Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
781 results about "Base address" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
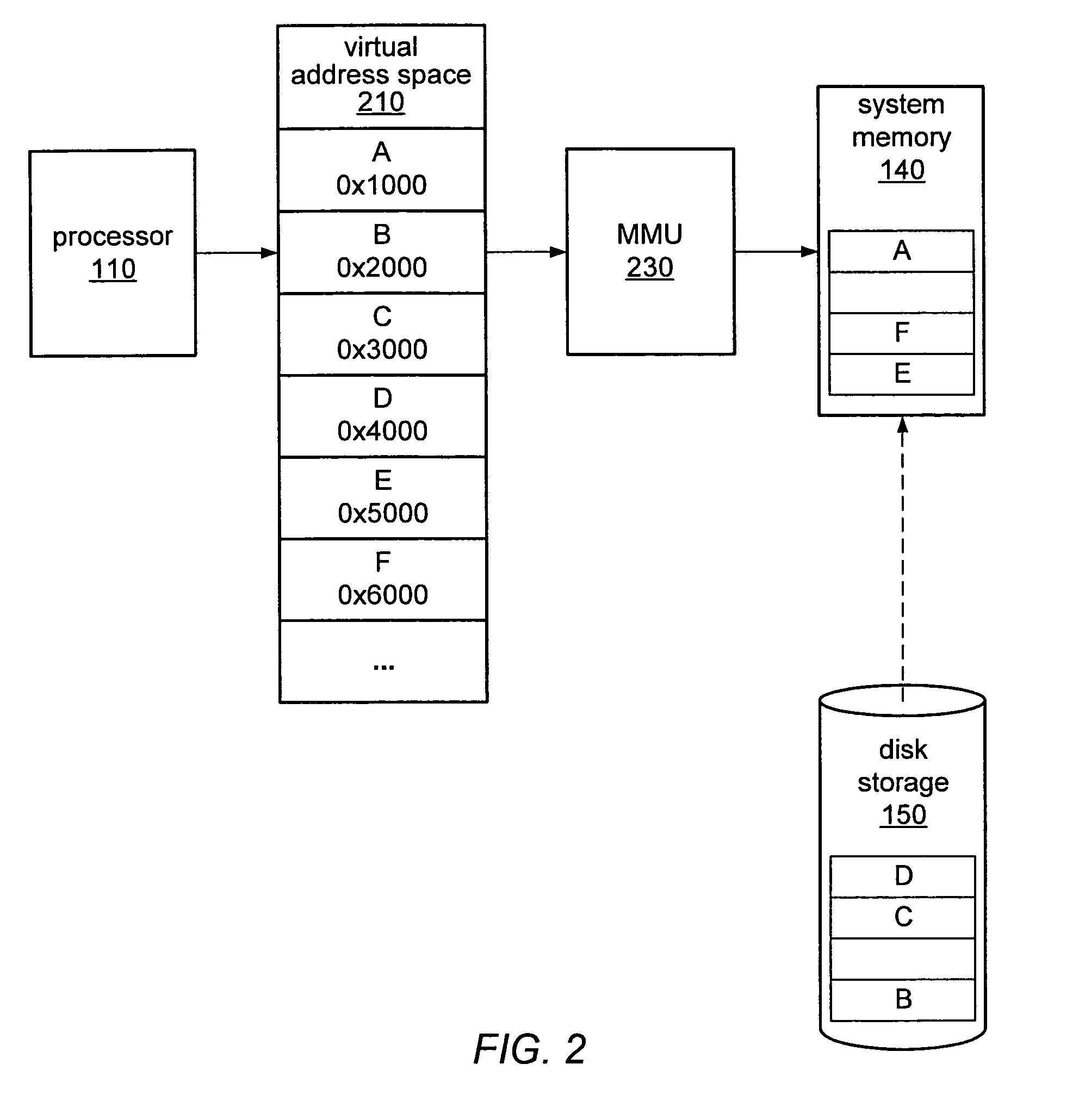
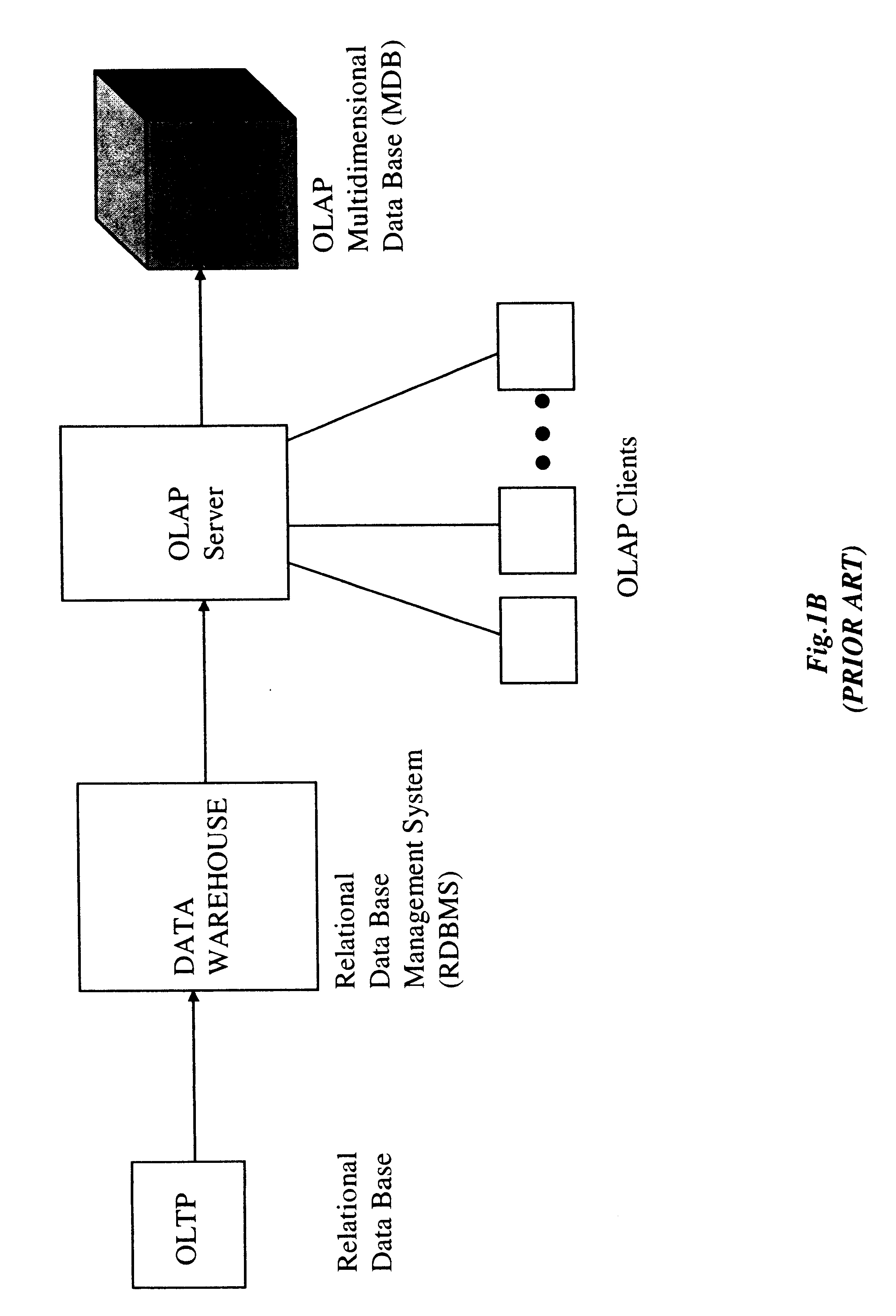
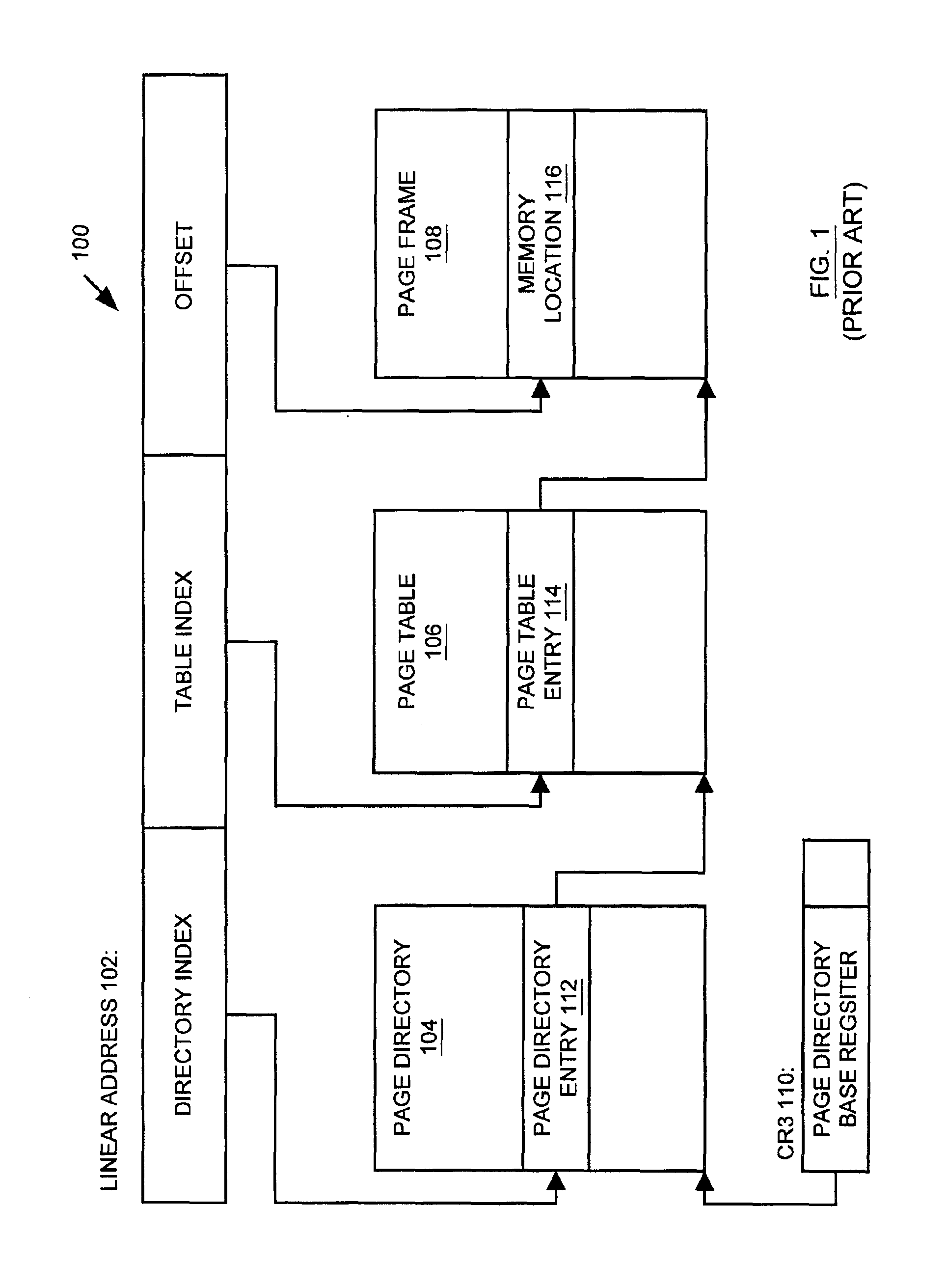
In computing, a base address is an address serving as a reference point ("base") for other addresses. Related addresses can be accessed using an addressing scheme. Under the relative addressing scheme, to obtain an absolute address, the relevant base address is taken and offset (aka displacement) is added to it. Under this type of scheme, the base address is the lowest numbered address within a prescribed range, to facilitate adding related positive-valued offsets.
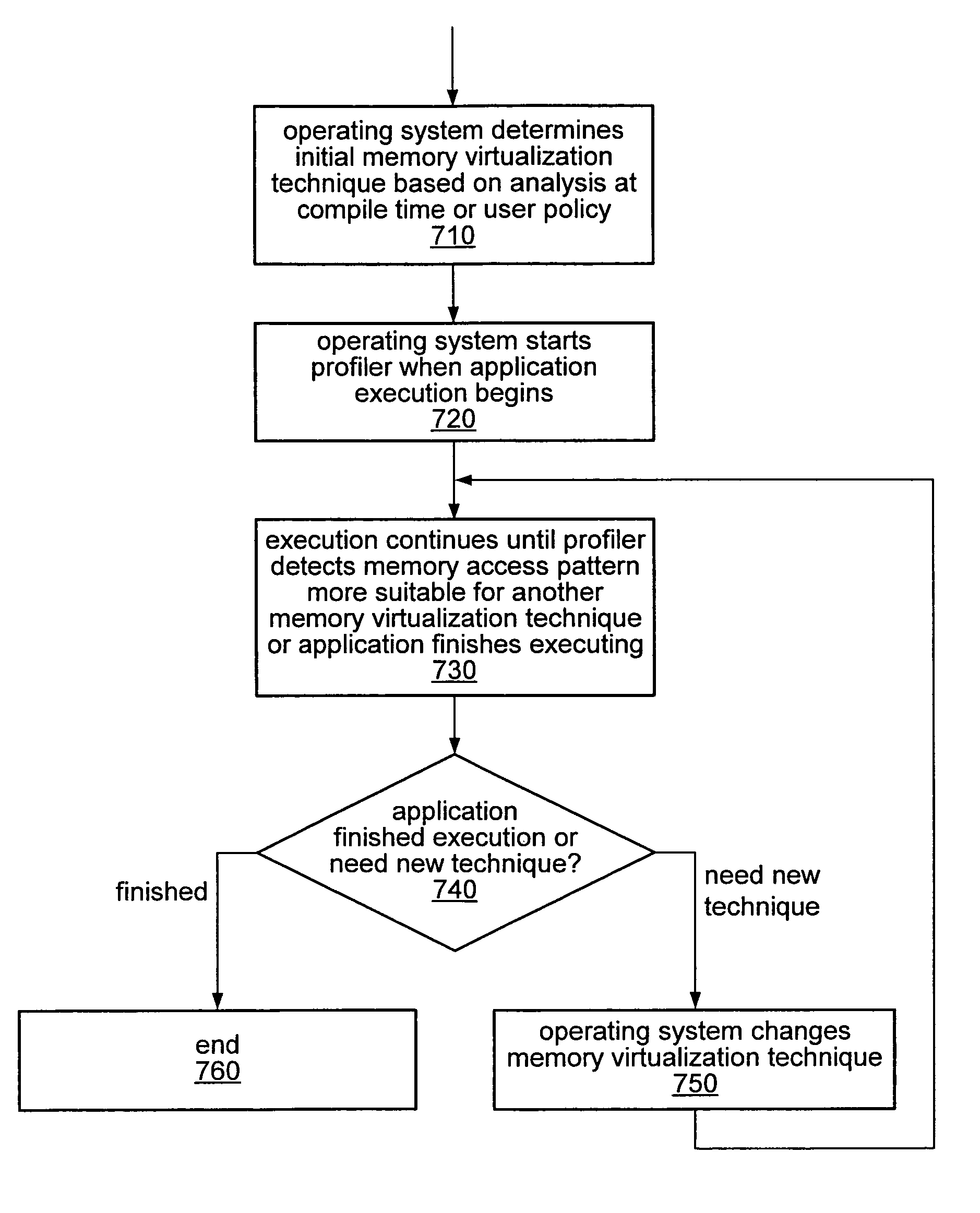
Dynamic selection of memory virtualization techniques
ActiveUS7752417B2Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtualizationComputerized system
A computer system may be configured to dynamically select a memory virtualization and corresponding virtual-to-physical address translation technique during execution of an application and to dynamically employ the selected technique in place of a current technique without re-initializing the application. The computer system may be configured to determine that a current address translation technique incurs a high overhead for the application's current workload and may be configured to select a different technique dependent on various performance criteria and / or a user policy. Dynamically employing the selected technique may include reorganizing a memory, reorganizing a translation table, allocating a different block of memory to the application, changing a page or segment size, or moving to or from a page-based, segment-based, or function-based address translation technique. A selected translation technique may be dynamically employed for the application independent of a translation technique employed for a different application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
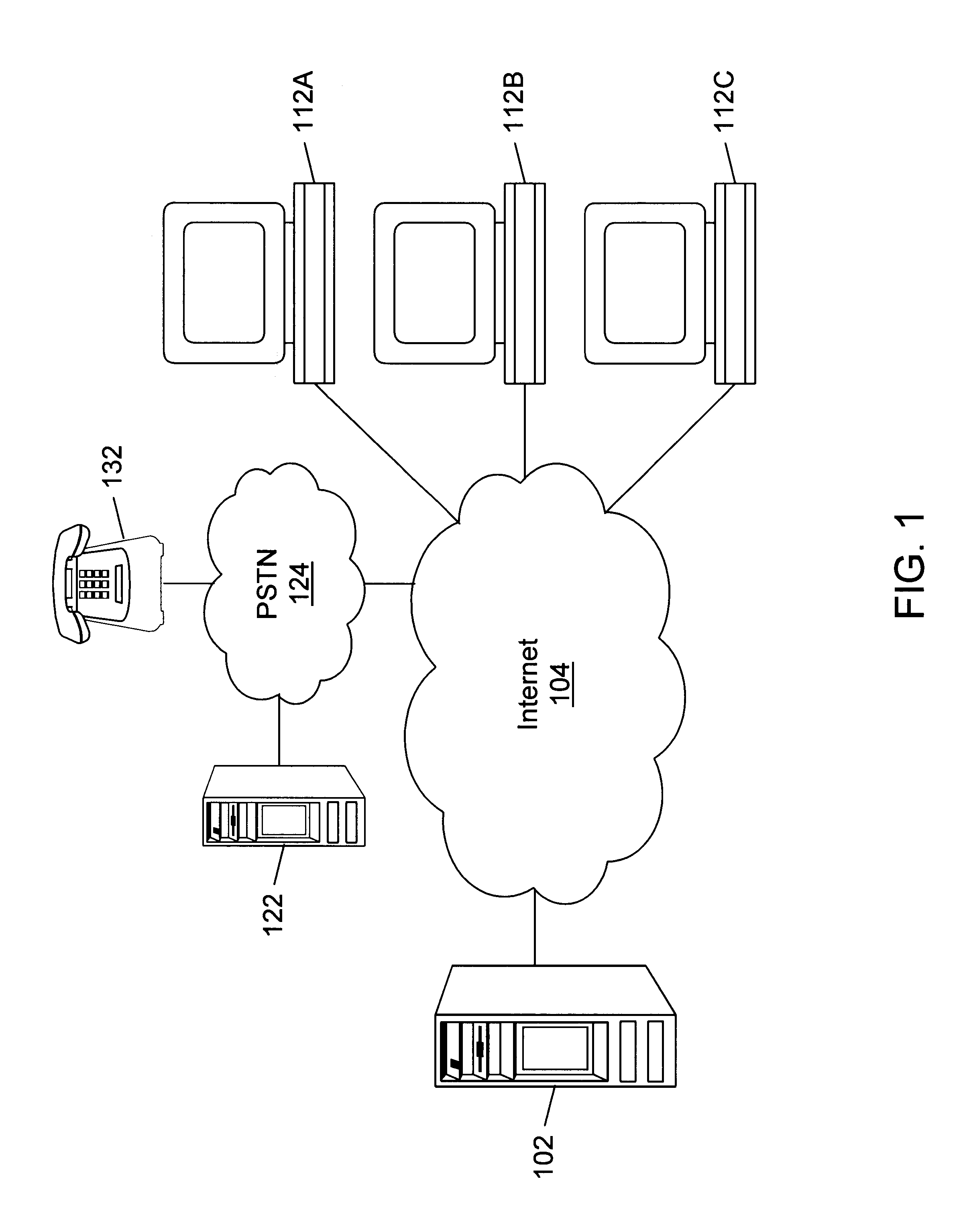
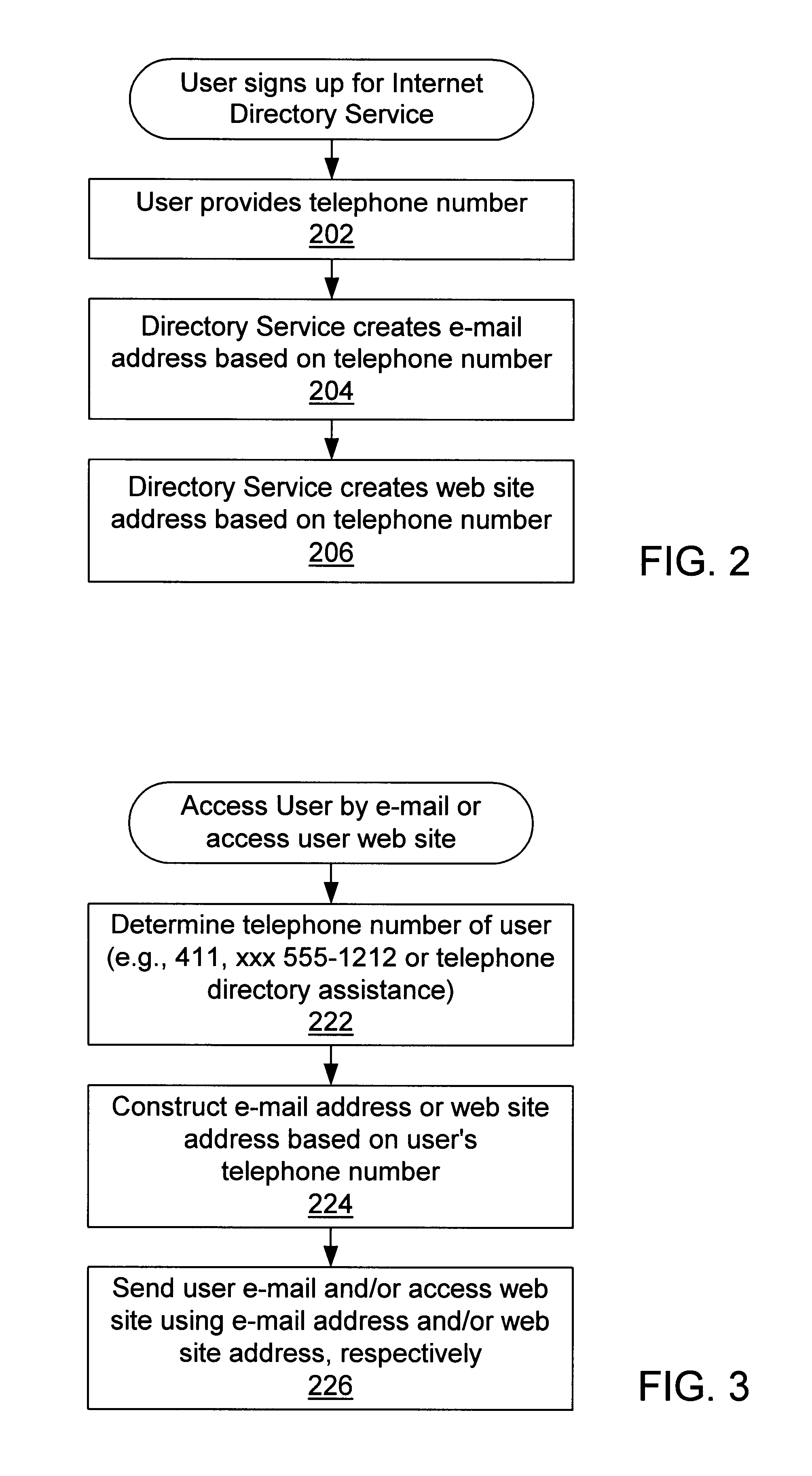
Internet directory system and method using telephone number based addressing
InactiveUS6788769B1Searches may be more readilyEasy to implementTelephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersDomain nameEmail address
An Internet directory system and method that is based on user telephone number addressing. The system includes an interactive white and yellow pages directory that is based on telephone numbers. Thus, a user's telephone number is a unique identifier used to key other information within the directory. The telephone number may also be used as the primary component of an email address, domain name, or web site URL for the user. The use of a telephone number as the primary component of an e-mail address or domain name greatly simplifies the process of locating a user. E-mail addresses and domain names may be readily found using standard telephone information services, such as "411", as well as other telephone-based methods for obtaining telephone directory information. This Internet directory system and method brings all communication methods and directory services together using one searchable key, a user's telephone number. The directory entry page may be created, edited and updated by the subscriber using simple html editing or using a voice telephone call or via fax, without the use of a personal computer. Thus, the present invention provides an open directory model wherein the end users construct the directory, and the directory is "living", i.e., dynamically changeable and updateable. The power of the directory is thus placed in the users' hands. The telephone based Internet directory system of the present invention also provides addressing for unified messaging as well as locality in addressing.
Owner:WEISMAN SANFORD P
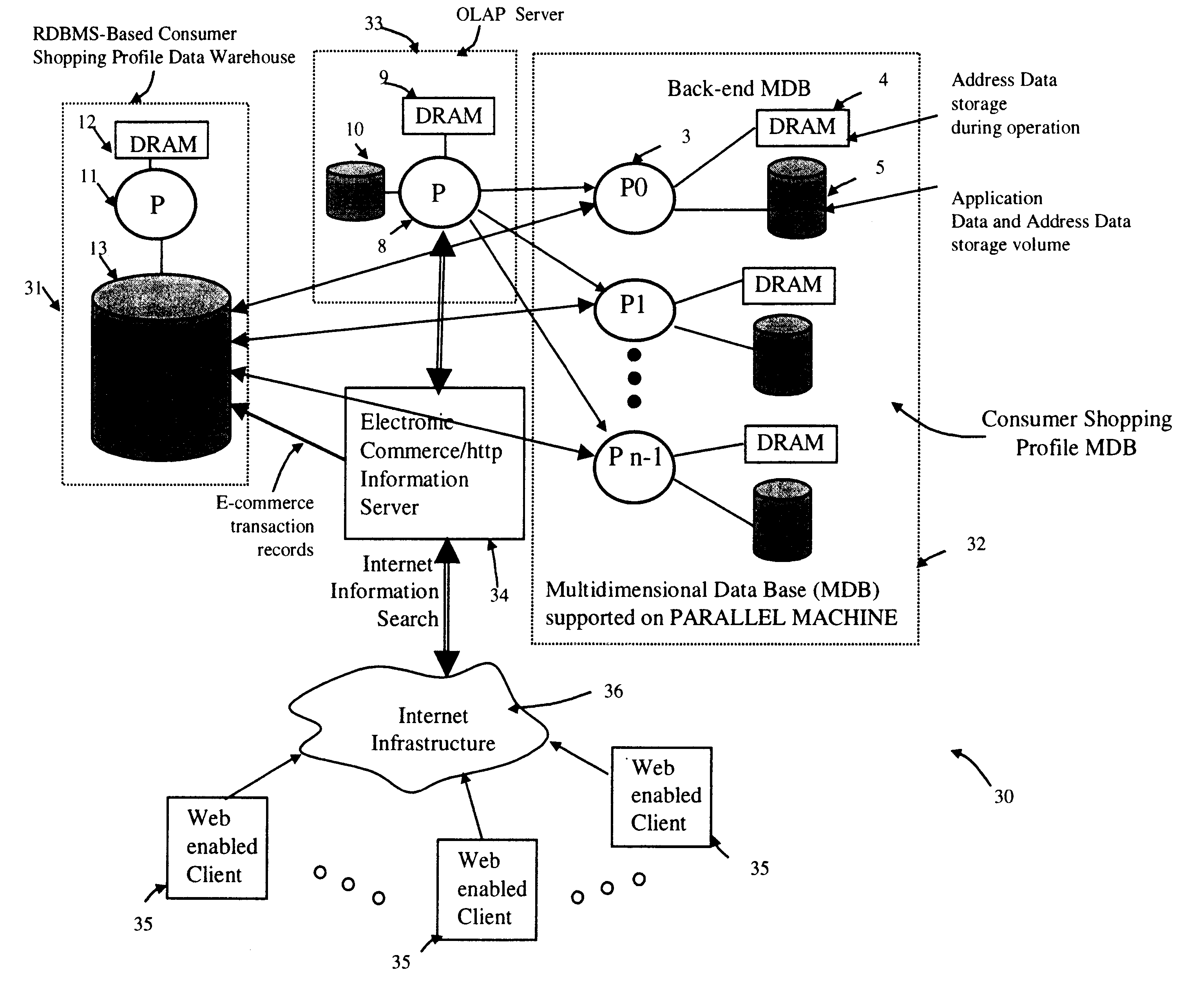
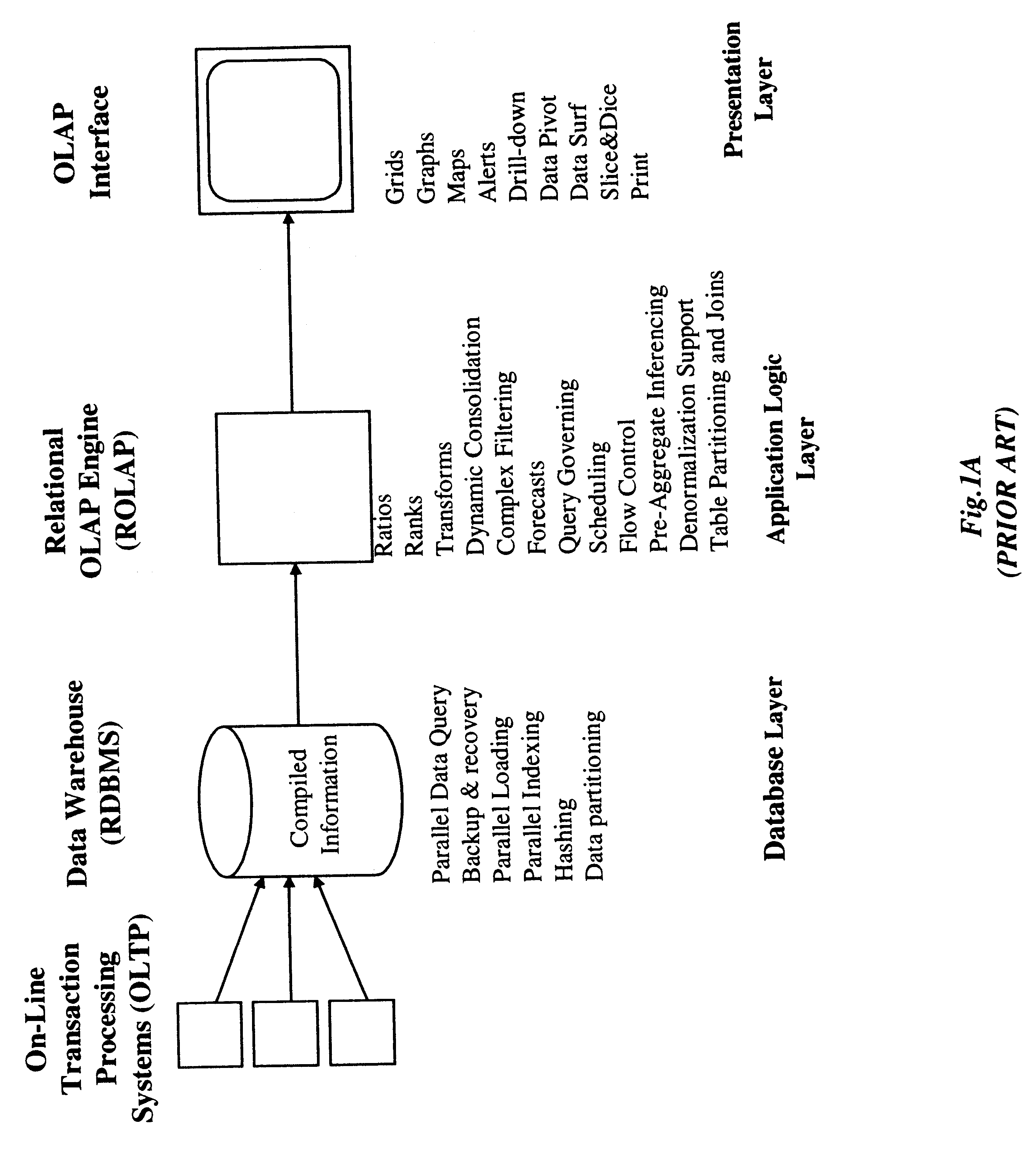
Method of and system for managing multi-dimensional databases using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping processes on integer-encoded business dimensions
InactiveUS6408292B1Improve performanceFast knowledge discoveryData processing applicationsMulti-dimensional databasesData warehouseThe Internet
An improved method of and a system for managing data elements in a multidimensional database (MDB) supported upon a parallel computing platform using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping (i.e. translation) processes on integer-encoded business dimensions. The parallel computing platform has a plurality of processors and one or more storage volumes for physically storing data elements therein at integer-encoded physical addresses in Processor Storage Space (i.e. physical address space in the one or more storage volumes associated with a given processor). The location of each data element in the MDB is specified in MDB Space by integer-encoded business dimensions associated with the data element. A data loading mechanism loads the integer-encoded business dimensions and associated data elements from a data warehouse. The address data mapping mechanism performs a two part address mapping processing. The first step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element to a given processor identifier (which uniquely identifies the processor amongst the plurality of processors of the parallel computing platform). The second step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element into an integer-encoded physical data storage address in Processor Storage Space associated with the processor identified by the processor identifier generated in the first mapping step. The mapping performed in this second step is based upon size of the integer encoded business dimensions. The data management mechanism manages the data elements stored in the storage volumes using the integer-encoded data storage addresses generated during the two-part address data mapping process. The use of modular-arithmetic functions in the two-part address data mapping mechanism ensures that the data elements in the MDB are uniformly distributed among the plurality of processors for balanced loading and processing. The present invention can be used to realize (i) an improved MDB for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations, (ii) an improved Internet URL Directory for supporting on-line information searching operations by Web-enabled client machines, as well as (iii) diverse types of MDB-based systems for supporting real-time control of processes in response to complex states of information reflected in the MDB.
