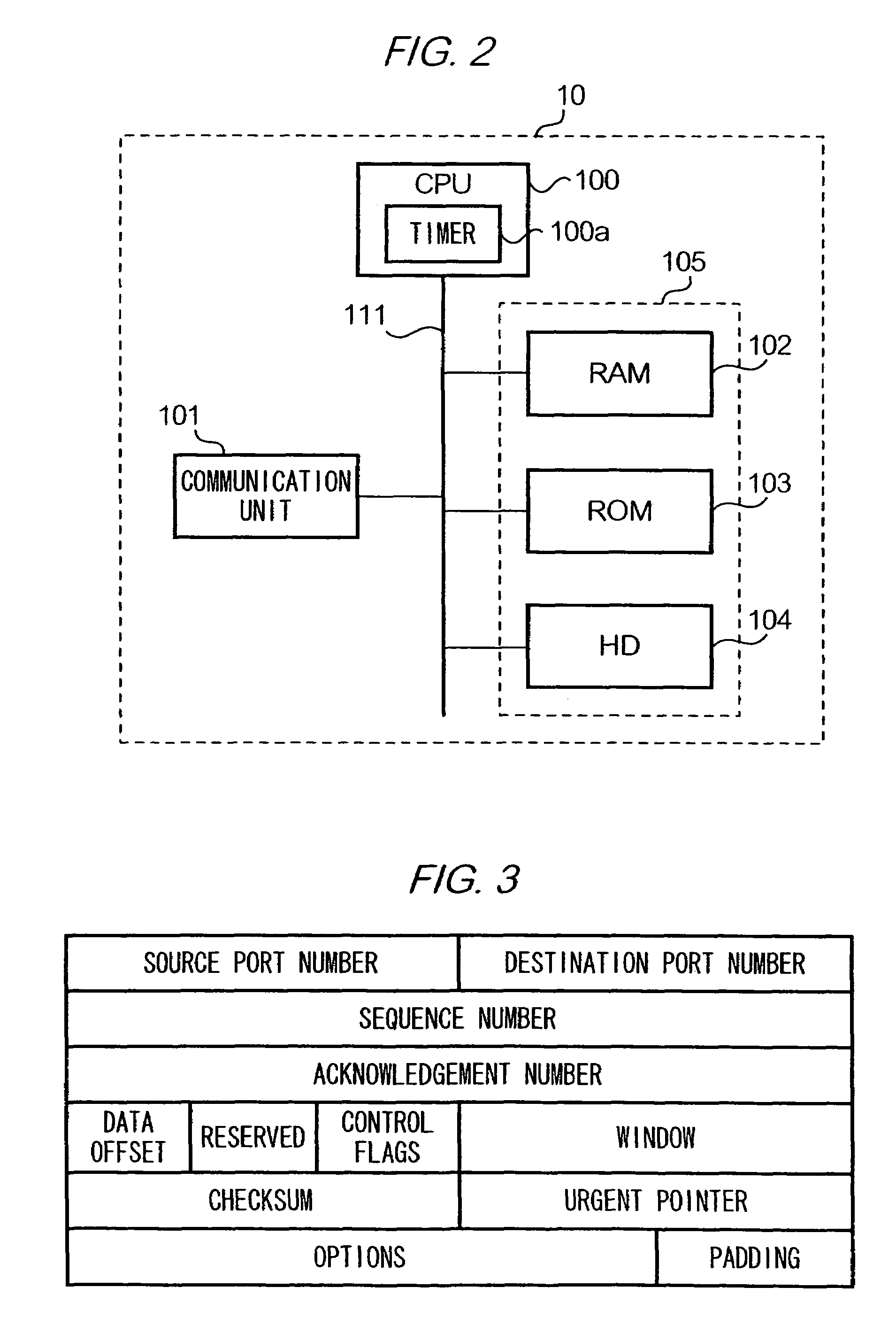
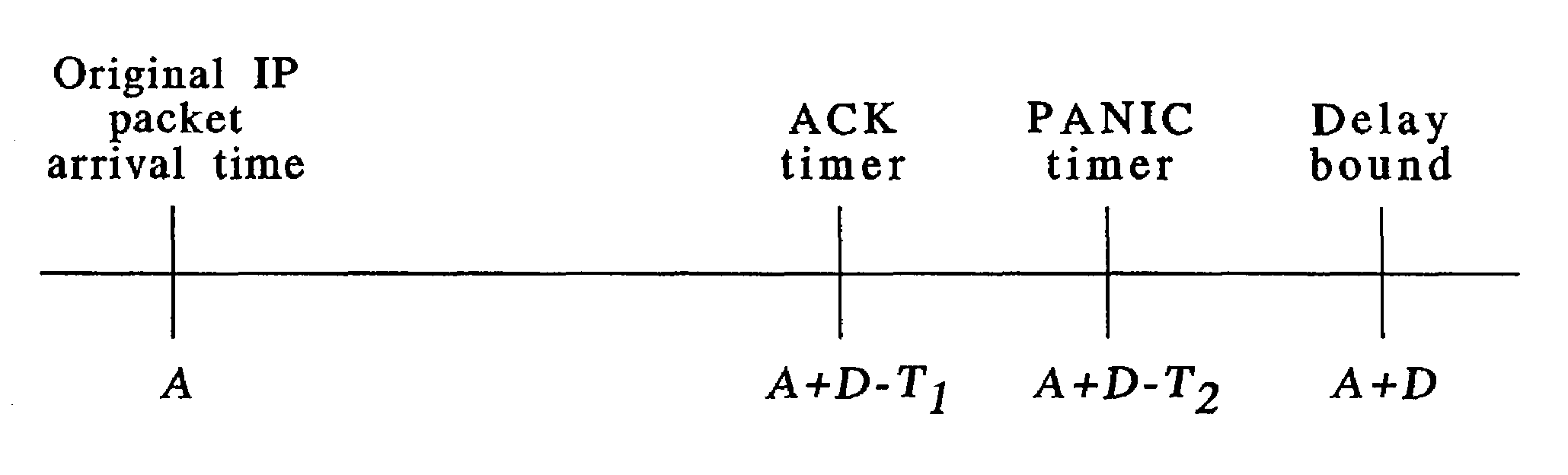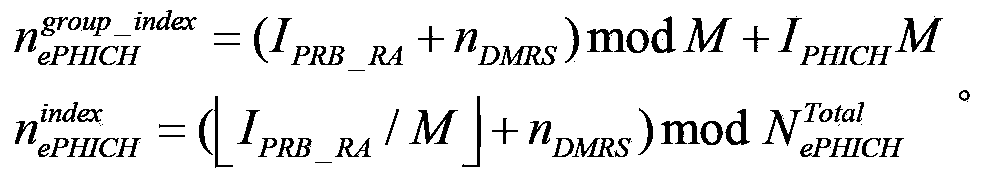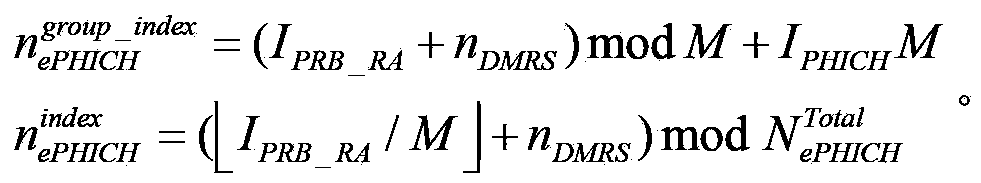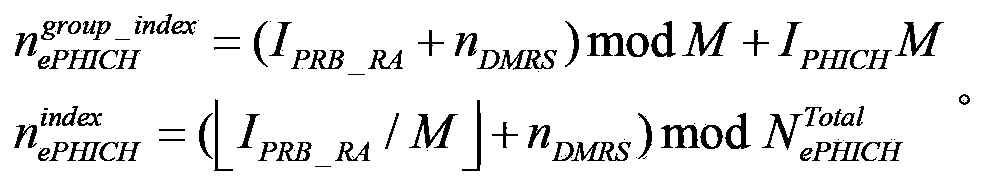Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1197 results about "Acknowledgement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In data networking, telecommunications, and computer buses, an acknowledgement (ACK) is a signal that is passed between communicating processes, computers, or devices to signify acknowledgement, or receipt of message, as part of a communications protocol. The negative-acknowledgement (NAK or NACK) signal is sent to reject a previously received message, or to indicate some kind of error. Acknowledgements and negative acknowledgements inform a sender of the receiver's state so that it can adjust its own state accordingly.
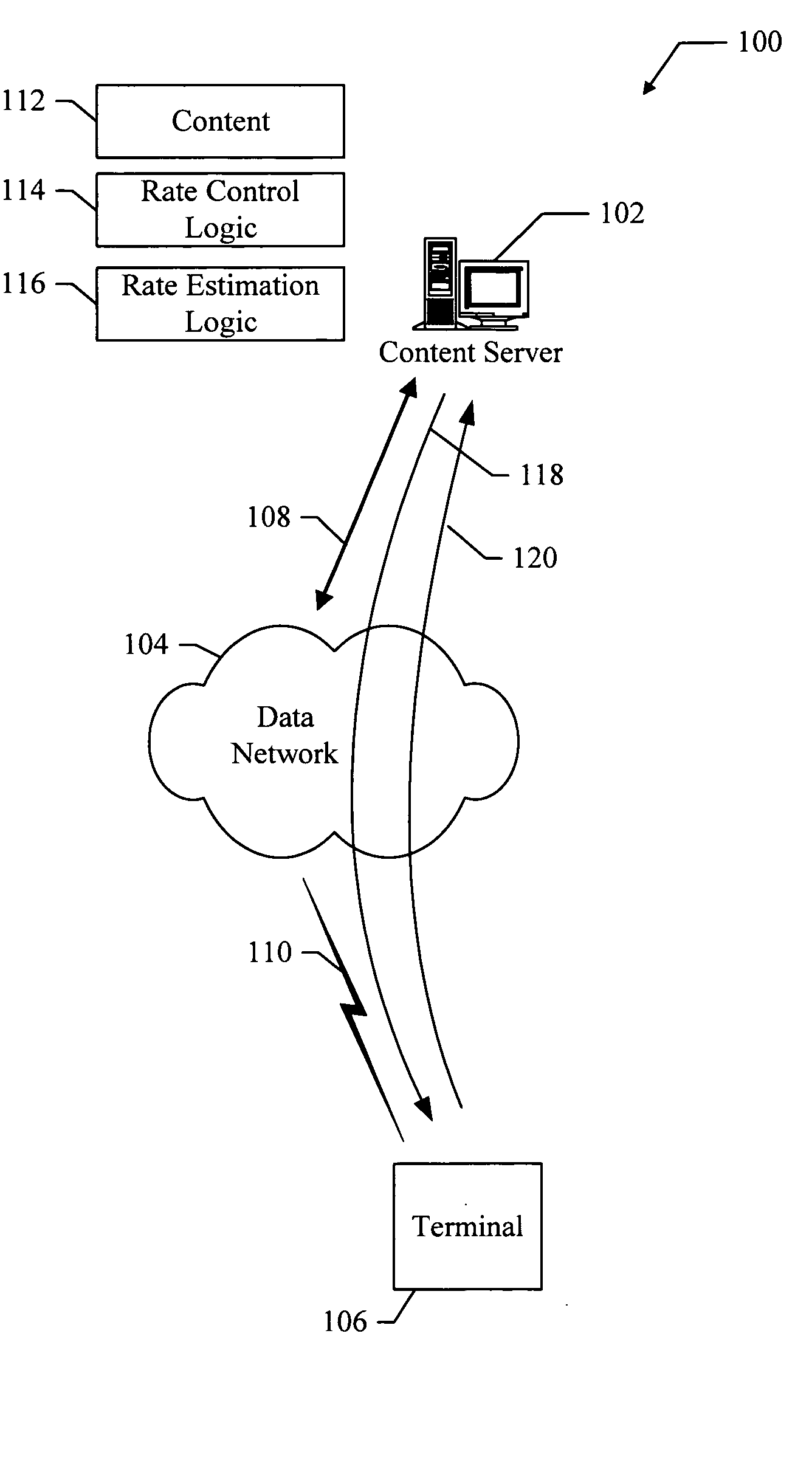
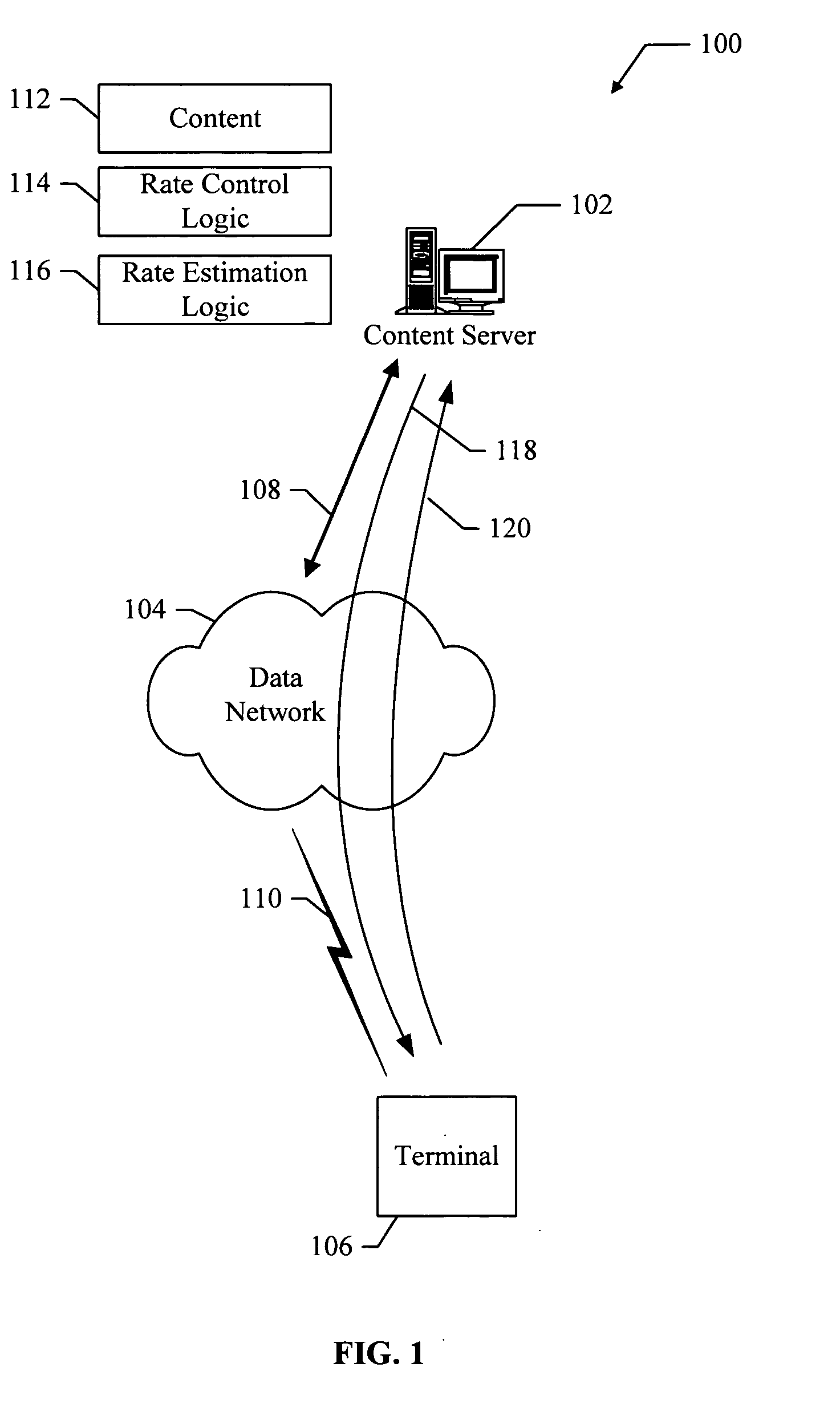
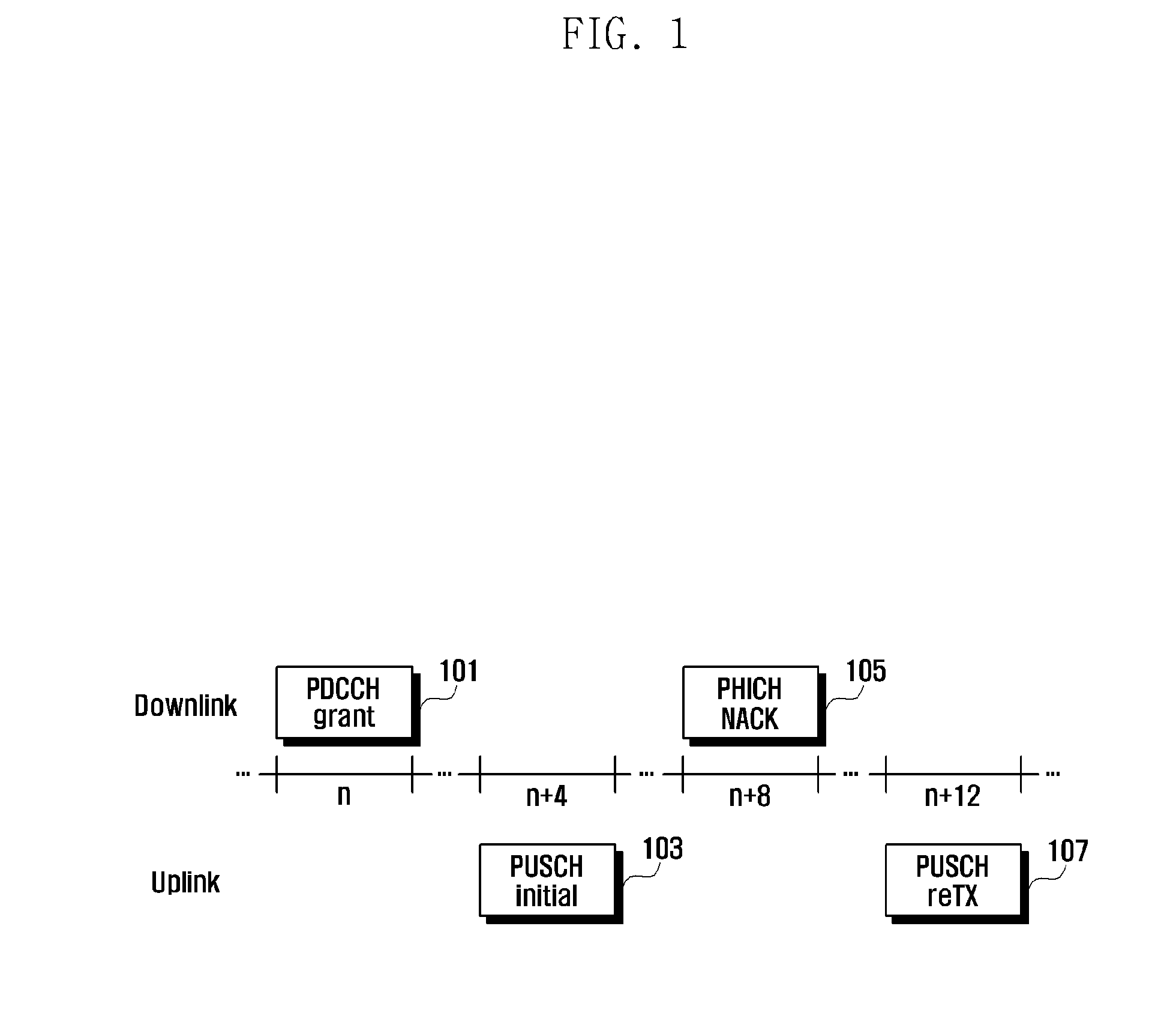
Method for optimizing the random access procedures in the cdma cellular networks
InactiveUS20030076812A1Limit collisionSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCellular networkSystem information
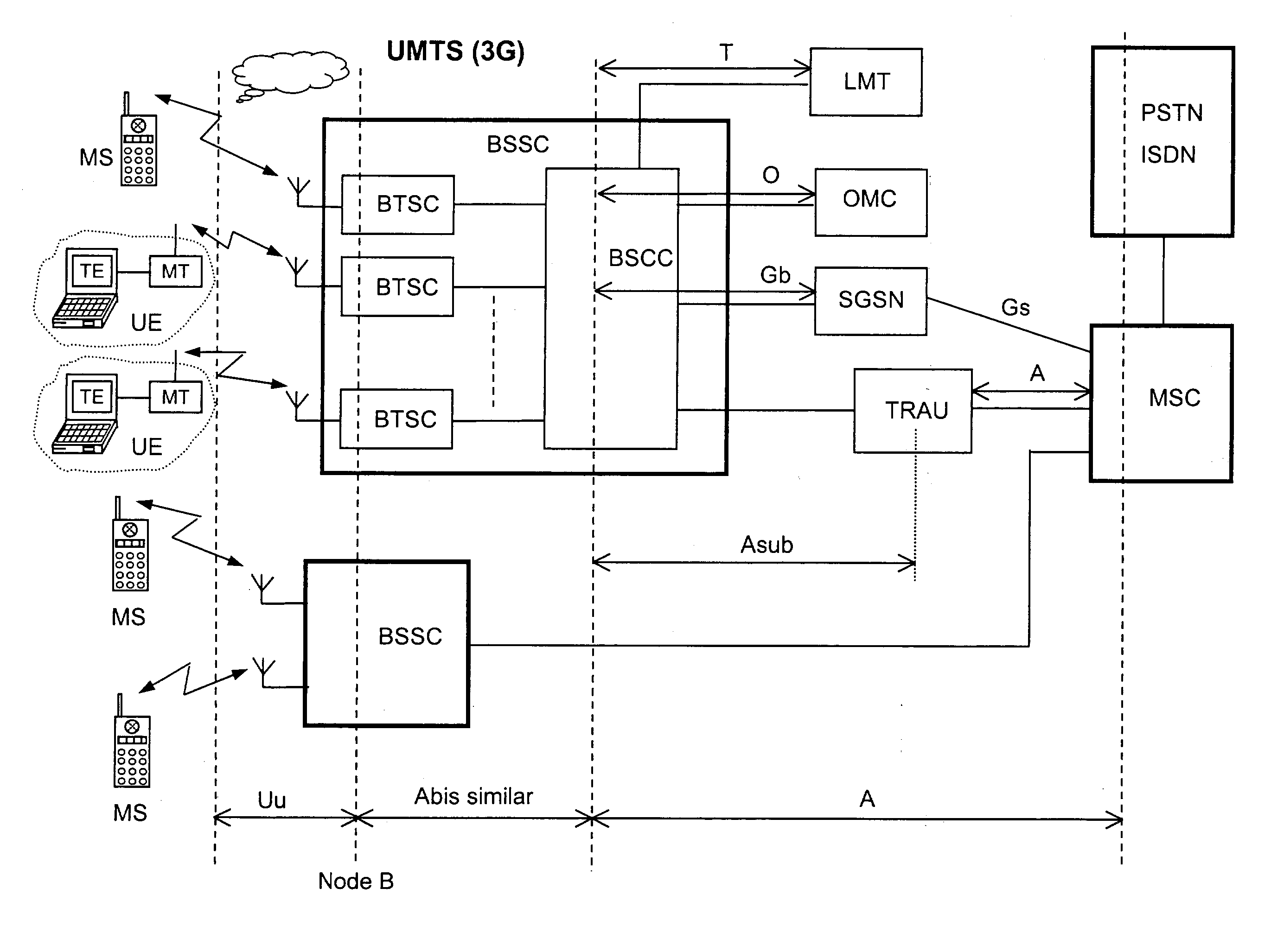
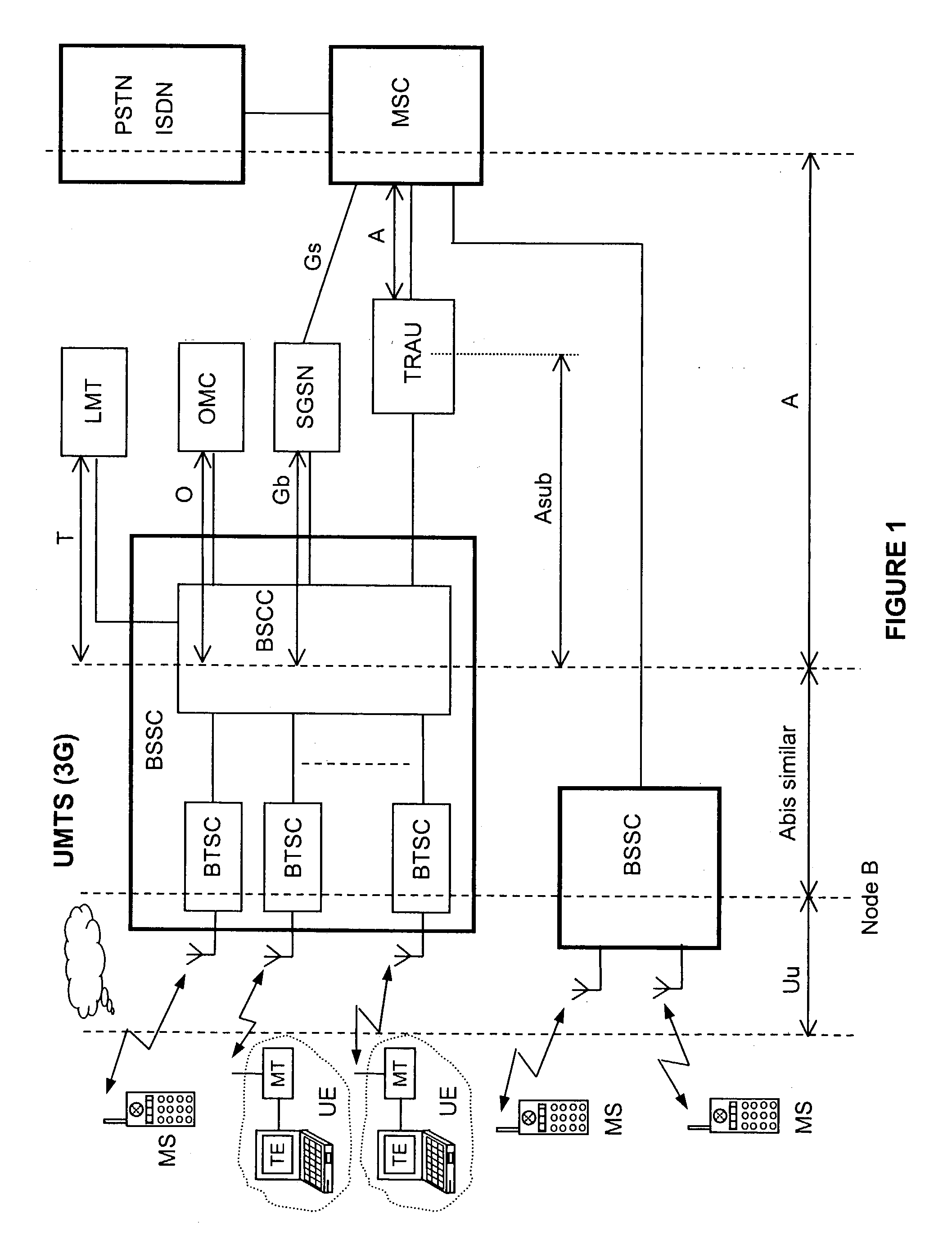
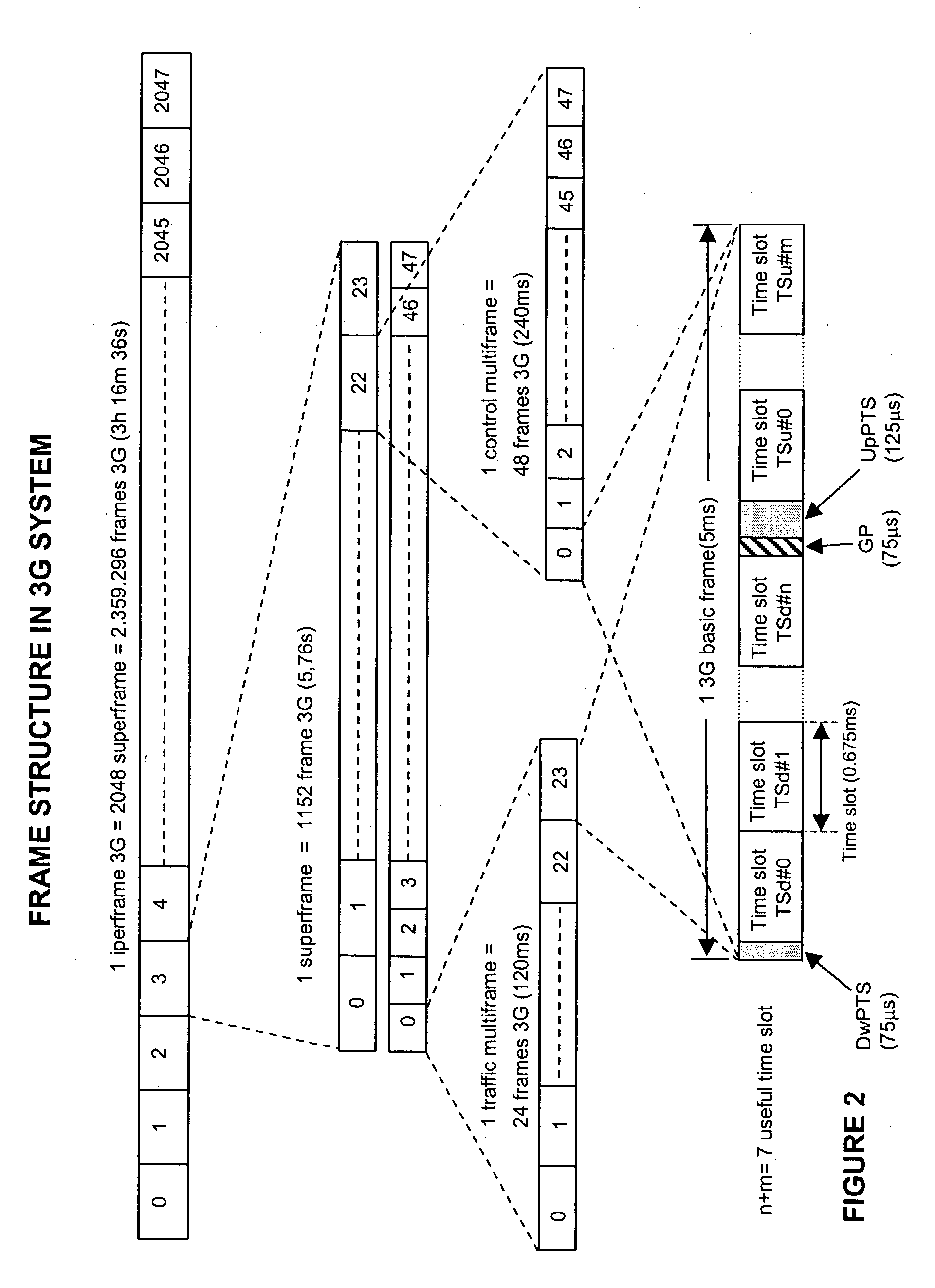
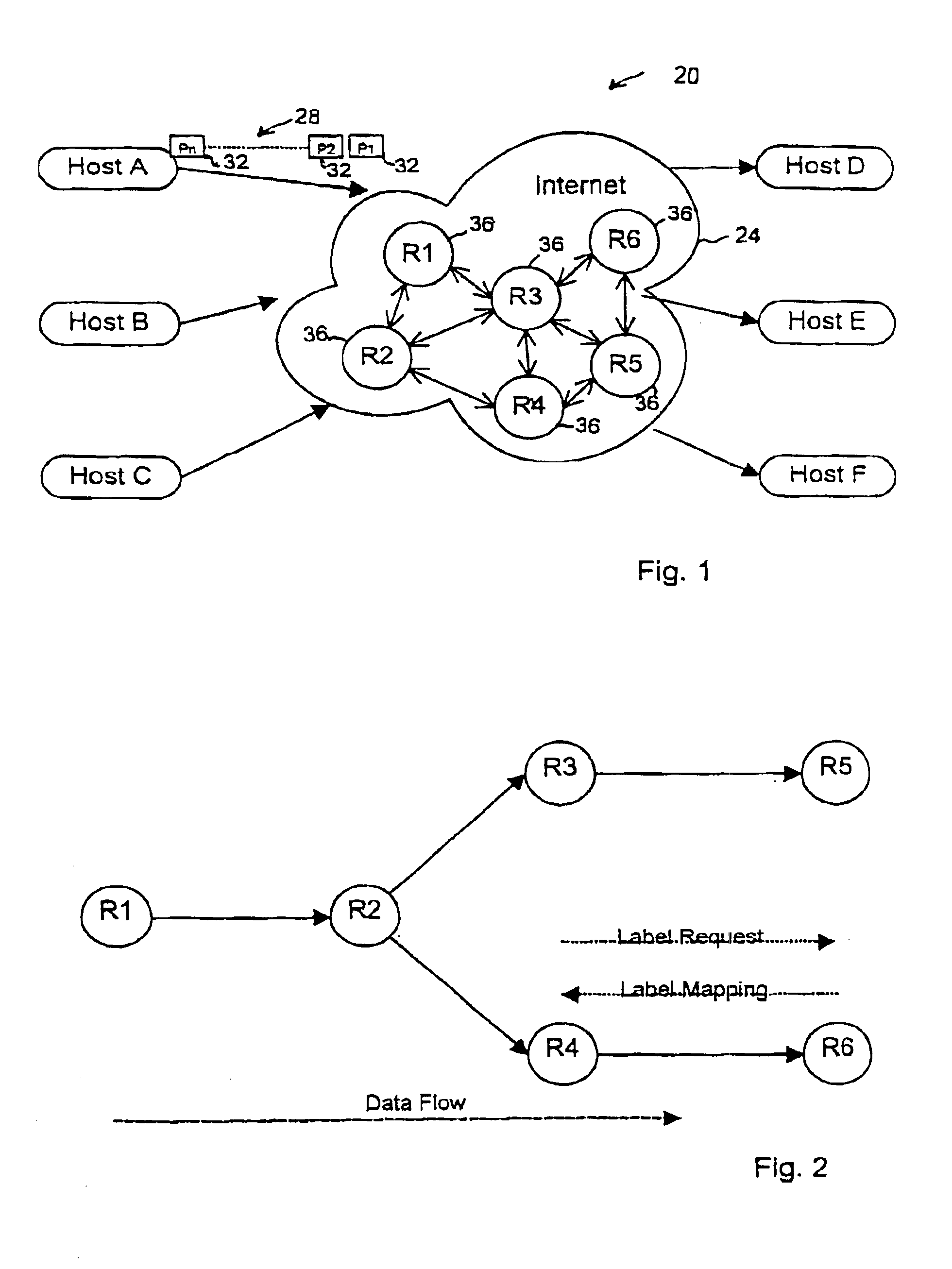
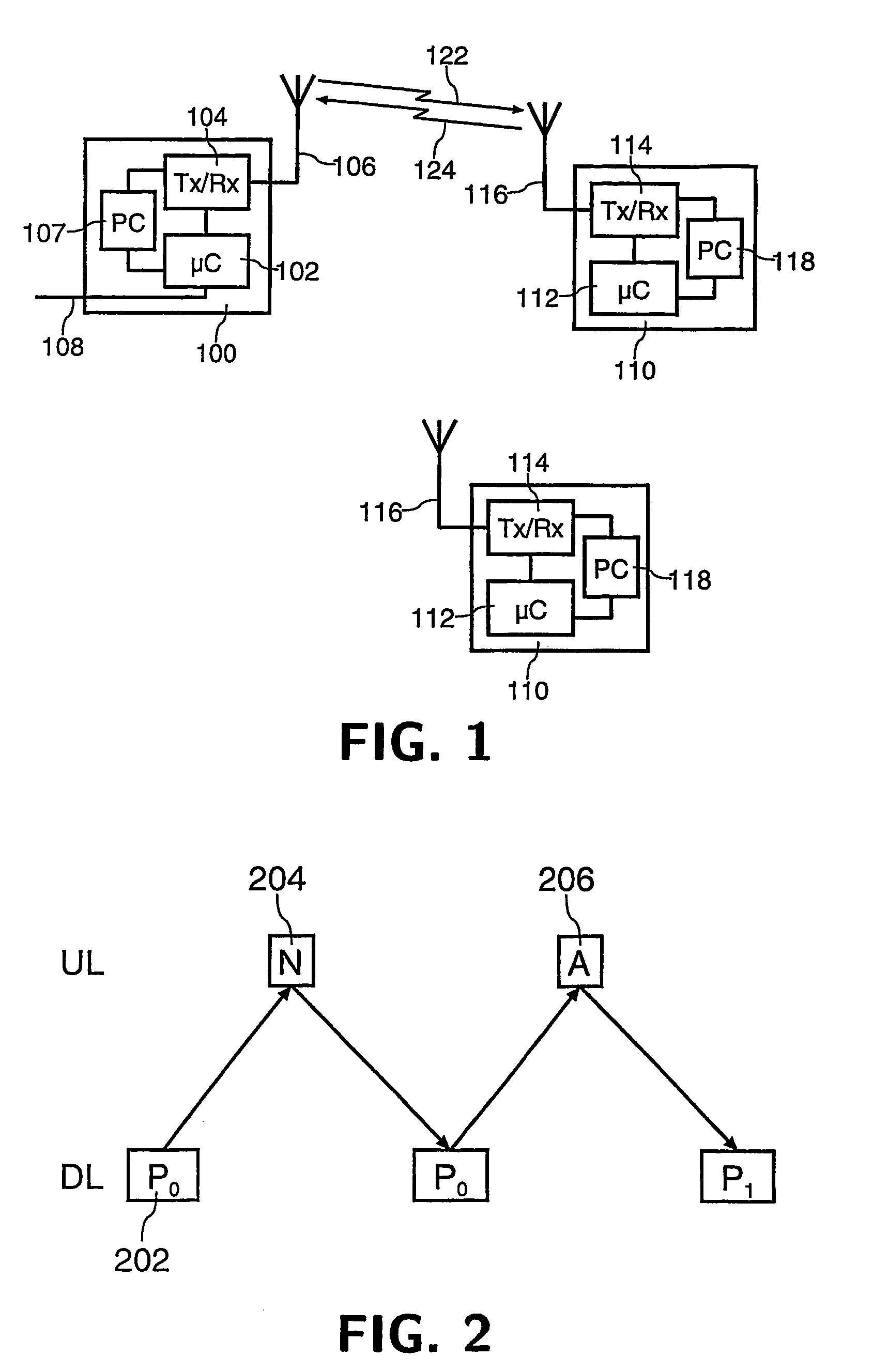
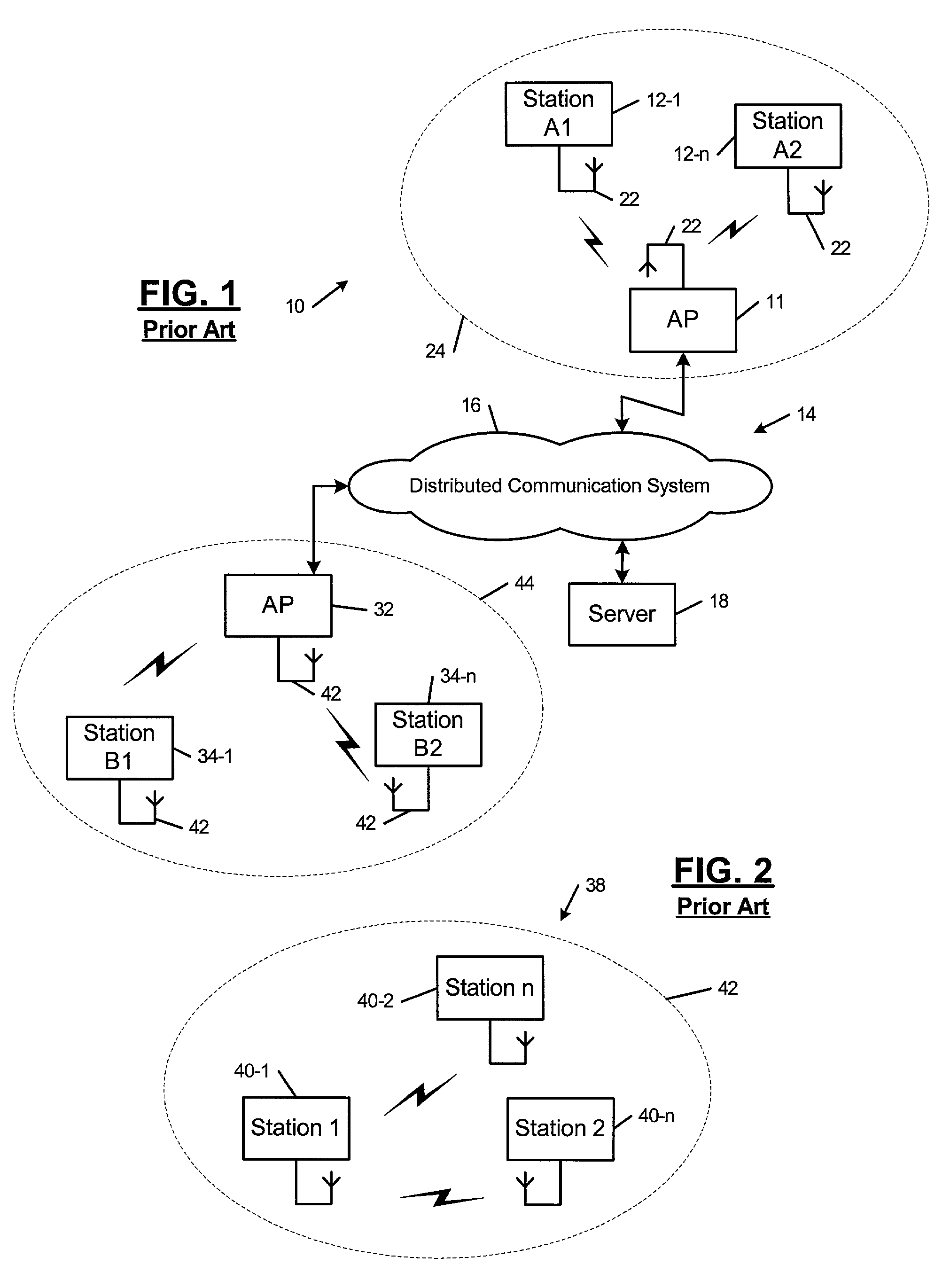
The disclosed invention is referred to a method for optimising the random access procedures in third generation CDMA cellular telephony systems. The particular embodiment of the example concerns a TD-SCDMA-TDD synchronous realization. The disclosed procedure includes a preliminary part charged to the network (BSSC, MSC) only for establishing the following associations between the configuration parameters of the involved physical channels: one signature burst (SYNC1) is associated to one forward access channel (P-FACH) only, in order to avoid any, ambiguity in the mobile stations about where to look for the expected acknowledgement from the network; one random access common channel (P-RACH) is associated to one forward access channel (P-FACH) only, in order to reduce collision on the latter (P-RACH); one access grant channel (P / S-CCPCH, AGCH) only is associated to one random access common channel (P-RACH), in order to avoid any ambiguity in the mobile stations about where to look for the expected answer from the network with the indication of the dedicated service channels (DPCH); and each complete associative link binding the involved physical channels is included in the system information and broadcasted into the serving cell to be read by the mobile stations (MS, UE) when entering an actual part of the procedure charged to exchange protocol messages with the network (BSSC, MSC) through said associative links that being signalling at once to the mobile stations the route towards the services offered by the network, simplifying the access procedure consequently. Suitable groupings among: Downlink pilot sequences, Uplink pilot sequences, scrambling codes, basic midambles, are carried out in a cell-discriminating way and broadcasted into the cell to simplify the serving cell selection procedure (<cross-reference target="DRAWINGS">FIG. 1< / cross-reference>).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
System and method for loop avoidance in multi-protocol label switching
InactiveUS6879594B1Overcome disadvantagesSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationMulti protocolLabel switching
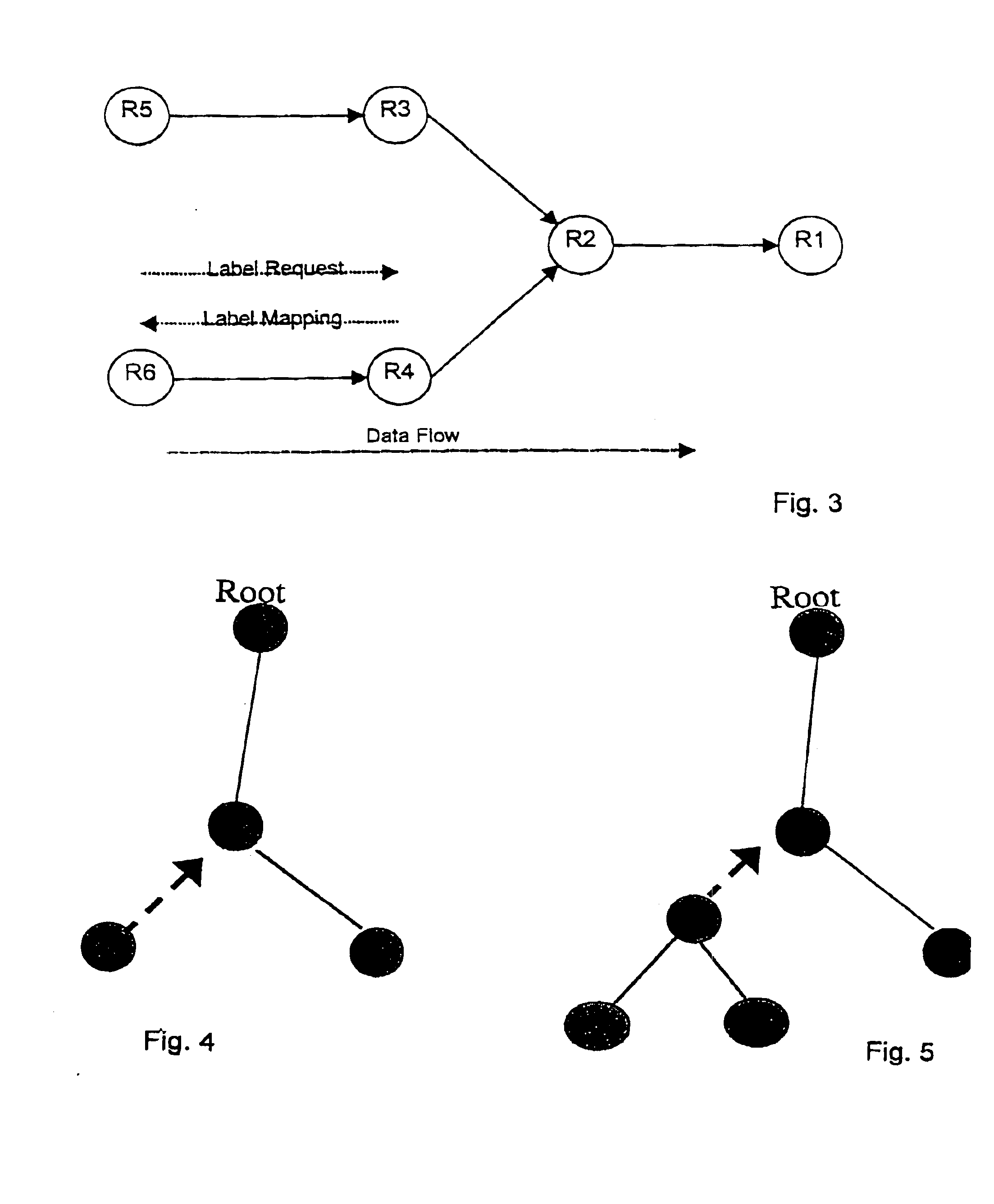
A method for avoiding loops from forming when setting up label switched paths is provided. The method uses a Label Splicing Message is followed by an Acknowledgment message to determine if loops are formed in the process of joining a new node or subtree to a multicast MPLS tree. By verifying that the path towards the root of the MPLS tree is loop-free during the construction of the tree, this method complements the loop detection mechanism provided by the label switched protocol (LDP).
Owner:BIOSPHERICS
Adaptive topology discovery in communication networks
