Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8440 results about "Random access memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Random-access memory (RAM / r æ m /) is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory. In contrast, with other direct-access data storage media such ...
Unipolar resistance random access memory (RRAM) device and vertically stacked architecture
InactiveUS20070132049A1Improve performanceGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesRandom access memoryEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention includes a low-cost unipolar rewritable variable-resistance memory device, made of cross-point arrays of memory cells, vertically stacked on top of one another and compatible with a polycrystalline silicon diode.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
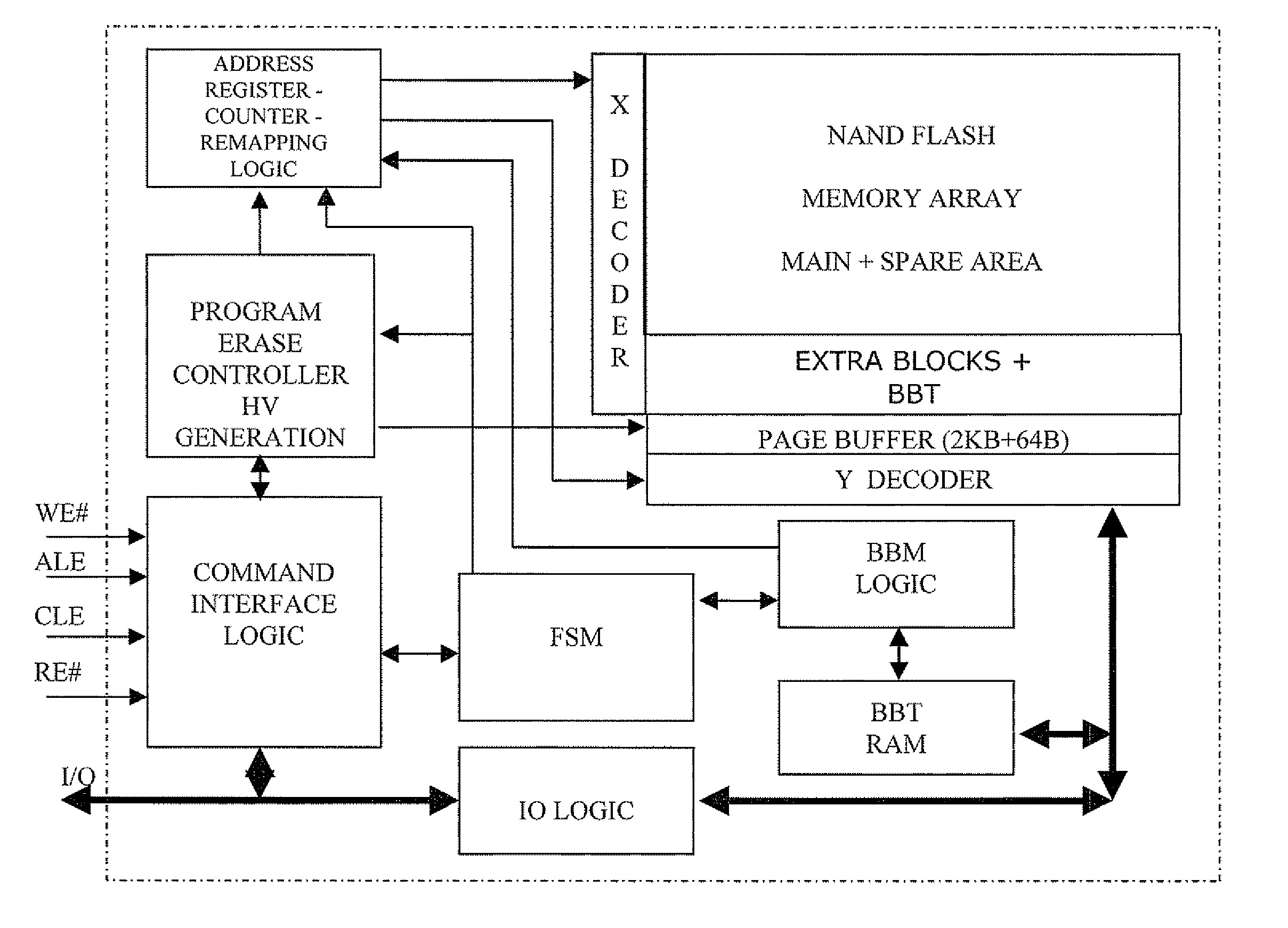
Method of managing fails in a non-volatile memory device and relative memory device
ActiveUS20070109856A1Easy to implementLow costRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectricityWorking life
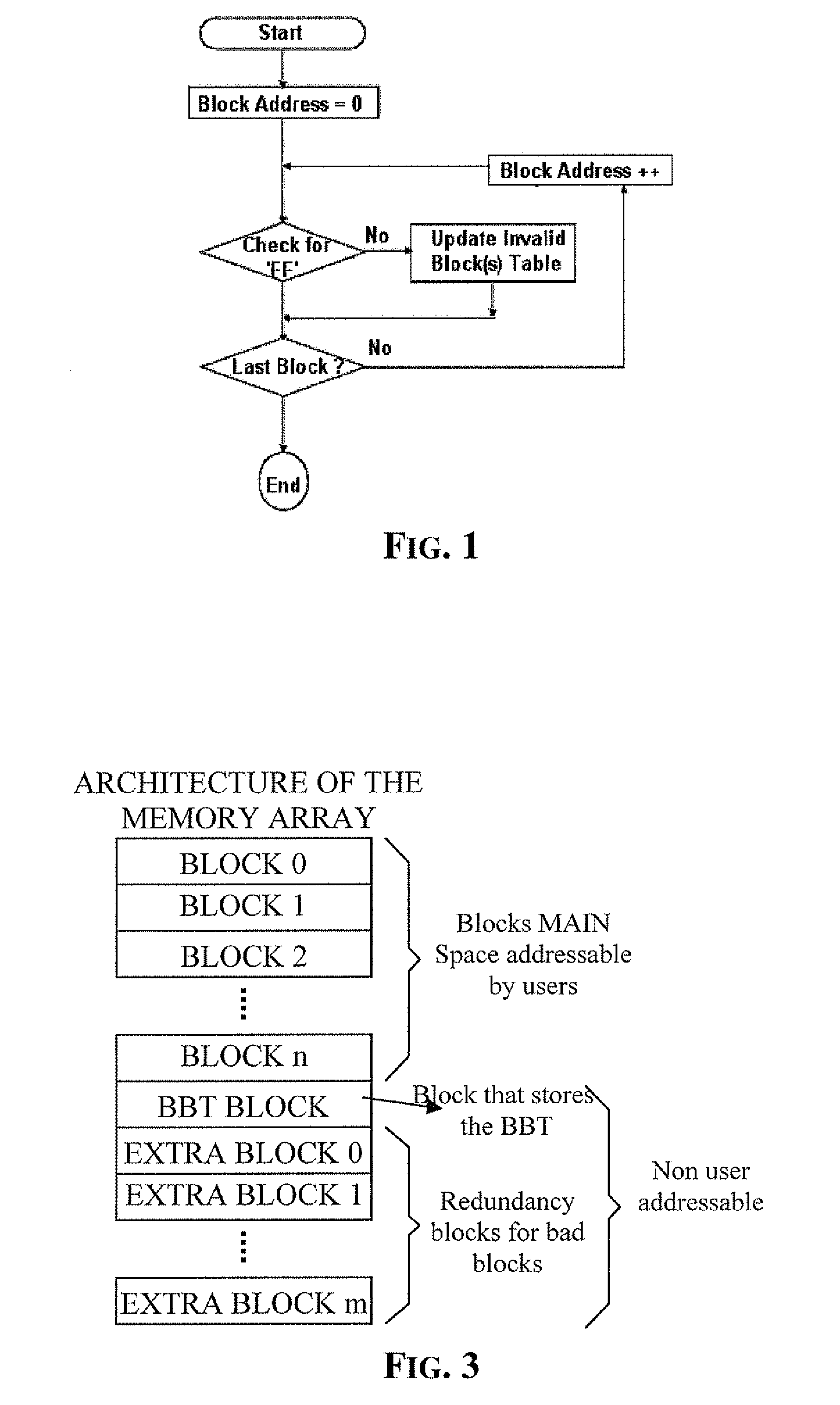
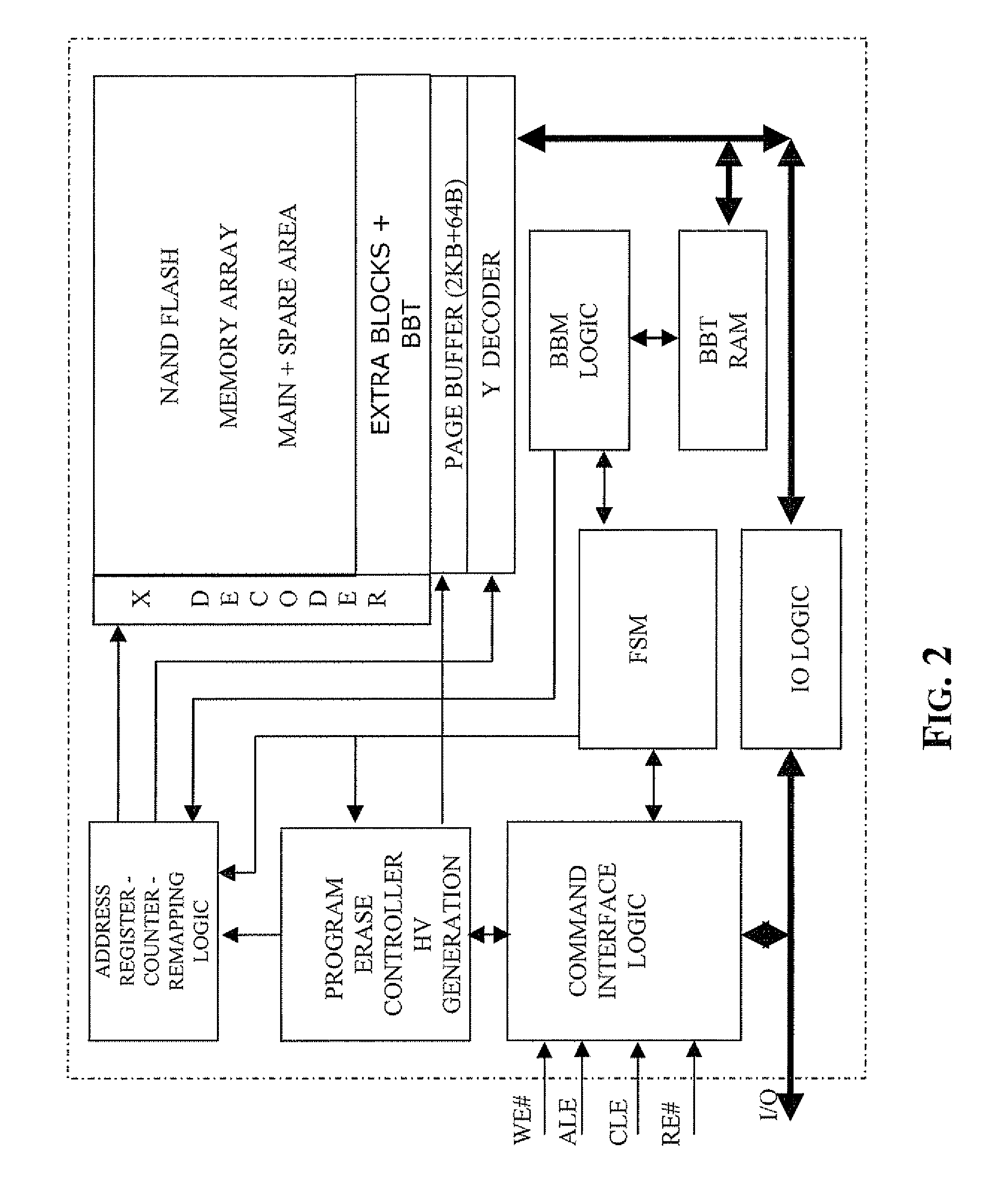
A method of managing fails in a non-volatile memory device including an array of cells grouped in blocks of data storage cells includes defining in the array a first subset of user addressable blocks of cells, and a second subset of redundancy blocks of cells. Each block including at least one failed cell in the first subset is located during a test on wafer of the non-volatile memory device. Each block is marked as bad, and a bad block address table of respective codes is stored in a non-volatile memory buffer. At power-on, the bad block address table is copied from the non-volatile memory buffer to the random access memory. A block of memory cells of the first subset is verified as bad by looking up the bad block address table, and if a block is bad, then remapping access to a corresponding block of redundancy cells. A third subset of non-user addressable blocks of cells is defined in the array for storing the bad block address table of respective codes in an addressable page of cells