Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4940 results about "Dual mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
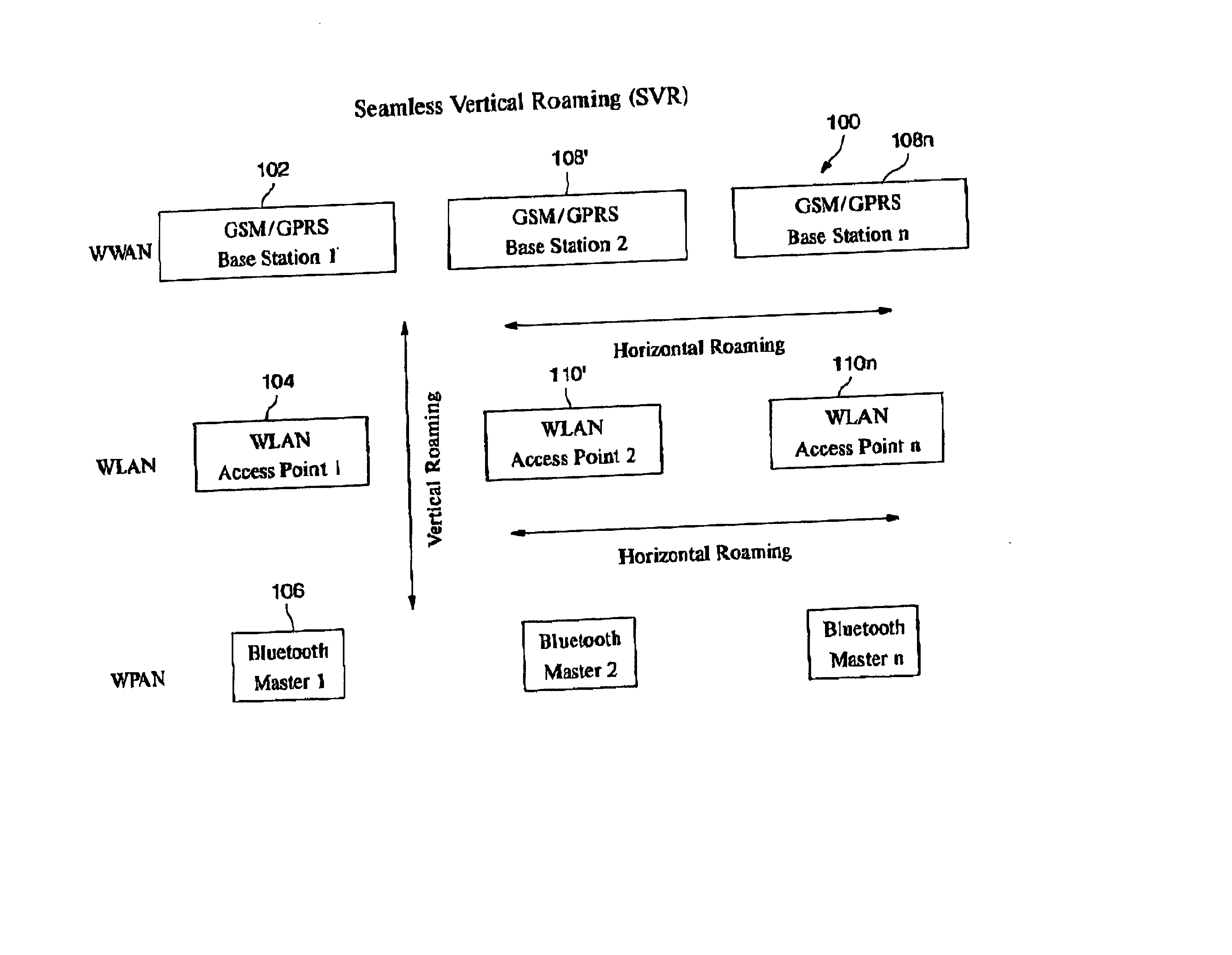
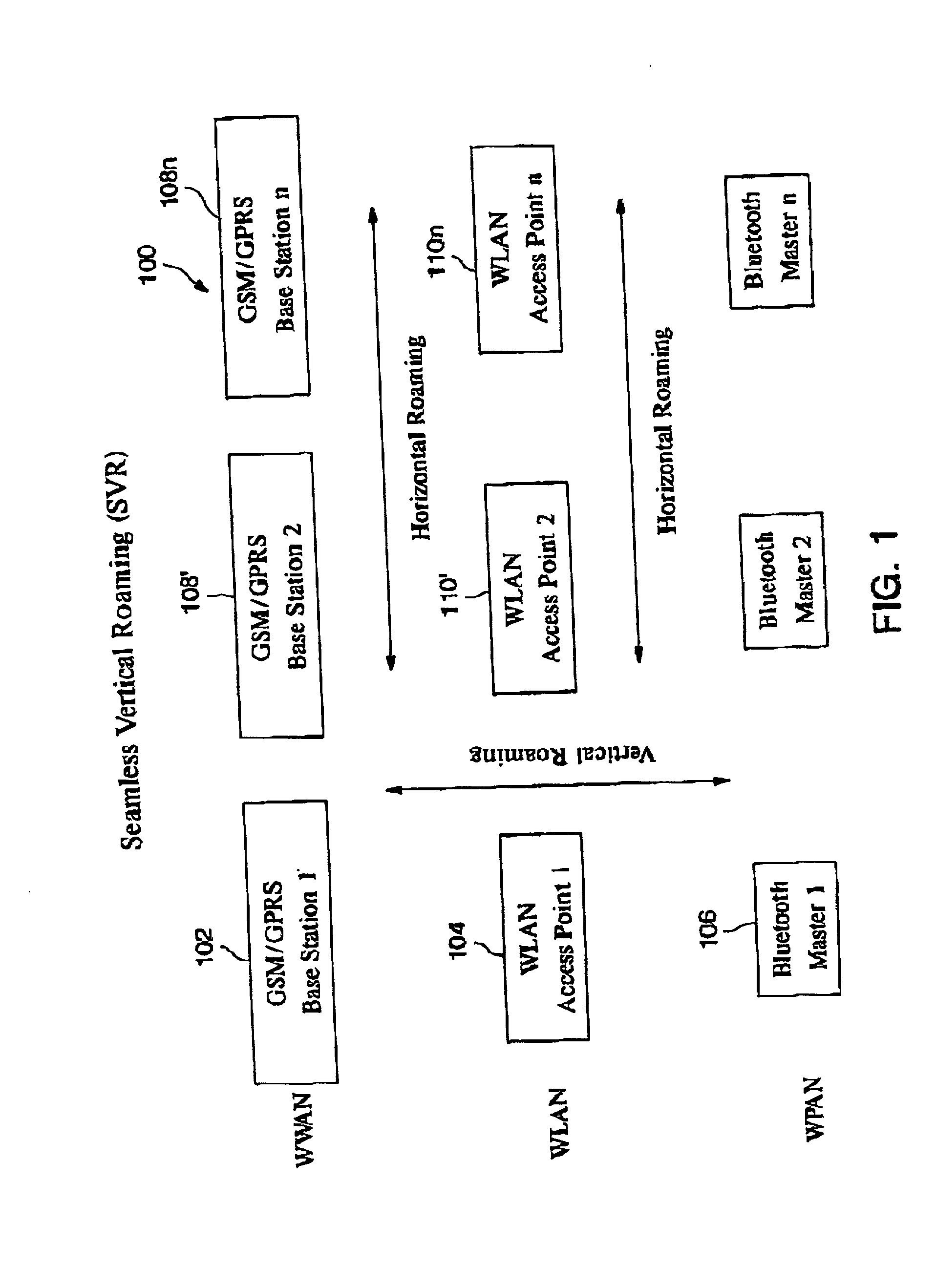
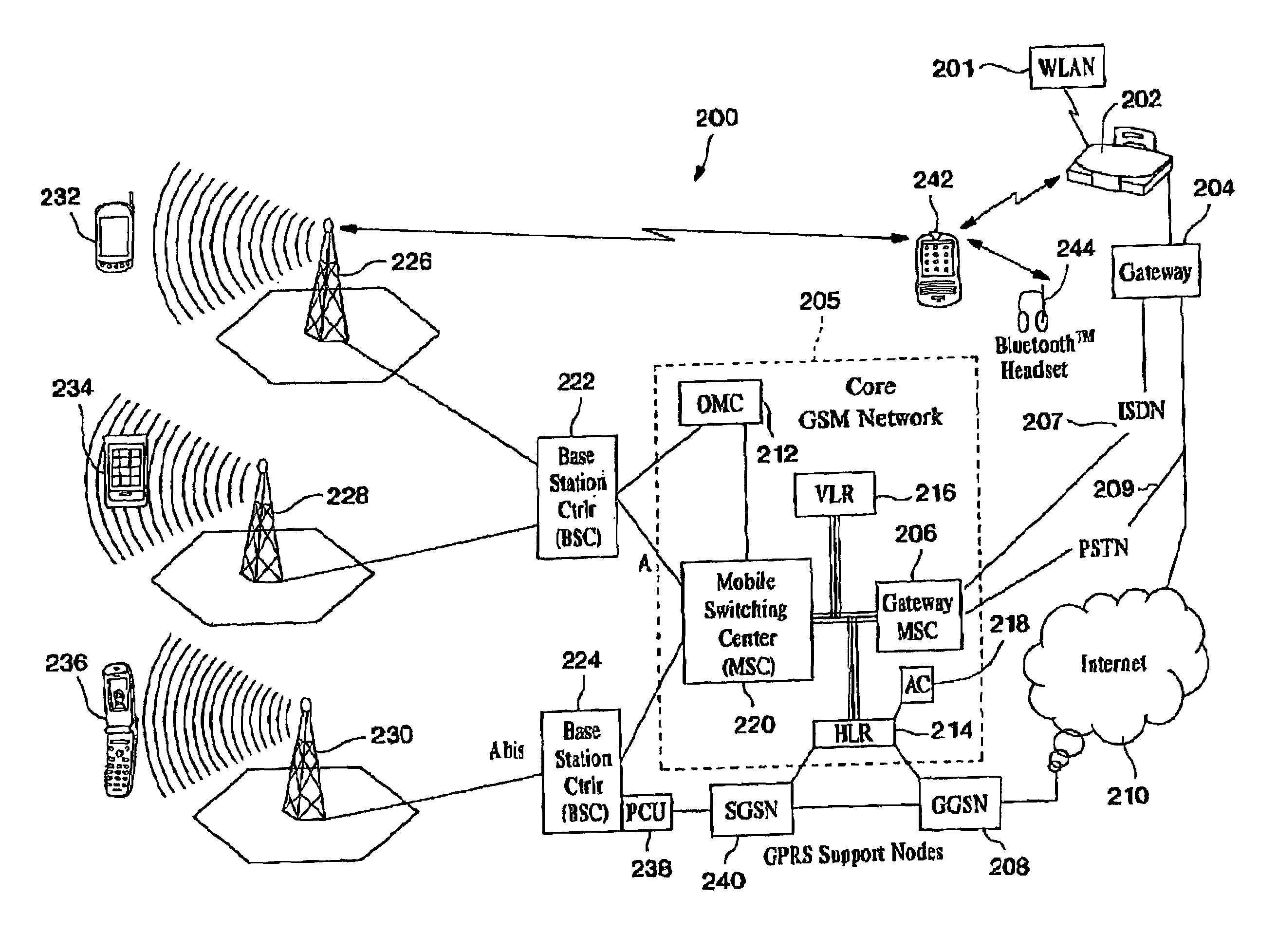
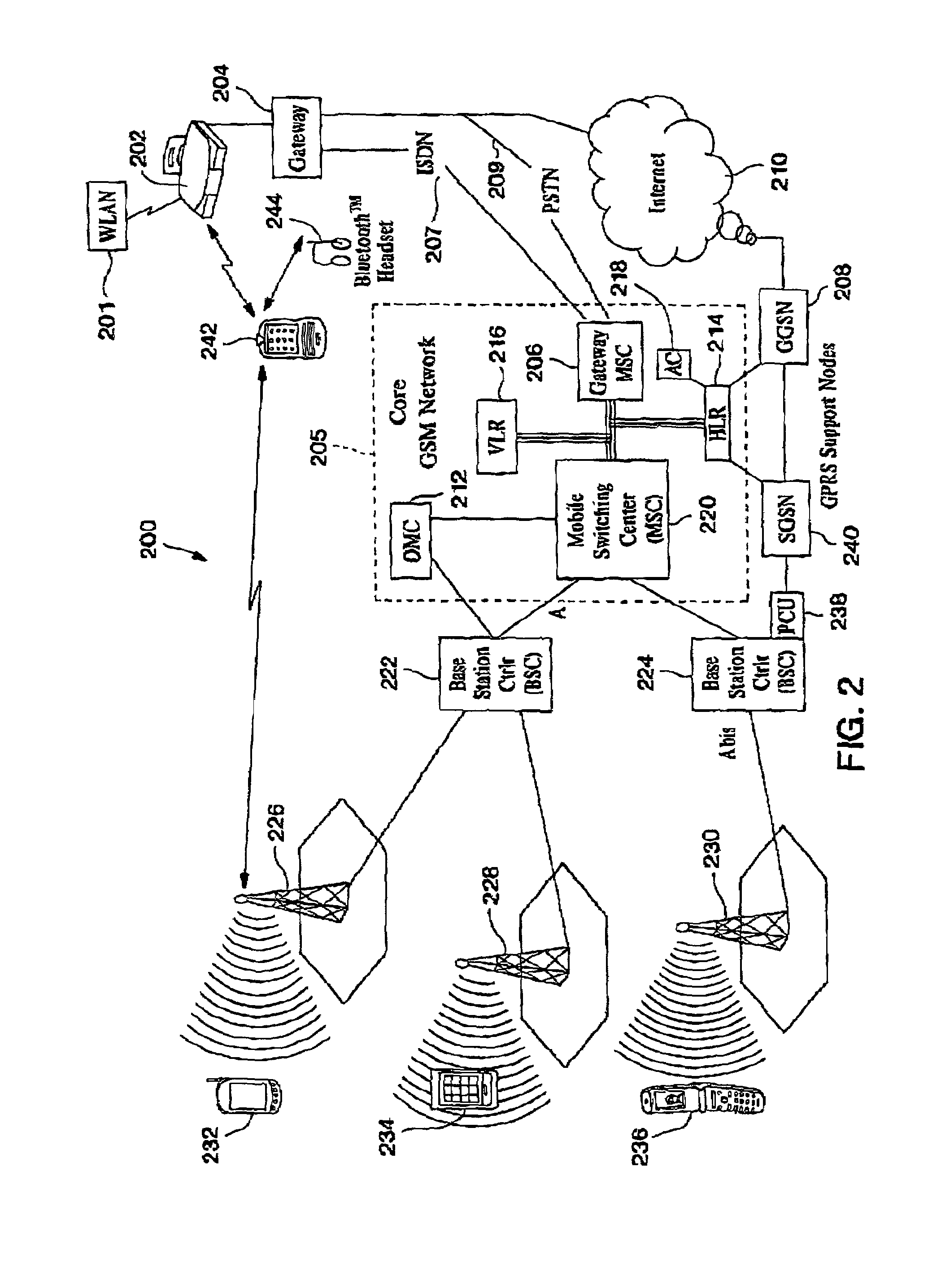
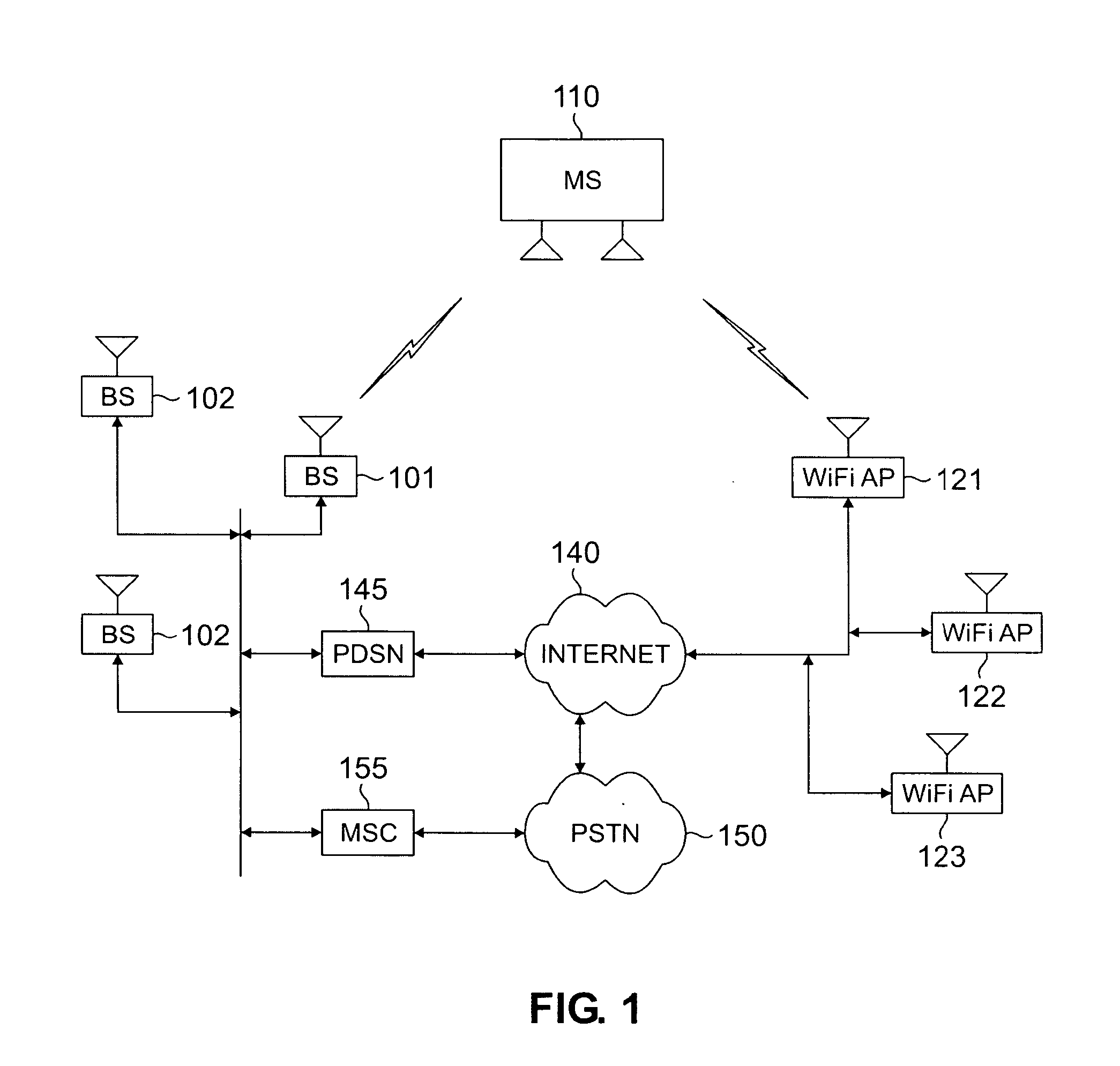
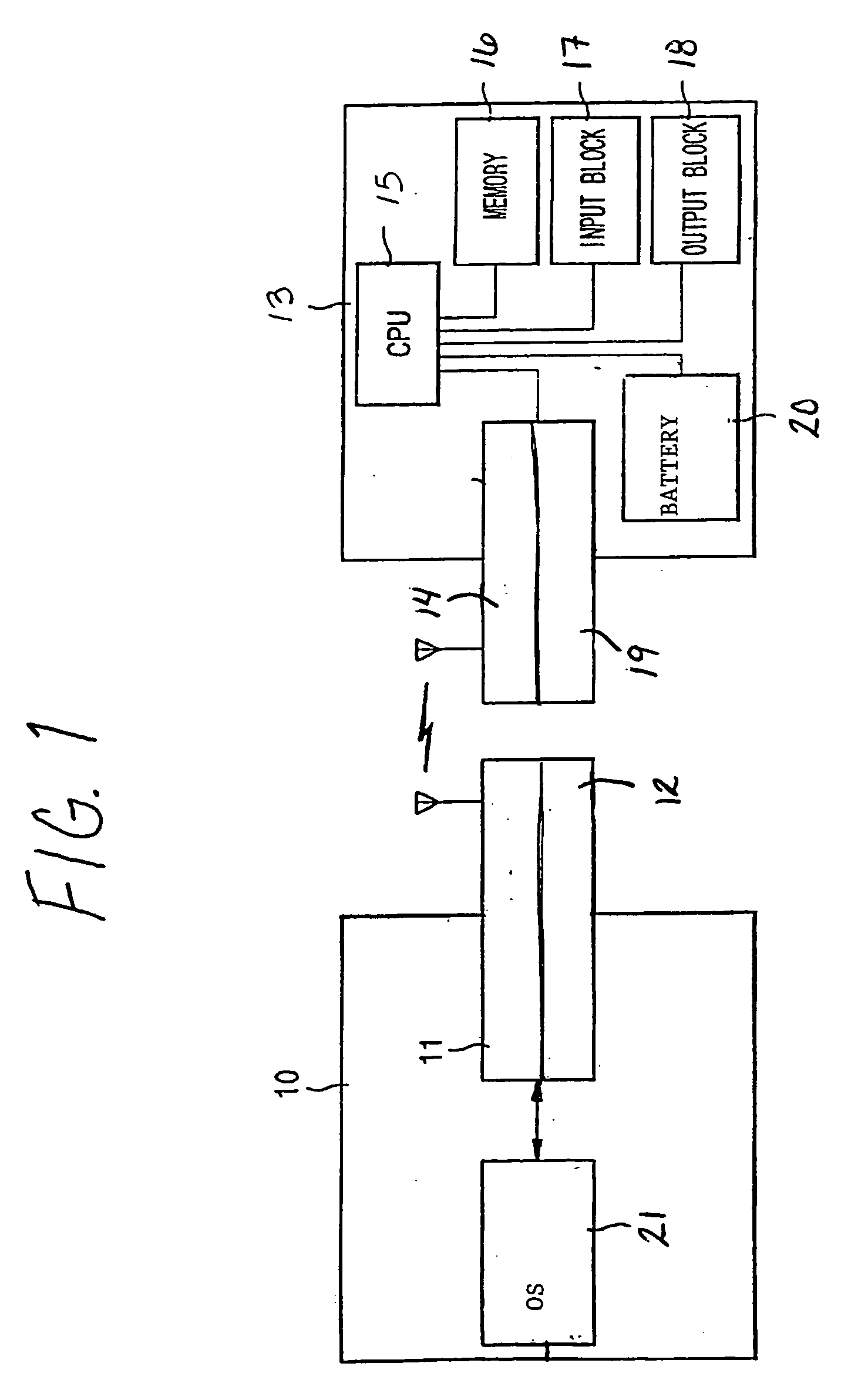
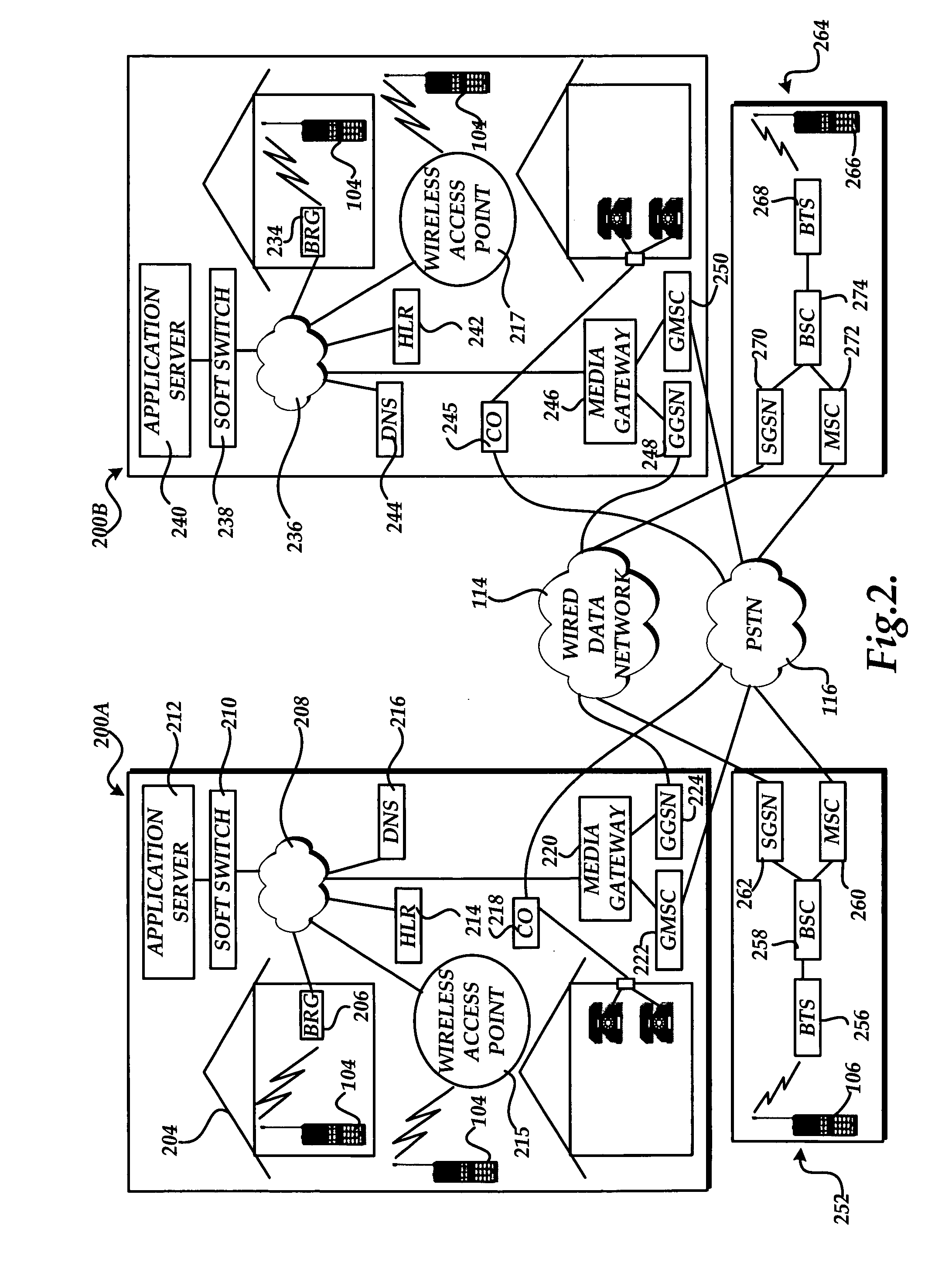
Automatic and seamless vertical roaming between wireless local area network (WLAN) and wireless wide area network (WWAN) while maintaining an active voice or streaming data connection: systems, methods and program products
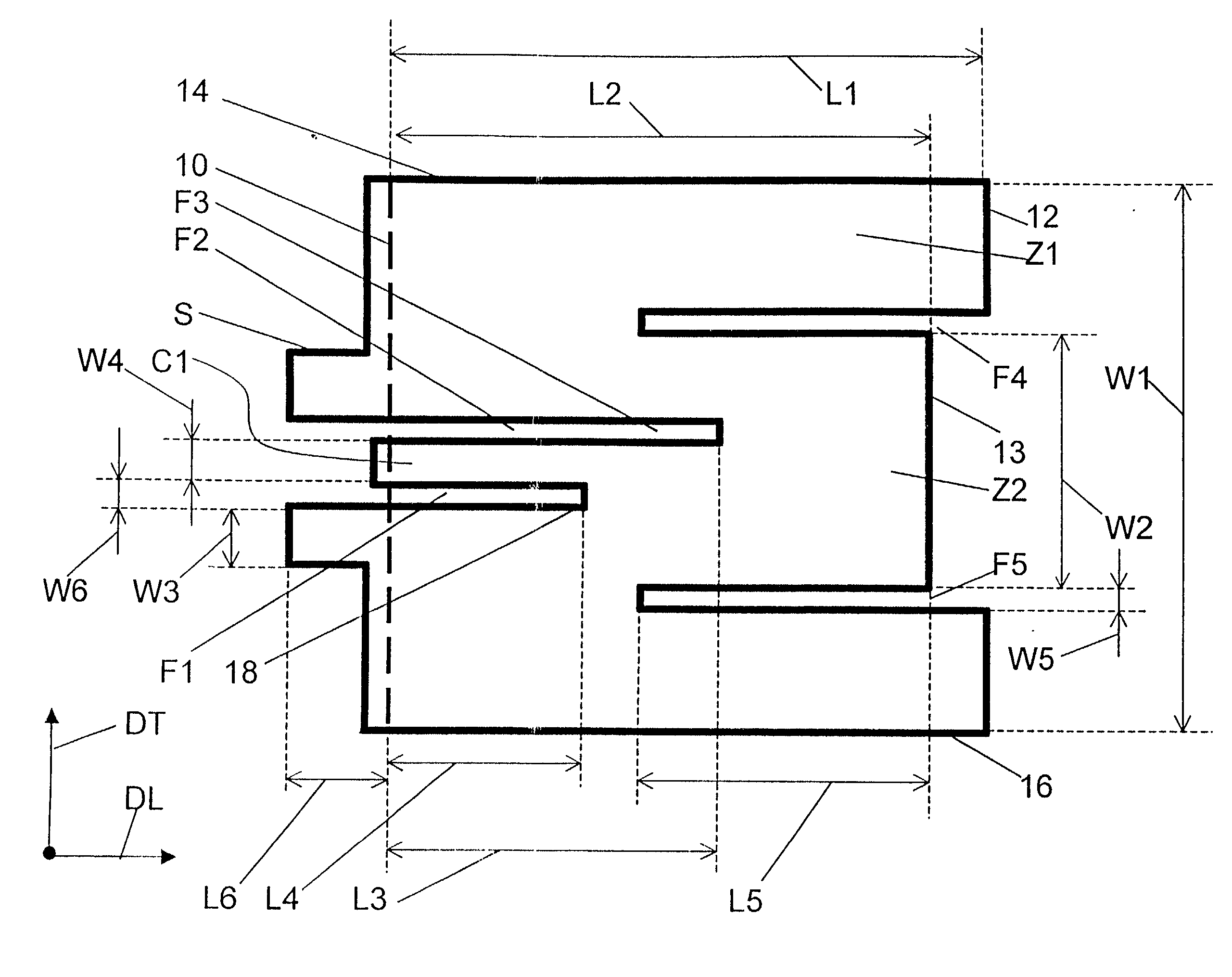
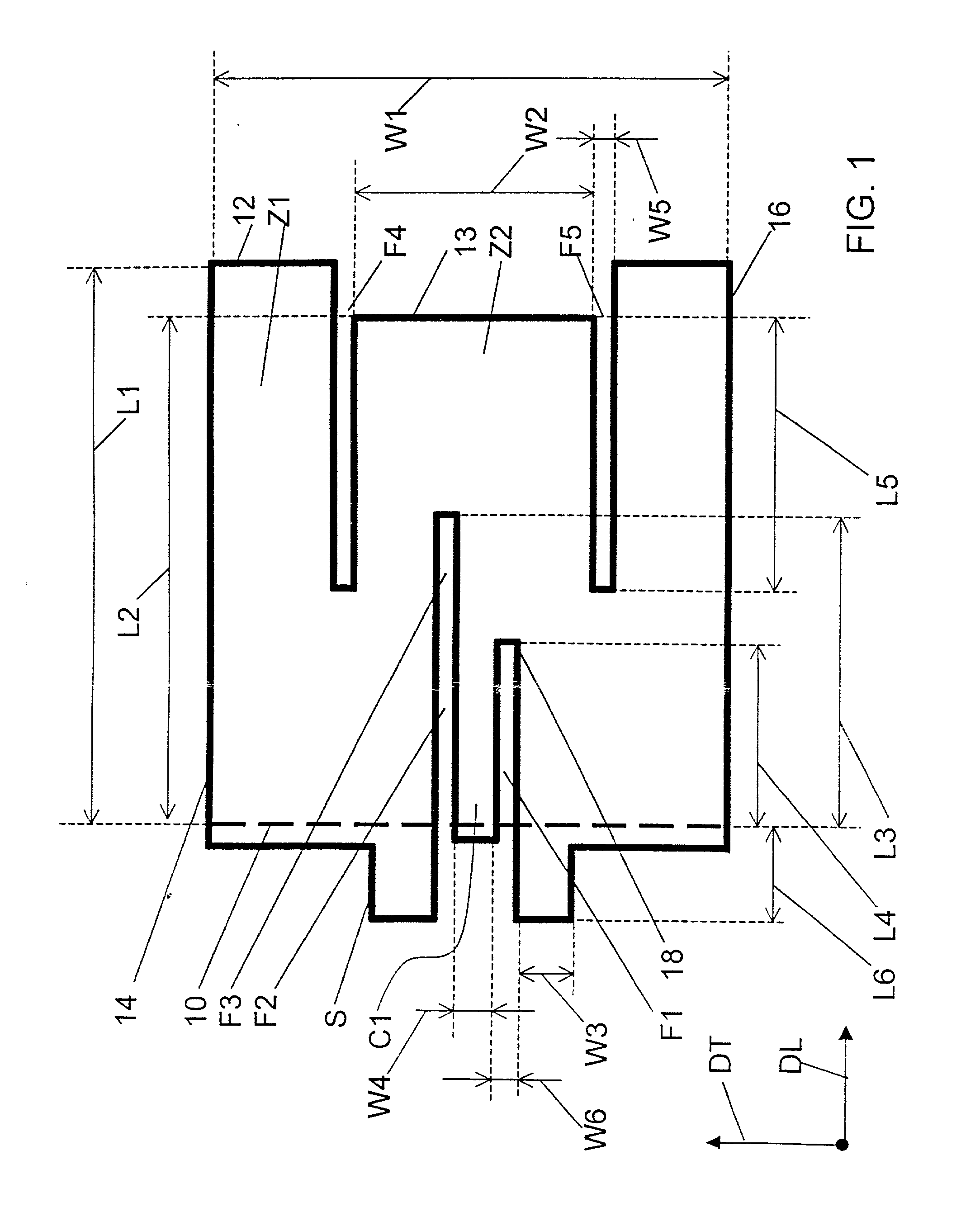
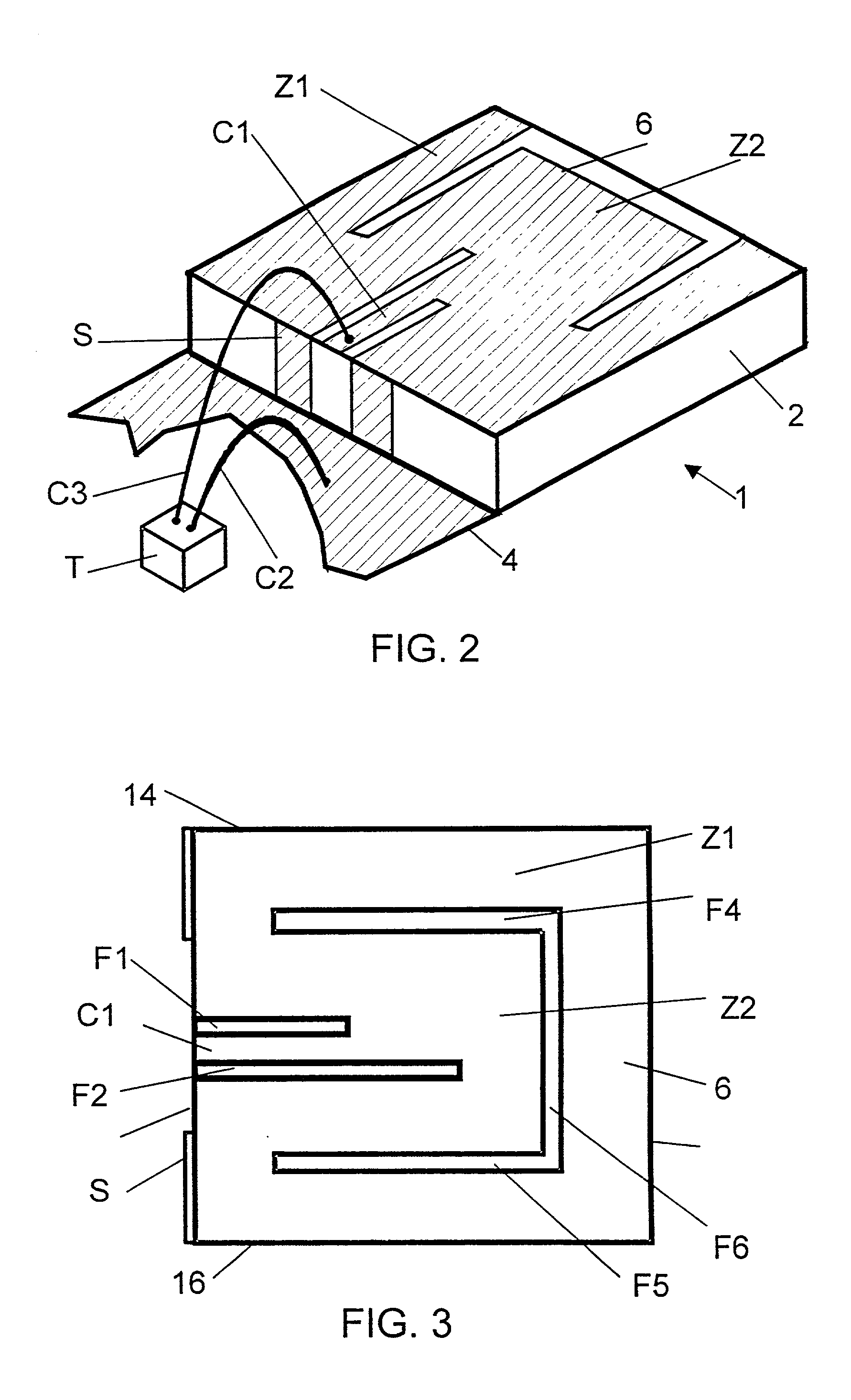
ActiveUS20020085516A1Data switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData connectionUser verification
A Mobile Station (MS) is able to vertically roam in either direction between two different network, i.e. WWAN and WLAN. The MS is equipped with a dual mode Radio for WWAN and WLAN transmissions. The WLAN Radio is linked to a WLAN Enterprise Gateway Controller (EGC) via a first air link and the WWAN Radio is linked to a WWAN Base Transceiver Station (BTS) via a second air link. The EGC is connected to a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) which is in turn connected to the BTS. An outgoing VoIP call from the WLAN Radio to a remote party on the WWAN will transition or seamlessly switch over to a WWAN connection when the MS detects packet error rates, frequent scale back or consistent signal degradation. Upon such conditions, the WLAN Radio requests the EGC to request an Explicit Call Transfer via the MSC to the MS integrated WWAN Radio portion which automatically accepts the call based on referenced information stored in the user's subscriber identification module (SIM). Once the WWAN Radio is confirmed connected to the remote party on the WWAN, the WLAN Radio drops the WLAN connection. An incoming call between the MS and a remote user via the WWAN will transition to the WLAN Radio when the MS enters WLAN coverage. The MS issues an ECT to the WLAN. After user verification by the WLAN Radio and the EGC signals acceptance of the call, the WWAN Radio connection is dropped and the call is now established between the WLAN Radio and the remote party on the WWAN.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
