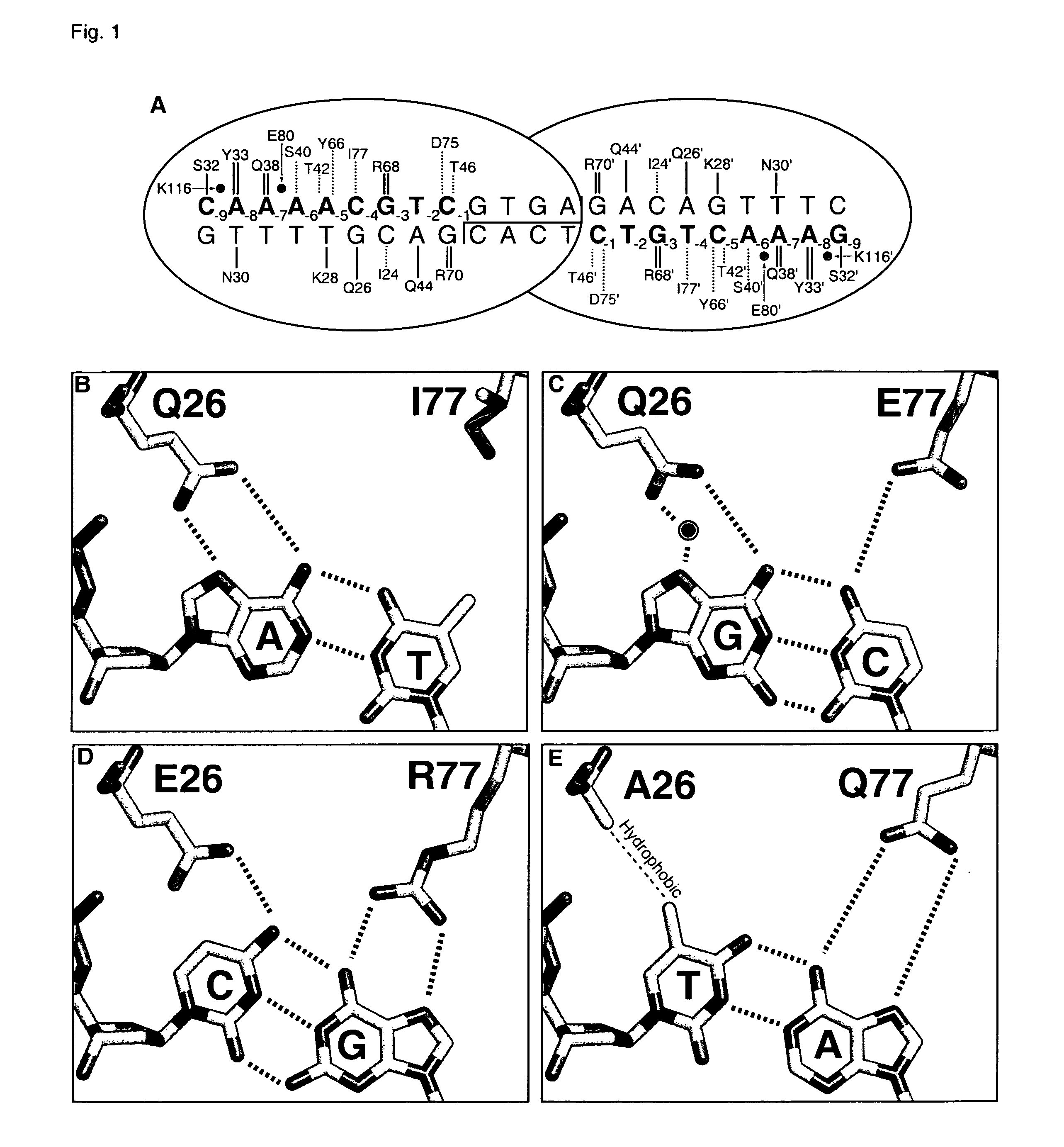
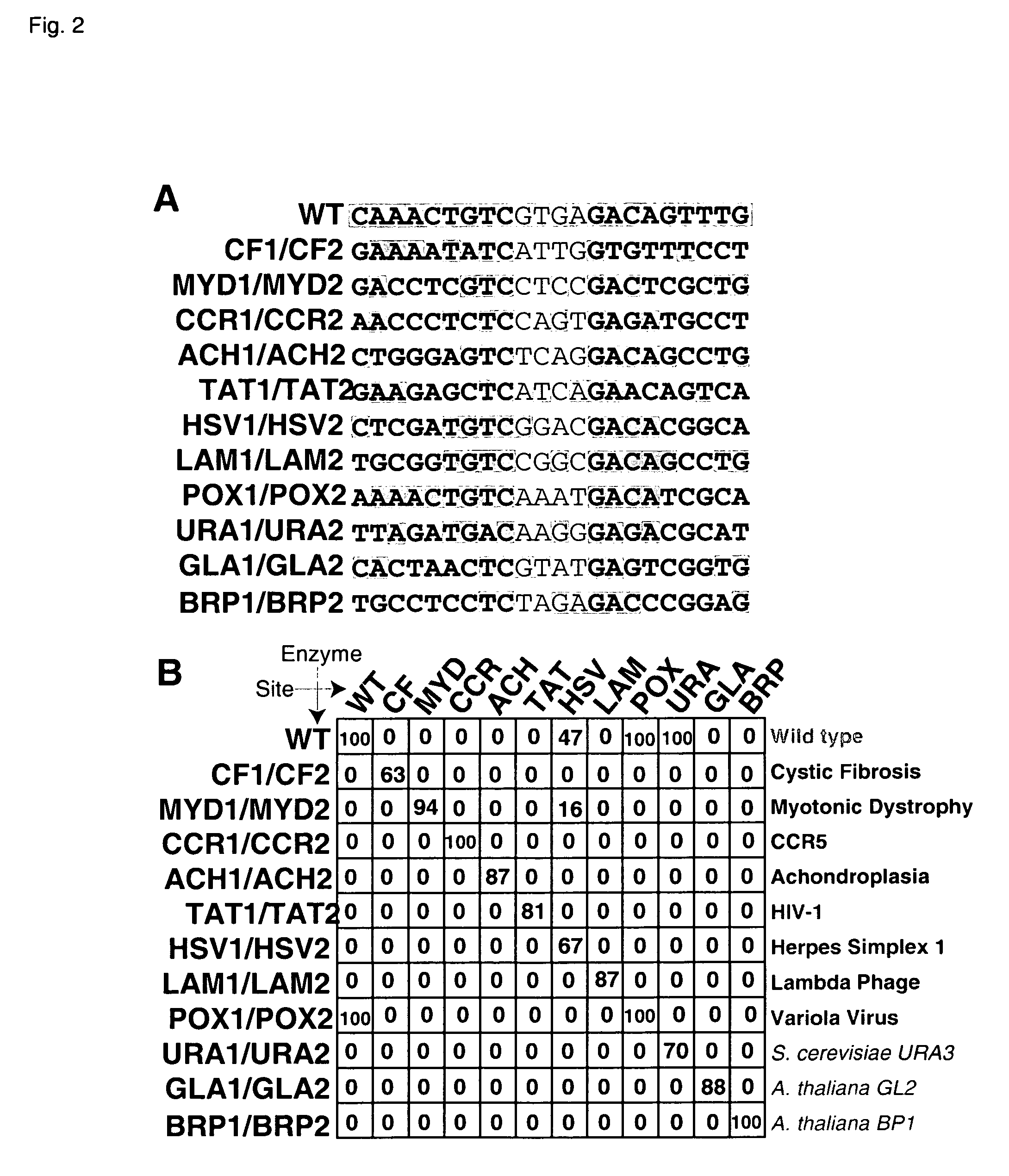
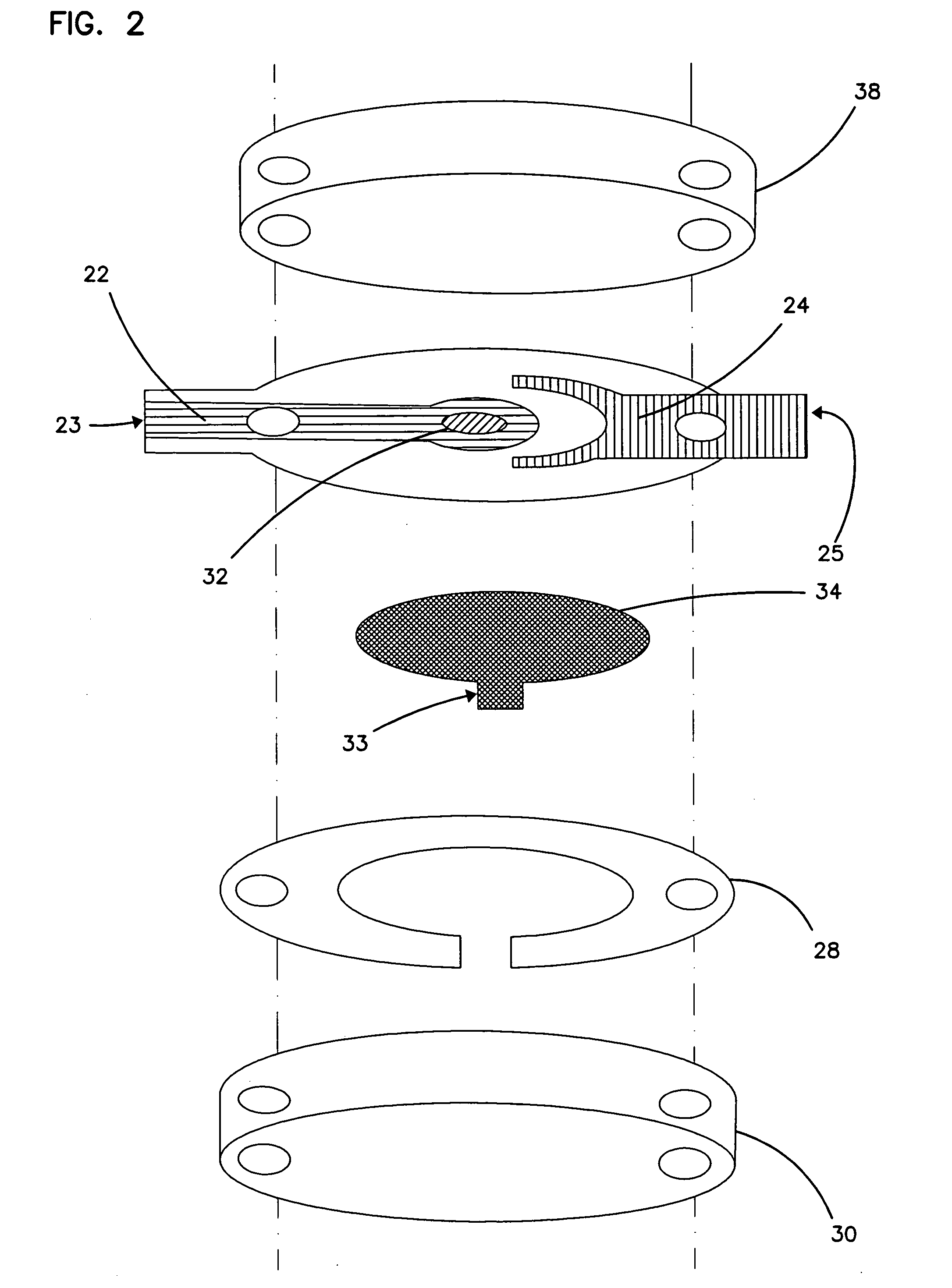
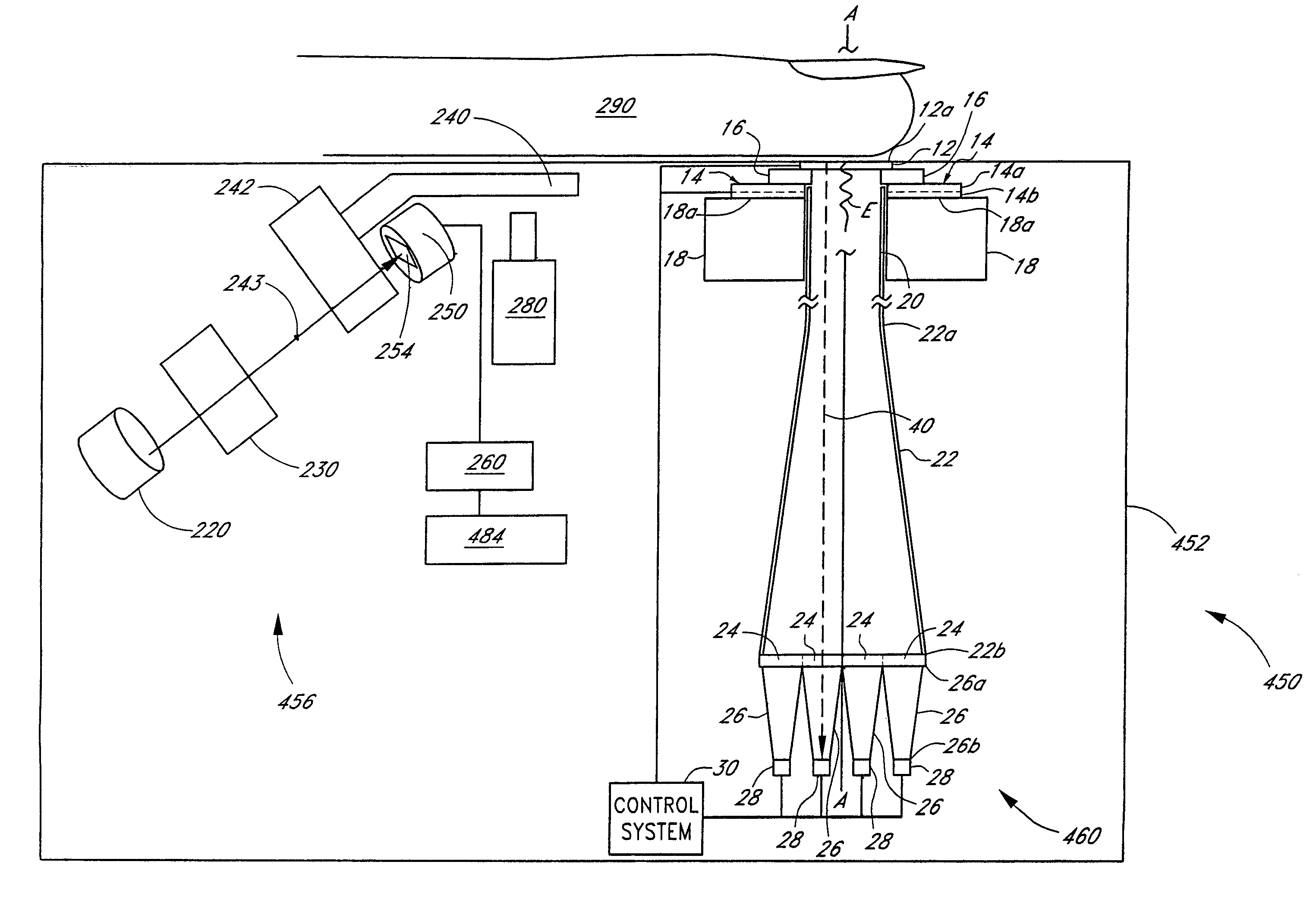
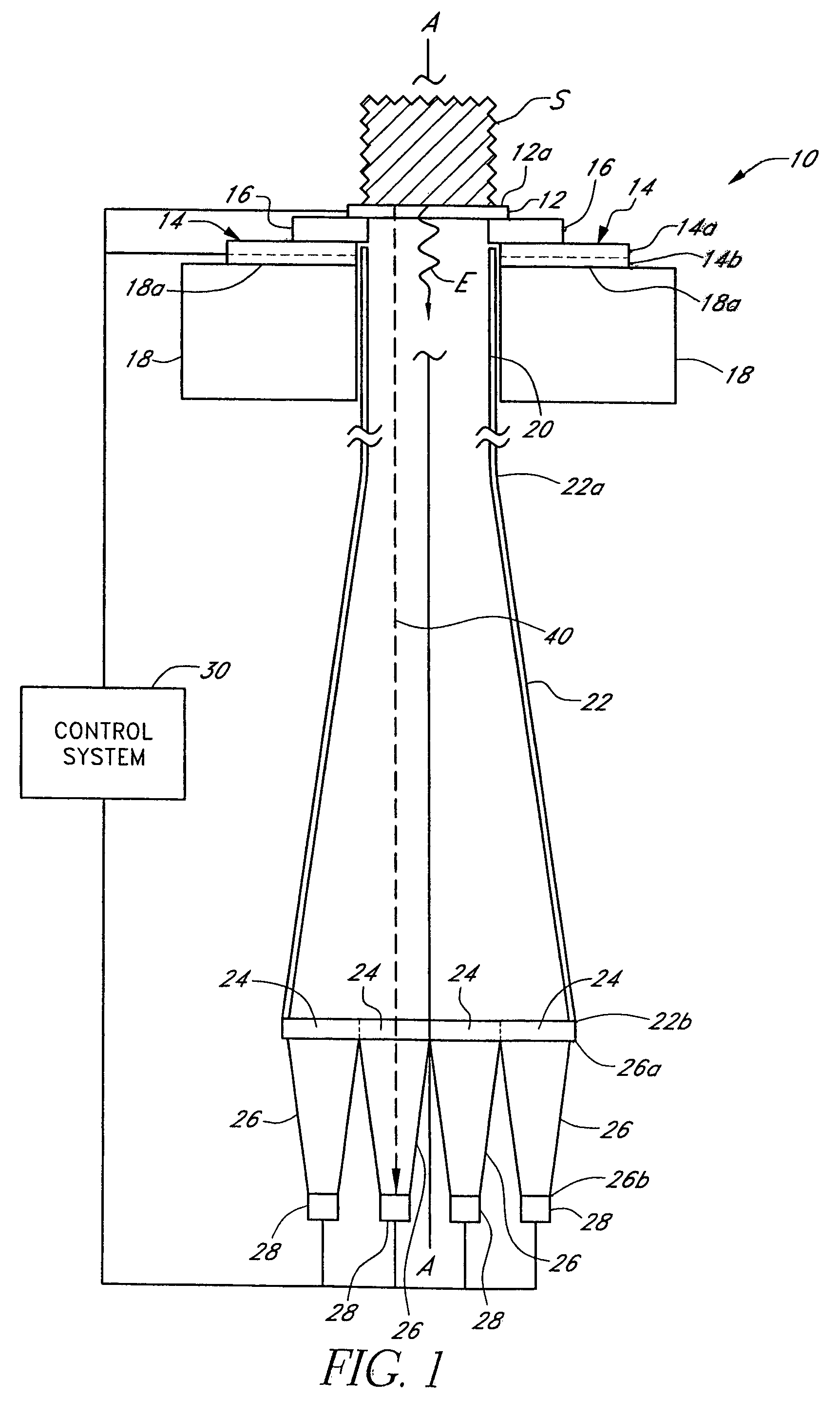
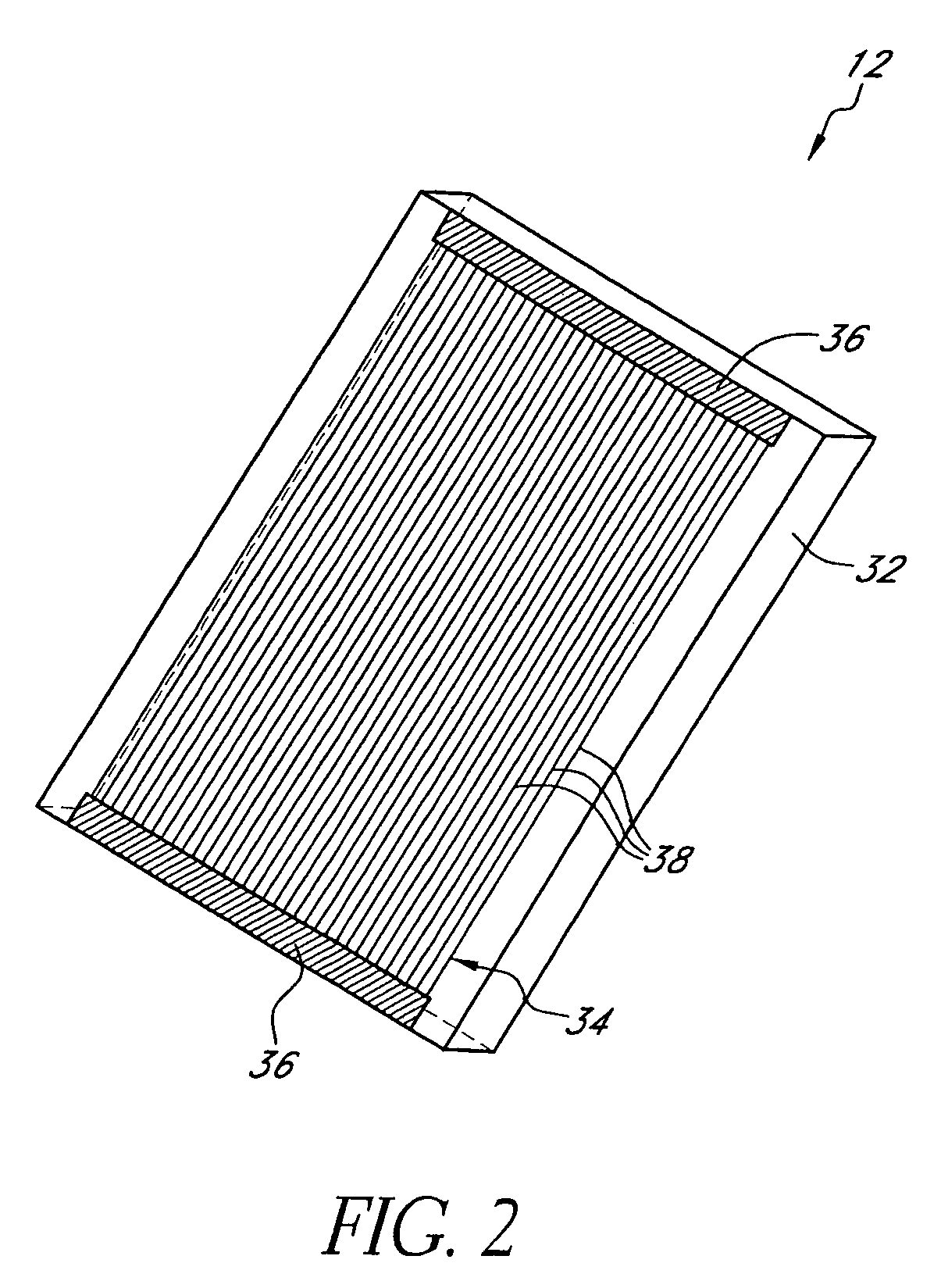
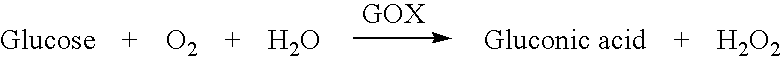Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
19062 results about "In vitro" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In vitro (meaning: in the glass) studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from in vitro experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to in vitro experiments, in vivo studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants.
