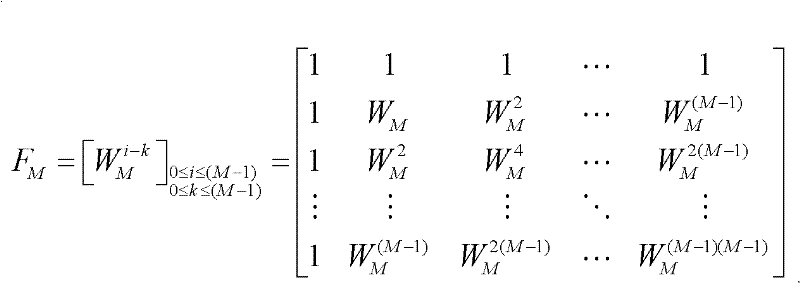Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
265 results about "Ofdm transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
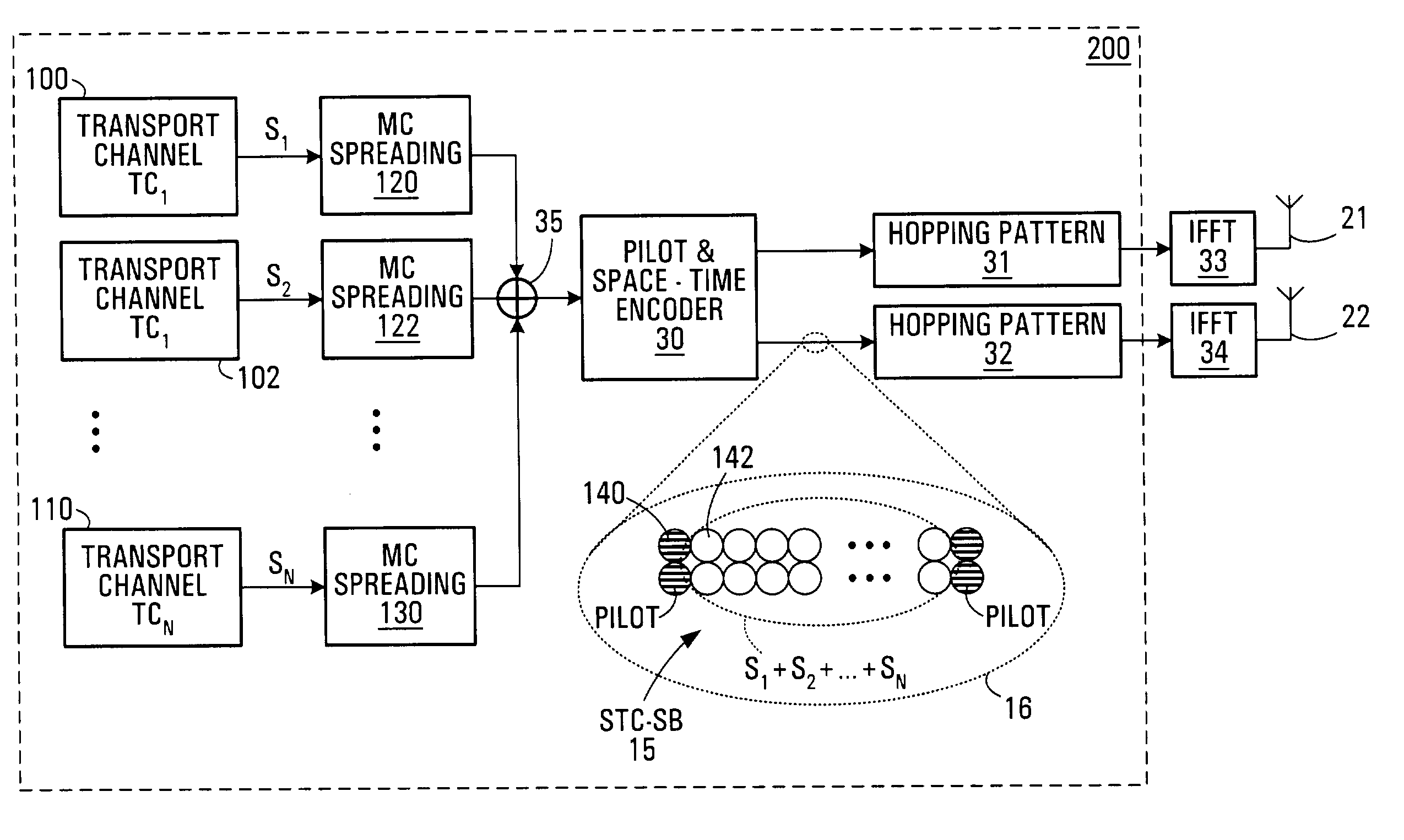
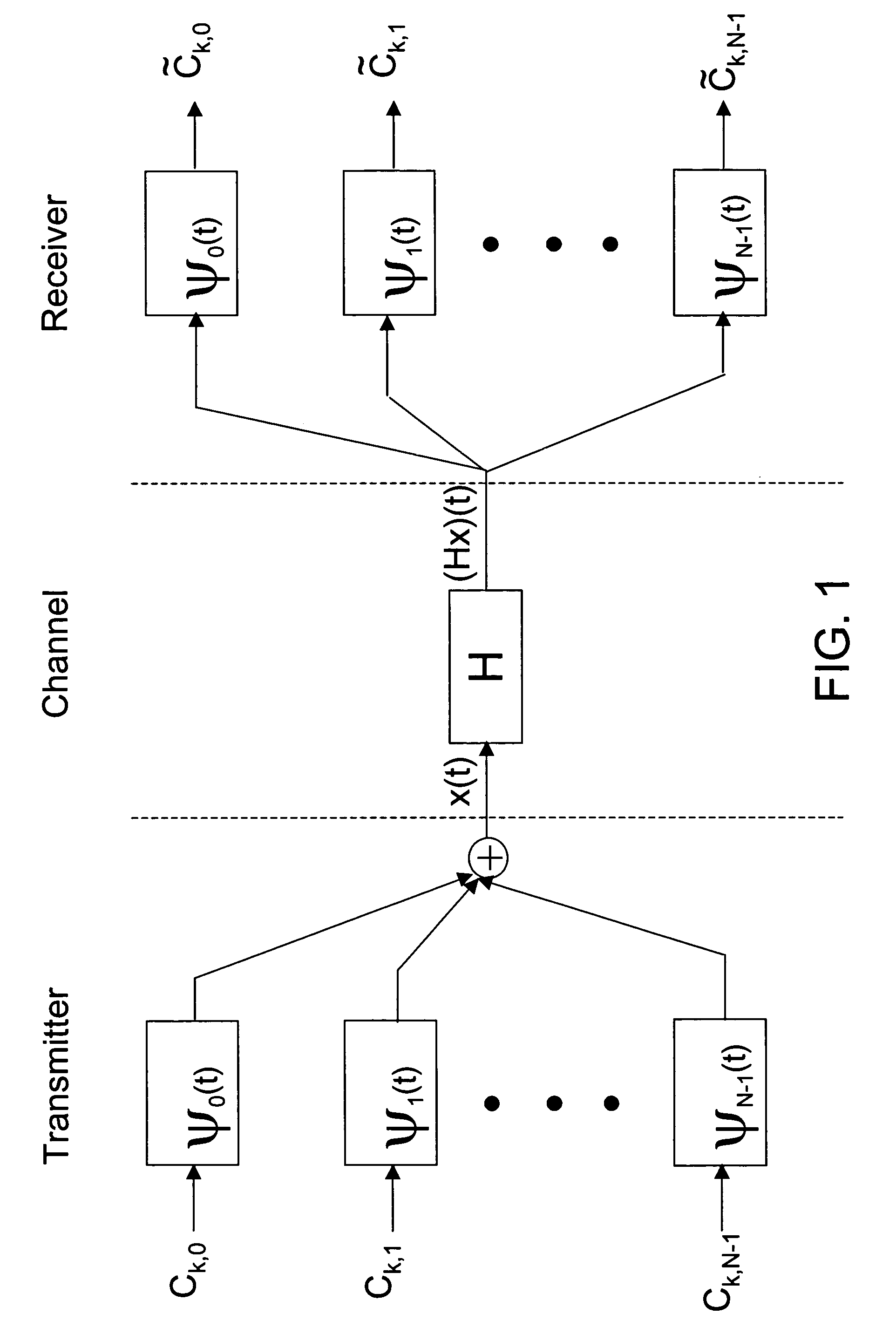
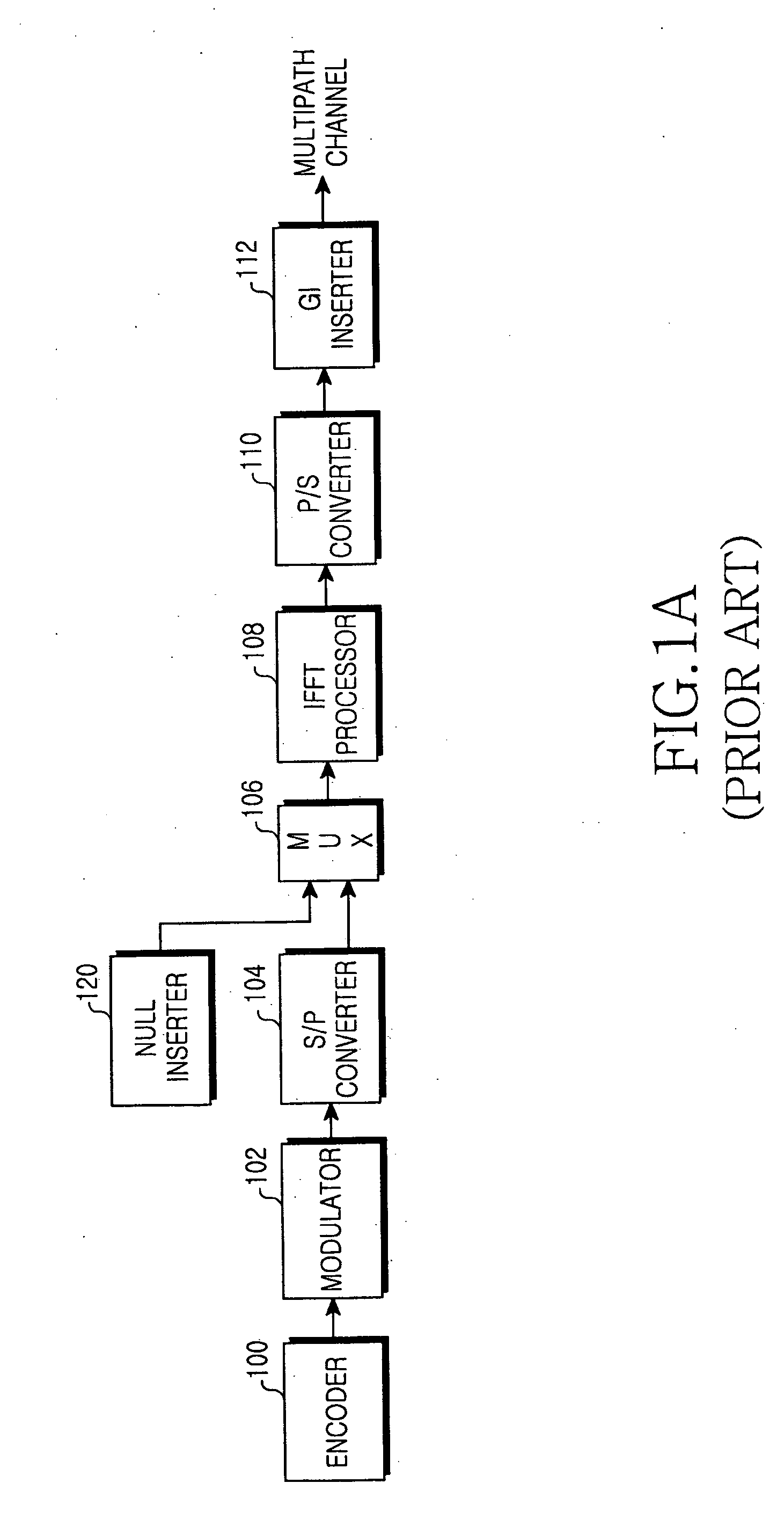
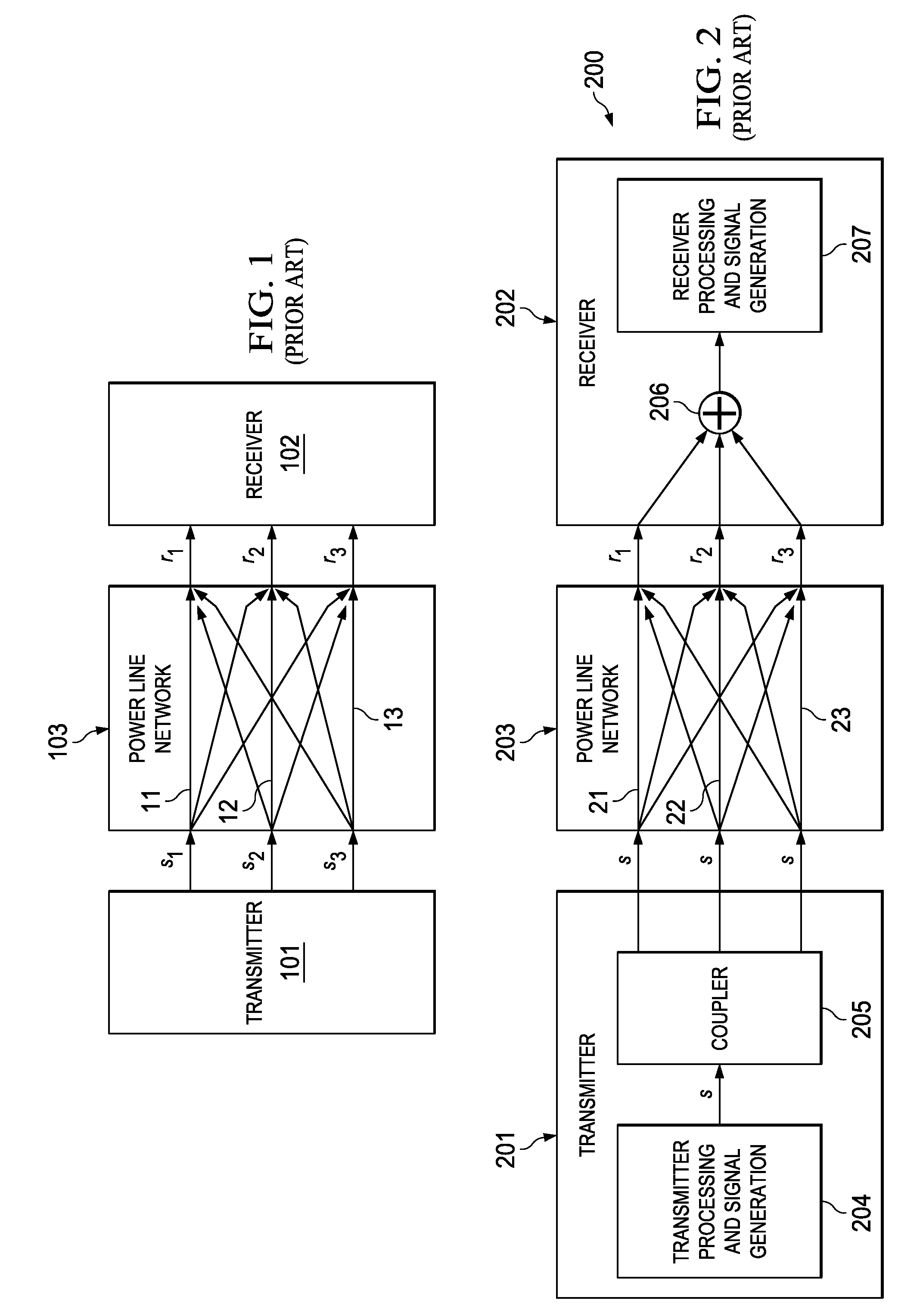
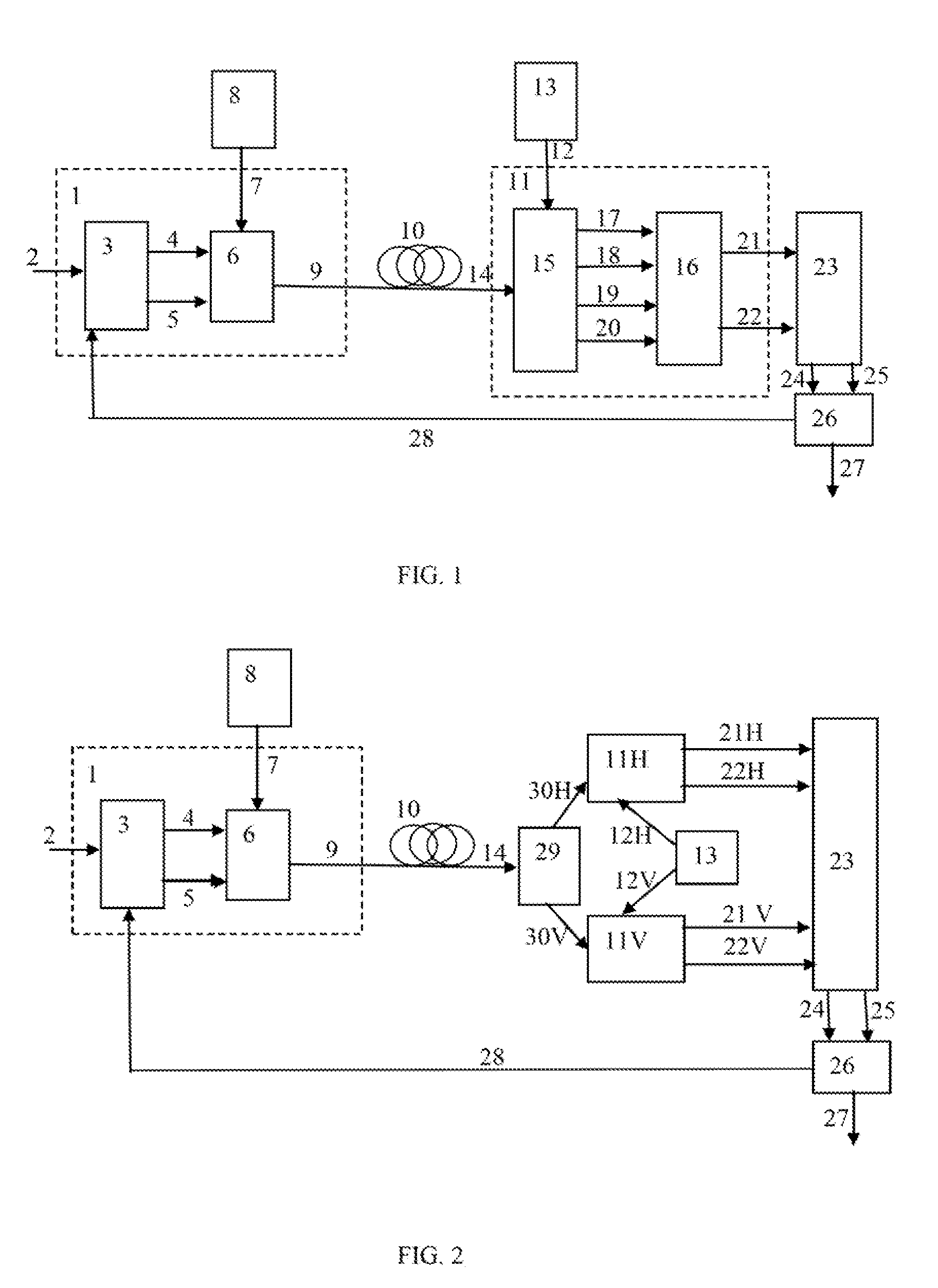
Dual-mode shared OFDM methods/transmitters, receivers and systems
ActiveUS7551546B2Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationNetwork terminationDual mode
A wireless terminal and network terminal are provided for implementing a new uplink OFDM protocol. In the new protocol, the wireless terminal has a first transmit chain for generating and transmitting a low rate mode OFDM transmission in a first frequency band of the OFDM band; and a second transmit chain for generating and transmitting a burst-mode transmission in a second frequency band of the OFDM band, the first frequency band being distinct from the second frequency band. An access channel is provided which is overlaid over the low rate mode transmissions of other users.
Owner:APPLE INC
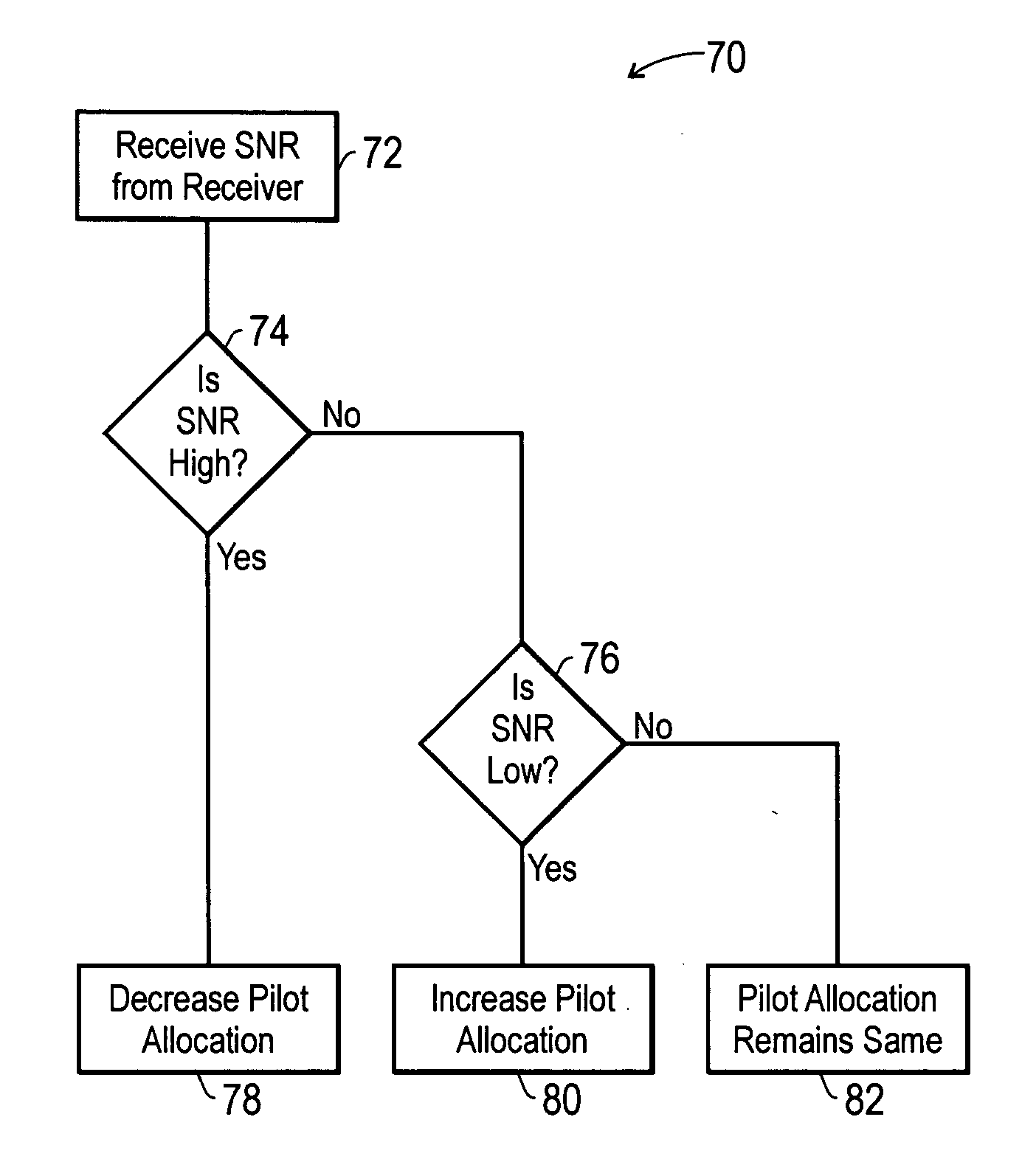
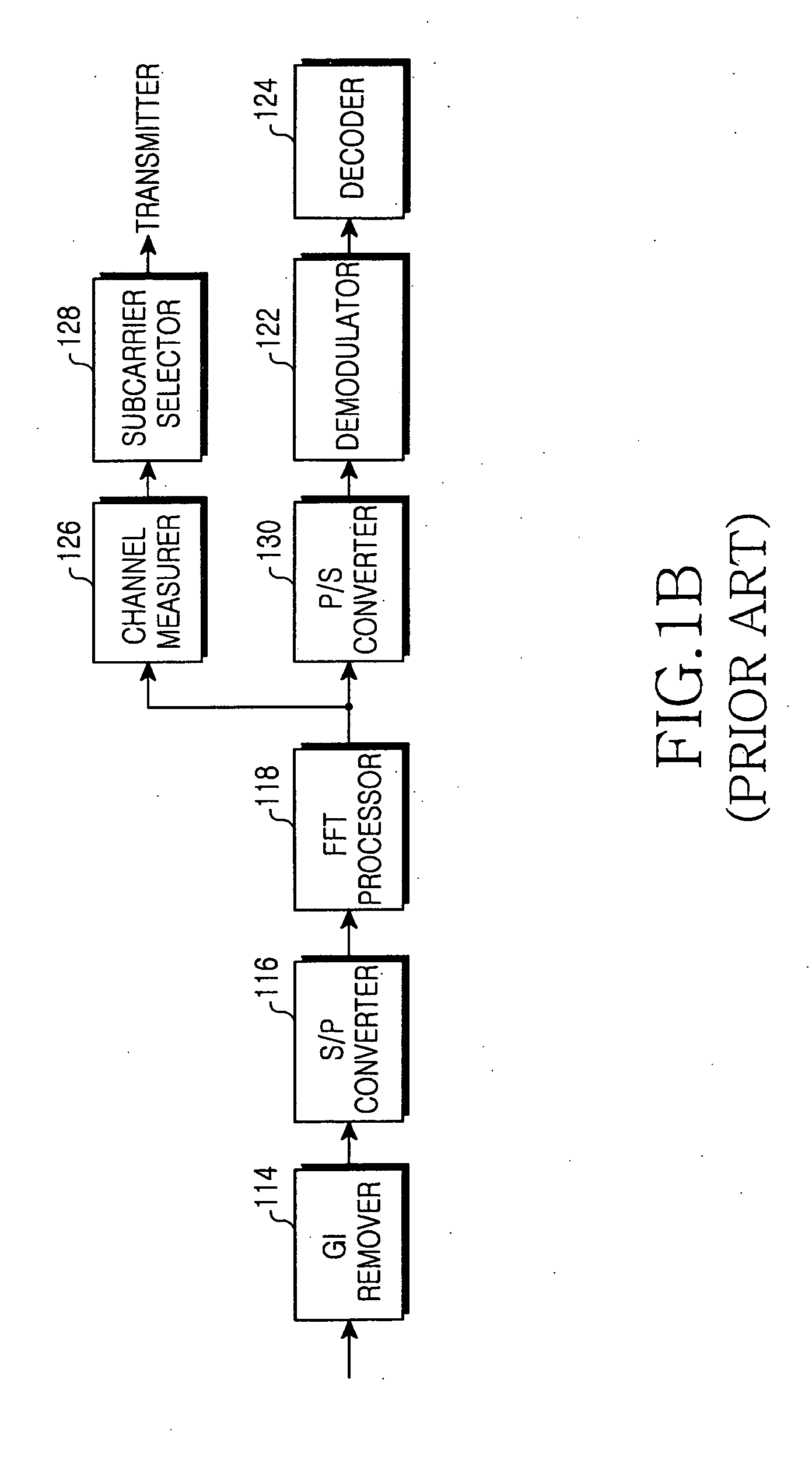
Method and apparatus for dynamic allocation of pilot symbols
InactiveUS20060280113A1Transmission path divisionCriteria allocationTelecommunicationsOrthogonal frequency code division multiplexing
There is provided a method and apparatus for dynamic allocation of pilot symbols in an OFDM transmission. More specifically, there is provided a method comprising transmitting a first orthogonal frequency division multiplexed signal with a first pilot symbol allocation, receiving a metric indicative of the quality of a transmitted signal, changing the location of pilot symbols within the first pilot symbol allocation based on the metric to create a second pilot symbol allocation, and transmitting a second orthogonal frequency division multiplexed signal with the second pilot symbol allocation.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
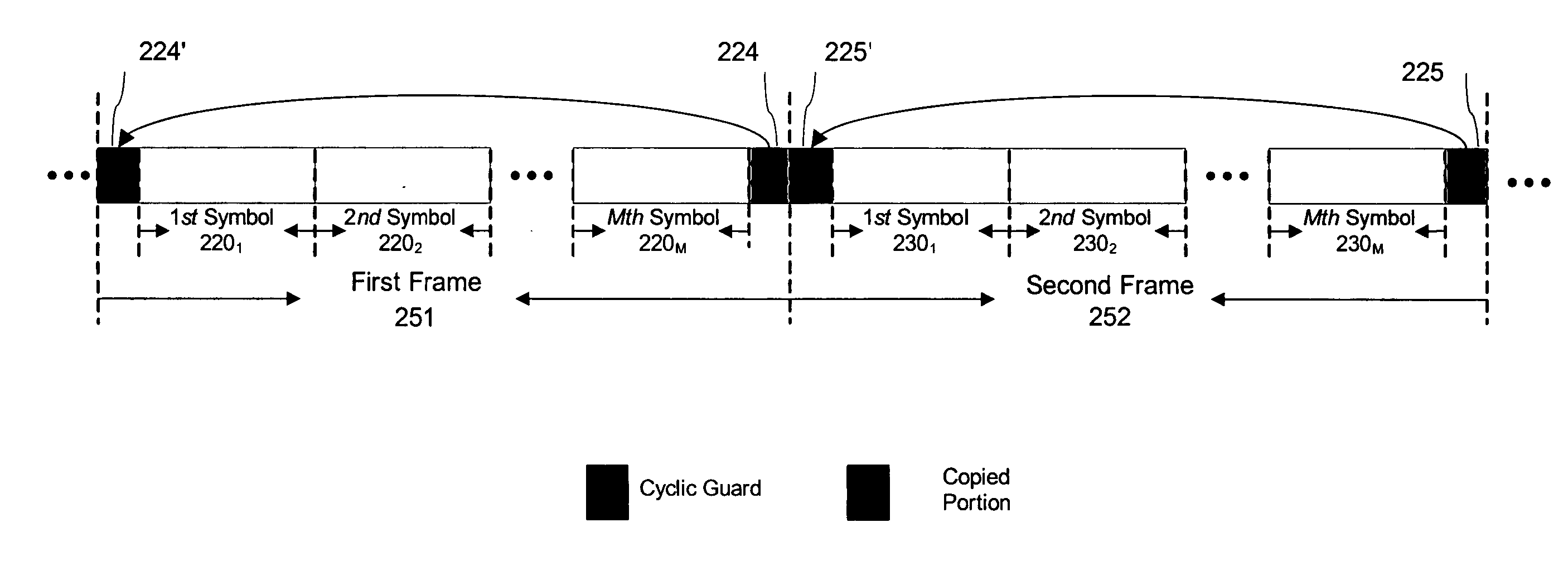
Multi-symbol encapsulated OFDM transmission
InactiveUS20050068886A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyReduce frequency offsetFrequency-division multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsHigh bandwidthCyclic prefix
A method and system for communication of information in OFDM format are disclosed. The method employs multi-symbol encapsulation (MSE), wherein multiple OFDM symbols are grouped together in cyclic frames having a single cyclic guard portion, for example a cyclic prefix, with multiple OFDM symbols sandwiched between each two consecutive cyclic guard portions. All OFDM symbols of one frame are equalized together at the receiver in a frequency domain using a single DFT / IDFT operation sequence. Embodiments of the MSE OFDM system are disclosed enabling high bandwidth efficiency, high tolerance to carrier frequency offset and low peak-to-average power ratio.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
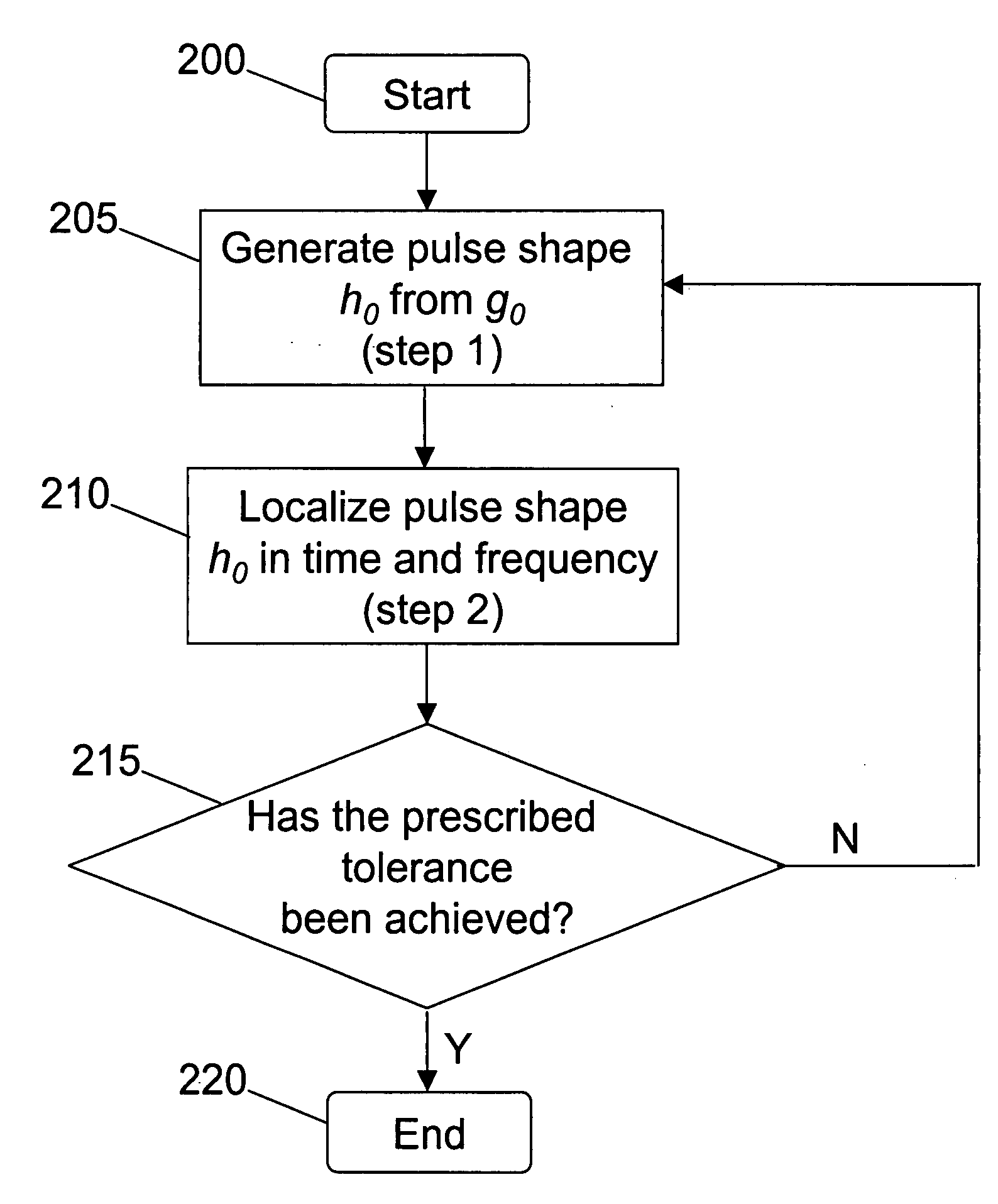
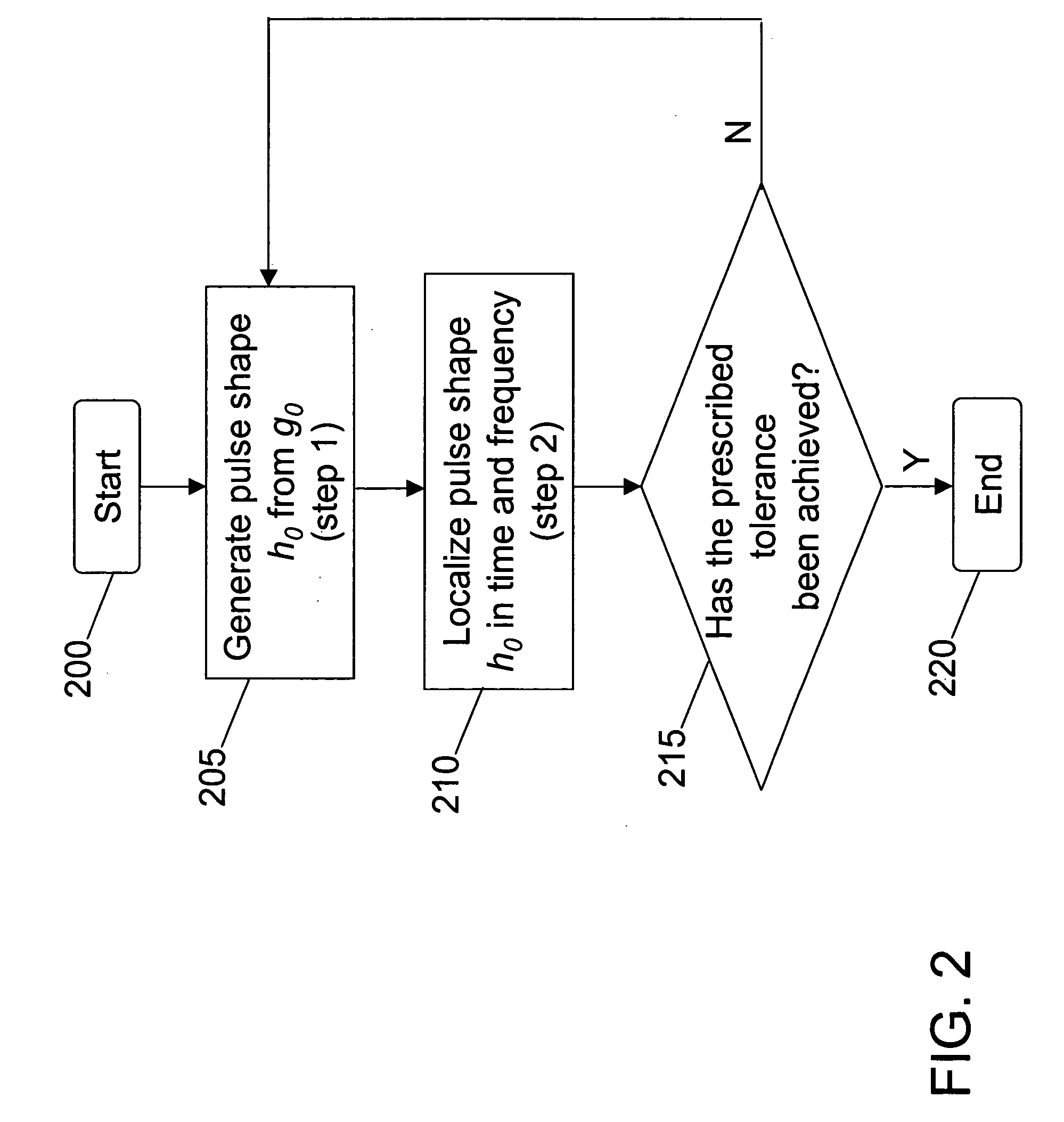
Method for pulse shape design for OFDM
InactiveUS20060039270A1Maximizing bit-error performanceIncrease data rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationFrequency spectrumWireless transmission