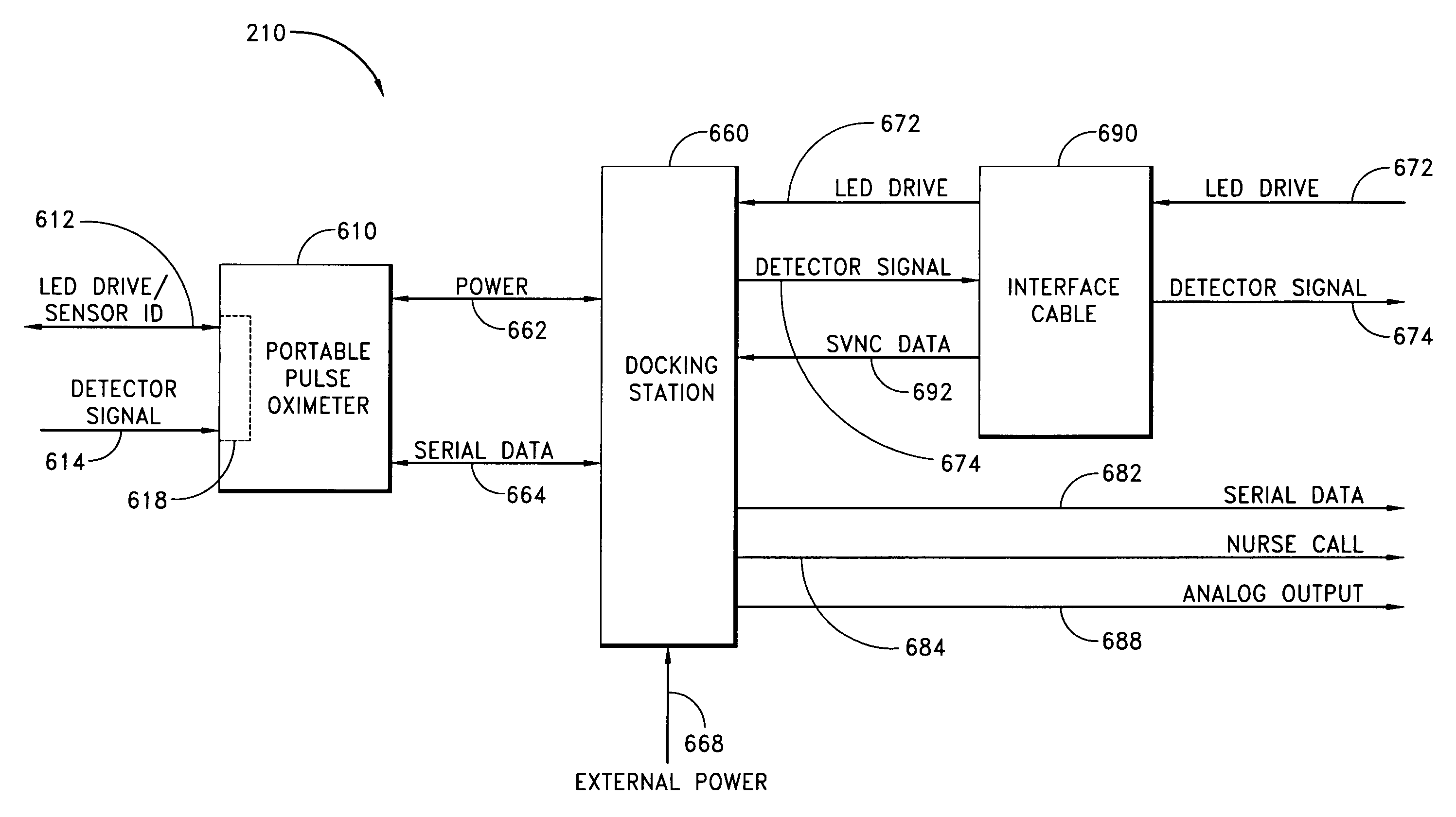
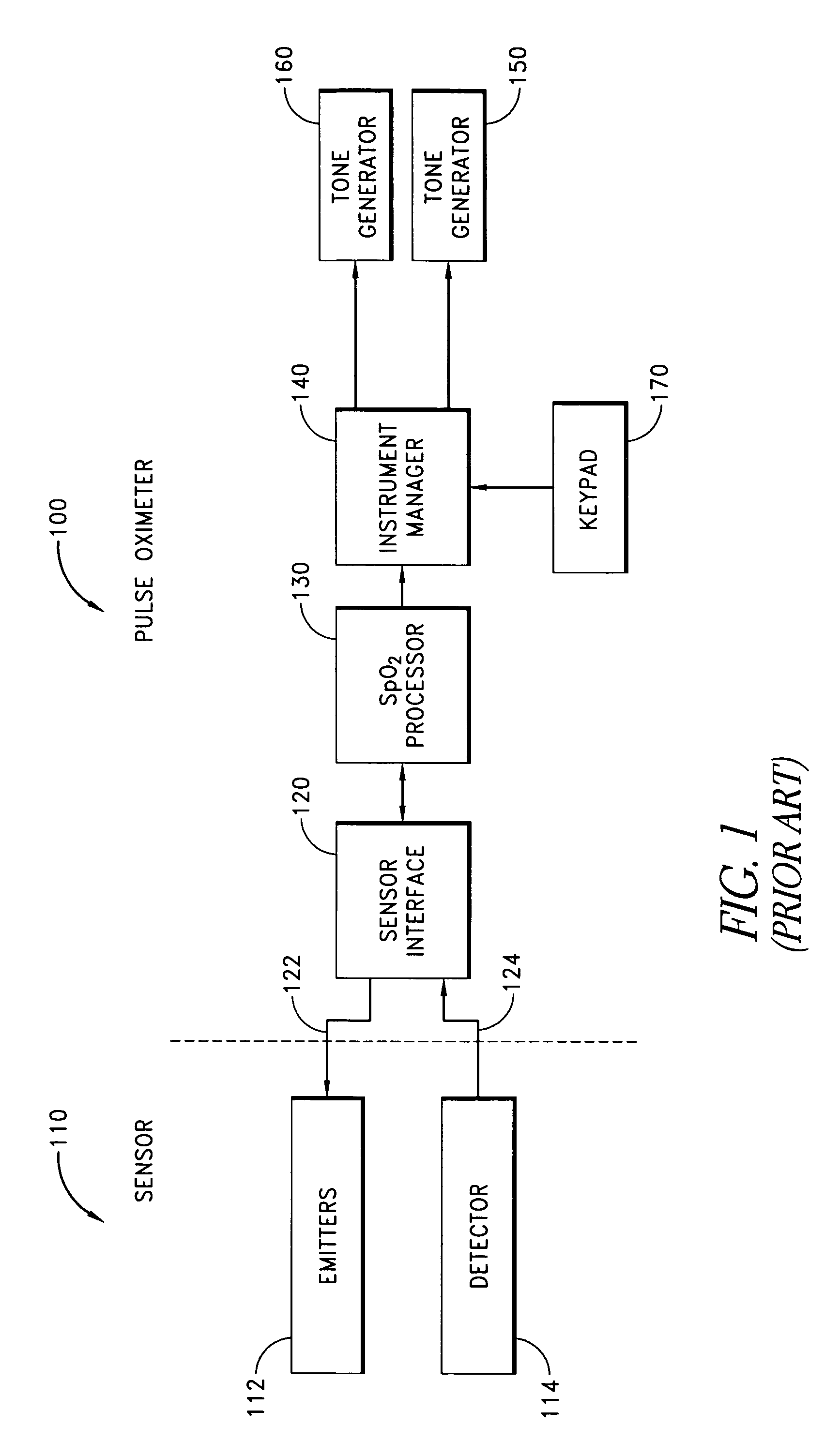
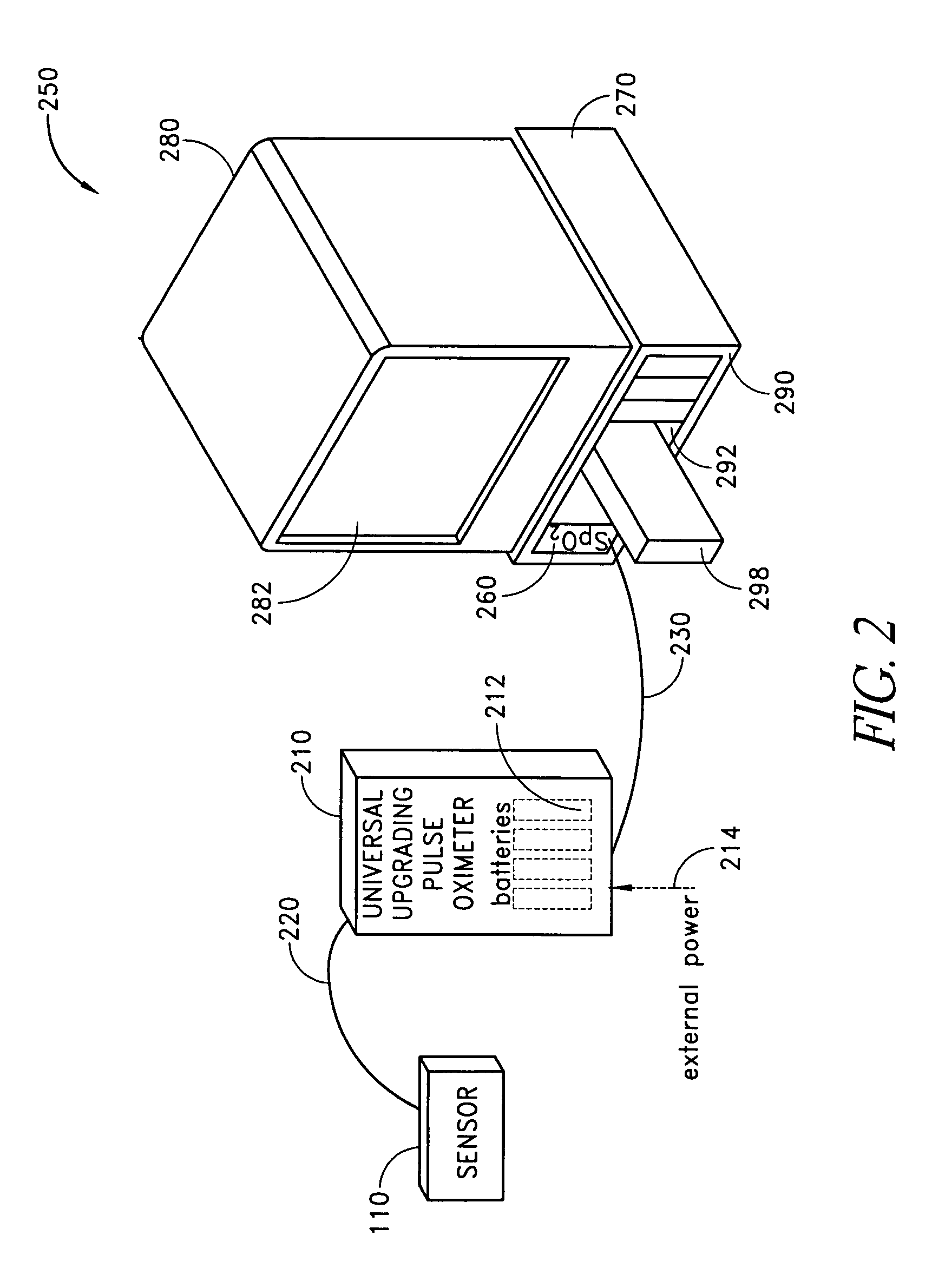
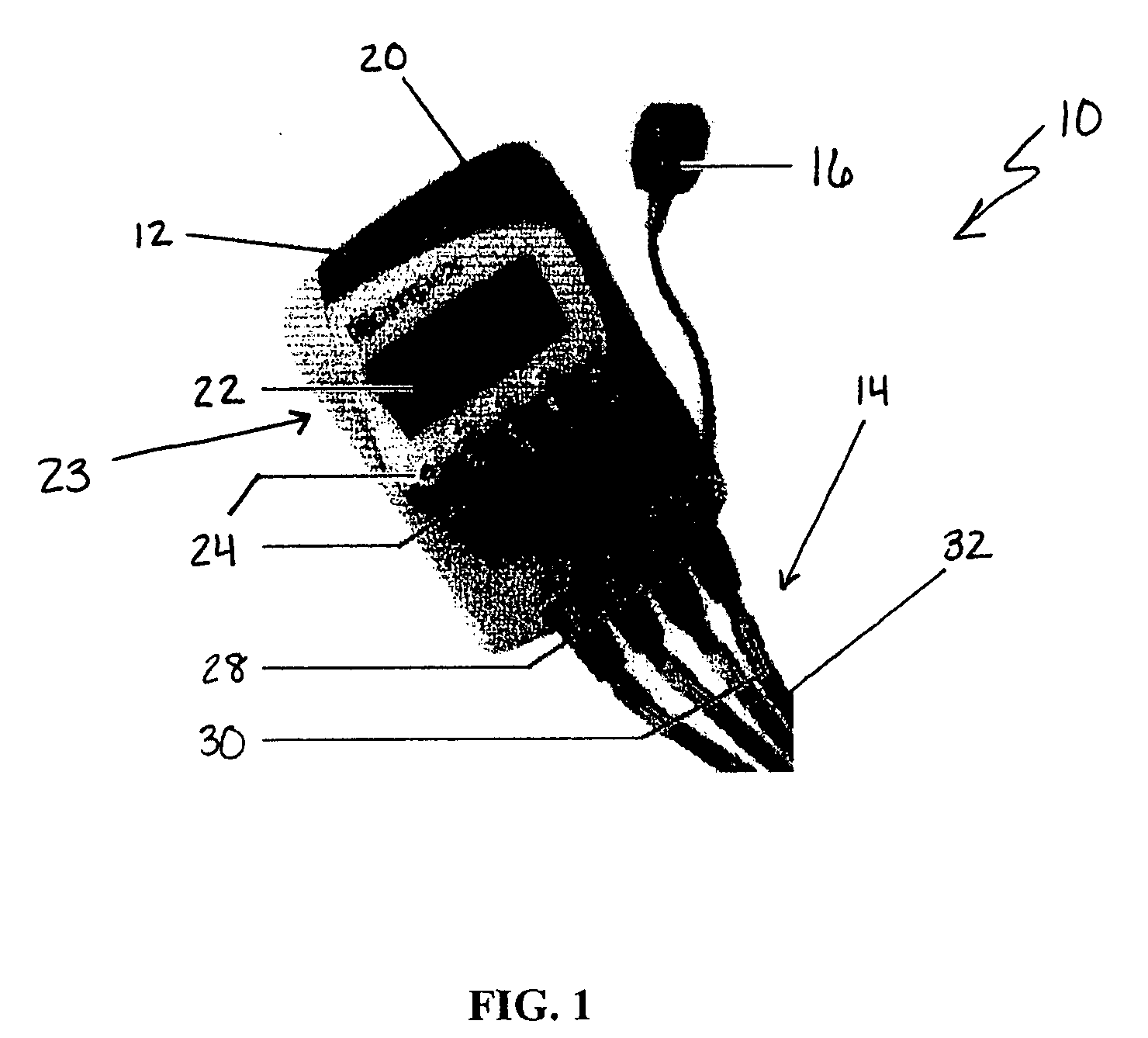
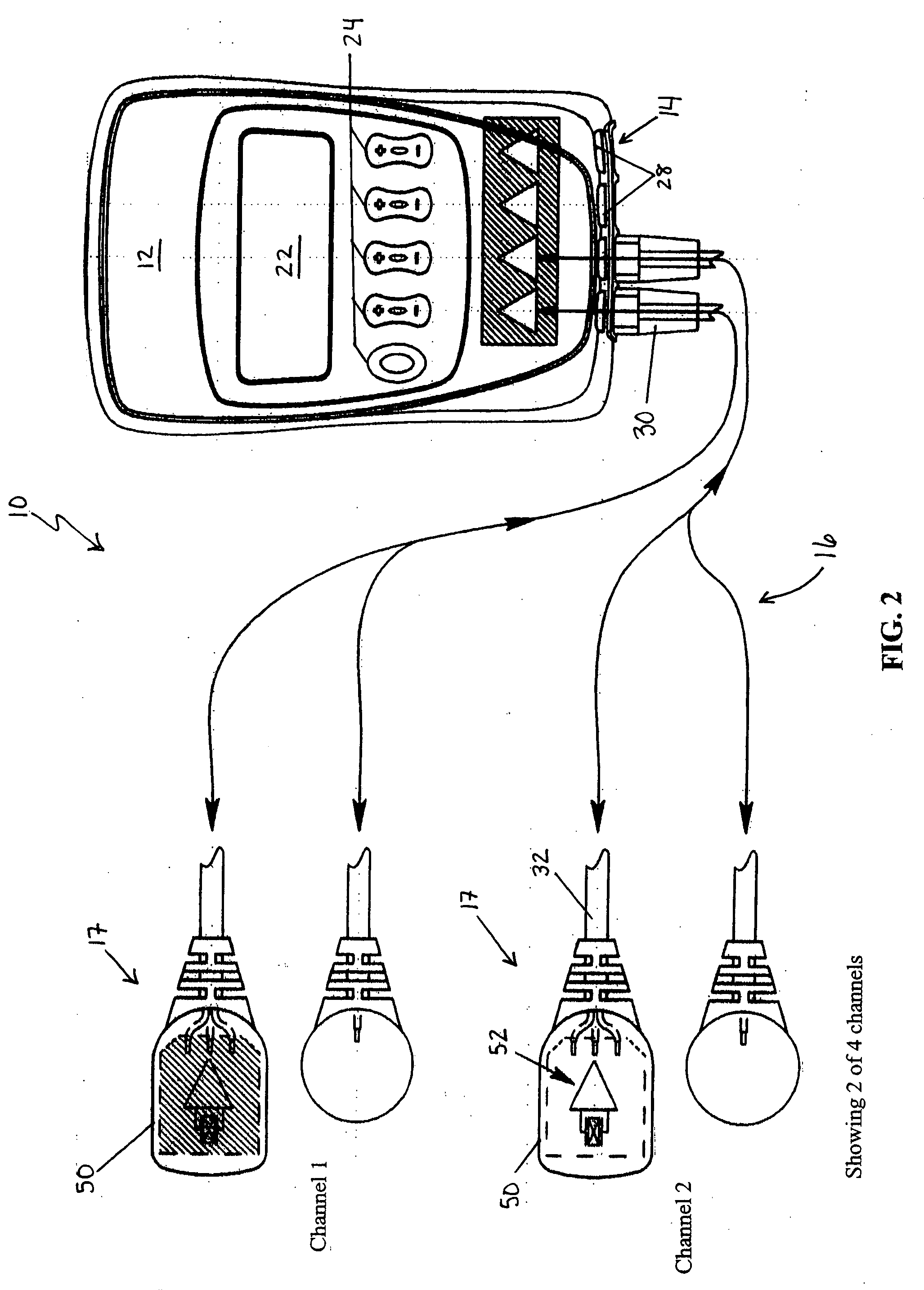
Dual-mode pulse oximeter
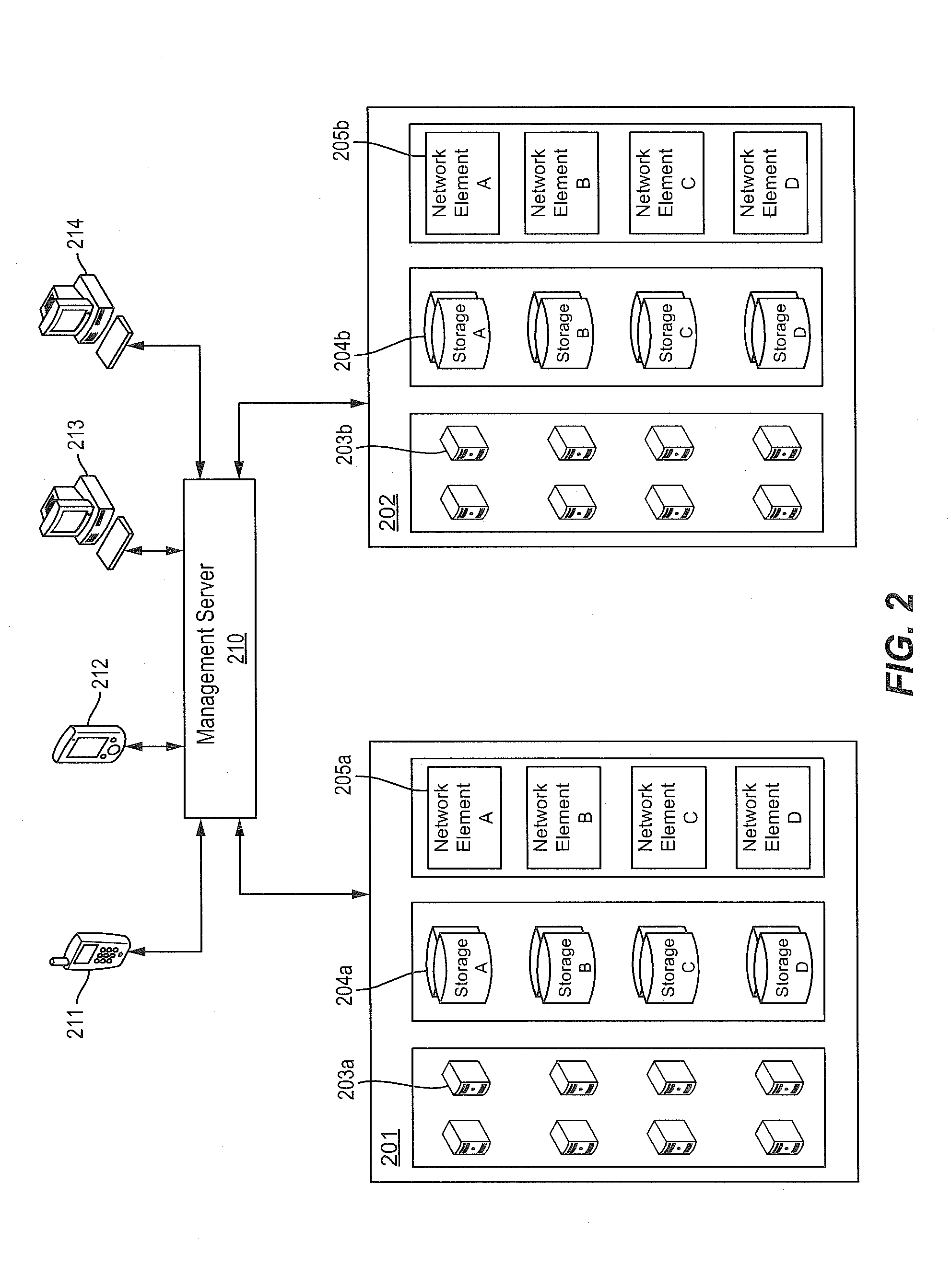
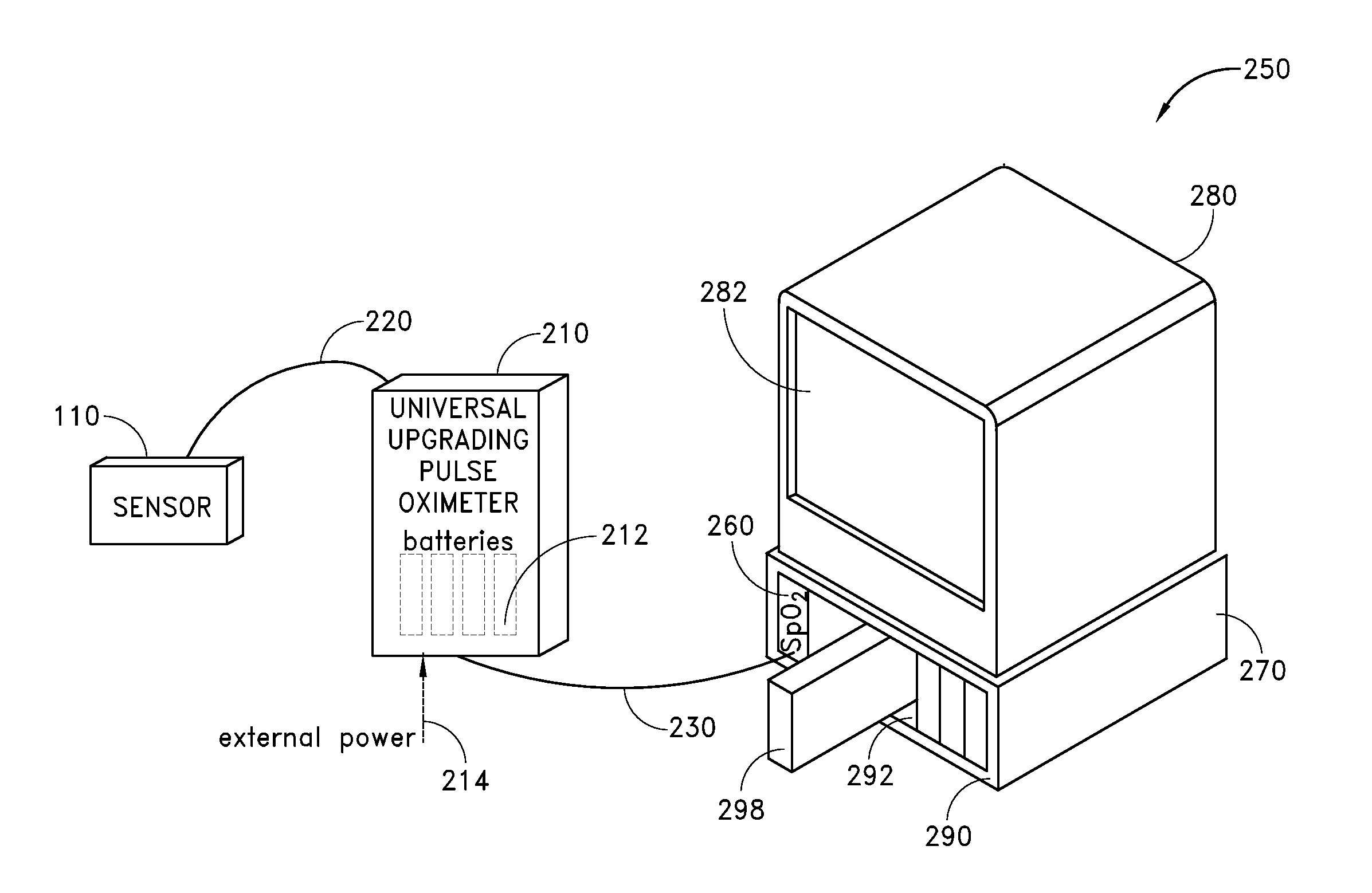
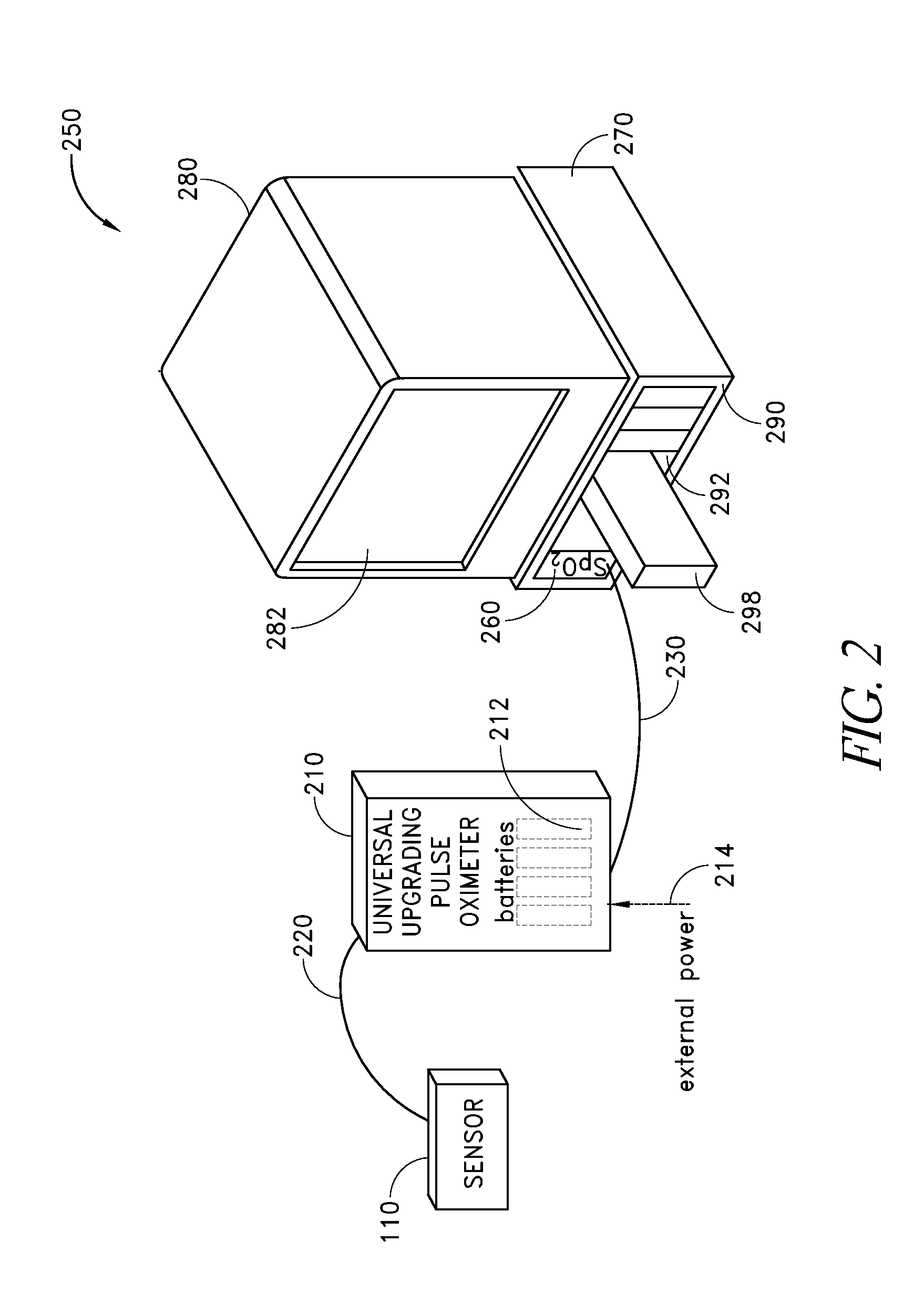
A pulse oximeter has an integrated mode in which it operates as a plug-in module for a multiparameter patient monitoring system (MPMS). The pulse oximeter also has a portable mode in which operates separately from the MPMS as a battery-powered handheld or standalone instrument. The pulse oximeter has a sensor port that receives a photo-plethysmographic signal as input to an internal processor. The pulse oximeter processes this sensor signal to derive oxygen saturation and pulse rate measurements. In the portable mode, this information is provided on its display, and stored in memory for trend capability. In the integrated mode, the pulse oximeter provides oxygen saturation and pulse rate measurements to the MPMS through a docking station to be displayed on a MPMS monitor. In the integrated mode, the portable pulse oximeter docks to the docking station, which in turn is inserted in one or more MPMS slots. The docking station can function as a simple electrical pass-through device between the docked portable pulse oximeter and the MPMS or it can provide a MPMS communications interface.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
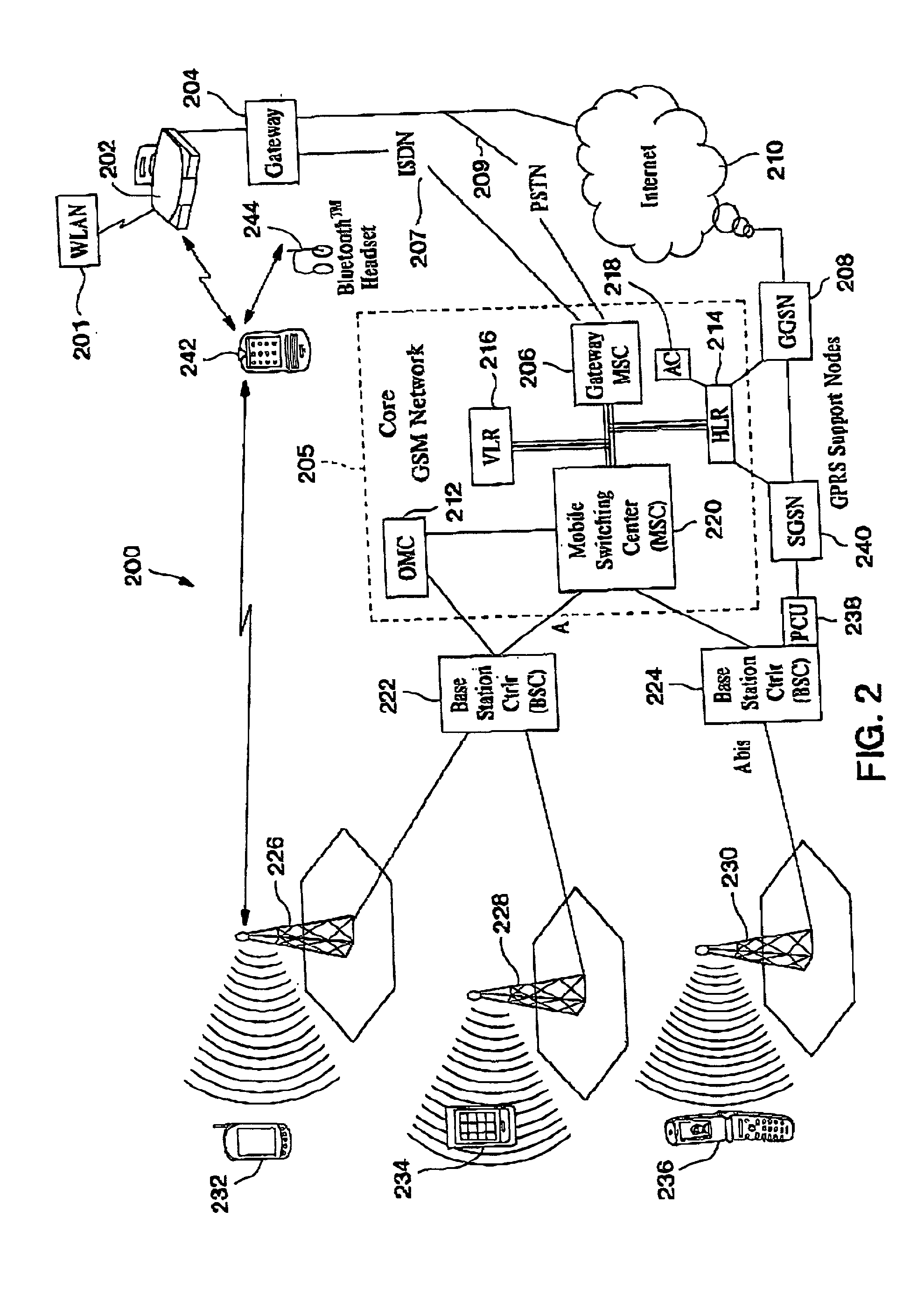
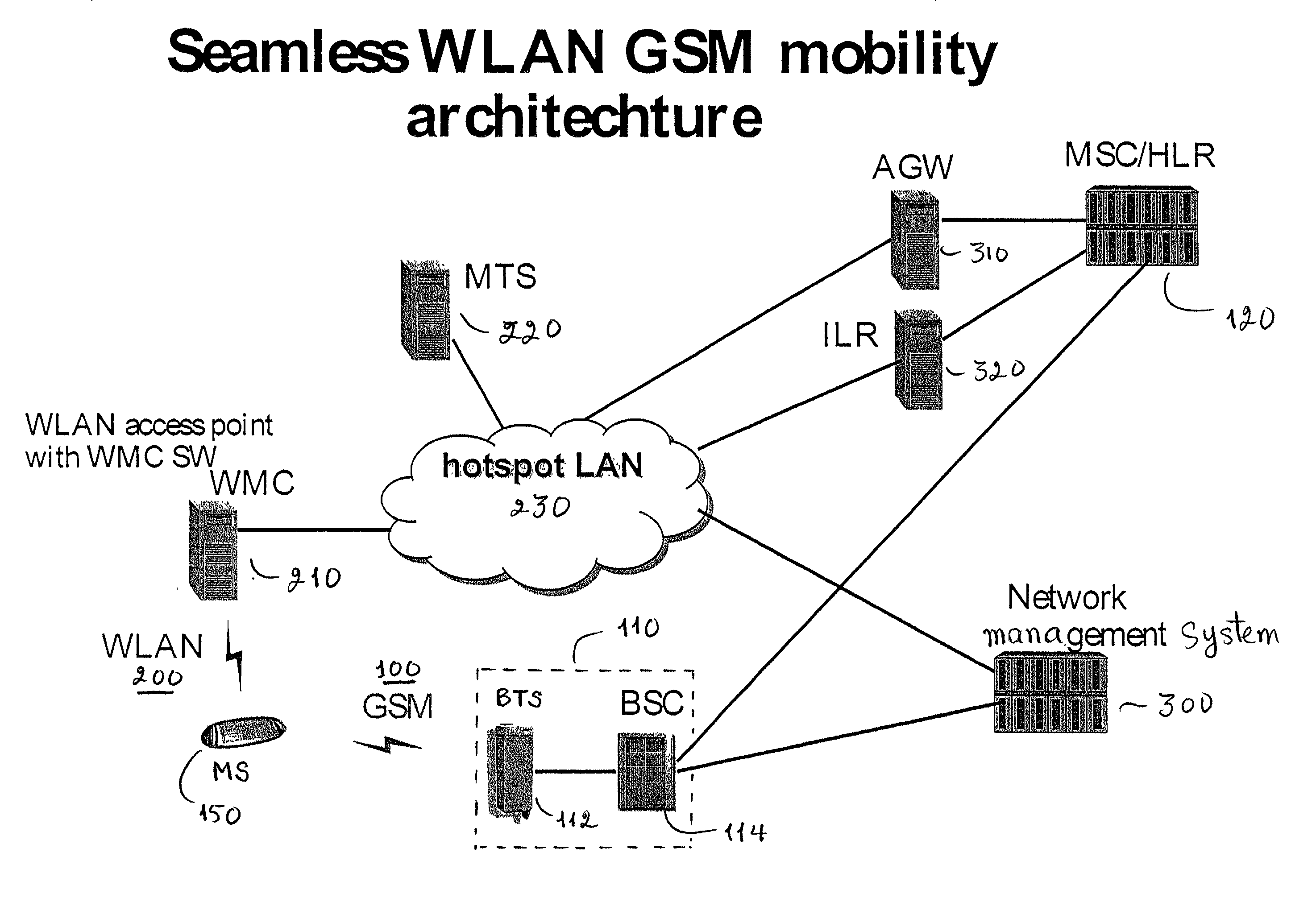
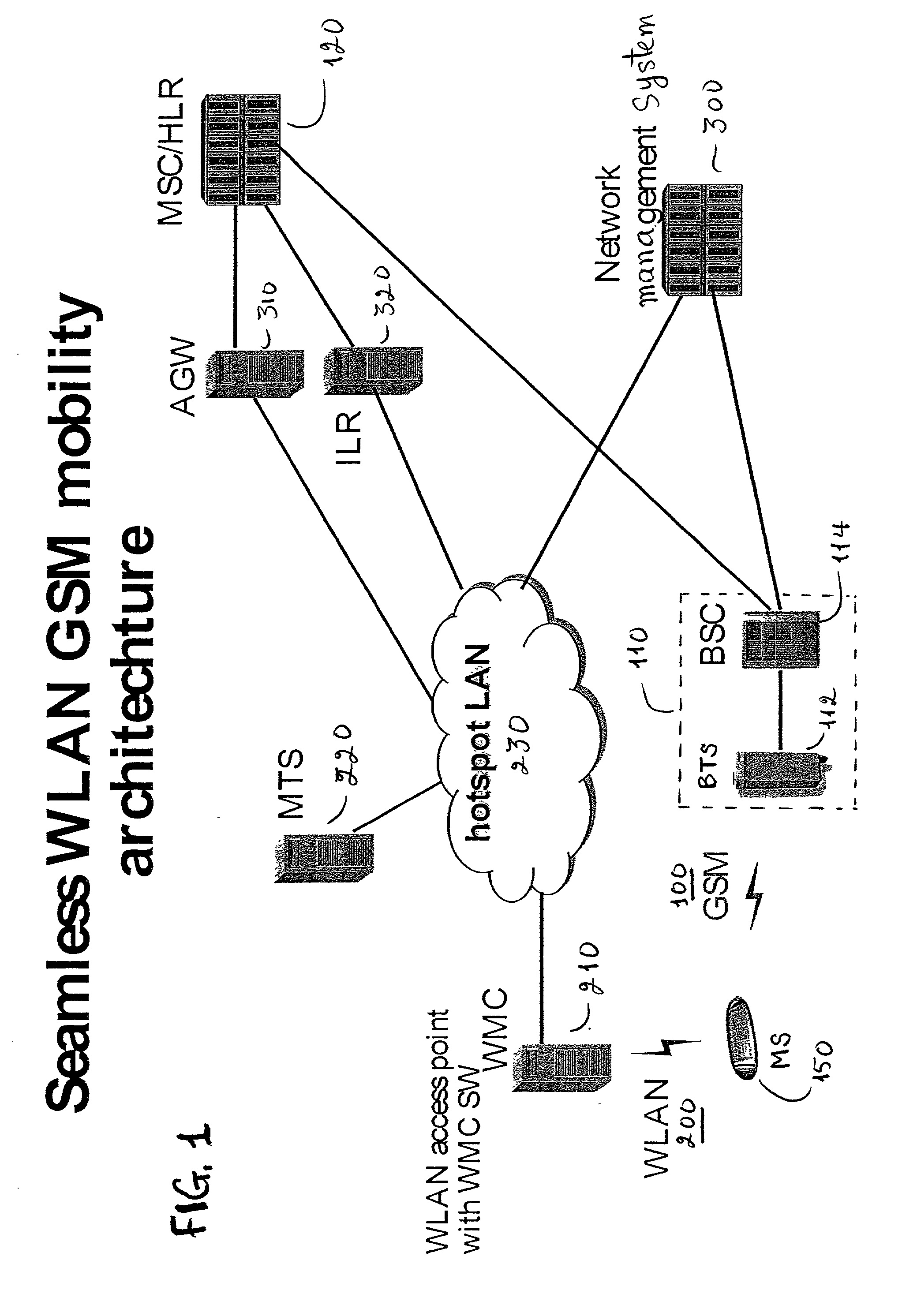
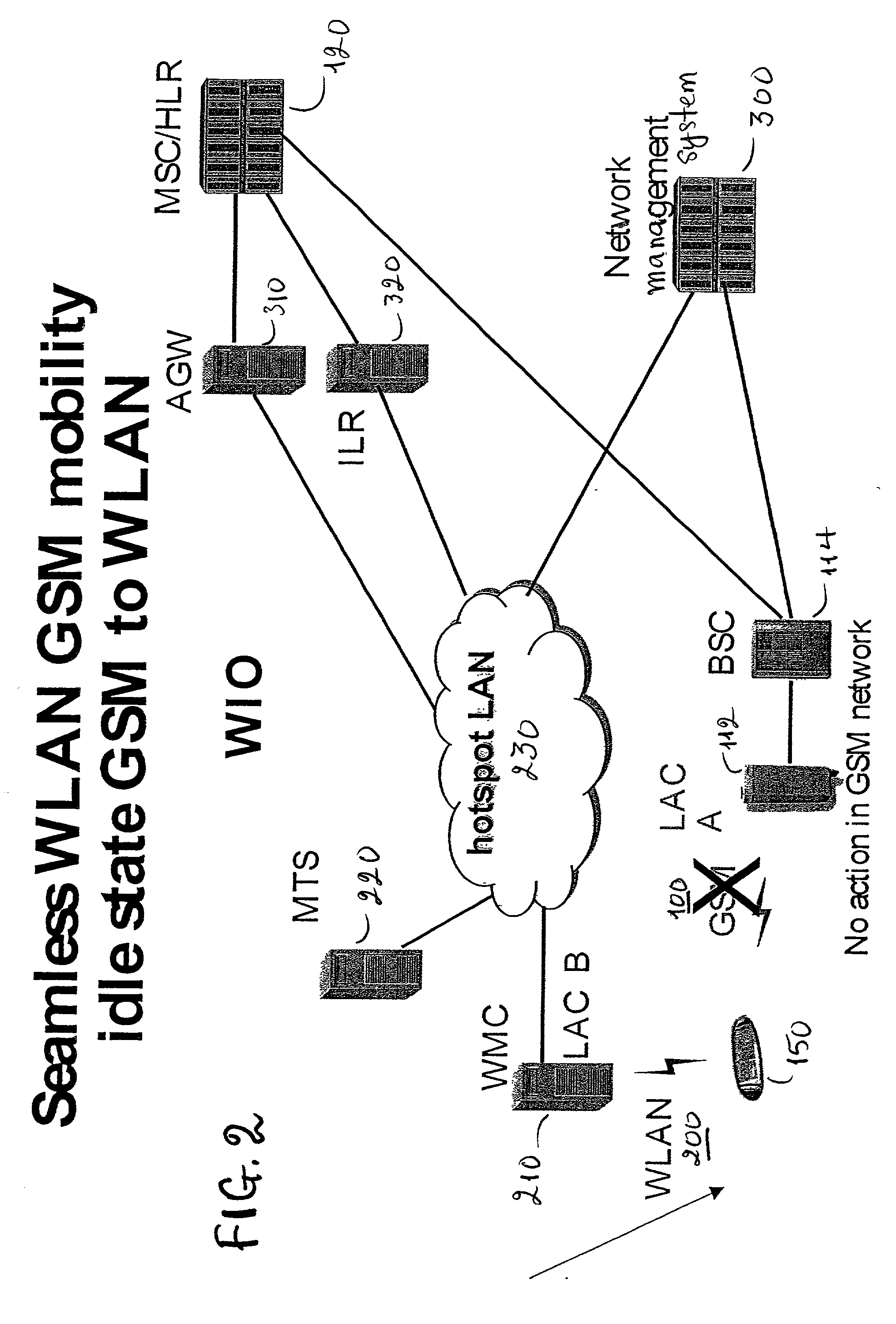
GSM Networks and solutions for providing seamless mobility between GSM Networks and different radio networks
