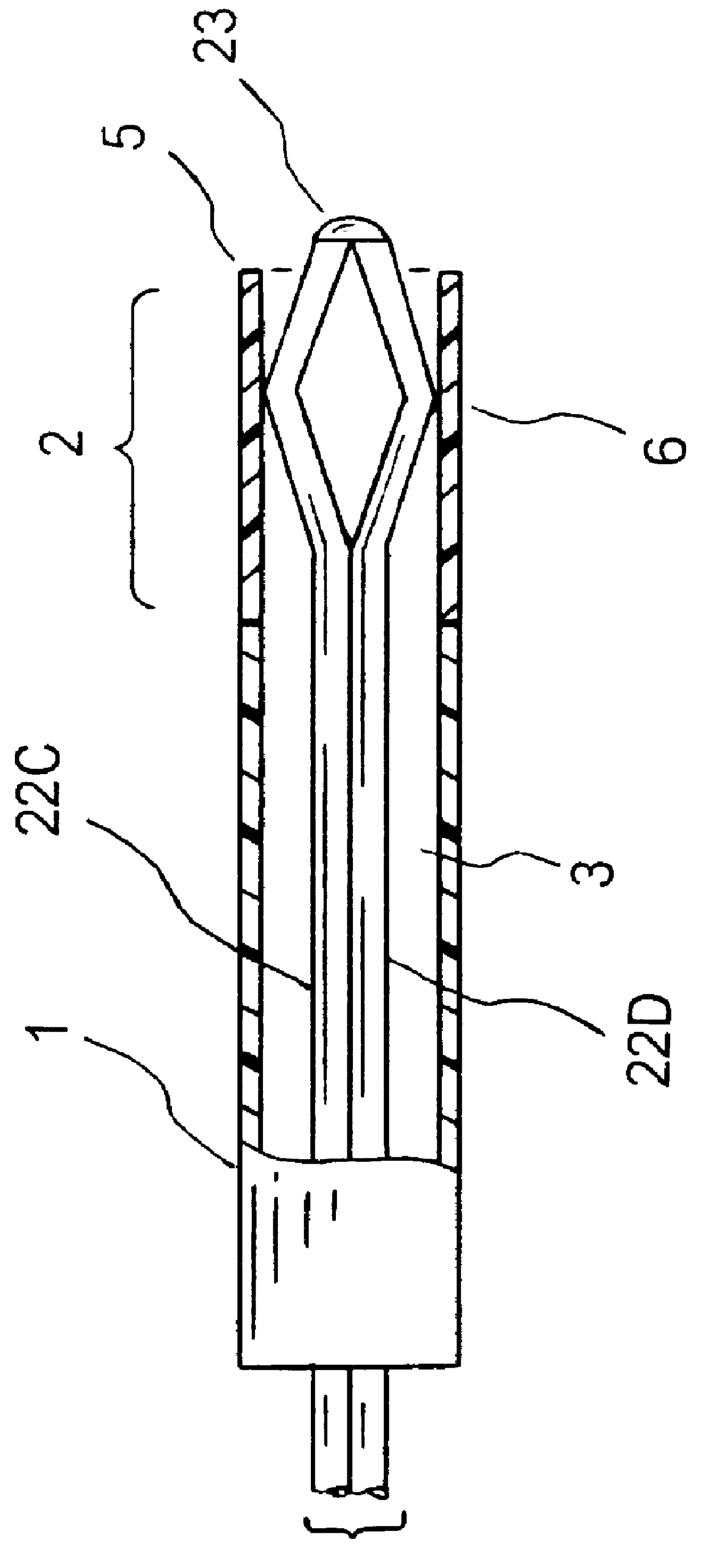
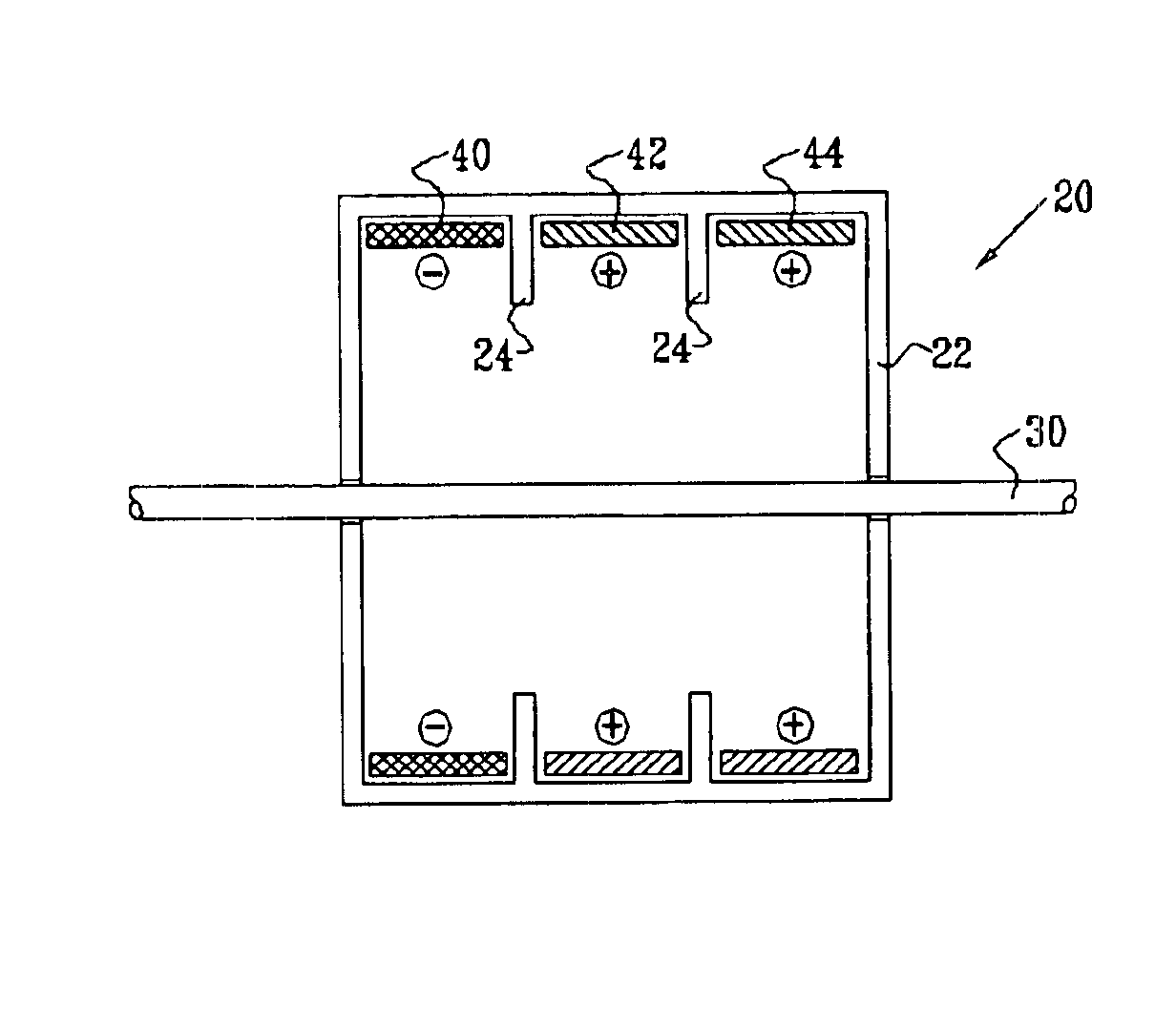
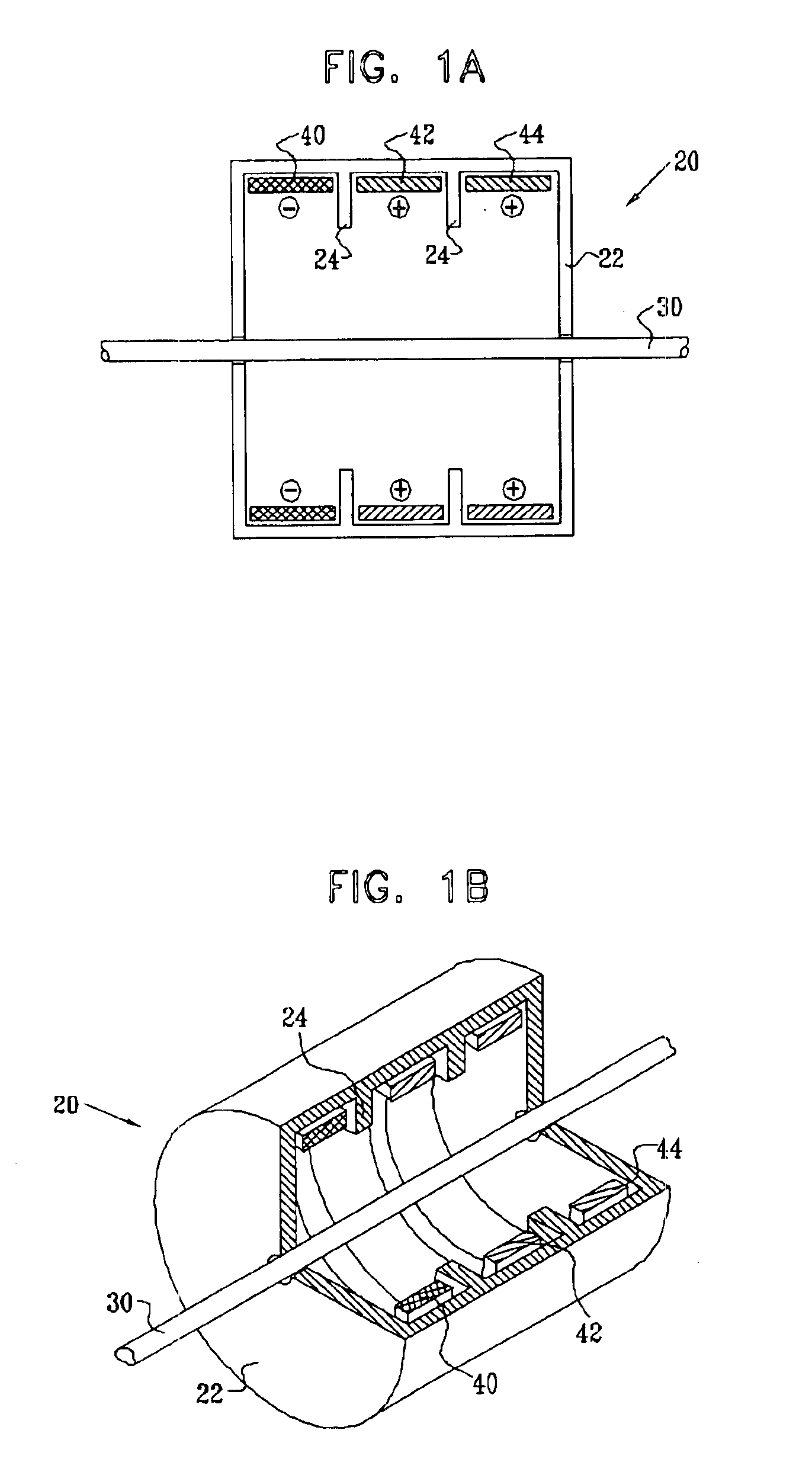
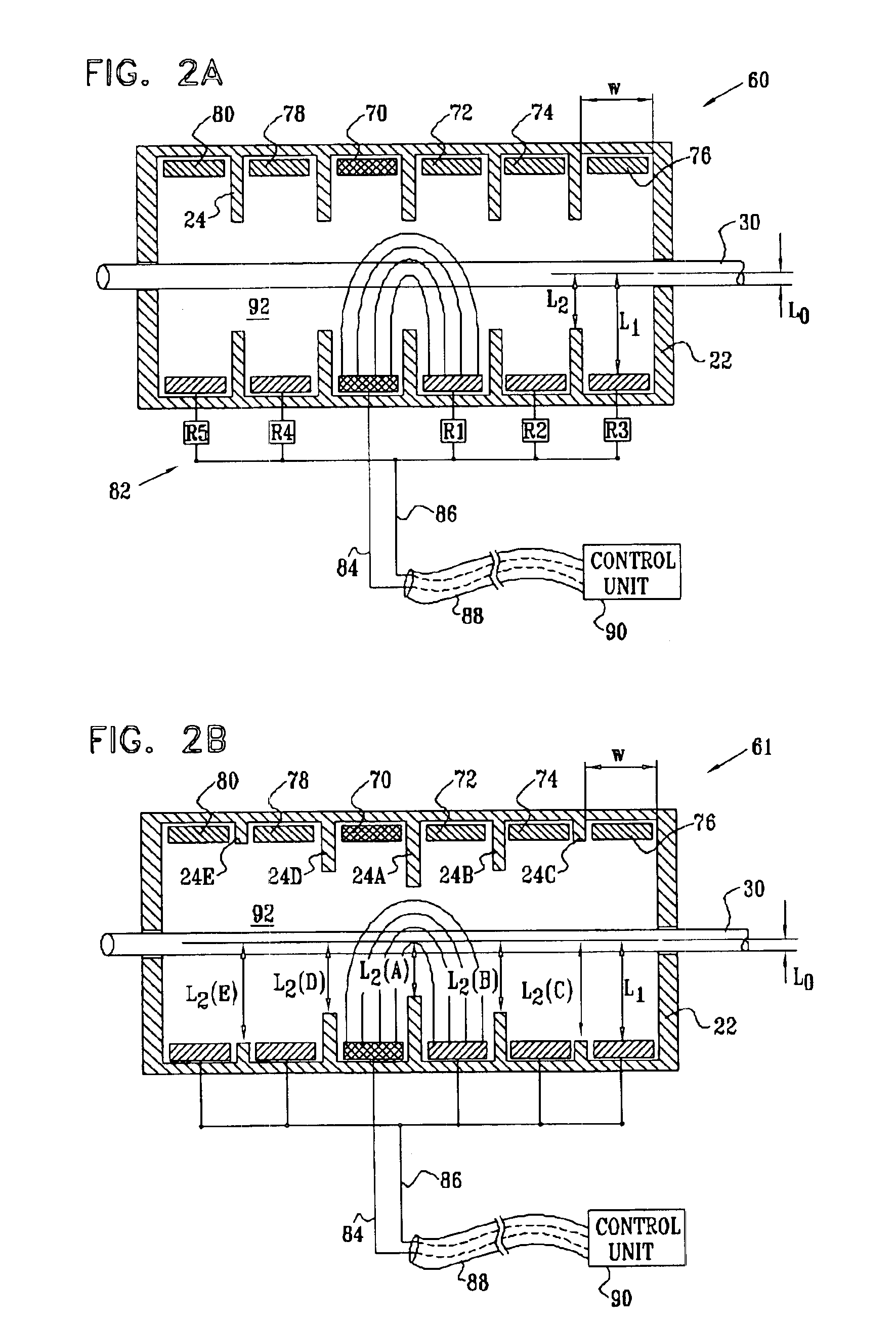
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57730 results about "Electric current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
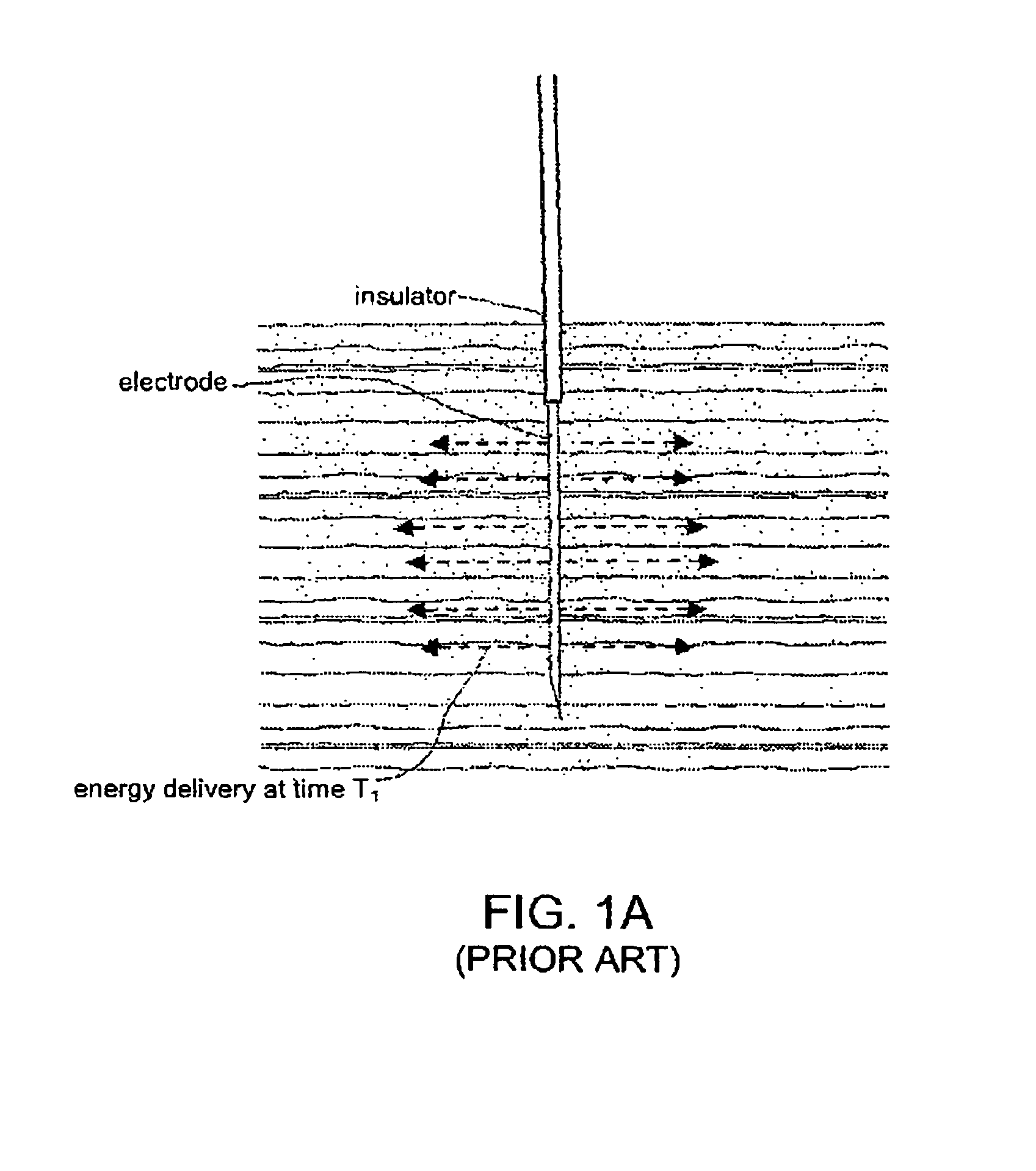
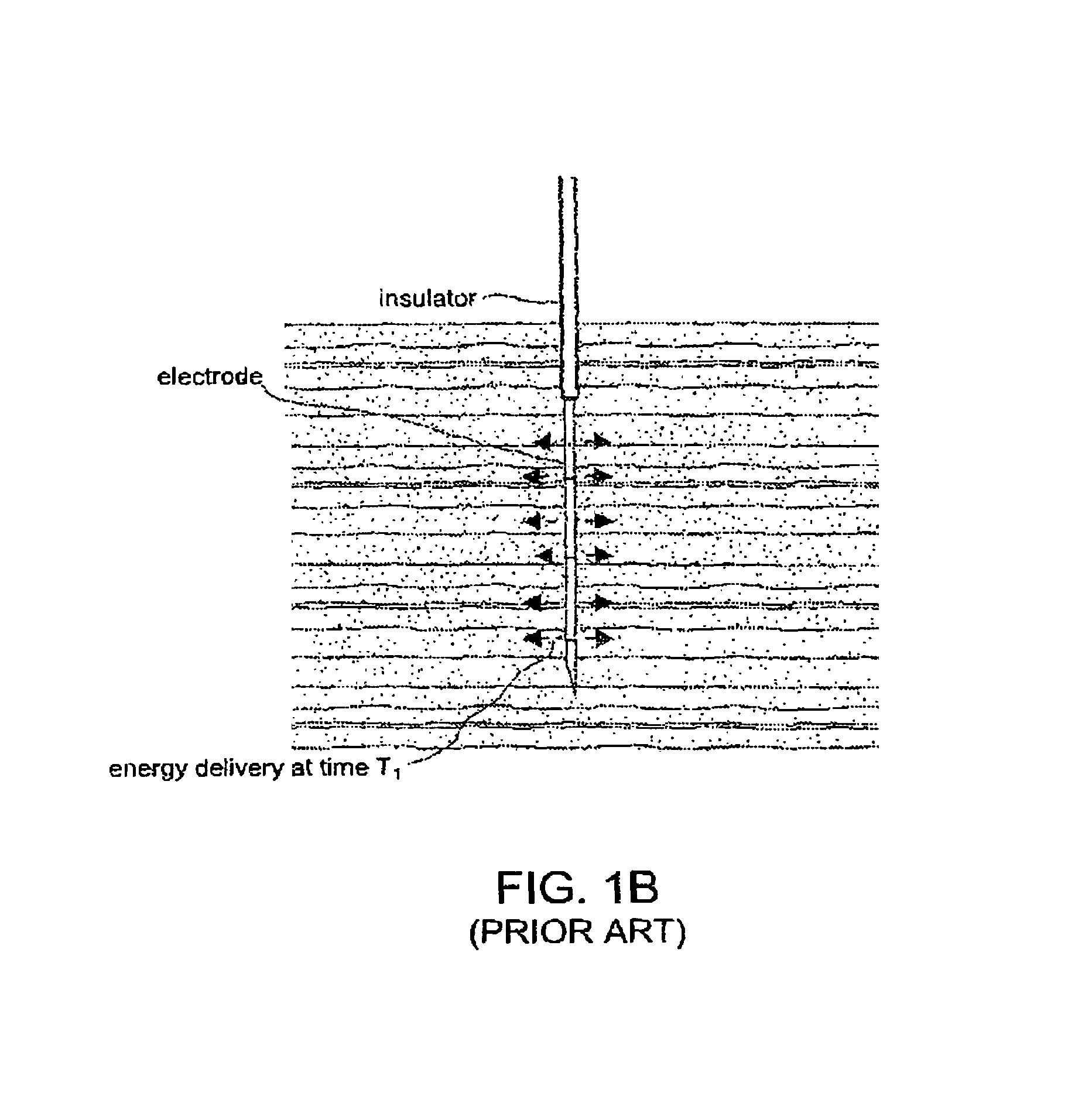
An electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge past a point or region. An electric current is said to exist when there is a net flow of electric charge through a region. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by electrons moving through a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in an ionized gas (plasma).
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090114910A1Uniform and high stabilityIncrease productionTransistorSolid-state devicesIn planeDevice material
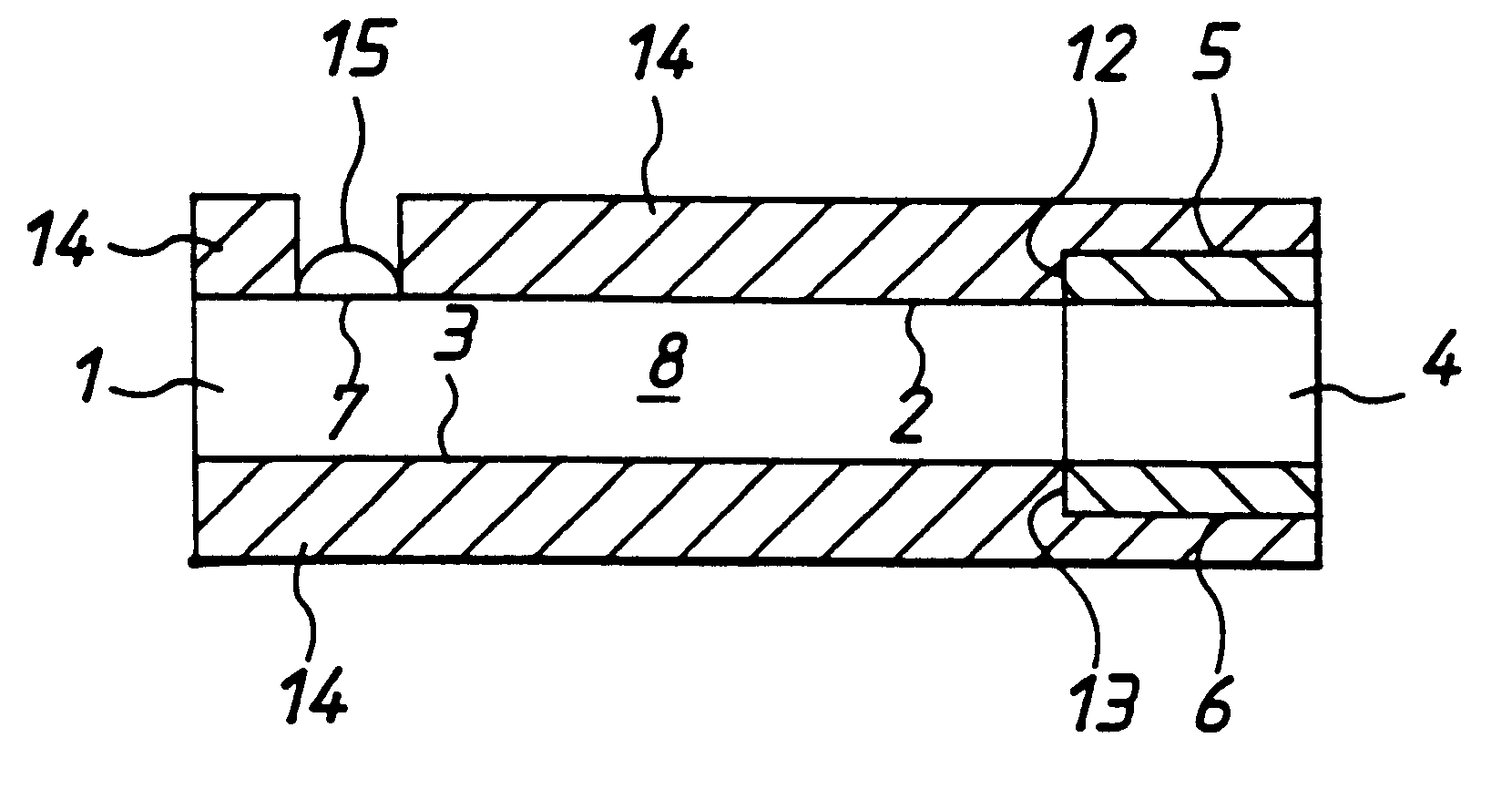
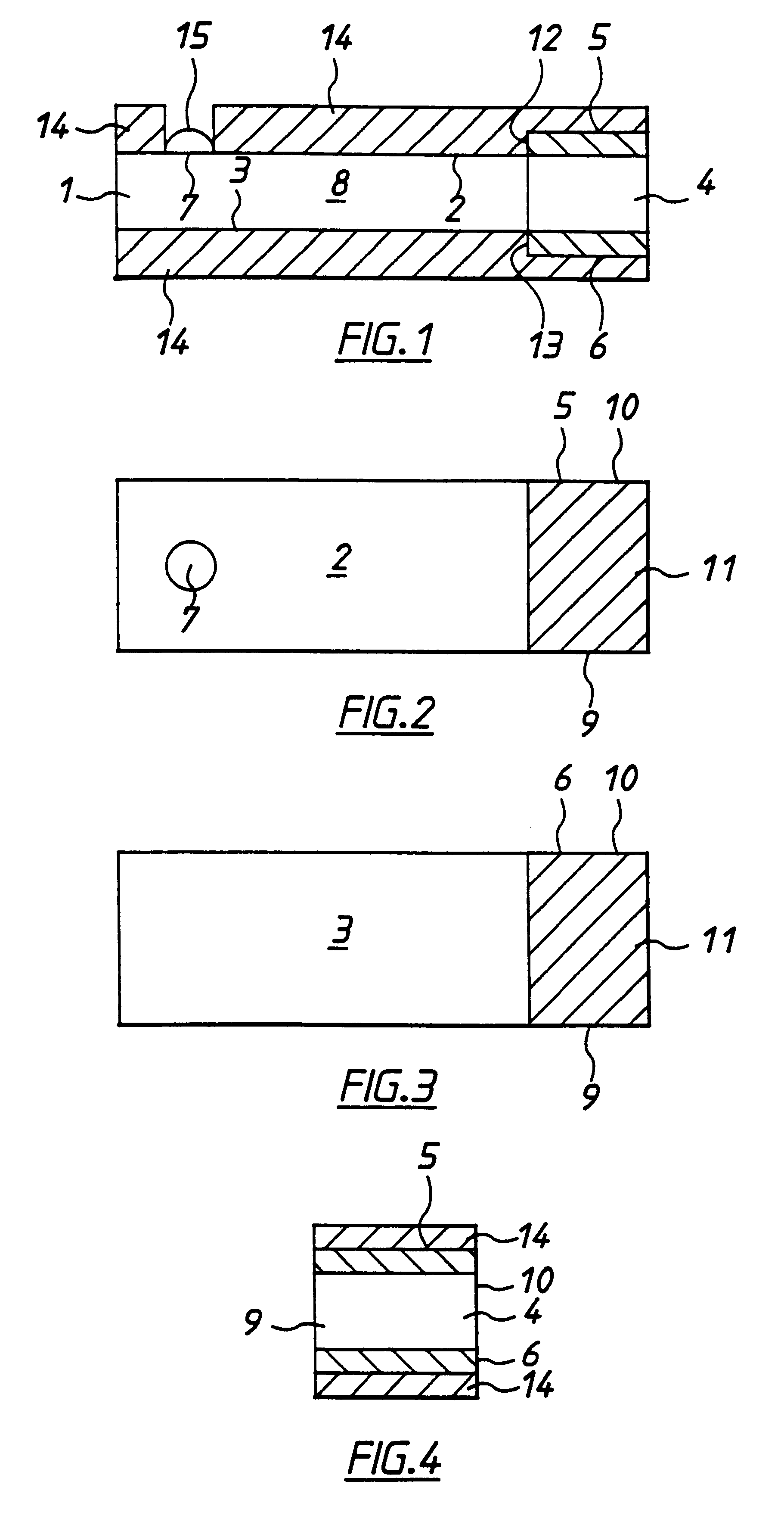
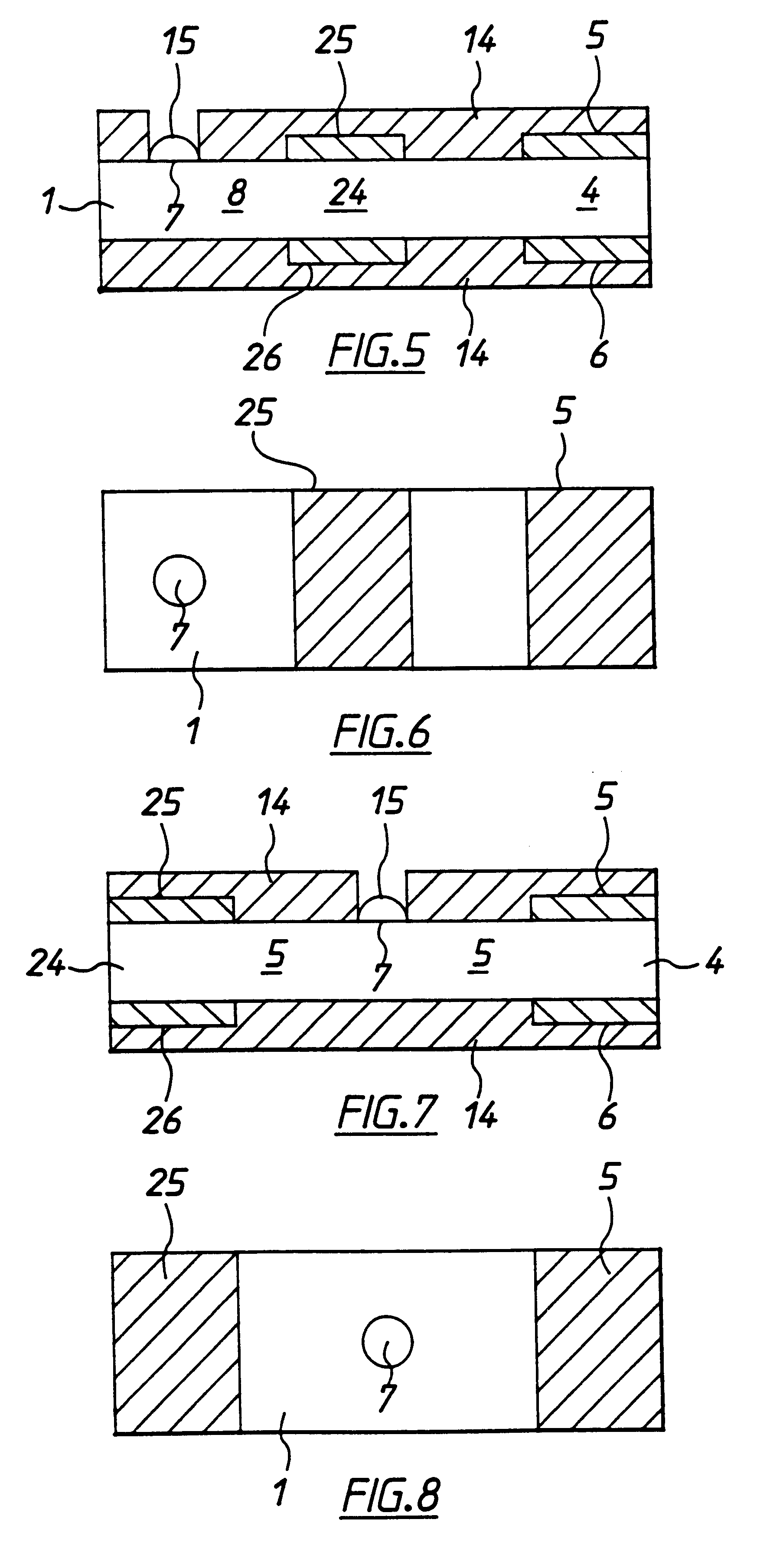
In the present invention, a thin film transistor is formed on a plastic film substrate (1) having anisotropy of thermal shrinkage rate or coefficient of thermal expansion in in-plane directions of the substrate. A channel is formed such thatthe direction (7) in which the thermal shrinkage rate or the coefficient of thermal expansion of the substrate is largest is nonparallel tothe direction (8) of a current flowing through the channel of the thin film transistor. Then, a thin film transistor having stable and uniform electrical characteristics, which is formed on the plastic film substrate, is provided.
