Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1546 results about "Transfer operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
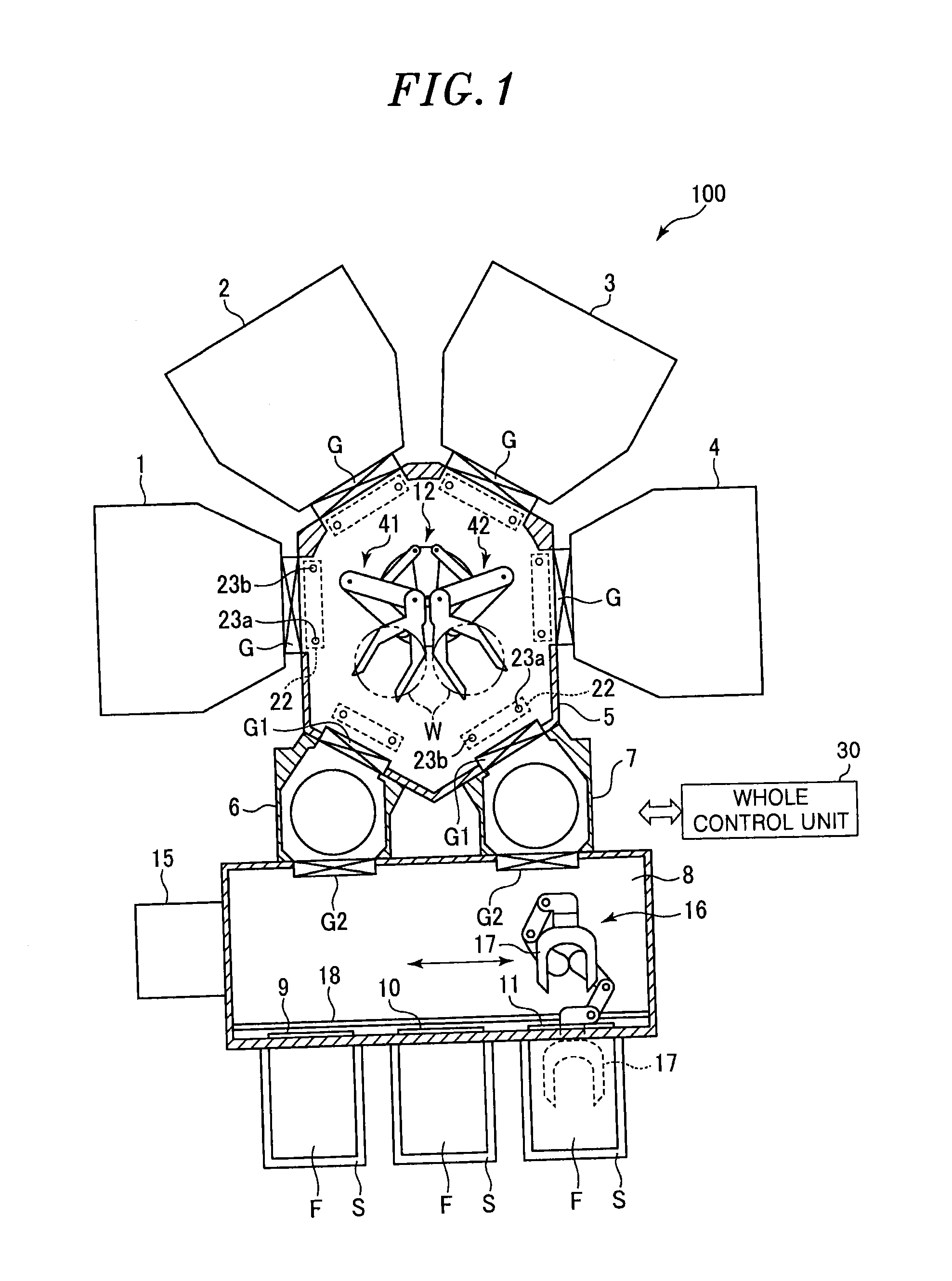
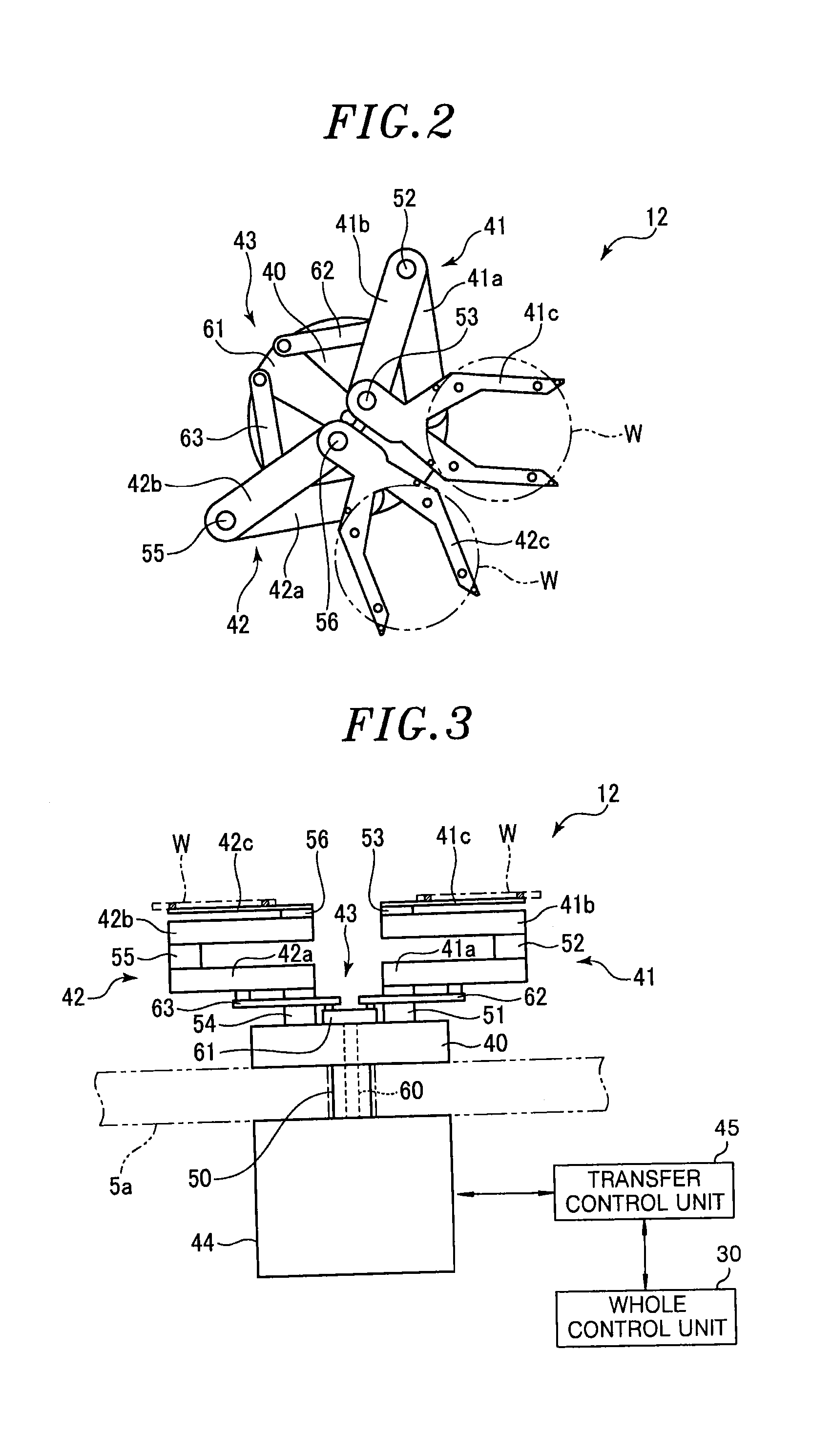
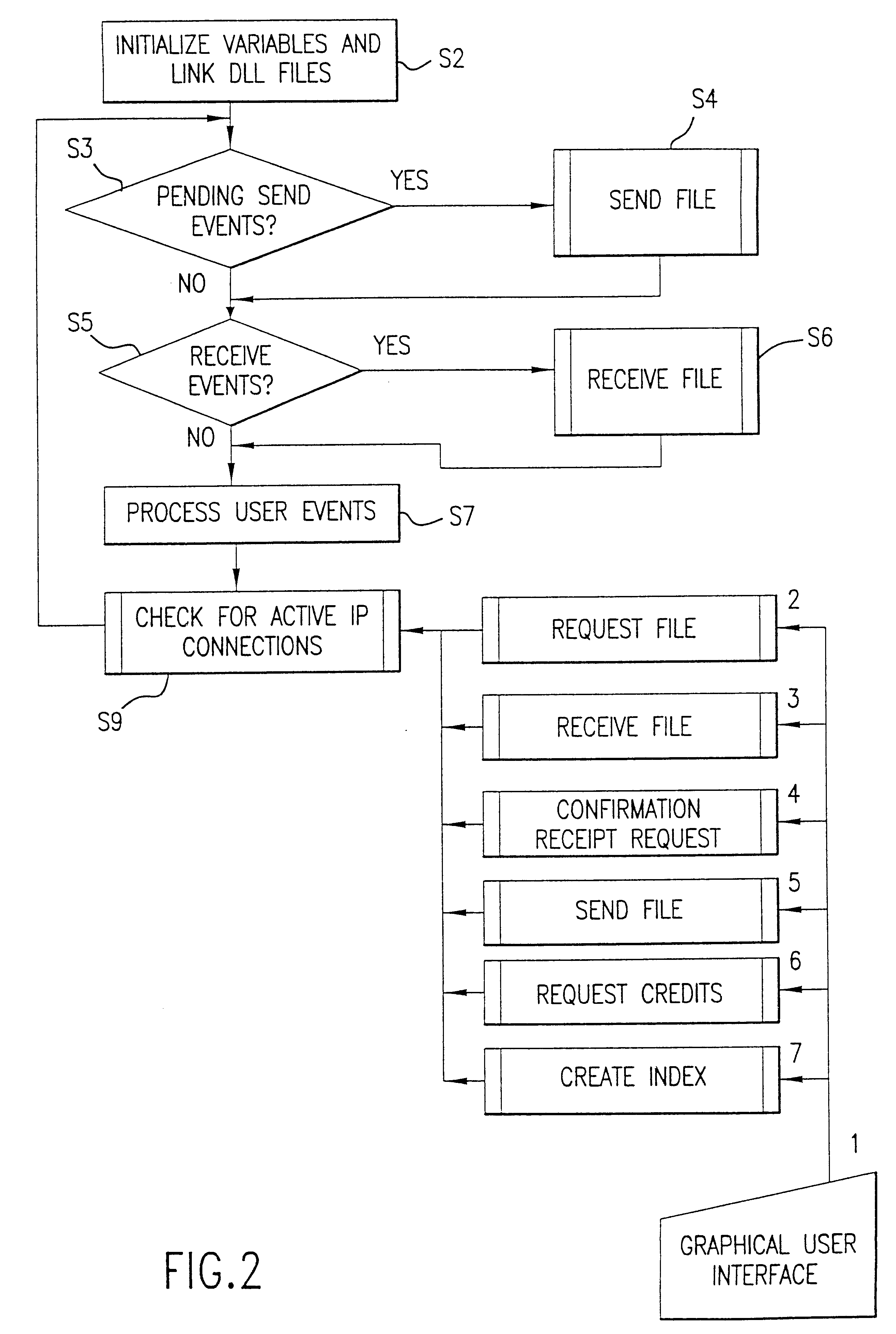
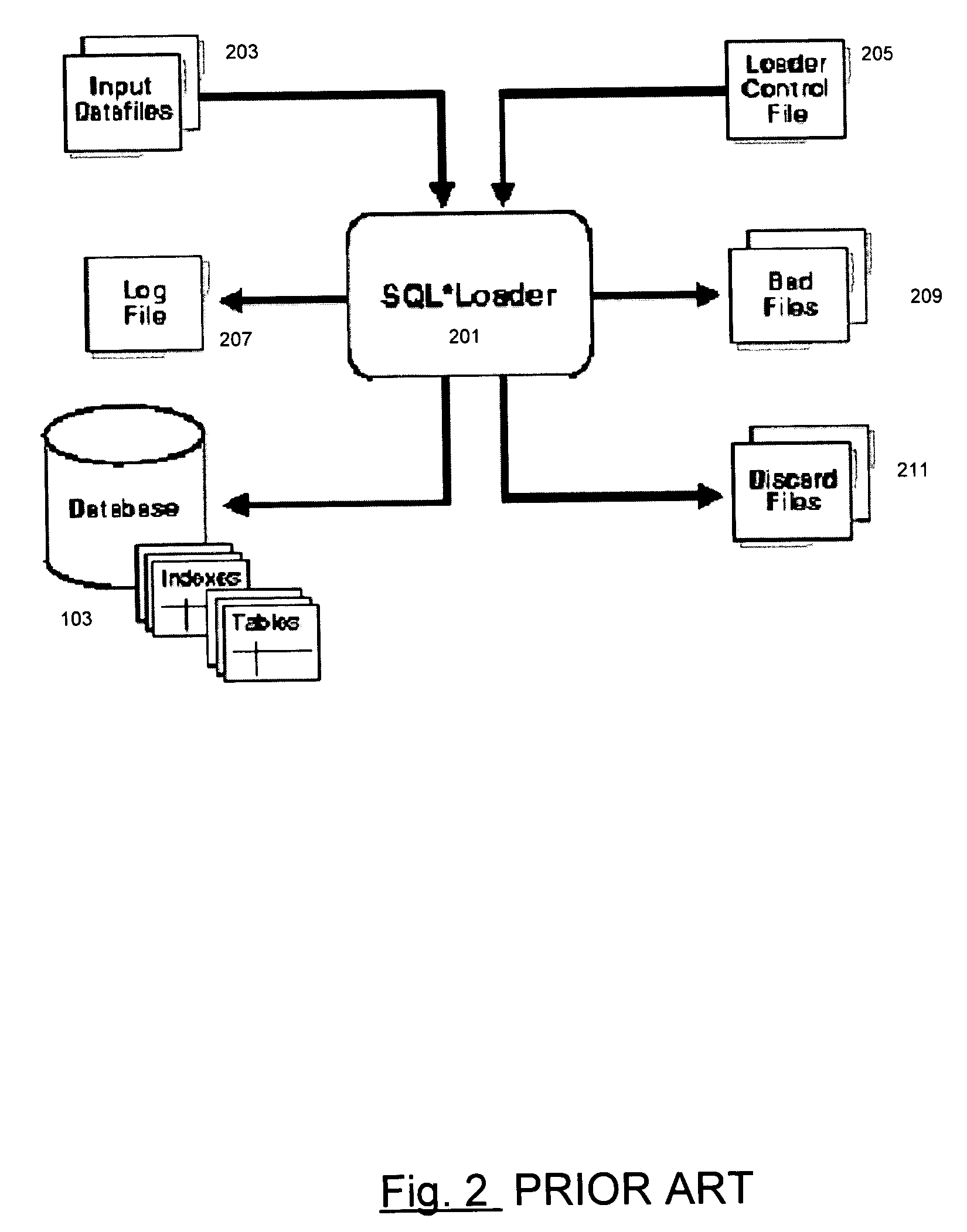
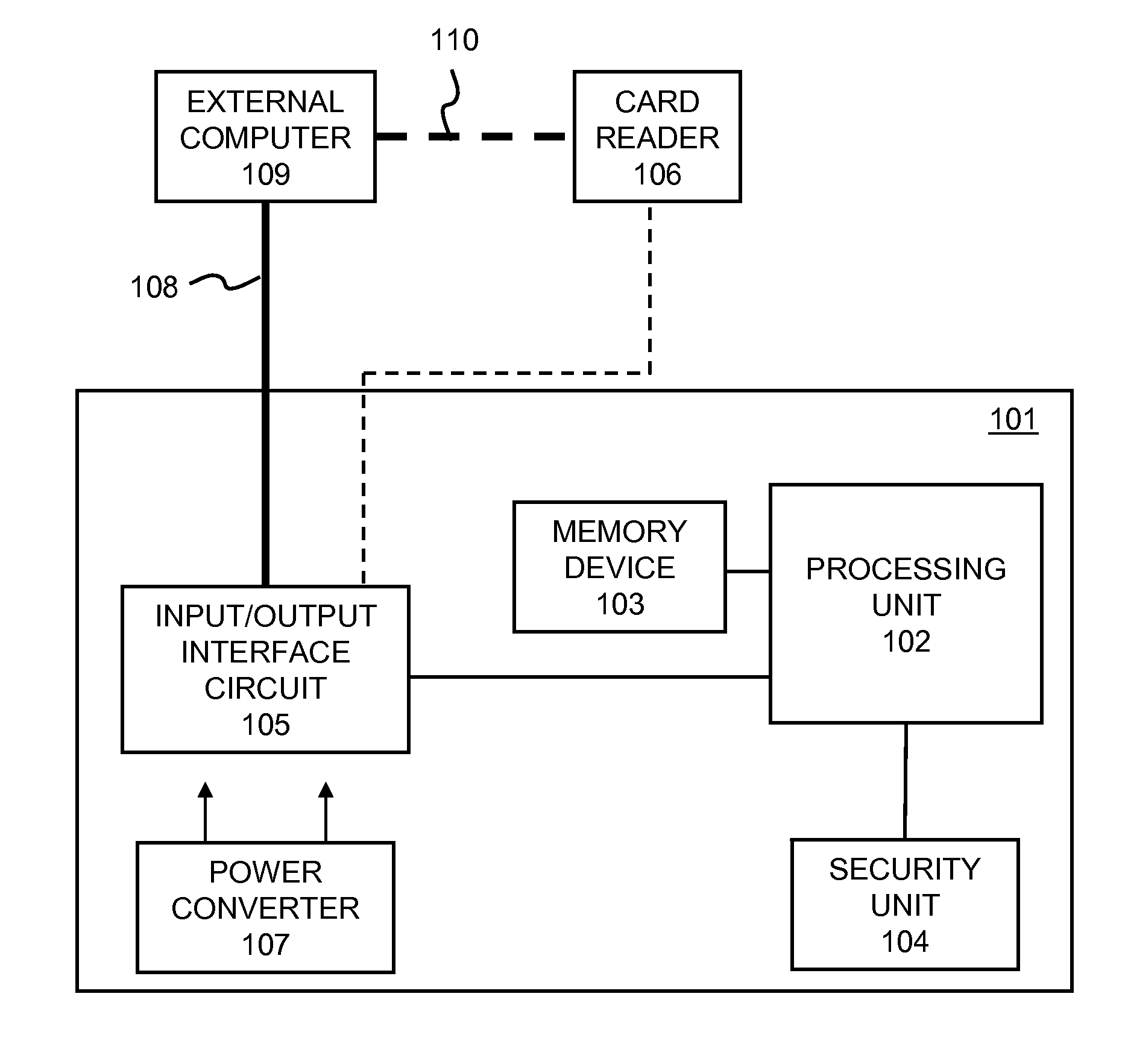
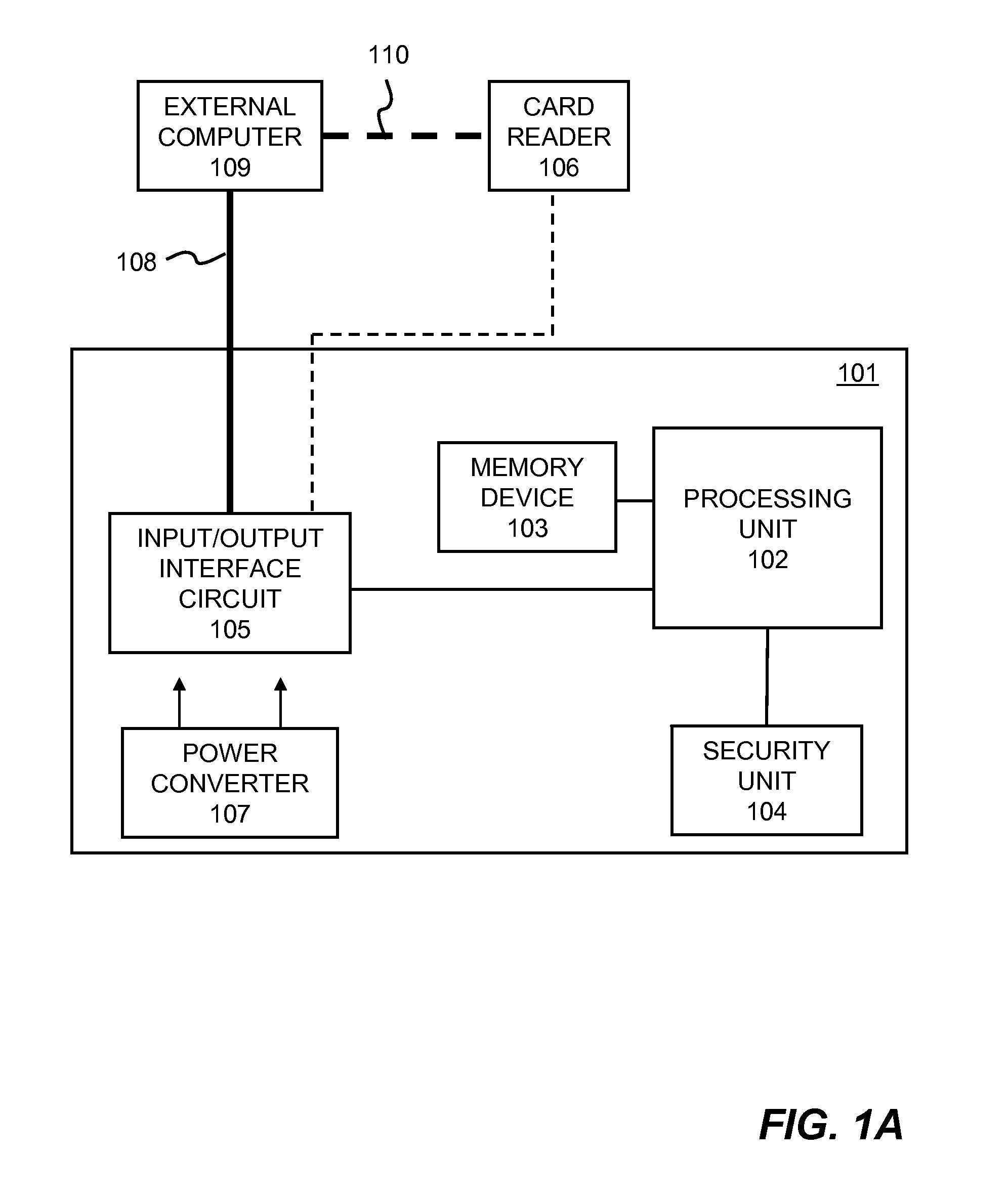
Distributed cache for state transfer operations
ActiveUS20020138551A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed cacheClient-side
A network arrangement that employs a cache having copies distributed among a plurality of different locations. The cache stores state information for a session with any of the server devices so that it is accessible to at least one other server device. Using this arrangement, when a client device switches from a connection with a first server device to a connection with a second server device, the second server device can retrieve state information from the cache corresponding to the session between the client device and the first server device. The second server device can then use the retrieved state information to accept a session with the client device.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Substrate transfer device and substrate processing system
InactiveUS20130180448A1Suppress position deviationHigh positioning accuracyLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRoom temperatureProcessing element
A substrate transfer device includes a pick which has positioning pins to position a substrate and holds a positioned substrate; a drive unit which drives the pick such that the substrate is loaded / unloaded to / from a vacuum processing unit by using a pick; and a transfer control unit which controls a transfer operation of the substrate using the pick. The transfer control unit obtains in advance information on a reference position of the substrate at room temperature when the substrate is loaded into the vacuum processing unit, calculates a positional deviation from the reference position of the substrate when the substrate is loaded into the vacuum processing unit in actual processing, and controls a drive unit such that the substrate is loaded into the vacuum processing unit by correcting the positional deviation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Methods and apparatus for secure electronic, certified, restricted delivery mail systems
A computer data signal embodied in a propagation medium is provided. The signal enables a variable number of data transfers and includes an initial connection source code segment and a data transfer source code segment. The initial connection source code segment establishes a connection between at least two devices via predetermined listening ports, with at least one predetermined listening port residing within each device. The initial connection source code segment also dynamically assigns a first data port within a first device, and transmits the address of the first data port to a remaining device via the predetermined listening ports. The data transfer source code segment is for each of the variable number of data transfer operations. The data transfer source code segment dynamically assigns a corresponding second data port within the remaining device and transfers data between the connected devices via the data ports so that the data is substantially simultaneously transferred between a variable number of devices via the data ports. Each pair of first and second data ports is established in response to each listening port connection.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
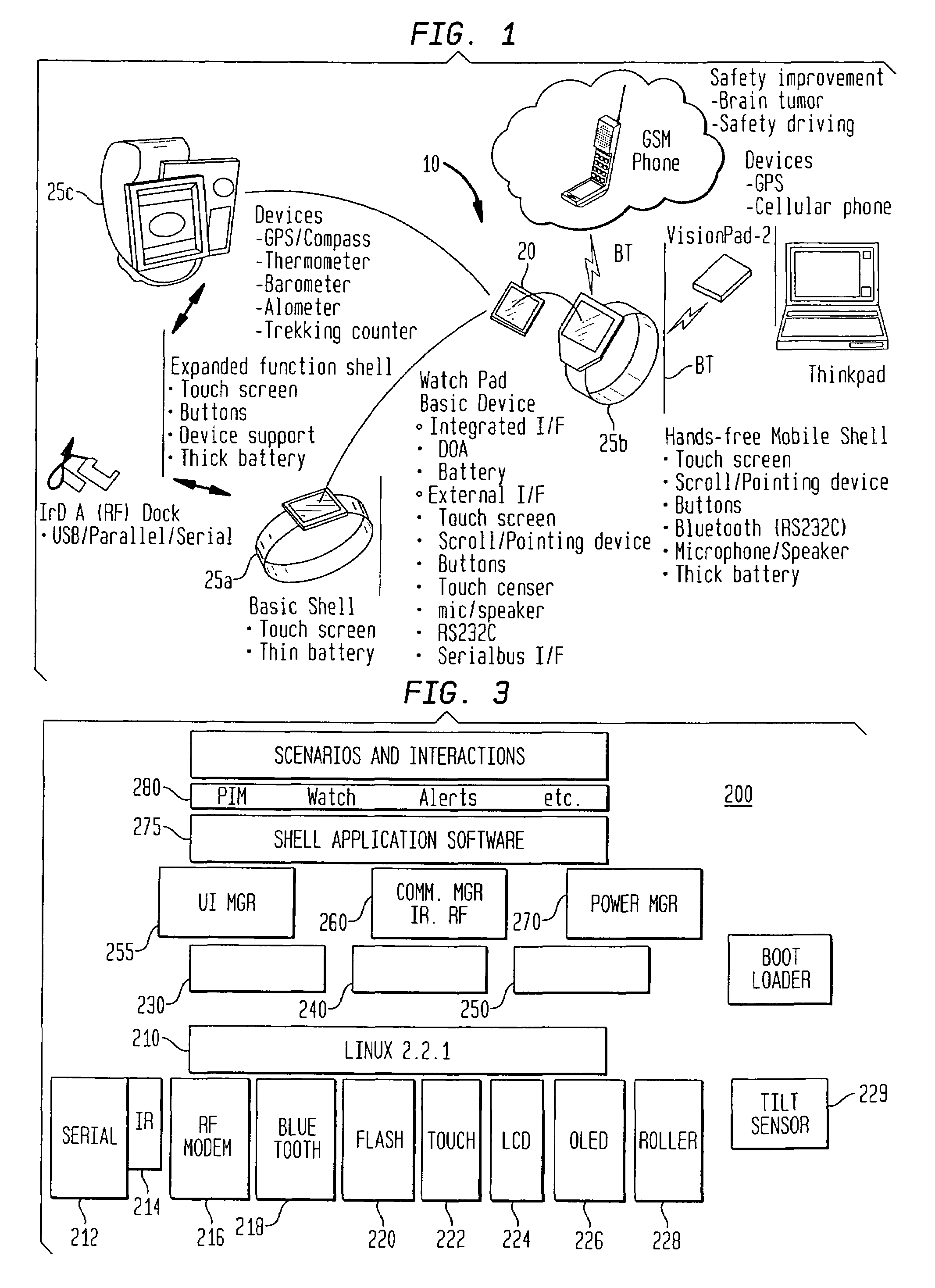
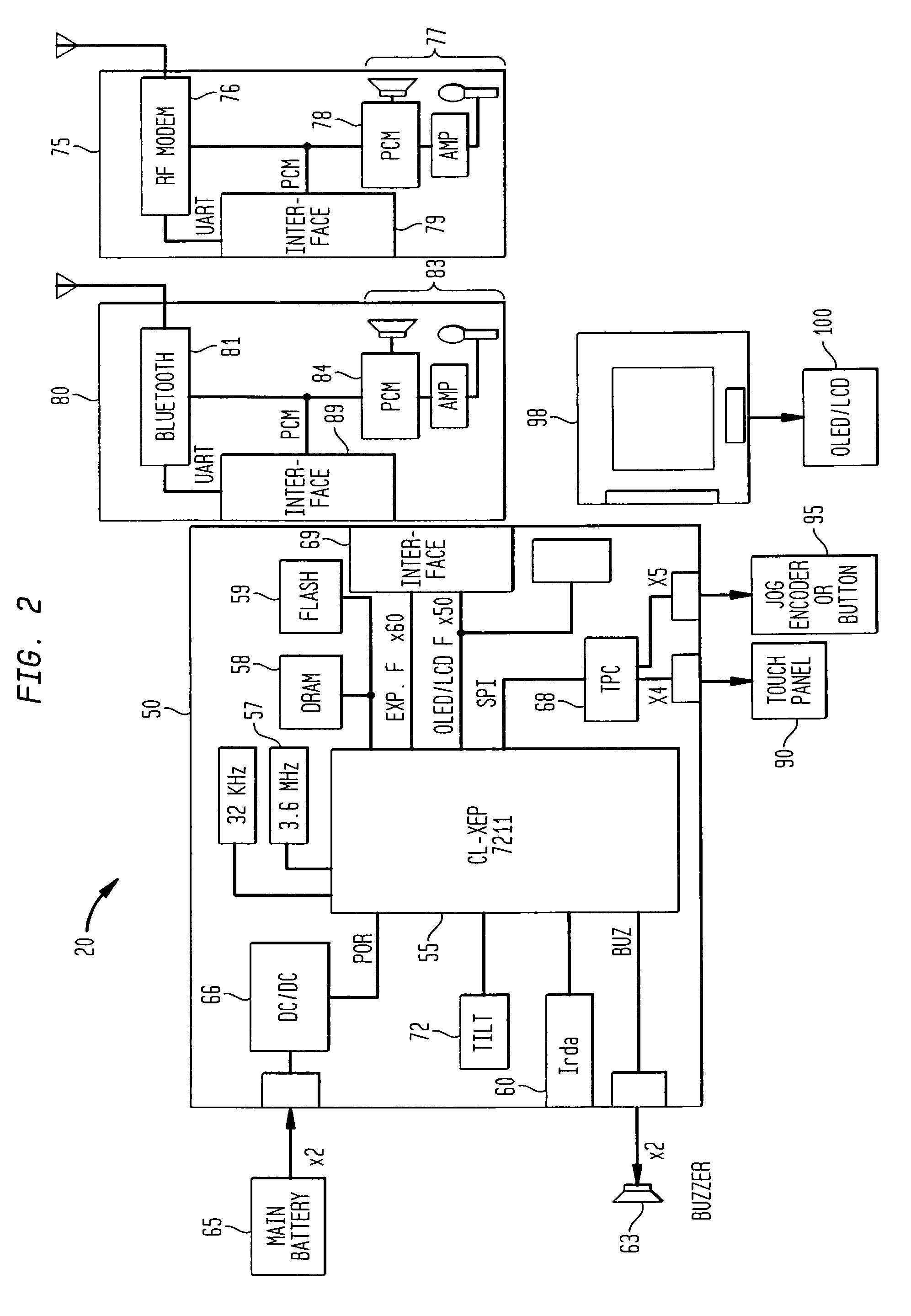
Demand pull-multichannel asynchronous data and application synchronization for pervasive devices
InactiveUS7477890B1Reduce wasteConvenient for userSpecial service for subscribersDevices with bluetooth interfacesData transmissionTransfer operation
A system and methodology for enabling a user to asynchronously request a data transfer operation (pull) via a first communication medium, and enable receipt of the requested data over a second communication medium, including a wireless channel for storage / presentation in a wearable mobile computing device / appliance (e.g., a wrist watch device) capable of wirelessly accessing information from a network or communications device.