of a block of the third subset. Each page of the third subset is associated to a corresponding redundancy block. If during the working life of the memory device a block of cells previously judged good in a test phase becomes failed, each block is marked as bad and the stored table in the random access memory is updated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
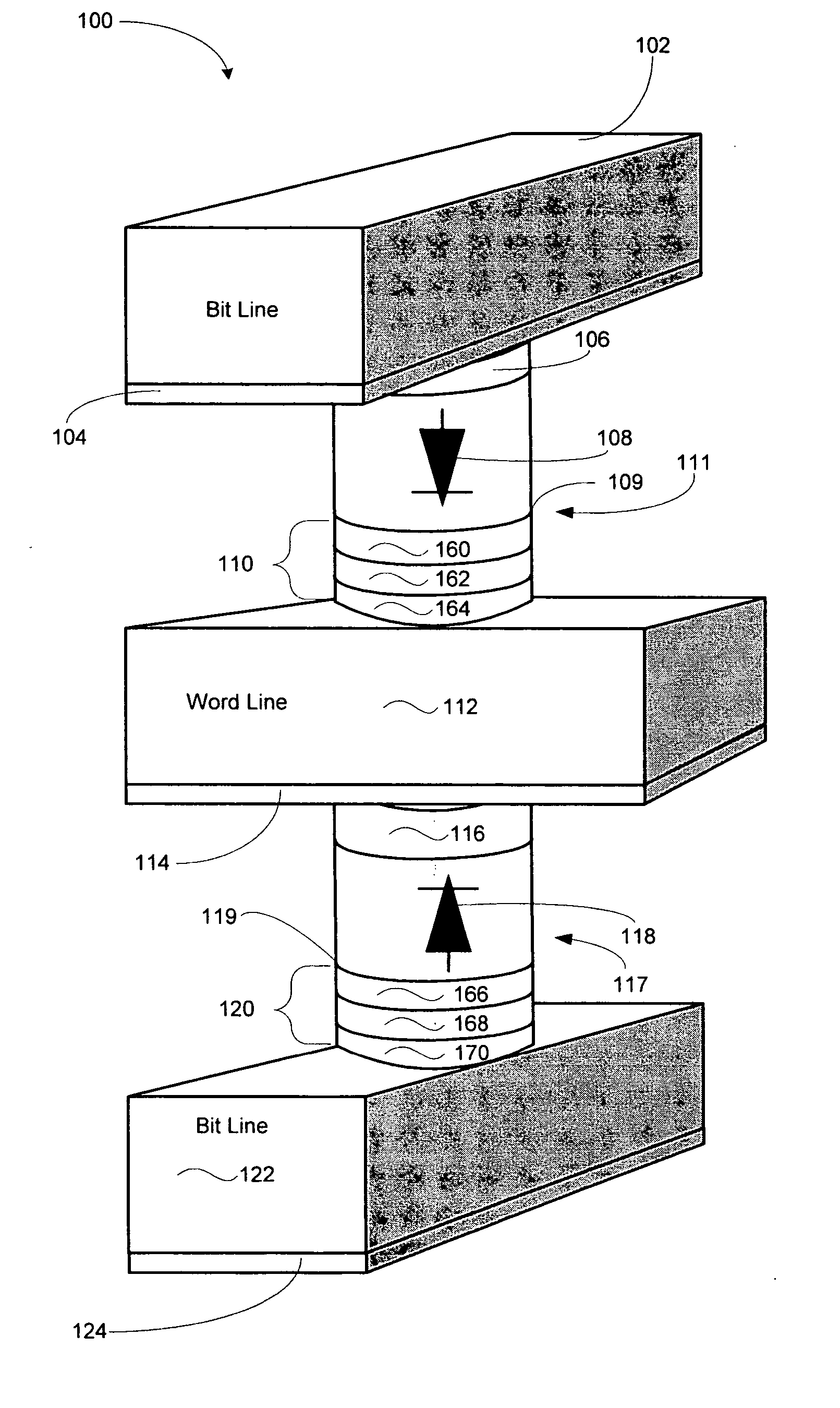
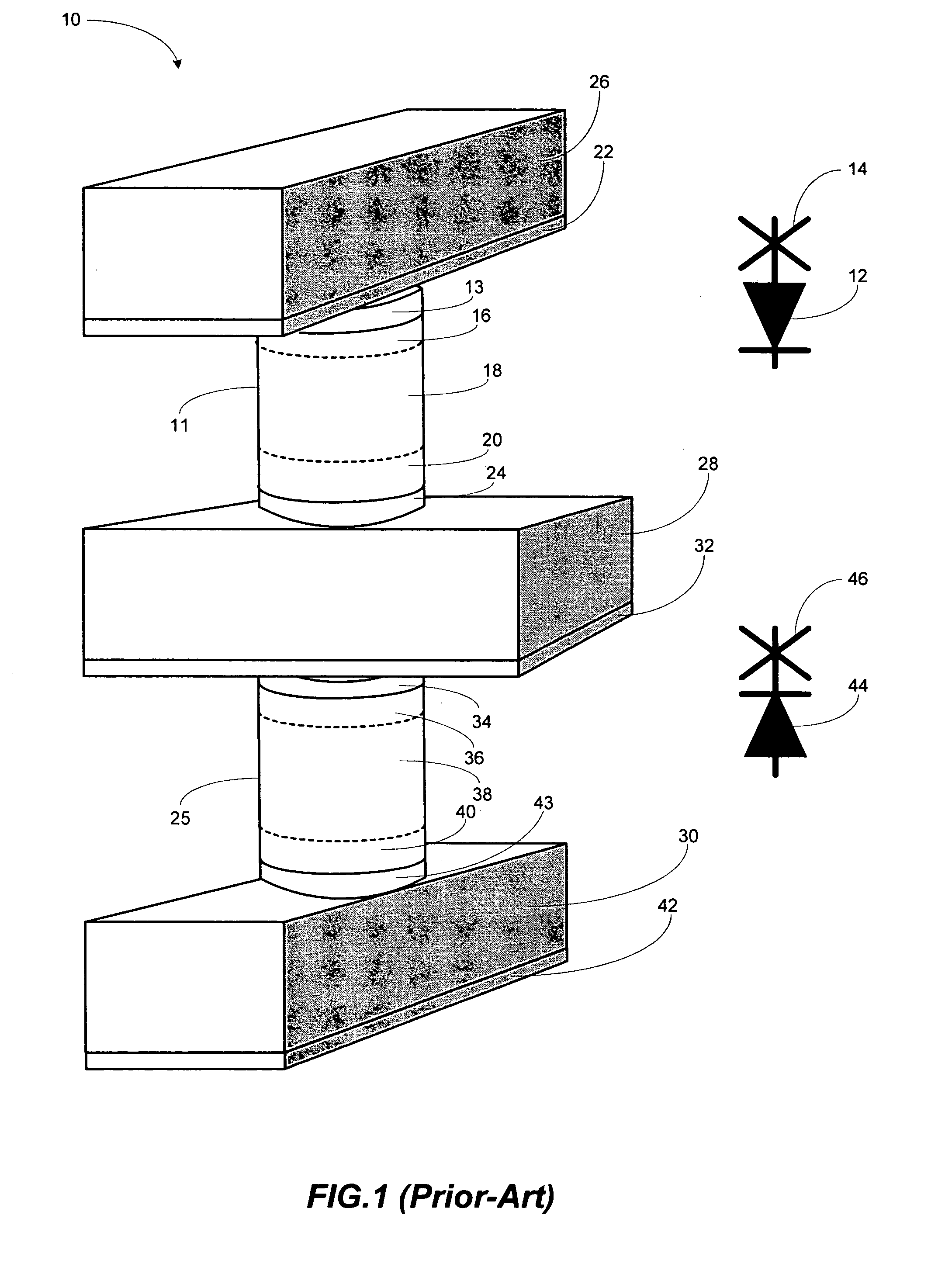
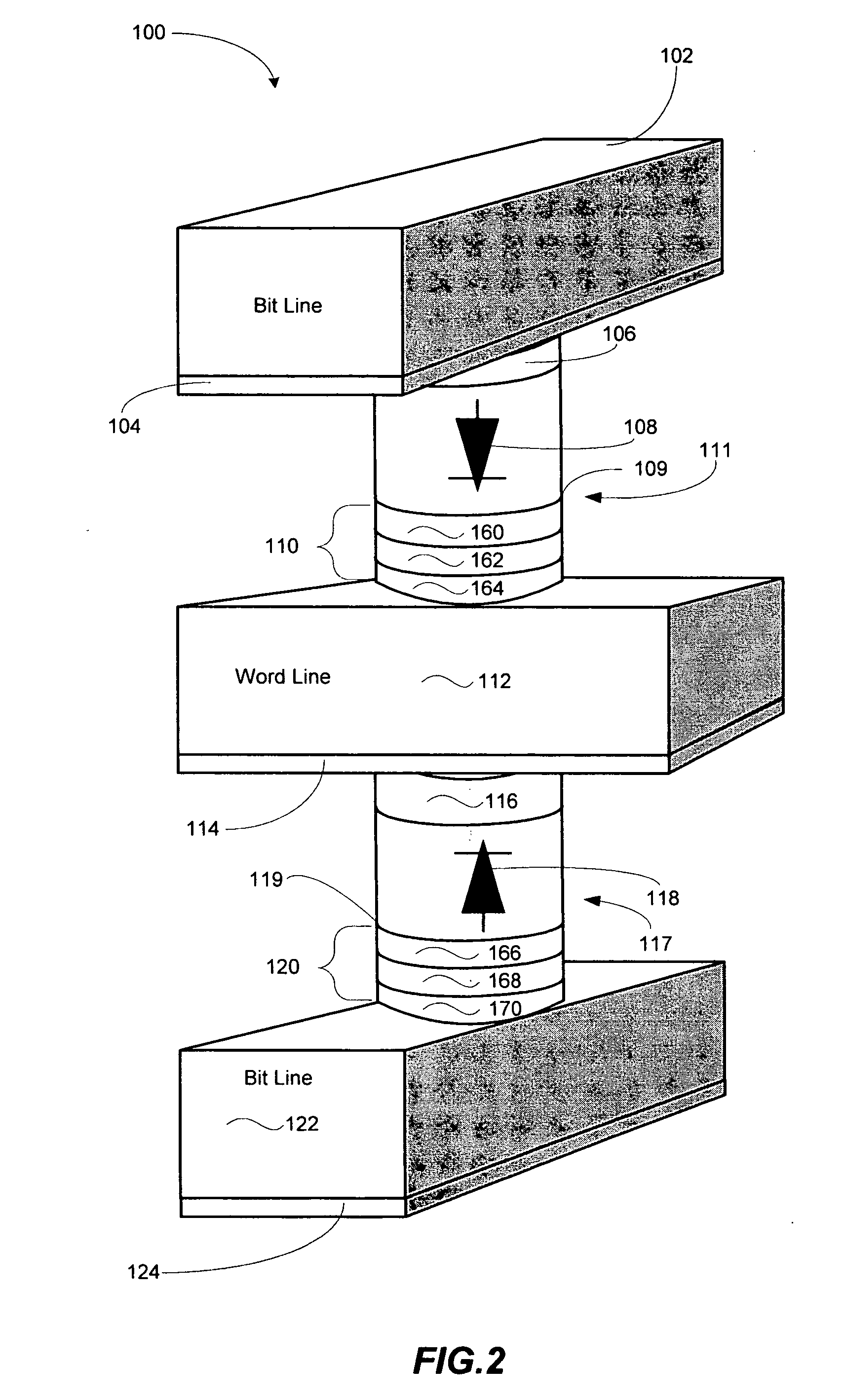
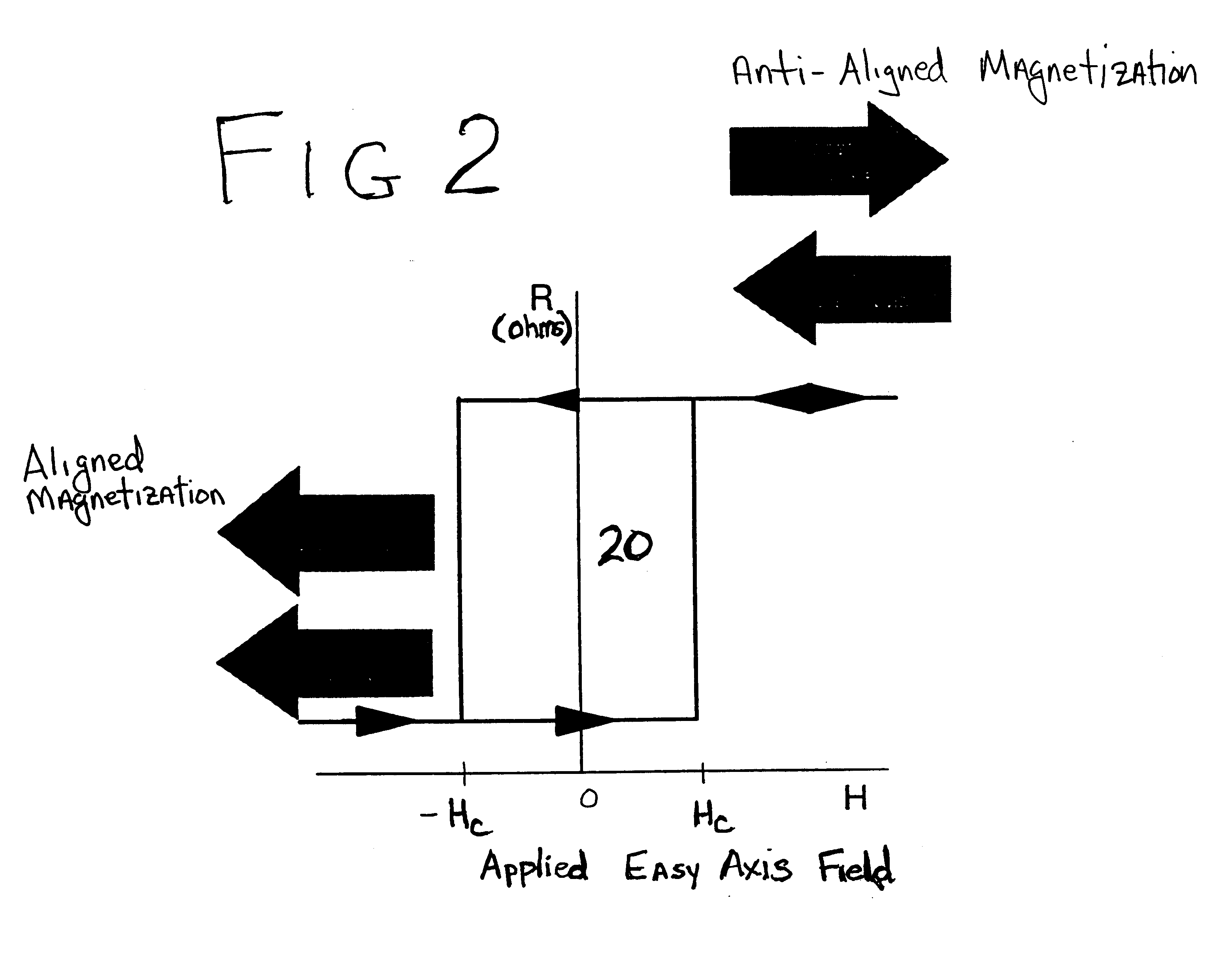
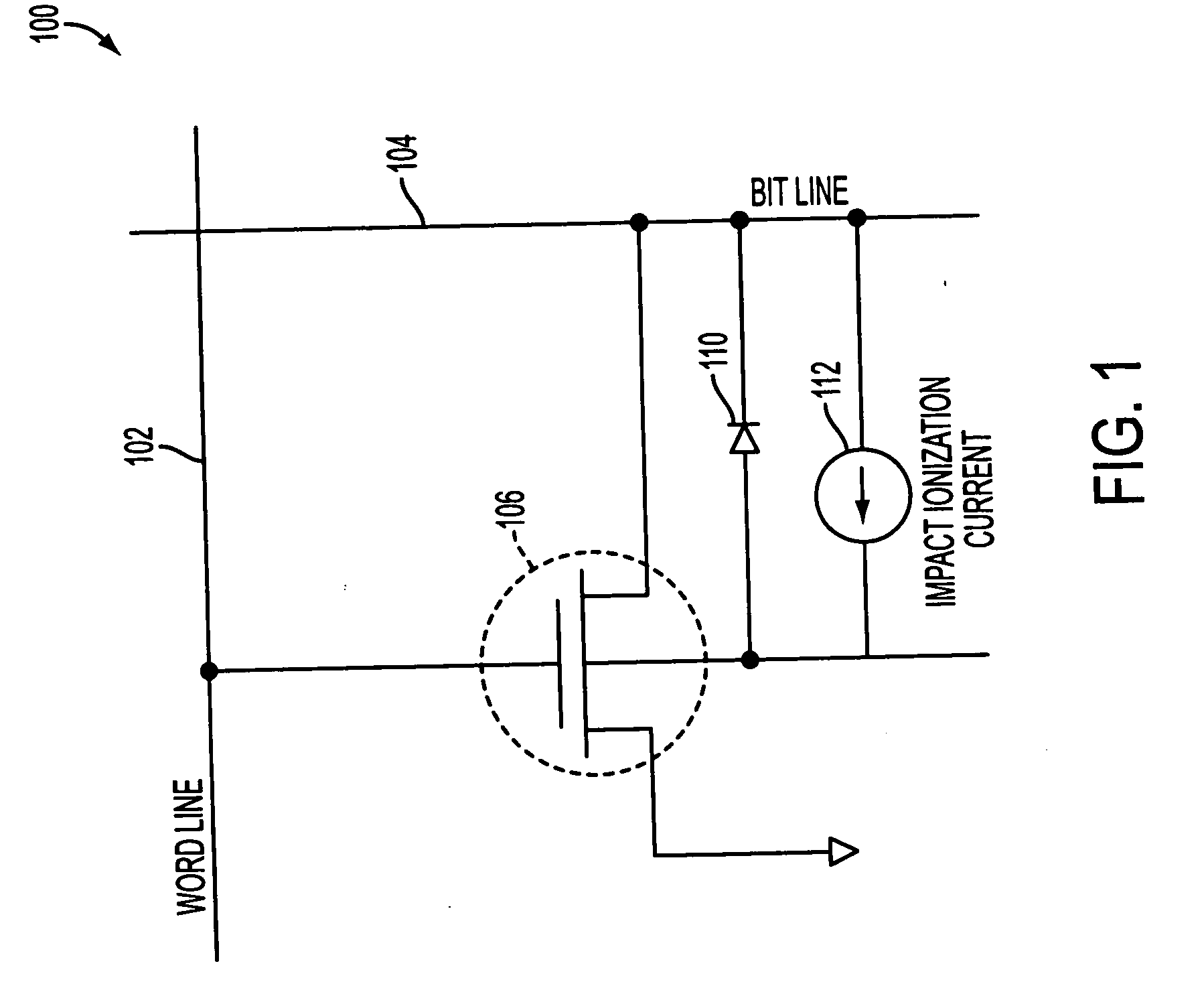
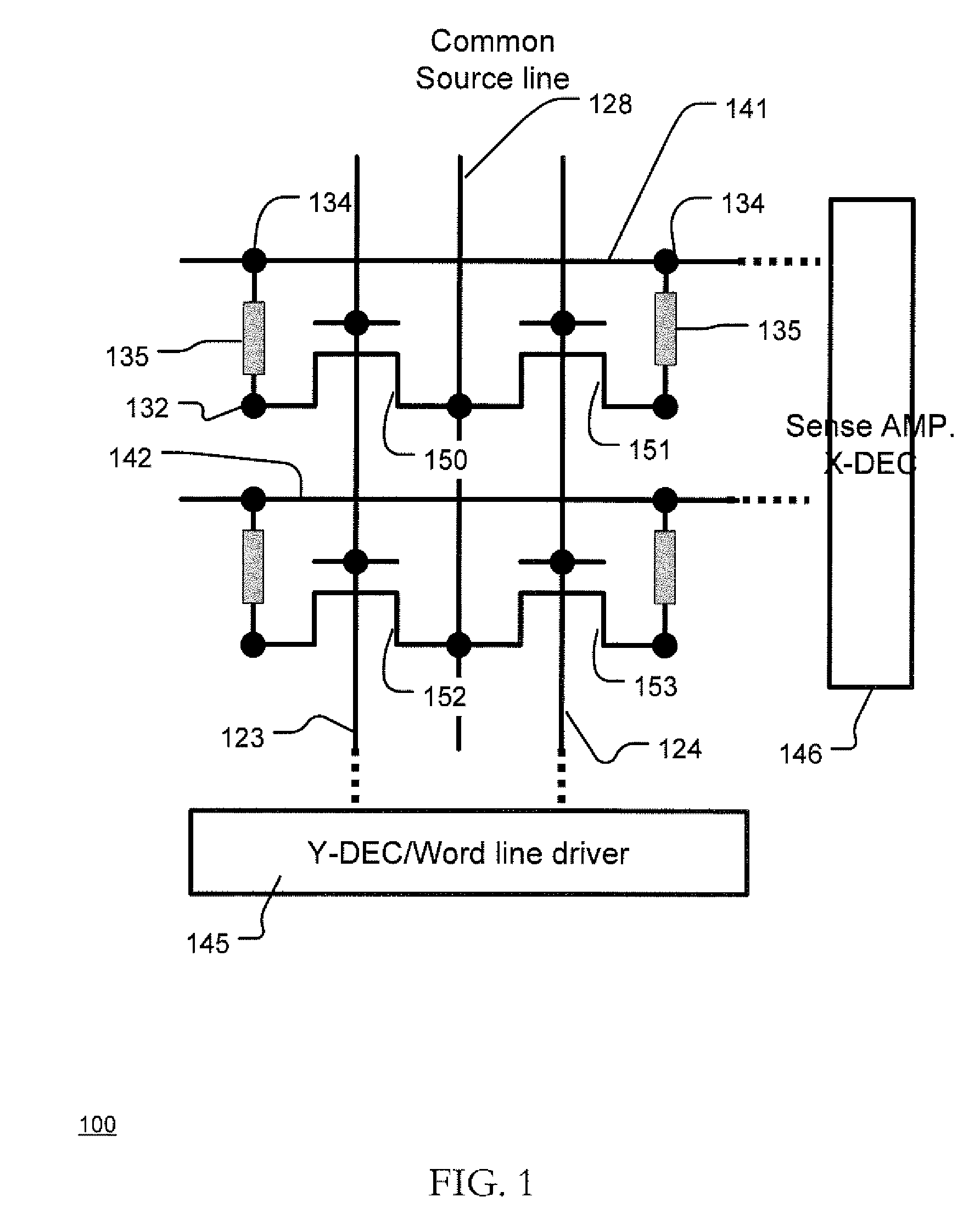
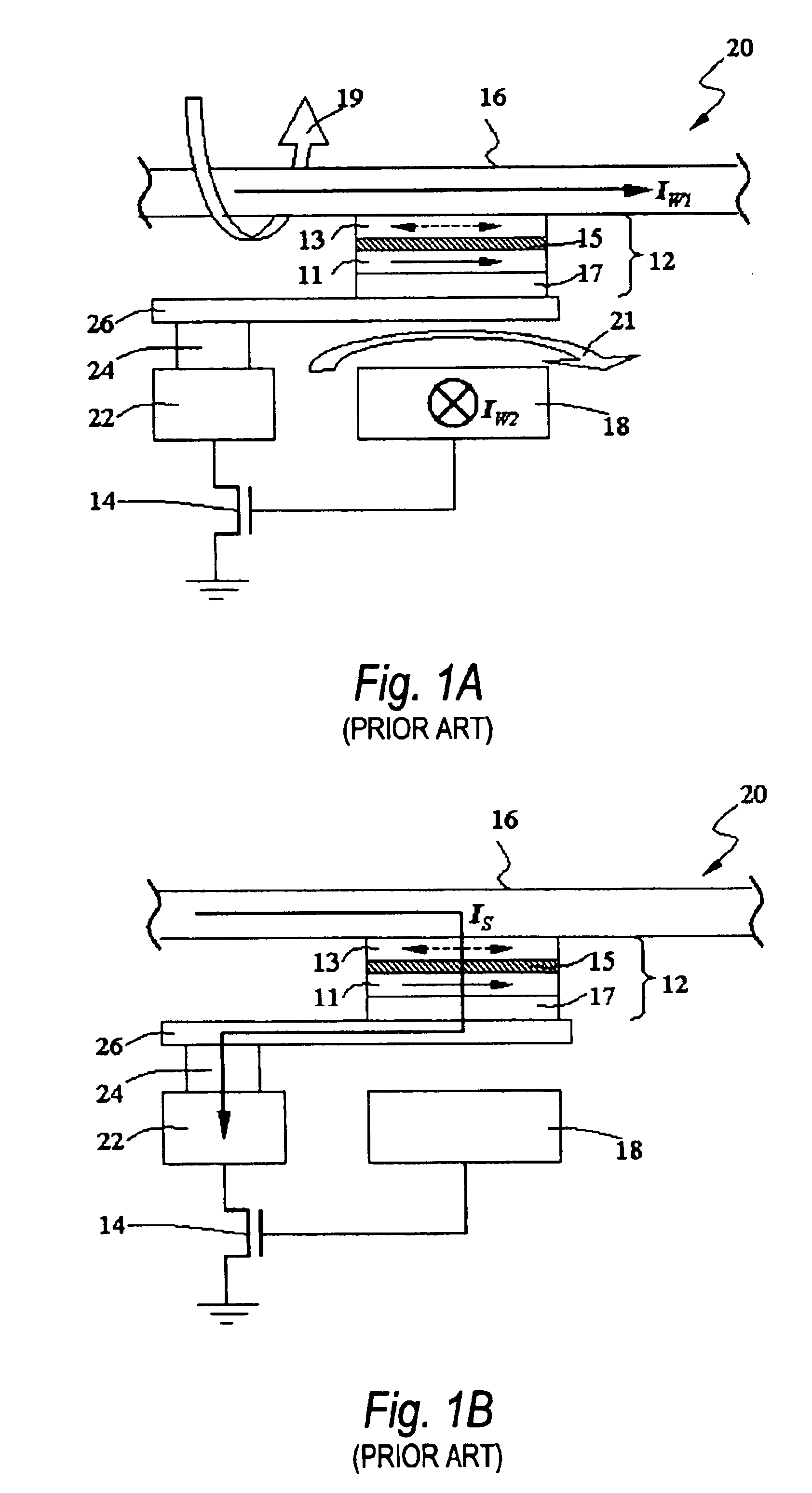
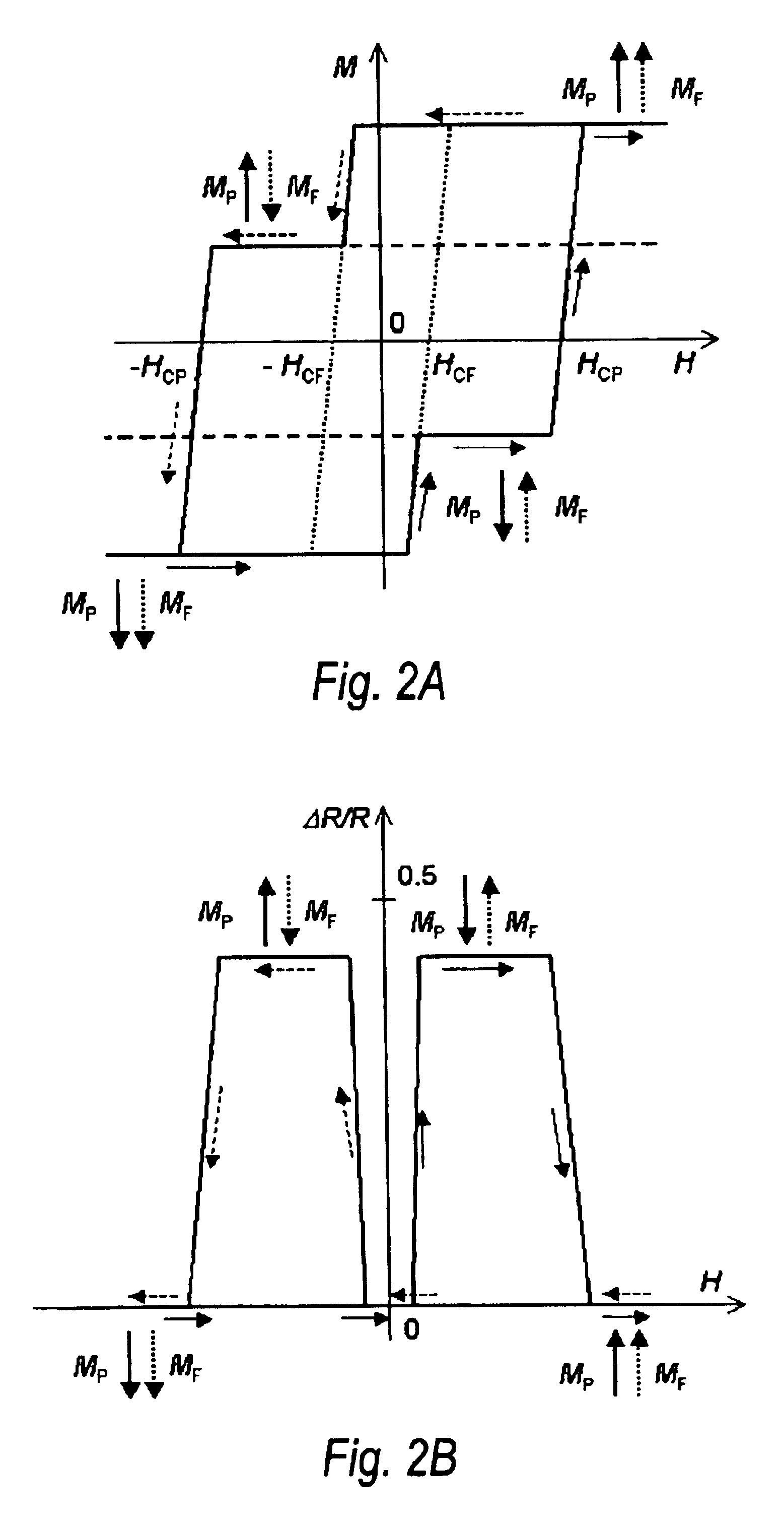
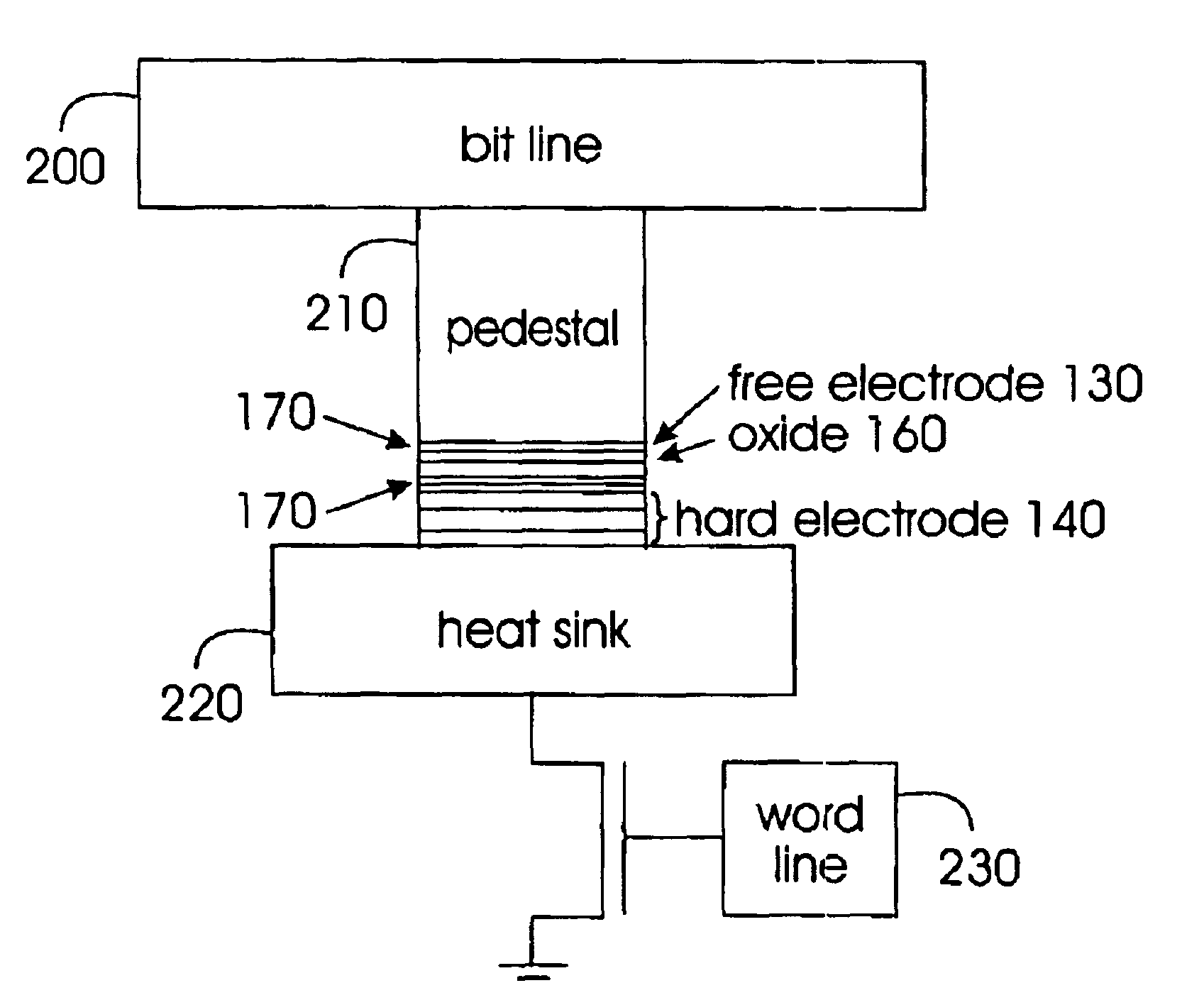
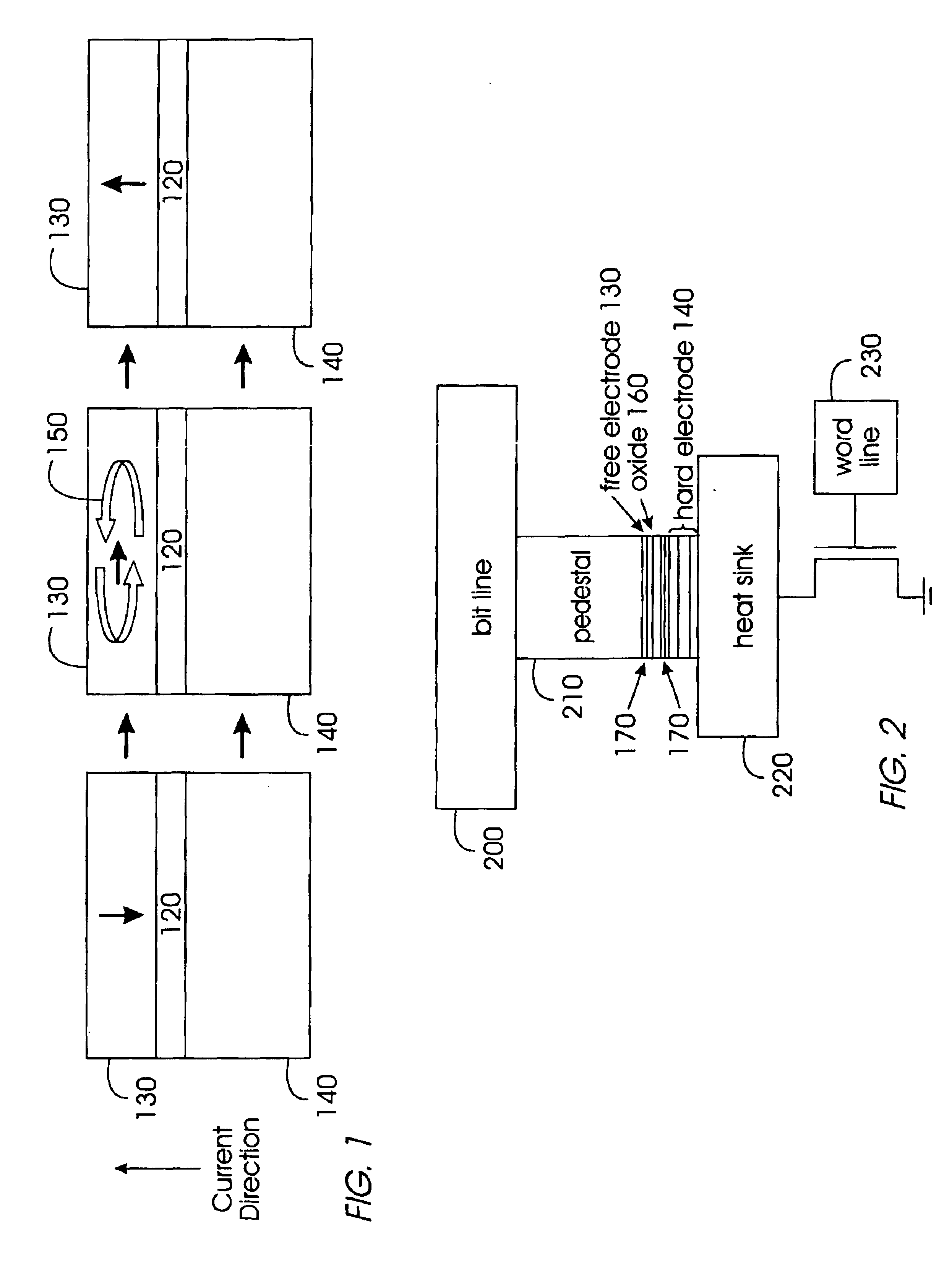
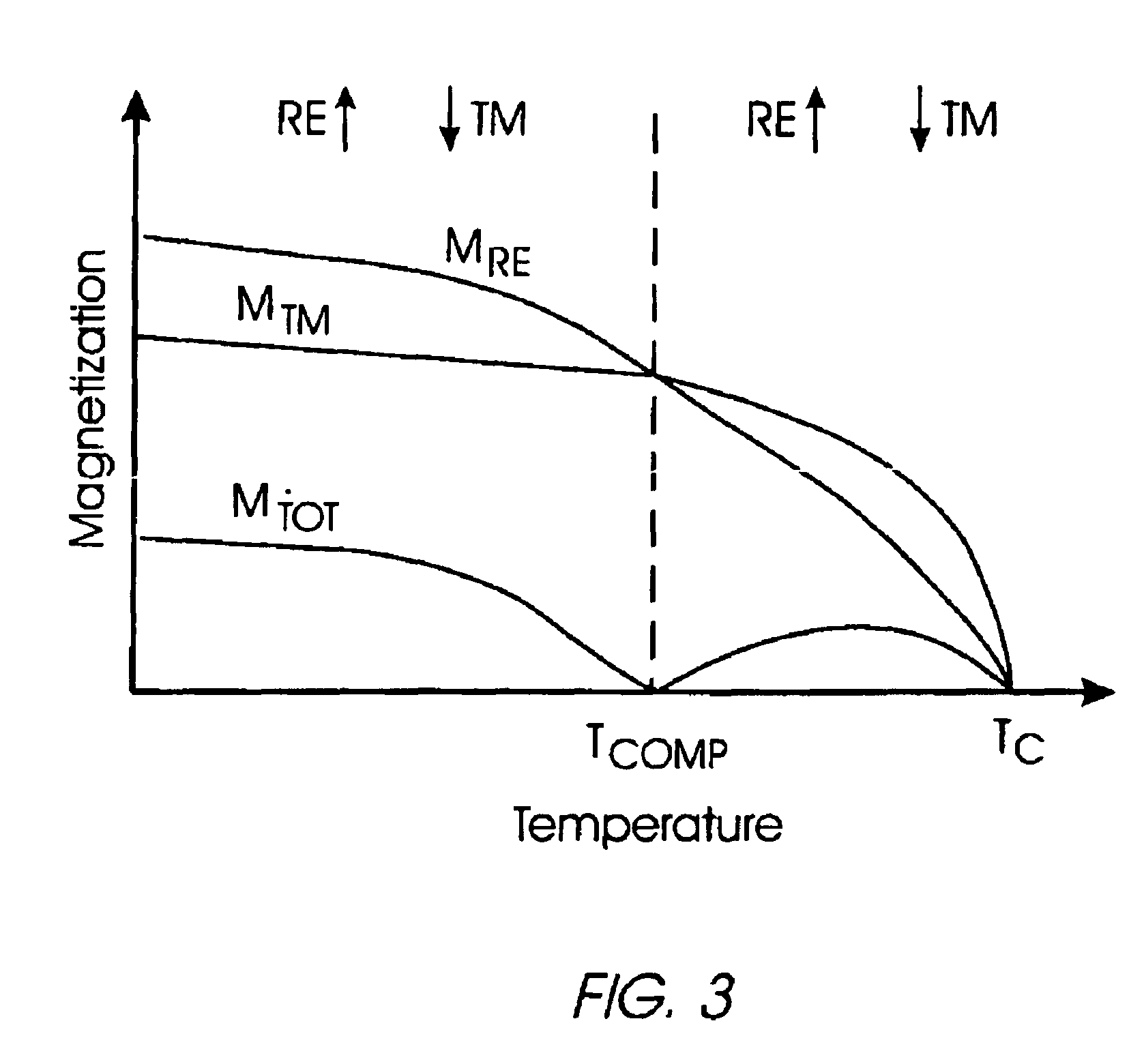
Thermally-assisted magnetic random access memory (MRAM)
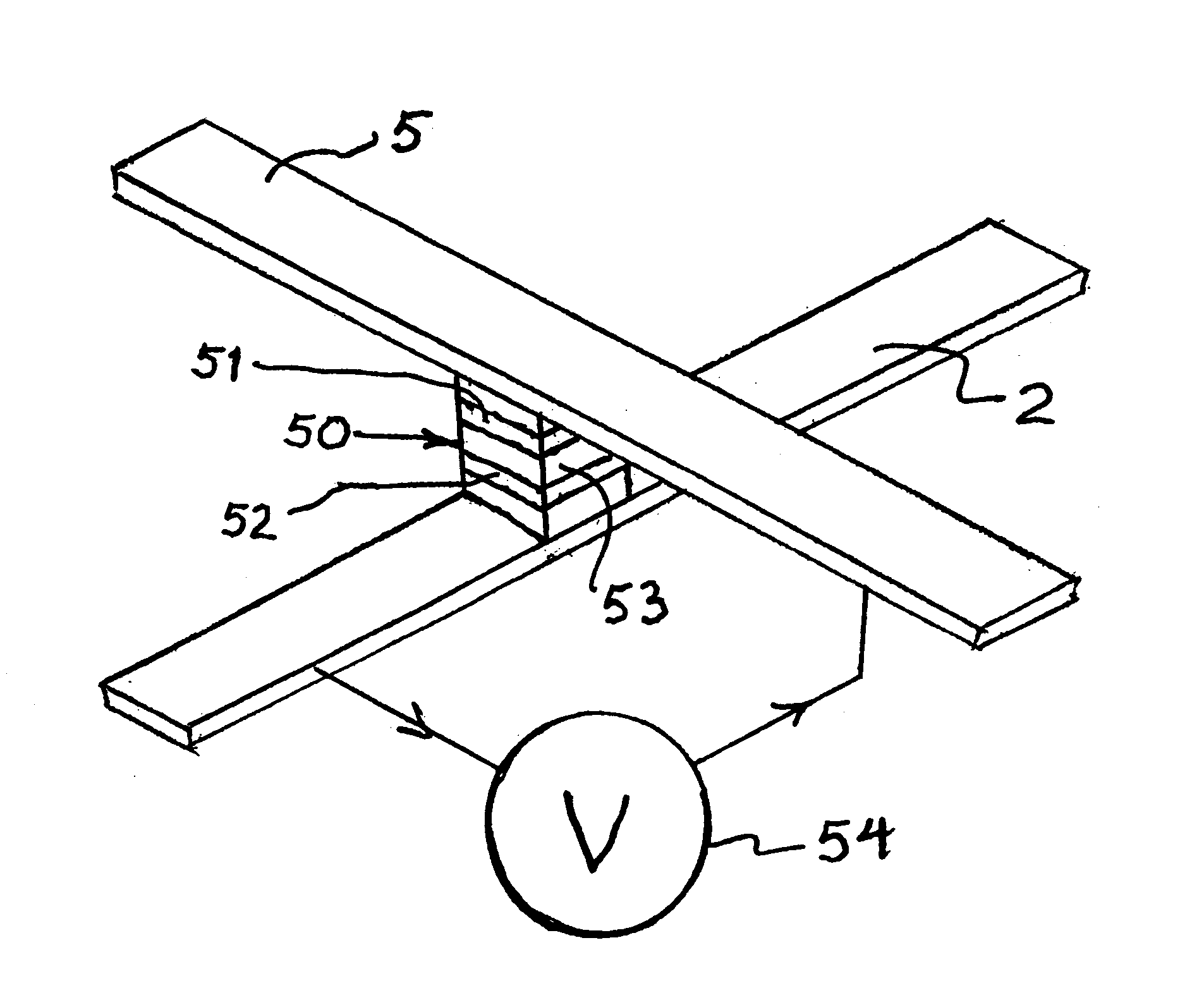
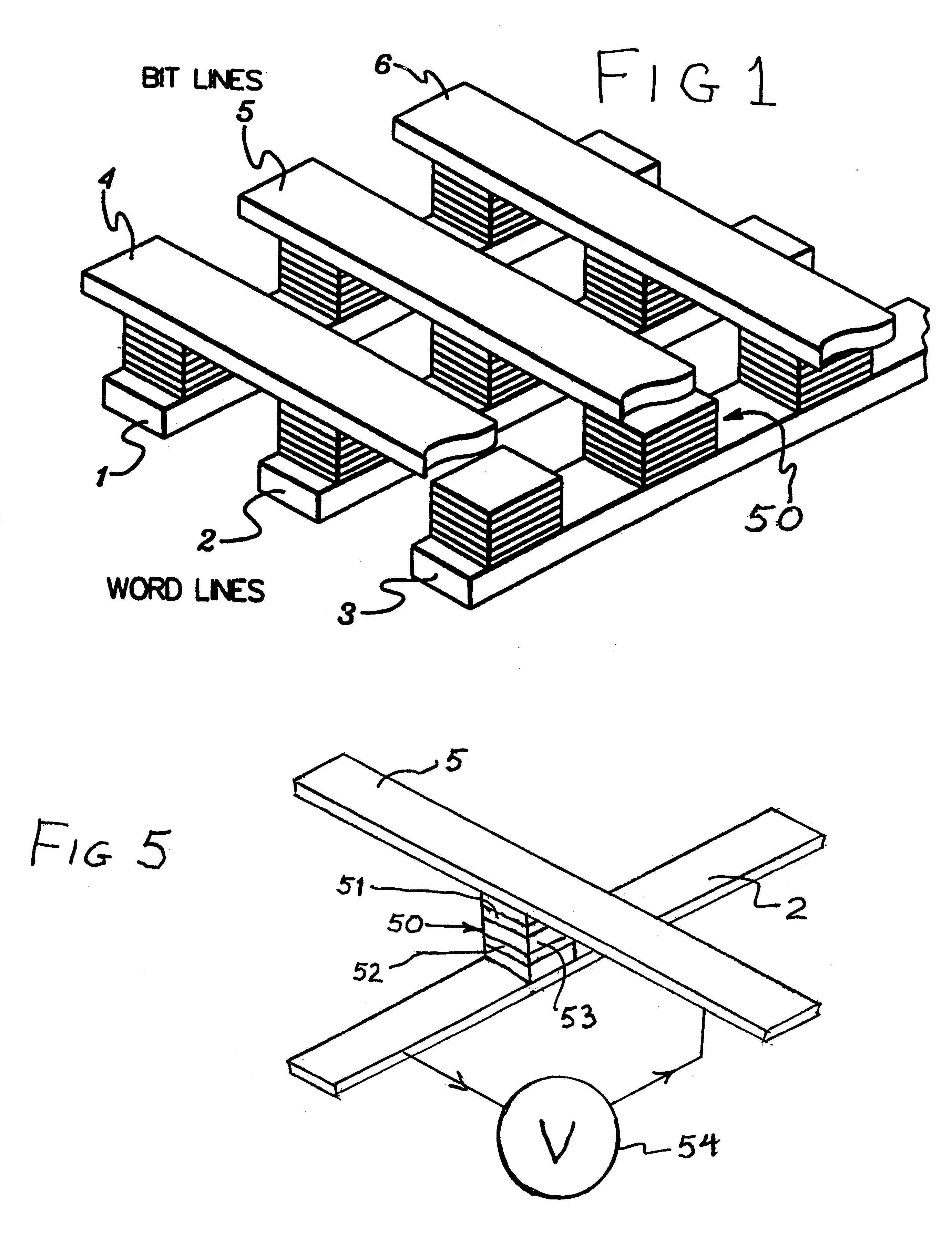
It is important to ensure good selectivity of a single magnetic tunnel junction storage cell within a memory array without affecting nearby storage cells. For this purpose, this memory array of storage cells preferably comprises a) an array of electrically conducting bit lines and electrically conducting word lines which form intersections therebetween, b) a storage cell disposed at each of said intersections, each storage cell comprising at least one reversible magnetic region or layer characterized by a magnetization state which can be reversed by applying thereto a selected external magnetic field, said reversible magnetic layer comprising a material whose magnetization state is more easily reversed upon a change in the temperature thereof, and c) a temperature change generator for changing the temperature of said reversible magnetic layer of only a selected one of said array of storage cells at any moment. To select a cell, it is preferable to select a cell by using a brief pulse of tunnelling current between the intersecting bit and word lines at that cell in order to provide sufficient Joule heating to facilitate a change in the magnetization state of its reversible magnetic layer, which preferably comprises a ferrimagnetic material.