InactiveUS7366113B1Increase elasticityImprove robustnessData switching by path configurationWireless communicationRouting tableTopology information
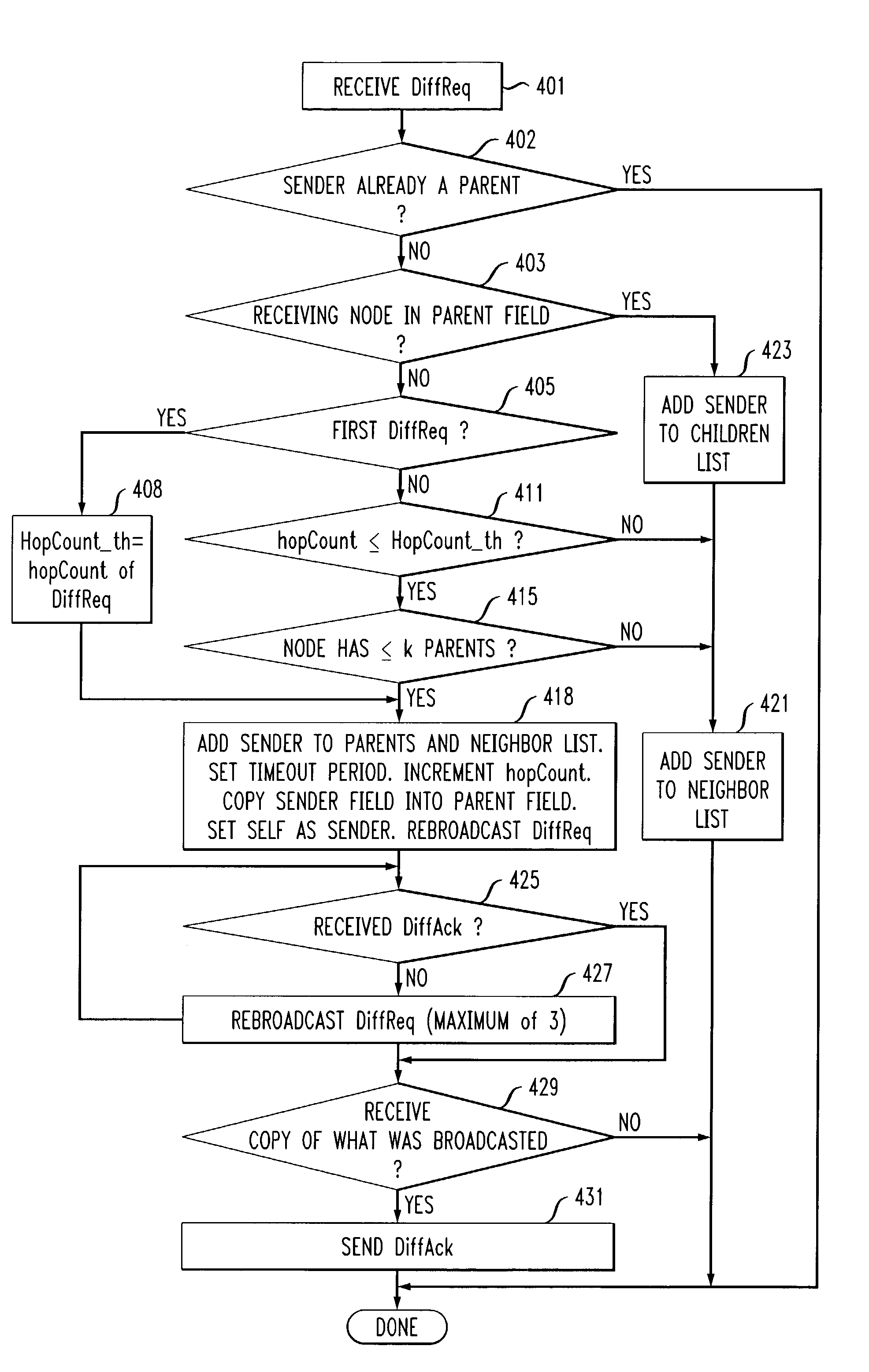
A topology discovery process is used to discover all of the links in an ad hoc network and thereby ascertain the topology of the entire network. One of the nodes of the network, referred to as the coordinator, receives the topology information which can then be used to, for example, distribute a routing table to each other node of the network. The process has a Diffusion phase in which a k-resilient mesh, k>1, is created by propagating a topology request message through the network. Through this process, the nodes obtain information from which they are able to discern their local neighbor information. In a subsequent, Gathering phase, the local neighbor information is reported upstream from a node to its parents in the mesh and thence to the parents' parents and so forth back to the coordinator. The robustness of the Diffusion phase is enhanced by allowing a node to have more than one parent as well as by a number of techniques, including use of a so-called diffusion acknowledgement message. The robustness of the Gathering phase is enhanced by a number of techniques including the use of timeouts that ensure that a node will report its neighbor information upstream even if it never receives neighbor information from one or more downstream neighbors and the use of a panic mode that enhances the probability that a node will get its neighbor information, and its descendents' neighbor information, reported upstream even if that node has lost connectivity with all of its parents.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method for determining location of wireless devices
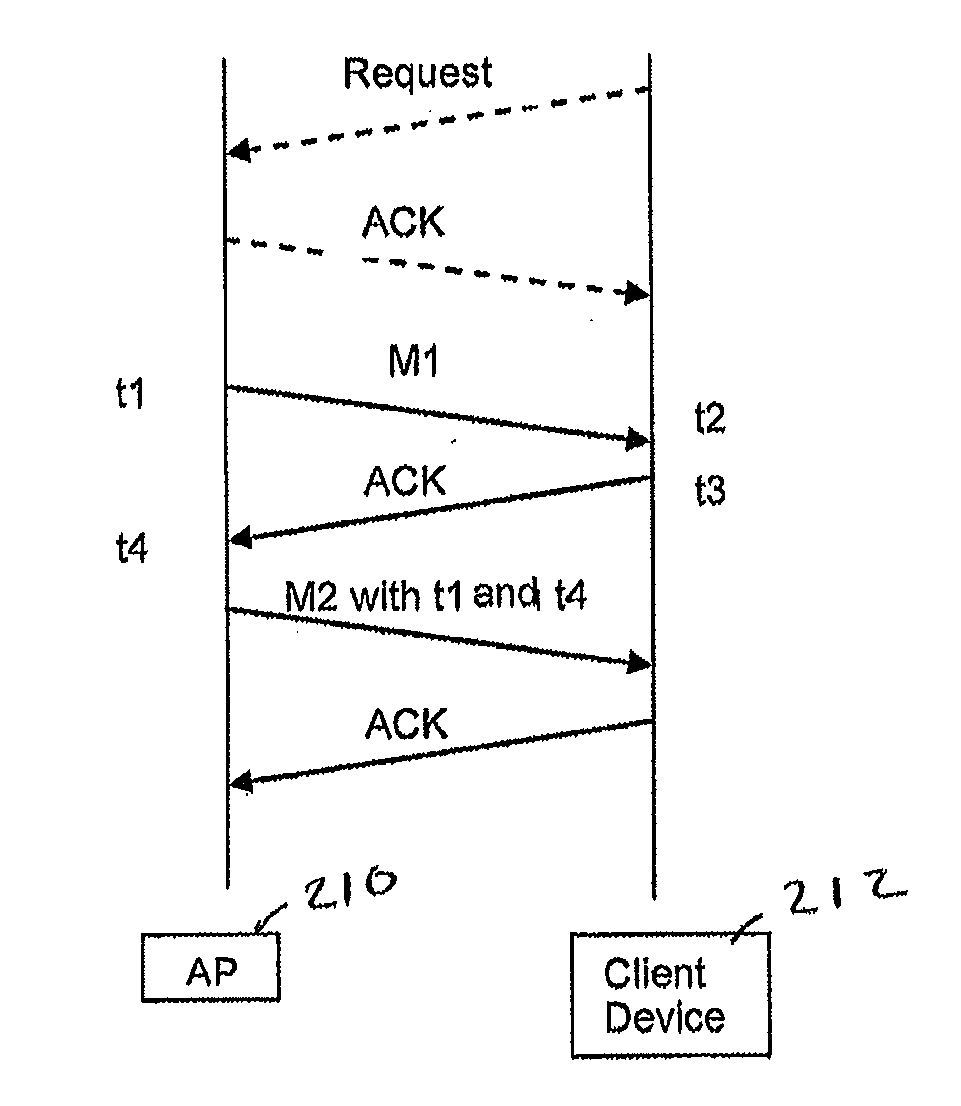
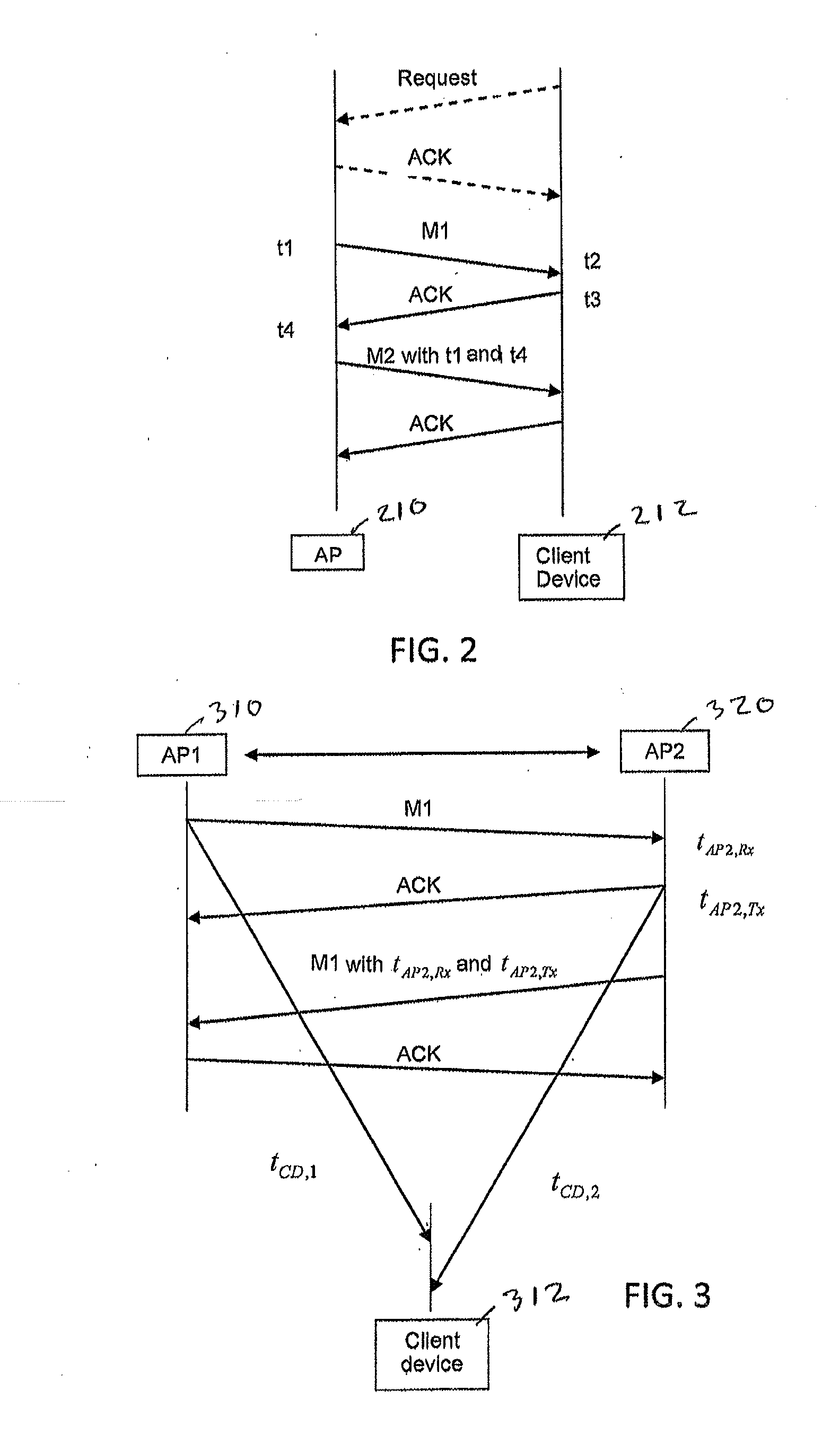
To determine a location of a client device in a wireless network having at least first and second network devices, with known locations, one of the network devices transmits a message to the other network device and the other network device responds with an acknowledgement message. A client device receives the message and the acknowledgement message as well as respective times indicating actual times at which the message and the acknowledgement message were processed by one of the first and second network devices. The client device determines its location based on the times at which it received the message and the acknowledgement message and the difference between the actual processing times. This location may be refined by determining an angle between the client device and at least one of the network devices having multiple antennas and being configured for steered beam communications.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Data mirroring system
ActiveUS7188292B2Significant processingError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsComputer terminalData shipping
Hitless Switching provides a method of delivering data to a remote point in a reliable fashion. However, no guarantee or acknowledgement is provided that data has been written to a remote storage device. This is problematic for remote data mirroring. Apparatus and methods are provided to guarantee that data arriving at a remote terminal is correctly stored. Interaction with hitless switching and remote optical mirroring systems are described.
Owner:CIENA
Transmission control method and system
InactiveUS7505412B2Increasing data amount of dataUnnecessary transmission of data can be preventedError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsData segmentComputer science
Upon receiving an acknowledgement after retransmission of a data segment, an acknowledgement number contained in the acknowledgement is compared with an acknowledgment number expected to be contained in an acknowledgement pertaining to the retransmitted data segment. When the former is larger than the latter, it is determined that the acknowledgement pertains to a data segment that was originally transmitted.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
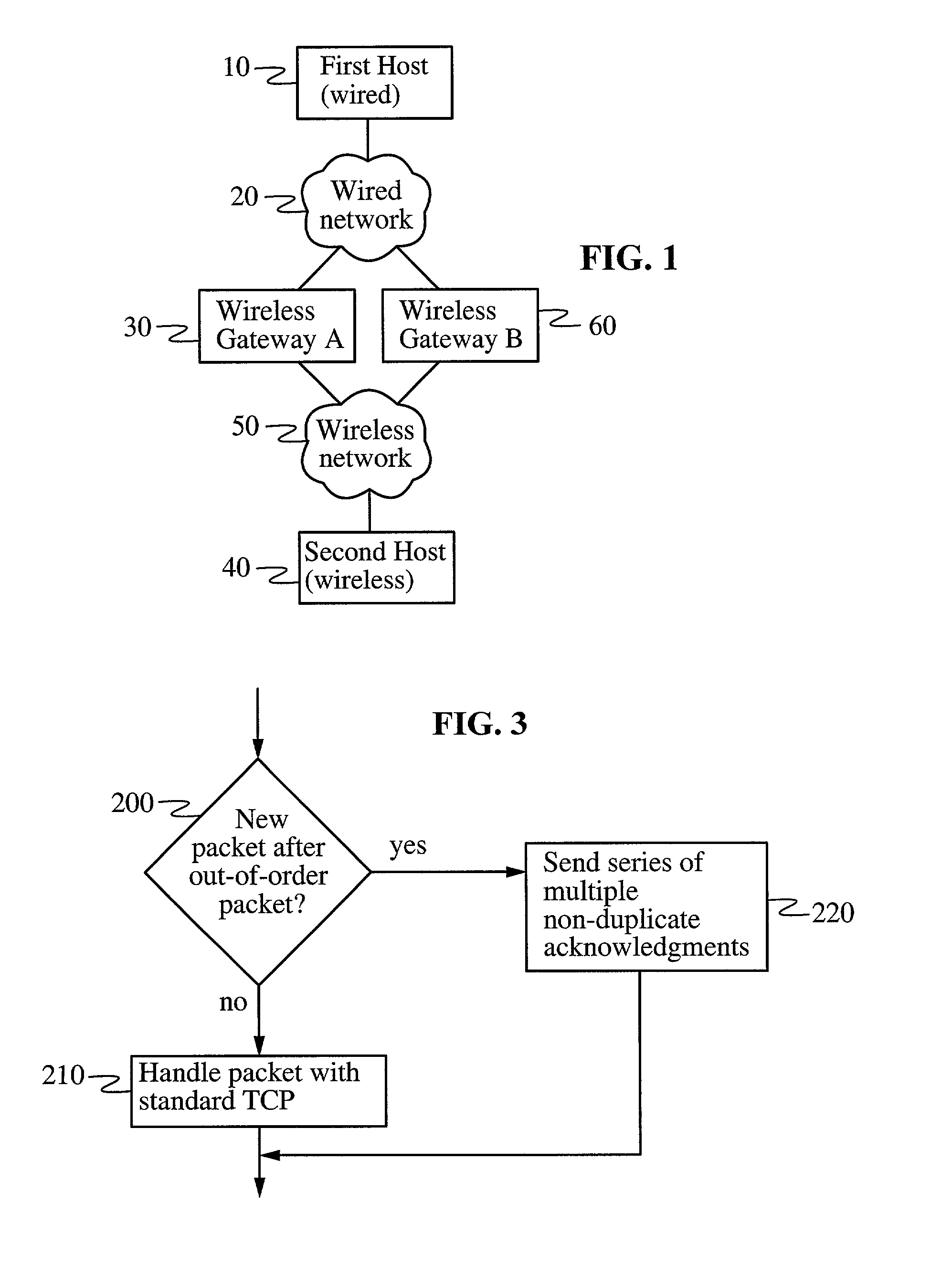
Data throughput over lossy communication links