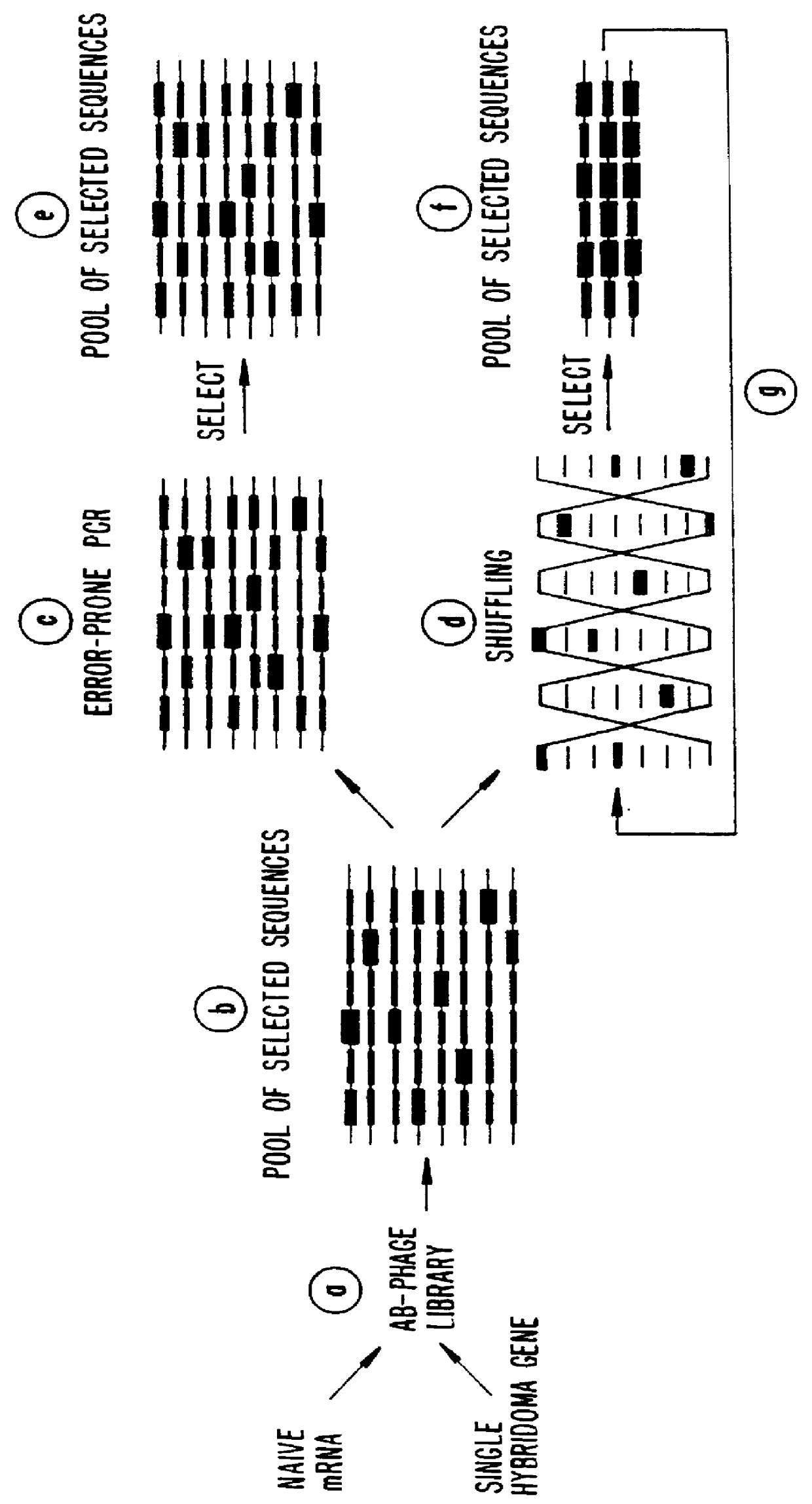
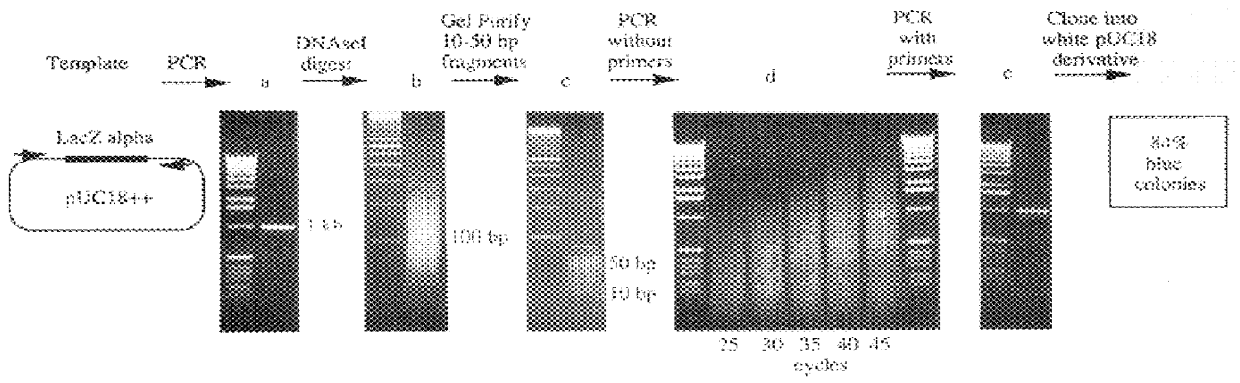
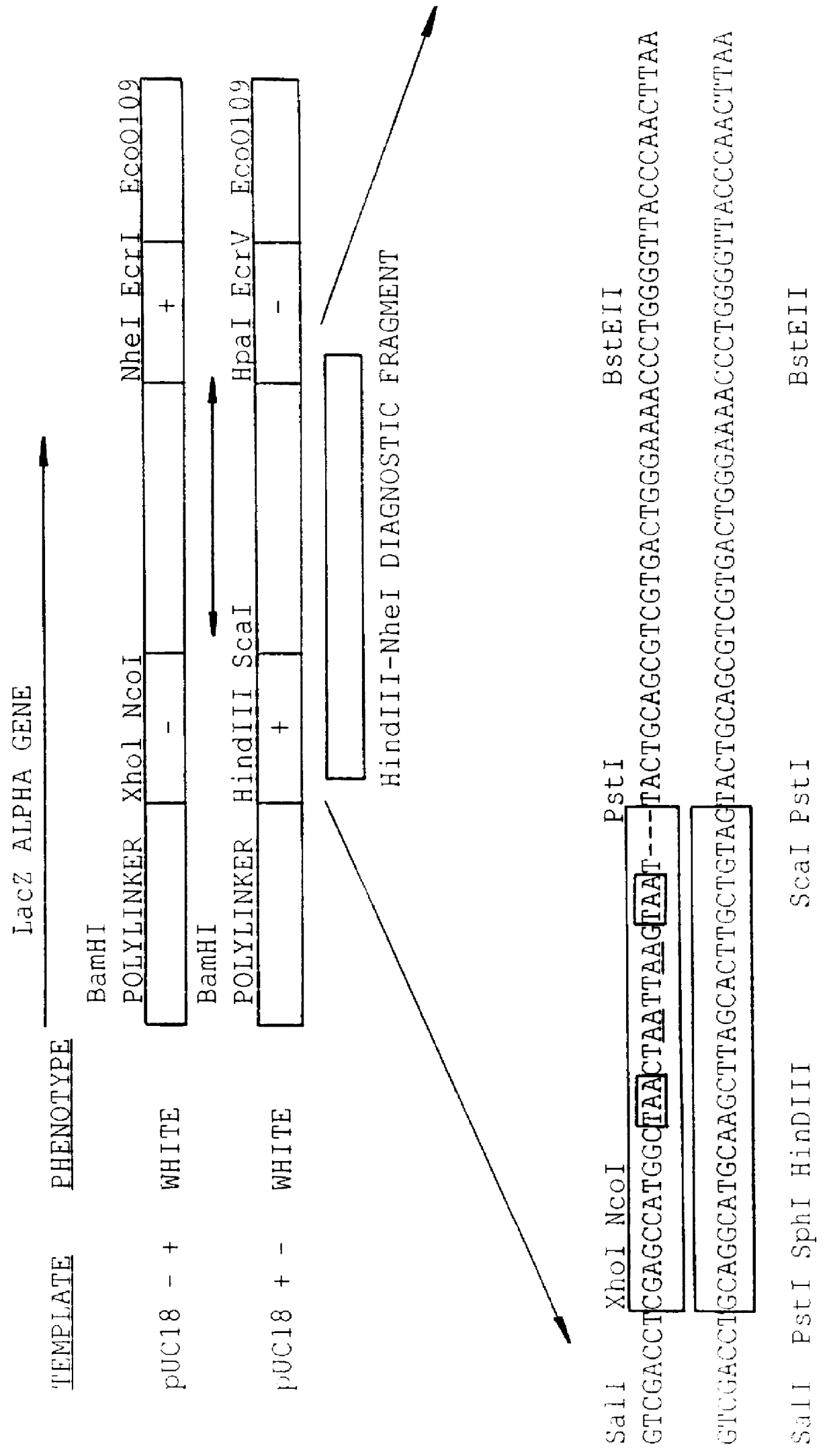
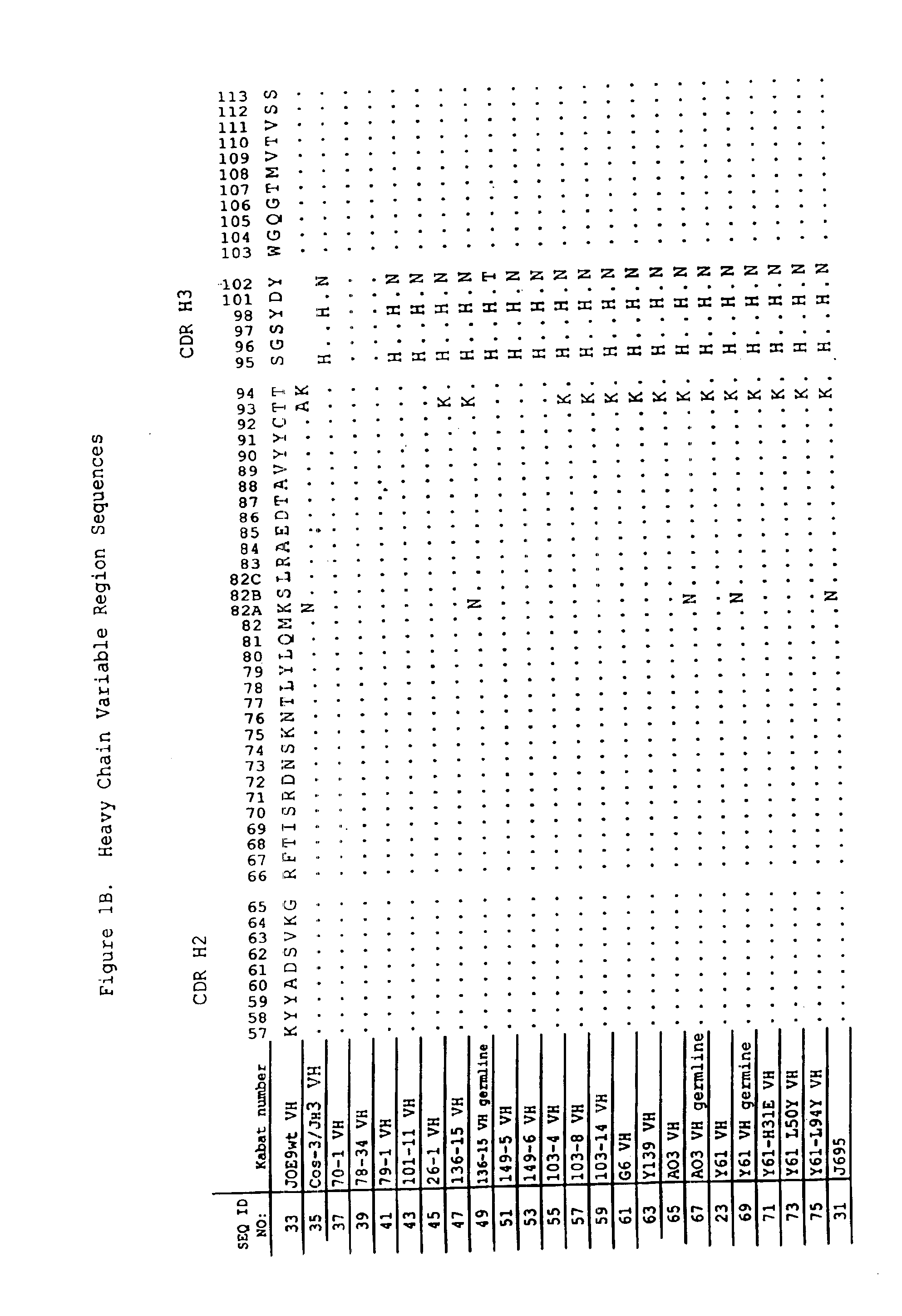
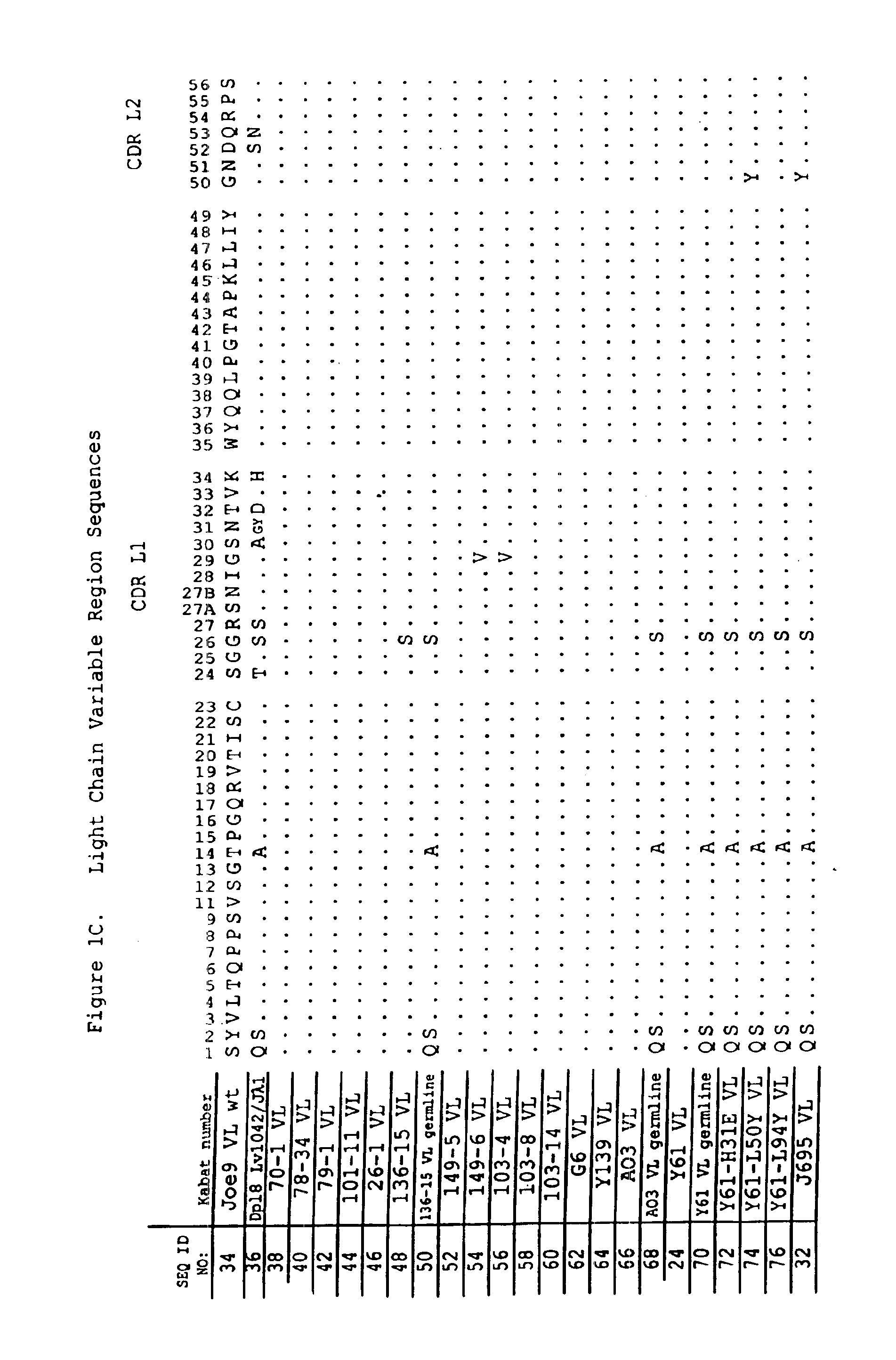
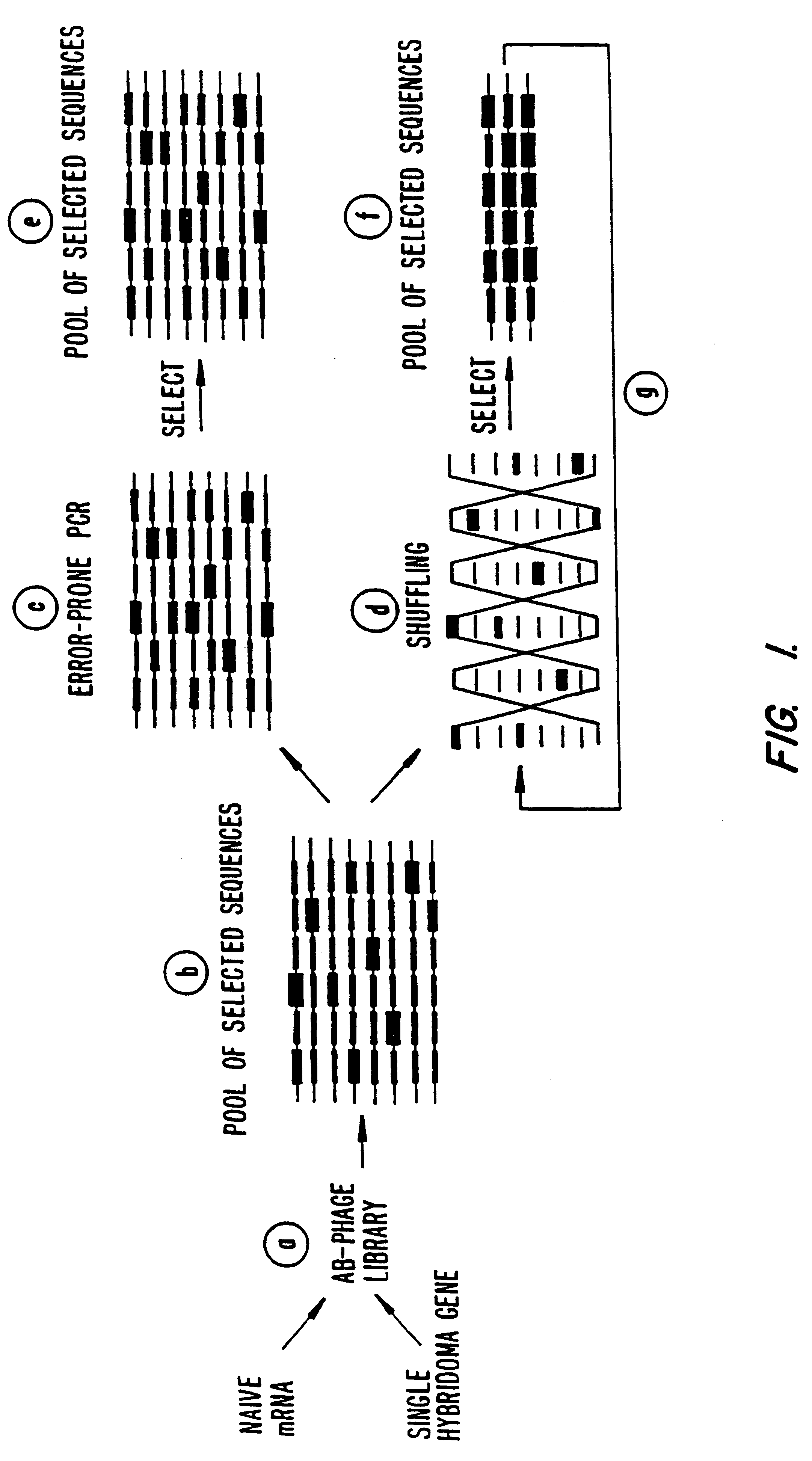
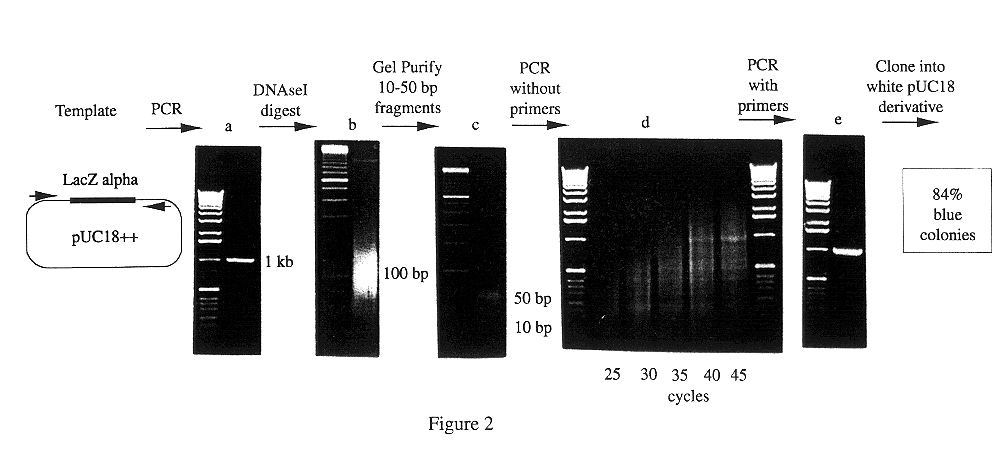
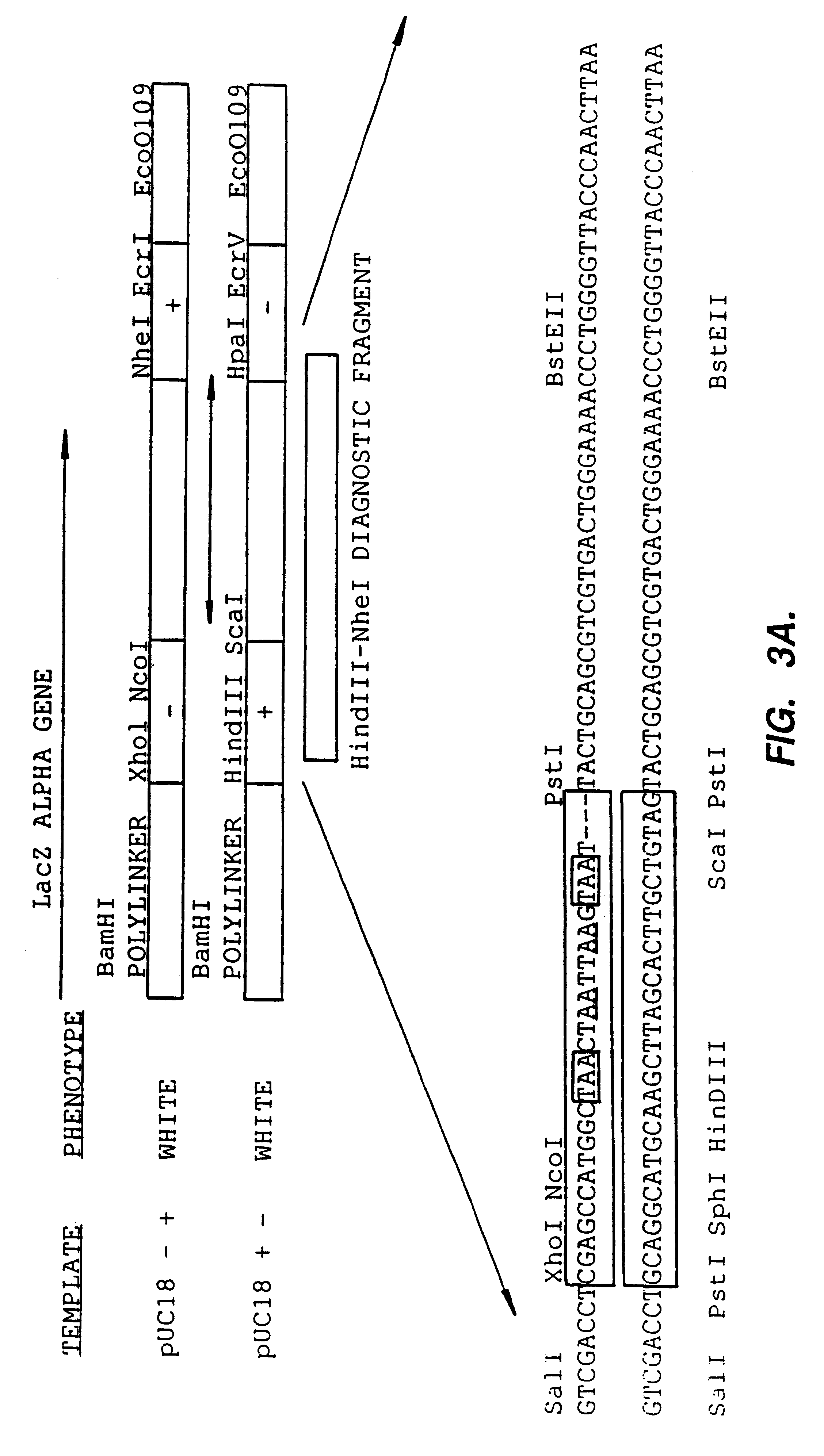
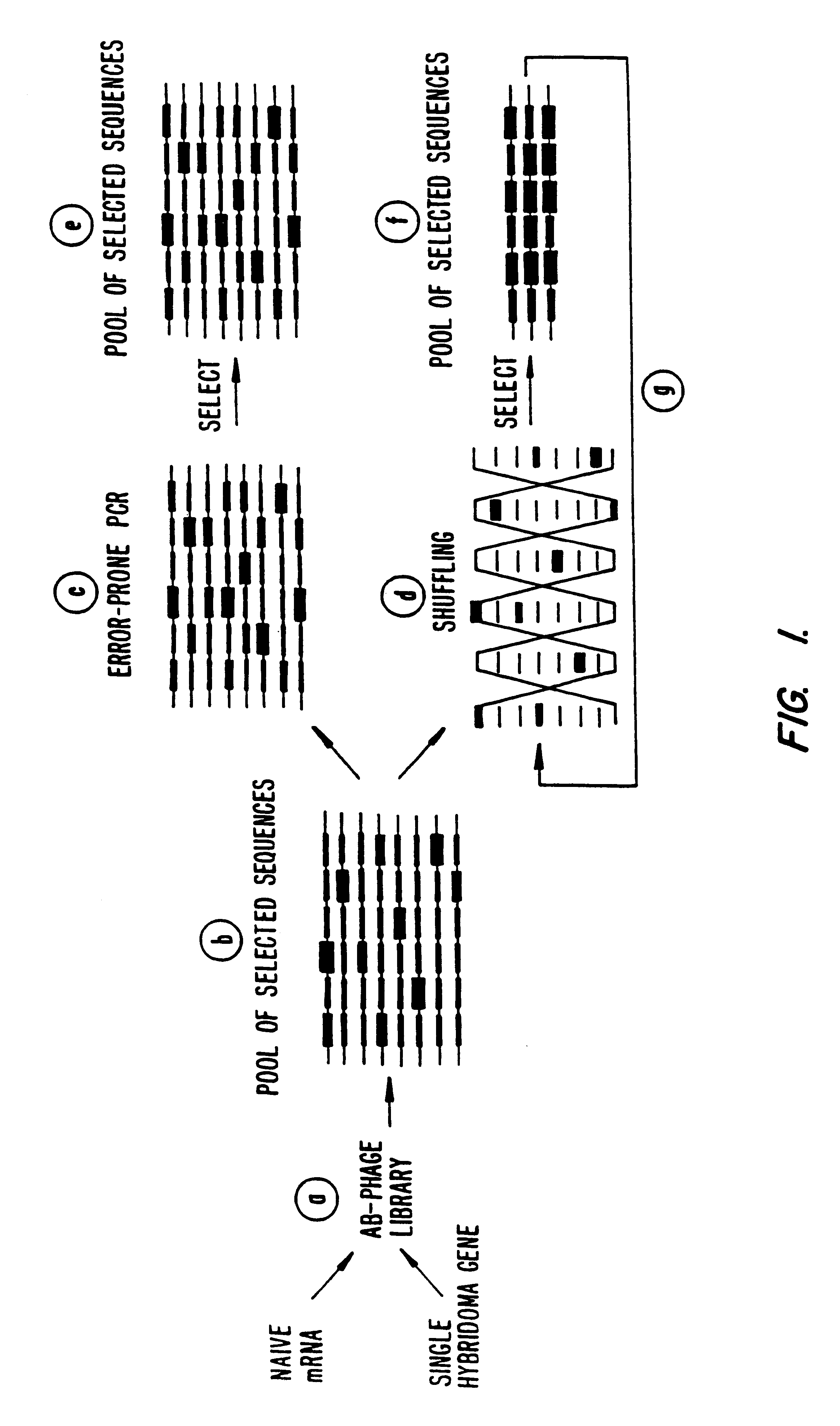
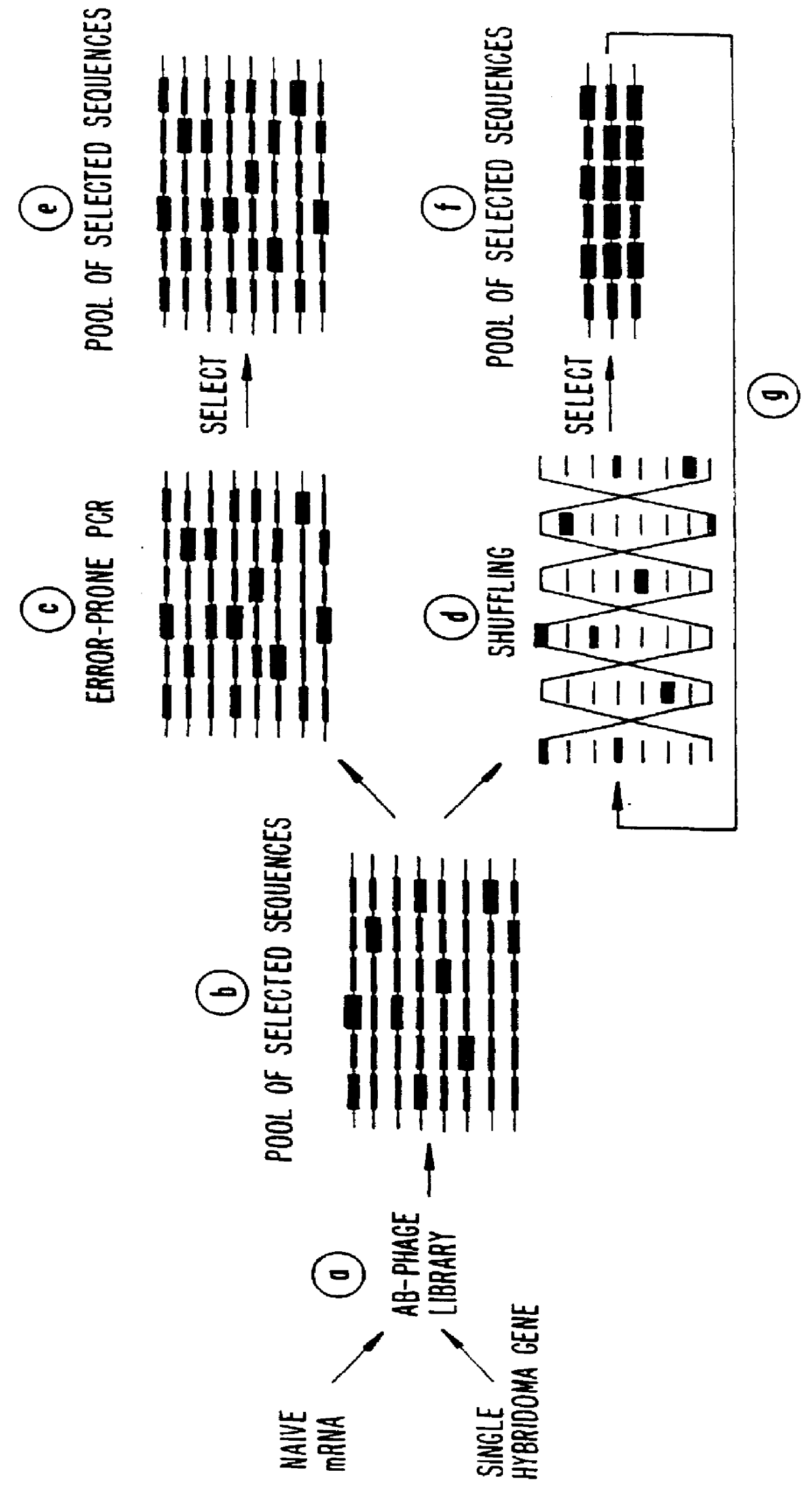
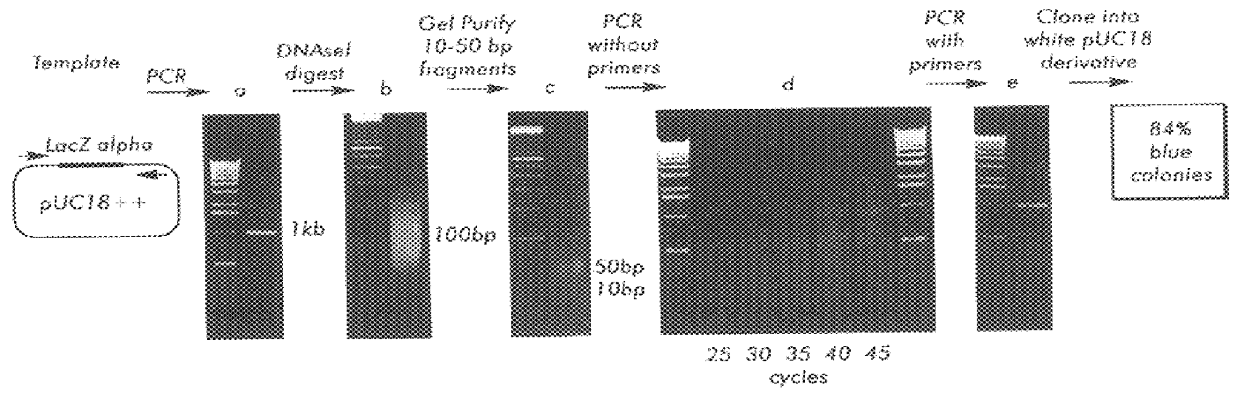
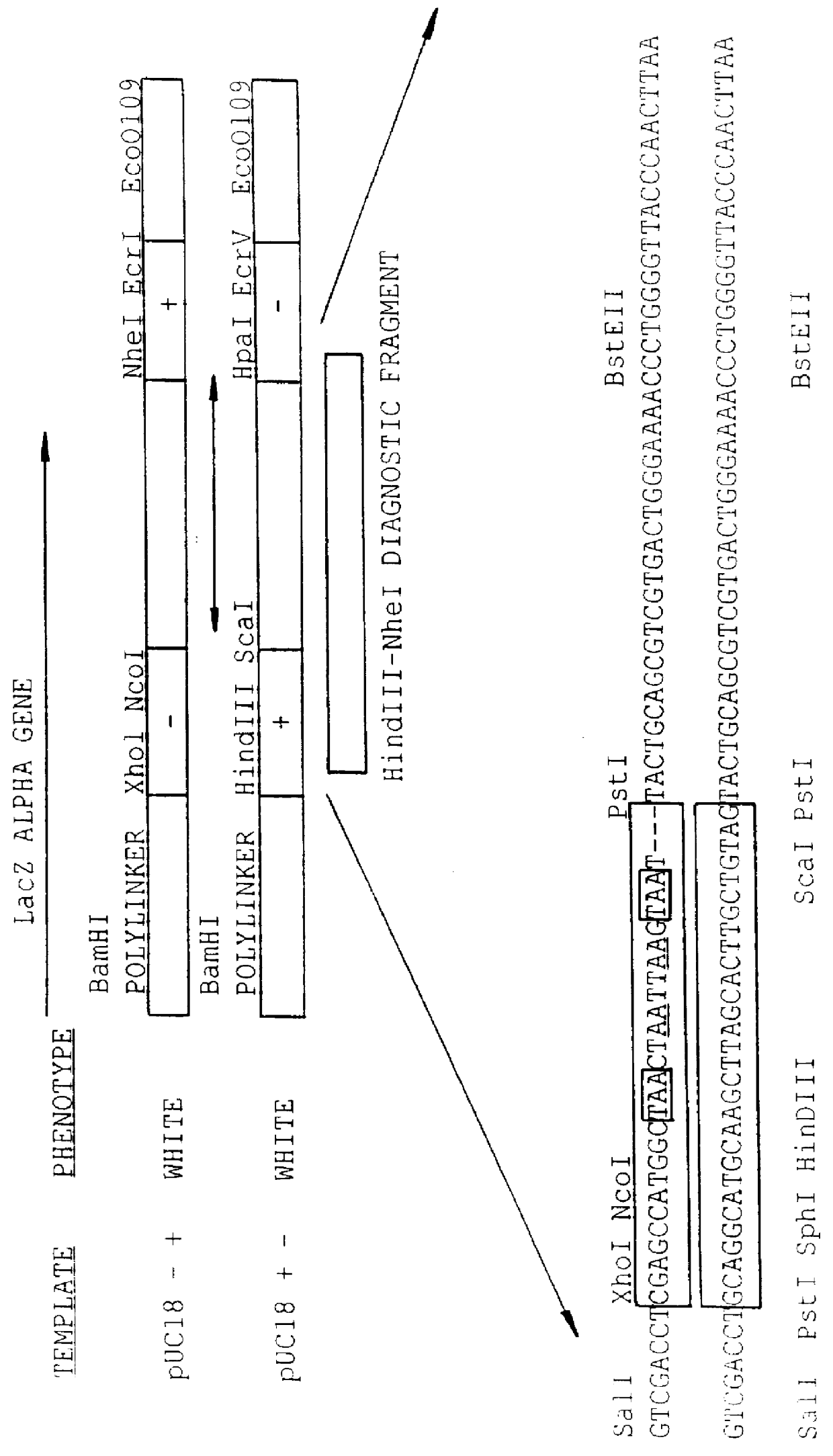
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
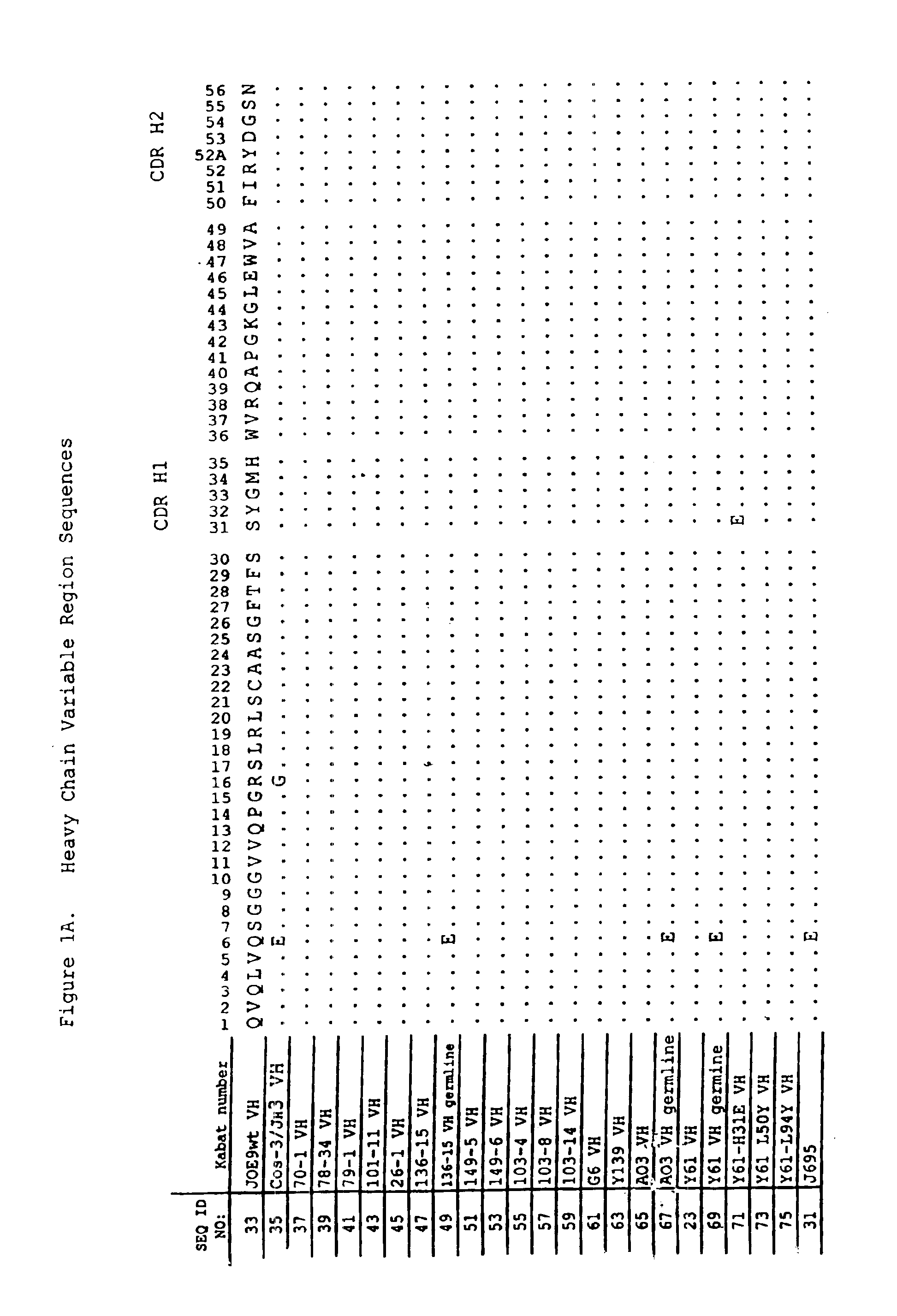
Human antibodies that bind human IL-12 and methods for producing
InactiveUS6914128B1Avoid interferencePreservationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigen bindingIn vivo
Human antibodies, preferably recombinant human antibodies, that specifically bind to human interleukin-12 (hIL-12) are disclosed. Preferred antibodies have high affinity for hIL-12 and neutralize hIL-12 activity in vitro and in vivo. An antibody of the invention can be a full-length antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof. The antibodies, or antibody portions, of the invention are useful for detecting hIL-12 and for inhibiting hIL-12 activity, e.g., in a human subject suffering from a disorder in which hIL-12 activity is detrimental. Nucleic acids, vectors and host cells for expressing the recombinant human antibodies of the invention, and methods of synthesizing the recombinant human antibodies, are also encompassed by the invention.