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
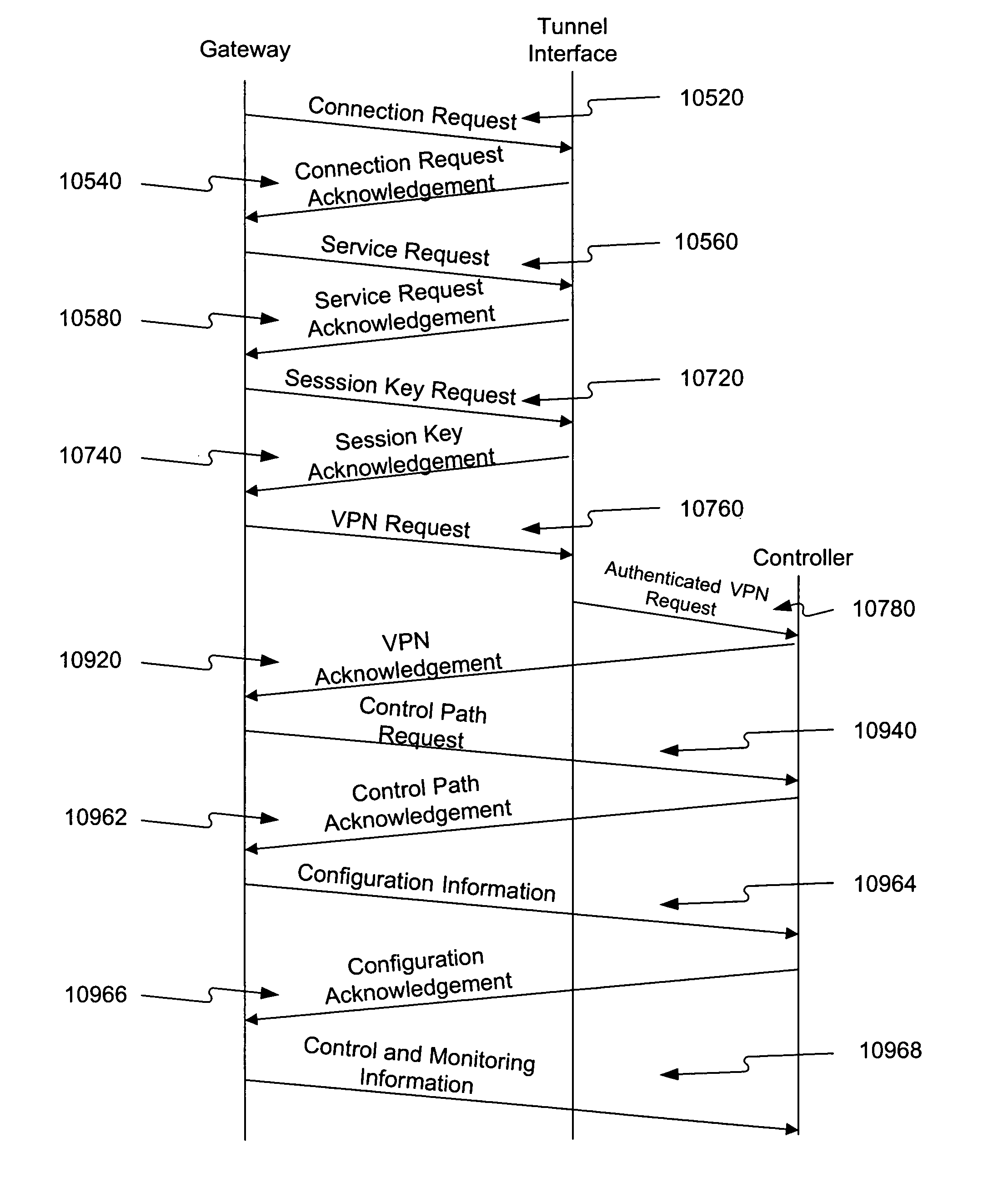
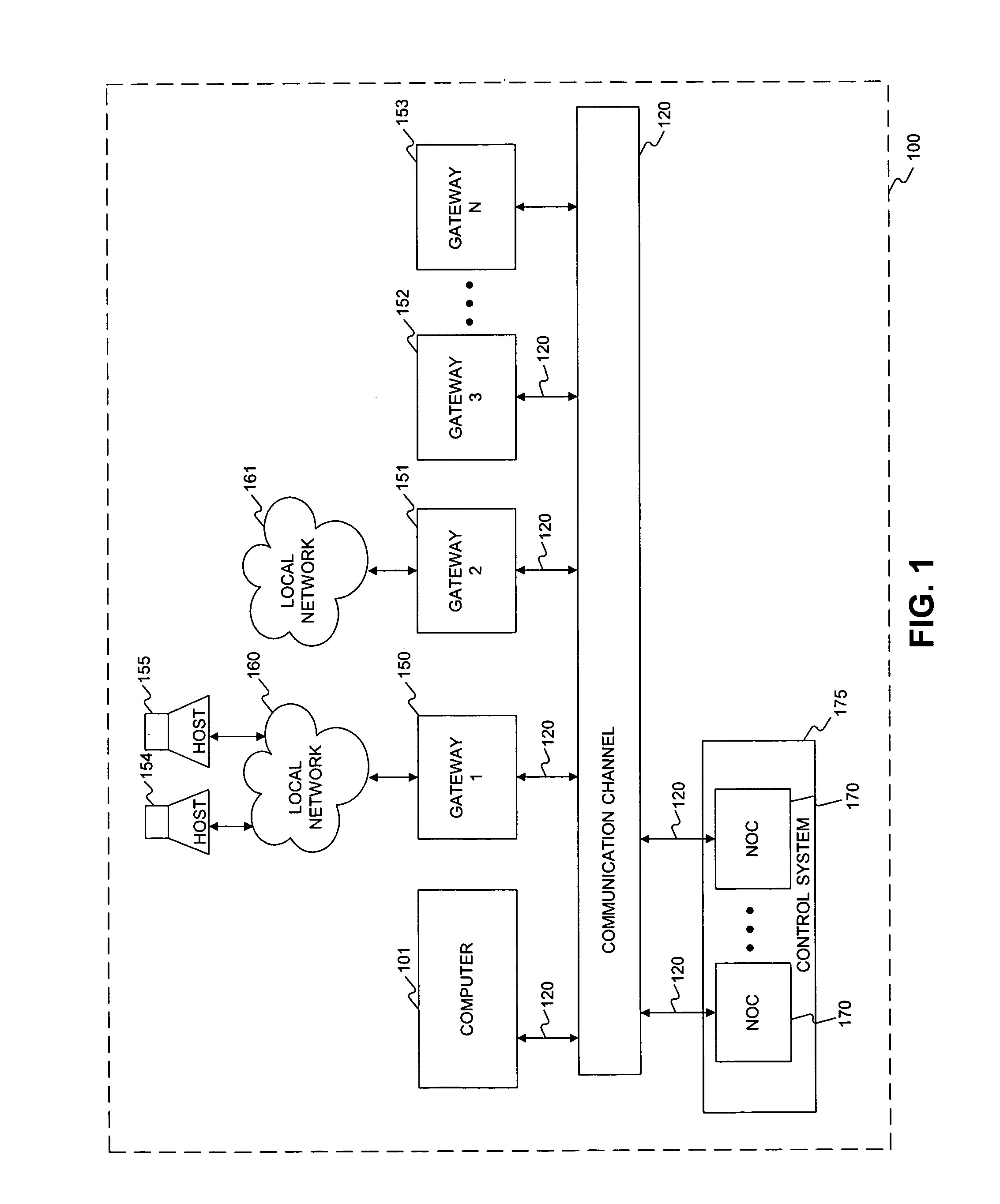
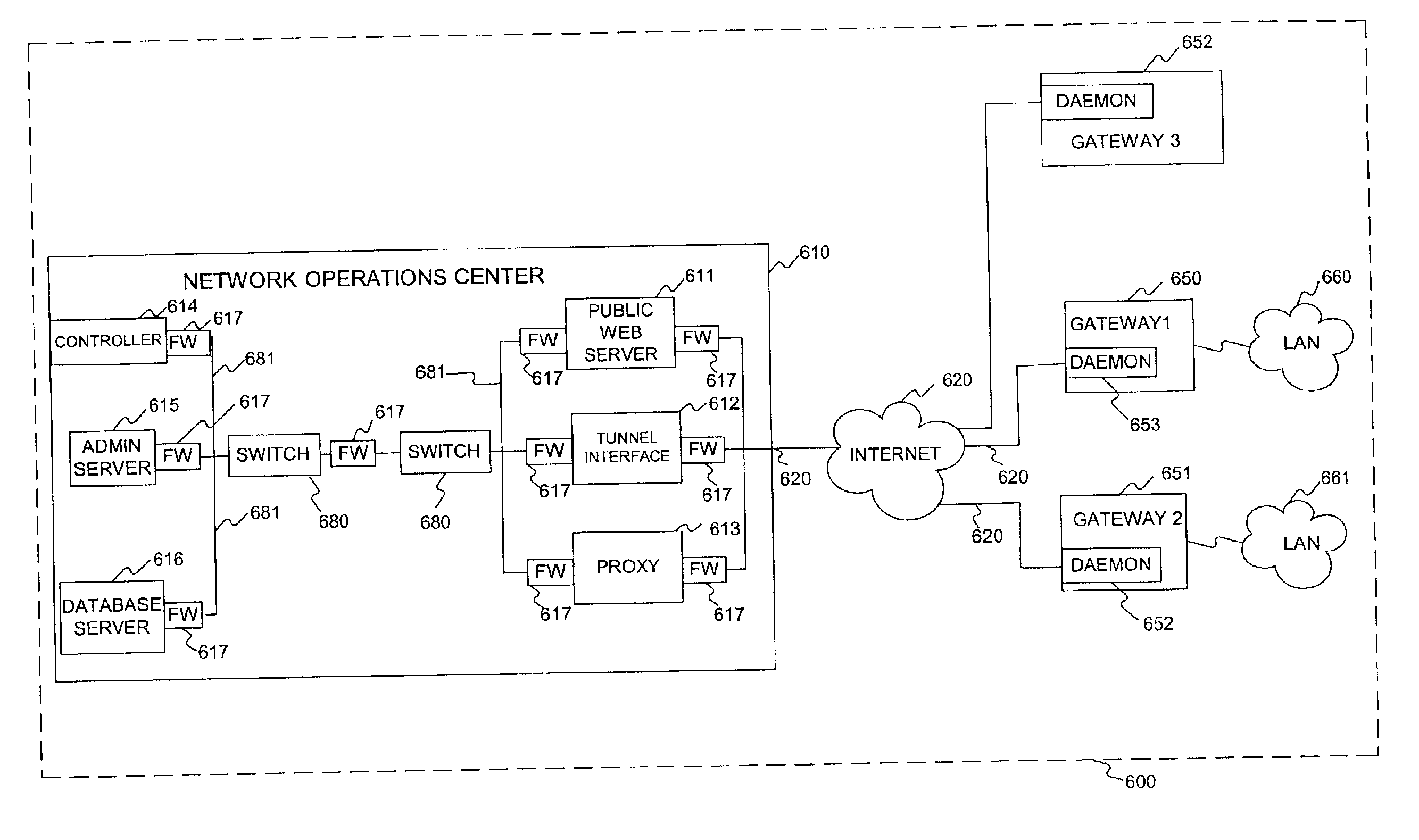
Methods and system for providing network services using at least one processor interfacing a base network
InactiveUS7181766B2Easily and effectively leverage powerWithout complexityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork operations centerNetwork code
Methods and systems are provided for providing network services using at least one processor, such as a network operations center that interfaces a base network. The network operations center may receive information identifying a user authorized to administer a first processor, which may be separate from the network operations center, and a base address that is routable in the base network. The network operations center may provide through the base network code and information for self-configuring the first processor as a gateway that interfaces the base network at the base address. The first processor may execute the provided code to self-configure itself as the gateway based on the provided information. The network operations center may then provide through the base network to the first processor additional information enabling at least one tunnel through the base network to a second processor, which may also be separate from the network operations center, when the first and second processors each provide to the network operations center a consent for enabling the tunnel.
Owner:ORACLE SYST CORP
Location-based addressing lighting and environmental control system, device and method
ActiveUS7889051B1Less bandwidthAttenuation bandwidthElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageLight equipmentControl system
Location-Based Addressing (LBA) is a method of controlling and commissioning networked lighting devices. The lighting devices communicate over a wireless network using radio frequency communication protocols. The lighting devices are commissioned or grouped based on their respective locations in a building floor plan or a building architecture. The lighting devices are commissioned to respond to radio frequency communications that correspond to their respective locations. This imposed location-based architecture reduces the amount of transmitted data required to control the lighting devices and, thus, reduces the radio bandwidth required to control the lighting devices. In other words, controlling devices “multicast” instructions and controlled devices “listen” for instructions and act only upon instructions that correspond to their respective location. Hand shaking or two-way communication between the controlling devices and the controlled devices is not required.
Owner:THE WATT STOPPER
Dynamic selection of memory virtualization techniques
ActiveUS20070283125A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtualizationComputerized system
A computer system may be configured to dynamically select a memory virtualization and corresponding virtual-to-physical address translation technique during execution of an application and to dynamically employ the selected technique in place of a current technique without re-initializing the application. The computer system may be configured to determine that a current address translation technique incurs a high overhead for the application's current workload and may be configured to select a different technique dependent on various performance criteria and / or a user policy. Dynamically employing the selected technique may include reorganizing a memory, reorganizing a translation table, allocating a different block of memory to the application, changing a page or segment size, or moving to or from a page-based, segment-based, or function-based address translation technique. A selected translation technique may be dynamically employed for the application independent of a translation technique employed for a different application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Methods and systems for managing virtual addresses for virtual networks
ActiveUS6996628B2Easily and effectively leverage powerWithout complexityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer scienceVirtual address space
Methods and systems are provided for enabling a virtual network between a first processor and a second processor using at least one additional processor separate from the first processor and the second processor. In one embodiment, the at the at least one additional processor may determine a first virtual address and a first base address for the first processor such that the first virtual address is routable through the virtual network and the first base address is routable through a base network and determine a second virtual address and a second base address for the second processor such that the second virtual address is routable through the virtual network and the second base address is routable through the base network. The at least one additional processor may provide the first virtual address and the first base address to the first processor and the second virtual address and the second base address to the second processor. Moreover, the virtual network may be enabled over the base network based on the first virtual address, the first base address, the second virtual address, and the second base address.
Owner:ORACLE SYST CORP
Capturing data changes utilizing data-space tracking
InactiveUS7085787B2Maximum efficiencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalOriginal dataData space
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus for automatic downloading of URLs and internet addresses
InactiveUS6393462B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalWeb browserUser input
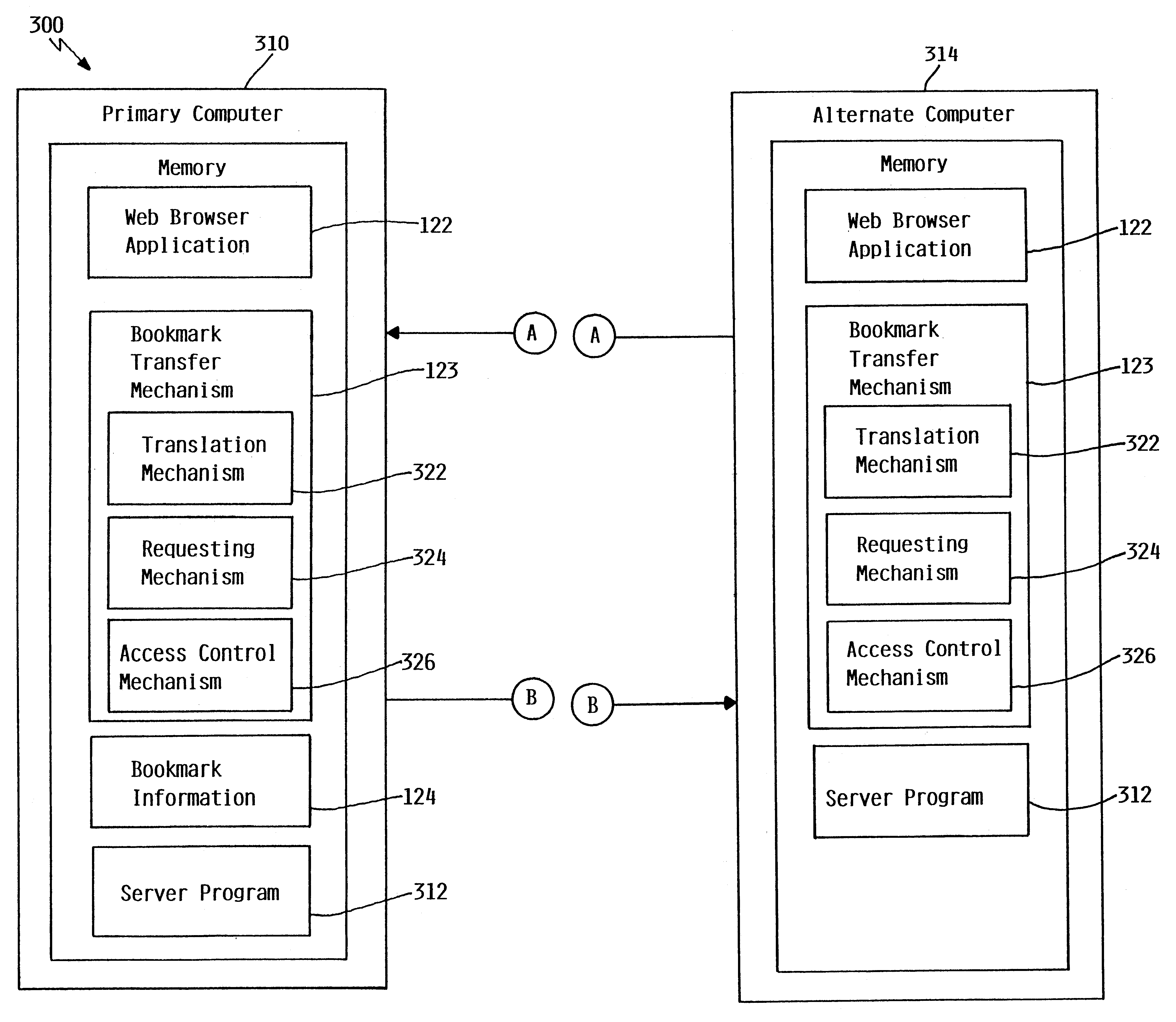
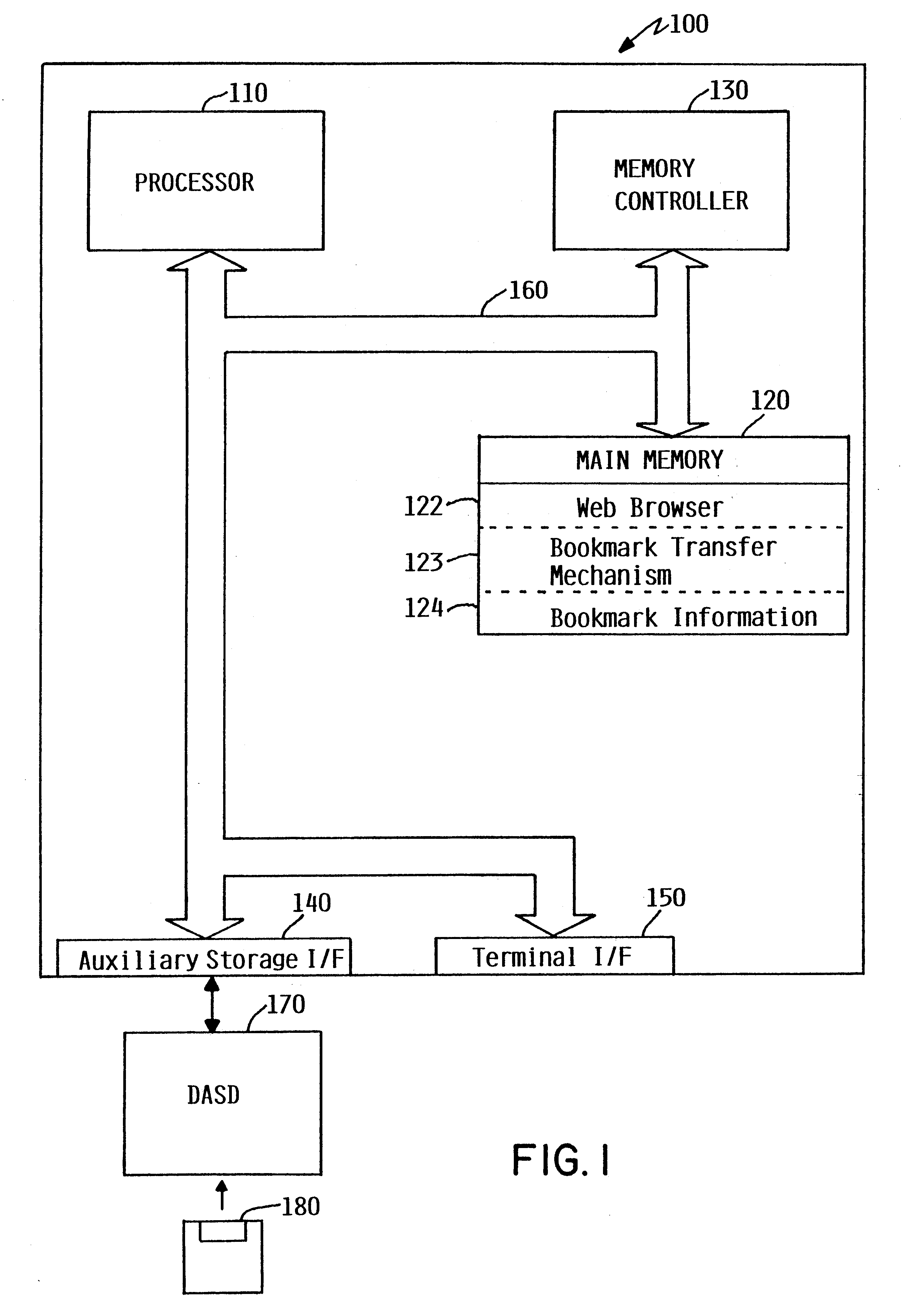
A bookmark transfer mechanism allows a user to transfer bookmark information from a primary computer to an alternate computer to customize a bookmarks menu on a web browser displayed on the alternate computer. The alternate computer prompts the user for a base address which is used by the web browser on the alternate computer to locate the primary computer where bookmark information is stored. The base address should correspond to a primary computer that has been configured for automatic download of bookmark information. Once the primary computer is located, the alternate computer transfers the base address and prompts the user for security information. The alternate computer then delivers the security information to the primary computer. The primary computer then authenticates the security information. If the security information is not valid, the primary computer delivers an error message to the alternate computer indicating that access to the primary computer has been denied. If the security information is valid, the primary computer transfers the bookmark information to the alternate computer. If necessary, the alternate computer translates the received bookmark information to the proper web browser format and updates the bookmarks menu on the web browser to include the transferred bookmark information. The bookmark information may be either temporarily or permanently incorporated into the web browser.
Owner:IBM CORP
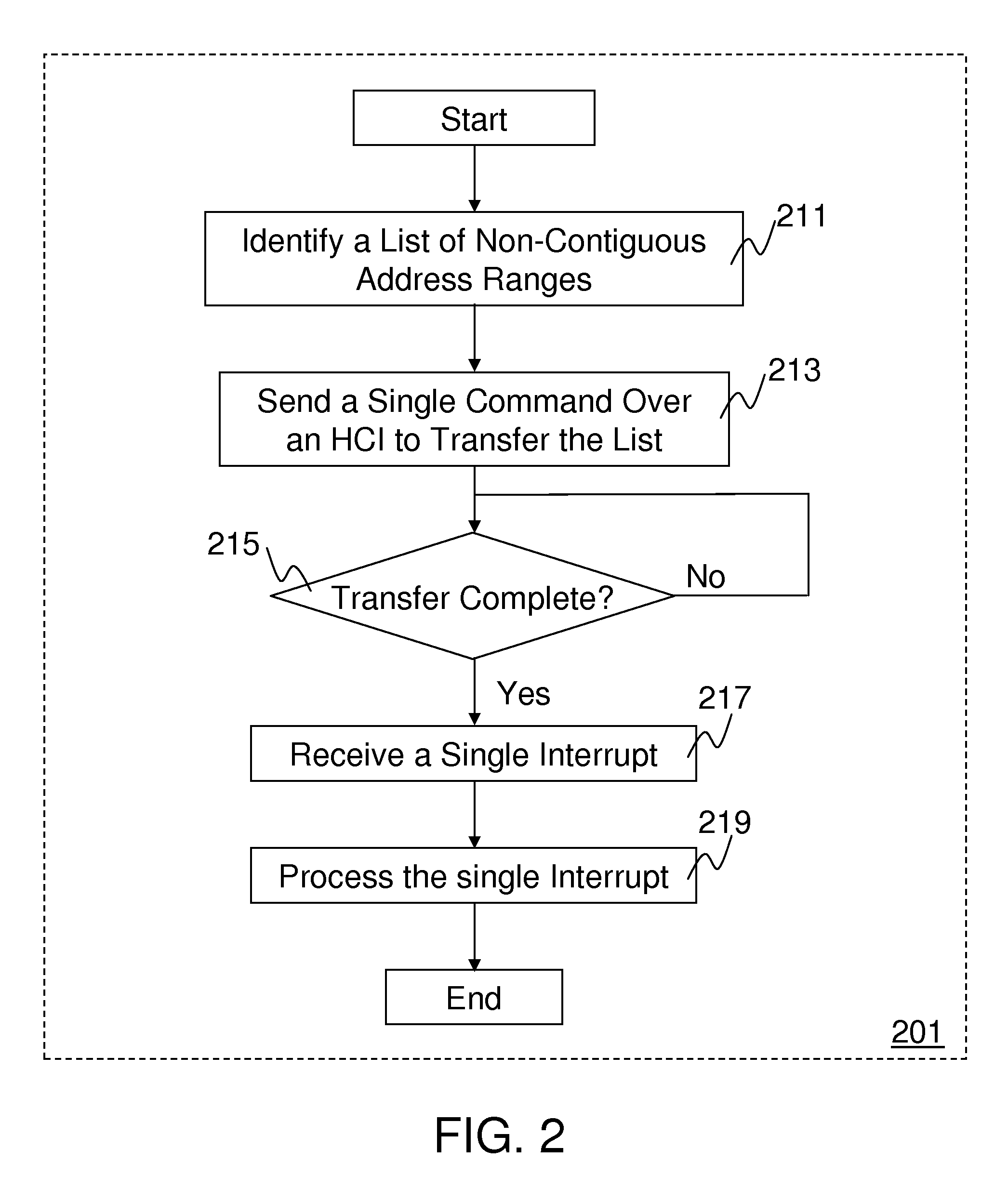
Method and system for queuing transfers of multiple non-contiguous address ranges with a single command
ActiveUS20100161936A1Input/output to record carriersProgram control using stored programsHost controller interfaceSoftware
Methods and systems for queuing transfers of multiple non-contiguous address ranges within a single command are disclosed. Embodiments of systems include system processors, memory to store data and executable software, and storage devices to receive transfer commands stored in system memory. A host controller interface driver is executed by one or more system processors and collects multiple non-continuous address ranges from storage-device transfer requests and records starting addresses and quantities of data to transfer for each non-continuous range in a tagged command list. It records the number of address ranges in the tagged command list, and a tagged-transfer opcode in a command, and stores the command and the tagged command list in a command table for the storage device. It records a base address for the command table in memory and an offset for the tagged command list into a command header, which is stored in a command queue.
