Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1066 results about "Data page" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
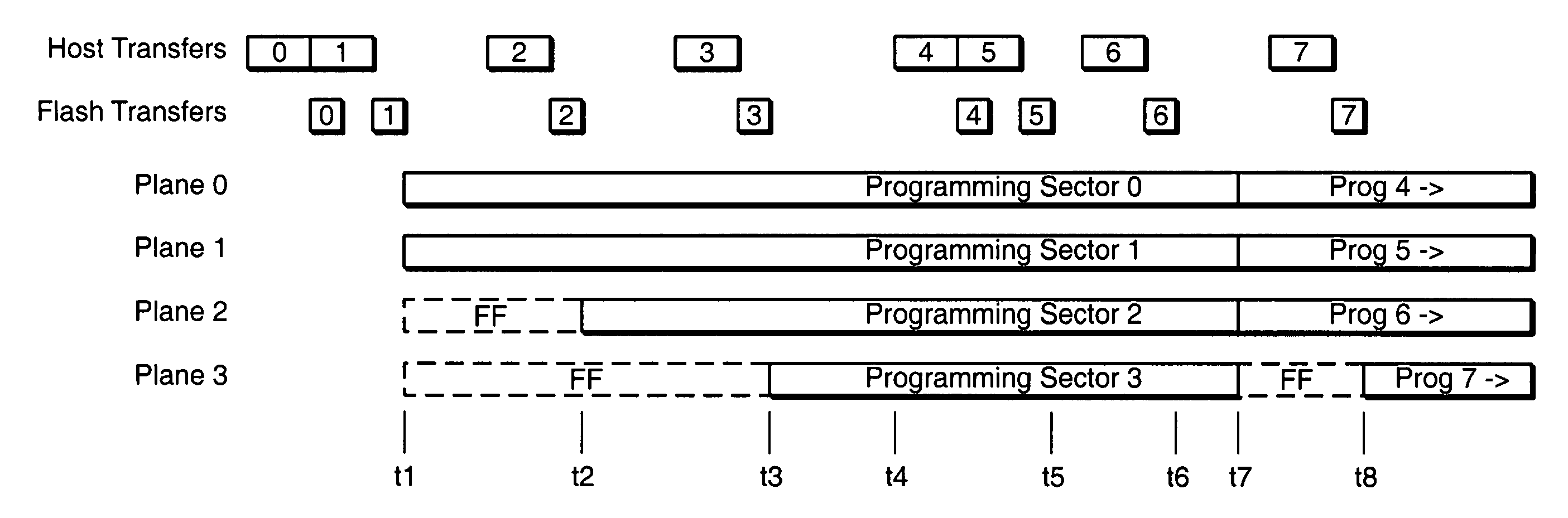
Pipelined programming of non-volatile memories using early data
ActiveUS20060126390A1Improve performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageFull dataProgramming process
The present invention presents techniques whereby a memory system interrupts a programming process and restarts it including additional data. More specifically, when a memory system programs data into a group of cells together as programming unit, programming can begin with less than the full data content which the group can hold. In one embodiment, the present invention allows overlapped programming of upper and lower data pages, where once the memory begins programming the lower logical data page, if data is received for the upper page assigned to the same physical page, programming is interrupted and recommenced with the concurrent programming of both the upper and the loser pages. In a complimentary embodiment, when a page contains multiple sectors of data, programming of the physical page can begin when one or more, but less than all, of the sectors forming the corresponding logical page have been received, stopped and restarted to include additional sectors of the page.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
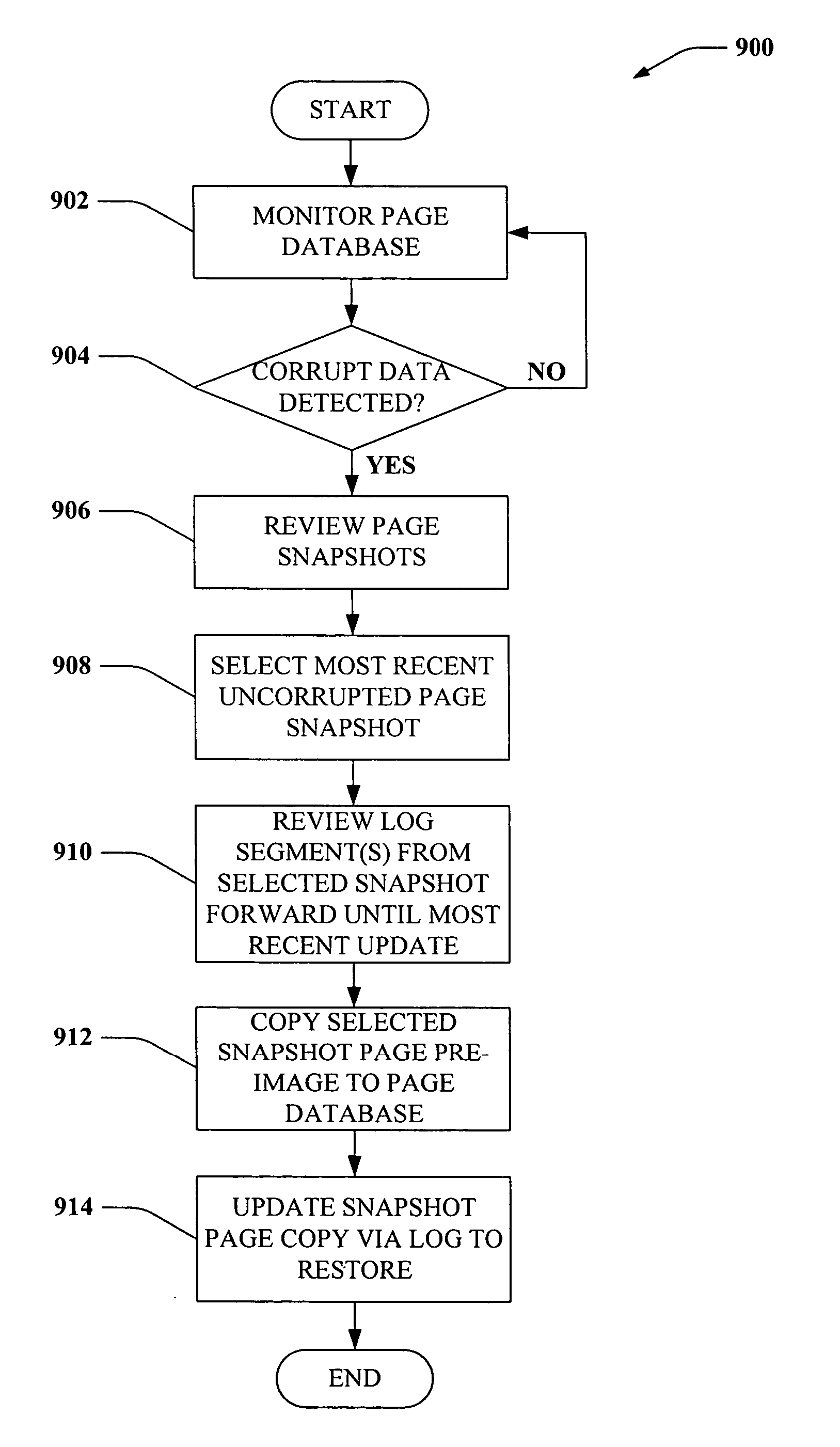
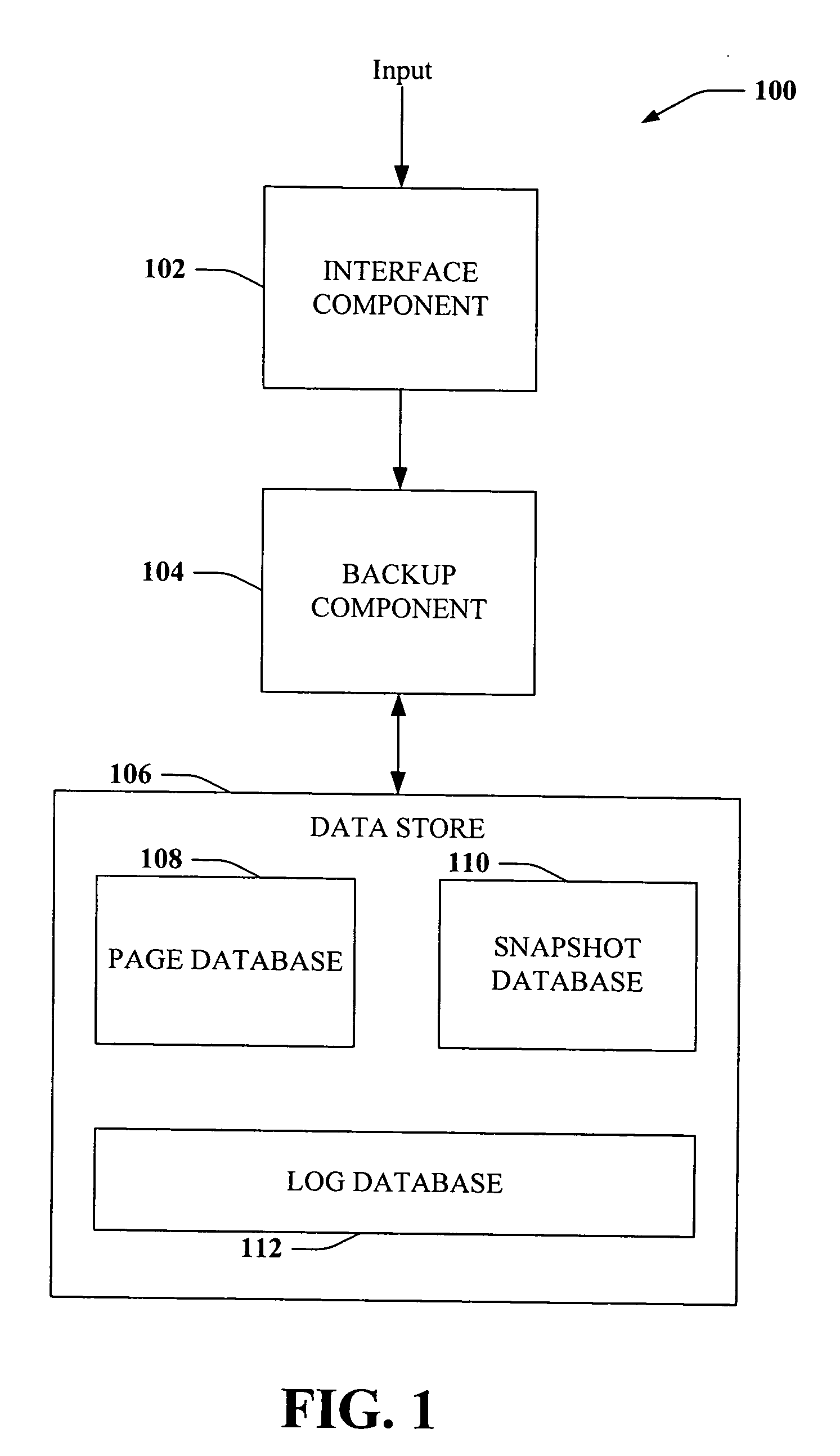
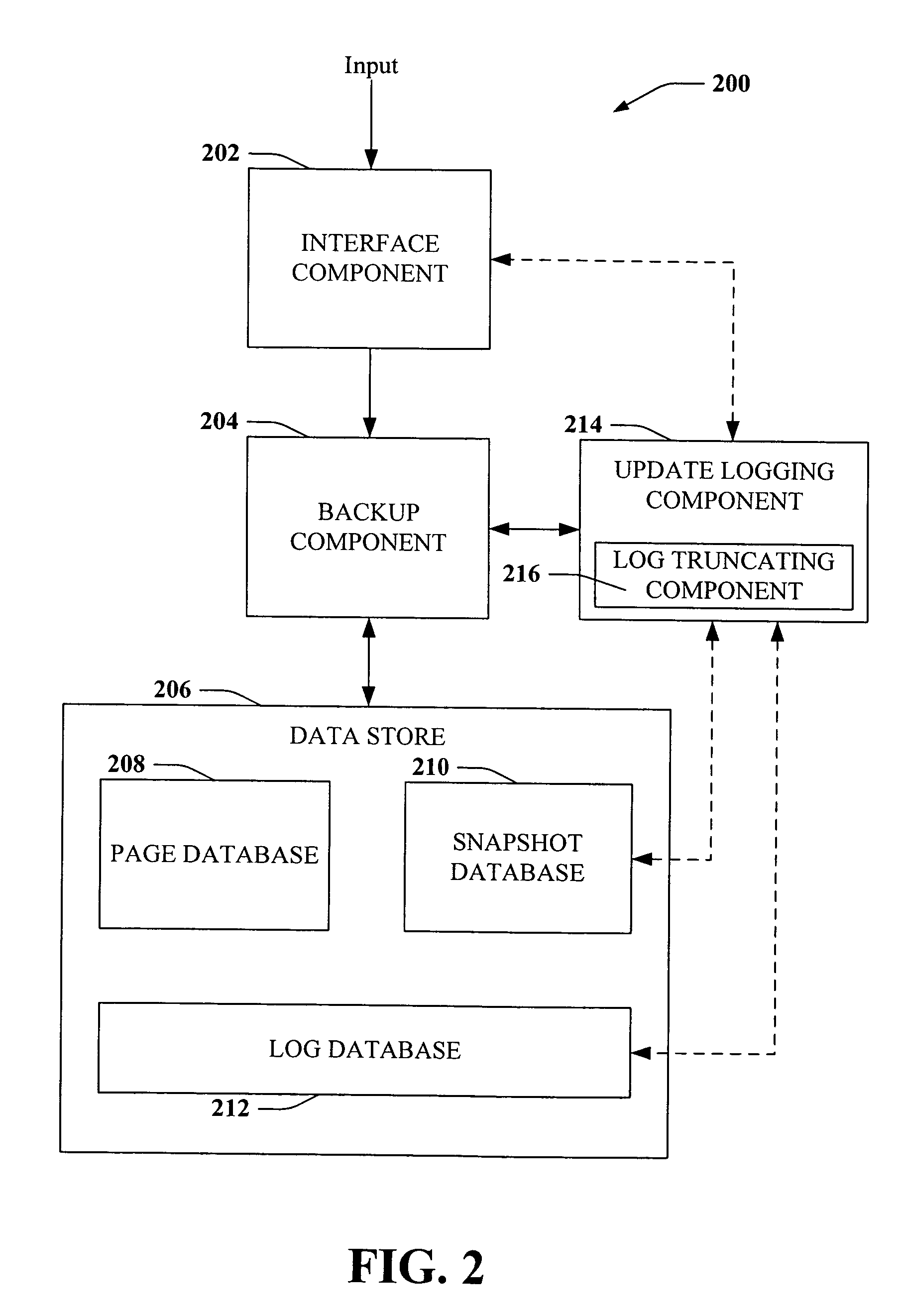
Page recovery using volume snapshots and logs
InactiveUS20060224636A1Promote recoveryImprove system efficiencyDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionDatabaseData page
Systems and methods are disclosed that facilitate providing page-level database restore functionality upon detection of a corruption event. Updates to a data page in a database can trigger generation of a snapshot of the data page, and an update log can be maintained that stores information related to page updates. Subsequent snapshots can be generated at predetermined intervals and can trigger truncation of a log segment and initiation of a new log segment. Upon detection of page corruption, a most-recent uncorrupt snapshot of the corrupt page can be identified, copied to the location of the corrupt page in the database, and modified according to the log segment associated with the uncorrupt snapshot to make the page current as of the corrupting event, all of which can be performed to restore the database without having to take the database offline.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and Apparatus for Addressing Actual or Predicted Failures in a FLASH-Based Storage System
ActiveUS20110040925A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionData storingData store
Methods and apparatuses for enhanced protection of data stored in a FLASH memory system involve a controller capable of adapting to the failure of one or more FLASH memory devices in the memory system. The controller stores data in the form of page stripes, each page stripe composed of data pages, and each data page stored in a different FLASH memory device. The controller also detects failure of a FLASH memory device in which a data page of a particular page stripe is stored, reconstructs the data page, and stores the reconstructed data page in a new page stripe, where the number of data pages in the new page stripe is less than the number of data pages in the particular page stripe, and where no page of the new page stripe is stored in a memory location within the failed FLASH memory device.
Owner:IBM CORP
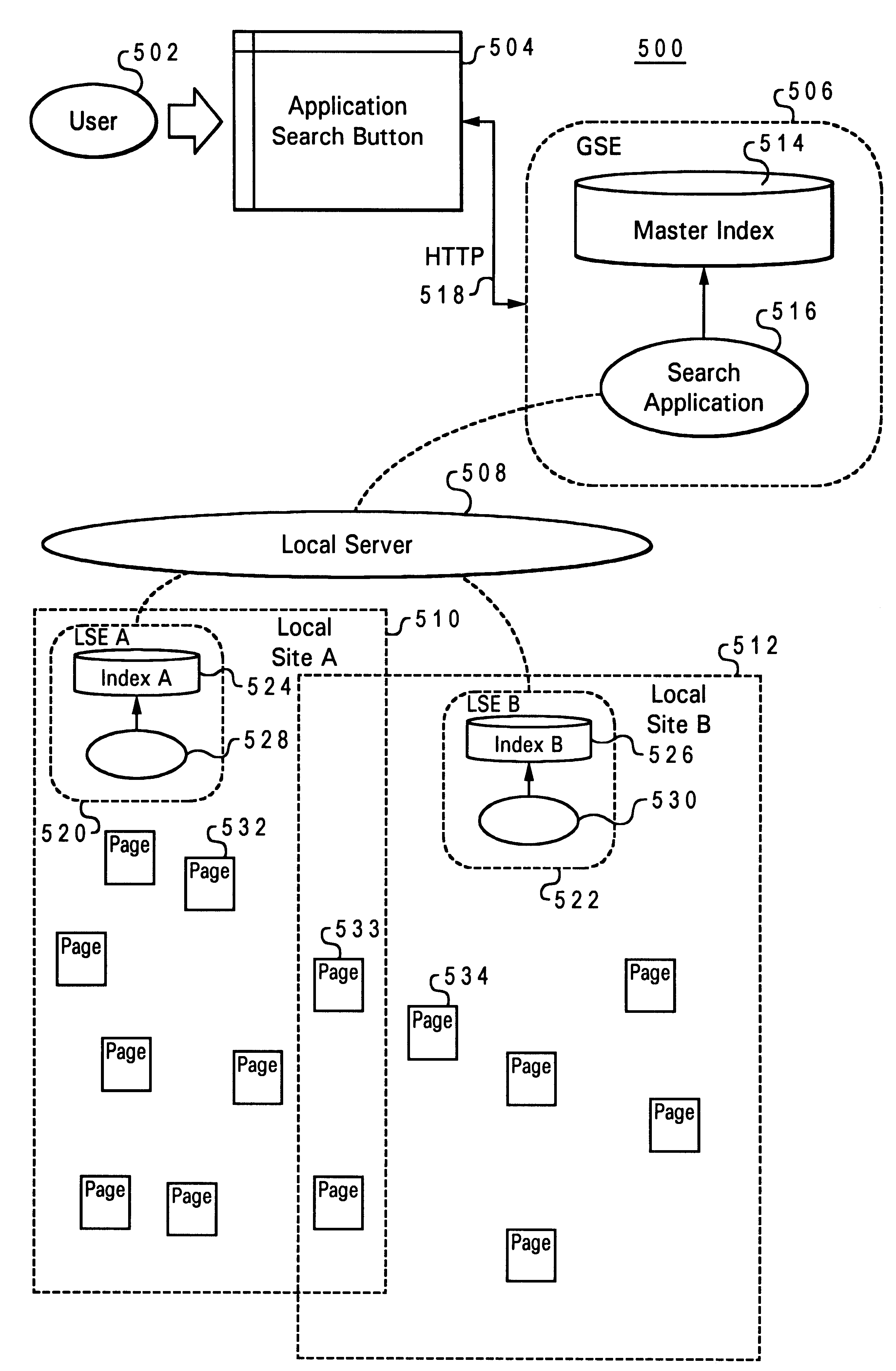
Distributed network search engine
InactiveUS6490575B1Efficient searchImprove search efficiencyData processing applicationsWeb data indexingCentral databaseComputer science
A method and system for facilitating a keyword search request initiated at a client station within a multilevel data network, wherein the multilevel data network includes multiple local sites each containing multiple data pages. Multiple keywords from each of the data pages within the local sites of the multilevel data network are stored locally and indexed such that each of the keywords points to one or more of the data pages in which the keywords are contained. The keywords and their index associations are locally updated. A central database is utilized to compile and index the locally indexed keywords from each of the local sites, such that each of the keywords in the central database points to one or more local sites from which those keywords came in response to a keyword search initiated at the client station.
