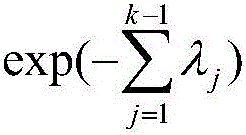Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1973 results about "Threat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
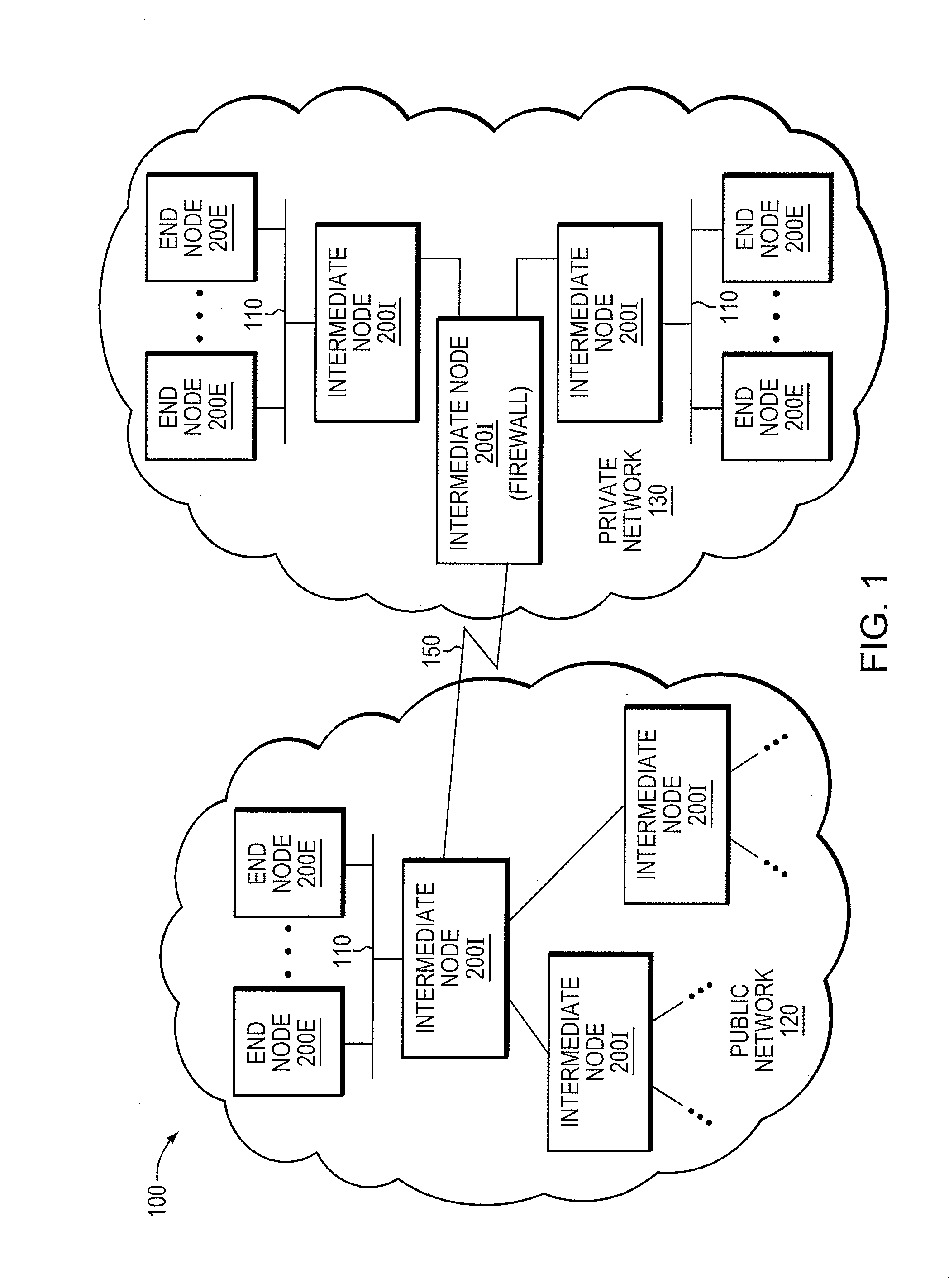
In computer security, a threat is a possible danger that might exploit a vulnerability to breach security and therefore cause possible harm. A threat can be either "intentional" (i.e. hacking: an individual cracker or a criminal organization) or "accidental" (e.g. the possibility of a computer malfunctioning, or the possibility of a natural disaster such as an earthquake, a fire, or a tornado) or otherwise a circumstance, capability, action, or event.
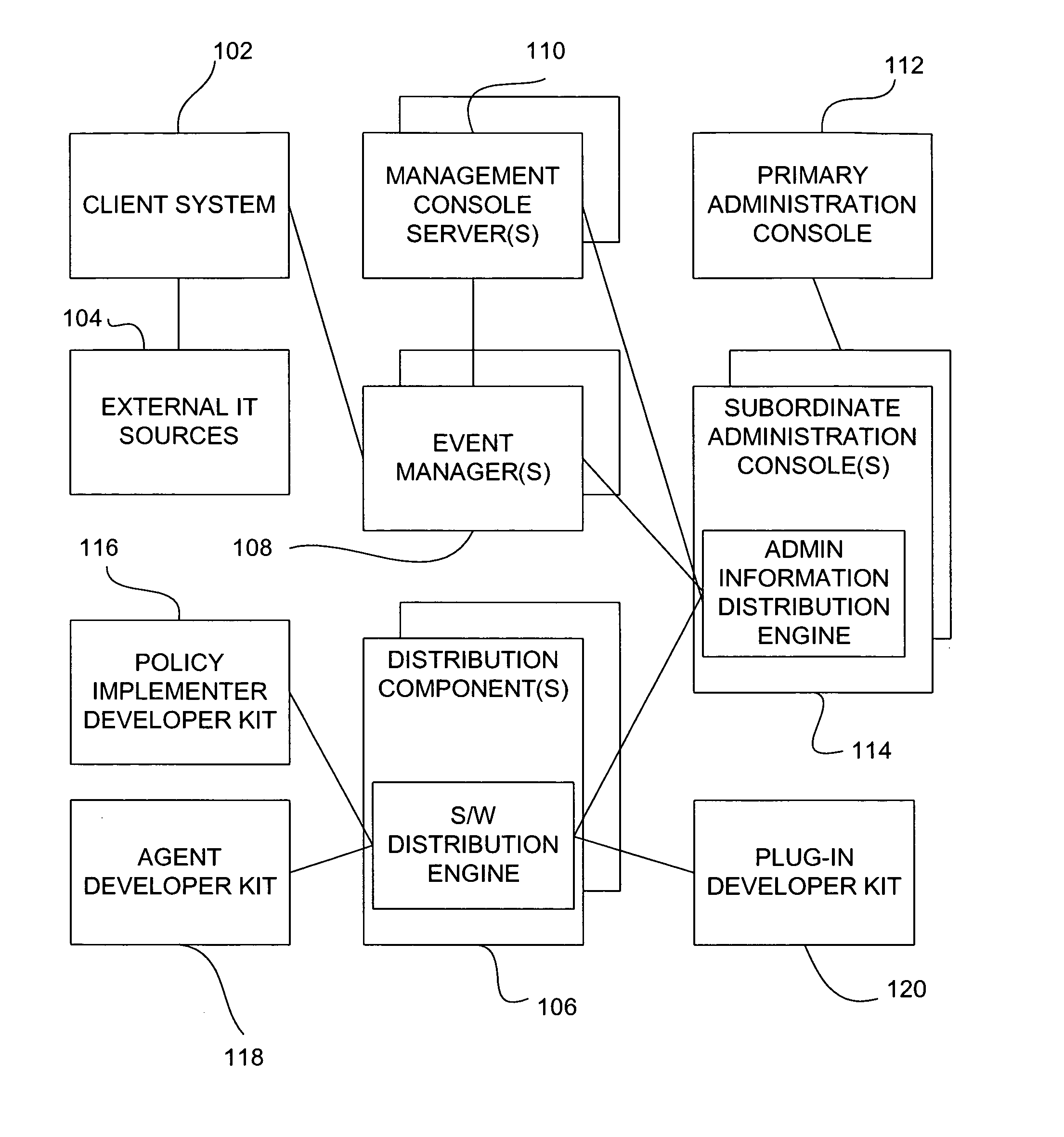
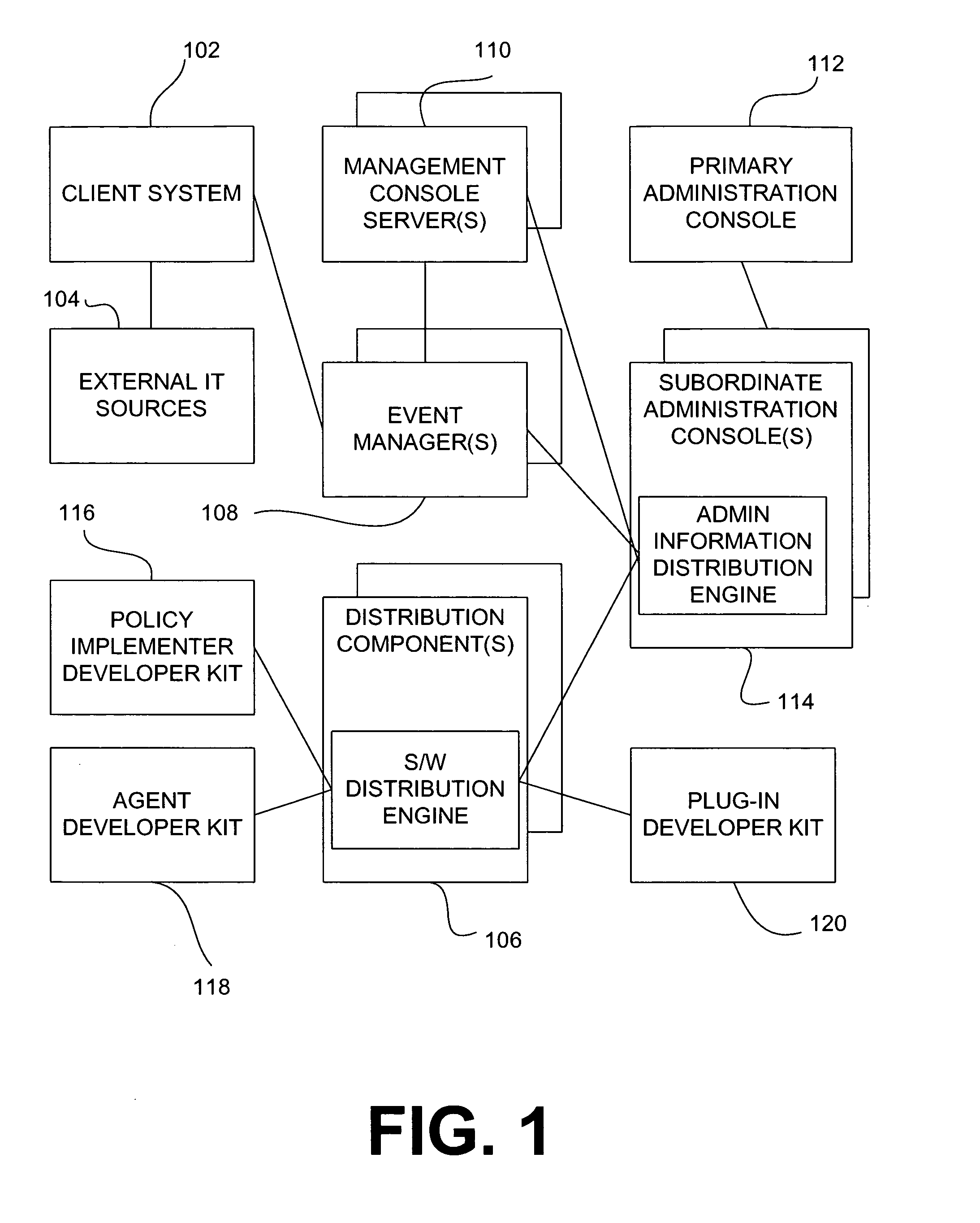
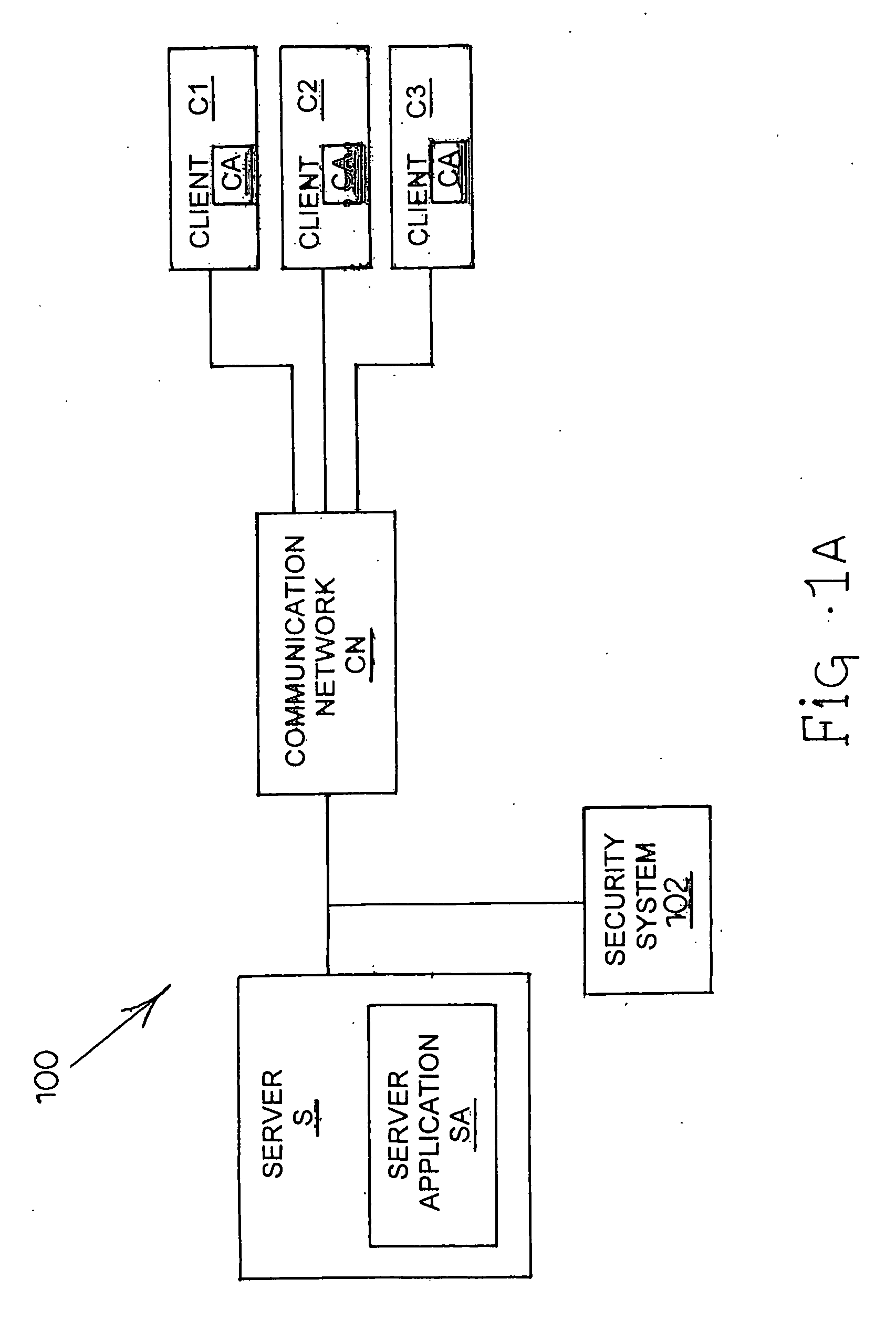
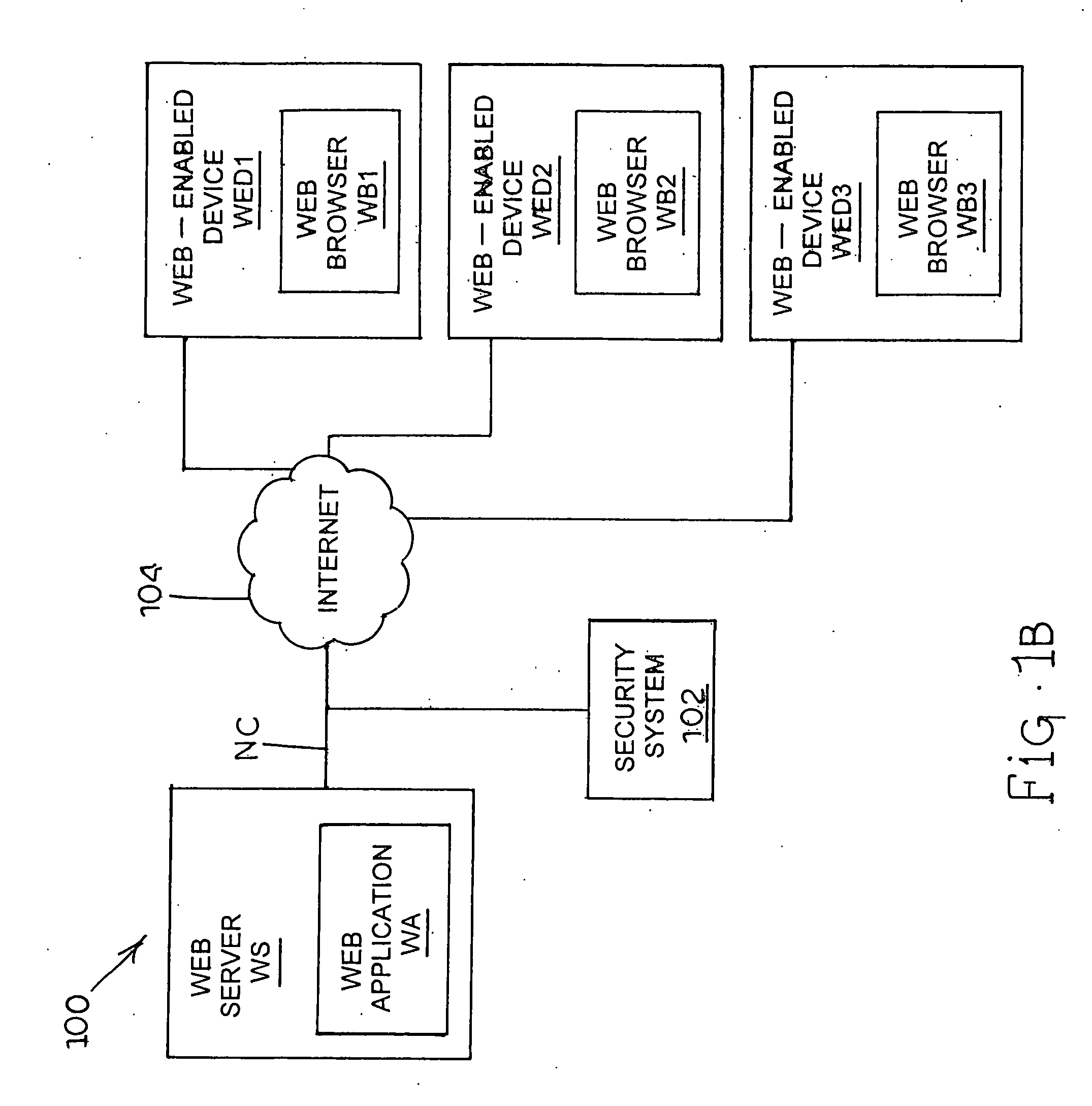
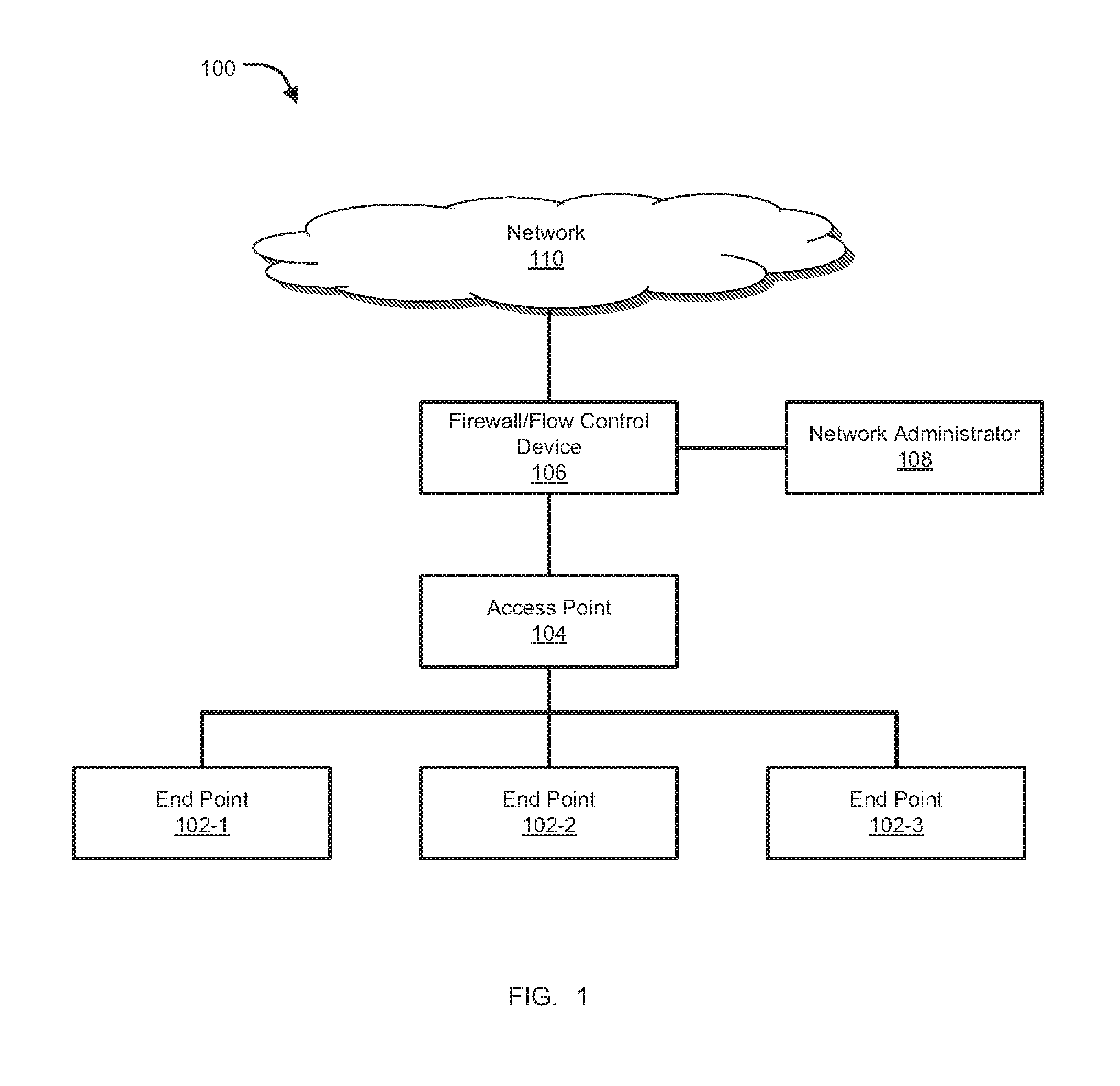
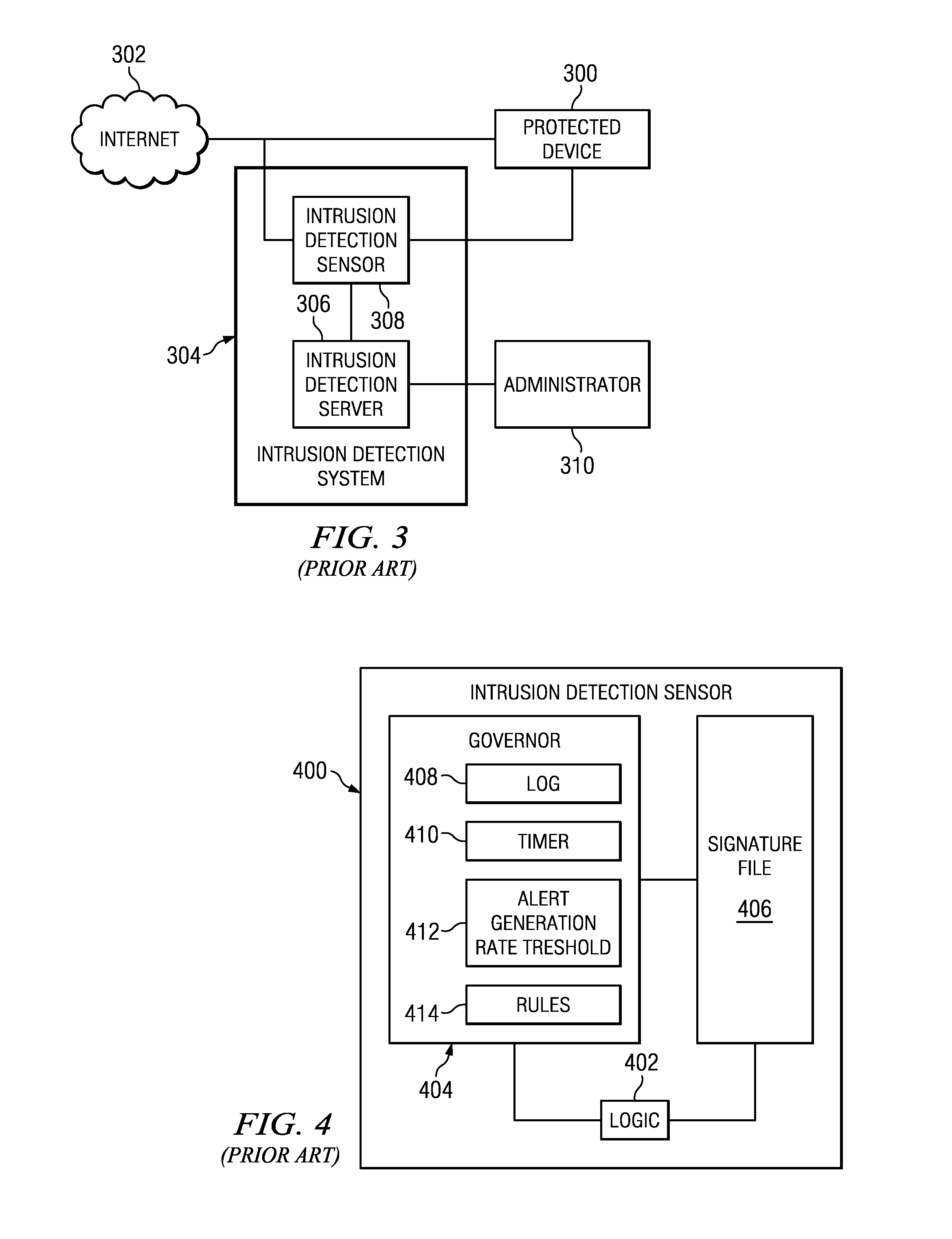
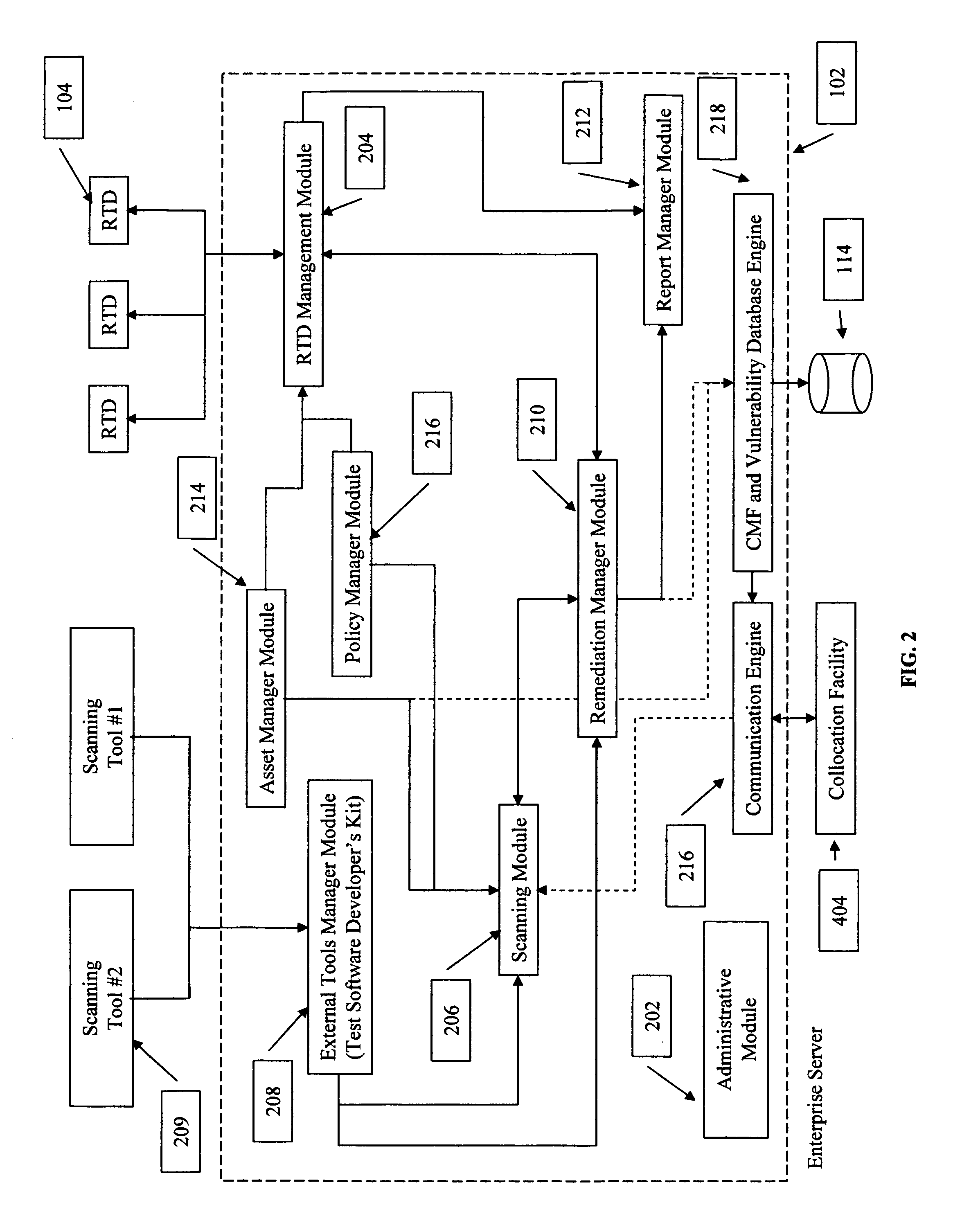
System and method for policy management
InactiveUS20070180490A1Computer security arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsStrategy makingComputer security
The invention provides a system and method for providing policy-based protection services. As a new threat is understood, one or more protection techniques are considered for protecting the asset, the organization assigns responsibilities to carry out or protect the asset, and a policy is constructed. After the policy is developed a plan is put into action to protect the asset, and a policy implementer is developed and / or purchased, distributed, configured, and managed. Finally, the policy, its enforcement, and its effectiveness, are reviewed to determine any changes needed, and new requirements are discovered, closing the lifecycle.
