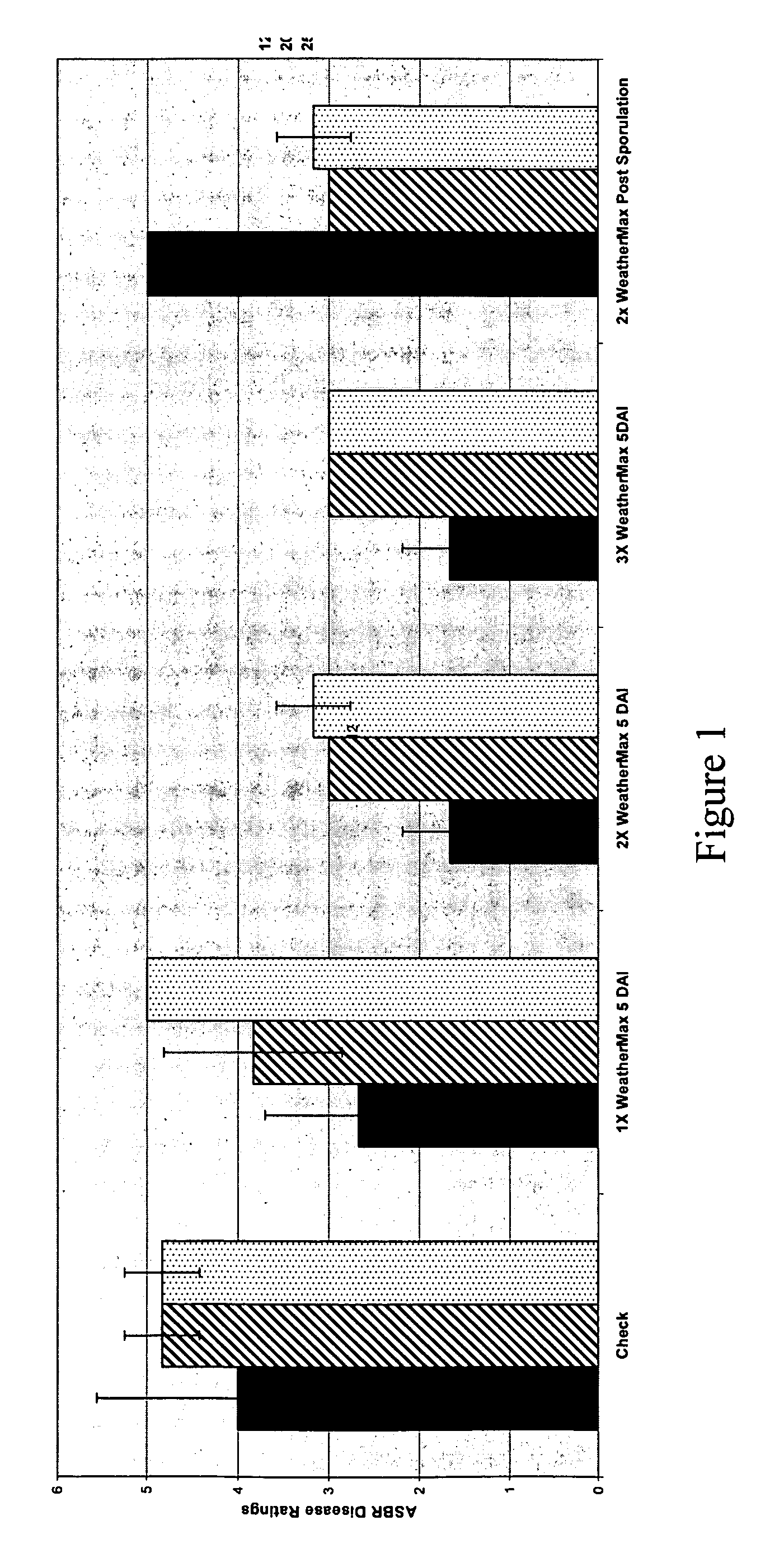
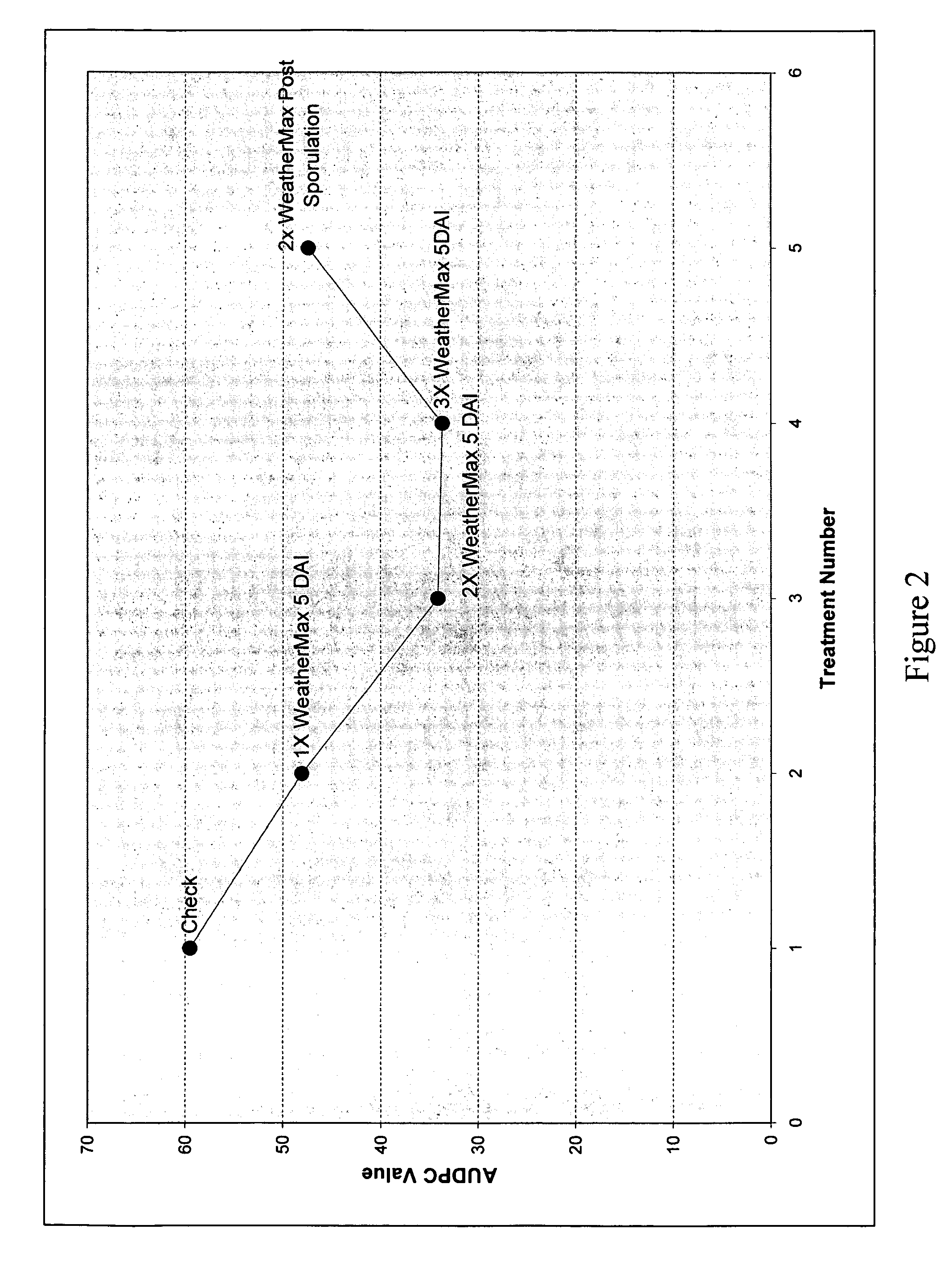
Method for disease control in MON89788 soybean
The present invention relates to a method to control diseases of MON89788 soybean by treatment with formulations and mixtures containing glyphosate. In particular, the formulations and mixtures are effective at controlling fungal diseases of MON89788. More specifically, the invention relates to a method to control the severity of leaf rust disease on MON89788.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
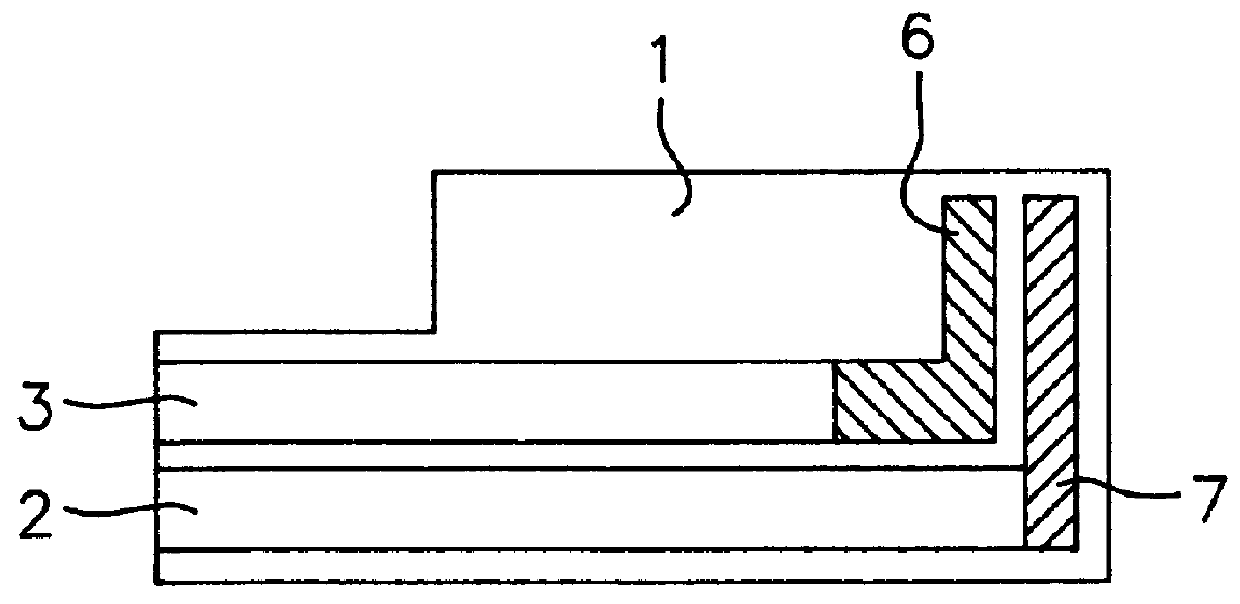
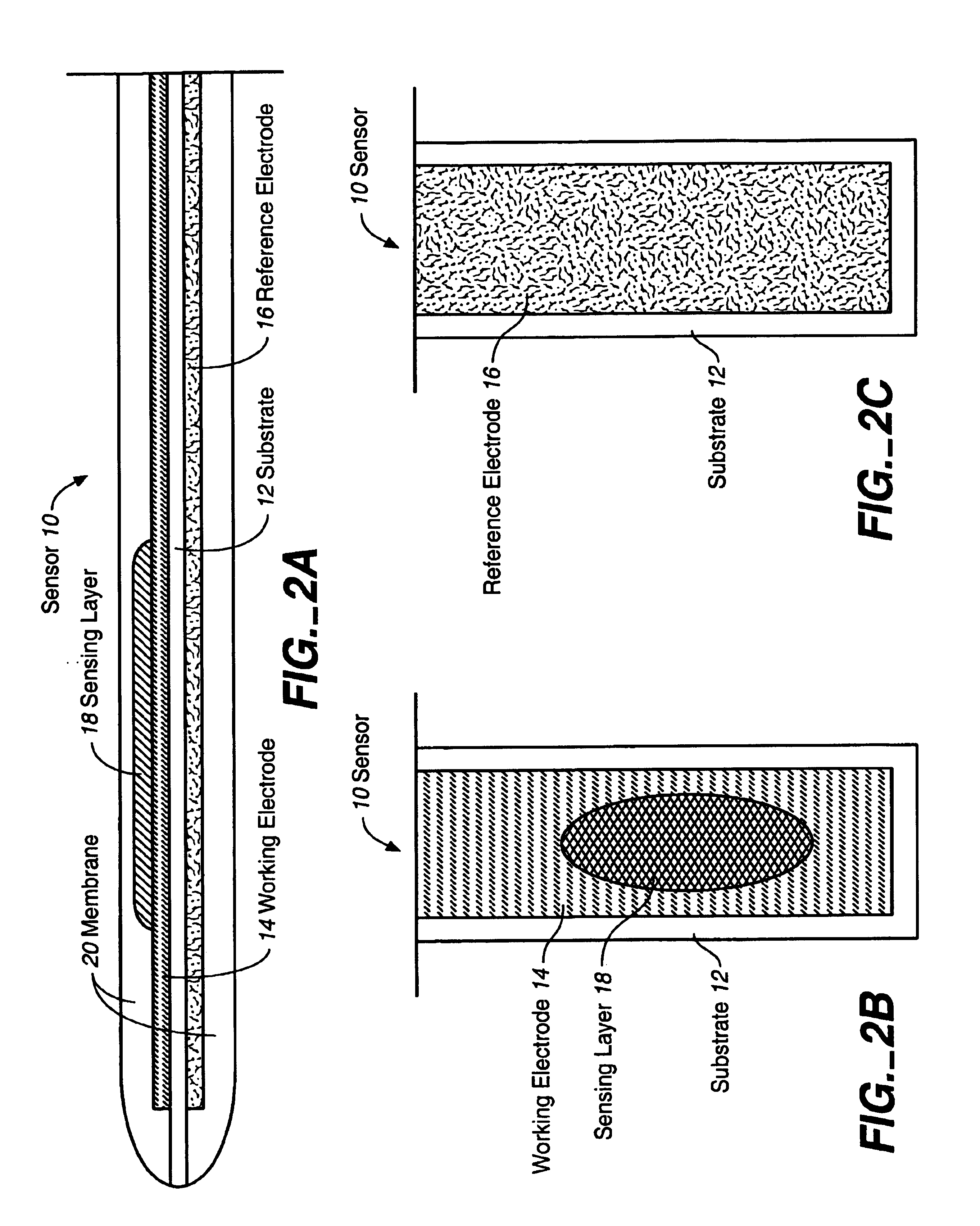
Enzyme electrode structure
InactiveUS6071391AEasy to manufactureEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzyme electrodeWorking electrode
A biosensor comprises a space part for sucking and housing a sample formed of two upper and lower plates, the two plates being stuck together by an adhesive layer, the space part for sucking and housing the sample being constituted so as to be partially opened in the peripheral part and partially closed by the adhesive layer, and has a working electrode having at least glucose oxidase immobilized thereon and a counter electrode on the same plane of the plate.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
