Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
175 results about "Mask" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
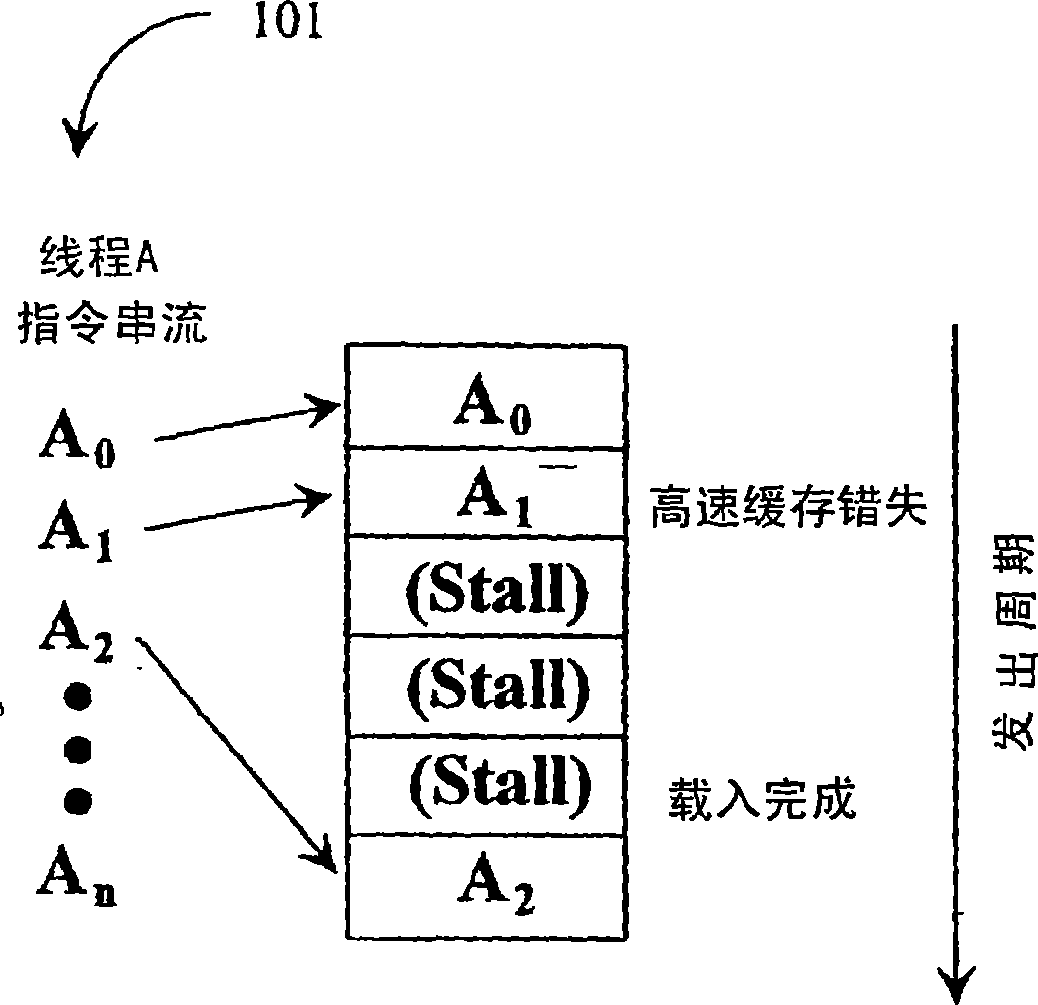
In computer science, a mask or bitmask is data that is used for bitwise operations, particularly in a bit field. Using a mask, multiple bits in a byte, nibble, word etc. can be set either on, off or inverted from on to off (or vice versa) in a single bitwise operation.
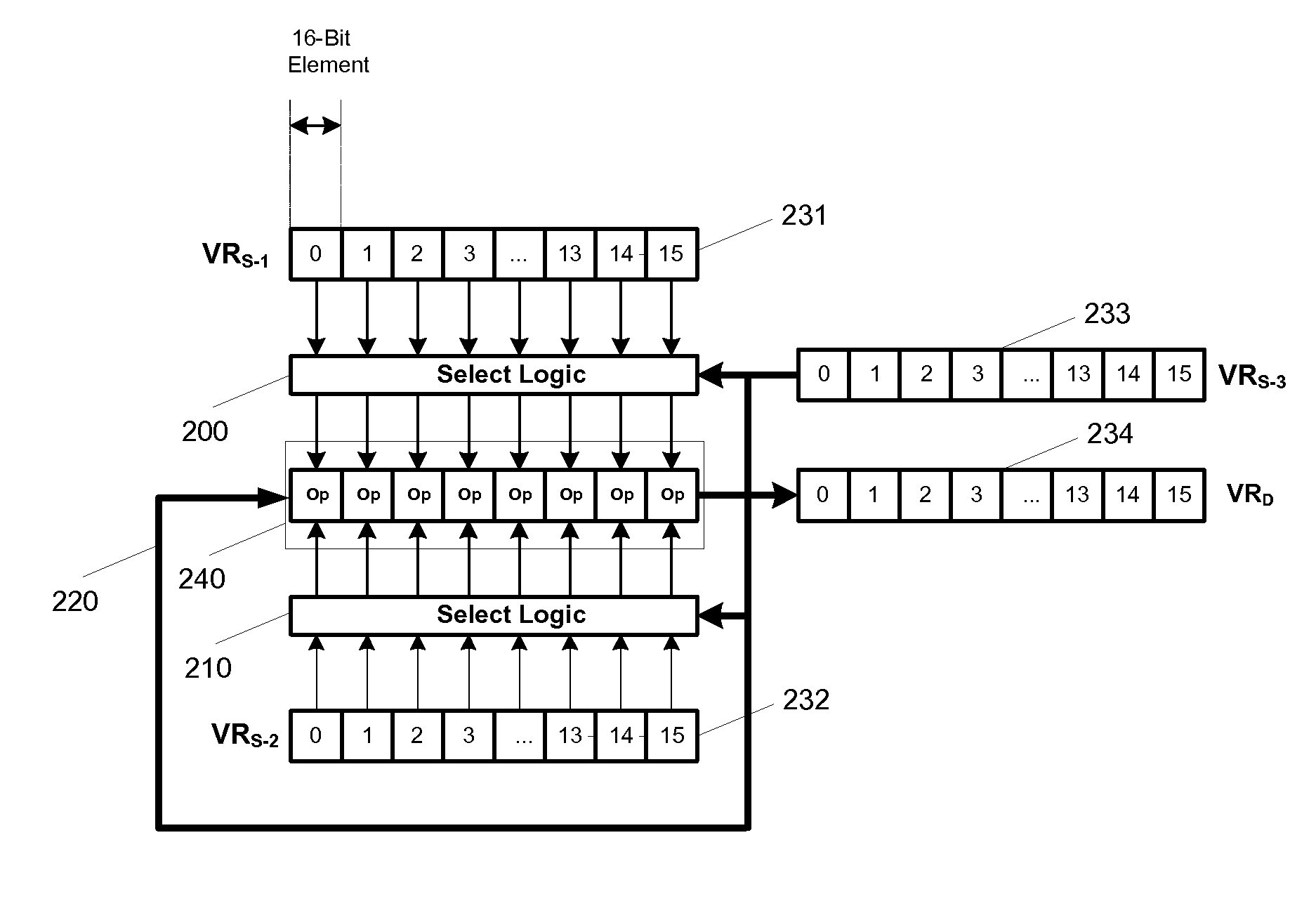
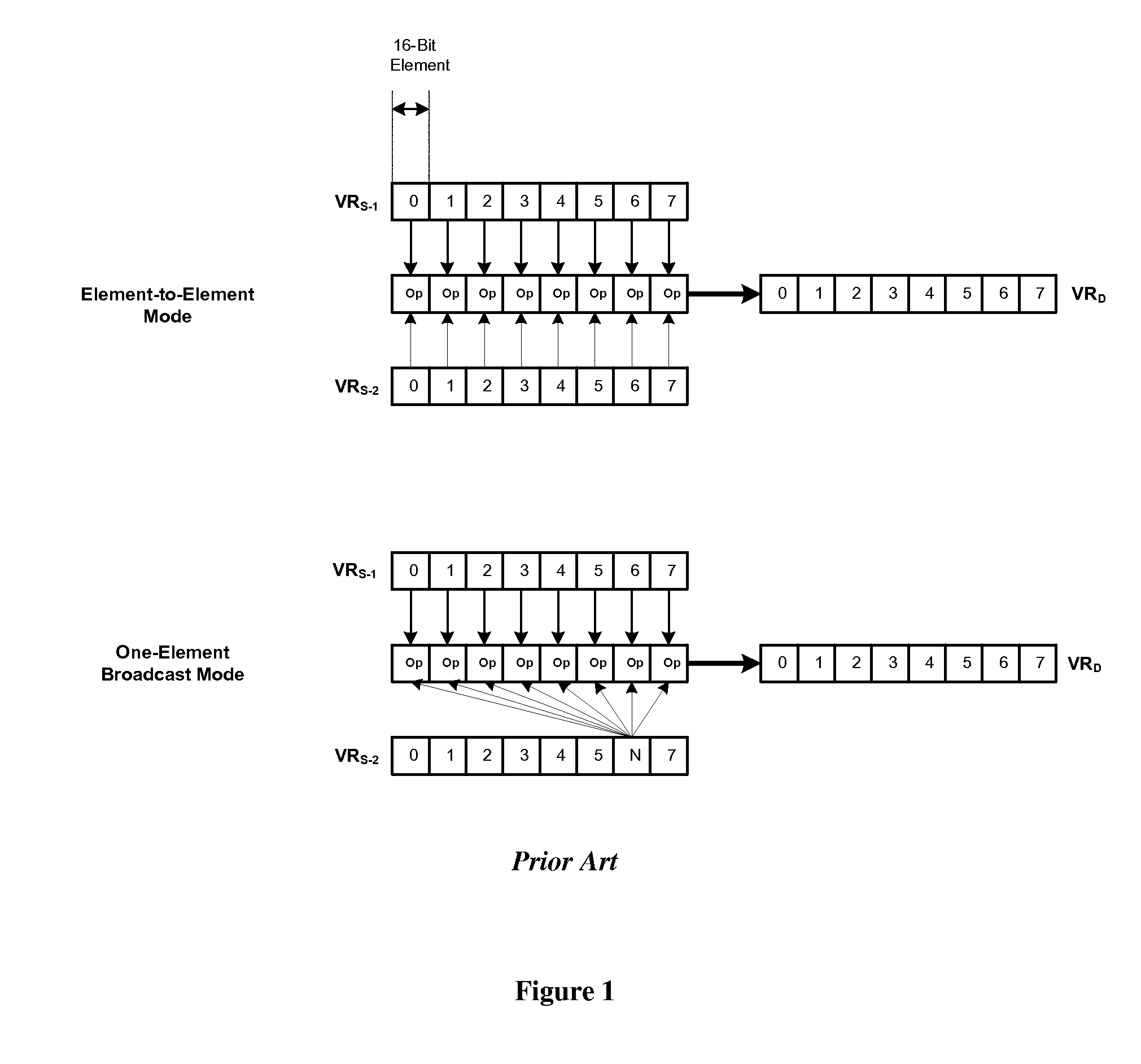
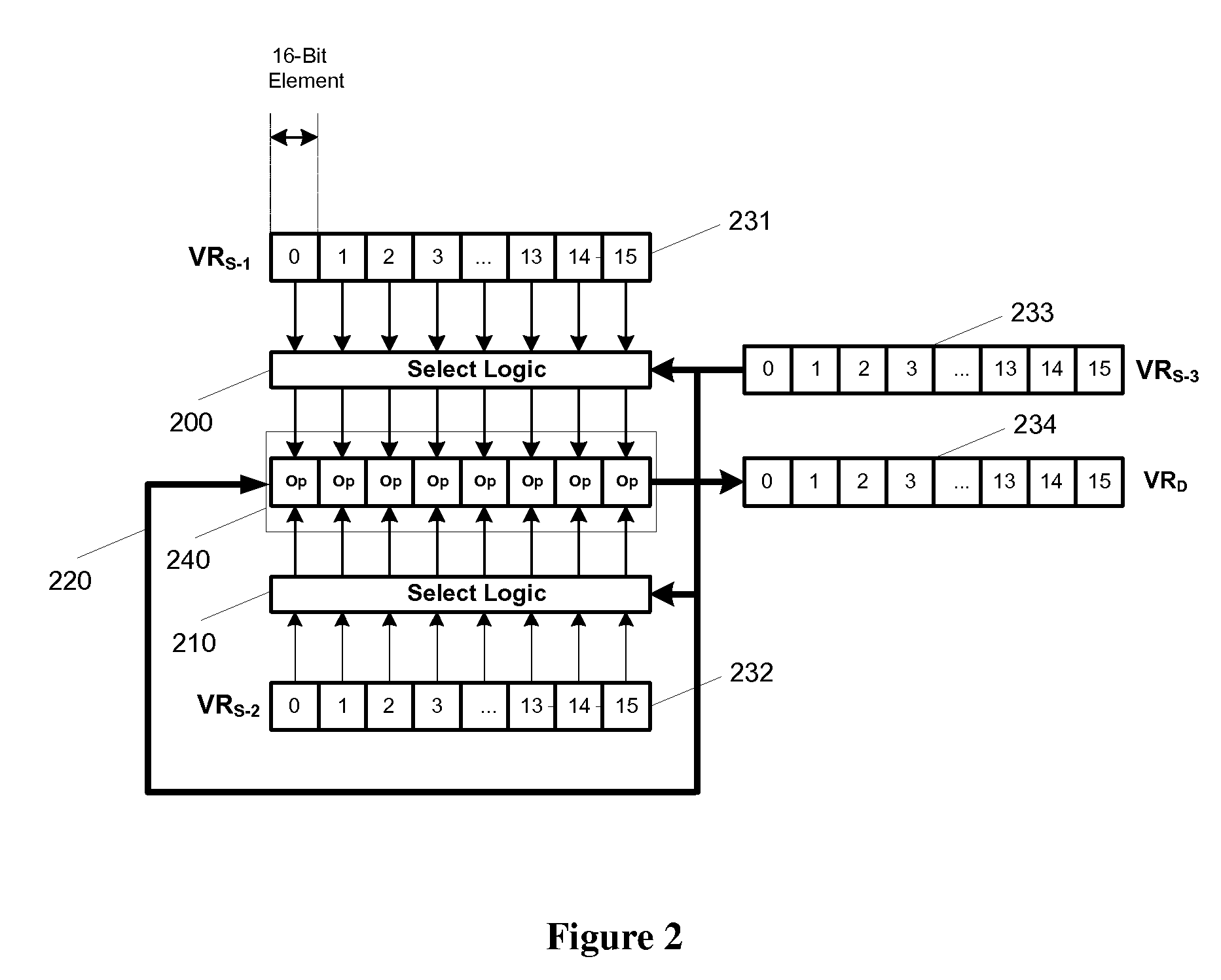
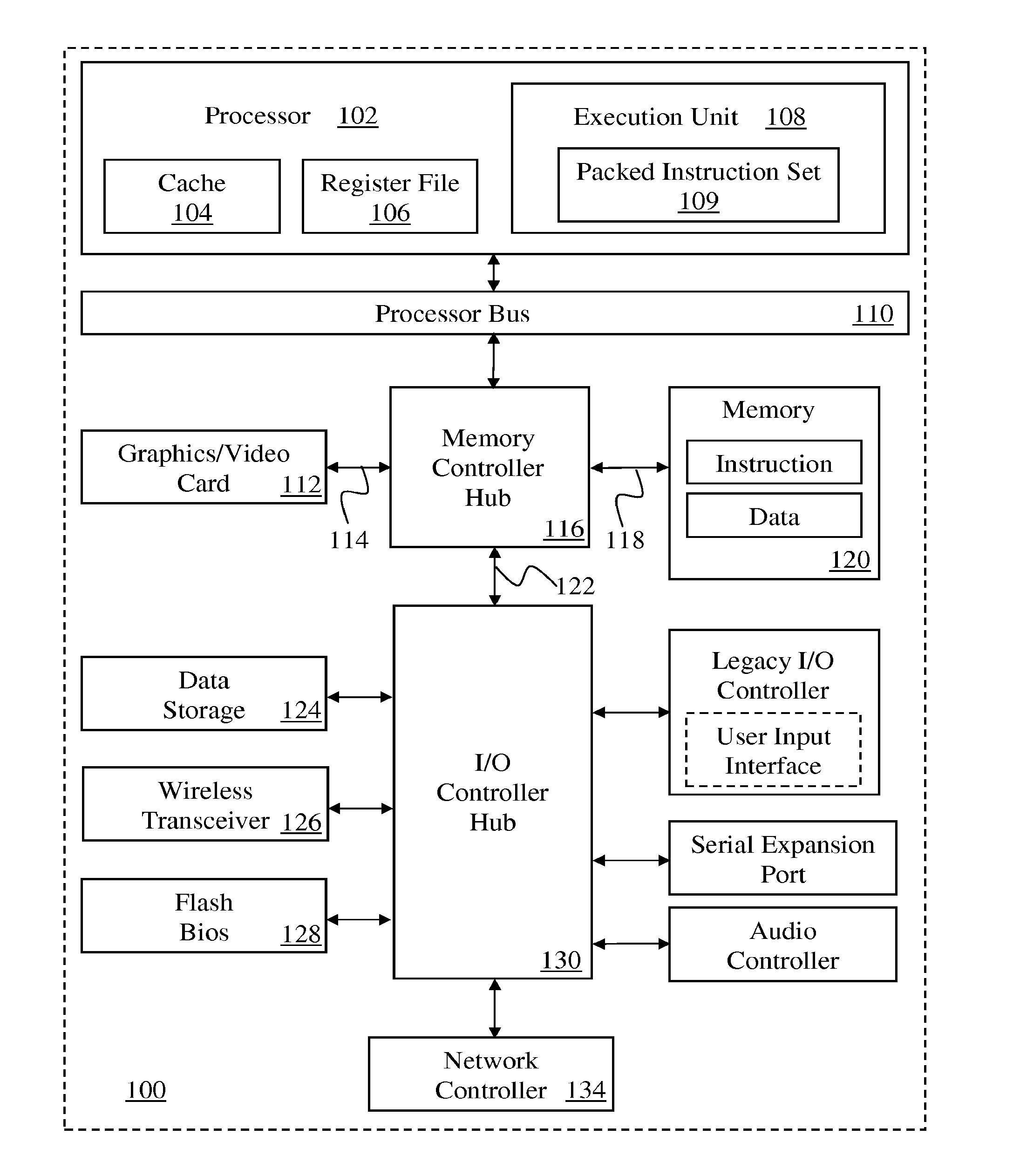
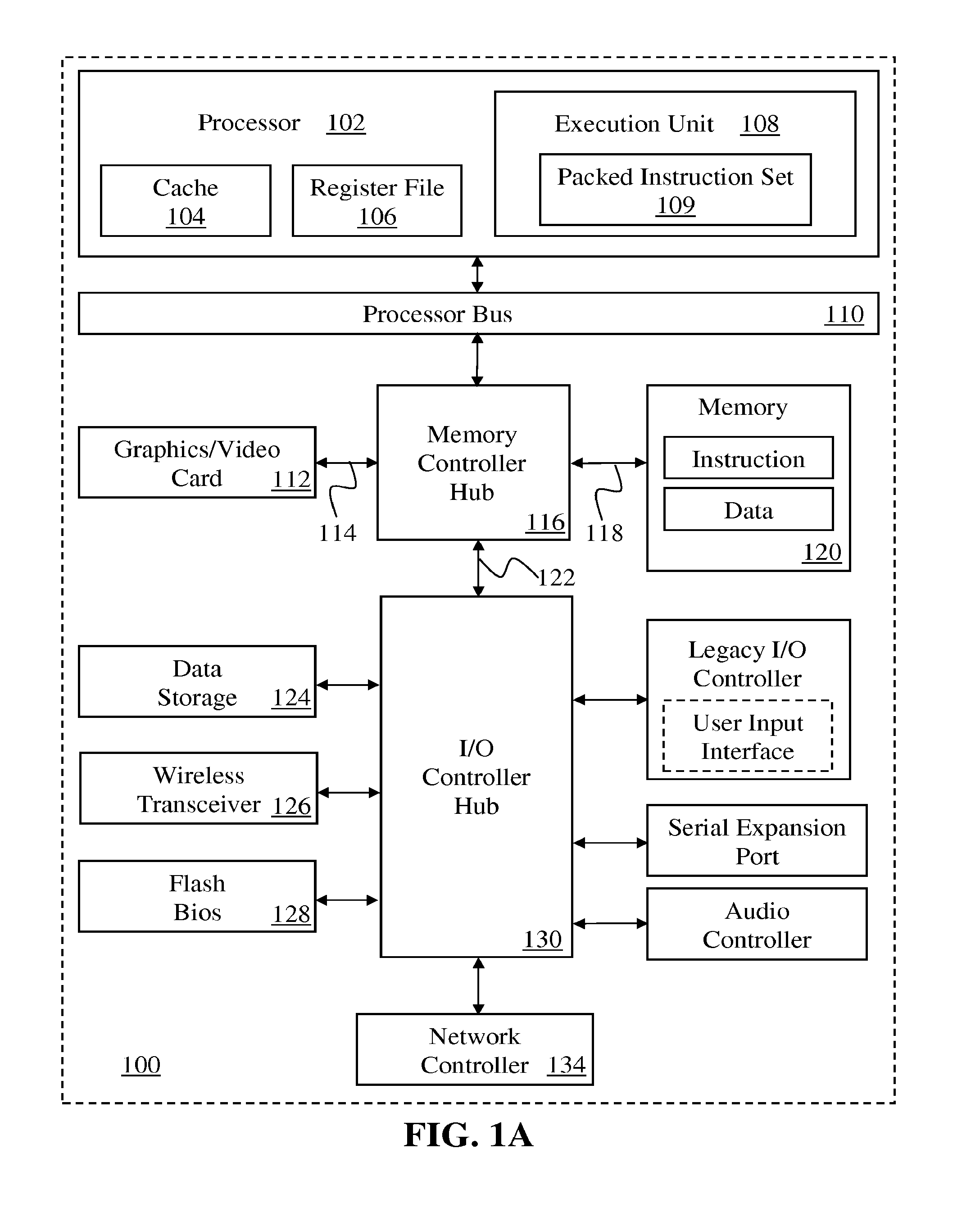
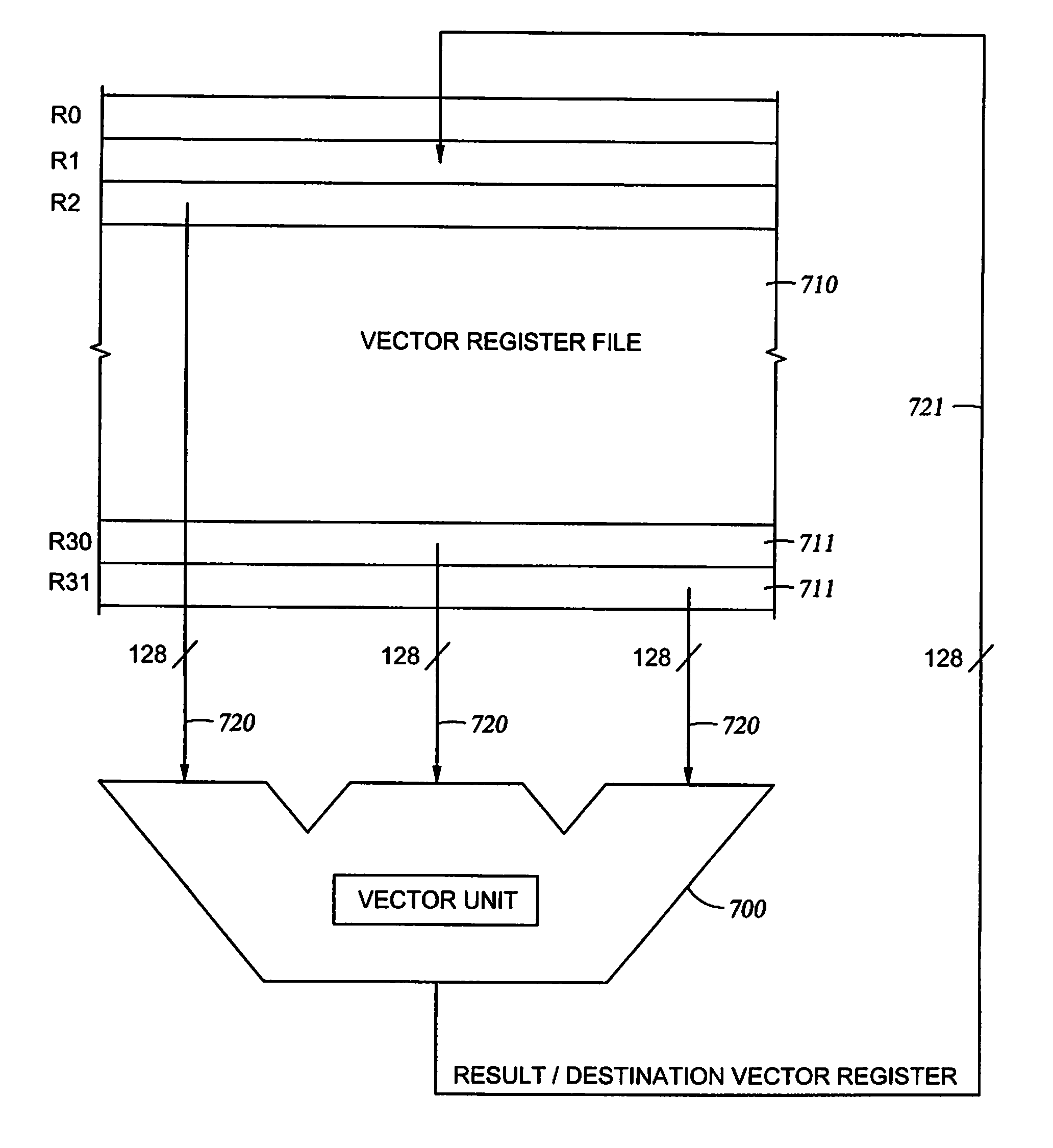
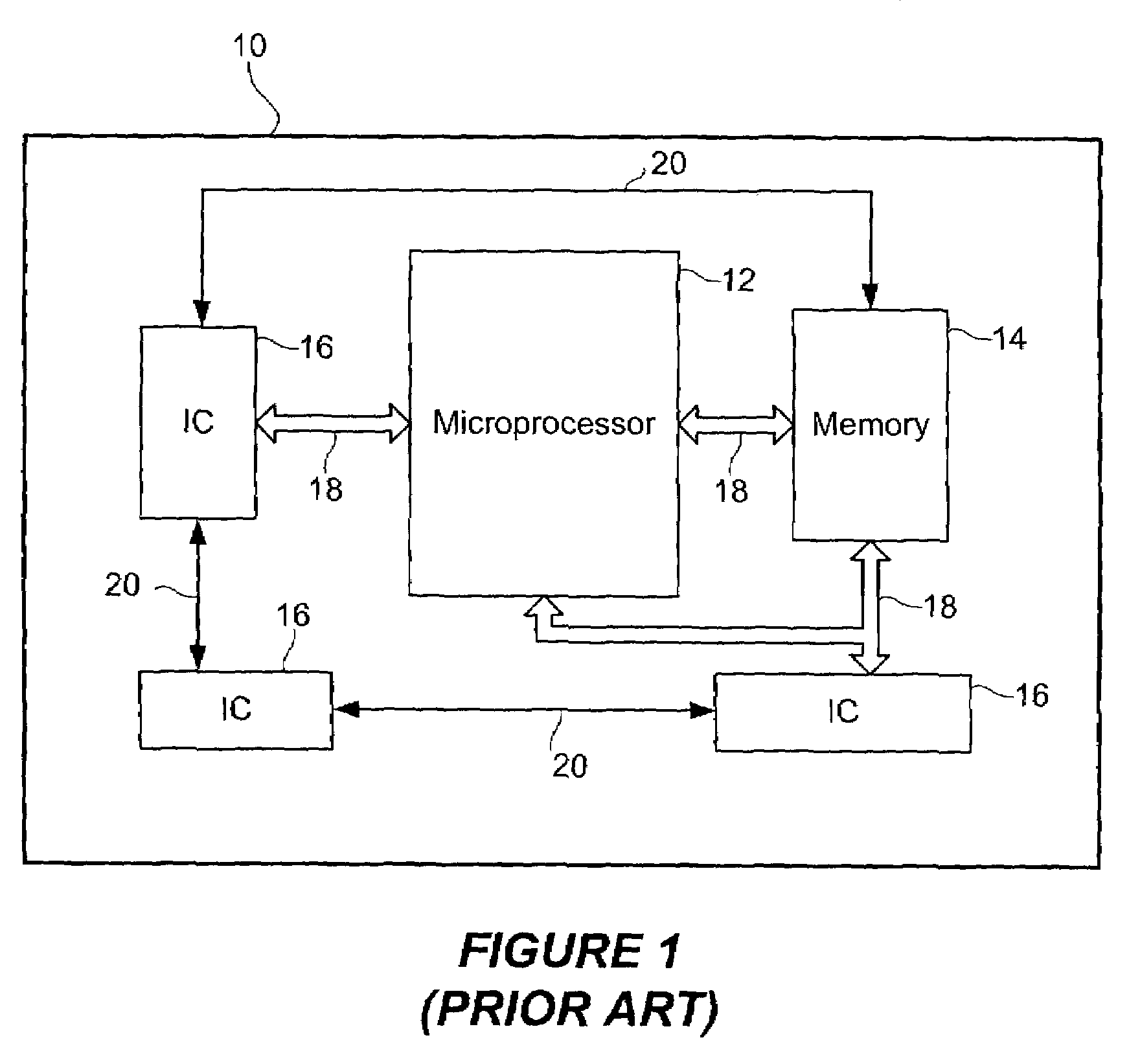
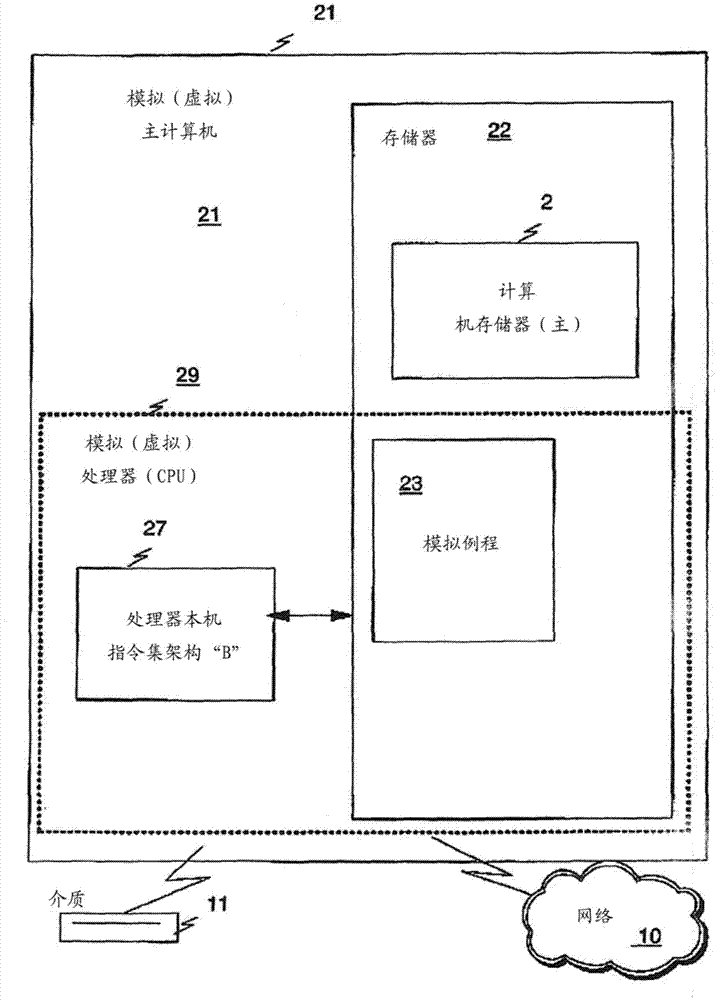
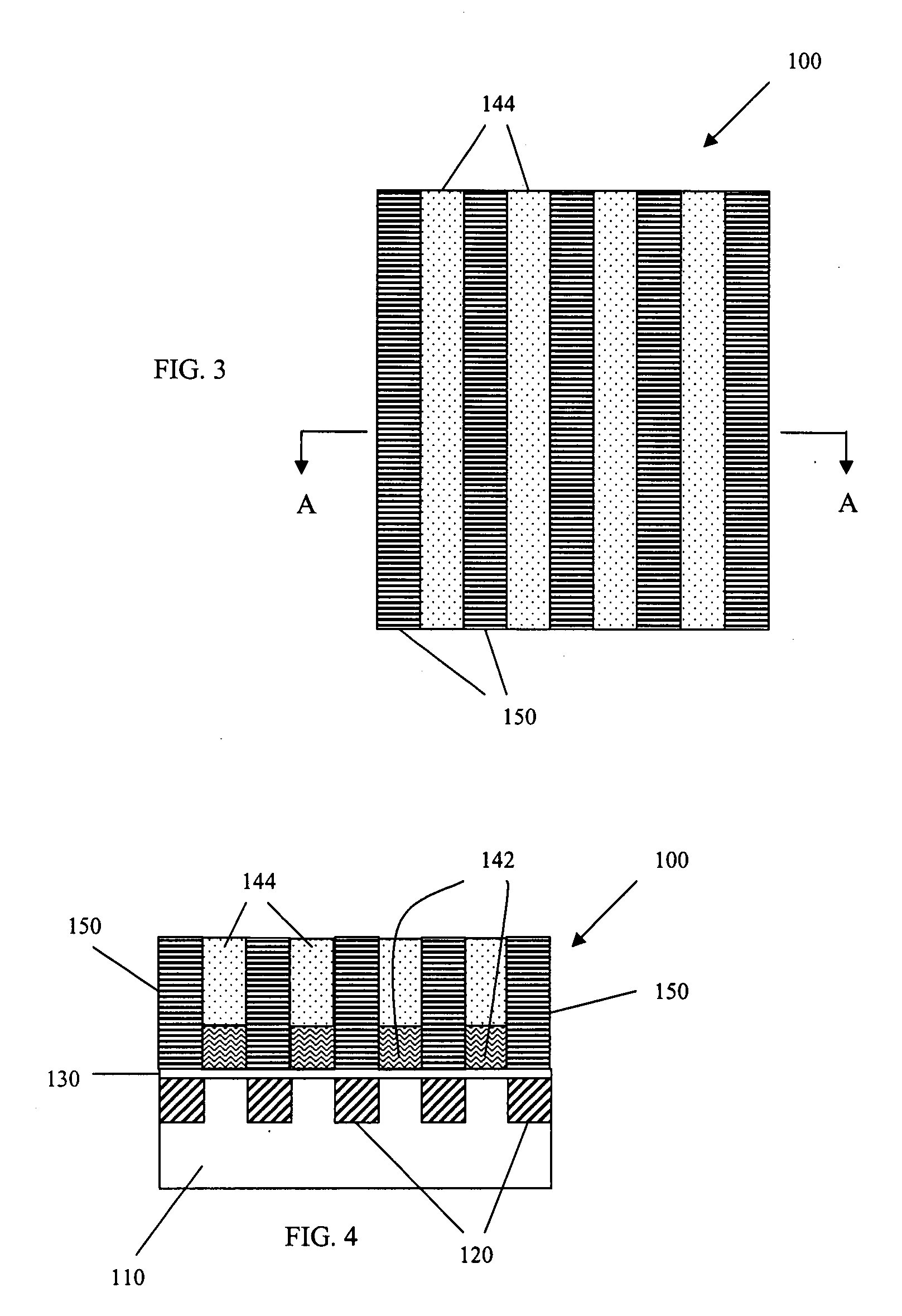
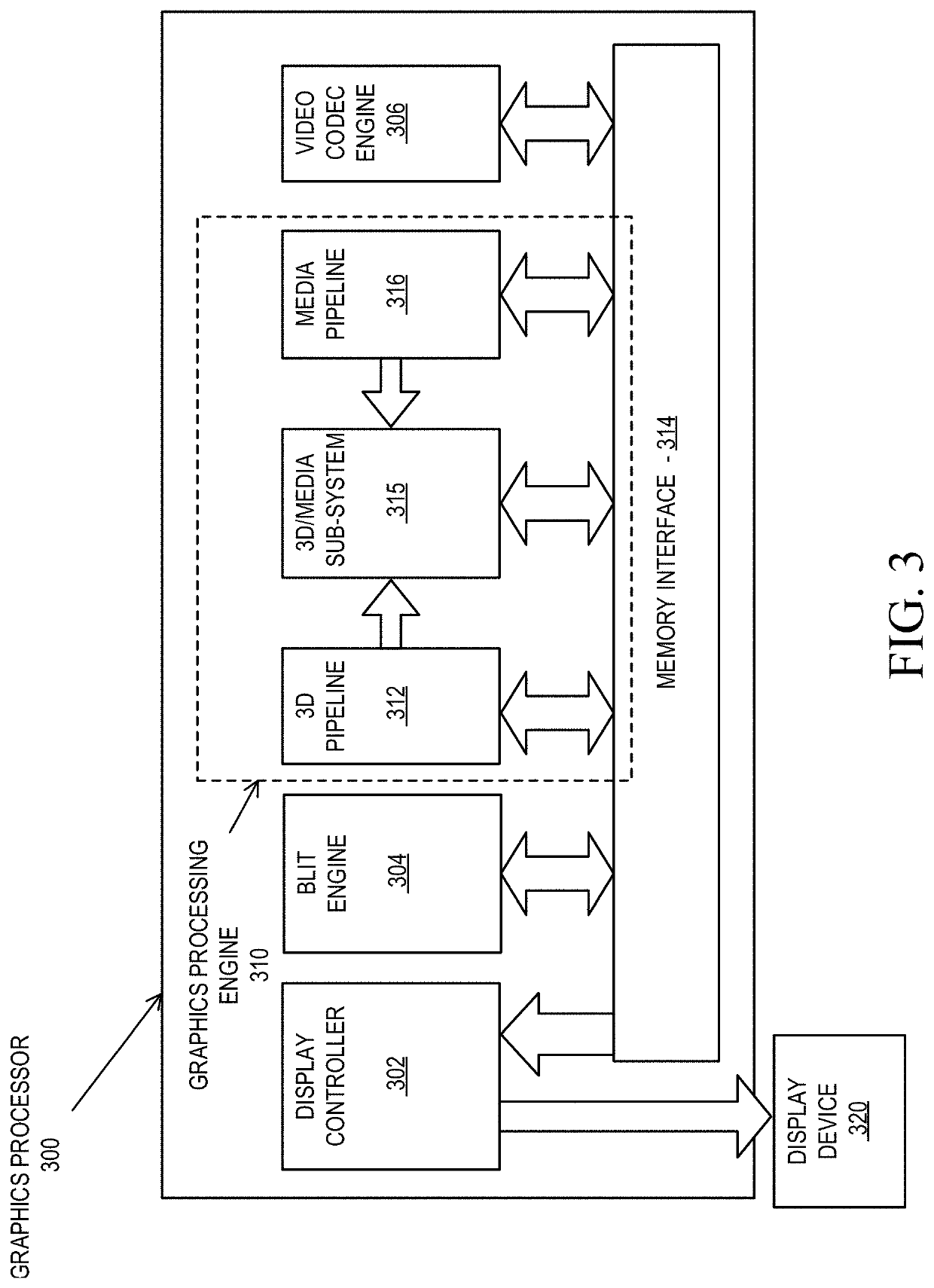
Flexible vector modes of operation for SIMD processor
InactiveUS20100274988A1General purpose stored program computerMachine execution arrangementsComputer architectureVector element
In addition to the usual modes of SIMD processor operation, where corresponding elements of two source vector registers are used as input pairs to be operated upon by the execution unit, or where one element of a source vector register is broadcast for use across the elements of another source vector register, the new system provides several other modes of operation for the elements of one or two source vector registers. Improving upon the time-costly moving of elements for an operation such as DCT, the present invention defines a more general set of modes of vector operations. In one embodiment, these new modes of operation use a third vector register to define how each element of one or both source vector registers are mapped, in order to pair these mapped elements as inputs to a vector execution unit. Furthermore, the decision to write an individual vector element result to a destination vector register, for each individual element produced by the vector execution unit, may be selectively disabled, enabled, or made to depend upon a selectable condition flag or a mask bit.