Owner:CANON KK
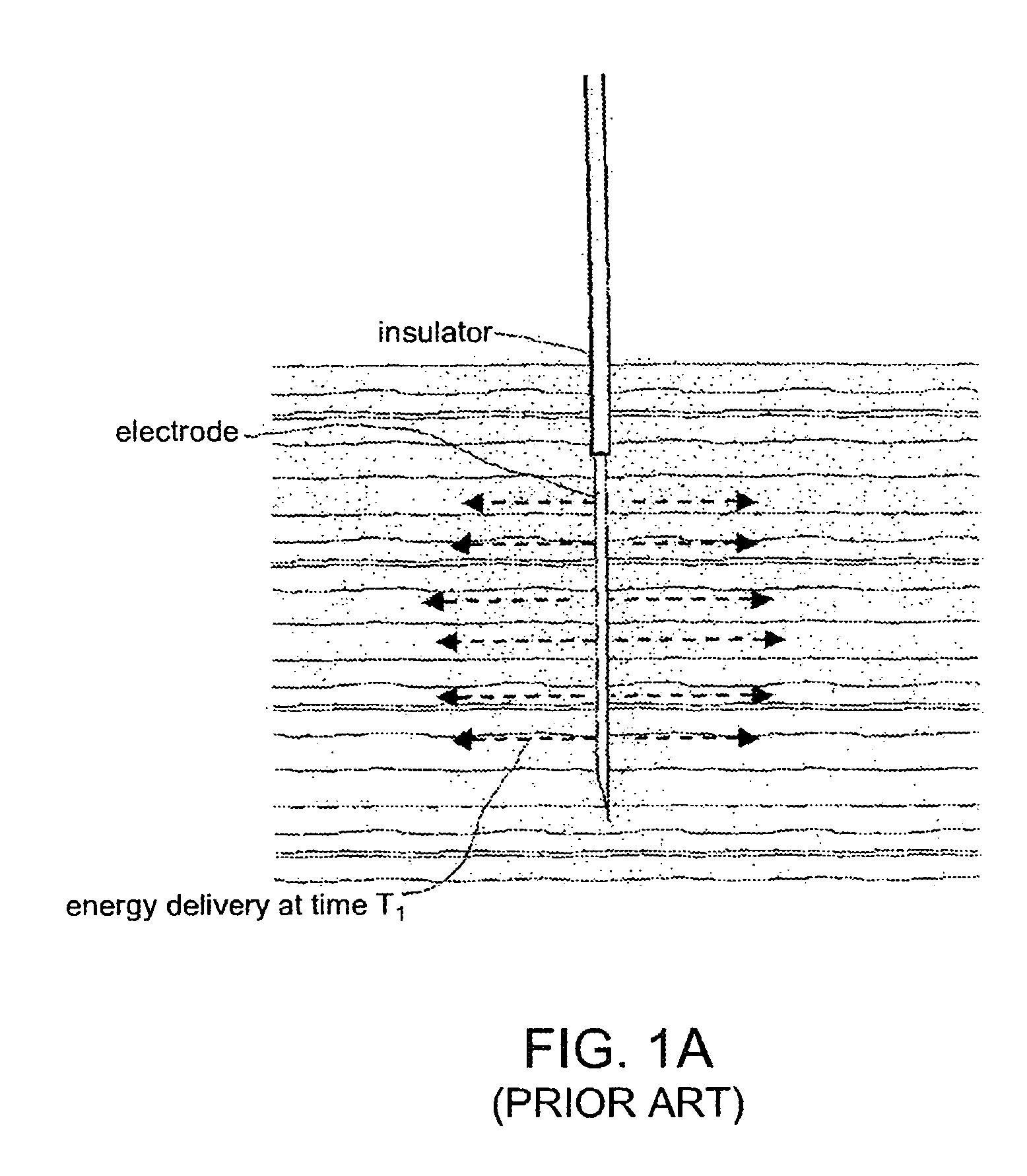
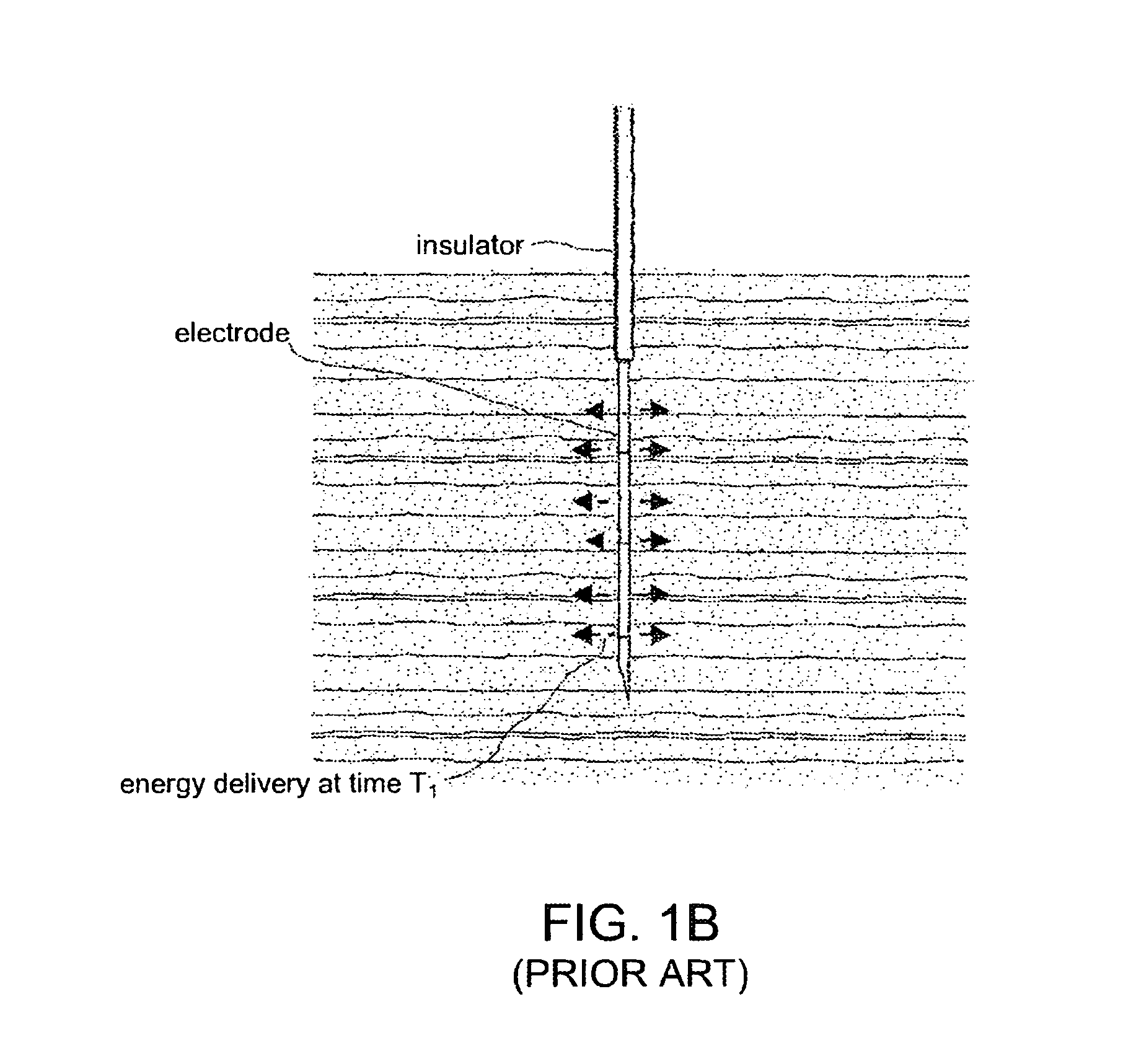
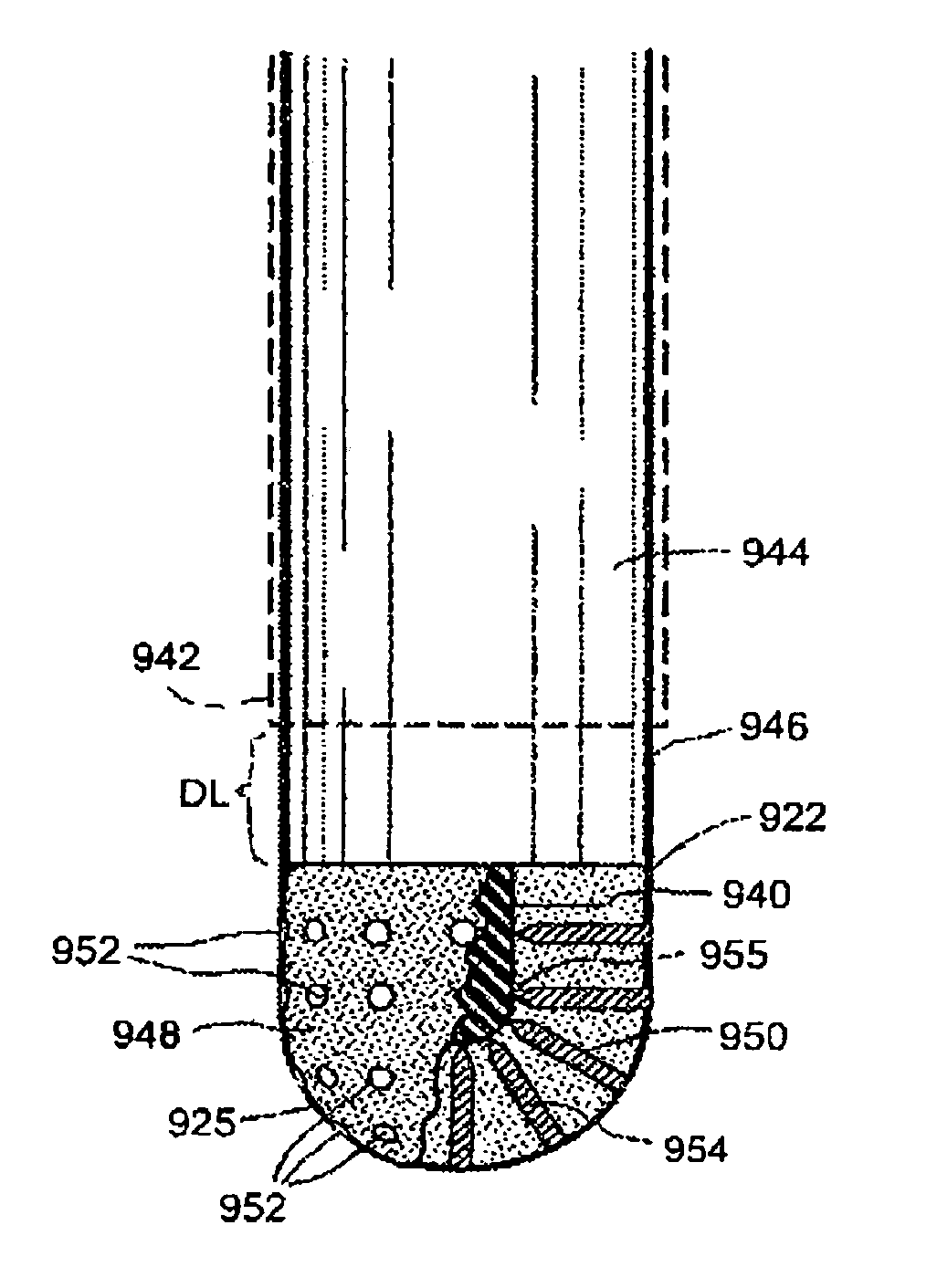
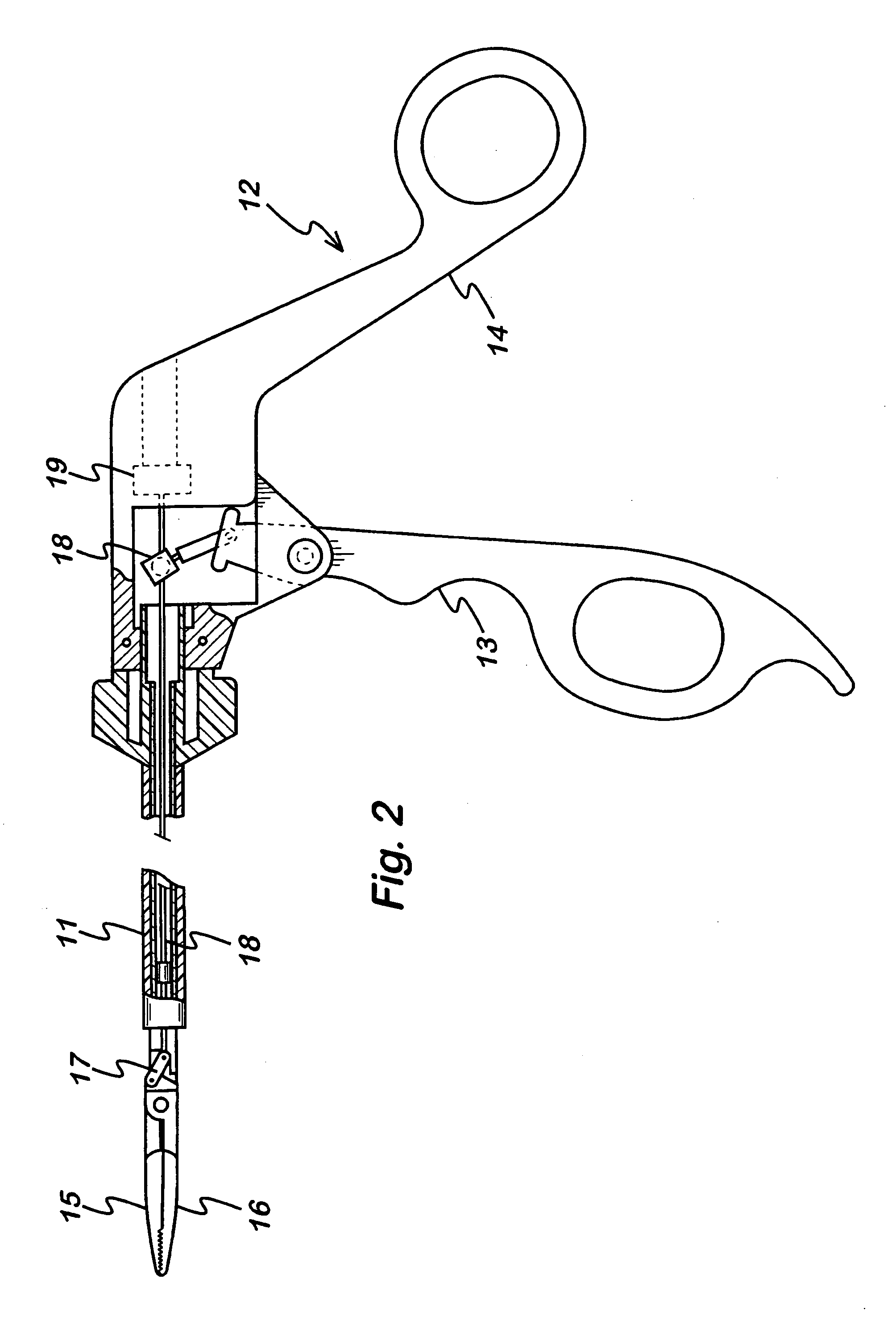
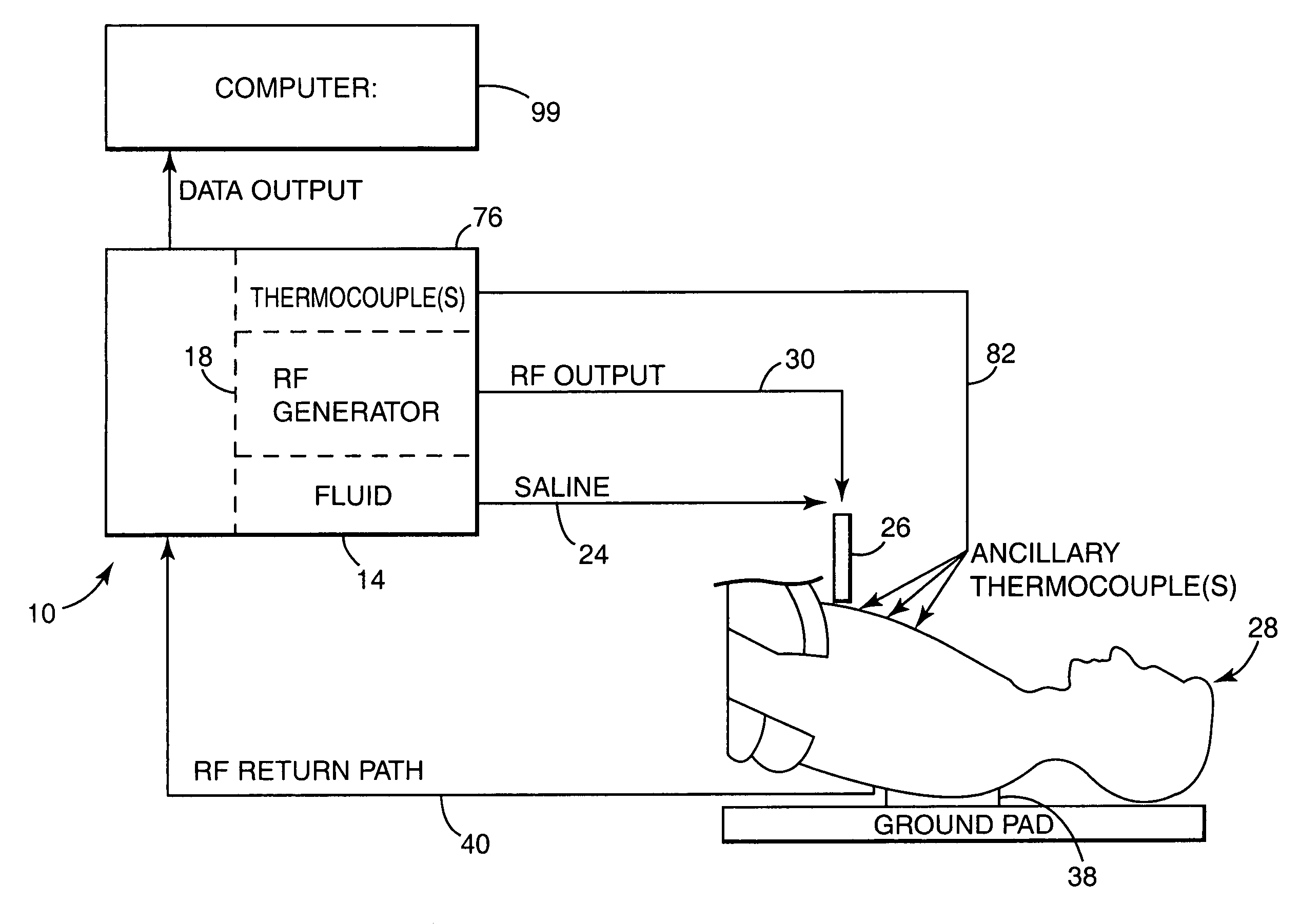
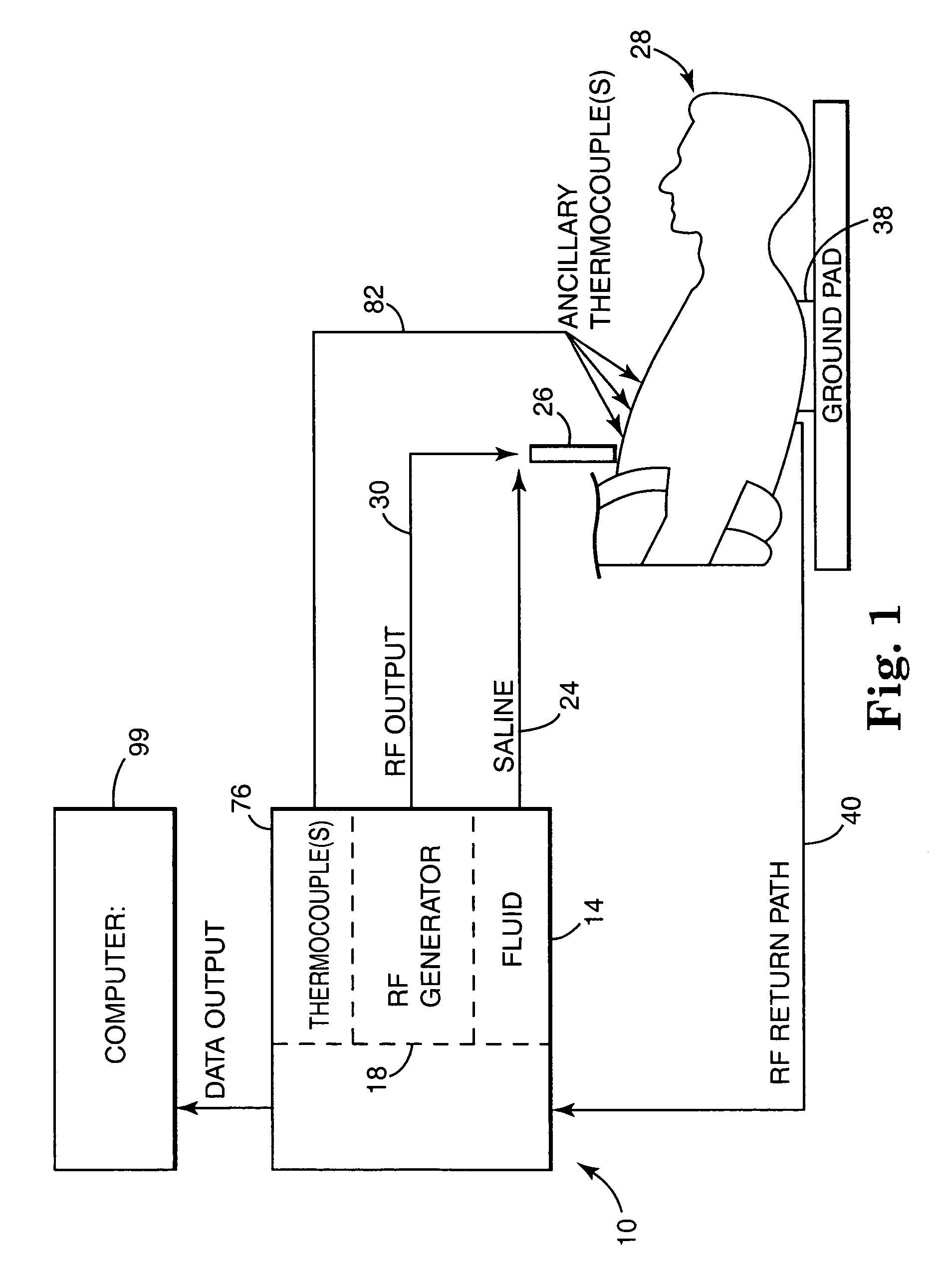
Electrosurgical working end for controlled energy delivery
InactiveUS7125409B2Prevent any substantial dehydrationEnergy efficiencySurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingElastomerEngineering
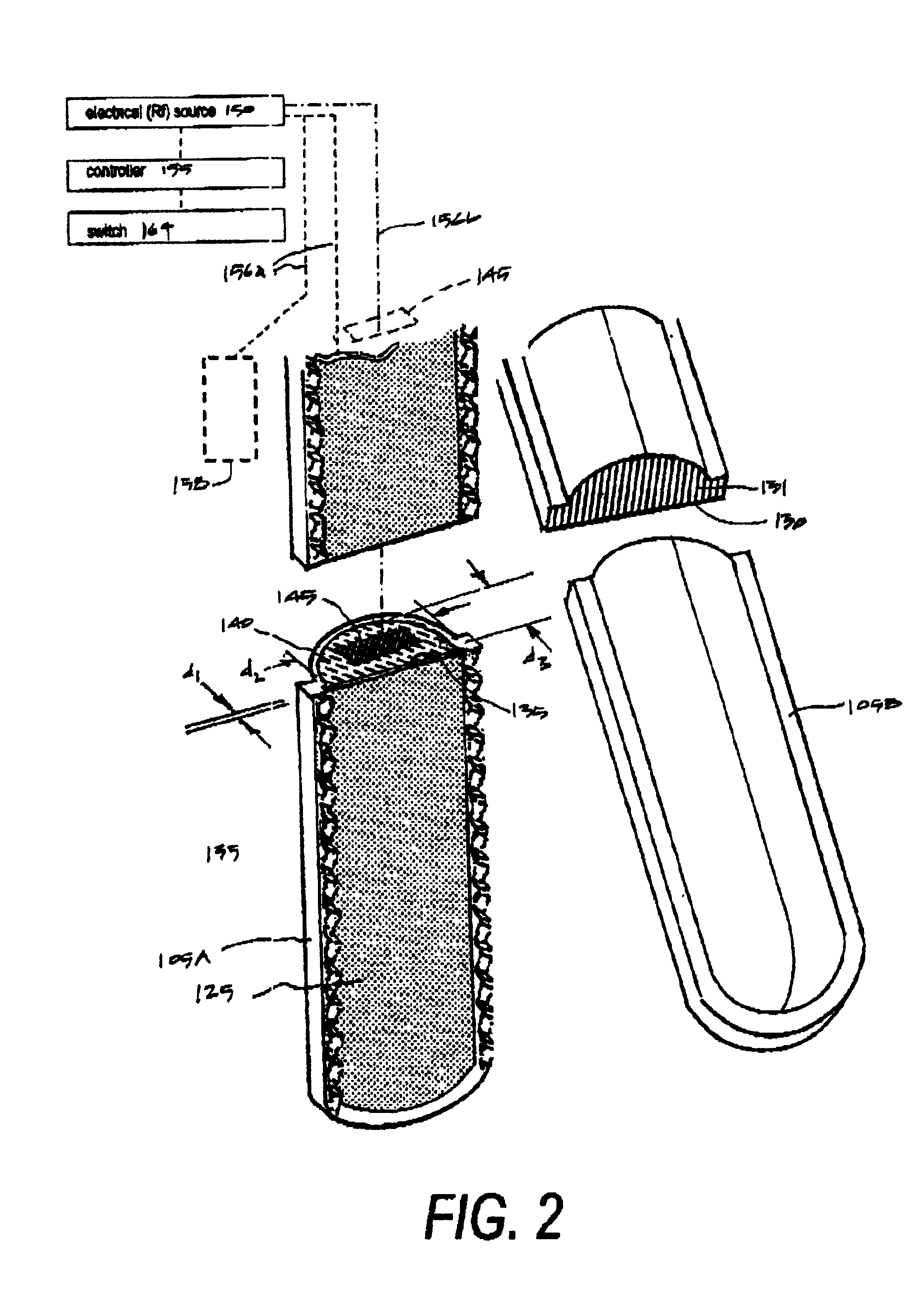
An electrosurgical working end for automatic modulation of active Rf density in a targeted tissue volume. The working end of the probe of the present invention defines a tissue-engagement surface of an elastomeric material with conductive elements that extend therethrough. In one embodiment, the expansion of the elastomeric material can de-couple the conductive elements from an interior electrode based temperature to modulate current flow. In another embodiment, the elastomeric material can couple and de-couple the conductive elements from an interior electrode based on engagement pressure to modulate current flow
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Electrosurgical jaw structure for controlled energy delivery
InactiveUS6929644B2Prevent any substantial dehydrationEnergy efficiencySurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsThermal energyConductive materials
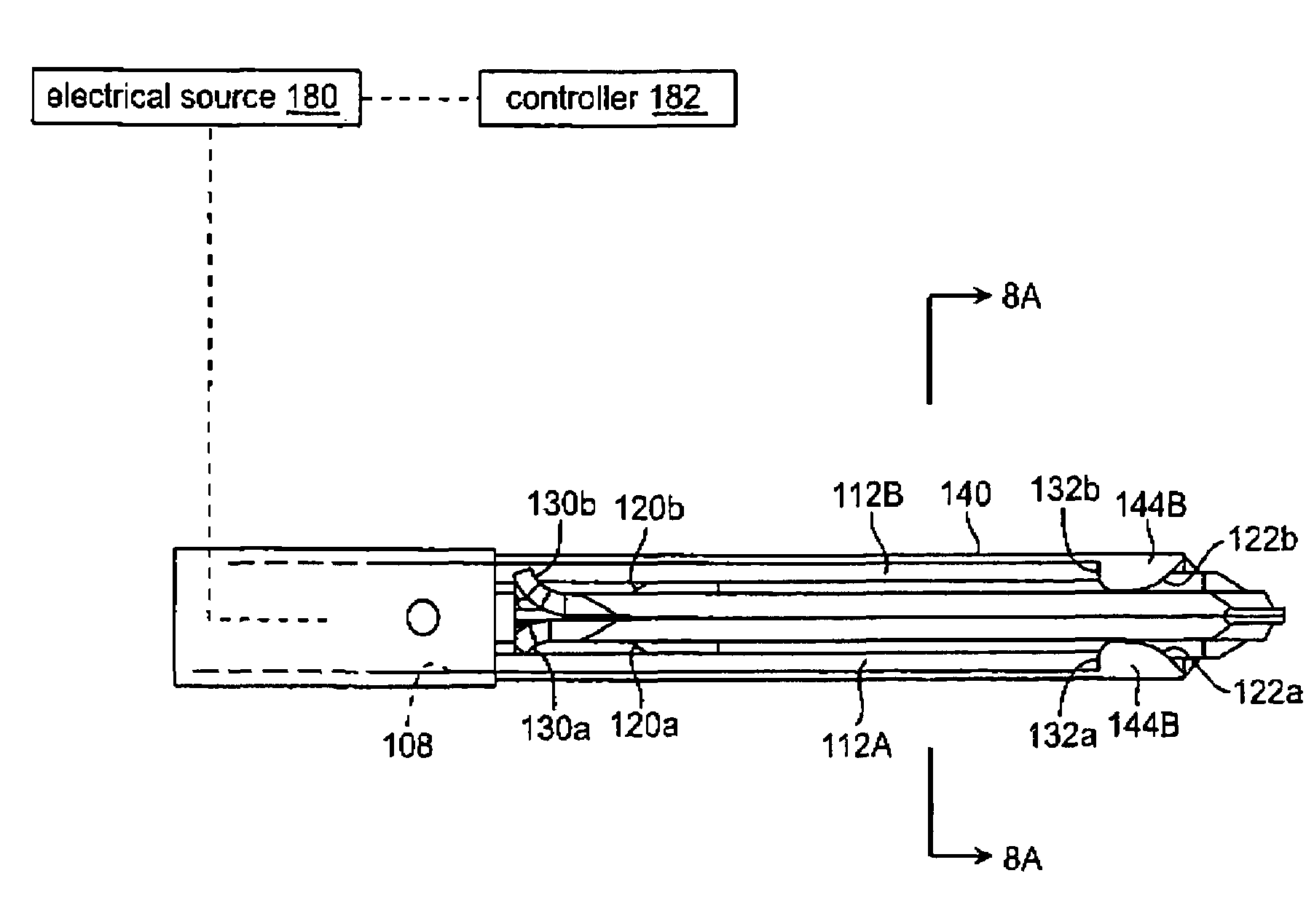
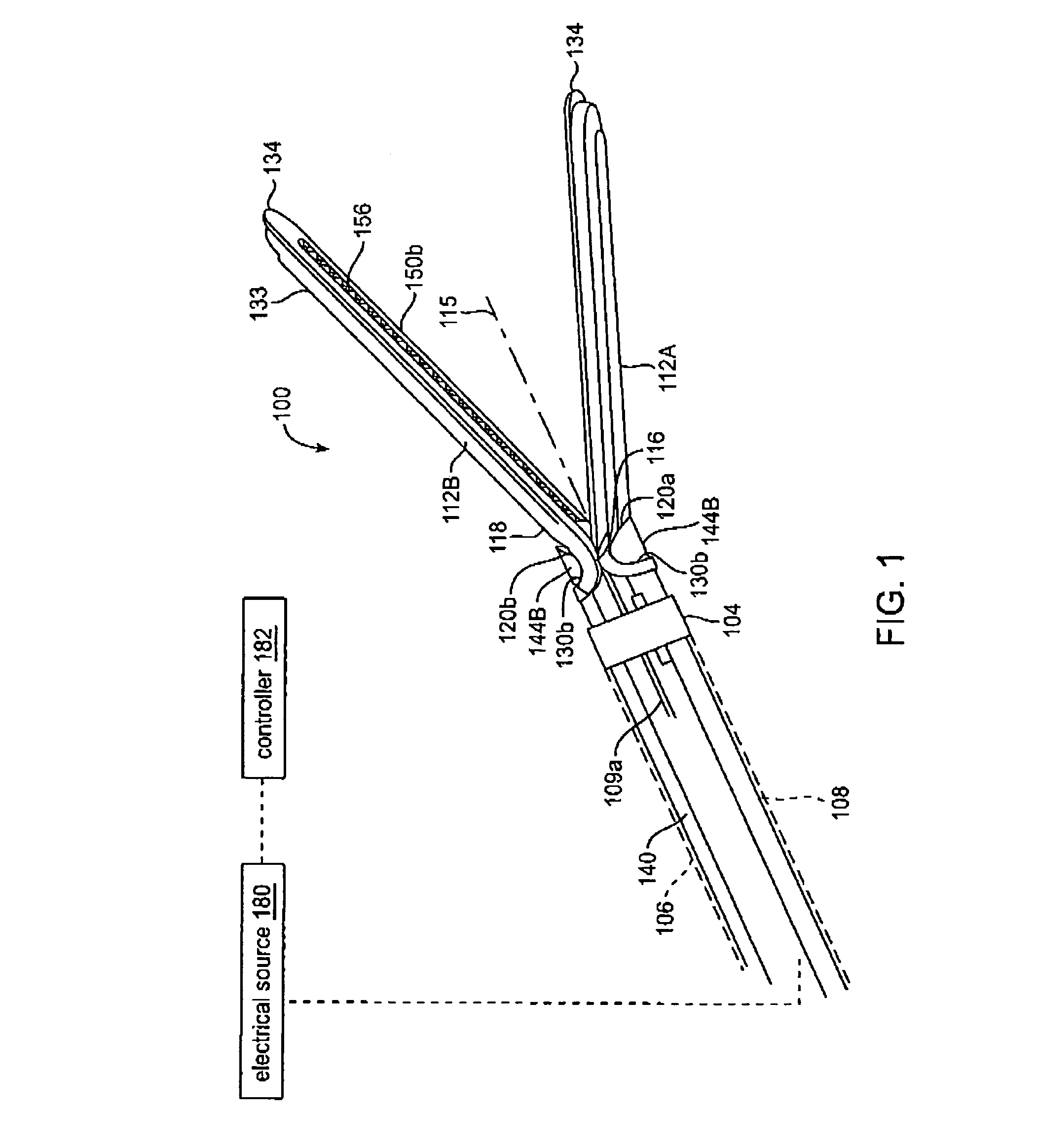
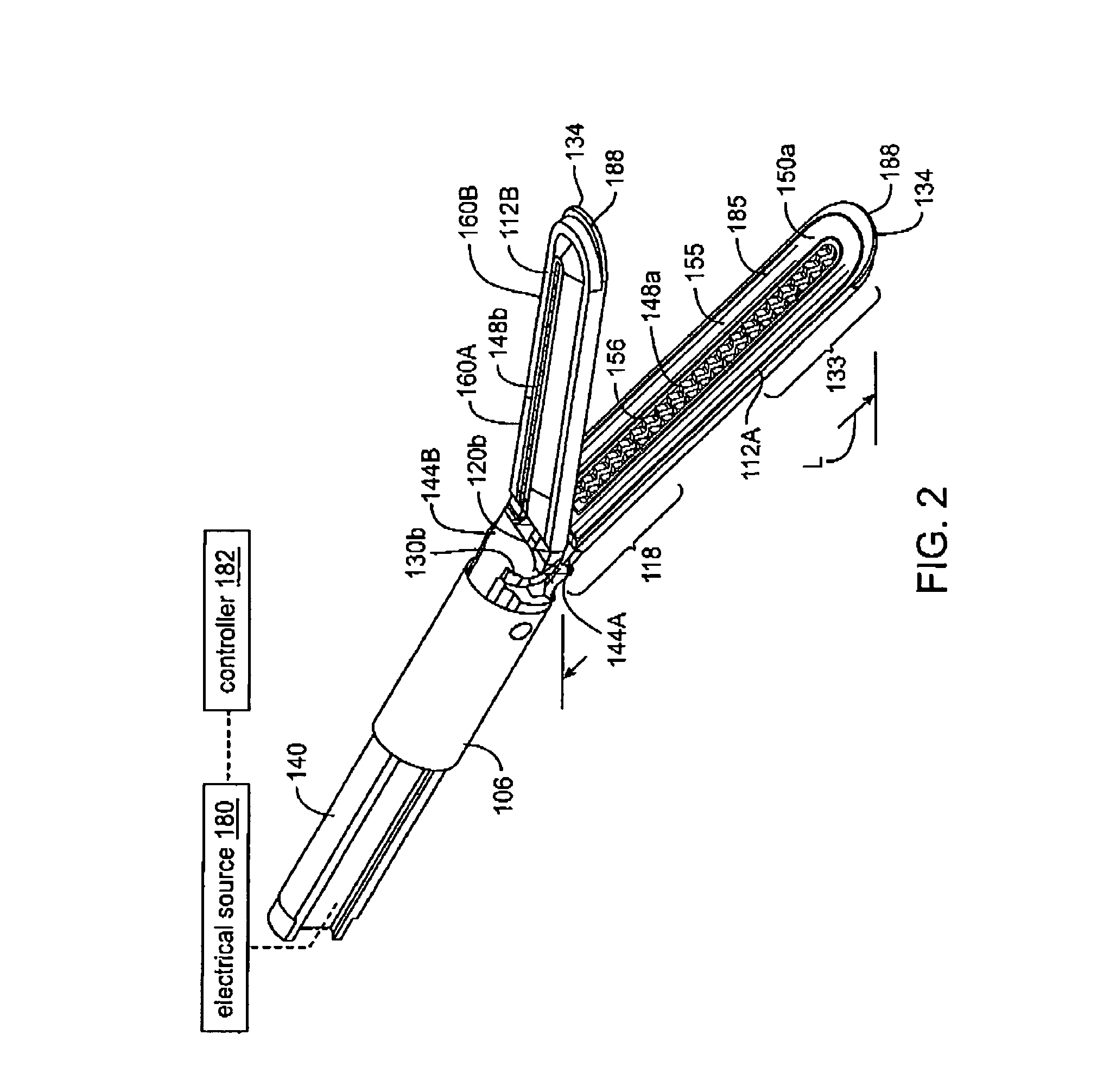
A working end of a surgical instrument that carries first and second jaws for delivering energy to tissue. In a preferred embodiment, at least one jaw of the working end defines a tissue-engagement plane that contacts the targeted tissue. The cross-section of the engagement plane reveals that it defines a surface conductive portion that overlies a variably resistive matrix of a temperature-sensitive resistive material or a pressure-sensitive resistive material. An interior of the jaw carries a conductive material or electrode that is coupled to an Rf source and controller. In an exemplary embodiment, the variably resistive matrix can comprise a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) material, such as a ceramic, that is engineered to exhibit a dramatically increasing resistance (i.e., several orders of magnitude) above a specific temperature of the material. In use, the engagement plane will apply active Rf energy to captured tissue until the point in time that the variably resistive matrix is heated to its selected switching range. Thereafter, current flow from the conductive electrode through the engagement surface will be terminated due to the exponential increase in the resistance of variably resistive matrix to provide instant and automatic reduction of Rf energy application. Further, the variably resistive matrix can effectively function as a resistive electrode to thereafter conduct thermal energy to the engaged tissue volume. Thus, the jaw structure can automatically modulate the application of energy to tissue between active Rf heating and passive conductive heating of captured tissue to maintain a target temperature level.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
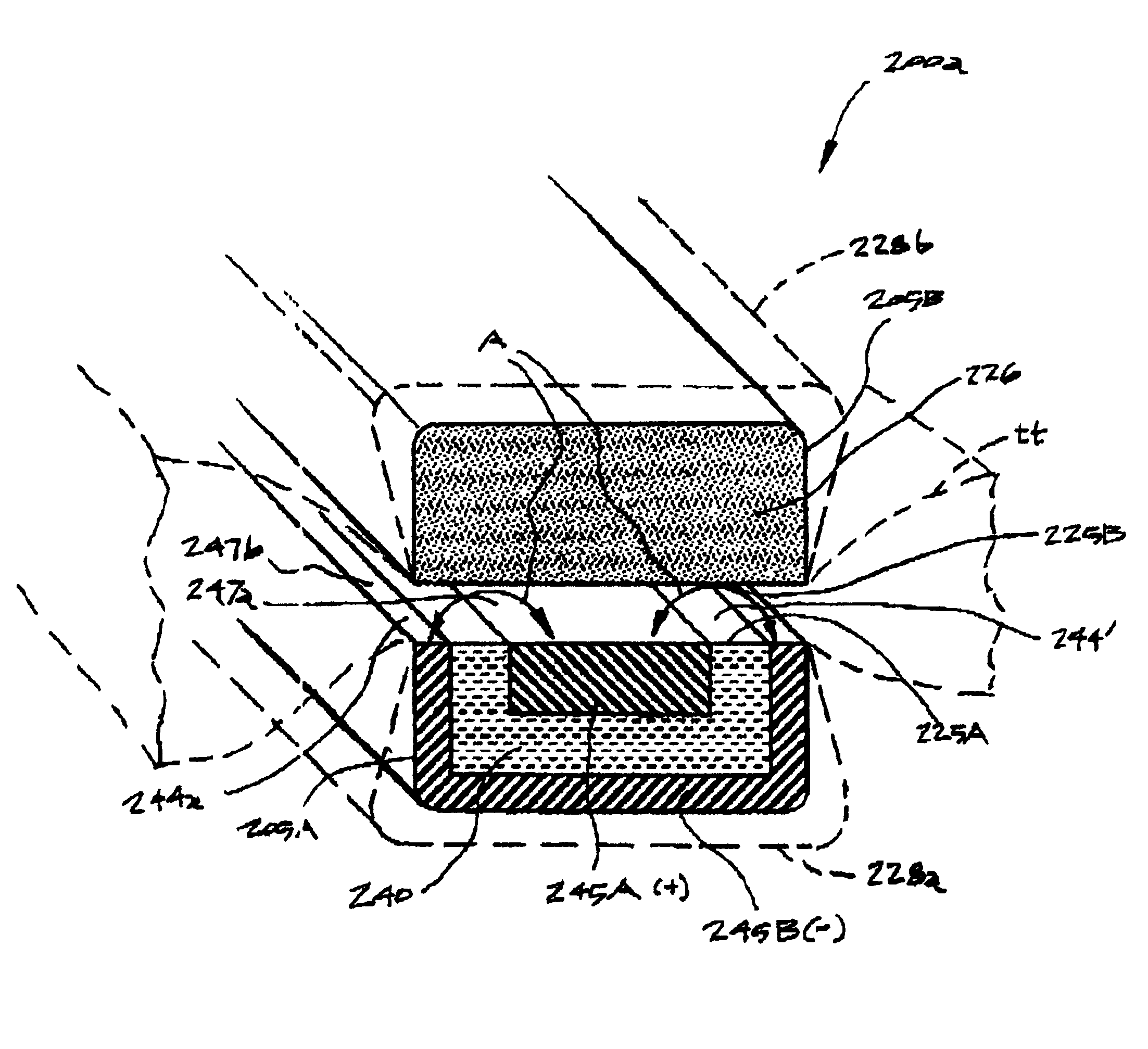
Jaw structure for electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7011657B2Improve the immunityEfficient weldingElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingTissue heatingVolumetric Mass Density
