Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5908 results about "Data channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
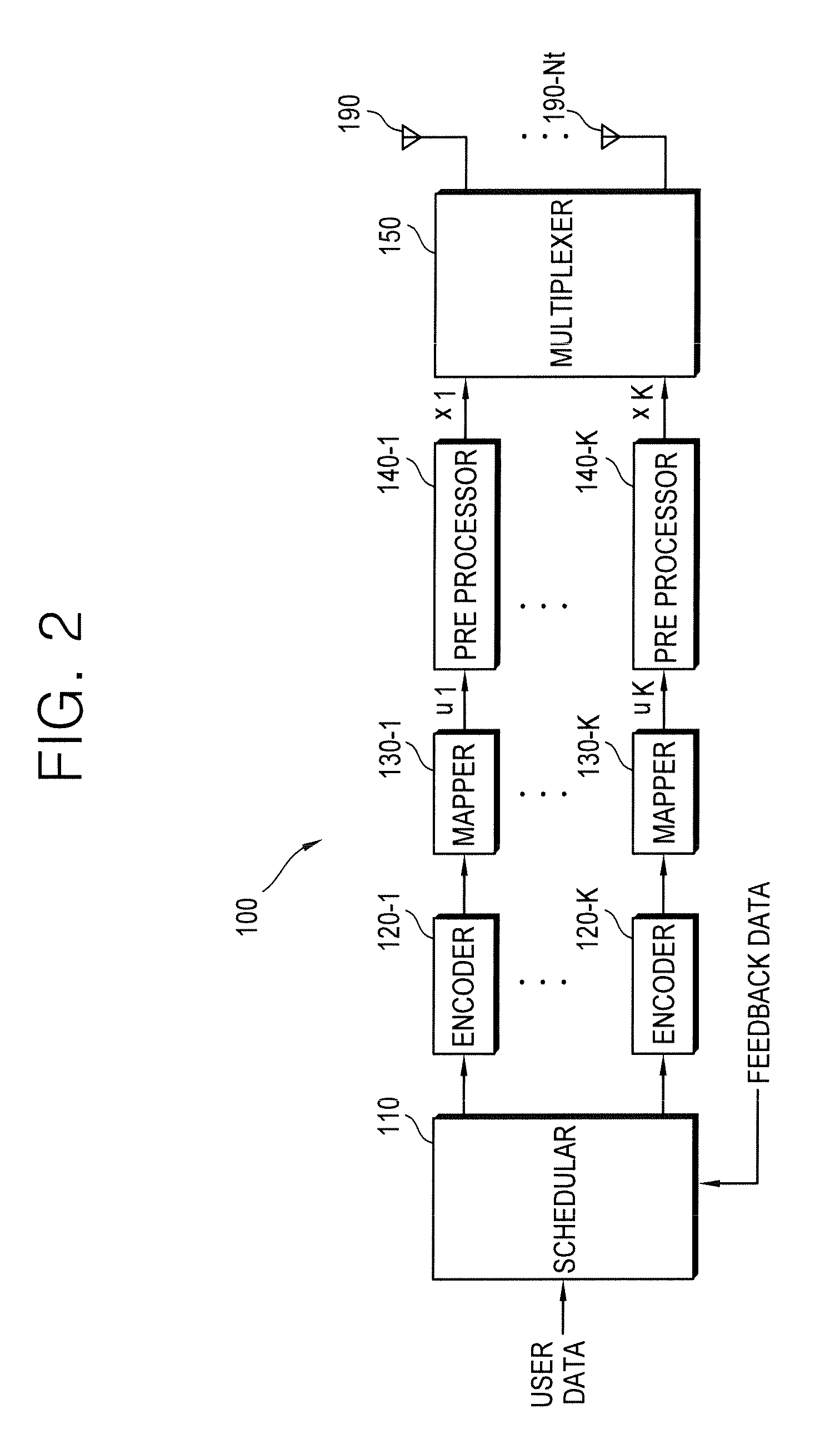
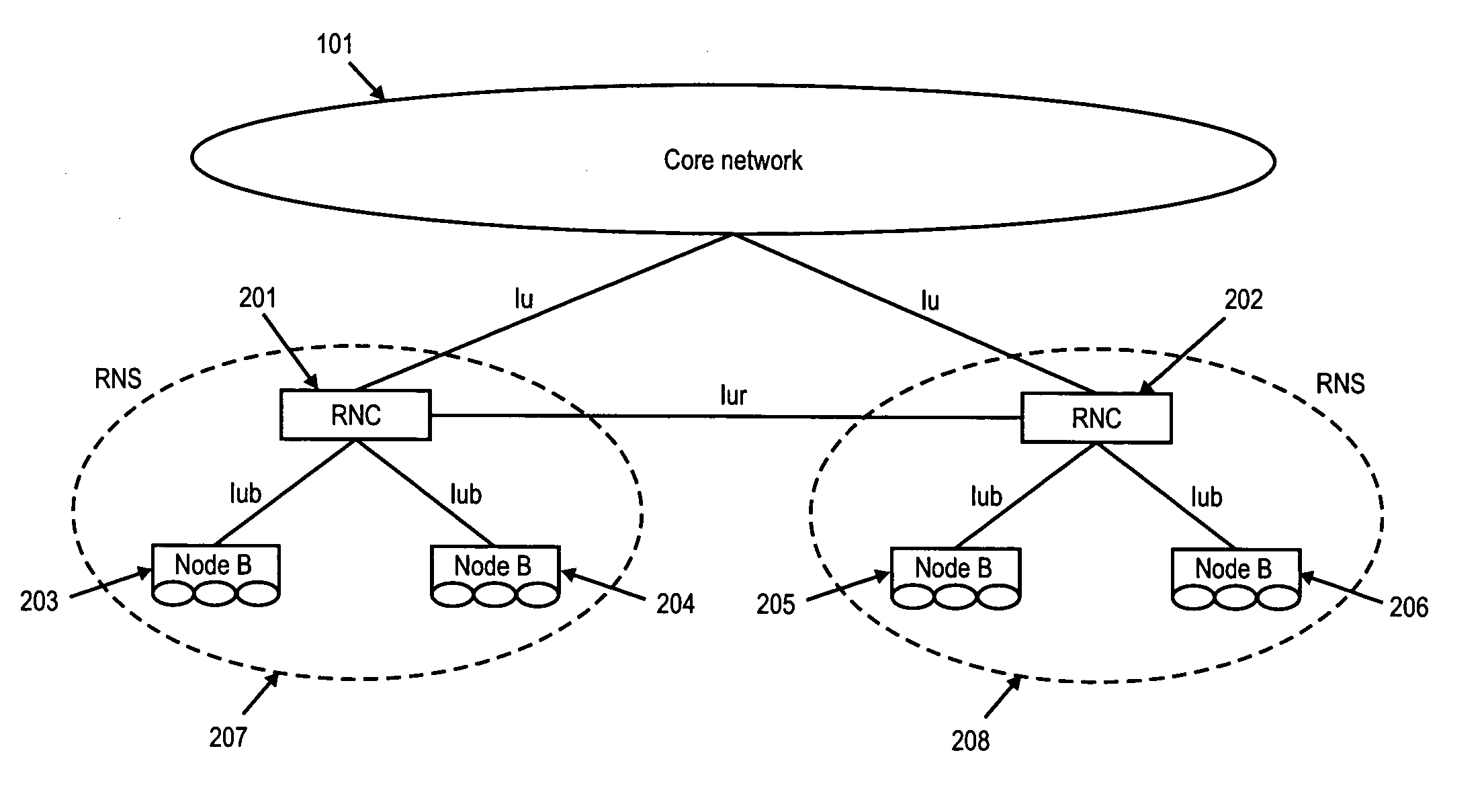
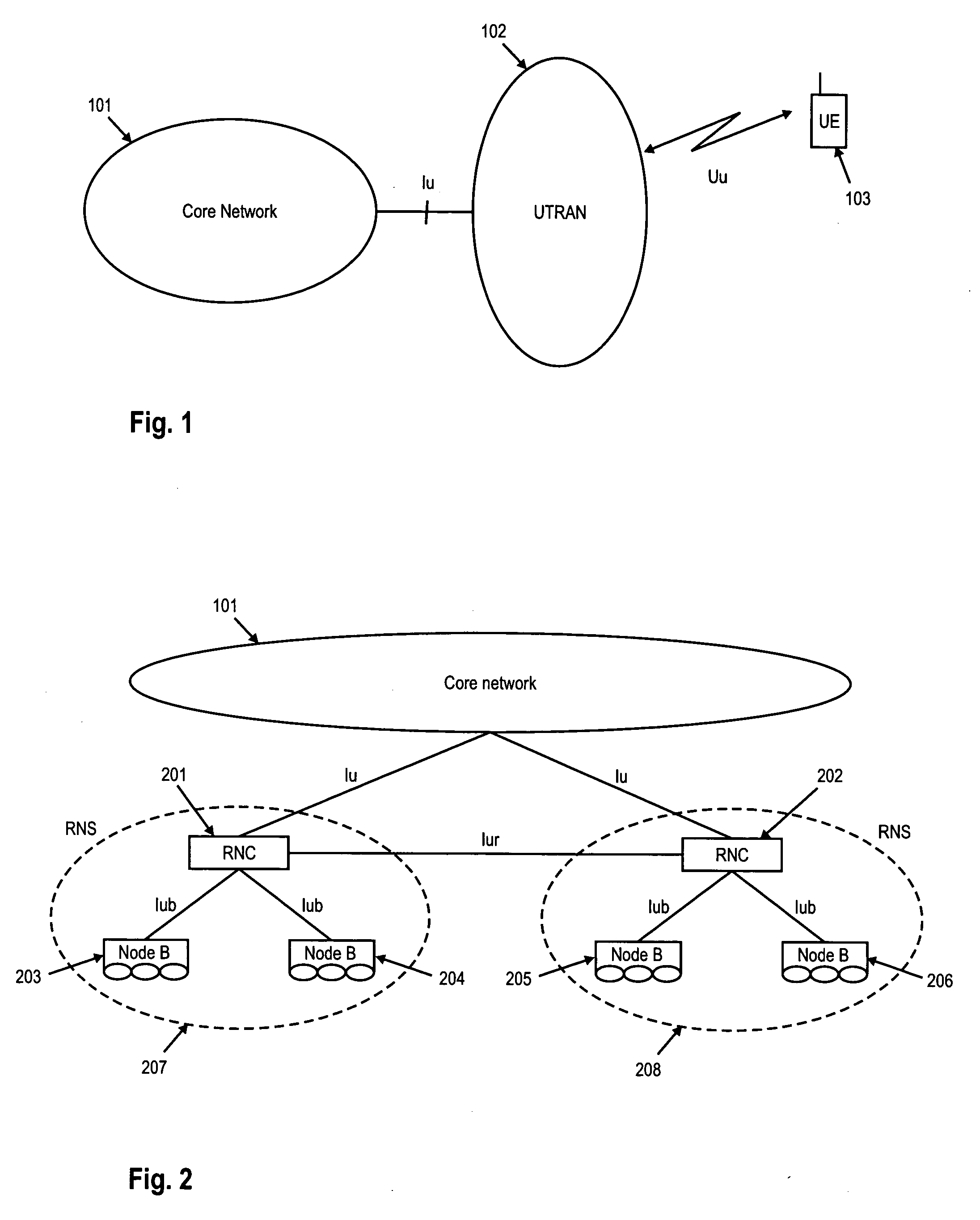
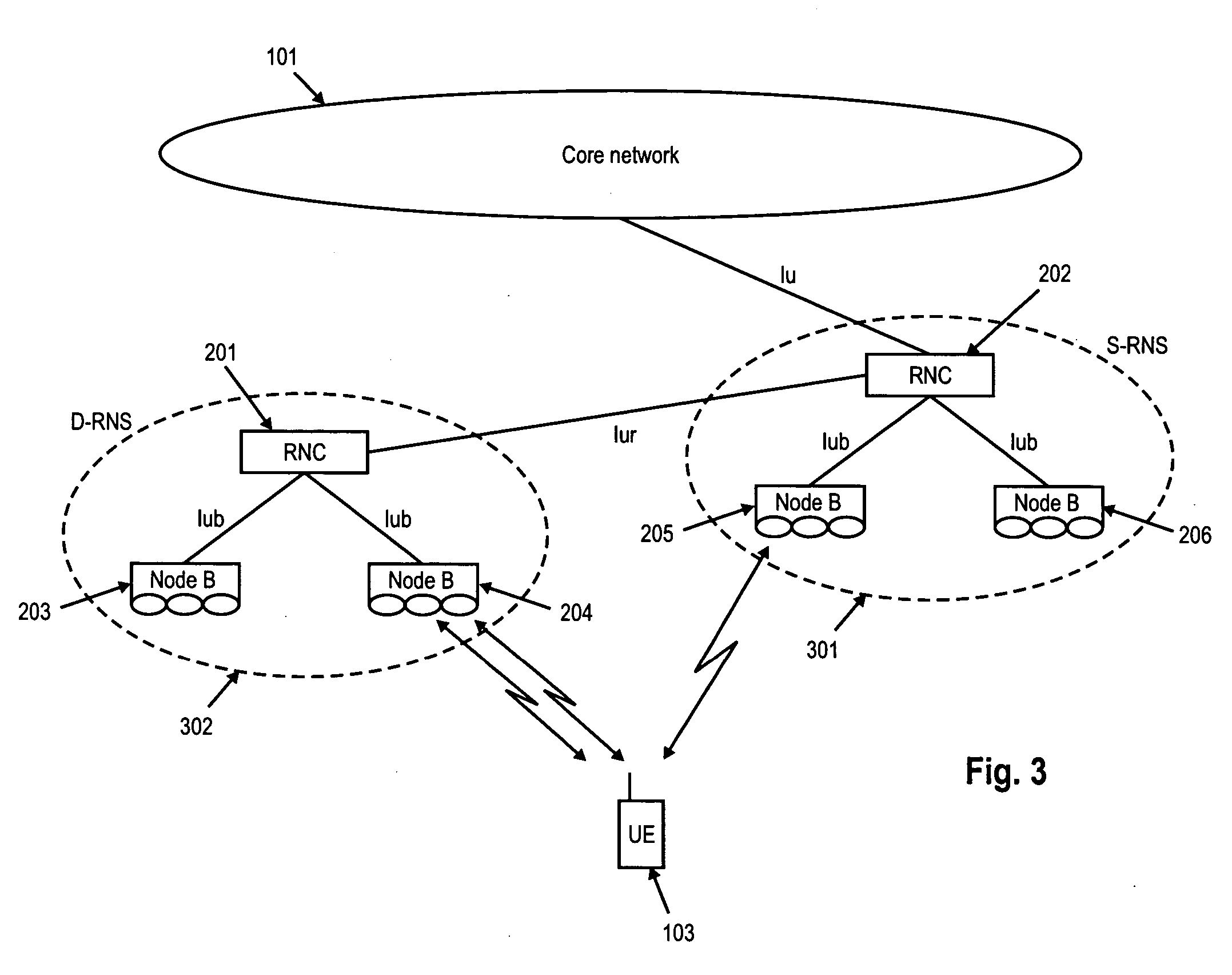
Data channel. A channel (on a BRI or PRI line) used to carry control information, to set up connections on the associated bearer channels. The name wasn't too bad back when users were sending voice (not data) over the bearer channels, but in 1997 it's quite a misnomer.
Reference signal for a coordinated multi-point network implementation
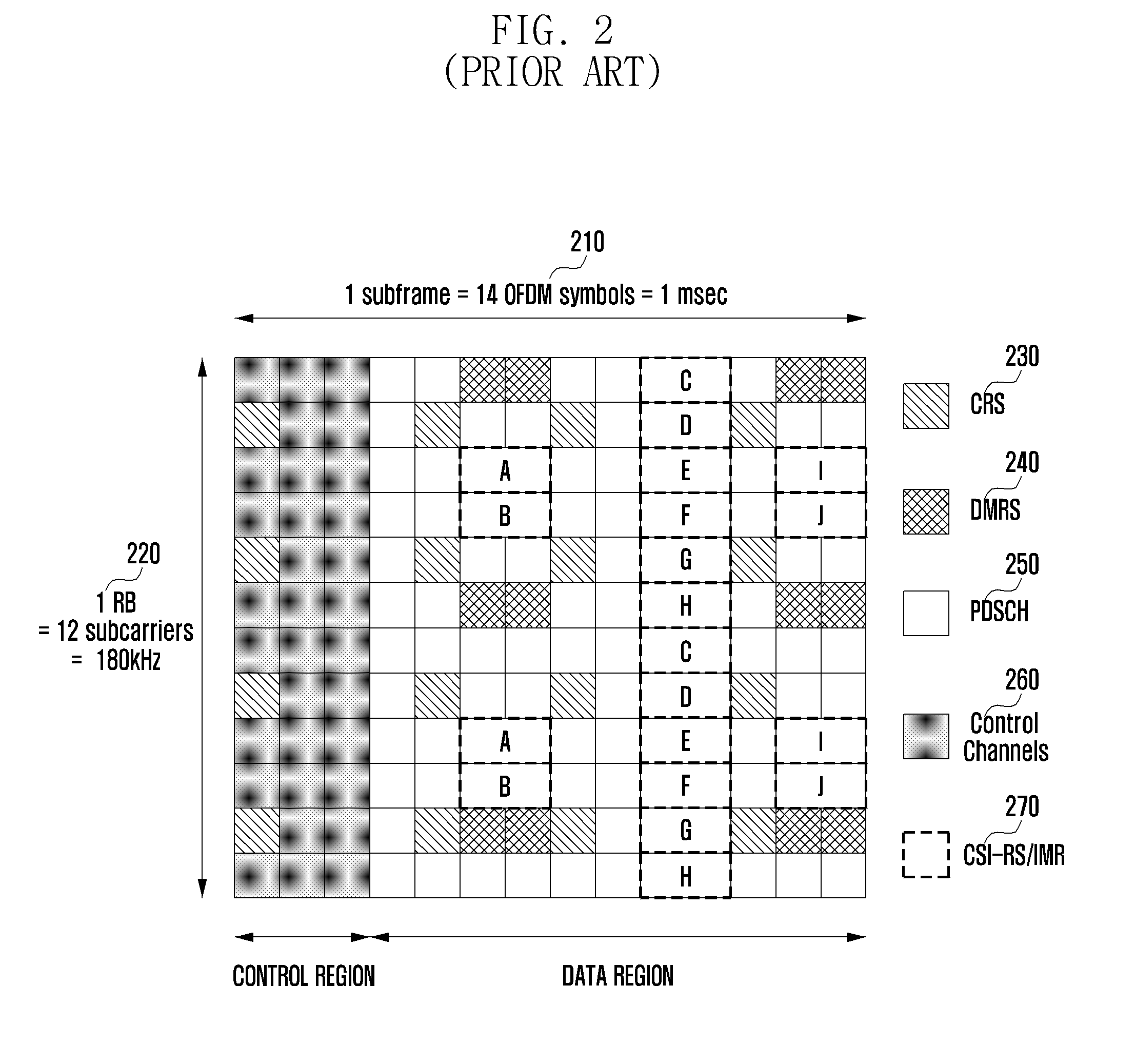
ActiveUS20110199986A1Criteria allocationSubstation equipmentChannel state informationResource element
Owner:OT PATENT ESCROW LLC
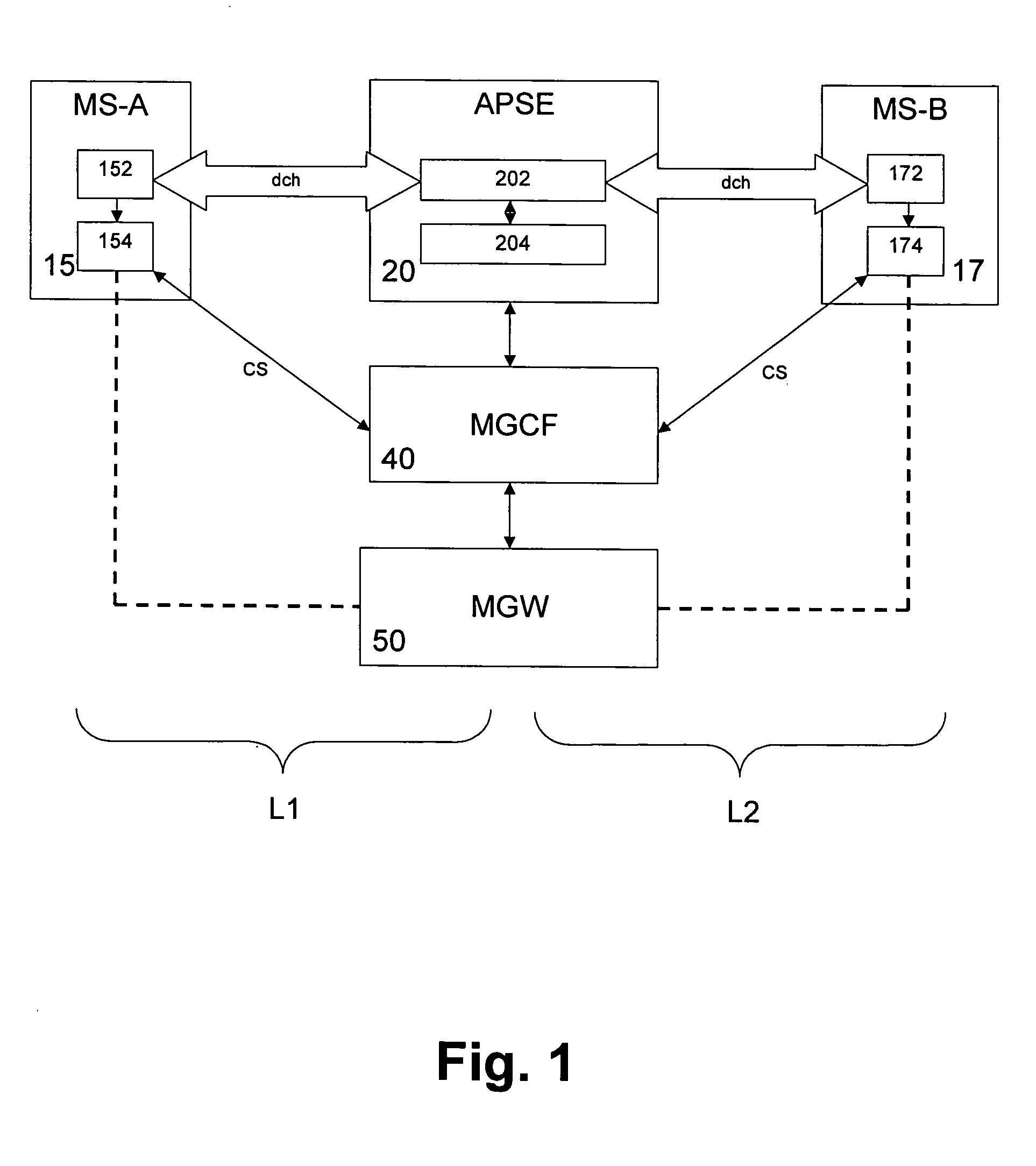
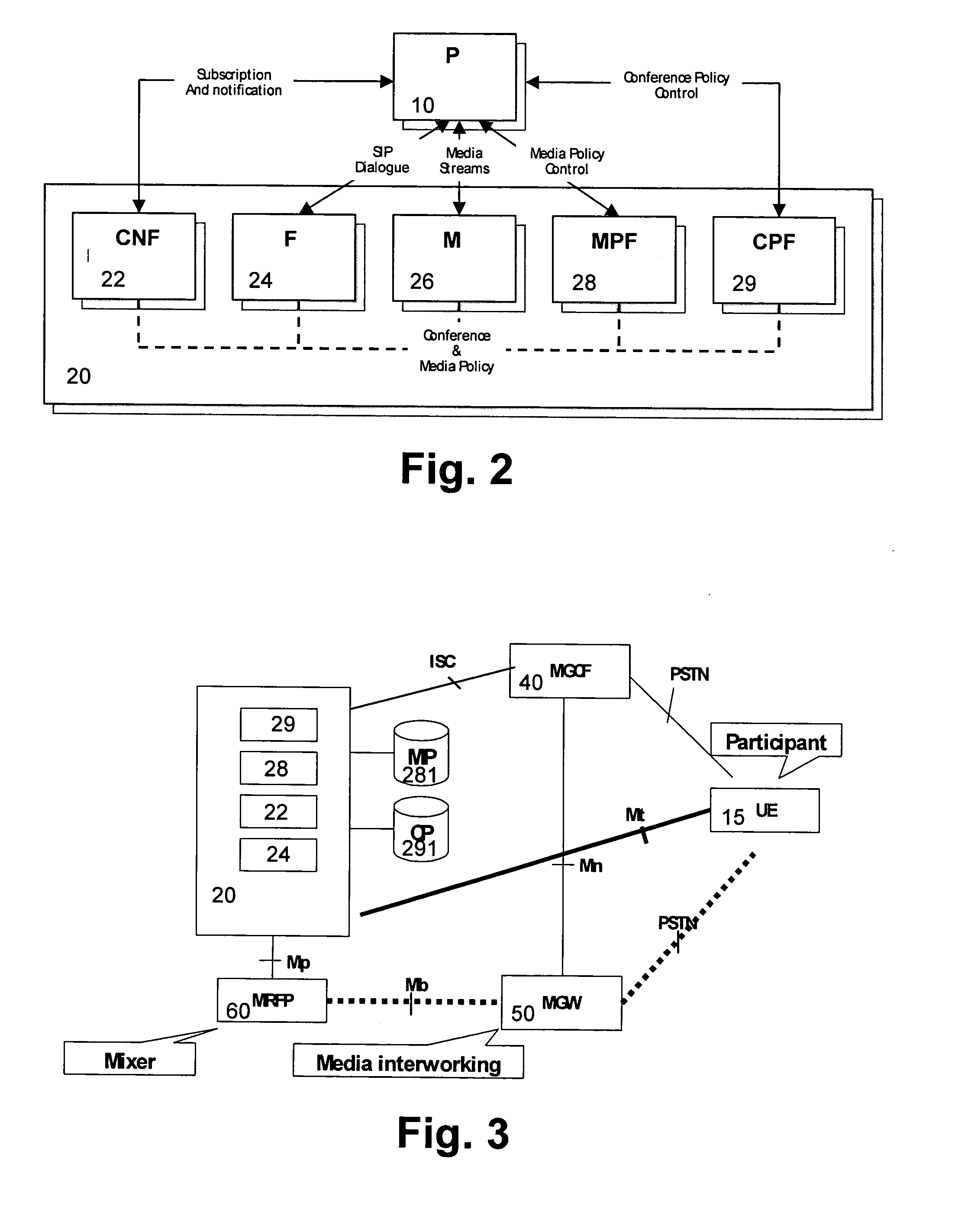
IP-based services for circuit-switched networks
ActiveUS20050058125A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsRadio access networkVoice over IP
A mechanism for providing a connection from an IP-based network to a circuit-switched network, such as a GSM network is disclosed. A temporary routing number for the circuit-switched network, such as an E.164 number, is delivered to a user terminal, and a circuit-switched call leg is established from the user terminal to the IP-based network using the routing number. Thereby, IMS-services are provided for end users which are located in the radio access network not having sufficient QoS required for voice over IP. In the example of a conference call service, a request for a conference call may forwarded via a data channel or data path to an application server which provides that conference call service. The application server then selects a conference routing number and returns the routing number to the conference host terminal via the data channel. Using the received conference routing number, the conference host terminal can then set up a circuit-switched connection as a call leg of the conference call.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