Owner:MIMAR TIBET
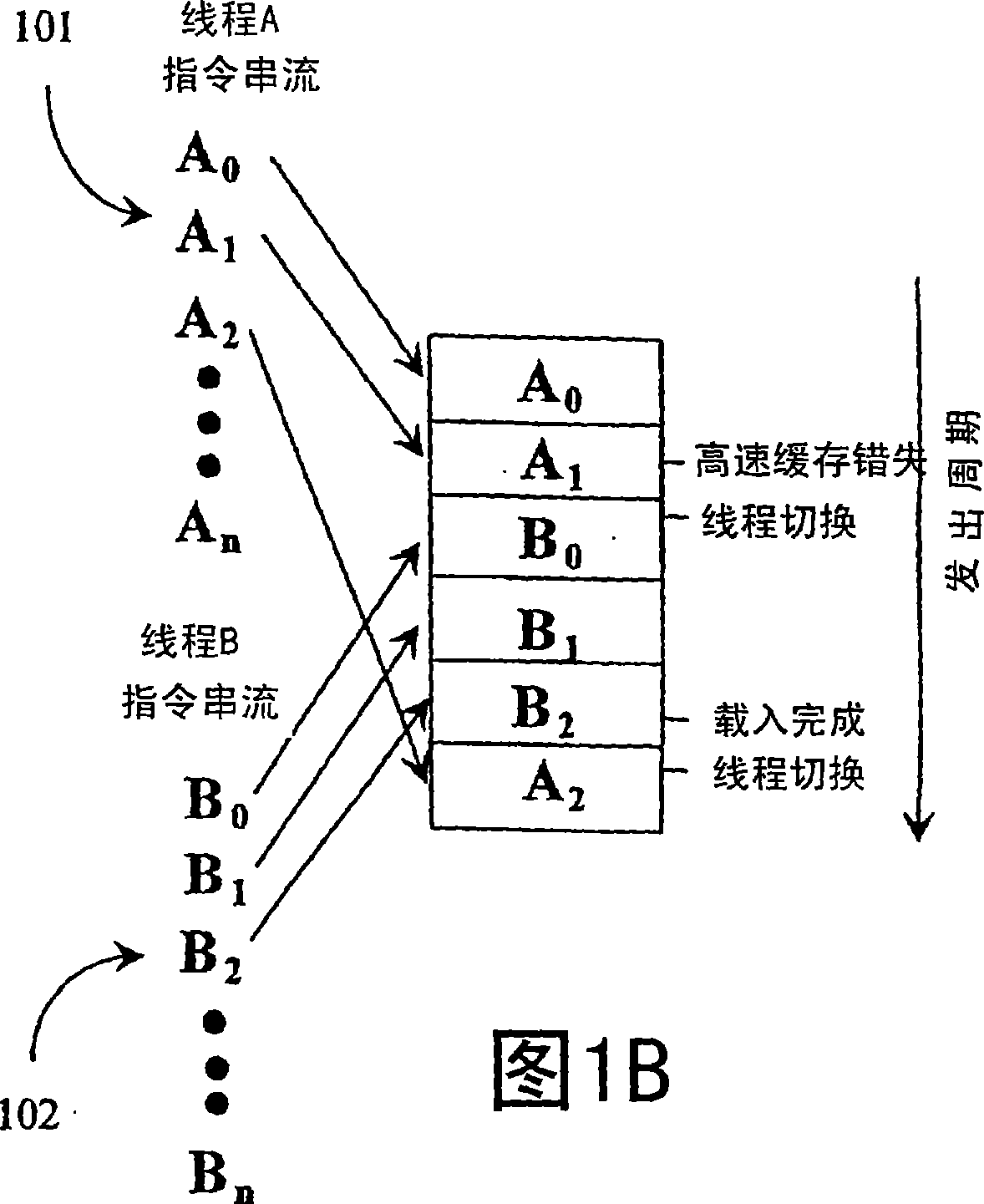
Integrated mechanism for suspension and deallocation of computational threads of execution in a processor
ActiveUS20050125795A1Valuable opcode spaceLittle overheadProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringOperandProgram Thread
A yield instruction for execution in a multithreaded microprocessor is disclosed. The yield instruction includes an operand. If the operand is zero the microprocessor terminates the program thread including the yield instruction. If the operand is −1 the microprocessor unconditionally reschedules the program thread. If the operand is a positive integer the microprocessor views the operand as a bit vector specifying one or more yield qualifier inputs, such as interrupt signals, and conditionally reschedules the thread based on the qualifier inputs and bit vector values. The microprocessor also includes a mask register that specifies a bit vector of the qualifier inputs. If the operand specifies a qualifier input not also specified in the mask register, an exception to the instruction is raised. The instruction returns a value specifying the values of the qualifier inputs qualified by the mask register value.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
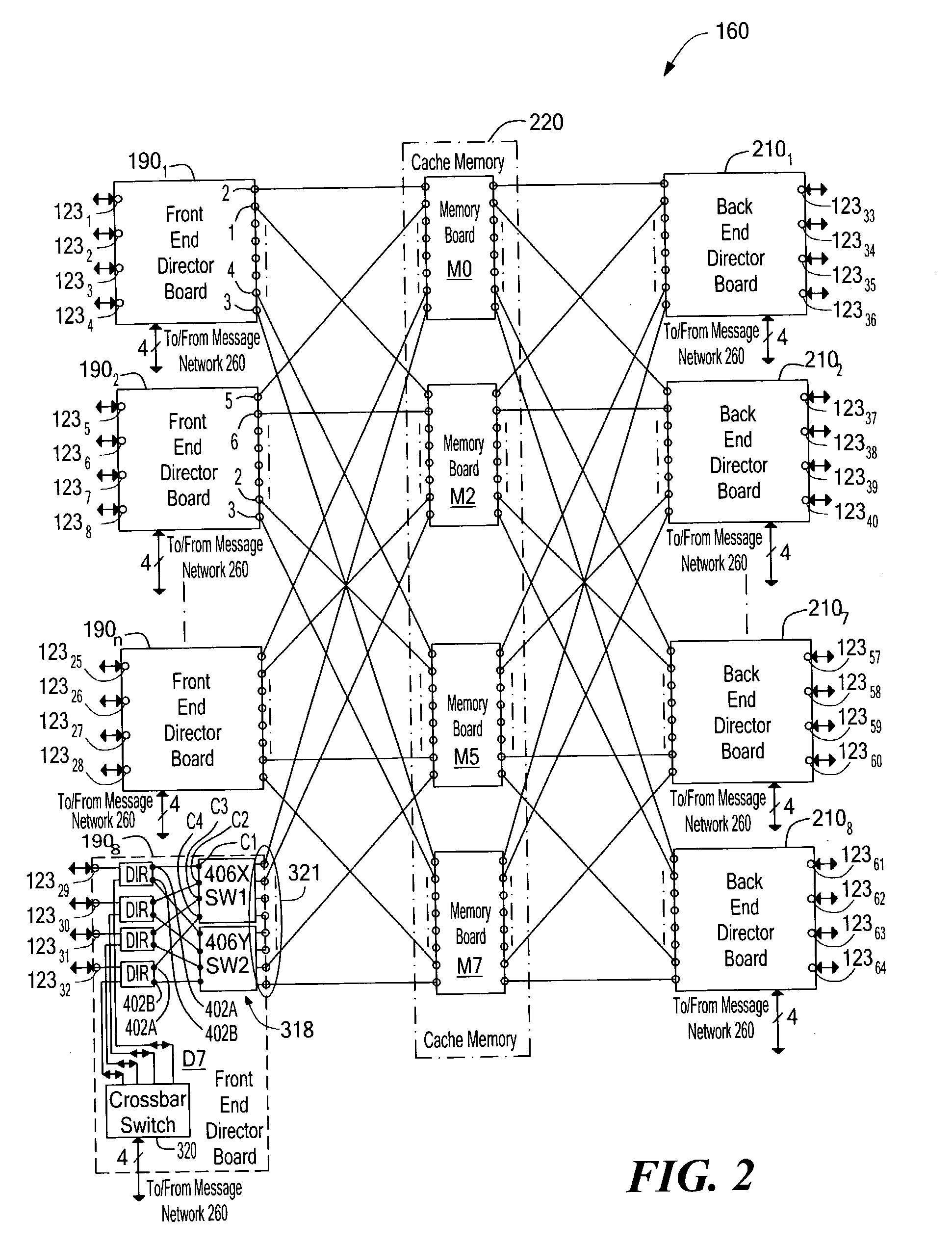
Data storage system having atomic memory operation
ActiveUS6973551B1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsData storage systemRead-modify-write
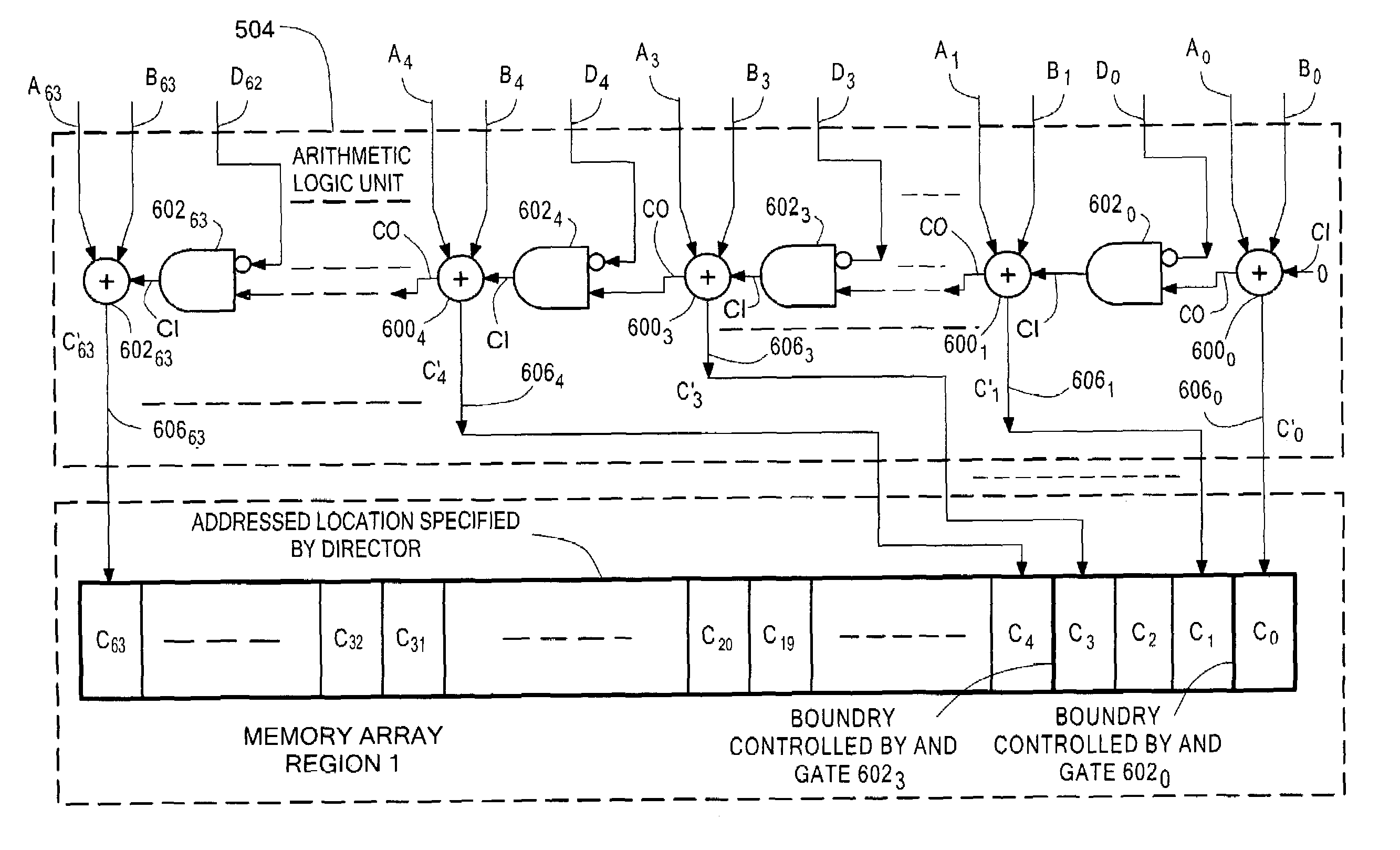
A method and system for enabling a director to perform an atomic read-modify-write operation on plural bit read data stored in a selected one of a plurality of memory locations. The method includes providing a plurality of successive full adders, each one of the full adders being associated with a corresponding one of the bits of the plural bit read data. Each one of the full adders has a summation output, a carry bit input and a carry bit output. The method includes adding in each one of the full adders: (a) a corresponding bit of plural bit input data provided by the director; (b) the corresponding one of the bits of the plural bit read data; and, (c) a carry bit fed the carry bit input from a preceding full adder. Each one of the full adders provides: (a) a carry bit on the carry output thereof representative of the most significant bit produced by the full adder; and, (b) a bit on the summation output representative of a least significant bit produced by the full adder. The bit on the summation output is stored in a corresponding bit location in the selected one of a plurality of memory locations. The method selectively couples, or inhibits coupling, the carry bit produced from one of the full adders to the carry bit input of a next successive full adder selectively in accordance with a corresponding bit of a plural bit carry bit mask provided by the director providing a full adder for each one of the bits of the plural bit read stored. The full adder has a carry bit input and a carry bit output. The method includes adding each one of a bits of plural bit input data provided by the director with a corresponding one of the bits of the plural bit read data in the provided full adder together with a carry bit fed the carry bit input of such provided full adder. The full adder provides: a carry output bit; and, a summation of the bits fed to such provided full adder to the corresponding bit location in the selected one of a plurality of memory locations. The method selectively couples, or inhibits coupling, a carry bit produced by one full adder provided for a lower order bit of the plural bit read data to the carry bit input of a second full adder provided by for next, successive higher order bit of the plural bit read data selectively in accordance with one of a plurality of bits of a carry bit mask provided by the director.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
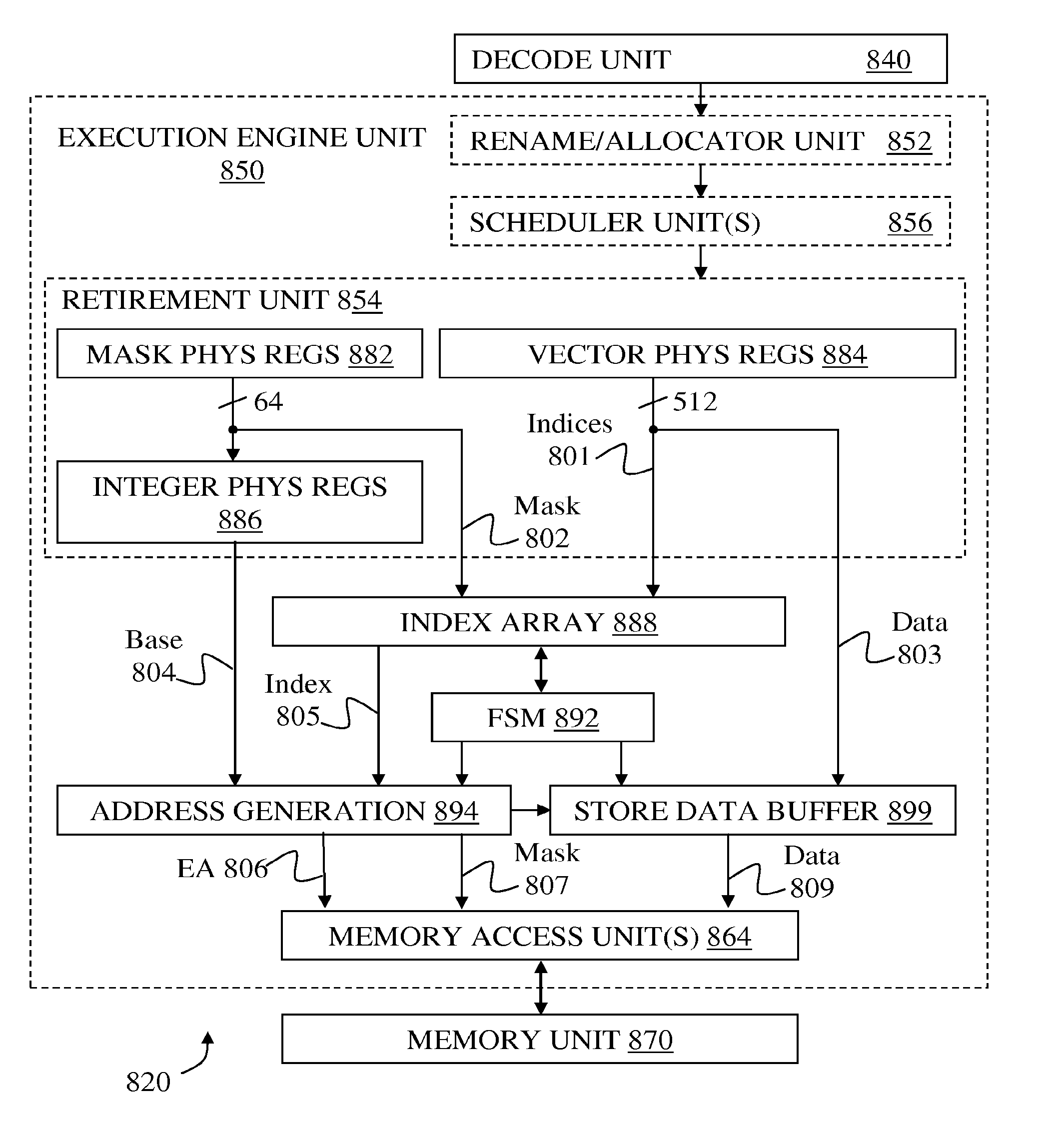
Scatter using index array and finite state machine
ActiveUS20150074373A1Instruction analysisArchitecture with single central processing unitMicro-operationFinite-state machine
Methods and apparatus are disclosed using an index array and finite state machine for scatter / gather operations. Embodiment of apparatus may comprise: decode logic to decode scatter / gather instructions and generate micro-operations. An index array holds a set of indices and a corresponding set of mask elements. A finite state machine facilitates the scatter operation. Address generation logic generates an address from an index of the set of indices for at least each of the corresponding mask elements having a first value. Storage is allocated in a buffer for each of the set of addresses being generated. Data elements corresponding to the set of addresses being generated are copied to the buffer. Addresses from the set are accessed to store data elements if a corresponding mask element has said first value and the mask element is changed to a second value responsive to completion of their respective stores.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Instruction and logic to provide vector scatter-op and gather-op functionality
ActiveUS20140201498A1Program control using stored programsInstruction analysisMemory addressIndex register
Instructions and logic provide vector scatter-op and / or gather-op functionality. In some embodiments, responsive to an instruction specifying: a gather and a second operation, a destination register, an operand register, and a memory address; execution units read values in a mask register, wherein fields in the mask register correspond to offset indices in the indices register for data elements in memory. A first mask value indicates the element has not been gathered from memory and a second value indicates that the element does not need to be, or has already been gathered. For each having the first value, the data element is gathered from memory into the corresponding destination register location, and the corresponding value in the mask register is changed to the second value. When all mask register fields have the second value, the second operation is performed using corresponding data in the destination and operand registers to generate results.
Owner:INTEL CORP
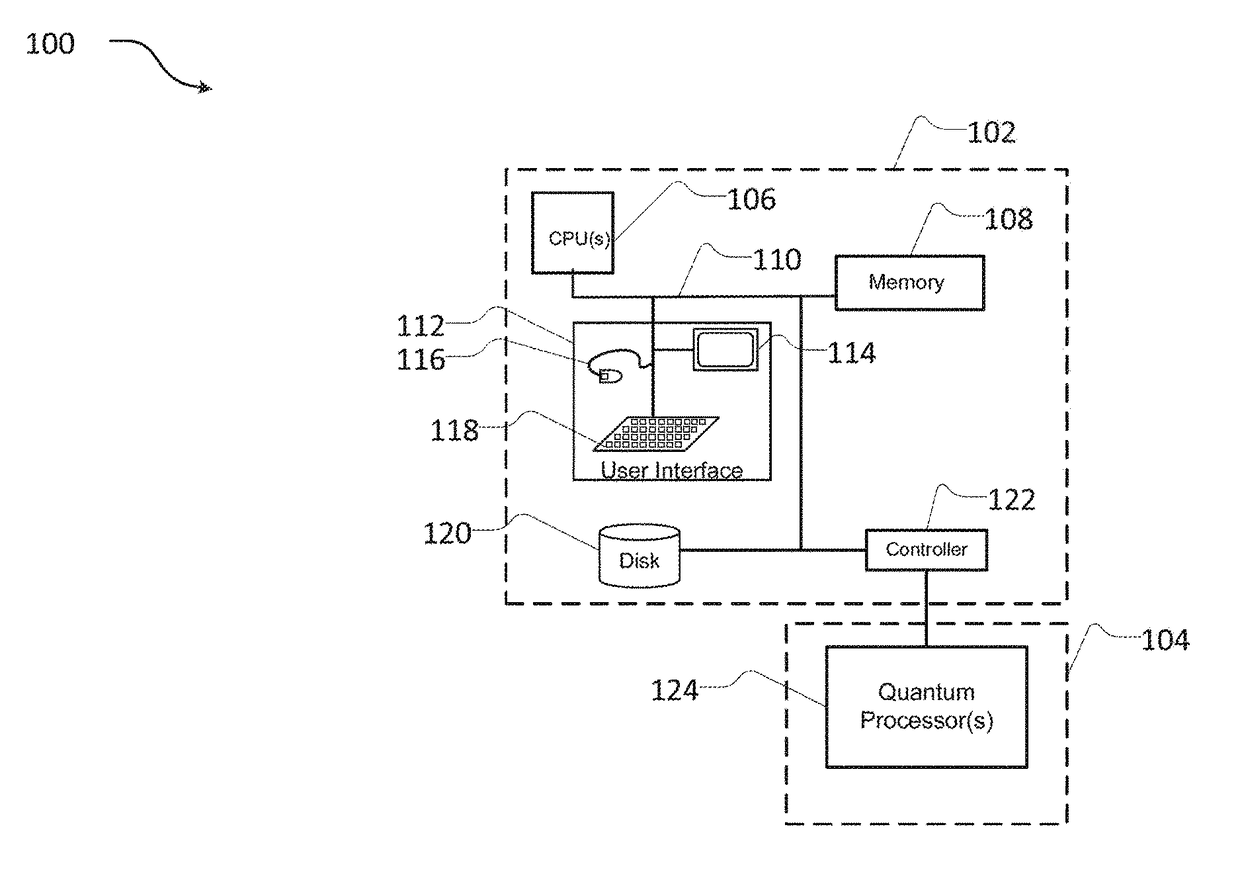
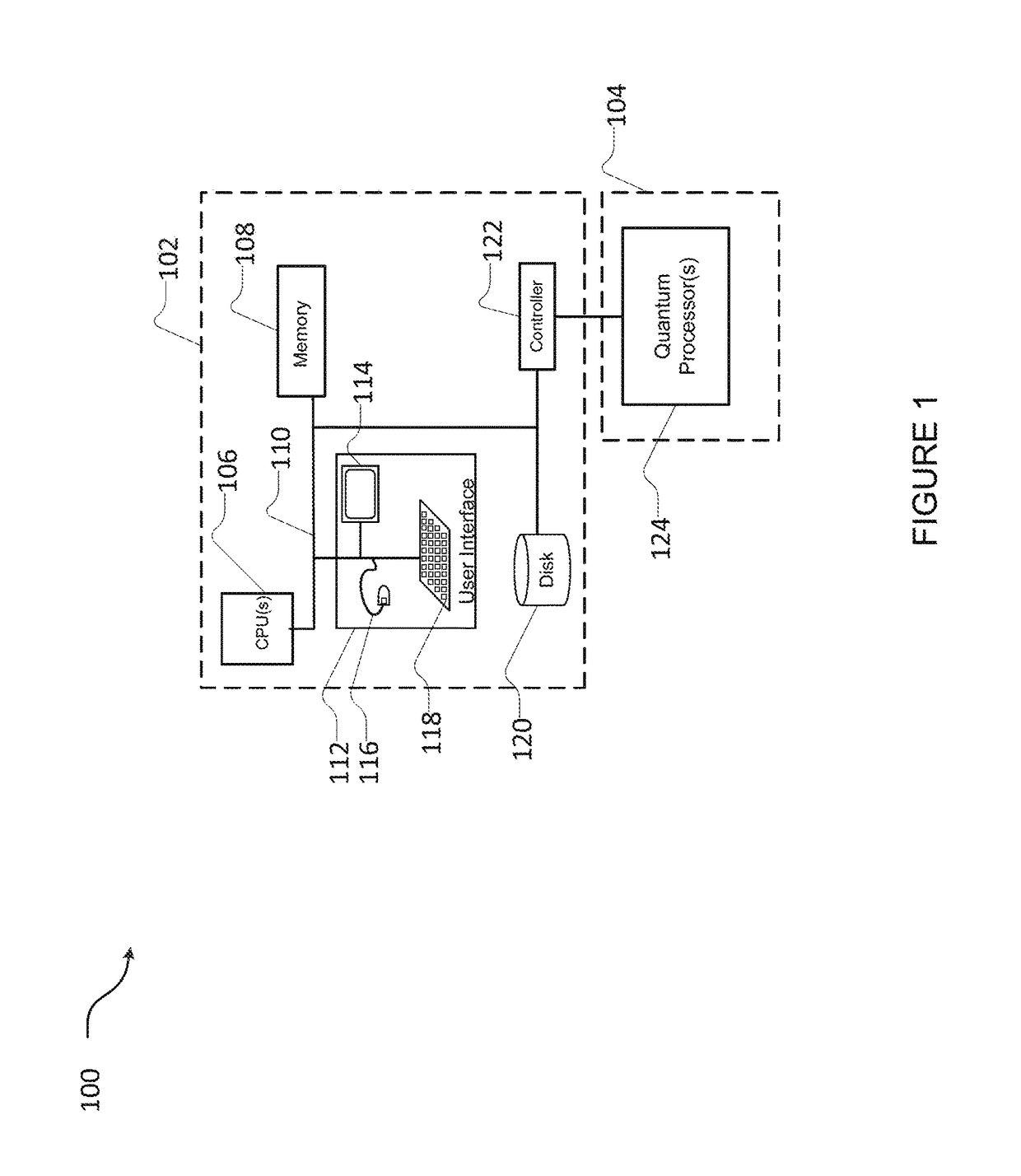
Systems and methods for embedding problems into an analog processor
ActiveUS20170300817A1Reduced strengthQuantum computersMachine learningAnalog processorGenetic algorithm
Generate an automorphism of the problem graph, determine an embedding of the automorphism to the hardware graph and modify the embedding of the problem graph into the hardware graph to correspond to the embedding of the automorphism to the hardware graph. Determine an upper-bound on the required chain strength. Calibrate and record properties of the component of a quantum processor with a digital processor, query the digital processor for a range of properties. Generate a bit mask and change the sign of the bias of individual qubits according to the bit mask before submitting a problem to a quantum processor, apply the same bit mask to the bit result. Generate a second set of parameters of a quantum processor from a first set of parameters via a genetic algorithm.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Single Precision Vector Permute Immediate with "Word" Vector Write Mask
The present invention is generally related to the field of image processing, and more specifically to an instruction set for processing images. Vector processing may involve performing a plurality of permute operations to arrange vector operands in desired locations of a register prior to performing vector operation, for example, a cross product. The permute instructions may be dependent on one another and may require the use of temporary registers. Embodiments of the invention provide a permute instruction wherein a mask field may be used to specify a particular location of a target register in which to transfer data, thereby reducing the number of instructions for arranging data, reducing dependencies between instructions, and the usage of temporary registers.