Owner:IBM CORP
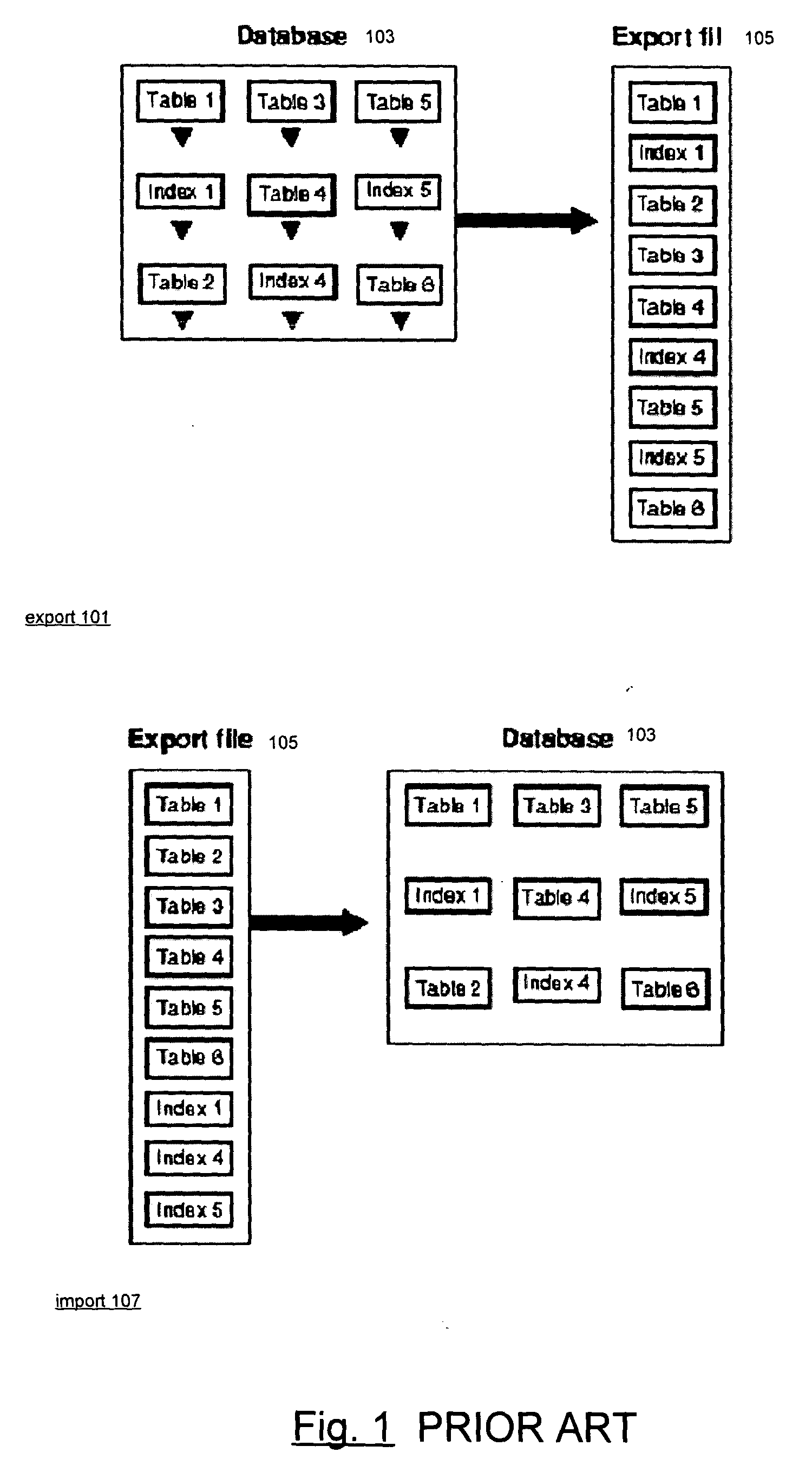
Apparatus and methods for transferring database objects into and out of database systems
ActiveUS20050055351A1Control performanceDatabase updatingDatabase management systemsRelational database management systemTransfer mechanism
Techniques for transferring objects between database systems. As implemented in a relational database management system, the techniques employ a data transfer mechanism that operates under control of a master table in the RDBMS that is performing the transfer operation. The master table specifies the kind of transfer operation to be performed, a set of objects to be transferred, operations to be performed on the objects as they are being transferred, and filters for selecting a subset of the objects. During execution of the transfer, the transfer mechanism maintains and updates state in the master table such that queries may be made on the master table to determine the current status of the operation and such that the transfer mechanism may restart the operation after it has been stopped either at the request of a client that is performing the operation or because of an error in the transfer. The master table's persistence and the status information it contains permit the client that is performing the operation to detach from the operation without stopping the operation and later again attach to the operation to determine the operation's status or to perform operations such as creating new files for the operation or changing the degree of parallelism with which the transfer operation is being performed. Another feature of the transfer mechanism is using an object's metadata to determine the most efficient way of transferring the object.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
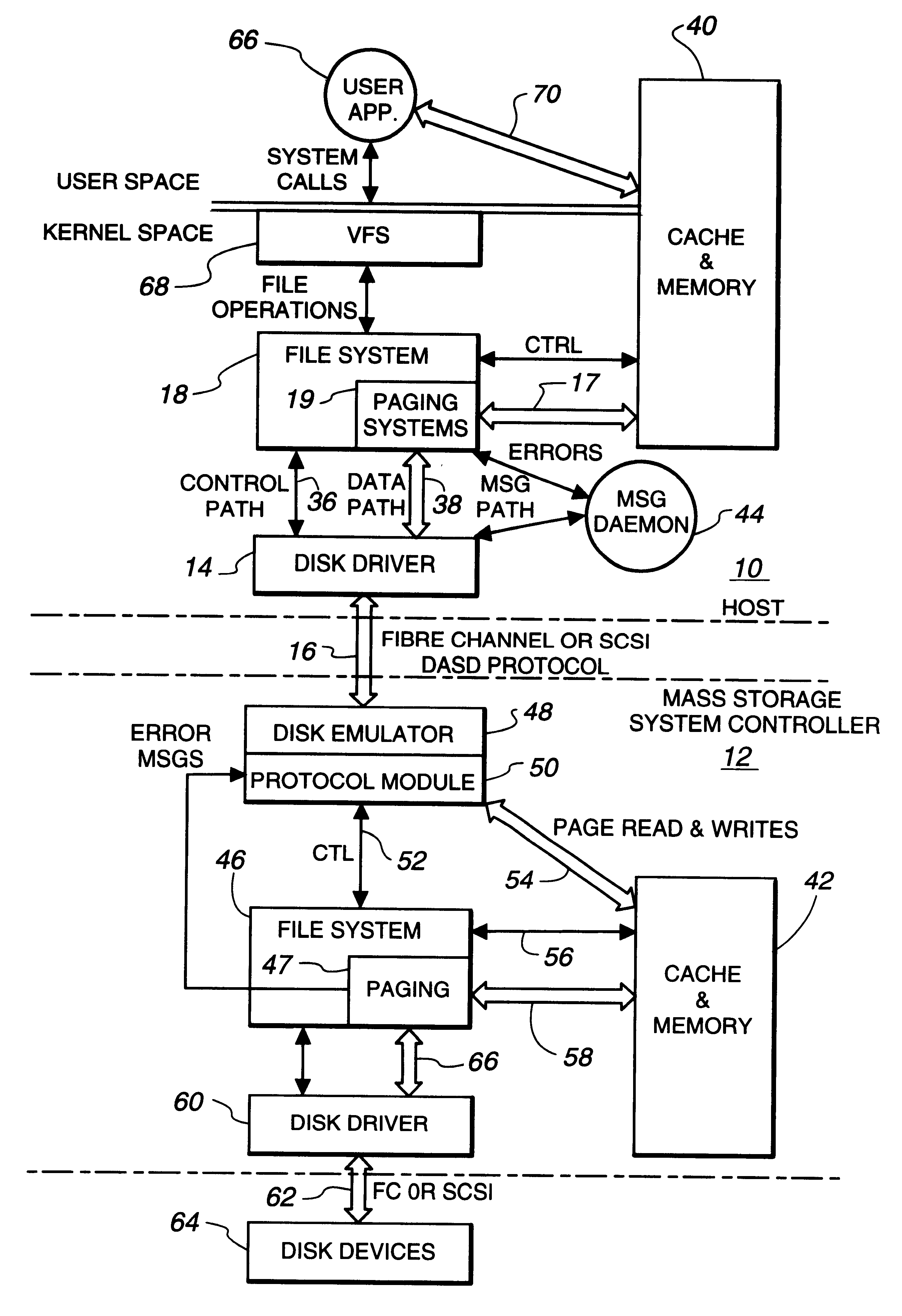
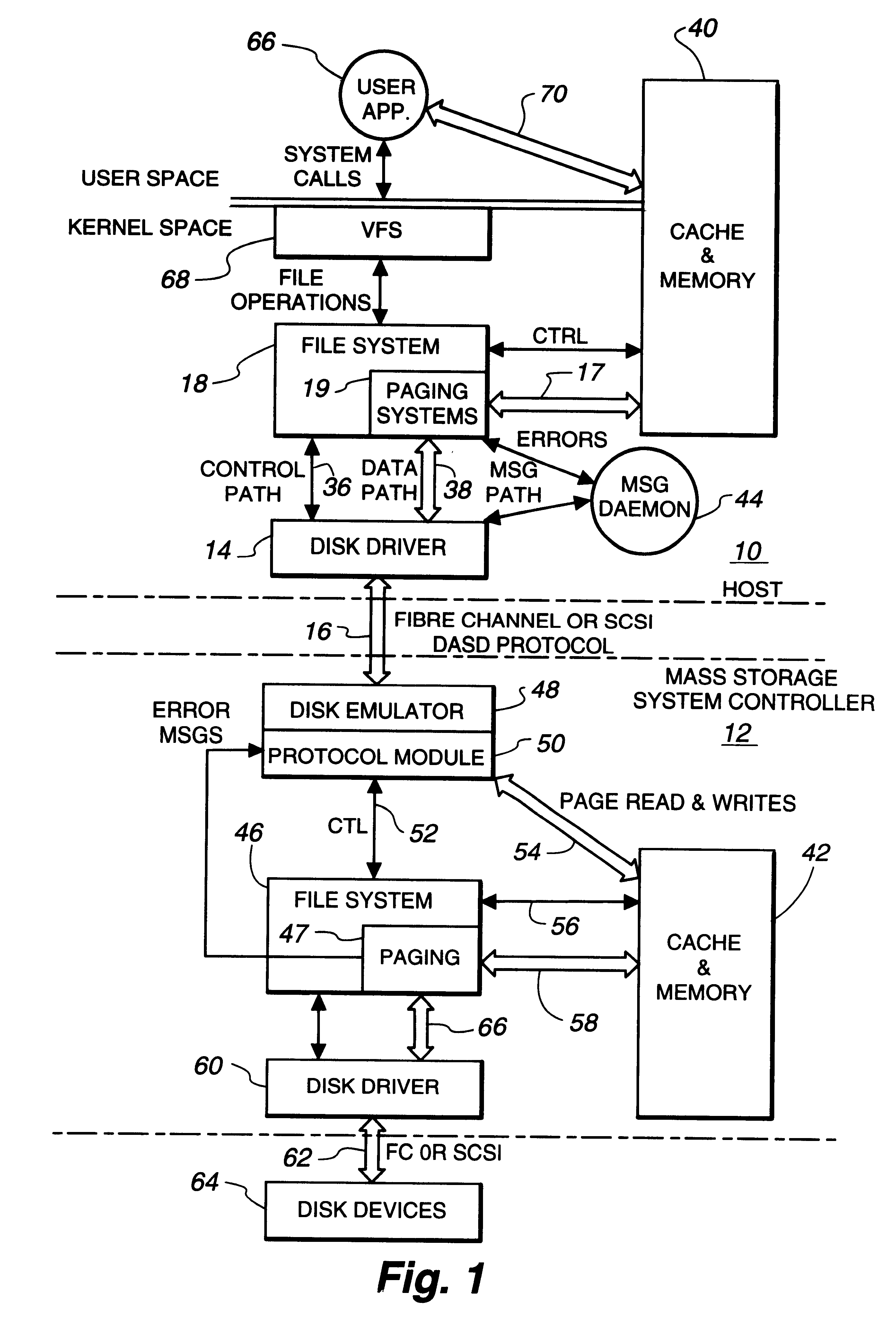
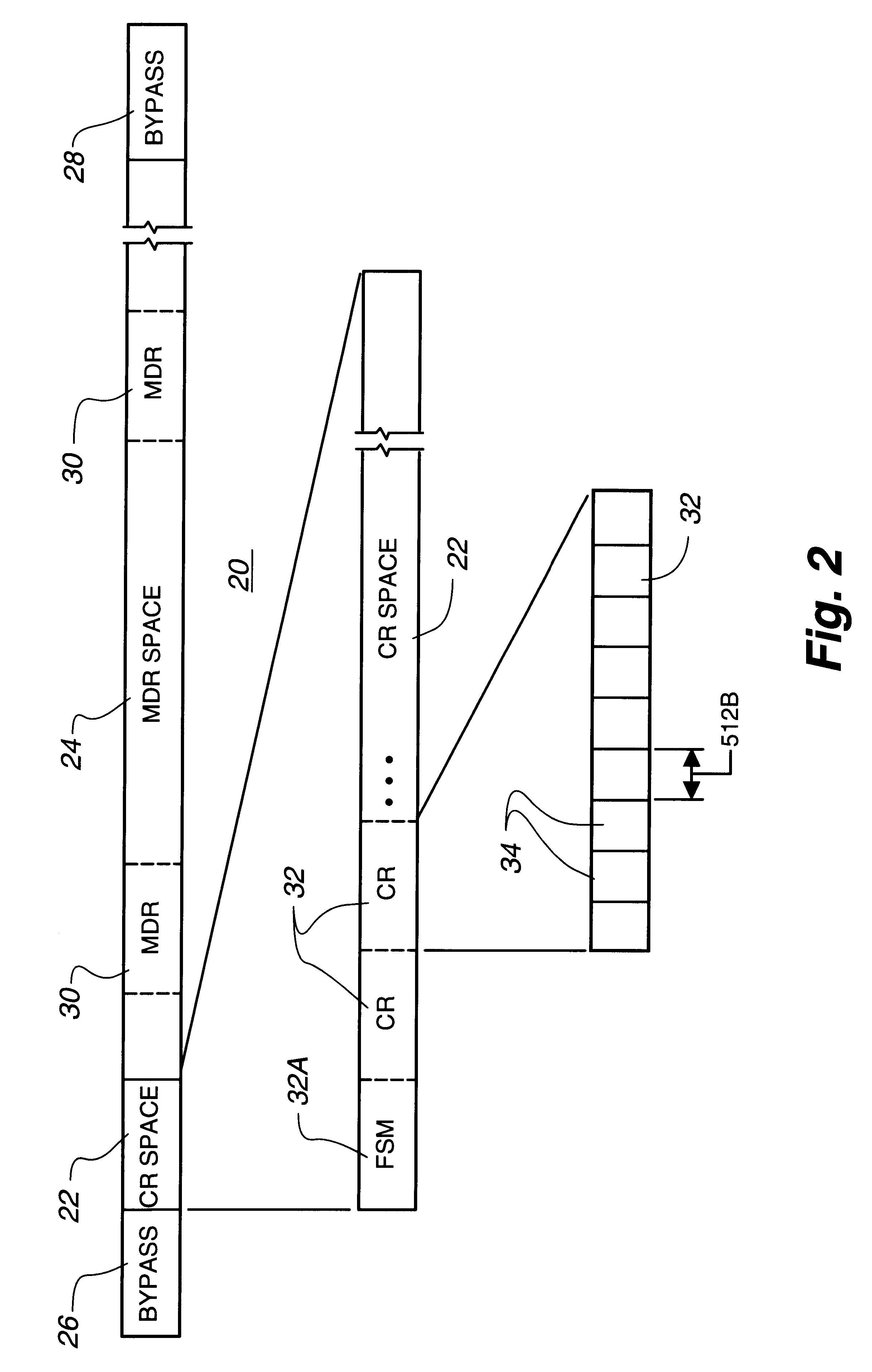
Intelligent controller accessed through addressable virtual space
InactiveUS6493811B1Remove restrictionsInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirect memory accessVirtual space
File operations on files in a peripheral system are controlled by an intelligent controller with a file processor. The files are accessed as if the intelligent controller were an addressable virtual storage space. This is accomplished first by communicating controller commands for the intelligent controller through read / write commands addressed to a Command Region of a virtual storage device. The controller commands set up a Mapped Data Region in the virtual storage device for use in controlling data transfer operations to and from the peripheral system. With the Mapped Data Regions set up, blocks of data are transferred between the host and the intelligent controller in response to read / write commands addressed to the Mapped Data Region of the virtual storage device.In an additional feature of the invention file operations are communicated between host and controller through a device driver at the host and a device emulator at the intelligent controller. If the address in the device write / read command is pointing to the Command Region of the virtual storage device, a Command Region process interprets and implements the controller operation required by the controller command embedded in the device write / read command. One of these controller commands causes the Command Region processor to map a requested file to a Mapped Data Region in the virtual storage device. If the address detected by the detecting operation is in a Mapped Data Region, a Mapped Data Region process is called. The Mapped Data Region process reads or writes requested data of a file mapped to the Mapped Data Region addressed by the read / write command. This mapped file read or write is accomplished as a transfer of data over a data path separate from a control path. In an additional feature of the invention, the data transfer between host system and intelligent controller is accomplished by performing a direct memory access transfer of data.