InactiveUS7061856B2Promote recoveryError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsData connectionTelecommunications link
In a heterogeneous data network including both wired and wireless / lossy links, a transport protocol method implemented at the wireless host is fully compatible with existing wired networks and wireless gateways, and requires no modification to transport protocols at existing wired hosts. The wireless host calculates a temperament parameter [100] characterizing the error-proneness of the data connection and uses this parameter to determine whether error-induced losses or congestion-losses dominate the data connection [110]. If congestion-losses dominate the data connection, then the host uses a standard technique for acknowledging data packets [130]. If, on the other hand, error-induced losses dominate the connection, the host uses a modified technique for acknowledging data packets [120]. According to this modified technique, the wireless host sends a plurality of non-duplicate acknowledgements of a single packet whenever a packet is received after an out-of-order packet is received. By acknowledging distinct fragments of the packet, rather than identical (i.e., duplicate) acknowledgments of the packet, the acknowledgments have the effect of accelerating recovery of maximal window size at the wired host and increasing data throughput.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
TCP selective acknowledgements for communicating delivered and missed data packets
ActiveUS20050063303A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic volumeReal-time computing
One or more flow control modules, implemented on various types of network topologies, provide a number of functionalities for controlling the flow of IP packets (such as TCP / IP packets) over a network connection. The flow control modules may be implemented within a sender and / or receiver or may be deployed into a network as a separate device without requiring significant additional resources.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method and apparatus to allocate resources for acknowledgments in communication systems
InactiveUS20080232307A1Effective distributionError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemControl channel
A method and apparatus for transmission between a plurality of units of user equipment and a base station in a wireless communication system. For each of the units of user equipment, a plurality of control channel elements are mapped to a plurality of downlink acknowledgement channel resources in accordance with a first mapping scheme, and the plurality of control channel elements are mapped to a plurality of uplink acknowledgement channel resources in accordance with a second mapping scheme. The first mapping scheme and the second mapping scheme may be different for different units of user equipment. Alternatively, the first mapping scheme and the second mapping scheme may change over time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
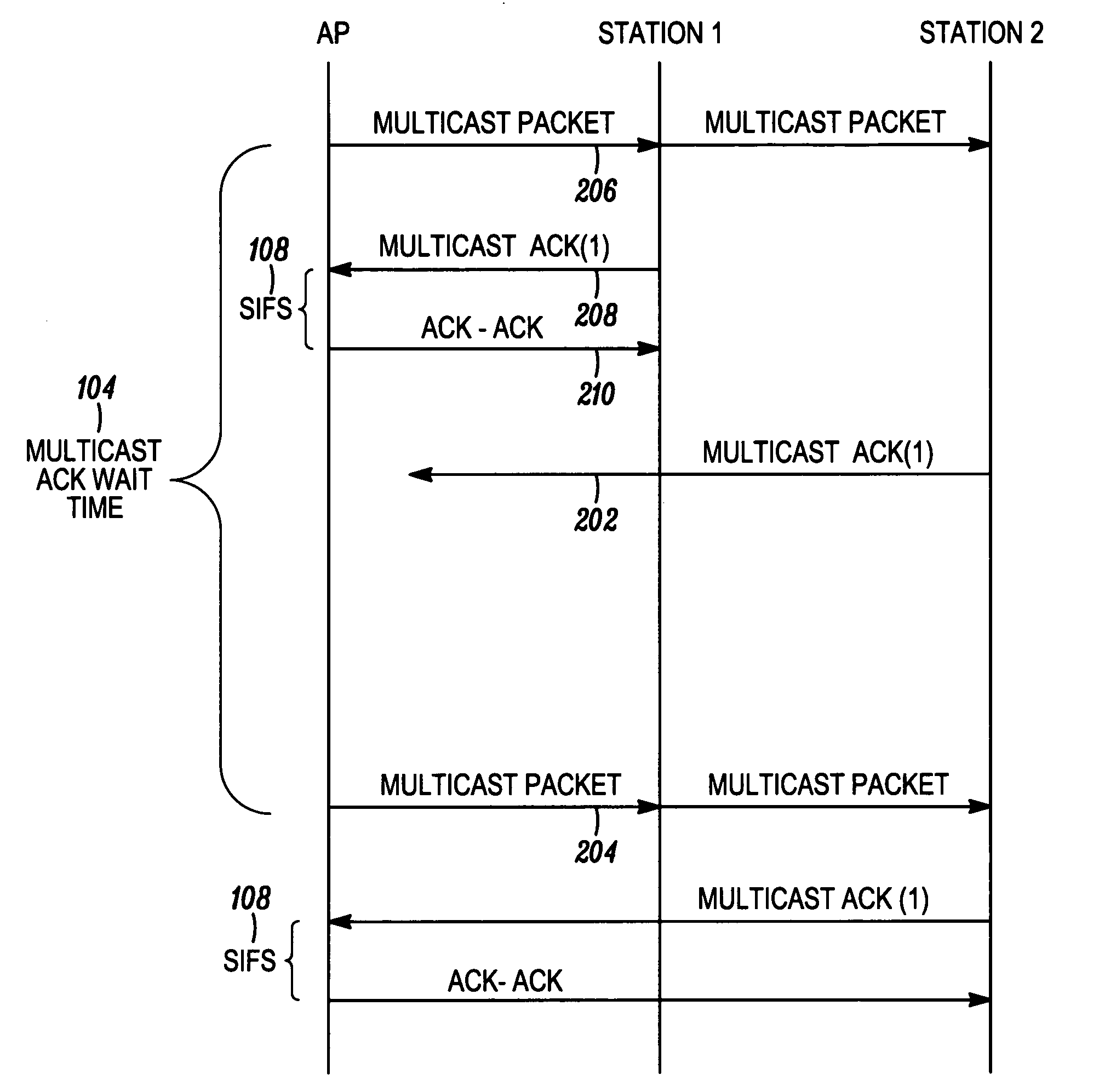
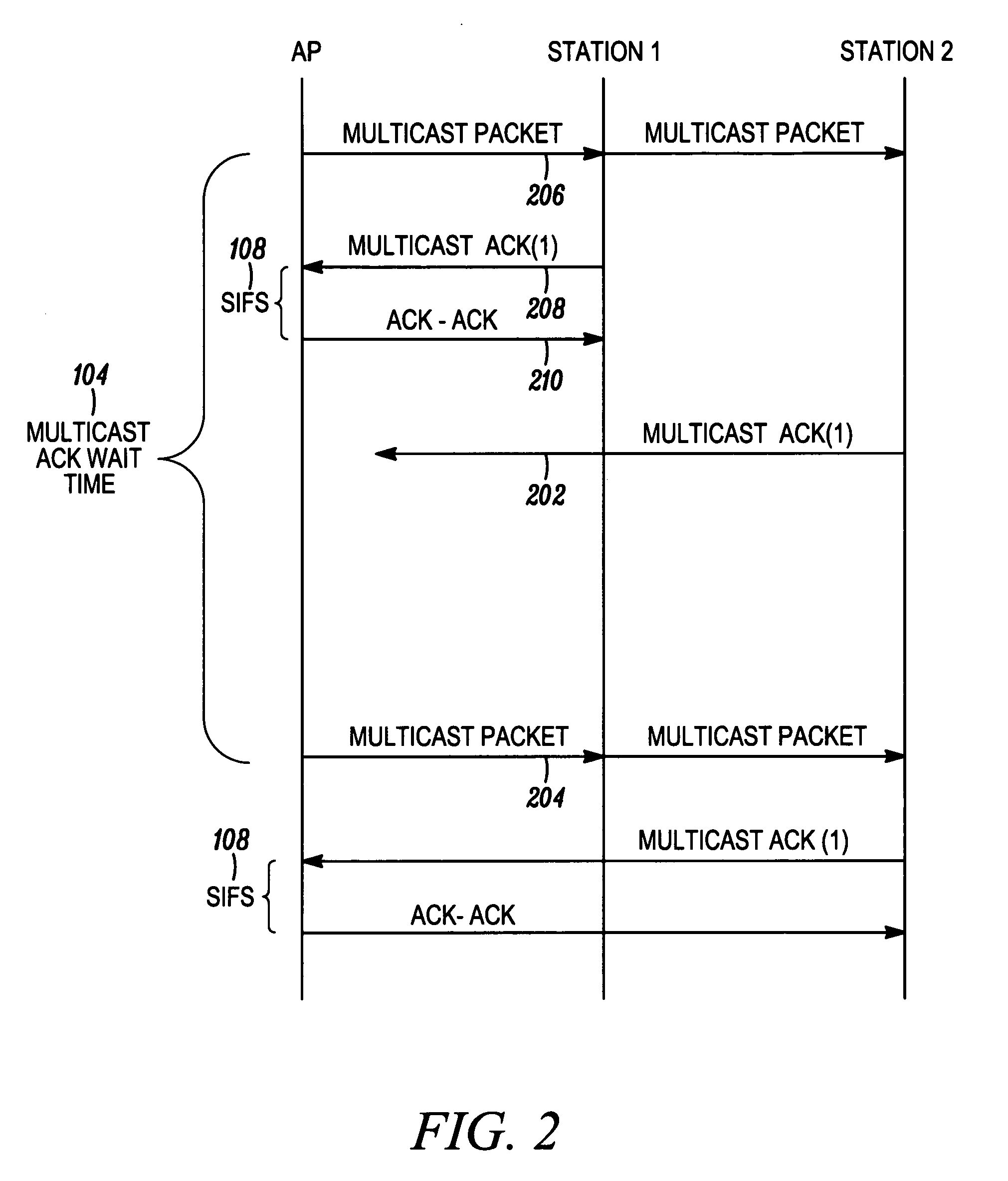
Reliable broadcast protocol in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS7280495B1Broadcast specific applicationsBroadcast transmission systemsThrough transmissionBroadcasting
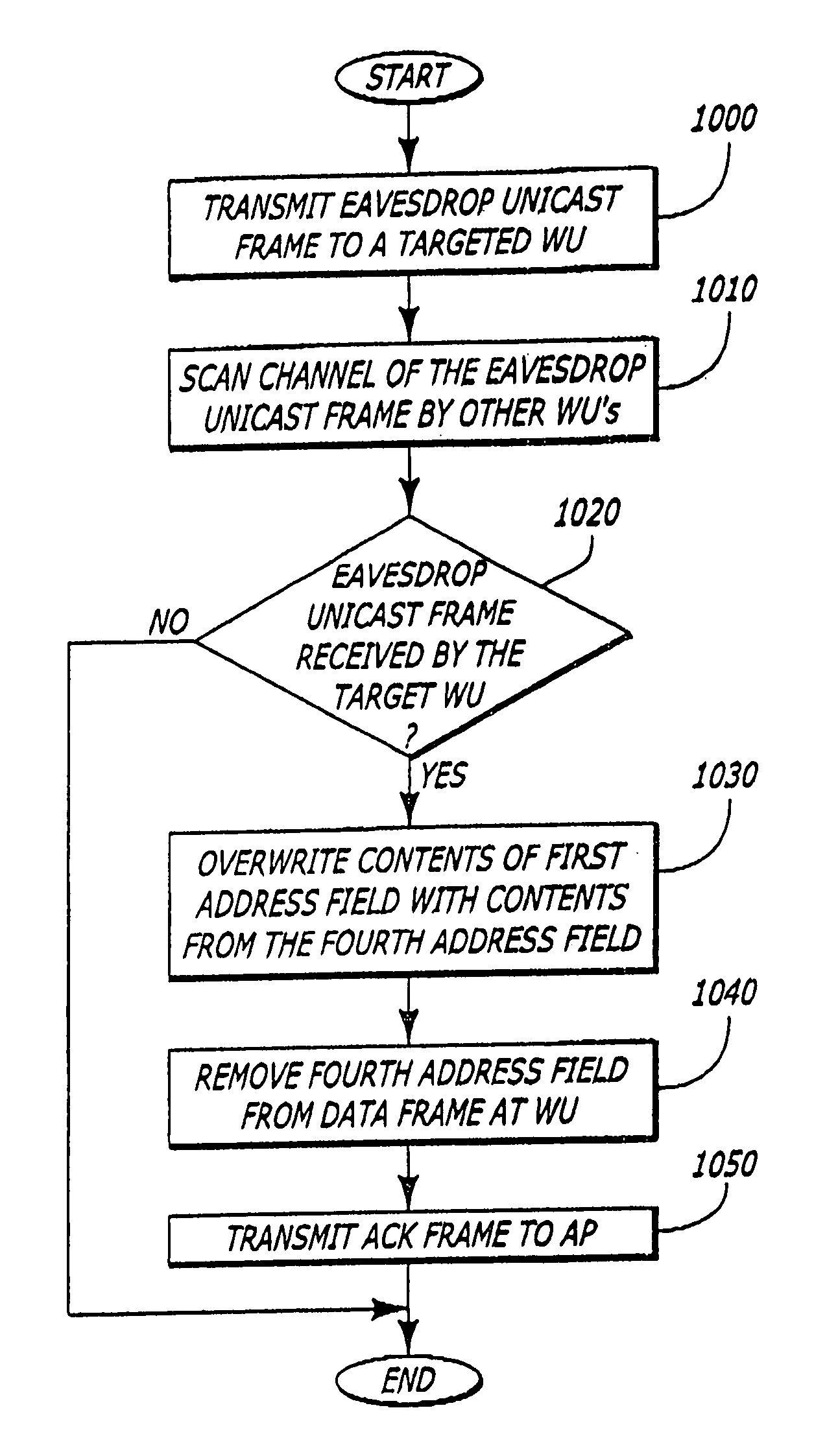
A protocol for acknowledging receipt of a multicast or broadcast frame by a wireless unit is described. One embodiment, an Eavesdrop Unicast frame is created for use in a wireless network operated in accordance with IEEE 802.11. The Eavesdrop Unicast frame allows the targeted wireless unit to transmit acknowledgement (ACK) frame but is configured so that other wireless units can scan and obtain information therefrom. Another embodiment is similar in configuration to the Eavesdrop Unicast frame but is fully compliant with IEEE 802.11. Therein, a multicast or broadcast frame is transmitted but one wireless unit is configured to acknowledge receipt of the multicast or broadcast frame. The acknowledgement is accomplished through transmission of a data frame. Yet another embodiment is the transmission of broadcast or multicast frames into corresponding unicast frames.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