A computationally efficient pulse shaping method for OFDM that produces mutually orthogonal transmission pulses having fast spectral decay is provided. The pulse shaping method comprises an iterative method for designing OFDM transmission pulses that satisfy prescribed time-frequency localization conditions. The iterative method may be implemented in a computationally efficient way and can be used to adapt the transmission pulses to time-varying channel conditions in real-time, thereby maximizing the bit-error performance of an OFDM system while maintaining high data rates in wireless transmission.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
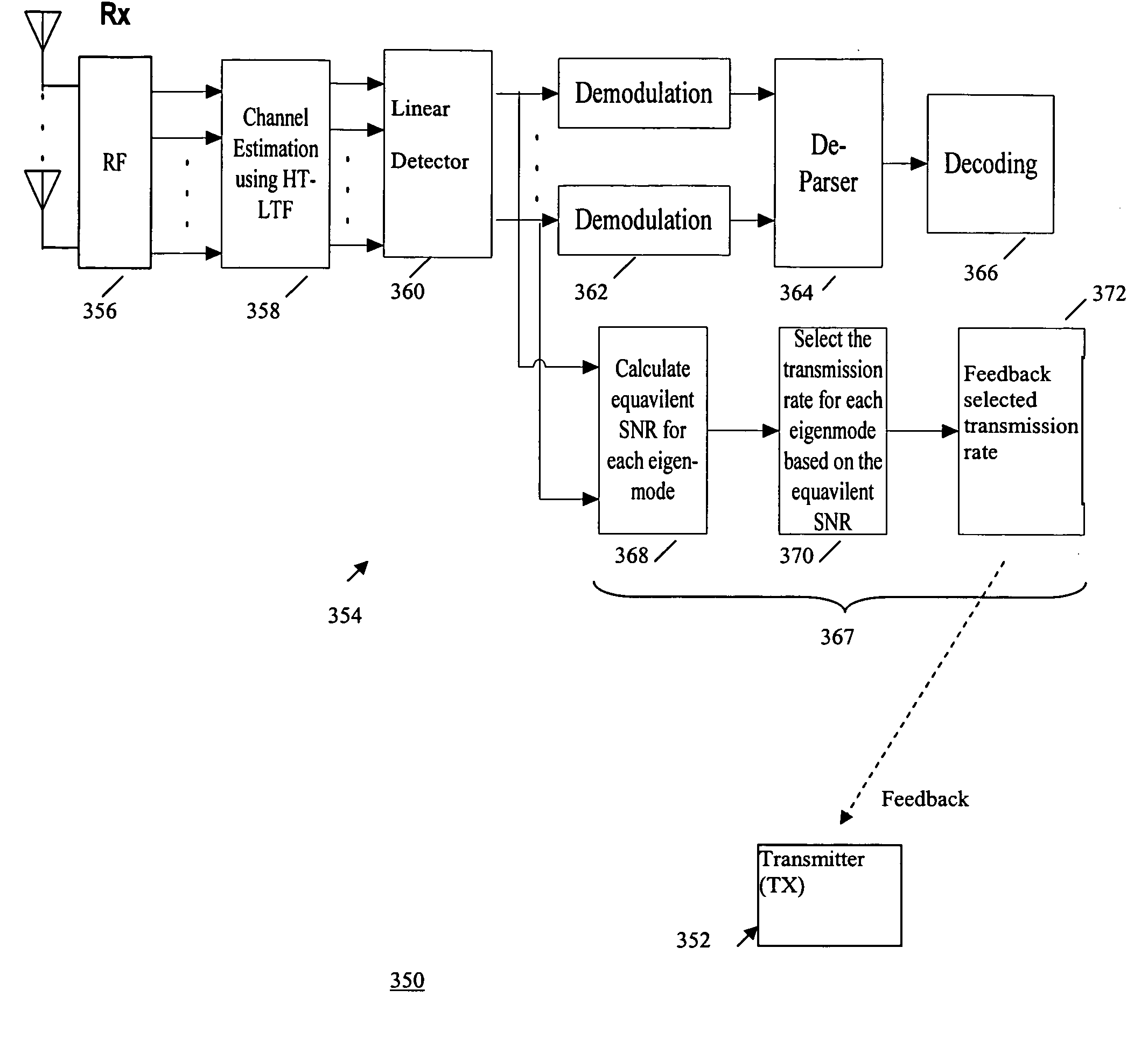
Method for rate adaptation with extended MCS set for wideband eigen-beamforming transmission
InactiveUS20070147535A1Simple and fast and efficient schemePower managementDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRate adaptationTransfer mode
A method for rate adaptation with extended MCS set for wideband eigen-beamforming transmission. A signaling method over multiple channels in a wireless telecommunication system including a transmitter and a receiver, performs the steps of obtaining an information bit stream, selecting the number of transmission streams, selecting different transmission rates for each MIMO OFDM transmission, and transmitting the information bit stream from the transmitter via said multiple channels over a plurality of transmitter antennas to the receiver according to the selected transmission rate per channel. Selecting transmission rates further includes the steps of selecting the transmission rates based on the diversity order of each stream. The method selects different transmission modes for each MIMO OFDM transmission and provides a simple, fast and efficient scheme to select the transmission rate for each eigen-mode transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
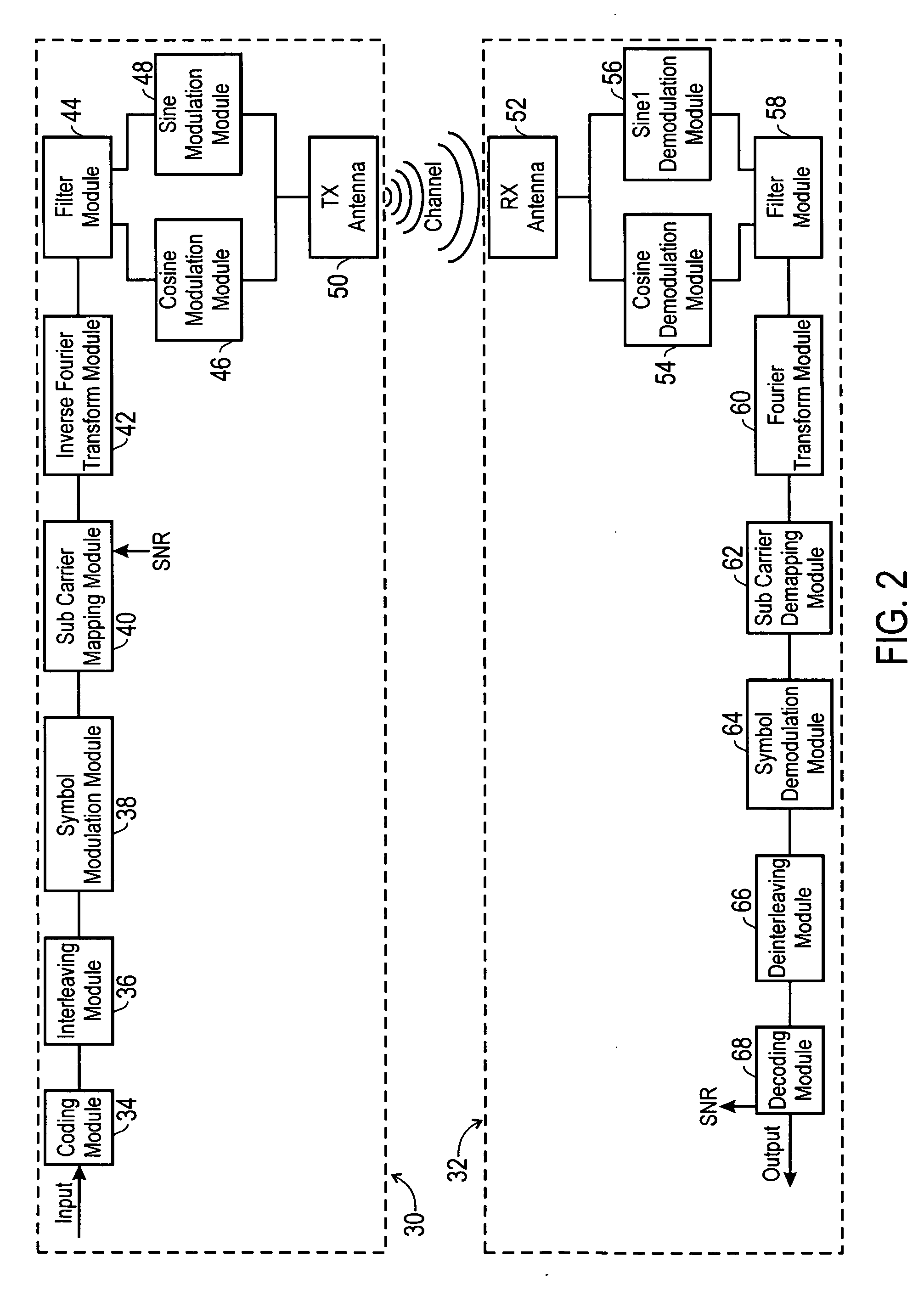
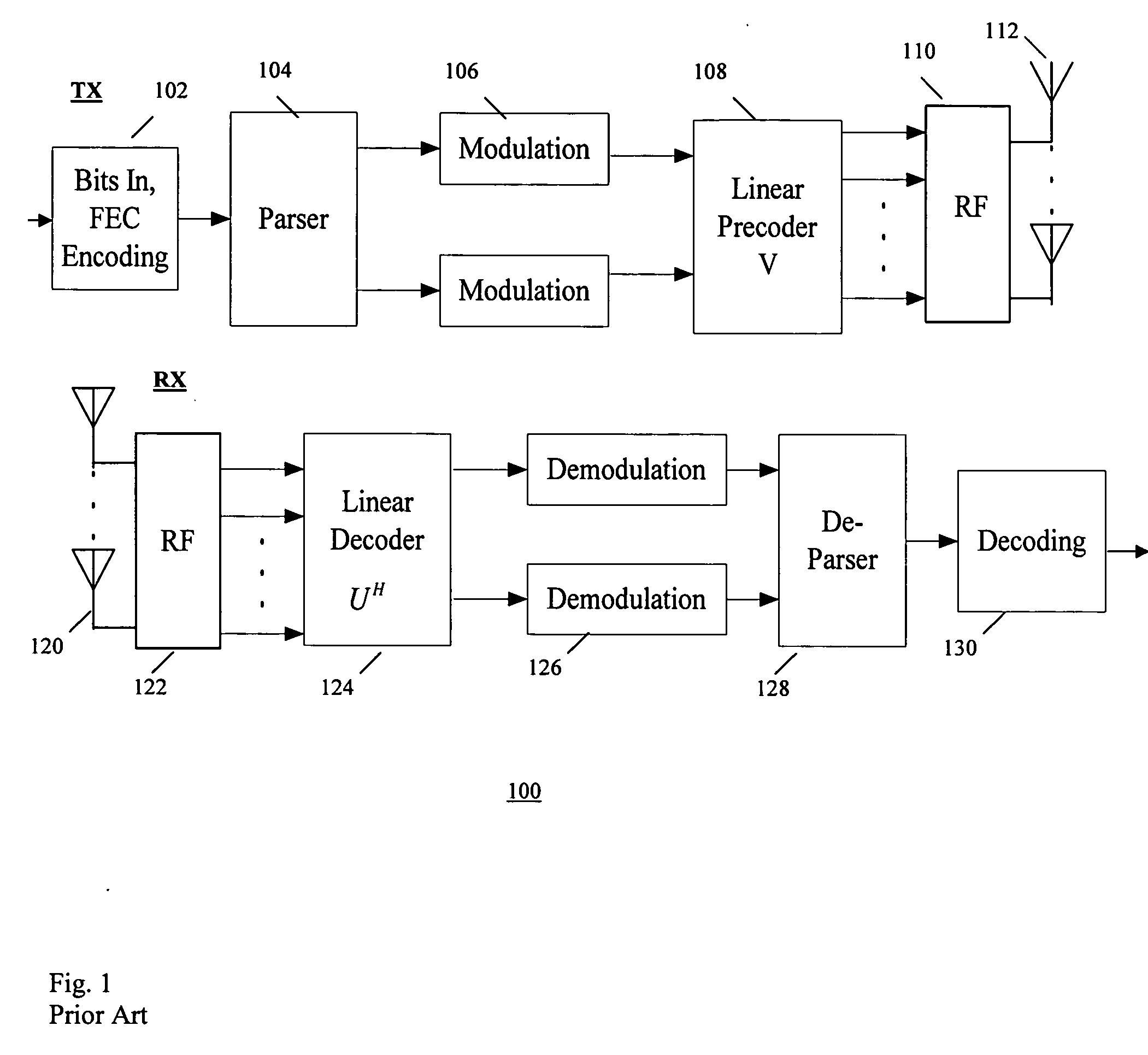
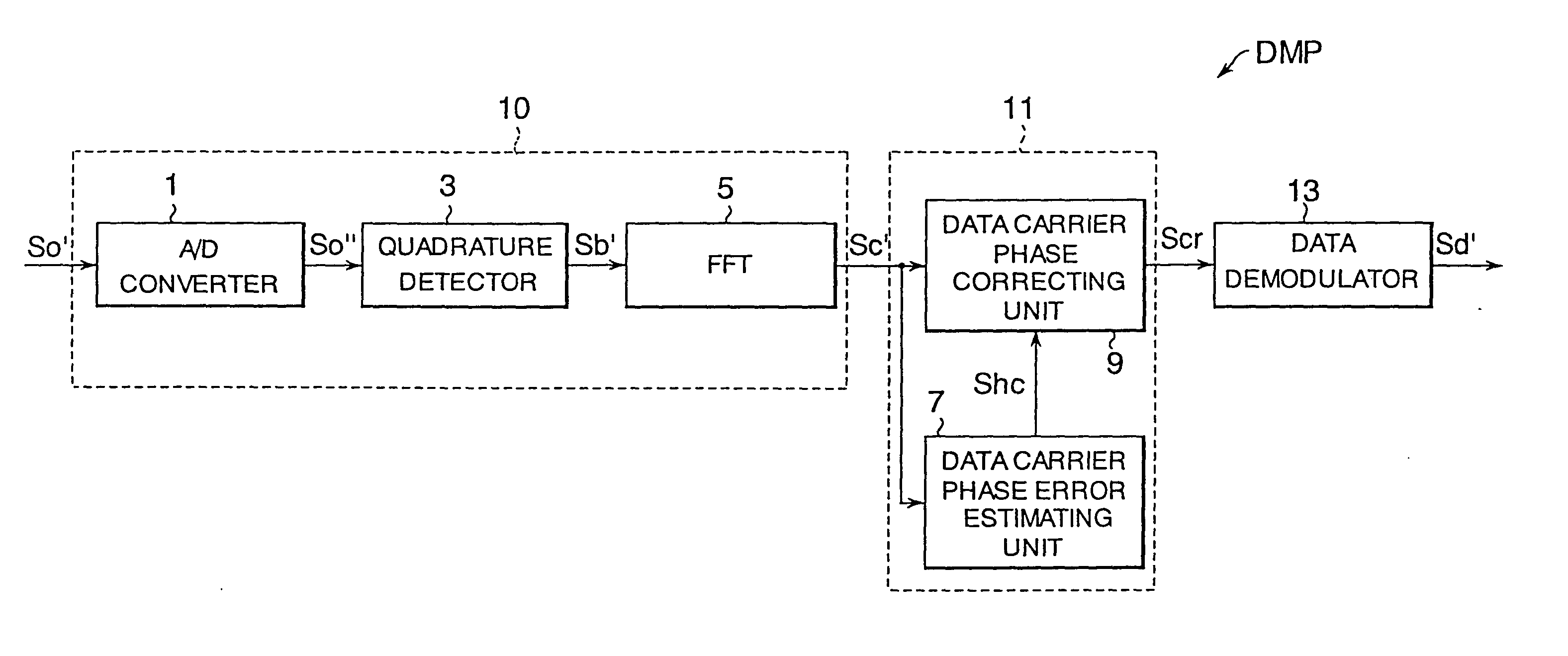
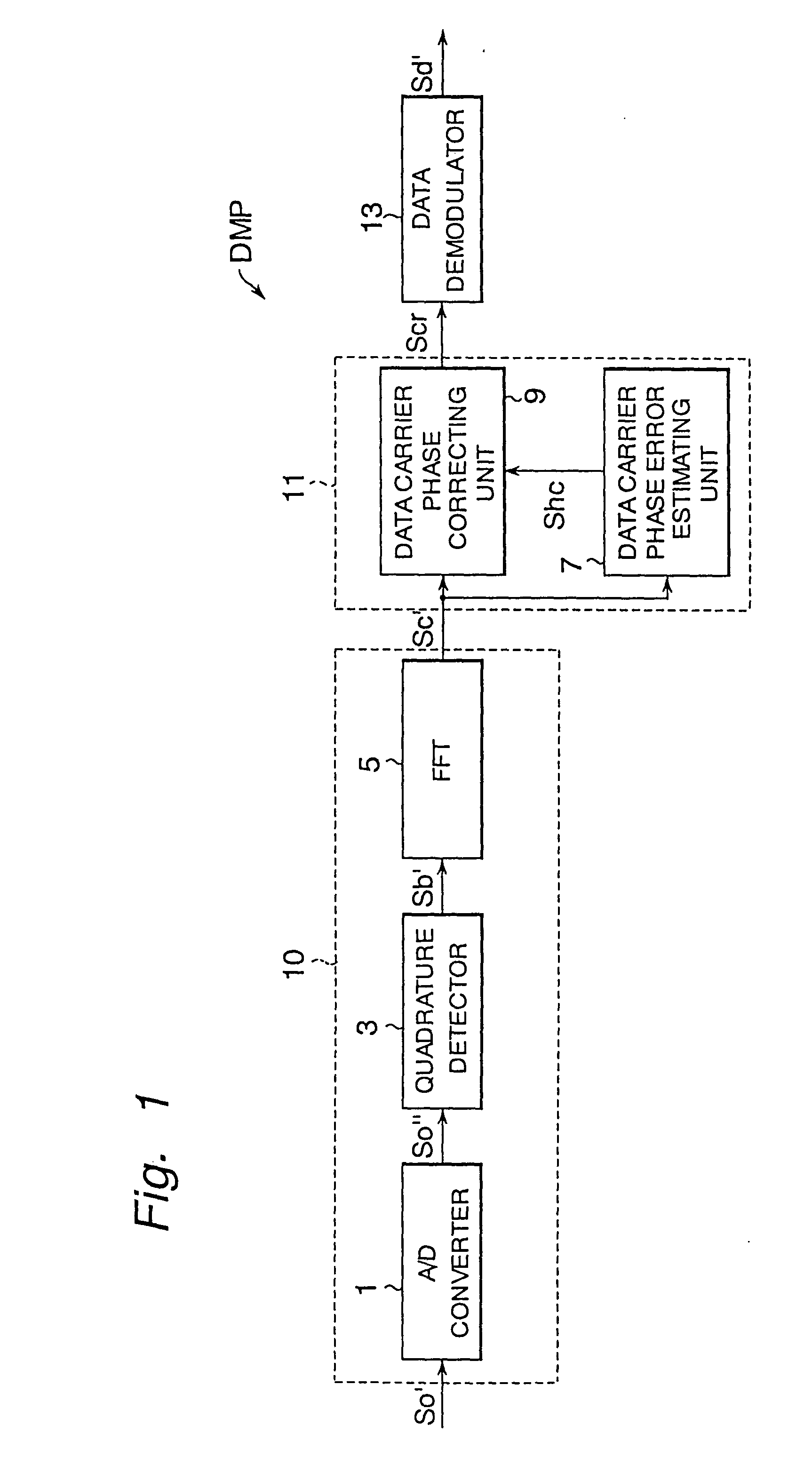
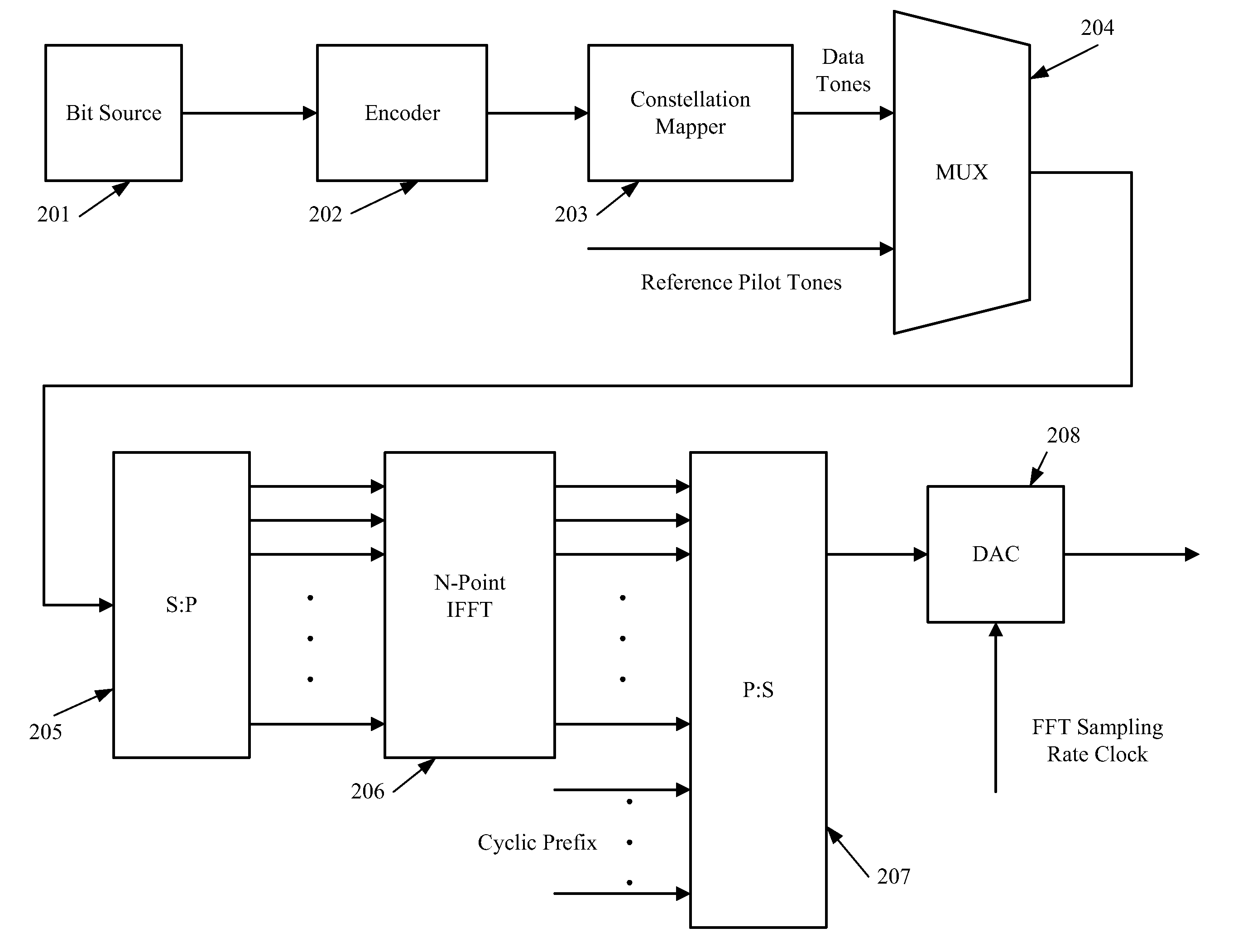
Modulator, demodulator, and transmission system for use in OFDM transmission
An input of an OFDM signal containing known pilot carriers among given subcarriers is separated into subcarriers through Fourier transform in a fast Fourier transform unit. A data carrier phase error estimating unit obtains an amount of phase correction of each subcarrier on the basis of the pilot carriers in the separated subcarriers. A data carrier phase correcting unit corrects the phase of the separated subcarrier signal on the basis of the amount of phase correction. Thus, the phase errors of the subcarriers can be corrected and the OFDM symbols can be demodulated even if a frequency error and a timing error are occurring between the transmitter and receiver.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
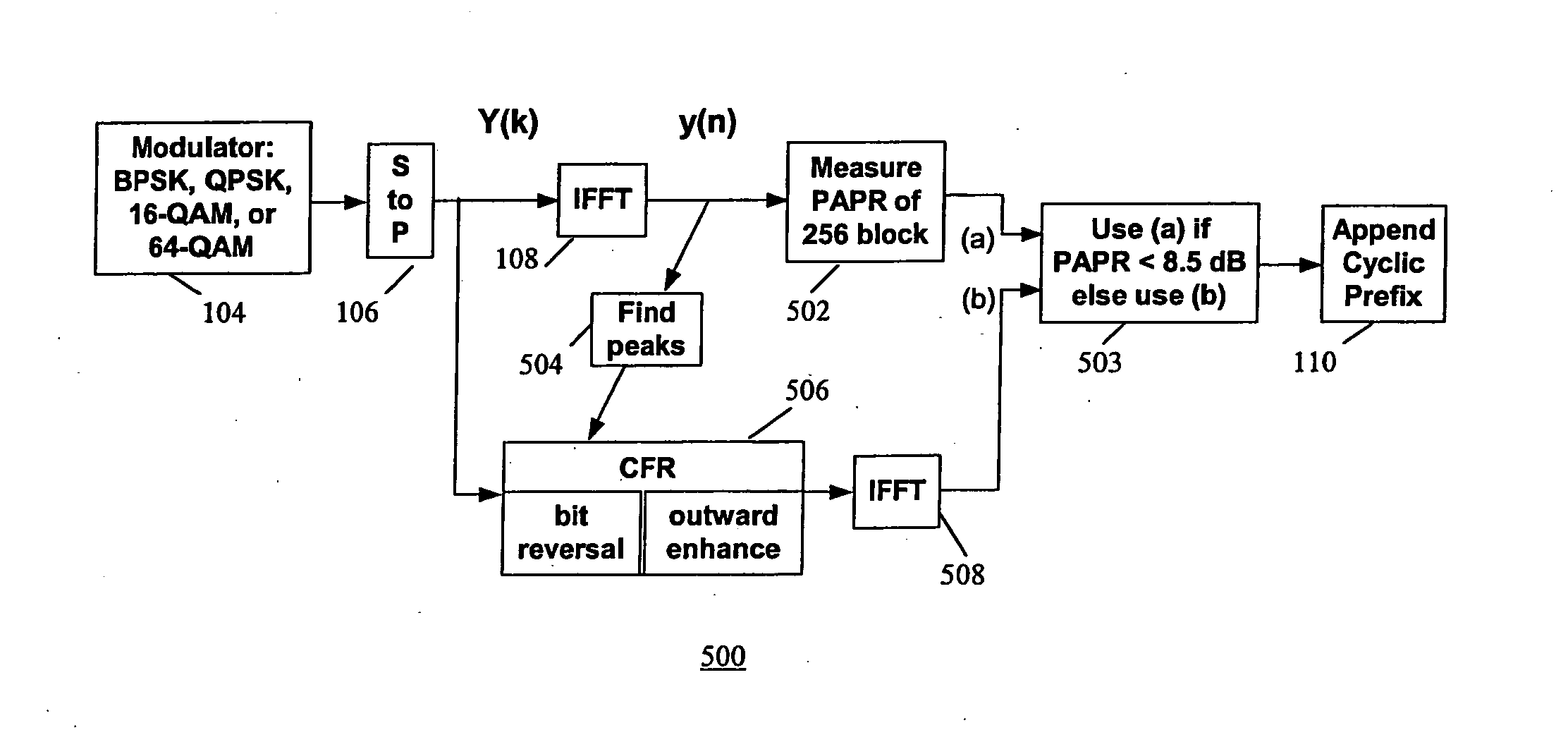
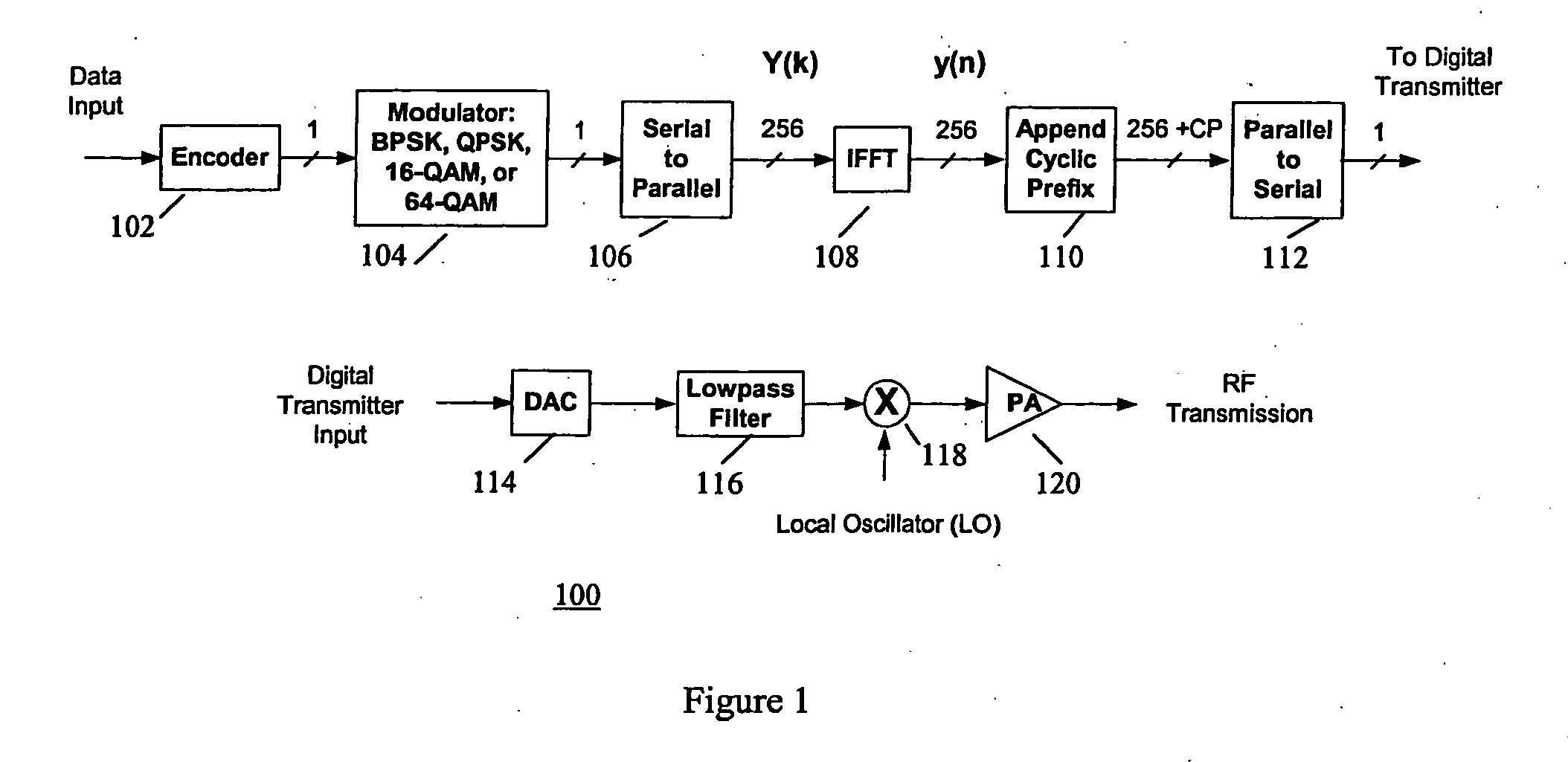
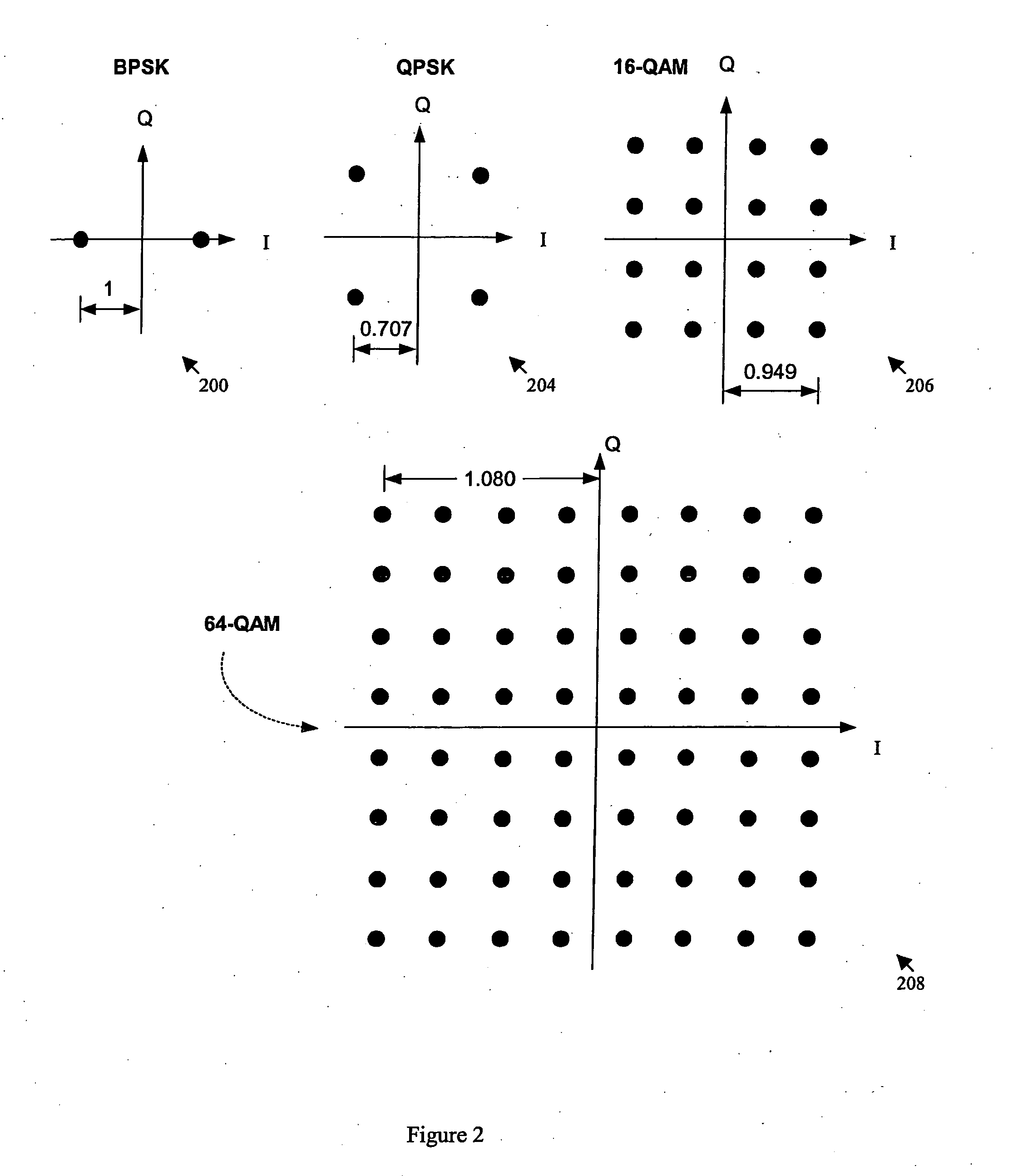
Peak-to-average power reduction for FM OFDM transmission
ActiveUS20050169411A1Reducing peak-to-average power ratioMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCarrier signalPeak value
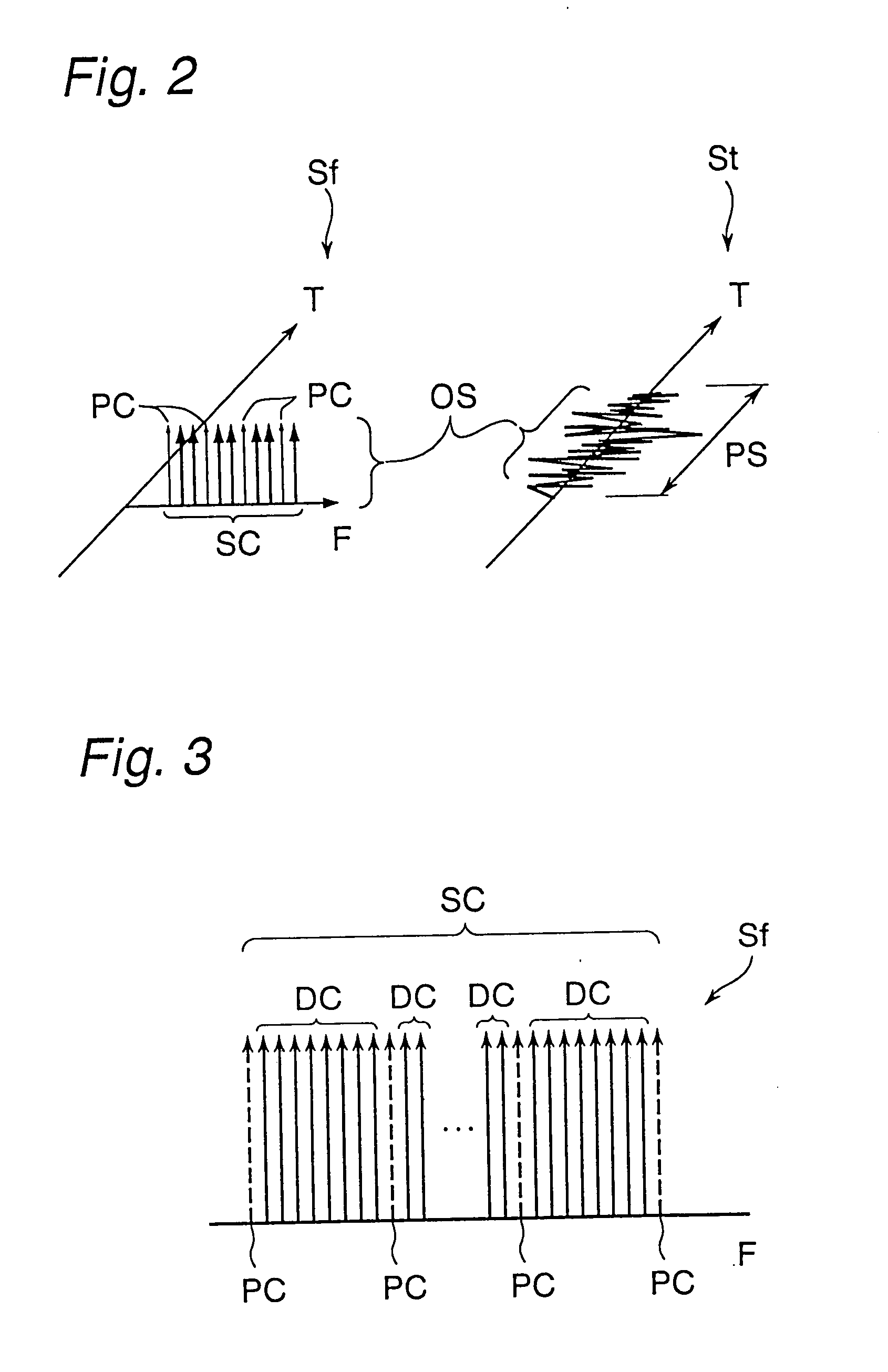