Owner:CA TECH INC
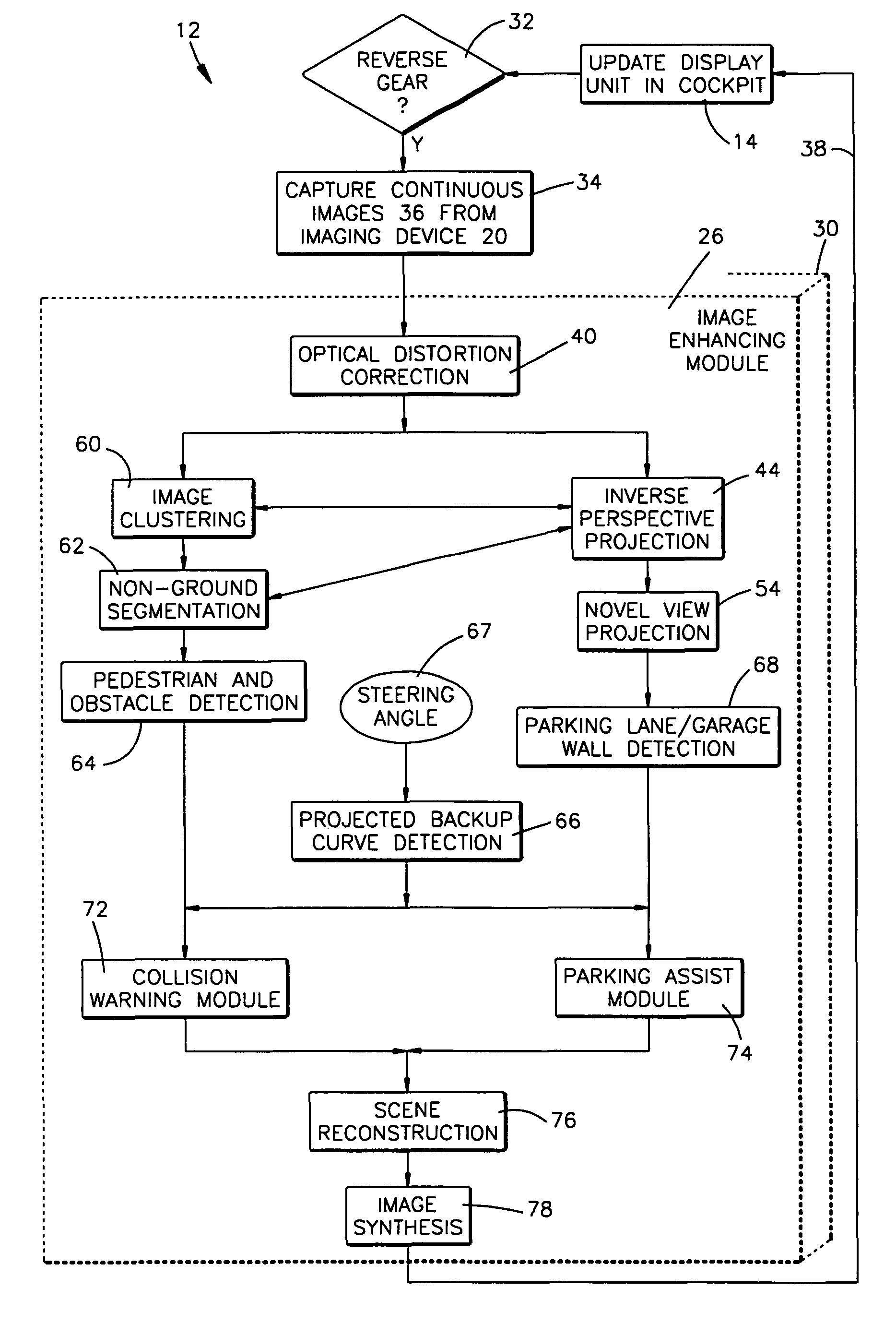
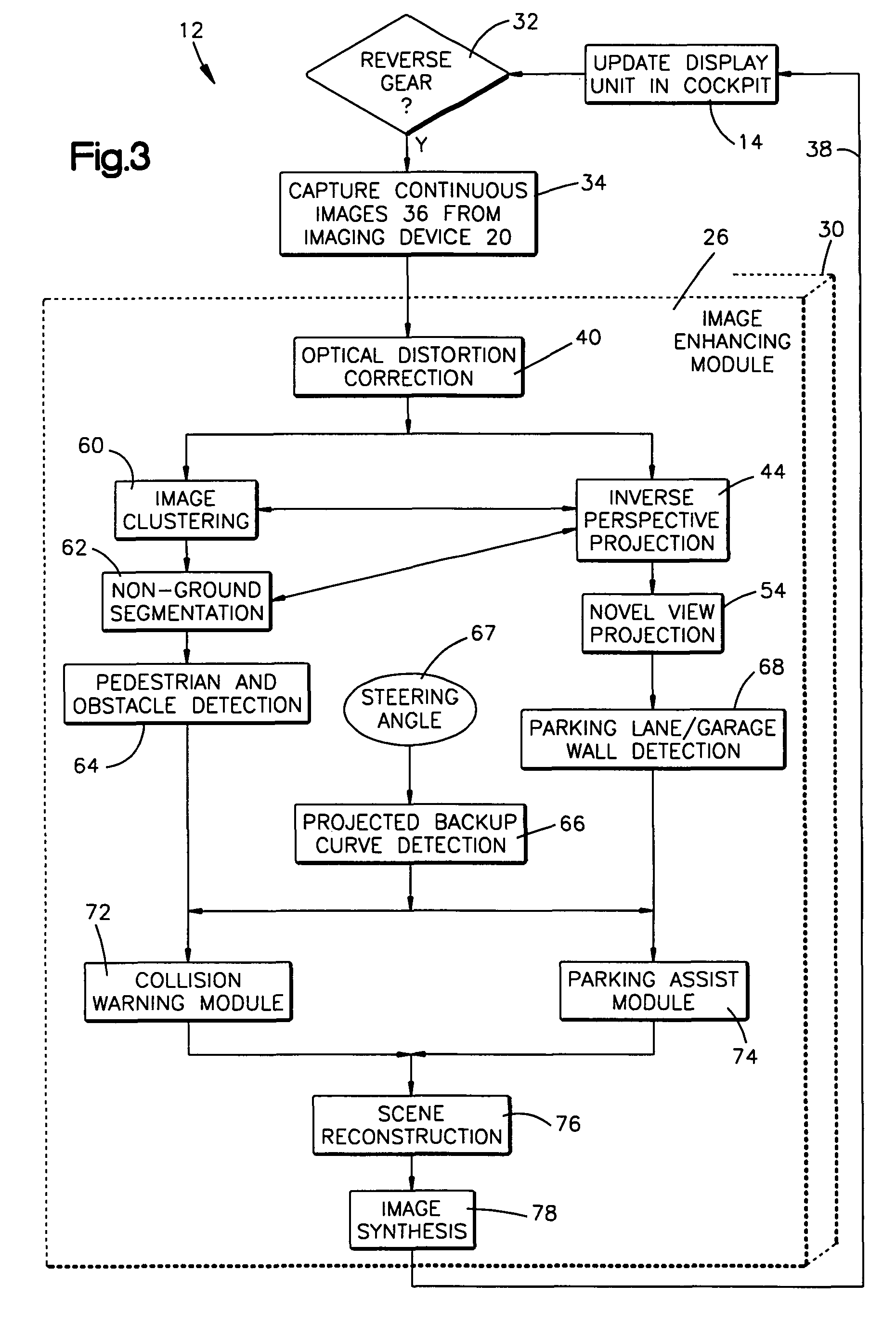
Method and apparatus for distortion correction and image enhancing of a vehicle rear viewing system
An image enhancing system for a vehicle comprises a display unit for displaying modified images and an imaging device for receiving captured images—enhanced by the image enhancing system. The system further includes an image enhancing module in communication with the display unit and the imaging device—such that pixels located in the captured images are enhanced by repositioning the pixels from a first position to a second position via a transfer operation.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
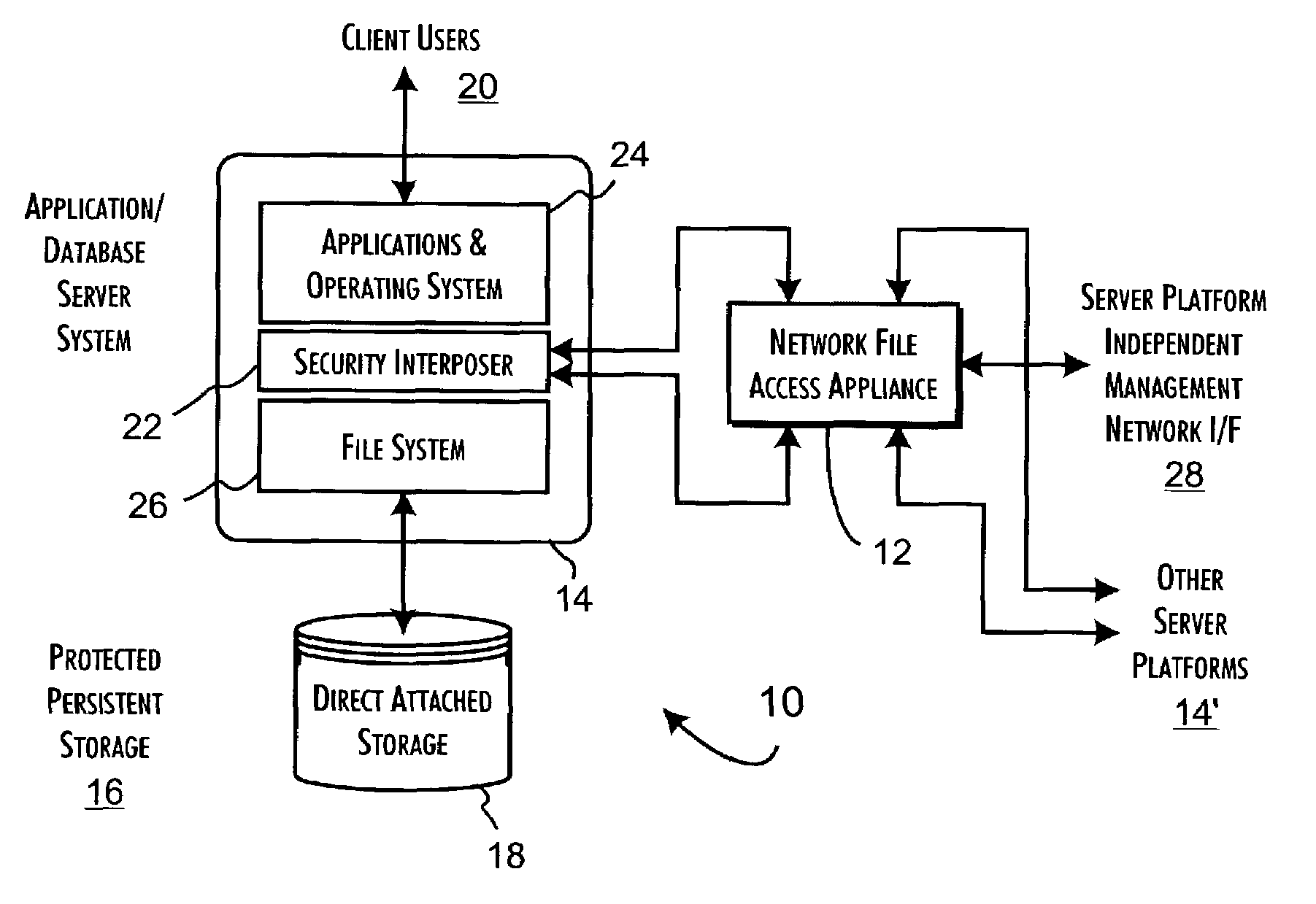
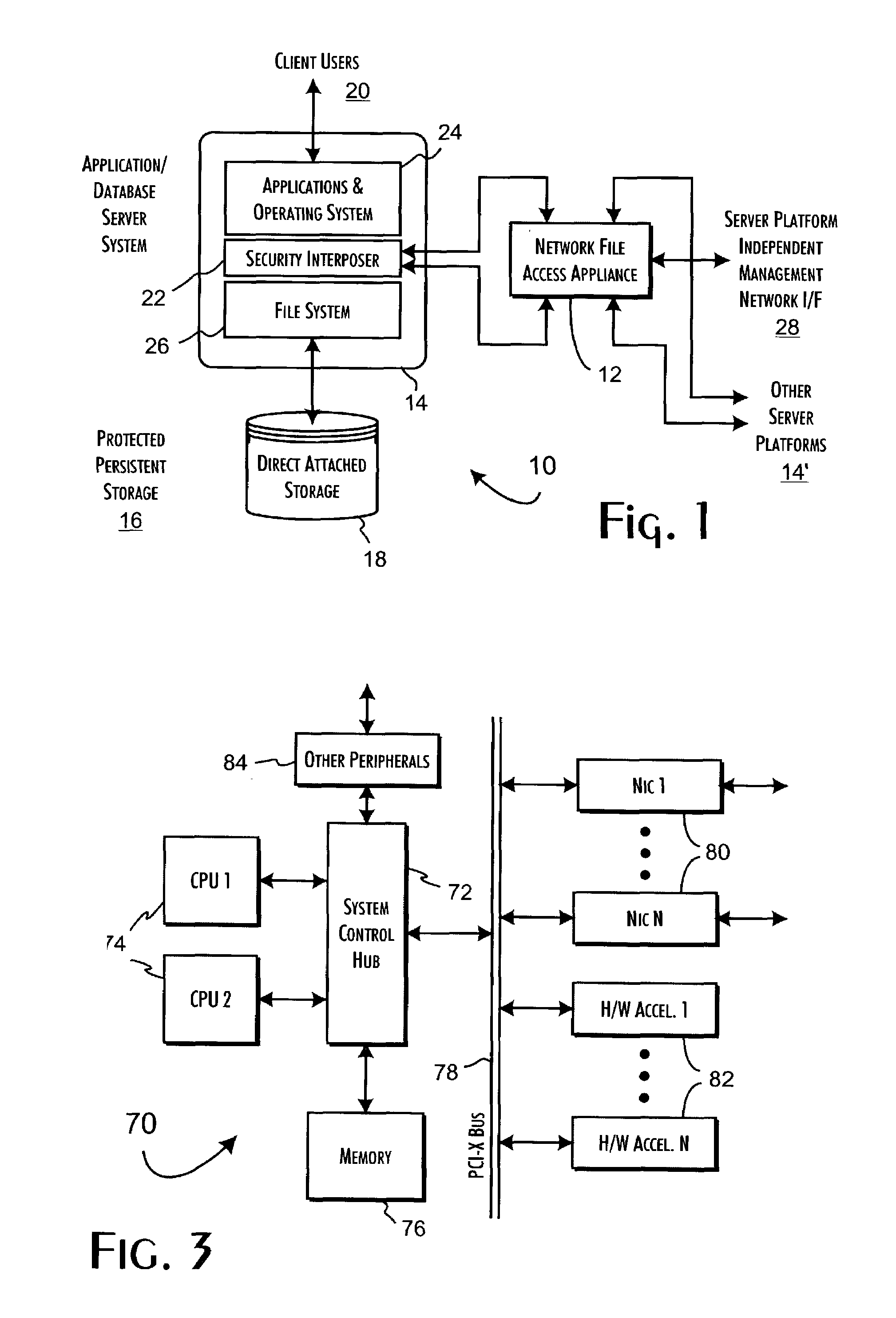
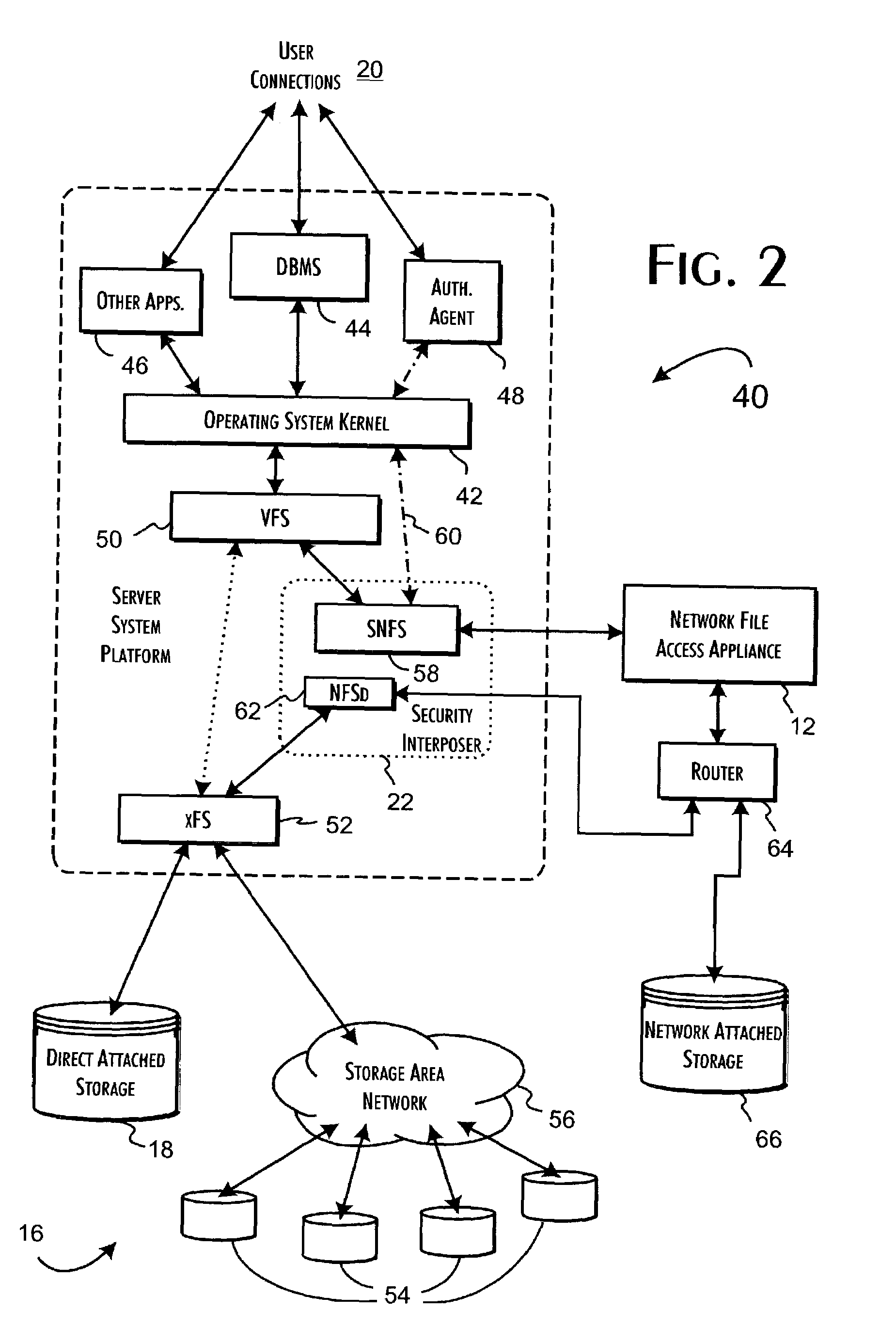
Secure file system server architecture and methods
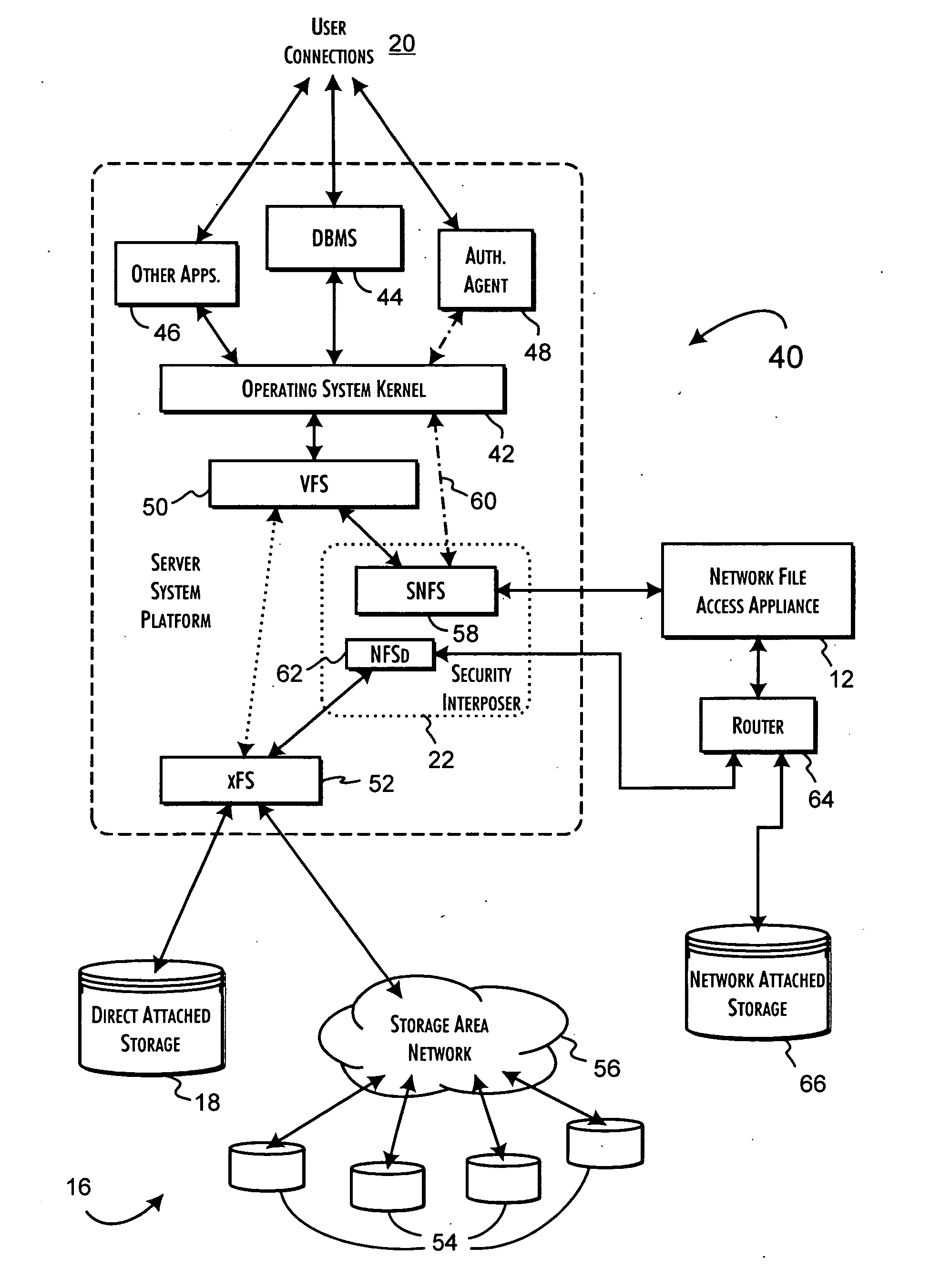
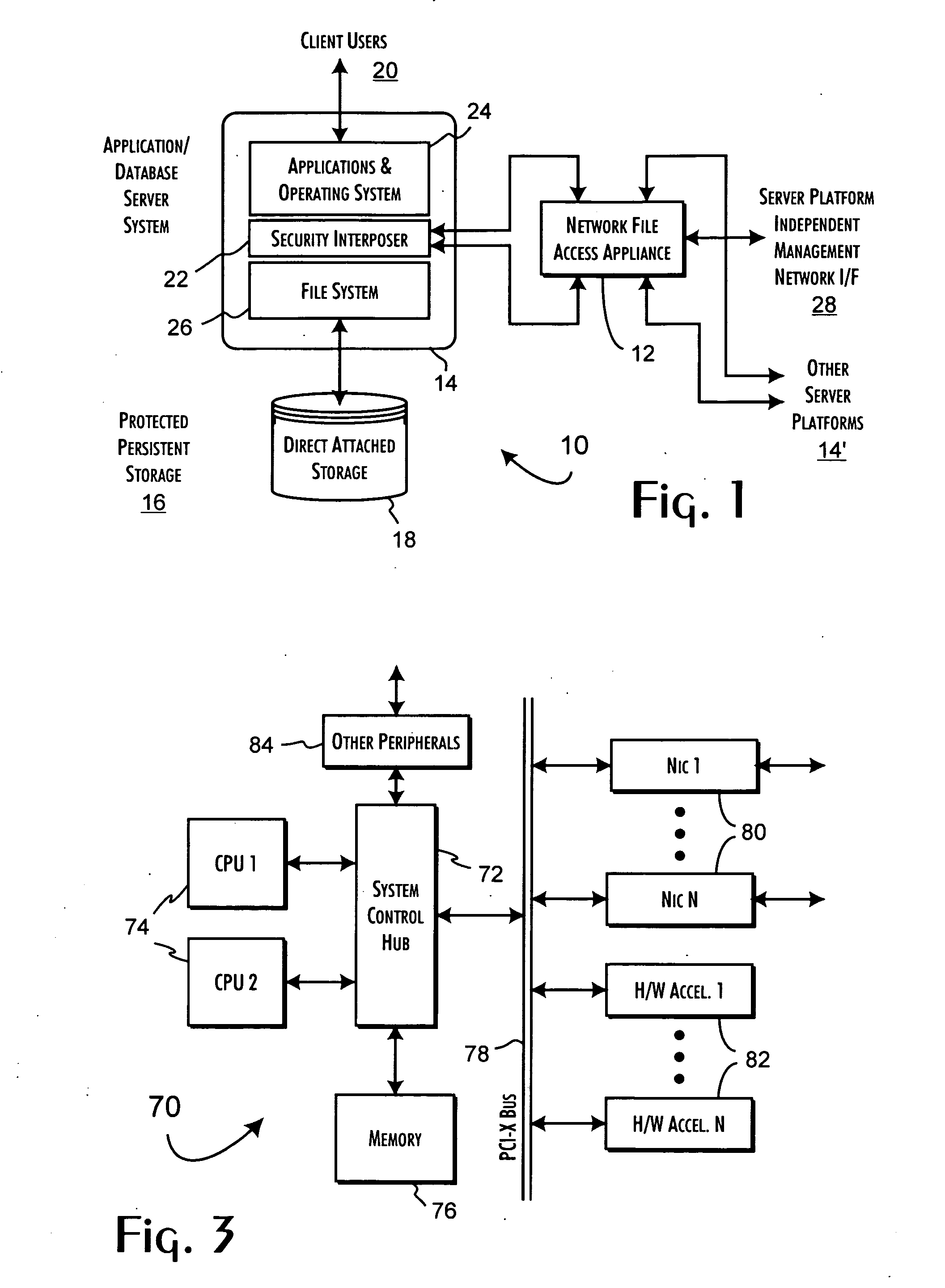
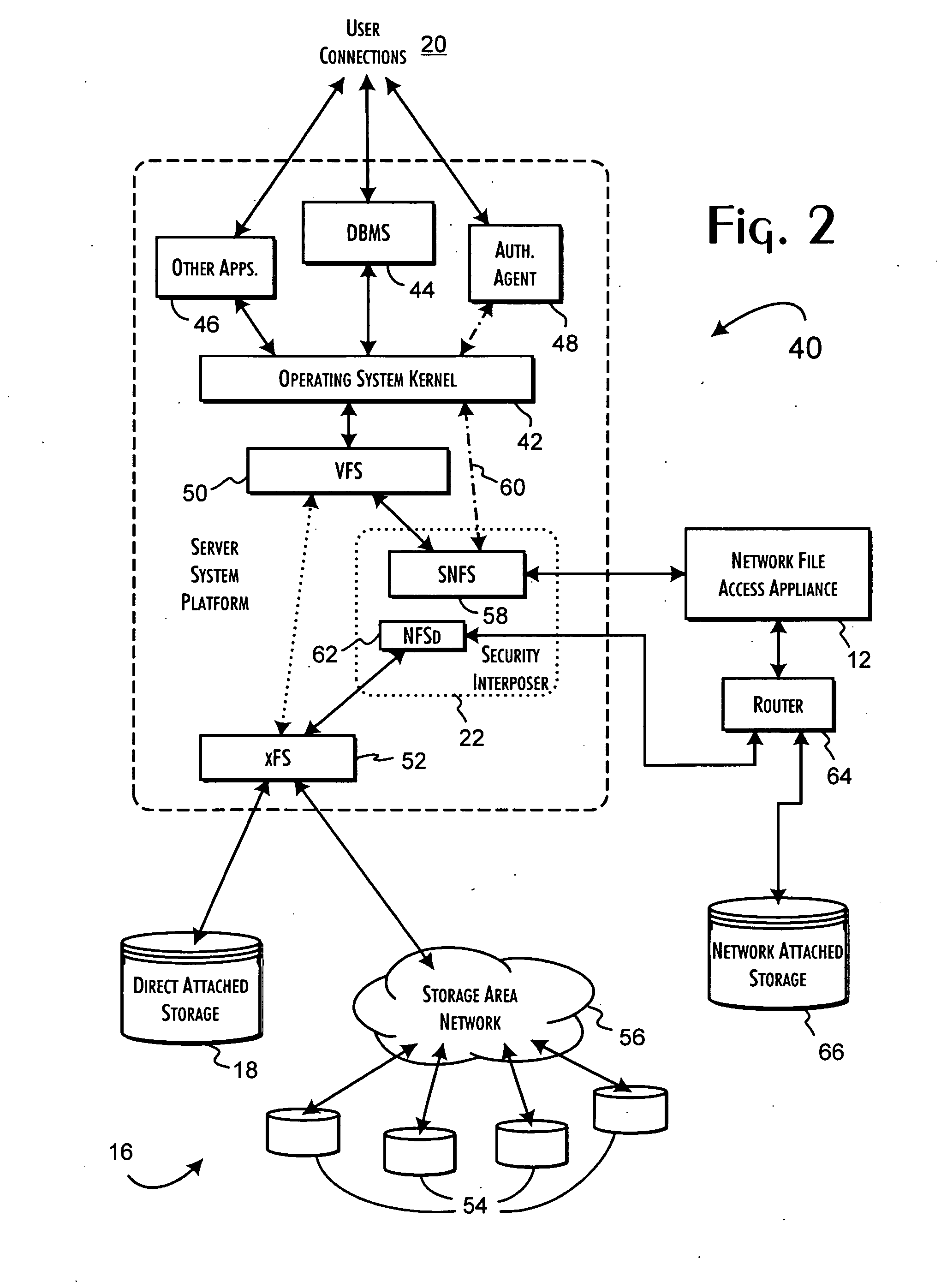
InactiveUS7143288B2Efficient collectionOperational safetyDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsOperational systemFile system
A data server platform includes a security file system layer interposed between the platform operating system kernel and file system. The secure file system layer is structured to implement a file access control function that selectively constrains data transfer operations initiated through the operating system kernel by an application program to transfer file data through the