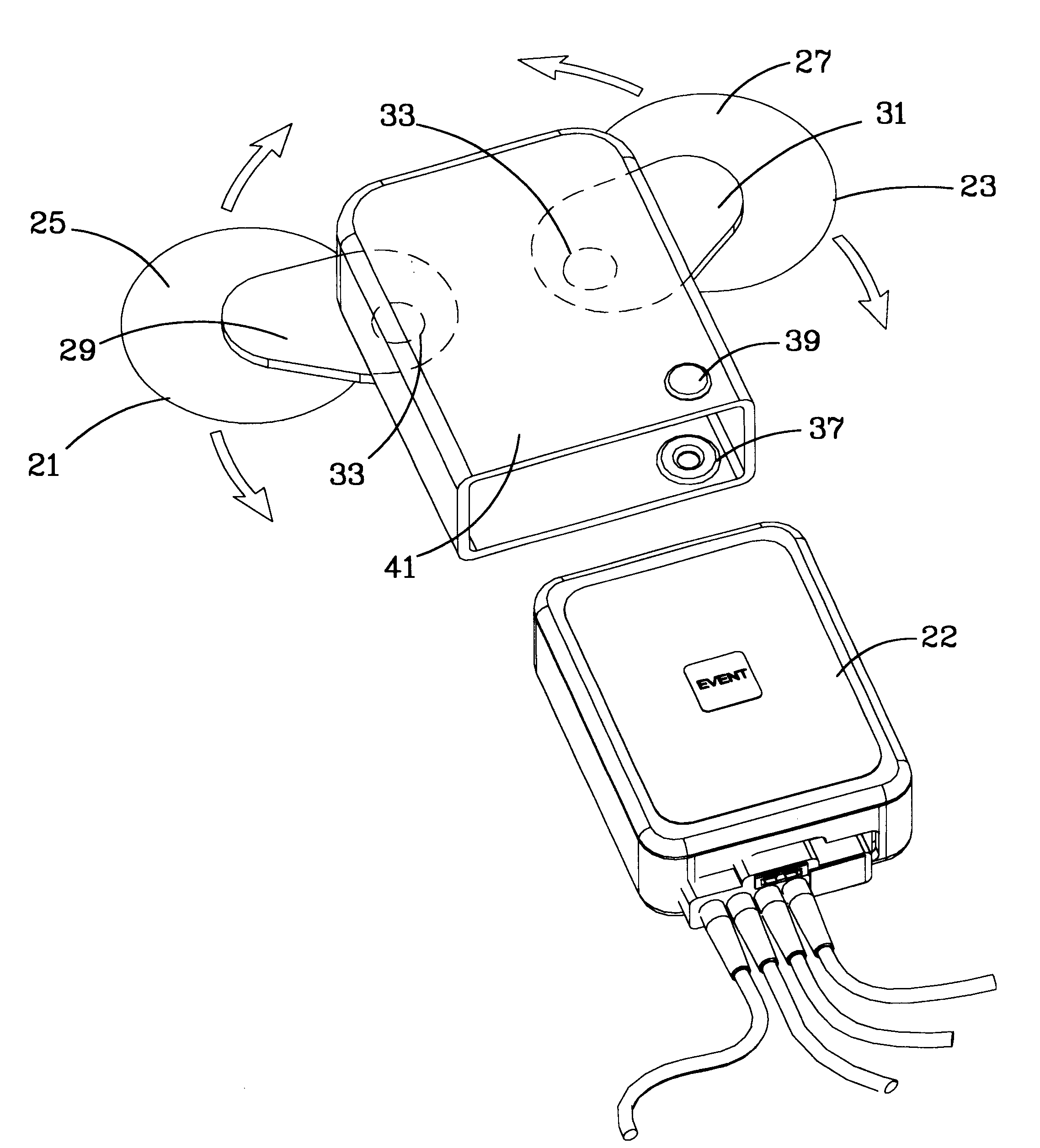
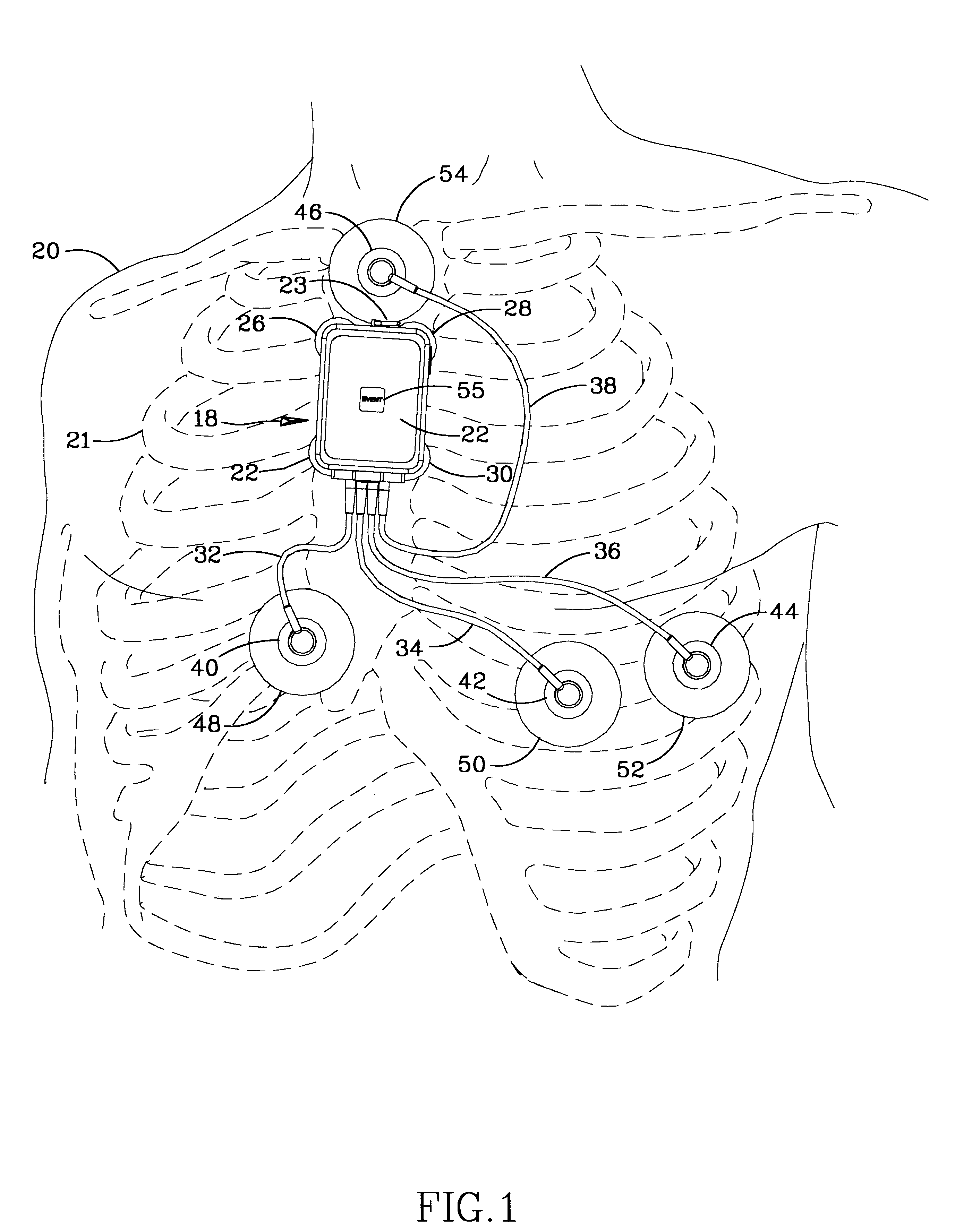
Ambulatory physio-kinetic monitor with envelope enclosure
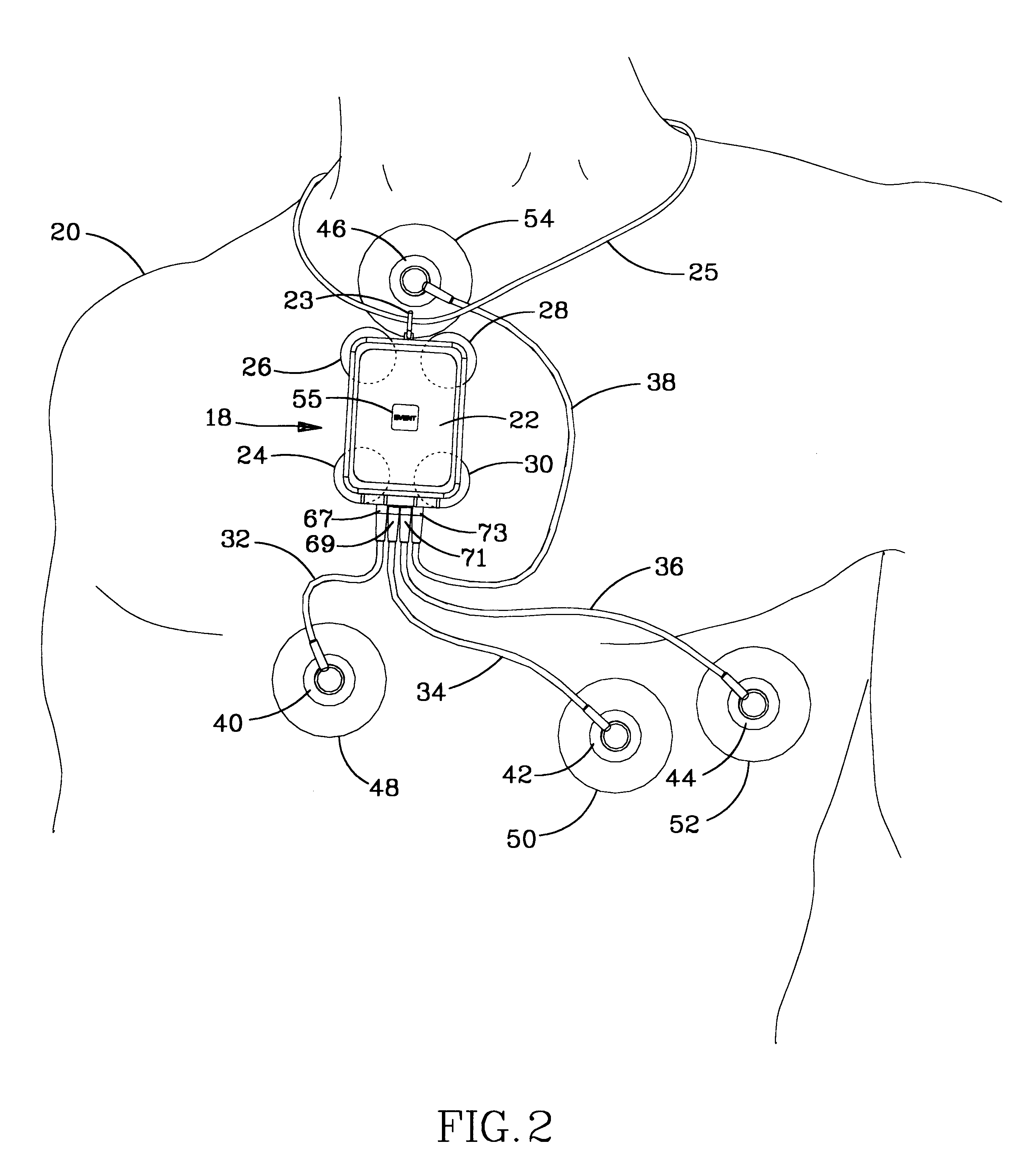
InactiveUS6605046B1Complete and reliableShorten the lengthElectrocardiographySurgeryAmbulatoryAccelerometer
A water and moisture sealed, self contained, compact, long term, ambulatory physio-kinetic monitor is designed for mounting directly to the skin of an athlete or fitness performer, preferably immediately adjacent to the organ or system that is to be monitored, and is adhesively held there in place, covertly and comfortably, under clothing by disposable electrode, adhesive skin pads. At least three positive electrodes and a common negative electrode extend from the monitor and attach by similar disposable adhesive electrode pads to detect physiological, e.g. ECG data. Accelerometer means disposed within the monitor detects body movement and likewise stores that data on a third ECG data channel.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
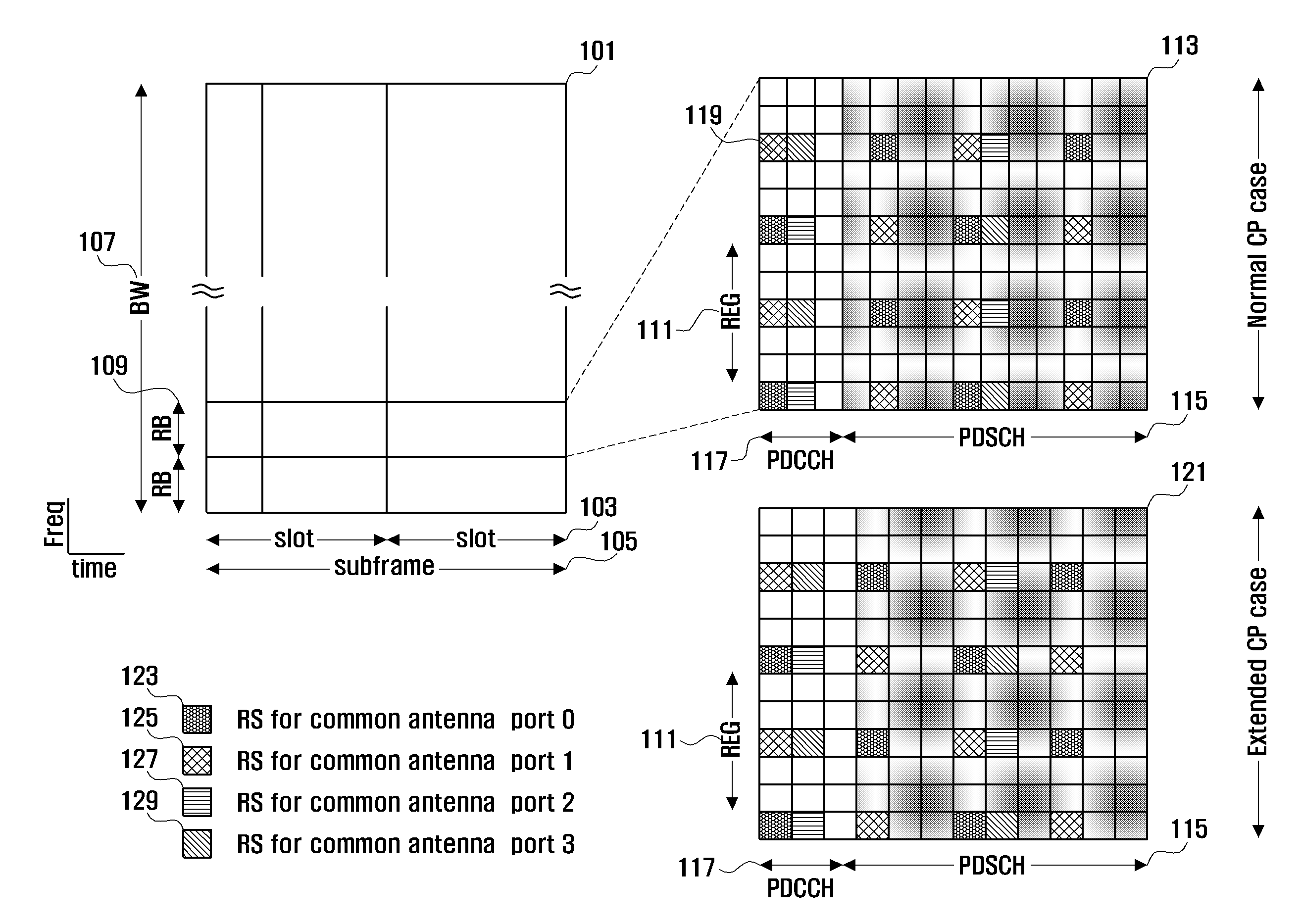
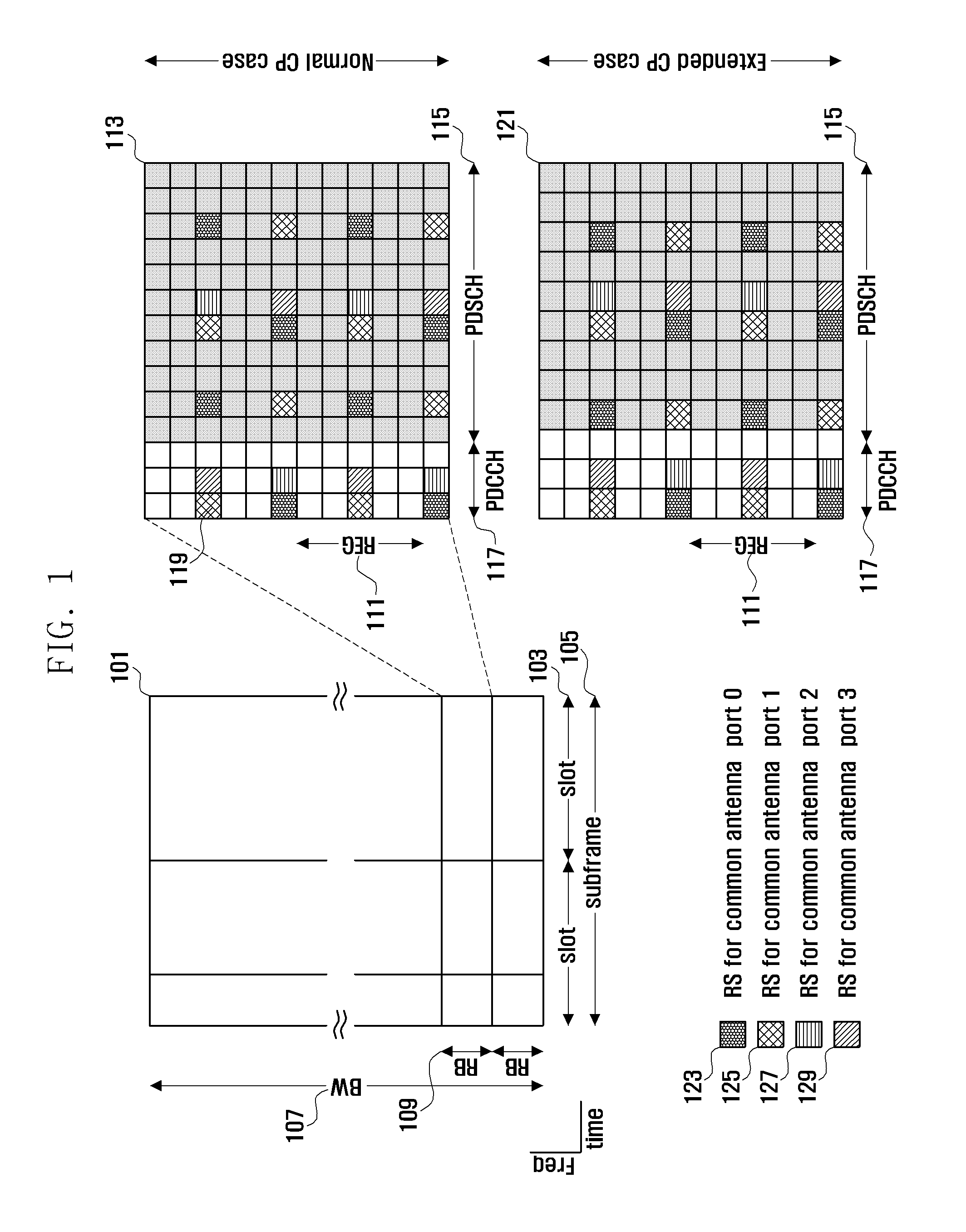
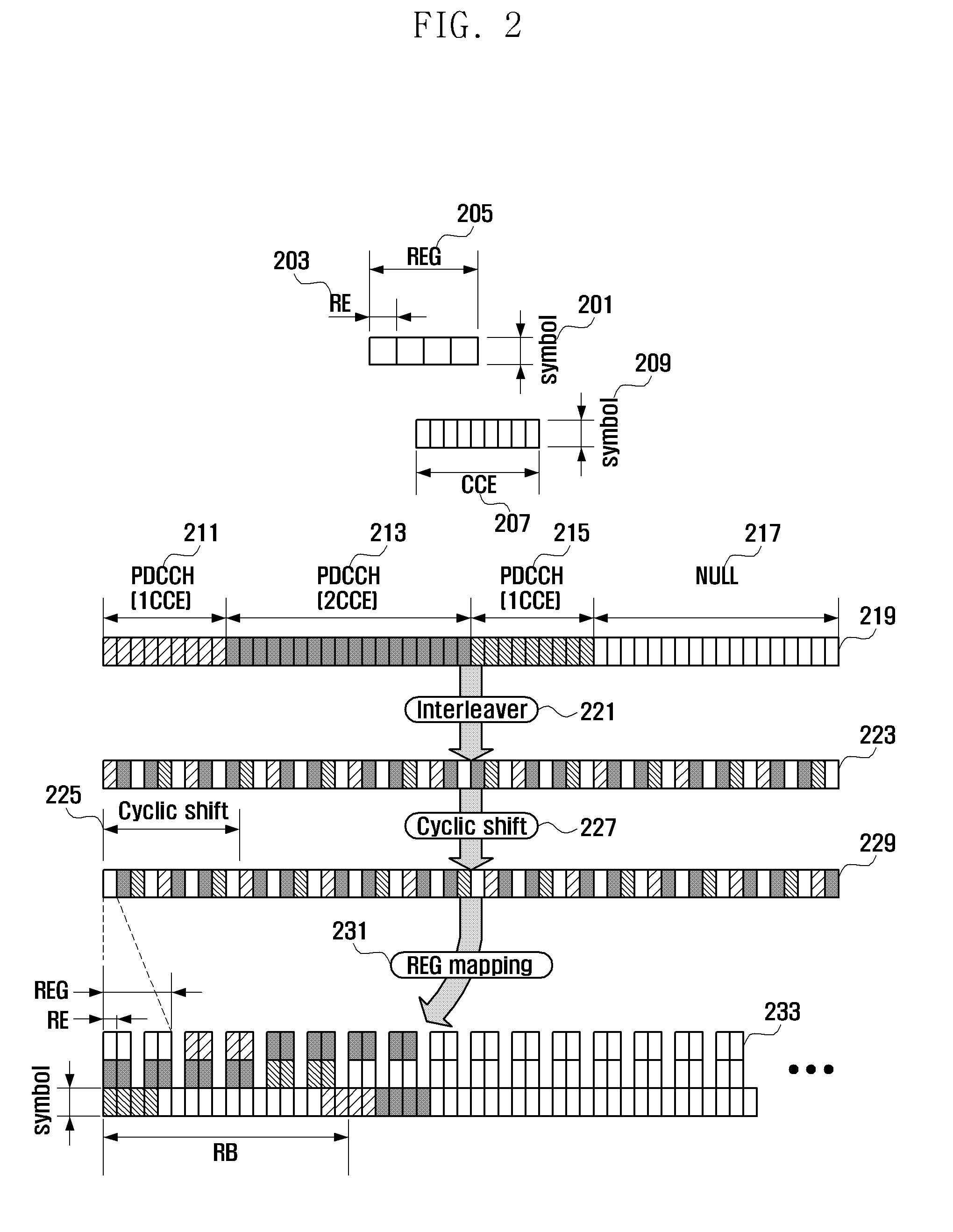
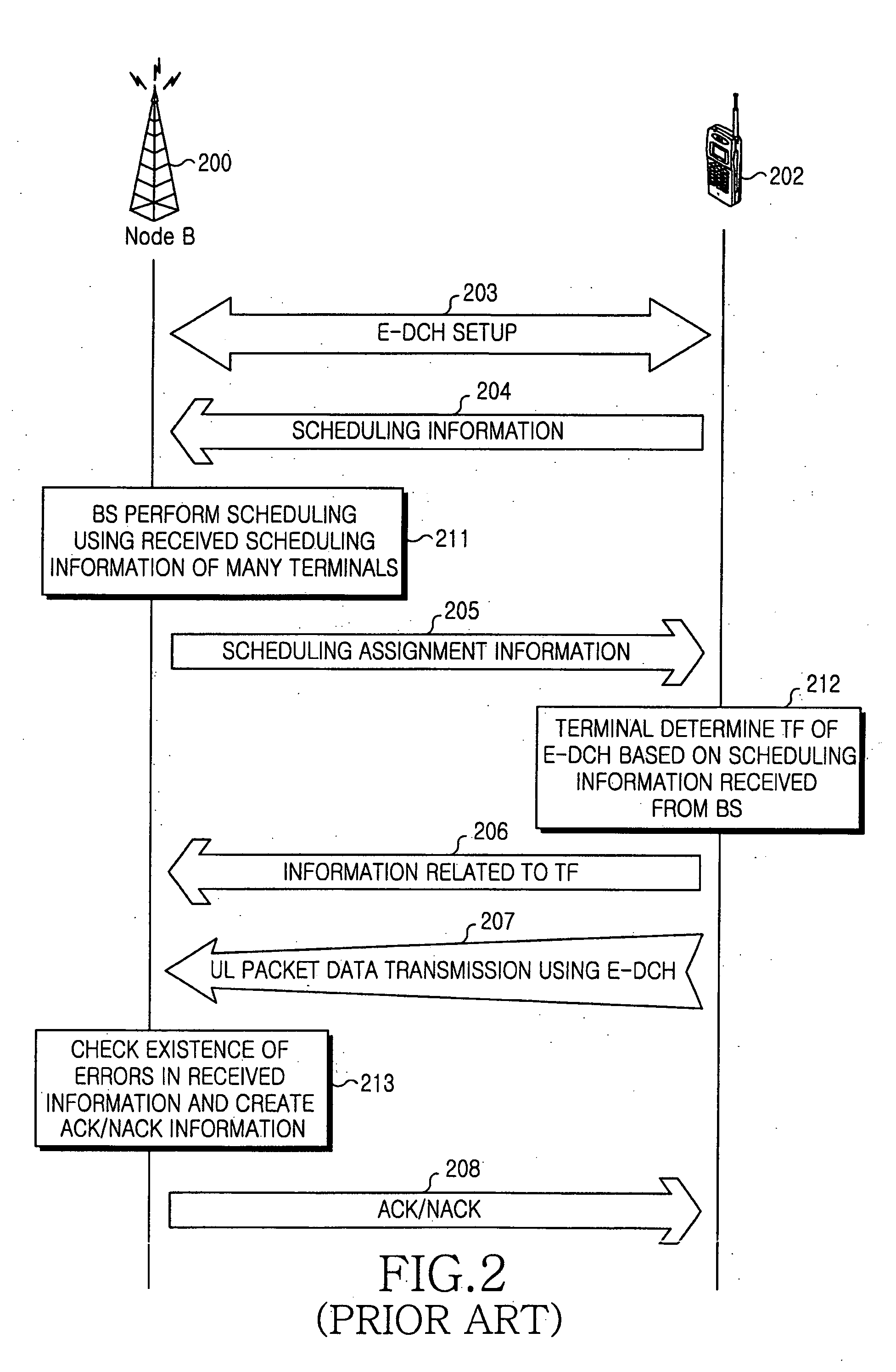
Method and apparatus for configuring control channel in OFDM system
InactiveUS20110044391A1Increasing control channel efficiencyIncreasing system coverageNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionTime domainCommunications system
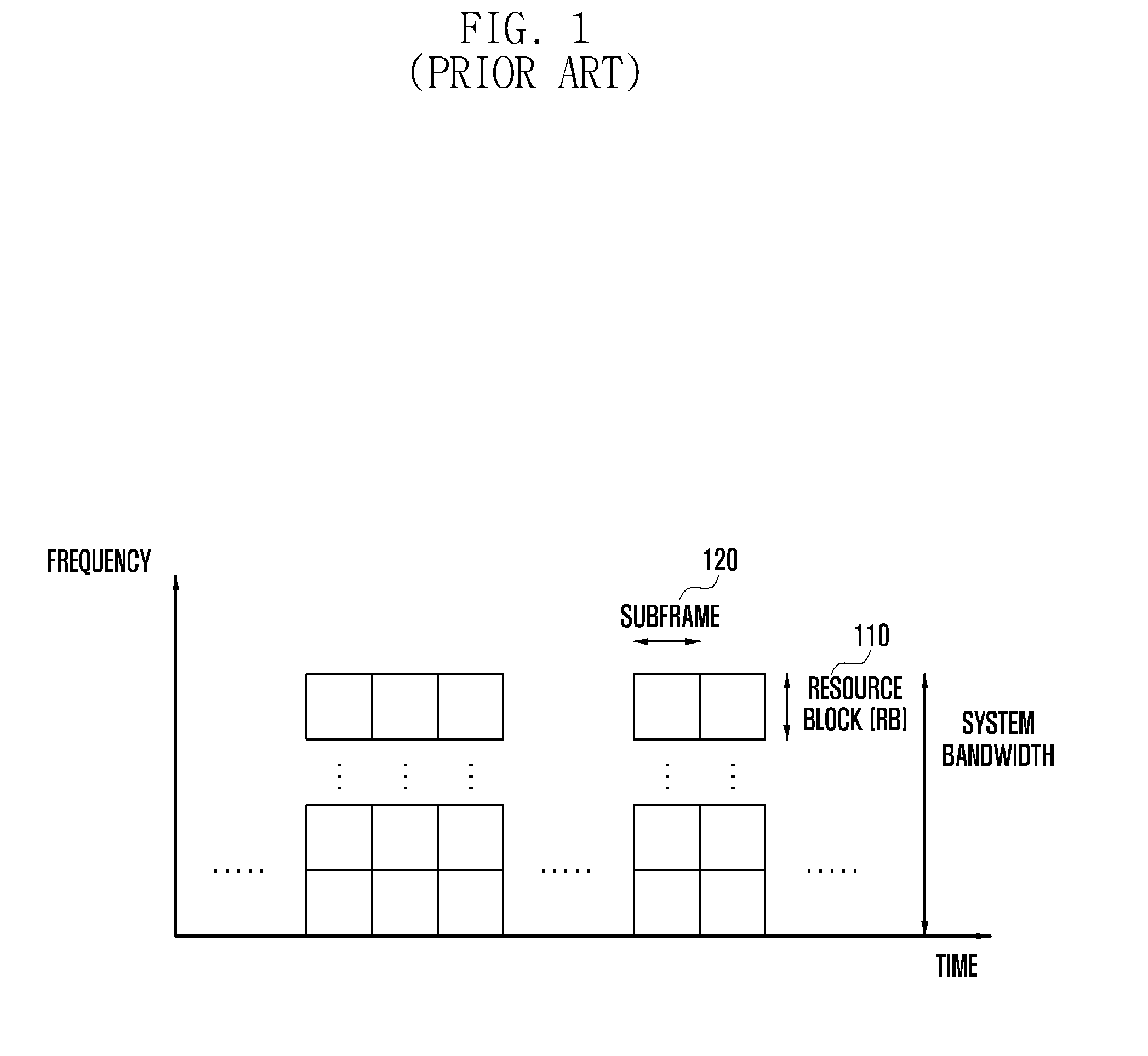