InactiveUS20020147008A1Data switching by path configurationSubstation equipmentRadio networksDual mode
A network architecture for Wireless Intranet Office (WIO) applications including a local radio network such as a wireless local area network (WLAN) which comprises a Wireless Mobile Center (WMC) arranged to serve as a WLAN access point; a GSM network which comprises a Mobile Station (MS) in a form of a dual-mode cellular phone to access both WLAN and GSM radio technologies, a Base Station (BS) arranged to convert a radio signal from the Mobile Station (MS) for communication, a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) arranged to establish call connection; and a Handover Module implemented in either the Mobile Station (MS) or the Wireless Mobile Center (WMC) for providing seamless mobility between the GSM network and the wireless LAN, when the Mobile Station (MS) roams between the GSM network and the wireless LAN.
Owner:RPX CORP
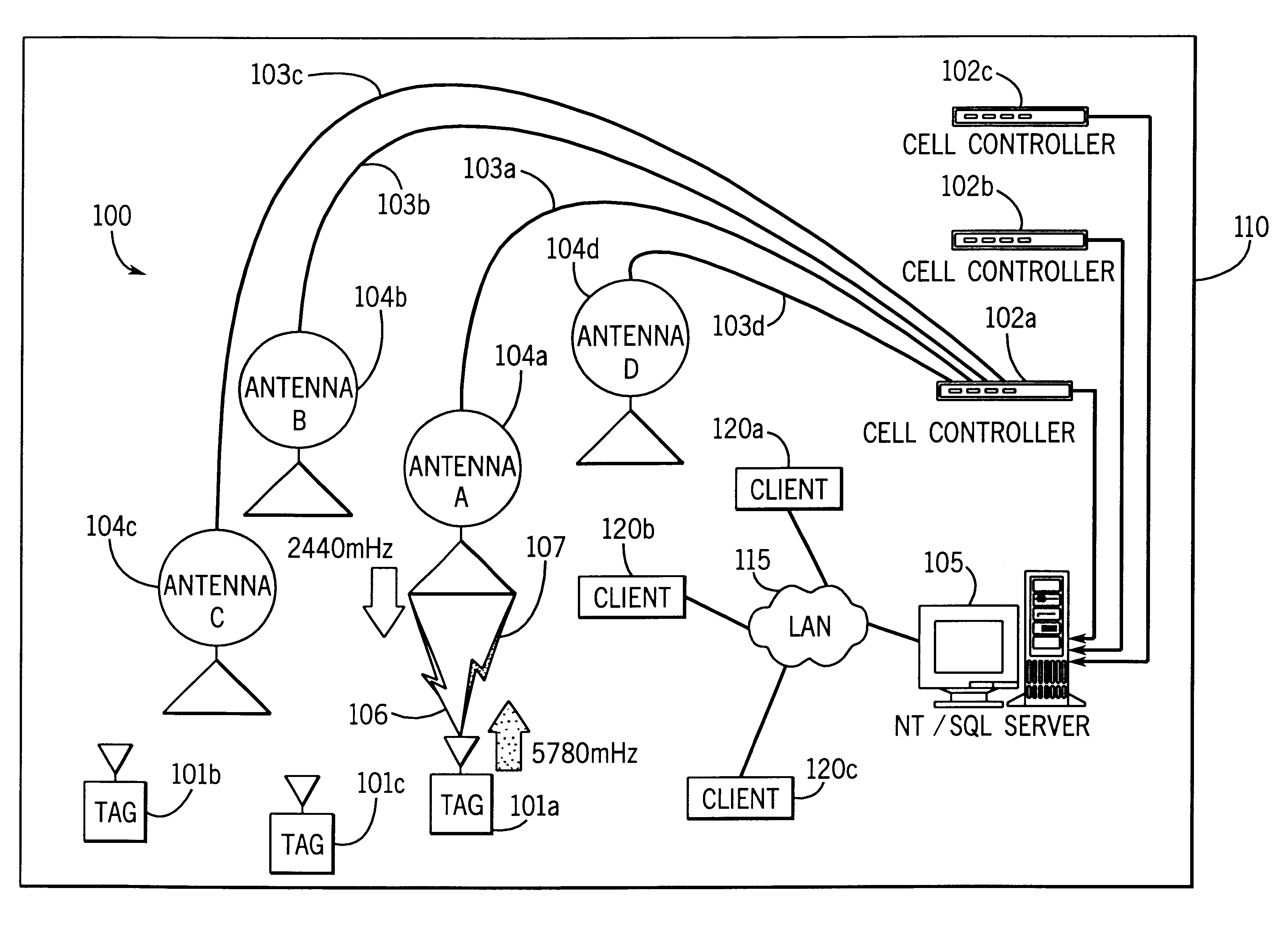
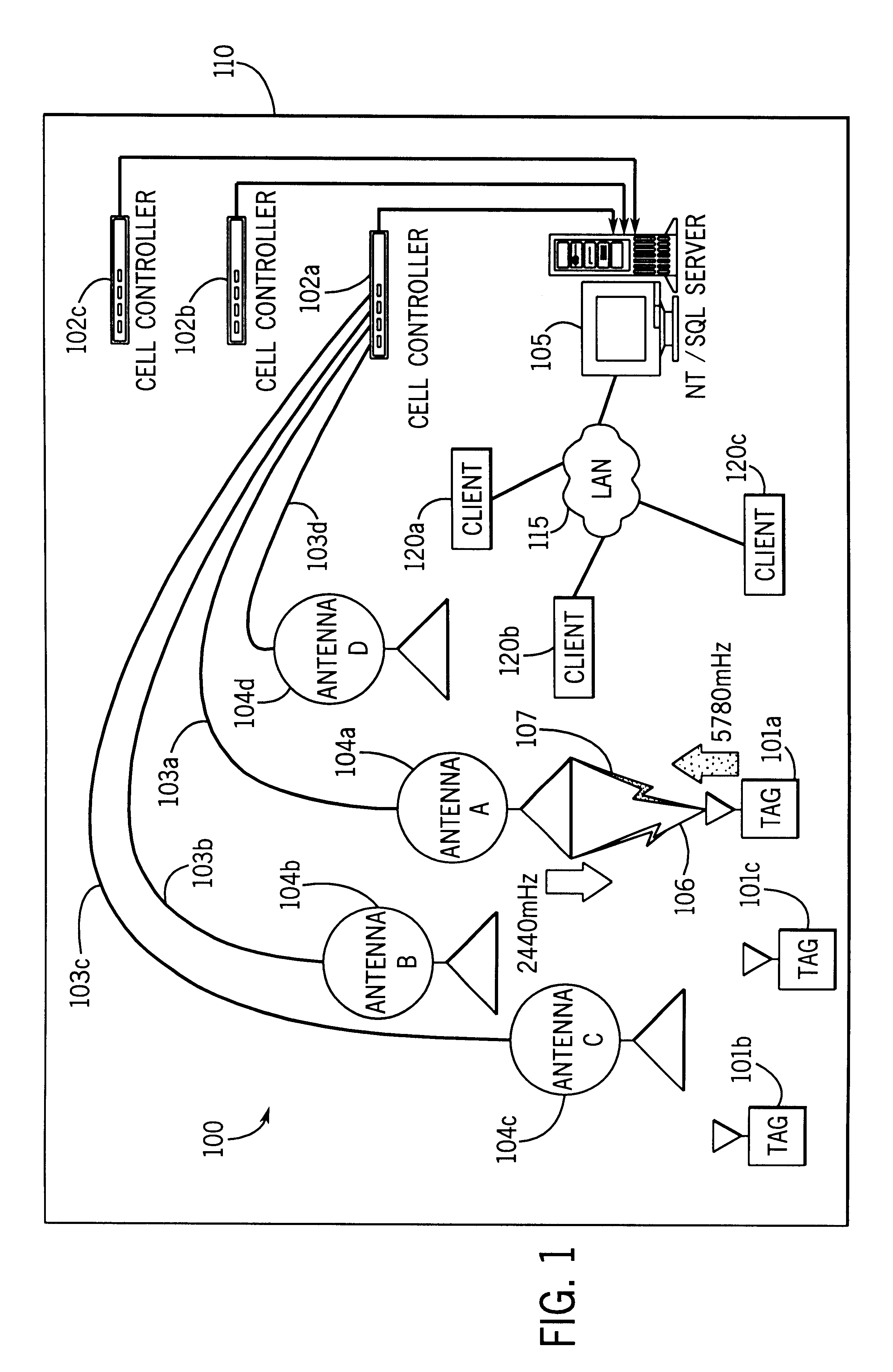
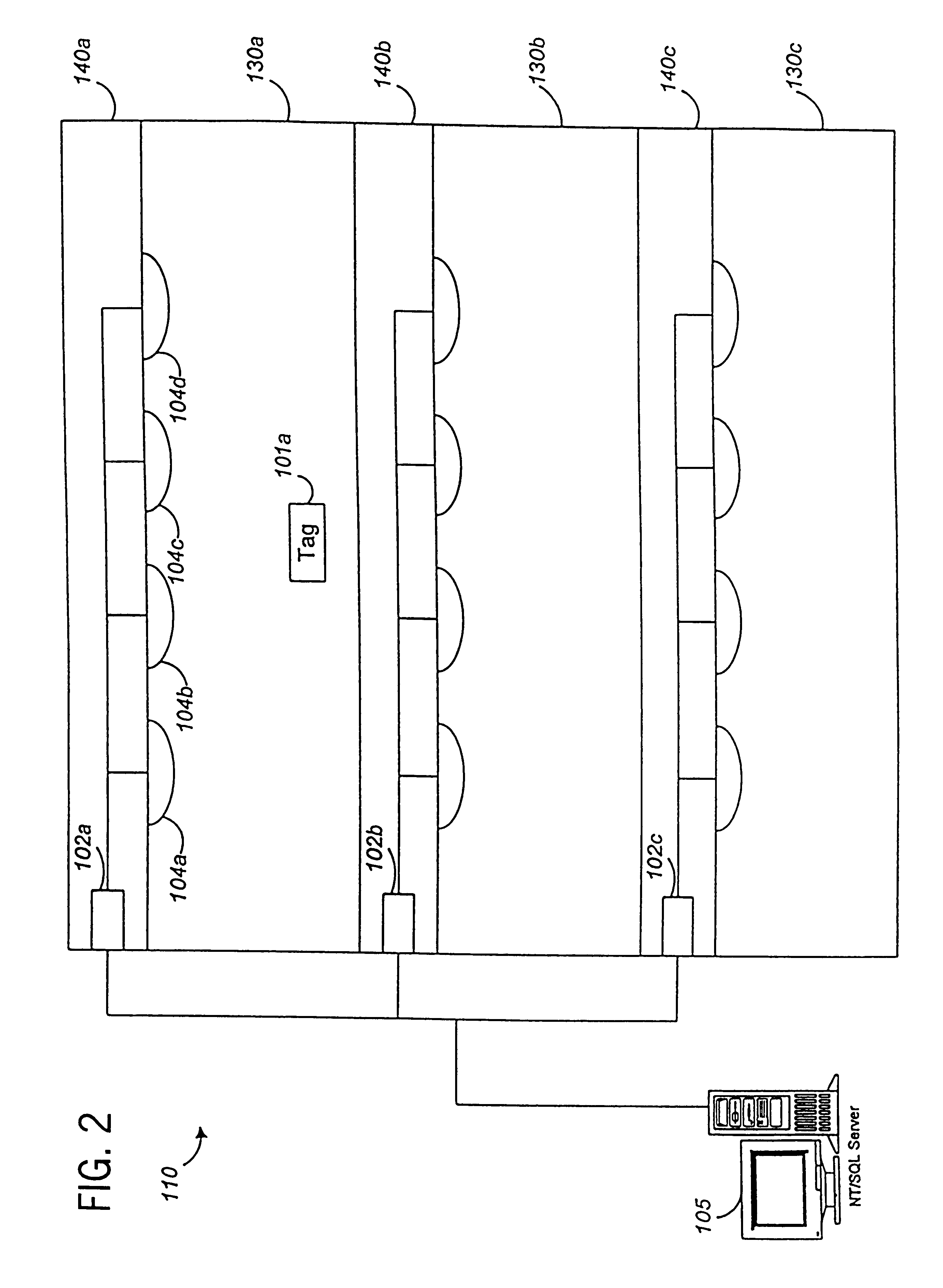
Dual mode tracking system
InactiveUS6353406B1Memory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsData warehouseDual mode
System for tracking mobile tags. Cell controllers with multiple antenna modules generate a carrier signal which is received by the tags. Tags shift the frequency of the carrier signal, modulate an identification code onto it, and transmit the resulting tag signal at randomized intervals. The antennas receive and process the response, and determine the presence of the tags by proximity and triangulation. The recursive-least squares (RLS) technique is used in filtering received signals. Distance of a tag from an antenna is calculated by measuring the round trip signal time. The cell controllers send data from the antenna to a host computer. The host computer collects the data and resolves them into positional estimates. Data are archived in a data warehouse, such as an SQL Server. Also disclosed is an article tracking system that supports both active and passive tags with a cell controller able to read both passive and active tag signals.