file system with respect to a persistent data store. A file access controller, implemented independent of the operating system kernel, is coupled to the security file system layer and supports the file access control function by defining permitted file data transfers through the file system. Management of the file access controller separate from the data server platform ensures that any security breach of the platform operating system kernel cannot compromise the function of the security file system layer.
Owner:THALES DIS CPL USA INC
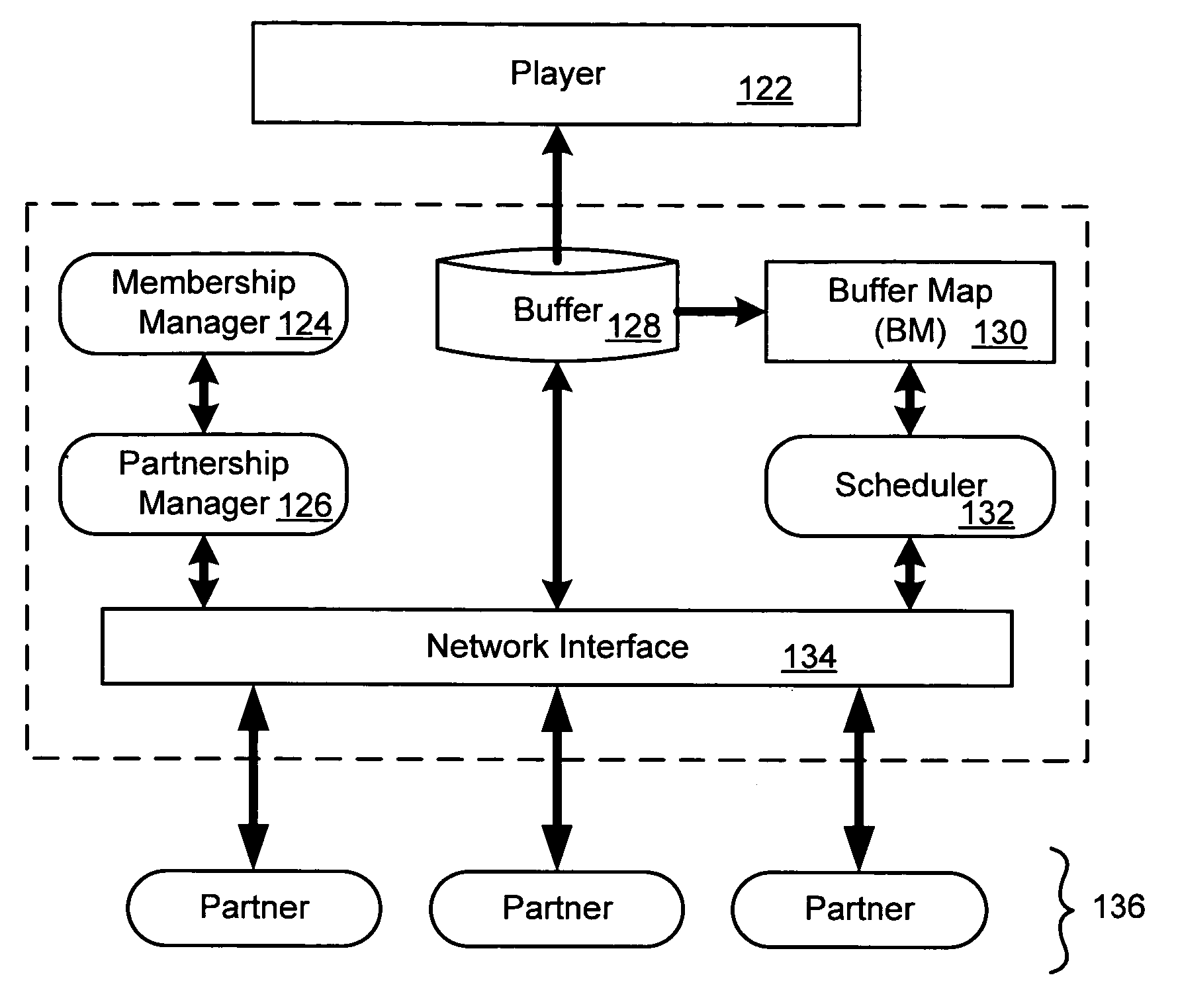
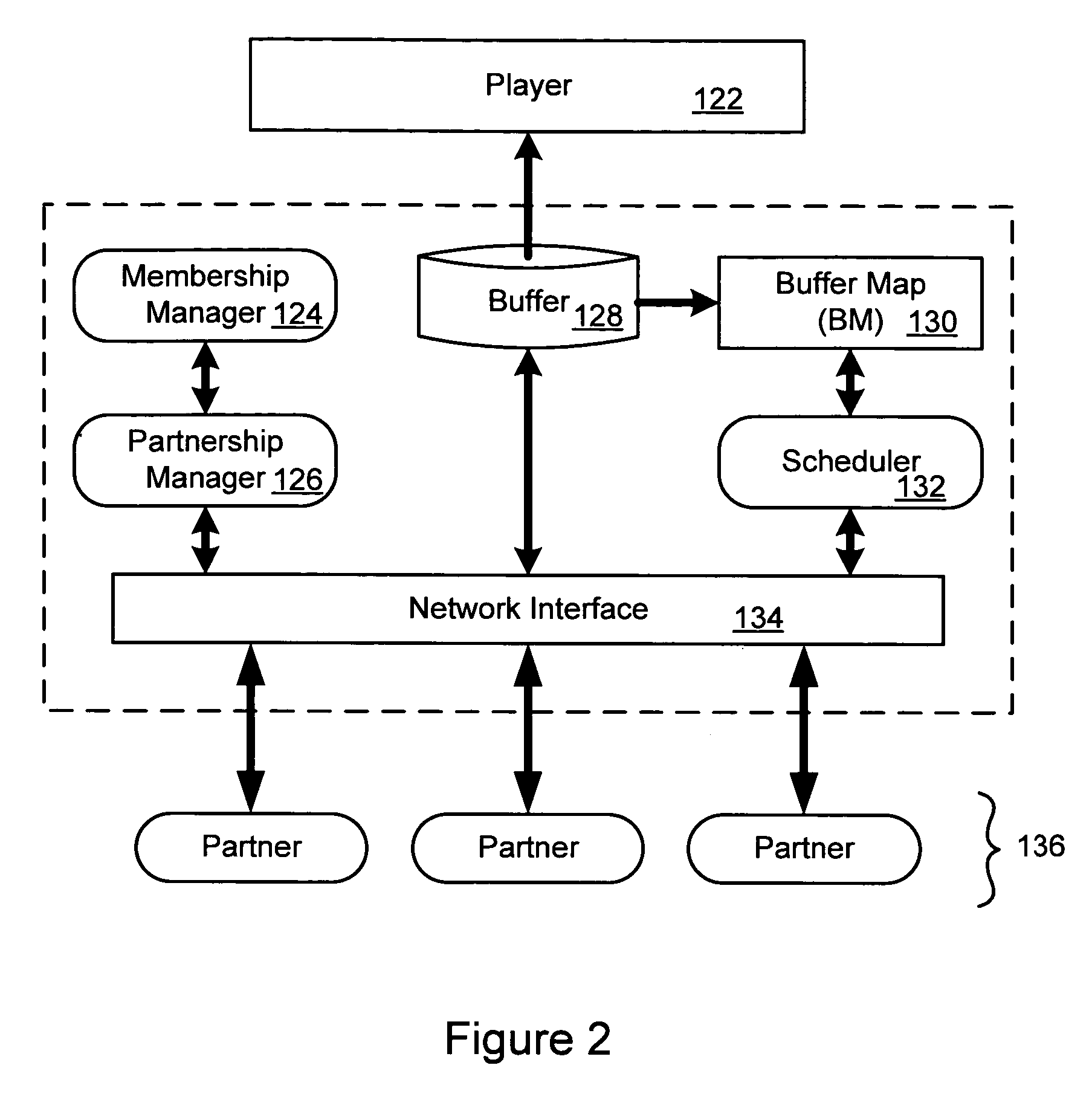
Distributed system for delivery of information via a digital network
A system for delivering streamed content over a large digital network such as the Internet. Distributed functionality executes on nodes in the network to achieve functions such as assigning partner nodes for transfer of content to or from a target node, scheduling transfer operations among nodes, adding or removing nodes from the network, maintaining security, and other operations. Different embodiments may use one or more of the functional features. In a preferred embodiment, video content is segmented and streamed through multi-path routing. An overlay network uses nodes in partnership groups so that a target node can obtain segments from multiple sources. Partner nodes can provide the segments within a given time window, including simultaneous delivery from multiple partner nodes, so that a more reliable data stream is supported.