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
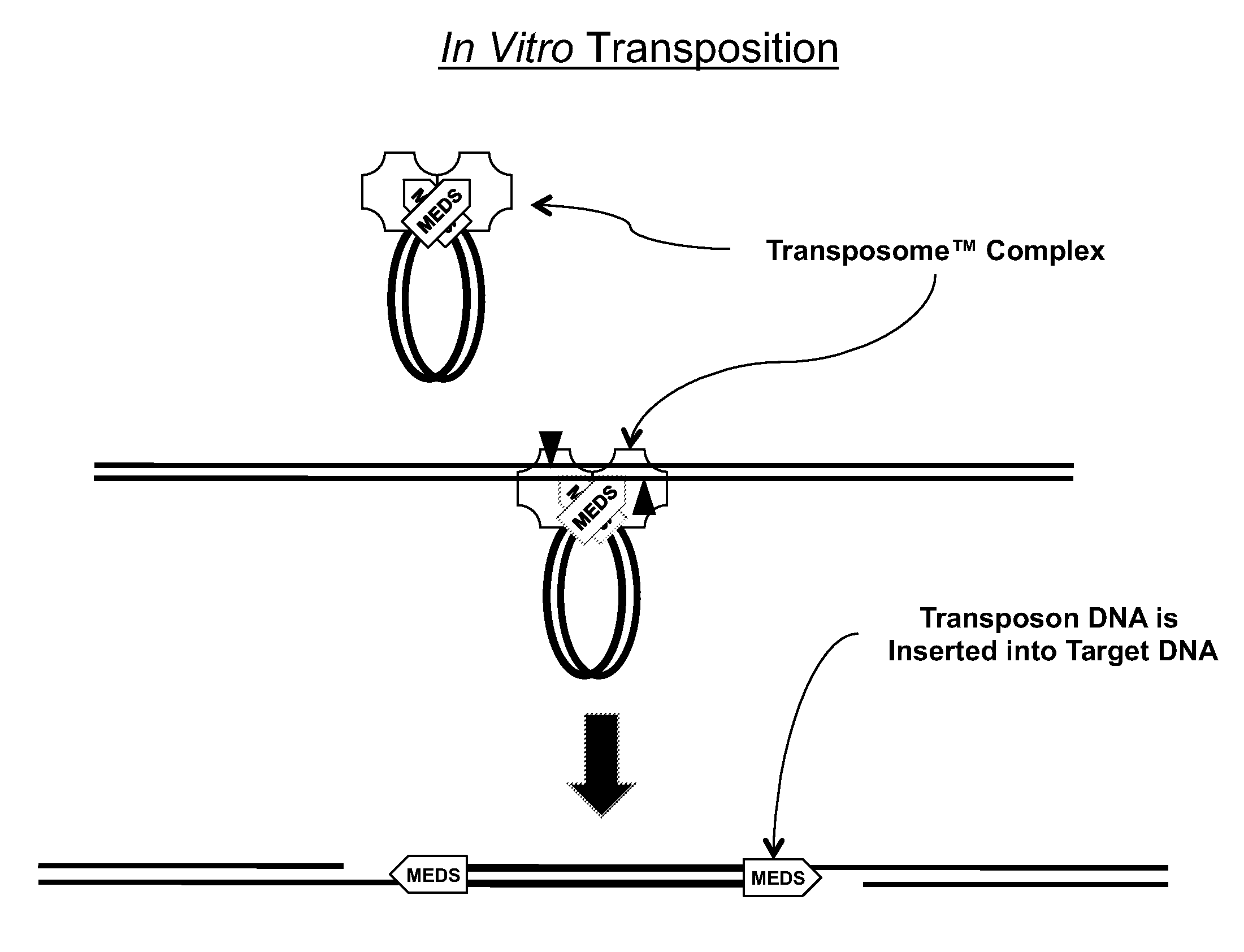
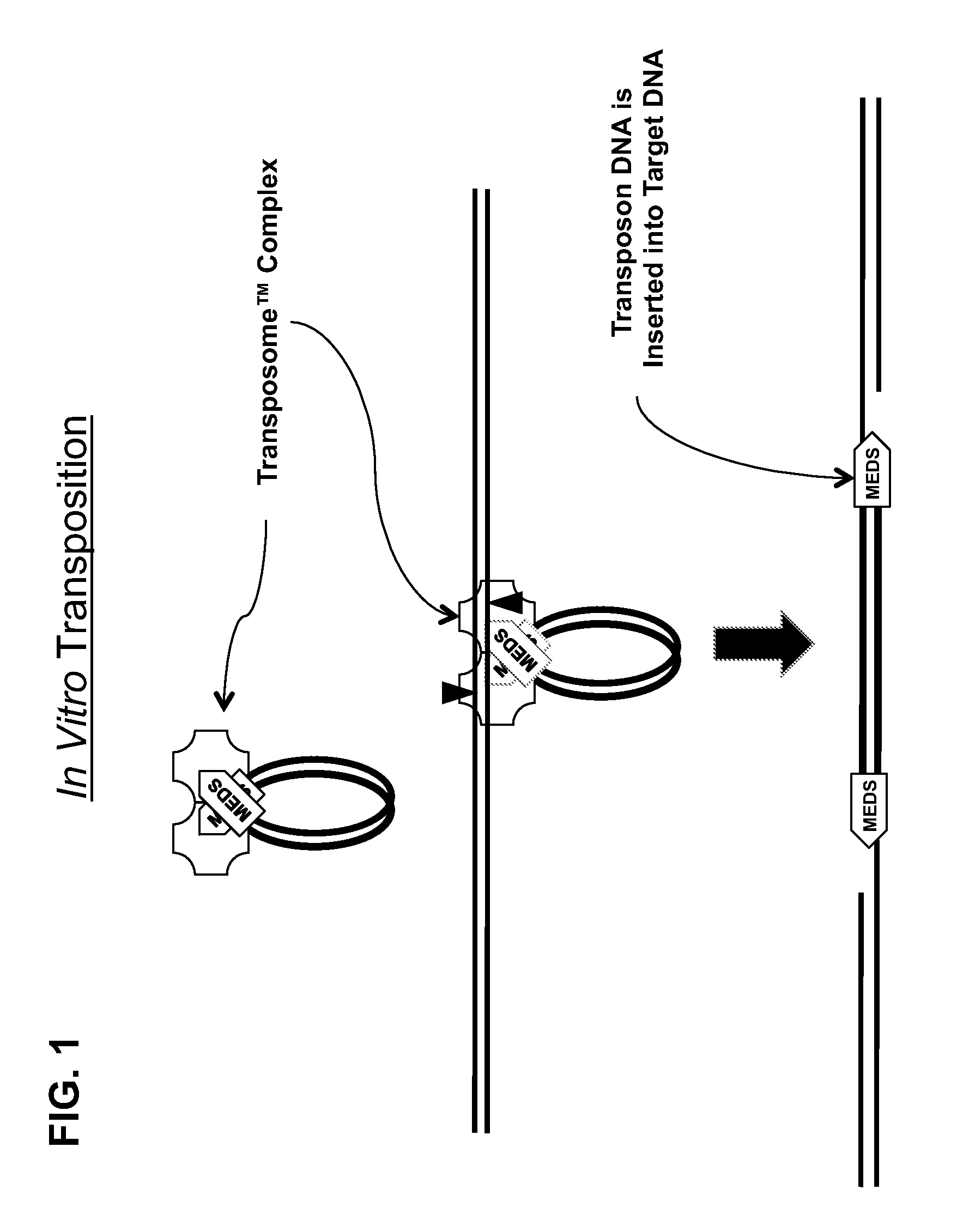
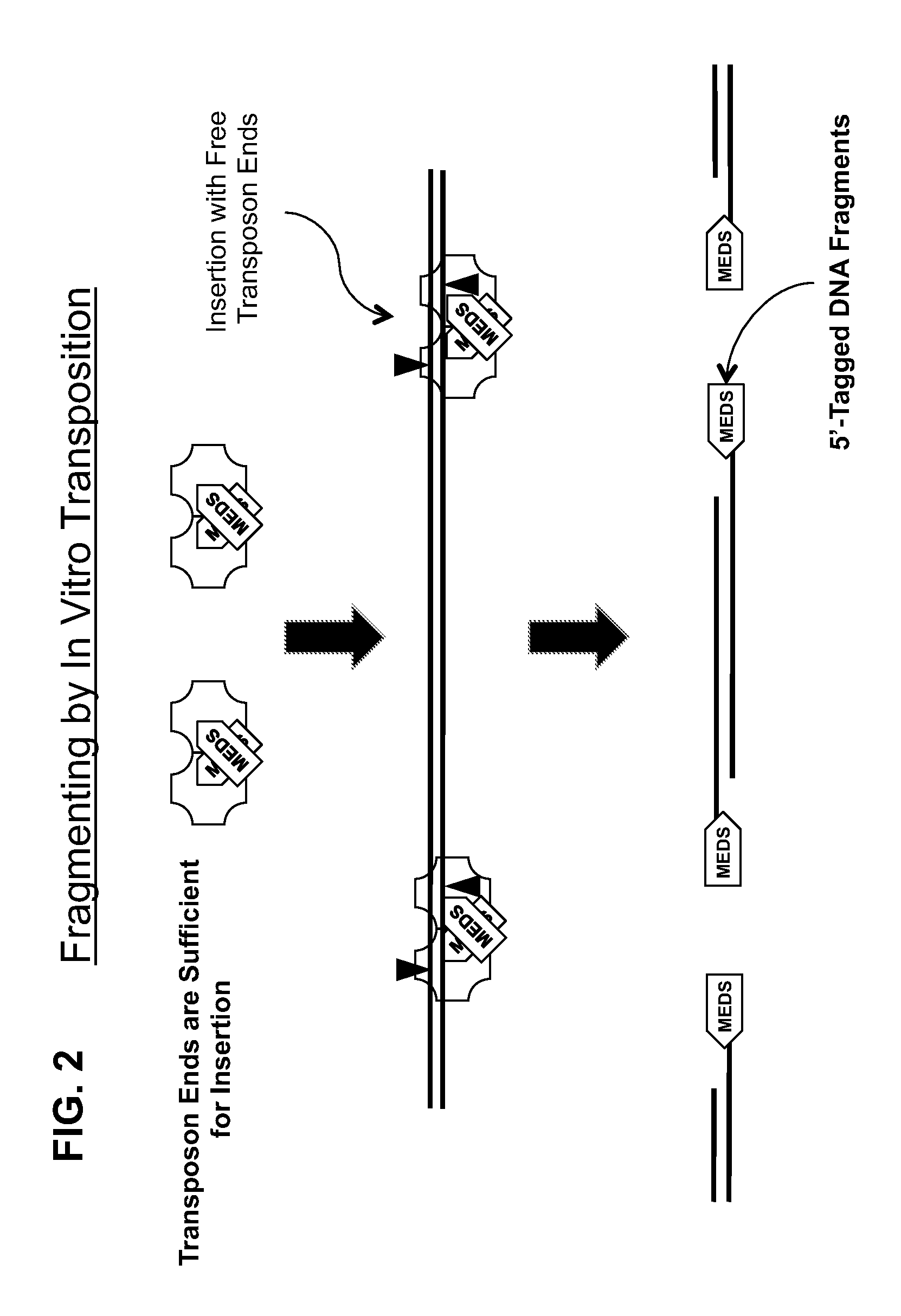
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100120098A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingPolymerase L
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for using a transposase and a transposon end for generating extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, then using a DNA polymerase for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged single-stranded DNA fragments without performing a PCR amplification reaction, wherein the first tag on the 5′-ends exhibits the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally, an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second tag on the 3′-ends exhibits a different sequence from the sequence exhibited by the first tag. The method is useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including processes for metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and comparative genomic sequencing (CGS), including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called “next-generation sequencing.)
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6165793ALess immunogenicDirected macromolecular evolutionImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
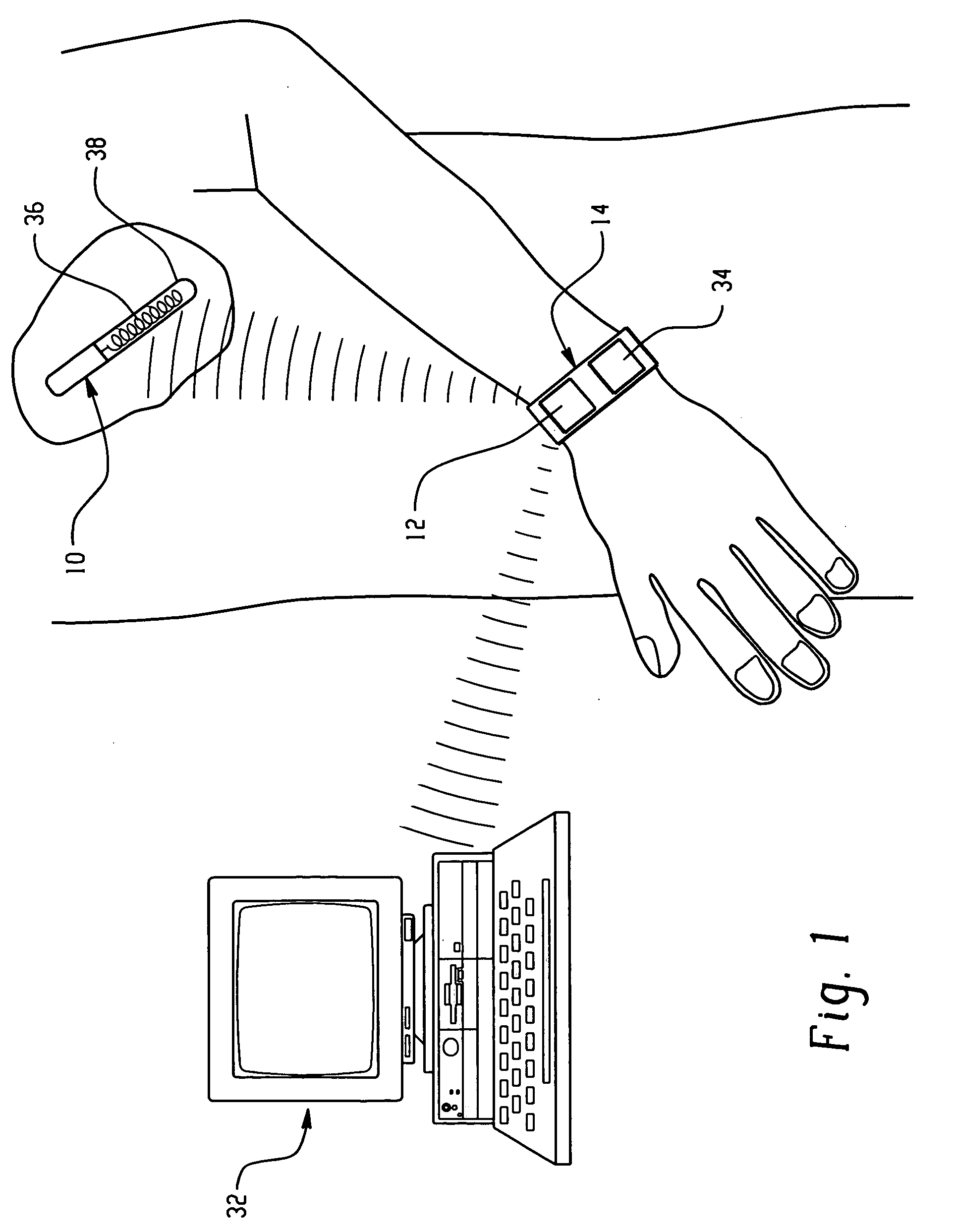
Microsensors for glucose and insulin monitoring
InactiveUS6893552B1Simultaneous measurementLacking and neededImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidative enzymeD-Glucose
A dual sensor for the simultaneous amperometric monitoring of glucose and insulin, wherein the glucose probe is based on the biocatalytic action of glucose oxidase, and the insulin probe is based on the electrocatalytic activity of metal oxide. Further provided is an oxidase enzyme composite electrode with an internal oxygen-rich binder. The present invention also optionally includes metallizing components within the carbon paste to eliminate signals from interfering compounds. The present invention includes embodiments for both in vitro and in vivo uses.
Owner:ARROWHEAD CENT
Three-dimensional culture of pancreatic parenchymal cells cultured living stromal tissue prepared in vitro
InactiveUS6022743AIncrease surface areaIncreased proliferationImmobilised enzymesSurgical needlesLigament structureIn vivo
A stromal cell-based three-dimensional cell culture system is prepared which can be used to culture a variety of different cells and tissues in vitro for prolonged periods of time. The stromal cells and connective tissue proteins naturally secreted by the stromal cells attach to and substantially envelope a framework composed of a biocompatible non-living material formed into a three-dimensional structure having interstitial spaces bridged by the stromal cells. The living stromal tissue so formed provides the support, growth factors, and regulatory factors necessary to sustain long-term active proliferation of cells in culture and / or cultures implanted in vivo. When grown in this three-dimensional system, the proliferating cells mature and segregate properly to form components of adult tissues analogous to counterparts in vivo, which can be utilized in the body as a corrective tissue. For example, and not by way of limitation, the three-dimensional cultures can be used to form tubular tissue structures, like those of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts, as well as blood vessels; tissues for hernia repair and / or tendons and ligaments; etc.
Owner:REGENEMED
Device and method for in vitro determination of analyte concentrations within body fluids
InactiveUS6989891B2Withdrawing sample devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSpectral bandsCell wall
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
In vitro analyte sensor and methods of use
ActiveUS20070068807A1Easy to fillEasy to recordImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteBiology
In vitro electrochemical sensors that provide accurate and repeatable analysis of a sample of biological fluid are provided. Embodiments include sensors that include a sample chambers having overhangs extending therefrom.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
In vitro evolution in microfluidic systems
ActiveUS20060078888A1High activitySpeed up the processSequential/parallel process reactionsFlow mixersGene productGenetic element
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; and (b) sorting the genetic elements which express the gene product having the desired activity; wherein at least one step is under microfluidic control. The invention enables the in vitro evolution of nucleic acids and proteins by repeated mutagenesis and iterative applications of the method of the invention.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Rationally-designed meganucleases with altered sequence specificity and DNA-binding affinity
ActiveUS8021867B2Affect specificityAffect activityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesBiological bodyNuclease