Owner:RF TECH +1
Automatic and seamless vertical roaming between wireless local area network (WLAN) and wireless wide area network (WWAN) while maintaining an active voice or streaming data connection: systems, methods and program products
ActiveUS7039027B2Data switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData connectionStreaming data
A Mobile Station (MS) is able to vertically roam in either direction between two different nerworks, i.e, WWAN and WLAN. The MS is equipped with a dual mode Radio for WWAN and WLAN transmissions. The WLAN Radio is linked to a WLAN Enterprise Gateway Controller (EGC) via a first air link and the WWAN Radio is linked to a WWAN Base Transceiver Station (BTS) via a second air link. An outgoing VoIP call from the WLAN Radio to a remote party on the WWAN will transition or seamlessly switch over to a WWAN connection when the MS detects packet error rates, frequent scale back or consistent signal degradation.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
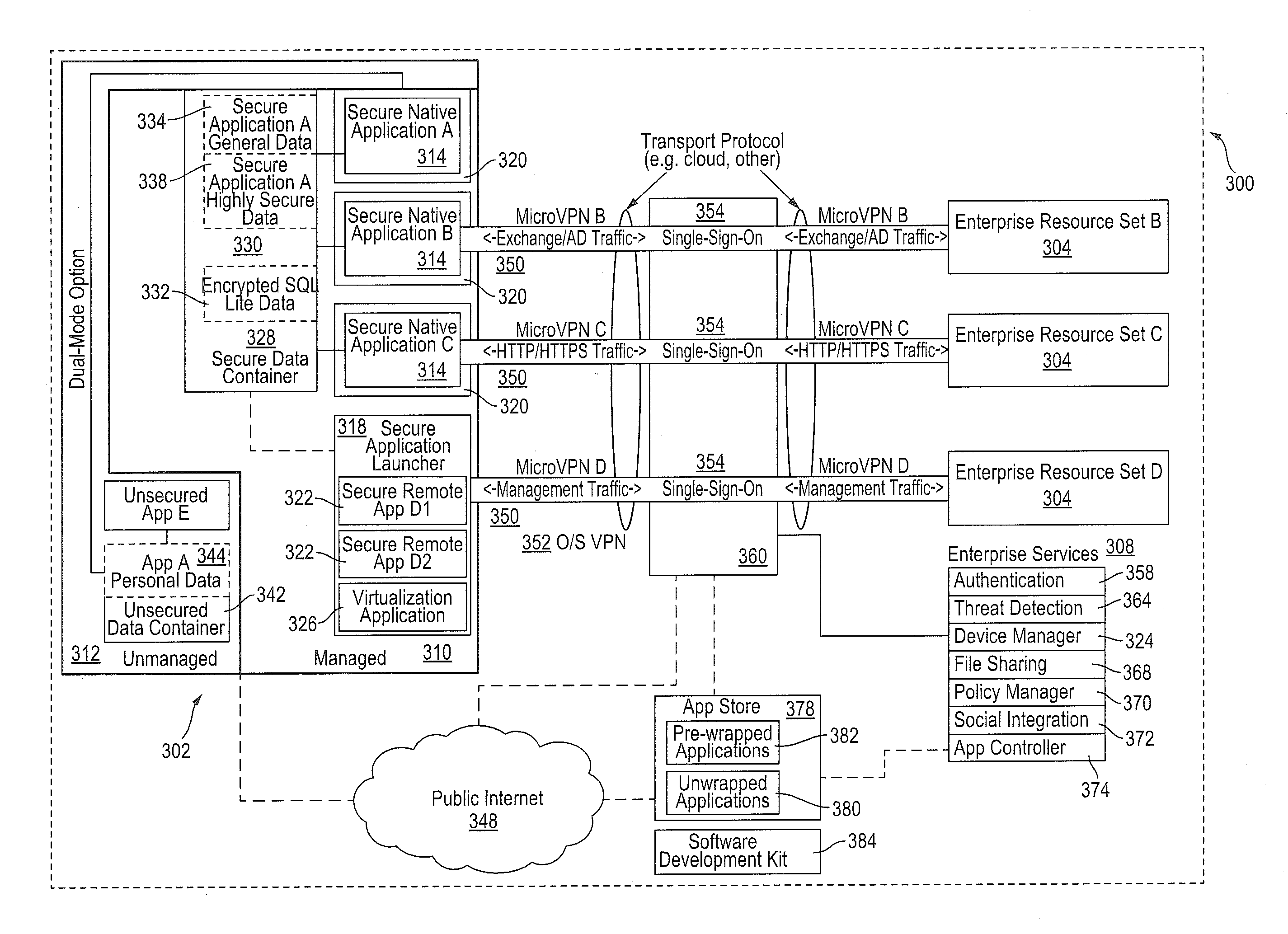
Policy-Based Application Management
Improved techniques for managing enterprise applications on mobile devices are described herein. Each enterprise mobile application running on the mobile device has an associated policy through which it interacts with its environment. The policy selectively blocks or allows activities involving the enterprise application in accordance with rules established by the enterprise. Together, the enterprise applications running on the mobile device form a set of managed applications. Managed applications are typically allowed to exchange data with other managed applications, but are blocked from exchanging data with other applications, such as the user's own personal applications. Policies may be defined to manage data sharing, mobile resource management, application specific information, networking and data access solutions, device cloud and transfer, dual mode application software, enterprise app store access, and virtualized application and resources, among other things.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Policy-Based Application Management
ActiveUS20140032691A1Digital computer detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionVirtualizationDual mode
Improved techniques for managing enterprise applications on mobile devices are described herein. Each enterprise mobile application running on the mobile device has an associated policy through which it interacts with its environment. The policy selectively blocks or allows activities involving the enterprise application in accordance with rules established by the enterprise. Together, the enterprise applications running on the mobile device form a set of managed applications. Managed applications are typically allowed to exchange data with other managed applications, but are blocked from exchanging data with other applications, such as the user's own personal applications. Policies may be defined to manage data sharing, mobile resource management, application specific information, networking and data access solutions, device cloud and transfer, dual mode application software, enterprise app store access, and virtualized application and resources, among other things.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Dual-mode patient monitor
InactiveUS20140012100A1Easy to disassembleElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyDual modeMonitoring system
A portable patient monitor has an integrated mode in which it operates as a plug-in module for a multiparameter patient monitoring system (MPMS). The patient monitor also has a portable mode in which it operates separately from the MPMS as a battery-powered handheld or standalone instrument. The patient monitor has a sensor port that receives a signal indicative of physiological parameters as input to an internal processor. The patient monitor processes this sensor signal to derive patient measurements. In the portable mode, this information is provided on its display. In the integrated mode, the patient monitor provides patient measurements to the MPMS to be displayed on a MPMS monitor.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Electrophoretic display with dual mode switching
InactiveUS7046228B2Low costIncrease contrastStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsIn planeDual mode
The present invention relates to an improved EPD which comprises both the traditional up / down switching and the in-plane switching modes. In other words, the improved EPD has dual switching modes.The monochrome EPDs of the present invention are capable of displaying highlight color of choice which is different from the text. For example, white background, blue text, and red highlight can be shown in any selected areas of the display. Furthermore, the full color EPDs of the present invention are capable of displaying high contrast images of high color saturation. Both high quality black and white states are possible in the full color displays of the present invention. The EPDs of the present invention do not need complex circuitry design, and are compatible with low cost and high yield roll-to-roll manufacturing processes.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
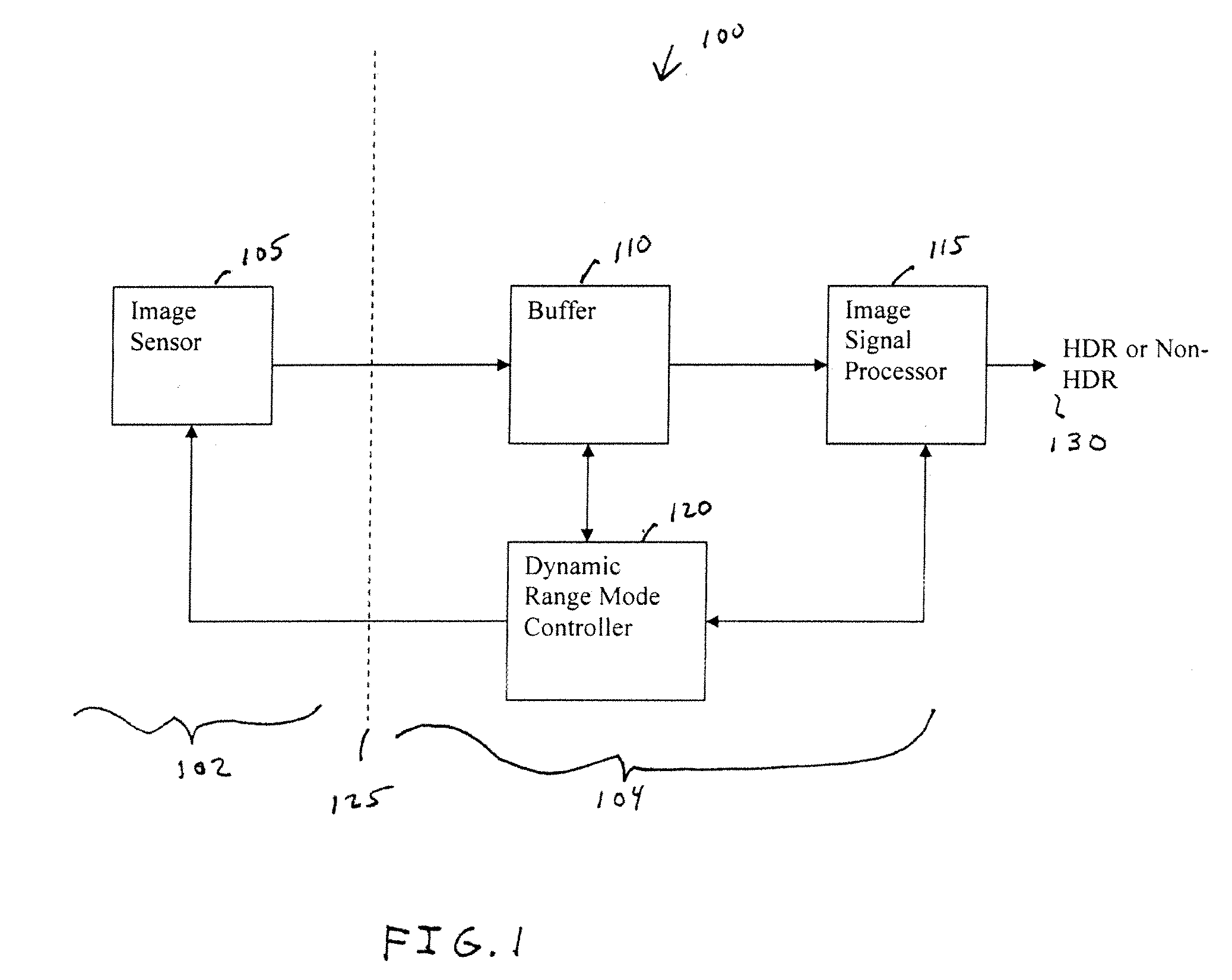
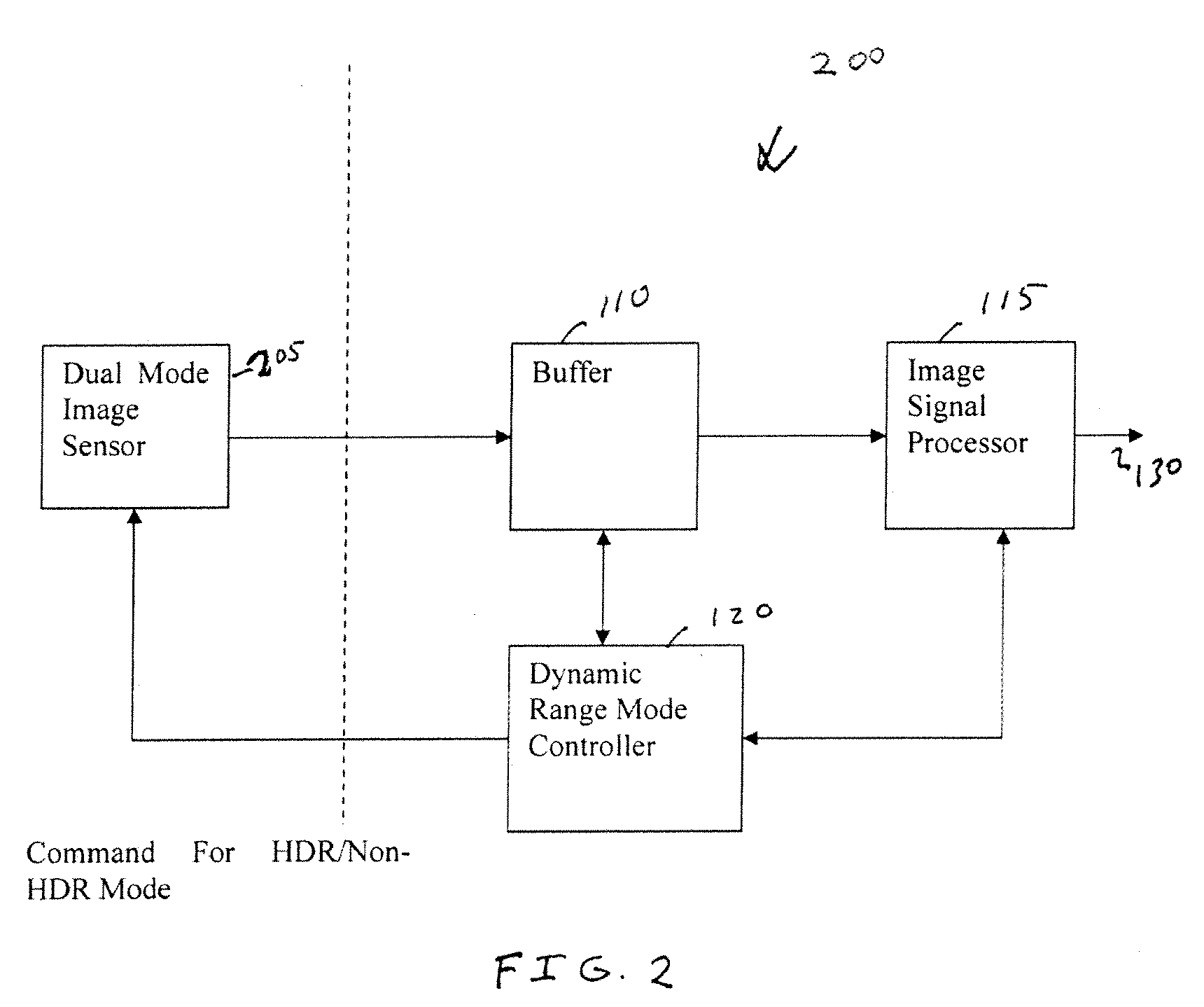
Dual mode camera solution apparatus, system, and method