Owner:ALLEGENT TECH GROUP
System and method for threat detection and response
InactiveUS20050018618A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetDistributed computing
In accordance with varying embodiments of the invention, systems, devices and methods for analyzing a network packet received from a remote source and destined for a network resource, the network packet having associated packet data, and for identifying a plurality of network threats are disclosed.
Owner:STRATACLOUD
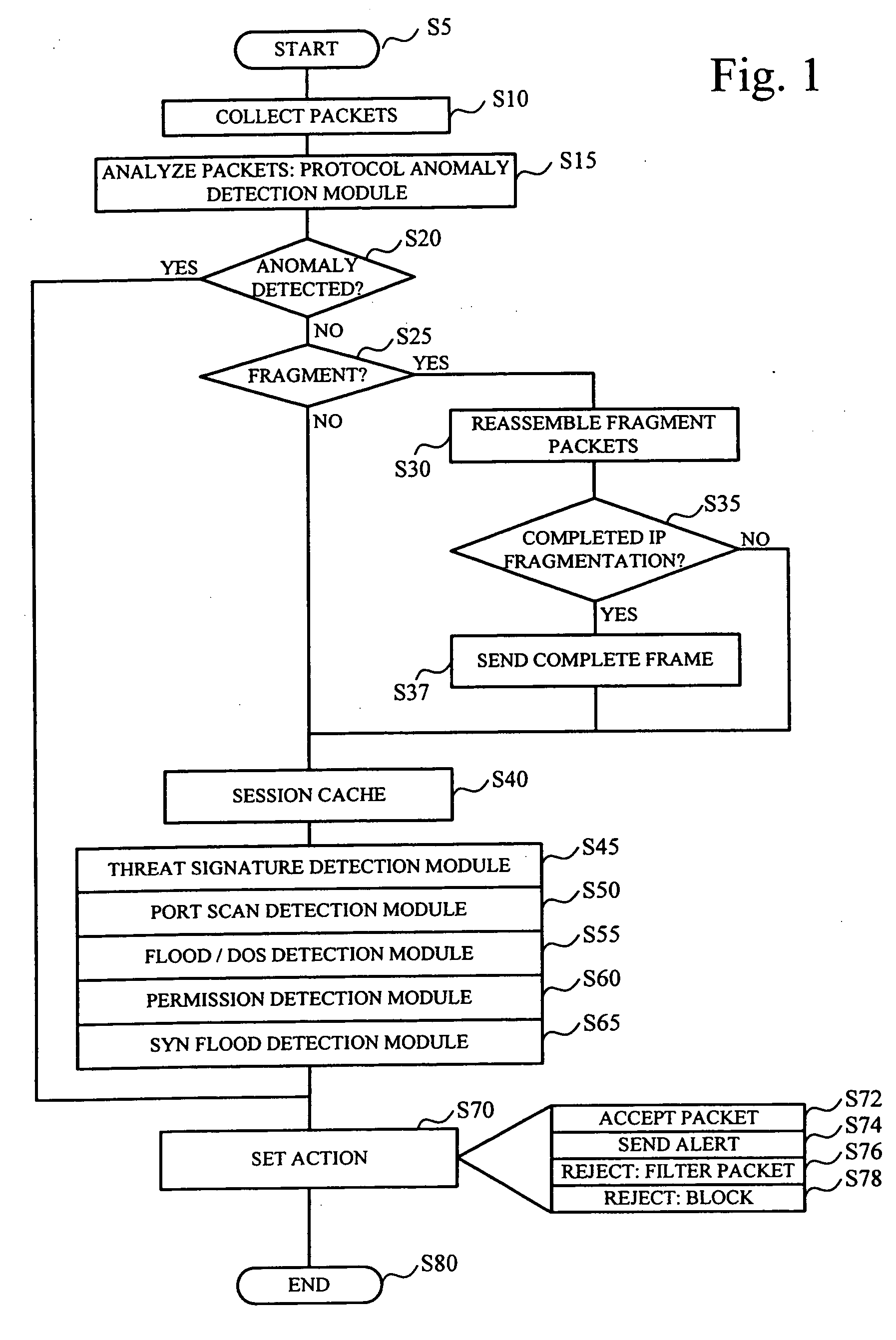
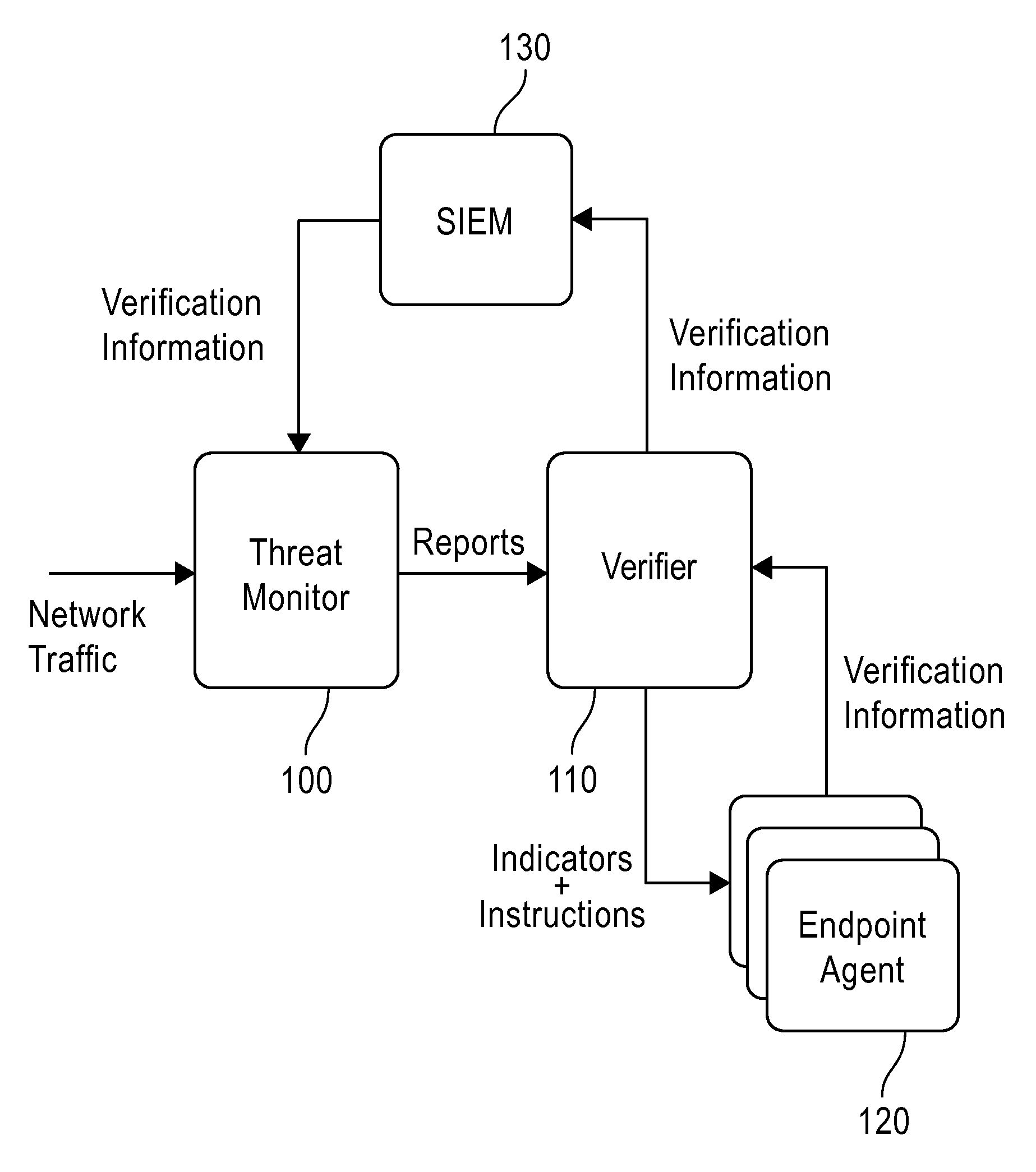
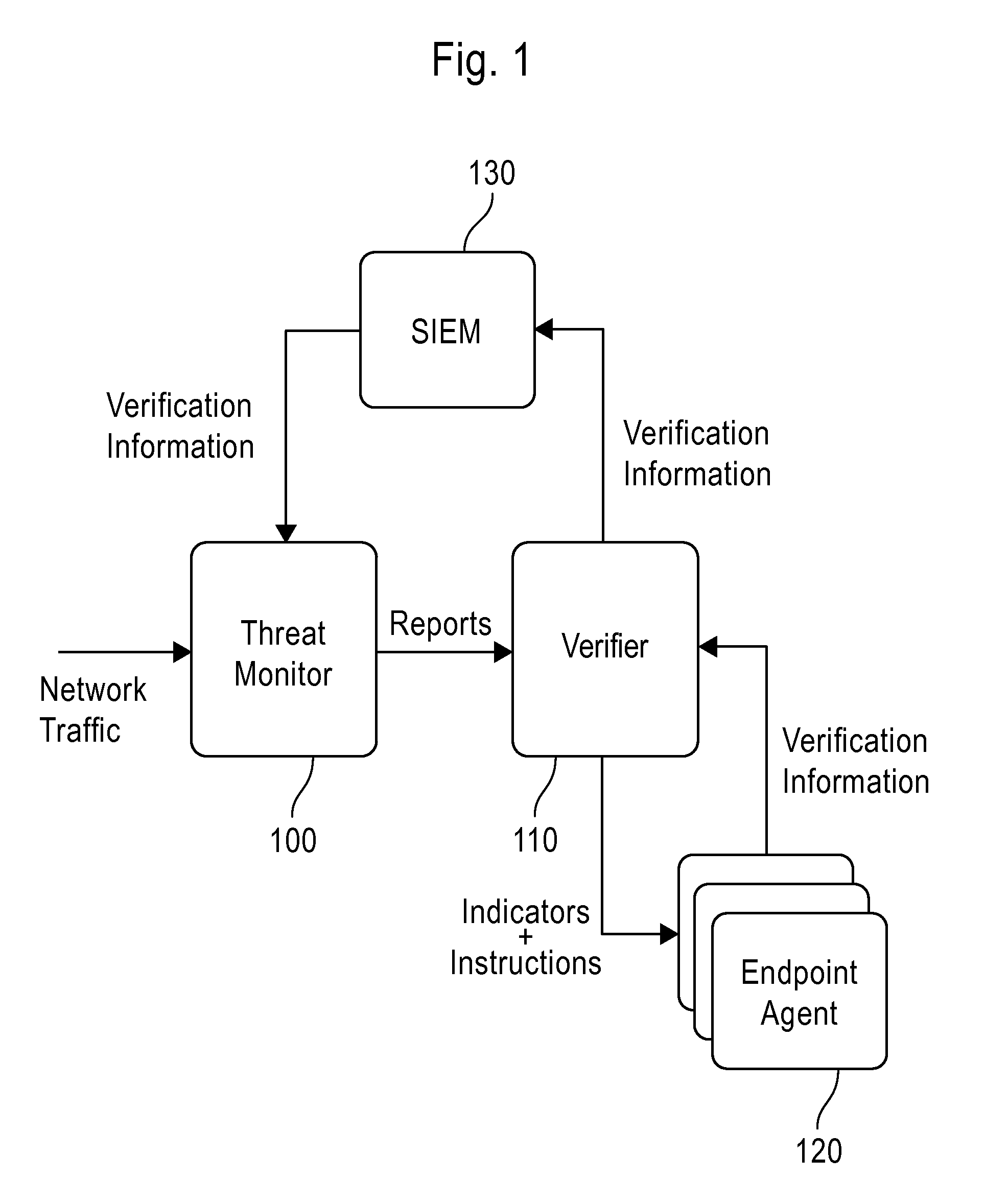
System and method employing structured intelligence to verify and contain threats at endpoints
ActiveUS20140344926A1Limiting the threat's ability to communicateMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet privacySecurity information and event management
A system and method to detect and contain threatening executable code by employing a threat monitor, verifier, endpoint agent, and a security information and event management module.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC +1
Methods, systems and computer program products for monitoring user login activity for a server application
InactiveUS20050188222A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsClient-sideDistributed computing
Methods, systems and computer program products are disclosed for monitoring user login activity for a server application in a computer network. The methods, systems, and computer program products can monitor communication data between a server application and a client. The methods, systems, and computer program products can also include applying one or more detectors to the communication data to identify a variety of predetermined activity. Further, the methods, systems, and computer program products can include generating a threat score associated with the predetermined activity by comparing the identified predetermined activity with a security threshold criteria.