Owner:IBM CORP
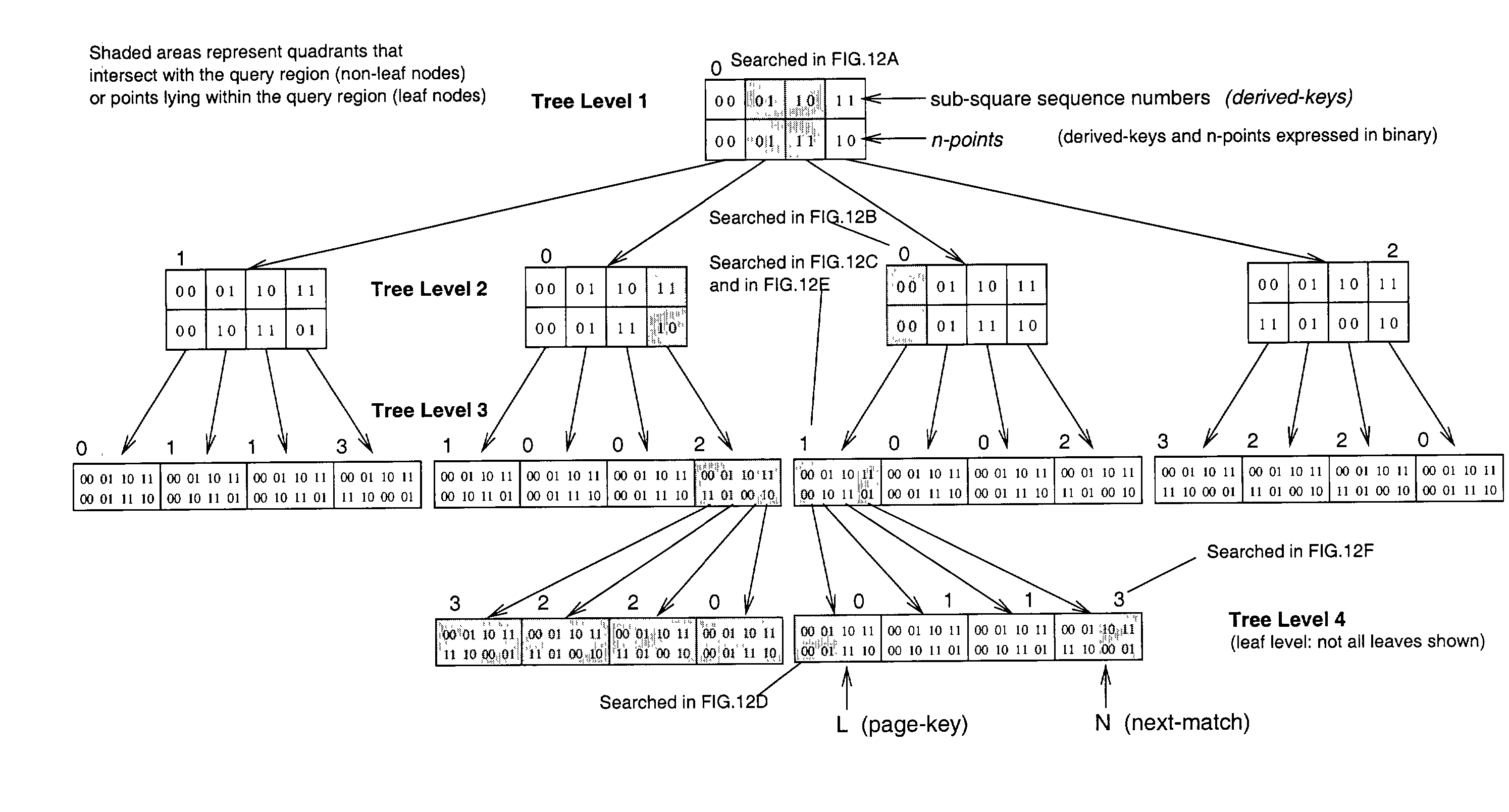
Method of storing and retrieving multi-dimensional data using the hilbert curve
InactiveUS20030004938A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData spaceHilbert space
An improved method of partitioning and indexing multi-dimensional data that maps the data to one-dimensional values according to the sequence in which an approximation of a Hilbert space-filling curve passes through all of the points corresponding to potential multi-dimensional data in a data space. Data is partitioned into pages, each corresponding to a length of Hilbert curve. A page identifier is the sequence of the first point on its corresponding Hilbert curve section. The mapping orders data and also orders the data pages that contain data within a database. Mapping multi-dimensional data to one-dimensional values enables the data to be indexed using any one-dimensional index structure. The practical application of the indexing method is made viable and useful by the provision of a querying algorithm enabling data to be selectively retrieved in response to queries wherein all or some of the data that lies within a rectangular space within multi-dimensional space is required to be retrieved. The querying algorithm identifies pages whose corresponding curve sections intersect with a query region. The first intersecting page is found by calculating the lowest one-dimensional value corresponding to a possible multi-dimensional data value or point within the query region, and looking up in the index to find which page may contain this point. The next intersecting page, if it exists, is found by calculating the lowest one-dimensional value equal to or greater than the identifier of the next page to the one just identified. This new lowest one-dimensional, if found, is used to look up in the index and find the next page intersecting with the query region. Subsequent pages to be found, if any, are determined in a similar manner until no more are found. Pages found to intersect the query region can be searched for data lying within the query region.
Owner:LAWDER JONATHAN KEIR
Mlc self-raid flash data protection scheme
ActiveUS20110228601A1Reduce data corruptionReduce rateMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionRAIDData storing
A two-dimensional self-RAID method of protecting page-based storage data in a MLC multiple-level-cell flash memory device. The protection scheme includes reserving one parity sector across each data page, reserving one parity page as the column parity, selecting a specific number of pages to form a parity group, writing into the parity page a group parity value for data stored in the pages of the parity group. The parity sector represents applying a RAID technique in a first dimension. The group parity represents applying a RAID technique in a second dimension. Data protection is achieved because a corrupted data sector can likely be recovered by the two dimensional RAID data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for protecting data using variable size page stripes in a FLASH-based storage system
ActiveUS7856528B1Efficient and enhanced protectionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionData storingData store
Methods and apparatuses for enhanced protection of data stored in a FLASH memory system involve a controller capable of using variable size page stripes in the memory system. The controller is configured to store data such that each page stripe comprises a plurality of data pages, with each data page in the page stripe being stored in a different FLASH memory chip. The controller is also configured to maintain one or more buffers containing information reflecting blocks of memory within the FLASH memory chips that have been erased and are available for information storage, and to dynamically determine the number of data pages to be included in a page stripe based on the information in the one or more buffers such that a first page stripe and a second page strip can have different numbers of data pages.
Owner:IBM CORP
Processing data pixels in a holographic data storage system
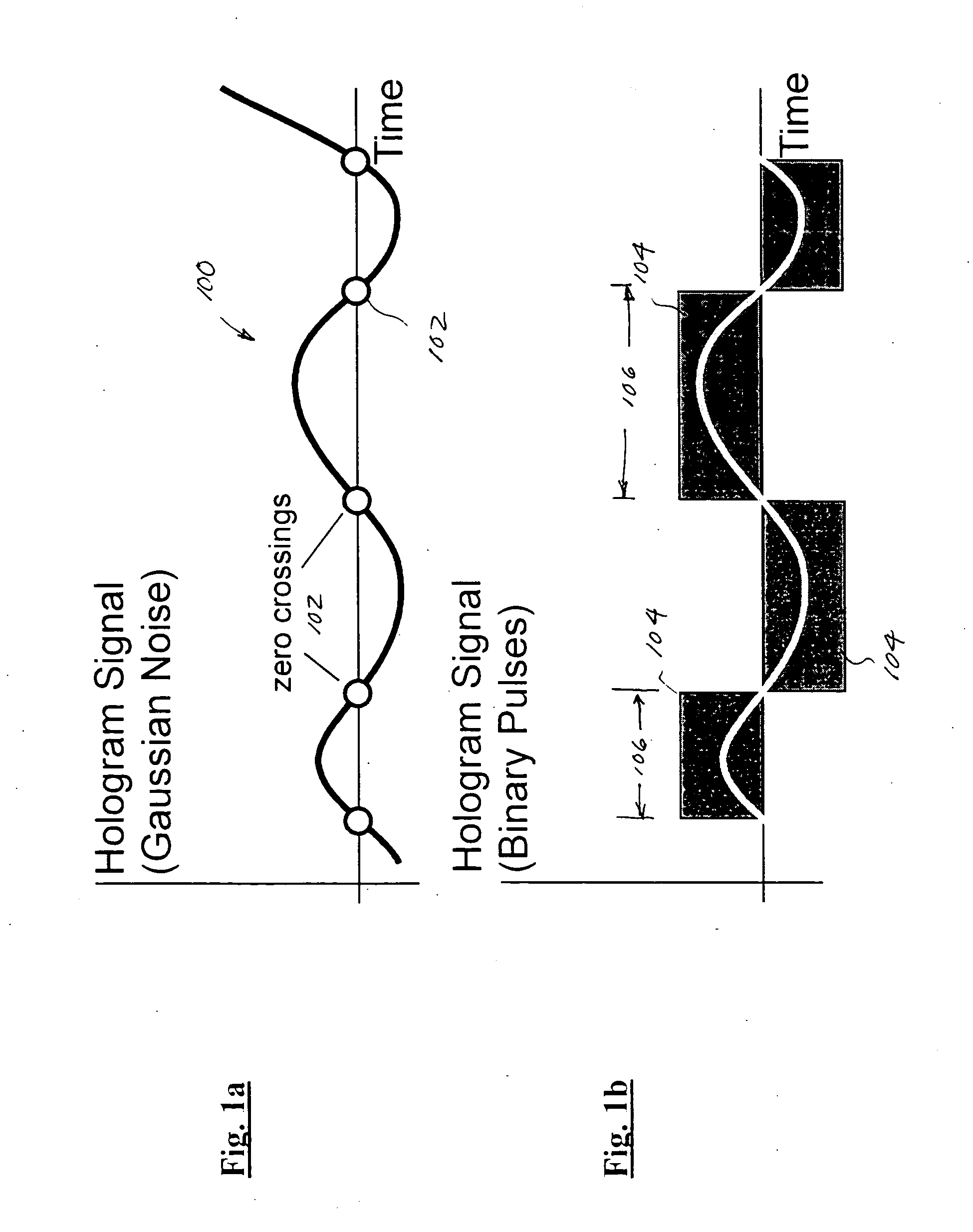