Owner:INTEL CORP
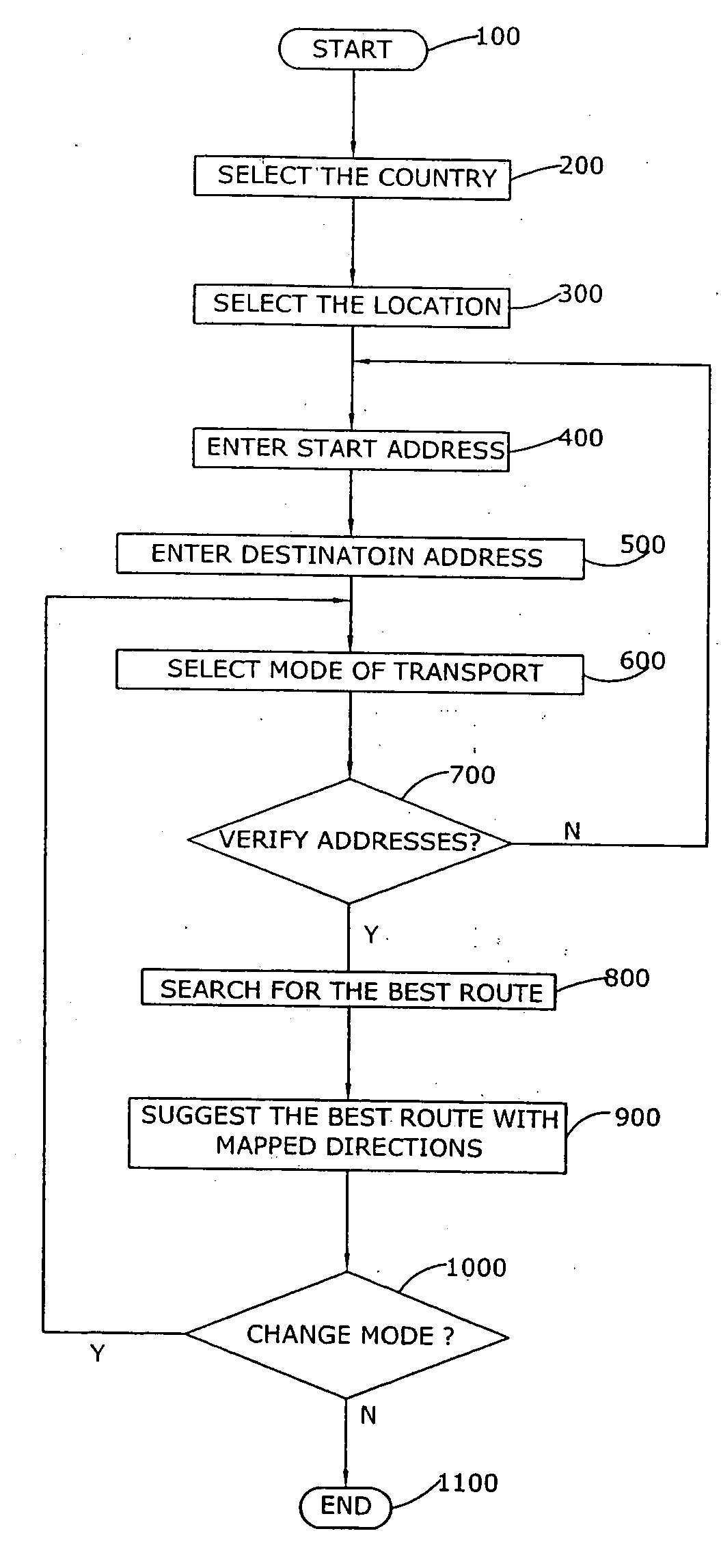
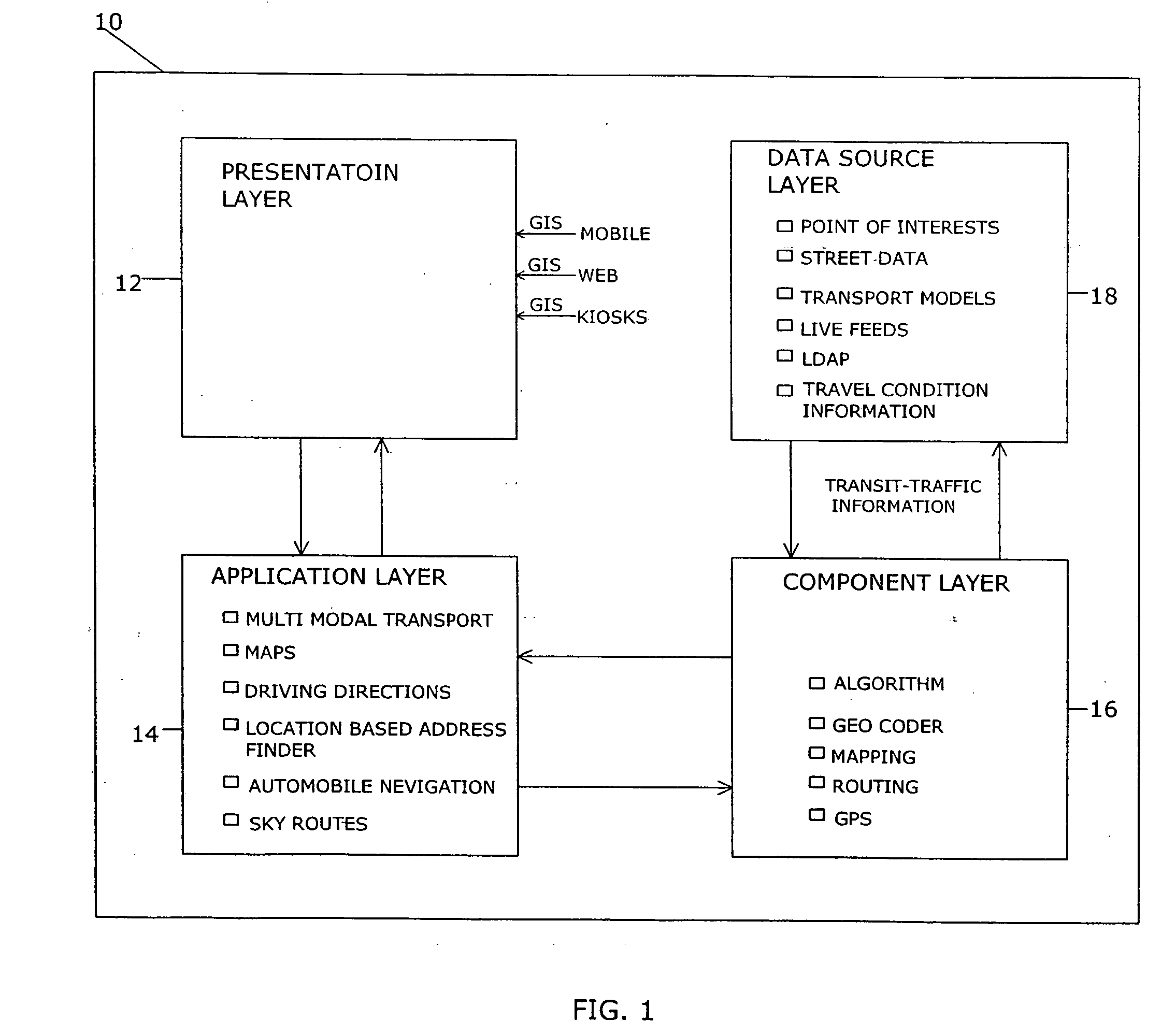
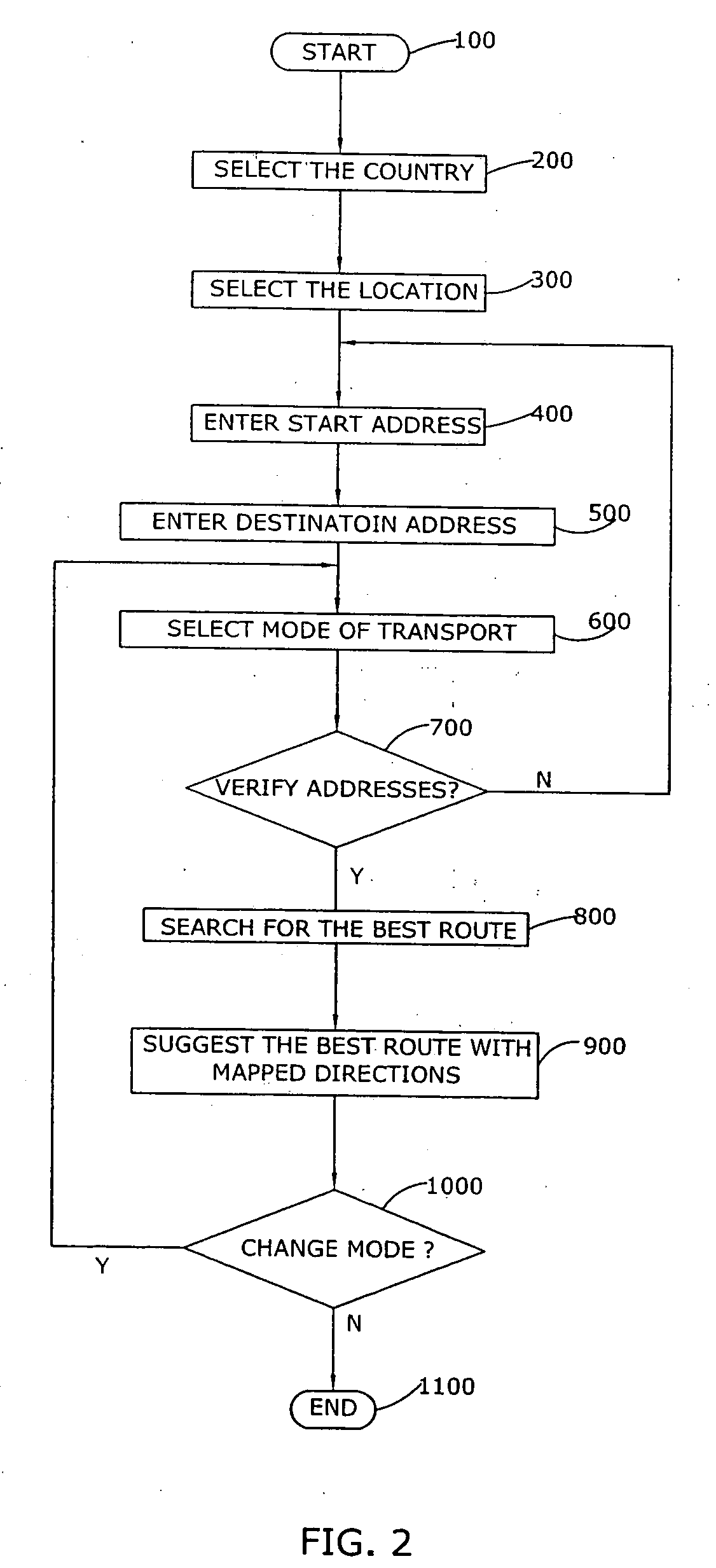
Method and system for finding multimodal transit route directions based on user preferred transport modes
InactiveUS20090119001A1Navigational calculation instrumentsDigital data processing detailsData bankSoftware
A method and system for finding multimodal transit route solutions with a computer software program is described that finds the most efficient transit routes based on user preferred modes of transport. The route finding system has four layers that include a presentation layer, an application layer, a component layer and a database layer. The system input includes a start address, a destination address and preferred mode of transport to find the most efficient transit routes. The transport mode includes public transport, private transport and combination of public and private transports. The system displays the detailed mapped route directions for the user input. The system also includes tools for location based address finder and local guidance.
Owner:PUBLIC ROUTES COM
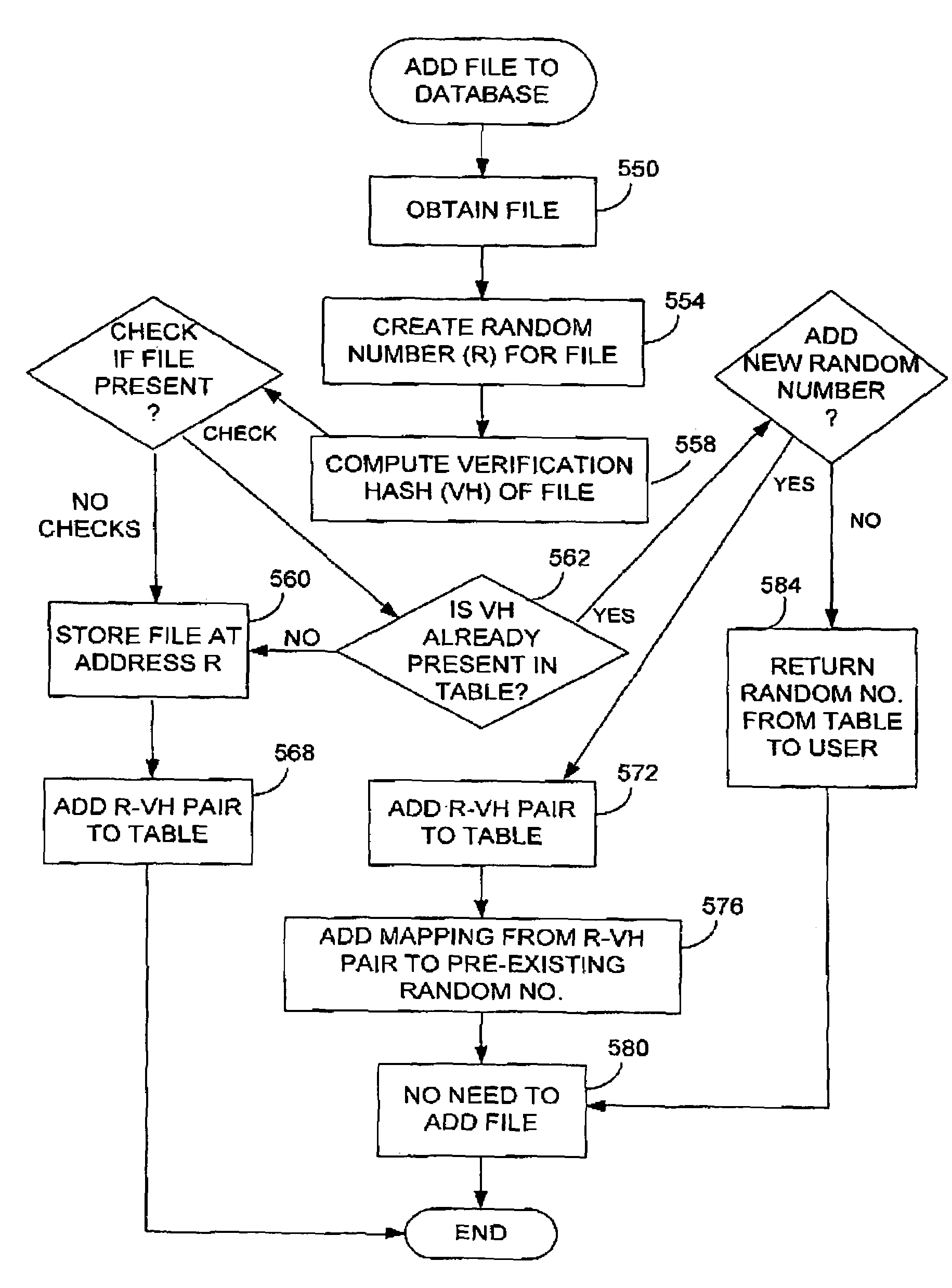
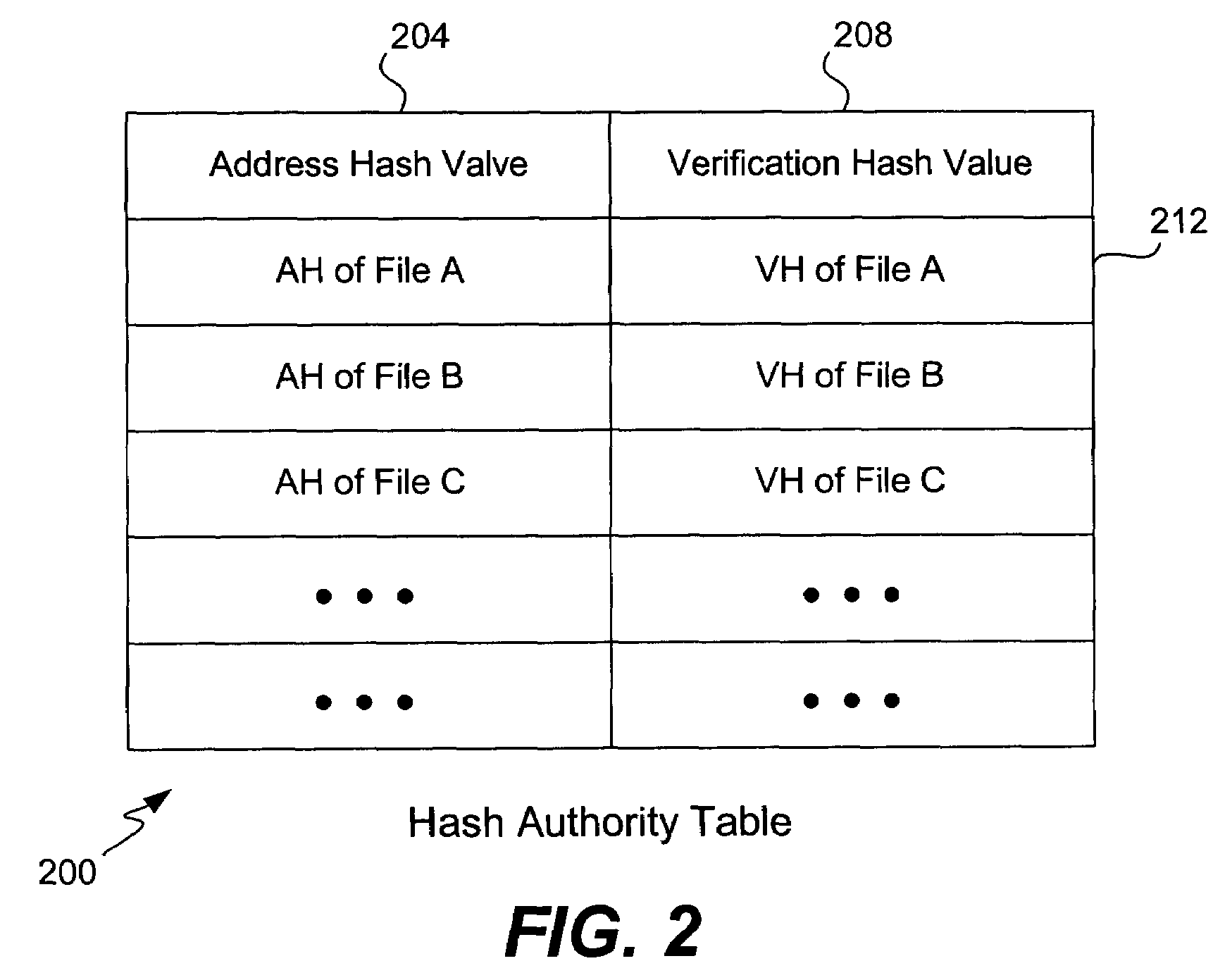
Additional hash functions in content-based addressing
ActiveUS7373345B2Eliminate malicious hash attackEliminate attackData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalComputer hardwareHash function
A hash function used for content addressing is different from the hash function used for content verification. Adding a file to a database involves storing both hash function values in a table as pair. Verifying the integrity of a file believed to be a duplicate in a database, or when retrieving a file, makes use of the verification hash function. Files can be continuously checked. A multi-level database can be used. A second hash function can be added to an existing system. A verification hash function can be upgraded and more than one content verification hash function can be used. In a variation, a random number generator is used instead of a hash function for content addressing; the verification hash function is also used. Files addressed using a random number are added or retrieved from a database and their verification hash values are checked. Time stamps and digital signatures are used for security.
