Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2886 results about "Data path" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
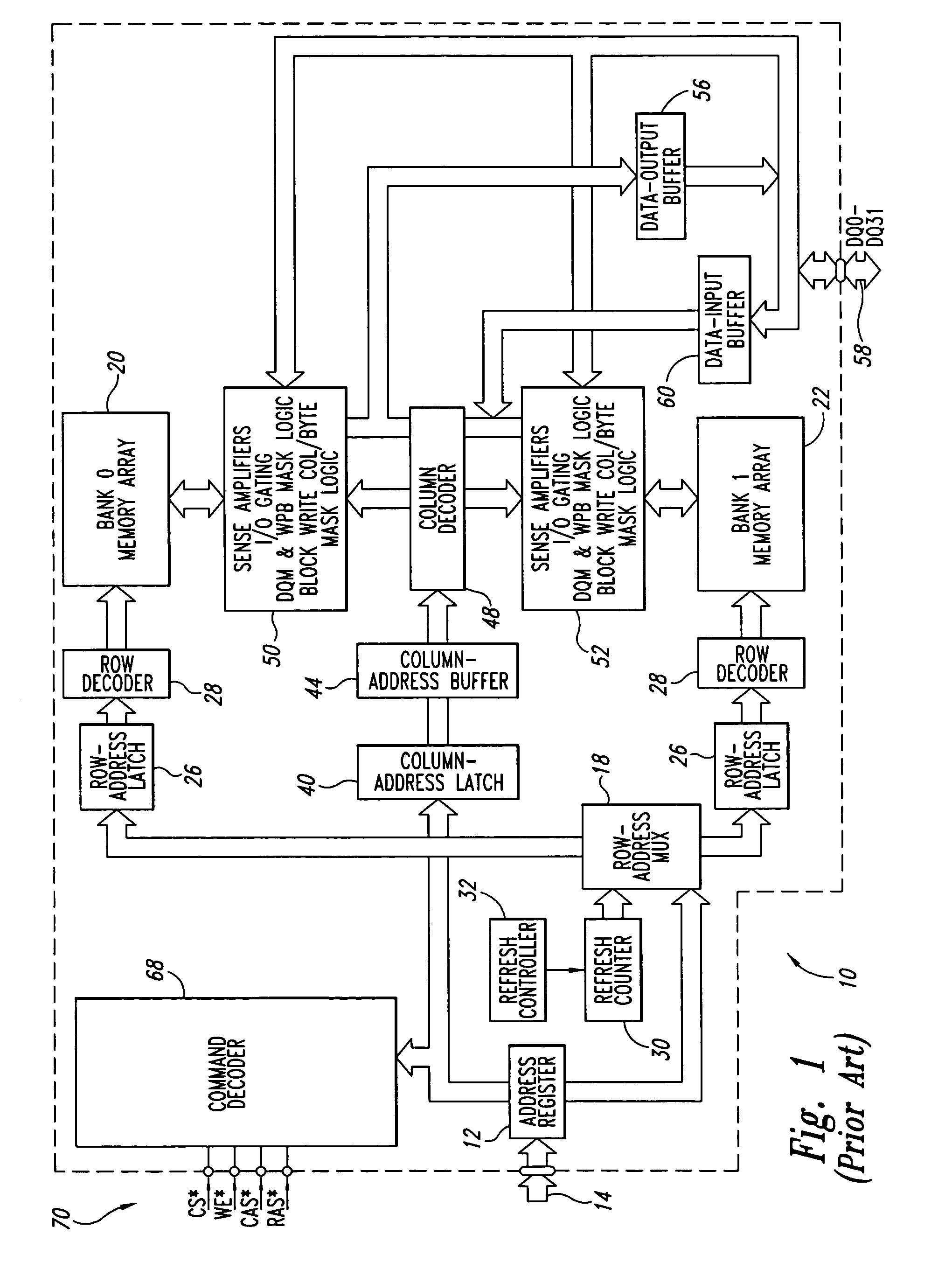
Data path. A data path (also written as datapath) is a set of functional units that carry out data processing operations. Datapaths, along with a control unit, make up the CPU (central processing unit) of a computer system. A larger data path can also be created by joining more than one together using multiplexers.
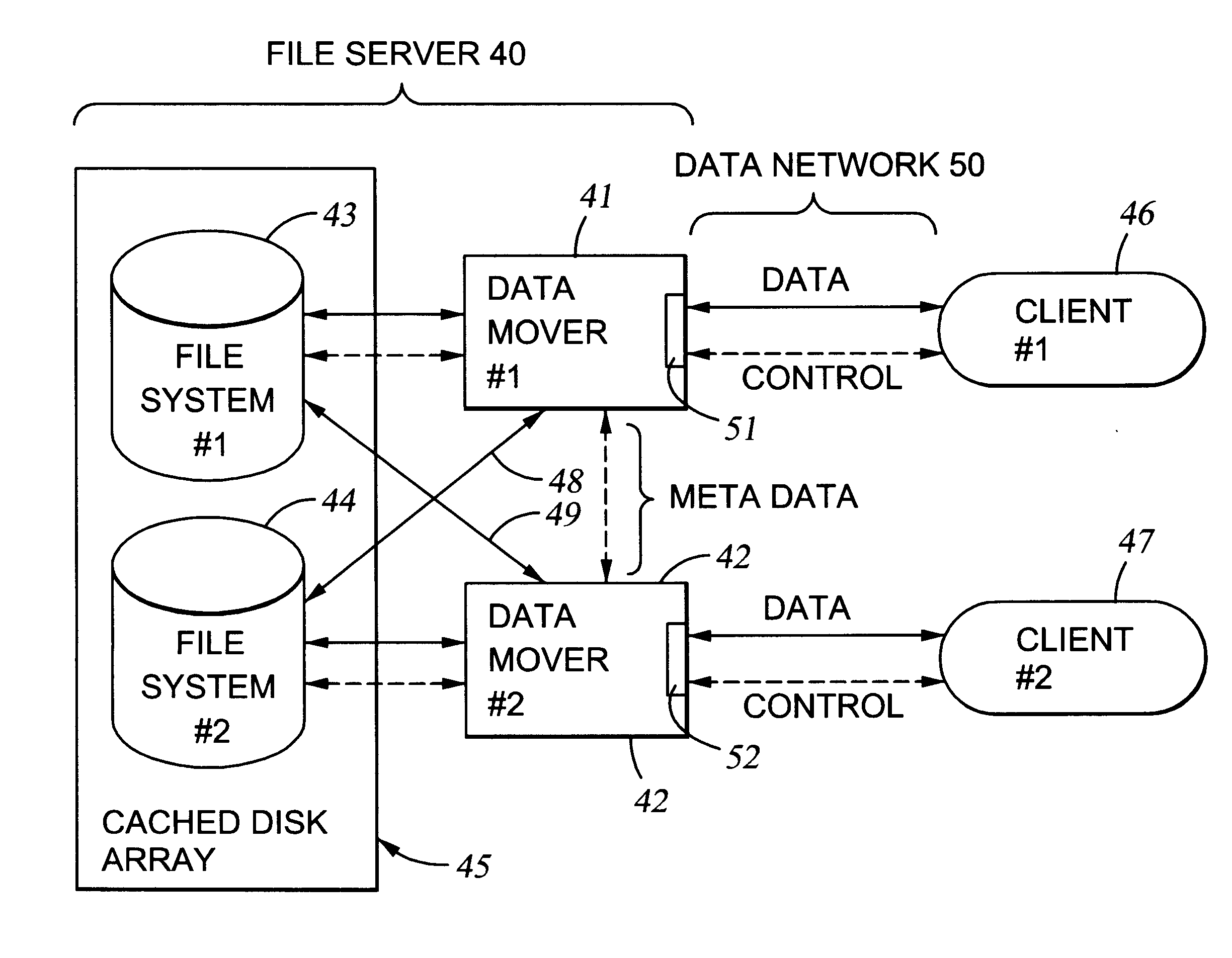
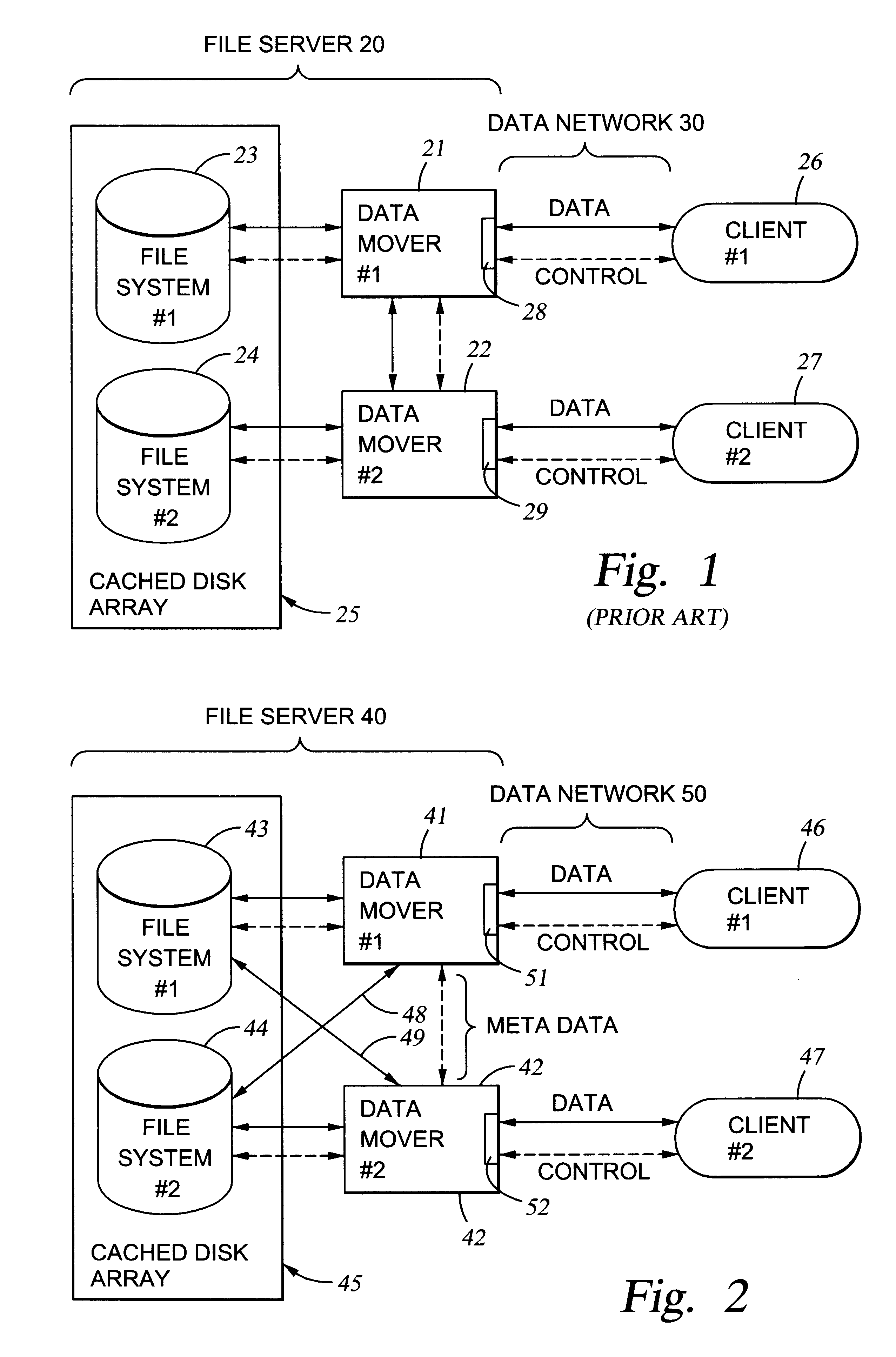
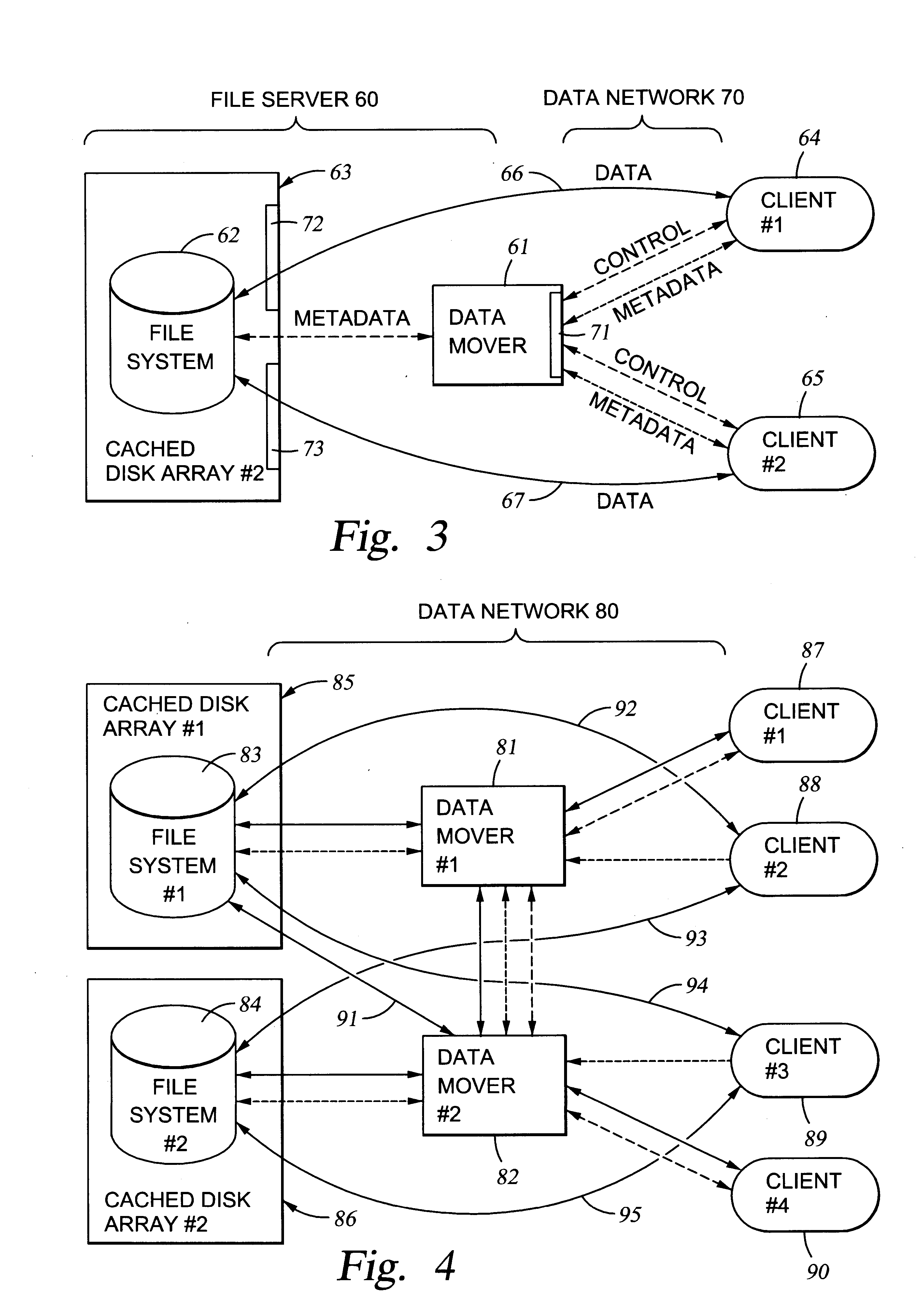
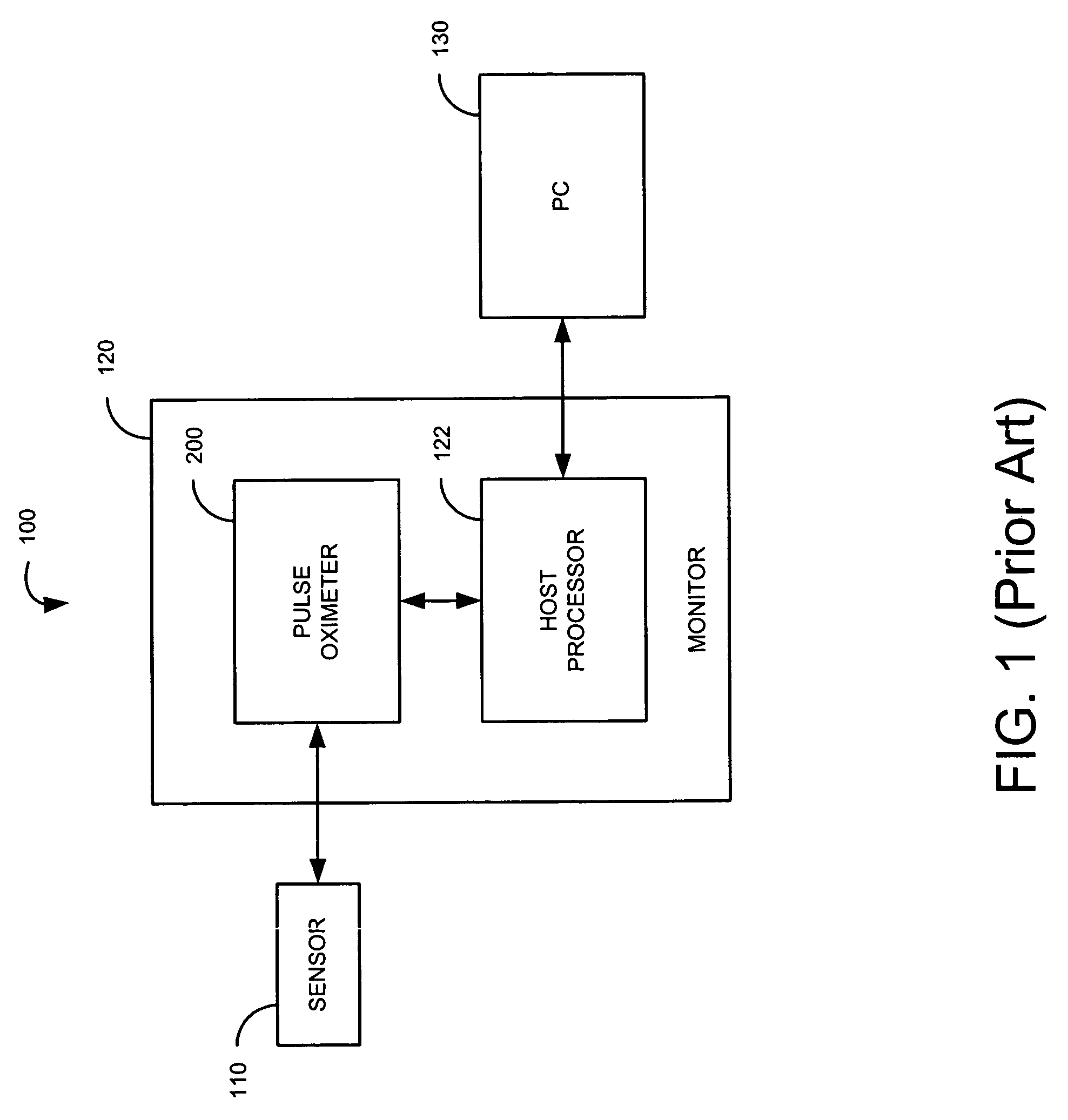
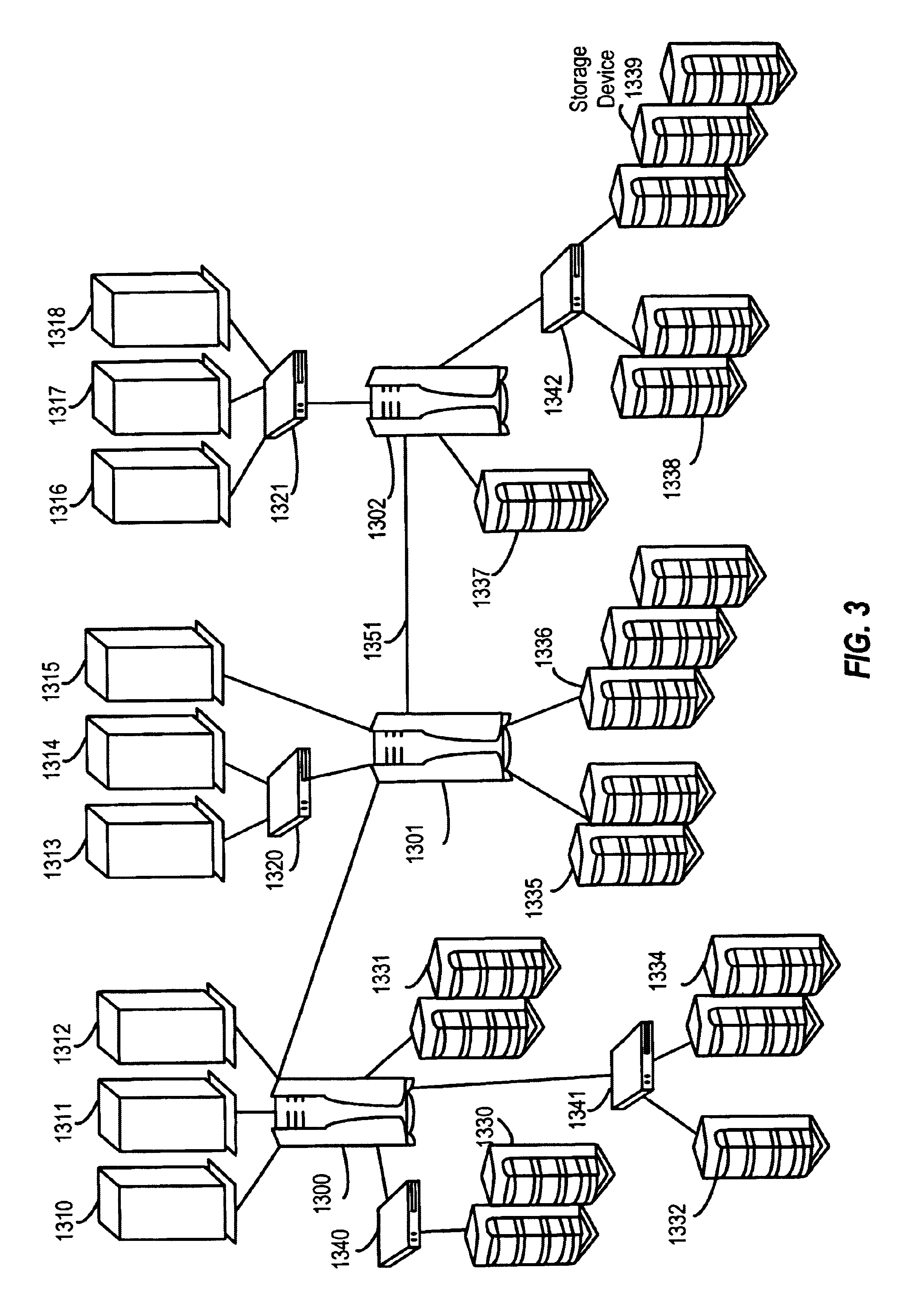
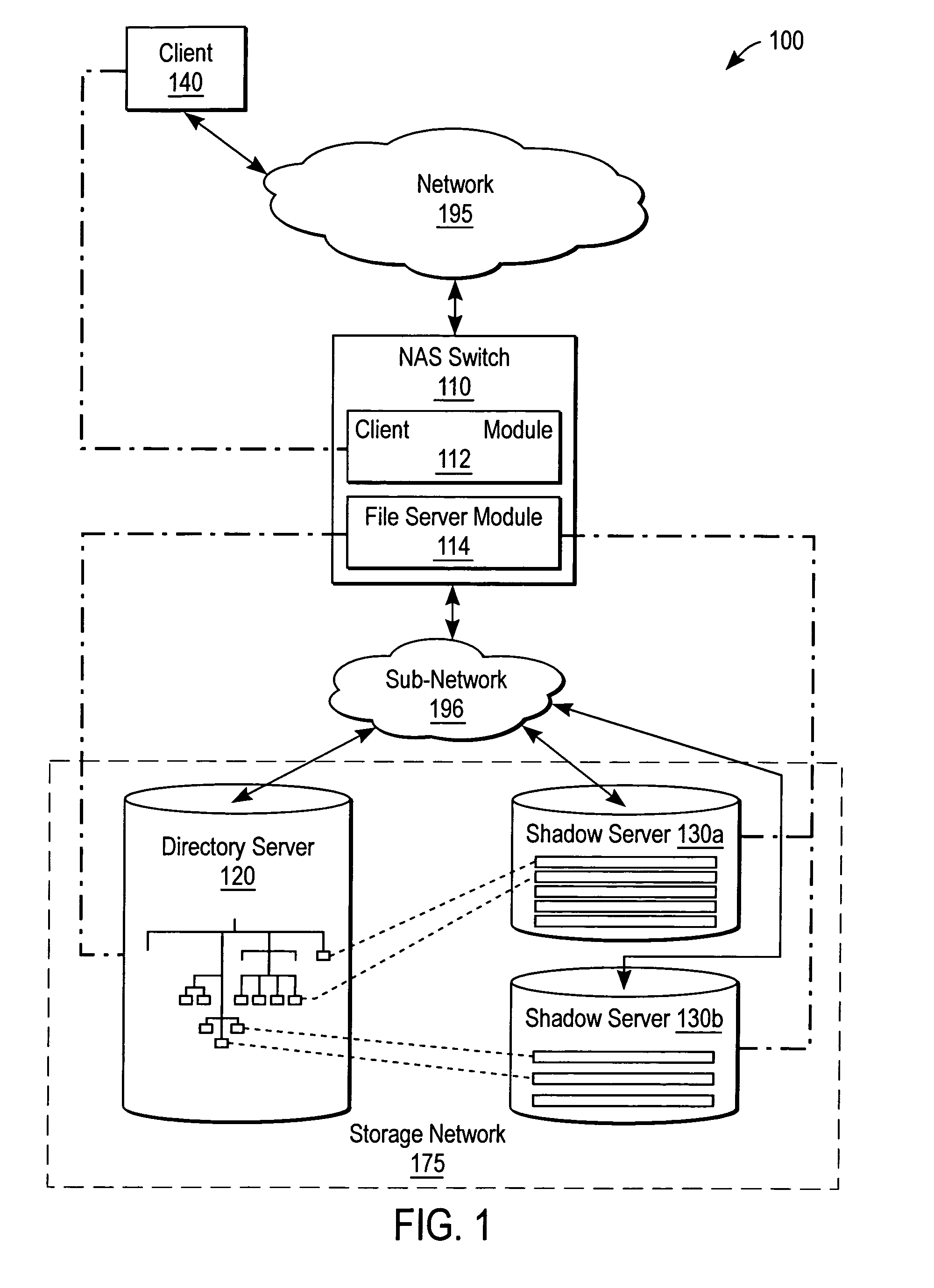
File server system using file system storage, data movers, and an exchange of meta data among data movers for file locking and direct access to shared file systems
InactiveUS6324581B1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsFile systemData access
A plurality of data mover computers control access to respective file systems in data storage. A network client serviced by any of the data movers can access each of the file systems. If a data mover receives a client request for access to a file in a file system to which access is controlled by another data mover, then the data mover that received the client request sends a metadata request to the data mover that controls access to the file system. The data mover that controls access to the file system responds by placing a lock on the file and returning metadata of the file. The data mover that received the client request uses the metadata to formulate a data access command that is used to access the file data in the file system over a bypass data path that bypasses the data mover computer that controls access to the file system.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
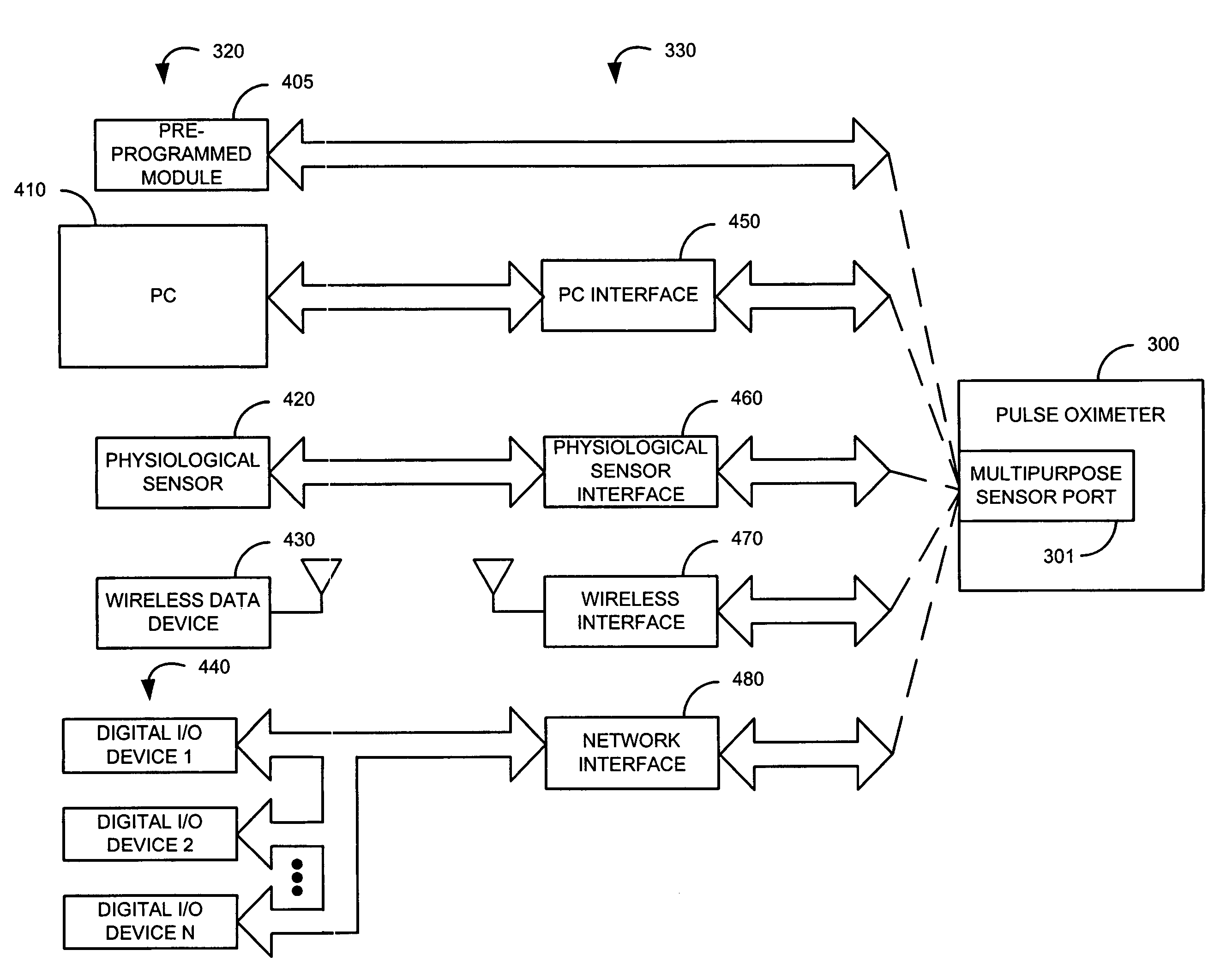
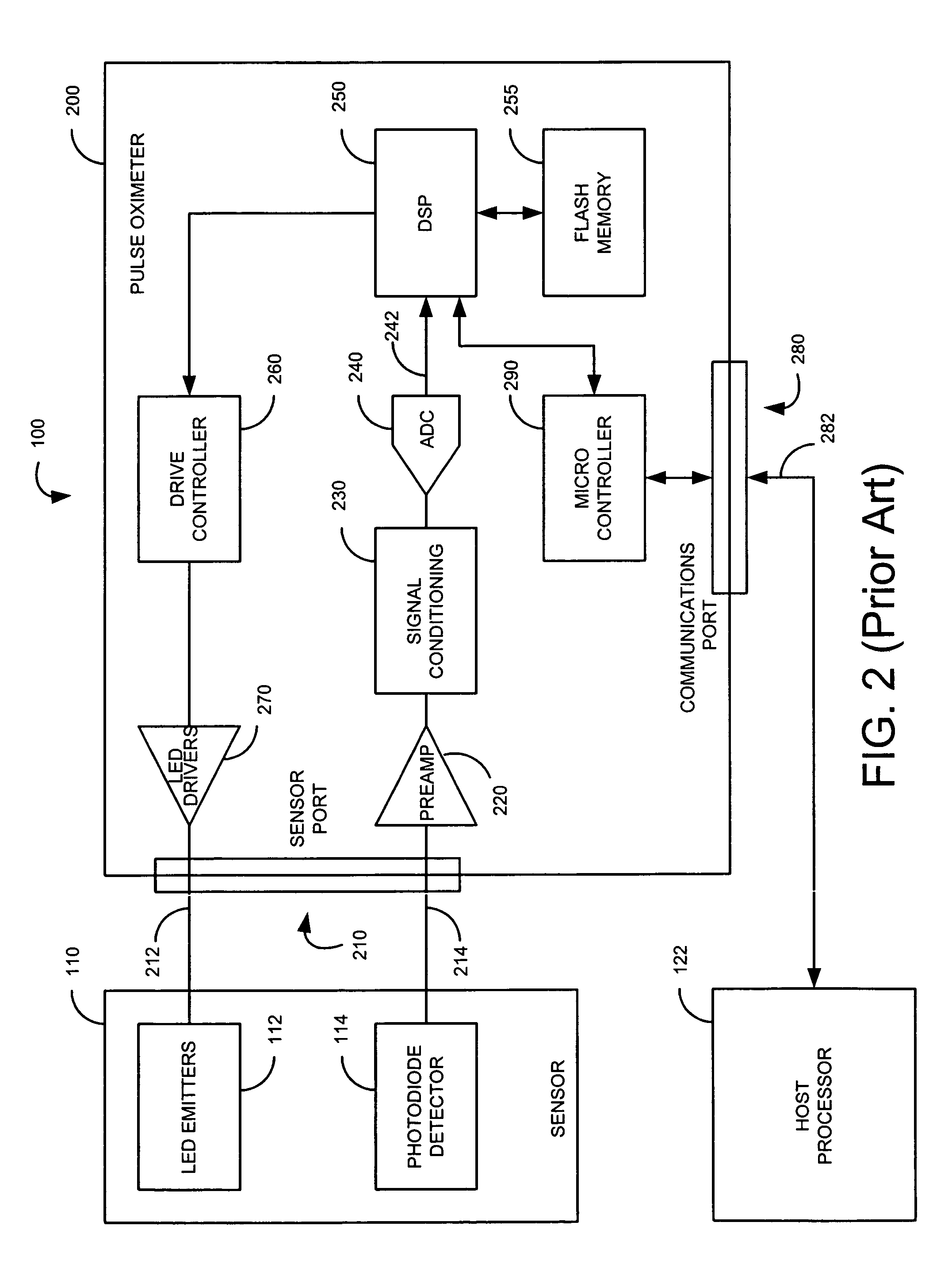
Multipurpose sensor port
A sensor port is adapted to connect to either a sensor or a data source. A reader is configured to identify which of the sensor and the data source is connected to the sensor port. A data path is configured to communicate an analog signal associated with the sensor and digital data associated with the data source to a signal processor according to the identification made by the reader.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
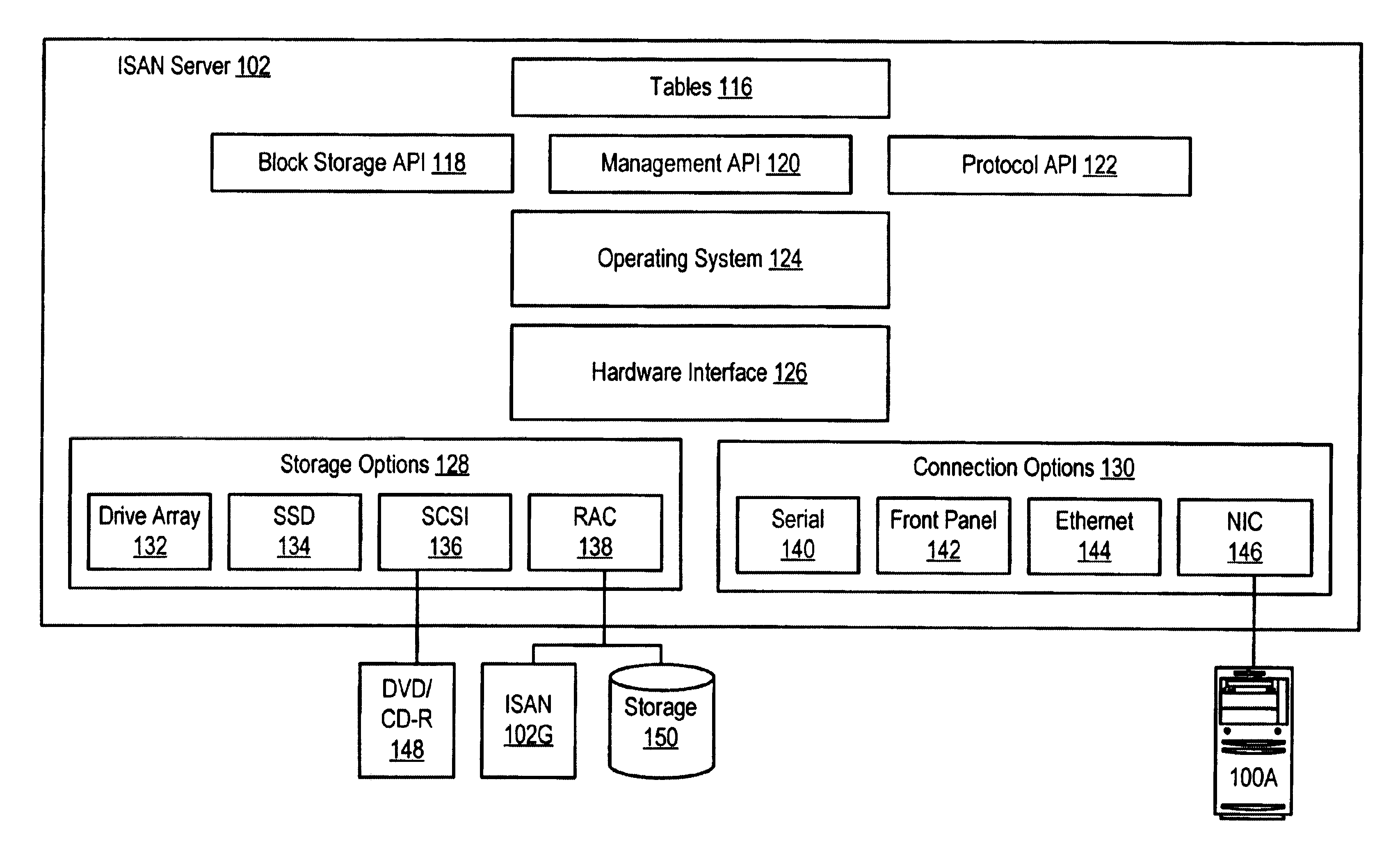
Method for configuration and management of storage resources in a storage network
InactiveUS6640278B1Improve performanceInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsCommunication interfaceStorage area network
A storage domain management system supports storage domains. The storage server includes a plurality of communication interfaces. A first set of communication interfaces in the plurality is adapted for connection to all kinds of users of data. A second set of communication interfaces in the plurality is adapted for connection to respective devices in a pool of storage devices for use in a storage domain. Data processing resources in the server are coupled to the plurality of communication interfaces for transferring data among the interfaces. The data processing resources comprise a plurality of driver modules and configurable logic linking driver modules into data paths. Each configured data path acts as a virtual circuit that includes a set of driver modules selected from the plurality of driver modules. A data storage transaction which is received at a communication interface is mapped to one of the configured data paths. A display and a user input device are included with data processing structures to manage images displayed on the display.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