An electrosurgical medical device and technique for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue that provides very high compressive forces. In one exemplary embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying first and second surface portions that comprise (i) an electrically conductive material and (ii) a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) material having a selected increased resistance that differs at each selected increased temperature over a targeted treatment range. One type of PTC material is a doped ceramic that can be engineered to exhibit a selected positively sloped temperature-resistance curve over about 37° C. to 100° C. The 70° C. to 100° C. range can bracket a targeted “thermal treatment range” at which tissue welded can be accomplished. The engineered resistance of the PTC matrix at the upper end of the temperature range will terminate current flow through the matrix. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane cause ohmic heating within tissue from Rf energy delivery tissue PTC matrix is heated to exceed the treatment range. Thereafter, energy density in the engaged tissue will be modulated as the conductivity of the second portion hovers within the targeted treatment range to thereby provide optical tissue heating for purposes of tissue welding.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
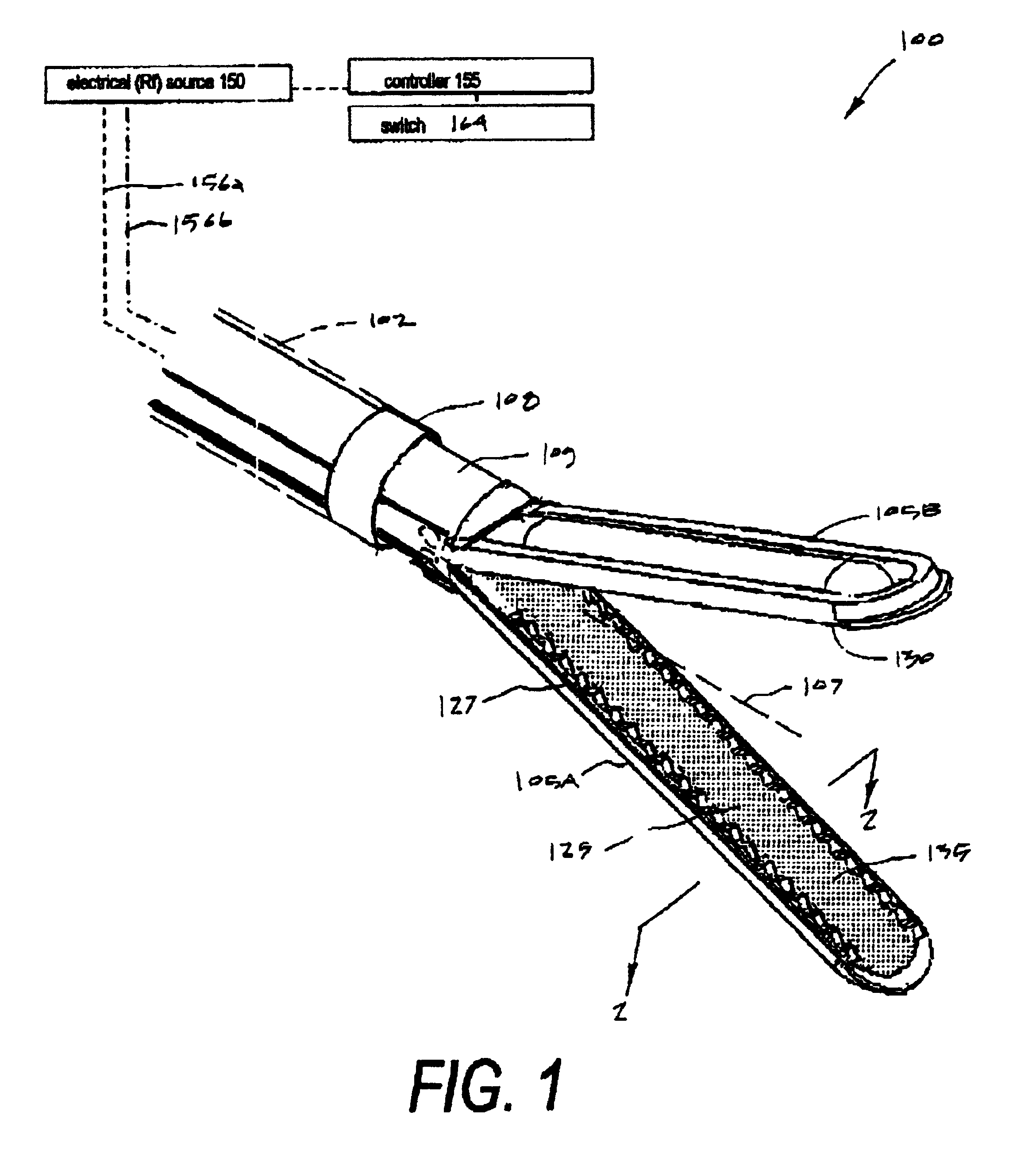
Electrosurgical working end for controlled energy delivery
InactiveUS7070597B2Prevent any substantial dehydrationEnergy efficiencySurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsElastomerVolumetric Mass Density
An electrosurgical working end for automatic modulation of active Rf density in a targeted tissue volume. The working end of the probe of the present invention defines a tissue-engagement surface of an elastomeric material with conductive elements that extend therethrough. In one embodiment, the expansion of the elastomeric material can de-couple the conductive elements from an interior electrode based temperature to modulate current flow. In another embodiment, the elastomeric material can couple and de-couple the conductive elements from an interior electrode based engagement pressure to modulate current flow.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
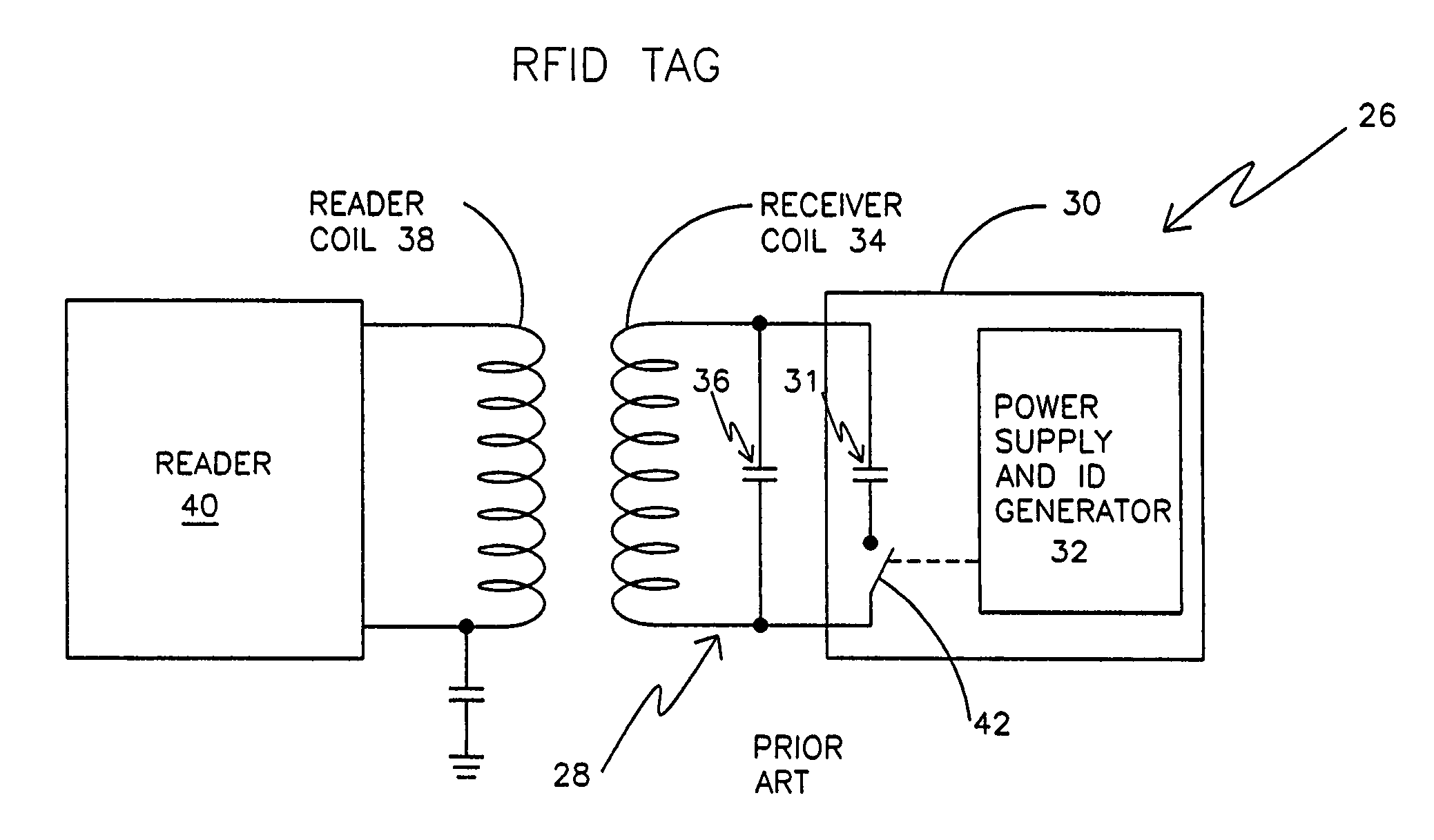
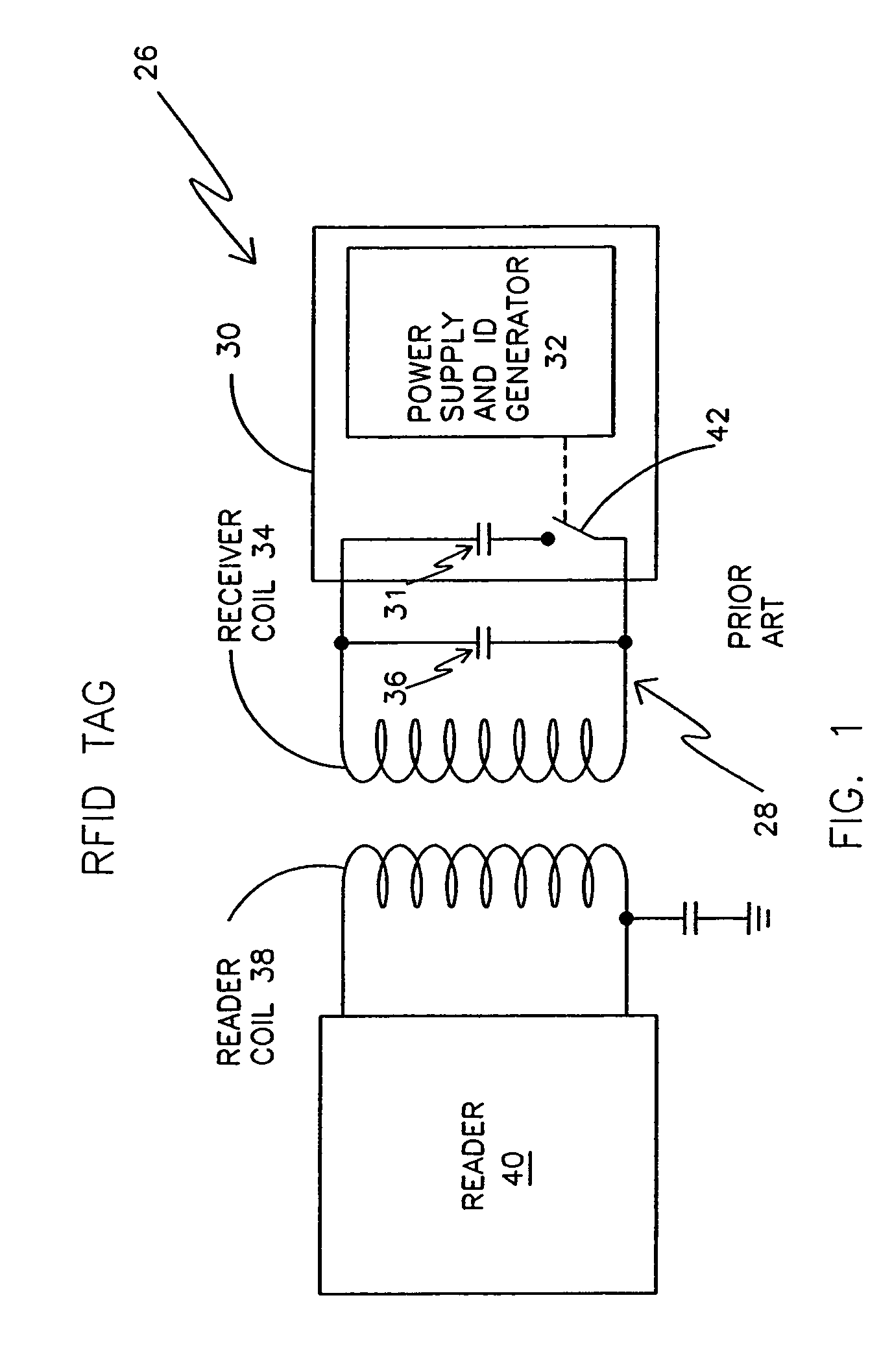
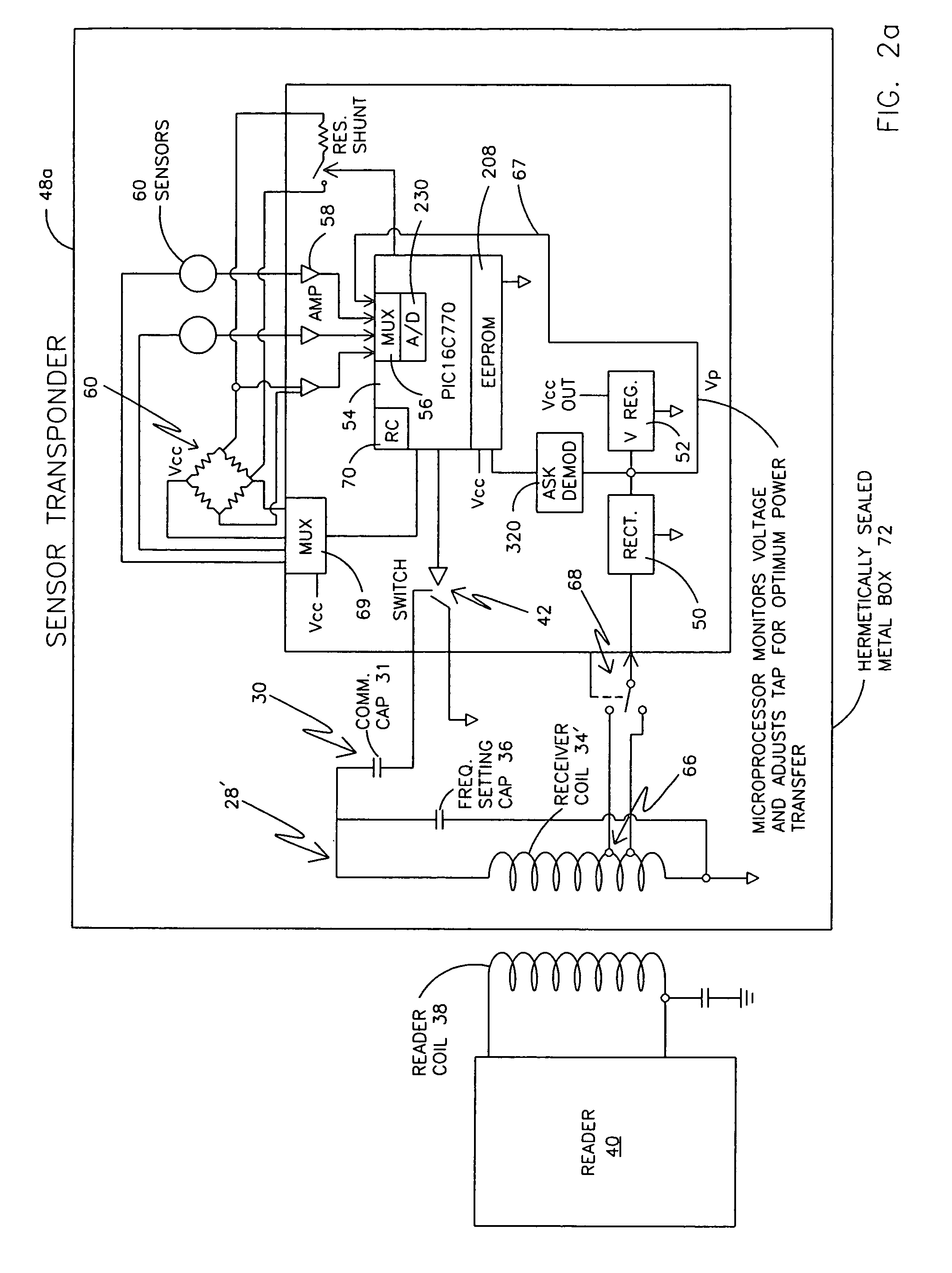
Remotely powered and remotely interrogated wireless digital sensor telemetry system
ActiveUS7256695B2More powerElectric signal transmission systemsElectrotherapyElectronic systemsPower flow
An electronic system includes a reader and a remotely powered and remotely interrogated sensor transponder. The sensor transponder includes a coil or an antenna, a switched reactance circuit, a processor, and a sensor. The sensor transponder receives power radiated from the reader to the coil or antenna. The sensor uses the power for sensing. The sensor transponder is capable of processing sensor data in the processor and transmitting the sensor data to the reader using the switched reactance circuit. In one embodiment, the receiver coil or antenna is part of a resonant tank circuit which includes an impedance matching circuit. The impedance matching circuit is connected to the receiver coil or antenna to provide greater current to the sensor or other power-using device than would be available to the sensor or other power-using device if the sensor or other power-using device were connected between the first and second end. The impedance matching circuit can be two or more taps to the coil or antenna.