System and apparatus for sequential processing of analytes
InactiveUS6969488B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMicroparticle
An apparatus and system are provided for simultaneously analyzing a plurality of analytes anchored to microparticles. Microparticles each having a uniform population of a single kind of analyte attached are disposed as a substantially immobilized planar array inside of a flow chamber where steps of an analytical process are carried out by delivering a sequence of processing reagents to the microparticles by a fluidic system under microprocessor control. In response to such process steps, an optical signal is generated at the surface of each microparticle which is characteristic of the interaction between the analyte carried by the microparticle and the delivered processing reagent. The plurality of analytes are simultaneously analyzed by collecting and recording images of the optical signals generated by all the microparticles in the planar array. A key feature of the invention is the correlation of the sequence of optical signals generated by each microparticle in the planar array during the analytical process.
Owner:SOLEXA
Biosensor membranes composed of polymers containing heterocyclic nitrogens
InactiveUS6932894B2Easy CalibrationConsider sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteNitrogen
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
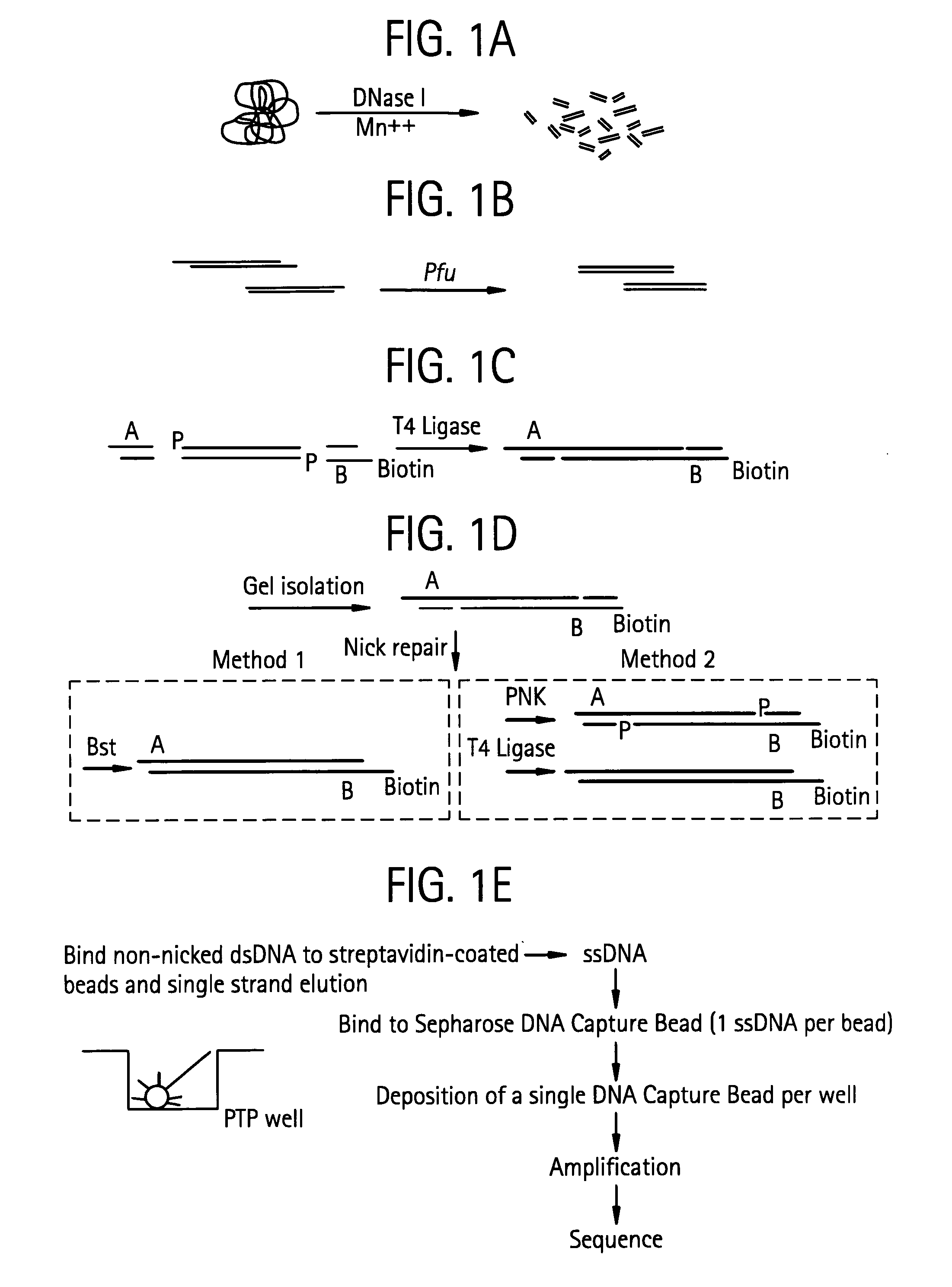
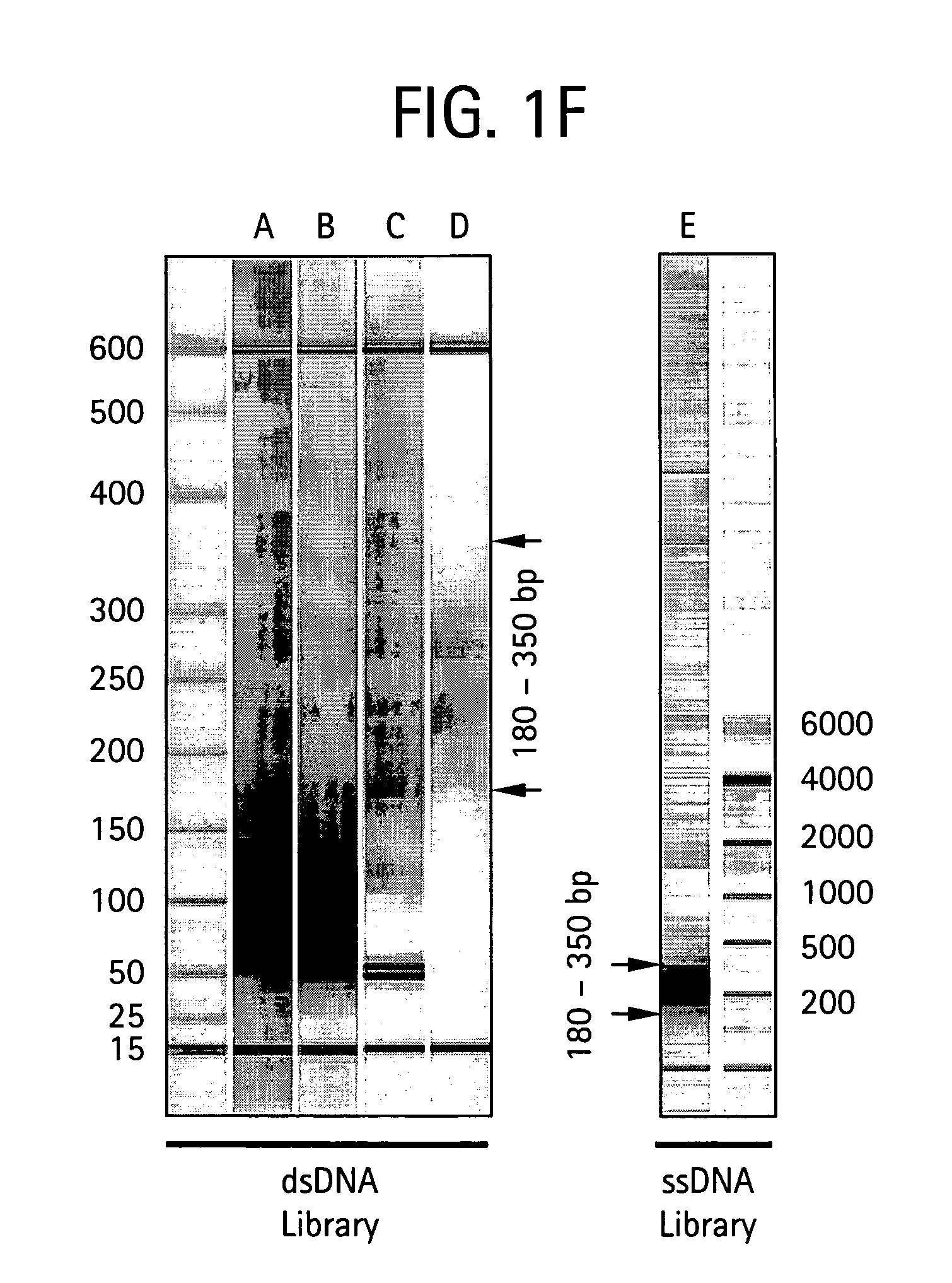
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Electrochemical sensors including electrode systems with increased oxygen generation
ActiveUS7108778B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteElectrochemical gas sensor
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for increasing oxygen generation in electrochemical sensors in order to overcome the oxygen limitations. The preferred embodiments employ electrode systems with at least two electrodes in relatively close proximity to each other; wherein at least one electrode is configured to generate oxygen and at least one other electrode is configured to sense an analyte or a product of a reaction indicative of the concentration of analyte. The oxygen generated by the oxygen-generating electrode is available to the catalyst within a membrane system and / or the counter electrode, thereby enabling the electrochemical sensors of the preferred embodiments to function even during ischemic conditions.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Phage antibodies