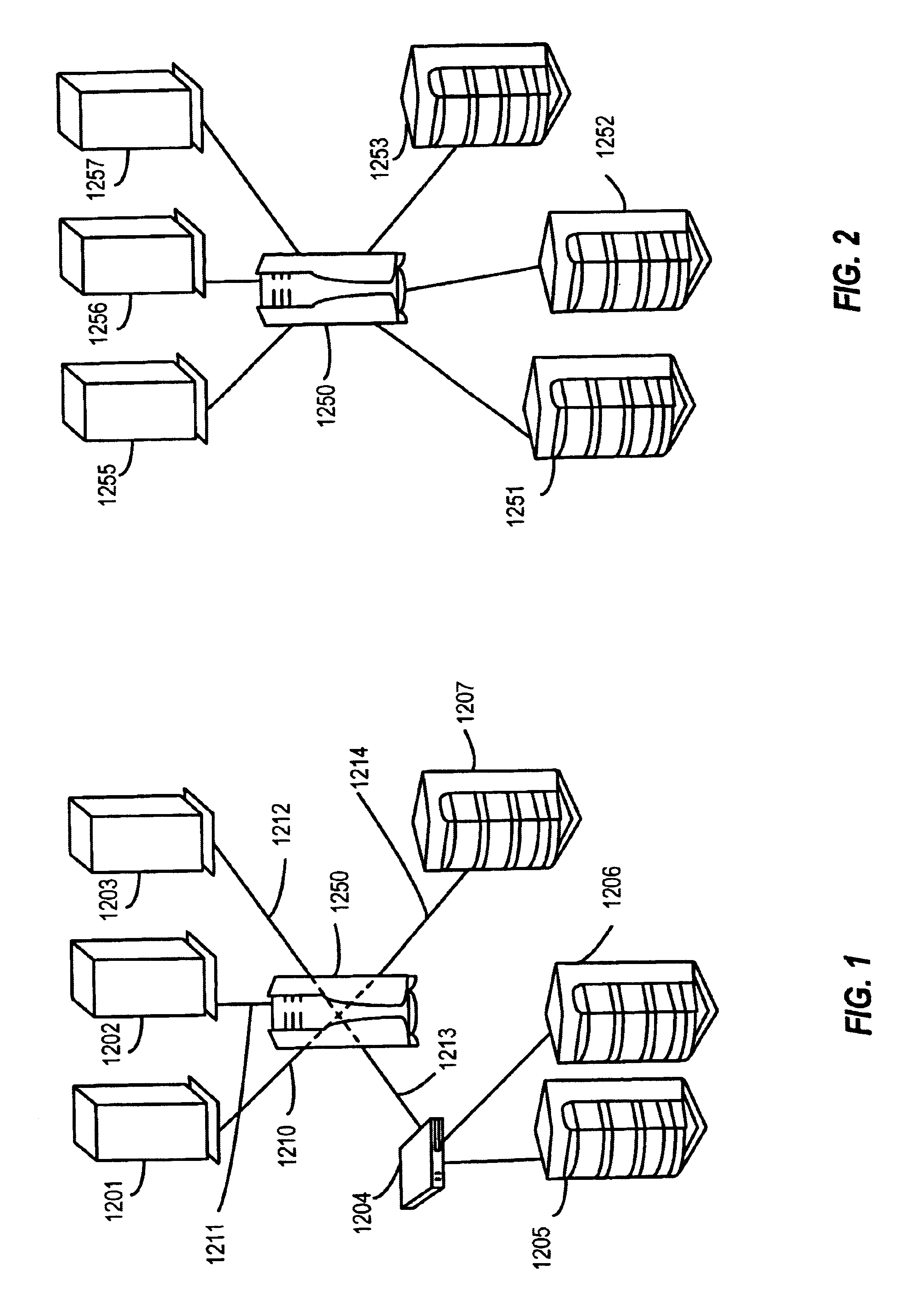
Method and apparatus for regulating data flow between a communications device and a network
ActiveUS7890612B2Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsTraffic capacityData stream
A network security device which acts as an “airlock” for traffic between a communications device and a network. Data is screened using rules based analysis by the security device to counter various threats, including viruses, phishing, attempts to “hijack” communications, communications with known malicious addresses or unknown addresses, and transmission of sensitive information. Data packets can be reassembled into files for screening, and decoded or expanded as necessary, but is never executed. The data path for the data being screened is kept separate from the operations of the network security device itself, so that the device is incorruptible—its programming cannot be compromised from outside sources. Updates for rules and entry of sensitive data for screening, etc., must be done through a physical interface, not via the normal data communications channel. The device is invisible—it cannot be “seen” by the network, and thus cannot be attacked.
Owner:ELECTRO GUARD CORP
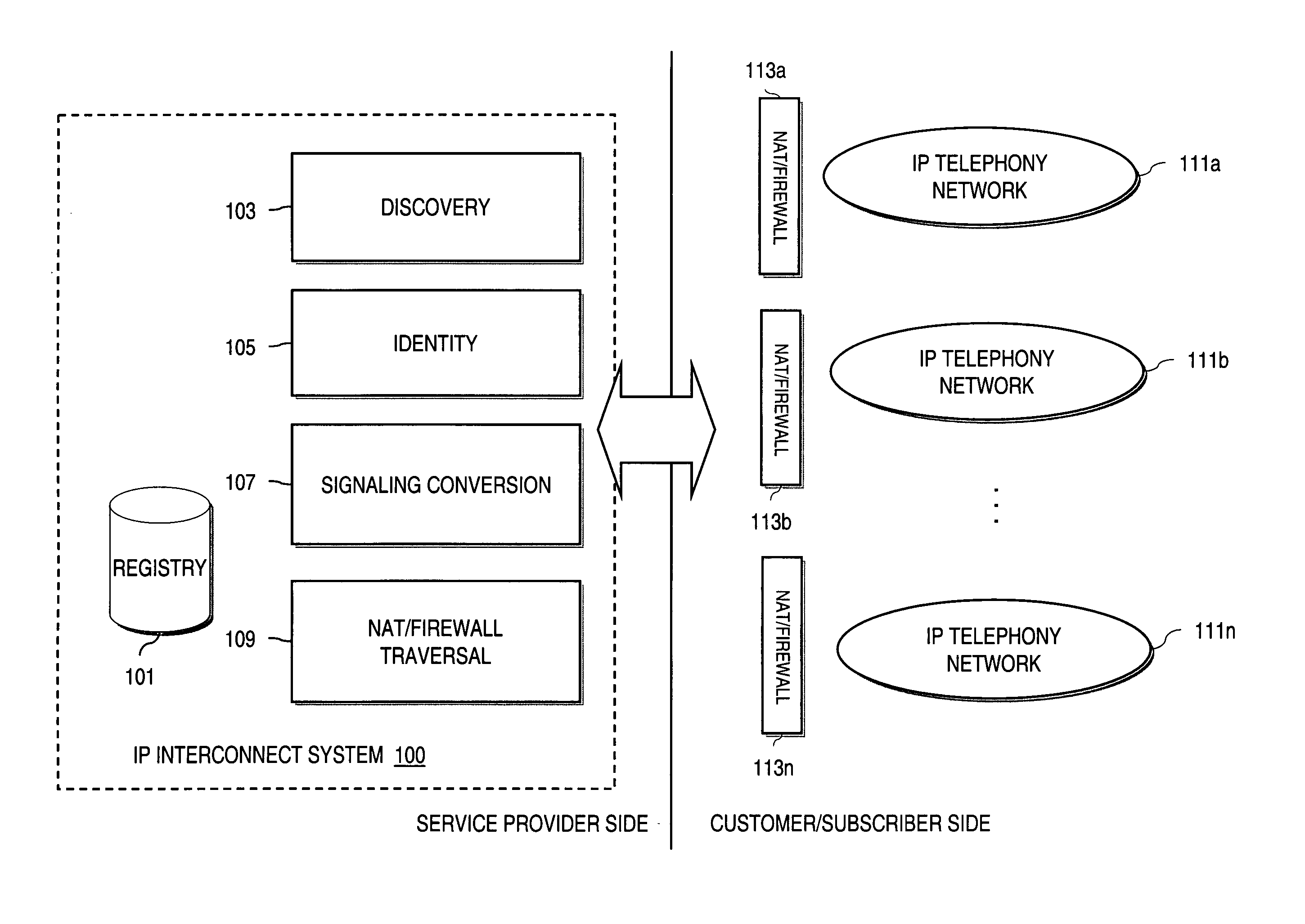
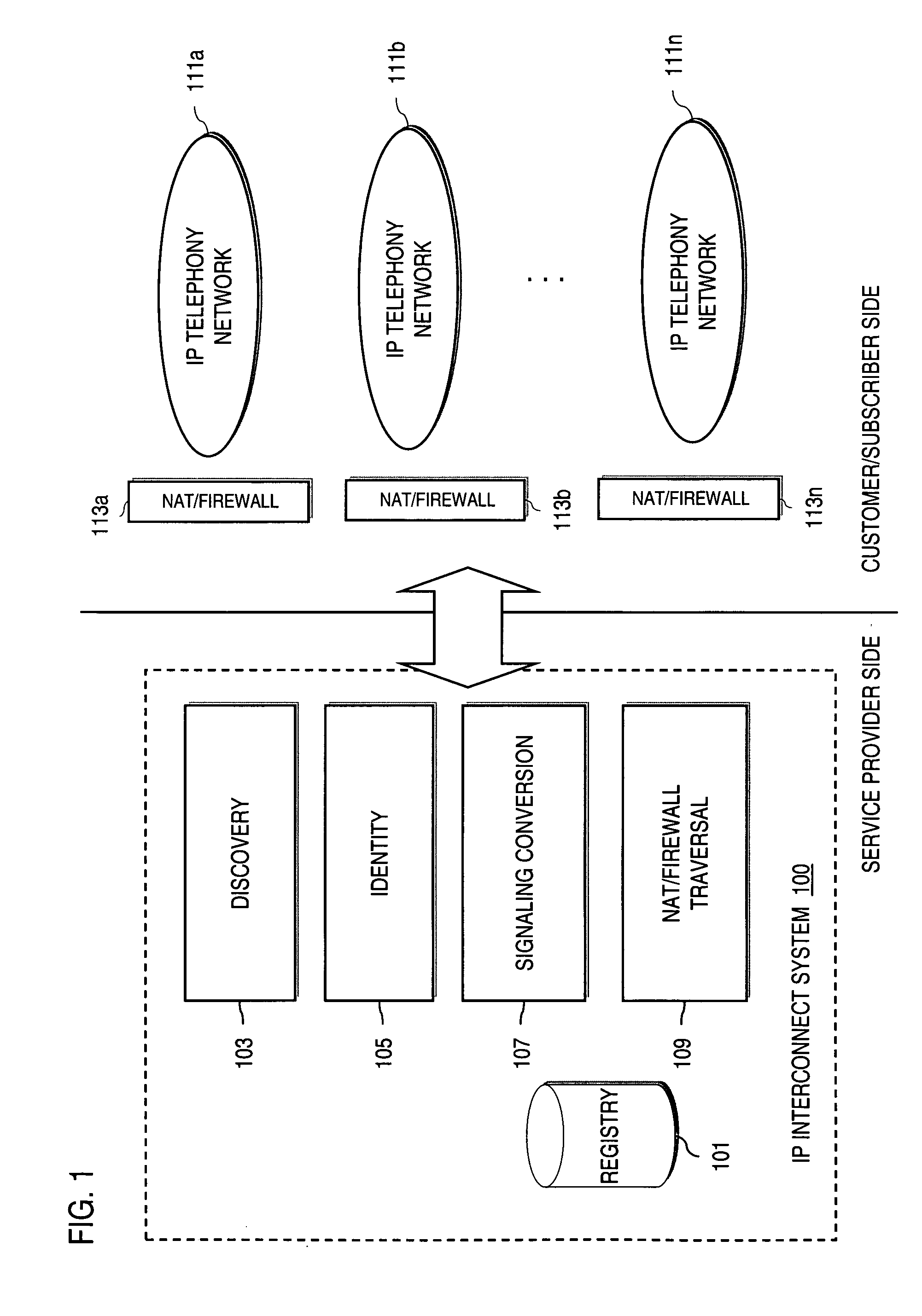
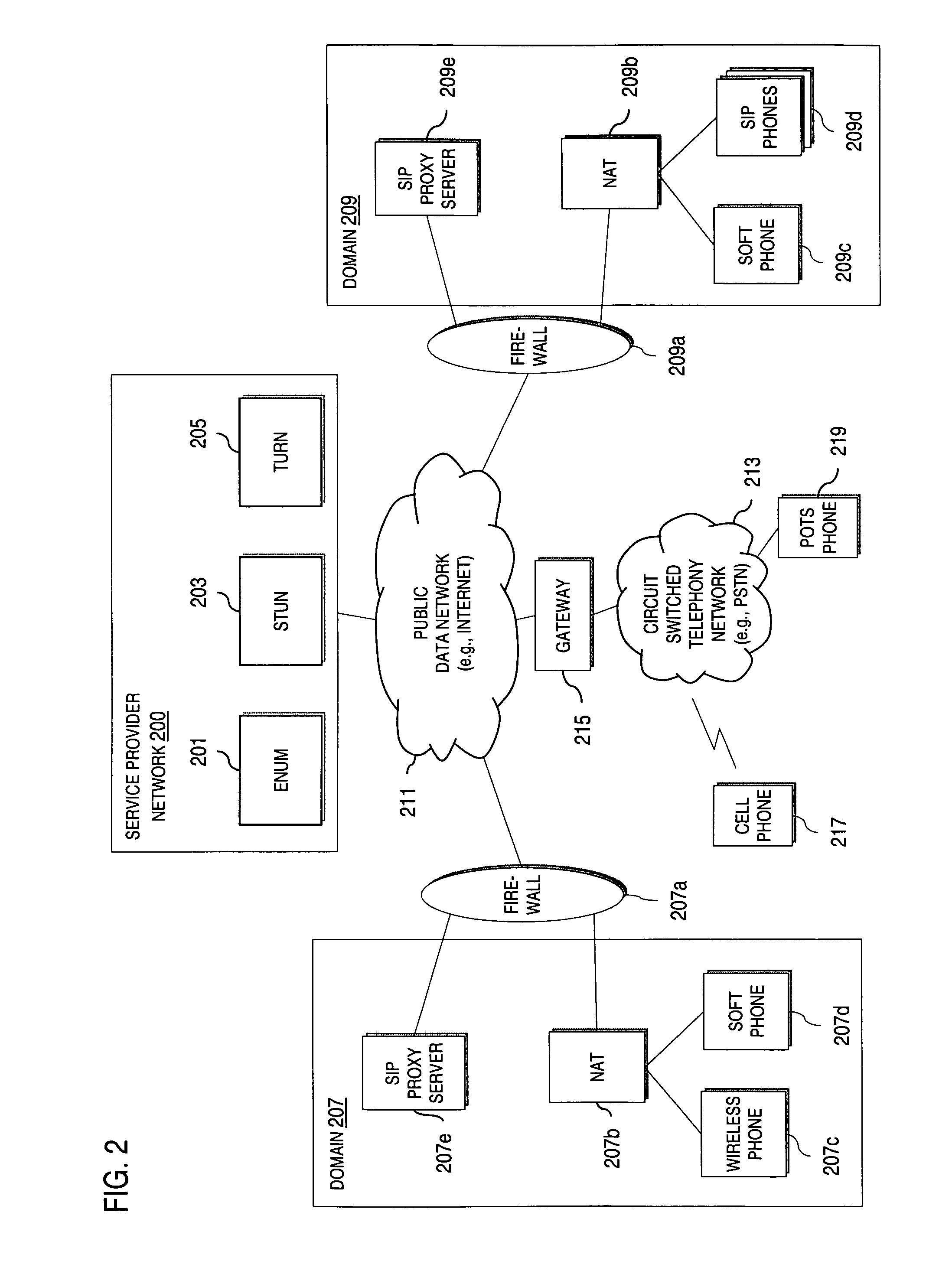
IP-based services for circuit-switched networks
ActiveUS20050058125A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsRadio access networkVoice over IP
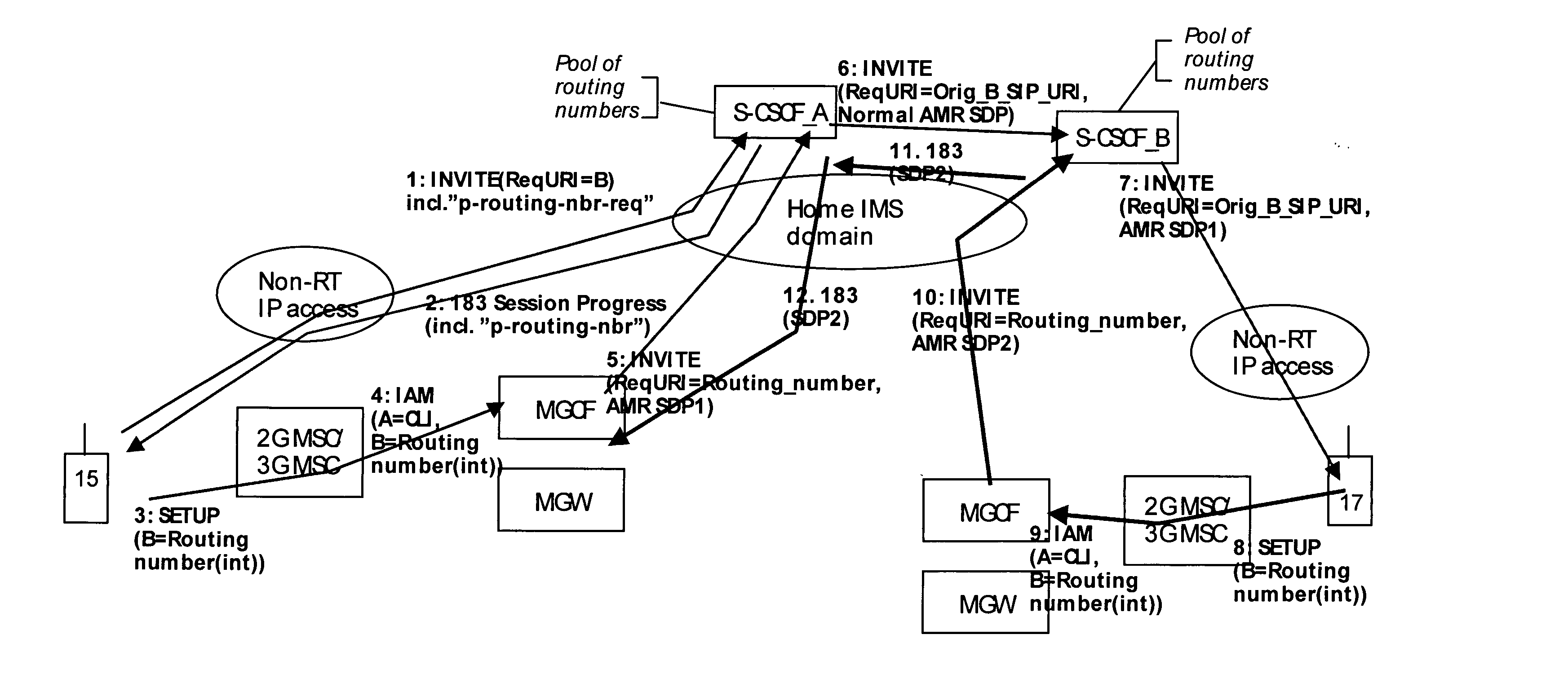
A mechanism for providing a connection from an IP-based network to a circuit-switched network, such as a GSM network is disclosed. A temporary routing number for the circuit-switched network, such as an E.164 number, is delivered to a user terminal, and a circuit-switched call leg is established from the user terminal to the IP-based network using the routing number. Thereby, IMS-services are provided for end users which are located in the radio access network not having sufficient QoS required for voice over IP. In the example of a conference call service, a request for a conference call may forwarded via a data channel or data path to an application server which provides that conference call service. The application server then selects a conference routing number and returns the routing number to the conference host terminal via the data channel. Using the received conference routing number, the conference host terminal can then set up a circuit-switched connection as a call leg of the conference call.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
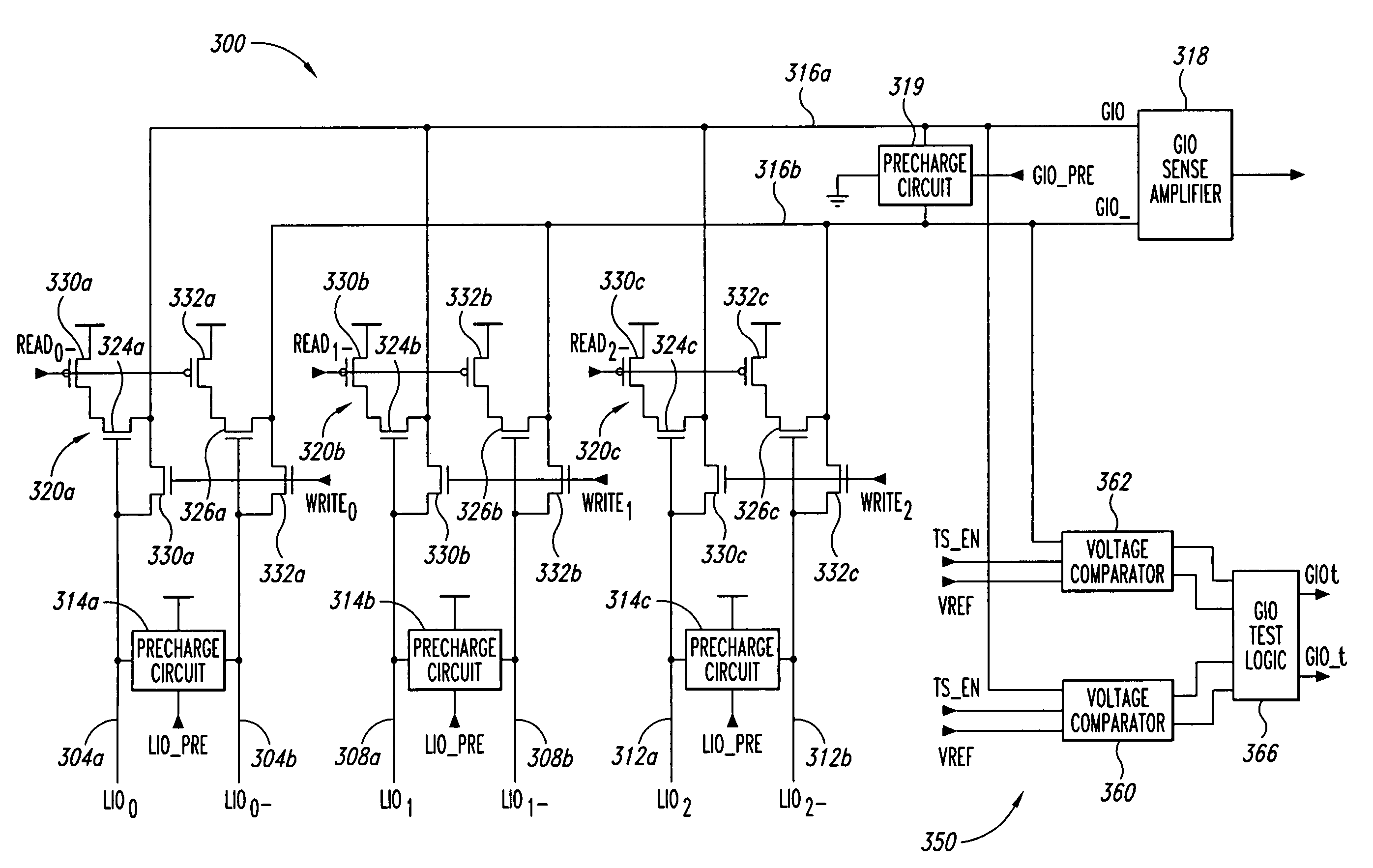
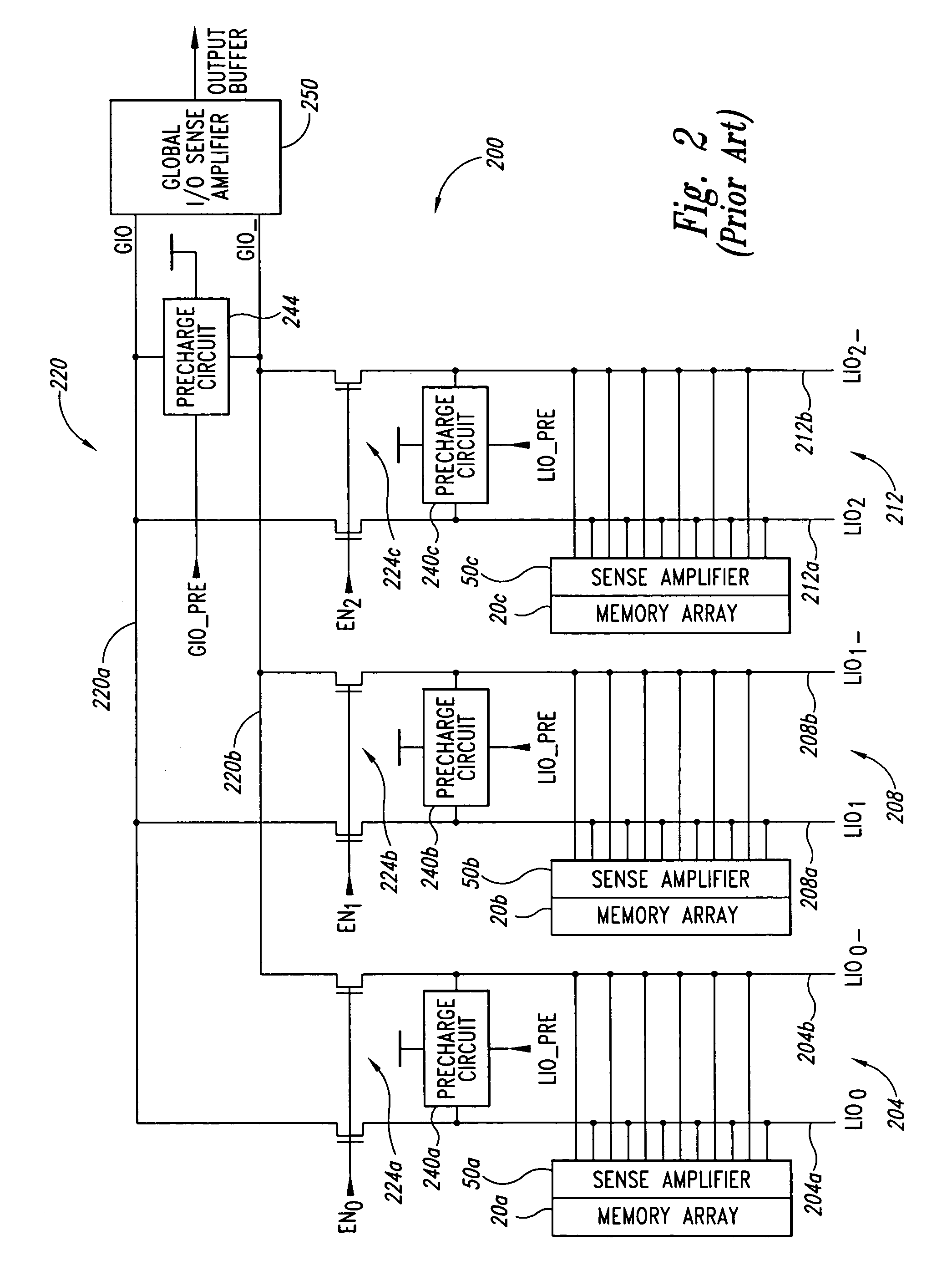
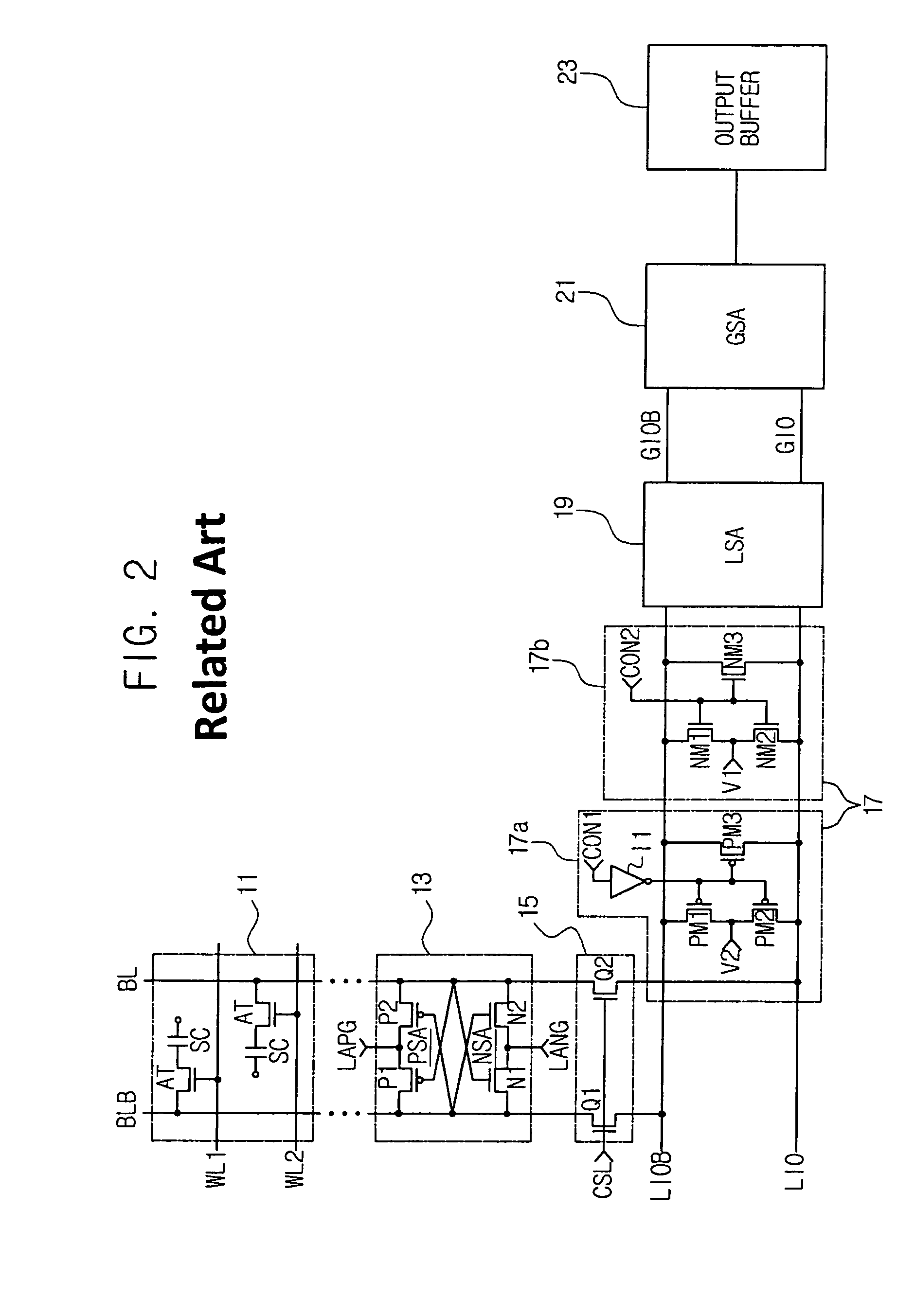
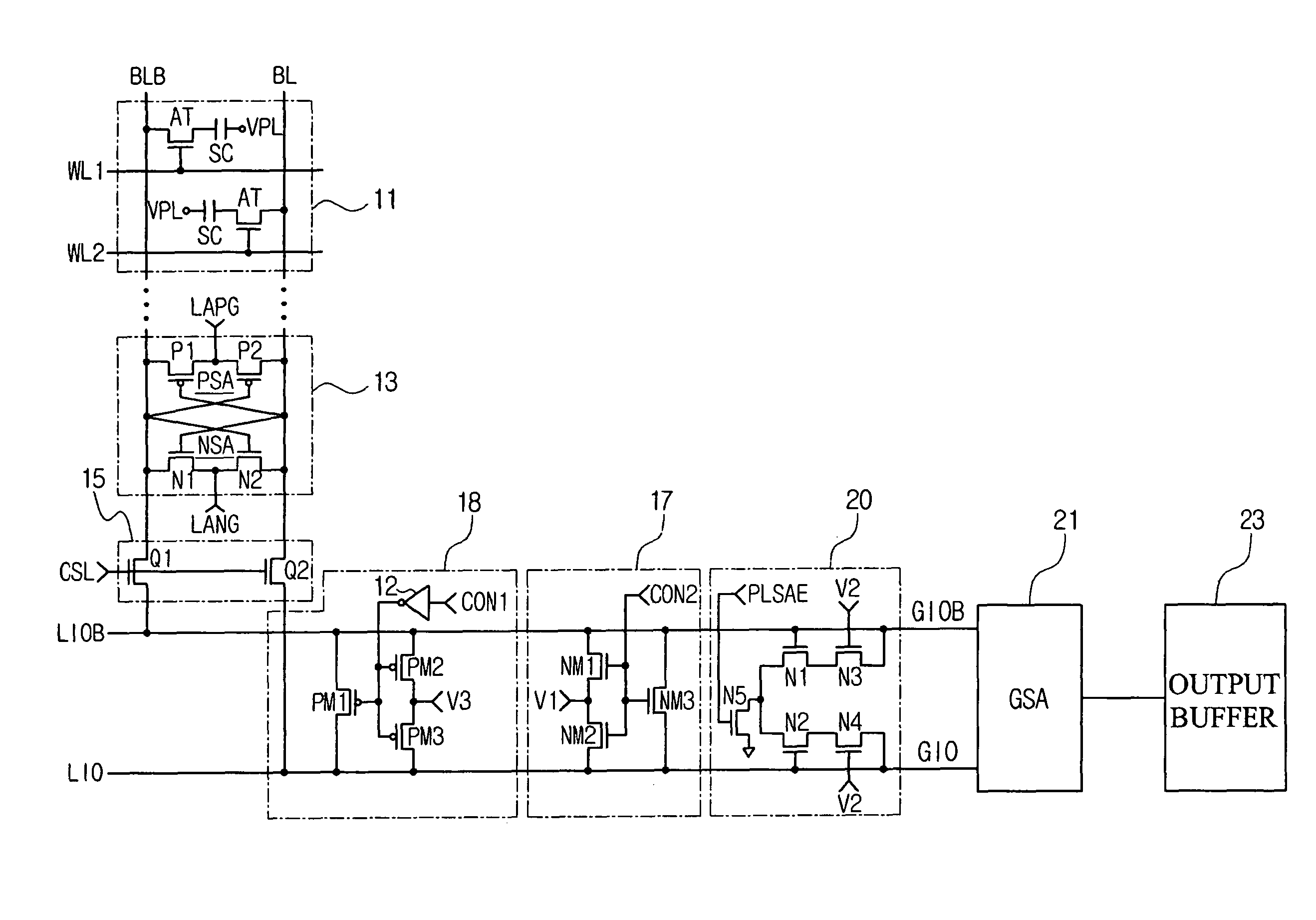
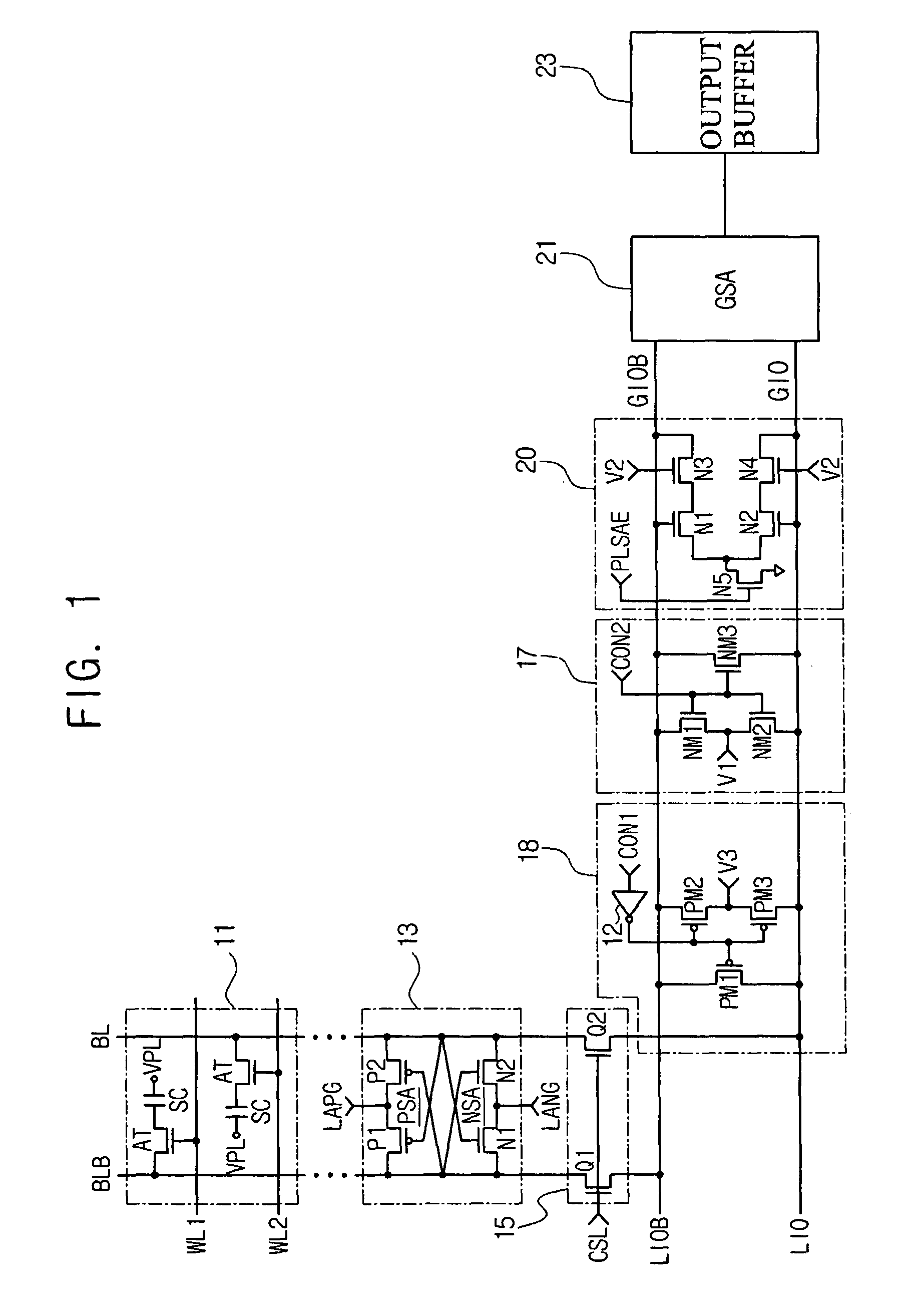
Data path having grounded precharge operation and test compression capability
A data path for coupling data between a memory cell and an input / output (IO) line sense amplifier. An IO line coupling circuit is coupled to a pair of global data lines and a pair of local data lines to couple and decouple each of the global data lines to and from a voltage supply based on the voltage levels of the local data lines for the memory read operation. For the memory write operation, the IO line coupling circuit couples and decouples each of the global data lines to and from a respective one of the local data lines. The data path also includes a first precharge circuit coupled to the global data lines to couple the global data lines to ground to precharge the signal lines prior to a memory read or write operation, and can further include a test compression circuit coupled to the global data lines.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