Owner:TV BANK
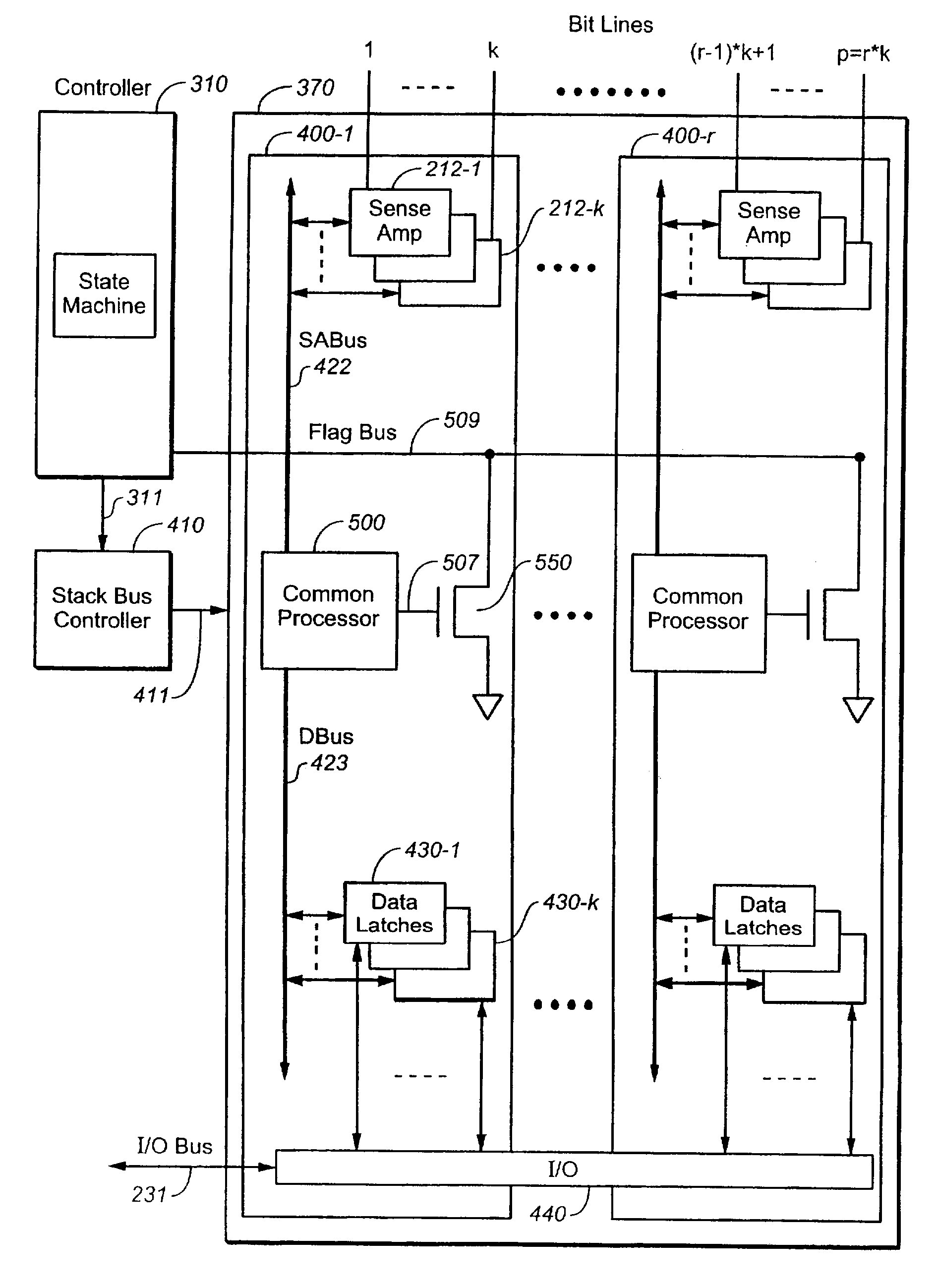
Method for Non-Volatile Memory with Background Data Latch Caching During Read Operations
ActiveUS20060221696A1Minimize perturbationSave transfer timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesTransfer operationNon-volatile memory
Part of the latency from memory read or write operations is for data to be input to or output from the data latches of the memory via an I / O bus. Methods and circuitry are present for improving performance in non-volatile memory devices by allowing the memory to perform some of these data caching and transfer operations in the background while the memory core is busy with a read operation. A scheme for caching read data is implemented so that even when the read for a current page on a current wordline must be preceded by a prerequisite read of data on an adjacent wordline, the prerequisite read along with any I / O access is preemptively done in the cycle for reading a previous page so that the current read can be performed while the previously read page is busy with the I / O access.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Distributed cache for state transfer operations
ActiveUS7383329B2Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed cacheClient-side
A network arrangement that employs a cache having copies distributed among a plurality of different locations. The cache stores state information for a session with any of the server devices so that it is accessible to at least one other server device. Using this arrangement, when a client device switches from a connection with a first server device to a connection with a second server device, the second server device can retrieve state information from the cache corresponding to the session between the client device and the first server device. The second server device can then use the retrieved state information to accept a session with the client device.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
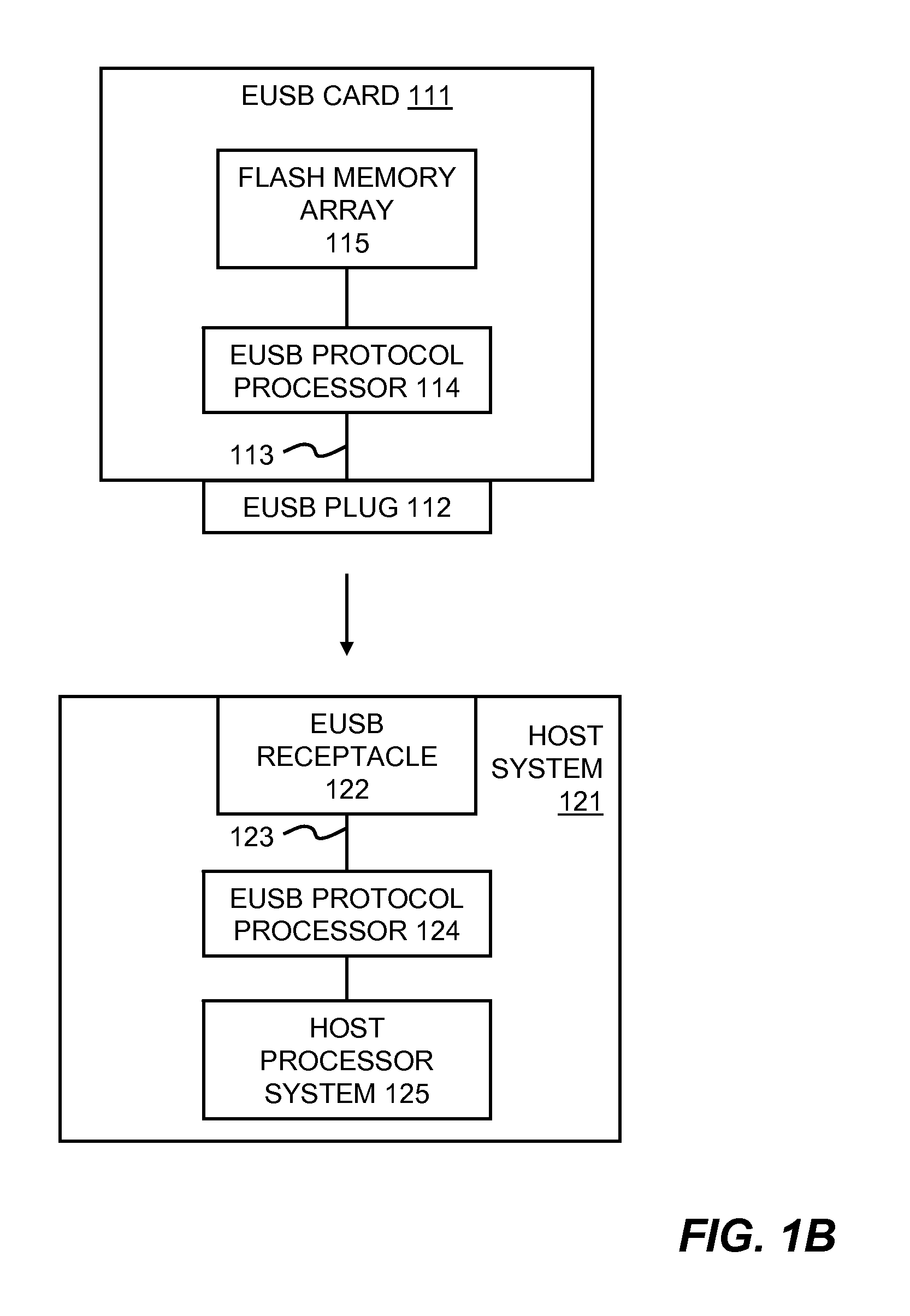
Methods and systems for storing and accessing data in uas based flash-memory device
ActiveUS20100185808A1Improve efficiencyEnsure performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesTransceiverRandom access memory
Methods and systems for storing and accessing data in UAS based flash memory device are disclosed. UAS based flash memory device comprises a controller and a plurality of non-volatile memories (e.g., flash memory) it controls. Controller is configured for connecting to a UAS host via a physical layer (e.g., plug and wire based on USB 3.0) and for conducting data transfer operations via two sets of logical pipes. Controller further comprises a random-access-memory (RAM) buffer configured for enabling parallel and duplex data transfer operations through the sets of logical pipes. In addition, a Smart Storage Switch configured for connecting multiple non-volatile memory devices is included in the controller. Finally, a security module / engine / unit is provided for data security via user authentication data encryption / decryption of the device. Furthermore, the flash memory device includes an optical transceiver configured for optical connection to a host also configured with an optical transceiver.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
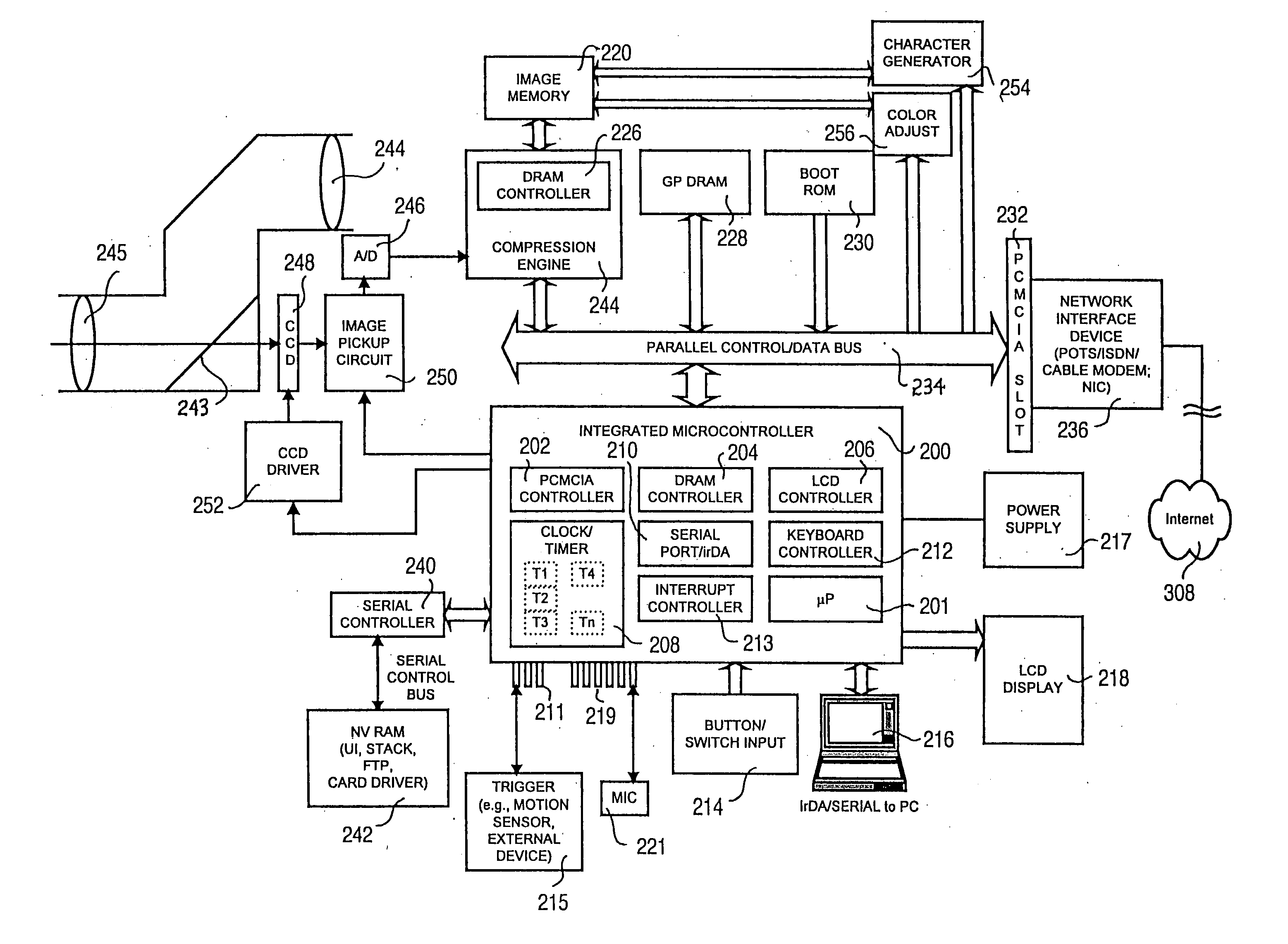
Integrated internet/intranet camera
InactiveUS20050055727A1Efficient and inexpensiveIncrease ratingsTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMicrocontrollerInternet communication
An integrated Internet camera includes, as embedded components contained within the camera body and controlled by a microcontroller, at least a network interface device for connecting to the Internet, a transport control device for packetizing according to Internet protocols, a file transfer device for communicating with a destination user directory on the Internet, and a transmission initiating device for initiating the connection and transfer operations of the file transfer device and transport control device. The network interface device may be a modem, network adapter, or adapter for connection to the Internet. Upon capturing the digital image, the camera initiates a connection to the Internet, connects to the destination user directory, and uploads the digital images. Thereafter, the digital images are available to authorized (or any) user having access to the Internet.
Owner:AXIS
Tracker sensing method for regulating synchronization of audit files between primary and secondary hosts
InactiveUS6446090B1Easy accessPromote recoveryData processing applicationsError detection/correctionFile synchronizationCritical level
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Connectivity between a scan tool and a remote device and method
InactiveUS20060101311A1Easy to upgradeEasy program upgrades/modificationsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesError detection/correctionModem deviceHand held
A hand-held diagnostic tool is designed to operate and easily upgrade software applications developed for automotive diagnostics. The diagnostic tool, which communicates with a plurality of motor vehicle control units, provides application upgrades and / or modifications and / or new algorithms that are developed / adapted via remote updating. The tool comprises full diagnostic capability capable of receiving diagnostic data from a motor vehicle for storage, analysis and / or further data transfer to a remote device. The tool may further comprise wireless capability to perform data transfer operations. Remote updating is accomplished through a number of external ports on the tool that facilitate modem, Ethernet and wireless communications, including point-to-point protocol connection to the Internet.
Owner:SPX CORP
Service desk data transfer interface
InactiveUS20060179070A1Data processing applicationsWeb data indexingApplication softwareNetwork data
A system, method and computer program product for importing data in a network-based customer relationship application is provided. First, data to be imported to a customer relationship application utilizing a network is identified. A set of predetermined rules associated with the customer relationship application are identified. The data is imported to the customer relationship application utilizing the network in accordance with the set of predetermined rules. The data is stored in memory accessible to the customer relationship application. The fields in which the data is stored in the memory are customized by a user. A system, method and computer program product for exporting data in a network-based customer relationship application is also provided. Data to be exported from a customer relationship application utilizing a network is identified. The data is stored in memory accessible to the customer relationship application, in fields which are user-customizable. A set of predetermined rules associated with the customer relationship application is identified. The data is exported from the customer relationship application utilizing the network in accordance with the set of predetermined rules. A system, method and computer program product are also provided for generating an application for managing network data transfer operations. A screen for receiving a designation of a type of application to be created is displayed. A screen for receiving a designation of an origin of the data is also displayed. A screen for receiving a designation of a destination for the data is further displayed. A mapping of fields between the origin of the data and the destination of the data is generated. The application is created. A screen is also displayed that allows a user to manipulate the mapping. A data transfer operation is performed upon execution of the application.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
Device facilitating efficient transfer of digital content from media capture device
InactiveUS20030146977A1Television system detailsColor television detailsDigital contentTransfer operation
A method facilitating the transfer of information from a media or data capture device to a larger device while providing valuable feedback about the transfer is described. A transfer device including a simple user interface that can be easily implemented on a media or data capture device provides feedback about the transfer operation, enabling the user to take action when necessary. For example, the user is advised if the transfer is complete or, alternatively, that the transfer has failed and needs to redone. Feedback is provided by visual signals and may also be accompanied by audible signals. All necessary transfer functionality is included on the media capture device, thereby avoiding the requirement for dedicated software on a host (or pipeline) device, such as a cellular phone. This expands the number of pipeline devices that can be utilized with particular media capture devices. As long as there is a correct interface between the data capture device and the pipeline device, all the necessary transfer functionality can be included in the data capture device.
