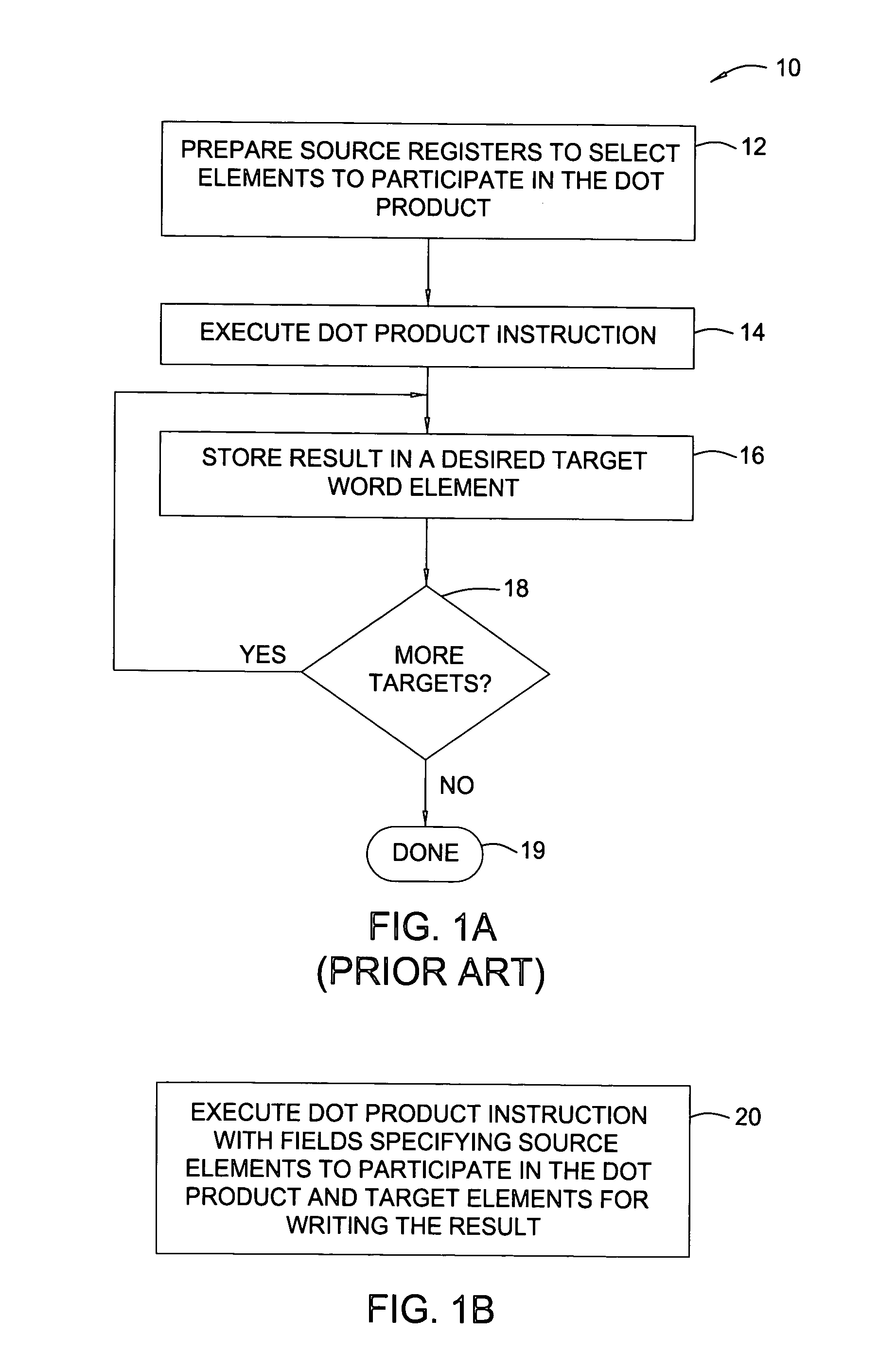
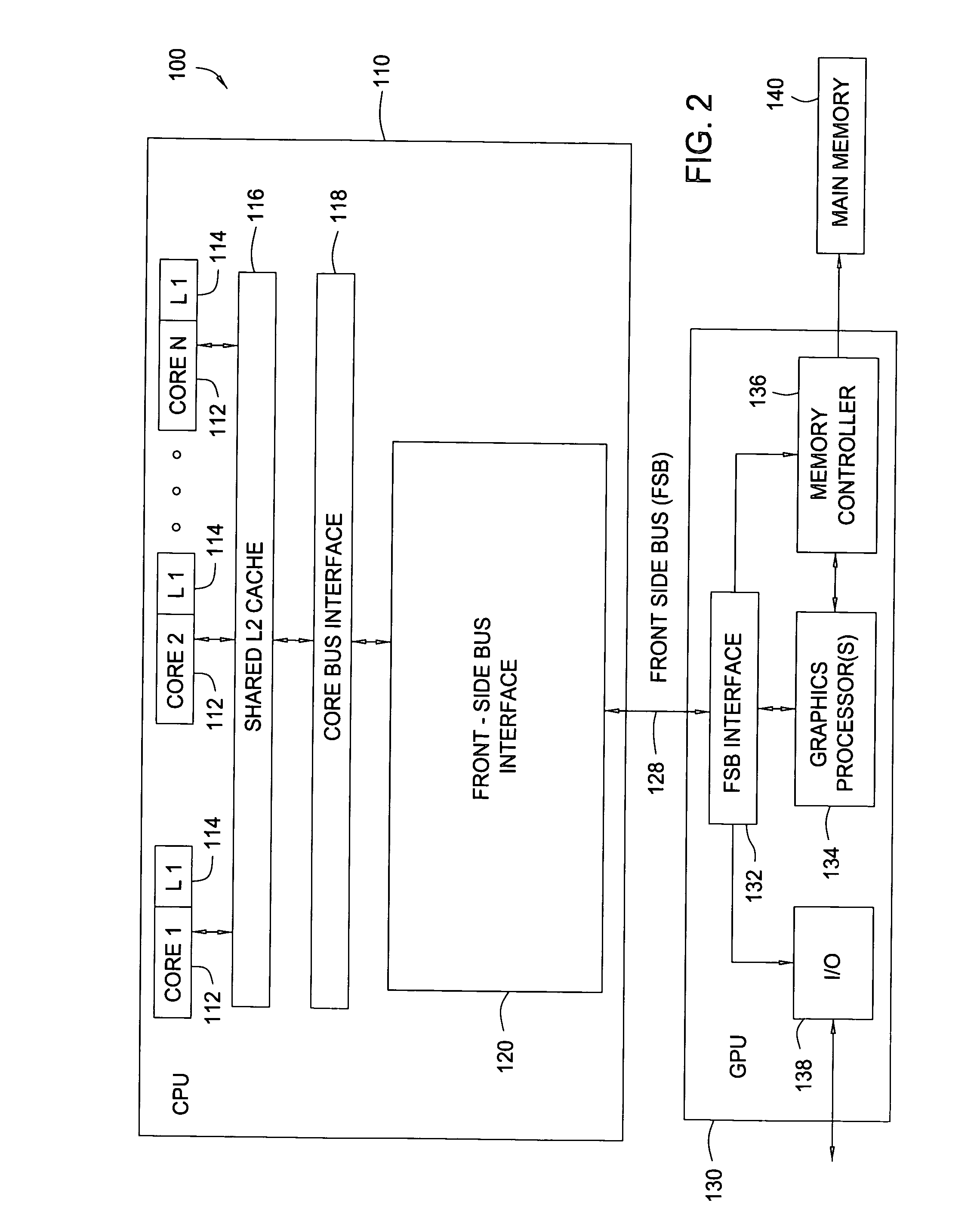
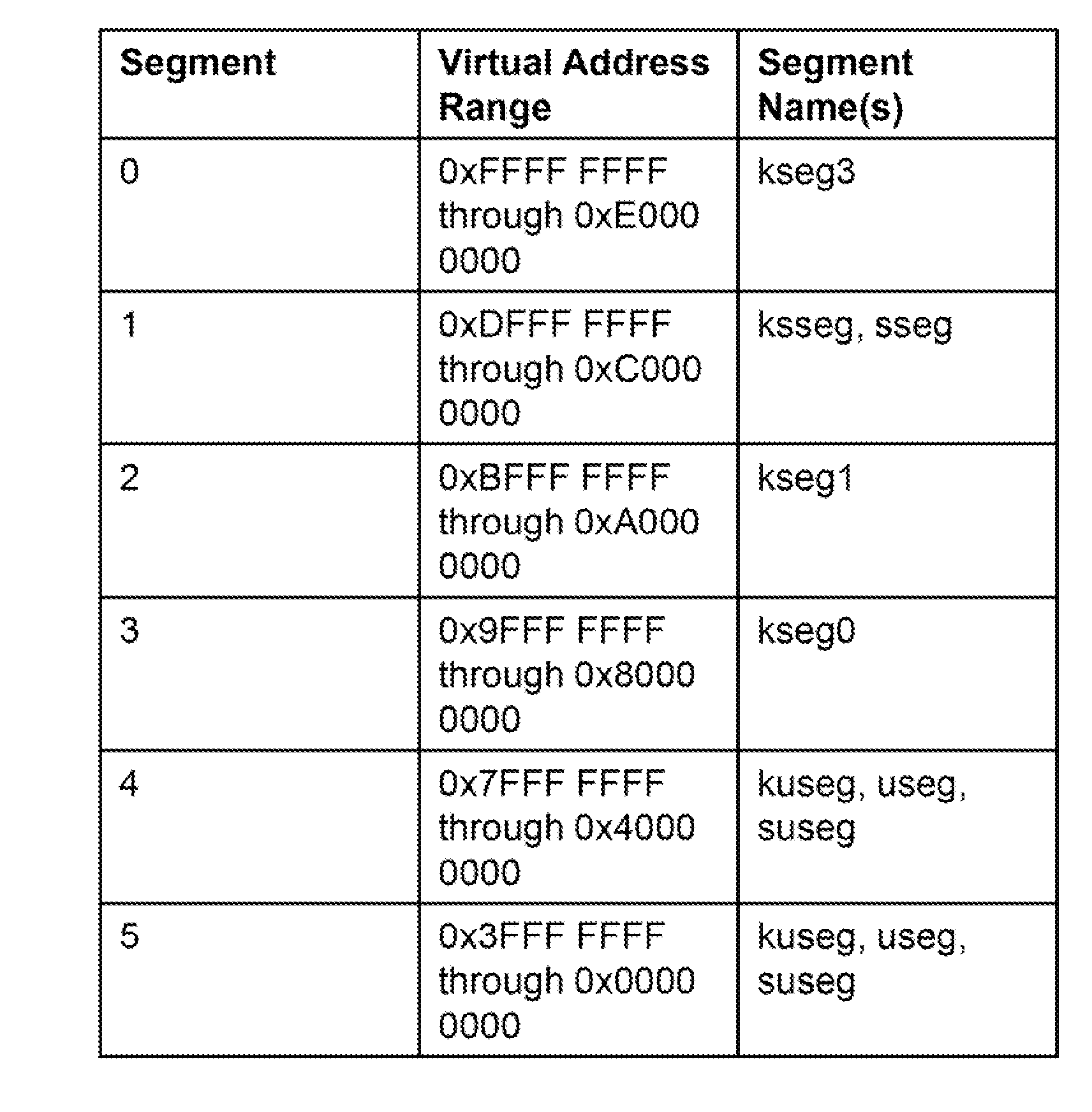
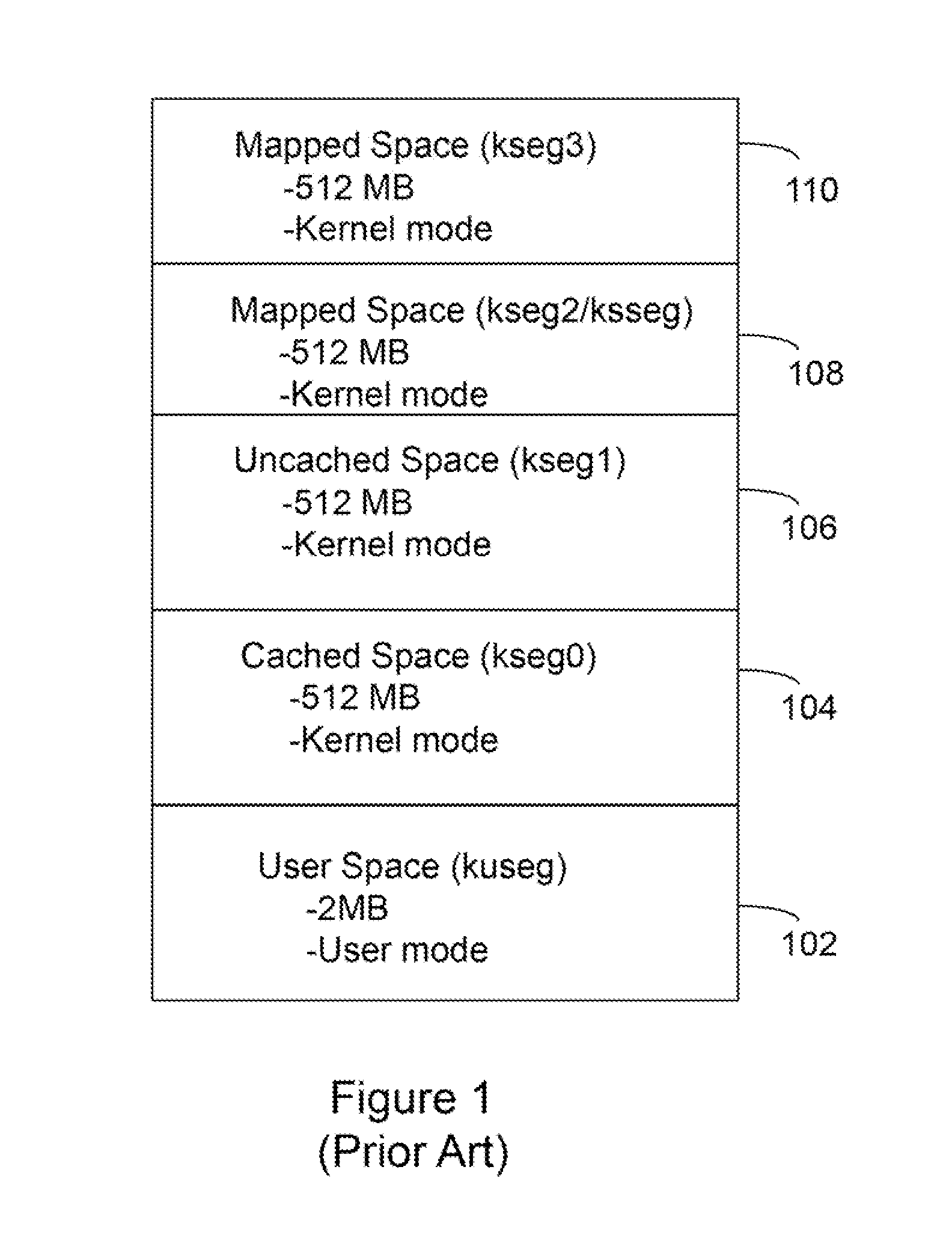
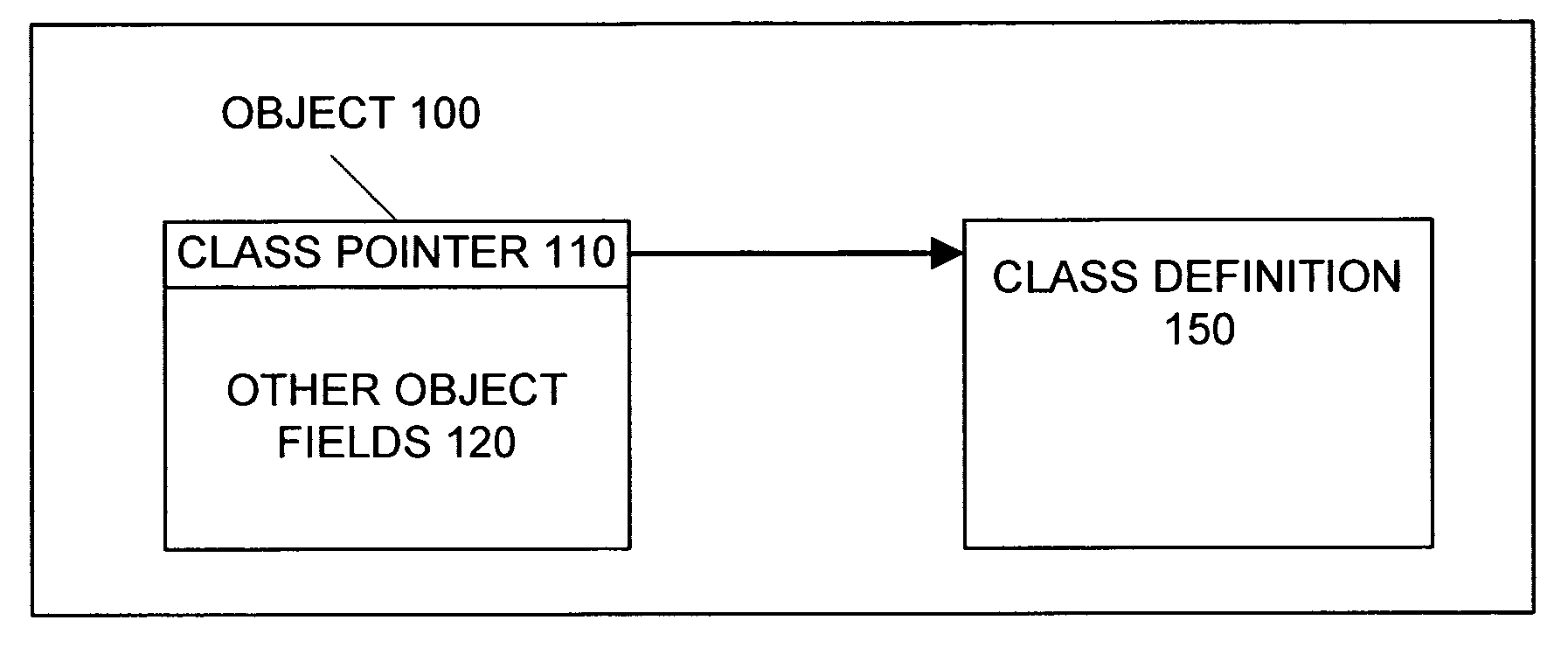
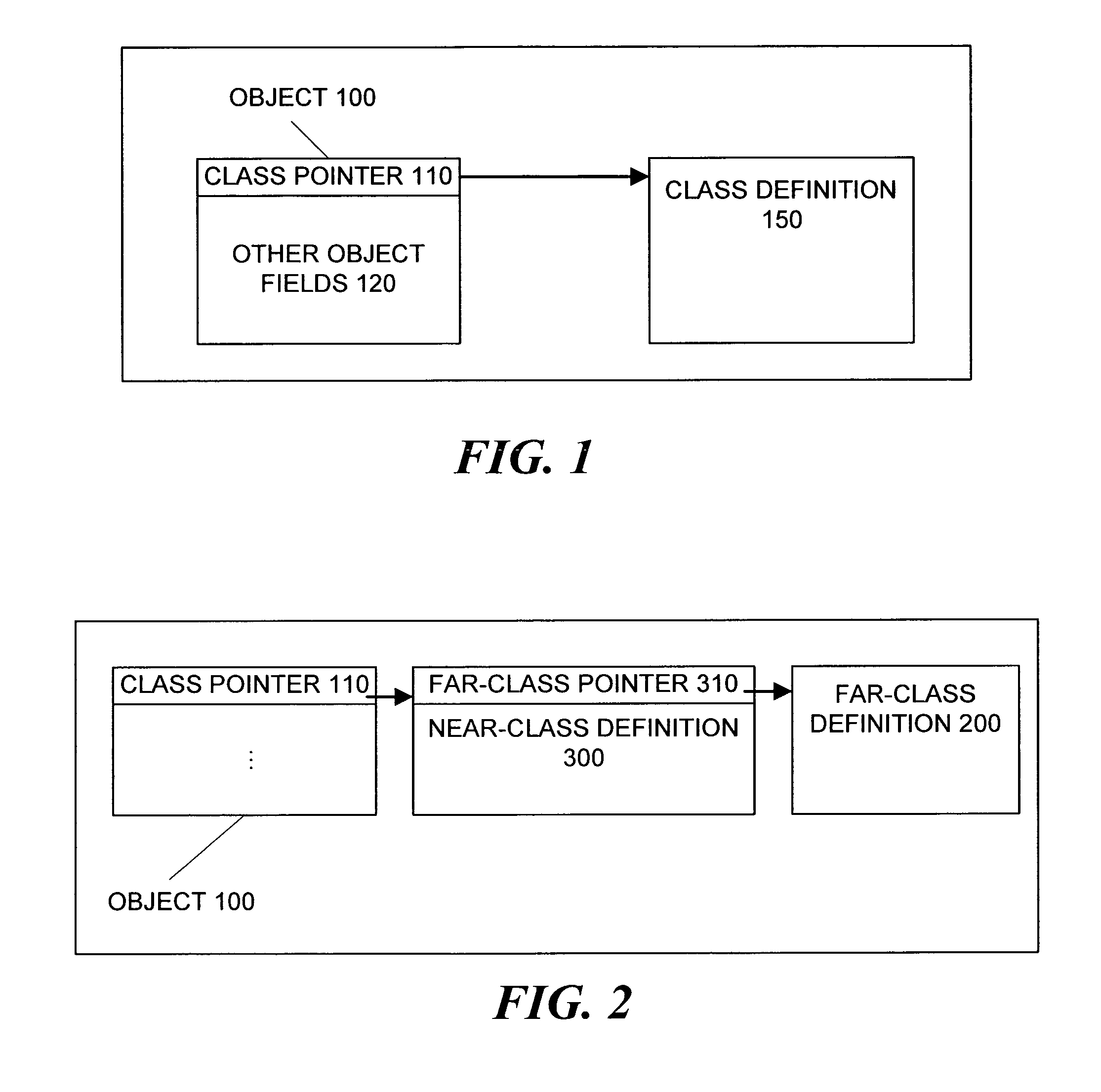
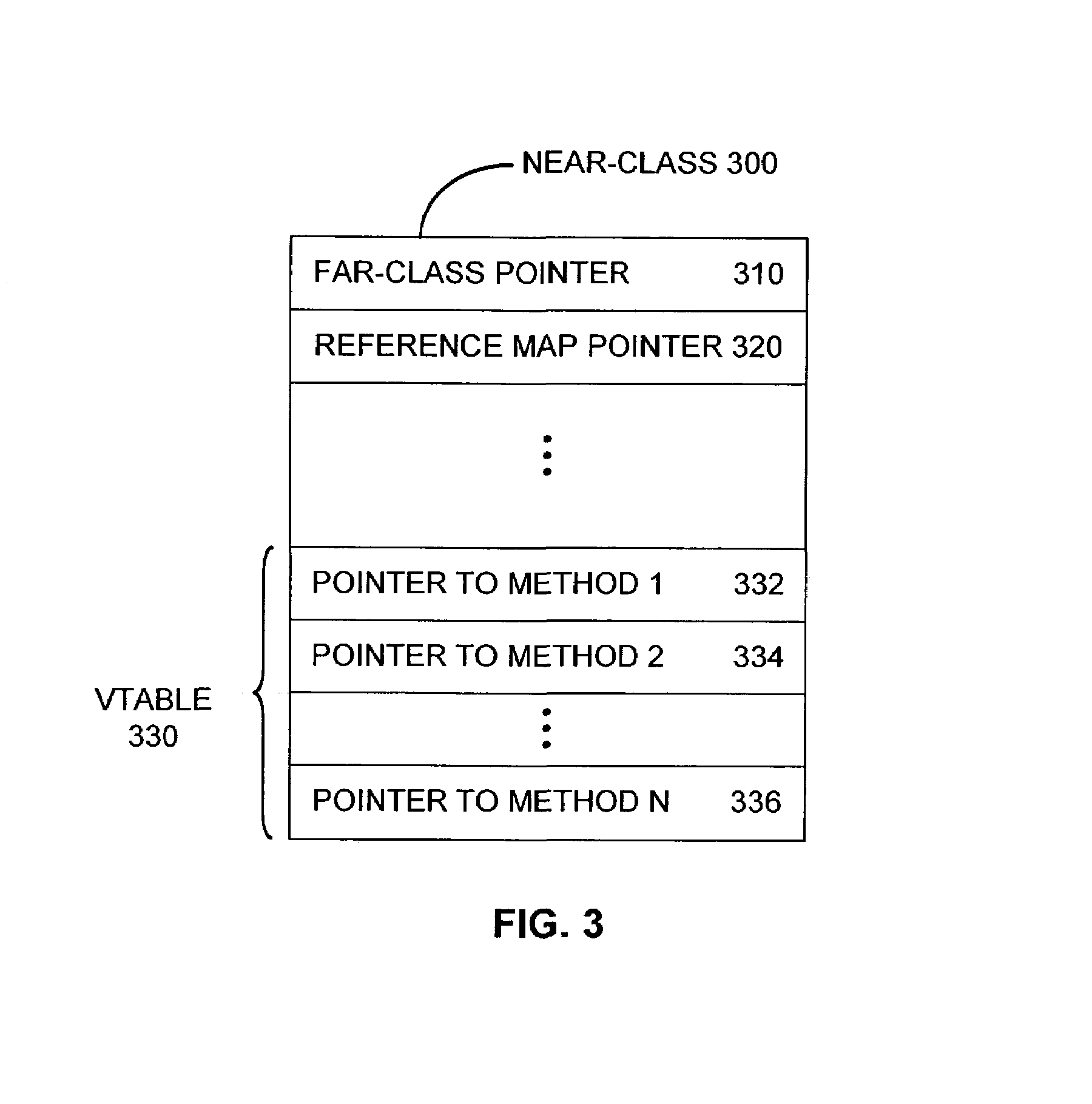
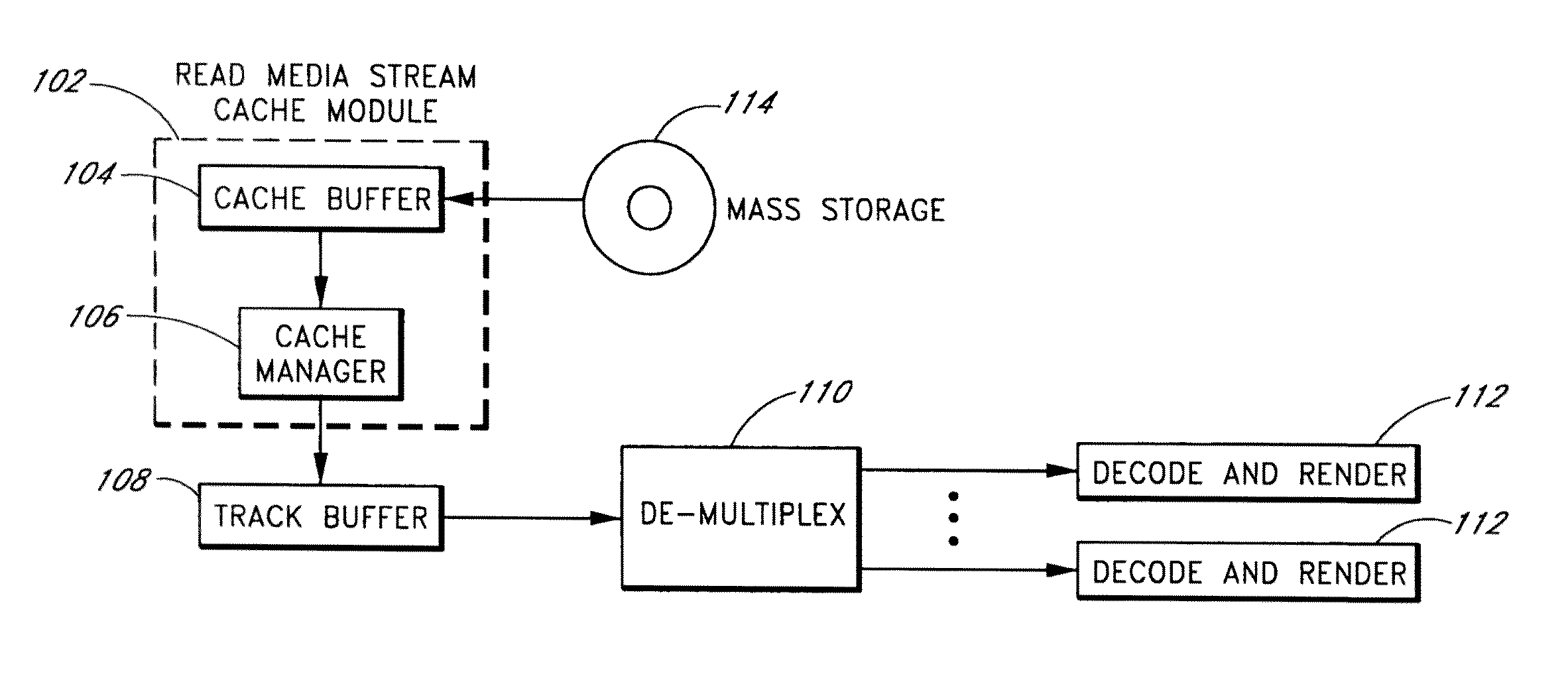
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41884 results about "Parallel computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
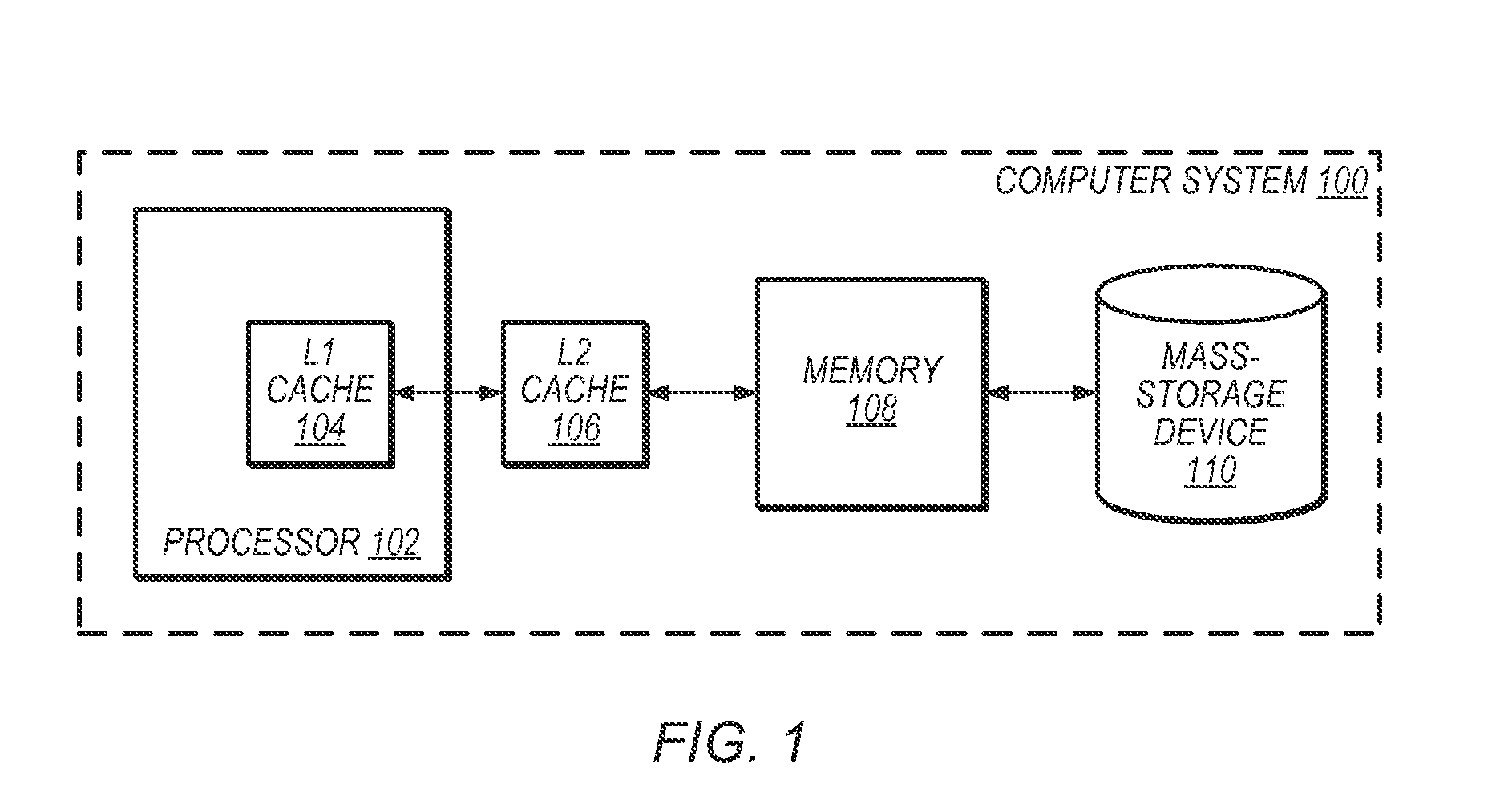
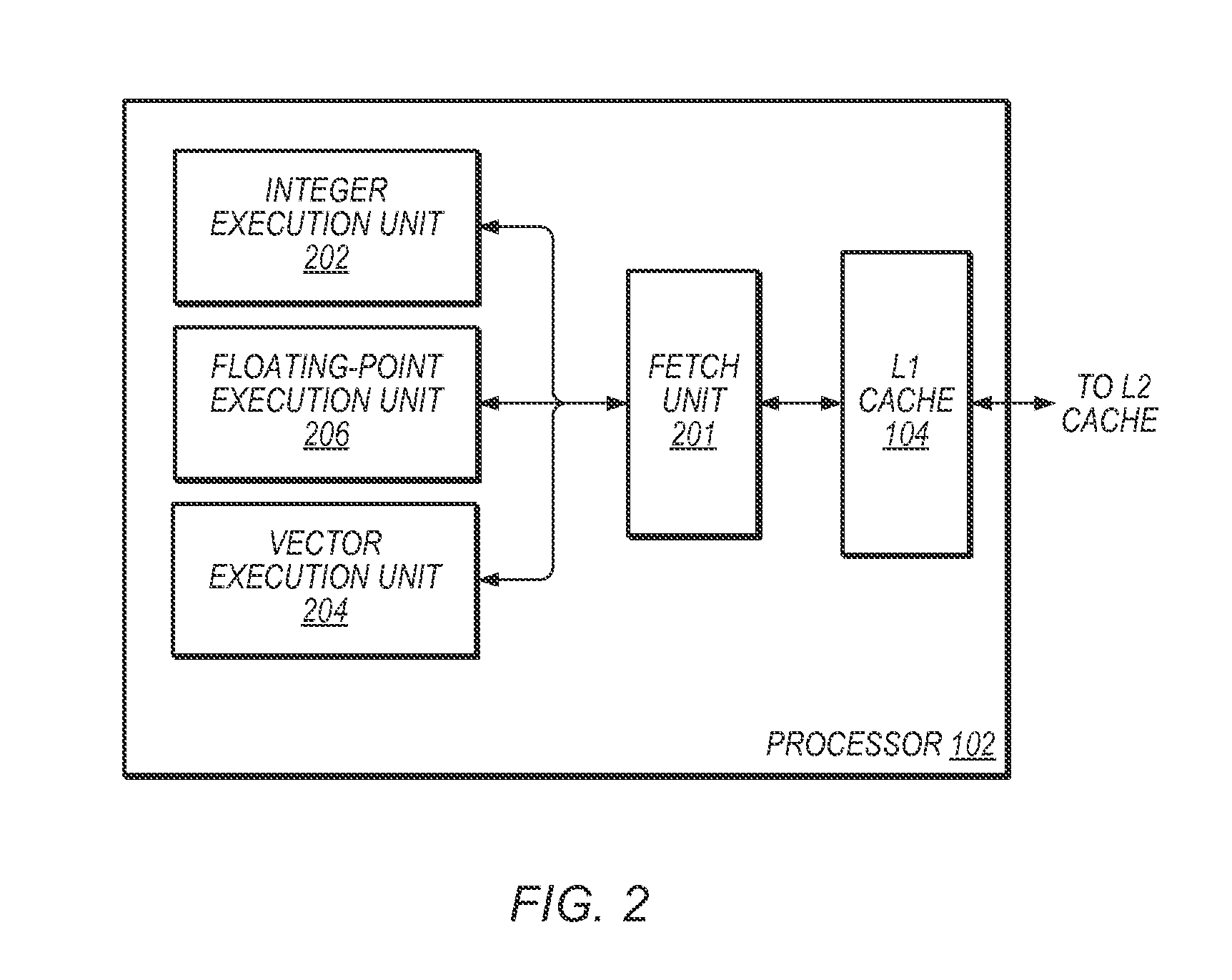
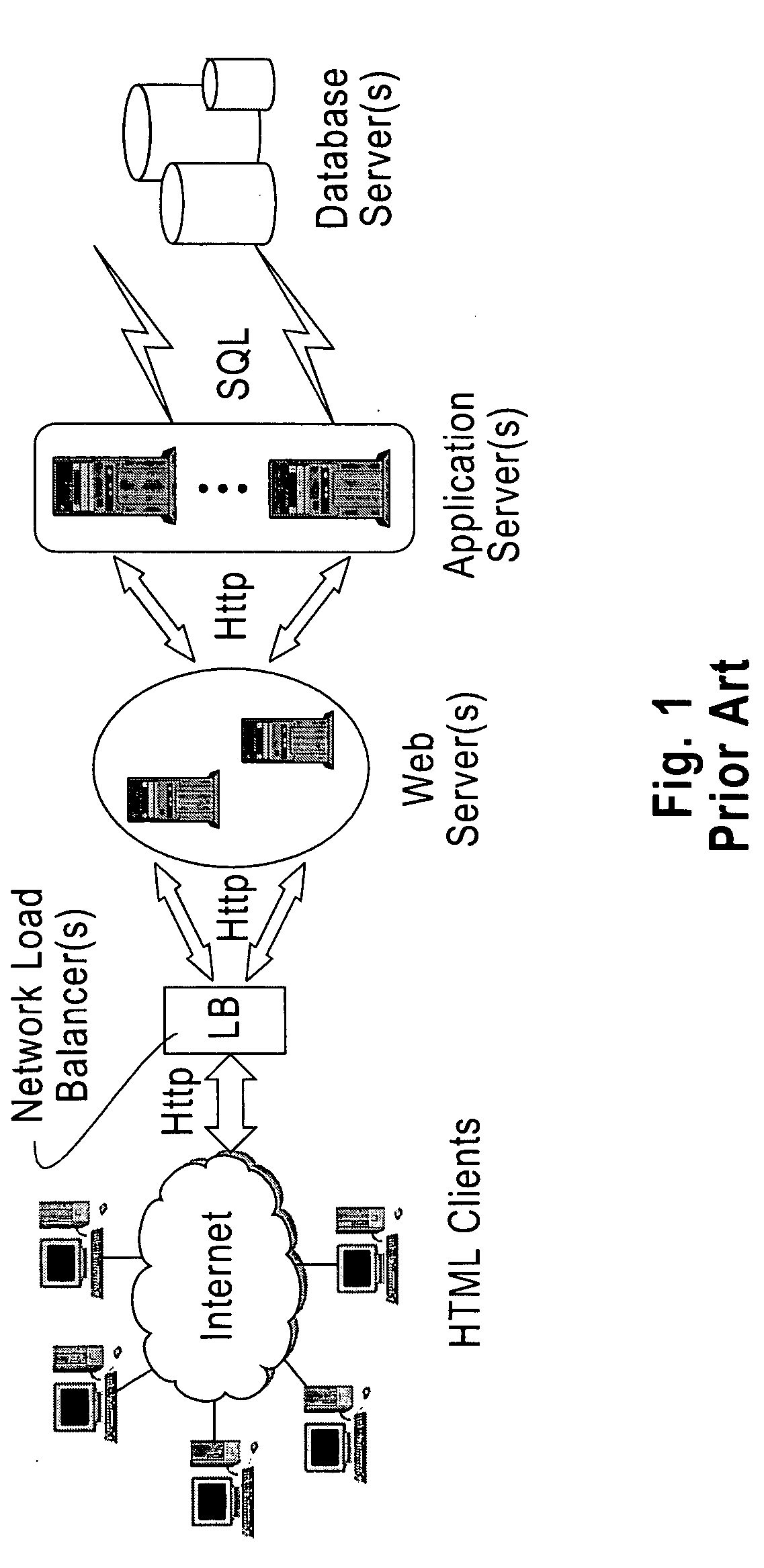
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or the execution of processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but it's gaining broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling. As power consumption (and consequently heat generation) by computers has become a concern in recent years, parallel computing has become the dominant paradigm in computer architecture, mainly in the form of multi-core processors.