Owner:BEIJING PIANRUOJINGHONG TECH CO LTD
Error detection for data storage and transmission
A check sum calculation on data coded with a Reed-Solomon error correcting code is performed by applying a byte based polynomial remaindering process to data bytes. The polynomial is X2+Xalpha2+alpha, over GF (28), where alpha is the primitive element GF (28) used to define redundancy coding for individual data groups. The roots of the polynomial used in the polynomial remaindering process differ from the roots of a generator polynomial of the Reed-Solomon error correcting code. The polynomial remaindering process is performed with a sub function mask containing the same mask function as used in defining redundancy coding for a data group or groups. The data group or groups are redundance coded using a Reed-Solomon code over GF (28)
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Apparatus and method for detecting identical elements within a vector register
InactiveUS20140089634A1Instruction analysisGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerTheoretical computer science
An apparatus, system and method are described for identifying identical elements in a vector register. For example, a computer implemented method according to one embodiment comprises the operations of: reading each active element from a first vector register, each active element having a defined bit position within the first vector register; reading each element from a second vector register, each element having a defined bit position within the second vector register corresponding to a bit position of a current active element in the first vector register; reading an input mask register, the input mask register identifying active bit positions in the second vector register for which comparisons are to be made with values in the first vector register, the comparison operations comprising: comparing each active element in the second vector register with elements in the first vector register having bit positions preceding the bit position of the current active element in the second vector register; and setting a bit position in an output mask register equal to a true value if all of the preceding bit positions in the first vector register are equal to the bit in the current active bit position in the second vector register.
Owner:INTEL CORP
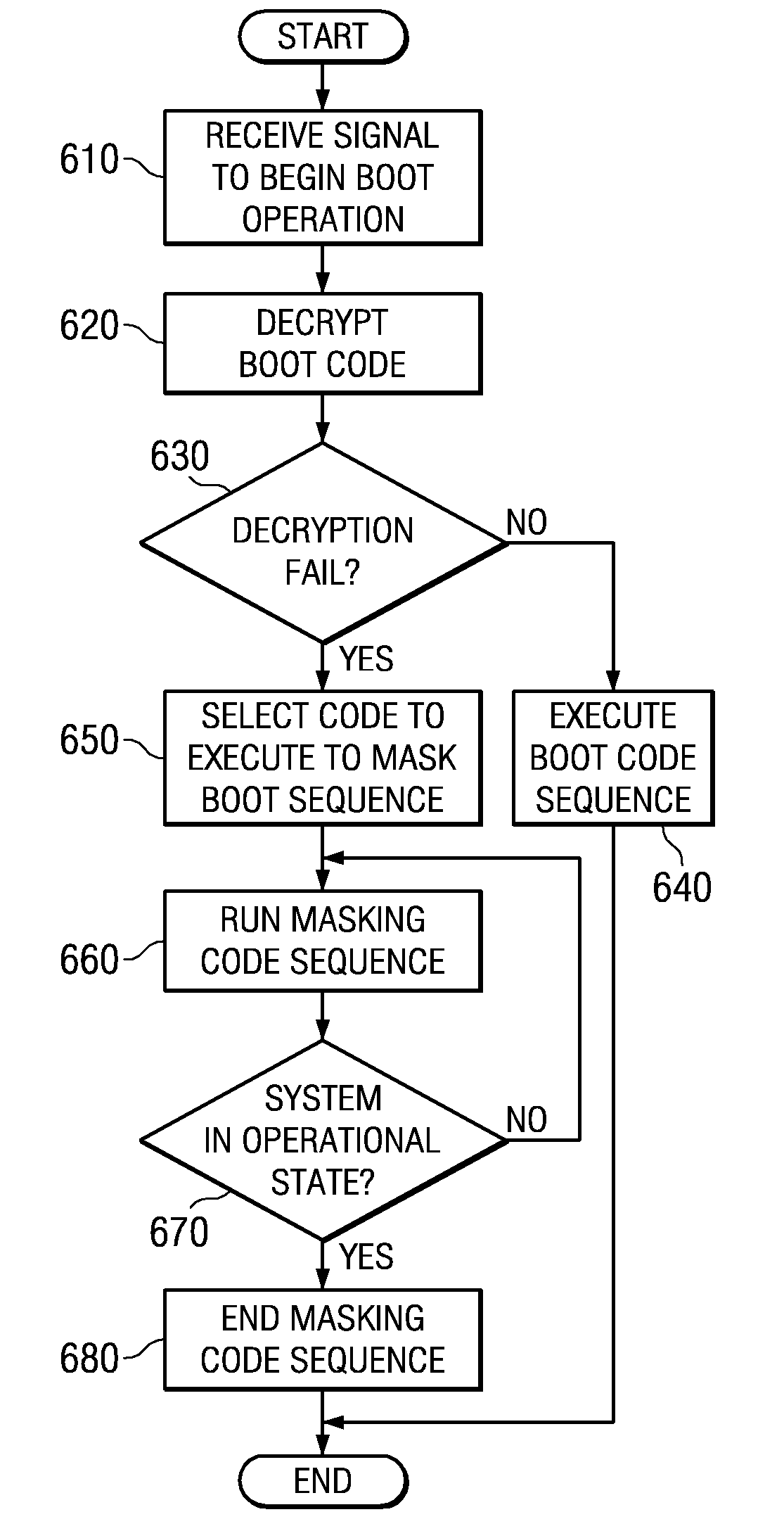
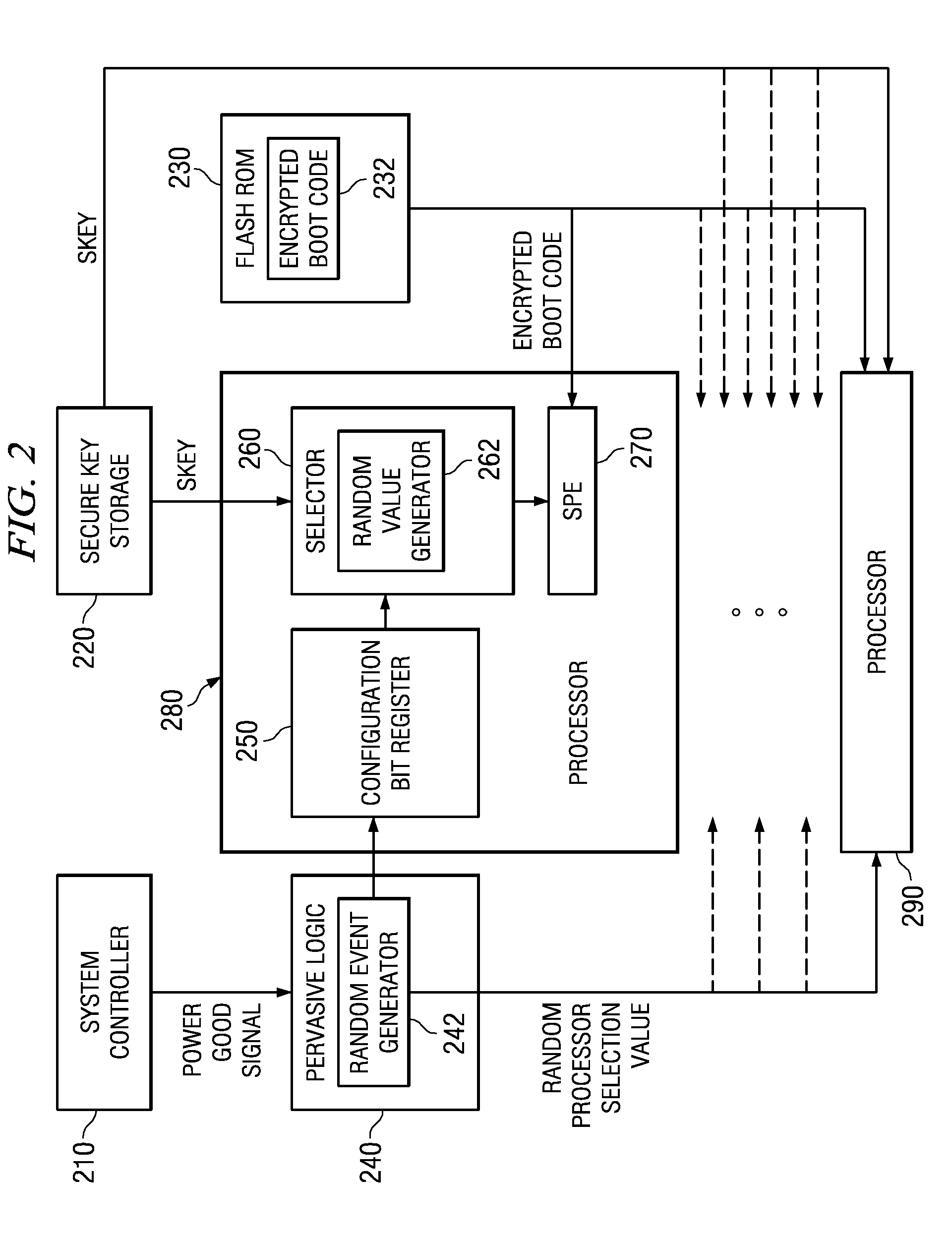
System and method for masking a boot sequence by running different code on each processor
InactiveUS20070288739A1Complete security measuresIncrease the number ofDigital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsMulti processorParallel computing
A system and method for masking a boot sequence by running different code on each processor of a multiprocessor system are provided. With the system and method, one of the processors of a multiprocessor system is chosen to be a boot processor. The other processors of the multiprocessor system execute masking code that generates electromagnetic and / or thermal signatures that mask the electromagnetic and / or thermal signatures of the actual boot processor. The masking code executed by each of the non-boot processors may be different from each other and may be randomly selected from a plurality of masking code sequences stored in a masking code storage device. Each execution of masking code on each of the non-boot processors may generate a different electromagnetic and / or thermal signature such that none of the processors appear to be unique from an external monitoring perspective.
Owner:IBM CORP
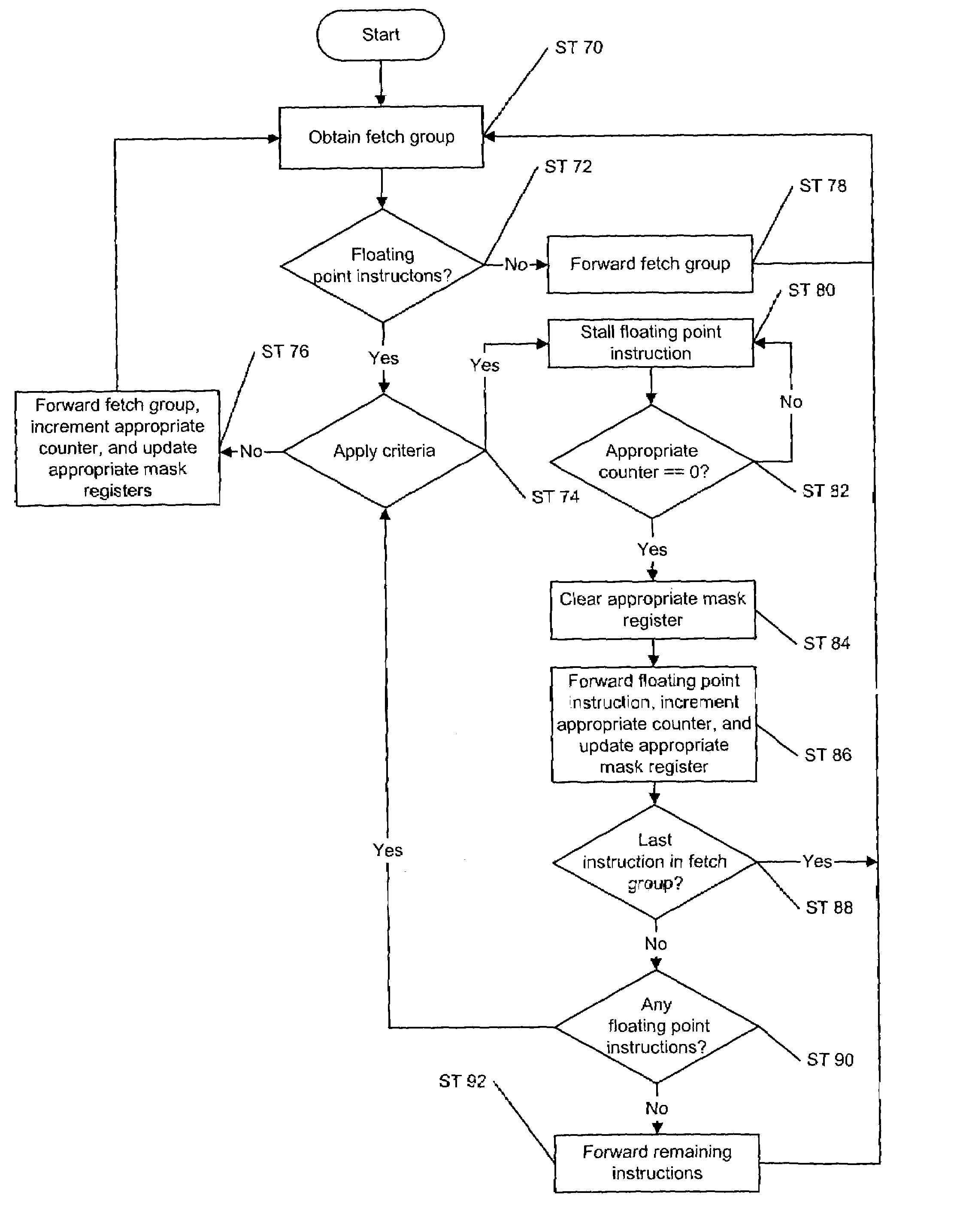
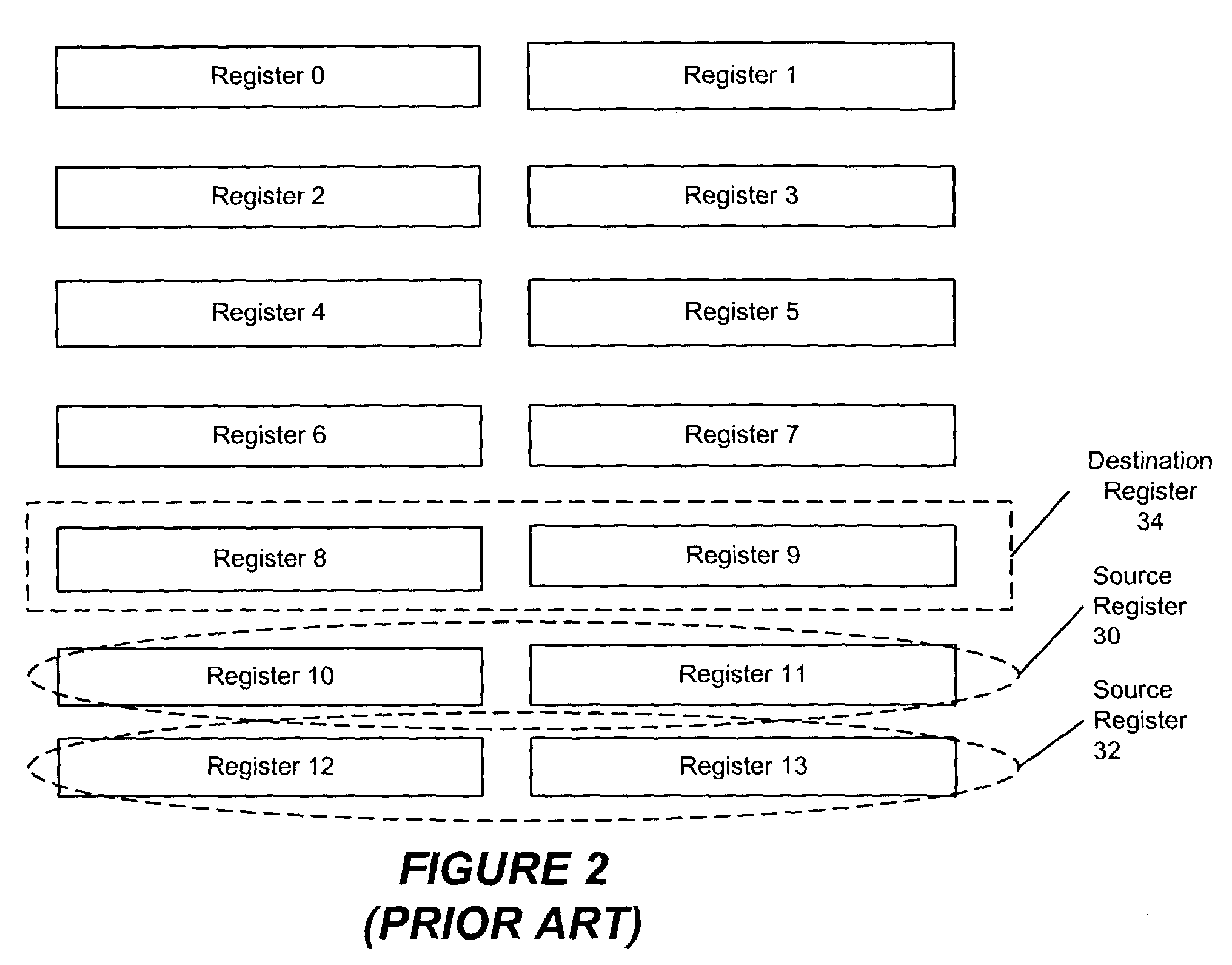
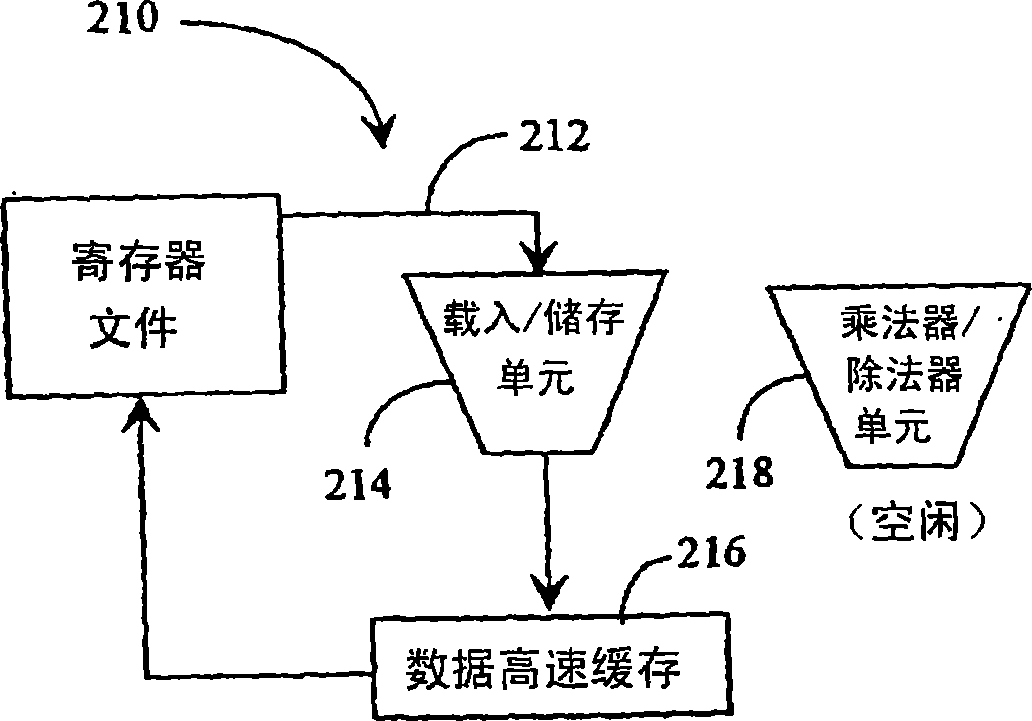
Method and a system for using same set of registers to handle both single and double precision floating point instructions in an instruction stream
ActiveUS7191316B2Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionProcessing InstructionProcessor register
A system for handling a plurality of single precision floating point instructions and a plurality of double precision floating point instructions that both index a same set of registers is provided. The system comprises a decode unit arranged to decode, stall, and forward at least one of the plurality of single precision and at least one of the plurality of double precision floating point instructions in a fetch group. The decode unit includes a first counter arranged to increment for each of the plurality of single precision floating point instructions forwarded down a pipeline; a second counter arranged to increment for each of the plurality of double precision floating point instructions forwarded down the pipeline; a first mask register and a second mask register. The first mask register is updated by each of the single precision floating point instructions forwarded and the second mask register is updated by each of the double precision floating point instructions forwarded.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Fast building of masks for use in incremental printing
InactiveUS6542258B1Digitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersImaging qualityDeterminism