Owner:COVELIGHT SYST
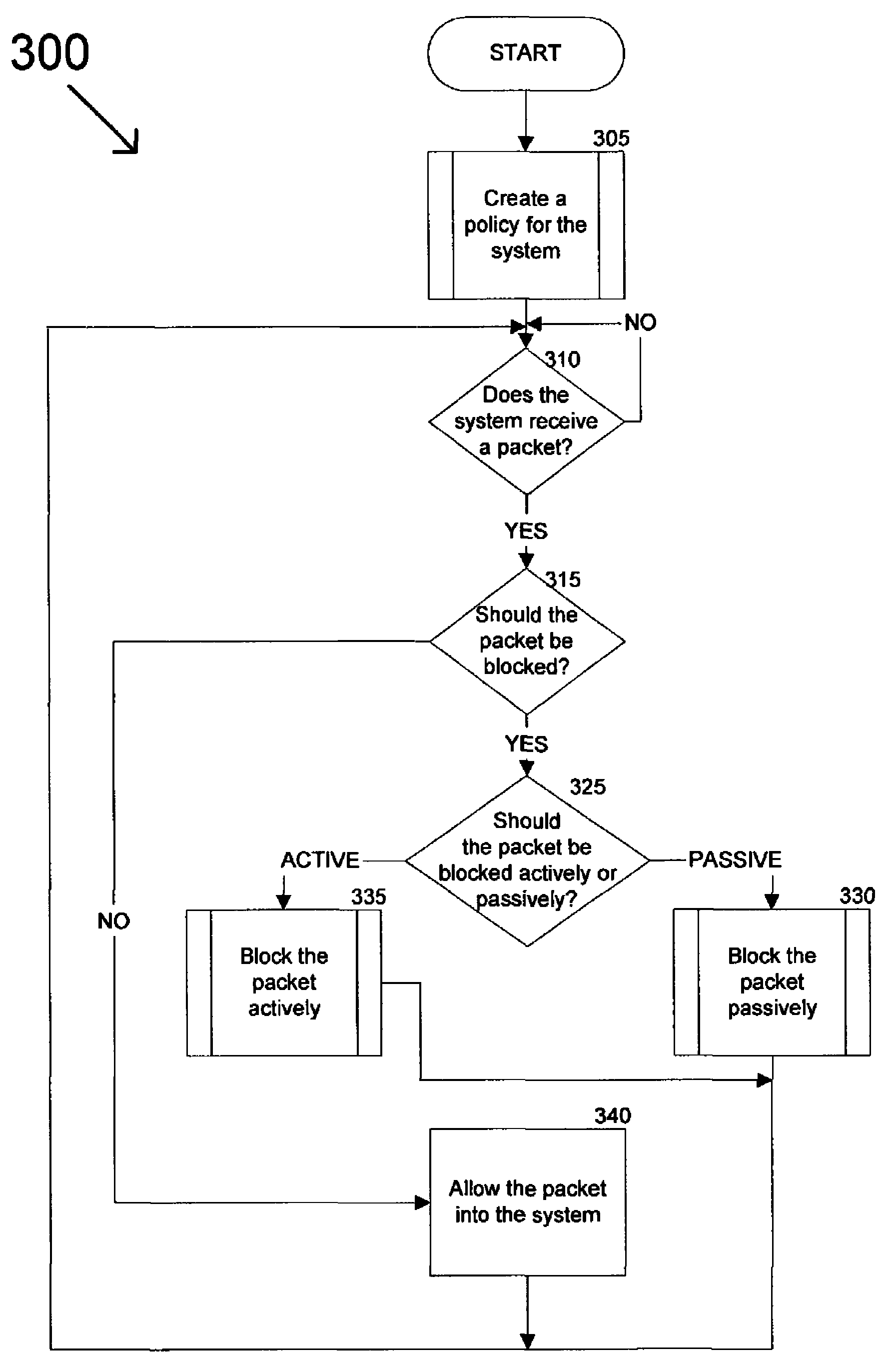
Method and system for dynamically protecting a computer system from attack
ActiveUS7913303B1Protection attackMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionProtection systemVulnerability
A dynamic protection system can analyze a computer system to determine its vulnerabilities to attack and generate a policy for protecting the computer system based on the identified vulnerabilities. Data received by the computer system can be analyzed to determine if it poses a threat to the system. This can prevent the data from entering the system or host based on a determination that the data poses a threat. Also, the dynamic protection system can receive policy updates to allow it to protect the system more efficiently and effectively. In other words, the dynamic protection system can protect an evolving computer system operating in an environment that is characterized by constantly changing methods of attack. Furthermore, by minimizing a need for manual intervention, attacks can be rapidly and accurately detected with a minimization of false positives, thereby lowering the cost of operation.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Method and system for evaluating network safety situation
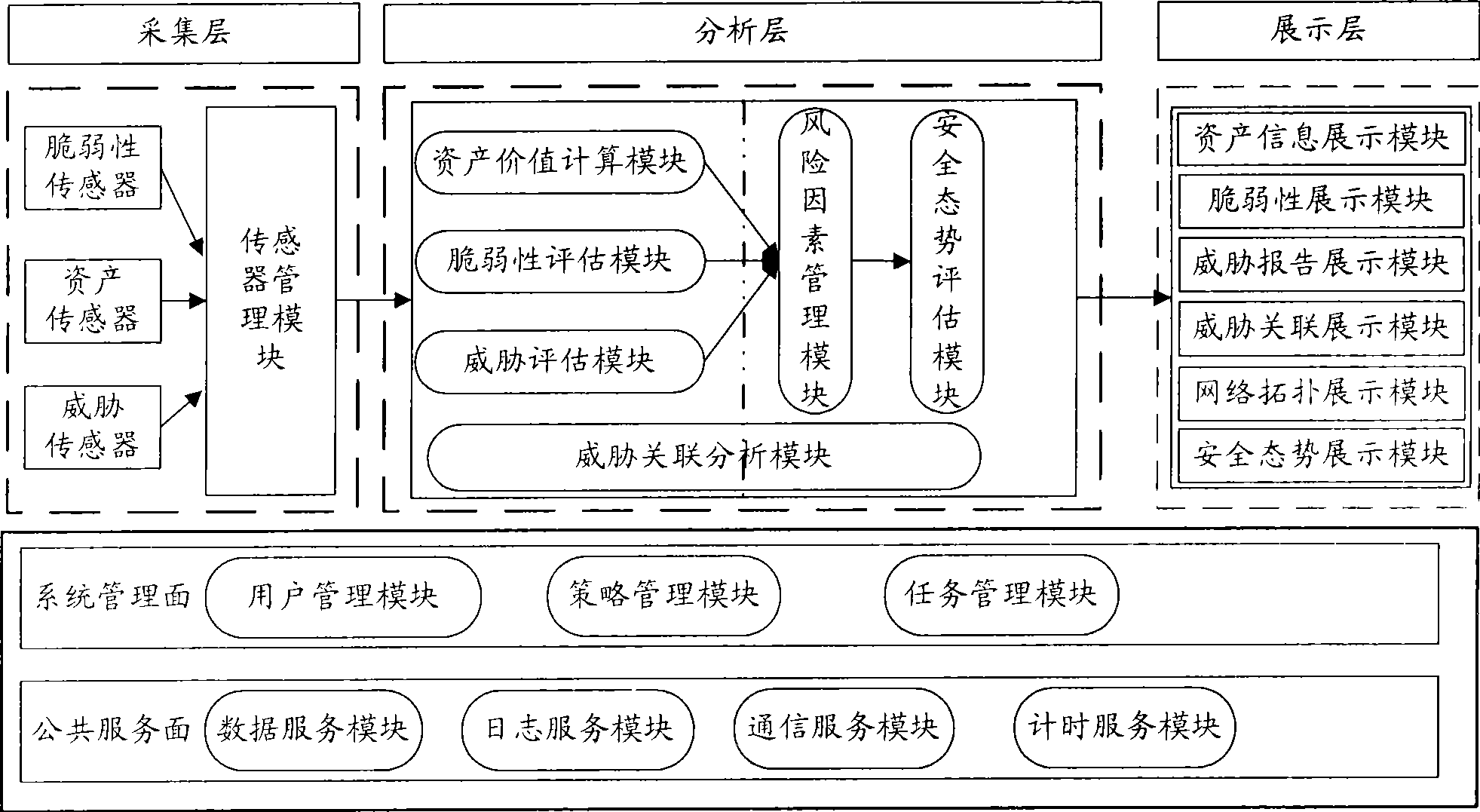
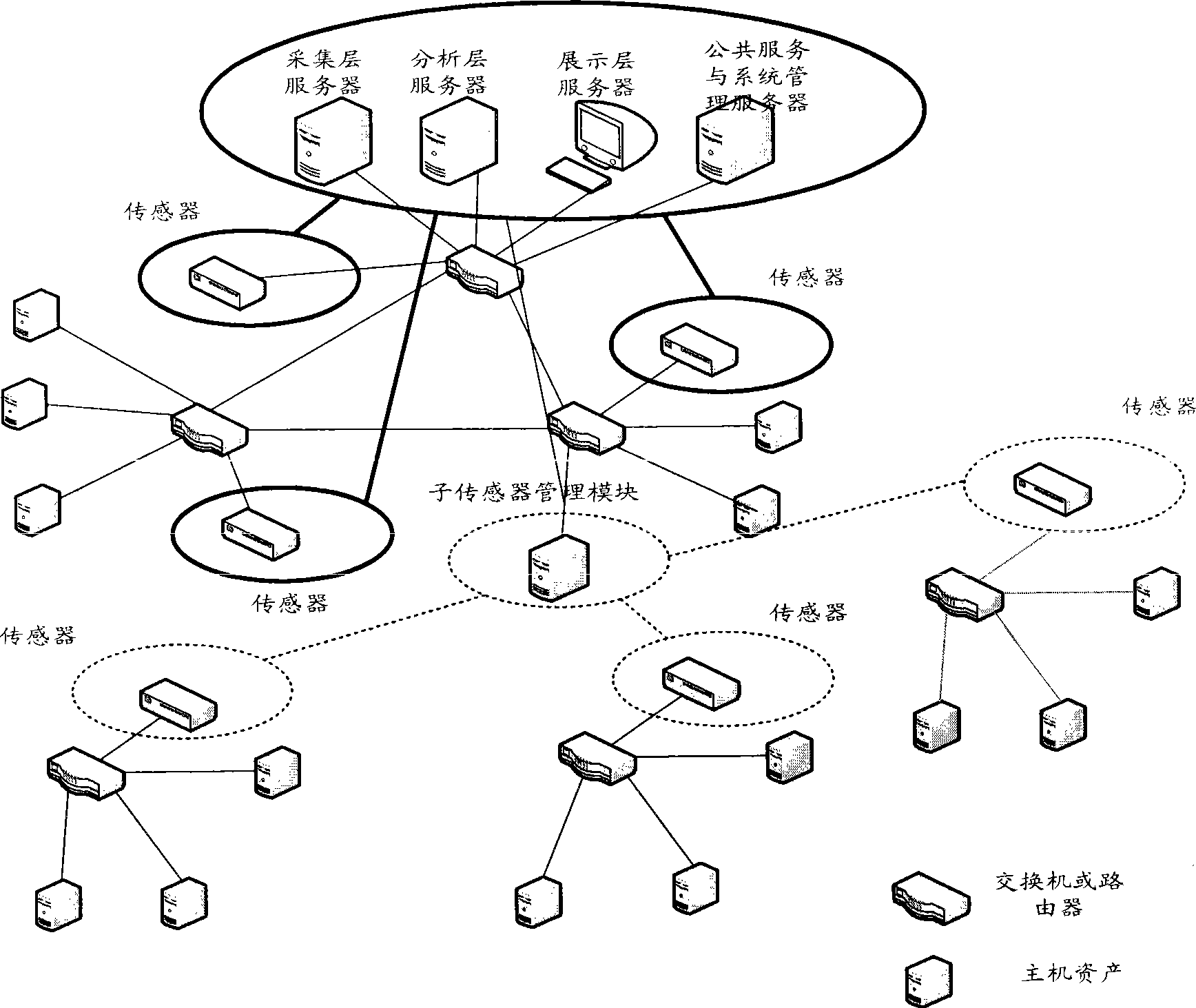
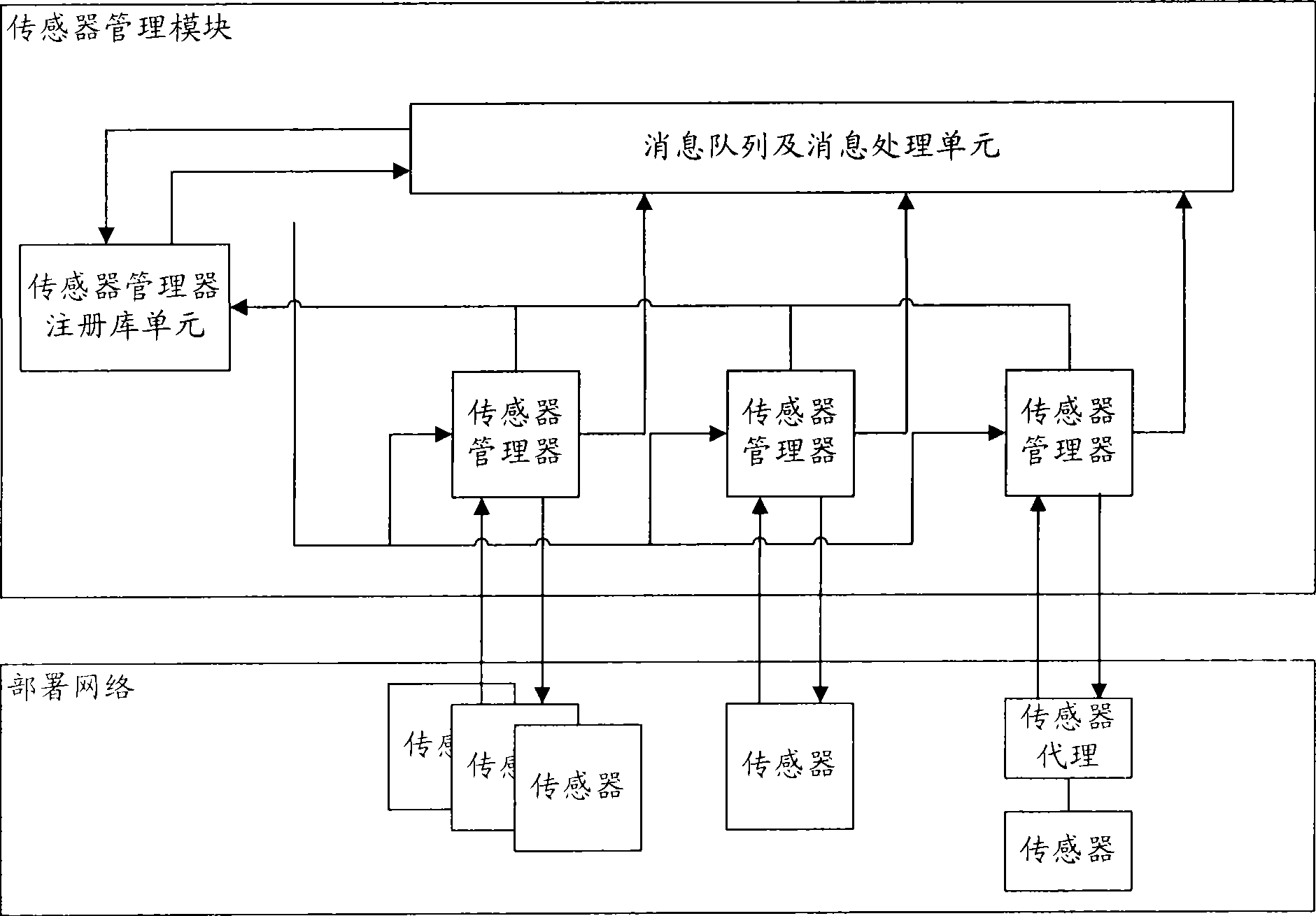
InactiveCN101436967AEasy to operateImprove securityData switching networksThree levelSecurity solution
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the security situation of a network and a system thereof. The system has a two-surface three-level framework and is provided with a public service surface and a service management surface for executing uniform coordinated management on each functional module of the system; according to a service logic processing flow, the system is divided into three levels: an acquisition level, an analysis level and an exhibition level for completing four evaluating operations of assets, frangibility, threat and security situation; the invention is based on the characteristic of service operation in the network, combines the prior risk evaluation method, the prior flow and the prior security detection tool and provides a set of a novel dynamic real-time evaluation method. The system can analyze the assets and service of the network and the risk of the whole network and carries out the evaluation of the security situation. The system can provide the security state of the whole network in macroscopy, can deepen to specific service and assets and know the specific security problem, thereby effectively helping network security personnel to analyze the root of the security problem and assisting to provide a security solution proposal and implement a defense measure.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
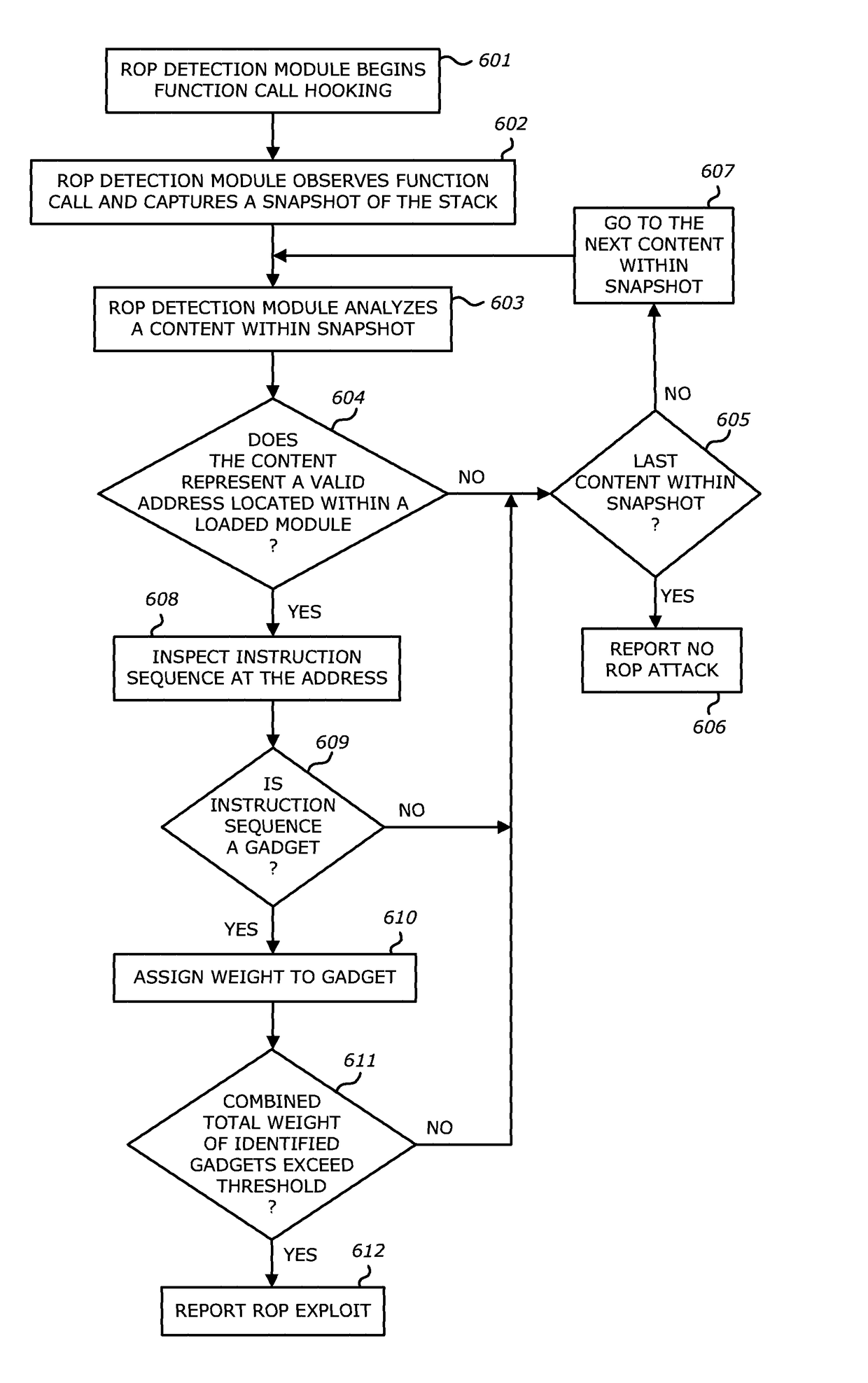
Return-oriented programming detection
ActiveUS9594912B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInternet trafficApplication procedure
According to one embodiment, a threat detection system is integrated with at least a dynamic analysis engine. The dynamic analysis engine is configured to automatically detect a function call by an application, responsive to detecting the function call, analyze contents located at one or more addresses located within a portion of memory allocated for the application, and, based on the analysis, determine whether one or more objects included in received network traffic is associated with a return-oriented programming (ROP) exploit.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
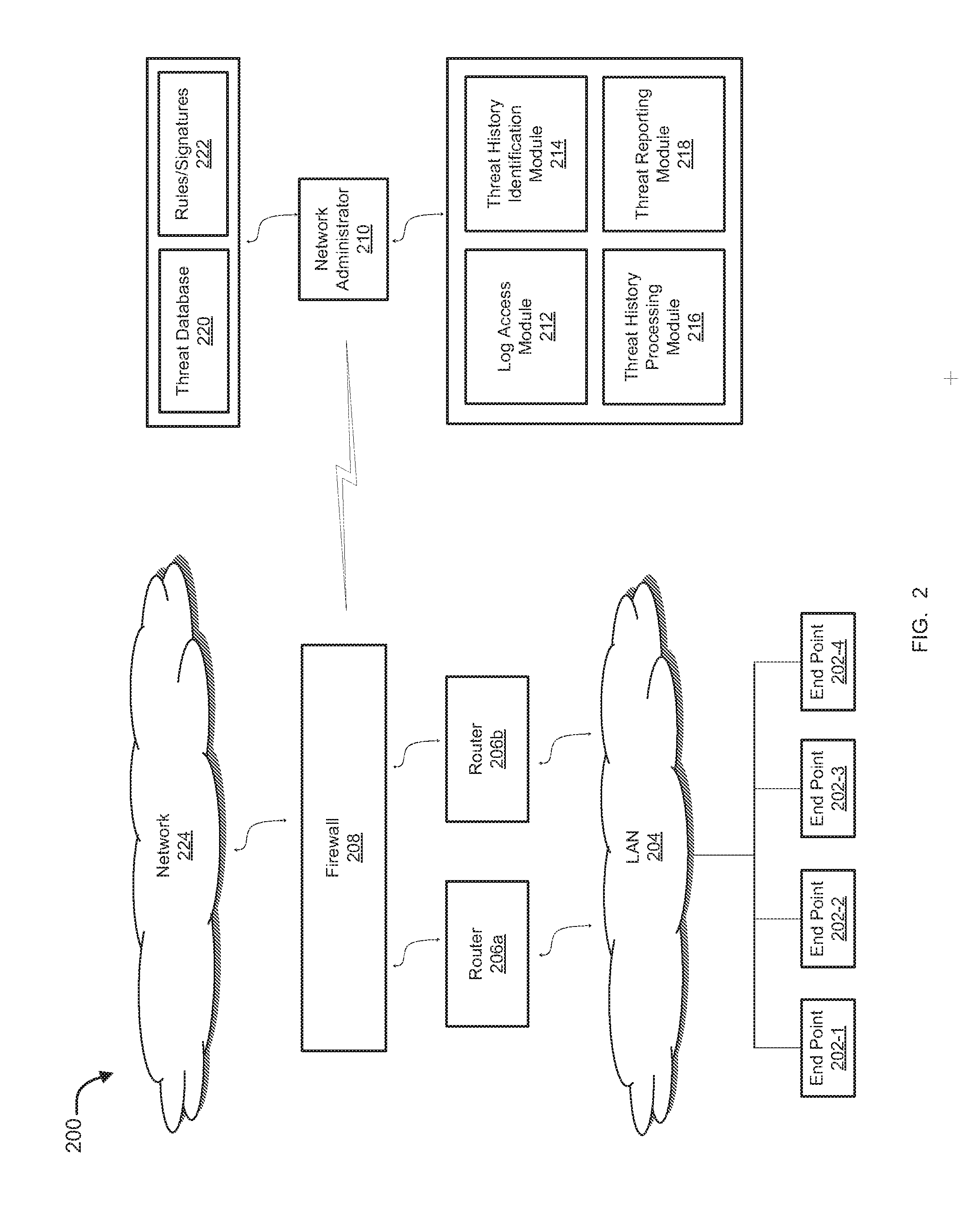
Presentation of threat history associated with network activity
ActiveUS20160173446A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlNetwork activityInternet privacy
Methods and systems for extracting, processing, displaying, and analyzing events that are associated with one or more threats are provided. According to one embodiment, threat information, including information from one or more of firewall logs and historical threat logs, is maintained in a database. Information regarding threat filtering parameters, including one or more of types of threats to be extracted from the database, parameters of the threats, network-level details of the threats, a time interval of detection of the threats and source-destination details of the threats, is received. Information regarding threats matching the threat filtering parameters are extracted from the database and is presented in a form of an interactive historical graph. Responsive to receiving from a user an indication regarding a selected subset of time in which to zoom into for further details, a list of threats within the selected subset is presented in tabular form.
