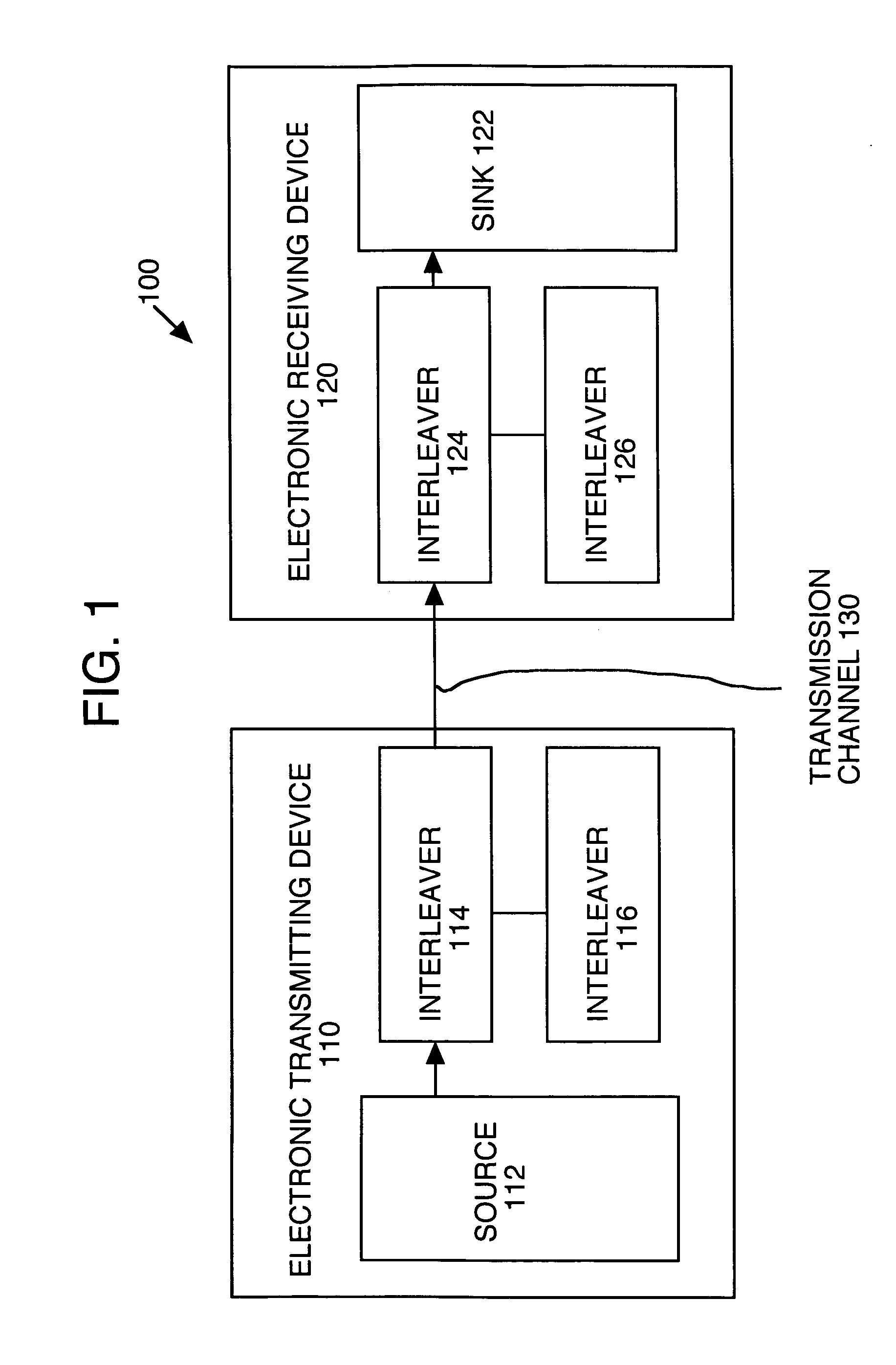
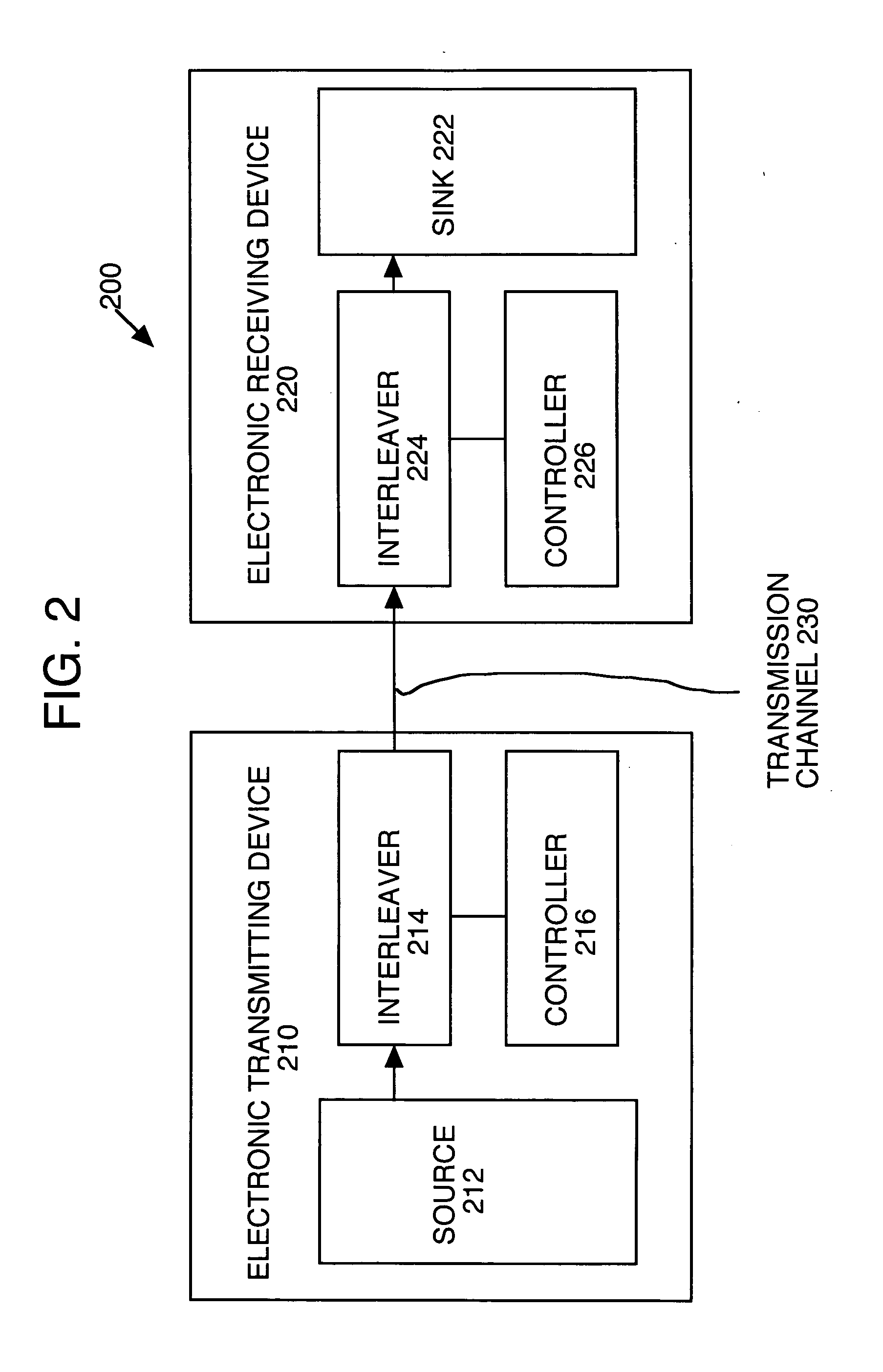
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Interleaving" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
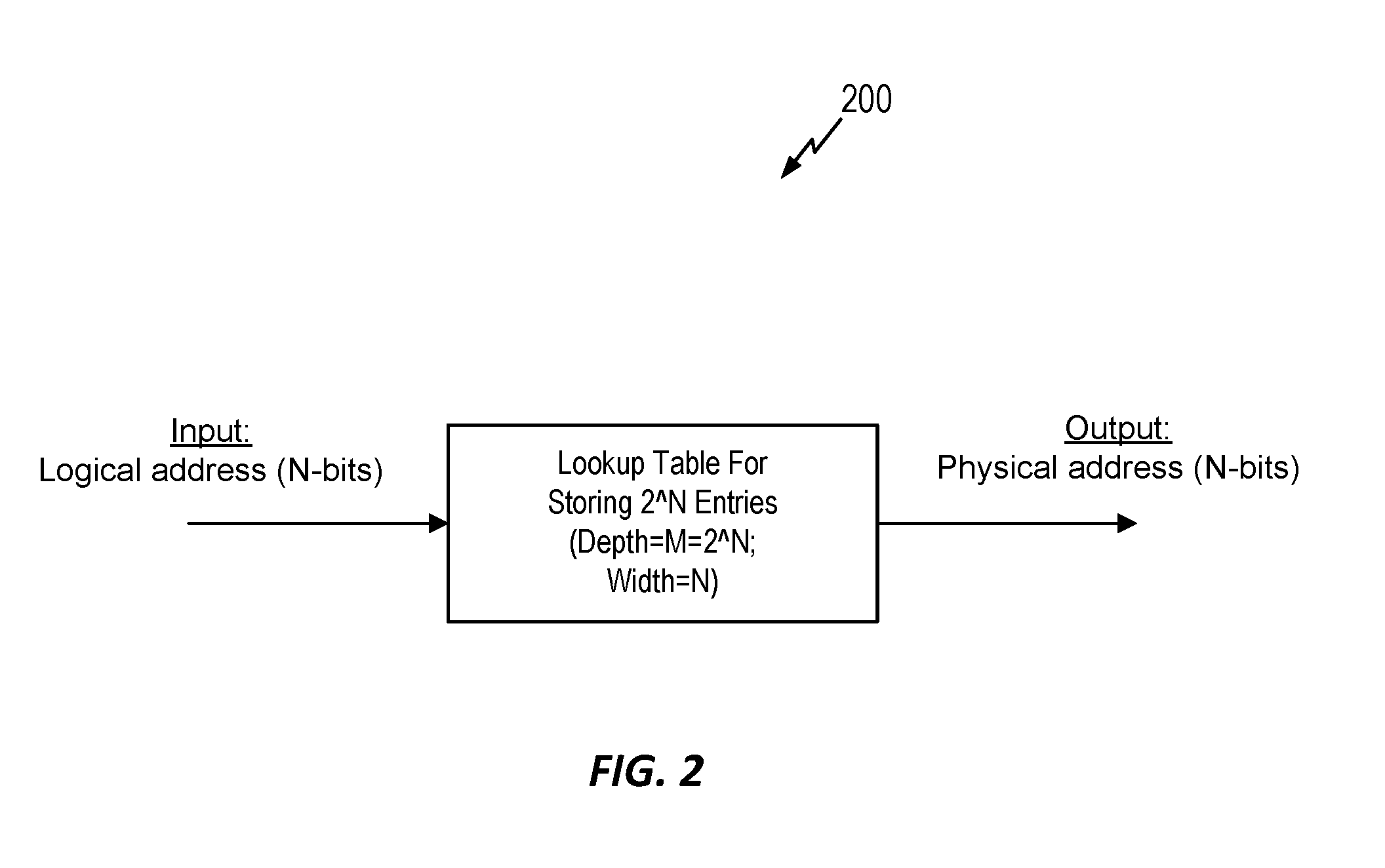
In disk storage and drum memory, interleaving is a technique used to improve access performance of storage by putting data accessed sequentially into non-sequential sectors. The number of physical sectors between consecutive logical sectors is called the interleave skip factor or skip factor.
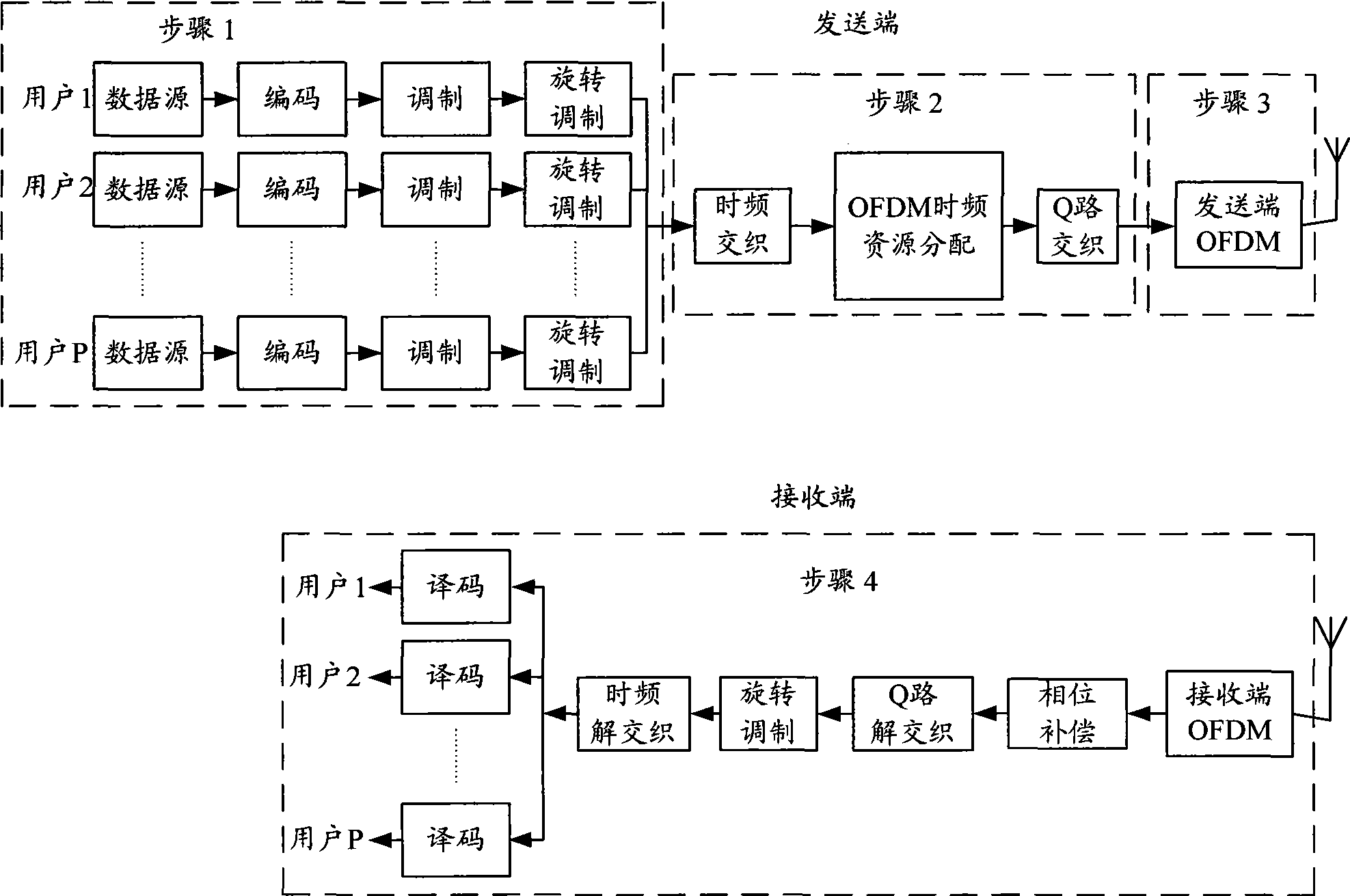
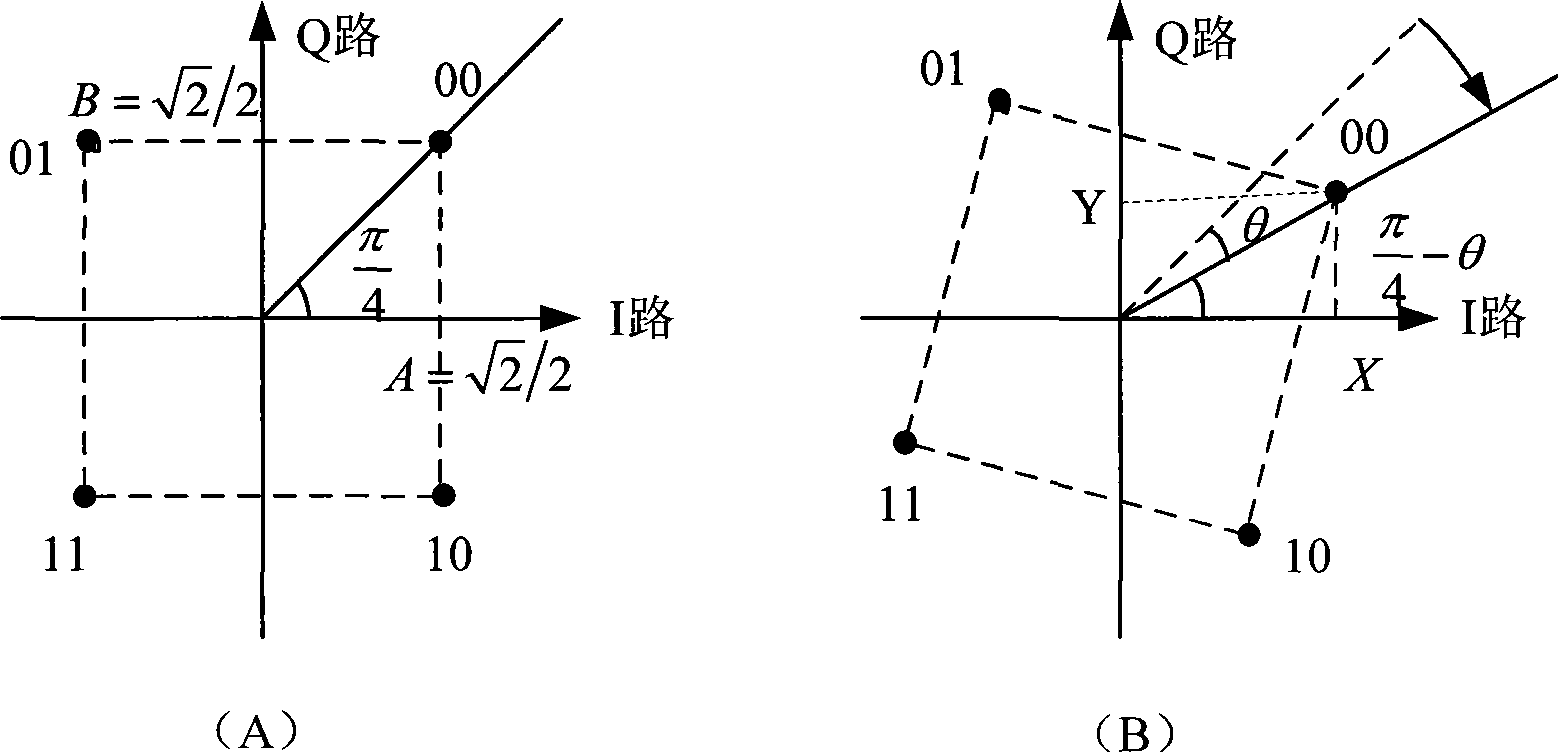
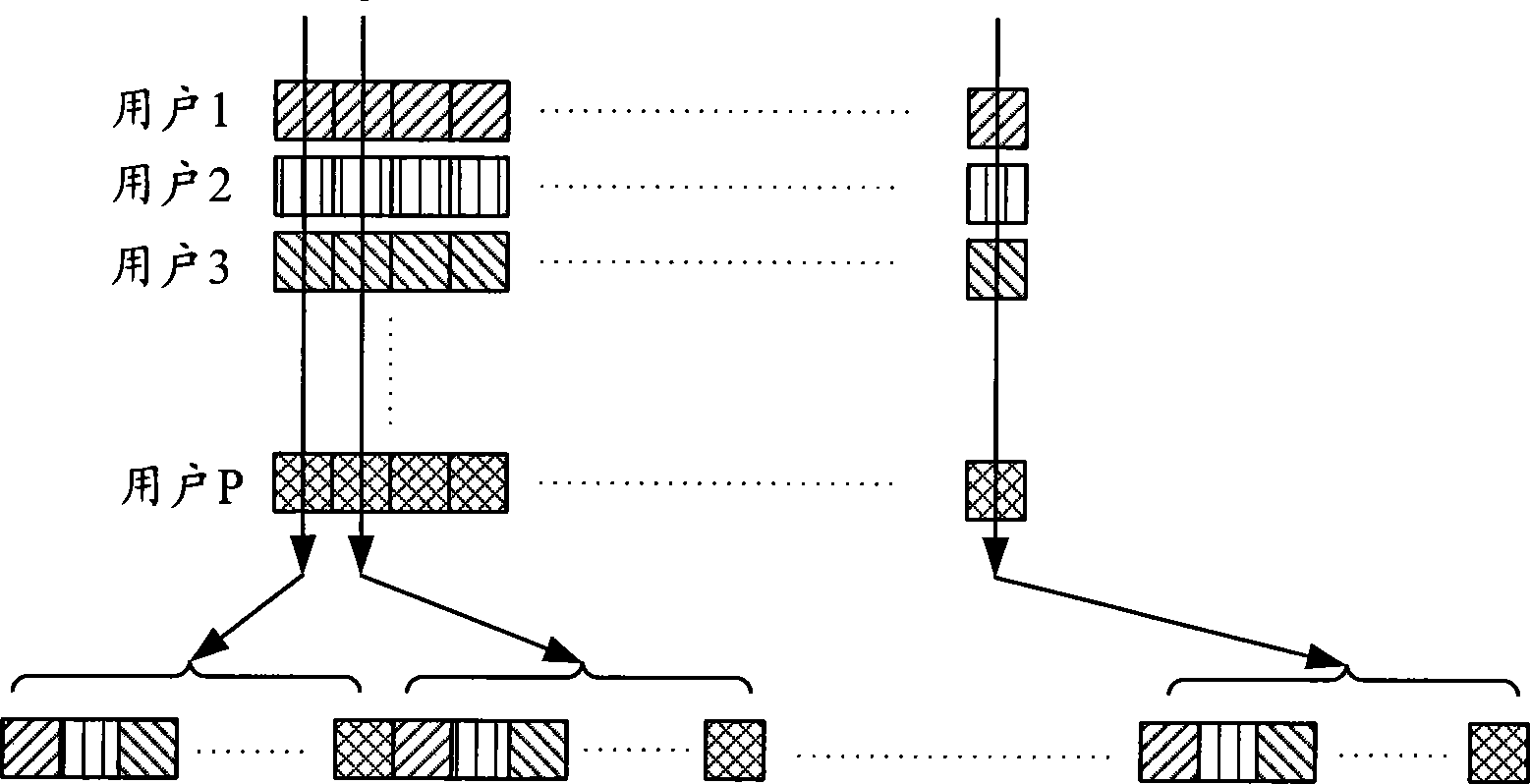
Signal diversifying method for OFDM system
InactiveCN101394392AImprove performanceEasy to operateMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsZero paddingData information
A signal diversity method of an OFDM system comprises the following steps: carrying out data decoding, modulation and rotation-modulation by a transmitting end, and storing the symbols of the processed data blocks; subjecting the symbols of the data blocks of a plurality of users in a memory to grouping and time-frequency interleaving, OFDM time-frequency resource allocation and Q-path interleaving according to the set number of the users, respectively subjecting the symbols of each data block to IFFT operation and CP addition after zero padding according to the OFDM modulation length, then transmitting the data; and subjecting the symbols of the data blocks to de-CP and FFT operations after a receiving end receives the data, carrying out phase compensation and zero removal, and sequentially subjecting the symbols of the obtained data blocks to Q-path de-interleaving, rotation demodulation, time-frequency de-interleaving and coding to obtain the desired data information. By adopting OFDM technique and rotation modulation technique and by selecting an optimal rotation angle, the method can acquire signal diversity gain and maximal performance improvement, thereby improving the system performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
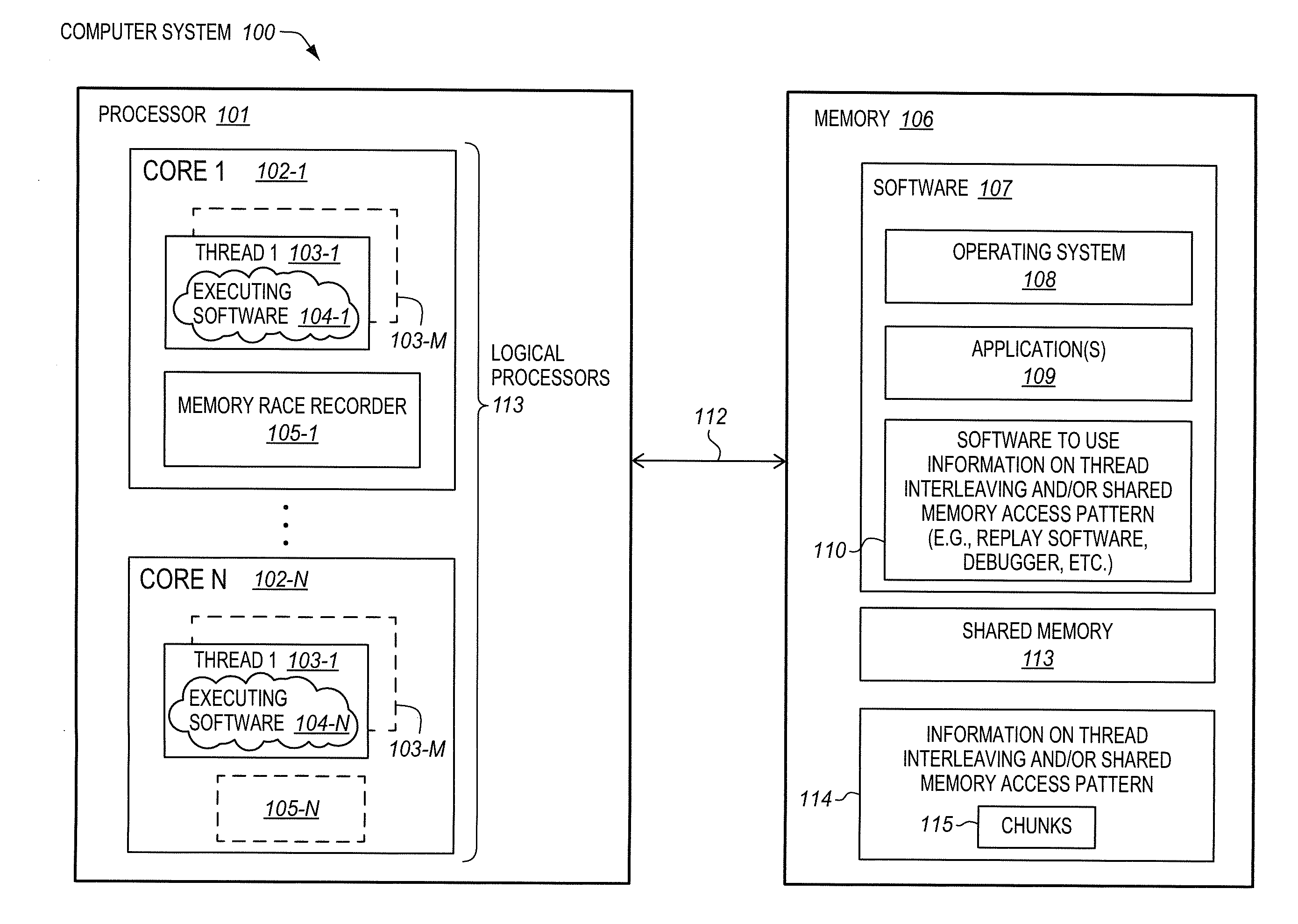
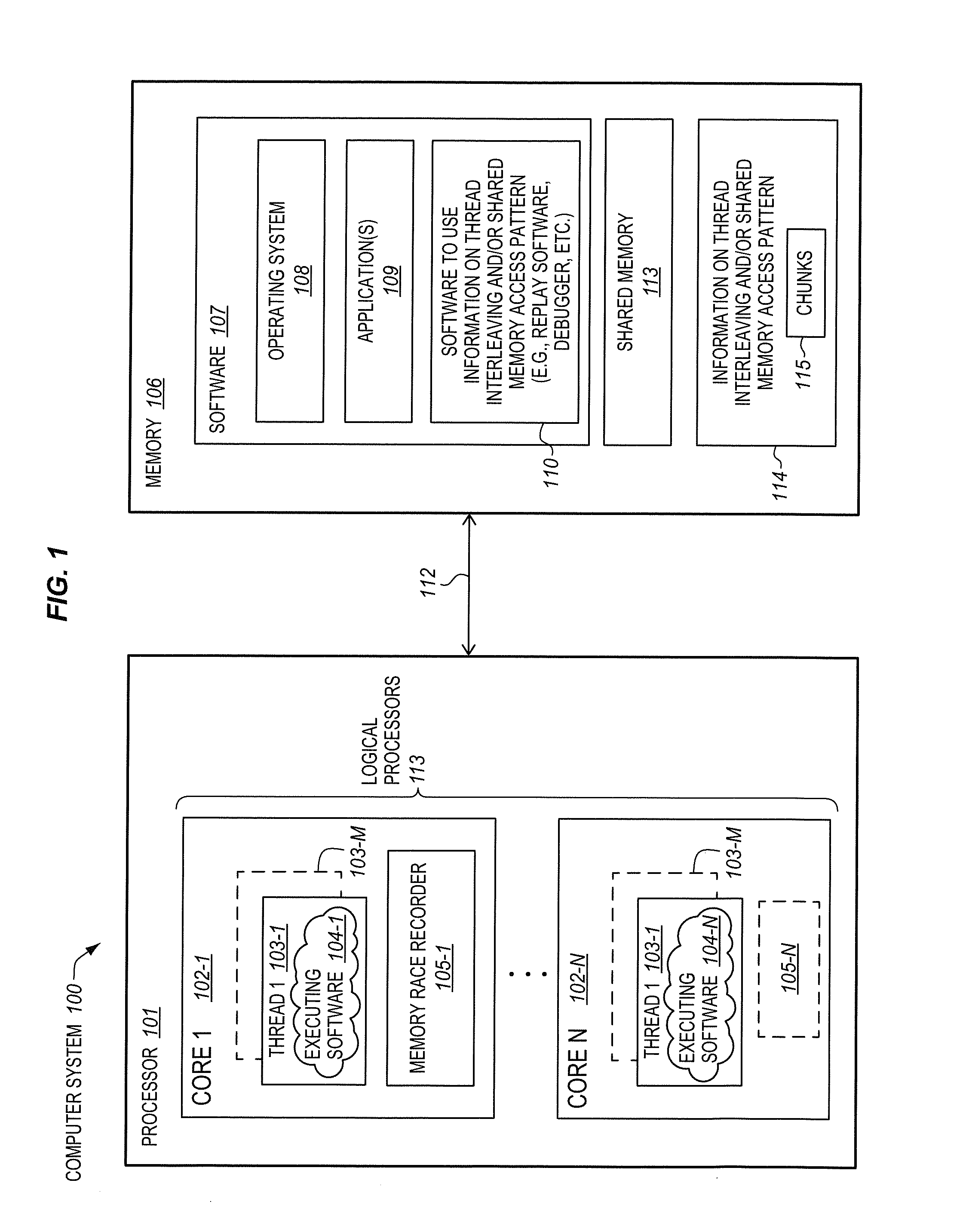
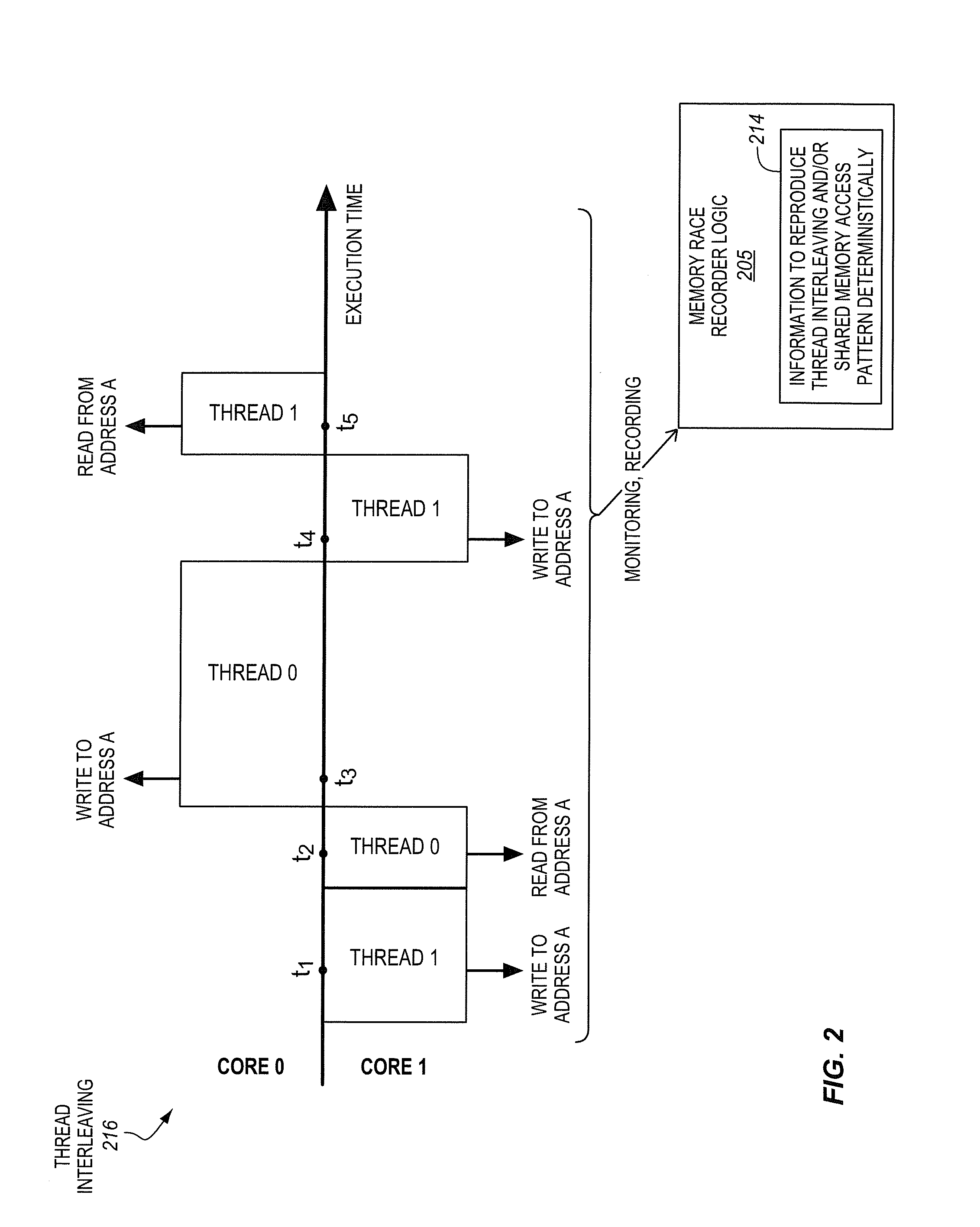
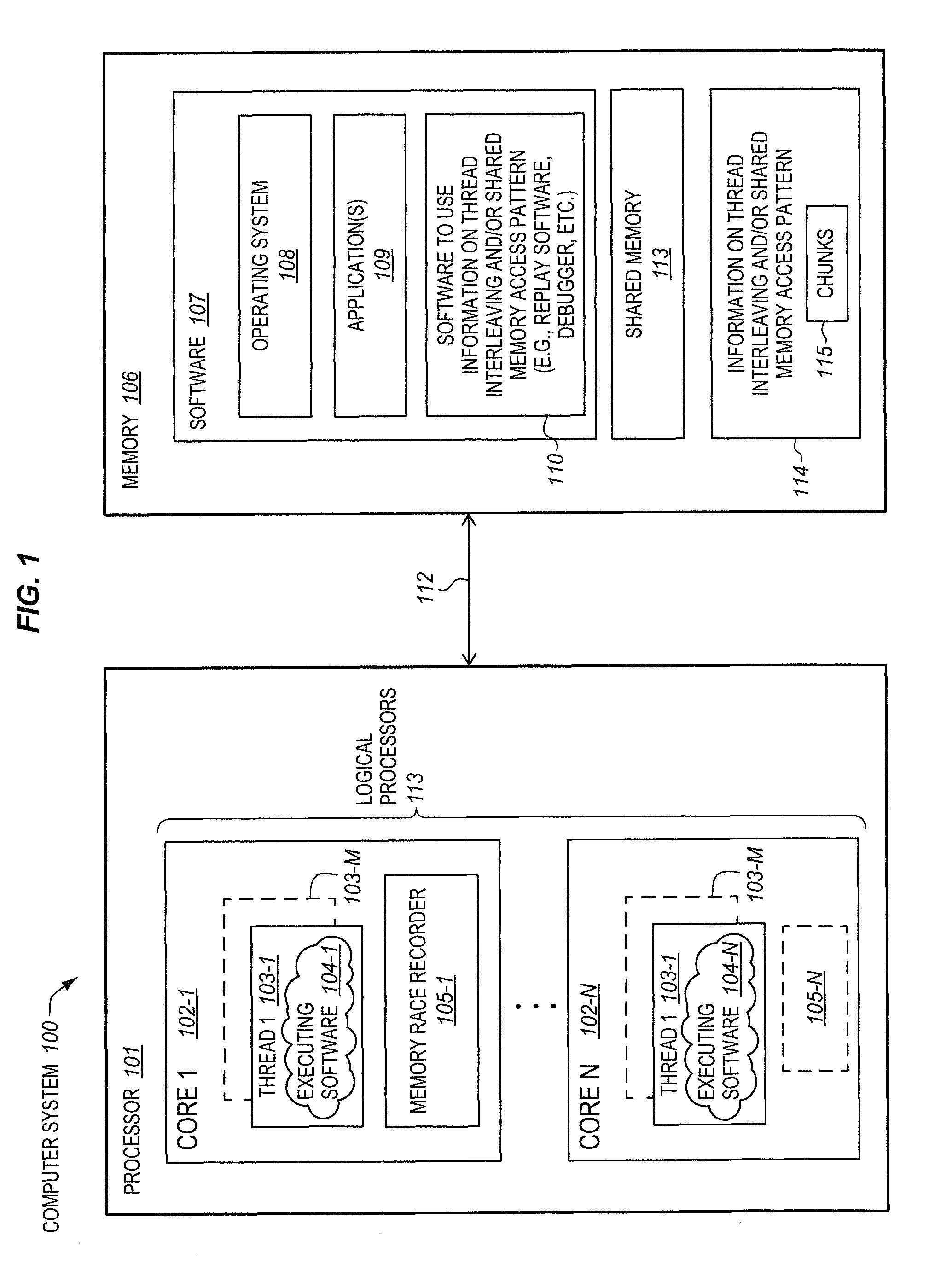
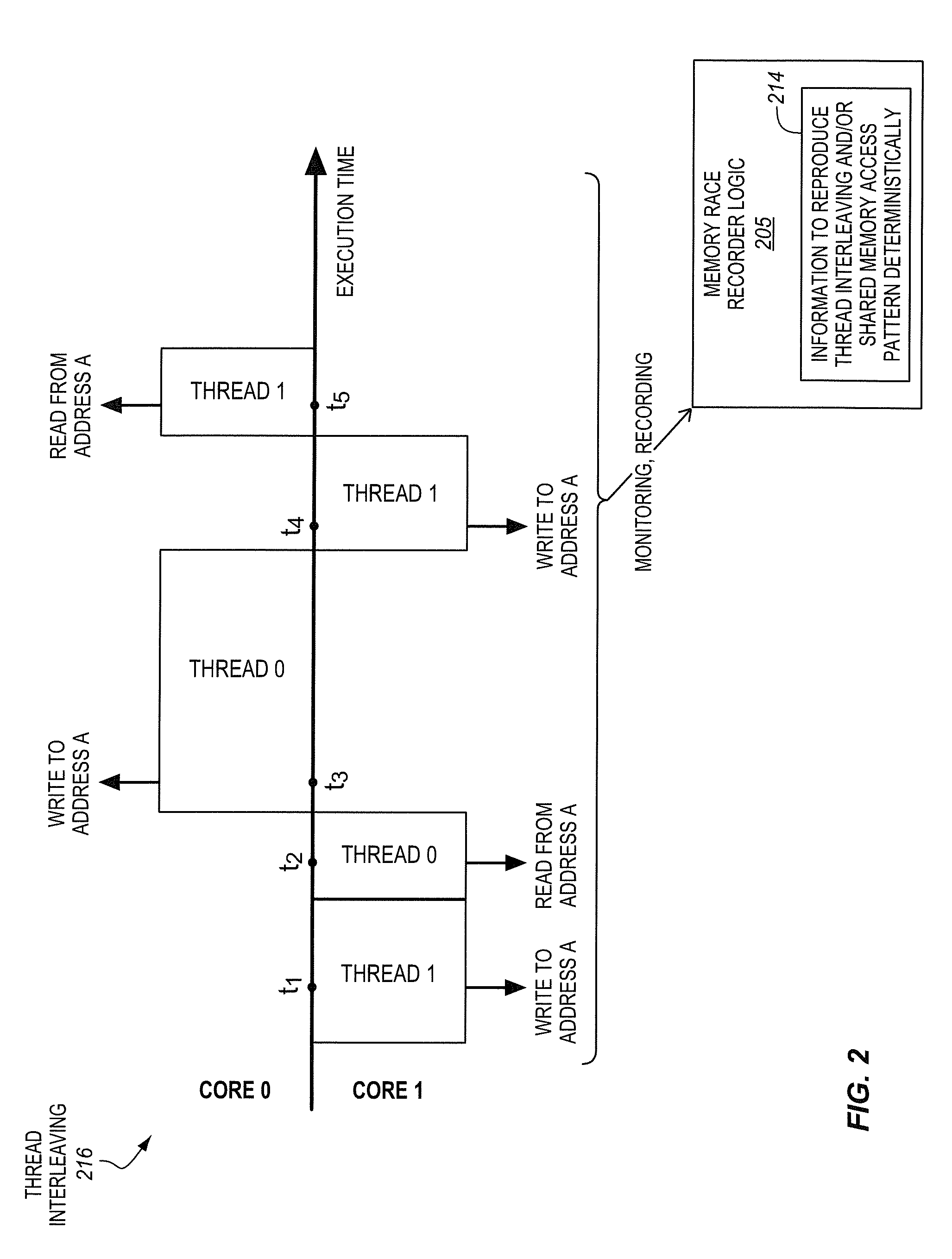
Processor with memory race recorder to record thread interleavings in multi-threaded software