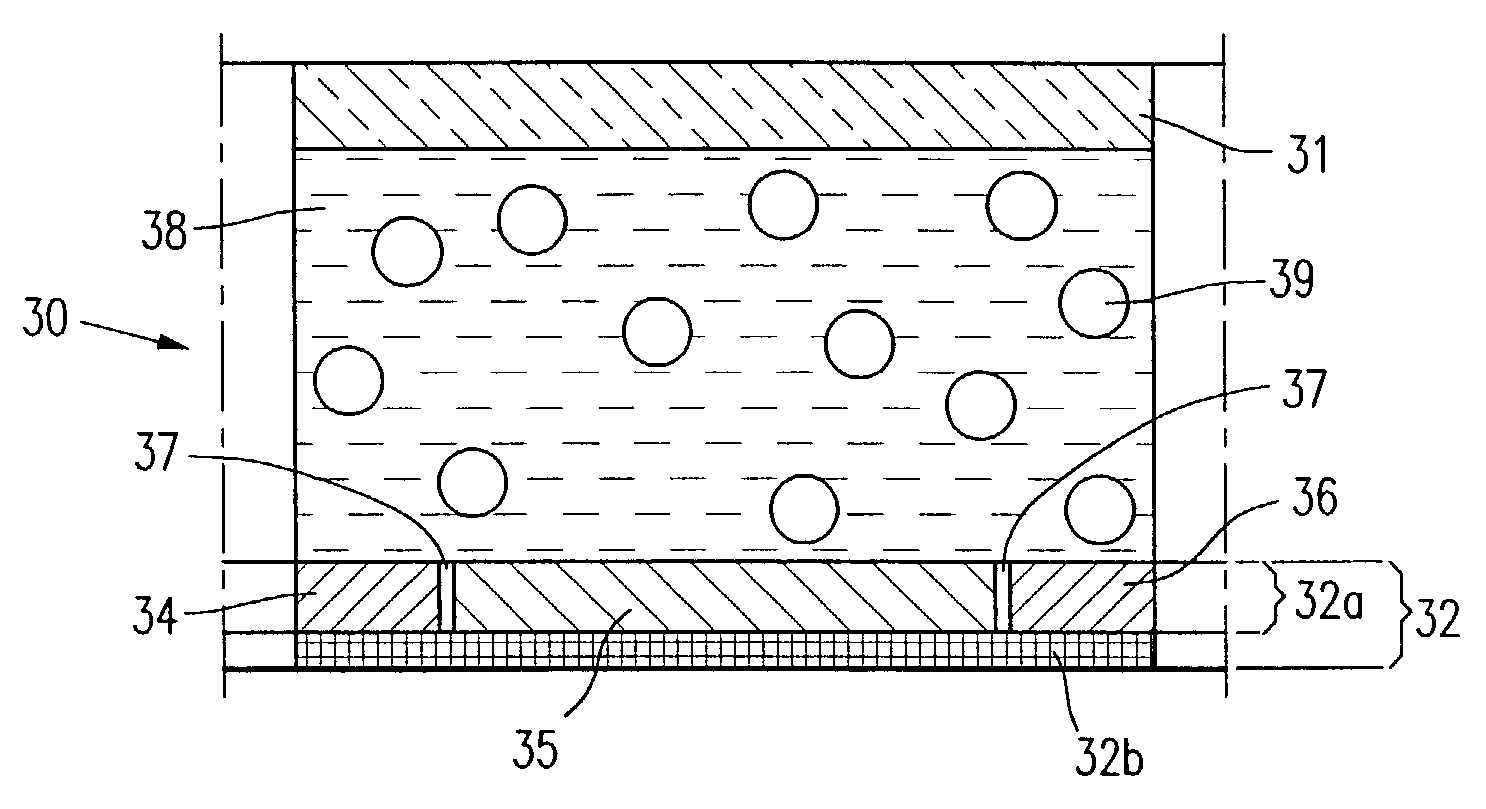
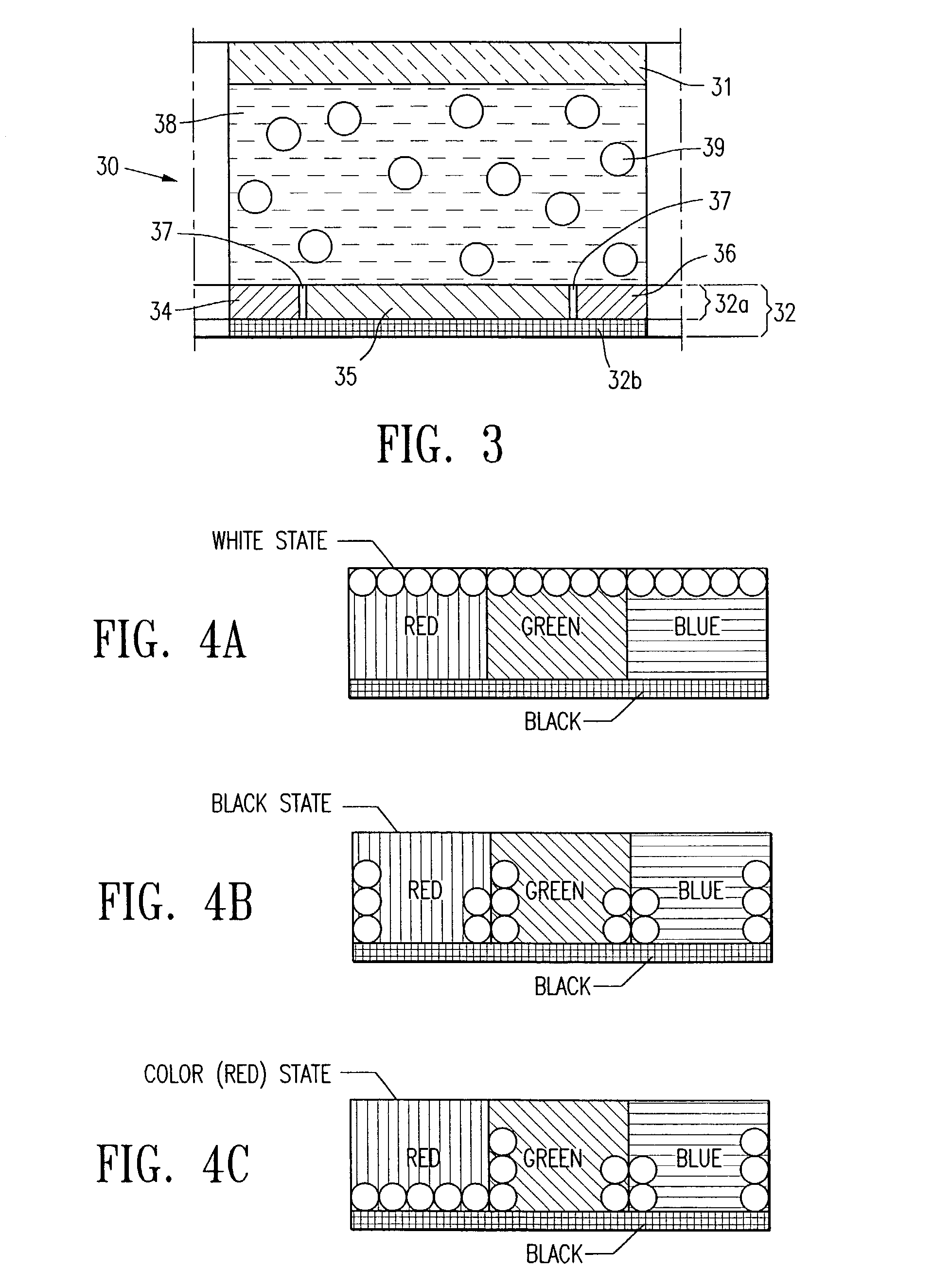
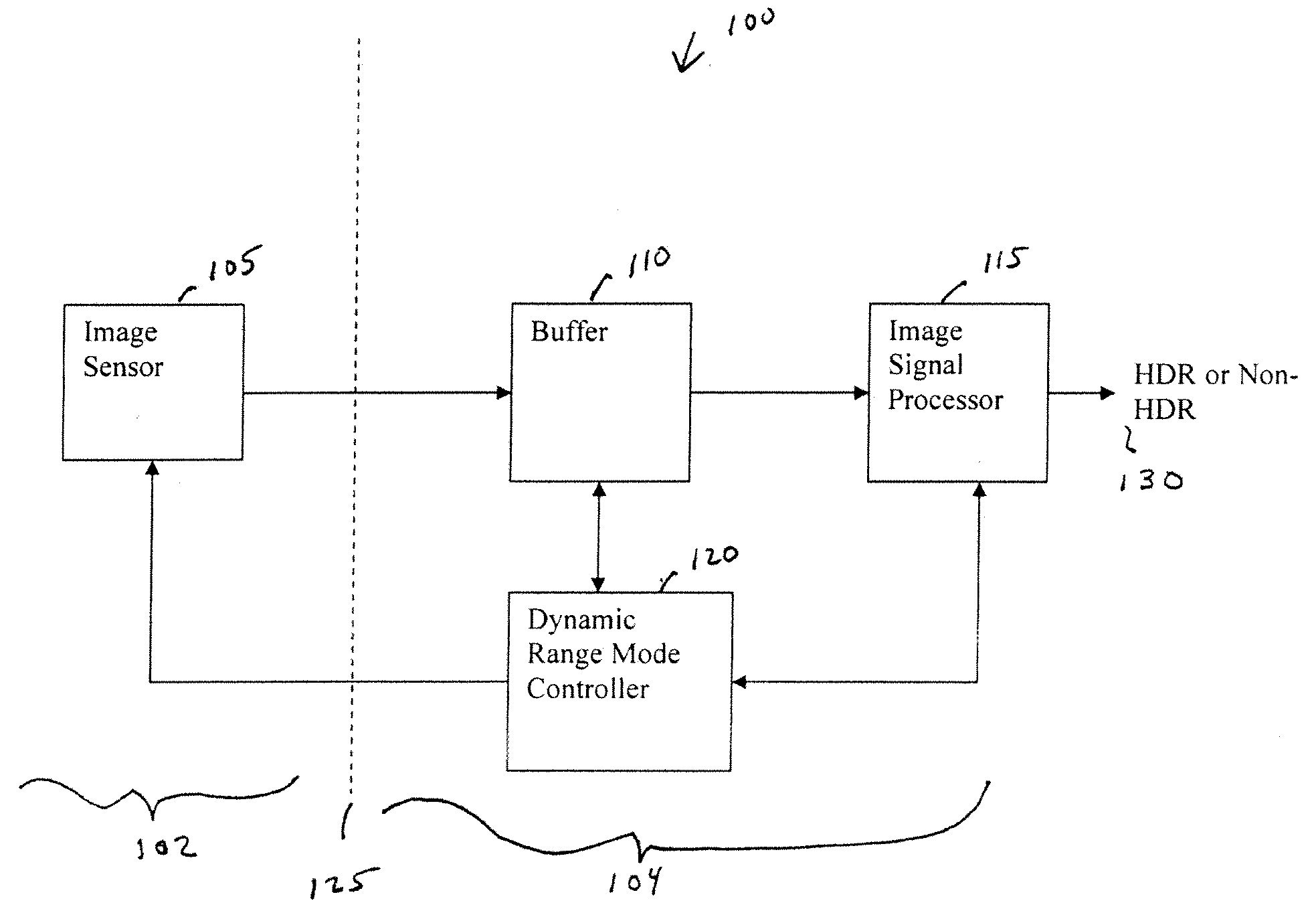
InactiveUS20090086074A1Improve dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingDual mode
A camera solution includes an image sensor and an image processing and control system. At least two different operating modes are supported, with one of the modes having a higher dynamic range. Control of the dynamic range is provided at the system level. The system supports statically or dynamically selecting an operating mode that determines the dynamic range of a camera. In one implementation, the system supports the use of either a conventional image sensor that does not natively support a high dynamic range or a dual-mode image sensor.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
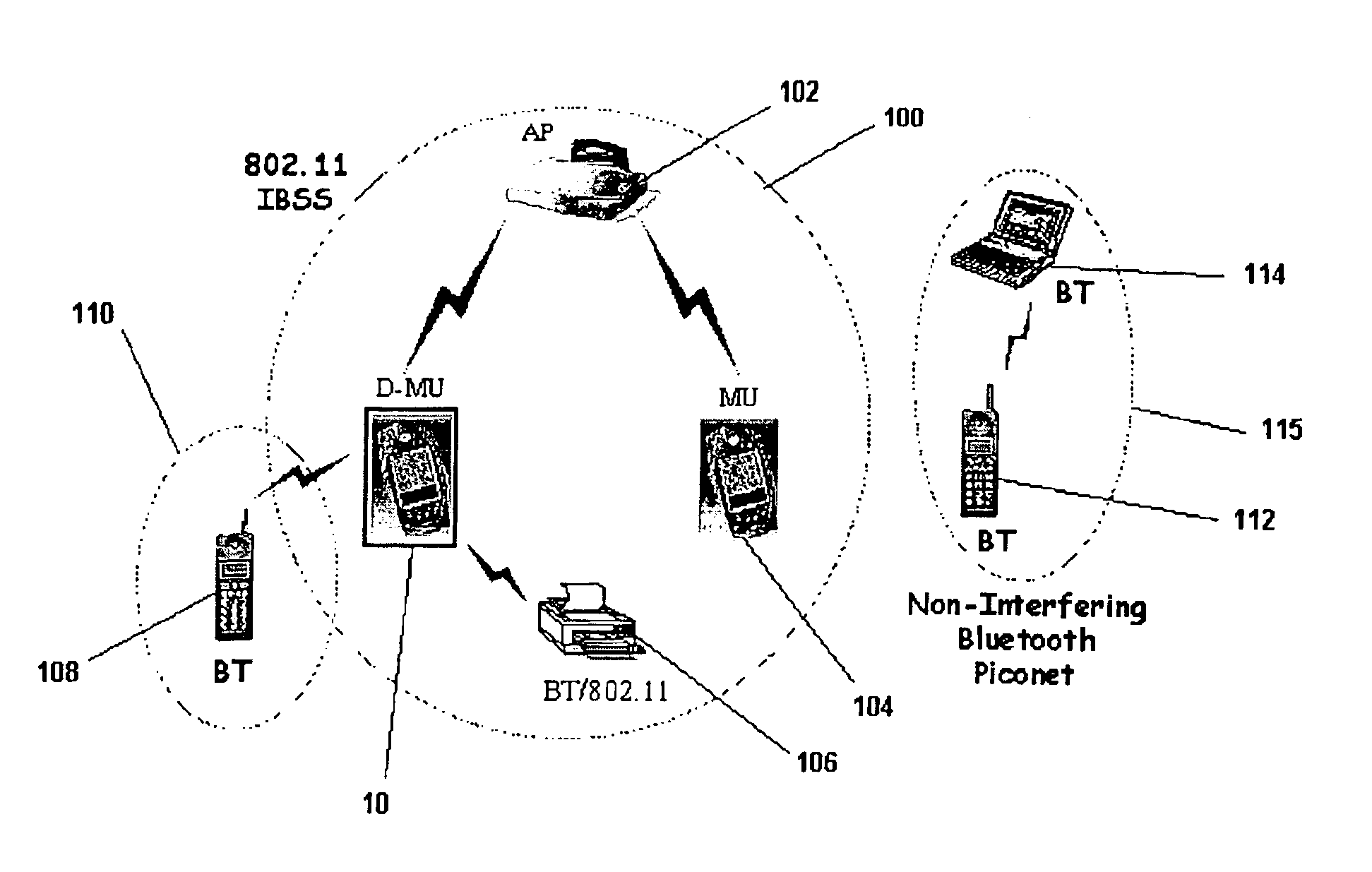
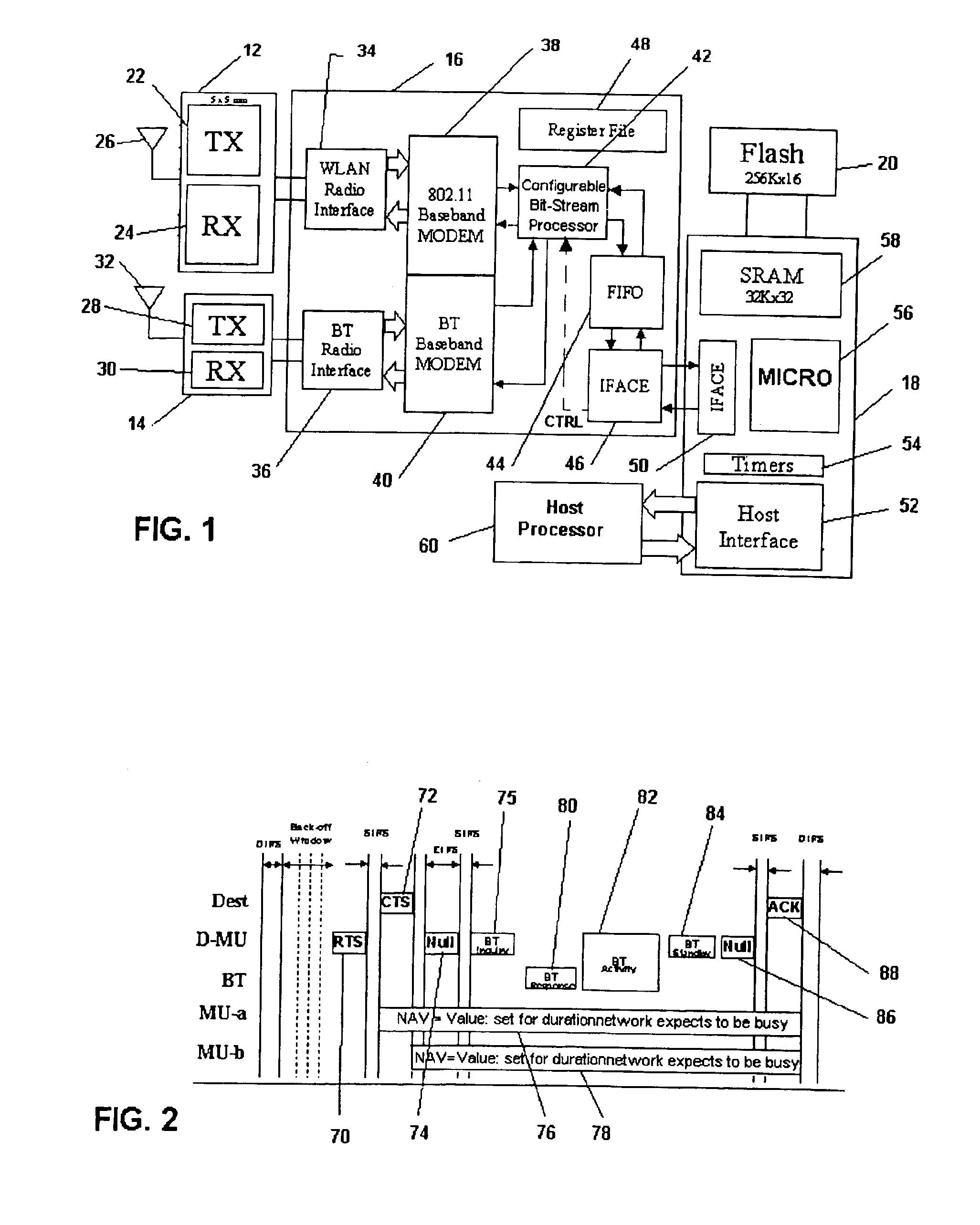
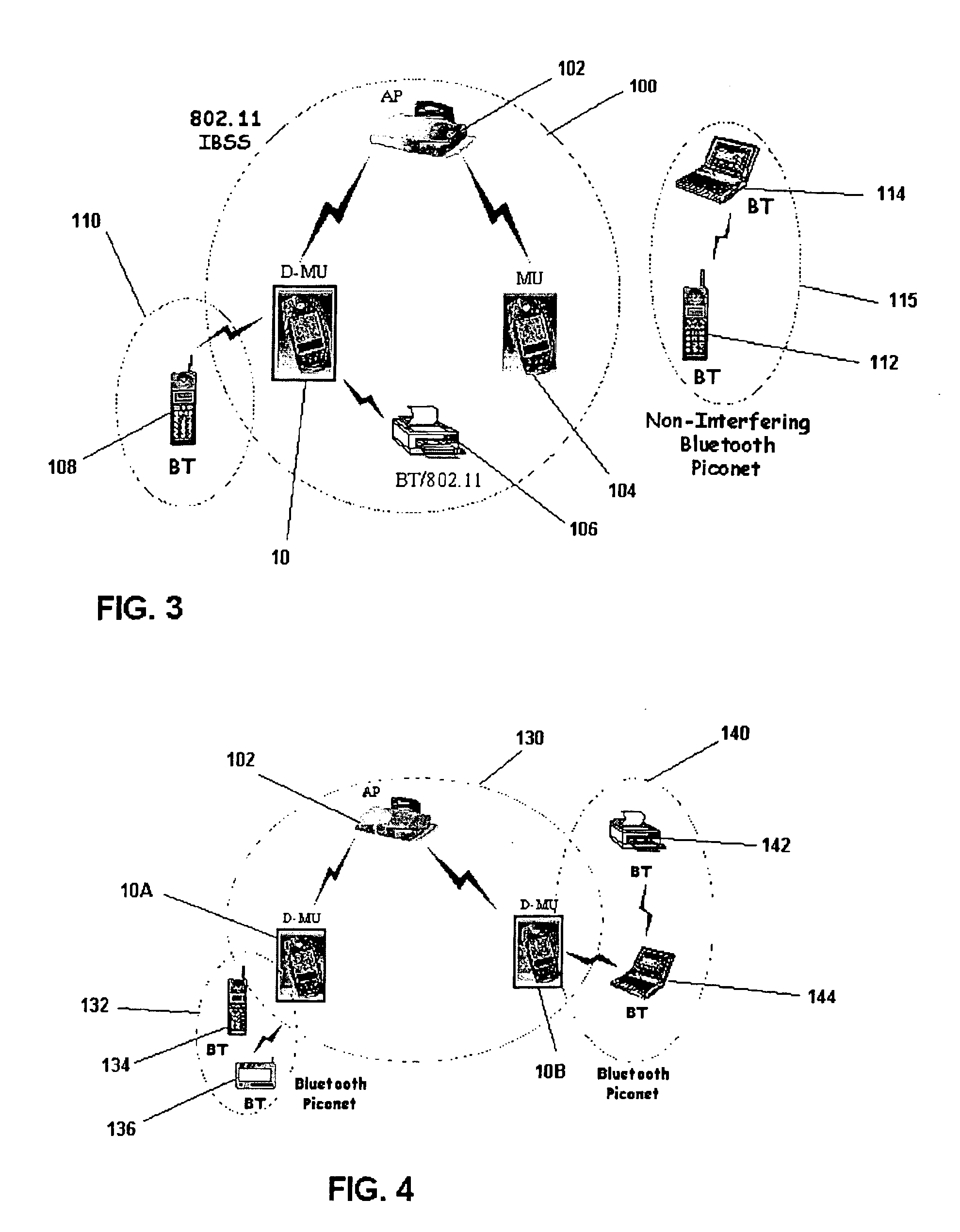
Dual mode wireless data communications
A dual mode mobile unit is arranged to communicate in either a first or second data communications standard, such as combined Bluetooth and 802.11 operation. An interface unit converts received Bluetooth or 802.11 format signals into 802.11 frame format data signals to be provided to a digital signal processor which is programmed to process signals in either standard. The dual mode mobile unit can operate in the 802.11 standard to reserve a time interval for Bluetooth activity during which other 802.11 units will avoid-transmissions to avoid interference.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Dual mode electrosurgical clamping probe and related methods
InactiveUS6974453B2Minimize damageAvoid and minimize currentCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsDual modeSurgical department
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue in order to ablate, contract, coagulate, or otherwise modify a target tissue or organ of a patients. An electrosurgical apparatus of the invention includes a shaft having a shaft distal end bearing an active electrode and a return electrode. At least one of the active electrode and the return electrode is moveable such that the shaft distal end can adopt a closed configuration or an open configuration. The apparatus can operate in an ablation mode or a sub-ablation mode. The closed configuration is adapted for clamping and coagulating a target tissue while the apparatus is operating in the sub-ablation mode, while the open configuration is adapted for ablating the target tissue via molecular dissociation of tissue components. A method of the present invention comprises clamping a target tissue or organ with an electrosurgical probe. A first high frequency voltage is applied between the active electrode and the return electrode to effect coagulation of the clamped tissue. Thereafter, a second high frequency voltage is applied to effect localized molecular dissociation of the coagulated tissue. The present invention allows the ablation or modification of the target tissue with minimal or no damage to surrounding, non-target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Wi-Fi/BPL dual mode repeaters for power line networks
ActiveUS7852837B1Stay connectedBridging the gapPower distribution line transmissionWireless systems/telephoneWi-FiPower line network
A method and apparatus for maintaining network connectivity over power lines is disclosed. Such network connectivity is maintained even if various customers are covered by different power line networks or if one or more power lines in a network are unavailable to transmit data. More particularly, in order to bridge a gap in a power line network, one or more messages are extracted from a first node in a power line network and are then transmitted to a second node via free space transmission, illustratively wireless radio frequency (RF) transmission conforming to one or more of the 802.11a, b or g standards. When those messages are received at the second node, the message is injected back into the power line on the other side of a gap in power line coverage. This method of transmission backup will continue until power line connectivity is restore upon which the preferred method will be selected and used.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
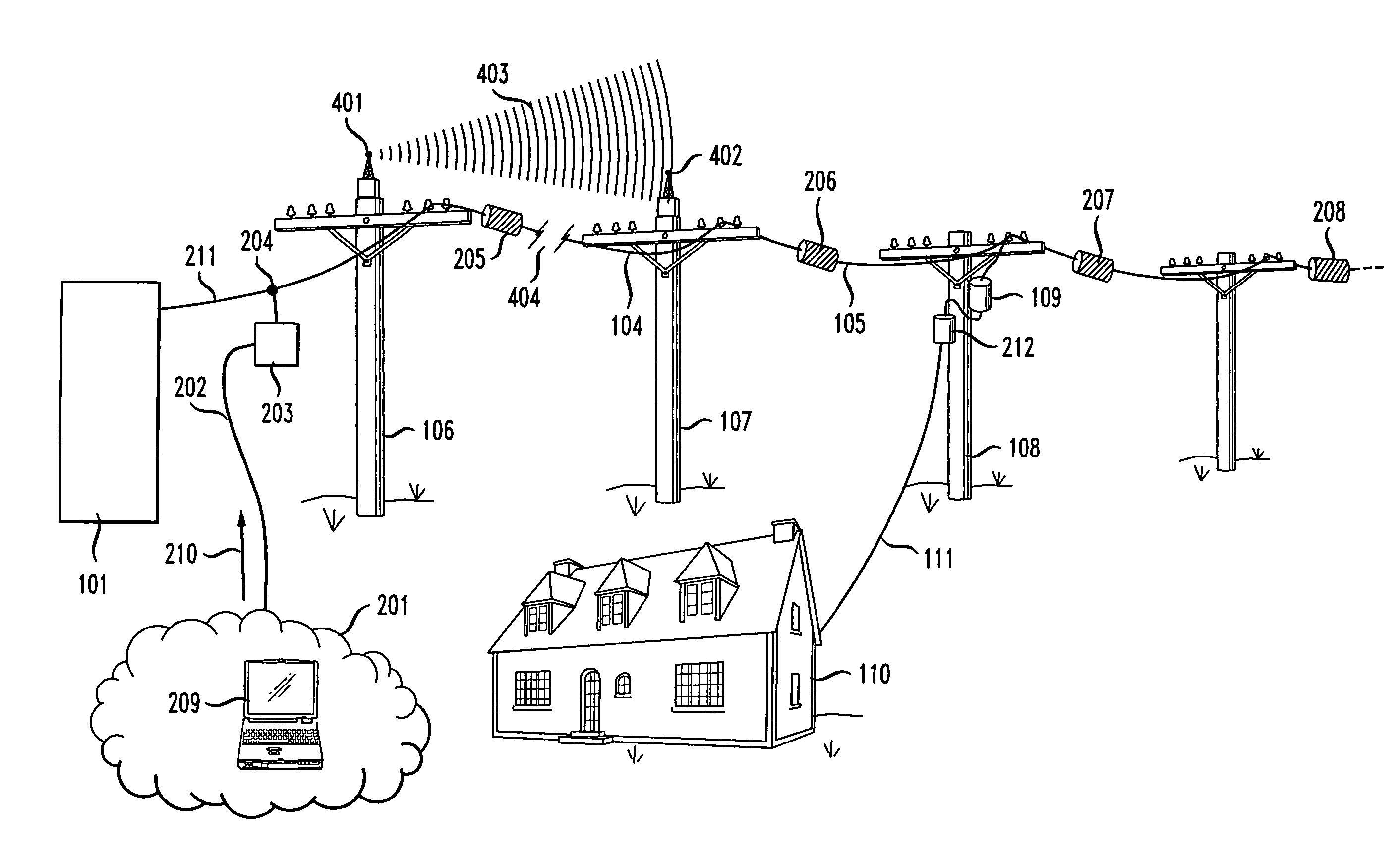
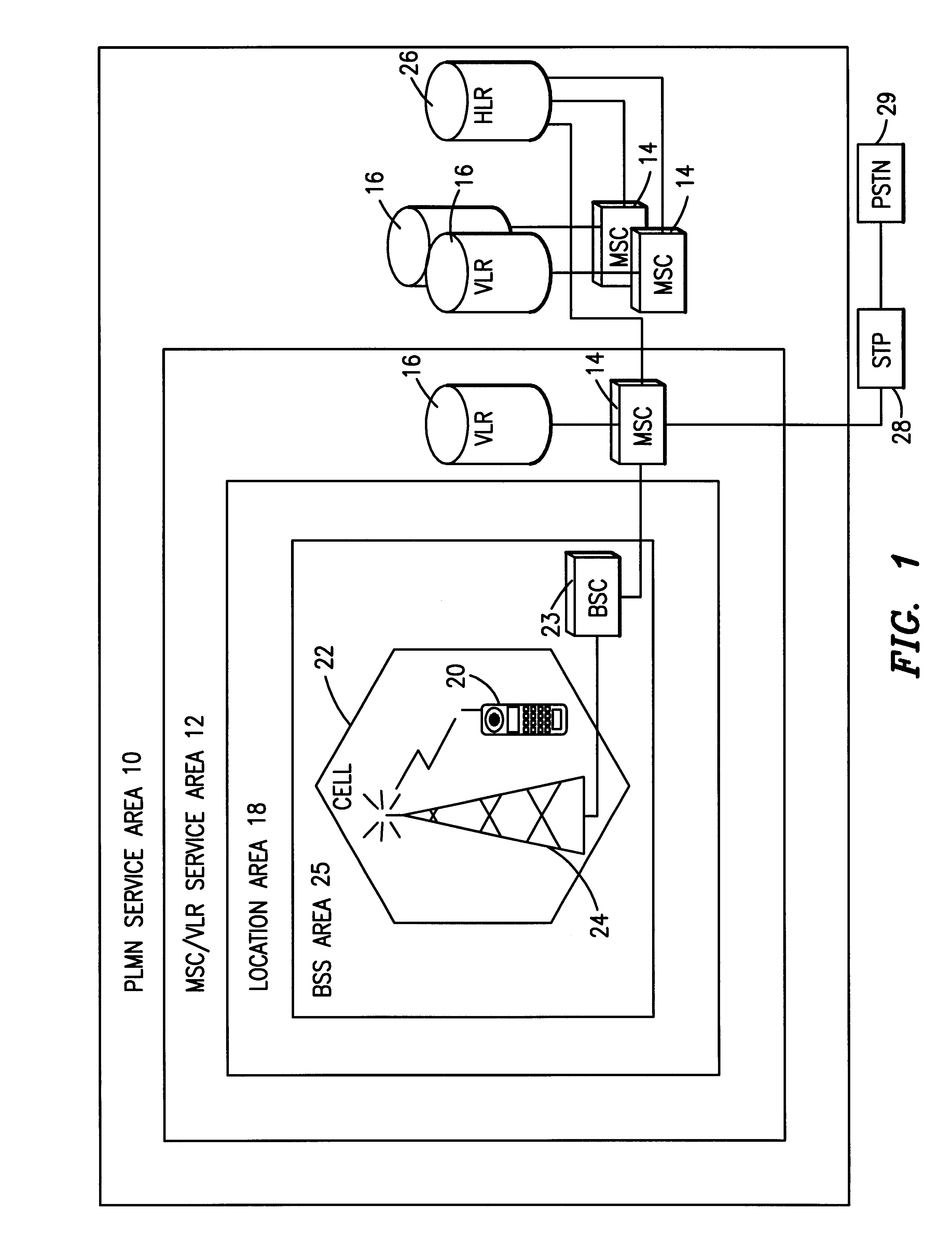
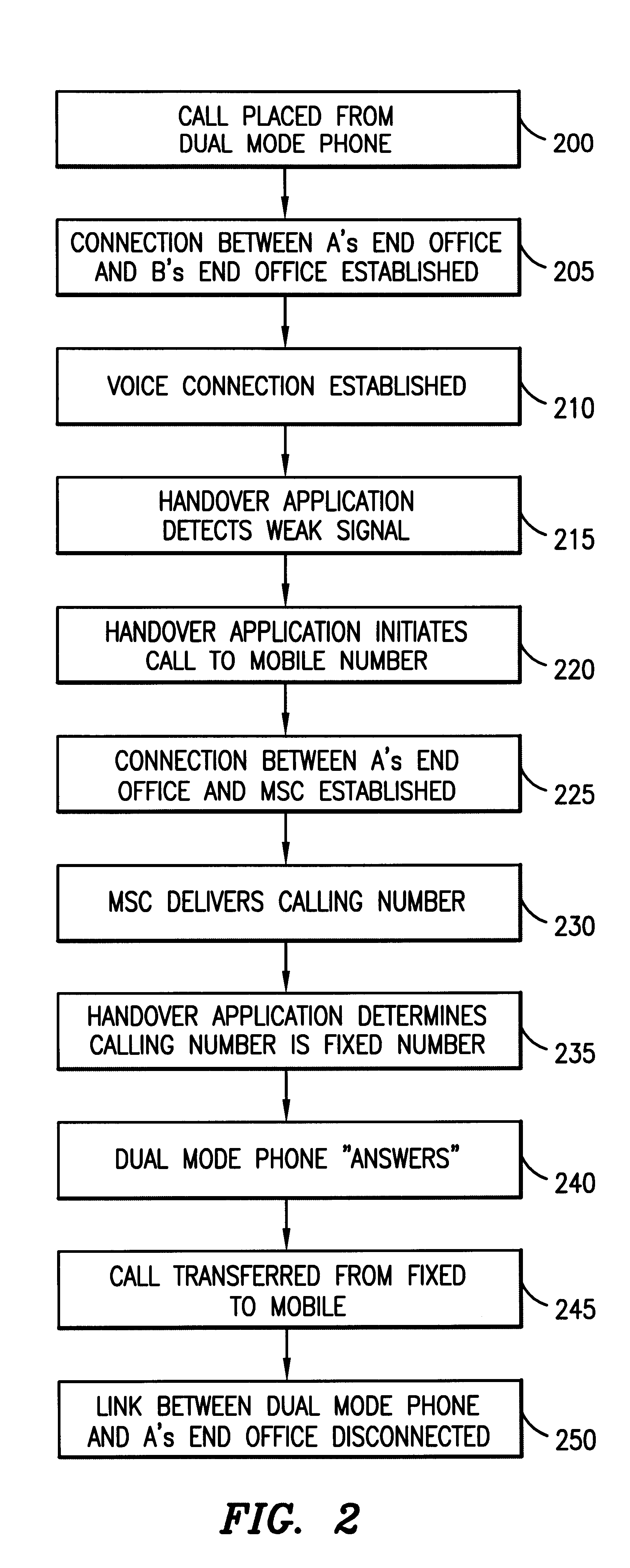
Handover between fixed and mobile networks for dual mode phones
InactiveUS6327470B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesData connectionCall forwarding
A telecommunications system and method for performing a handover between the fixed (wireline) network and a mobile network during a call placed to or from a dual mode device, without any interruption in the voice or data connection. Therefore, for calls initiated in the fixed network, once the subscriber leaves the coverage area for the fixed mode of the dual mode device, the call continues as normal by transferring the call to the mobile network. Similarly, for calls initiated in the mobile network, once the subscriber moves back into the fixed mode coverage area, the call can be transferred to the fixed network in order to provide a lower rate to the subscriber, without any service interruption.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
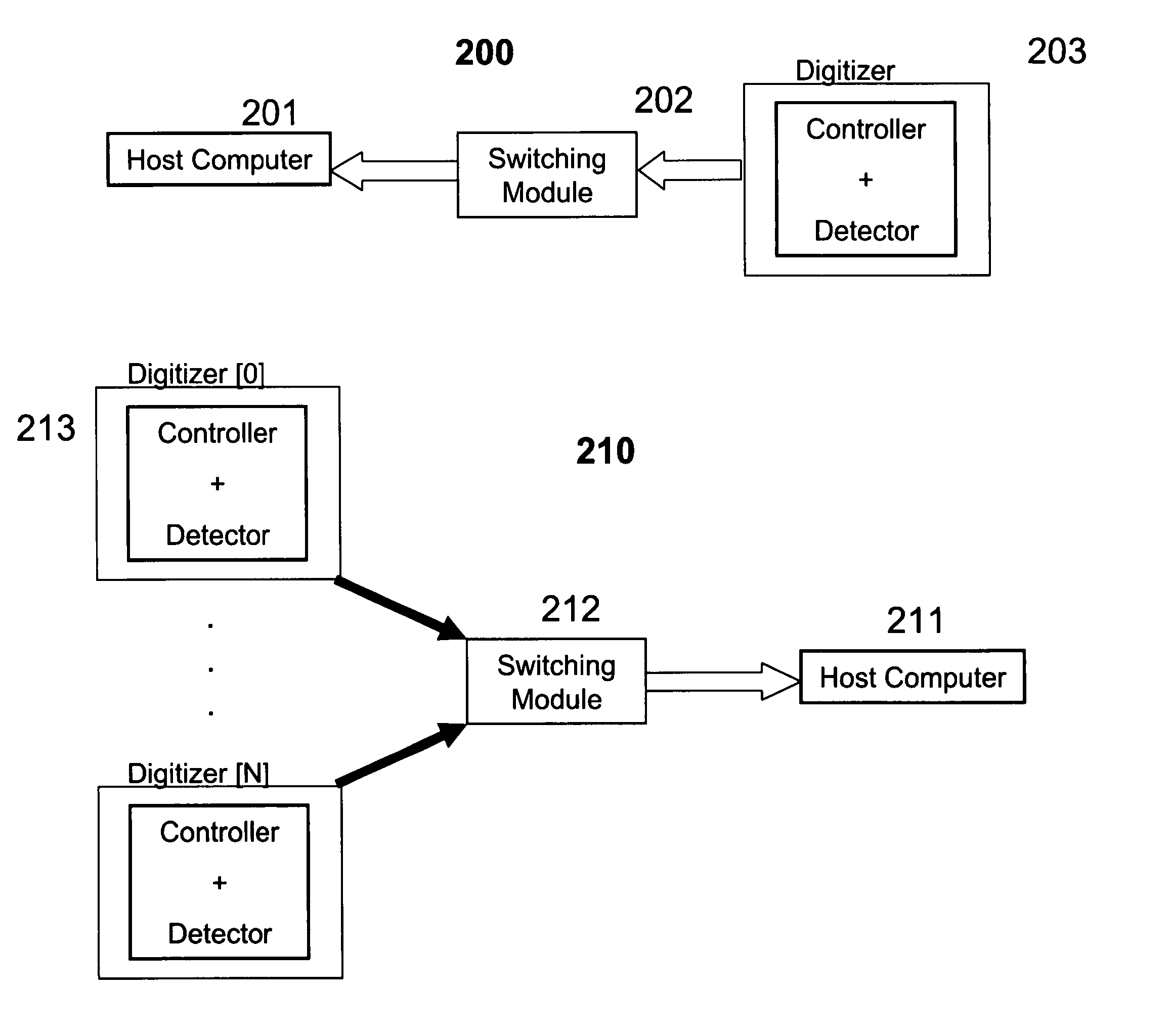