Owner:IBM CORP
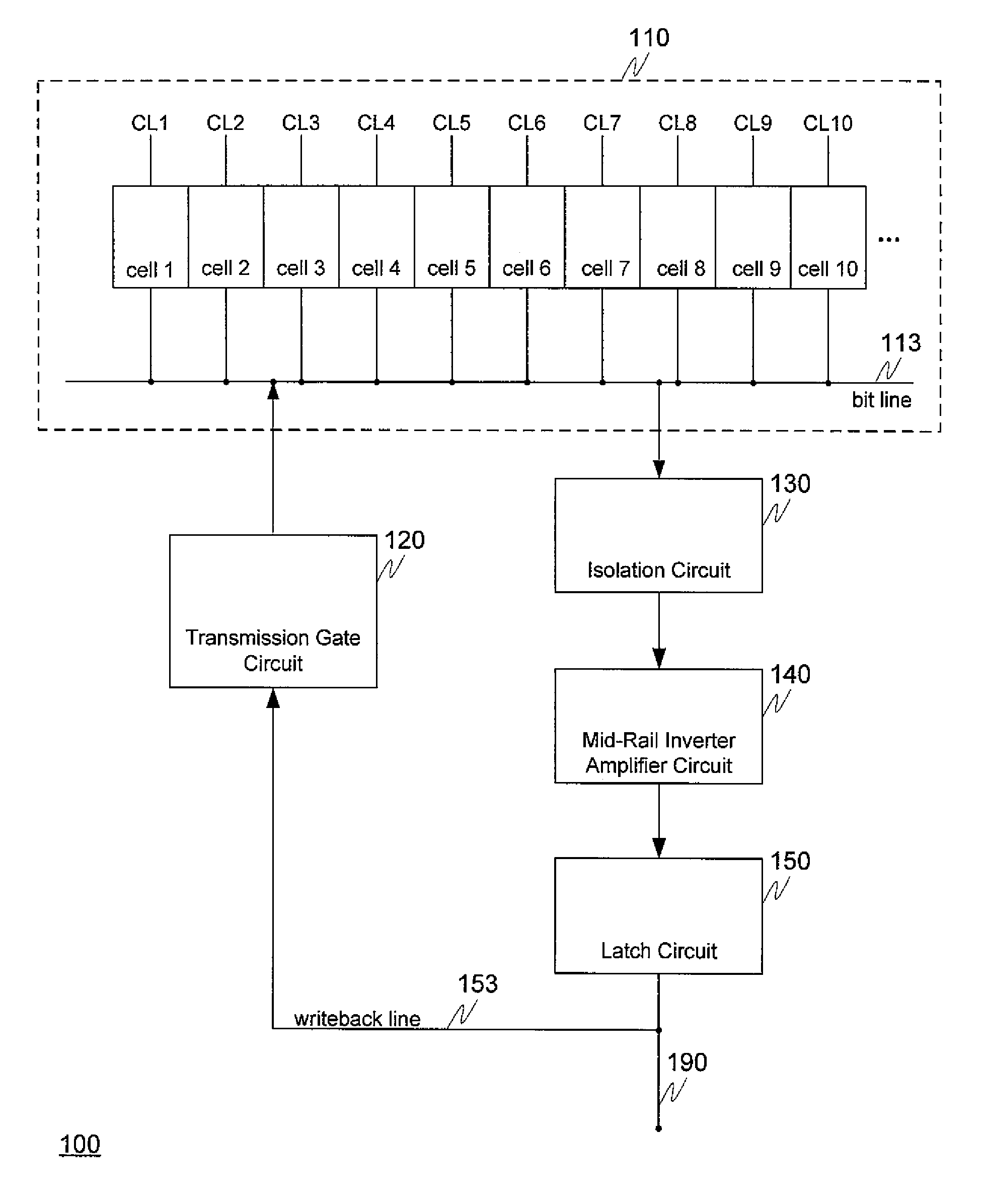
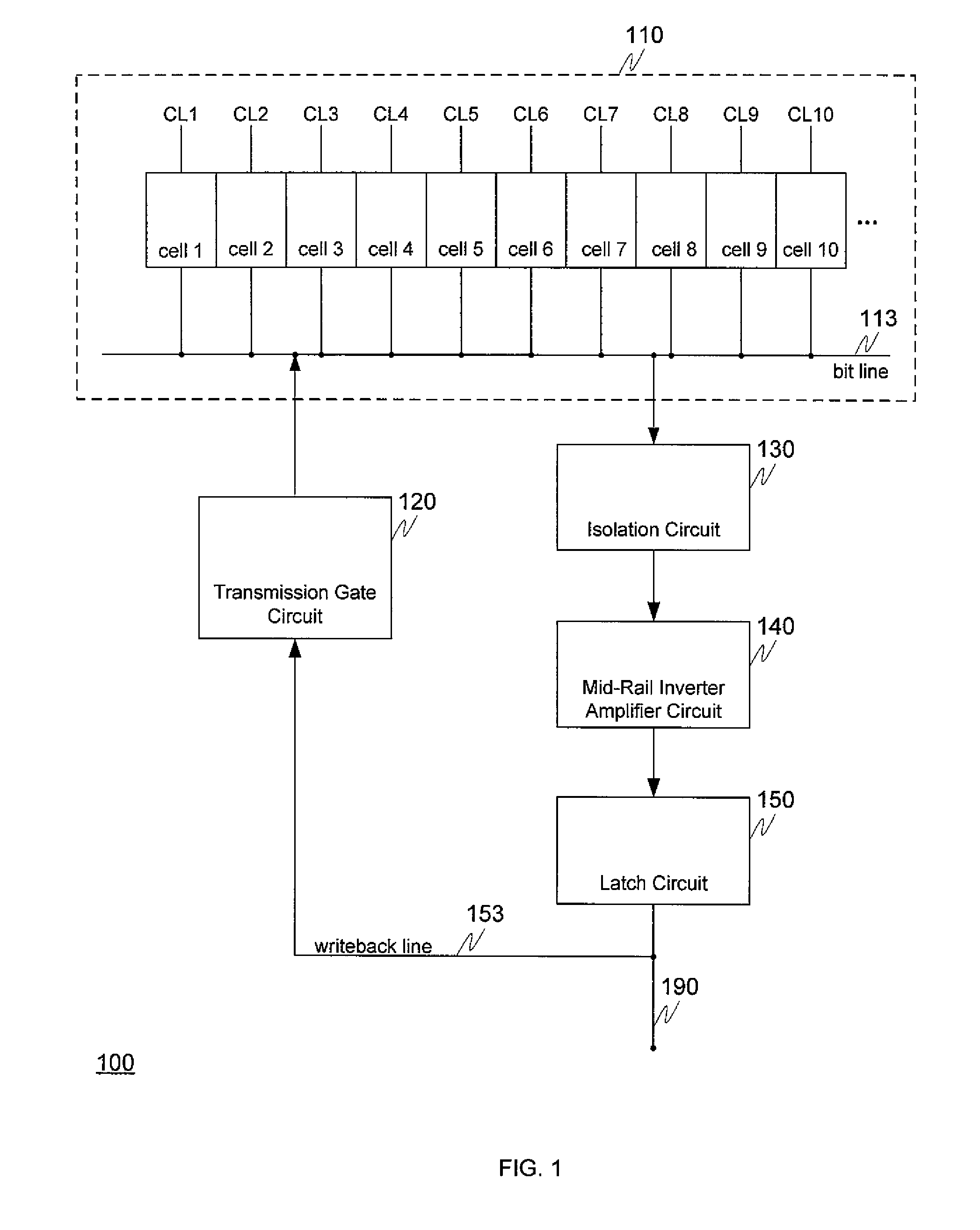
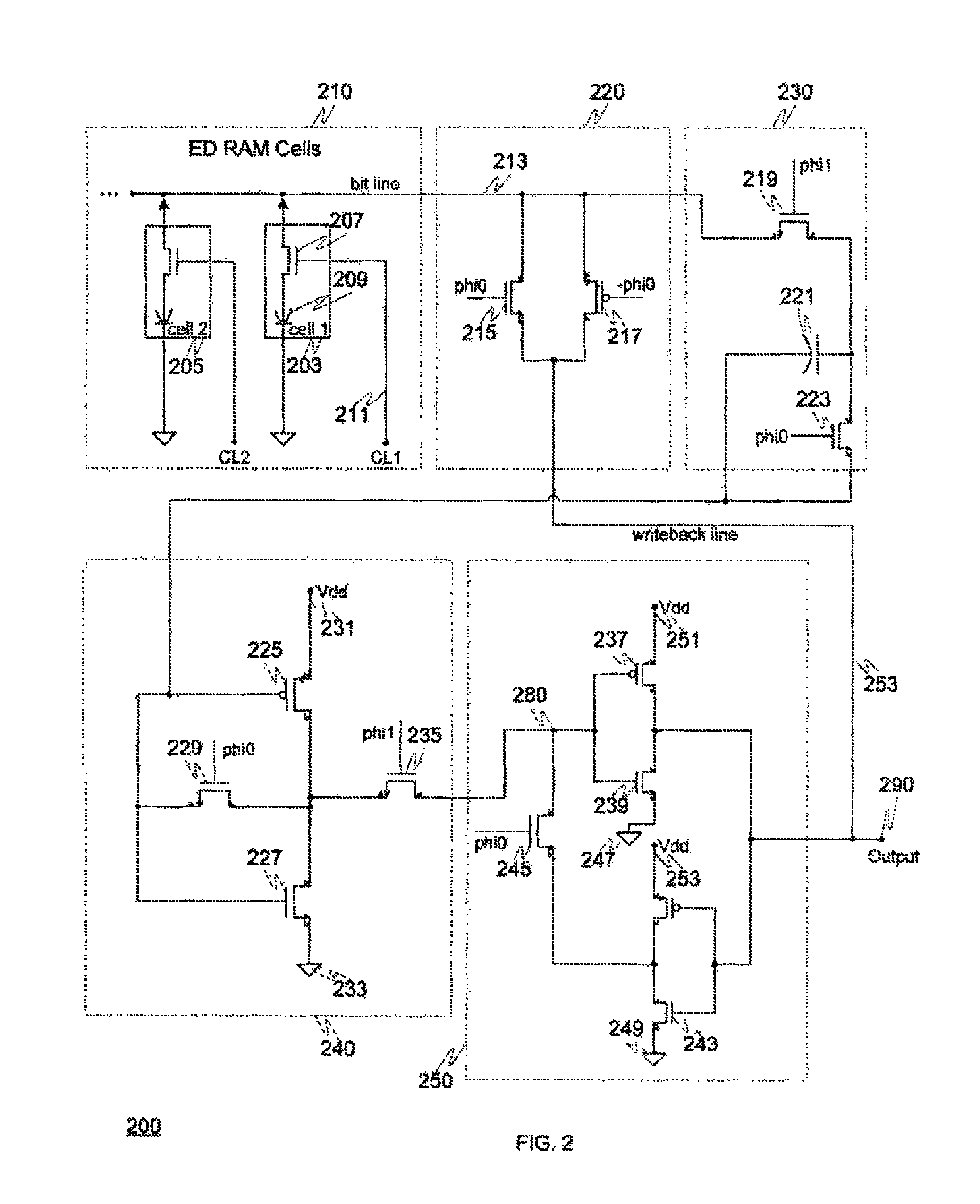
High performance eDRAM sense amplifier
Embedded dynamic random access memory (eDRAM) sense amplifier circuitry in which a bit line connected to each of a first plurality of eDRAM cells is controlled by cell control lines tied to each of the cells. During a READ operation the eDRAM cell releases its charge indicating its digital state. The digital charge propagates through the eDRAM sense amplifier circuitry to a mid-rail amplifier inverter circuit which amplifies the charge and provides it to a latch circuit. The latch circuit, in turn, inverts the charge to correctly represent at its output the logical value stored in the eDRAM cell being read, and returns the charge through the eDRAM sense amplifier circuitry to replenish the eDRAM cell.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
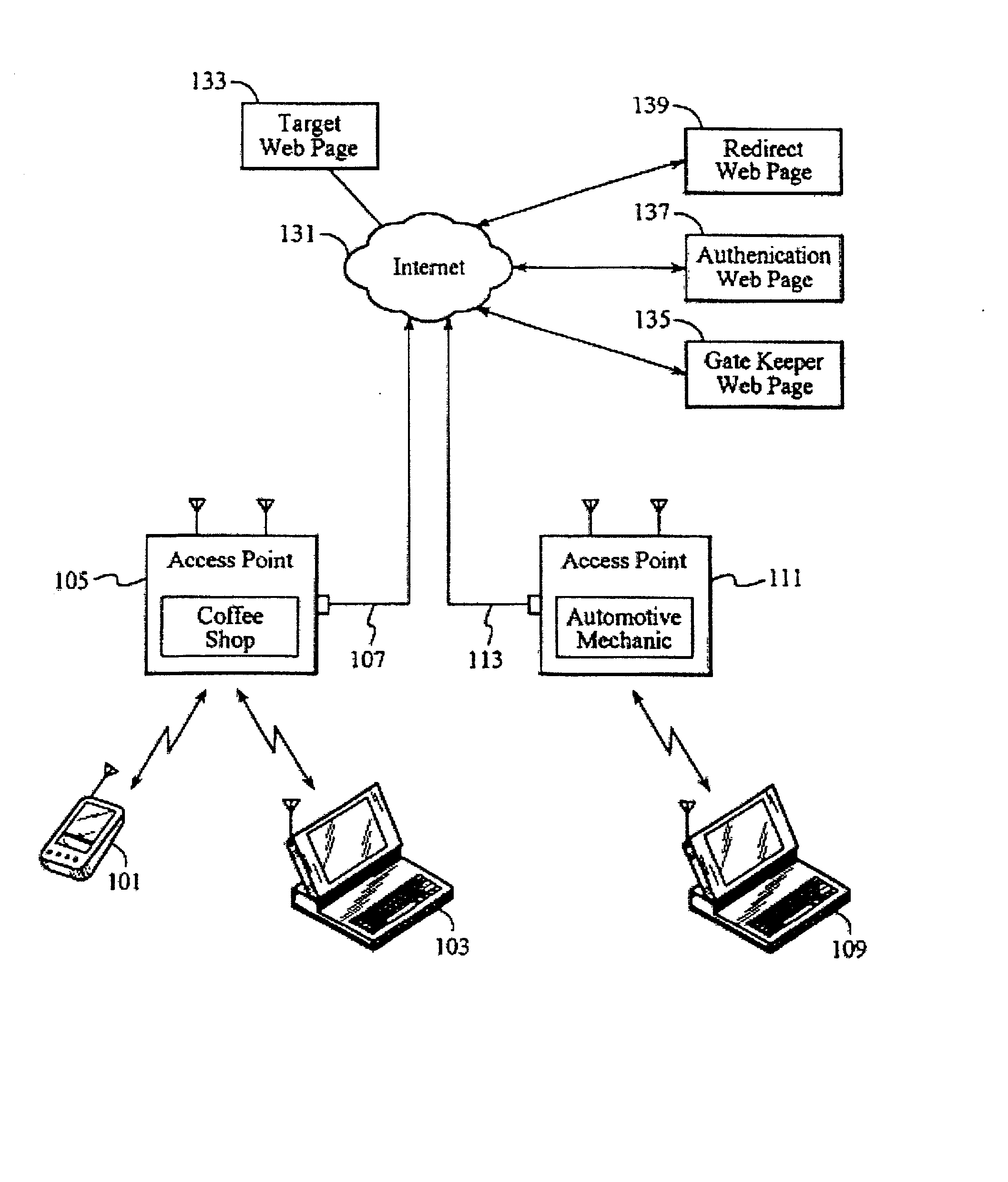
Automated updating of access points in a distributed network
InactiveUS20020157090A1Data switching by path configurationProgram loading/initiatingProgrammable read-only memoryRandom access memory
A method and system for maintaining network access point equipment including installing and upgrading software. The system includes a network server, and access point equipment including one or more access point devices, with each device equipped with a CPU including a random access memory (RAM) and a programmable read only memory (PROM). The server is configured for receiving software for maintaining the programming of access point devices. Both the access point devices and the server are programmed with authentication software for identifying each other prior to transmission of maintenance data. The access point devices are further programmed to periodically do a software check with the server. If the current software version in the device is the same as that stored in the server, no action is taken. If the version in the server is different, then the server and device automatically load the current software version into the device.