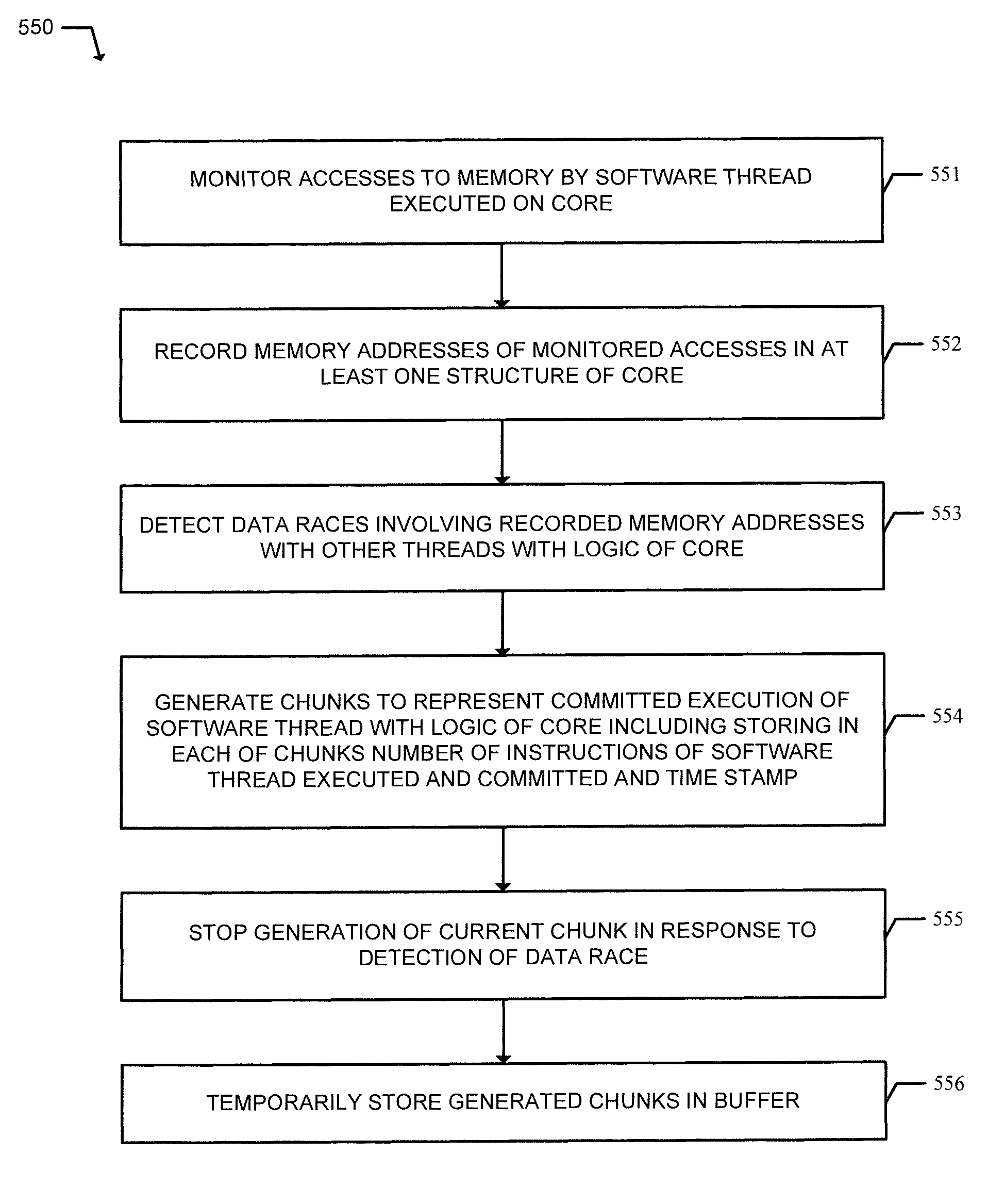
InactiveUS20140189256A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationSoftware testing/debuggingMemory addressComputer architecture
A processor includes a first core to execute a first software thread, a second core to execute a second software thread, and shared memory access monitoring and recording logic. The logic includes memory access monitor logic to monitor accesses to memory by the first thread, record memory addresses of the monitored accesses, and detect data races involving the recorded memory addresses with other threads. The logic includes chunk generation logic is to generate chunks to represent committed execution of the first thread. Each of the chunks is to include a number of instructions of the first thread executed and committed and a time stamp. The chunk generation logic is to stop generation of a current chunk in response to detection of a data race by the memory access monitor logic. A chunk buffer is to temporarily store chunks until the chunks are transferred out of the processor.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Error-correcting code interleaver
InactiveUS6839870B2Efficient and reliable to useData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionParallel computingError correcting
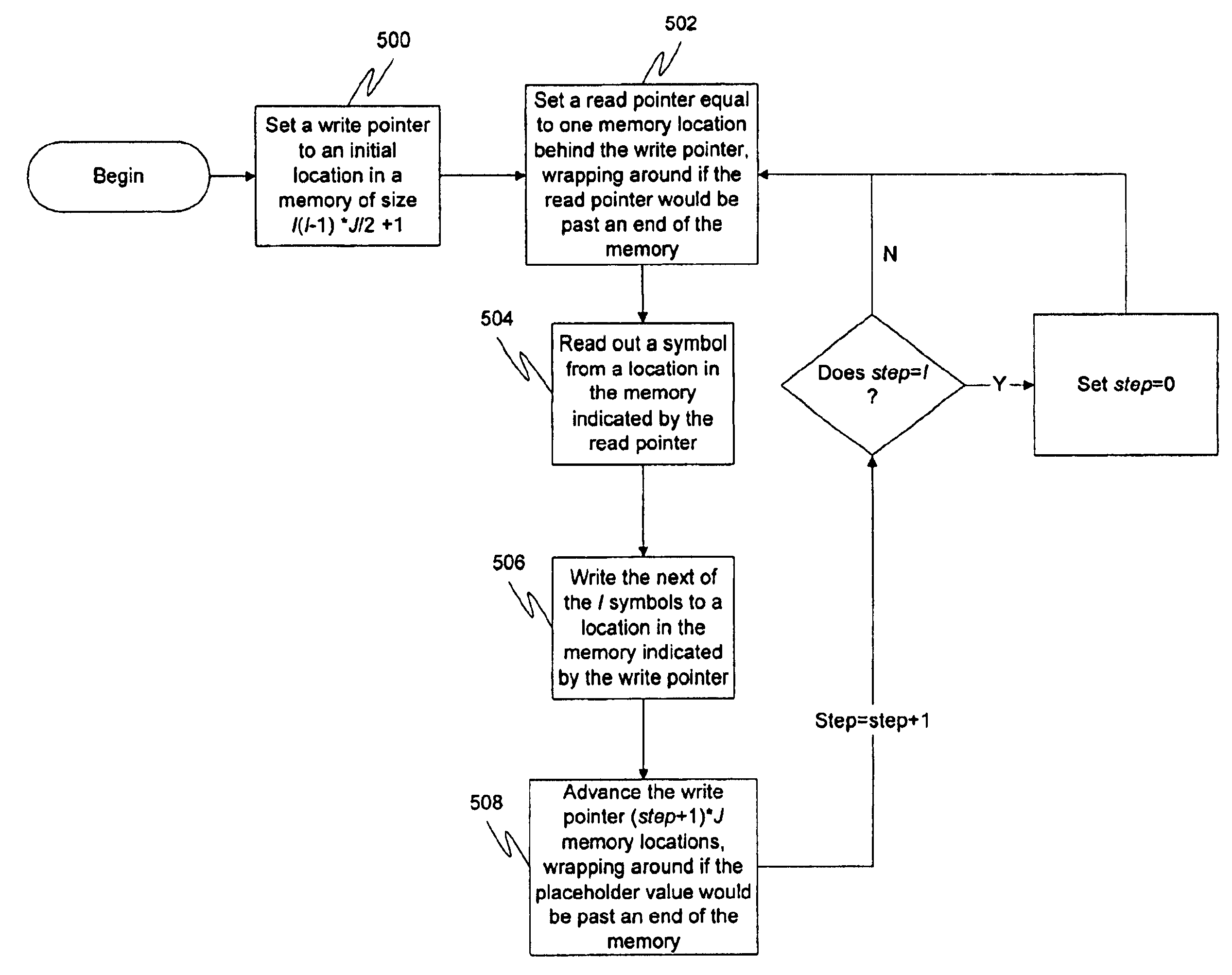
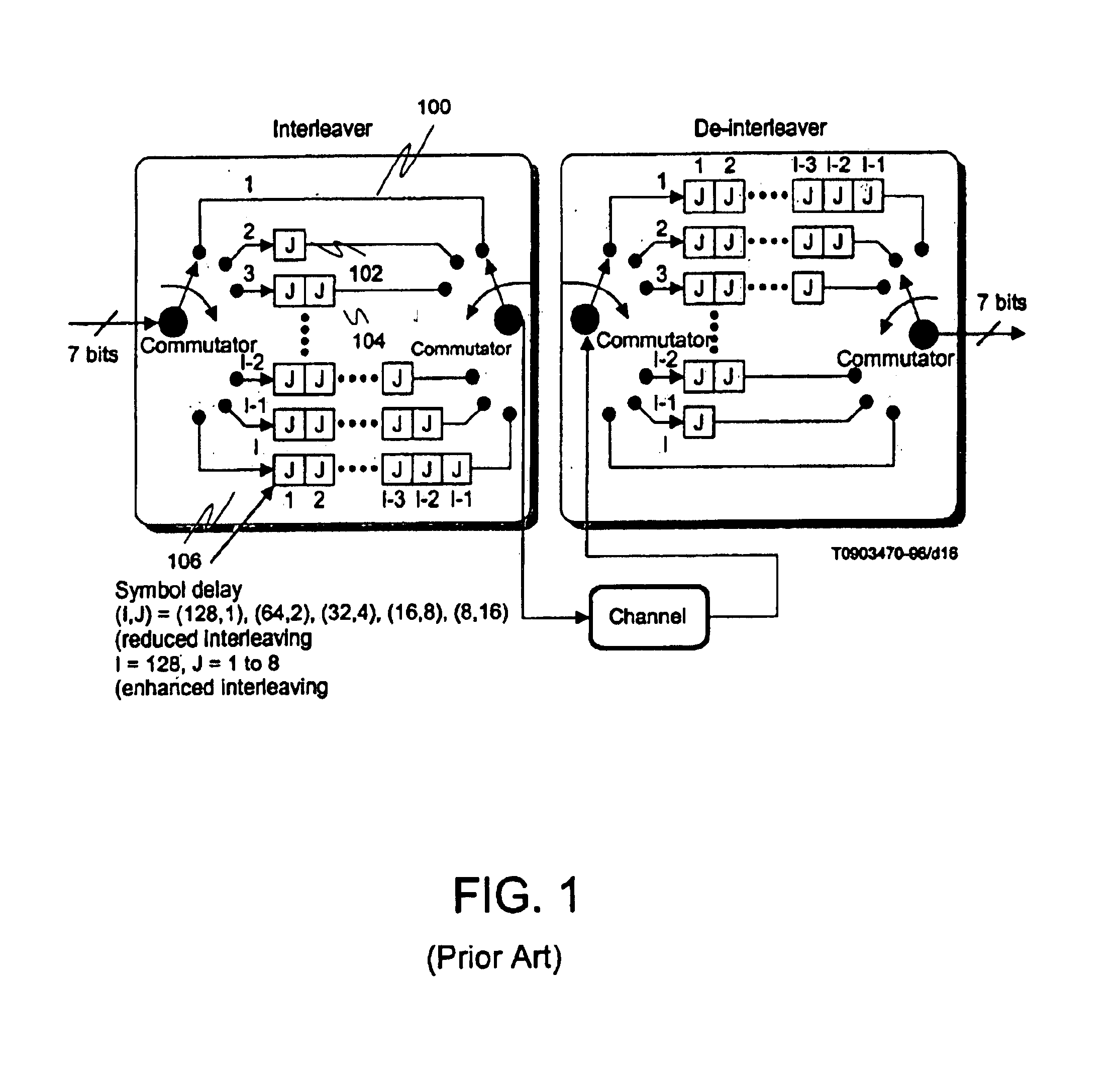
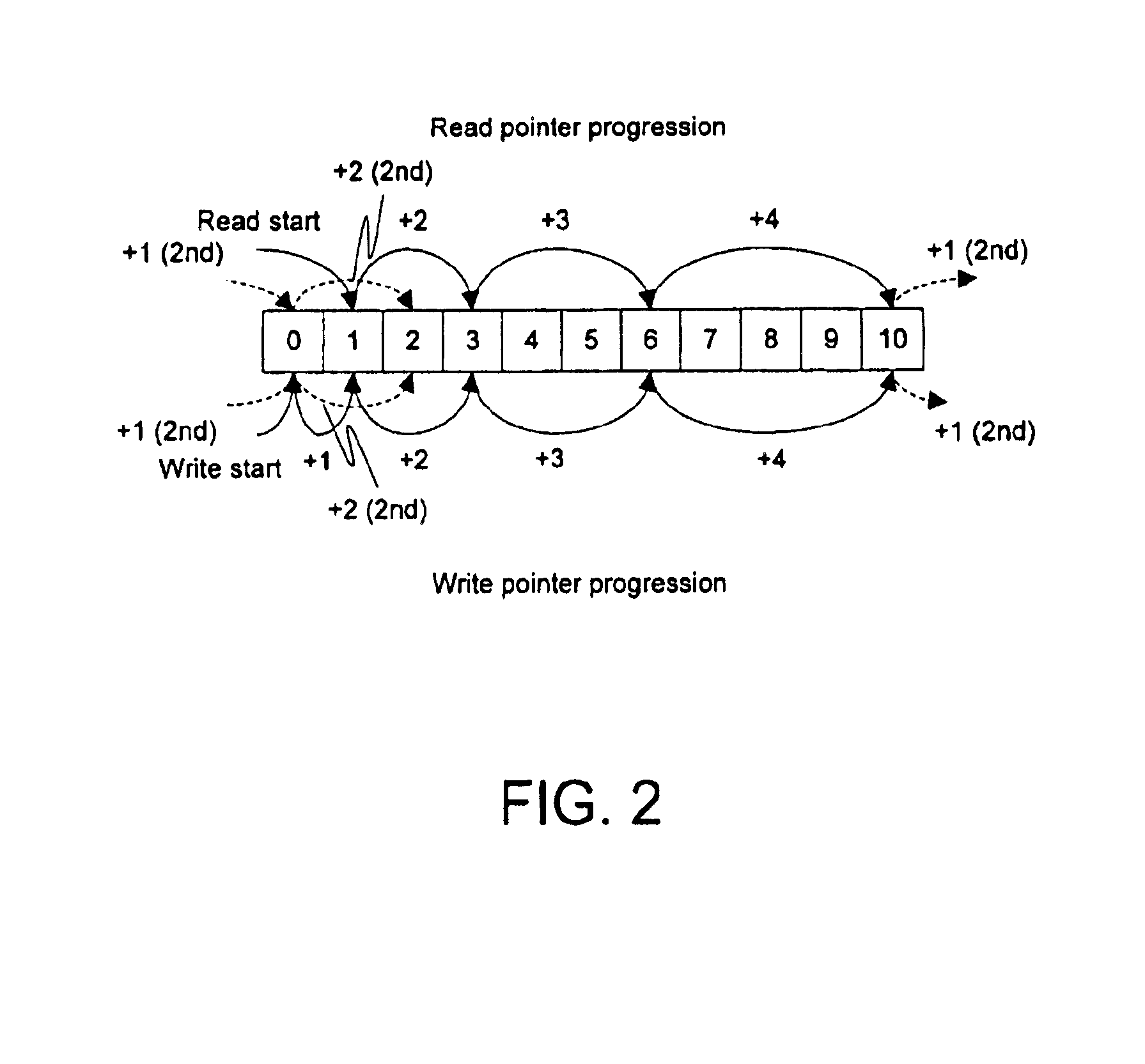
Memory may be partitioned into ever-sliding FIFOs. Each of the FIFOs may be stacked end-to-end in memory with the oldest data at the base offset and the newest at the end (or vice-virsa). Each symbol, the pointer may be incremented (modulo the set size) by an appropriate amount (typically J more than for the previous symbol). After each set, the pointers may be incremented by J more than the previous increment and the process starts over, wrapping around the memory if the end of the memory is reached. After a preset number of symbols, the process may restart from an increment of J. Alternatively, the pointers may be decremented rather than incremented. Thus, the newest symbol cannibalizes the memory position vacated by the oldest symbol in the current FIFO, causing the FIFOs to “slide”, providing for a very efficient and reliable use of memory for error-correcting code interleaving.