Peripheral blood leucocytes incubated with a semi-synthetic phage antibody library and fluorochrome-labeled CD3 and CD20 antibodies were used to isolate human single chain Fv antibodies specific for subsets of blood leucocytes by flow cytometry. Isolated phage antibodies showed exclusive binding to the subpopulation used for selection or displayed additional binding to a restricted population of other cells in the mixture. At least two phage antibodies appeared to display hithereto unknown staining patterns of B lineage cells. This approach provides a subtractive procedure to rapidly obtain human antibodies against known and novel surface antigens in their native configuration, expressed on phenotypically defined subpopulations of cells. Importantly, this approach does not depend on immunization procedures or the necessity to repeatedly construct phage antibody libraries.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
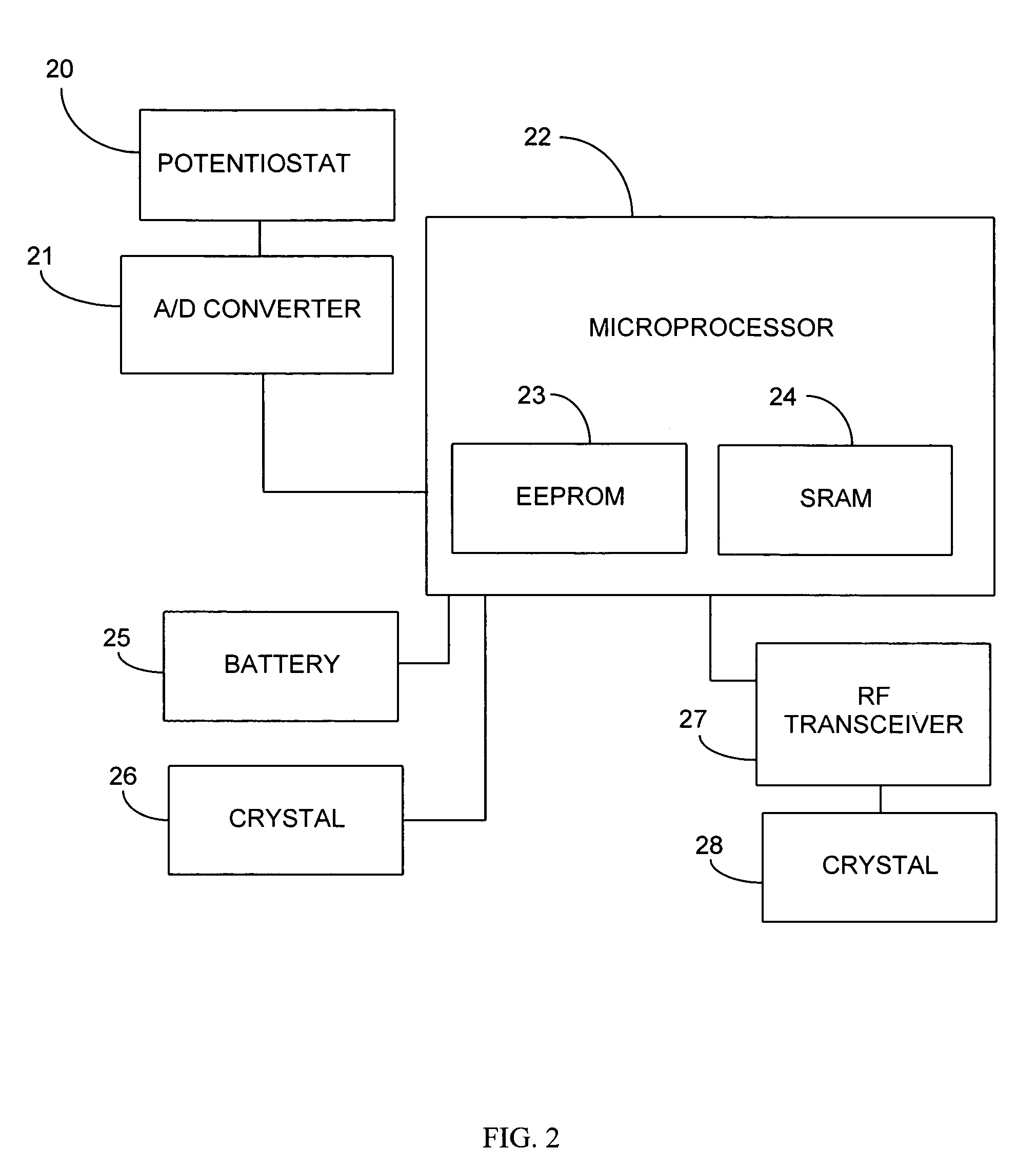
Implantable analyte sensor
ActiveUS20050245795A1Improved patient convenienceConvenient careImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteEngineering
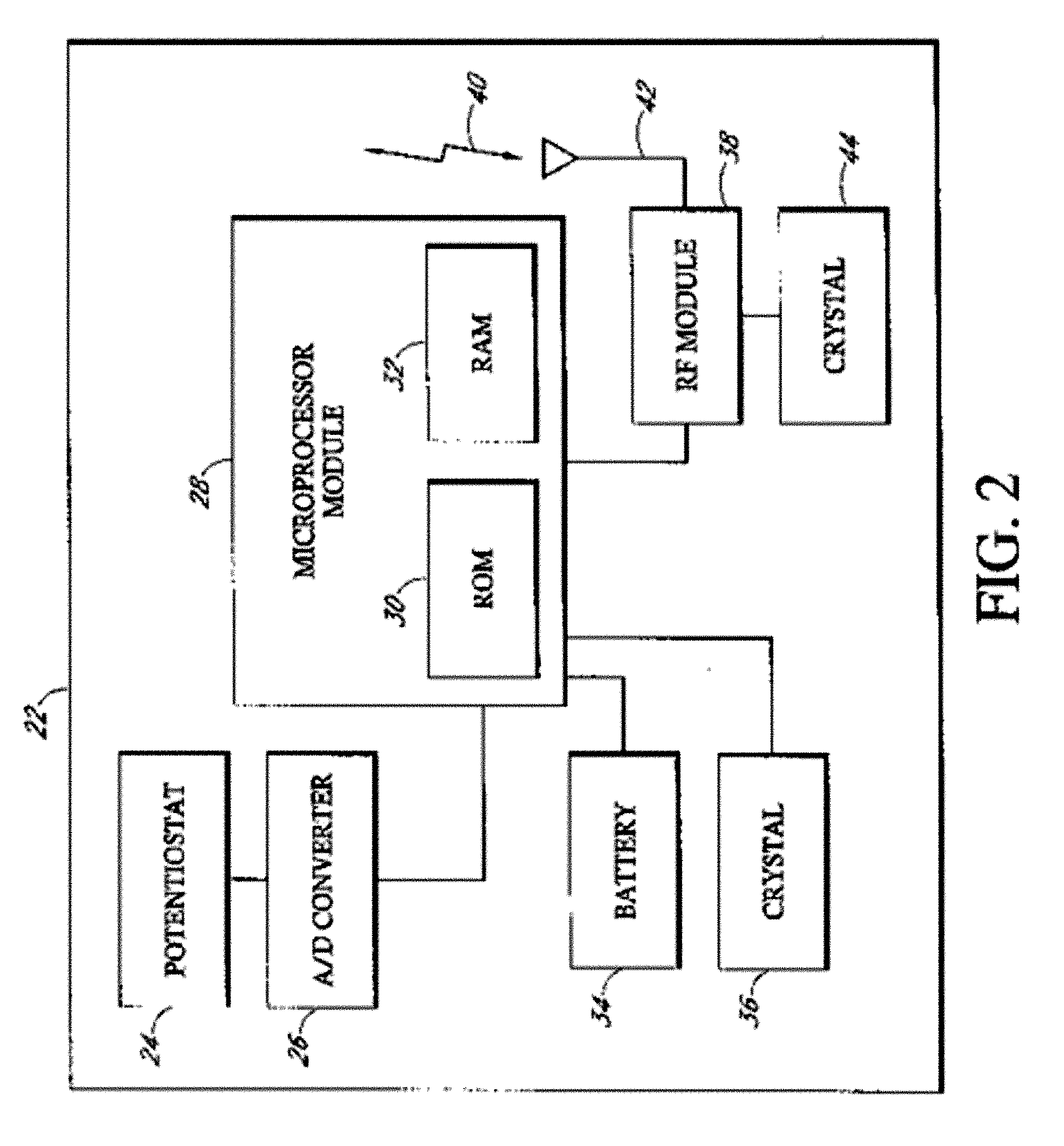