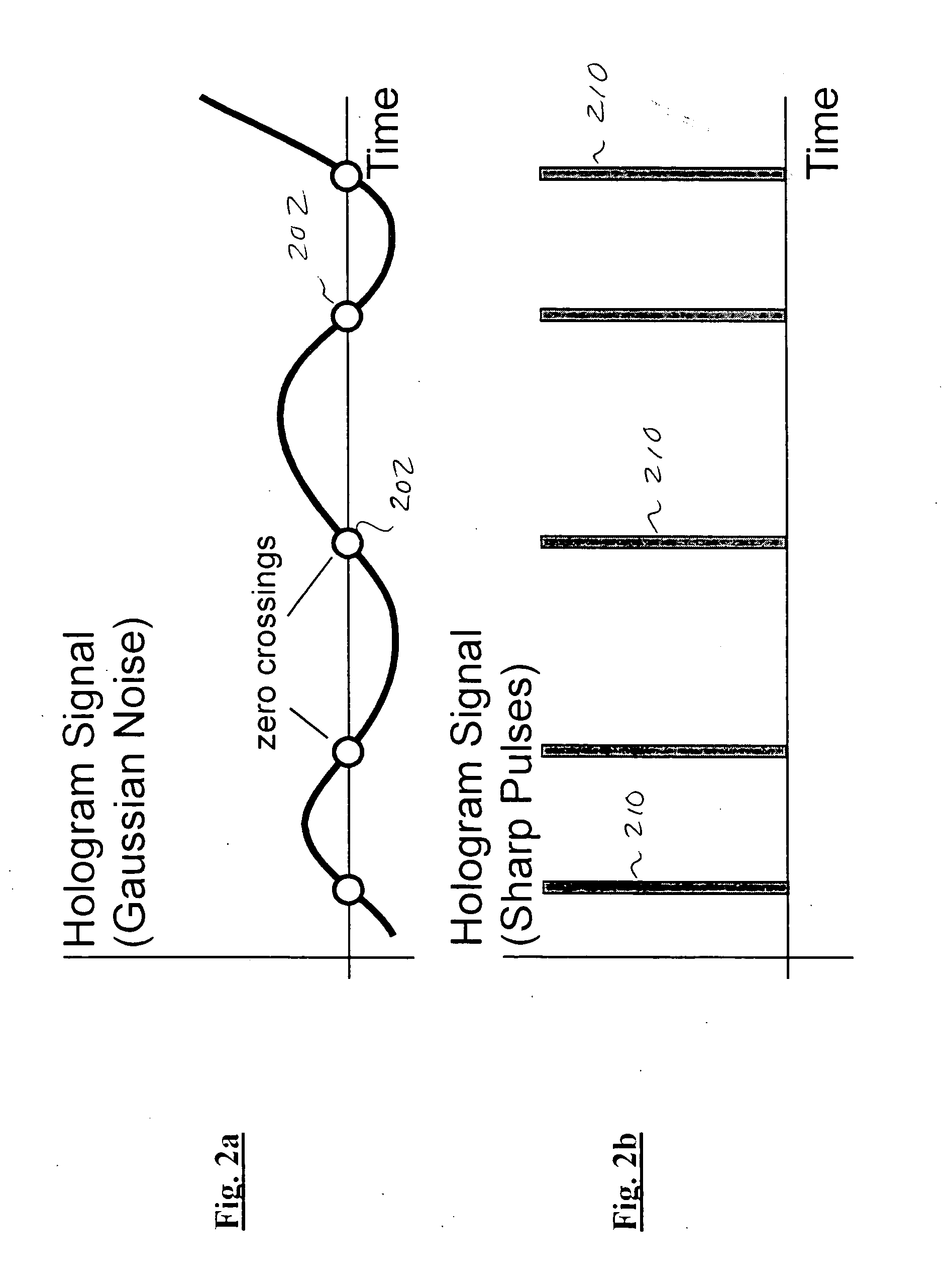
InactiveUS20050286388A1Record information storageCharacter and pattern recognitionHolographic Data Storage SystemPosition error
A method for processing data pixels in a holographic data storage system is disclosed. The method includes assigning predetermined reserved blocks throughout each data page, where each reserved block comprises known pixel patterns, determining position errors of the data page by computing the best match between regions of the data page and the predetermined reserved blocks, and compensating the data pixels at the detector in accordance with the corresponding position errors of the data page.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
System and method for providing dynamic tactile feedback on hand-held electronic devices
InactiveUS20050231489A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersElectronic documentData page
Various dynamic tactile feedback is provided to the user of a handheld electronic device through a scrollwheel depending on the types of data, priority of particular data and user preferences. In one embodiment the type of feedback is determined by a software module, which analyses the data being displayed on a display screen, and provides differing types and levels of feedback including resistance to rotational movement, such as free slides, partially resisted rotation, and full stops, as well as lateral motion feedback such as “bumps,”“holes,” and plateaus, to the user through a scrollwheel or scrollwheel. Intelligent software decides what if any feedback should be associated with a particular type of feedback In another embodiment of the invention, information telling the software application to use a particular feedback type is embedded in the data. The system then provides tactile feedback at specified locations according to the embedded data. For example, software reads tactile triggers embedded into a data page, such as an email, electronic document or web page, and then translate these tactile triggers into dynamic tactile feedback which is provided to the user of the handheld device through the scrollwheel.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
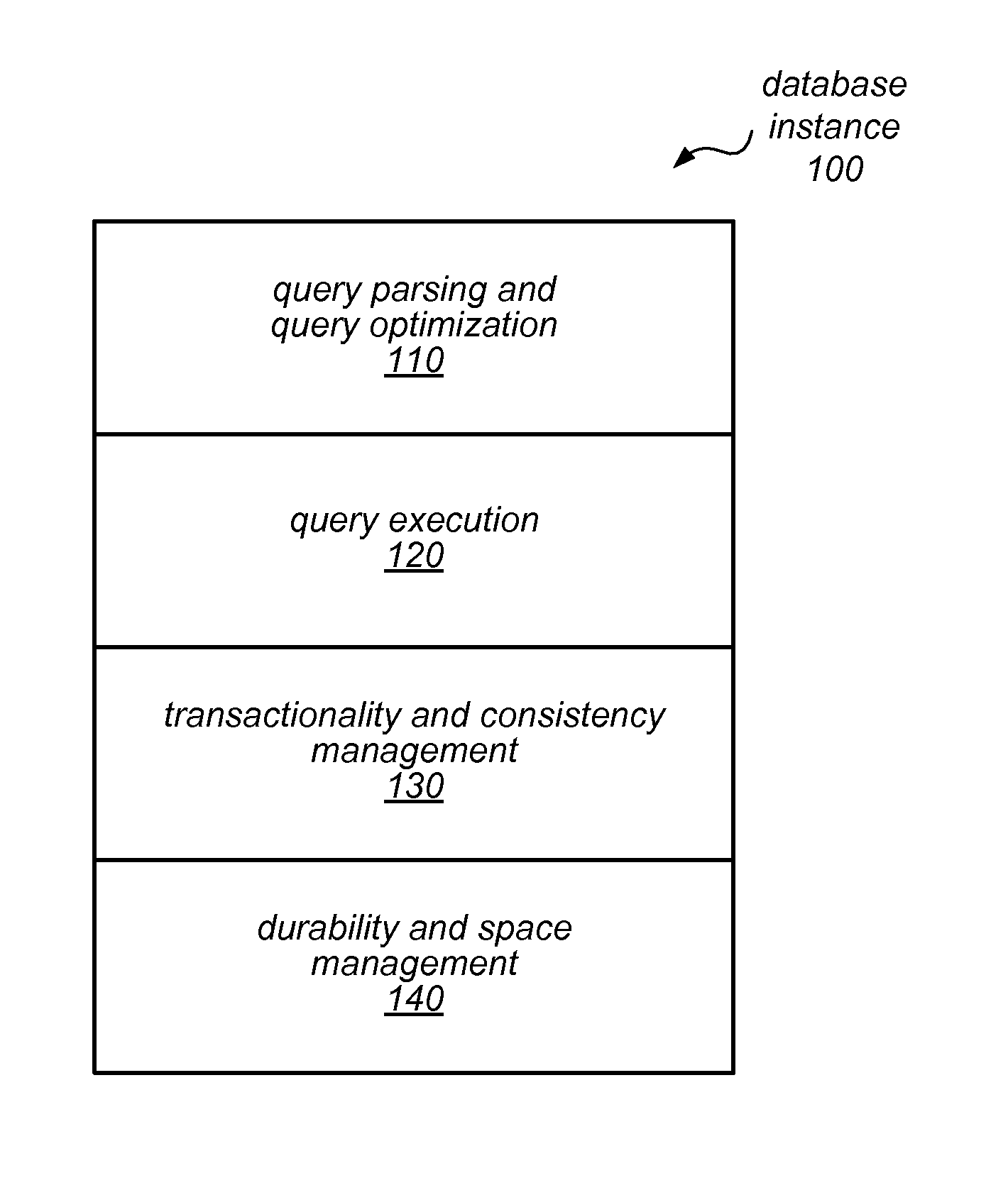
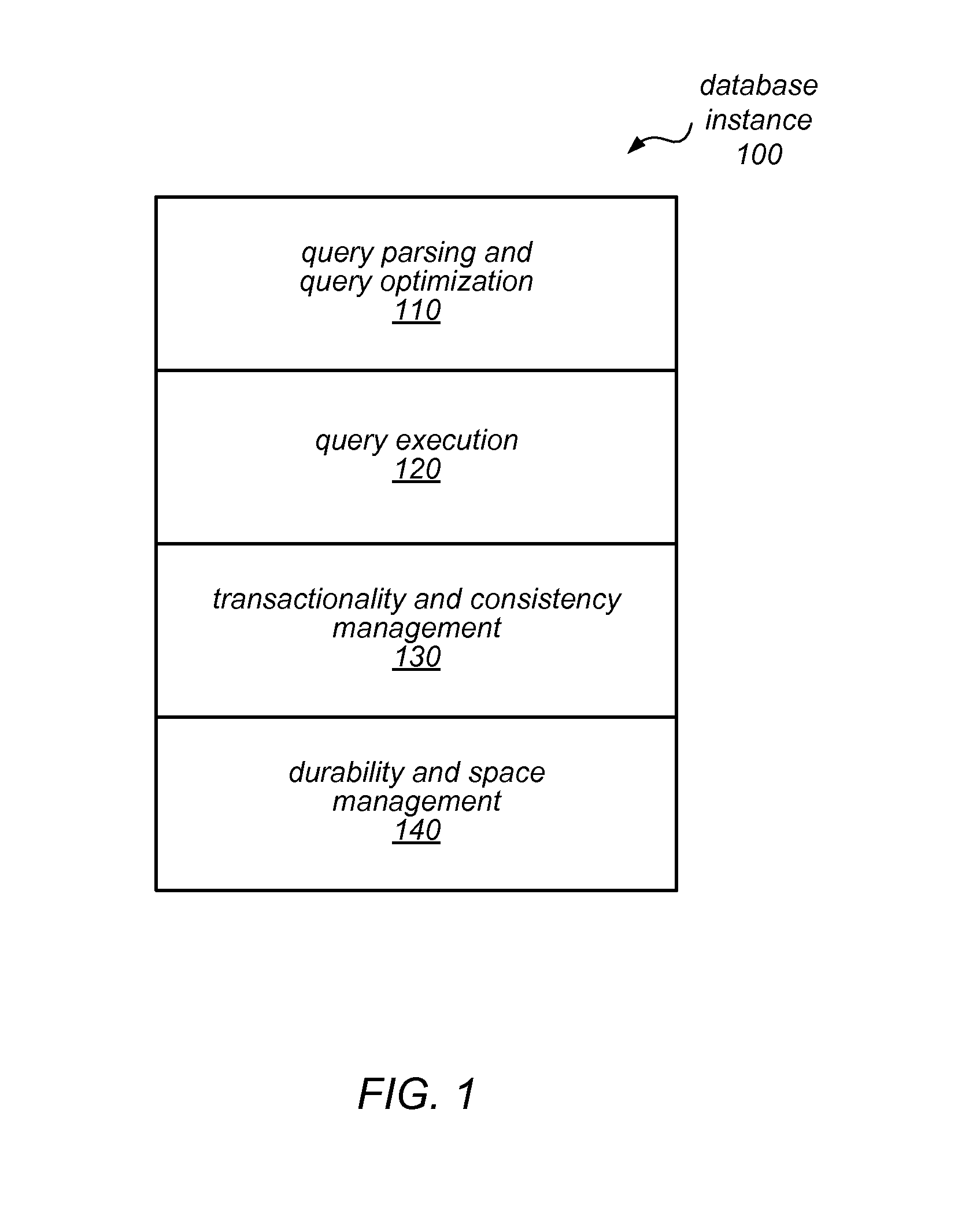
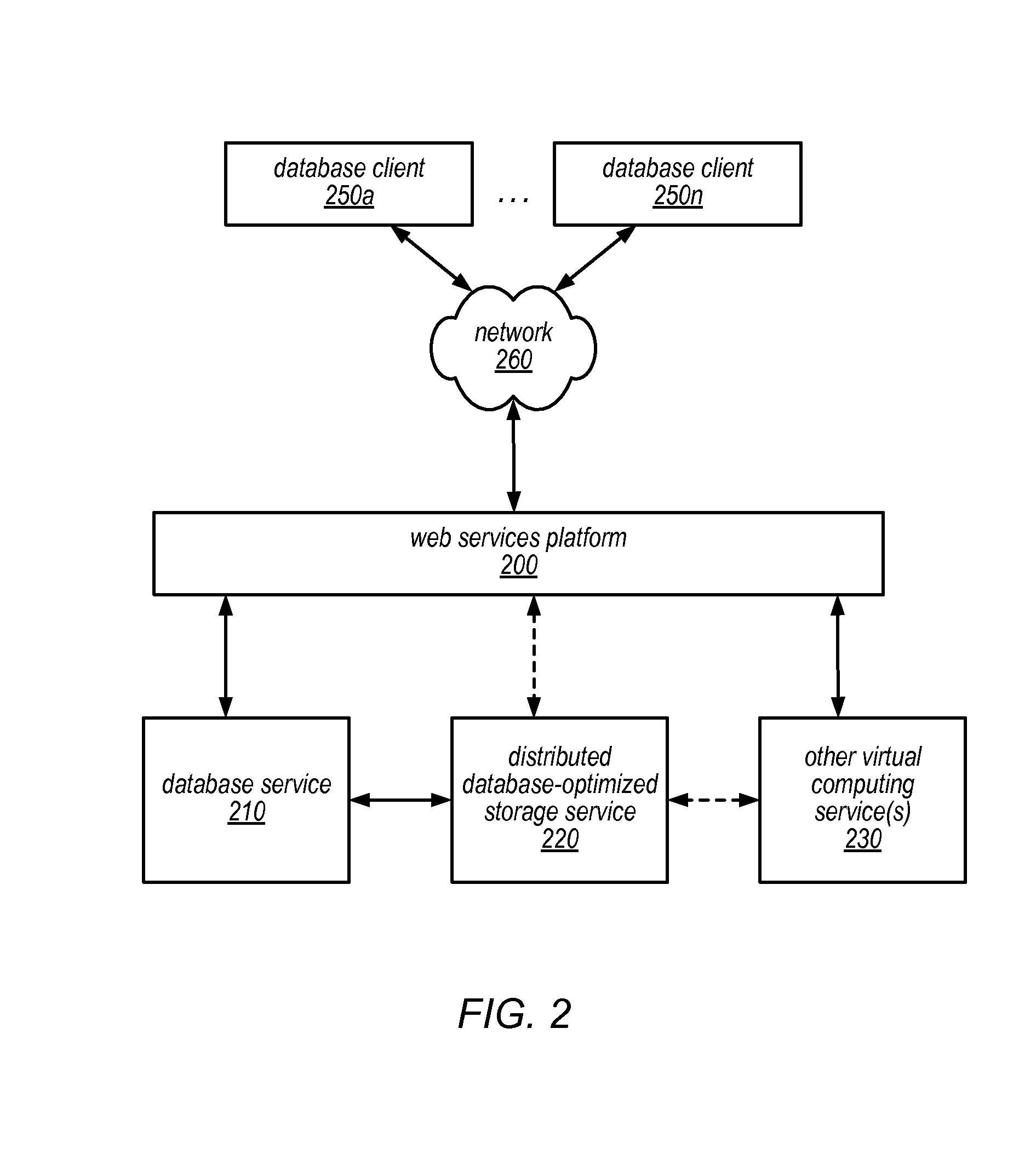
Database system with database engine and separate distributed storage service
ActiveUS20140279929A1Database updatingDigital data processing detailsDatabase servicesDatabase engine
A database system may include a database service and a separate distributed storage service. The database service (or a database engine head node thereof) may be responsible for query parsing, optimization, and execution, transactionality, and consistency, while the storage service may be responsible for generating data pages from redo log records and for durability of those data pages. For example, in response to a write request directed to a particular data page, the database engine head node may generate a redo log record and send it, but not the data page, to a storage service node. The storage service node may store the redo log record and return a write acknowledgement to the database service prior to applying the redo log record. The server node may apply the redo log record and other redo log records to a previously stored version of the data page to create a current version.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Memory device and memory programming method
ActiveUS20100002506A1Reduce errorsRead-only memoriesDigital storageMulti-level cellReal-time computing
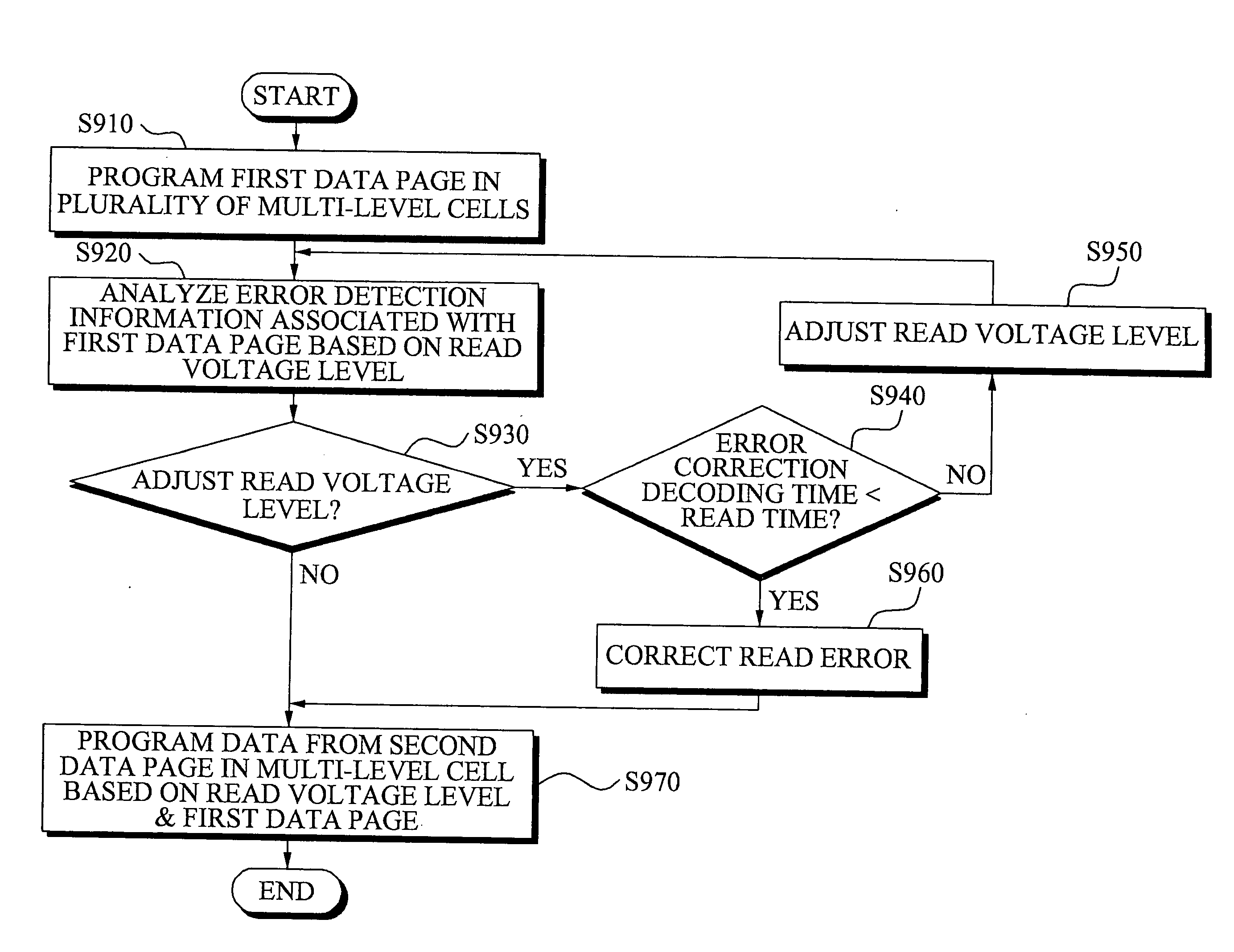
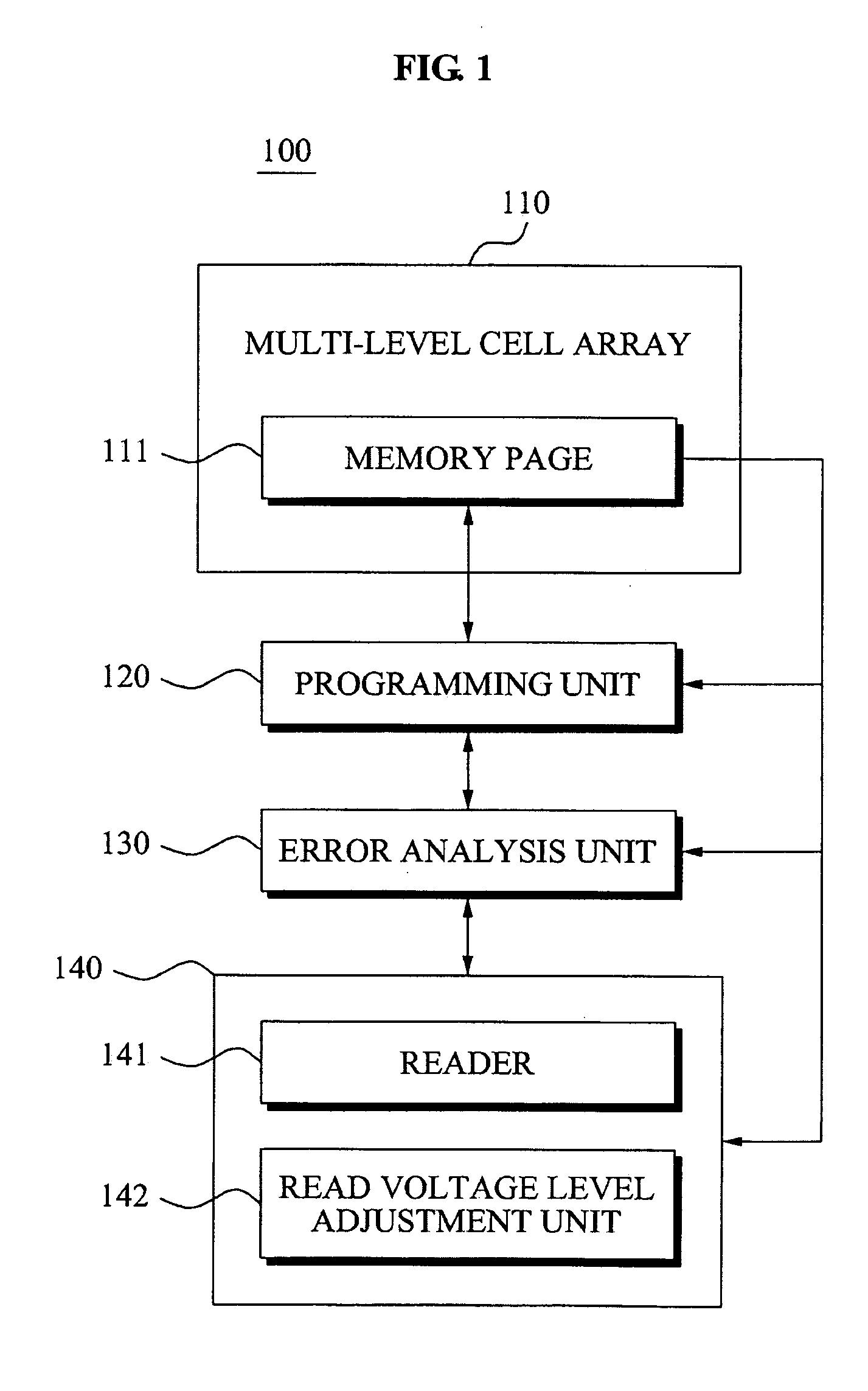
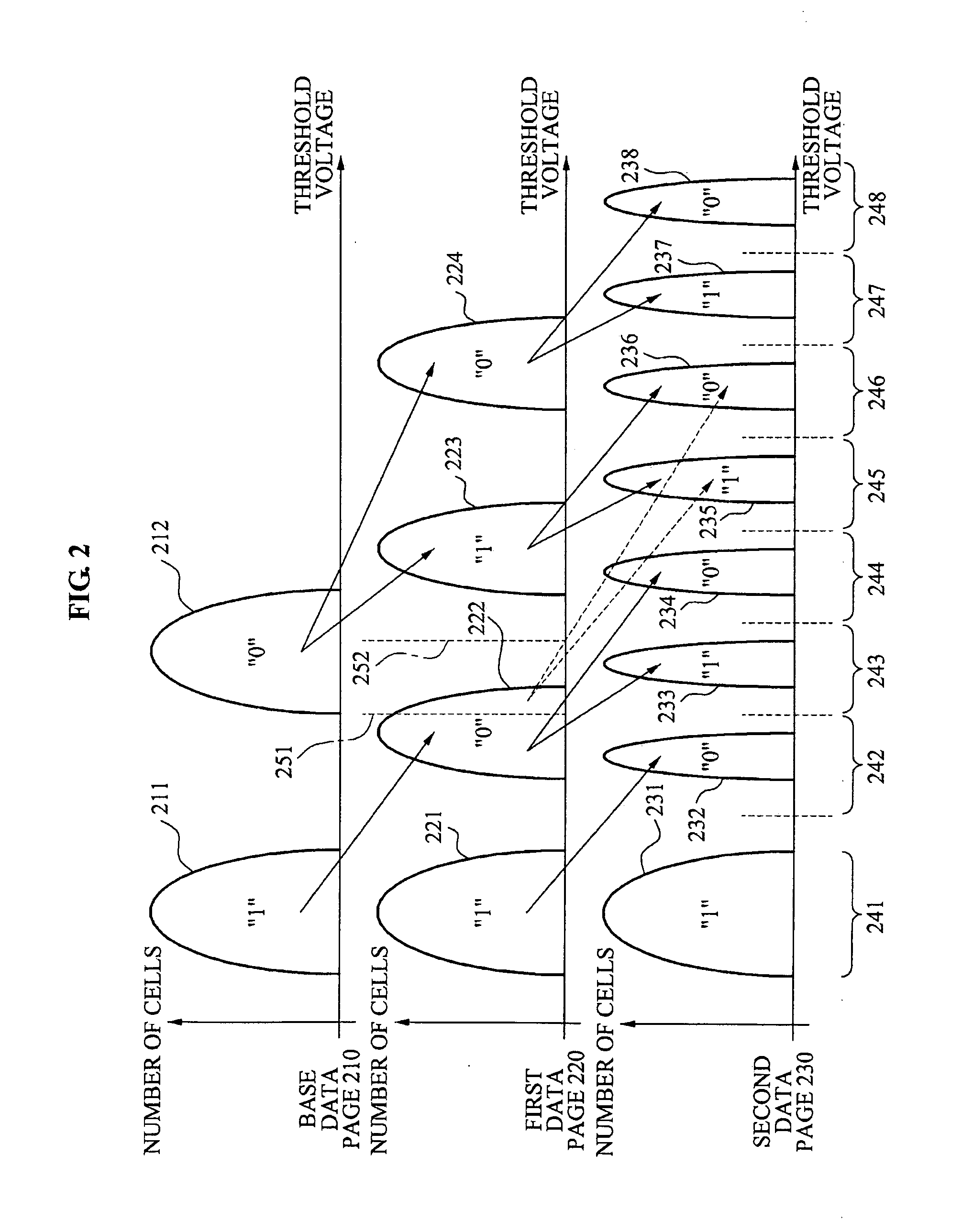
Provided are memory devices and memory programming methods. A memory device may include: a multi-level cell array that includes a plurality of multi-level cells; a programming unit that programs a first data page in the plurality of multi-level cells and programs a second data page in a multi-level cell from among the plurality of multi-level cells in which the first data page is programmed; an error analysis unit that analyzes read error information corresponding to the first data page based on a read voltage level to determine whether to correct a read error based on the analyzed read error information; and a controller that adjusts the read voltage level of the first data page depending on the determination result. Through this, it is possible to reduce an error occurrence when reading and / or programming a data page.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