A program with complete conditions for a usable mask yields a unitary mask, each try. One mask pattern is used throughout an image, but may be "tiled". Preferably the program, for given mask position, expresses favorability of several candidate pass numbers as a "neighborhood constraint" in the form of a weight; distills the weights into one weight for each pass number; based on that, chooses a number for the position; and iterates for all positions. Many preferences are very useful, e.g. automatically balancing randomness vs. determinism, and several generalized relative notations. Another invention facet uses an input text file of mask constraints; a program reads constraints from the file, applies them, forms a mask and stores / uses it. Another reprocesses a mask for best image quality, fixing its own imperfections of first-round mask forming.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Apparatus and method for conversion of data between different formats
InactiveUS6411395B1Code conversionTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsData transformationHeuristic
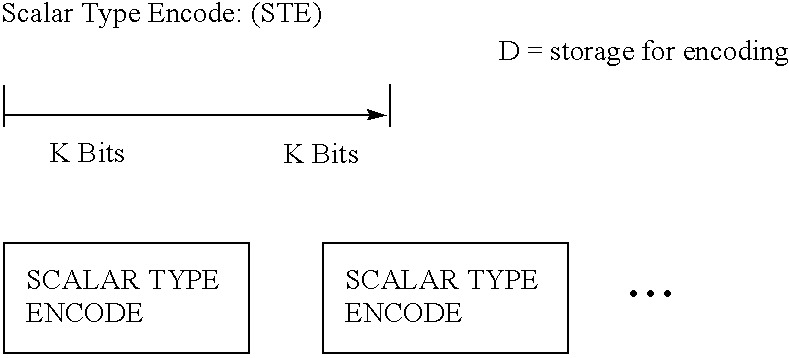
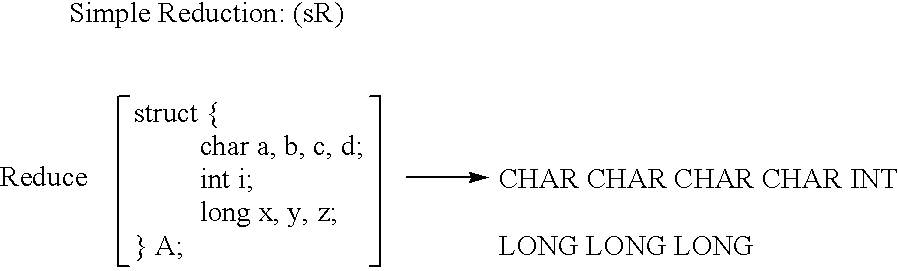
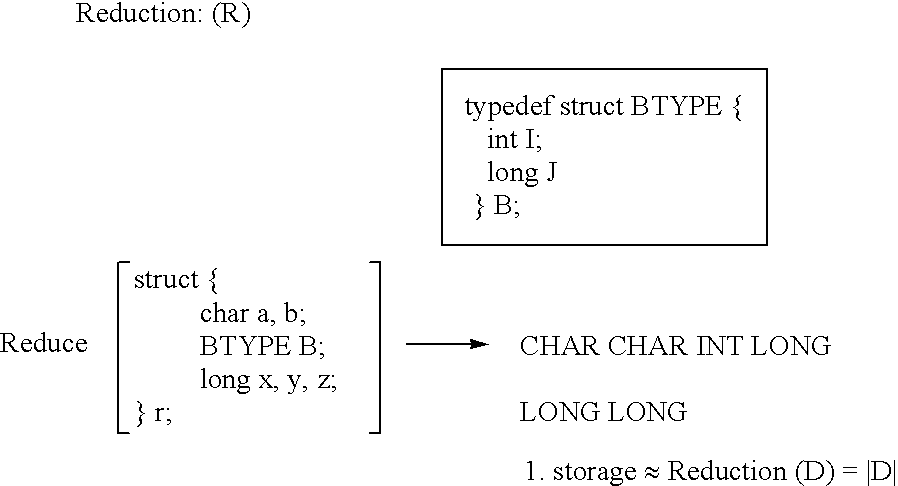
Apparatus and method for performing hierarchial type mask encoding and data transformation includes locating a data source, loading the data source into a temporary storage, encoding heuristics for buffer transformation, and delivery of data for transformation and scalar type encoding, reduction, compression, iteration, type extension and versioning if required.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for masking arbitrary boolean functions
ActiveUS20090116644A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsBoolean functionSide channel attack
A method and system for protecting an arbitrary Boolean function of arbitrary number of variables, N, including in a computing device, if N=1, protecting one or more definitions of the arbitrary Boolean function by applying a predetermined masking algorithm, if N>1, reiteratively defining the arbitrary Boolean function of number of variables, N, in terms of intermediate functions, G and H, of a fewer number of variables, N−M, where M<N, until N−M=1, applying the predetermined masking algorithm for to the two or more intermediate functions, G and H, and combining the masked intermediate functions G and H according to a predetermined scheme to generate a masked arbitrary Boolean function of the number of variables, N. A method and system for protecting an arbitrary Boolean function, F, for an arbitrary number of variables, N, from side-channel attacks, including in a computing device, if N=1, protecting one or more definitions of the arbitrary Boolean function by applying a predetermined masking algorithm, and if N>1, defining the arbitrary Boolean function, F of the number of variables, N, in terms of two or more single variable functions, G and H, applying the predetermined masking algorithm for N=1 to the two or more intermediate functions, G and H, and combining the masked intermediate functions G and H according to a predetermined scheme to generate a masked arbitrary Boolean function for the number of variables, N. Other embodiments are described and claimed
Owner:ARM LTD
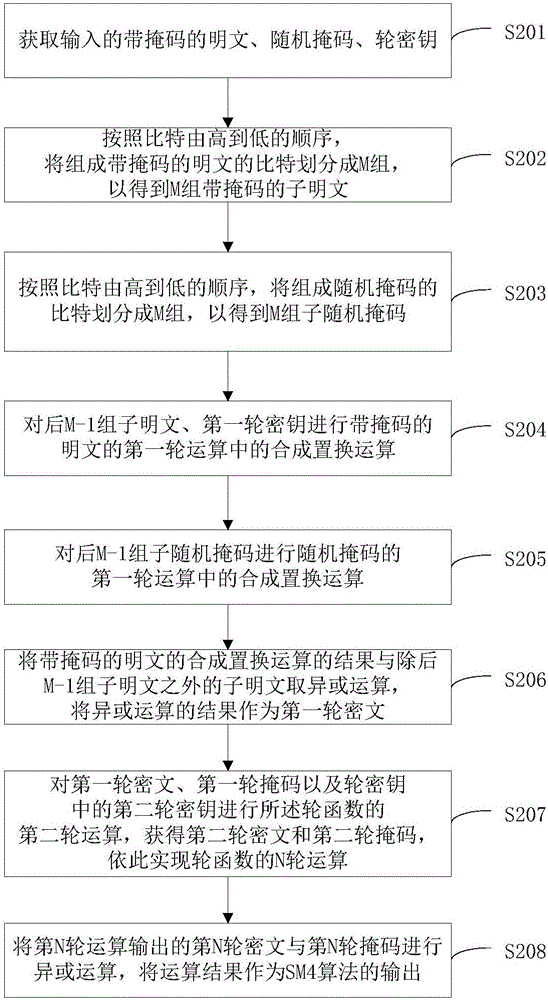
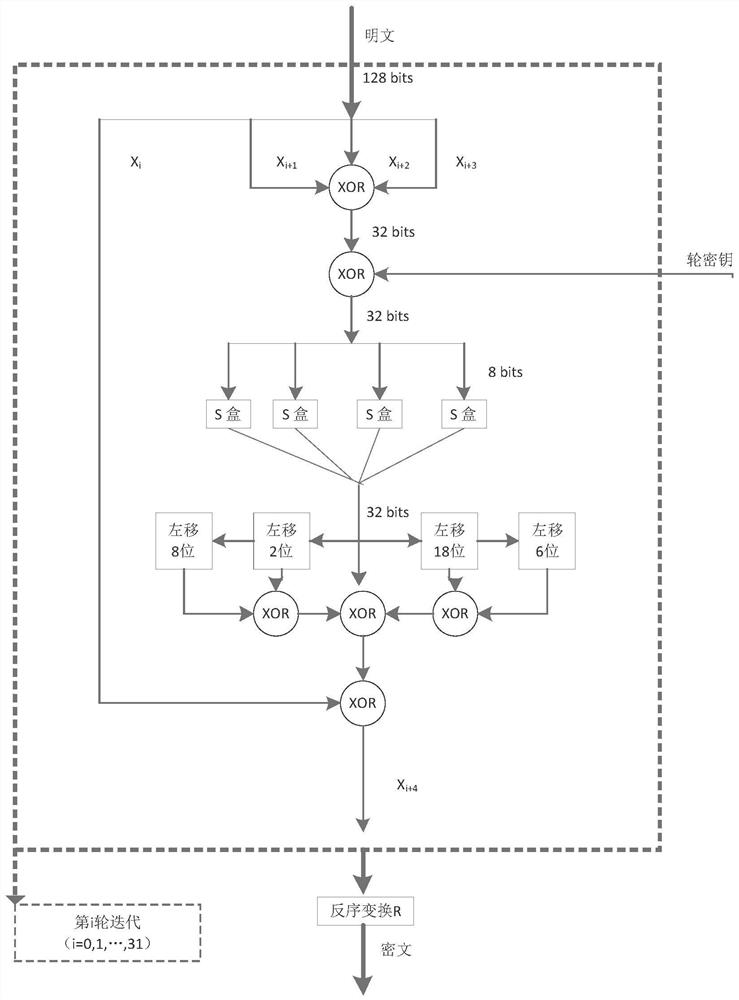
Mask method and mask device for SM4 algorithm
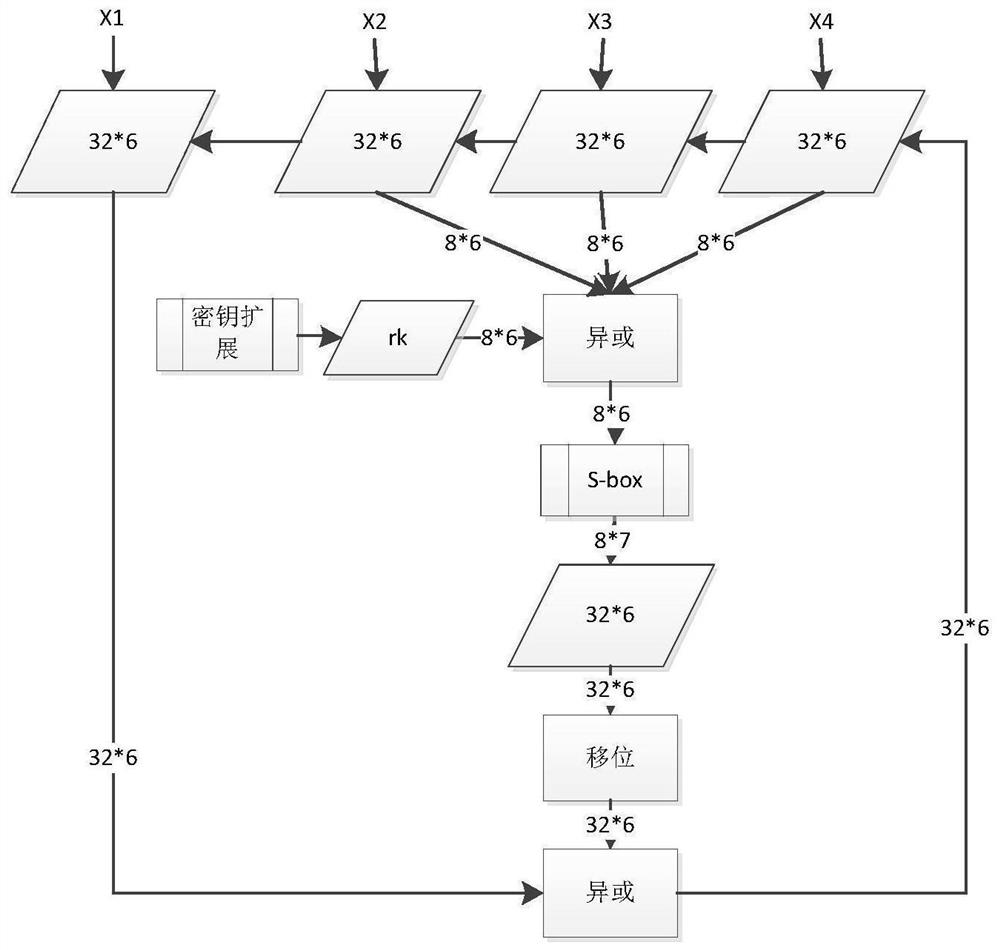
The invention discloses a mask method and a mask device for an SM4 algorithm. The mask method comprises the following steps: acquiring an inputted masked plain text, a random mask and round keys; carrying out a first round operation of a round function on the masked plain text, the random mask and a first round key in the round keys, to obtain a first round ciphertext and a first round mask; carrying out a second round operation of the round function on the first round ciphertext, the first round mask and a second round key in the round keys, to obtain a second round ciphertext and a second round mask, so as to realize N rounds of operation of the round function in turn; and carrying out an XOR operation an N round ciphertext and an N round mask outputted from the N round operation, wherein the operation result is taken as an output of the SM4 algorithm. Namely, except for the first round operation in the N rounds of operation of the round function, masks required for each round operation are all obtained by the output of the last round operation next to the current round operation, and therefore a demask on an intermediate value of the N rounds of operation is not required by adopting the technical solution disclosed by the invention, so that a resistance to an energy attack is realized.
Owner:CHINA INFORMATION TECH SECURITY EVALUATION CENT
Branch prediction preloading
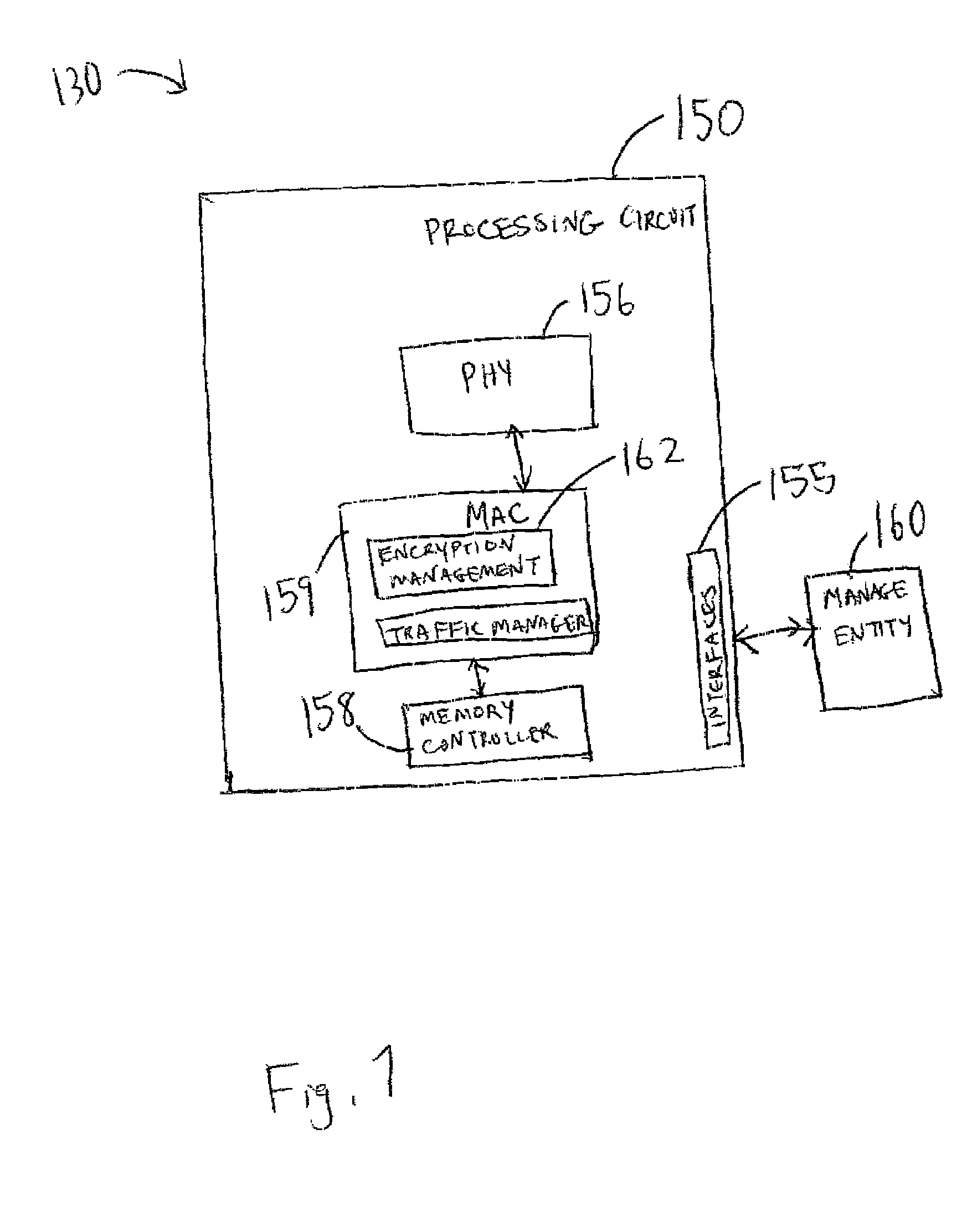
Embodiments relate to branch prediction preloading. A method for branch prediction preloading includes fetching a plurality of instructions in an instruction stream, and decoding a branch prediction preload instruction in the instruction stream. The method also includes determining, by a processing circuit, an address of a predicted branch instruction based on the branch prediction preload instruction, and determining, by the processing circuit, a predicted target address of the predicted branch instruction based on the branch prediction preload instruction. The method further includes identifying a mask field in the branch prediction preload instruction, and determining, by the processing circuit, a branch instruction length of the predicted branch instruction based on the mask field. Based on executing the branch prediction preload instruction, a branch target buffer is preloaded with the address of the predicted branch instruction, the branch instruction length, and the predicted target address associated with the predicted branch instruction.