Owner:LORD CORP
Surgical instrument
An electrosurgical instrument for use in cutting and / or coagulating tissue includes a dielectric material, the dielectric material being positioned in the current pathway between the tissue-treatment regions of first and second electrodes. This can be achieved by providing one or more electrode surfaces coated with a dielectric material having a reactive impedance of less than 3,000 ohms / sq. mm. at 450 kHz. The dielectric coating acts to couple the RF signal into the tissue primarily by capacitive coupling, providing a more even heating of the tissue and the elimination of “hot spot”. Examples of electrosurgical instruments employing such coated electrodes include forceps, scissors or scalpel blade instruments.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Apparatus and method for creating, maintaining, and controlling a virtual electrode used for the ablation of tissue
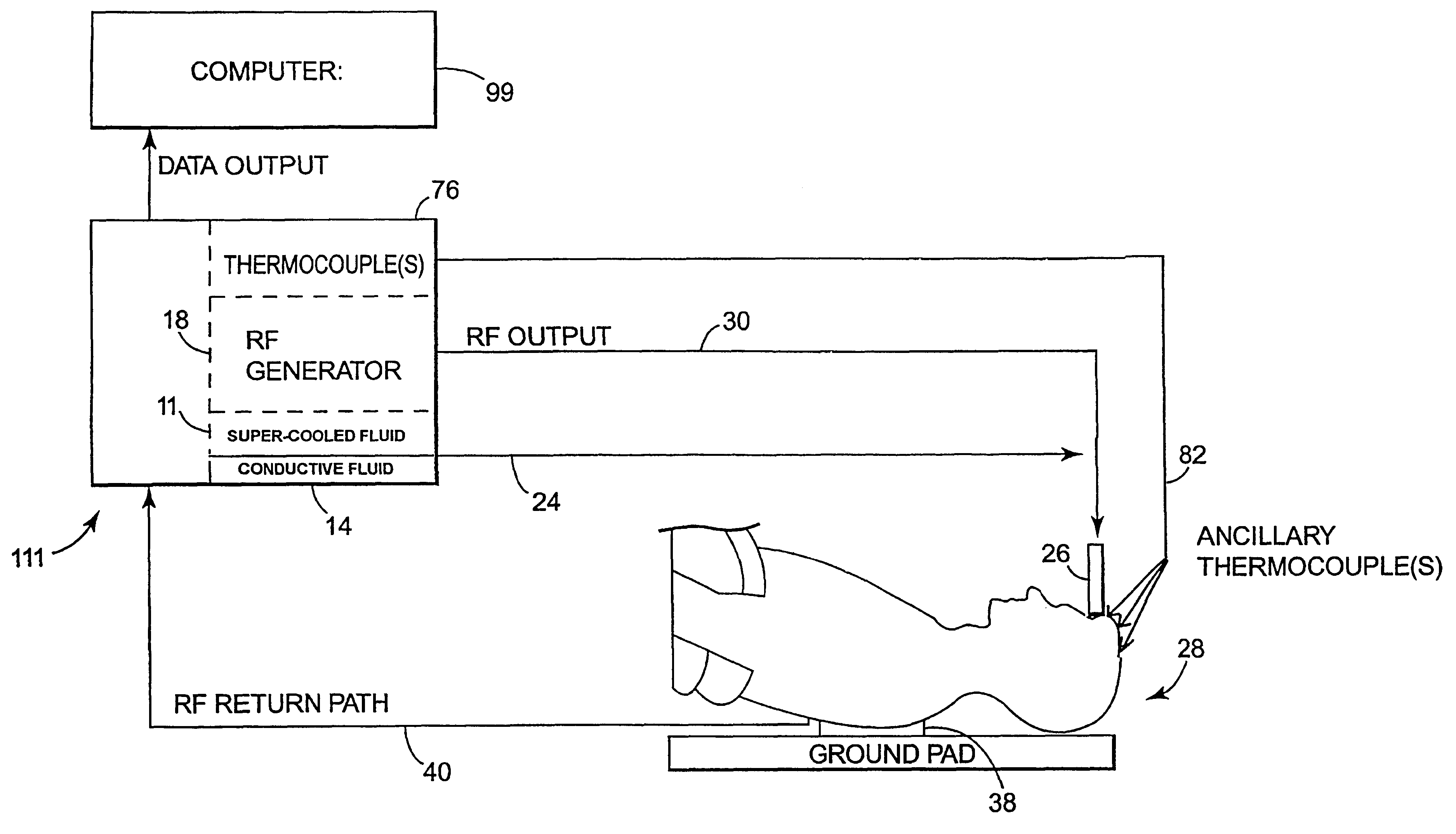
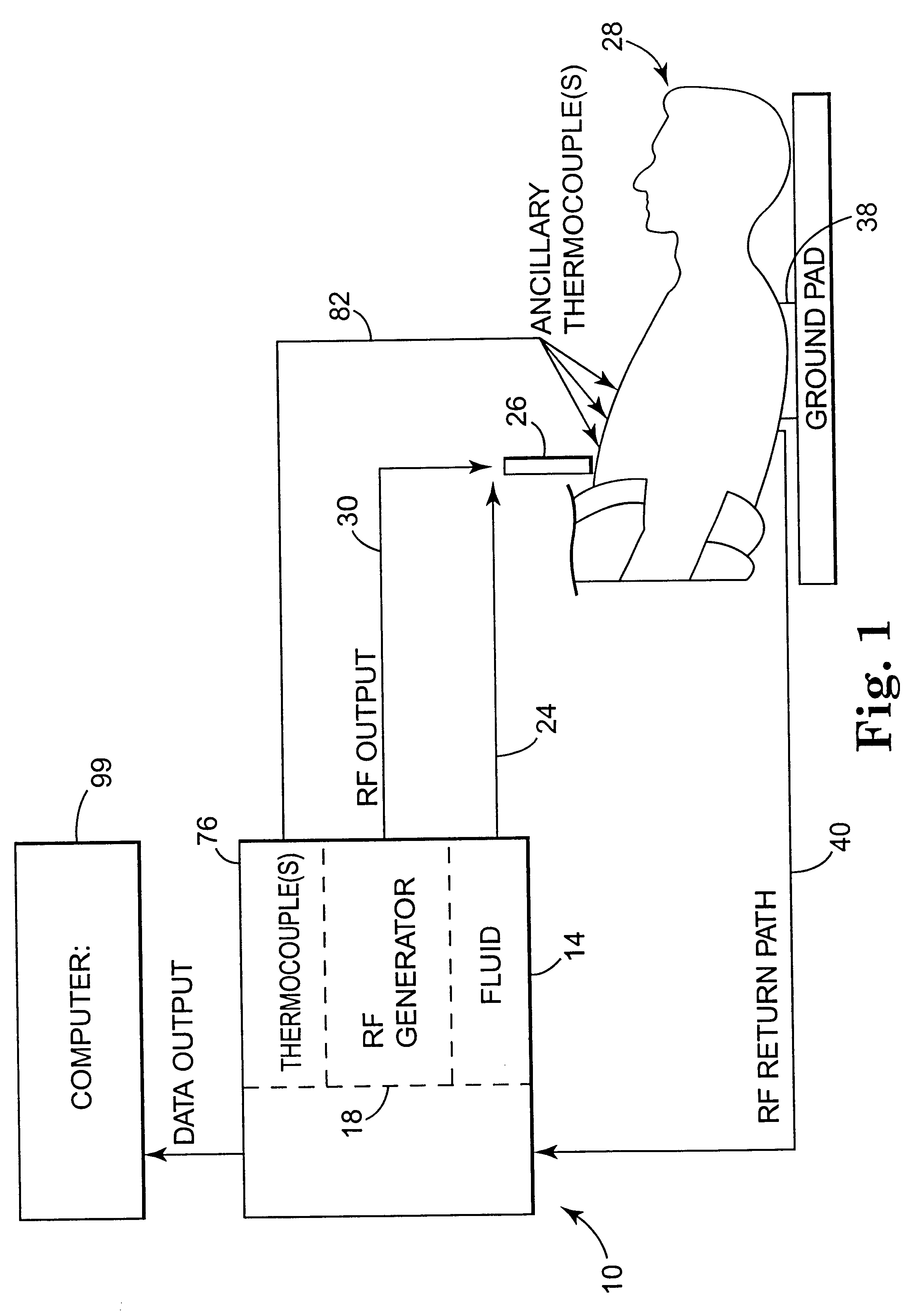
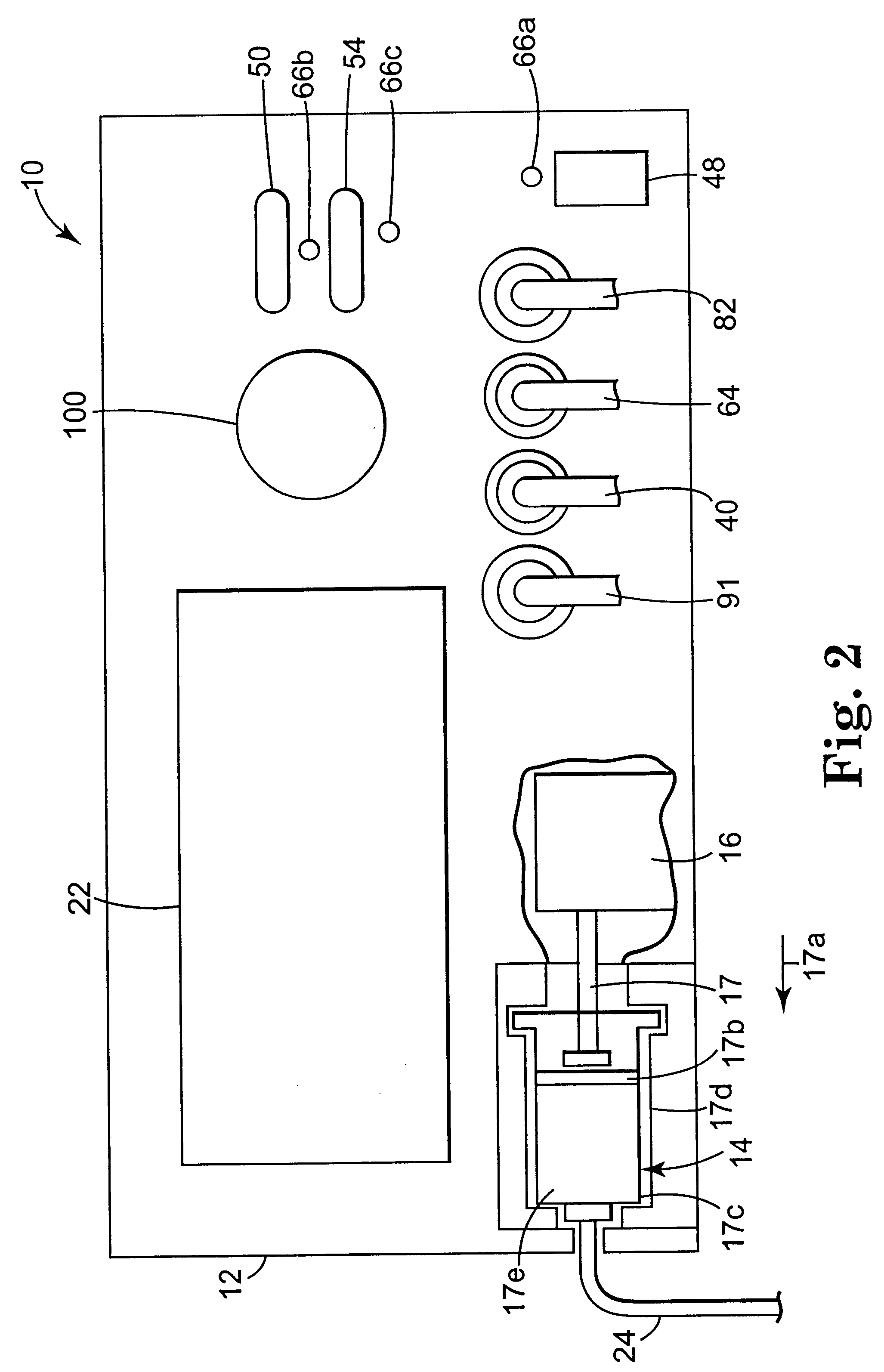
InactiveUS6537272B2Improving impedanceReduce the possibilitySurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingBlood Vessel TissueVascular tissue
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for producing a virtual electrode within or upon a tissue to be treated with radio frequency alternating electric current, such tissues including but not limited to brain, liver, cardiac, prostate, breast, and vascular tissues and neoplasms. An apparatus in accordance with the present invention includes a source of super-cooled fluid for selectively providing super-cooled fluid to the target tissue to cause a temporary cessation of cellular or electrical activity, a supply of conductive or electrolytic fluid to be provided to the target tissue, and alternating current generator, and a processor for creating, maintaining, and controlling the ablation process by the interstitial or surficial delivery of the fluid to a tissue and the delivery of electric power to the tissue via the virtual electrode. A method in accord with the present invention includes delivering super-cooled fluid to the target tissue to cause a temporary cessation of cellular or electrical activity, evaluating whether the temporary cessation of cellular or electrical activity is the desired cessation of cellular or electrical activity, and if so, delivering a conductive fluid to the predetermined tissue ablation site for a predetermined time period, applying a predetermined power level of radio frequency current to the tissue, monitoring at least one of several parameters, and adjusting either the applied power and / or the fluid flow in response to the measured parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Electrochemical cell
InactiveUS6284125B1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectricityDiffusion
A method for determining the concentration of a reduced (or oxidised) form of a redox species in an electrochemical cell of the kind comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode spaced from the working electrode by a predetermined distance, said method comprising the steps of: (1) applying an electric potential difference between the electrodes; (2) selecting the potential of the working electrode such that the rate of electro-oxidation of the reduced form (or electro-reduction of the oxidised form) of the species is diffusion controlled, (3) selecting the spacing between the working electrode and the counter electrode so that reaction products from the counter electrode arrive at the working electrode; (4) determining current as a function of time after application of the potential and prior to achievement of a steady state; (5) estimating the magnitude of the steady state current, and (6) obtaining from the change in current with time and the magnitude of the steady state current, a value indicative of the diffusion coefficient and / or of the concentration of the reduced form (or the oxidised form) of the species. Also disclosed is an apparatus for determining the concentration of a redox species in an electrochemical cell comprising: an electrochemical cell having a working electrode and a counter (or counter / reference) electrode, means for applying and electric potential difference between said electrodes, means for measuring the change in current with time, and characterised in that the working electrode is spaced from the counter electrode by less than 500 mum.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Tissue electroperforation for enhanced drug delivery
The present invention relates to a method and a device for transporting a molecule through a mammalian barrier membrane of at least one layer of cells comprising the steps of: ablating the membrane with an electric current from a treatment electrode; and utilizing a driving force to move the molecule through the perforated membrane.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
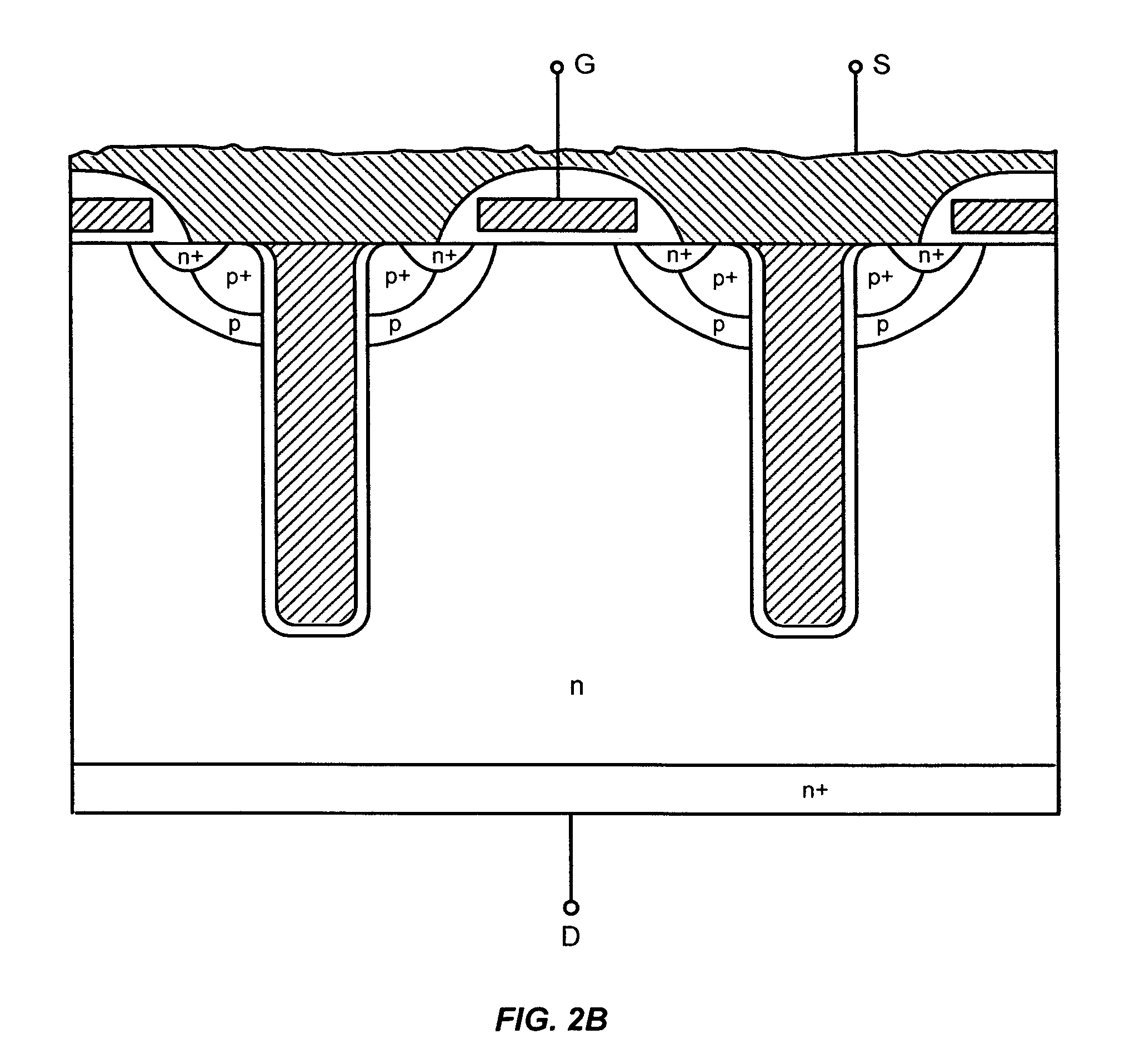
ActiveUS20050167742A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh voltage
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Surgical machine and method for controlling and/or regulating a surgical machine
ActiveUS7362062B2Guaranteed uptimeEasy to startElectronic commutation motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlMotor controllerControl theory
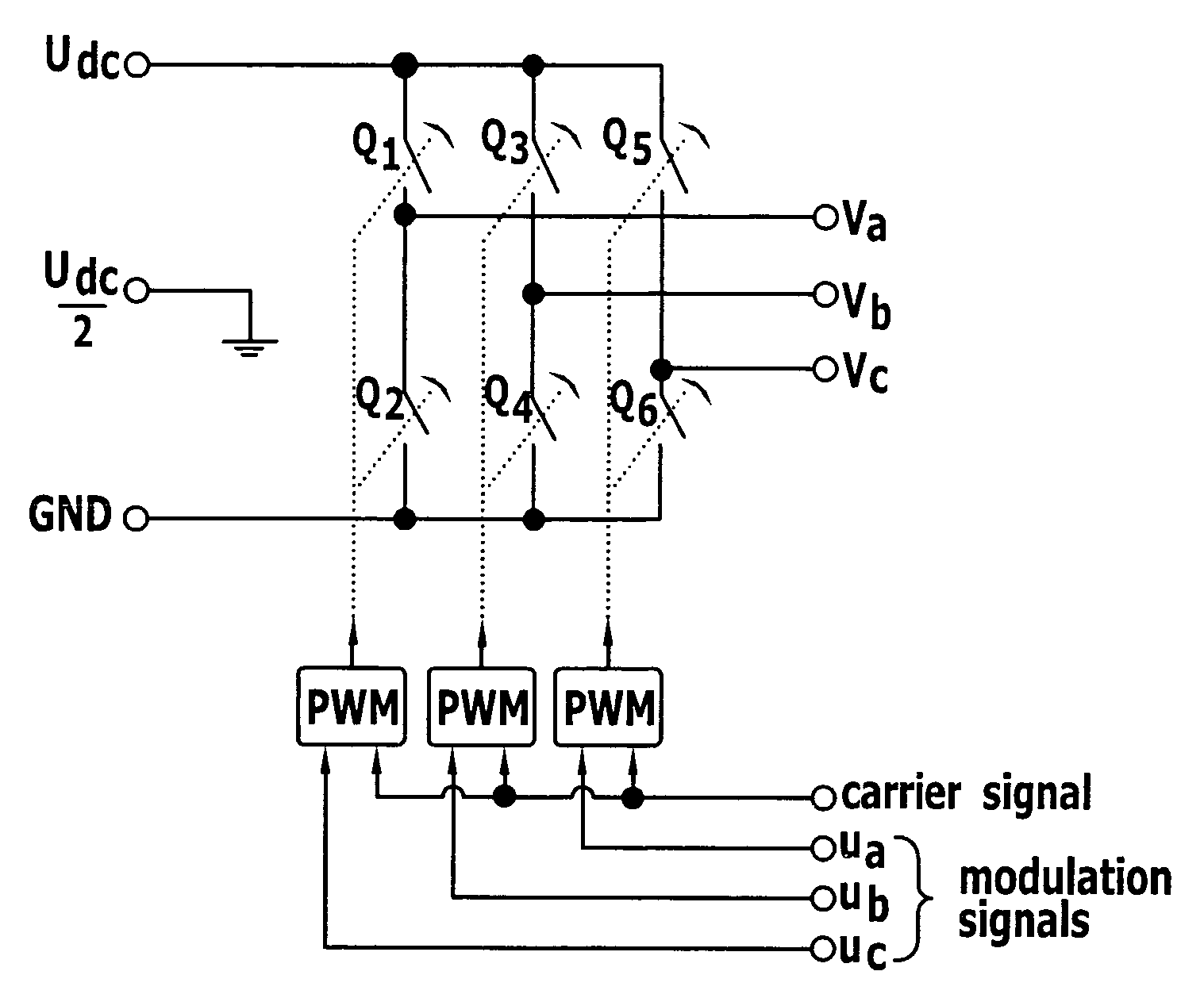
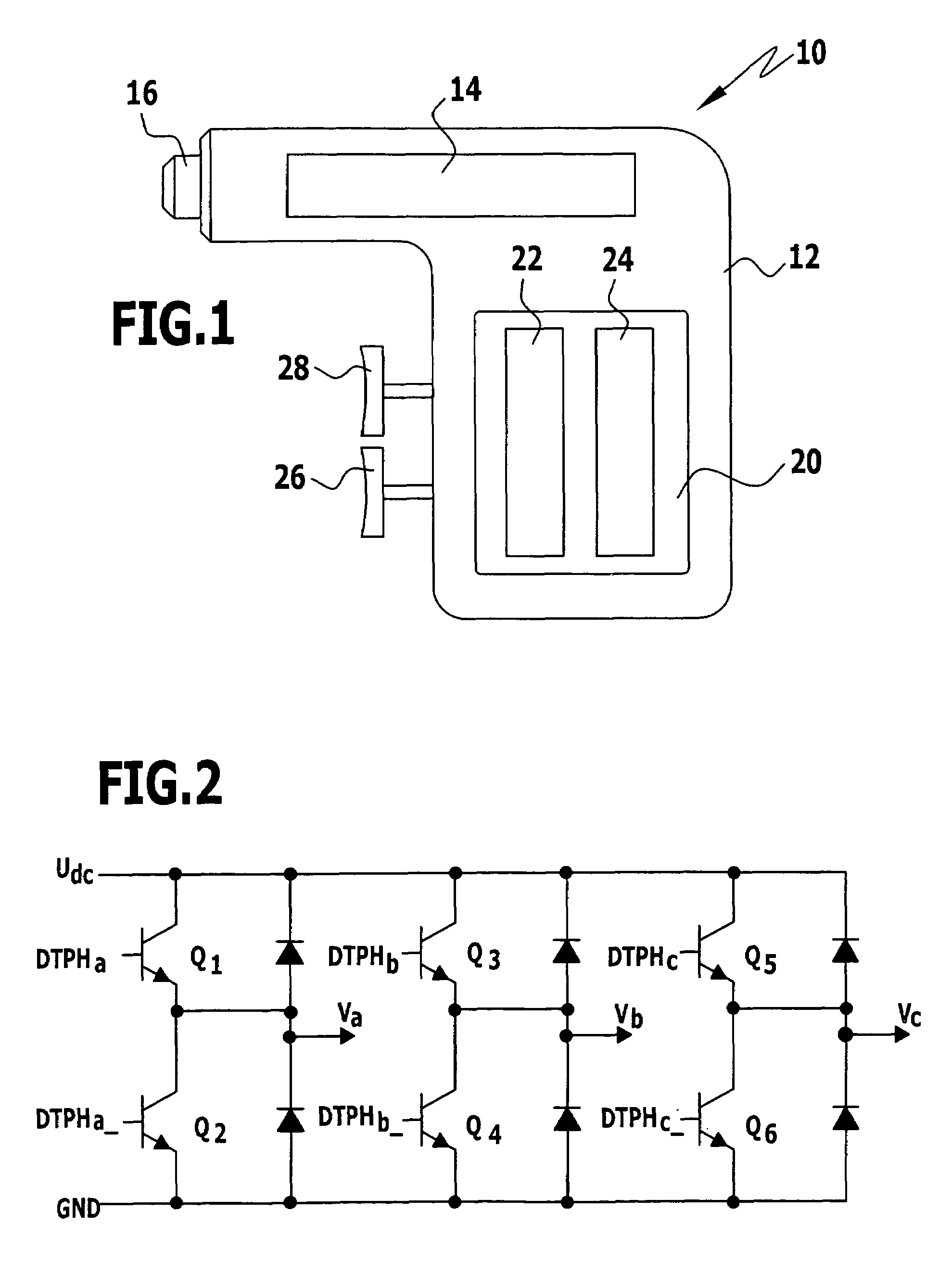
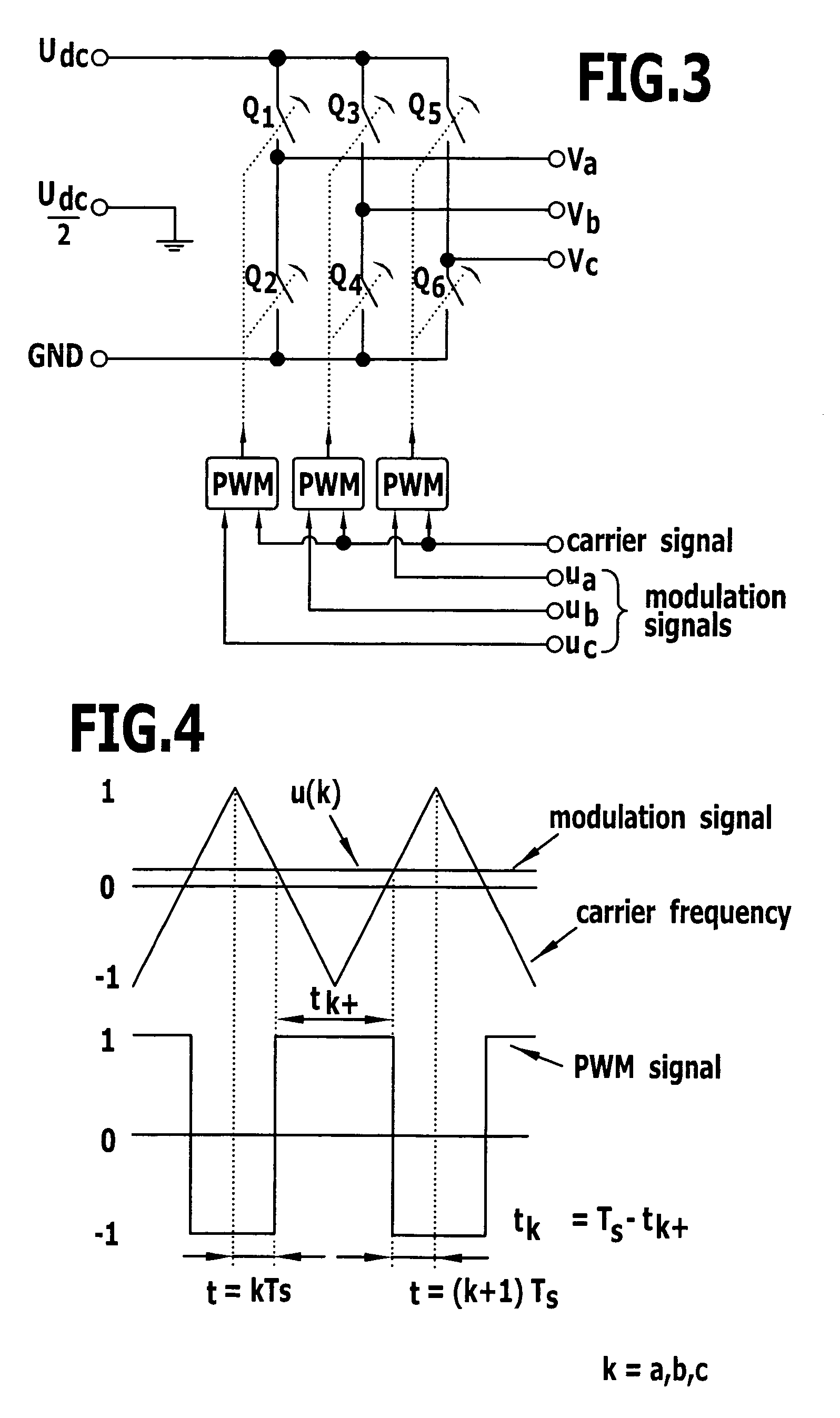