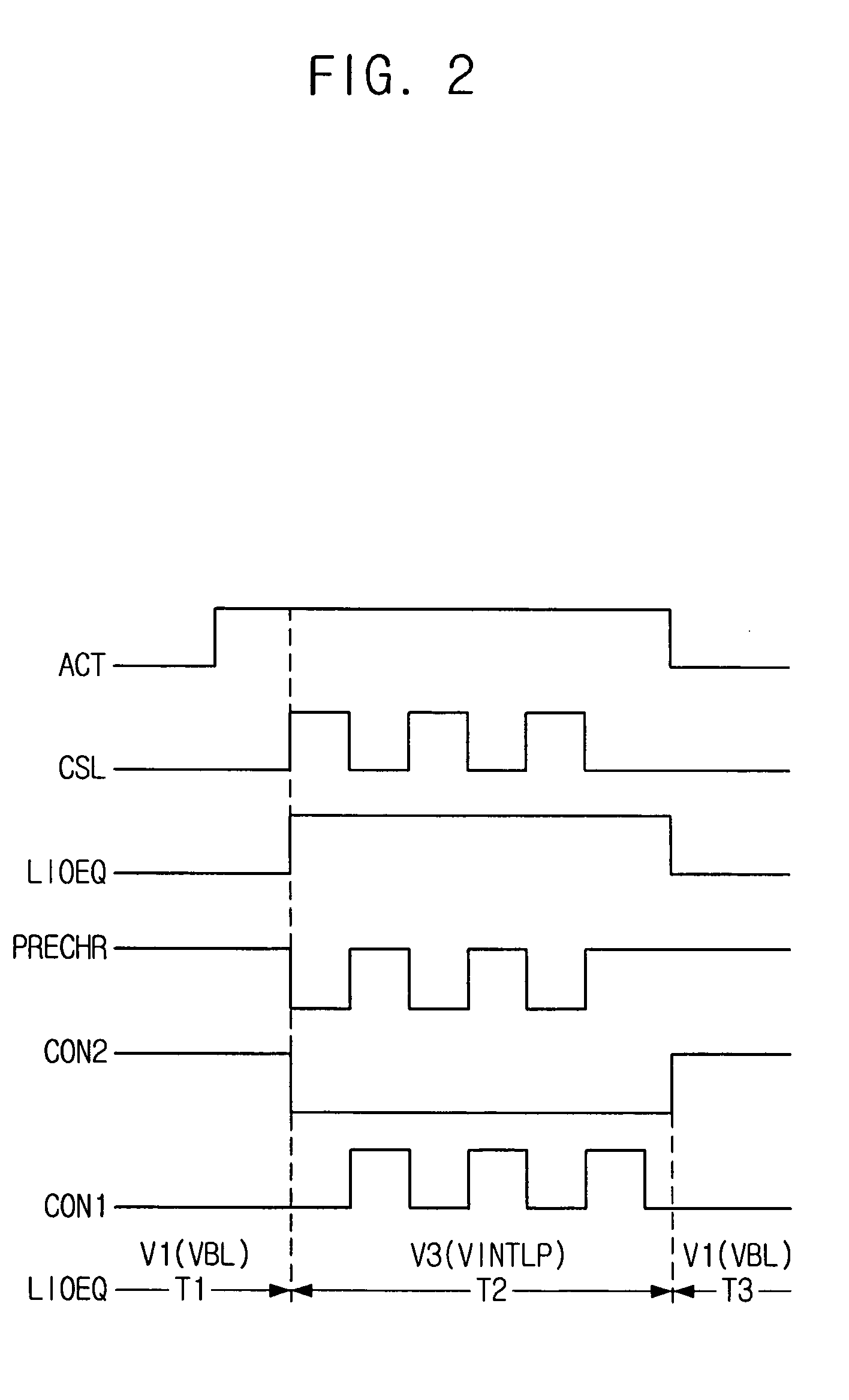
Semiconductor memory device adopting improved local input/output line precharging scheme
A semiconductor memory device capable of preventing or minimizing bit line disturbance and performing a low-voltage high-speed operation includes a read data path circuit including a bit line sense amplifier, a local input / output line sense amplifier, a column selecting unit to operationally connect bit lines connected to the bit line sense amplifier to local input / output lines connected to the local input / output line sense amplifier in response to a column selection signal, and a local input / output line precharging unit to precharge the pair of local input / output lines by a first precharging unit, equalizing the pair of local input / output lines by an equalizing unit, and to precharge the local input / output lines by a second precharging unit following an elapsed time after the bit line sense amplifier is activated, while the column selection is deactivated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
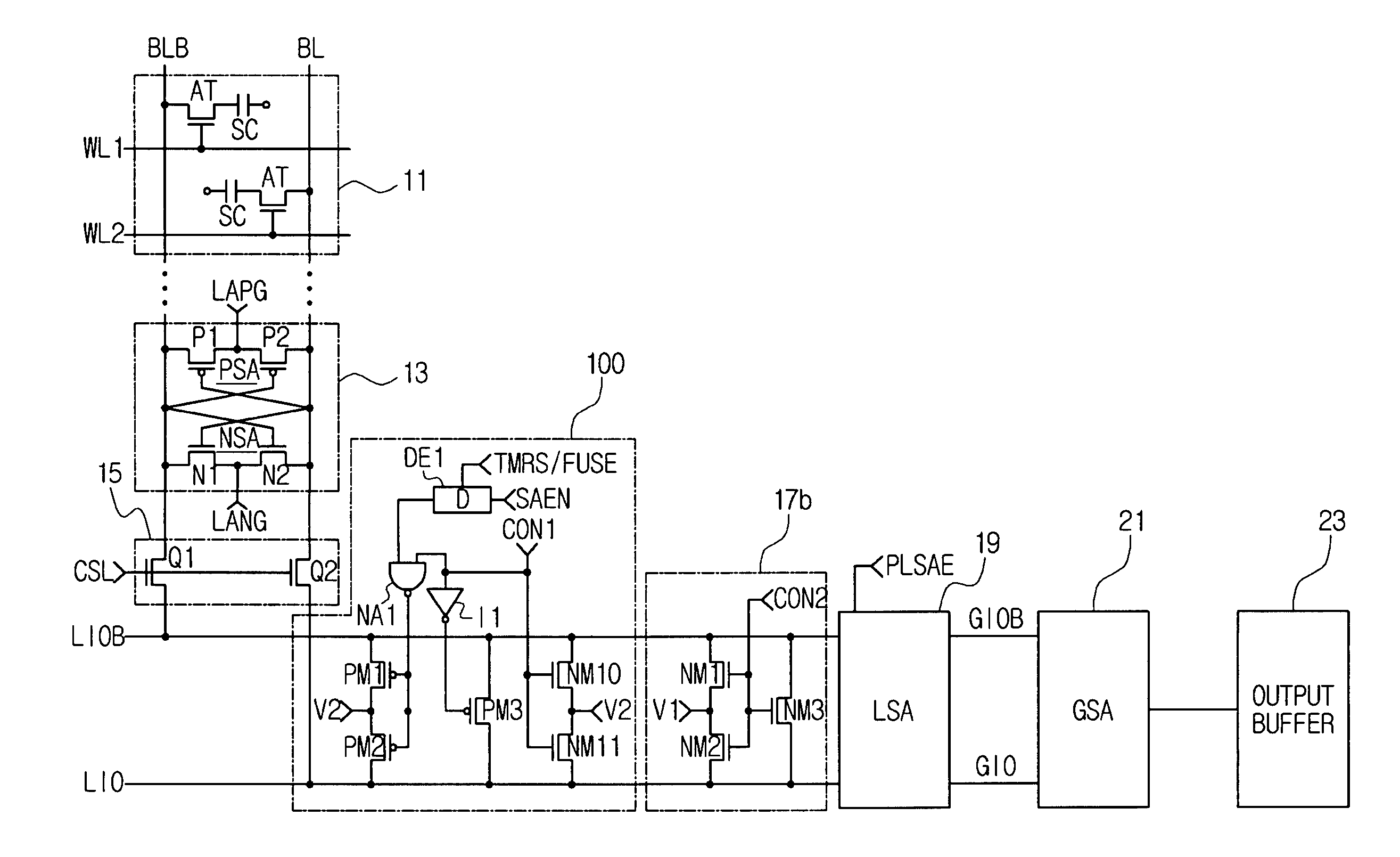
Semiconductor memory device having improved local input/output line precharge scheme
ActiveUS8213248B2Preventing bit line disturbanceRun at high speedDigital storageBit lineDatapath circuits
A data path circuit of a semiconductor memory device includes: a bit line sense amplifier driven by a first power supply voltage; a local input / output line sense amplifier; a column selecting unit operatively connecting a pair of bit lines connected to the bit line sense amplifier and a pair of local input / output lines connected to the local input / output line sense amplifier in response to a column selection signal; and a local input / output line precharge unit precharging the pair of local input / output lines with a second power supply voltage different from the first power supply voltage during a period for which the column selection signal is in an inactive state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for providing voice over IP managed services utilizing a centralized data store
ActiveUS20070036143A1Interconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationVoice over IPData memory
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A centralized data store, maintained by a service provider, stores one or more user identifiers and an associated directory number. The centralized data store also stores routing information including one or more communication paths corresponding to the user identifier, wherein the routing information includes a data path or a circuit-switched path for establishing a call to the user. In response to a request for establishing the call to the directory number, the data store retrieves the routing information for use to establish the call.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
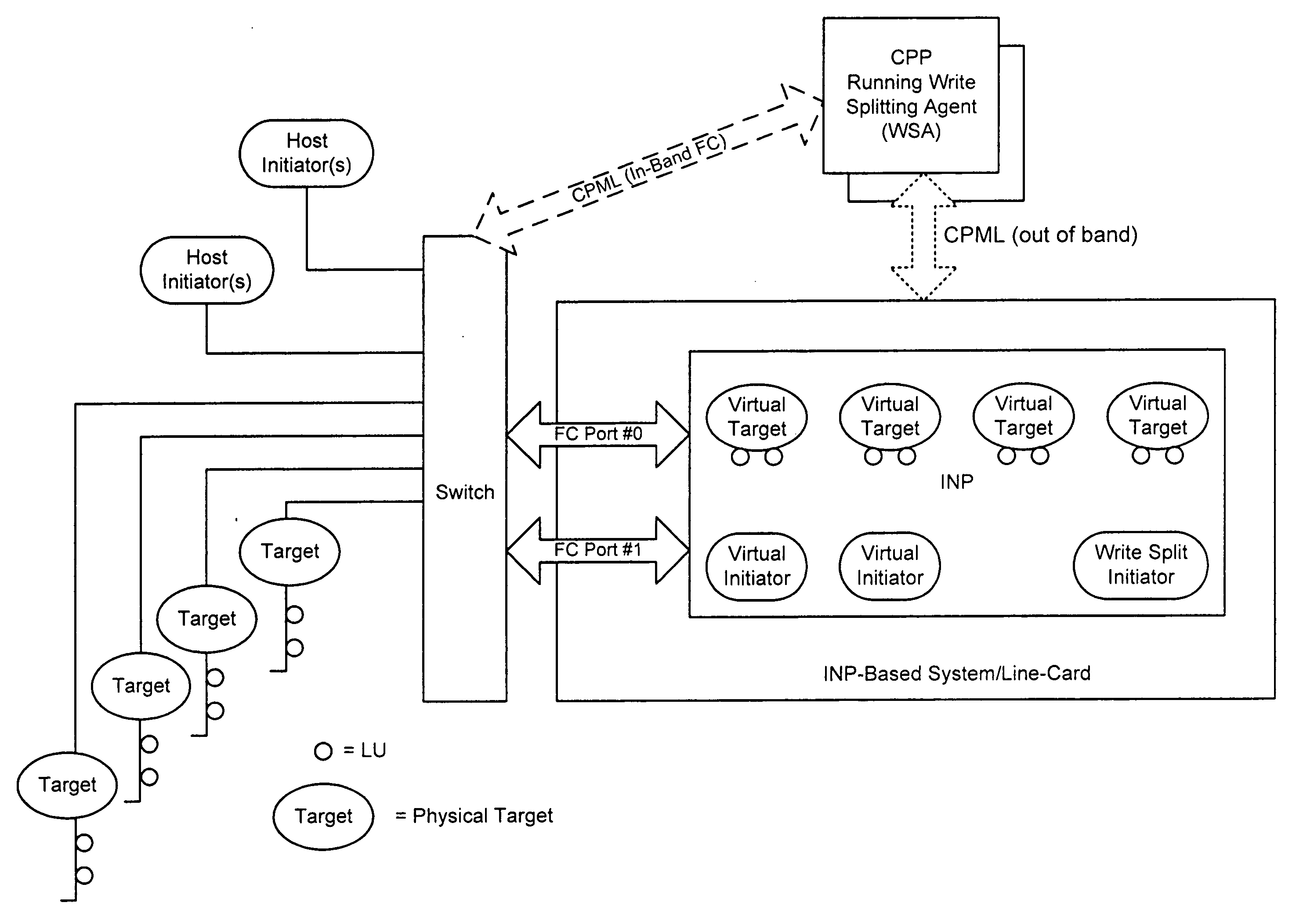
Apparatus for performing storage virtualization
ActiveUS20070239944A1Simplify writingIncrease overheadError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual targetData management
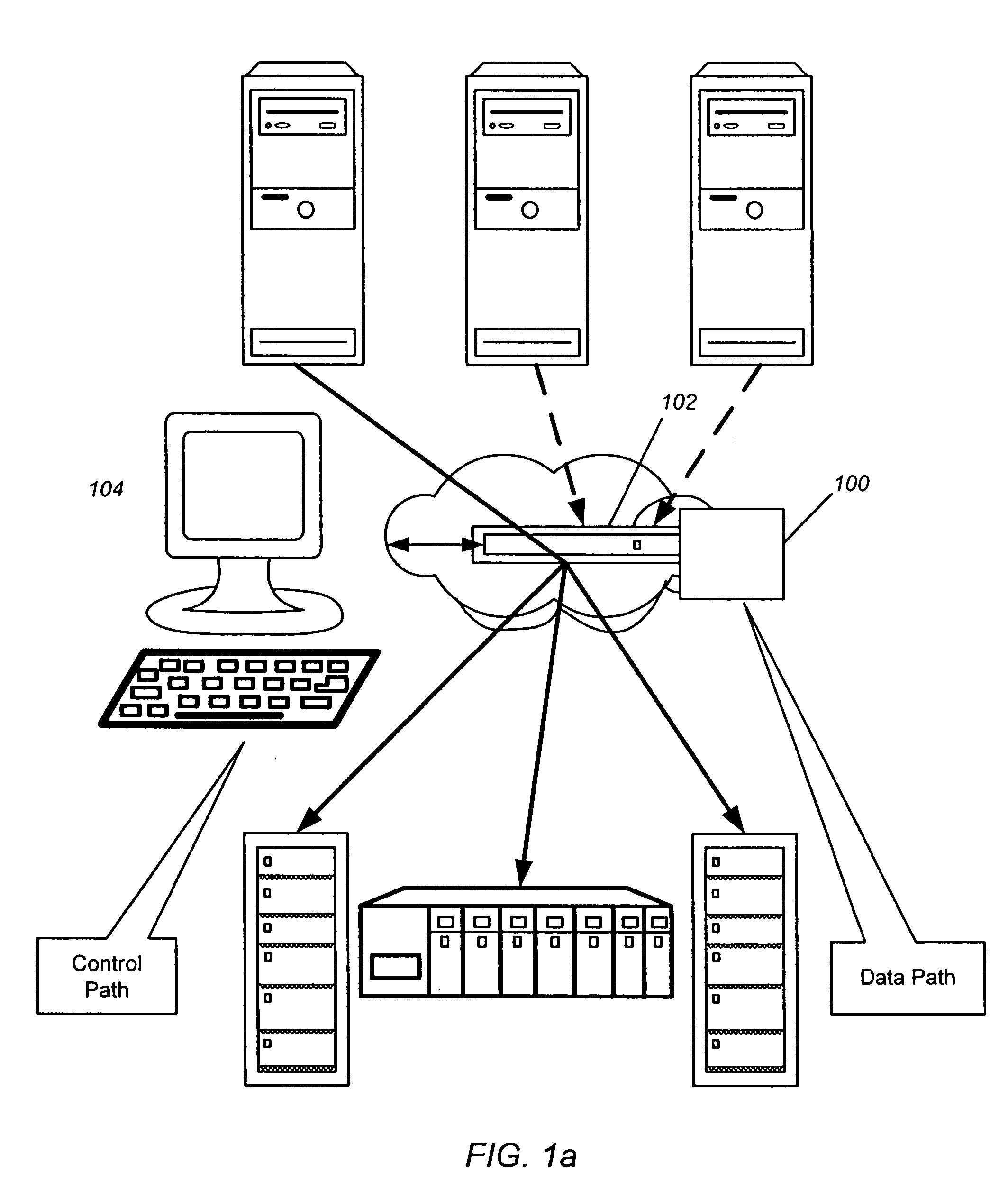
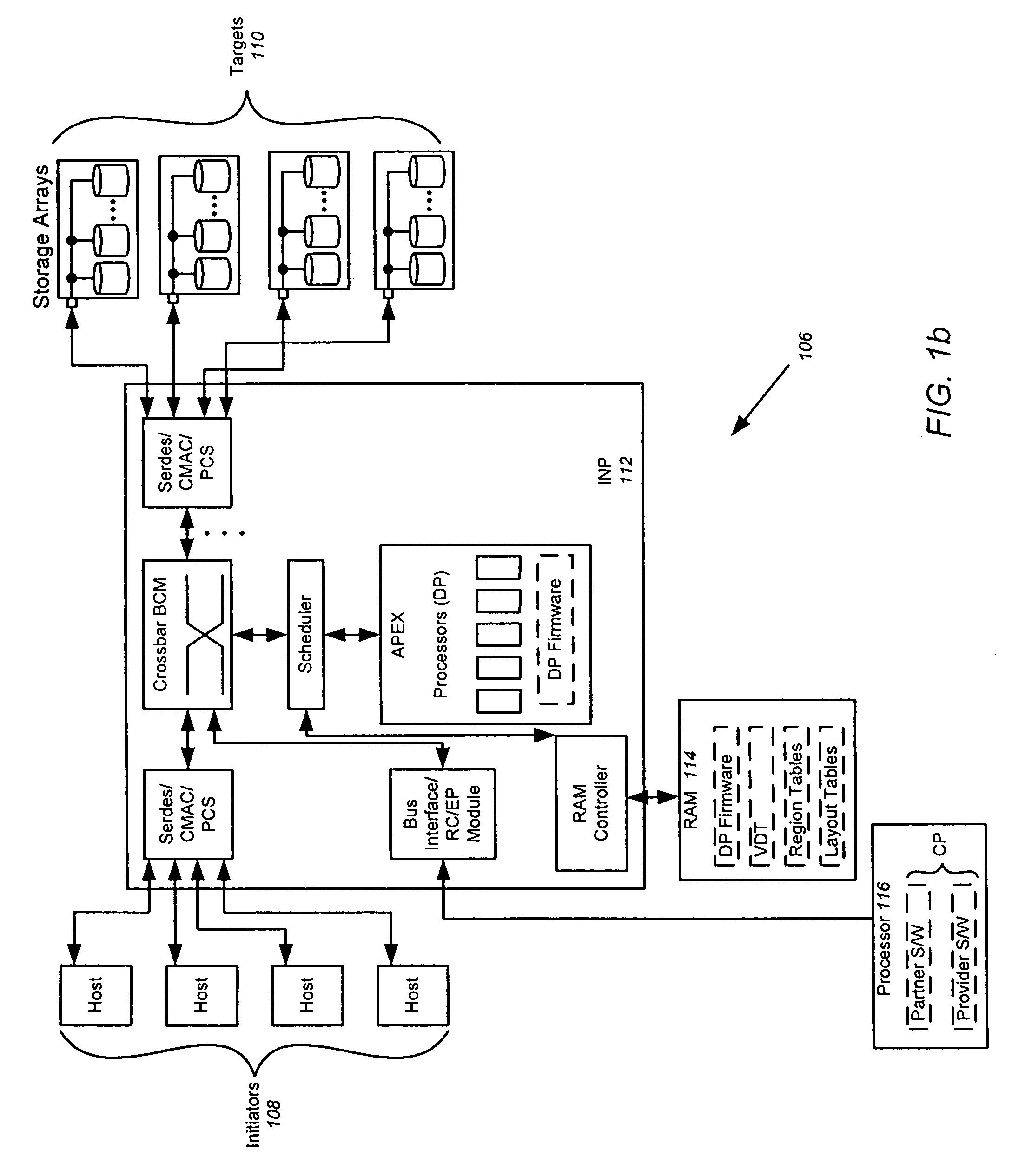
