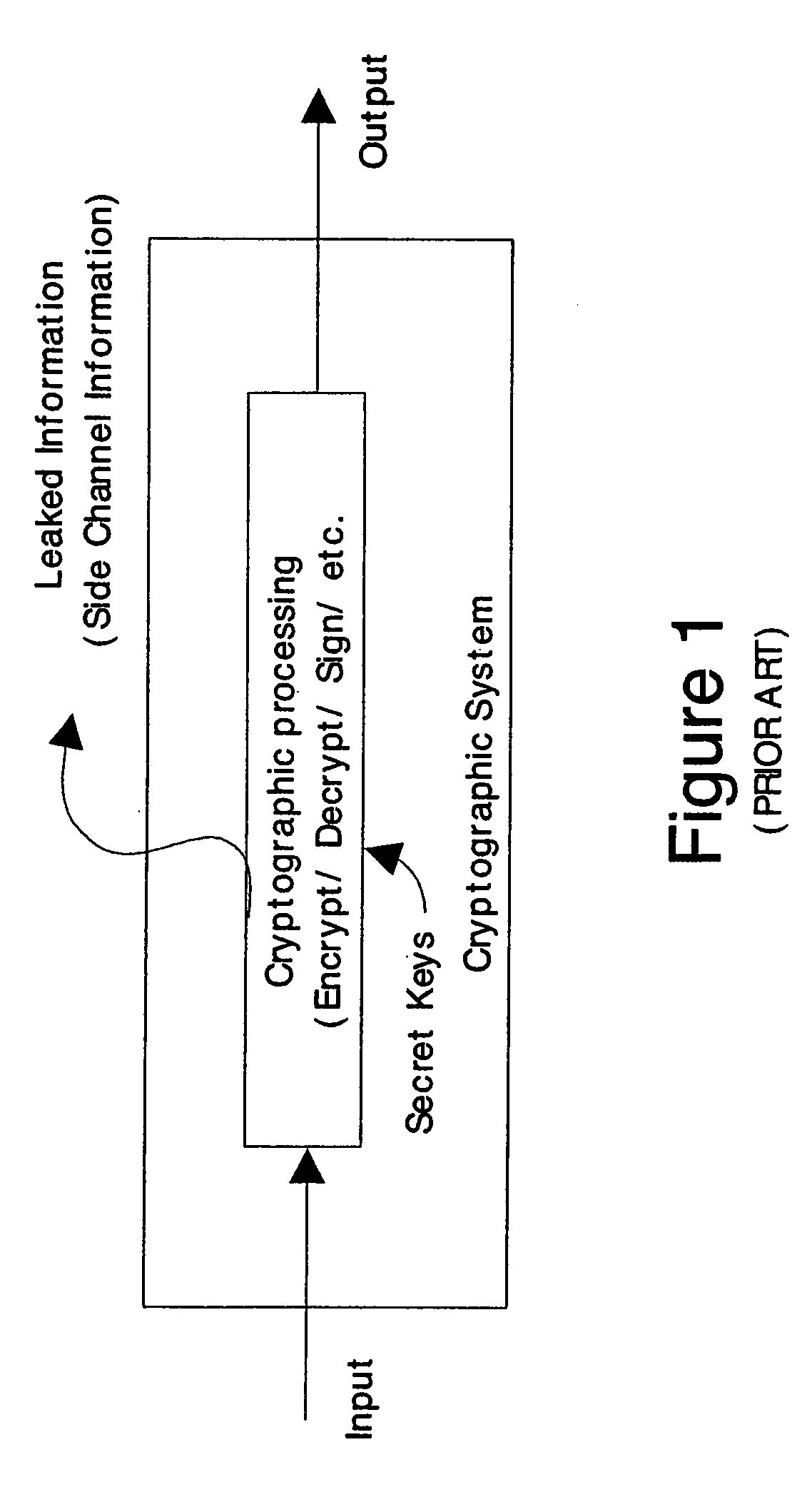
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2388results about "Cryptographic attack countermeasures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
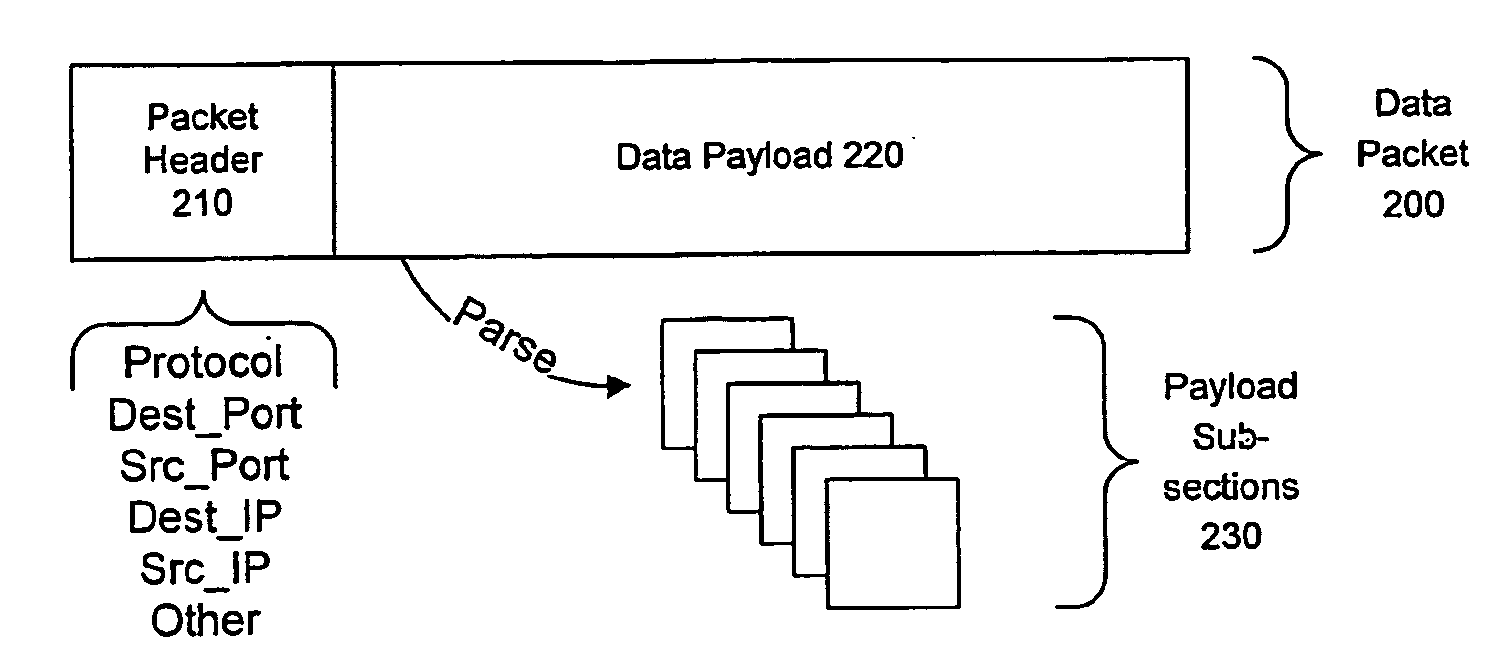
Detecting Public Network Attacks Using Signatures and Fast Content Analysis
ActiveUS20080307524A1Memory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwarePrivate network
Network worms or viruses are a growing threat to the security of public and private networks and the individual computers that make up those networks. A content sifting method if provided that automatically generates a precise signature for a worm or virus that can then be used to significantly reduce the propagation of the worm elsewhere in the network or eradicate the worm altogether. The content sifting method is complemented by a value sampling method that increases the throughput of network traffic that can be monitored. Together, the methods track the number of times invariant strings appear in packets and the network address dispersion of those packets including variant strings. When an invariant string reaches a particular threshold of appearances and address dispersion, the string is reported as a signature for suspected worm.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
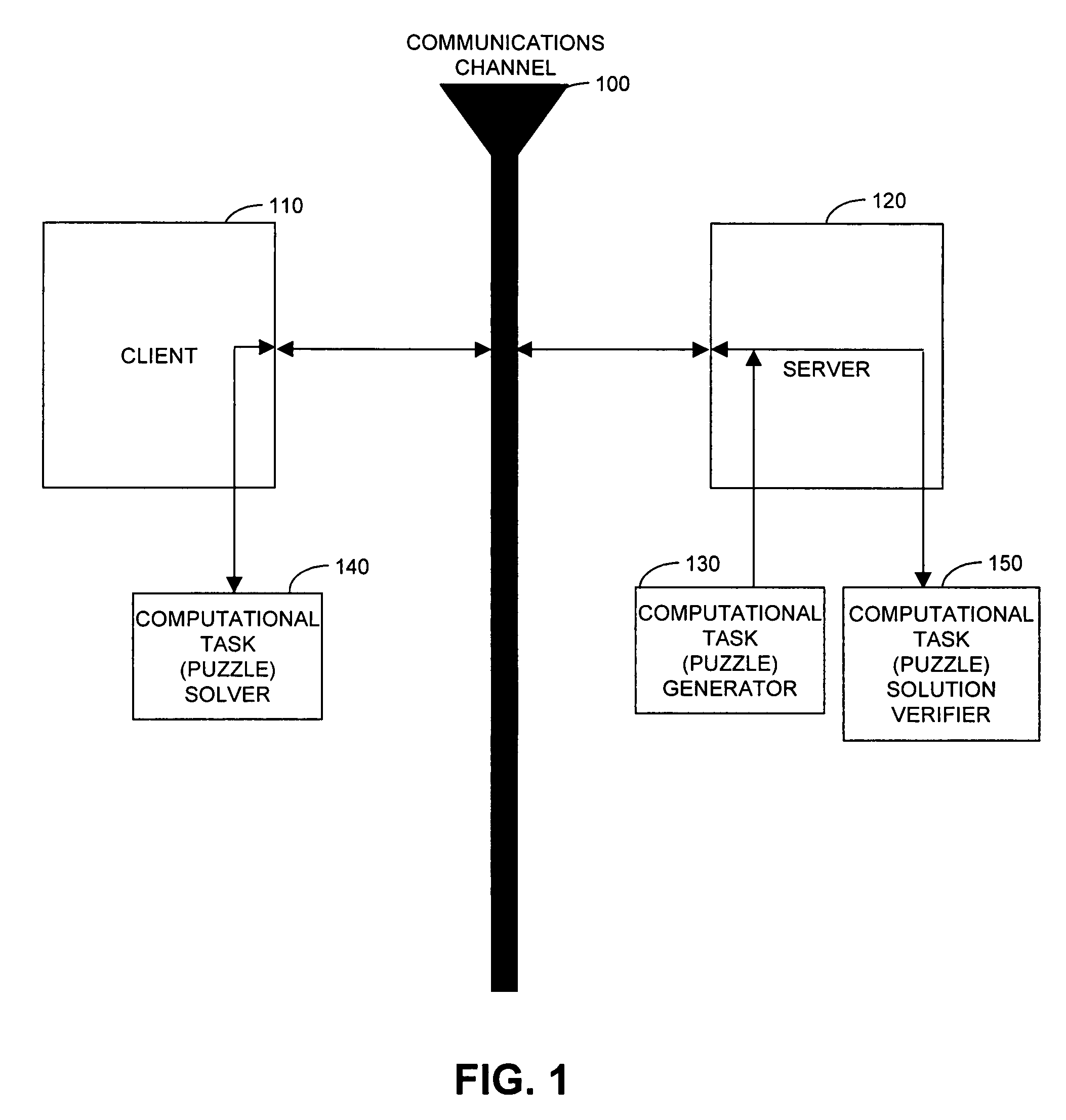
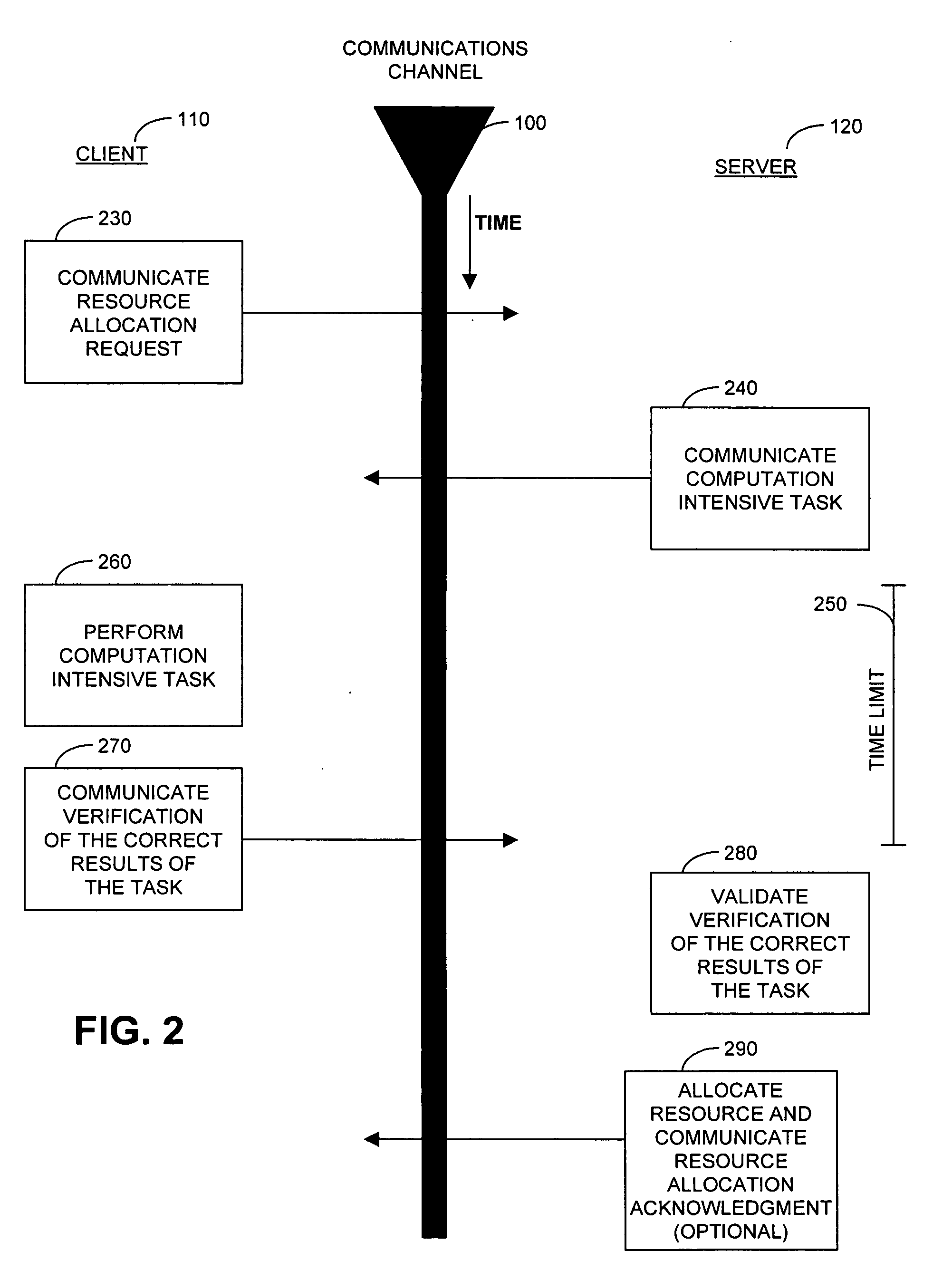
Cryptographic countermeasures against connection depletion attacks
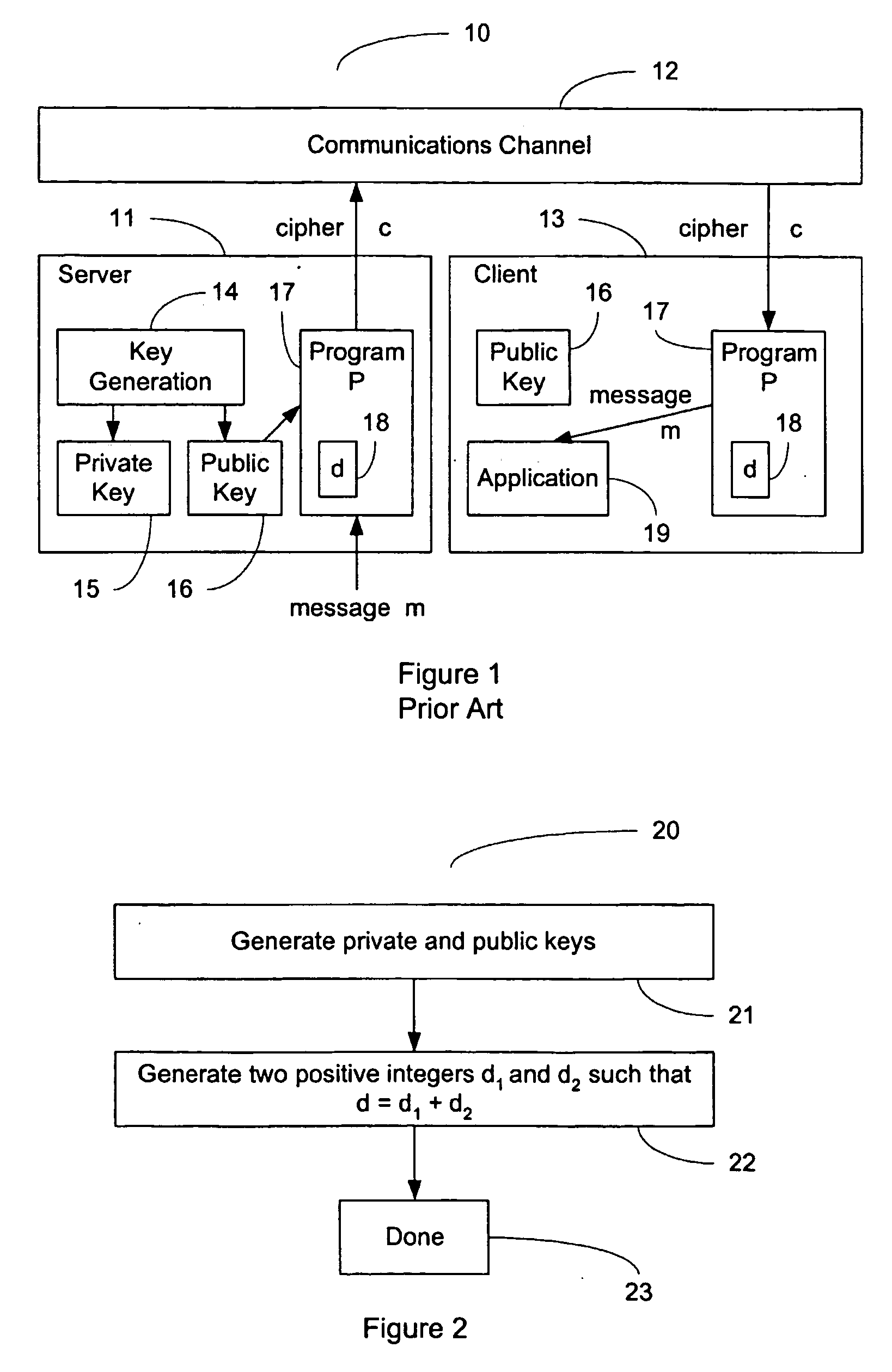
InactiveUS7197639B1Ensure correct executionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCountermeasureTime limit
This invention relates to cryptographic communications methods and systems that protect a server from a connection depletion attack. Specifically, the invention presents a method for allocating a resource comprising the steps of receiving a resource allocation request from a client, imposing a computational task and a time limit for correct completion of the task upon the client, verifying that the task was performed correctly within the time limit, and allocating the resource if the task was correctly performed within the time limit.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
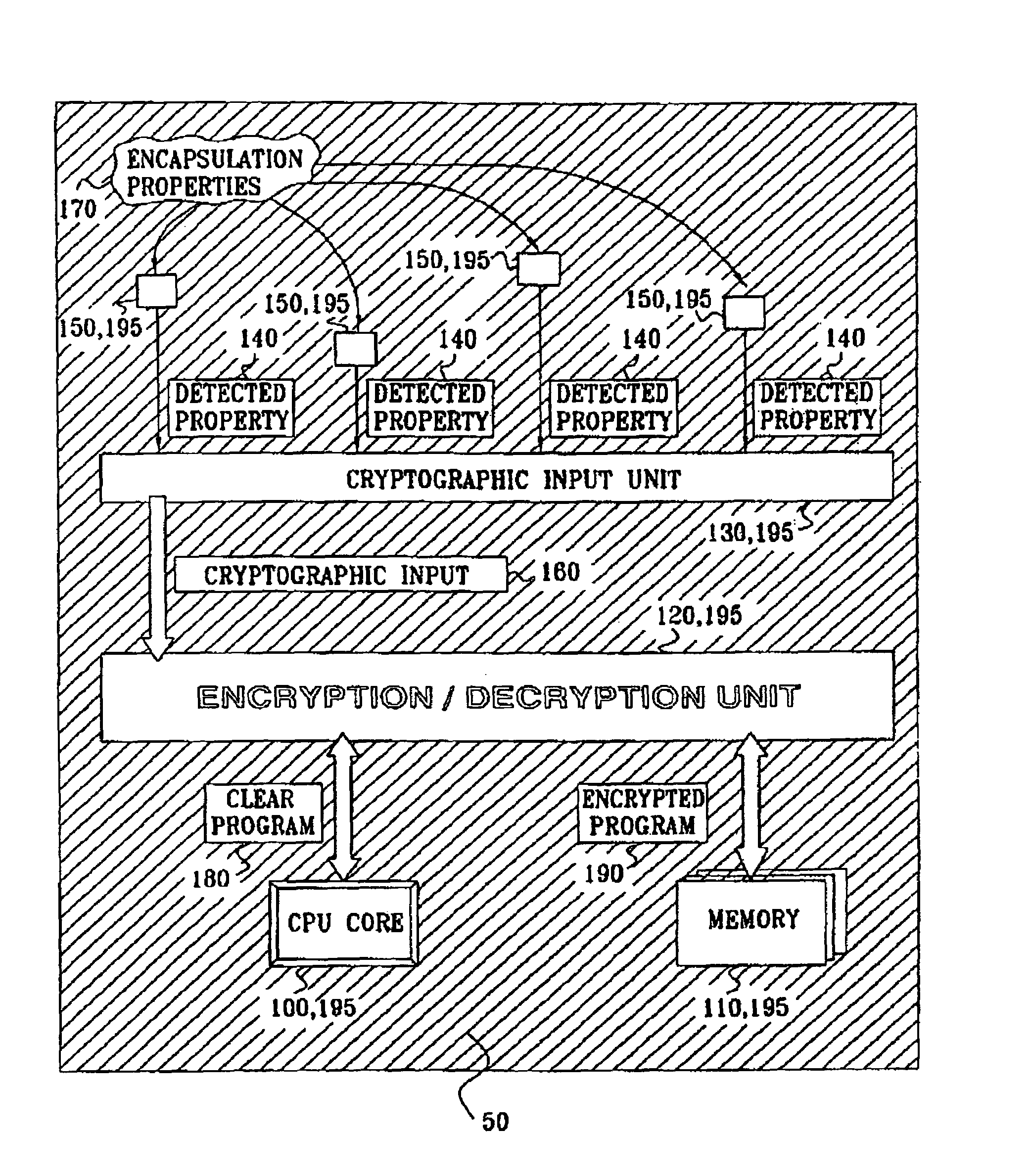
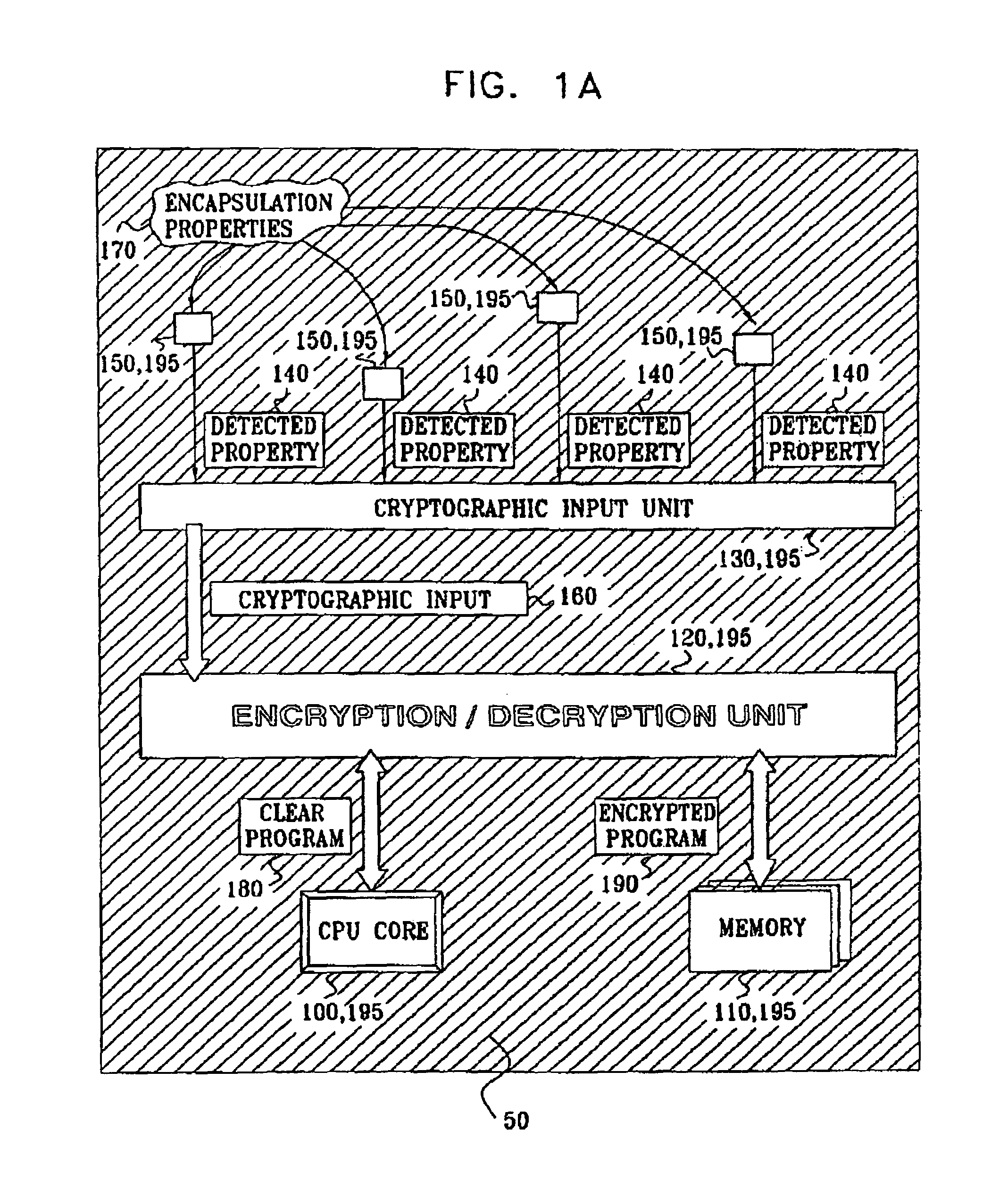
Anti tamper encapsulation for an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7005733B2Protected contentReduce accessKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareEncryption
An integrated circuit device comprising: a circuit which uses encryption; and an encapsulation packaging layer; in which the circuit is responsive to at least one physical parameter of the encapsulation to apply the encryption and / or decryption by reading the key therefrom, so that tampering with the encapsulation to gain access to the circuit causes the encryption and / or decryption to fail.