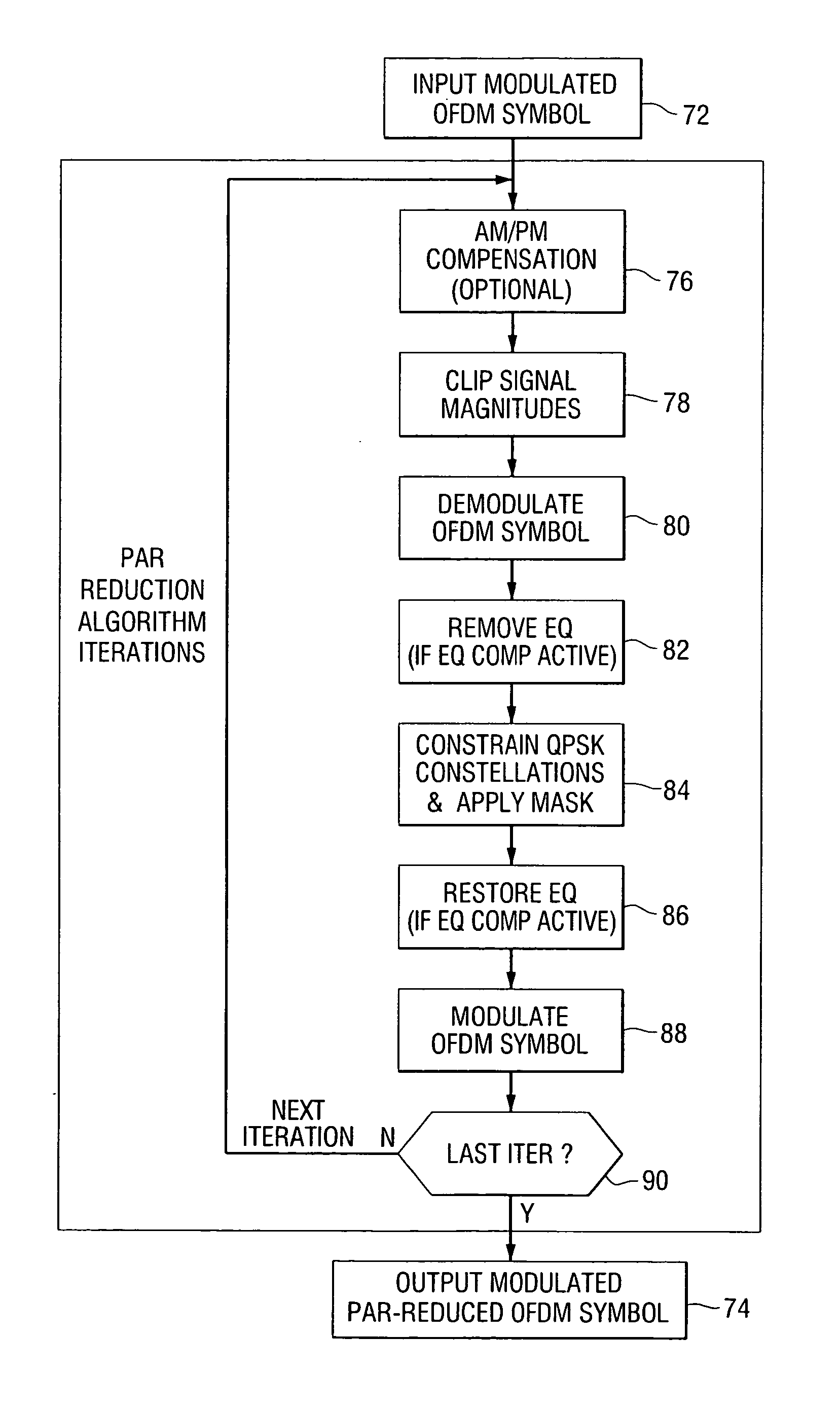
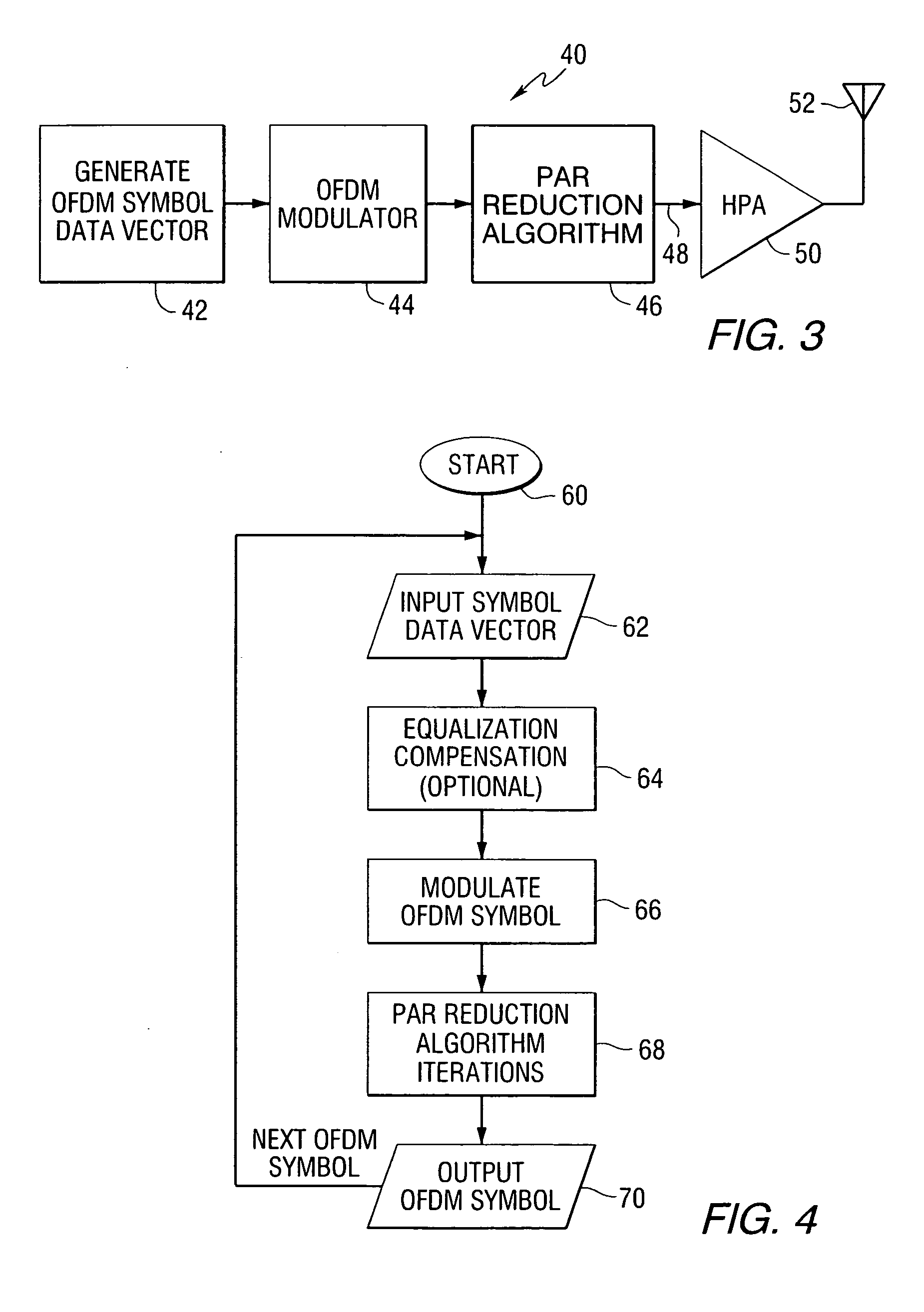
A method of reducing peak-to-average power ratio in an OFDM signal comprises the steps of modulating a set of subcarriers with a set of data symbol vectors to produce a first modulated signal, limiting the magnitude of the first modulated signal to produce a first limited modulated signal, demodulating the first limited modulated signal to recover distorted input symbol vectors, constraining the distorted input symbol vectors to values greater than or equal to a minimum threshold value to produce constrained data symbol vectors, constraining out-of-band spectral components to lie within a predetermined mask, and remodulating the constrained data symbol vectors. A transmitter that performs the method is also included.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
OFDM signal transmission scheme, and OFDM signal transmitter/receiver
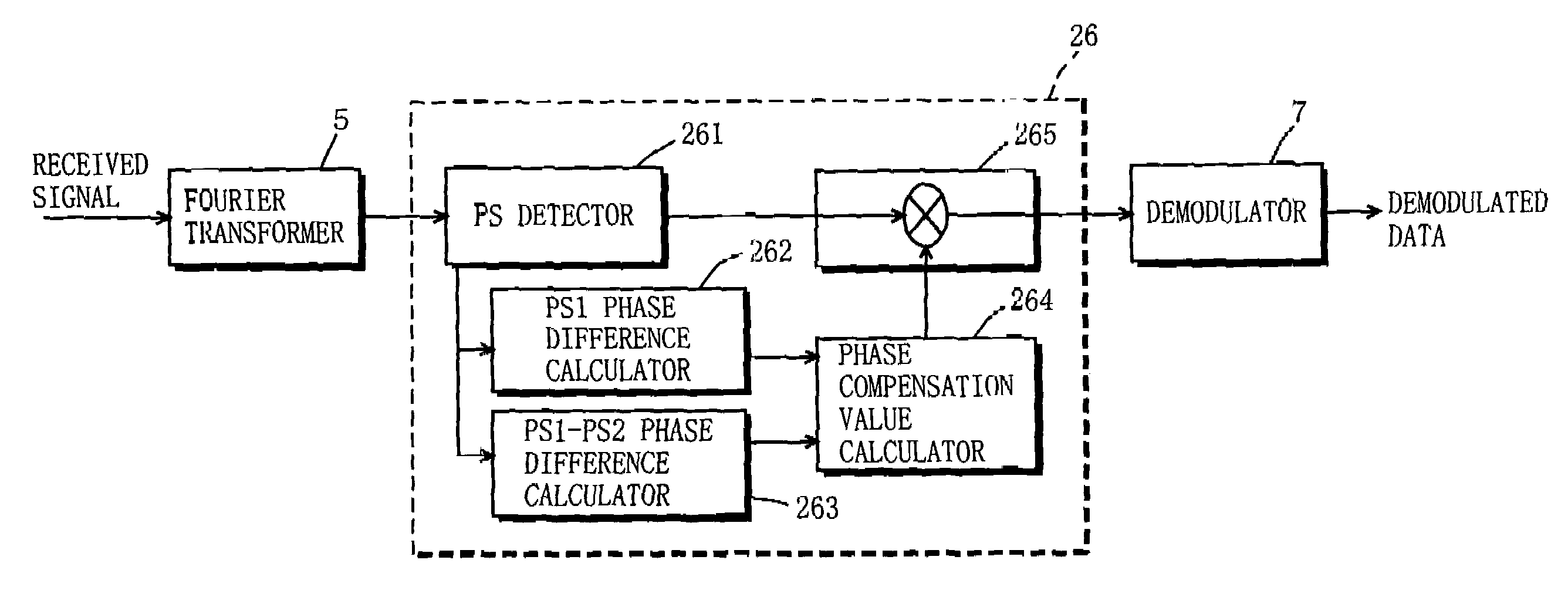
InactiveUS7027464B1Reduce error rateAccurate compensationModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionPhase shiftedEngineering
In an OFDM transmission scheme, in order to compensate any frequency response variations time wise resulted from any distortion in a transmission path, out-of-synchronization with passage of time, frequency drift, and phase shift, and to improve a demodulation characteristic, a PS detector in a receiver receiving an OFDM signal detects a pilot symbol. A PS1 TPFR calculator calculates a frequency response of the transmission path for a first pilot symbol, while a PS2 TPFR calculators calculates a frequency response of the transmission path for a second pilot symbol for a second pilot symbol. Thereafter, a compensation vector calculator calculates compensation vectors from the frequency responses of the transmission path for both of the first and second pilot symbols by linear approximation. A frequency response compensatory compensates the frequency response variation of subcarriers in a data symbol based on the calculated compensation vectors.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Bi-directional communication channel
InactiveUS7133352B1Extended transfer timeReduce remaining sidelobesPower managementTransmission path divisionAutomatic frequency controlGuard time
A communication system using OFDM transmission from a base station to subscriber units, includes means for achieving a bi-directional channel. These means comprise transmitting means in the subscriber units for the transmission of signal synchronous with the guard time interval in the OFDM transmission, and receiving means in the base station for the reception of the transmitted signals. The system also includes signal shaping means in the receiver of the base station and / or the subscriber unit for the application of a window in time to signals received therein. A communication system includes a combination of CDMA modulation codes and OFDM coding / decoding means to achieve orthogonality between signals from the various users in the uplink. A communication system includes a combination of OFDM and channeling means for achieving orthogonality between signals from the various users in the uplink. Automatic Frequency Control is achieved with means in the mobile unit for achieving a frequency-lock to the base station.