Owner:DATACORE SOFTWARE
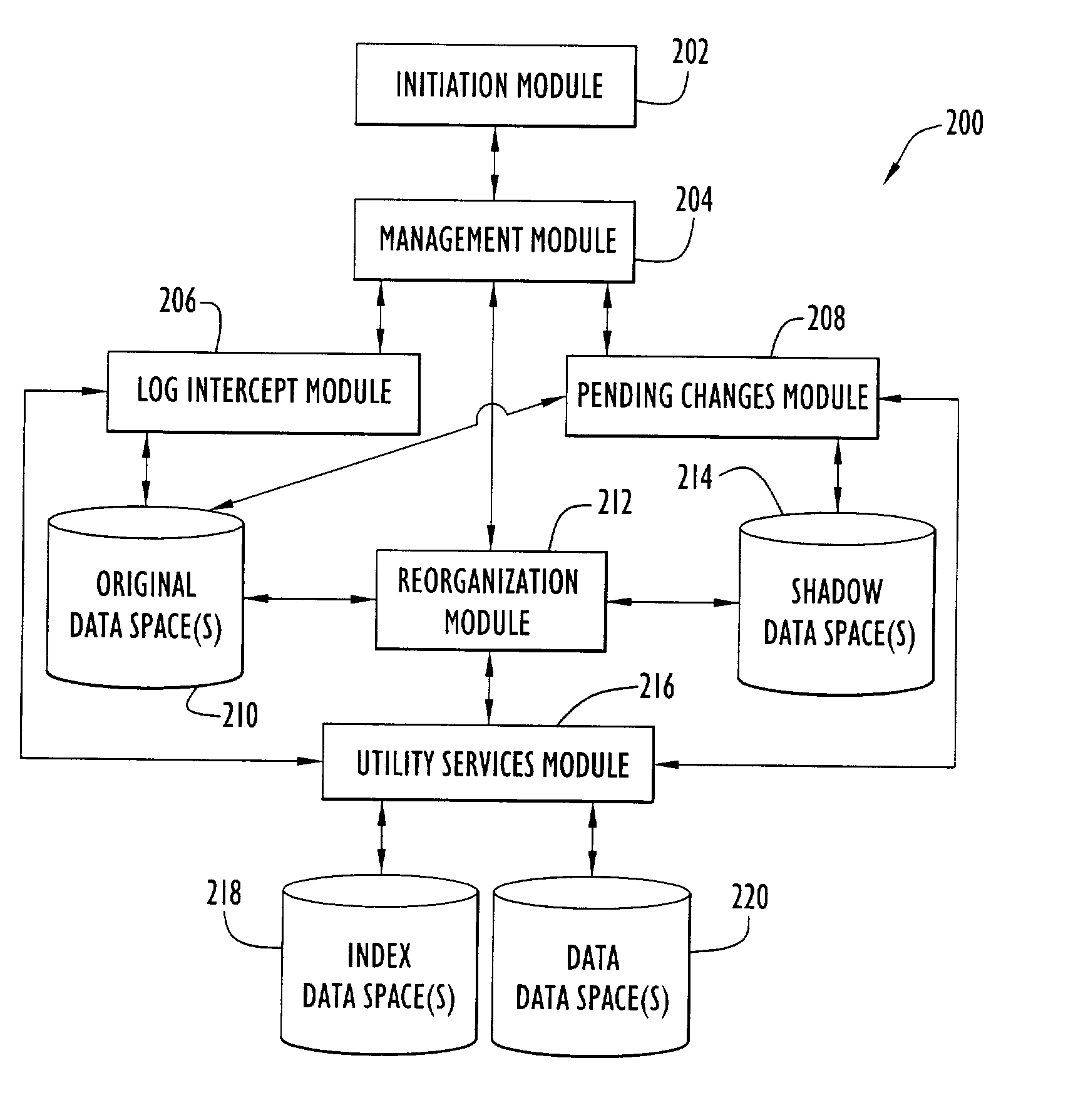
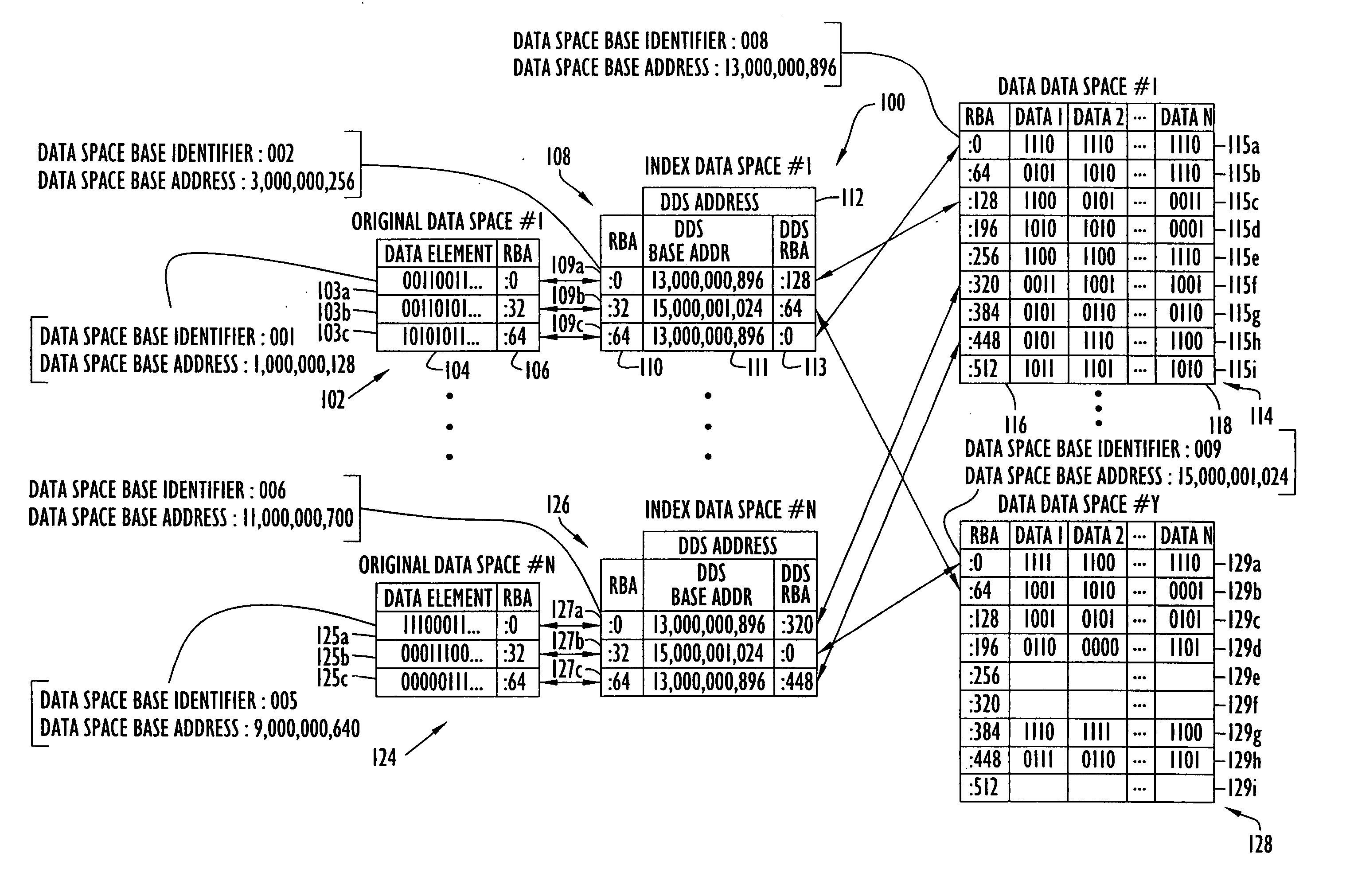
Capturing data changes utilizing data-space tracking
InactiveUS20060074951A1Significant storage space efficiencySignificant processing efficiencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData spaceOriginal data
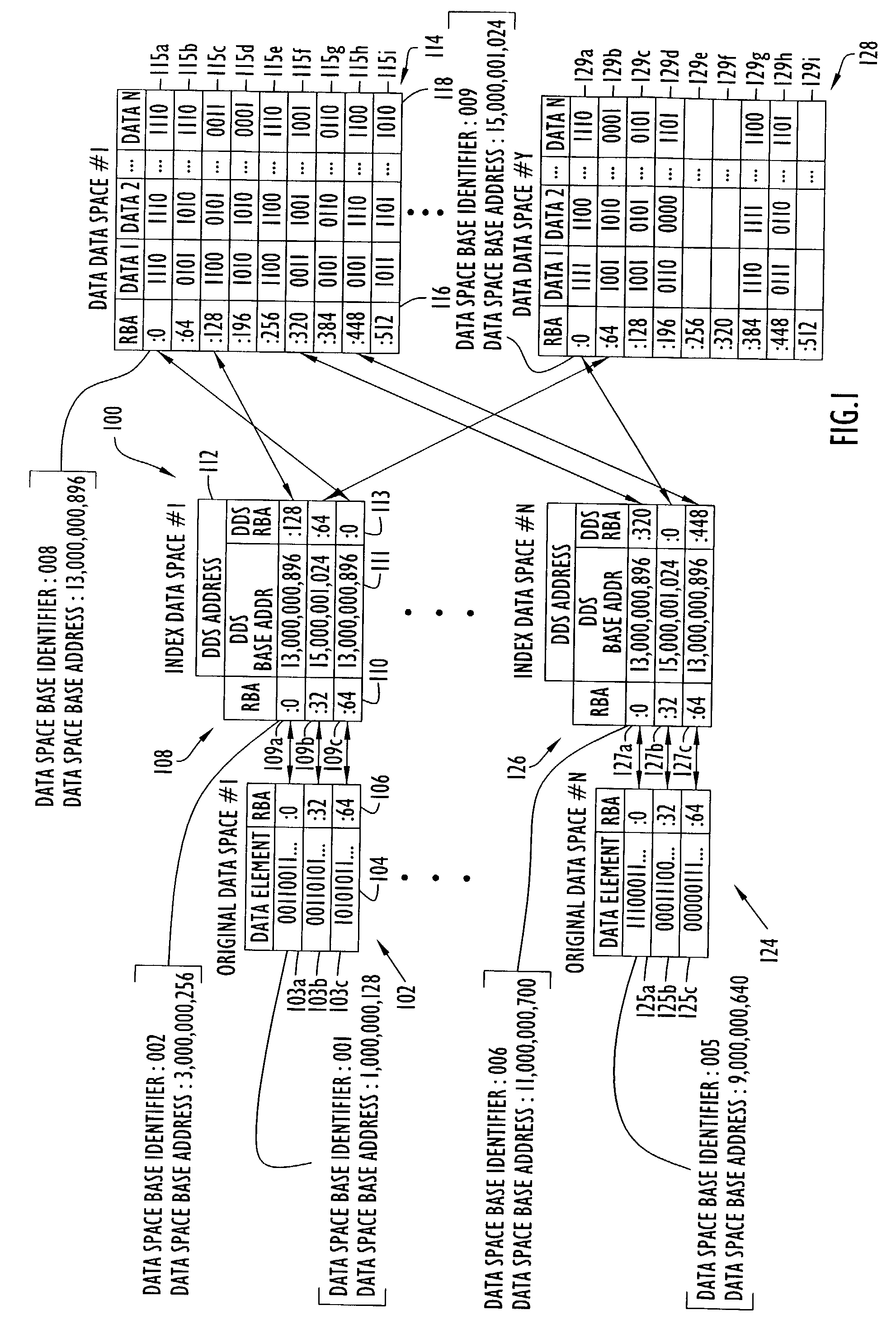
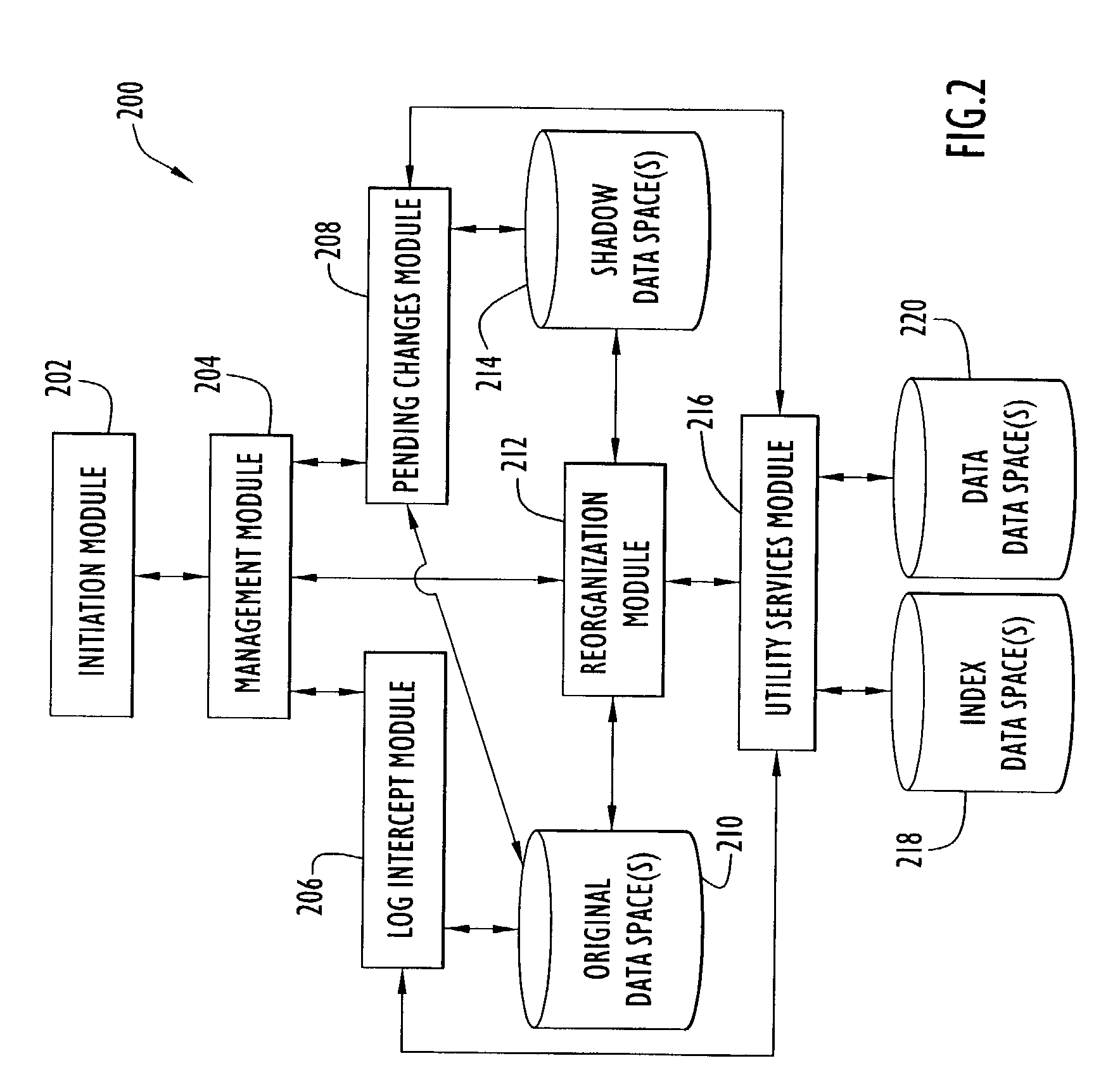
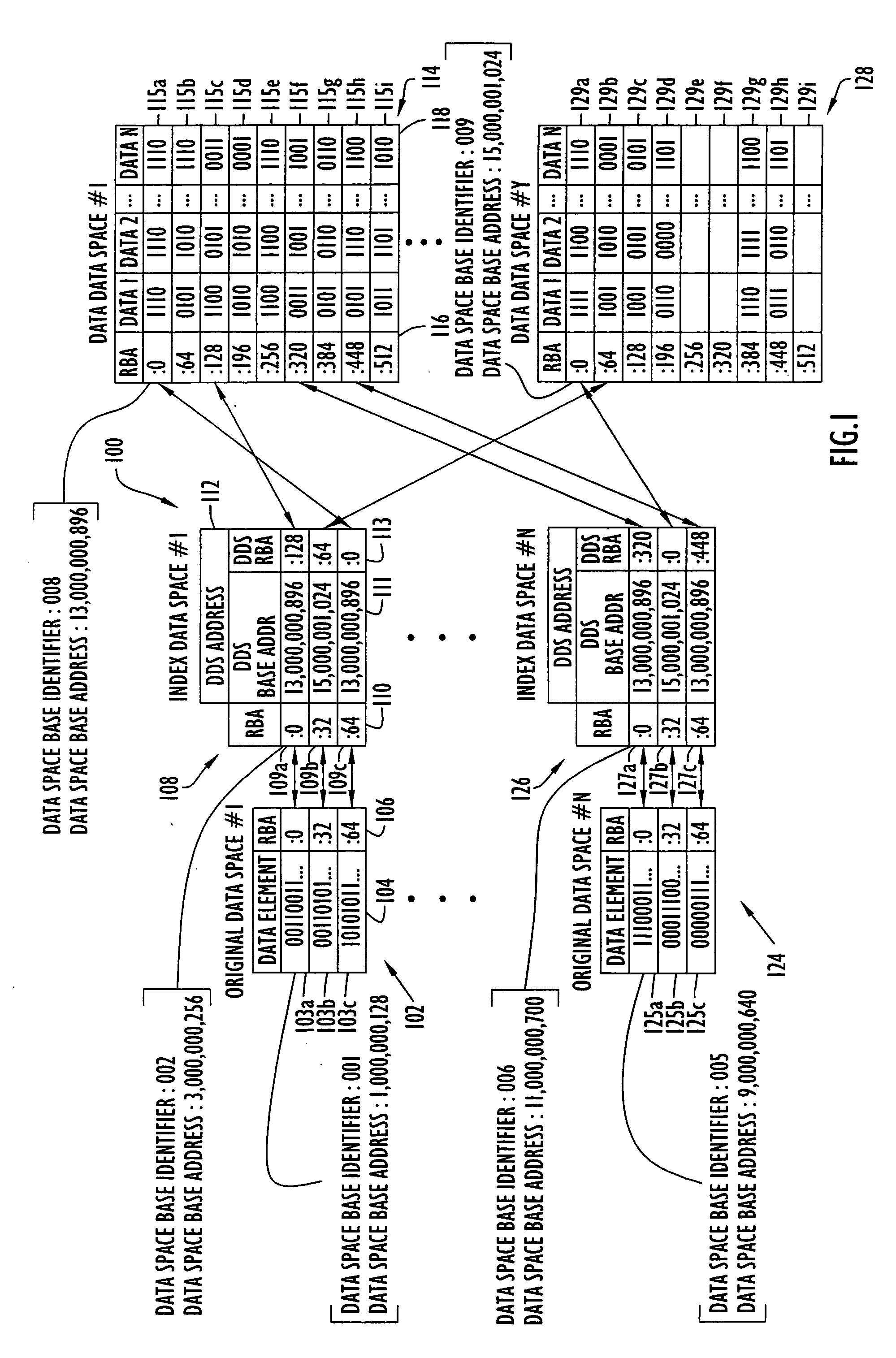
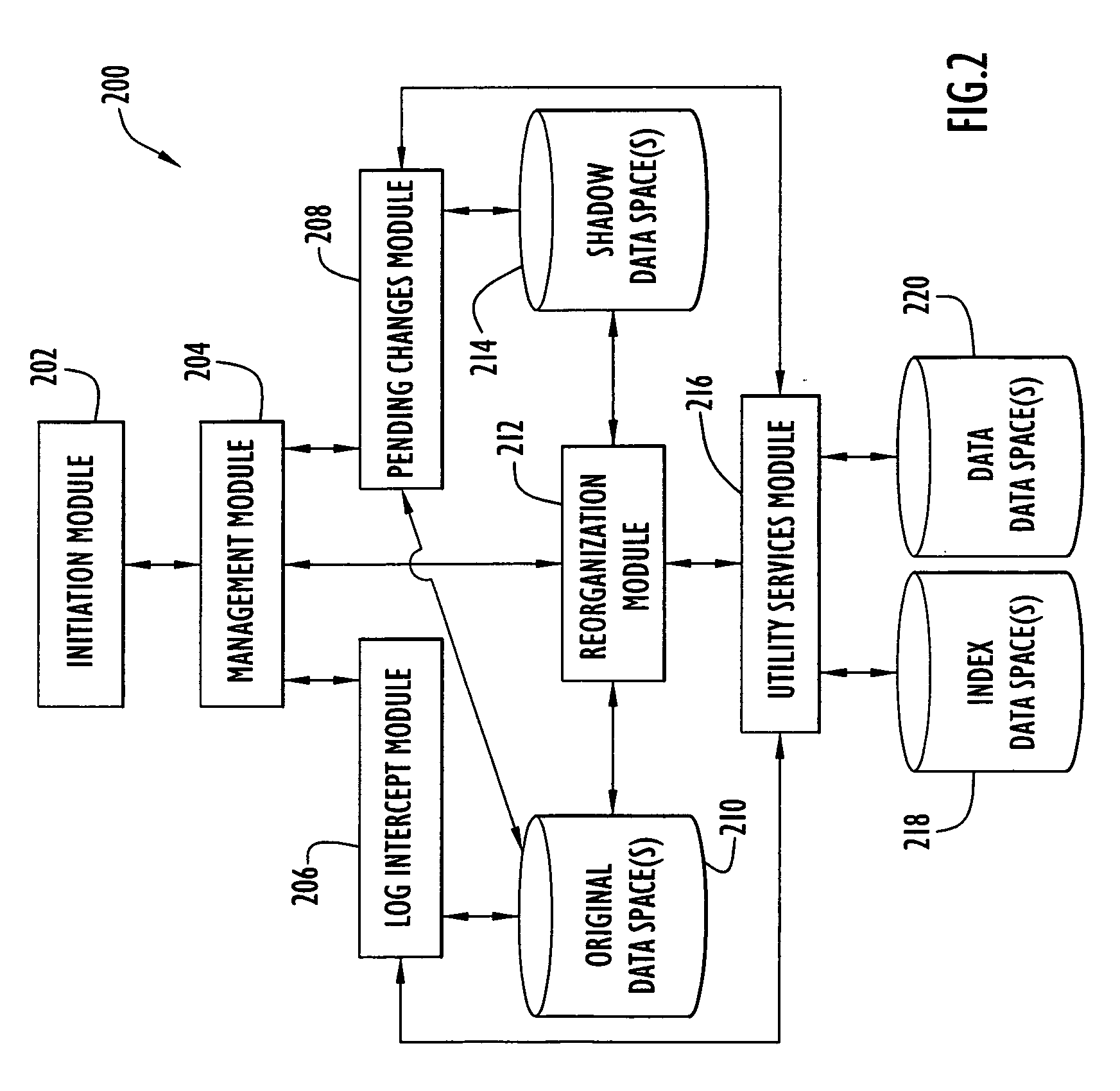
An on-line reorganization facility (ORF) uses index data-spaces that point to other data-spaces, referred to as data data-spaces, to efficiently track and coordinate information about the data-elements in an original data-space operated upon by a reorganization process. A relative base address of a data-element in an index data-space can be derived from a relative base address of a data-element in an original data-space, and vice versa. An index data-space data-element contains a location of a data-element in a data data-space that tracks change information related to a corresponding data-element in the original data-space. Tracked changes are later applied to the newly reorganized data-space to assure consistency and integrity of the data. Tracked changes include the location in the original data-space where the change occurred and a flag indicting the type of change.
Owner:IBM CORP
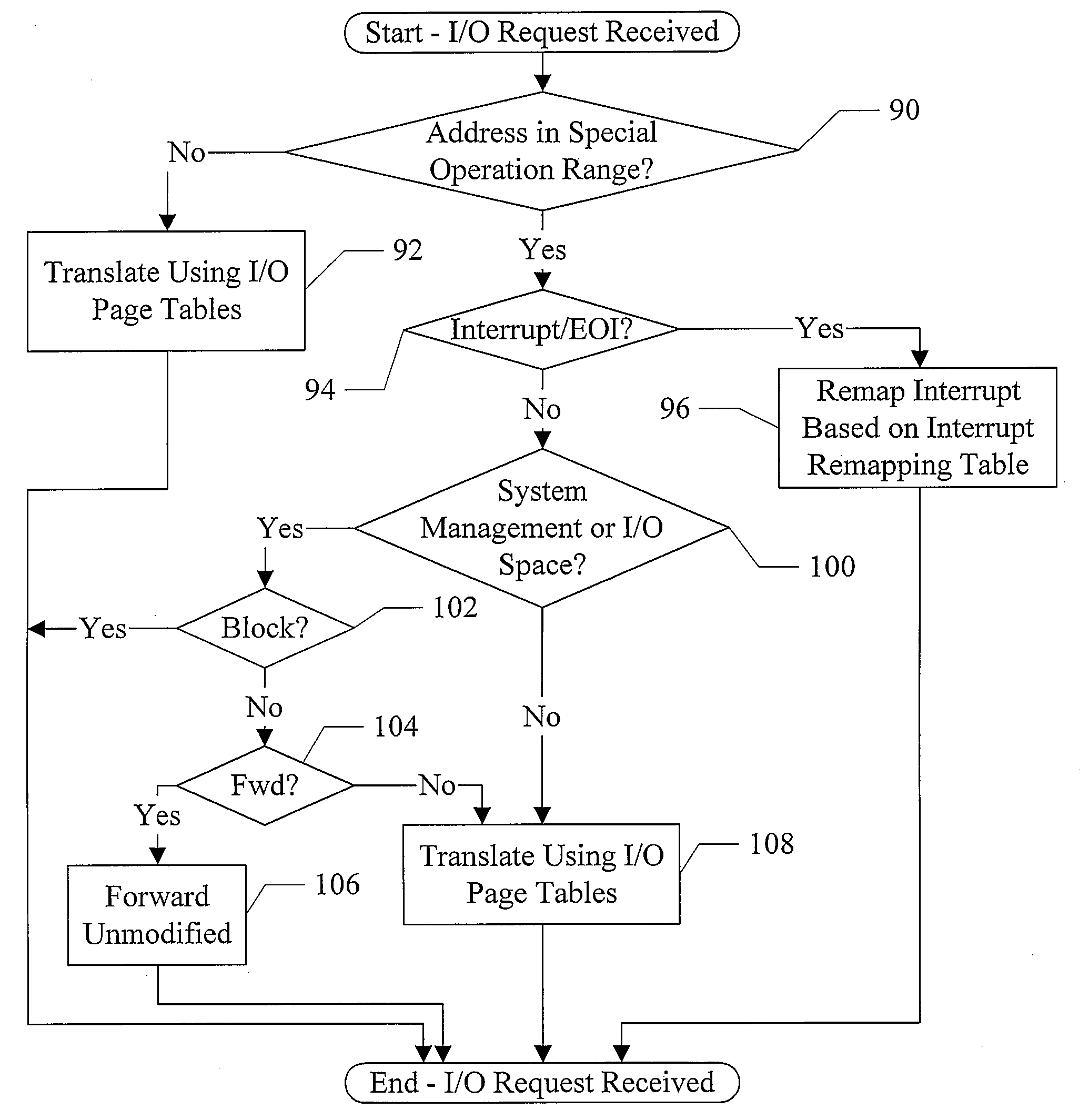
Filtering and Remapping Interrupts
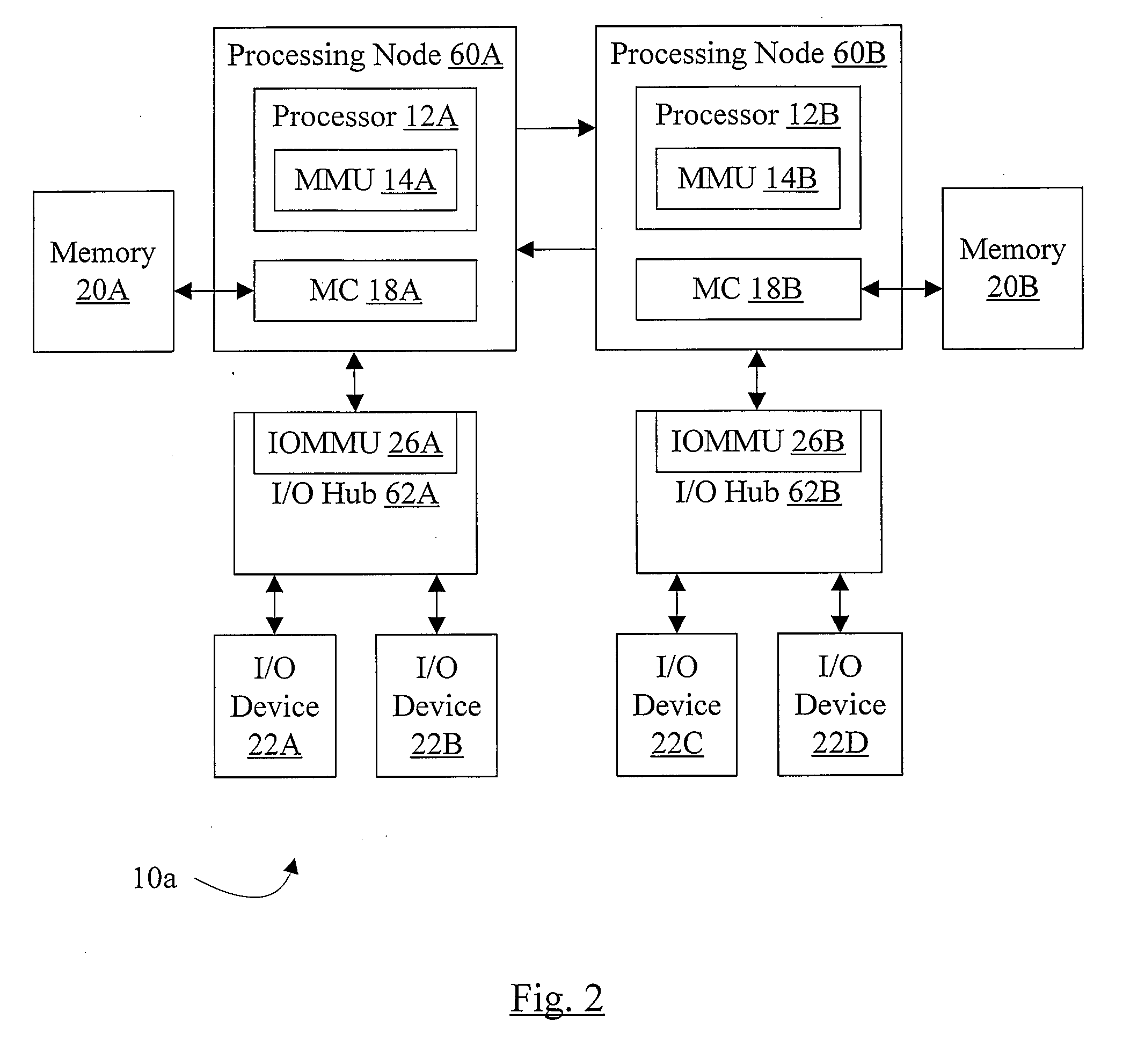
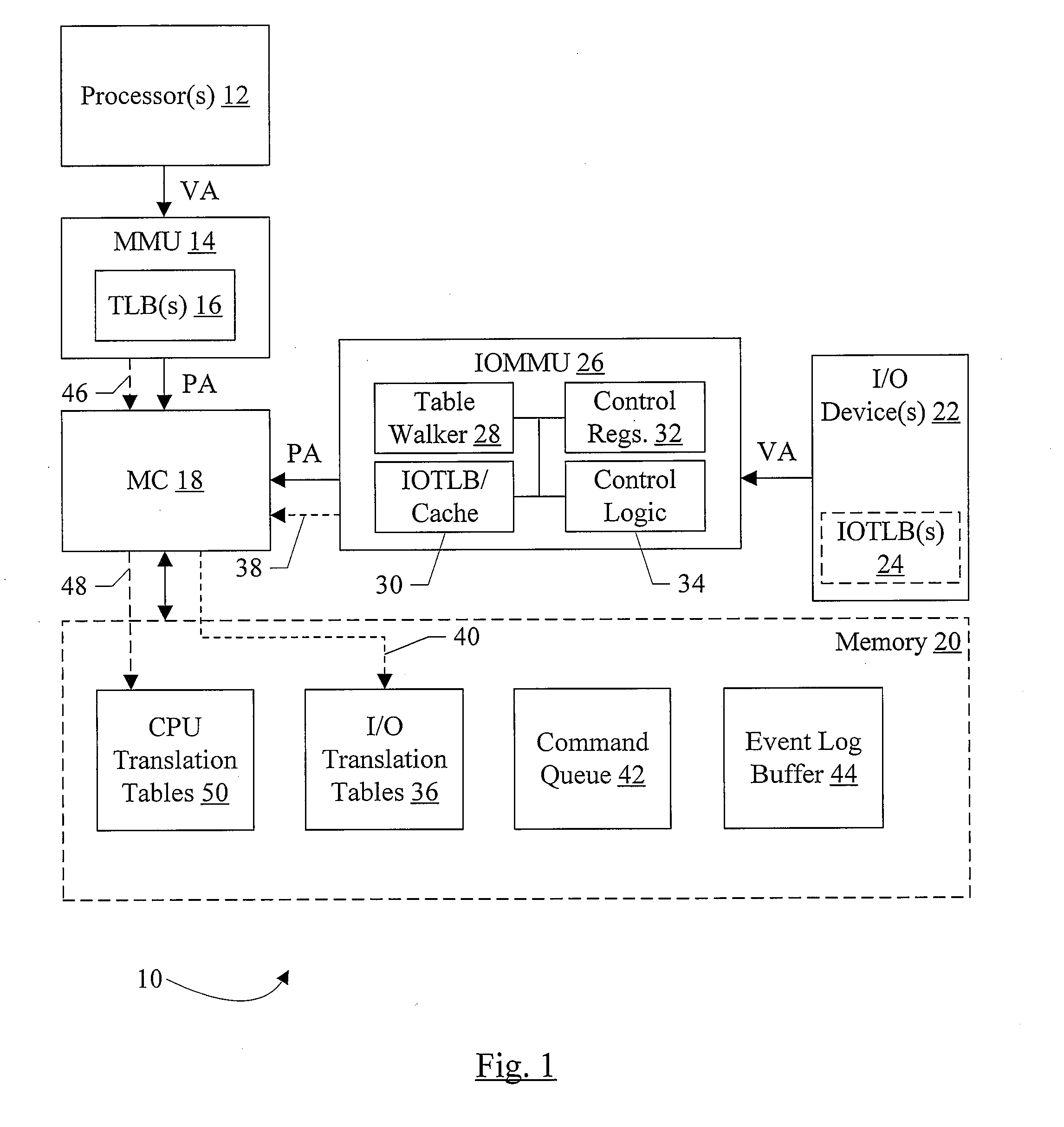
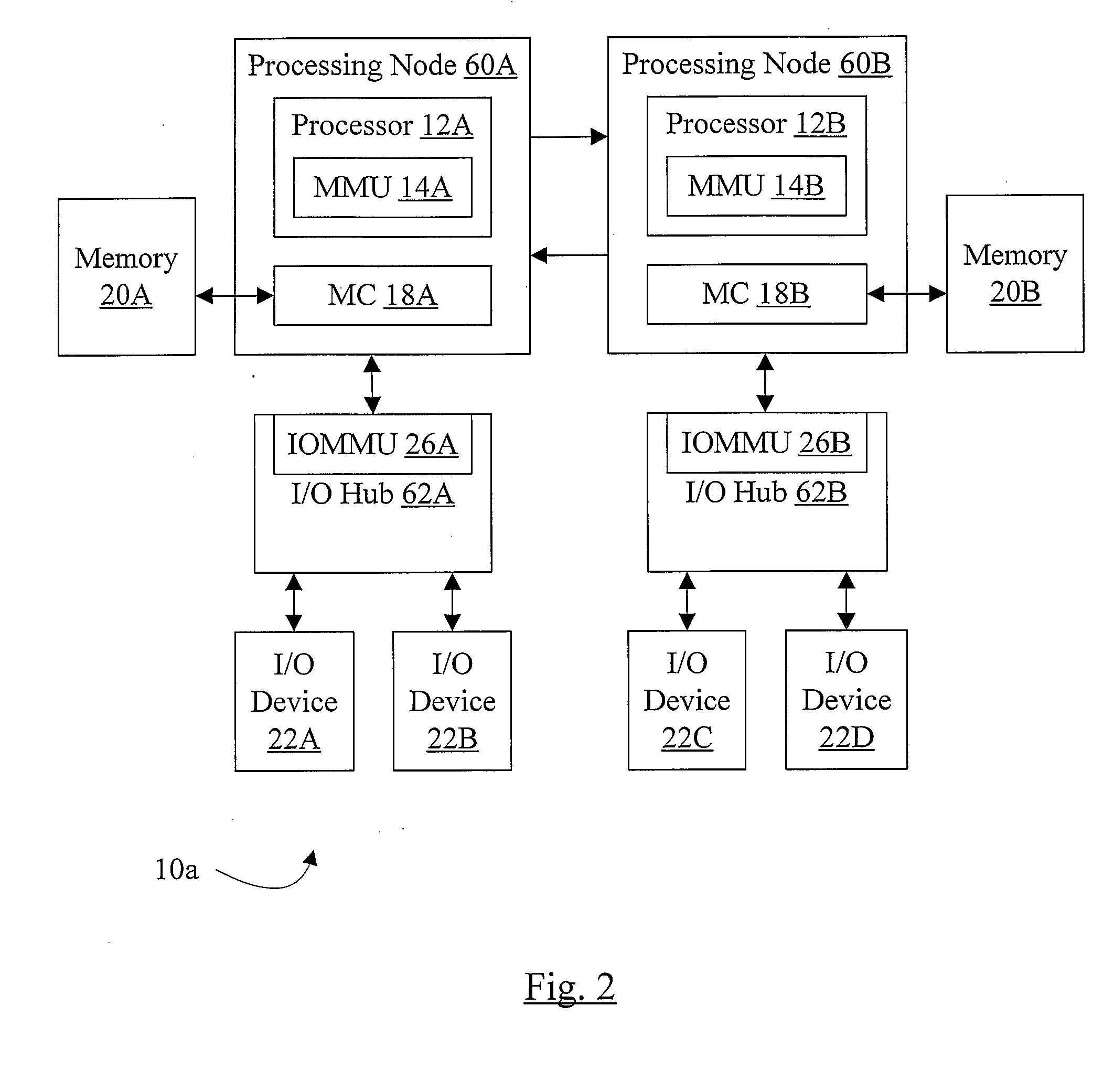
ActiveUS20080114916A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsManagement unitProcessor register
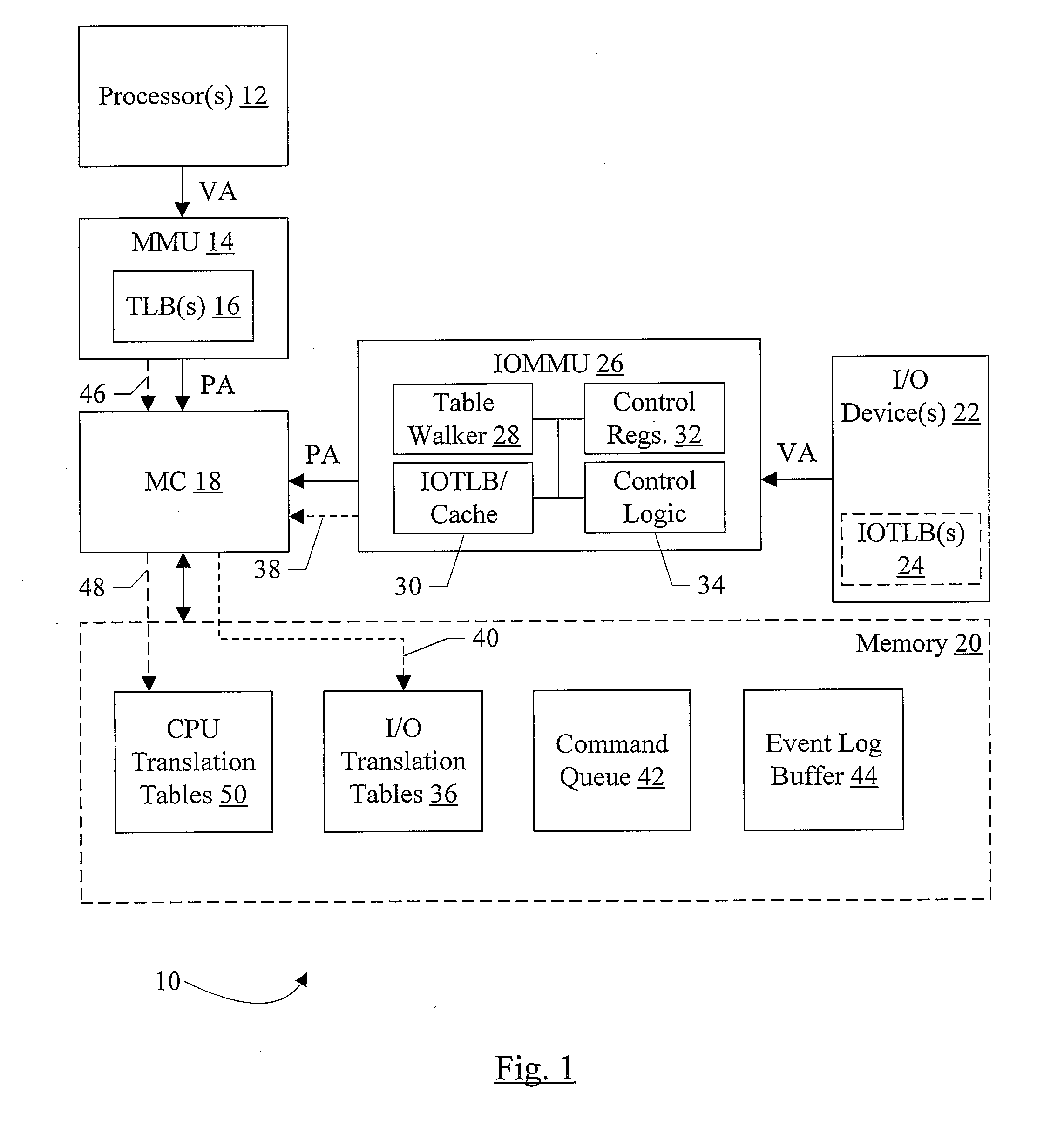
In one embodiment, an input / output memory management unit (IOMMU) comprises a control register and control logic coupled to the control register. The control register is configured to store a base address of a device table, wherein a given input / output (I / O) device has an associated device identifier that selects a first entry in the device table. The first entry comprises a pointer to an interrupt remapping table. The control logic is configured to remap an interrupt specified by an interrupt request received by the IOMMU from the given I / O device if the interrupt remapping table includes an entry for the interrupt.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Memory management system and method providing increased memory access security
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Data structure describing logical data spaces
InactiveUS20070156729A1Automatic and efficientAvoid disadvantagesData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData storingData store
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Efficiently Controlling Special Memory Mapped System Accesses
ActiveUS20080114906A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsManagement unitControl register
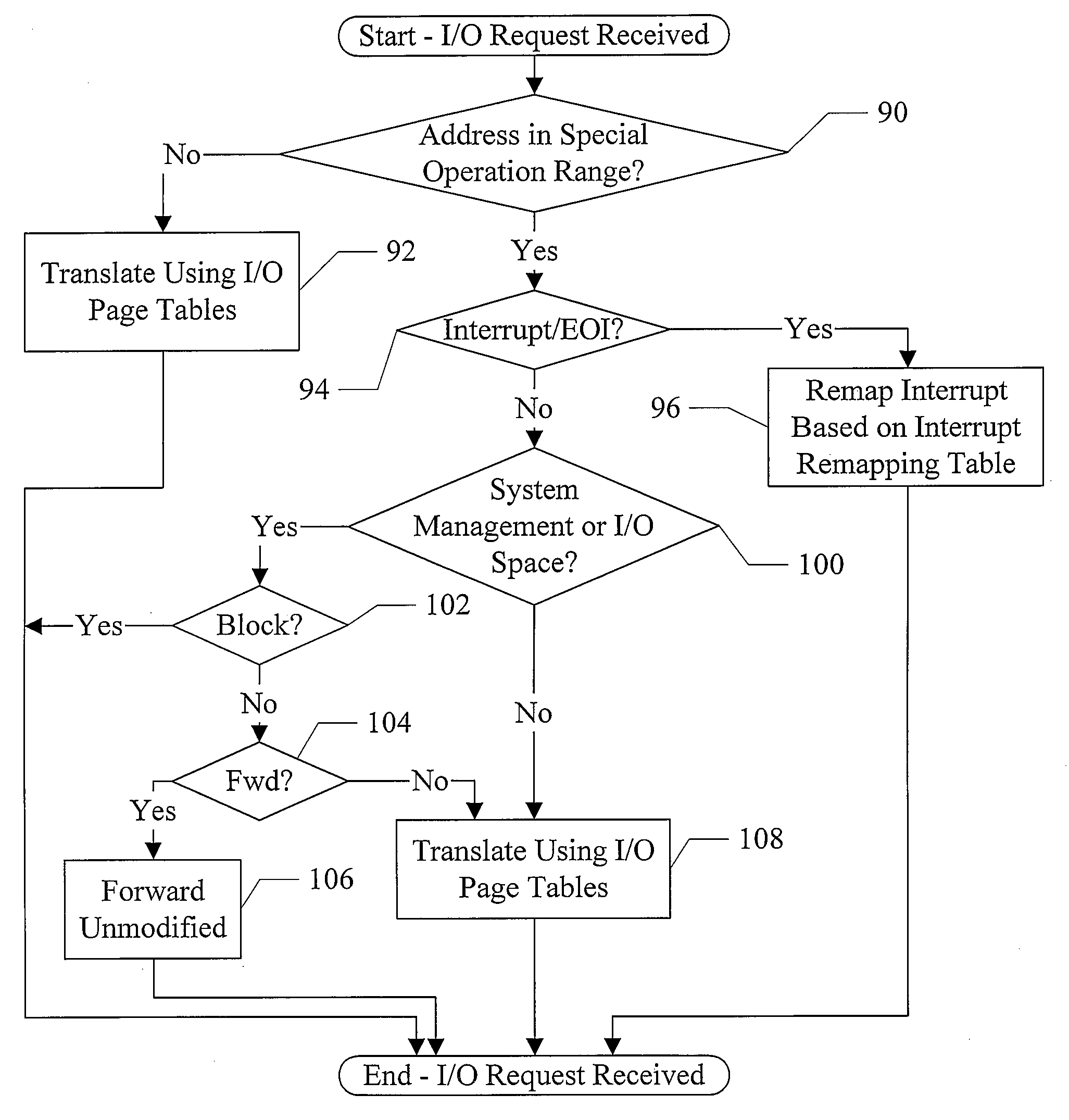
In one embodiment, an input / output memory management unit (IOMMU) comprises a control register configured to store a base address of a set of translation tables and control logic coupled to the control register. The control logic is configured to respond to an input / output (I / O) device-initiated request having an address within an address range of an address space corresponding to a peripheral interconnect. One or more operations other than a memory operation are associated with the address range, and the control logic is configured to translate the address to a second address outside of the address range if the translation tables specify a translation from the address to the second address, whereby a memory operation is performed in response to the request instead of the one or more operations associated with the address range.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
System and method for ecmp load sharing
A packet classifier and a method for routing a data packet are provided. The packet classifier includes a content addressable memory, a translation table and a parameter memory. The method includes looking up a content addressable memory for a base address into a parameter memory using a header of the data packet. The base address is related to the routes under ECMP for forwarding the data packet. From among these addresses, using multiple headers of the data packet, an adjustment to the base address is computed. The adjustment specifies an actual address to the parameter memory corresponding to a selected route for forwarding the data packet. The parameter memory is then accessed using the actual address to obtain parameter values relevant to the selected route. The data packet is then forwarded according to the parameter values thus obtained.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