Owner:UNIVERSAL IMAGING IND LLC
System and method providing disconnected authentication
ActiveUS20050166263A1Minimize the possibilityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHash functionPassword
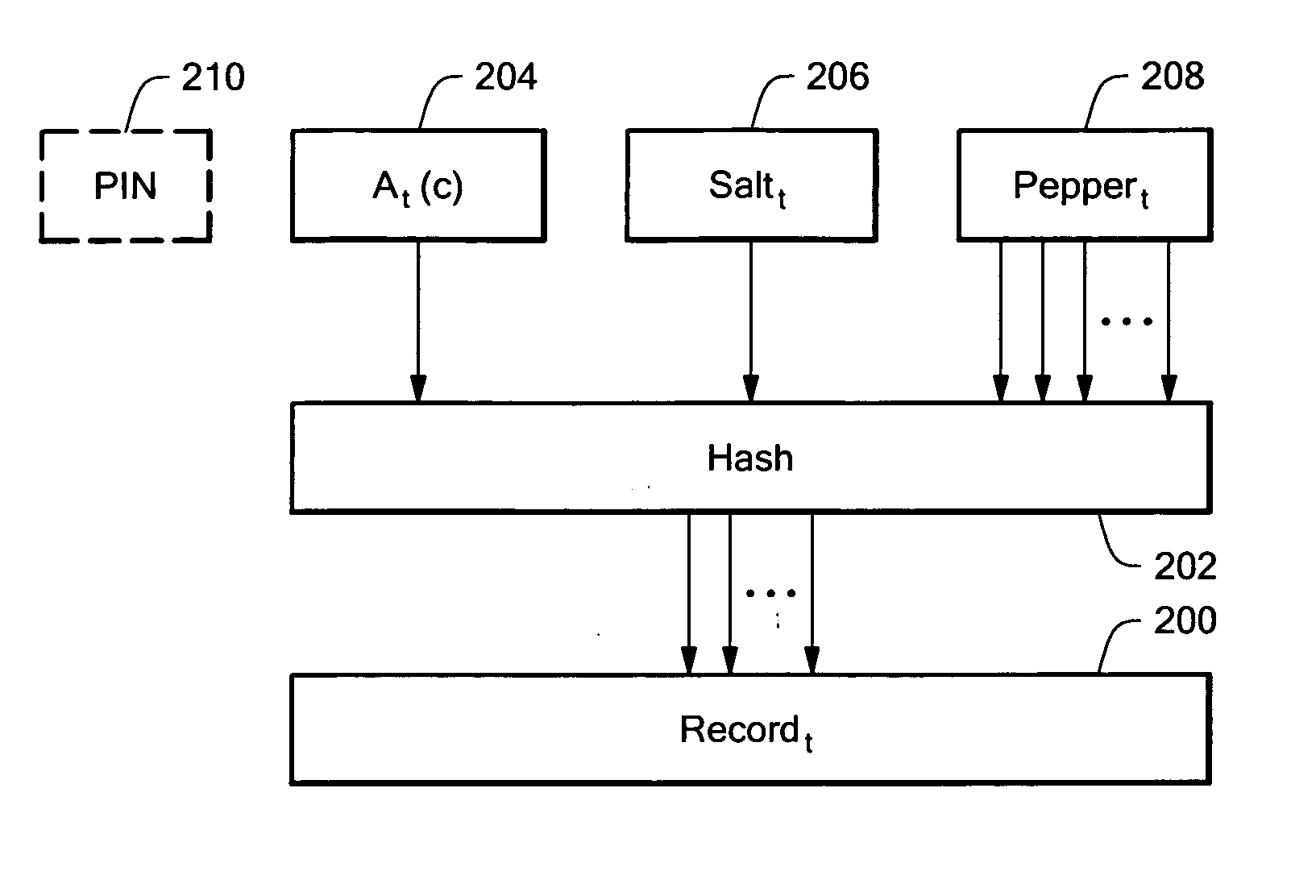
In a system for disconnected authentication, verification records corresponding to given authentication token outputs over a predetermined period of time, sequence of events, and / or set of challenges are downloaded to a verifier. The records include encrypted or hashed information for the given authentication token outputs. In one embodiment using time intervals, for each time interval, token output data, a salt value, and a pepper value, are hashed and compared with the verification record for the time interval. After a successful comparison, a user can access the computer. A PIN value can also be provided as an input the hash function. A portion of the hash function output can be used as a key to decrypt an encrypted (Windows) password, or other sensitive information.
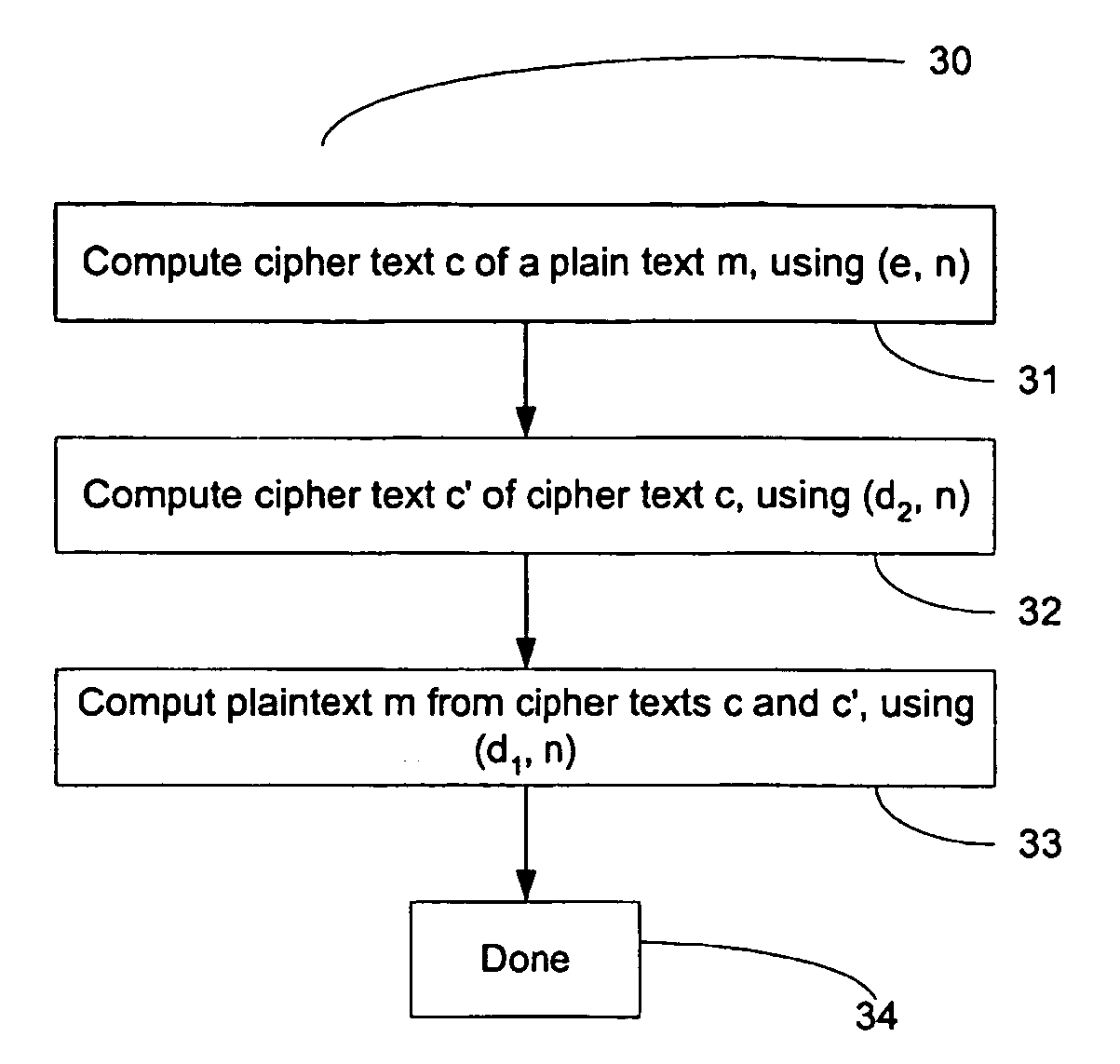
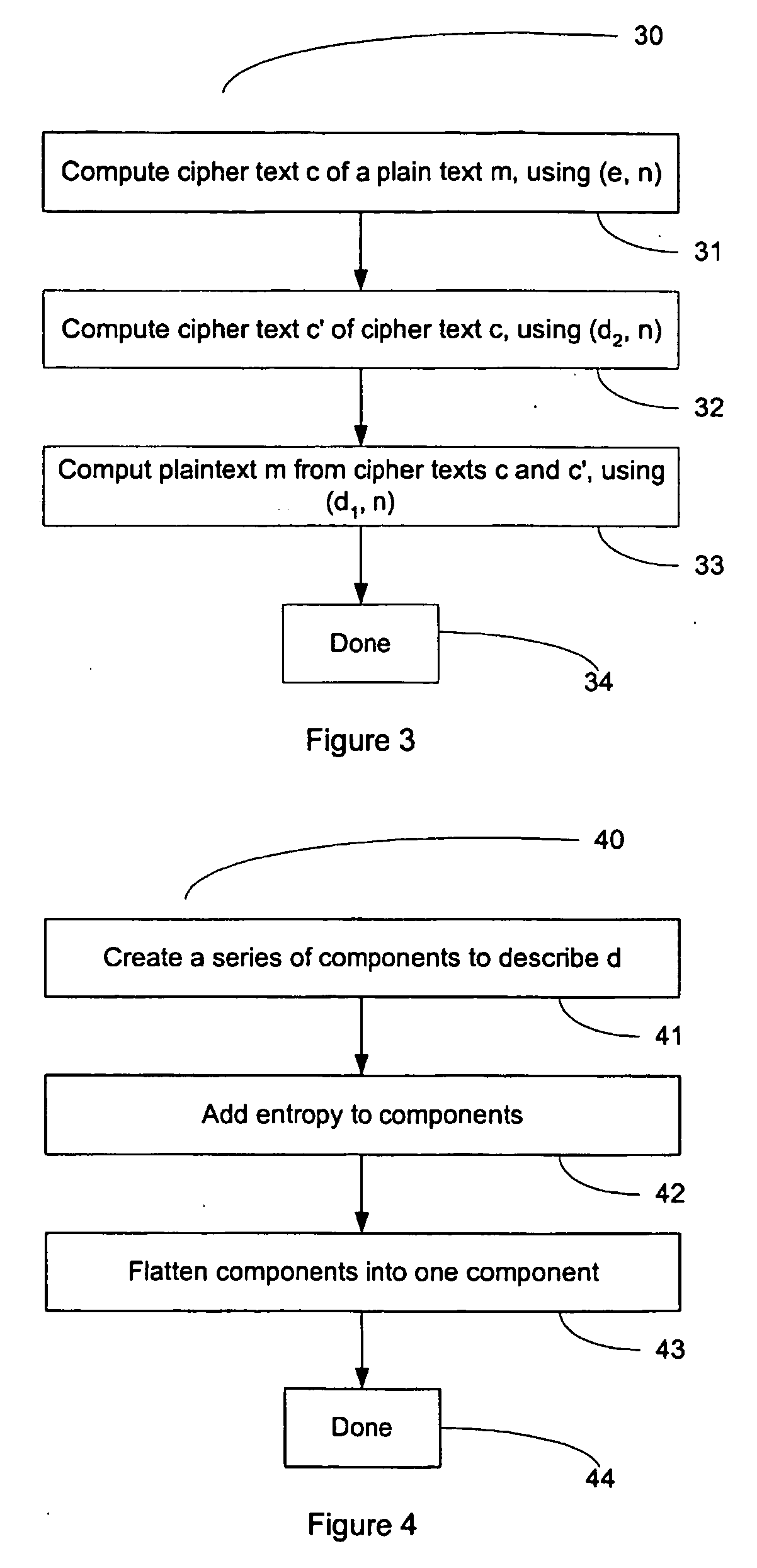
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method for Protecting IC Cards Against Power Analysis Attacks
ActiveUS20080019507A1Prevent power analysis attackImprove automationInternal/peripheral component protectionSecret communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
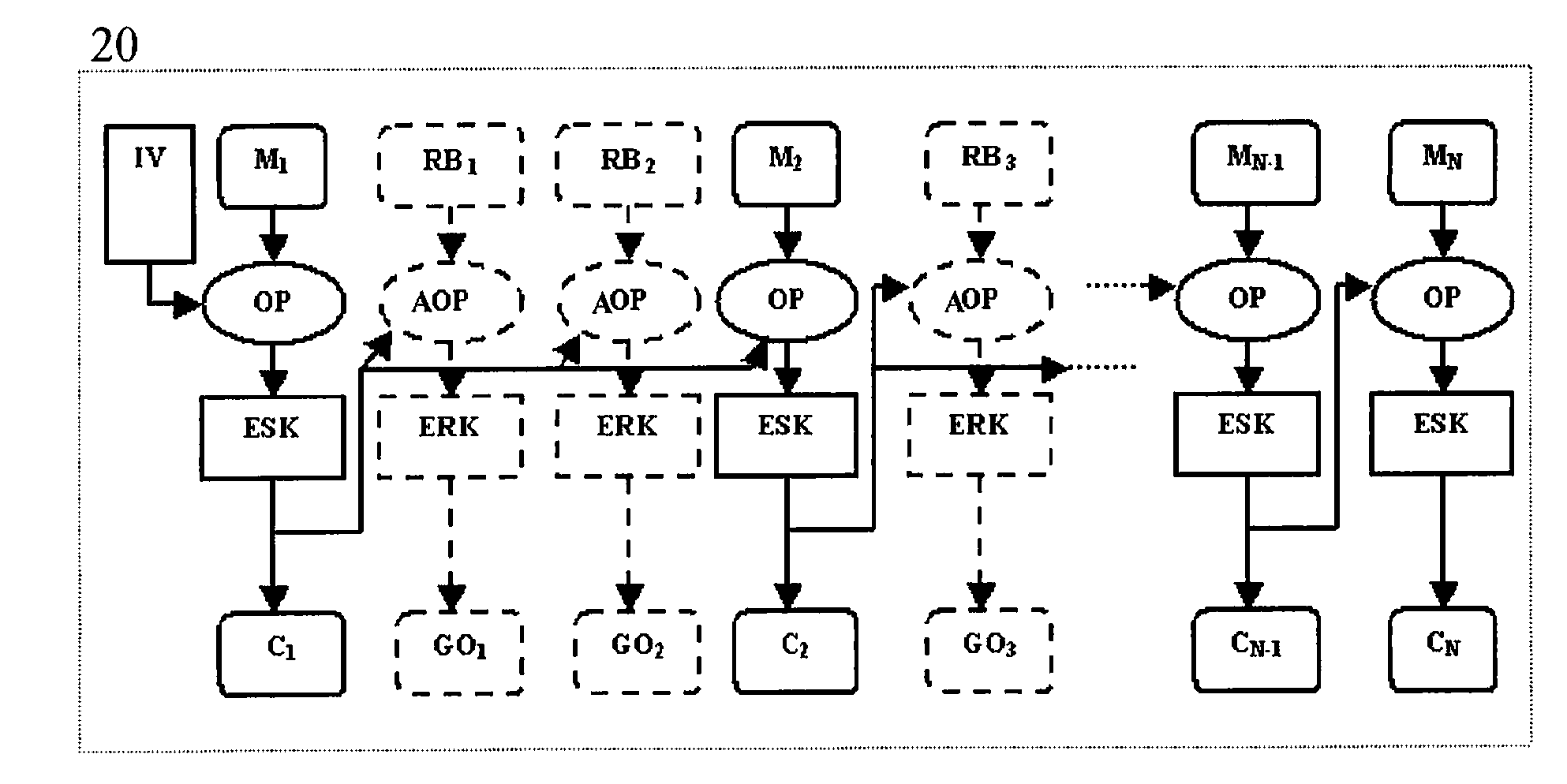
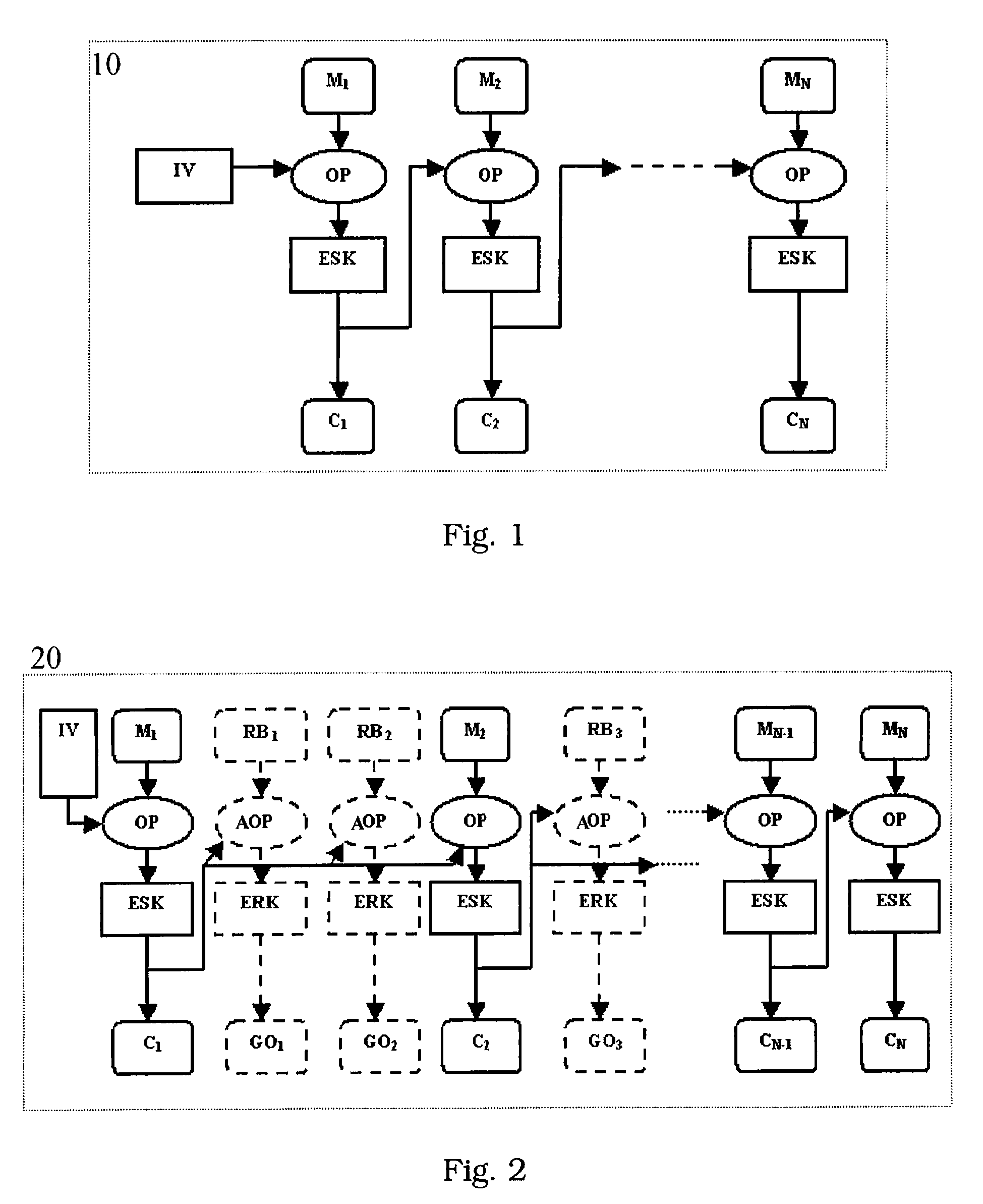
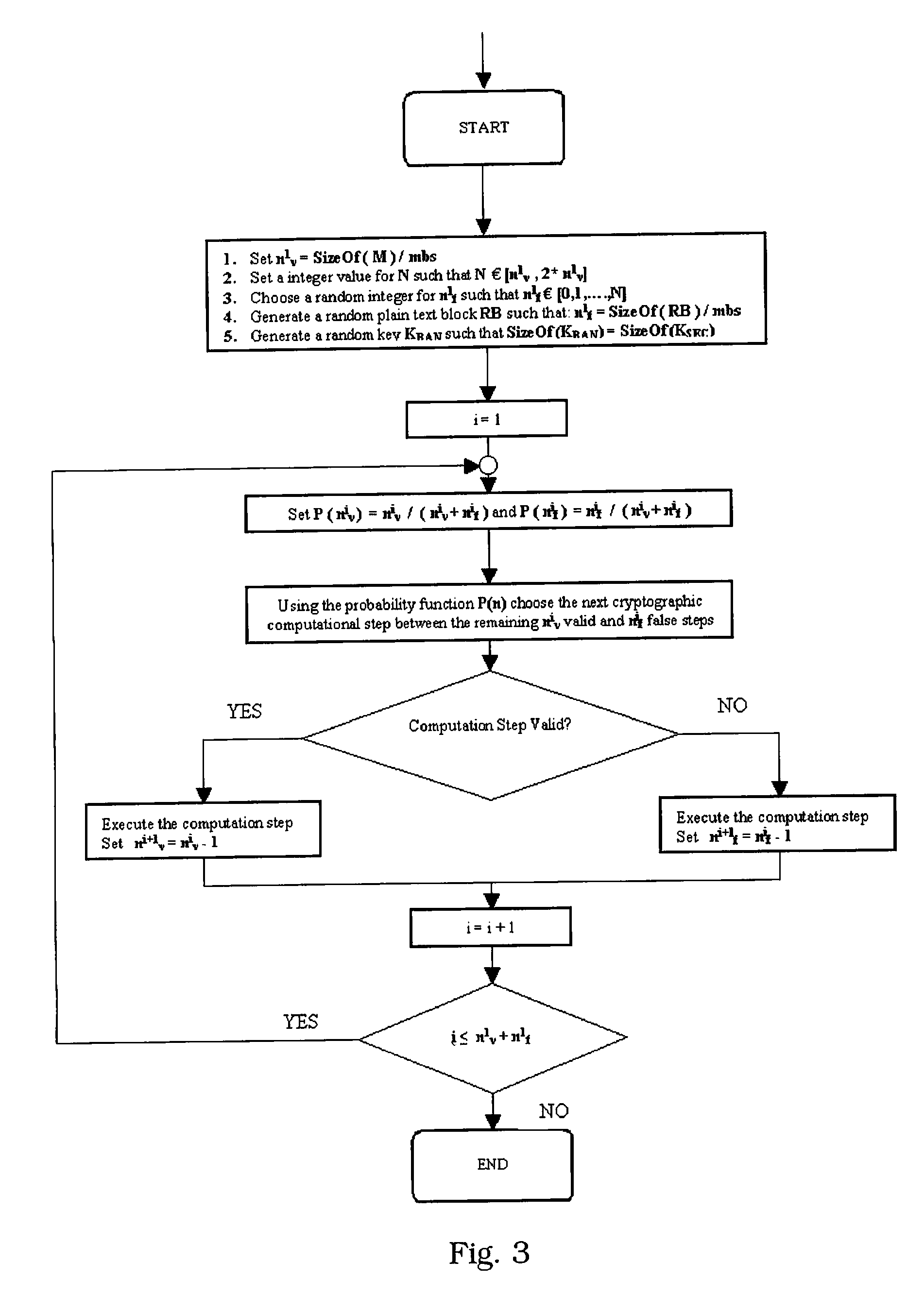
A method for protecting data against power analysis attacks includes at least a first phase of executing a cryptographic operation for ciphering data in corresponding enciphered data through a secret key. The method includes at least a second phase of executing an additional cryptographic operation for ciphering additional data in corresponding enciphered additional data. An execution of the first and second phases is undistinguishable by the data power analysis attacks. Secret parameters are randomly generated and processed by the at least one second phase. The secret parameters include an additional secret key ERK for ciphering the additional data in the corresponding enciphered additional data.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