Owner:ZION HADAD COMM
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a signal in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
InactiveUS20060018250A1Efficiently provideCriteria allocationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemCyclic prefix
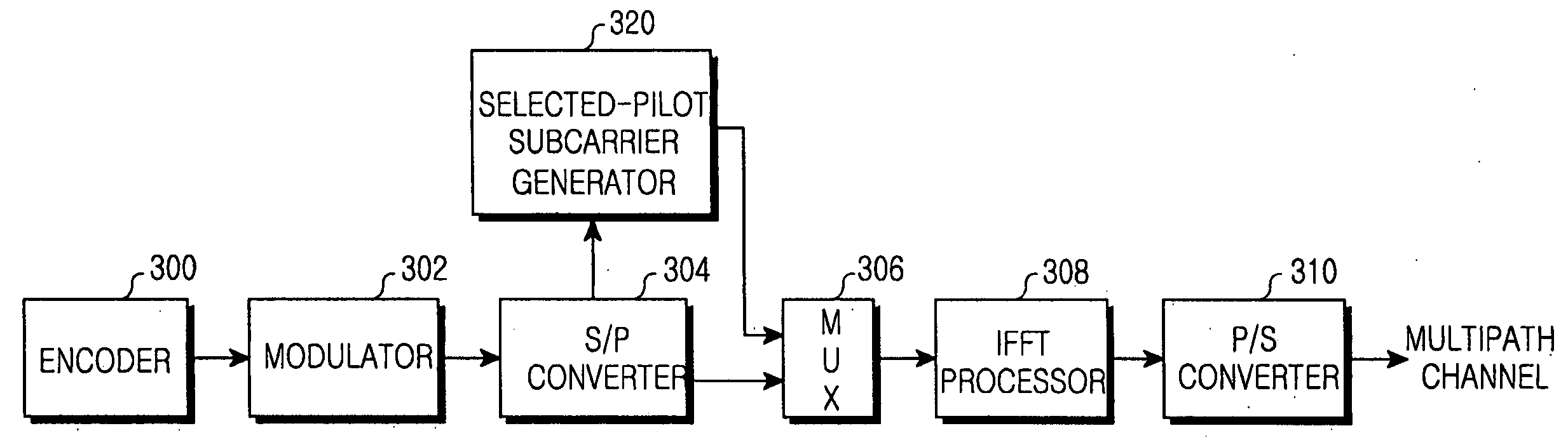
A system and method for effectively providing an adaptive modulation scheme and known-cyclic prefix (CP) technology in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system. An OFDM transmission system variably generates a known CP while considering a channel state. Pilot subcarrier position information for generating the known CP is sent to a transmitter. Pilot subcarriers are selected on the basis of a channel state of an OFDM symbol through which data is transmitted and the known CP is generated, such that data transmission is provided efficiently.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
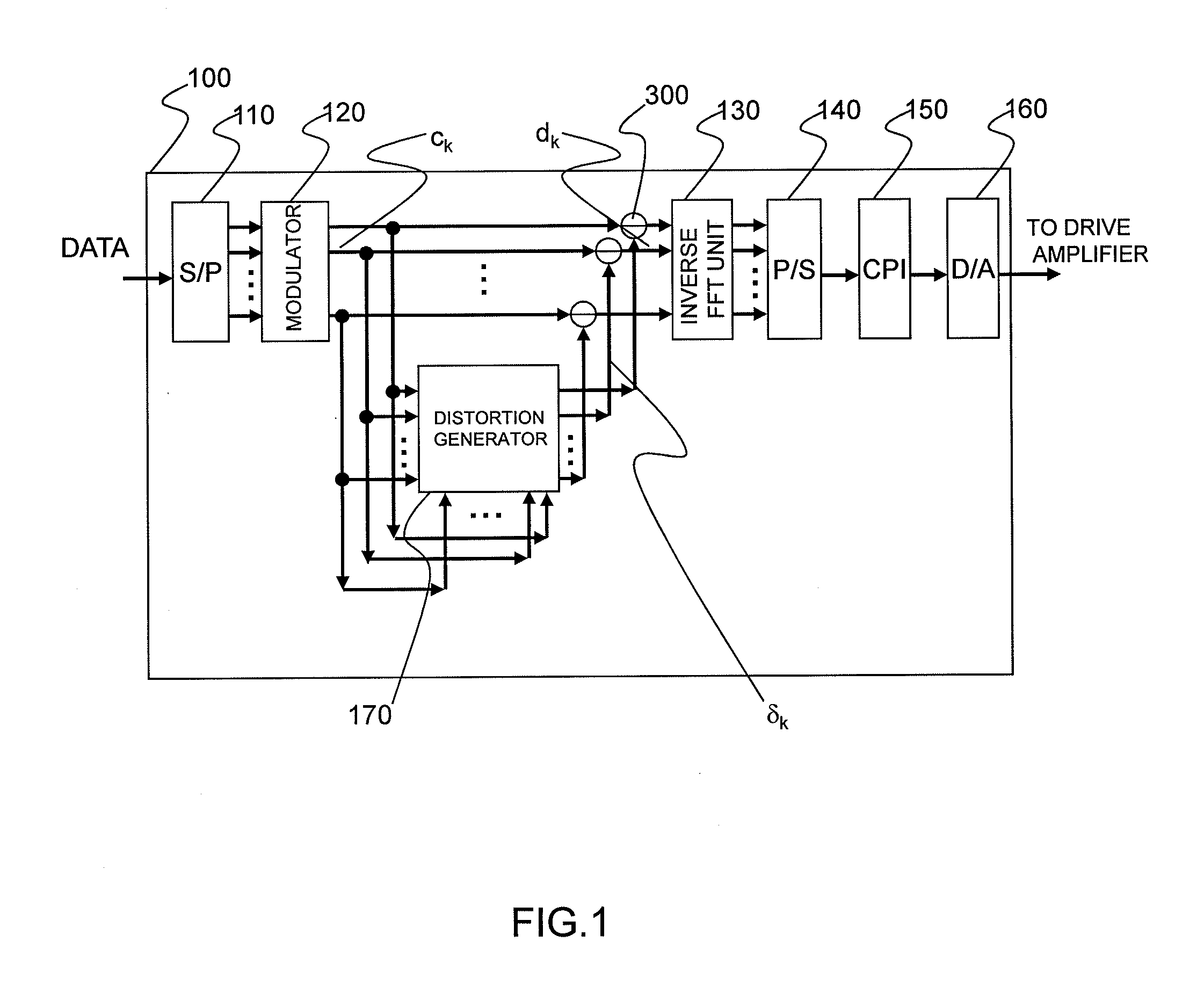
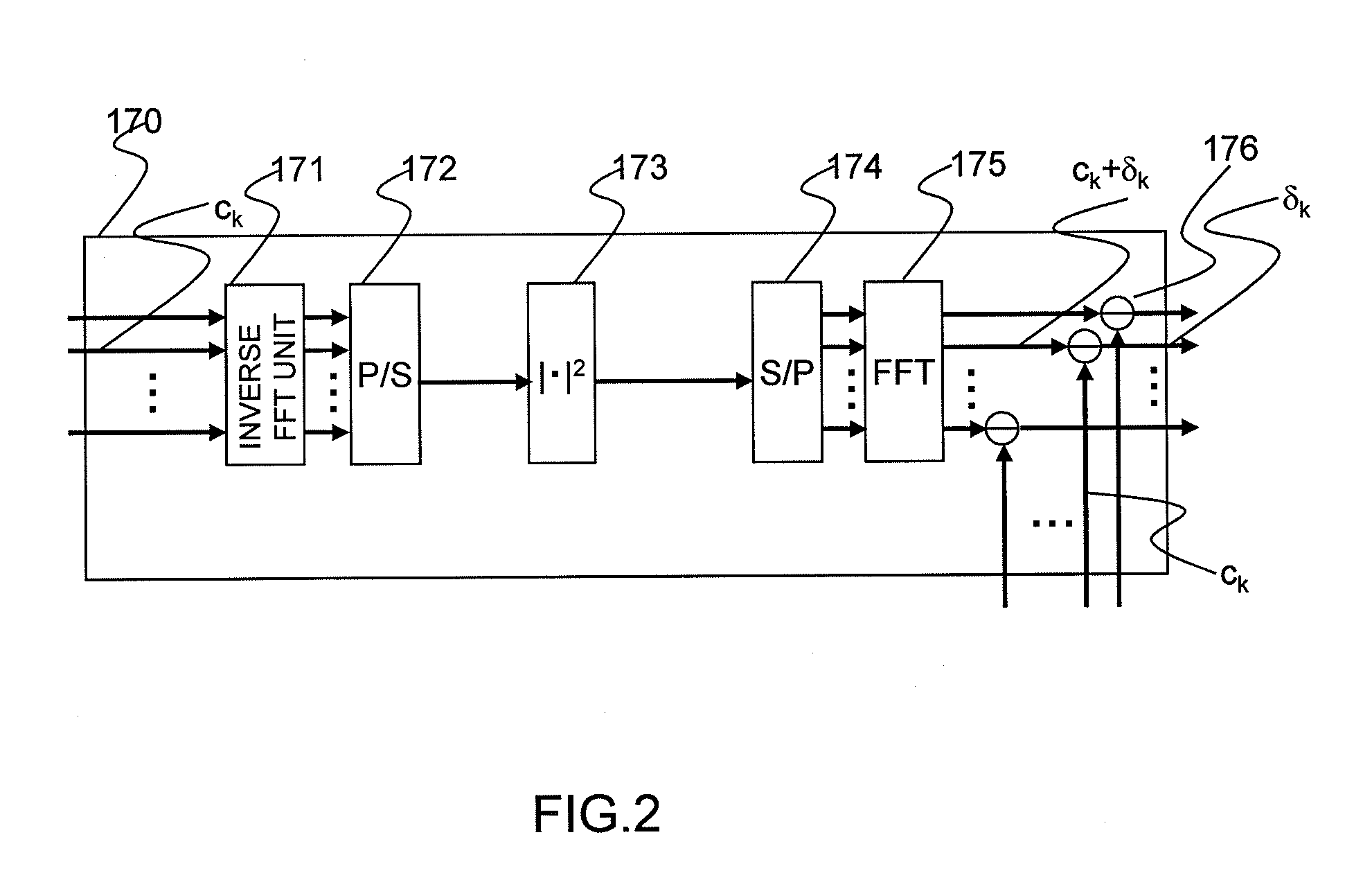
Optical Transmitter and Optical OFDM Communication System
InactiveUS20110249978A1Reduce signalingReduce impactModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOriginal dataCarrier signal
Distortion of a reception signal which is attributable to interference between subcarriers during photoelectric conversion is reduced in an optical OFDM communication system without broadening the signal band. A transmission signal processing unit (100) in a transmitter is provided with a distortion generating circuit (distortion generating unit) (170). A subcarrier signal is utilized as an input signal for the circuit. The distortion generating circuit (170) generates a baseband OFDM signal by means of inverse FFT calculation using the input signal, computes the square of the absolute value of the signal, and restores the subcarrier signal by mean of FFT calculation. Because interference between subcarriers is also included in the signal, the distortion element generated by the interference between the subcarriers can be extracted when the difference from the input signal is found. The signal obtained by subtracting the distortion element from the subcarrier signal, which has been modulated using the original data to be communicated, is used as the transmission signal. The transmission signal is photoelectrically converted with a receiver. The interference between subcarriers generated at this time is smaller than when the aforementioned processing is not performed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
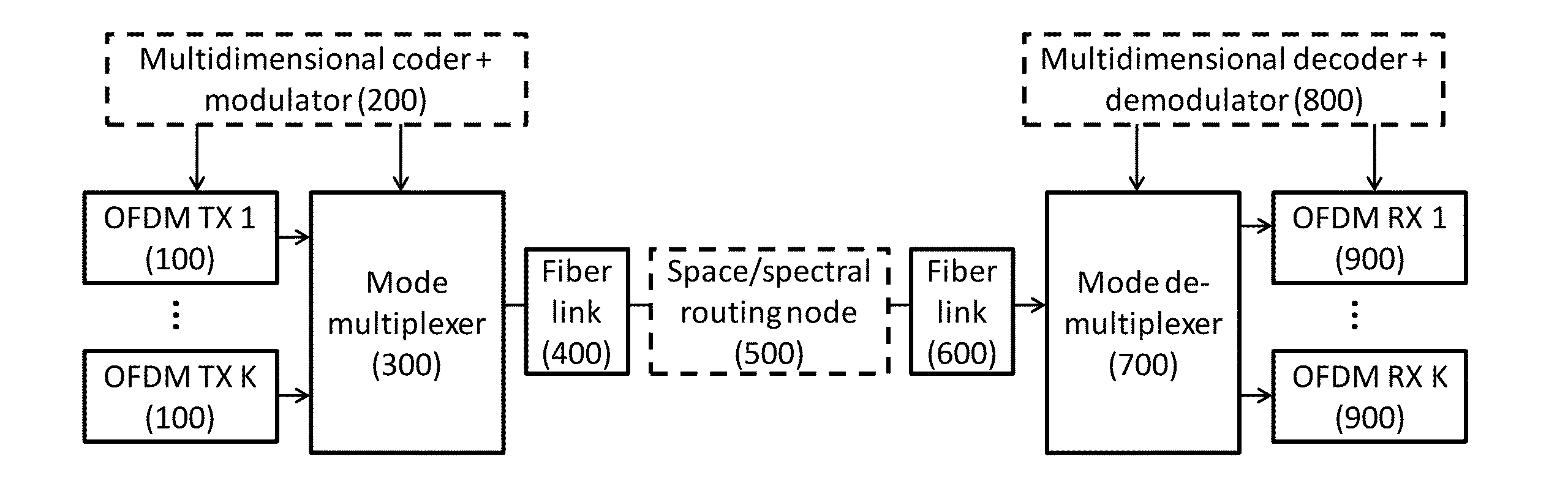
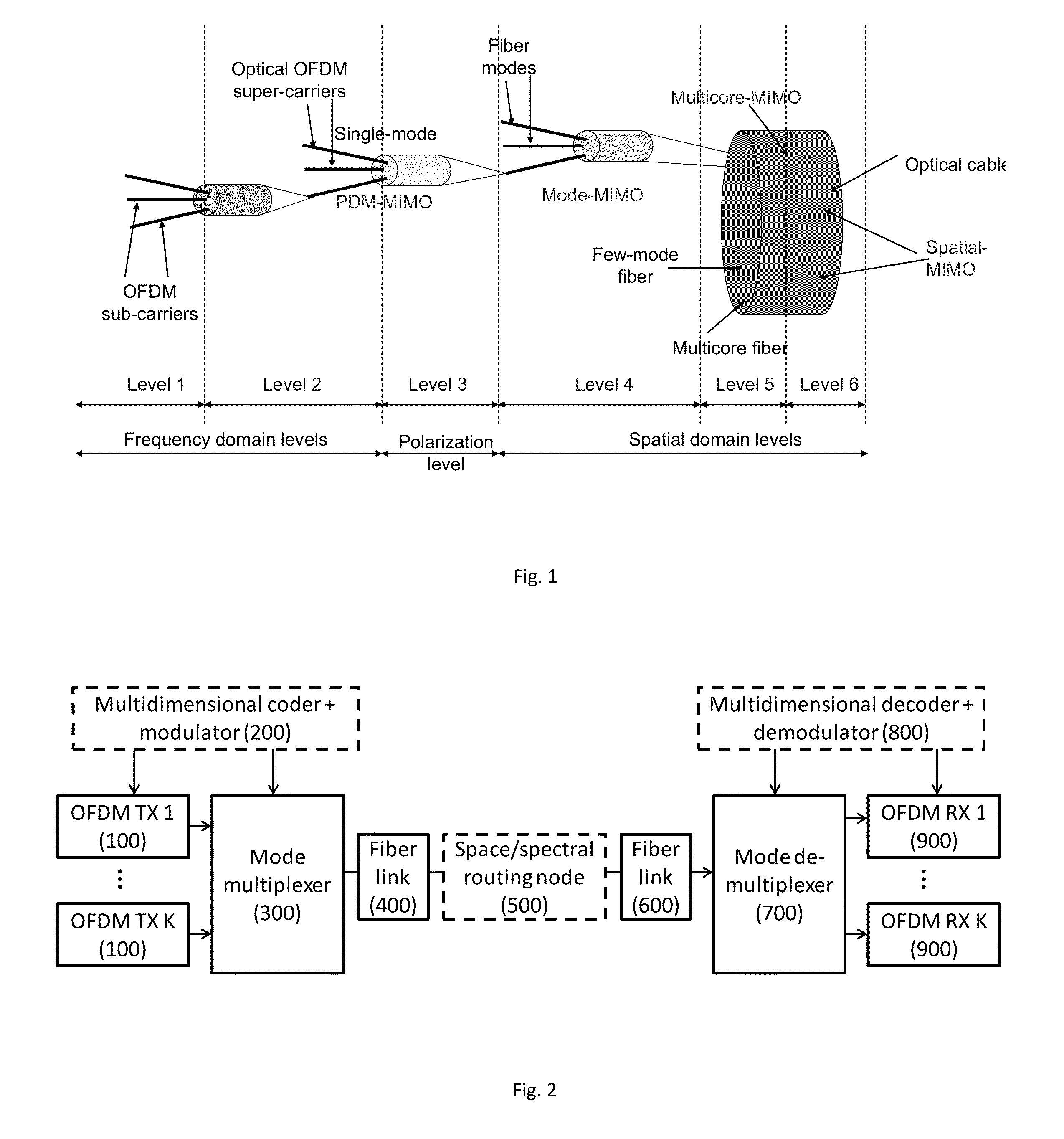
Dynamic Multidimensional Optical Networking Based on Spatial and Spectral Processing
An optical network includes a multidimensional coder and modulator for handling multiple-in-multiple-out MIMO spatial lightpath properties and content of any specific supercarrier, a spatial mode multiplexer responsive to orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM transmissions and the multidimensional coder, a spatial-spectral routing node coupled over a fiber link to the spatial mode multiplexer for performing switching granularity by a spatial mode reconnection, a multidimensional decoder and demodulator; and a spatial mode demultiplexer coupled over a fiber link to the spatial-spectral routing node and responsive to the multidimensional decoder and demodulator.
Owner:NEC CORP
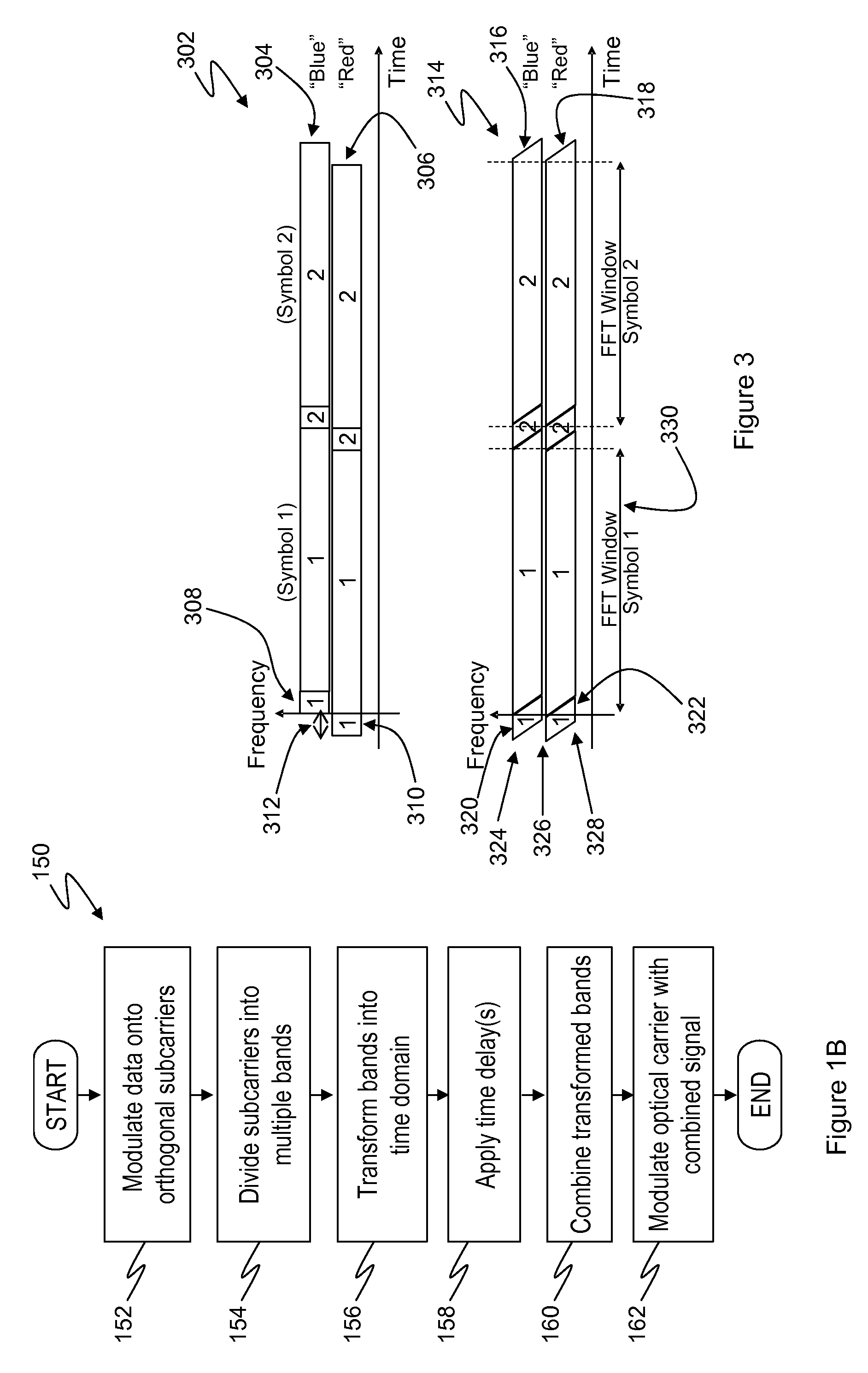
Optical OFDM transmission with improved efficiency
InactiveUS7693429B1Avoid Intersymbol InterferenceReduce impactModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTime delaysTime transformation
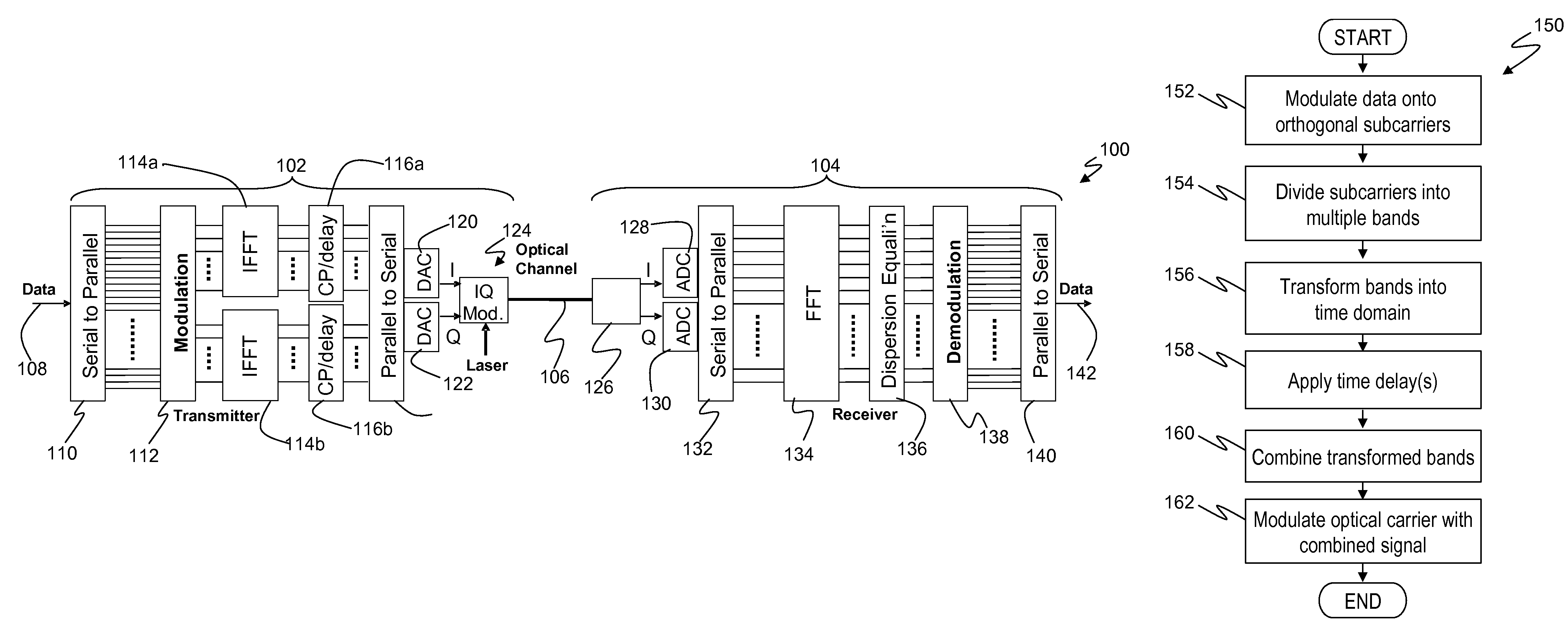
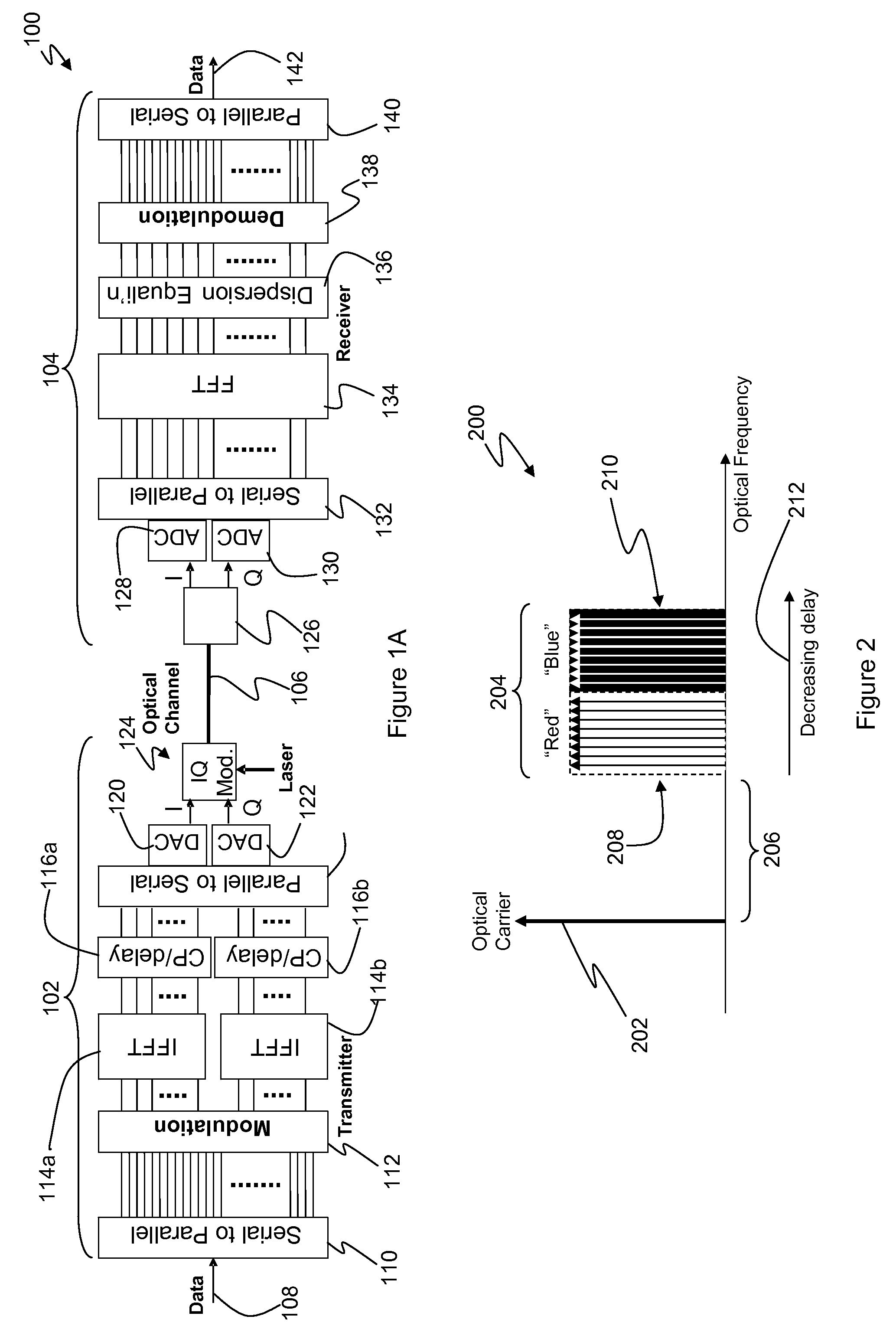
A method of transmitting digital information over a dispersive optical channel includes encoding the digital information into a series of data blocks, wherein each block comprises a plurality of substantially orthogonal frequency domain subcarriers. Each data block is then divided into at least two frequency bands, each band comprising a plurality of contiguous subcarriers. A frequency / time transformation is then performed, in order to form a corresponding plurality of transformed bands, each transformed band comprising a sequence of time domain data samples. A time delay is applied to at least one of the transformed bands relative to at least one other of the transformed bands. The bands are then combined to produce an electrical signal waveform embodying the digital information. Finally, an optical source is modulated using the electrical signal waveform, to produce a corresponding optical signal for transmission over the dispersive optical channel. The invention enables a reduction in the duration of guard intervals that may need to be inserted into the transmitted data blocks, in order to avoid received signal degradation due to inter-symbol interference caused by dispersion in the optical channel. Transmission overheads may thereby be reduced, resulting in an improvement in transmission efficiency.