Owner:SYNIVERSE ICX LLC
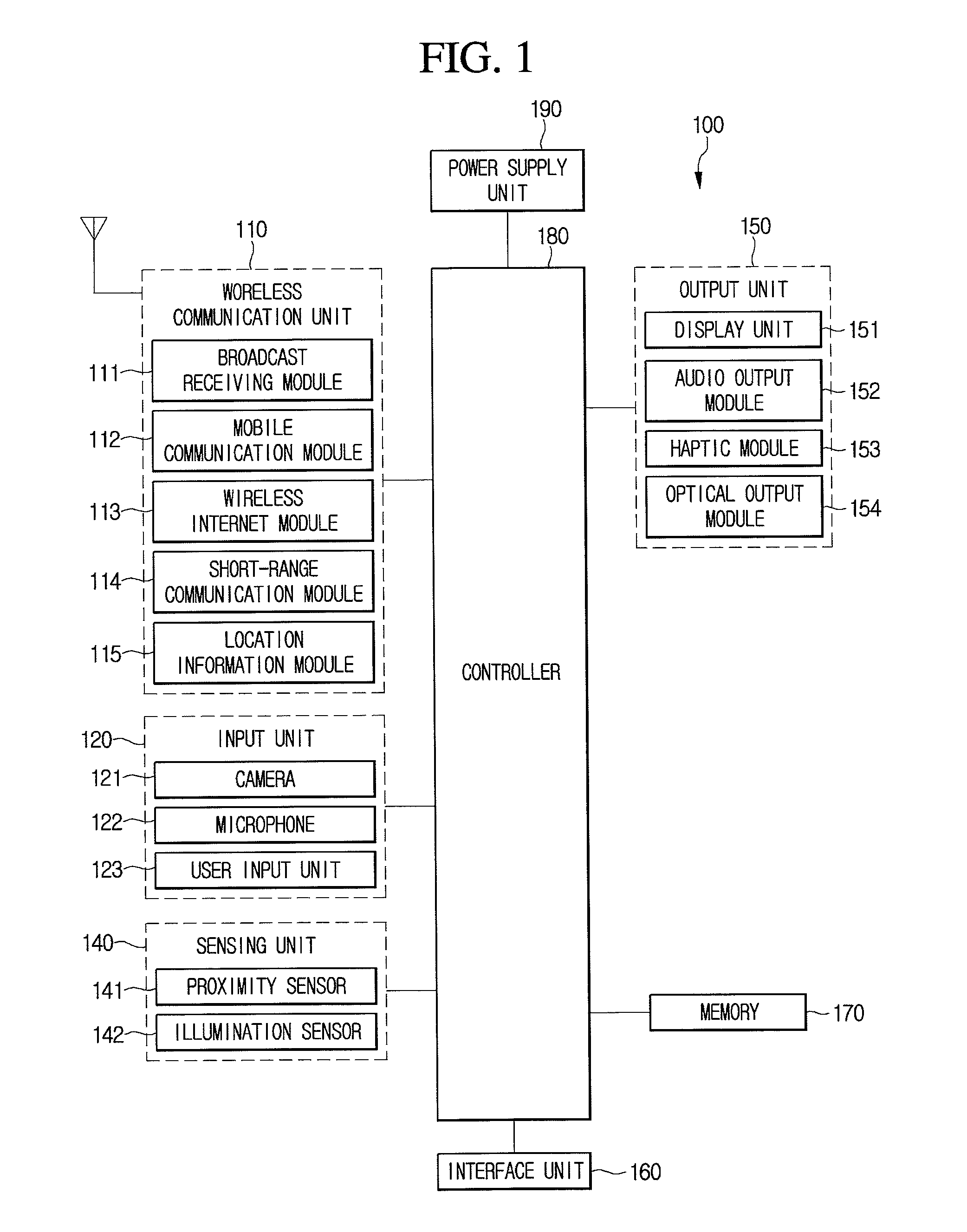
Wearable device and mobile terminal for supporting communication with the device
InactiveUS20160110012A1Improve user convenienceInput/output for user-computer interactionDevices with sensorComputer hardwareCommunication unit
A mobile terminal including a wireless communication unit configured to perform wireless communication with a wearable device; a touch screen; a sensor unit configured to sense at least one of a mobile terminal acceleration signal and a mobile terminal vibration signal; and a controller configured to display a screen corresponding to an application executing on the mobile terminal, receive first state information from the wearable device indicating at least one of a wearable device acceleration signal and a wearable device vibration signal of the wearable device, receive second state information from the sensor unit indicating said at least one of the mobile terminal acceleration signal and the mobile terminal vibration signal of the mobile terminal, and transfer operations of the application executing on the mobile terminal to the wearable device, based on the first and second state information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
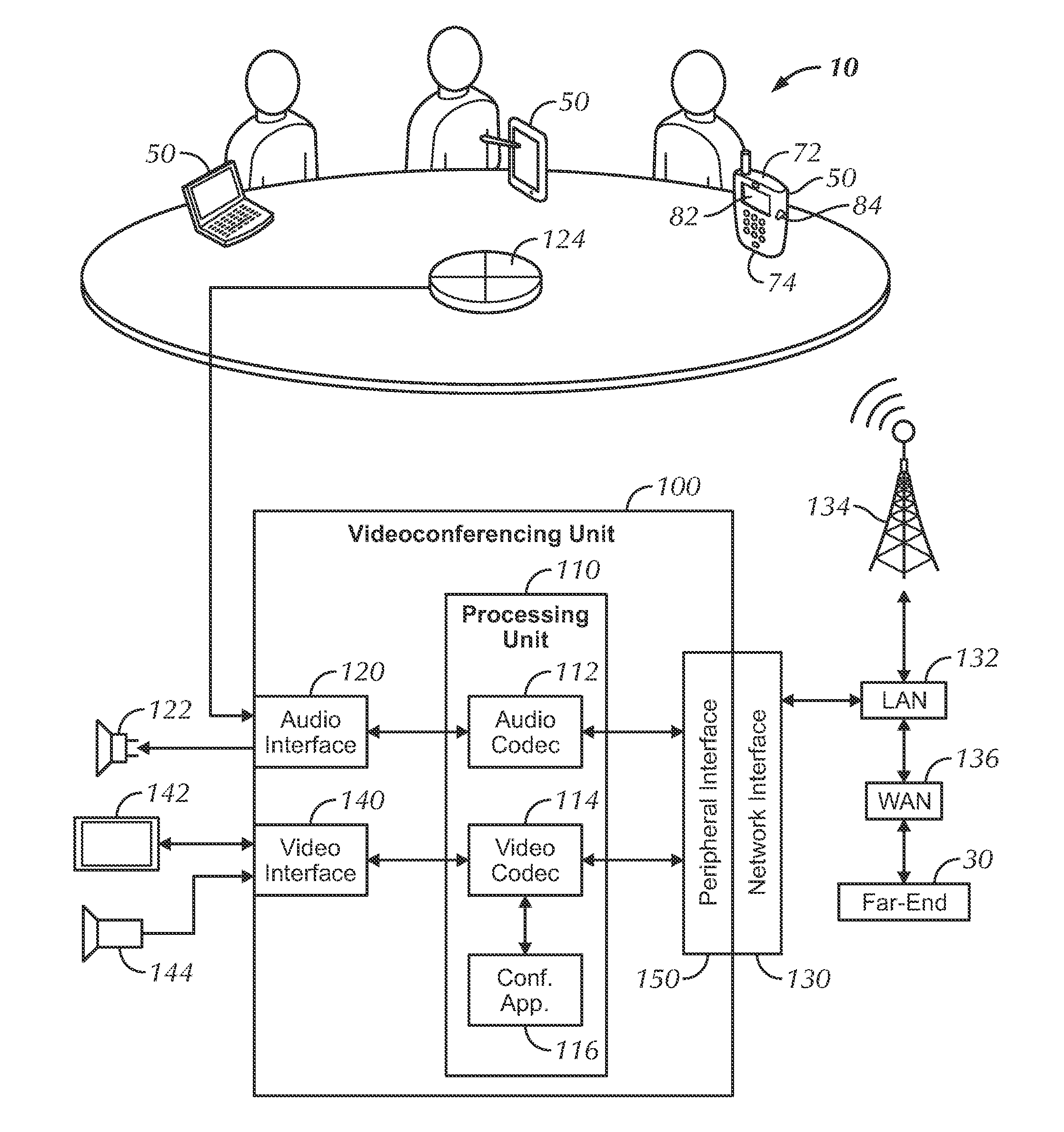
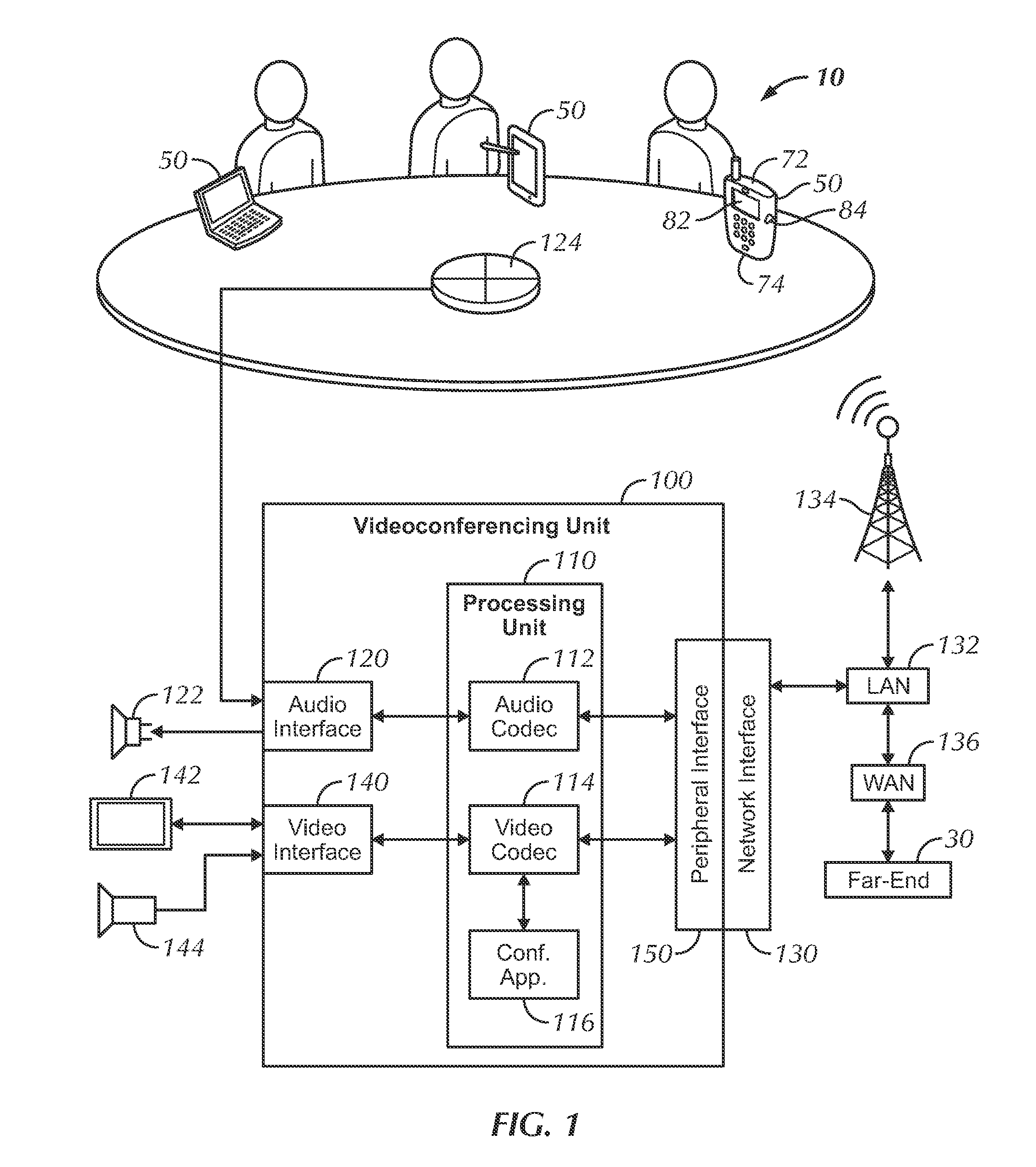
Pairing Devices in Conference Using Ultrasonic Beacon
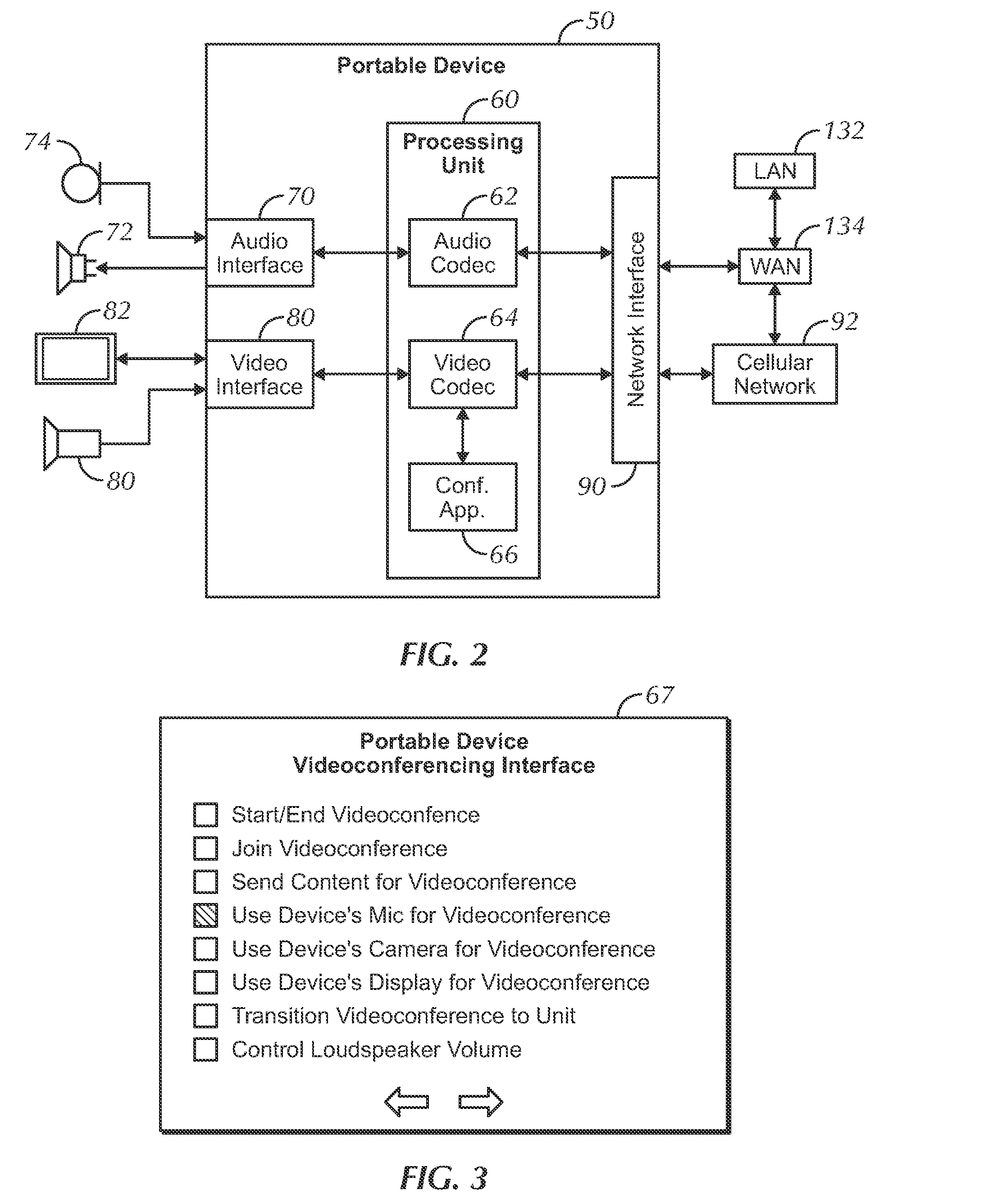
InactiveUS20130106977A1Reduced effectivenessSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsCouplingProximal point
A videoconferencing system has a videoconferencing unit that use portable devices as peripherals for the system. The portable devices obtain near-end audio and send the audio to the videoconferencing unit via a wireless connection. In turn, the videoconferencing unit sends the near-end audio from the loudest portable device along with near-end video to the far-end. The portable devices can control the videoconferencing unit and can initially establish the videoconference by connecting with the far-end and then transferring operations to the videoconferencing unit. To deal with acoustic coupling between the unit's loudspeaker and the portable device's microphone, the unit uses an echo canceller that is compensated for differences in the clocks used in the A / D and D / A converters of the loudspeaker and microphone.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Docking Station And Device Adapter For Use In A Docking Station
ActiveUS20110134601A1Coupling device connectionsDigital data processing detailsDocking stationElectrical battery
The embodiments disclosed herein relate generally to a docking station for charging batteries used in portable electronic devices and / or for transferring data to or from portable electronic devices. The docking station is adapted to receive a rechargeable battery either directly and / or through its portable electronic device, which can be fitted with or without a cover case. For example, the docking station has a receiving area configured to receive and hold a portable electronic device including a rechargeable battery and / or a rechargeable battery after being removed from the corresponding portable electronic device. The invention also relates to a removable device adapter for use with a docking station to receive a rechargeable battery directly and / or through its portable electronic device fitted with or without a cover case. For example, the device adapter can be removably used in a docking station during a charging operation of a rechargeable battery and / or a data transferring operation of a portable electronic device.
Owner:UNKNOWN
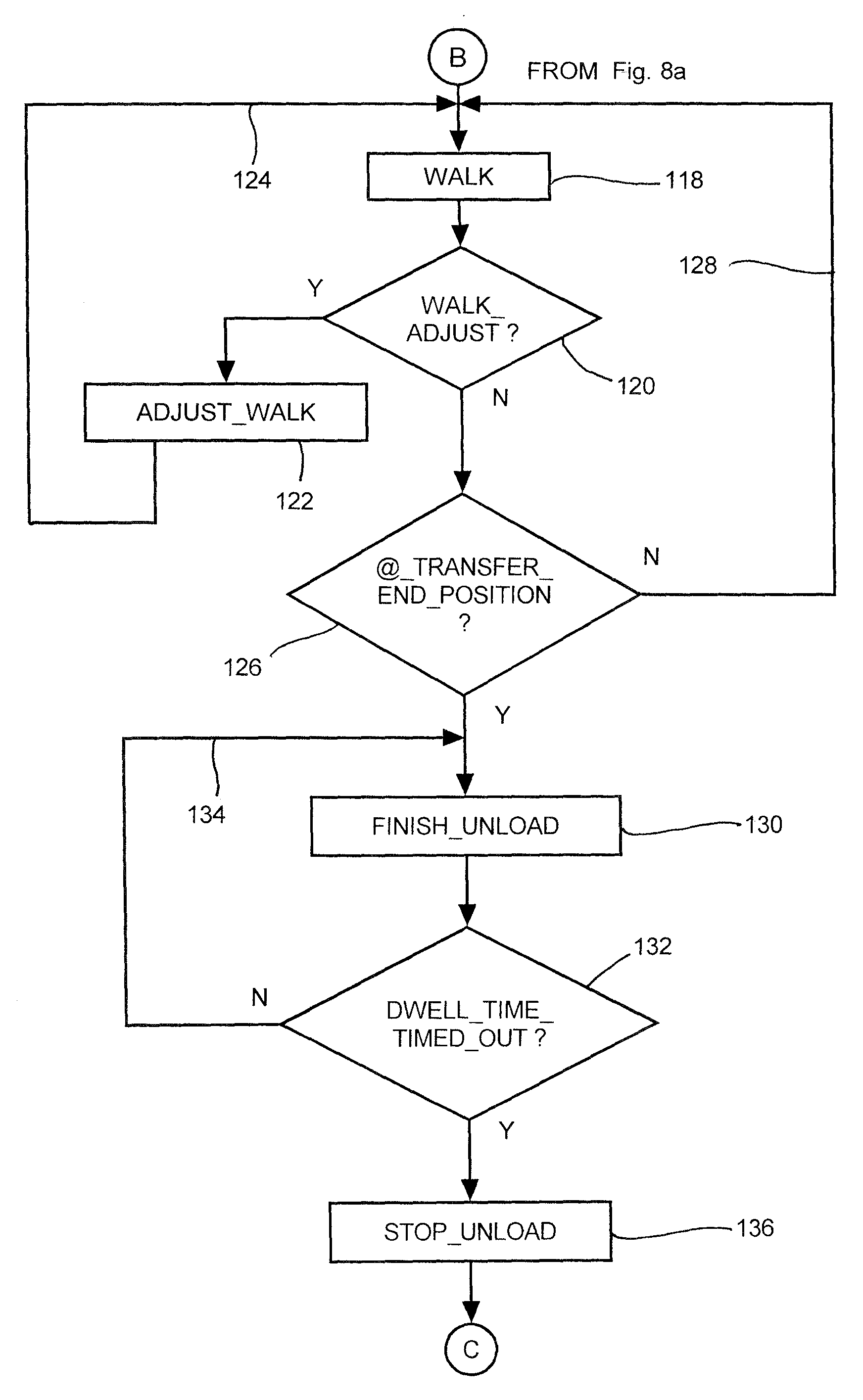
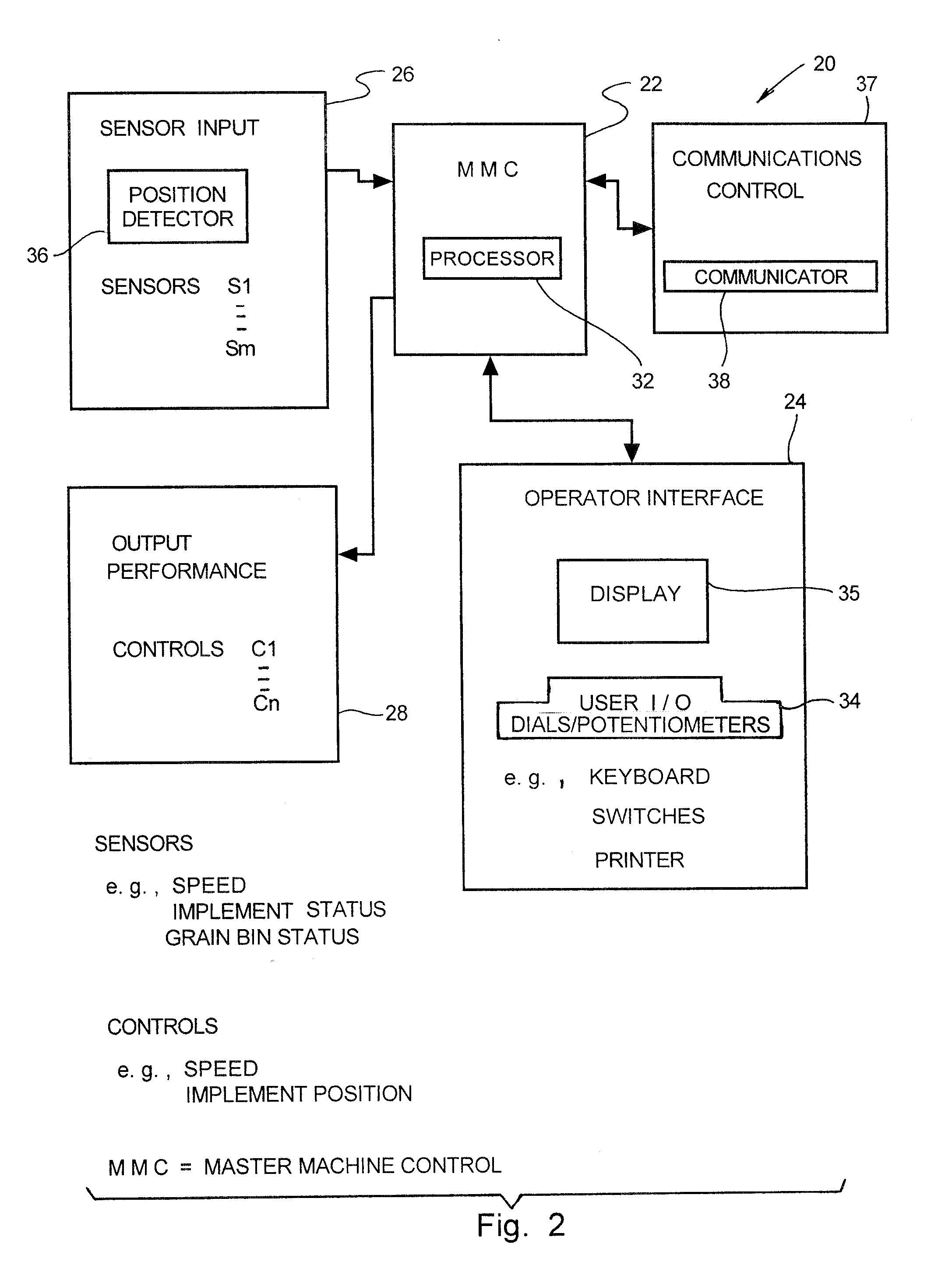
Grain transfer control system and method
ActiveUS20100274452A1Evenly filledDigital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlAutomatic controlControl system
A grain transfer control system, and method of use thereof, for automatedly controlling the transfer of grain from a mobile transferor-type vehicle, such as a combine harvester, to a mobile transferee-type vehicle, such as a crop transport, by varying the position and speed of the transferor-type and transferee-type vehicles relative to one another during the transfer operation, especially by varying the position and rate of walk of the discharge spout along at least a portion of the length of a grain holding receptacle of the transferee-type vehicle, to effect a generally even fill of the grain holding receptacle of the transferee-type vehicle along the length of the grain holding receptacle.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