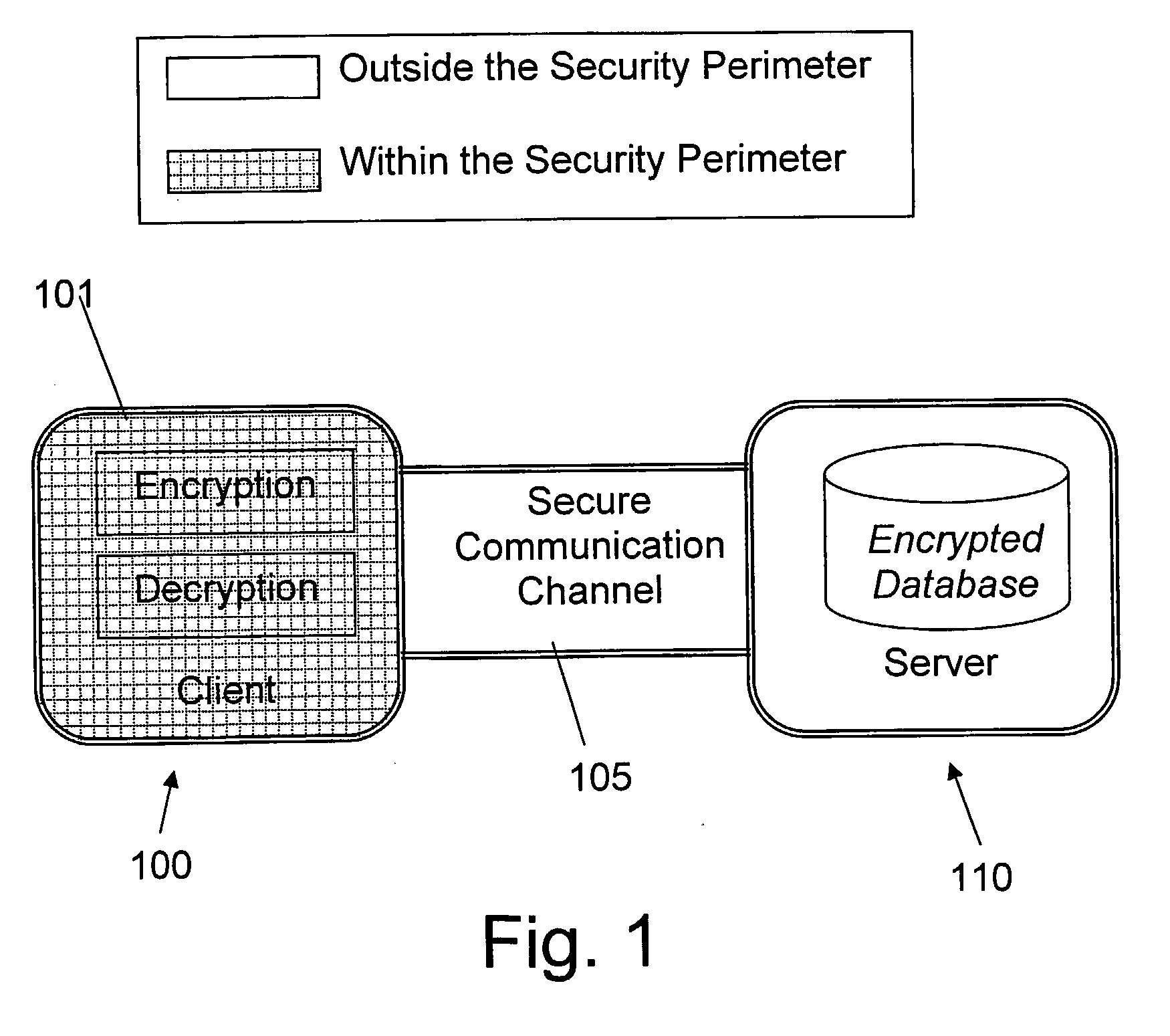
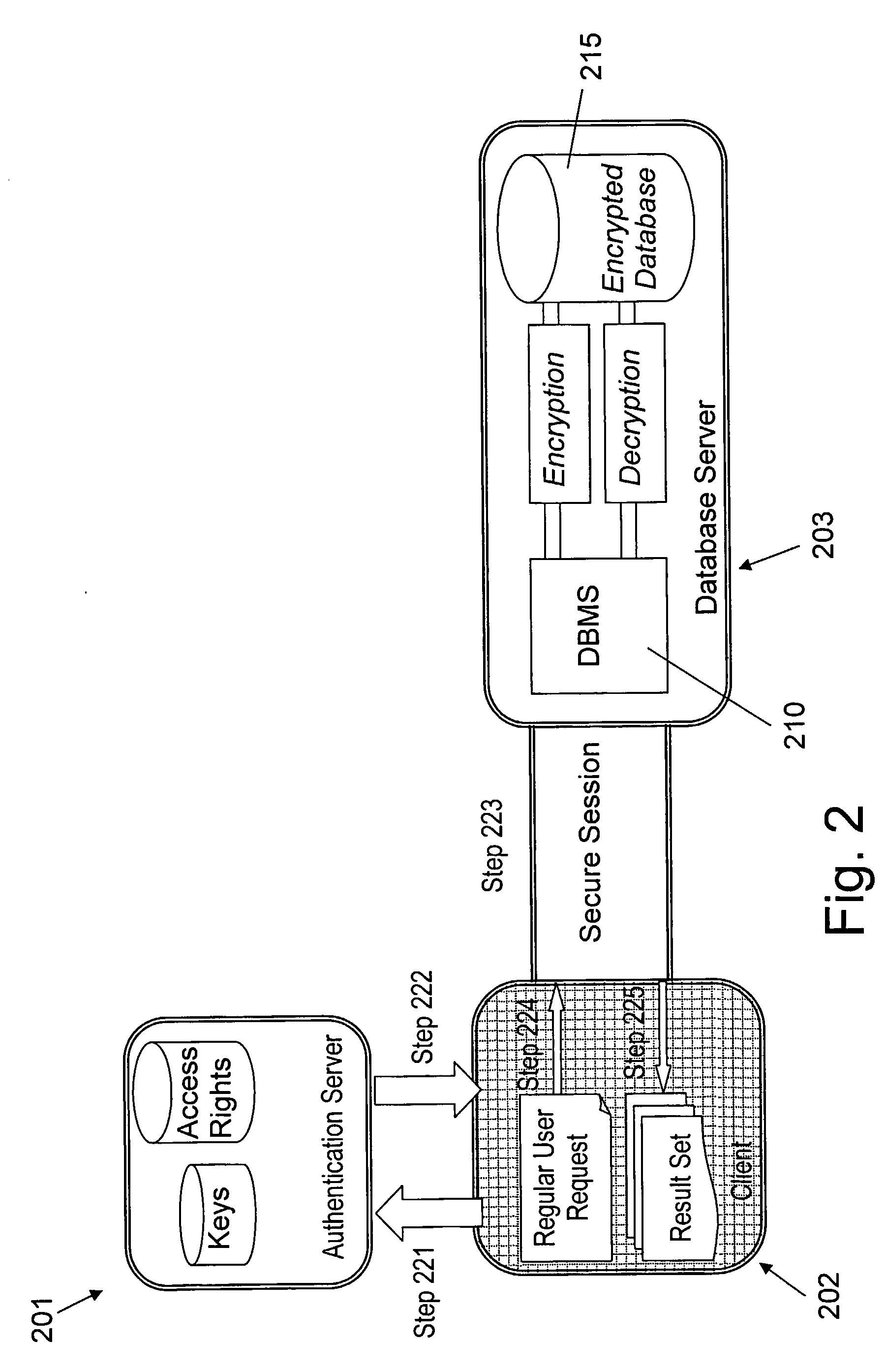
Structure Preserving Database Encryption Method and System
ActiveUS20080133935A1Easy accessAvoid contactKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageDatabase indexMulti user environment
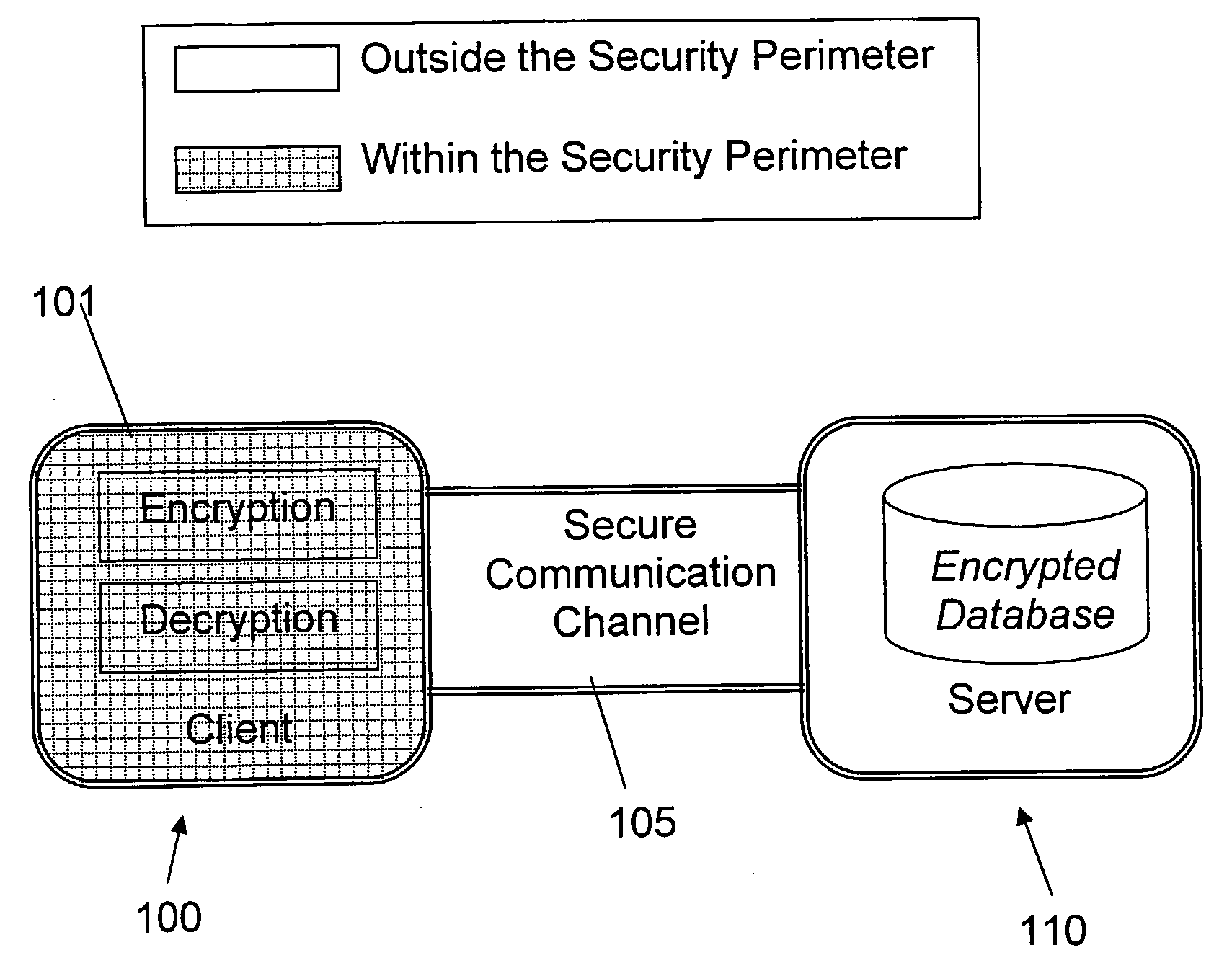
A database encryption system and method, the Structure Preserving Database Encryption (SPDE), is presented. In the SPDE method, each database cell is encrypted with its unique position. The SPDE method permits to convert a conventional database index into a secure one, so that the time complexity of all queries is maintained. No one with access to the encrypted database can learn anything about its content without the encryption key. Also a secure index for an encrypted database is provided. Furthermore, secure database indexing system and method are described, providing protection against information leakage and unauthorized modifications by using encryption, dummy values and pooling, and supporting discretionary access control in a multi-user environment.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
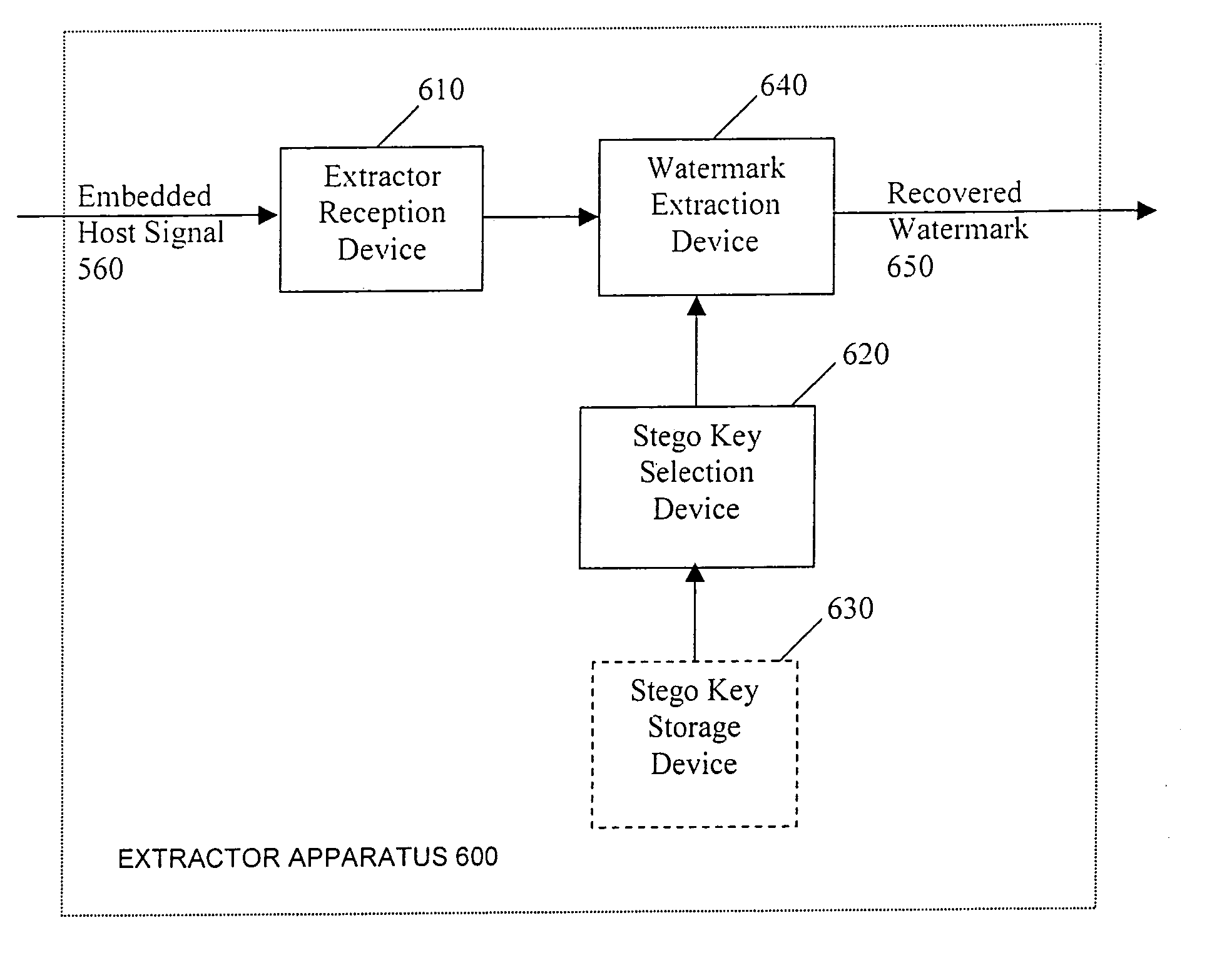
System reactions to the detection of embedded watermarks in a digital host content
InactiveUS7369677B2Increase payload capacitySacrificing complexityUser identity/authority verificationSpeech analysisSystem requirementsSystem recovery
Methods for adapting the operation of a system in response to the detection of embedded watermarks from a digital host content are provided. A digital host content is received and examined for the presence of watermarks. In response to the detection of embedded watermarks and in accordance with the value, type, density or spacing of the detected watermarks, one or more system reactions may take place. These reactions include conditionally allowing the system to resume its normal operation, prohibiting the system from resuming its normal operation, degrading the quality of the digital host content or changing the security status of the digital host content. In response to the extraction of weak watermarks that do not meet the desired system requirements, the extraction operation may be modified or extended to enable the detection of strong watermarks.