A control channel configuration method and apparatus is provided for supporting Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) in an OFDM-based communication system. The control channel configuration method includes determining a Resource Block (RB) to be used for configuring control channels; configuring the control channels by mapping the control channels in a data channel region within the RB; and transmitting the configured control channels, wherein configuring the control channels includes mapping the control channels in units of Resource Element Groups (REGs) formed by binding one or more Resource Elements (REs) in a time domain-preferred allocation manner within the same RB.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
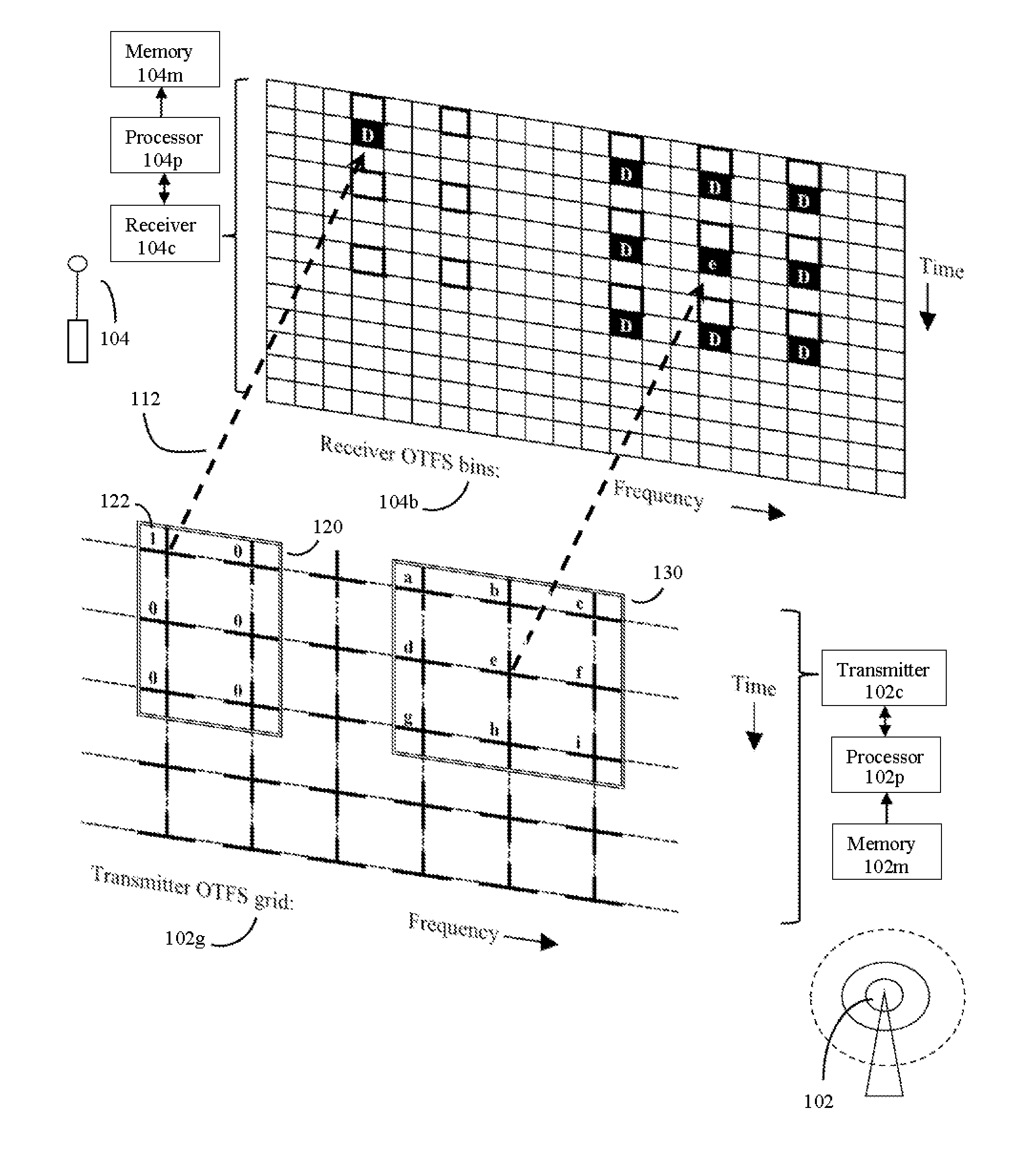
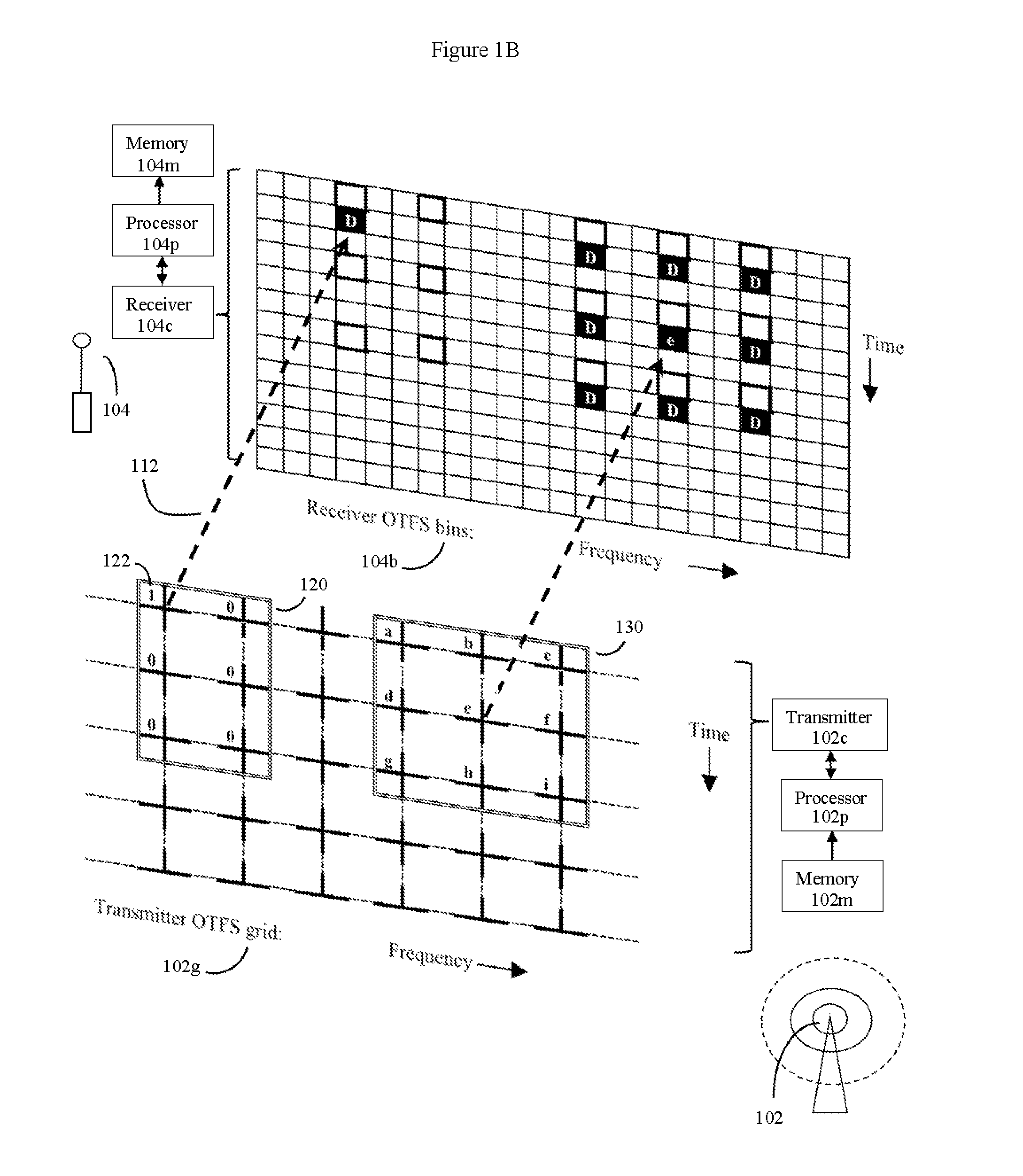
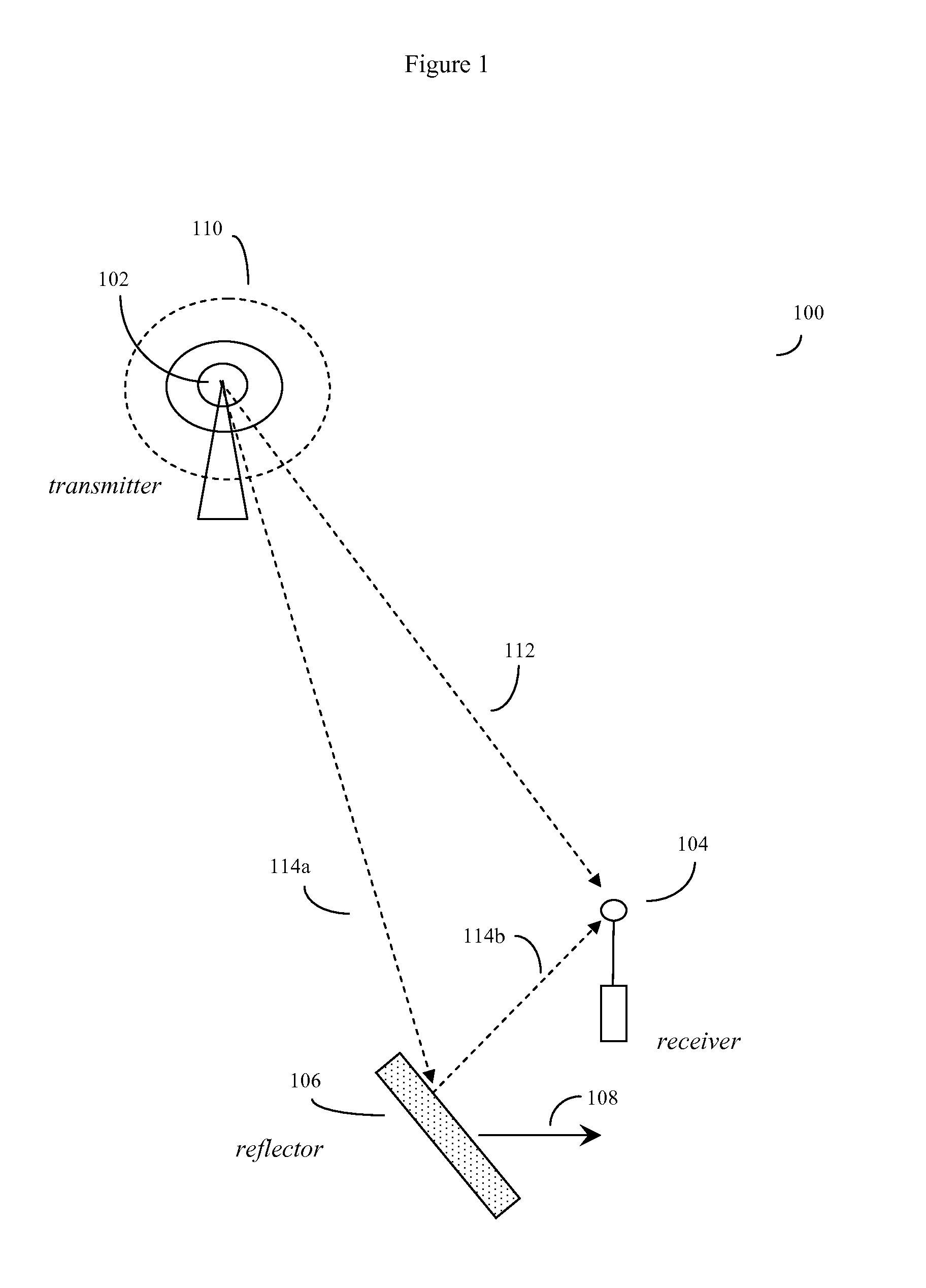
Otfs methods of data channel characterization and uses thereof
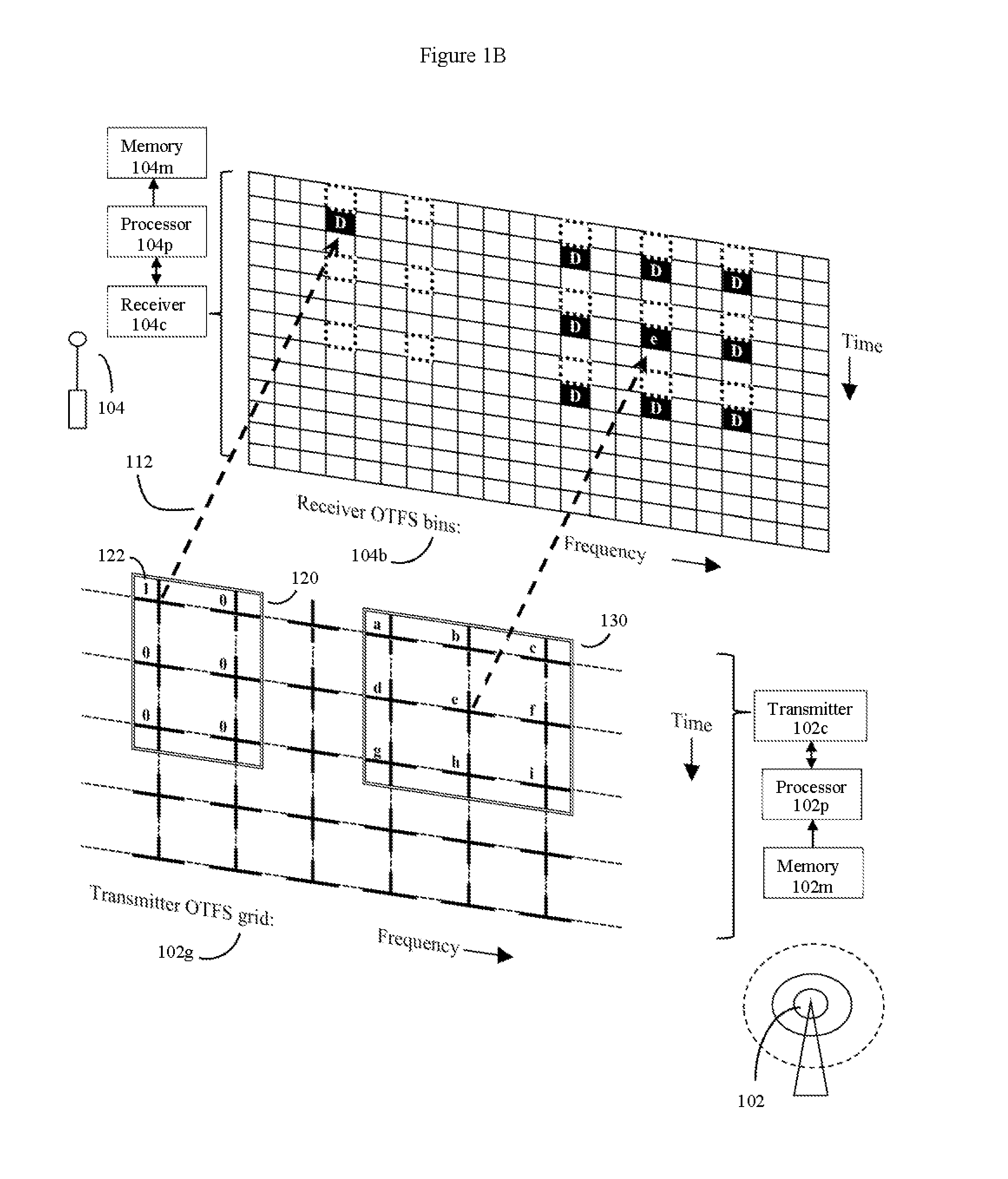
Fiber, cable, and wireless data channels are typically impaired by reflectors and other imperfections, producing a channel state with echoes and frequency shifts in data waveforms. Here, methods of using OTFS pilot symbol waveform bursts to automatically produce a detailed 2D model of the channel state are presented. This 2D channel state can then be used to optimize data transmission. For wireless data channels, an even more detailed 2D model of channel state can be produced by using polarization and multiple antennas in the process. Once 2D channel states are known, the system turns imperfect data channels from a liability to an advantage by using channel imperfections to boost data transmission rates. The methods can be used to improve legacy data transmission modes in multiple types of media, and are particularly useful for producing new types of robust and high capacity wireless communications using non-legacy OTFS data transmission methods.