Owner:FORTINET
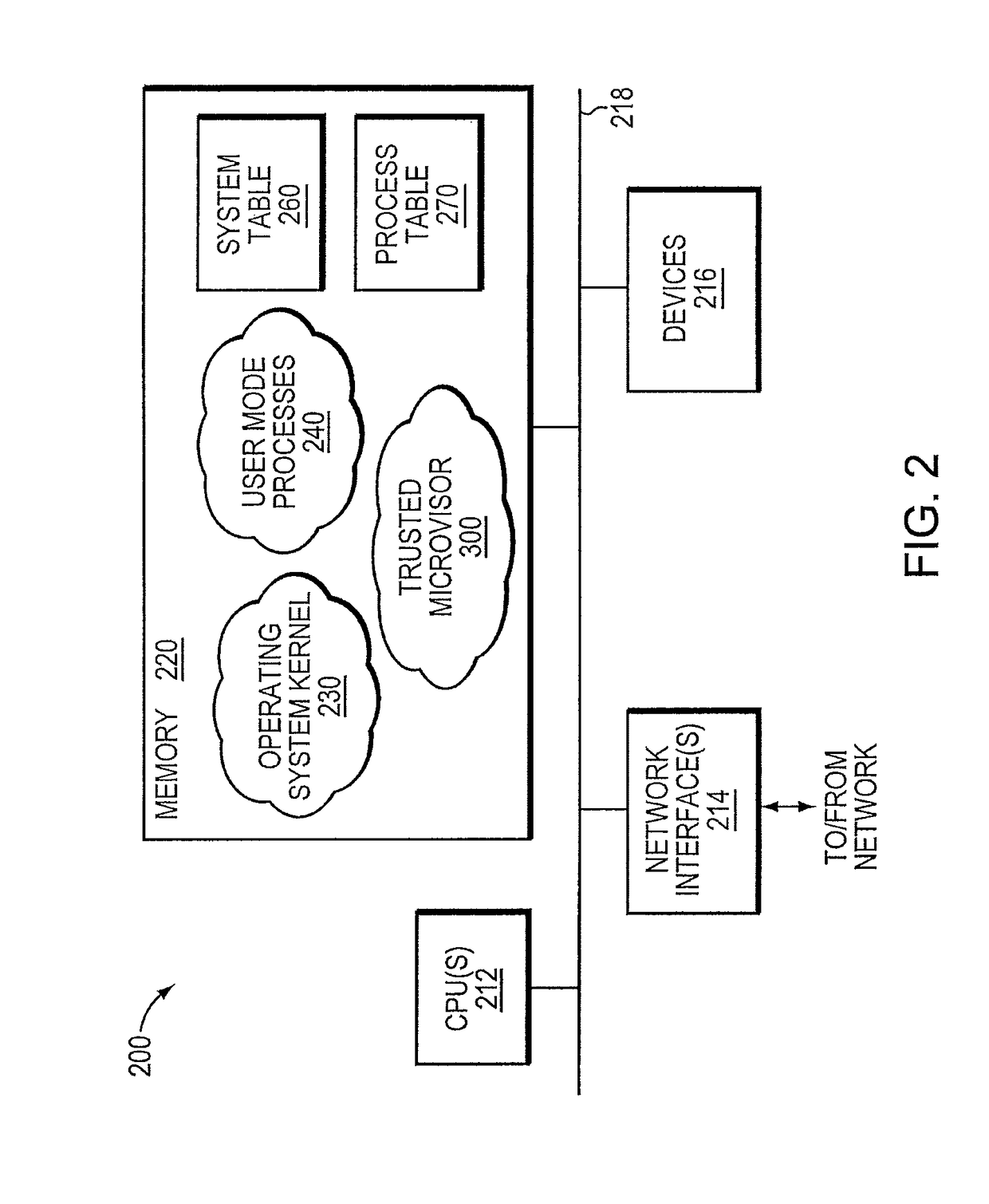
Exploit detection system with threat-aware microvisor
ActiveUS20150199531A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVulnerability detectionThreat intelligence
An exploit detection system deploys a threat-aware microvisor to facilitate real-time security analysis, including exploit detection and threat intelligence, of an operating system process executing on a node of a network environment. The microvisor may be organized as a main protection domain representative of the operating system process. In response to the process attempting to access a kernel resource for which it does not have permission, a capability violation may be generated at the main protection domain of the microvisor and a micro-virtual machine (VM) may be spawned as a container configured to encapsulate the process. The main protection domain may then be cloned to create a cloned protection domain that is representative of the process and that is bound to the spawned micro-VM. Capabilities of the cloned protection domain may be configured to be more restricted than the capabilities of the main protection domain with respect to access to the kernel resource. The restricted capabilities may be configured to generate more capability violations than those generated by the capabilities of the main protection domain and, in turn, enable further monitoring of the process as it attempts to access the kernel resource.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
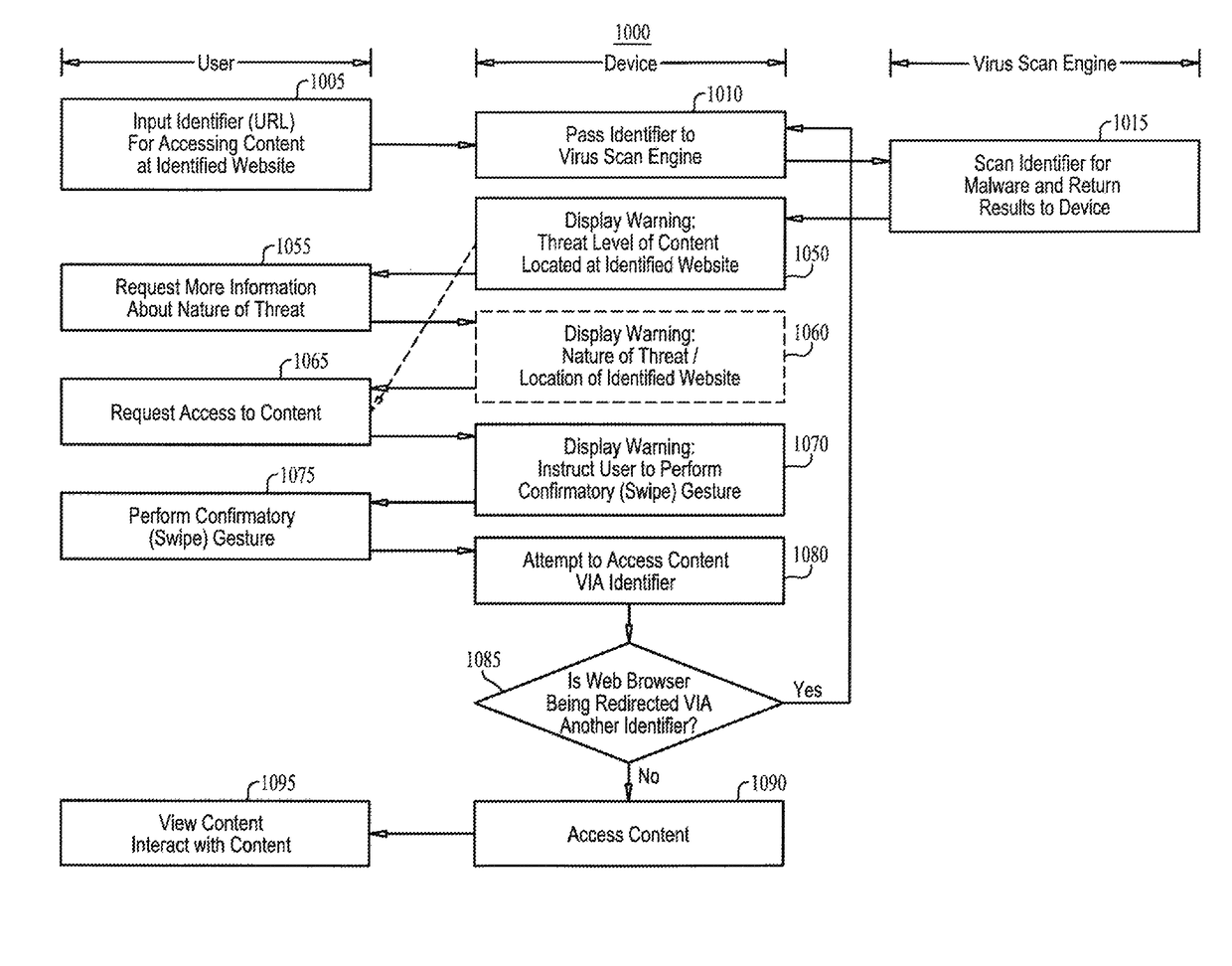
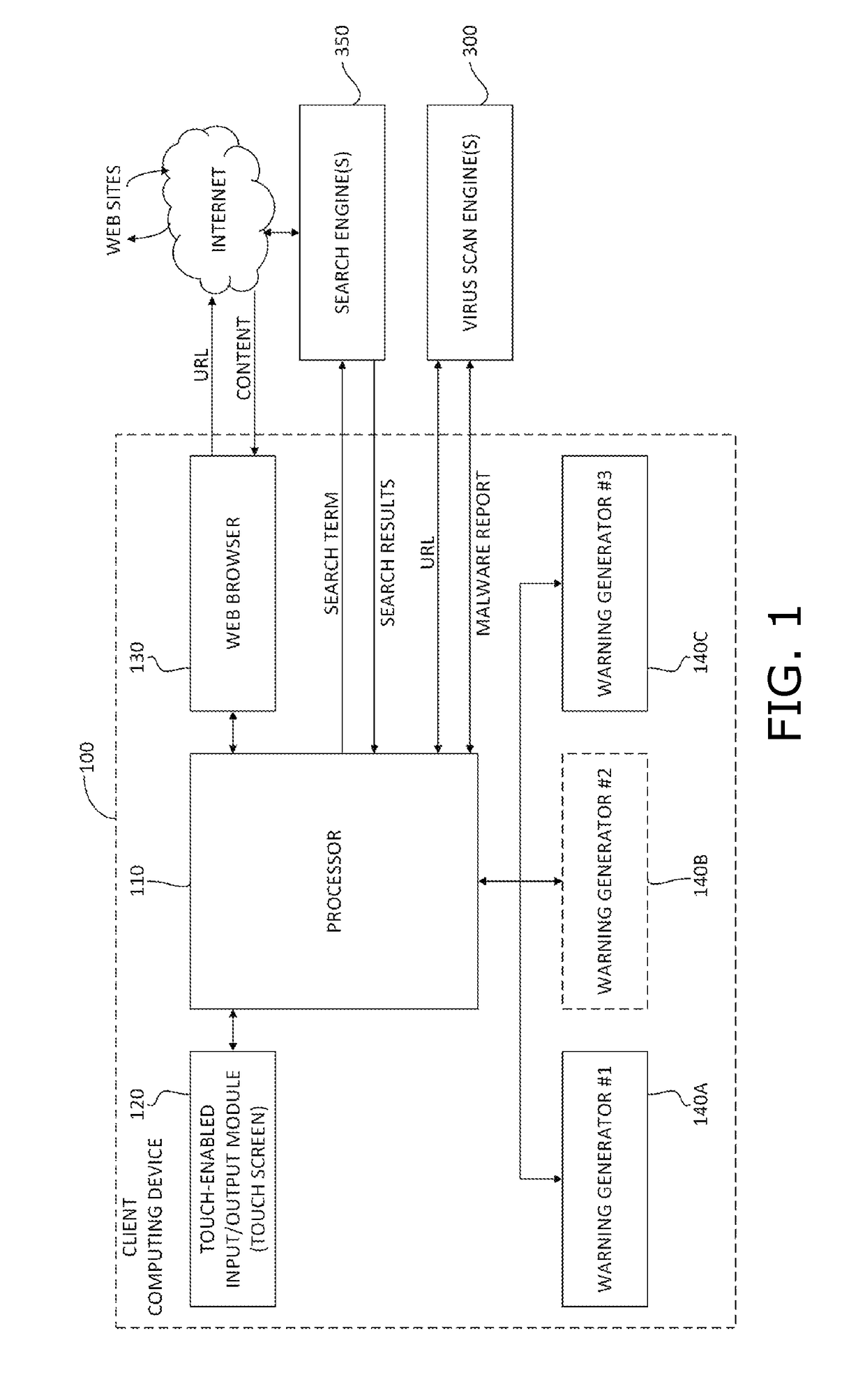
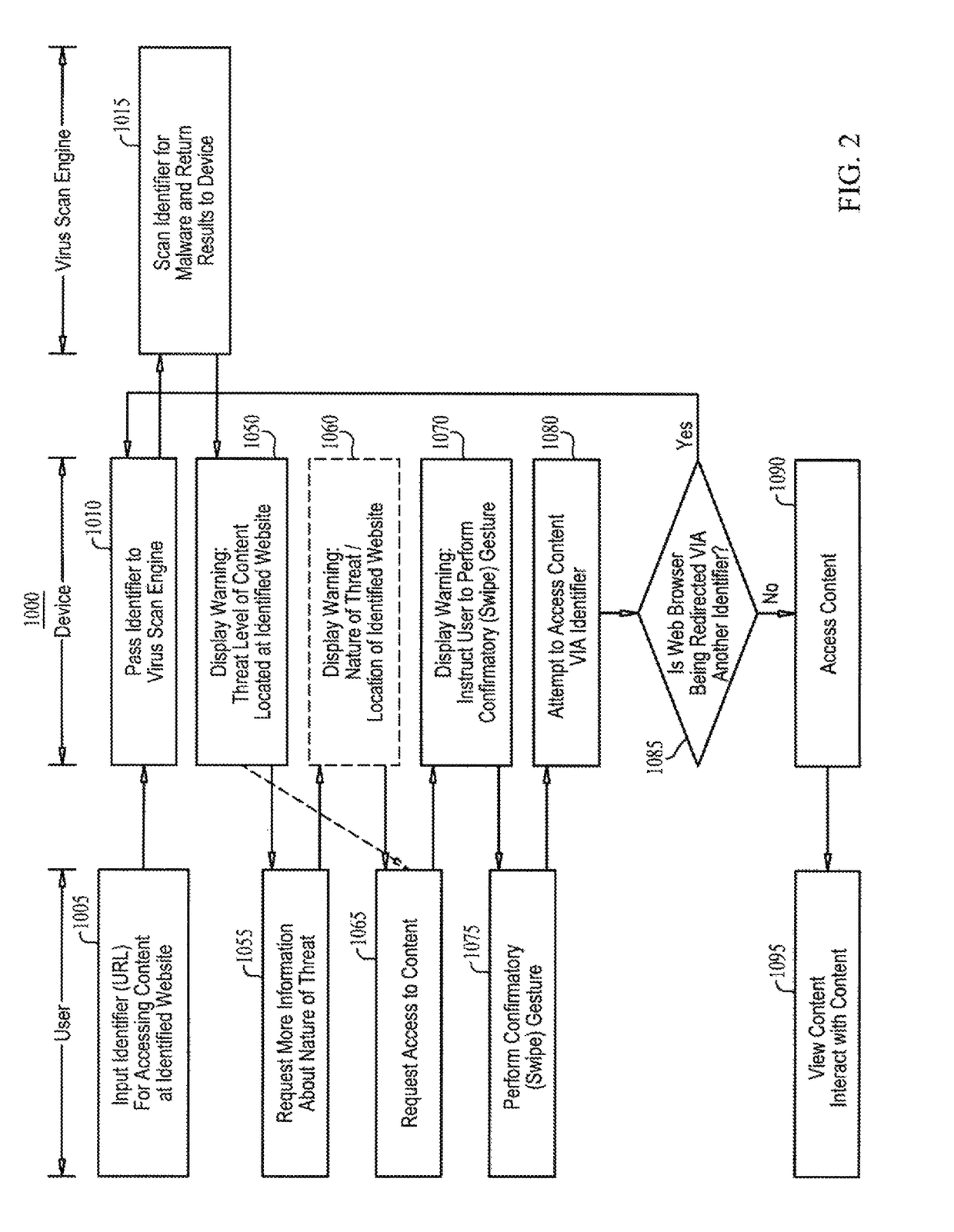
Malware warning
A malware warning system, including a client sending requests to and receiving replies from a server, and a server, including a first warning generator sending to the client a warning including a threat level of content located at a web site, in response to receiving from the client a URL for accessing content at the web site, a second warning generator sending to the client a warning including information about at least one of the nature of the threat of the content located at the web site and a location of the web site, in response to receiving from the client a request for more information about the nature of the threat, and a third warning generator, sending to the client a warning including an instruction to perform a swipe gesture to confirm a request to access the URL, in response to receiving that request from the client.
Owner:FINJAN MOBILE LLC
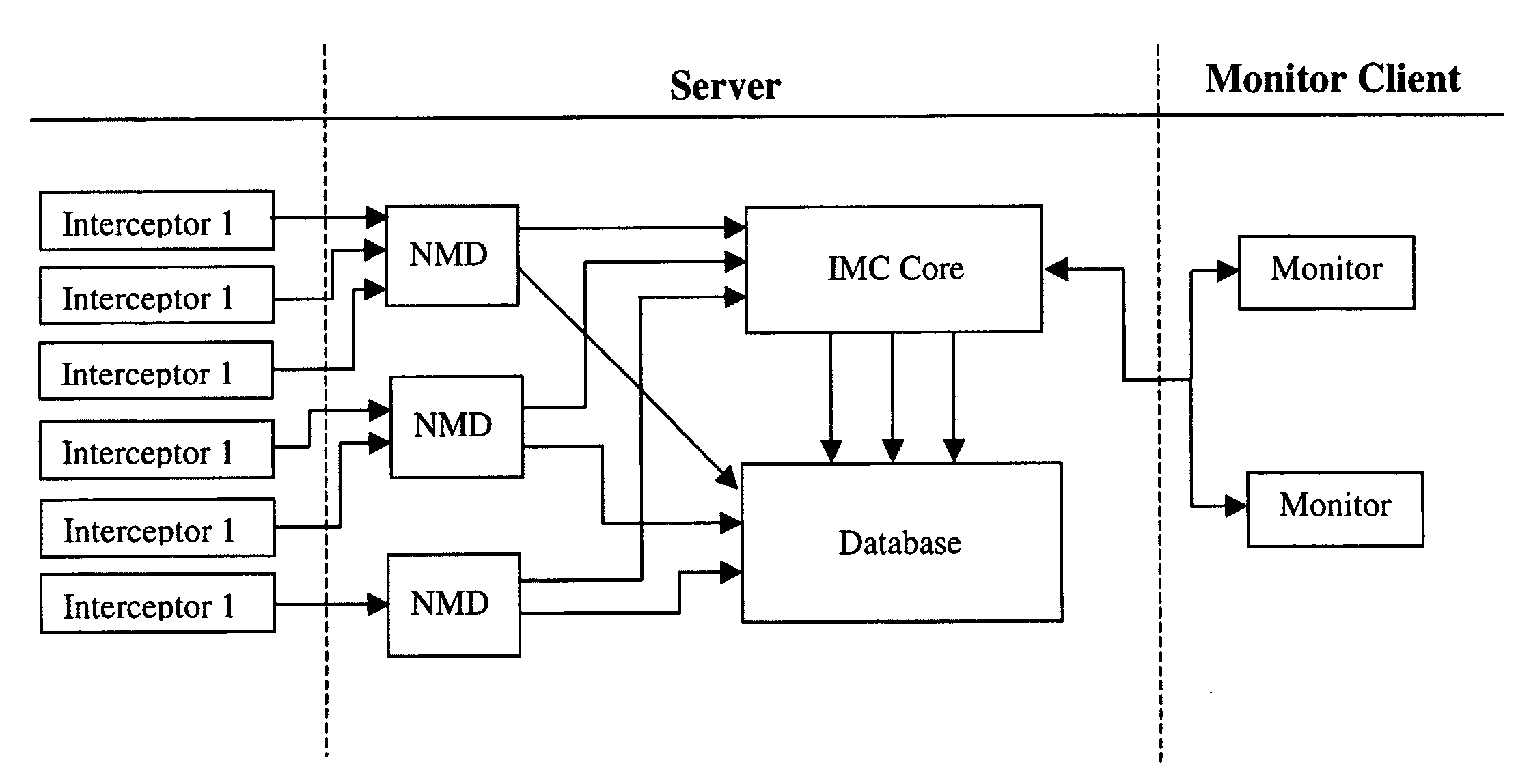
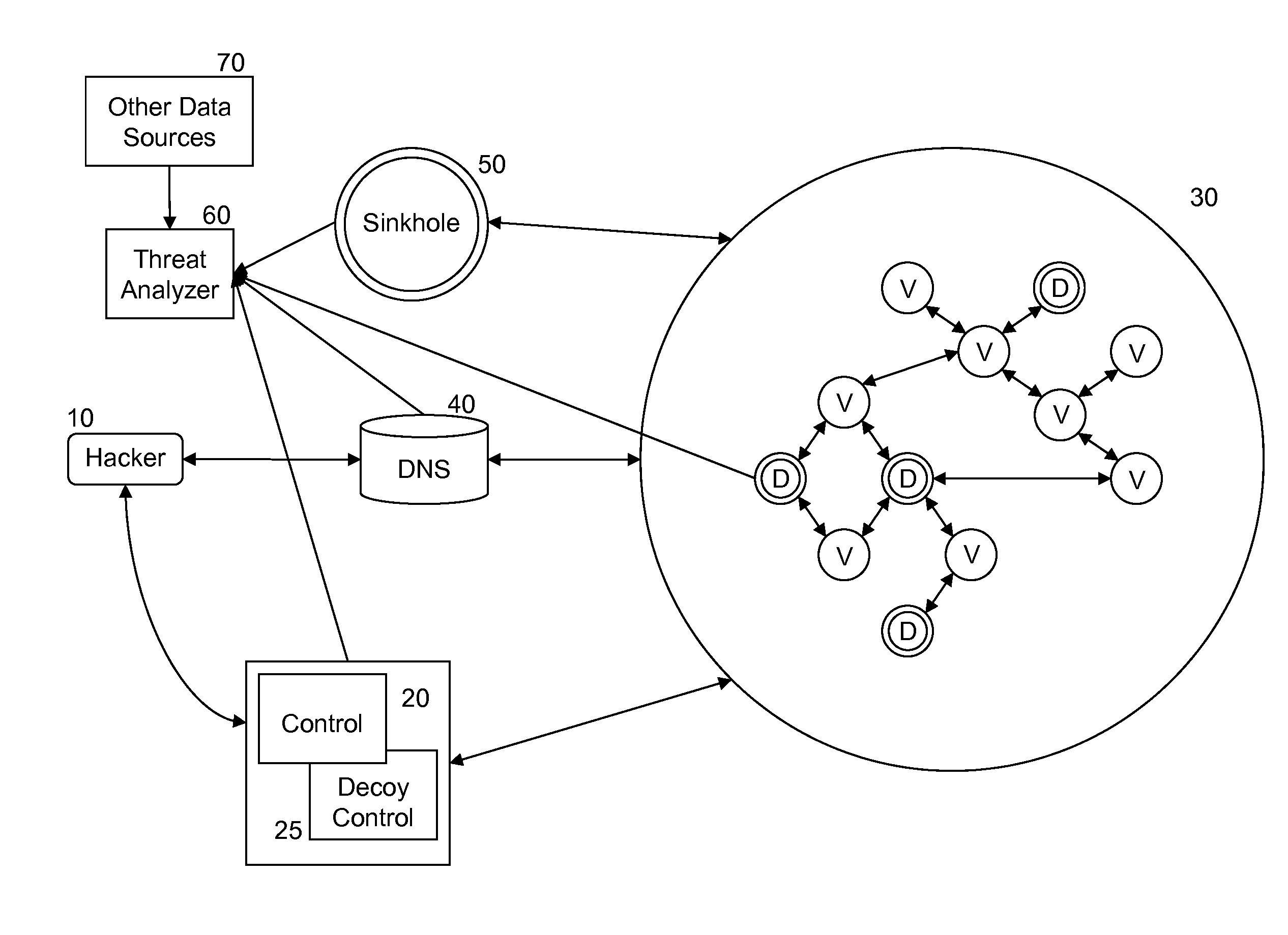
Method and system for detecting network compromise
ActiveUS9356942B1Eliminate the problemMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet privacyEngineering
A method and system are described for detecting unauthorized access to one or more of a plurality of networked victim computers in a victim cloud. The networked victim computers connect to one or more DNS servers. The system includes one or more decoy bot computers, which are operated as victim computers in the victim cloud. The system also includes one or more decoy control computers, which are operated as control computers that communicate with victim computers in the victim cloud. Threats are identified by analyzing data traffic communicated with the decoy bot computers and decoy control computers for information suspected of having being sent from a victim's computer without proper authorization, and by monitoring whether behavior of a DNS server deviates from expected behaviors.
Owner:SECURITY SERVICES LLC
Cooperative intrusion detection ecosystem for IP reputation-based security
ActiveUS20140059683A1Easy to operateImprove system response timeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionPattern matchingContinuous data
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is enhanced to operate in a cluster of such systems, and IDSs organized into a cluster cooperate to exchange IP reputation influencing events information between or among the cooperating systems in real-time to enhance overall system response time and to prevent otherwise hidden attacks from damaging network resources. An IDS includes an IP reputation analytics engine to analyze new and existing events, correlate information, and to raise potential alerts. The IP reputation analytics engines may implement an algorithm, such as a pattern matching algorithm, a continuous data mining algorithm, or the like, to facilitate this operation. Clustering IDS endpoints to share IP reputation influencing events, using the cluster-wide view to determine IP reputation, and feeding the cluster-wide view back to the IDS endpoints, provides for enhanced and early detection of threats that is much more reliable and scalable as compared to prior art techniques.