The splitting of storage applications and functions into a control path (CP) component and a data path (DP) component is disclosed. Reads and writes may be handled primarily in the DP. The CP may be responsible for discovery, configuration, and exception handling. The CP can also be enabled for orchestrating complex data management operations such as snapshots and migration. Storage virtualization maps a virtual I / O to one or more physical I / O. A virtual target (vTarget) in the virtual domain is associated with one physical port in the physical domain. Each vTarget may be associated with one or more virtual LUNs (vLUNs). Each vLUN includes one or more vExtents. Each vExtent may point to a region table, and each entry in the region table may contain a pointer to a region representing a portion of a pExtent, and attributes (e.g. read / write, read only, no access) for that region.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Wide area network using internet with quality of service
InactiveUS7111163B1Reduces monthly costQuality improvementDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsQuality of serviceTTEthernet
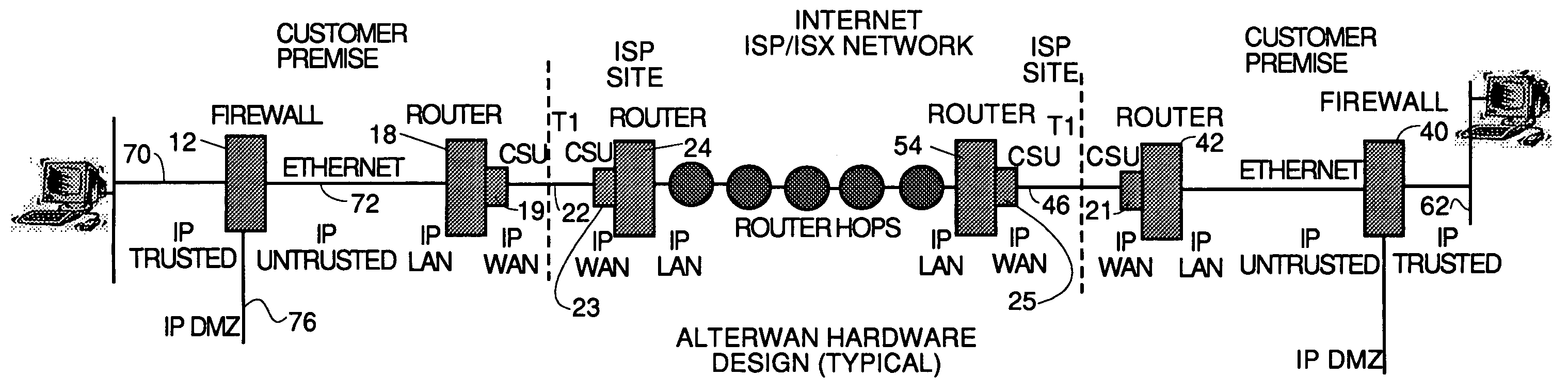
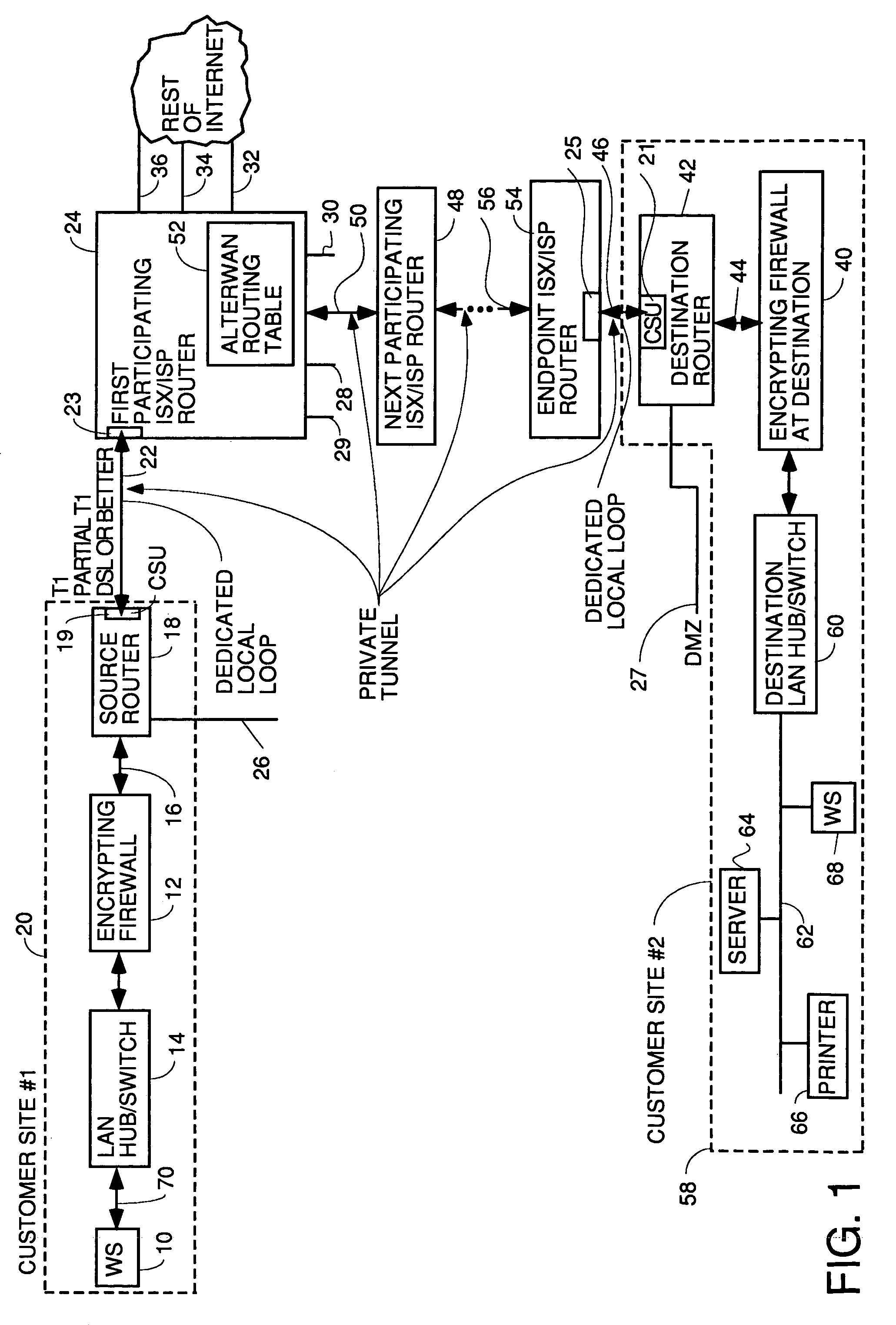
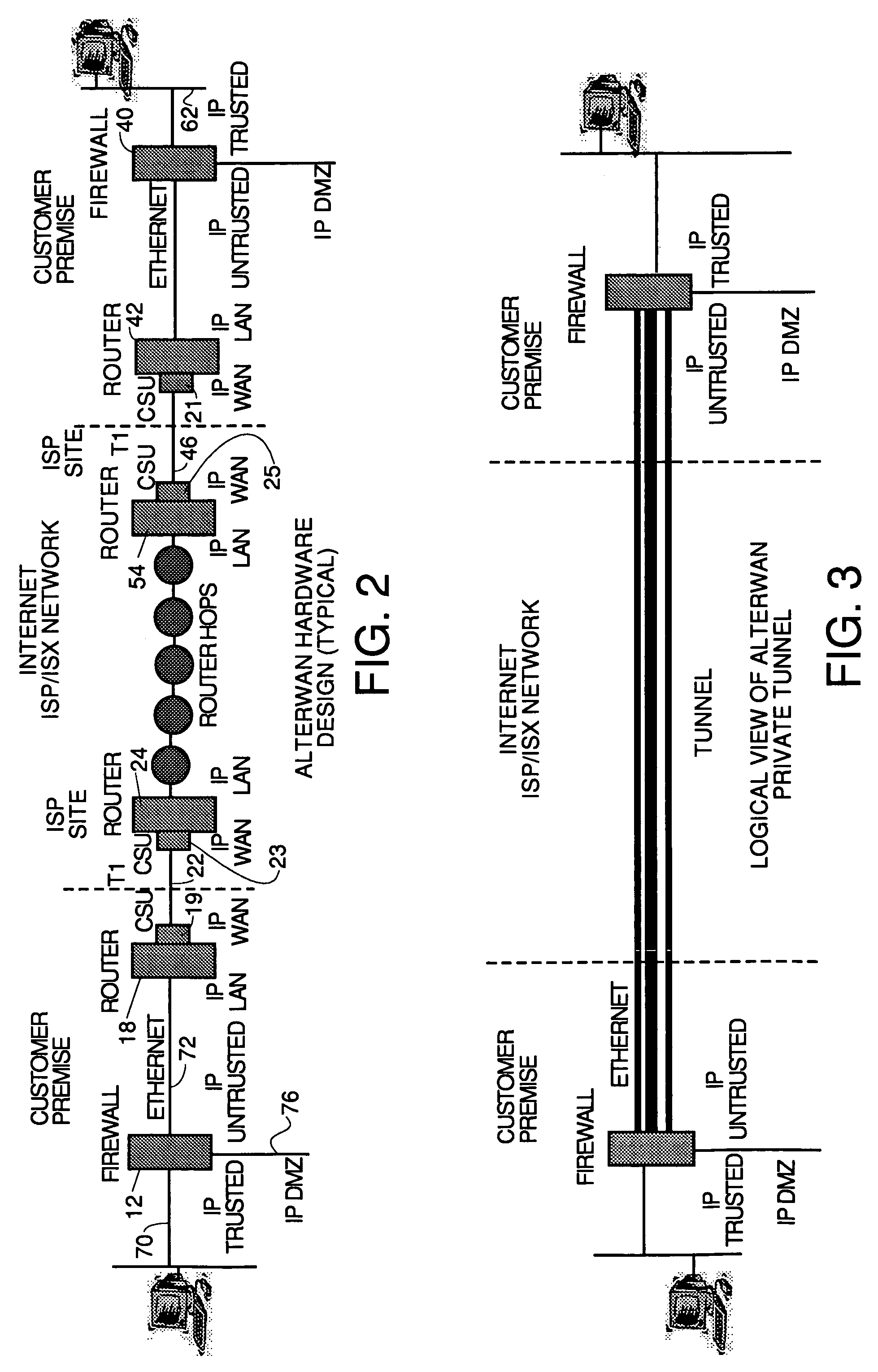
A wide area network using the internet as a backbone utilizing specially selected ISX / ISP providers whose routers route AlterWAN packets of said wide area network along private tunnels through the internet comprised of high bandwidth, low hop-count data paths. Firewalls are provided at each end of each private tunnel which recognize IP packets addressed to devices at the other end of the tunnel and encapsulate these packets in other IP packets which have a header which includes as the destination address, the IP address of the untrusted side of the firewall at the other end of the tunnel. The payload sections of these packets are the original IP packets and are encrypted and decrypted at both ends of the private tunnel using the same encryption algorithm using the same key or keys.
Owner:ALTERWAN
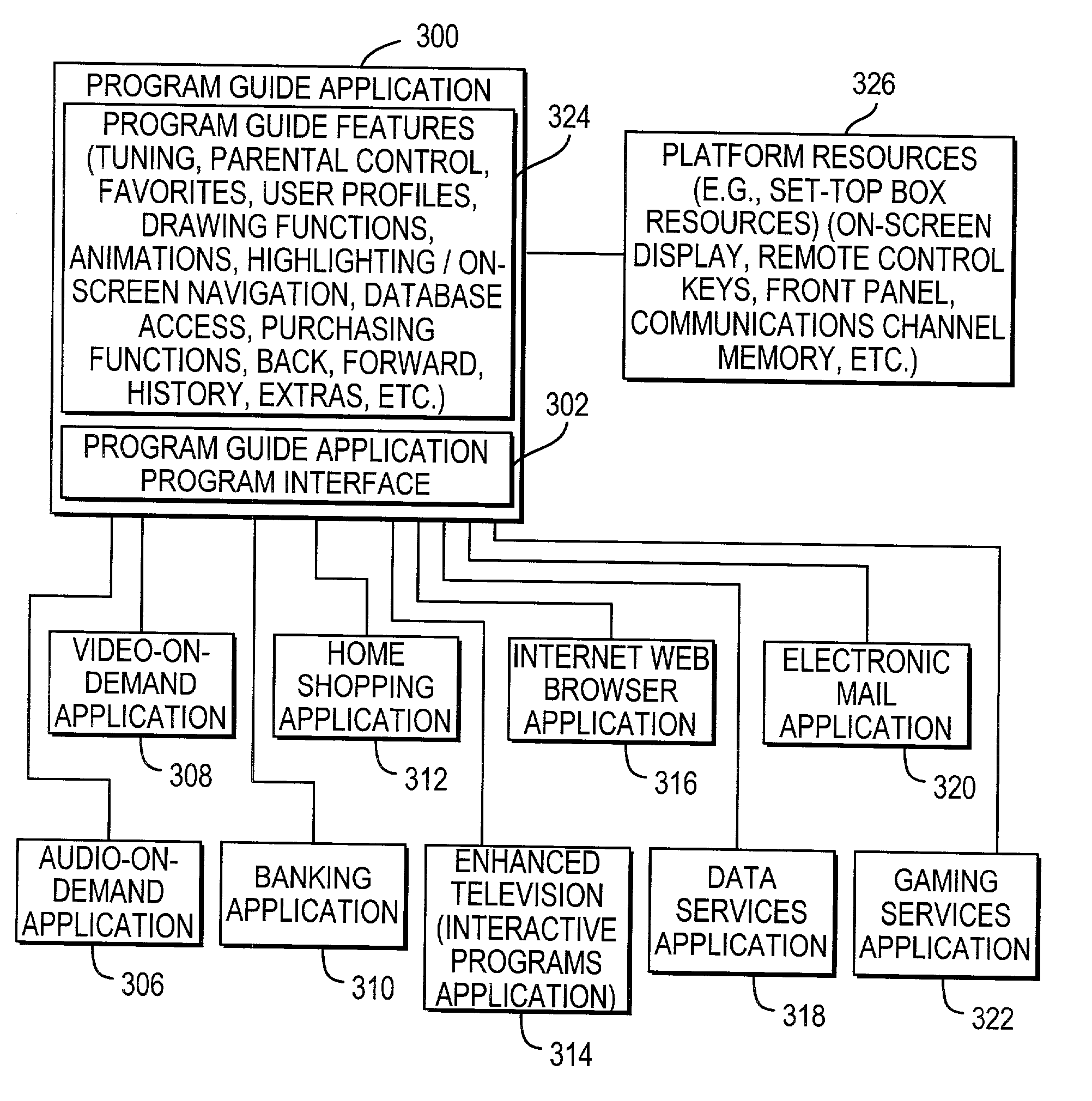
Features for use with advanced set-top applications on interactive television systems
InactiveUS20050235319A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTelevision systemInteractive television
Advanced features for interactive television applications are described, including a back feature, a forward feature, a history feature, a go to feature, an extras feature, a reminder feature, a favorites feature, a parental control feature, and a search feature. Features may be inter-resource. Support for multiple data paths, Internet access, interactive services, and user profiles are also described.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
Method and apparatus for efficient scalable storage management
ActiveUS7181578B1Improve performanceSolve the lack of spaceMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingHandling systemDatapath
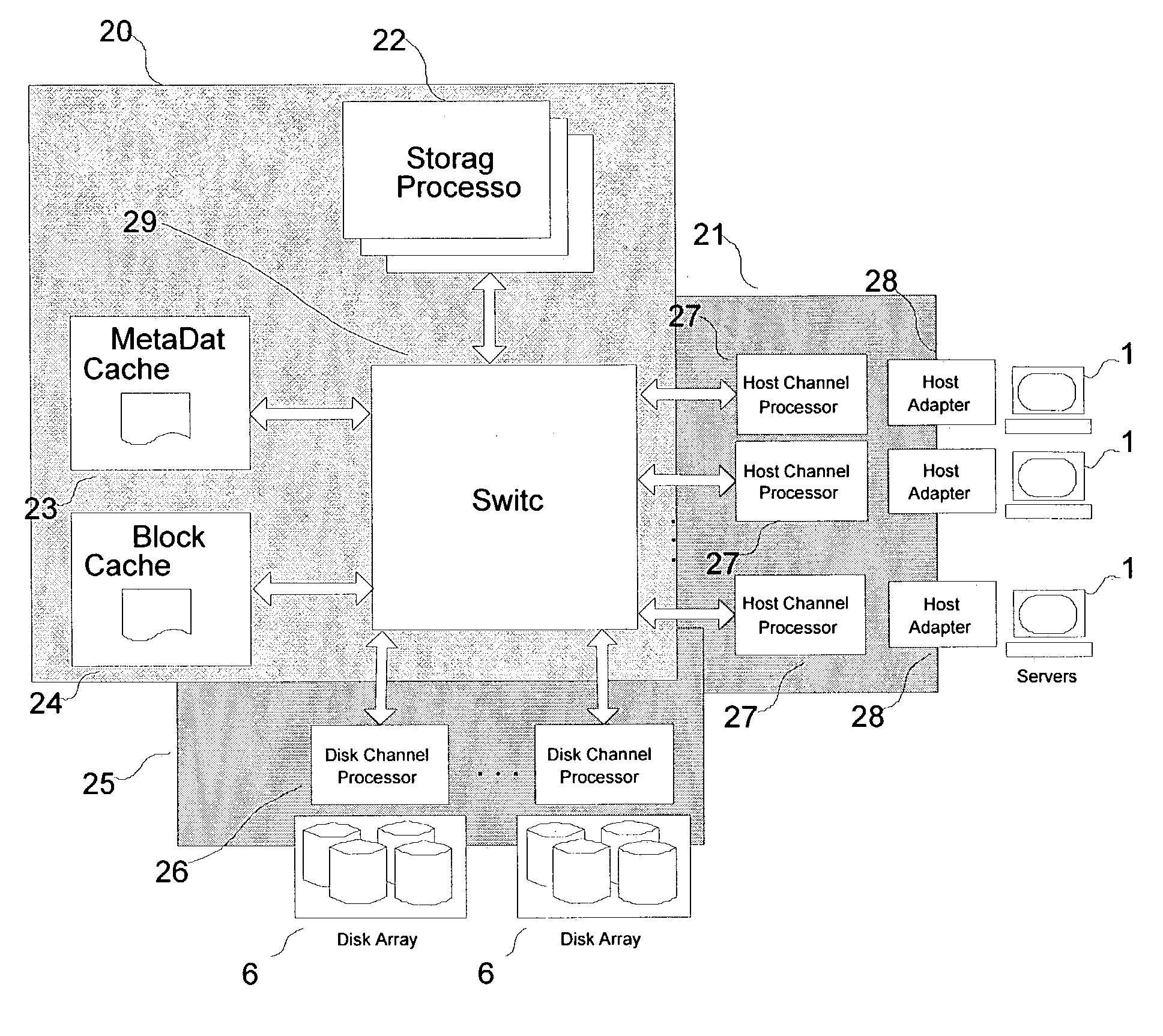
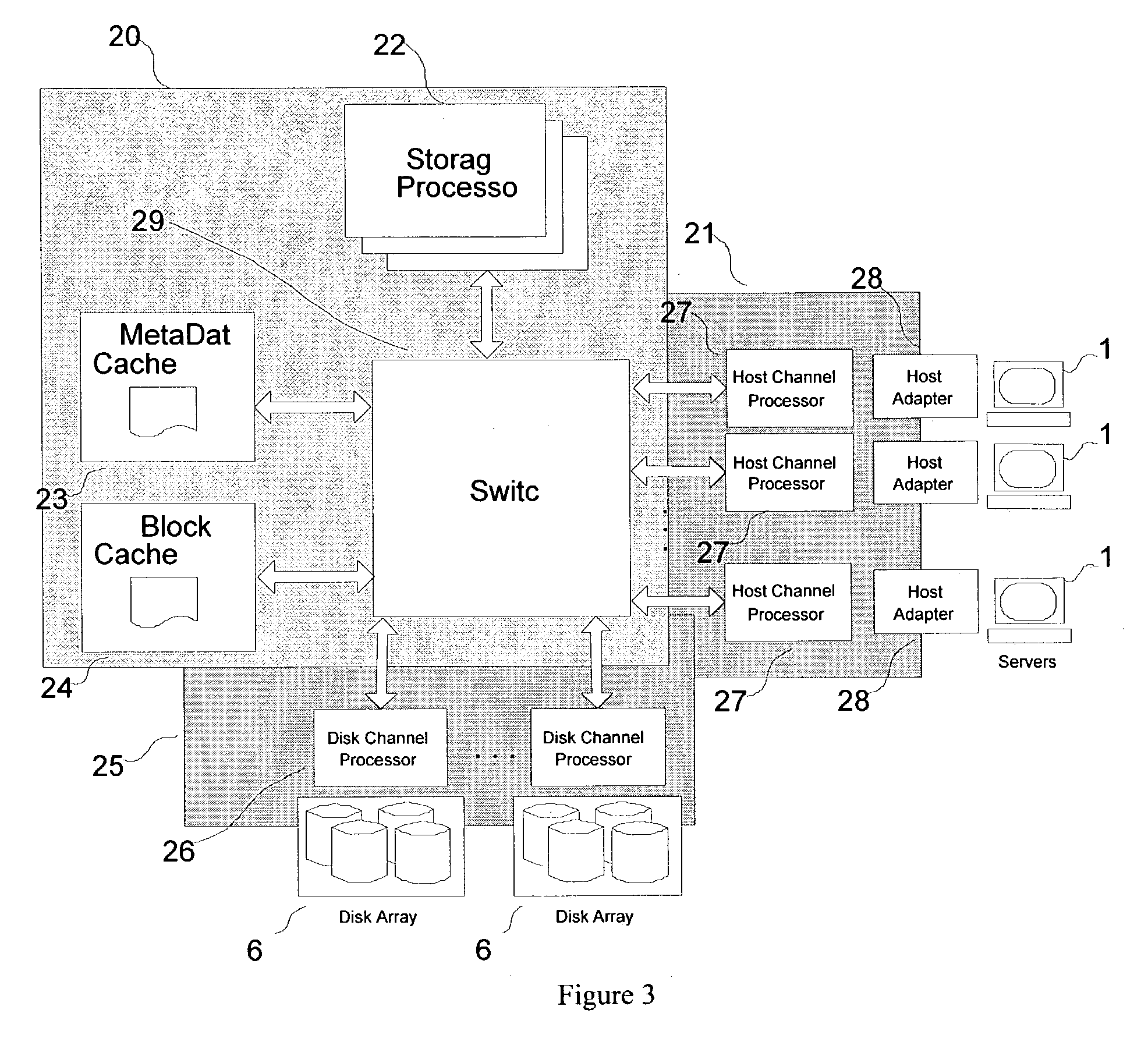
A hybrid centralized and distributed processing system includes a switching device that connects a storage processor to one or more servers through a host channel processor. The switching device also connects the storage processor to one or more storage devices such as disk drive arrays, and to a metadata cache and a block data cache memory. The storage processor processes access request from one or more servers in the form of a logical volume or logical block address and accesses the metadata cache to determine the physical data address. The storage processor monitors the performance of the storage system and performs automatic tuning by reallocating the logical volume, load balancing, hot spot removal, and dynamic expansion of storage volume. The storage processor also provides fault-tolerant access and provides parallel high performance data paths for fail over. The storage processor also provides faster access by providing parallel data paths for, making local copies and providing remote data copies, and by selecting data from a storage device that retrieves the data the earliest.