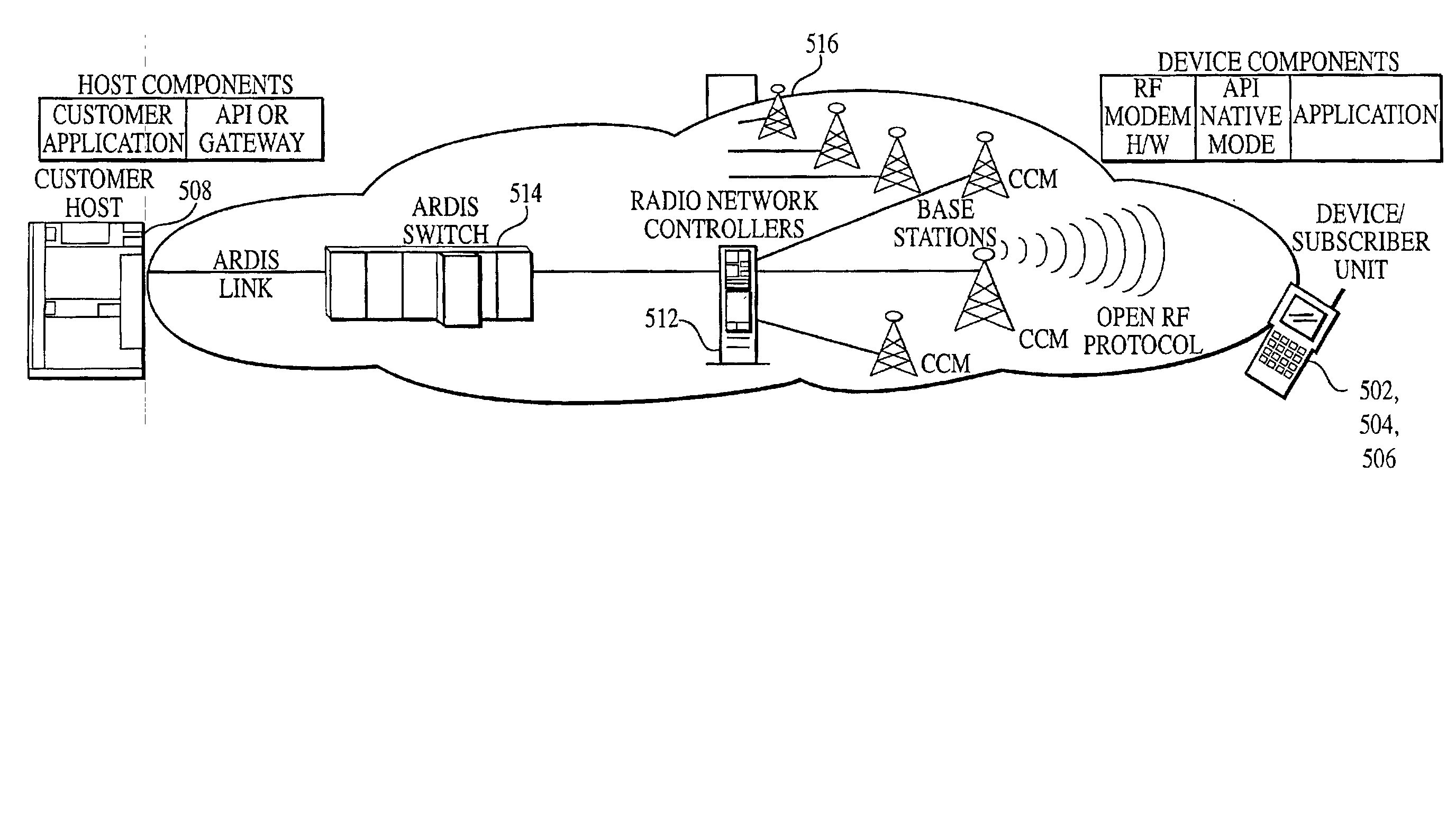
System and method of transmitting data messages between subscriber units communicating with/between Complementary/Disparate Networks
InactiveUS20020160771A1Accounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementData messagesMessage format
A system and method for enabling a first device (502, 504, 506) that may optionally roam between at least first and second wireless networks (500, 1102) to communicate with a second device (502, 504, 506) that may optionally roam between the at least first and second wireless networks (500, 1102). The devices (502, 504, 506) are preferably registered to each network in which the device may roam. A routing switch (1112) first transmits a data message to the receiving device at the last known location of the receiving device. If a negative acknowledgement is received, the message is routed to all other networks to which the receiving device is registered, either serially or in parallel, depending upon the configuration of the transmitting network. Routing devices (1112) and / or gateways (1110) are preferably provided for each network (500, 1102) to provide any required protocol and / or message format conversions.
Owner:XRS CORPORATION
Method of reliable multicasting
ActiveUS20070064718A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsEngineering
Disclosed is a method for reliable multicasting. The method comprises receiving a multicast packet, sending a first acknowledgement for having received the multicast packet, and receiving a second acknowledgement in response to having sent the first acknowledgement.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting data over a network within a specified time limit
ActiveUS7058085B2Facilitate communicationAvoid lostError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
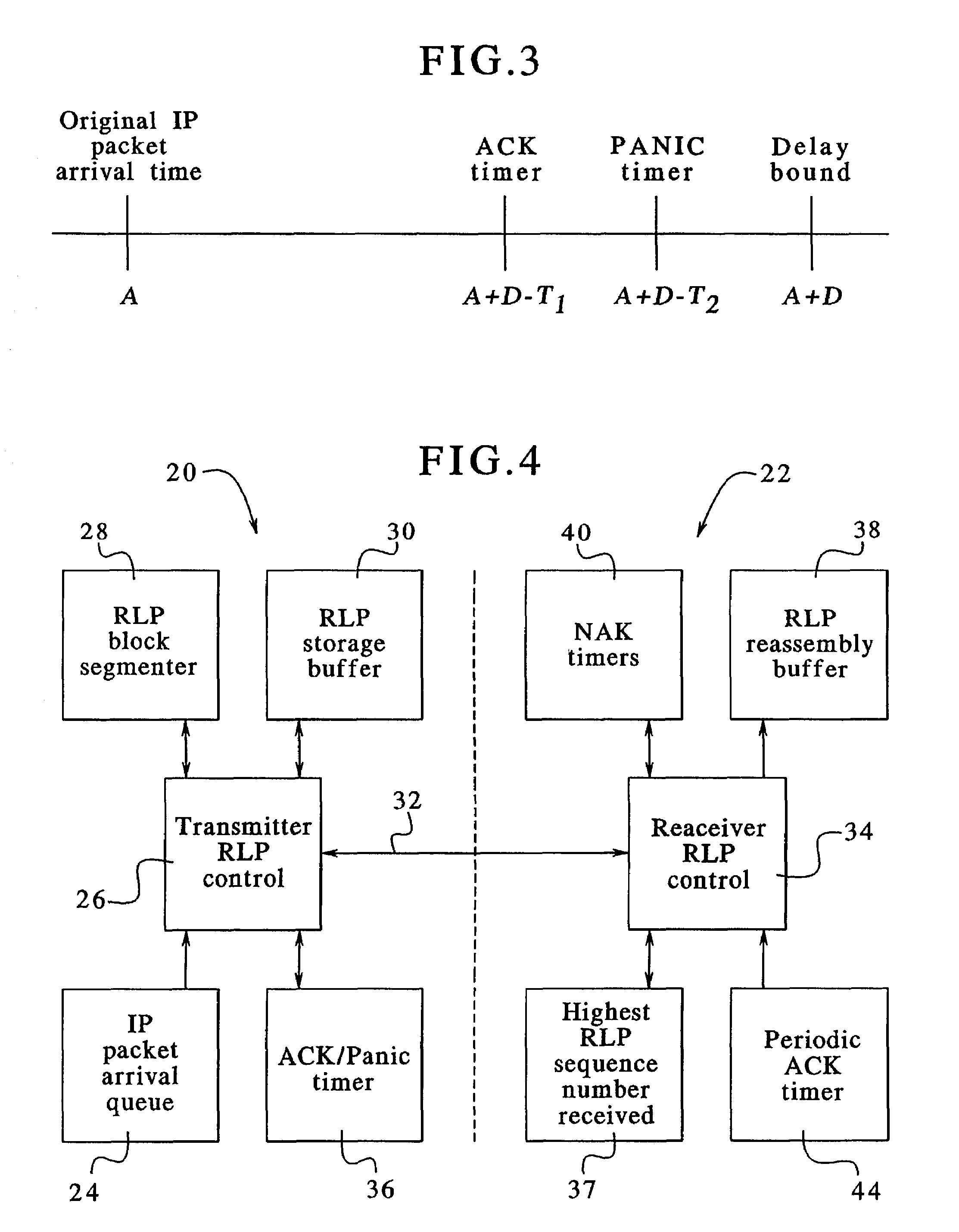
A radio link protocol for a communications system ensures that delivery of Internet protocol data packets occurs within a set delay bound for the packets, in order to satisfy specified quality of service levels. Data packets arriving at a transmitter are subdivided into data blocks. As each block is transmitted, the transmitter starts an associated acknowledgement timer. The timer is turned off, before it expires, if the transmitter timely receives from a receiver a message informing the transmitter that the associated block was successfully received. If such message is not received, the timer expires and the transmitter sends an acknowledgement request signal to the receiver and starts an associated panic timer. The panic timer is turned off, before it expires, if the transmitter subsequently timely receives a message that the associated block was successfully received. If such message not received, the panic timer expires and the transmitter sends one of more copies of the corresponding block to the receiver before occurrence of the delay bound. If the transmitter receives a negative acknowledgement message from the receiver, that a block is missing or corrupted, the transmitter retransmits a copy of the block to the receiver. To reduce messaging traffic, the transmitter cancels acknowledgement and panic timers based upon information contained in negative acknowledgement messages, and the receiver can periodically send acknowledgement messages to inform the transmitter of successfully received blocks.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems, methods, apparatuses and computer program products for providing notification of items for pickup and delivery
ActiveUS11392902B2Conserve computing resource and bandwidthOffice automationLogisticsEngineeringEmbedded system
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
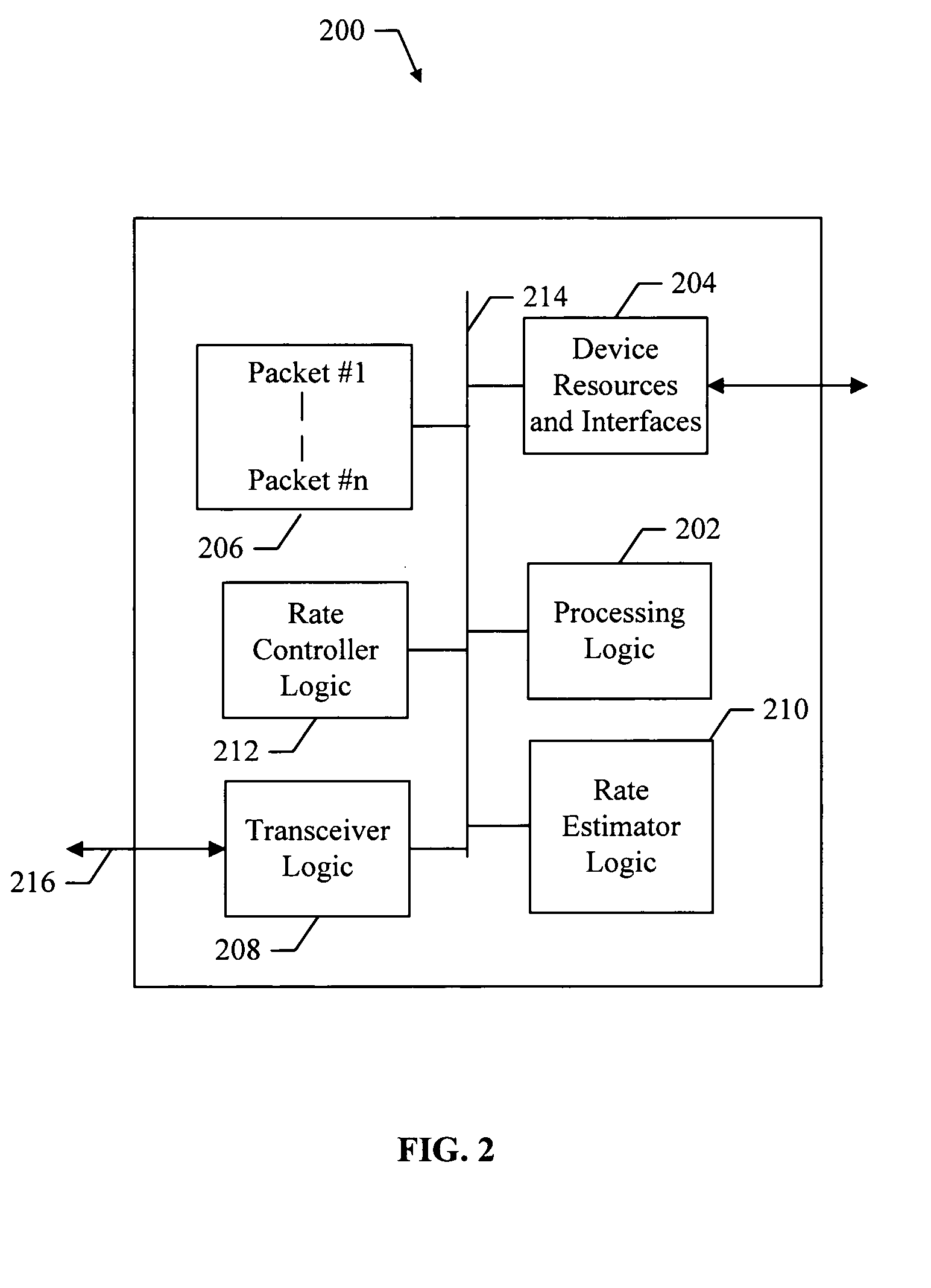
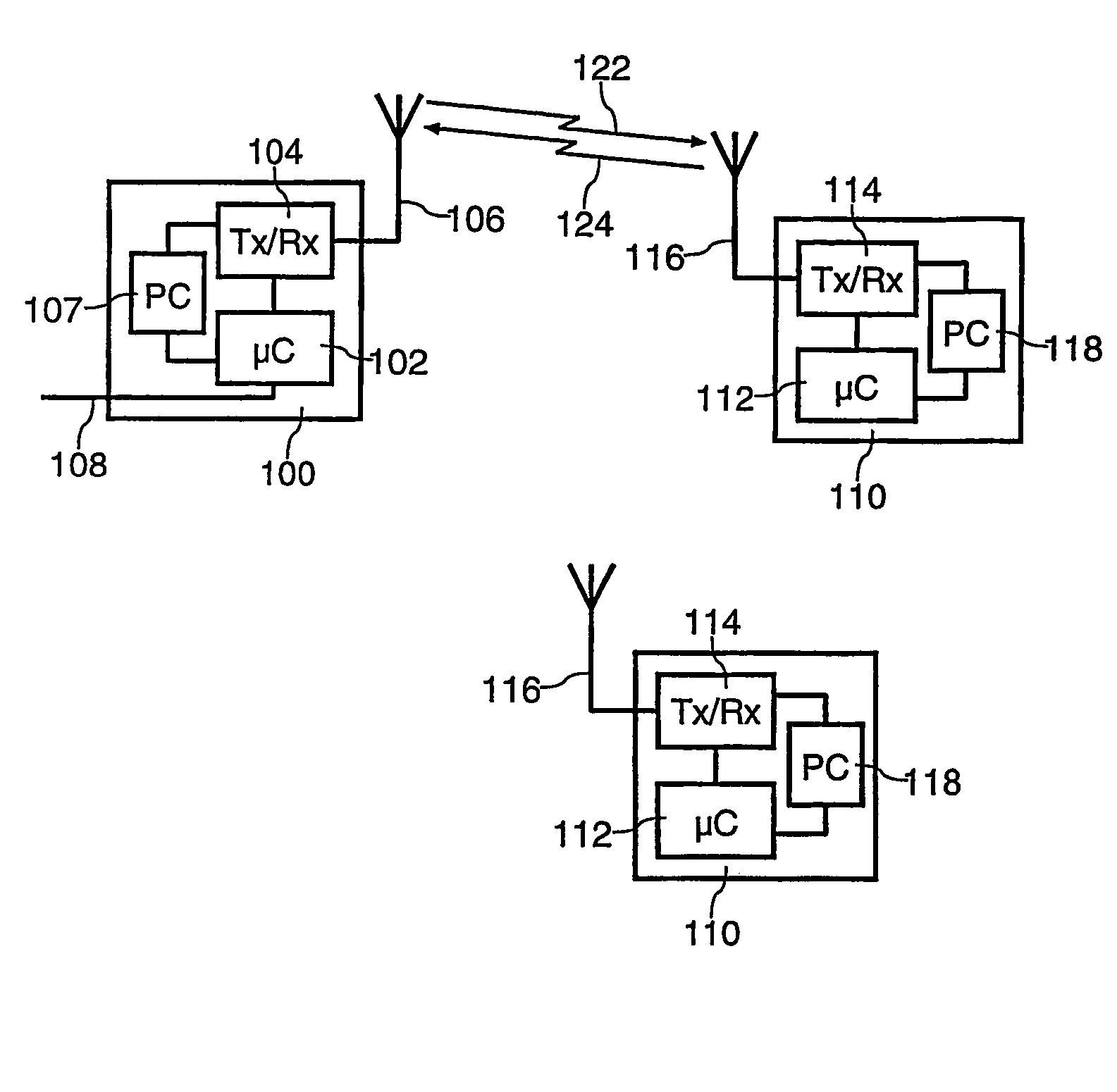
Methods and apparatus for optimum file transfers in a time-varying network environment
InactiveUS20060026296A1Efficient deliveryNetwork usageSpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTWeb environmentFile transfer