Owner:HEREUARE COMMUNICATIOINS
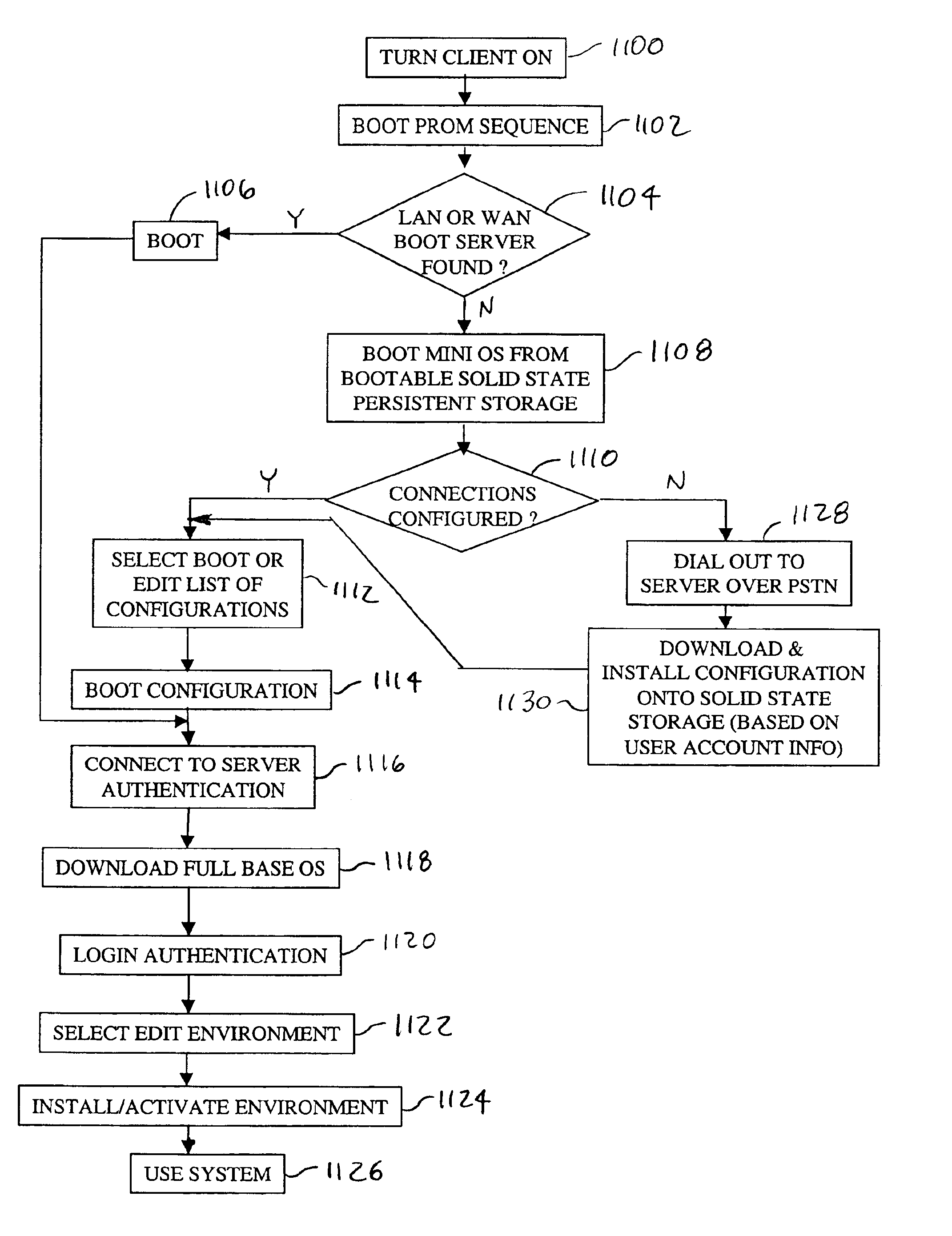
Networked computer system
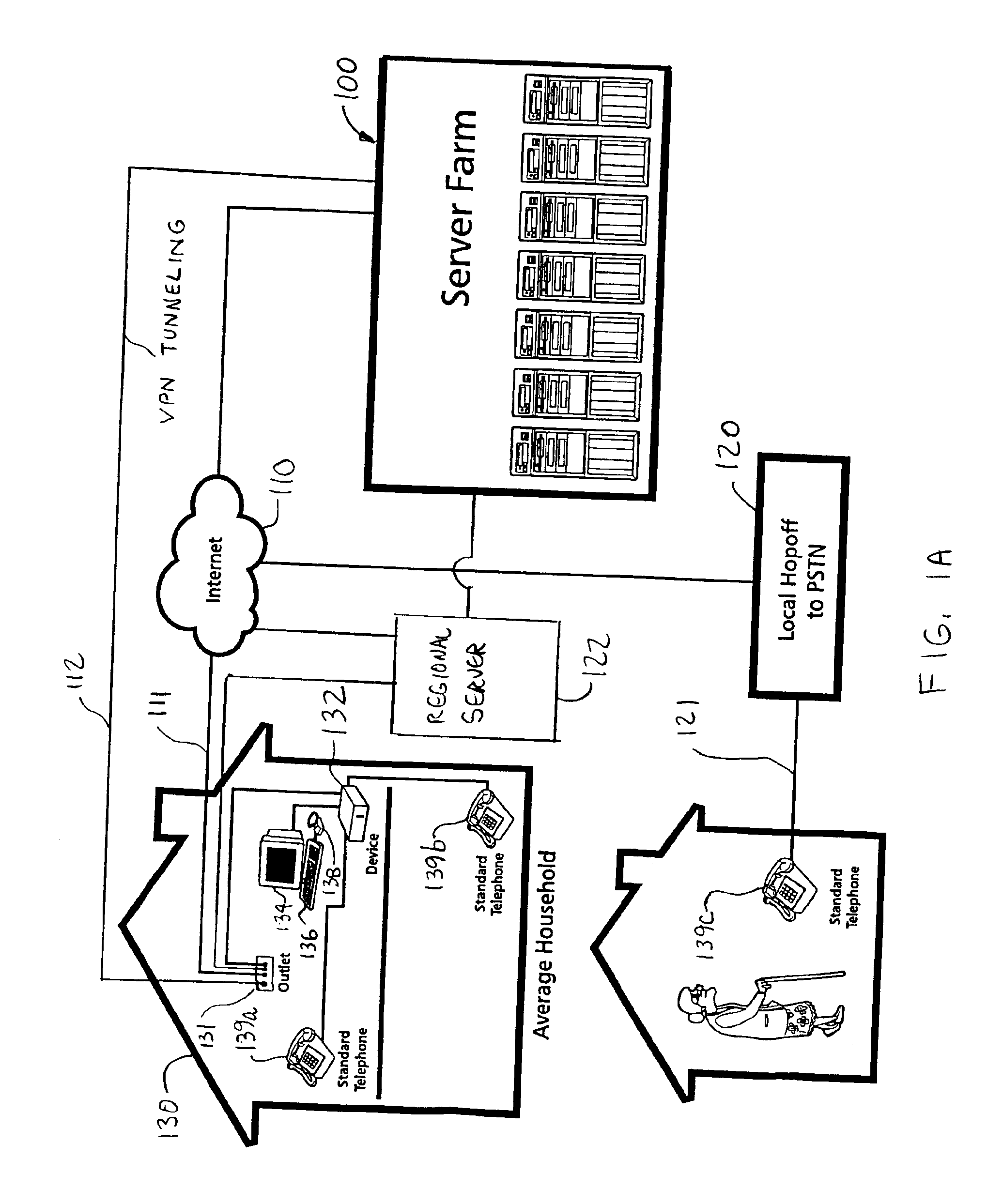
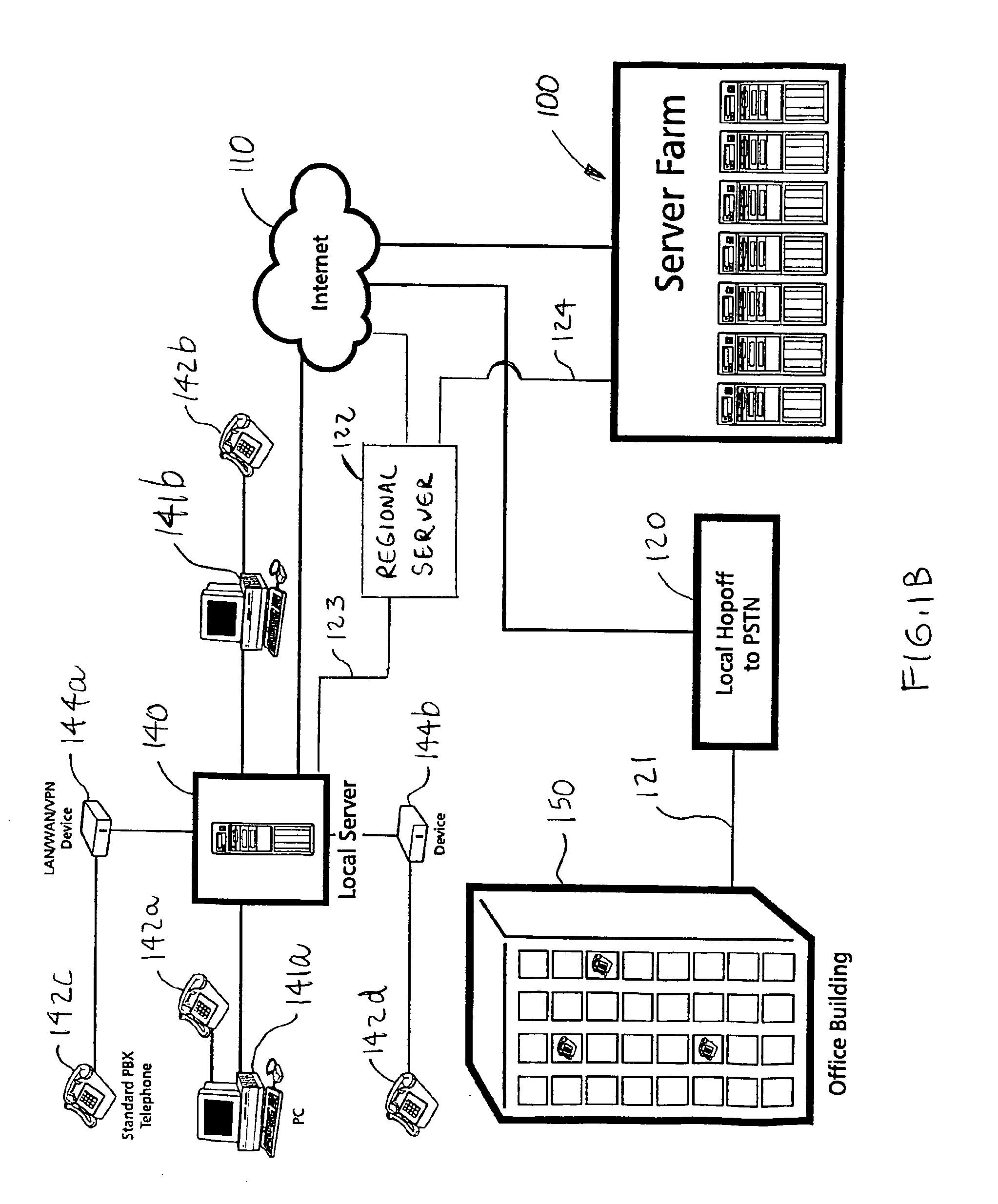
InactiveUS6854009B1Multiple digital computer combinationsBootstrappingOperational systemRandom access memory
A networked computer system has a plurality of servers and a plurality of distributed clients, which may be devices or computers. Each client has a boot operating system (OS). Upon startup, the boot OS in each client automatically initiates a connection to one of the servers via the Internet. The boot OS can detect the type of medium (e.g., cable modem, DSL) to which the client is connected. The server automatically downloads a base OS and dynamically configures a suite of applications on the client without running the standard installation programs. One included application is an Internet telephony application, allowing a user to plug a standard telephone into the client appliance or computer, pick up the telephone, and automatically dial out using long distance Internet telephony. Optionally, the server may download a plurality of operating systems that are automatically initiated to run concurrently on the client. The clients use a random access memory (RAM) caching technique. A first portion of each OS or application is downloaded at startup and maintained in the client RAM, containing the files needed to launch the OS or application. If the client processes a request for an OS or application program file not in the client's RAM, the requested file is automatically downloaded from the server.
Owner:CA TECH INC
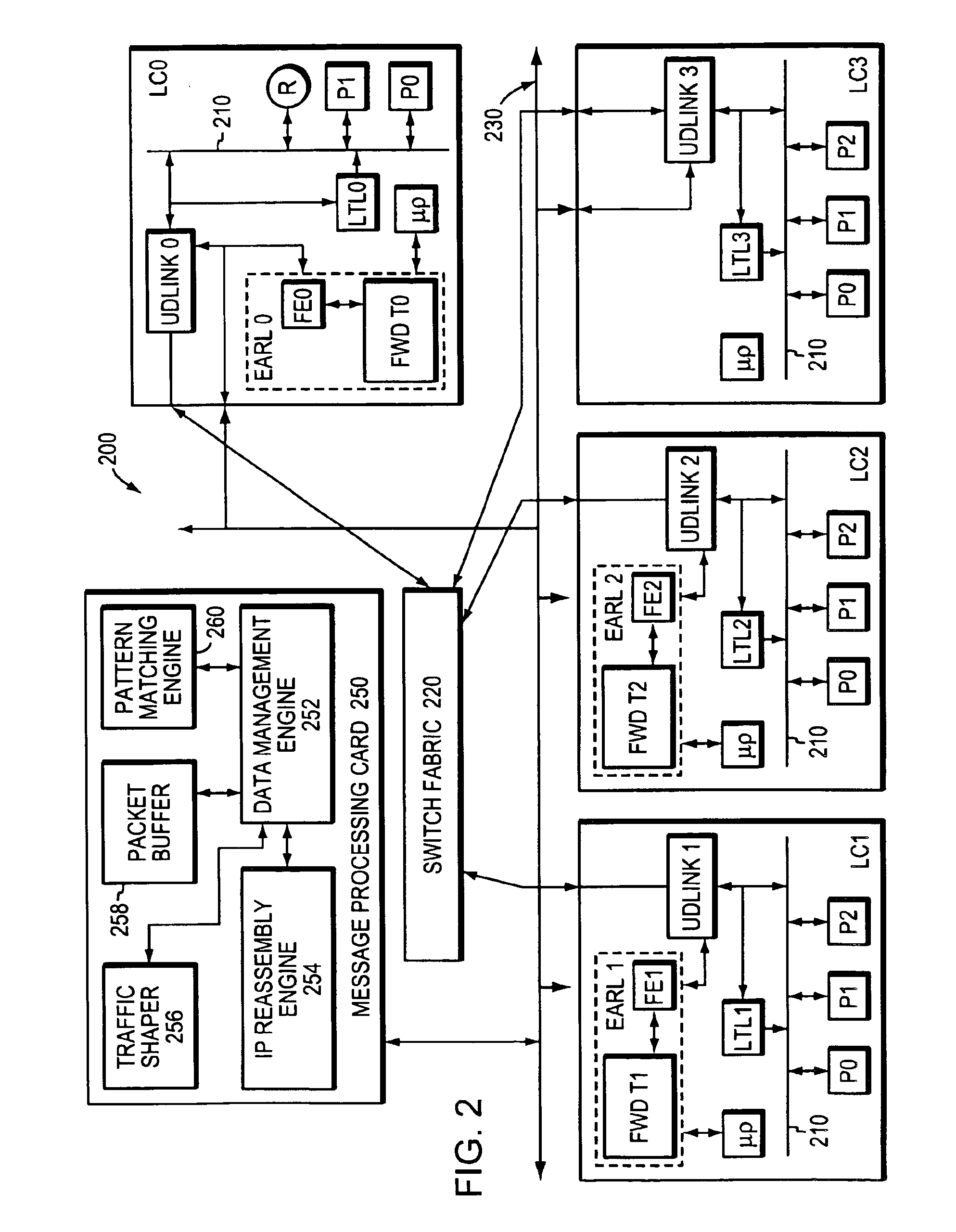
Virtual channels in a network switch
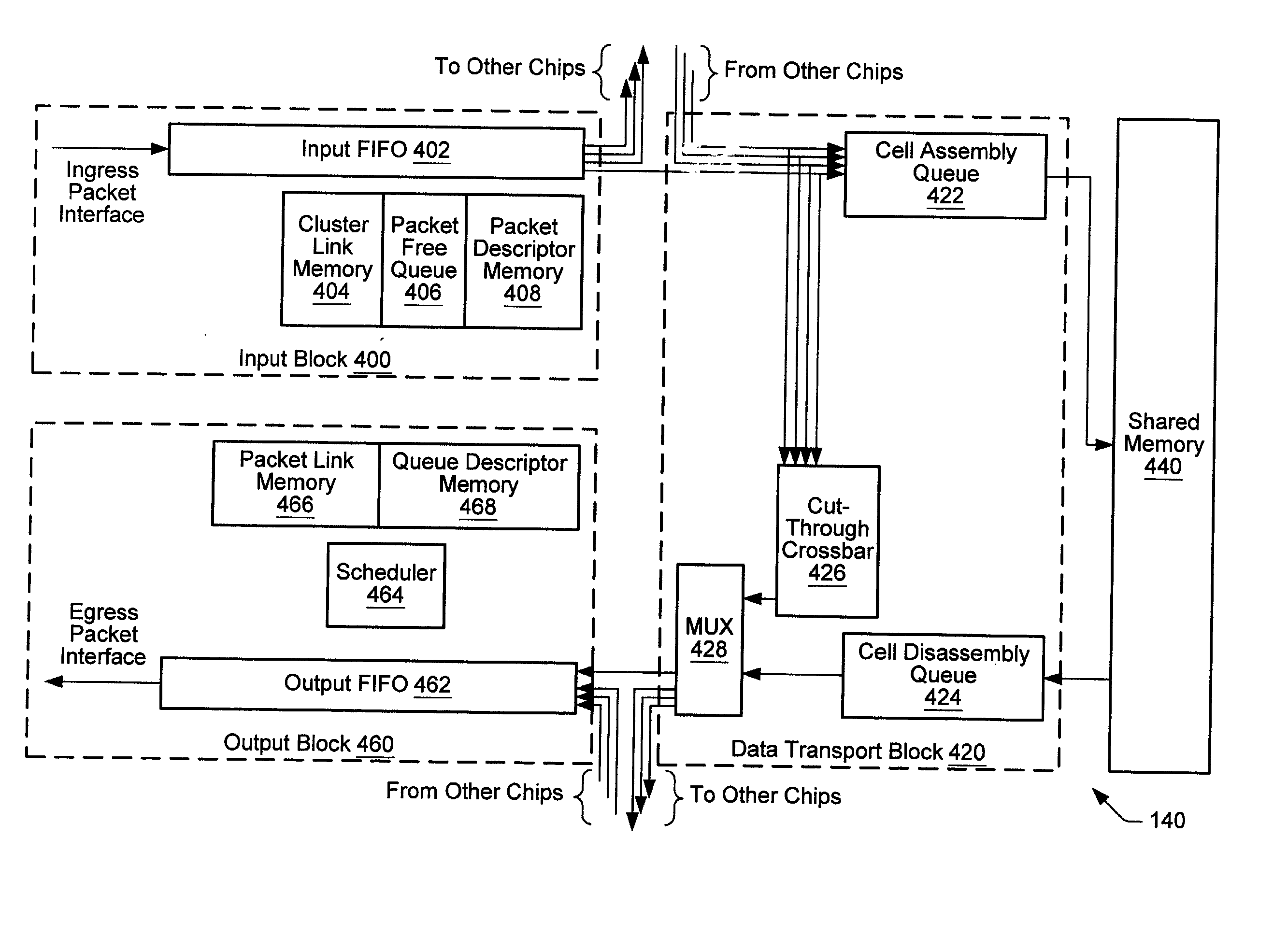
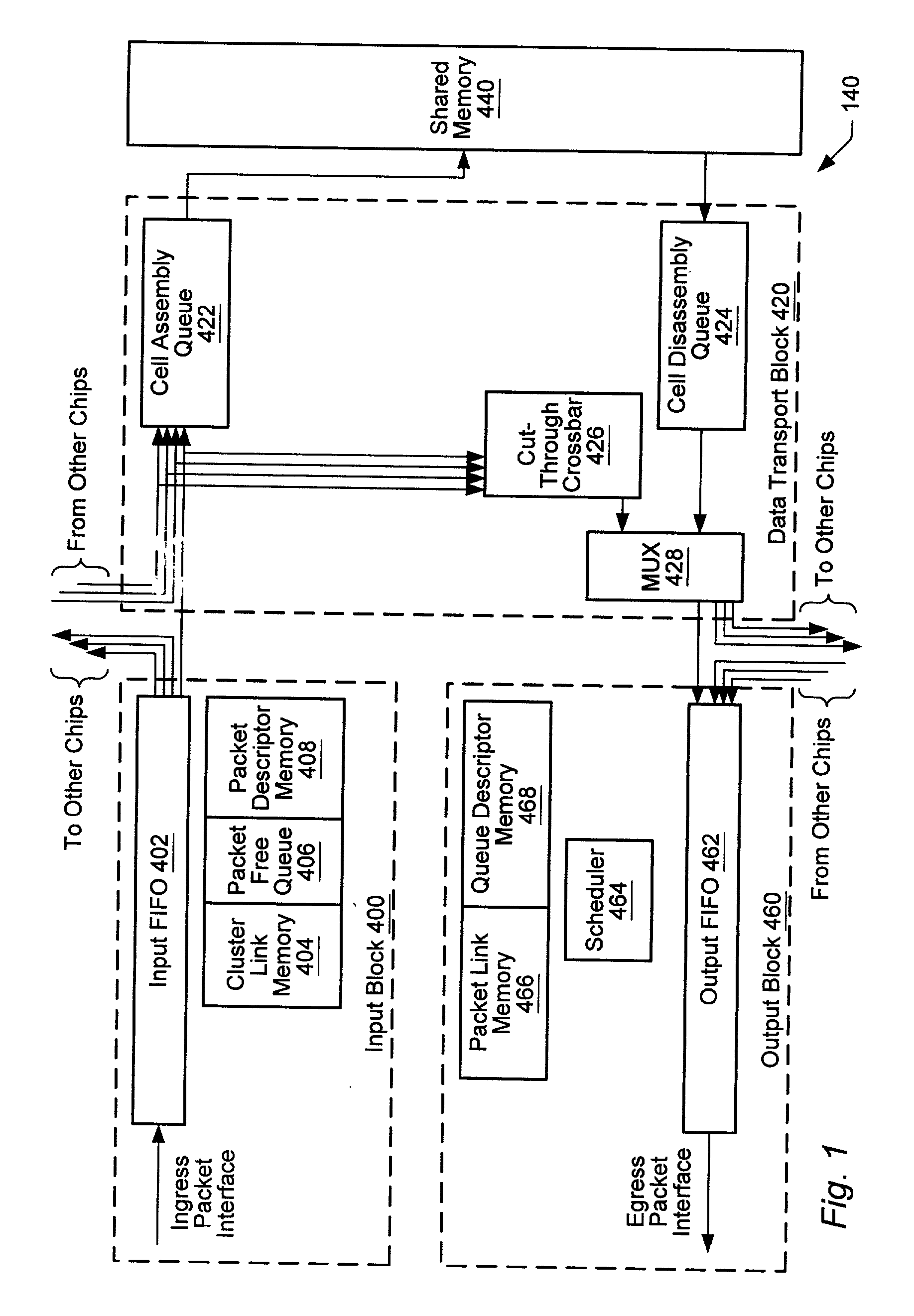
A system and method providing virtual channels with credit-based flow control on links between network switches. A network switch may include multiple input ports, multiple output ports, and a shared random access memory coupled to the input ports and output ports by data transport logic. Two network switches may go through a login procedure to determine if virtual channels may be established on a link. A credit initialization procedure may be performed to establish the number of credits available to the virtual channels. Credit-based packet flow may then begin on the link. A credit synchronization procedure may be performed to prevent the loss of credits due to errors. On detecting certain error conditions, a virtual channel may be deactivated. In one embodiment, the link is a Gigabit Ethernet link, and the packets are Gigabit Ethernet packets. The packets may encapsulate storage format (e.g. Fiber Channel) frames.