Rationally-designed LAGLIDADG (SEQ ID NO: 37) meganucleases and methods of making such meganucleases are provided. In addition, methods are provided for using the meganucleases to generate recombinant cells and organisms having a desired DNA sequence inserted into a limited number of loci within the genome, as well as methods of gene therapy, for treatment of pathogenic infections, and for in vitro applications in diagnostics and research.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor with diffusible or non-leachable redox mediator
InactiveUS20060025662A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteRedox mediator
A region of skin, other than the fingertips, is stimulated. After stimulation, an opening is created in the skin (e.g., by lancing the skin) to cause a flow of body fluid from the region. At least a portion of this body fluid is transported to a testing device where the concentration of analyte (e.g., glucose) in the body fluid is then determined. It is found that the stimulation of the skin provides results that are generally closer to the results of measurements from the fingertips, the traditional site for obtaining body fluid for analyte testing.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Device and method for in vitro determination of analyte concentrations within body fluids
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Single-primer nucleic acid amplification methods
ActiveUS7374885B2Reduce appearanceHigh levelMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
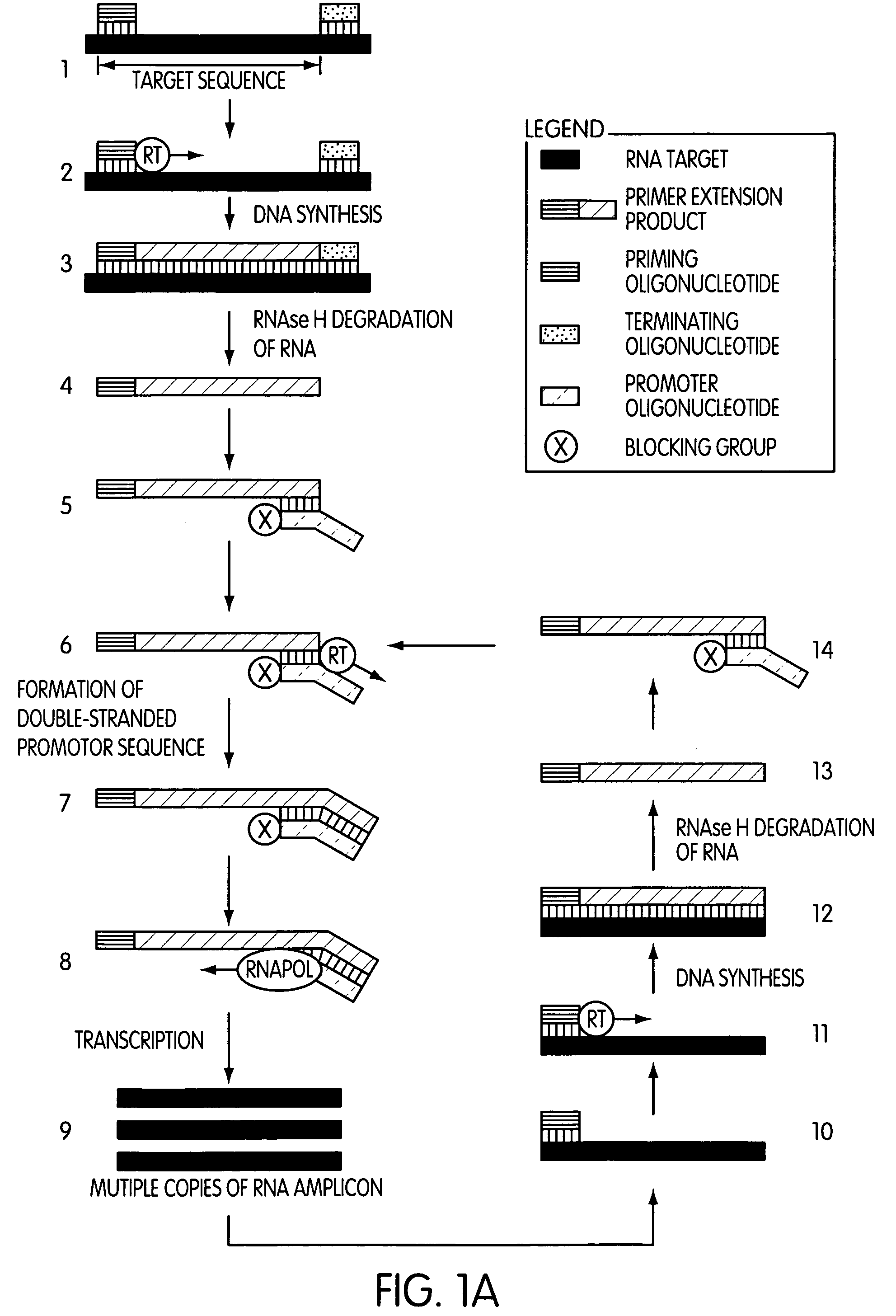
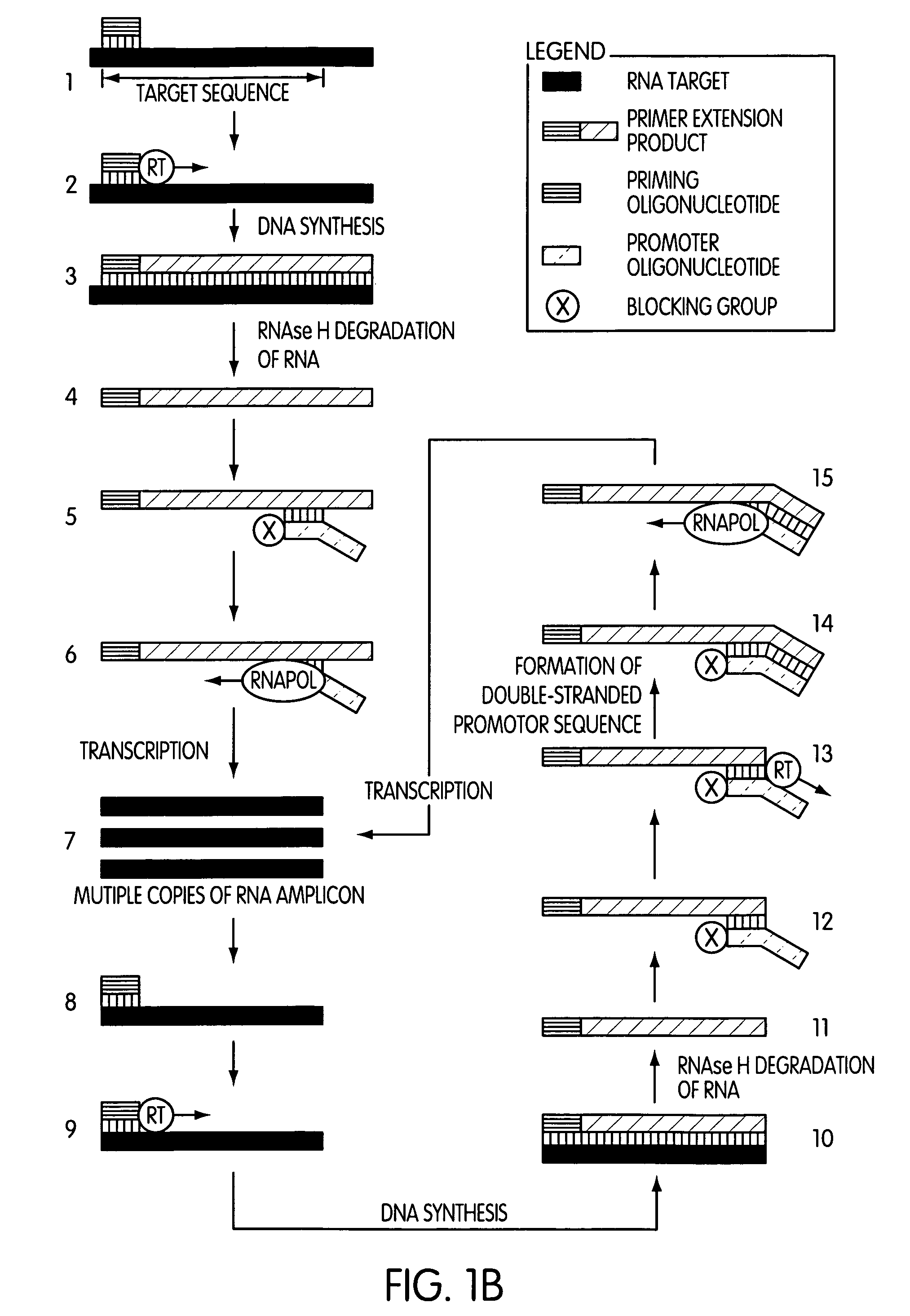
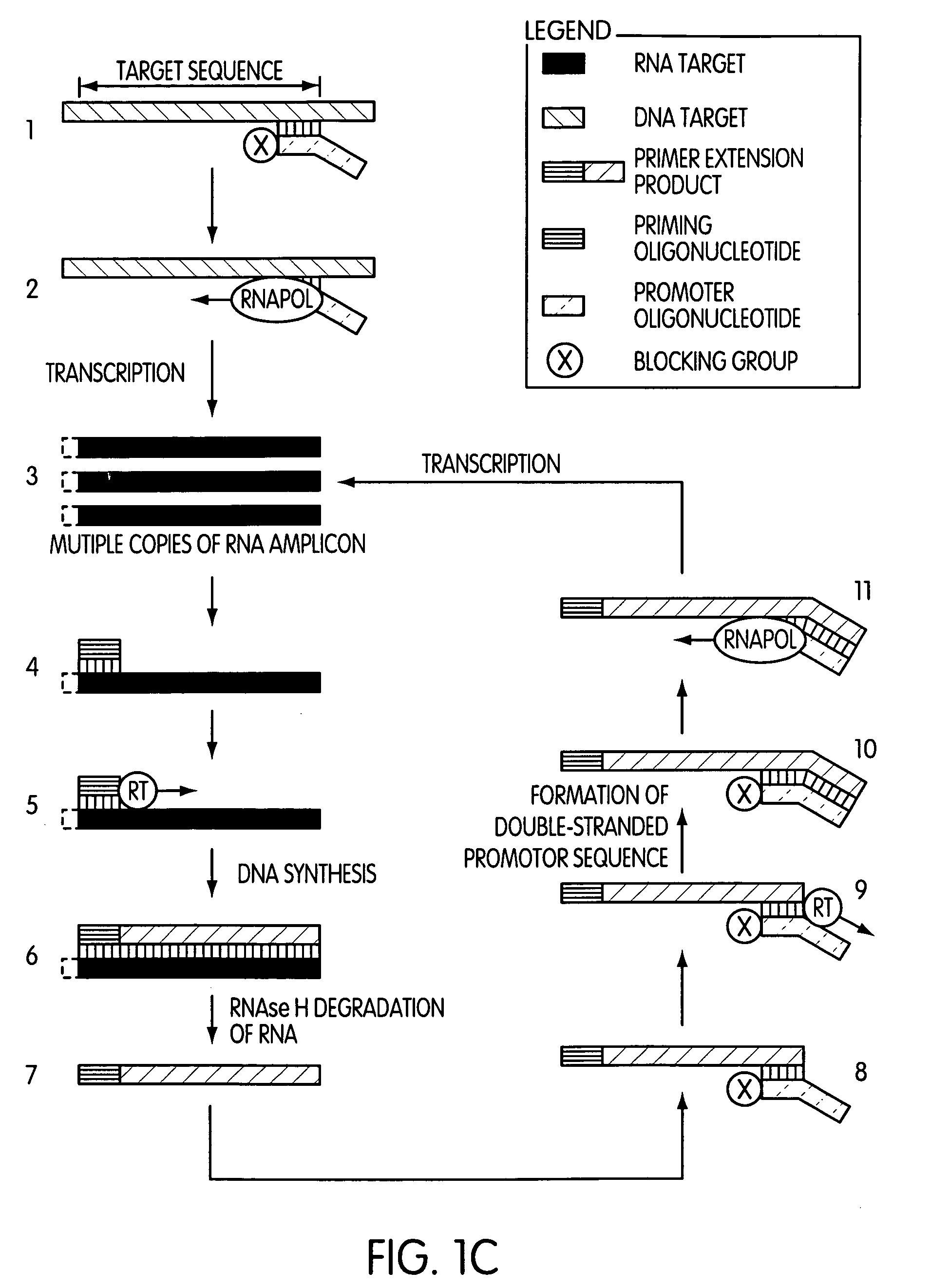
The present invention is directed to novel methods of synthesizing multiple copies of a target nucleic acid sequence which are autocatalytic (i.e., able to cycle automatically without the need to modify reaction conditions such as temperature, pH, or ionic strength and using the product of one cycle in the next one). In particular, the present invention discloses a method of nucleic acid amplification which is robust and efficient, while reducing the appearance of side-products. The method uses only one primer, the “priming oligonucleotide,” a promoter oligonucleotide modified to prevent polymerase extension from its 3′-terminus and, optionally, a means for terminating a primer extension reaction, to amplify RNA or DNA molecules in vitro, while reducing or substantially eliminating the formation of side-products. The method of the present invention minimizes or substantially eliminates the emergence of side-products, thus providing a high level of specificity. Furthermore, the appearance of side-products can complicate the analysis of the amplification reaction by various molecular detection techniques. The present invention minimizes or substantially eliminates this problem, thus providing an enhanced level of sensitivity.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
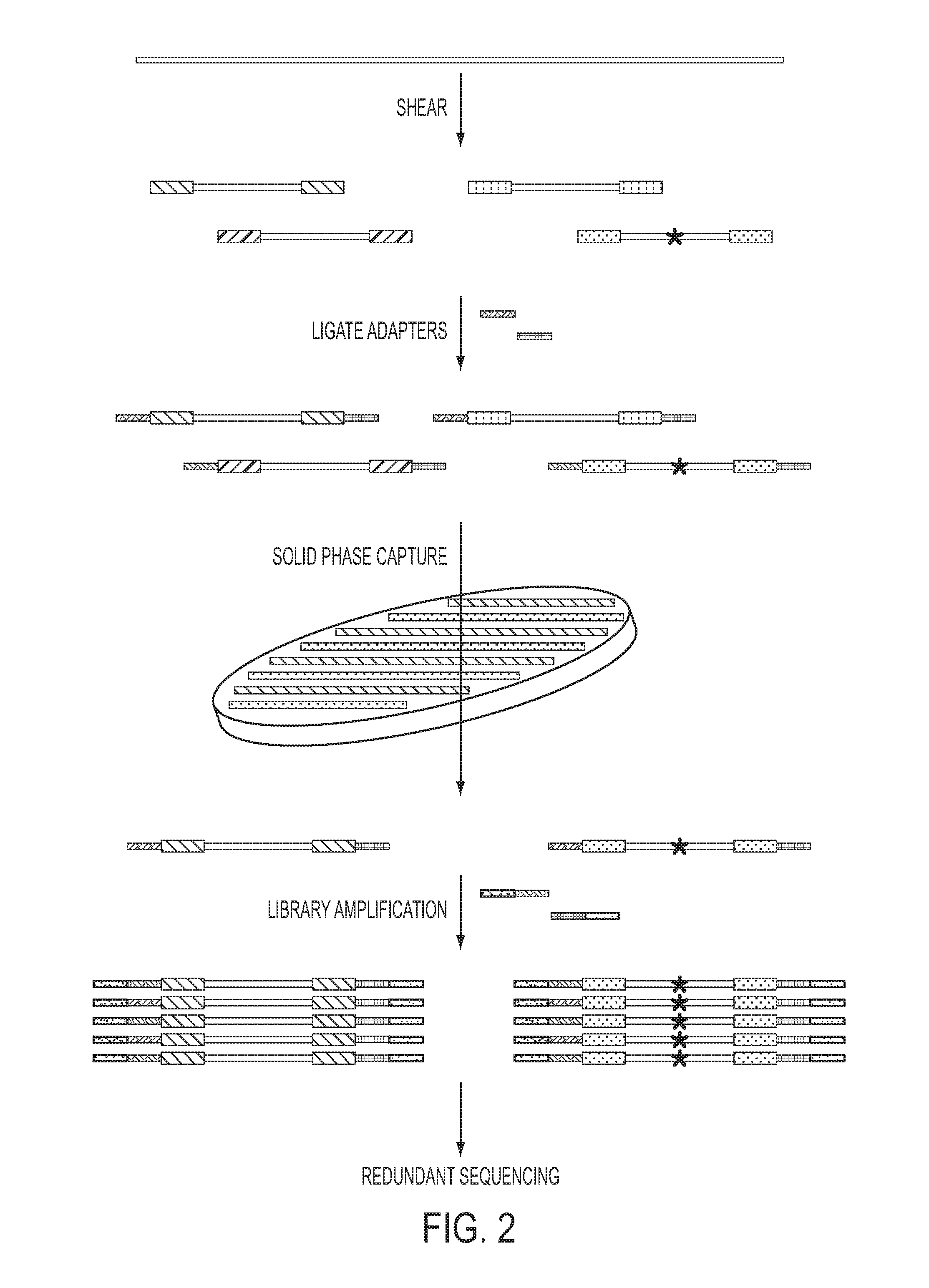
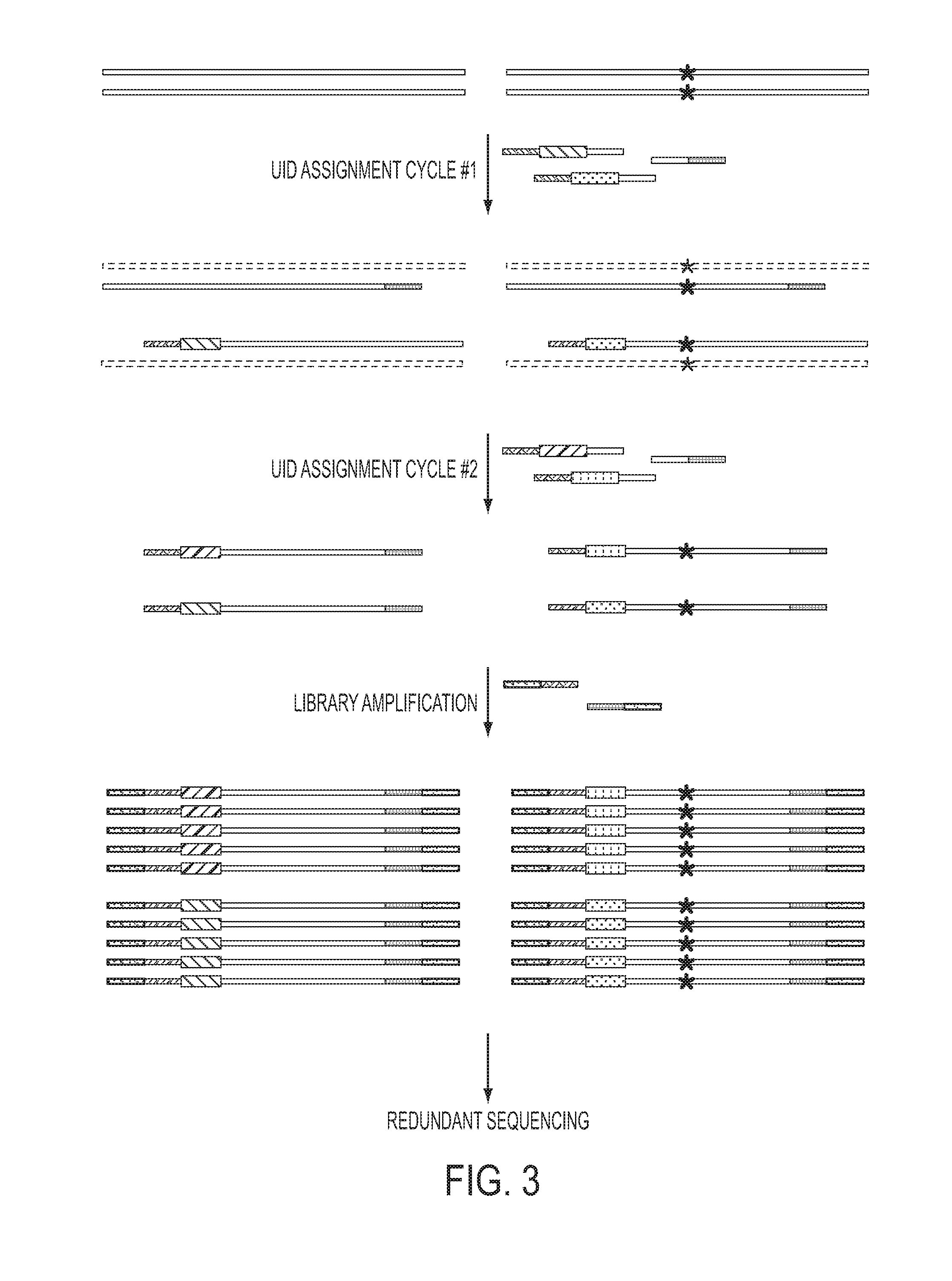
Safe sequencing system
ActiveUS20140227705A1Sensitively accurately determiningMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideInstrumentation
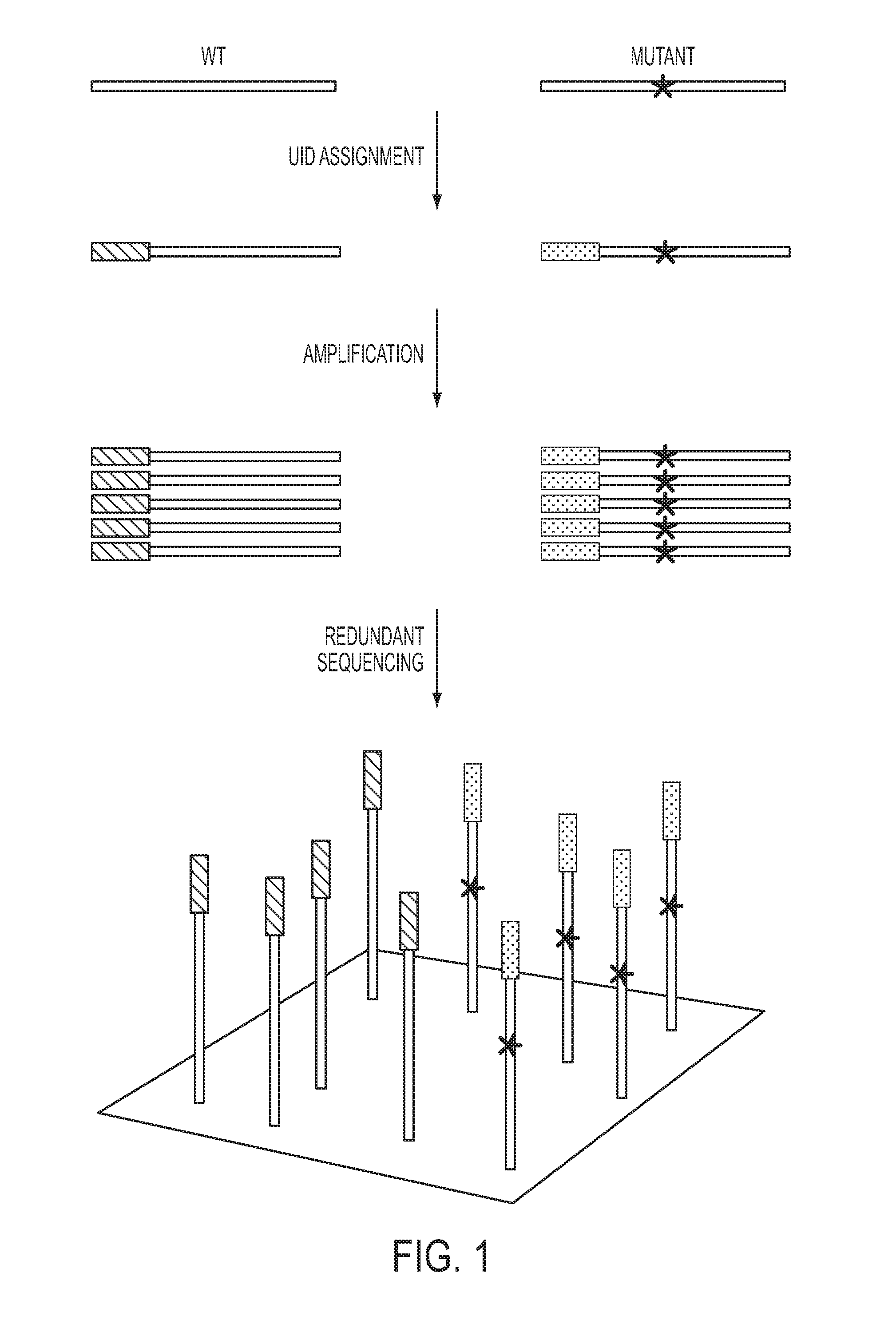
The identification of mutations that are present in a small fraction of DNA templates is essential for progress in several areas of biomedical research. Though massively parallel sequencing instruments are in principle well-suited to this task, the error rates in such instruments are generally too high to allow confident identification of rare variants. We here describe an approach that can substantially increase the sensitivity of massively parallel sequencing instruments for this purpose. One example of this approach, called “Safe-SeqS” for (Safe-Sequencing System) includes (i) assignment of a unique identifier (UID) to each template molecule; (ii) amplification of each uniquely tagged template molecule to create UID-families; and (iii) redundant sequencing of the amplification products. PCR fragments with the same UID are truly mutant (“super-mutants”) if ≧95% of them contain the identical mutation. We illustrate the utility of this approach for determining the fidelity of a polymerase, the accuracy of oligonucleotides synthesized in vitro, and the prevalence of mutations in the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes of normal cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
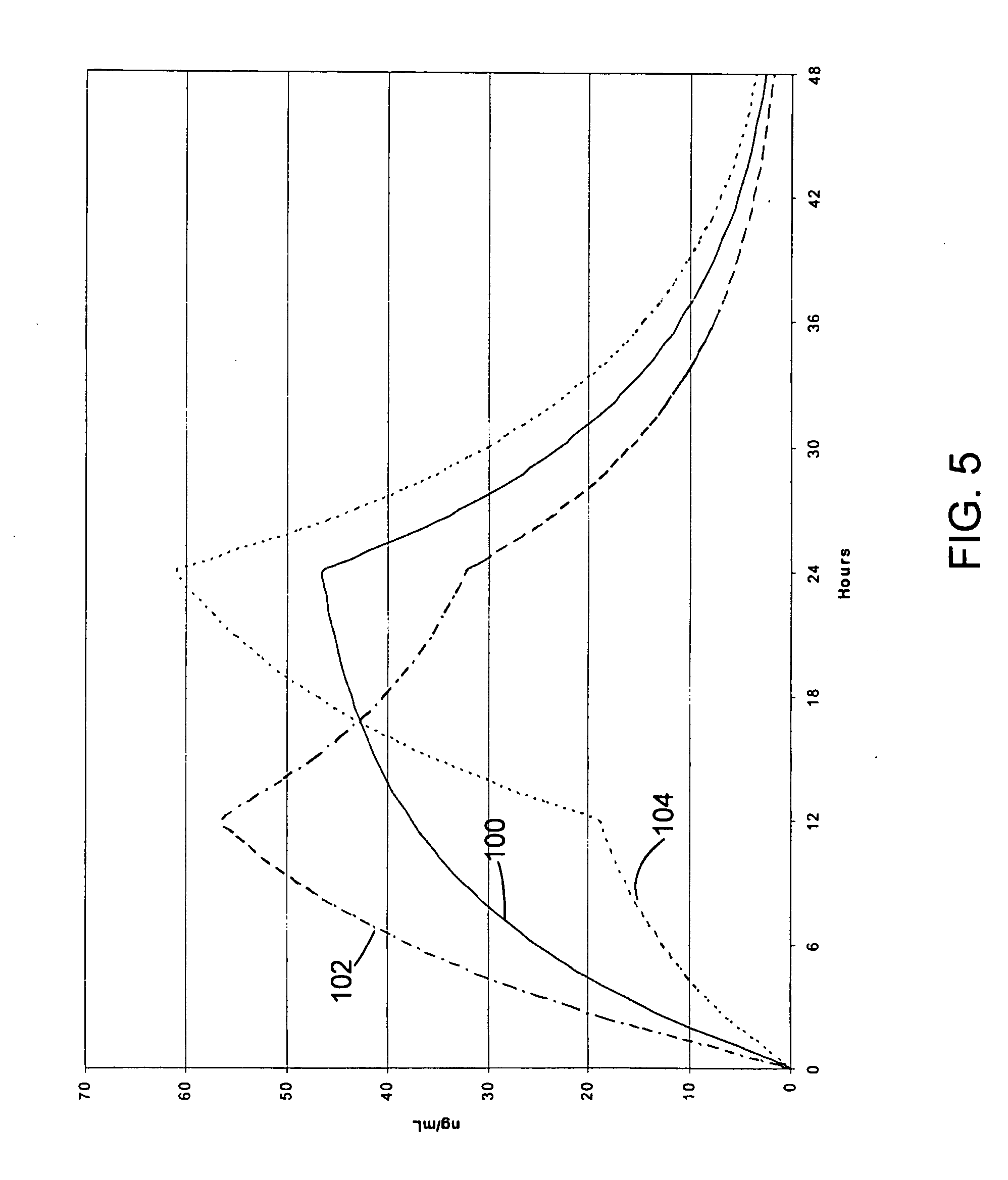
Once-a-day, oral, controlled-release, oxycodone dosage forms
Oxycodone formulations are provided which produce substantially flat in vivo steady state plasma profiles. Tolerance levels associated with such profiles and tolerance levels associated with biphasic profiles are shown not to be statistically different. The substantially flat in vivo steady state plasma profiles are produced by dosage forms having substantially zero order in vitro release profiles. Such release profiles produce low single dose in vivo Cmax levels which can reduce the probability of adverse side effects.