Owner:IP ACQUISITIONS LLC
Method and system for establishing cryptographic communications between a remote device and a medical device
ActiveUS8472630B2Less processing powerKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareMaster key
A method and system establishing cryptographic communications between a remote device and a medical device, with the medical device having less processing power than the remote device are disclosed. The method may comprise establishing unencrypted communication between the remote device and the medical device, generating an asymmetric key pair by the remote device comprising a public key and a private key, generating a key request message and sending of the key request message together with the public key to the medical device, generating a pre-master key and encryption of the pre-master key with the received public key by the medical device, generating a key response message and sending of the key response message together with the encrypted pre-master key from the medical device to the remote device, decrypting the encrypted pre-master key with the private key by the remote device, and deriving a master key as a symmetric key from the pre-master key.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
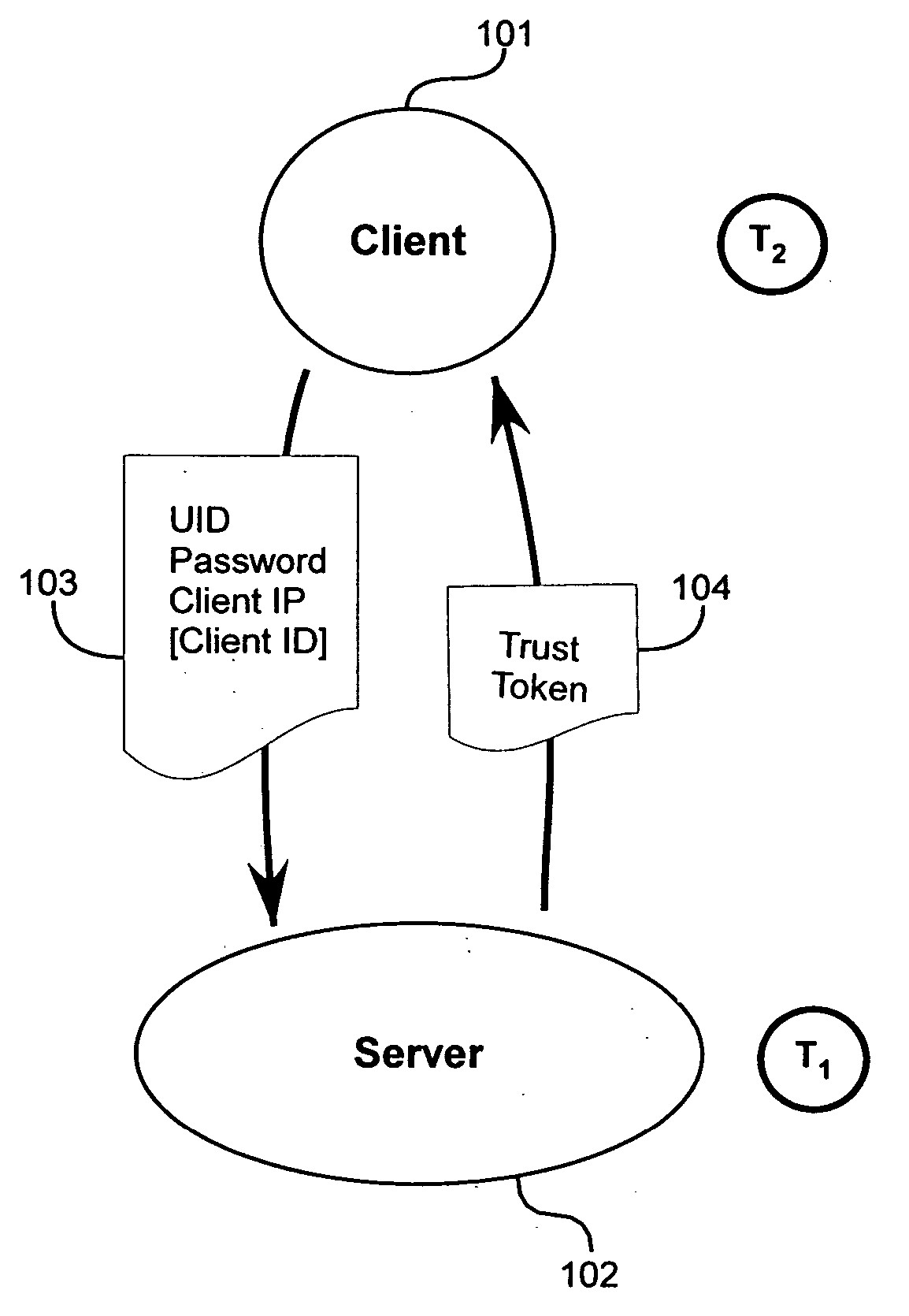
Method and apparatus for trust-based, fine-grained rate limiting of network requests
ActiveUS20050108551A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRate limitingInternet traffic
A method and apparatus for fine-grained, trust-based rate limiting of network requests distinguishes trusted network traffic from untrusted network traffic at the granularity of an individual user / machine combination, so that network traffic policing measures are readily implemented against untrusted and potentially hostile traffic without compromising service to trusted users. A server establishes a user / client pair as trusted by issuing a trust token to the client when successfully authenticating to the server for the first time. Subsequently, the client provides the trust token at login. At the server, rate policies apportion bandwidth according to type of traffic: network requests that include a valid trust token are granted highest priority. Rate policies further specify bandwidth restrictions imposed for untrusted network traffic. This scheme enables the server to throttle untrusted password-guessing requests from crackers without penalizing most friendly logins and only slightly penalizing the relatively few untrusted friendly logins.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Method for checking an m out of n code
InactiveUS20140230055A1Inhibit outputReliably recognizeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionProgramming languageReducer
A method and a circuit system for checking an m out of n code are provided. The method uses a code checker, to which at least one code reducer is assigned, a reduction of the code word width to in each case half being carried out using the at least one code reducer until a 1 out of x (x=n / 2, n / 4, n / 8 . . . ) code or another code which is not reducible further in this way is provided, each step of the code reducer additionally being connected to different bits of a counter, the 1 out of x code or the code which is not further reducible being checked and additionally the signal pairs of each step being checked.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method, system and computer program for protecting user credentials against security attacks
InactiveUS20090055642A1Eliminate needEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCryptographic attack countermeasuresThird partyClient-side
A method, system and computer program is provided for protecting against one or more security attacks from third parties directed at obtaining user credentials on an unauthorized basis, as between a client computer associated with a user and a server computer is provided. The server computer defines a trusted Public Key Cryptography utility for use on the client computer. The Public Key Cryptography utility is operable to perform one or more cryptographic operations consisting of encrypting / decrypting data, authenticating data, and / or authenticating a sender, decrypting and / or verifying data. The user authenticates to the Public Key Cryptography utility, thereby invoking the accessing of user credentials associated with the user, as defined by the server computer. The Public Key Cryptography Utility facilitates the communication of the user credentials to the server computer, whether directly or indirectly via an authentication agent, the server computer thereby authenticating the user. In response, the server computer providing access to one or more system resources linked to the server computer to the user. The present invention also provides a series of methods enabling the server computer to authenticate the user by operation of the Public Key Cryptography utility and / or based on enrolment of the user and providing the Public Key Cryptography utility to the user.
Owner:ECHOWORX CORP
Systems and methods to securely generate shared keys
ActiveUS20050251680A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMaster keyRe keying
A method for secure bidirectional communication between two systems is described. A first key pair and a second key pair are generated, the latter including a second public key that is generated based upon a shared secret. First and second public keys are sent to a second system, and third and fourth public keys are received from the second system. The fourth public key is generated based upon the shared secret. A master key for encrypting messages is calculated based upon a first private key, a second private key, the third public key and the fourth public key. For re-keying, a new second key pair having a new second public key and a new second private key is generated, and a new fourth public key is received. A new master key is calculated using elliptic curve calculations using the new second private key and the new fourth public key.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Communication system and security assurance device
InactiveUS20060048228A1Memory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationCountermeasureCommunications system
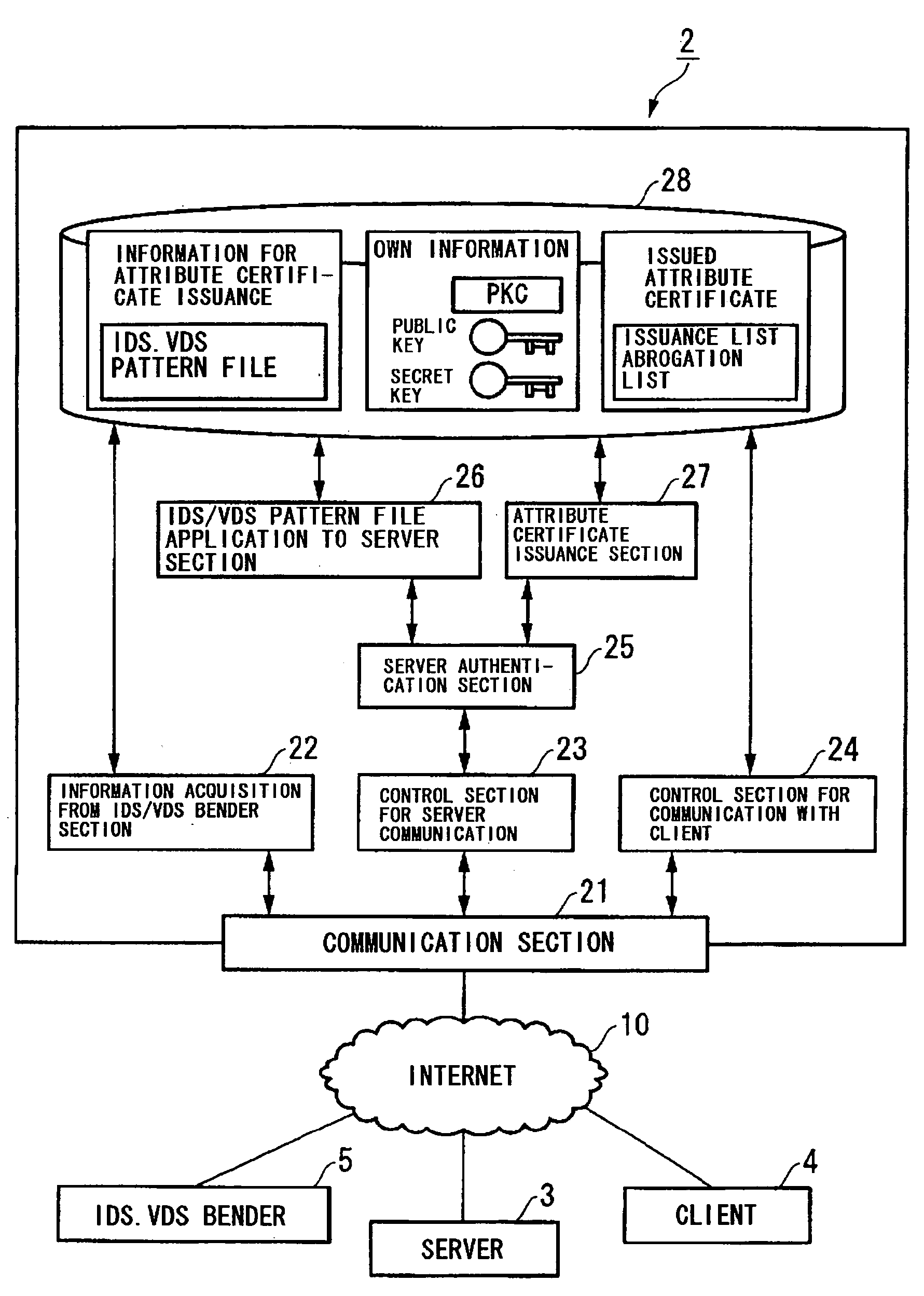
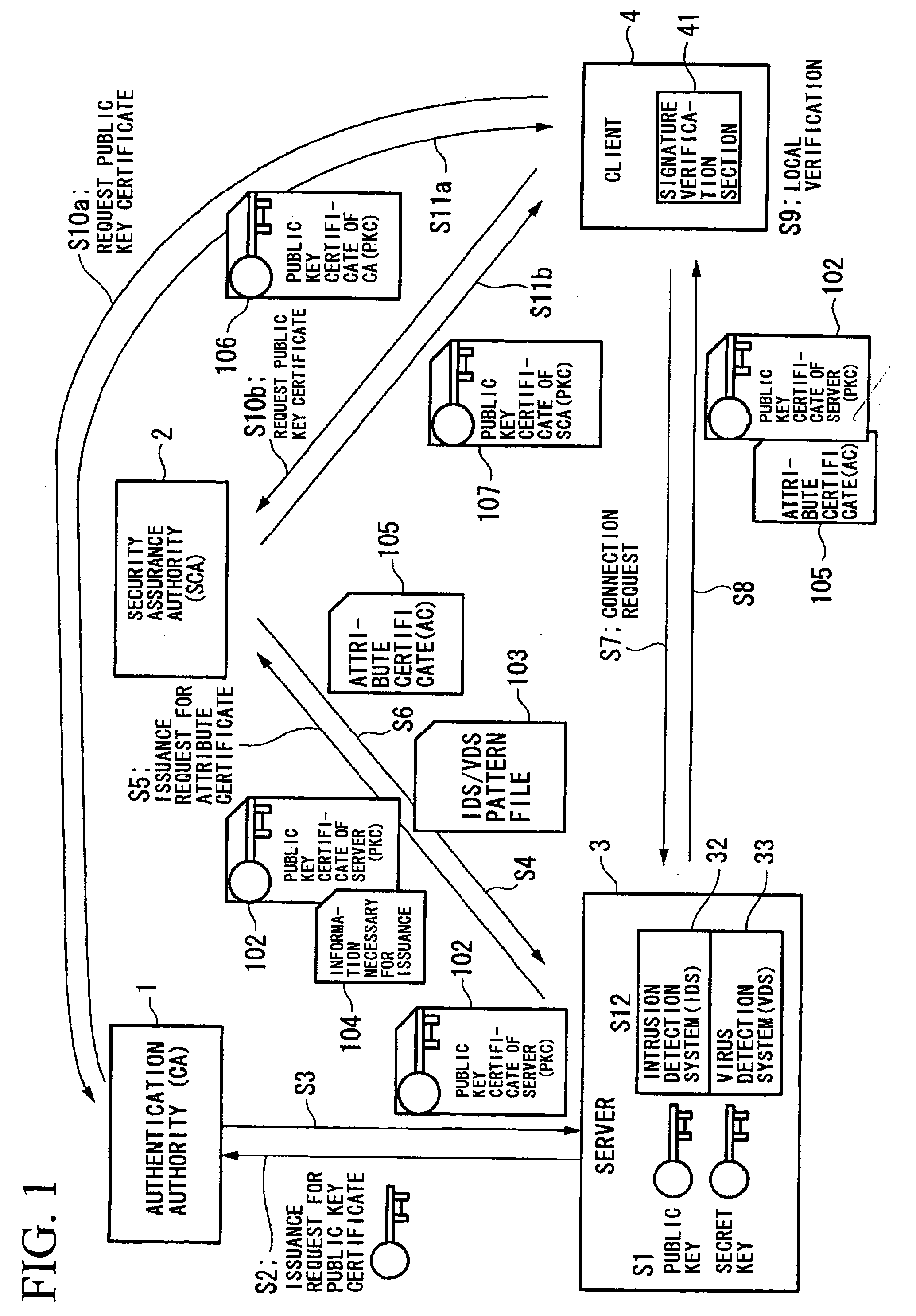
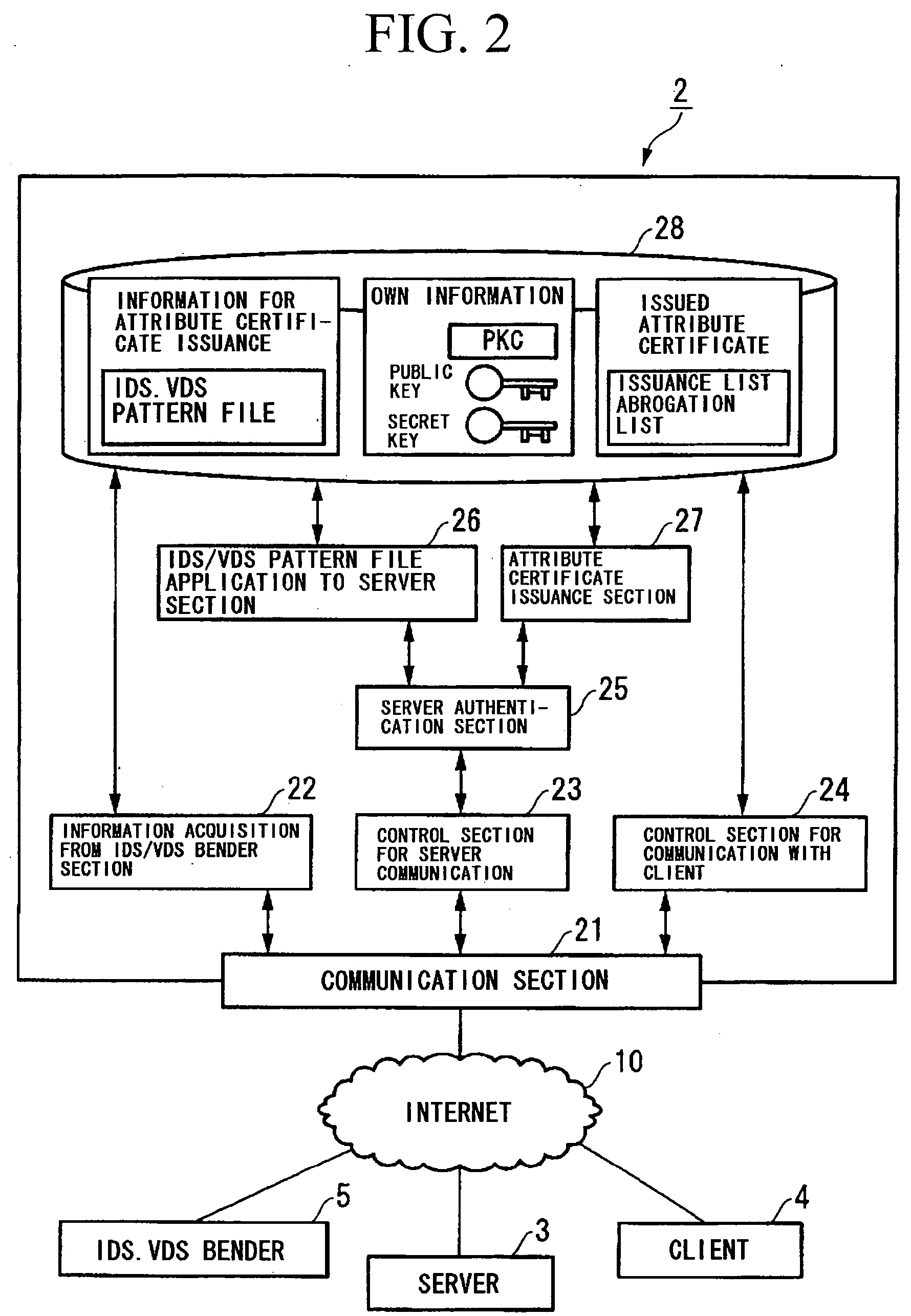
A communication system and a security assurance device are proposed, which are capable of assuring that a target party for communication is implementing security countermeasures. A server 3 transmits information 104 necessary for AC issuance to a security assurance authority 2. The security assurance authority 2 verifies the security of the server 3 during communication based upon this information necessary for AC issuance 104. And, when the security of the server 3 during communication is confirmed, the security assurance authority 2 issues an AC 105 which proves the security of the server 3 during communication, and transmits it to the server 3. Upon receipt of this AC 105, the server 3 transmits the AC 105 to a client 4, according to a connection request from the client 4. And, upon receipt of this AC 105, the client 4 verifies the security during communication of the server 3, based upon the AC 105.
Owner:KDDI CORP +1
Methods and apparatus for secure data sharing
ActiveUS20130013921A1User identity/authority verificationCryptographic attack countermeasuresData sharingElectronic mail
This disclosure relates to methods and apparatus for securely and easily sharing data over a communications network. As communications services on a communications network are continuously becoming cheaper, faster, and easier to use, more users are becoming receptive to the idea of sharing data over the communications network. However, although E-mails and web folders, to a certain degree, provide easy-to-use or secure data sharing mechanisms, none of the existing data sharing methods is both easy-to-use and highly secure. This disclosure provides methods and apparatus for easily and securely sharing data over a communications network.