Owner:OFIDIUM PTY LTD
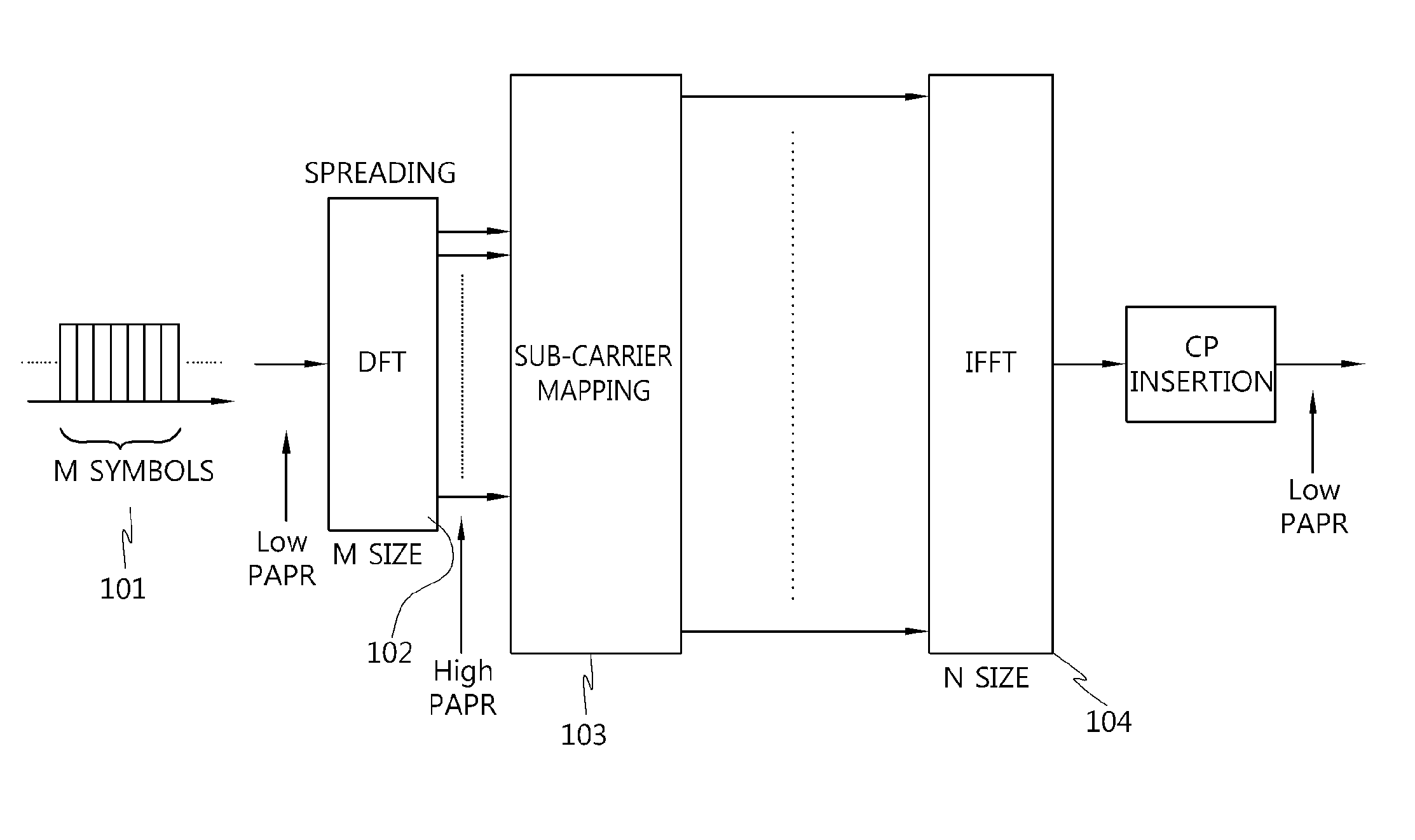
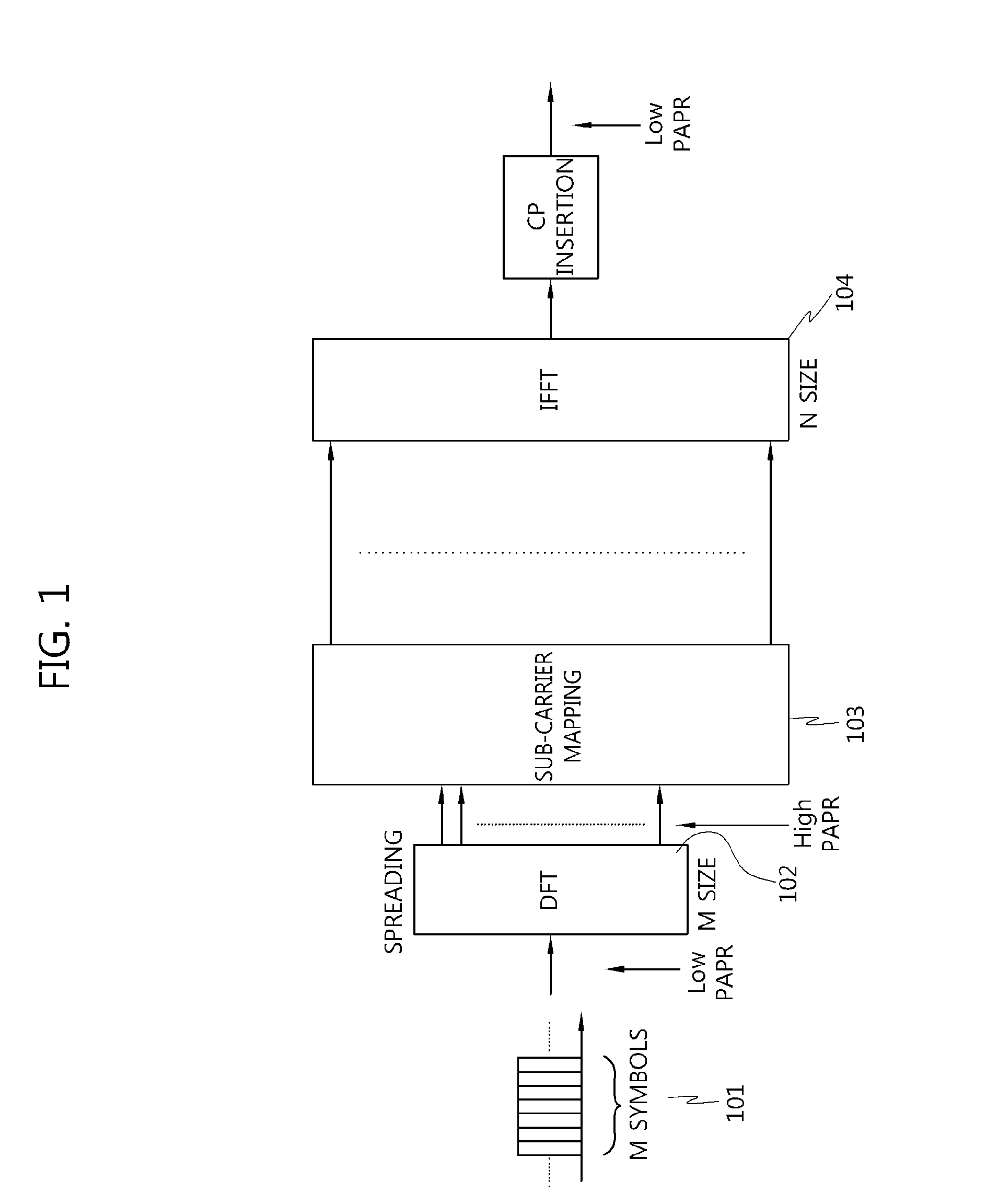
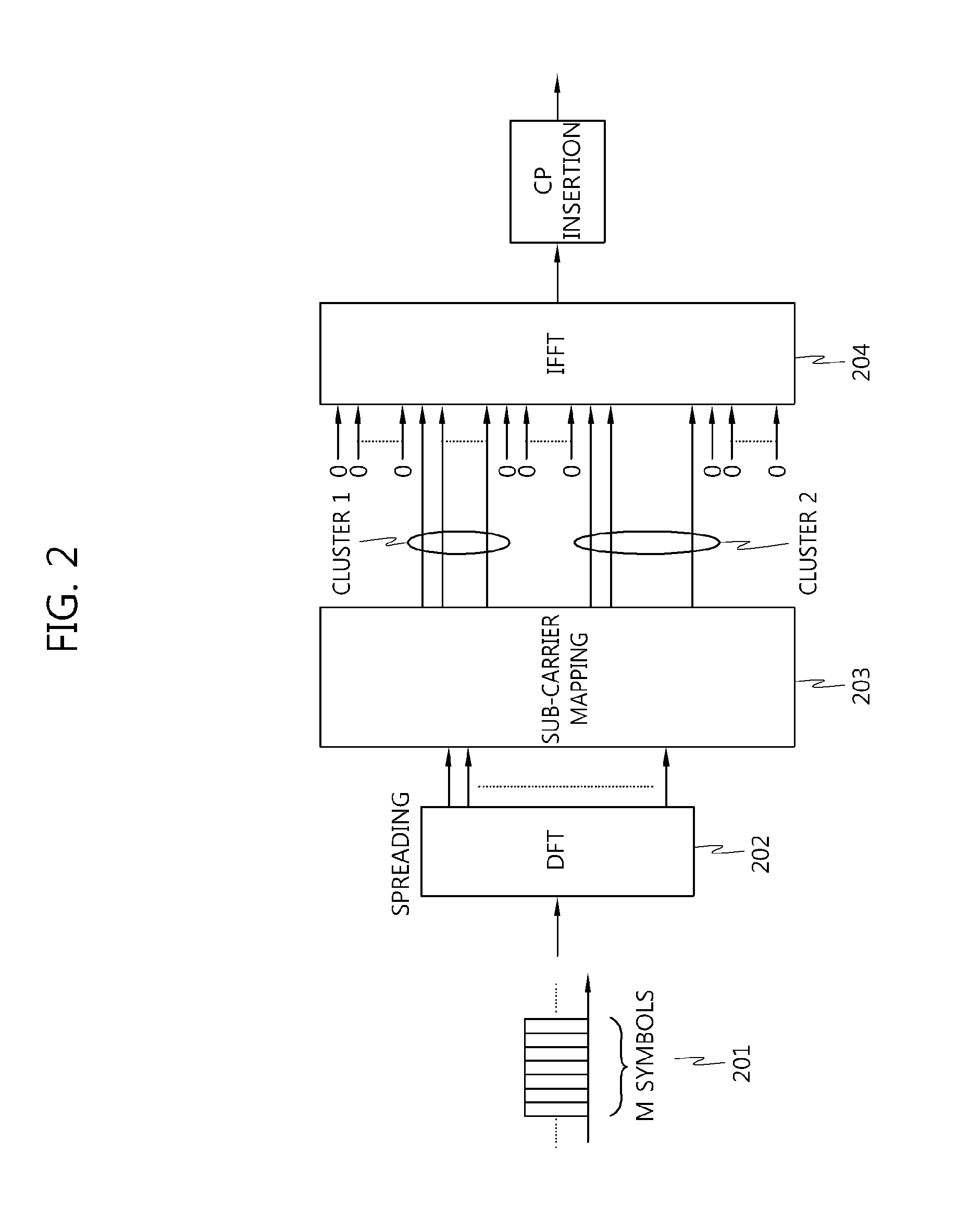
Method for generating and transmitting a reference signal for uplink demodulation in a clustered dft-spread OFDM transmission scheme
ActiveUS20120269285A1Reduce Inter-Cell InterferenceModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionUplink transmissionComputer science
Disclosed is a method for generating and transmitting a reference signal in a clustered DFT-spread OFDM transmission scheme. A method for generating and transmitting a DM-RS in a clustered DFT-spread-OFDM scheme comprises: a step of generating DM-RS sequences corresponding to the number of clusters allocated for an uplink transmission; and a step of mapping the generated DM-RS sequences to the relevant DM-RS symbol positions for each cluster. Accordingly, the method for generating and transmitting a reference signal according to the present invention, in which DM-RS sequences are allocated and transmitted on a cluster basis, uses a complete DM-RS sequence for each cluster, and therefore inter-cell interference can be weakened, and problems which might occur when applied to a multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) scheme can be solved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
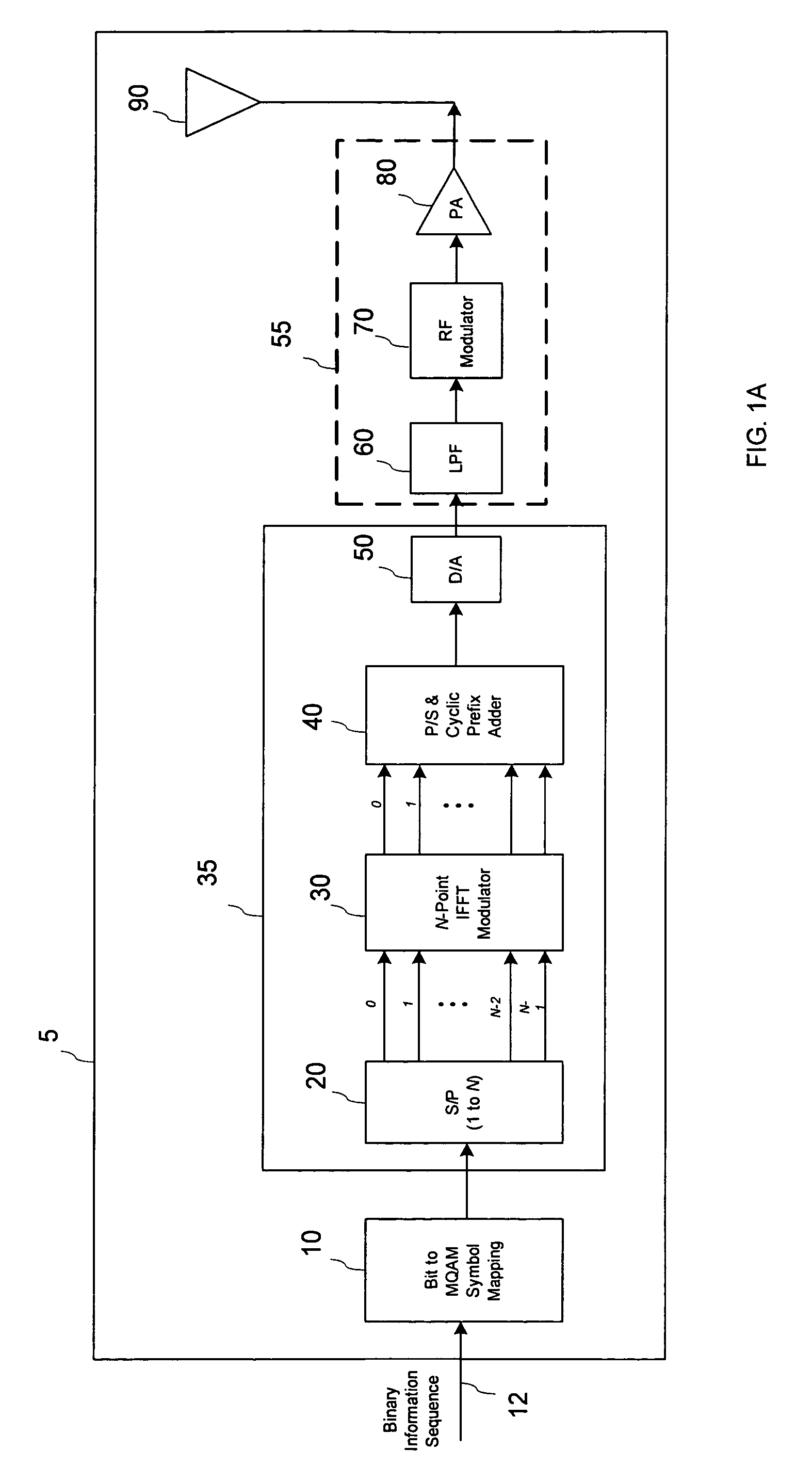
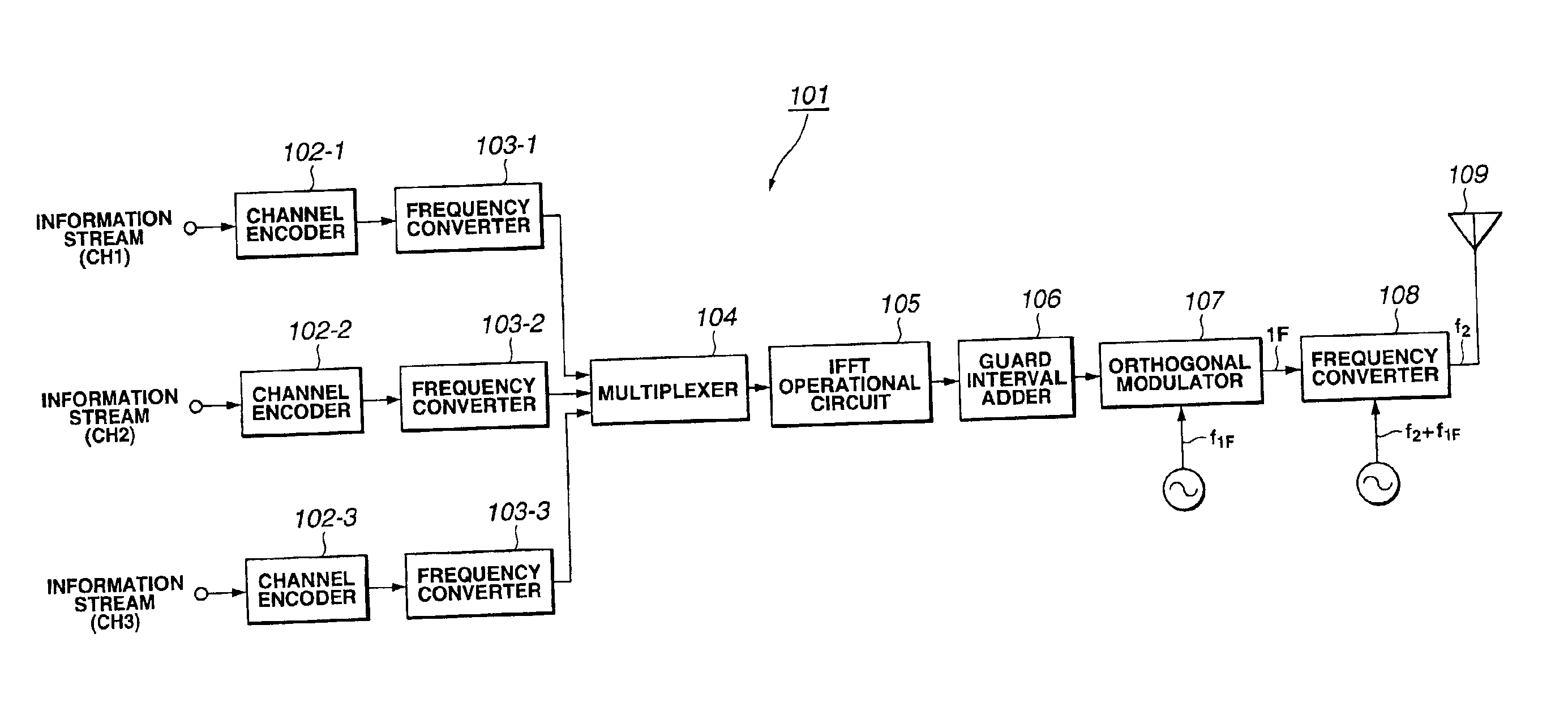
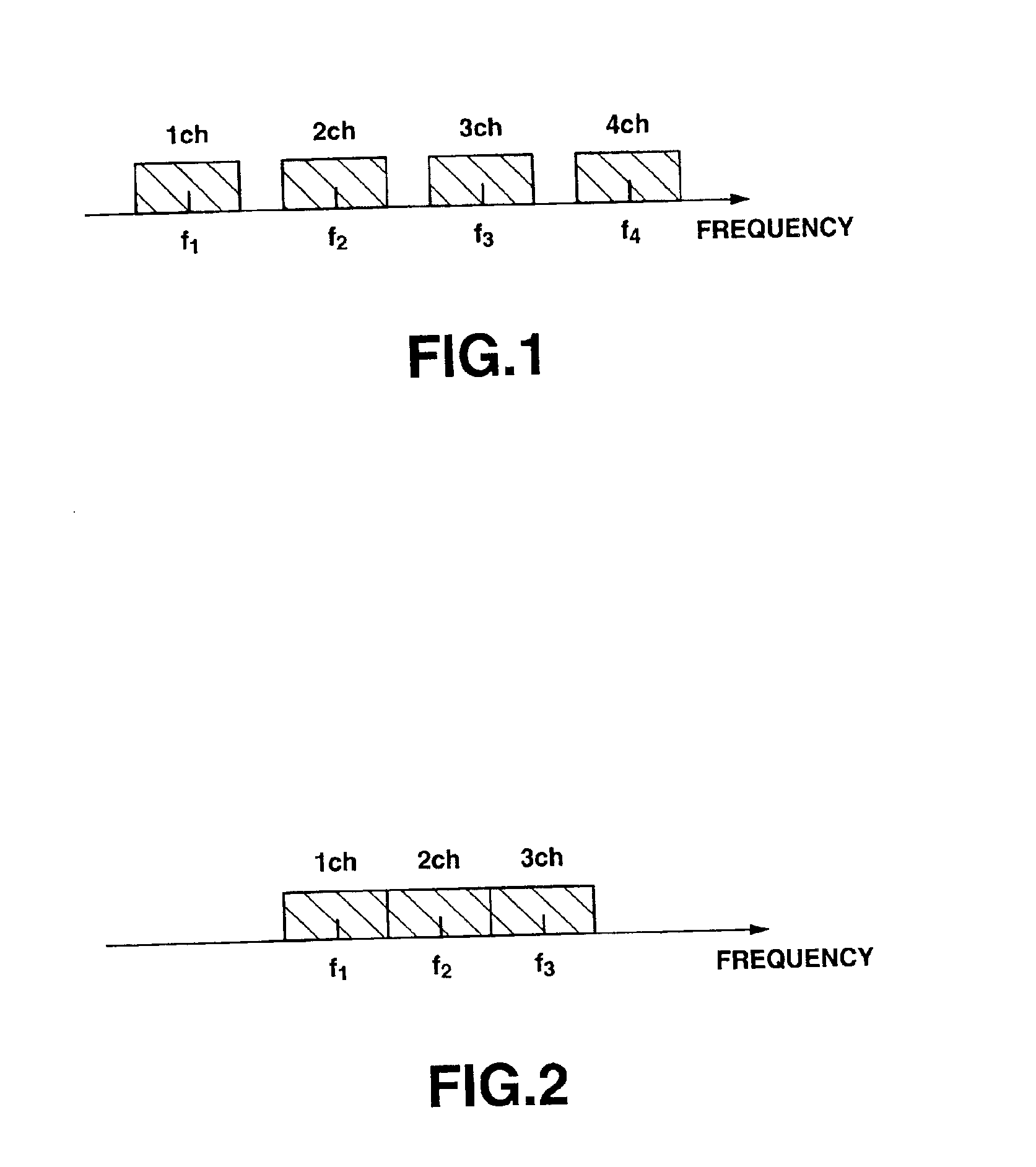
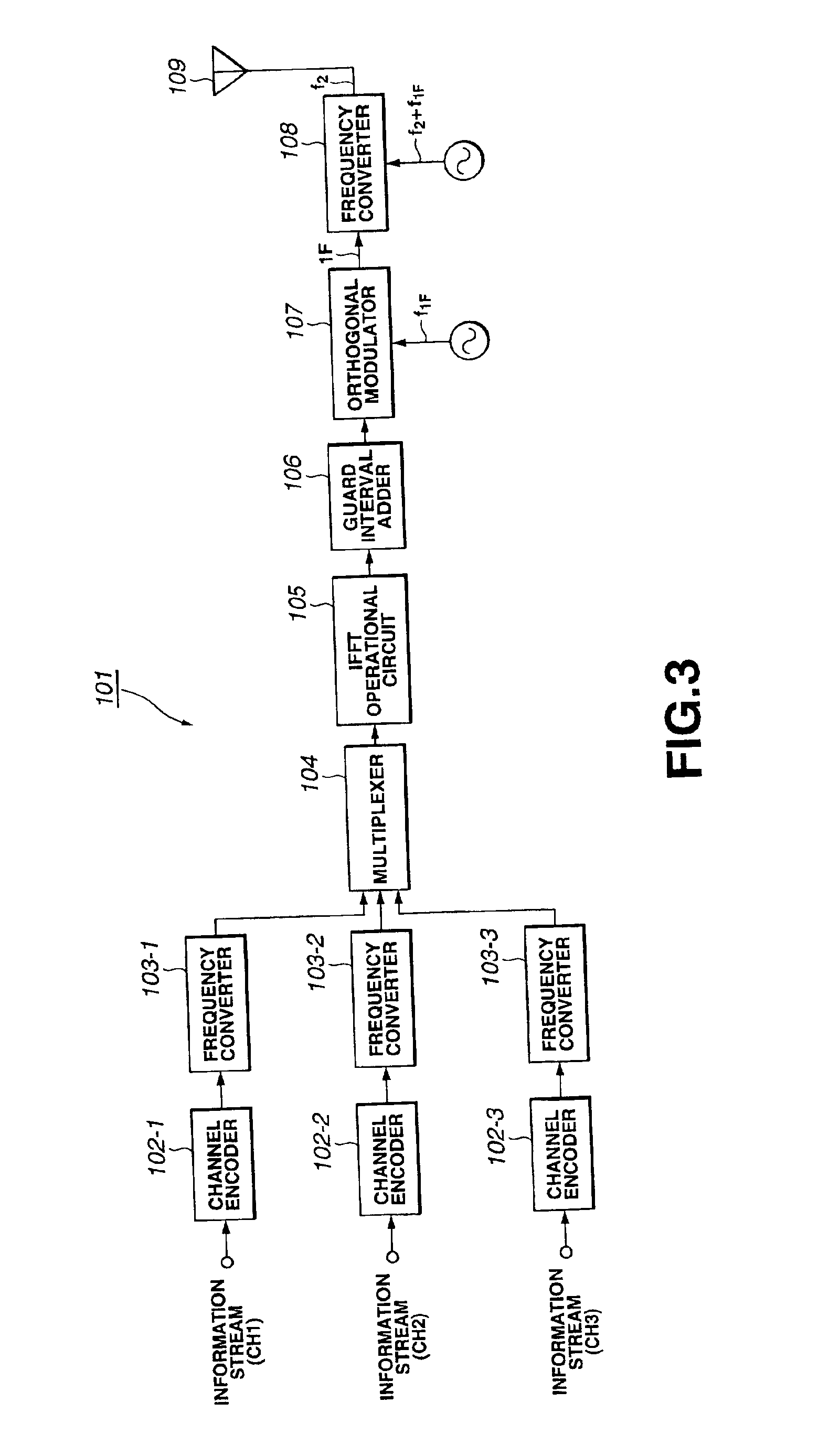
OFDM transmission device and OFDM transmission method
InactiveUS6856590B2Shorten the timeShorten the switching timeSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlOrthogonal multiplexElectrical and Electronics engineeringOfdm transmission
The time required for switch the channel can be remarkably curtailed. When broadcasting signals through a plurality of information channels with an OFDM system, the plurality of information channels are multiplexed in the sense of frequency and collectively subjected to IFFT modulation for connected transmission instead of subjecting the plurality of information channels independently to OFDM modulation for transmission. With this arrangement, the efficiency of exploitation of frequencies is improved. According to the invention, the OFDM frames are synchronized for each information channel for the purpose of connected transmission. Then, the OFDM receiver can switch the information channel for signal reception, maintaining the frame synchronizing signals.