Owner:IBM CORP
Policy/rule engine, multi-compliance framework and risk remediation
Owner:ALERT ENTERPRISE
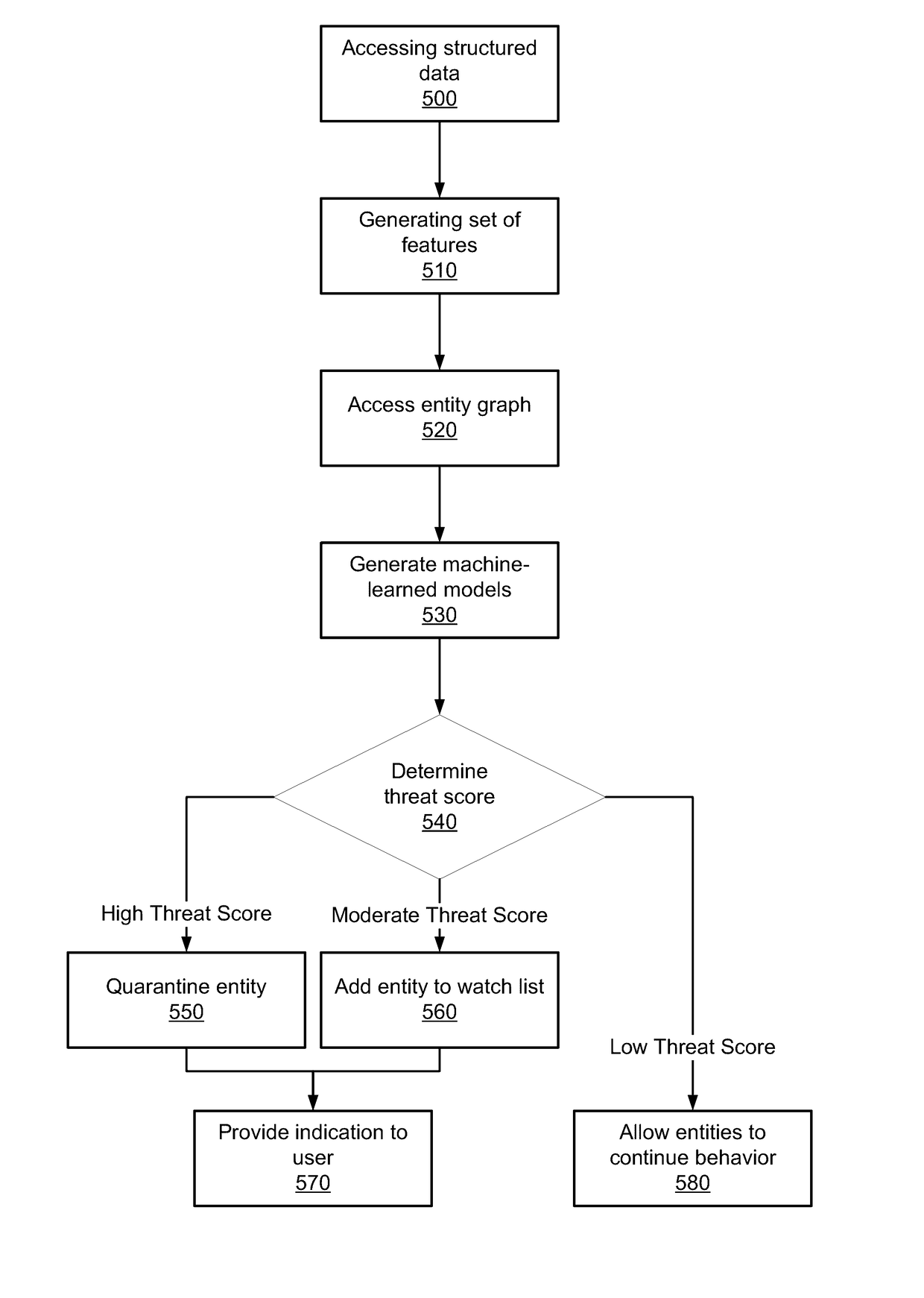
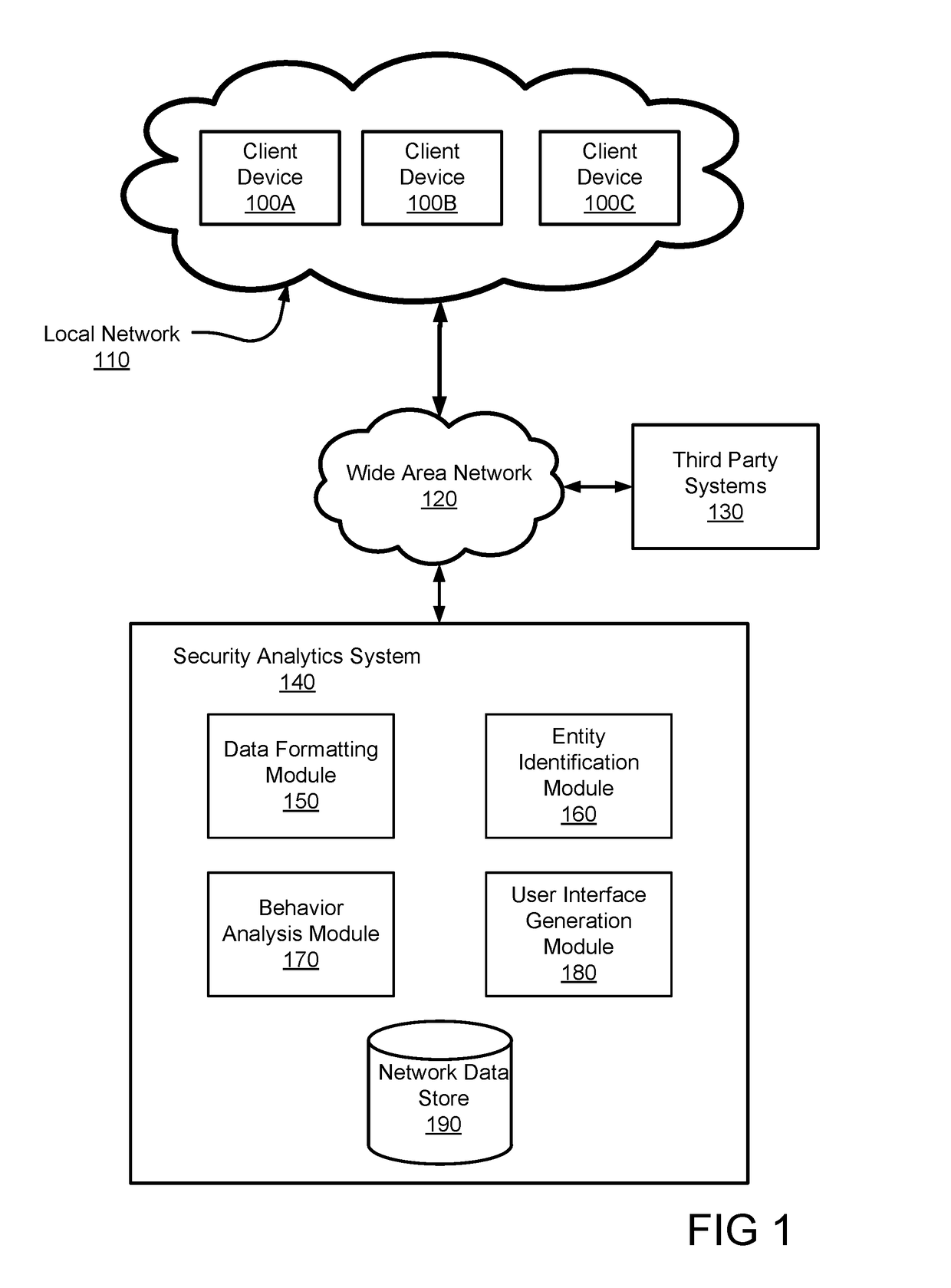
Detecting security threats in a local network
ActiveUS20170118240A1Mathematical modelsKnowledge representationEntity–relationship modelOriginal data
Disclosed is a system for detecting security threats in a local network. A security analytics system collects data about entities in the local network. The security analytics system identifies the entities in the raw data and determines a set of properties about each of the identified entities. The entity properties contain information about the entity and can be temporary or permanent properties about the entity. The security analytics system determines relationships between the identified entities and can be determined based on the entity properties for the identified properties. An entity graph is generated that describes the entity relationships, wherein the nodes of the entity graph represent entities and the edges of the entity graph represent entity relationships. The security analytics system provides a user interface to a user that contains the entity graph and the relationships described therein.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Trusted threat-aware microvisor
ActiveUS9680862B2Digital data protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceTrusted ComputingSecurity properties
A trusted threat-aware microvisor may be deployed as a module of a trusted computing base (TCB) that also includes a root task module configured to cooperate with the microvisor to load and initialize one or more other modules executing on a node of a network environment. The root task may cooperate with the microvisor to allocate one or more kernel resources of the node to those other modules. As a trusted module of the TCB, the microvisor may be configured to enforce a security policy of the TCB that, e.g., prevents alteration of a state related to security of the microvisor by a module of or external to the TCB. The security policy of the TCB may be implemented by a plurality of security properties of the microvisor. Trusted (or trustedness) may therefore denote a predetermined level of confidence that the security property is demonstrated by the microvisor.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
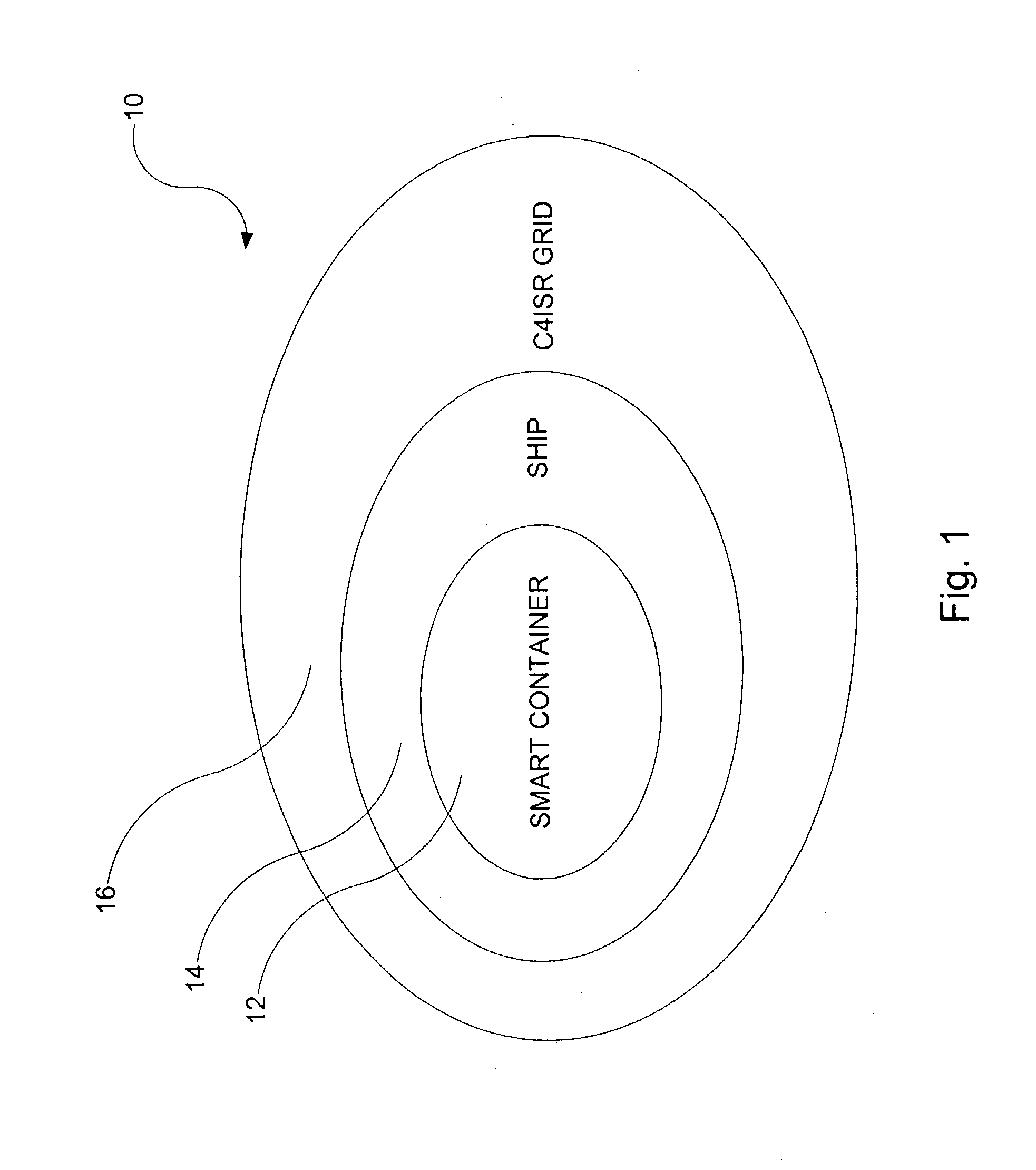
Smart and secure container
ActiveUS7002472B2Road vehicles traffic controlLarge containersTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A smart container configured for transporting cargo on a transportation vehicle and a method for transporting the smart container on the transportation vehicle are disclosed. The smart container includes a container housing that has an opening for loading and unloading cargo. The opening can be sealed and unsealed. Disposed within the container housing is at least one detector for detecting deviations that could be indicative of possible threats (security concerns). A communications link is also disposed within the container housing. The communications link is capable of transmitting the possible threat information to a central cargo data collection location. For example, the container(s) on a transportation vehicle (e.g., a ship) transport information about the container to a central data collector onboard the ship. The central data collector may then transmit that information off of the ship, e.g., to a C4ISR grid.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
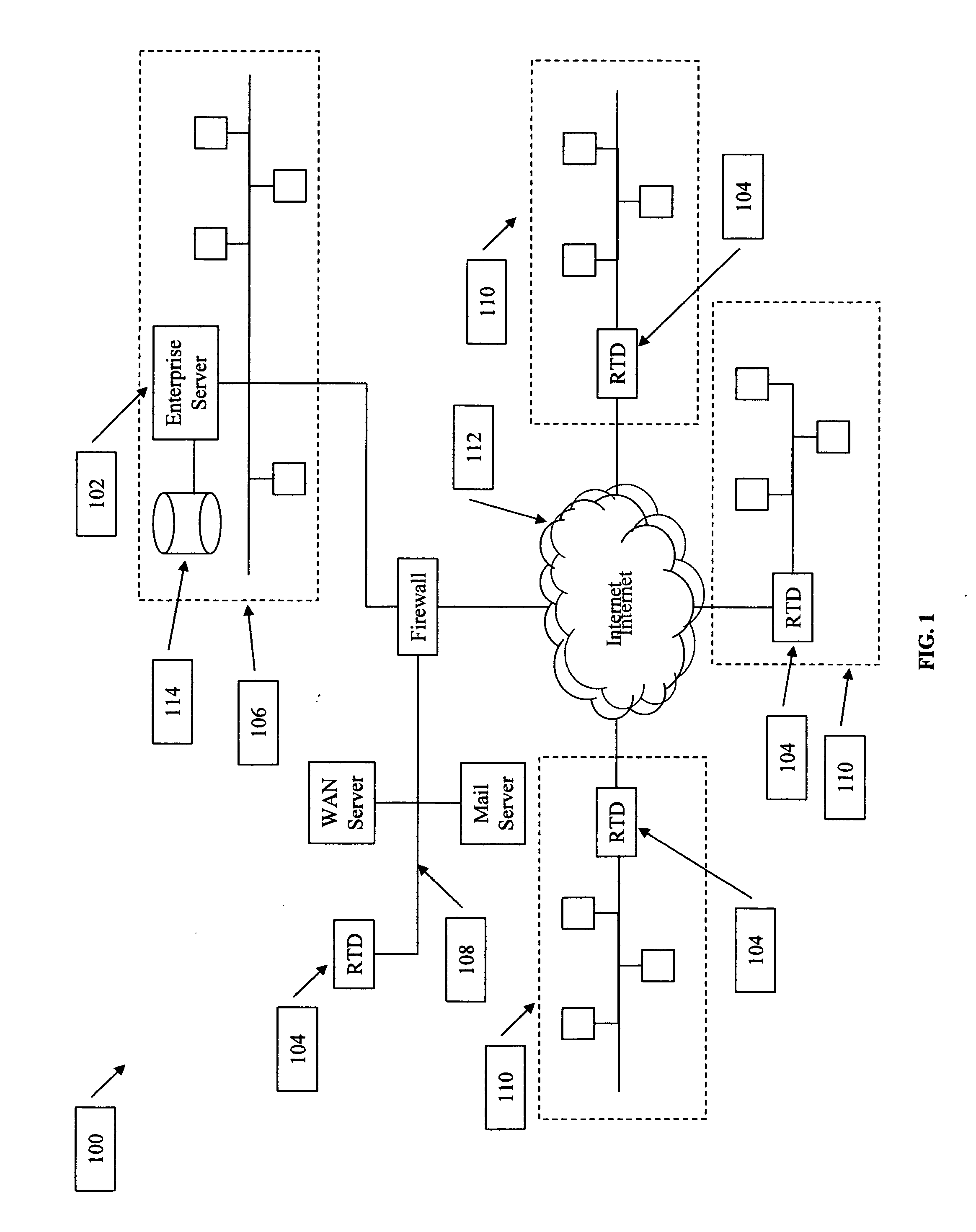
Method to generate a quantitative measurement of computer security vulnerabilities
InactiveUS20060101518A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionCollocationSecurity management
The present invention provides a system and method to provide a measurement of the risk that a computer network may have to computer security threats. The system includes a collocation facility that is coupled to a plurality of computer security management systems. Some or all of the vulnerability information is reported to the collocation facility. At the collocation facility, this information is compared to a standard. This comparison yields a number or other measurement of that organization's risk in its computer security. The collocation facility can then report this measurement to any information user that wishes to know what the vulnerability is for that organization.
Owner:SCHUMAKER TROY T +1
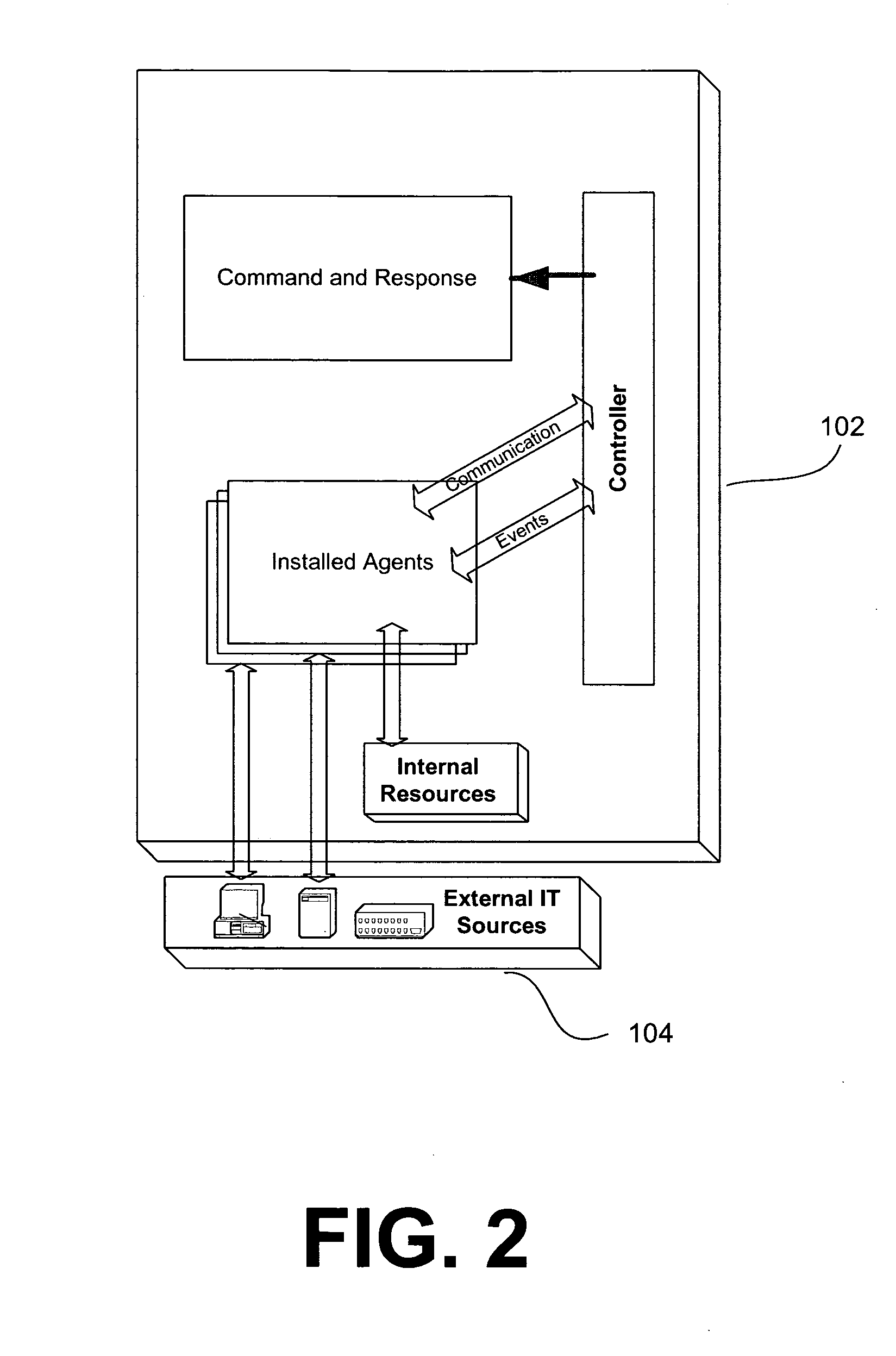
Method and system for securing and monitoring a wireless network
InactiveUS20050054326A1Limited accessUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsNetwork controlSystem usage
A common software interface simplifies a process of configuring the network security features provided by network controlled devices. A real-time threat entity detection system automatically scans the network using various protocols and builds entity profile data for each detection. The entity profile data is saved and updated every time the entity is detected on the network. Once the scan is complete, the system user is prompted to classify each newly detected node as a member or non-member of the network. The system user can then define automatic actions to take upon identification of the existence of the defined threat entity on the network at any point in the future. For example, a typical action could include notifying the threat entity of its detection or sending continuous requests to the threat entity over the network to effectively eliminate the usefulness of its membership on the network. The software also contacts the network gateway or router and configures MAC address filtering and disables broadcast of the router's SSID, effectively making the network invisible to any devices other than the devices allowed on the network. Additionally, the solution provides a process to add new members to the network while security features are enabled.
Owner:ROGERS TODD
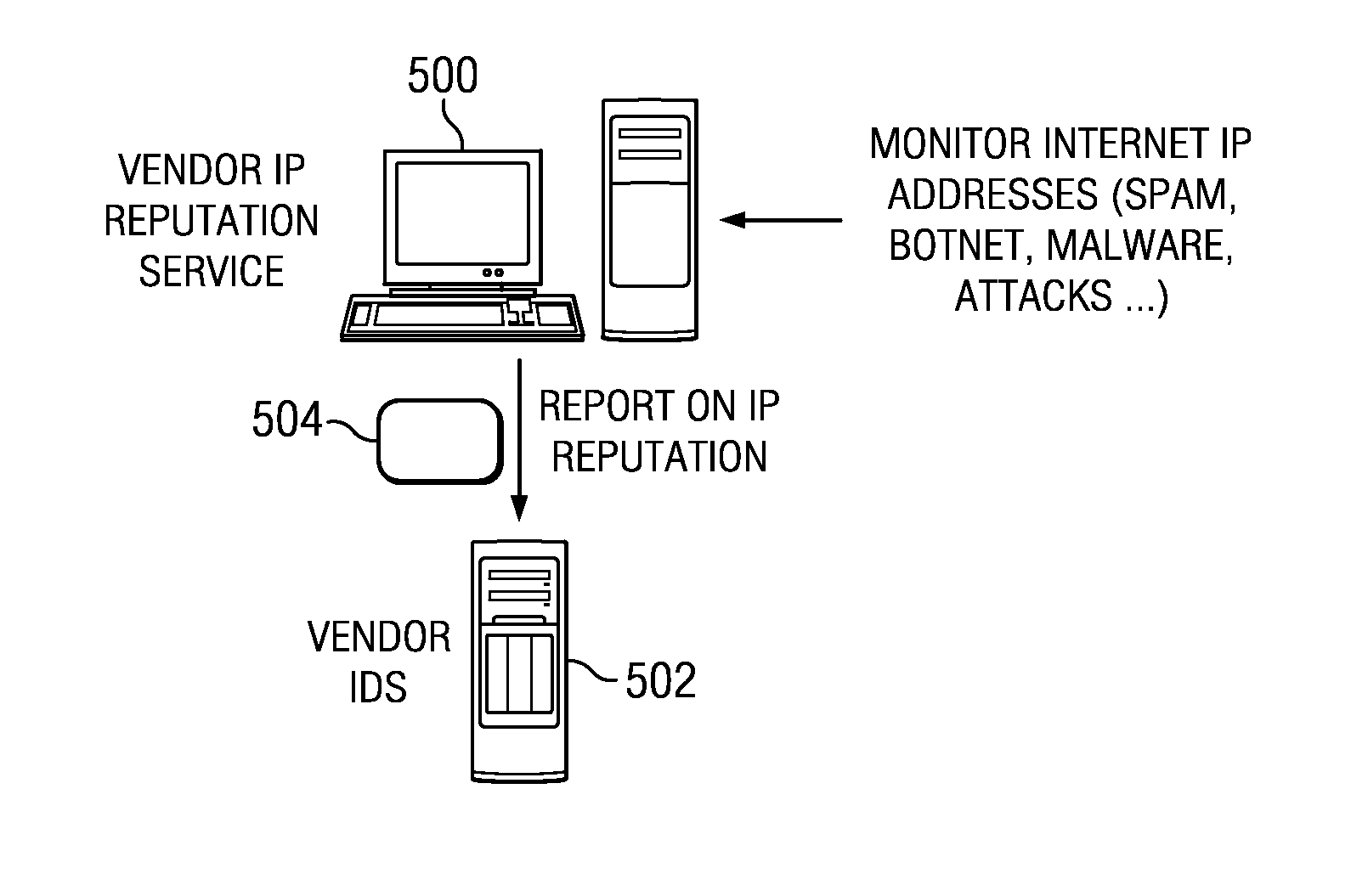
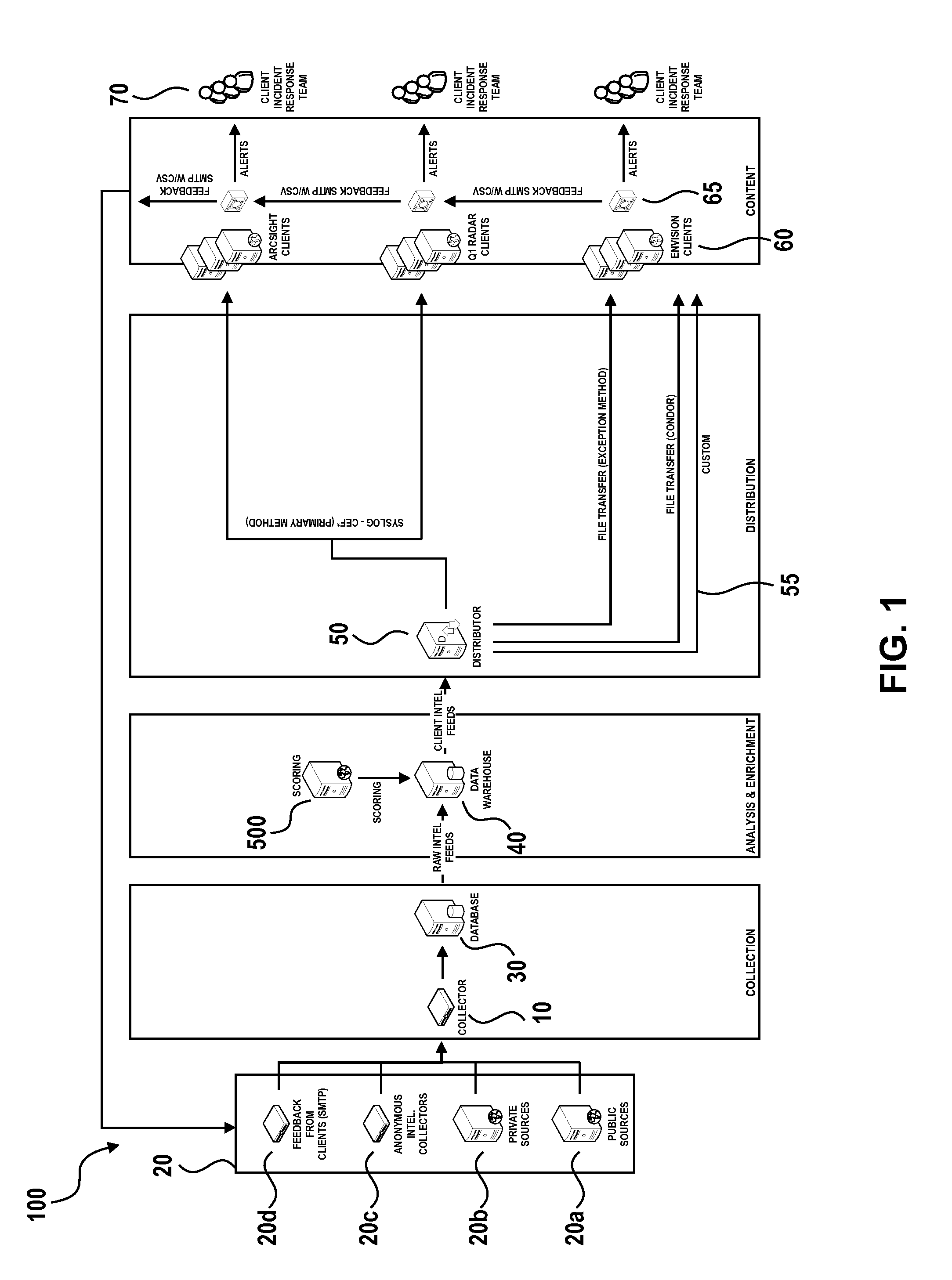
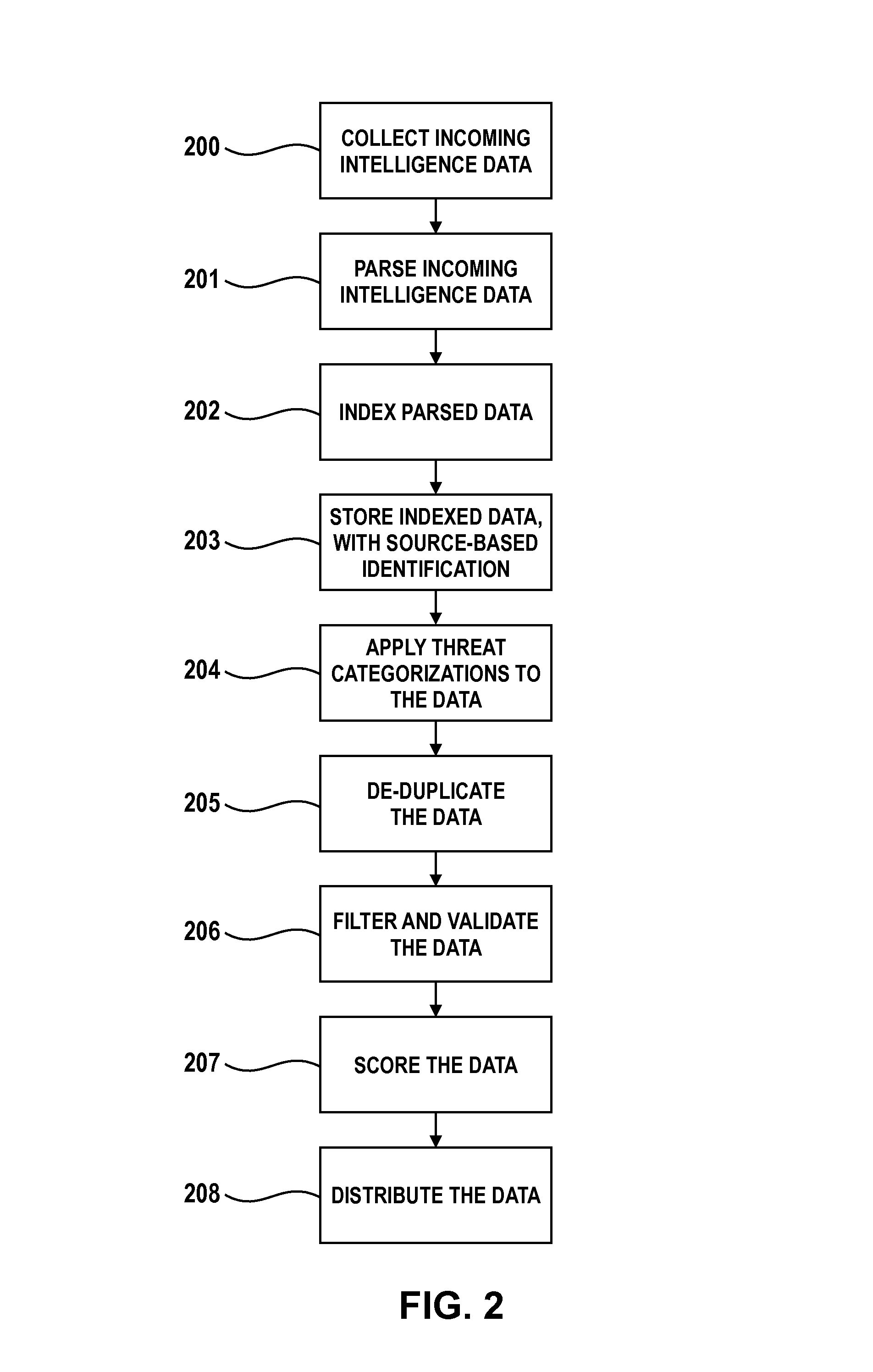
Collective threat intelligence gathering system
ActiveUS8813228B2Quality improvementMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionIp addressInternet privacy
Threat intelligence is collected from a variety of different sources. The threat intelligence information is aggregated, normalized, filtered and scored to identify threats to an information network. Threats are categorized by type, maliciousness and confidence level. Threats are reported to network administrators in a plurality of threat feeds, including for example malicious domains, malicious IP addresses, malicious e-mail addresses, malicious URLs and malicious software files.