Owner:IBM CORP
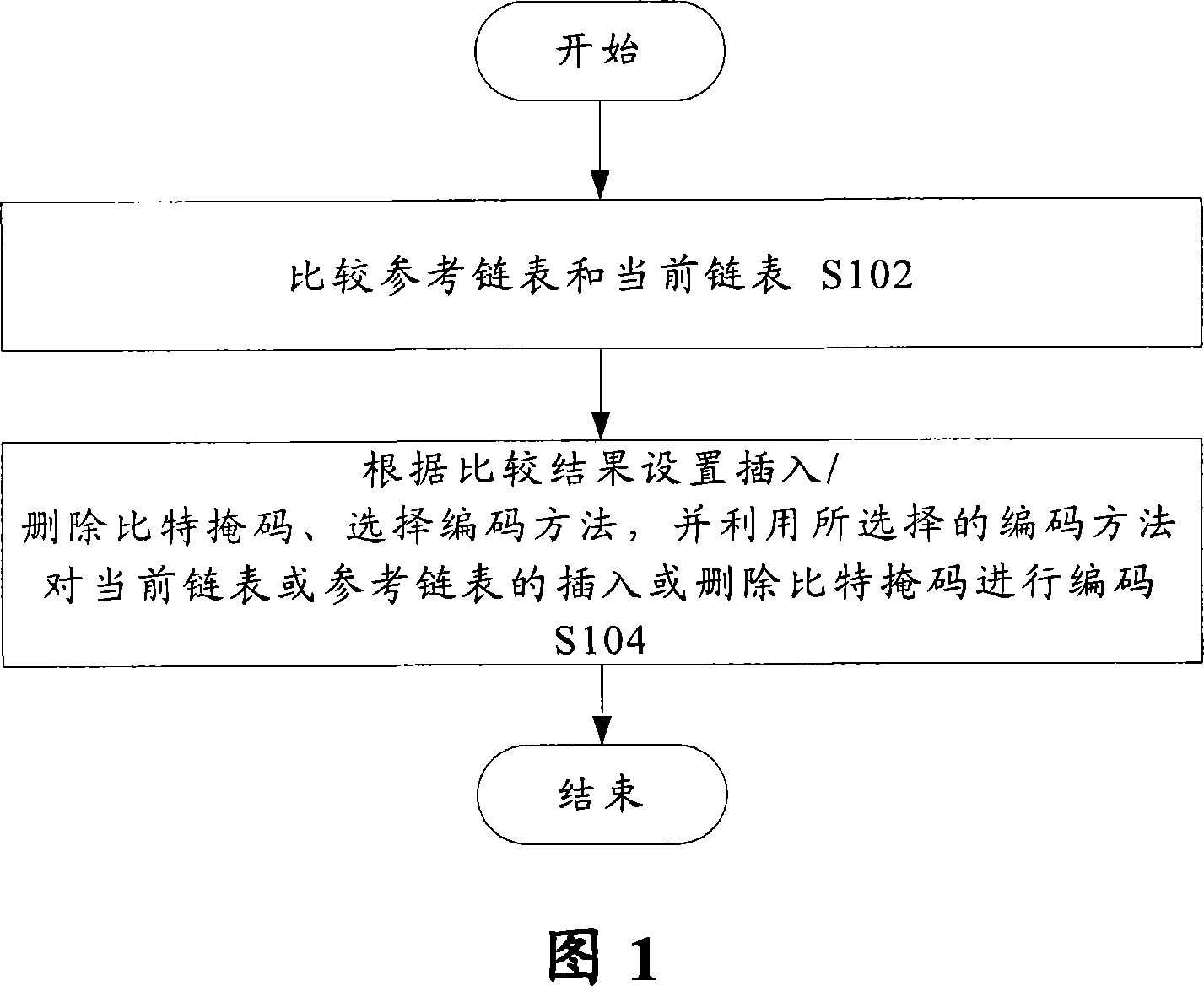
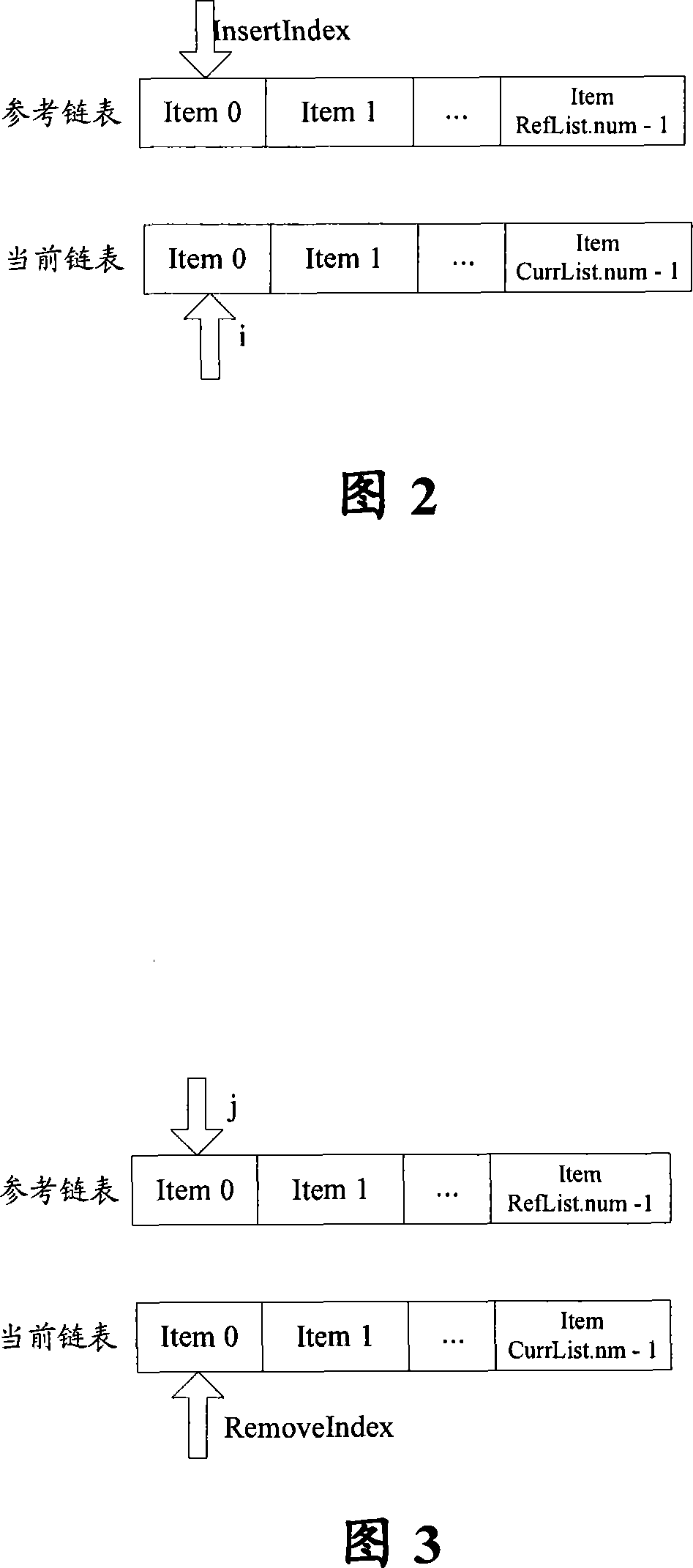
Chain table encoding method and system
InactiveCN101110638AReduce the number of comparisonsImprove reusabilityError preventionRadio transmission for post communicationReusabilityLinked list
Owner:ZTE CORP
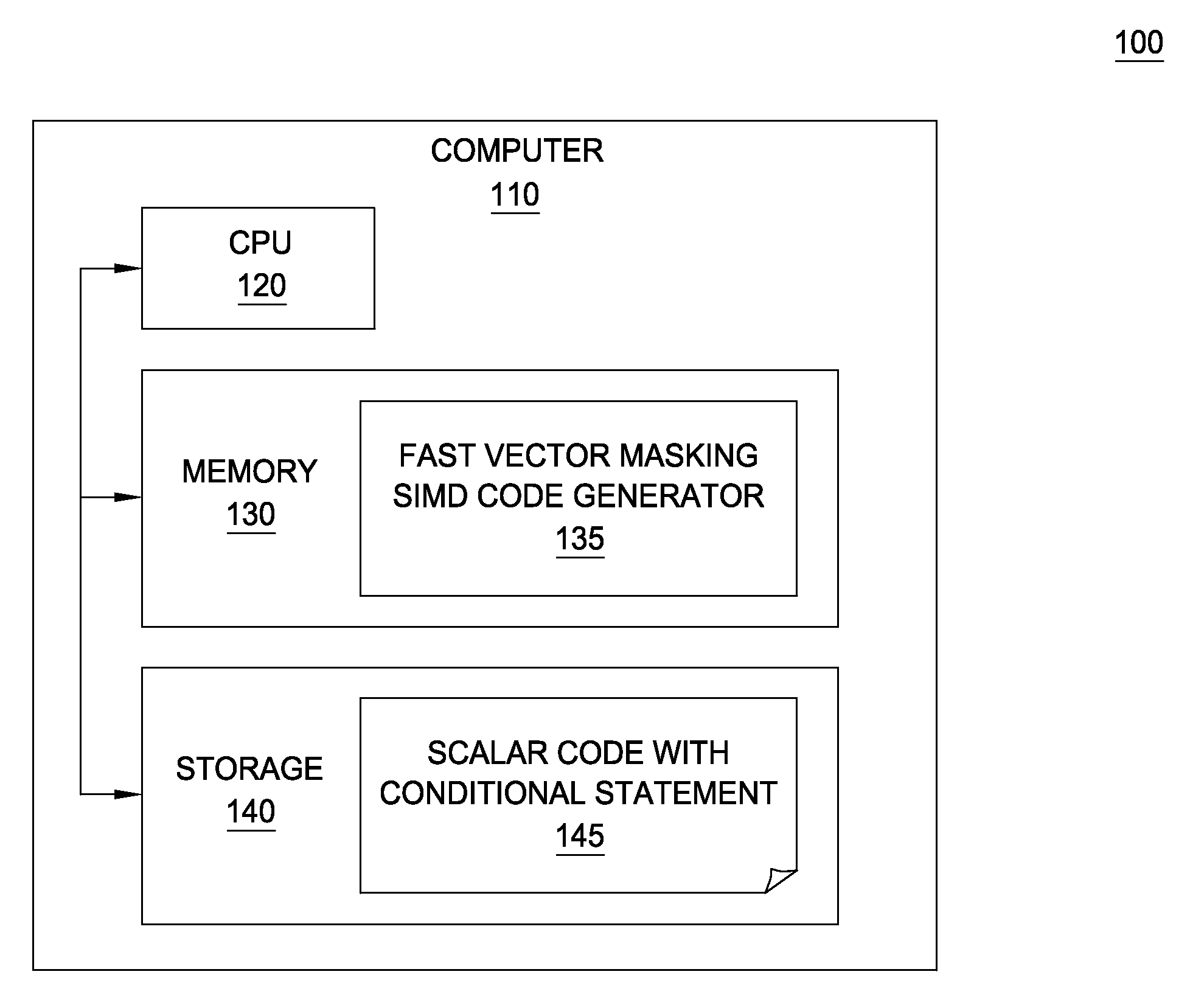
Fast vector masking algorithm for conditional data selection in SIMD architectures
InactiveUS8418154B2Transformation of program codeConcurrent instruction executionComputational scienceData selection
Owner:IBM CORP
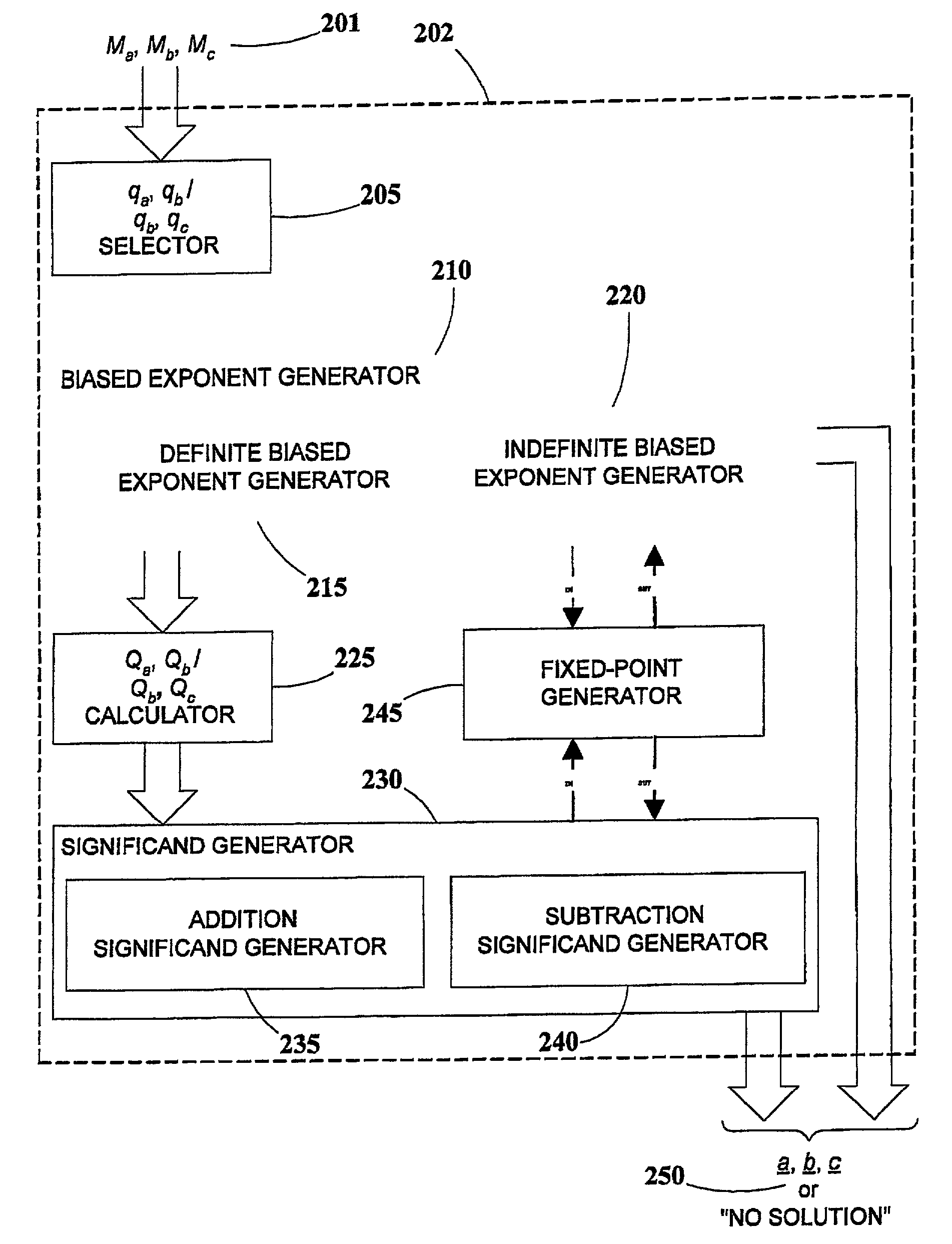
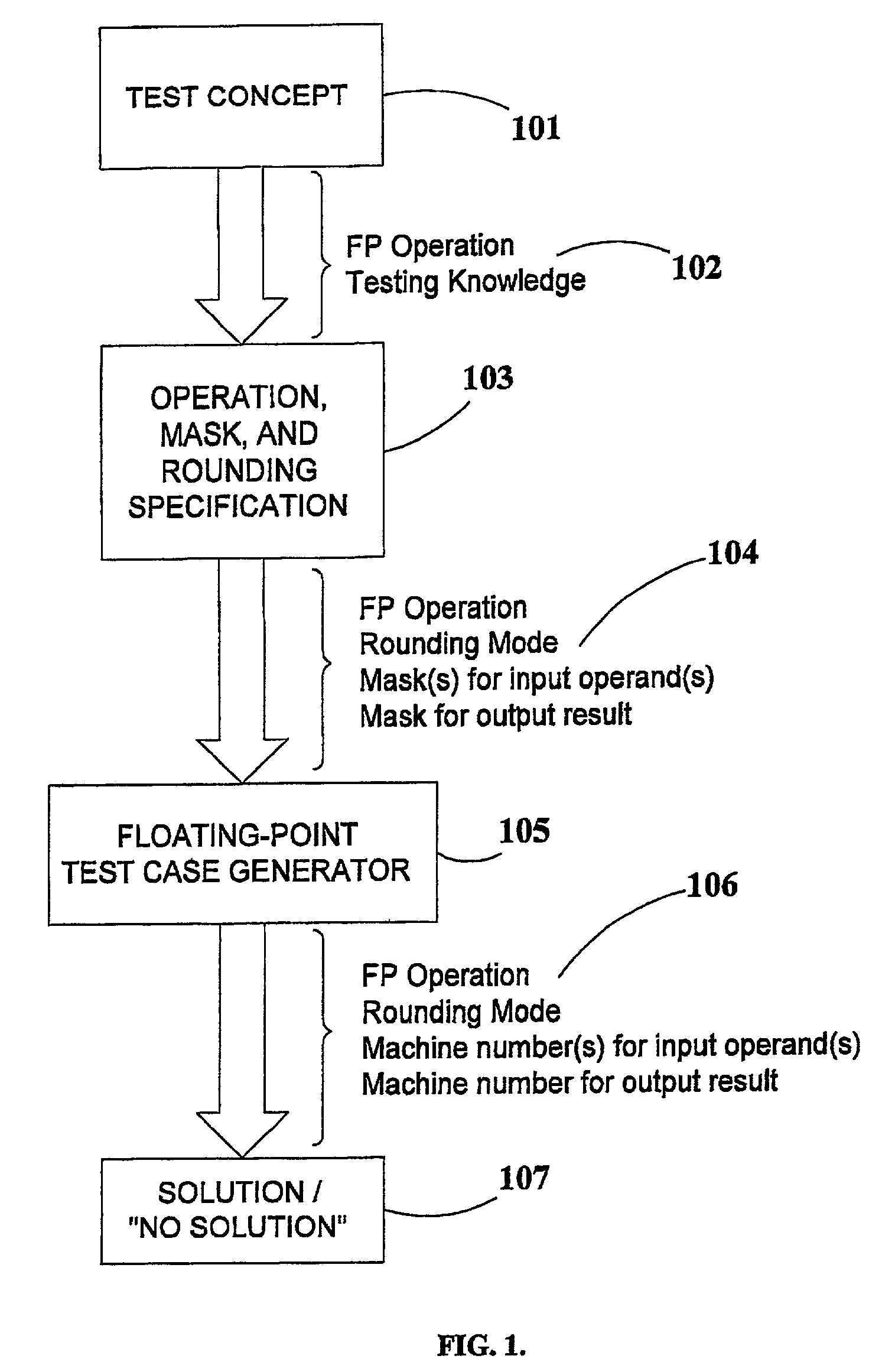
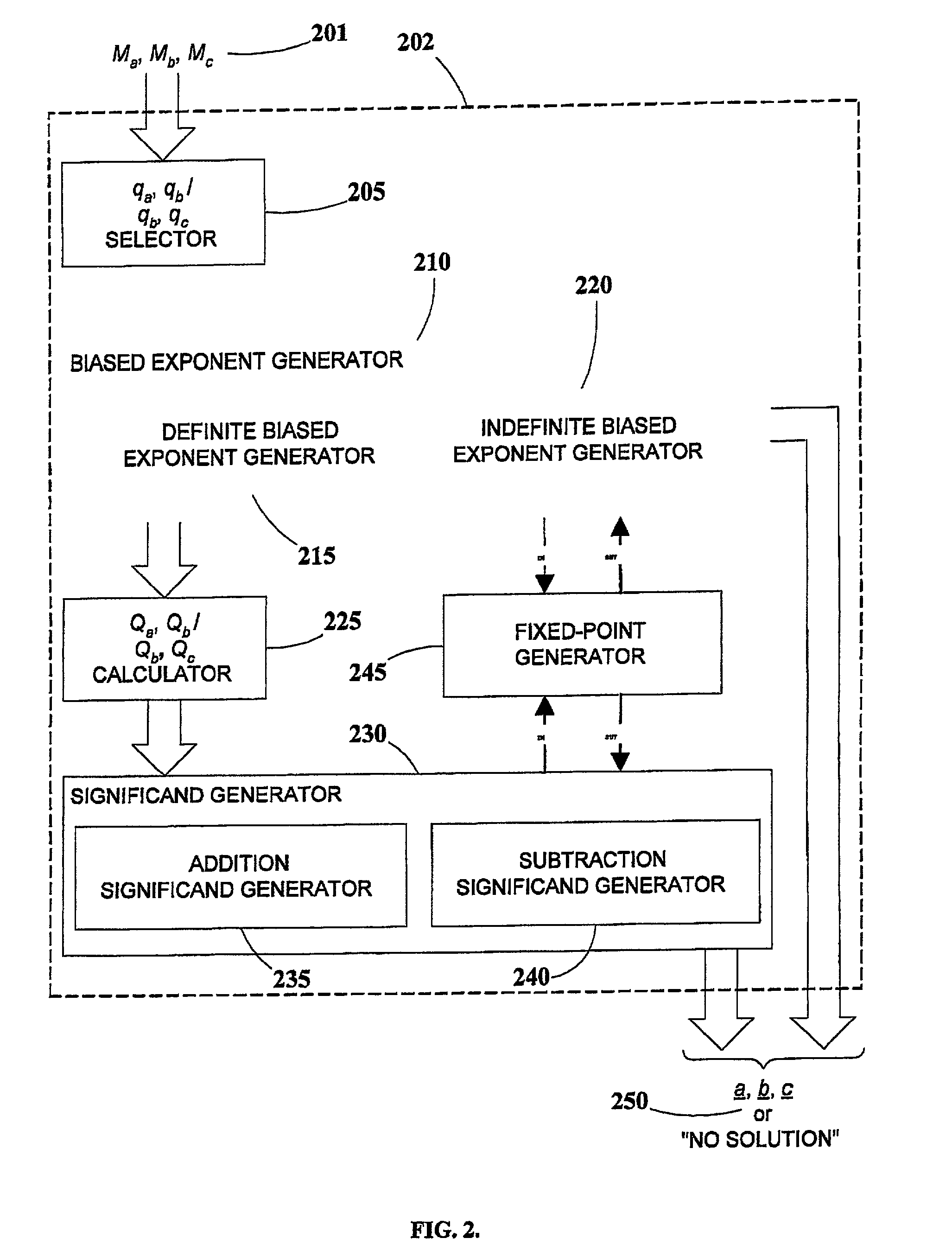
Generation of mask-constrained floating-point addition and subtraction test cases, and method and system therefor
ActiveUS7028067B2Comprehensive verificationElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionSignificandIEEE floating point
A method and system for generating numerical test cases for testing binary floating-point arithmetic units for addition and subtraction operations, in order to verify the proper operation of the units according to a specified standard. The space for eligible test-cases is compatible with masks which stipulate the allowable forms of the operands and the result, including constant as well as variable digits in both the exponent and significand fields. The test-cases, which are generated randomly, cover the entire solution space without excluding any eligible solutions. All standard rounding modes are supported, and if a valid solution does not exist for a given set of masks, this fact is reported. The method is general and can be applied to any standard, such as the IEEE floating-point standard, in any precision. A system according to the present invention utilizes a set of sub-generators for biased exponents and significands, and also incorporates a fixed-point generator for performing calculations common to the other generators. The method relies on searching for solutions based on feasible carry sequences, and is also capable of generating test-cases for mask-constrained carry sequences.