Owner:COHERE TECH
System And Method For Camera Imaging Data Channel
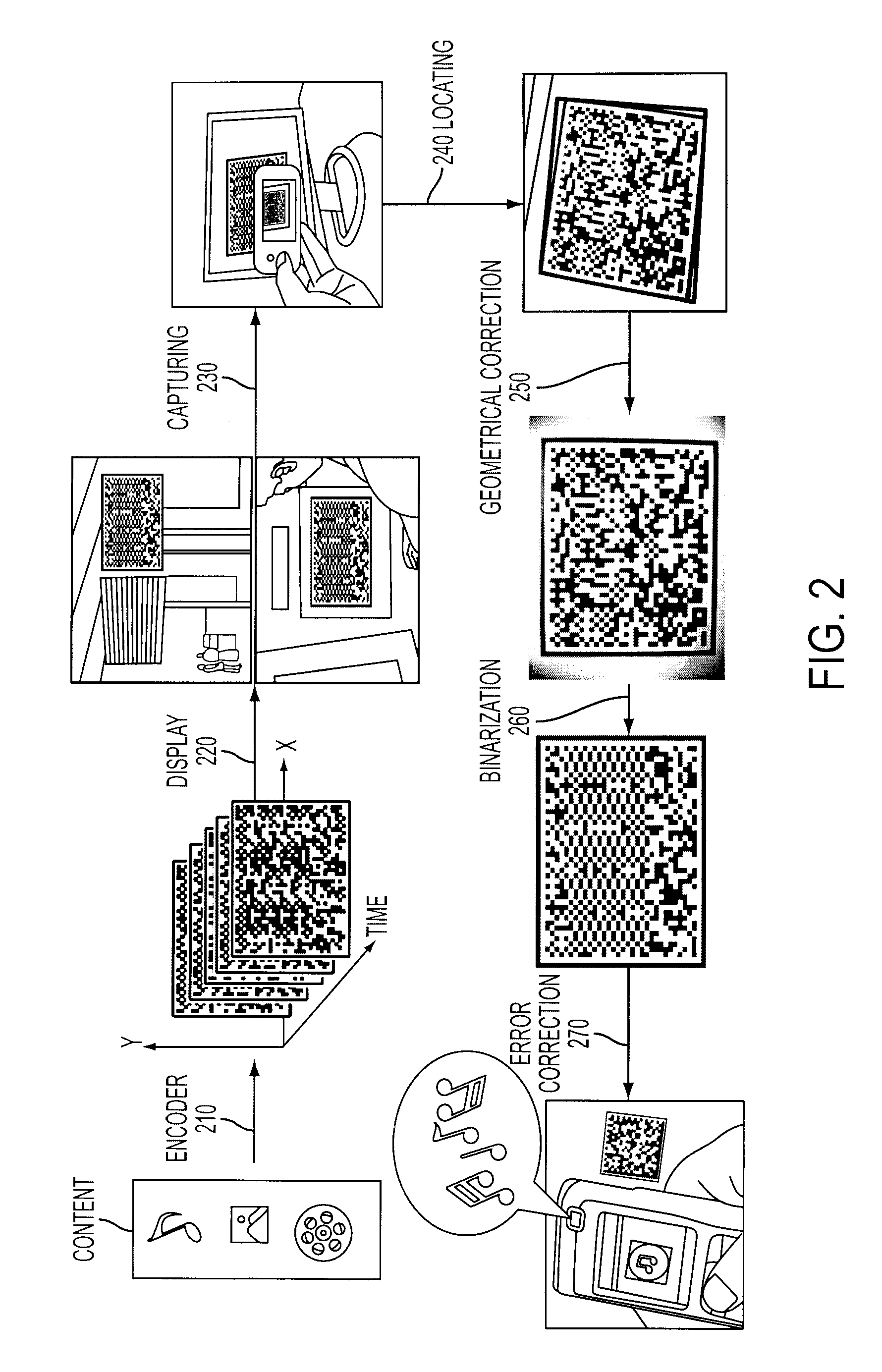
InactiveUS20100020970A1Low data costLow costCode conversionSecret communicationBarcodeDisplay device
A system and method for using cameras to download data to cell phones or other devices as an alternative to CDMA / GPRS, BlueTooth, Infrared or cable connections. The data is encoded as a sequence of images such as 2D bar codes, which can be displayed in any flat panel display, acquired by a camera, and decoded by software embedded in the device. The decoded data is written to a file. The system and method meet the following challenges: (1) To encode arbitrary data as a sequence of images. (2) To process captured images under various lighting variations and perspective distortions while maintaining real time performance. (3) To decode the processed images robustly even when partial data is lost.
Owner:LIU XU +2
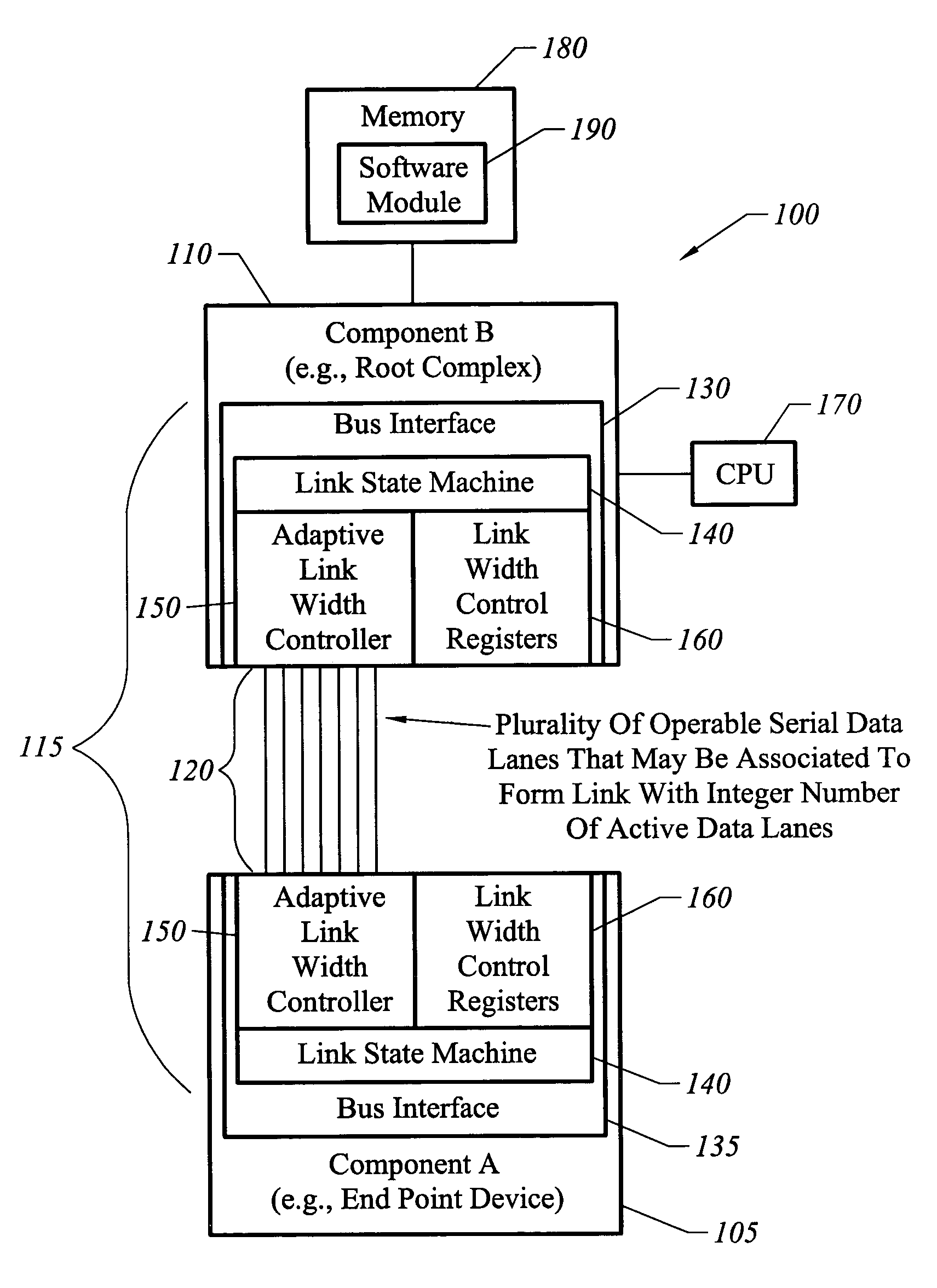
Apparatus, system, and method for bus link width optimization
ActiveUS7136953B1High bandwidthReducing bus power requirementEnergy efficient ICTStatic indicating devicesBus interfaceBandwidth requirement
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving uplink data retransmission request in a CDMA communication system
InactiveUS20050013263A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemUplink transmission
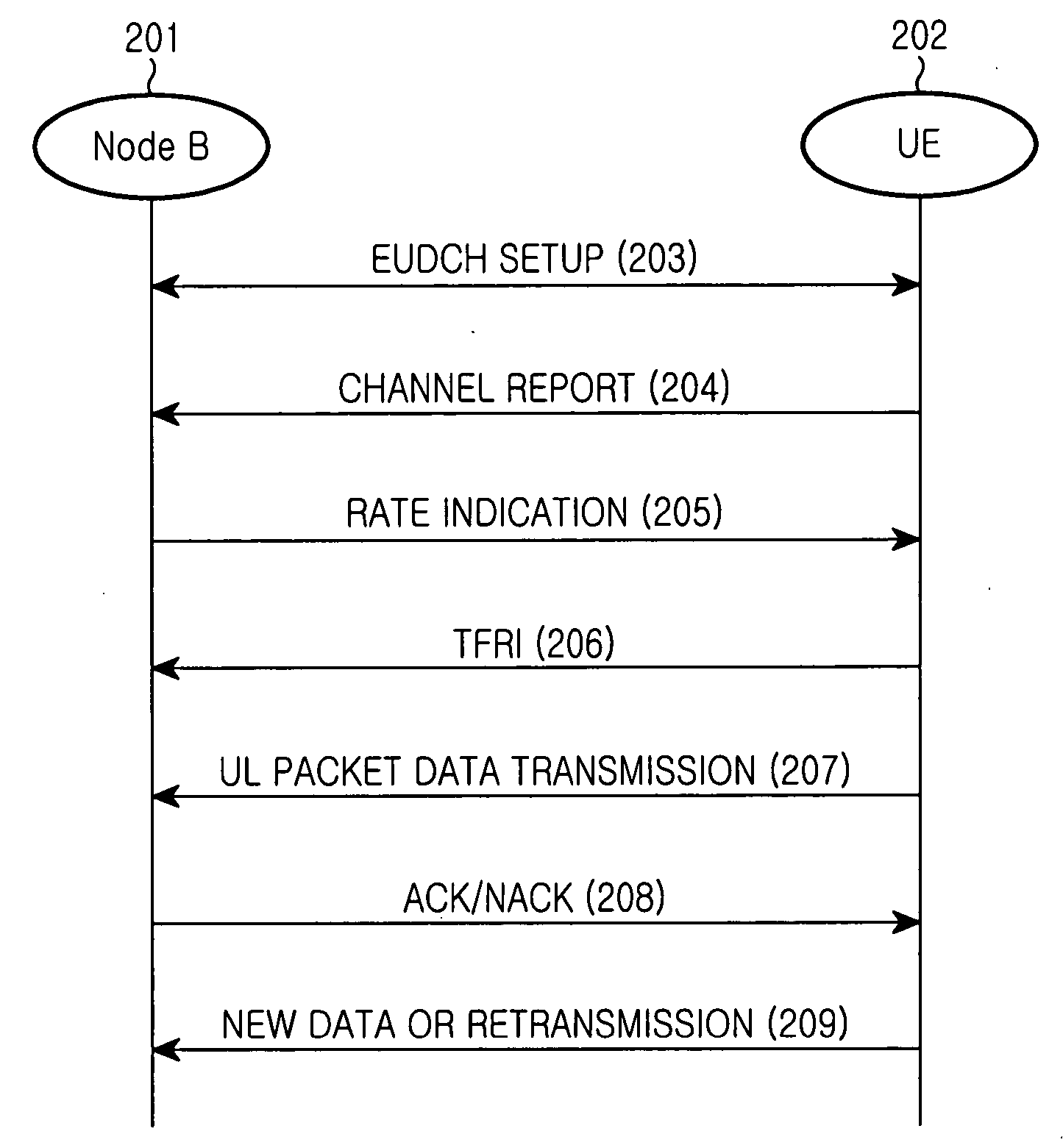
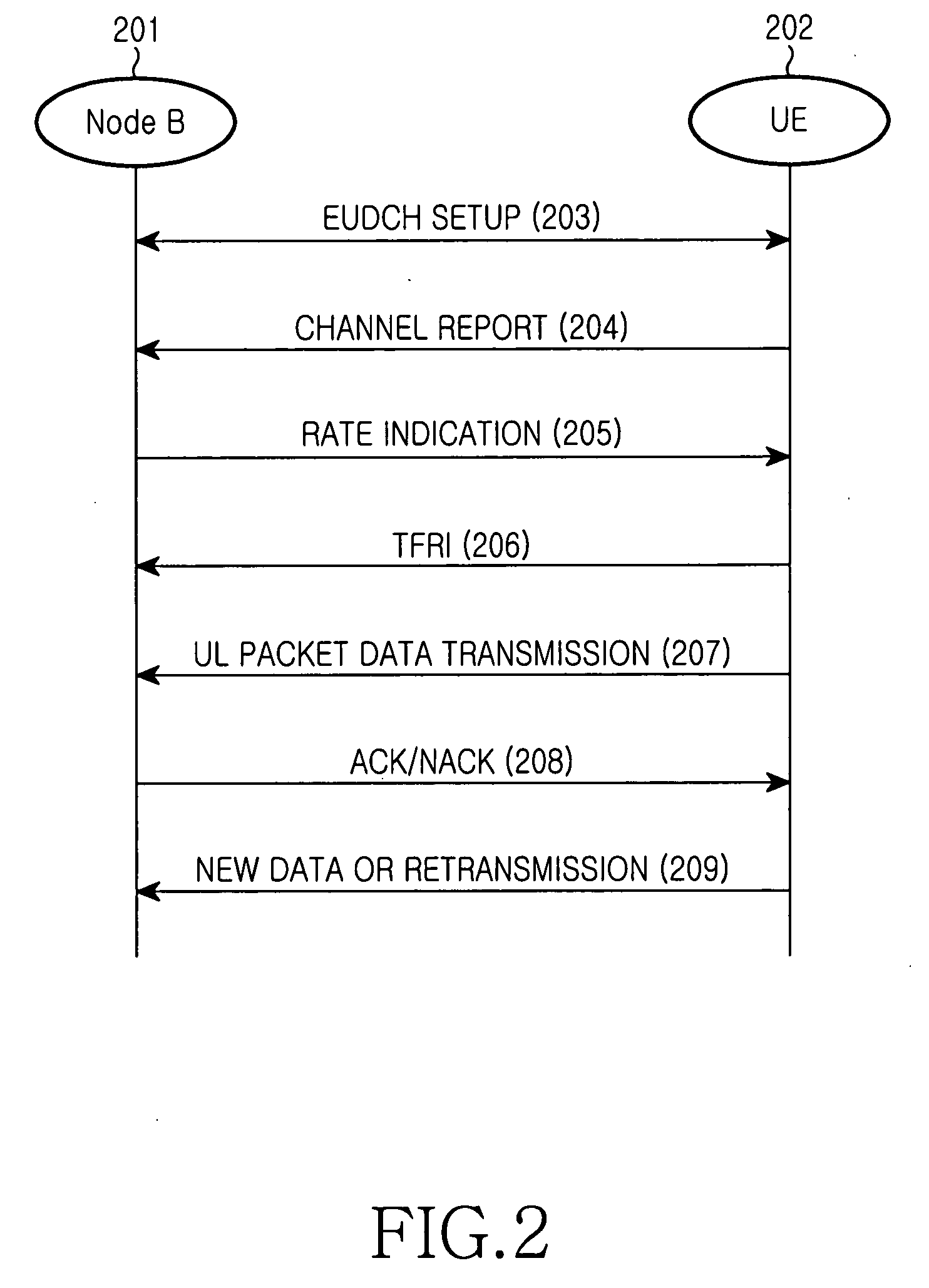
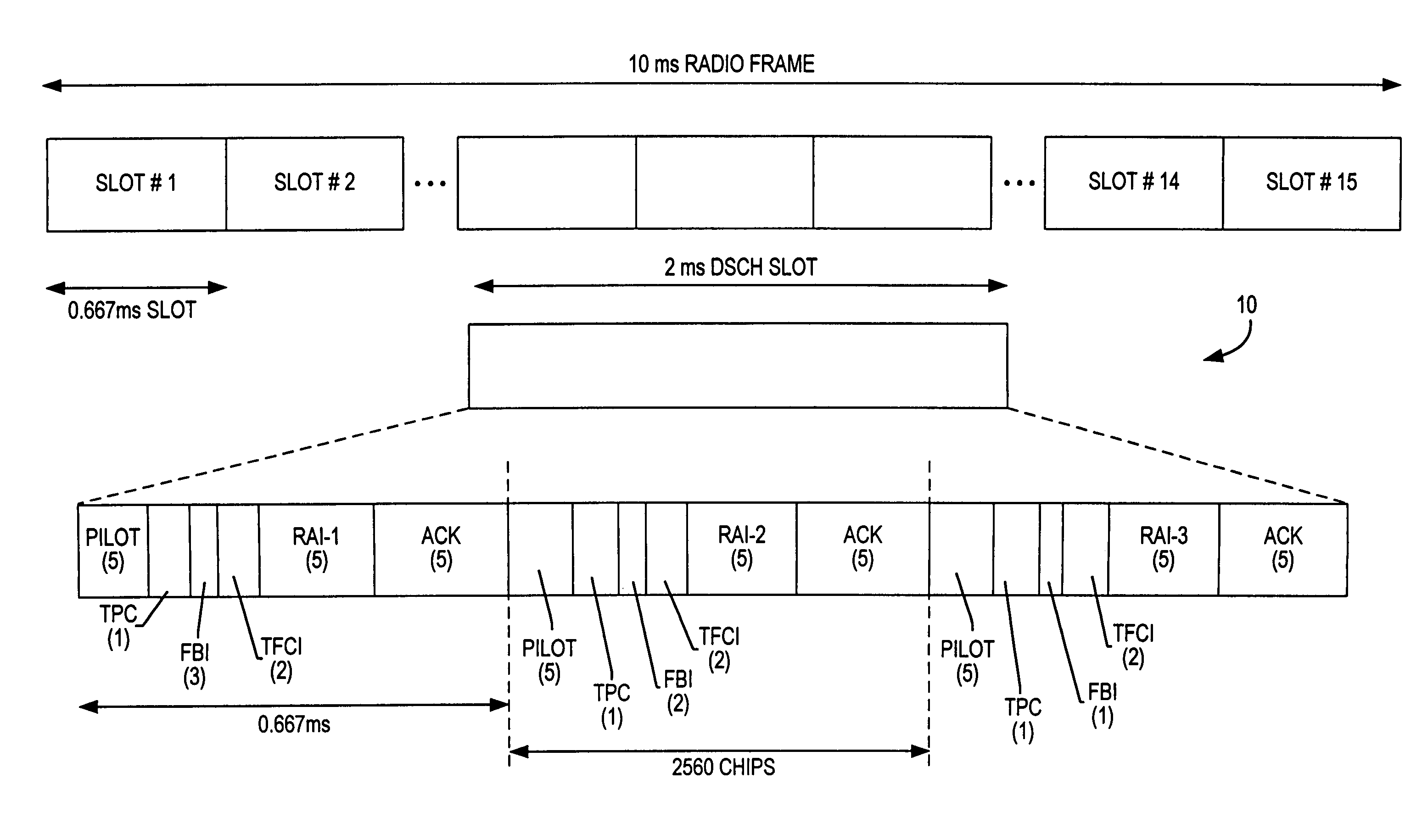
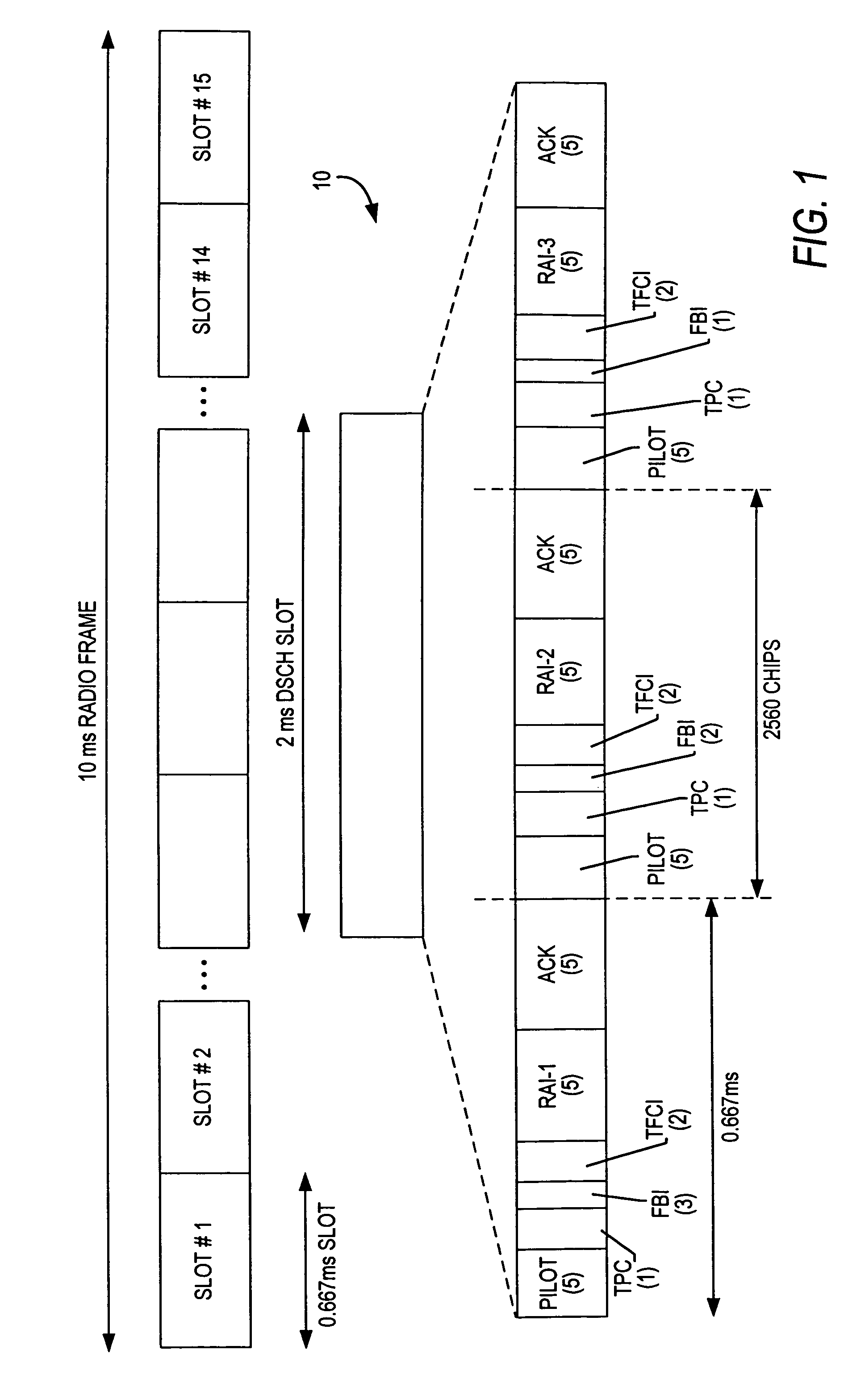
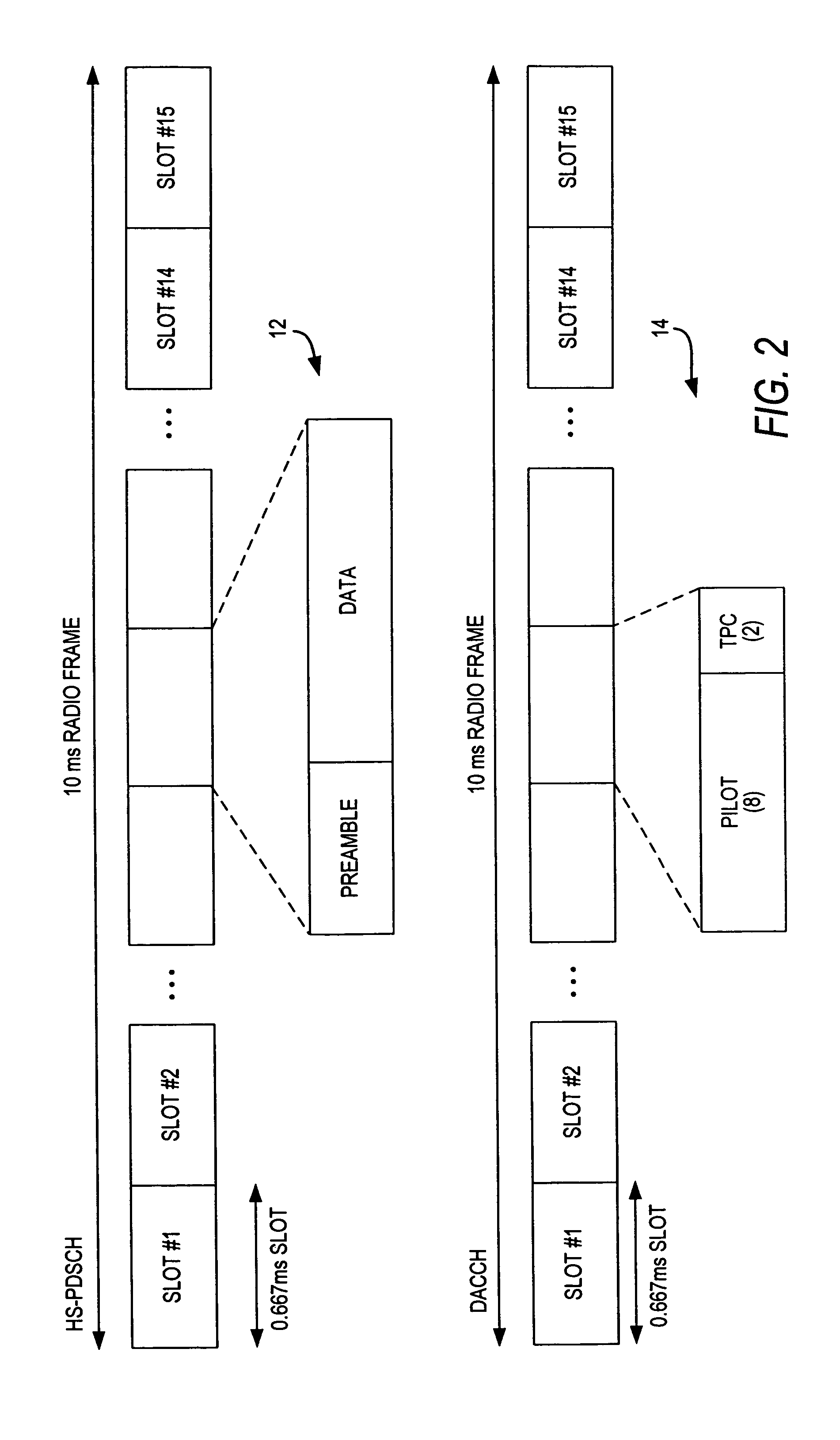
Disclosed is a code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system having a downlink dedicated physical channel (DL_DPCH) having a downlink dedicated physical control channel (DL_DPCCH) and a downlink dedicated physical data channel (DL_DPDCH). The DL_DPCCH having a transport power control (TPC) field transmitting a TPC command for controlling uplink transport power, a transport format combination indicator (TFCI) field transmitting TFCI indicating a transport format combination of a currently transmitted channel, and a pilot field transmitting a pilot. The DL_DPDCH has first and second data fields transmitting downlink data. If data is normally received over an enhanced uplink dedicated channel (EUDCH), ACK information is generated, and if data is abnormally received over the EUDCH, NACK information is generated. Bits corresponding to the ACK or NACK information are punctured at a position randomly selected from the first and second data fields of the DL_DPDCH, and the ACK or NACK information is inserted into the punctured position before being transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling interference in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20140254516A1Cancel any interferenceModulated-carrier systemsCriteria allocationCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A