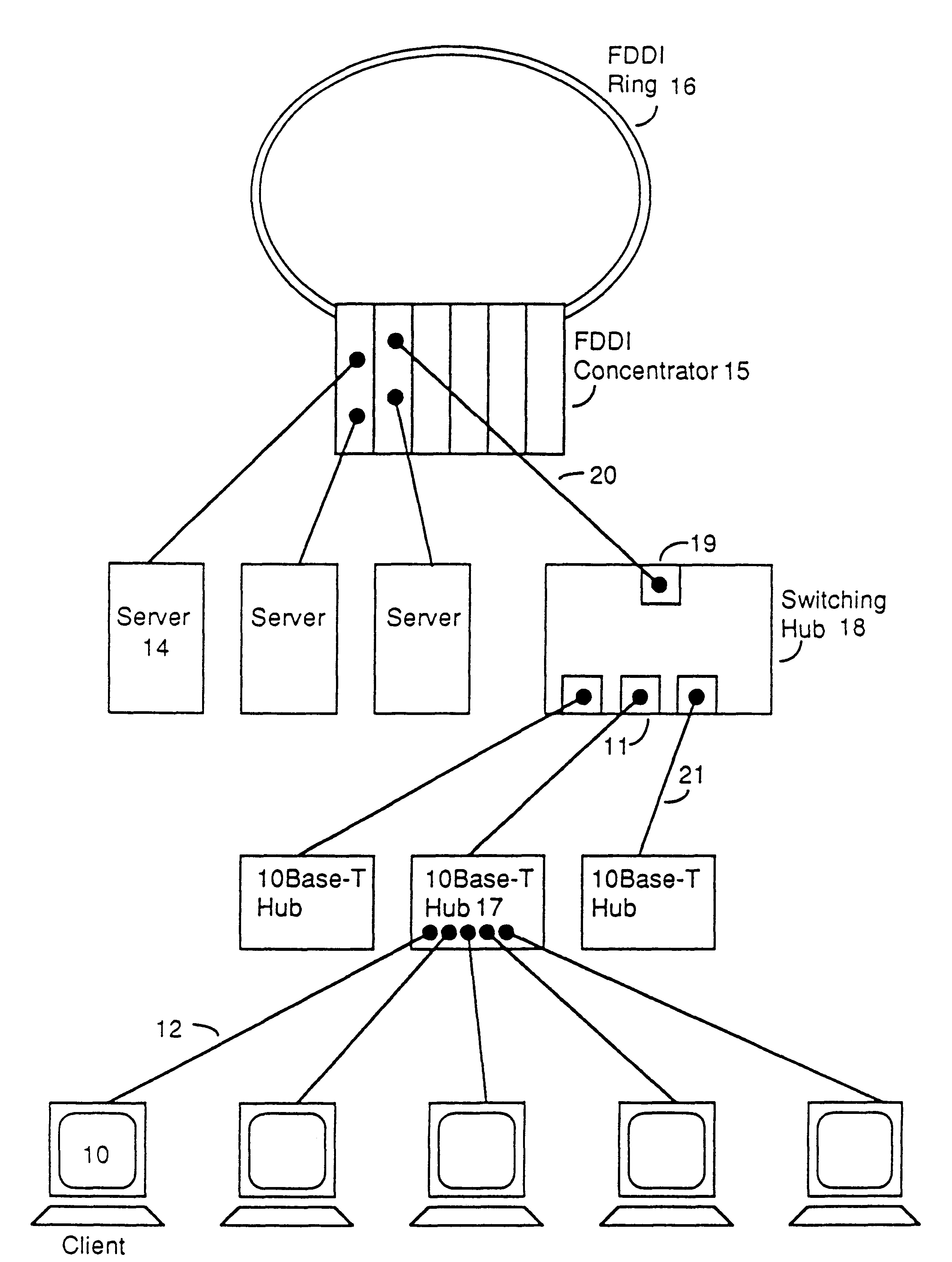
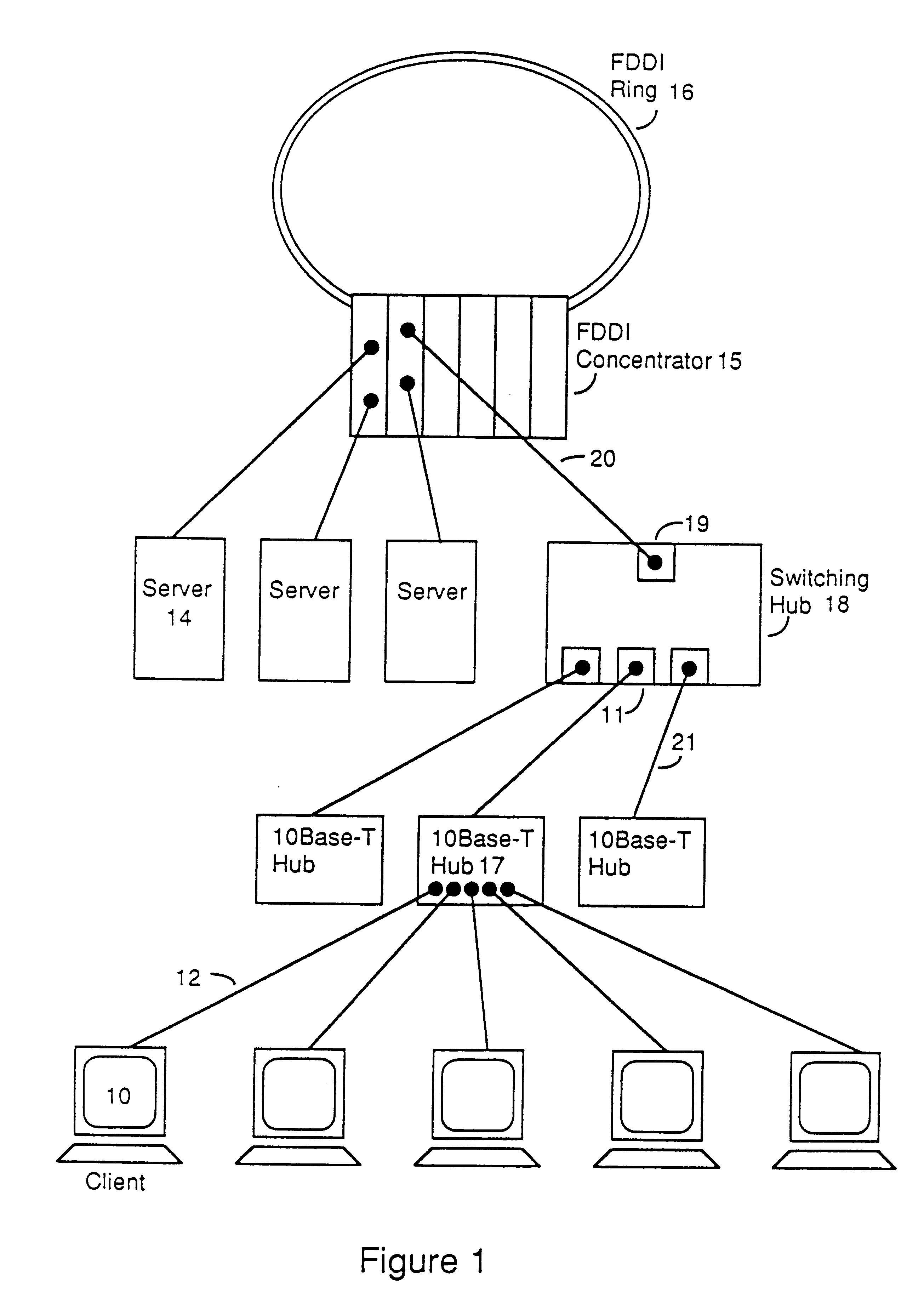
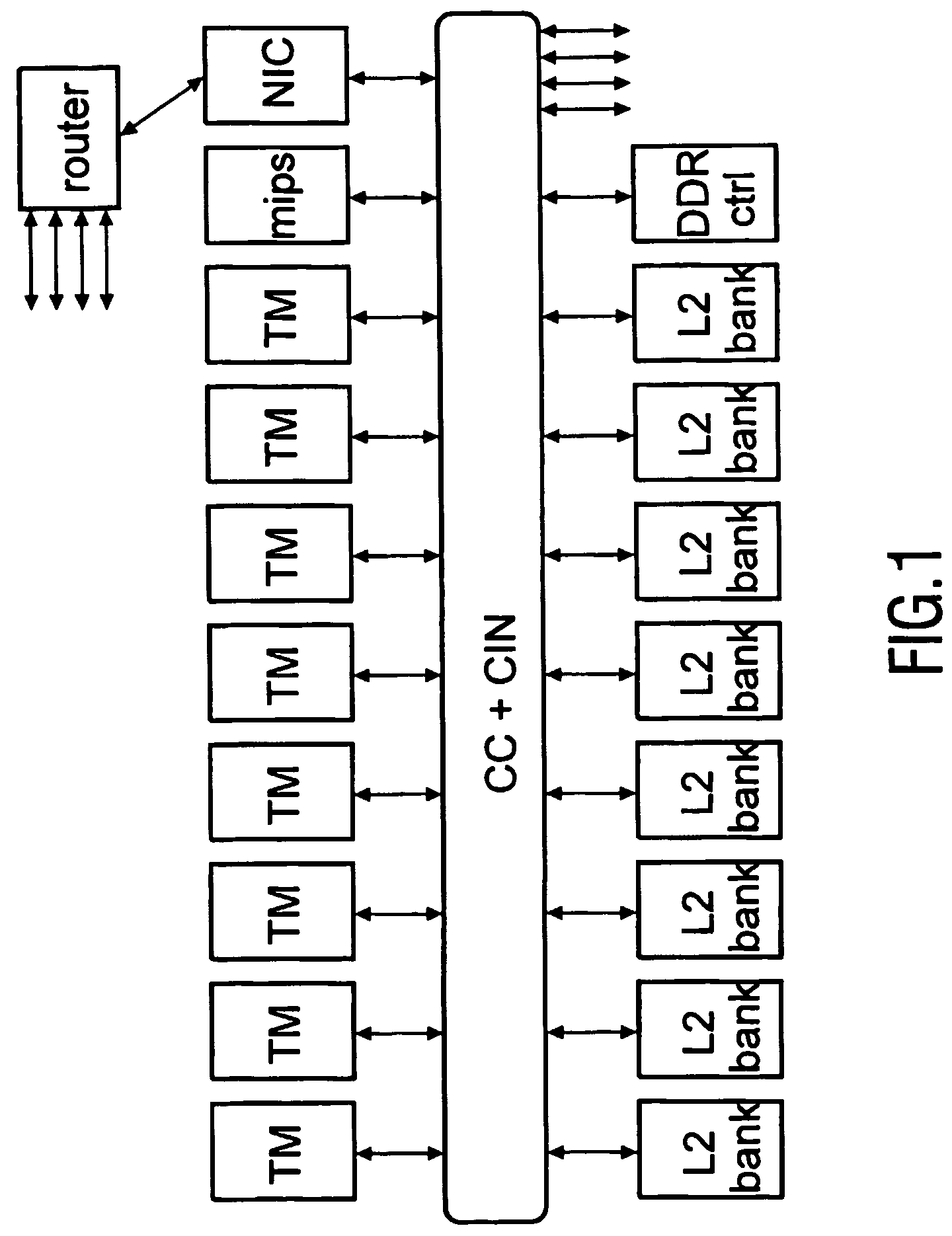
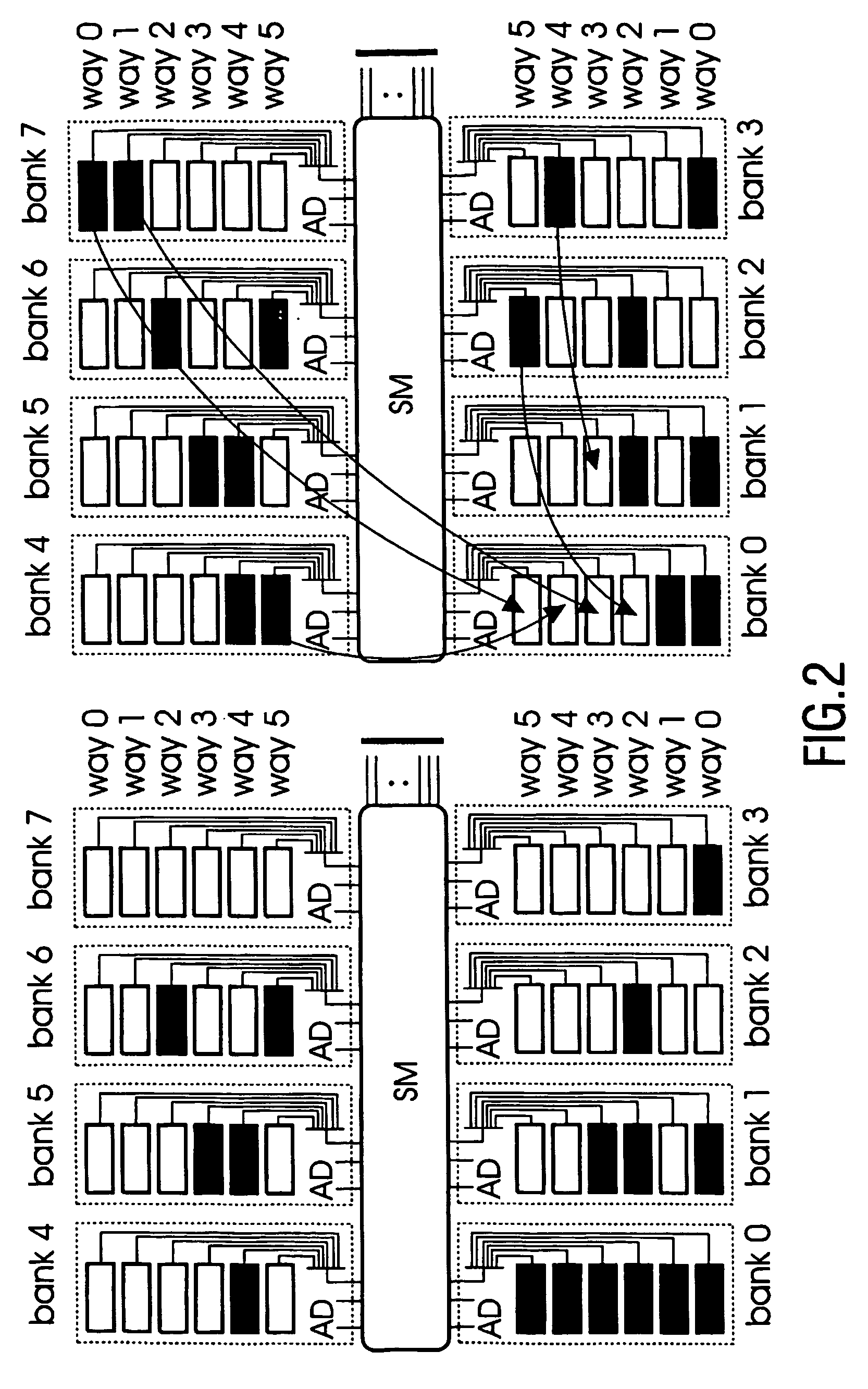
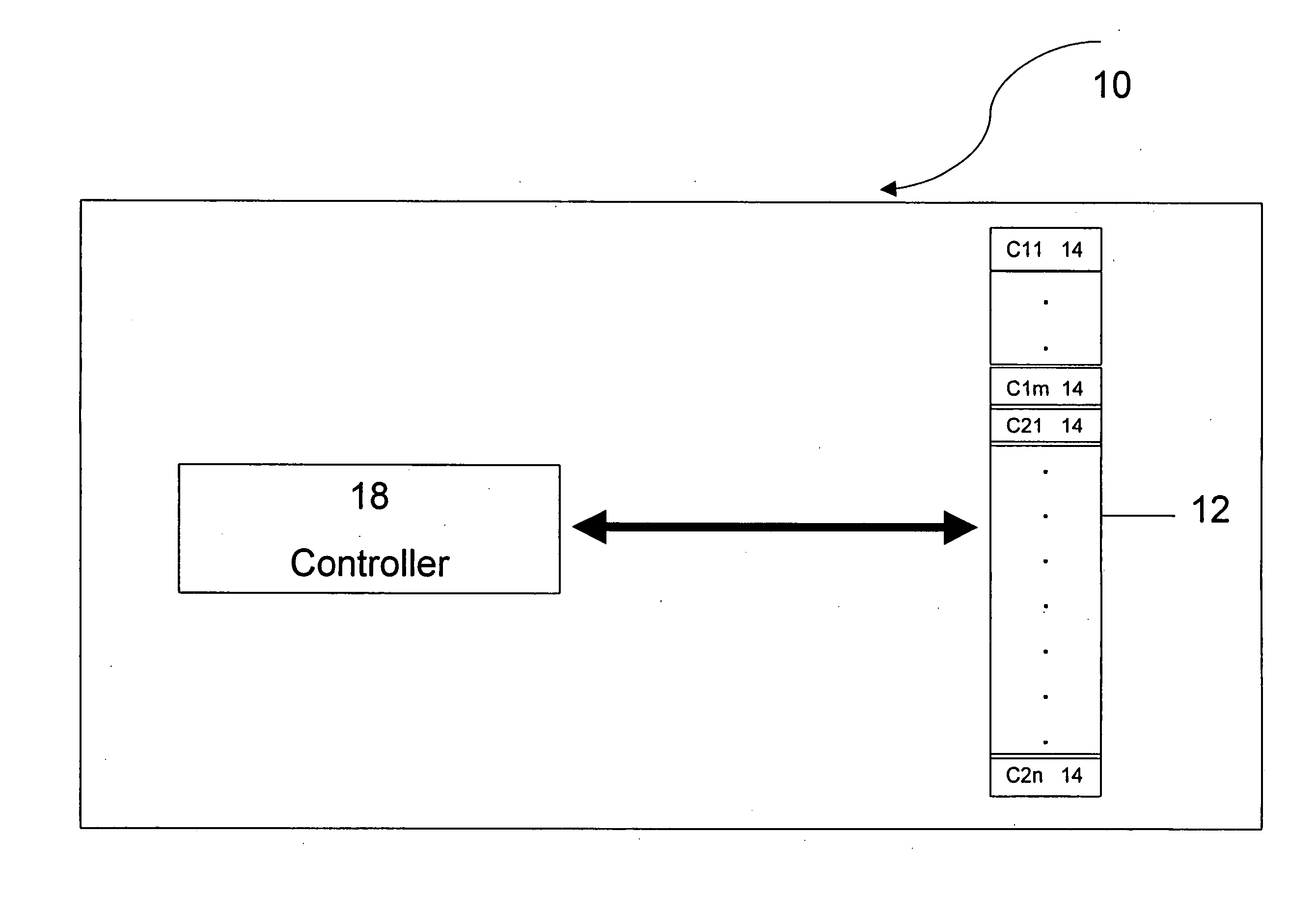
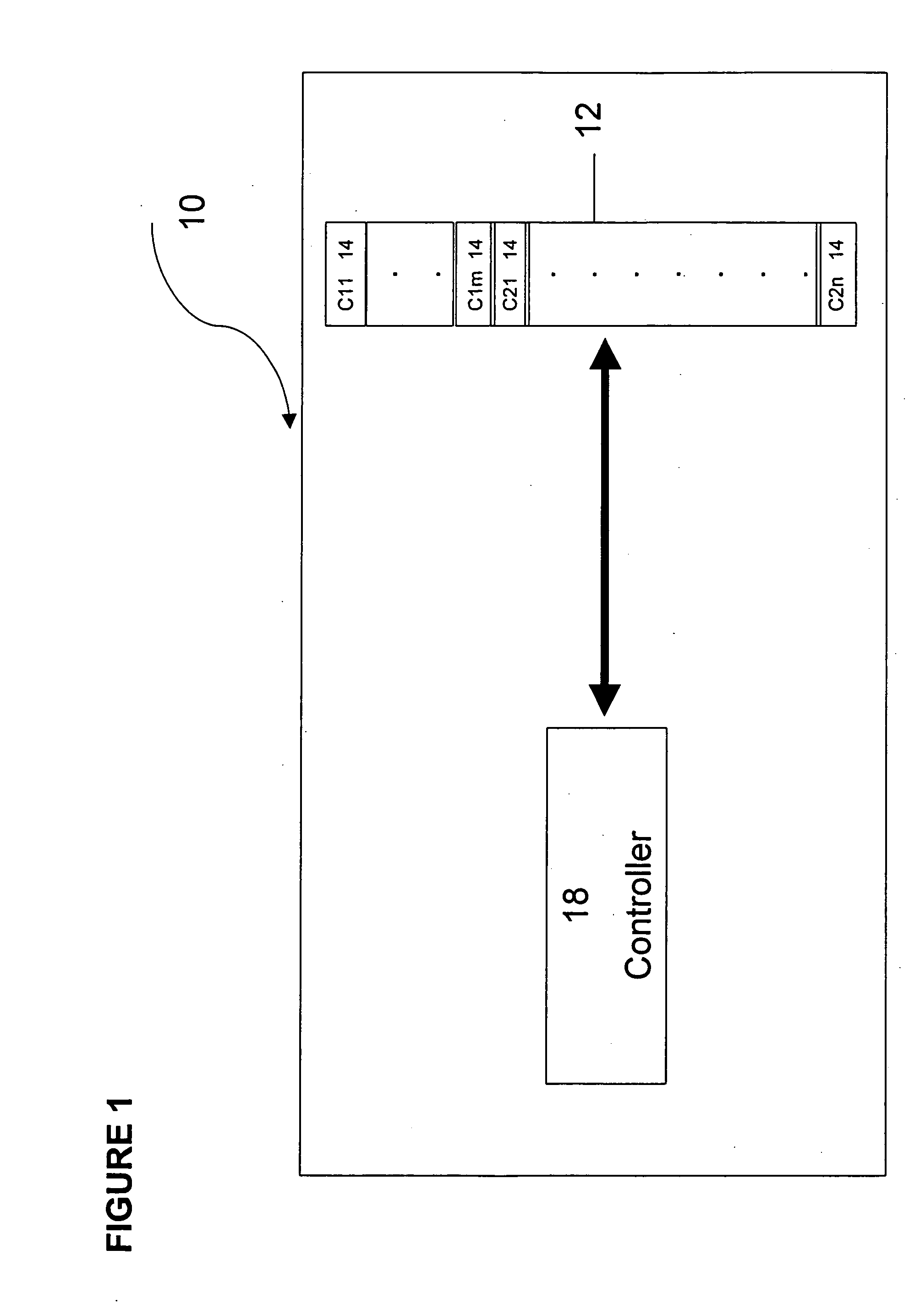
Distributed memory switching hub
InactiveUS6175571B1Quick rinseHigh frame forwarding rateTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationStore and forwardDistributed memory architecture
A distributed memory switching hub interconnecting heterogeneous local area networks operating at different transmission speeds for receiving, storing and forwarding frames of data. The distributed memory switching hub employs a distributed memory architecture in which memory storage for frames of data received and to be transmitted is located at each low speed LAN port of the distributed memory switching hub. A distributed memory architecture renders unnecessary the need for a central programmable processor or shared common memory to store and forward frames received by the distributed memory switching hub.