Owner:TERAYON COMM SYST
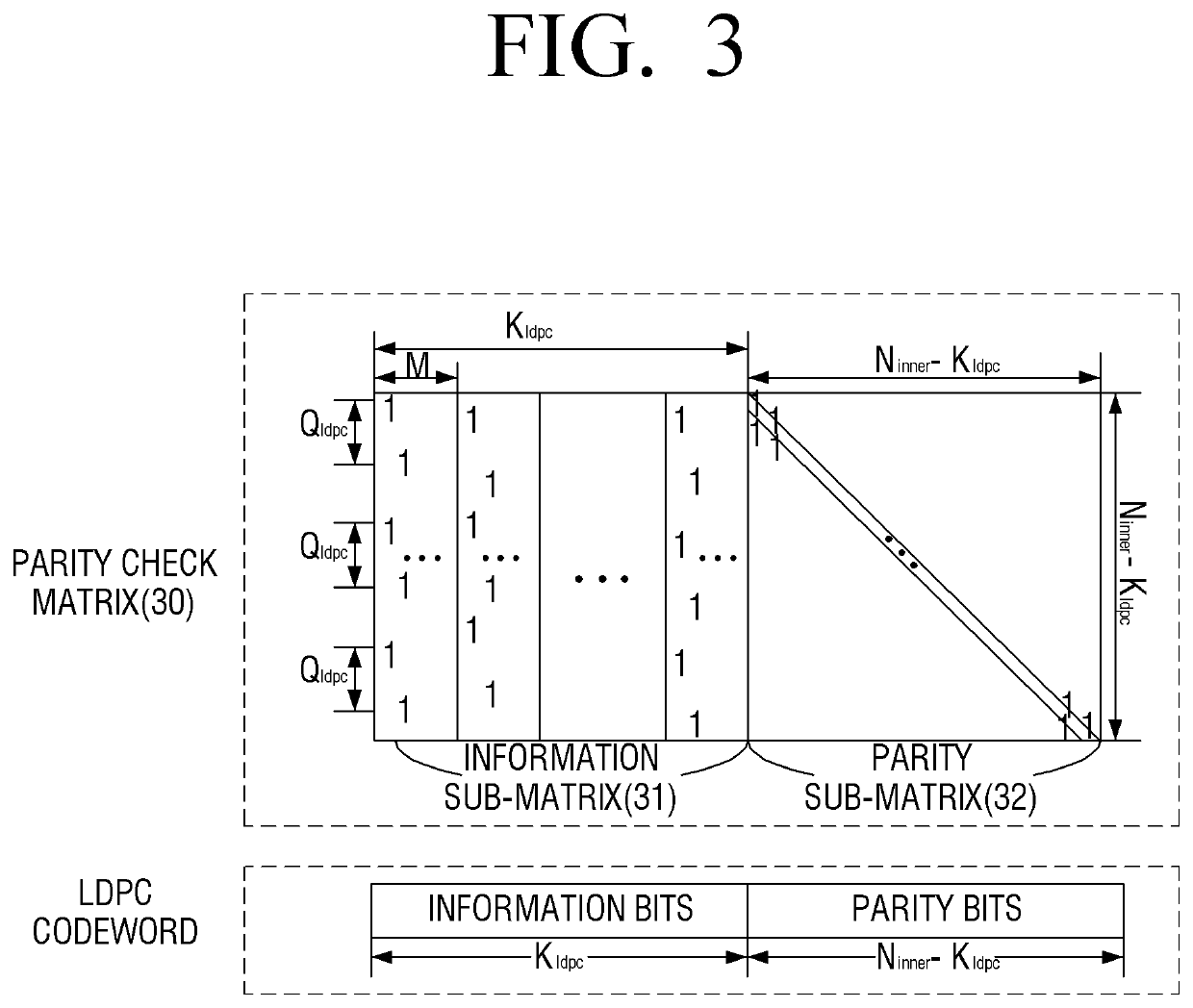
Multi-level signal memory with LDPC and interleaving
ActiveUS7971130B2Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using LDPC codesParallel computingLow density
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Interleaving and rate matching and de-interleaving and rate de-matching methods
InactiveCN101547064AReduce read and write operationsError preventionMatching methodsComputer science
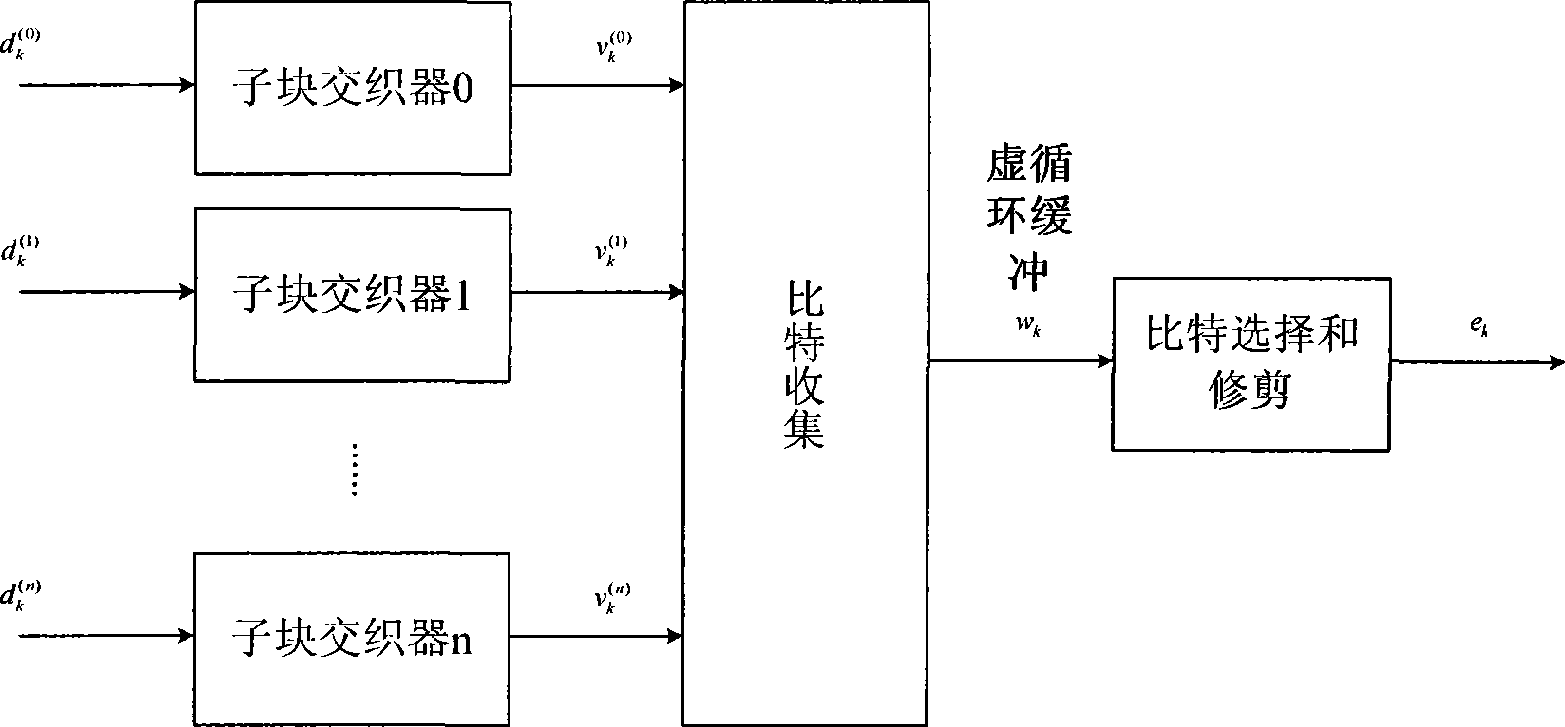
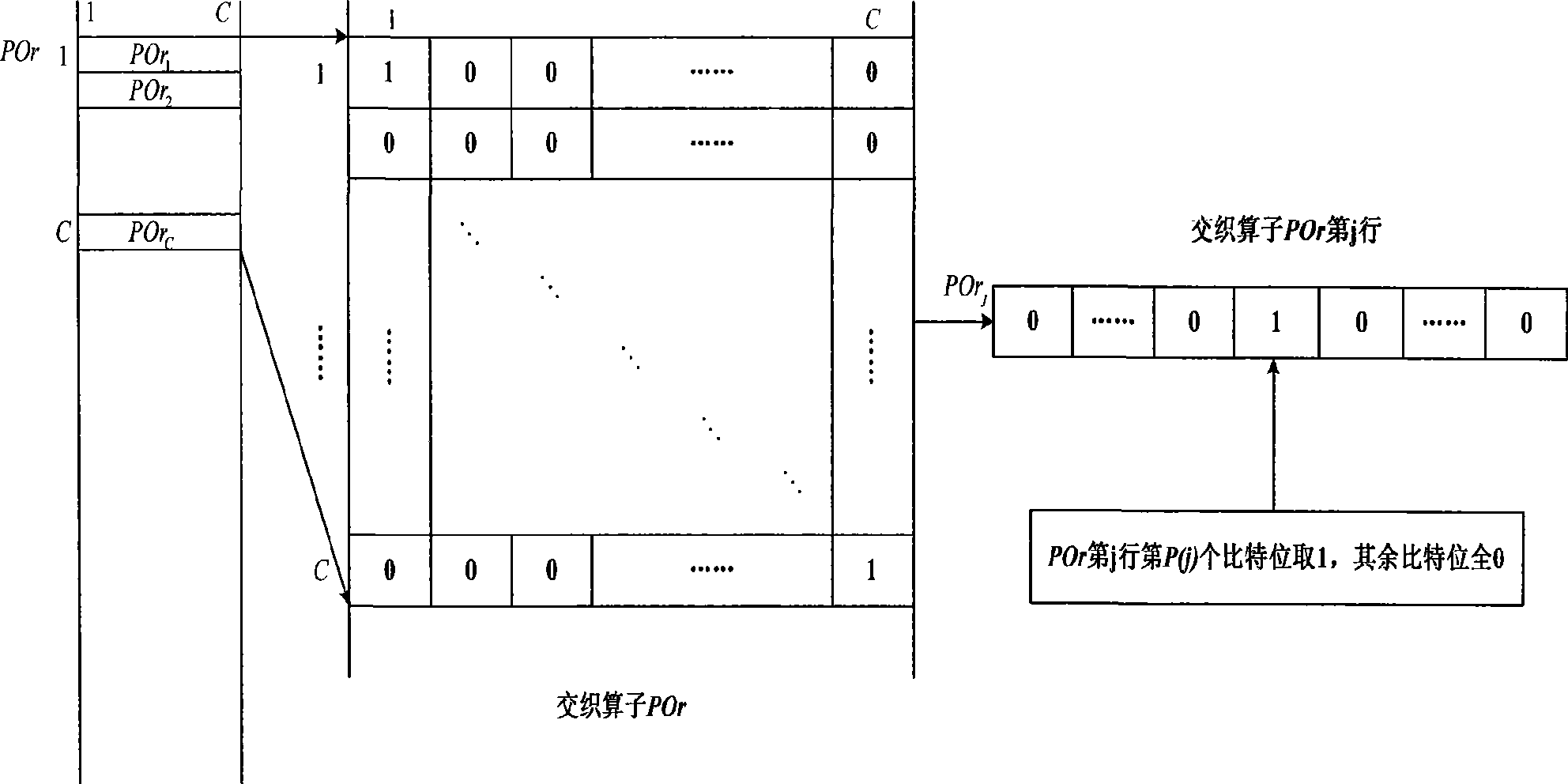
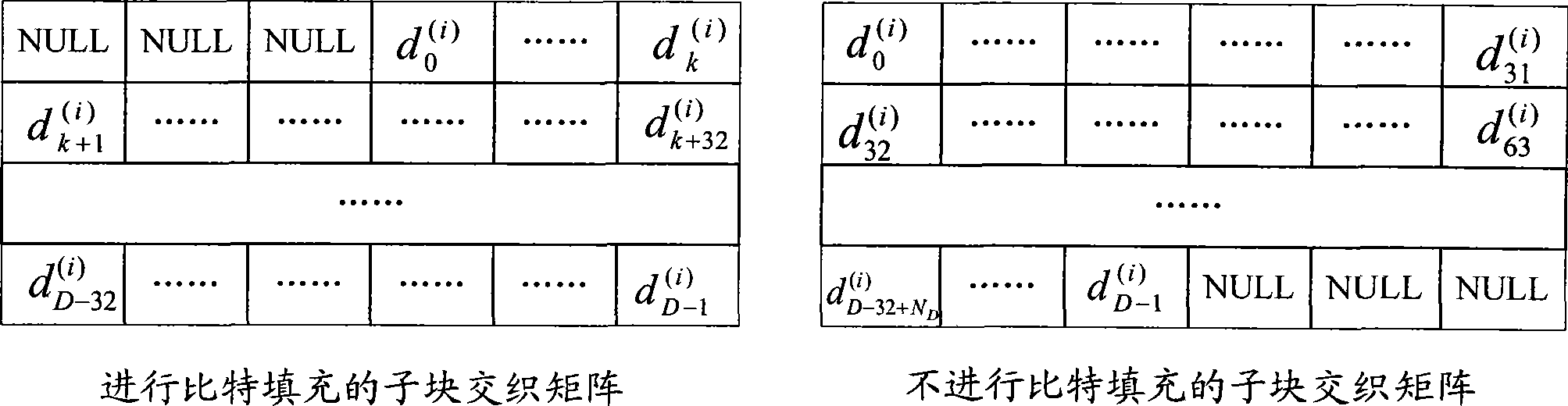
The invention discloses an interleaving and rate matching method. A correction interleaving mode is determined according to a column interleaving mode and head filling bits, an interleaving operator is determined according to the correction interleaving mode, and the interleaving operator is utilized to perform interleaving processing on subblock interleaving matrices in sequence; one mode can utilize the interleaving operator to perform the interleaving processing on bits required to be output in the subblock interleaving matrices according to the requirement of redundancy version, directly output subblock interleaving results after protocol sorting while completing the interleaving of subblocks until meeting the corresponding requirement of the code rate; and the other mode can utilize the interleaving operator to perform the interleaving processing on the subblock interleaving matrices one by one, output the subblock interleaving results after protocol sorting to a circulating buffer while completing the interleaving of subblocks, and then output corresponding bits after the interleaving according to the requirement of the redundancy version. Furthermore, the invention also discloses a de-interleaving and rate de-matching method corresponding to the interleaving and rate matching method. The methods can greatly reduce buffers to be used and read-write operation of the buffers in the interleaving and rate matching and de-interleaving and rate de-matching processes.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
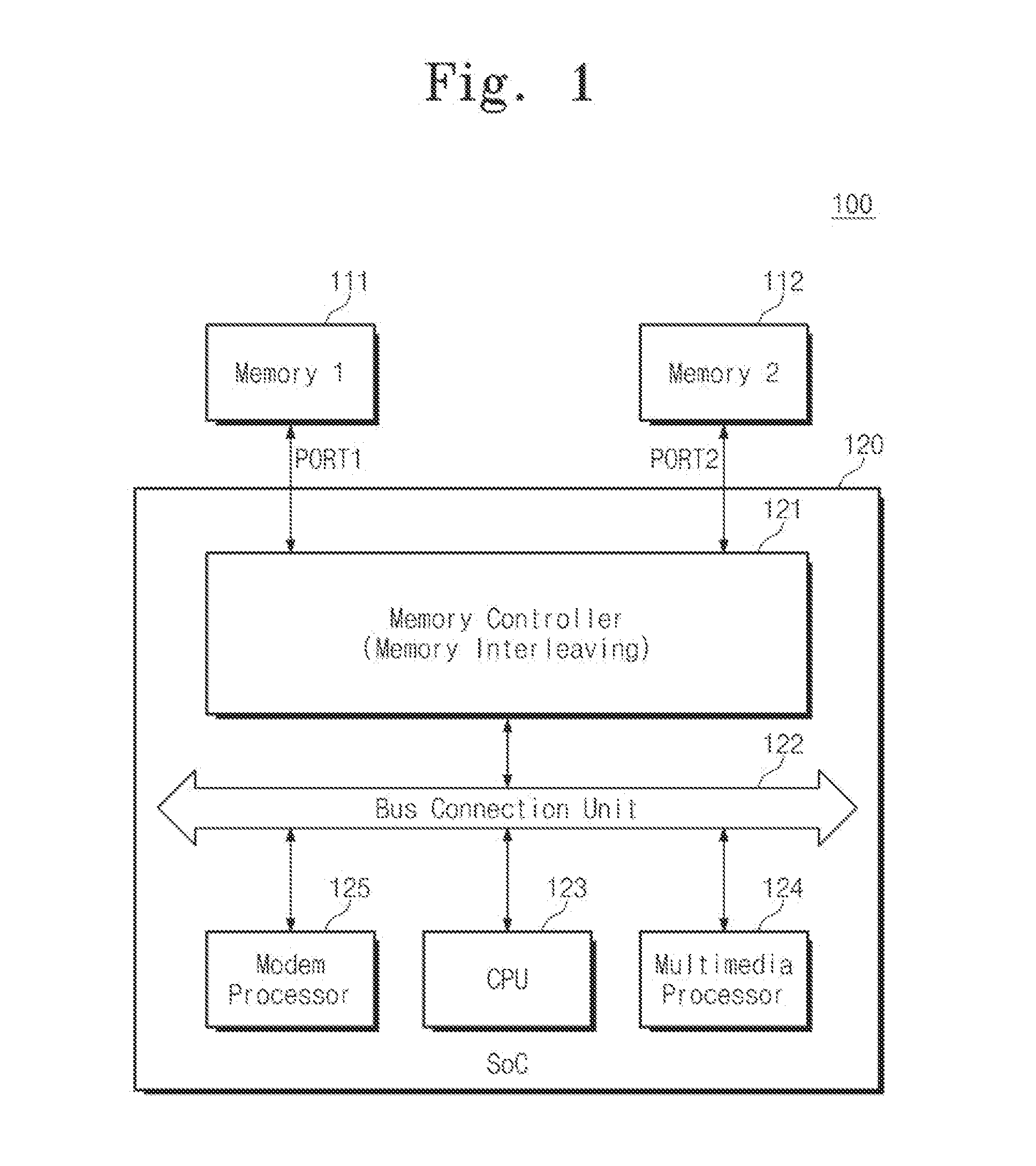
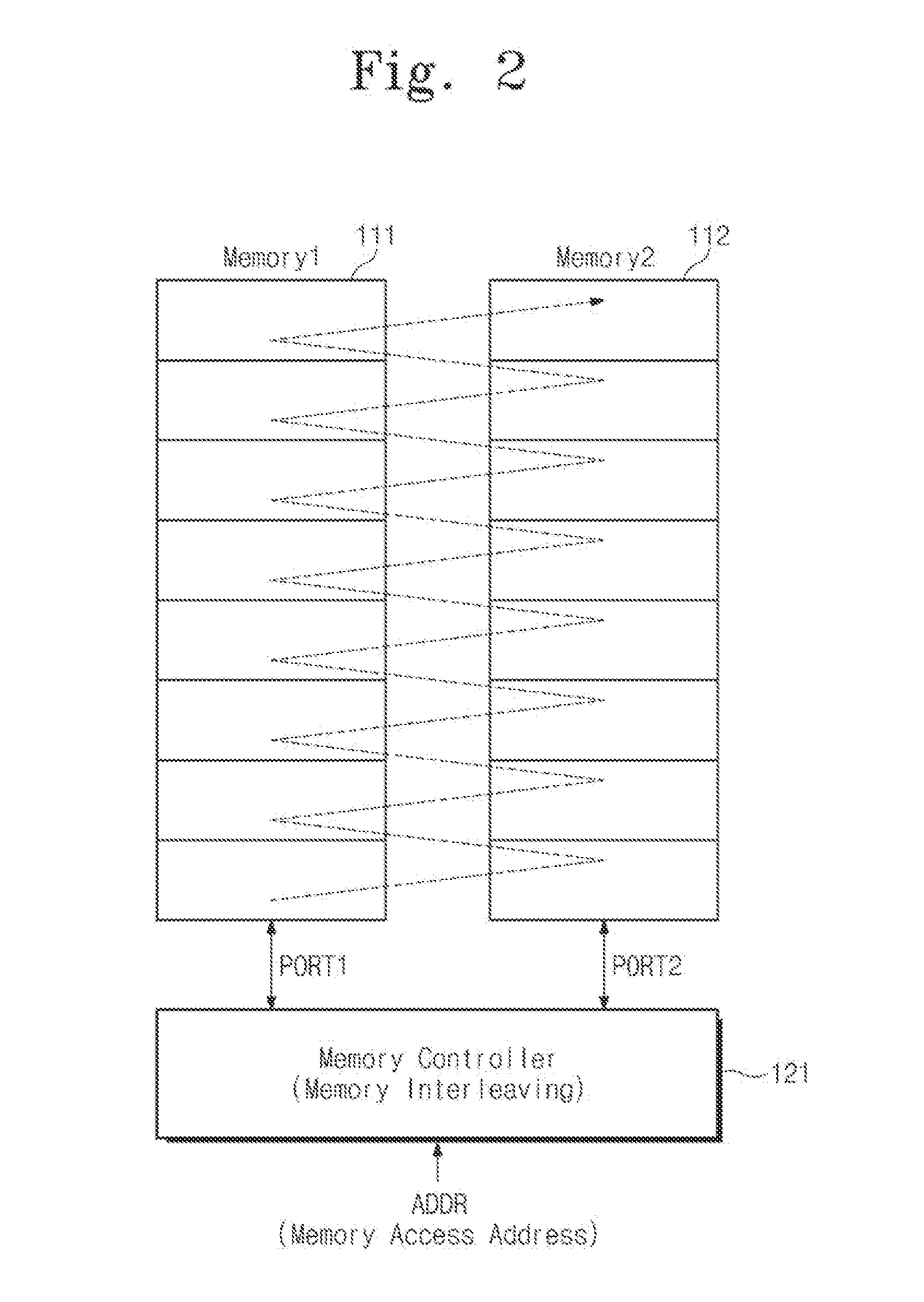
Memory system and soc including linear addresss remapping logic
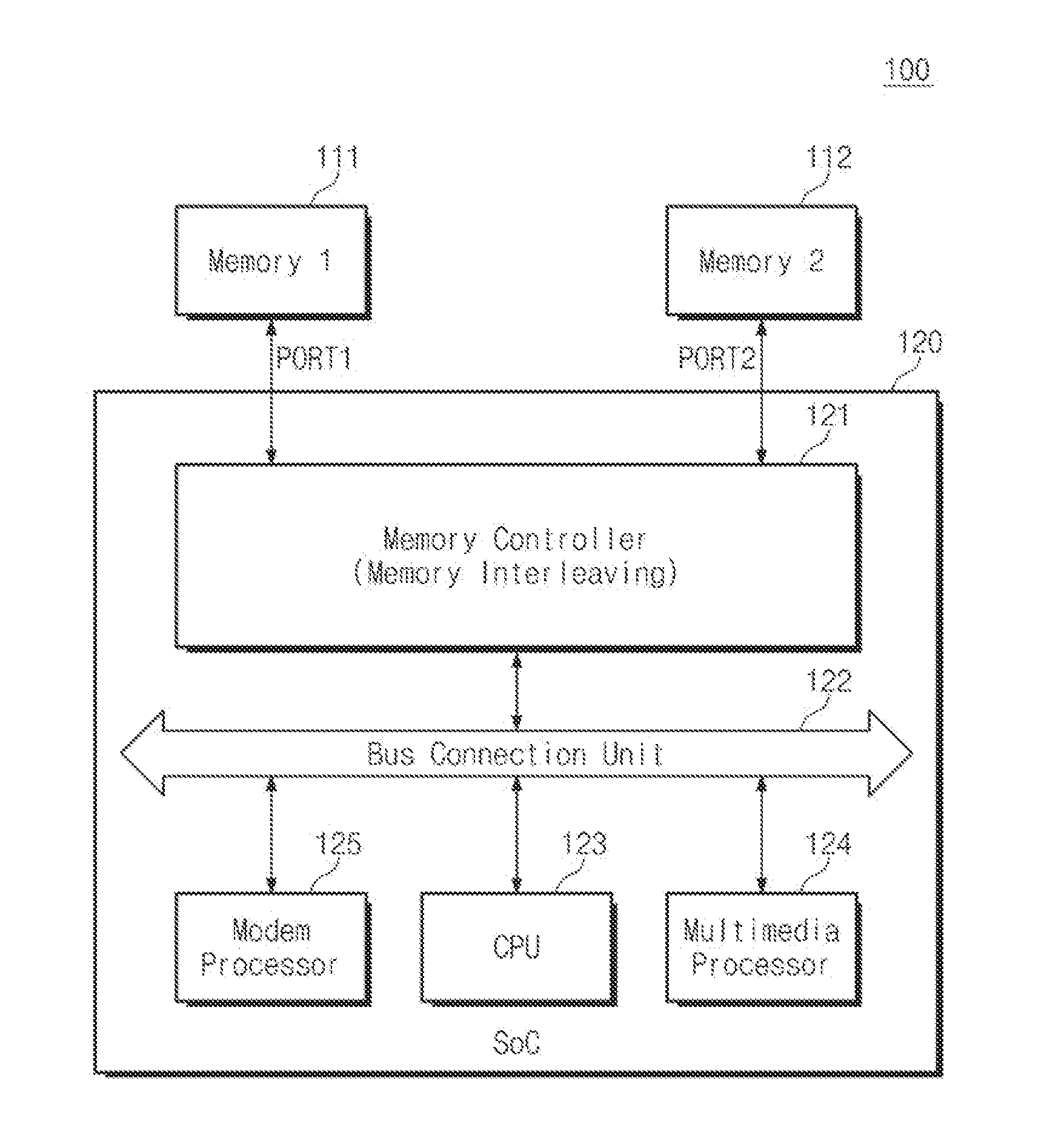
ActiveUS20130339640A1Increase data bandwidthReduce power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationModem deviceTerm memory
A system-on-chip is connected to a first memory device and a second memory device. The system-on-chip comprises a memory controller configured to control an interleaving access operation on the first and second memory devices. A modem processor is configured to provide an address for accessing the first or second memory devices. A linear address remapping logic is configured to remap an address received from the modem processor and to provide the remapped address to the memory controller. The memory controller performs a linear access operation on the first or second memory device in response to receiving the remapped address.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