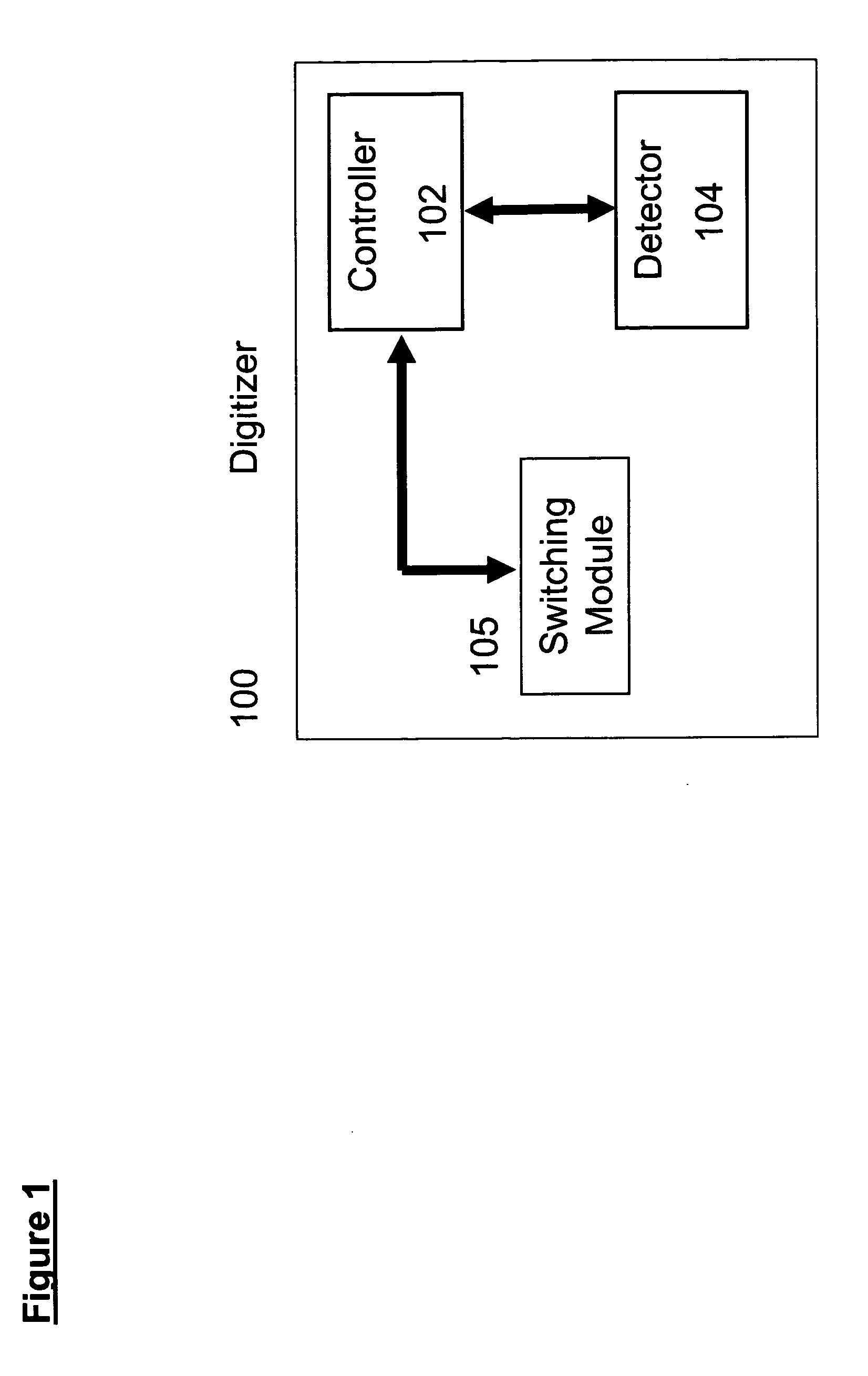
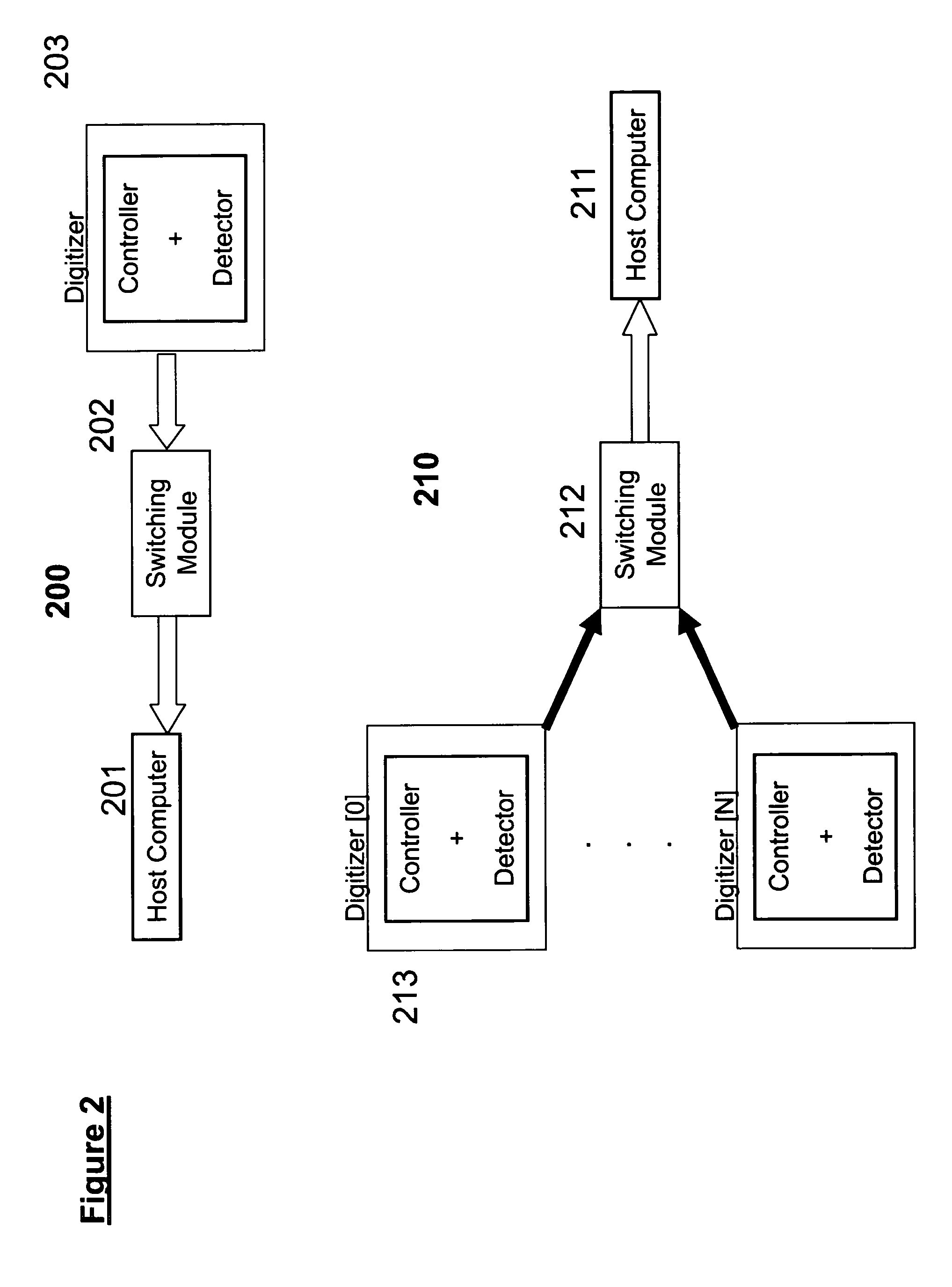
Automatic switching for a dual mode digitizer
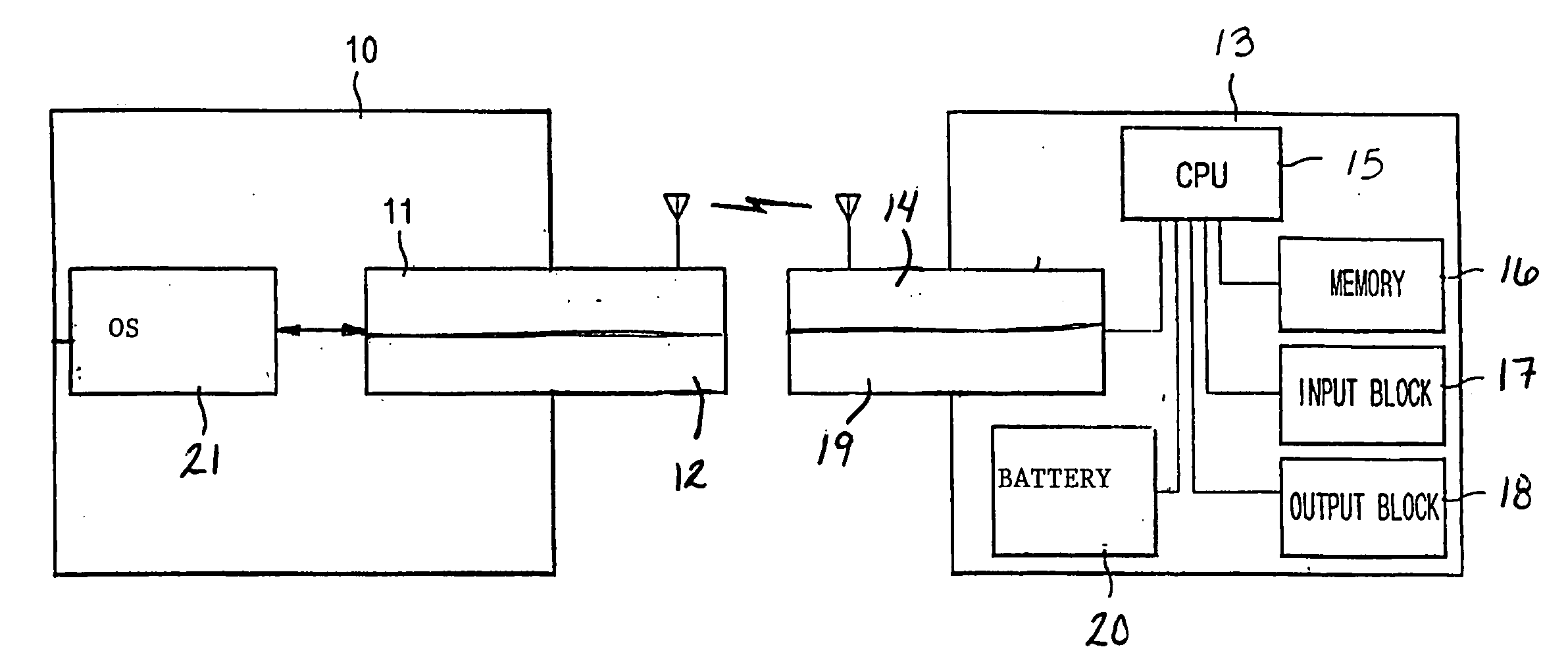
InactiveUS20060012580A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDual modeComputer science
An apparatus for detecting a plurality of user interactions, comprising: at least one detector for sensing the user interactions, a respective controller, associated with each of the detectors, for finding positions of the user interactions, and a switcher, associated with the controllers, for handling the user interactions, according to a defined policy.
Owner:N TRIG
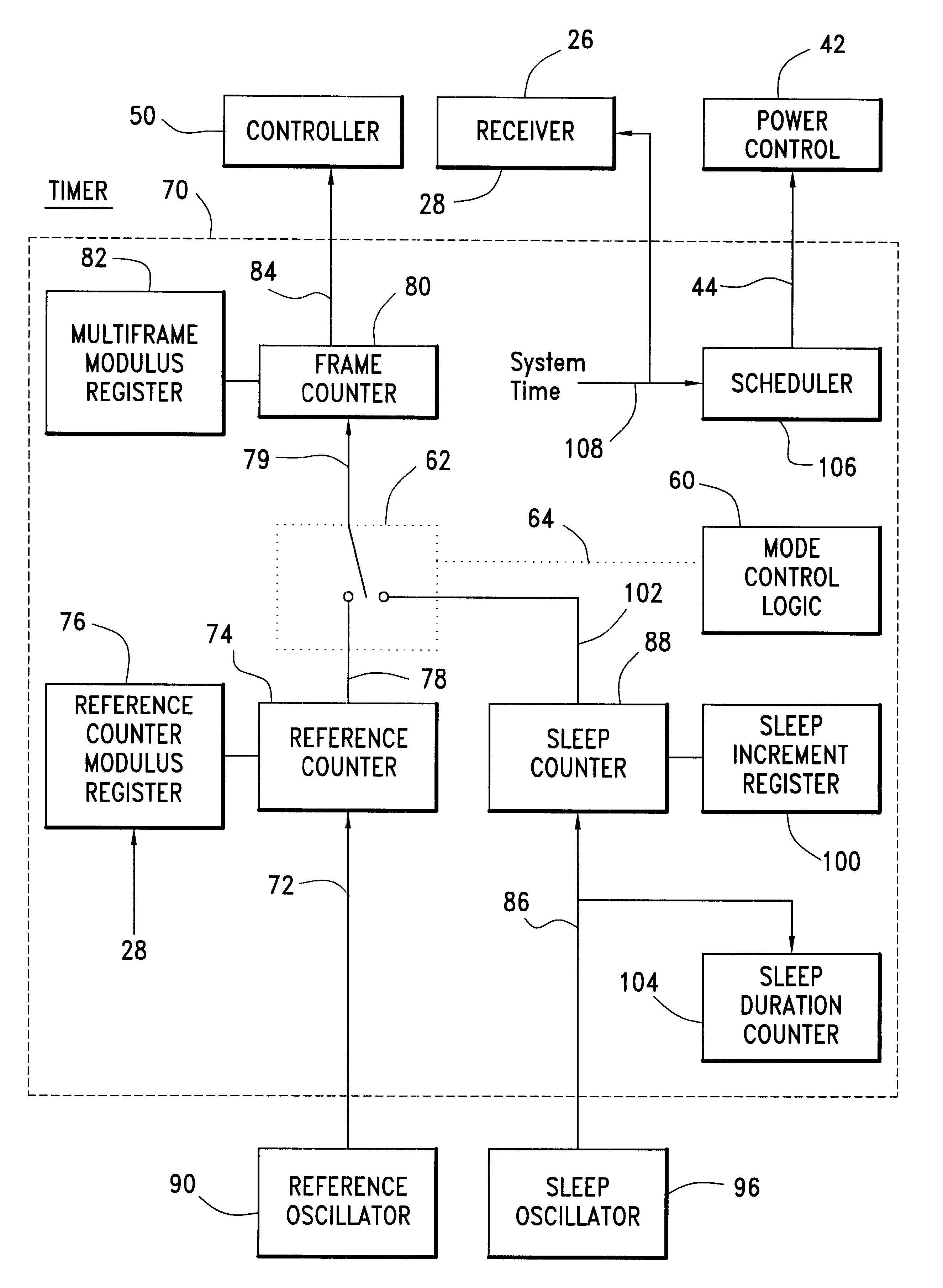
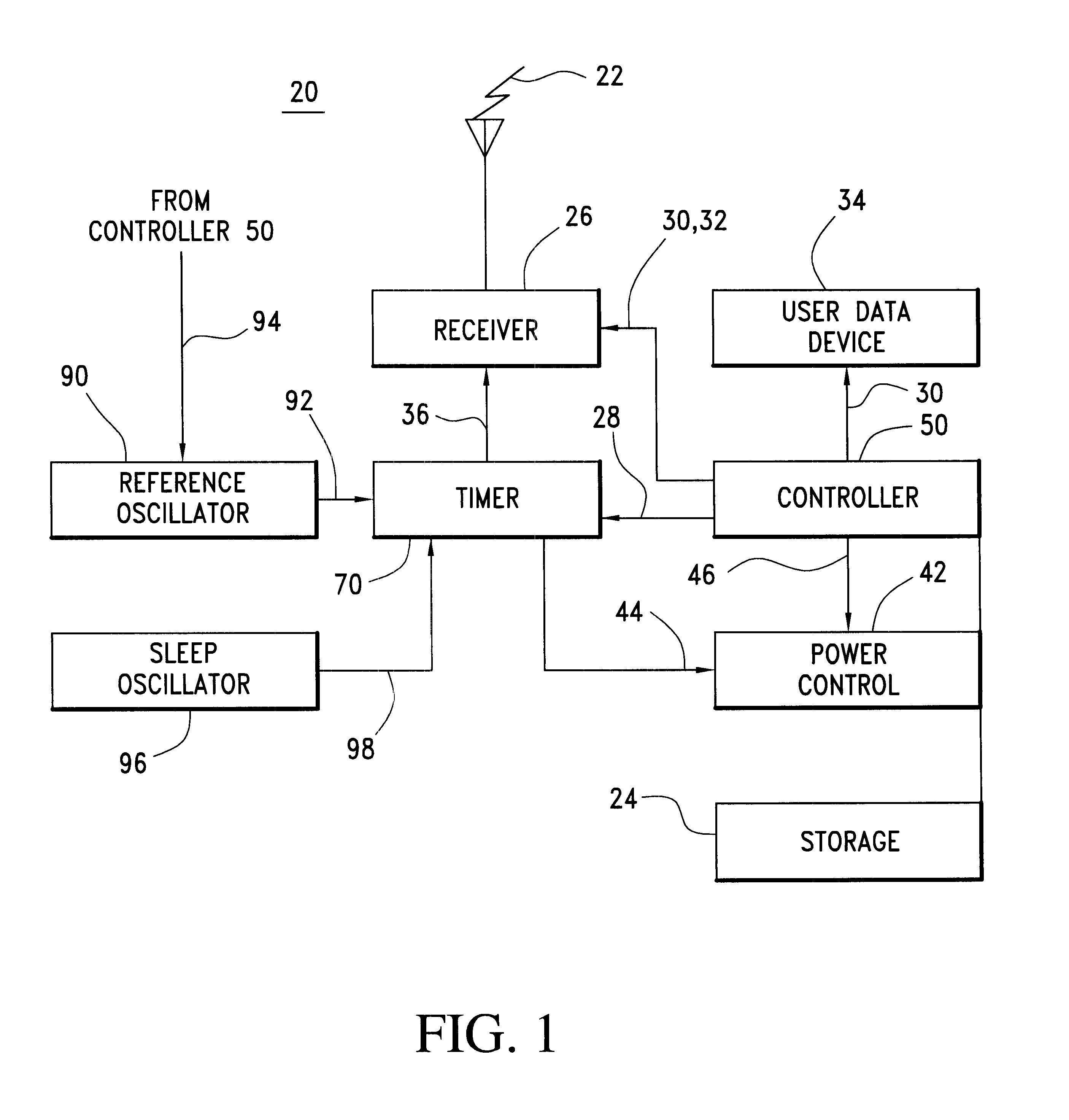
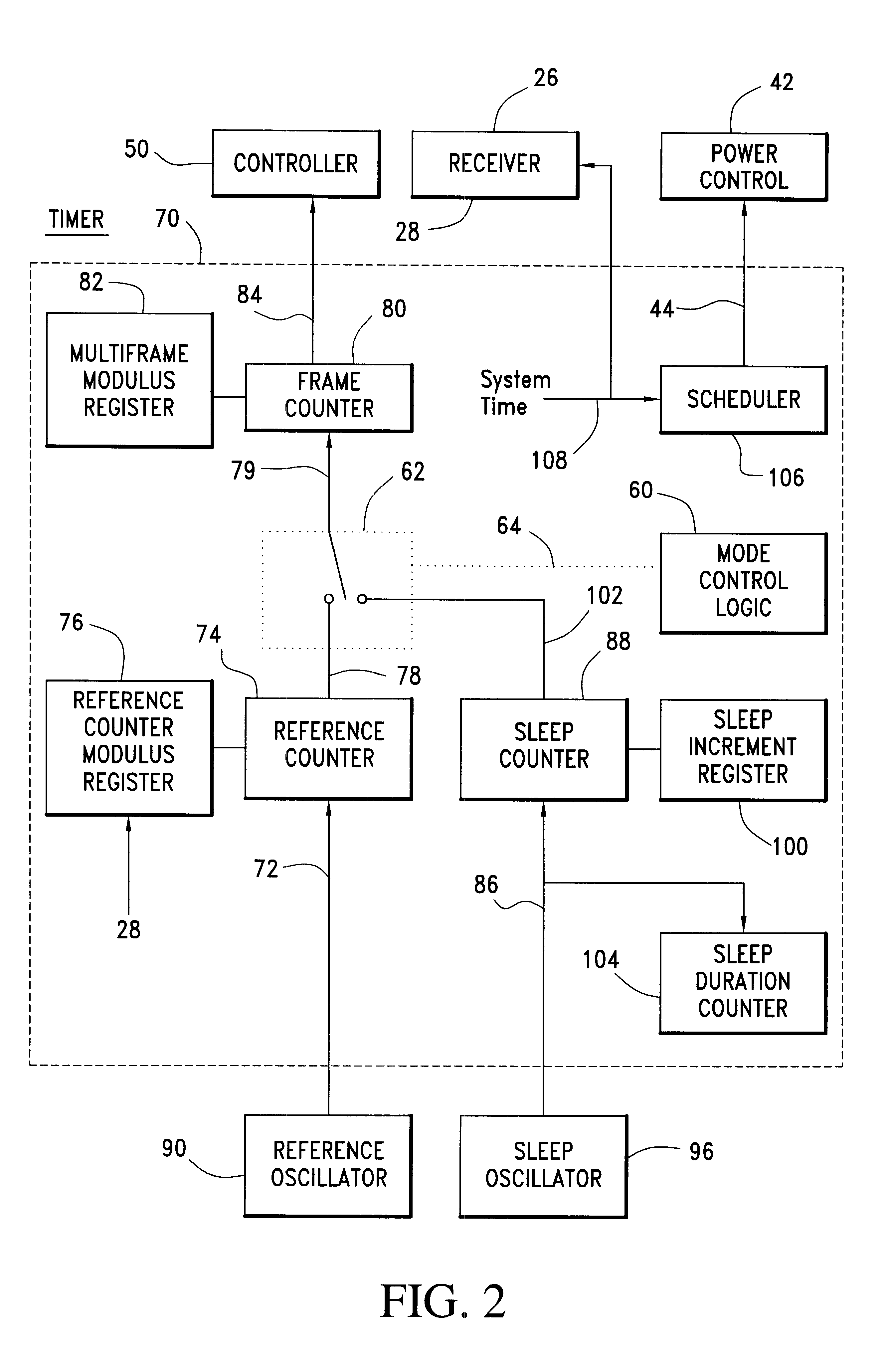
Communication device with a self-calibrating sleep timer
The present invention provides for a system for operating a communication device (20) for reception of scheduled intermittent information messages (22) with a dual mode timer (70) that extends battery life. A controller (50) schedules the timer (70) to power down all idle components of the device (20) between message receptions in a power saving sleep mode to conserve battery power. During active mode when the device is fully active in reception of messages, the timer (70) uses a reference oscillator (90) with a relatively high frequency to support digital processing by the receiver (26). During sleep mode when only the timer is powered on, a much lower frequency sleep oscillator (96) is used to maintain the lowest possible level of power consumption within the timer itself. The timer (70) has provision for automatic temperature calibration to compensate for timing inaccuracies inherent to the low-power low-frequency crystal oscillator (96) used for the sleep mode. The resultant improvement in timer accuracy during sleep mode eliminates the need for an initial reacquisition period following wake up in active mode, thereby reducing battery drain in active mode as well.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
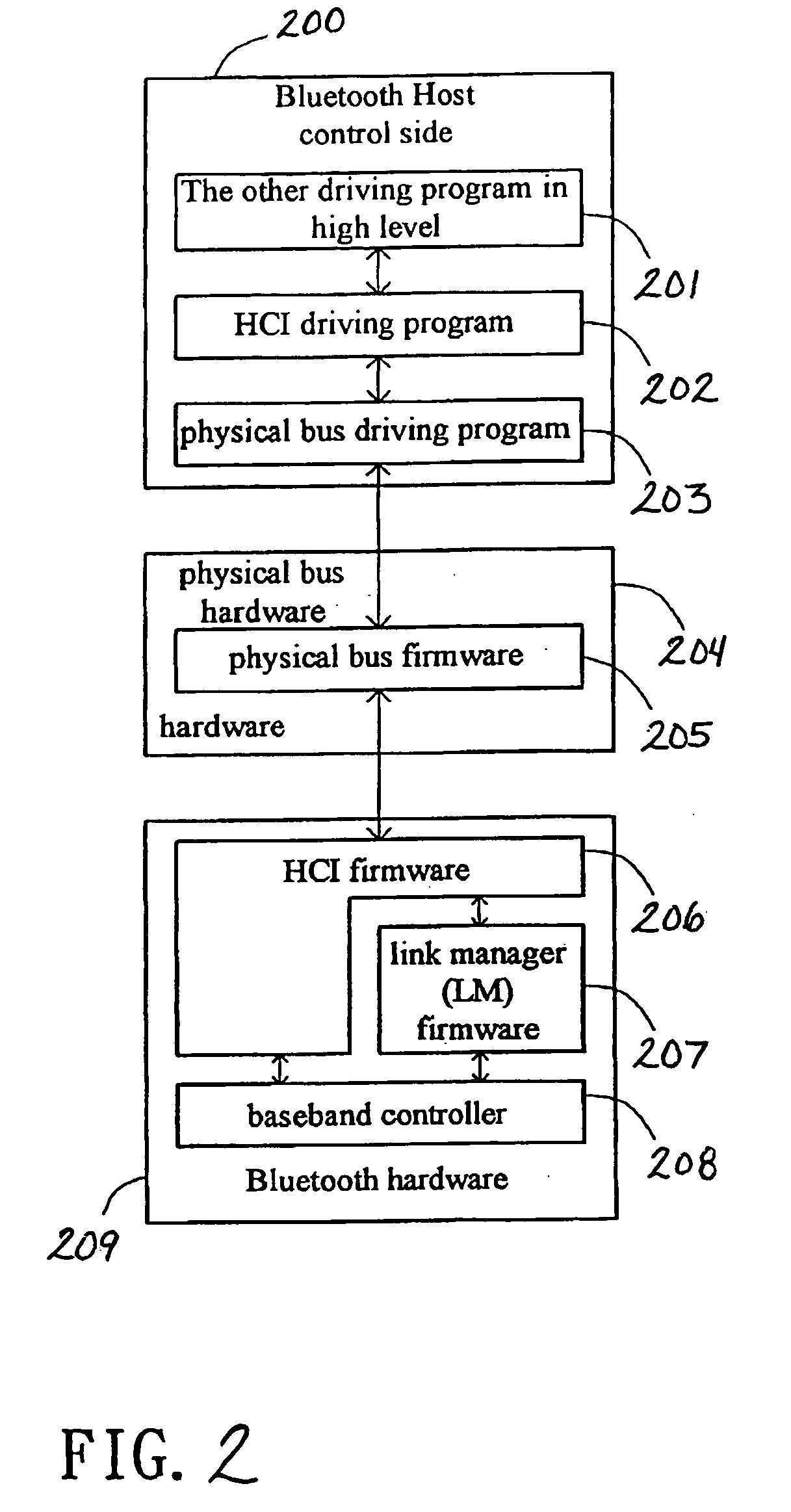
Data link control proctocol for 3G wireless system
InactiveUS6542490B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelElectronic circuit testingTelecommunications linkDual mode
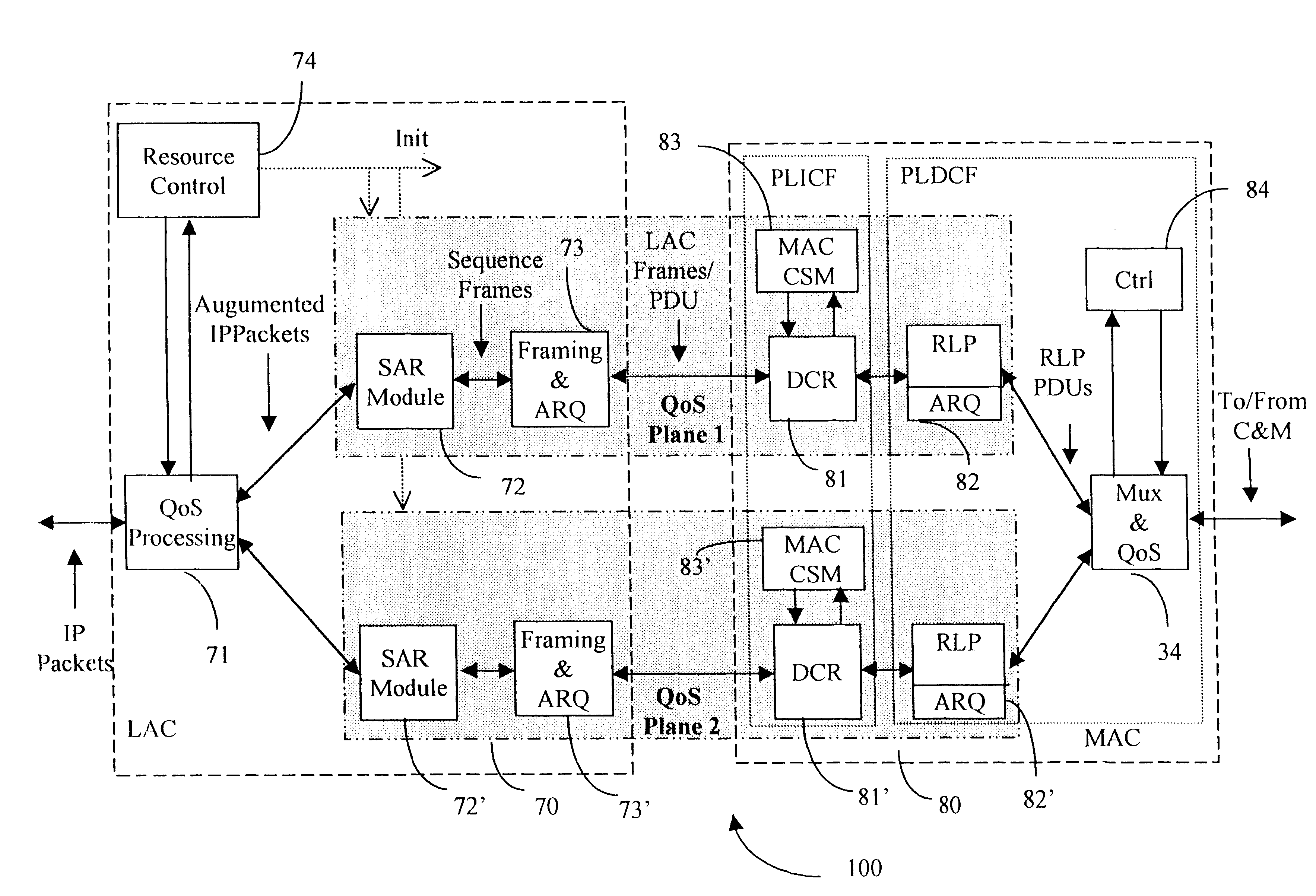
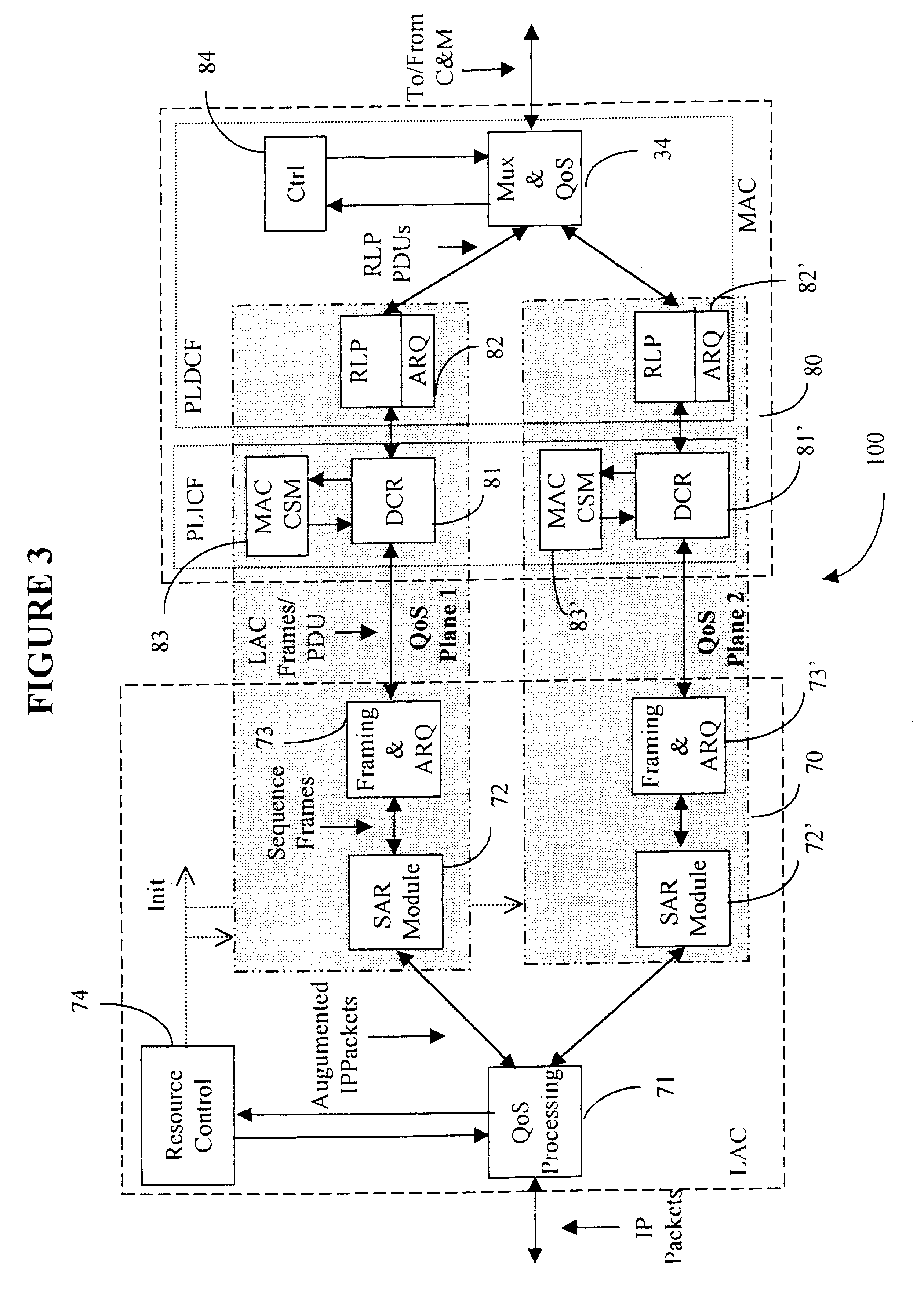
A Data Link Control protocol for 3G wireless communication system for direct support for network layer protocols, e.g. the Internet Protocol (IP), is provided. The Link Layer disclosed comprises a Link Access Control (LAC) sublayer and a Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer. At a transmit end of the wireless system, a plurality of Quality of Service (QoS) data planes are created to directly support the IP QoS. Each QoS data plane is optimized to handle QoS requirements for a corresponding Class of Service (CoS). Data packets received at the LAC sublayer are directed to a QoS data plane according to the particular QoS information they contain and processed according to the particular QoS requirement to generate variable size LAC frames. The variable size LAC frames are transmitted to the MAC sublayer for generating radio link protocol data units (RLP PDUs) to be transmitted to a receiving end. A new level of error correction is provided at the LAC sublayer as the size of the LAC PDUs can be dynamically adjusted in response to the conditions of the communication link. A dual mode ARQ is provided at the MAC sublayer to improve the quality of the air transmission for bursty as well as non-bursty traffic conditions.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
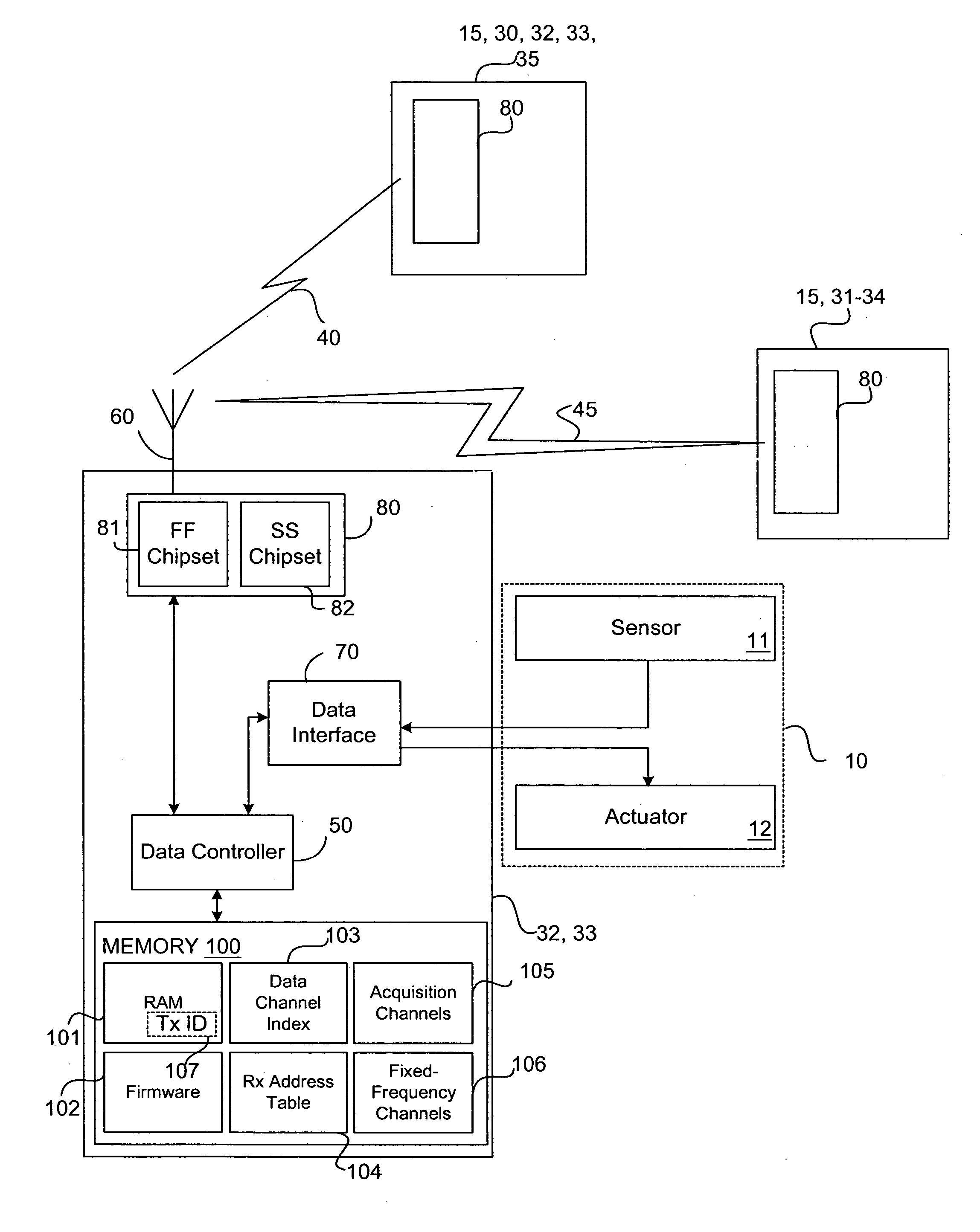
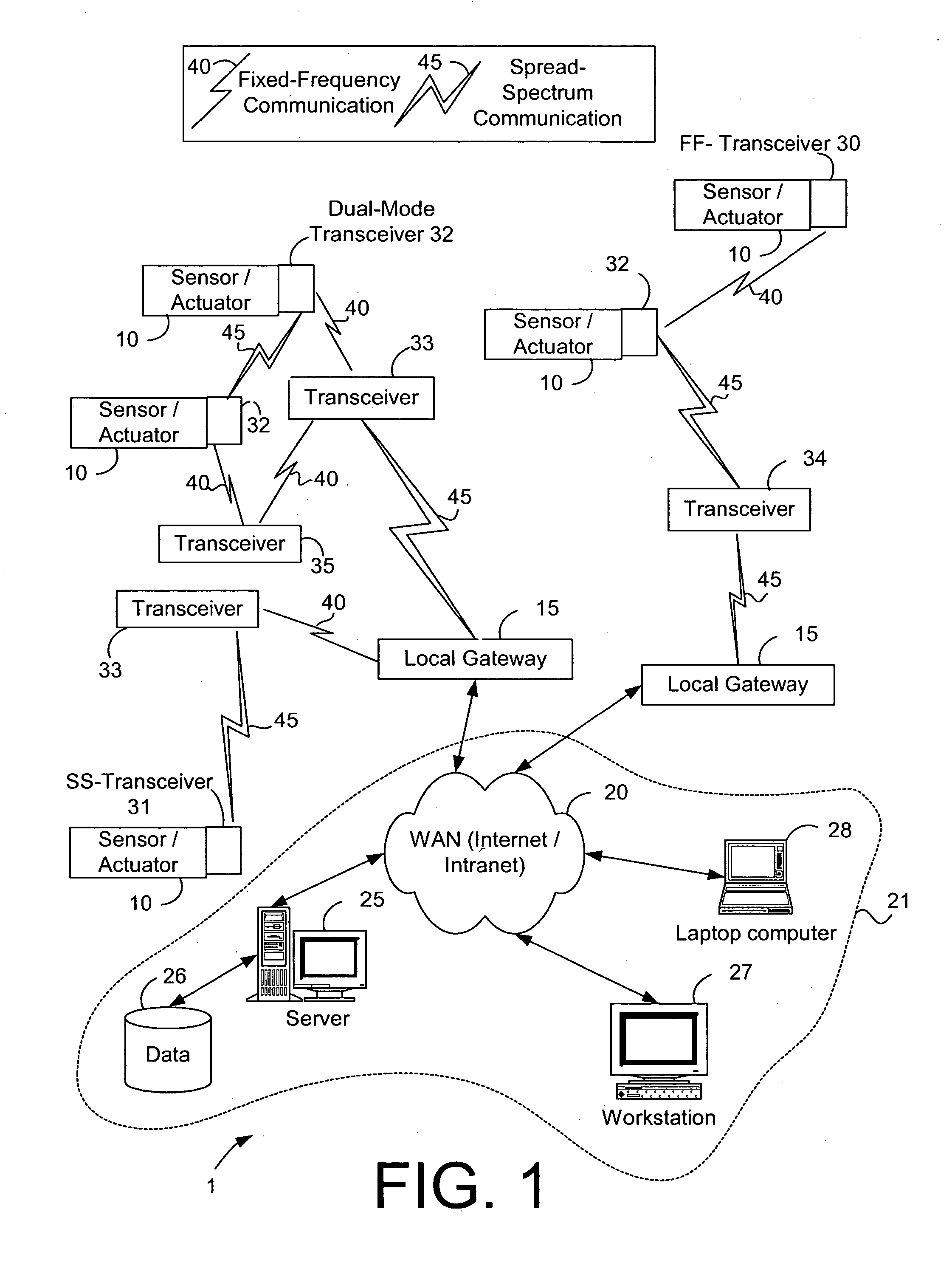
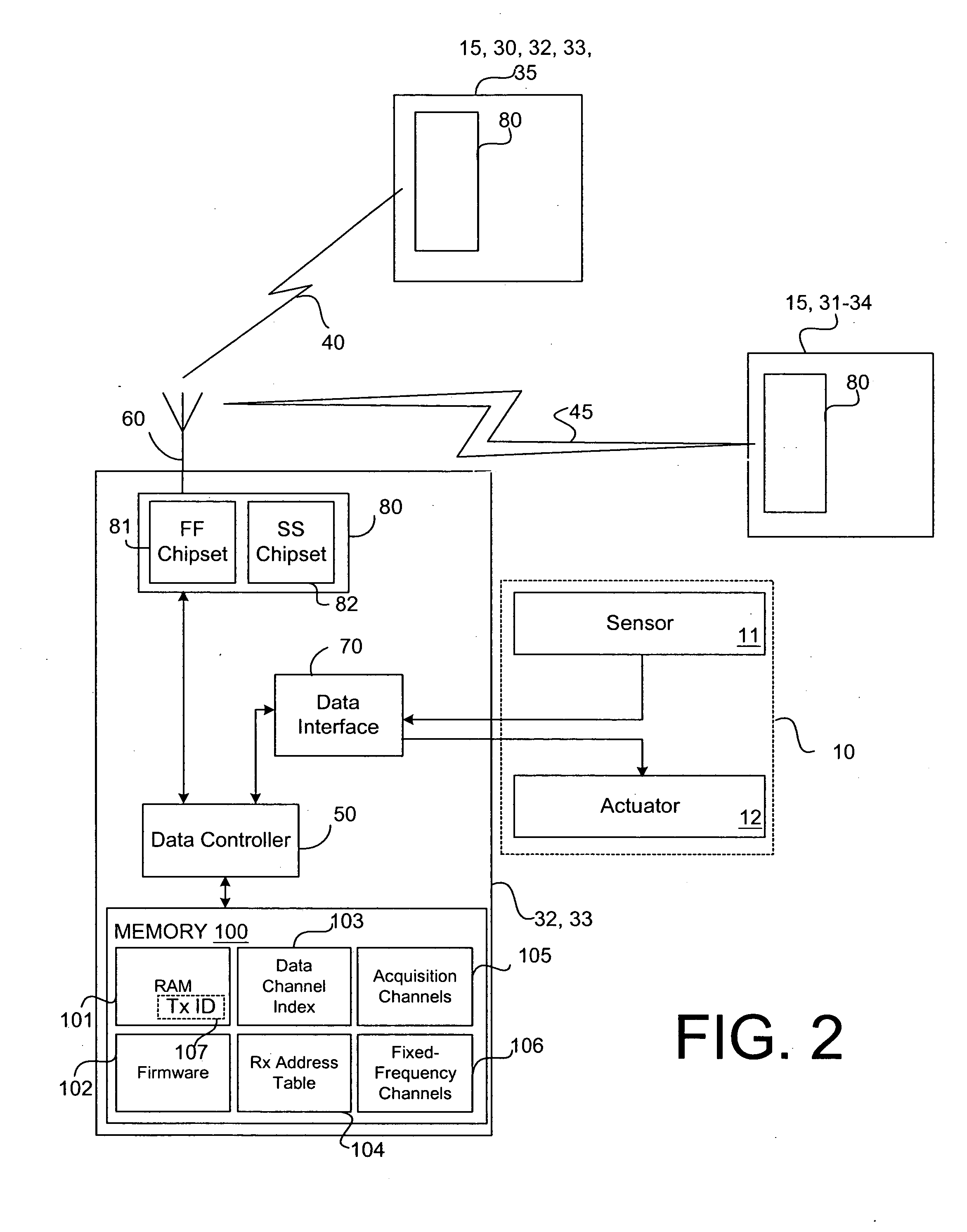
System and method for monitoring remote devices with a dual-mode wireless communication protocol
ActiveUS20050195775A1Electric signal transmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless transceiverTransceiver
The present invention is generally directed to systems and device for monitoring remote device with a wireless, dual-mode communication protocol. As such, a representative embodiment is a system for monitoring and controlling remote devices. The system includes a first- and a second remote device; and a first and a second wireless transceiver integrated with the respective remote devices. The wireless transceivers are configured to communicate with at least one of a spread-spectrum communication protocol and a fixed-frequency communication protocol.
Owner:STATSIGNAL IPC
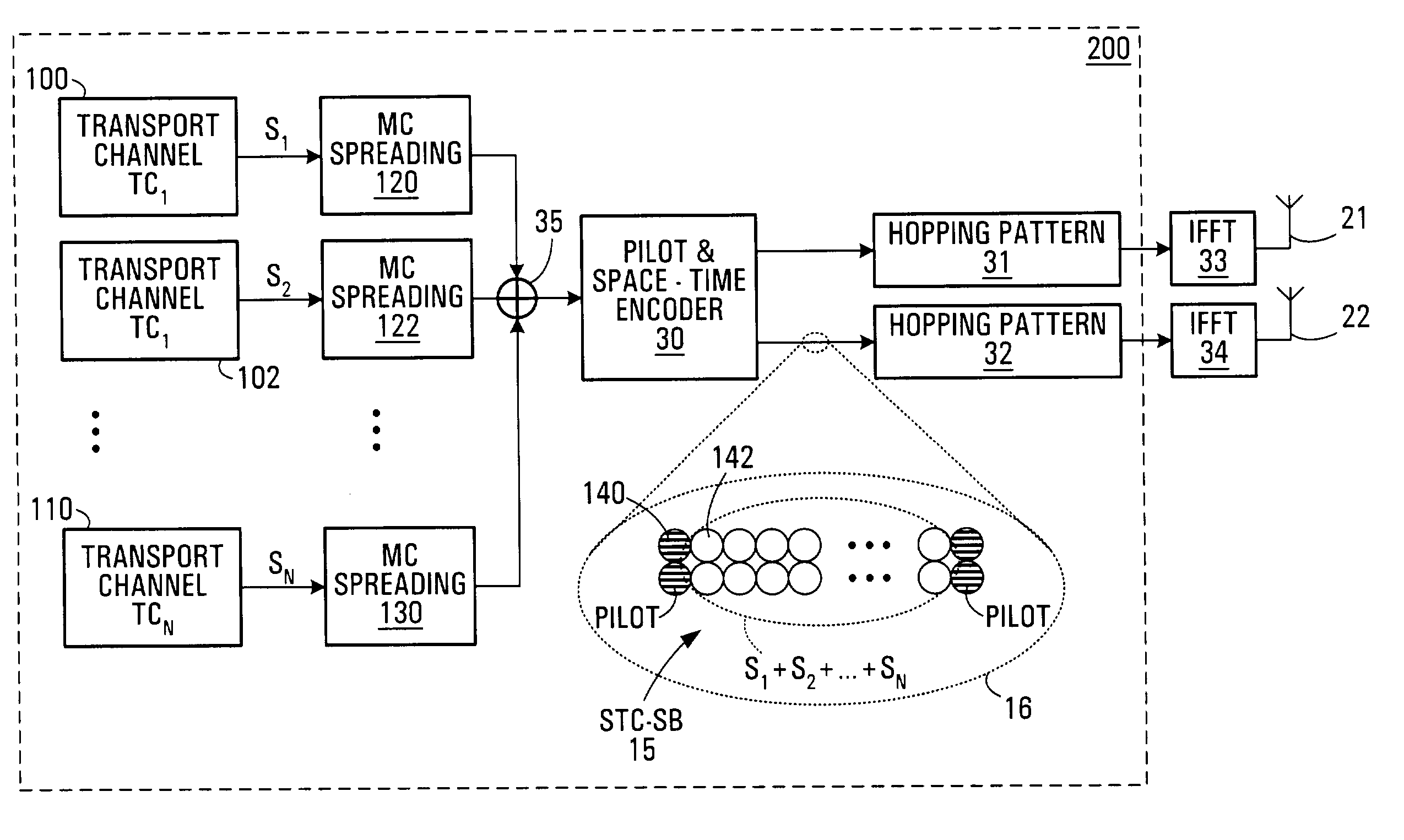
Dual-mode shared OFDM methods/transmitters, receivers and systems
ActiveUS7551546B2Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationNetwork terminationDual mode
A wireless terminal and network terminal are provided for implementing a new uplink OFDM protocol. In the new protocol, the wireless terminal has a first transmit chain for generating and transmitting a low rate mode OFDM transmission in a first frequency band of the OFDM band; and a second transmit chain for generating and transmitting a burst-mode transmission in a second frequency band of the OFDM band, the first frequency band being distinct from the second frequency band. An access channel is provided which is overlaid over the low rate mode transmissions of other users.