Owner:ALZA CORP
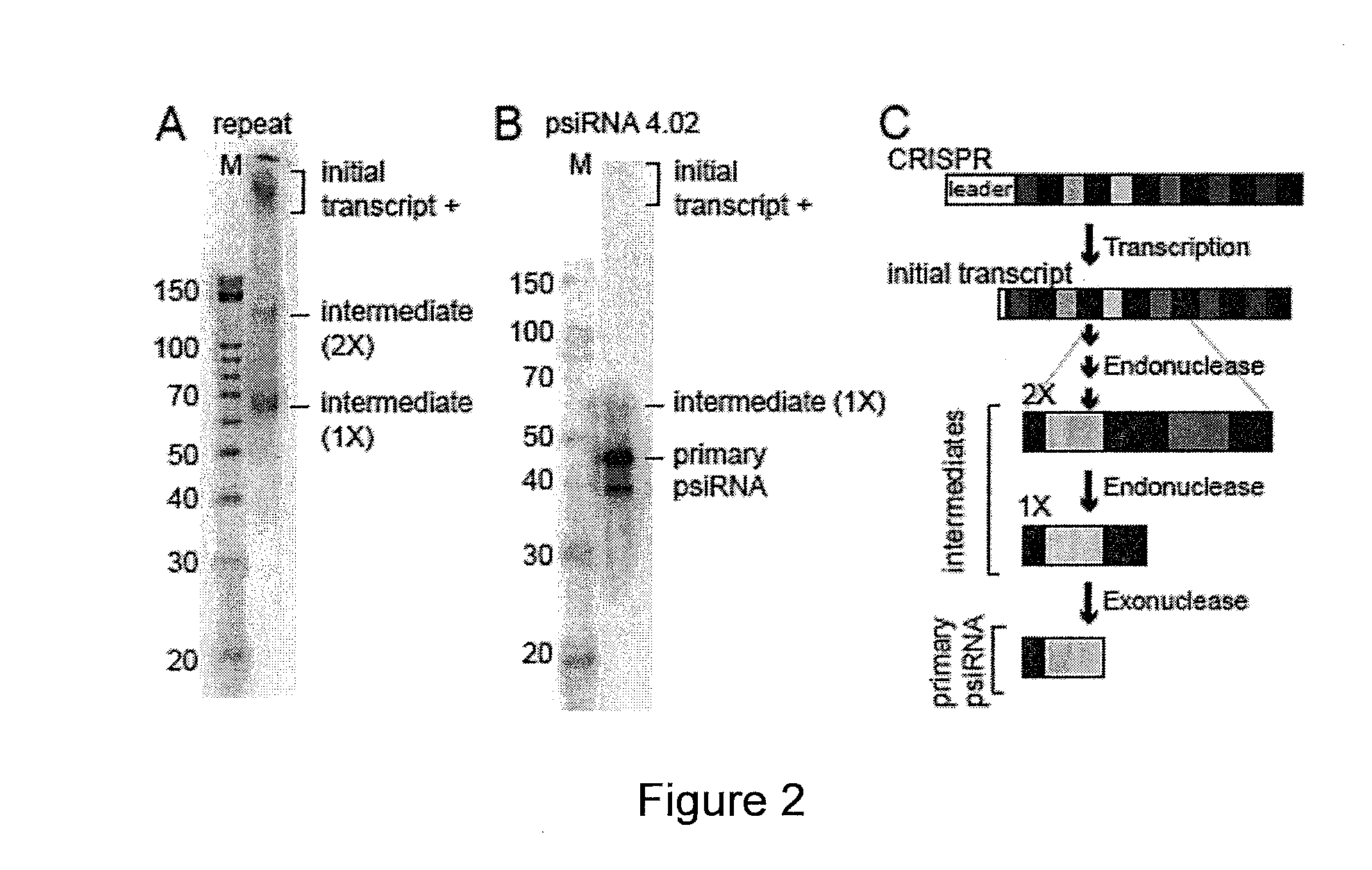
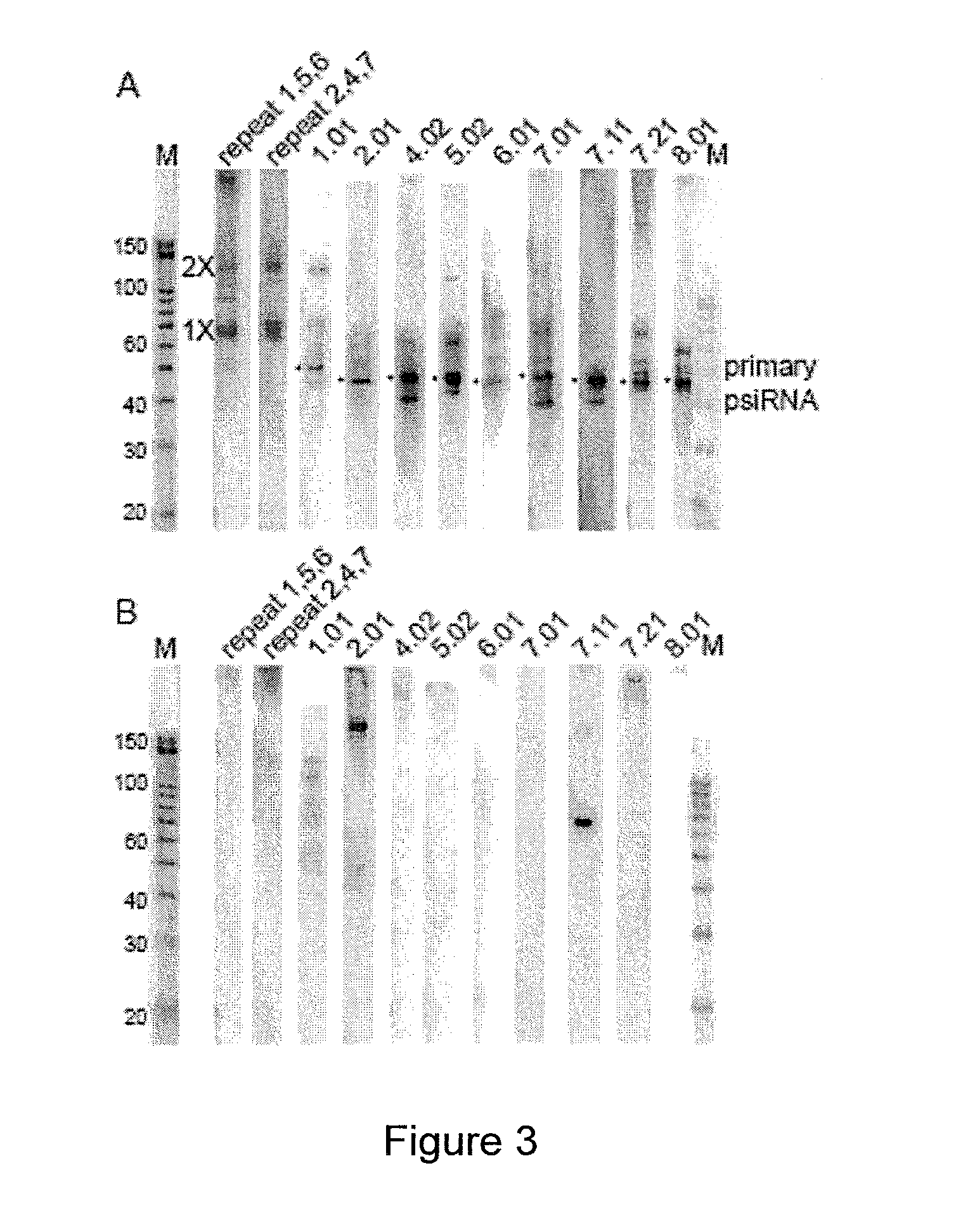
PROKARYOTIC RNAi-LIKE SYSTEM AND METHODS OF USE
Provided herein are methods for inactivating a target polynucleotide. The methods use a psiRNA having a 5′ region and a 3′ region. The 5′ region includes, but is not limited to, 5 to 10 nucleotides chosen from a repeat from a CRISPR locus immediately upstream of a spacer. The 3′ region is substantially complementary to a portion of the target polynucleotide. The methods may be practiced in a prokaryotic microbe or in vitro. Also provided are polypeptides that have endonuclease activity in the presence of a psiRNA and a target polynucleotide, and methods for using the polypeptides.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Sliver type autonomous biosensors
InactiveUS20040180391A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoElectrochemistry
In vivo or in vitro monitoring of chemical and biochemical species (e.g., pH, or glucose levels) in the interstitial fluid of patients or in a sample of a fluid to be analyzed is provided by a probe (10, 70, 210, 270). For in vivo monitoring, the probe is readily inserted by a minimally invasive method. Optical or electrochemical sensing methods are employed to detect a physical or chemical change, such as pH, color, electrical potential, electric current, or the like, which is indicative of the concentration of the species or chemical property to be detected. Visual observation by the patient may be sufficient to monitor certain biochemicals (e.g., glucose) with this approach. A CAP membrane allows high enzyme loadings, and thus enables use of microminiature probes, and / or diagnosis of low levels of the analyte(s), with sufficient signal-to-noise ratio and low background current.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
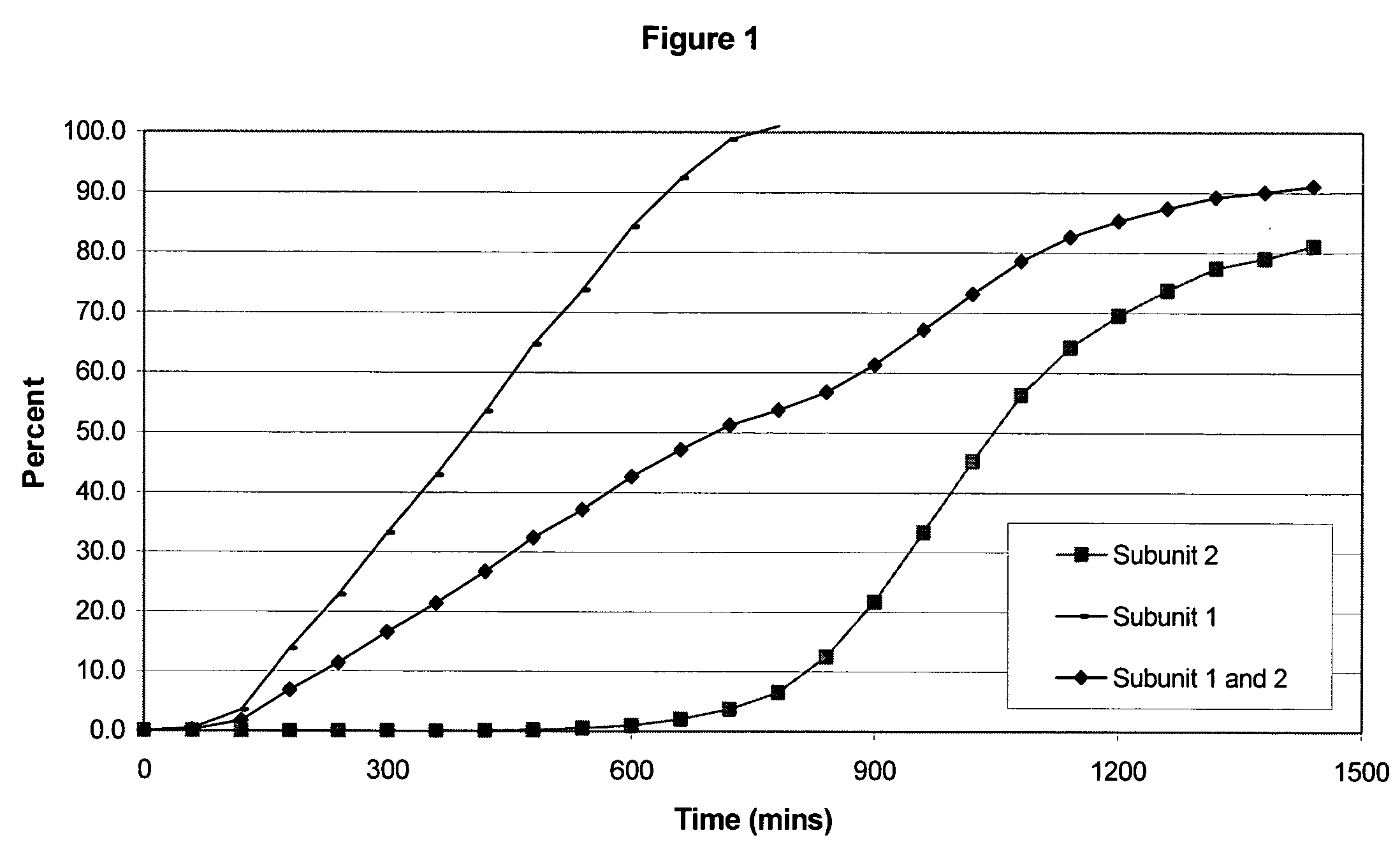
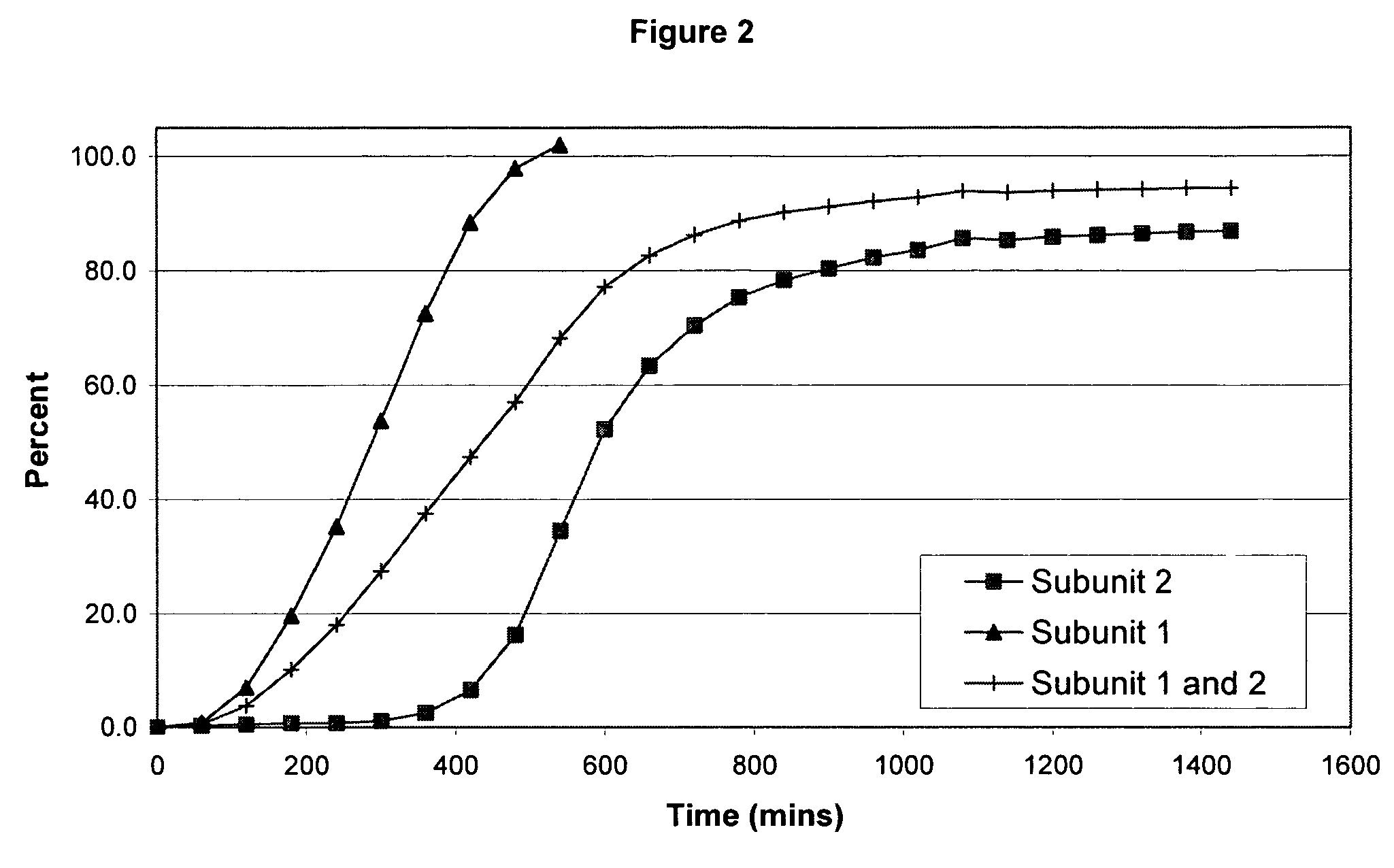
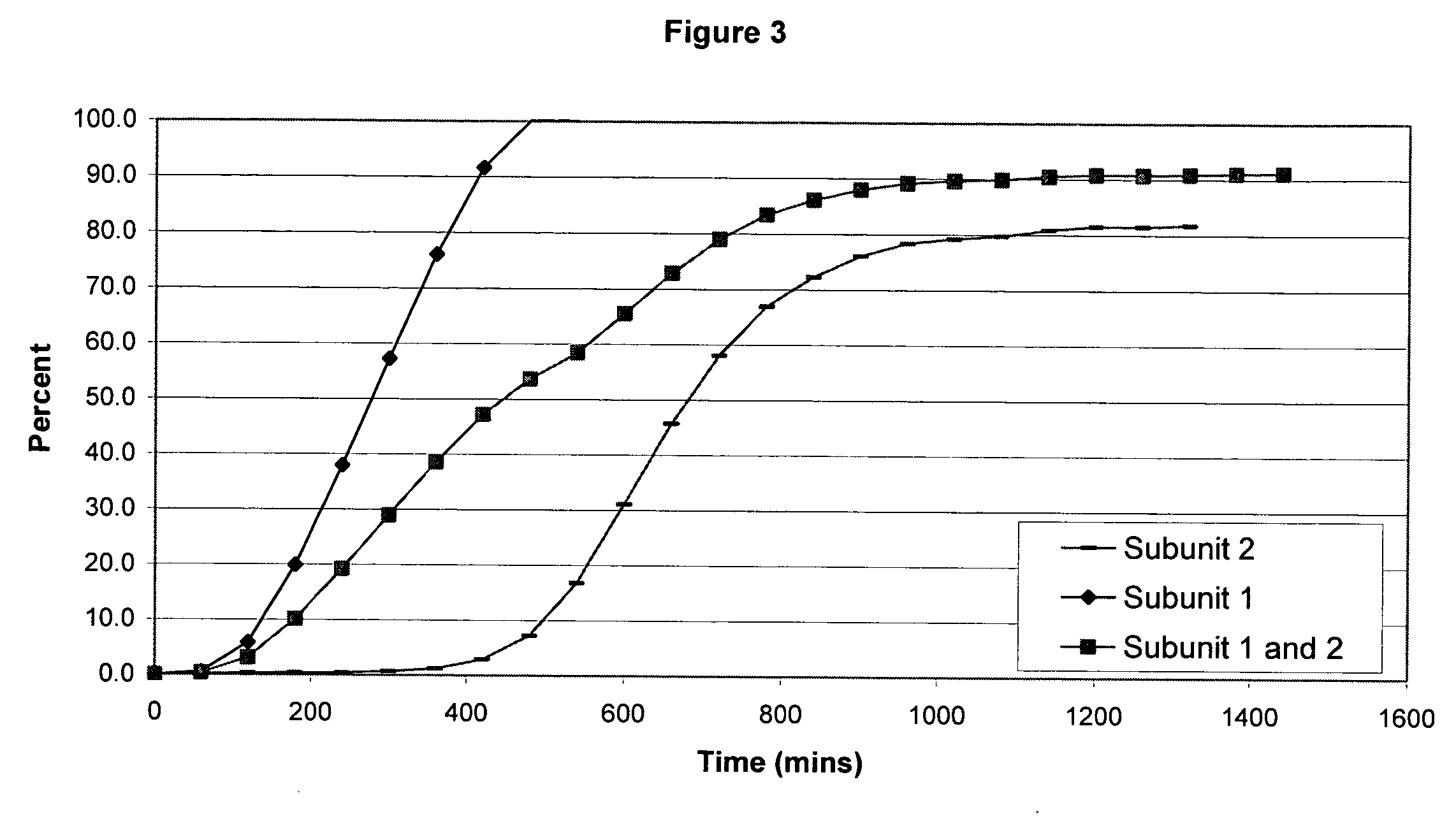
Sustained release opioid formulations and method of use
The invention combines two different subunits with different release profiles in novel sustained-release oral dosage forms. In particular, the oral dosage forms include a subunit that comprises an opioid analgesic and a sustained-release material, wherein the dissolution rate in-vitro of the subunit, when measured by the standard USP Drug Release test of U.S. Pharmacopeia XXVI (2003) <724>, is less than about 10% within about 6 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; less than about 10% within about 8 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; less than about 10% within about 10 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; or less than about 10% within about 12 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; the dosage form providing a duration of therapeutic effect of about 24 hours.