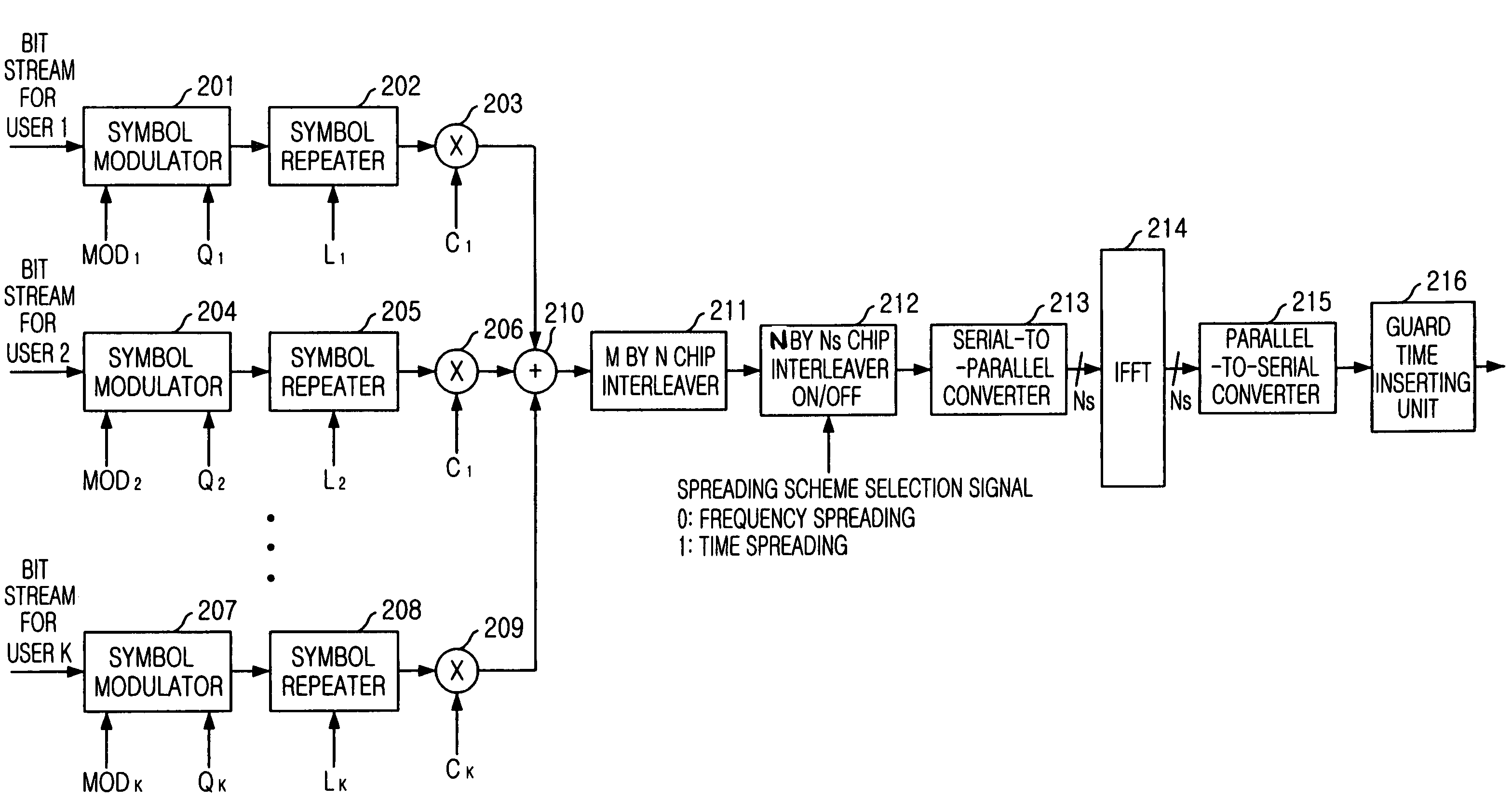
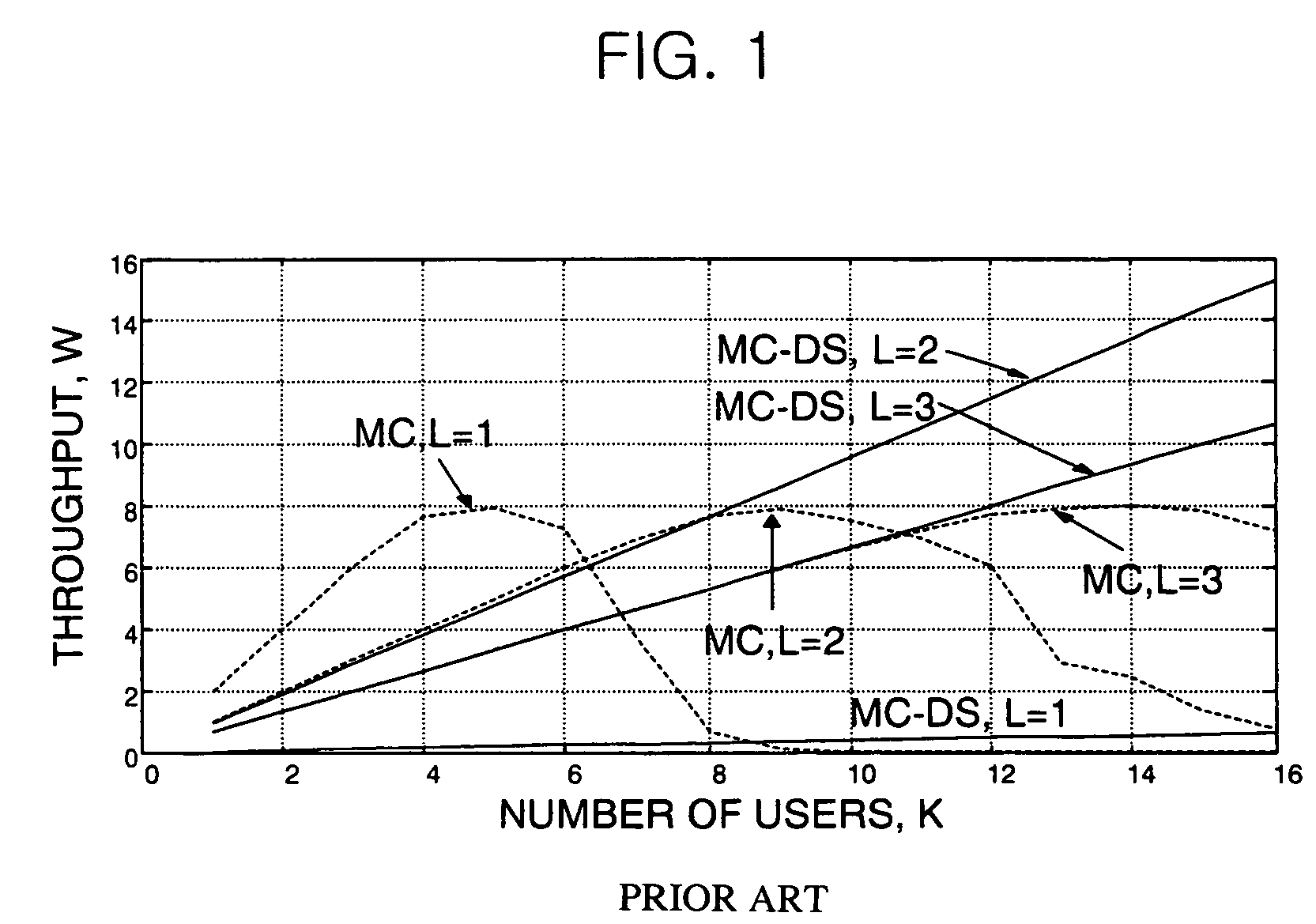
MC/MC-DS dual-mode adaptive multi-carrier code division multiple access (CDMA) apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS7349460B2Maintaining flexibilityStay flexibleMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTime-division multiplexCdma systemsTransfer mode
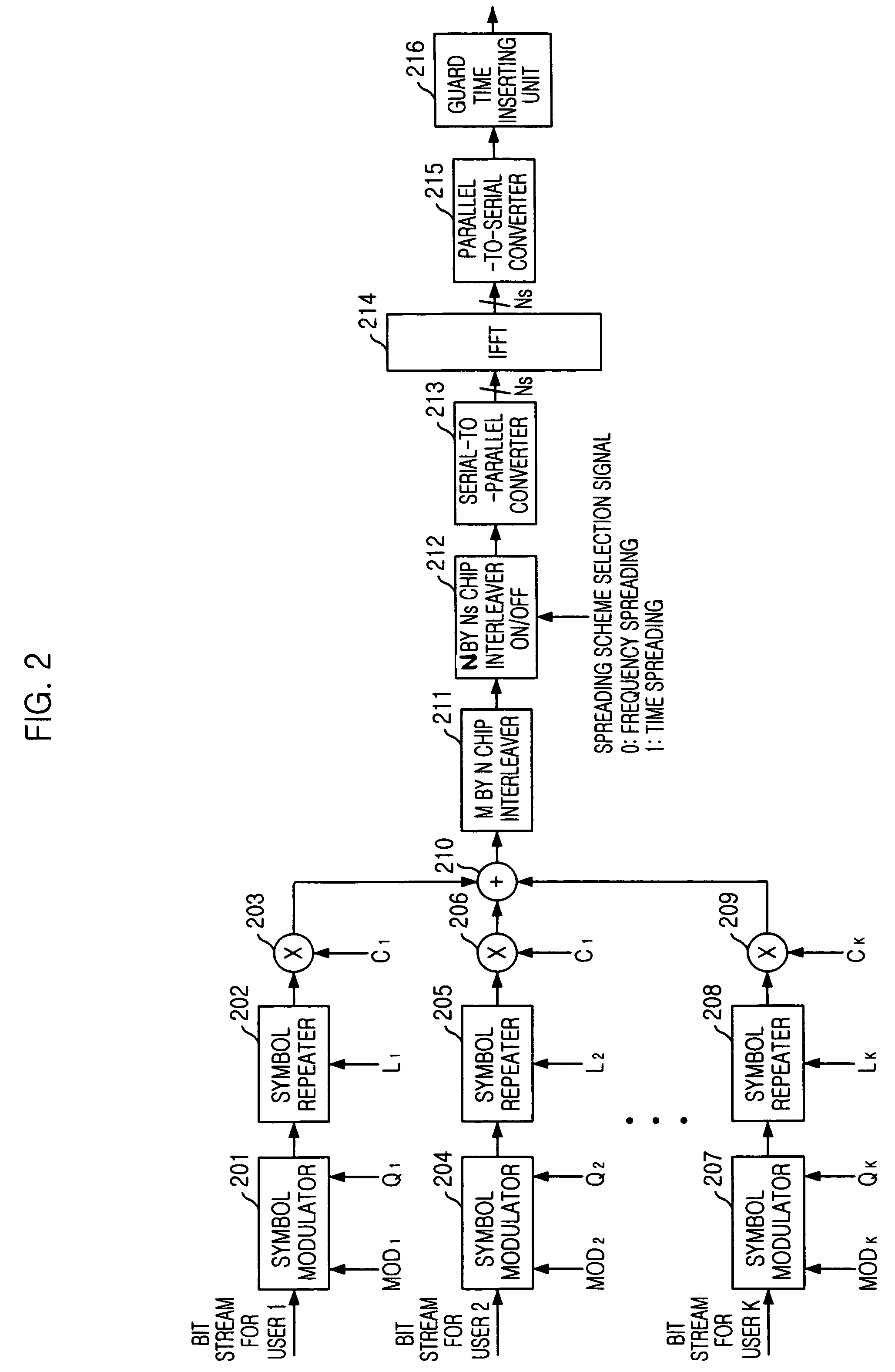
Provided are multi-carrier (MC) / multi-carrier direct sequence (MC-DS) dual-mode adaptable CDMA apparatus, the method thereof, and a computer program that implements the method. The apparatus can vary the user modulation degree and the transmission repetition degree independently, and convert a spreading scheme between the time-based spreading scheme (MC-DS-CDMA) and the frequency-based spreading scheme (MC-CDMA) in a MC-CDMA system. The apparatus includes: a user signal processing unit for performing symbol modulation, repetition and spreading of bit stream for each user based on a transmission mode suitable for channel environment of each user, and generating spread chip streams for the user; a combining unit for adding up all the spread chip streams for the users; a first interleaving unit for interleaving the chip streams added up in the combining unit and generating a first interleaved stream; and a second interleaving unit for optionally performing a second interleaving on the first interleaved stream.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Convolution interleaving/de-interleaving method in digital transmission
InactiveCN101404555AError preventionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesConvolutionReal-time computing
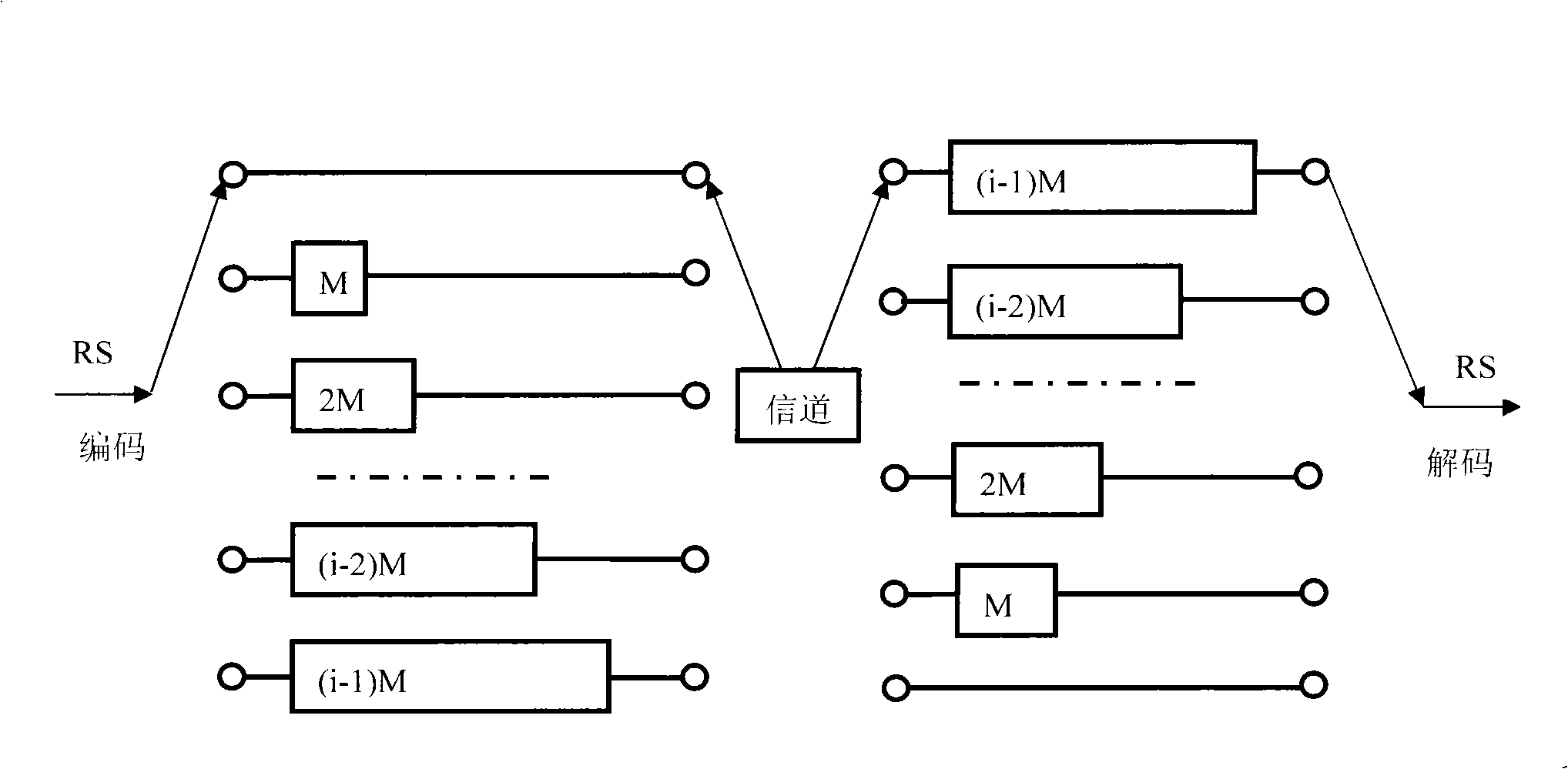
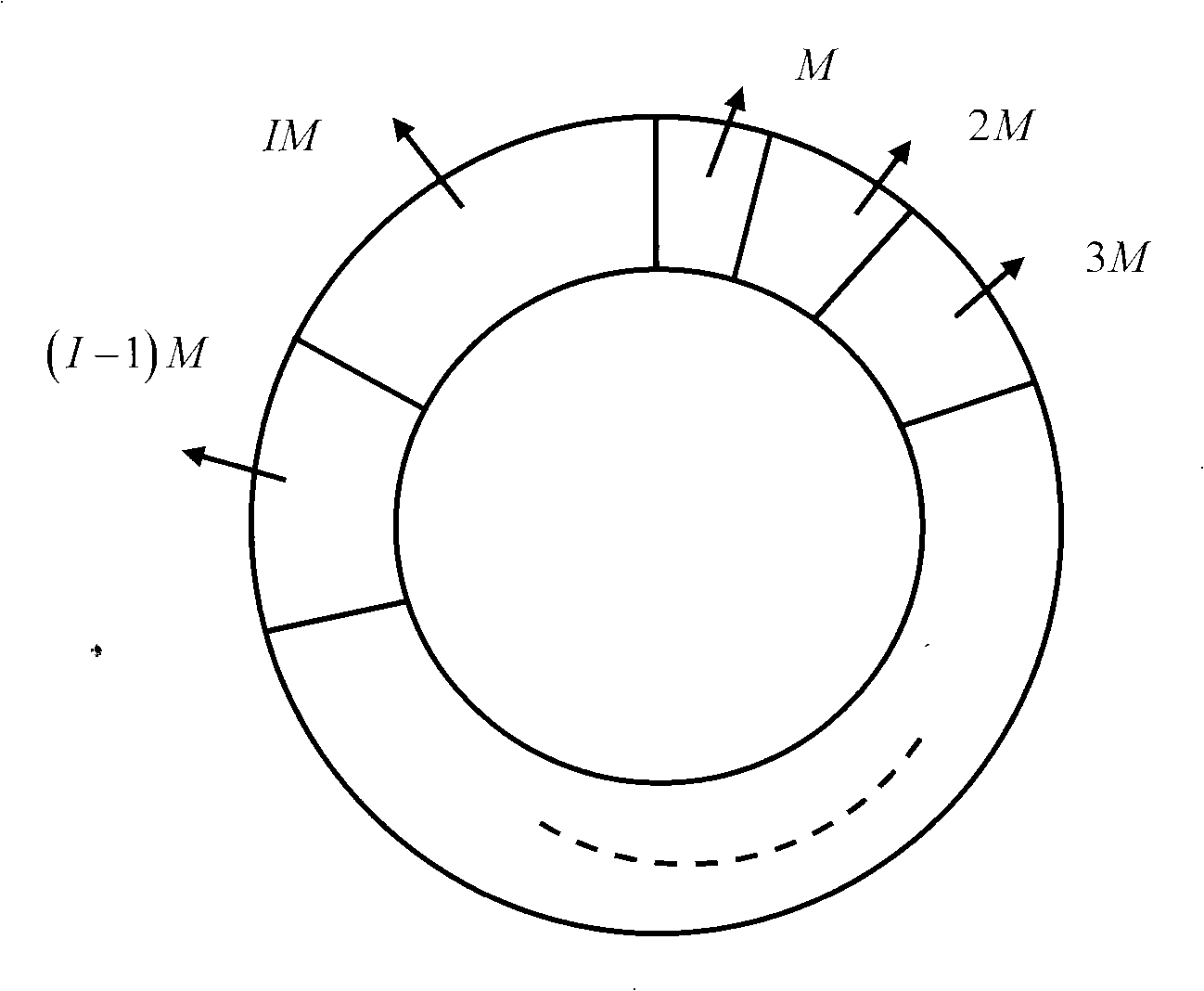
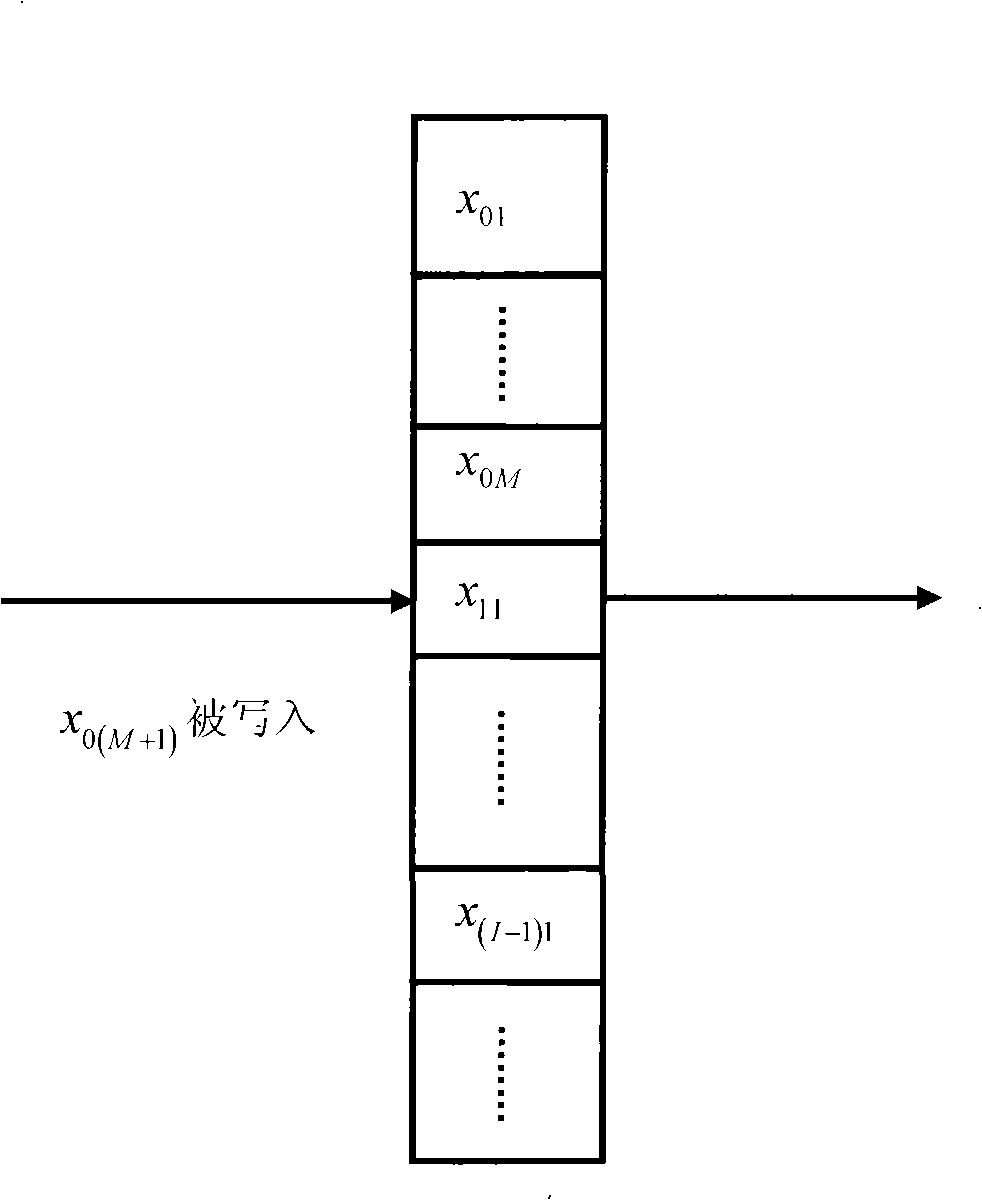
The invention discloses a method for interleaving and deinterleaving a convolution in digital transmission. The method regards an RAM as a ring with end-to-end addresses, and occupies RAM I(I+1)M / 2 space while interleaving according to the I and M information. While interleaving, the RAM is subject to writing-after-reading operations round by round. Differences among various addresses that are read and written in each round are M, 2M, to IM, and the address of the next round is close to that of the prior round. RAM I(I+3)M / 2 space is occupied while deinterleaving, and reading-reading-writing operations are performed round by round. Differences among various addresses that are read for the first time in each round are (I+1)M, IM, to 2M, and the address of the next round is close to that of the prior round. The address that is read for the second time and the address that is read for the first time are separated by 2M+1 space, namely having a distance of the 2M (shown as in the figure). The written address is the same as the address that is read for the first time. The convolution process is simply controlled, and a deinterleaver and an RS decoder can share an RAM, which saves the resources.