Owner:ETSY INC
System and method of hiding cryptographic private keys
ActiveUS20050002532A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareEnd user
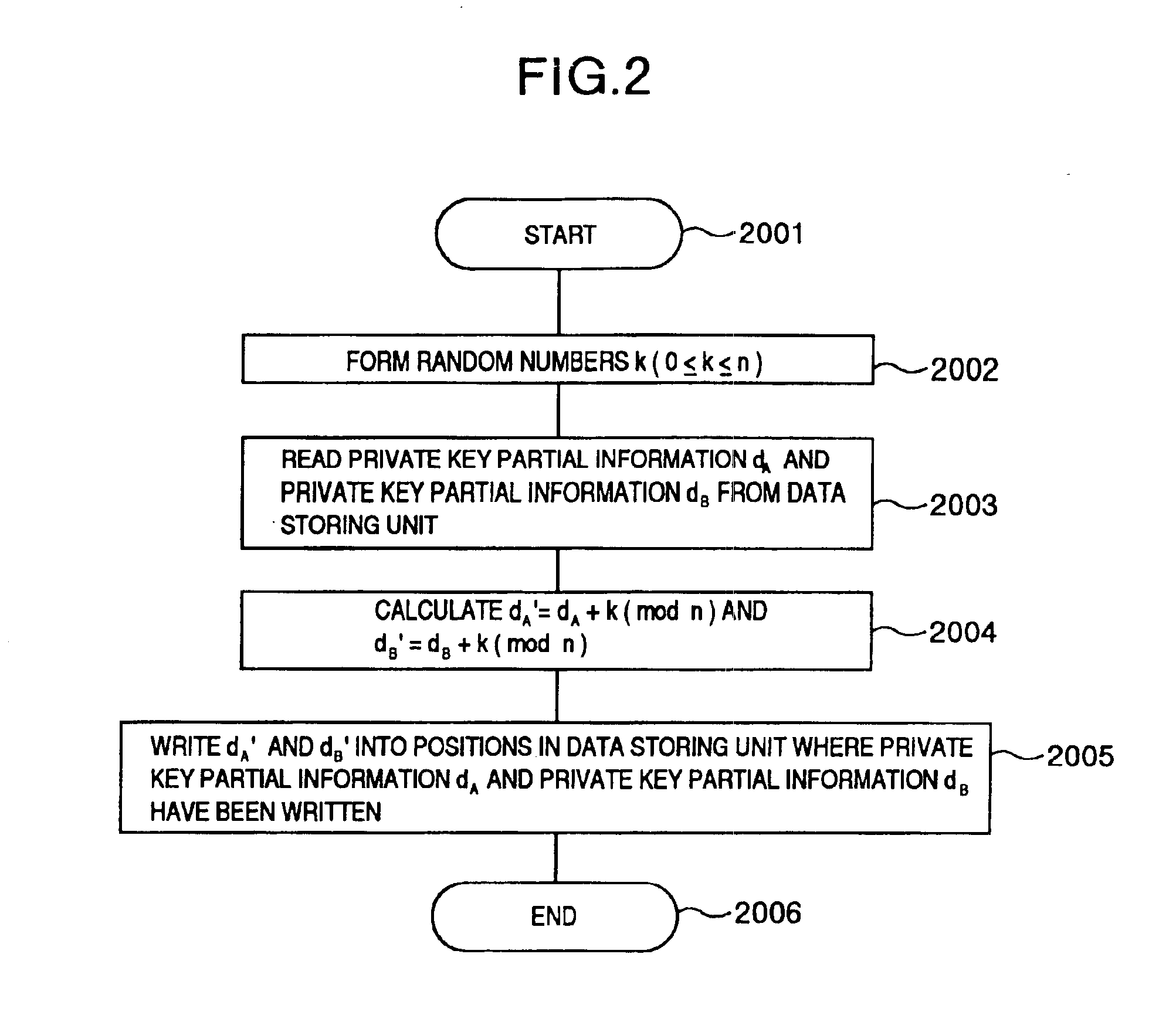
The invention relates to a system and method of hiding cryptographic private keys. While public / private key encryption systems are considered to be secure, the private keys ultimately must be stored in some location—in fact, in some digital commerce systems the private key is sent to the end user as part of an executable file such as an audio player and audio file. Thus, attackers can obtain access to the private key. The broad concept of the invention is to split the private key up into parts which are obfuscated, but still kept in a form that allows the encrypted data to be decrypted. One technique for obfuscating the private key uses modulo arithmetic.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS
System and method for protecting computer software from a white box attack
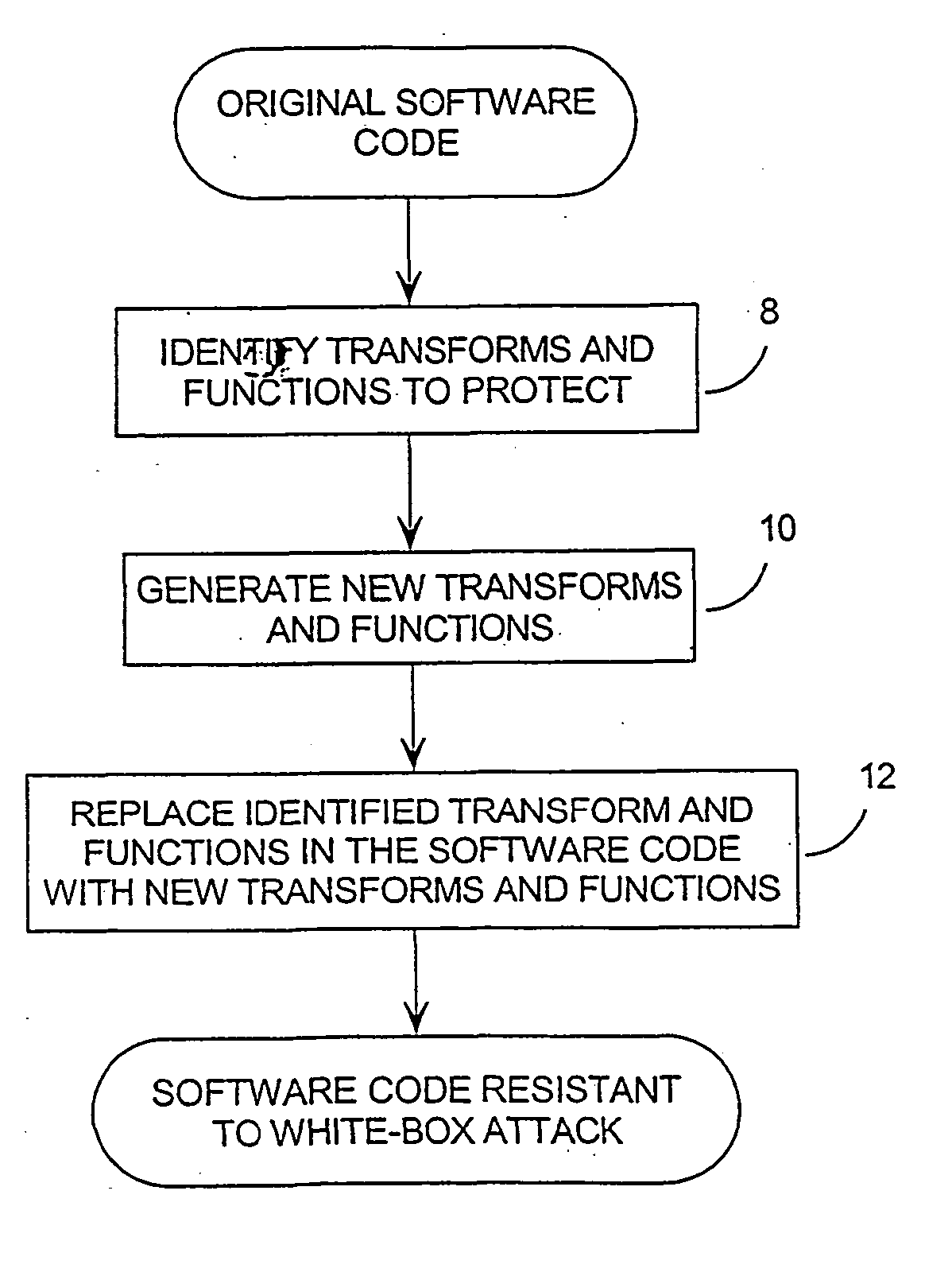
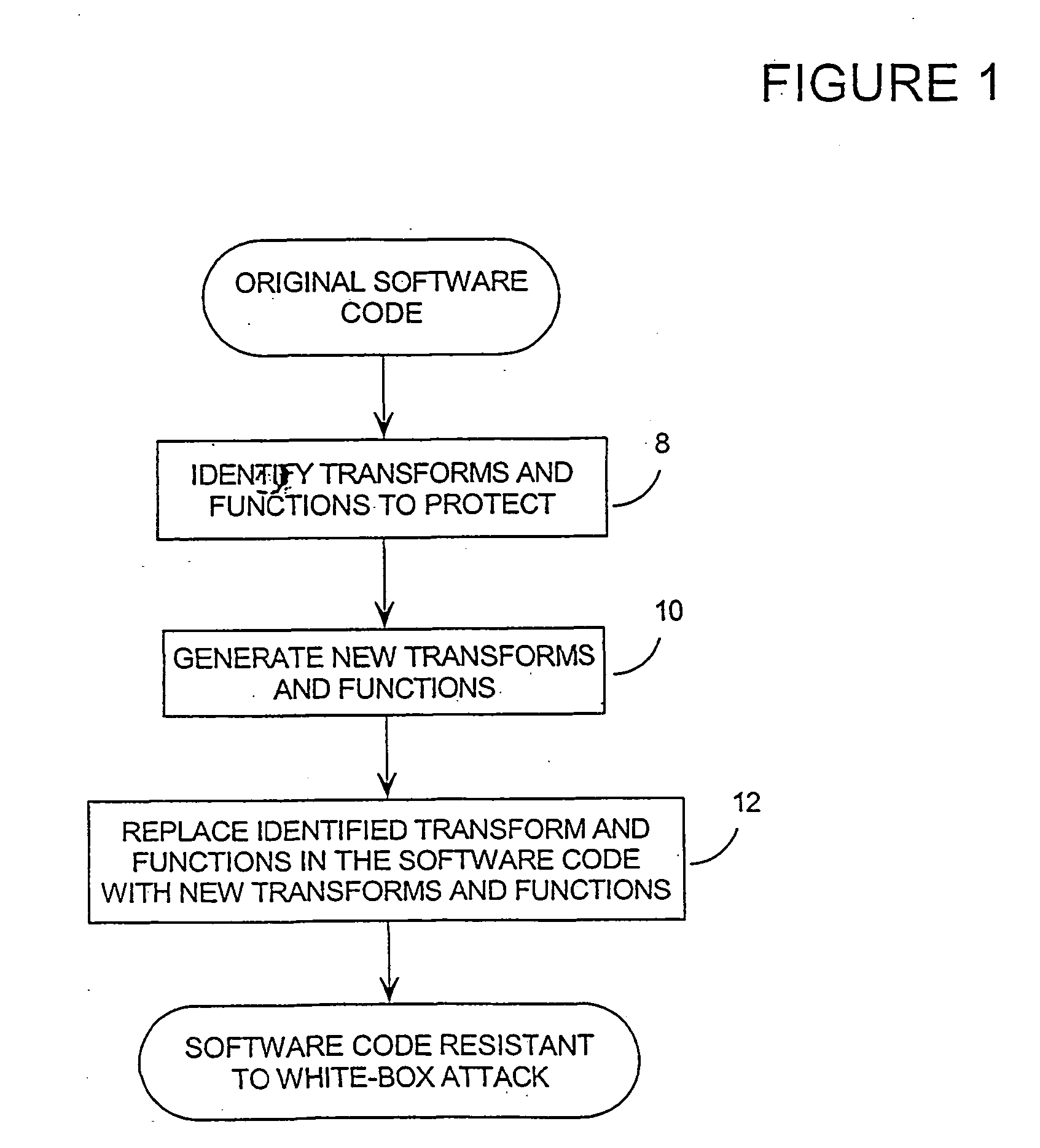
InactiveUS20060140401A1Improve securityIncreased complexityDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSoftware engineeringComputer software
Methods and systems related to increasing the cryptographic security of keys used by software with cryptographic functions. This is done by increasing the mathematical complexity of the software. The components and functions used by the software are first determined and, using these components, functions, and the data exchanged between them, the software is made more resistant to analysis. The methods used in increasing analytical resistance are grouped into 3 general types: adjusting the information exchanged between the components, replacing some components with different but related components, and adjusting the data flow between the components.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS
Processing apparatus, program, or system of secret information
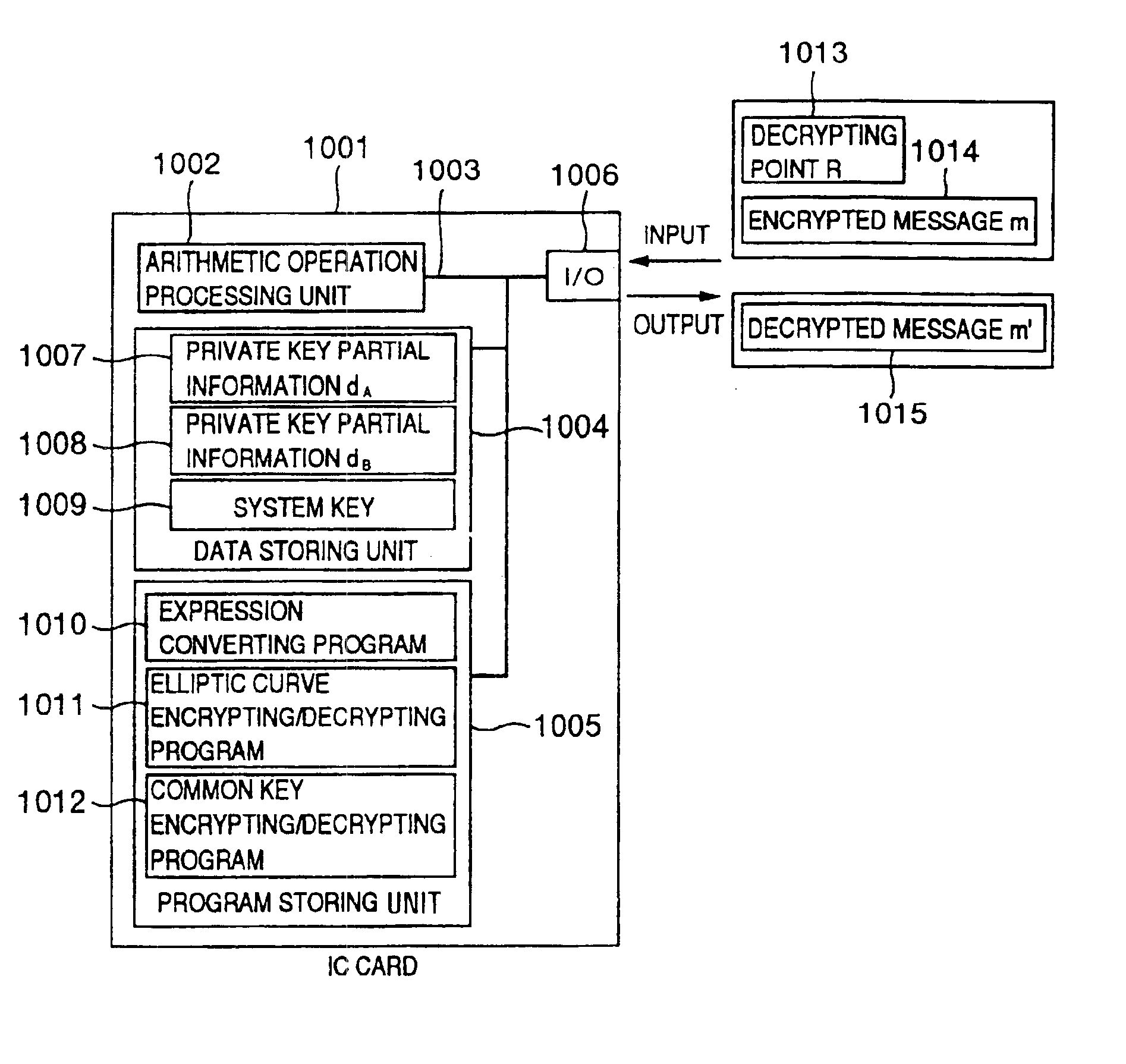
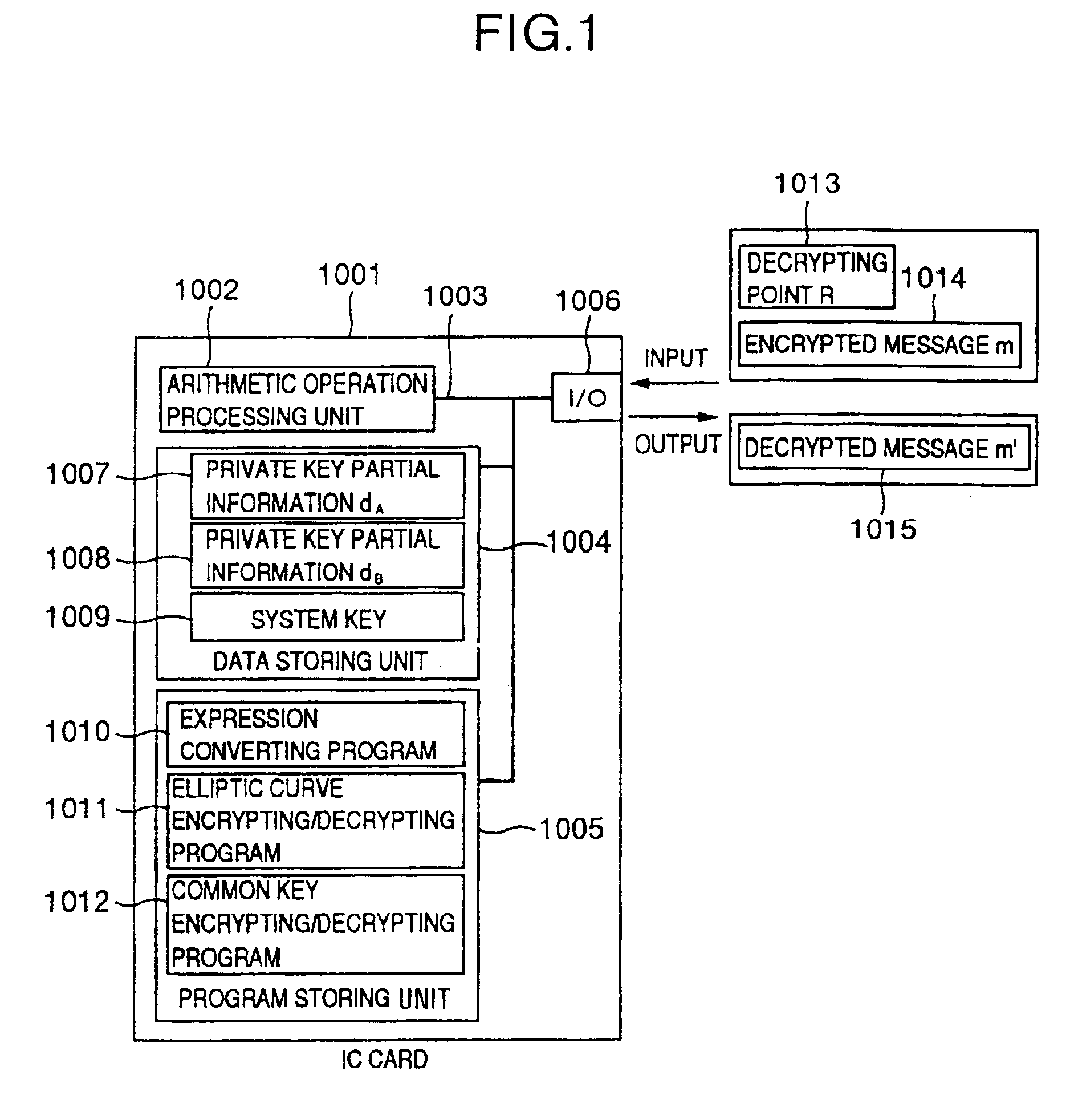
InactiveUS6873706B1Reduce correlationTotal current dropKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
To provide a secure cryptographic device such as an IC card which can endure TA (Timing Attack), DPA (Differential Power Analysis), SPA (Simple Power Analysis), or the like as an attaching method of presuming secret information held therein, when the secret information held in the card or another information which is used in the secret information or an arithmetic operation using such secret information when such an arithmetic operation is performed is shown by a plurality of expressing methods and the arithmetic operation is performed, thereby making an arithmetic operation processing method different each time the arithmetic operation is performed and making each of an arithmetic operation time, an intensity of a generated electromagnetic wave, and a current consumption different.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
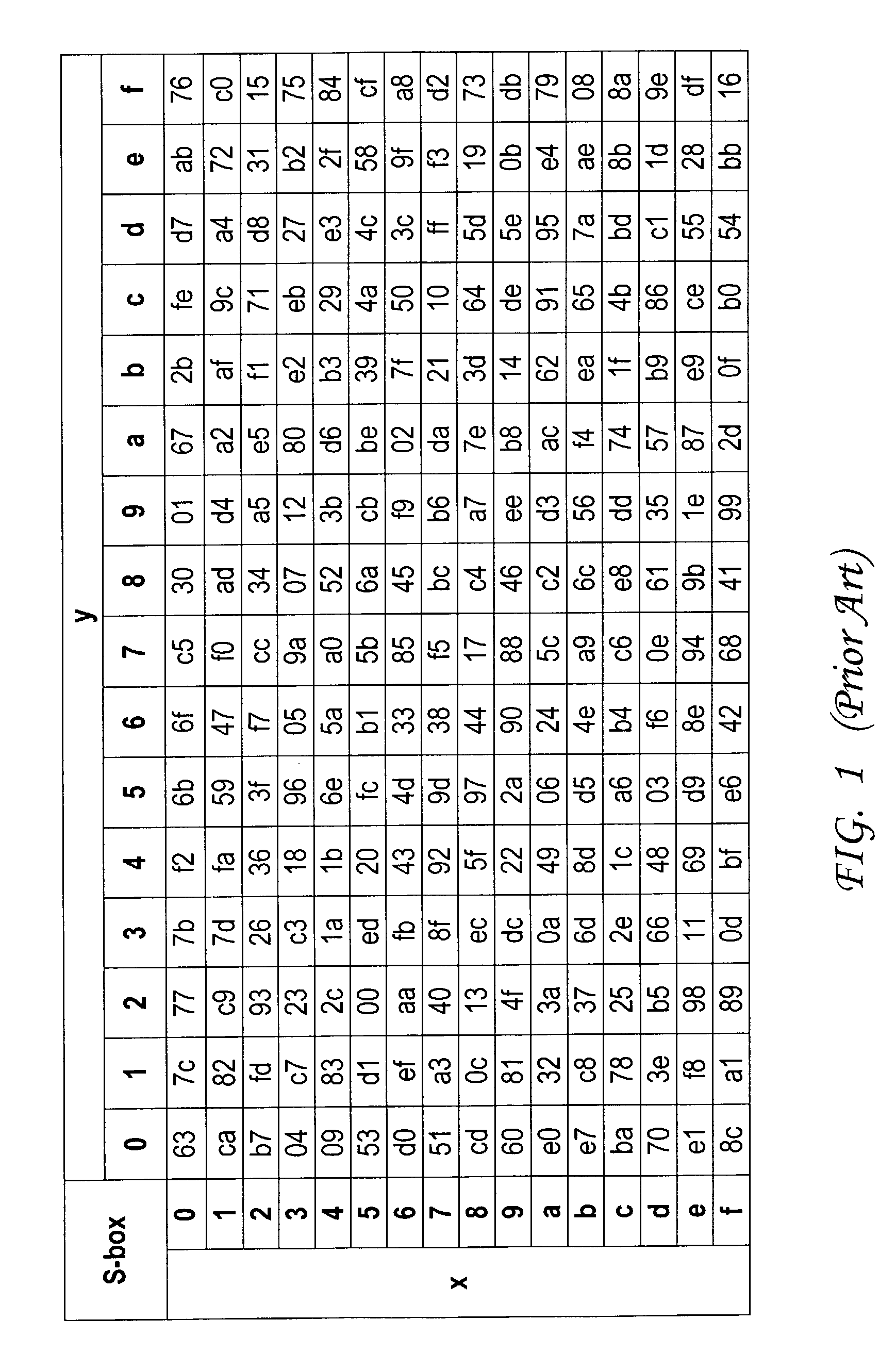
Encryption protection method
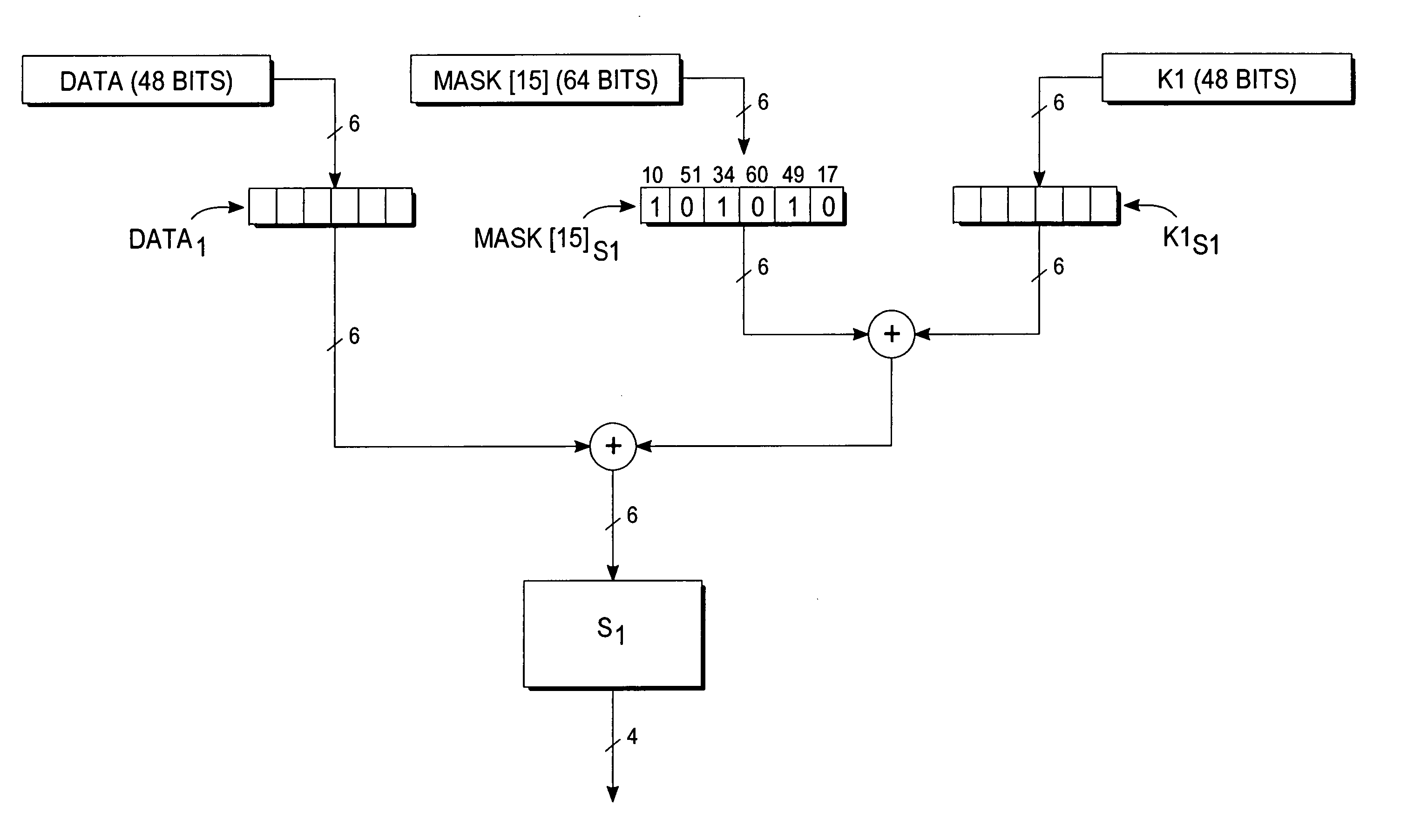
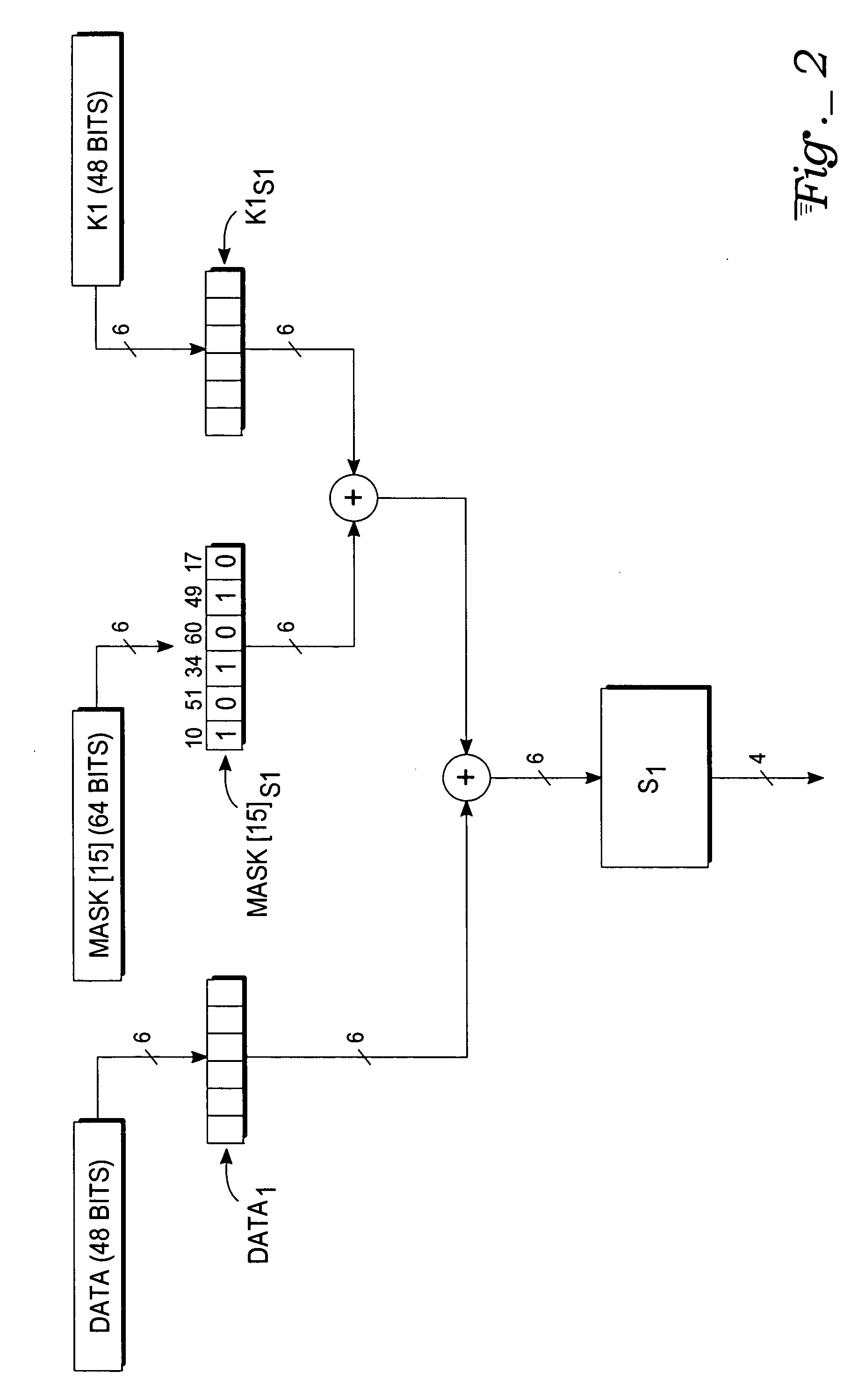
InactiveUS20080019503A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecret communicationComputer hardwareS-box
A deterministic blinding method for cipher algorithms that employ key-mixing and substitution (S-box) operations uses a masking table constructed with a true mask and a plurality of dummy masks corresponding to every possible S-box input. Each mask is applied in the key-mixing operation (e.g., bitwise XOR) to the cipher key or to round subkeys to generate true and dummy keys or subkeys that are applied to the data blocks within the overall cipher algorithm or within individual cipher rounds. The mask values prevent side-channel statistical analyses from determining the true from the dummy keys or subkeys. The true mask is identifiable to the cipher but not by external observers.