Owner:NISHAN SYST
Methods for identifying malicious software
ActiveUS7644441B2Memory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesGraphicsEncrypted function
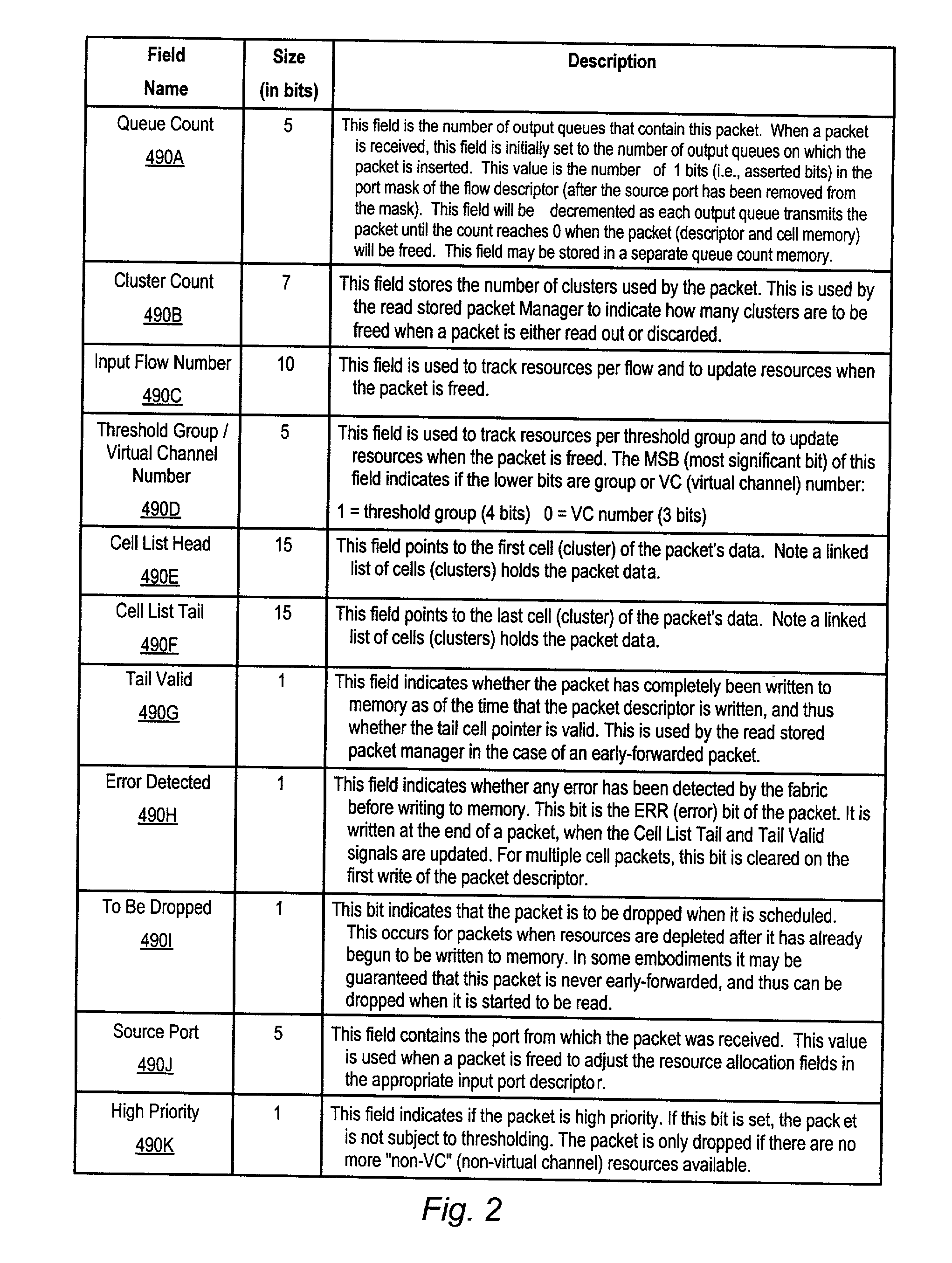
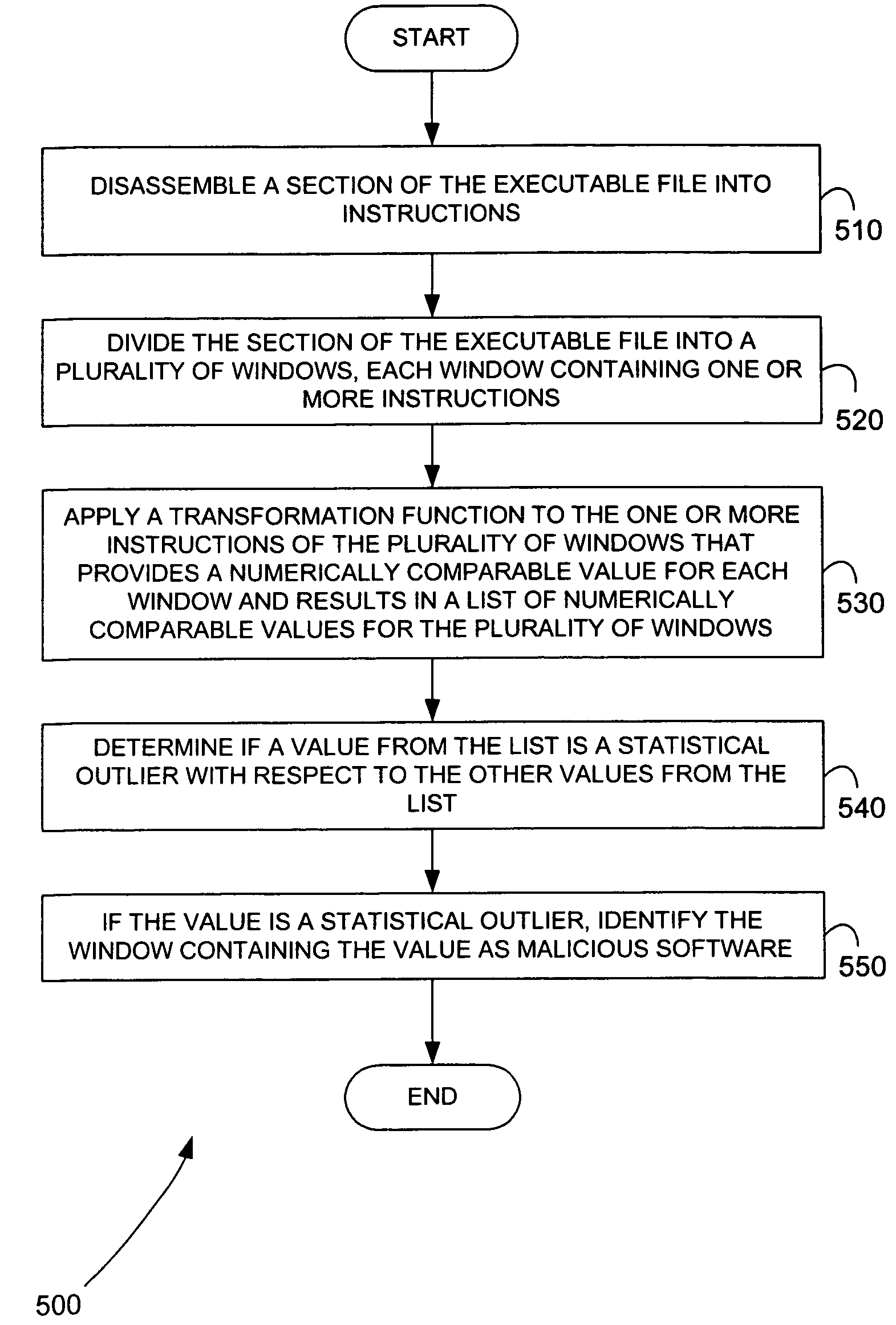
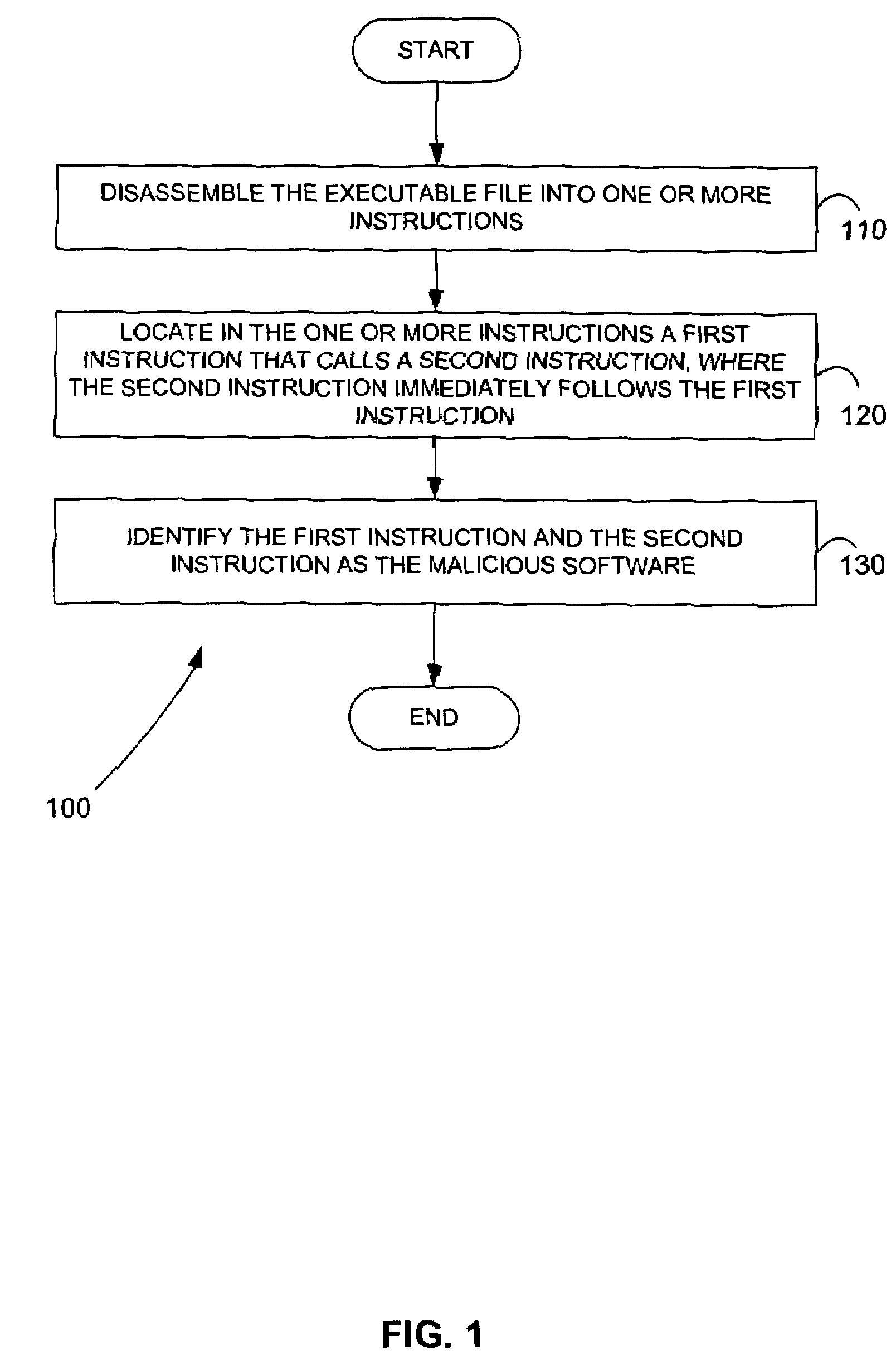
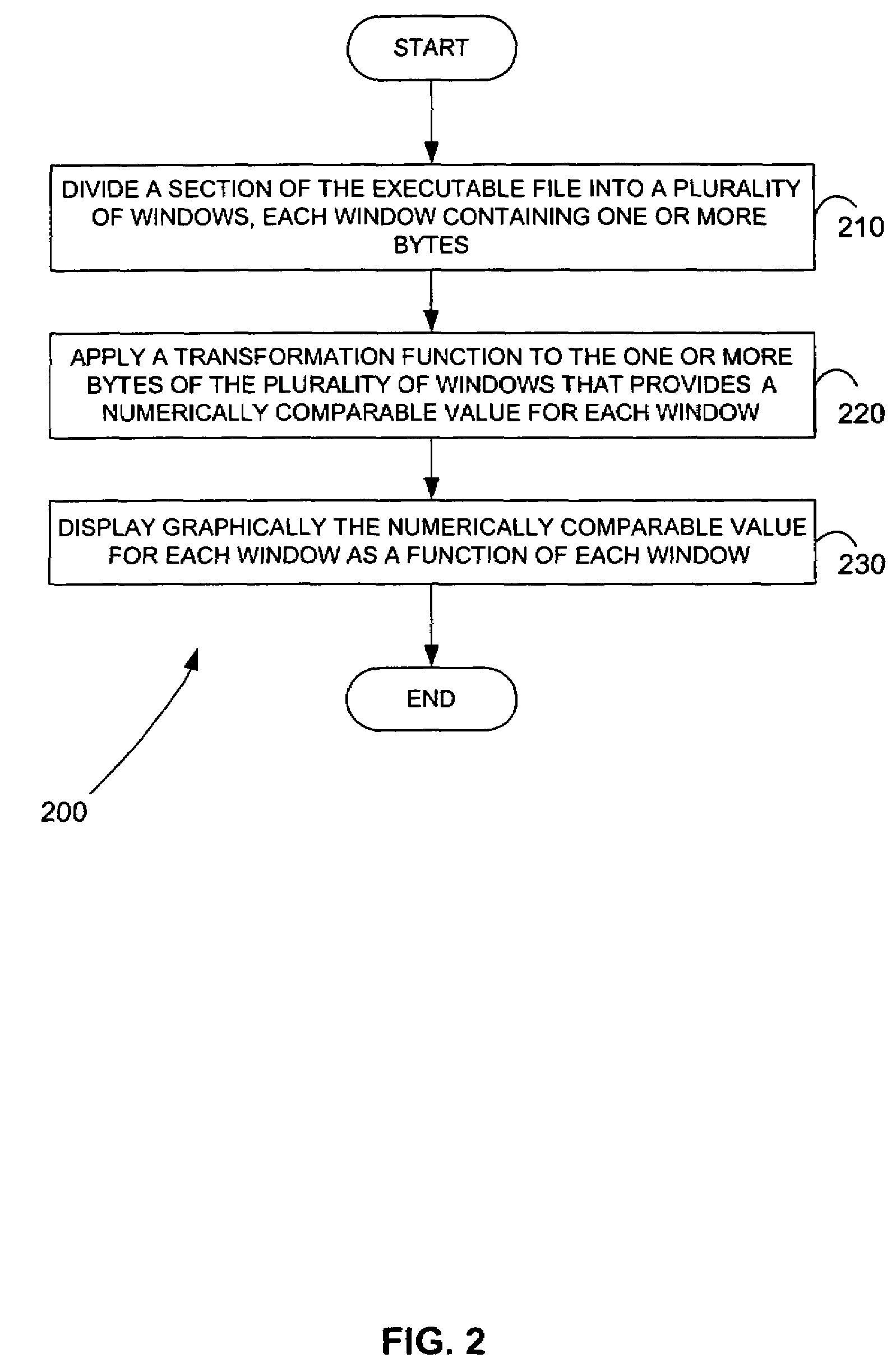
Malicious software is identified in an executable file by identifying malicious structural features, decryption code, and cryptographic functions. A malicious structural feature is identified by comparing a known malicious structural feature to one or more instructions of the executable file. A malicious structural feature is also identified by graphically and statistically comparing windows of bytes or instructions in a section of the executable file. Cryptography is an indicator of malicious software. Decryption code is identified in an executable file by identifying a tight loop around a reversible instruction that writes to random access memory. Cryptographic functions are identified in an executable file be obtaining a known cryptographic function and performing a string comparison of the numeric constants of the known cryptographic function with the executable file.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
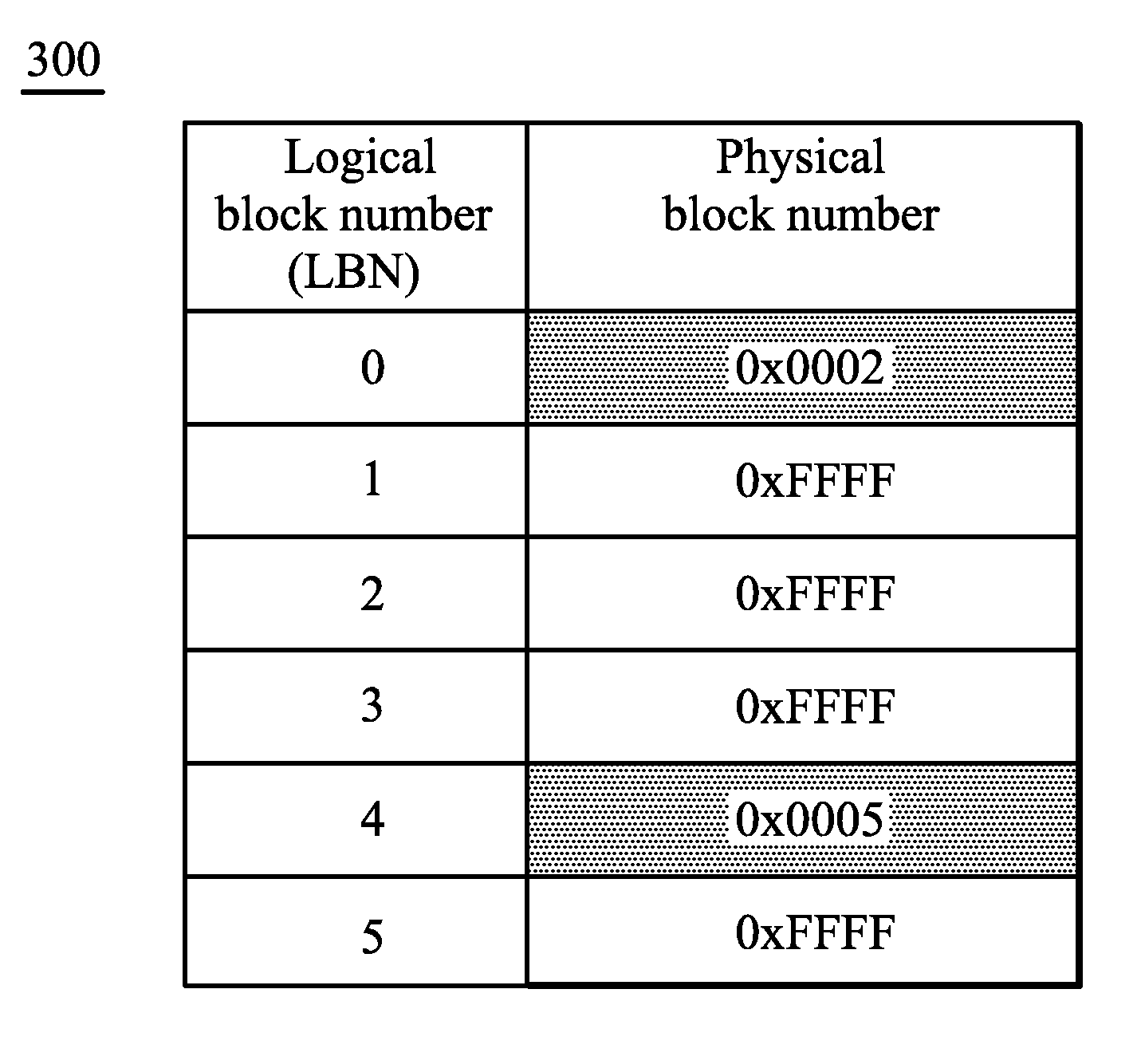
Two-Level RAM Lookup Table for Block and Page Allocation and Wear-Leveling in Limited-Write Flash-Memories
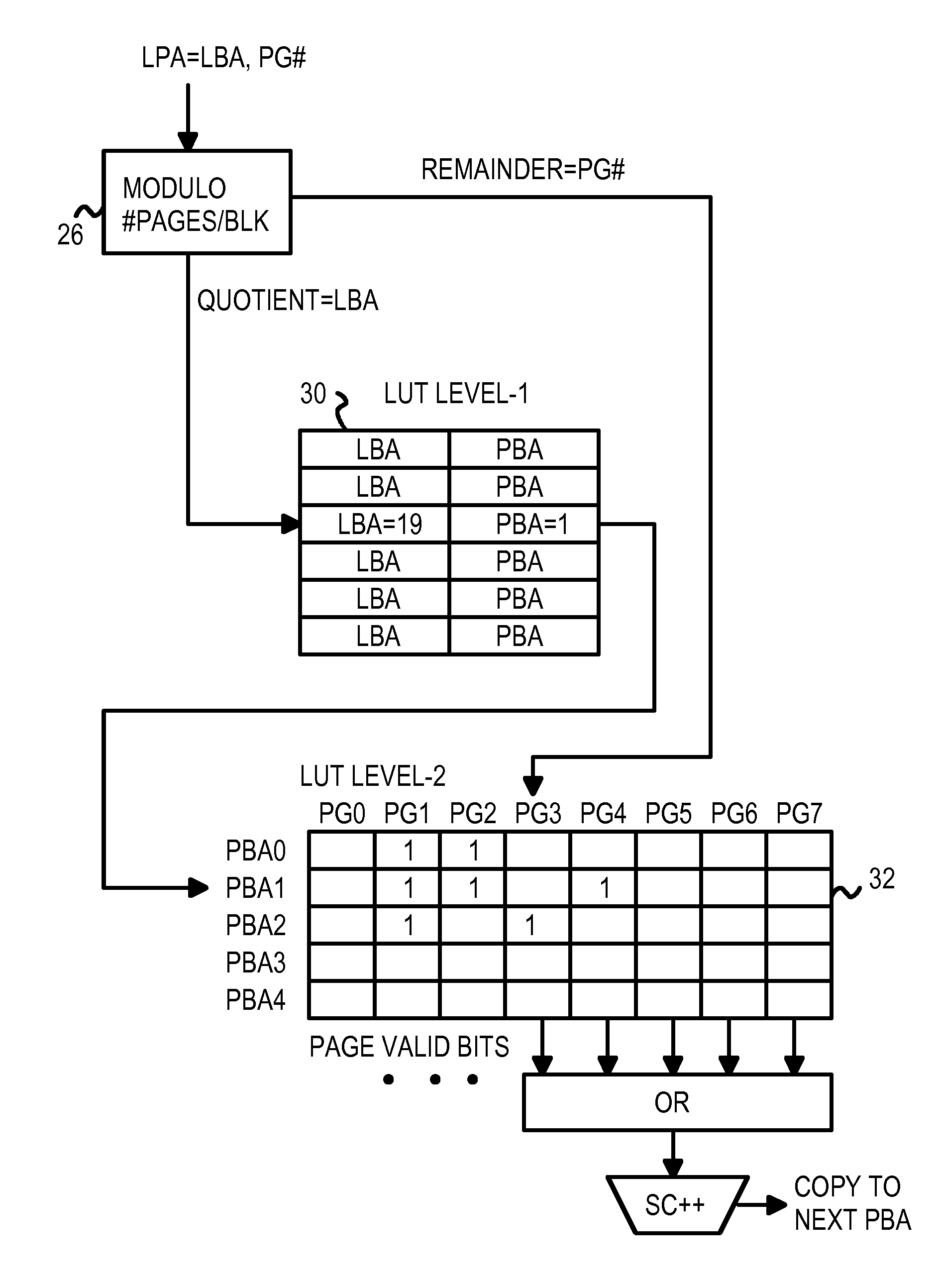
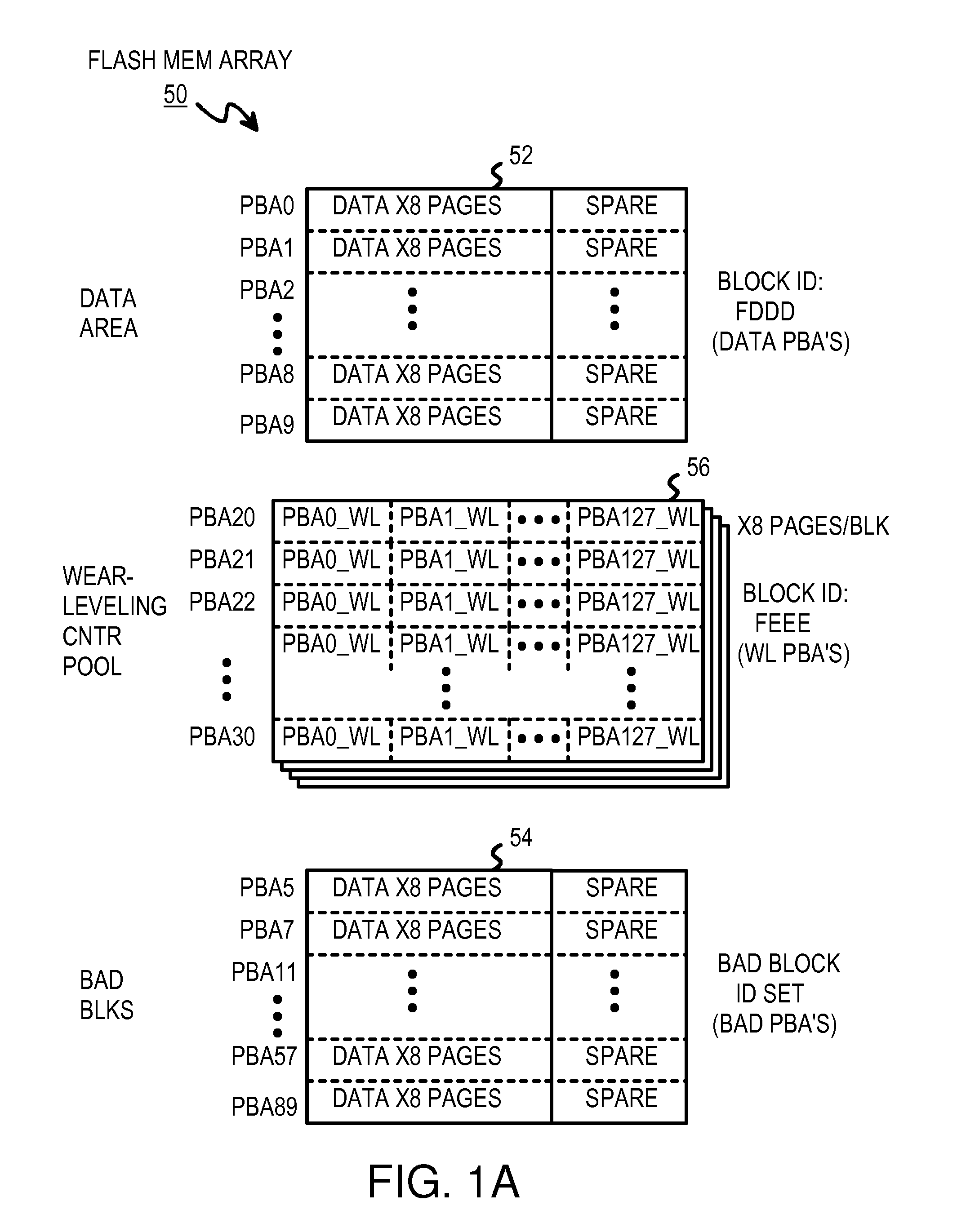
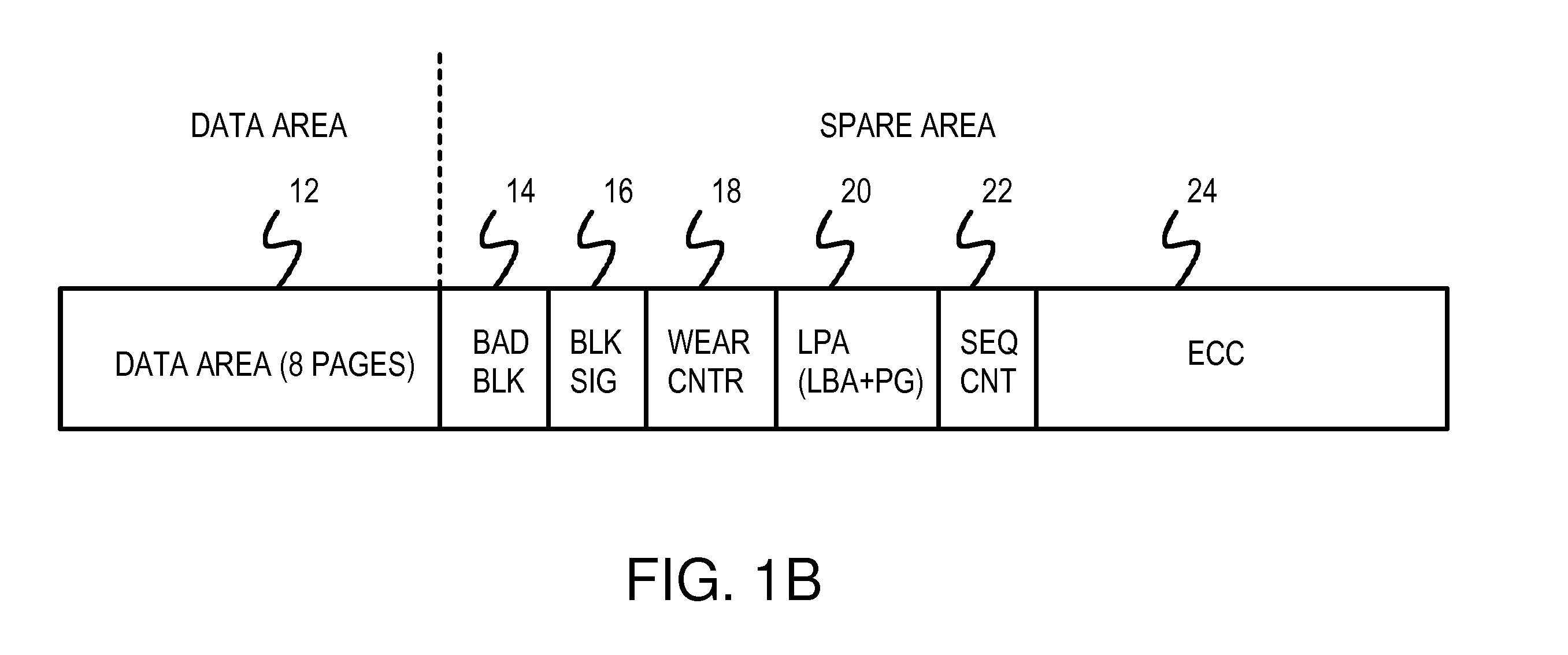
InactiveUS20070204128A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesRandom access memoryLogical block addressing
A restrictive multi-level-cell (MLC) flash memory prohibits regressive page-writes. When a regressive page-write is requested, an empty block having a low wear-level count is found, and data from the regressive page-write and data from pages stored in the old block are written to the empty block in page order. The old block is erased and recycled. A two-level look-up table is stored in volatile random-access memory (RAM). A logical page address from a host is divided by a modulo divider to generate a quotient and a remainder. The quotient is a logical block address that indexes a first-level look-up table to find a mapping entry with a physical block address that selects a row in a second-level look-up table. The remainder locates a column in the row in the second-level look-up table. If any page-valid bits above the column pointed to by the remainder are set, the write is regressive.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
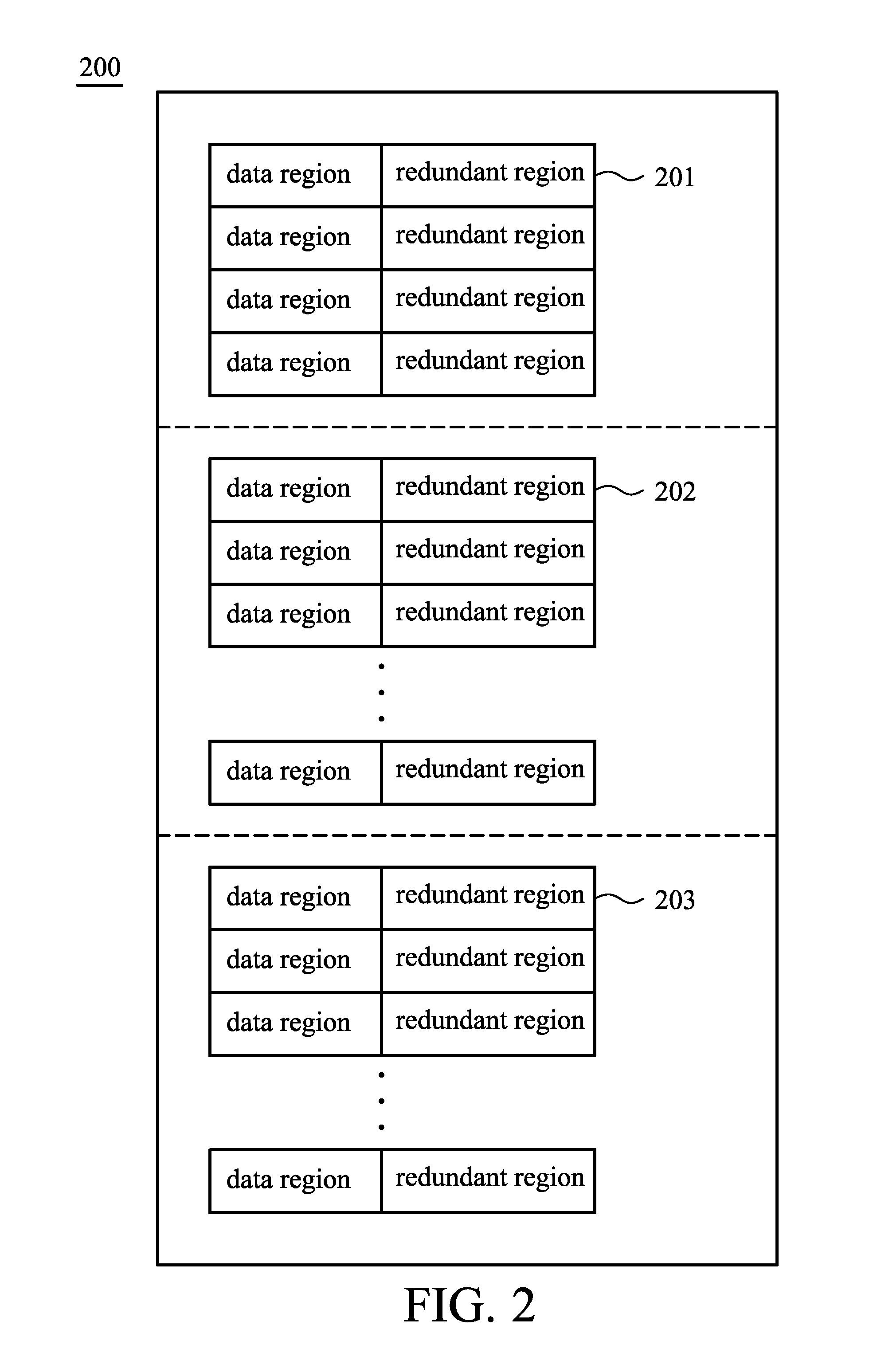
Data boundary management
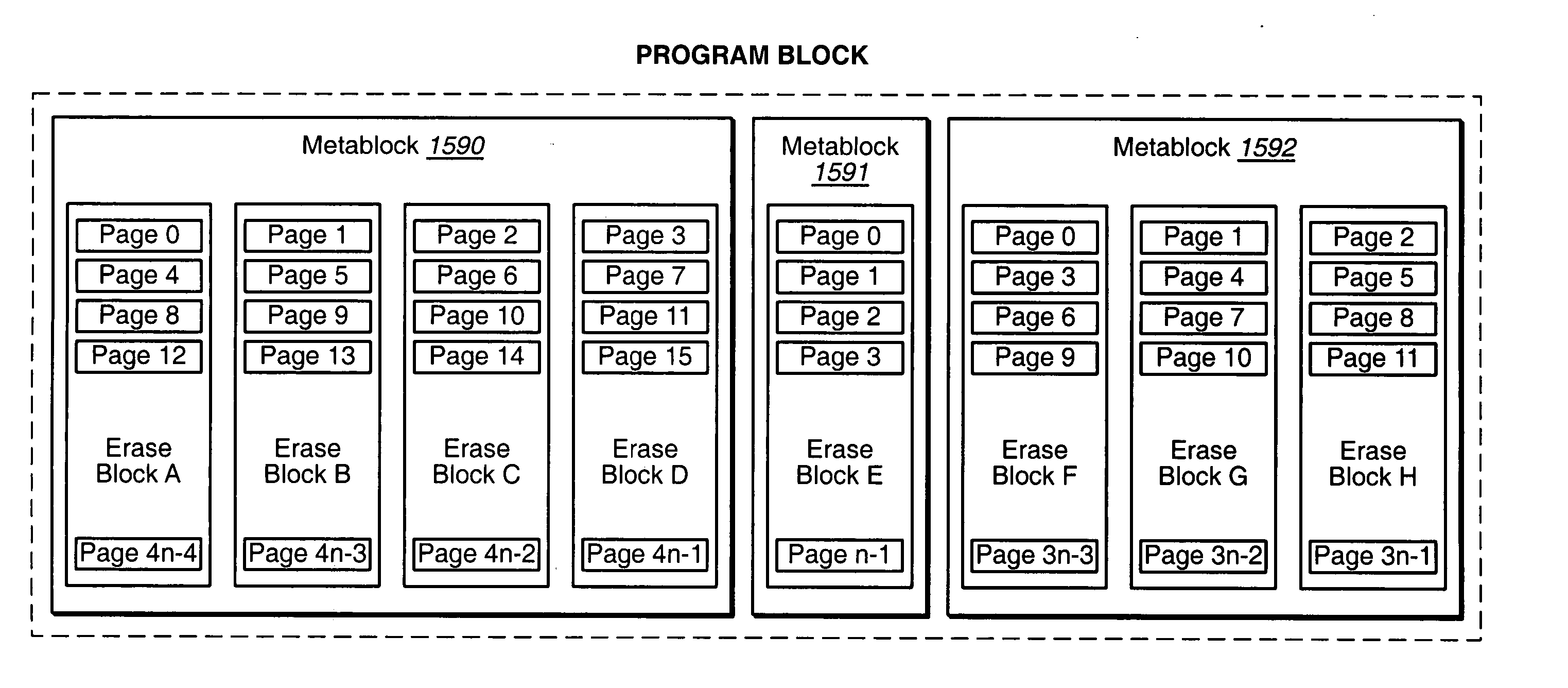