Owner:BEIJING BM ELECTRONICS HIGH TECH
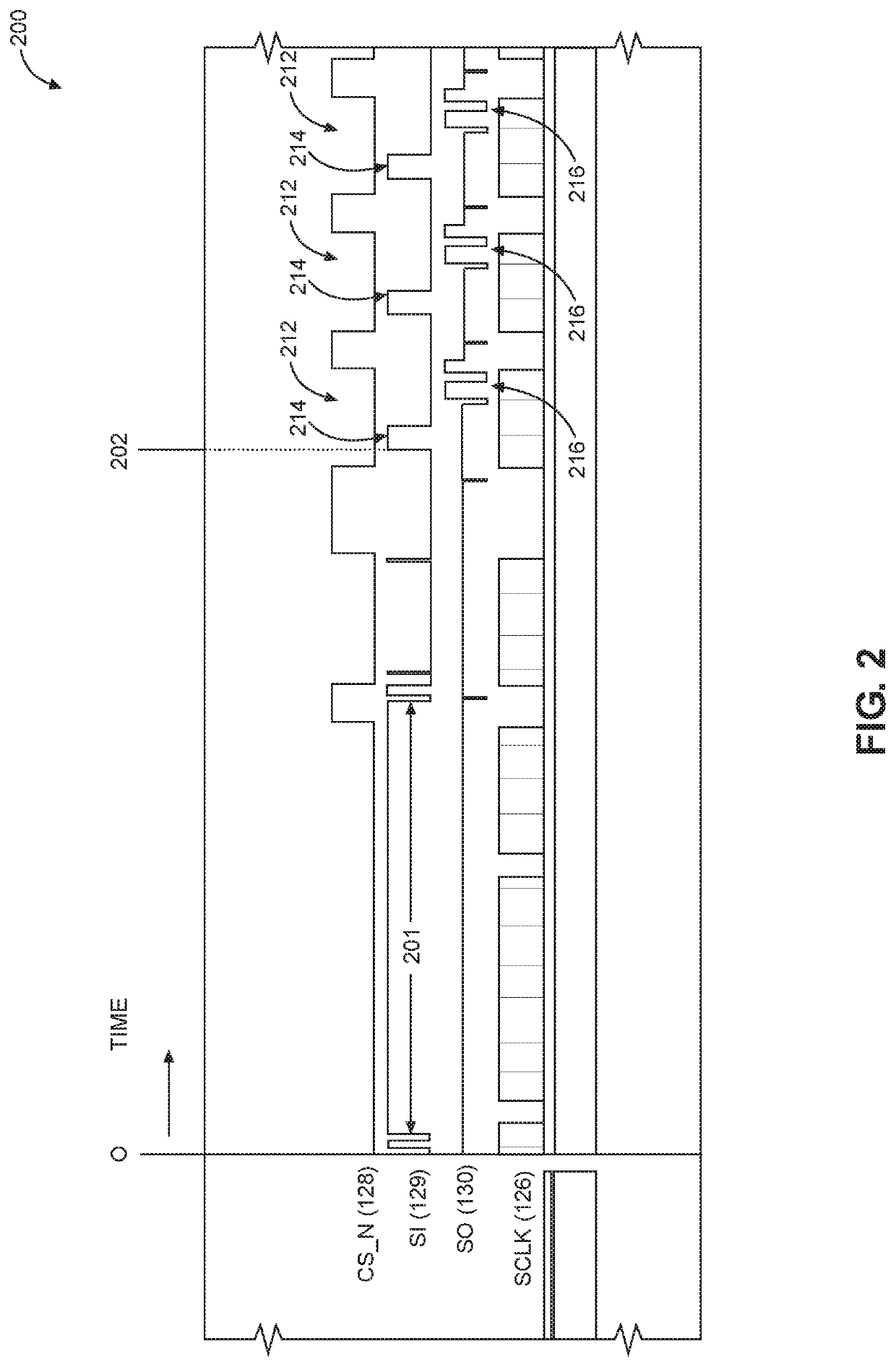
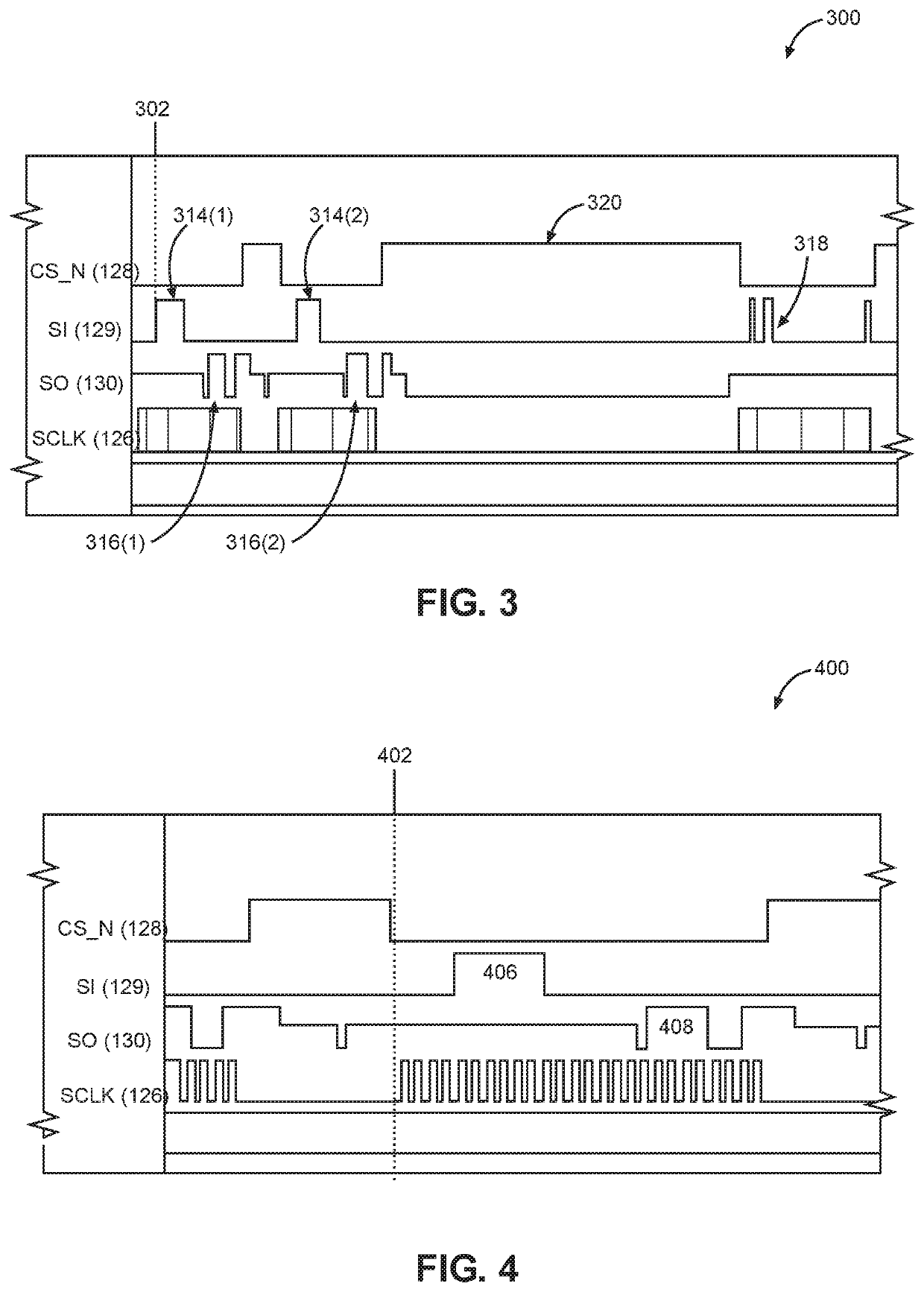
Reducing power consumption of communication interfaces by clock frequency scaling and adaptive interleaving of polling
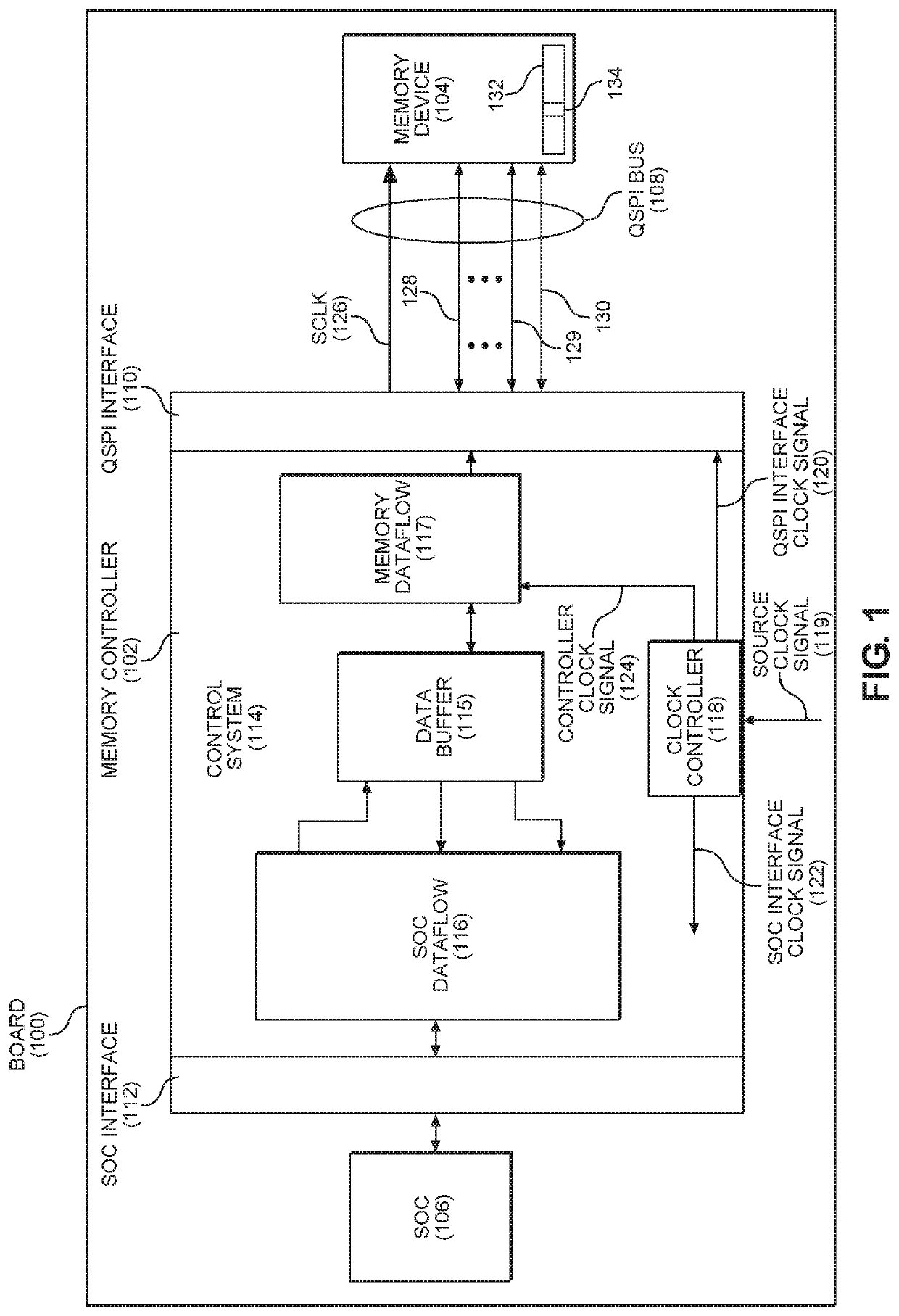
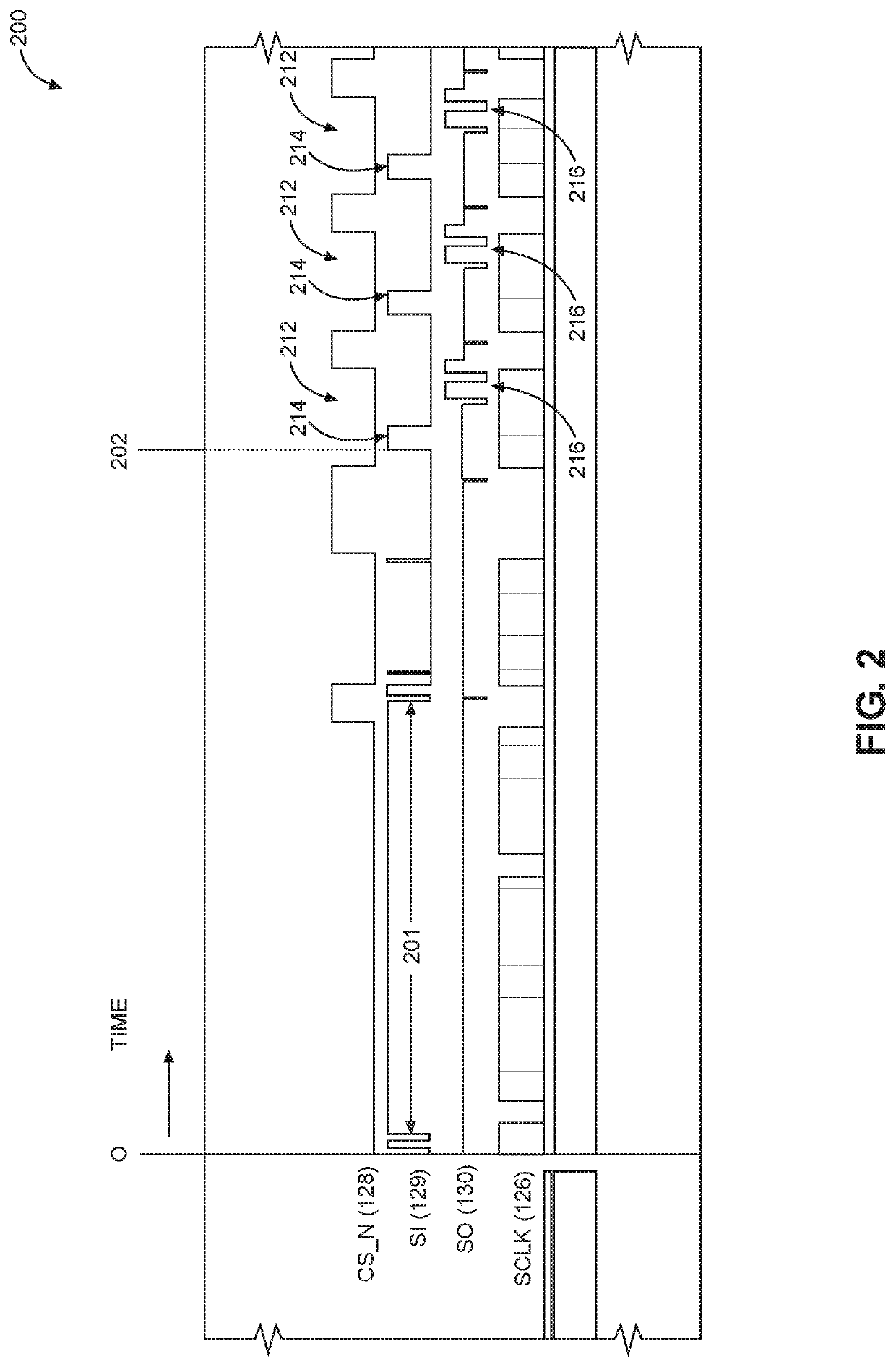
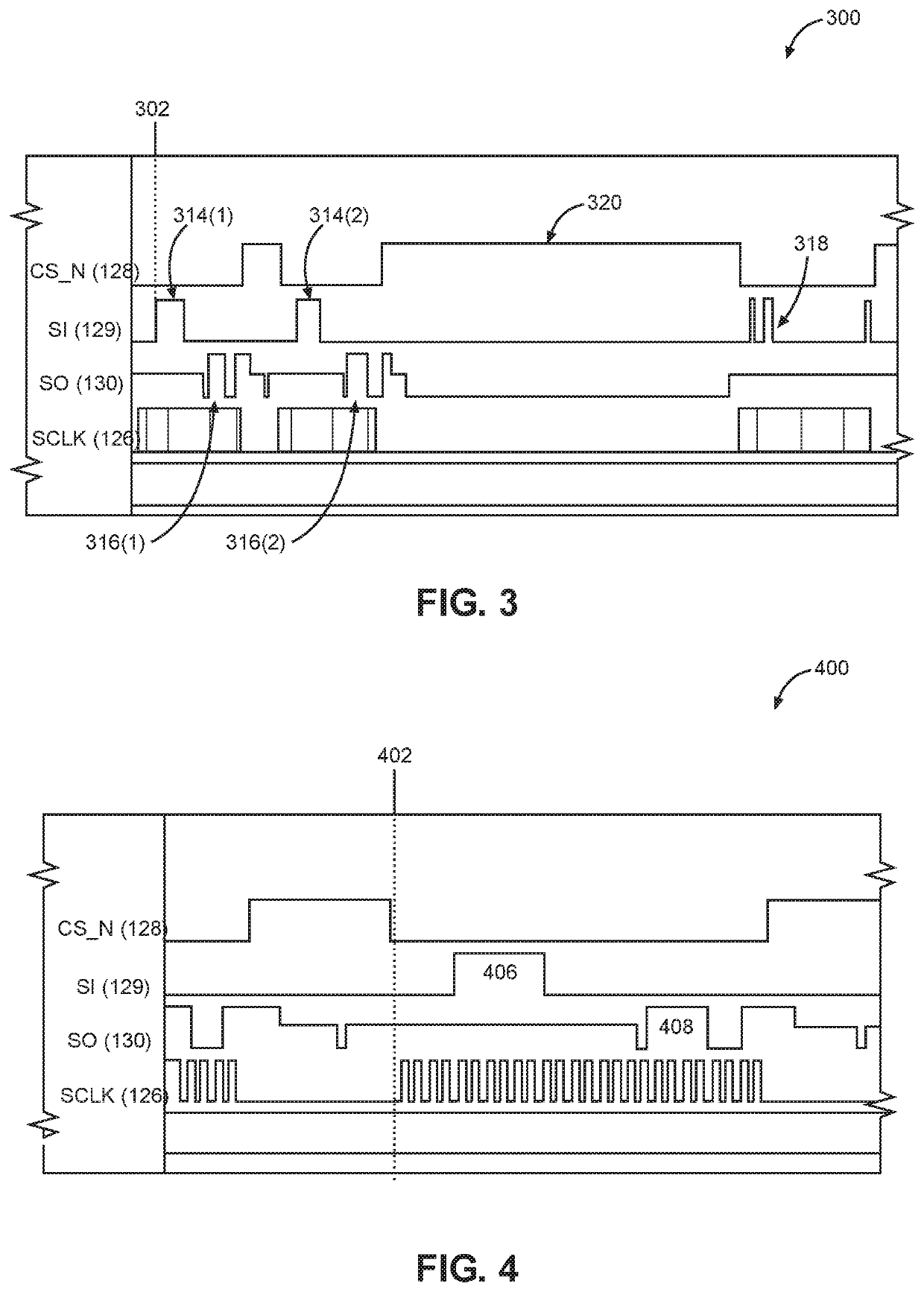
ActiveUS20200192455A1Reduce power consumptionImprove latencyDigital data processing detailsEnergy efficient computingCommunication interfaceCompletion time
Reducing power consumption of communication interfaces by clock frequency scaling and adaptive interleaving of polling is disclosed. In a first aspect, a control system controls transmission of a command via a serial interface at a higher clock frequency. After transmission, the control system and the interface are operated at a lower clock frequency to save power during command execution. In this aspect, a reduction in polling corresponds to the reduction in clock signal frequency. When the command is complete, the interface is operated at the higher frequency to send another command. In a second aspect, after the control system sends a command to the receiving device, polling is suspended and an execution time of the command is tracked. Polling begins when the tracked execution time almost equals an expected completion time. Both aspects disclosed above may be implemented to reduce power consumption in exchange for a small increase in latency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Processor with memory race recorder to record thread interleavings in multi-threaded software
InactiveUS9128781B2Program synchronisationSoftware testing/debuggingMemory addressComputer architecture
A processor includes a first core to execute a first software thread, a second core to execute a second software thread, and shared memory access monitoring and recording logic. The logic includes memory access monitor logic to monitor accesses to memory by the first thread, record memory addresses of the monitored accesses, and detect data races involving the recorded memory addresses with other threads. The logic includes chunk generation logic is to generate chunks to represent committed execution of the first thread. Each of the chunks is to include a number of instructions of the first thread executed and committed and a time stamp. The chunk generation logic is to stop generation of a current chunk in response to detection of a data race by the memory access monitor logic. A chunk buffer is to temporarily store chunks until the chunks are transferred out of the processor.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Transmitting interleaved multiple data flows
ActiveUS20060126591A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexChannel dataComputer hardware
Multiple transport channels (405, 406, 407) are multiplexed and transmitted in a single physical channel. A code (TFCI) is added to the transport channel data flows to indicate which processing schemes, from a set of available schemes, are being employed and the resultant blocks are interleaved. The depth of the interleaving is set in dependence on the transmission time intervals associated with the schemes in the set of processing schemes.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
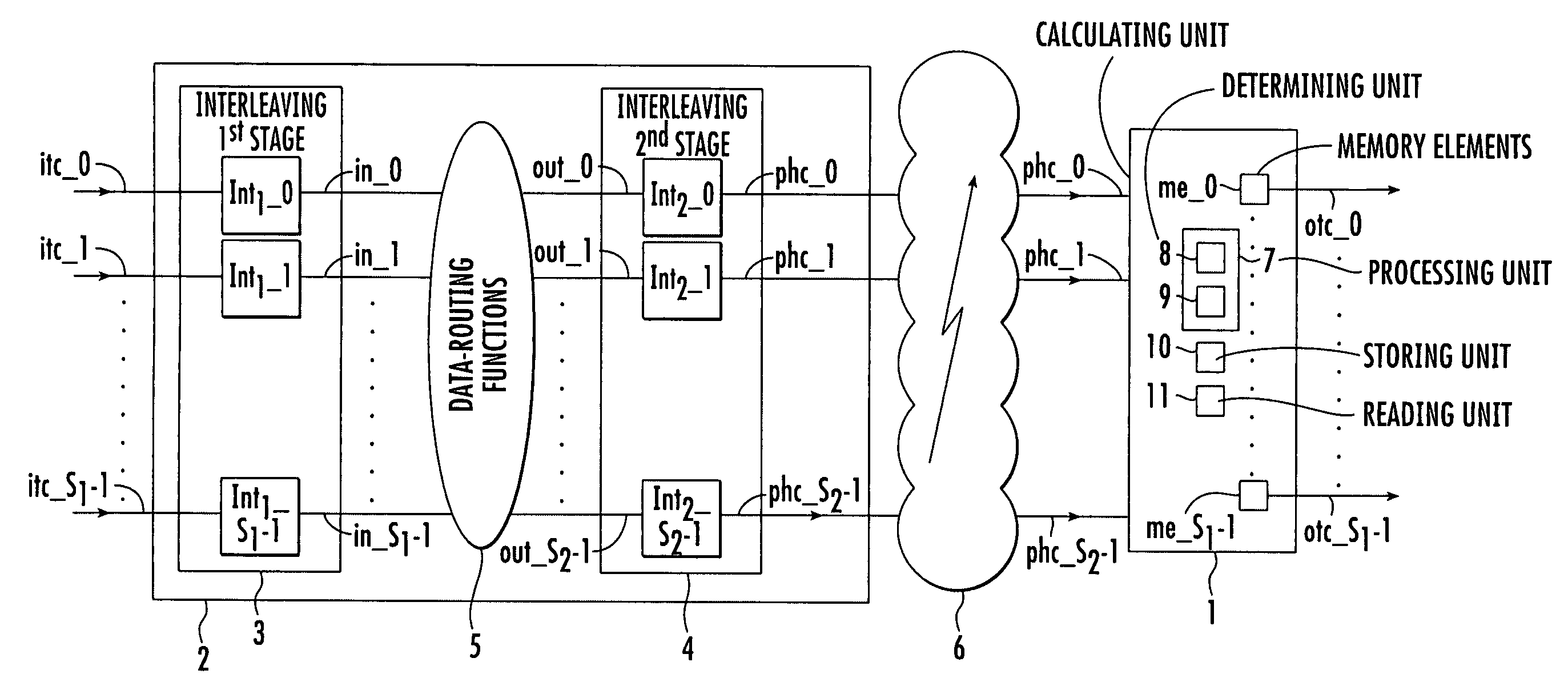
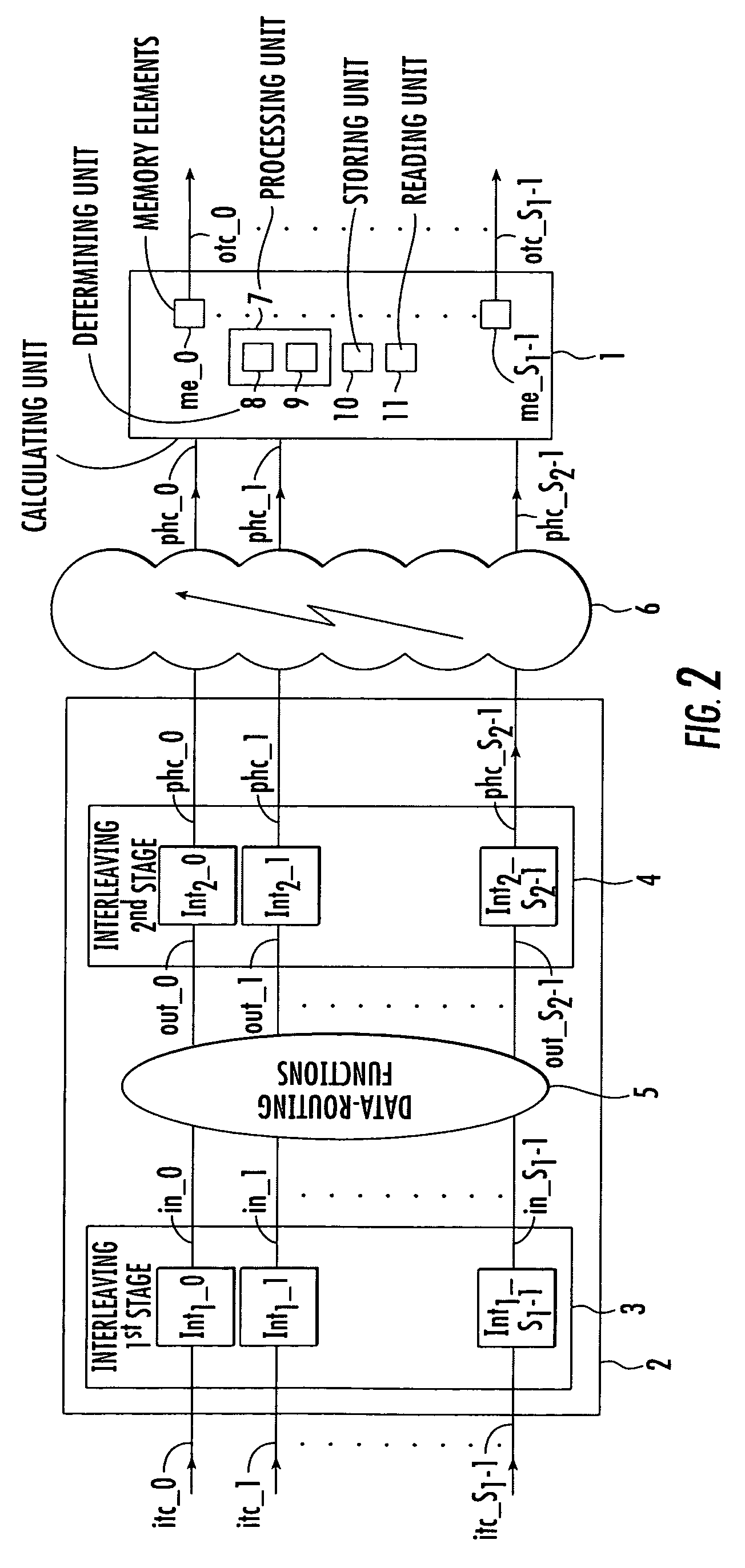
Method and device for interleaving and method and device for de-interleaving
InactiveUS20050005223A1Good effectError detection/correctionUnequal/adaptive error protectionEmbedded systemComputer hardware
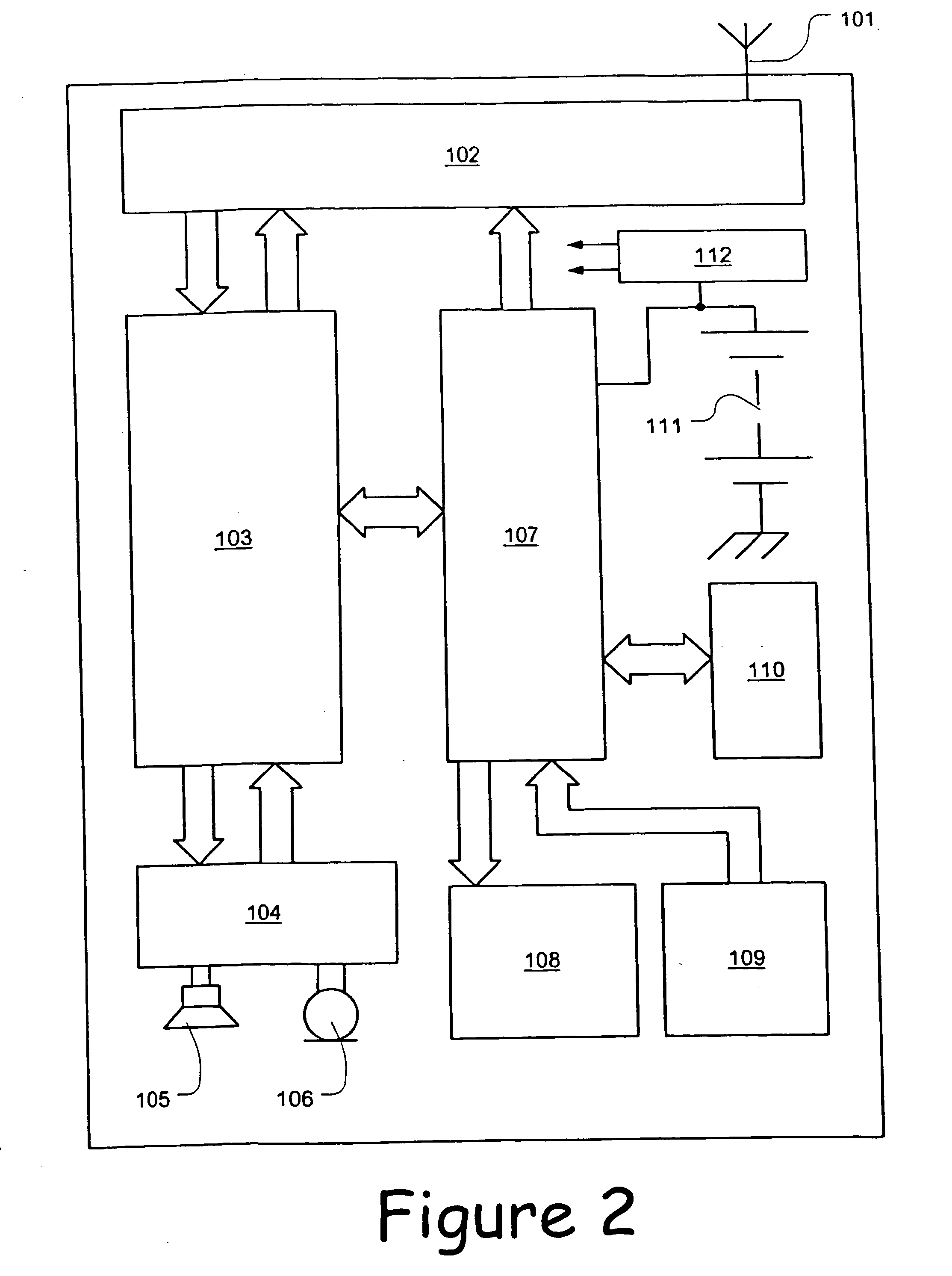
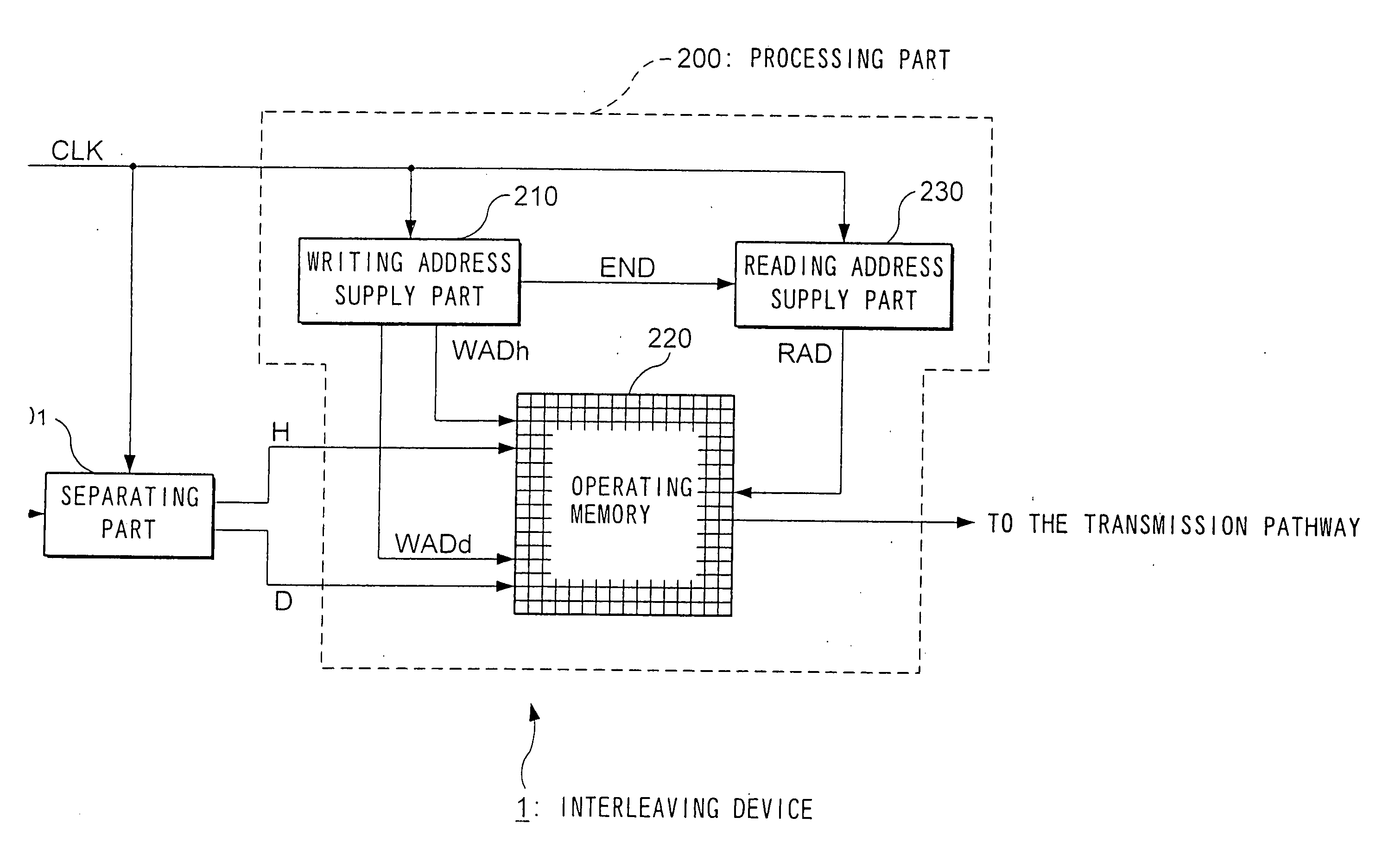
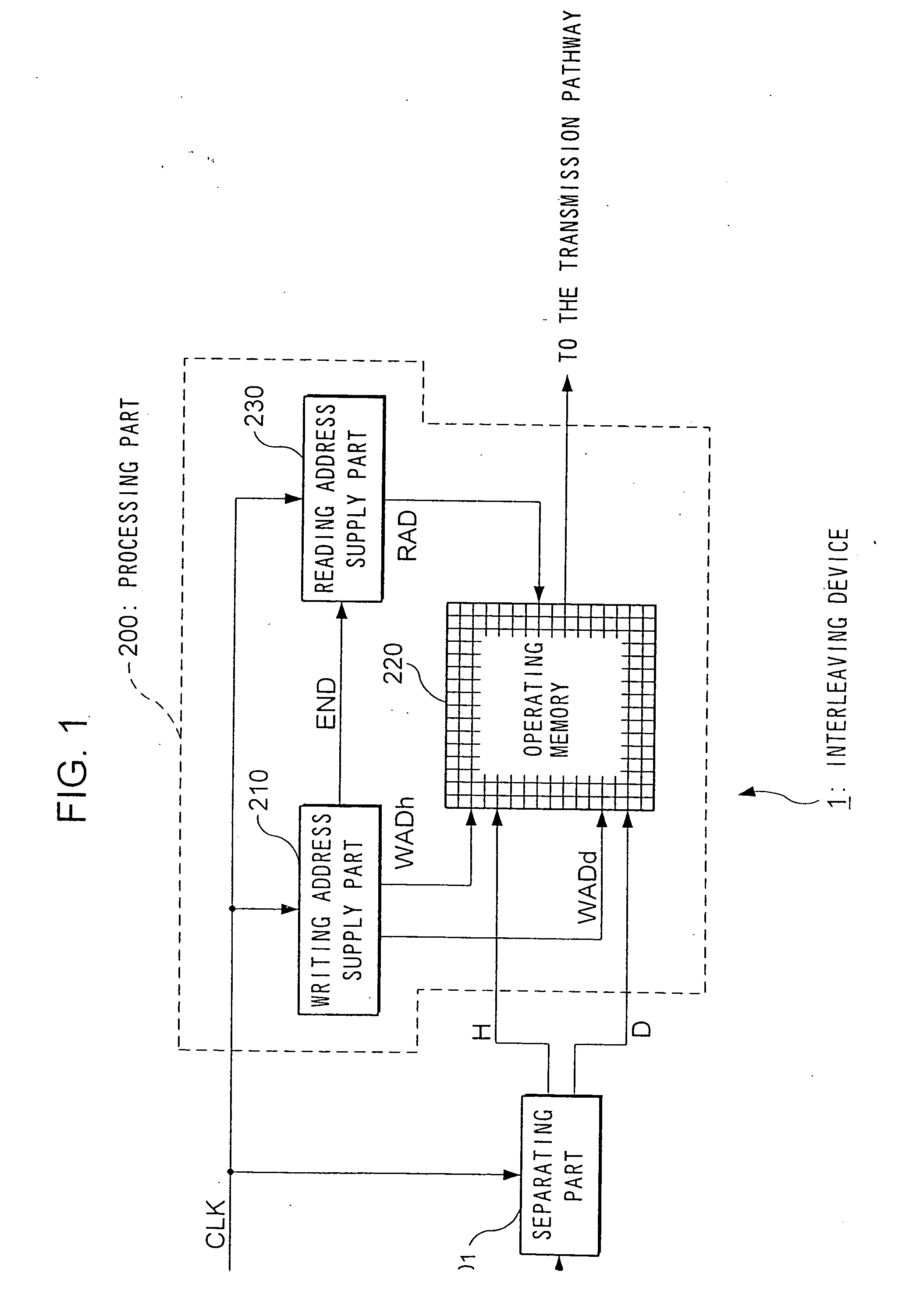
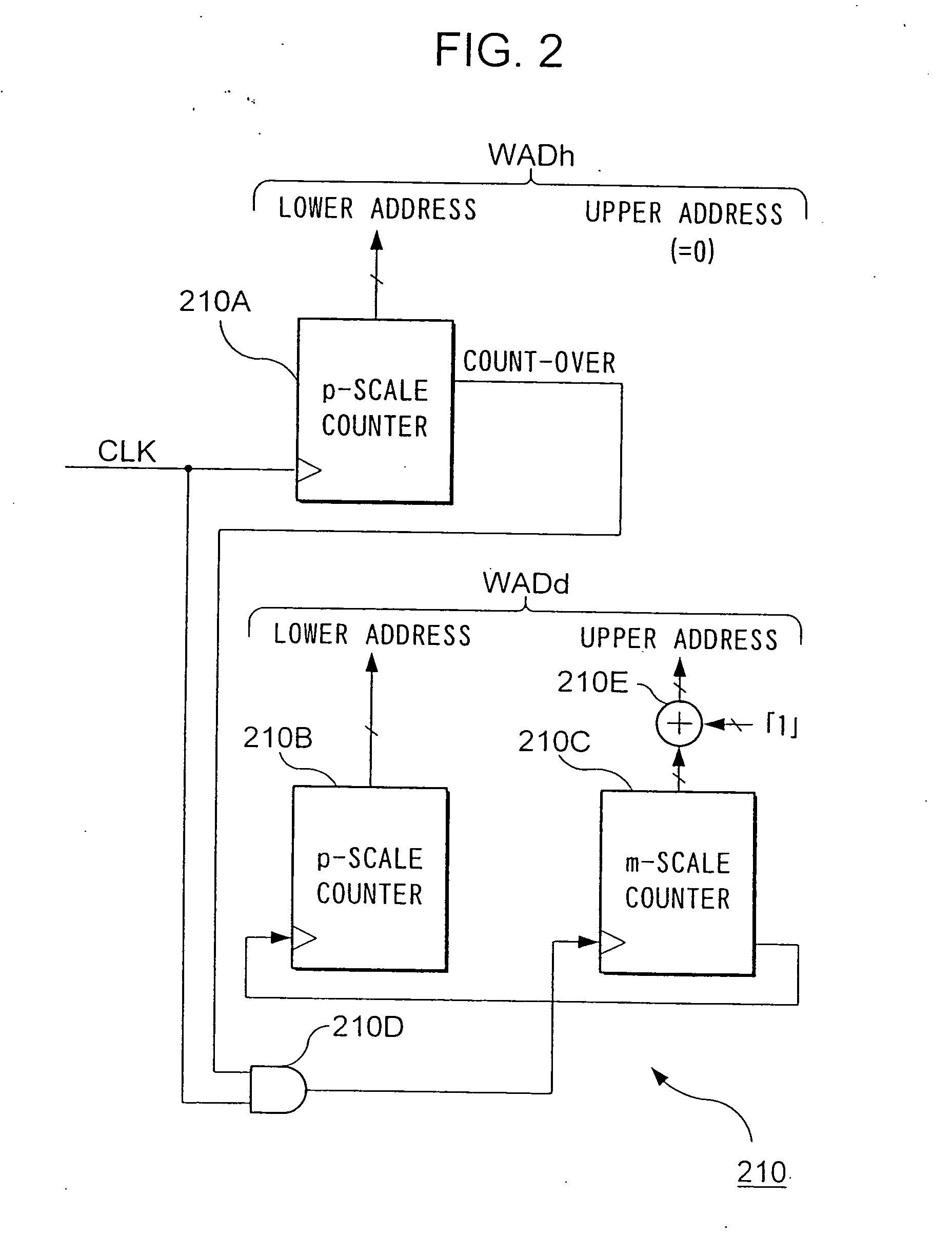
The writing address supply part 210 supplies writing addresses for writing the bits forming bit sequences corresponding to the header H contained in a frame to be transmitted or stored and bit sequences corresponding to the data D, into the operating memory 220. The reading address supply part 230 alternately supplies to the operating memory 220 a plurality of addresses for reading a plurality of continuous bits corresponding to the header H from the operating memory 220, and an address for reading 1 bit corresponding to the data D from the operating memory 220, and reads the bit sequence such that the bits forming the bit sequence corresponding to the header H are scattered and arranged within the bit sequence forming the data D, from the operating memory. In accordance with such an interleaving device, it is possible to individually randomize frames according to their constituent data, and it is possible to transmit the bits that make up such data in a format which is most suited for said data.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Generation of random address mapping in non-volatile memories using local and global interleaving
ActiveUS20170017578A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationProgram synchronisationParallel computingTheoretical computer science