Owner:NETWORK PERIPHERALS
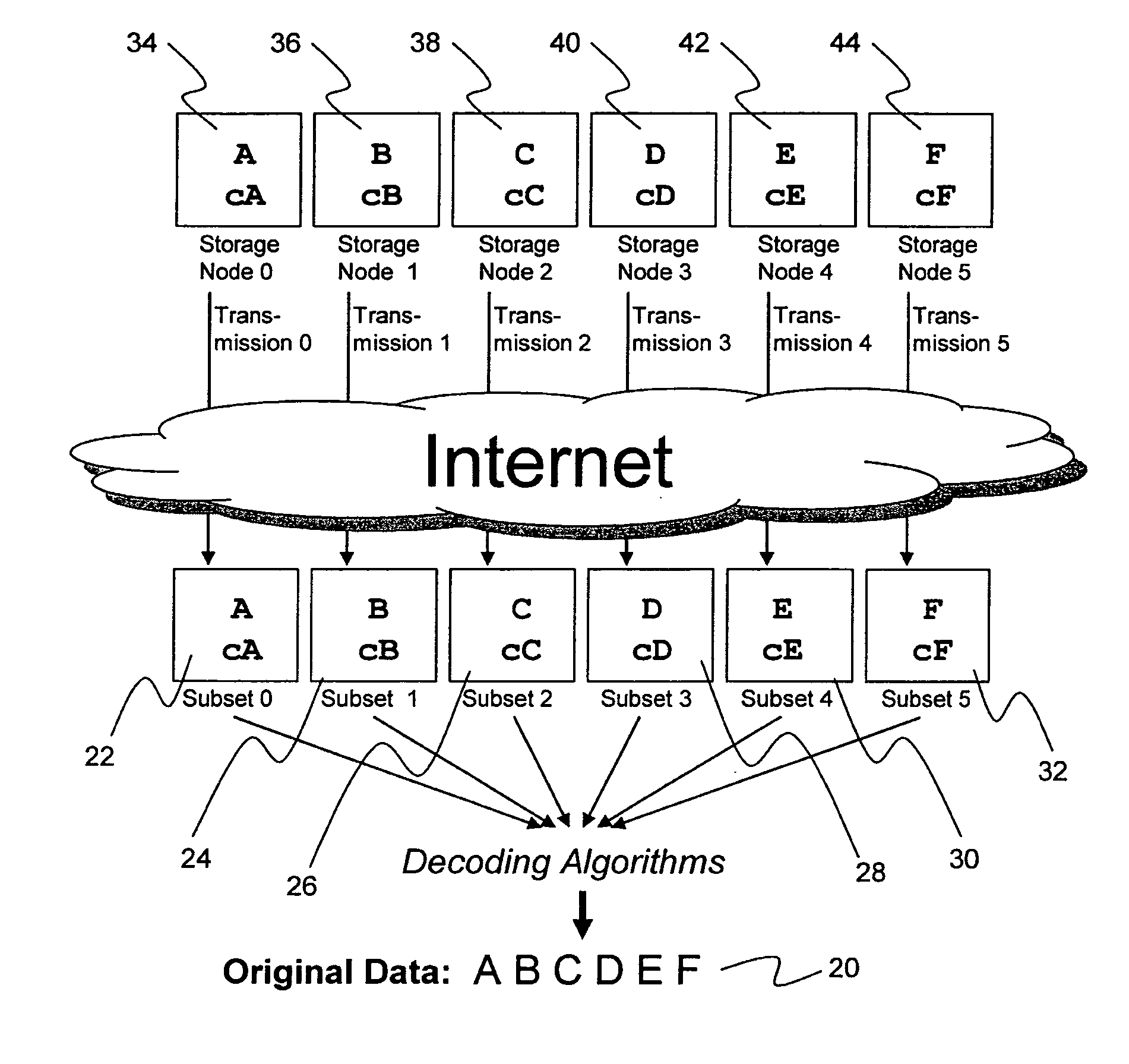
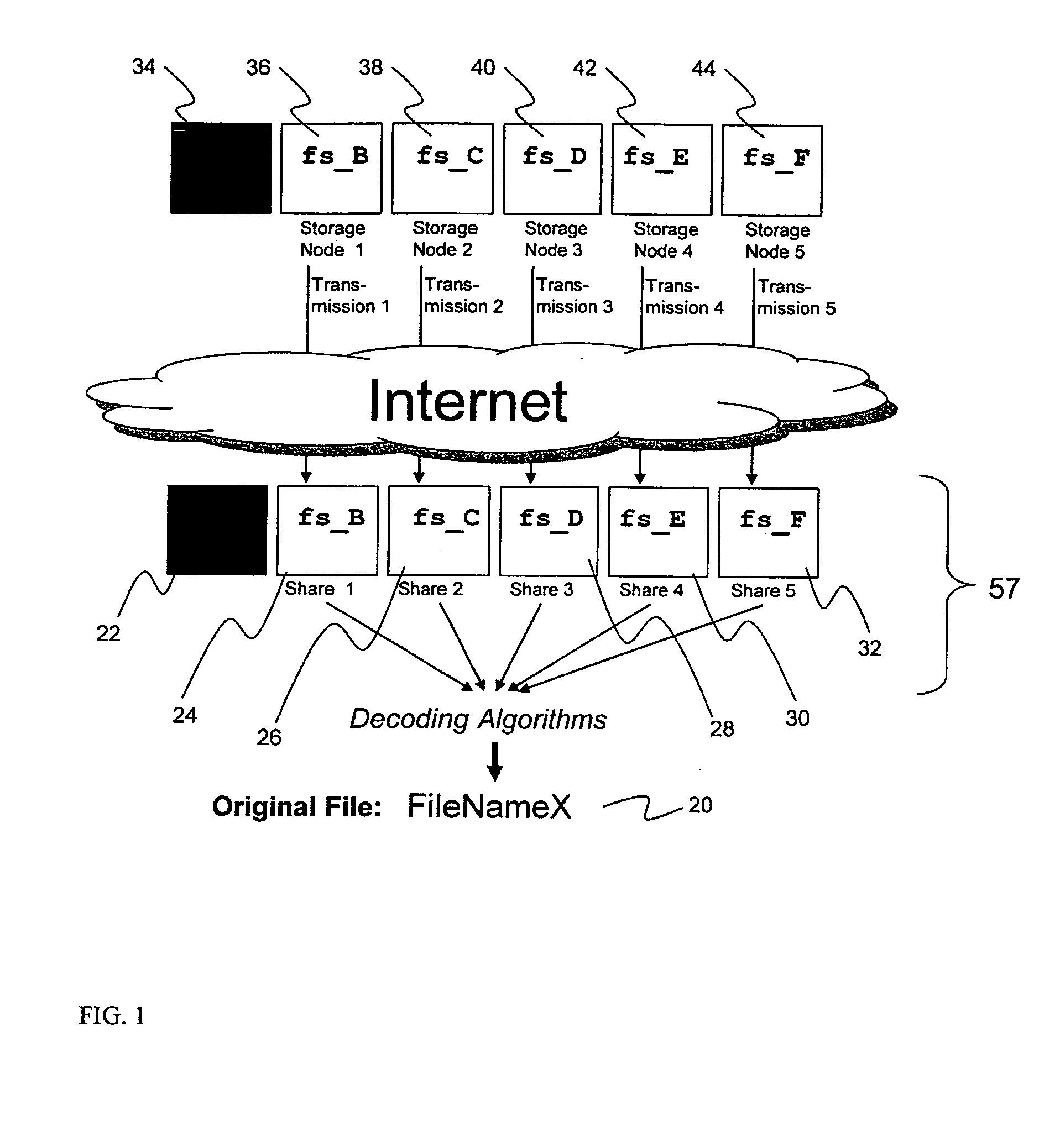
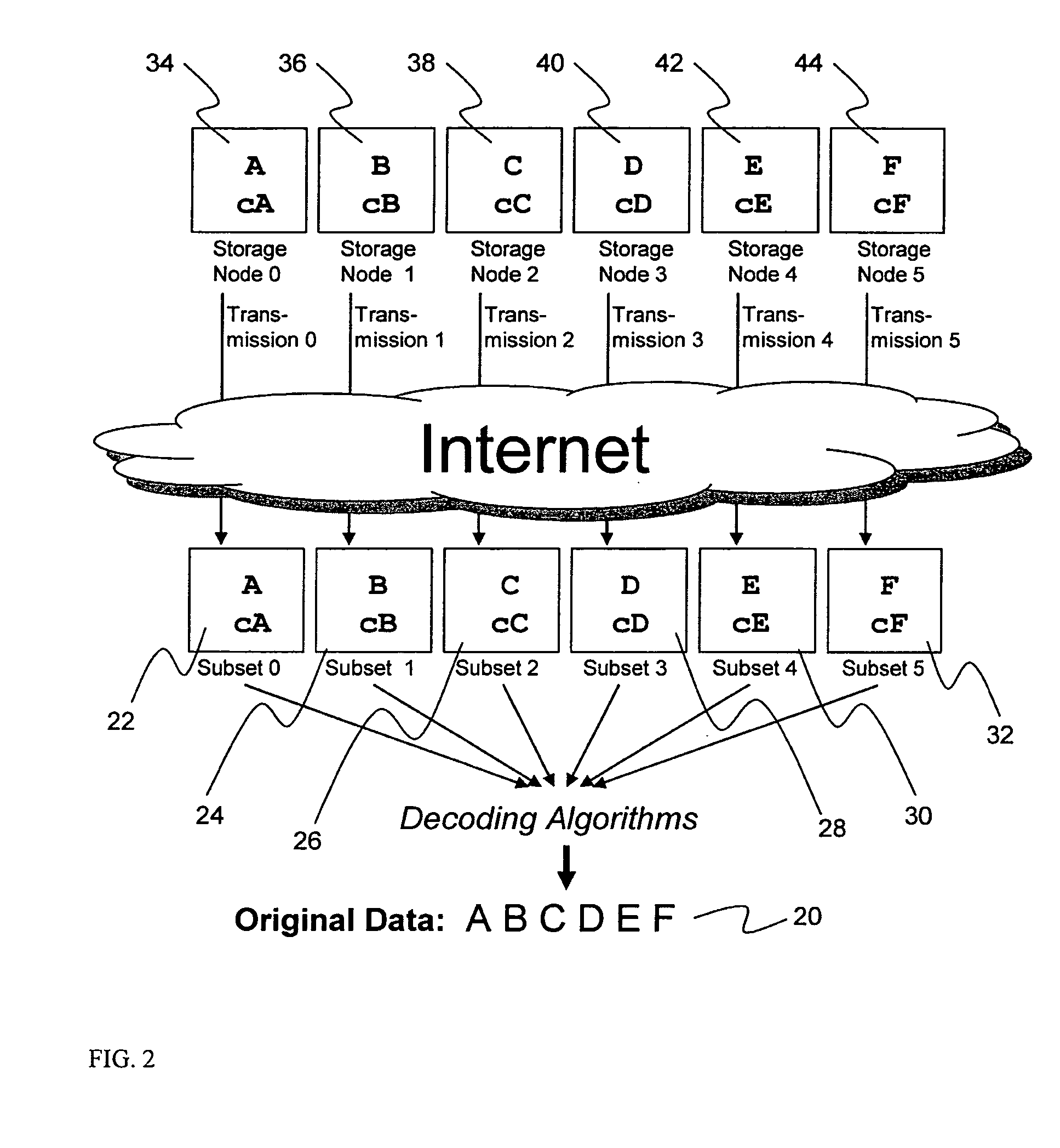
System for rebuilding dispersed data
ActiveUS20070079082A1Reliably and securely protectImprove privacyError detection/correctionDigital data protectionGrid resourcesInformation dispersal
A digital data file storage system is disclosed in which original data files to be stored are dispersed using some form of information dispersal algorithm into a number of file “slices” or subsets in such a manner that the data in each file share is less usable or less recognizable or completely unusable or completely unrecognizable by itself except when combined with some or all of the other file shares. These file shares are stored on separate digital data storage devices as a way of increasing privacy and security. As dispersed file shares are being transferred to or stored on a grid of distributed storage locations, various grid resources may become non-operational or may operate below at a less than optimal level. When dispersed file shares are being written to a dispersed storage grid which not available, the grid clients designates the dispersed data shares that could not be written at that time on a Rebuild List. In addition when grid resources already storing dispersed data become non-available, a process within the dispersed storage grid designates the dispersed data shares that need to be recreated on the Rebuild List. At other points in time a separate process reads the set of Rebuild Lists used to create the corresponding dispersed data and stores that data on available grid resources.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
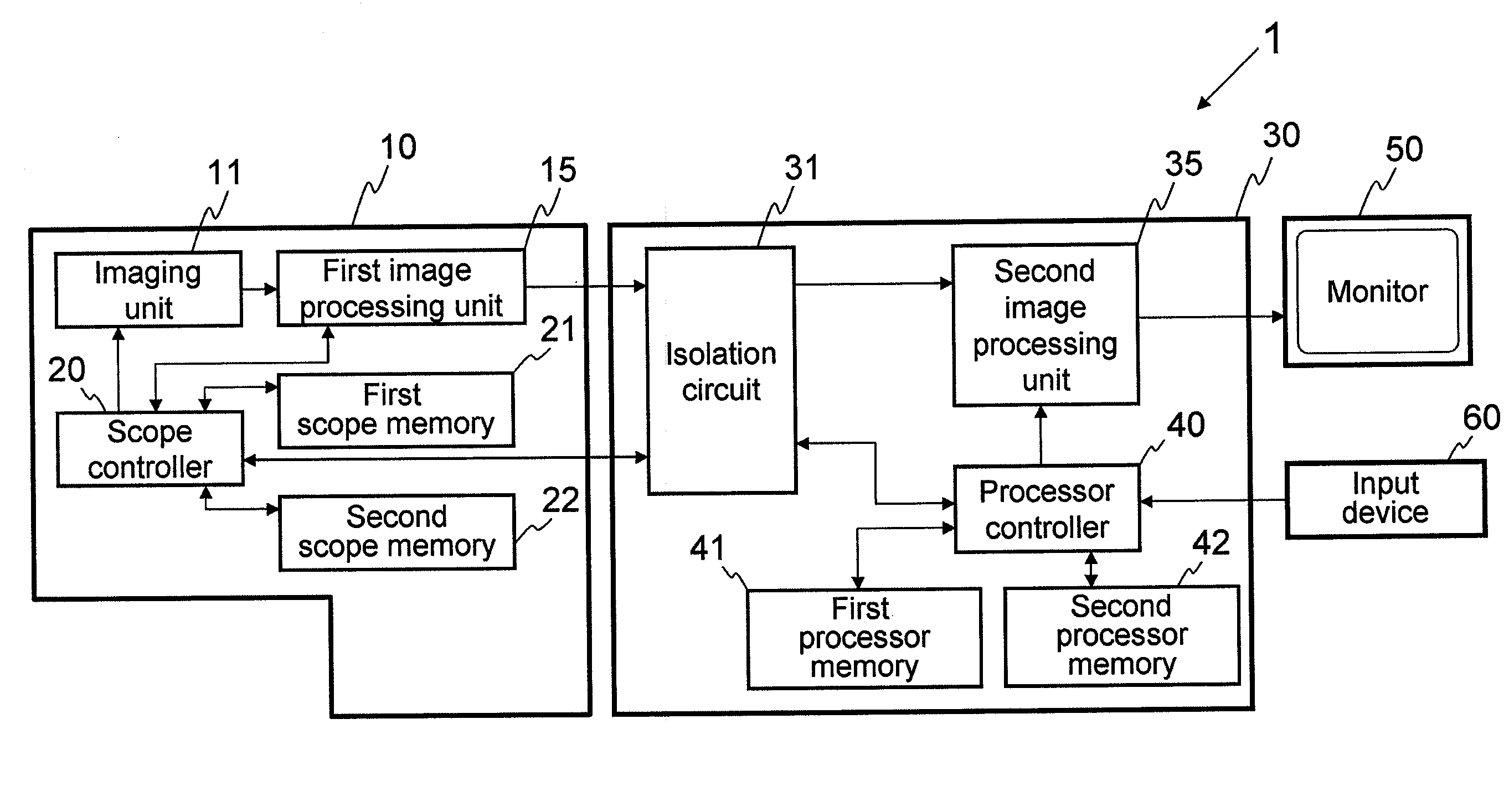
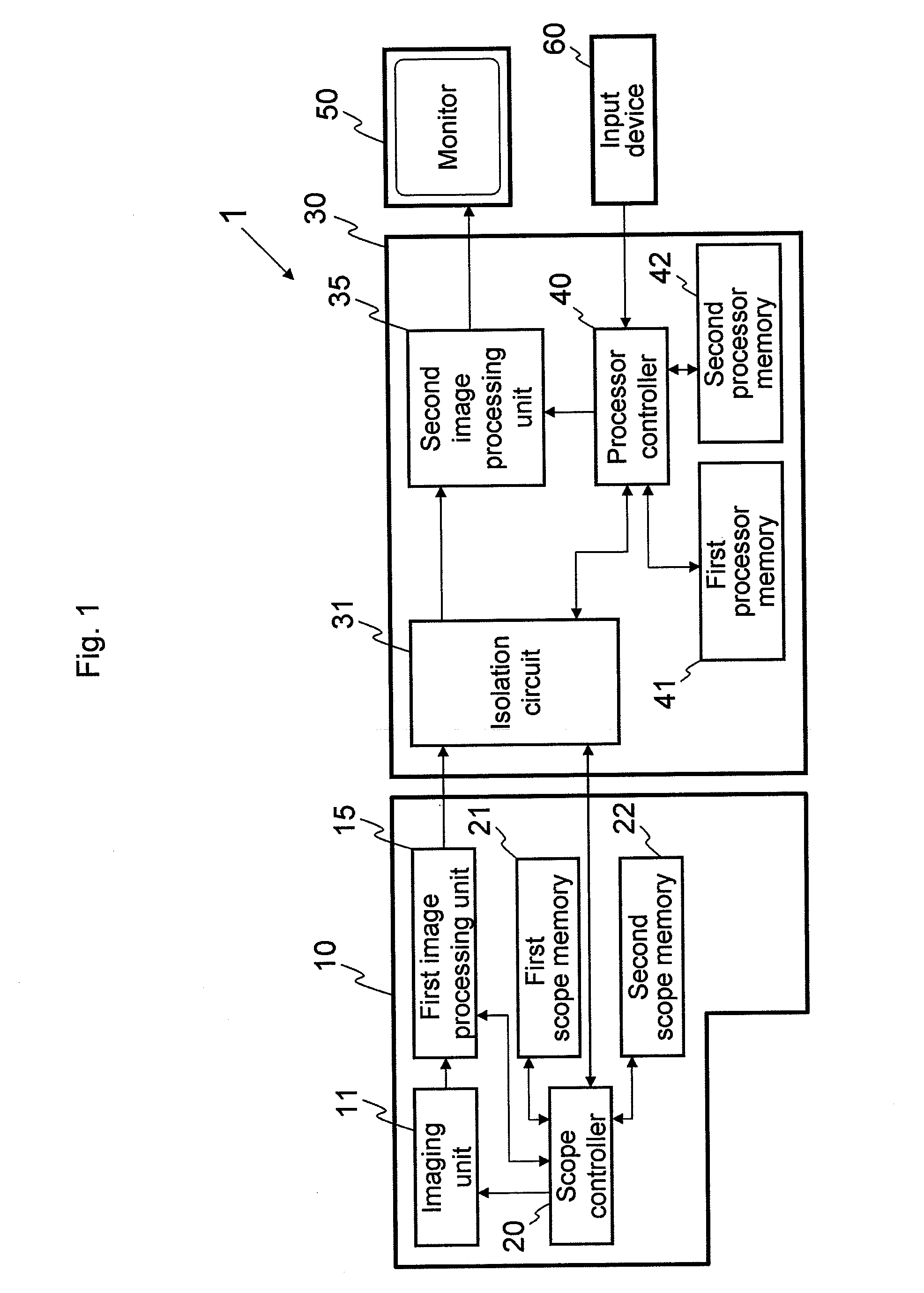
Endoscope system
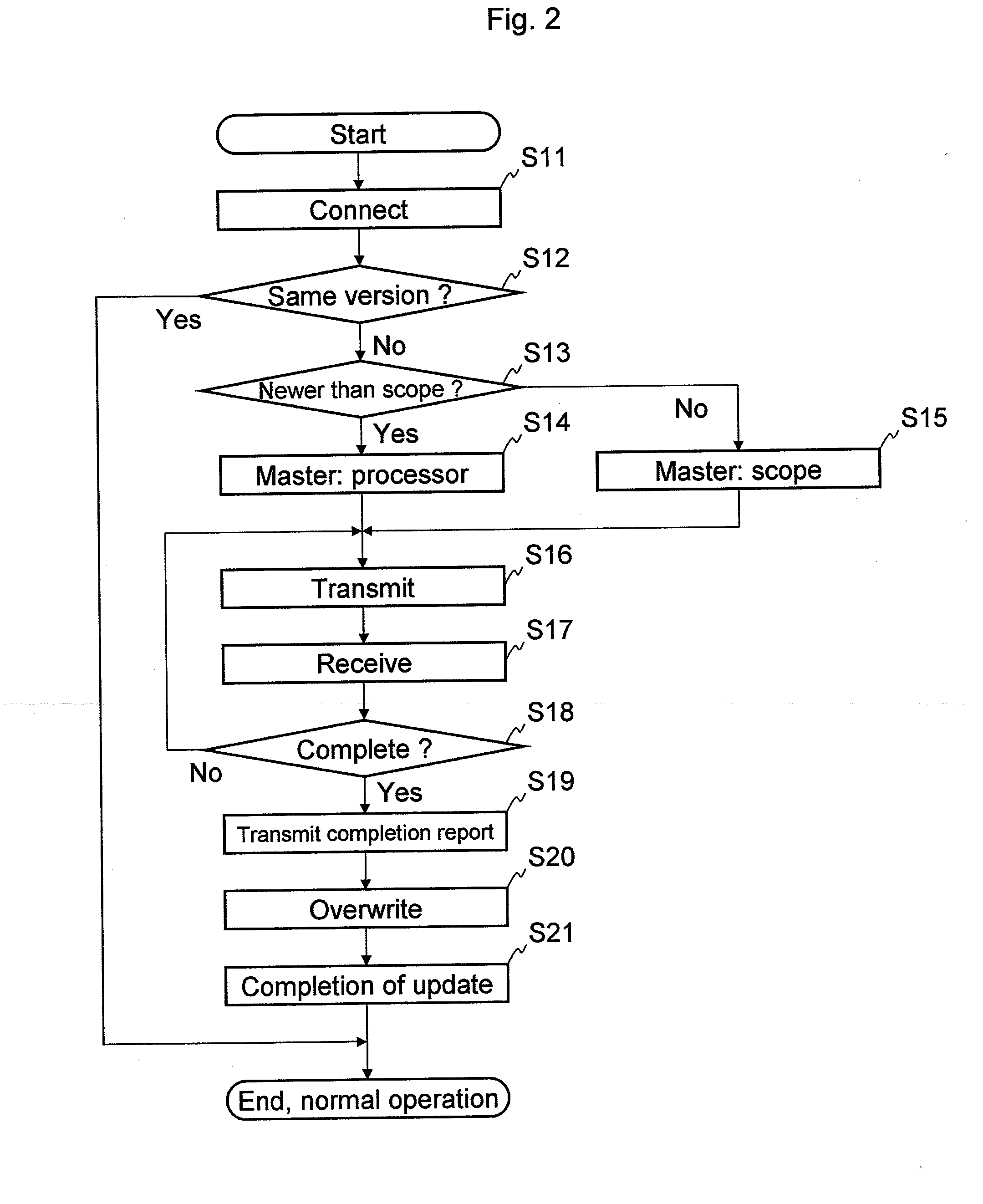
InactiveUS20090290016A1Easy to updateEndoscopesColor television detailsImaging processingParallel computing
An endoscope system comprises a scope and a processor. The scope has an imaging sensor, a first image-processing unit that performs primary image processing, a first memory, and a second memory. The first and second memories are non-volatile. The processor has a second image-processing unit that performs secondary image processing, and a processor memory that is non-volatile. The first memory stores an system data that includes parameters for the primary and secondary image processing. The processor memory stores the system data. The second memory is used for storing the system data stored in the processor memory when it is determined that the system data stored in the first memory is older than the system data stored in the processor memory. The system data stored in the second memory is overwritten onto the first scope memory after the system data is stored in the second memory.