Owner:SONY CORP
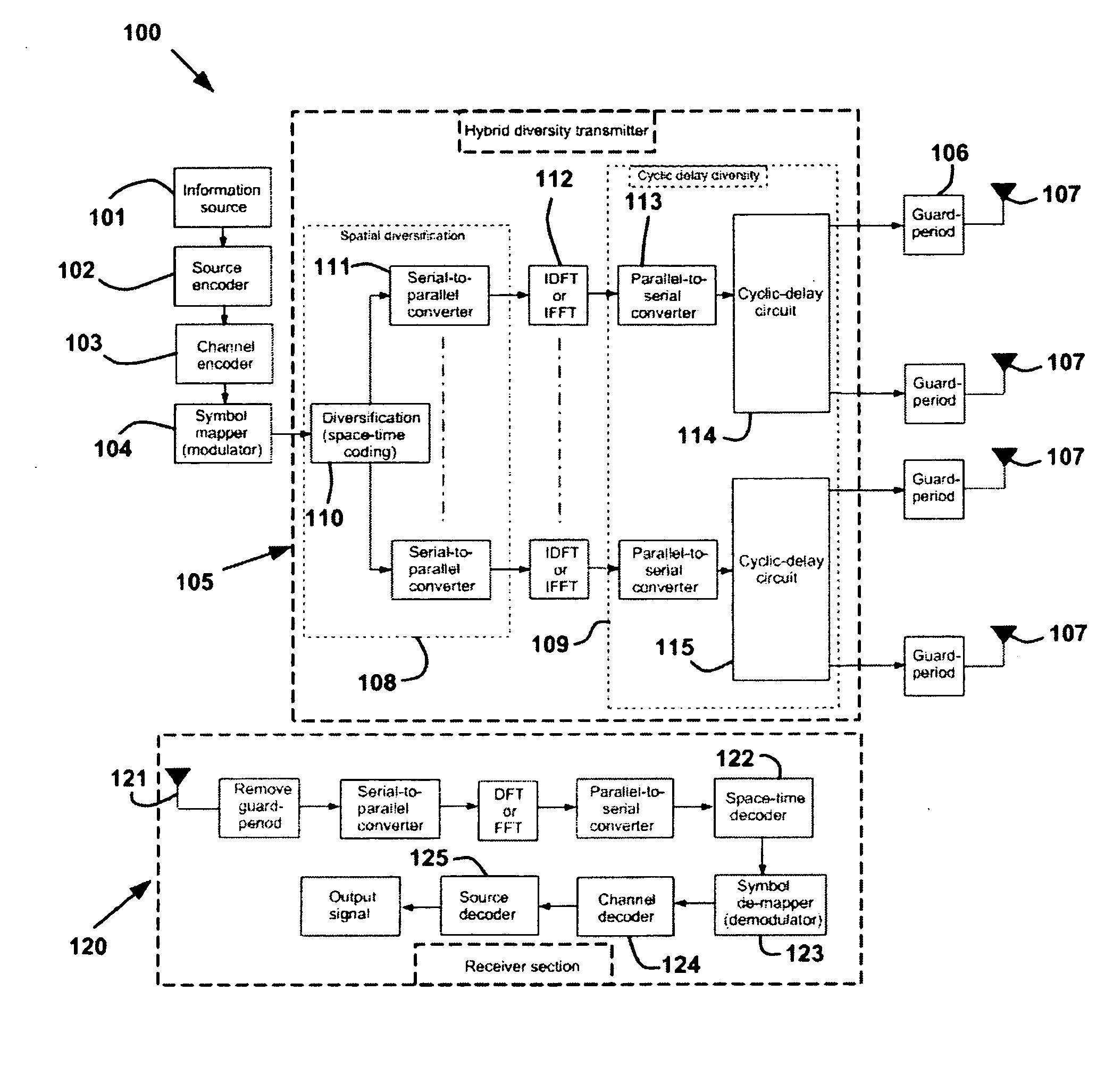
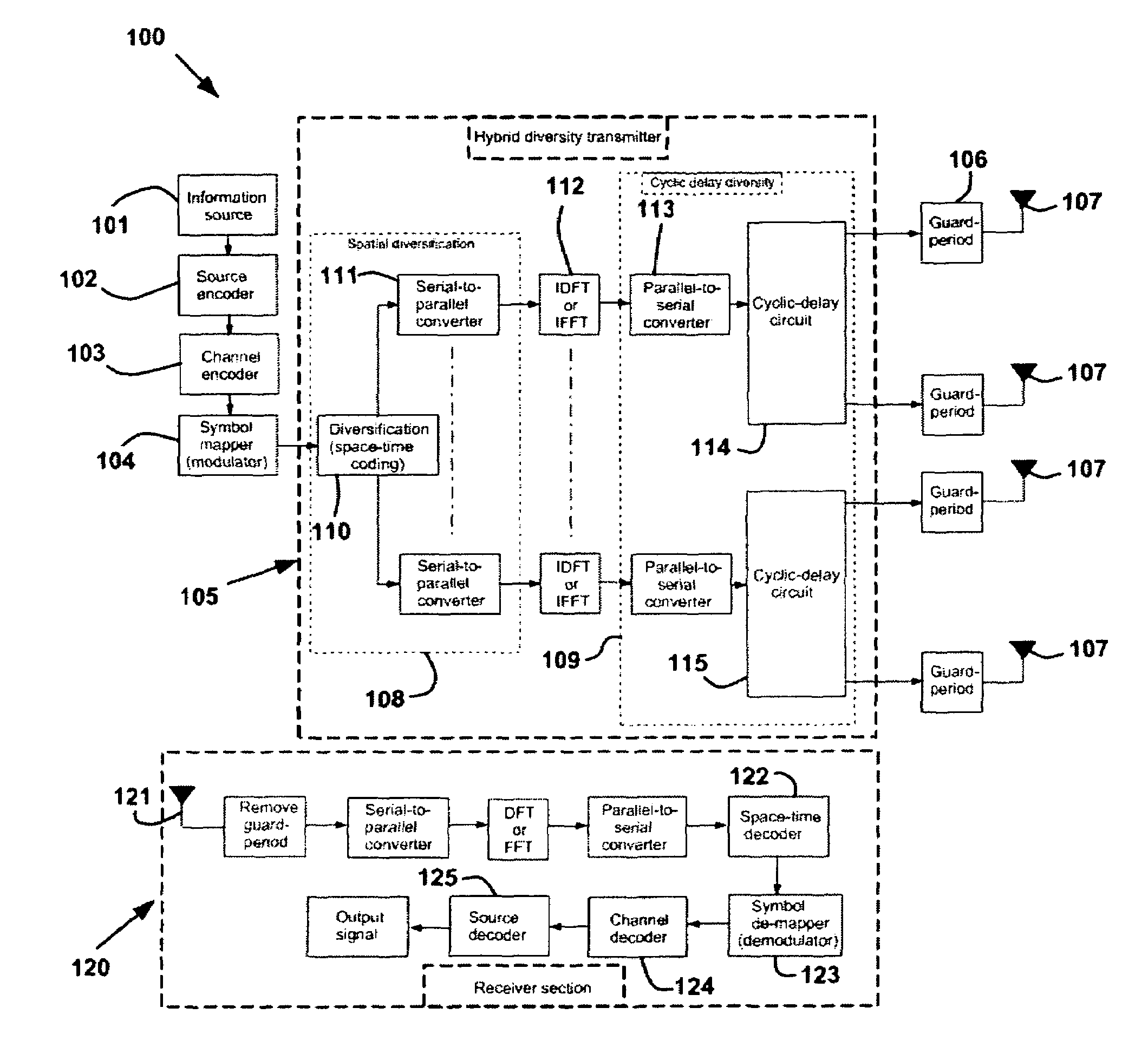
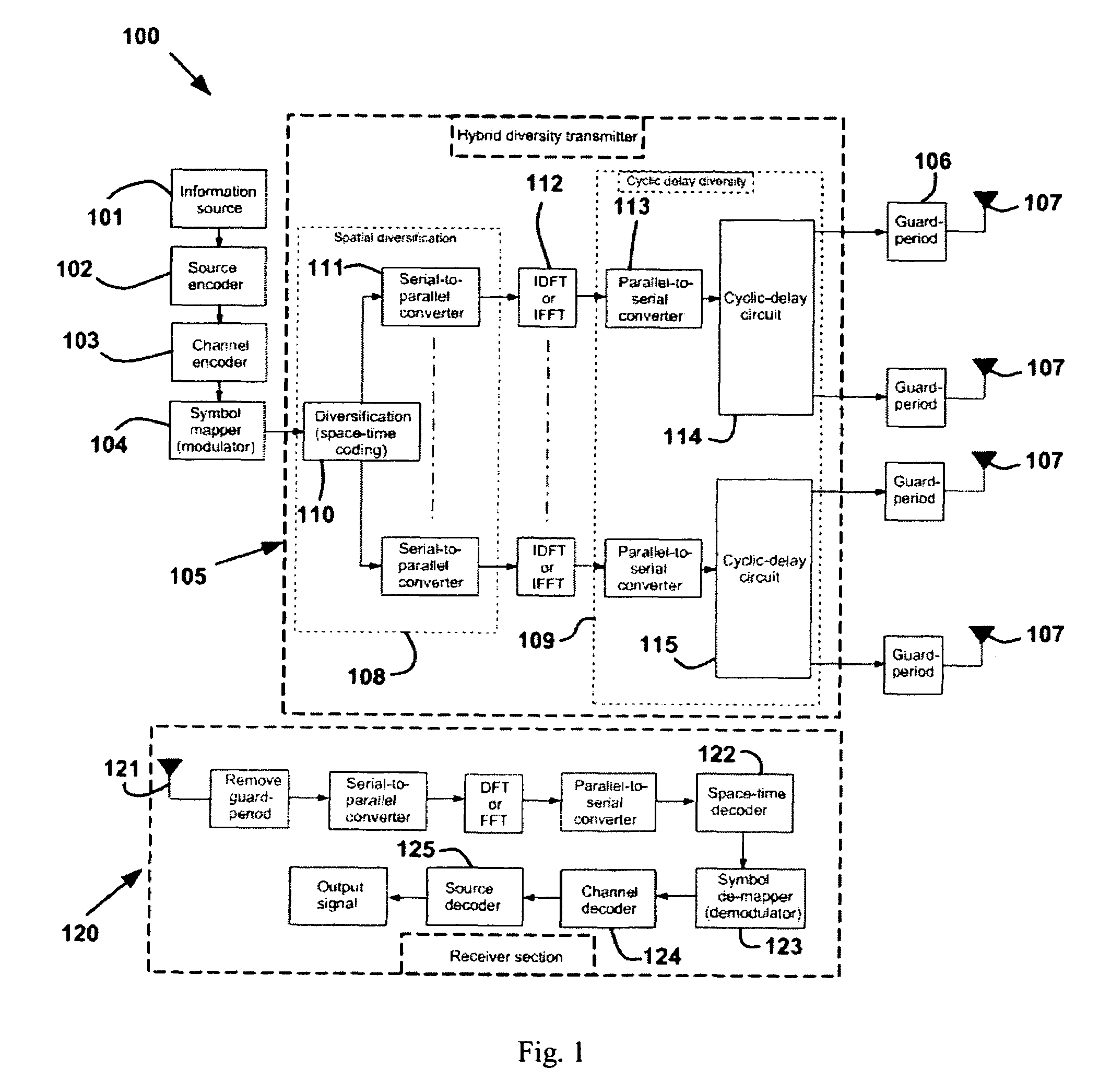
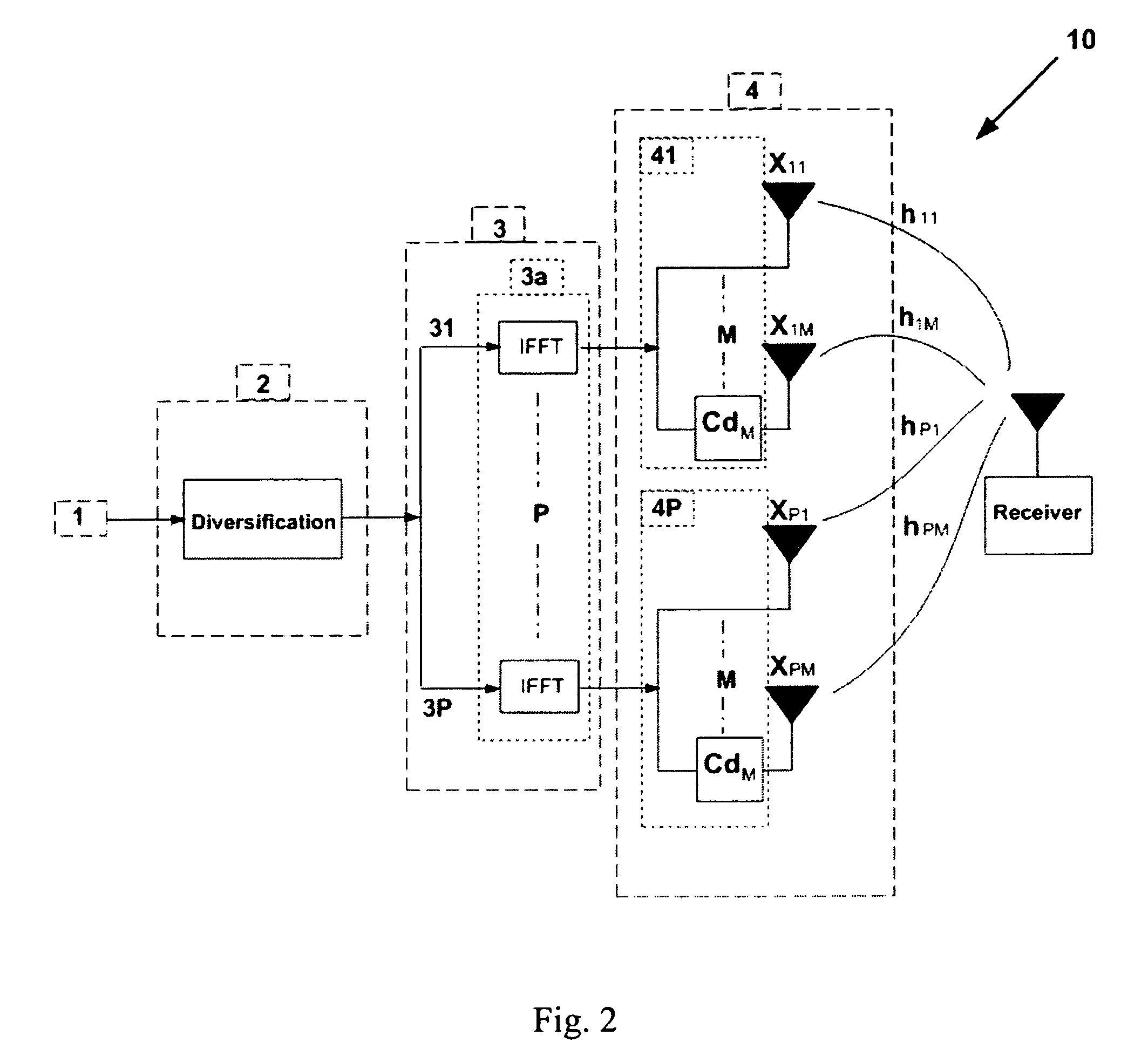
Diversity transmitter and method
InactiveUS20060193245A1More frequency selectiveIncrease the number ofSpatial transmit diversityError preventionTime domainTime shifting
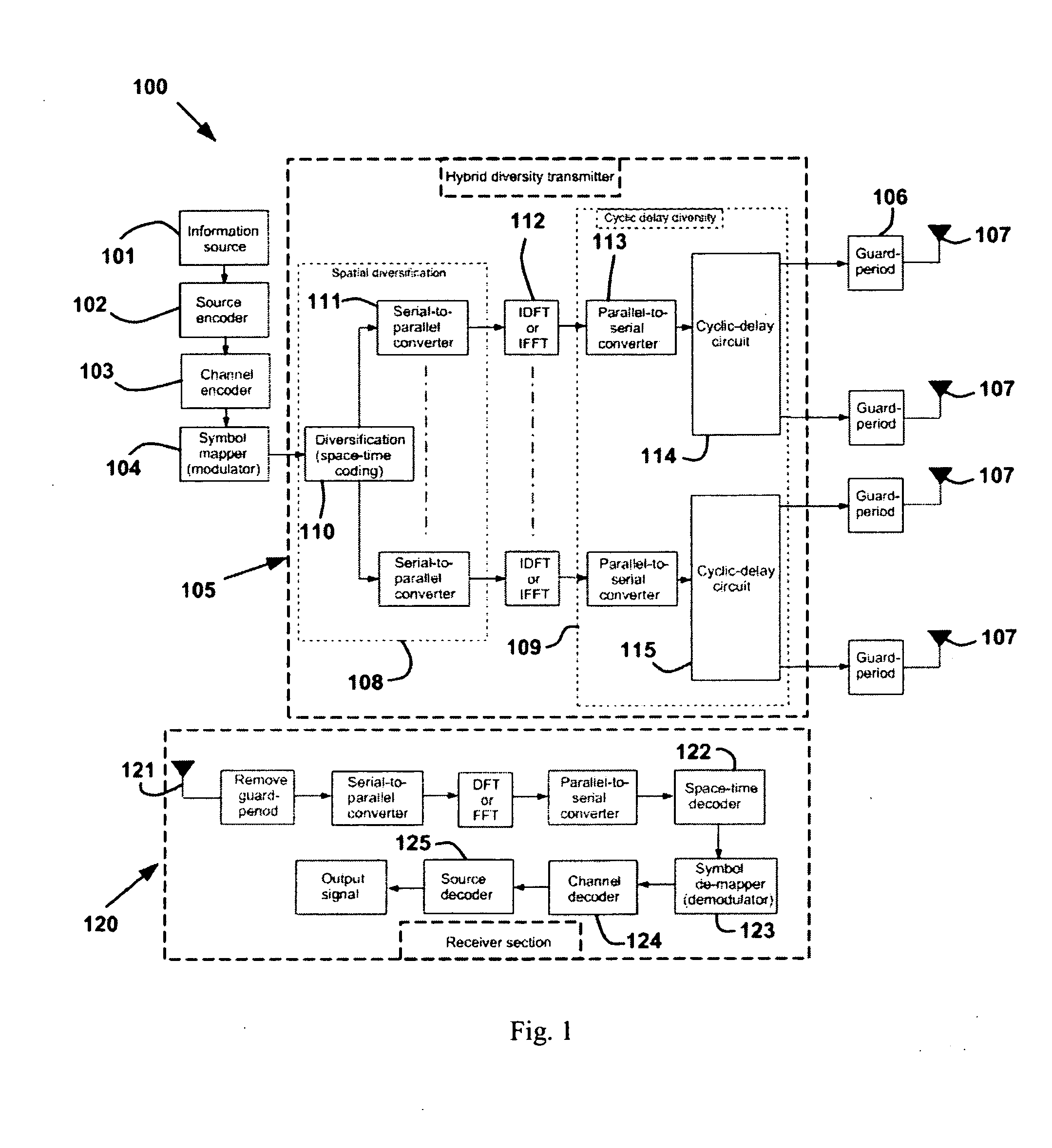
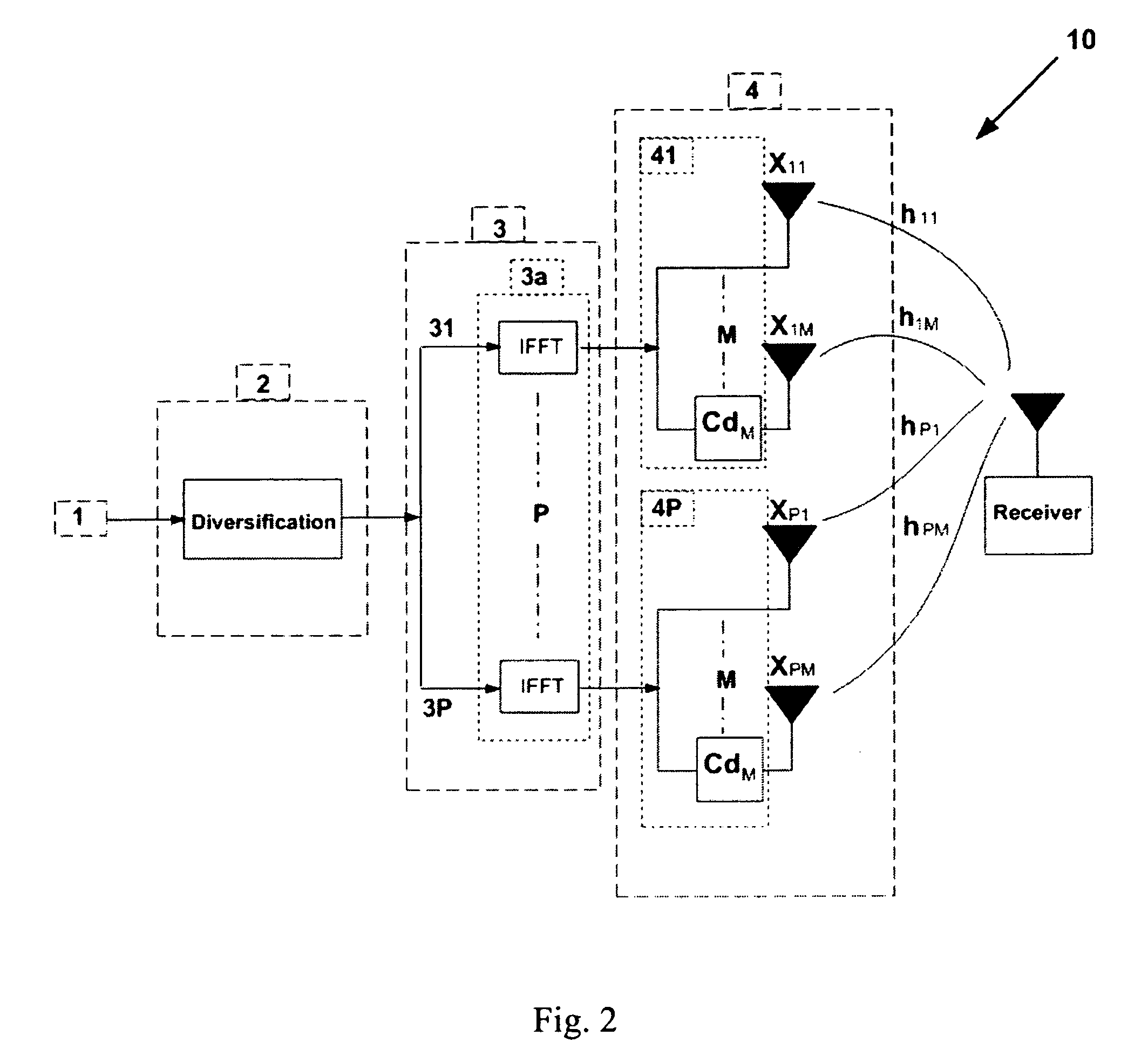
A diversity transmitter for use in an OFDM transmission protocol which diversity transmitter comprises: a diversity generator (2) for receiving and diversifying OFDM transmit symbols, and outputting diversified OFDM symbol matrices (DOSM), DOSM symbols within each DOSM being divided into at least two primary streams each comprising different DOSM symbols, a transmit processor for receiving said at least two primary streams of DOSM symbols, and for transforming said each DOSM symbol from the frequency domain into the time domain, and outputting time domain OFDM symbols (TDOSs), a cyclic delay circuit (41 . . . 4P) for dividing at least one of said primary streams of TDOSs into at least two branches of identical TDOSs, each branch for supplying a respective spatial channel for transmission to a receiver, the arrangement being such that, in use, said cyclic delay circuit (41 . . . 4P) applies a cyclic time shift to a TDOS symbol in at least one of said branches before transmission.
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON
Covert OFDM Transmission Using Cyclic Prefix
ActiveUS20060050626A1Reduce bandwidth lossImprove immunityModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumTheoretical computer science
Methods for secure OFDM communications include changing the length of OFDM symbols in a pseudo-random fashion by appending a totally random signal to some of the OFDM symbols. An adaptive cyclic prefix is provided for covert and spectrally efficient communication. A developed PN based random data addition provides further security by removing the chance of combining synchronization information over several OFDM symbols.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
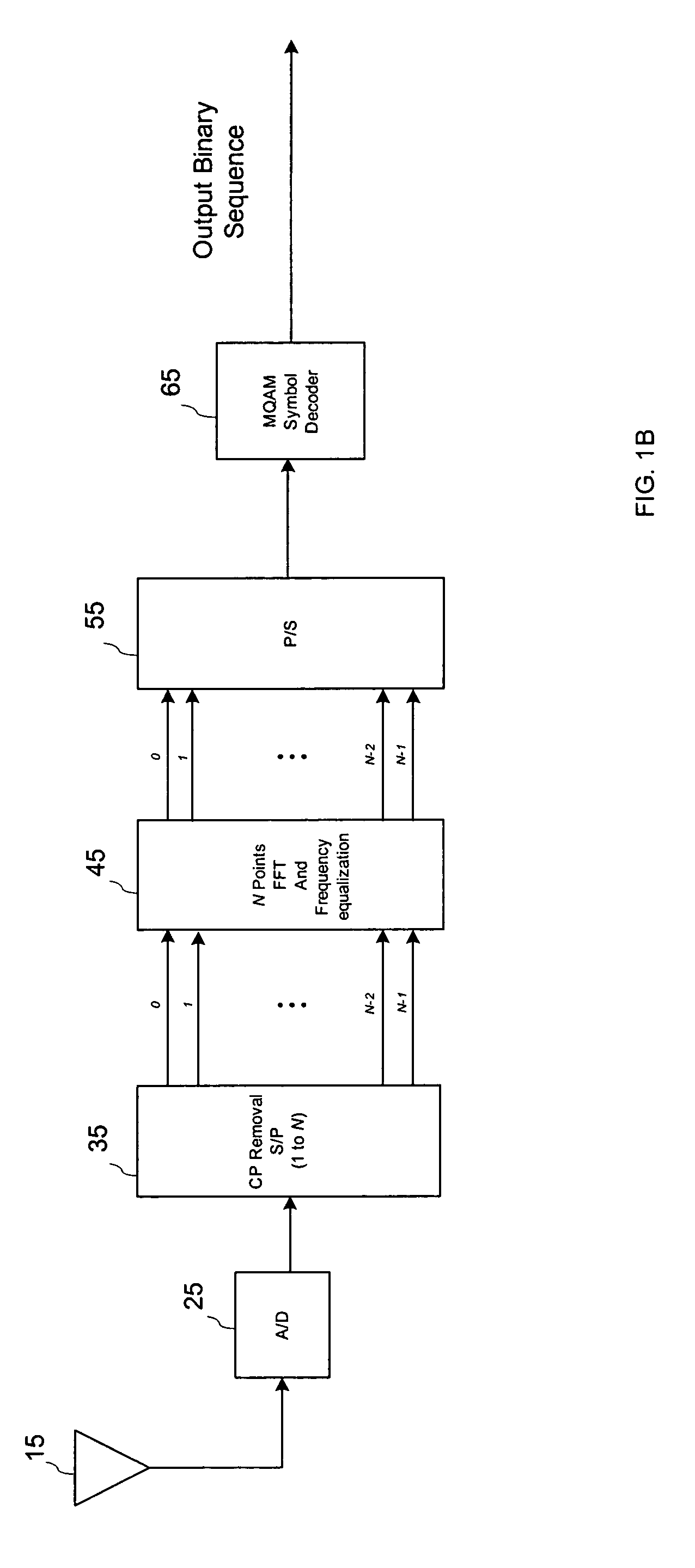
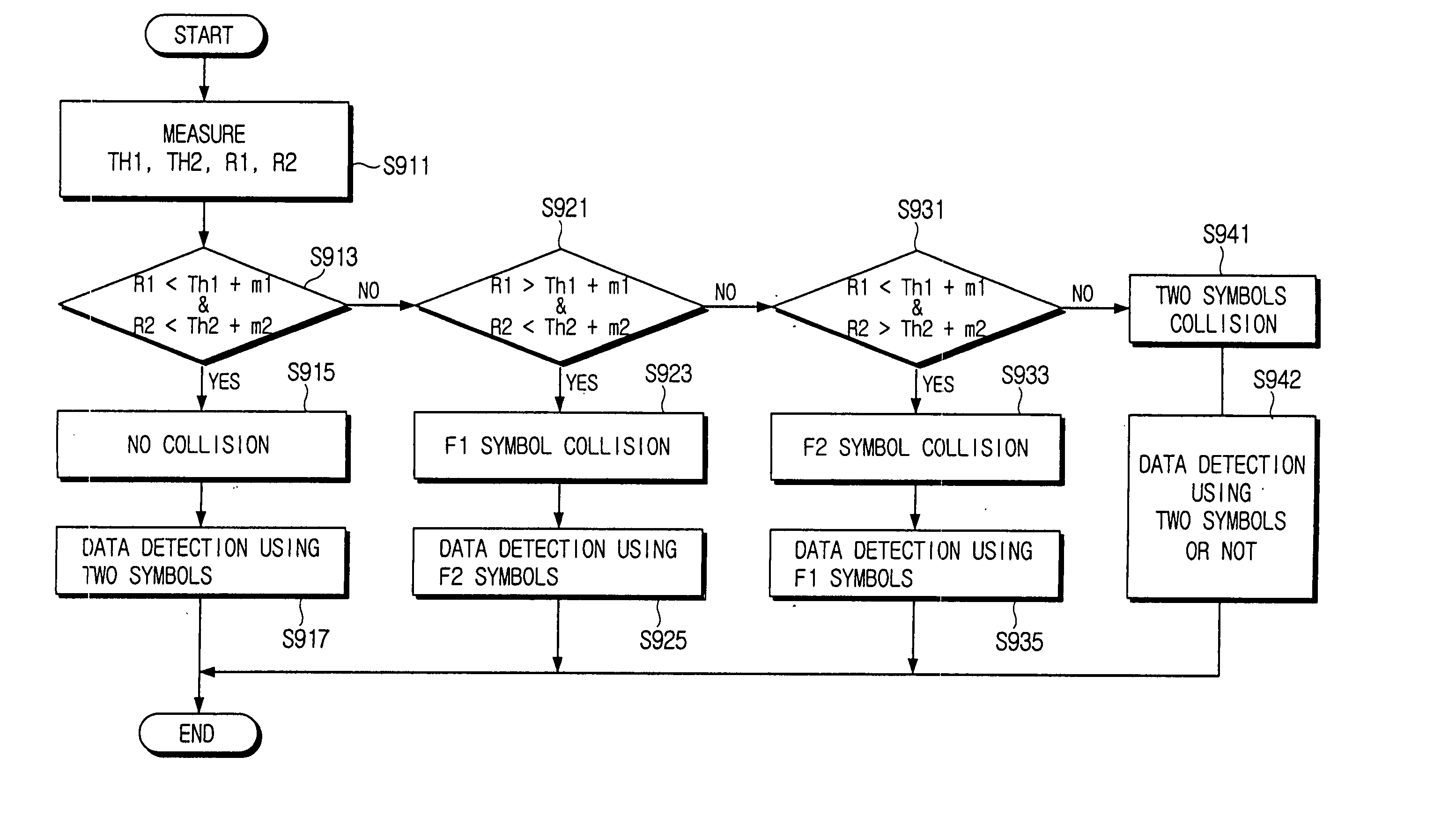
Receiving apparatus in OFDM transmission system
InactiveUS7362832B2Easy to codeIncrease in the BER can be suppressedError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransfer systemGuard interval
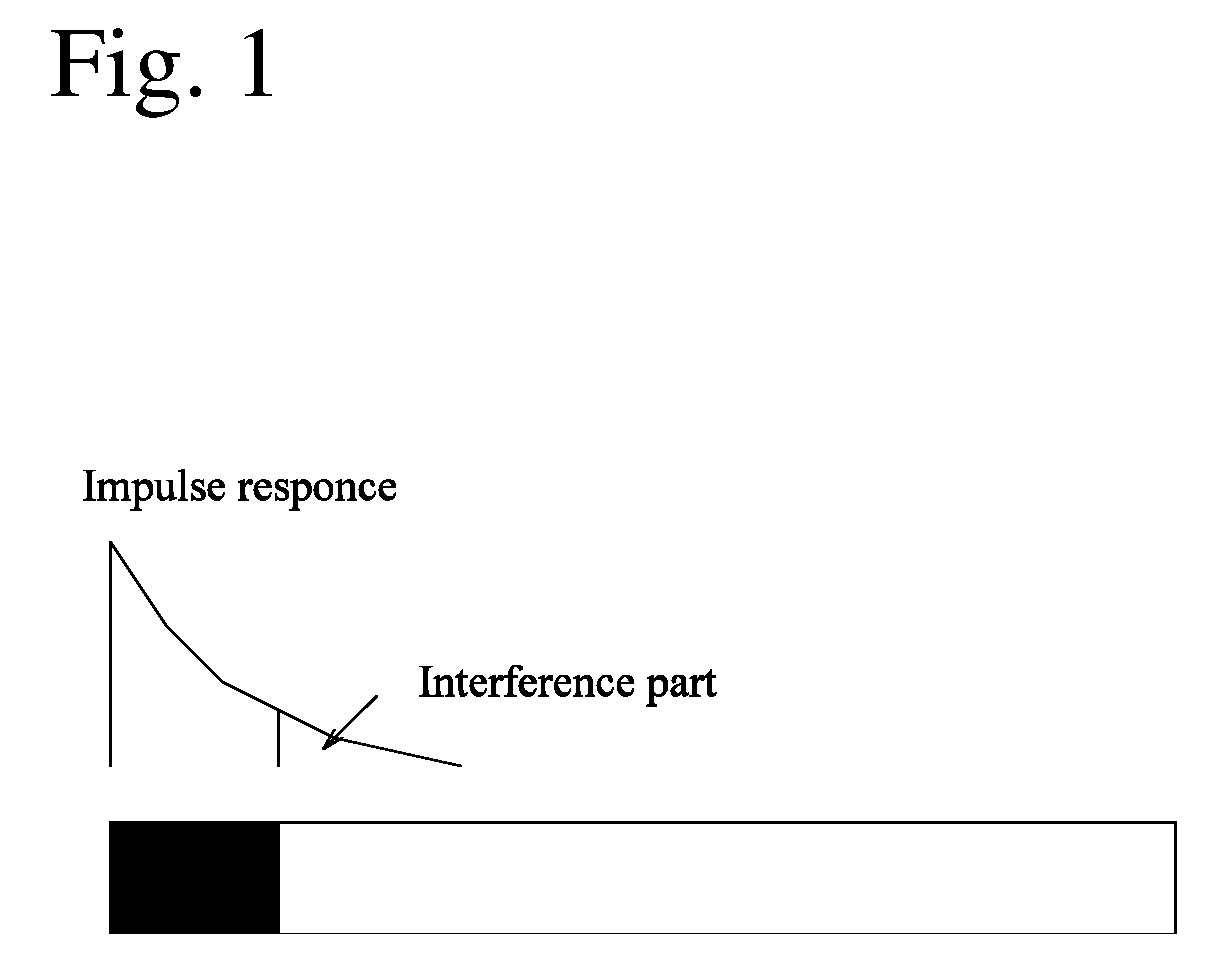
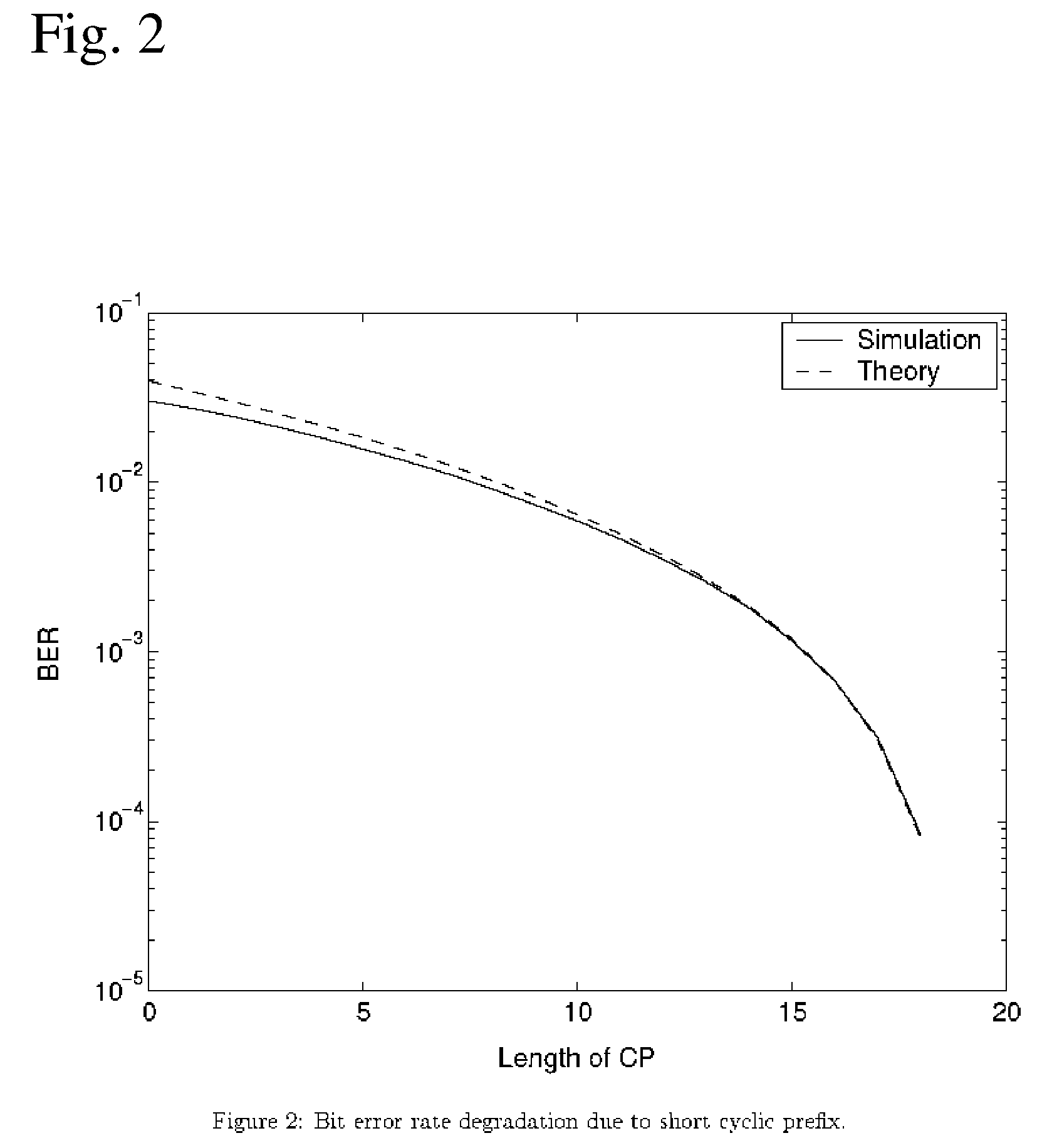
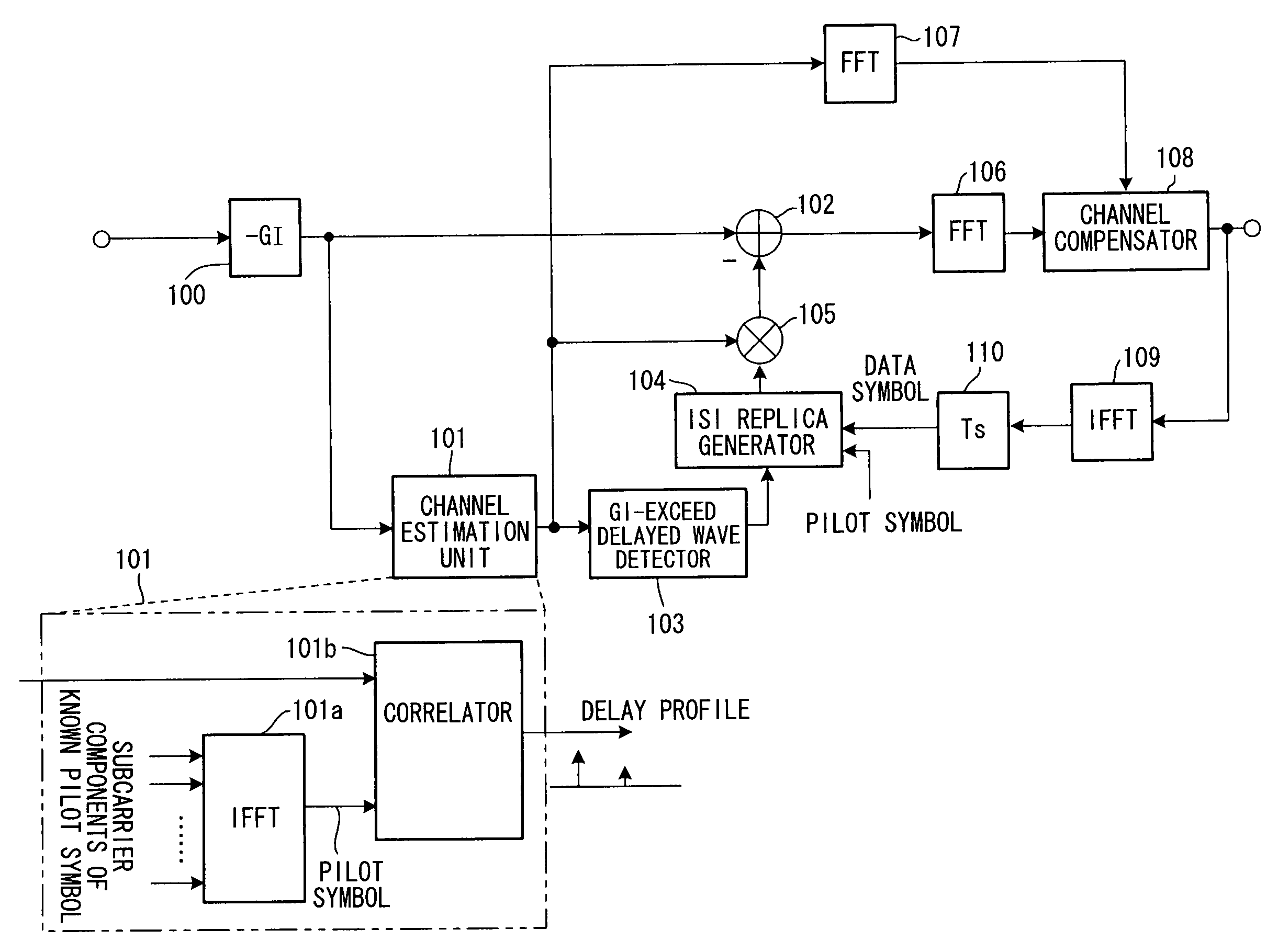
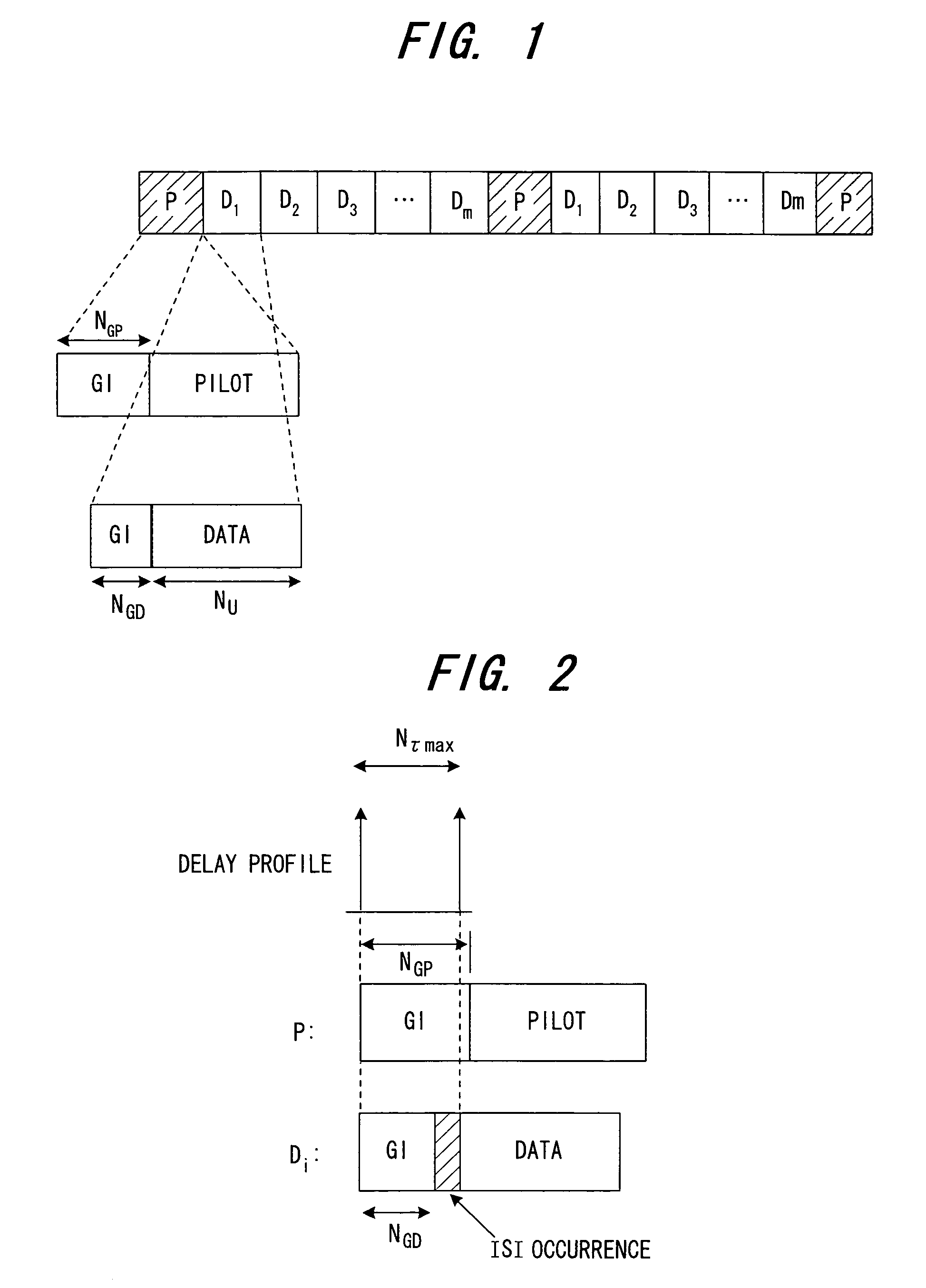
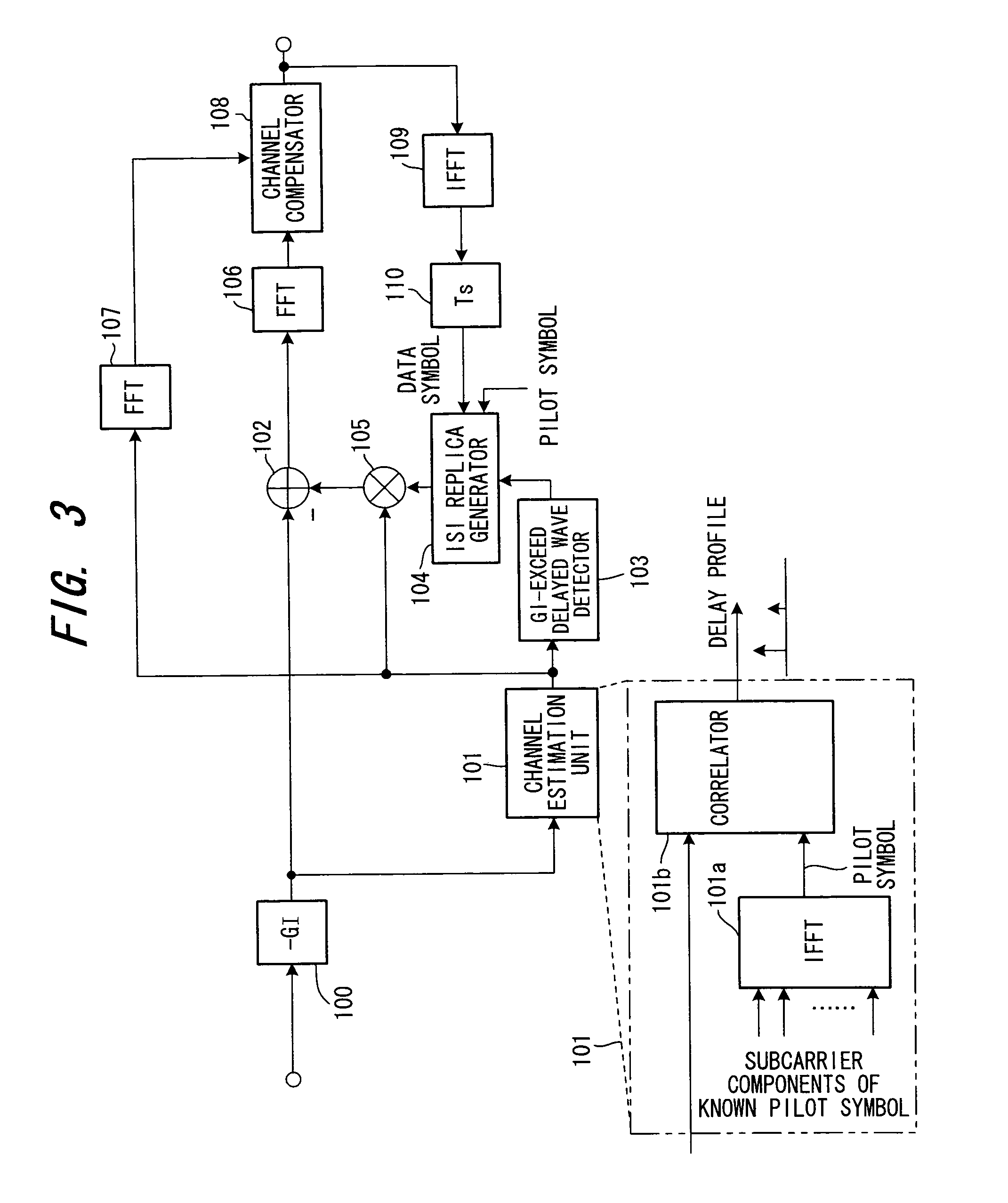
A receiving apparatus in an OFDM transmission system includes a channel estimation unit (101) for measuring a delay profile of a delayed wave having a delay greater than a guard interval of data; a guard-interval-exceed delayed wave detector (103) for detecting, from the delay profile as an intersymbol interference (ISI) portion, a delay-time portion greater than the guard interval of the data; a ISI replica generator (104) for generating, as the ISI replica, a time-waveform portion of a known symbol conforming to the ISI portion, or a time-waveform portion of the preceding symbol; subtractor (102) for subtracting the ISI replica from a receive signal; and an FFT arithmetic unit (106) for demodulating data by applying FFT processing to the result of subtraction.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Cyclic delay diversity and space coded-hybrid diversity transmitter
InactiveUS7609613B2Easy to implementHigh selectivitySpatial transmit diversityError preventionCyclic delay diversityTime domain
A diversity transmitter for use in an OFDM transmission protocol which diversity transmitter comprises:a diversity generator (2) for receiving and diversifying OFDM transmit symbols, and outputting diversified OFDM symbol matrices (DOSM), DOSM symbols within each DOSM being divided into at least two primary streams each comprising different DOSM symbols,a transmit processor for receiving said at least two primary streams of DOSM symbols, and for transforming said each DOSM symbol from the frequency domain into the time domain, and outputting time domain OFDM symbols (TDOSs),a cyclic delay circuit (41 . . . 4P) for dividing at least one of said primary streams of TDOSs into at least two branches of identical TDOSs, each branch for supplying a respective spatial channel for transmission to a receiver,the arrangement being such that, in use, said cyclic delay circuit (41 . . . 4P) applies a cyclic time shift to a TDOS symbol in at least one of said branches before transmission.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
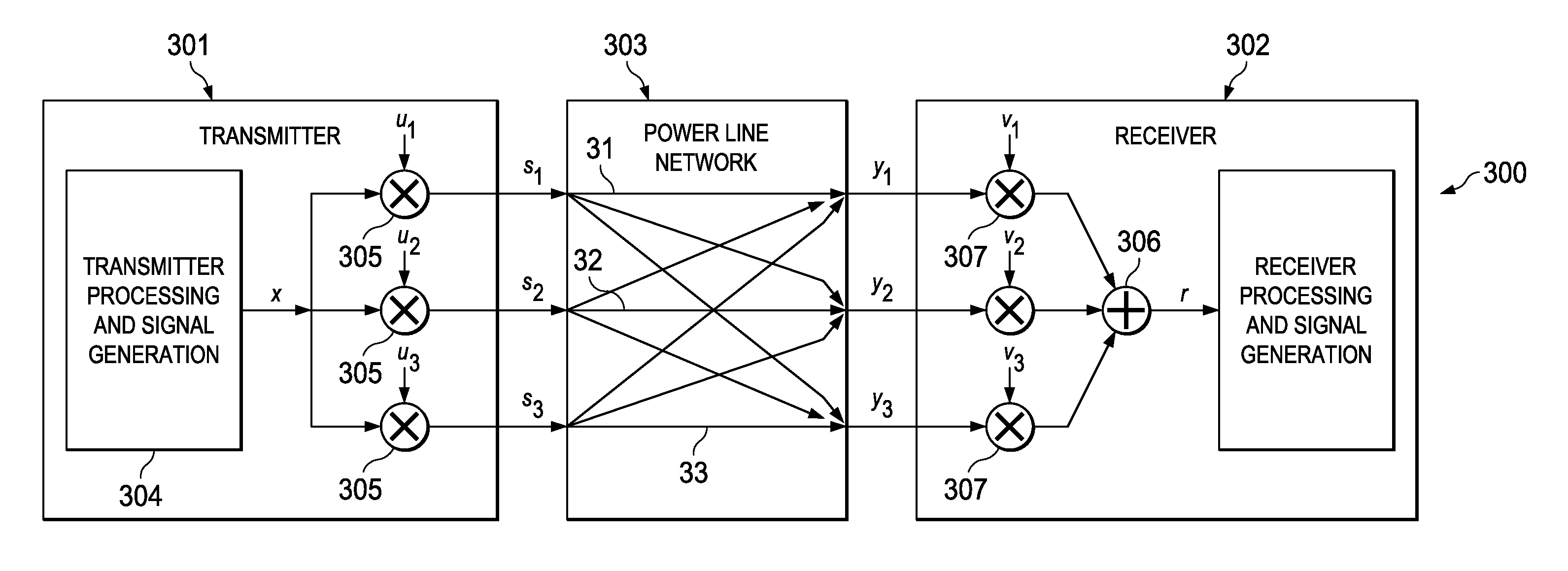
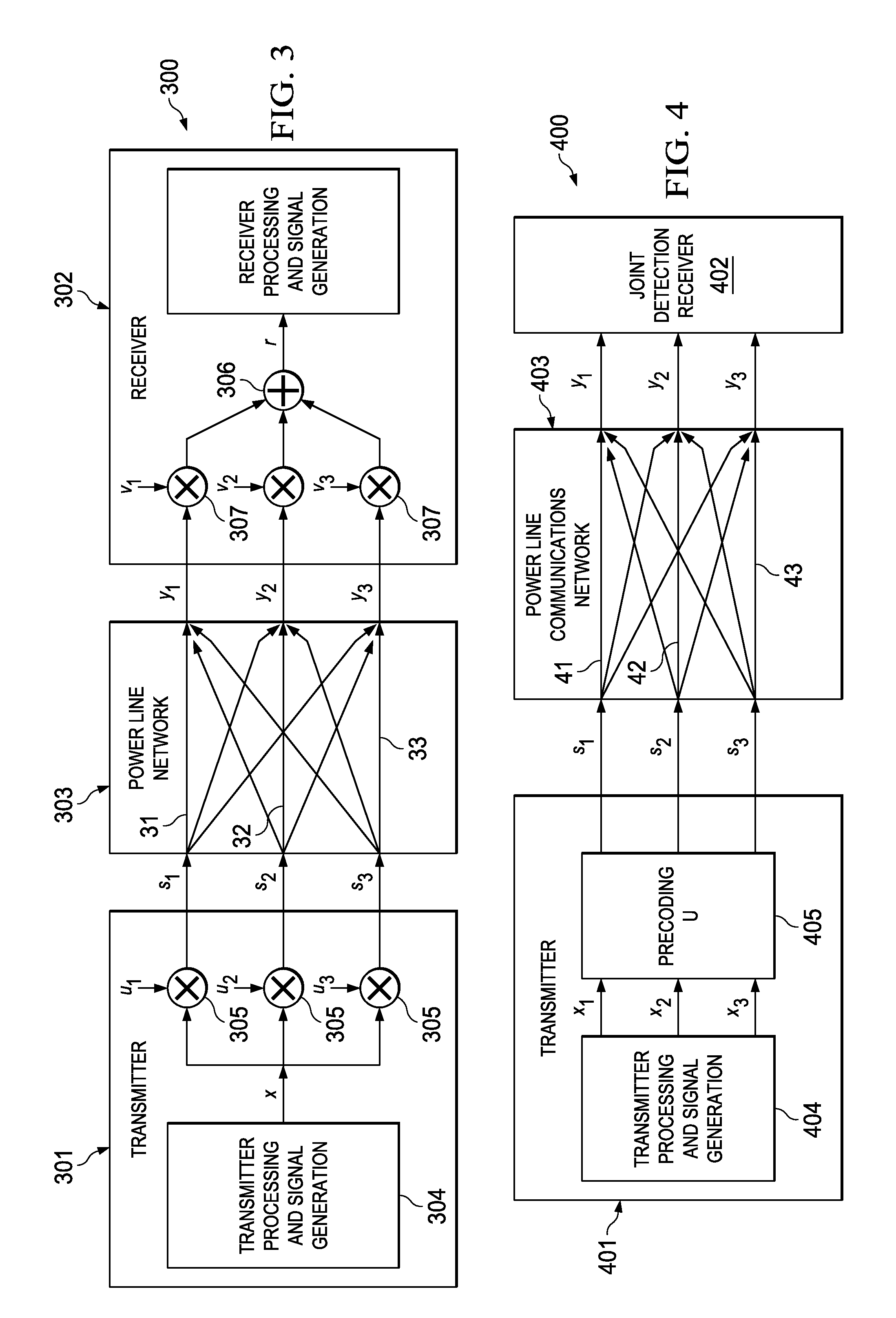
OFDM transmission methods in three phase modes
ActiveUS20110026621A1Neutralize effectMultiple-port networksTransmission/receiving by adding signal to wavePower line networkThree-phase
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
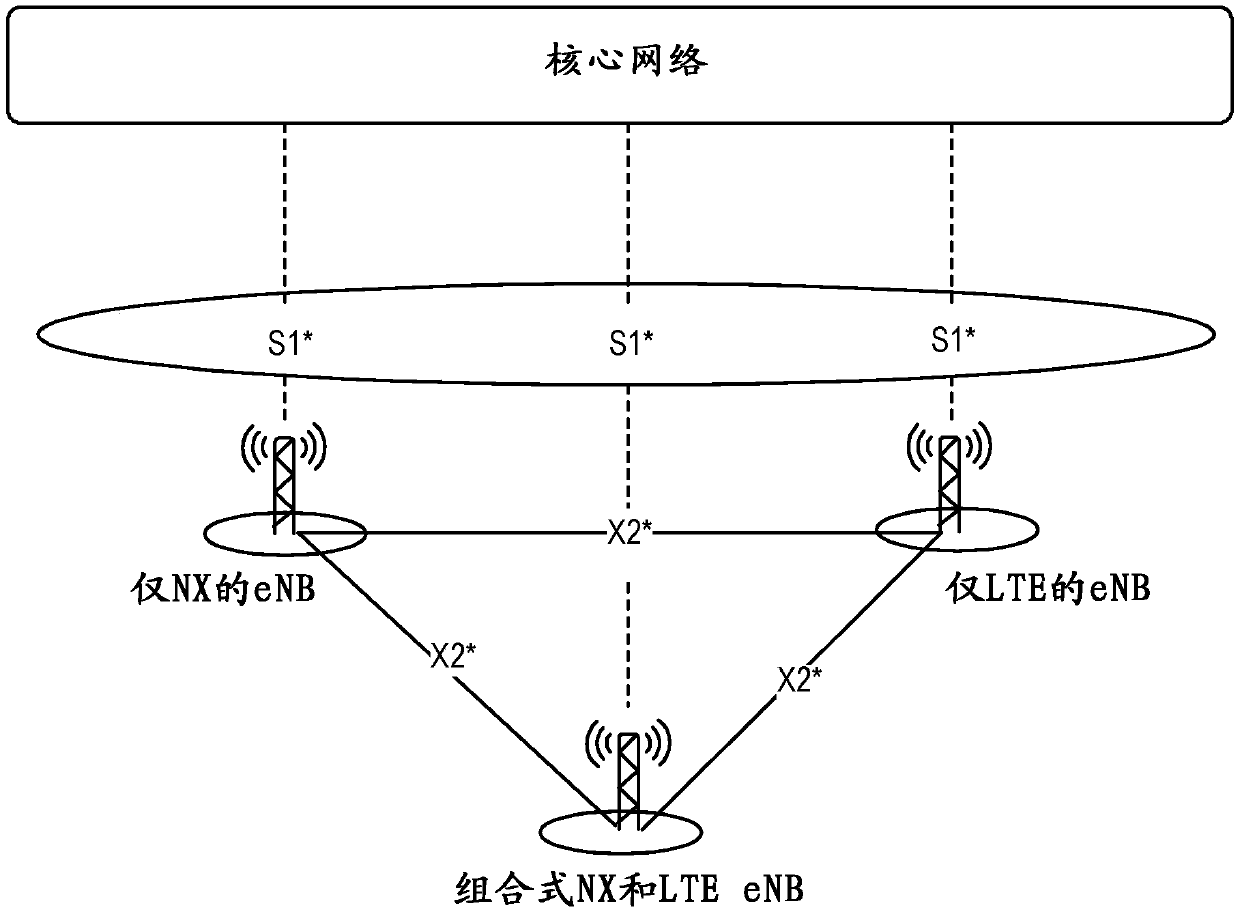
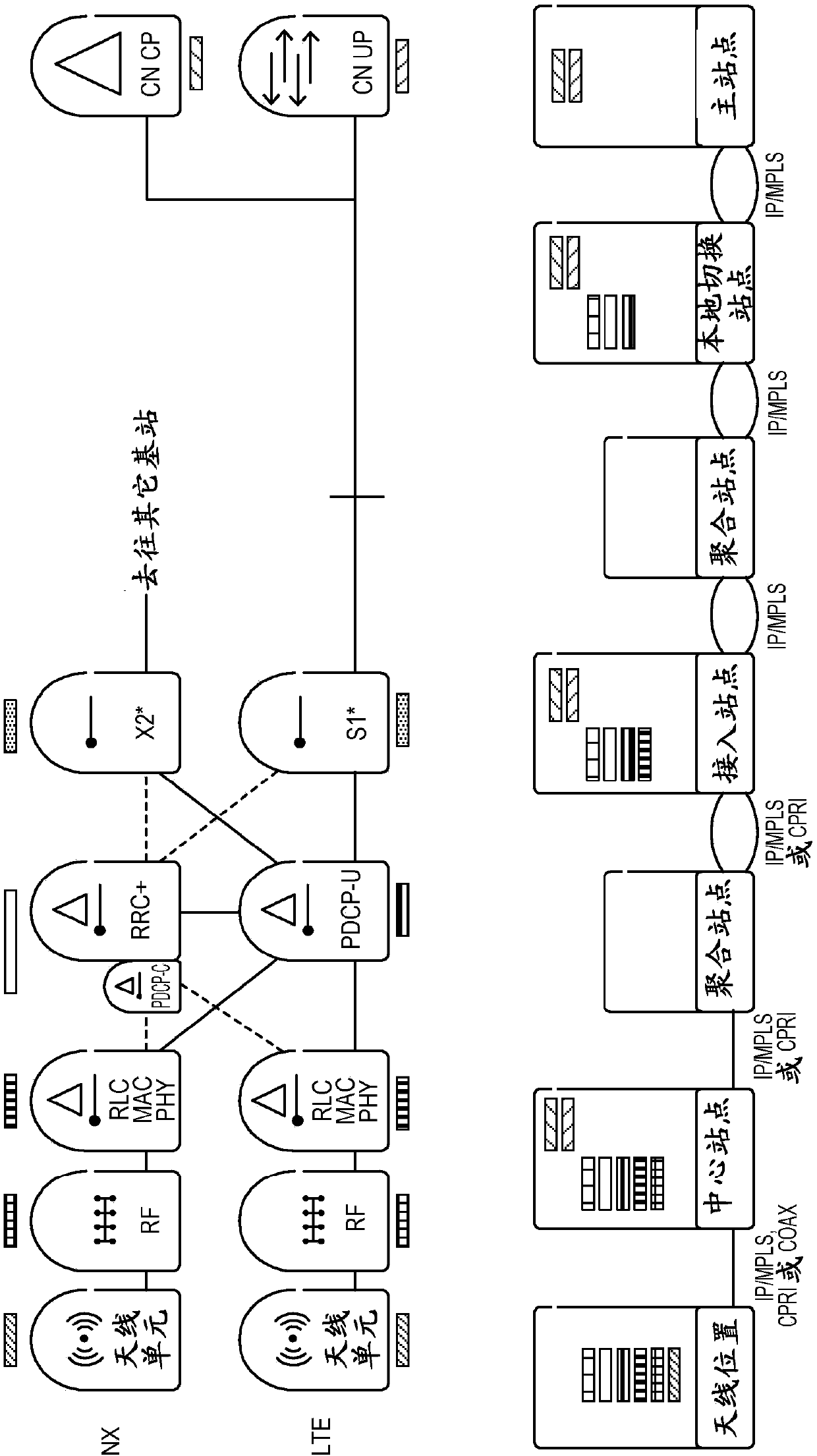
Network architecture, methods, and devices for a wireless communications network
ActiveCN109588059AIncrease peak rateWide carrier bandwidthTransmission path divisionAssess restrictionMultiplexingNetwork architecture