InactiveUS20050144363A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Data may be stored in a non-volatile memory array in adaptive metablocks that are configured according to the locations of data boundaries in the data. Data may be stored in an intermediate format and later copied to adaptive metablocks configured for the data. Data in intermediate format may be stored in non-volatile random access memory or in a portion of the non-volatile memory array.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for high-speed parsing of network messages
InactiveUS6892237B1Efficient analysisIncrease speedMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksPattern matchingRandom access memory
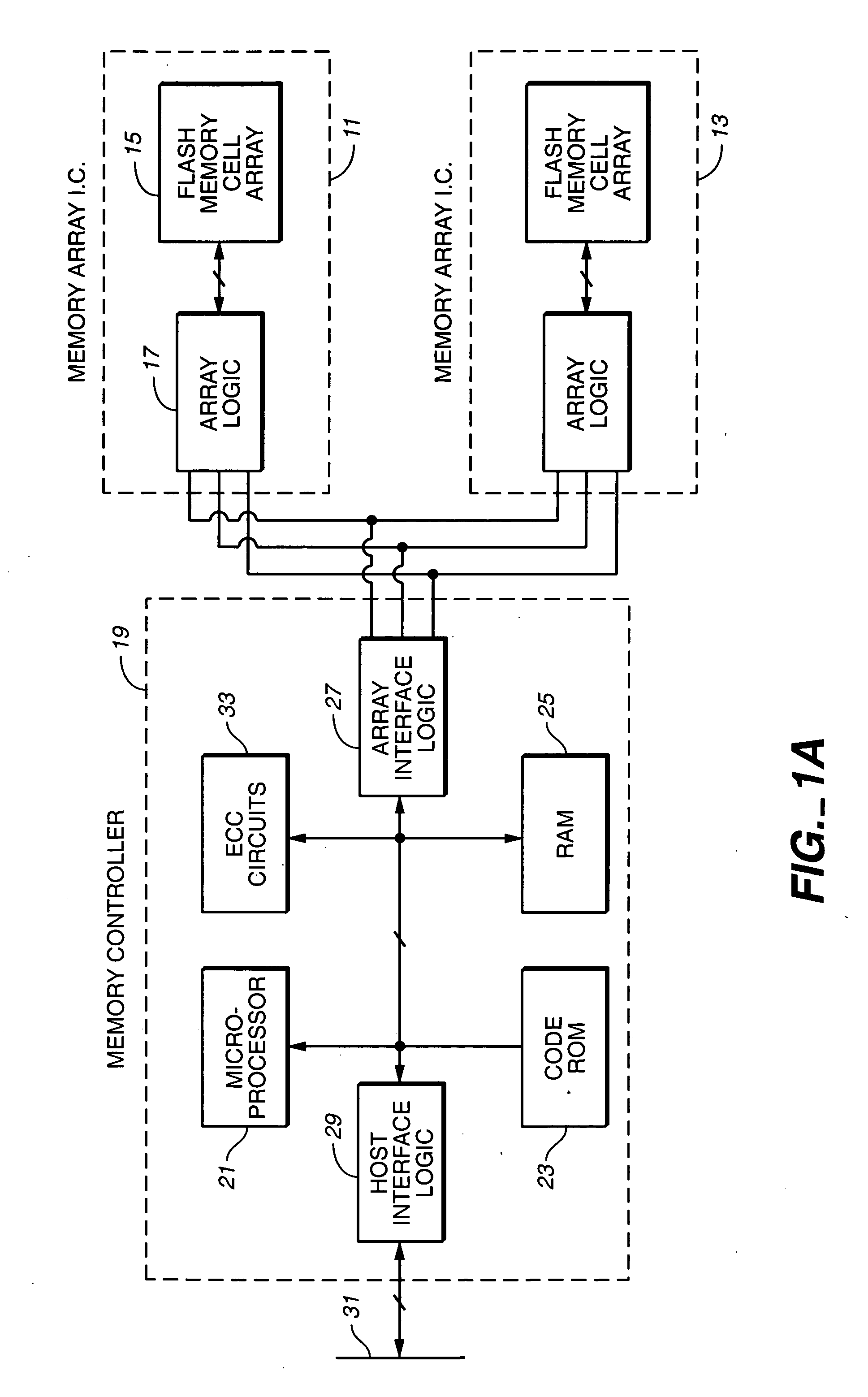
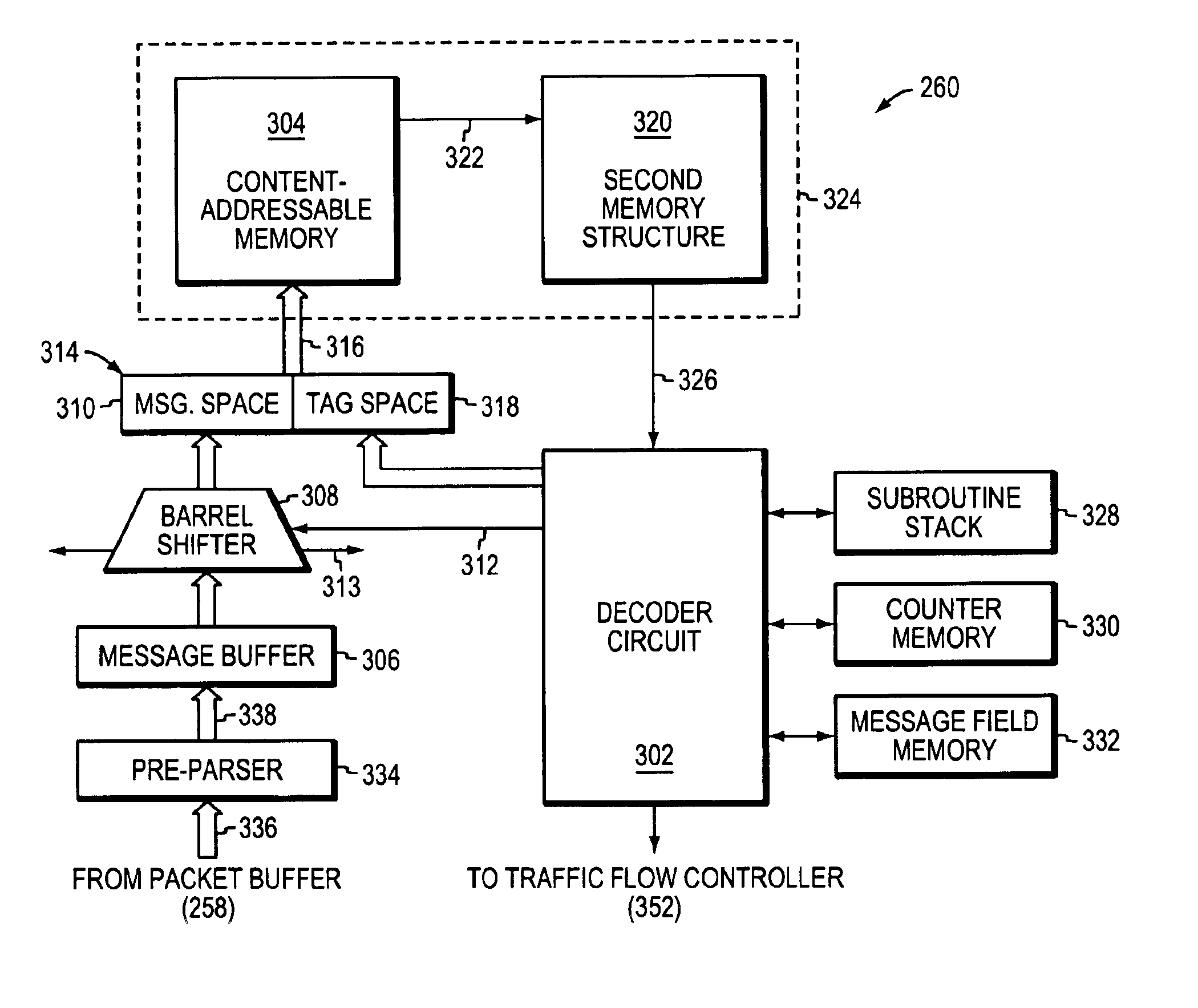
A programmable pattern matching engine efficiently parses the contents of network messages for regular expressions and executes pre-defined actions or treatments on those messages that match the regular expressions. The pattern matching engine is preferably a logic circuit designed to perform its pattern matching and execution functions at high speed, e.g., at multi-gigabit per second rates. It includes, among other things, a message buffer for storing the message being evaluated, a decoder circuit for decoding and executing corresponding actions or treatments, and one or more content-addressable memories (CAMs) that are programmed to store the regular expressions used to search the message. The CAM may be associated with a second memory device, such as a random access memory (RAM), as necessary, that is programmed to contain the respective actions or treatments to be applied to messages matching the corresponding CAM entries. The RAM provides its output to the decoder circuit, which, in response, decodes and executes the specified action or treatment.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
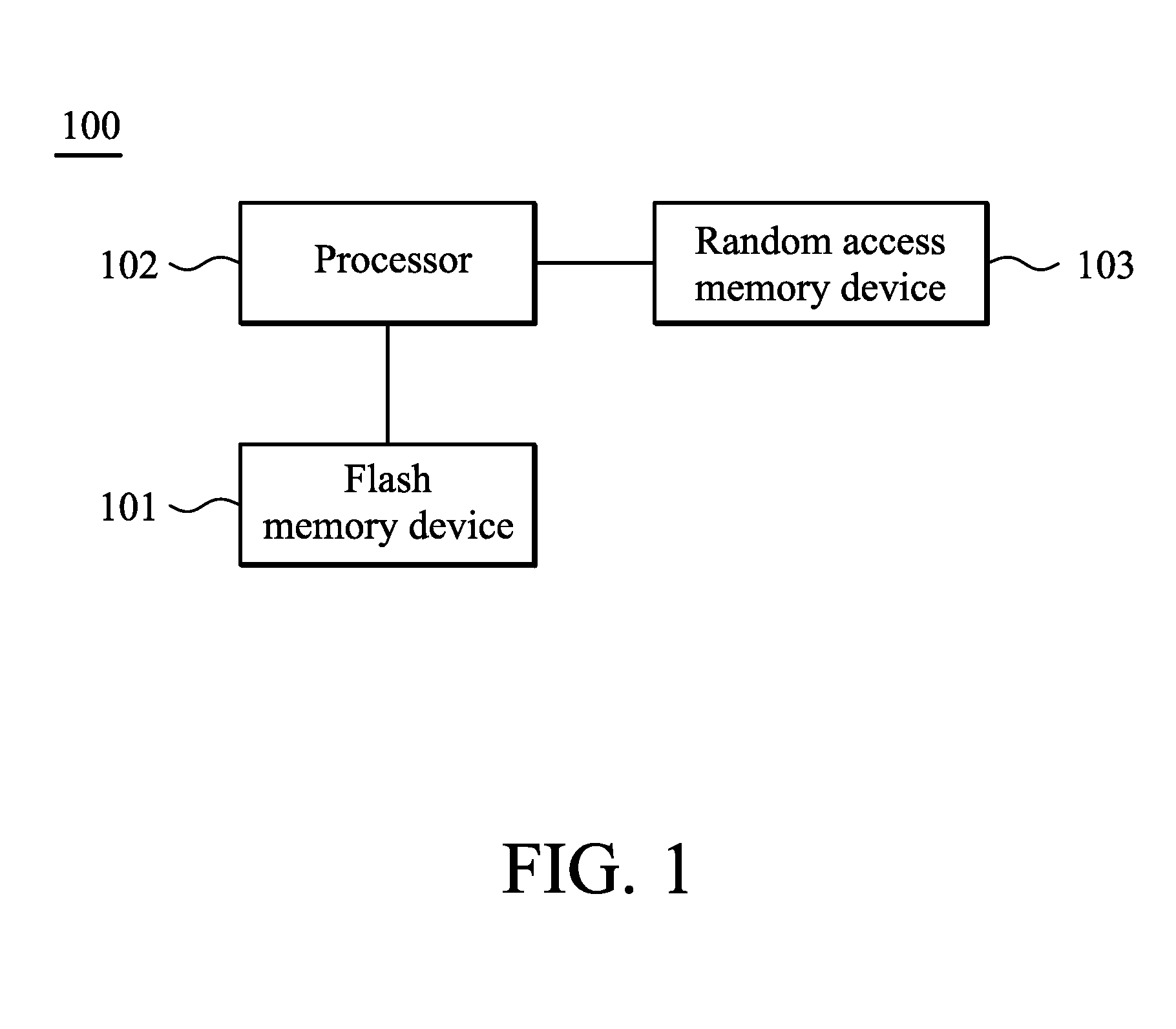
Computing systems and methods for managing flash memory device
InactiveUS20100287327A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRandom access memoryData field
A computing system is provided. A flash memory device includes at least one mapping block, at least one modification block and at least one cache block. A processor is configured to perform: receiving a write command with a write logical address and predetermined data, loading content of a cache page from the cache block corresponding to the modification block according to the write logical address to a random access memory device in response to that a page of the mapping block corresponding to the write logical address has been used, the processor, reading orderly the content of the cache page stored in the random access memory device to obtain location information of an empty page of the modification block, and writing the predetermined data to the empty page according to the location information. Each cache page includes data fields to store location information corresponding to the data has been written in the pages of the modification block in order.