Owner:ALPHARMA PHARMA
Poly(beta-amino alcohols), their preparation, and uses thereof
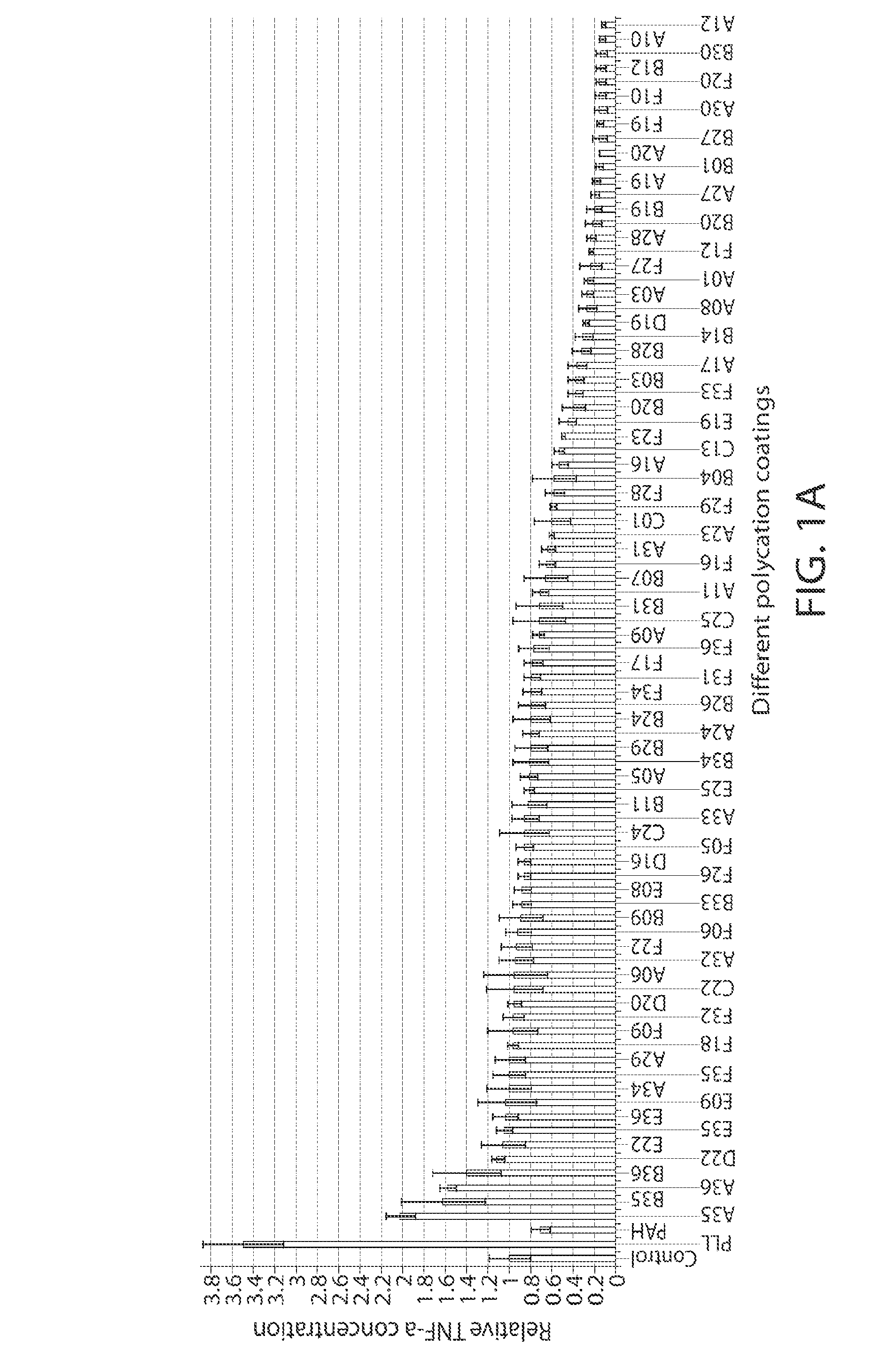
ActiveUS20130302401A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical structureFibrosis
A new class of poly(beta-amino alcohols) (PBAAs) has been prepared using combinatorial polymerization. The inventive PBAAs may be used in biotechnology and biomedical applications as coatings (such as coatings of films or multilayer films for medical devices or implants), additives, materials, excipients, non-biofouling agents, micropatterning agents, and cellular encapsulation agents. When used as surface coatings, these PBAAs elicited different levels of inflammation, both in vitro and in vivo, depending on their chemical structures. The large chemical diversity of this class of materials allowed us to identify polymer coatings that inhibit macrophage activation in vitro. Furthermore, these coatings reduce the recruitment of inflammatory cells, and reduce fibrosis, following the subcutaneous implantation of carboxylated polystyrene microparticles. These polymers may be used to form polyelectrolyte complex capsules for cell encapsulation. The invention may also have many other biological applications such as antimicrobial coatings, DNA or siRNA delivery, and stem cell tissue engineering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
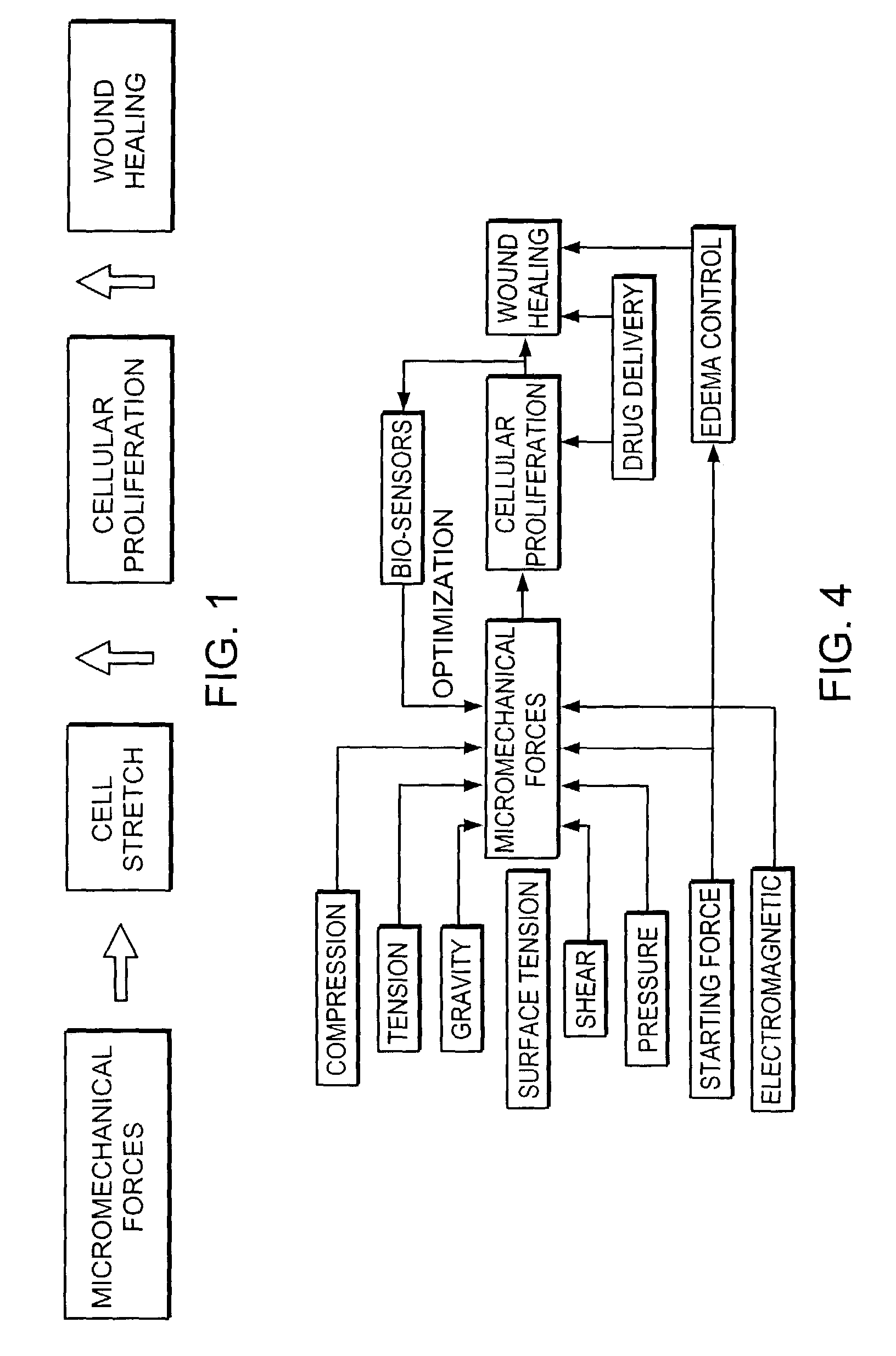
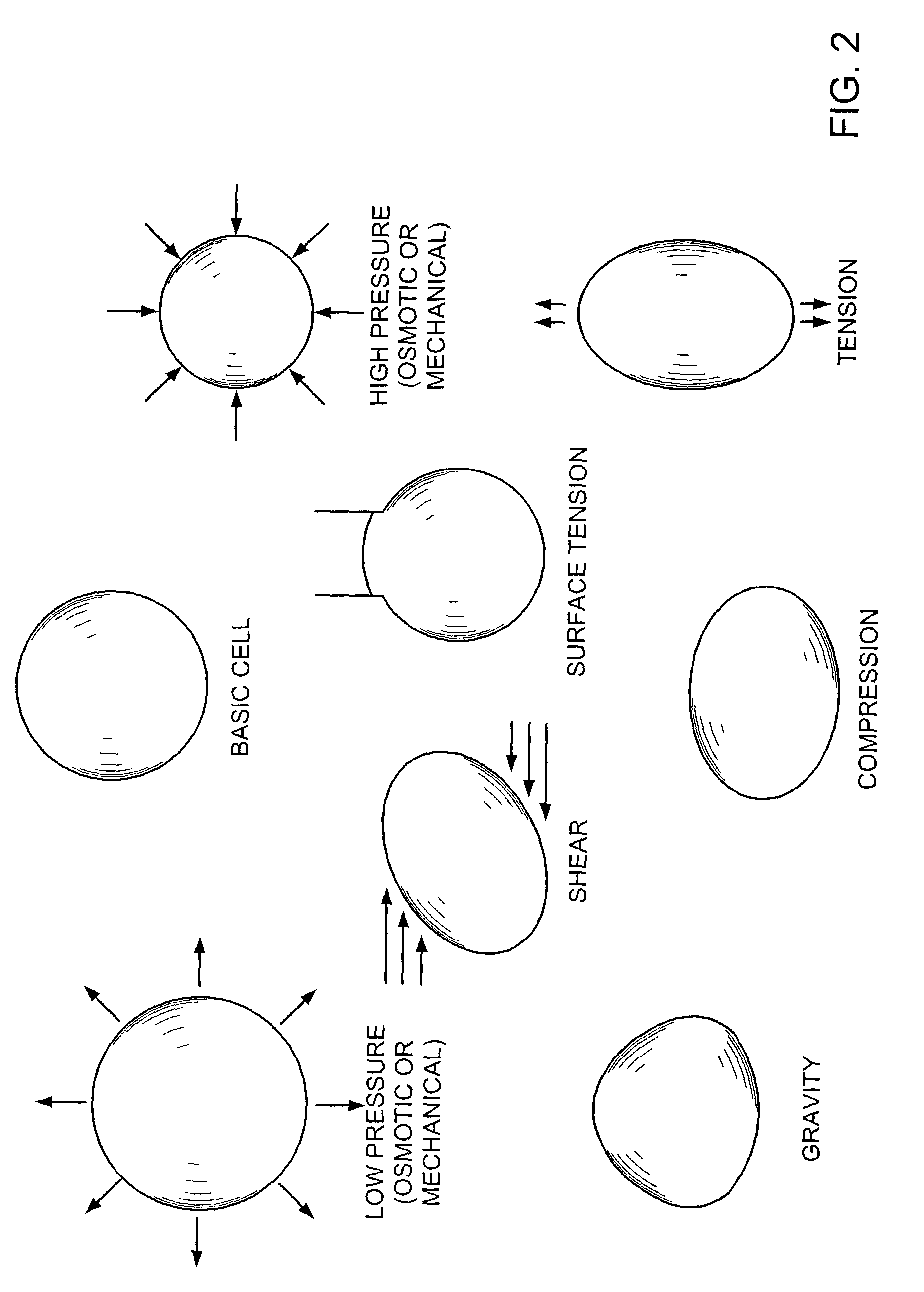
Methods and apparatus for application of micro-mechanical forces to tissues
InactiveUS7494482B2Accelerate tissue ingrowthEnhancing tissue repairNon-adhesive dressingsBone implantMicron scaleCell-Extracellular Matrix
Methods and devices for transmitting micromechanical forces locally to induce surface convolutions into tissues on the millimeter to micron scale for promoting wound healing are presented. These convolutions induce a moderate stretching of individual cells, stimulating cellular proliferation and elaboration of natural growth factors without increasing the size of the wound. Micromechanical forces can be applied directly to tissue, through biomolecules or the extracellular matrix. This invention can be used with biosensors, biodegradable materials and drug delivery systems. This invention will also be useful in pre-conditioned tissue-engineering constructs in vitro. Application of this invention will shorten healing times for wounds and reduce the need for invasive surgery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
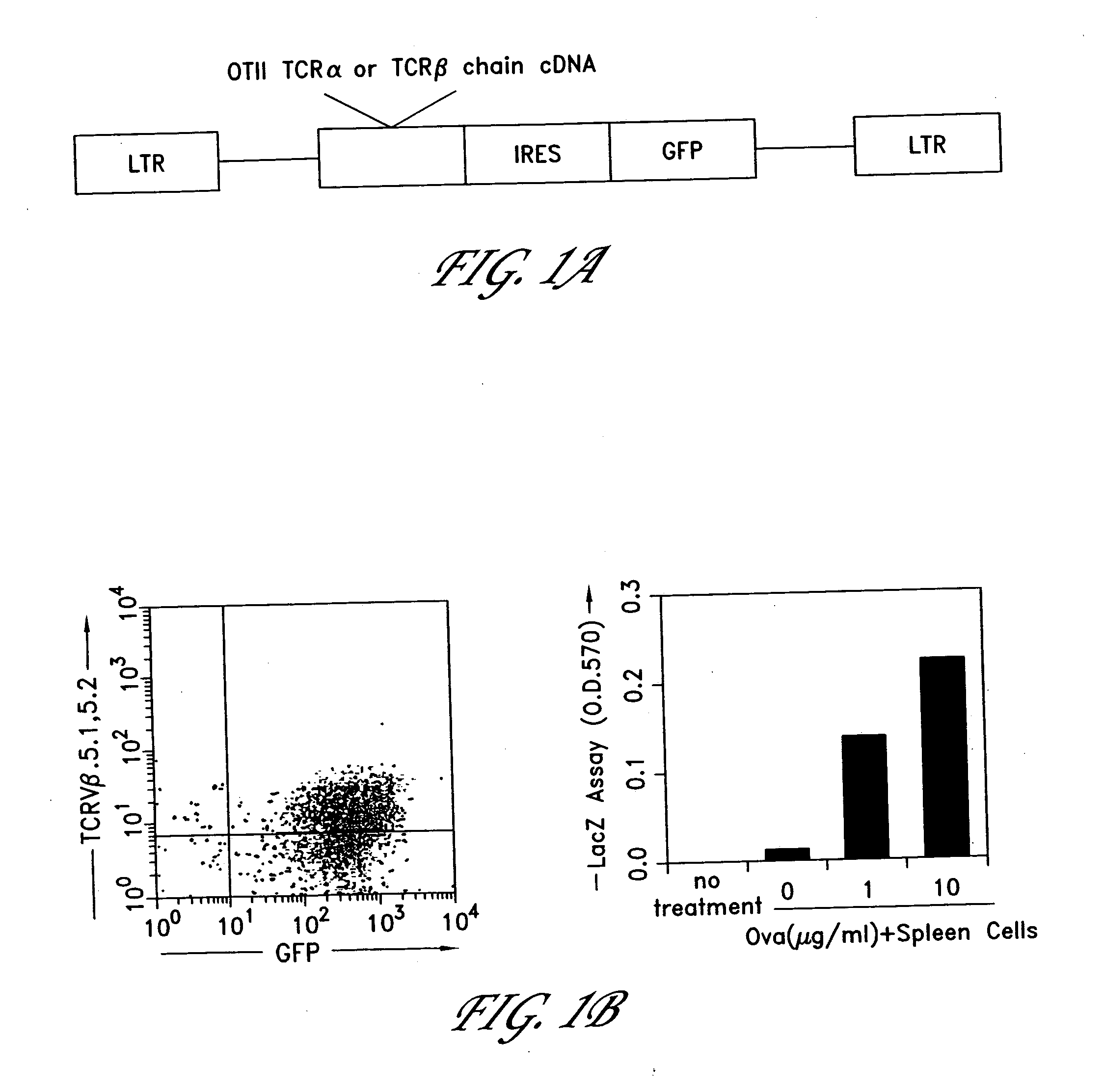
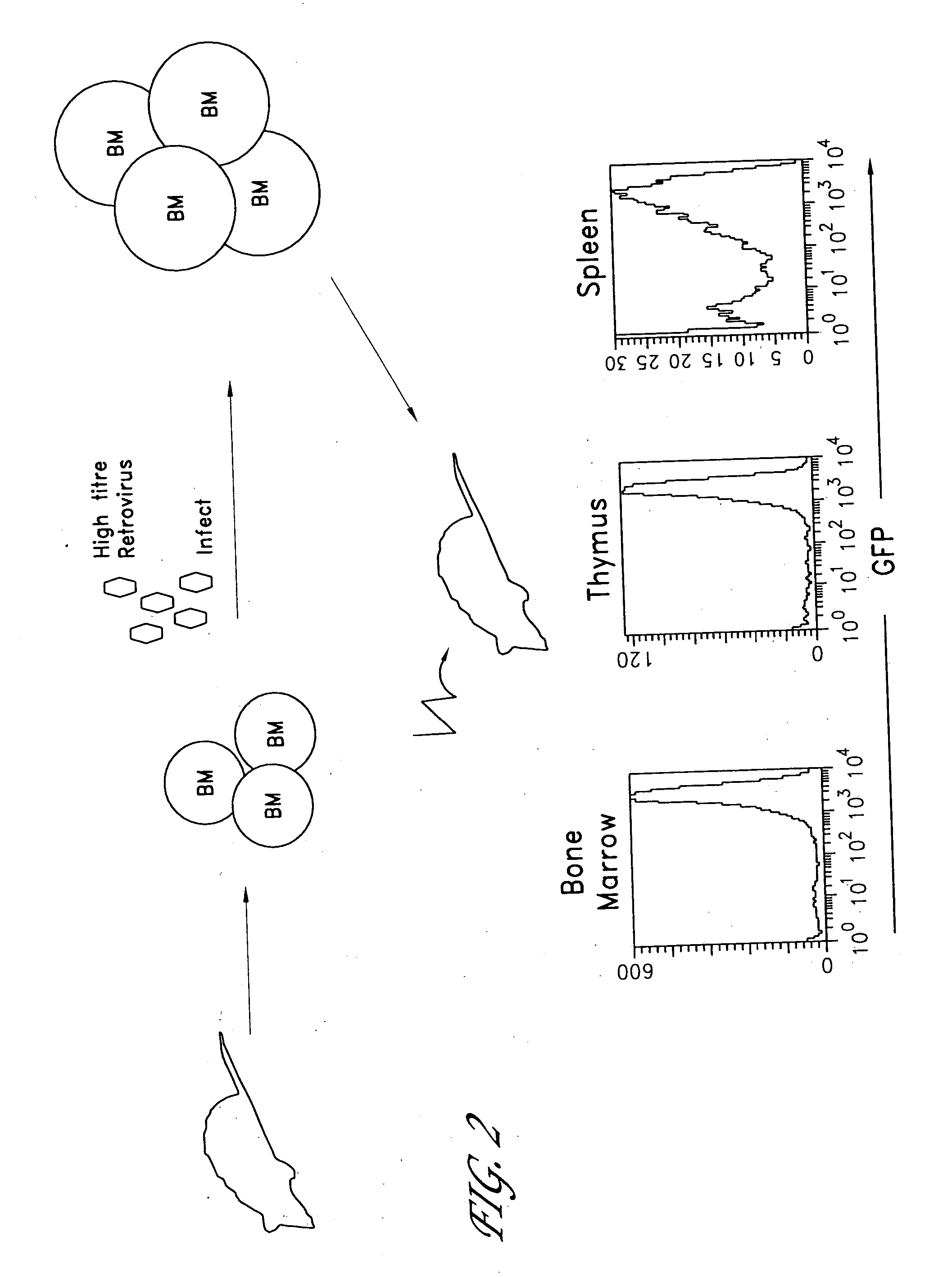
Method for the generation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
InactiveUS20070116690A1Function increaseEnhancing function of T cellBiocideVirusesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
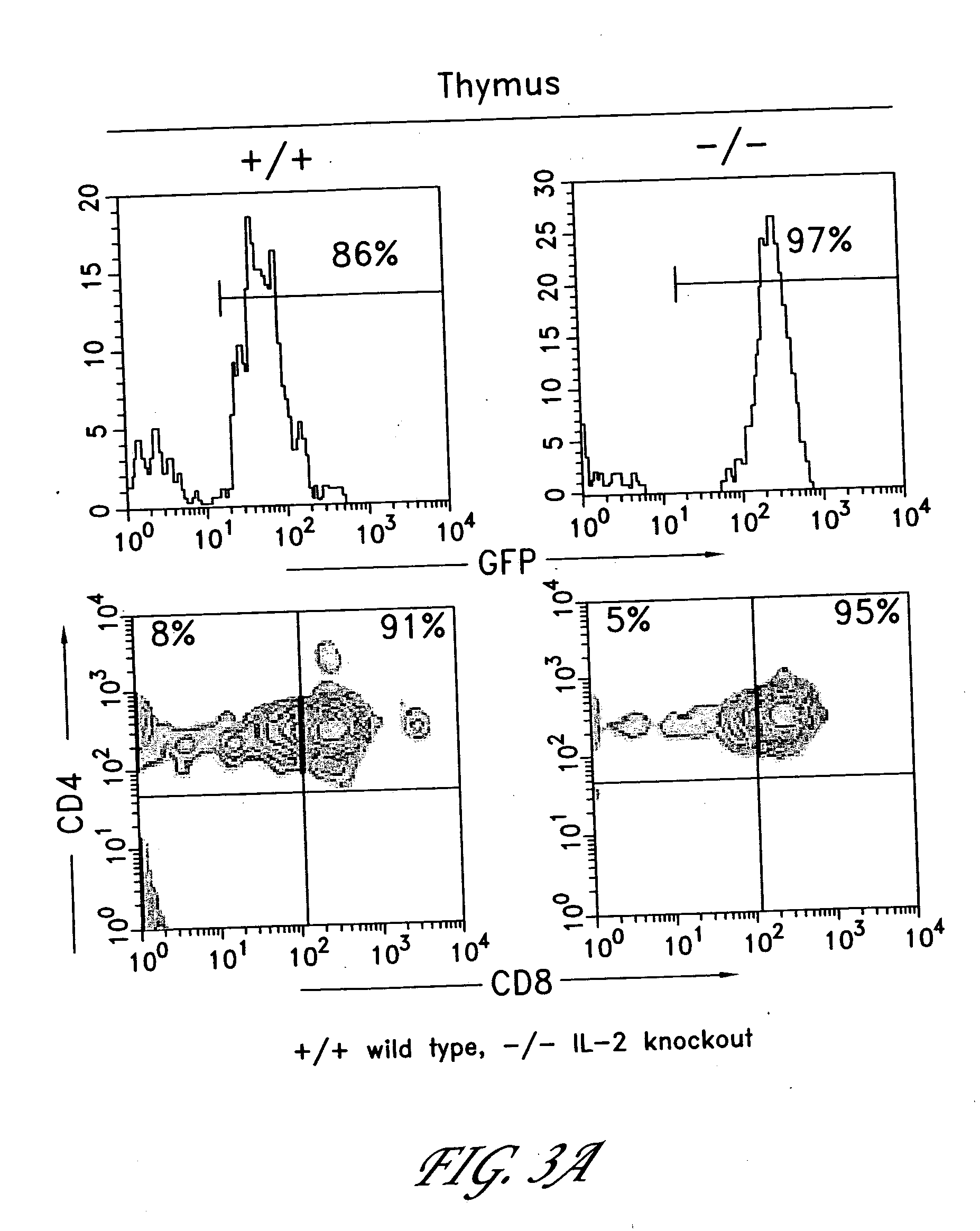
The invention provides systems and methods for the generation of lymphocytes having a unique antigen specificity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of virally infecting cells from bone marrow with one or more viral vectors that encode antigen-specific antibodies for the production of, for example B cells and T cells. In some embodiments, the viral vectors include an IRES or 2A element to promote separation of, for example, the α subunit and β subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR) or heavy and light chains of a B-cell antibody. The resulting lymphocytes, express the particular antibody that was introduced in the case of B cells and TCR in the case of T cells. The lymphocytes generated can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes including the treatment of various cancers and the generation of a desired immune response to viruses and other pathogens. The resulting cells develop normally and respond to antigen both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that it is possible to modify the function of lymphocytes by using stem cells from different genetic backgrounds. Thus our system constitutes a powerful tool to generate desired lymphocyte populations both for research and therapy. Future applications of this technology may include treatments for infectious diseases, such as HIV / AIDS, cancer therapy, allergy, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
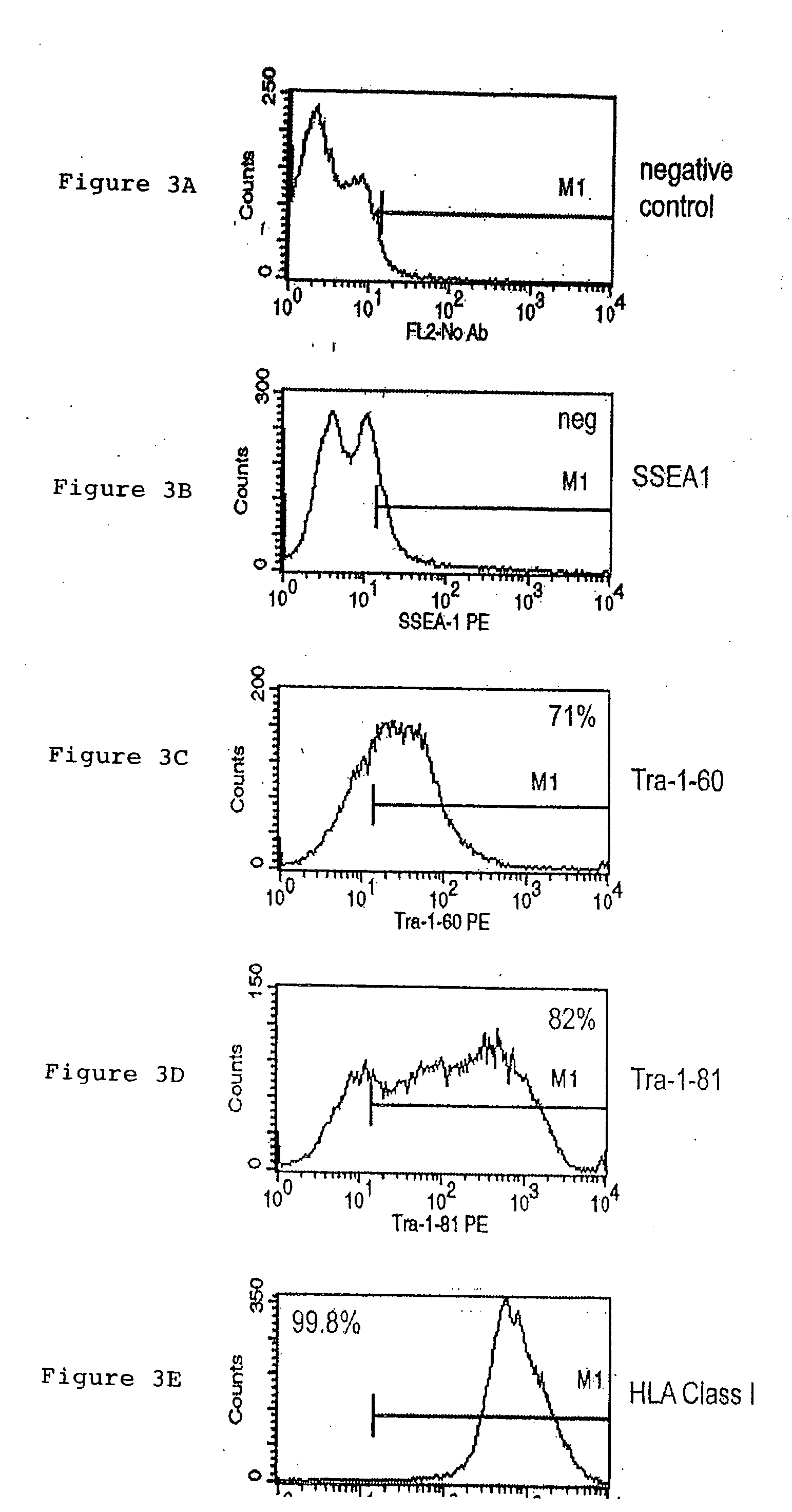
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
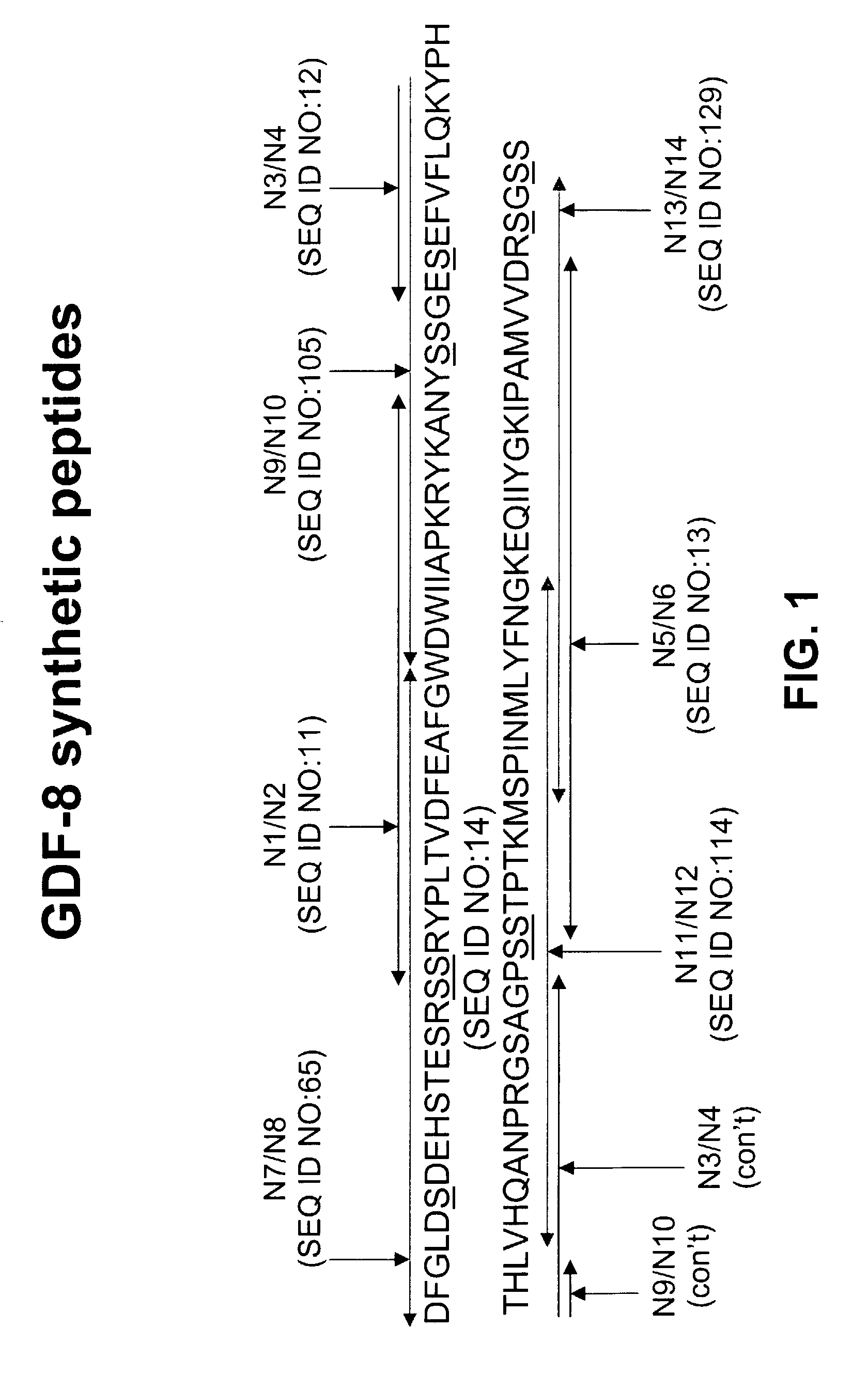
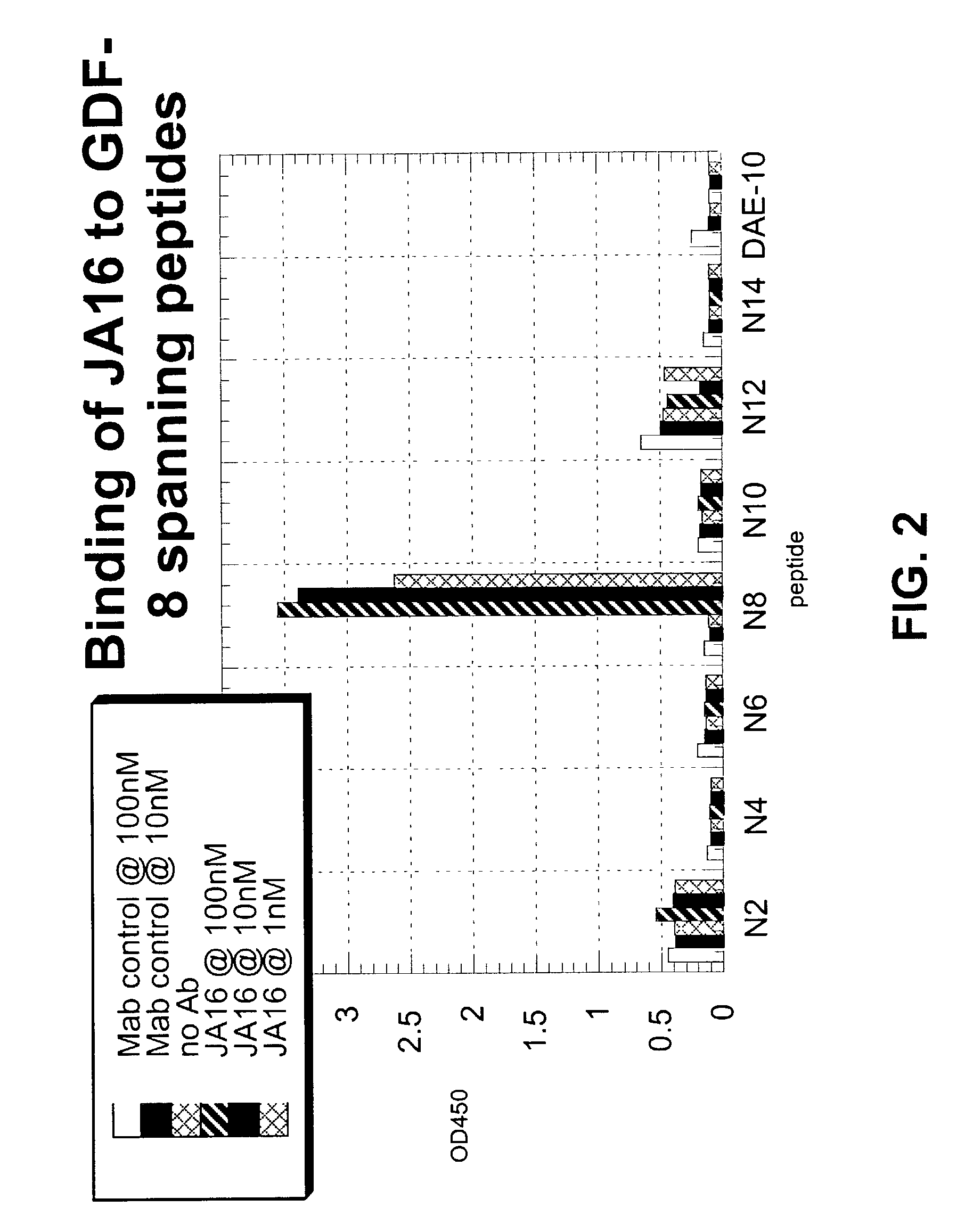
Antibody inhibitors of GDF-8 and uses thereof
ActiveUS7320789B2Reduction in one or more of the biological activitiesReduced activityNervous disorderMuscular disorderAntibody inhibitorAntibody fragments