Owner:DELOITTE DEV
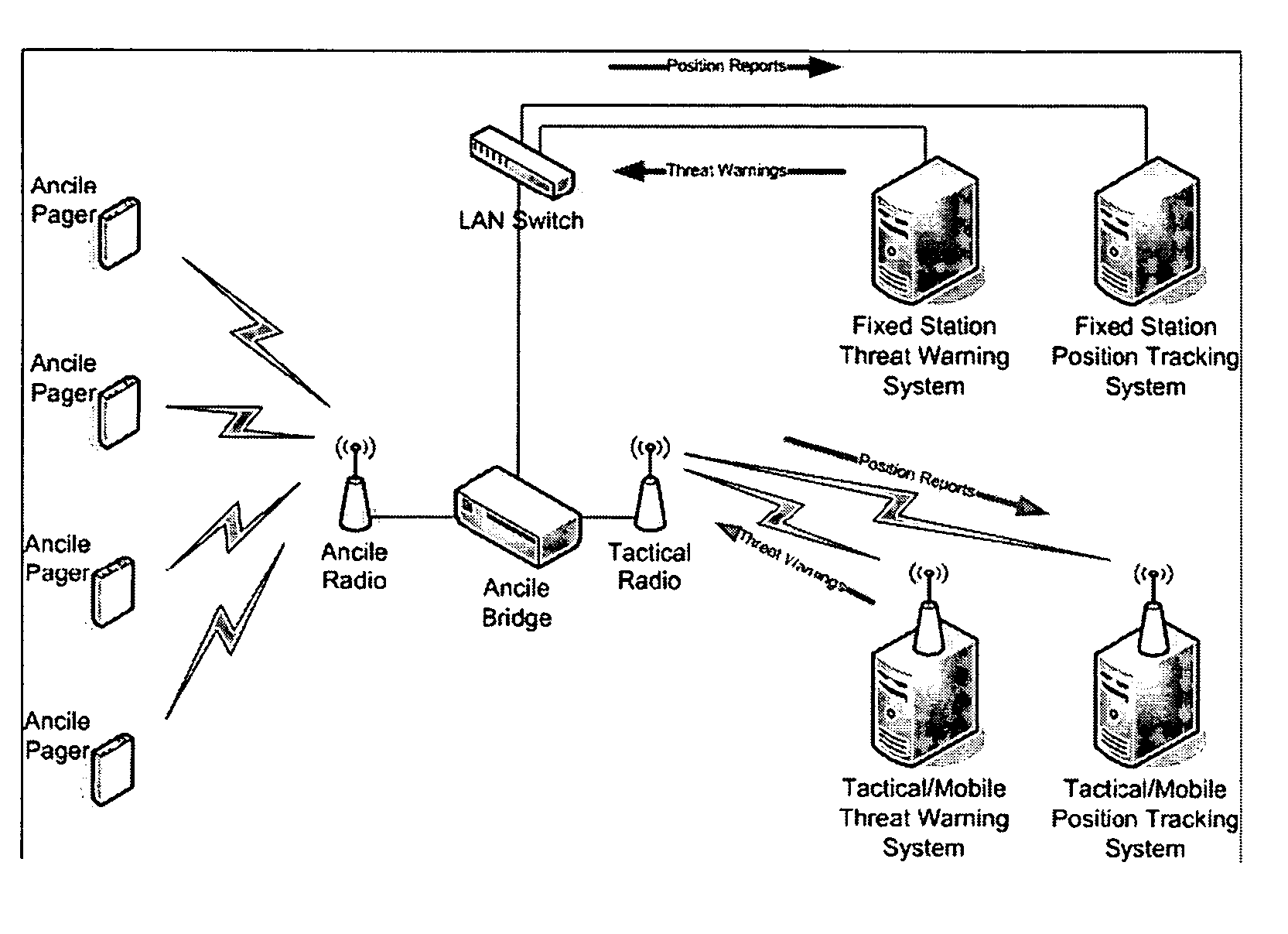
System, user warning and positioning device for use therein, and computer program product therefor, for tactical distributed event warning notification for individual entities
ActiveUS7764185B1Prevent basic triangulation effortEmergency connection handlingElectric testing/monitoringCommand and controlControl system
A system, device, and computer program product is provided for the centralized or distributed warning of existing or developing significant events and / or threats to users of the device within their locale, while reporting the location of all users of the system to existing command and control systems. A pager-like user warning and positioning device, worn by or carried by the individual user, or mounted in a vehicle or vessel, having a geographical positioning means therein, periodically transmits the geographical location of the individual user, vehicle or vessel, and listens for warning / notification event messages transmitted by a network bridge or central station. When an event / threat warning is received by the device, the device alerts the user via indicia relative to the event / situation, including audible spoken warnings and instructions on how to react, and may retransmit the event / threat warning to other nodes in the network.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE UNITED STATE OF AMERICA +1
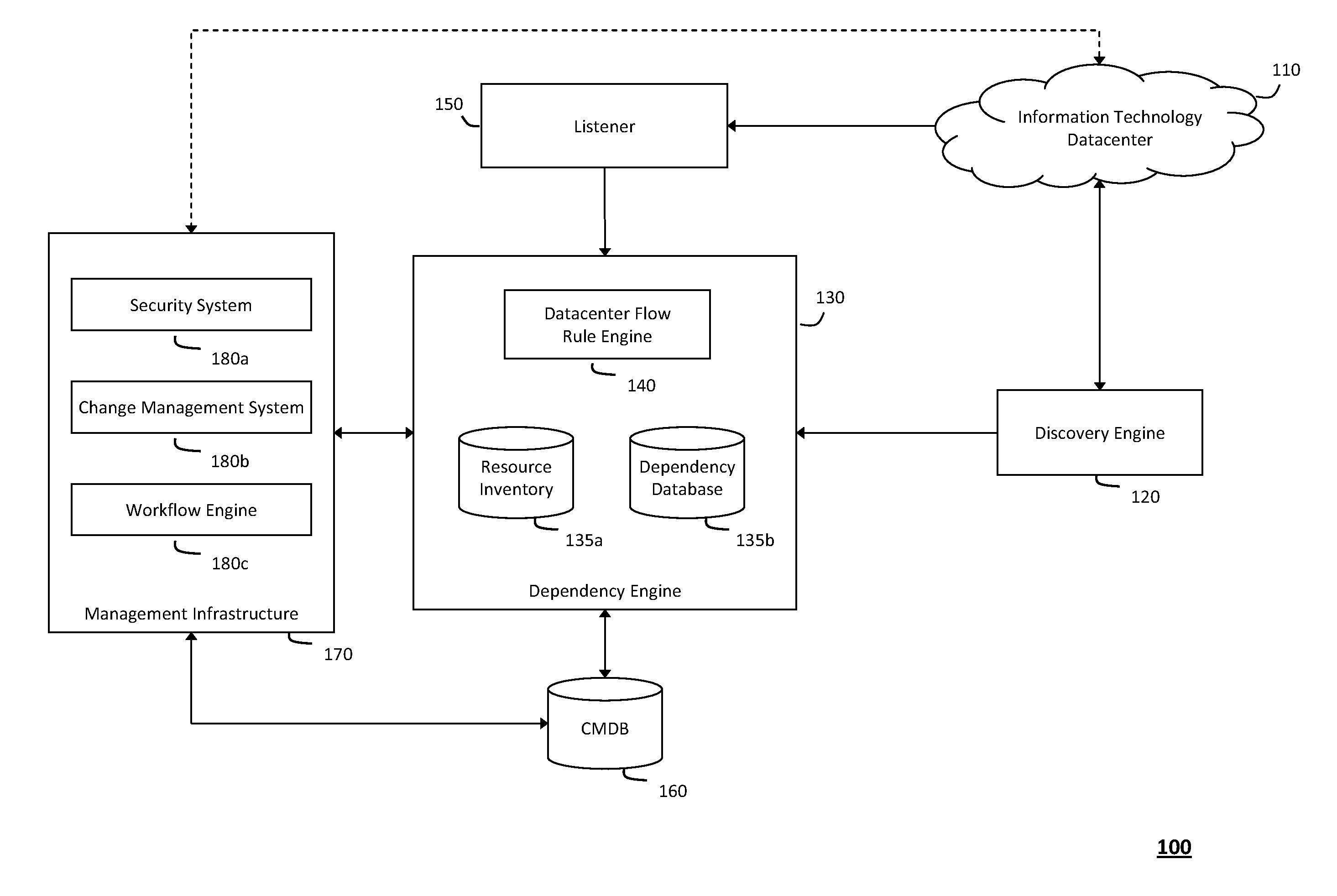
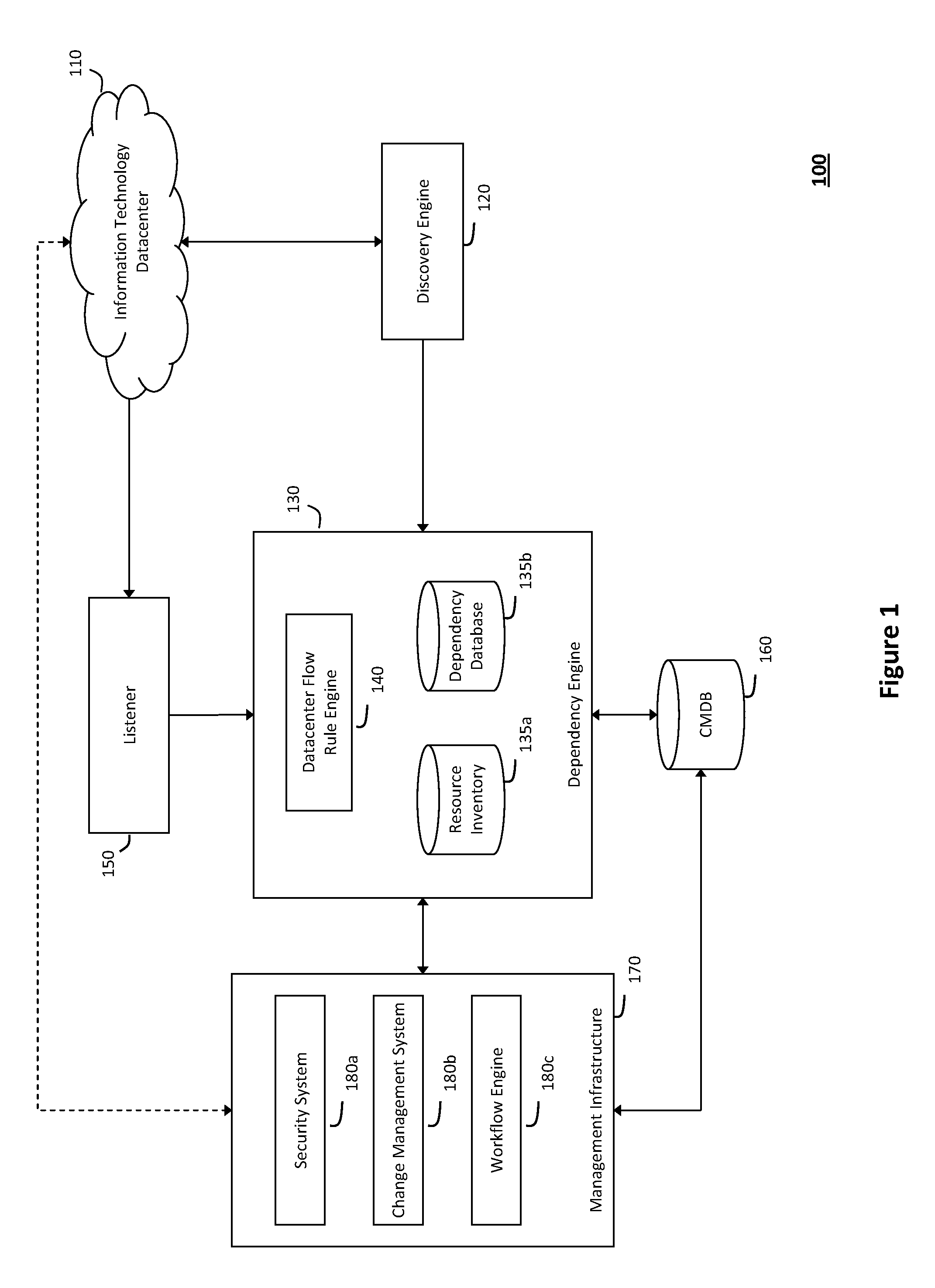
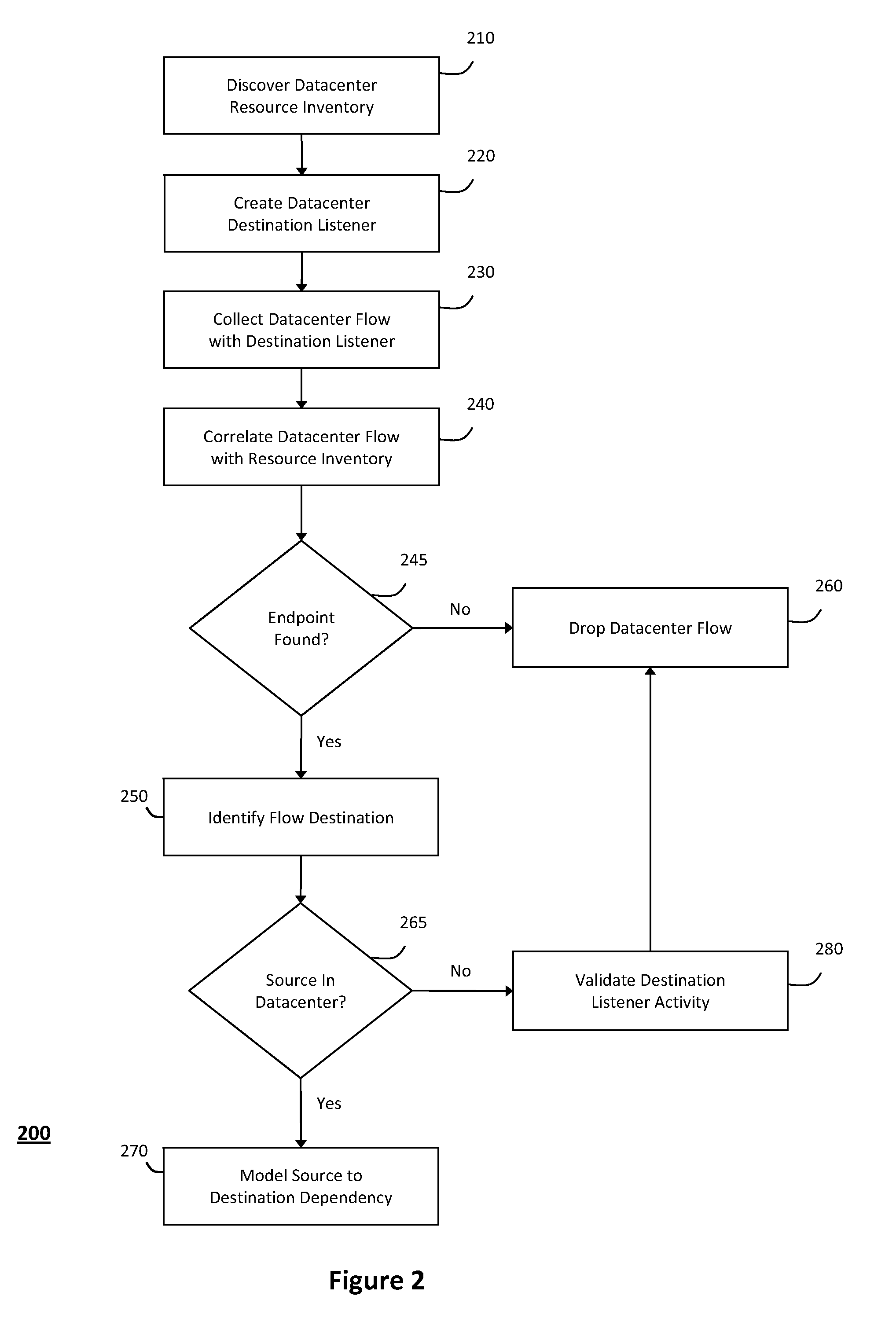
System and method for detecting real-time security threats in a network datacenter
InactiveUS20110302652A1Impact operationDamper and reduce impactMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionEngineeringNetwork data
The system and method described herein may include a configuration management database that describes every known service endpoint in a network datacenter to represent a steady state for the datacenter. One or more listeners may then observe traffic in the datacenter in real-time to detect network conversations initiating new activity in the datacenter, which may be correlated, in real-time, with the information in the configuration management database representing the steady state for the datacenter. Thus, in response to the new activity failing to correlate with the known service endpoints, a real-time security alert may be generated to indicate that any network conversations initiating such activity fall out-of-scope from the steady state for the information technology datacenter.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
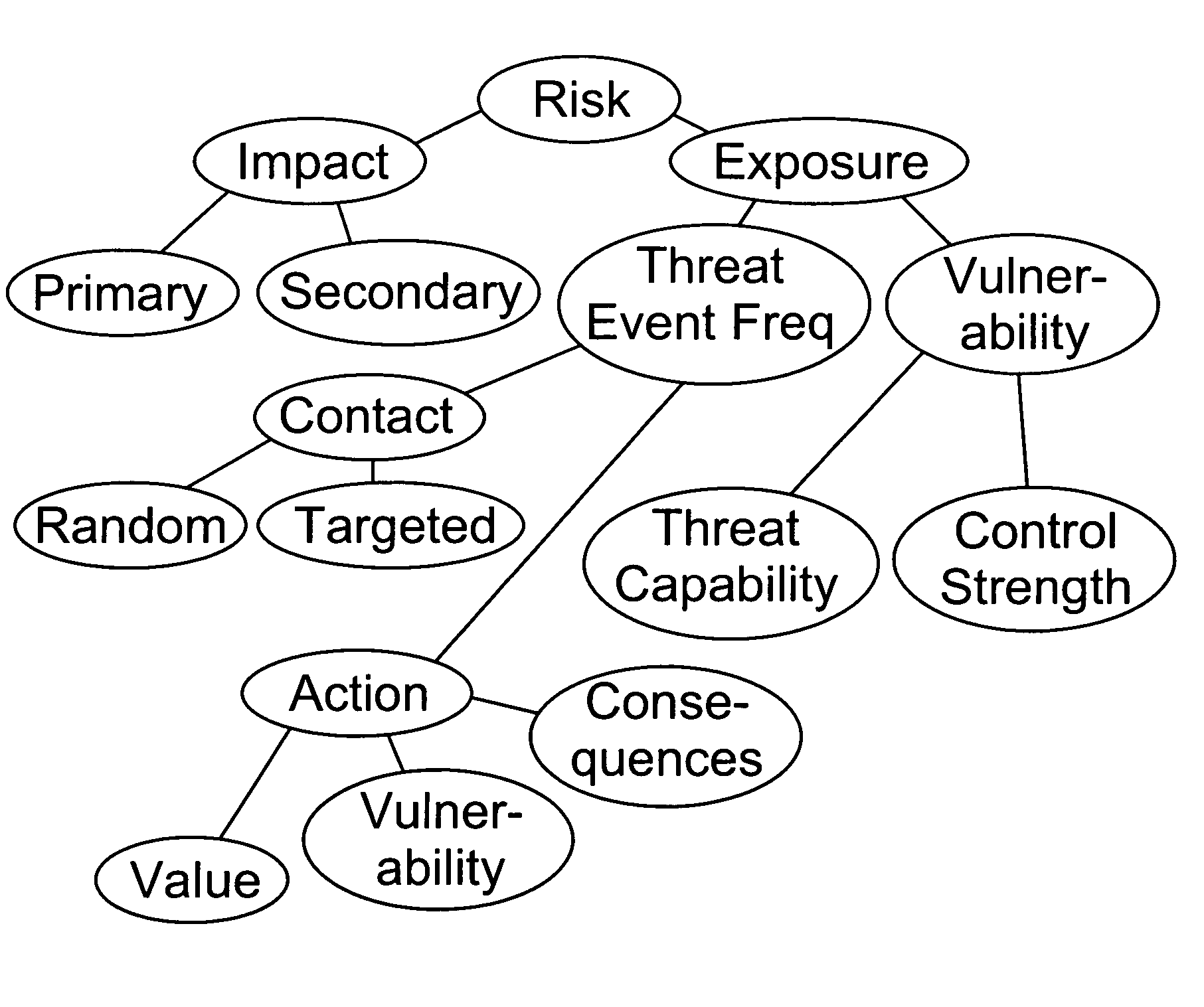
Factor analysis of information risk
InactiveUS20050066195A1Risk management decisions can become more effective and efficientGood return on investmentDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsSalient objectsObject definition
The invention is a method of measuring and representing security risk. The method comprises selecting at least one object within an environment and quantifying the strength of controls of at least one object within that environment. This is done by quantifying authentication controls, quantifying authorization controls, and then quantifying structural integrity. In the preferred method, the next step is setting global variables for the environment, for example, whether the environment is subject to regulatory laws, and then selecting at least one threat community, for example, professional hackers, and then calculating information risk. This calculation is accomplished by performing a statistical analysis using the strengths of controls of said at least one object, the characteristics of at least one threat community, and the global variables of the environment, to compute a value representing information risk. The method identifies the salient objects within a risk environment, defines their characteristics and how they interact with one another, utilizing a means of measuring the characteristics, and a statistically sound mathematical calculation to emulate these interactions and then derives probabilities. The method then represents the security risk, such as the risk to information security, such as by an integer, a distribution or some other means.