Methods and apparatus for optimum file transfers in a time-varying network environment. A method is provided for transmitting content in a data network. The method includes transmitting content at a selected transmission rate, and receiving one or more acknowledgement signals. The method also includes estimating a network delivery rate from the one or more acknowledgment signals, and adjusting the selected transmission rate of the content based on the network delivery rate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Communication system using arq
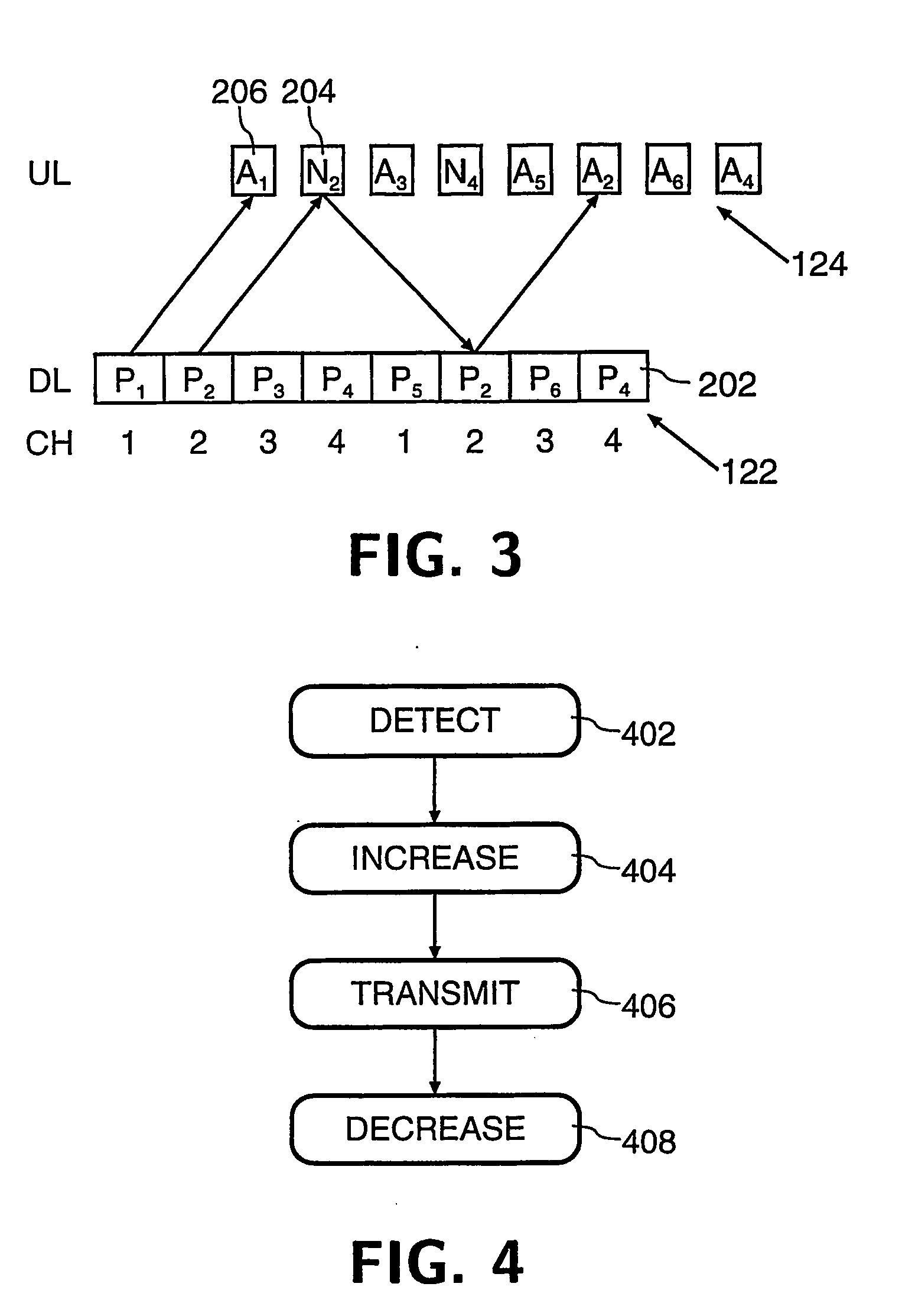
ActiveUS20050143114A1Improve accuracyImproved channel estimationPower managementEnergy efficient ICTPrimary stationCommunications system
A communication system comprises a downlink data channel for the transmission of data packets from a primary station to a secondary station and two uplink control channels, a first channel for transmission of status signals to indicate the status of received data packets and a second channel for transmission of pilot information. In operation, on detection (402) of a data packet the secondary station increases (404) the transmission power of the second channel, thereby enabling the primary station to obtain a better estimate of uplink channel properties and hence increase the accuracy with which it can decode the status signal. The secondary station transmits (406) the status signal, typically either an acknowledgement (ACK) or negative acknowledgement (NACK), and decreases (408) the transmission power of the second control channel signal. The increase and decrease in power are not necessarily identical, for example as a result of the effects of power control.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods and apparatus for managing a buffer of events in the background
InactiveUS7032226B1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsData processing systemPacket processing
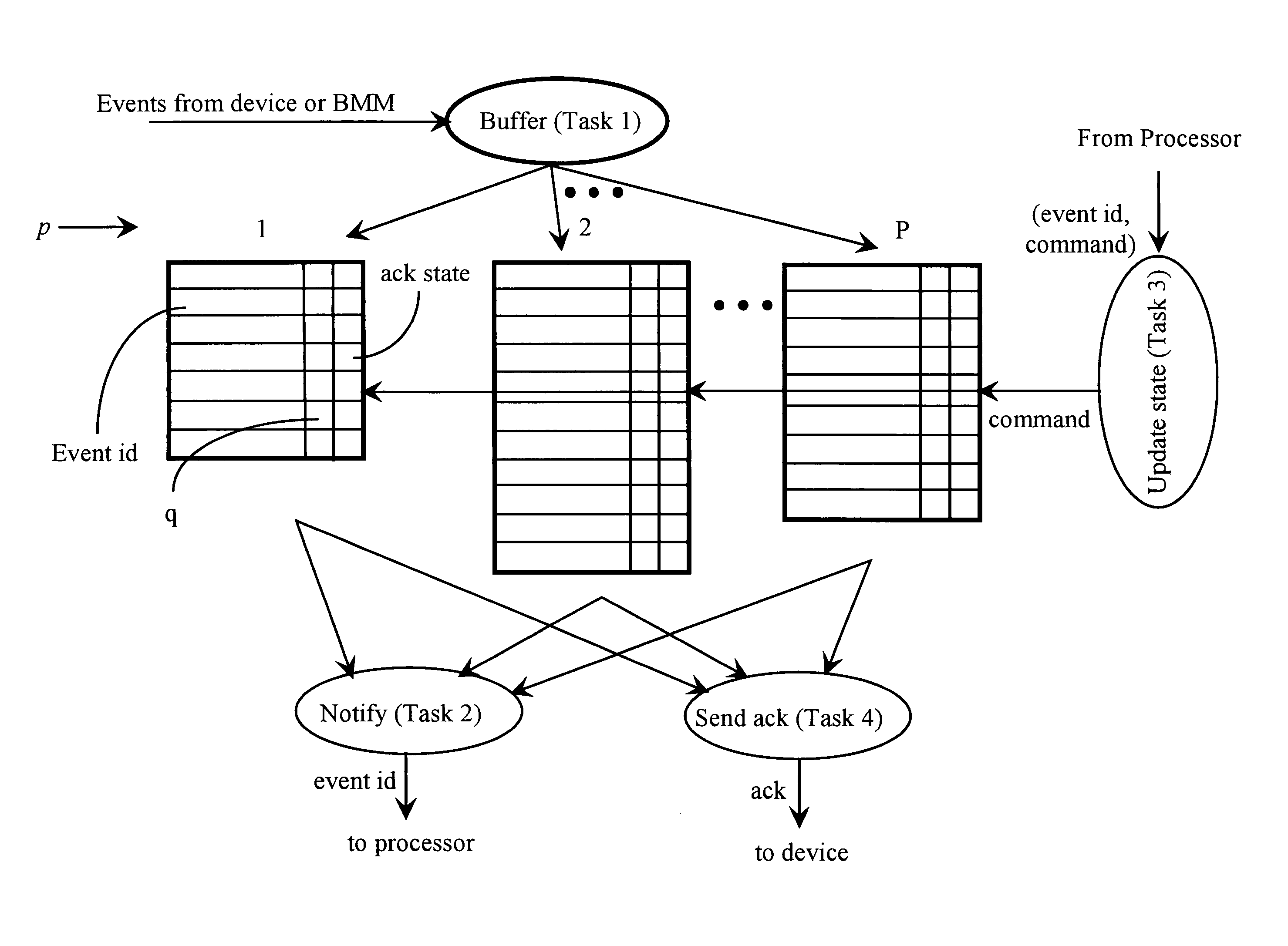
A background event buffer manager (BEBM) for ordering and accounting for events in a data processing system having a processor includes a port for receiving event identifications (IDs) from a device, a queuing function enabled for queuing event IDs received, and a notification function for notifying the processor of queued event IDs. The BEBM handles all event ordering and accounting for the processor. The BEBM in preferred embodiments queues events by type with priority and by priority within type, and also handles sending acknowledgement to the device when processing on each event is concluded, and buffers the acknowledgement process. In particular embodiments the apparatus and method is taught as a packet processing router engine.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
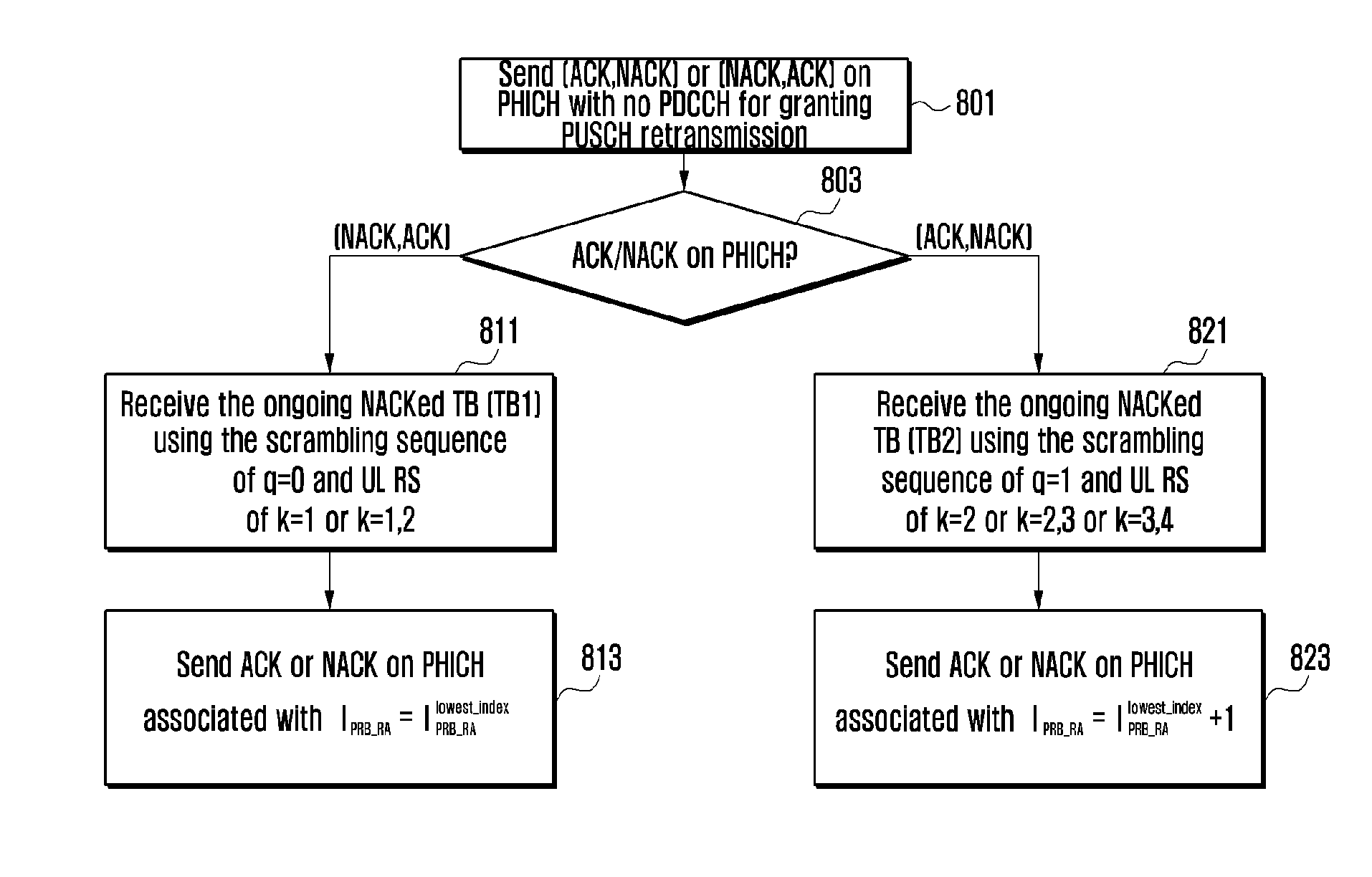
Method for sending and receiving ACK/NACK information, base station and terminals
ActiveCN103973397AResolving resource allocation conflictsError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionReliable transmissionSmall cell
Disclosed are methods for sending and receiving ACK / NACK information, a base station, and a terminal. The method for sending ACK / NACK information comprises: dividing acknowledgement (ACK) / negative acknowledgement (NACK) information of multiple terminals into X groups according to a present indication parameter, X being a positive integer greater than or equal to 1; separately performing combined coding on ACK / NACK information corresponding to each group in the foregoing X groups, so as to obtain X first blocks of bits; and mapping the foregoing X first blocks of bits to a predetermined ACK / NACK physical source and sending the foregoing X first blocks of bits. By means of the present invention, reliable transmission of HARQ-ACK information of a terminal on the NCT is implemented, the reliability of transmission of uplink data in a Low Cost terminal is improved, and problems such as a conflict of PHICH resource allocation and ICIC of a frequency domain in a small cell are solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for transmitting harq-ack feedback information
InactiveUS20130114575A1Reduce the impactImprove throughput performanceSignal allocationTime-division multiplexCarrier signalControl channel