Owner:CRYPTOGRAPHY RESEARCH
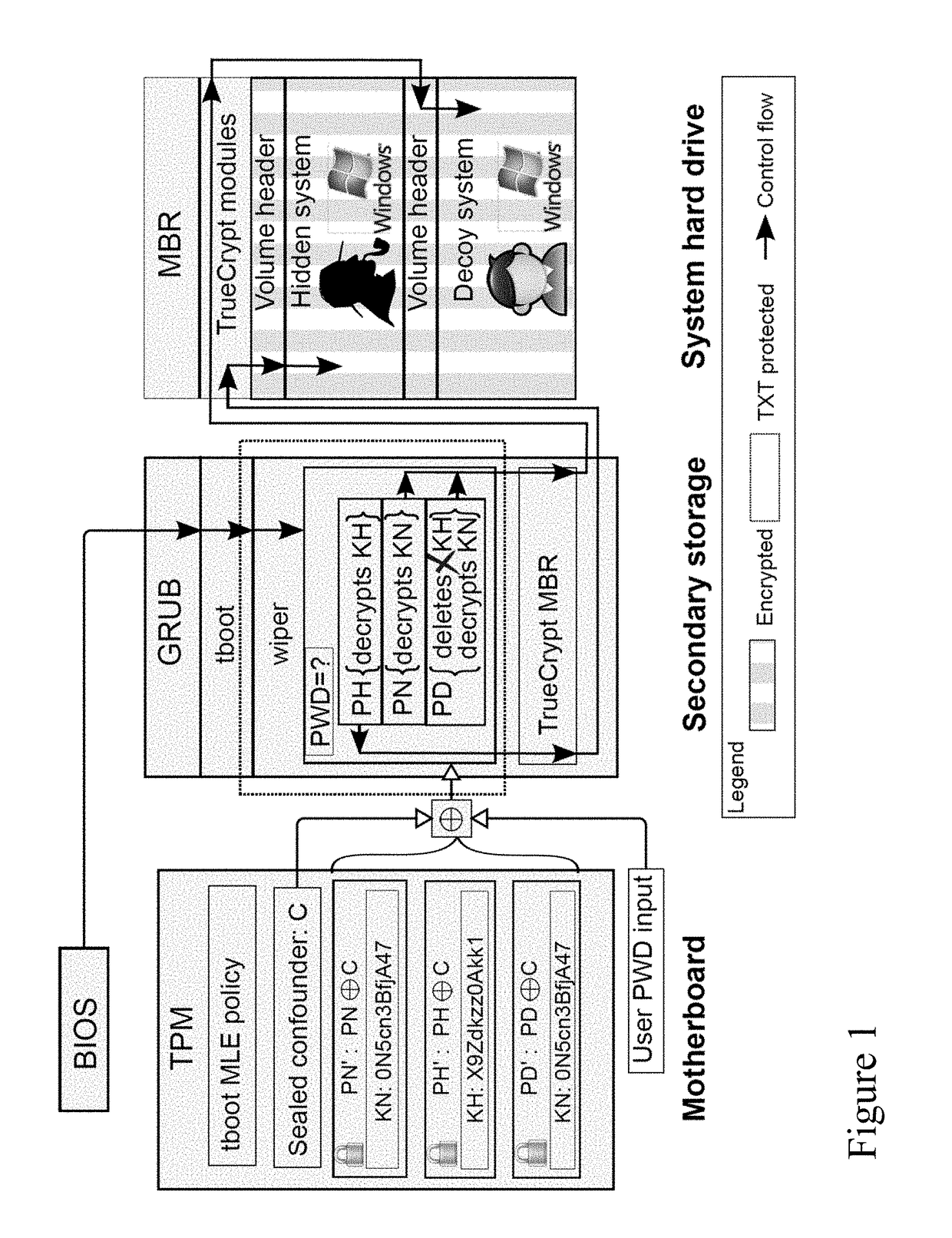
Password triggered trusted encrytpion key deletion
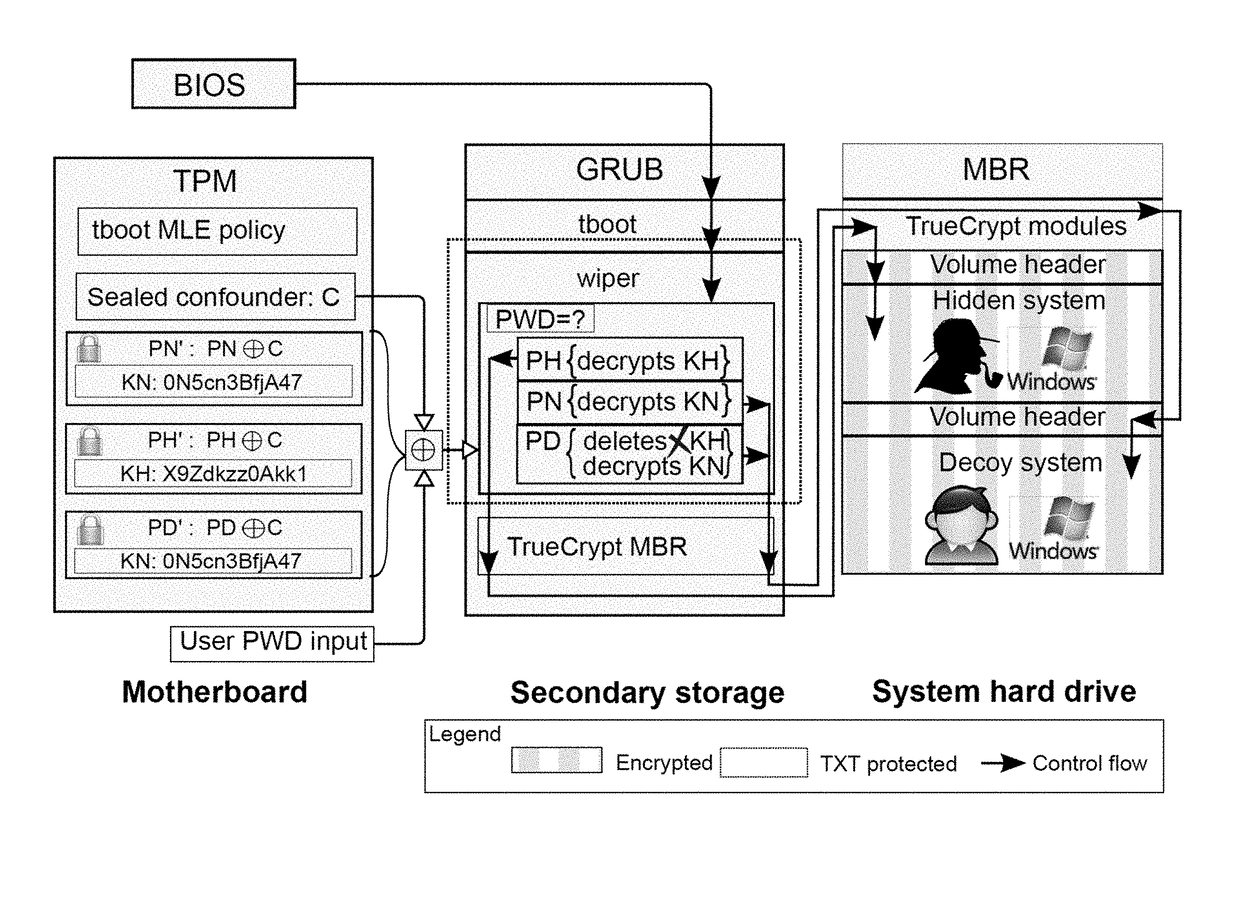
ActiveUS20170230179A1Reduce restrictionsGood plausibilityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionGraphicsPassword
Owner:MANNAN MOHAMMAD
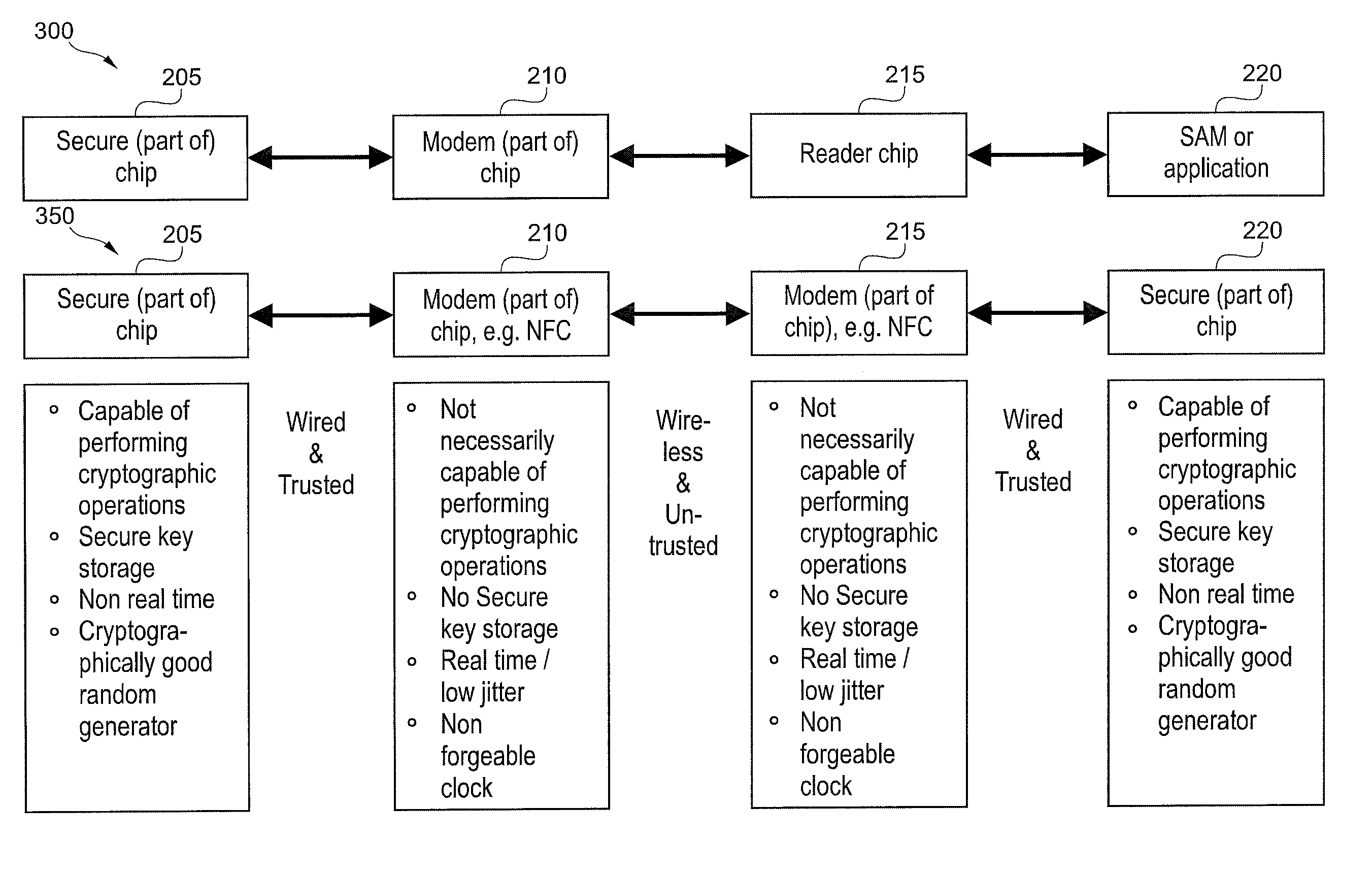
Decoupling of measuring the response time of a transponder and its authentication
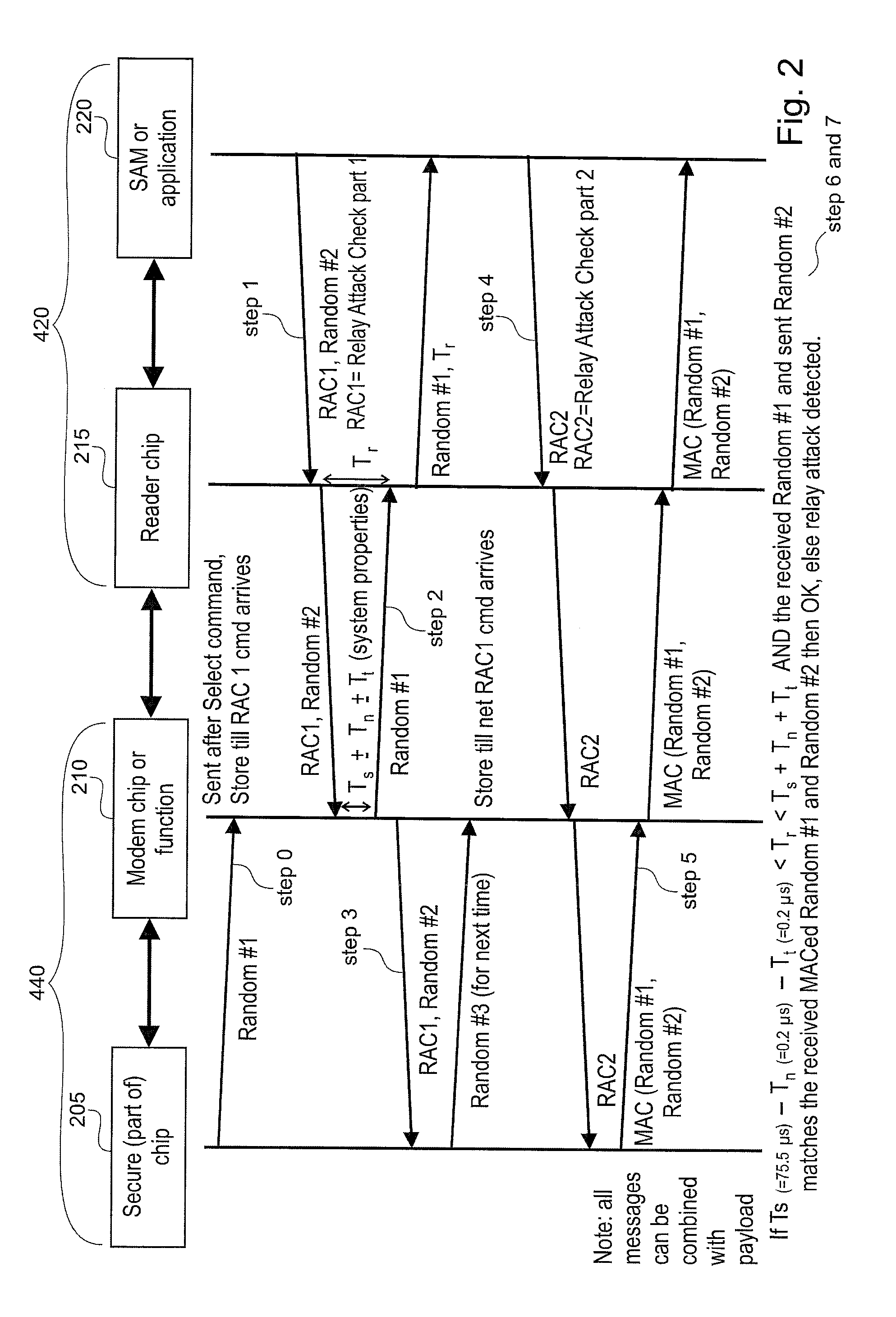
ActiveUS20110078549A1Short response timeImprove reliabilityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringAuthentication
Reader (420) for determining the validity of a connection to a transponder (440), designed to measure a response time of a transponder (440) and to authenticate the transponder (440) in two separate steps. Transponder (440) for determining the validity of a connection to a reader (420), wherein the transponder (440) is designed to provide information for response time measurement to said reader (420) and to provide information for authentication to said reader (420) in two separate steps, wherein at least a part of data used for the authentication is included in a communication message transmitted between the reader (420) and the transponder (440) during the measuring of the response time.