Owner:JONES JACK A
Techniques for discovering and managing security of applications
Techniques for discovery and management of applications in a computing environment of an organization are disclosed. A security management system discovers use of applications within a computing environment to manage access to applications for minimizing security threats and risks in a computing environment of the organization. The security management system can obtain network data about network traffic to identify unique applications. The security management system can perform analysis and correlation, including use of one or more data sources, to determine information about an application. The system can compute a measure of security for an application (“an application risk score”) and a user (“a user risk score”). The score may be analyzed to determine a threat of security posed by the application based on use of the application. The security system can perform one or more instructions to configure access permitted by an application, whether access is denied or restricted.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Countering security threats with the domain name system
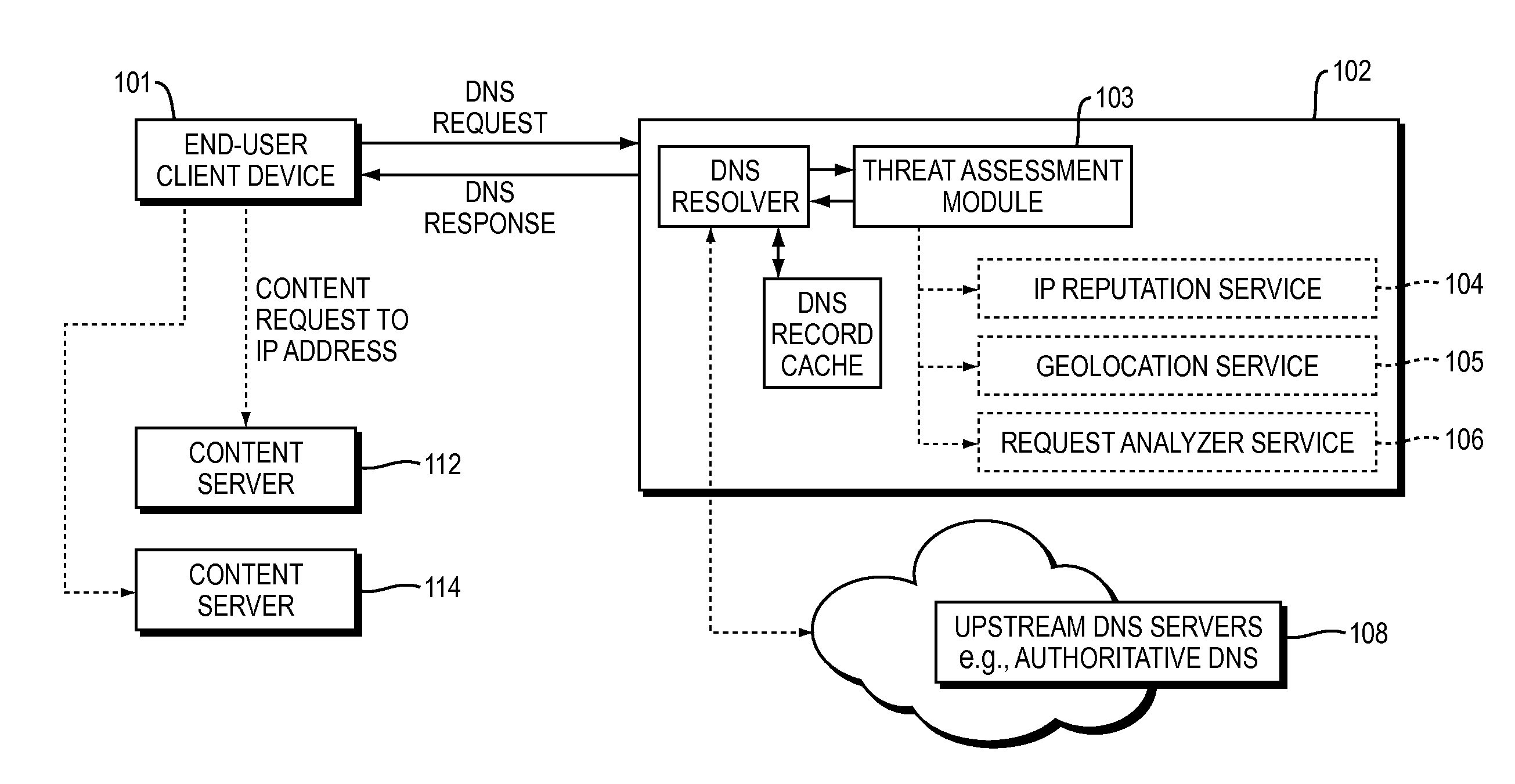
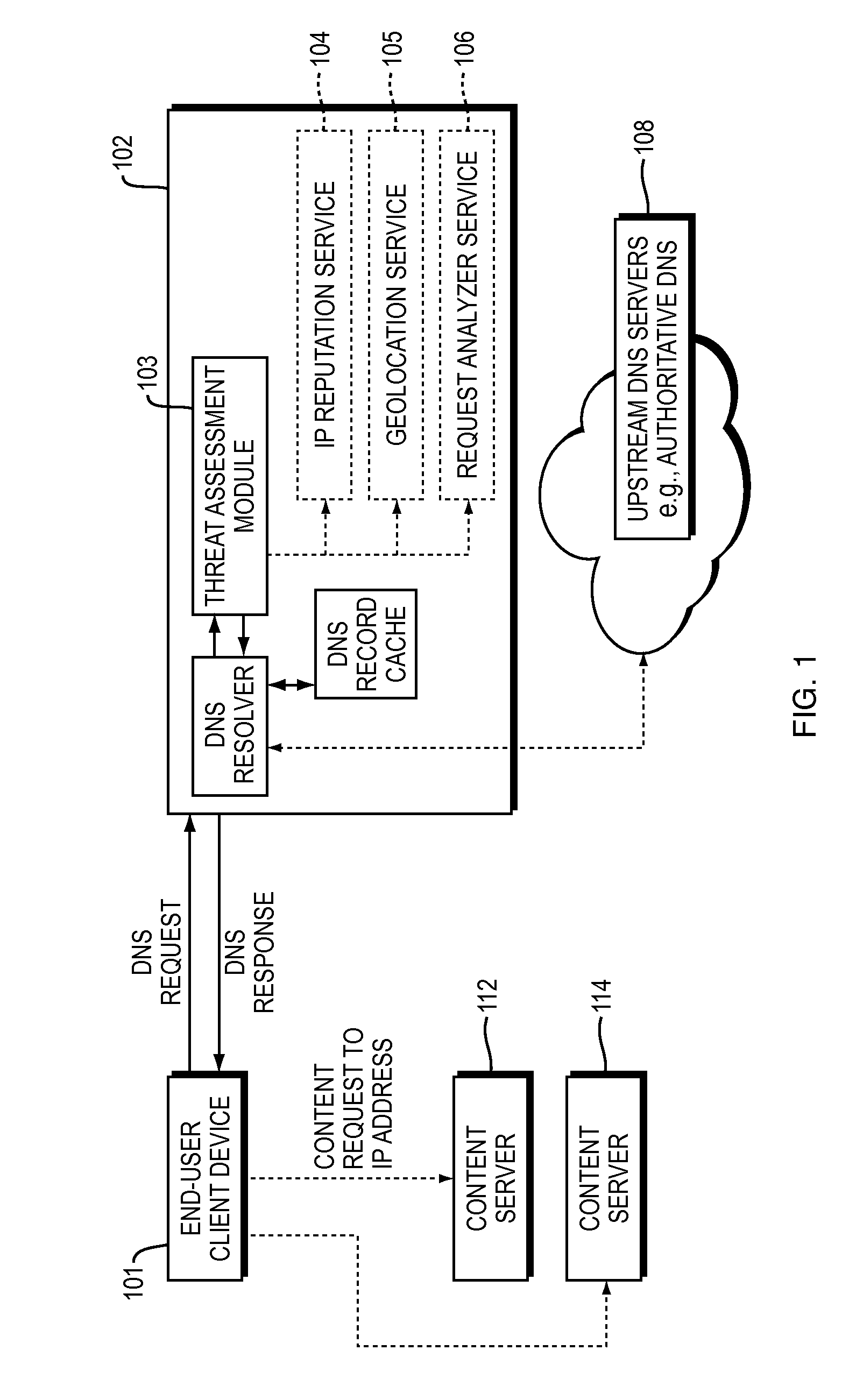
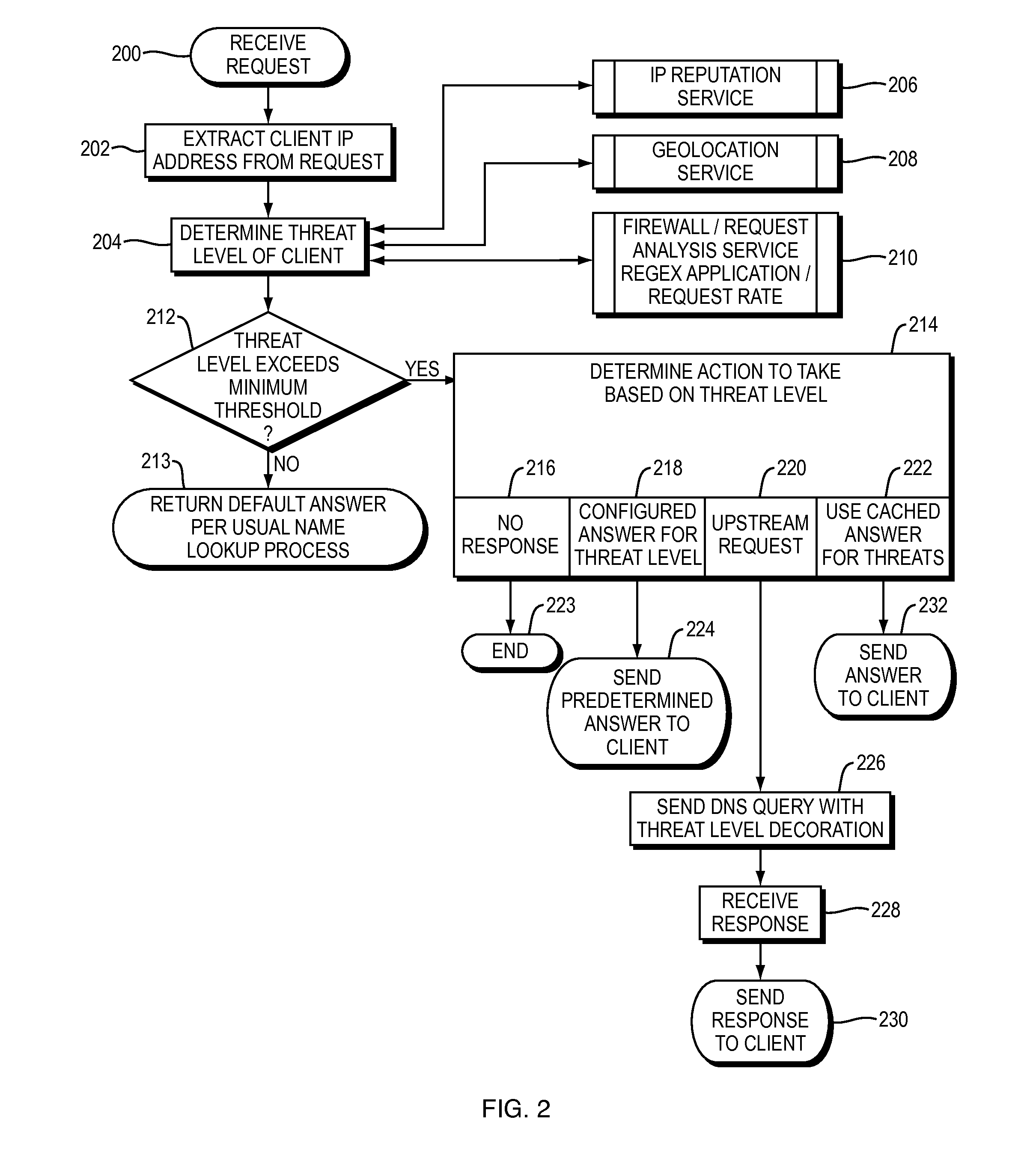
ActiveUS20150180892A1Easy to controlGood mitigateMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionDomain nameDomain Name System
Described herein are methods, systems, and apparatus in which the functionality of a DNS server is modified to take into account security intelligence when determining an answer to return in response to a requesting client. Such a DNS server may consider a variety of security characteristics about the client and / or the client's request, as described more fully herein. Such a DNS server can react to clients in a variety of ways based on the threat assessment, preferably in a way that proactively counters or mitigates the perceived threat.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
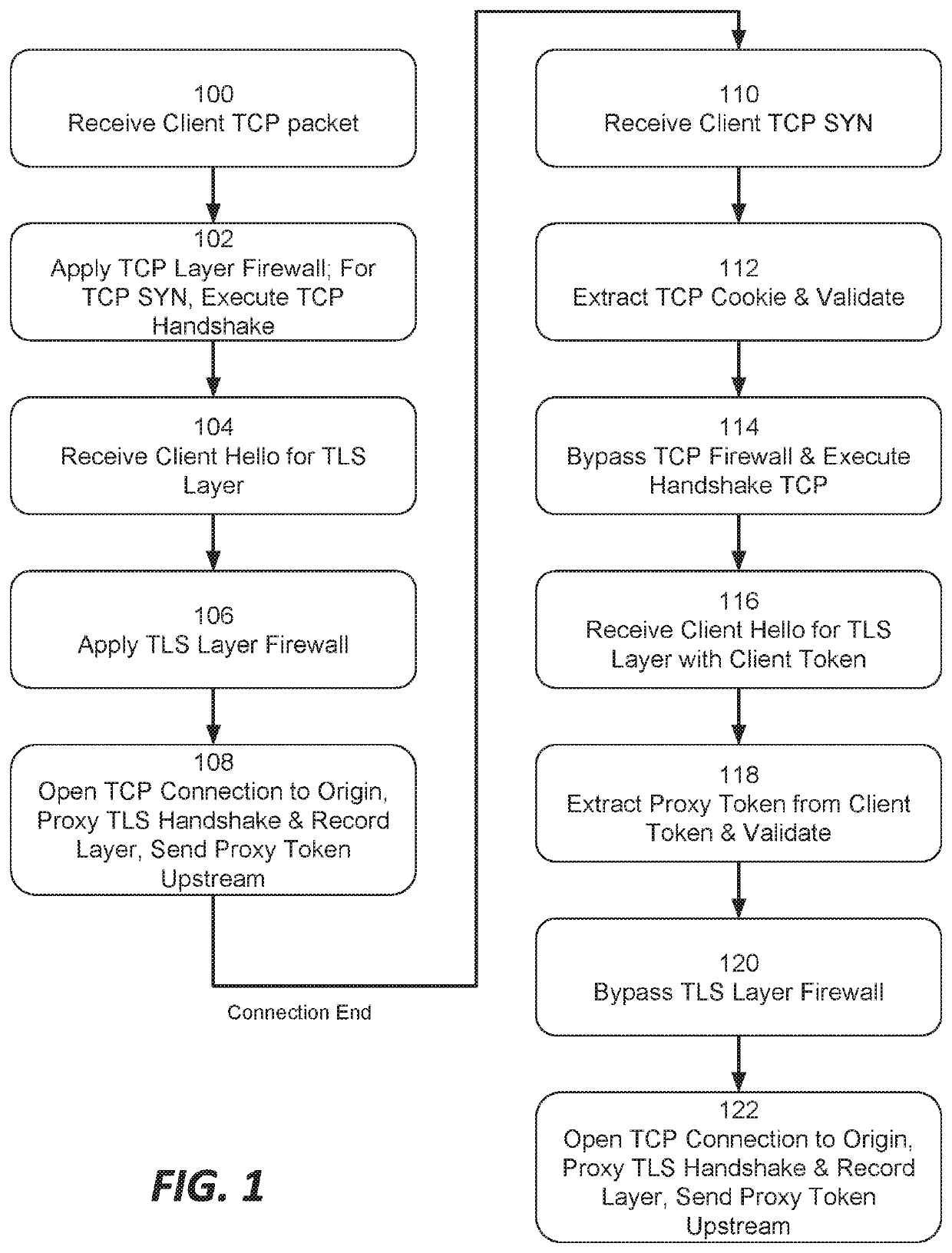
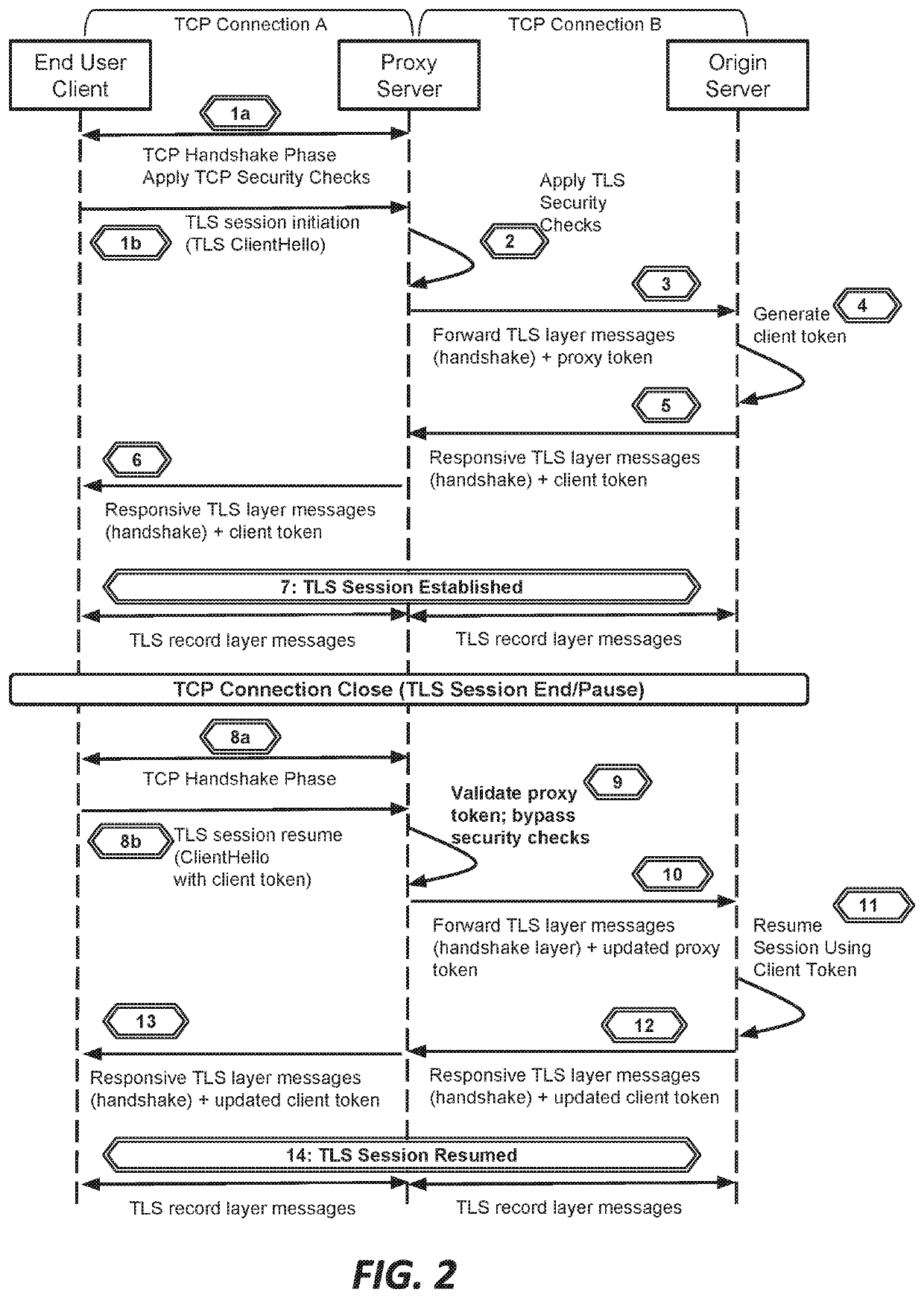
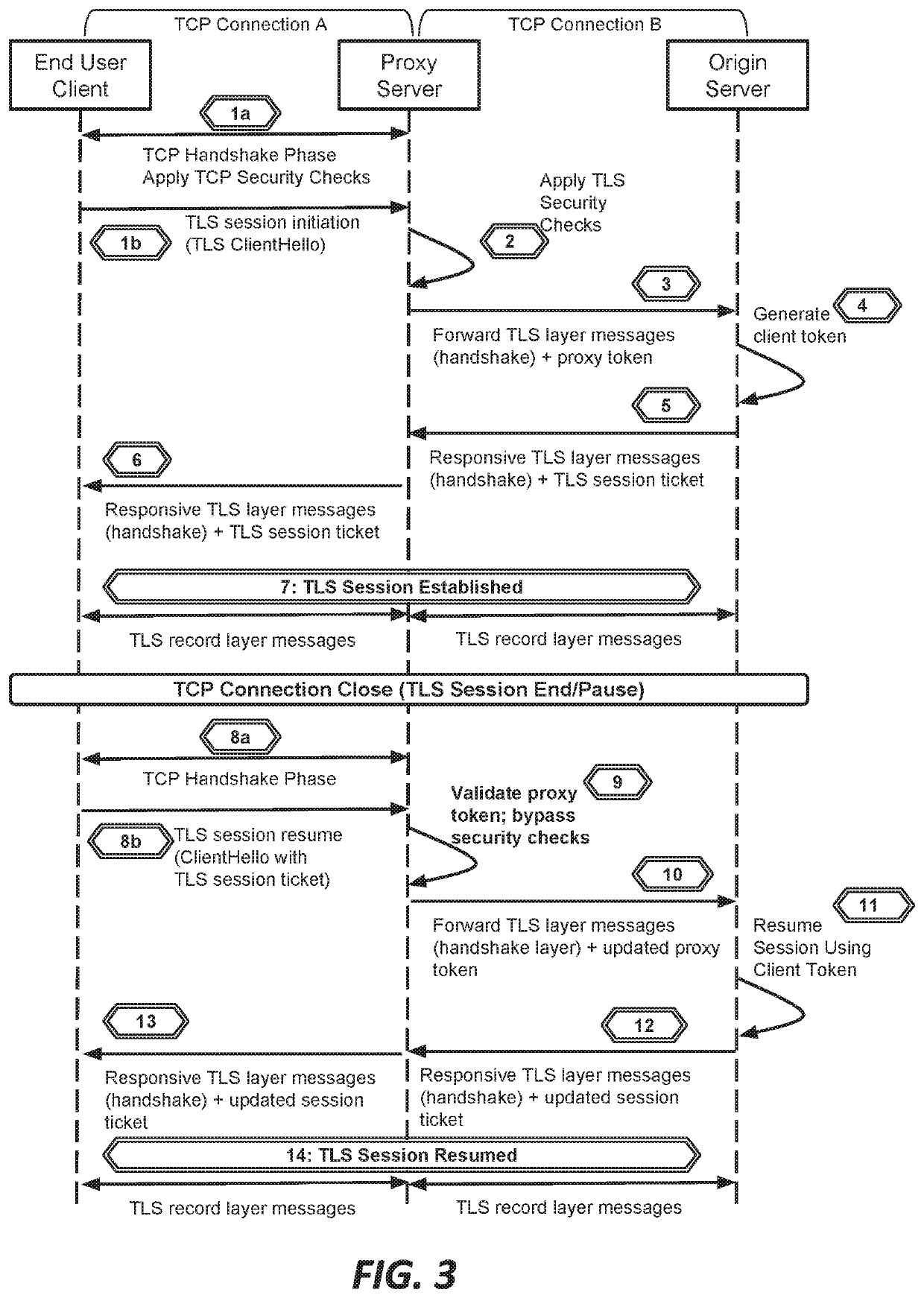
Systems and methods for proxying encrypted traffic to protect origin servers from internet threats
This document describes, among other things, systems and methods for more efficiently resuming a client-to-origin TLS session through a proxy layer that fronts the origin in order to provide network security services. At the time of an initial TLS handshake with an unknown client, for example, the proxy can perform a set of security checks. If the client passes the checks, the proxy can transmit a ‘proxy token’ upstream to the origin. The origin can incorporate this token into session state data which is passed back to and stored on the client, e.g., using a TLS session ticket extension field, pre-shared key extension field, or other field. On TLS session resumption, when the client sends the session state data, the proxy can recover its proxy token from the session state data, and upon successful validation, bypass security checks that it would otherwise perform against the client, thereby more efficiently handling known clients.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
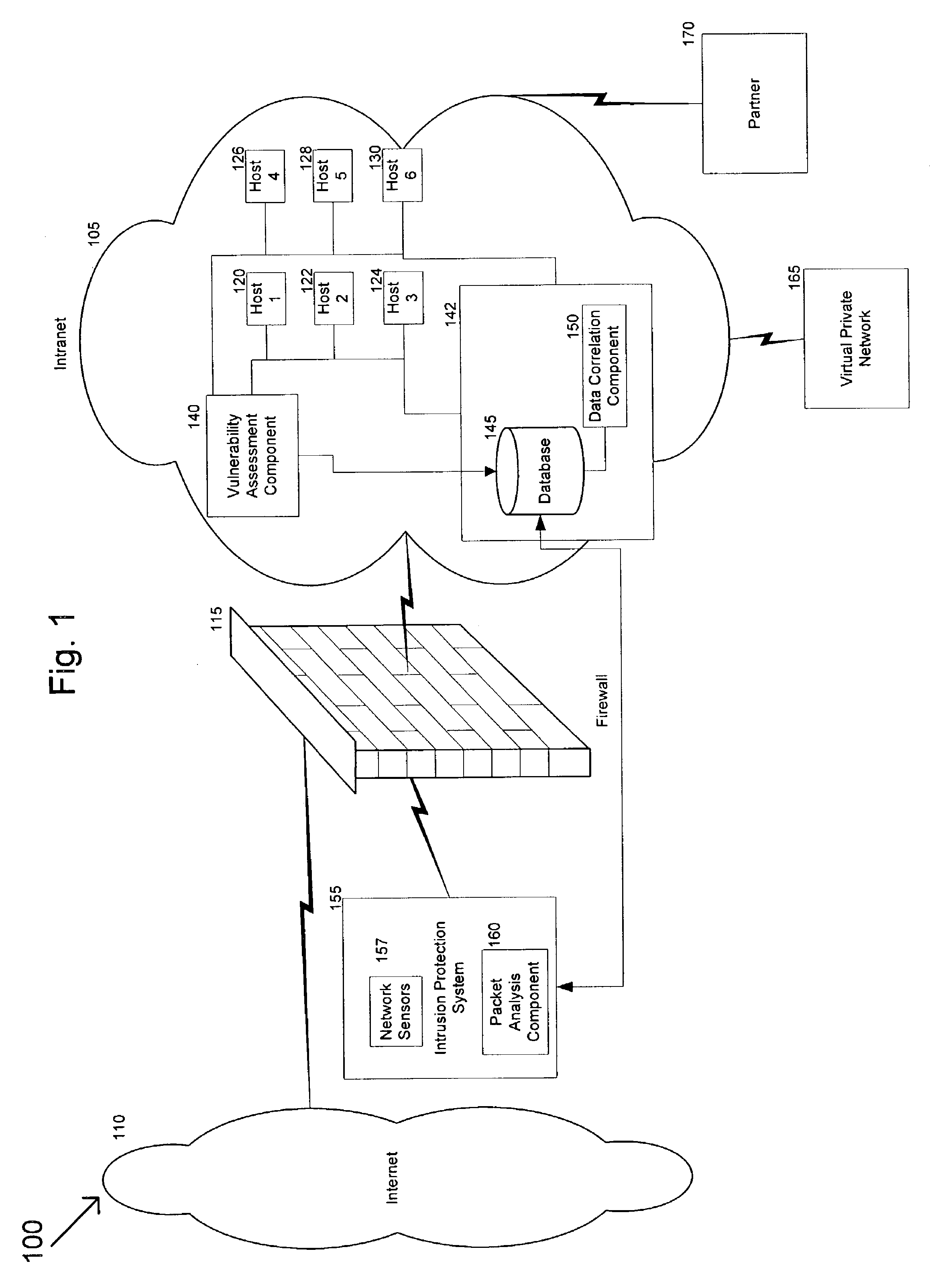
Methods, computer program products and data structures for intrusion detection, intrusion response and vulnerability remediation across target computer systems
ActiveUS20060015941A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationGoal systemVulnerability
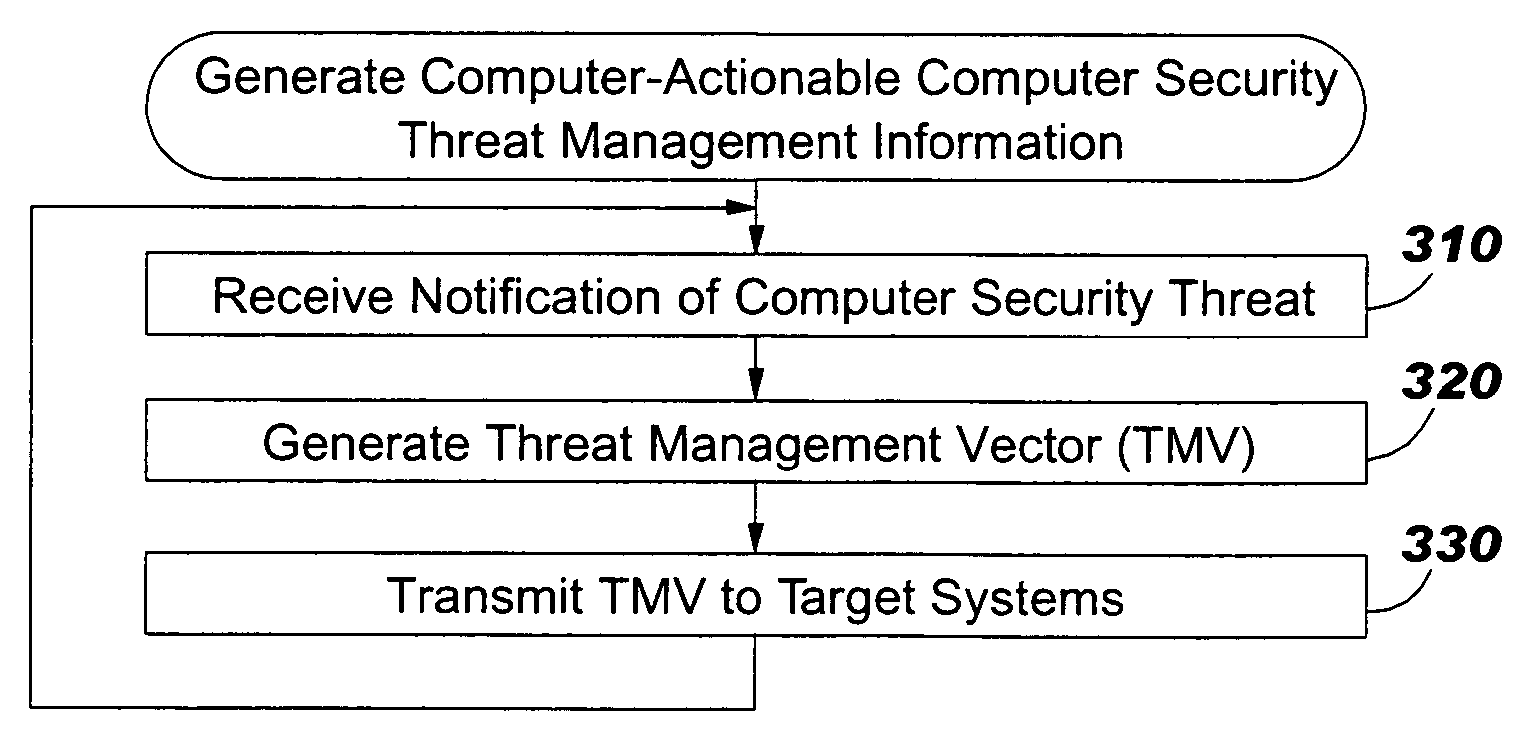
Computer security threat management information is generated by receiving a notification of a security threat and / or a notification of a test that detects intrusion of a computer security threat. A computer-actionable TMV is generated from the notification that was received. The TMV includes a computer-readable field that provides identification of at least one system type that is effected by the computer security threat, a computer-readable field that provides identification of a release level for a system type, and a computer-readable field that provides identification of the test that detects intrusion of the computer security threat for a system type and a release level, a computer-readable field that provides identification of a method to reverse the intrusion exploit of the computer security threat for a system type and a release level, and a computer-readable field that provides identification of a method to remediate the vulnerability subject to exploit of the computer security threat for a system type and a release level. The TMV is transmitted to target systems for processing by the target systems.