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
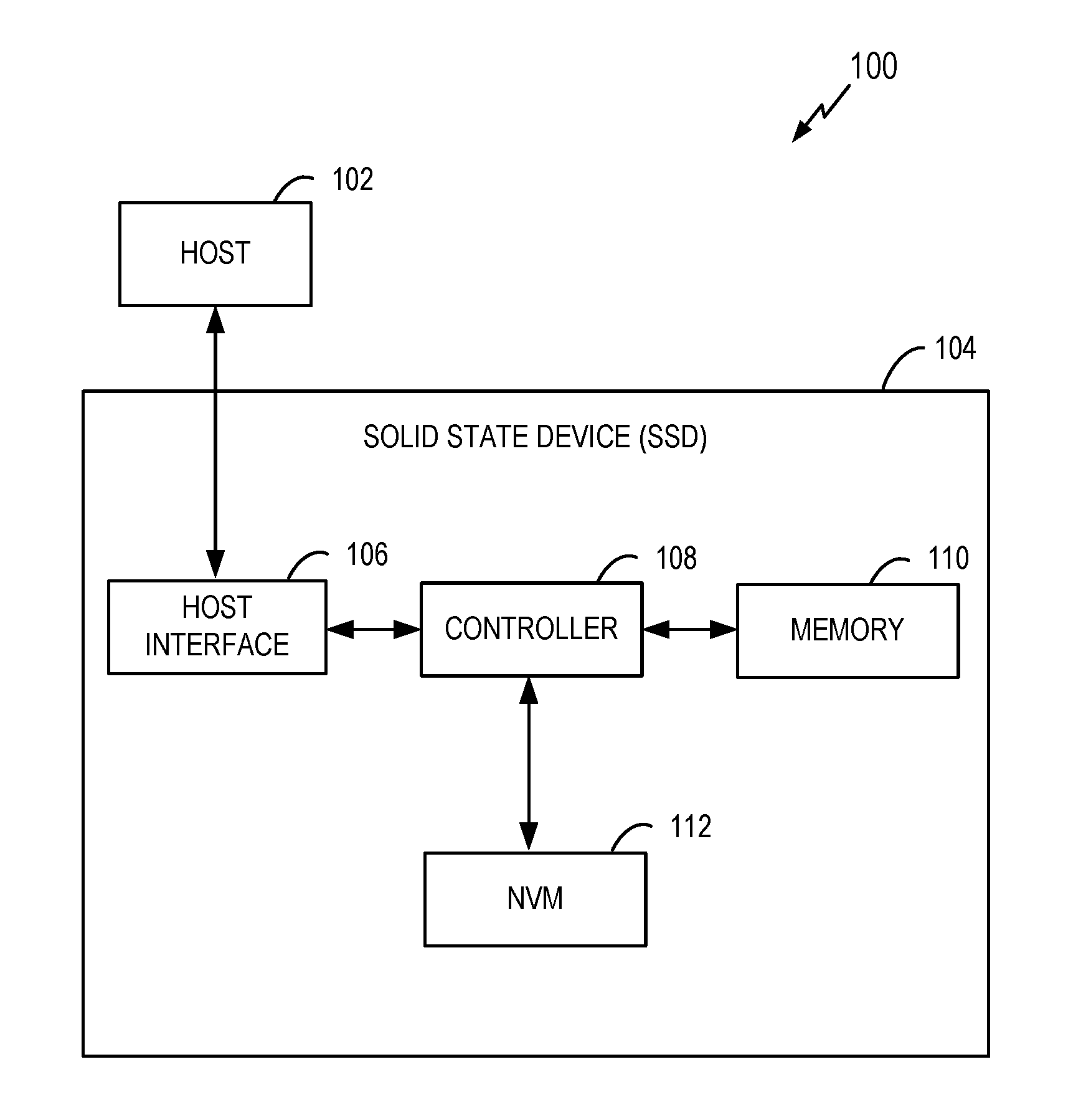
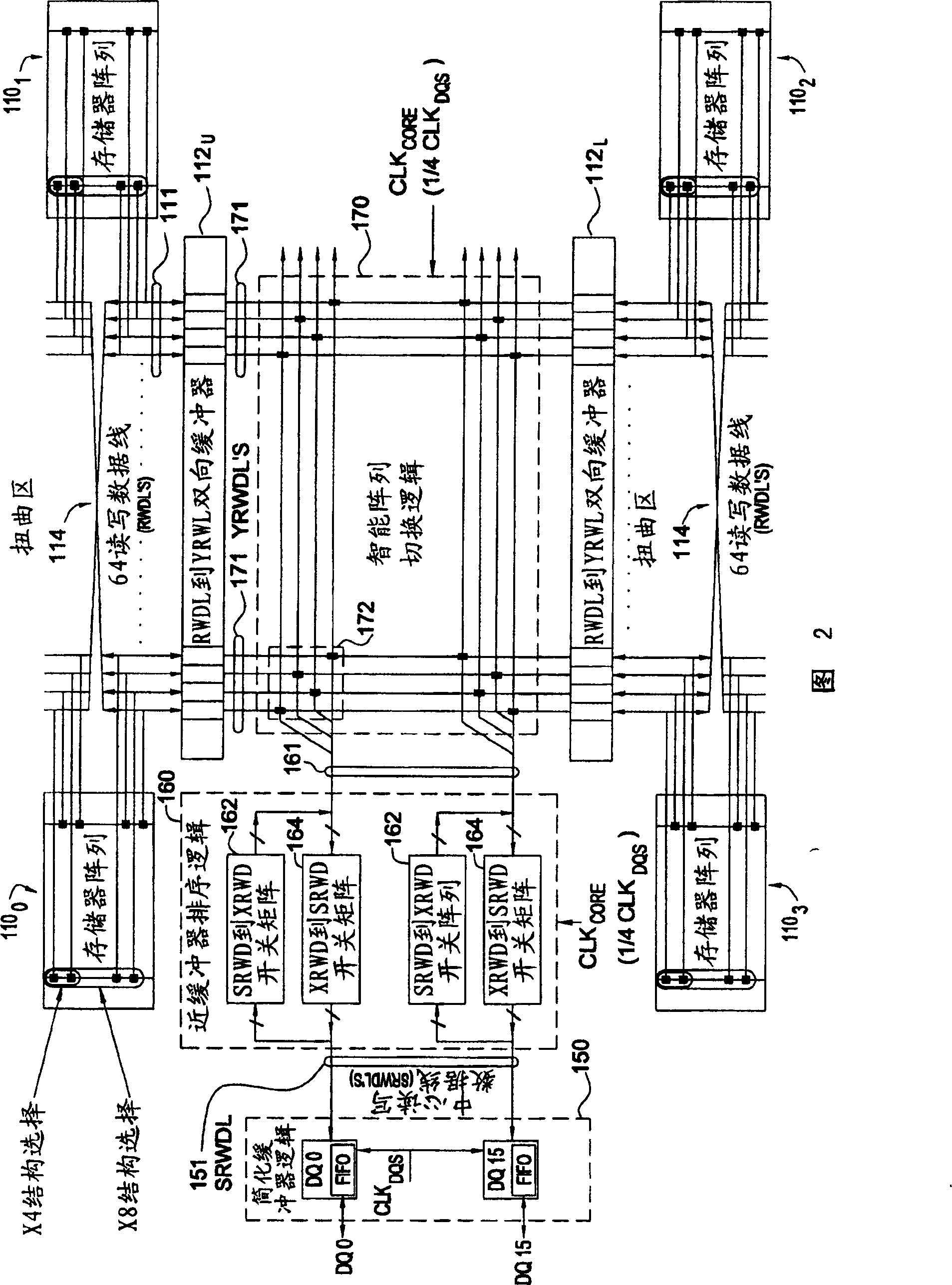
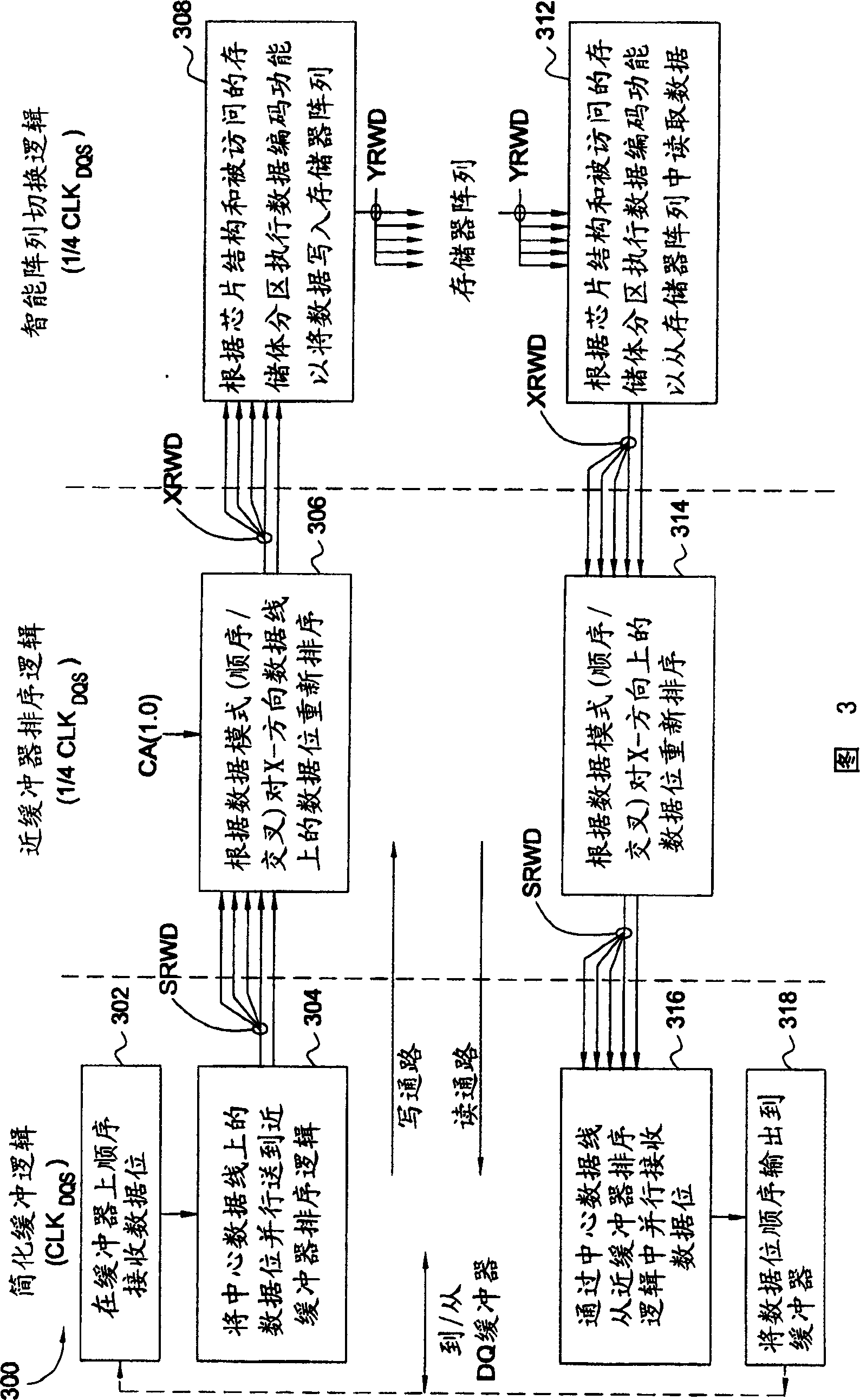
Improved DDR II dram data path
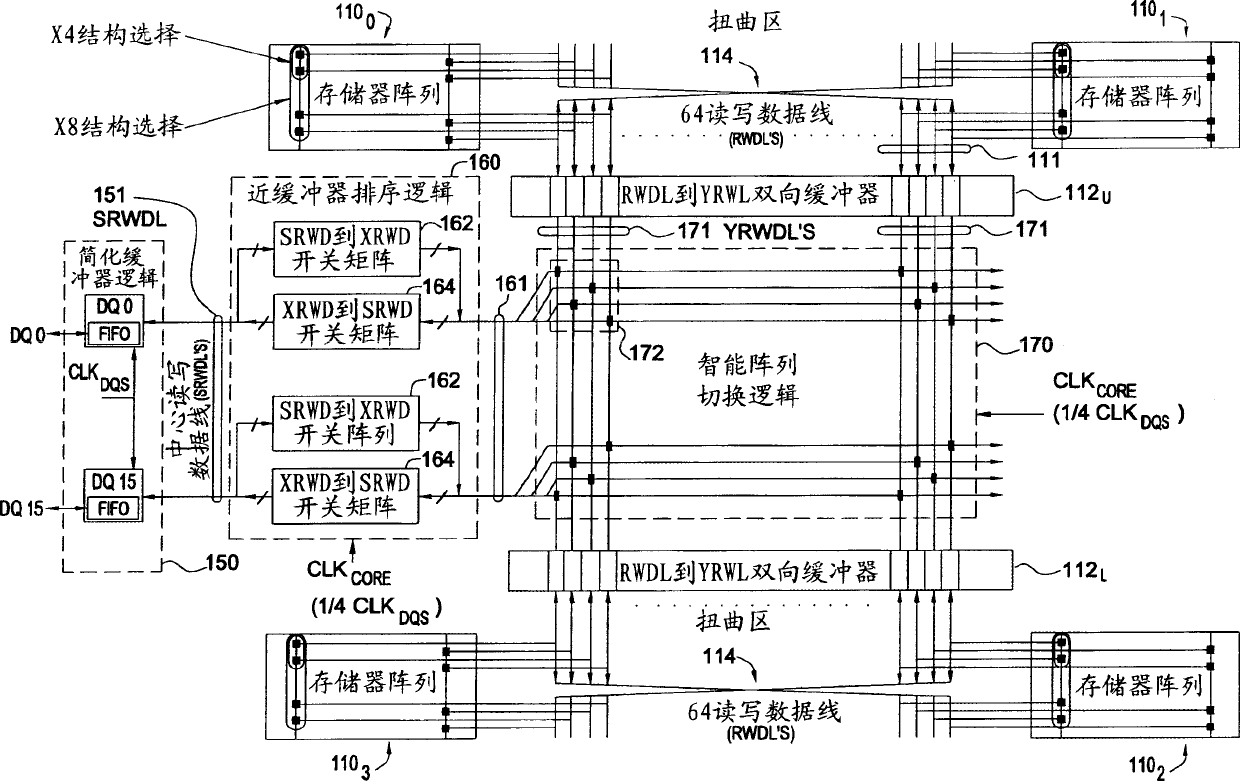
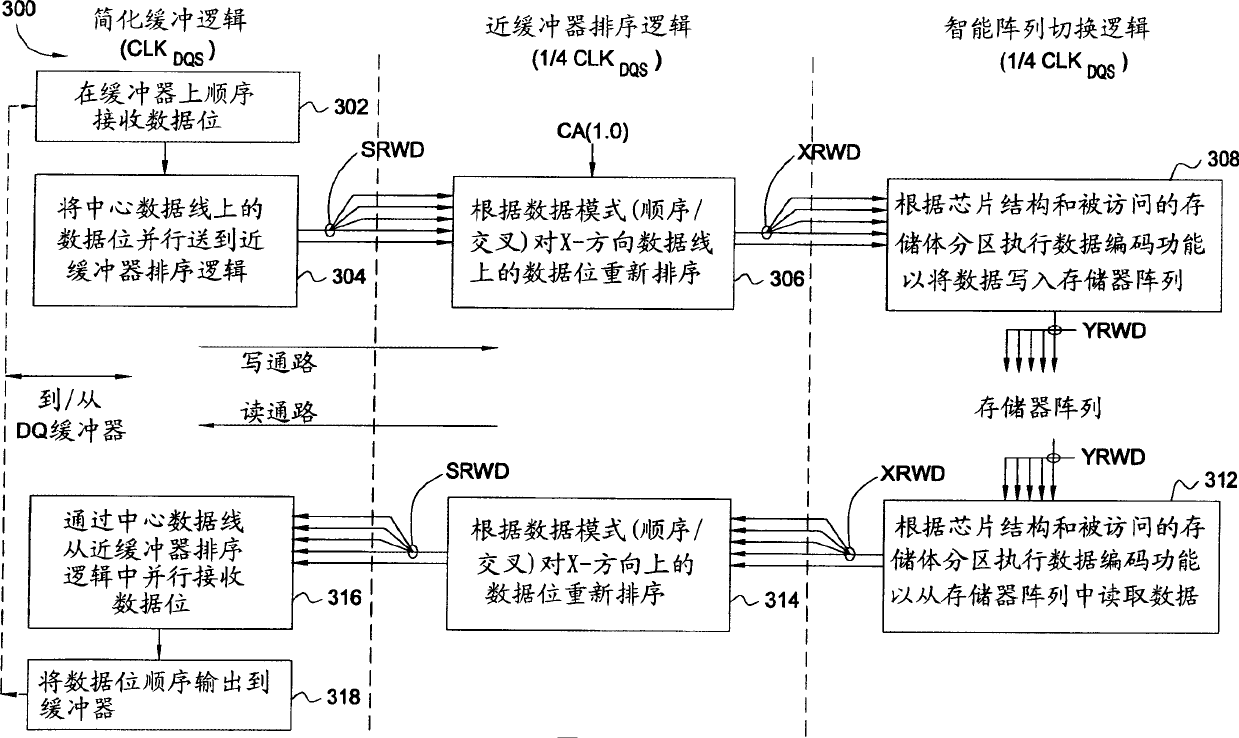
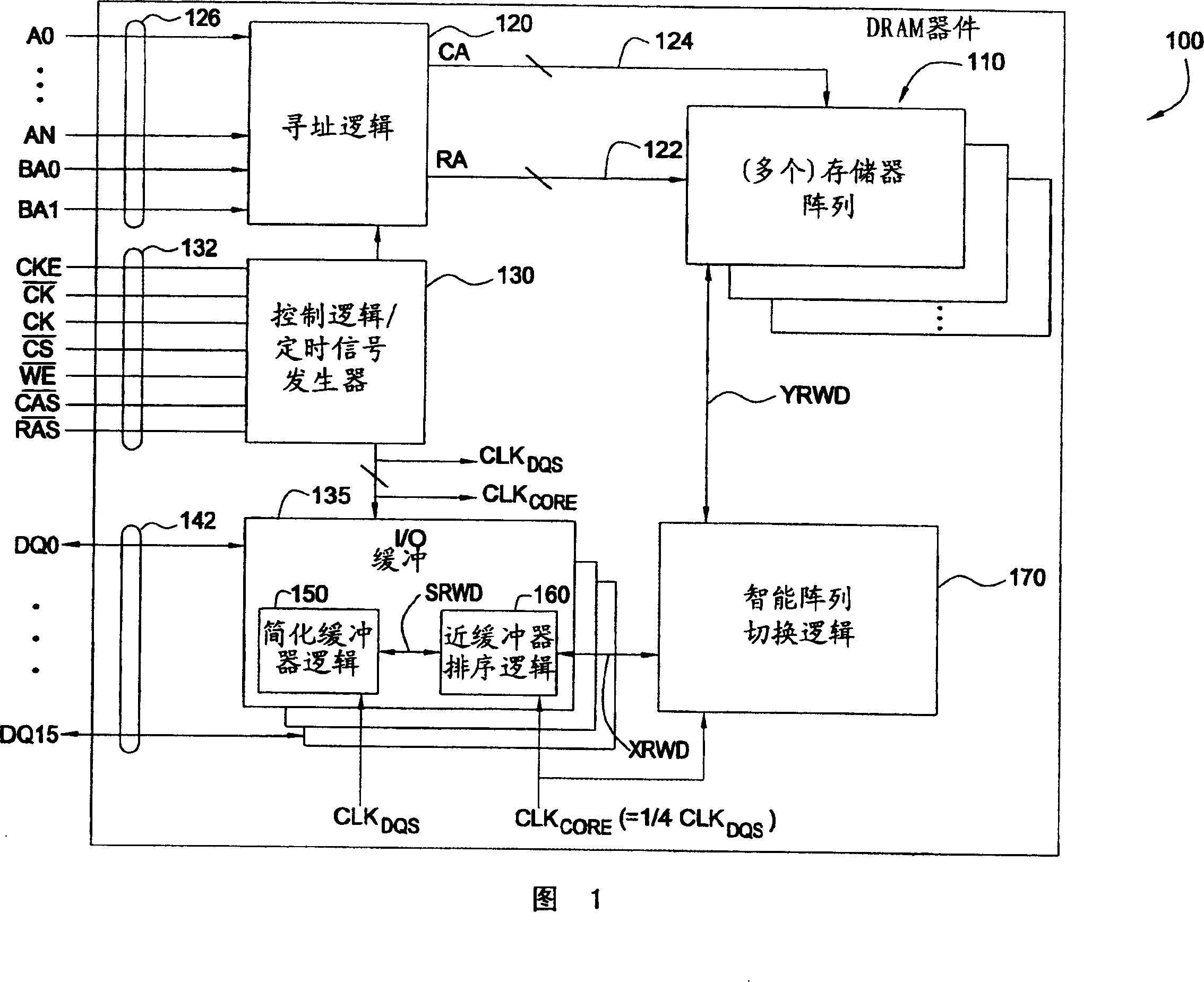
An improved doubled data rate (DDR)-II type dynamic random access memory (DRAM) device data path is disclosed. Techniques and circuitry that support switching operations required to exchange data between memory arrays and external data pads are provided. In a write path, such switching operations may include latching in and assembling a number of bits sequentially received over a single data pad, reordering those bits based on a type of access mode (e.g., interleaved or sequential), and performing scrambling operations based on chip organization (e.g., x4, x8, or x16) a bank location being accessed. Through separation the high speed buffer logic from switching logic which can perform other various logic functions, the switching logic performing the functions can work under a lower clock frequency, thus the time that data is transmitted from the memory arrays to the DQ pads is saved and associated timing requirements is relaxed and the latency is improved, otherwise.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
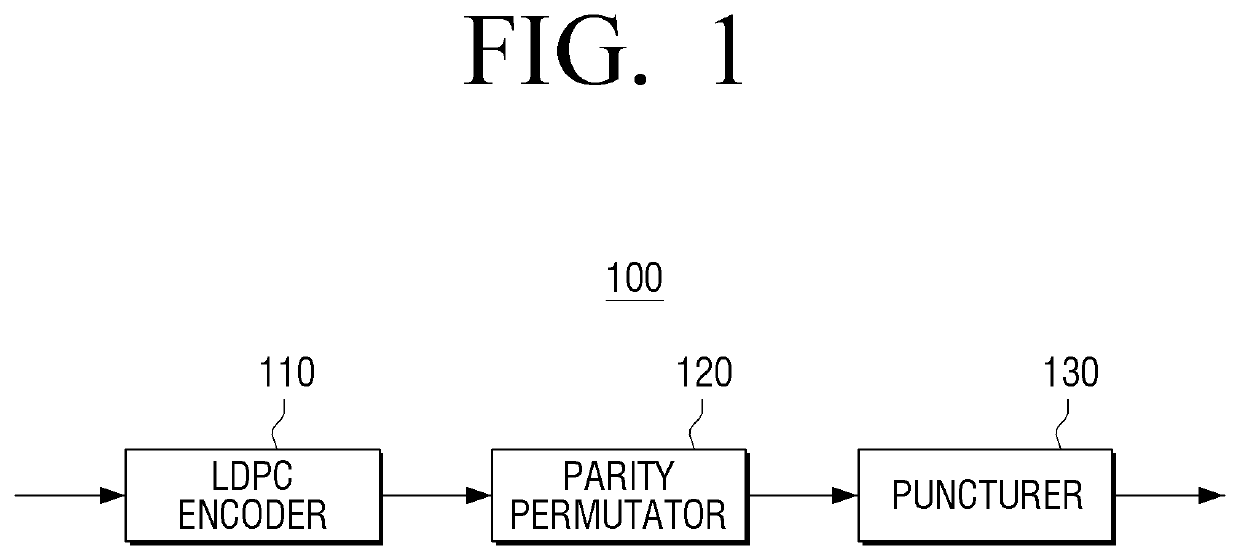
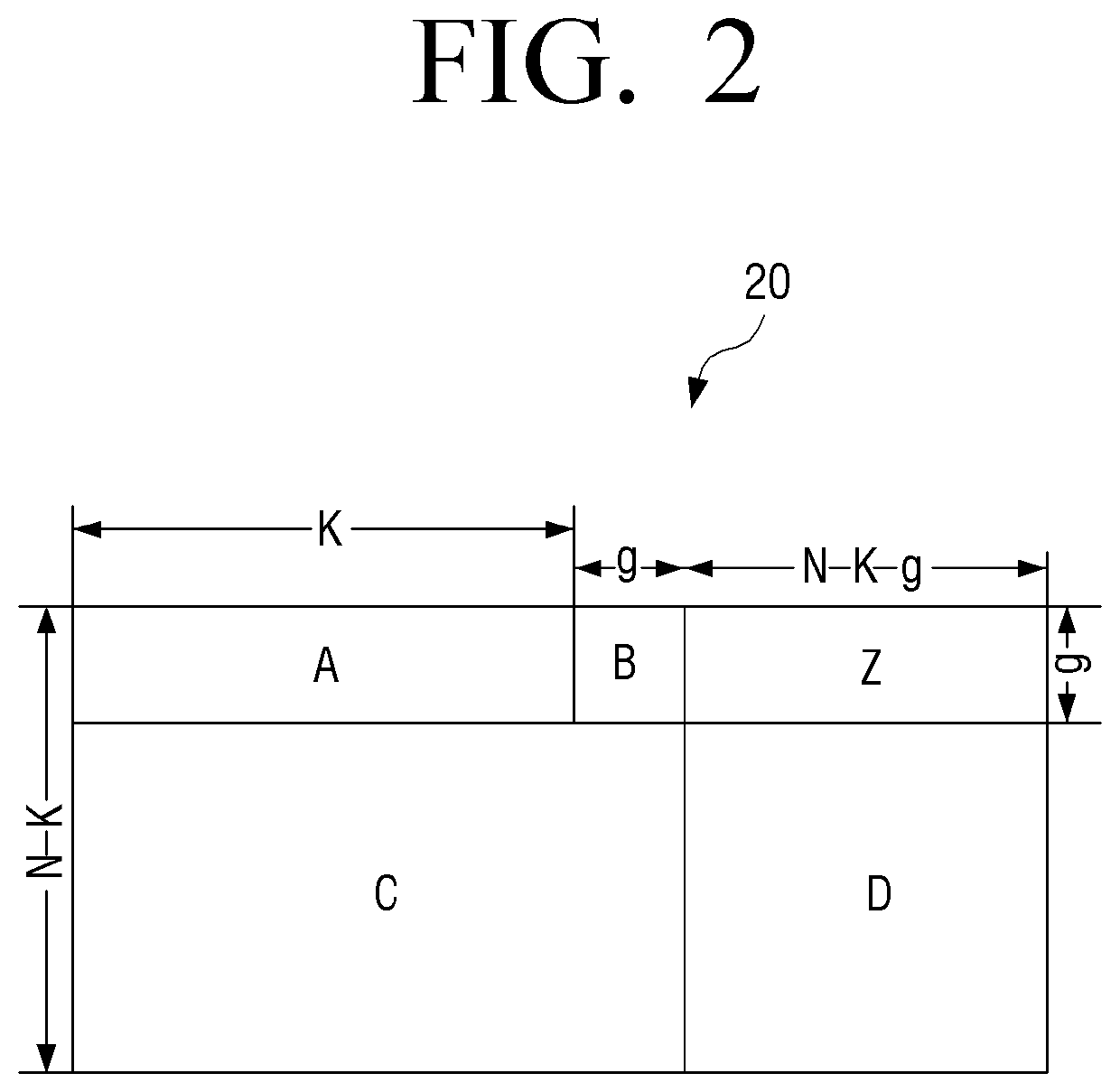
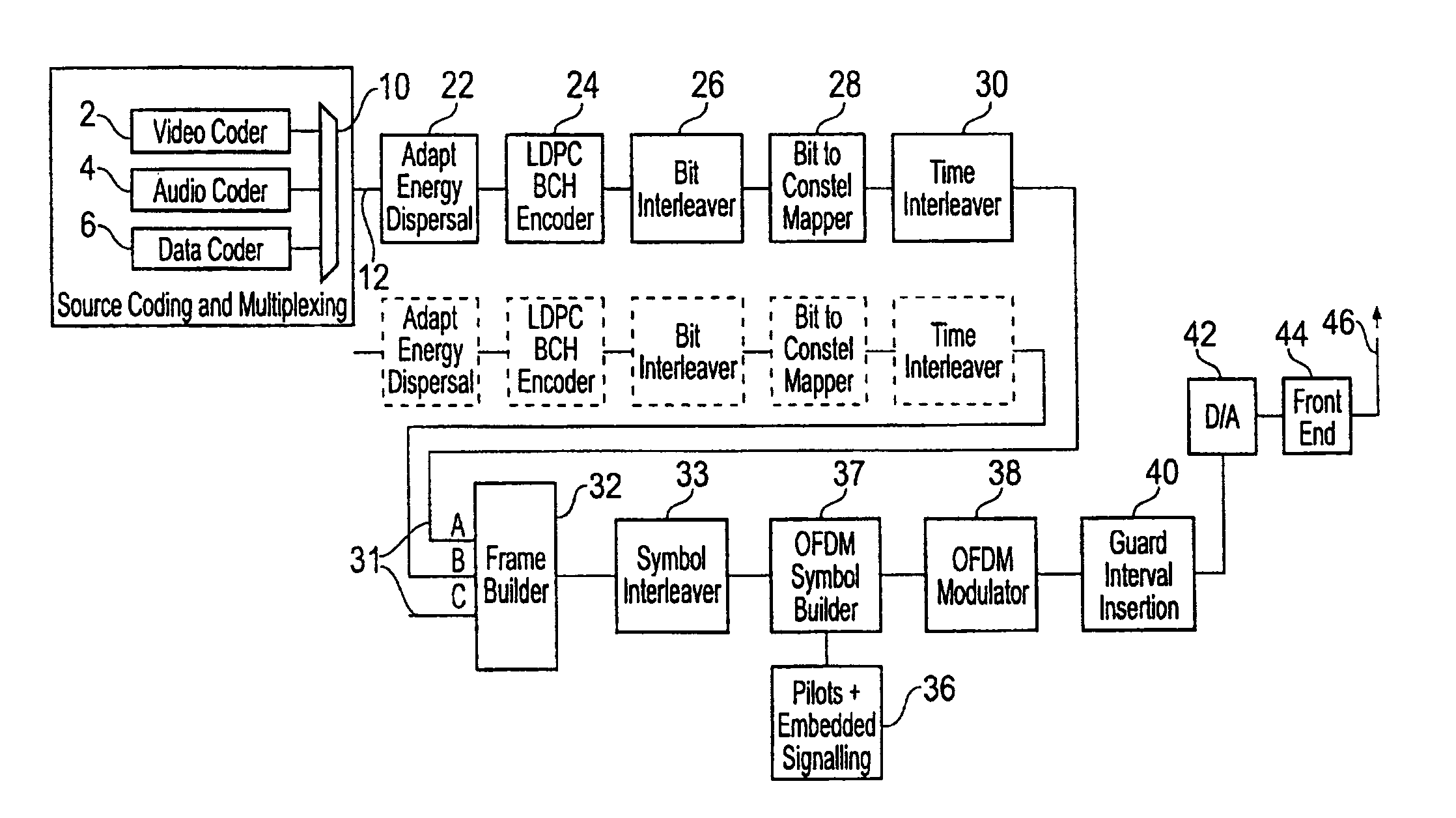
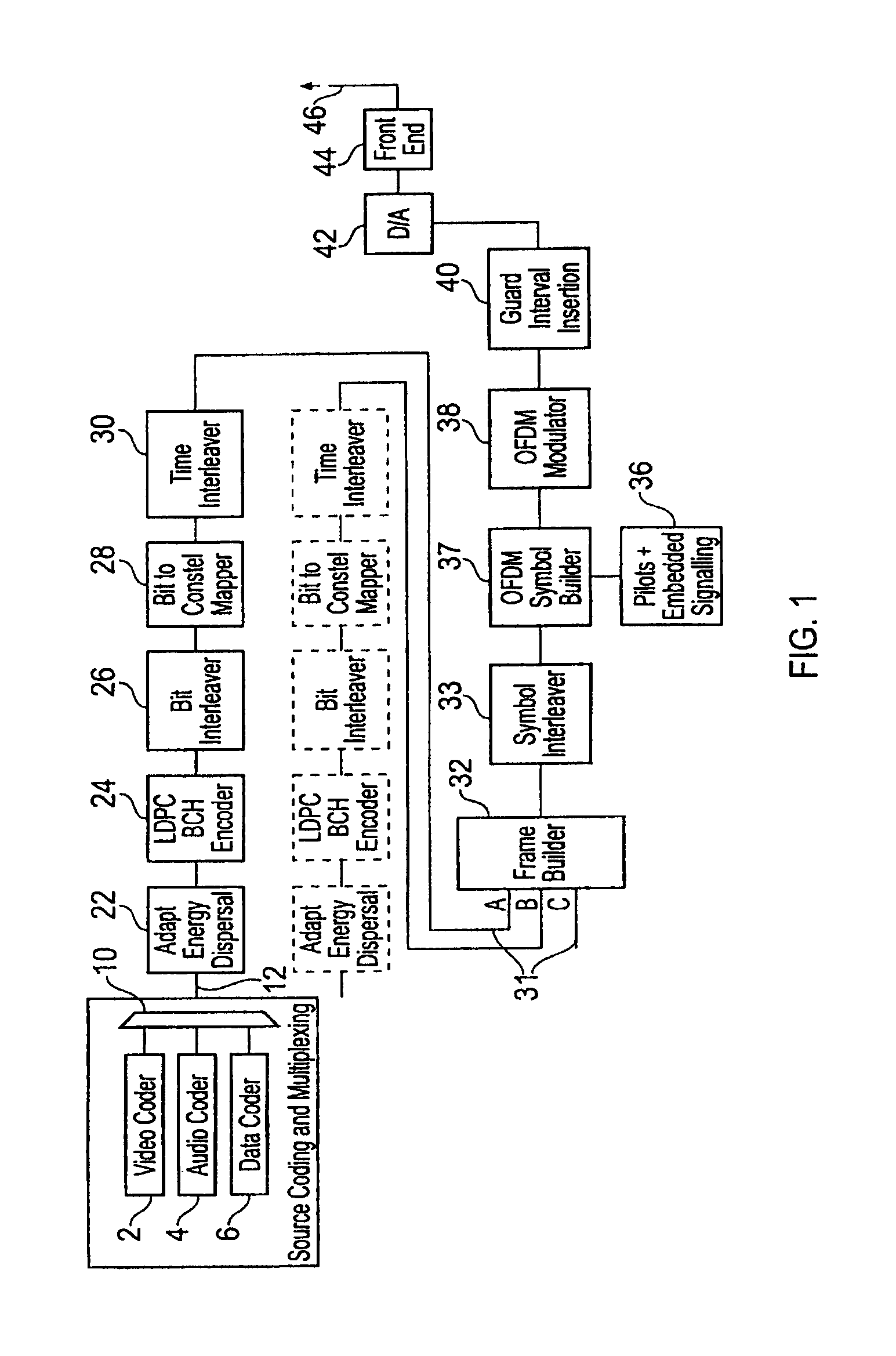
Transmitter and parity permutation method thereof
ActiveUS10554222B2Improve decoding performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTransmitterComputer engineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
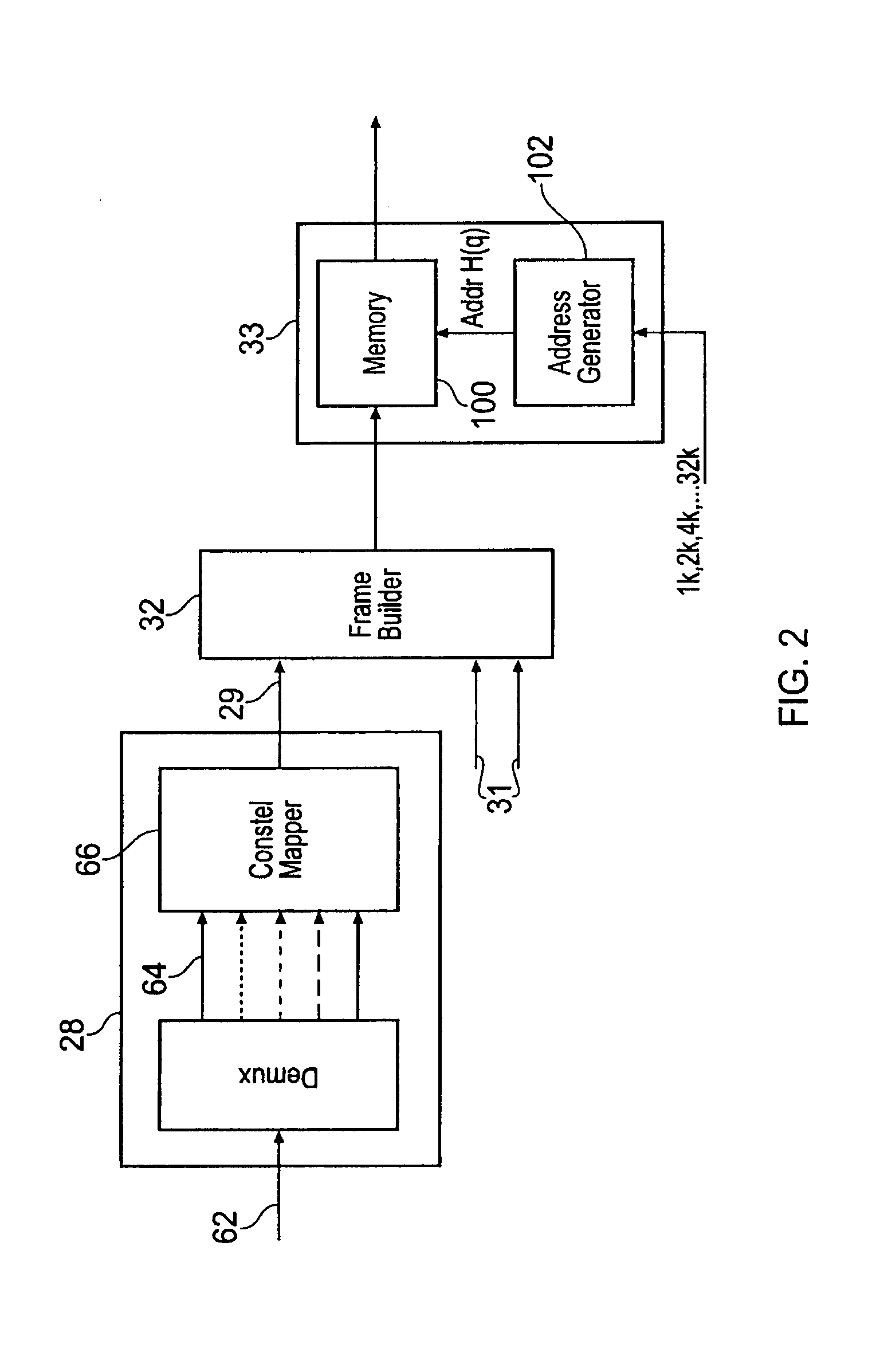
2k mode interleaver with odd interleaving only and per OFDM symbol permutaion code change in a digital video broadcasting (DVB) standard
InactiveUS20120127372A1Improve integrityGuaranteed to workPulse modulation television signal transmissionColor signal processing circuitsCarrier signalAddress generator
Owner:SONY CORP
LDPC codeword interleaving and mapping method and LDPC codeword de-interleaving and de-mapping method
InactiveCN105337691AImprove performanceError preventionMultiple carrier systemsTheoretical computer scienceConstellation diagram
The invention discloses an LDPC codeword interleaving and mapping method and an LDPC codeword de-interleaving and de-mapping method. The method comprises the following steps: performing bit interleaving of a coded LDPC codeword according to a certain bit interleaving method and an interleaving pattern; and performing constellation mapping of the bit interleaved LDPC codeword according to a constellation diagram so as to obtain a symbolic stream. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, specific mapping and de-mapping methods are selected for an LDPC code having a specific code rate, such that the system performance is improved better.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
Interleaving with iterative calculation of interleaving addresses
ActiveCN101133559ACode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresDigital dataData stream
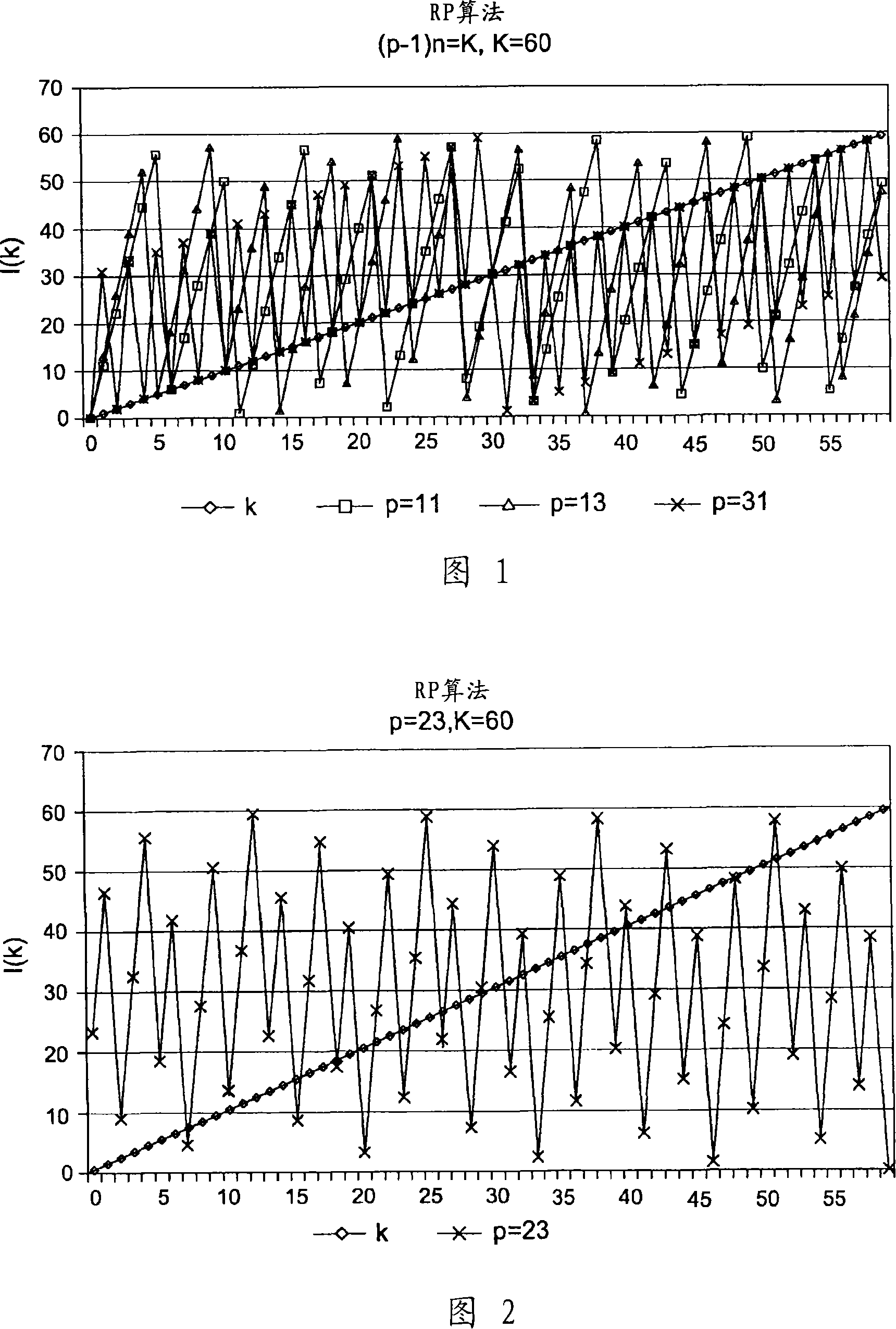
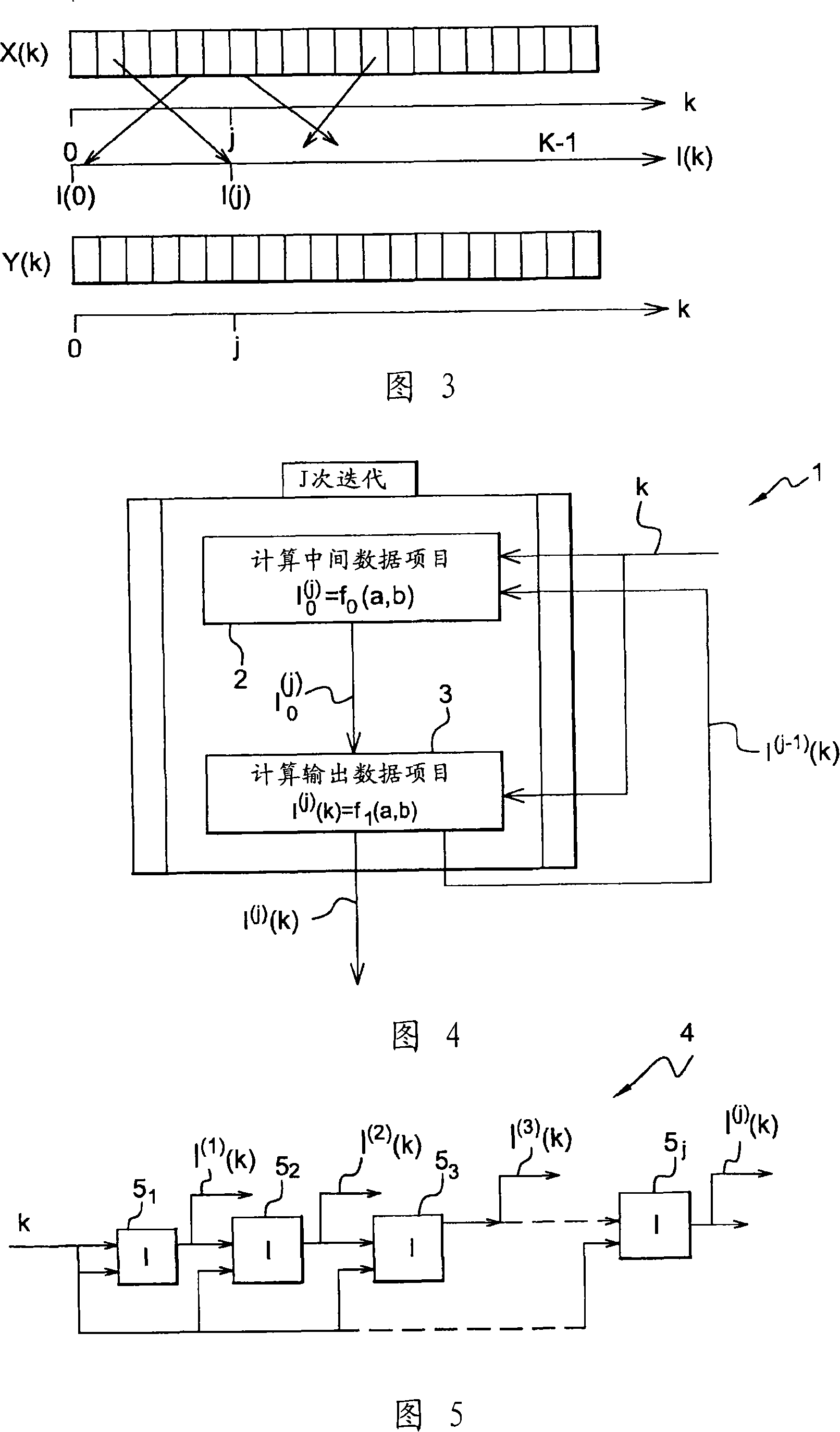
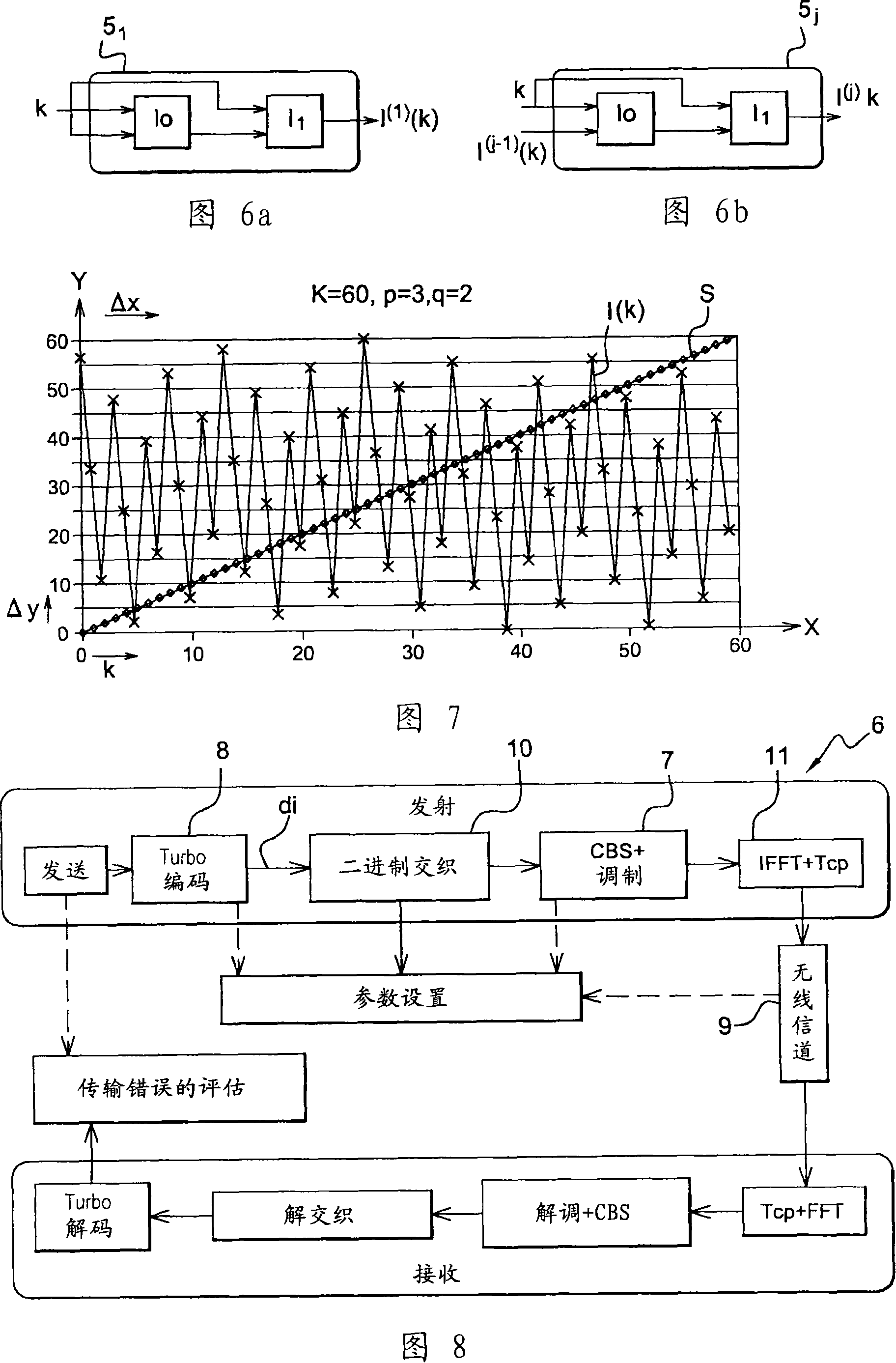
The invention concerns a method and a device (4) for block interleaving of size K with N iterations of index j, N being not less than 1, of input digital data indexed by a variable k = {0,...., K - 1}. The interleaving method uses a turbo structure having two inputs and one output. At the end of each iteration j, the interleaving law I(J)(k) in the interleaver output (4) is modified in accordance with an input sequence formed by the position indices of the data prior to interleaving (typically a ramp) and in accordance with an interleaved sequence (which provides the position of the data after interleaving) resulting from the previous iteration of the same interleaving algorithm. The invention enables the overall position of p multiplexed data streams to be maintained.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Memory efficient interleaving
InactiveUS20060071843A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersArtificial intelligenceComputer hardware
A method and system using a single interleaver at a either a receiving device or a transmitting device where a first symbol set is read from the single interleaver and concurrently with a second symbol set is written to the single interleaver, and a controller that synchronizes the reading of the first symbol set from the interleaver and the writing of the second symbol set to the interleaver so that a particular symbol of the second symbol set is only written to a location of the interleaver after a particular symbol of the first symbol set has been read from the location. The controller may switch between orders, e.g., row order and column order, of reading and / or writing symbols to the single interleaver when all of the symbols for a particular set of symbols associated with the single interleaver have been read, according to another embodiment.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