RAID system for performing efficient mirrored posted-write operations
InactiveUS7340555B2Reduce needMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionRAIDPCI Express
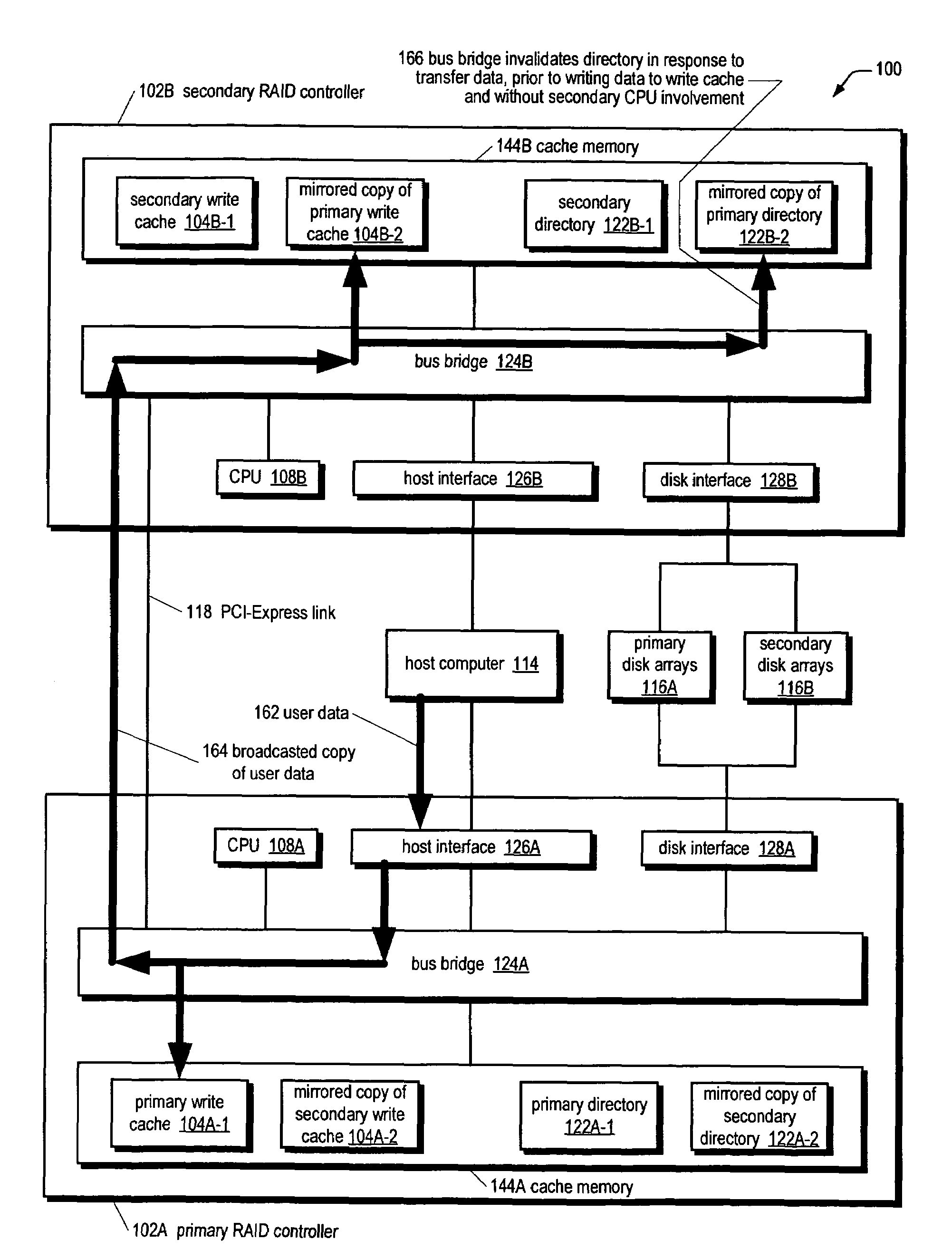
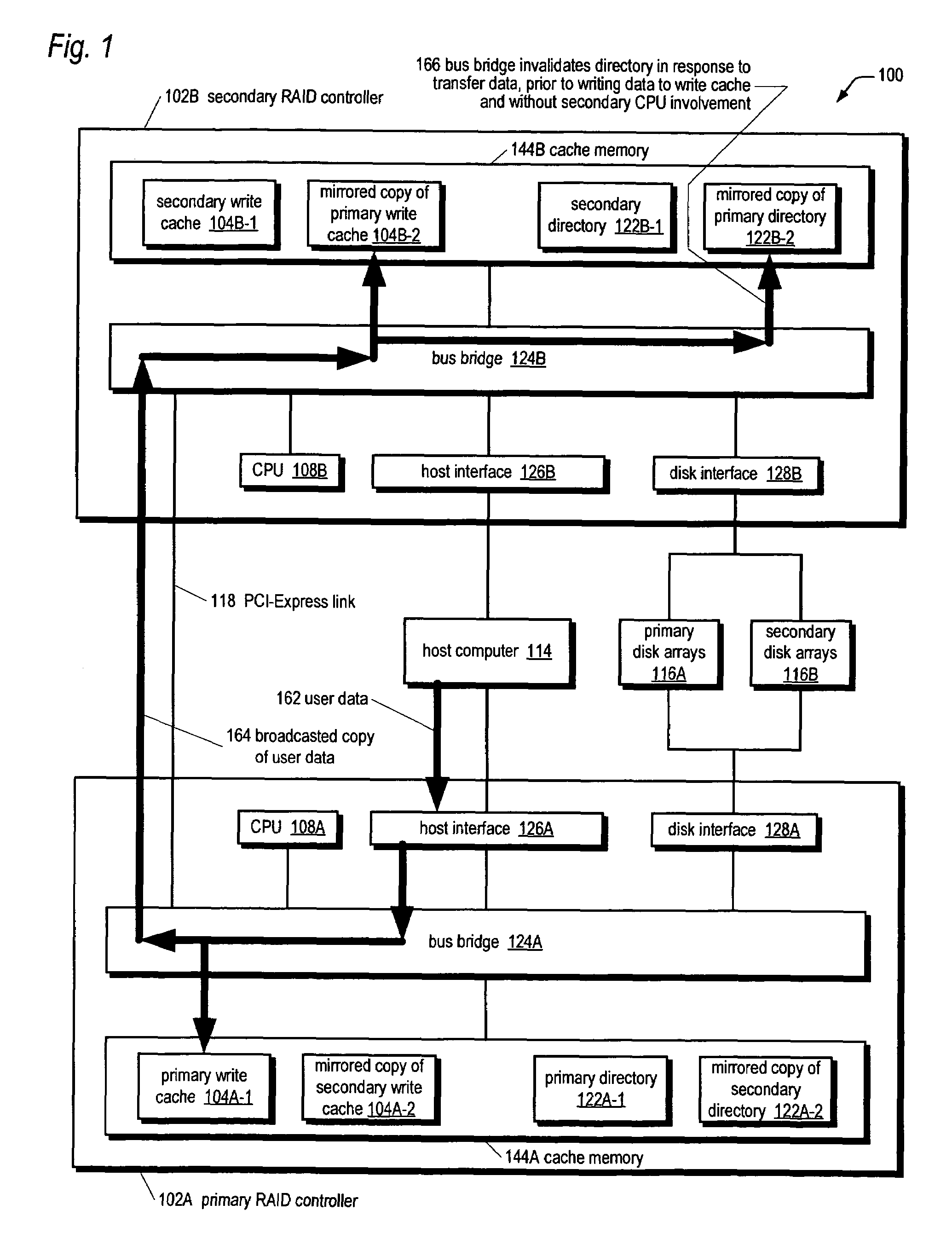
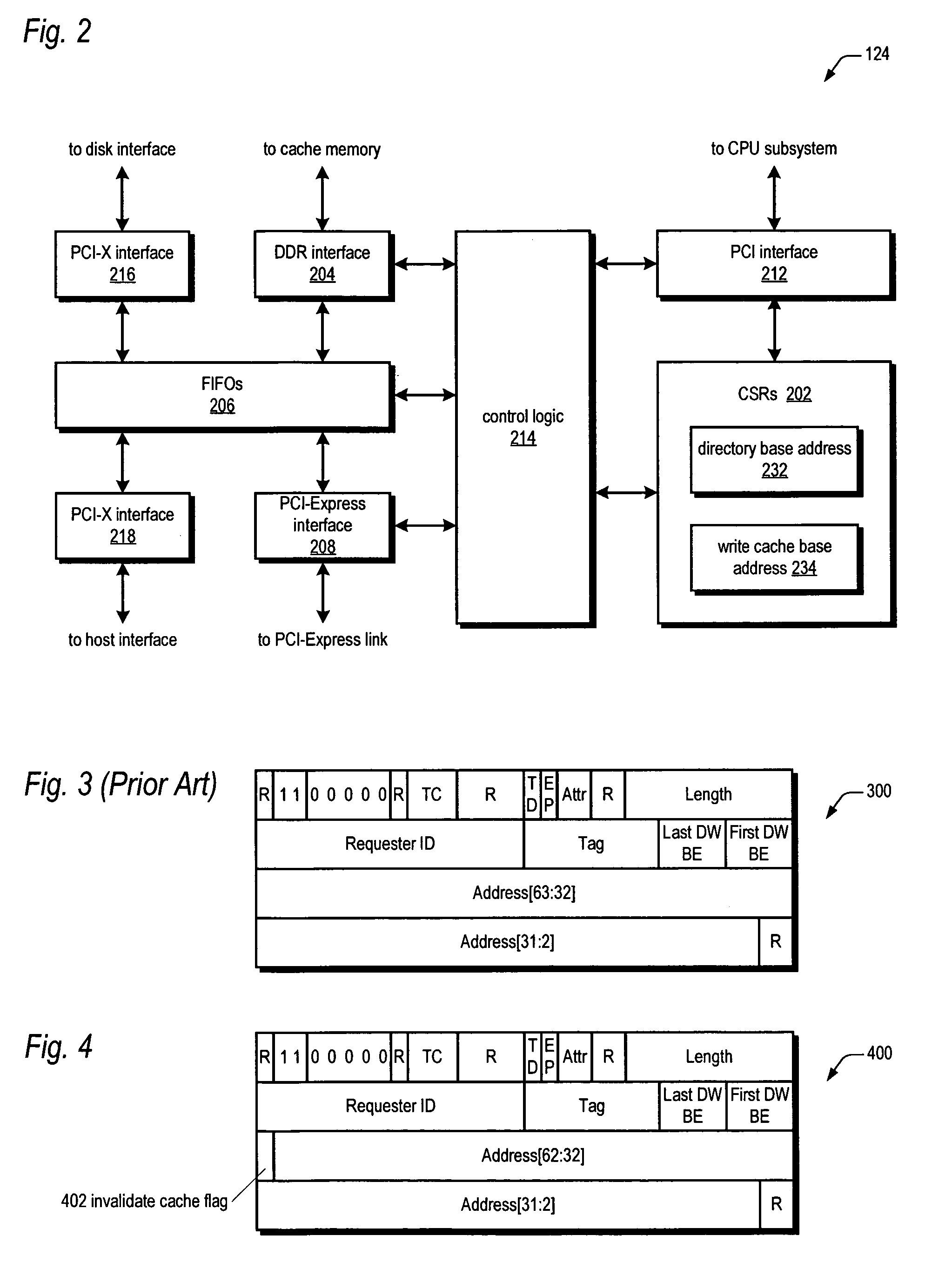
A bus bridge on a primary RAID controller receives user write data from a host and writes the data to its write cache and also broadcasts the data over a high speed link (e.g., PCI-Express) to a secondary RAID controller's bus bridge, which writes the data to its mirroring write cache. However, before writing the data, the second bus bridge automatically invalidates the cache buffers to which the data is to be written, which alleviates the primary controller's CPU from sending a message to the secondary controller's CPU to instruct it to invalidate the cache buffers. The secondary controller CPU programs its bus bridge at boot time with the base address of its mirrored write cache to enable it to detect that the cache buffer needs invalidating in response to the broadcast write, and with the base address of its directory that includes the cache buffer valid bits.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
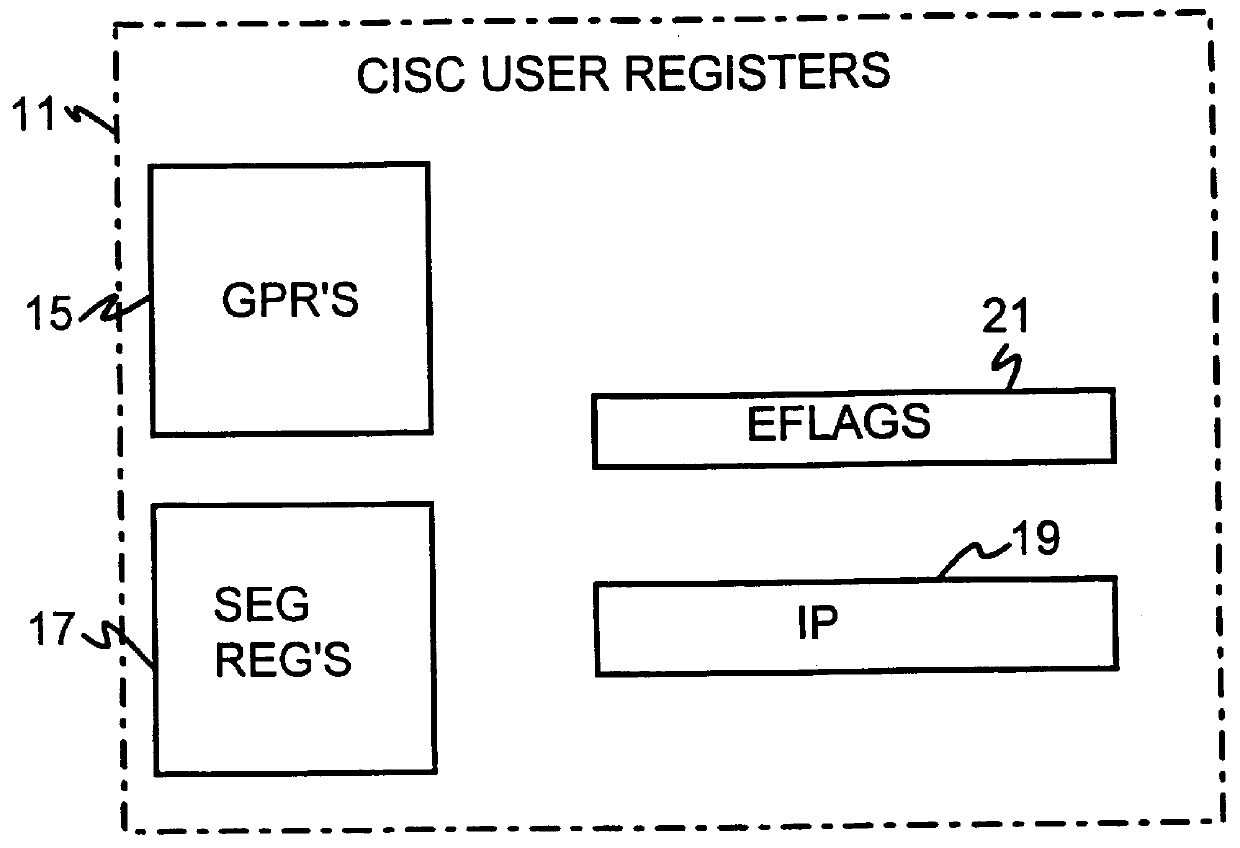
Shared register architecture for a dual-instruction-set CPU to facilitate data exchange between the instruction sets
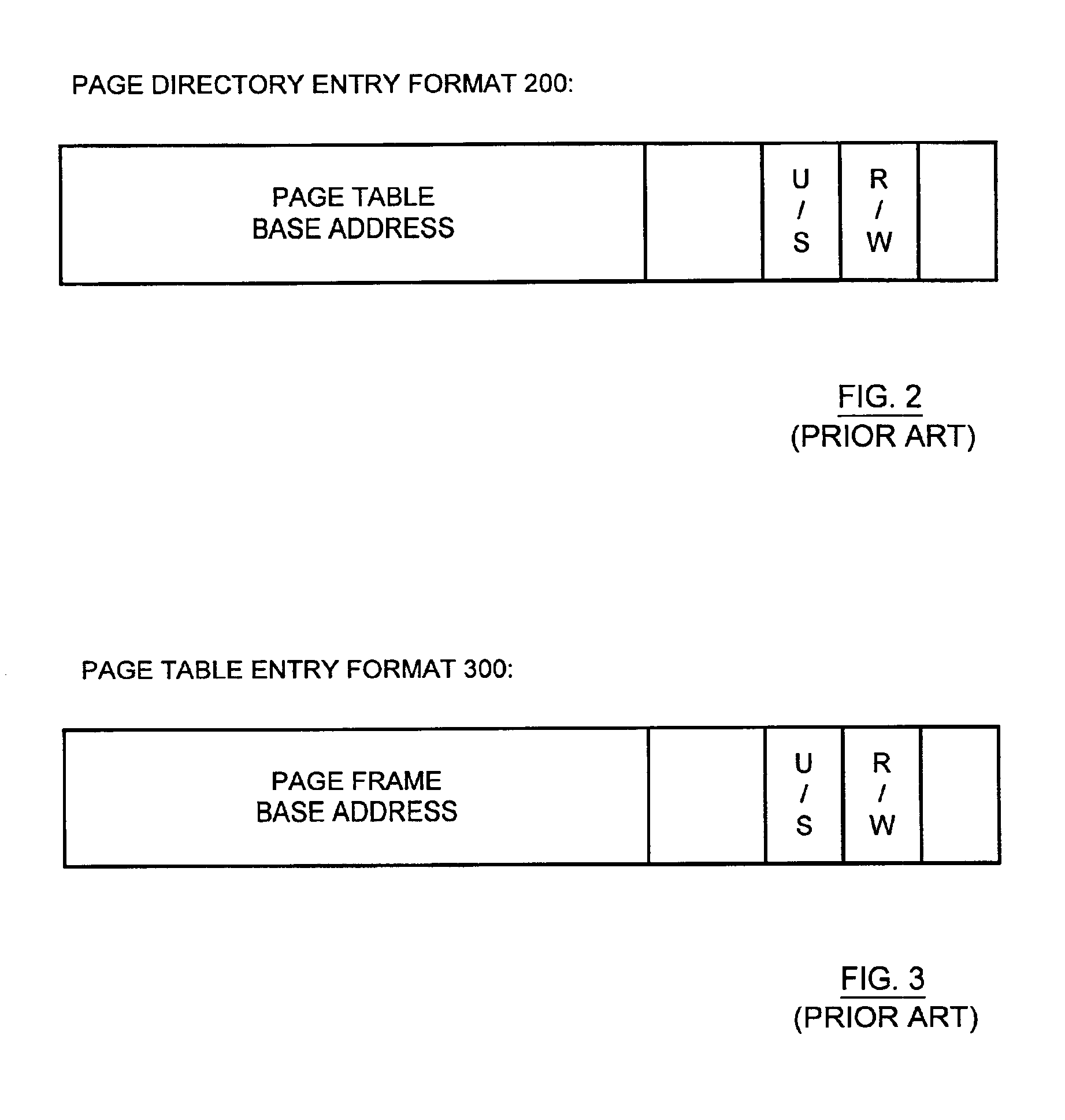
A dual-instruction set central processing unit (CPU) is capable of executing instructions from a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set and from a complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set. Data and address information may be to transferred from a CISC program to a RISC program running on the CPU by using shared registers. The architecturally-defined registers in the CISC instruction set are merged or folded into some of the architecturally-defined registers in the RISC architecture so that these merged registers are shared by the two instructions sets. In particular, the flags or condition code registers defined by each architecture are merged together so that CISC instructions and RISC instructions will implicitly update the same merged flags register when performing computational instructions. The RISC and CISC registers are folded together so that the CISC flags are at one end of the register while the frequently used RISC flags are at the other end, but the RISC instructions can read or write any bit in the merged register. The CISC code segment base address is stored in the RISC branch count register, while the CISC floating point instruction address is stored in the RISC branch link register. The general-purpose registers (GPR's) are also merged together, allowing a CISC program to pass data to a RISC program merely by writing one of its GPR's, switching control to the RISC program, and the RISC program reading one of its GPR's that is merged with and corresponds to the CISC GPR that was written to by the CISC program.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information processing device
ActiveUS20110029696A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingInformation processingInternal memory
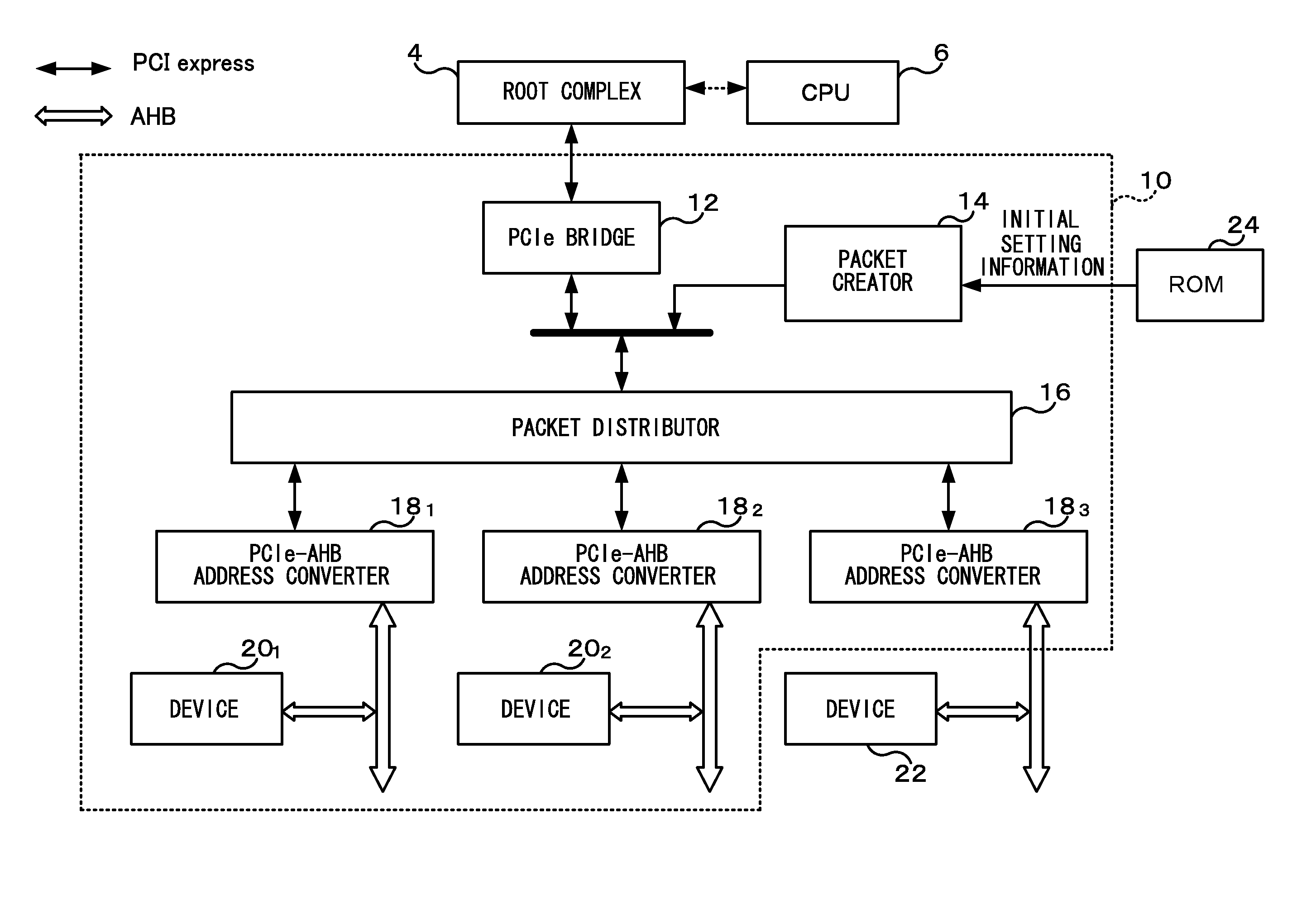
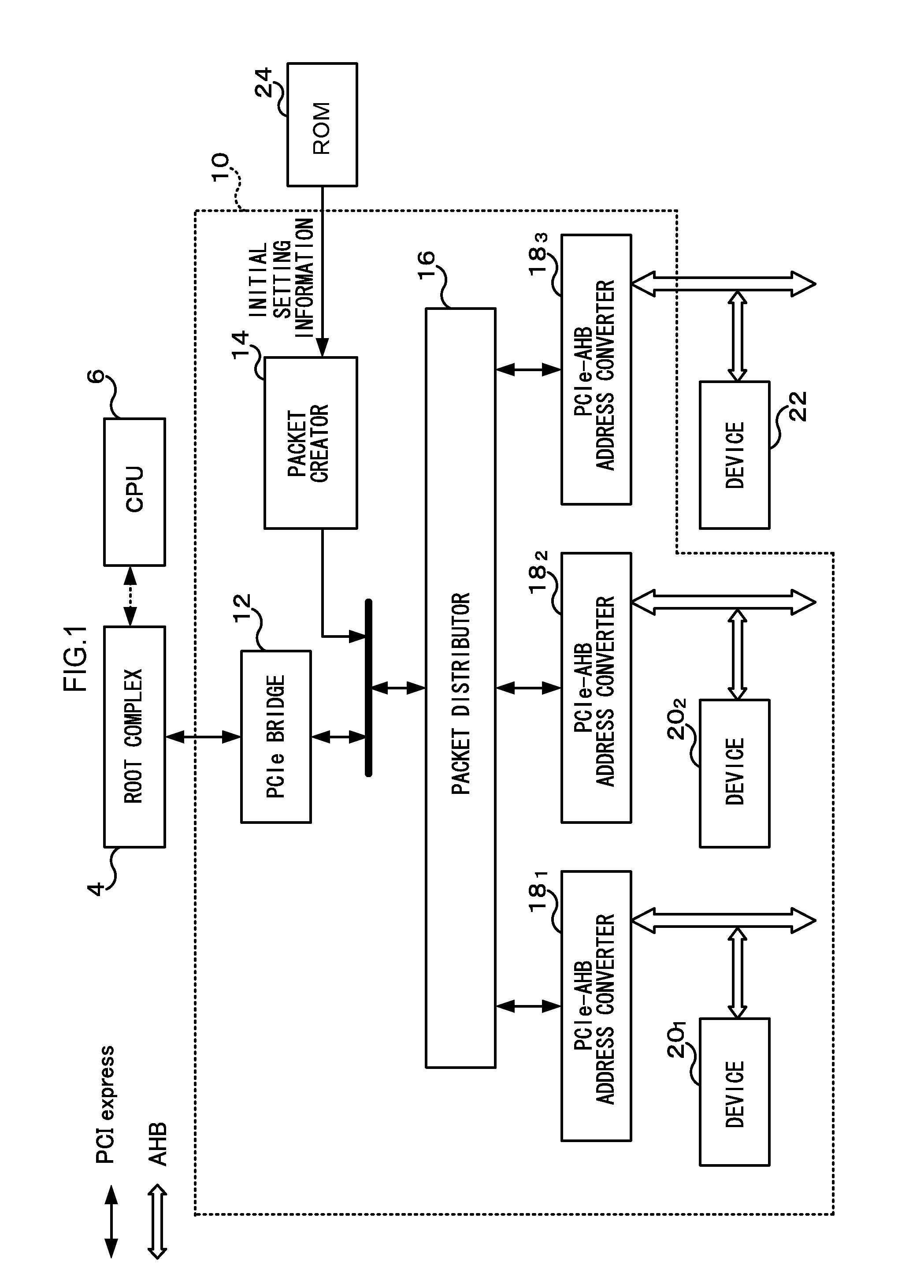
An information processing device includes: an address converter including a base address register in which address conversion information is stored and a conversion circuit that converts a PCI Express standard bus address of an inputted packet to a non-PCI Express standard bus address; and a packet generator. When first configuration information of a first device that has a device-unique unique address, is connected to a non-PCI Express standard bus and is unaware of the unique address is stored, the packet generator generates an address setting-use configuration write request packet, and when second configuration information including change information for changing the base address register to a base address register of a second device where at least one of an address width and an internal memory address is a device-unique unique value, the packet generator generates a change setting-use configuration write request packet and outputs the generated packet to the address converter.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