To improve a surgical machine with a sensorless electric motor comprising a rotor and at least two motor windings, and with a motor controller for controlling and / or regulating the electric motor, so that the electric motor is operable with optimum efficiency at low rotational speeds and a starting of the motor in accordance with the purpose, also under load, is enabled, it is proposed that a space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) method for controlling and / or regulating the electric motor, in which all motor windings are able to be simultaneously supplied with electric current, be performable with the motor controller. A method for controlling and / or regulating a surgical machine is also proposed.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Apparatus and method for creating, maintaining, and controlling a virtual electrode used for the ablation of tissue
InactiveUS7169144B2Maintain temperatureImproving impedanceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesBlood Vessel TissueVascular tissue
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for producing a virtual electrode within or upon a tissue to be treated with radio frequency alternating electric current, such tissues including but not limited to liver, lung, cardiac, prostate, breast, and vascular tissues and neoplasms. An apparatus in accord with the present invention includes a supply of a conductive or electrolytic fluid to be provided to the patient, an alternating current generator, and a processor for creating, maintaining, and controlling the ablation process by the interstitial or surficial delivery of the fluid to a tissue and the delivery of electric power to the tissue via the virtual electrode. A method in accord with the present invention includes delivering a conductive fluid to a predetermined tissue ablation site for a predetermined time period, applying a predetermined power level of radio frequency current to the tissue, monitoring at least one of several parameters, and adjusting either the applied power and / or the fluid flow in response to the measured parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Minimally-invasive system and method for monitoring analyte levels
InactiveUS6952604B2Improve responseImprove signal and performanceCatheterSensorsAnalyteStratum corneum
A minimally-invasive analyte detecting device and method for using the same. The system and method employ a device having an active electrode optionally coated with a substance, and a counter-electrode that is configured at least partially surround the active electrode. The configuration of the auxiliary electrode and active electrode improves the current flow through the device and increases the sensitivity of the device. When the device is placed against the patient's skin, the active electrode is adapted to enter through the stratum corneum of a patient to a depth less than a depth in the dermis at which nerve endings reside. An electric potential is applied to the active electrode and the analyte level is determined based on the amount of current or charge flowing through the device.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Position sensing and detection of skin impedance
ActiveUS7756576B2Improve accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringLiving bodyMoisture
Apparatus and methods are provided for determining in near realtime the position of a probe placed within a living body. Electric currents are driven between one or more electrodes on the probe and electrodes placed on the body surface. The impedance between the probe and each of the body surface electrodes is measured, and three-dimensional position coordinates of the probe are determined based on the impedance measurements. Dynamic compensation is provided for changing impedance of the body surface and its interface with the electrodes, resulting from such causes as electrode peel-off and changes in moisture and temperature. The compensation improves the accuracy of, inter alia, medical procedures, such as mapping the heart or performing ablation to treat cardiac arrhythmias.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
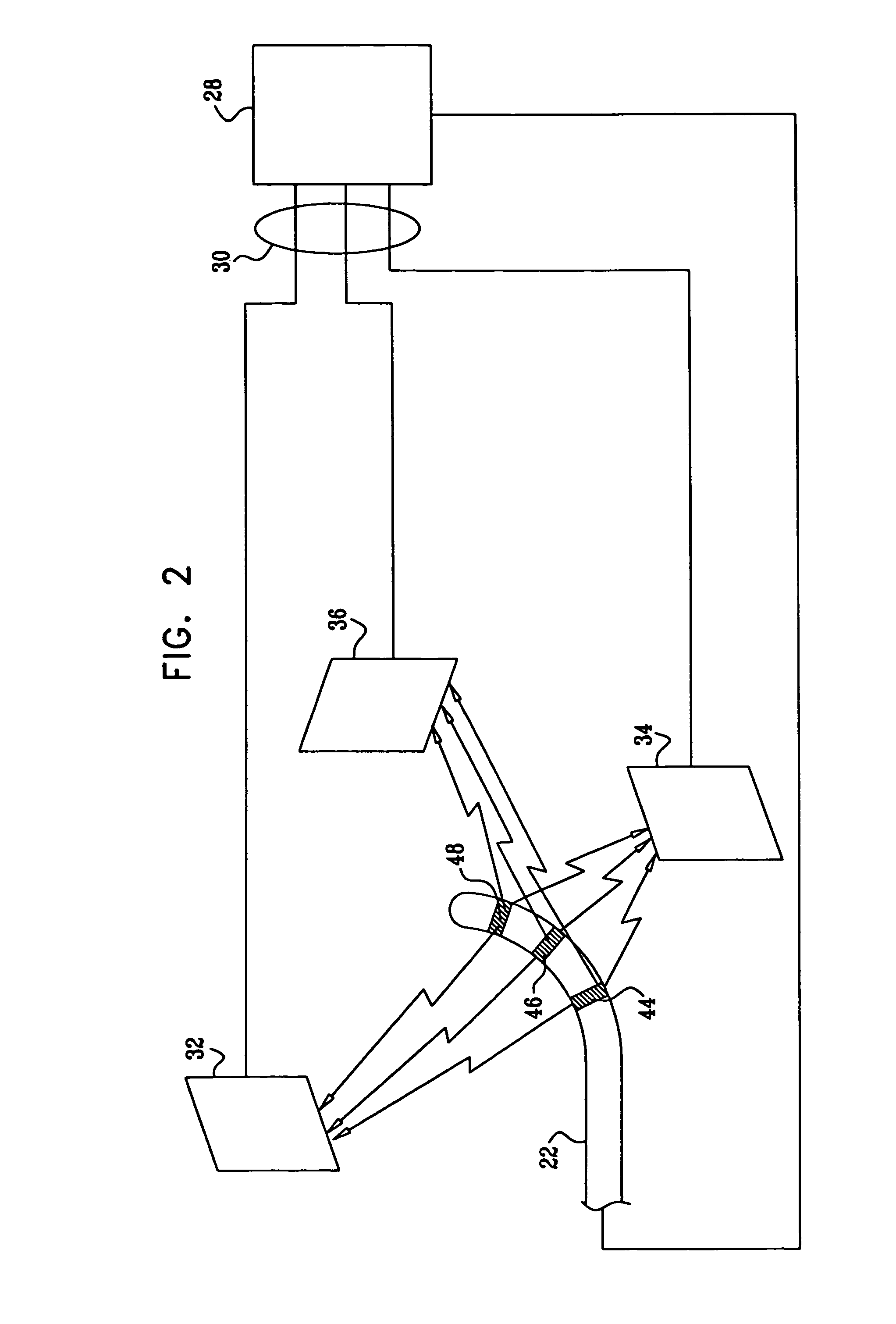
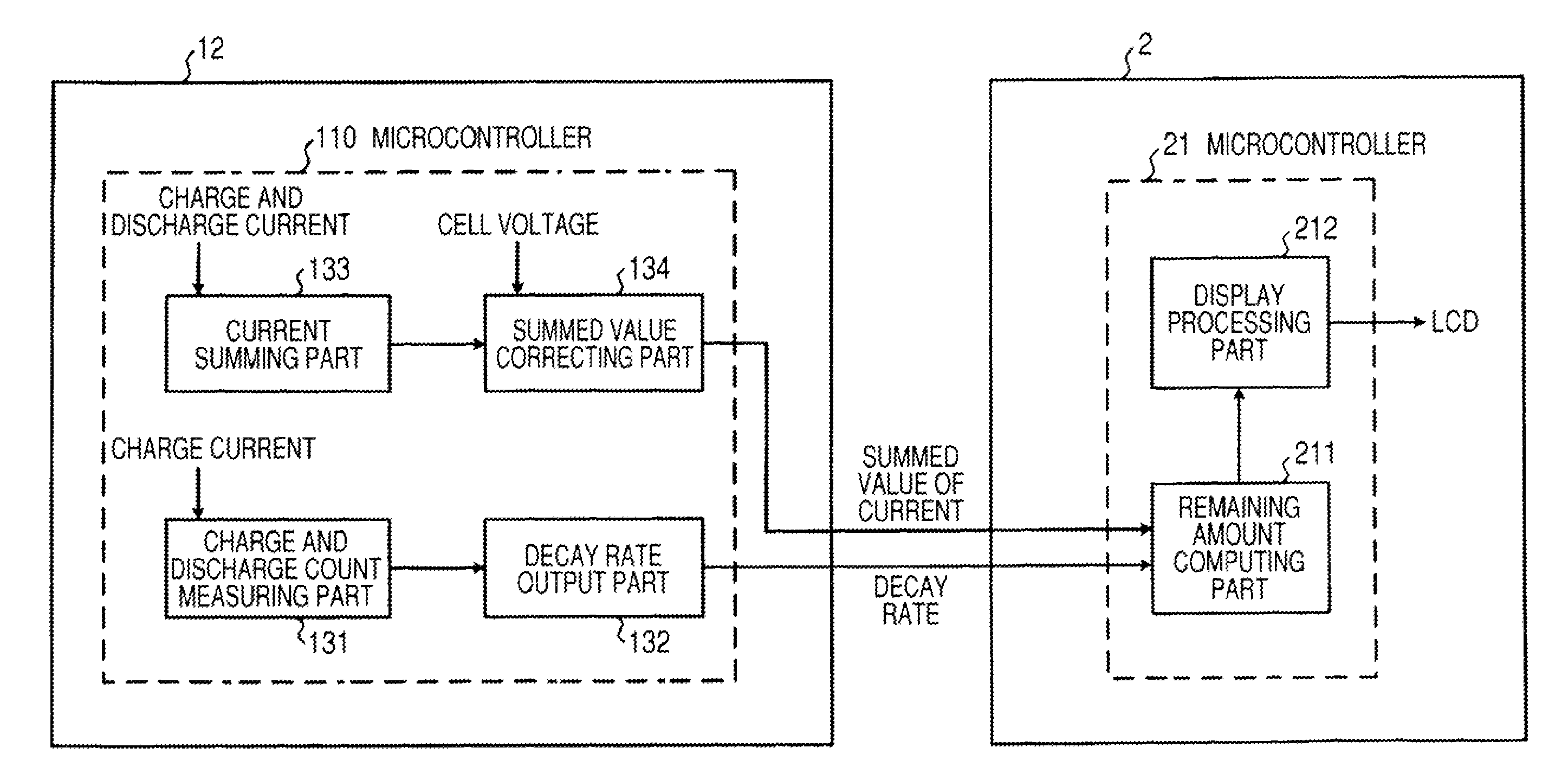
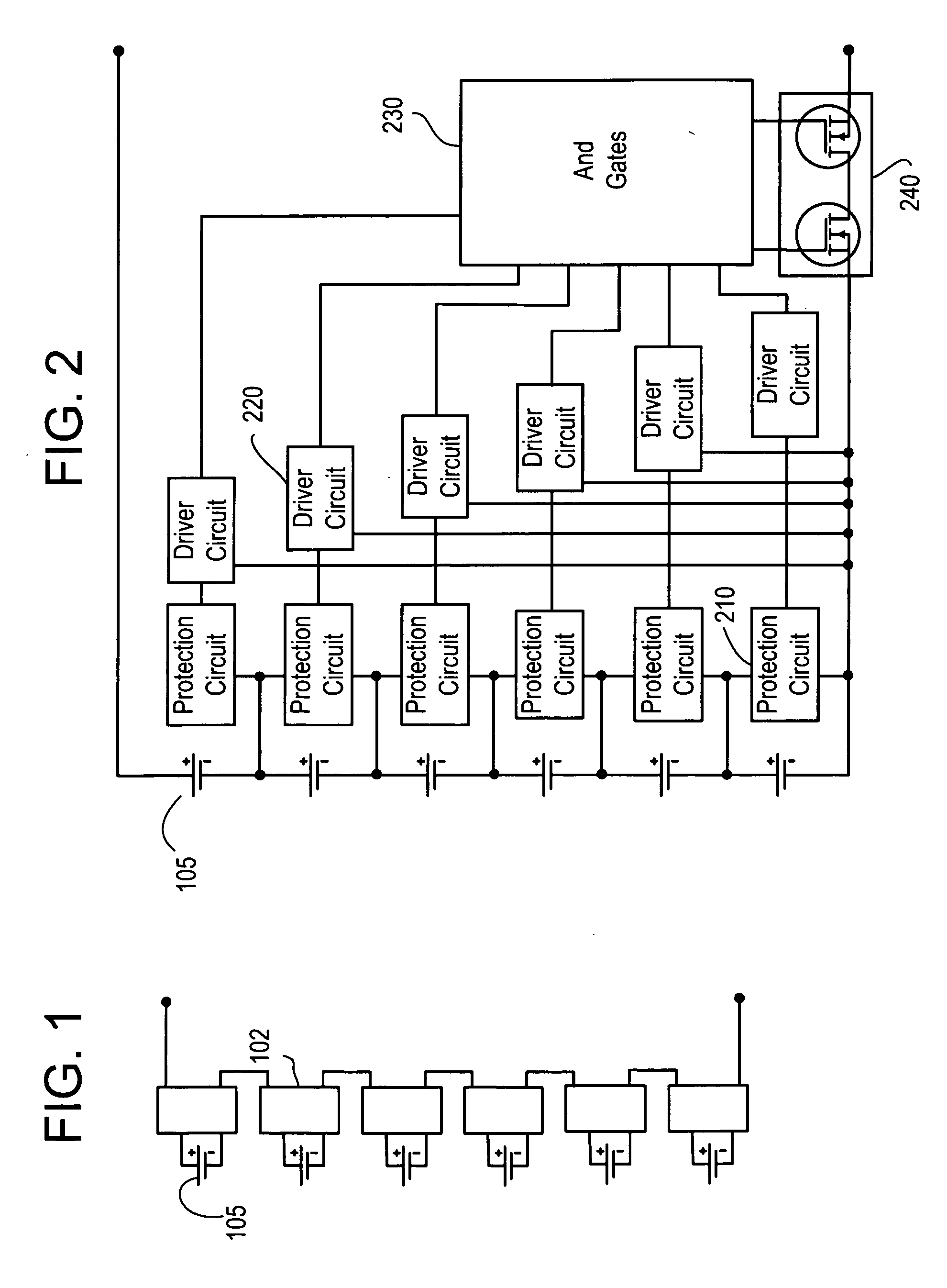
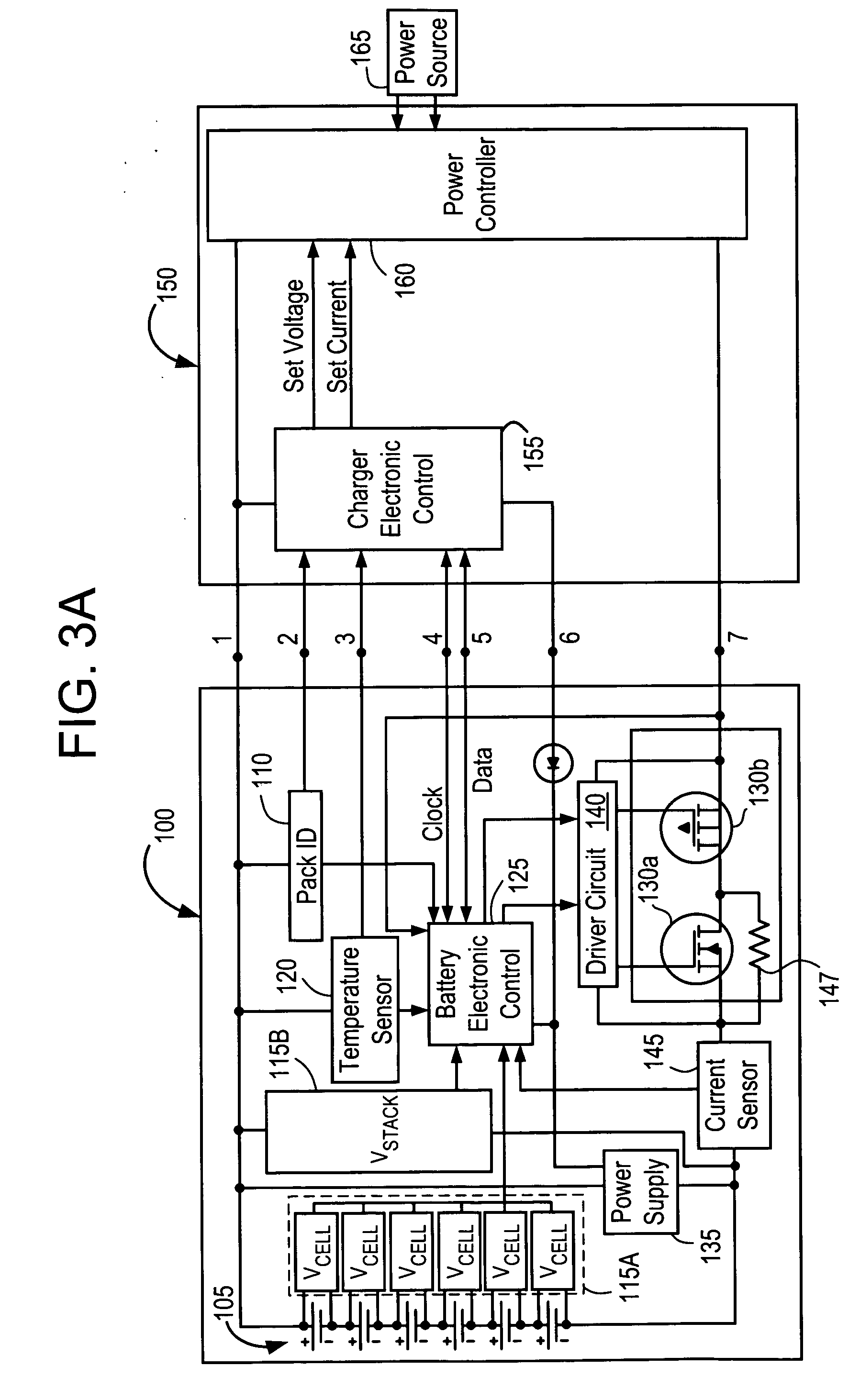
Battery pack, electronic appliance, and method of detecting remaining amount of battery
InactiveUS8359174B2Accurate detectionCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingPower flowCharge current
A battery pack has a charge and discharge count measuring part (131) configured to measure the number of times of charges and discharges of a secondary battery based on the summed value of the charge current for the secondary battery, and a decay rate output part (132) configured to compute a decay rate that indicates a degree of decay of the secondary battery based on the number of times of charges and discharges measured by the charge and discharge count measuring part (131) and to output it to a device being a discharge load. For example, the charge and discharge count measuring part (131) repeatedly sums the detected values of the charge current to a predetermined threshold, and counts up the number of times of charges and discharges every time when the summed value reaches the threshold. Accordingly, even though charges and discharges are repeated at finer steps in a relatively narrow voltage range, the number of times of charges and discharges can be counted accurately, and the computing accuracy of the decay rate is improved. In the battery pack in which the secondary battery is accommodated, parameters for detecting the remaining amount of the battery are detected more accurately.