A method for transmitting Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest-ACKnowledgement (HARQ-ACK) feedback information is provided. The method includes obtaining HARQ-ACK feedback information, a total number of bits of which is less than or equal to four through performing group bundling on the HARQ-ACK feedback information of all sub-frames in a current HARQ-ACK bundling window of two Component Carriers (CCs), determining a number of Physical Uplink Control Channel (PUCCH) resources provided for transmission of the HARQ-ACK feedback information according to data transmission modes of the two CCs, and a number of elements in the bundling window, and transmitting the HARQ-ACK feedback information after the group bundling to a base station on PUCCH channel resources adopting a PUCCH format 1b of channel selection according to the PUCCH channel resources mapped from the HARQ-ACK feedback information after the group bundling and modulation symbols.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmission/reception method and apparatus for uplink MIMO retransmission in LTE system
ActiveUS20120076078A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionPrecodingTelecommunications
A transmission / reception method and apparatus for a mobile communication system supporting uplink MIMO is provided. In the transmission method, a User Equipment (UE) transmits two transport blocks according to a predetermined number of layers and respective precoding indices, an evolve Node B (eNB) transmits, when one of the transport blocks is lost, a negative acknowledgement for the lost transport block, and the UE sets a precoding index for the lost transport block to a predetermined value to retransmit the lost transport block while maintaining the number of layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for the exchange of data packets in a network of distributed stations, device for compression of data packets and device for decompression of data packets
InactiveUS20070165635A1Avoid possibilityAvoid transitSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementRobust Header CompressionNetwork communication
The invention is related with network communication, in particular wireless networking. In order to improve bandwidth utilization, a header compression protocol is implemented in most wireless network systems, such as robust header compression ROHC for WLAN systems. When using multicast groups for data communication problems with ROHC are related with relative late initiation of stations that newly enter the multicast group. The invention proposes an improved state machine for the compressor in order to overcome this drawback. It is also proposed an improvement for the decompressors which omit sending positive acknowledgements in order to further improve compression efficiency. The invention also concerns an accordingly improved method for the exchange of data packets in a network of distributed stations.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving uplink control channels in a wireless communication system
A method and apparatus for transmitting / receiving pilot symbols for demodulation of control channel information in the uplink of a wireless communication system are provided. When an Evolved Node B (ENB) expects to receive both the Channel Quality Information (CQI) and the Acknowledgement (ACK) / Negative ACK (NACK) from a User Equipment (UE) in a certain subframe, if the UE transmits only the CQI channel, the ENB is prevented to detect the nonexistent ACK / NACK information from the CQI channel, thereby avoiding false alarm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
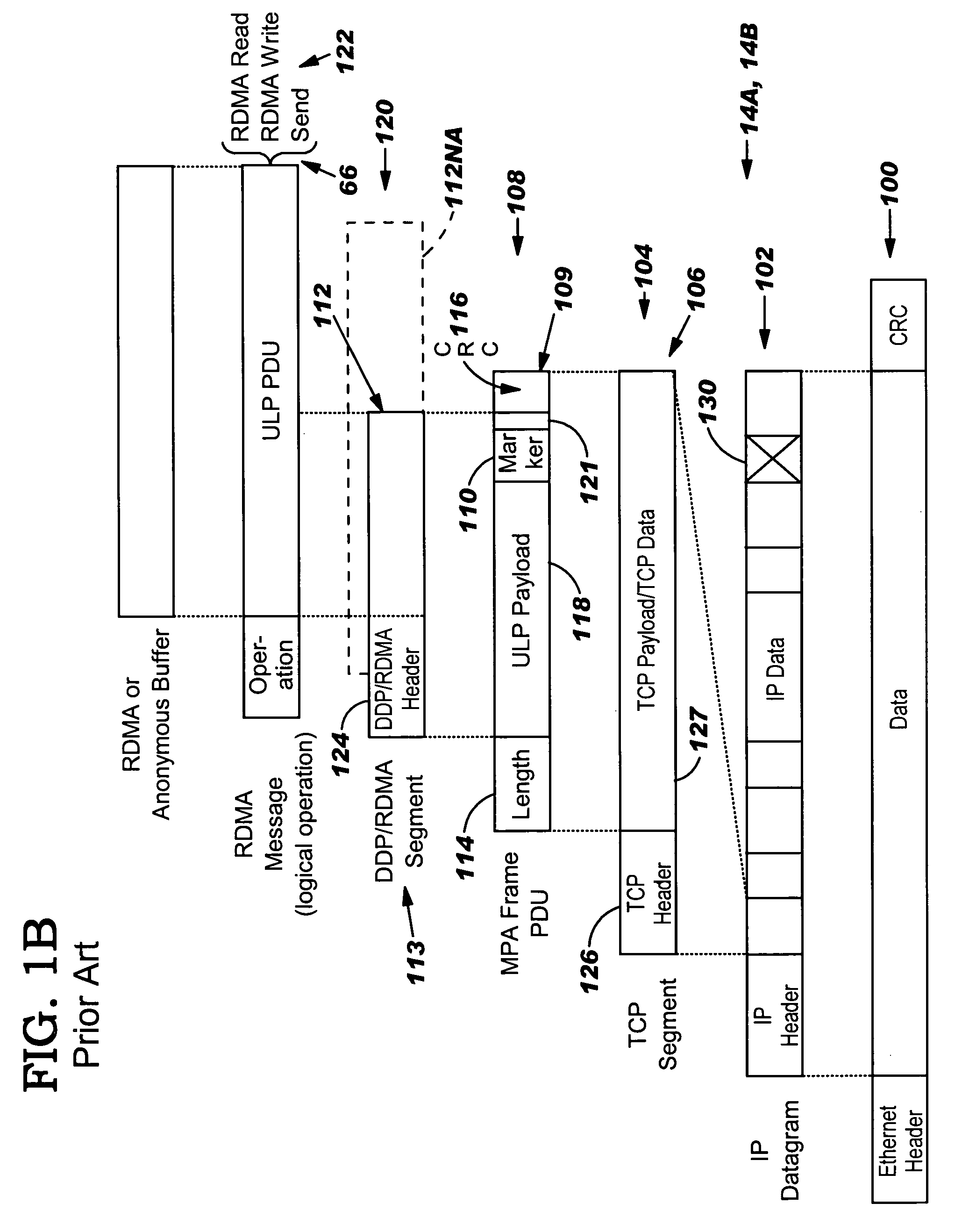
In-order delivery of plurality of RDMA messages
InactiveUS20050144310A1Increase probabilityAttenuation bandwidthMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionConnection typeData placement
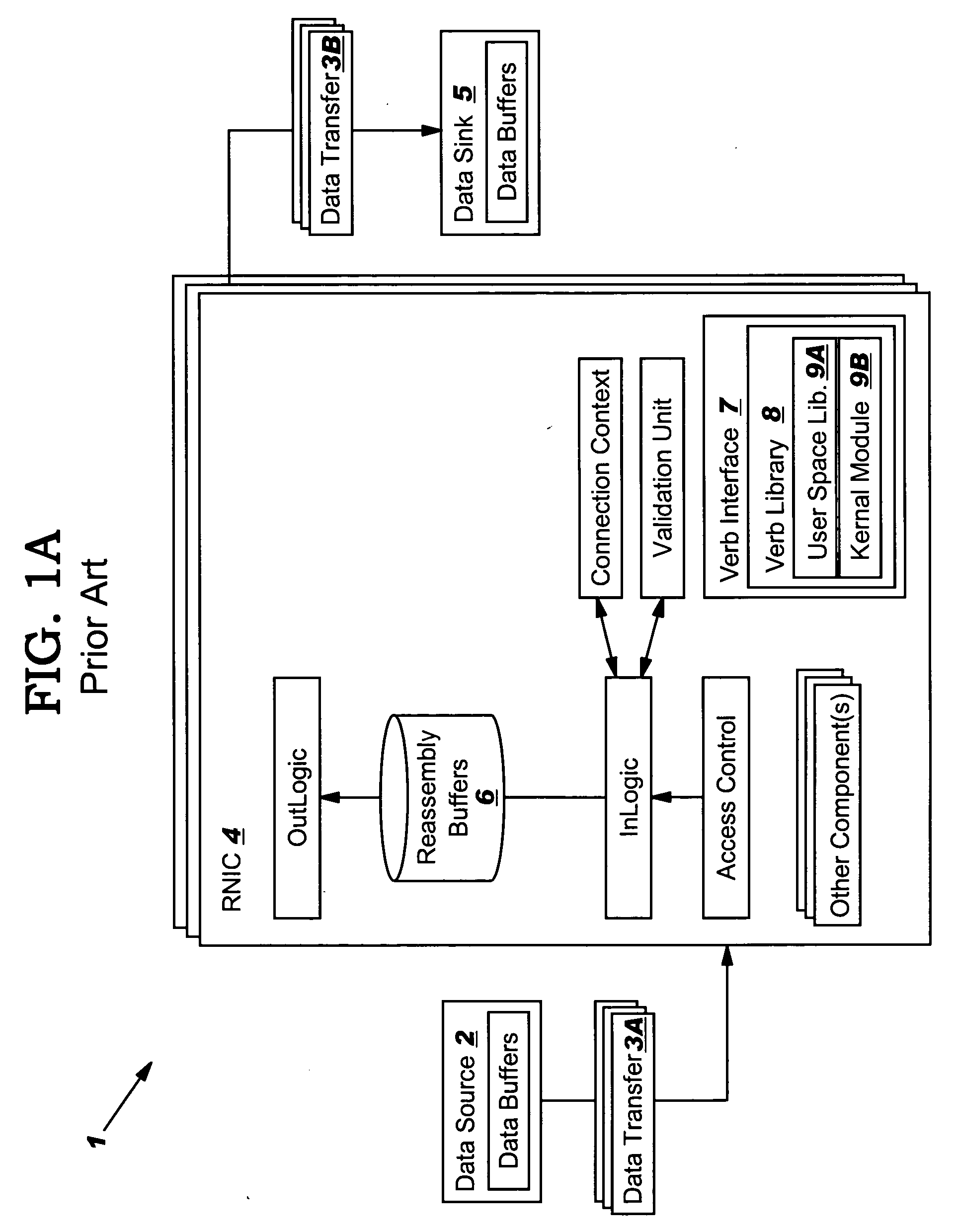