Owner:INTEL CORP
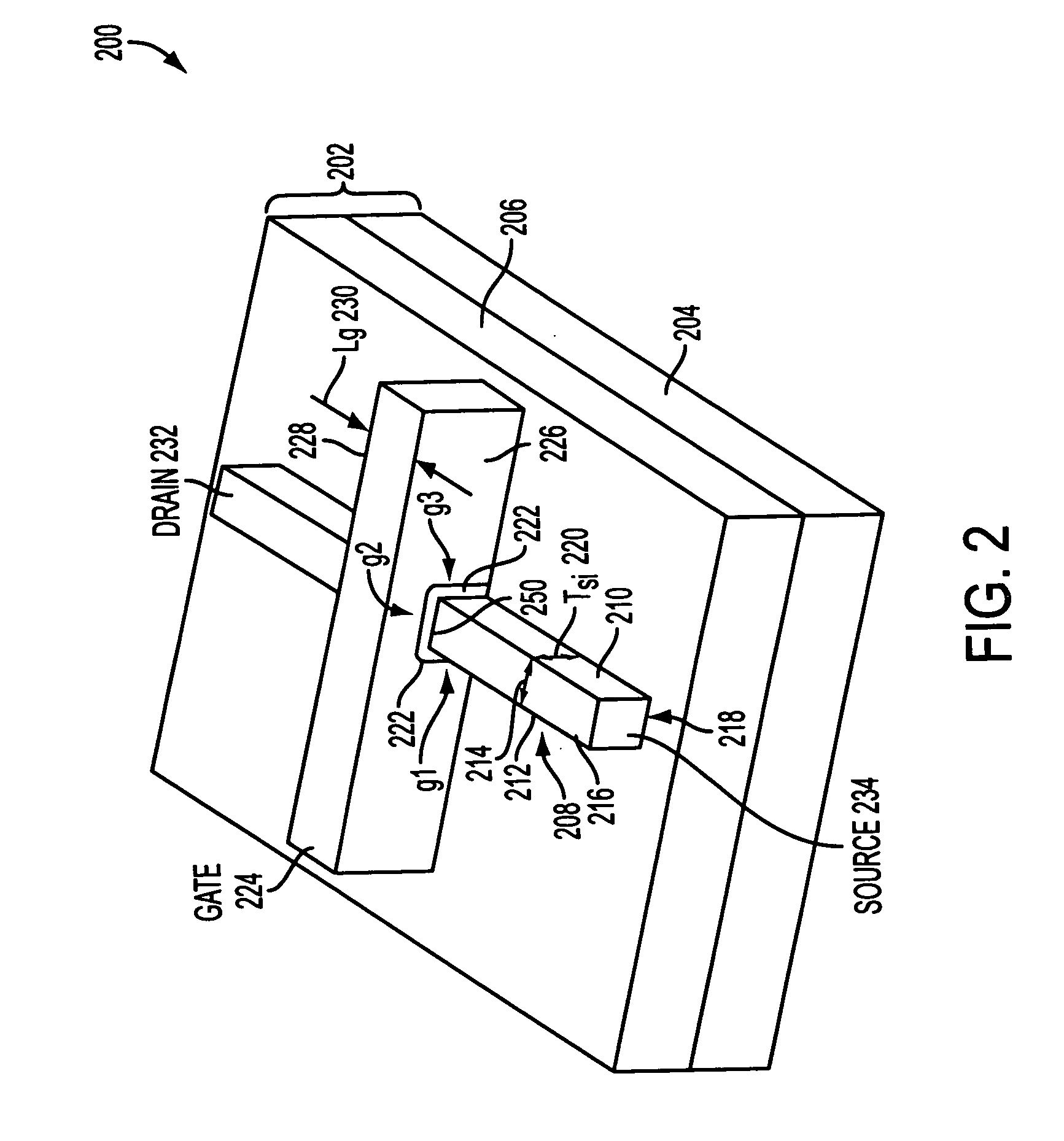
Floating-body DRAM in tri-gate technology
A floating-body dynamic random access memory device may include a semiconductor body having a top surface and laterally opposite sidewalls formed on a substrate. A gate dielectric layer may be formed on the top surface of the semiconductor body and on the laterally opposite sidewalls of the semiconductor body. A gate electrode may be formed on the gate dielectric on the top surface of the semiconductor body and adjacent to the gate dielectric on the laterally opposite sidewalls of the semiconductor body. The gate electrode may only partially deplete a region of the semiconductor body, and the partially depleted region may be used as a storage node for logic states.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Resistive random access memory and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100112810A1Improve the immunityReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A resistive random access memory including, an insulating layer, a hard mask layer, a bottom electrode, a memory cell and a top electrode is provided. The insulating layer is disposed on the bottom electrode. The insulating layer has a contact hole having a first width. The hard mask layer has an opening. A portion of the memory cell is exposed from the opening and has a second width smaller than the first width. The top electrode is disposed on the insulating layer and is coupled with the memory cell.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
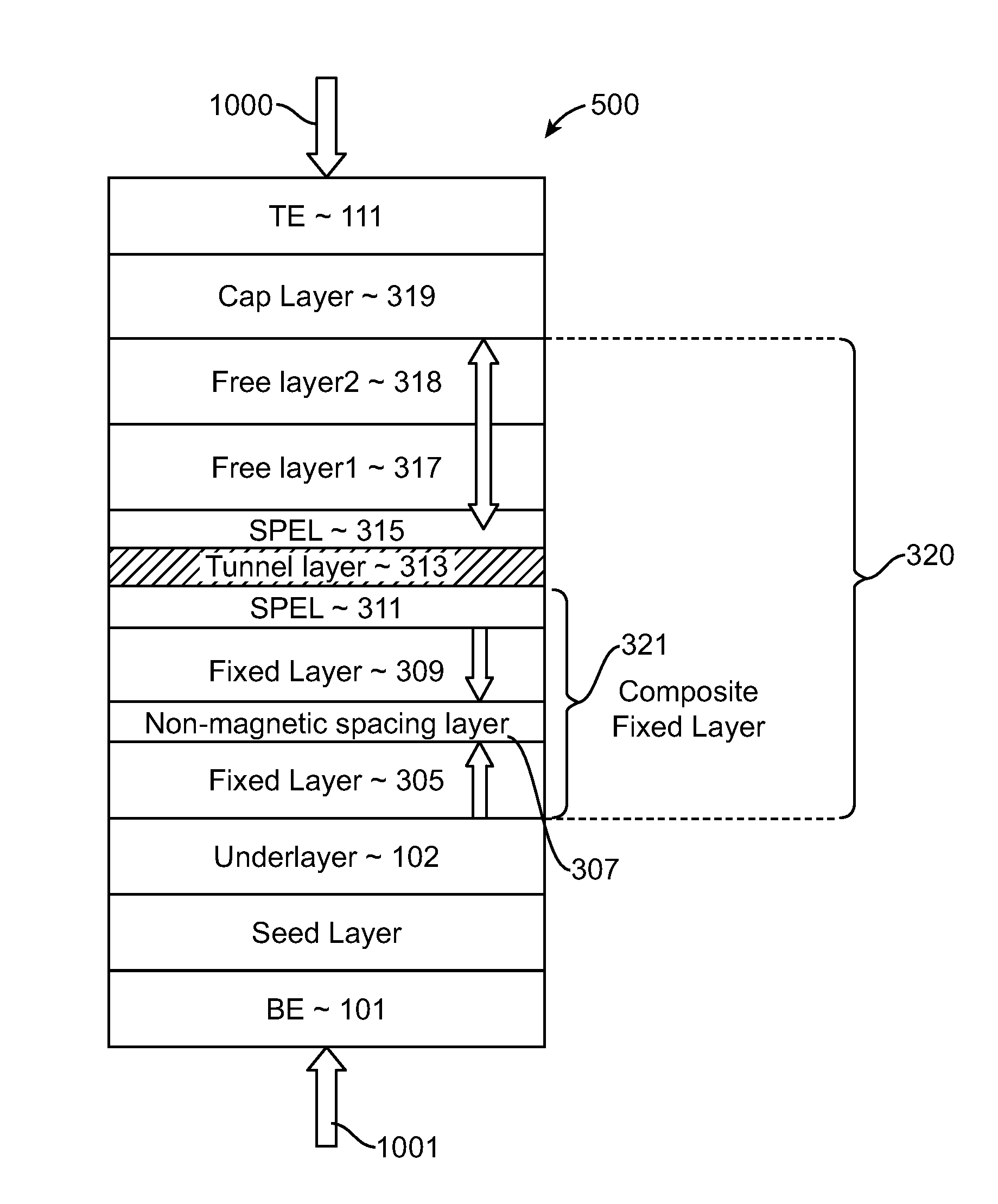
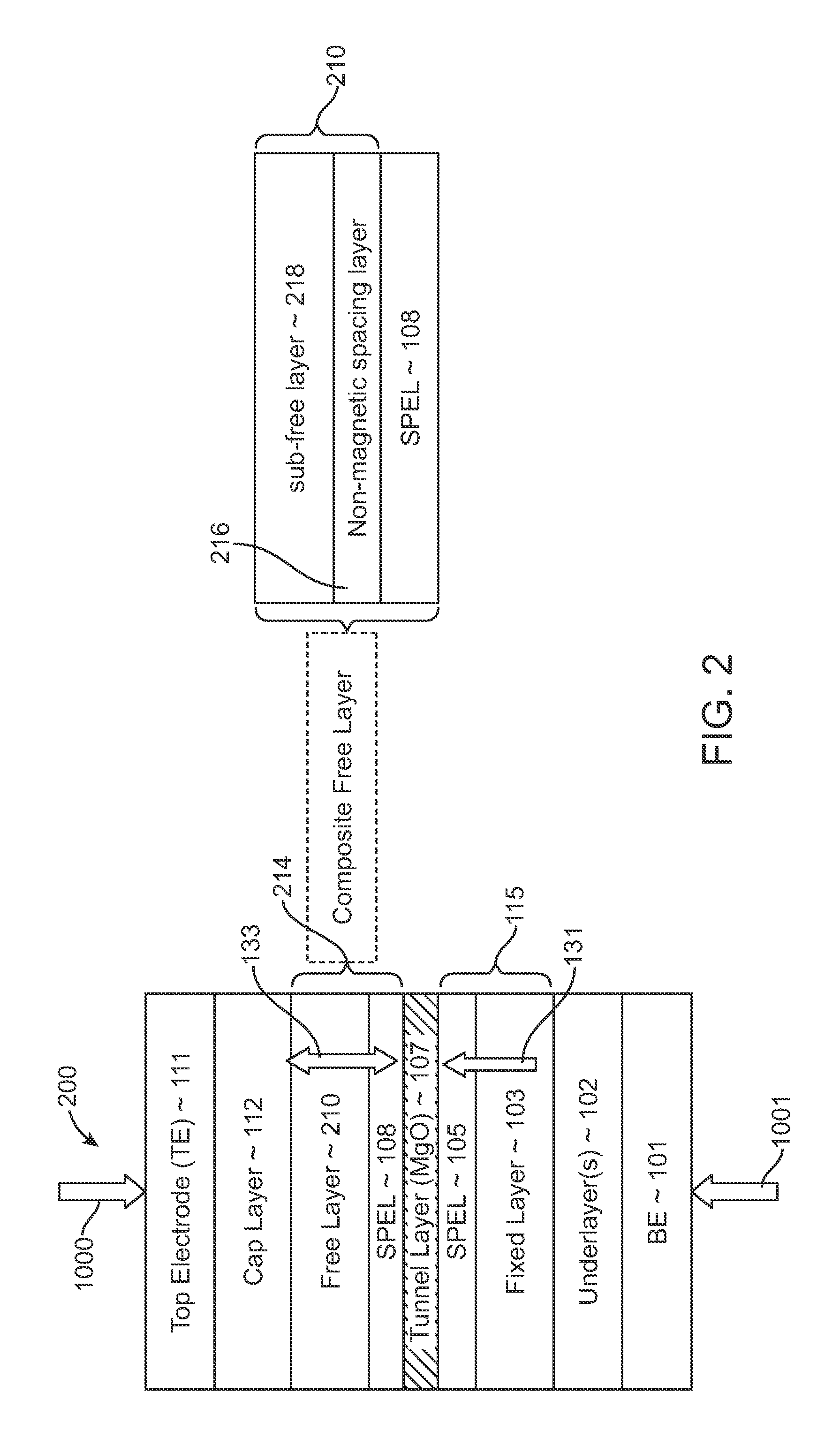
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Bridge resistance random access memory device with a singular contact structure
ActiveUS7608848B2Reduced dimensionSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesBit lineEdge surface
A resistance random access memory in a bridge structure is disclosed that comprises a contact structure where first and second electrodes are located within the contact structure. The first electrode has a circumferential extending shape, such as an annular shape, surrounding an inner wall of the contact structure. The second electrode is located within an interior of the circumferential extending shape and separated from the first electrode by an insulating material. A resistance memory bridge is in contact with an edge surface of the first and second electrodes. The first electrode in the contact structure is connected to a transistor and the second electrode in the contact structure is connected to a bit line. A bit line is connected to the second electrode by a self-aligning process.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
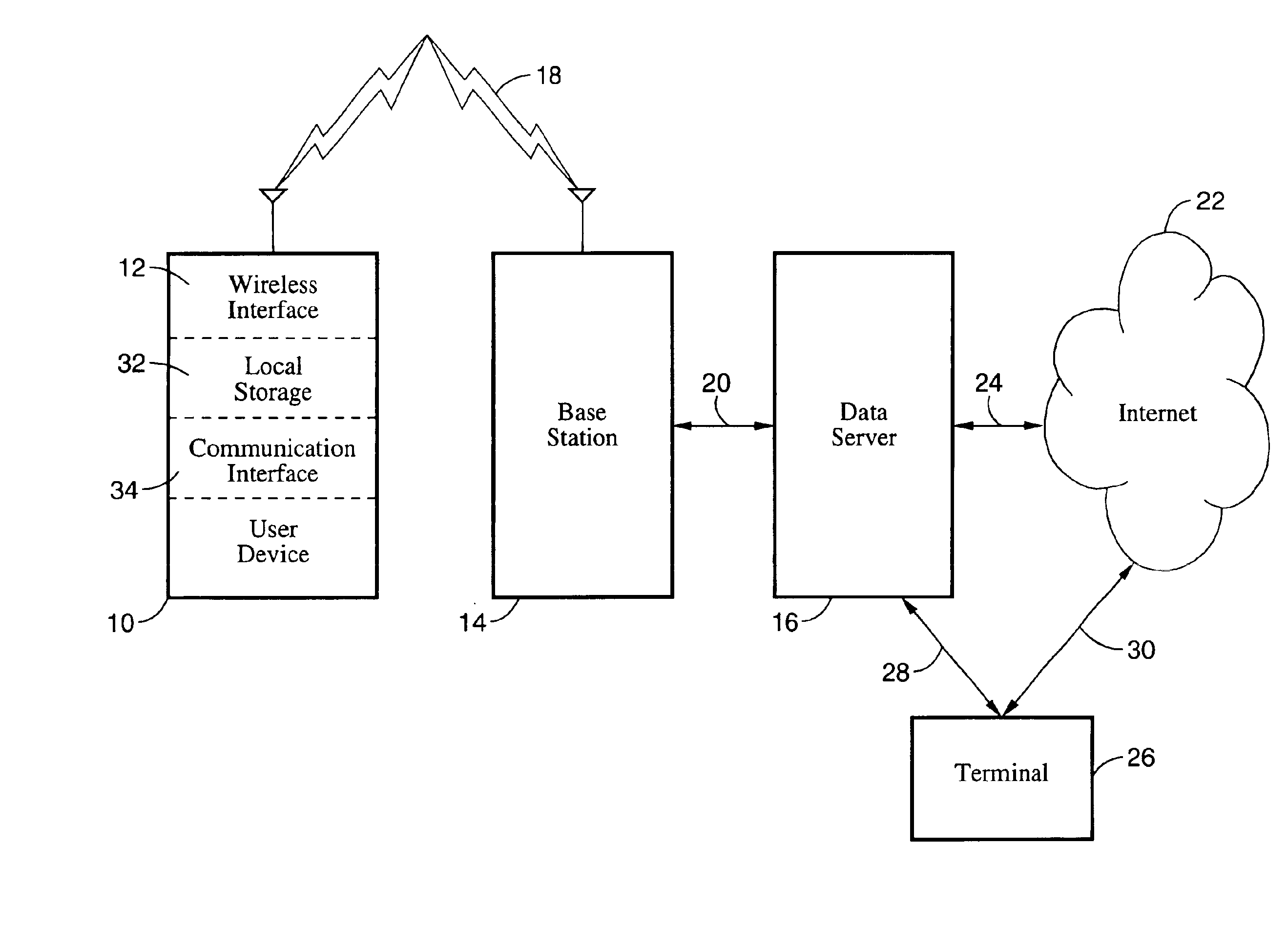
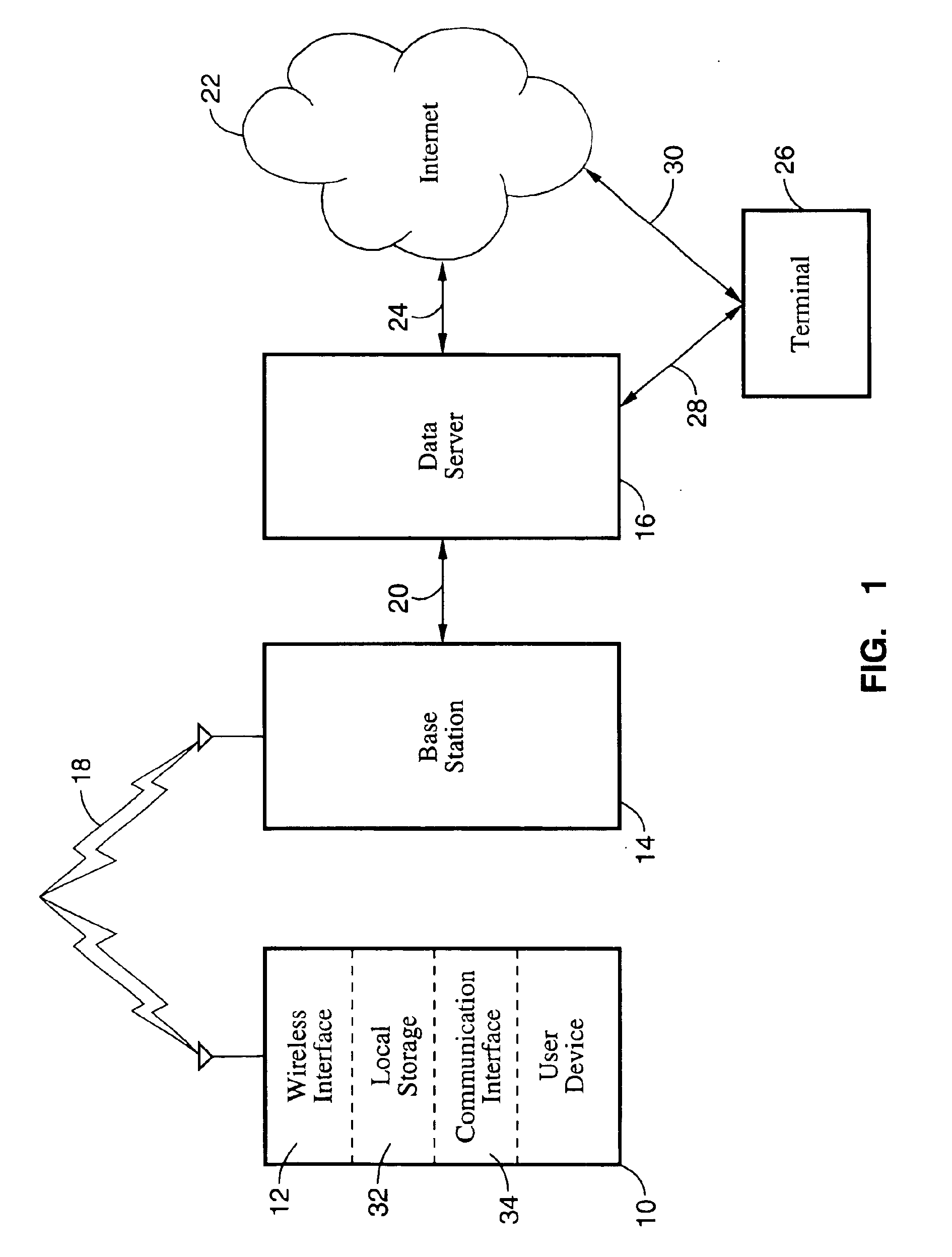
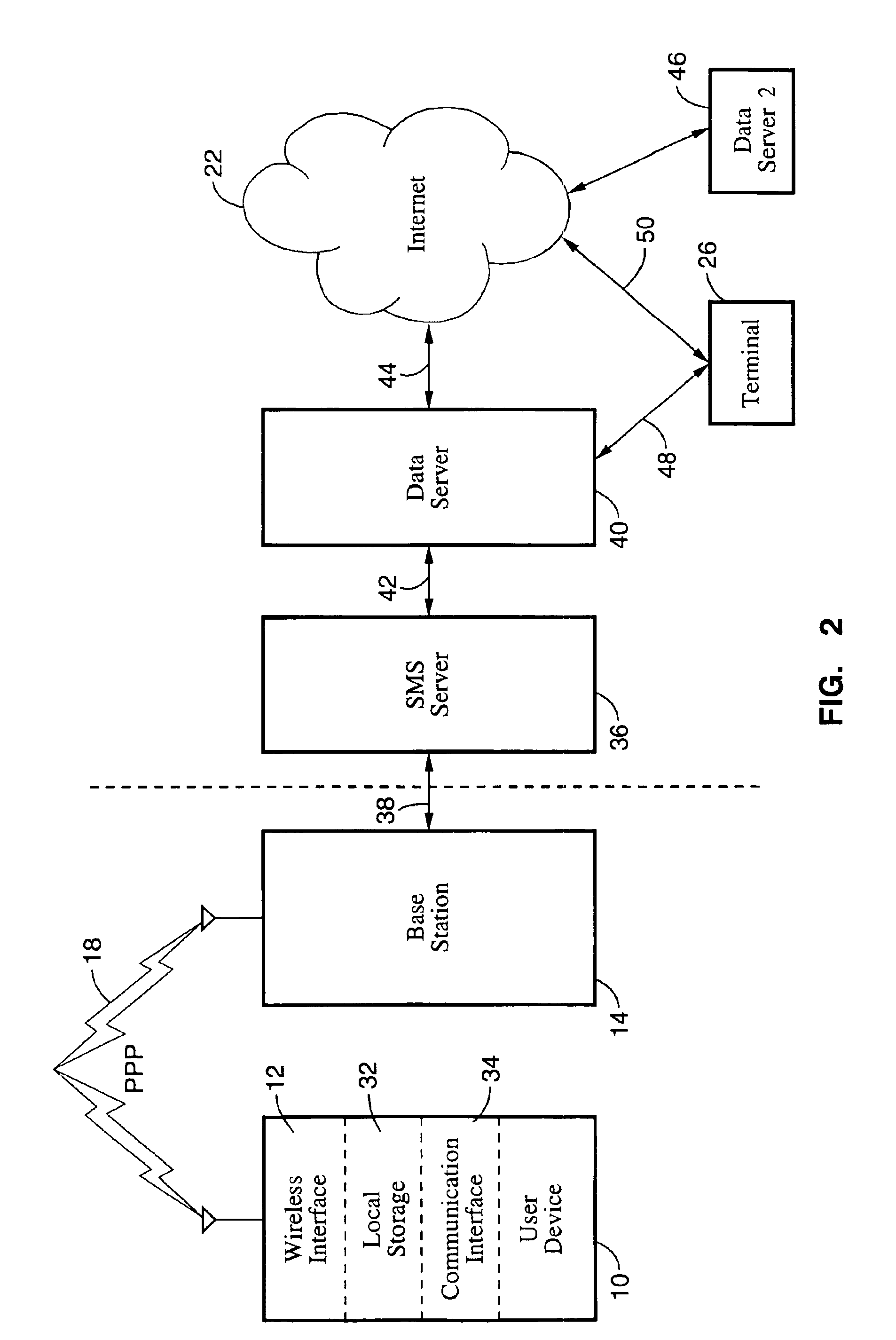
Method, system and devices for wireless data storage on a server and data retrieval
InactiveUS6956833B1Reduce and eliminate needMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless commuication servicesUser deviceData retrieval
A method and system for remotely storing data on a server through a wireless connection instead of storing data locally in a consumer device, as well as devices for use with the method and system. More particularly, a video camera, still camera, laptop computer, or other consumer device which normally stores data in local memory such as film, disk, random access memory, memory sticks, or other forms of storage would transmit the data to a remote server through a wireless connection. The data would be saved on the remote server for subsequent retrieval through, for example, the Internet or a wireless connection to the server. In addition, data not originating from the user device could be downloaded to the consumer device. The data to be retrieved can be specified by the user, or sent to the user according to a user profile stored on the server.