Owner:COPAN SYST INC +1
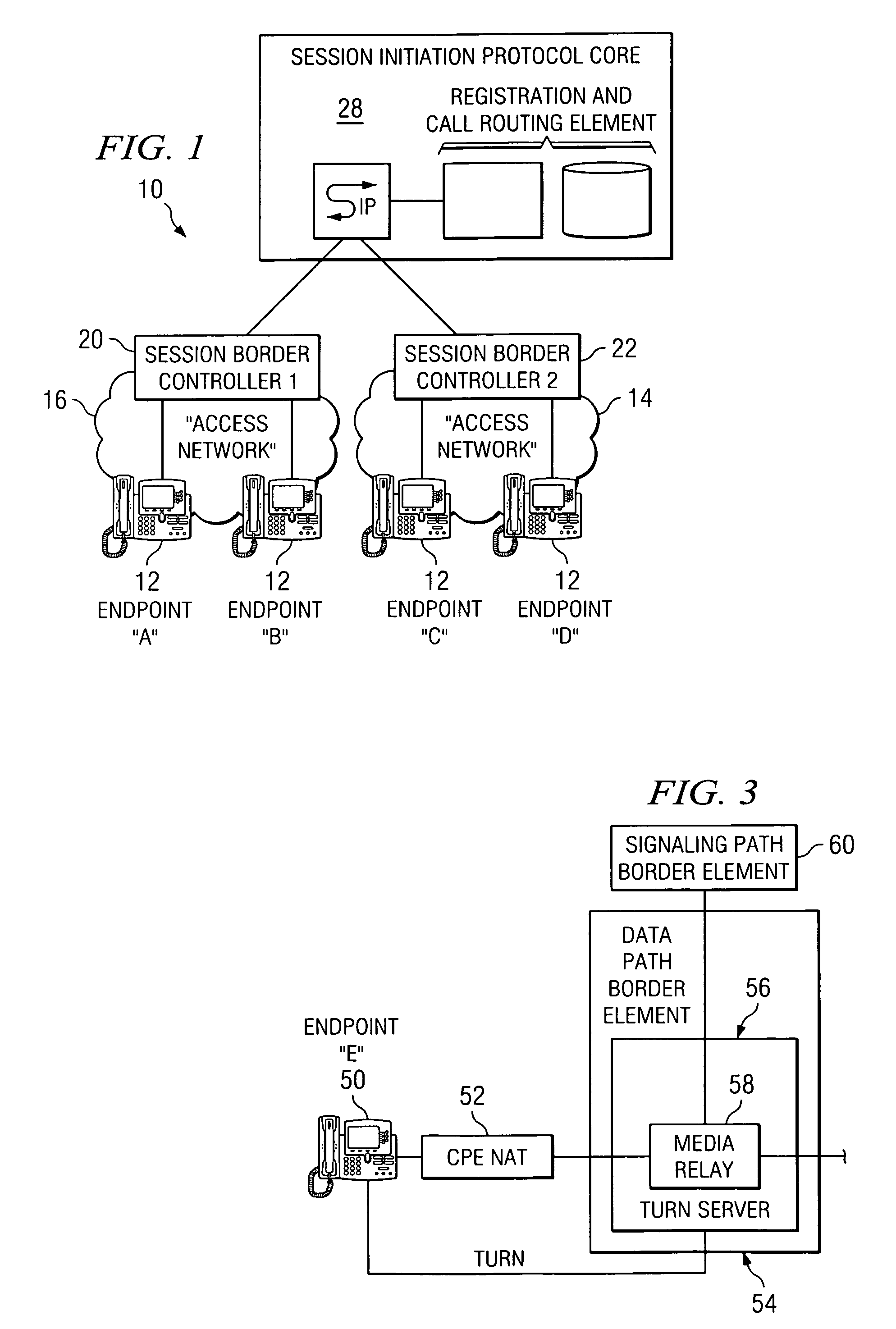
System and method for optimizing communications between session border controllers and enpoints in a network environment
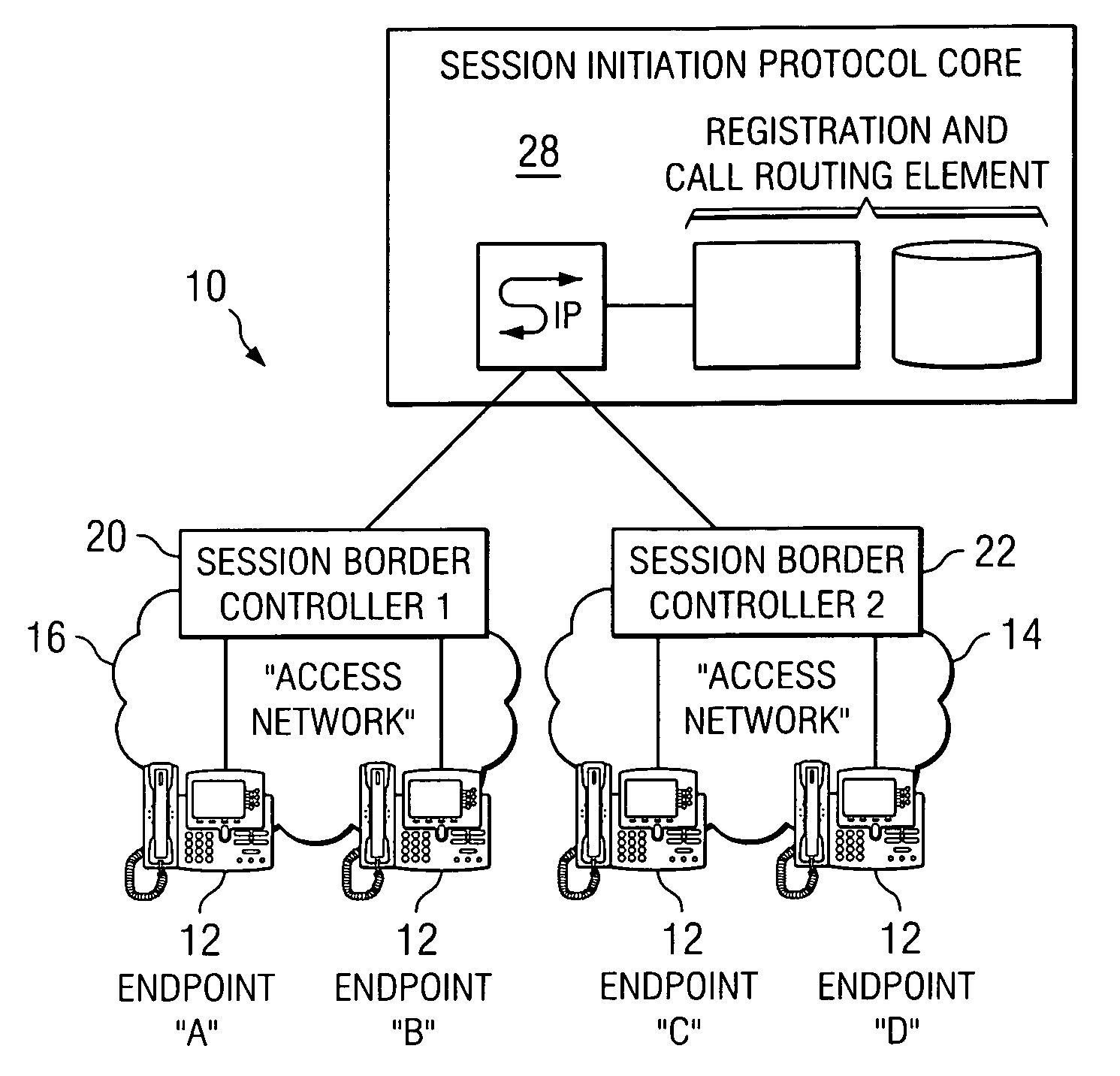
ActiveUS20070019619A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationDatapathSession border controller
An apparatus for optimizing communications between session border controllers in a network environment is provided that includes a session border controller (SBC) operable to communicate with a first endpoint and a second endpoint. The SBC is also operable to communicate with a data path border element (DBE) and a signaling path border element (SBE). The DBE is operable to provide a media relay for a communication session involving the endpoints, the media relay being invoked by either of the endpoints using a traversal using relay network address translation (TURN) protocol, which allows the SBC to operate in either of two modes depending on protocol support present in the endpoints.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
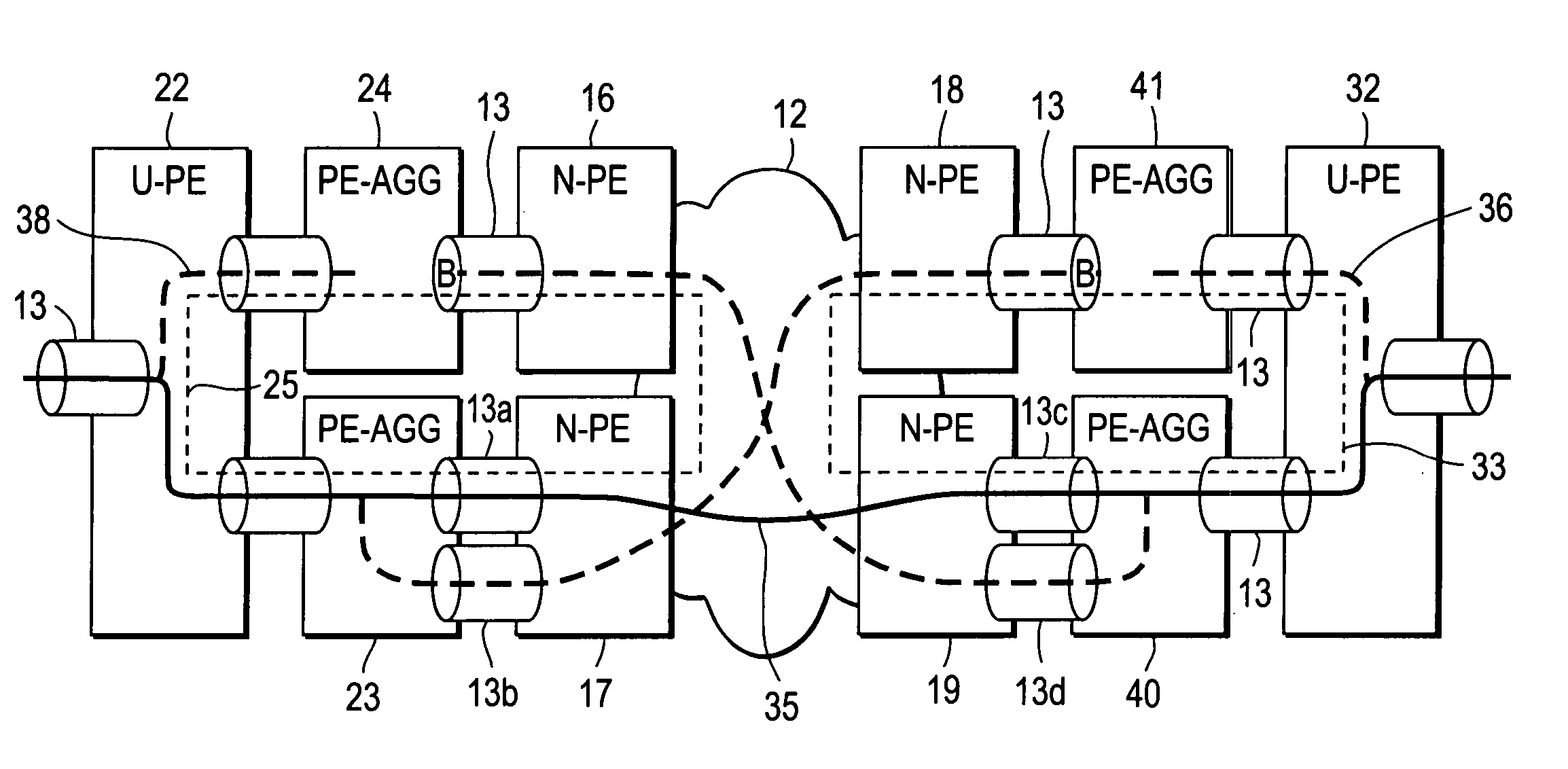
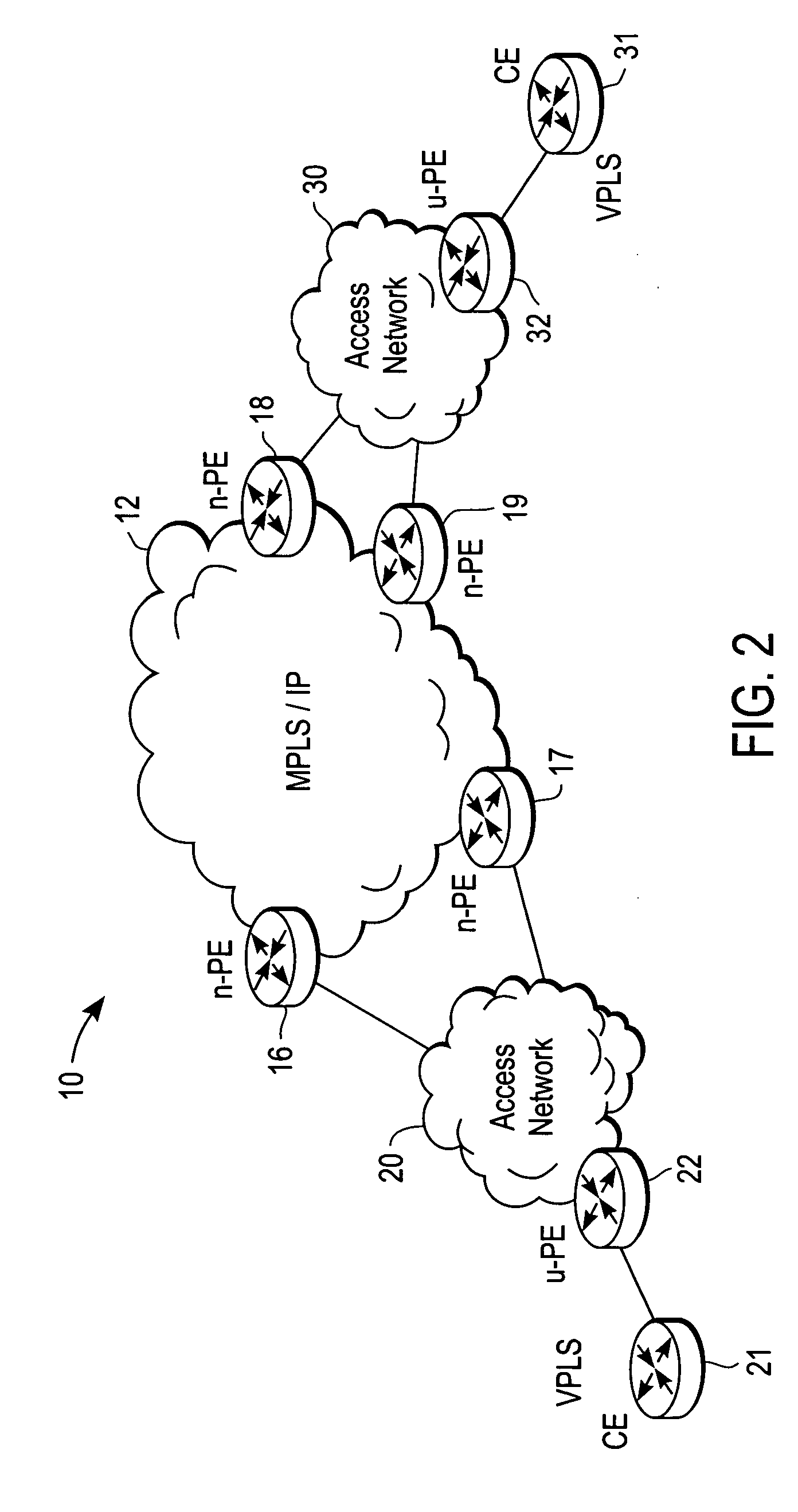
Computer network with point-to-point pseudowire redundancy
A computer network includes a core network connected with first and second Ethernet access domain networks, each of Ethernet access domain networks including a user-facing provider edge (u-PE) device, a primary network-facing provider edge (n-PE) device, a redundant n-PE device, and a plurality of aggregation provider edge (Agg-PE) devices providing connectivity between to the u-PE device and the primary and redundant n-PE devices, the Agg-PE devices running a spanning-tree protocol (STP) algorithm. A primary data path is provided along with first and second redundant data paths that include first and second redundant pseudowires (PWs), respectively, connected across the core network, the first and second redundant data paths being blocked by the STP algorithm when the primary data path is available, the STP algorithm unblocking either the first or second redundant data path in response to a failure of the primary data path. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods of implementing dynamic QoS and/or bandwidth provisioning and related data networks, data service providers, routing gateways, and computer program products
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
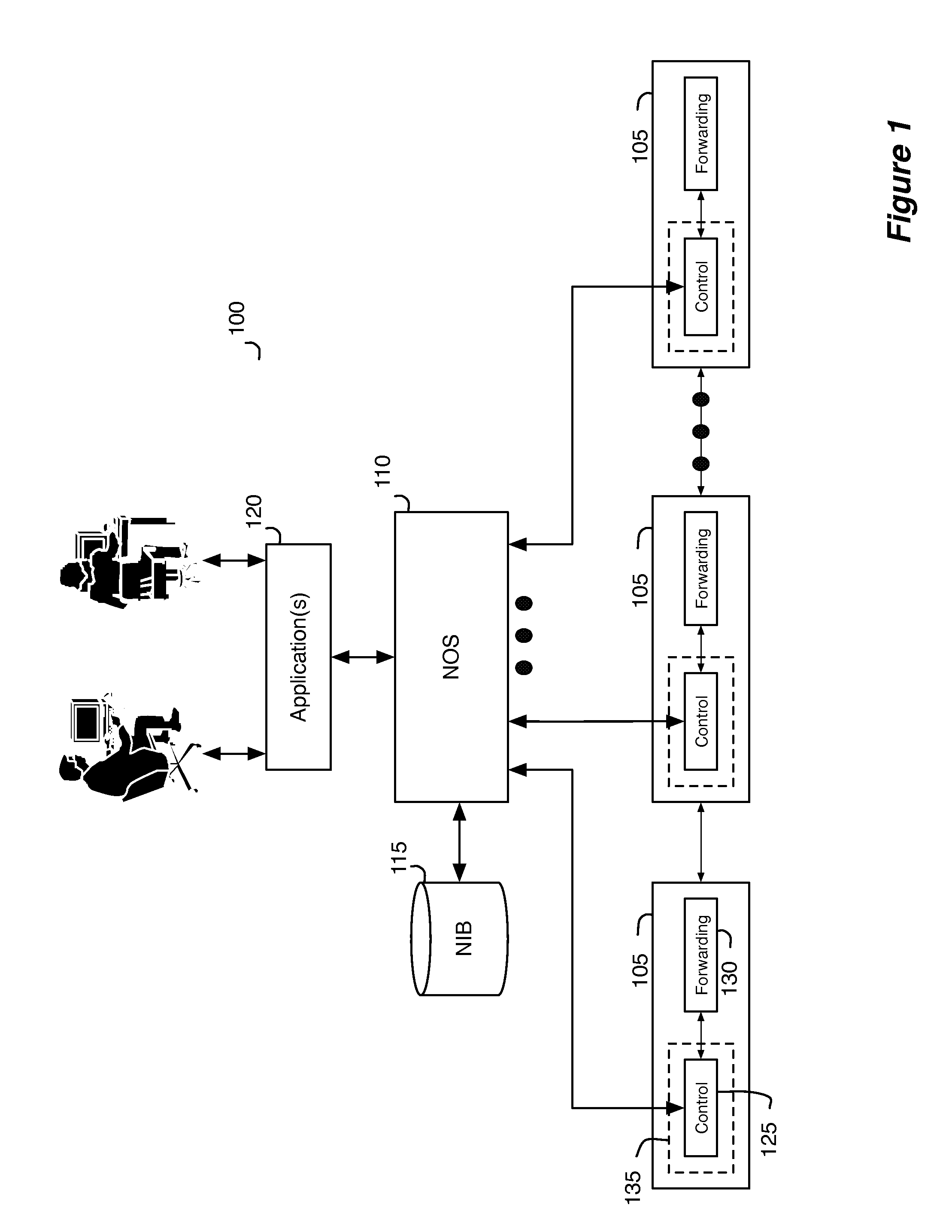
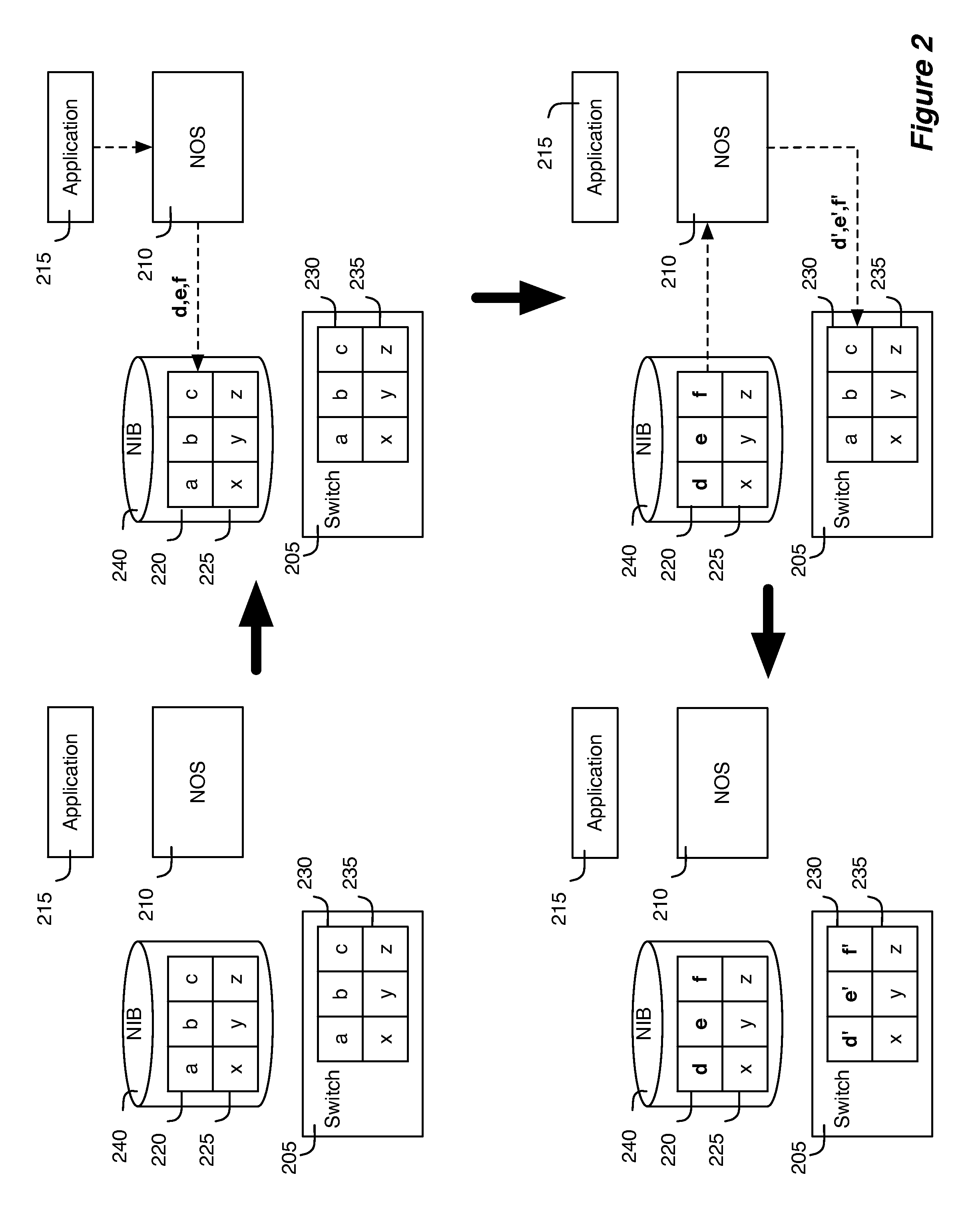
Packet processing for logical datapath sets
Some embodiments provide a method that processes network data through a network. The method receives a packet destined for a network host associated with a logical datapath set implemented by a set of managed edge switching elements and a set of managed non-edge switching elements in the network. The method determines whether the packet is a known packet. When the packet is a known packet, the method forwards the packet to a managed switching element in the set of managed edge switching elements for forwarding to the network host. When the packet is not a known packet, the method forwards the packet to a managed switching element in the set of managed non-edge switching elements for further processing.
Owner:NICIRA
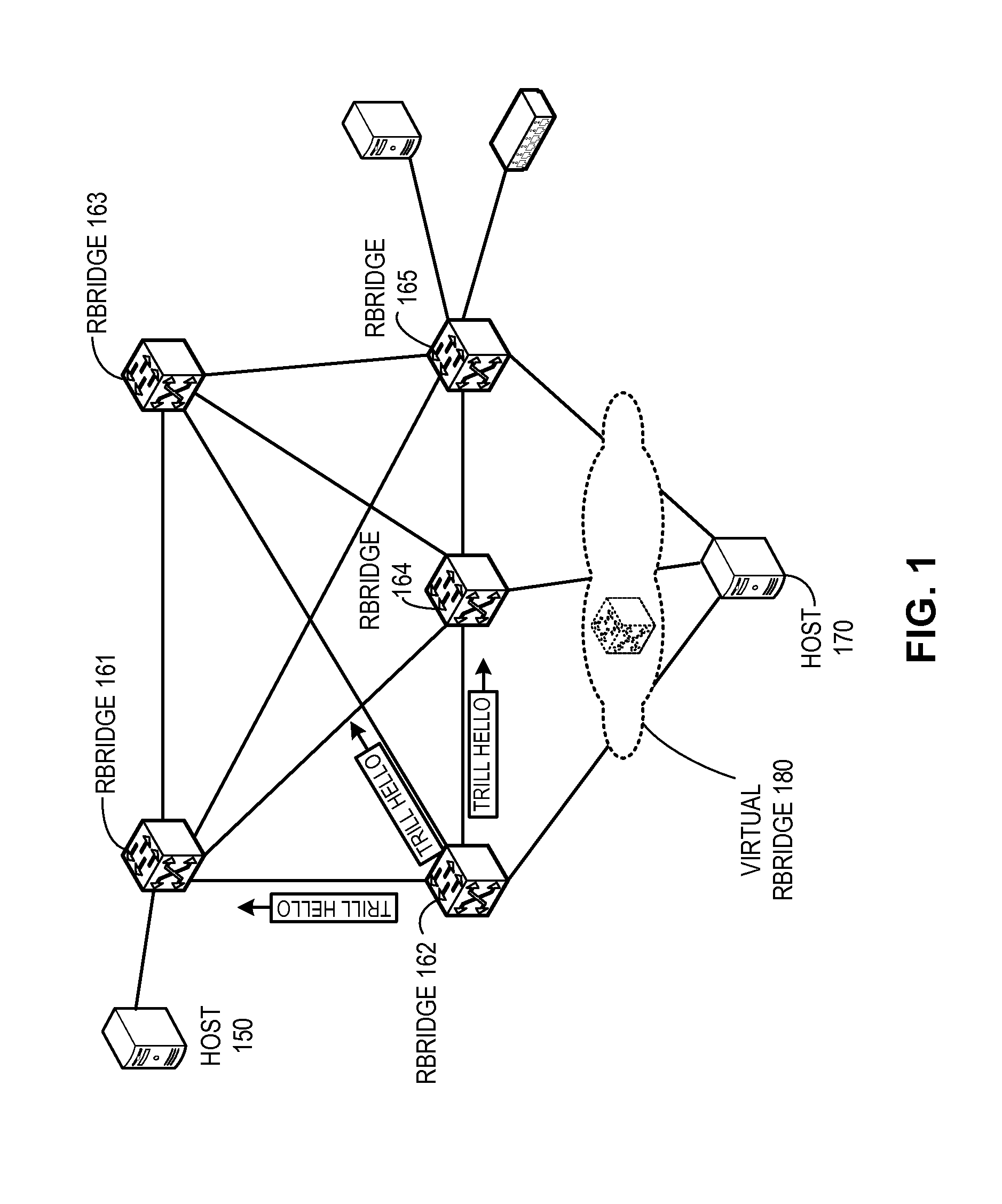
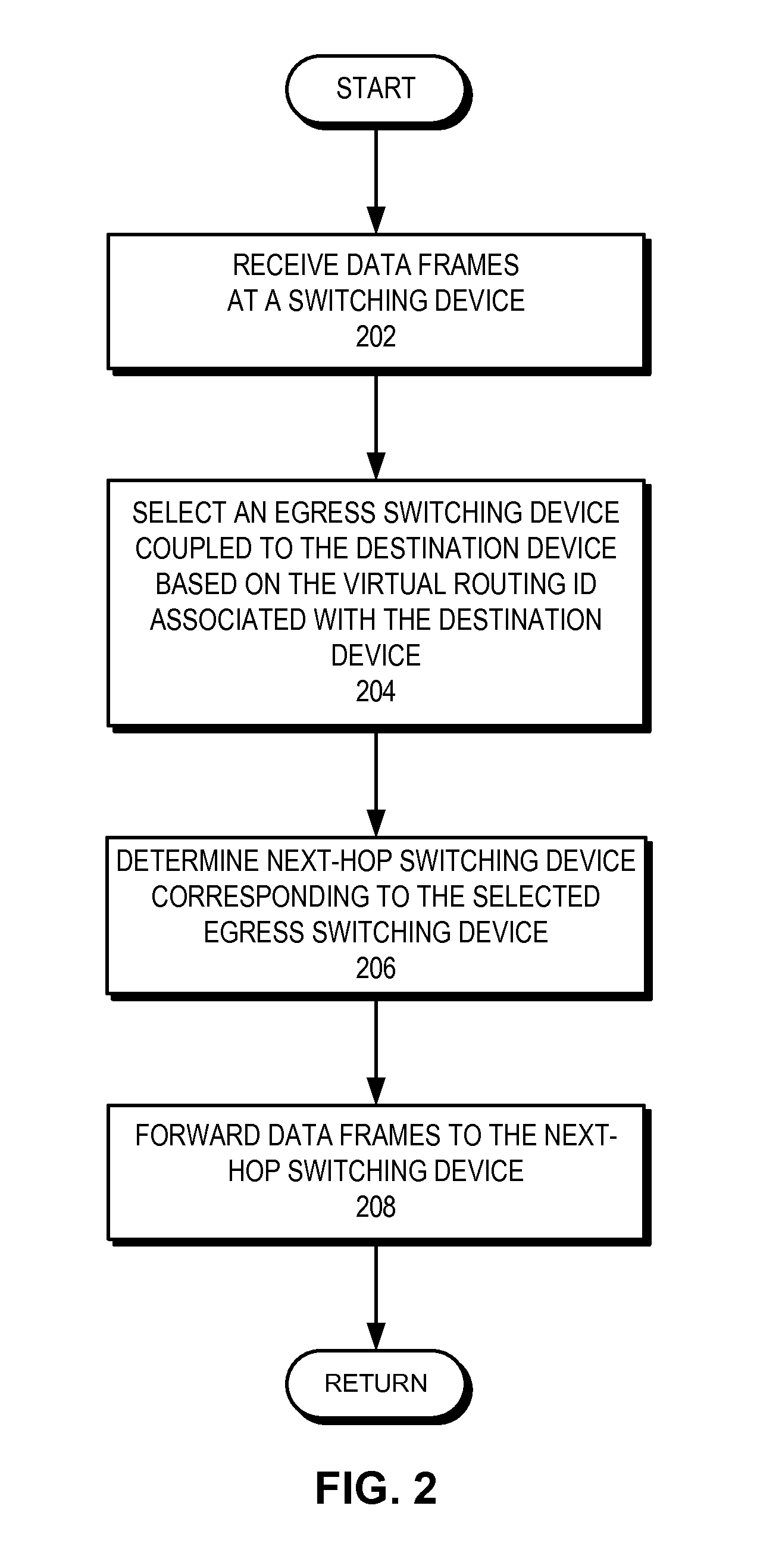
Method and system for remote load balancing in high-availability networks
InactiveUS20120163164A1To achieve load balancingFacilitating remote load balancingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHigh availabilityDatapath