method and apparatus for transmitting control information is provided for use in detection of interference an signal in a wireless communication system. An interference control method of a base station of a mobile communication system includes scheduling data to be transmitted to a terminal and transmitting control information including data channel information on the scheduled data and interference signal information to the terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for end-to-end communication between a universal integrated circuit card and a remote entity over an IP-based wireless wide area network and the internet
InactiveUS20050259673A1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsBrick and mortarWide area network
End-to-end communication between a UICC and a remote node on a network without requiring implementation of special purpose protocols at the remote node. The UICC operates to transmit a command using a first protocol from the UICC to the terminal to request the terminal to open a data channel to the network. The wireless terminal operates to, in response to the request to open a data channel, attempt to open a channel to the network. Upon indication that a data channel has successfully been opened: the UICC operates to transmit datagrams of a second protocol to the wireless terminal using the first protocol. The wireless terminal operates to receive the datagrams from the UICC and to transmit the datagrams received from the UICC to the network using the second protocol. The wireless terminal operates to receive datagrams of the second protocol from the remote entity and to transmit the datagrams from the remote entity to the UICC using the first protocol.
Owner:AXALTO SA
Multimedia messaging service routing system and method
InactiveUS6947738B2Special service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingThe InternetMobile device
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Detachable shaft flexible endoscope
ActiveUS9107573B2Good adhesionEasy detachmentSurgeryEndoscopesElectric power transmissionFlexible endoscopy
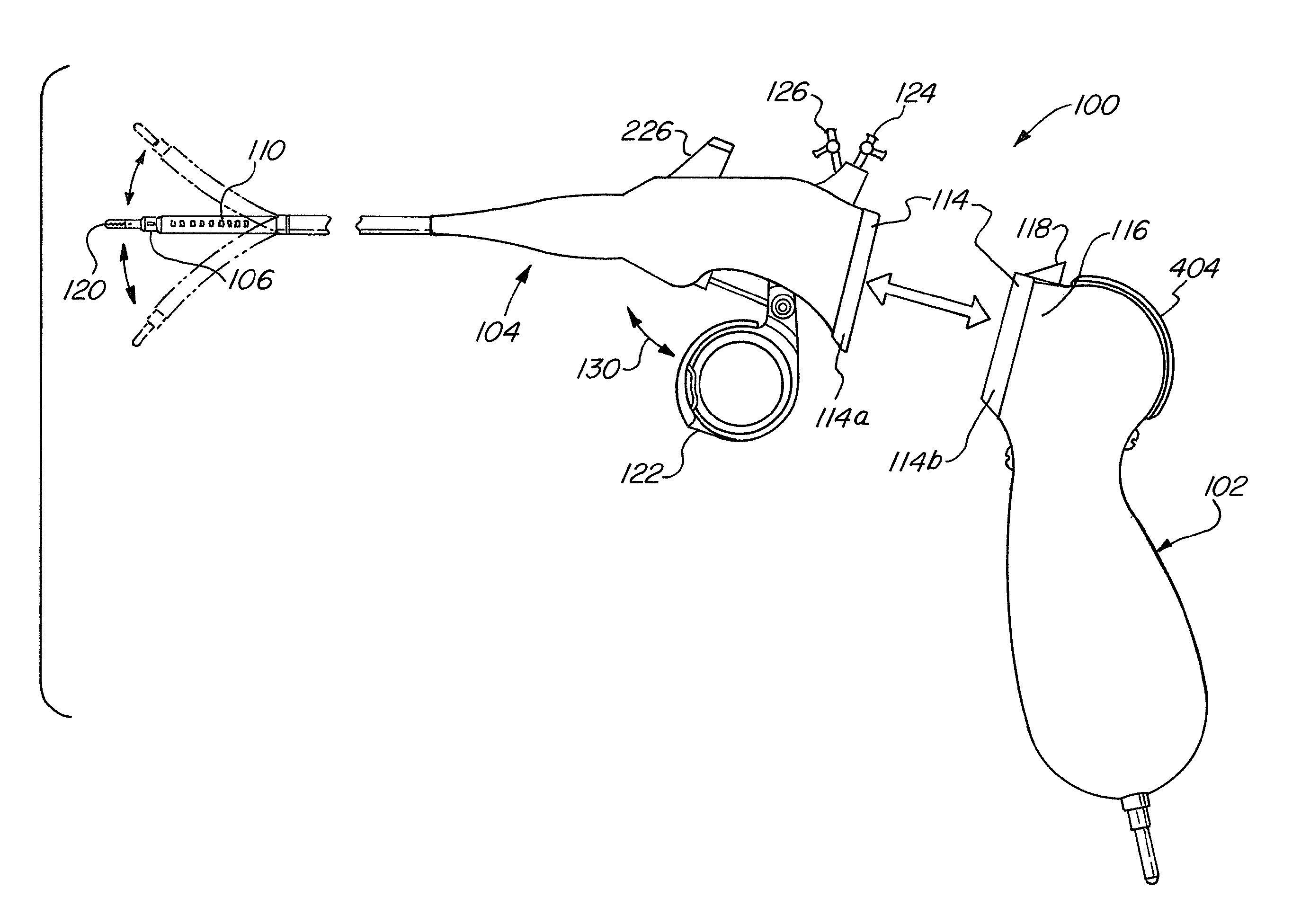
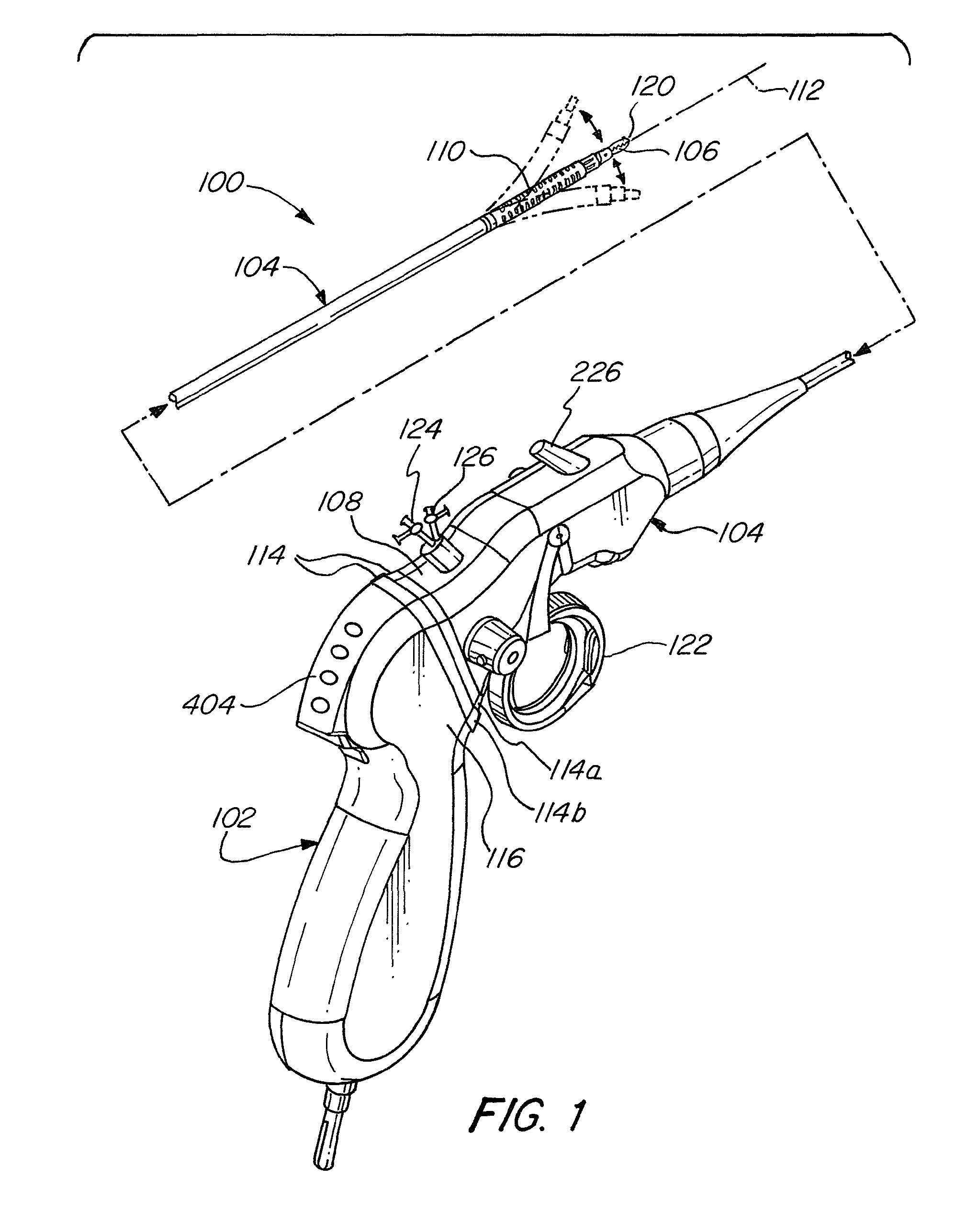
A flexible endoscope includes a handle, a flexible shaft having a distal end and a proximal end, a coupling mechanism releasably attaching the handle to the distal end of the flexible shaft, an illumination unit disposed in the flexible shaft, the illumination unit providing light to an area in front of the distal end of the flexible shaft, and an imaging unit disposed in the flexible shaft, the imaging unit generating image data of the area in front of the distal end of the flexible shaft, wherein the coupling mechanism includes an electrical channel for transmitting electrical power to the illumination unit and the imaging unit, and a data channel for transmitting the image data from the imaging unit.