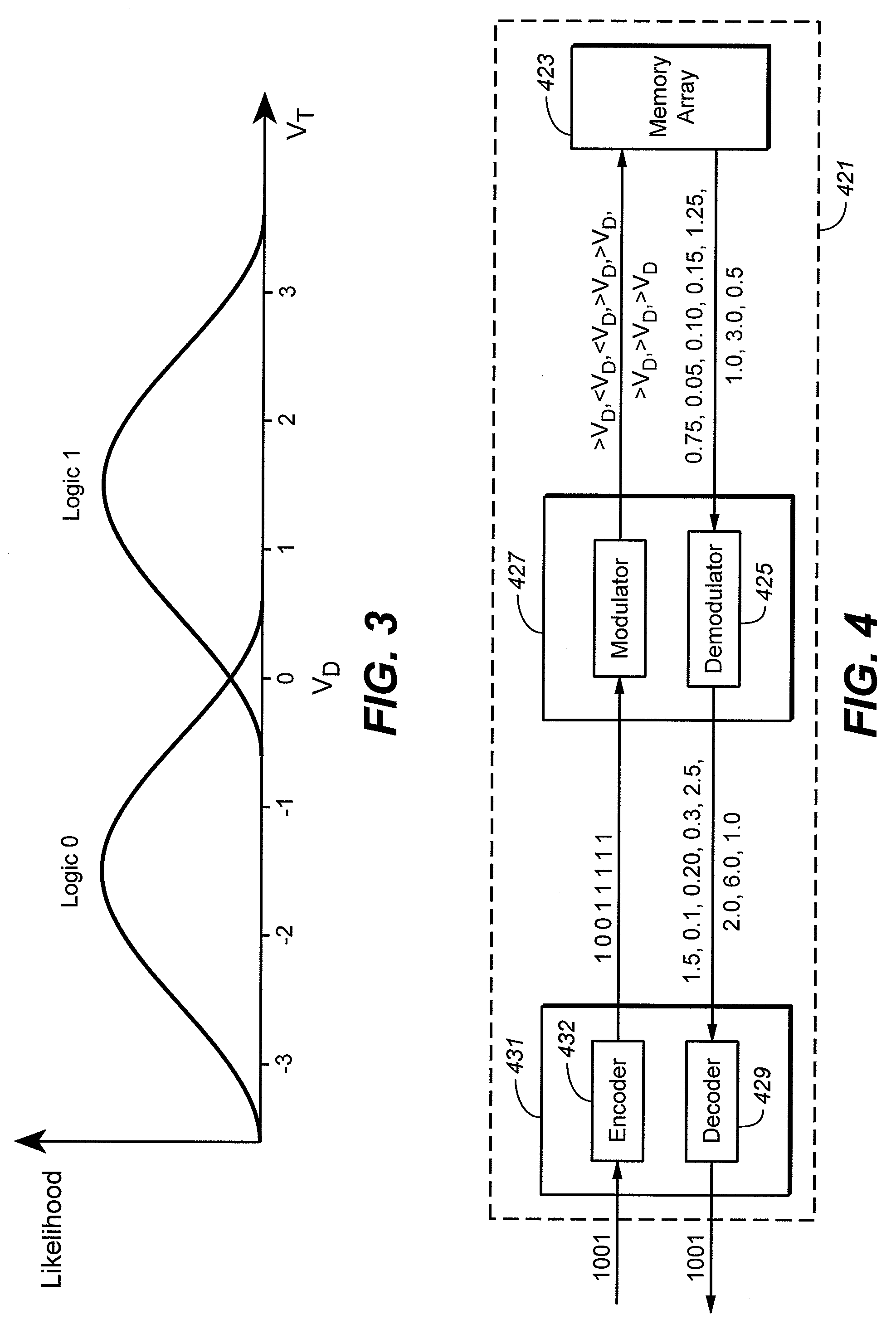
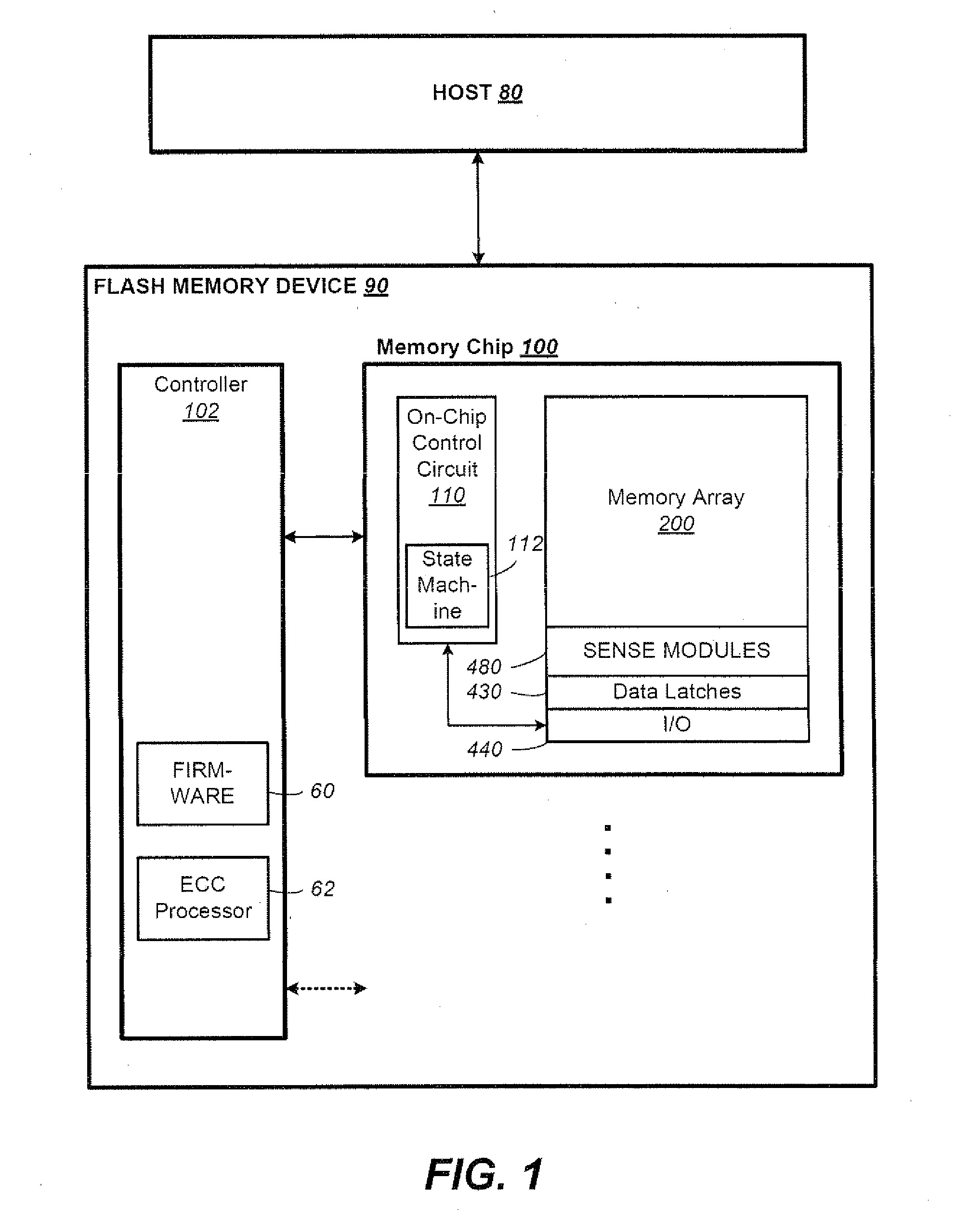
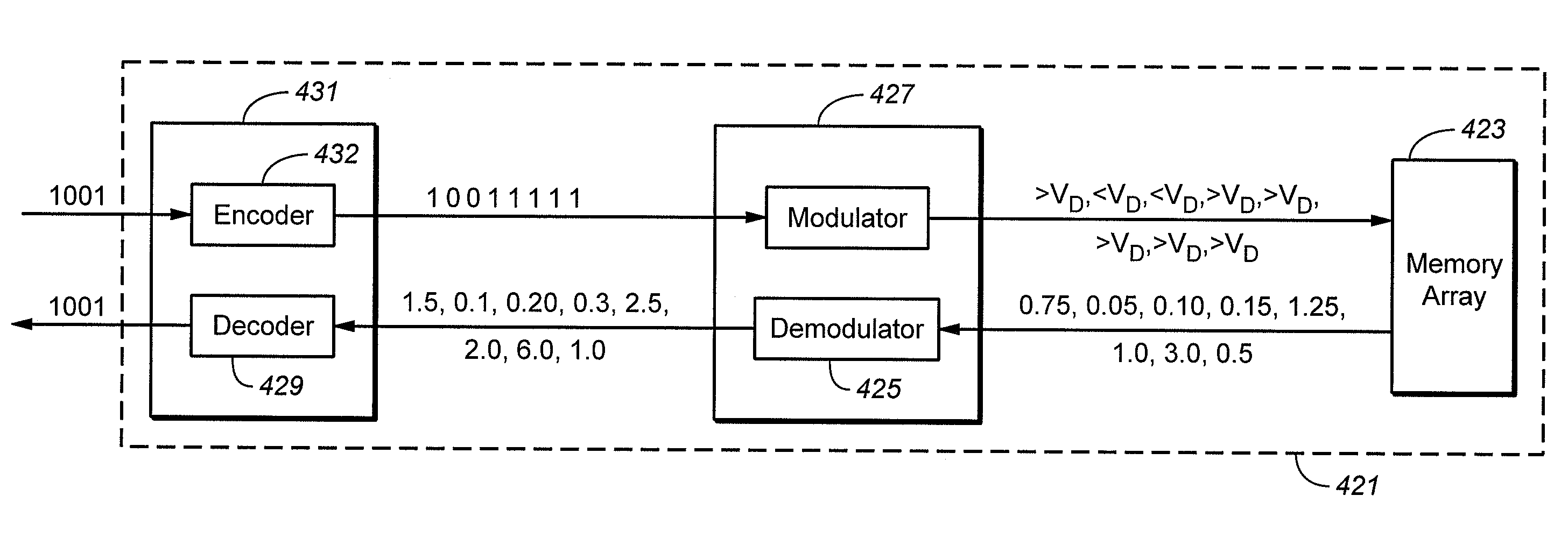
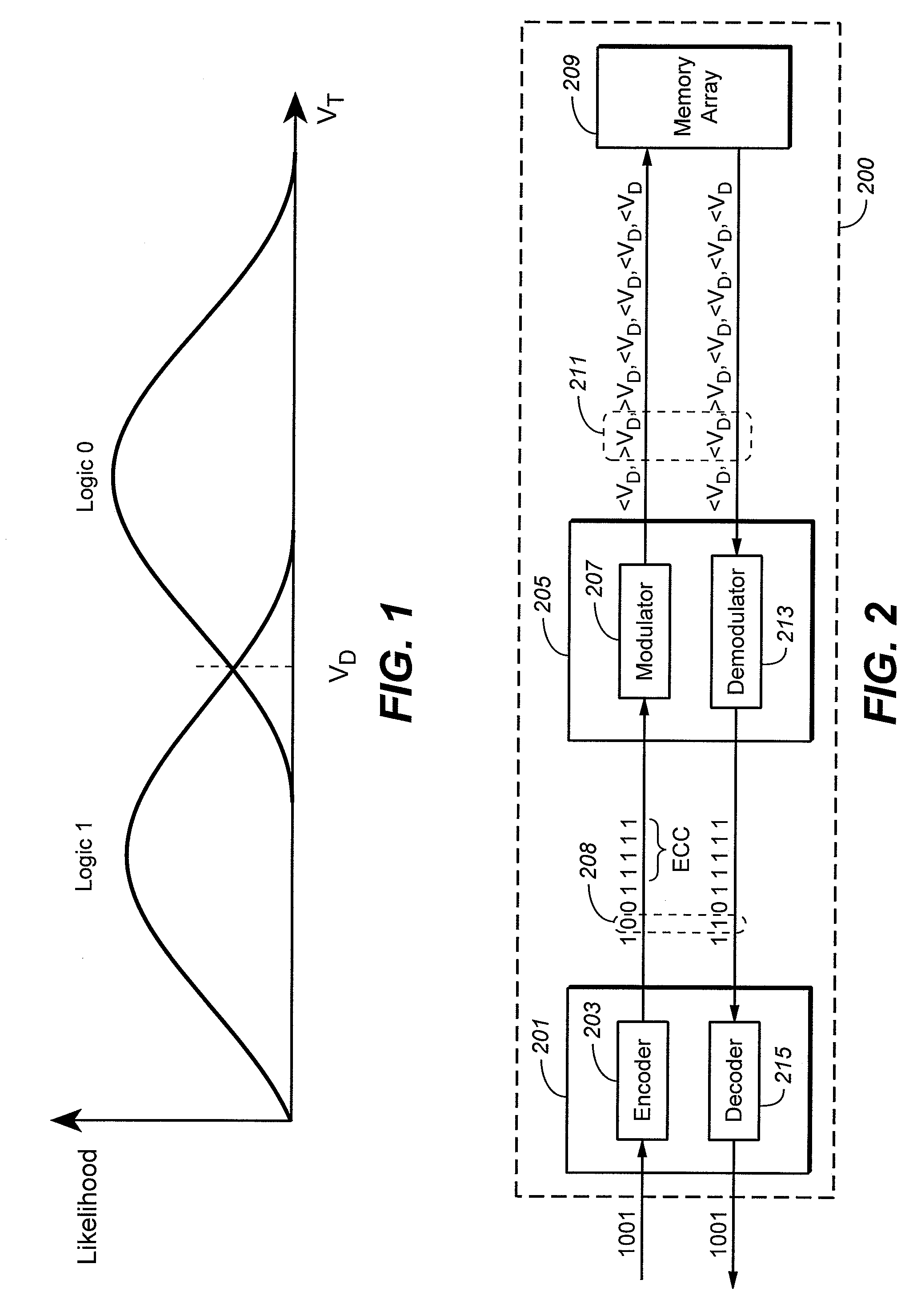
Nonvolatile Memory With Modulated Error Correction Coding
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
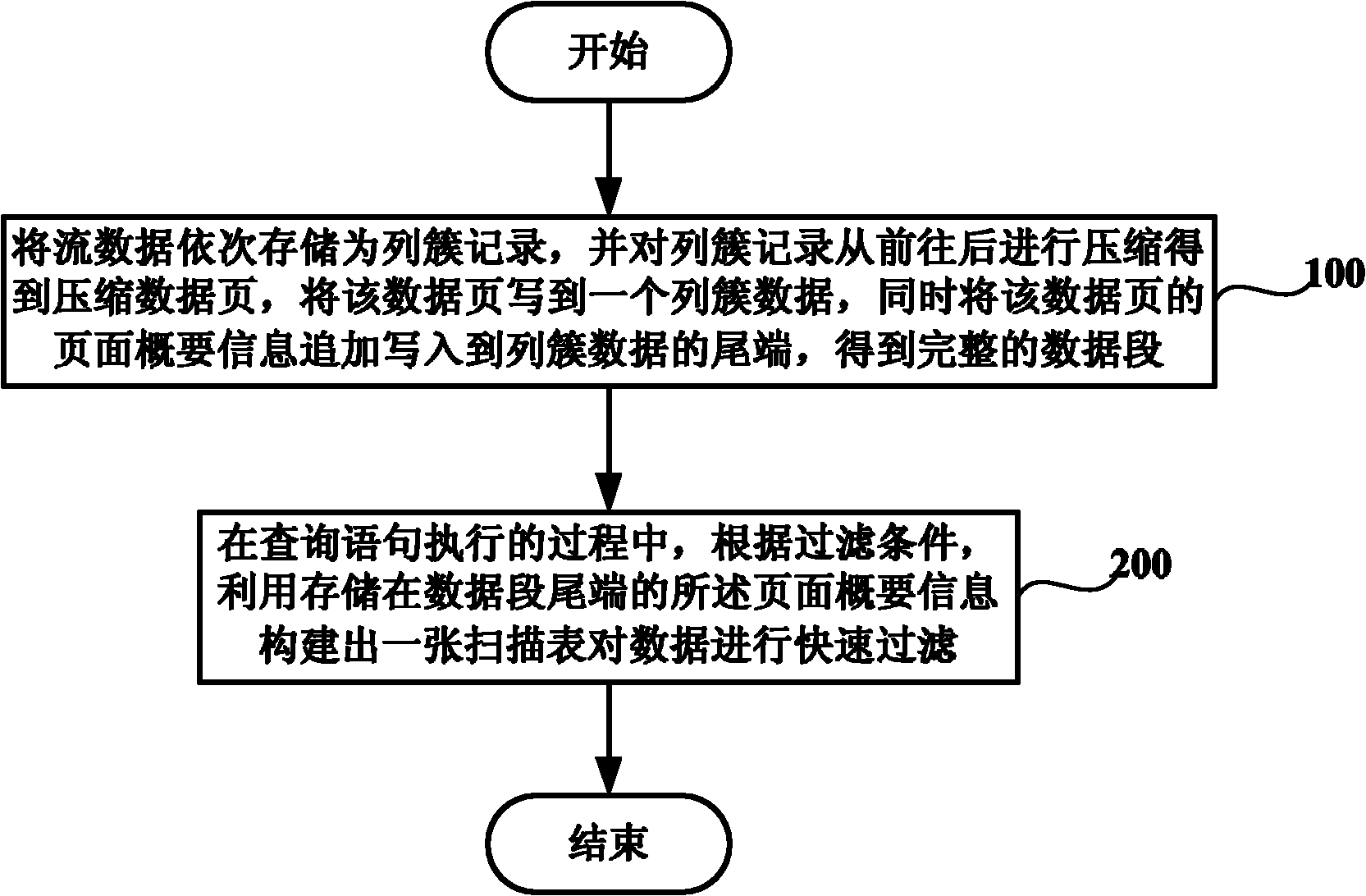
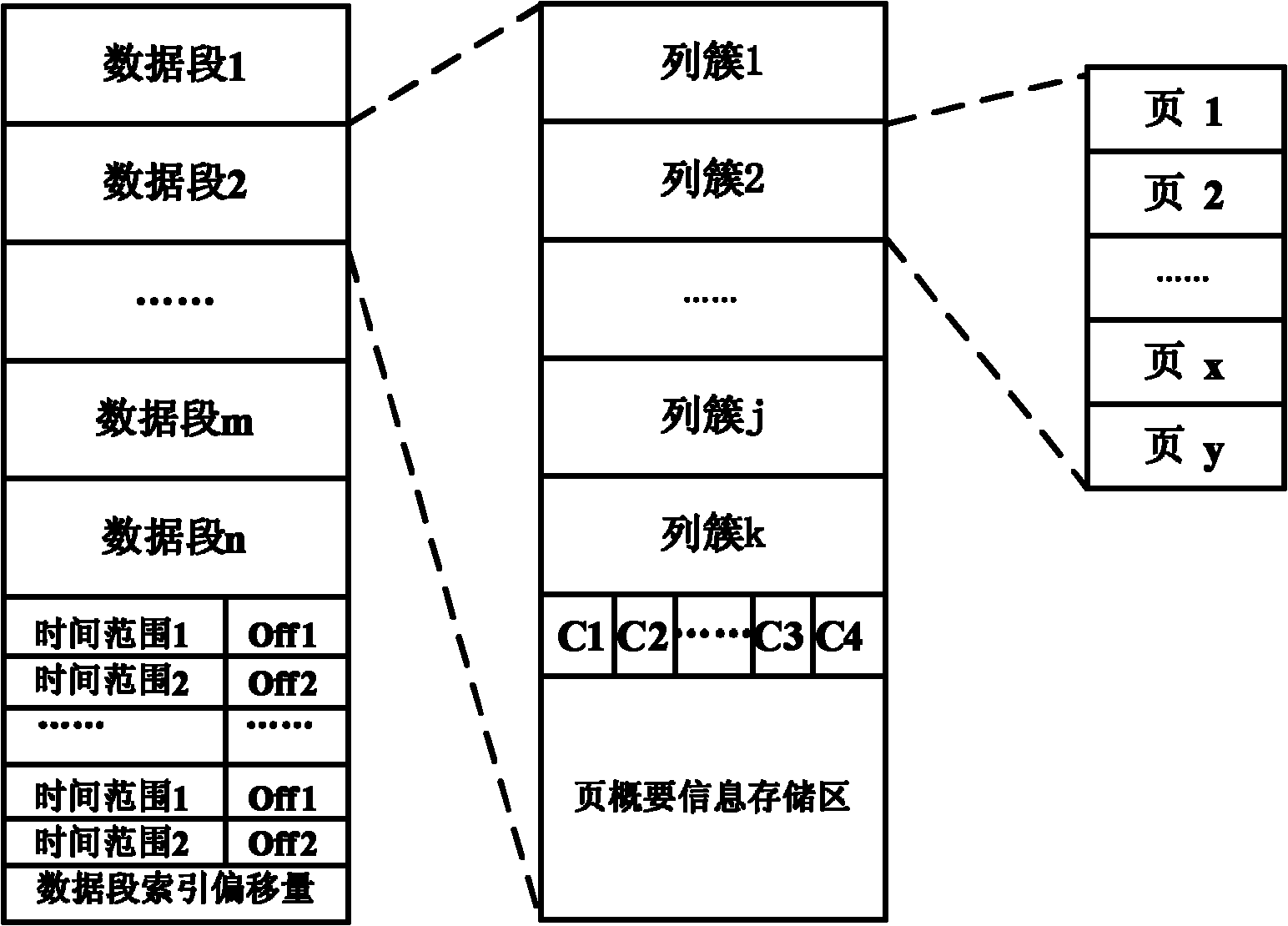
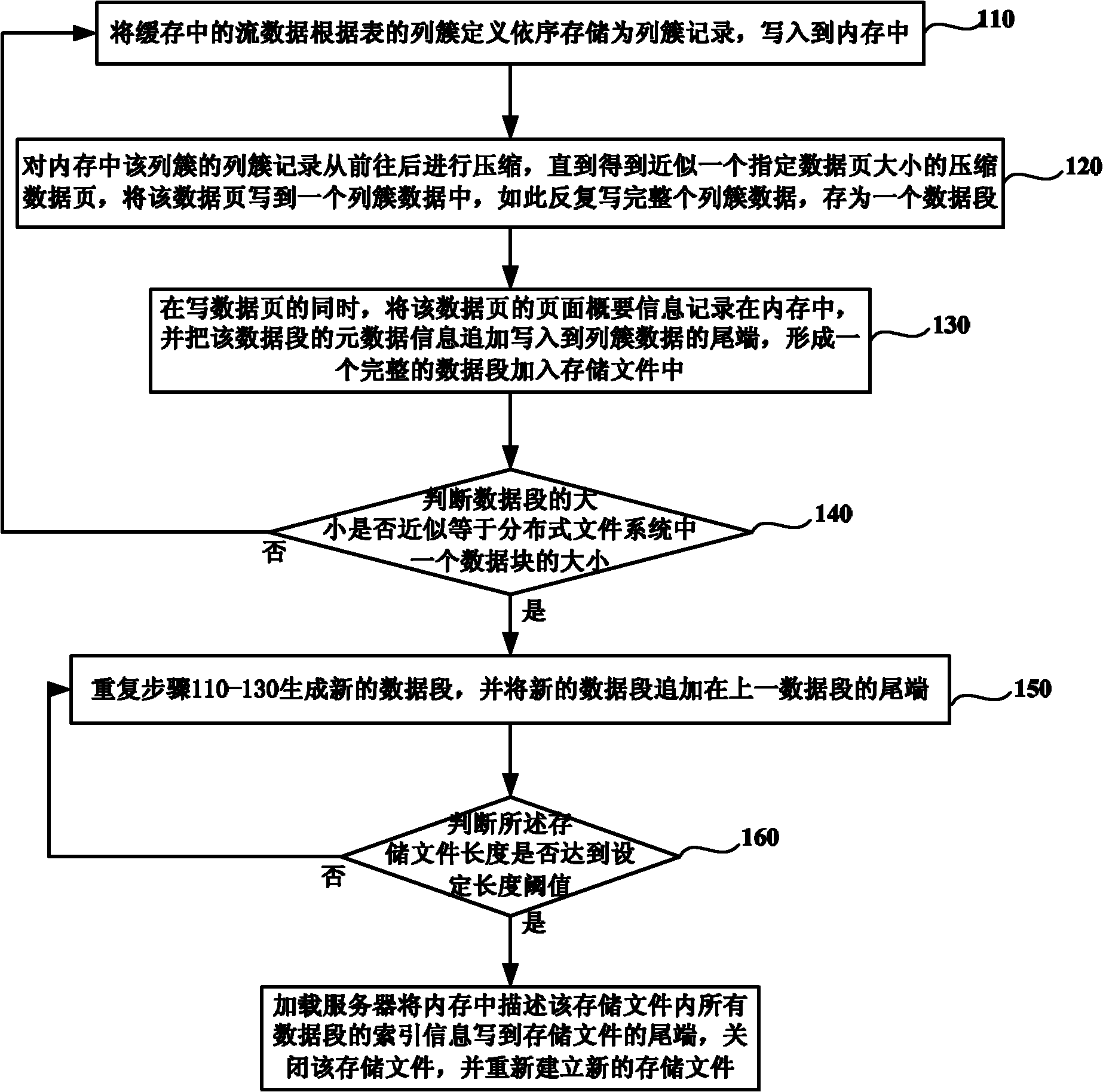
Hadoop-based mass stream data storage and query method and system
InactiveCN101996250AReduce data volumeQuick filterSpecial data processing applicationsStreaming dataClustered data
The invention discloses a Hadoop-based mass stream data storage and query method and a Hadoop-based mass stream data storage and query system. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a segmented column cluster type storage structure; sequentially storing stream data as column cluster records, compressing the column cluster records from front to back to obtain compressed data pages, writing each compressed data page into a piece of column cluster data, and simultaneously additionally writing the page outline information of the compressed data pages into the tail ends of the column cluster data to obtain an integrated data segment; and in the process of executing query statements, constructing a scan table according to filtering restraints by utilizing the page outline information at the tail ends of data segments to quickly filter the data.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
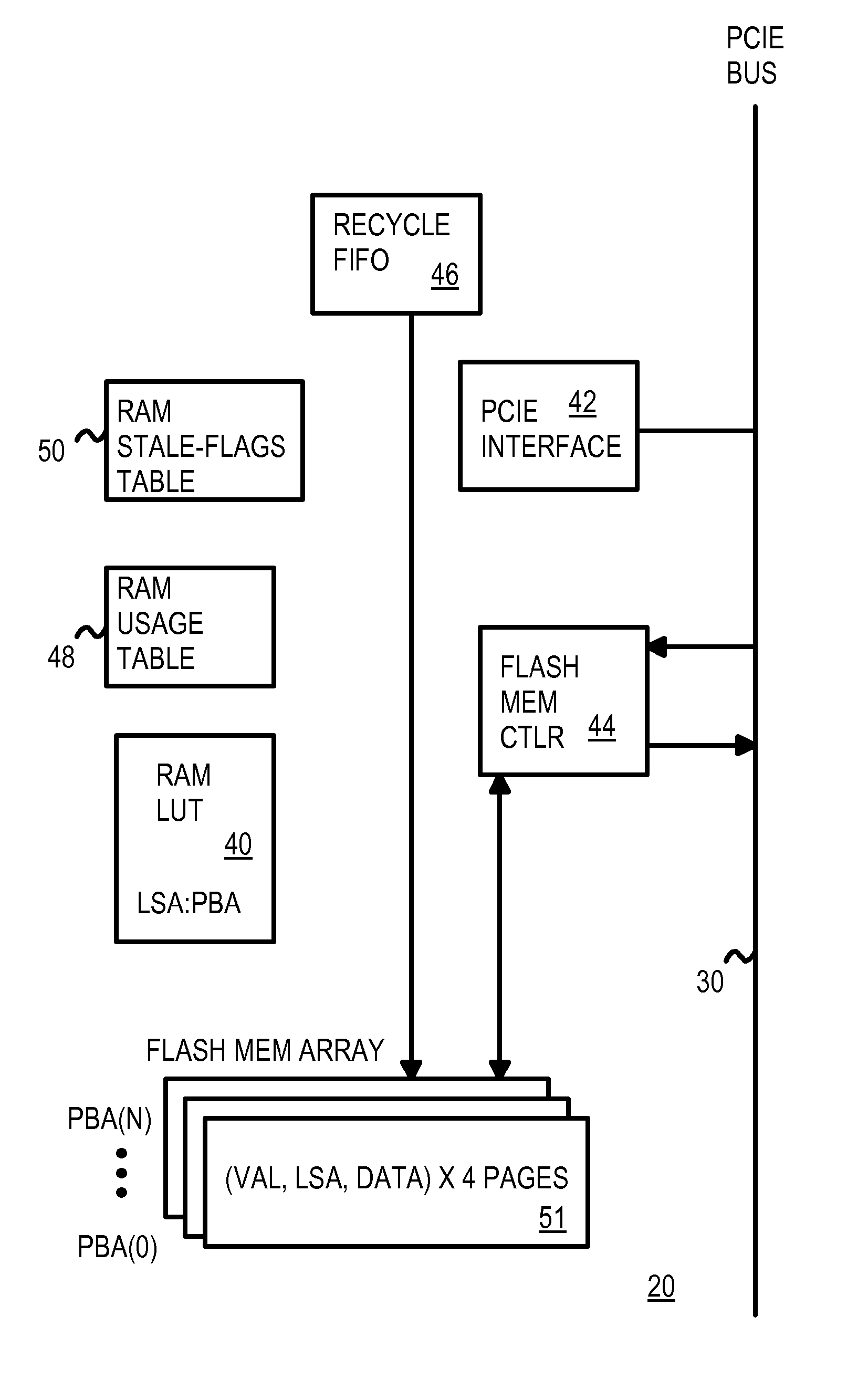
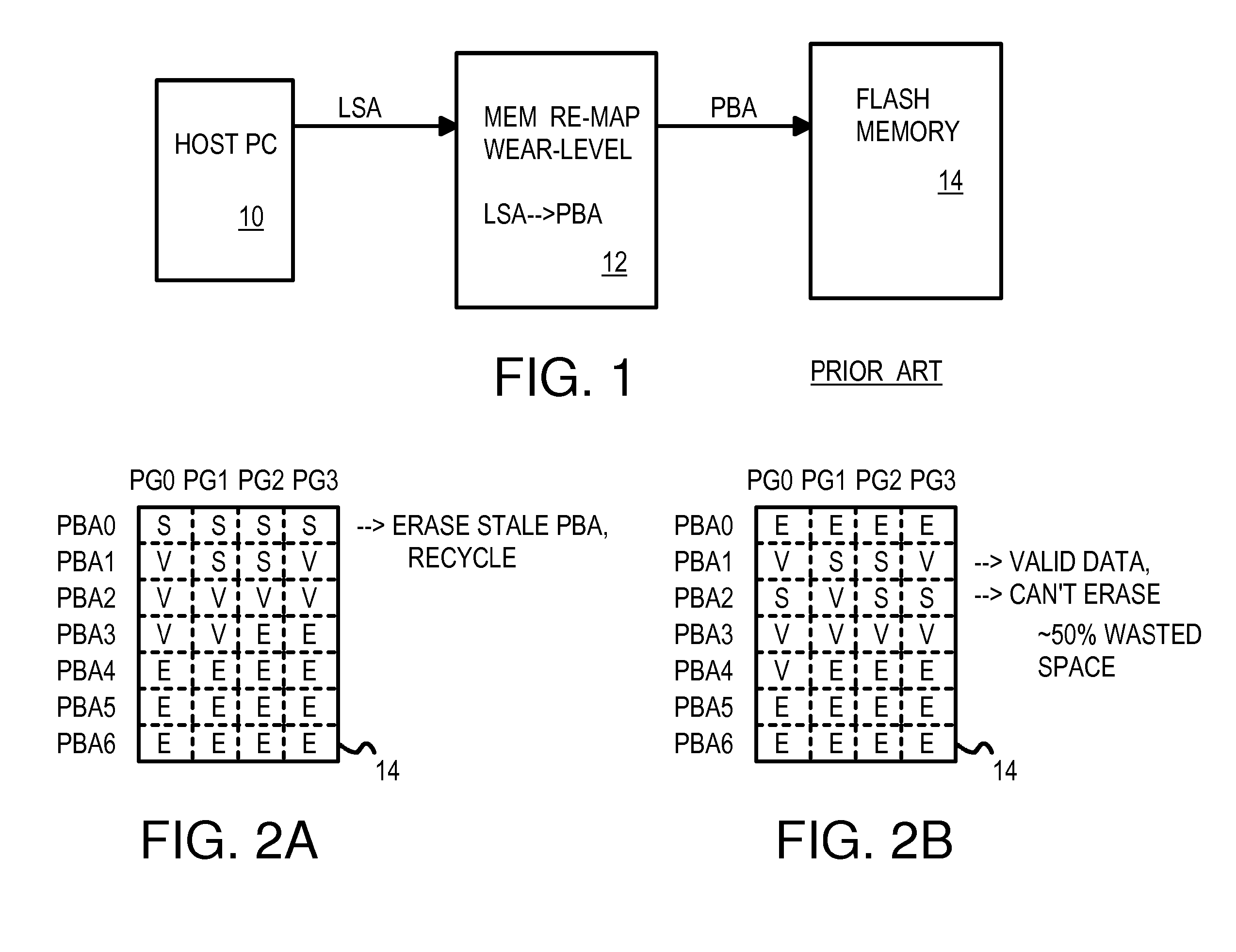
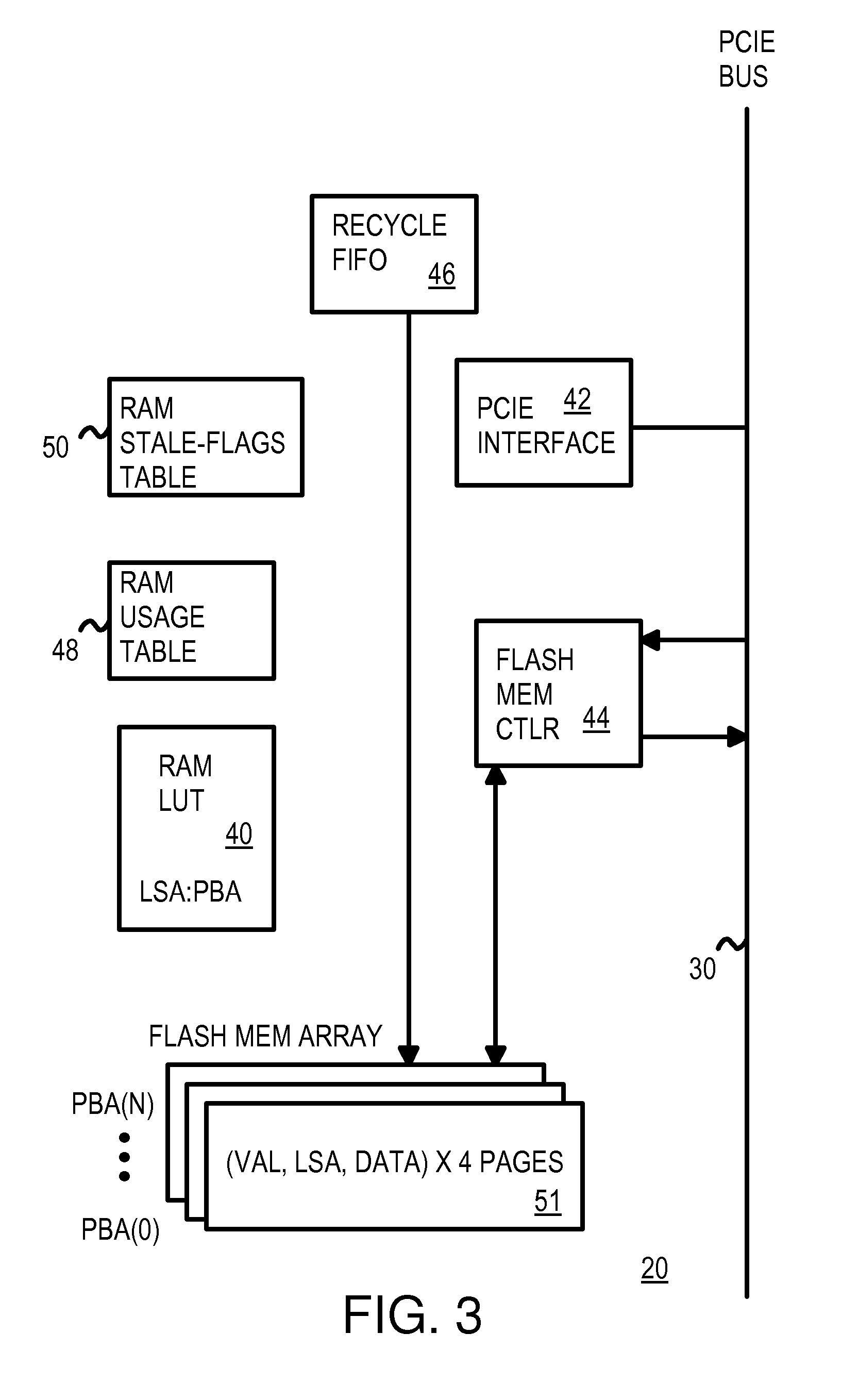
Recycling Partially-Stale Flash Blocks Using a Sliding Window for Multi-Level-Cell (MLC) Flash Memory
InactiveUS20070268754A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationCoupling device detailsSlide windowMulti-level cell
A sliding window of flash blocks is used to reduce wasted space occupied by stale data in a flash memory. The sliding window slides downward over a few flash blocks. The oldest block is examined for valid pages of data, and the valid pages are copied to the end of the sliding window so that the first block has only stale pages. The first block can then be erased and eventually re-used. A RAM usage table contains valid bits for pages in each block in the sliding window. A page's valid bit is changed from an erased, unwritten state to a valid state when data is written to the page. Later, when new host data replaces that data, the old page's valid bit is set to the stale state. A RAM stale-flags table keeps track of pages that are full of stale pages.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
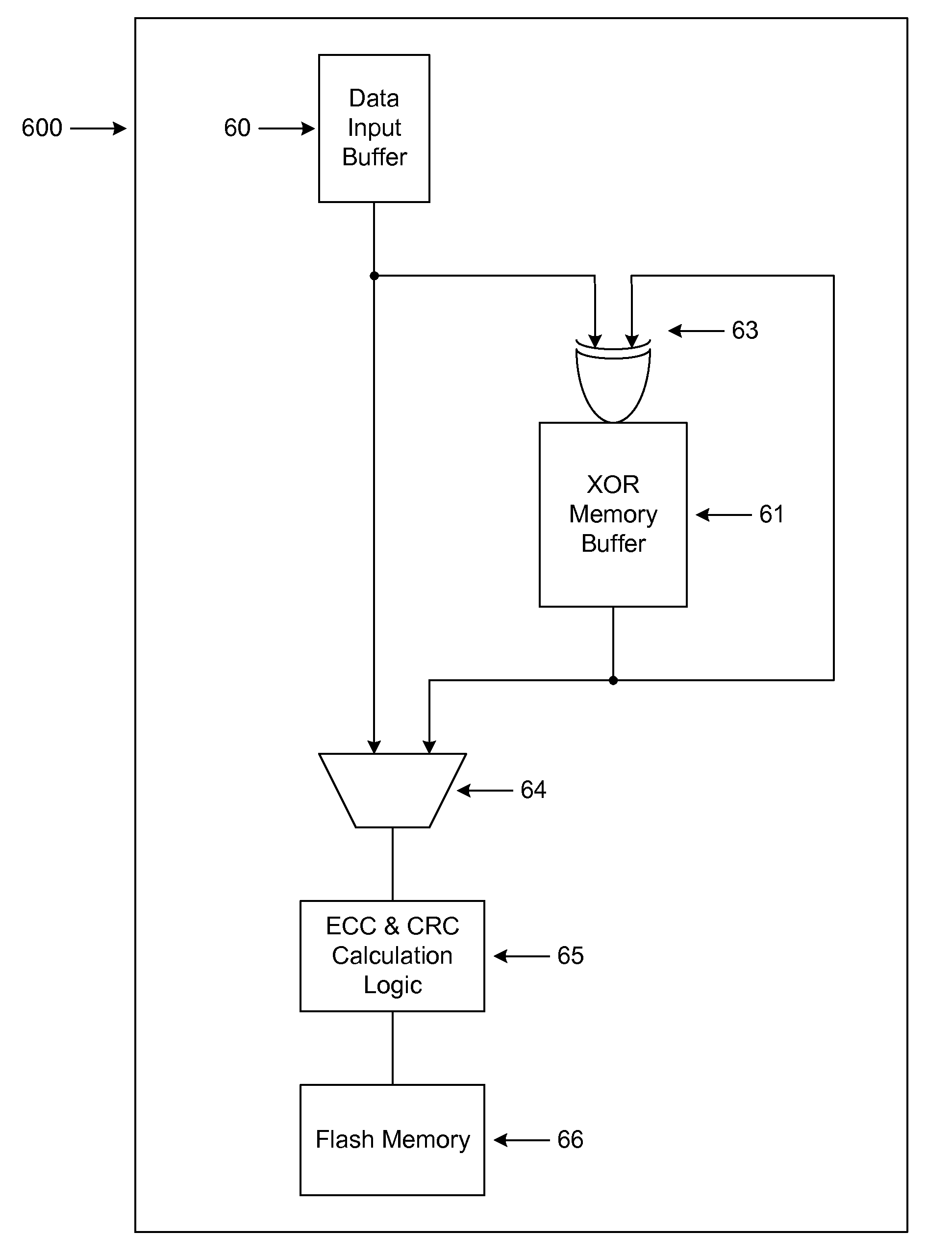
Data Recovery for Defective Word Lines During Programming of Non-Volatile Memory Arrays
The recovery of data during programming, such as in the case of a broken word-line, is considered. The arrangement described assumes that k pages may be corrupted when the system finishes programming a block. Then these corrupted pages can be recovered using an erasure code. In order to recover any k pages, the system will compute and temporarily store k parity pages in the controller. These k parity pages may be computed on-the-fly as the data pages are received from the host. Once programming of the block is finished, a post-write read may be done in order to validate that the data is stored reliably. If no problem is detected during EPWR, then the parity pages in the controller may be discarded. In case a problem is detected, and data in up to k pages is corrupt on some bad word-lines, then the missing data is recovered using the k parity pages that are stored in the controller and using the other non-corrupted pages that are read from the block of the memory array and decoded. Once the recovery is complete the block can be reprogrammed and the temporary parity pages in the controller may be discarded upon successfully reprogramming.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Methods of Modulating Error Correction Coding