A system is provided for facilitating remote load balancing in a high-availability network. During operation, the system receives a plurality of data frames destined for a destination device, wherein the destination device is coupled to a network via a trunk link, the trunk link coupling the destination device to at least two separate egress switching devices. The system then forwards the data frames via at least two data paths, each of which leads to a respective egress switching device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Scalable block data storage using content addressing
ActiveUS9104326B2Unlimited in capacityUnlimited in performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsComputer moduleDatapath
A device for scalable block data storage and retrieval uses content addressing. Data storage devices store data blocks, and are connected over a network to computing modules. The modules comprise control modules and data modules and carry out content addressing for both storage and retrieval. The network defines separate control paths via the control modules and data paths via the data modules.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
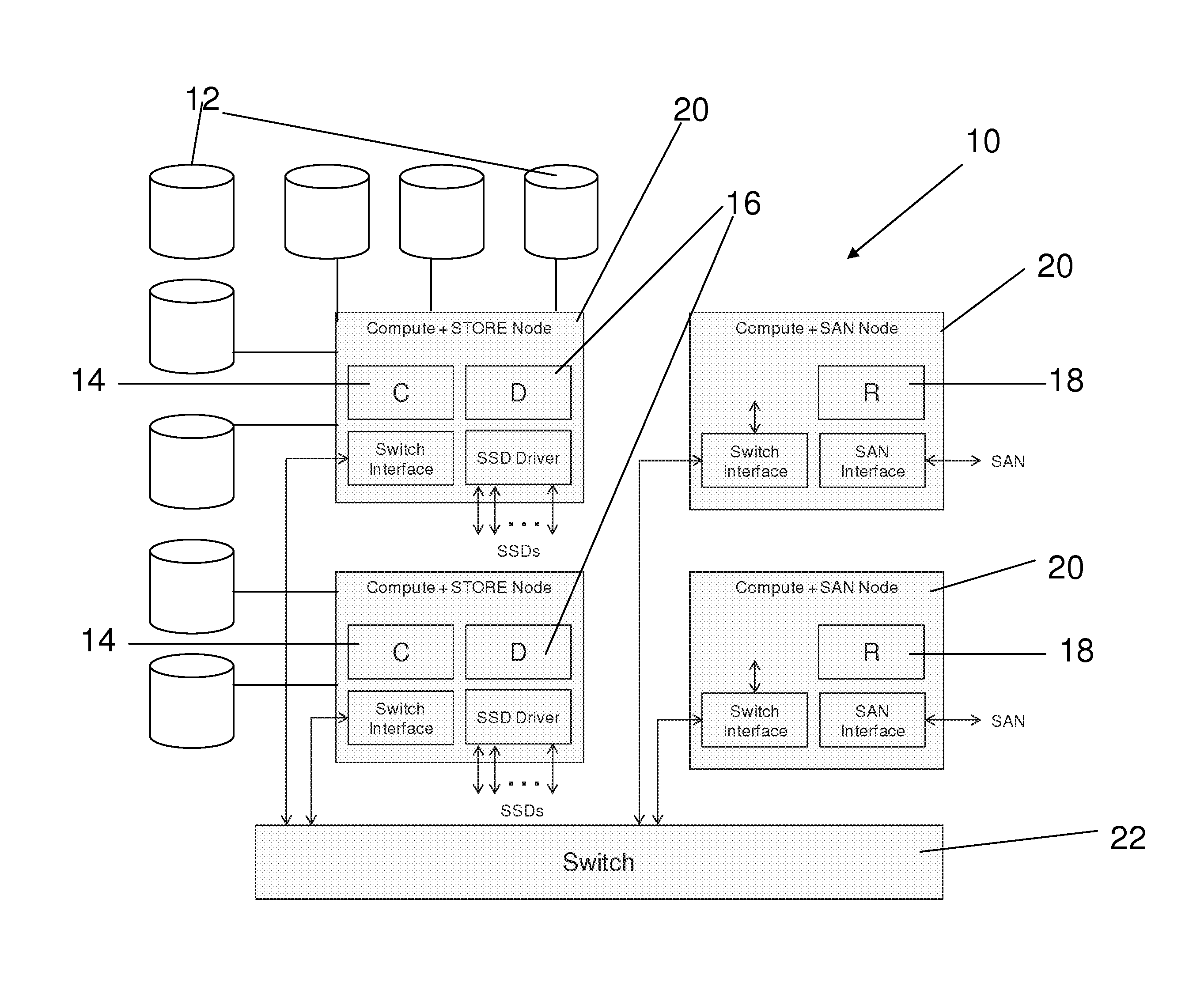
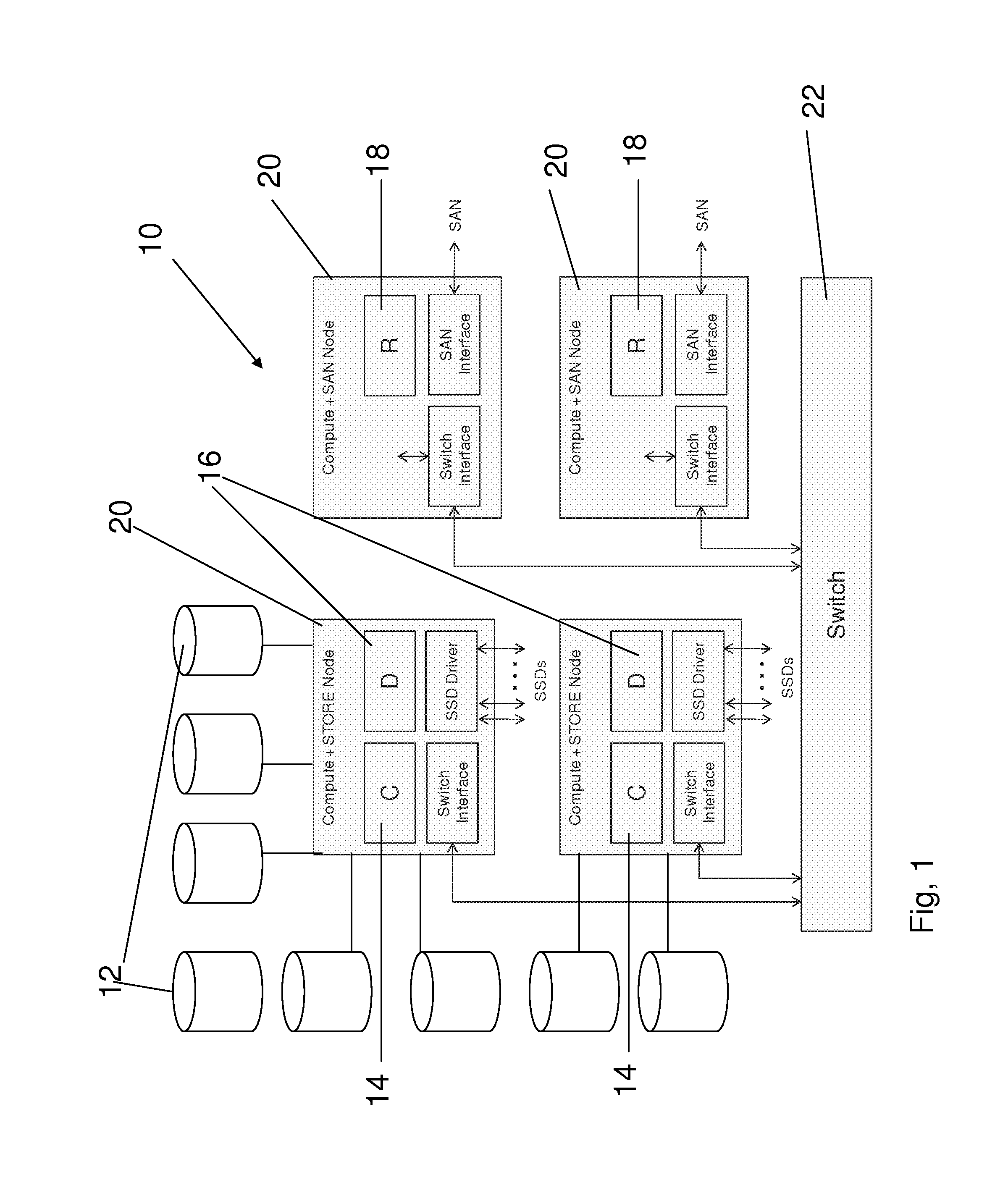
Method and apparatus for providing high-performance and highly-scalable storage acceleration
ActiveUS9390019B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLatency (engineering)Datapath
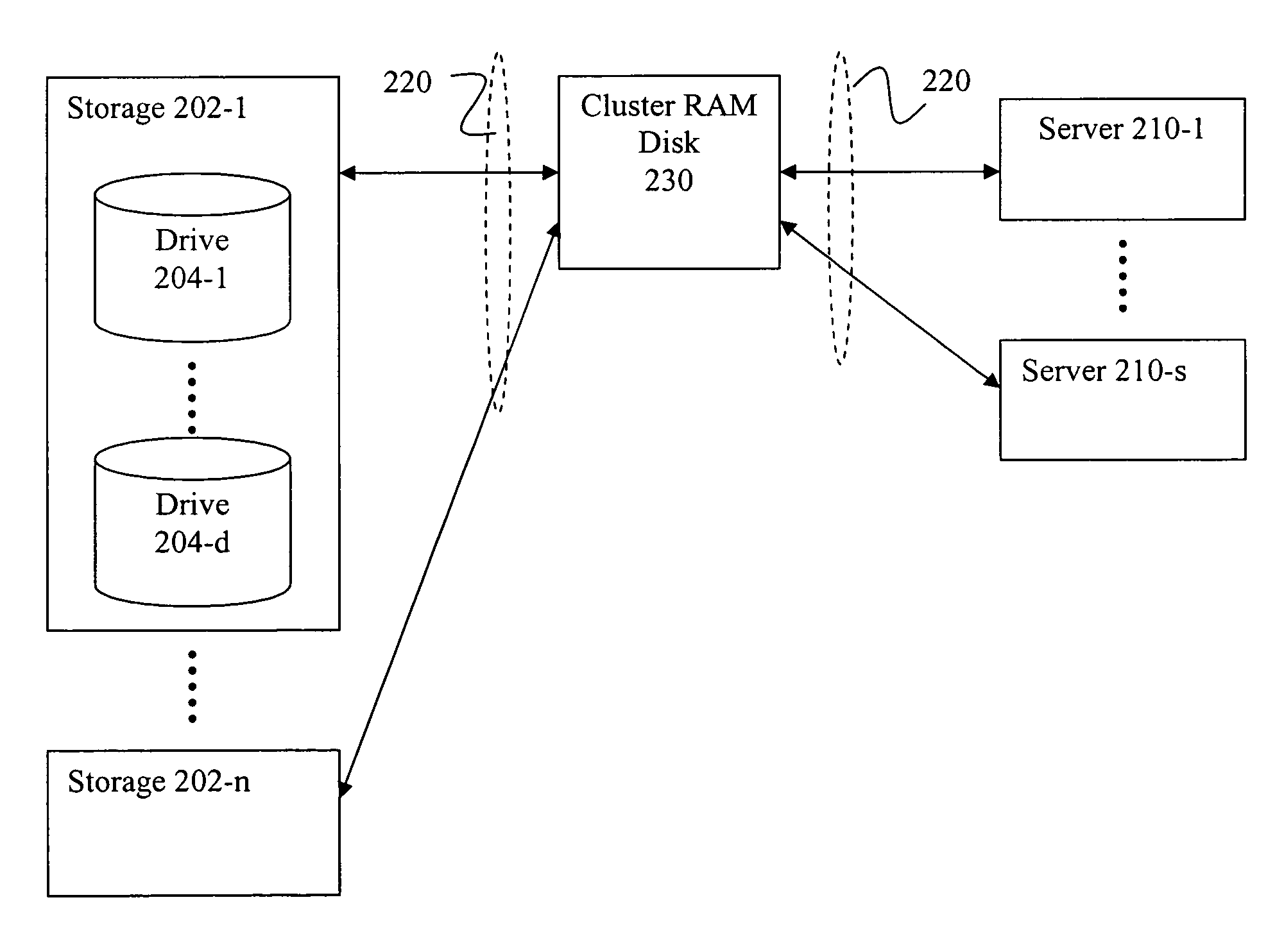
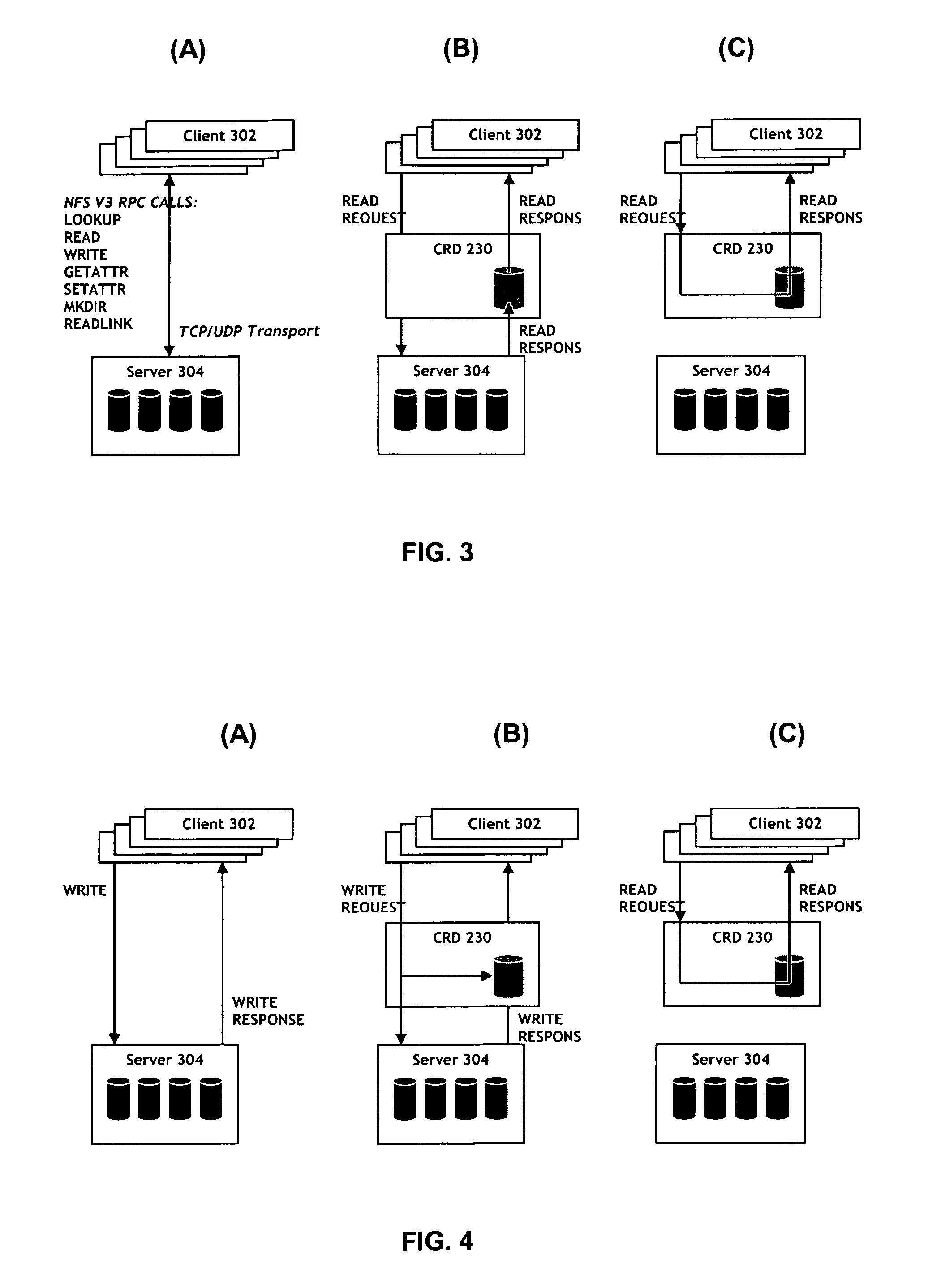
A method and apparatus of providing high performance and highly scalable storage acceleration includes a cluster node-spanning RAM disk (CRD) interposed in the data path between a storage server and a computer server. The CRD addresses performance problems with applications that need to access large amounts of data and are negatively impacted by the latency of classic disk-based storage systems. It solves this problem by placing the data the application needs into a large (with respect to the server's main memory) RAM-based cache where it can be accessed with extremely low latency, hence improving the performance of the application significantly. The CRD is implemented using a novel architecture which has very significant cost and performance advantages over existing or alternative solutions.
Owner:INNOVATIONS IN MEMORY LLC
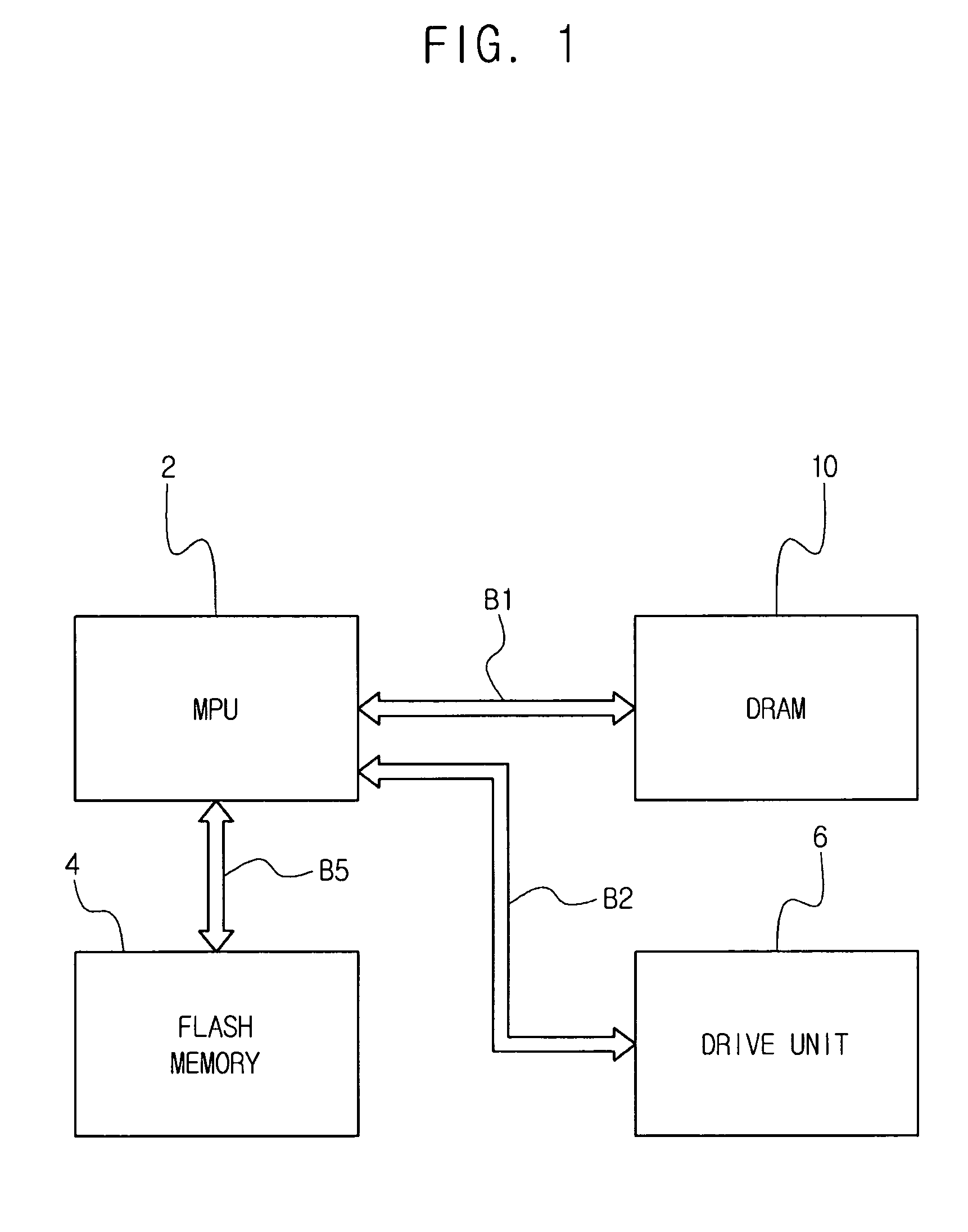
Data processing system and method
InactiveUS20060013473A1Eliminate informationImage enhancementImage analysisStatic random-access memoryHigh memory
A powerful, scaleable, and reconfigurable image processing system and method of processing data therein is described. This general purpose, reconfigurable engine with toroidal topology, distributed memory, and wide bandwidth I / O are capable of solving real applications at real-time speeds. The reconfigurable image processing system can be optimized to efficiently perform specialized computations, such as real-time video and audio processing. This reconfigurable image processing system provides high performance via high computational density, high memory bandwidth, and high I / O bandwidth. Generally, the reconfigurable image processing system and its control structure include a homogeneous array of 16 field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) and 16 static random access memories (SRAM) arranged in a partial torus configuration. The reconfigurable image processing system also includes a PCI bus interface chip, a clock control chip, and a datapath chip. It can be implemented in a single board. It receives data from its external environment, computes