Owner:KARL STORZ ENDOVISION INC
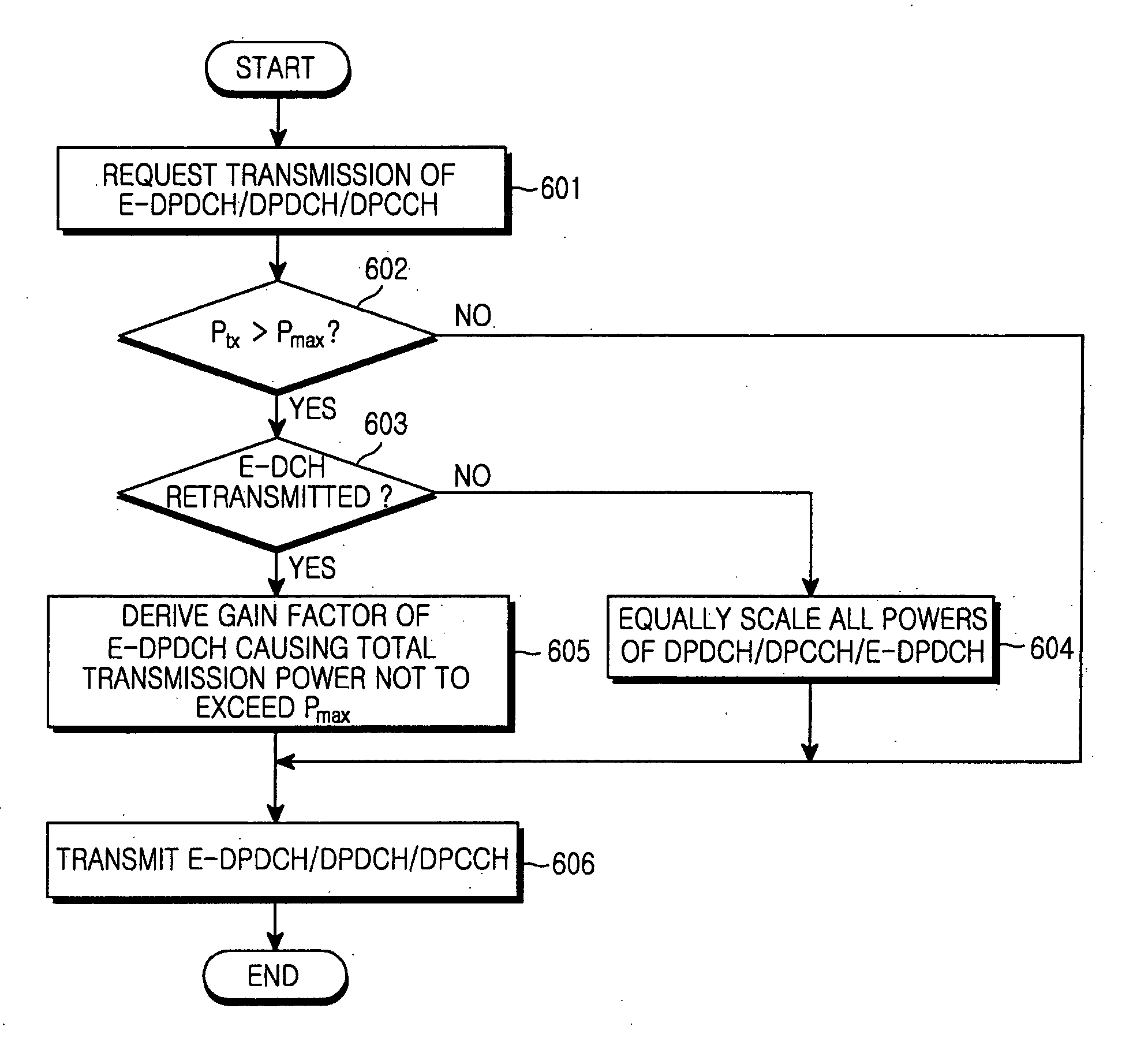
Method and apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system supporting enhanced uplink service
ActiveUS20060003787A1Effective controlReduce transmit powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingTransmitted powerControl channel
A method and an apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system supporting an enhanced uplink service are provided. A Transport Format Combination (TFC) selector determines TF information for data to be transmitted through a first data channel not supporting Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) and a second data channel supporting HARQ, and determines gain factors for the first and second data channel, and first and second control channel carrying control information for the first and second data channel. The gain factors are input to a physical channel transmission controller, and the physical channel transmission controller reduces the gain factor for the second channel if total transmit power required for transmission of the channels exceeds the predetermined maximum allowed power. A gain scaler adjusts transmit powers of the channels using the scaled gain factor and gain factors for the first data channel, the first control channel and the second control channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
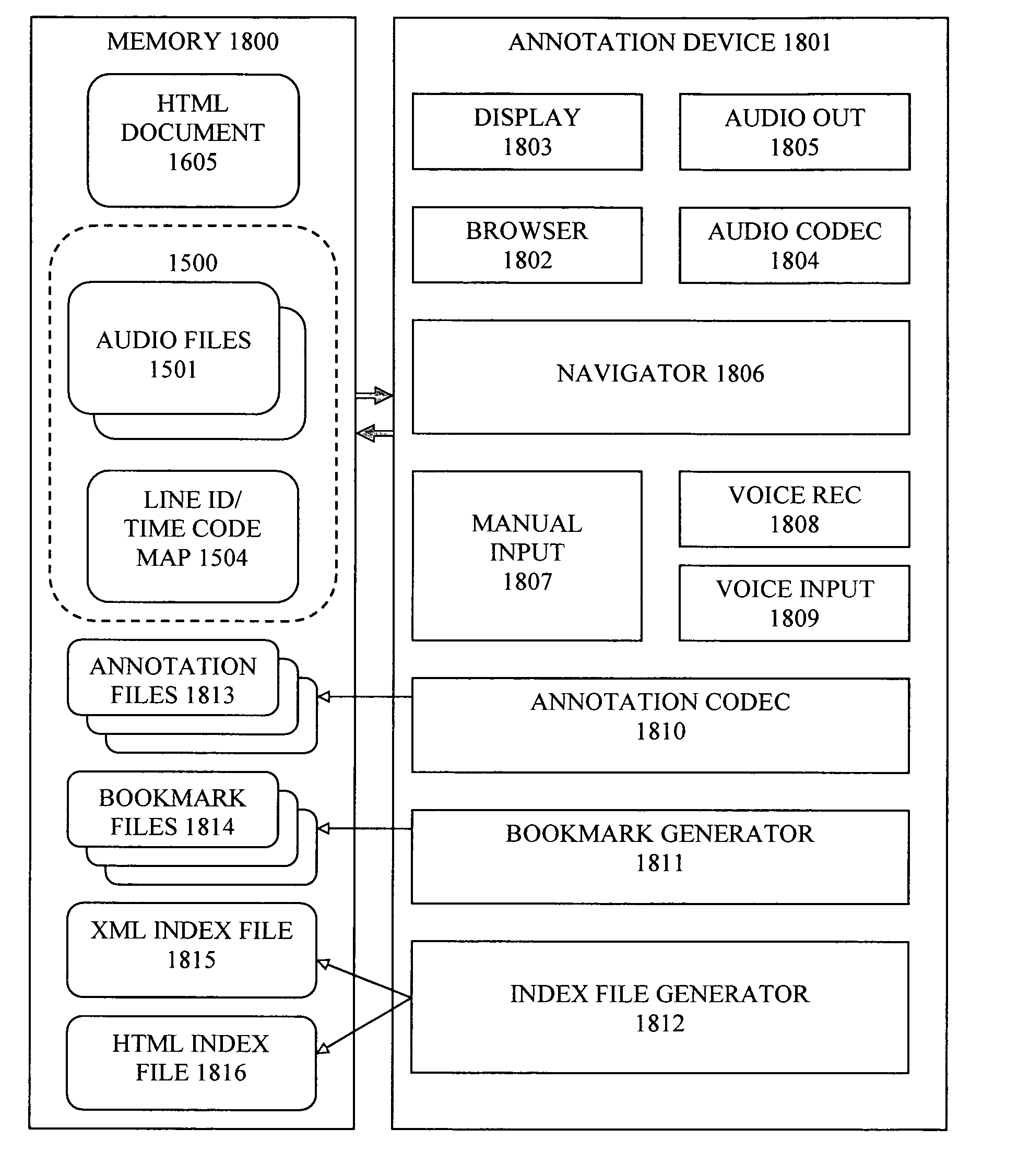
Method and apparatus for annotating a line-based document
InactiveUS20060143559A1Way of increaseSimple methodNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionNumber timesText annotation
To facilitate the use of audio files for annotation purposes, an audio file format, which includes audio data for playback purposes, is augmented with a parallel data channel of line identifiers, or with a map associating time codes for the audio data with line numbers on the original document. The line number-time code information in the audio file is used to navigate within the audio file, and also to associate bookmark links and captured audio annotation files with line numbers of the original text document. An annotation device may provide an output document wherein links to audio and / or text annotation files are embedded at corresponding line numbers. Also, a navigation index may be generated, having links to annotation files and associated document line numbers, as well as bookmark links to selected document line numbers.
Owner:COPERNICUS INVESTMENTS
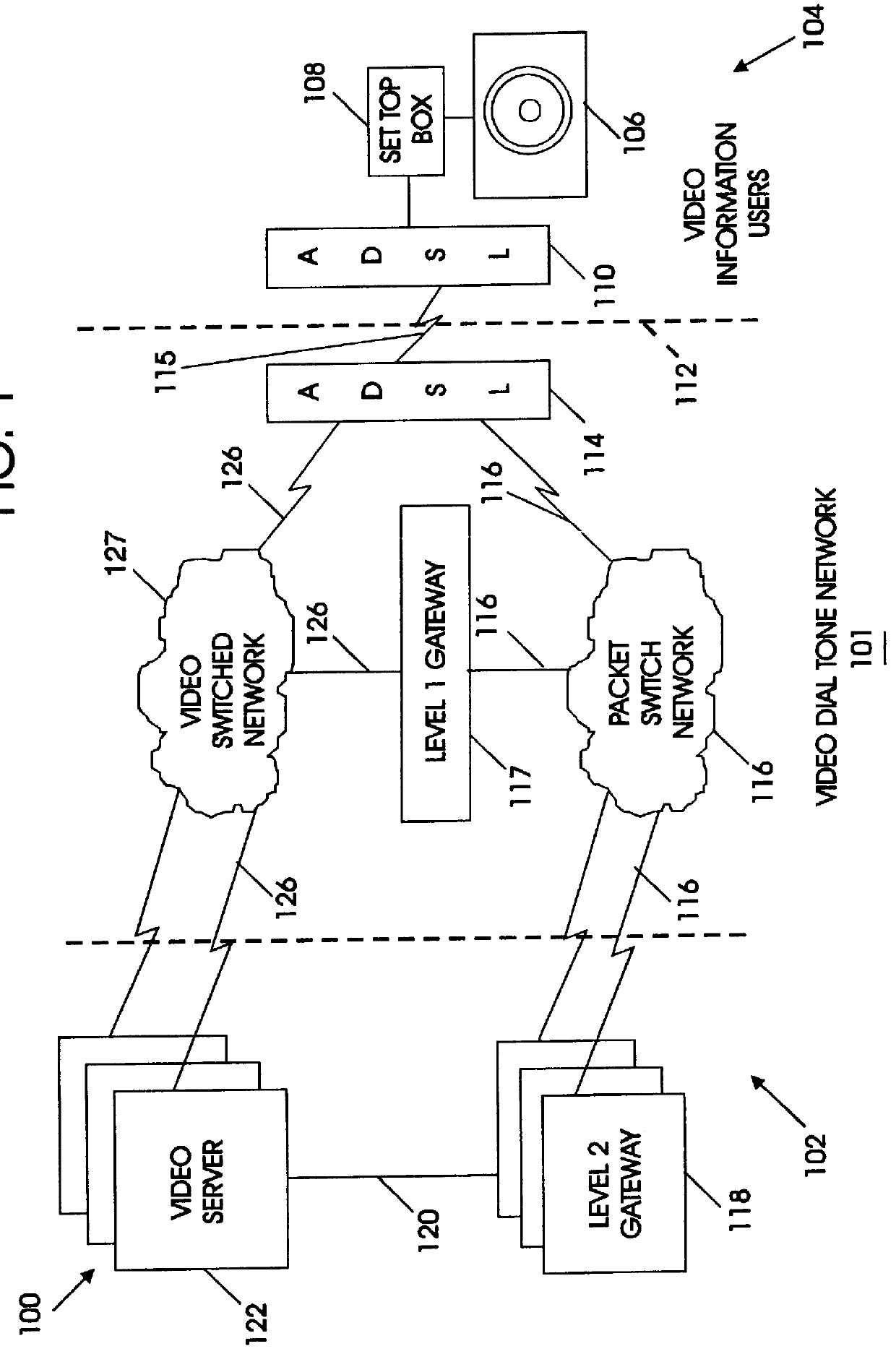
System and method to provide interactivity for a networked video server
InactiveUS6055560AMinimizes burden and hence costRapid responseTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVideo serverData channel
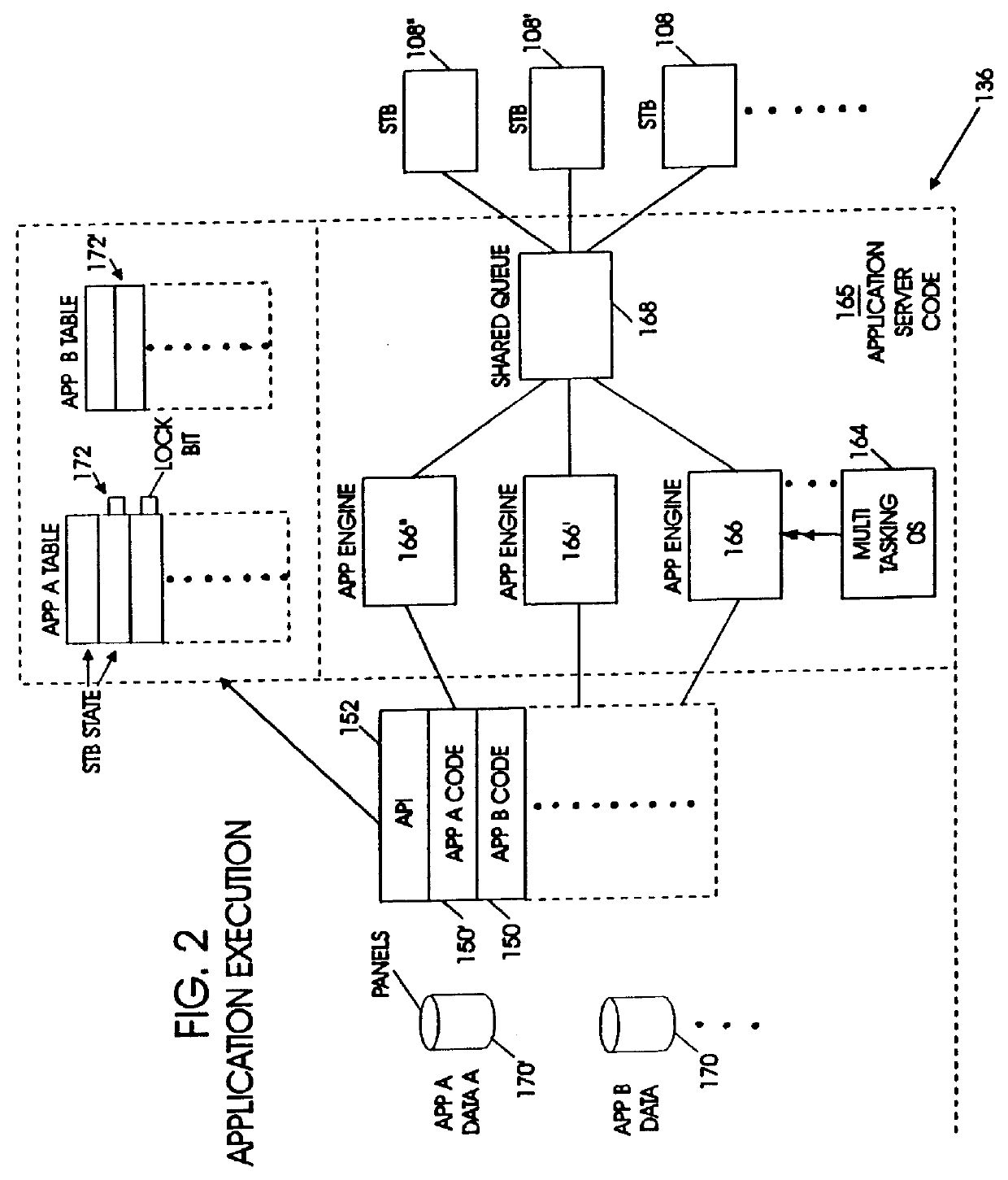
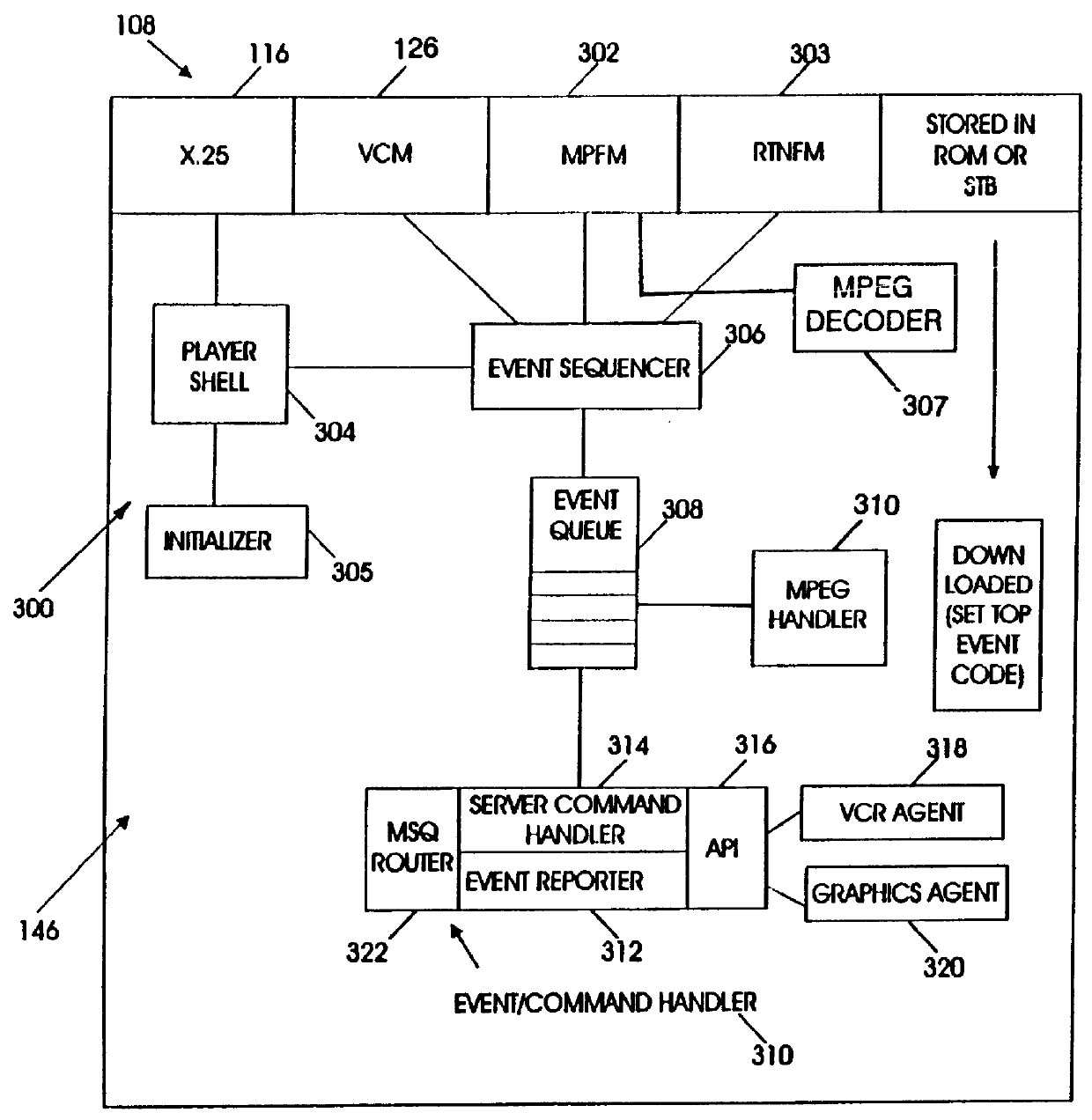
An interactive video system supports functions typically expected with a VCR such as play, pause, fast forward and rewind. A set top box is coupled to a display terminal and a first interface. The set top box includes a memory for storing an operating system in set top enabling codes. A video dial tone network includes a control channel and a data channel coupled to a second interface linked to the first interface. A first gateway controls establishment of a video session between a video server and the display terminal. A second gateway establishes connection between the video server and the set top box over a data channel in response to an input from the first gateway. An application server coupled to the first gateway and the video server contains executable code for transferring video data, video and audio information from the video server to the display terminal. The application server includes a shared queue coupled to a plurality of application engines and set top boxes and includes program code for multi-tasking operation. The code operates the application engines in response to application tables to provide video transmission as a panel object indicative of the state of set top boxes in a video session.
Owner:IBM CORP
Updating malware definition data for mobile data processing devices
ActiveUS7210168B2Quickly reachPush behaviour is further enhancedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareDigital signature
The malware definition data of mobile data processing devices is updated via a data channel associated with a wireless telephony link to that mobile data processing device. The data channel may be the same channel wed for SMS messaging and the transfer of control information. The mobile data processing device is typically a mobile telephone. The update data may be digitally signed to increase security.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Downlink and uplink channel structures for downlink shared channel system
InactiveUS7006464B1Improve spectral efficiencyAdapt quicklyPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCode spaceTransmitted power
An uplink and downlink channel structure supports a shared downlink data channel. The new structure accommodates advanced physical and Medium Access Control (MAC) layer techniques, such as incremental redundancy (IR), fast adaptation to channel conditions, and multiple input multiple output (MIMO) antenna configuration. The proposed changes are intended to lead to a downlink structure that achieves higher spectral efficiency for the packet oriented services over then shared downlink channel. Additionally, the new structure uses the base station transmit power information and of the channelization (OVSF) code space more efficiently.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Otfs methods of data channel characterization and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150117395A1Increase chanceGood knowledgePolarisation/directional diversityTransmission path divisionWireless dataFrequency shift
Fiber, cable, and wireless data channels are typically impaired by reflectors and other imperfections, producing a channel state with echoes and frequency shifts in data waveforms. Here, methods of using OTFS pilot symbol waveform bursts to automatically produce a detailed 2D model of the channel state are presented. This 2D channel state can then be used to optimize data transmission. For wireless data channels, an even more detailed 2D model of channel state can be produced by using polarization and multiple antennas in the process. Once 2D channel states are known, the system turns imperfect data channels from a liability to an advantage by using channel imperfections to boost data transmission rates. The methods can be used to improve legacy data transmission modes in multiple types of media, and are particularly useful for producing new types of robust and high capacity wireless communications using non-legacy OTFS data transmission methods.
Owner:COHERE TECH
Method of transmitting data in multiple antenna system
ActiveUS20090059844A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsSignal allocationCommunications systemControl channel
A method of transmitting data in a wireless communication system comprises receiving feedback data on an uplink data channel, the feedback data comprising a precoding matrix indicator (PMI), wherein the value of the PMI corresponds to an index in a codebook, transmitting a precoding scheme for downlink data on a downlink control channel, wherein the preceding scheme is determined as one of at least two of a transmit diversity irrespective of the received PMI, an acknowledgement indicating preceding according to the received PMI and a new PMI indicating that it is used in precoding downlink data to be transmitted, and transmitting the downlink data on a downlink data channel after applying precoding according to the determined preceding scheme.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Uplink control channel allocation
ActiveUS20080233964A1Network traffic/resource managementSignal allocationCommunications systemControl channel
Various methods of allocating uplink control channels in a communication system are implemented at a resource scheduler or a user equipment (UE). In one method the scheduler reserves resources for a downlink data channel and signals a corresponding downlink data channel grant and also reserves resources for a persistent uplink control channel for a longer duration than the data channel grant. Signaling overhead associated with a grant for this persistent uplink control channel is reduced over a full dynamic grant. A predetermined rule can be used at the scheduler and at the UE to avoid overhead signaling associated with a grant for this persistent control channel. Predetermined rules at the UE and scheduler can also be used to reserve appropriate resources and select appropriate MCS levels for control information and the control information and uplink data can be transported over a common uplink channel when a time overlap occurs between an uplink data channel and the persistent control channel.