Owner:HOYA CORP
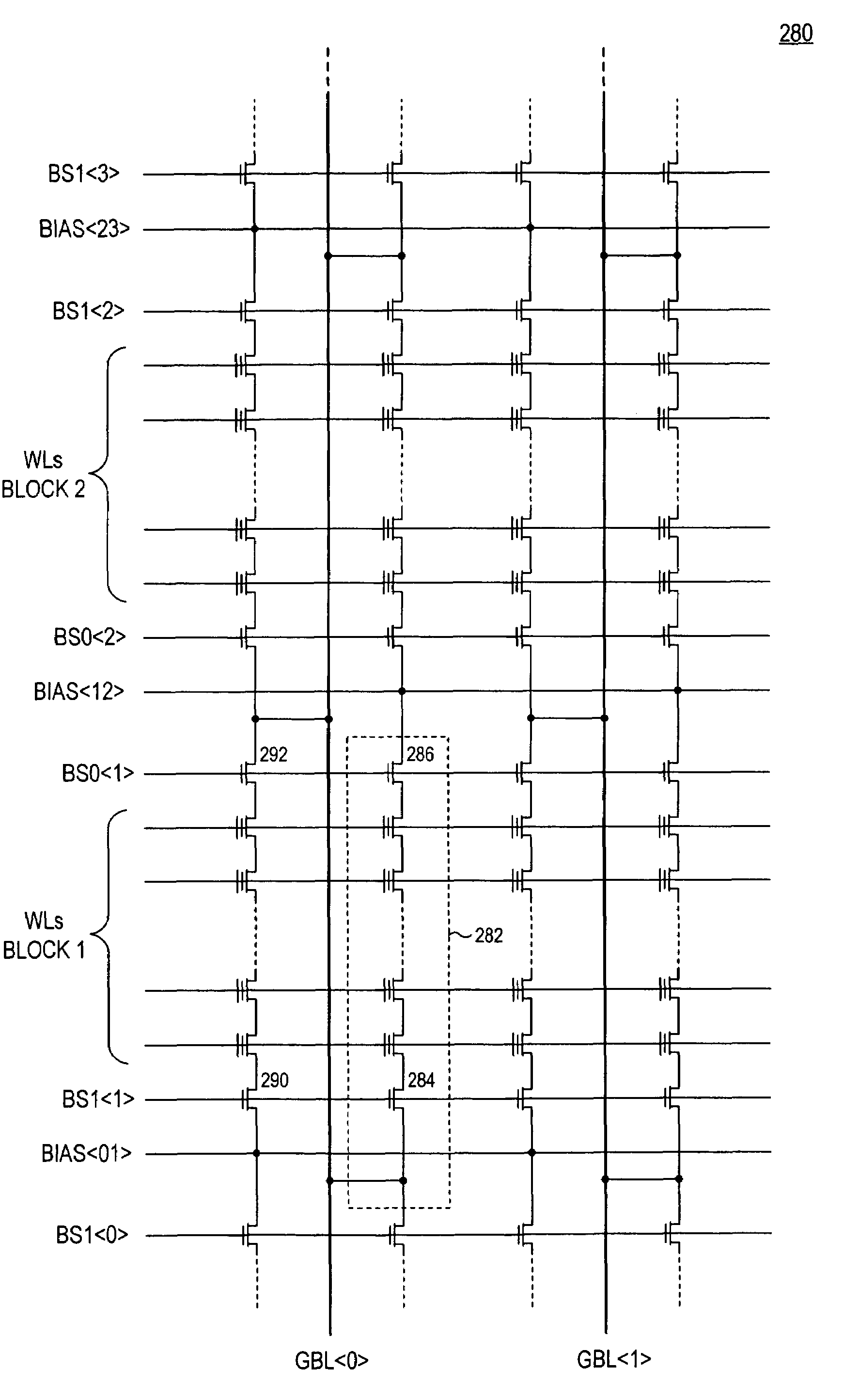
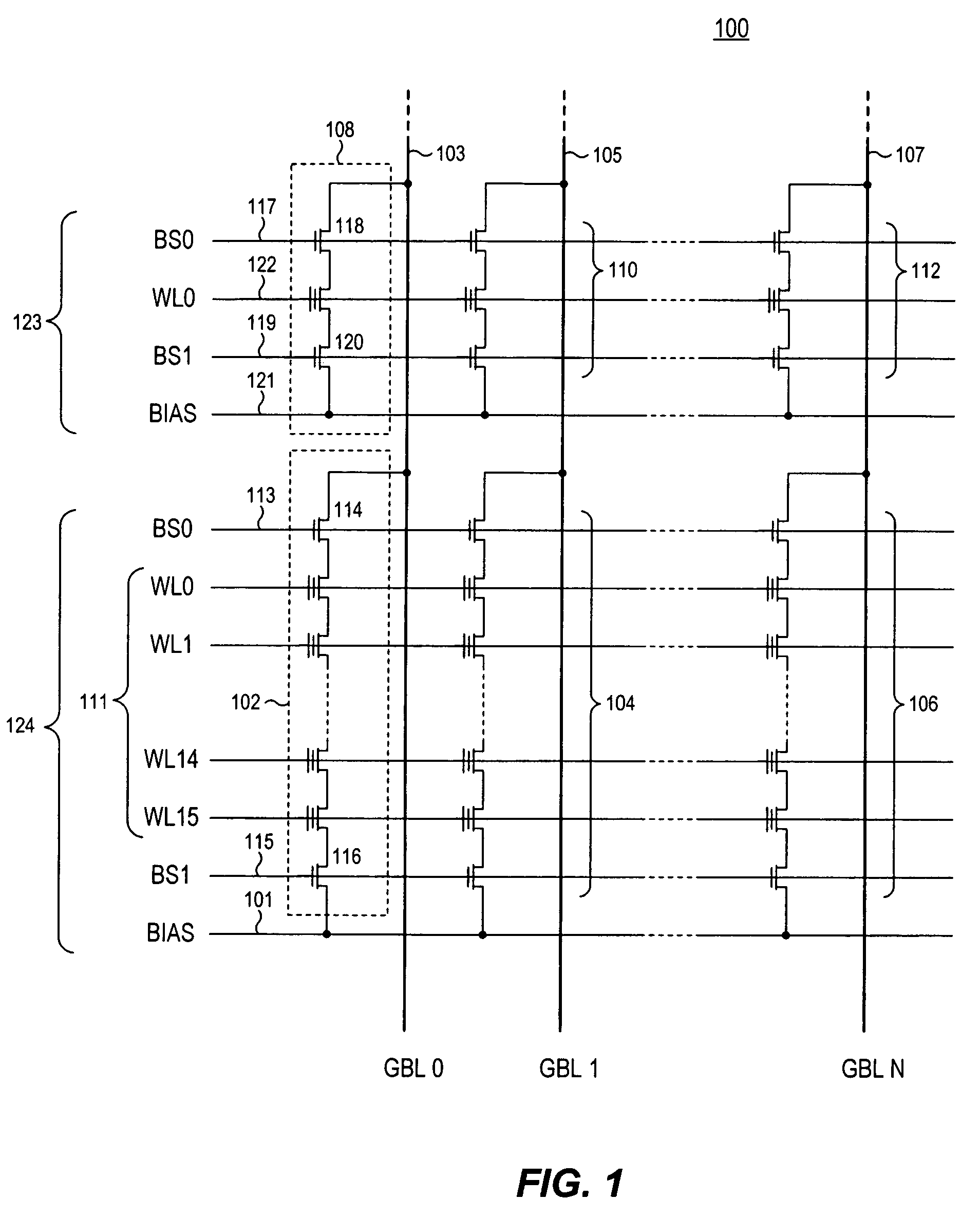
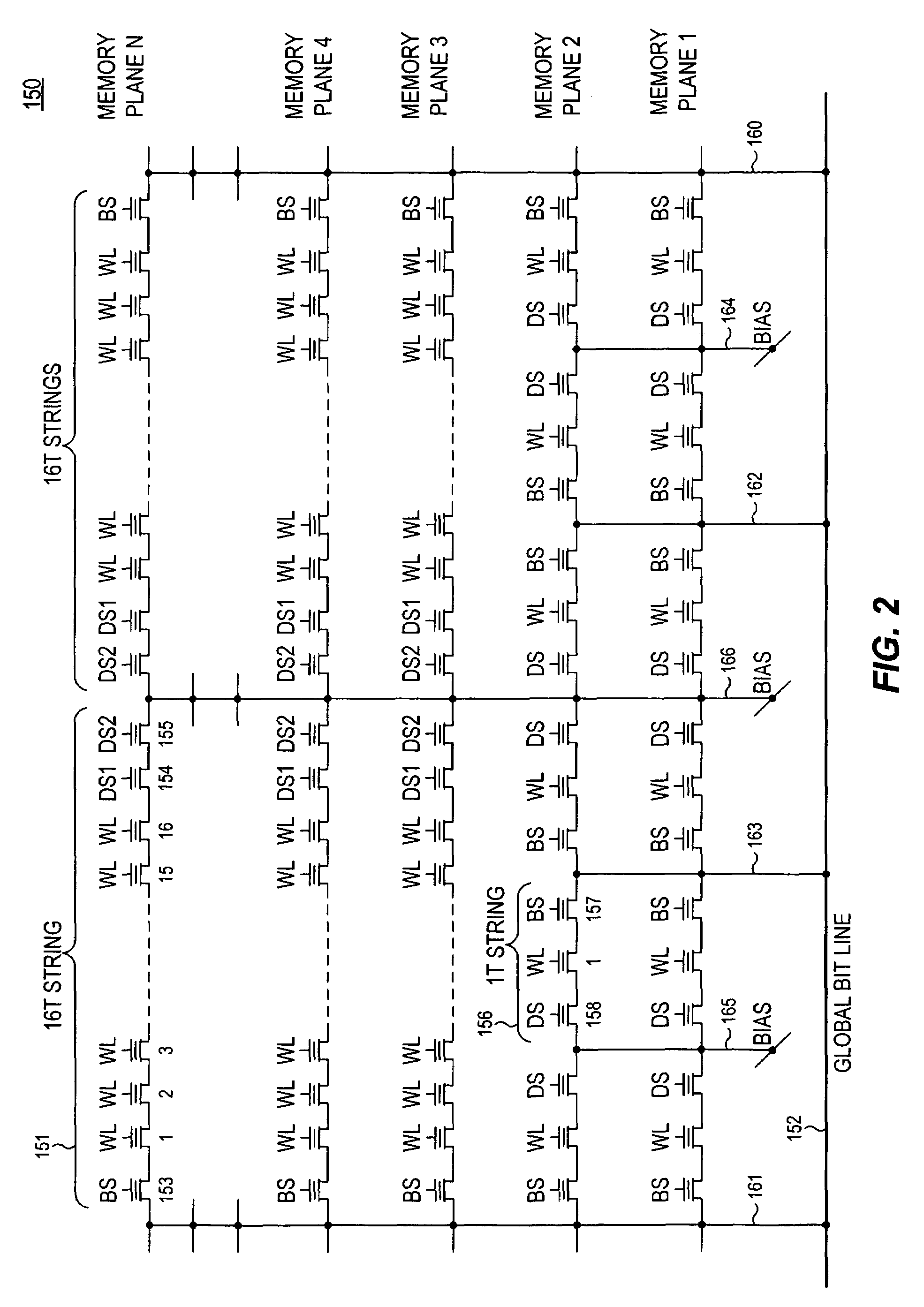
Non-volatile memory and method with reduced neighboring field errors
InactiveUS6987693B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageNon-volatile memoryParallel programing
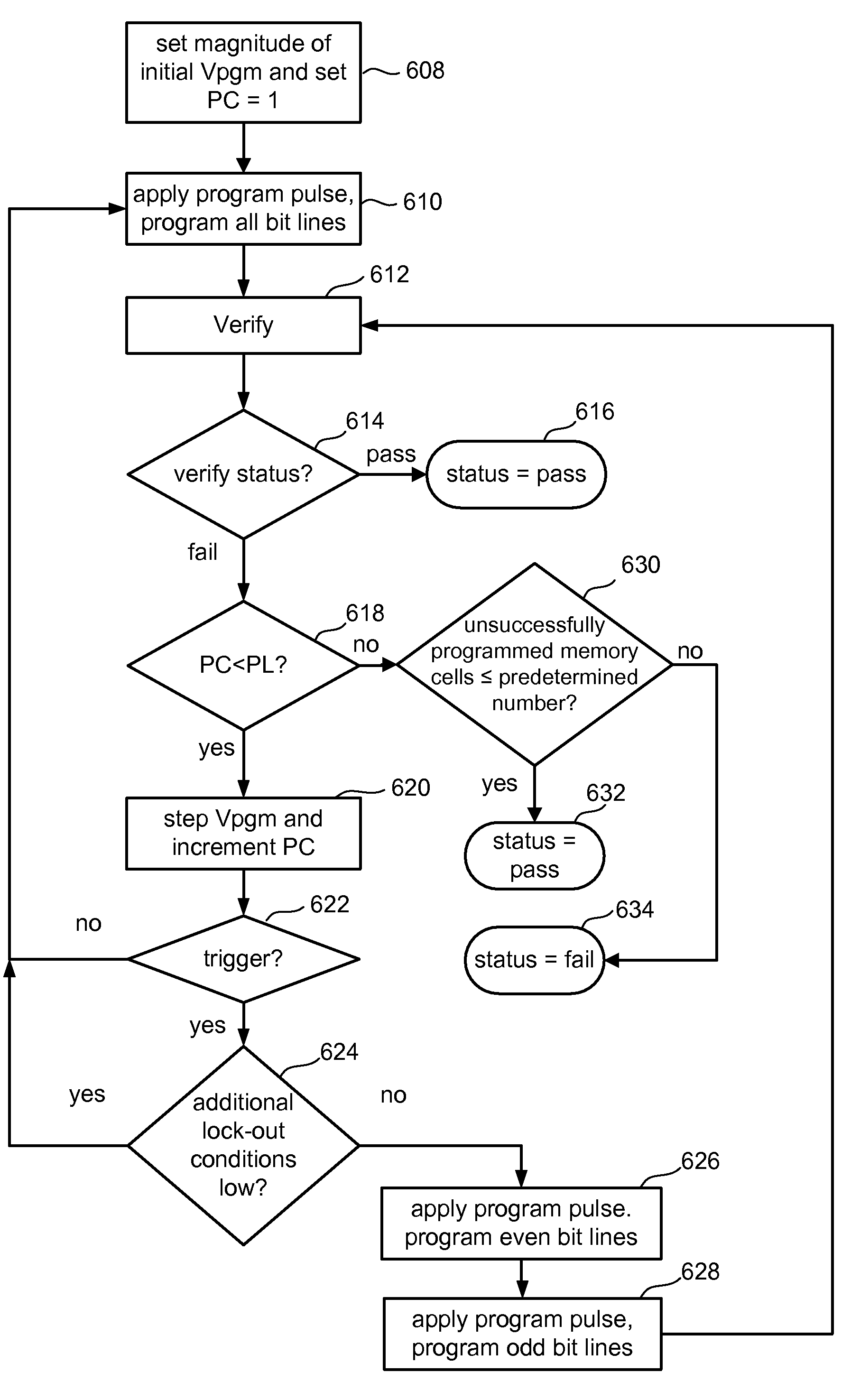
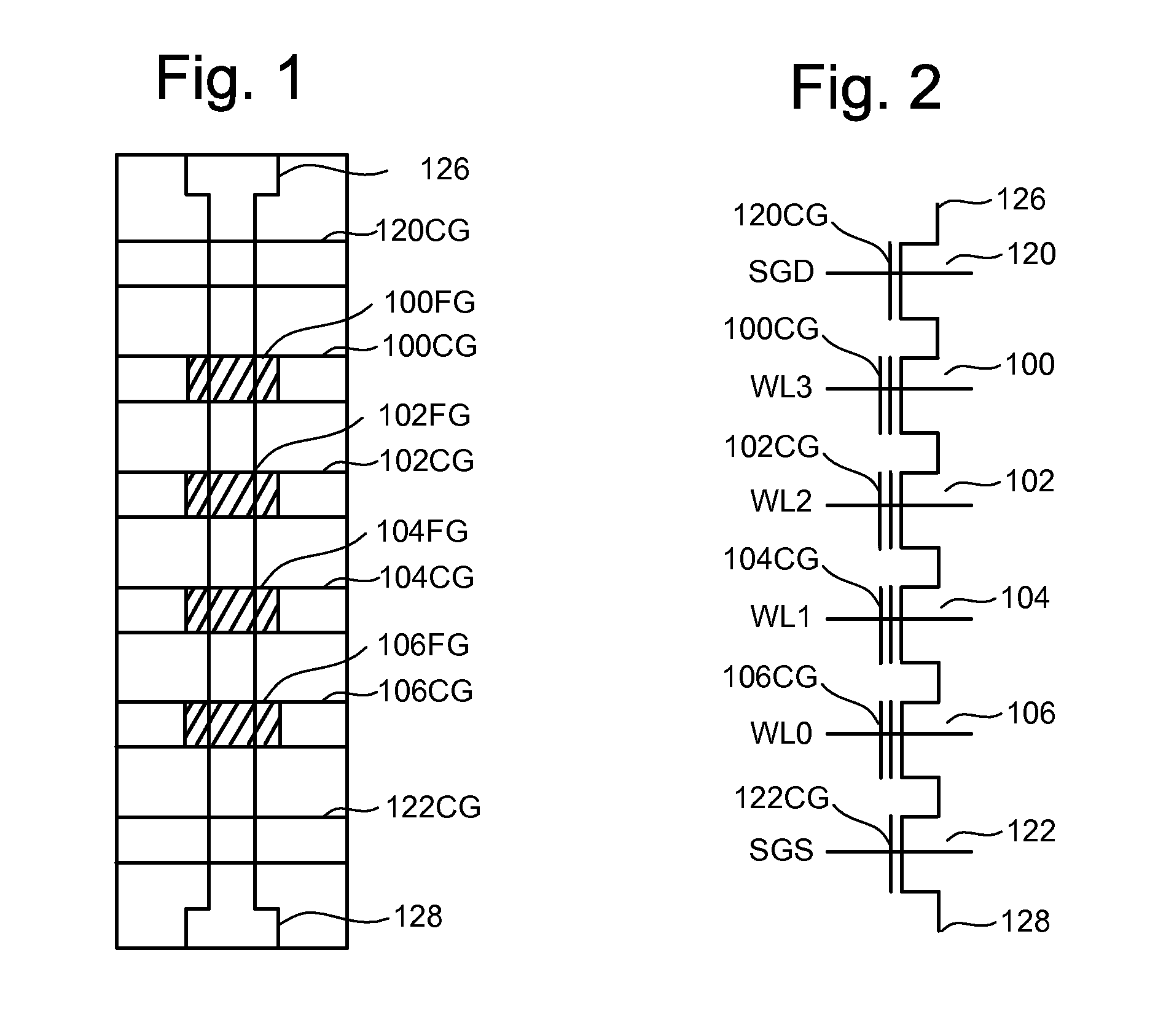
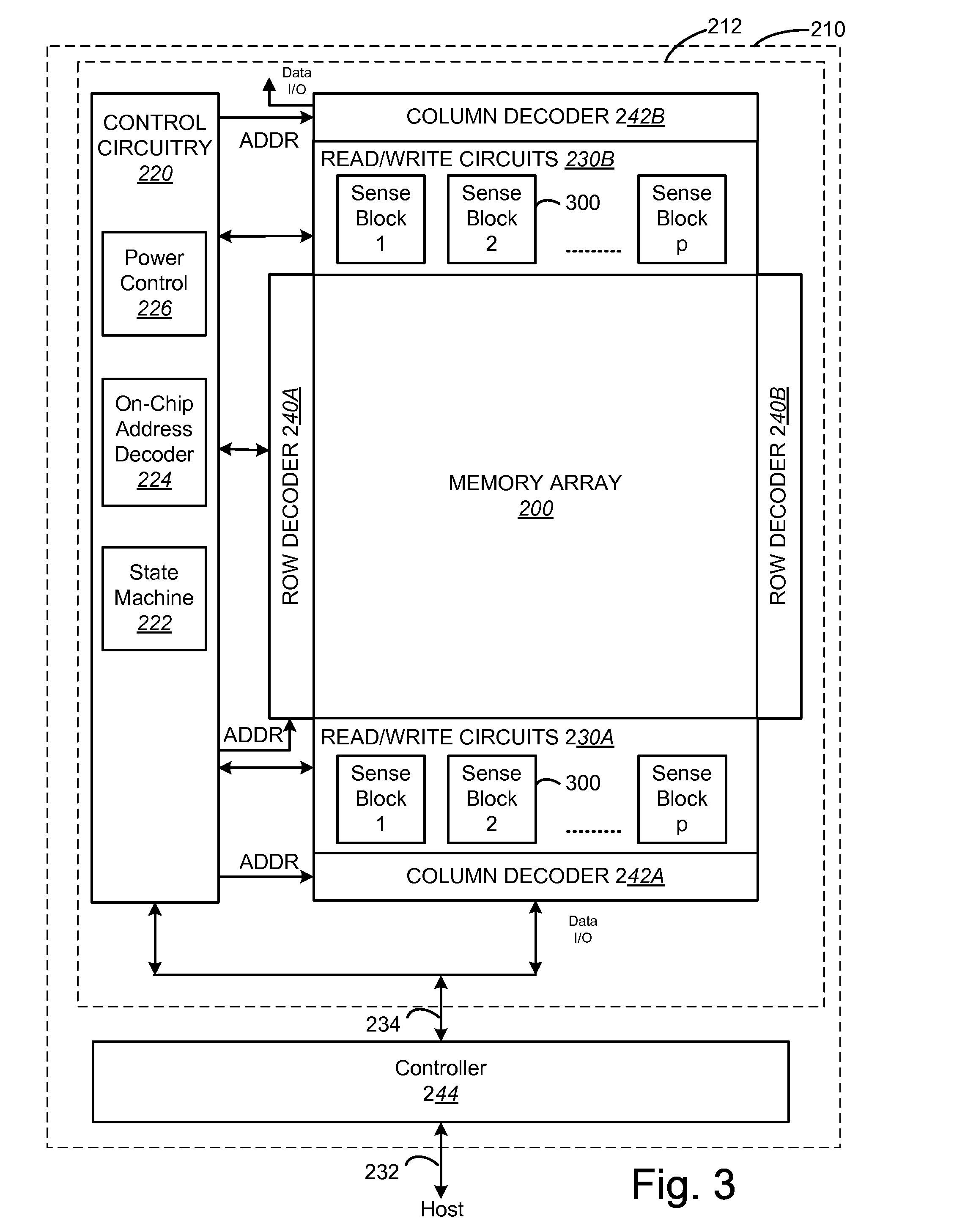
A memory device and a method thereof allow programming and sensing a plurality of memory cells in parallel in order to minimize errors caused by coupling from fields of neighboring cells and to improve performance. The memory device and method have the plurality of memory cells linked by the same word line and a read / write circuit is coupled to each memory cells in a contiguous manner. Thus, a memory cell and its neighbors are programmed together and the field environment for each memory cell relative to its neighbors during programming and subsequent reading is less varying. This improves performance and reduces errors caused by coupling from fields of neighboring cells, as compared to conventional architectures and methods in which cells on even columns are programmed independently of cells in odd columns.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
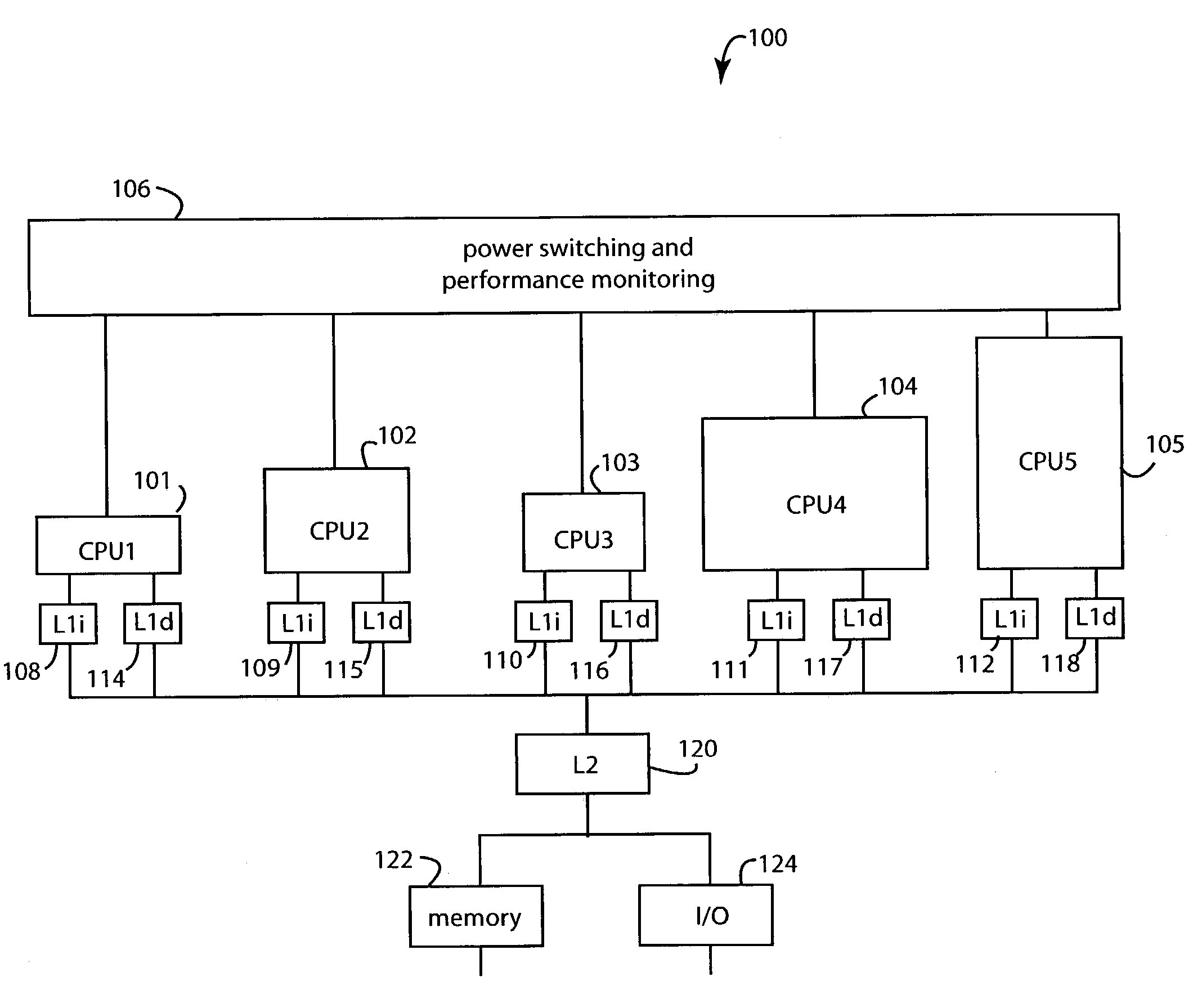
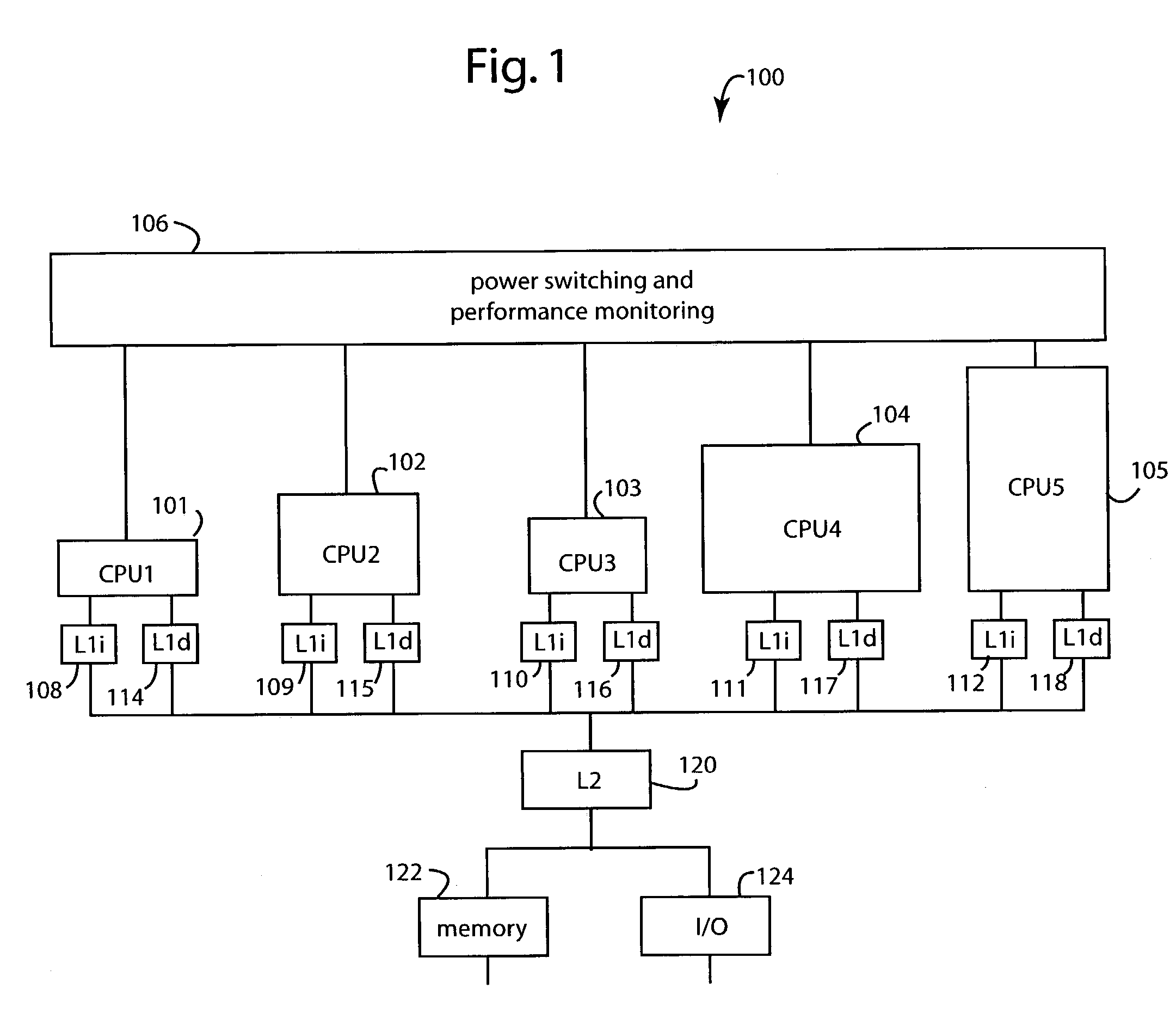
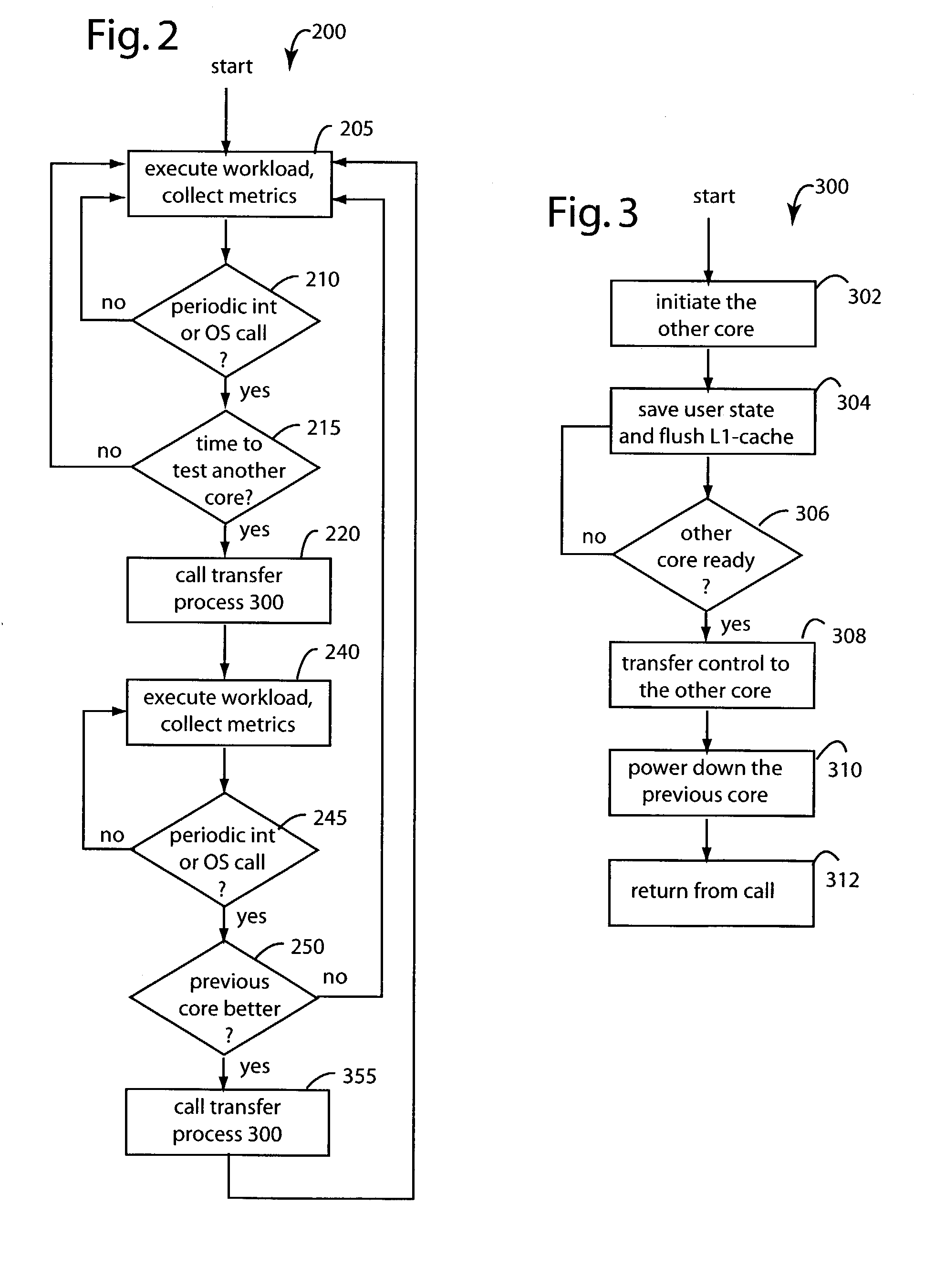
Dynamically selecting processor cores for overall power efficiency
ActiveUS7093147B2Save battery powerSave powerEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperating pointParallel computing
A computer system for conserving operating power includes a number of computer hardware processor cores that differ amongst themselves in at least in their respective operating power requirements and processing capabilities. A monitor gathers performance metric information from each of the computer hardware processor cores that is specific to a particular run of application software then executing. A workload transfer mechanism transfers the executing application software to a second computer hardware processor core in a search for reduced operating power. A transfer delay mechanism is connected to delay a subsequent transfer of the executing application software if the system operating power may be conserved by such delay.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
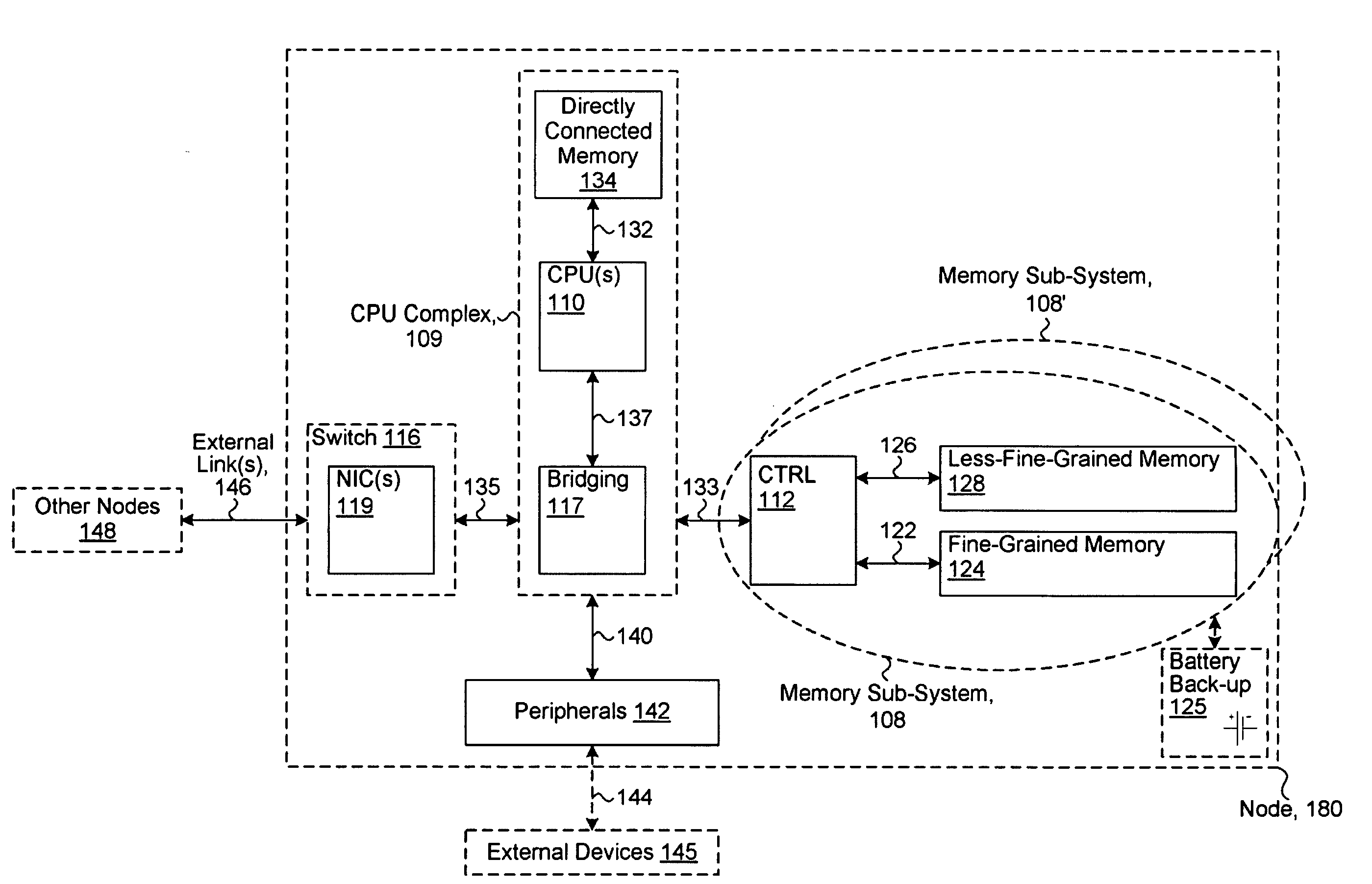
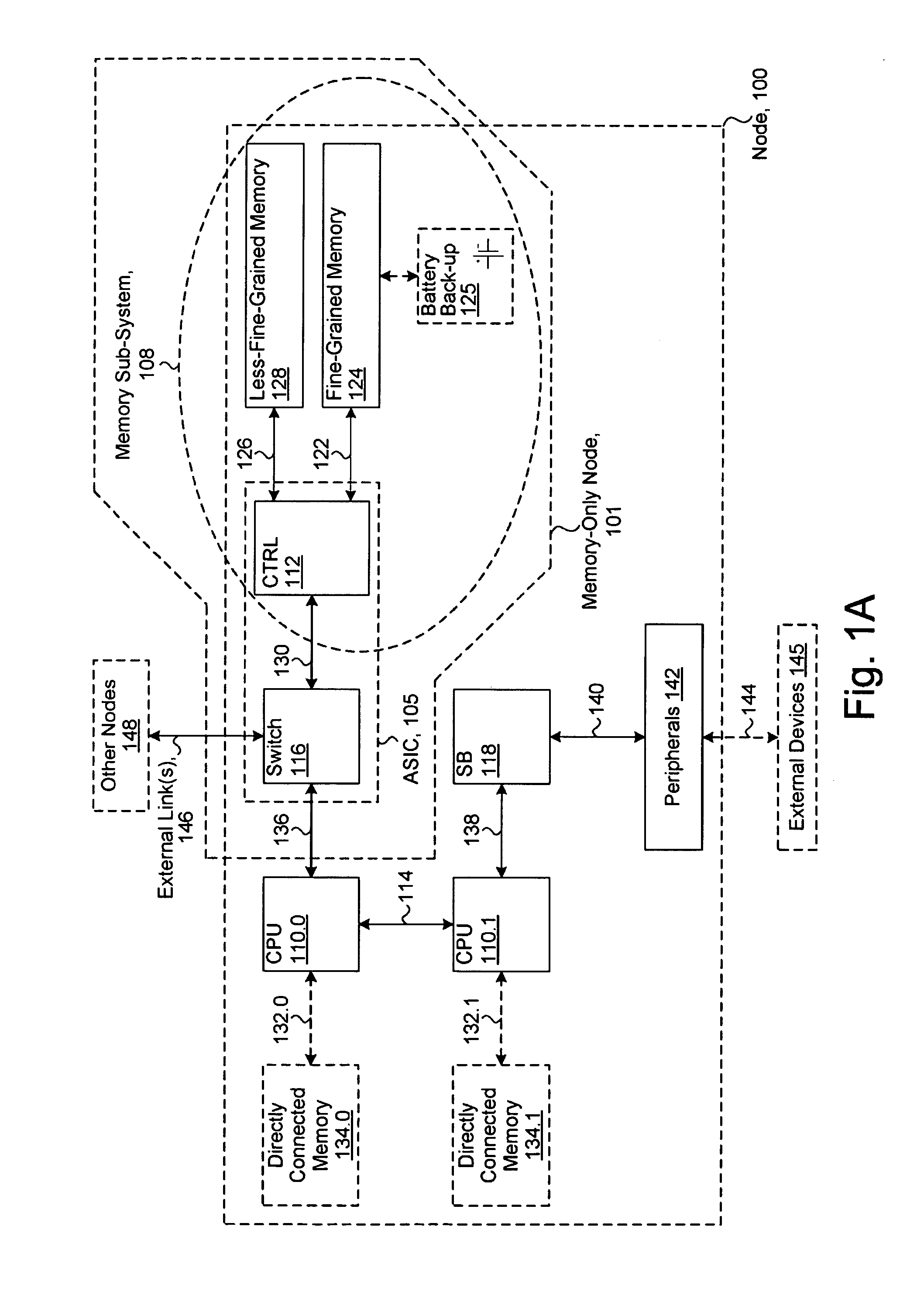