correspondence, and uses the results of the correspondence computations for various post-processing industrial applications. The reconfigurable image processing system determines correspondence by using non-parametric local transforms followed by correlation. These non-parametric local transforms include the census and rank transforms. Other embodiments involve a combination of correspondence, rectification, a left-right consistency check, and the application of an interest operator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Network control apparatus and method for populating logical datapath sets
For a network control system that receives, from a user, logical datapath sets that logically express desired forwarding behaviors that are to be implemented by a set of managed switching elements, a controller for managing several managed switching elements that forward data in a network that includes the managed switching elements is described. The controller includes a set of modules for detecting a change in one or more managed switching elements and for updating logical datapath set based on the detected change. The logical datapath set is for subsequent translation into a set of physical forwarding behaviors of the managed switching elements.
Owner:NICIRA
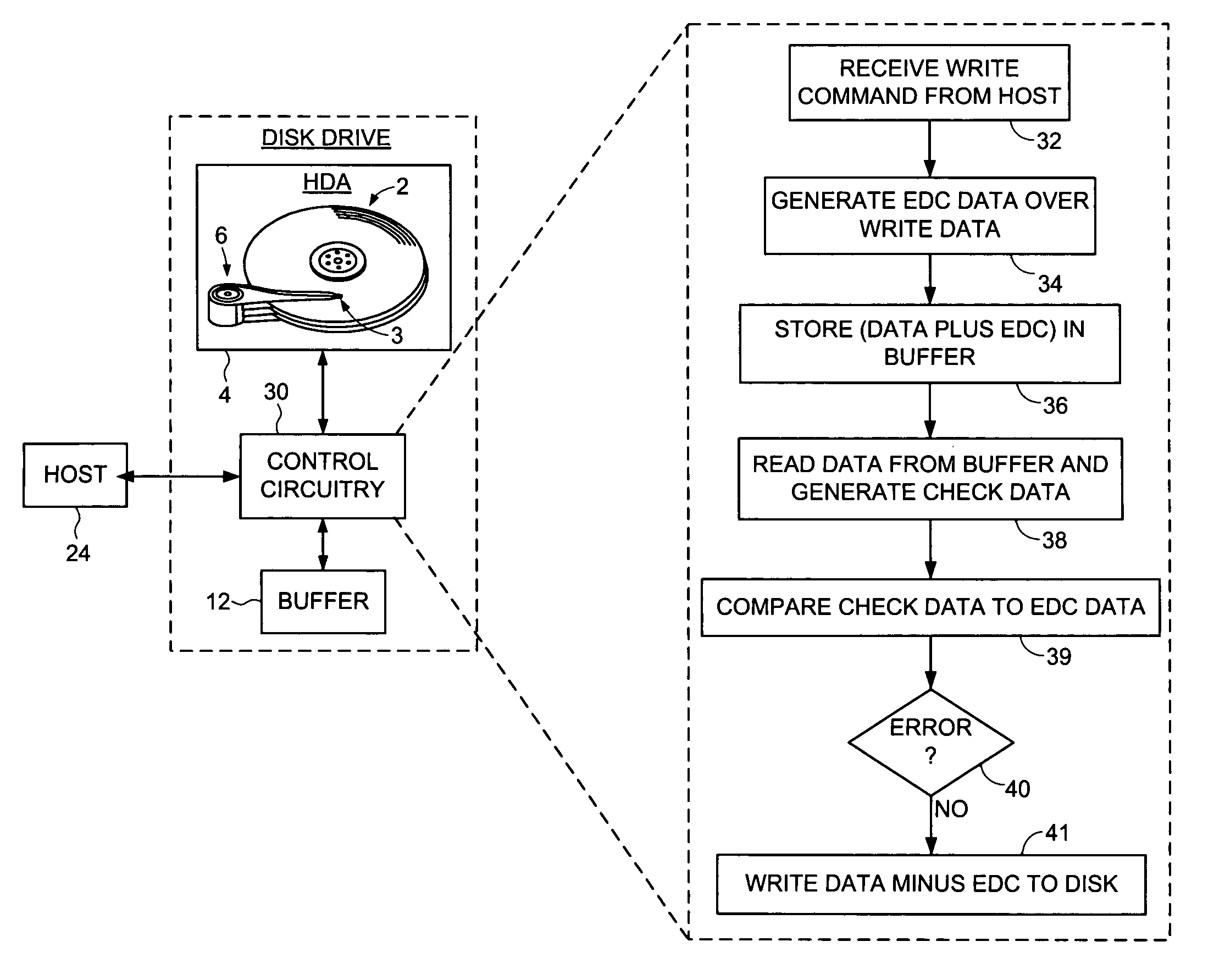
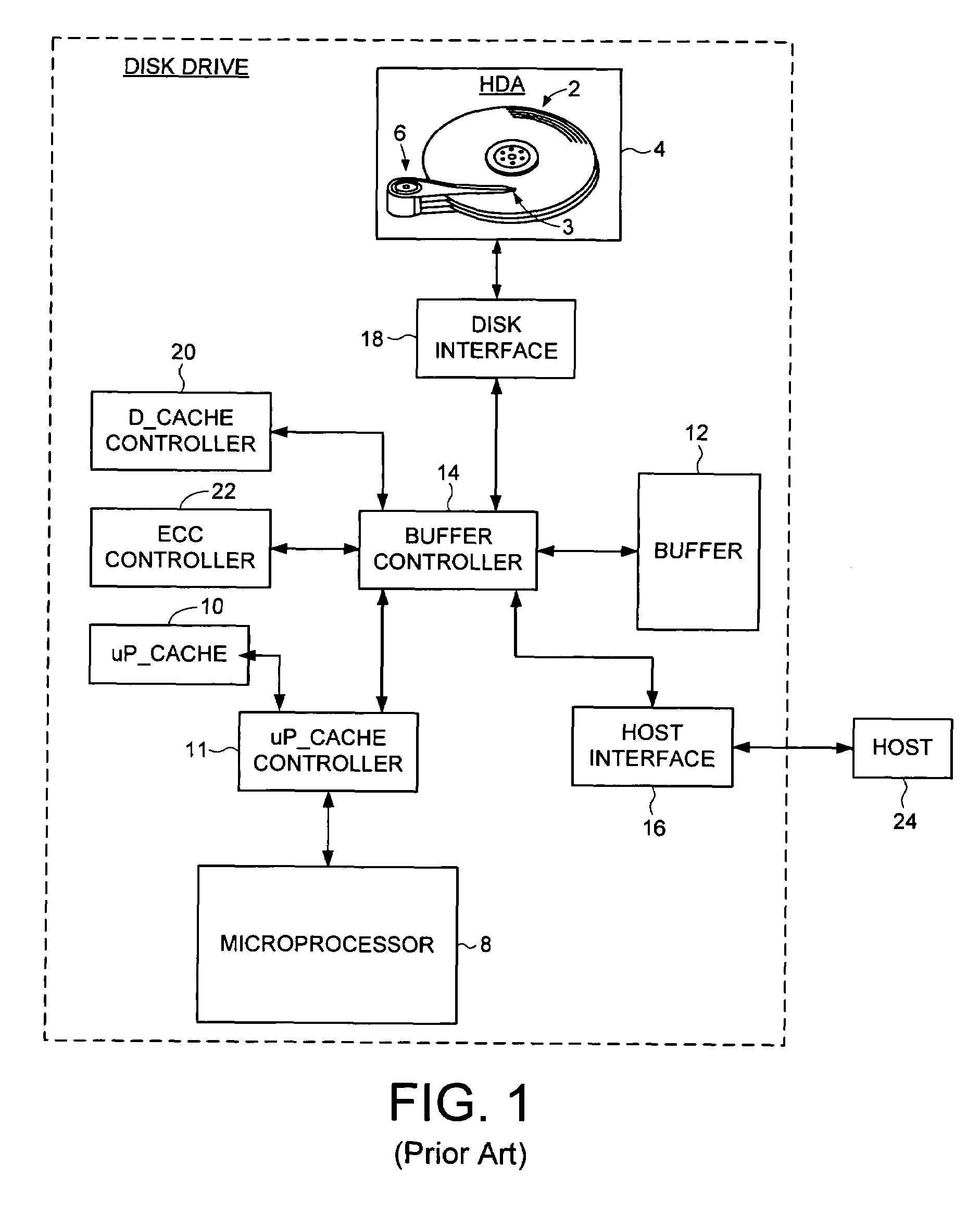
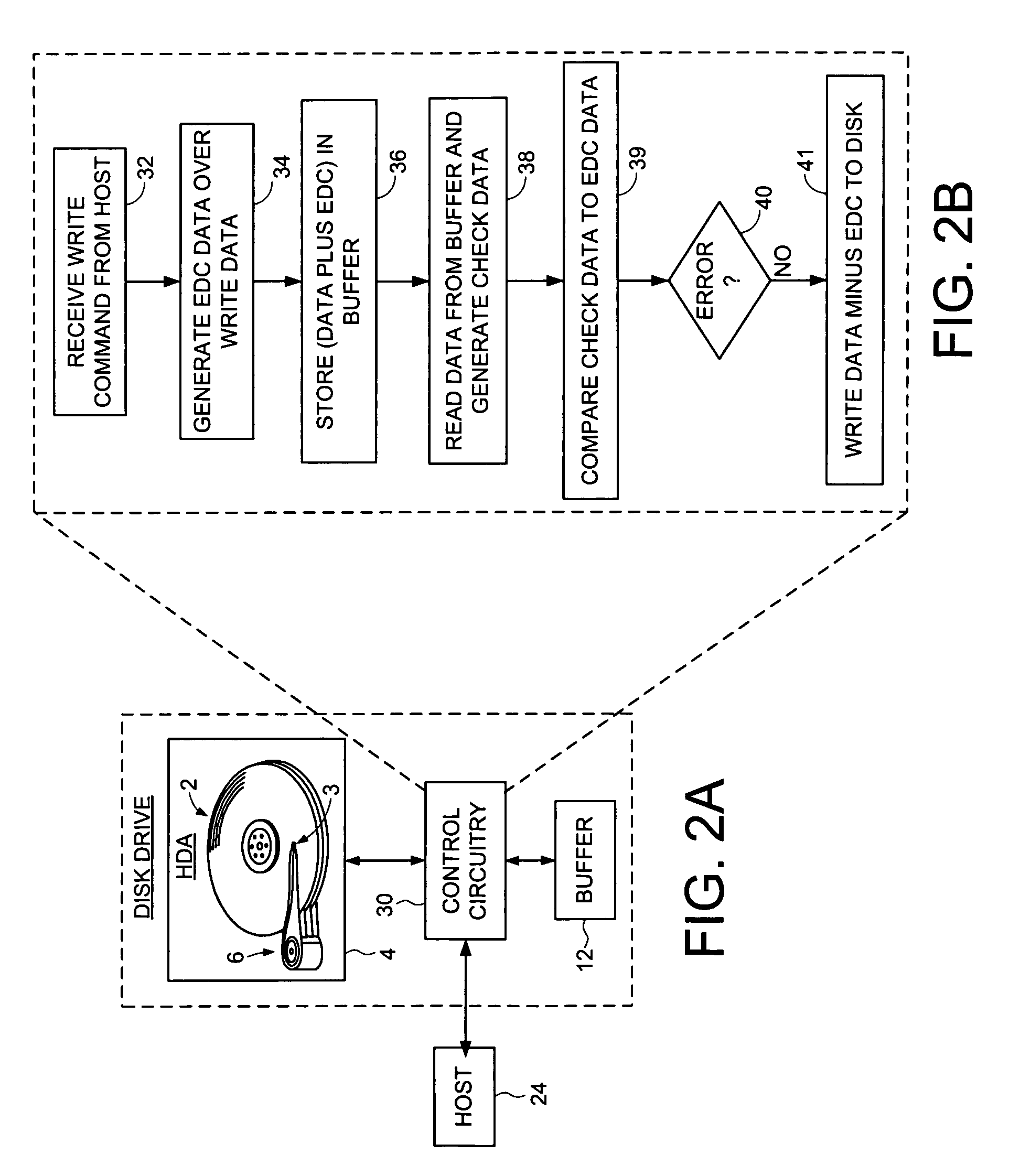
Disk drive implementing data path protection without writing the error detection code data to the disk
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
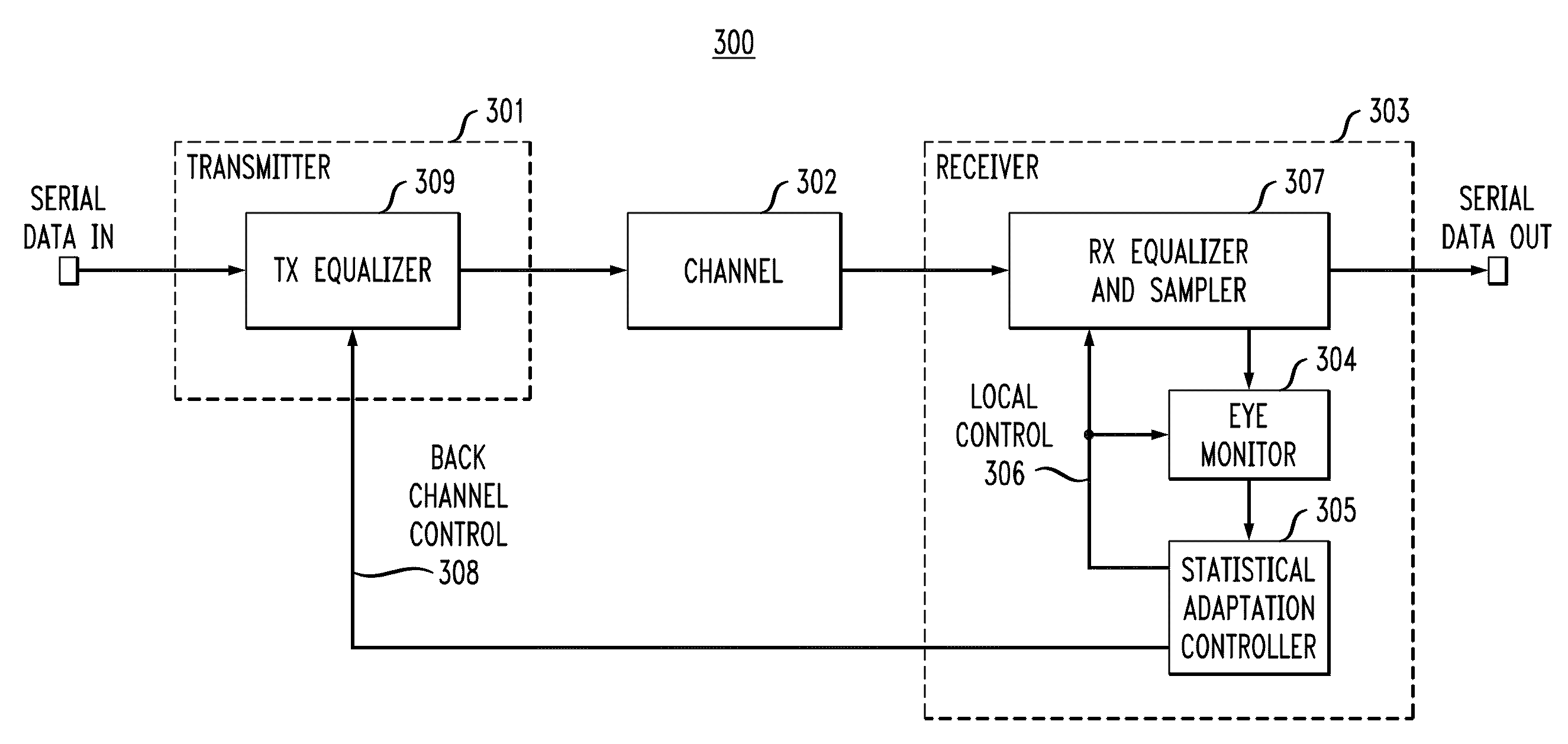
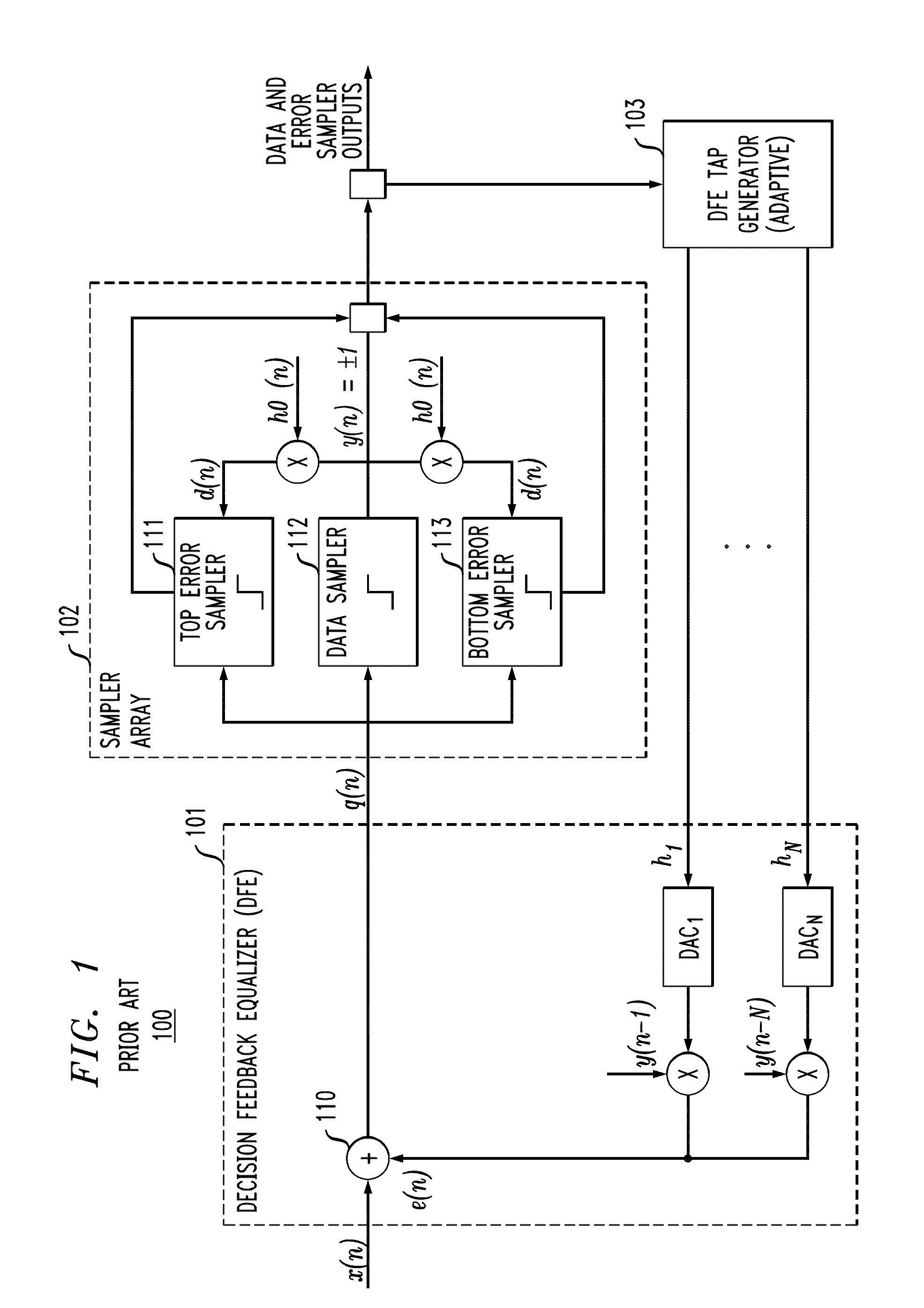
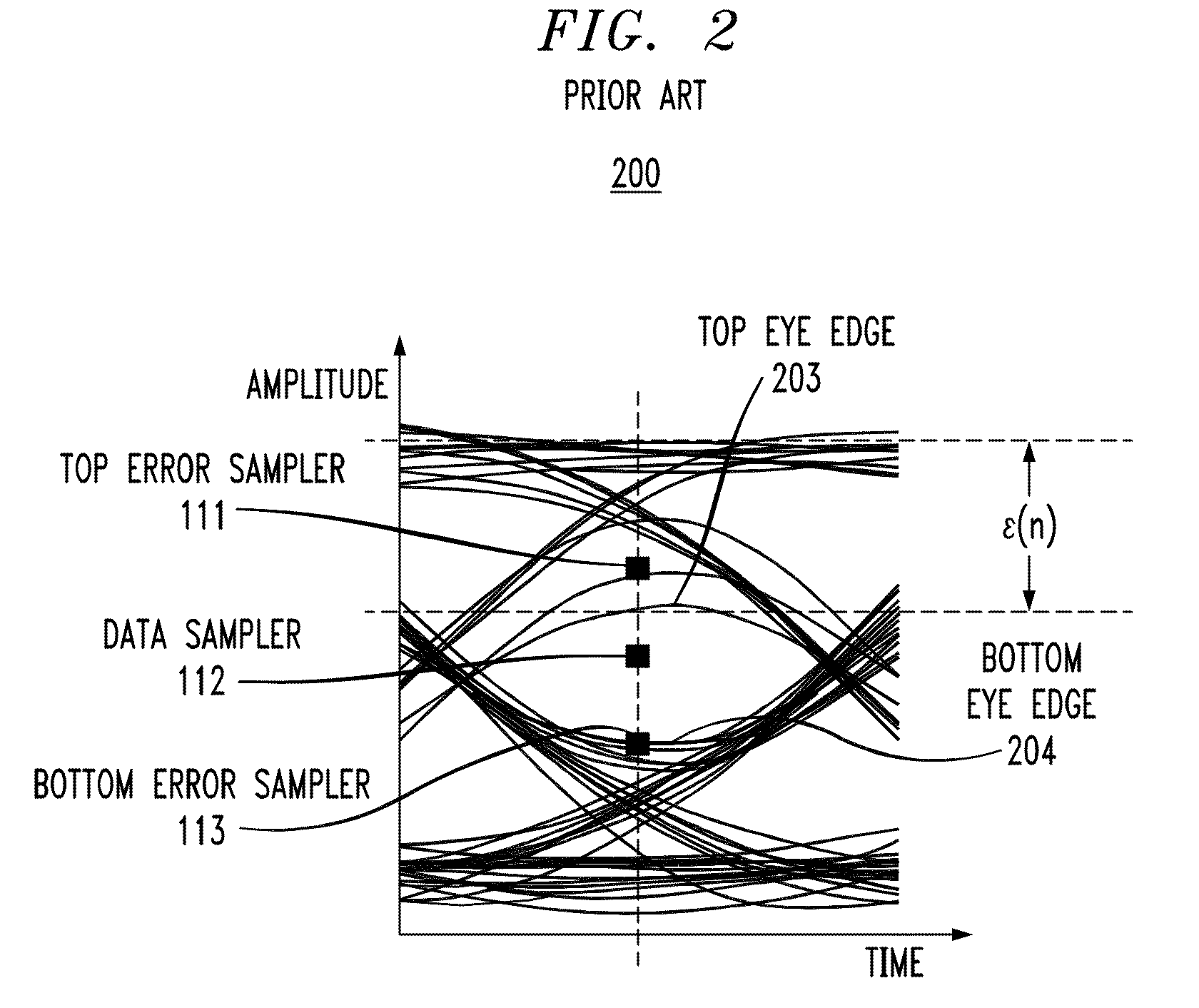
Statistically-Adapted Receiver and Transmitter Equalization
InactiveUS20100329325A1High error rateReduce error rateMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTraining periodData integrity
In described embodiments, adaptive equalization of a signal in, for example, Serializer / De-serializer transceivers by a) monitoring a data eye in a data path with an eye detector for signal amplitude and / or transition; b) setting the equalizer response of at least one equalizer in the signal path while the signal is present for statistical calibration of the data eye; c) monitoring the data eye and setting the equalizer during periods in which received data is allowed to contain errors (such as link initiation and training periods) and periods in which receive data integrity is to be maintained (such as normal data communication).
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
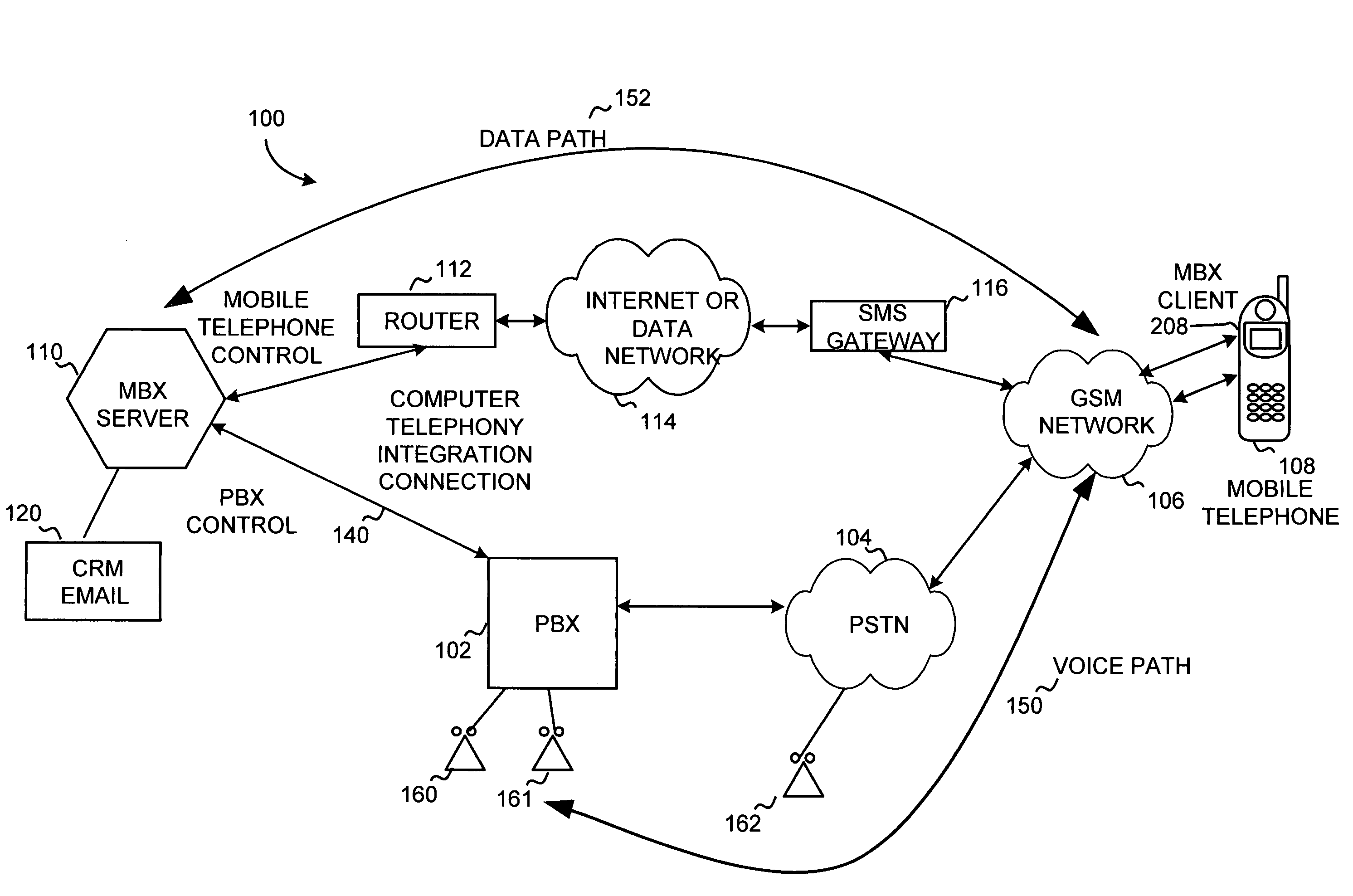
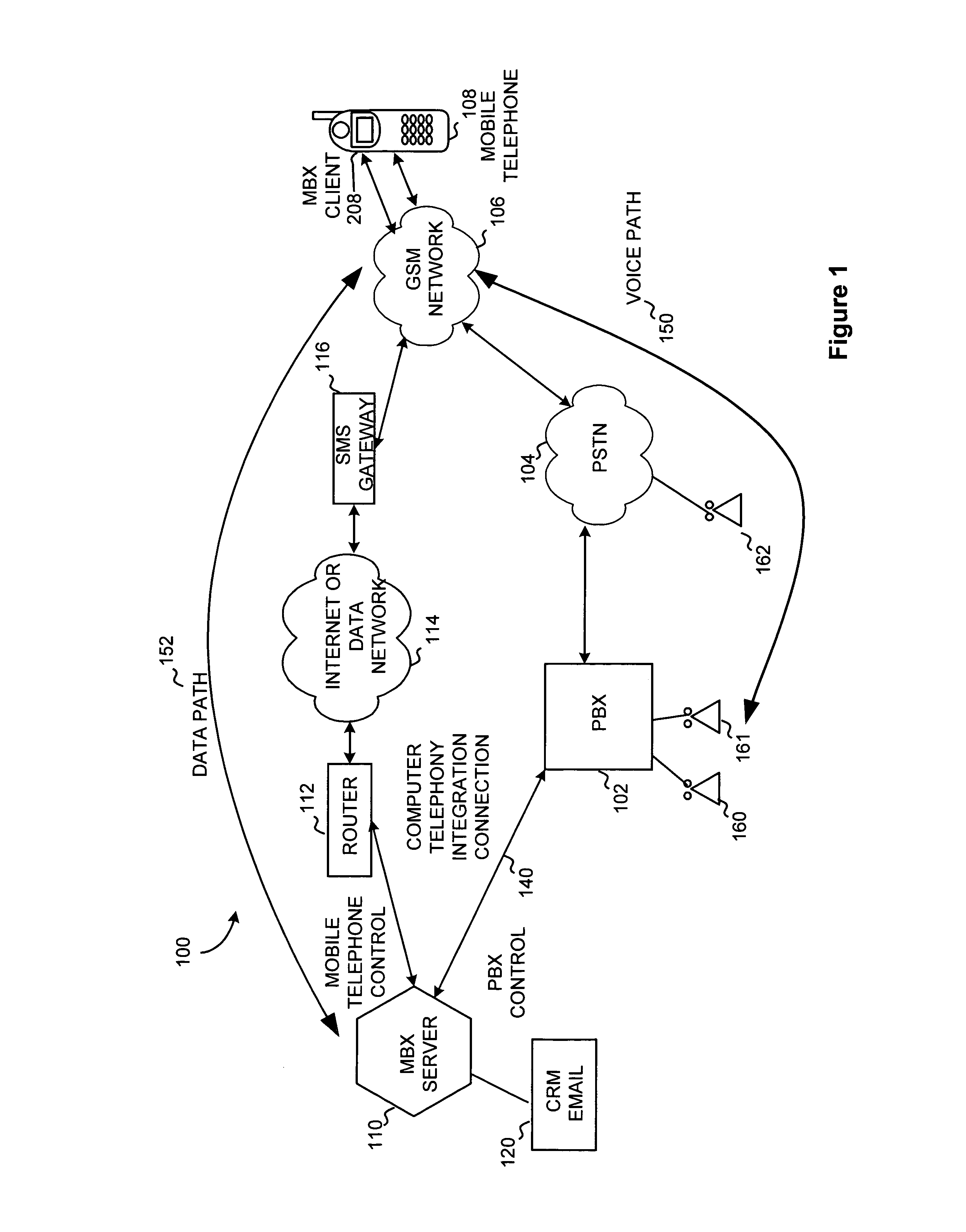
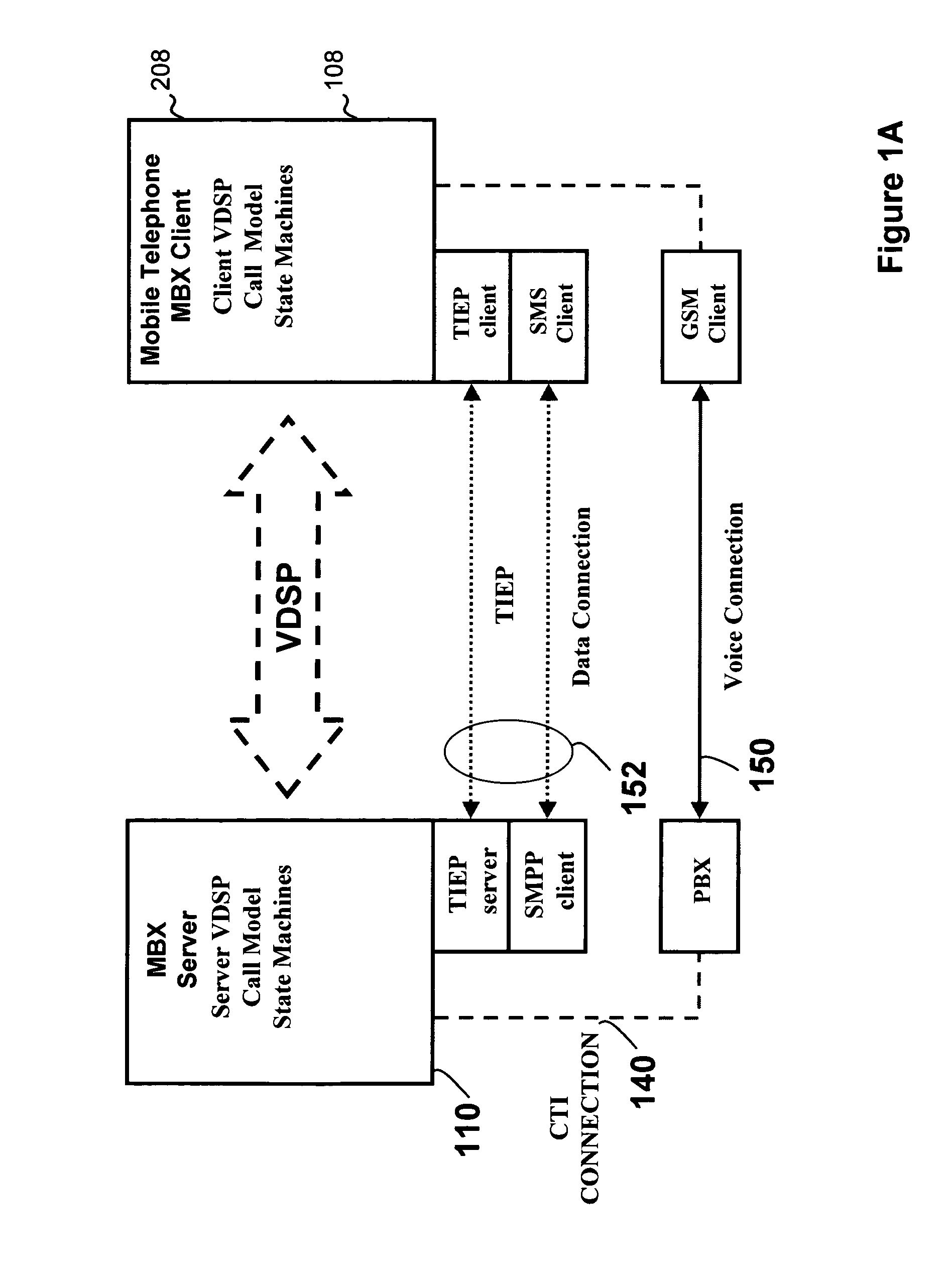
Mobile branch exchange
InactiveUS6993360B2Improve functionalityExtend functionalitySpecial service for subscribersCalled number recording/indicationClient-sideSoftware
A mobile branch exchange (MBX) allows a user of a mobile telephone to exploit the functionality of a private branch exchange (PBX) as if the user were using a PBX-connected wire line telephone in an office setting. A server is placed on corporate premises and the server is configured to communicate with corresponding client software programmed into a programmable mobile telephone. The server directly interfaces with the PBX to control call placement and connectivity and operates as an intermediary proxy for the mobile telephone. In a preferred embodiment, the server establishes a data pathway to the mobile telephone that is, from a network point of view, independent of a parallel voice pathway established between the PBX and mobile telephone.