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method for recording event logs and database engine
ActiveCN103729442AReduce lock granularityHigh speedError detection/correctionDatabase distribution/replicationGranularityTransaction log
The invention discloses a method for recording event logs and a database engine, and belongs to the technical field of databases. The method includes the steps that an SQL request is received; according to the SQL request, data pages corresponding to the SQL request are modified; corresponding event logs are generated for the modification; the event logs are partitioned to obtain a plurality of log segments, the log segments are written into a plurality of buffer queues, and the log segments in the buffer queues are written into a log file. The database engine comprises a receiving module, a modifying module, a generating module and writing-in module. According to the method for recording event logs and the database engine, the event logs can be recorded in parallel; due to the fact that the buffer queues are multiple and written into the log file in a parallel processing mode, not only is the lock granularity of the event log buffer queues reduced, but also the speed for writing the log file into a disk is greatly increased, the performance of a database system is improved, and user experience is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI CLOUD COMPUTING TECH CO LTD
Storing Compressed Data
ActiveUS20100017578A1Lower requirementSimple and efficient storageMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram control using stored programsVirtual memoryParallel computing
A method of processing data for storage in a storage medium coupled to a processing unit adapted to access data stored in the storage medium as one or more pages of data, each page having a predetermined page size and a corresponding virtual memory address, the method comprising: obtaining a compressed data item including compressed data corresponding to a first memory page of uncompressed data; dividing the compressed data item into an initial part and a supplementary part, the initial part having an initial part size; determining respective second memory locations for the supplementary parts so as to reduce the number of sectors occupied by the supplementary parts; allocating the initial part together with an index data item at a first memory location associated with the first memory page, the index data item being indicative of a second memory location; allocating the supplementary part at the second memory location.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method, terminal and system of data presentation
ActiveCN103703789AAvoid complex operationsRecording carrier detailsRecord information storageComputer terminalComputer science
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Secure Flash-based Memory System with Fast Wipe Feature
ActiveUS20120166715A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionEmergent systemsLogical operations
A Flash-based storage system, card, and / or module comprises a Flash controller configured to encrypt the data pages of a page stripe by shuffling the data pages, including loading each data page into a data shuffling buffer in a sequential order relative to other data pages in the page stripe, and thereafter unloading each data page in a non-sequential order relative to other data pages in the page stripe. The Flash controller is also configured to scramble the data pages of the page stripe by performing a bitwise logical operation on the data pages that are unloaded from the data shuffling buffer. A user key and one or more system keys are used to perform the shuffling and scrambling. The Flash controller is further configured to flush the user key by bypassing the system's backup power supply and performing an emergency system shutdown without backing up system data.