Owner:APPLE INC
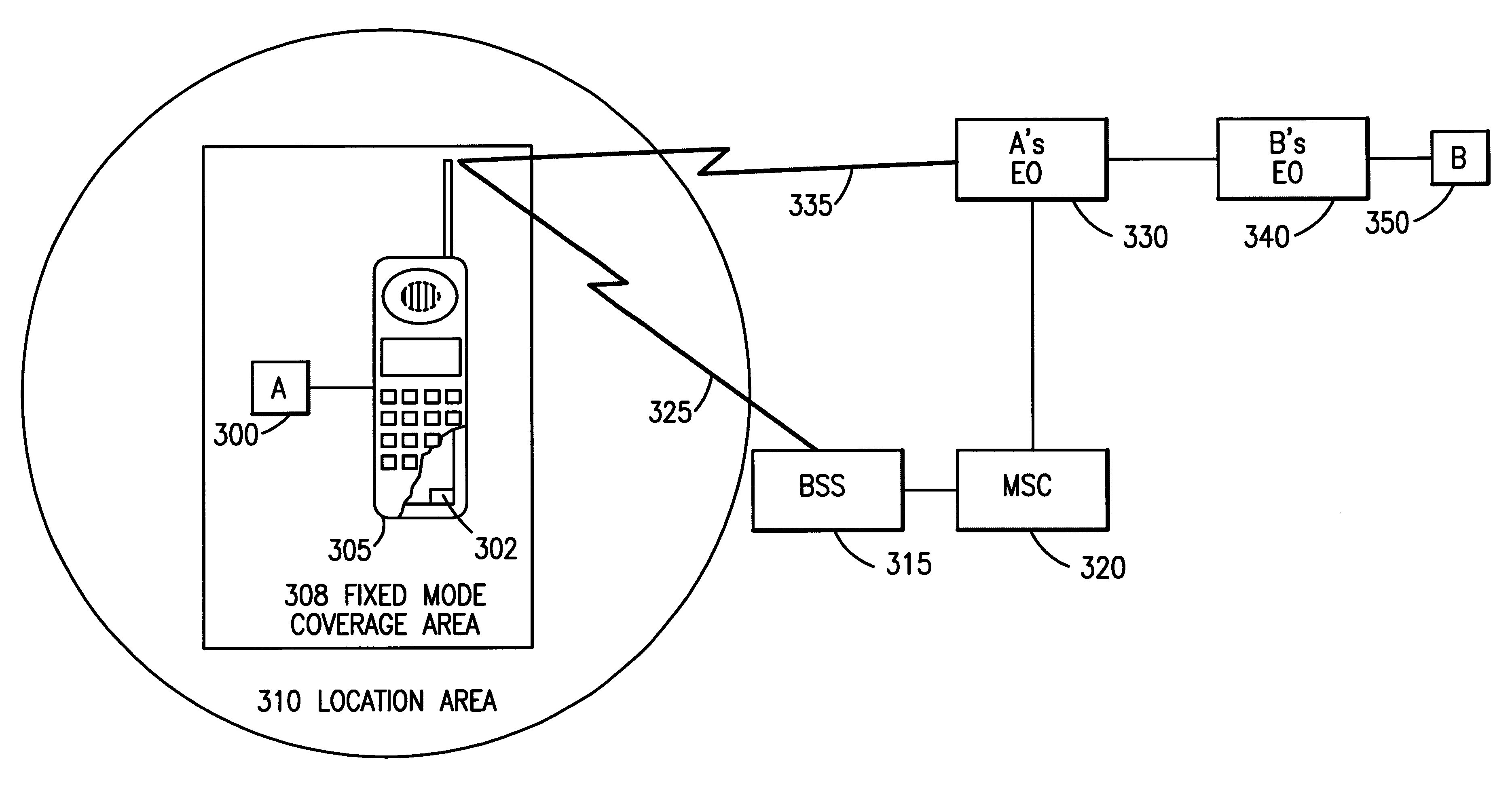
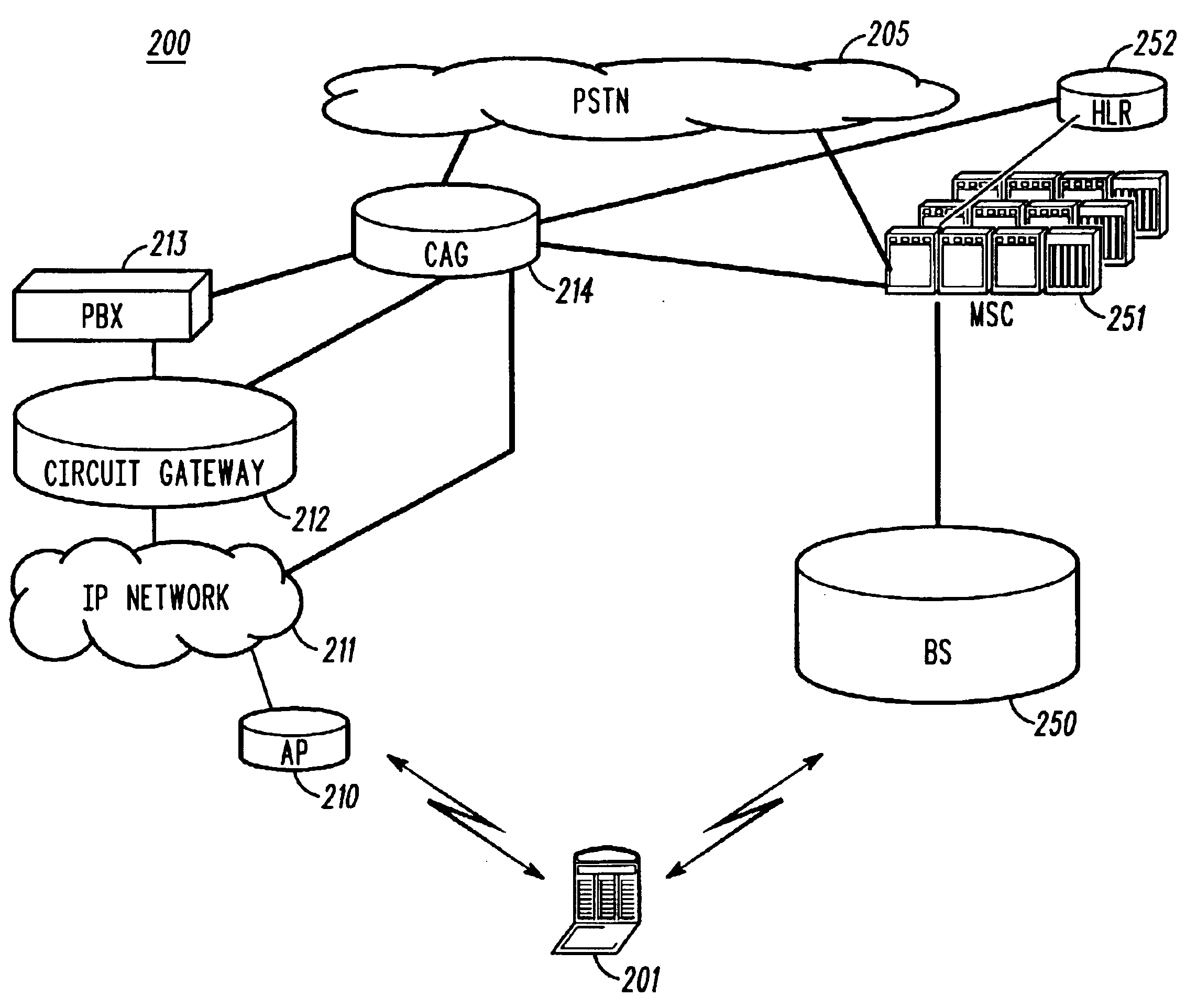
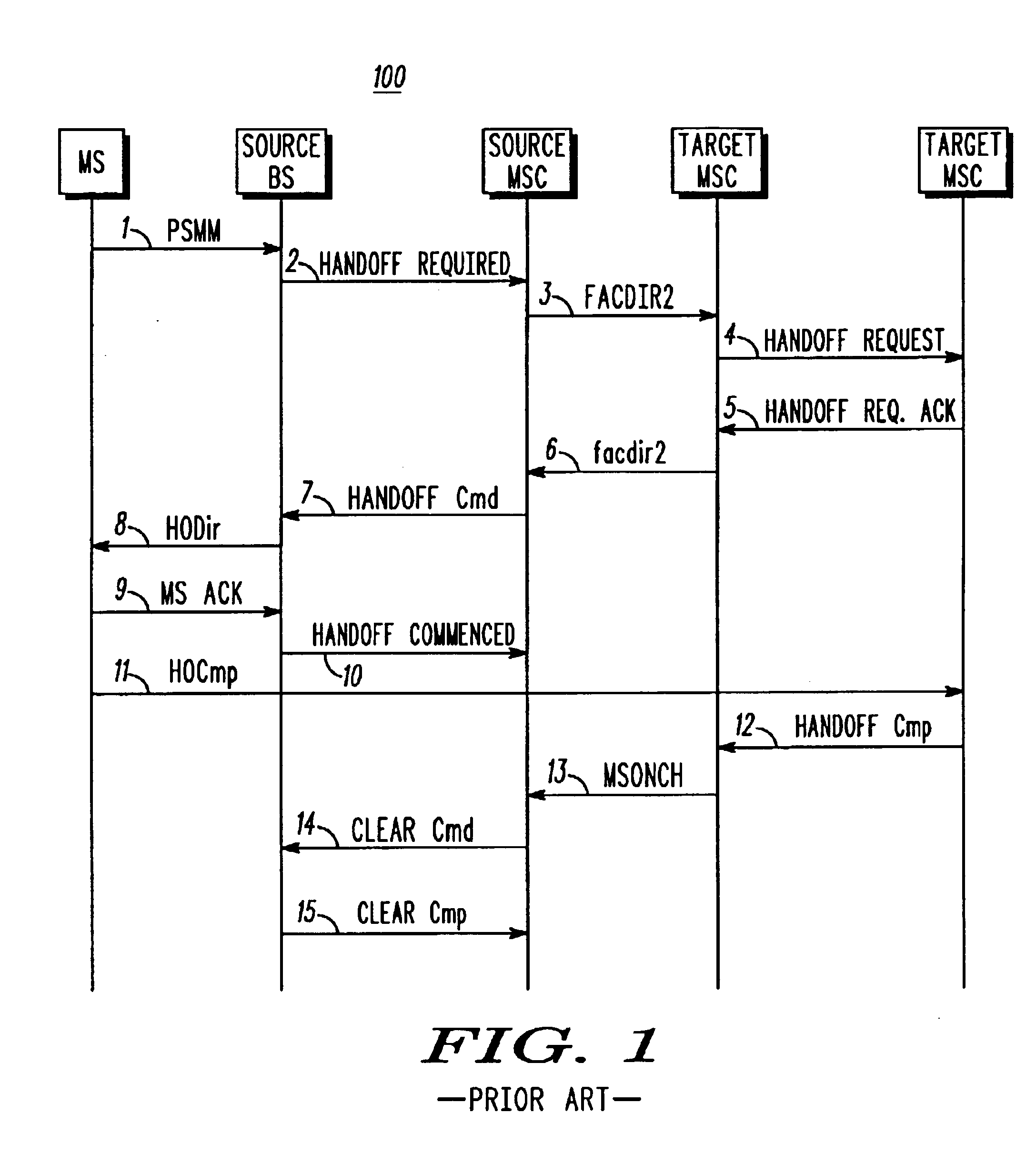
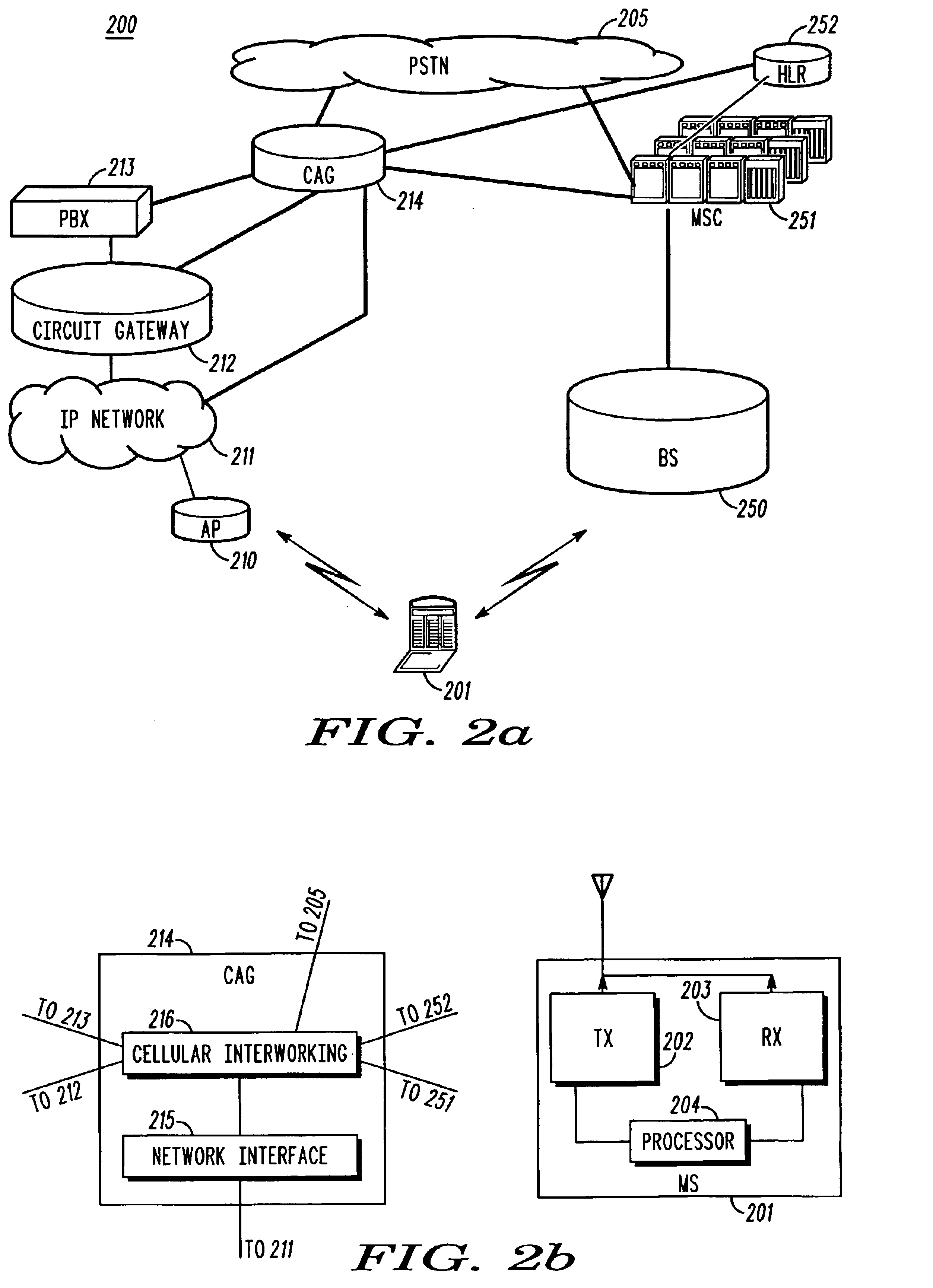
Method and apparatus for a source-initiated handoff from a source cellular wireless network to a target non-cellular wireless network
To address the need for an apparatus and method for handoff from a cellular wireless network to a non-cellular wireless network (WLAN, e.g.), the present application describes an access gateway (214) and a dual mode mobile station (201) that enable such handoffs. Dual mode MSs can determine when a handoff to a non-cellular network is preferred and request a handin (302) from the non-cellular network. The access gateway provides information to the MS (304) so that it can initiate a handoff through the serving cellular network. Triggering handoffs in this manner, allows cellular networks to handle handoffs to non-cellular networks in much the same way they handle inter-MSC handoffs today, i.e., source initiated.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Dual-mode phone using GPS power-saving assist for operating in cellular and WiFi networks
InactiveUS20060063560A1Low powerReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTWireless network protocolsWide areaTransceiver
A dual-mode mobile station for accessing a wide-area wireless network according to a first wireless protocol and a small-area wireless network according to a second wireless protocol. The dual-mode mobile station comprises a controller that switches the dual-mode mobile station between a first mode in which the dual-mode mobile station communicates with the wide-area wireless network and a second mode in which the dual-mode mobile station communicates with the small-area wireless network. The controller switches the dual-mode mobile station between the first and second modes depending on a distance between the dual-mode mobile station and an access point of the small-area wireless network. When the dual-mode transceiver enters the first mode, the controller turns off a transceiver that operates in the second mode in order to save power.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
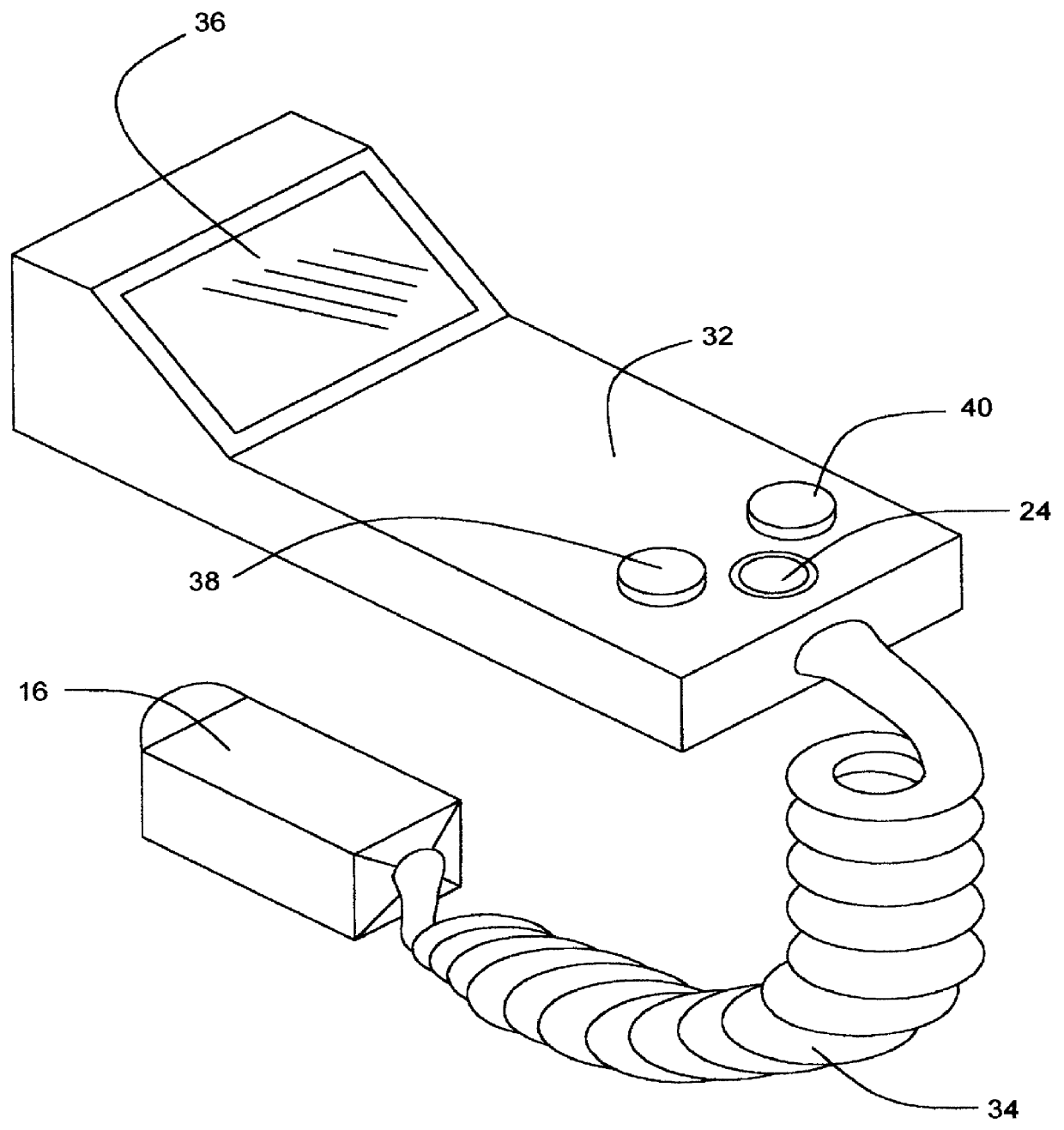
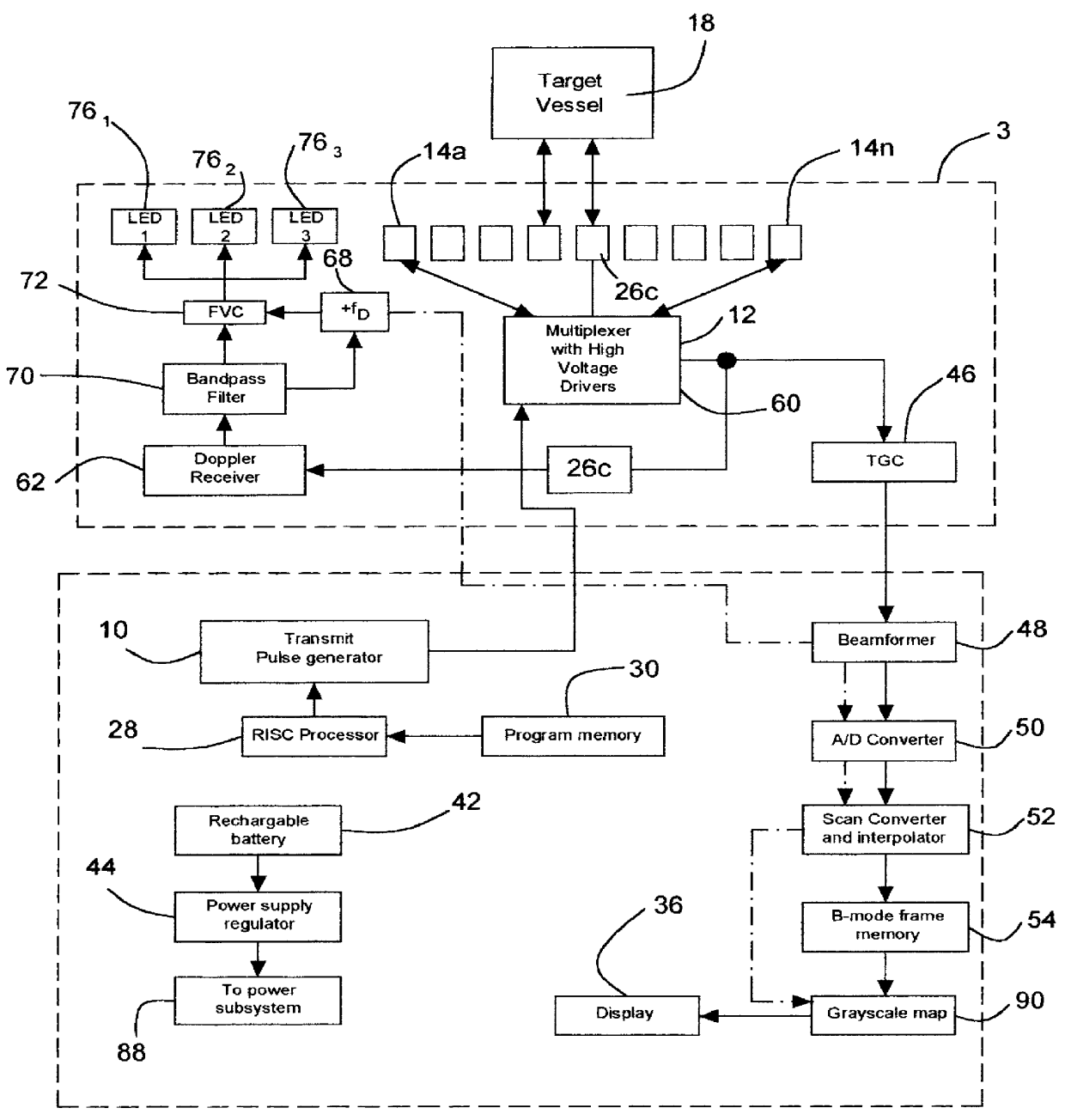
Method and apparatus for ultrasound guided intravenous cannulation
InactiveUS6132379AEasy to operateQuick buildBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionVenous accessDual mode
A dual mode handheld ultrasonic device is provided for guiding a venous access catheter into a patient's peripheral vein. It provides B-mode imaging with a predetermined aperture and operating frequency which locates and displays a gray scale cross-sectional image of the target blood vessel. A single doppler beam in a separate mode detects the same blood vessel and creates a single scanline image superimposed to such B-mode cross-sectional image. Simultaneously, the intensity of the positive doppler shift detected by the single doppler beam as it hits the target blood vessel activates a plurality of light emitting diode (LED) indicator lights with varying voltage requirements mounted in the scanhead. Activated LED indicator lights forms an arrow pointing inferiorly perpendicular to the target vessel which guides a physician or a paramedical professional to the precise catheter insertion spot on a patient's extremity while simultaneously viewing the target blood vessel's cross-section on the display screen.
Owner:PATACSIL ESTELITO G +1
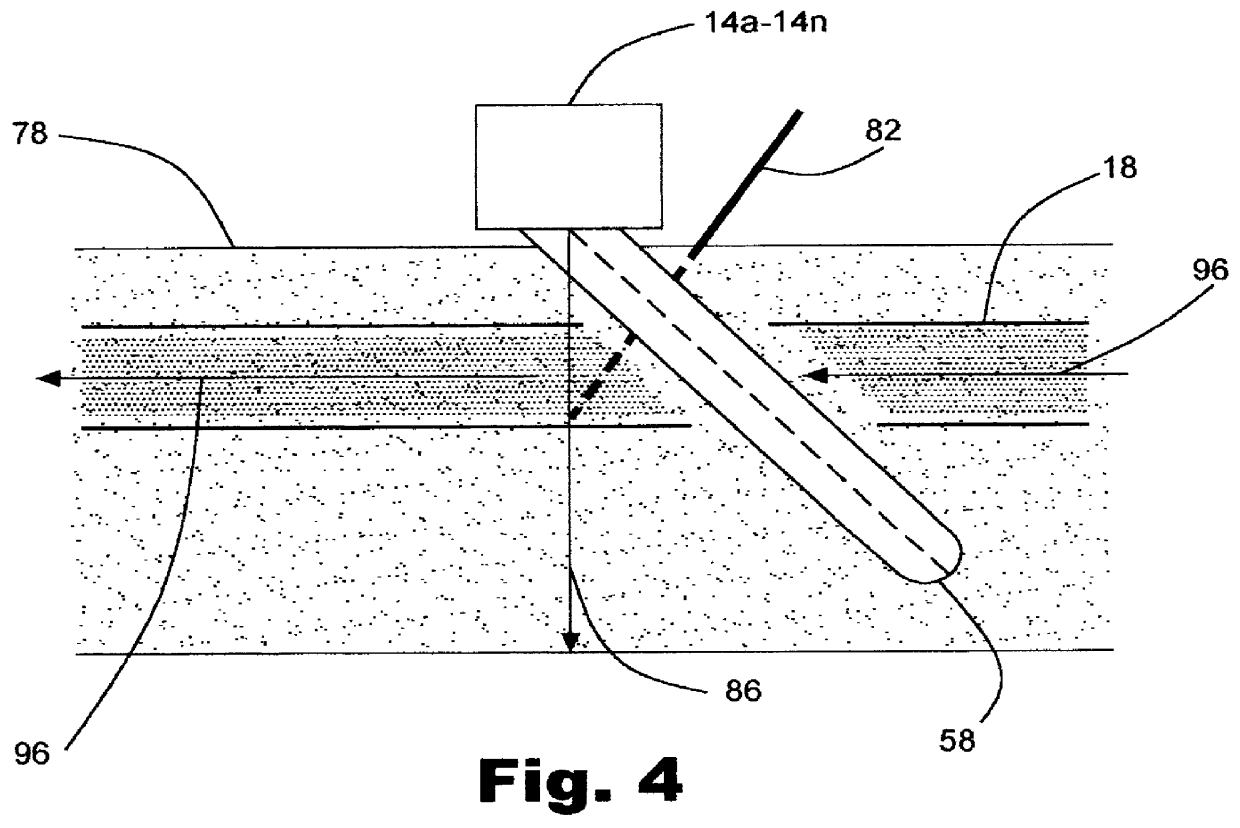
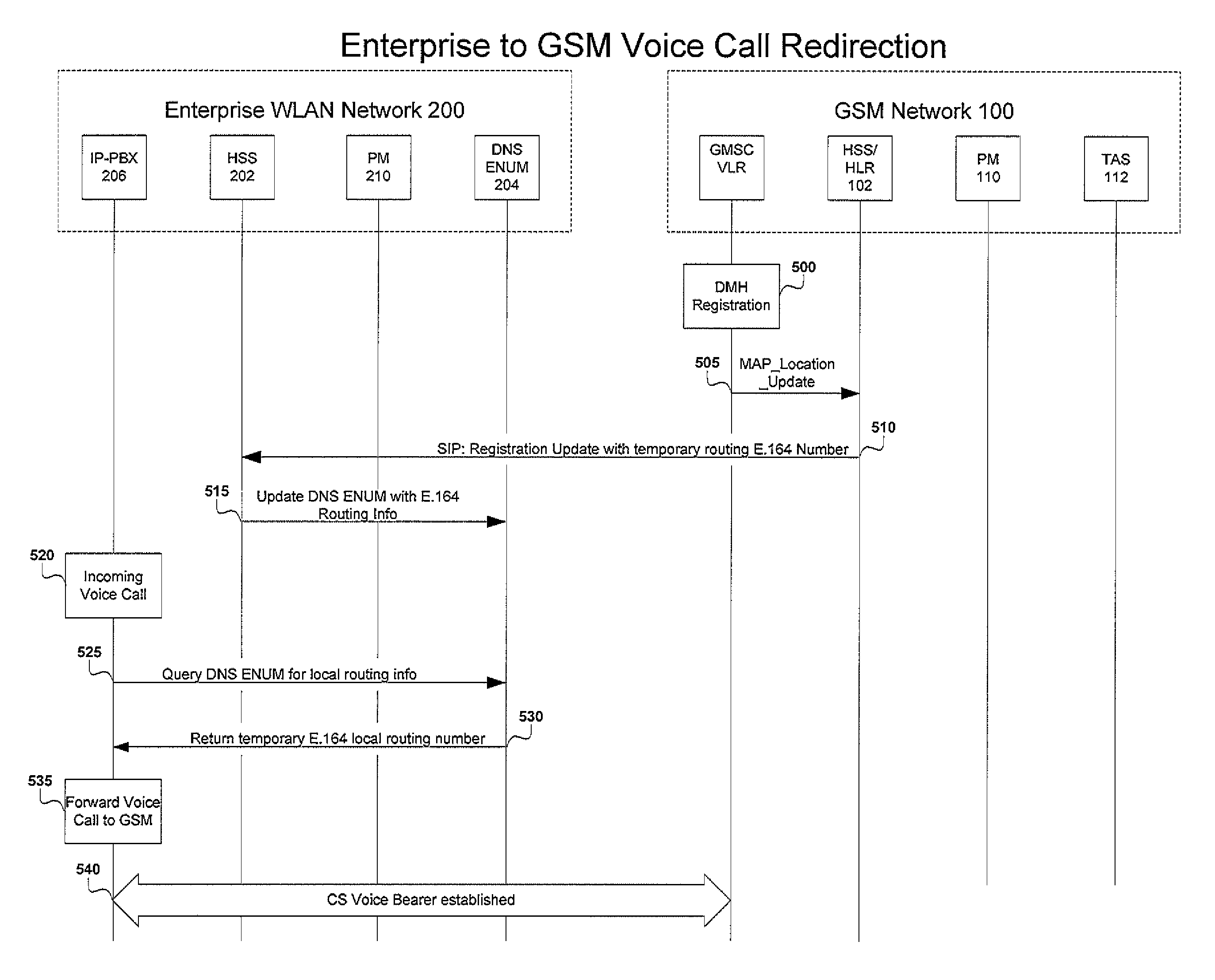
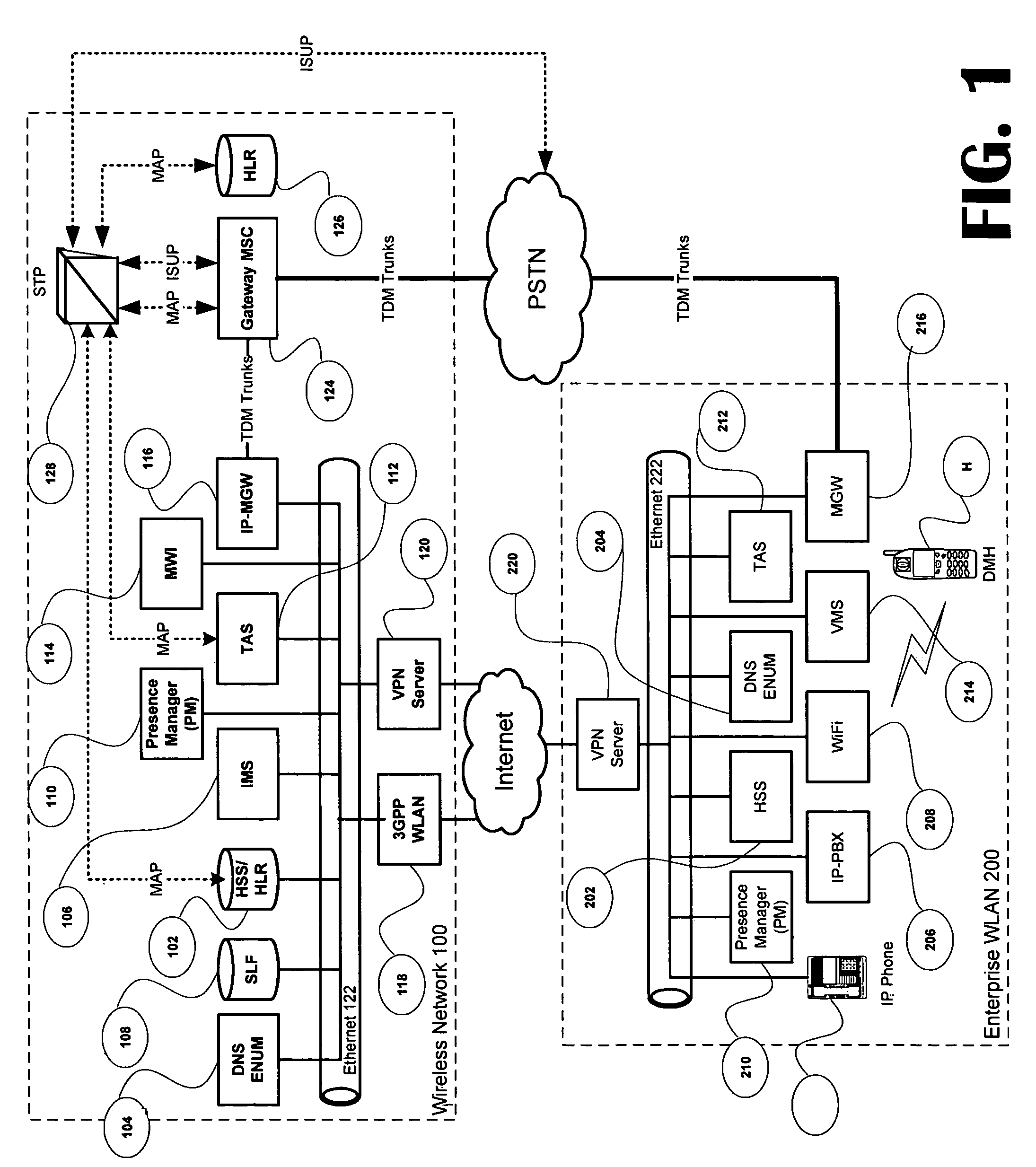
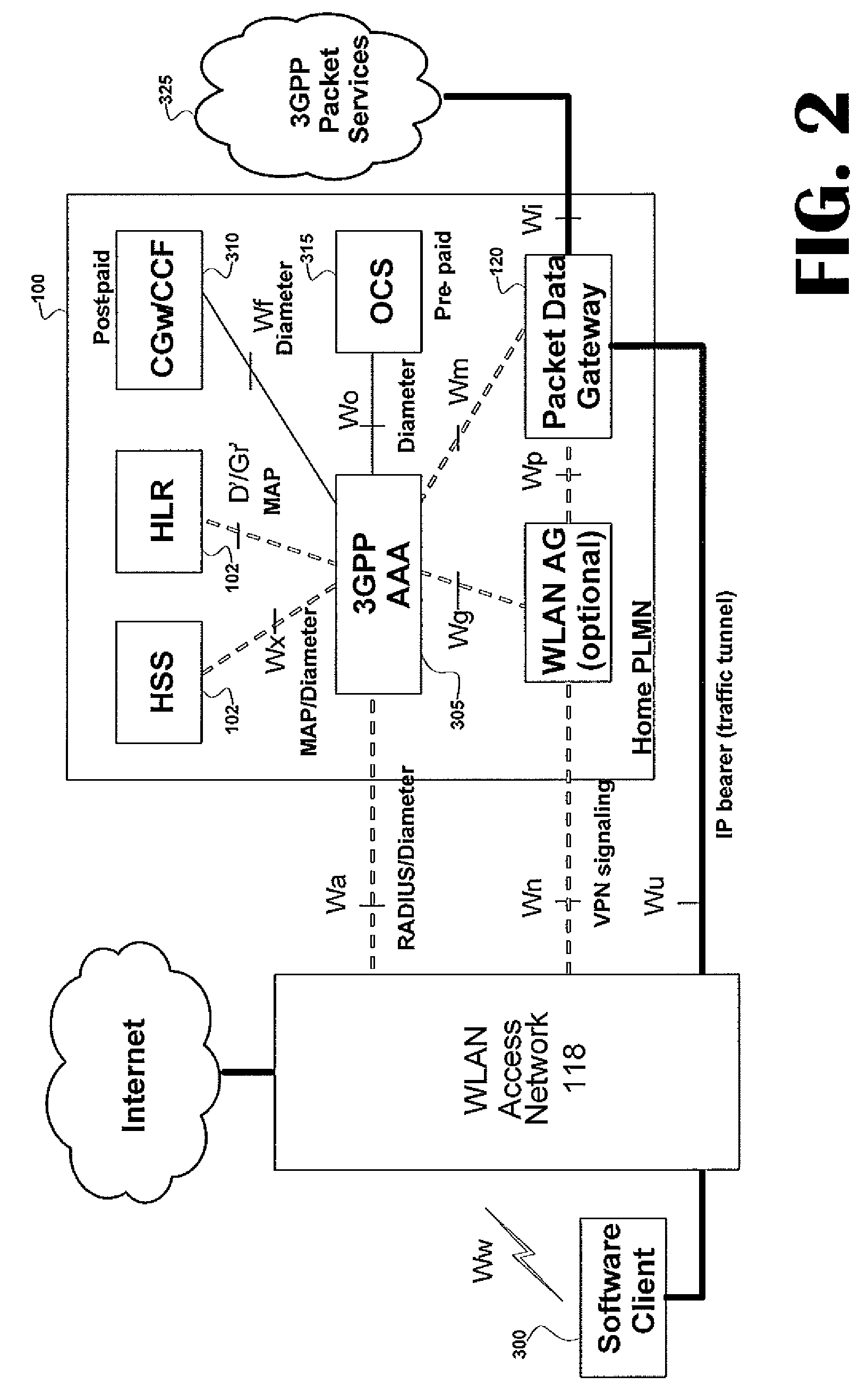
Voice call redirection for enterprise hosted dual mode service
ActiveUS7664495B1Network topologiesCommmunication supplementary servicesDevice registerSpecific function
Systems and methods provide a single E.164 number for voice and data call redirection and telephony services such as caller identification, regardless of in which type of network a dual mode mobile device operates. When the dual mode device registers and is active in a GSM network, temporary routing and status updates are triggered and resultant information is maintained in both networks. A mobile terminated call is routed through an enterprise WLAN with call control within the enterprise being handled by SIP or H.323 signaling, and the call is redirected to the mobile device in the GSM network, where call control is assumed by the SS7 network. Services are provided using the protocols native to the active network, and the single E.164 is used consistently along with or lieu of the temporary routing information for subscriber identity specific functions, such as caller identification and voice mail.