Owner:ONRELAY
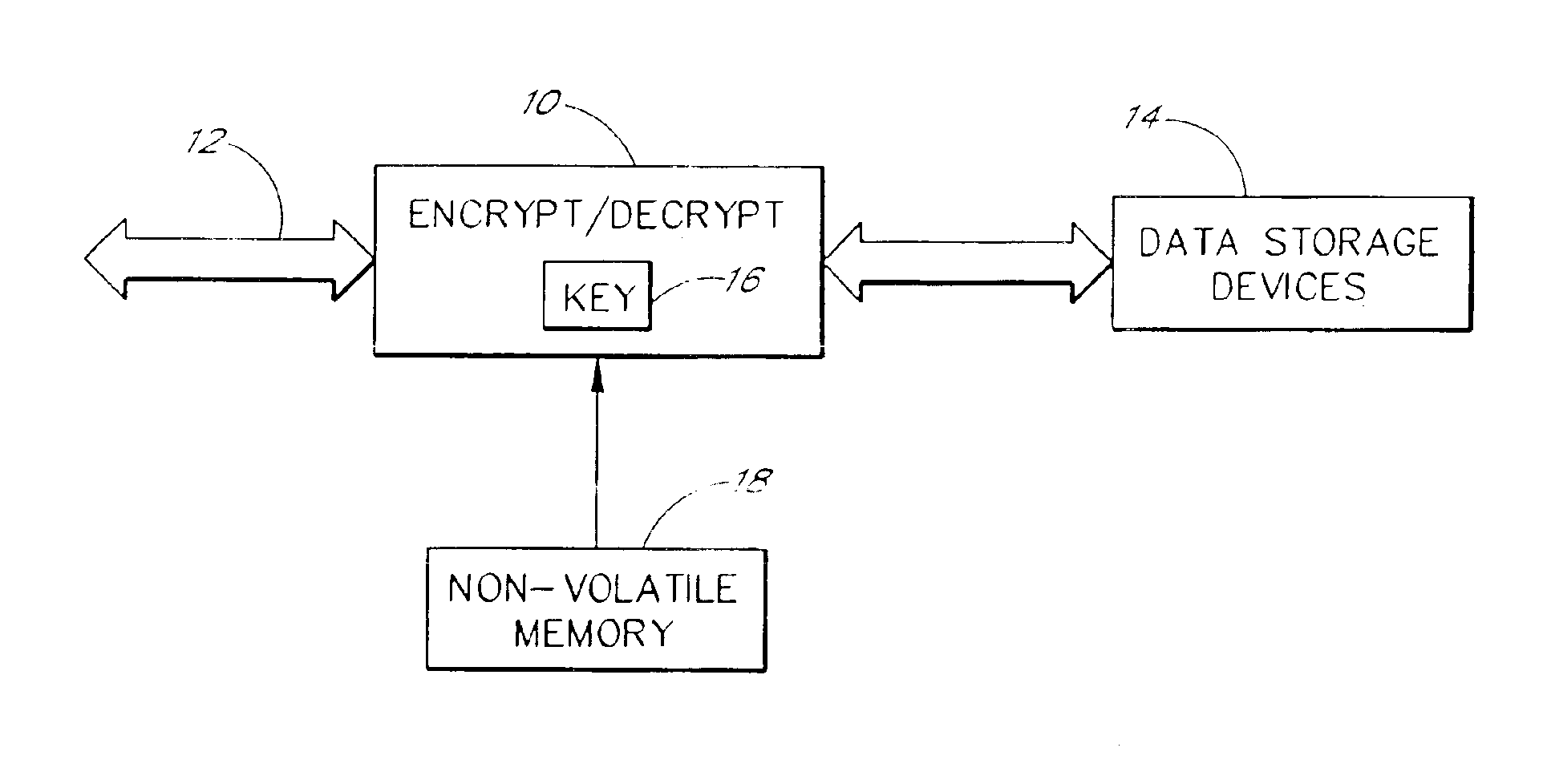
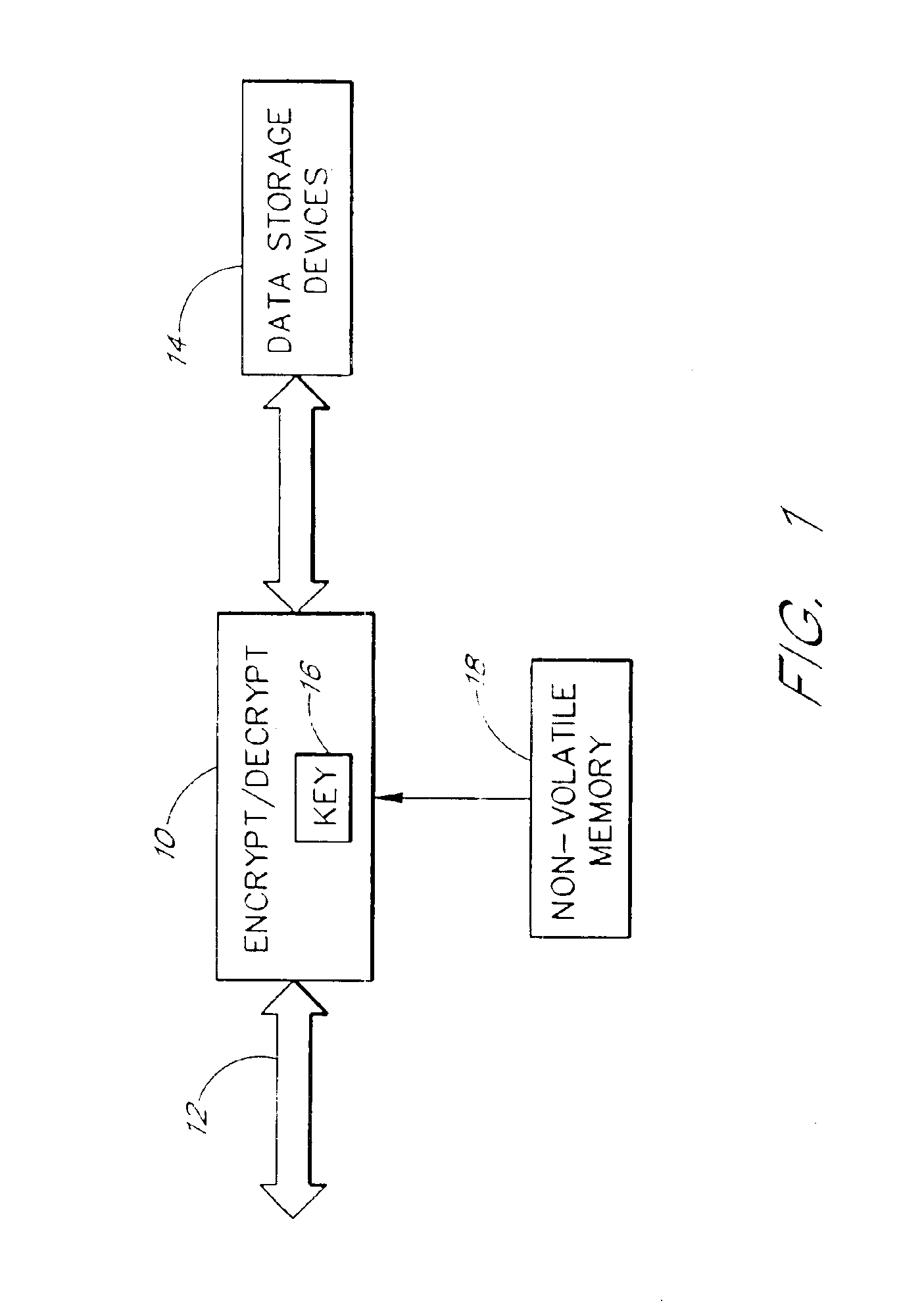
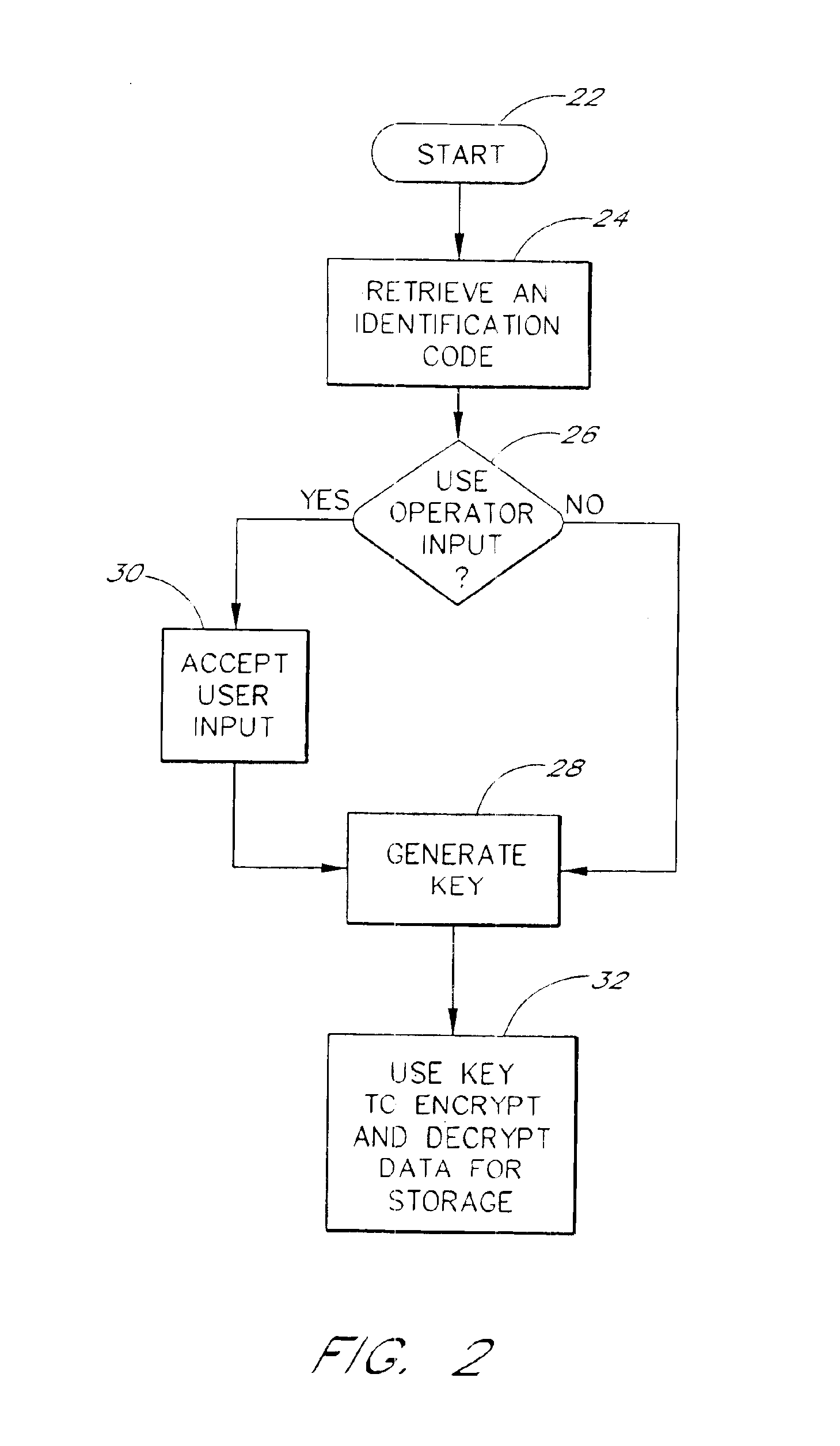
Data security for digital data storage
InactiveUS6857076B1Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionUser inputData source
A computing system includes data encryption in the data path between a data source and data storage devices. The data encryption may utilize a key which is derived at least in part from an identification code stored in a non-volatile memory. The key may also be derived at least in part from user input to the computer.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
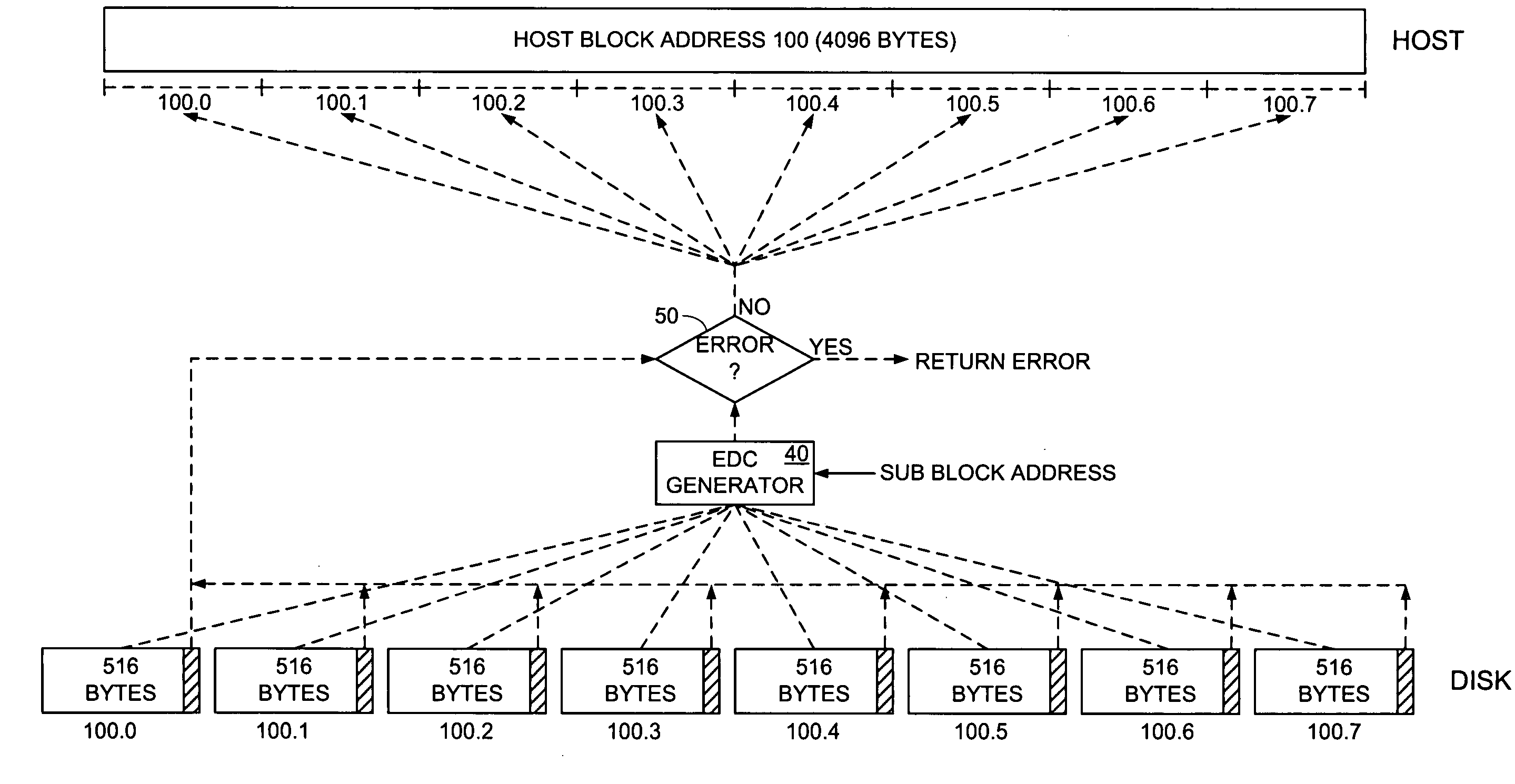
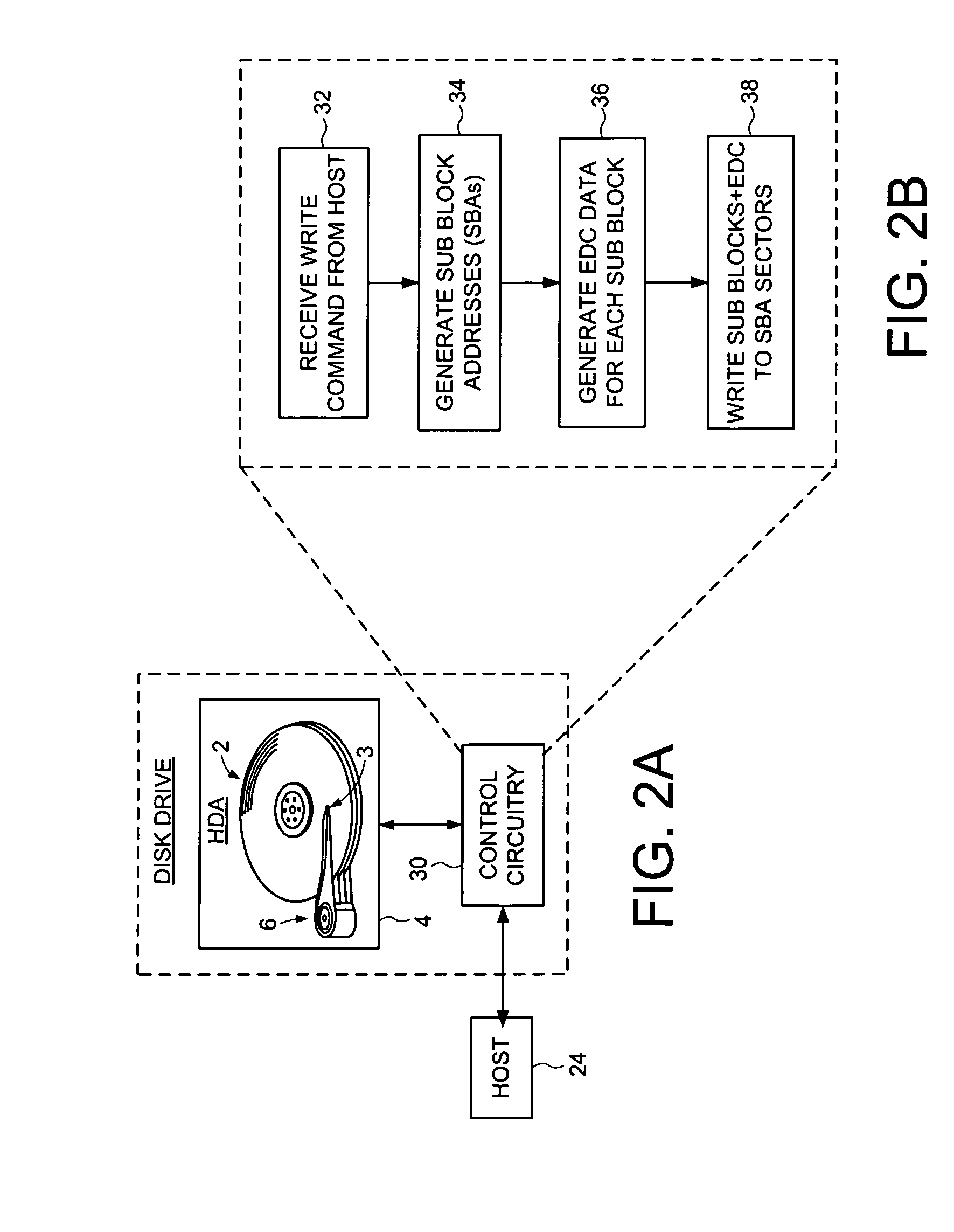
Disk drive implementing data path protection by encoding large host blocks into sub blocks
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk having a plurality of data tracks, wherein each data track includes a plurality of data sectors. A head is actuated over the disk for accessing the data sectors. A write command is received from a host, wherein the write command includes a host block and corresponding host block address. The host block is partitioned into a plurality of sub blocks, and a plurality of sub block addresses are generated in response to the host block address, wherein each sub block address corresponds to one of the sub blocks. Error detection code (EDC) data is generated for each sub block in response to the sub block and corresponding sub block address. Each sub block and corresponding EDC data are combined to generate a plurality of partial codewords that are written to the data sectors corresponding to the sub block addresses.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
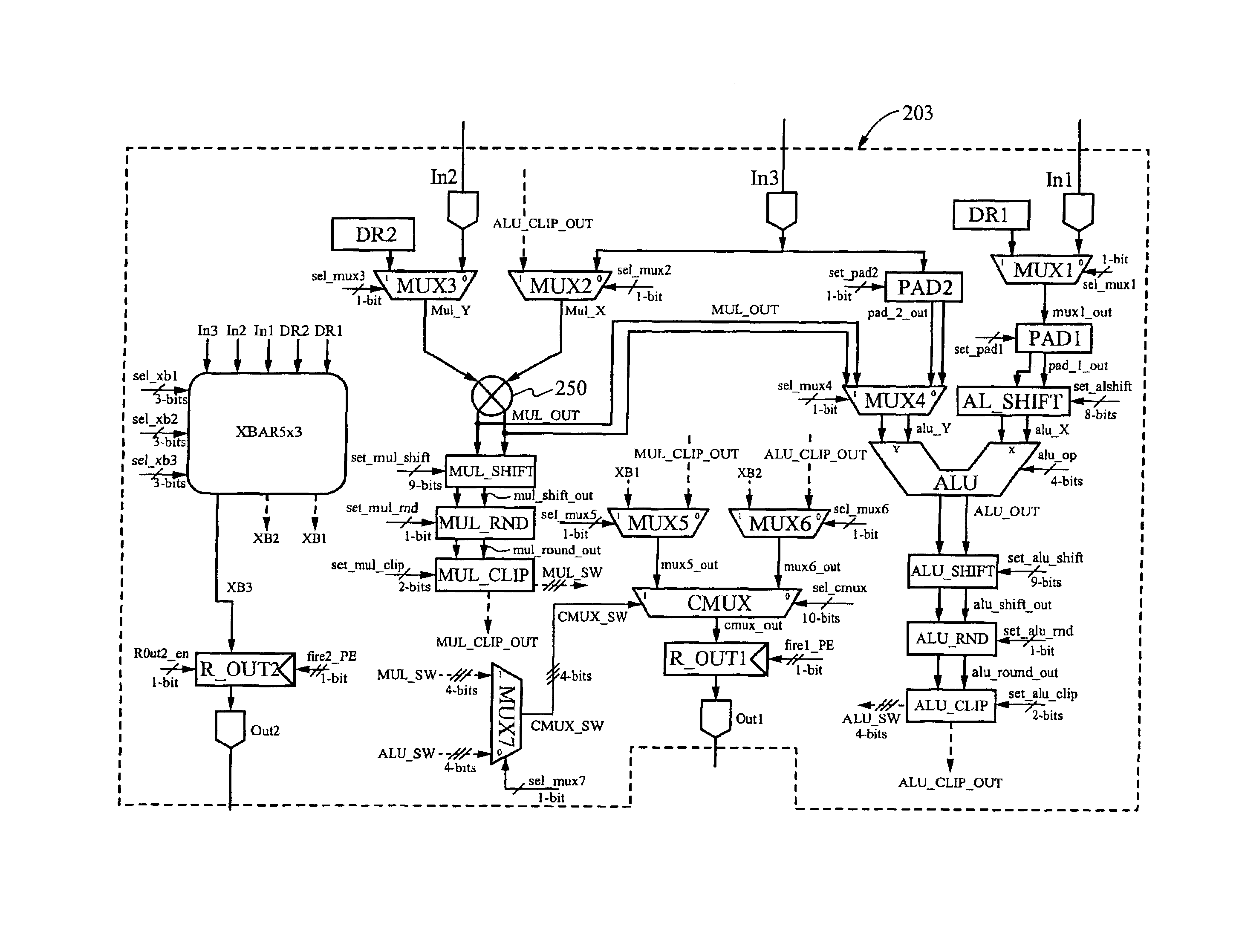
Reconfigurable data path processor
InactiveUS6883084B1Eliminates branchingCycle simpleEnergy efficient ICTConditional code generationMultiplexerProcessing element
A reconfigurable data path processor comprises a plurality of independent processing elements. Each of the processing elements advantageously comprising an identical architecture. Each processing element comprises a plurality of data processing means for generating a potential output. Each processor is also capable of through-putting an input as a potential output with little or no processing. Each processing element comprises a conditional multiplexer having a first conditional multiplexer input, a second conditional multiplexer input and a conditional multiplexer output. A first potential output value is transmitted to the first conditional multiplexer input, and a second potential output value is transmitted to the second conditional multiplexer output. The conditional multiplexer couples either the first conditional multiplexer input or the second conditional multiplexer input to the conditional multiplexer output, according to an output control command. The output control command is generated by processing a set of arithmetic status-bits through a logical mask. The conditional multiplexer output is coupled to a first processing element output. A first set of arithmetic bits are generated according to the processing of the first processable value. A second set of arithmetic bits may be generated from a second processing operation. The selection of the arithmetic status-bits is performed by an arithmetic-status bit multiplexer selects the desired set of arithmetic status bits from among the first and second set of arithmetic status bits. The conditional multiplexer evaluates the select arithmetic status bits according to logical mask defining an algorithm for evaluating the arithmetic status bits.
Owner:STC UNM +1
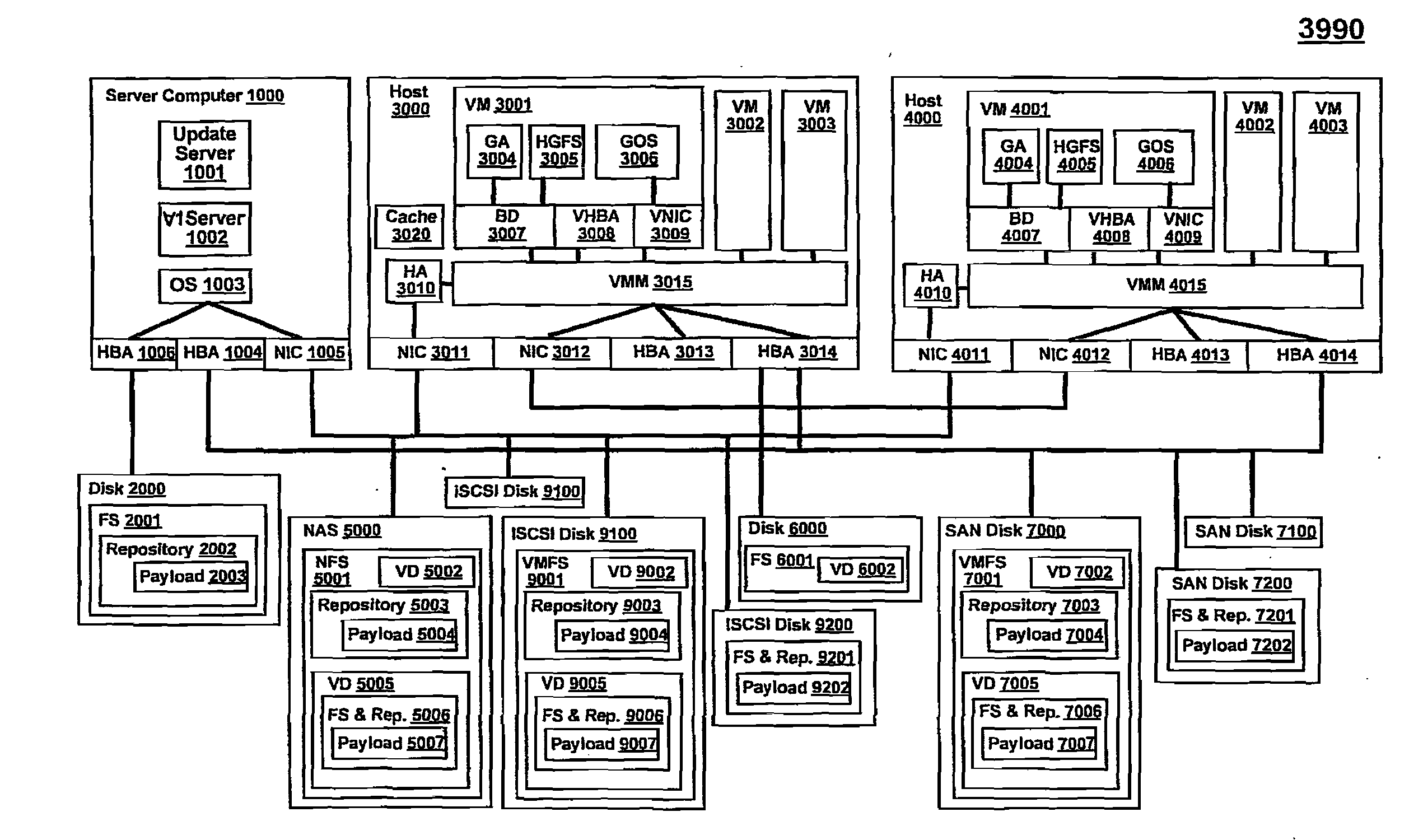
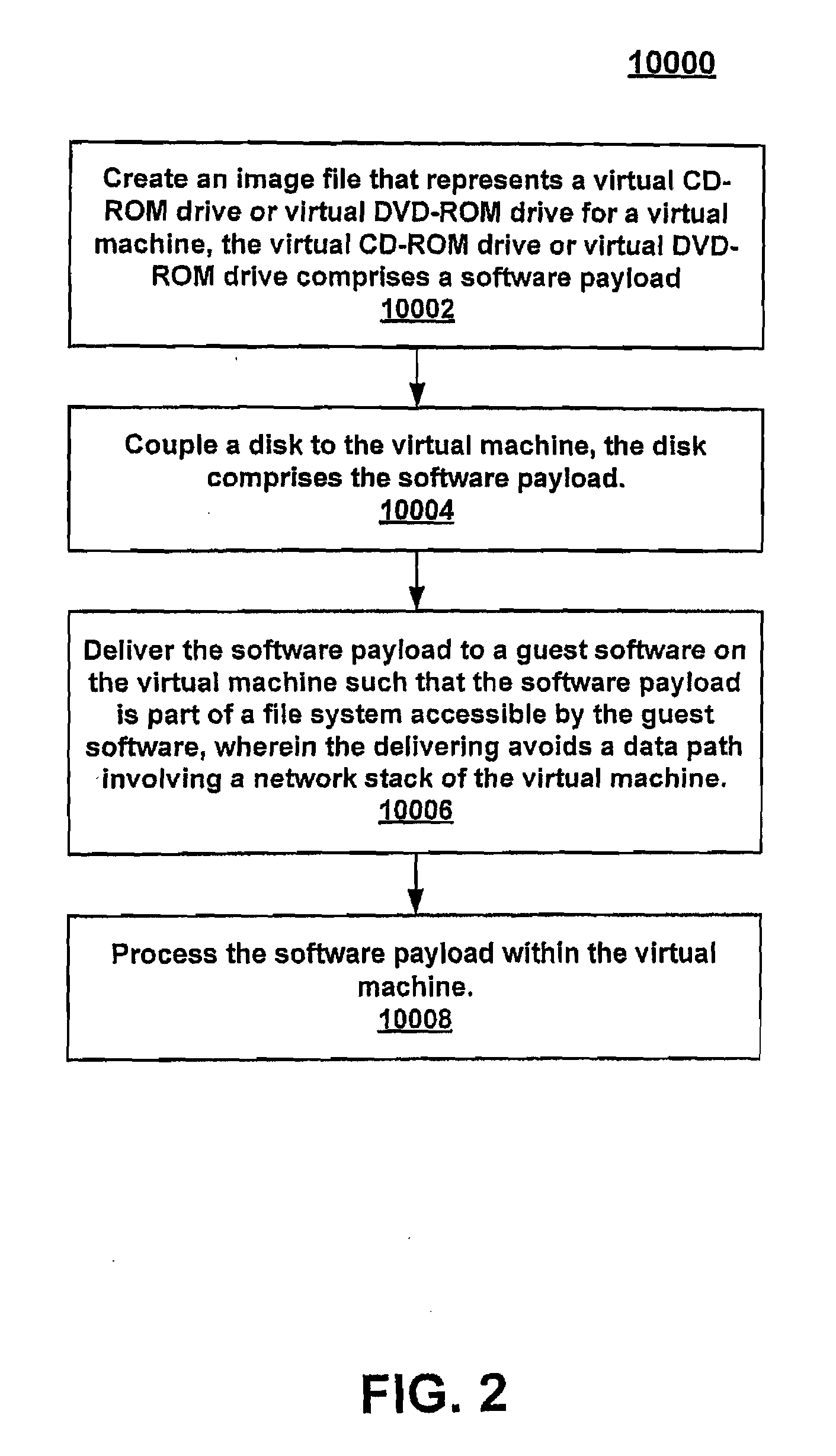
Software delivery for virtual machines
ActiveUS20080244577A1Program synchronisationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFile systemDatapath
Owner:VMWARE INC
Extended storage capacity for a network file server
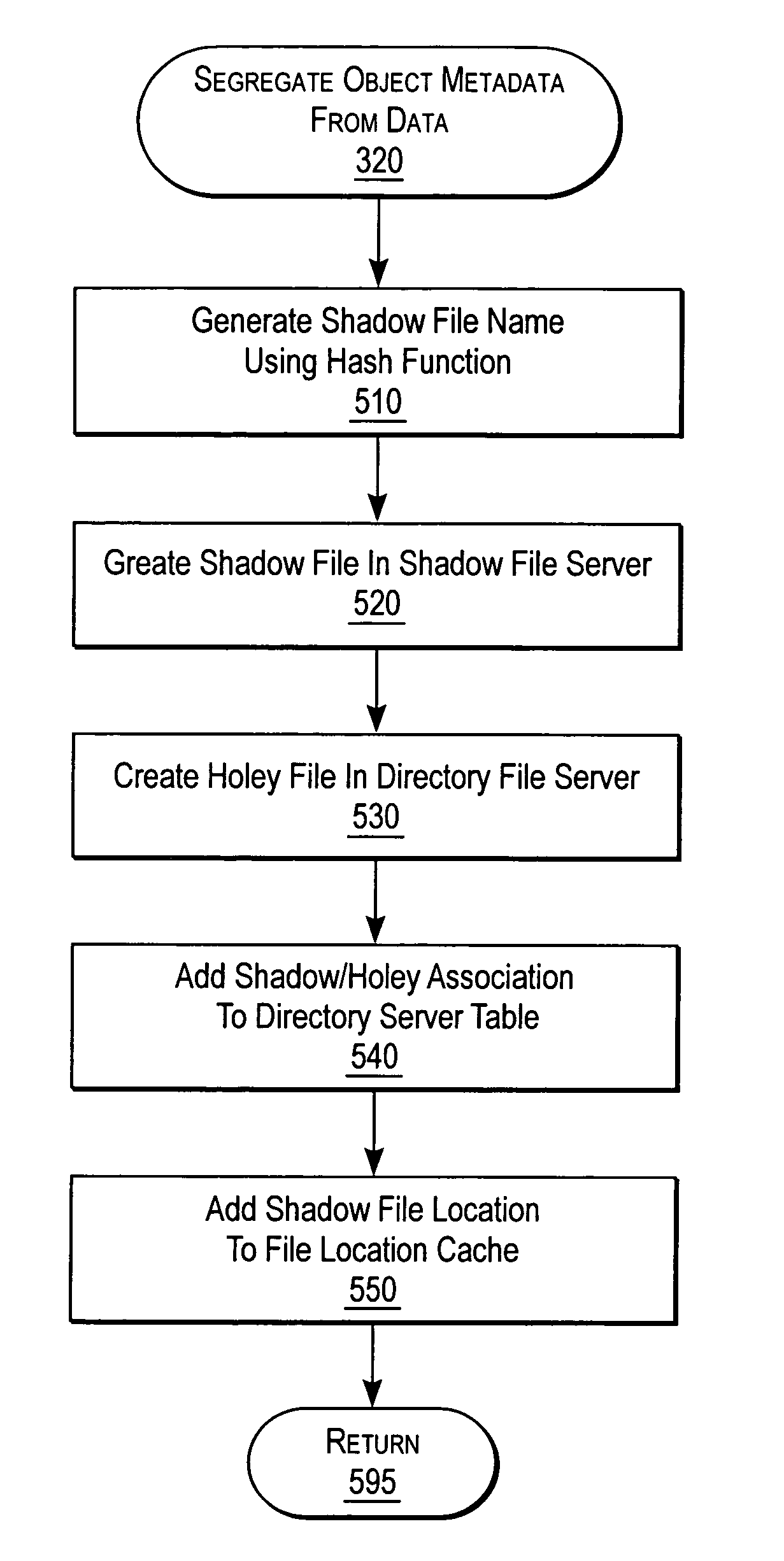
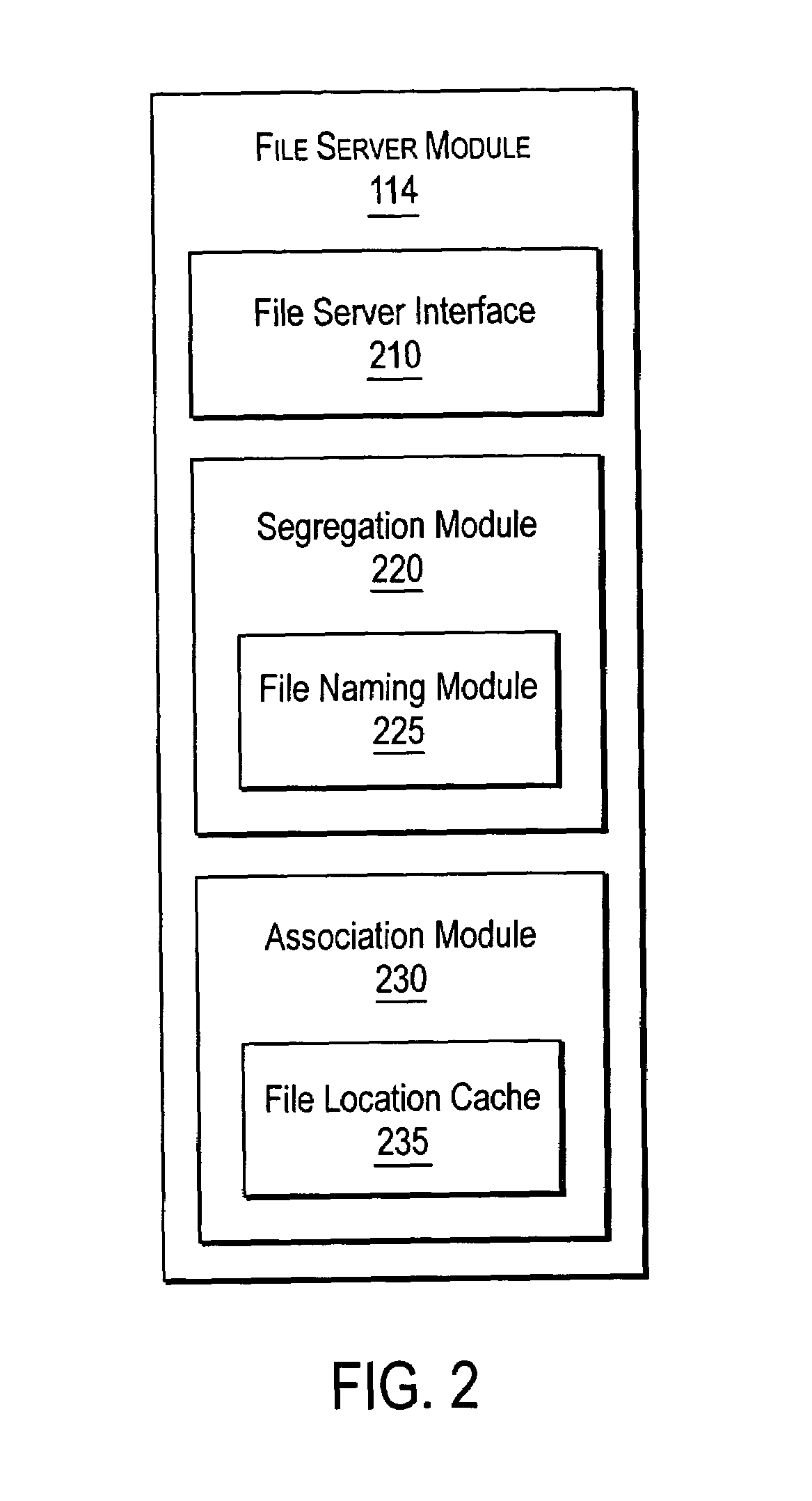
ActiveUS7072917B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsServer replicationData operations
A NAS switch provides extended storage capacity to a file server in a decentralized storage network such as a NAS (Network Attached Storage) storage network. The NAS switch sits in the data path of a client on the front end and a directory file server and shadow file servers on the back end. A segregation module in the NAS switch replicates data from the directory file server to a shadow file server, and then replaces the data in the directory file server with holey files. Holey files, which store a range of consecutive values such as zero with negligible storage space, retain the attributes of the data without retaining its storage consumption. Thus, the directory file server can server as a single directory hierarchy for several shadow file servers containing data beyond a capacity of the directory file server. When the NAS switch receives operations from the client, an association module forwards directory operations to the directory file server and data operations to the shadow file server. The NAS switch also provides services to several shadow file servers from a single directory file server.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com