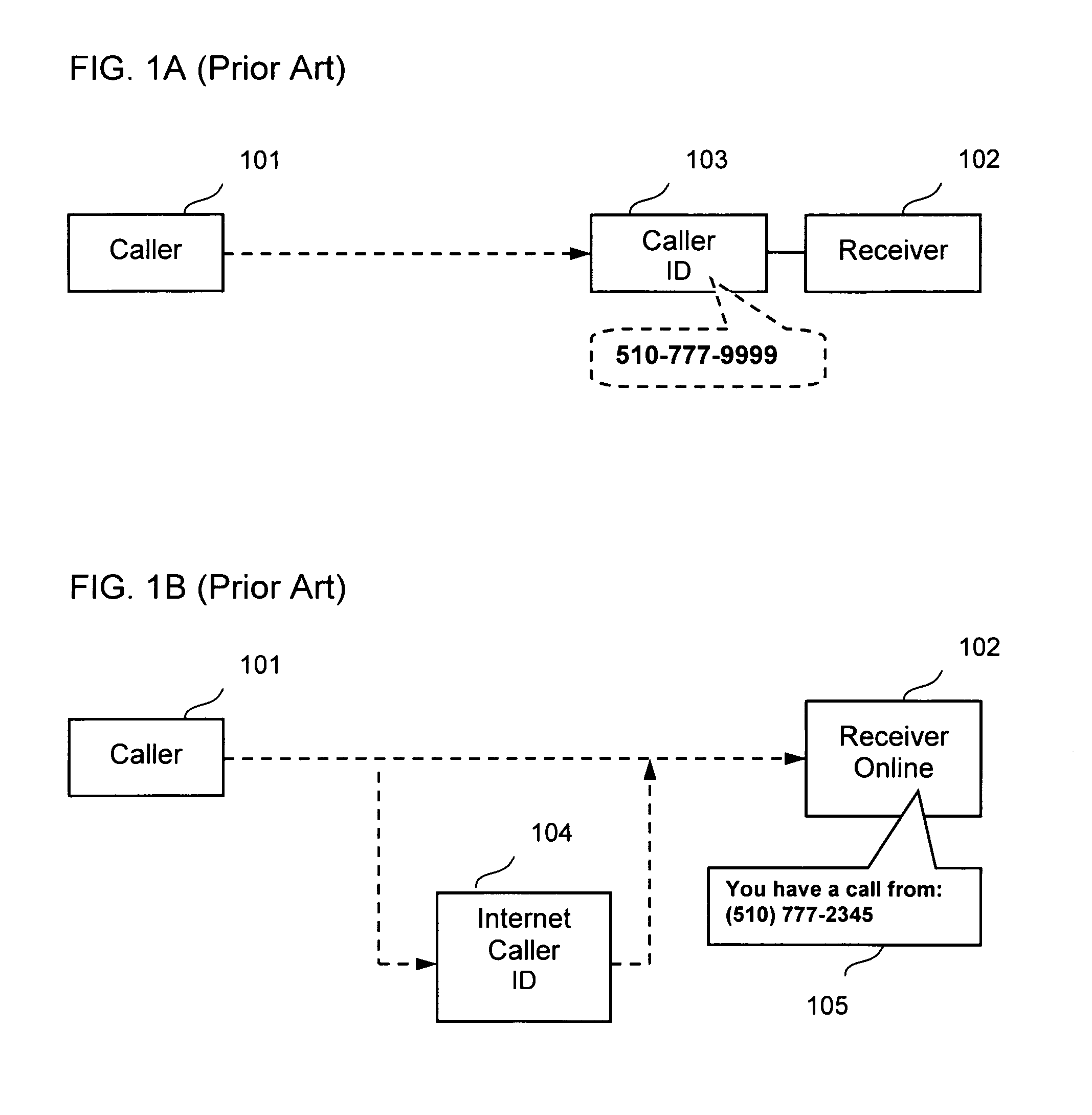
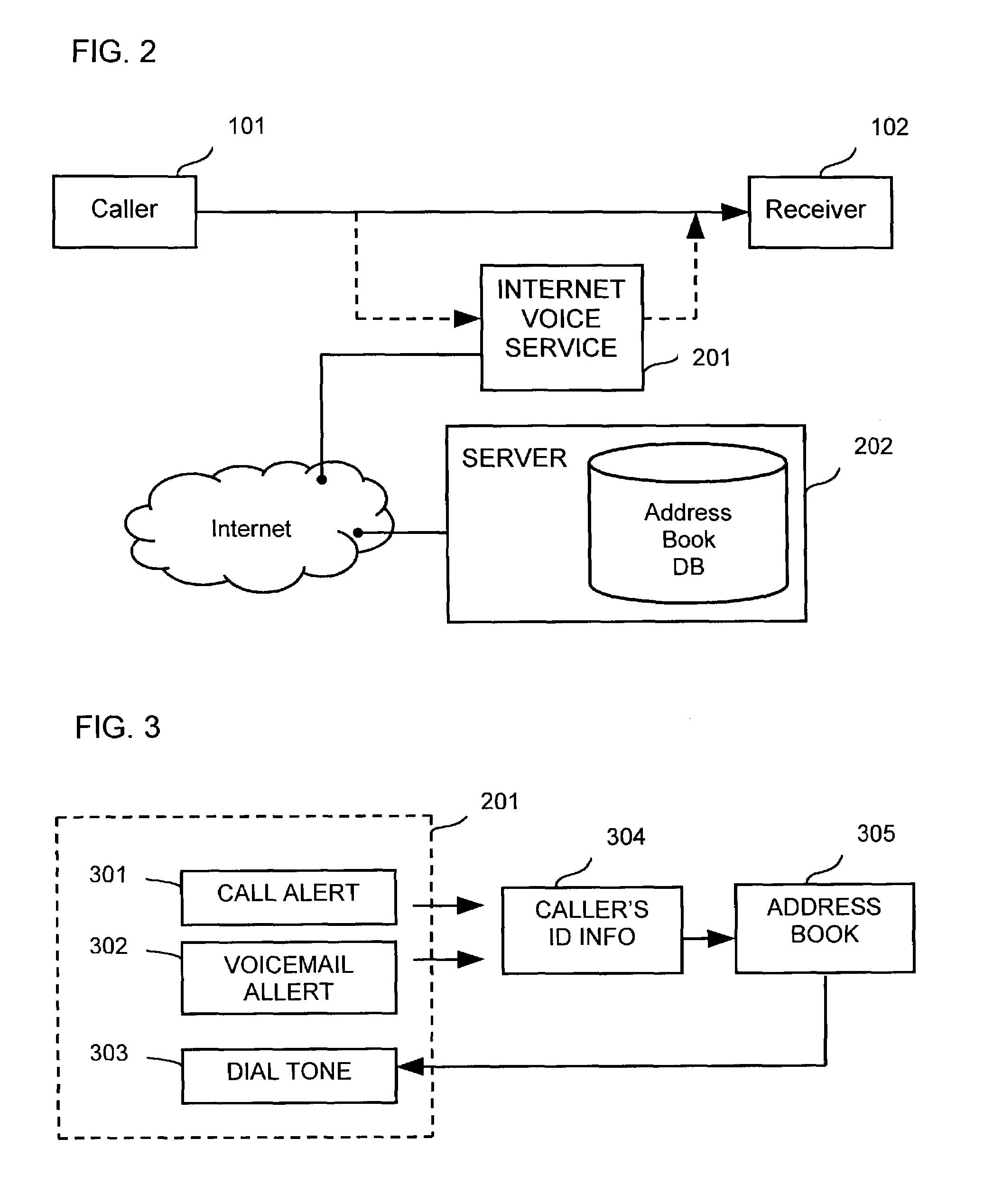
Method for populating a caller's information to a host-based address book
InactiveUS7068768B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersAddress bookOperating system
A method and apparatus is provided to populate a caller's information to a host-based address book automatically or by a single click on a virtual button included in a popup window or by a series of simple commands.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
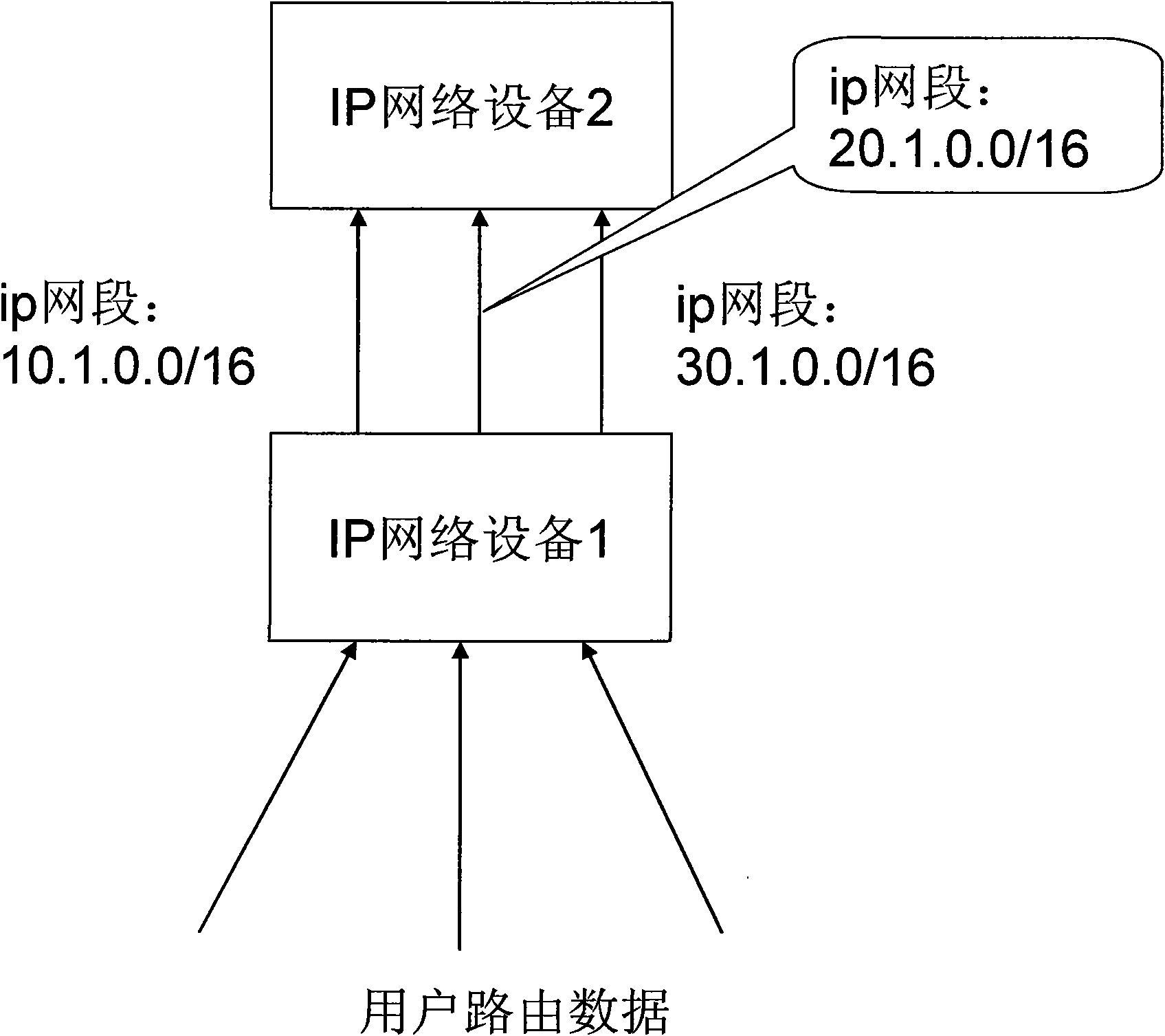
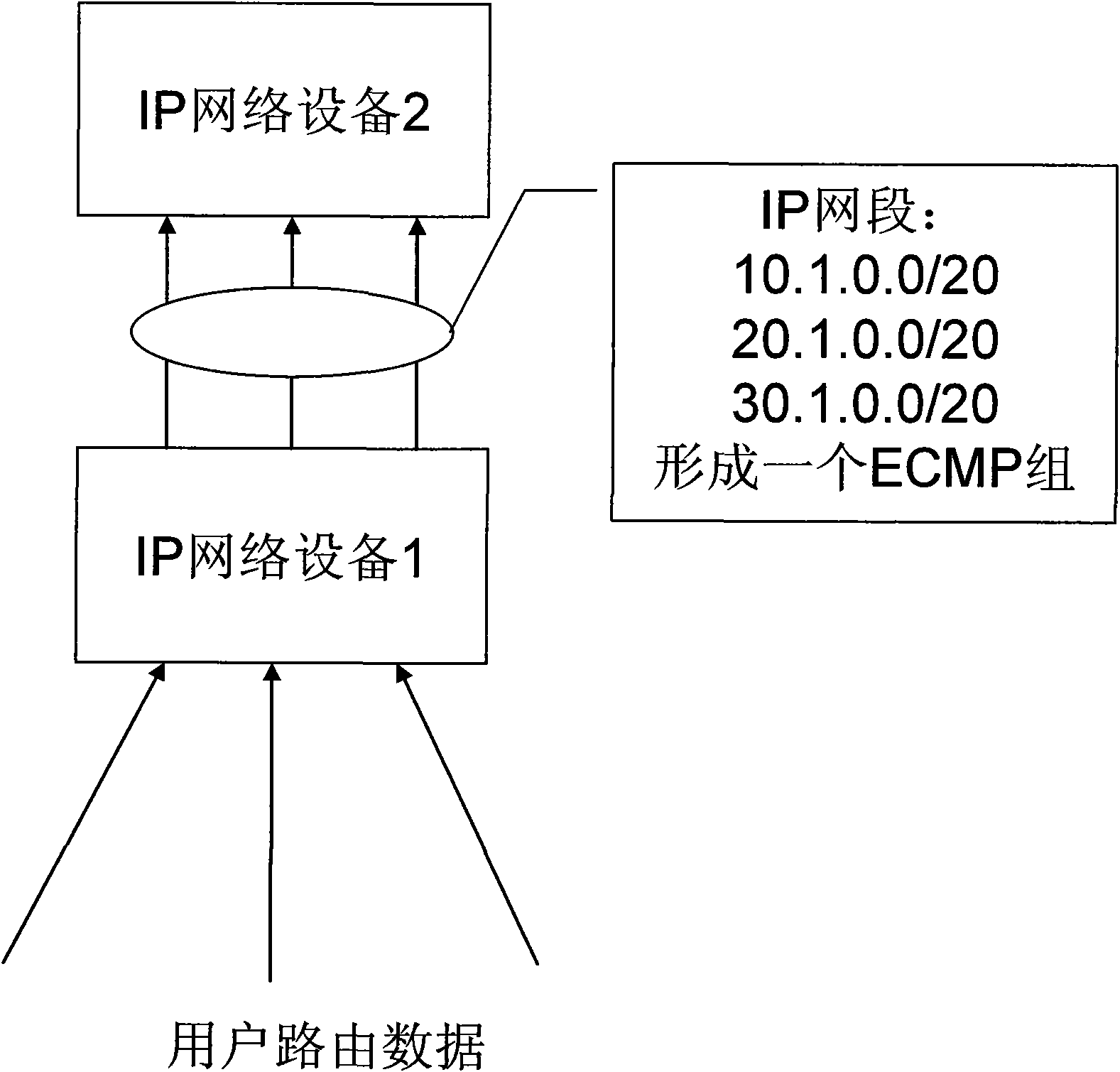
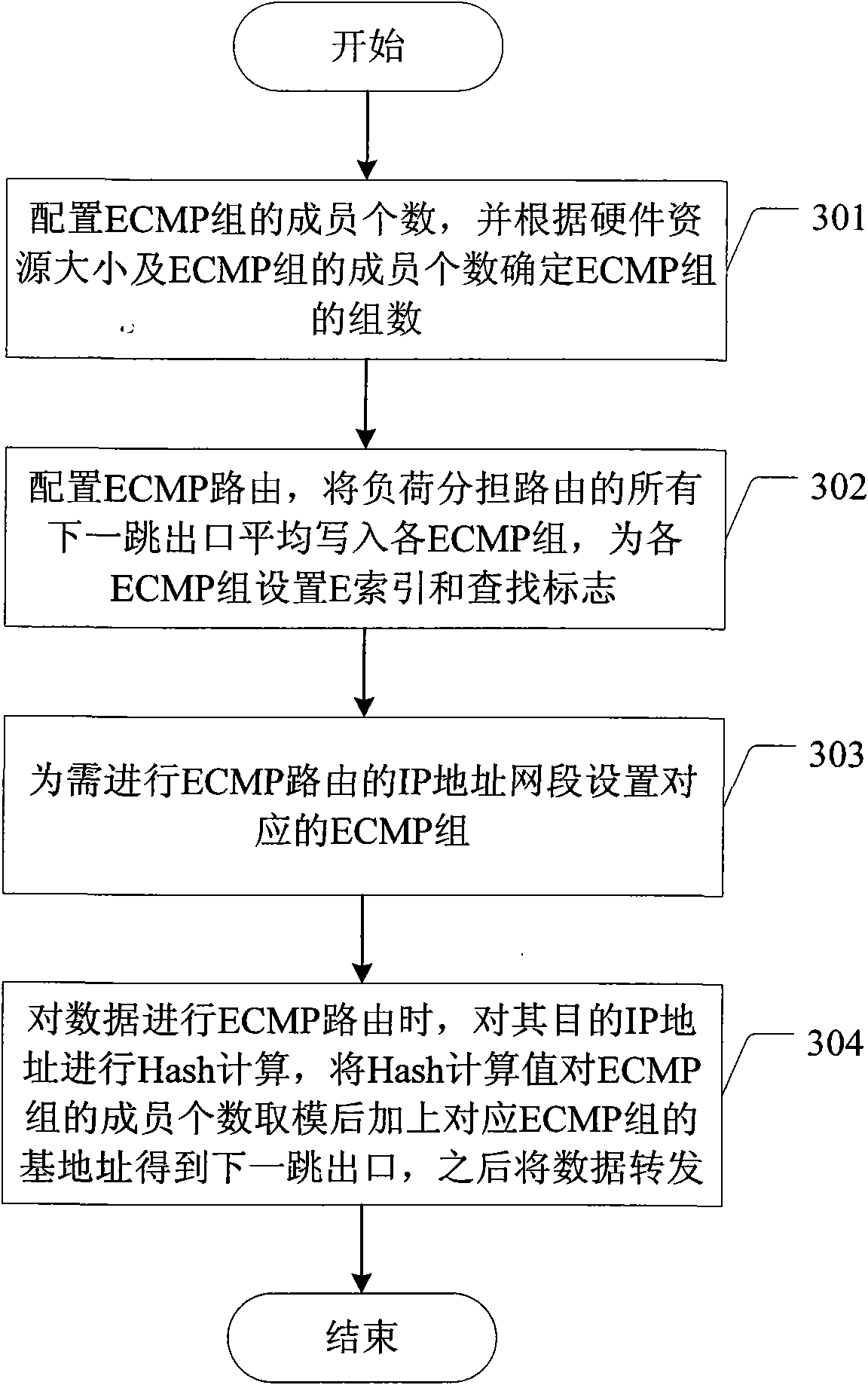
Method for realizing equal cost multipath of IP route and device
ActiveCN101572667ASolve the problem of routing load sharingEasy to routeData switching networksIp addressTerminal equipment
The invention discloses a method for realizing equal cost multipath of IP route and a device; wherein the device comprises an ECMP group generation module, a route ECMP configuration module, a route ECMP searching module; the corresponding method has the following steps: the ECMP group generation module configures the number of members of the ECMP group and determines the number of groups of the ECMP group; the route ECMP configuration module averagely writes all next hop outlets of a load sharing module into the ECMP groups and sets corresponding ECMP groups for IP address network segments which need ECMP routing; when ECMP routing is carried out on data, the route ECMP searching module carries out Hash calculation on target IP addresses of the data, and then uses the Hash calculation values to carry out modulo on the number of members of the ECMP groups and adds base addresses of the ECMP groups corresponding to the data to obtain the next hop outlet, and finally transfers the data from the next hop outlet. With the method and the device of the invention adopted, data can be conveniently, flexibly and uniformly routed to opposite terminal equipment.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Long Instruction Word Controlling Plural Independent Processor Operations
InactiveUS20080077771A1Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesIntegrated circuitStatus register
This invention is a data processing apparatus which operates on instruction controlling plural processor actions. Each instruction includes a data unit section and a data transfer section. These instruction sections are independent and may include differing options. In the preferred embodiment, each instruction is 64 bits. The data unit section includes a data operation field that indicates the type of arithmetic logic unit operation and six operand fields. The six operand fields include four source data register fields and two destination register fields. The data unit (110) includes a multiplication unit (220) and an arithmetic logic unit (230). The data unit (110) may include a barrel rotator (235) for one input of the arithmetic logic unit (230). The rotated data may be stored in the first destination register instead of the multiply result. The address unit (120) operations according to the data transfer operation field. This could be a load, a store or a register to register move. Operations may be conditional based upon conditions stored in a status register (210). The status register (210) is set by a prior output of the arithmetic logic unit (230) and the instruction may specify some of the status bits protect from change. The address unit (120) preferably includes a plurality of base address registers (611), a full adder (615) and a left shifter (614). The full adder (615) may add an index as scaled by the left shifter to the base address or subtract the scaled index from the base address. The full adder (615) output may update the base address register (611), either before supply of the address or following supply of the address. The index may be recalled from an index register (612) or an immediate value. In the preferred embodiment of this invention, the data unit (110) including the data registers (200), the multiplication unit (220) and the arithmetic logic unit (230), the address unit (120) and the instruction decode logic (250, 660) are embodied in at least one digital image / graphics processor (71, 72, 73, 74) as a part of a multiprocessor (100) formed in a single integrated circuit used in image processing.