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Crest factor reduction system and method for OFDM transmission systems using selective sub-carrier degradation
ActiveUS20070140367A1Positive correlationReducing the primary peakSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainTransfer system
A system and method for crest factor reduction of OFDM transmission systems using selective sub-carrier degradation, is disclosed. A modulated communications signal comprising a series of symbols is converted into parallel format in groups of plural symbols in the frequency domain. Crest factor reduction reduces a primary peak of the groups of plural symbols by selective sub-carrier degradation, to generate peak reduction symbols. The groups of plural symbols are converted into time domain symbols, and combined with the peak reduction symbols to provide peak reduced symbols in time domain.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Spectral shaping for optical OFDM transmission
InactiveUS7580630B2Reduce the differenceImprove reliabilityTransmission monitoringOptical multiplexFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Visible light communication system and method thereof
InactiveCN102244635AImprove transmission qualityImprove performanceClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsEngineeringOptical communication
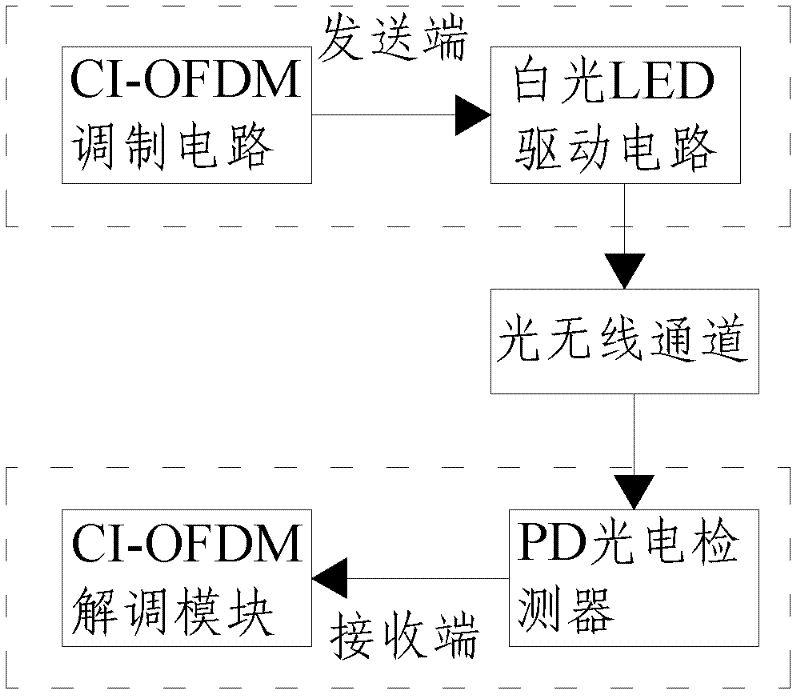
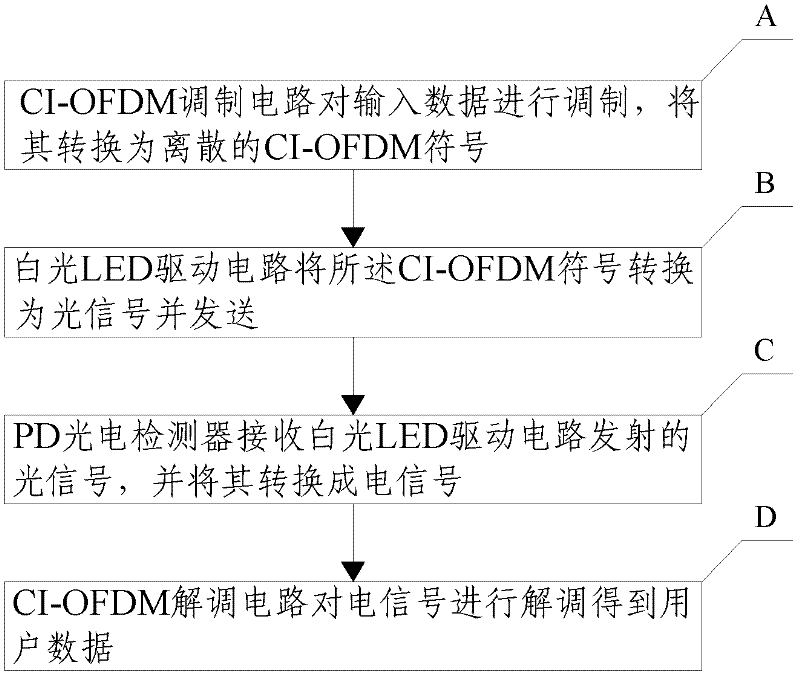
The invention discloses a visible light communication system and a visible light communication method thereof, which relate to the technical field of wireless optical communication. The system comprises a transmitter and a receiver. An input signal is converted into an optical signal by the transmitter, the optical signal is transmitted to the receiver by a wireless optical channel, and the receiver converts the optical signal into an electrical signal and outputs the electrical signal. The transmitter comprises a carrier interferometry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CI-OFDM) modulation circuit and a white light-emitting diode (LED) drive circuit which are connected, wherein the CI-OFDM modulation circuit is used for performing CI-OFDM modulation on data input by a user; and the white LED drive circuit is used for converting the electrical signal generated by the CI-OFDM modulation circuit into the optical signal. The receiver comprises a PD photoelectric detector and a CI-OFDM demodulation circuit which are connected, wherein the PD photoelectric detector is used for performing P / D conversion on the received optical signal to convert the optical signal into the electrical signal; and the CI-OFDM demodulation circuit is used for performing CI-OFDM demodulation on the received data. By the system and the method, the transmission quality of the visible light communication system can be effectively improved, and the peak-to-average power ratio of an OFDM transmitted signal can be reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
OFDM transmission signal processing equipment, method and radio frequency far-end unit
InactiveCN101136811AReduce transmission bandwidth requirementsHigh spectral resolutionOrthogonal multiplexData switching networksFrequency spectrumCyclic prefix
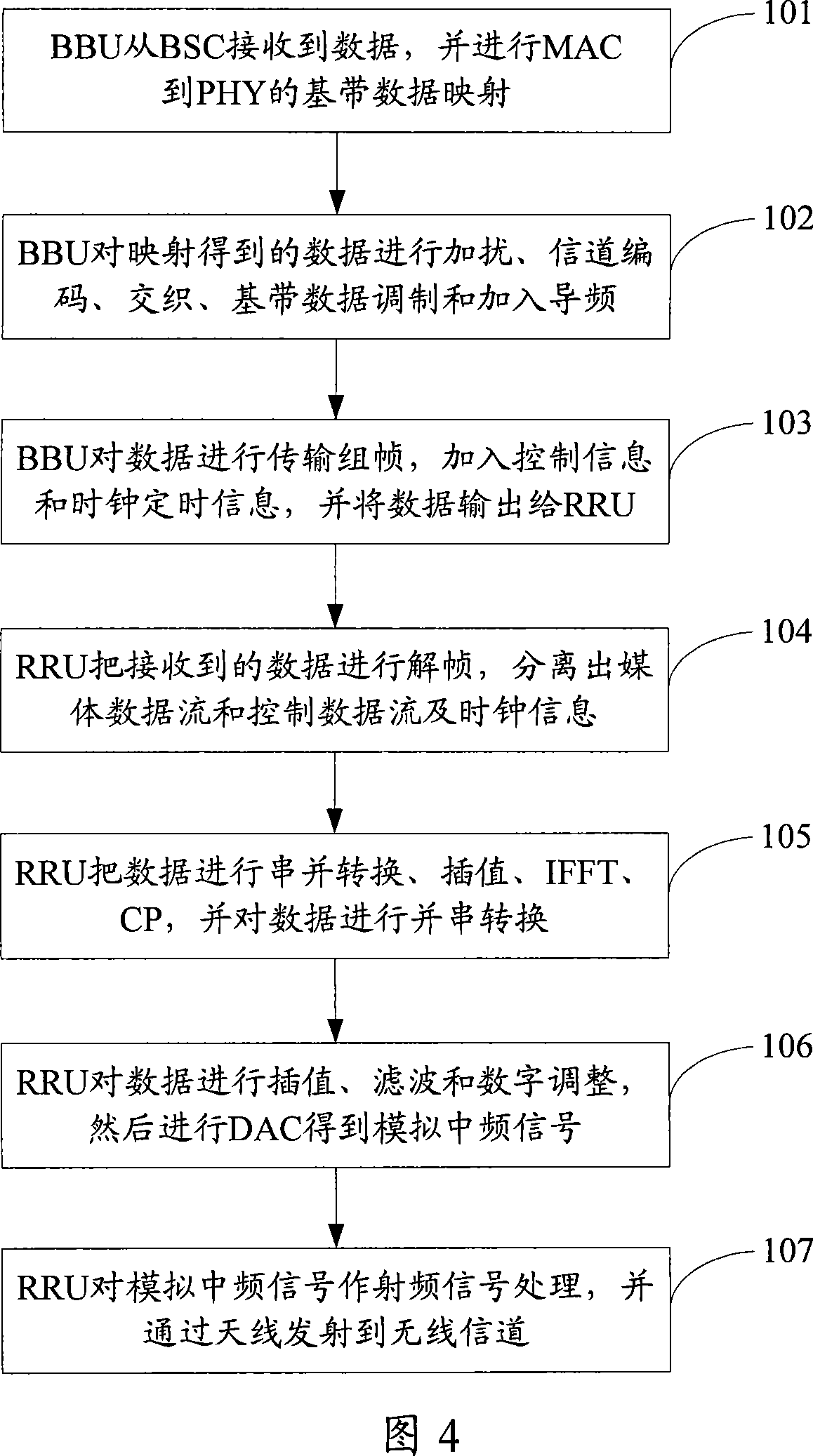
The device for processing OFDM transmission signal includes radio remote unit (RRU) and base band unit (BBU). BBU is in use for carrying out data mapping from media access layer to physical layer as well as scrambling baseband data, and coding, interlacing, demodulating channel, then sending them to RRU. RRU also includes post-processing module for baseband data. The post-processing module is in use for carrying out serial-parallel conversion for baseband data, interpolation, fast reverse Fourier transform, adding circulation prefix, parallel-serial conversion, and outputting. The invention raises resolution and sampling rate of signal spectrum, saves bandwidth of transmission link between BBU and RRU as well as improves quality of transmission signal.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Secure orthogonal frequency multiplexed optical communications
InactiveUS20110170690A1Improve securityMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsDigital signal processingOptical communication
The invention provides a system and method for secure communication that involve encoding and transmitting an optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) signal. Each subcarrier of an optical carrier in OFDM transmission is modulated with data individually, and a variety of data format are used, such as QPSK, OOK, QAM, etc. The data format of each subcarrier may change in time according to a predetermined pattern. An optical receiver uncovers the data transmitted via an optical link. It is based on a coherent optical receiver and a digital signal processing (DSP) unit. A key to the data mapping and change is transmitted via the same optical link or by a separate channel. In one embodiment, the key is transmitted using quantum encryption technique. Besides subcarrier modulation encoding, the system may provide additional layers of security: optical carrier frequency hopping and polarization scrambling.