Owner:SONY CORP
Rechargeable electric device
InactiveUS20130169217A1Accurate displayImprove accuracyCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingCharge currentSwitching signal
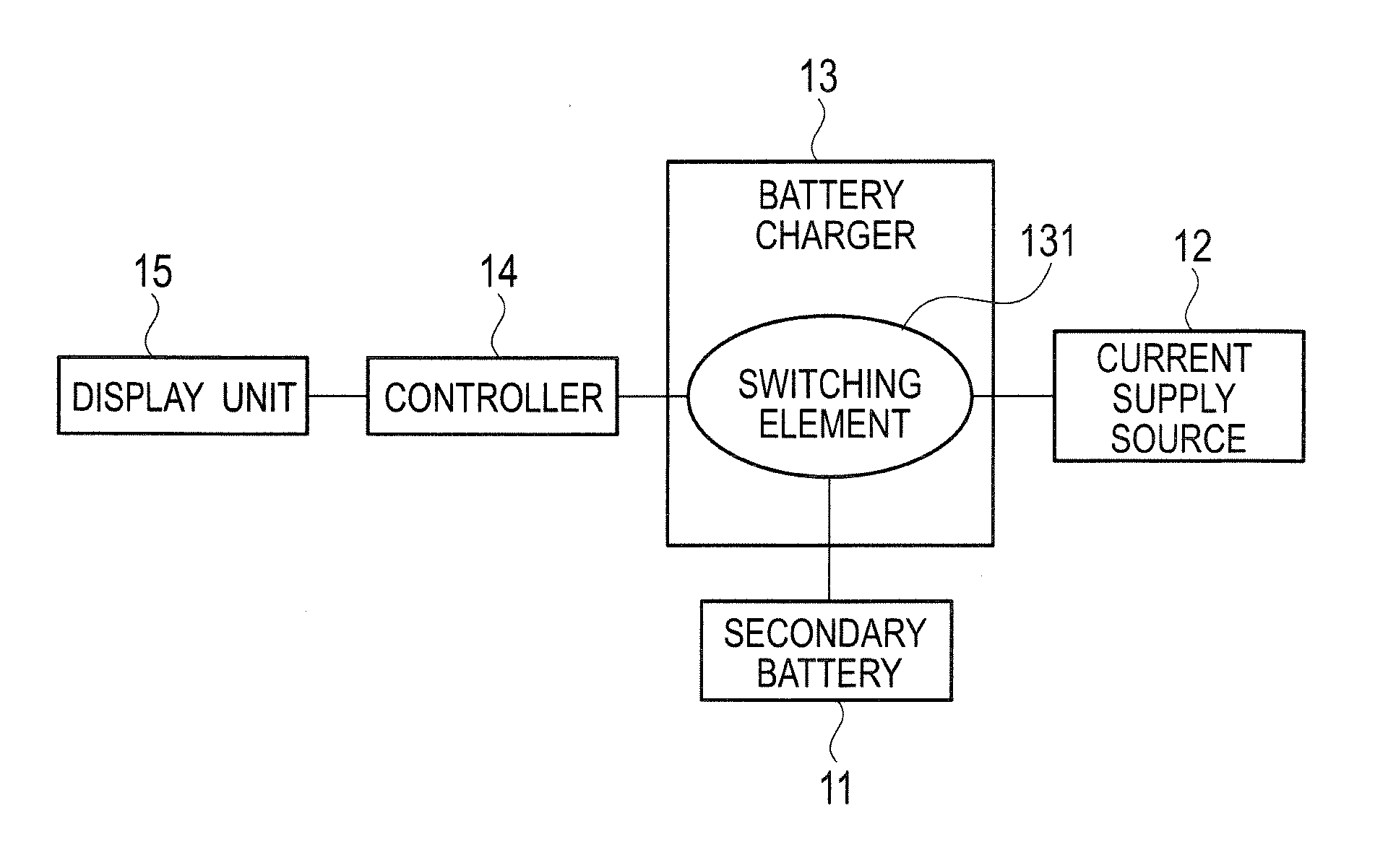
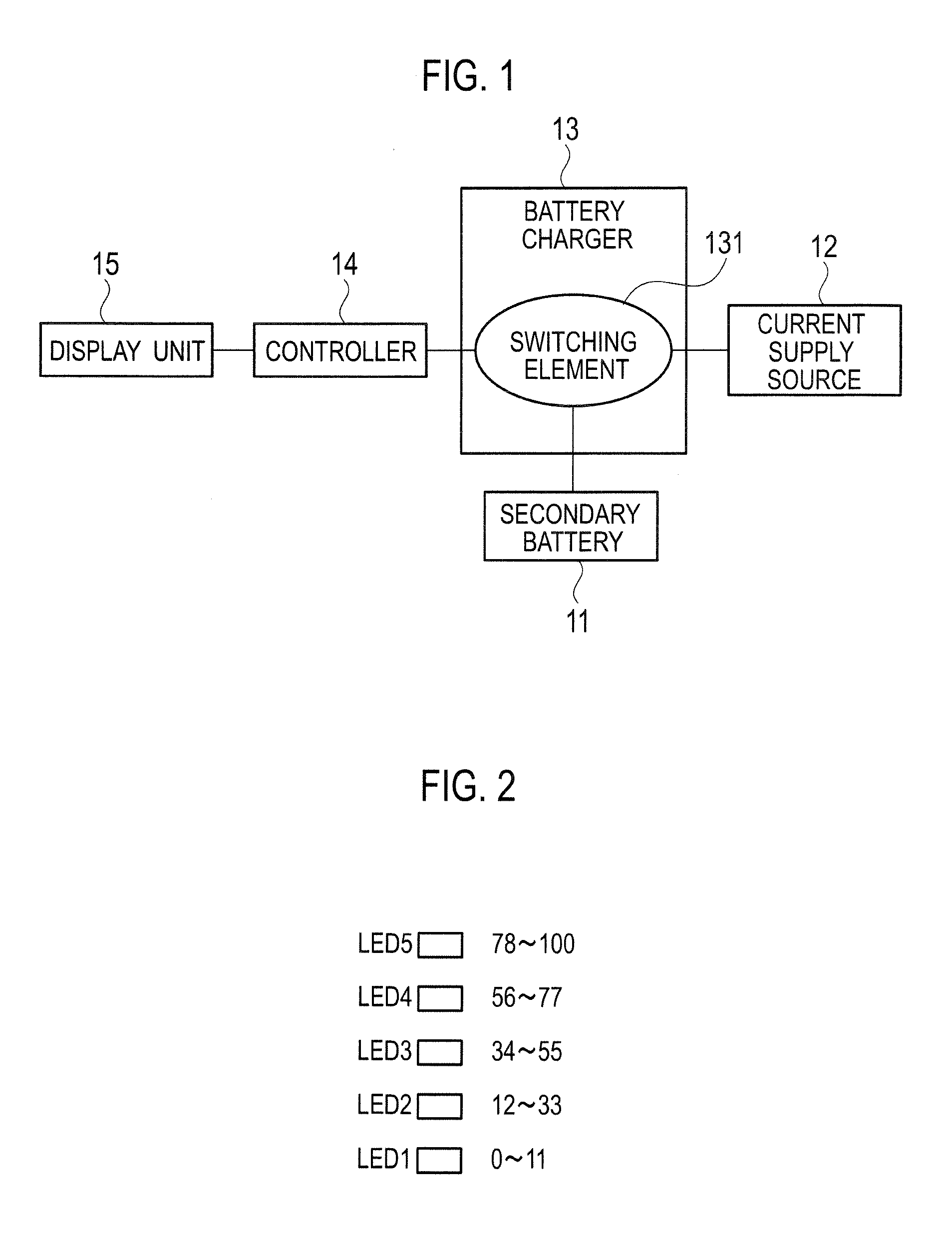
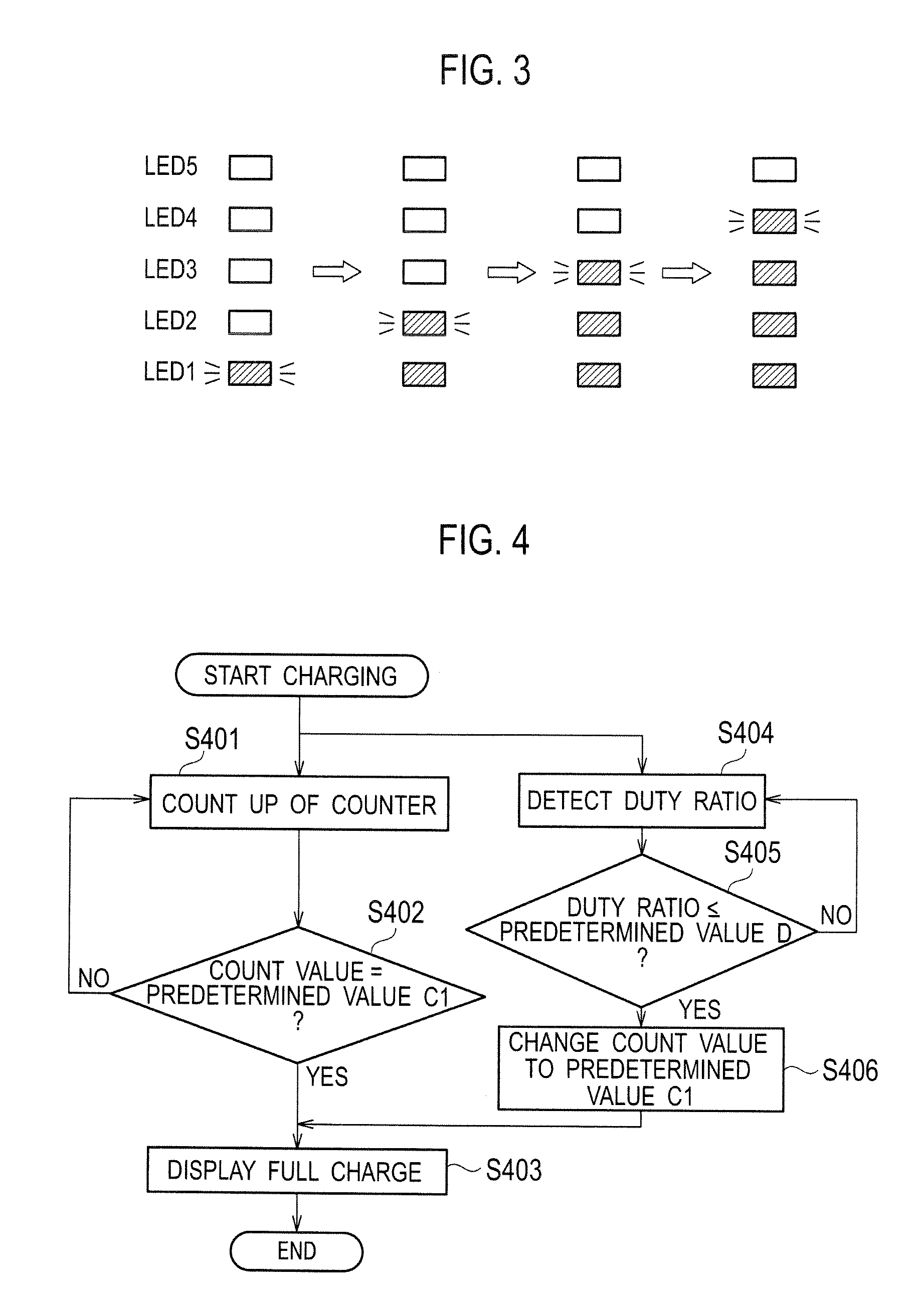
Under a control by a controller (14), a rechargeable electric device makes a full charge display to display on a display unit (15) that a secondary battery (11) is fully charged, after a start of charging the secondary battery (11) in a case where either when a count value of a counter reaches a first predetermined value (C1) corresponding to the full charge of the secondary battery (11), or when a duty ratio of switching signals which make an on / off control of a switching element (131) becomes smaller than or equal to a predetermined value (D) corresponding to the charge current obtained at a time of the full charge of the secondary battery (11).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
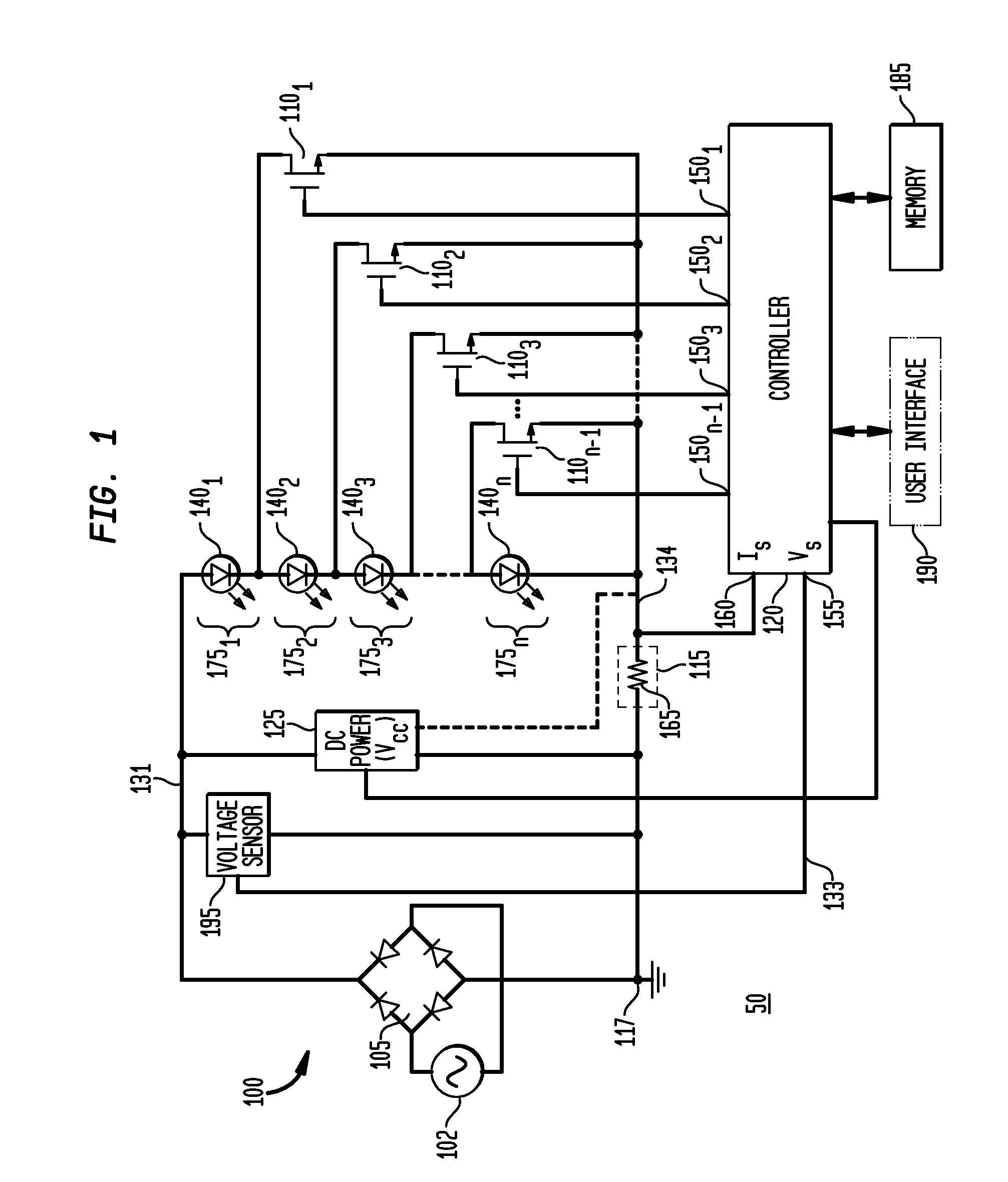
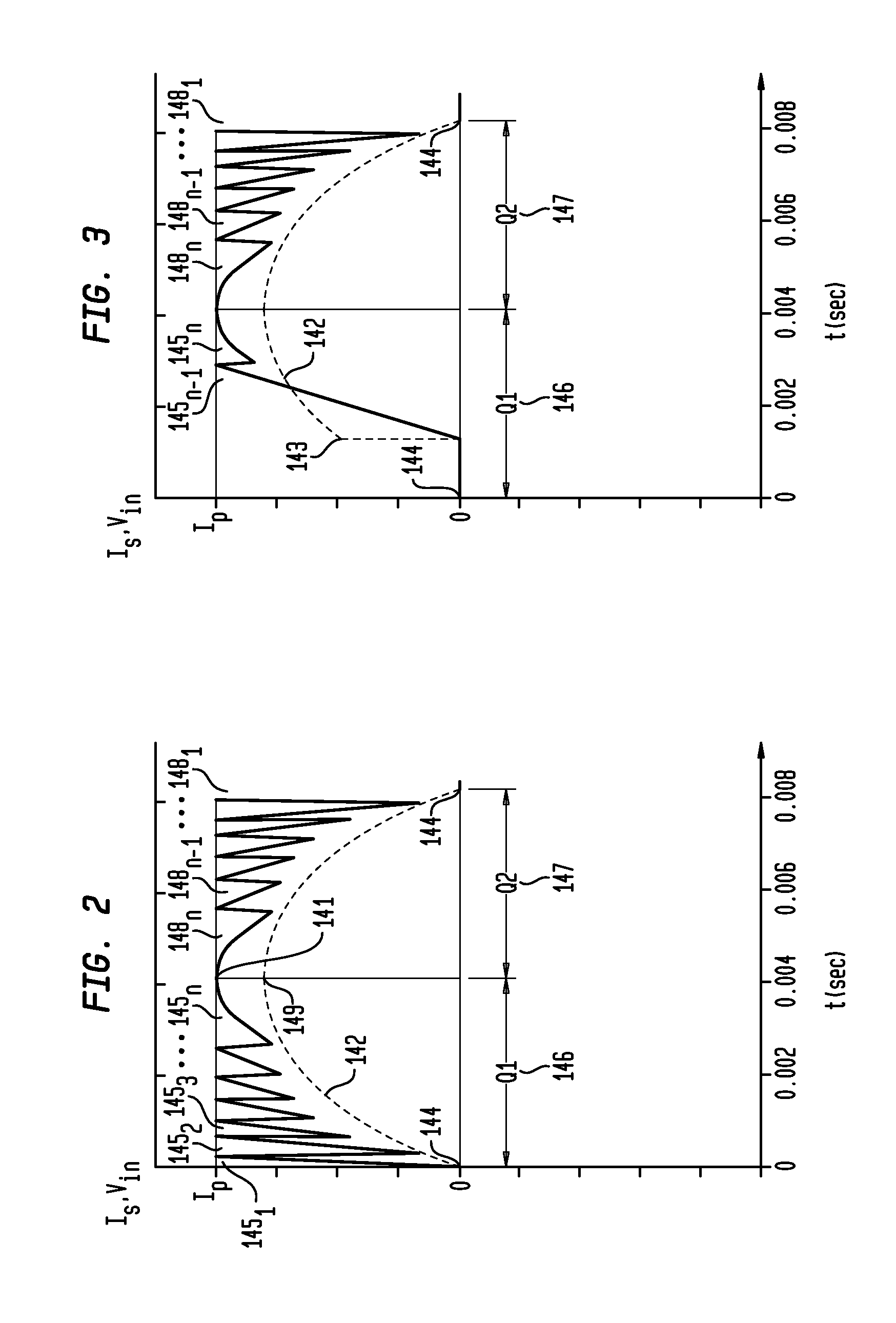
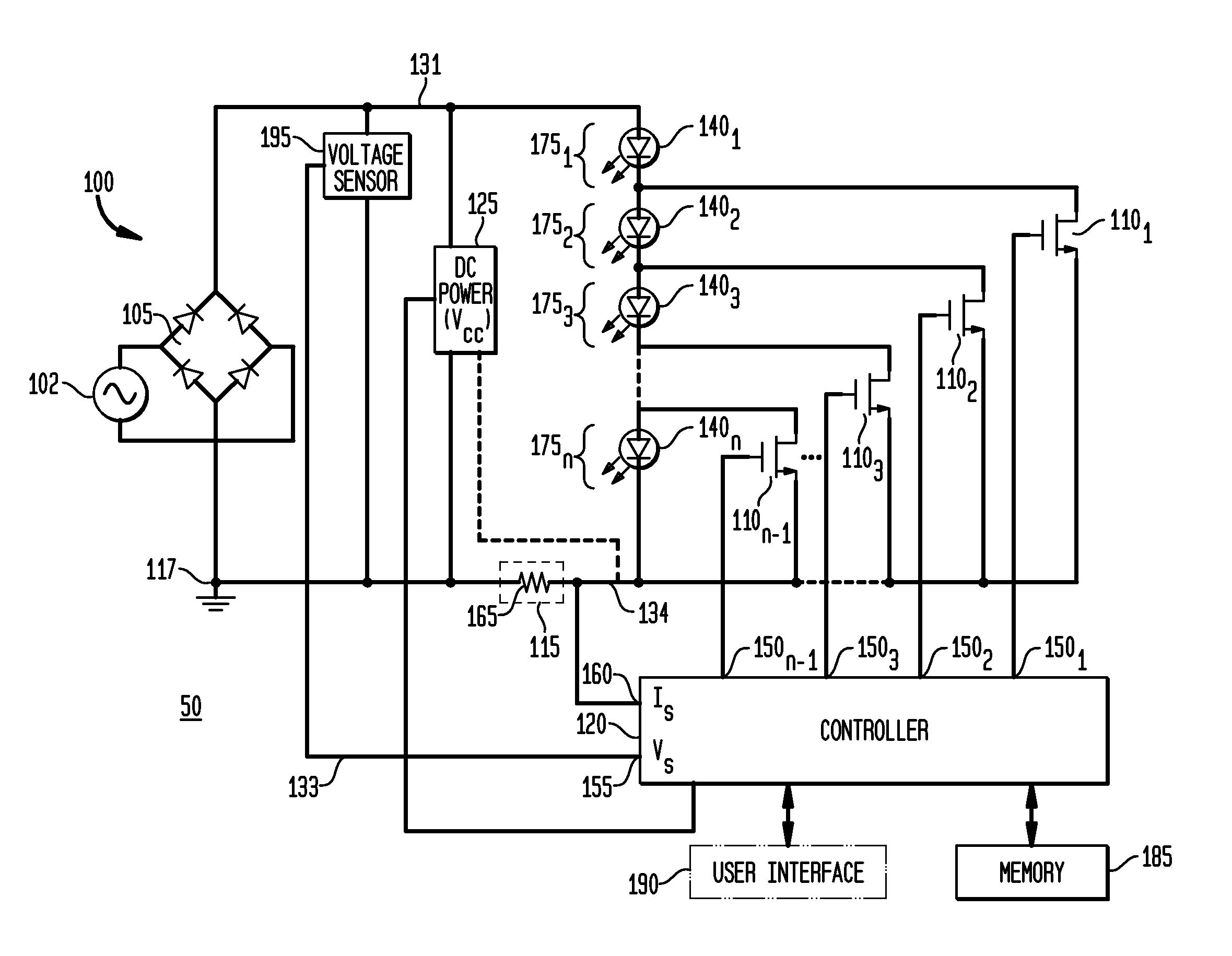
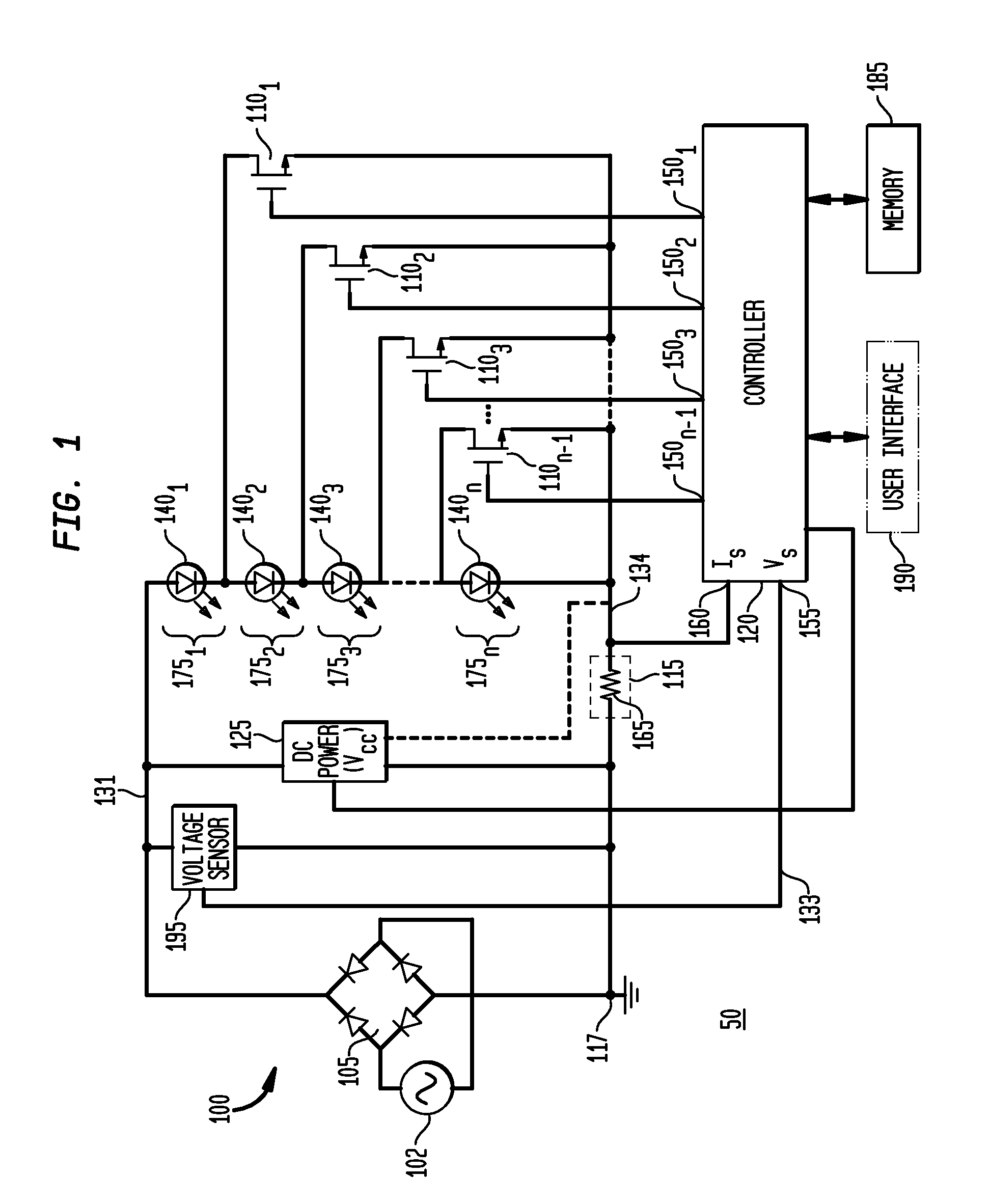
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
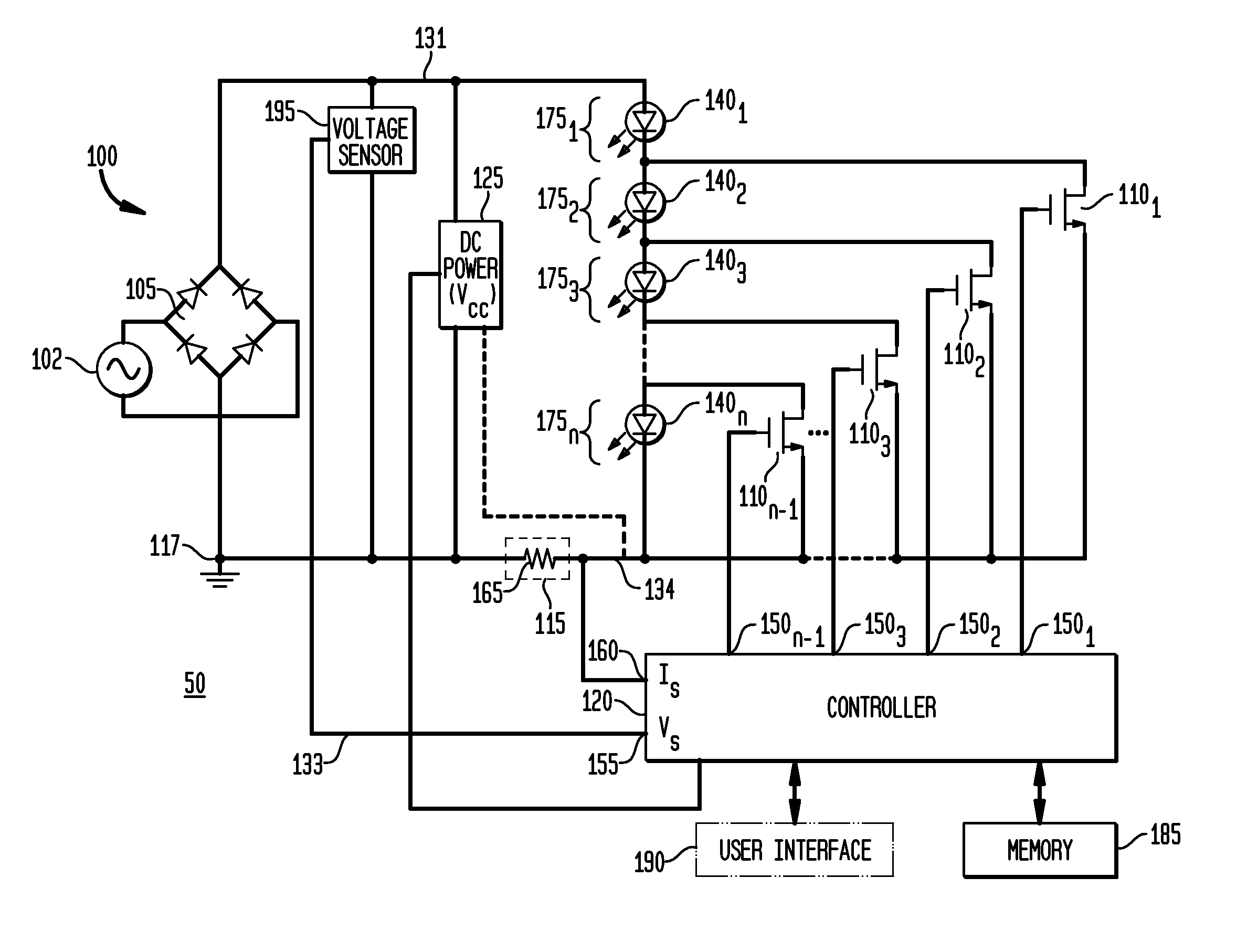
ActiveUS20120081009A1Reduction in size and costImprove Utilization and EfficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentVoltage regulation
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a plurality of segments of LEDs; first and second current regulators; a current sensor; and a controller to monitor a current level through a series LED current path, and to provide for first or second segments of LEDs to be in or out of the series LED current path at different current levels. A voltage regulator is also utilized to provide a voltage during a zero-crossing interval of the AC voltage. In an exemplary embodiment, first and second segments of LEDs are both in the series LED current path regulated at a lower current level compared to when only the first segment of LEDs is in the series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
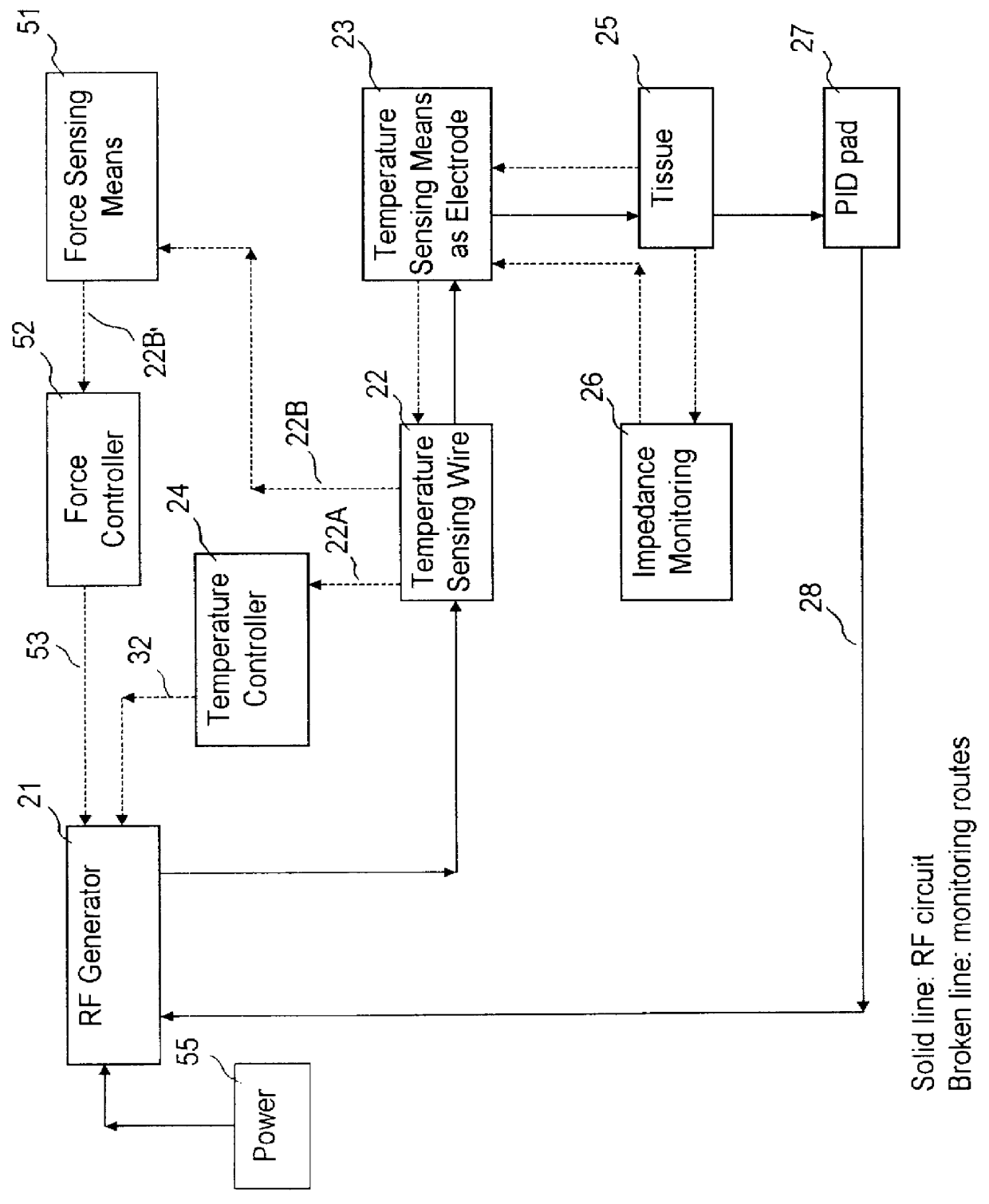
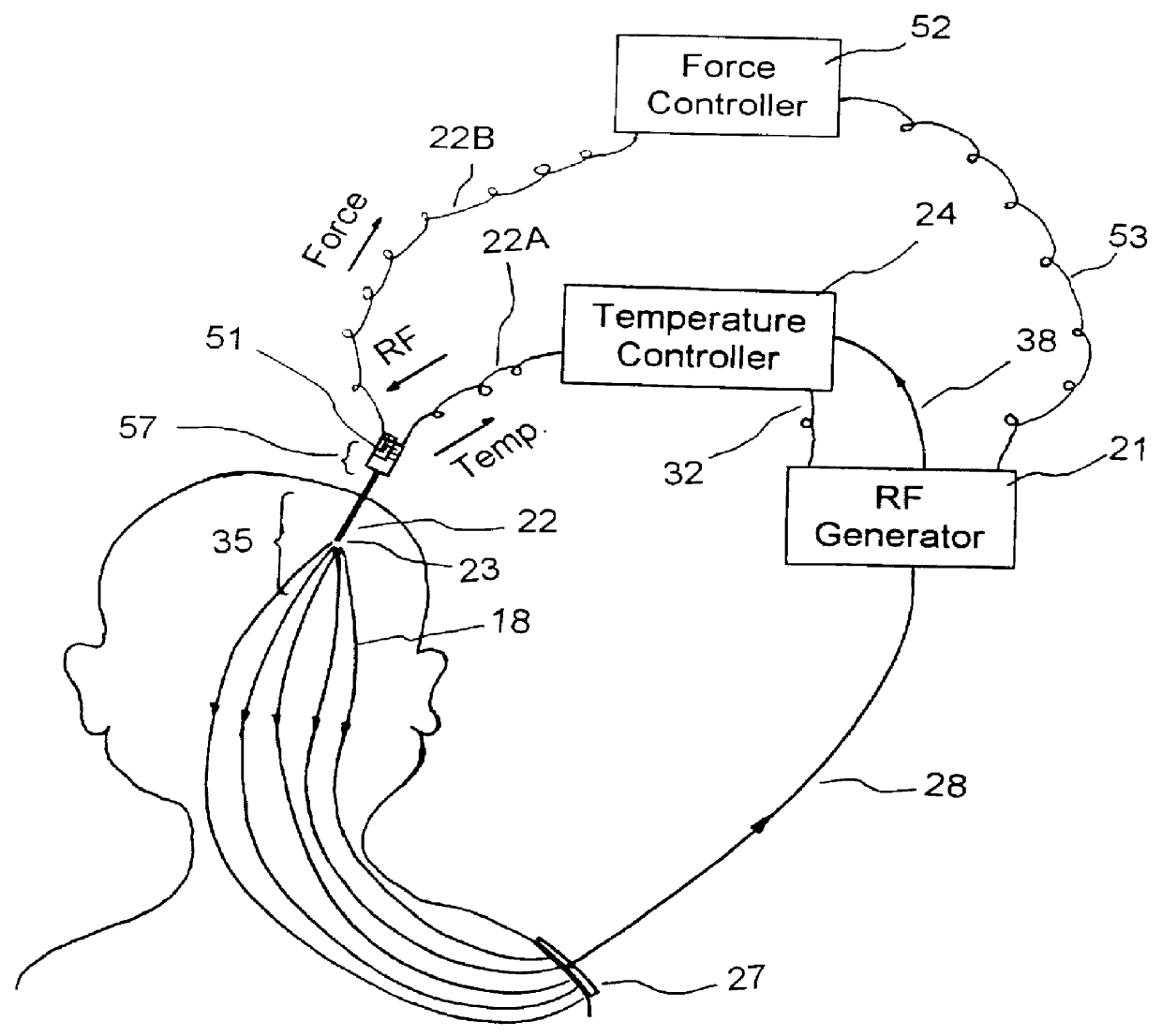
Ablation apparatus having temperature and force sensing capabilities
InactiveUS6113593AGood effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMeasurement deviceBiomedical engineering
An ablation apparatus system for treating tissues in a patient, the ablation apparatus comprising temperature sensing means for measuring a temperature, wherein said temperature sensing means comprises a temperature sensing probe and at least one temperature sensing wire secured to the temperature sensing probe; force measuring means for measuring force exerted onto the temperature sensing probe by a tissue; and RF current generating means for generating RF current, wherein the RF current generating means is connected to and controlled by the temperature sensing means and force measuring means, adapted for supplying RF current to the temperature sensing probe as an electrode for tissue treatment.