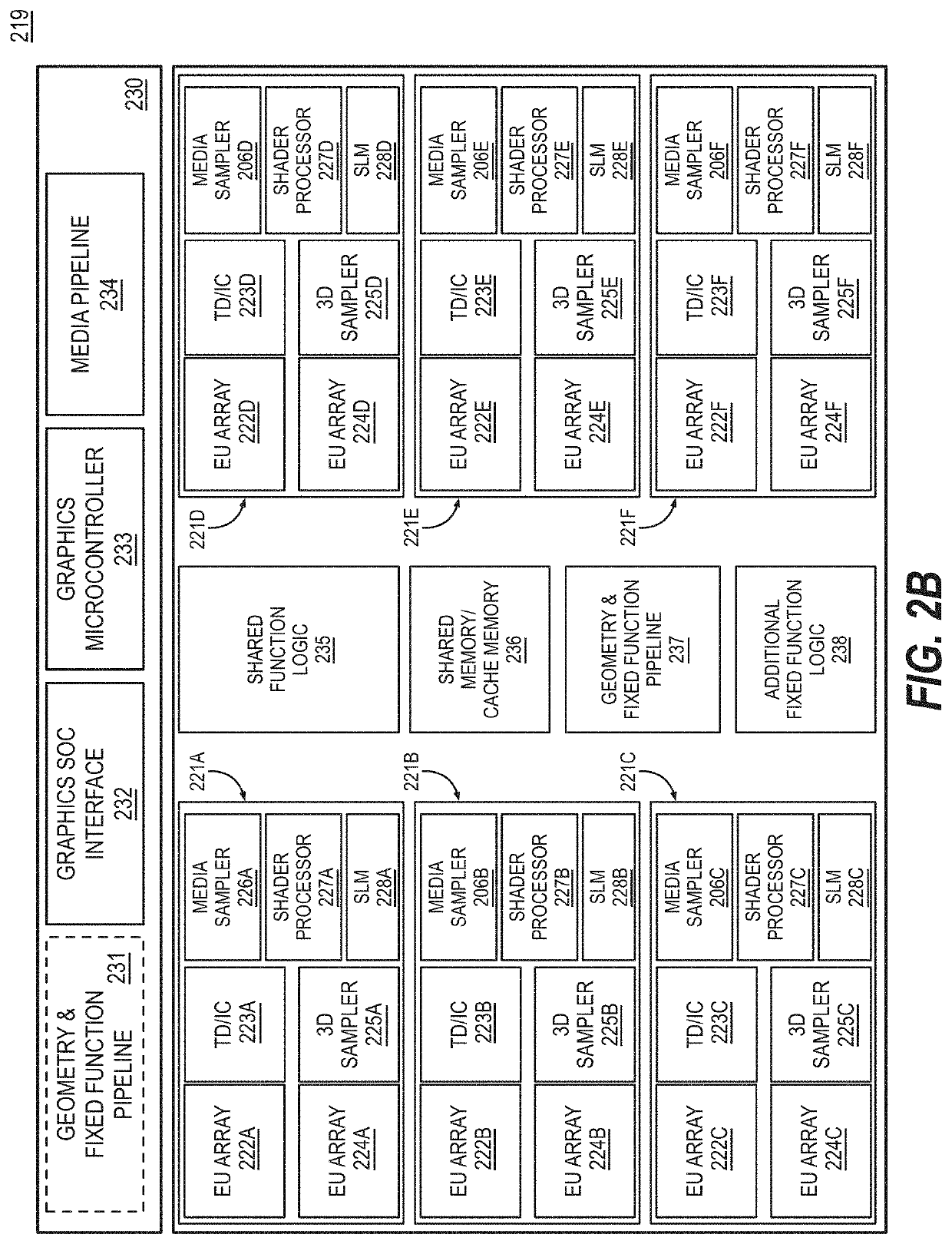
Variable width interleaved coding for graphics processing
Variable width interleaved coding for graphics processing is described. An example of an apparatus includes one or more processors including a graphic processor; and memory for storage of data including data for graphics processing, wherein the graphics processor includes an encoder pipeline to provide variable width interleaved coding and a decoder pipeline to decode the variable width interleaved coding, and wherein the encoder pipeline is to receive a plurality of bitstreams from workgroups; perform parallel entropy encoding on the bitstreams to generate a plurality of encoded bitstreams for each of the workgroups; perform variable interleaving of the bitstreams for each workgroup based at least in part on data requirements for decoding received from the decoder pipeline; and compact outputs for each of the workgroups into a contiguous stream of interleaved data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method of de-interleaving interleaved data samples sequences, and associated system
ActiveUS7506220B2Optimized areaIncrease power consumptionError detection/correctionCode conversionSample sequenceSecondary stage
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
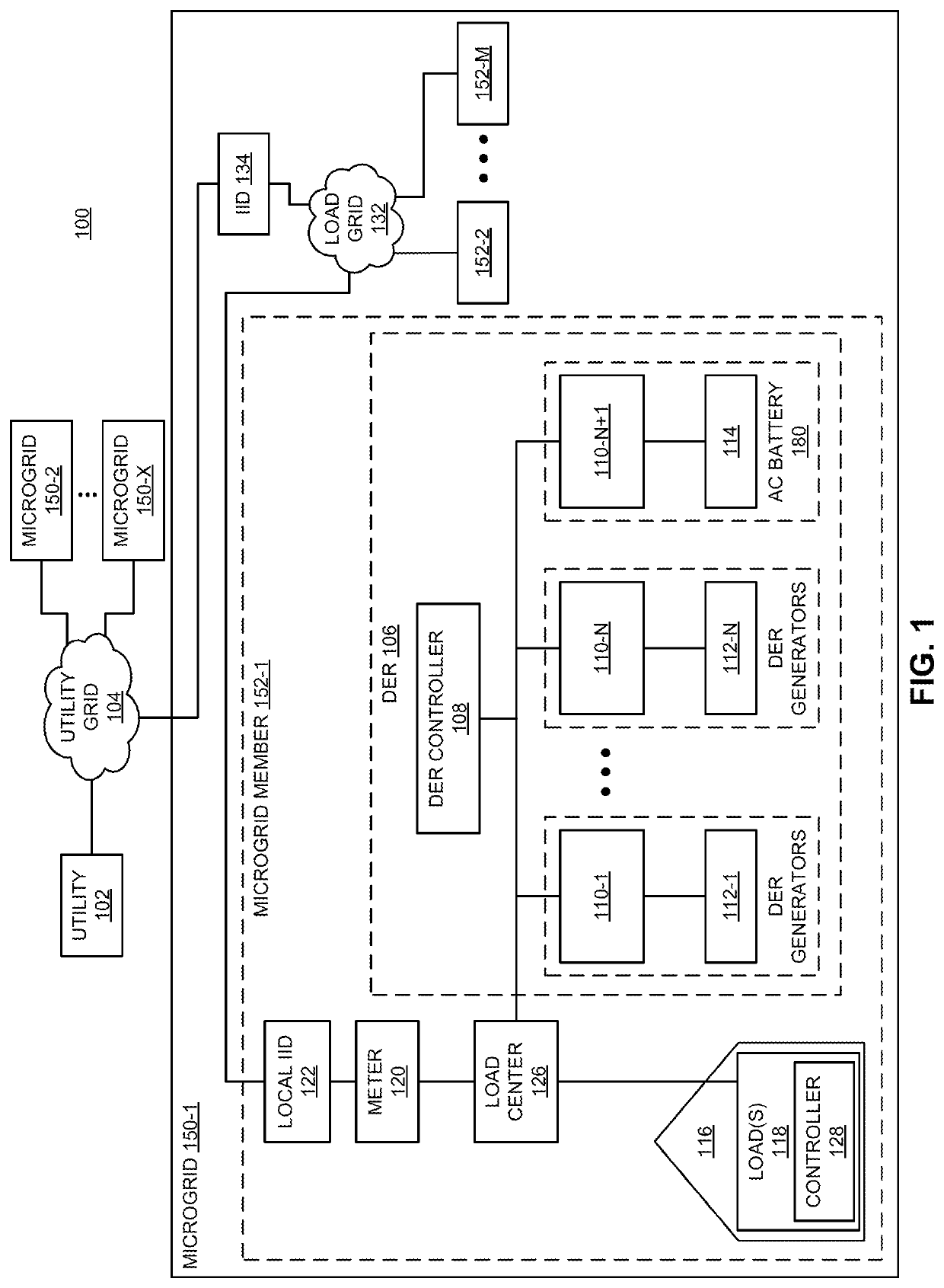
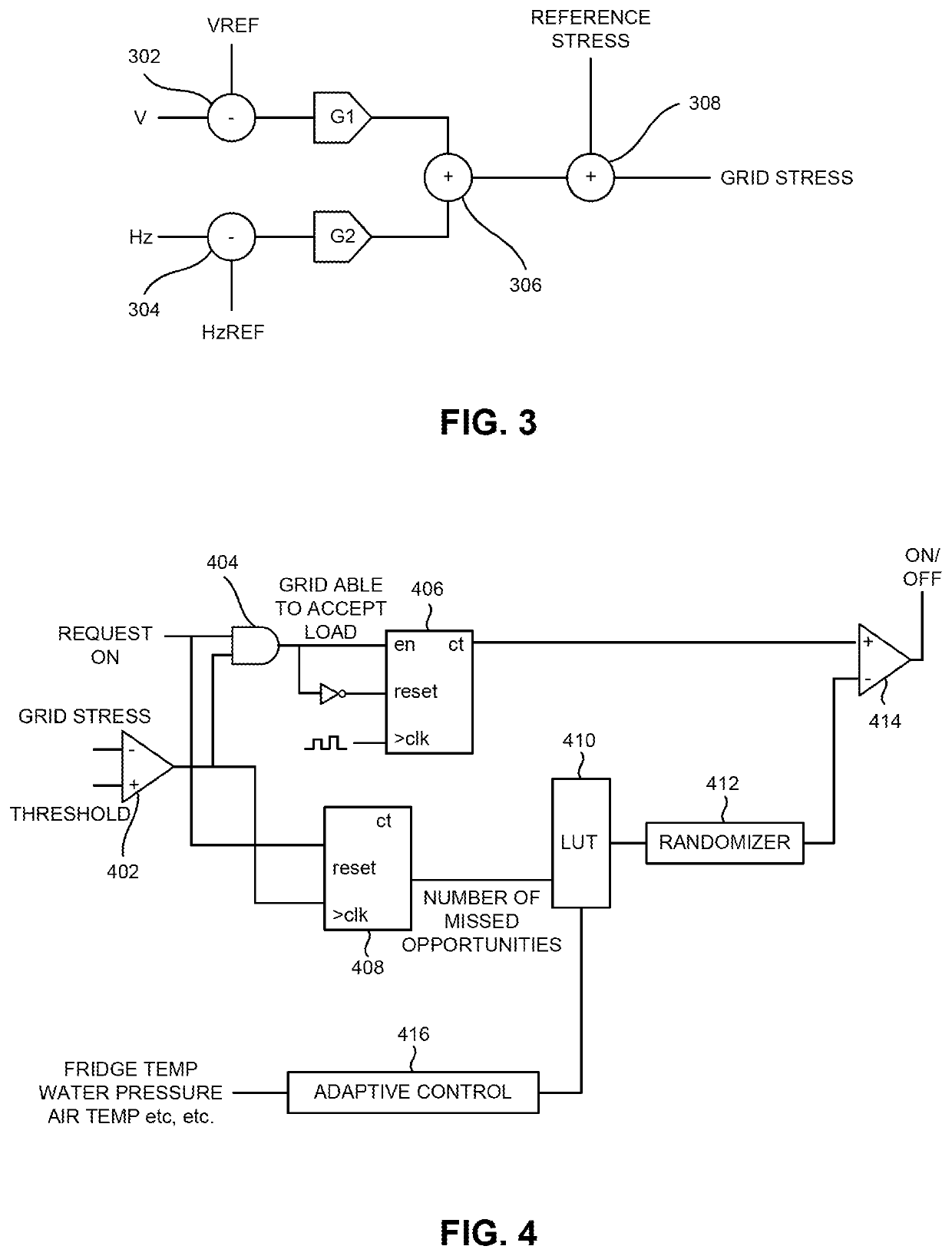
Method and apparatus for automatic interleaving of cycled loads in a microgrid
A method and apparatus for autonomous, automatic interleaving of cycled loads coupled to a grid. In one or more embodiments, the method comprises (i) determining, by a smart load coupled to a grid, a first grid stress value; (ii) comparing, by the smart load, the first grid stress value to an activation threshold; (iii) waiting, by the smart load, when the first grid stress value is less than the activation threshold, a delay period; (iv) determining, by the smart load and after the delay period ends, a second grid stress value; (v) comparing, by the smart load, the second grid stress value to the activation threshold; and (iv) activating, by the smart load, when the second grid stress value is less than the activation threshold.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
Reducing power consumption of communication interfaces by clock frequency scaling and adaptive interleaving of polling
ActiveUS11249536B2Reduce power consumptionSave power during command executionPower supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingLow power dissipationEmbedded system
Reducing power consumption of communication interfaces by clock frequency scaling and adaptive interleaving of polling is disclosed. In a first aspect, a control system controls transmission of a command via a serial interface at a higher clock frequency. After transmission, the control system and the interface are operated at a lower clock frequency to save power during command execution. In this aspect, a reduction in polling corresponds to the reduction in clock signal frequency. When the command is complete, the interface is operated at the higher frequency to send another command. In a second aspect, after the control system sends a command to the receiving device, polling is suspended and an execution time of the command is tracked. Polling begins when the tracked execution time almost equals an expected completion time. Both aspects disclosed above may be implemented to reduce power consumption in exchange for a small increase in latency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
IC die to IC die interconnection using error correcting code and data path interleaving
PendingCN112655088AReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHemt circuitsDie (integrated circuit)
A multi-chip module includes a first integrated circuit (IC) die a second IC die. The first IC die includes an array of first bond pads, a plurality of first code group circuits, and first interleaved interconnections between the plurality of first code group circuits and the array of first bond pads, and the first interleaved interconnections include a first interleaving pattern causing data from different code group circuits to be coupled to adjacent first bond pads. The second IC die includes a second array of bond pads that electrically couple to the array of first bond pads, a plurality of second code group circuits, and second interleaved interconnections between the plurality of second code group circuits and the array of second bond pads, and the second interleaved interconnections include a second interleaving pattern causing data from different code groups to be coupled to adjacent second bond pads.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A kind of interweaving method and device