Abstract of the DisclosureAn implantable analyte sensor including a sensing region for measuring the analyte and a non-sensing region for immobilizing the sensor body in the host. The sensor is implanted in a precisely dimensioned pocket to stabilize the analyte sensor in vivo and enable measurement of the concentration of the analyte in the host before and after formation of a foreign body capsule around the sensor. The sensor further provides a transmitter for RF transmission through the sensor body, electronic circuitry, and a power source optimized for long-term use in the miniaturized sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM
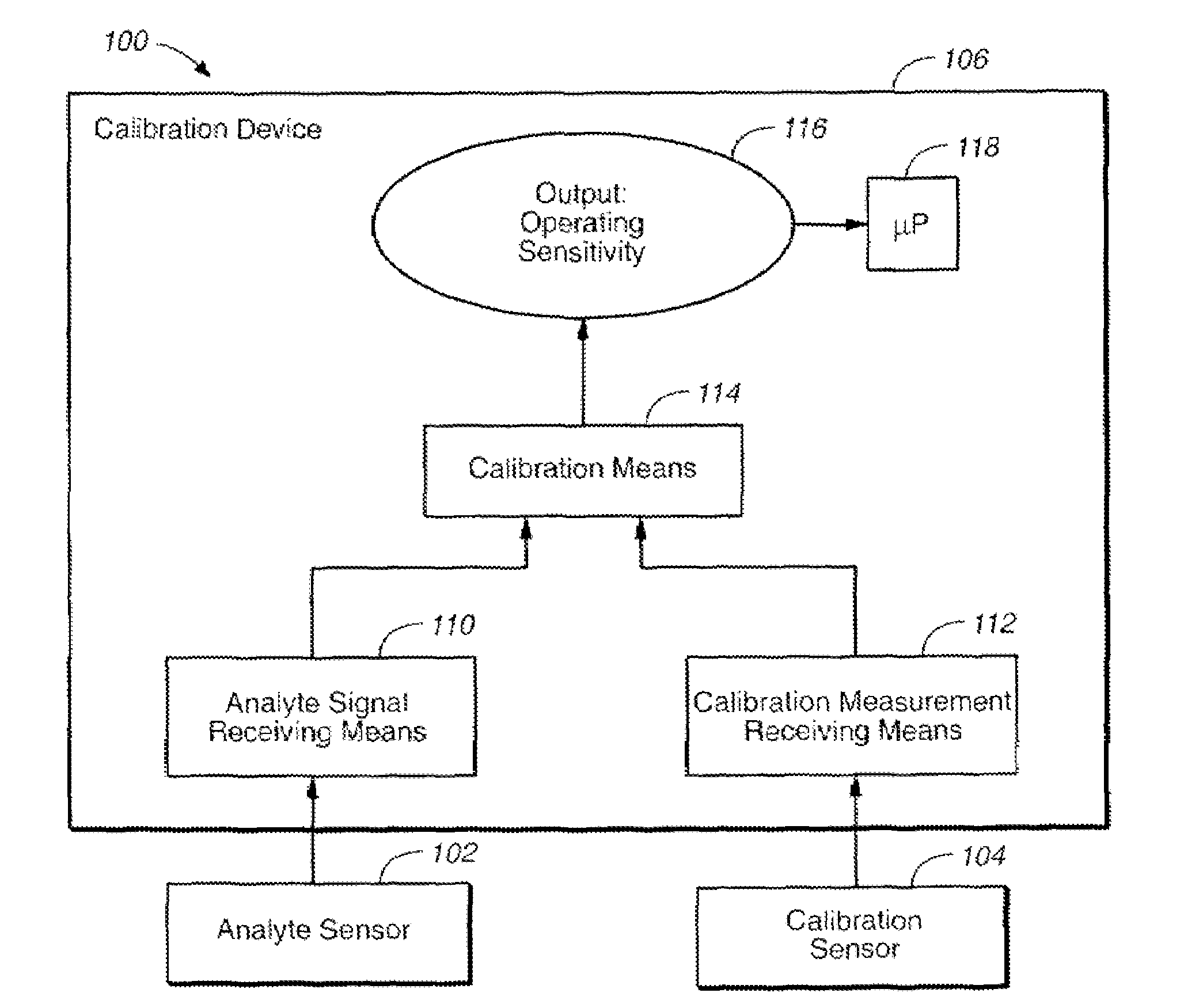
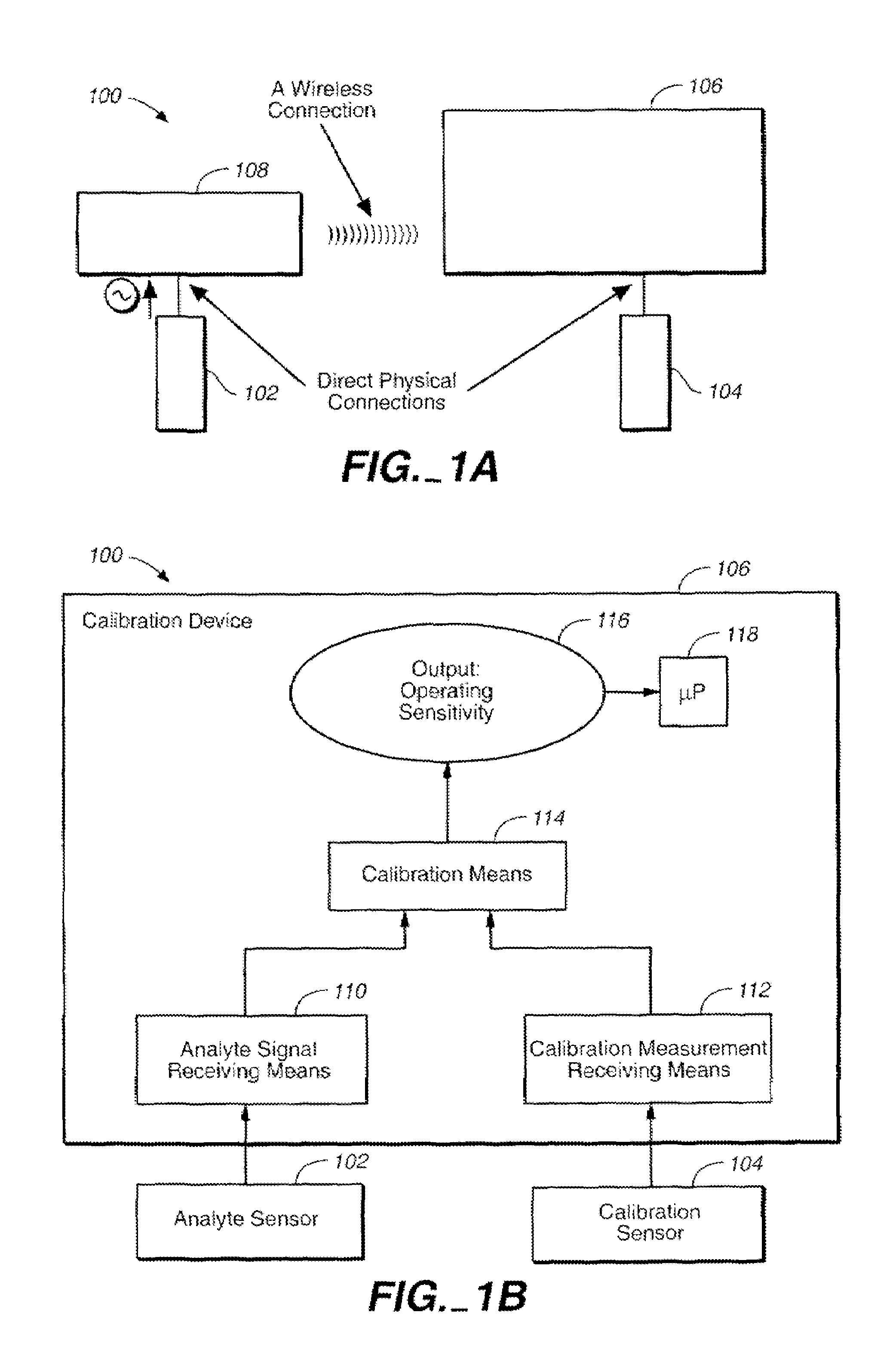
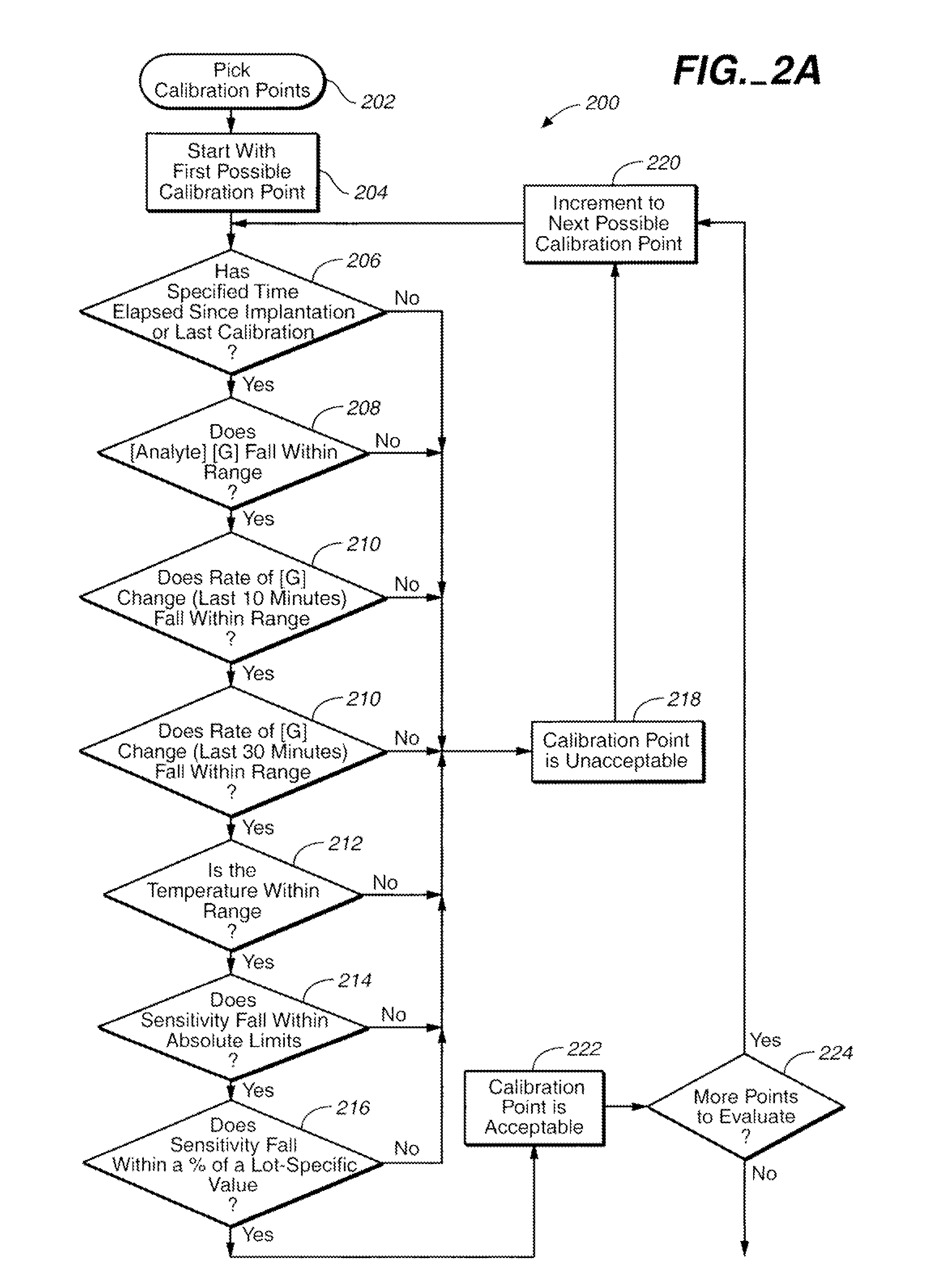
Method of calibrating an analyte-measurement device, and associated methods, devices and systems
ActiveUS7299082B2Improve mobilityAvoid high pressureMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterMeasurement deviceAnalyte
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Use of chimeric nucleases to stimulate gene targeting
ActiveUS20050026157A1Ameliorate genetic disorderIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsFusion with DNA-binding domainGene targetsGenetic Change