Owner:IRVINE BIOMEDICAL
Electrode assembly for nerve control
InactiveUS6907295B2Minimize cathode effectWeakening rangeSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsPower flowAnatomy
Apparatus is provided for applying current to a nerve. A cathode is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of a cathodic longitudinal site of the nerve and to apply, a cathodic current to the nerve. A primary inhibiting anode is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of a primary anodal longitudinal site of the nerve and to apply a primary anodal current to the nerve. A secondary inhibiting anode is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of a secondary anodal longitudinal site of the nerve and to apply a secondary anodal current to the nerve, the secondary anodal longitudinal site being closer to the primary anodal longitudinal site than to the cathodic longitudinal site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Low profile compact multi-band meanderline loaded antenna
InactiveUS7079079B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectrical conductor
An antenna for transmitting and receiving radio frequency energy. The antenna comprises a conductive radiator comprising a first and a second conductive region for providing a first and a second current path length. A feed conductor and a ground conductor operate as meanderline (or slow wave) elements to provide an electrical length longer than a physical length.
Owner:SKYCROSS INC
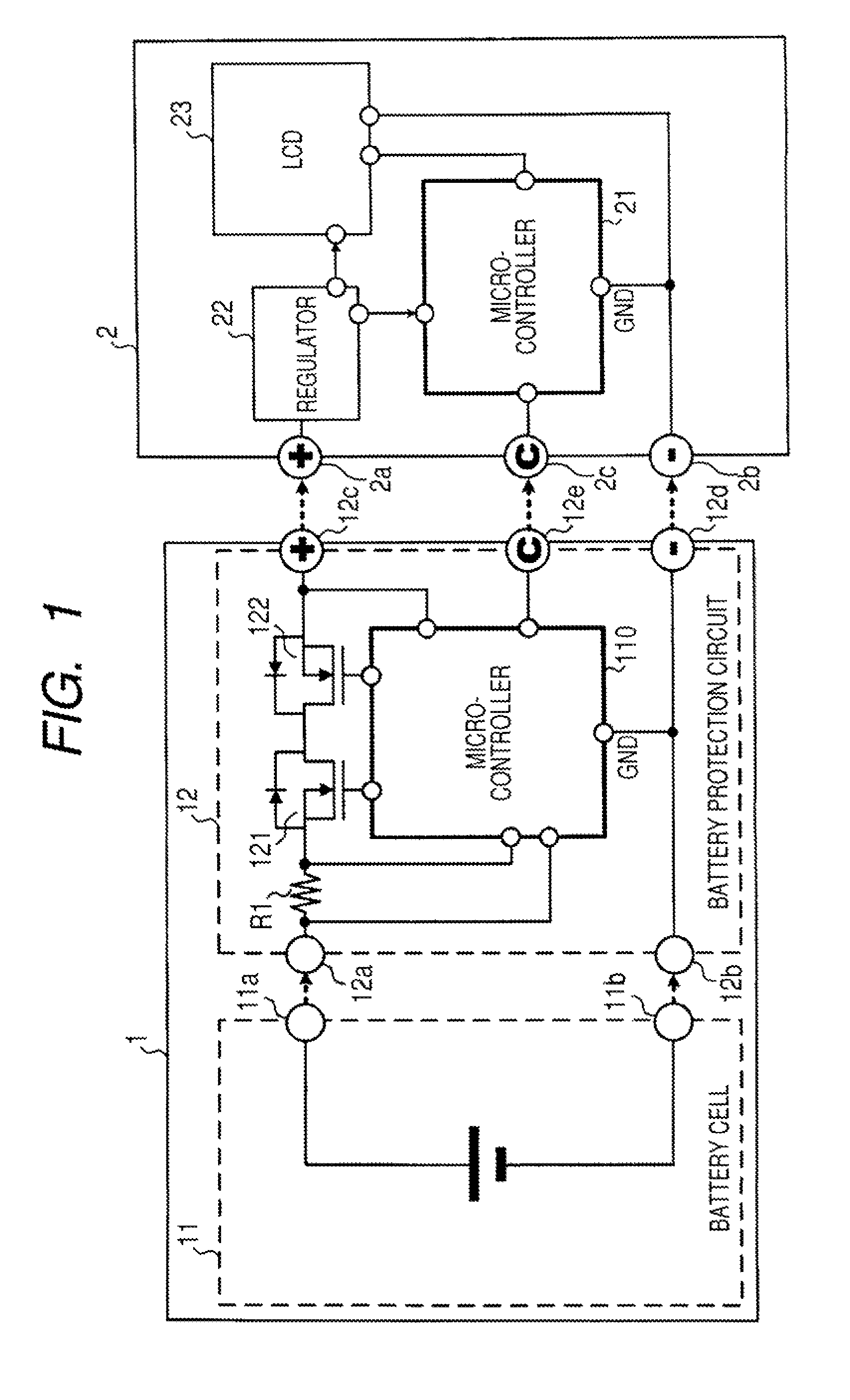
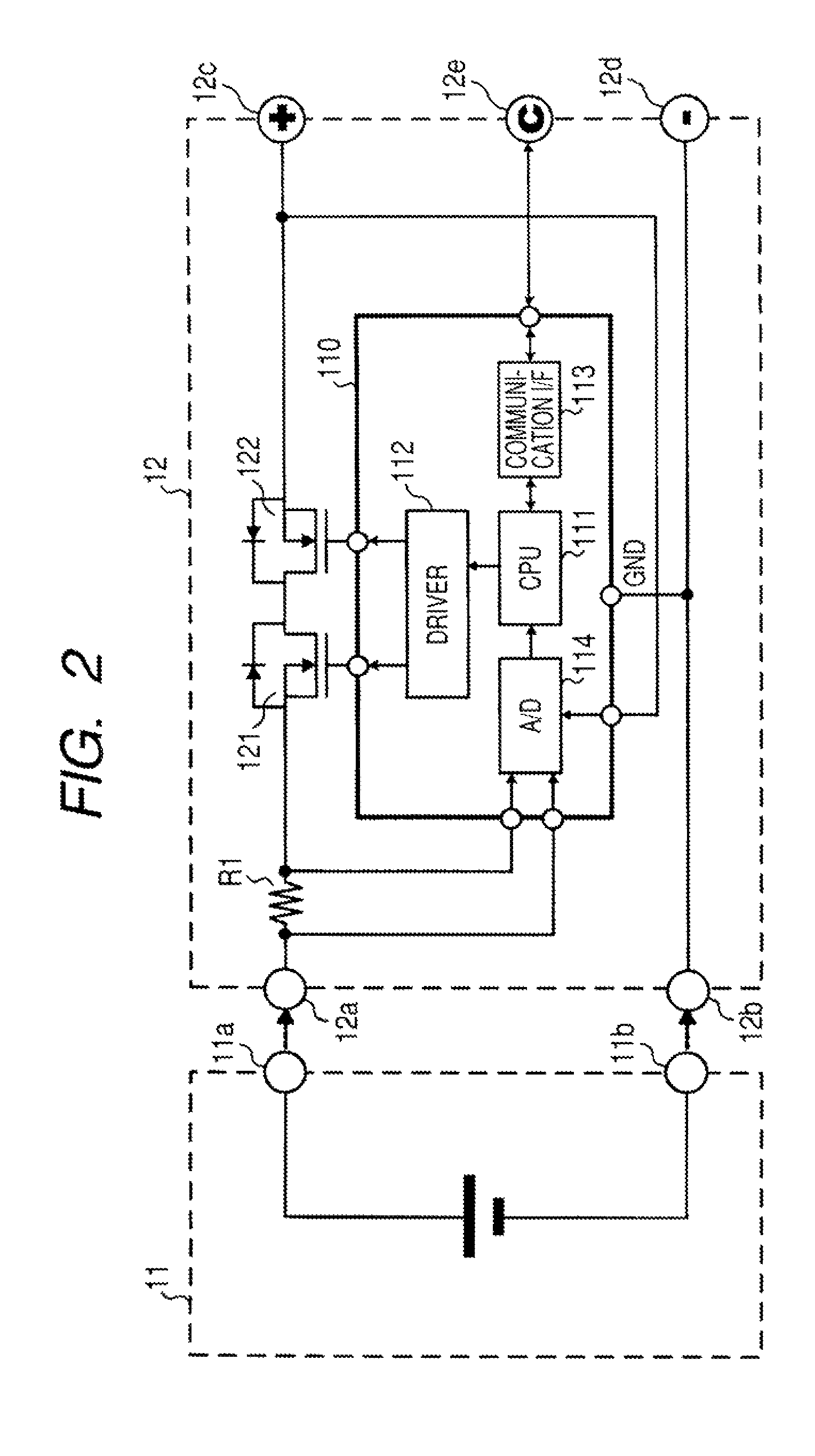
Protection methods, protection circuits and protective devices for secondary batteries, a power tool, charger and battery pack adapted to provide protection against fault conditions in the battery pack
InactiveUS20050077878A1Primary cell to battery groupingCharge equalisation circuitElectrical batteryEngineering
In a cordless power tool system, protection methods, circuits and devices are provided to protect against fault conditions within a battery pack that is operatively attached to a power tool or charger, so as to prevent internal or external damage to the battery pack or attached tool or charger. The exemplary methods, circuits and devices address fault conditions such as over-charge, over-discharge, over-current, over-temperature, etc.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
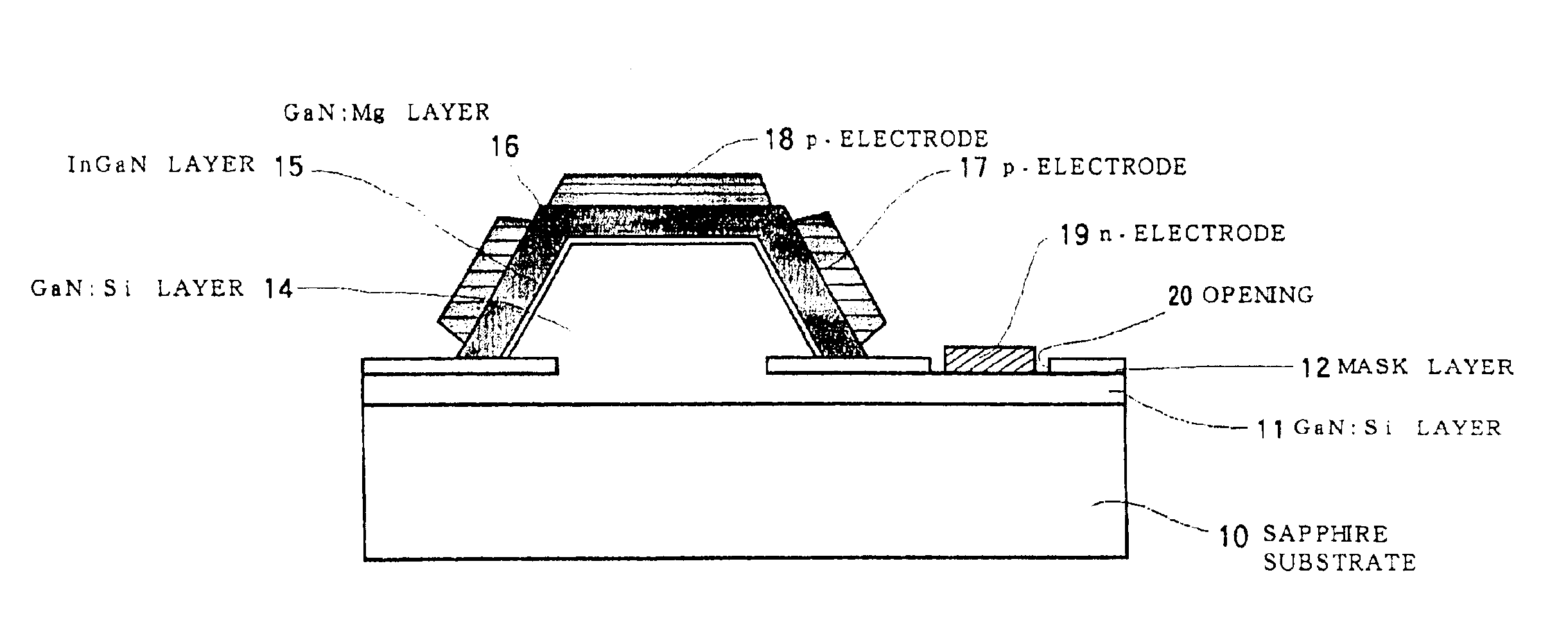
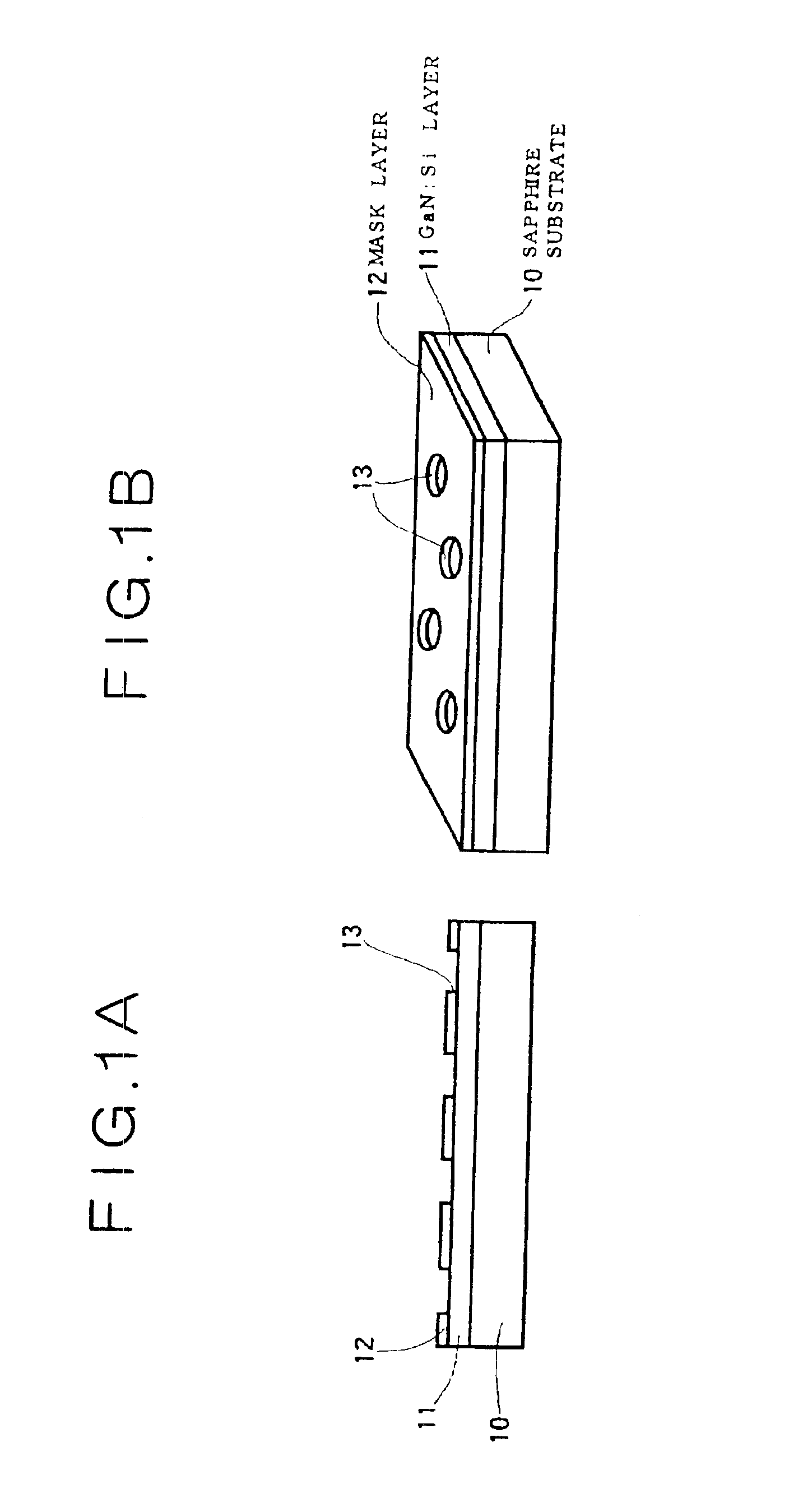
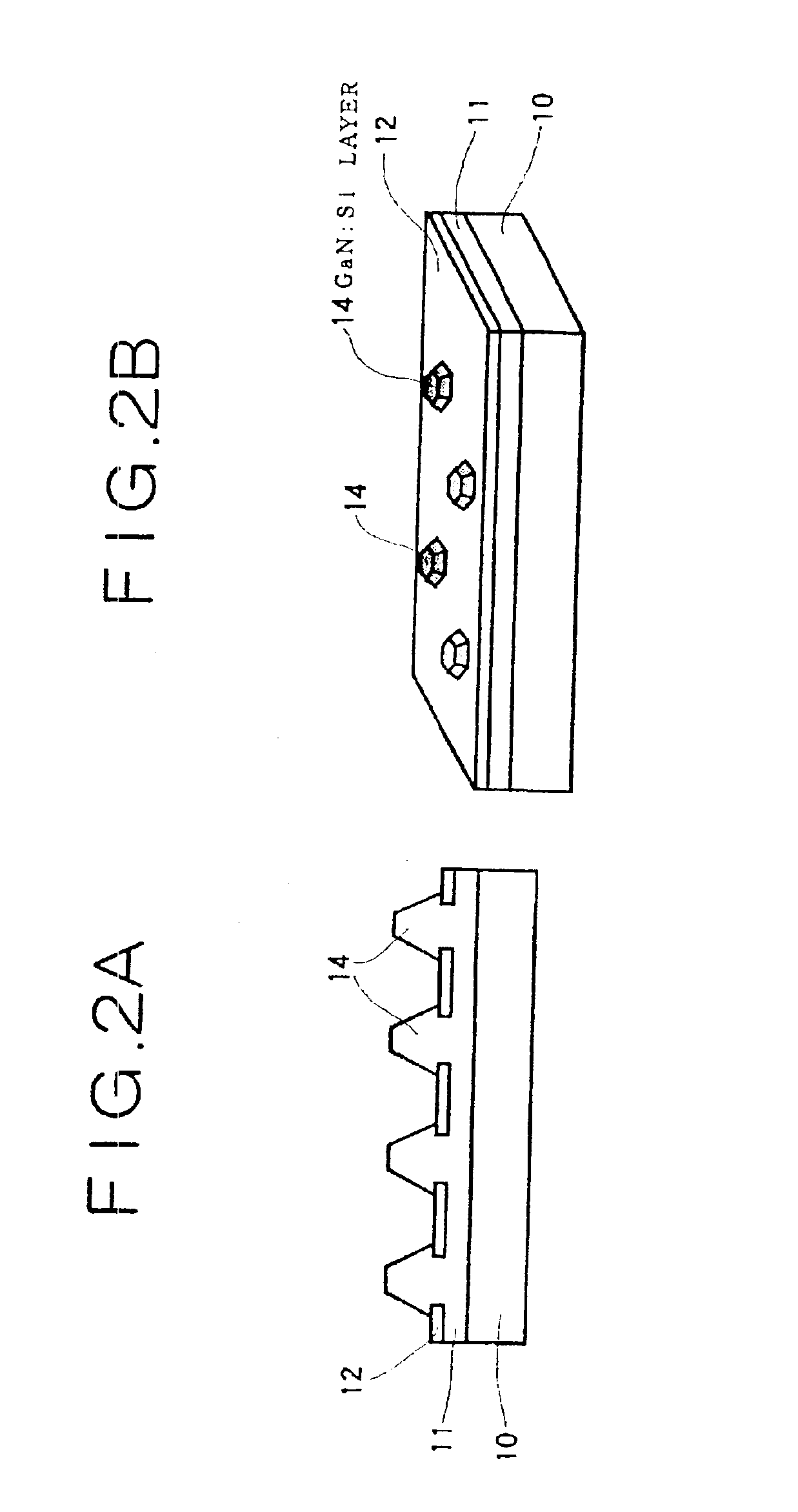
Semiconductor light-emitting device and semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS7087932B2Well formedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal planeCrystallinity
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and methods of bioelectrical impedance analysis of blood flow
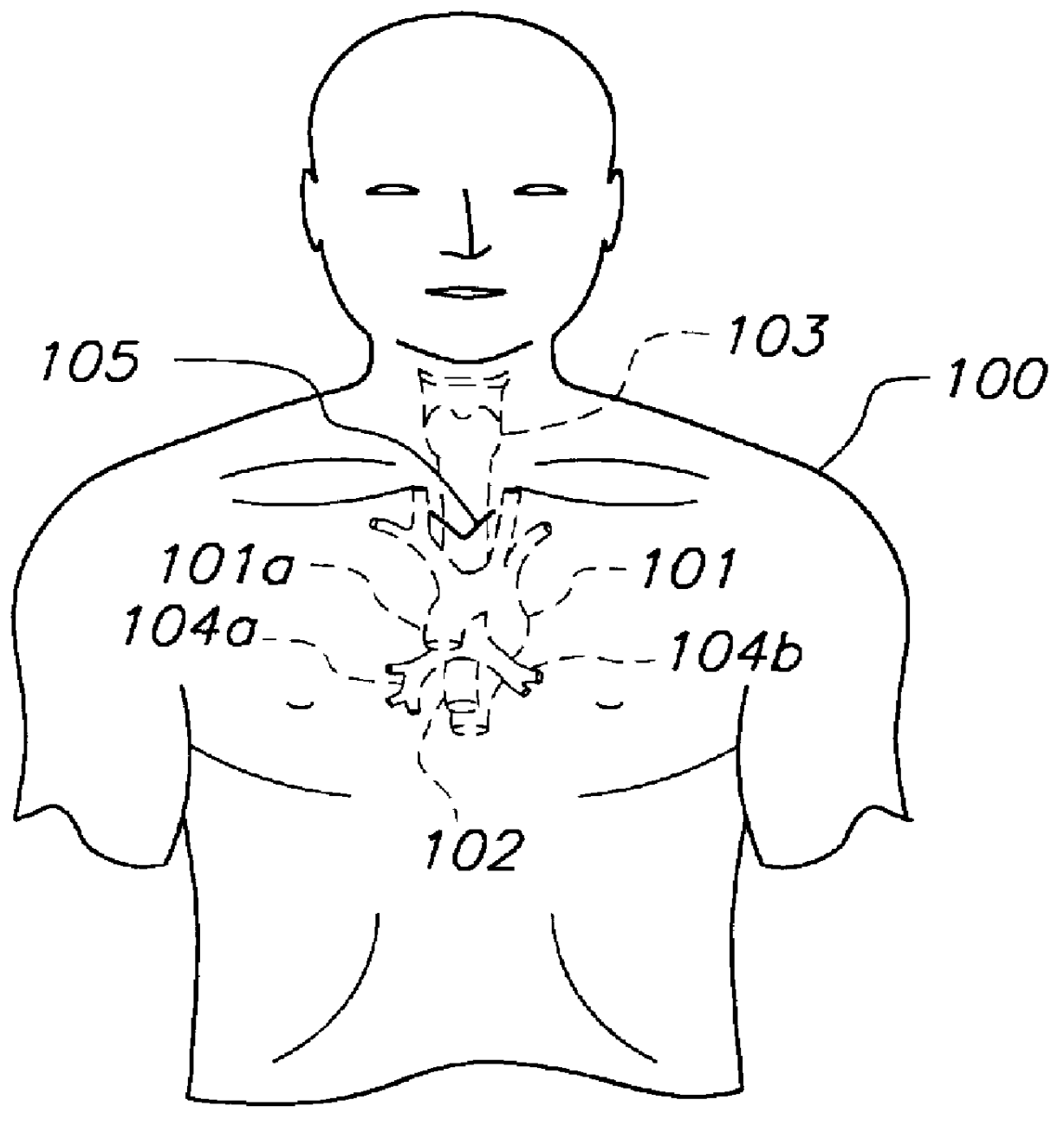
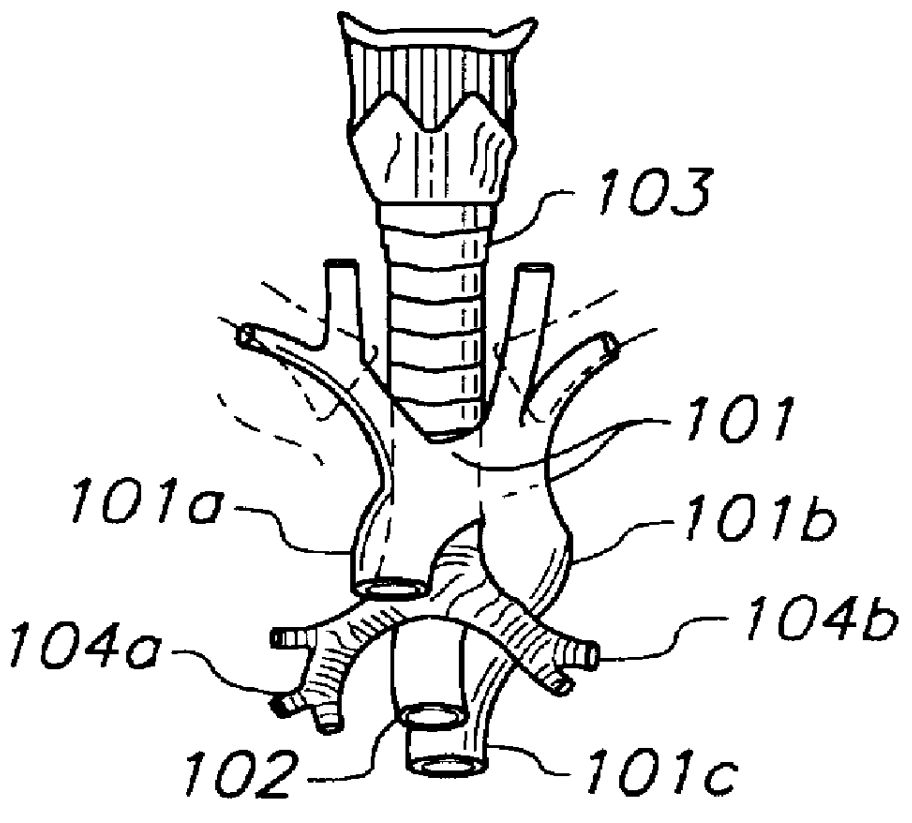
InactiveUS6095987AAccurately and non-invasively and continuously measuring cardiac outputCatheterSensorsBioelectrical impedance analysisCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus and methods are provided for monitoring cardiac output using bioelectrical impedance techniques in which first and second electrodes are placed in the trachea and / or bronchus in the vicinity of the ascending aorta, while an excitation current is injected into the thorax via first and second current electrodes, so that bioelectrical impedance measurements based on the voltage drop sensed by the first and second electrodes reflect voltage changes induced primarily by blood flow dynamics, rather than respiratory or non-cardiac related physiological effects. Additional sense electrodes may be provided, either internally, or externally, for which bioelectrical impedance values may be obtained. Methods are provided for computing cardiac output from bioelectrical impedance values. Apparatus and methods are also provided so that the measured cardiac output may be used to control administration of intravenous fluids to an organism or to optimize a heart rate controlled by a pacemaker.