Owner:NXP BV
System and method for automatically verifying storage of redundant contents into communication equipments, by data comparison
InactiveUS9130918B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationContent IdentifierRedundant code
A method is intended for verifying storage of contents into communication equipments connected to at least one communication network. This method consists, when a first communication equipment stores a content and wants to verify that this content is still stored into a second communication equipment: i) in transmitting a first request, comprising at least an identifier of this content and first data representative of this content and requiring verification of the storage of this content into the second communication equipment, to an auxiliary communication equipment acting as an interface between the communication network and the second communication equipment, ii) in transmitting a second request, comprising at least the content identifier, to the second communication equipment, to require transmission of second data representative of the content to the auxiliary communication equipment, and in triggering a timeout having a chosen duration, and iii) if the auxiliary communication equipment has received the second data before expiration of this timeout, in comparing these received second data, possibly after having processed them, to the received first data, and in transmitting a message representative of the result of this comparison to the first communication equipment.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
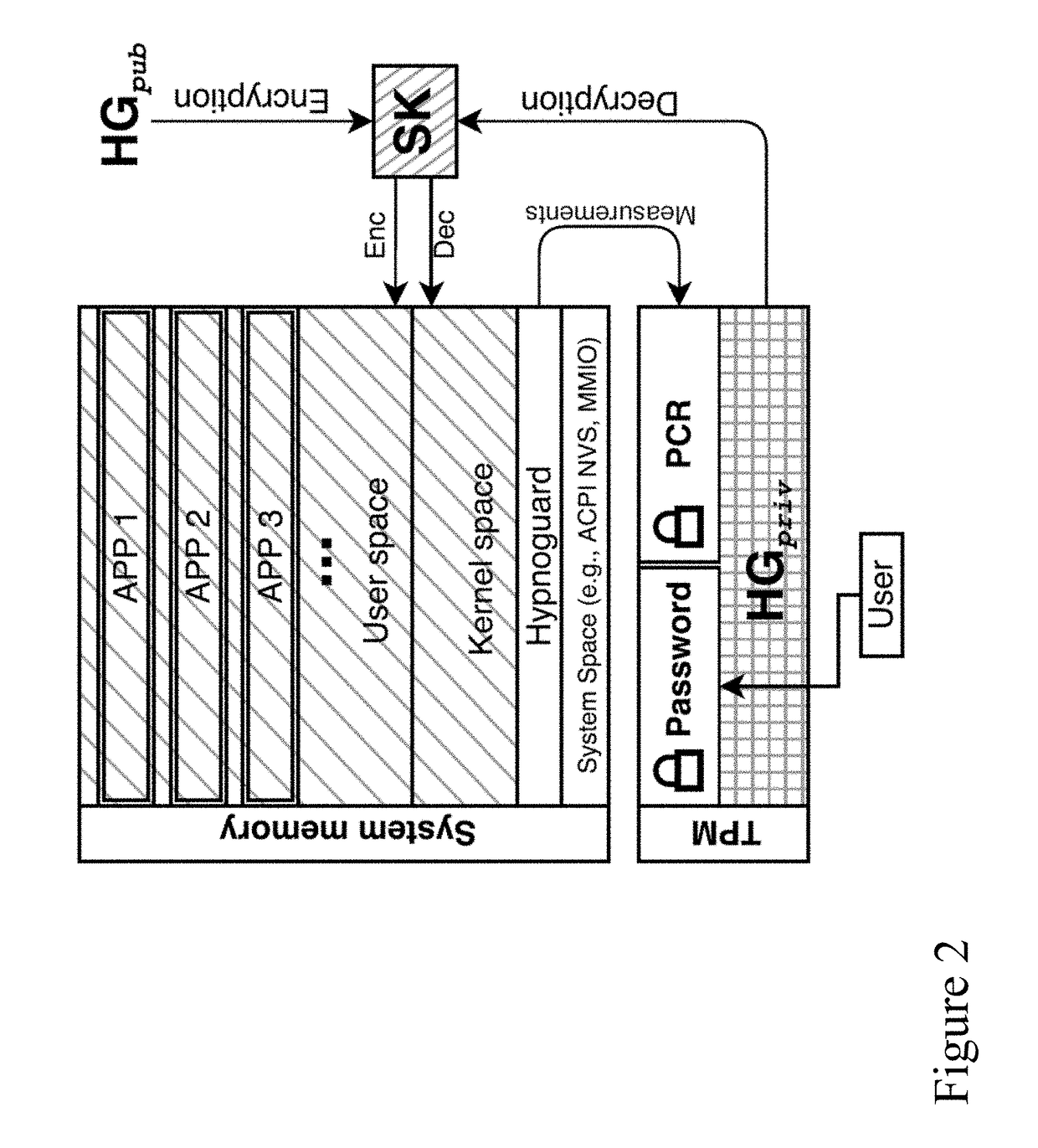
Physically unclonable function with tamper prevention and Anti-aging system
ActiveUS20120179952A1Avoids freezing attackReduce the impactMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInternal/peripheral component protectionComputer hardwarePhysical unclonable function
Owner:INTRINSIC ID
Attack-resistant implementation method
InactiveUS6986054B2Improve efficiencyEliminate characteristicKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareInformation processing
The present invention makes it difficult for unauthorized parties to estimate processing and a secret key based upon the waveforms of power consumption of an IC card chip by changing a processing order in the IC card chip so that it is not estimated by the attackers. In an information processing apparatus comprising storing means having a program storing part for storing programs and a data storing part for storing data, an operation processing unit, means for inputting data to be operated on in the operation processing unit, and means for outputting operation processing results on the data by the operation processing unit, an arithmetic operation method is provided which comprises the steps of: for two integers K1 and K2, when finding a value F(K, A) of a function F satisfying F(K1+K2, A)=F(K1, A)◯F(K2, A) (◯ denotes an arithmetic operation in a communtative semigroup S. K designates an integer and A designates an element of S), decomposing the K to the sum of m integers K[0]+K[1]+ . . . K[m−1]; using T(0), T(1), . . . T(m−1) resulting from rearranging a string of the m integers 0, 1, . . . m−1 by permutation T (the result corresponds one for one to the integer string 0, 1, . . . m−1); and operating on terms F(K[T(0)], A) to F(K[T(m−1)], A) on the right side ofF(K, A)=F(K[T(0)], A)◯F(K[T(1)], A)◯ . . . F(K[T(m−1)], A) . . . (expression 1)in the order of F(K[T(0)], A), F(K[T(1)], A), . . . F(K[T(m−1)], A) to find F(K, A).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for enhancing network application security
InactiveUS8302170B2Improve securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationEmbedded security
Owner:RICHEMONT INT
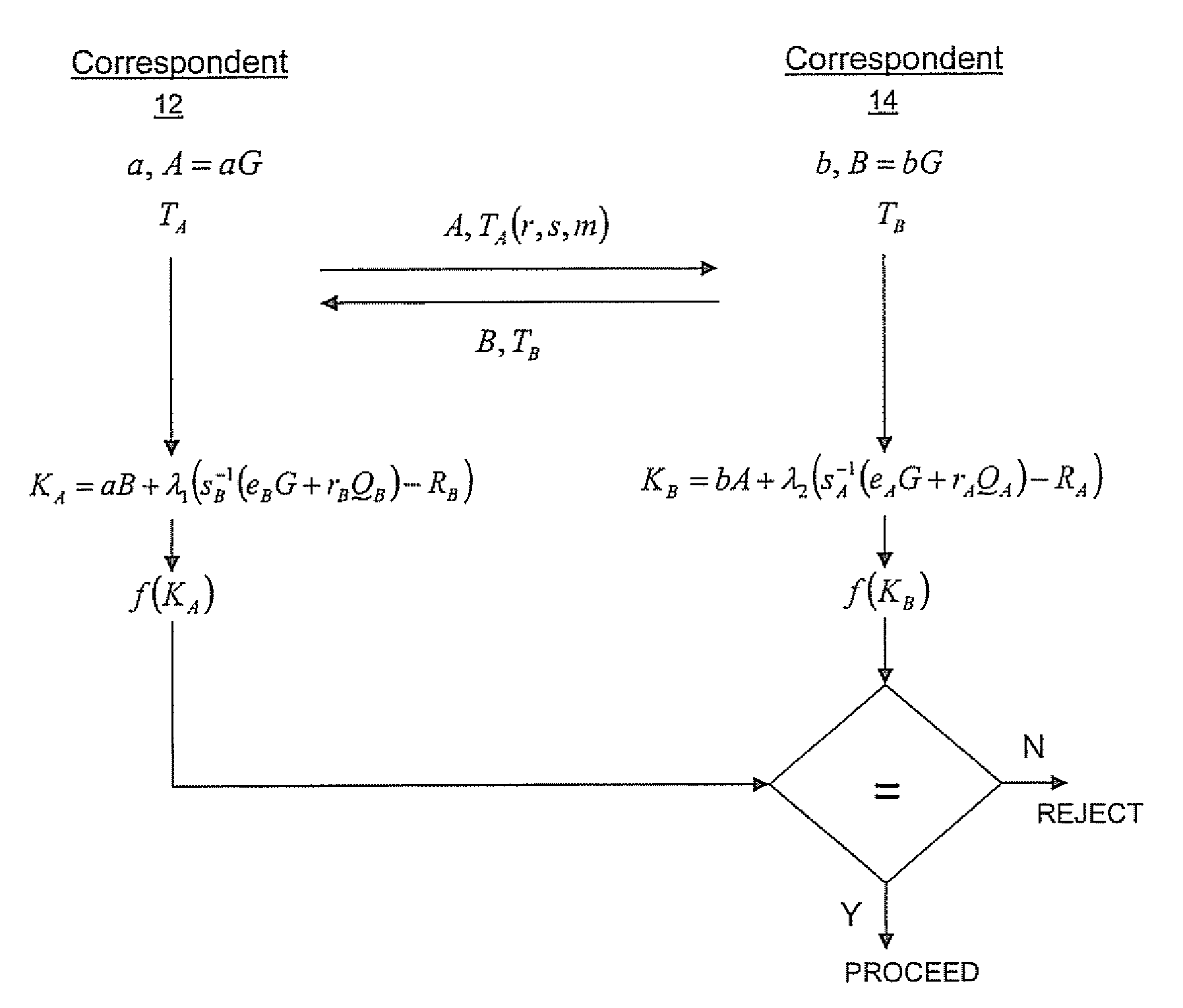
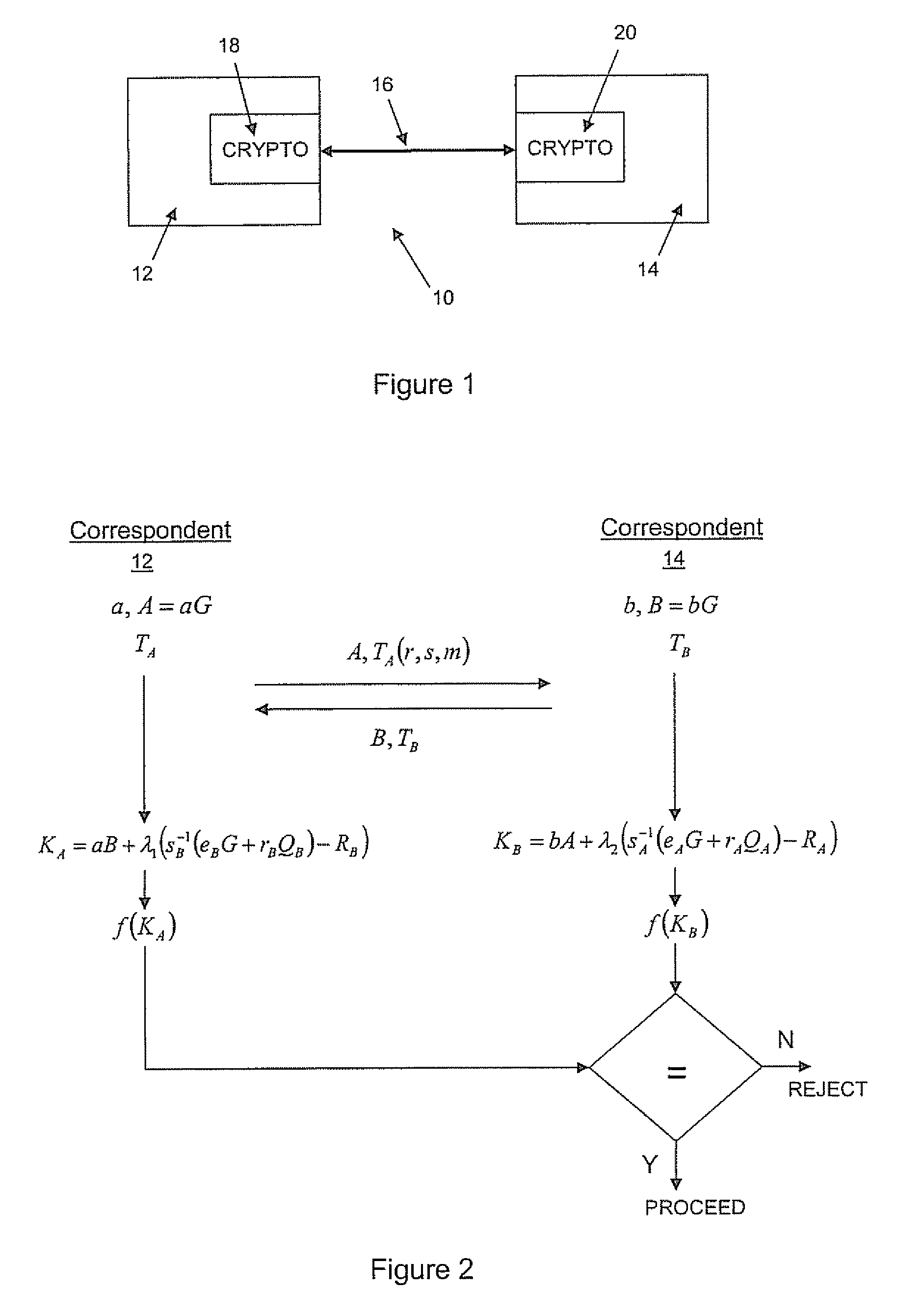
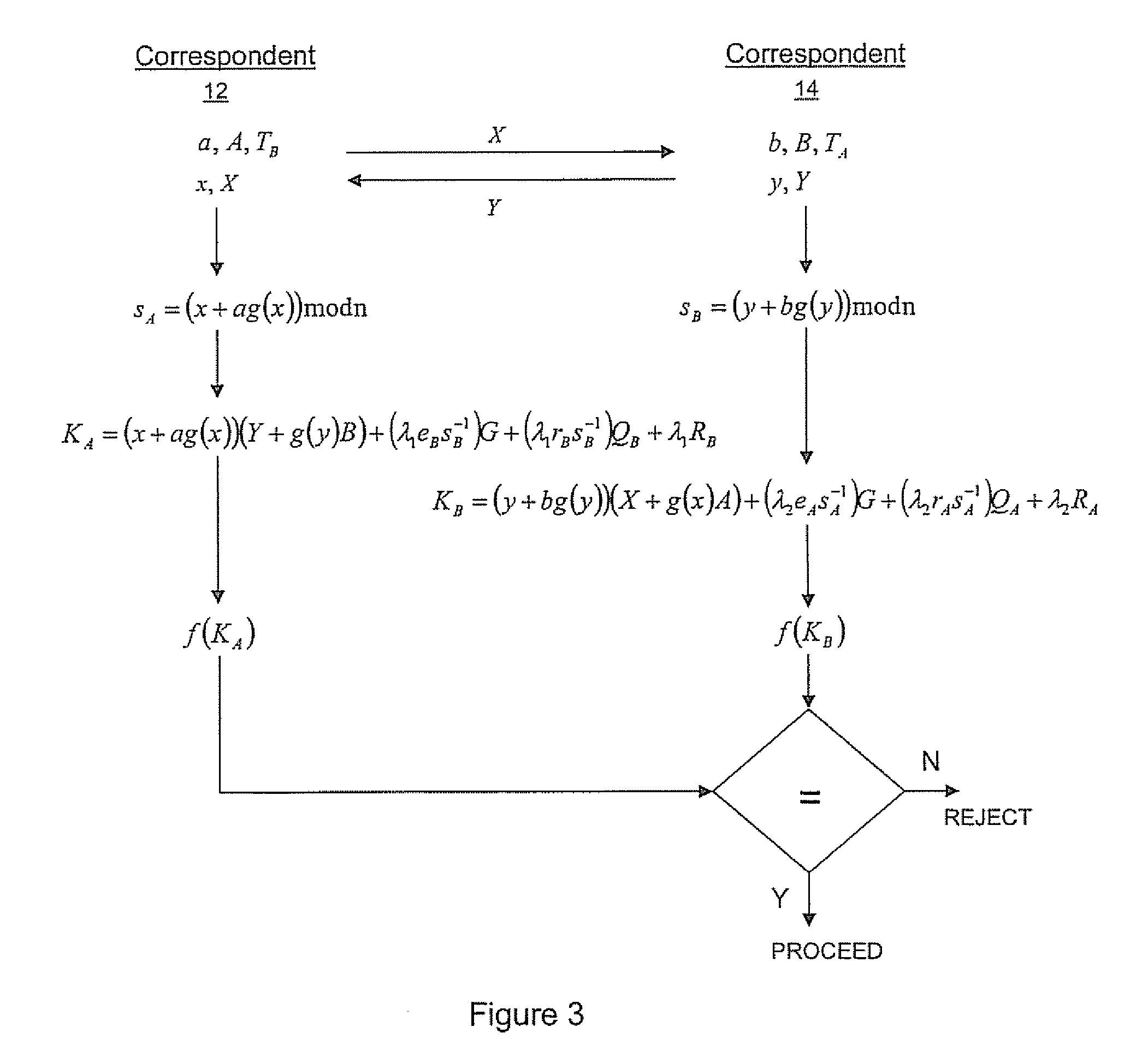
Implicit certificate verification
ActiveUS20100023771A1Heavy calculationPublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsCryptographic key typesCryptographic nonce
A method of computing a cryptographic key to be shared between a pair of correspondents communicating with one another through a cryptographic system is provided, where one of the correspondents receives a certificate of the other correspondents public key information to be combined with private key information of the one correspondent to generate the key. The method comprises the steps of computing the key by combining the public key information and the private key information and including in the computation a component corresponding to verification of the certificate, such that failure of the certificate to verify results in a key at the one corespondent that is different to the key computed at the other correspondent.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