Owner:CELIGHT
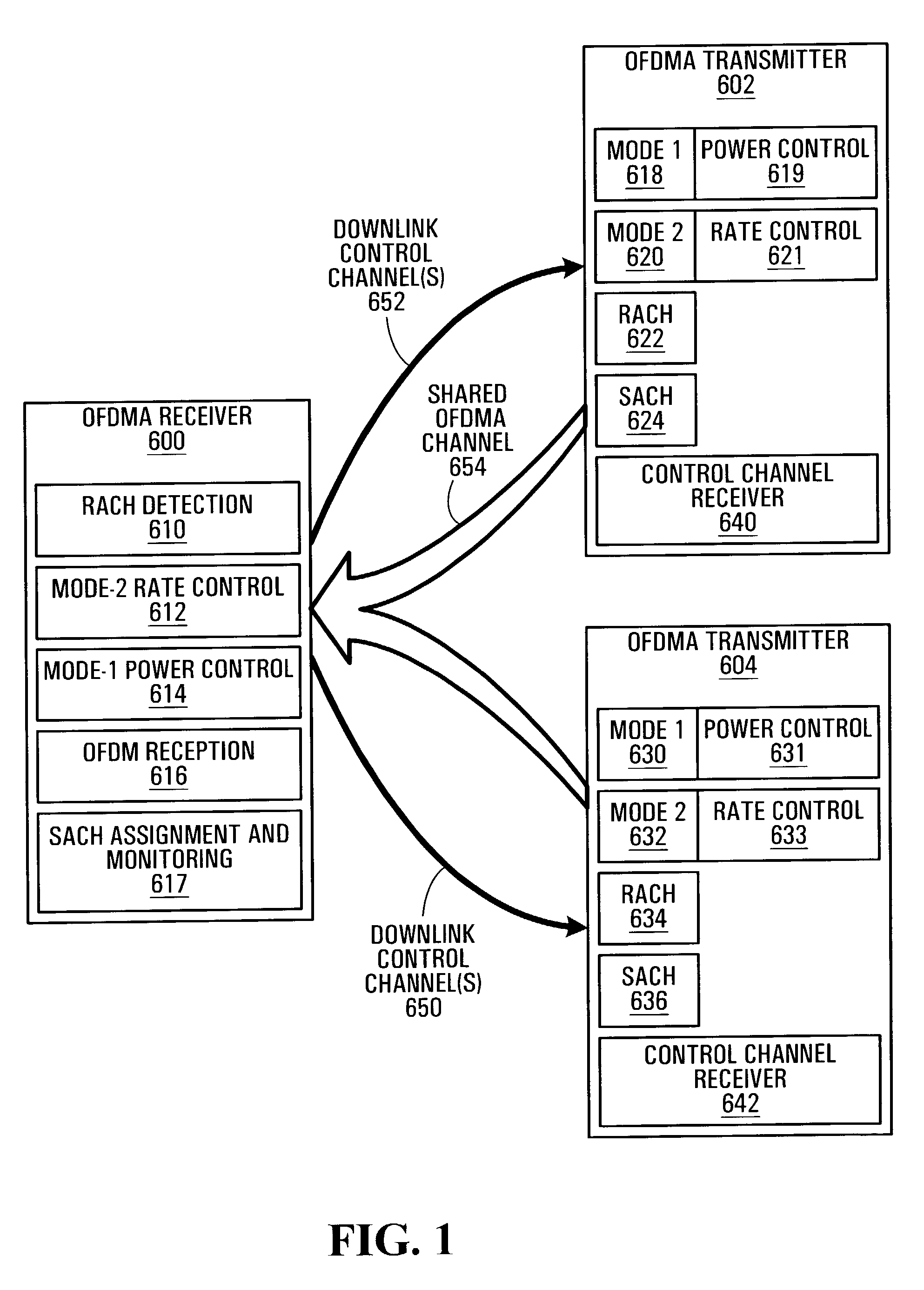
Fft numerology for an OFDM transmission system
An exemplary fast Fourier transform (FFT) numerology for an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) downlink transmission system is described. The exemplary FFT numerology reduces the FFT sampling rate for a given transmission bandwidth, thereby increasing the battery life of a UE. The FFT numerology increases robustness against Doppler spread, phase noise, and frequency offset, enabling operation in channels with high delay spread, such as occurs in mountainous regions. The described numerology might provide the following without altering standard sub-frame duration: increased intercarrier spacing; reduced FFT sampling frequency across the transmission bandwidths; reduced FFT size across all transmission bandwidths; increased number of OFDM symbols per sub-frame; and / or increased cyclic prefix length choices.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
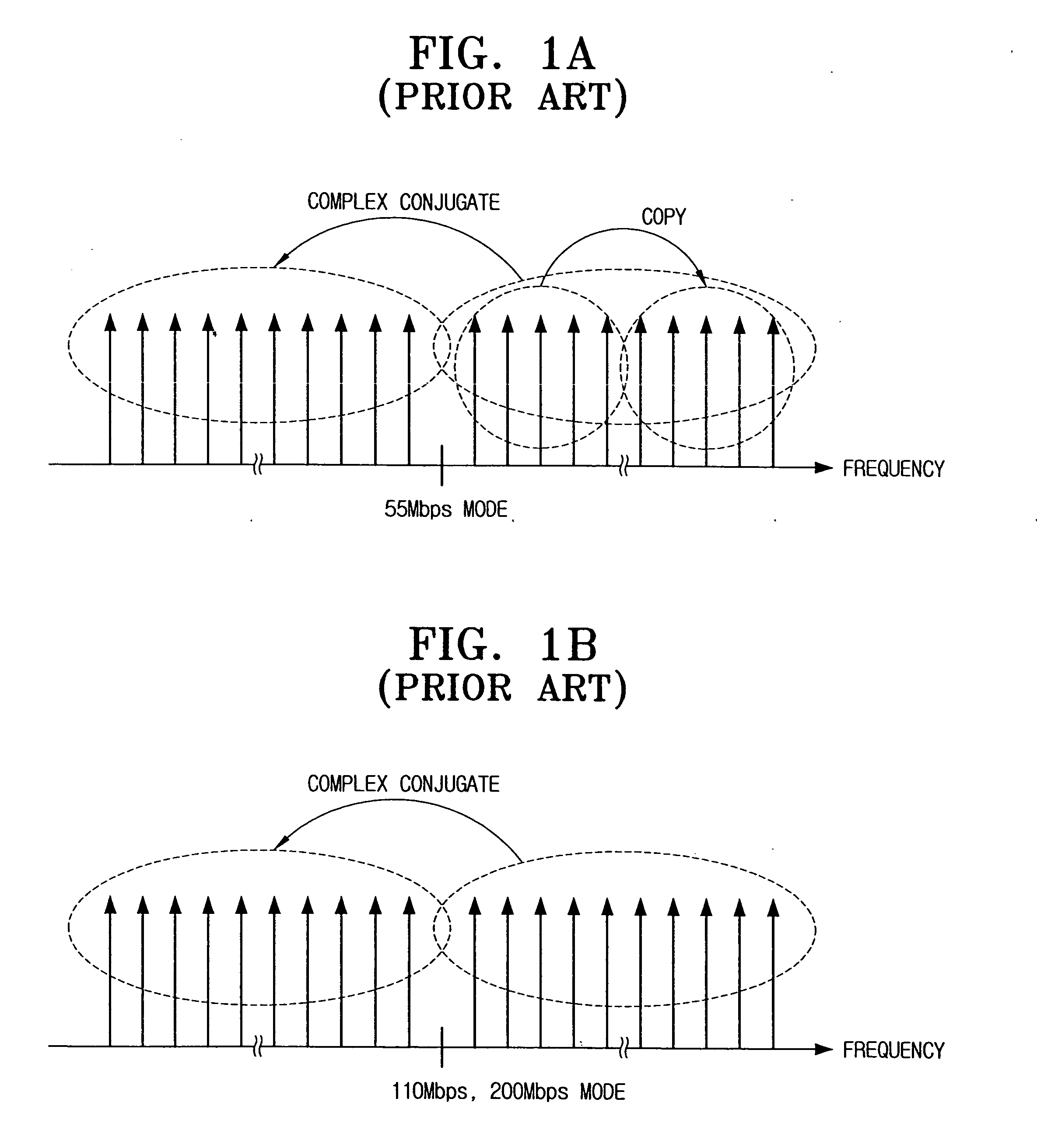
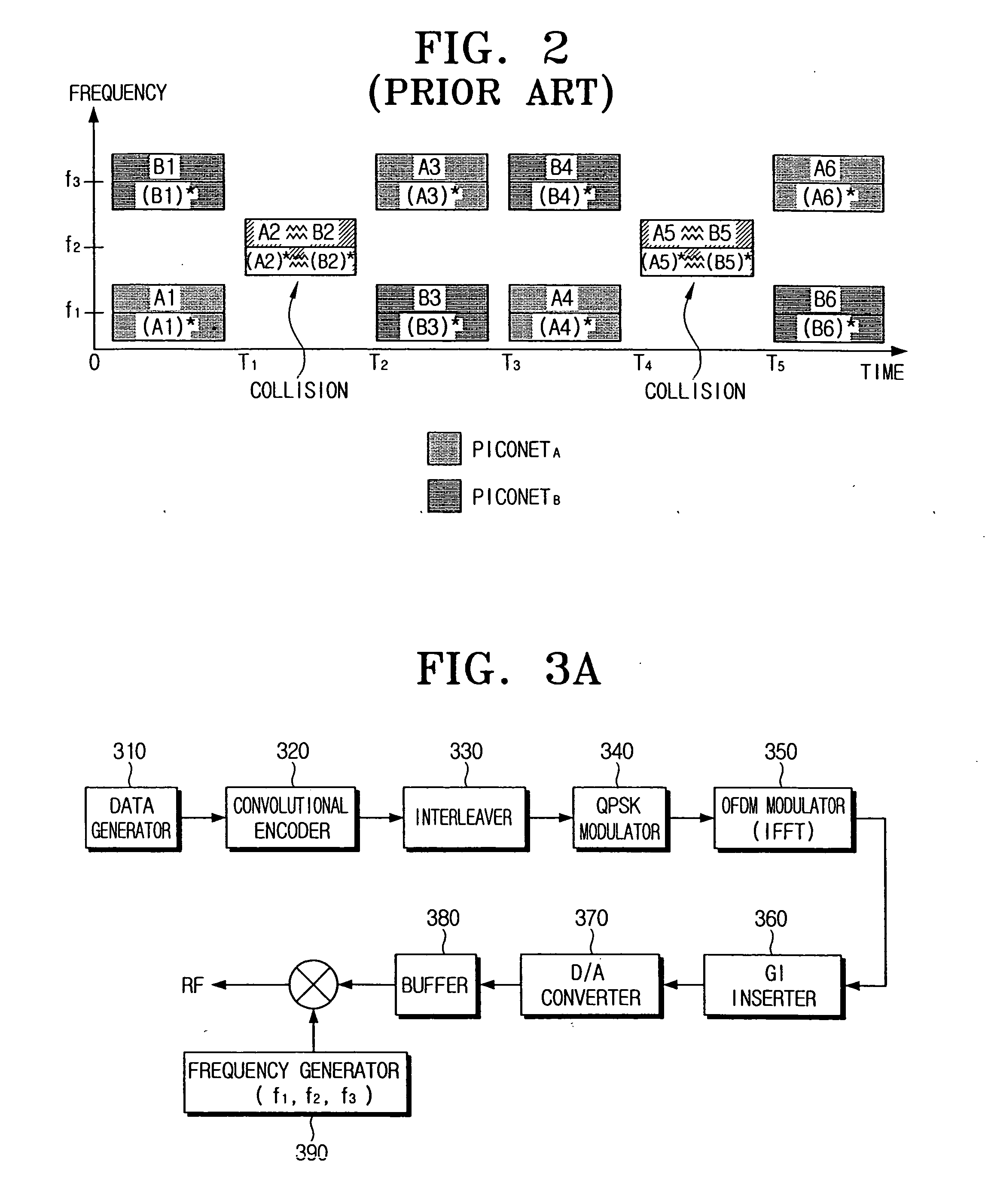
TFI-OFDM transmission/reception systems for UWB communication and methods thereof for mitigating interference from simultaneously operating piconets
ActiveUS20050047444A1Frequency-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTime domainTransfer system
A TFI-OFDM transmission system includes a data generator generating data having a speed corresponding to a transmission speed mode; a convolutional encoder convolutional-encoding the data, an interleaver bit-interleaving the encoded data, an OFDM modulator inputting a first data group into a positive frequency domain and a second data group into a negative frequency domain, executing an IFFT, and outputting OFDM symbols; a buffer temporarily storing the OFDM symbols in order to sequentially transmit the OFDM symbols in a time domain at least two times; and a frequency generator generating certain frequencies to transmit the OFDM symbols in a certain number of frequency bands corresponding to transmission channels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
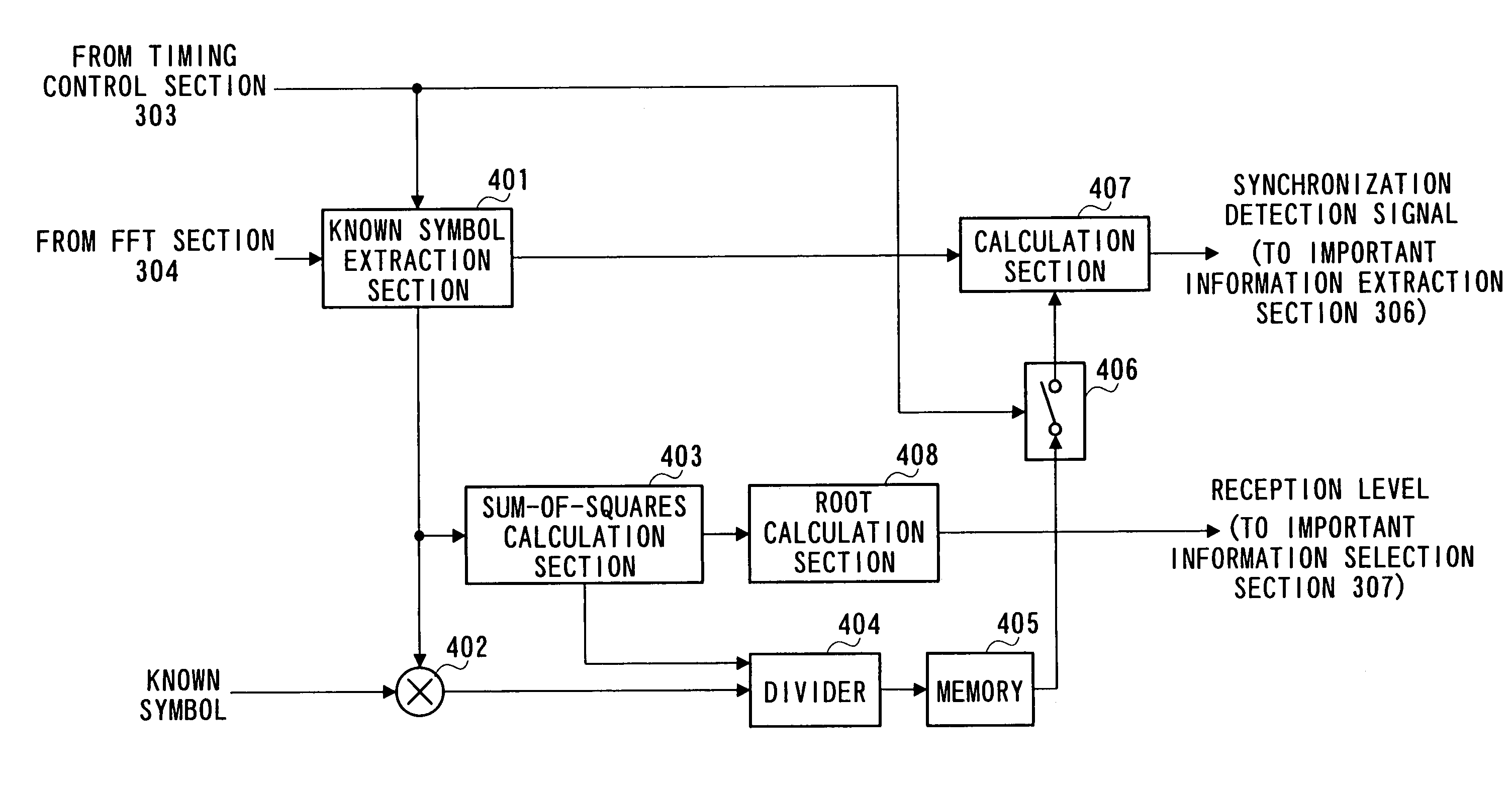
OFDM transmission/reception apparatus
InactiveUS7106689B1Quality improvementError prevention/detection by using return channelCriteria allocationCarrier signalSubcarrier
Modulation section 201 performs modulation processing on transmission data. Mapping control section 202 controls mapping of the baseband signal onto the subcarriers so that the important information conventionally transmitted by one subcarrier is transmitted by two subcarriers and one of the two subcarriers should be the subcarrier with a carrier frequency signal of frequency 0 which was conventionally not used. IFFT section 203 performs IFFT processing on the modulated transmission data. Transmission section 204 performs transmission processing on the IFFT-processed transmission data and transmits the processed transmission data from antenna 205.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
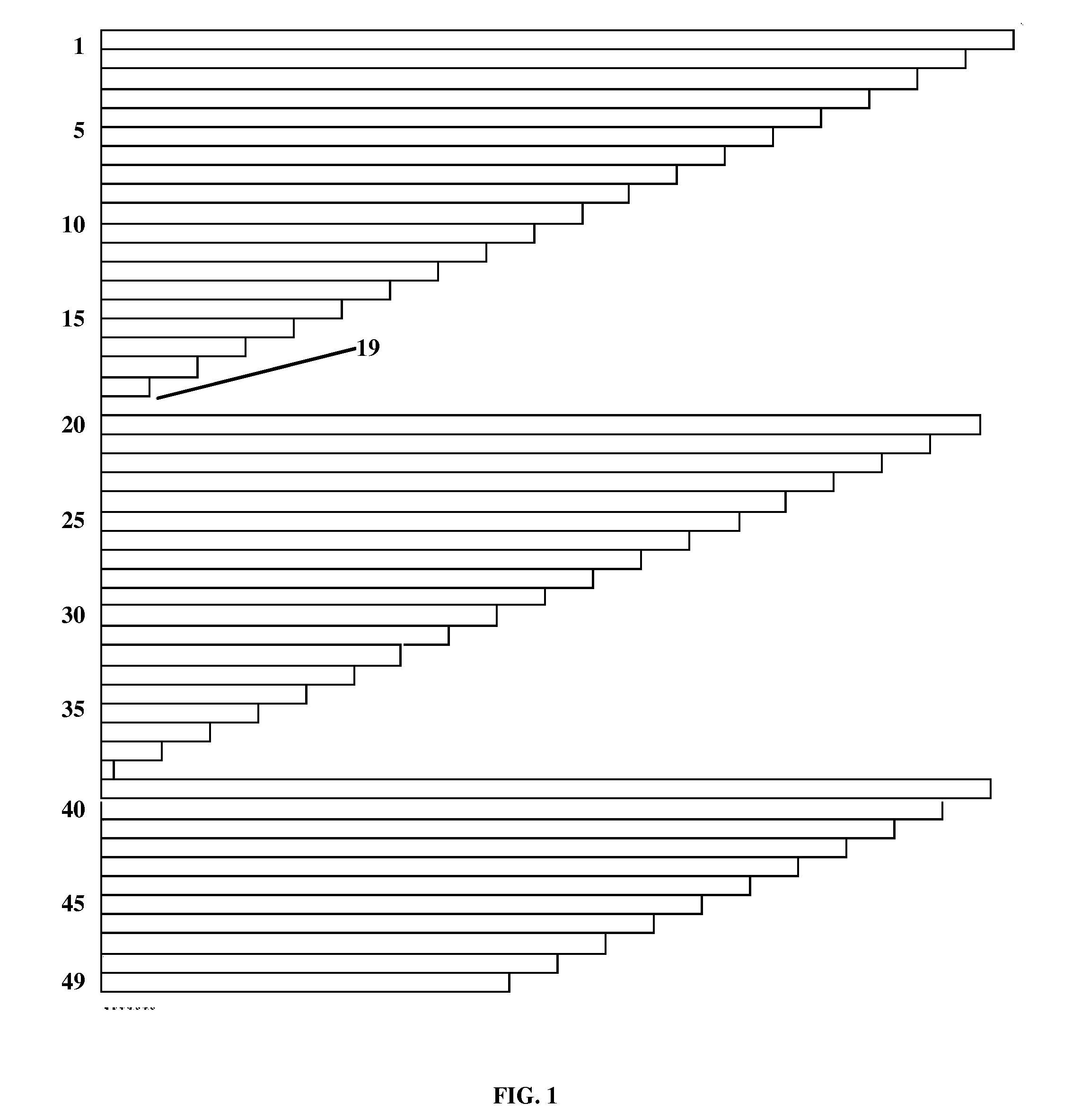
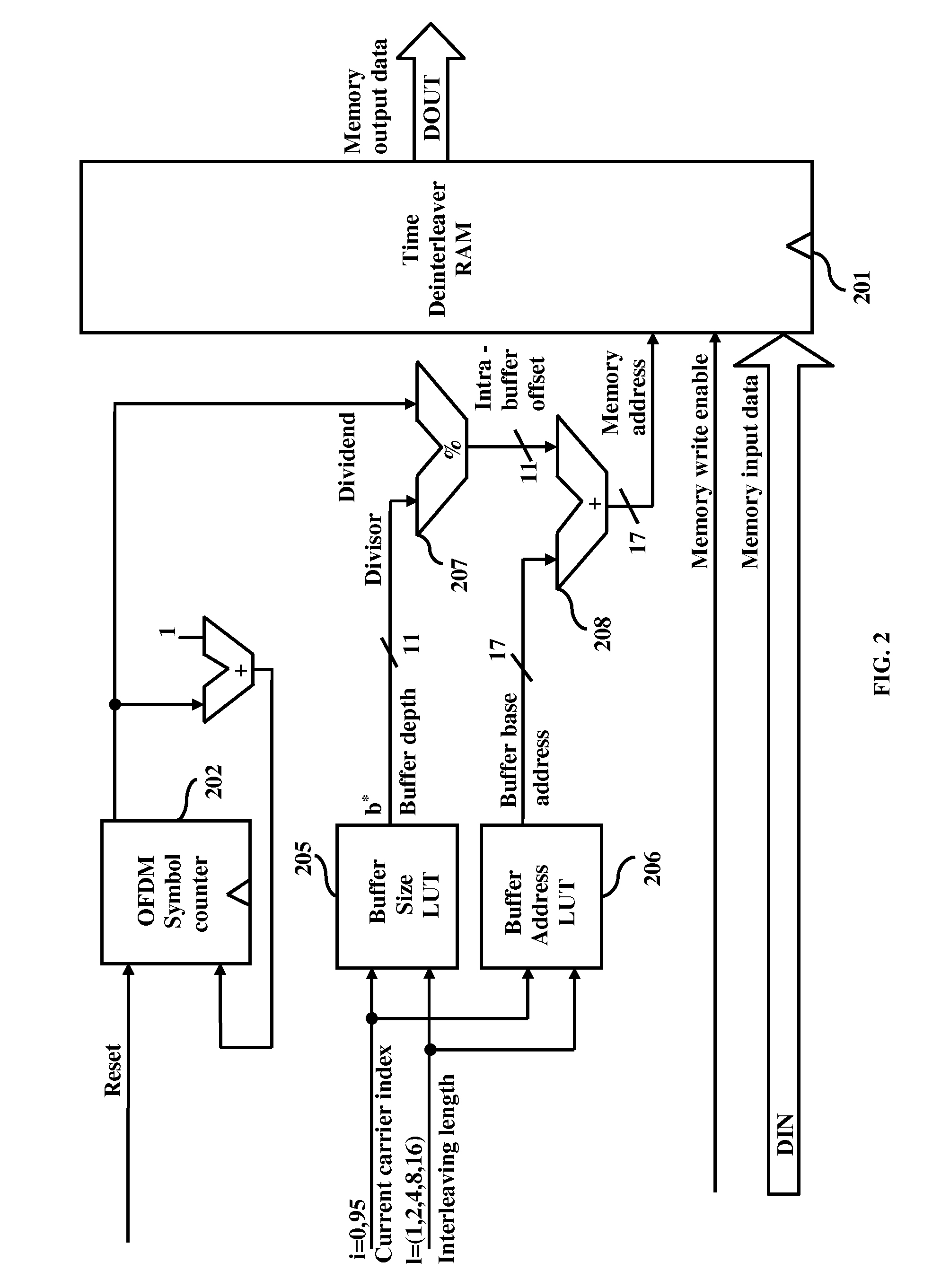
Area and power efficient architectures of time deinterleaver for isdb-t receivers
A method and apparatus for de-interleaving interleaved data in a deinterleaver memory in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) based Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Terrestrial (ISDB-T) receiver. In different embodiments, the apparatus comprises of a OFDM symbol counter along with a divider or a buffer pointer RAM with circular pointer logic, a first lookup table to obtain delay buffer size and interleaving lengths for a given OFDM transmission layer, and a second lookup table to obtain buffer base address and interleaving lengths for a given OFDM transmission layer.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com