An RNIC implementation that performs direct data placement to memory where all segments of a particular connection are aligned, or moves data through reassembly buffers where all segments of a particular connection are non-aligned. The type of connection that cuts-through without accessing the reassembly buffers is referred to as a “Fast” connection because it is highly likely to be aligned, while the other type is referred to as a “Slow” connection. When a consumer establishes a connection, it specifies a connection type. The connection type can change from Fast to Slow and back. The invention reduces memory bandwidth, latency, error recovery using TCP retransmit and provides for a “graceful recovery” from an empty receive queue. The implementation also may conduct CRC validation for a majority of inbound DDP segments in the Fast connection before sending a TCP acknowledgement (Ack) confirming segment reception.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
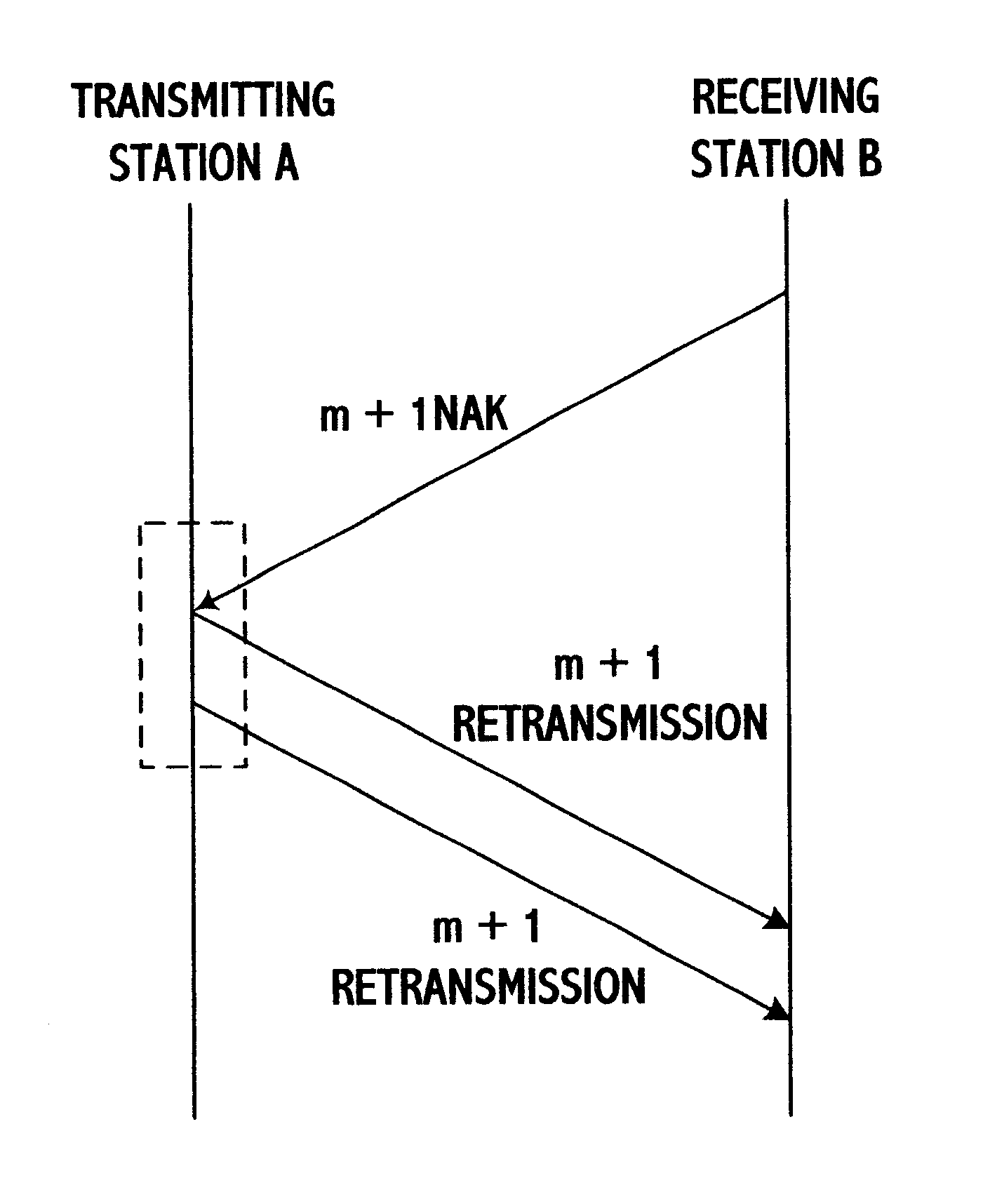
Method for transmitting control frames and user data frames in mobile radio communication system
InactiveUS6581176B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexCommunications systemStation
In a method for transmitting radio link protocol frames in a mobile radio communication system, if an error occurs on a radio section when user data frames of a radio link protocol (RLP) having respective different series numbers are transferred from a transmitting station to a receiving station, at least one missed user data frame is caused at the receiving station. At this time, the receiving station transmits, repeatedly by first times, a negative acknowledgement (NAK) control frame of the RLP for at least one missed user data frame, to the transmitting station. The transmitting station sends, by second times different from the first times, at least one missed user data frame in response to the received NAK control frame, to the receiving station. Particularly, series numbers of respective missed user data frames are sent through one NAK control frame to the transmitting station, at equal time when a timer for an NAK is expired, to accordingly result in reducing the number of the total NAK control frames and increasing a throughput per unit time.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
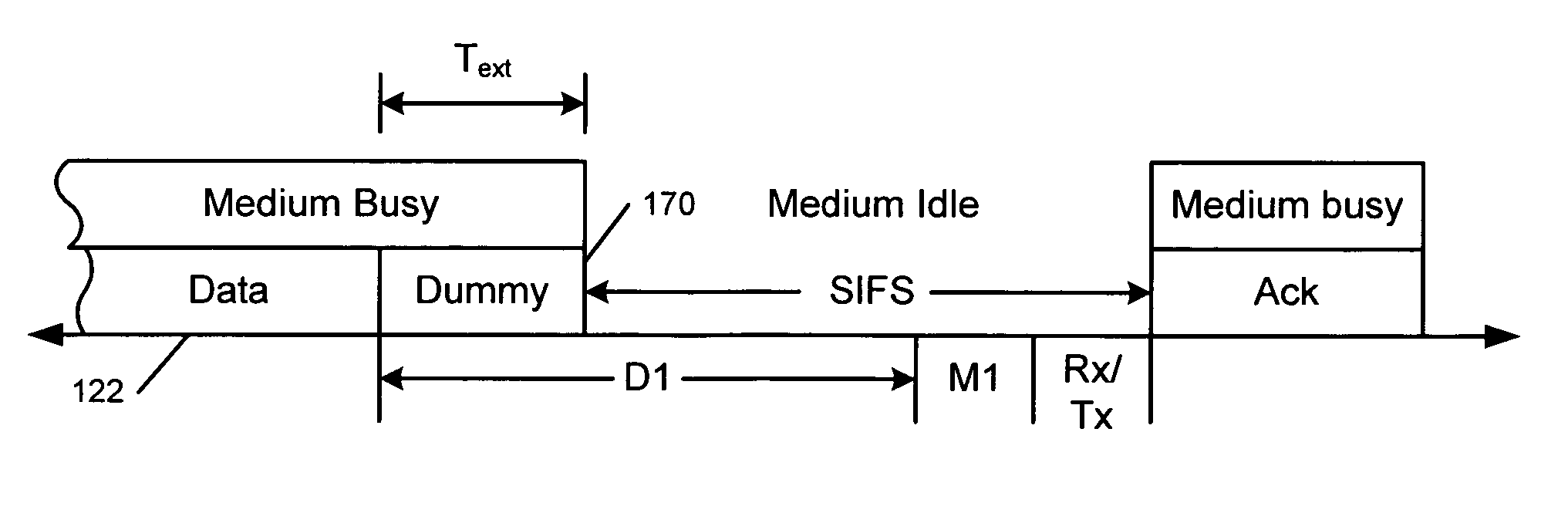
Extension mode for wireless lans complying with short interframe space requirement
A method and apparatus enables advanced signal processing in a wireless local area network (WLAN). First and second WLAN transceivers are provided with advanced signal processing capabilities. A maximum interframe period between data and an acknowledgement is required by the WLAN for compatibility. A duration of the interframe period is shorter than a duration that is required to perform the advanced signal processing. The first WLAN transceiver transmits a header and data. A first data field in the header is specified that enables the advanced signal processing. A second data field is specified that defines a data time period and an extension time period. The first WLAN transceiver transmits data during the data time period and dummy data during the extension time period. The second WLAN transceiver receives the header and initiates receiver processing during the extension time period.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
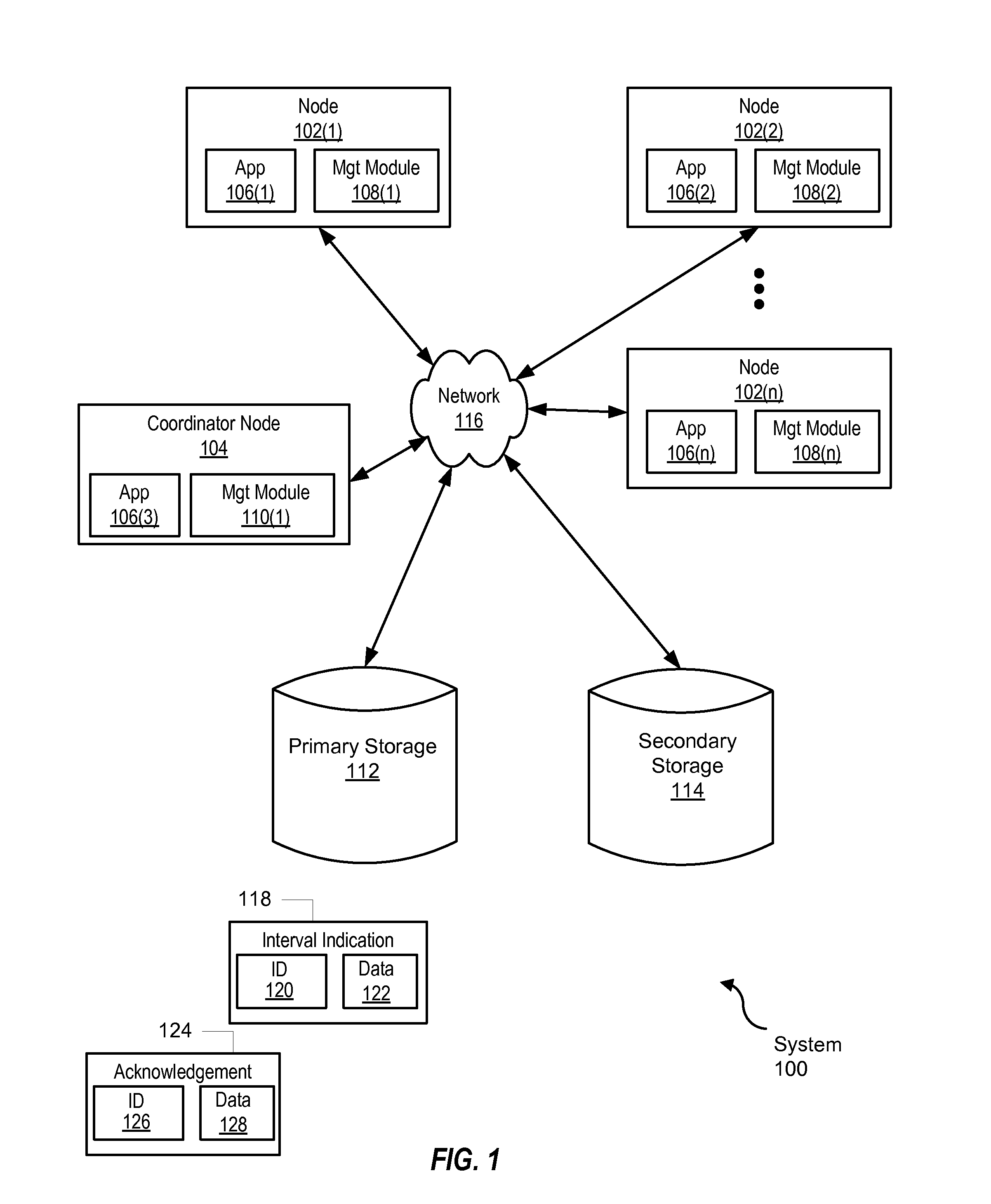
Interval-controlled replication
InactiveUS20130226870A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionComputer scienceOperating system
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Method and apparatus for updating information in a low-bandwidth client/server object-oriented system
InactiveUS20070078978A1Efficiently maintaining updated informationImprove performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData packObject based
Methods and apparatus for efficiently maintaining updated information on client / server object-oriented computing systems are disclosed. In accordance with one aspect of the present invention, a method for transmitting a packet of data from a first computing system to a second computing system in a client / server object-based computing system includes identifying the packet of data using the first computing system and attempting to send the packet of data from the first computing system to the second computing system. Once the attempt is made to send the packet of data, it is determined whether the packet of data is received by the second computing system. An acknowledgment is sent from the second computing system to the first computing system when it is determined that the packet of data is received by the second computing system. The acknowledgement indicates that the packet of data is received by the second computing system. In one embodiment, the method includes re-attempting to send the packet of data from the first computing system to the second computing system when the packet of data is not successfully received by the second computing system.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