Owner:TWITTER INC
System and method for modification of coded instructions in read-only memory using one-time programmable memory
InactiveUS20150242213A1Reduce in quantitySave spaceDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionMask ROMController (computing)
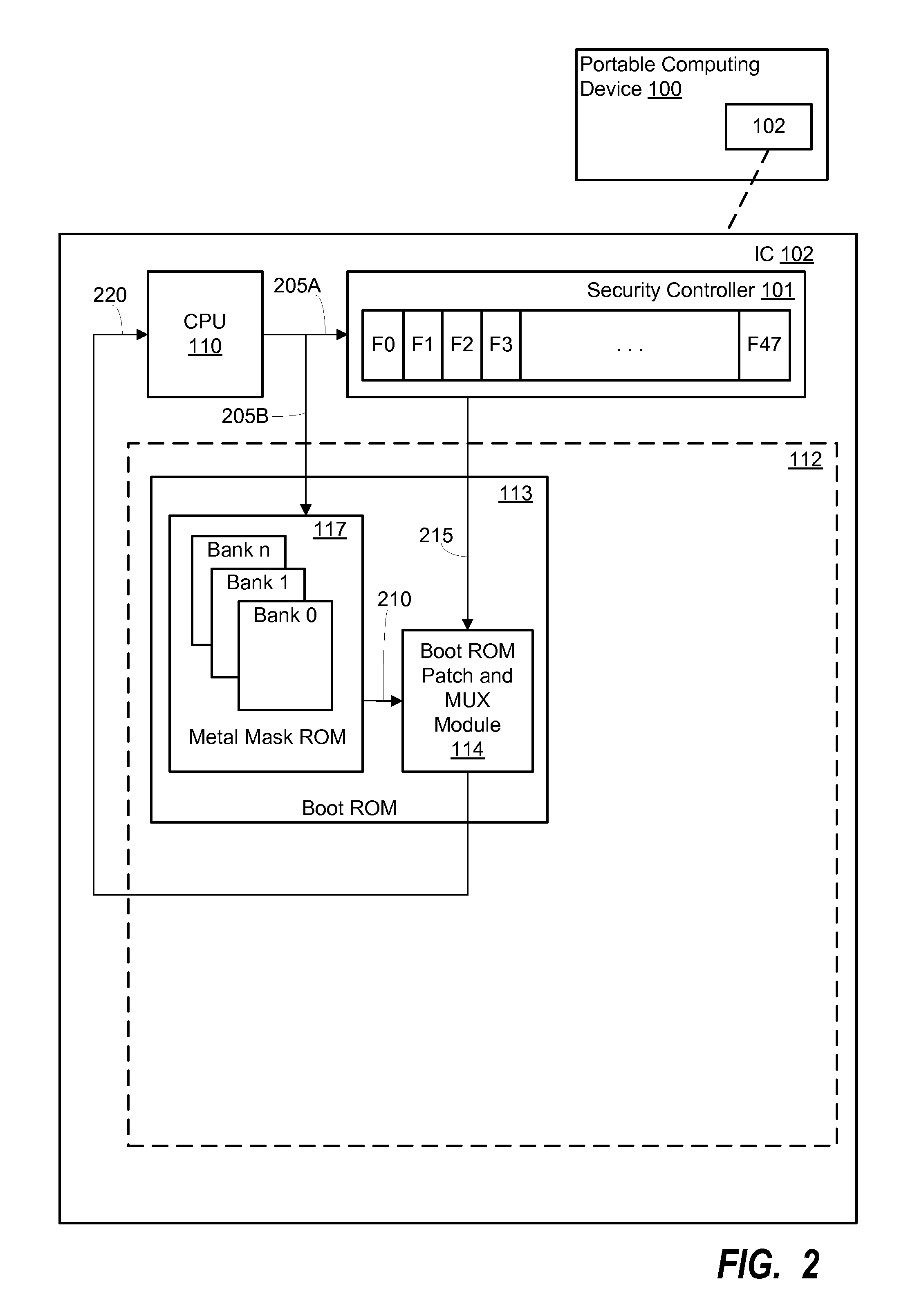
Various embodiments of methods and systems for flexible read only memory (“ROM”) storage of coded instructions in a portable computing device (“PCD”) are disclosed. Because certain instructions and / or data associated with a primary boot loader (“PBL”) may be defective or in need of modification after manufacture of a mask ROM component, embodiments of flexible ROM storage (“FRS”) systems and methods use a closely coupled one-time programmable (“OTP”) memory component to store modified instructions and / or data. Advantageously, because the OTP memory component may be manufactured “blank” and programmed at a later time, modifications to code and / or data stored in an unchangeable mask ROM may be accomplished via pointers in fuses of a security controller that branch the request to the OTP and bypass the mask ROM.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Semantic understanding model training method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN111444311APromote joint trainingImprove understandingSemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a semantic comprehension model training method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a total word sequence corresponding to a training text from a training set; randomly selecting a preset number of continuous word vectors from the total word sequence, replacing the continuous word vectors with a mask sequence to obtain an input word sequence, and taking the preset number of continuous word vectors as a test output word sequence; inputting the input word sequence into an encoder-attention-decoder model for training to obtain a prediction output word sequence; according to the difference between the prediction output word sequence and the test output word sequence, adjusting model parameters of the encoder-attention-decoder model to reduce the difference; and returning to input the input word sequence into the encoder-attention-decoder model for training to obtain a prediction output word sequence, continuing training, and stopping training until a preset training stop condition is met to obtain a semantic understanding model. According to the invention, the understanding accuracy of the computer to the natural language is improved.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Steiner tree based approach for polygon fracturing
ActiveCN101689215AOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsMask data preparationComputer science
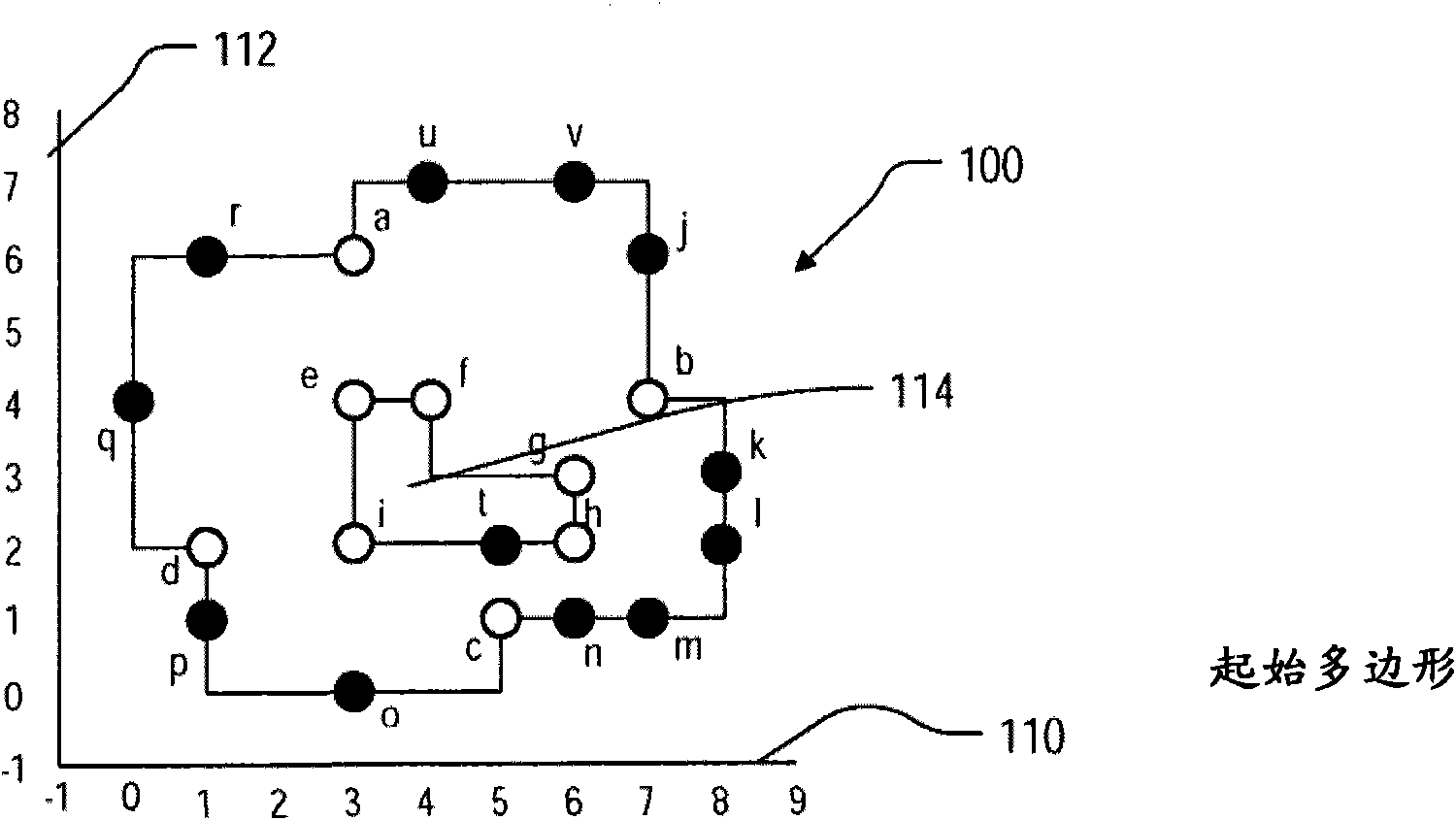
Roughly described, a method for mask data preparation is described, for use with a preliminary mask layout that includes a starting polygon, the vertices of the starting polygon including I-points (vertices of the starting polygon having an interior angle greater than 90 degrees), including steps of developing a rectilinear partition tree on at least the I-points of the starting polygon, and usingthe edges of the partition tree to define the partition of the starting polygon into sub-polygons for mask writing.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Read-only memory device coded with selectively insulated gate electrodes
ActiveUS7192811B2Increased process windowSize of ROM can be downSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsDielectric layer
During fabrication of a mask read-only memory (ROM) device, a dielectric layer is grown on a substrate. Strip-stacked layers are formed on the dielectric layer, with each strip-stacked layer including a polysilicon and a silicon nitride layer. Source / drain regions are formed in the substrate between the strip-stacked layers, and spacers are then deposited between the strip-stacked layers. The strip-stacked layers are patterned into gates, which are disposed over every code position, with silicon nitride pillars being disposed on the gates. Additional spacers are formed on gate sidewalls. The silicon nitride pillars are removed, exposing the gates. A mask is then formed to cover active code positions, in accordance with the desired programming code. Insulating layers are then deposited through the mask onto the exposed gates. When the mask is removed, word lines are formed, interconnecting the gates without the insulating layers.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
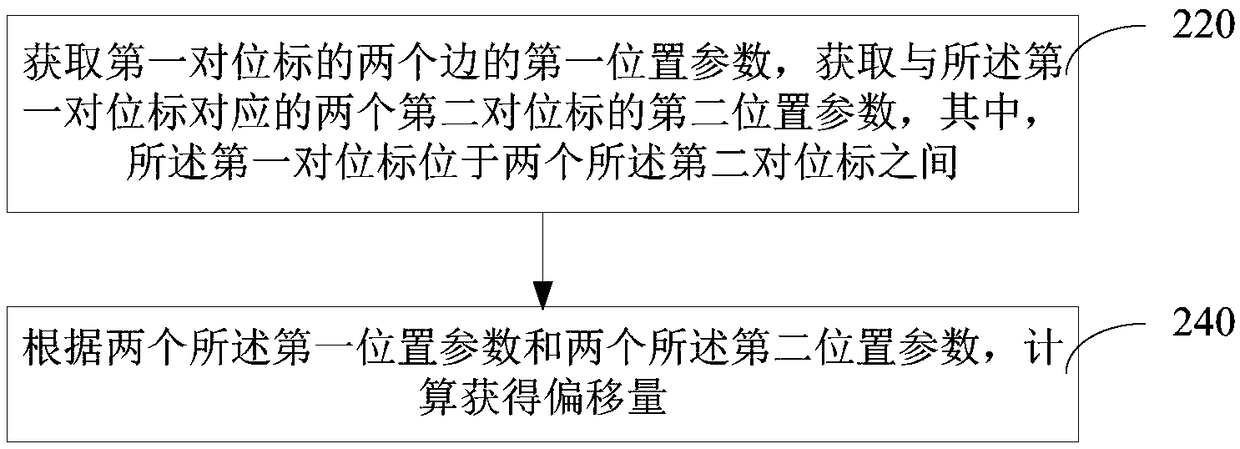
Mask exposure offset detection method, mask exposure offset detection device, computer and storage medium
ActiveCN108762005AImprove detection accuracyImprove detection efficiencyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringExposure
The invention relates to a mask exposure offset detection method, a mask exposure offset detection device, a computer and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring first position parameters of two sides of a first register guide, and acquiring second position parameters of two second register guides corresponding to the first register guide, wherein the first register guide is located between the two second register guides; and calculating the offset according to the two first position parameters and the two second position parameters. The two first position parameters and the two second position parameters are obtained to calculate the offset, so the detection accuracy and the detection efficiency of the mask exposure offset are effectively improved.
Owner:TRULY HUIZHOU SMART DISPLAY
Apparatus and method for vectorization with speculation support
An apparatus and method are described for detecting and responding to fault conditions in a processor. For example, one embodiment of a method comprises: reading each active element in succession from a first vector register, each active element specifying an address for a gather or load operation; detecting one or more fault conditions associated with one or more of the active elements; for each active element read in succession prior to a detected fault condition on an element other than the first active element, storing the data loaded from an address associated with the active element in a first output vector register; and for each active element associated with the detected fault condition and following the detected fault condition, setting a bit in an output mask register to indicate the detected fault condition.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Computer system and method of controlling computer system