Owner:GUTTAG KARLM +2
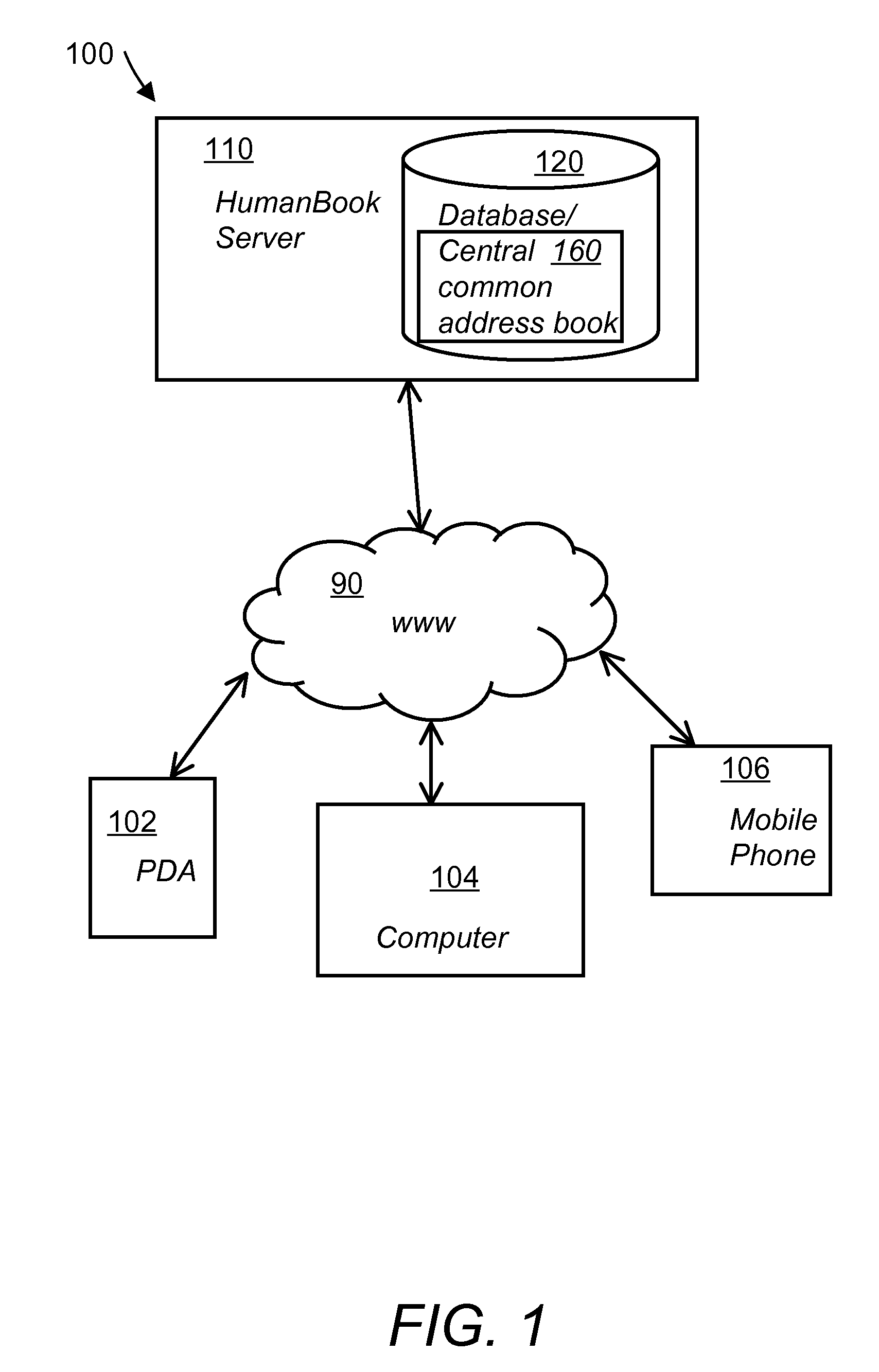
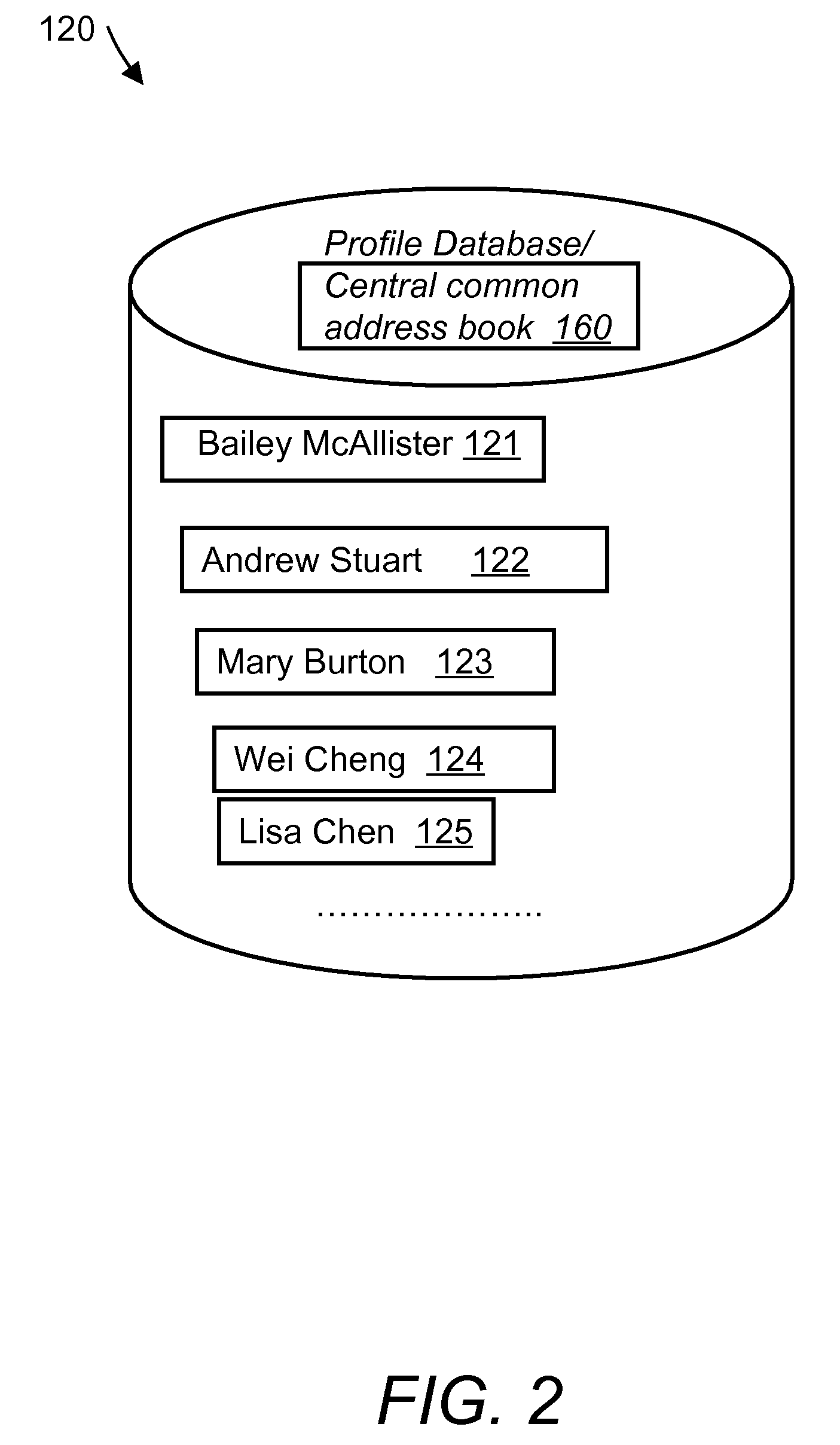
System and method for a web-based address book
An online system and a method for a web-based address book that allows collaborative updating and synchronization of the listed persons' contact information. The method includes creating profile templates for each person within a group and storing these profile templates in a central database. Next, populating the profile templates with publicly available basic information and then publishing the public profile information in the web-based address book. Users login into the address book website, update their own profile information and upload their personal address book. The system then cross-correlates and matches contact information retrieved from users' personal address books to the contact information listed in other persons' profiles.
Owner:HUMANBOOK
Method and system for dynamically assigning addresses to an input/output device
InactiveUS6185638B1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingDirect-access storage deviceComputerized system
Disclosed is a system for dynamically assigning alias addresses to base addresses referencing an I / O device, such as a direct access storage device (DASD). In the system, at least one base control block indicates a base address and a plurality of alias control blocks indicate a plurality of alias addresses. Each control block is associated with an address for addressing an I / O device. A processing unit, such as a host computer system, processes at least one alias control block associated with the I / O device and determines a base control block associated with the I / O device with which the alias control blocks are associated. The processing unit then binds at least one alias control block to the determined base control block. The bound base and alias control blocks provide different addresses to address the same I / O device. Further, the bound base and alias addresses address the same I / O device for subsequent I / O operations until the processing unit detects a reassignment of the association of base and alias addresses.
Owner:IBM CORP
Efficient Streaming of Un-Aligned Load/Store Instructions that Save Unused Non-Aligned Data in a Scratch Register for the Next Instruction
InactiveUS20070106883A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsGeneral purposeLoad instruction
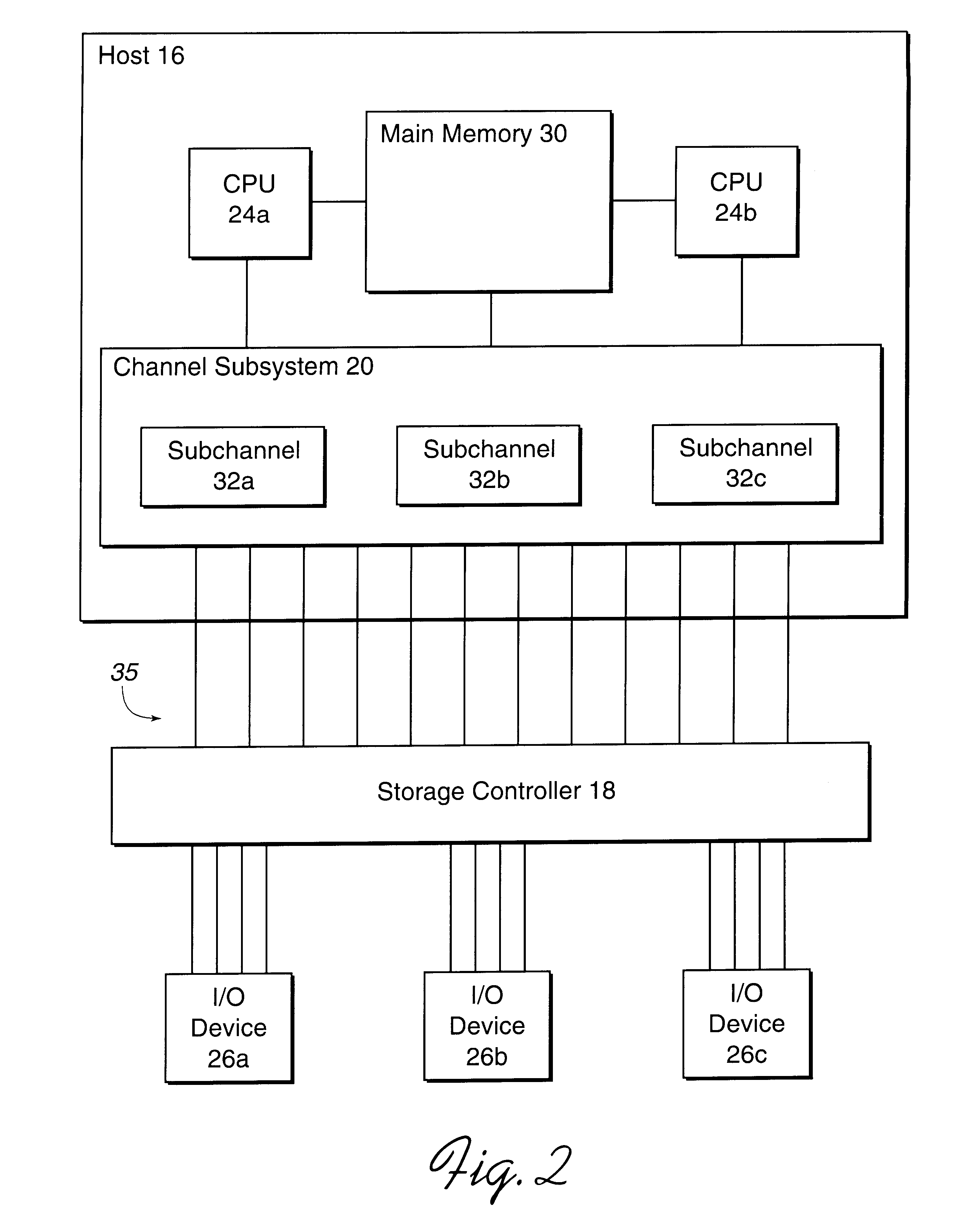
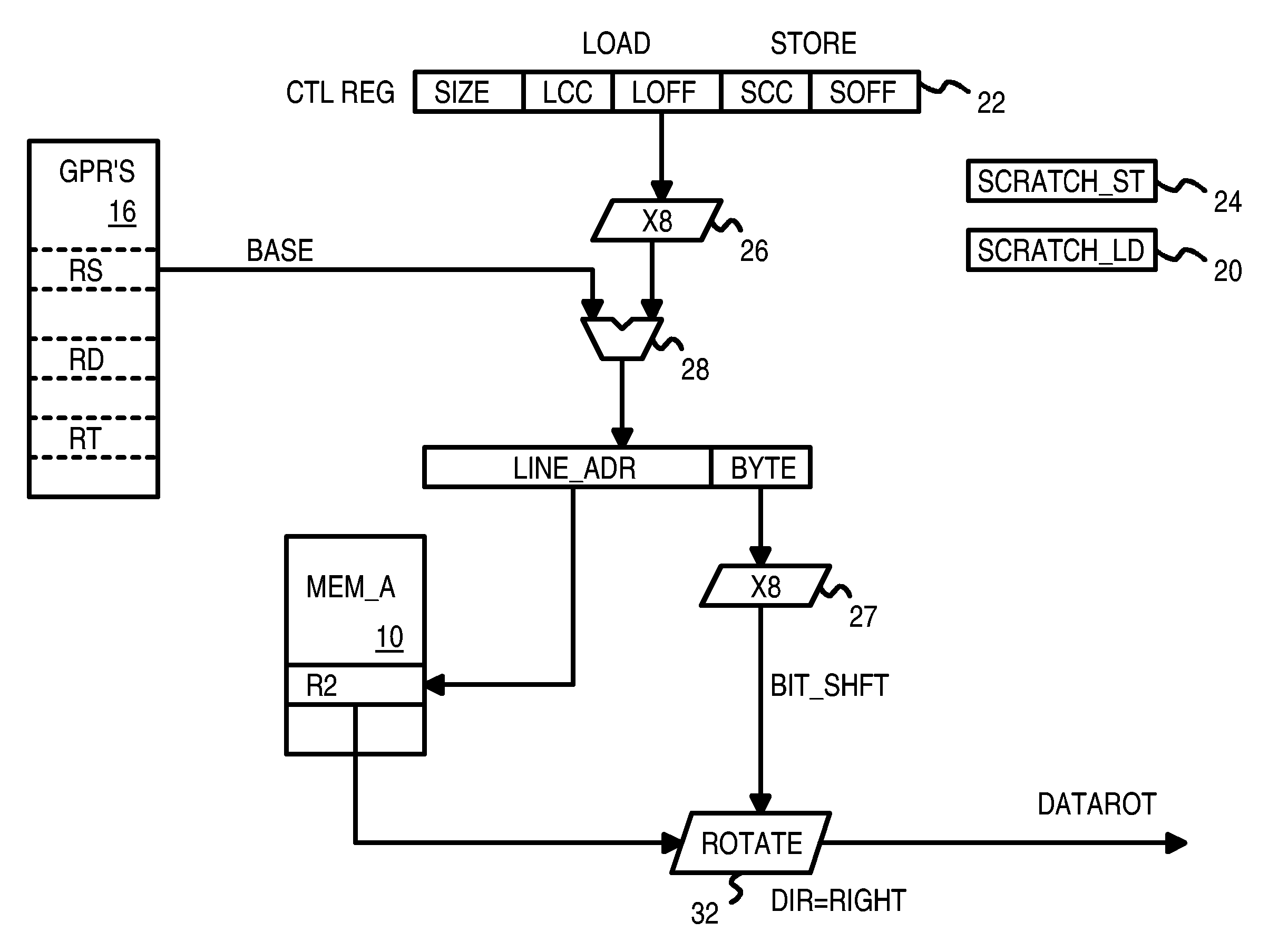
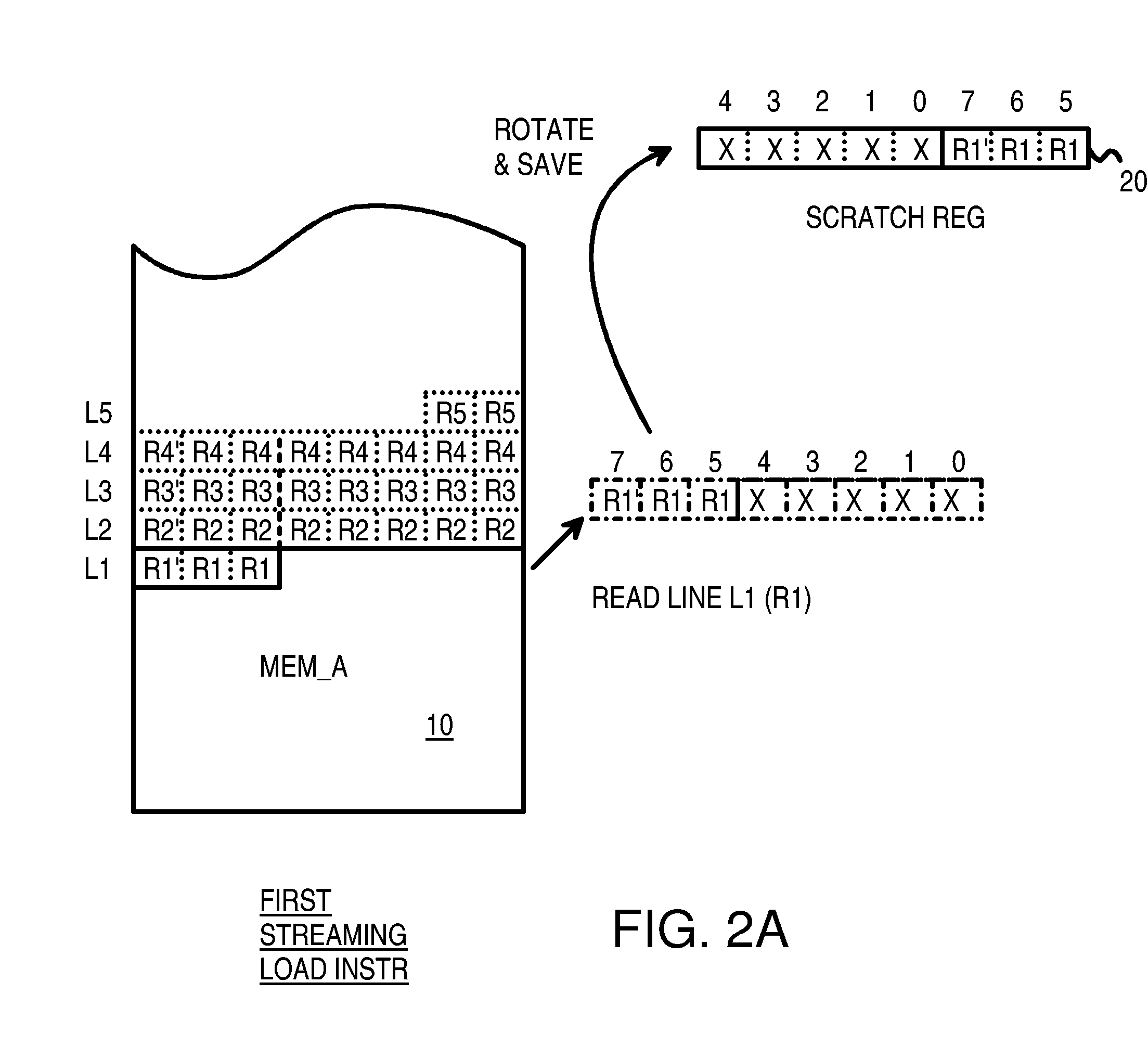
A memory block with any source alignment is streamed into general-purpose registers (GPRs) as aligned data using a streaming load instruction. A streaming store instruction reads the aligned data from the GPRs and writes the data into memory with any destination alignment. Data is streamed from any source alignment to any destination alignment. Memory accesses are aligned to memory lines. The data is rotated using the offset within a memory line of the base address. The rotated data is stored in a scratch register for use by the next streaming load instruction. Rotated data just read from memory is combined with rotated data in the scratch register read by the last streaming load instruction to generate result data to load into the destination GPR. Streaming condition codes are set when the block's end is detected to disable future streaming instructions. Aligned memory accesses at full bandwidth read the un-aligned block.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
Method and system for prefetching data
InactiveUS6918010B1Eliminate and greatly reduce disadvantageEliminate and greatly reduce and problemMemory adressing/allocation/relocationNext instruction address formationArray data structureParallel computing
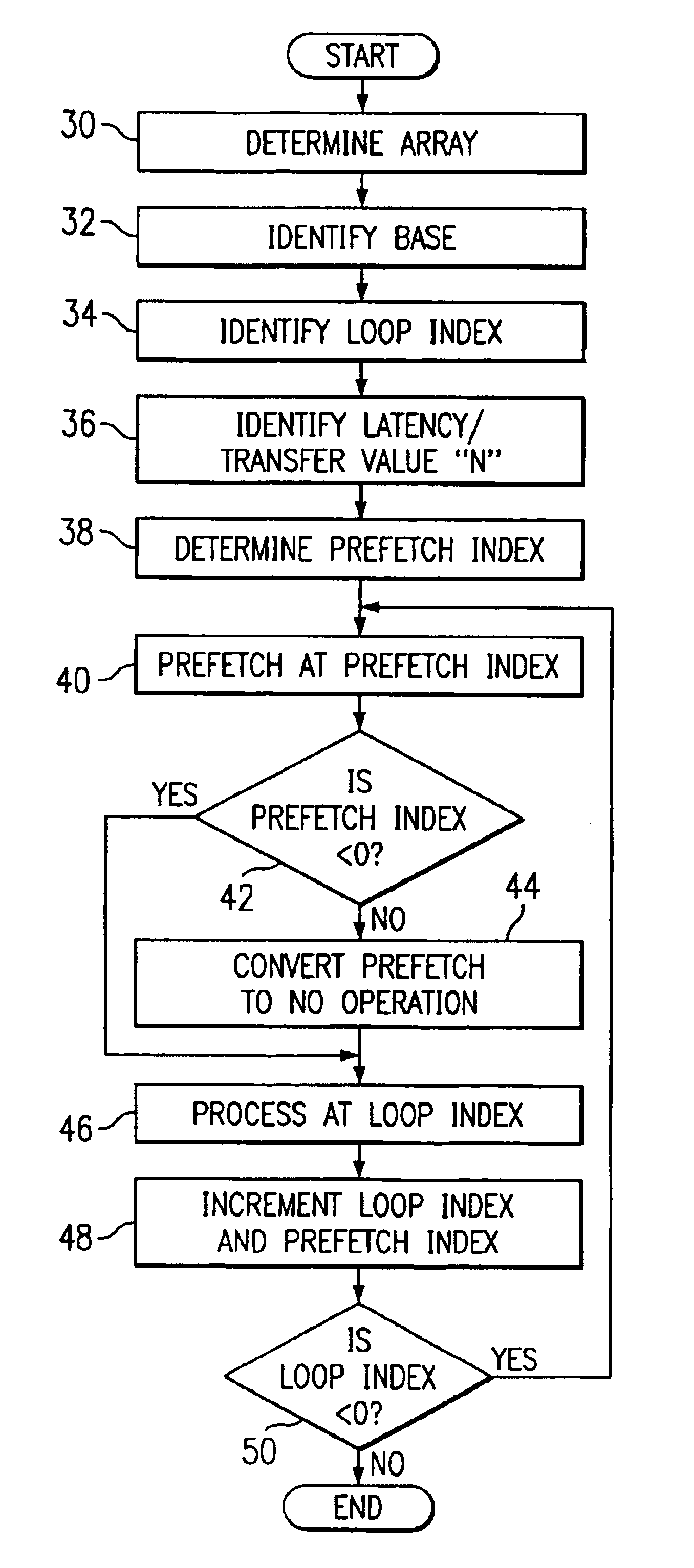
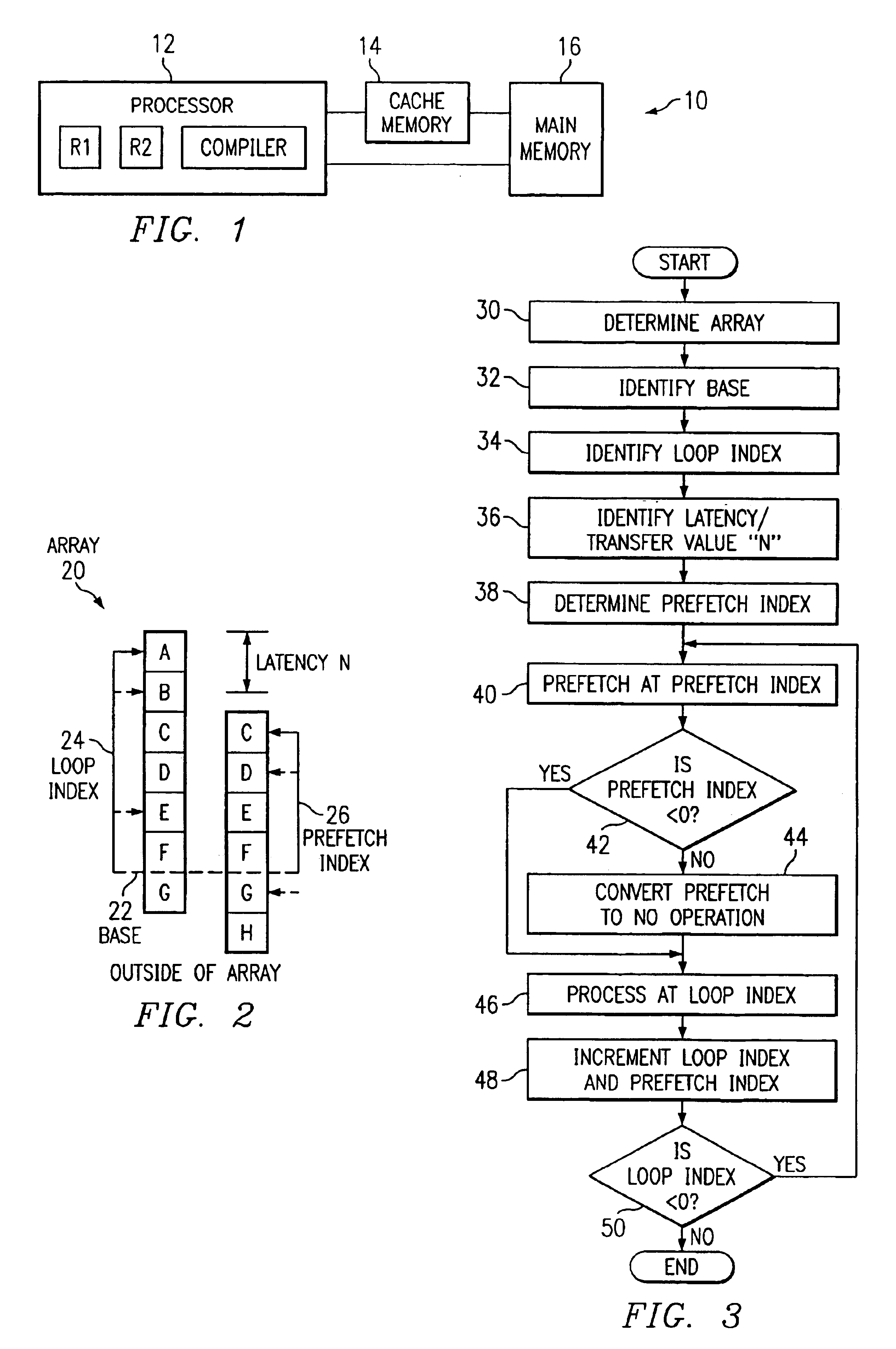