Owner:APPLE INC
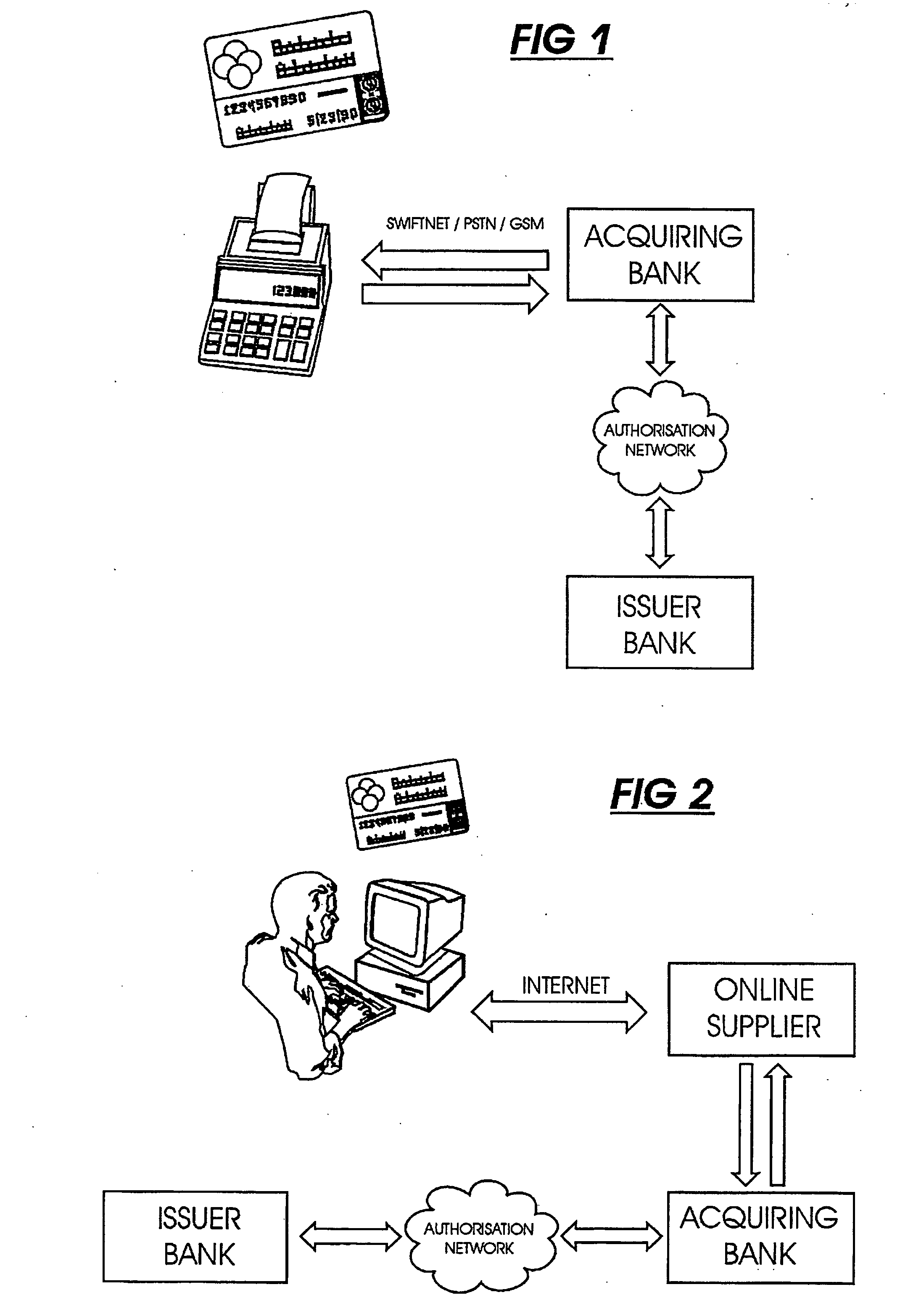
Transaction verification system
This invention uses separate, parallel communication channels to authorise and authenticate a transaction. A primary data channel (PSTN, radio or the like) is used to communicate between the merchant terminal and the bank, and a parallel data channel (a mobile phone network for instance) is used for the authentication process. In the example, the transaction is initiated (on a primary data channel), using a POS terminal as a transaction processing client. The transaction processing server and financial services provider fulfill their normal functions. At this point, the process loops into a transaction authorisation component using the parallel data channel, that requires authentication of the transaction initiator (the card holder). In the example, communications on the parallel data channel are by way of SMS. In the authorisation process, the card holder receives an SMS requesting authorisation of the transaction. If the card holder is not the transaction initiator, the card holder can cancel the transaction. If the transaction can be authorised, an authentication process is initiated in which the mobile phone is programmed to require the entry of a normally secret code (such as a personal identification number (PIN)) that serves to authenticate the card holder and to give final authorisation of the transaction.
Owner:NARAINSAMY SELVANATHAN
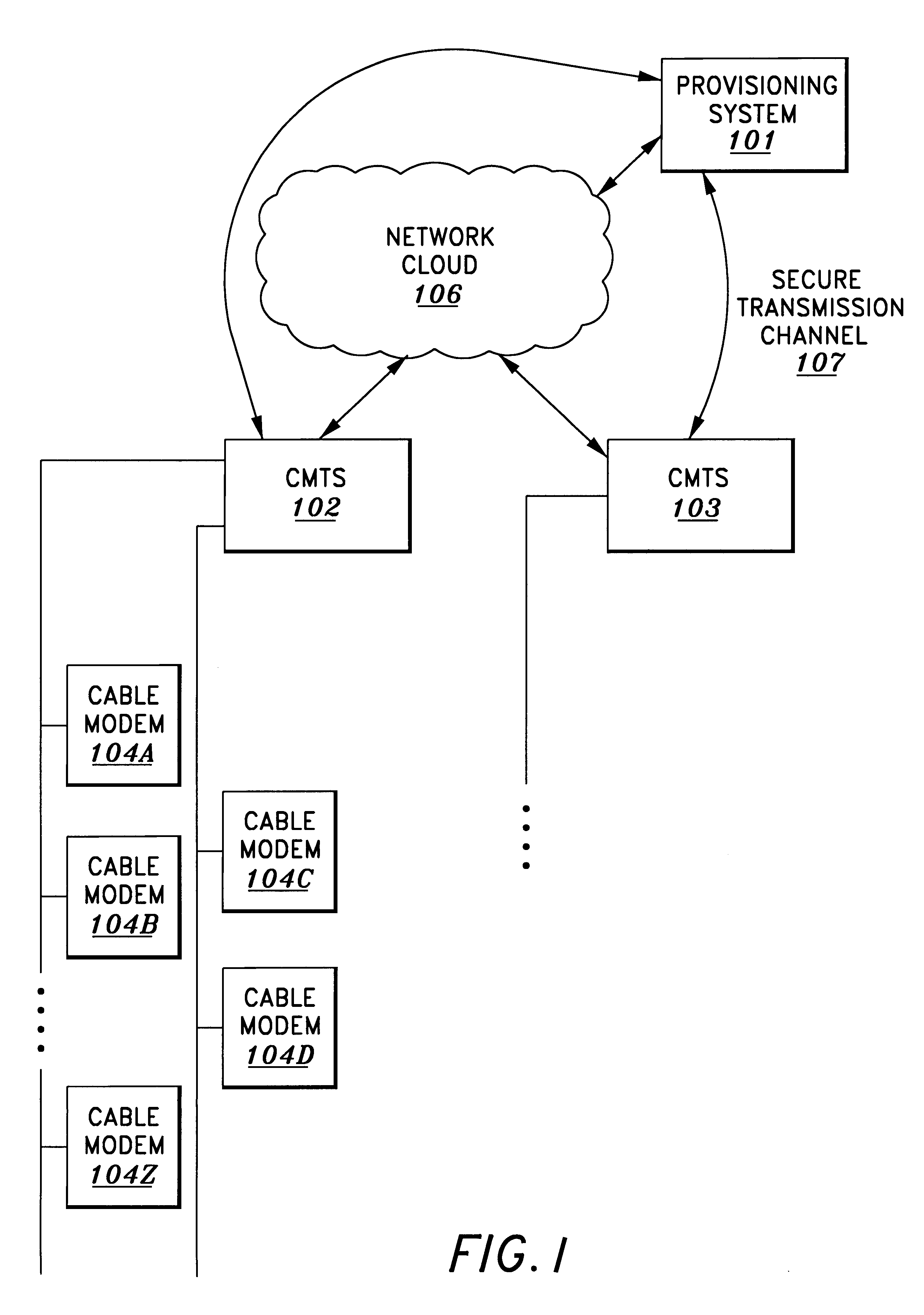
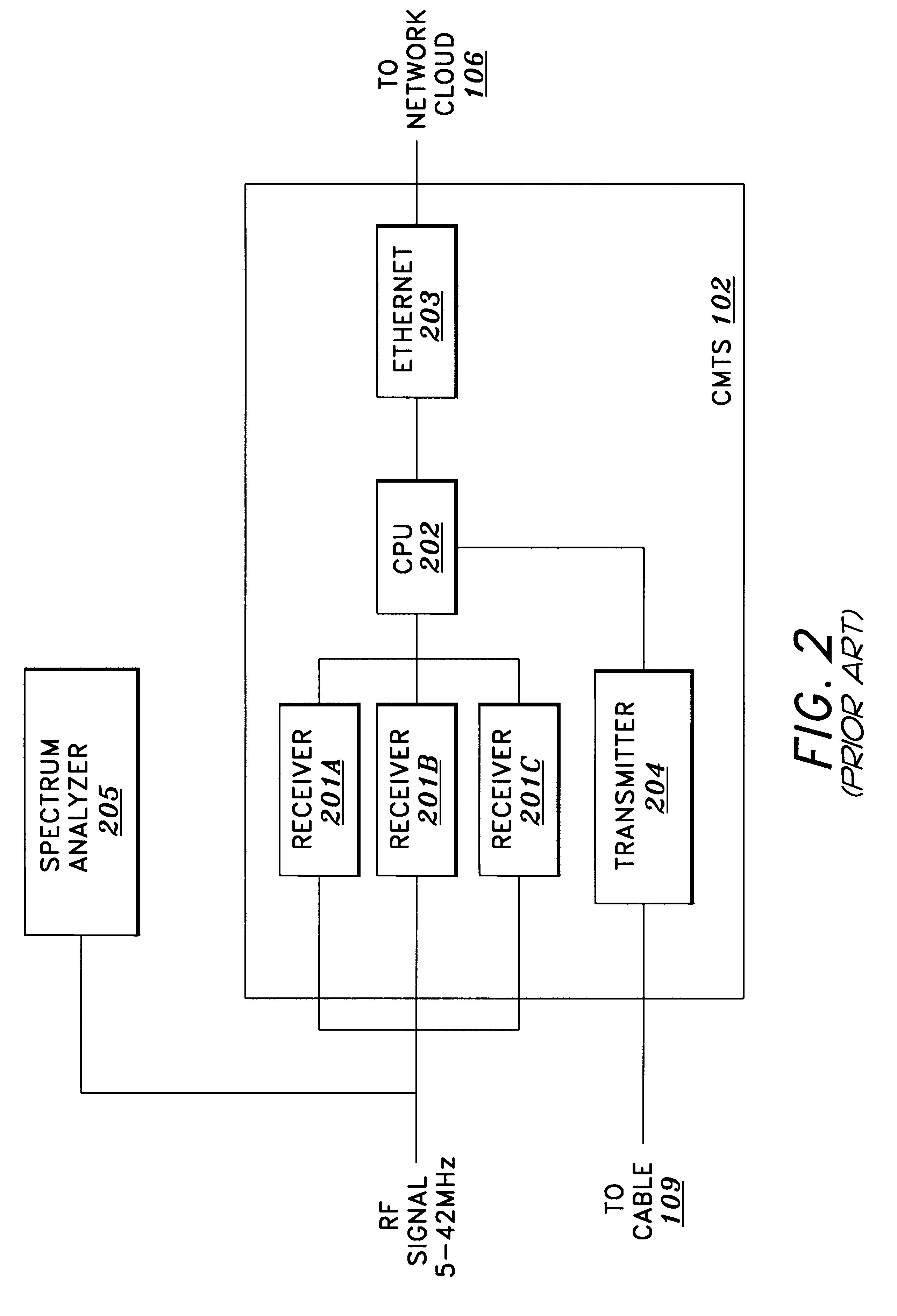
Method and apparatus for initialization of a cable modem
A method and apparatus for initialization and operation of cable modems comprising initializing the cable modems over management channels and transferring the cable modems to a data channel for operation. Initialization over a management channel overcomes certain prior art constraints associated with initialization over the data channel.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Support of guaranteed bit-rate traffic for uplink transmissions
ActiveUS20060182065A1Frequent occurrenceReduce loadPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementUplink transmissionRadio Network Controller
The invention relates to a method for providing measurements on a bit-rate provided to scheduled data having a guaranteed bit-rate and being transmitted on at least one dedicated uplink data channel by at least user equipment via a C-RNC. Further, the invention also relates to a method for initiating congestion control for scheduled data of at least one guaranteed bit-rate priority class in a mobile communication system. Moreover, the invention relates to a C-RNC as well as a serving radio network controller performing these methods. To enable the C-RNC within a mobile communication system to perform congestion control for uplink transmissions having a guaranteed bit-rate the invention suggests to provide the C-RNC with a bit-rate being provided to scheduled data of the guaranteed bit-rate priority class using common or dedicated measurement procedures. This provided bit-rate is evaluated and taken as a basis for deciding on whether congestion control for data of the priority class needs to be performed.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method for communicating in dual-modes
ActiveUS20050195768A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsConnection managementTelecommunicationsDual mode
The present invention is generally directed to methods for communicating in a dual-mode communication protocol. A representative embodiment of the present invention comprises: enabling communication in a spread-spectrum communication protocol, comprising: receiving a first portion of a communication frame at a first frequency channel, wherein the first portion of the communication frame comprises a data channel index that indicates a second frequency channel for receiving a second portion of the communication frame; switching to the second frequency channel; and receiving the second portion of the communication frame at the second frequency channel.
Owner:SIPCO
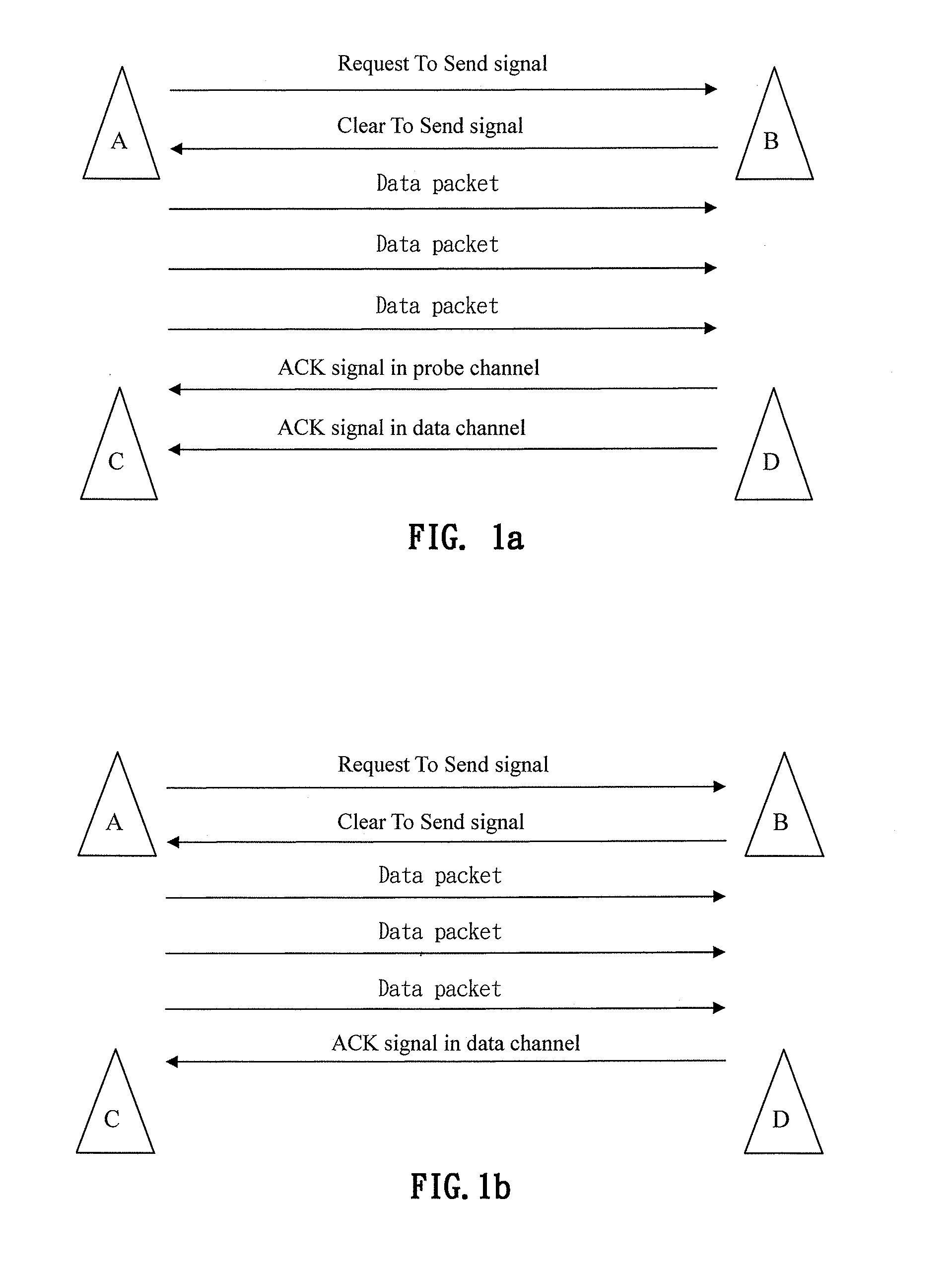
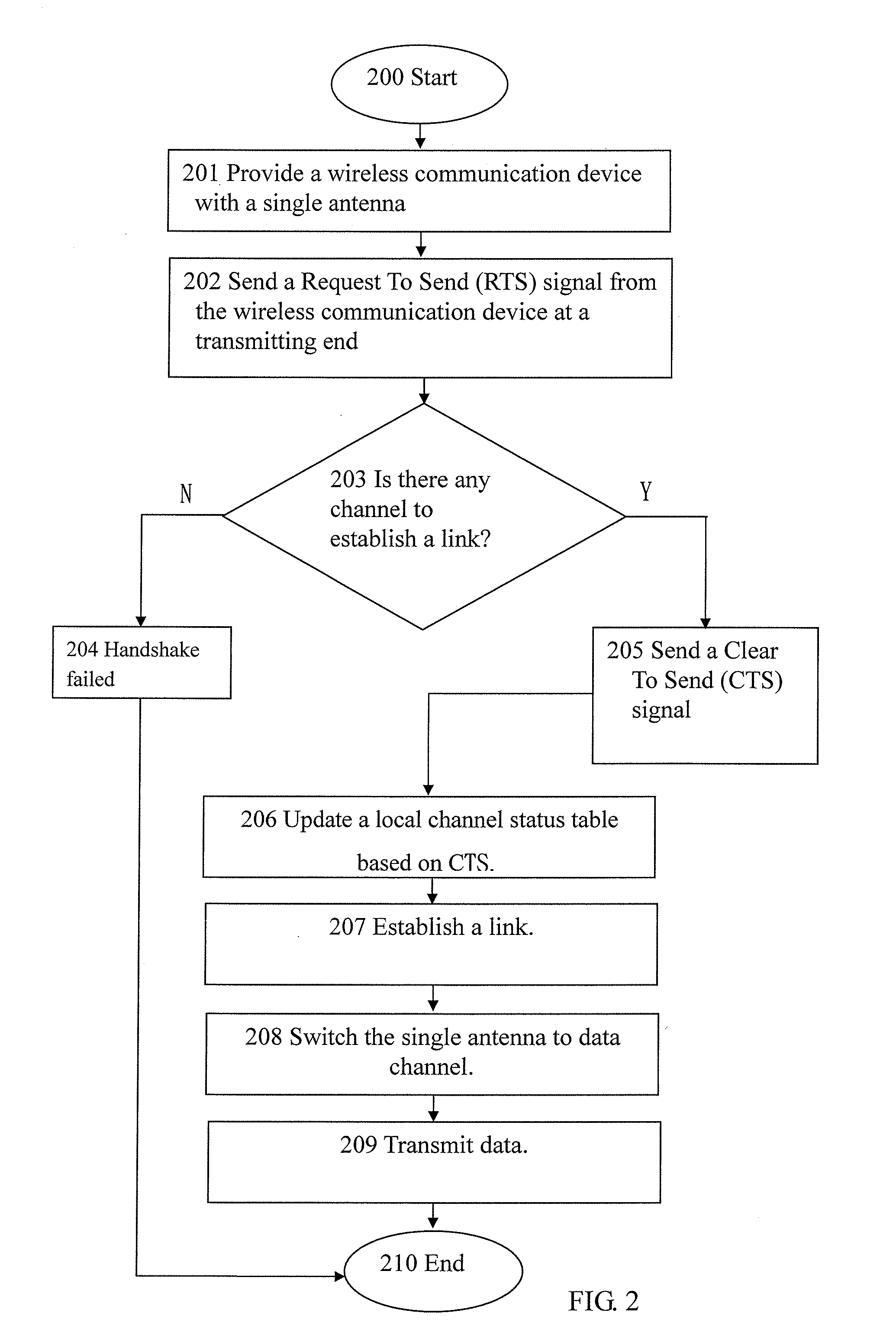
Wireless communication methods utilizing a single antenna with multiple channels and the devices thereof
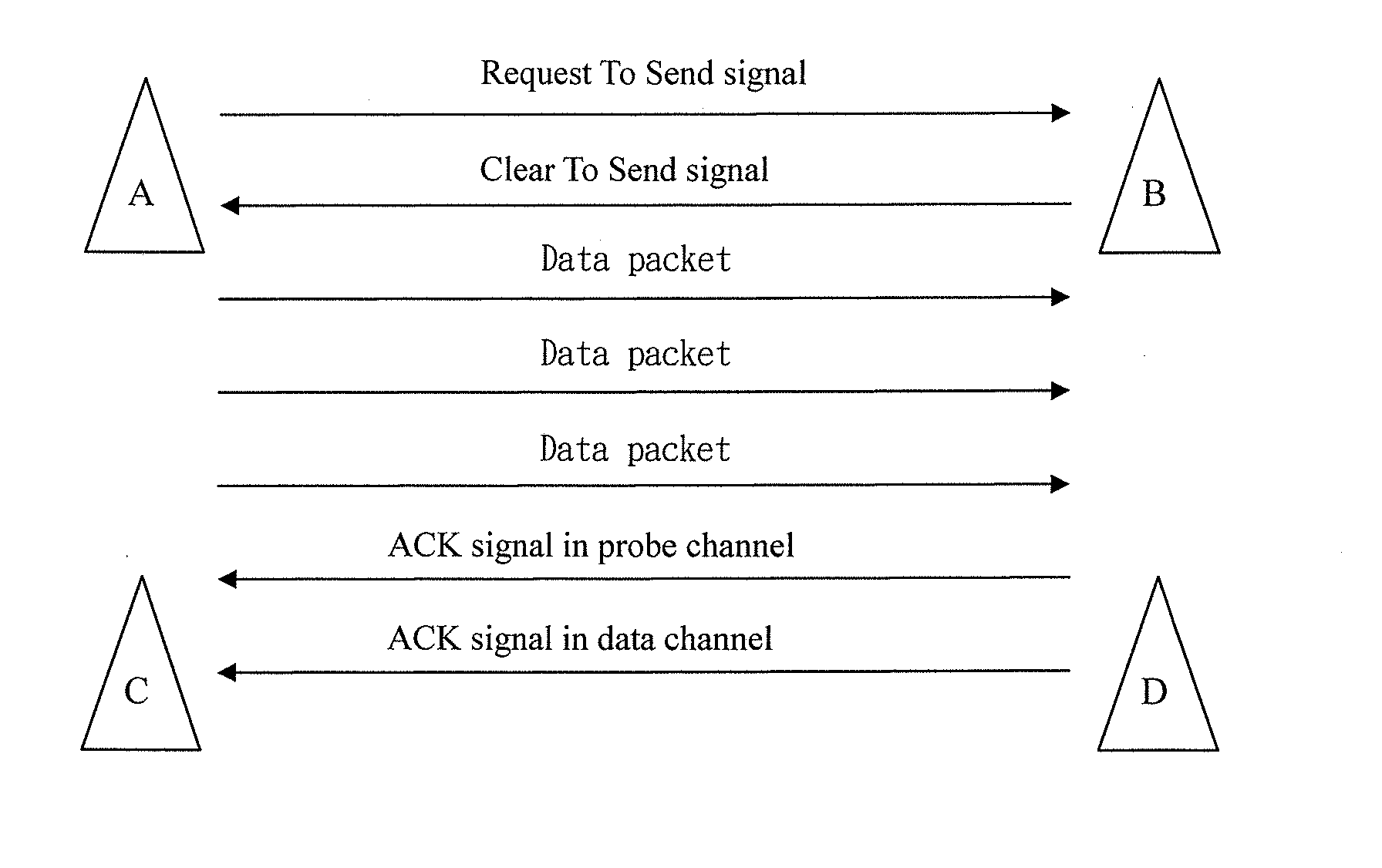
InactiveUS20100091712A1Improve noiseImprove throughputError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData transmissionProbe signal
The present invention provides wireless communication methods utilizing a single antenna with multiple channels and the devices thereof. The method includes providing a plurality of communication channels within the single antenna. The plurality of communication channels may include a probe channel and a data channel. The single antenna may selectively switch between the probe channel and the data channel based on a probe signal transmitted in the probe channel so as to facilitate data transmission.