Owner:MITEL NETWORKS INC +1
Antenna with a conductive layer and a two-band transmitter including the antenna
InactiveUS20020003499A1Improve matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual modeTwo band
The antenna of said transmitter is a microstrip antenna. A rear edge of its patch is provided with a short circuit by means of which a quarter-wave primary resonance can be excited by a coplanar line formed by two coupling slots in an area. Separator slots separate said area from another area in which a secondary resonance can be established at twice the frequency of the primary resonance from a slotted line extending one slot of the coplanar line. The invention applies in particular to the production of a dual-mode mobile telephone to the GSM and DCS standards.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
System and method for pairing dual mode wired/wireless devices
InactiveUS20060068760A1Near-field transmissionNetwork topologiesCommunication interfaceComputer network
A method and apparatus for establishing wireless communication between a first and a second dual mode device, each dual mode device having a wired communication interface and a wireless communication interface. A wired connection between the first dual mode device and the second dual mode device is established via the wired communication interfaces. The second dual mode device is detected by the first dual mode device and a link key is created. The link key and the first device address are transferred to the second device via the wired connection and the second device address is retrieved via the wired connection by the first device. A wireless link is then established.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
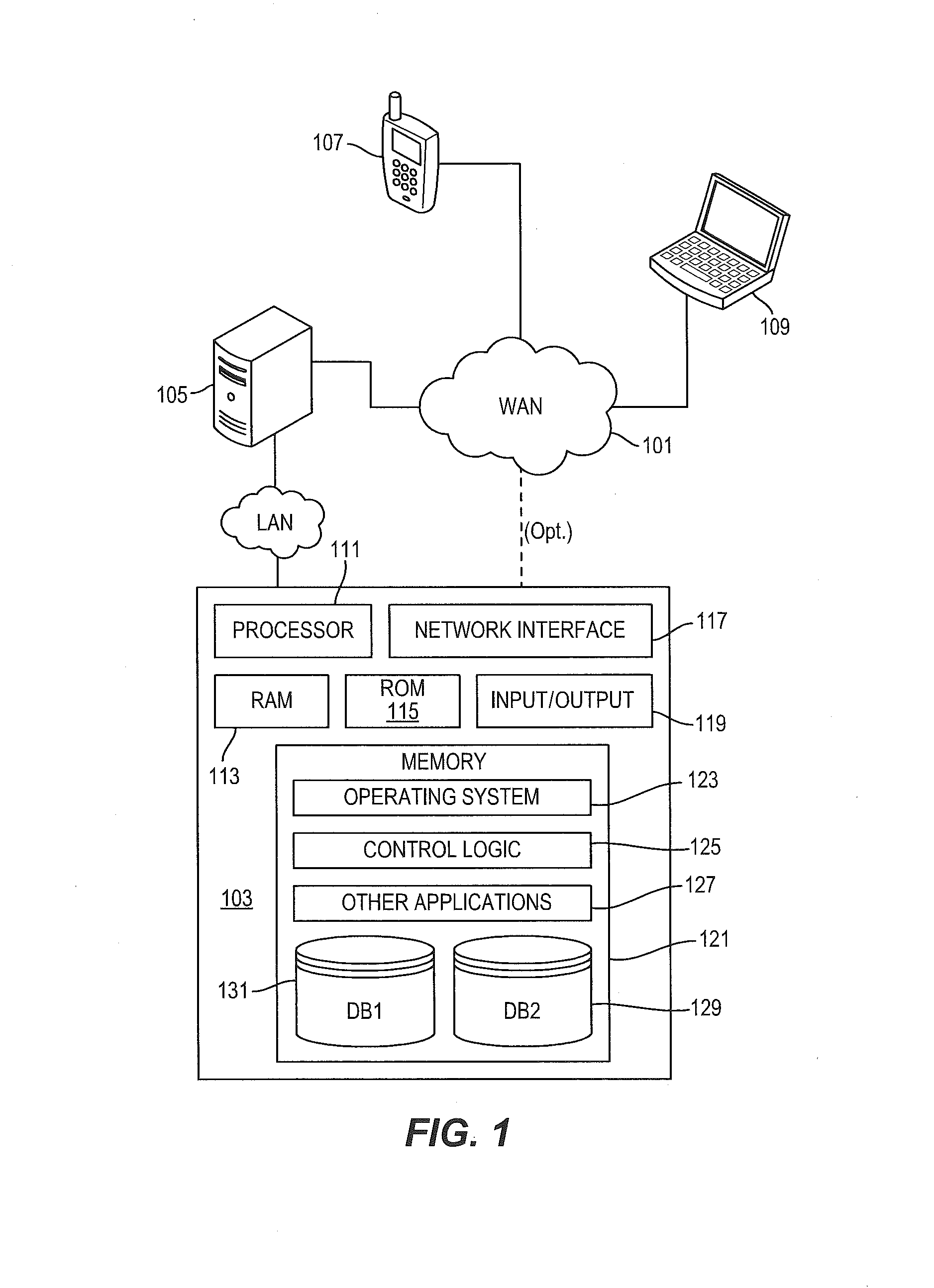
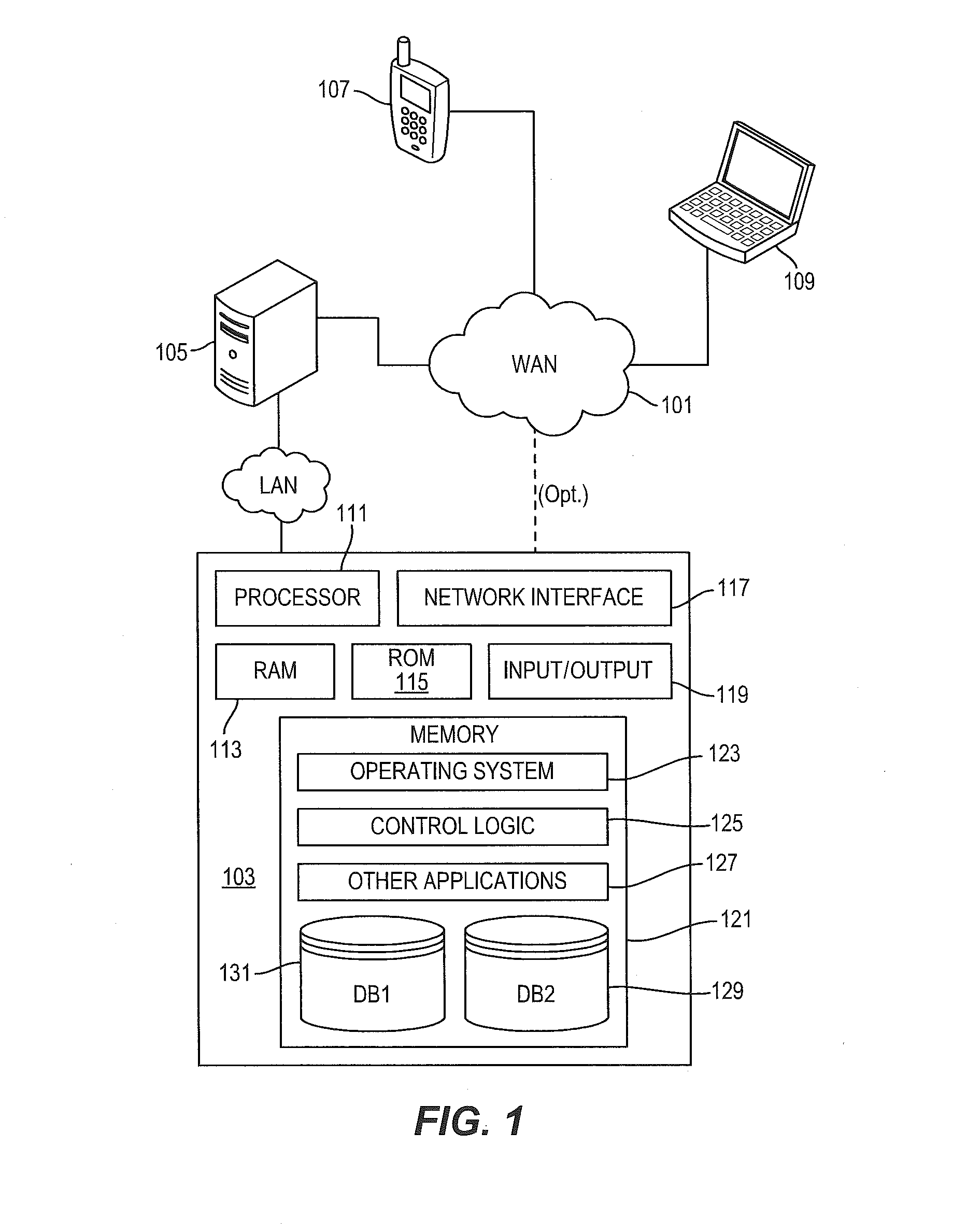
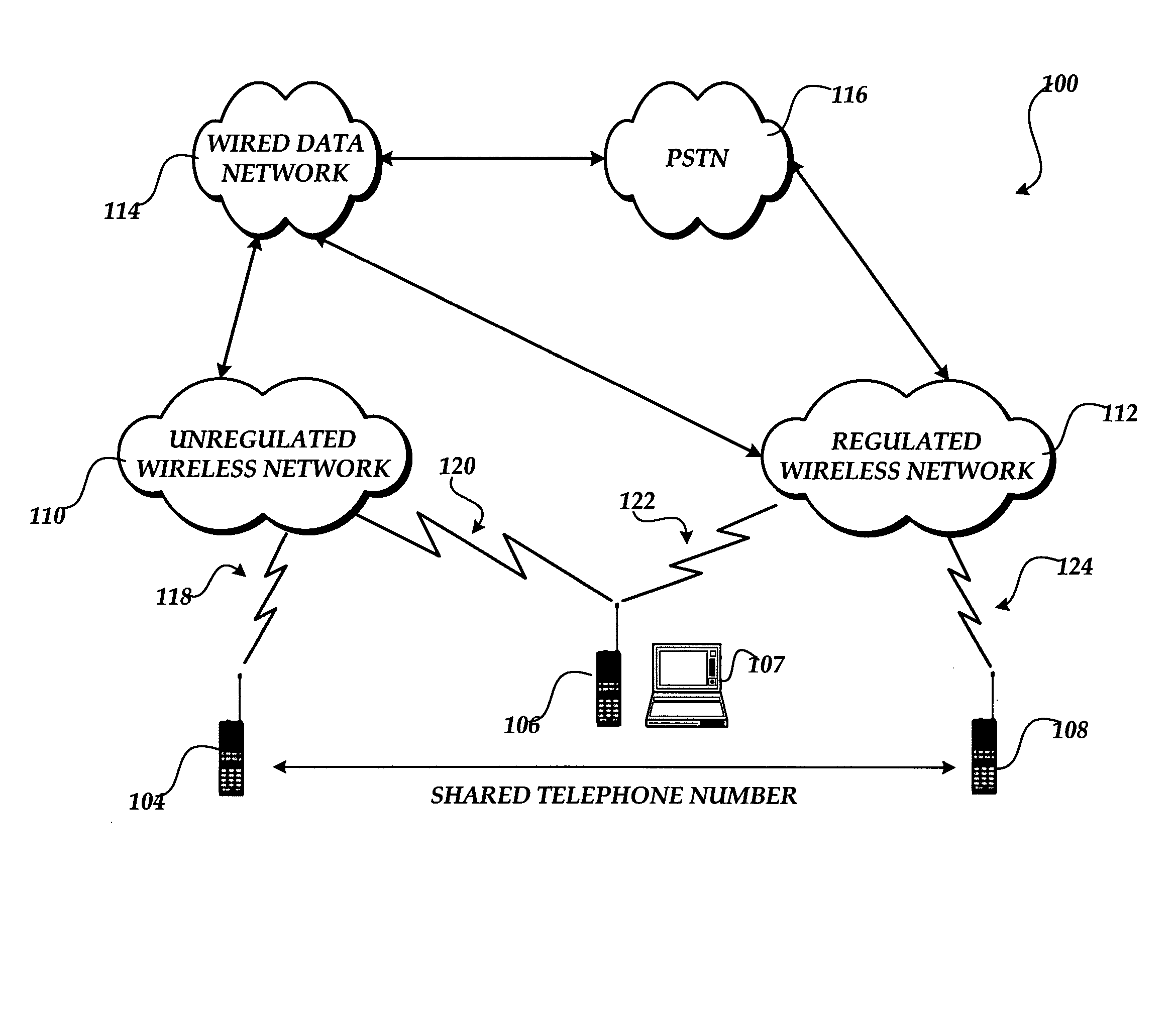
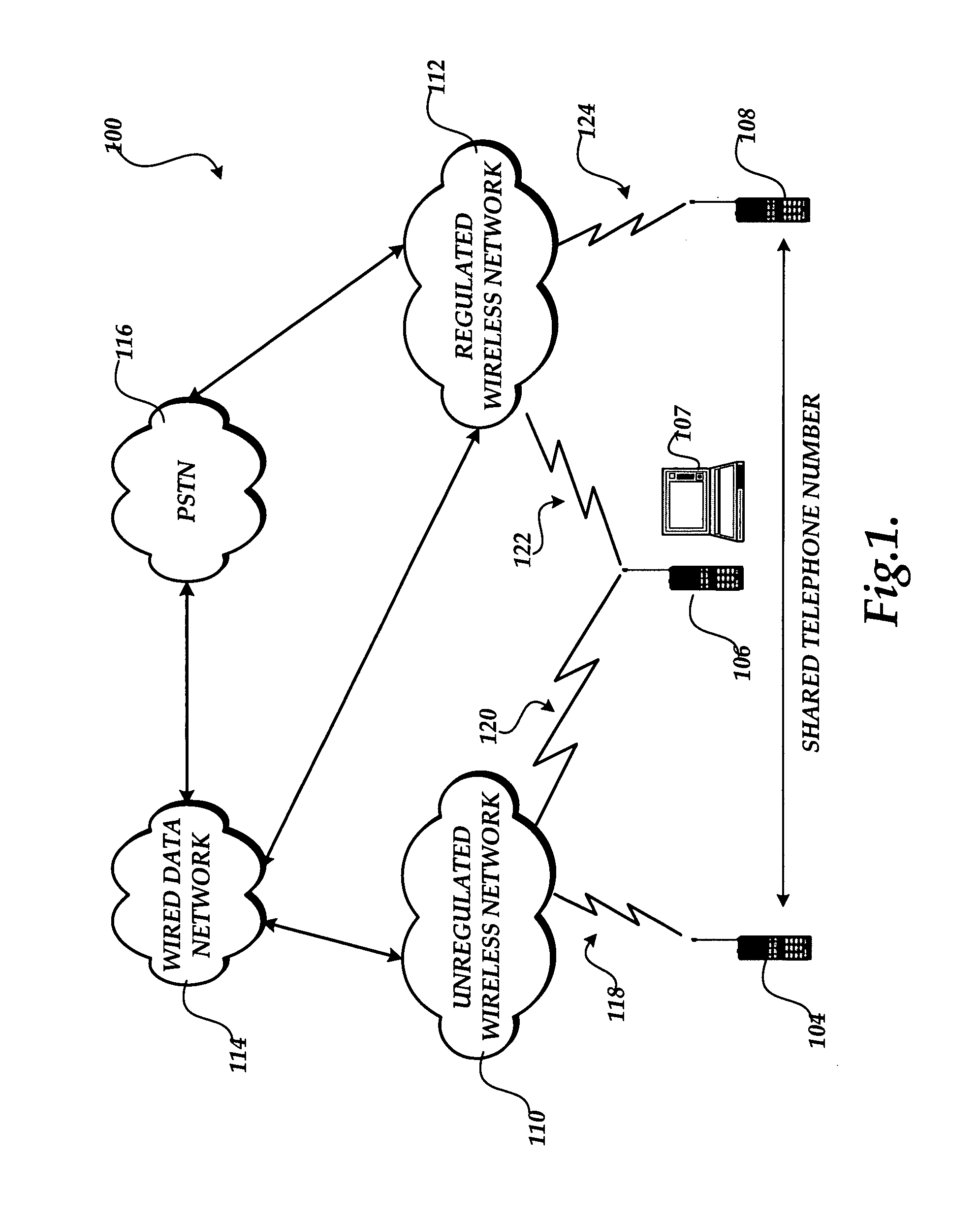
System and method for providing integrated voice and data services utilizing wired cordless access with unlicensed spectrum and wired access with licensed spectrum
InactiveUS20060019667A1Special service for subscribersConnection managementFrequency spectrumDual mode
Systems and methods for providing integrated wireless and wired data voice and data services via a dual mode telecommunications device are provided. A communication directed to an address associated with a dual mode device is received. If the dual mode device is in range of a wireless access point connected to a wired data network, then a determination is made whether the address of the dual mode device is associated with an address of at least one other device associated with the wired data network. If the address of the dual mode device is associated with an address of at least one other device associated with the wired data network, then the communication is routed over the wired data network to the dual mode device and the at least one other device.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
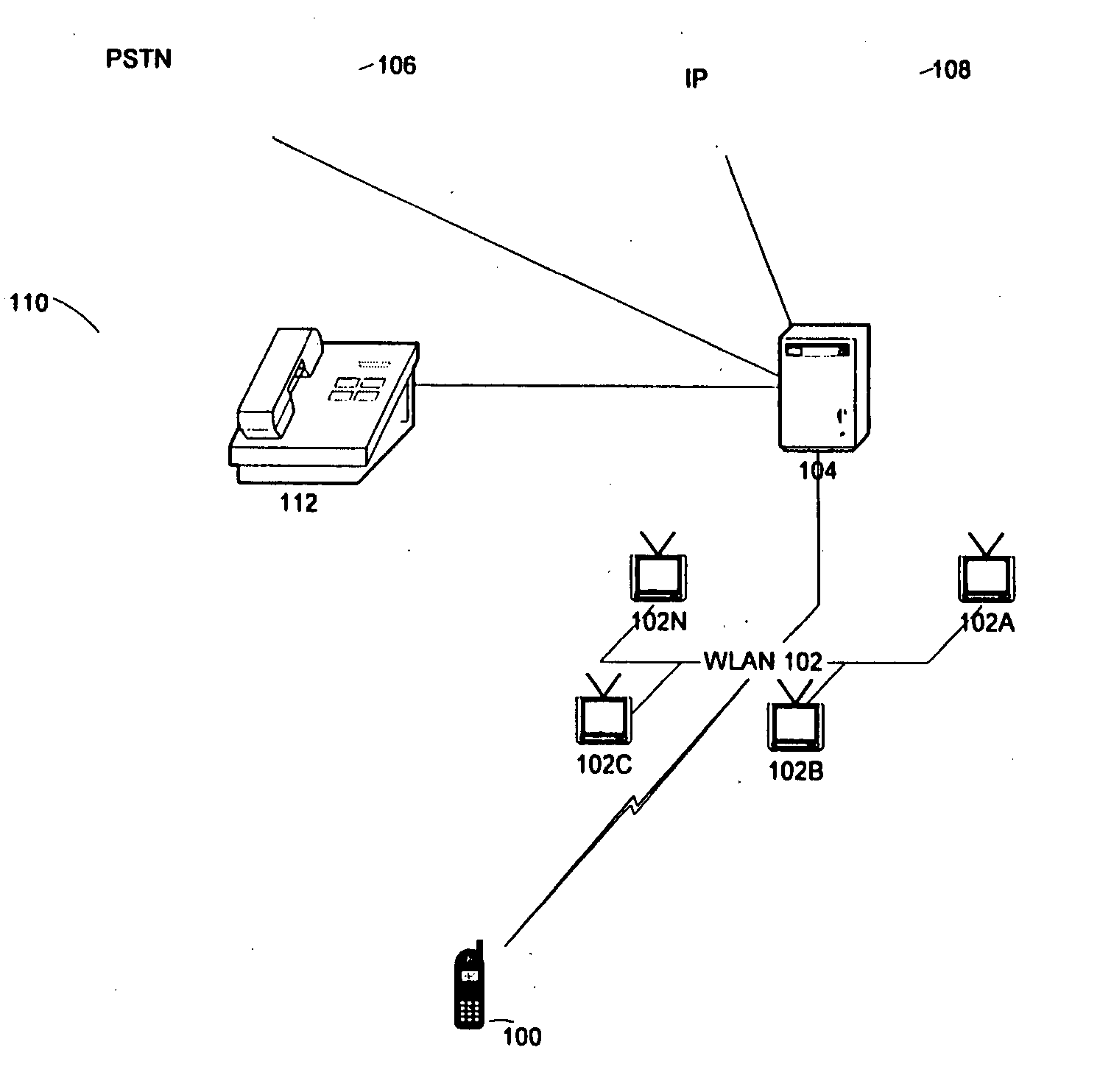
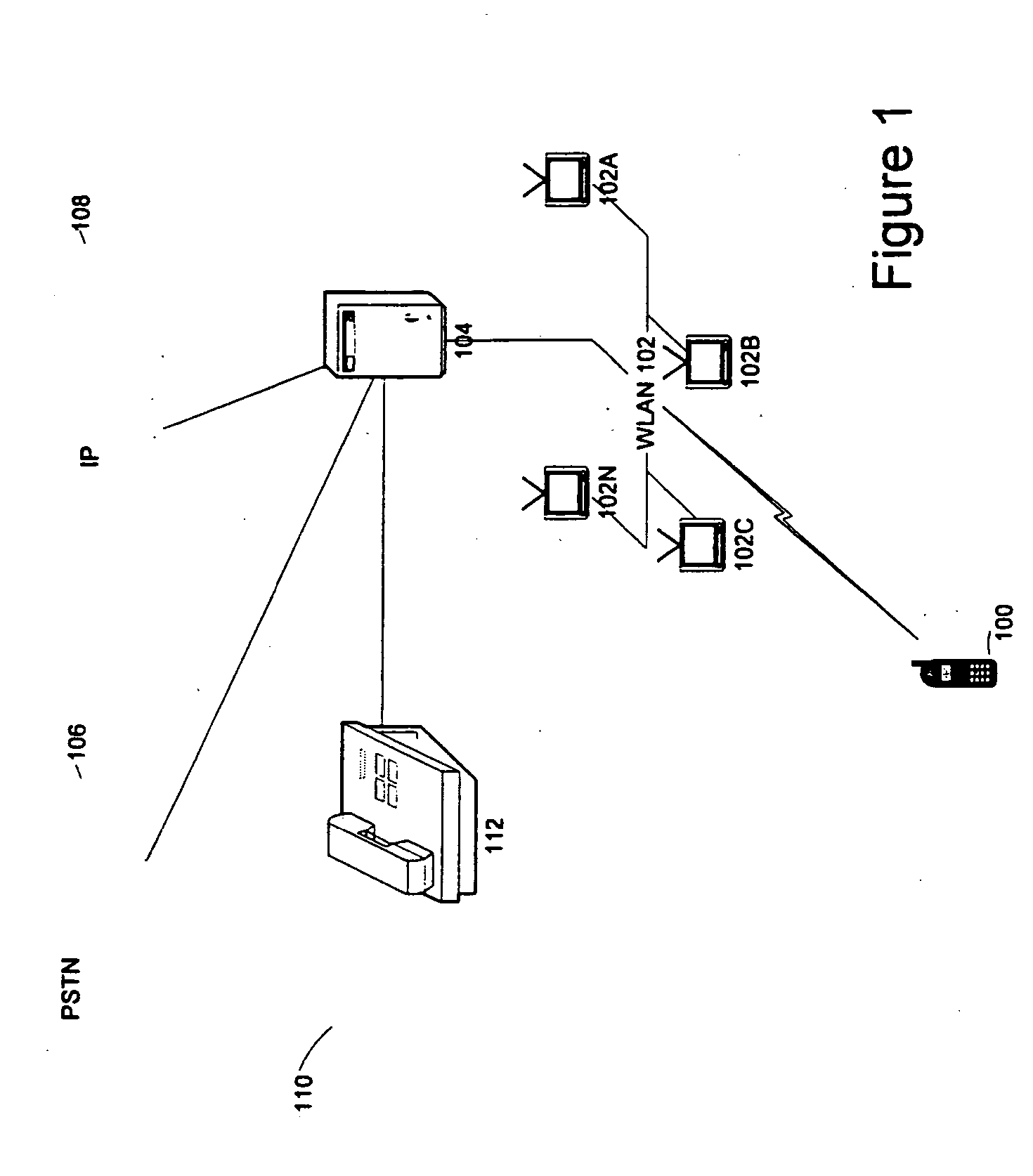
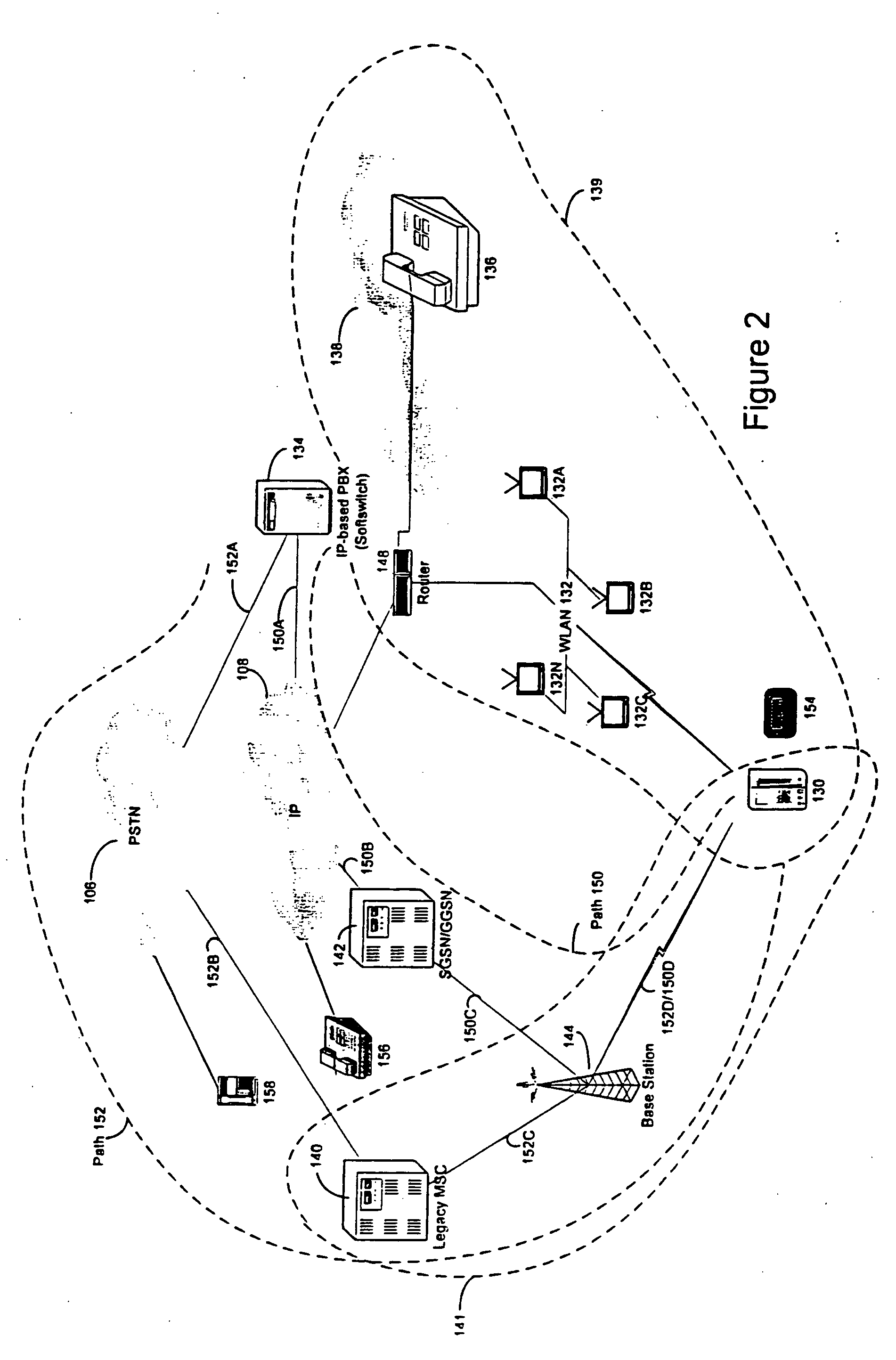
Extension of a local area phone system to a wide area network
InactiveUS20060205436A1Telephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersSession Initiation ProtocolDual mode
A soft switch 134 providing wireless PBX voice services to a local area network (WLAN) is used to extend PBX functionality to the cellular domain. A dual mode remote unit is capable of receiving signals both in the cellular system as well as the WLAN. The cellular system is comprised of a data-bearing path and a voice-bearing path. When the dual mode remote unit is within the WLAN, it communicates both voice over IP (VoIP) signaling as well as session initiation protocol (SIP) control signaling over the WLAN. When the remote unit is outside the WLAN, it communicates voice signaling over the voice-bearing path of the cellular network using a standard cellular voice channel. In parallel, it uses the data-bearing path of the cellular network to transmit SIP control signaling.
Owner:LON COMM MGMT
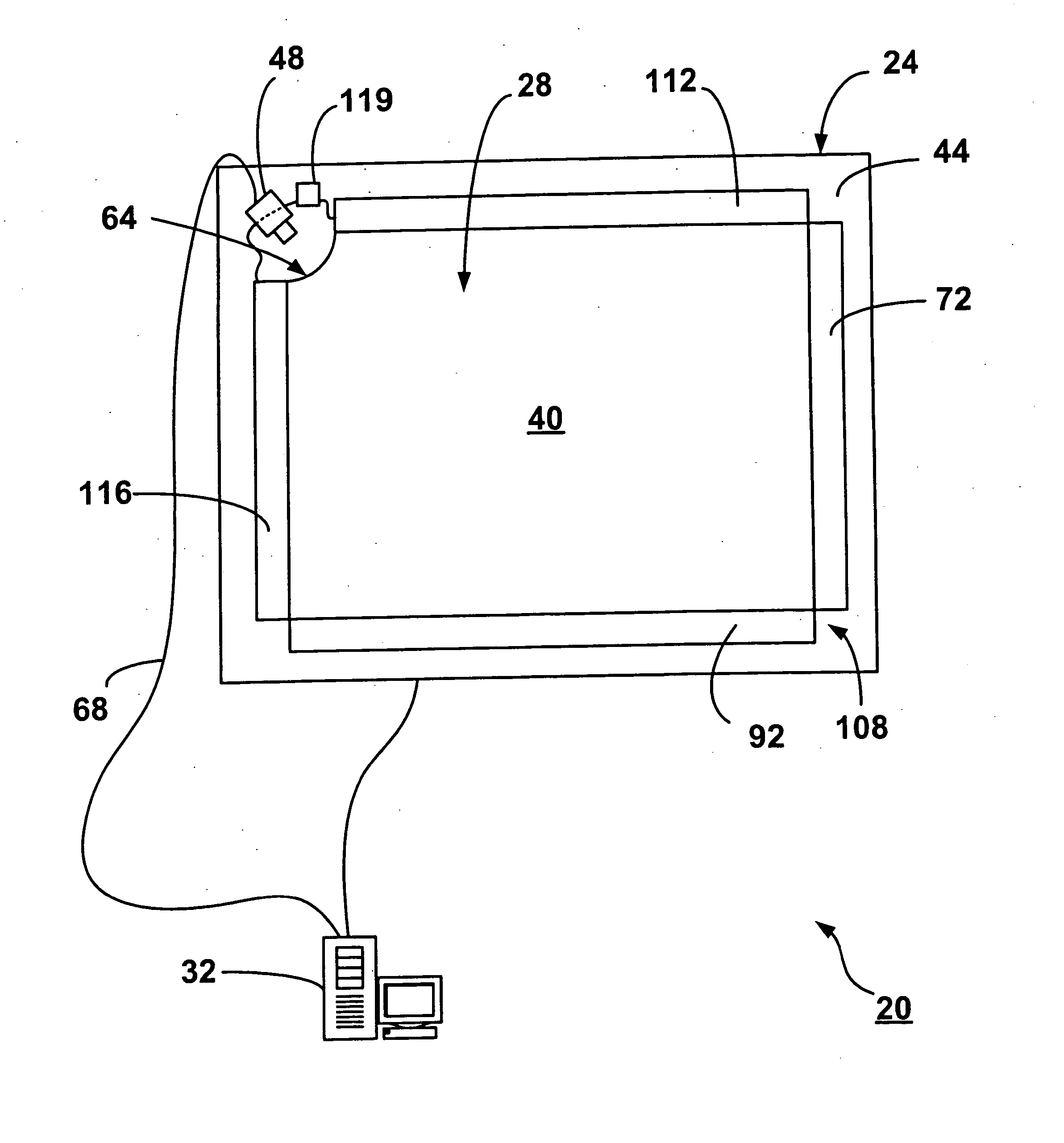
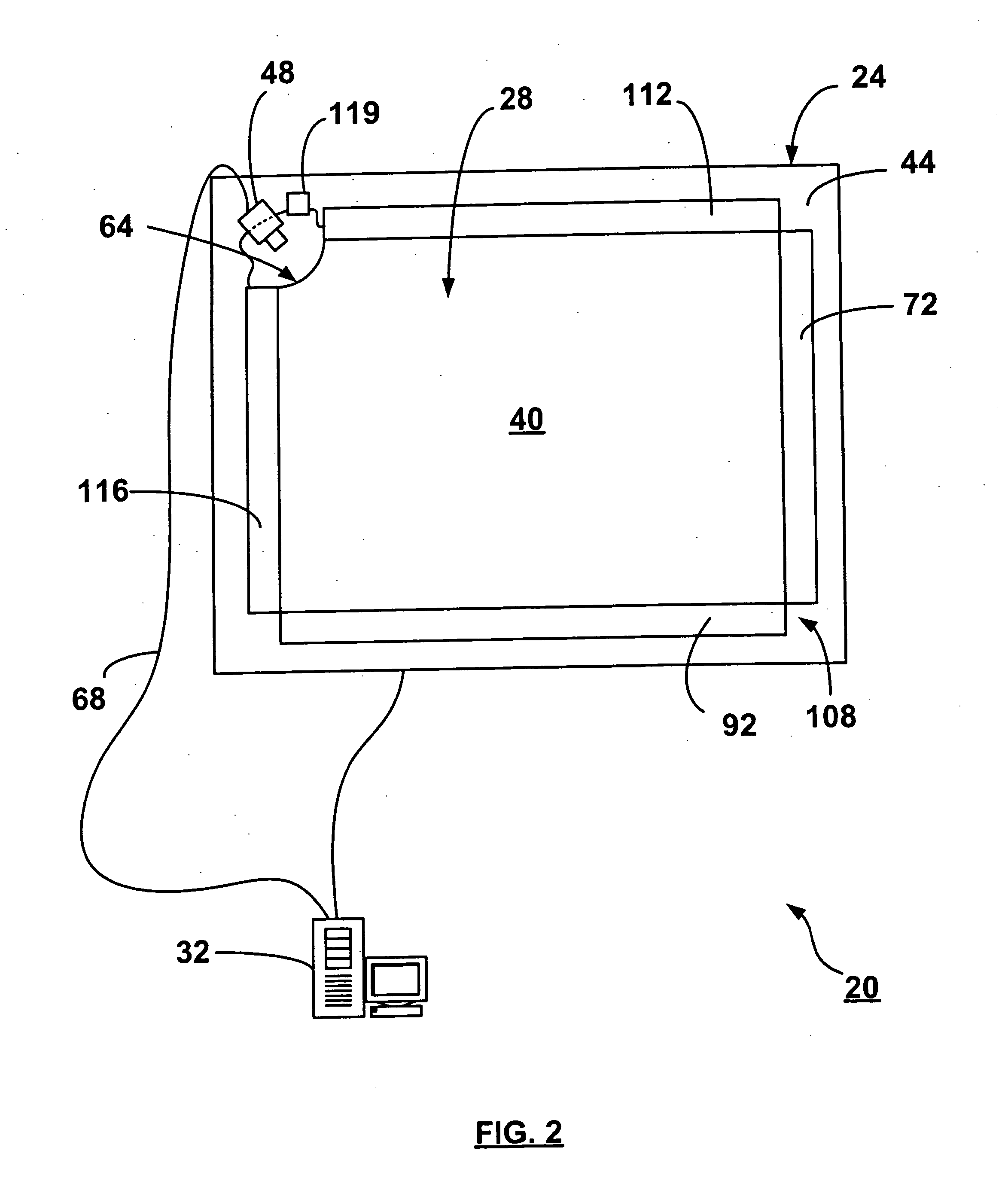
Dual mode touch system
An apparatus for detecting a pointer includes a waveguide and a touch surface over the waveguide on which pointer contacts are to be made. At least one reflecting device extends along a first side of the waveguide and touch surface. The reflecting device defines an optical path between the interior of the waveguide and the region of interest above the touch surface. At least one imaging device looks across the touch surface and into the waveguide. The imaging device captures images of the region of interest and within the waveguide including reflections from the reflecting device.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Automated adaptive muscle stimulation method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050283204A1Easy to integrateEnhancing user comfortElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An automated adaptive muscle stimulation system and method are disclosed. The stimulation system includes at least one electrode assembly adapted to deliver a muscle stimulation signal to the tissue of a user, a sensor system adapted to detect a muscle response, and an electrical stimulation device operably coupled to the at least on electrode assembly and the sensor system, the electrical stimulation device including a control system operable to automatically diagnose at least one characteristic of a muscle from the detected muscle response and adjust at least one parameter of the muscle stimulation signal in response thereto to deliver an adjusted muscle stimulation signal. A dual mode muscle stimulation system adapted to accept first and second data sets and provide first and second levels of treatment data is also disclosed.
Owner:DJO GLOBAL SWITZERLAND SARL
Dual mode hemodialysis machine
A compact portable dual mode hemodialysis machine system is provided. The system includes a sorbent dialysis module with a sorbent cartridge that purifies a dialysate fluid that flows therethrough, where the sorbent dialysis module returns the purified dialysate fluid from the sorbent cartridge to an inlet of a dialyzer. The system also includes a single-pass dialysis module with an acetate pump, a bicarbonate pump and a mixing chamber, where the acetate and bicarbonate pumps flow acetate and bicarbonate mixtures, respectively, into the mixing chamber. The single-pass dialysis module receives a desired amount of water from a reverse osmosis device, the single-pass dialysis module operated to direct used dialysate from the dialyzer to a drain. The machine system can be operated to replace the sorbent cartridge with the single-pass dialysis module to switch the operation of the dual mode hemodialysis machine system from a sorbent dialysis mode to a single-pass dialysis mode
Owner:C TECH BIOMEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com