Owner:IBM CORP
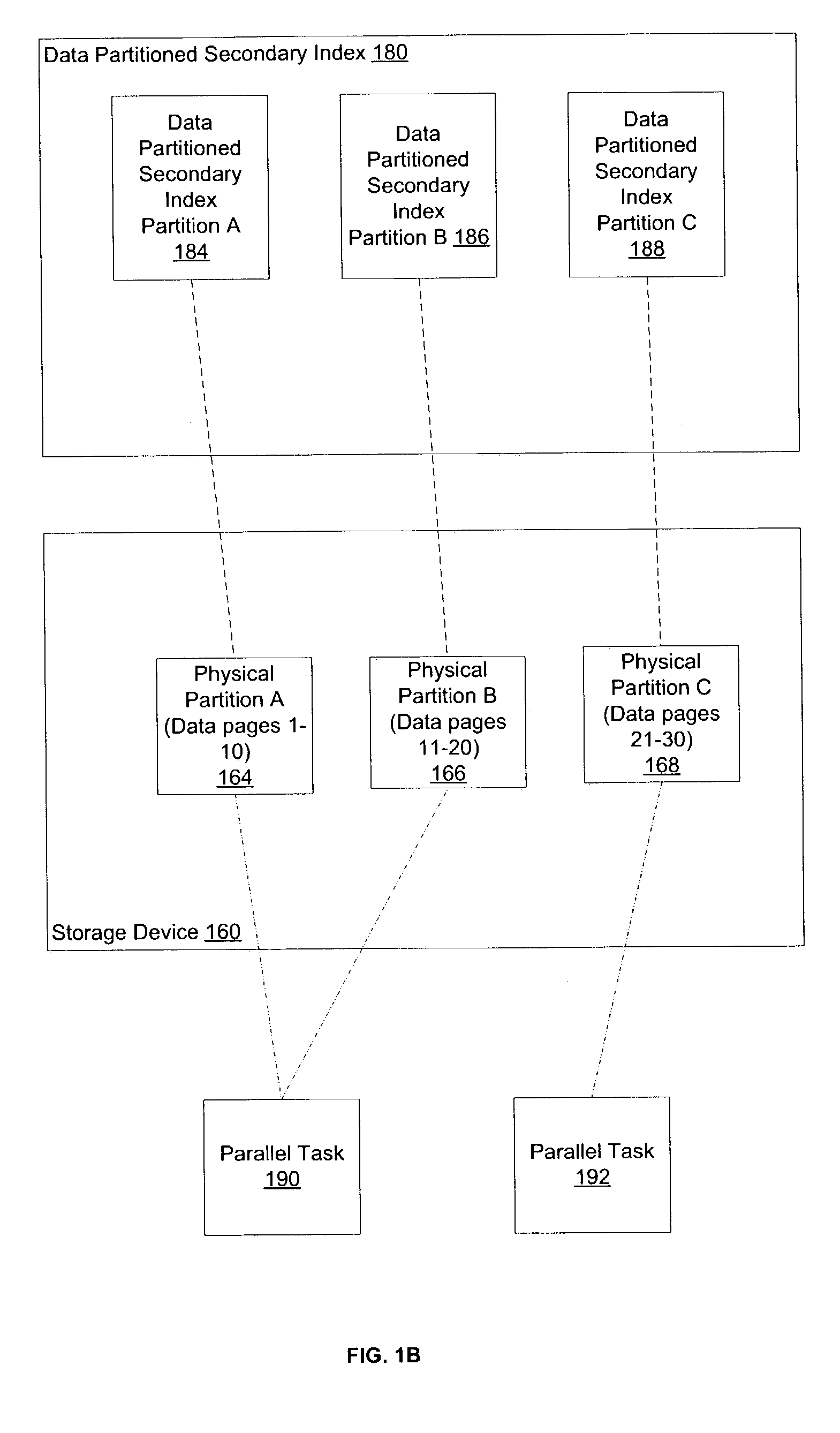
Method, system, and program for optimizing database query execution
Disclosed is a method, system, and program for database query execution. A range of data pages is assigned to each of multiple parallel tasks. For each of the multiple parallel tasks, the range of data pages is mapped to one or more physical partitions, and a data partitioned secondary index partition associated with each of the one or more physical partitions is identified. Each of the multiple parallel tasks is executed to process the database query against the assigned range of data pages using the one or more data partitioned secondary index partitions.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
FLASH-based Memory System With Variable Length Page Stripes Including Data Protection Information
ActiveUS20110040926A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVariable lengthData storing
Methods and apparatuses for enhanced protection of data stored in a FLASH memory system involve a controller capable of protecting data using different size page stripes. The controller is configured to store data in FLASH memory devices in the form of page stripes, each page stripe comprising a plurality of pages of information, each page of information being stored in a different FLASH memory chip. The controller stores the data in a manner such that the pages making up each page stripe includes a plurality of data pages and at least one data protection page. In one implementation, the page stripes stored by the controller include a first page stripe having N data pages and one data protection page, and a second page stripe having M data pages and one data protection page, where N is an integer greater than three and M is an integer less than N.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Multiple access holographic communications apparatus and methods
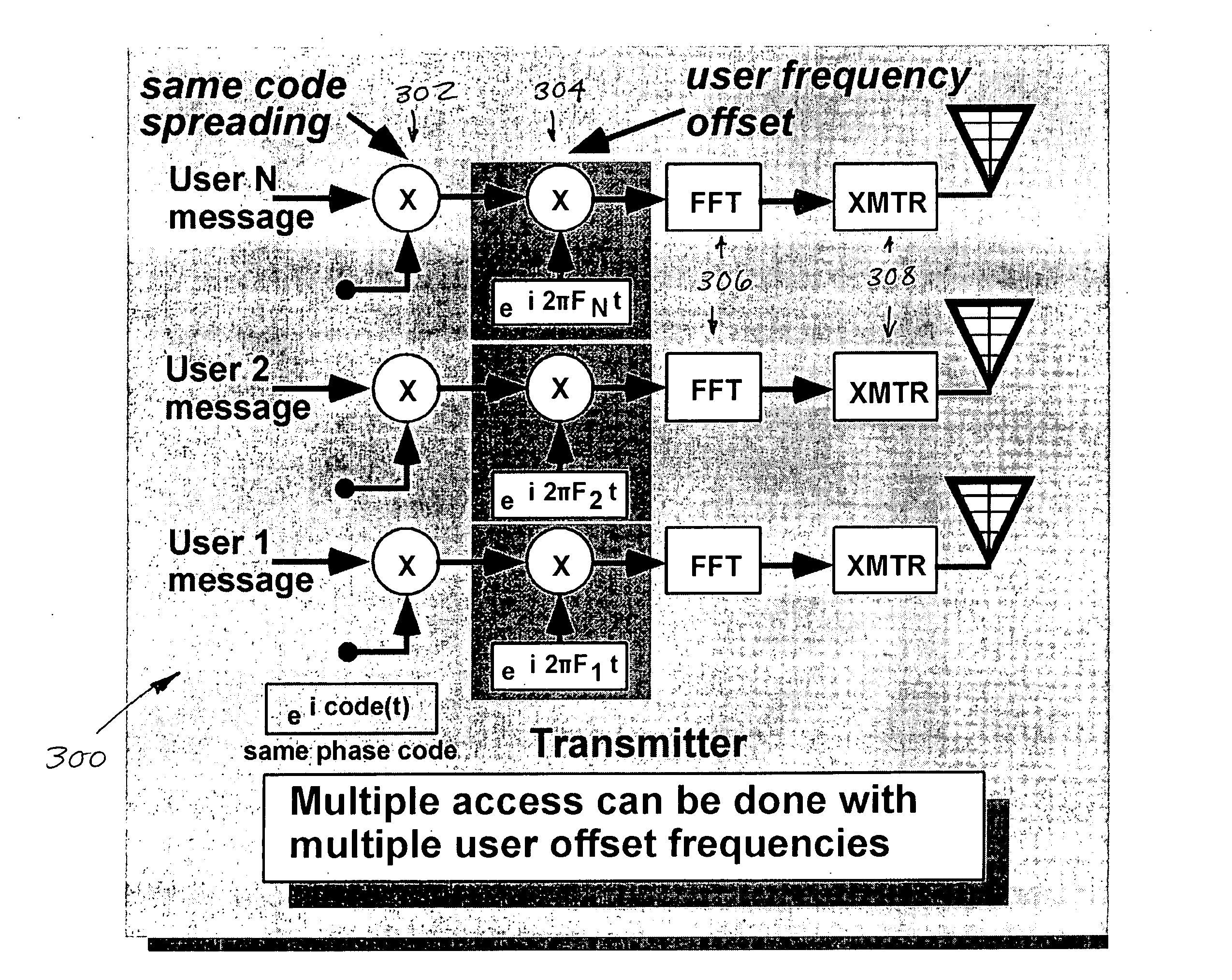
Improved apparatus and methods for utilizing holographic waveforms for a variety of purposes including communication, ranging, and detection. In one exemplary embodiment, the holographic waveforms are transmitted over an RF bearer medium to provide, inter alia, highly covert communications, radar systems, and microwave data links. The bearer (i.e., carrier) is optionally frequency-hopped, and various pulse modulation techniques applied in order to further increase communications efficiency and covertness. Methods of providing multiple access including multiple data “pages”, and high bandwidth data transmission, are also disclosed. Improved apparatus utilizing these features; e.g., a wireless miniature covert transceiver / locator, are also disclosed.
Owner:HOLOWAVE
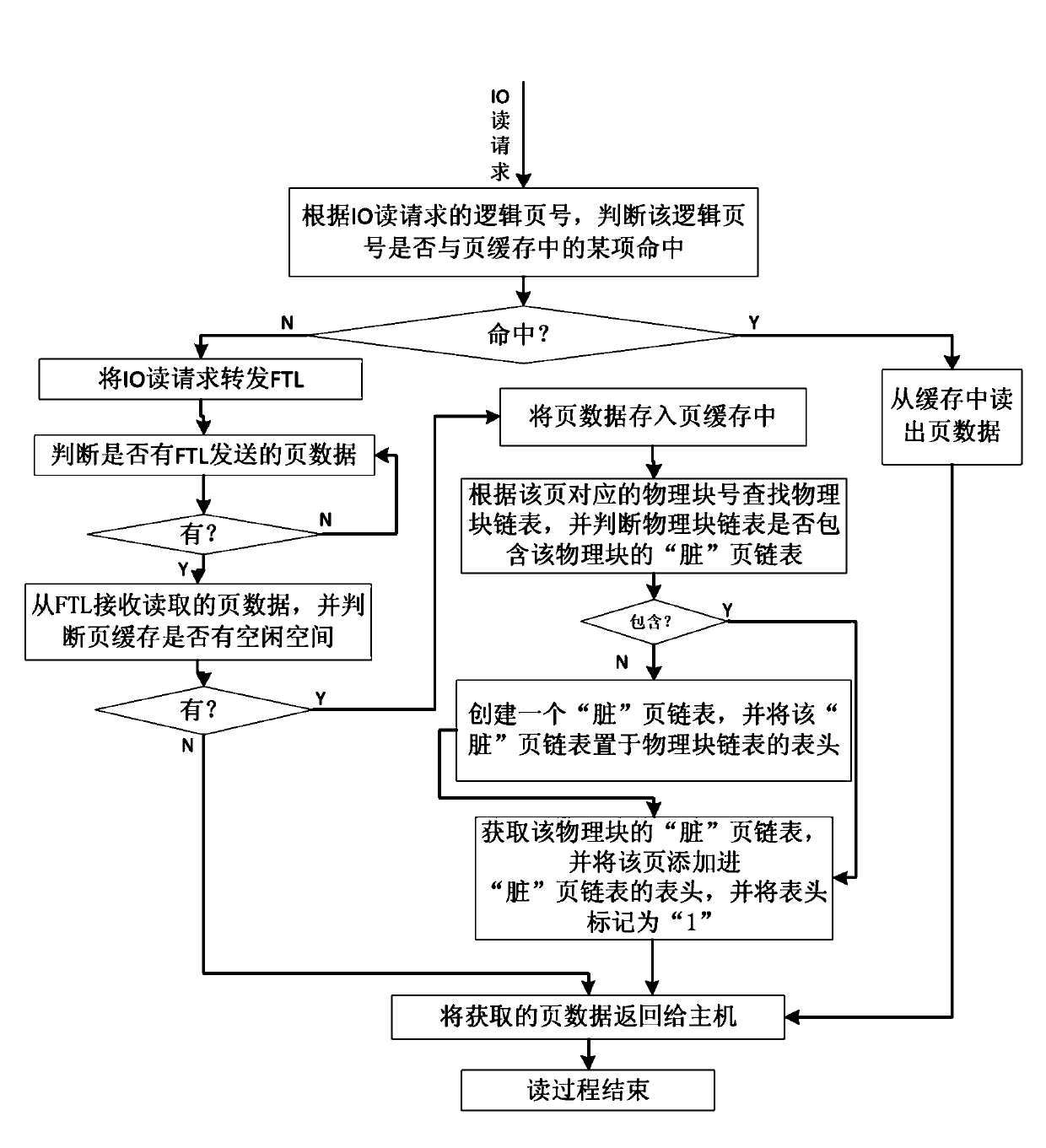
Cache management method for solid-state disc
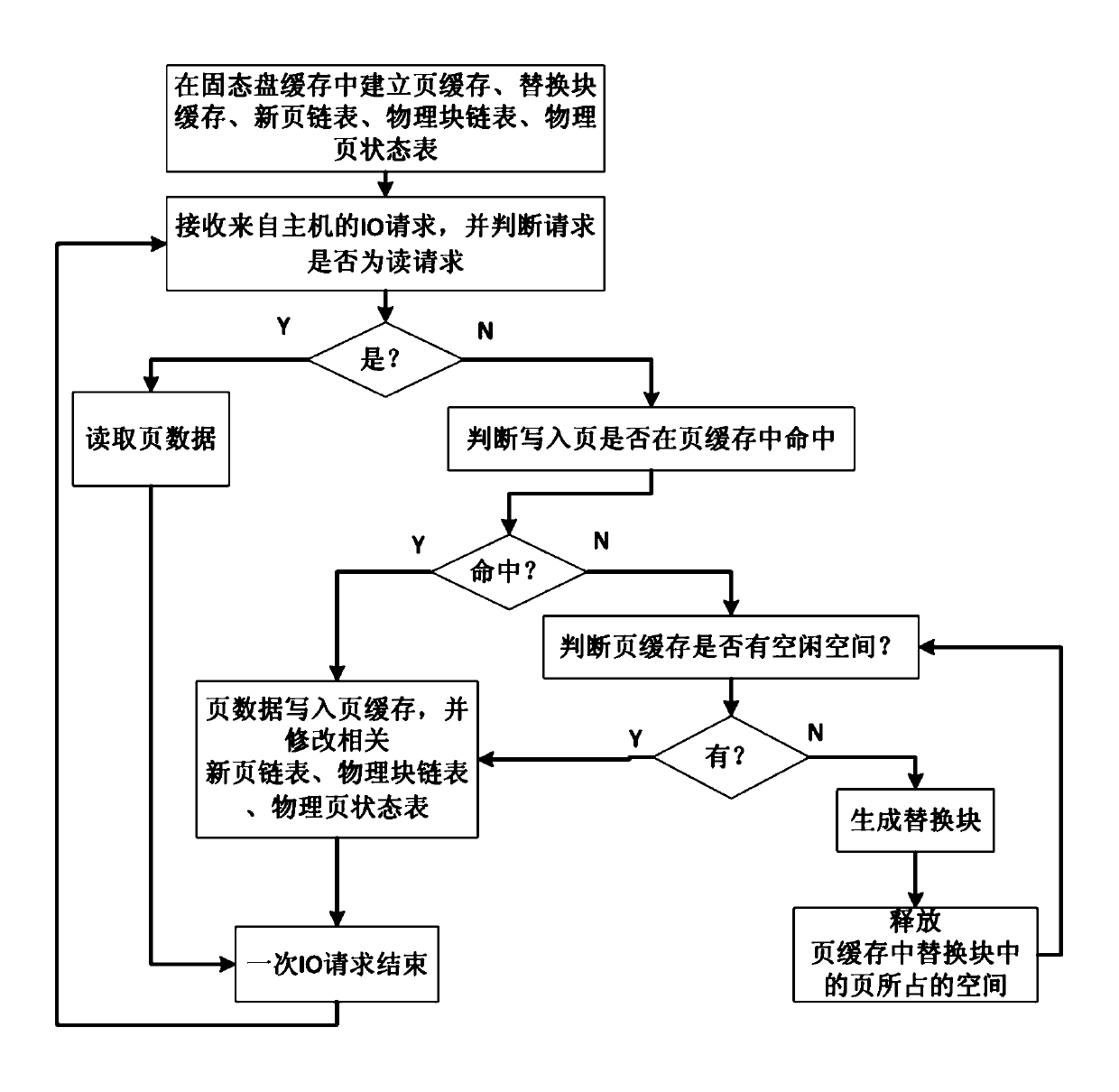
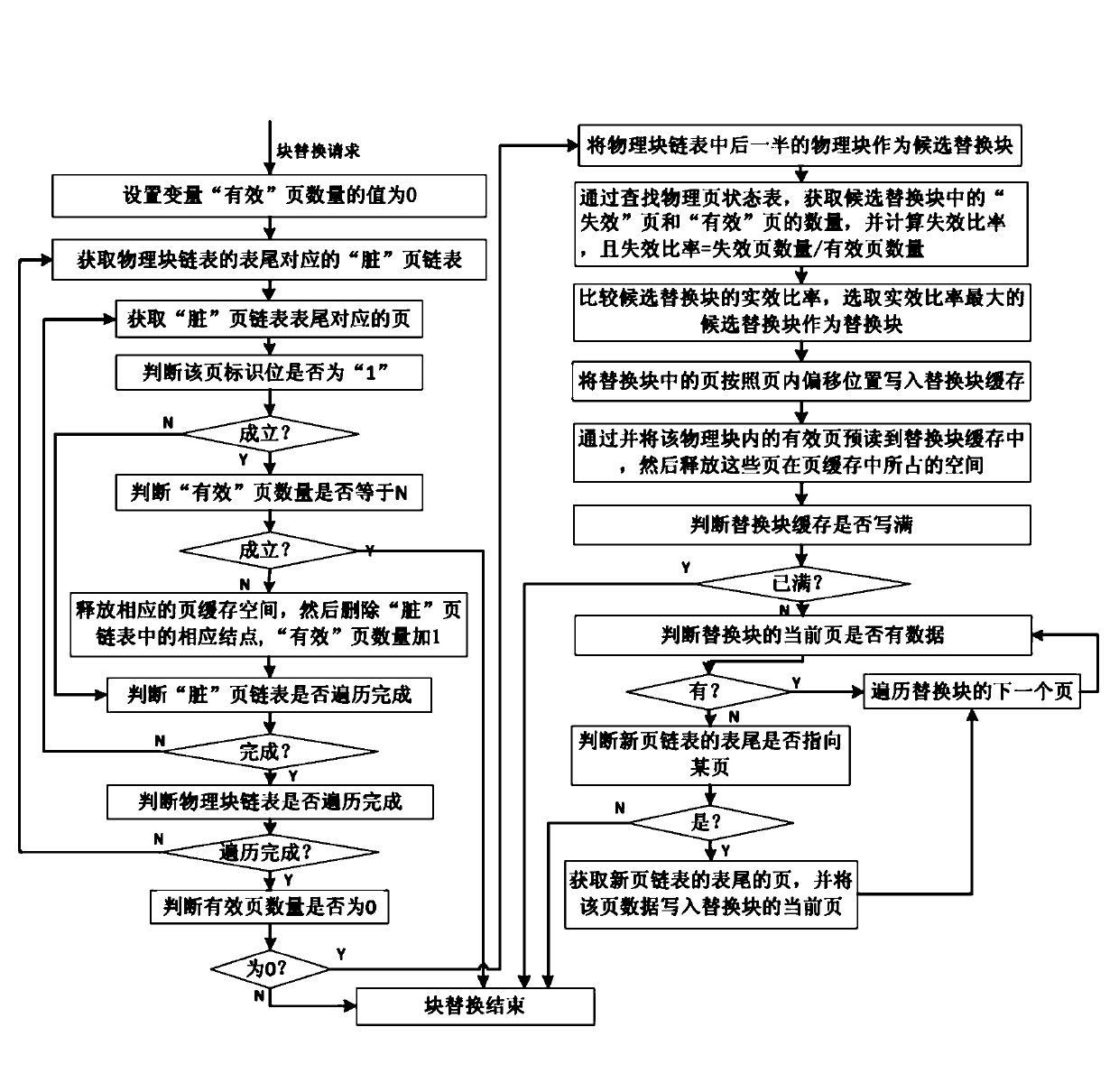
ActiveCN103136121AImprove hit chanceImprove read and write speedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirty dataCache management
The invention discloses a cache management method for a solid-state disc. The method comprises the following implement steps that a page cache, a replace block module, a new page linked list, a physical block chain list and a physical page state list are established; an input and output (IO) request from a host is received and is executed through the page cache, when a writing request is executed, if the page cache is missed, and the page cache has no spare space, a block replace process of the solid-state disc is executed, namely an 'effective' page space in the page cache is preferential released; when the number of 'effective' pages in the page cache is zero, a candidate replace block with the largest failure ratio in a rear half physical block of the physical block chain list is selected to serve as a replace block, and the replace block cache is utilized to execute a replace writing process. The cache management method for the solid-state disc can effectively use a limited cache space and increase hit rate of the cache, enables a block written in a flash medium to comprise as many dirty data pages as possible and as few effective data pages as possible to reduce erasure operation and page copy operations and sequential rubbish recovery caused by the dirty data pages. The cache management method for the solid-state disc is easy to operate.