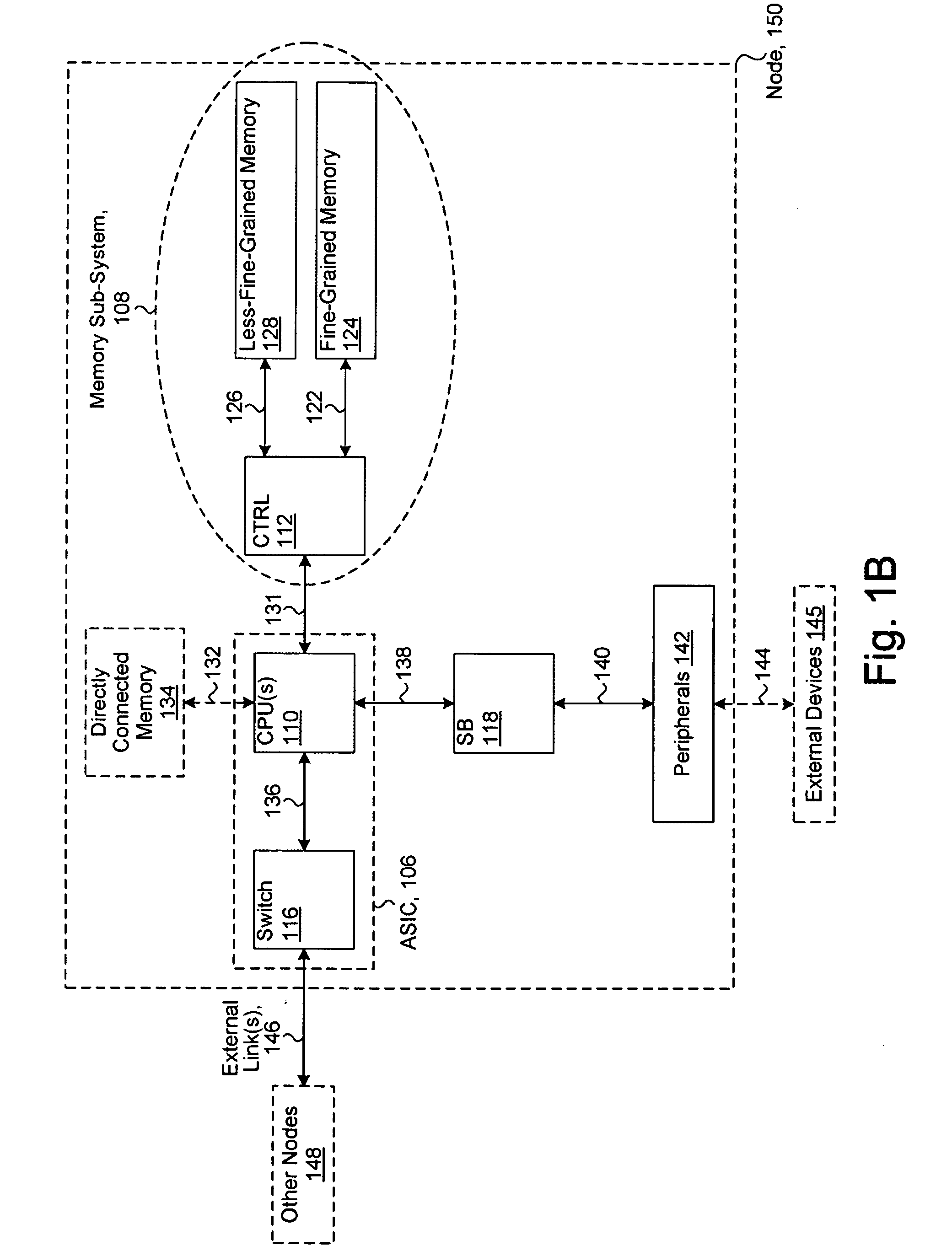
System including a fine-grained memory and a less-fine-grained memory
ActiveUS20080301256A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTData processing systemWrite buffer
A data processing system includes one or more nodes, each node including a memory sub-system. The sub-system includes a fine-grained, memory, and a less-fine-grained (e.g., page-based) memory. The fine-grained memory optionally serves as a cache and / or as a write buffer for the page-based memory. Software executing on the system uses n node address space which enables access to the page-based memories of all nodes. Each node optionally provides ACID memory properties for at least a portion of the space. In at least a portion of the space, memory elements are mapped to locations in the page-based memory. In various embodiments, some of the elements are compressed, the compressed elements are packed into pages, the pages are written into available locations in the page-based memory, and a map maintains an association between the some of the elements and the locations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
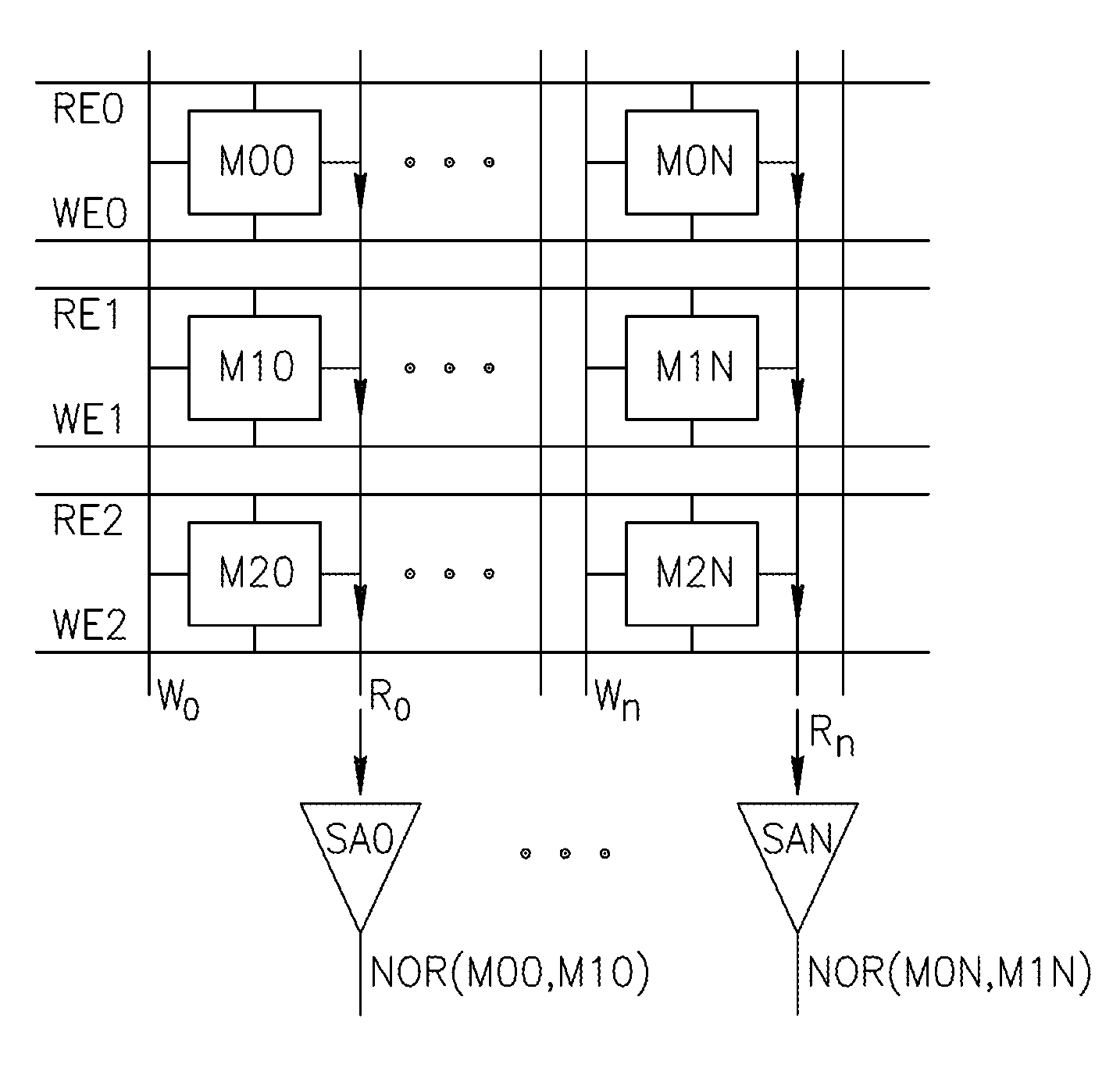
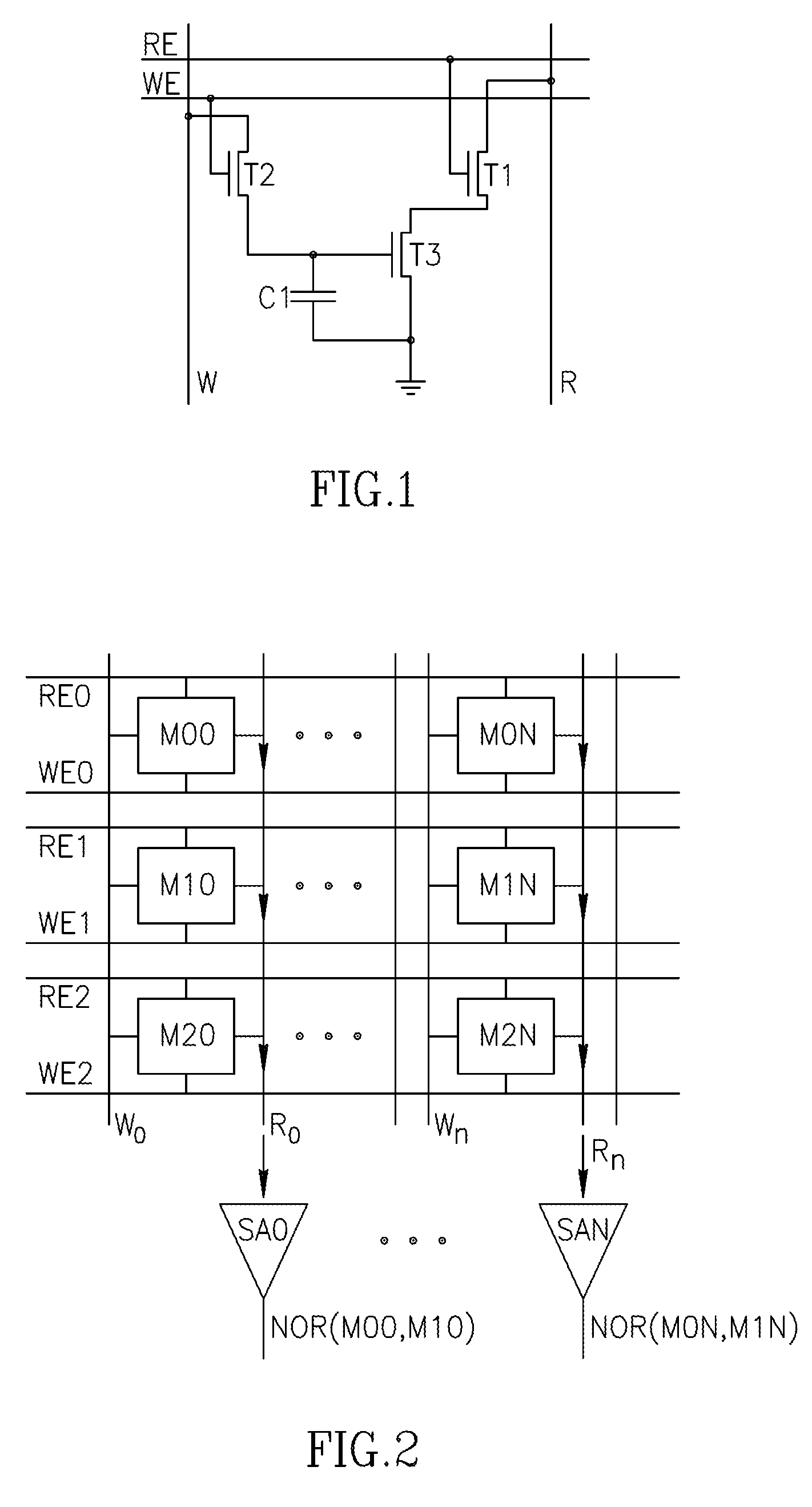
Using storage cells to perform computation
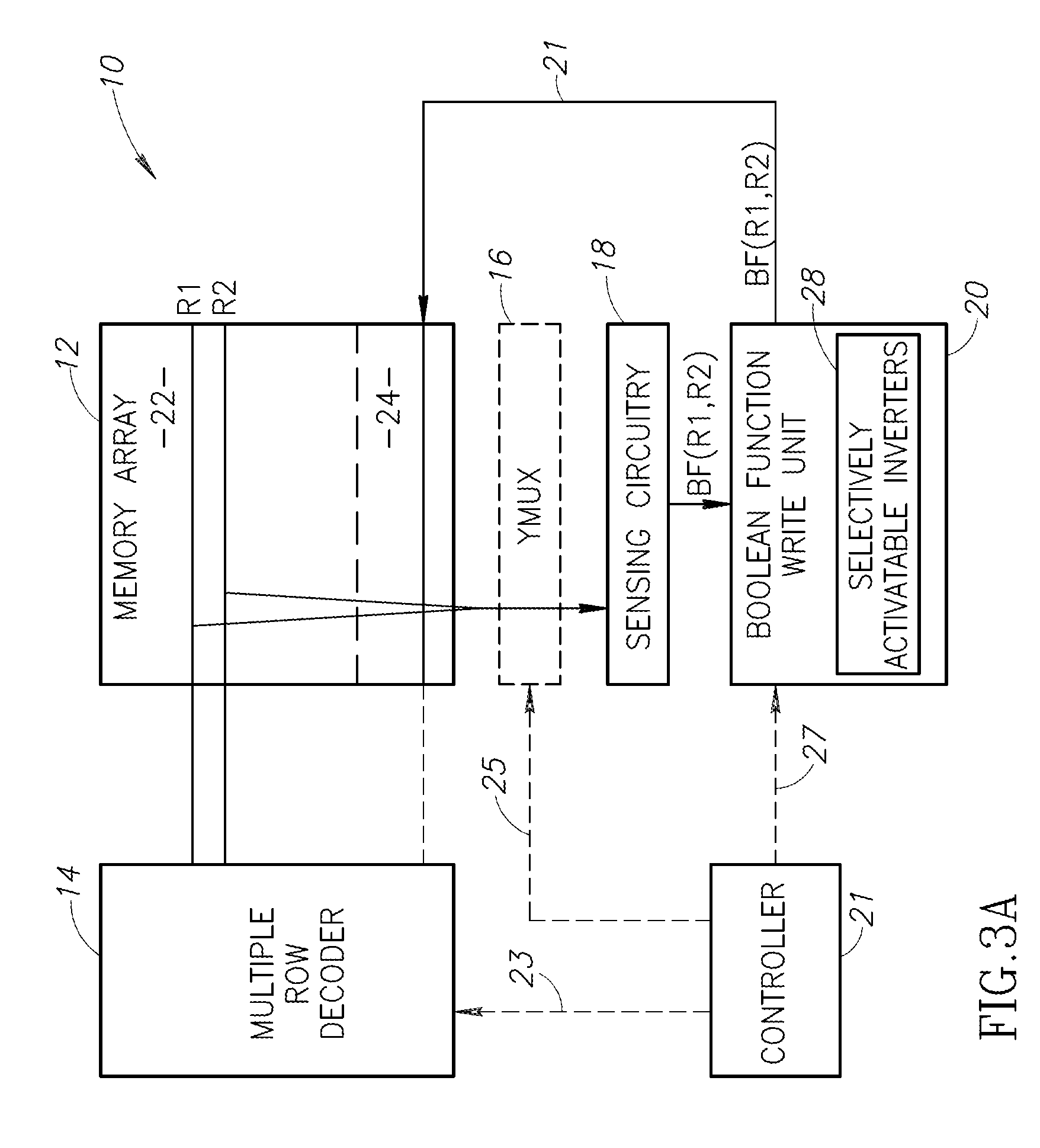
An in-memory processor includes a memory array which stores data and an activation unit to activate at least two cells in a column of the memory array at generally the same time thereby to generate a Boolean function output of the data of the at least two cells. Another embodiment shows a content addressable memory (CAM) unit without any in-cell comparator circuitry.
Owner:GSI TECH
Reducing the impact of interference during programming
ActiveUS7869273B2Reduce the impact of interferenceRead-only memoriesDigital storageParallel computingNon-volatile memory
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
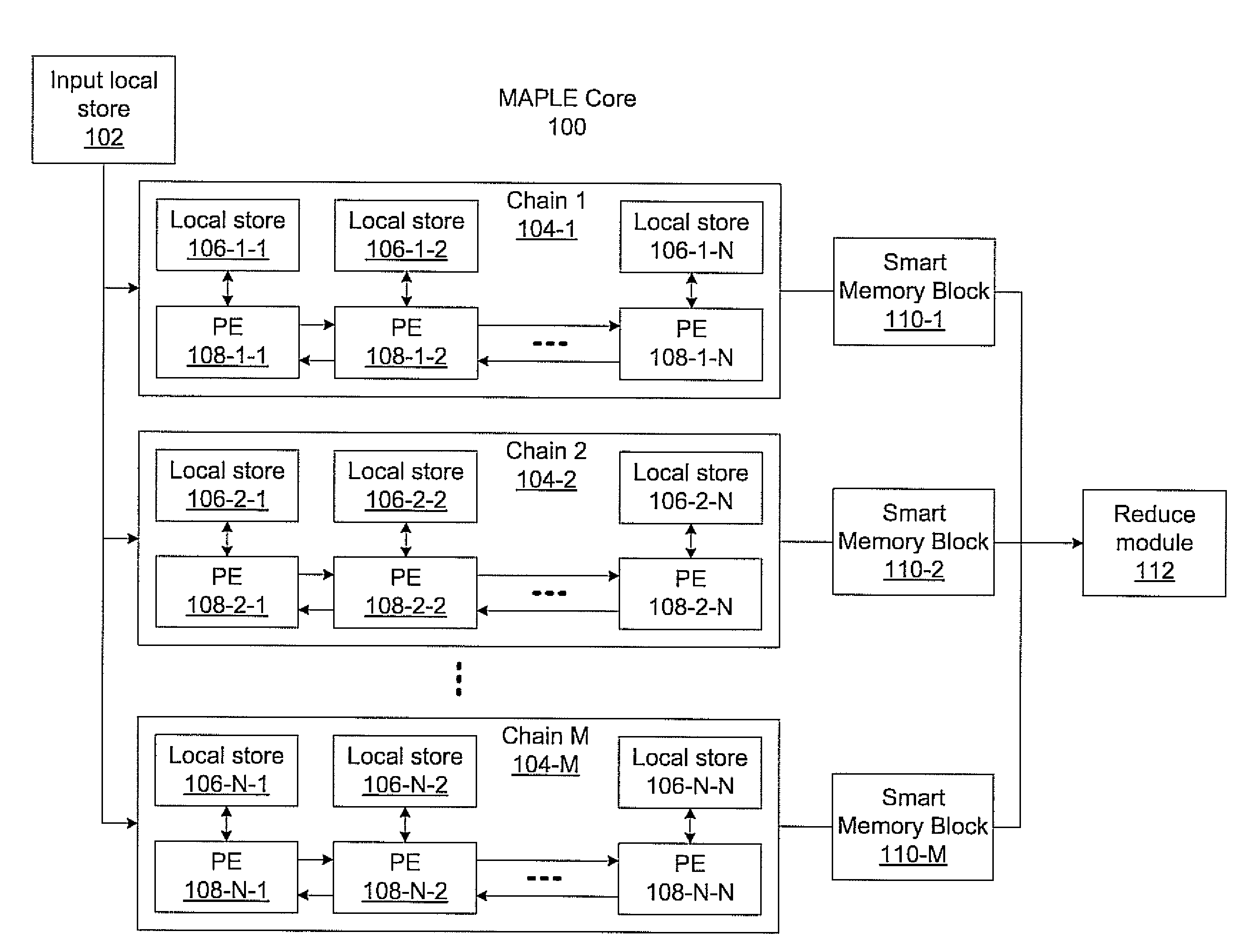
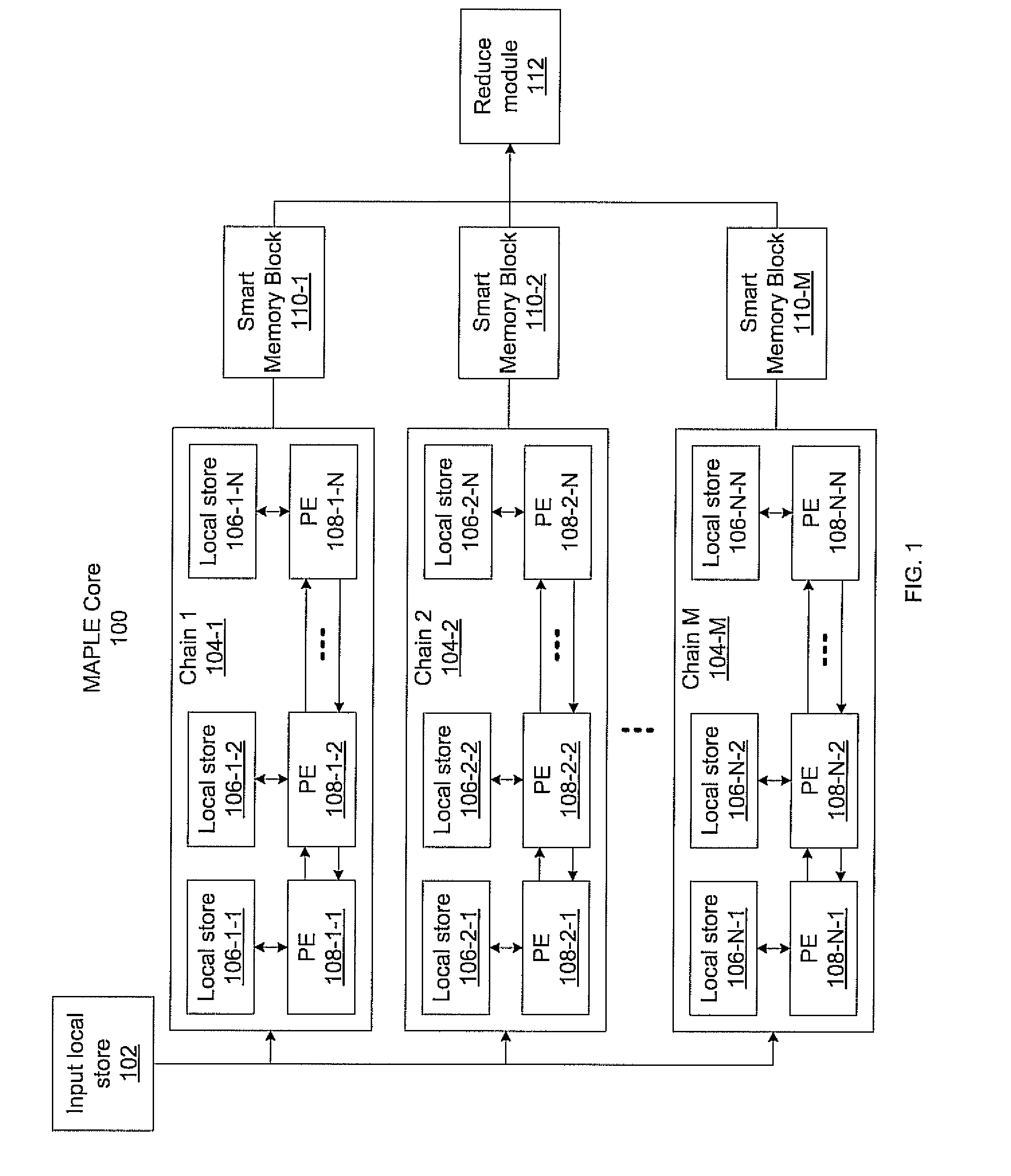
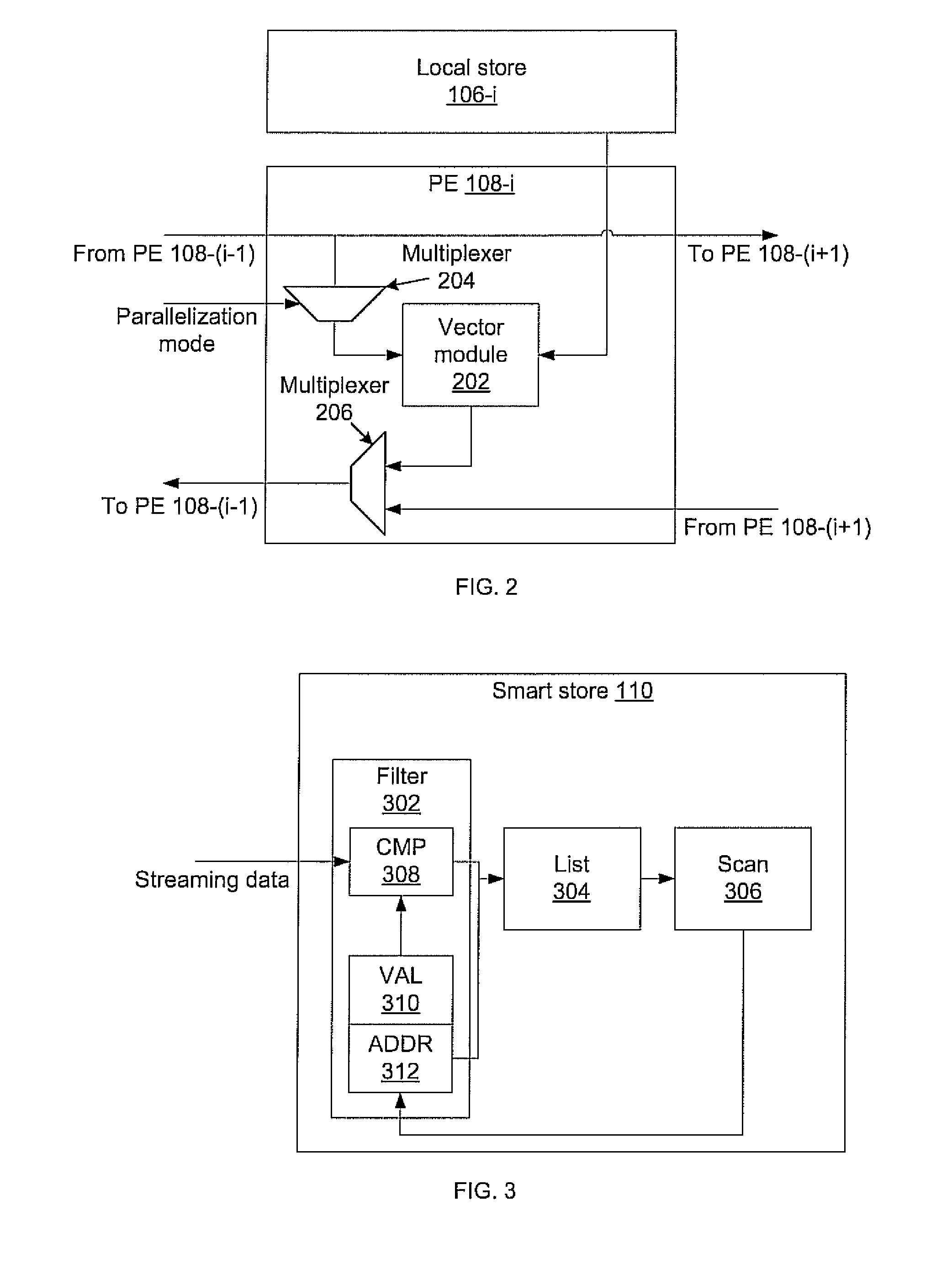
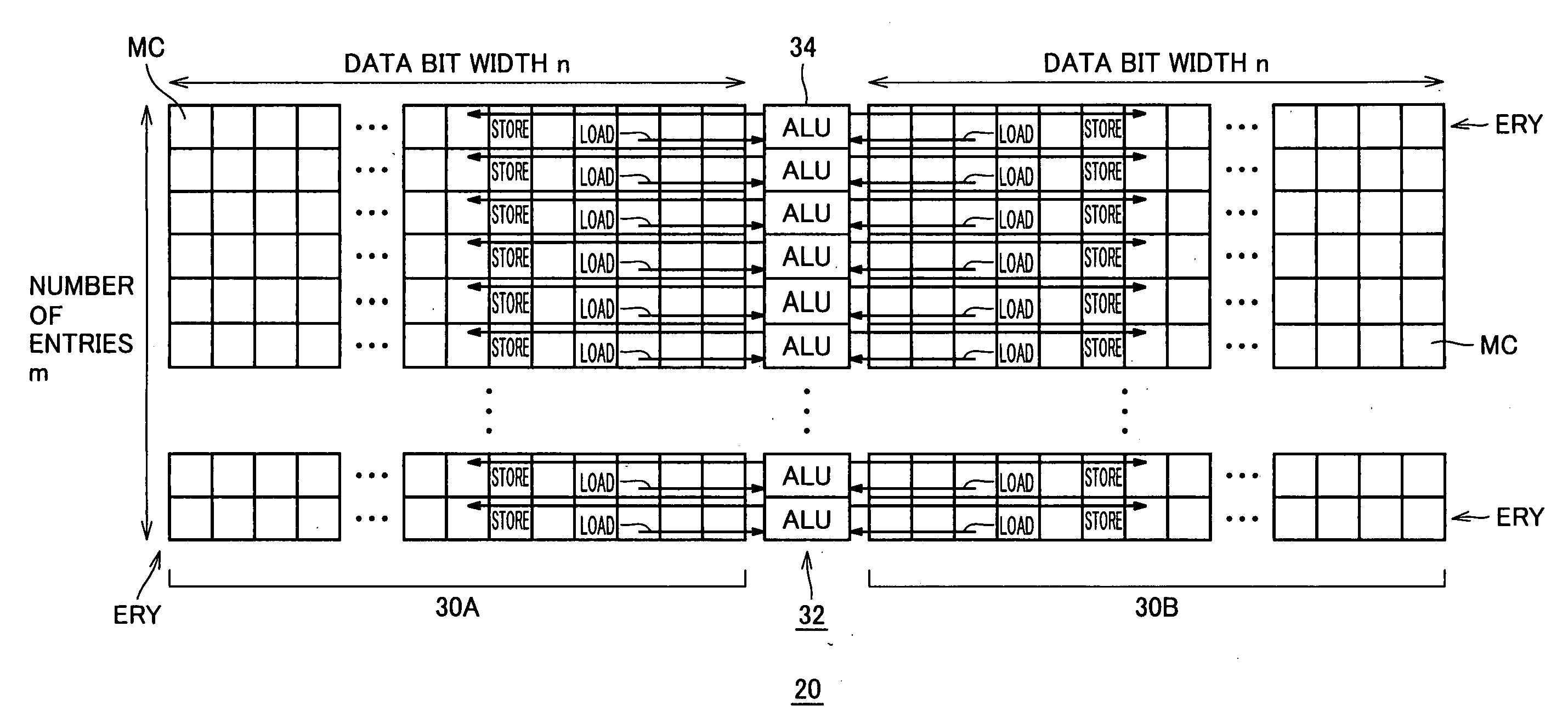
Massively parallel, smart memory based accelerator
Systems and methods for massively parallel processing on an accelerator that includes a plurality of processing cores. Each processing core includes multiple processing chains configured to perform parallel computations, each of which includes a plurality of interconnected processing elements. The cores further include multiple of smart memory blocks configured to store and process data, each memory block accepting the output of one of the plurality of processing chains. The cores communicate with at least one off-chip memory bank.