Gene targeting is a technique to introduce genetic change into one or more specific locations in the genome of a cell. For example, gene targeting can introduce genetic change by modifying, repairing, attenuating or inactivating a target gene or other chromosomal DNA. In one aspect, this disclosure relates to methods and compositions for gene targeting with high efficiency in a cell. This disclosure also relates to methods of treating or preventing a genetic disease in an individual in need thereof. Further disclosed are chimeric nucleases and vectors encoding chimeric nucleases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
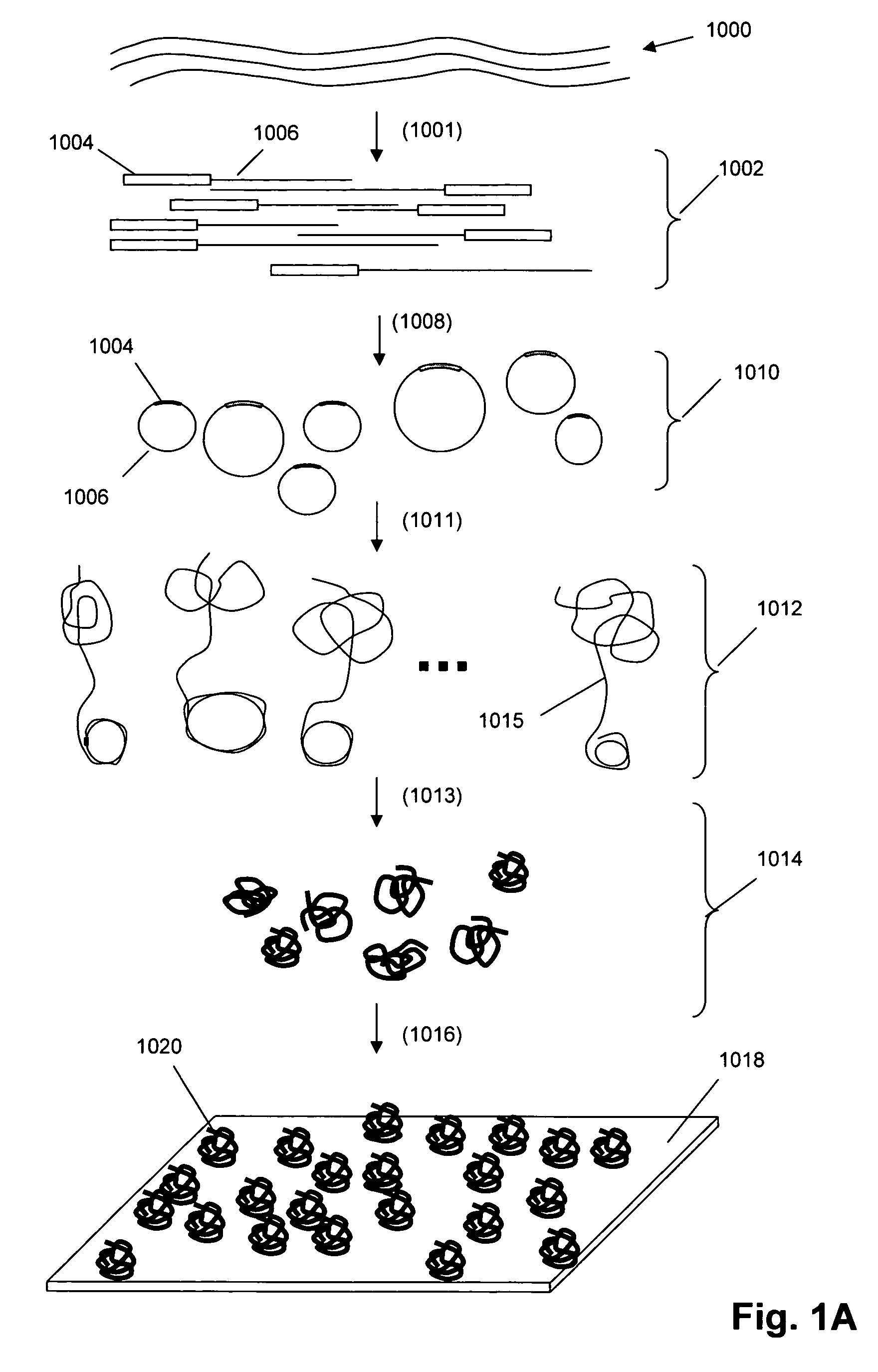
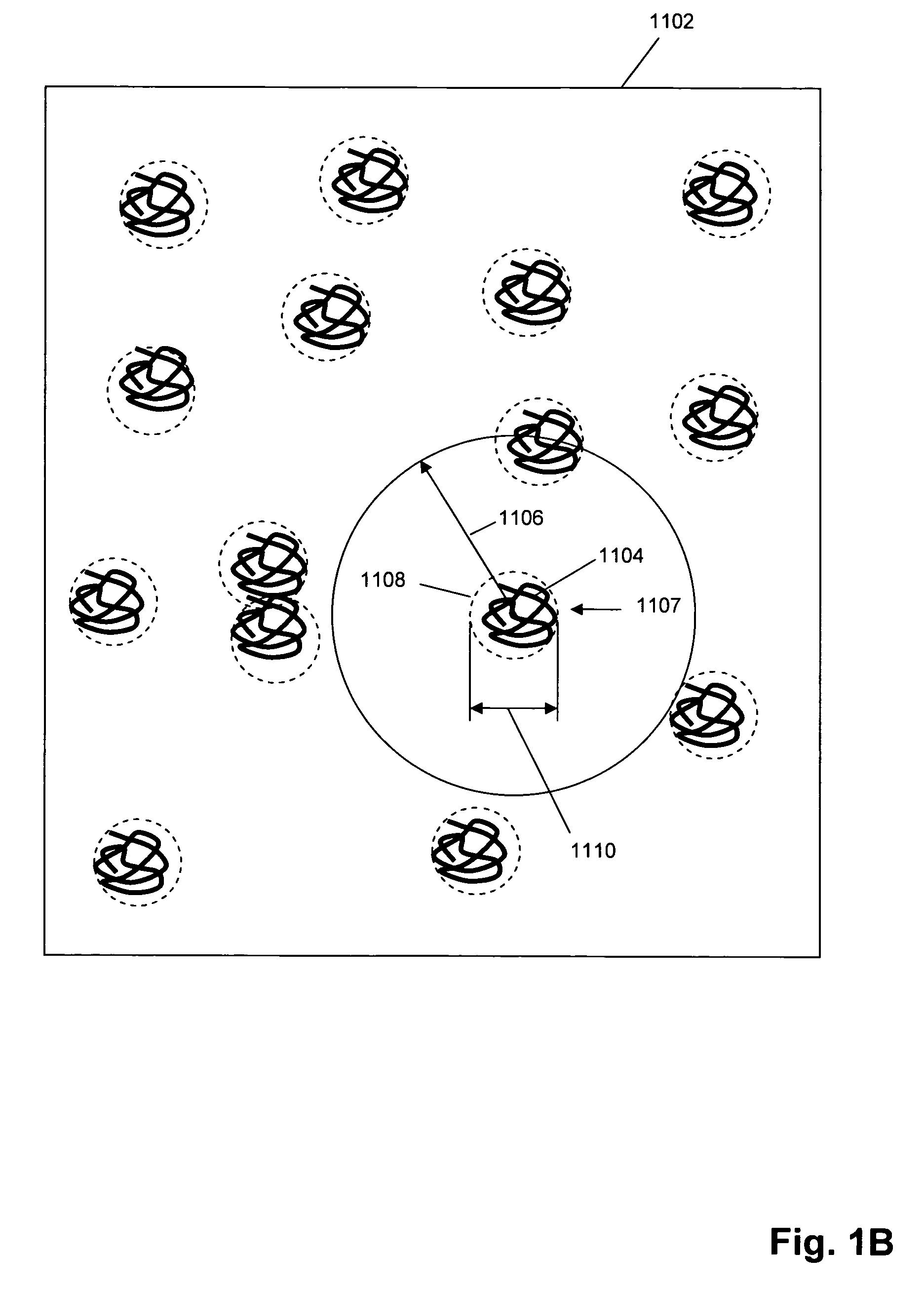
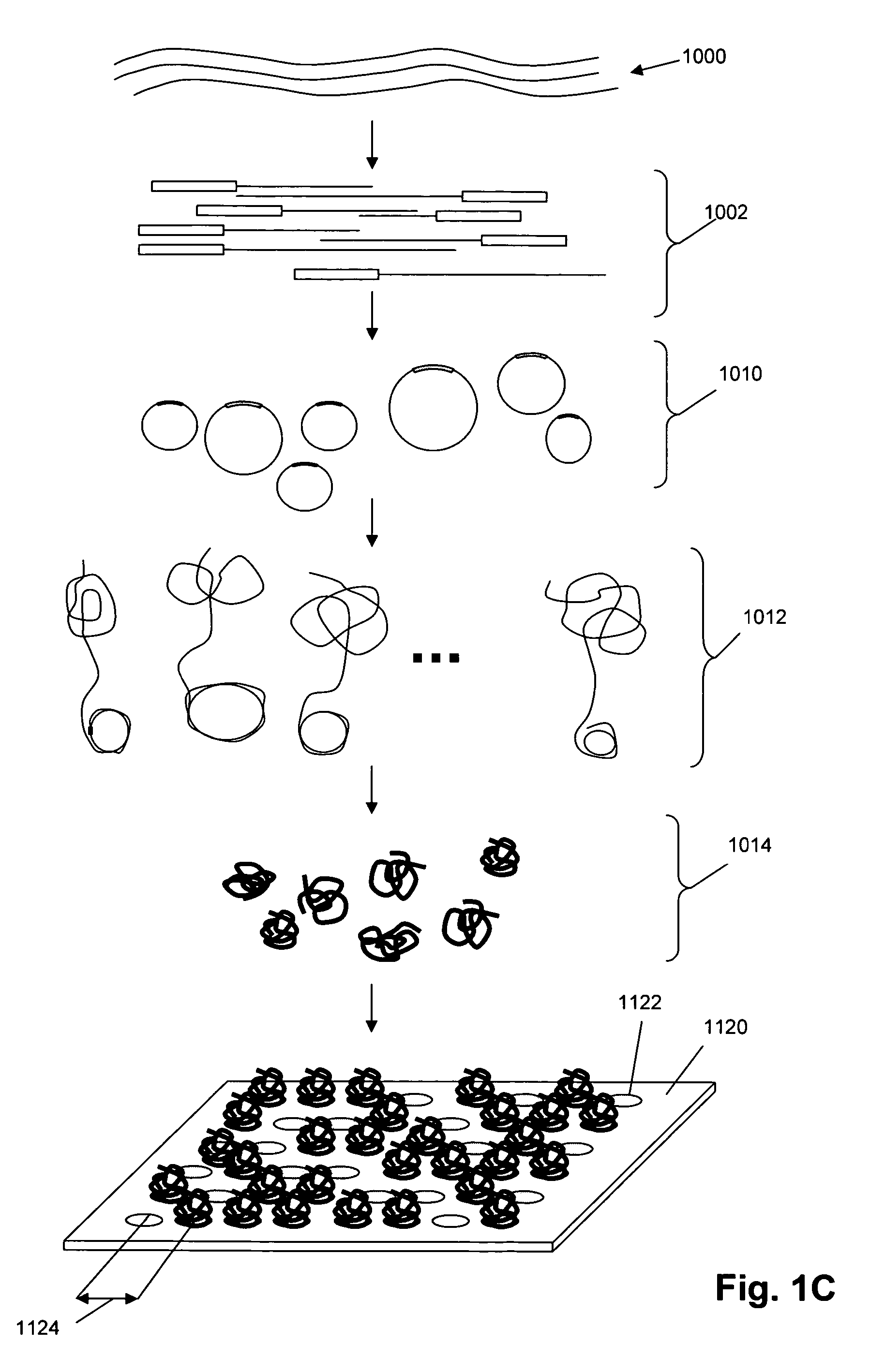
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Method of sequencing a nucleic acid
InactiveUS7244559B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyNucleic acid detectionOligonucleotide
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
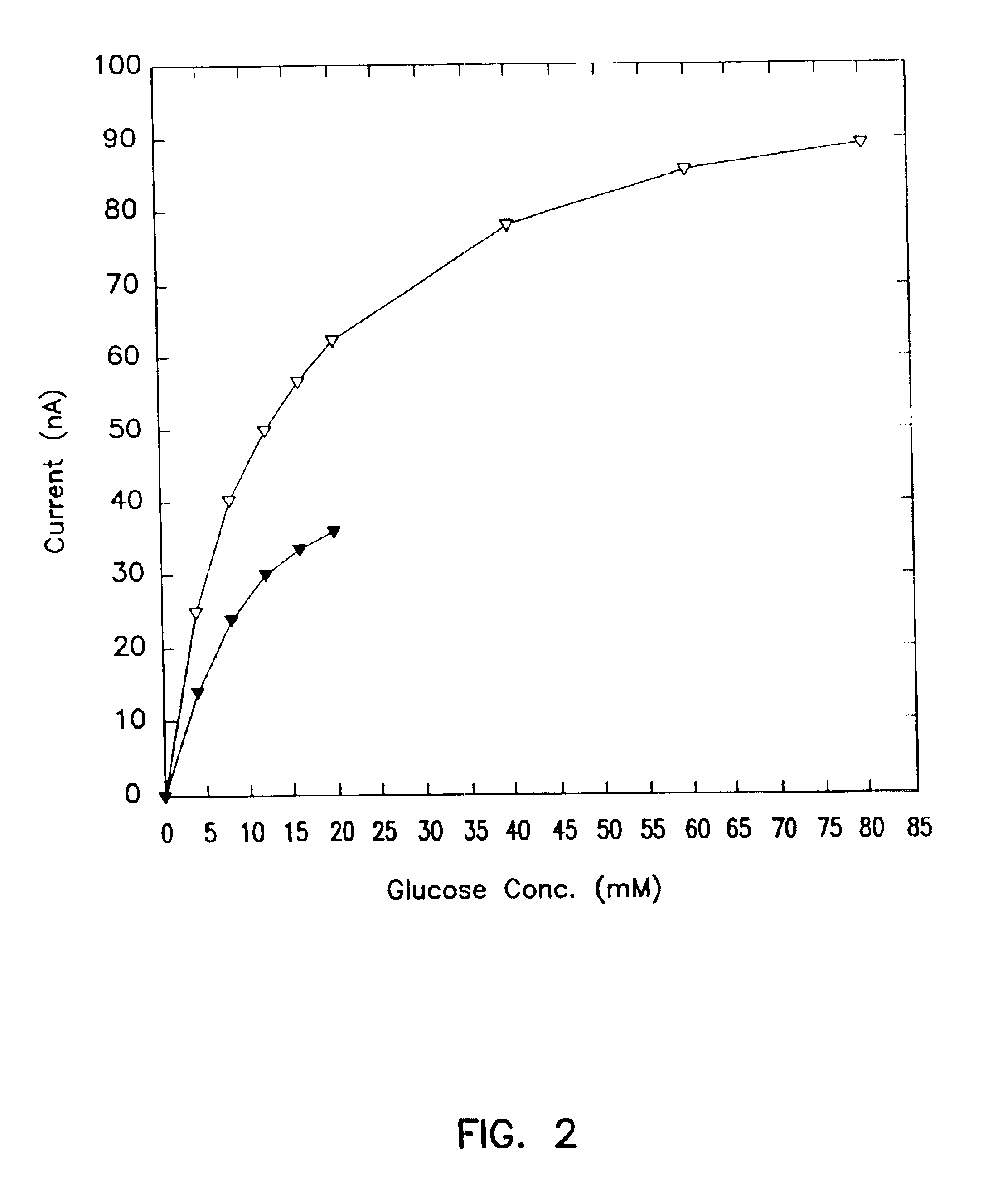
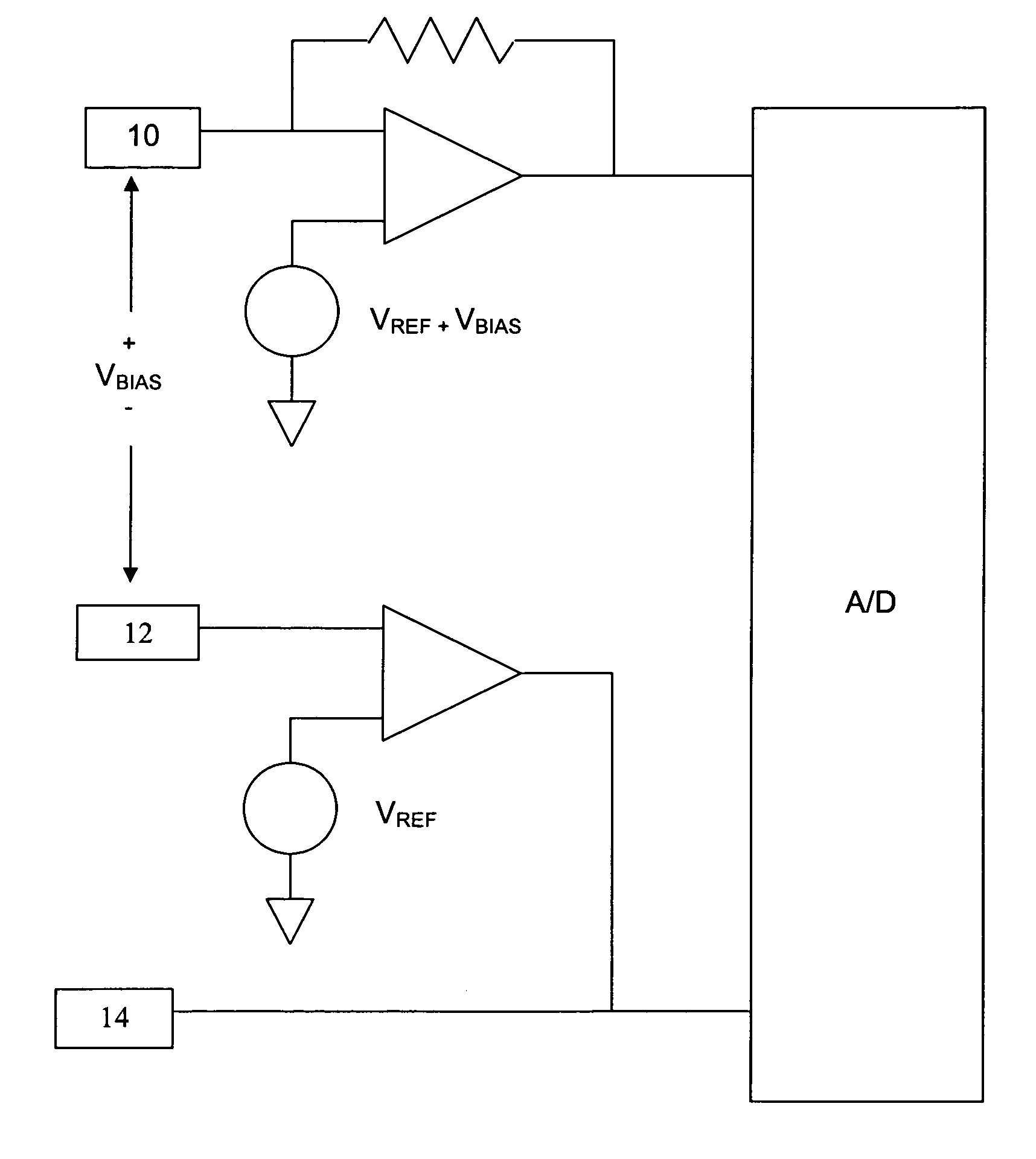
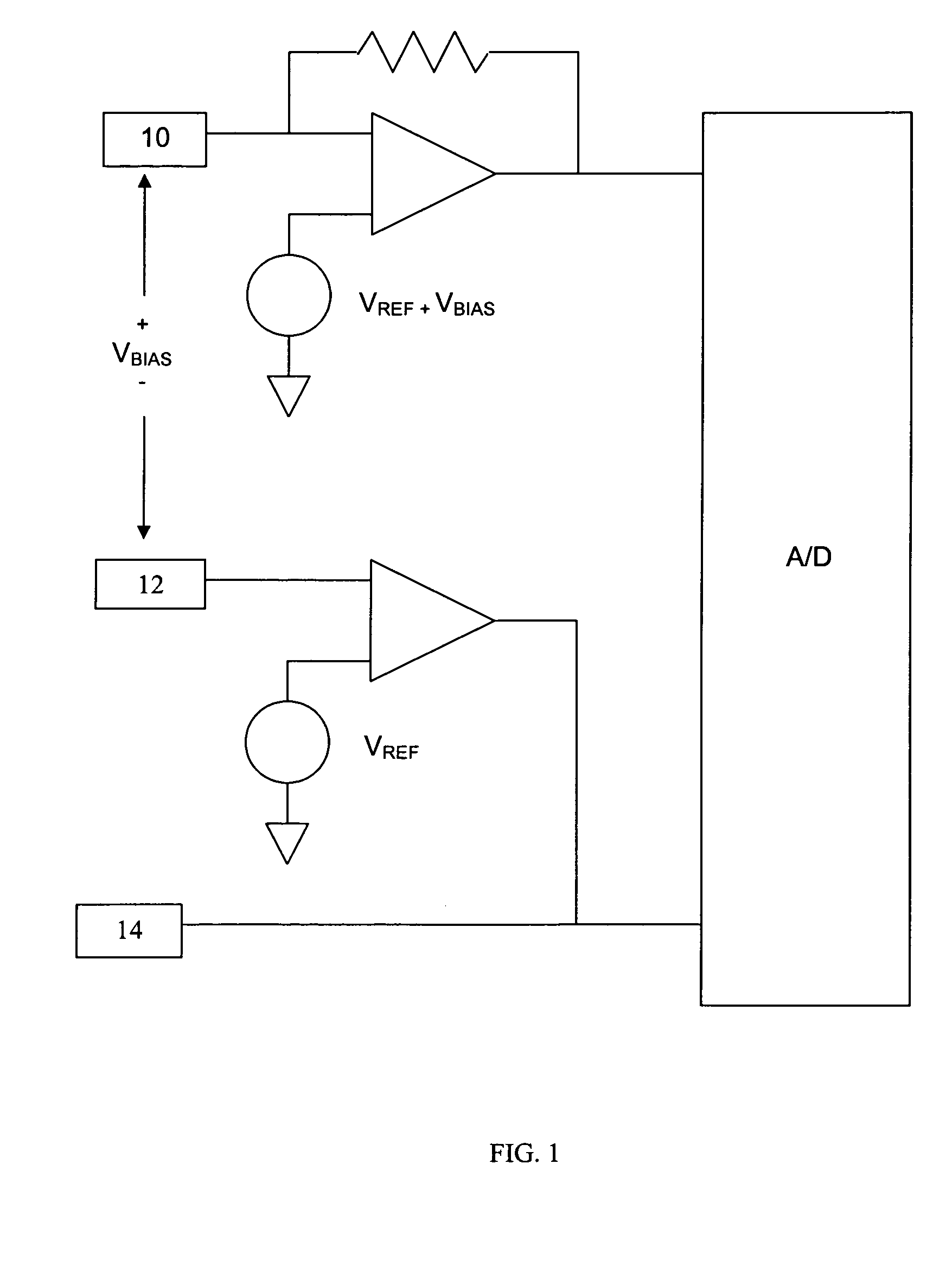
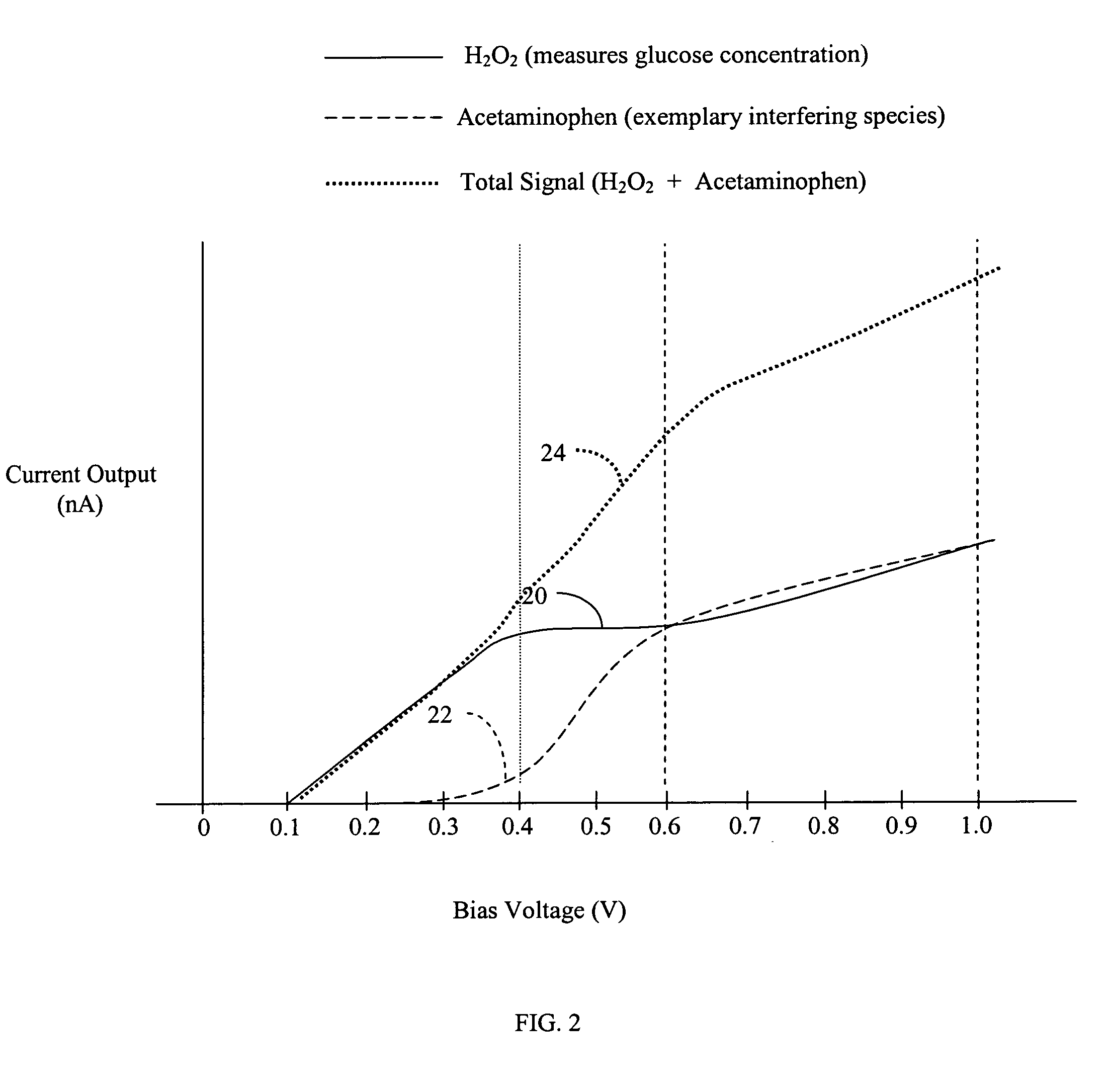
Systems and methods for improving electrochemical analyte sensors
ActiveUS7081195B2Quality improvementReducing and eliminating effectImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteD-Glucose