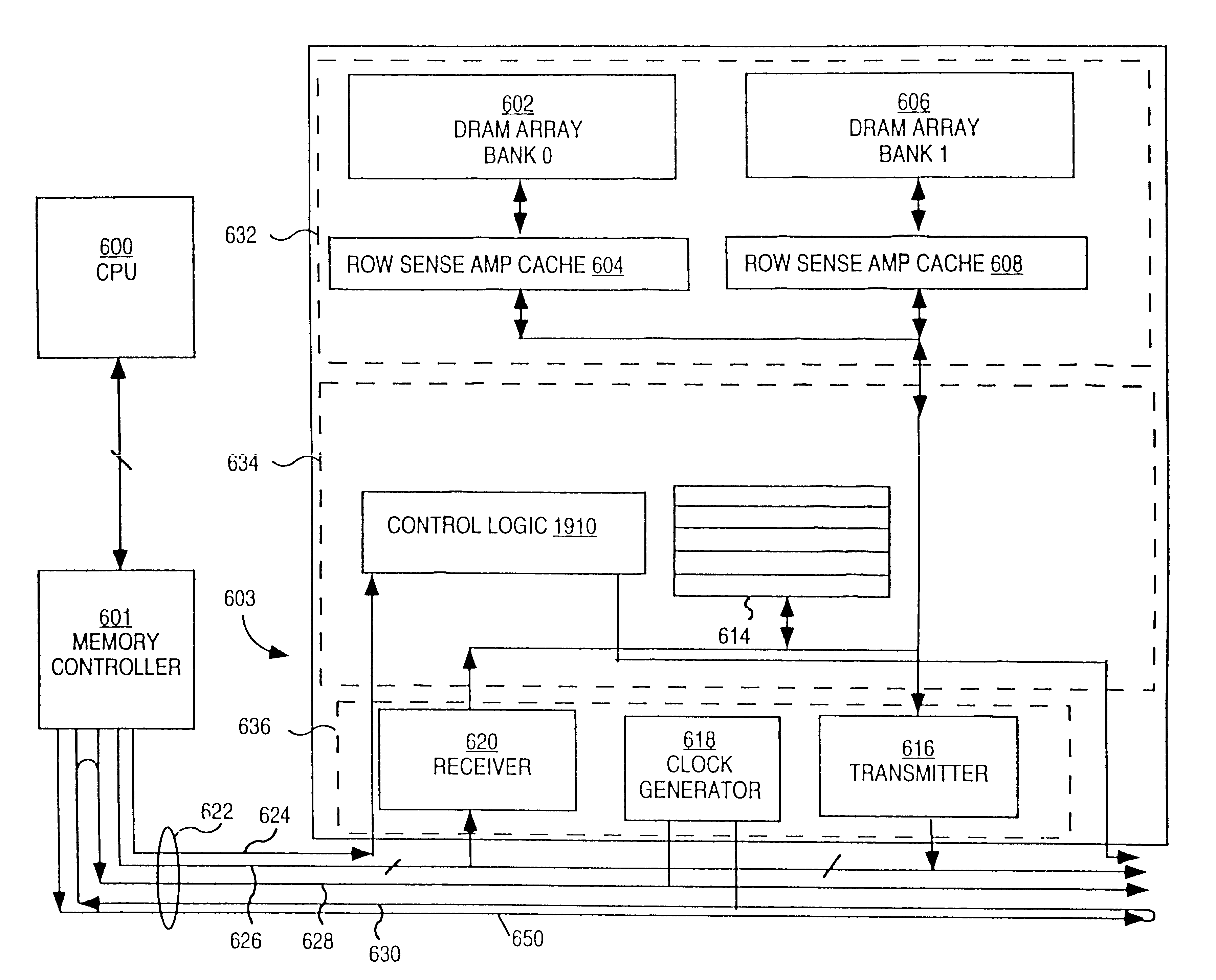
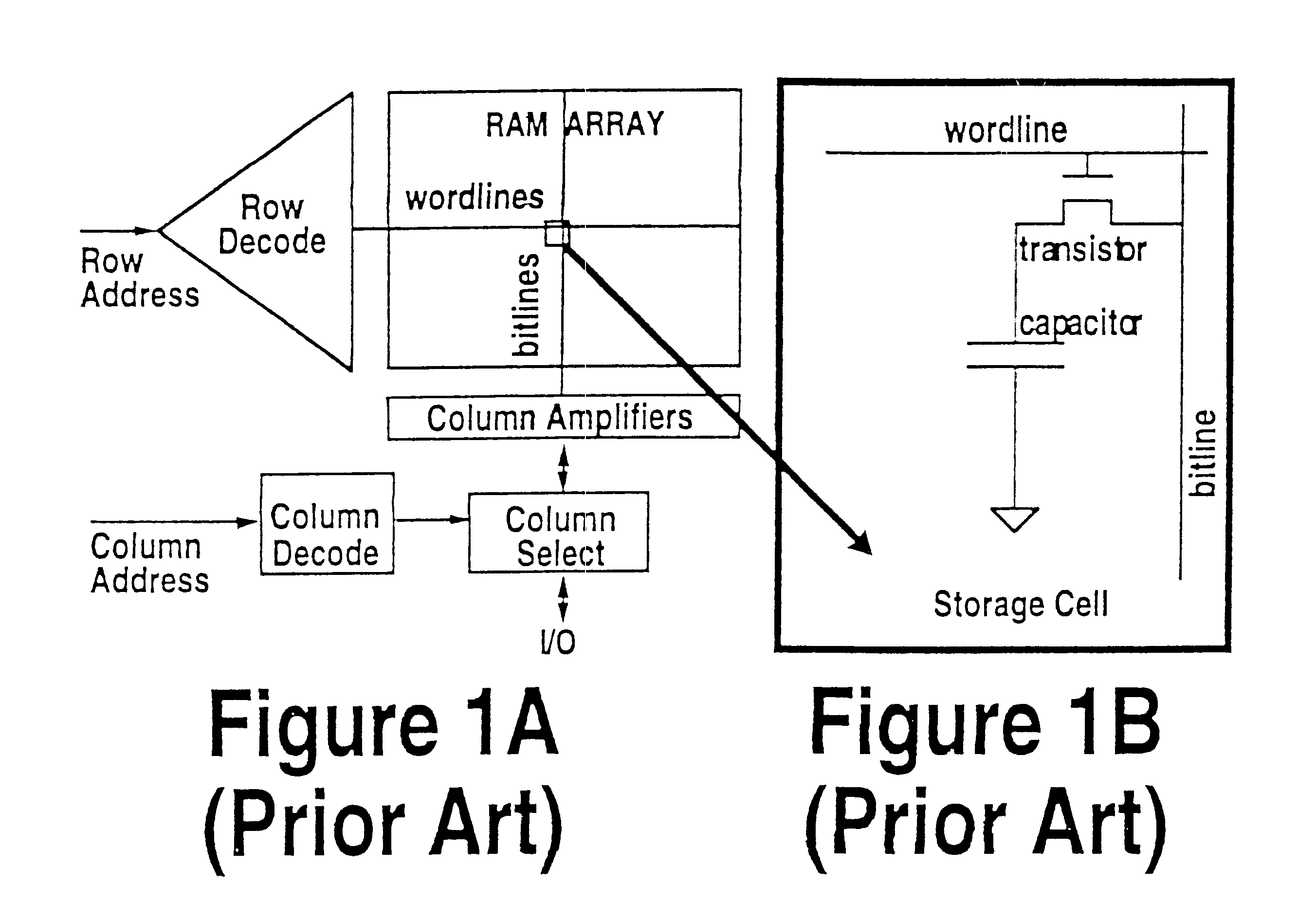
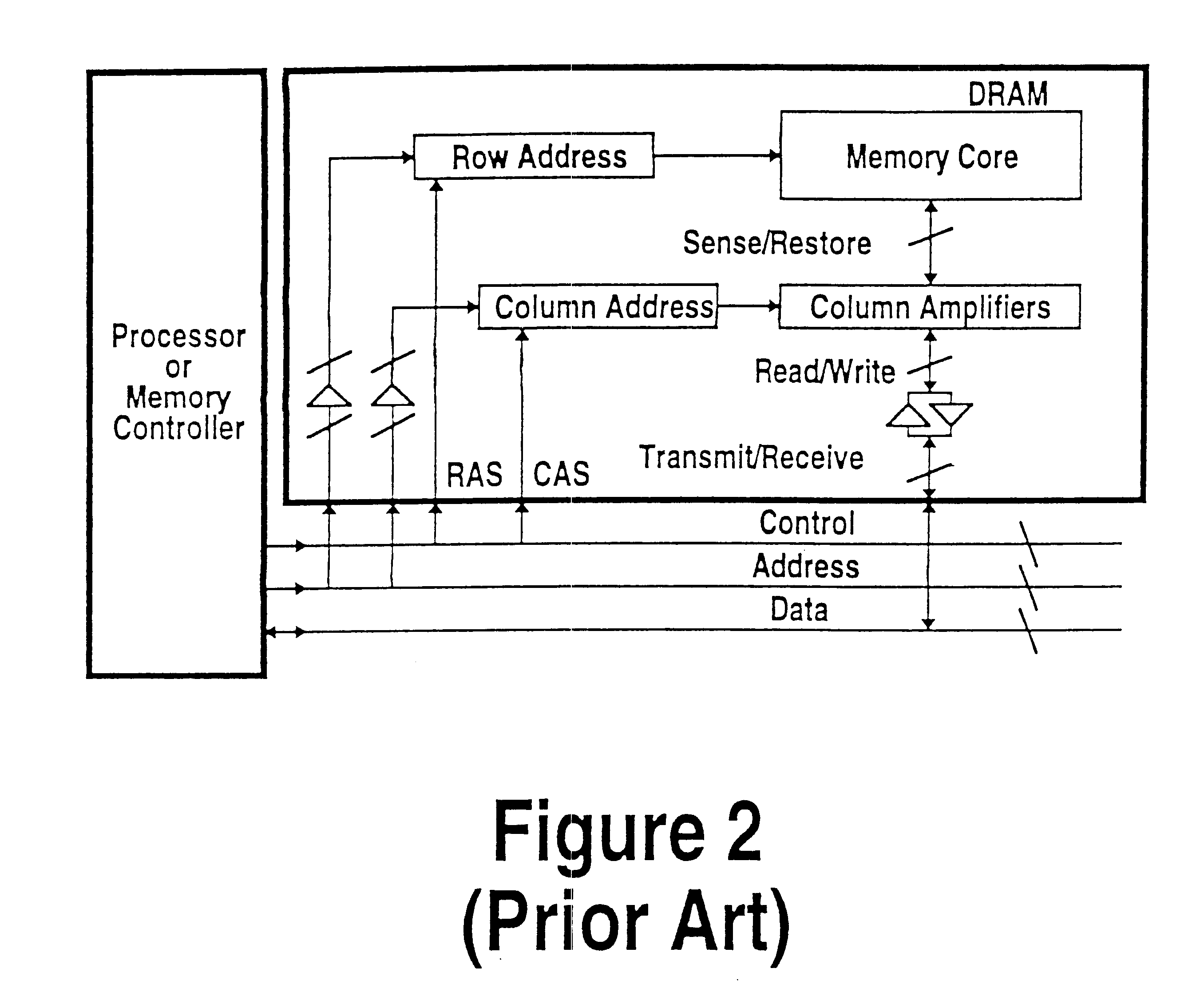
Protocol for communication with dynamic memory
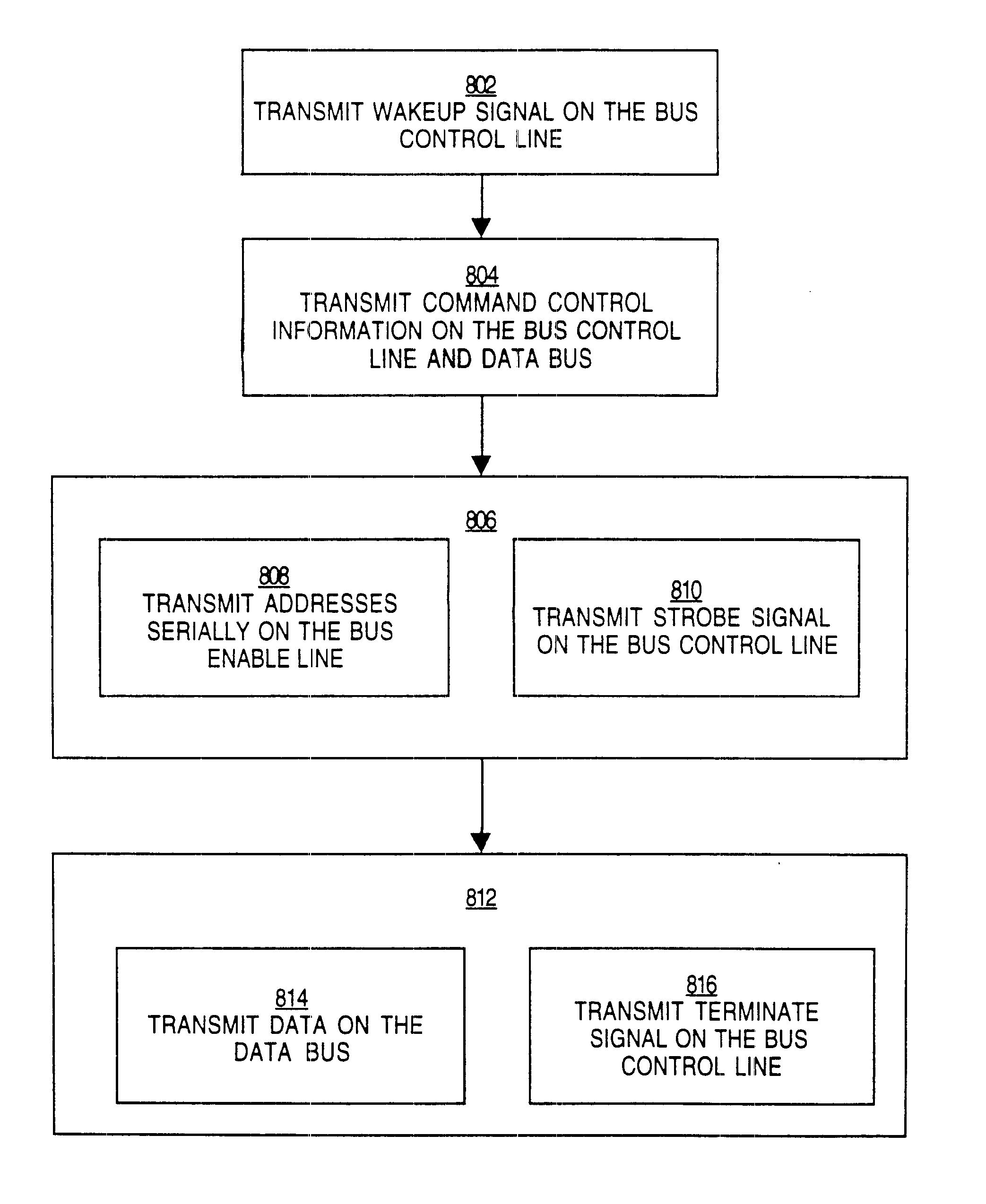
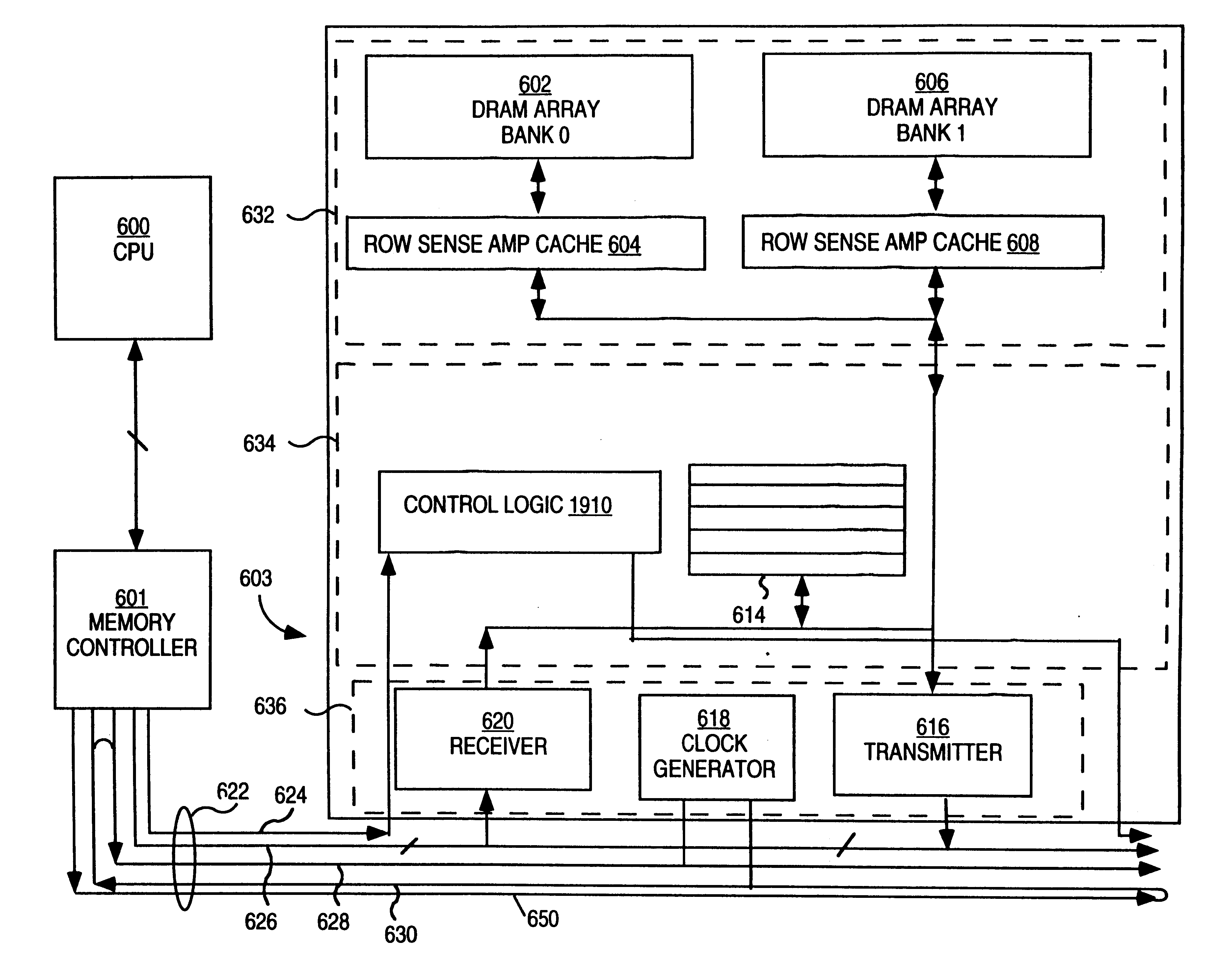
InactiveUS6470405B2Minimum bandwidthDelay minimizationDigital storageElectric digital data processingMemory bankControl signal
A system and method for performing data transfers within a computer system is provided. The system includes a controller configured to dynamically adjust the interleave of the communications required to perform a series of data transfer operations to maximize utilization of the channel over which the communications are to be performed. The controller is able to vary the time interval between the transmission of control information that requests a data transfer and the performance of the data transfer by signaling the beginning of the data transfer with a strobe signal sent separate from the control information. The controller is able to defer the determination of how much data will be transferred in the operation by initiating the termination of a data transfer with a termination signal. The method provides a technique for distinguishing between identical control signals that are carried on the same line. The system includes a memory device with control circuitry that allows no more than one memory bank powered by any given power supply line to perform sense or precharge operations.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Protocol for communication with dynamic memory
InactiveUS6591353B1Minimum bandwidthDelay minimizationDigital storageMemory systemsMemory bankControl signal
A system and method for performing data transfers within a computer system is provided. The system includes a controller configured to dynamically adjust the interleave of the communications required to perform a series of data transfer operations to maximize utilization of the channel over which the communications are to be performed. The controller is able to vary the time interval between the transmission of control information that requests a data transfer and the performance of the data transfer by signaling the beginning of the data transfer with a strobe signal sent separate from the control information. The controller is able to defer the determination of how much data will be transferred in the operation by initiating the termination of a data transfer with a termination signal. The method provides a technique for distinguishing between identical control signals that are carried on the same line. The system includes a memory device with control circuitry that allows no more than one memory bank powered by any given power supply line to perform sense or precharge operations.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Secure file system server architecture and methods
InactiveUS20070050620A1Efficient collectionOperational safetyDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsOperational systemFile system
A data server platform includes a security file system layer interposed between the platform operating system kernel and file system. The secure file system layer is structured to implement a file access control function that selectively constrains data transfer operations initiated through the operating system kernel by an application program to transfer file data through the file system with respect to a persistent data store. A file access controller, implemented independent of the operating system kernel, is coupled to the security file system layer and supports the file access control function by defining permitted file data transfers through the file system. Management of the file access controller separate from the data server platform ensures that any security breach of the platform operating system kernel cannot compromise the function of the security file system layer.