Owner:NEC CORP
Parallel operational processing device
InactiveUS20070180006A1Easy to operateReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsAudio power amplifierParallel computing
In a parallel operational processing device having an operational processing unit arranged between memory blocks each having a plurality of memory cells arranged in rows and columns, the respective columns of each memory block are alternately connected to the operational processing units on the opposite sides of the memory block. By selecting one word line in one memory block, data can be transferred to two operational processing units. The number of the word lines selected per one operational processing unit is reduced, and power consumption is reduced. The bit operation units and sense amplifiers / write drivers of the operational processing units have arrangement pitch conditions mitigated and are reduced in number, and an isolation region between the memory blocks is not required and the layout area is reduced. Thus, the parallel operational processing device with a layout area and the power consumption reduced, can achieve a fast operation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
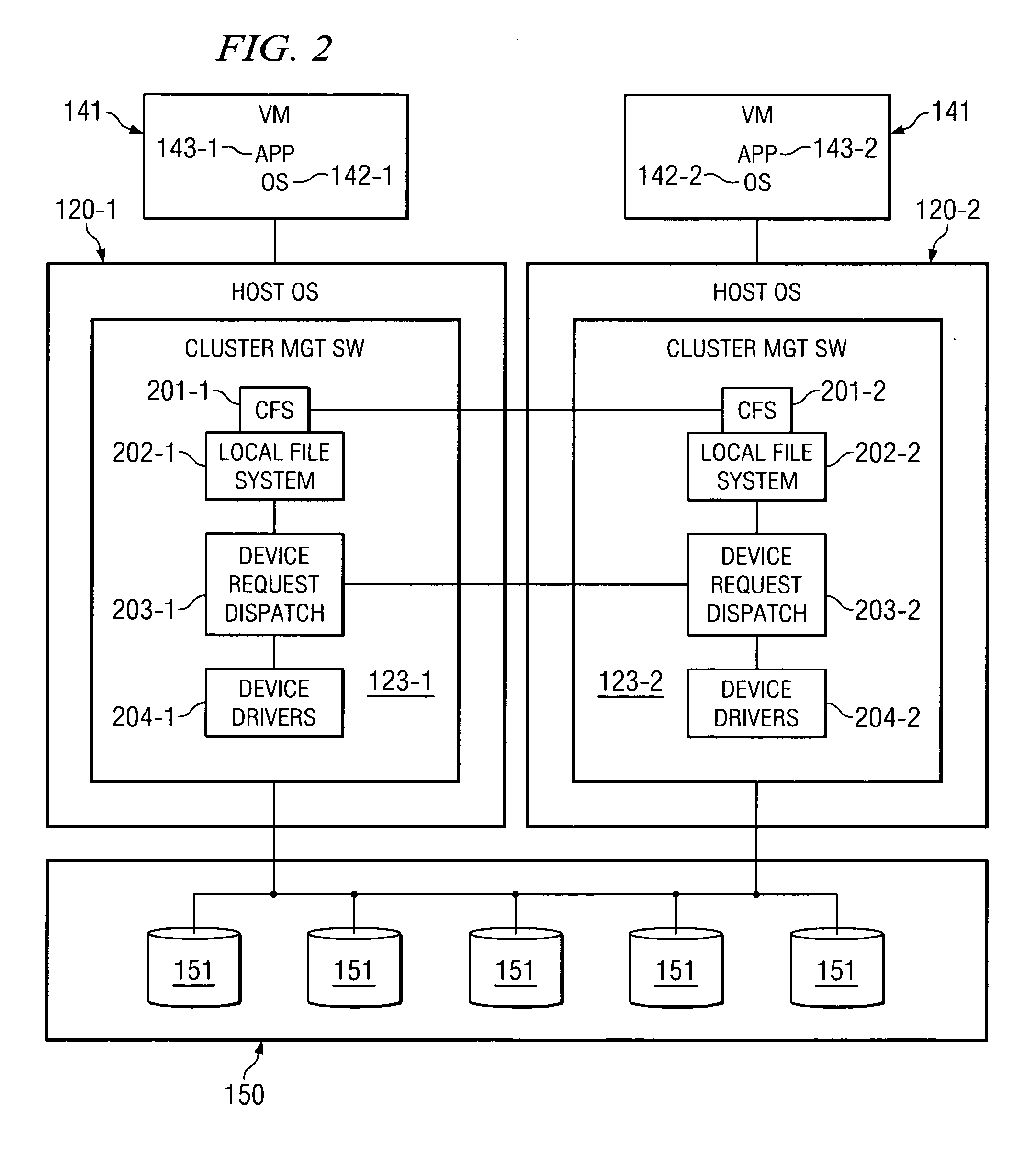
System and method for migrating virtual machines on cluster systems
ActiveUS20060195715A1Satisfactory operationError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsManagement processCluster systems
In one embodiment, a method comprises executing a plurality of virtual machines on a plurality of nodes of a cluster computing system, wherein at least one application is executed within each of the plurality of virtual machines, generating data that is related to performance of applications in the virtual machines, analyzing, by a management process, the data in view of parameters that encode desired performance levels of applications, and migrating, by the management process, a virtual machine on a first node to a second node of the plurality of nodes in response to the analyzing.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
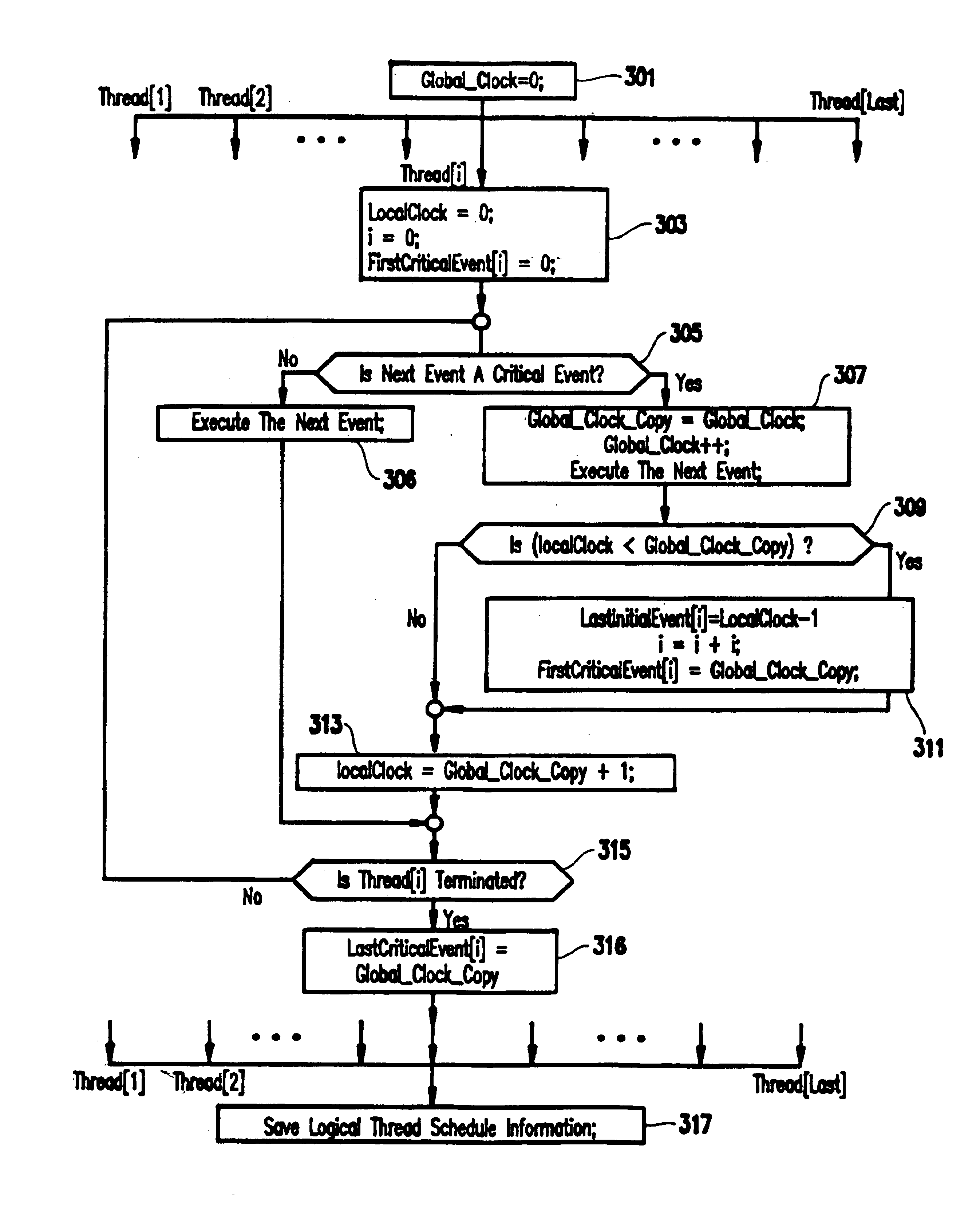
Method and system for recording and replaying the execution of distributed java programs
InactiveUS6832367B1Easy to copyGuaranteed orderError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsStream socketThread scheduling
A method for recording and replaying execution of distributed programs on a computer system in a distributed environment, includes identifying an execution order of critical events of a program, generating groups of critical events of the program, wherein for each group, critical events belonging to the group belong to a common execution thread, and generating for each execution thread a logical thread schedule that identifies a sequence of the groups so as to allow deterministically replaying a non-deterministic arrival of stream socket connection requests, a non-deterministic number of bytes received during message reads, and a non-deterministic binding of stream sockets to local ports.
Owner:IBM CORP
Memory addressing controlled by PTE fields
ActiveUS7805587B1Reduce accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsMemory addressDram memory
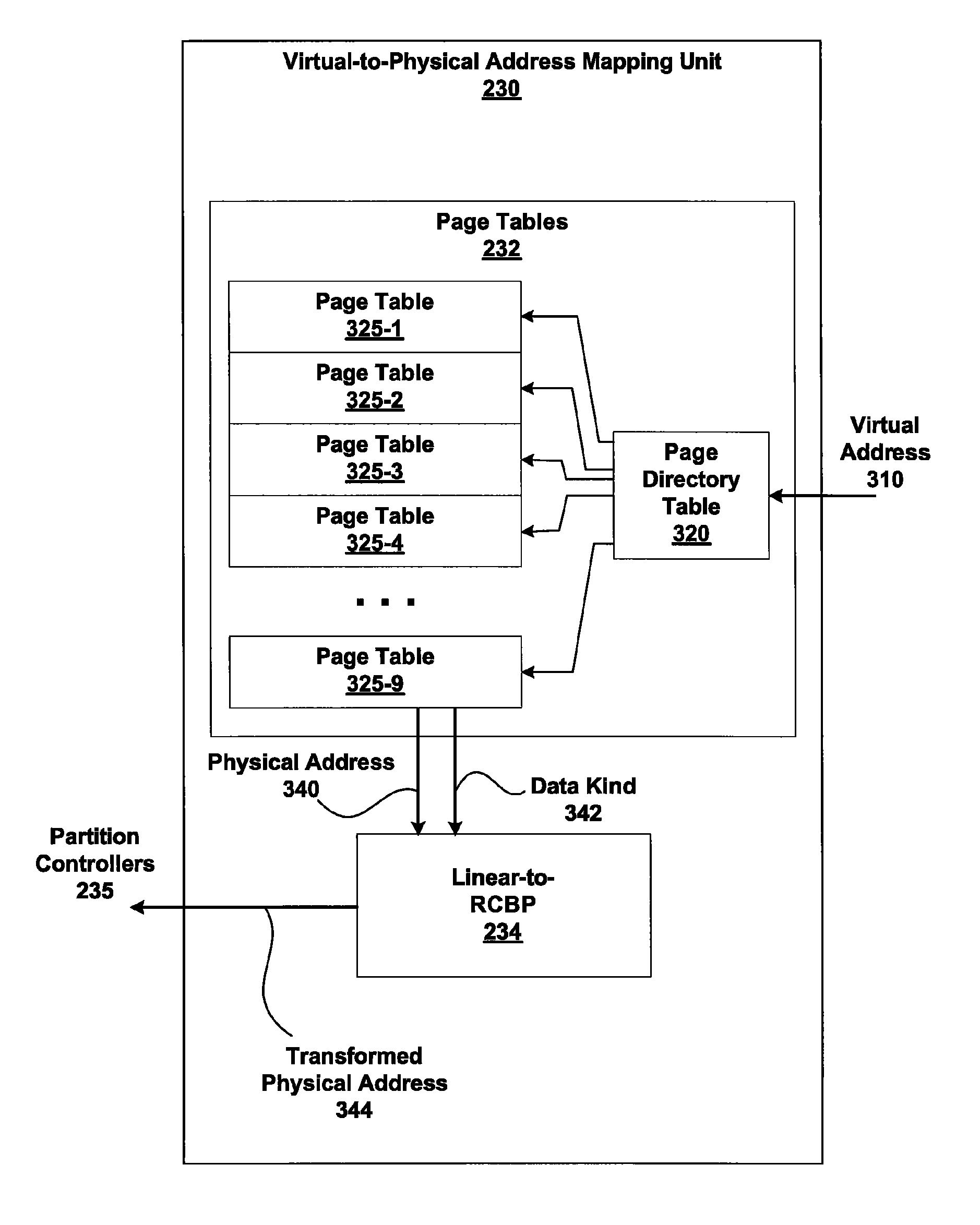
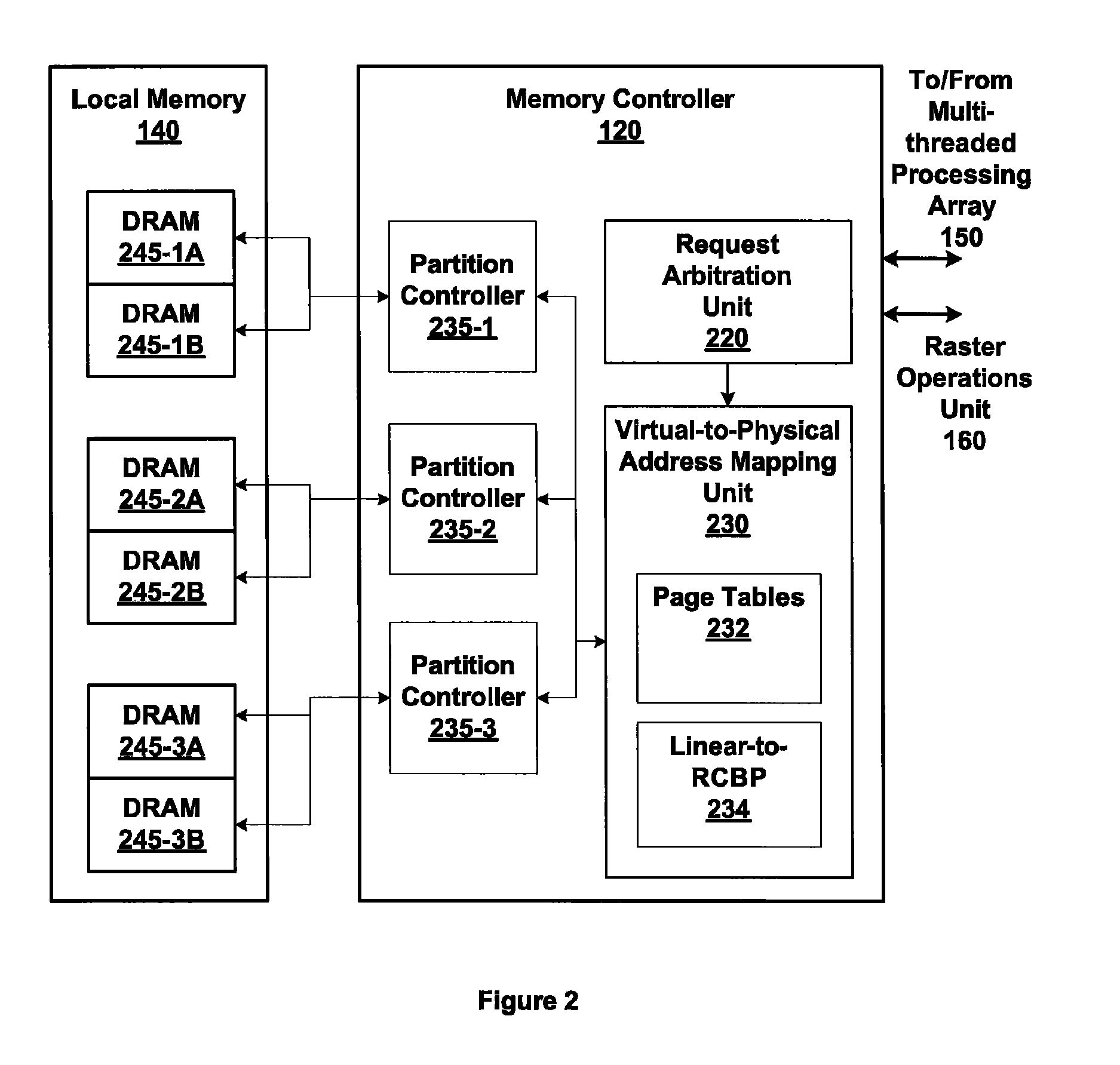
Embodiments of the present invention enable virtual-to-physical memory address translation using optimized bank and partition interleave patterns to improve memory bandwidth by distributing data accesses over multiple banks and multiple partitions. Each virtual page has a corresponding page table entry that specifies the physical address of the virtual page in linear physical address space. The page table entry also includes a data kind field that is used to guide and optimize the mapping process from the linear physical address space to the DRAM physical address space, which is used to directly access one or more DRAM. The DRAM physical address space includes a row, bank and column address. The data kind field is also used to optimize the starting partition number and partition interleave pattern that defines the organization of the selected physical page of memory within the DRAM memory system.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
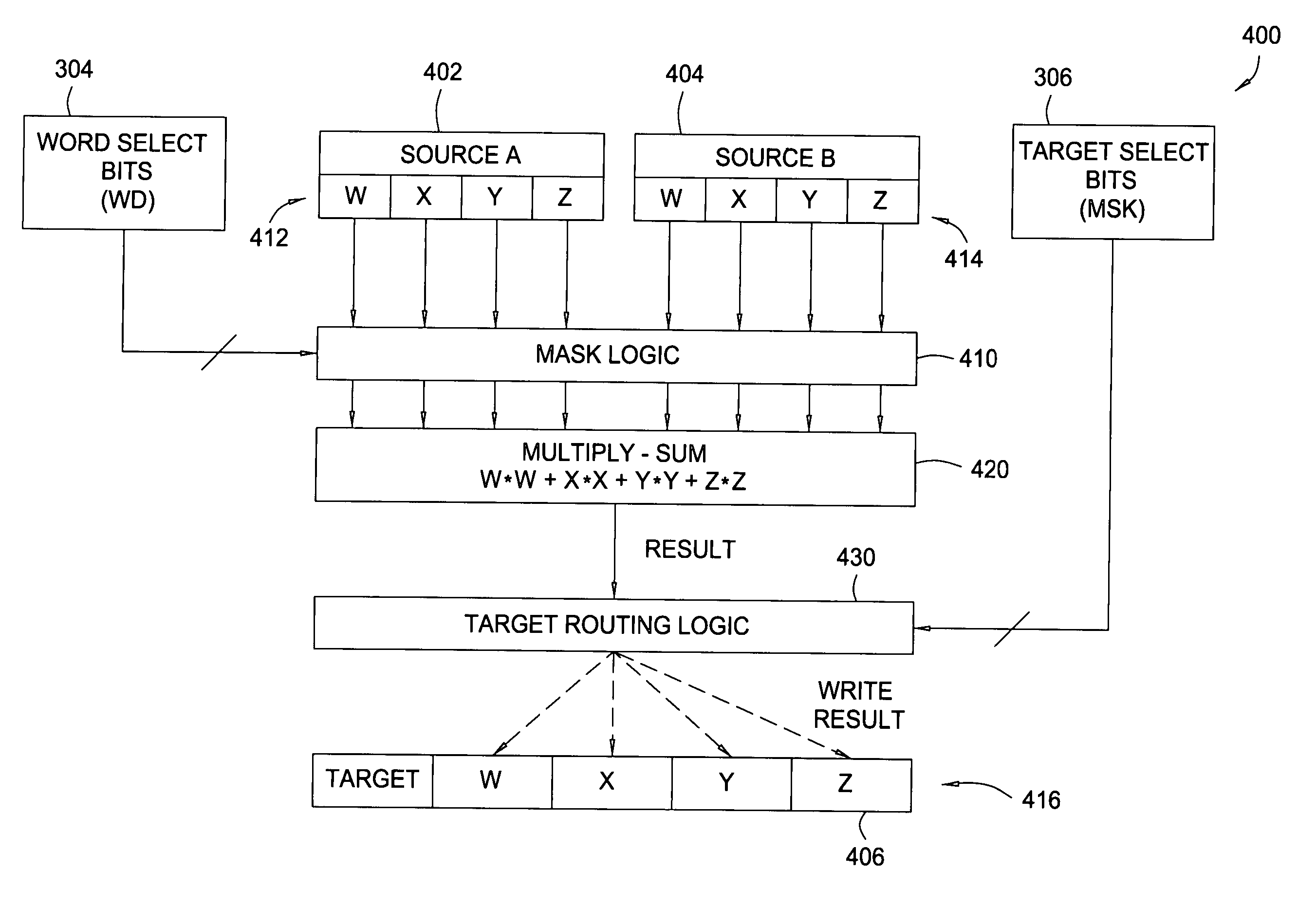
Multiply-sum dot product instruction with mask and splat
Owner:IBM CORP
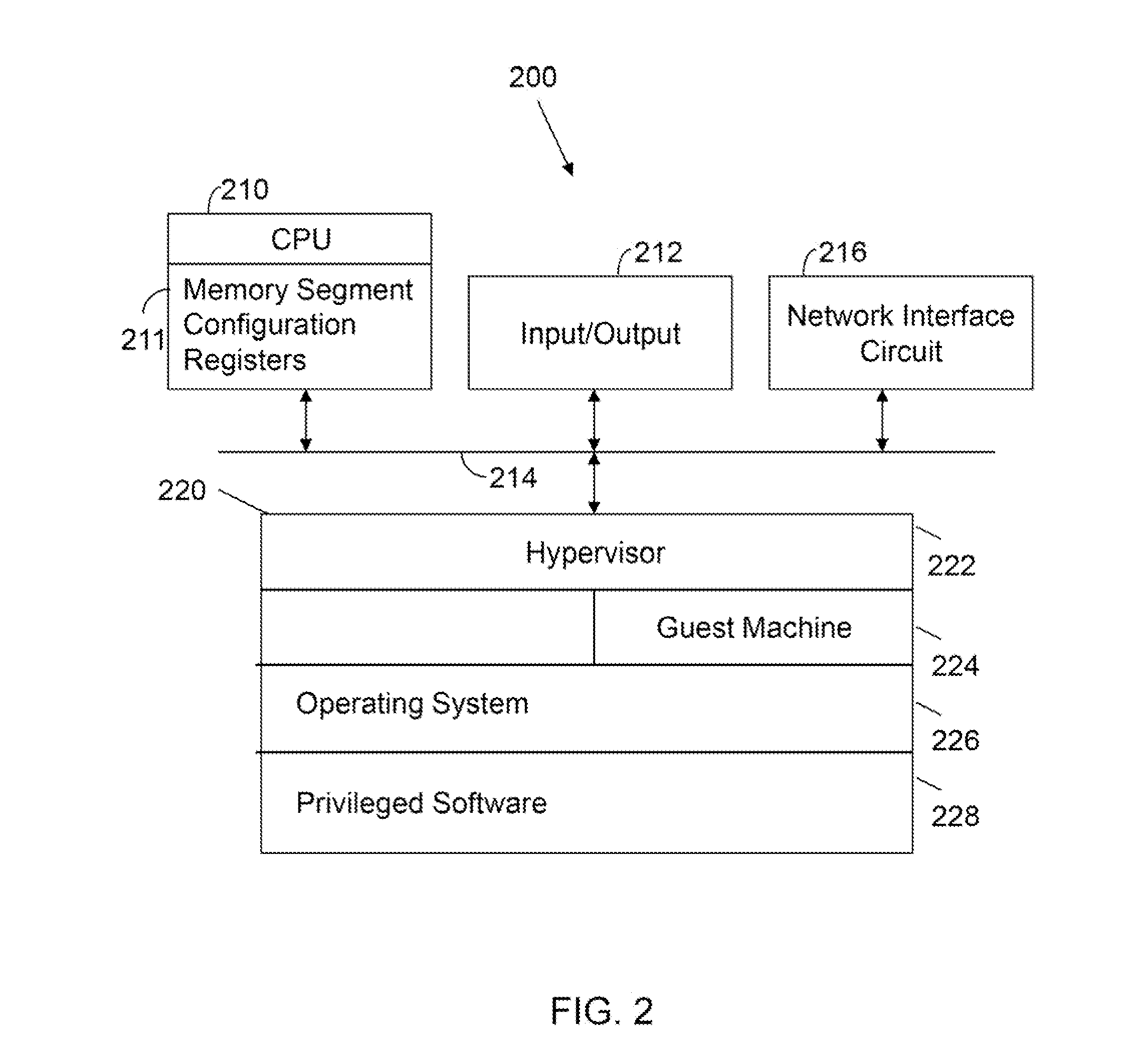
Processor with Kernel Mode Access to User Space Virtual Addresses
ActiveUS20130132702A1Enhanced kernel mode memory capacityIncrease memory capacityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionMemory addressParallel computing
A computer includes a memory and a processor connected to the memory. The processor includes memory segment configuration registers to store defined memory address segments and defined memory address segment attributes such that the processor operates in accordance with the defined memory address segments and defined memory address segment attributes to allow kernel mode access to user space virtual addresses for enhanced kernel mode memory capacity.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
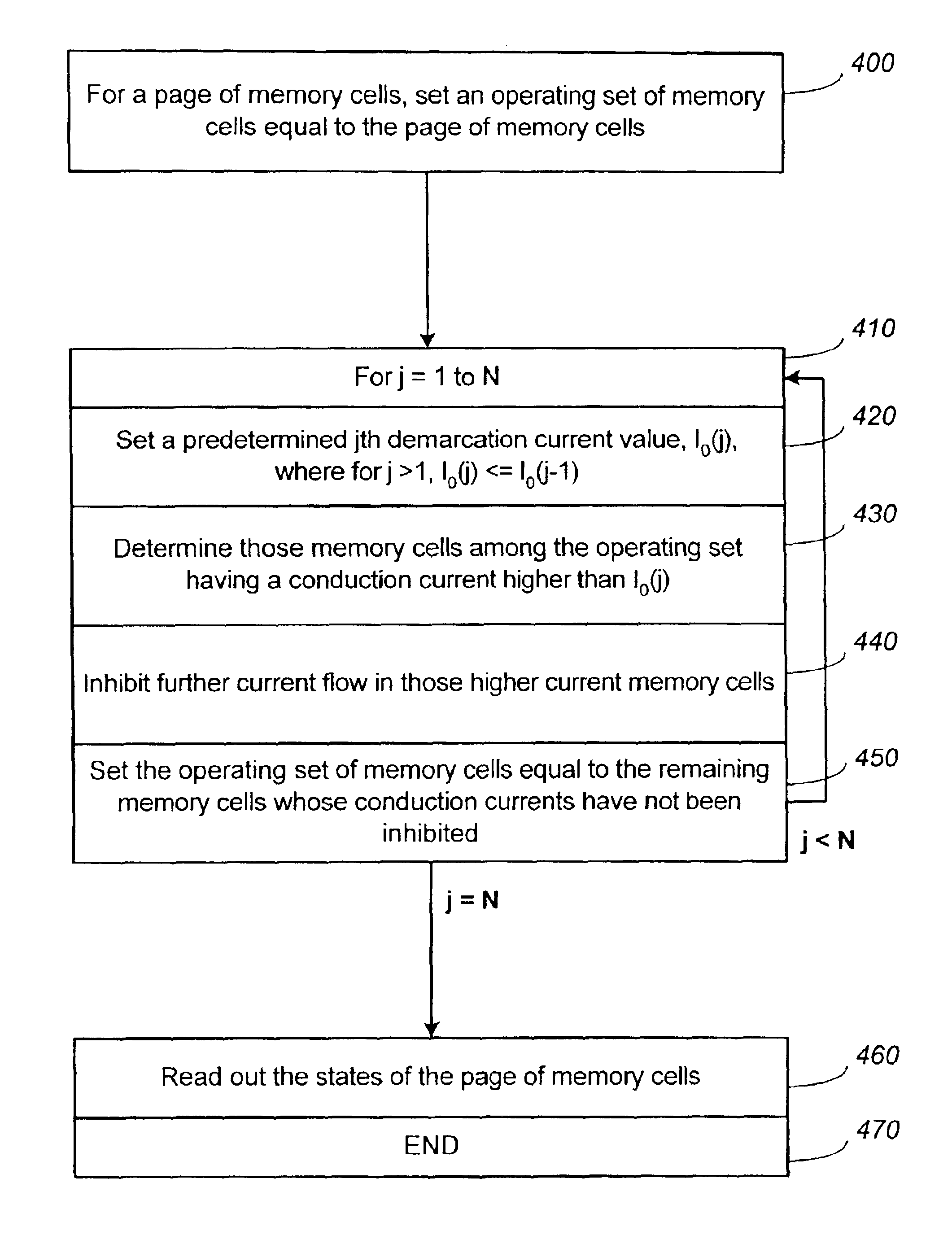
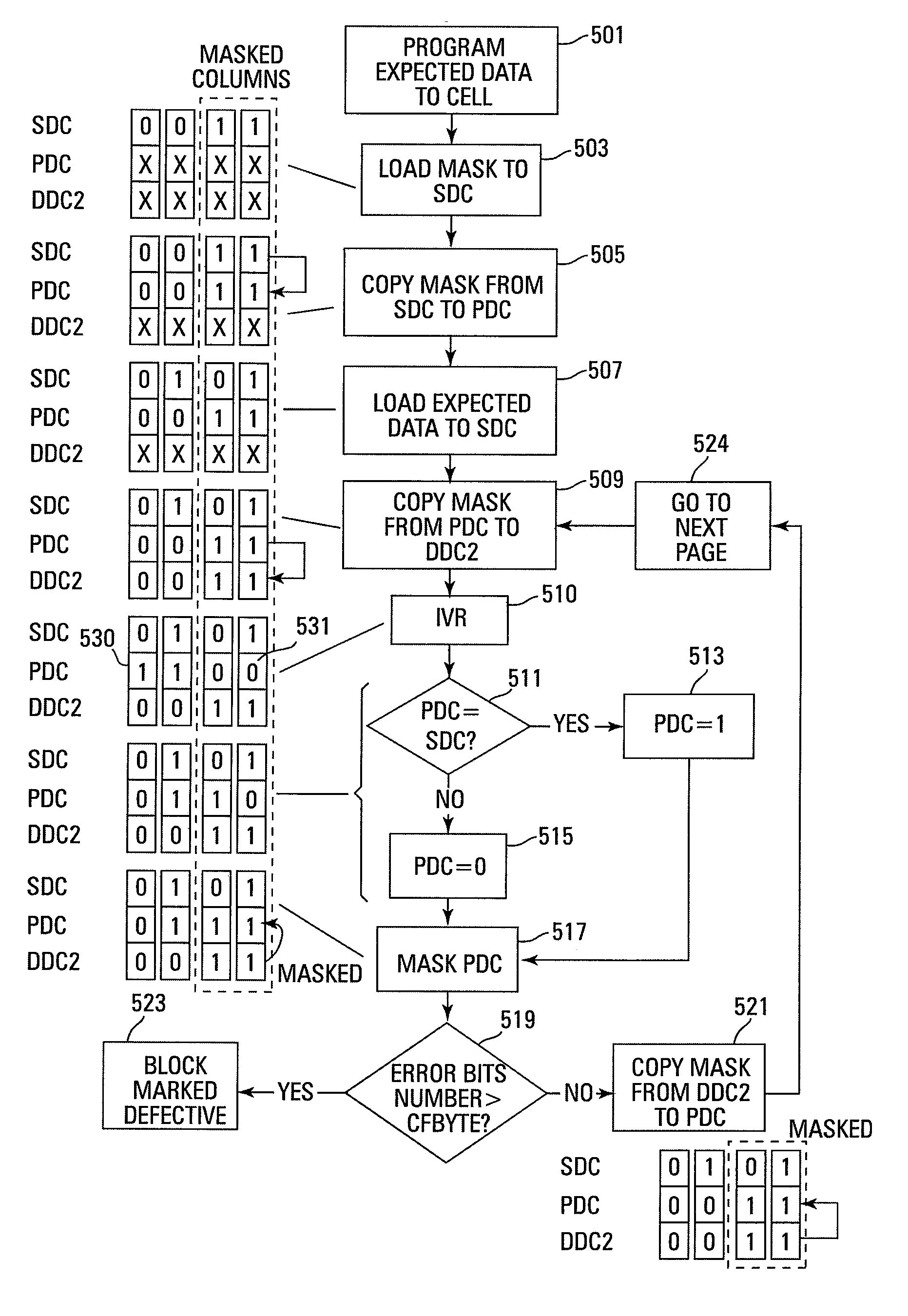
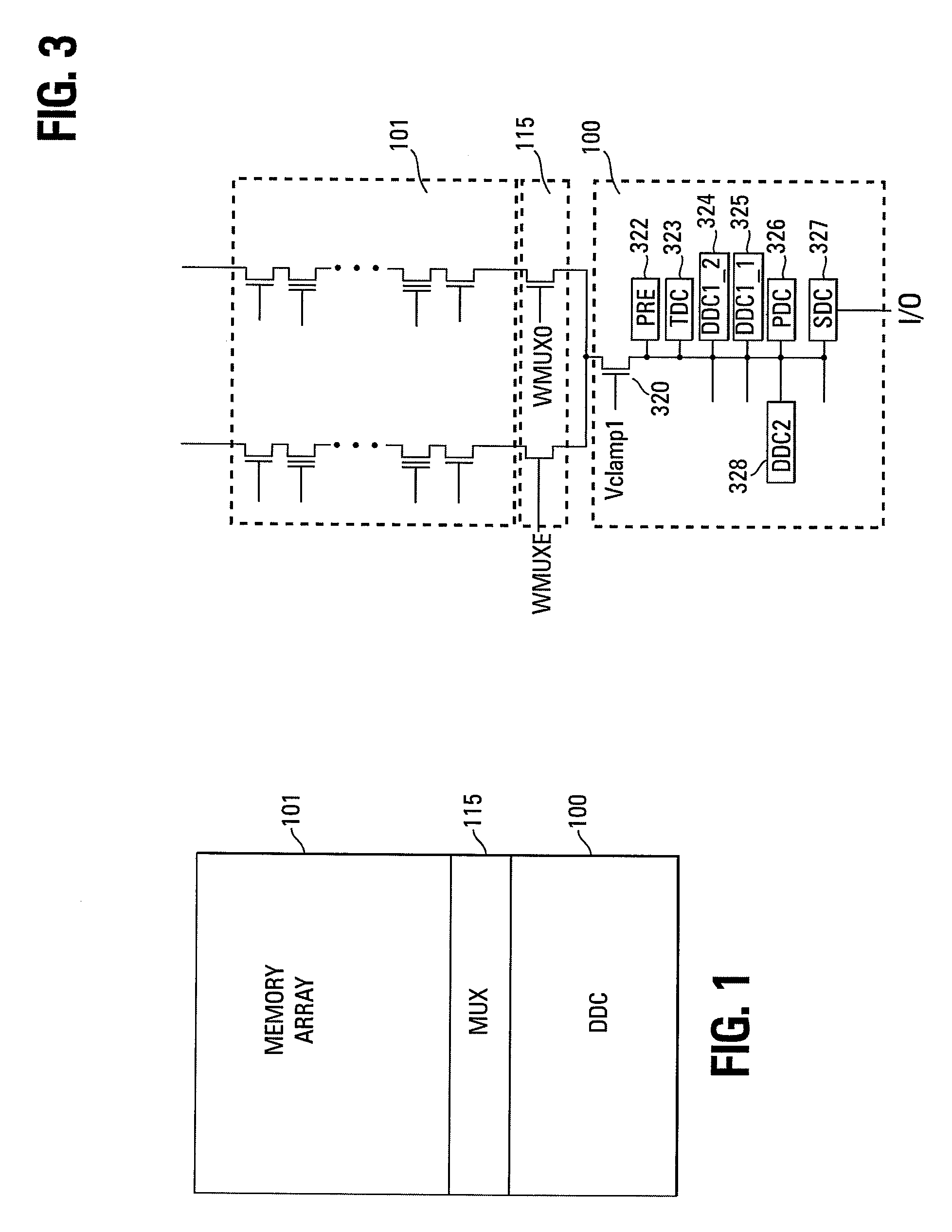
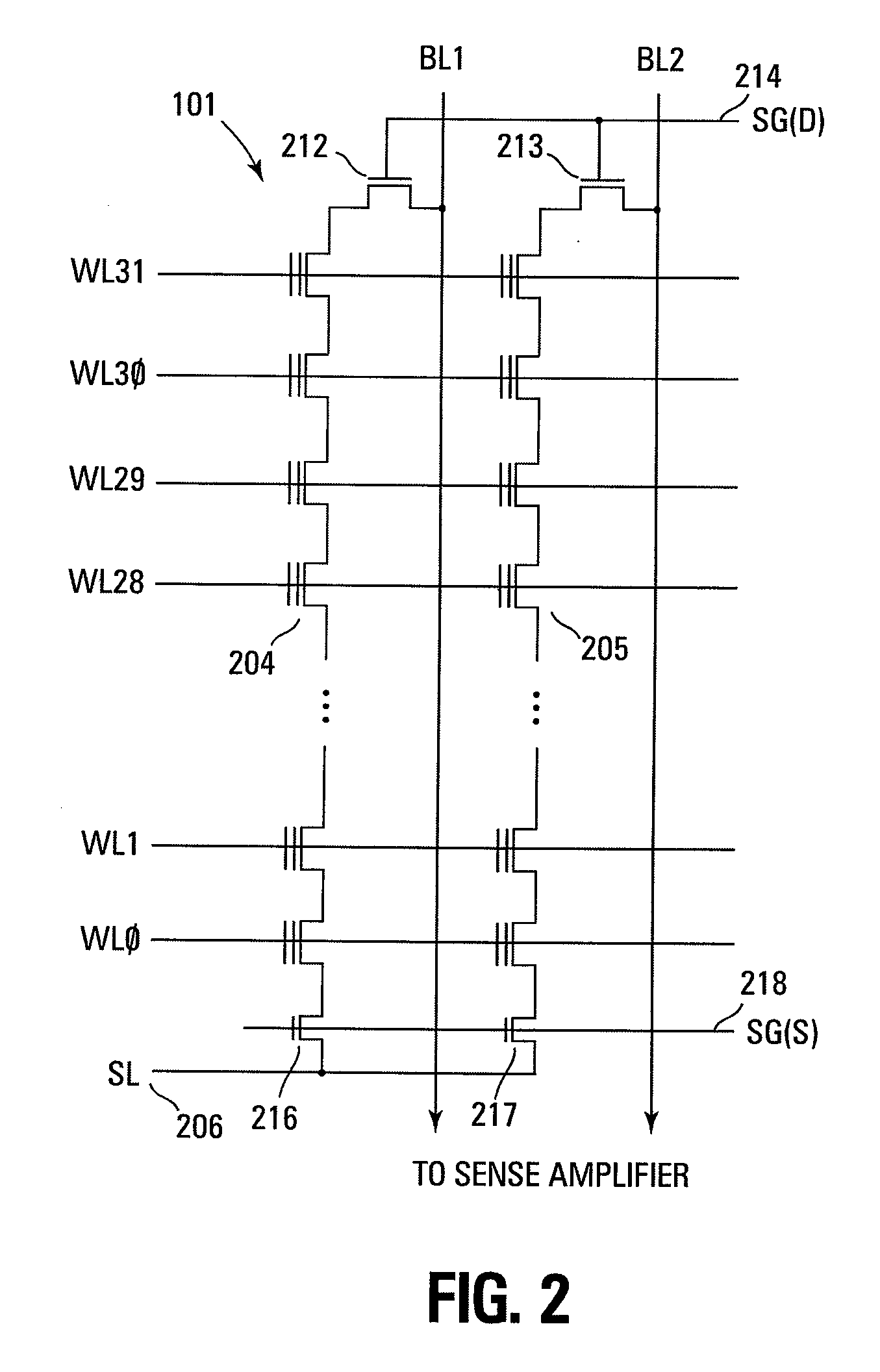
Small unit internal verify read in a memory device
Methods for small unit internal verify read operation and a memory device are disclosed. In one such method, expected data is programmed into a grouping of columns of memory cells (e.g., memory block). Mask data is loaded into a third dynamic data cache of three dynamic data caches. The expected data is loaded into a second data cache. After a read operation of programmed columns of memory cells, the read data is compared to the expected data and error bit indicators are stored in the second data cache in the error bit locations. The second data cache is masked with the mask data so that only those error bits that are unmasked are counted. If the number of unmasked error bit indicators is greater than a threshold, the memory block is marked as unusable.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