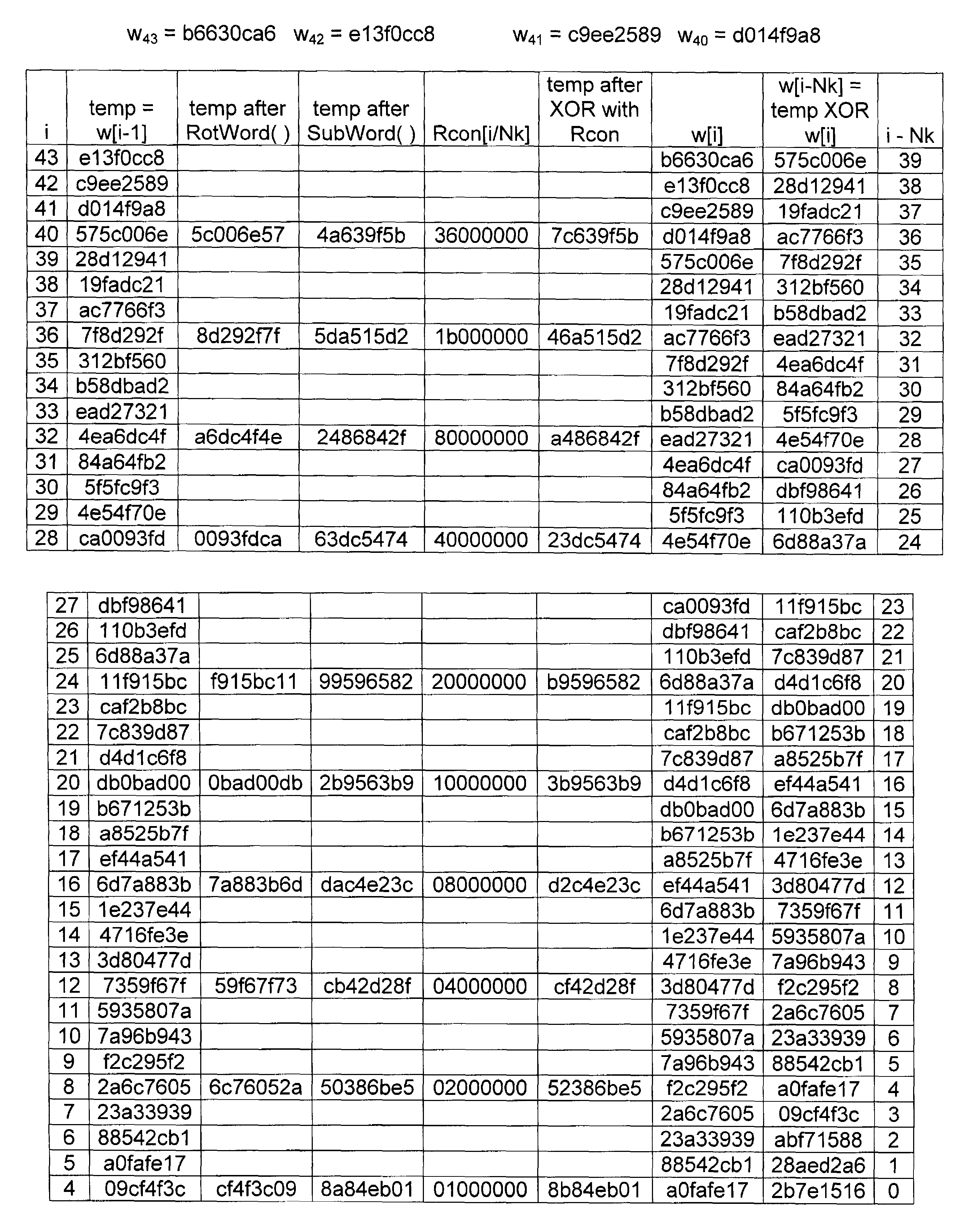
Advanced encryption standard (AES) hardware cryptographic engine
ActiveUS7295671B2Reduce in quantityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageS-boxAdvanced Encryption Standard
A cryptographic method and related implements the Rijndael—AES encryption standard. In one improvement, the decryption round keys are generated on a round by round basis from the final Nk round keys saved from a previous encryption key scheduling operation. Latency and memory requirements are thereby minimized. S-boxes for the AES key generation and cipher operation itself, may be implemented multiple times in different ways with different power signatures, with a pseudo-random selection of the pathway for the different bytes to be substituted. The premix operation occurs simultaneously with the generation of first round keys, and a dummy circuit with substantially identical timing as the real premix circuitry adds power consumption noise to the premix.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
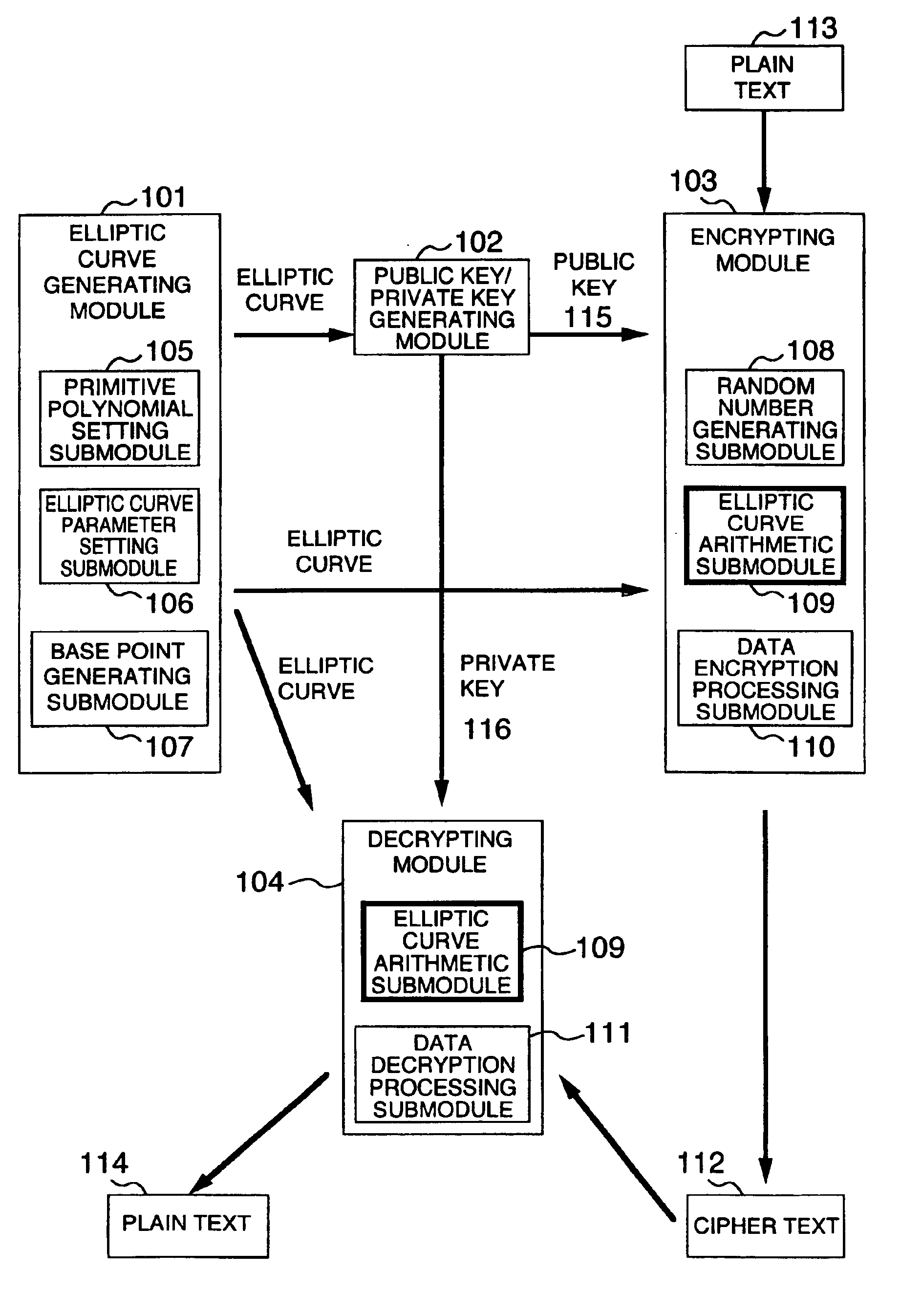
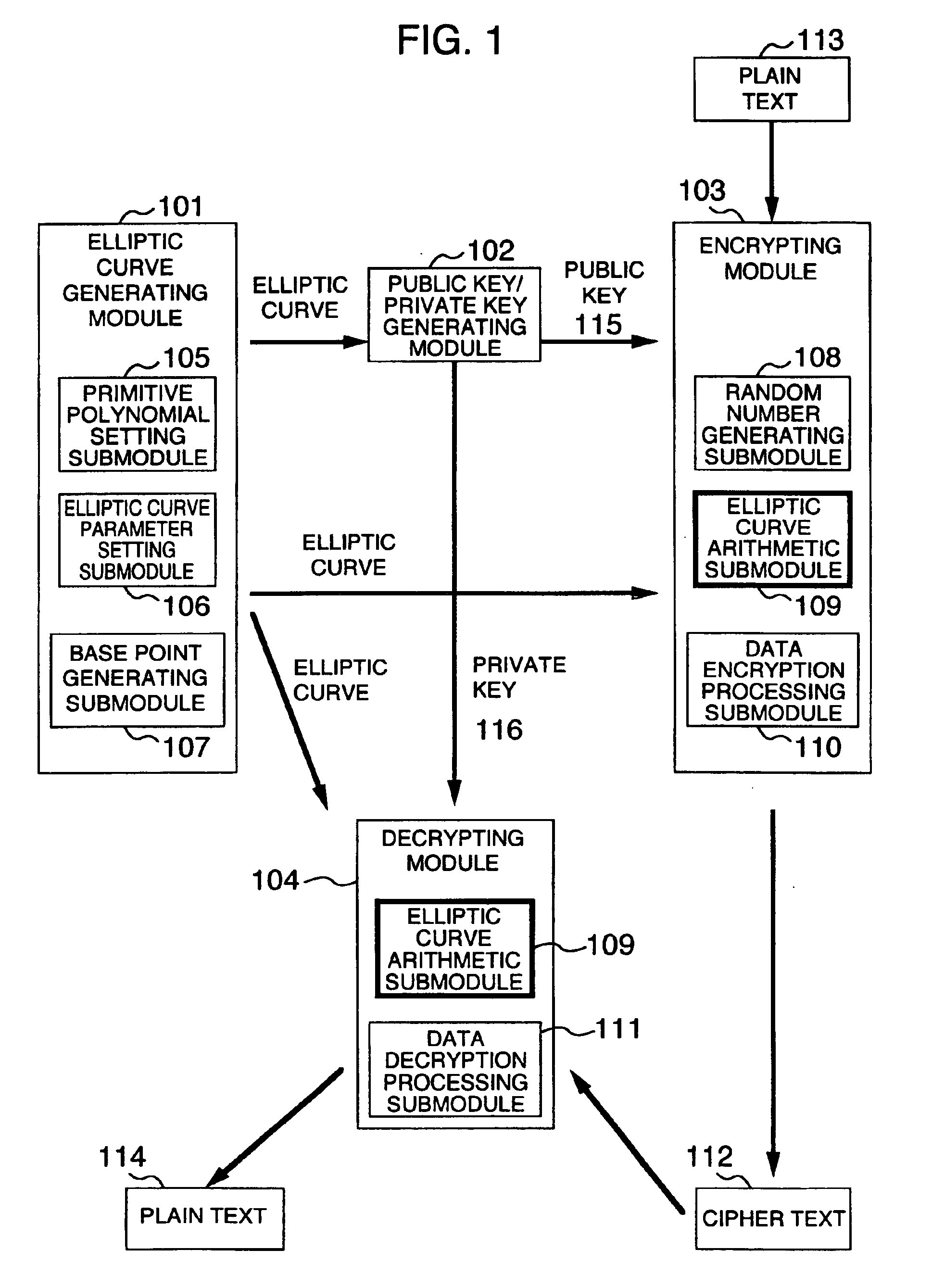
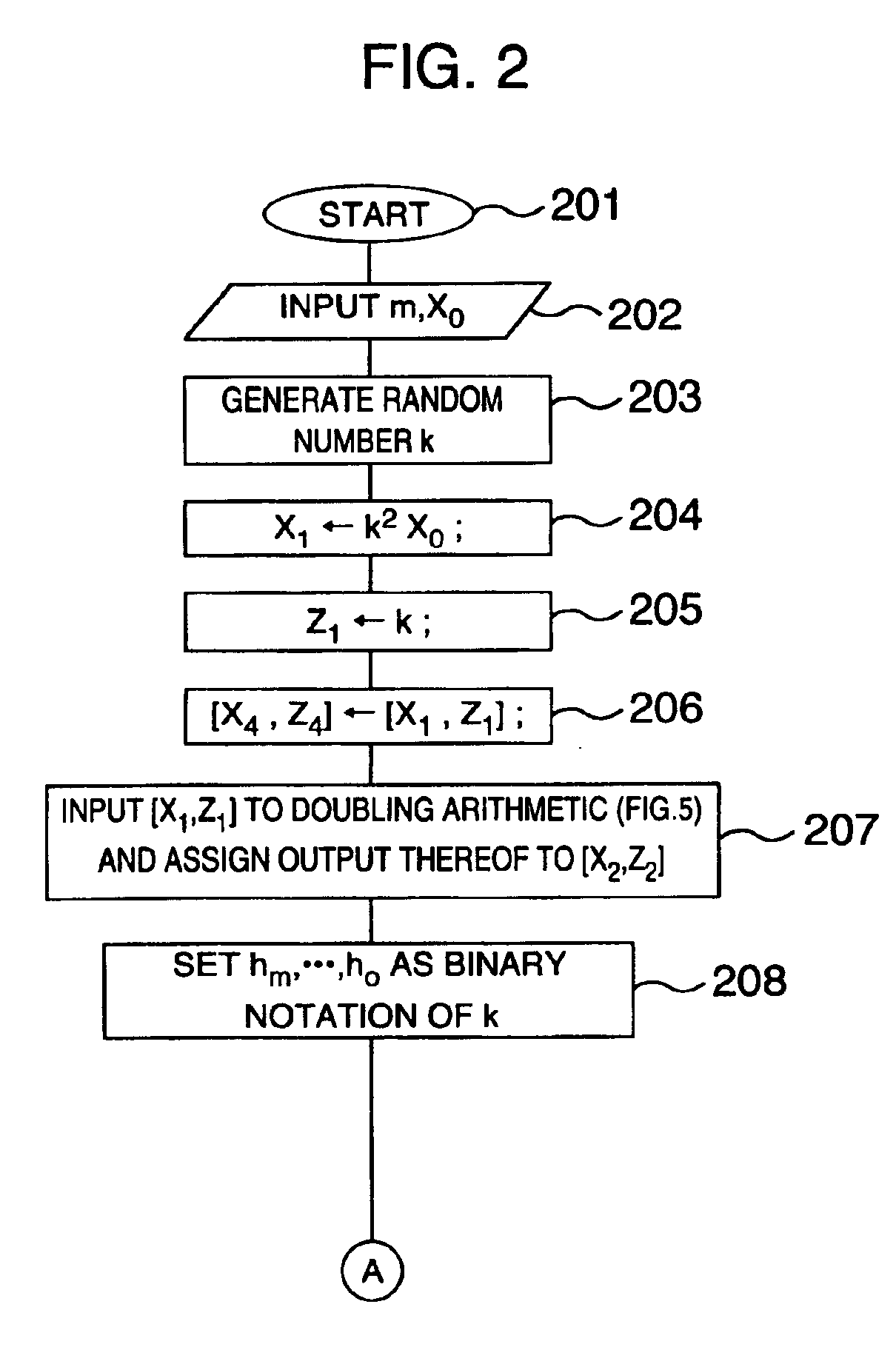
Method and apparatus for elliptic curve cryptography and recording medium therefore
InactiveUS6876745B1Prevent leakageRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
A method and an apparatus capable of realizing at a high speed an elliptic curve cryptography in a finite field of characteristic 2, in which the elliptic curve is given by y2+xy=x3+ax2+b (b≠0) and an elliptic curve cryptography method which can protect private key information against leaking from deviation information of processing time to thereby defend a cipher text against a timing attack and a differential power analysis attack are provided. To this end, an arithmetic process for executing scalar multiplication arithmetic d(x, y) a constant number of times per bit of the private key d is adopted. Further, for the scalar multiplication d(x, y), a random number k is generated upon transformation of the affine coordinates (x, y) to the projective coordinates for thereby effectuating the transformation (x, y)→[kx, ky, k] or alternatively (x, y)→[k2x, k3y, k]. Thus, object for the arithmetic is varied by the random number (k).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Cryptographic architecture with random instruction masking to thwart differential power analysis
ActiveUS20050271202A1Memory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePower analysis
An apparatus and method for preventing information leakage attacks that utilize timeline alignment. The apparatus and method inserts a random number of instructions into an encryption algorithm such that the leaked information can not be aligned in time to allow an attacker to break the encryption.
Owner:HRL LAB
Implementing carbon nanotube based sensors for cryptographic applications
InactiveUS8797059B2Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A method and circuit for implementing security protection with carbon nanotube based sensors for cryptographic applications, and a design structure on which the subject circuit resides are provided. A carbon nanotube layer is incorporated with a polymeric encapsulation layer of a security card. Electrical connections to the carbon nanotube layer are provided for electrical monitoring of electrical resistance of the carbon nanotube layer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
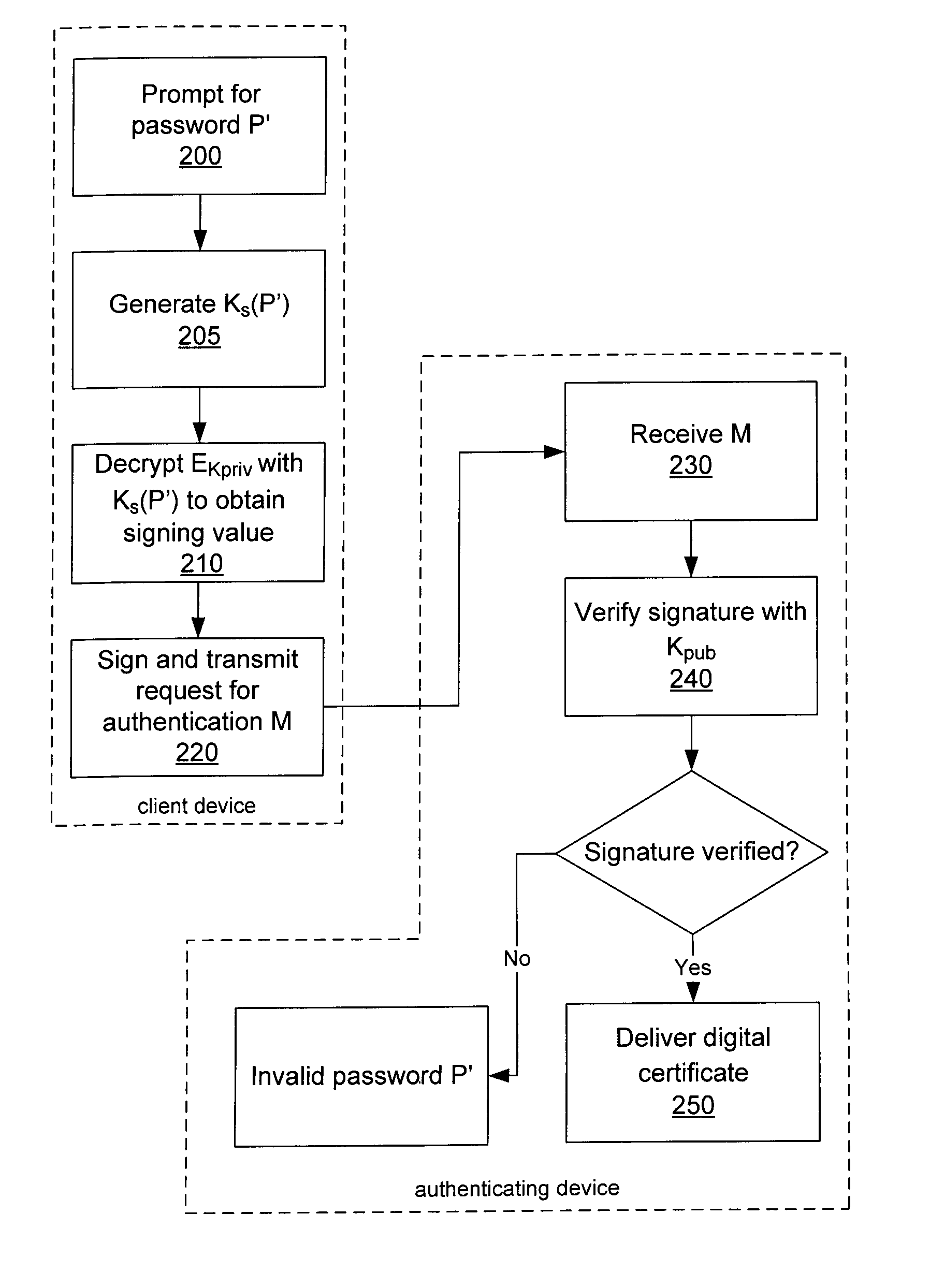
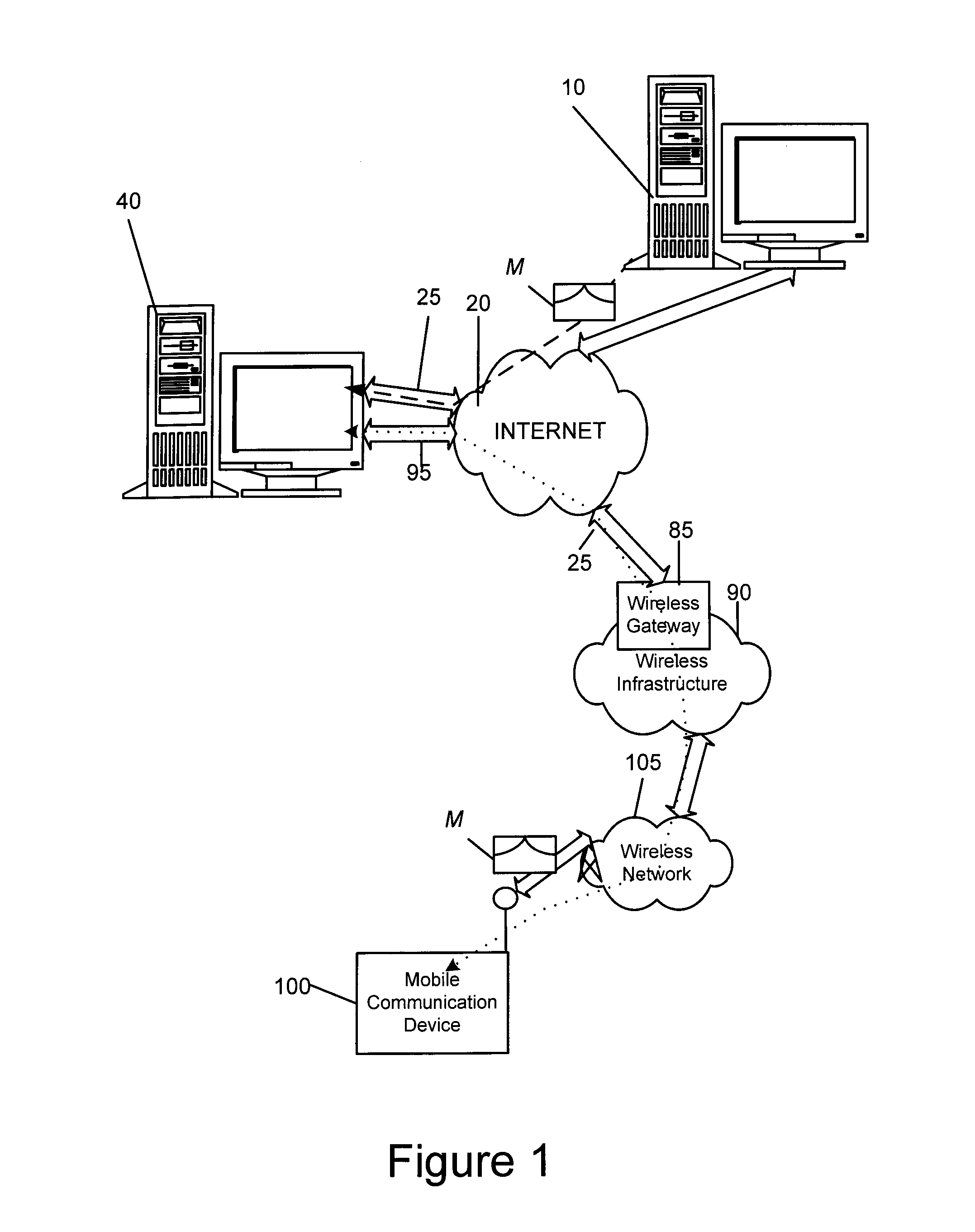
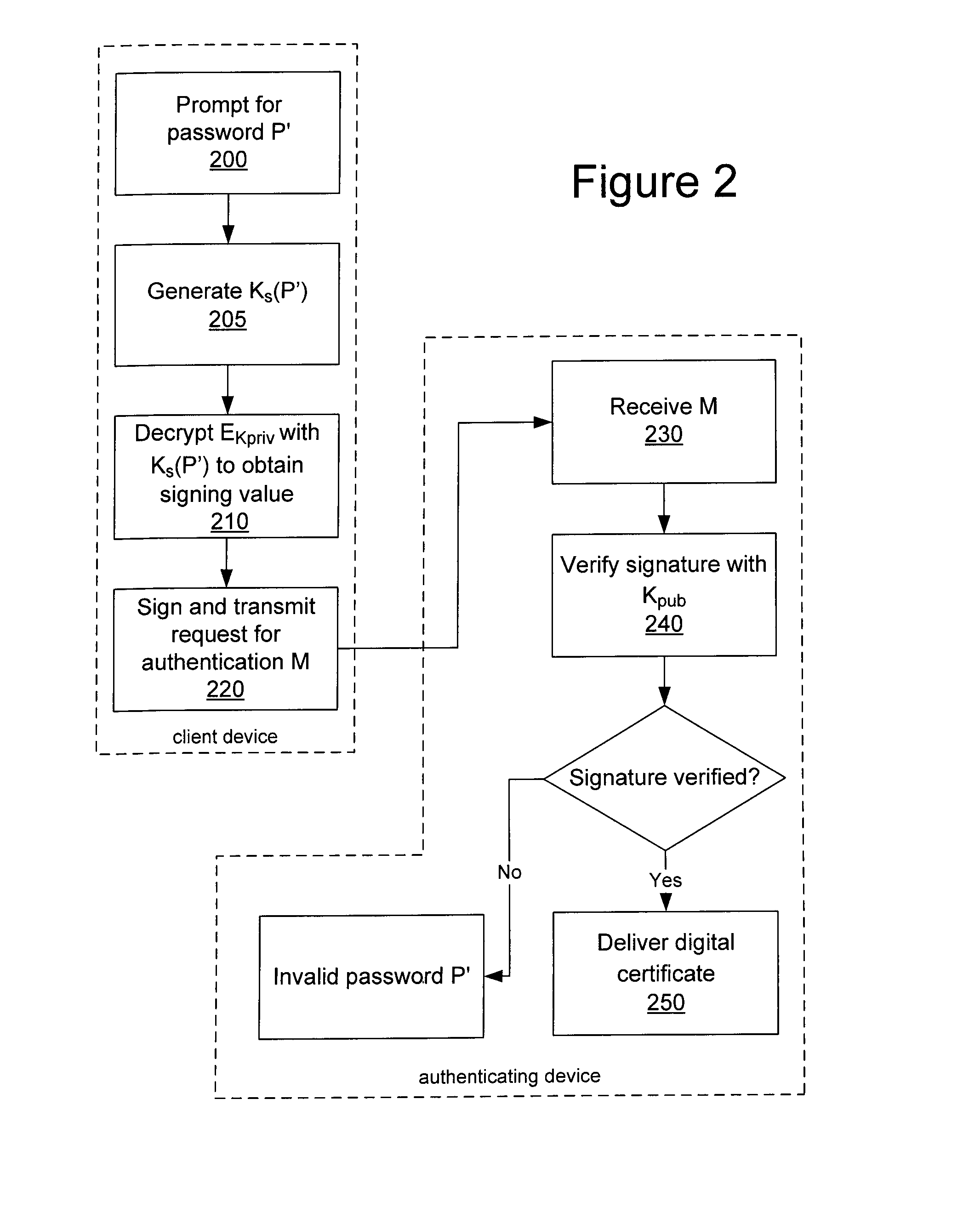
System and method for protecting a password against brute force attacks
ActiveUS20080120504A1User identity/authority verificationCryptographic attack countermeasuresBrute forcePassword
In a system and method for authenticating a client device by an authentication device, the client device user is assigned a PIN generated by the authentication device. The user provides the PIN and a password to the client device, from which the client device generates a symmetric key and further generates a public / private key pair. The private key is encrypted using the symmetric key and stored in encrypted form only. The public key and a message authentication code generated from the PIN are provided to the authentication device, which stores the public key. Subsequently, when the user seeks to be authenticated, the user enters a password at the client device, which is used to generate a symmetric key to decrypt the encrypted private key. A message to the authentication device is signed using the resultant value. The authentication device uses the public key to verify the signature of the message.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com