ActiveCN109391363BCode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesRound complexityParallel computing
The present application relates to the field of communication technology, and discloses an interleaving method and device, which are used to reduce the complexity of implementing Polar code interleaving and rate matching. The method is as follows: obtain the coded bits encoded by the Polar code, sort the coded bits according to the priority order of performing the rate matching operation, and obtain a first bit sequence, and the first bit sequence includes j subsequences, and j is positive integer, write the first bit sequence into the interleaver of row i and column j, wherein the bit in one column in the interleaver contains one subsequence in the j subsequences, and from the interleaver The bits are read out column by column until M bits are read, wherein at least two adjacent columns read in opposite directions, and M is the target code length.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Parallel turbo decoding with non-uniform window sizes
Owner:阿塞勒康姆有限公司
Decoding method based on dvb-s2 standard ldpc code parallel decoding fpga implementation architecture
ActiveCN110278000BImprove throughputError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDecoding methodsComputer architecture
Owner:南京中科晶上通信技术有限公司
Low-density parity-check rate matching in communication systems
PendingUS20220303052A1Channel coding adaptationForward error control useCommunications systemStation
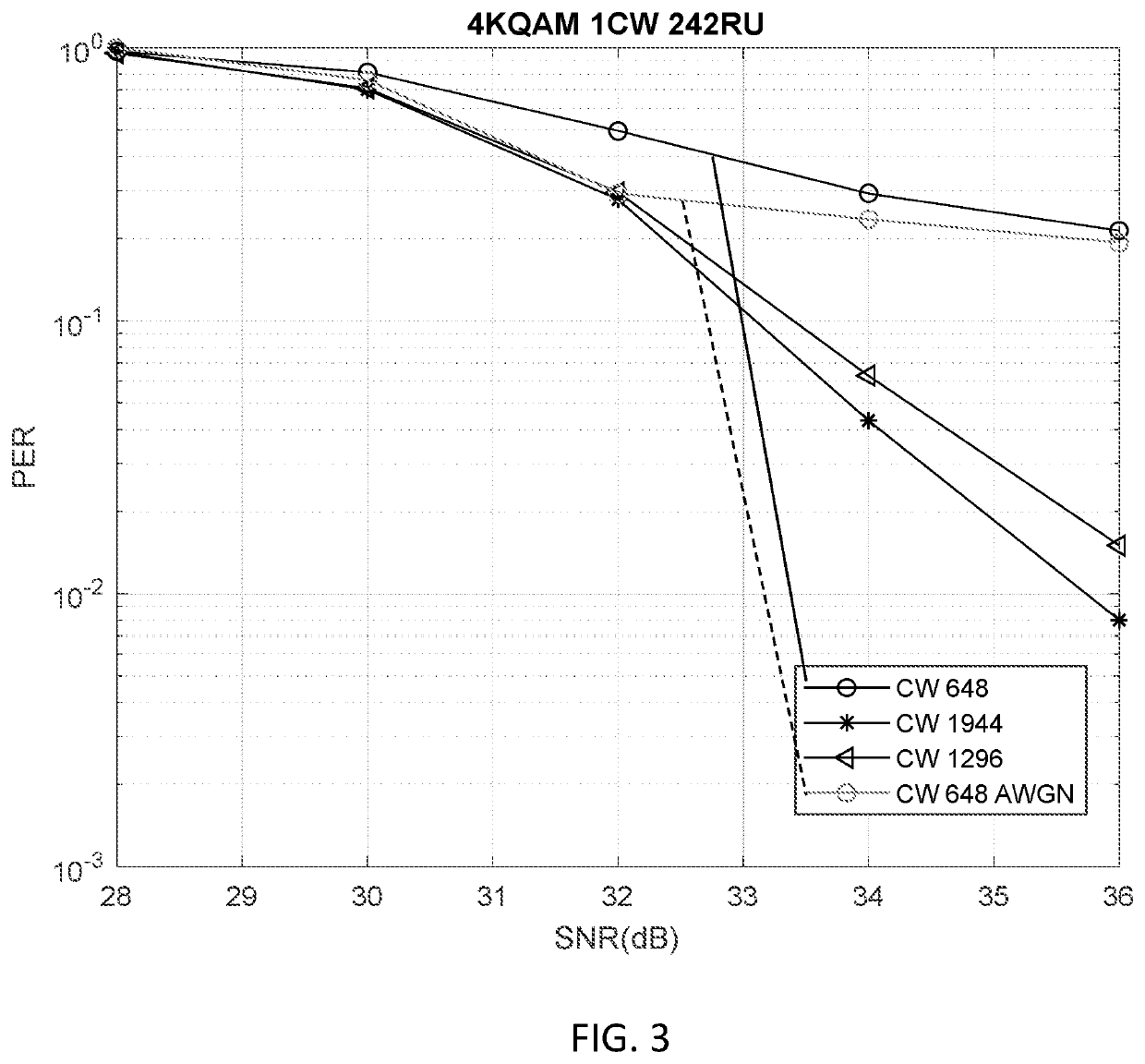
An apparatus and system for decreasing packet error rate (PER) in a station (STA) are described. The STA determines that an Extremely High Throughput (EHT) physical layer protocol data unit (PPDU) is to be constructed for transmission and that Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) encoding is to be used to encode a data field of the EHT PPDU. In response, the STA constructs the EHT PPDU in accordance with a construction constraint of the data field of the EHT PPDU when a LDPC codeword (CW) size 648 is to be used for the data field of the EHT PPDU. The construction constraint includes using bit level interleaving or preventing use of LDPC CW size 648 for a modulation coding scheme (MCS) that is larger than 256 quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) or 64 QAM or for all QAMs.
Owner:INTEL CORP
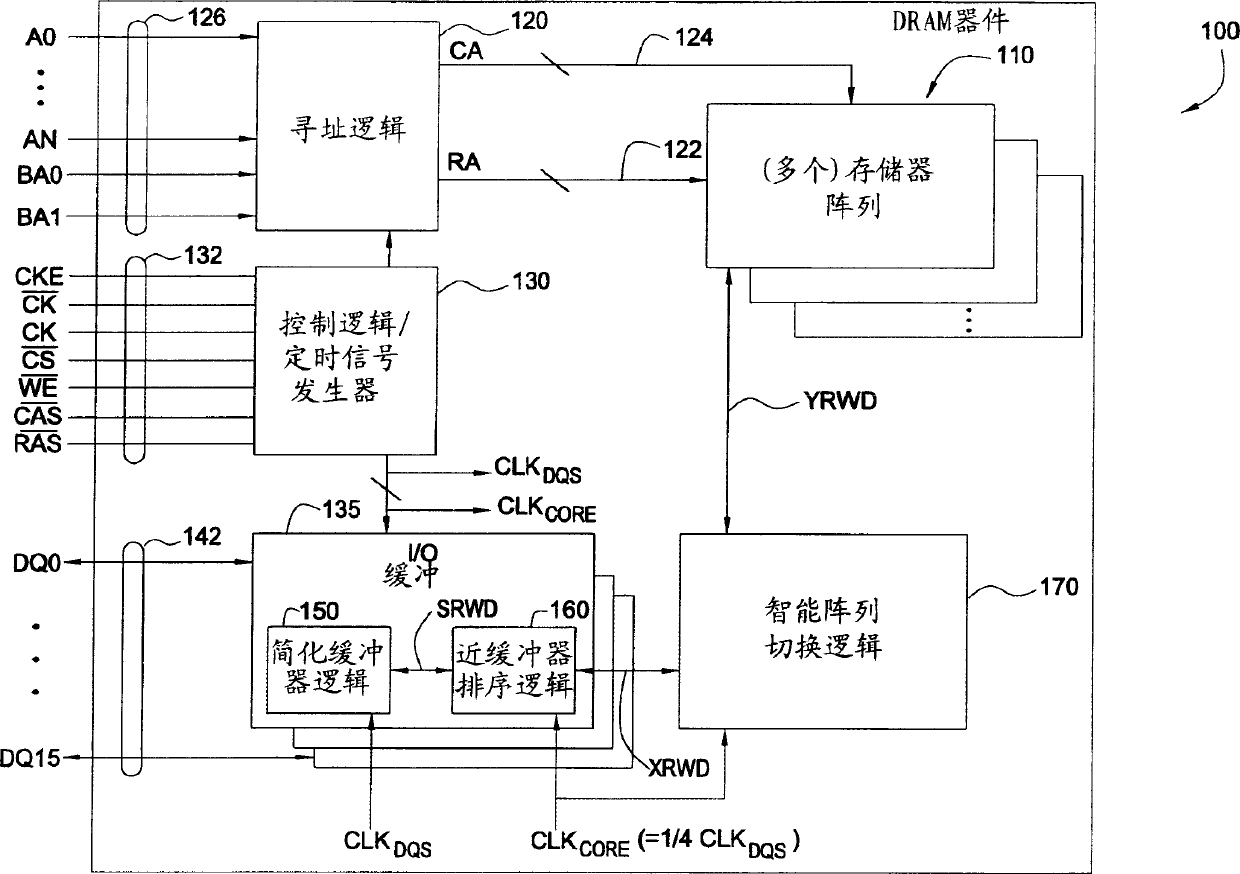
Memory device and method for exchanging data with memory device
Improved double data rate type II dynamic random access memory data path. The present invention proposes techniques and circuits to support the switching operations required to exchange data between a memory array and an external data buffer. In the write path, this switching operation can include latching and assembling some of the data bits received sequentially on a single data buffer, rearranging the data bits based on the type of access pattern (for example, interleaved or sequential). Sort and perform encoding operations on the accessed bank locations based on the chip structure (eg ×4, ×8, ×16). Similar operations are performed in the read path (in reverse order) to assemble the data to be read from the slave device. By separating the cache logic from the switching logic that can perform various other logic functions, the switching logic that performs those functions can operate at a lower clock frequency, saving the time of data transfer from the memory array to the DQ buffer, which can Alleviate the associated timing needs and improve latency, and vice versa.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
De-convolutional interleaver and de-convolutional interleaving method
The present invention provides a de-convolutional interleaver applied to process multi-group convolutional interleaving data. The multi-group convolutional interleaving data package includes multiple convolutional interleaving data which is formed by processing multi-group non-interleaving data through convolutional interleaving processing, each non-interleaving data includes L data, and adjacent two data corresponds a delay depth gap in each non-interleaving data after the convolutional interleaving processing, wherein L is a positive integer. The de-convolutional interleaver includes: an input data buffer configured to temporarily store multi-group convolutional interleaving data; a memory controller configured to store the multi-group convolutional interleaving data temporarily stored in the input data buffer in the memory to perform de-convolutional interleaving processing, the memory address of each stored convolutional interleaving data being determined by the delayed depth, the L value and the delay depth distance corresponding to the data; and an output data buffer configured to temporarily store multi-group convolutional interleaving data read from the memory.
Owner:MSTAR SEMICON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com