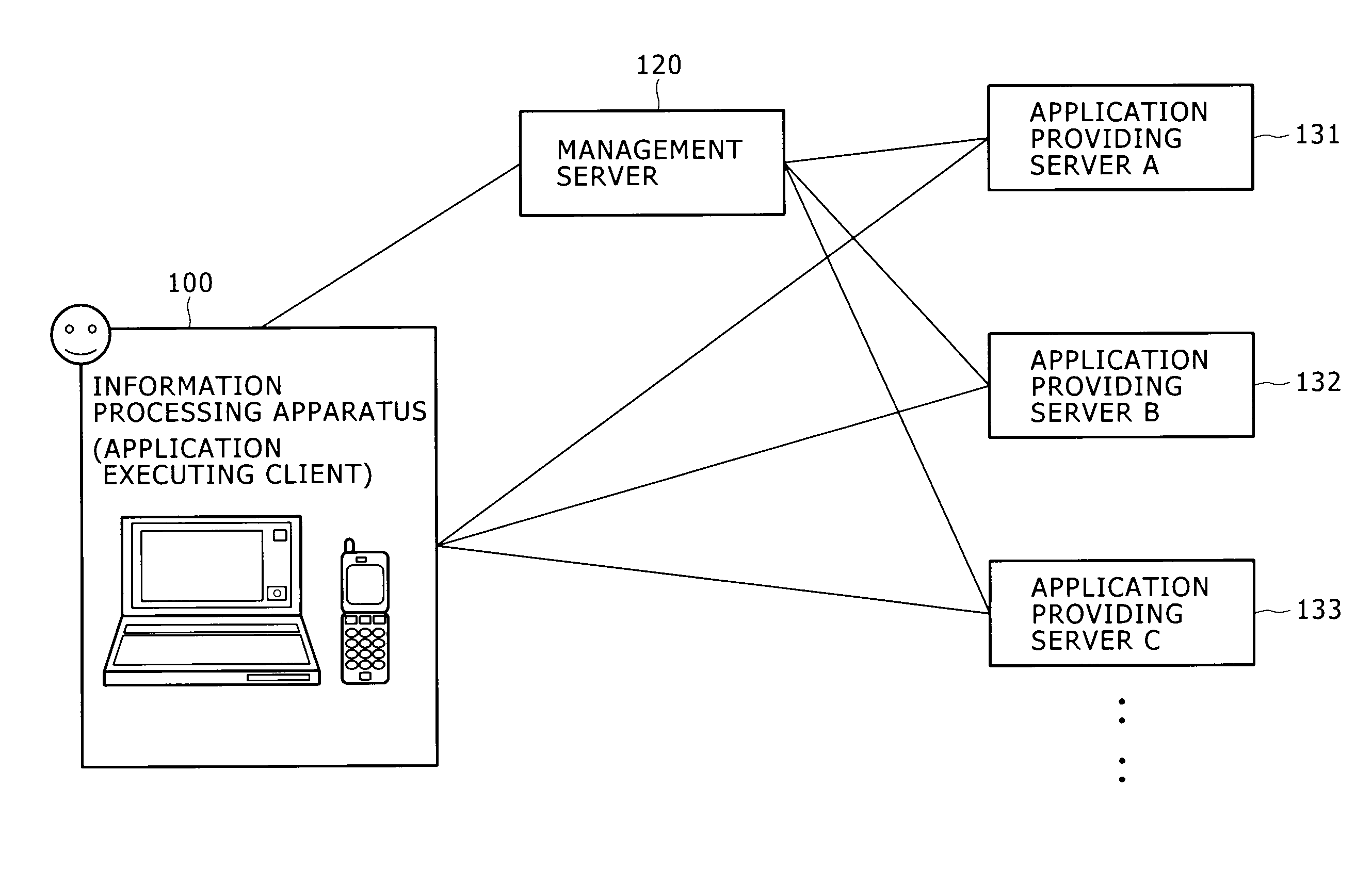
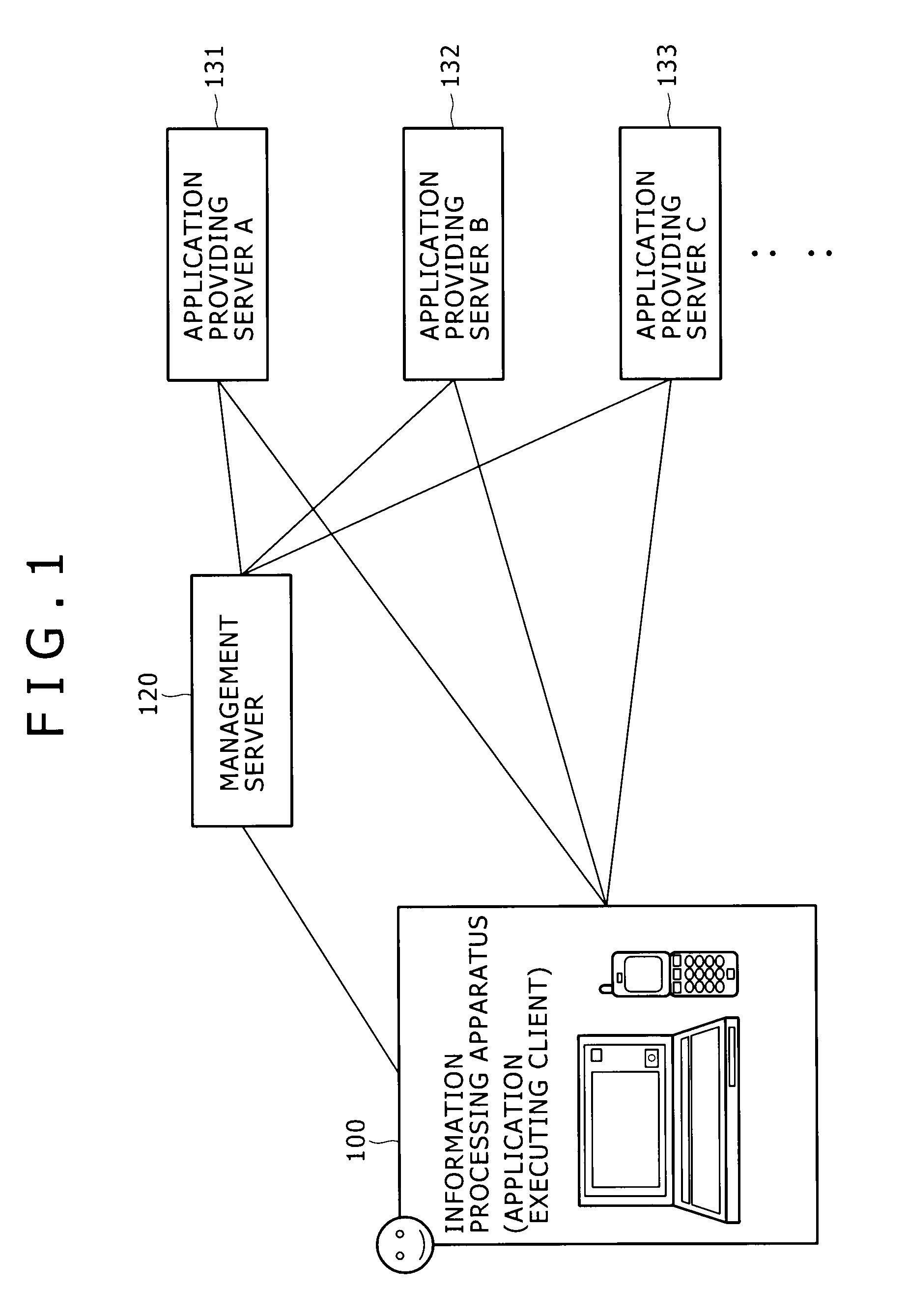
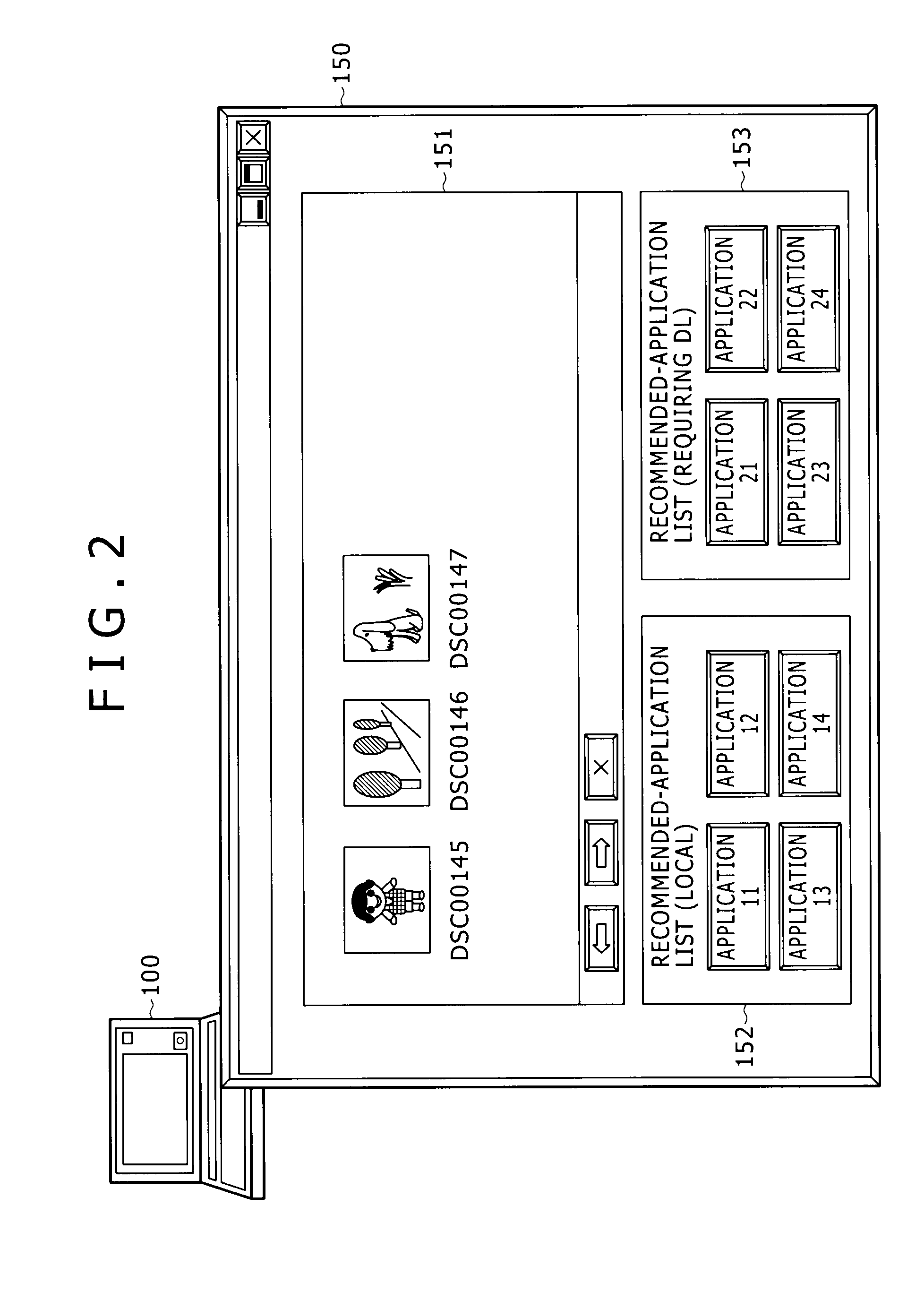
Information processing apparatus and information processing method
ActiveUS20100146442A1Easy to getMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationInformation processingRelevant information
Disclosed herein is an information processing apparatus including: a communication section configured to acquire application programs from external apparatus; a memory used for storing at least an application program and information relevant to the application program; an application execution section configured to execute the application program stored in the memory; and a control section configured to determine other application programs to be recommended in the course of execution of the application program in the application execution section, wherein information stored in the memory as the information relevant to the application program includes first relevant information and second relevant information which are used for determining the other application programs to be recommended in the course of execution of the application program in the application execution section
Owner:SONY CORP
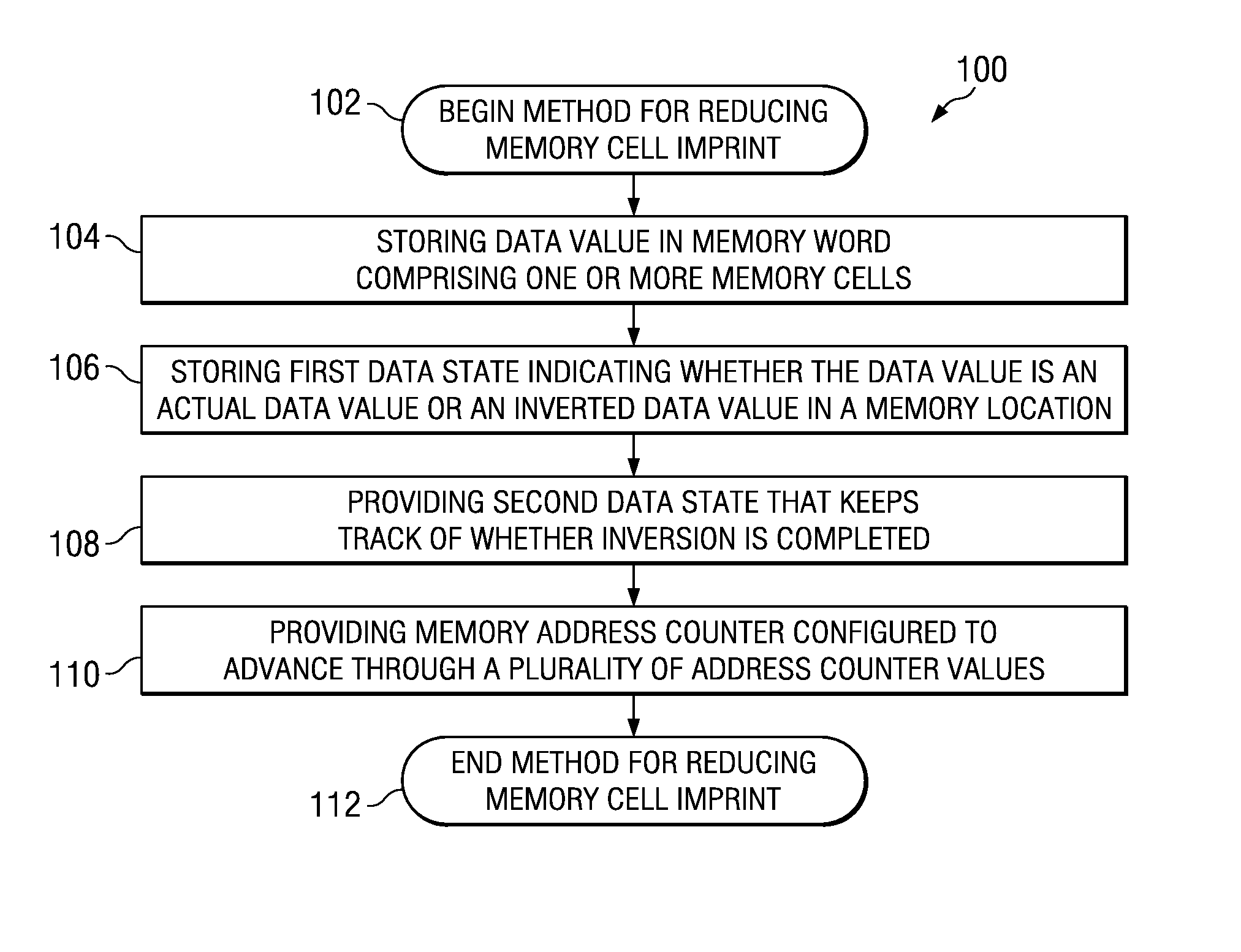
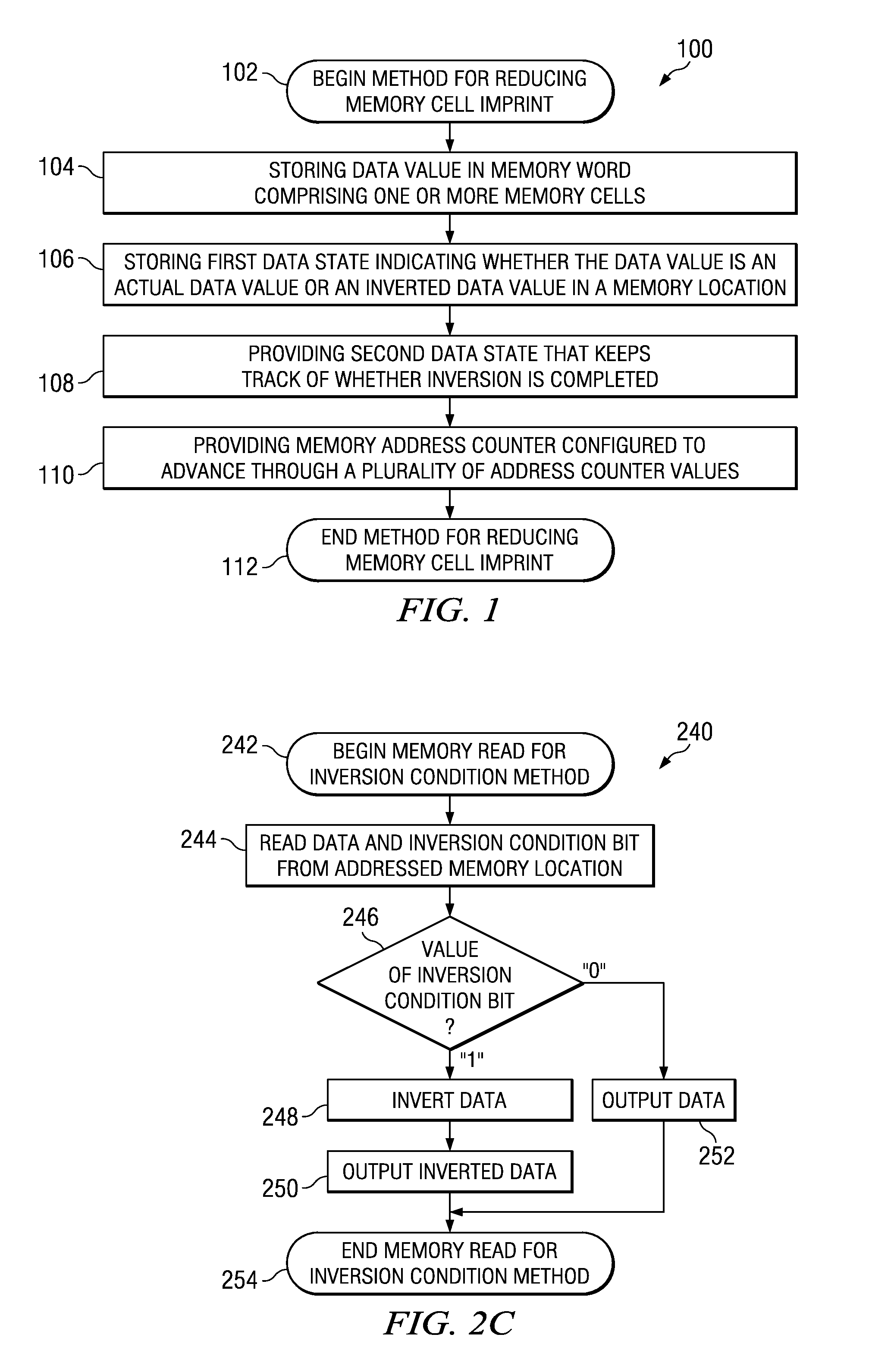
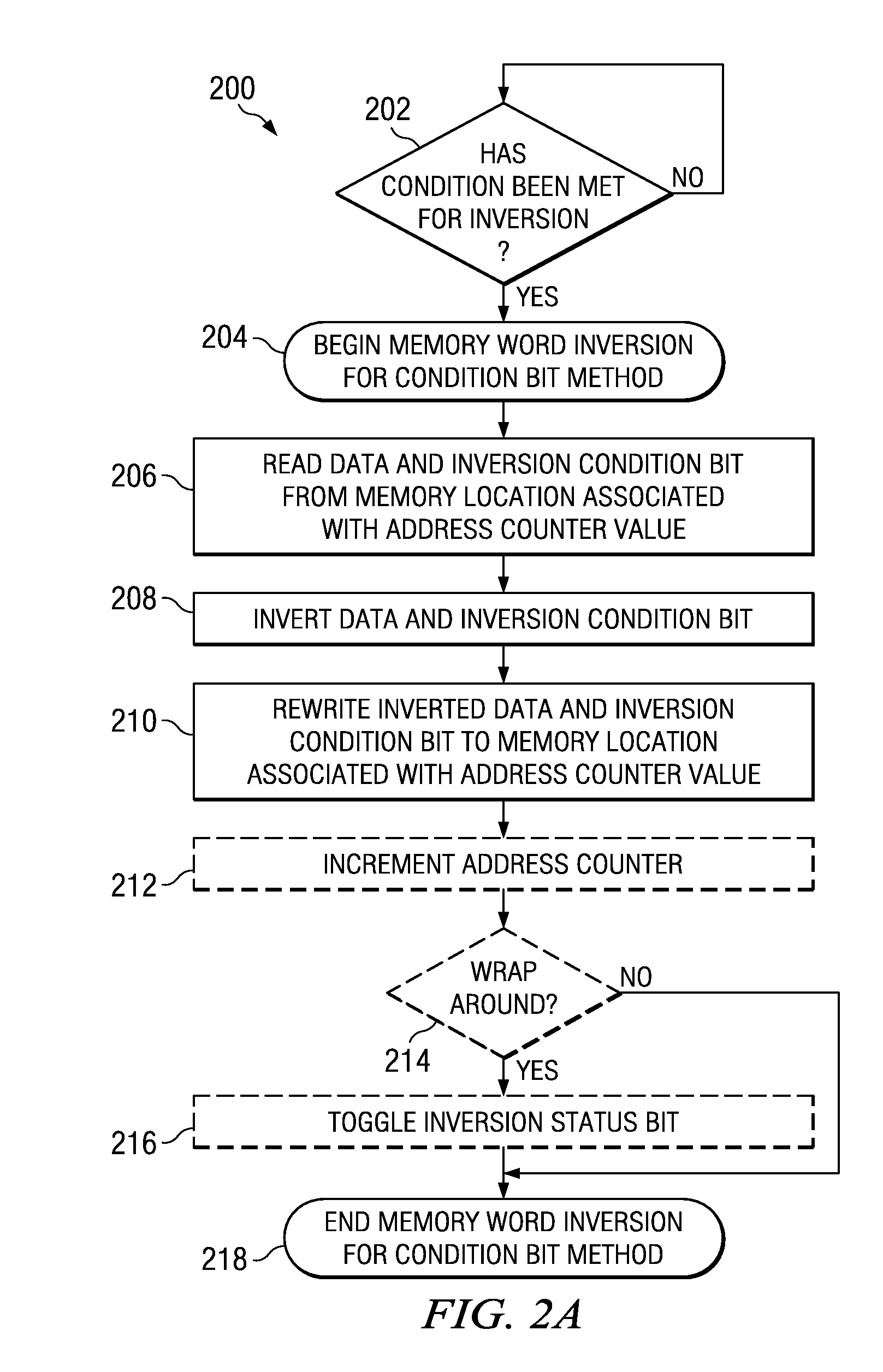
Technique for memory imprint reliability improvement
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of reducing imprint of a memory cell. The method comprises adding an inversion condition bit operably associated with one or more memory cells storing a memory word. The inversion condition bit indicates whether the memory word represents an actual payload or an inversion of the actual payload. The inversion condition bit and memory word are selectively toggled by a control circuitry. Inversion is performed by reading the inversion condition bit and memory word and rewriting the memory word back to the one or more memory cells in an inverted or non-inverted state, depending on an inversion condition bit. The inversion condition bit is then written to the inversion status bit value. The memory address is incremented, and the inversion status data state is toggled once the address counter addresses the entire memory array. Other methods and circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Intergrated circuit and a method of cache remapping
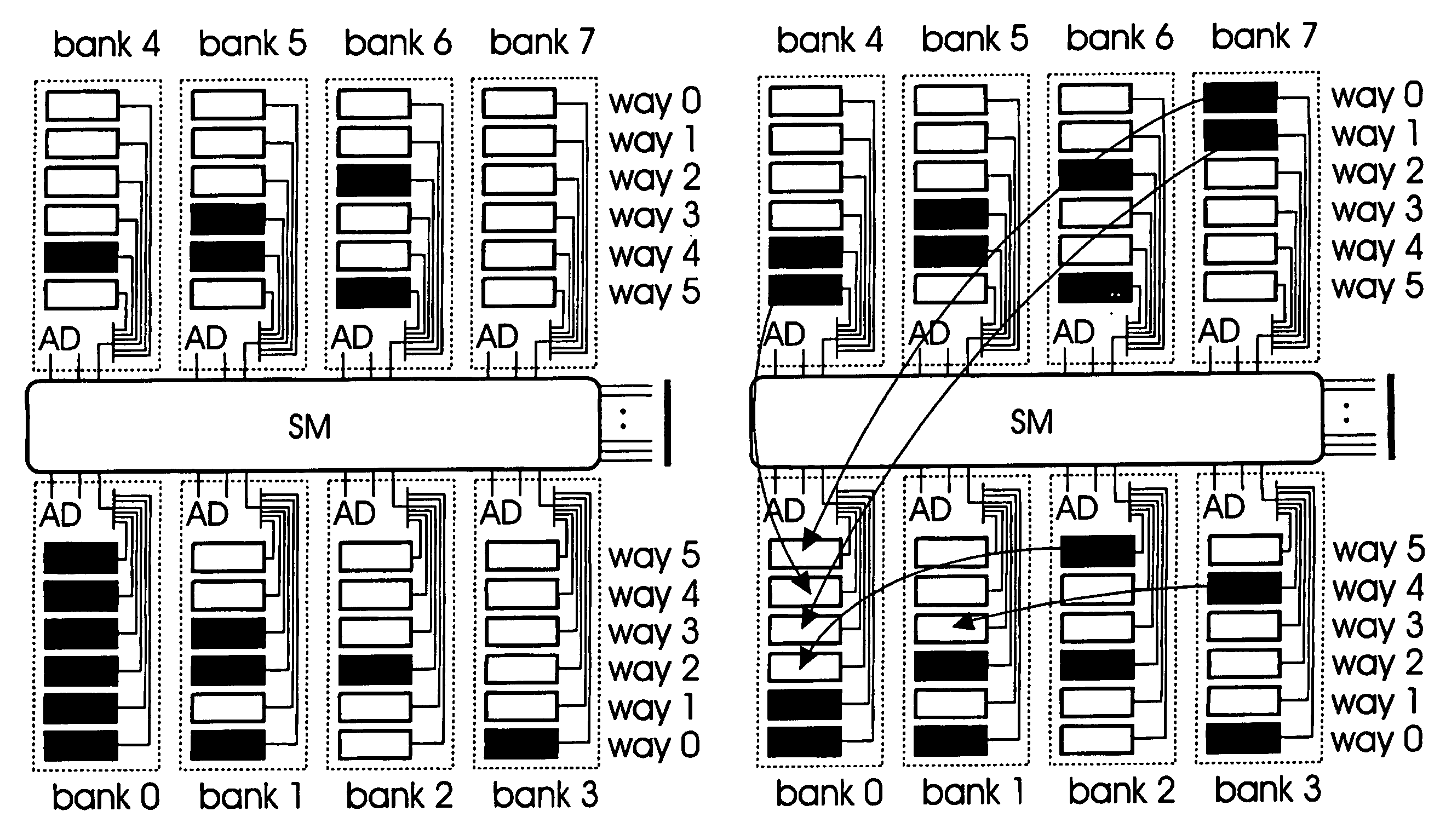
InactiveUS7827372B2Improve overall utilizationRapid cachingError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit is provided with at least one processing unit (TM), a cache memory (L2 BANK) having a plurality of memory modules, and remapping means (RM) for performing an unrestricted remapping within said plurality of memory modules. Accordingly, faulty modules can be remapped without limitations in order to optimise the utilization of the memory modules by providing an even distribution of the faulty modules.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Integrated circuit including memory array incorporating multiple types of NAND string structures
ActiveUS7177191B2High densityGood flexibilitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDevice formParallel computing
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
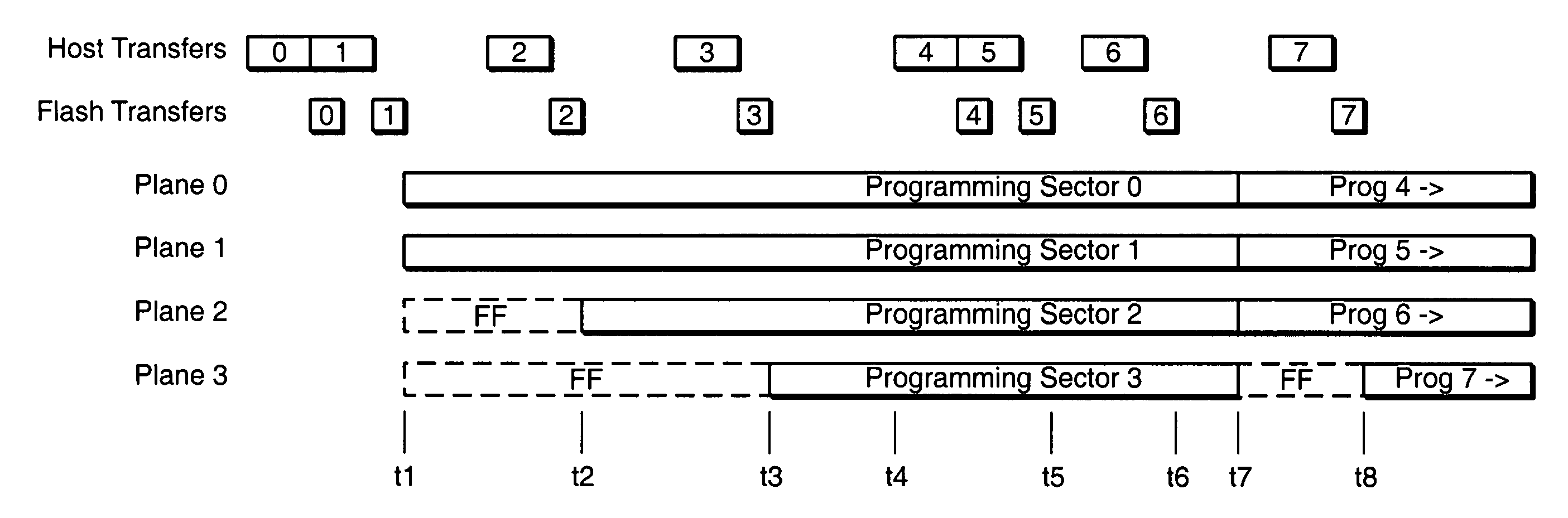
Pipelined programming of non-volatile memories using early data
ActiveUS20060126390A1Improve performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageFull dataProgramming process
The present invention presents techniques whereby a memory system interrupts a programming process and restarts it including additional data. More specifically, when a memory system programs data into a group of cells together as programming unit, programming can begin with less than the full data content which the group can hold. In one embodiment, the present invention allows overlapped programming of upper and lower data pages, where once the memory begins programming the lower logical data page, if data is received for the upper page assigned to the same physical page, programming is interrupted and recommenced with the concurrent programming of both the upper and the loser pages. In a complimentary embodiment, when a page contains multiple sectors of data, programming of the physical page can begin when one or more, but less than all, of the sectors forming the corresponding logical page have been received, stopped and restarted to include additional sectors of the page.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
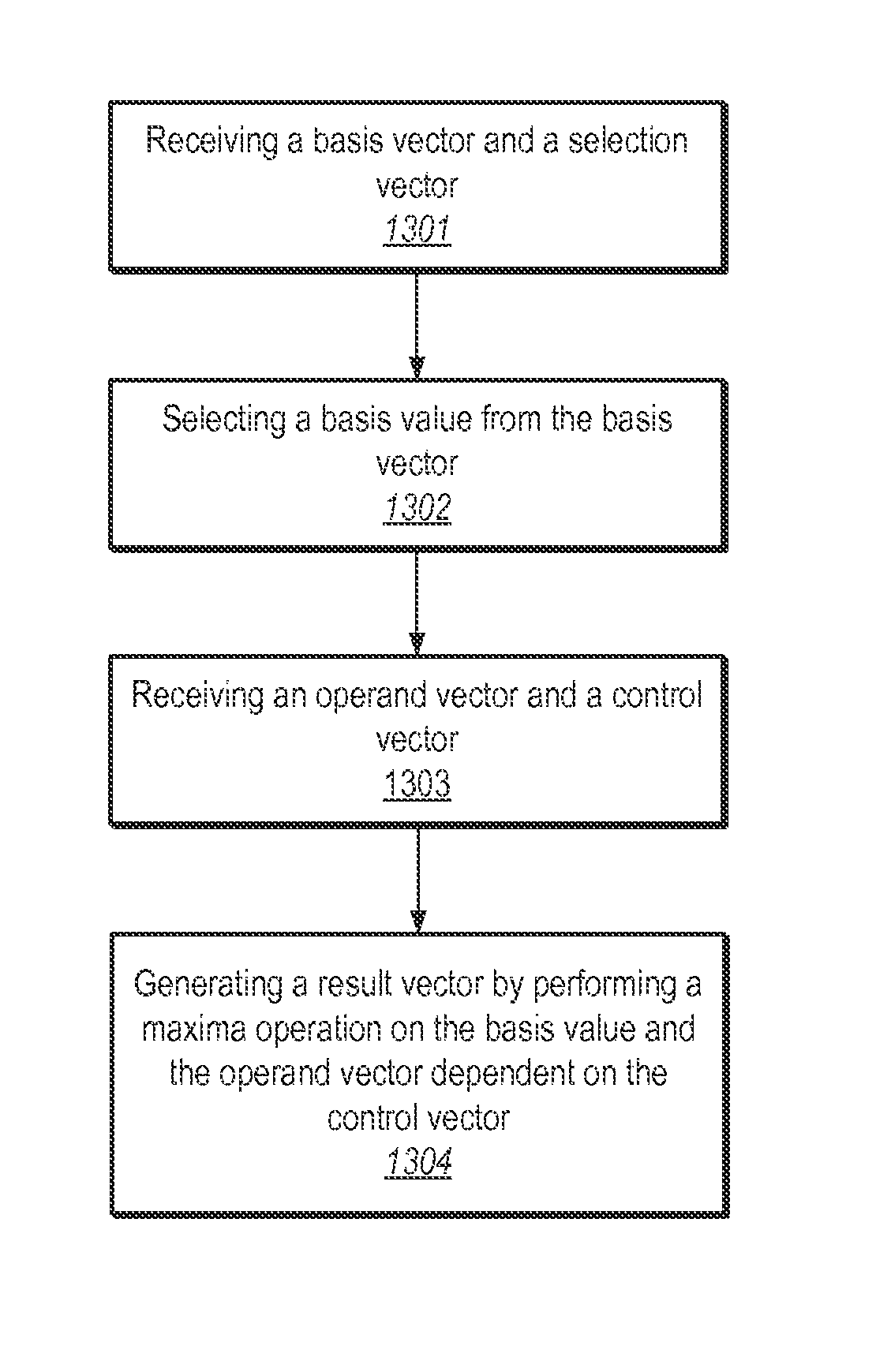
Processing vectors using wrapping minima and maxima instructions in the macroscalar architecture
ActiveUS8555037B2Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerControl vectorParallel computing
Embodiments of a system and a method in which a processor may execute instructions that cause the processor to receive an input vector and a control vector are disclosed. The executed instructions may also cause the processor to perform a minima or maxima operation on another input vector dependent upon the input vector and the control vector.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method for replicating, integrating and synchronizing distributed information
InactiveUS20050086384A1Database distribution/replicationMultiple digital computer combinationsReal-time computingParallel computing
An extensible protocol to replicate, integrate and synchronize distributed information is described which may be implemented in a computer system. A system and method for replicating, integrating and synchronizing distributed information is also described.