Owner:SKYPHY NETWORKS
Method and system for power saving in wireless communications
A method and a system for wireless communication is provided which involves maintaining a data communication module in a power saving mode, detecting channel reservation for communication on a wireless data channel during one or more reserved time periods, and upon successful data channel reservation, transitioning the data communication module from the power saving mode to an active mode for data communication on the reserved data channel. Preferably, the data communication module is transitioned back to the power saving mode upon completion of data communication on the data channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
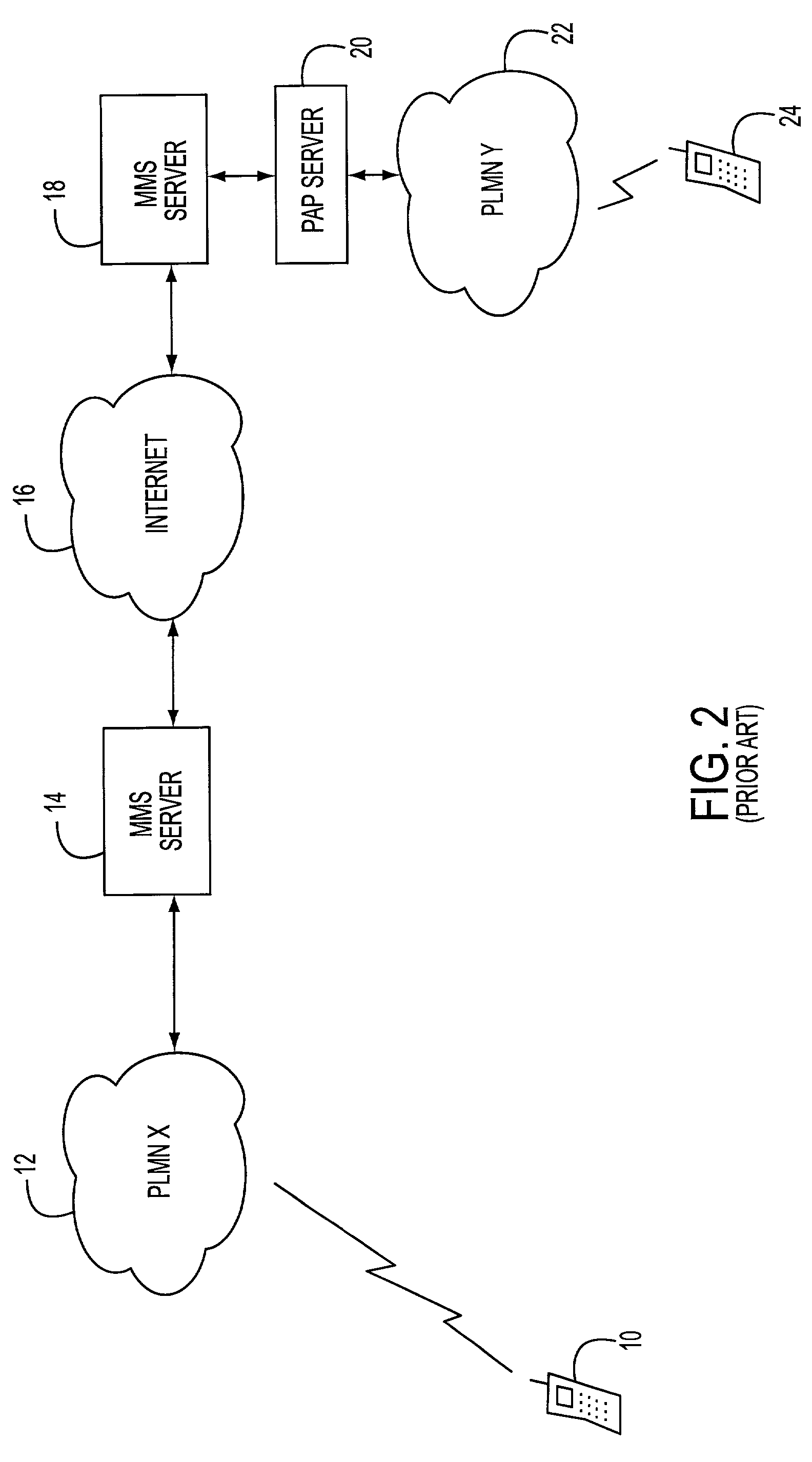
Multimedia messaging service routing system and method
InactiveUS20020126708A1Special service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingThe InternetMobile device
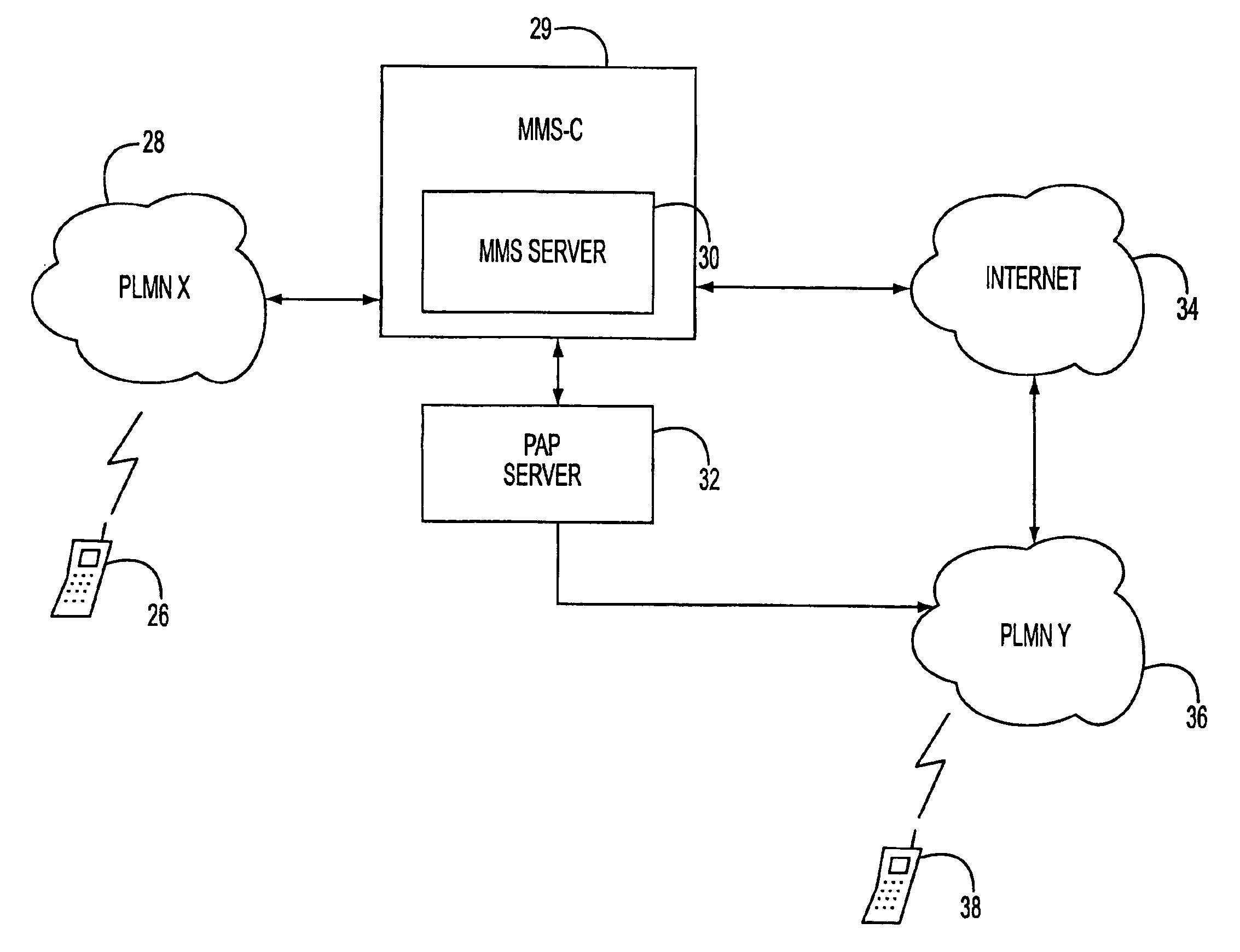
A multimedia messaging system for sending and receiving multimedia MMS messages. The MMS messages are sent to a MMS server and addressed to the recipient's MSISDN number. MMS server sends a notification to a PAP server that sends the notification as a WAP Push to the recipient mobile device telling the mobile device to retrieve the message. If the recipient mobile device is engaged in an on going or dedicated session with the Internet, the notification is sent to the recipient mobile device during the session. The recipient mobile device then initiates a HTTP GET request to retrieve the multimedia message via the voice or data channel of a PLMN. If the recipient mobile device is not engaged in an on going or dedicated session with the Internet, the notification is sent to the recipient mobile device as a WAP Push using SMS as bearer via the signaling channel of the PLMN. The recipient mobile device then initiates a HTTP GET request to retrieve the multimedia message via the voice or data channel of the PLMN.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
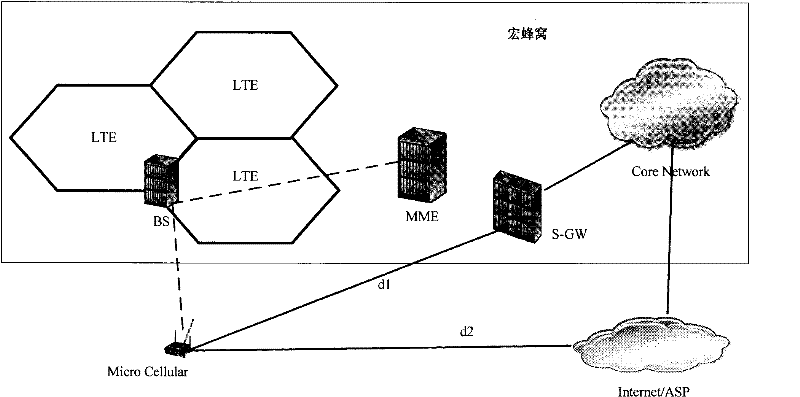
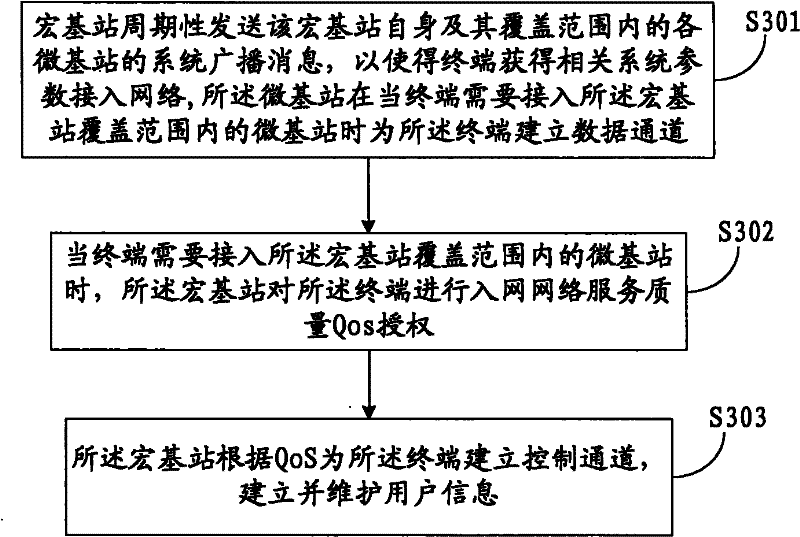
Cellular communication system, method for inter-cell handover of terminal and macro base station
InactiveCN102348244AReduce negative impactAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesMacro base stationsMicro cell
The invention discloses a cellular communication system, a method for the inter-cell handover of a terminal and a macro base station. The cellular communication system comprises the macro base station and at least one micro base station within the coverage of the macro base station. The macro base station is used for establishing a control channel for the terminal of the micro base station, performing accessing management operations on the micro base stations within the coverage, receiving a handover request of the terminal and realizing the handover of the terminal to another micro base station within the coverage. The micro base station is used for establishing a data channel for an accessing terminal to perform data transmission with the terminal. By the system, the method and the macro base station, a user control plane and a data plane under a micro cell can be separated, so that the resources of the micro base station can be better used for data communication. Therefore, negative impact on the system can be reduced in a macro cell-micro cell coexisting networking way.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
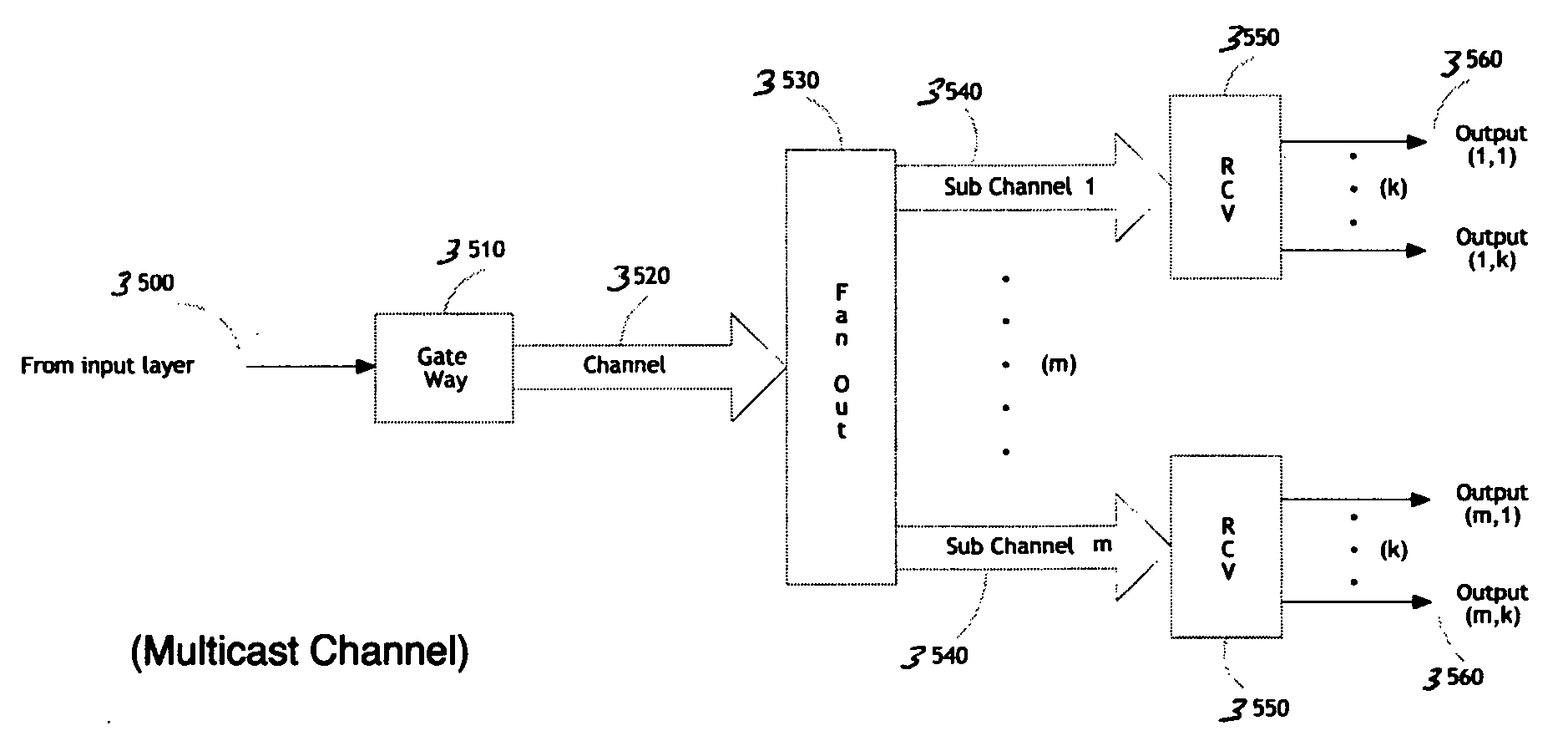
N-way serial-channel interconnect
Methods and apparatus are described for an n-Way, Serial-Channel interconnect. An apparatus includes a communications network interconnect including an input layer including a plurality of input channels; a multicast channel branching fabric coupled to the input layer; and a modular output layer coupled to the multicast channel branching fabric layer, the modular output layer including a plurality of individual serial data channels; and a plurality of sets of endpoints, each set of endpoints coupled to one of the plurality of individual serial data channels.
Owner:LIGHTFLEET CORP
Methods of operating and implementing wireless otfs communciations systems
ActiveUS20150326273A1Improve featuresSimple structureModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityThree-dimensional spaceTime shifting
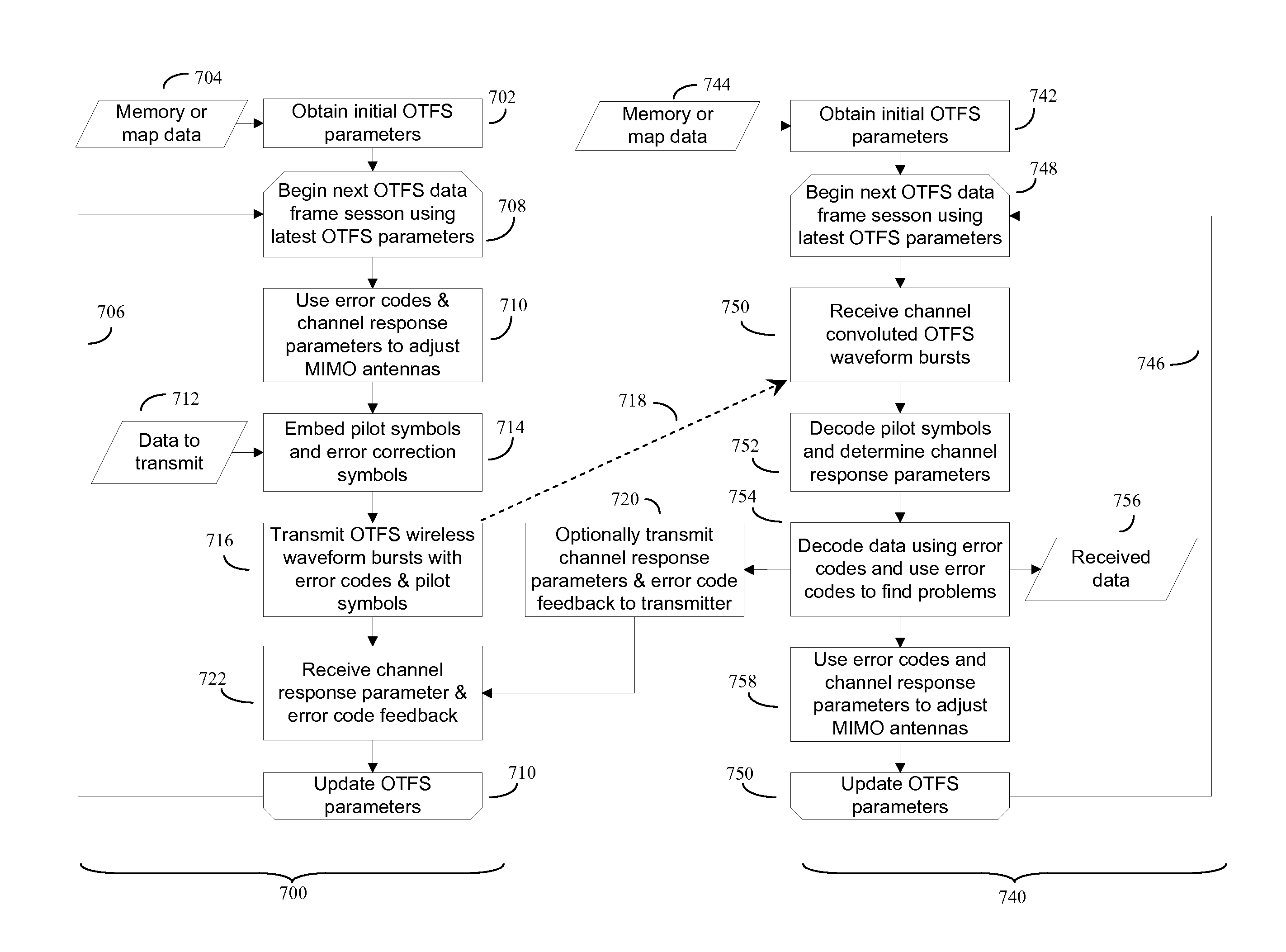
Computerized wireless transmitter / receiver system that automatically uses combinations of various methods, including transmitting data symbols by weighing or modulating a family of time shifted and frequency shifted waveforms bursts, pilot symbol methods, error detection methods, MIMO methods, and other methods, to automatically determine the structure of a data channel, and automatically compensate for signal distortions caused by various structural aspects of the data channel, as well as changes in channel structure. Often the data channel is a two or three dimensional space in which various wireless transmitters, receivers and signal reflectors are moving. The invention's modulation methods detect locations and speeds of various reflectors and other channel impairments. Error detection schemes, variation of modulation methods, and MIMO techniques further detect and compensate for impairments. The invention can automatically optimize its operational parameters, and produce a deterministic non-fading signal in environments in which other methods would likely degrade.
Owner:COHERE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com