Owner:FINJAN BLUE INC
Detecting attacks using compromised credentials via internal network monitoring
ActiveUS20180007087A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityDigital data authenticationTransmissionPasswordNetwork monitoring
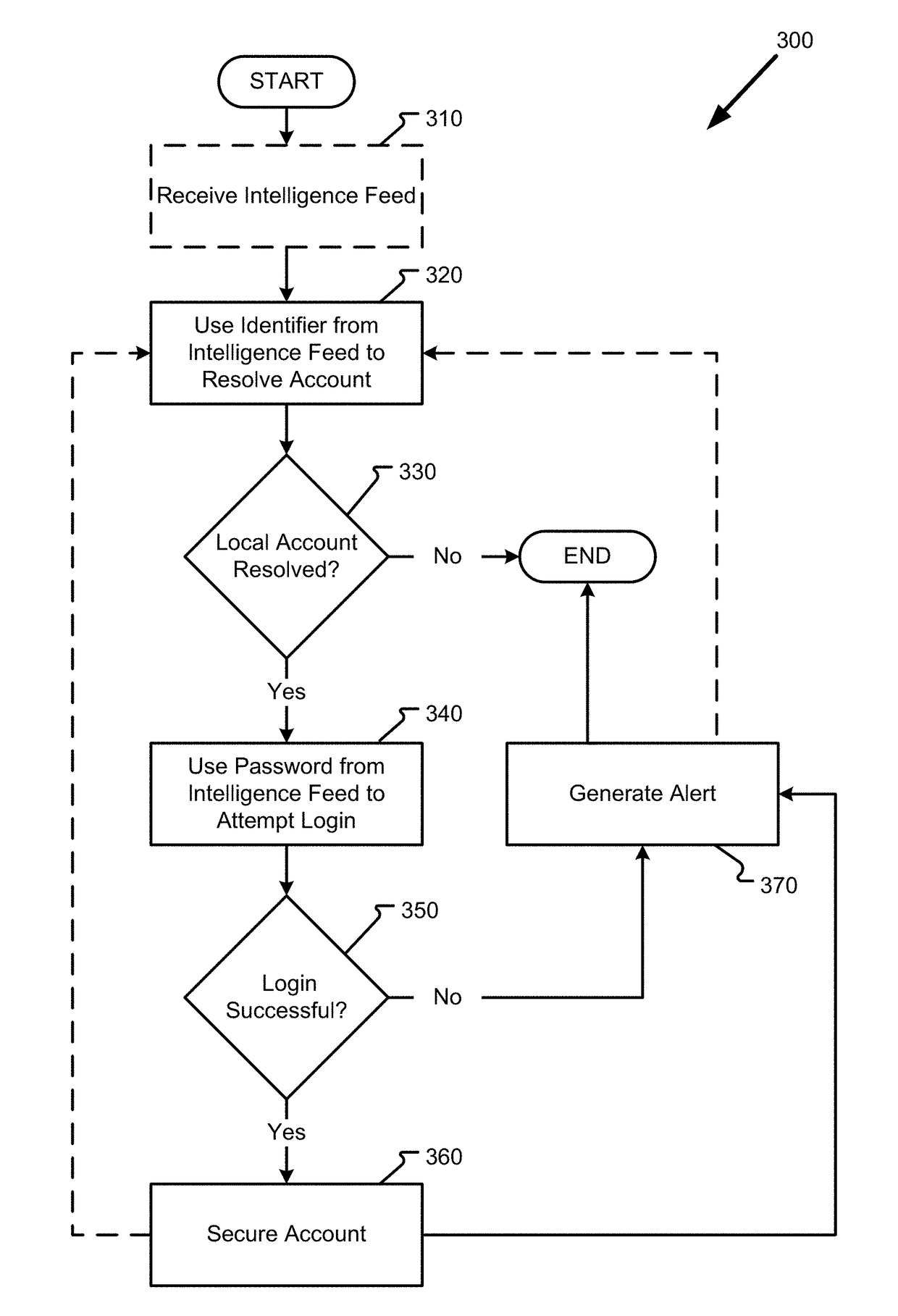
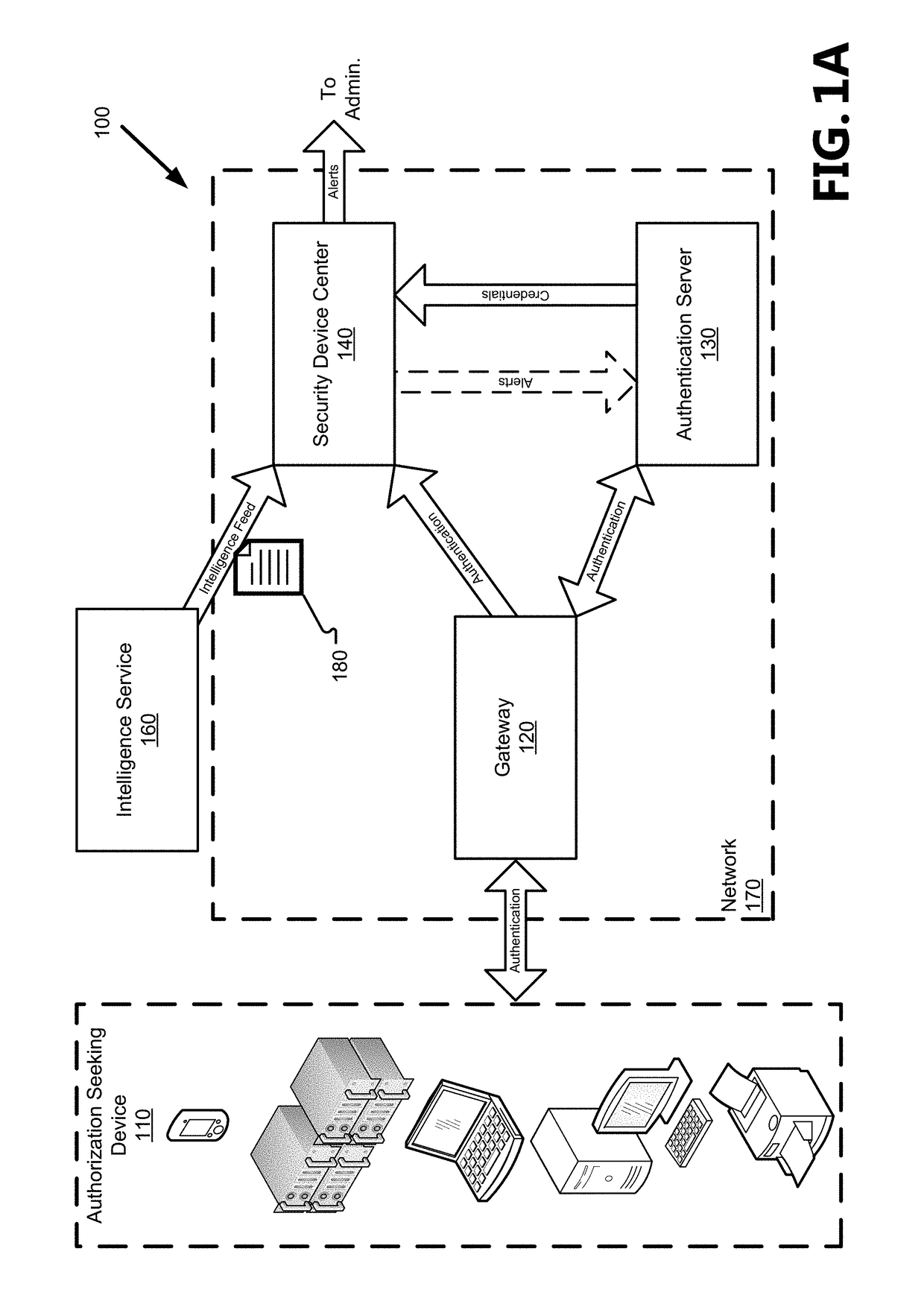
The threat of malicious parties exposing users' credentials from one system and applying the exposed credentials to a different system to gain unauthorized access is addressed in the present disclosure by systems and methods to preemptively and reactively mitigate the risk of users reusing passwords between systems. A security device passively monitors traffic comprising authorization requests within a network to reactively identify an ongoing attack based on its use of exposed credentials in the authorization request and identifies accounts that are vulnerable to attacks using exposed credentials by actively attempting to log into those accounts with exposed passwords from other networks. The systems and methods reduce the number of false positives associated with attack identification and strengthens the network against potential attacks, thus improving the network's security and reducing the amount of resources needed to securely manage the network.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System, method and apparatus for authenticating and protecting an IP user-end device
ActiveUS20100107230A1Raise security concernsInterconnection arrangementsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionInternet privacyAttack
A system, method and apparatus authenticates and protects an Internet Protocol (IP) user-end device by providing a client-based security software resident on the IP user-end device, authenticating the IP user-end device using the client-based security software and a network security node communicably coupled to the IP user-end device, authenticating a user of the IP user-end device whenever a trigger condition occurs using an in-band channel between the client-based security software and the network security node, and protecting the IP user-end device by: (a) screening incoming IP traffic to the IP user-end device using the client-based security software, and (b) detecting an attack or a threat involving the IP user-end device using the network security node.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Network-security-risk analysis method based on network node vulnerability and attack information
ActiveCN105871882AAccurately calculate the threat levelImprove risk analysis resultsData switching networksAnalysis methodNetwork topology
The invention discloses a network-security-risk analysis method based on network-node vulnerability and attack information. The network-security-risk analysis method includes the following steps that 1, the index required by computing the threat degree of a network system is determined; 2, the network topology structure, the network asset property and network asset vulnerability information are obtained; 3, a vulnerability correlation relationship module based on a Petri network is built; 4, attack information detected by an IDS safety device is obtained, and the correlation relationship module is perfected through the attack information; 5, the threat degrees of all nodes in the network system are computed; 6, the network security risk is analyzed according to the threat degree value of all the nodes. According to the network-security-risk analysis method, the vulnerability correlation relationship module of the Petri network built in static analysis is updated in real time through the detected attack information in real time, the threat degrees of all the nodes are accurately computed, the network-risk analysis result is perfected, the analytical ability of the network risk is improved, and the safety of the network is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +5
System, computer program, and method of cooperative response to threat to domain security
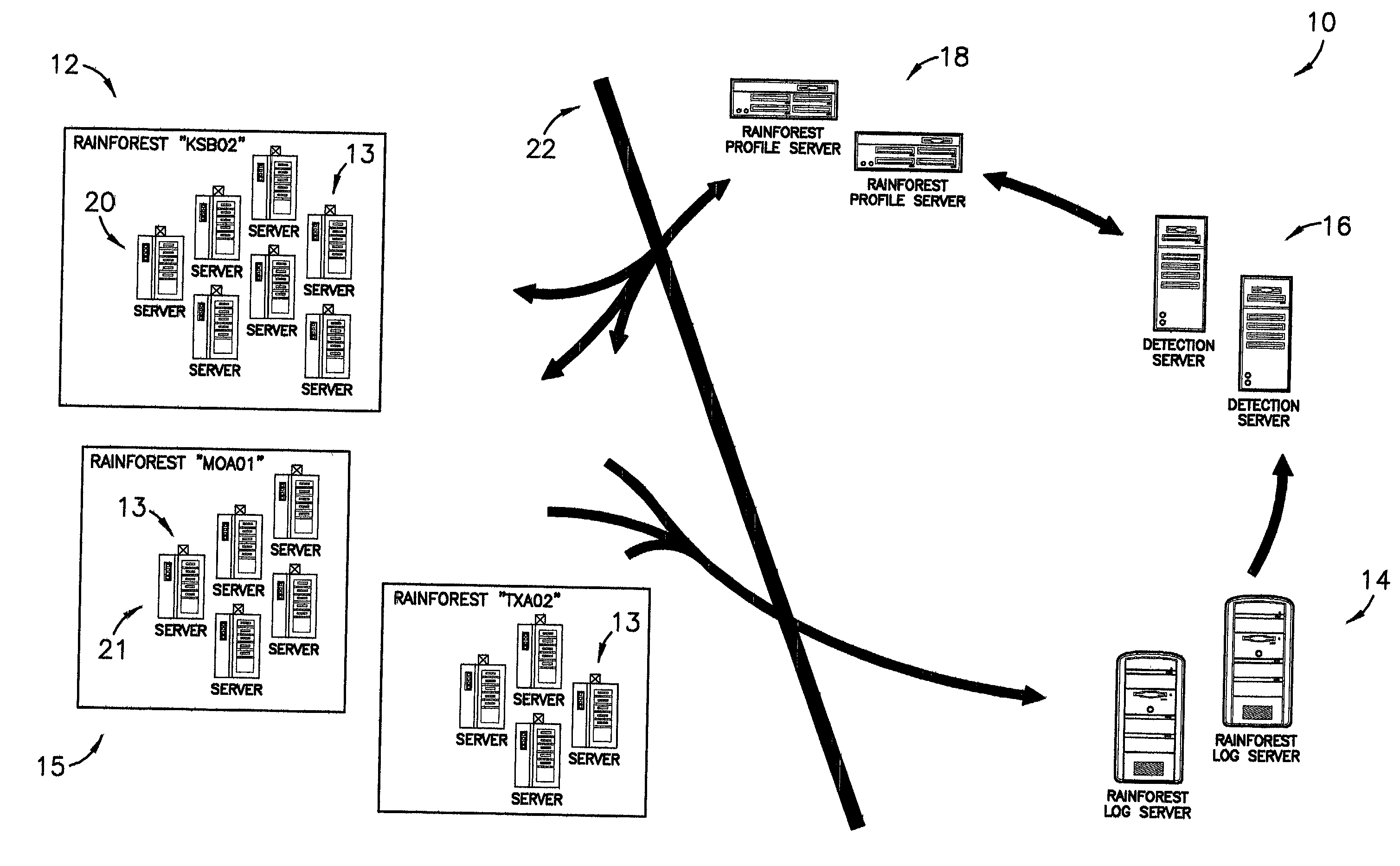
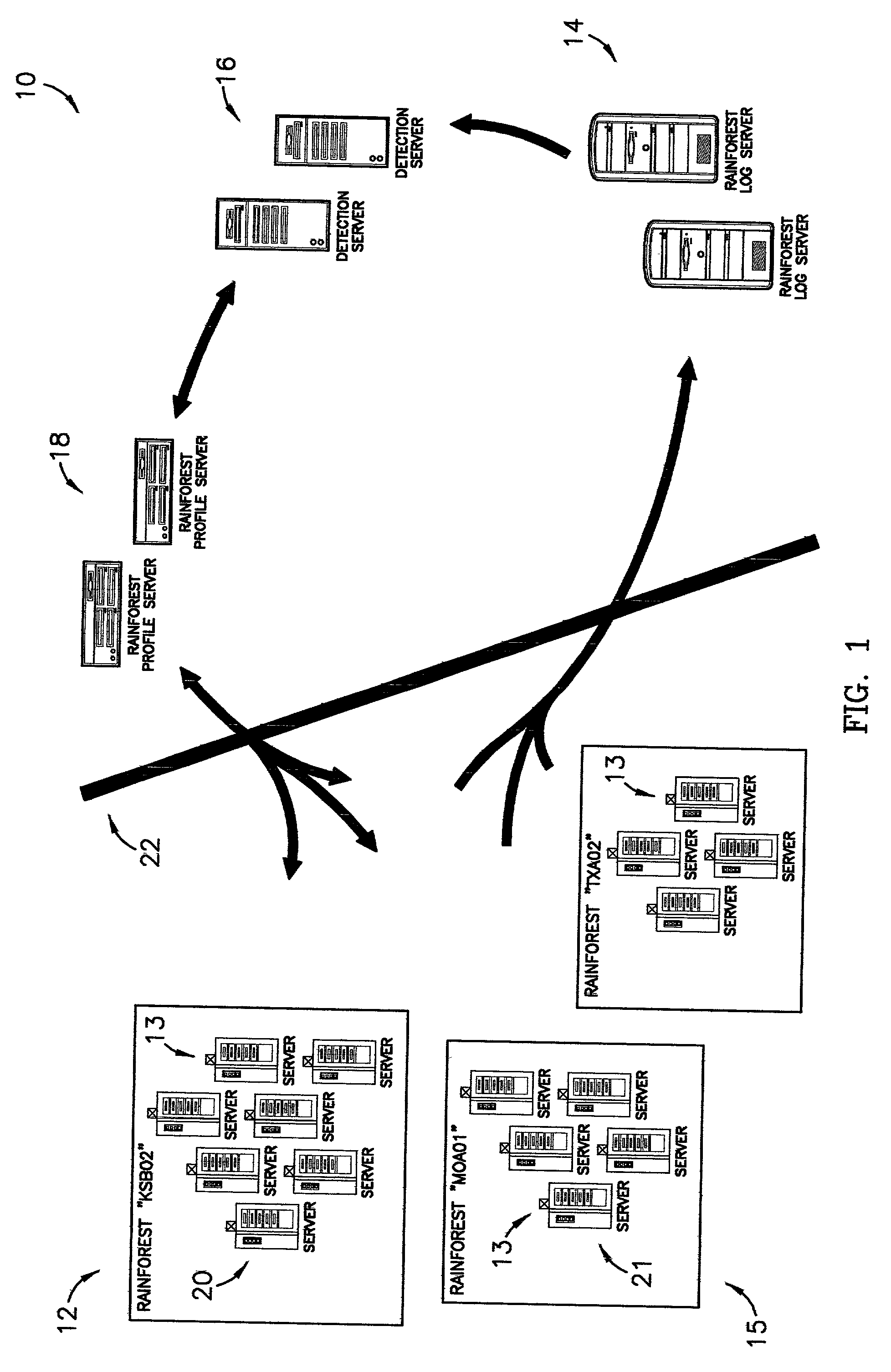
ActiveUS7028338B1Minimize impactMinimizes resourceMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsDomain nameRisk profiling
A system, computer program, and method of providing an automatic cooperative response ability to all members of a domain in light of a detected threat or other suspicious activity, such as, for example, a virus or denial of service attack, directed, at least initially, at less than all members of the domain. The system broadly comprises the domain; a log server; a detection server; and a profile server. The domain comprises a logical grouping of members having similar risk profiles. The detection server monitors and parses log and audit records generated by the members and copied to the log server. When the detection server identifies threatening or other suspicious activity it sets an alert status in a security profile stored on the profile server. The members periodically query the profile server for updates to the alert status and are thereby apprised of the alert.
Owner:SPRING SPECTRUM LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com