Owner:R OBJECTS
Locking technique for control and synchronization
InactiveUS6973549B1Digital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsFast pathLocking mechanism
Described are techniques used in a computer system for handling data operations to storage devices. A switching fabric includes one or more fast paths for handling lightweight, common data operations and at least one control path for handling other data operations. A control path manages one or more fast paths. The fast path and the control path are utilized in mapping virtual to physical addresses using mapping tables. The mapping tables include an extent table of one or more entries corresponding to varying address ranges. The size of an extent may be changed dynamically in accordance with a corresponding state change of physical storage. The fast path may cache only portions of the extent table as needed in accordance with a caching technique. The fast path may cache a subset of the extent table stored within the control path. A set of primitives may be used in performing data operations. A locking mechanism is described for controlling access to data shared by the control paths.
Owner:IBM CORP
Flash memory storage system and method
ActiveUS20070061502A1Overcome disadvantagesEqually distributedMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesParallel computingStorage cell
A flash memory storage system includes a memory array containing a plurality of memory cells and a controller for controlling the flash memory array. The controller dedicates a first group of memory cells to operate with a first number of bits per cell and a second, separate group of memory cells to operate with a second number of bits per cell. A mechanism is provided to apply wear leveling techniques separately to the two groups of cells to evenly wear out the memory cells.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Processor having a trace access instruction to access on-chip trace memory
InactiveUS6314530B1Hardware monitoringSoftware testing/debuggingComputerized systemParallel computing
A computer system includes a memory for storing instructions executable by a processor and an on-chip trace memory having a plurality of locations for storing trace information that indicates execution flow in the processor. A trace access instruction provides for access to the on-chip trace memory on the processor. The trace access instruction can be a write instruction or a read instruction. Typically, both read and write to the trace memory is provided. The system also has the capability to trace on start or restart of an executable thread by providing to the processor an indication of which executable thread to trace via a debug port. That indicates to the processor to provide trace information when the executable thread starts. When execution of the executable thread starts, the processor places an identifier corresponding to the executable thread into the trace memory to indicate that subsequent entries placed into the trace memory are part of said executable thread. The processor may also provide an entry indicating when the thread stops executing.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
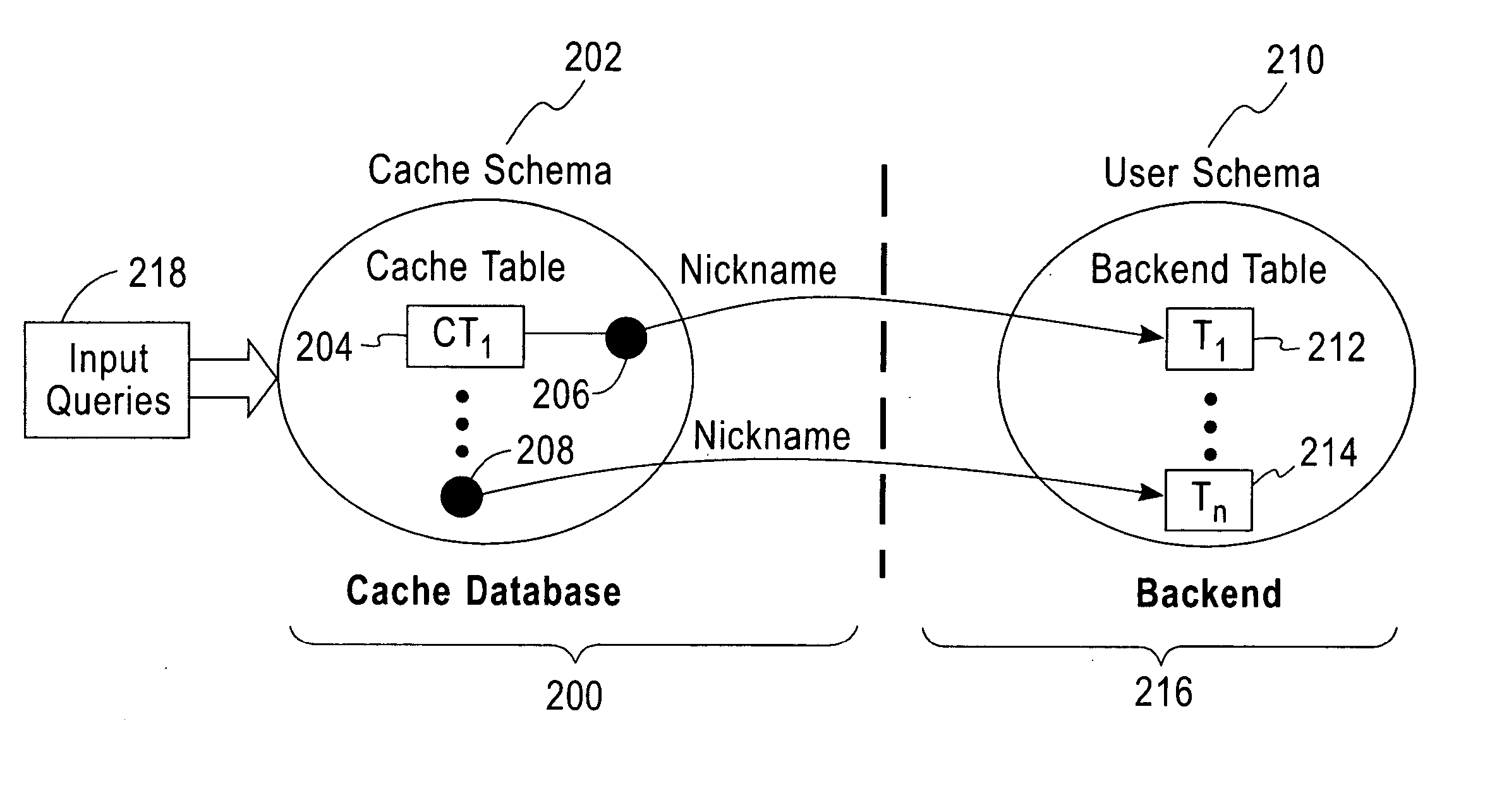
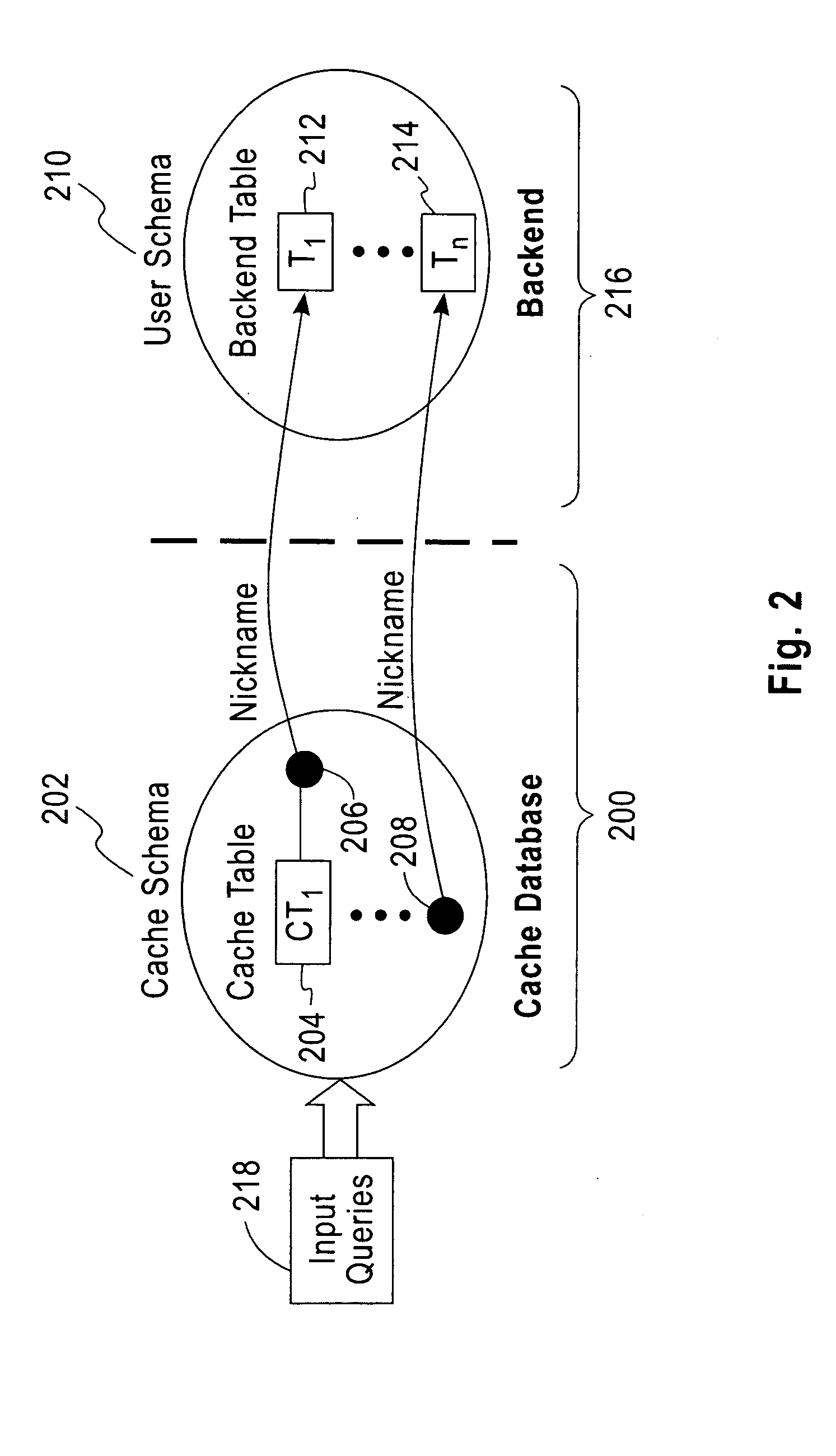
System and method for adaptive database caching
ActiveUS20060026154A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalQuery planUser input
A local database cache enabling persistent, adaptive caching of either full or partial content of a remote database is provided. Content of tables comprising a local cache database is defined on per-table basis. A table is either: defined declaratively and populated in advance of query execution, or is determined dynamically and asynchronously populated on-demand during query execution. Based on a user input query originally issued against a remote DBMS and referential cache constraints between tables in a local database cache, a Janus query plan, comprising local, remote, and probe query portions is determined. A probe query portion of a Janus query plan is executed to determine whether up-to-date results can be delivered by the execution of a local query portion against a local database cache, or whether it is necessary to retrieve results from a remote database by executing a remote query portion of Janus query plan.
Owner:IBM CORP
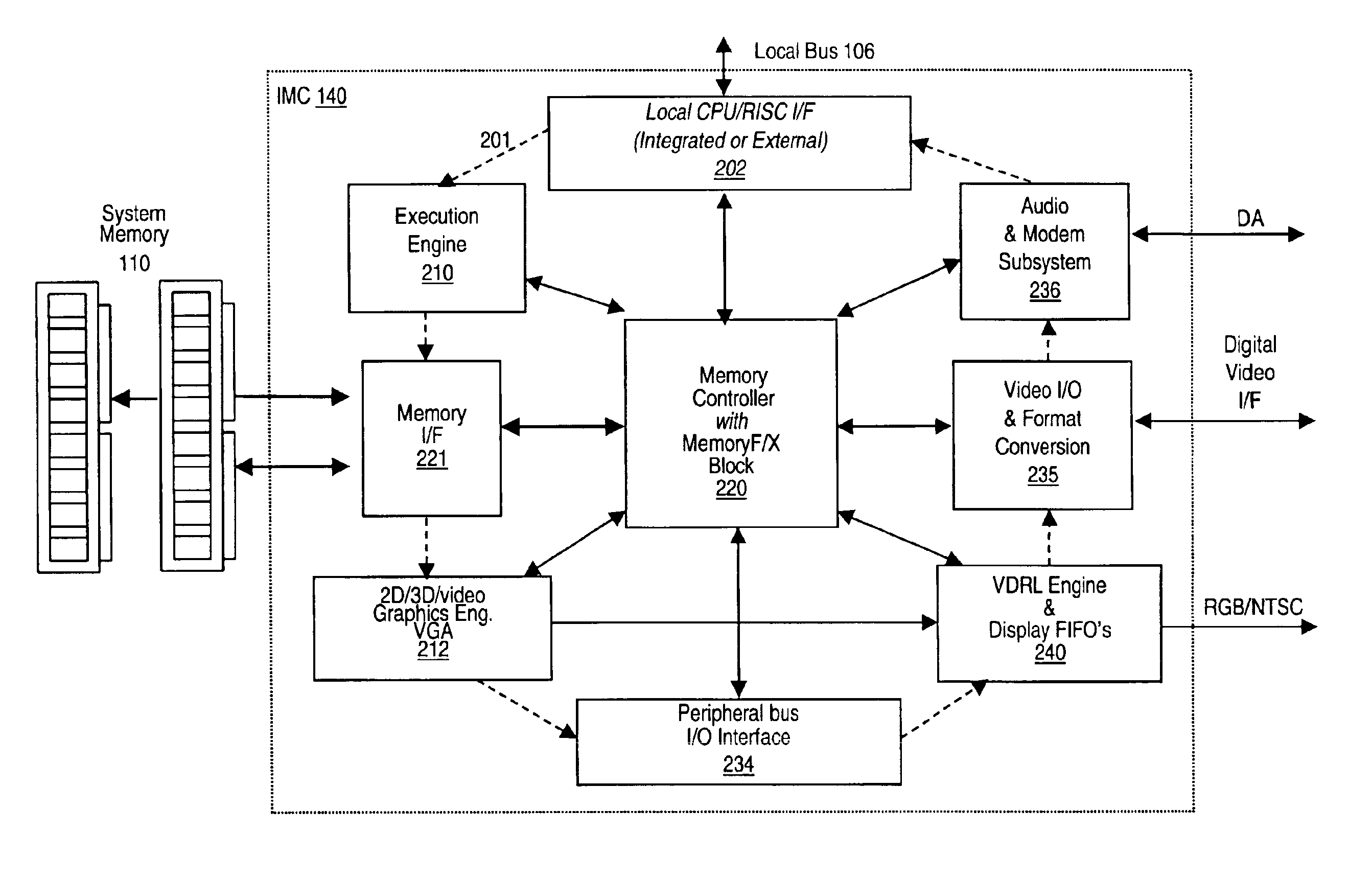
Memory module including scalable embedded parallel data compression and decompression engines
InactiveUS6879266B1Low costSmall data storage requirementMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel compressionParallel computing
An memory module including parallel data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory module includes MemoryF / X Technology. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high-speed parallel decompression operation. The memory module-integrated data compression and decompression capabilities remove system bottlenecks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Specializing write-barriers for objects in a garbage collected heap
ActiveUS7089272B1Reduce in quantityWithout compromising garbage collector performanceData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingWaste collection
A technique is provided for reducing the number of write barriers executed in mutator code without compromising garbage collector performance. Advantageously, a compiler generates two forms of a mutator code—a first version with write barriers and a second version substantially without write barriers. In operation, the first version of the code may be accessed by a vtable in a “mature” near-class and the second version may be accessed by a vtable in a “nascent” near-class. According to the invention, mapping of functionally equivalent points in the first and second versions of the mutator code may be facilitated by an associated pcmap. Further, each of the first and second versions may also be associated with a respective nr_map that facilitates mapping functionally equivalent points within different branches of guard code sequences corresponding to reference-writes to non-receiver objects.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
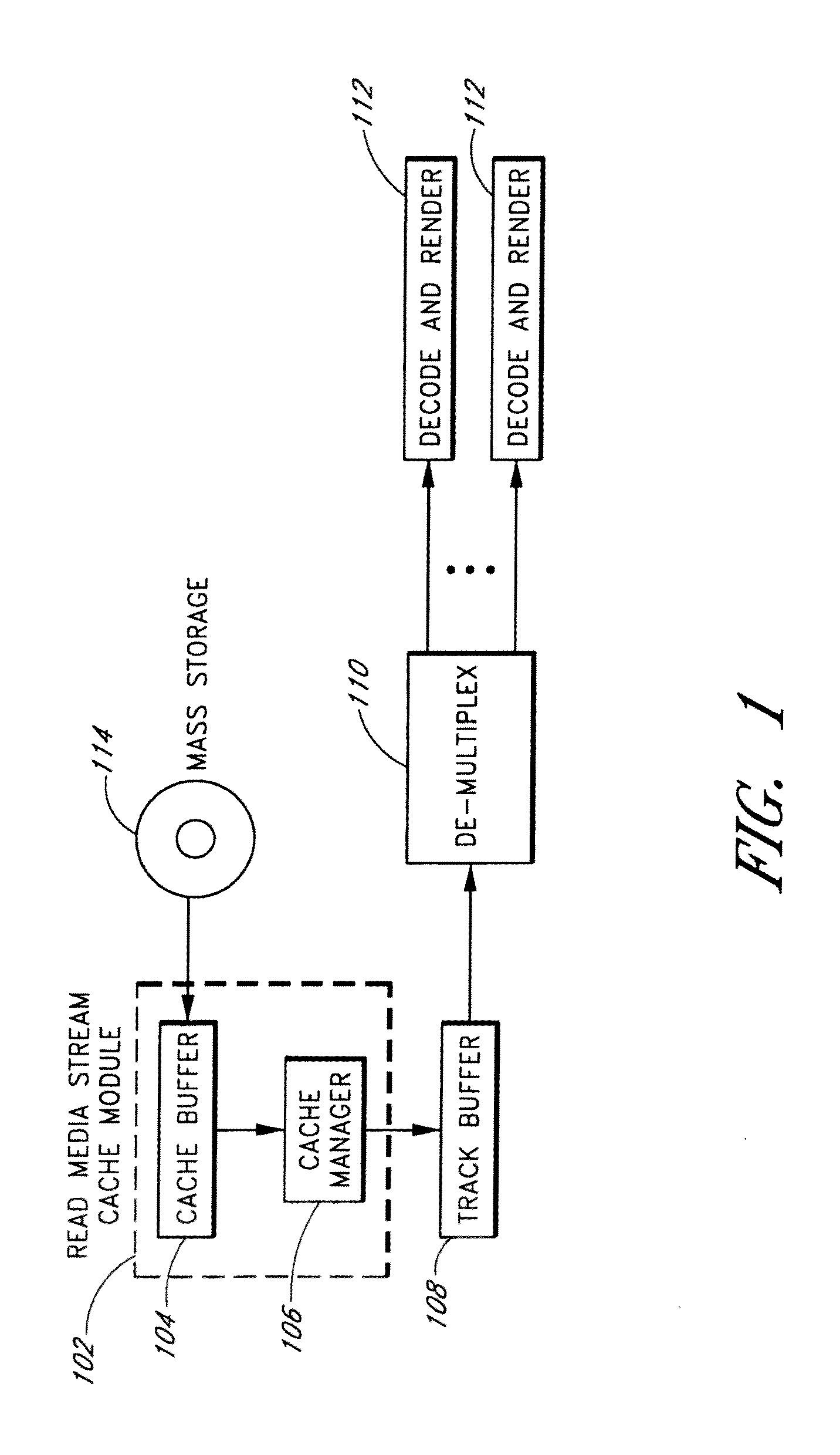
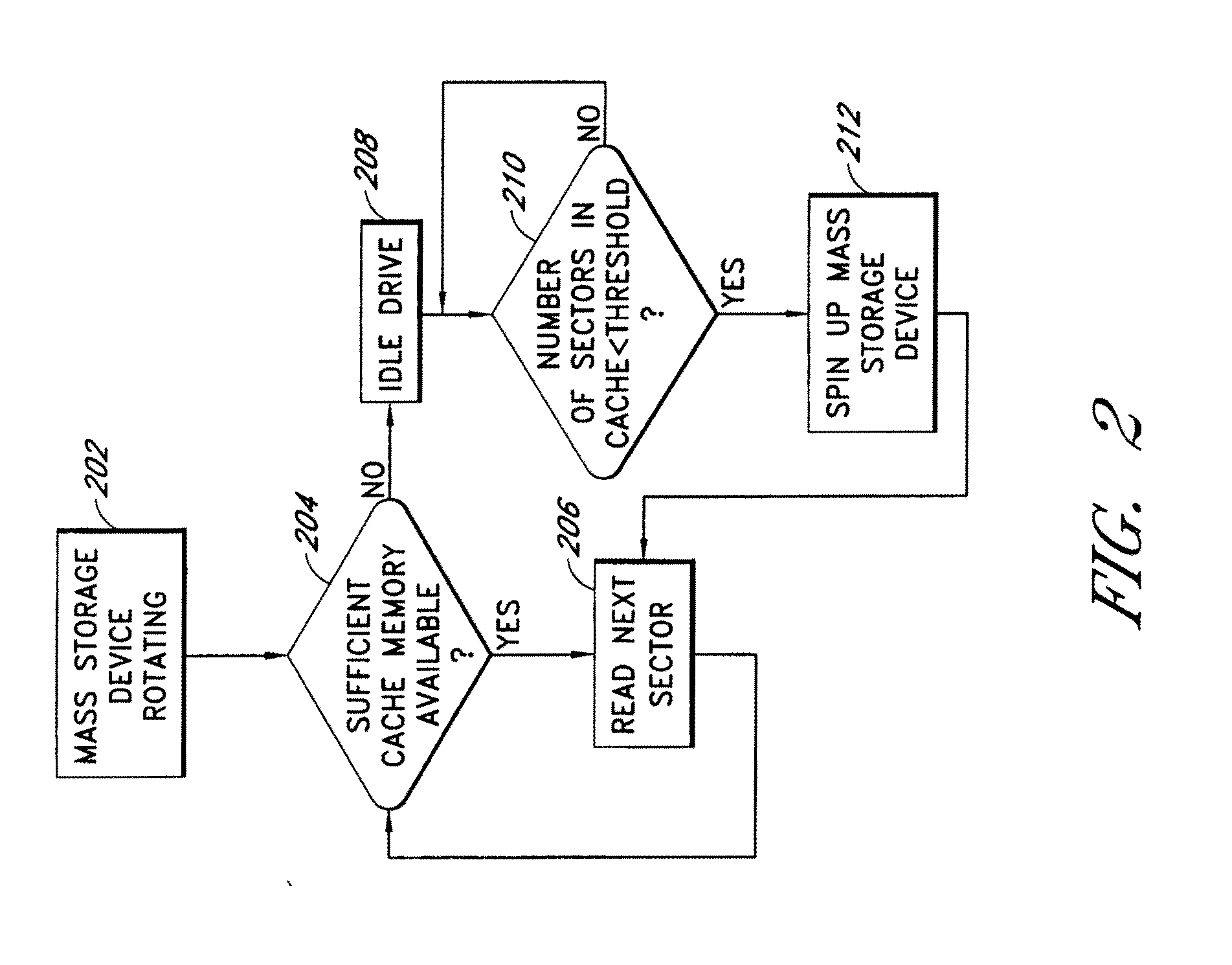
System and Method for Caching Multimedia Data
InactiveUS20100332754A1Data augmentationImprove functionalityMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel computingData system
Systems and methods are provided for caching media data to thereby enhance media data read and / or write functionality and performance. A multimedia apparatus, comprises a cache buffer configured to be coupled to a storage device, wherein the cache buffer stores multimedia data, including video and audio data, read from the storage device. A cache manager coupled to the cache buffer, wherein the cache buffer is configured to cause the storage device to enter into a reduced power consumption mode when the amount of data stored in the cache buffer reaches a first level.
Owner:COREL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com