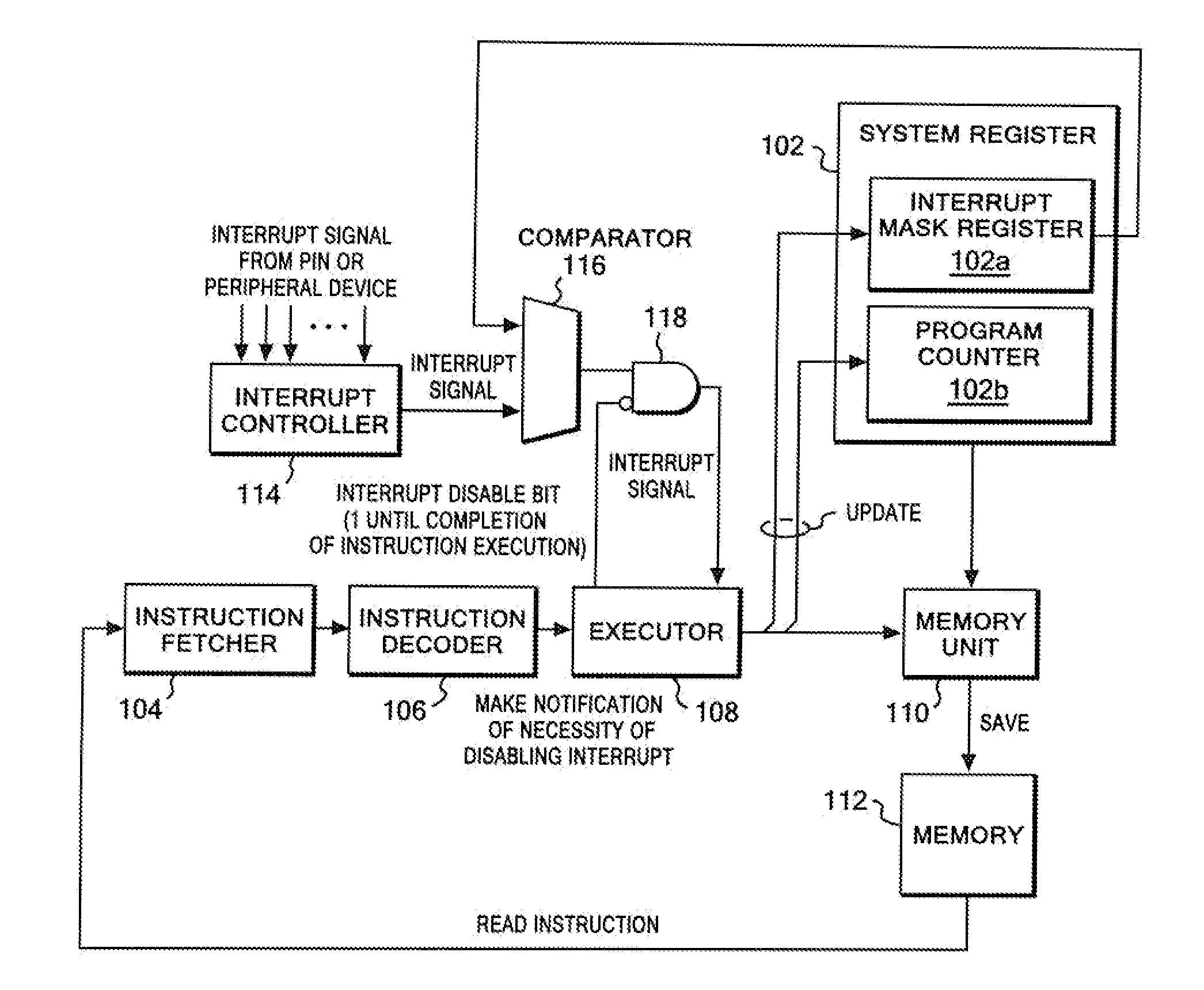
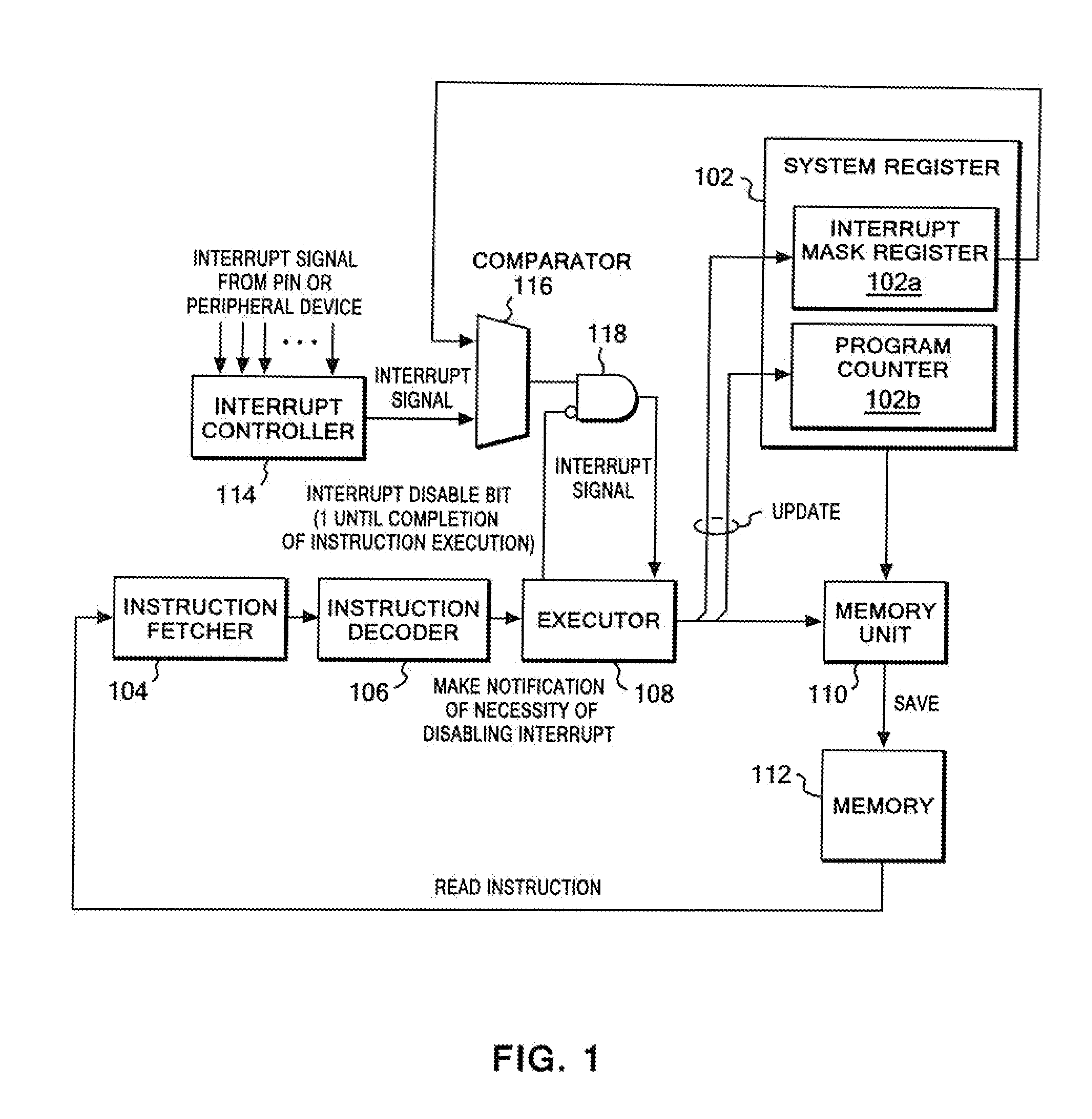
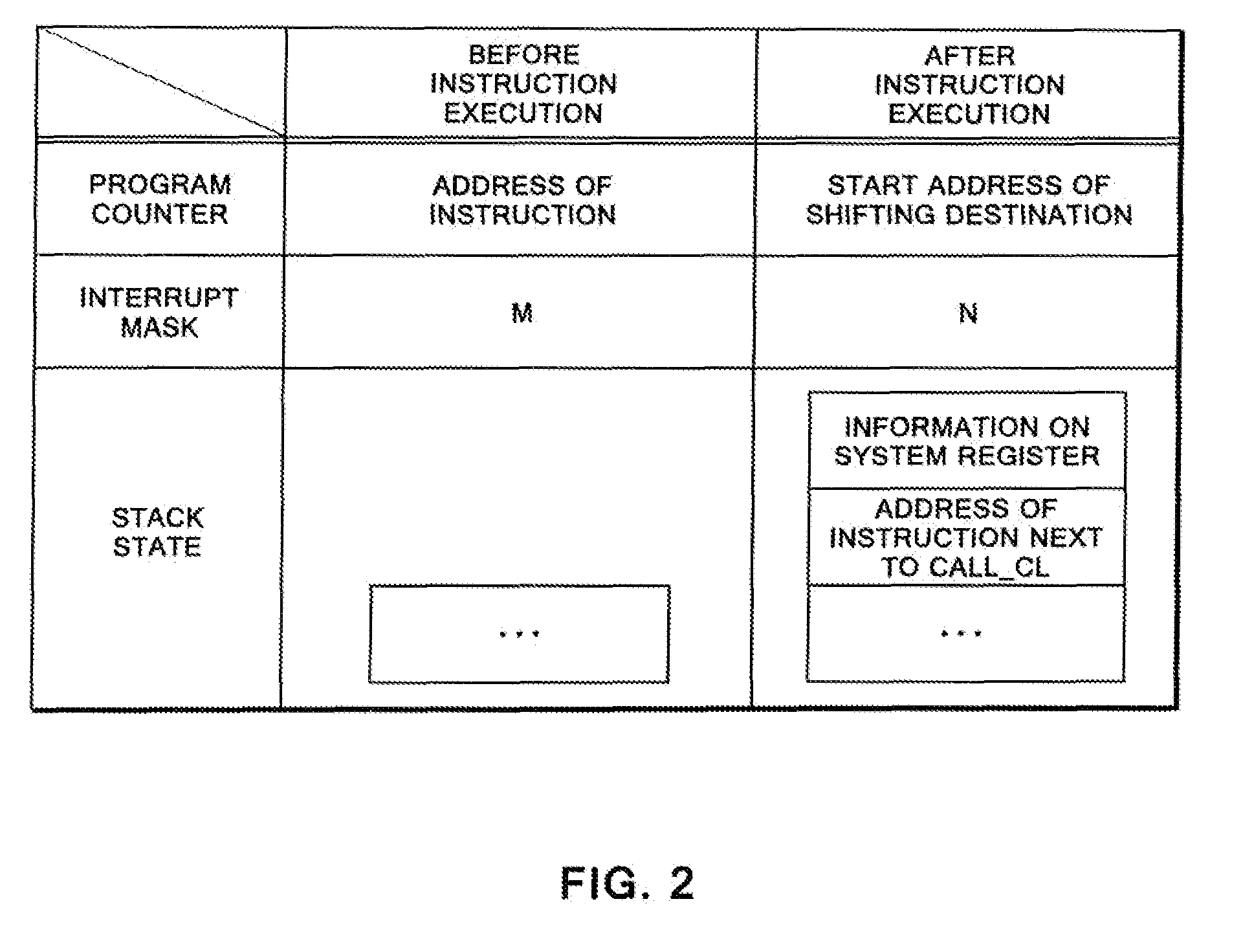
CPU architecture is modified so that content of the interrupt mask register can be changed directly based on a decoding result of an instruction decoder of a CPU. Such modification does not require a great deal of labor in changing a CPU design. In addition, an extended CALL instruction and an extended software interrupt instruction are added to the CPU, and each of the extended CALL instruction and the extended software interrupt instruction additionally has a function of changing the value of the interrupt mask register. Atomicity is achieved by: allowing such a single instruction to concurrently execute a call of a process and a value change of the interrupt mask register; and disabling other interrupts during execution of the single instruction.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for ray tracing with grid primitives
ActiveUS20200211264A1Processor architectures/configurationDetails involving image processing hardwareComputational scienceRay
Apparatus and method for ray tracing acceleration using a grid primitive. For example, one embodiment of an apparatus comprises: a grid primitive generator to generate a grid primitive comprising a plurality of adjacent interconnected primitives; a bitmask generator to generate a bitmask associated with the grid primitive, the bitmask comprising a plurality of bitmask values, each mask value associated with a primitive of the grid primitive; a ray tracing engine comprising traversal and intersection hardware logic to perform traversal and intersection operations in which rays are traversed through a hierarchical acceleration data structure and intersections between the rays and one or more of the adjacent interconnected primitives identified, wherein the ray tracing engine is to read the bitmask to determine a first set of primitives from the grid primitive on which to perform the traversal and intersection operations and a second set of primitives from the grid primitive on which the traversal and intersection operations will not be performed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
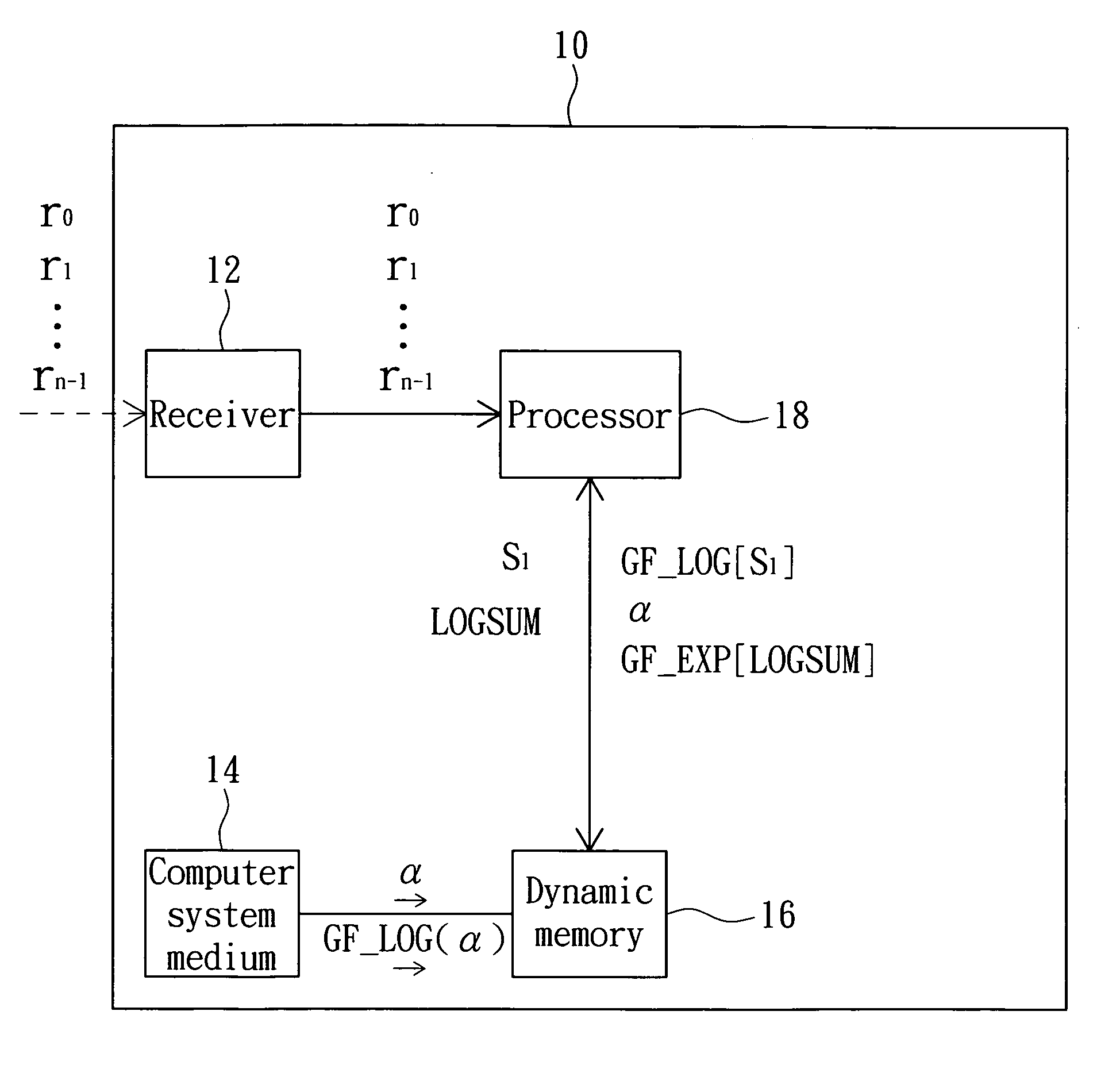
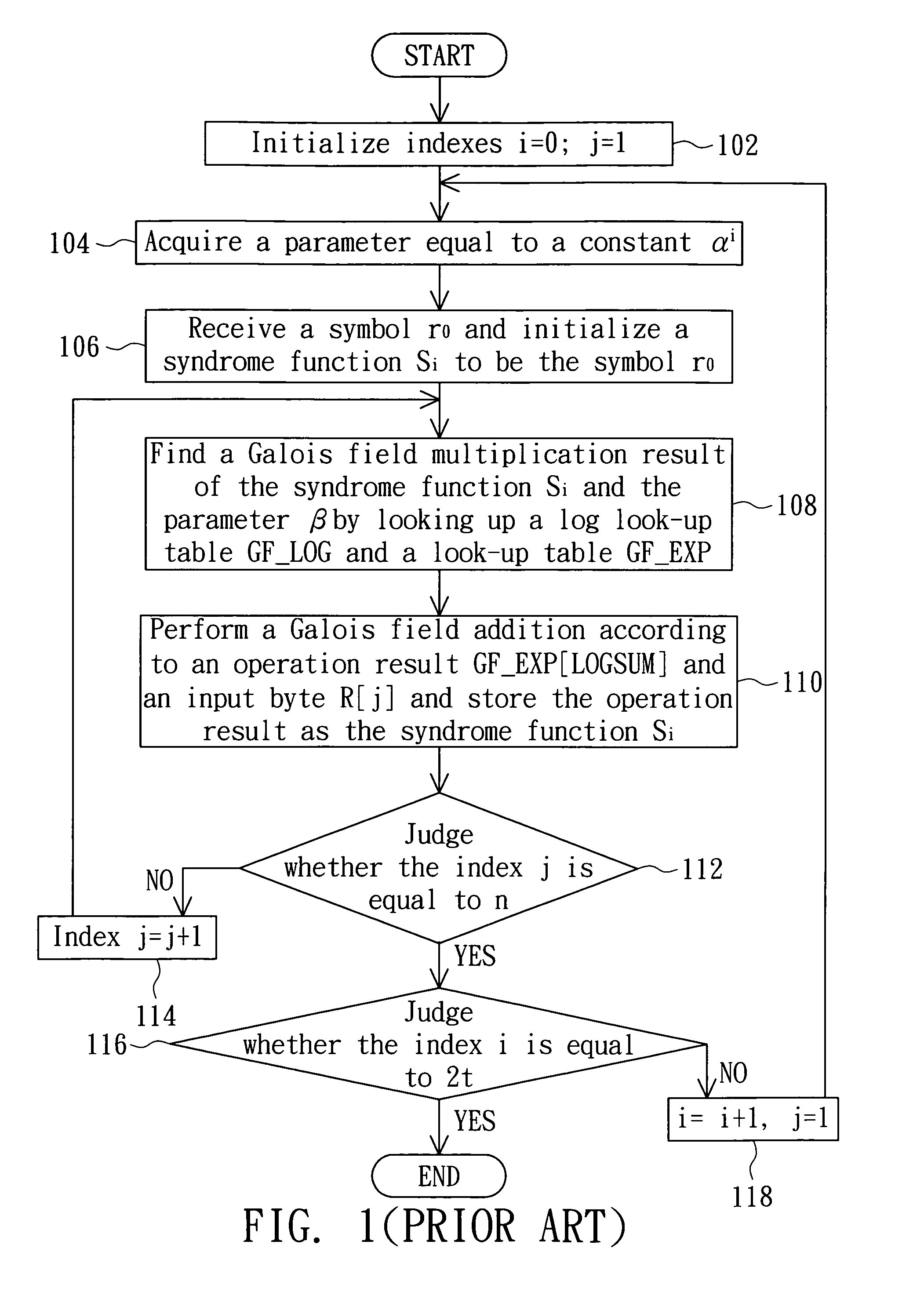
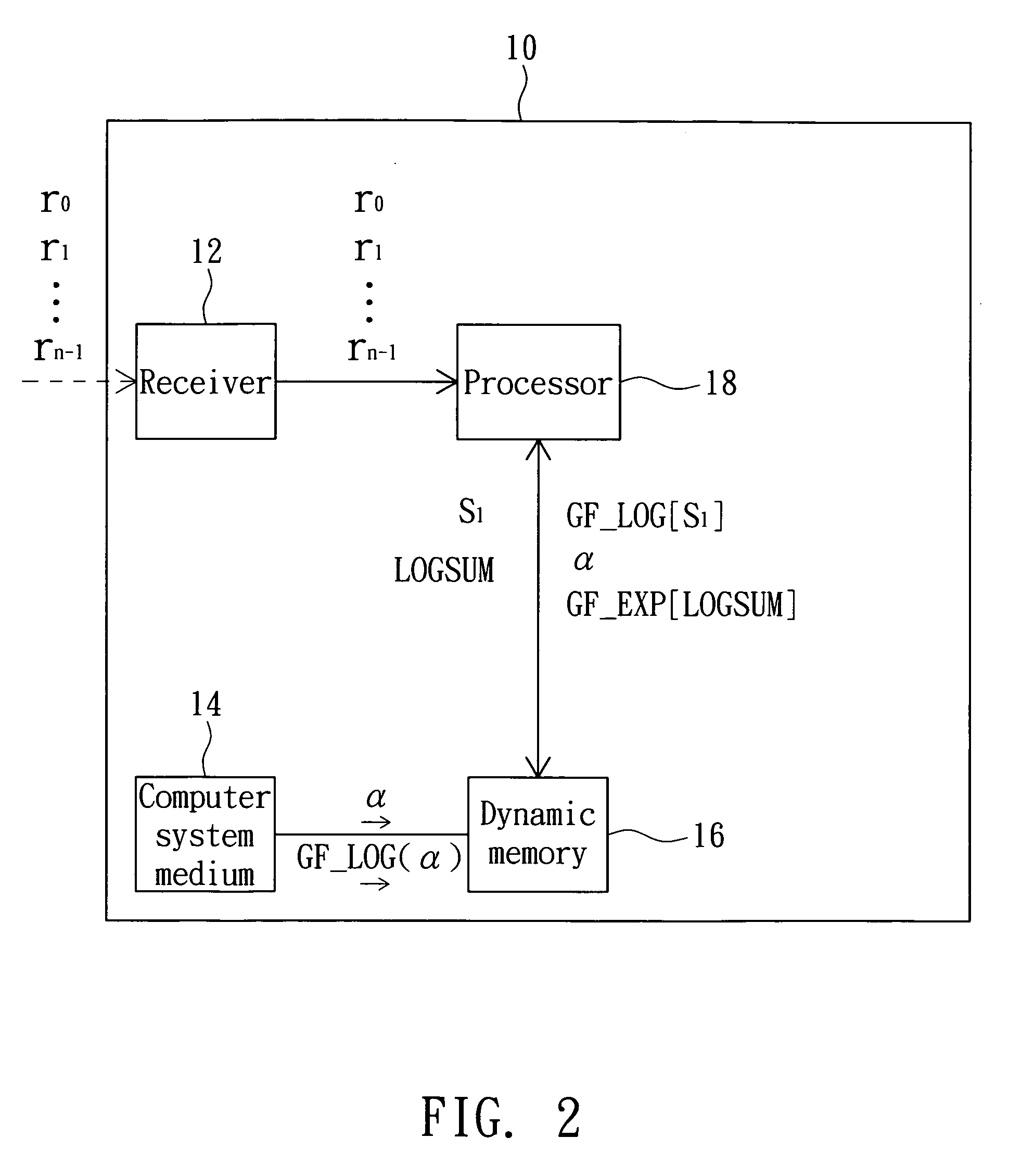
Data processing method and computer system medium thereof
InactiveUS20090055712A1Increase computing speedFew operation resourceCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesComputerized systemData mining
A data processing method includes the steps of: initializing a syndrome vector to be an (n−1)th symbol; finding a corresponding mask based on the syndrome vector, wherein the mask is zero when the (n−1)th symbol is zero; correcting a known constant, which is zero when the syndrome vector is zero, based on the mask; inputting the syndrome vector to a log look-up table to correspondingly find log data; performing a modulo addition operation corresponding to log maximum data to find a log sum based on the log data and a log known constant; and inputting the log sum to an anti-log look-up table to correspondingly find operational data.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP
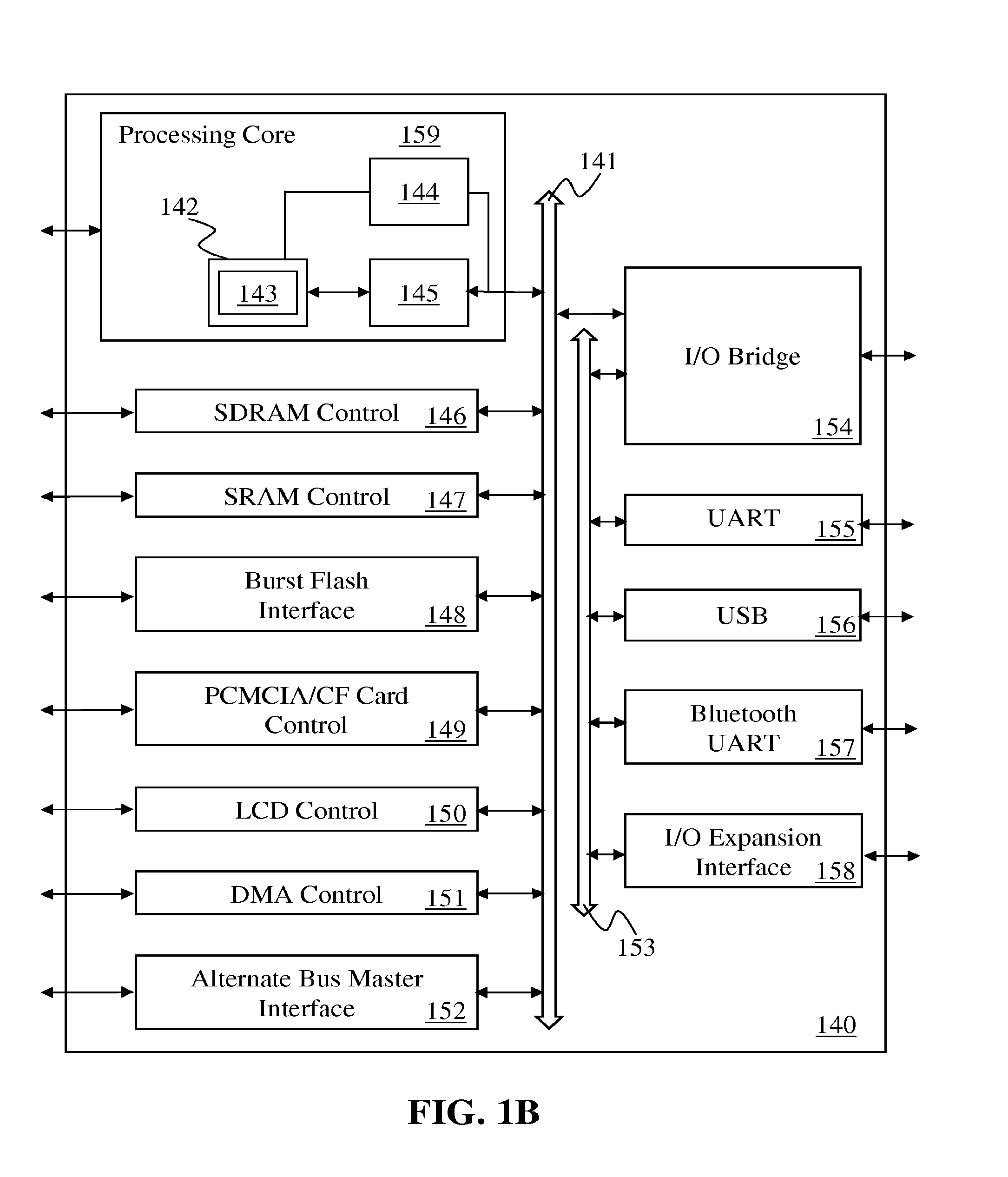
Integrated mechanism for suspension and deallocation of computational threads of execution in a processor
InactiveCN1846194ASave spaceEffective executionMultiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionComputer architectureParallel computing
A yield instruction for execution in a multithreaded microprocessor is disclosed. The yield instruction includes an operand. If the operand is zero the microprocessor terminates the program thread including the yield instruction. If the operand is -1 the microprocessor unconditionally reschedules the program thread. If the operand is a positive integer the microprocessor views the operand as a bit vector specifying one or more yield qualifier inputs, such as interrupt signals, and conditionally reschedules the thread based on the qualifier inputs and bit vector values. The microprocessor also includes a mask register that specifies a bit vector of the qualifier inputs. If the operand specifies a qualifier input not also specified in the mask register, an exception to the instruction is raised. The instruction returns a value specifying the values of the qualifier inputs qualified by the mask register value.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Comprehensive protection method for resisting side channel and fault attacks
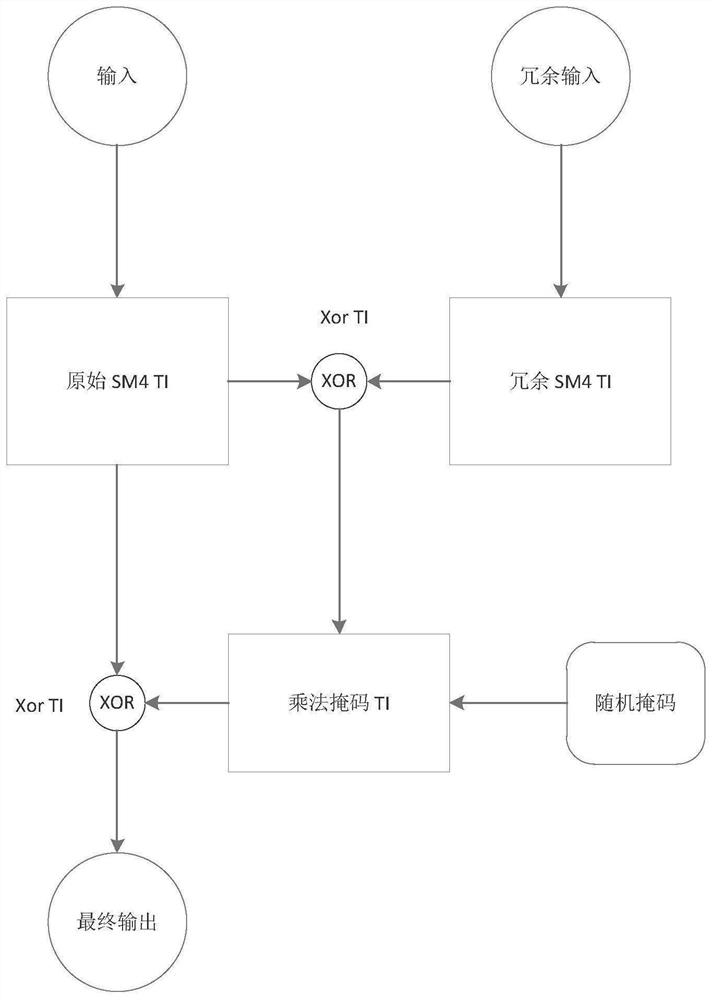
InactiveCN112187444AImprove protectionExcellent areaEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCryptographic attack countermeasuresCiphertextExclusive or
The invention discloses a comprehensive protection method for resisting side channel and fault attacks, which comprises the following steps of: 1) for a target algorithm to be protected, constructingan algorithm which is the same as the target algorithm as a redundancy algorithm of the target algorithm; respectively constructing the same d-order threshold protection scheme for the target algorithm and the redundant algorithm thereof, wherein the same d-order threshold protection scheme is used for protecting the d-order side channel attack; 2) carrying out exclusive OR on the output of the target algorithm and the output of the redundant algorithm, then carrying out multiplication mask operation on the output of the target algorithm and a random number, and protecting the multiplication operation by adopting a threshold implementation technology; 3) carrying out exclusive OR on the processing result of the step 2) and the d-order threshold implementation structure of the target algorithm or the d-order threshold implementation structure of the redundant algorithm to obtain a result, and taking the result as a final output result of the target algorithm. The method can resist faultsensitivity attacks not based on ciphertext, differential fault attacks based on ciphertext and side channel attacks.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com