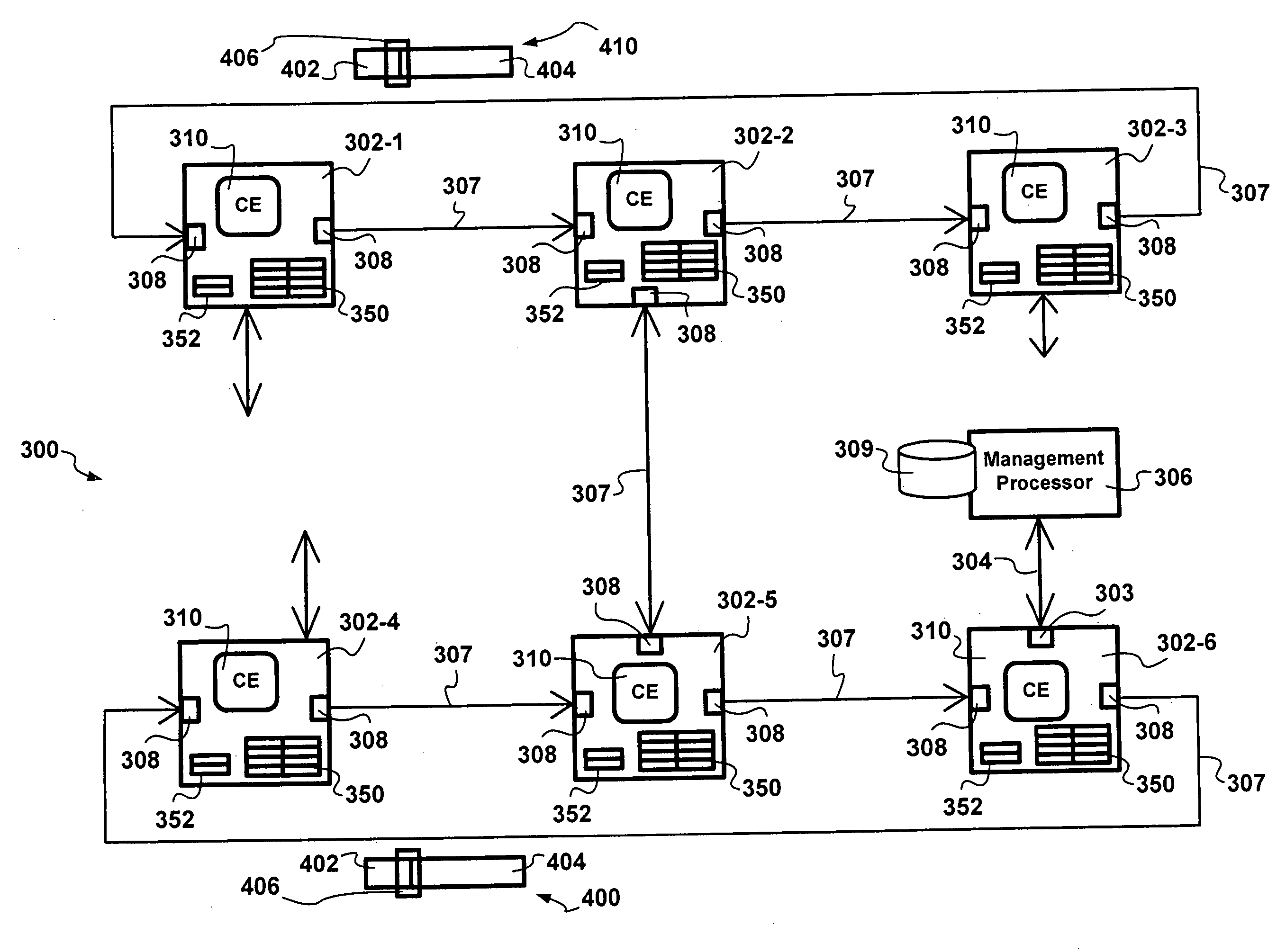
Remote control of a switching node in a stack of switching nodes
InactiveUS20060023640A1Reduce deploymentReduce configurationMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationExchange networkRemote control
A methods and apparatus for remote management of switching network nodes in a stack via in-band messaging are presented. Switching nodes in the stack default to reserved switching node identifiers and stacking ports default to a blocking state upon startup, restart, and reset. Each command frame received via a blocking state is forwarded to a command engine at each switching node and is acknowledged with the current switching node identifier. Each acknowledgement frame bearing the reserved network node identifier triggers configuration of the acknowledging switching node. Switching nodes and the management processor track interrupt state vectors regarding events. An interrupt acknowledgement process is employed to track raised interrupts. Configuration of switching node is performed via command frames transmitted by the management processor and destined to a command engine associated with the switching node. Services provided by the management processor are requested via control frames destined to the switching node to which the management processor is attached and destined to the management port thereof. The advantages are derived from engineered switching node deployments wherein an appropriate number of management processors, less than the number of switching nodes in the stack, are employed to provide services to corresponding switching nodes in the stack, based on processing, control, and configuration bandwidth requirements. The in-band configuration and control of the switching nodes in the stack reduce deployment, configuration, management, and maintenance overheads.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Selection of acknowledgment timing in wireless communications
ActiveUS20140010128A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSite diversityAutomatic repeat requestCarrier signal
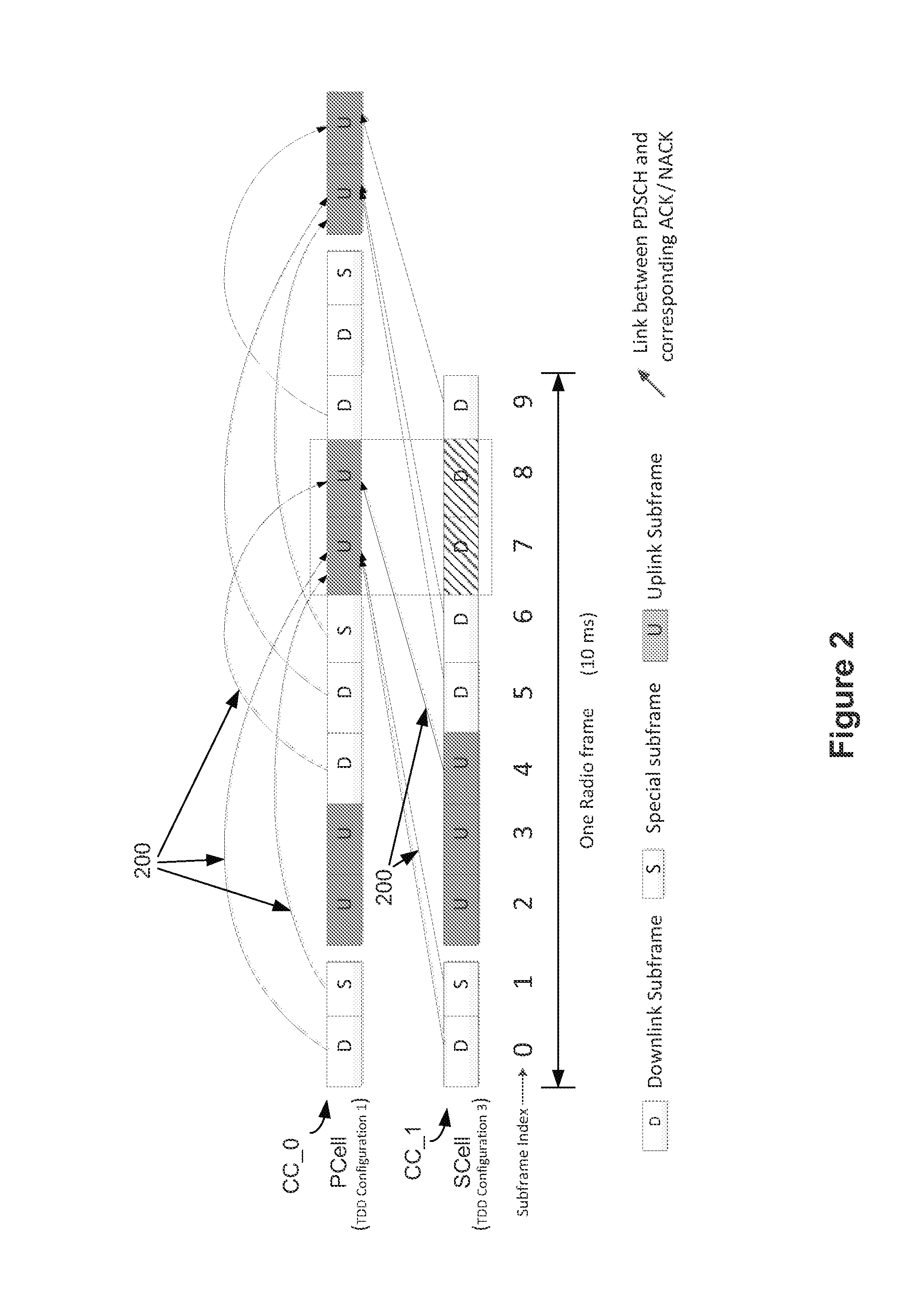
Disclosed is a method including communicating, by a mobile device, with a base station via first and second component carriers having different frequency bands and time division duplexing (TDD) configurations. The method may include receiving one or more downlink transmissions via the second component carrier. The method may include selecting a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) timing sequence based on the TDD configurations of the first and second component carriers. The method may include transmitting one or more positive acknowledgment and / or negative acknowledgement (ACK / NACK) signals, associated with the one or more downlink transmissions, according to the selected HARQ timing sequence. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for sending very high throughput wlan acknowledgment frames
InactiveCN102948101AError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless transmissionPhysical layer
One of a normal acknowledgement (ACK) and block ACK may be selectively enabled for wireless transmissions using a Very High Throughput Physical Layer Protocol Data Unit (PPDU). At least one designated bit may be set in a Physical Layer header of the PPDU for transmission from a transmitter to a receiver to indicate an ACK type selected from at least at least two of a normal ACK, a Block ACK, or no ACK. The PPDU may be transmitted in a Very High Throughput frame to the receiver where the designated bit can be used to provoke a normal ACK or Block ACK response to the PPDU, depending on the bit value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com