Owner:湖南长城银河科技有限公司
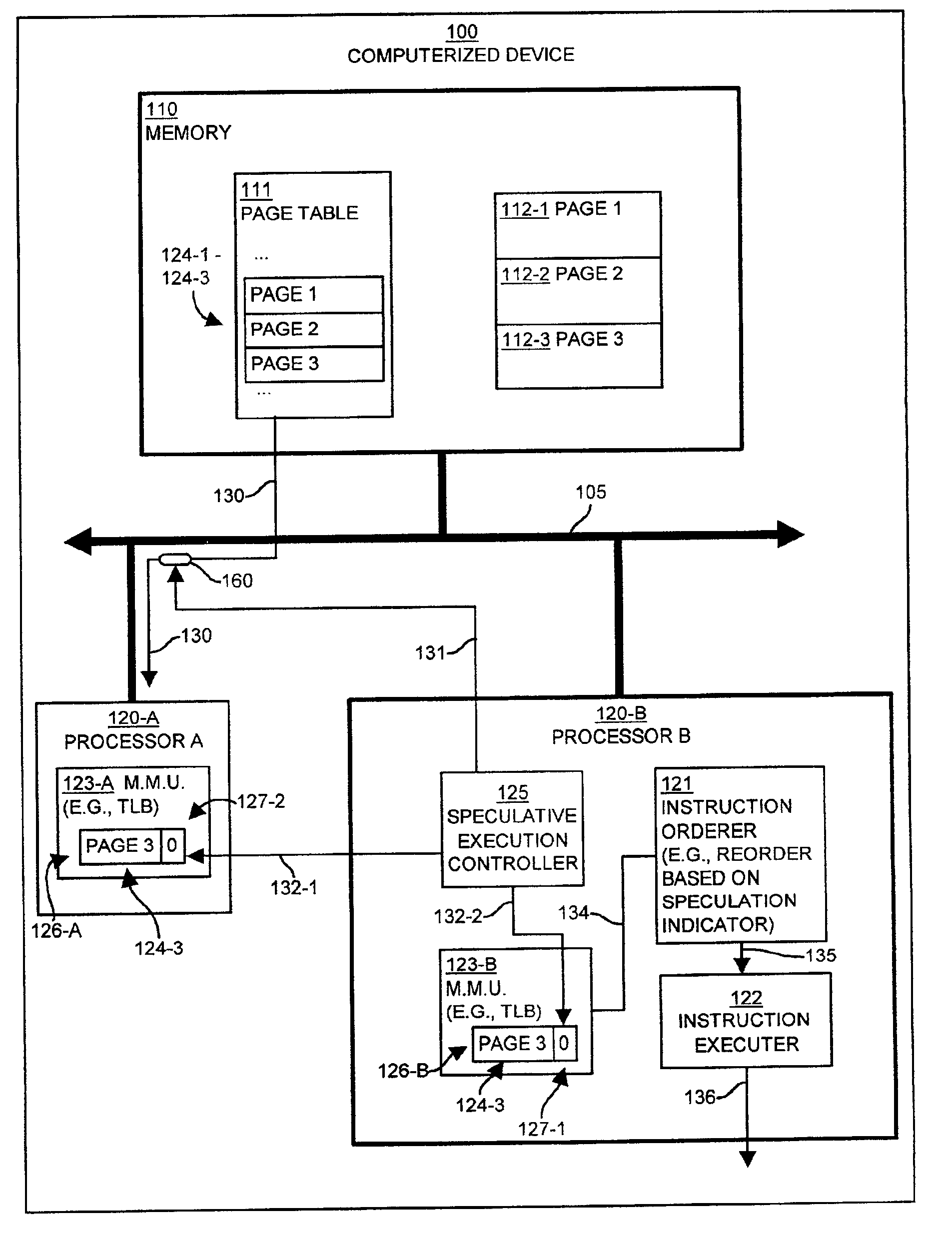
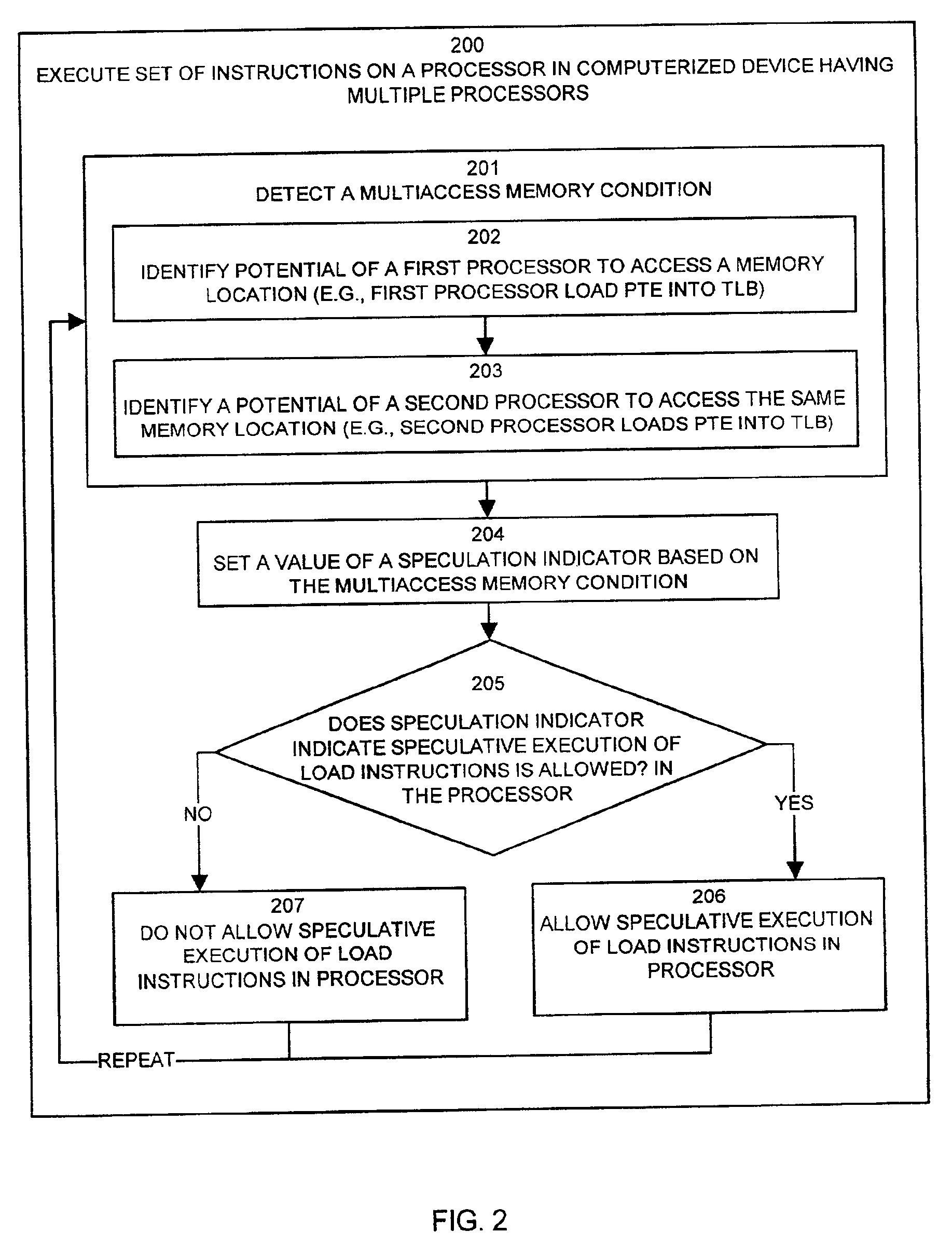
Methods and apparatus for controlling speculative execution of instructions based on a multiaccess memory condition
InactiveUS6877088B2Lower performance requirementsEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpeculative executionPage table
Mechanisms and techniques operate in a computerized device to enable or disable speculative execution of instructions such as reordering of load and store instructions a multiprocessing computerized device. The mechanisms and techniques provide a speculative execution controller that can detect a multiaccess memory condition between the first and second processors, such as concurrent access to shared data pages via page table entries. This can be done by monitoring page table entry accesses by other processors. The speculative execution controller sets a value of a speculation indicator in the memory system based on the multiaccess memory condition. If the value of the speculation indicator indicates that speculative execution of instructions is allowed in the computerized device, the speculative execution controller allows speculative execution of instructions in at least one of the first and second processors in the computerized device. If the value of the speculation indicator indicates that speculative execution of instructions is not allowed in the computerized device, the speculative execution controller does not allow speculative execution of instructions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
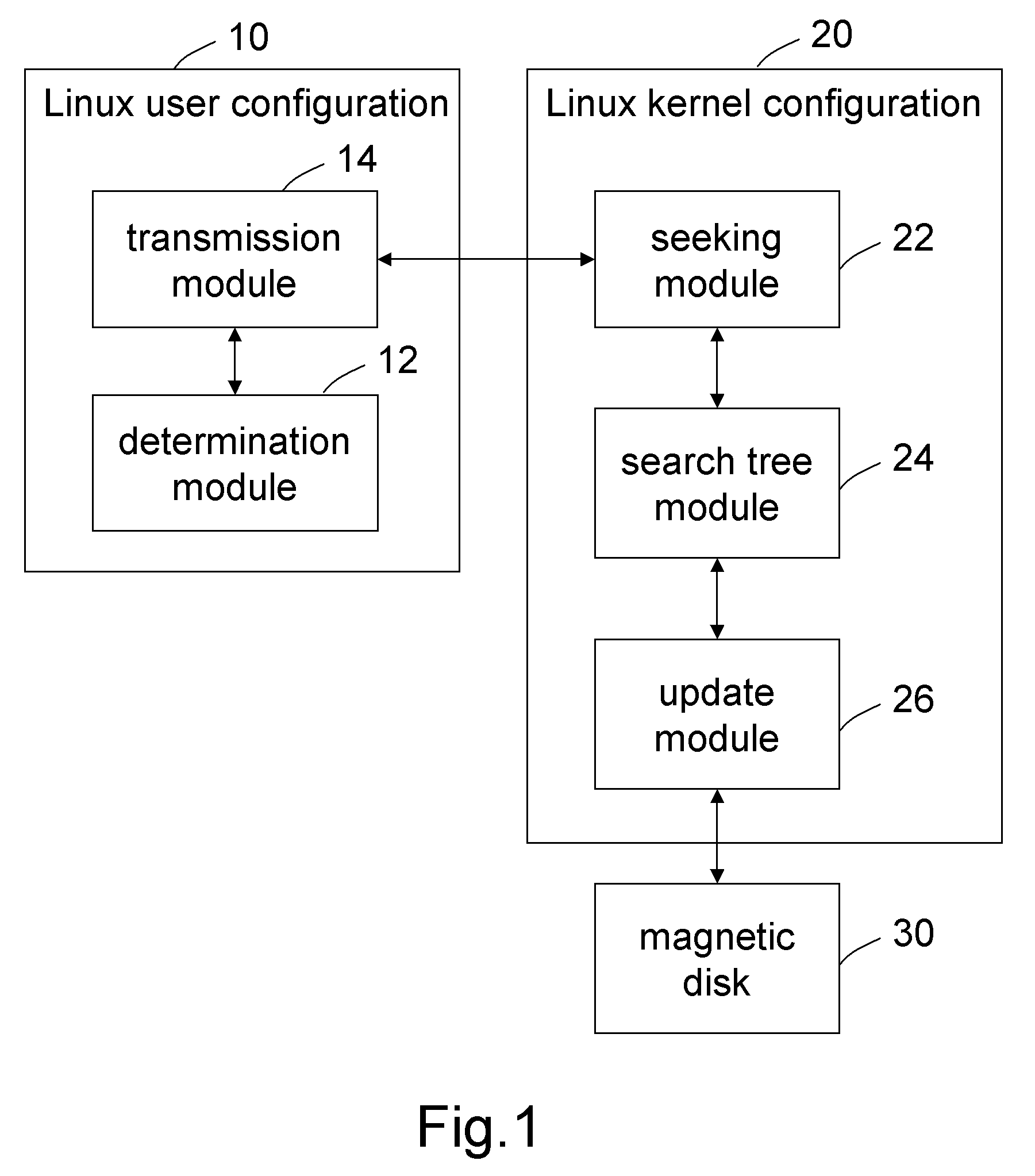
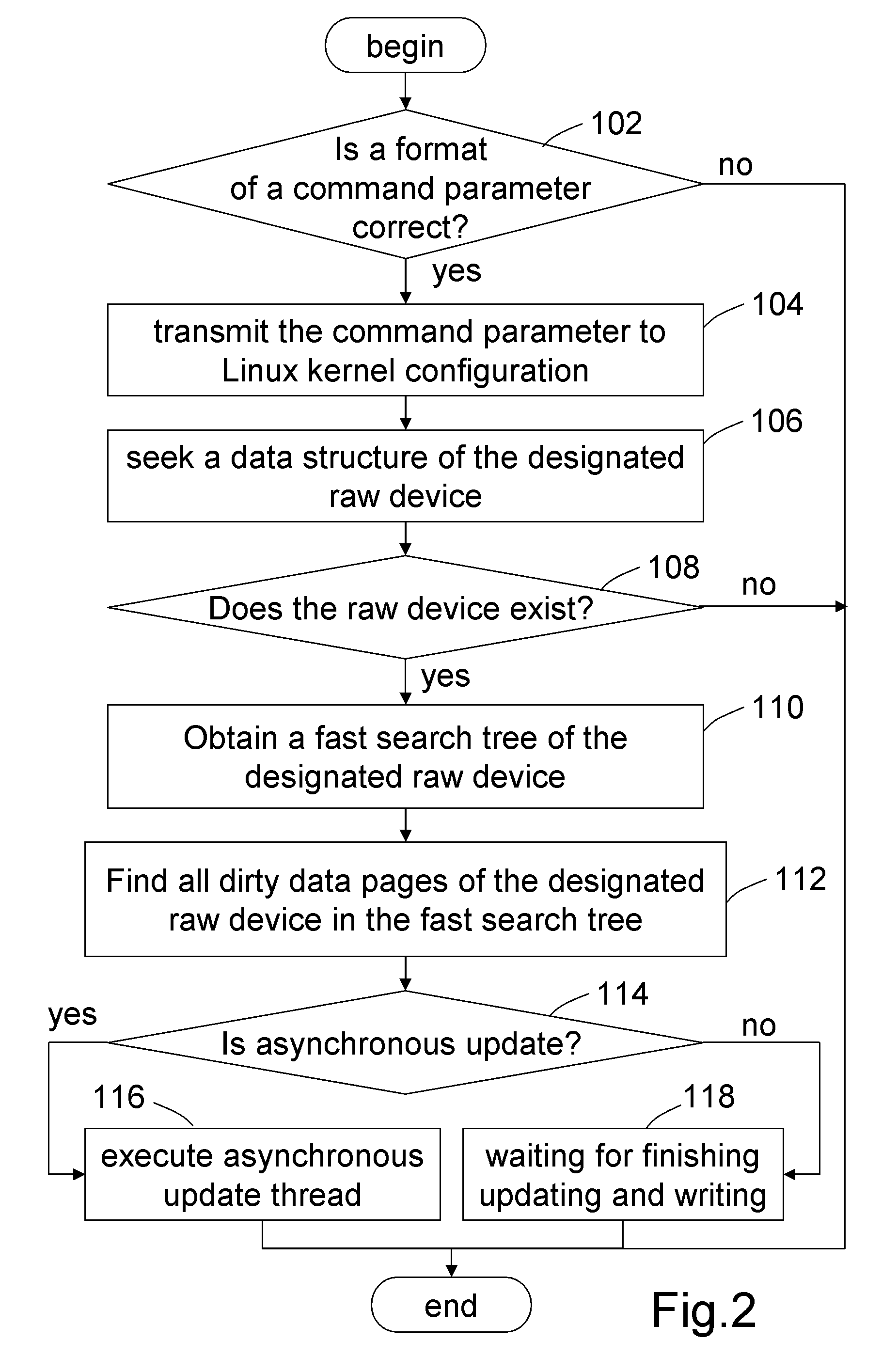
System and method for updating dirty data of designated raw device
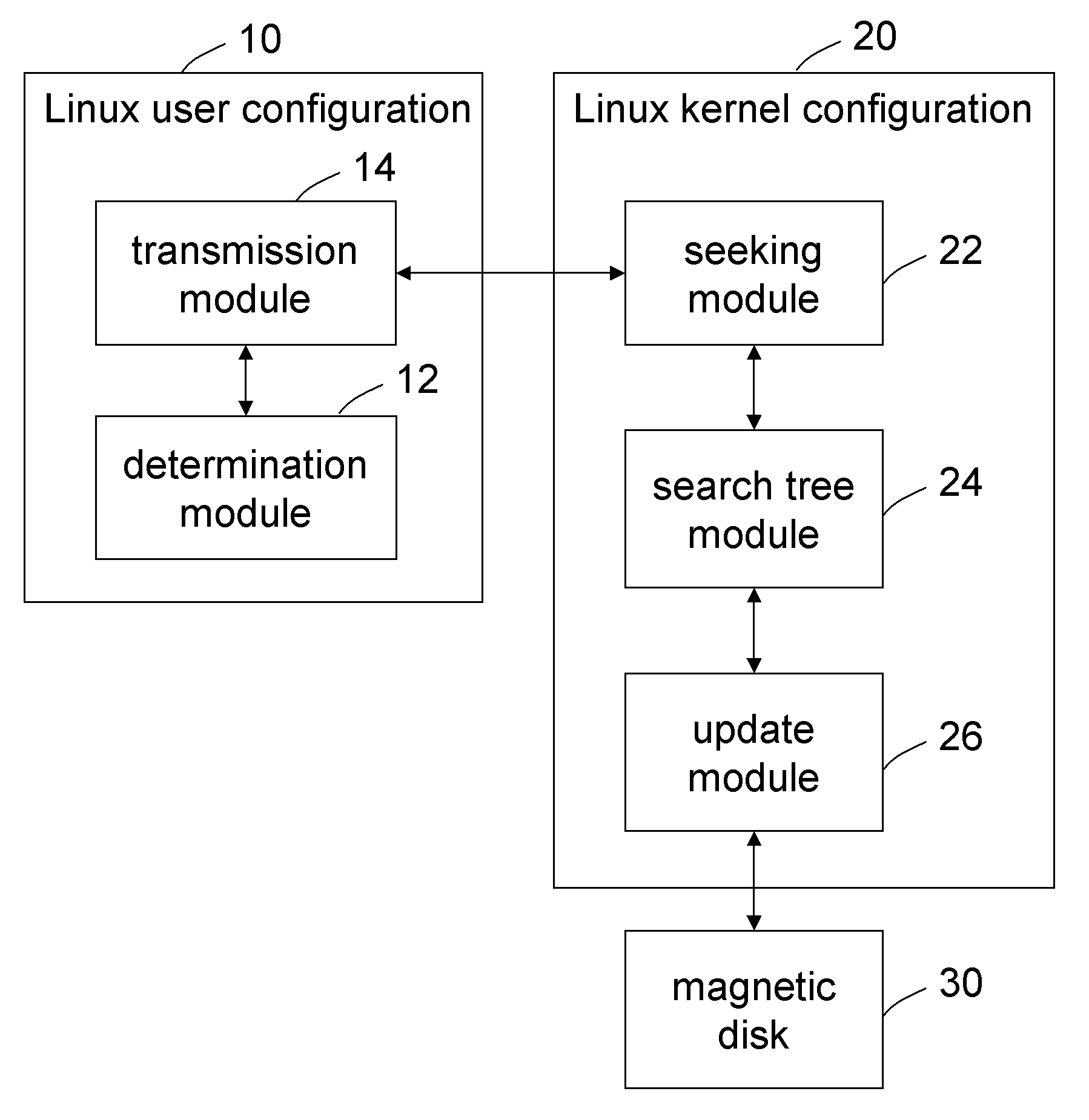
ActiveUS20090113130A1Shorten the timeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationGNU/LinuxDirty data
A system and method for updating dirty data of designated raw device is applied in Linux system. A format of a command parameter for updating the dirty data of the designated raw device is determined, to obtain the command parameter with the correct format and transmit it into the Kernel of the Linux system. Then, a data structure of the designated raw device is sought based on the command parameter, to obtain a fast search tree of the designated raw device. Finally, all dirty data pages of the designated raw device are found by the fast search tree, and then are updated into a magnetic disk in a synchronous or asynchronous manner. Therefore, the dirty data of an individual raw device can be updated and written into the magnetic disk without interrupting the normal operation of the system, hereby ensuring secure, convenient, and highly efficient update of the dirty data.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
Data storage system employing a hot spare to proactively store array data in absence of a failure or pre-failure event
ActiveUS20180165169A1Input/output to record carriersRedundant hardware error correctionComputer hardwareData store
A data storage system includes a controller, a hot spare storage device and a plurality of primary storage devices. The controller utilizes the hot spare storage device to mirror only a subset of each stripe of logical pages written across the data storage array, where the subset includes a logical page determined by a write input / output operation (IOP) policy. In response to receipt of a write IOP, the controller writes a stripe including a plurality of logical data pages and a logical data protection page across the plurality of primary storage devices and mirrors the logical page determined by the write IOP policy on the hot spare storage device. In response to a failure of a storage device among the plurality of primary storage devices, contents of the failed storage device not already mirrored on the hot spare storage device are rebuilt on the hot spare storage device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Print control method, apparatus, computer-readable storage medium, and program embodied in a computer-readable medium for managing document information on a page basis
In printing a plurality of pages of print data on one paper sheet upon combining the pages, a print control apparatus inputs layout data for determining a layout of the respective pages, extracts a page data portion to be printed as a single page from the print data in accordance with the input layout data, holds the page data portion, and outputs print data generated from the held page data. In this apparatus, when paper sheets are folded to form printed matter with an appearance of a book, a plurality of print page data can be printed in each print area. The apparatus includes a designation unit for making designation with respect to layout data to combine and lay out a plurality of print data pages on one page of bound paper sheets on which printing is performed, and a generating unit for generating print data print data having a plurality of page data laid out on one page of the bound paper sheets in accordance with the layout data.