Owner:ECOM MED
Deep brain stimulation current steering with split electrodes
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead having a longitudinal surface, a proximal end, a distal end and a lead body. The device also includes a plurality of electrodes disposed along the longitudinal surface of the lead near the distal end of the lead. The plurality of electrodes includes a first set of segmented electrodes comprising at least two segmented electrodes disposed around a circumference of the lead at a first longitudinal position along the lead; and a second set of segmented electrodes comprising at least two segmented electrodes disposed around a circumference of the lead at a second longitudinal position along the lead. The device further includes one or more conductors that electrically couple together all of the segmented electrodes of the first set of segmented electrodes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method for fabricating programmable memory array structures incorporating series-connected transistor strings
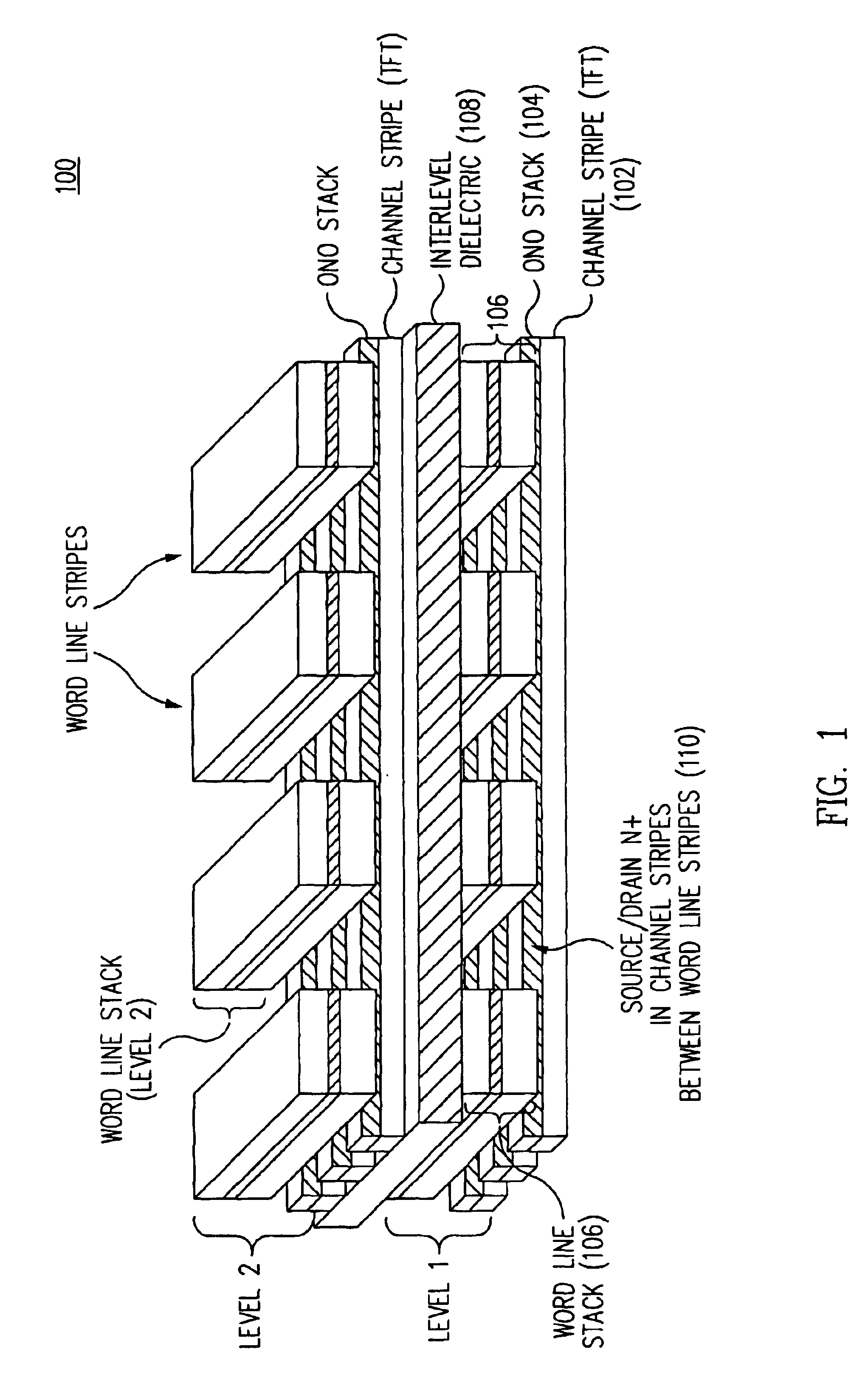
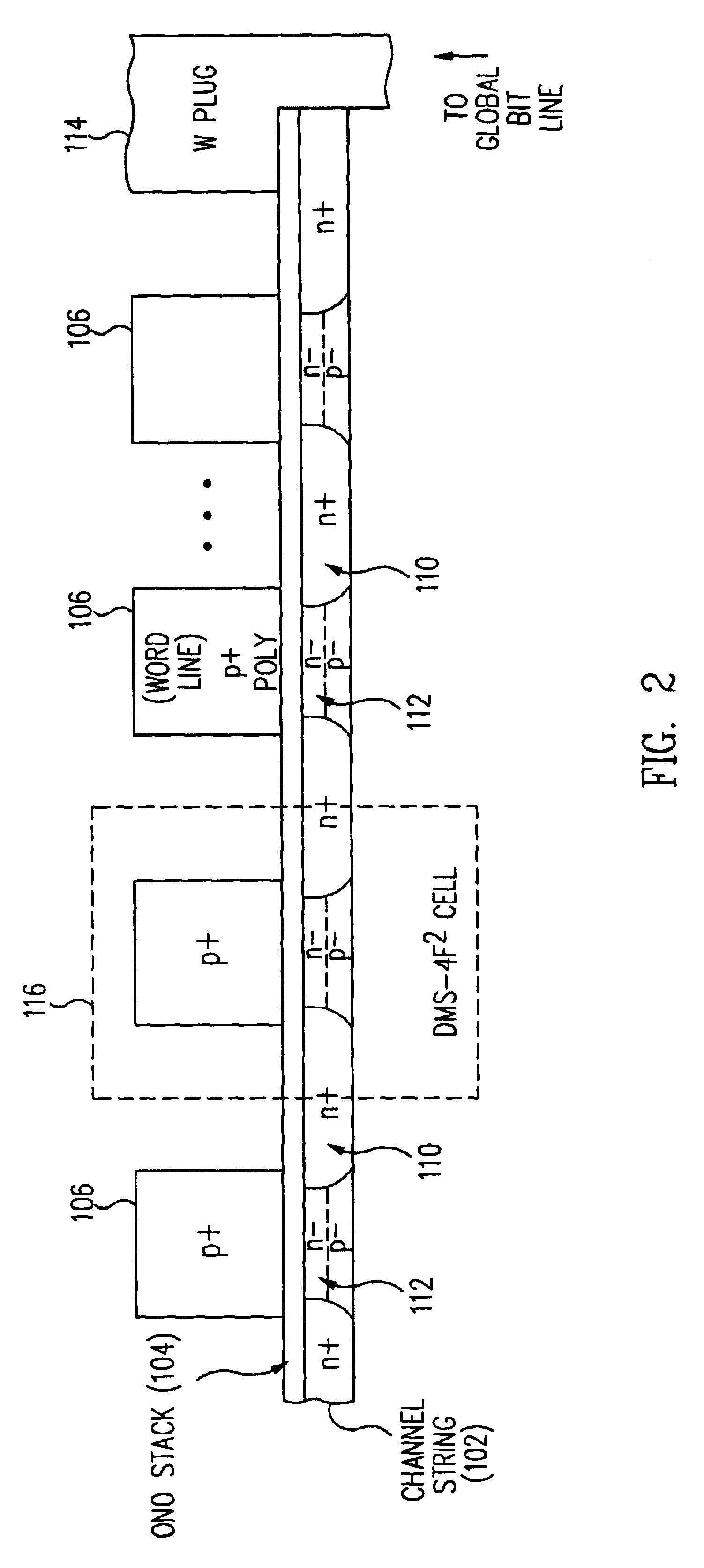
InactiveUS7005350B2Reduce in quantityDense memory arraySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineComputer architecture
A three-dimensional flash memory array incorporates thin film transistors having a charge storage dielectric arranged in series-connected NAND strings to achieve a 4F2 memory cell layout. The memory array may be programmed and erased using only tunneling currents, and no leakage paths are formed through non-selected memory cells. Each NAND string includes two block select devices for respectively coupling one end of the NAND string to a global bit line, and the other end to a shared bias node. Pairs of NAND strings within a block share the same global bit line. The memory cells are preferably depletion mode SONOS devices, as are the block select devices. The memory cells may be programmed to a near depletion threshold voltage, and the block select devices are maintained in a programmed state having a near depletion mode threshold voltage. NAND strings on more than one layer may be connected to global bit lines on a single layer. By interleaving the NAND strings on each memory level and using two shared bias nodes per block, very little additional overhead is required for the switch devices at each end of the NAND strings. The NAND strings on different memory levels are preferably connected together by way of vertical stacked vias, each preferably connecting to more than one memory level. Each memory level may be produced with less than three masks per level.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Semiconductor substrate process using a low temperature deposited carbon-containing hard mask
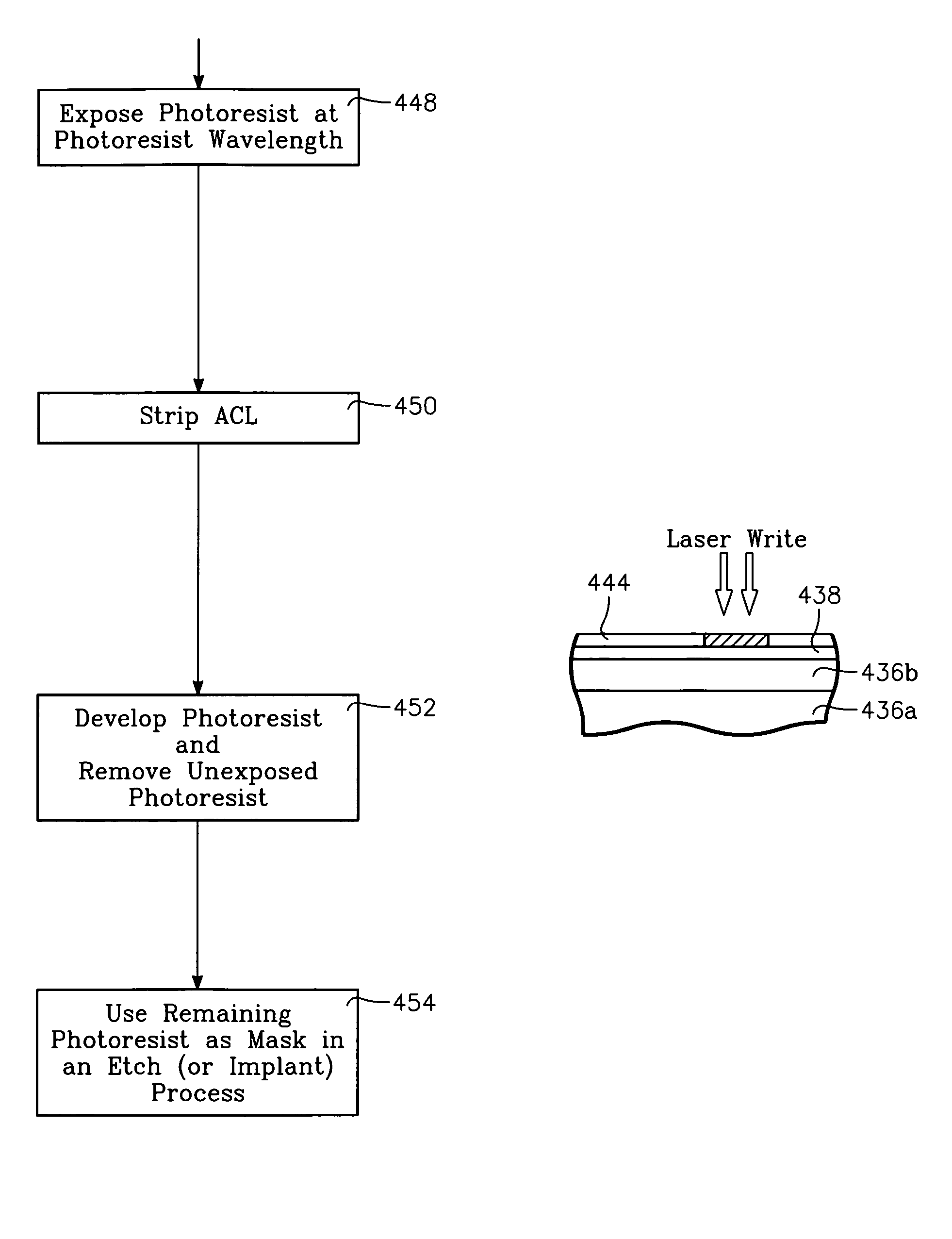
InactiveUS7323401B2Electric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsLow temperature depositionPlasma current
A method of processing a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate using an optically writable mask includes placing the substrate in a reactor chamber, the substrate having on its surface a target layer to be etched in accordance with a predetermined pattern, and depositing a carbon-containing hard mask layer on the substrate by (a) introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, (b) generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and (c) coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece. The method further includes photolithographically defining the predetermined pattern in the carbon-containing hard mask layer, and etching the target layer in the presence of the hard mask layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Portable contact-less power transfer devices and rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS7248017B2Maximise currentMaximise voltageTransformersTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
There is disclosed a system and method for transferring power without requiring direct electrical conductive contacts. There is provided a primary unit having a power supply and a substantially laminar charging surface having at least one conductor that generates an electromagnetic field when a current flows therethrough and having an charging area defined within a perimeter of the surface, the at least one conductor being arranged such that electromagnetic field lines generated by the at least one conductor are substantially parallel to the plane of the surface or at least subtend an angle of 45° or less to the surface within the charging area; and at least one secondary device including at least one conductor that may be wound about a core. Because the electromagnetic field is spread over the charging area and is generally parallel or near-parallel thereto, coupling with flat secondary devices such as mobile telephones and the like is significantly improved in various orientations thereof.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Non-contact power transmission device
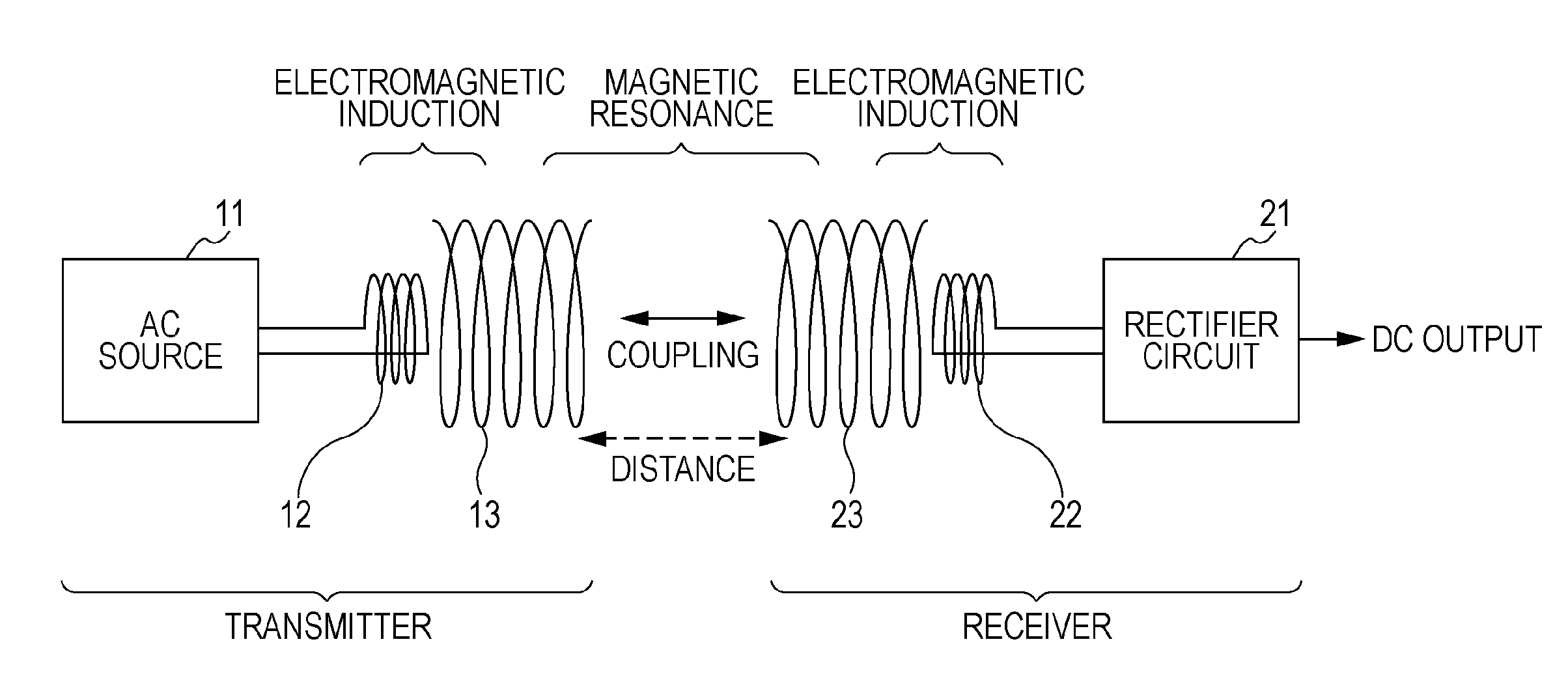
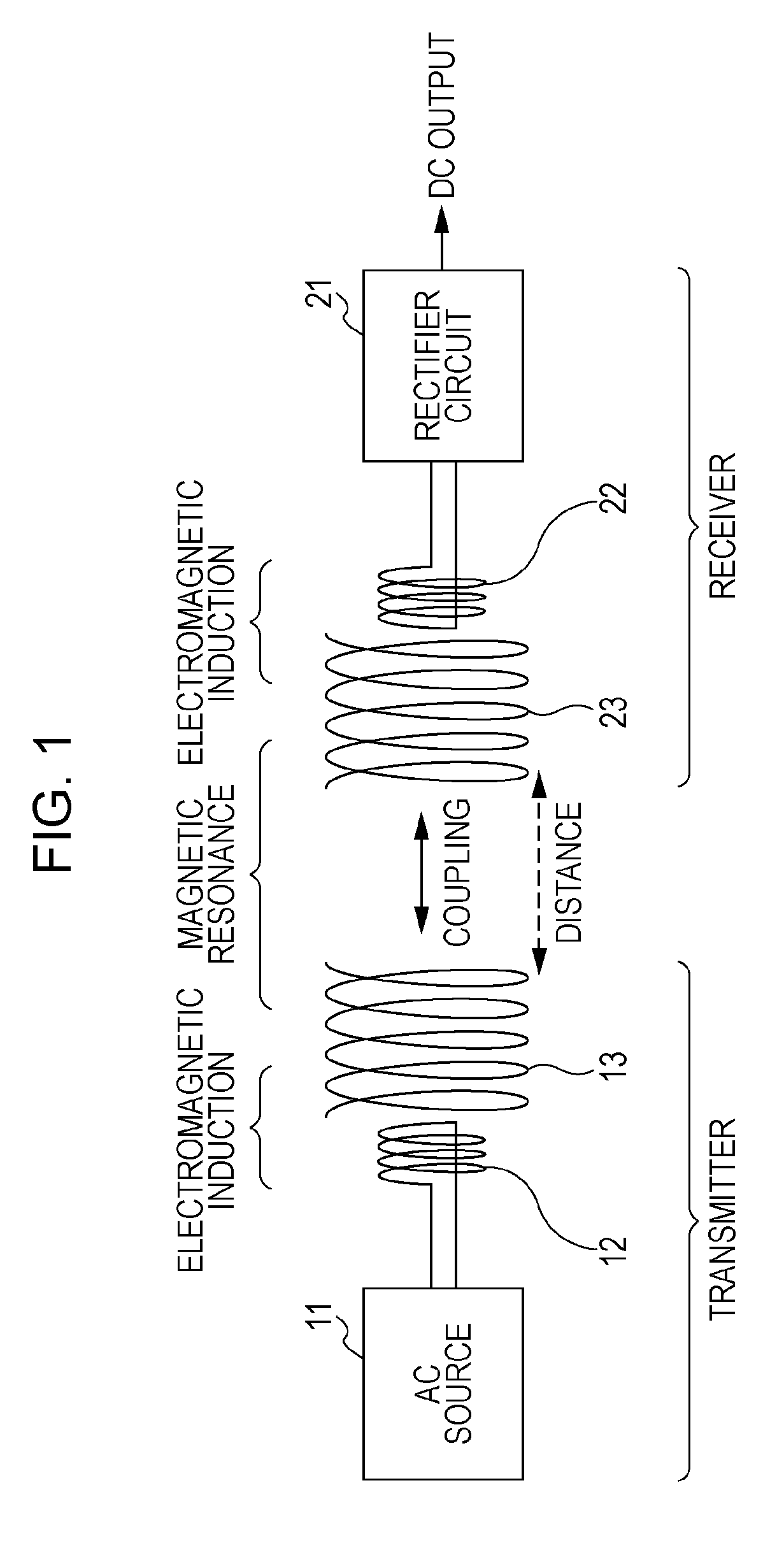
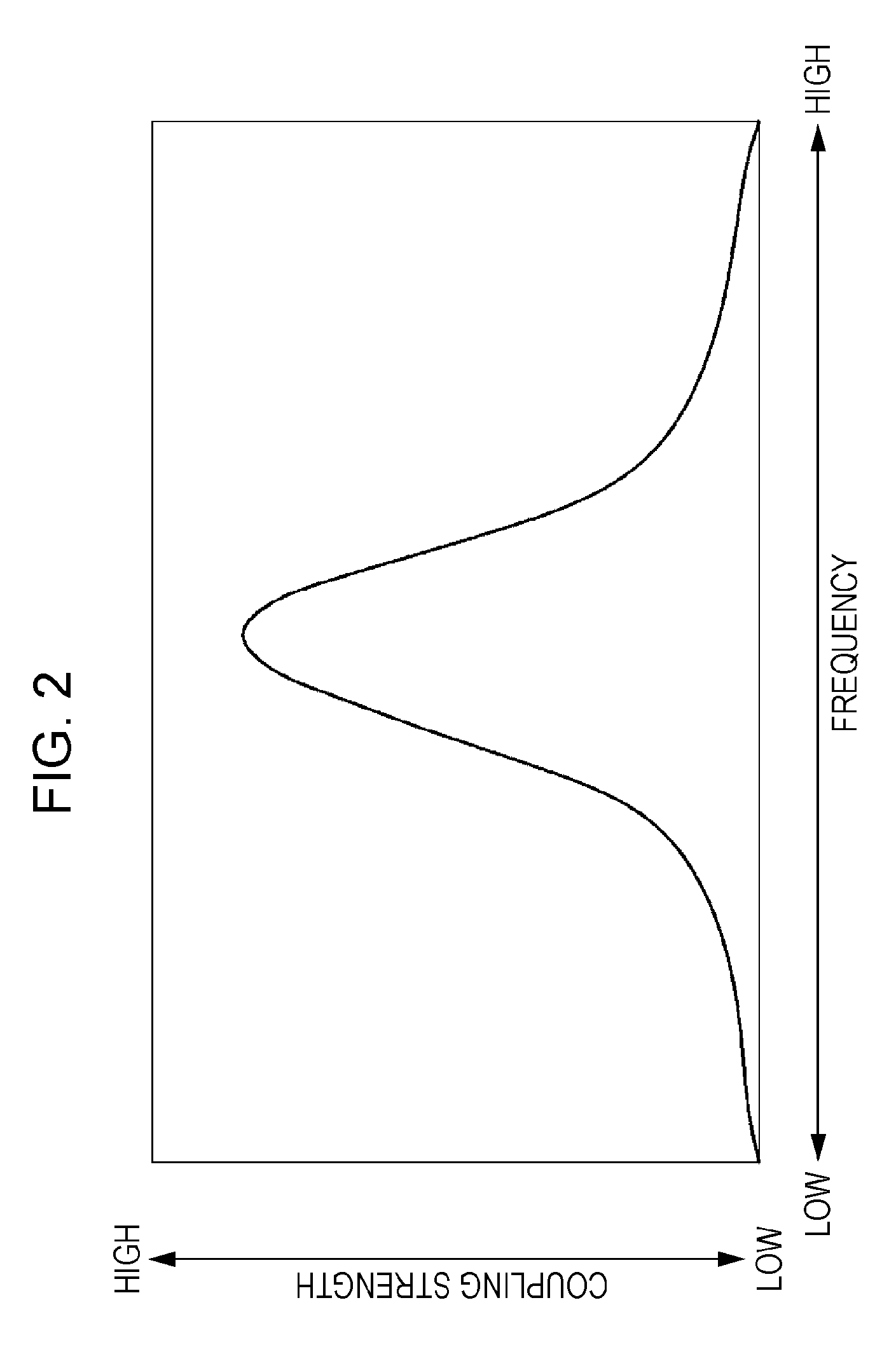
An electromagnetic resonance non-contact power transmission device includes a transmitter including a transmitter resonance element having a mechanism for discretely or continuously varying a resonant frequency, a transmitter excitation element coupled to the transmitter resonance element by electromagnetic induction, and an alternating current source for applying an alternating current at the same frequency as the resonant frequency to the transmitter excitation element, and a plurality of receivers each including a receiver resonance element having a specific resonant frequency, a receiver excitation element coupled to the receiver resonance element by electromagnetic induction, and an output circuit for outputting an electric current induced by the receiver excitation element. Electric power is transmitted selectively from the transmitter to any of the receivers having different specific resonant frequencies by changing the resonant frequency of the transmitter.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20100308739A1Reduction in size and costImprove Utilization and EfficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentControl signal
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a first plurality of segments of LEDs; a plurality of switches coupled to the plurality of segments of LEDs to switch a selected segment into or out of a series LED current path in response to a control signal; a memory; and a controller which, in response to a first parameter and during a first part of an AC voltage interval, determines and stores in the memory a value of a second parameter and generates a first control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs into the series LED current path; and during a second part of the AC voltage interval, when a current value of the second parameter is substantially equal to the stored value, generates a second control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs out of the first series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com