An analyte-measuring device, particularly an electrochemical sensor, is provided for measuring current values at multiple bias potential settings to assess the quality of the analyte measurement, identify interference in the signal, and calculate substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements. The device and method are suitable for calculating substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements when glucose is the analyte and acetaminophen is an interfering species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensor
ActiveUS20090018424A1Sufficient flow rateReduce the amount requiredLocal control/monitoringDrug and medicationsAnalyteVascular Access Devices
Systems and methods of use for continuous analyte measurement of a host's vascular system are provided. In some embodiments, a continuous glucose measurement system includes a vascular access device, a sensor and sensor electronics, the system being configured for insertion into communication with a host's circulatory system.
Owner:DEXCOM
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS7110803B2Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesAnalyteImplanted device
Owner:DEXCOM
Afinity domain for analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050176136A1Reduce impactBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteSorbent
Abstract of the DisclosureThe preferred embodiments provide a membrane system, particularly for use on an electrochemical sensor, wherein the membrane system includes an affinity domain that dampens the effects of target interferant(s) on the sensor. The affinity domain can be layer, surface, region, and / or portion of the membrane system formed using sorbents that have an affinity for the target interferant. The sorbents can be adapted to adsorb the interferants, for example using adsorbents such as chromatography packing materials. The sorbents can also be adapted to absorb the interferants by imprinting a molecular structure on the material that forms the affinity domain such that target interferants bind to the imprinted surfaces at the molecular level.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte measuring device
InactiveUS20050033132A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteCell layer
An implantable analyte-measuring device including a membrane adapted to promote vascularization and / or interfere with barrier cell layer formation. The membrane includes any combination of materials, architecture, and bioactive agents that facilitate analyte transport to provide long-term in vivo performance of the implantable analyte-measuring device.
Owner:DEXCOM
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com