The disclosure provides novel antibodies against growth and differentiation factor-8 (GDF-8), including antibody fragments, which inhibit GDF-8 activity in vitro and in vivo. The disclosure also provides methods for diagnosing, preventing, or treating degenerative disorders of muscle, bone, or insulin metabolism.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Pseudo-antibody constructs
InactiveUS20030211078A1Reduce productionInhibit synthesisOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHalf-lifeIn vivo
This invention relates to novel pharmaceutically useful compositions that bind to a biological molecule, having improved circulatory half-life, increased avidity, increased affinity, or multifunctionality, and methods of use thereof. The present invention provides a pseudo-antibody comprising an organic moiety covalenty coupled to at least two target-binding moieties, wherein the target-binding moieties are selected from the group consisting of a protein, a peptide, a peptidomimetic, and a non-peptide molecule that binds to a specific targeted biological molecule. The pseudo-antibody of the present invention may affect a specific ligand in vitro, in situ and / or in vivo. The pseudo-antibodies of the present invention can be used to measure or effect in an cell, tissue, organ or animal (including humans), to diagnose, monitor, modulate, treat, alleviate, help prevent the incidence of, or reduce the symptoms of, at least one condition.
Owner:CENTOCOR
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6093695ARemarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaBacillus thuringiensisCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta -endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against colcopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneur). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Cell viability detection using electrical measurements
InactiveUS6927049B2Quantitative measurementEnhanced informationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityCell membrane
A method of determining information about cell viability and other characteristics relating to cell membrane permeability is disclosed. The method involves determining the effect of a cell on current flow and relating that effect to a known standard which standard may be a known healthy cell and thereby deducing the viability of the cell being tested. The cells being tested can be subjected to different environmental conditions such as surrounding chemicals, temperature, pH and pressure to determine the effects of such conditions on cell viability and / or cell permeability. The cell being tested can be in a cell suspension, grown on s ubstarte, in tissue in vitro or in tissue in vivo. The method provides substantially instantaneous results and need not include the use of dyes or other markers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Implants for replacing hyaline cartilage, with hydrogel reinforced by three-dimensional fiber arrays
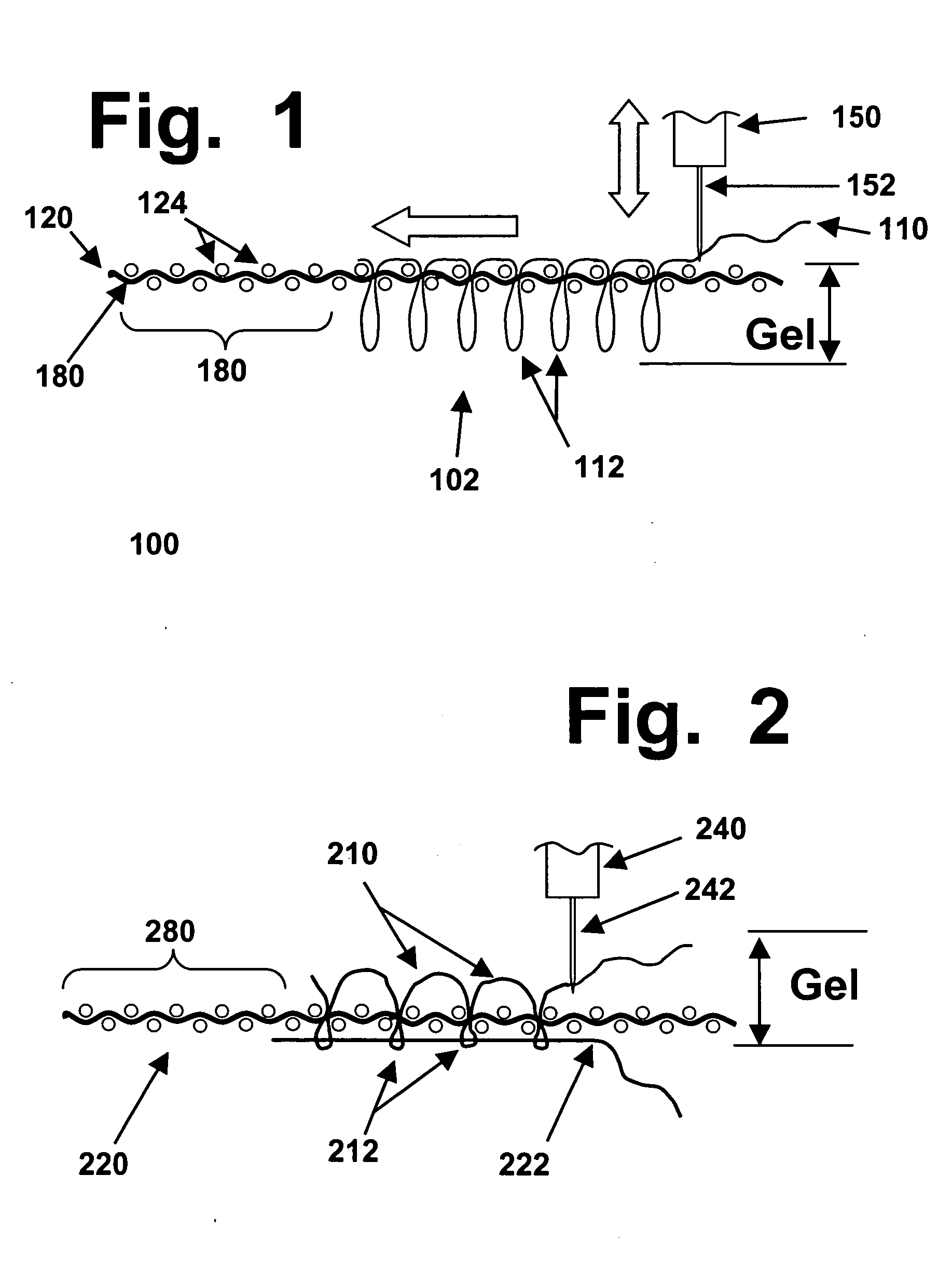
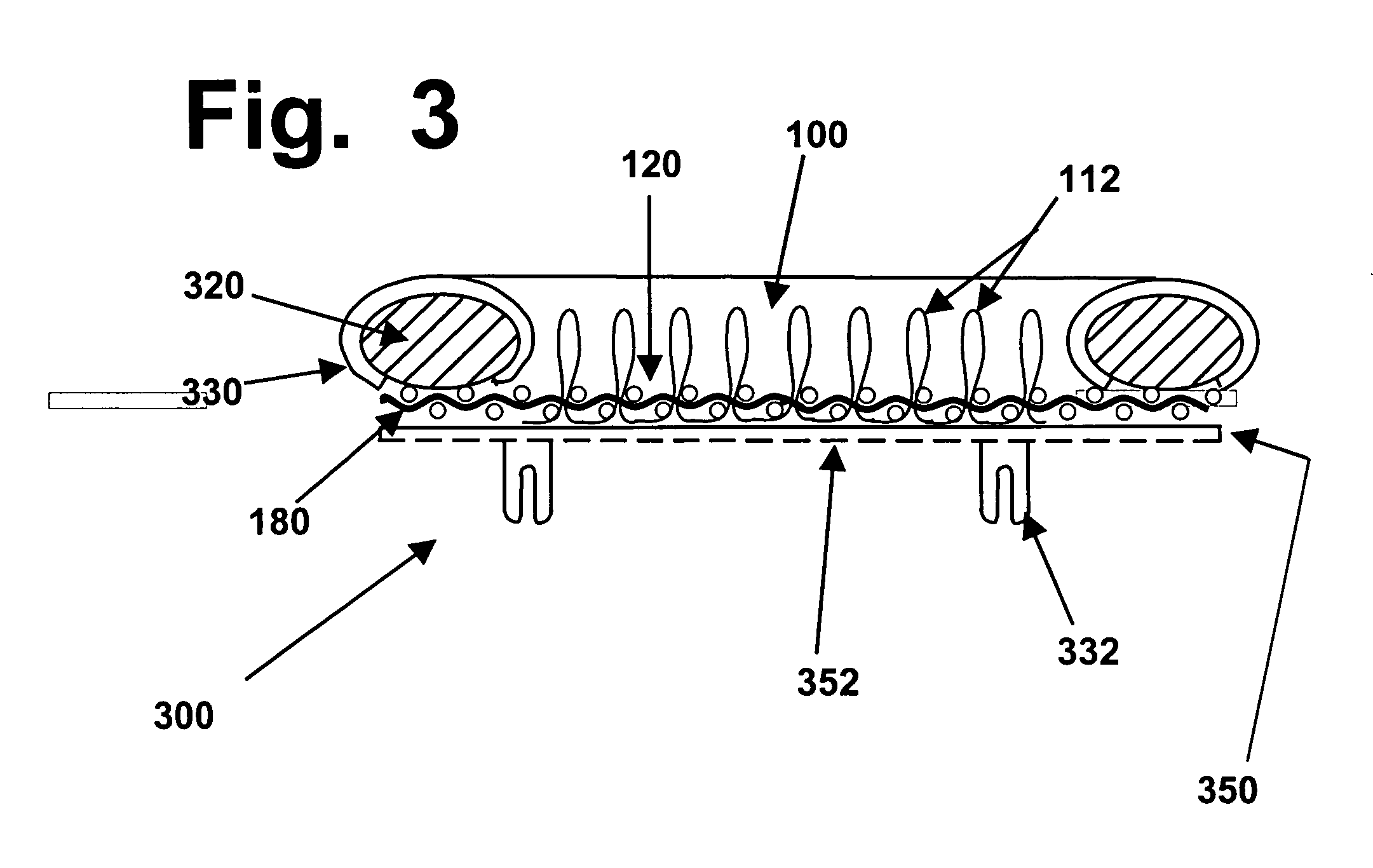
Implants with hydrogel layers reinforced by three-dimensional fiber arrays can replace hyaline cartilage. Such implants should replace an entire cartilage segment, rather than creating a crevice around a plug, so these implants must be thin and flat, they must cover large areas, the tips of any tufts or stitches must not reach the hydrogel surface, and they must be flexible, for arthroscopic insertion. The use of computerized stitching machines to create such arrays enables a redesigned and modified test sample to be made with no delays, and no overhead or startup costs. This provides researchers with improved tools for making and testing implants that will need to go through extensive in vitro, animal, and human testing before they can be approved for sale and use. Fiber-reinforced hydrogels also can be secured to strong shape-memory rims, for securing anchoring to bones.
Owner:FORMAE
Mutated Tn5 transposase proteins and the use thereof
Transposase proteins that are modified relative to and have higher transposase activities than the wild-type Tn5 transposase are disclosed. A transposase protein of the present invention differs from the wild-type Tn5 transposase at amino acid position 41, 42, 450, or 454 and has greater avidity than the wild-type Tn5 transposase for at least one of a Tn5 outside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:3, a Tn5 inside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:4, and a modified Tn5 outside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:5. Also disclosed are various systems and methods of using the transposase proteins of the present invention for in vitro or in vivo transposition.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com