In prefetching cache lines from a main memory to a cache memory, an array of memory locations to be prefetched is determined and a base address indicating a highest address in the array is identified as well as a loop index used to point to the first address in the array. A prefetch index, which is the loop index plus a latency / transfer value, is used to prefetch memory locations as the array is processed. After a memory location is prefetched and initialized, the loop index and the prefetch index are incremented. The prefetch index is compared to a threshold value. If the prefetch index is less than the threshold value, then the next memory location in the array is prefetched and the prefetch index is again incremented and compared to the threshold value. If the prefetch index is equal to or greater than the threshold value, then the prefetch instruction is converted to a no operation instruction to prevent memory locations outside of the array from being prefetched during the processing of the array.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
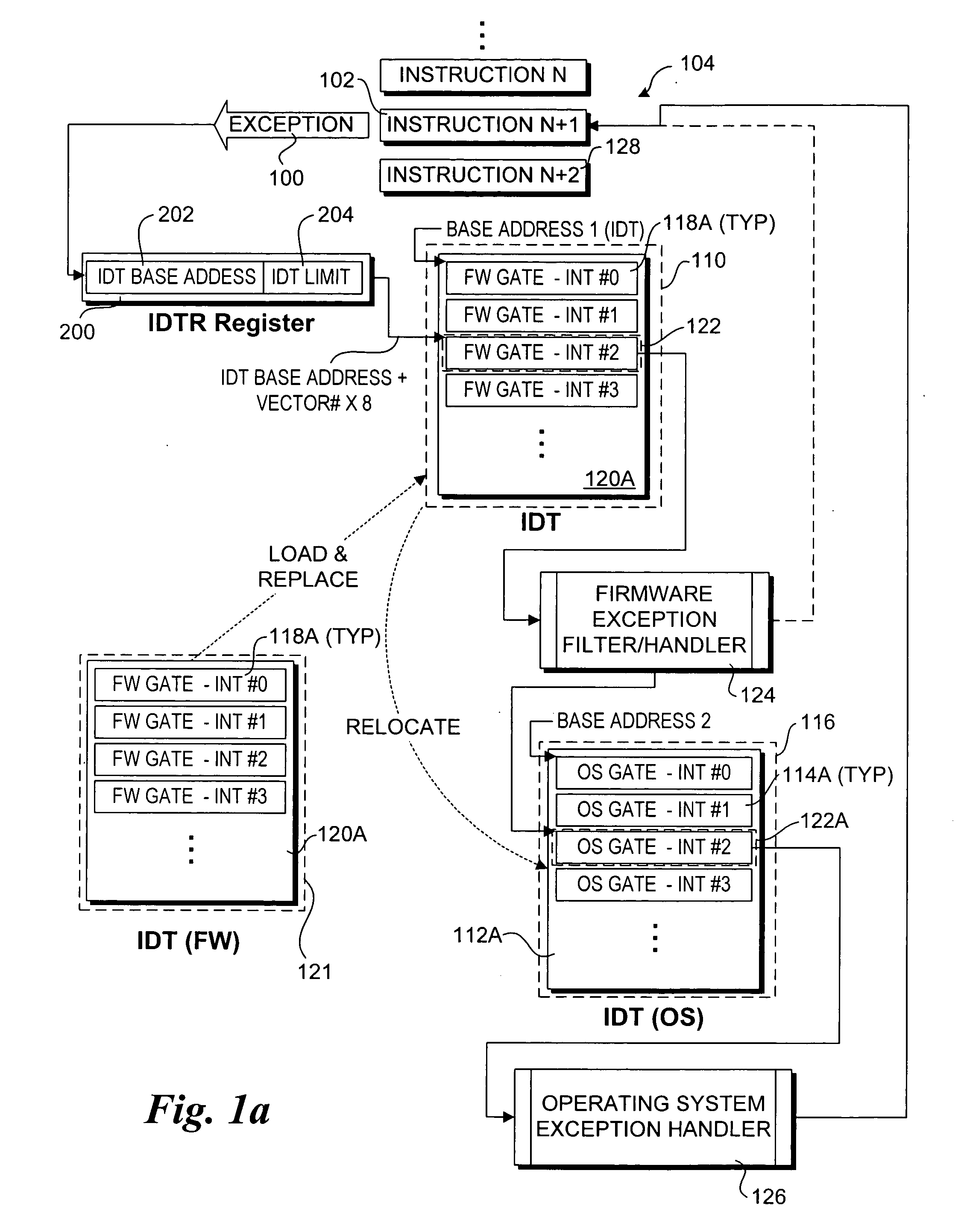
Method and system for firmware-based run time exception filtering
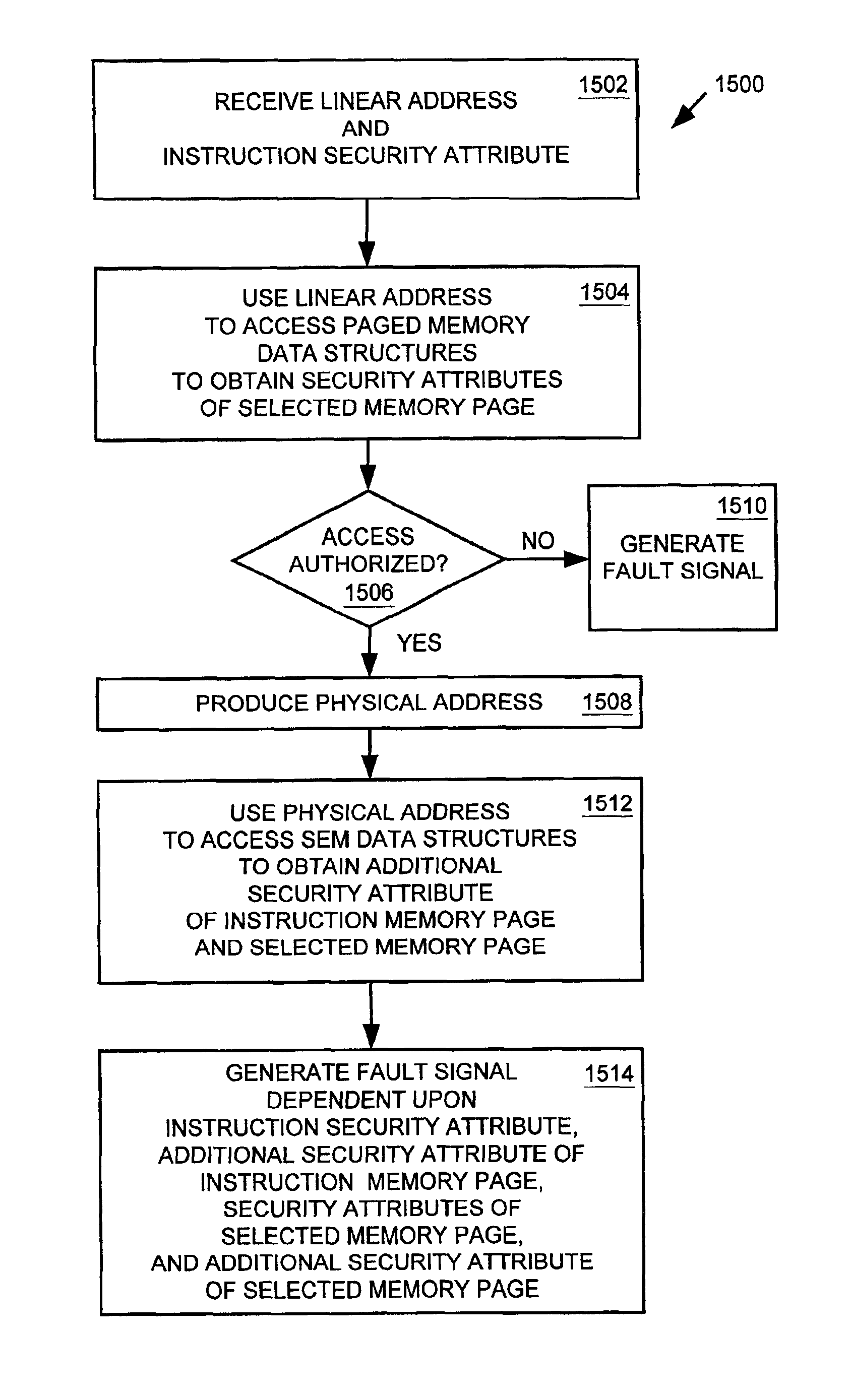
InactiveUS20050149711A1Program initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsBase addressPhysical address
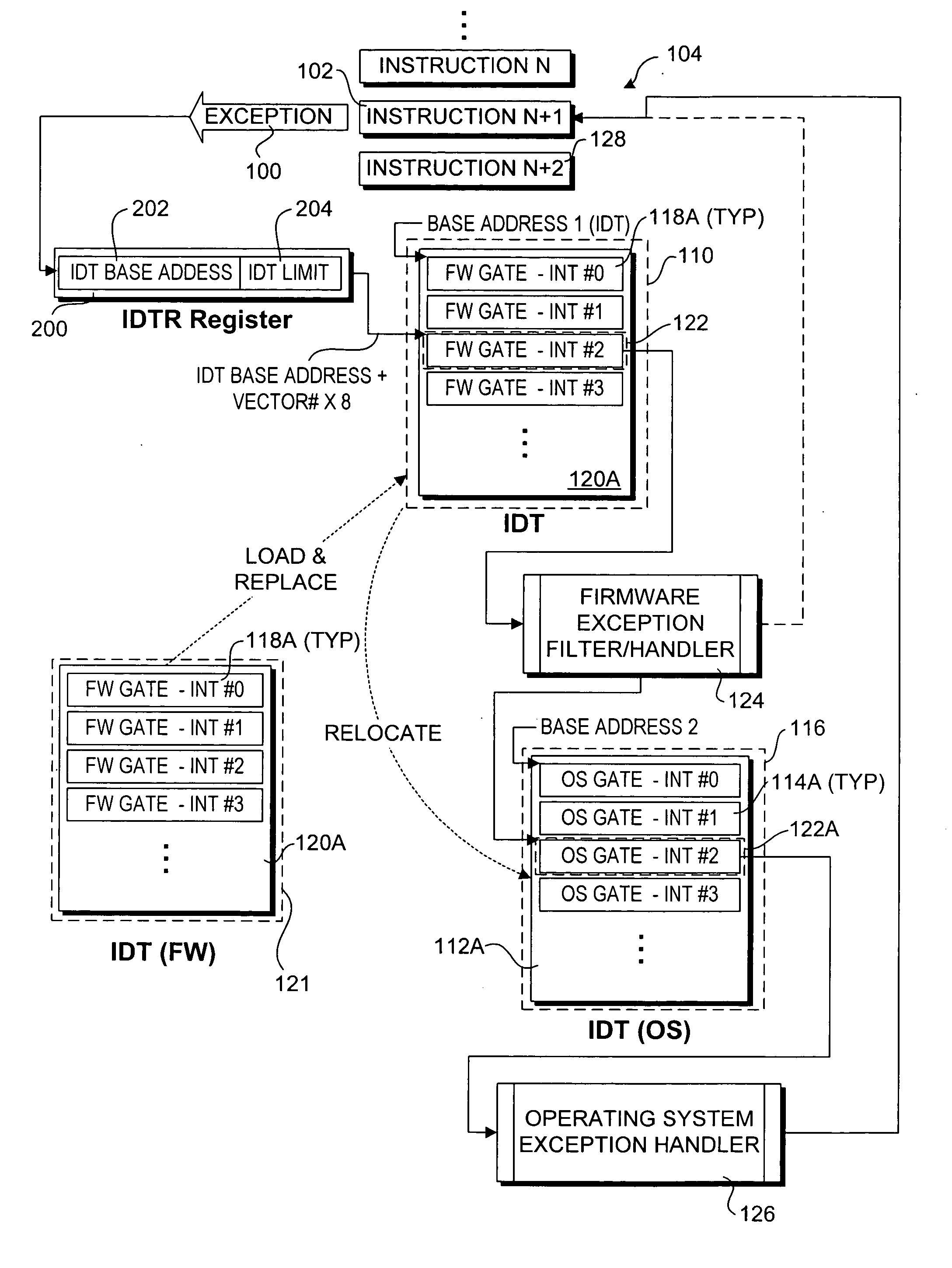
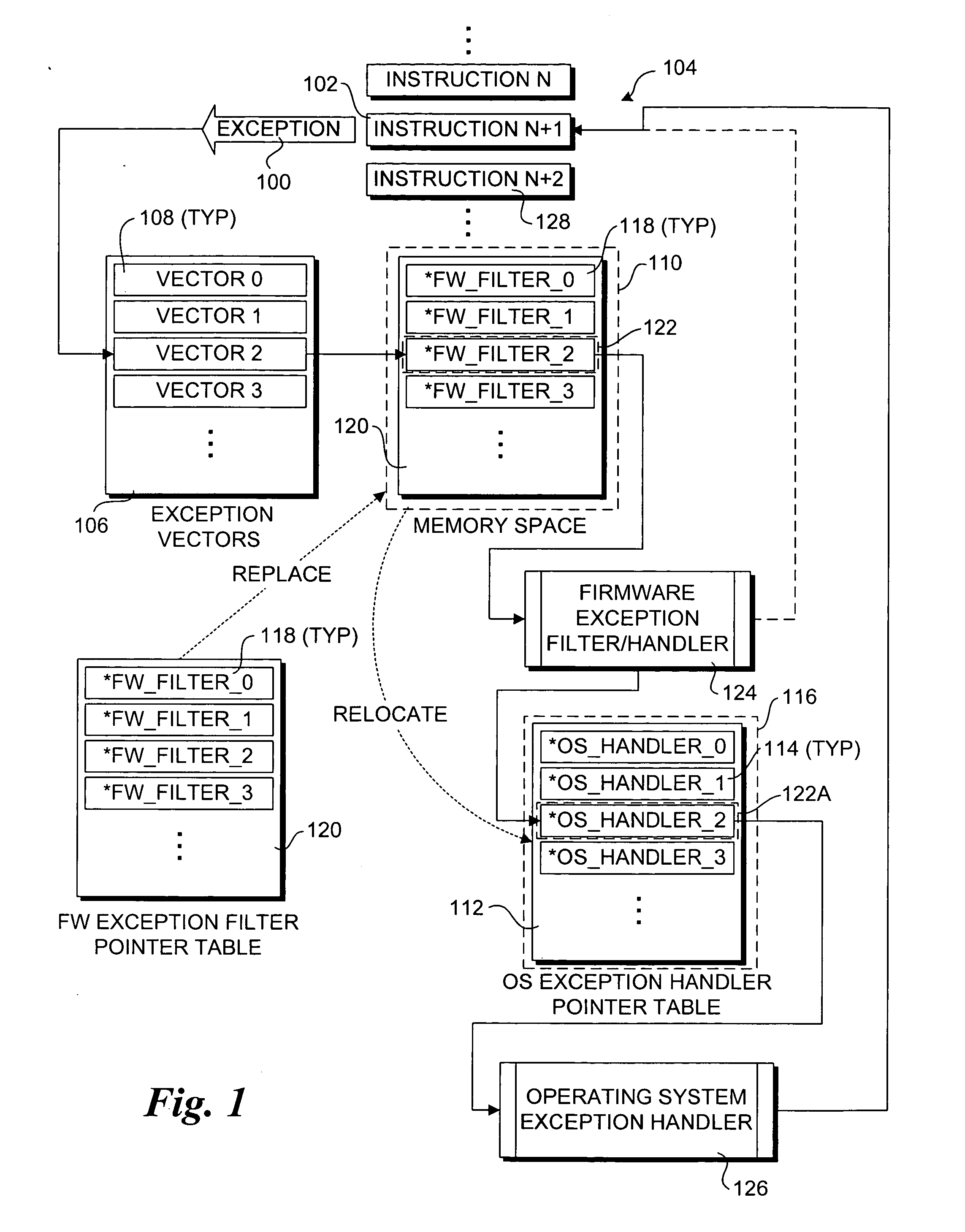
A method and system for filtering and / or handling operating system (OS) runtime exceptions using firmware-based components. OS-based exception handling components and corresponding pointers, as applicable, are set up in a conventional manner during the OS load. The OS-based components are then physically or logically relocated (moved from a physical to virtual address in one embodiment, re-referencing a base address for the OS-based components in another embodiment) and physically or logically replaced with corresponding firmware-based exception filters / handler components. In response to a runtime exception, the execution stream (i.e., instruction pointer) is vectored to a firmware-based exception filter / handler that performs exception filtering and / or handling for the exception. Upon completion, the execution stream may be re-vectored to a corresponding OS-based exception handler. A firmware-based exception filter / handler may be used to augment an OS-based exception handler, or replace it.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Web-based address book
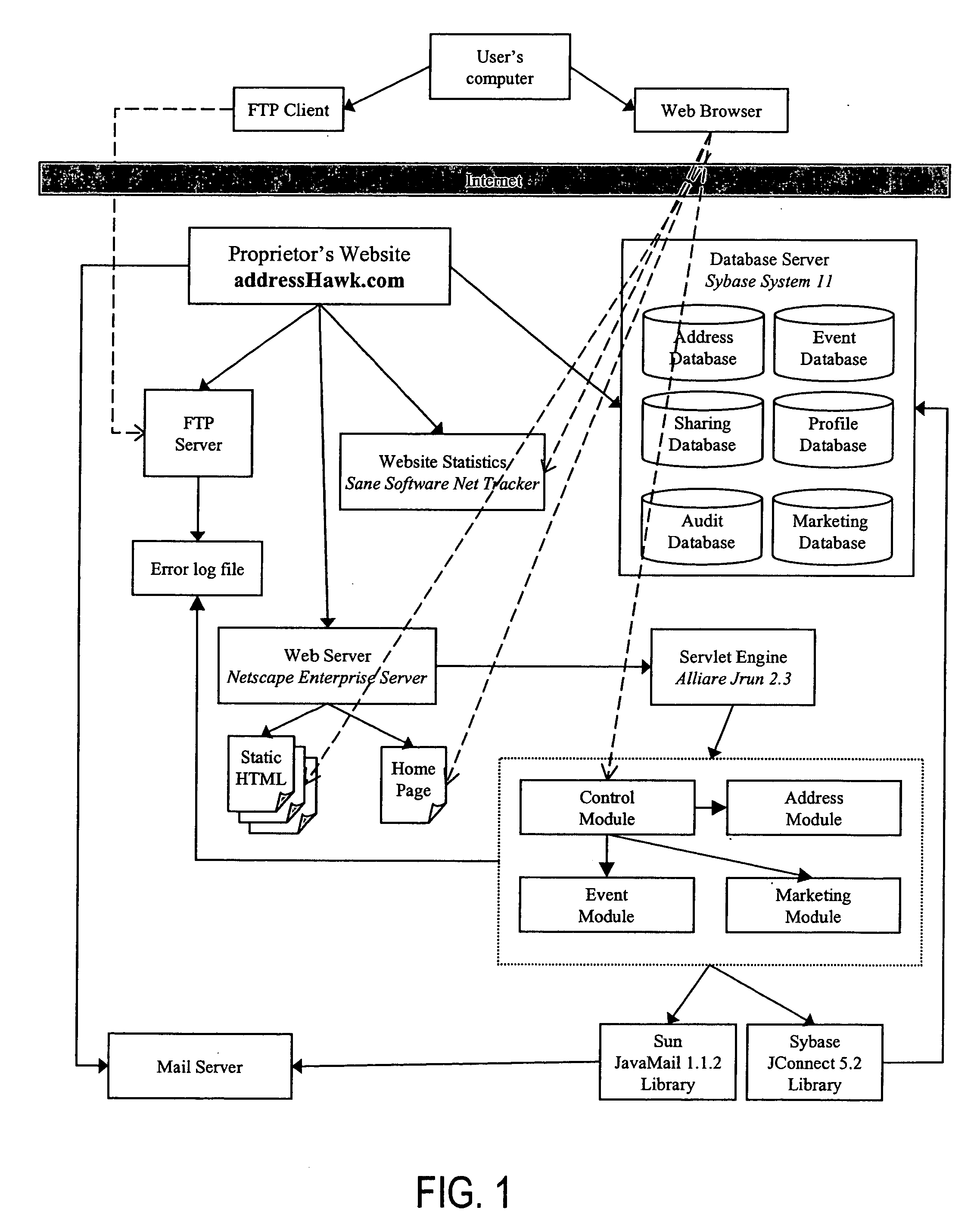
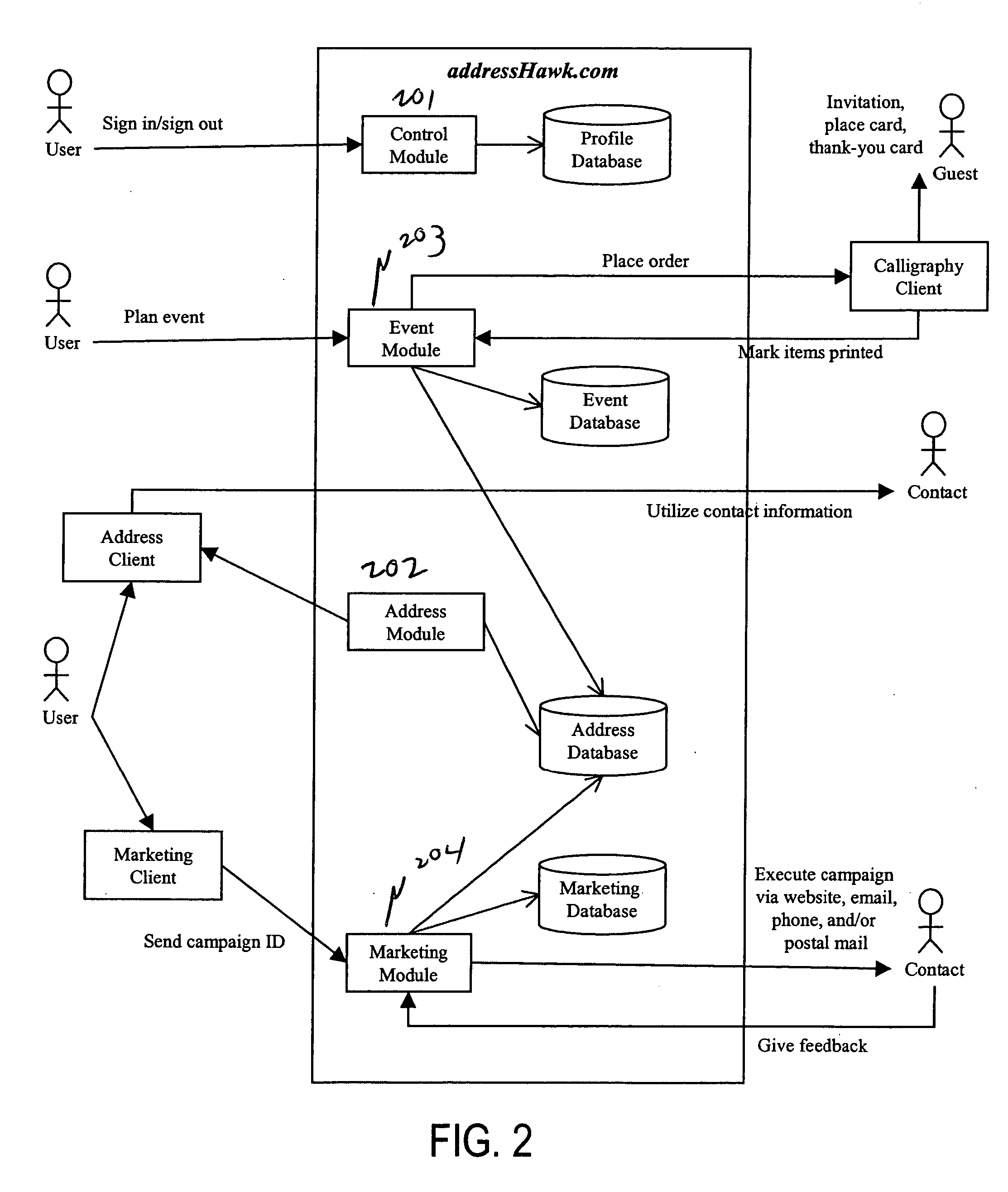
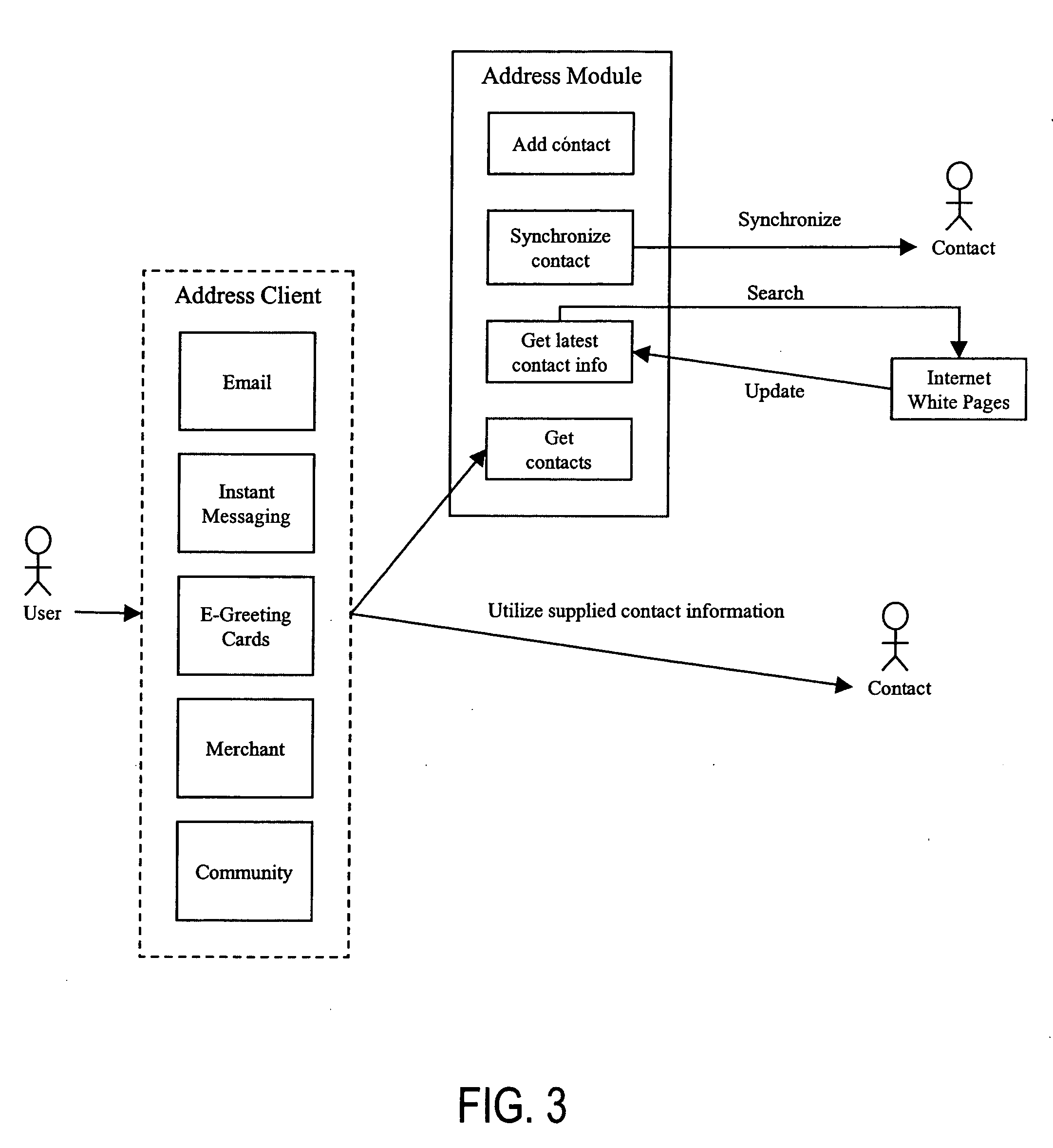
InactiveUS20050075925A1Value maximizationMore serviceMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsNegative feedbackAddress book
Disclosed is an Internet-based address book that enables individuals (“users”) or (“members”) to use people (“contacts”) from their address book for event planning, purchasing gifts, marketing, and anything else anyone dreams up. The system includes the following modules: an address book whose information can be utilized by any client for any purpose, a full-fledged event planner suitable for planning formal events such as weddings, a marketing module that allows people to refer products and information to people who would be interested, and a recipient transaction module that makes recipient-based transactions such as gifts and money transfer assessable and convenient. Features of the event planner include automatic generation and reprinting of invitations, placement cards, and thank-you cards with proper etiquette. Features of the marketing module includes the ability (a) to restrict the contacts that can be marketed to based on demographics, negative feedback, missing requisite information, or other reasons, (b) to reward users that market merchandise to their contacts with a discount on the merchandise itself, and (c) to bundle all the marketing sent by all users to one contact and deliver it as a single consolidated information package. Features of the recipient transactions module include the ability to (a) send one person a gift through postal mail or email, (b) send many people a gift, and (c) allow many people to purchase a single gift together.
Owner:SASH YAAKOV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com