Owner:THALES ESECURITY INC
Utility meter with external signal-powered transceiver
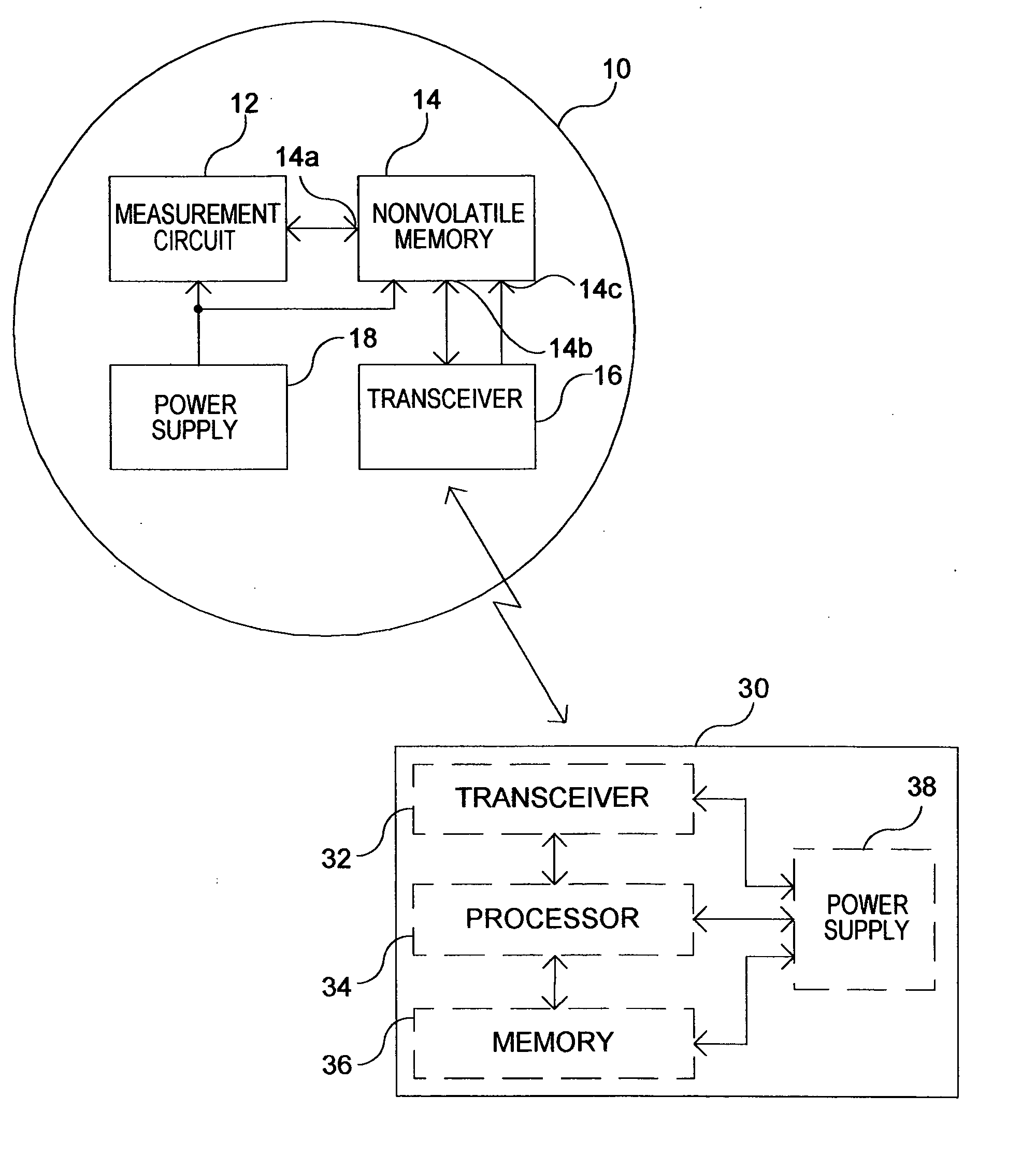
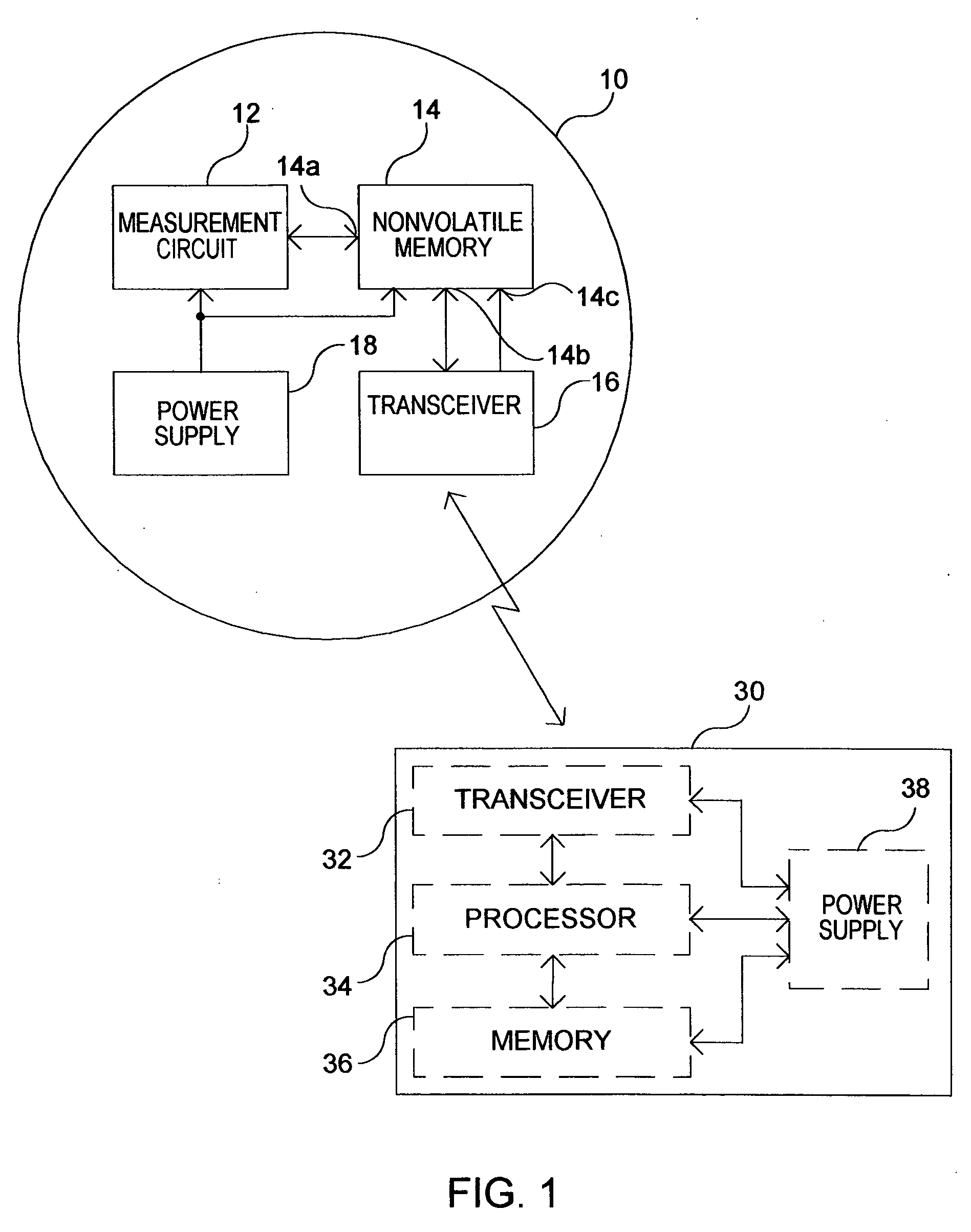
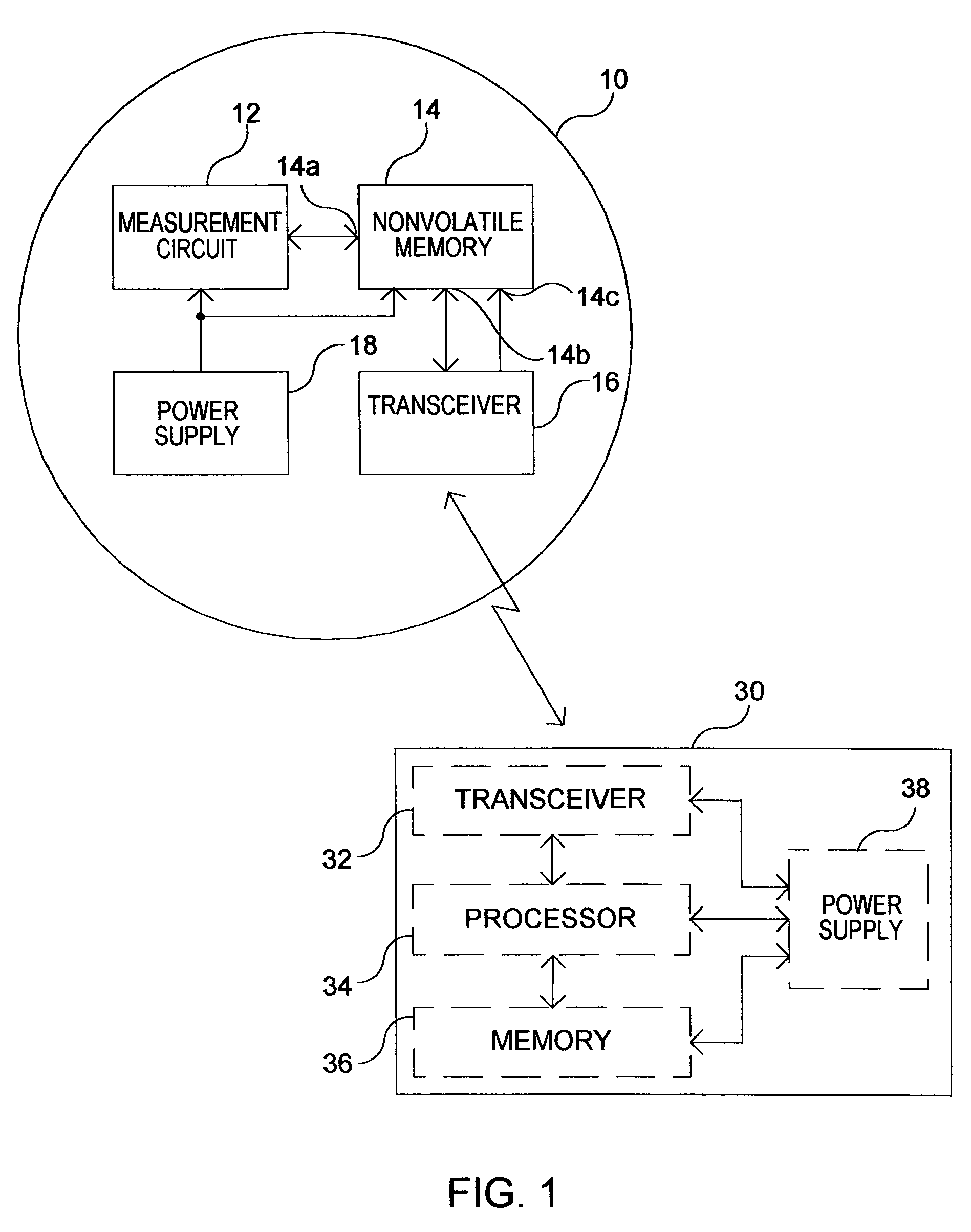
InactiveUS20060145890A1Electric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusTransceiverData transmission
An arrangement for use in a utility meter includes a non-volatile memory and an RF transceiver. The non-volatile memory has a first and a second port, the first port configured to obtain commodity consumption data. The radio frequency (RF) transceiver is configured to receive and RF signal from an external source and obtain energy from the RF signal and provide the energy to a bias voltage input of the non-volatile memory. The RF transceiver is further operable to perform a data transfer operation responsive to the received RF signal, the data transfer operation including a transfer of meter-related data between the non-volatile memory and the RF transceiver using the second port of the non-volatile memory.
Owner:LANDIS GYR LLC
Utility meter with external signal-powered transceiver
InactiveUS7126493B2Electric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusTransceiverEngineering
Owner:LANDIS GYR LLC
Protocol for communication with dynamic memory
InactiveUS6810449B1Minimum bandwidthDelay minimizationDigital storageInput/output processes for data processingMemory bankControl signal
A system and method for performing data transfers within a computer system is provided The system includes a controller configured to dynamically adjust the interleave of the communications required to perform a series of data transfer operations to maximize utilization of the channel over which the communications are to be performed. The controller is able to vary the time interval between the transmission of control information that requests a data transfer and the performance of the data transfer by signaling the beginning of the data transfer with a strobe signal sent separate from the control information. The controller is able to defer the determination of how much data will be transferred in the operation by initiating the termination of a data transfer with a termination signal. The method provides a technique for distinguishing between identical control signals that are carried on the same line. The system includes a memory device with control circuitry that allows no more than one memory bank powered by any given power supply line to perform sense or precharge operations.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Method for Non-Volatile Memory with Background Data Latch Caching During Erase Operations
ActiveUS20060233023A1Save transfer timeImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTTransfer operationNon-volatile memory
Part of the latency from memory read or write operations is for data to be input to or output from the data latches of the memory via an I / O bus. Methods and circuitry are present for improving performance in non-volatile memory devices by allowing the memory to perform some of these data caching and transfer operations in the background while the memory core is busy with an erase operation. In the exemplary embodiment, a read operation is inserted just prior to the erase operation or one or more read operations are inserted during a soft programming phase of the erase operation. In this way, the read data could be output while the erase operation is taking place, thereby making use of otherwise waiting time.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
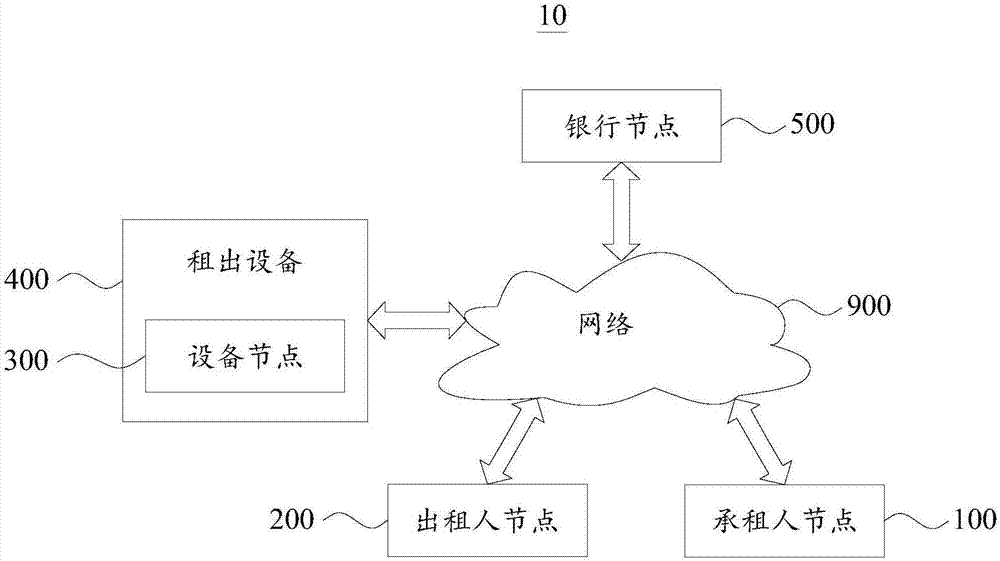
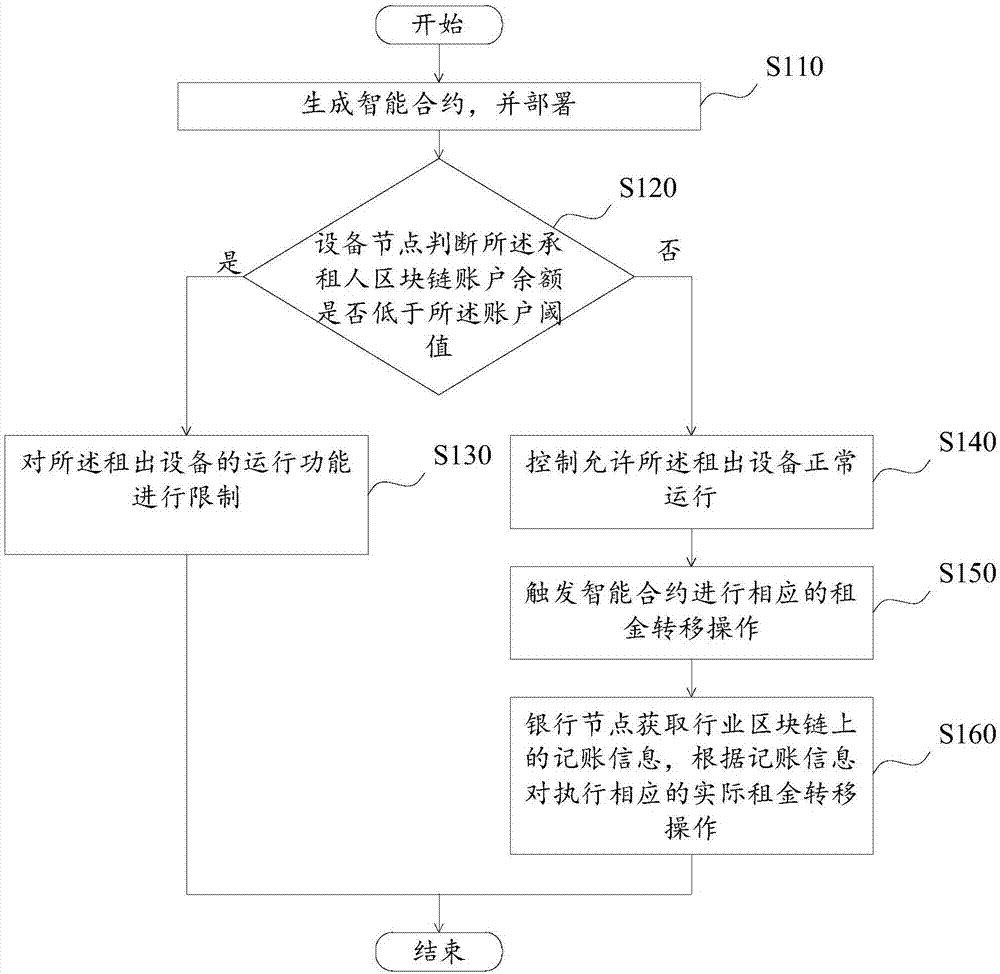
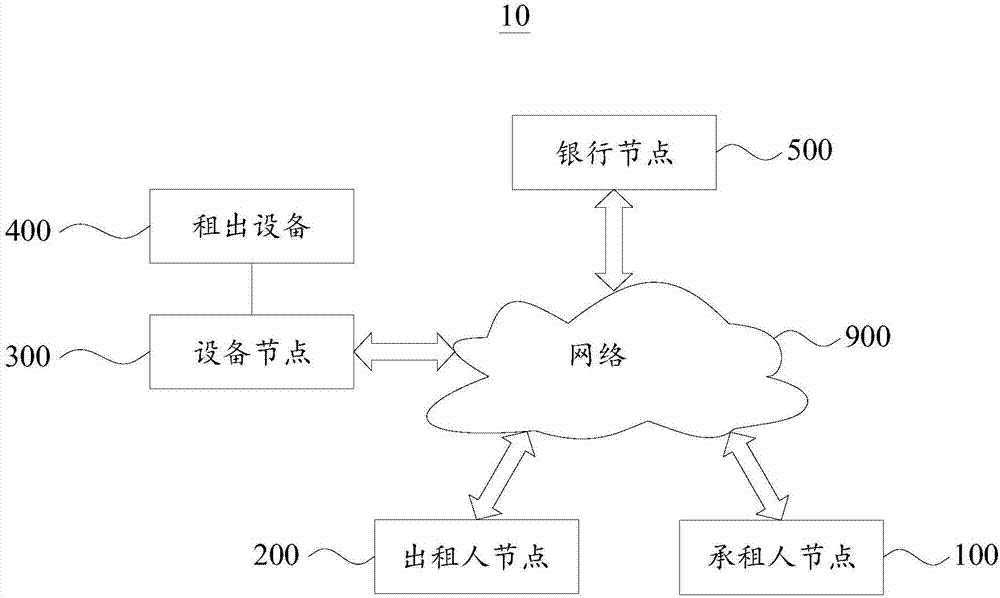
Equipment leasing method and system based on blockchain
InactiveCN107194778AAchieve publicityImprove efficiencyPayment protocolsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsTransaction managementIntelligent management
The invention provides an equipment leasing method and system based on a blockchain. The method comprises the following steps that: a leaser node generates an intelligent contract according to a leasing protocol of a leaser and a lessee, and deploys the intelligent contact on an industrial blockchain; an equipment node obtains the blockchain account information, which is recorded by the industrial blockchain, of the lessee, and whether the blockchain account amount of the lease is lower than the appointed threshold value of the account or not is judged; when the account balance is lowered than the appointed threshold value of the account, the operation function of leased equipment is restricted; when the virtual currency balance of the account is not lower than the appointed threshold value of the account, the leased equipment is controlled to permit to normally operate; and the equipment node triggers the intelligent contact according to the operation situation of the leased equipment to carry out a corresponding rent transfer operation on the blockchain account of the leaser and the lessee. Therefore, the public, transparent, traceable and untamped recording of the automatic and intelligent management and transaction process of the leased equipment and rent transaction can be realized, and leasing transaction managing or auditing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:金立彦
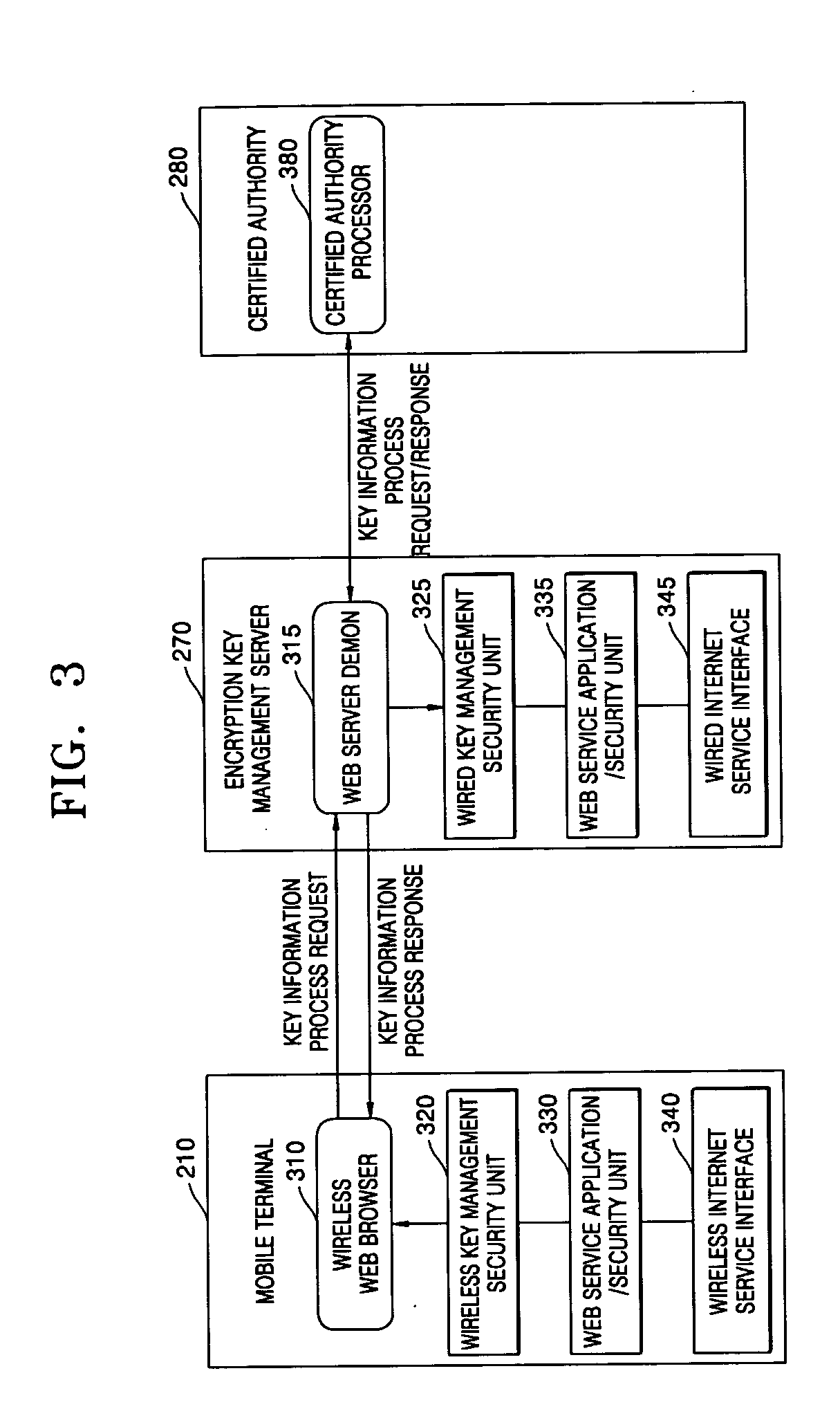
System and method of managing encryption key management system for mobile terminals
InactiveUS20050144439A1Reduce hardware loadKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageTransfer operationManagement system
An encryption key management method for mobile terminals for providing at least one mobile terminal which is connected to a network to use services with an encryption key required for issuing a certificate which is needed for the services and managed by a certification authority by using an encryption key management server is provided. The method includes operations of: a registration requesting operation where the mobile terminal generates an encryption key registration request; an encryption key managing operation where the encryption key management server generates and manages the encryption key in response to the encryption key registration request; a transferring operation of sending the generated encryption key to the mobile terminal; and a security service providing operation of receiving the certificate managed by the certification authority and providing selective security services specific to the content of the services provided to the mobile terminal. The method can relieve the hardware load of mobile terminals while providing a security service using various conventional certification authorities.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com