Owner:CANON KK
Data processing method, device thereof and flash-memory storage system
ActiveCN101526923AImprove space utilizationImprove data access performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCold treatmentData access
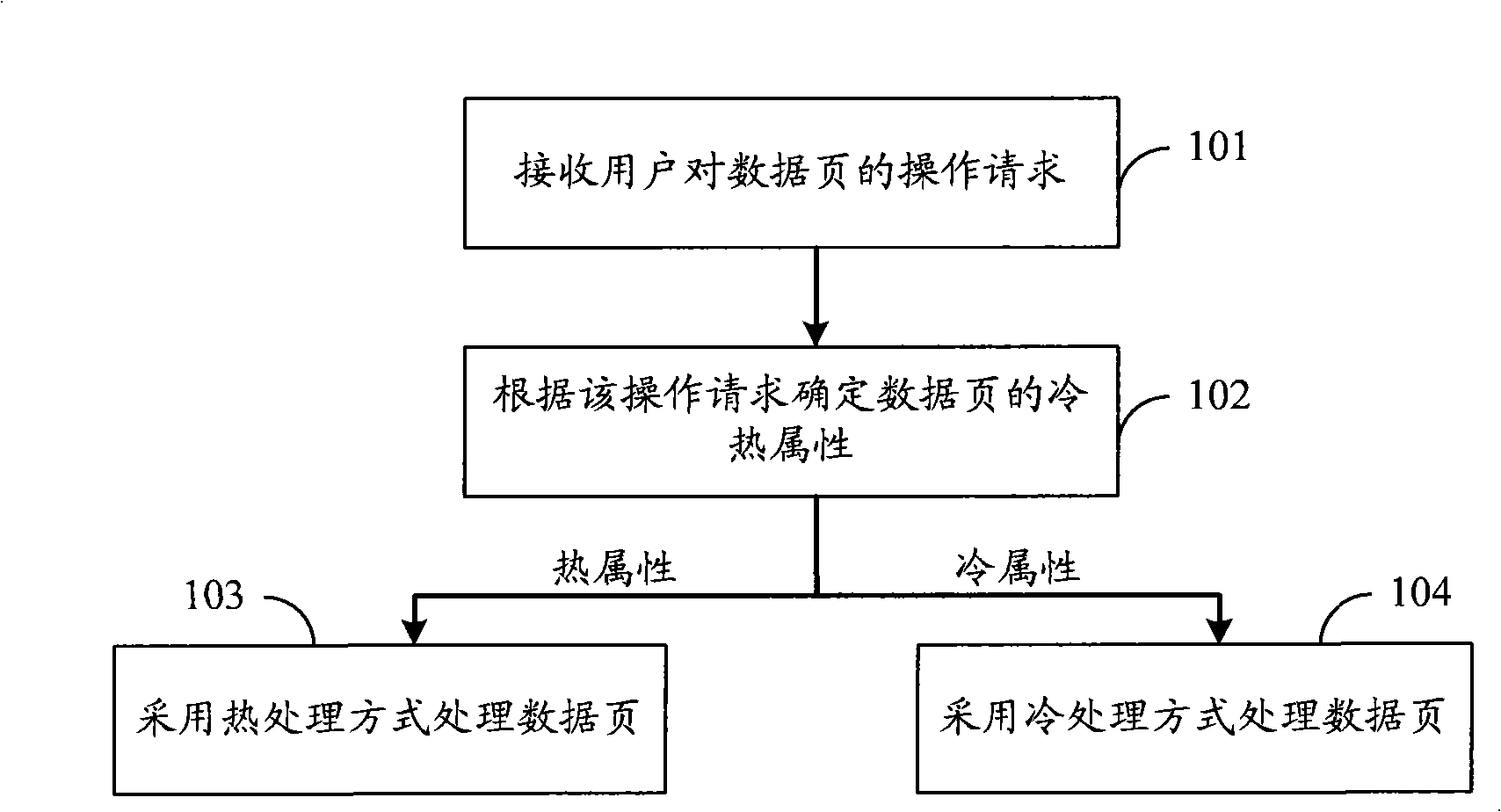
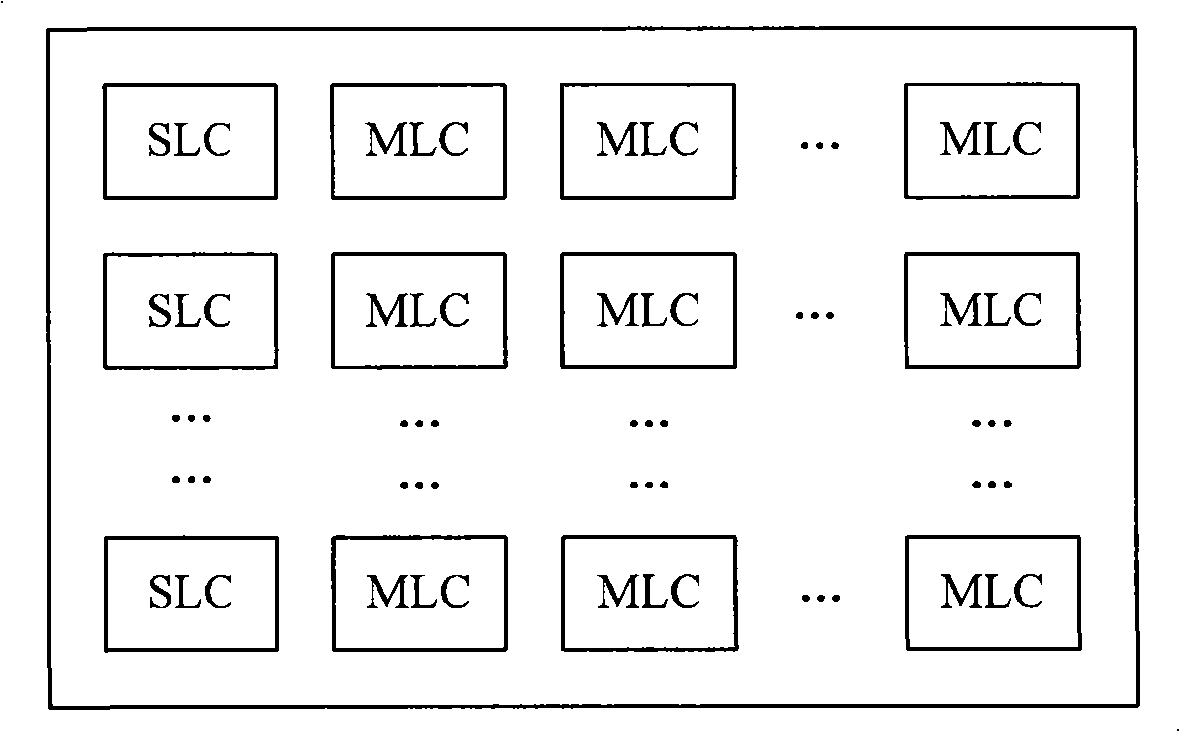
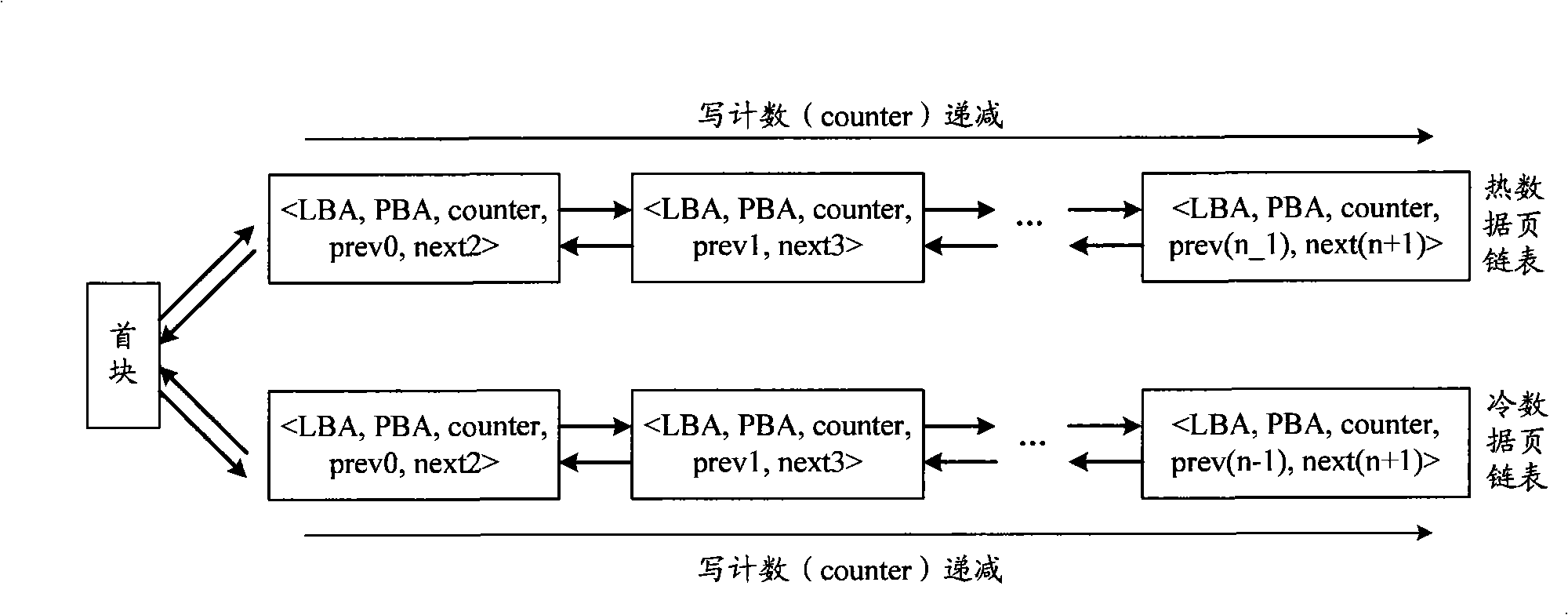
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data processing method, a device thereof and a flash-memory storage system. The data processing method comprises the steps as follows: an operation request towards a data page of the user is received; whether the writing count of the data page is larger than a preset threshold value is judged according to the operation request; if the data page is larger than a preset threshold value, the data page is confirmed as thermal property, and the data page is processed in a way of heat treatment; if the data page is not larger than a preset threshold value, the data page is confirmed as cold property, and the data page is processed in a way of cold treatment, wherein, the cold property and the thermal property indicate the accessing frequency towards the data page of the user. The data processing device comprises a receiving unit and a processing unit. A flash memory comprises the receiving unit and a memory unit. A flash-memory storage system comprises the data processing device and the flash memory. The proposal provided by the embodiment of the invention can realize the high space utilization rate of the flash memory and also has high data accessing performance.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
Data page caching method for file system of solid-state hard disc
ActiveCN102156753AReduce overheadImprove hit rateSpecial data processing applicationsDirty pageExternal storage
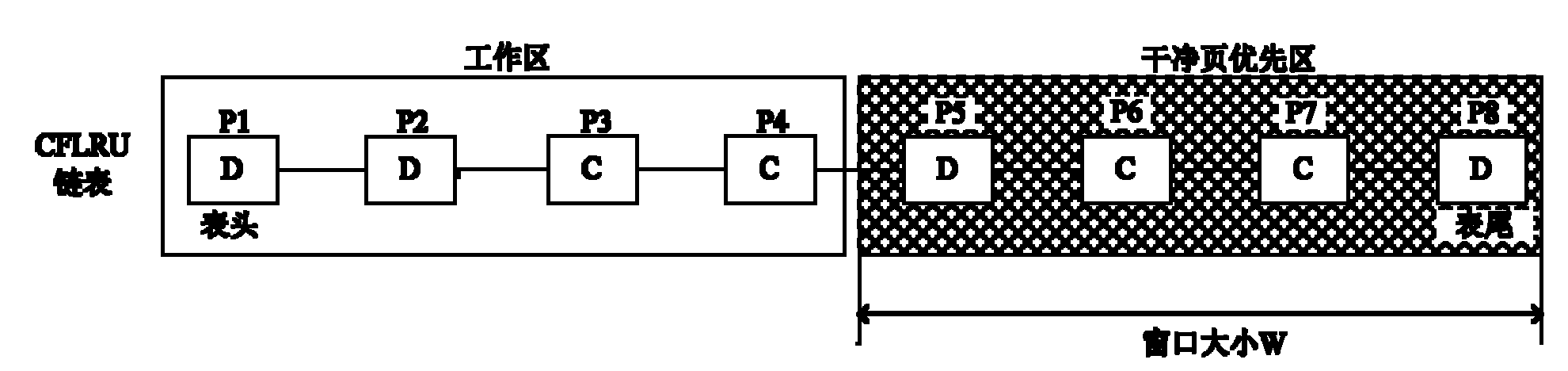
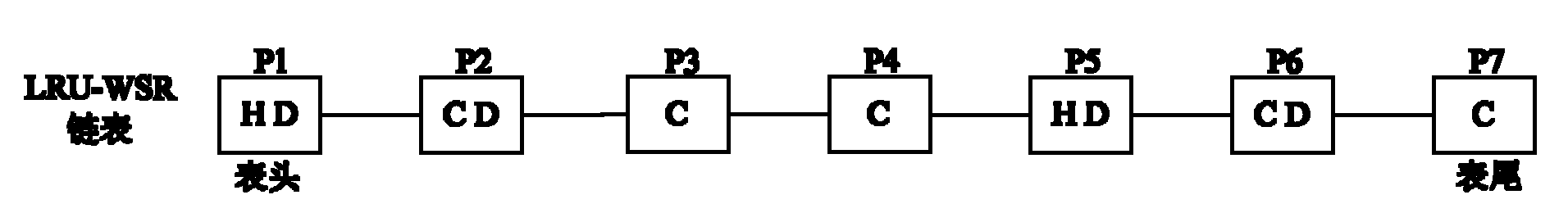
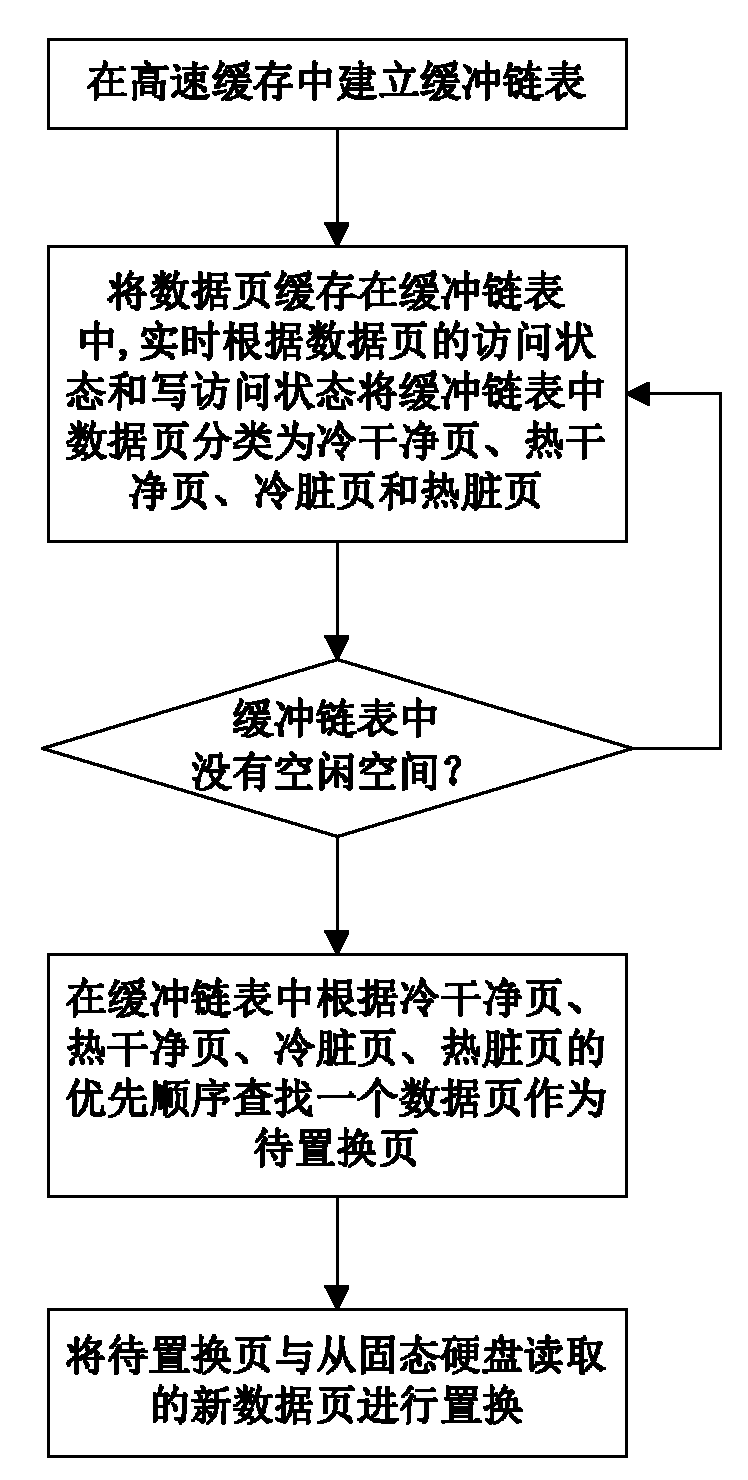
The invention discloses a data page caching method for a file system of a solid-state hard disc, which comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) establishing a buffer link list used for caching data pages in a high-speed cache; (2) caching the data pages read in the solid-state hard disc in the buffer link list for access, classifying the data pages in the buffer link list into cold clean pages, hot clean pages, cold dirty pages and hot dirty pages in real time according to the access states and write access states of the data pages; (3) firstly searching a data page as a page to be replaced in the buffer link list according to the priority of the cold clean pages, the hot clean pages, the cold dirty pages and the hot dirty pages, and replacing the page to be replaced with a new data page read from the solid-state hard disc when a free space does not exist in the buffer link list. In the invention, the characteristics of the solid-state hard disc can be sufficiently utilized, the performance bottlenecks of the external storage can be effectively relieved, and the storage processing performance of the system can be improved; moreover, the data page caching method has the advantages of good I / O (Input / Output) performance, low replacement cost for cached pages, low expense and high hit rate.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com