Owner:SONY CORP +2
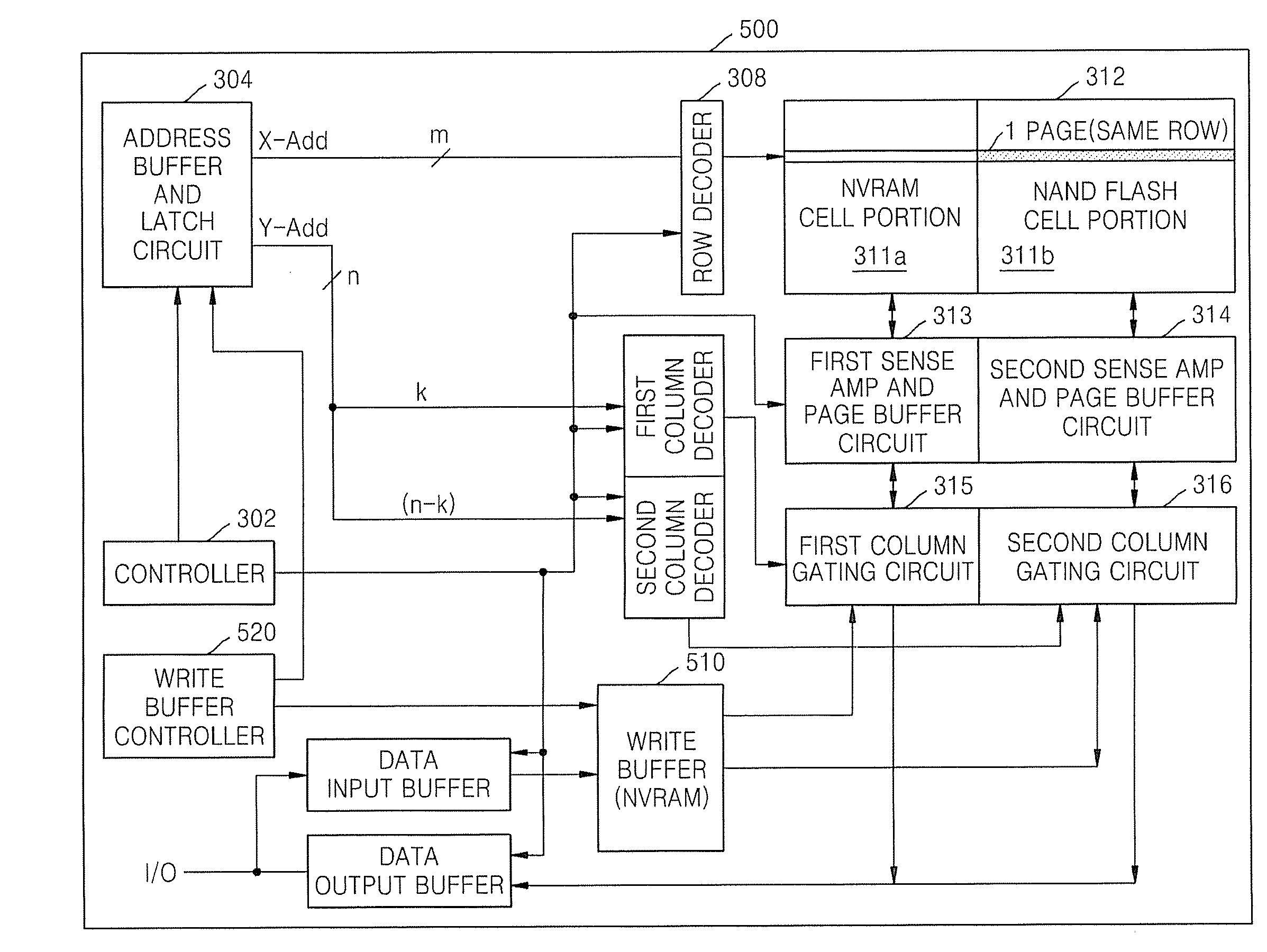
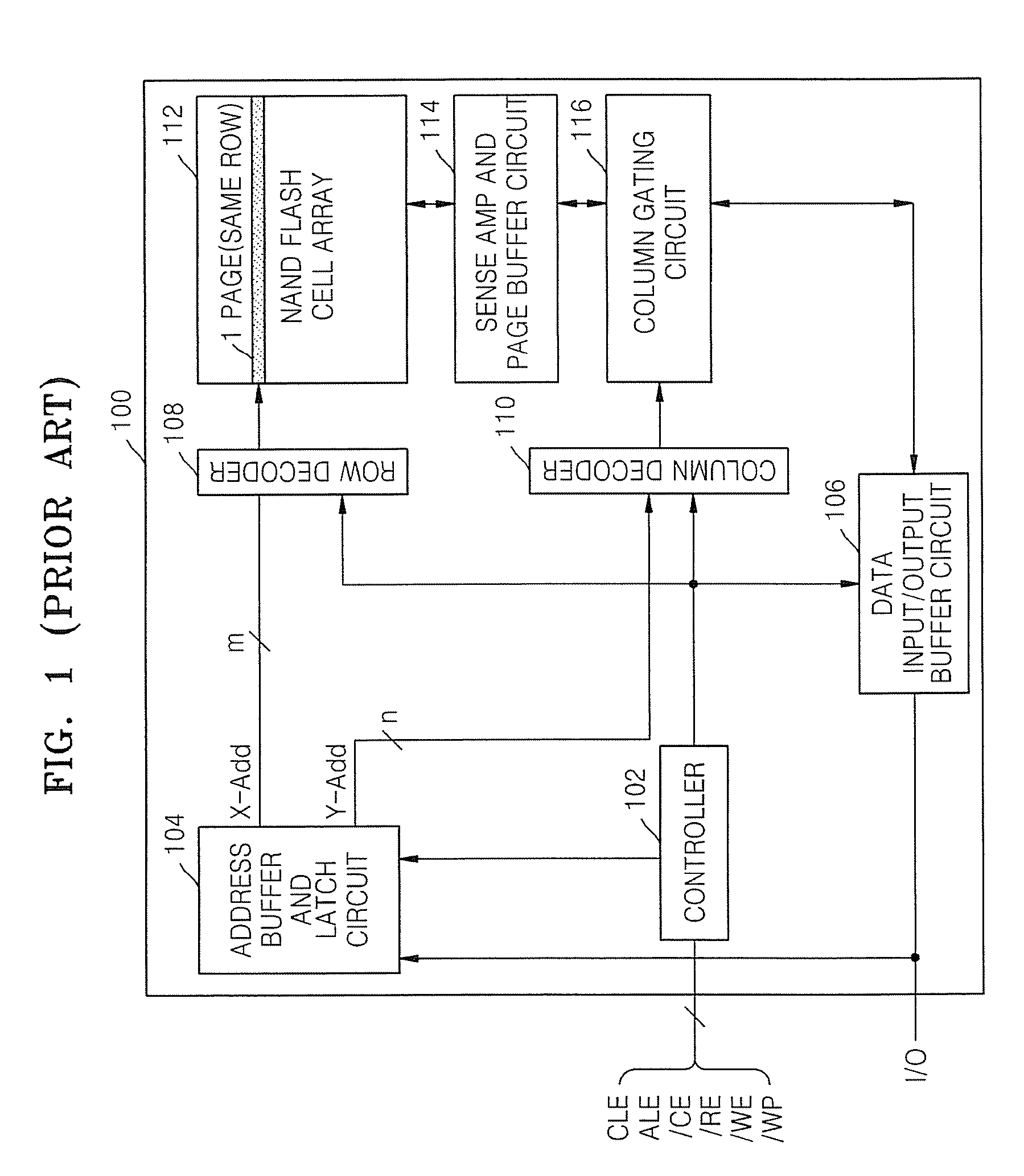
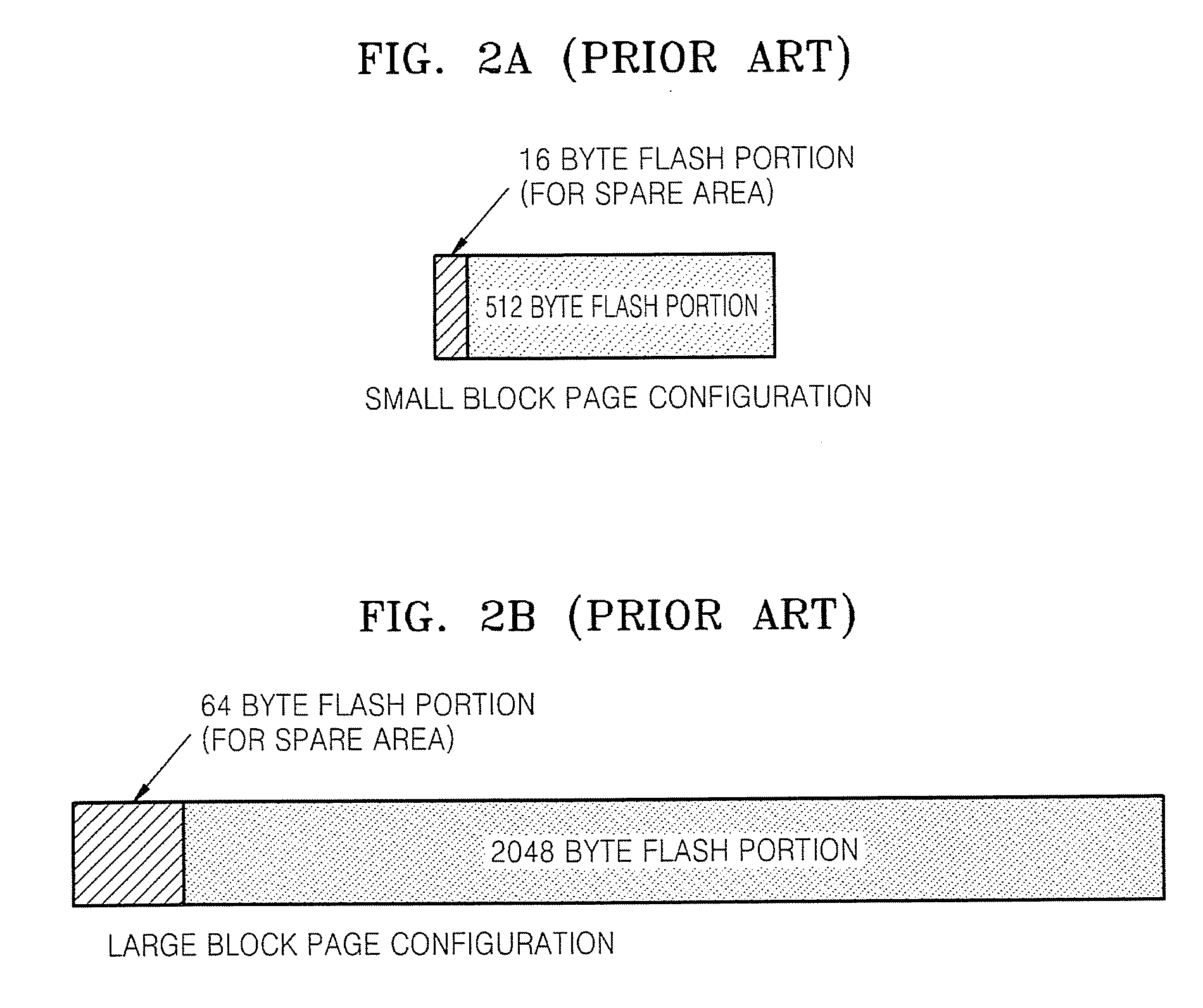
Memory device employing NVRAM and flash memory cells
A memory device includes a memory cell array including a NAND flash cell portion including a plurality of first columns of serially-connected flash memory cells and a non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) cell portion including a plurality of second columns of NVRAM cells. The flash memory cells and the NVRAM cells are arranged such that respective word lines are connected to flash memory cells and NVRAM cells in each of respective rows, which may correspond to page units including flash memory cells and NVRAM cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
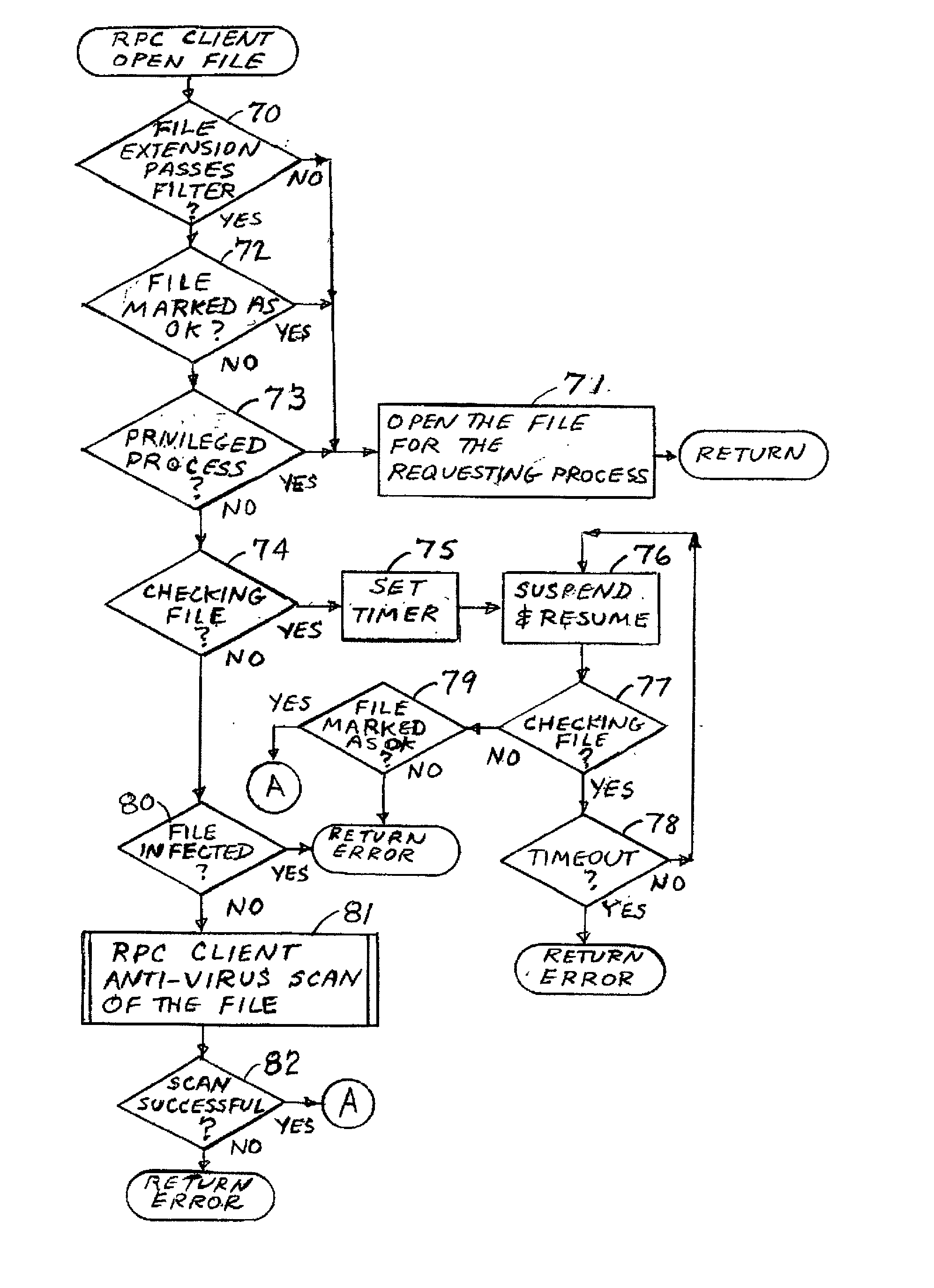
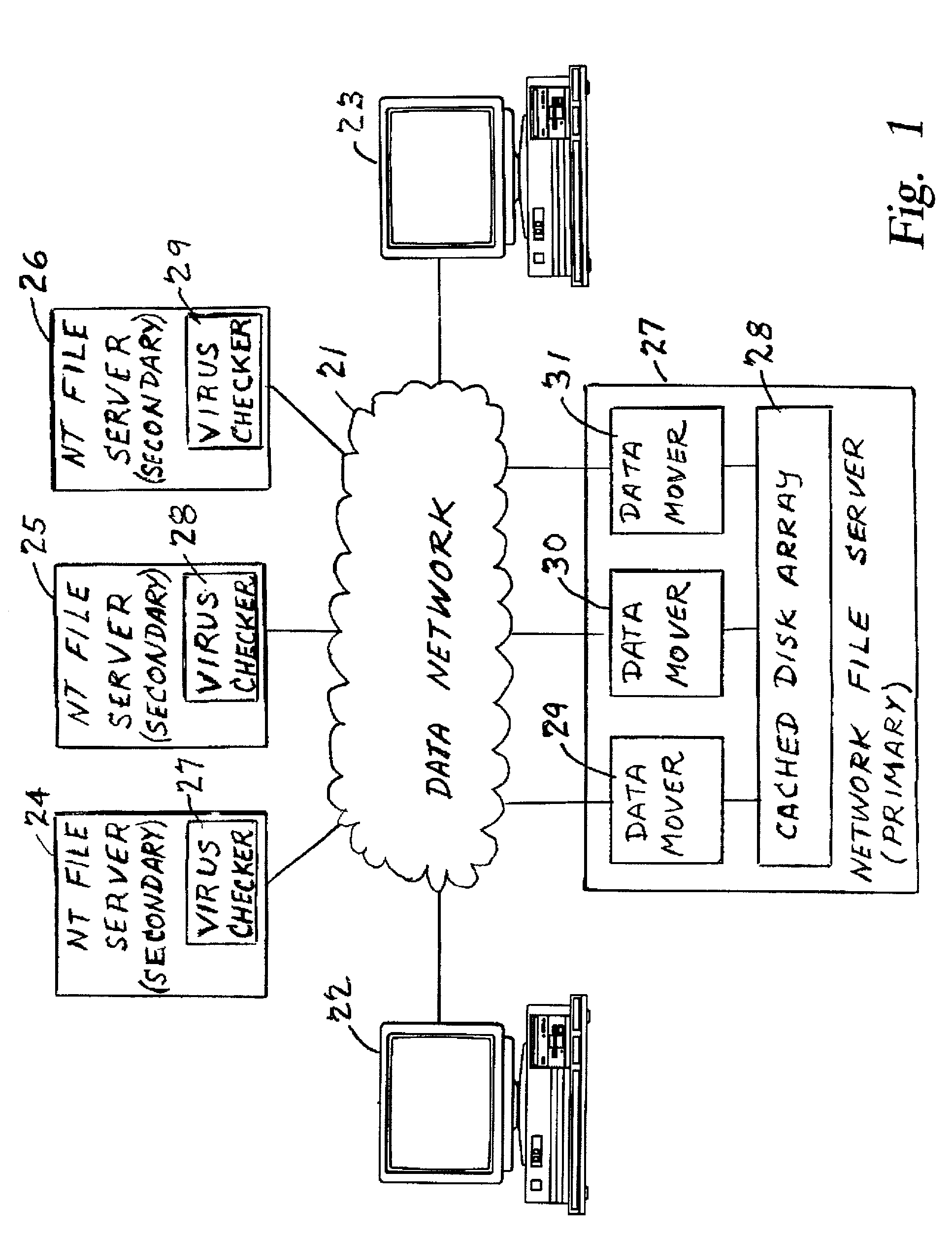
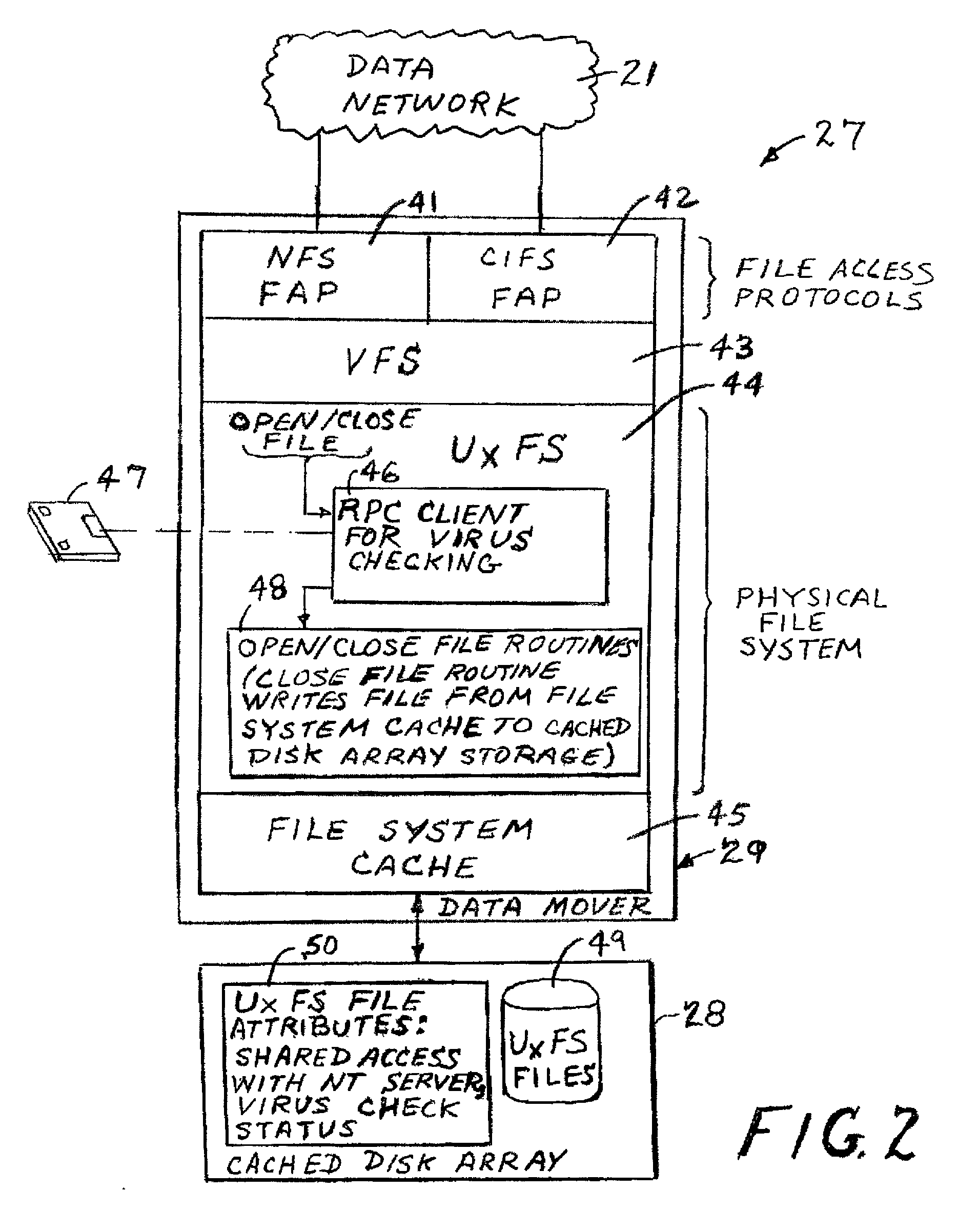
Using a virus checker in one file server to check for viruses in another file server
ActiveUS20020129277A1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionAnti virusRandom access memory
When a network client accesses a file in a network file server, the network file server invokes a conventional virus checker program in an NT file server to transfer pertinent file data from the network file server to random access memory in the NT file server to perform an anti-virus scan. Users may interact with the virus checker program in the usual fashion, to select file types to check, and actions to perform when a virus is detected. This method eliminates the need for porting the virus checker program to the network file server, and avoids maintenance problems when the virus checker program is updated or upgraded. Moreover, a kernel mode driver in the NT file server may provide an indirect interface to the virus checker program for initiating an anti-virus scan. Therefore, the driver supports a wide variety of virus checker programs and ensures continued operation when the virus checker program is upgraded.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
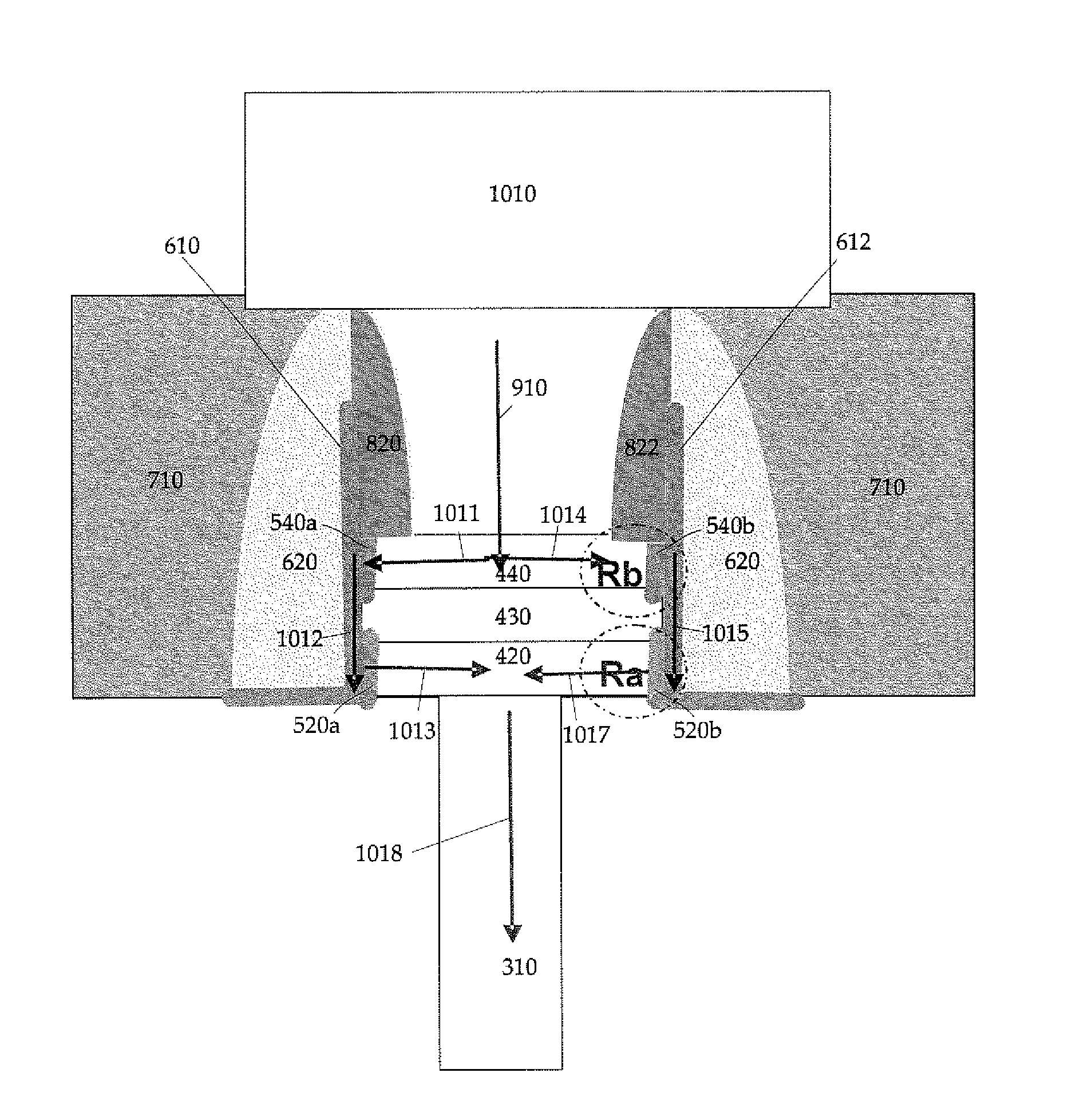
Multi-level cell resistance random access memory with metal oxides
ActiveUS7697316B2High densityElectrical apparatusElectric analogue storesRandom access memoryElectrical battery
A bistable resistance random access memory comprises a plurality of programmable resistance random access memory cells where each programmable resistance random access memory cell includes multiple memory members for performing multiple bits for each memory cell. The bistable RRAM includes a first resistance random access member connected to a second resistance random access member through interconnect metal liners and metal oxide strips. The first resistance random access member has a first resistance value Ra, which is determined from the thickness of the first resistance random access member based on the deposition of the first resistance random access member. The second resistance random access member has a second resistance value Rb, which is determined from the thickness of the second resistance random access member based on the deposition of the second resistance random access member.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
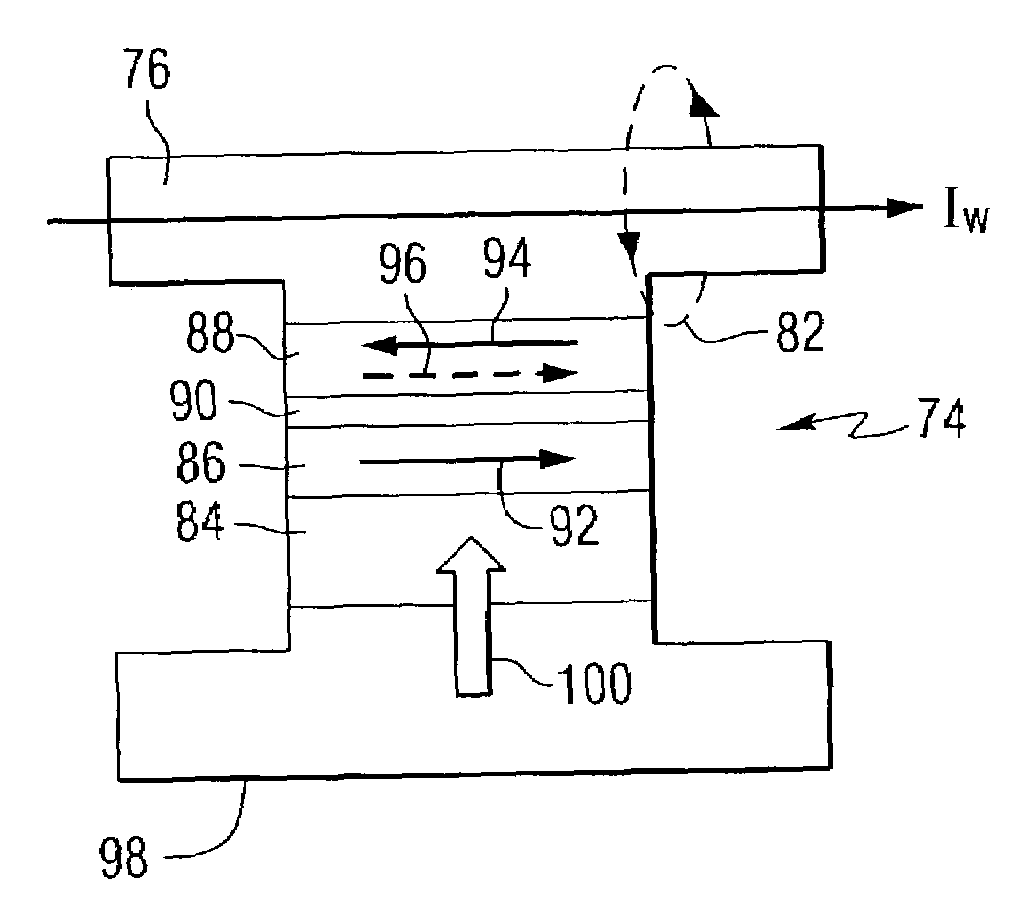
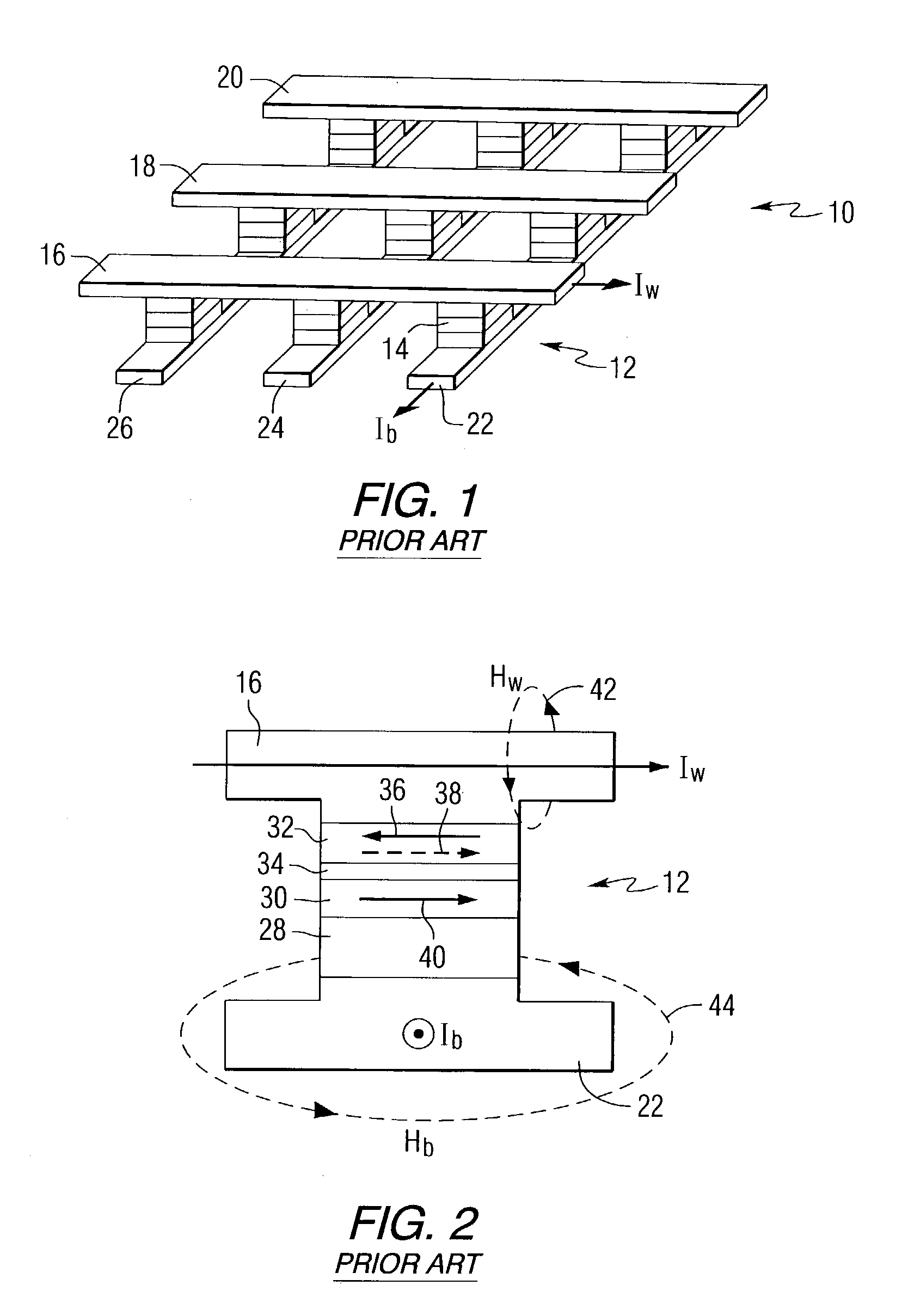
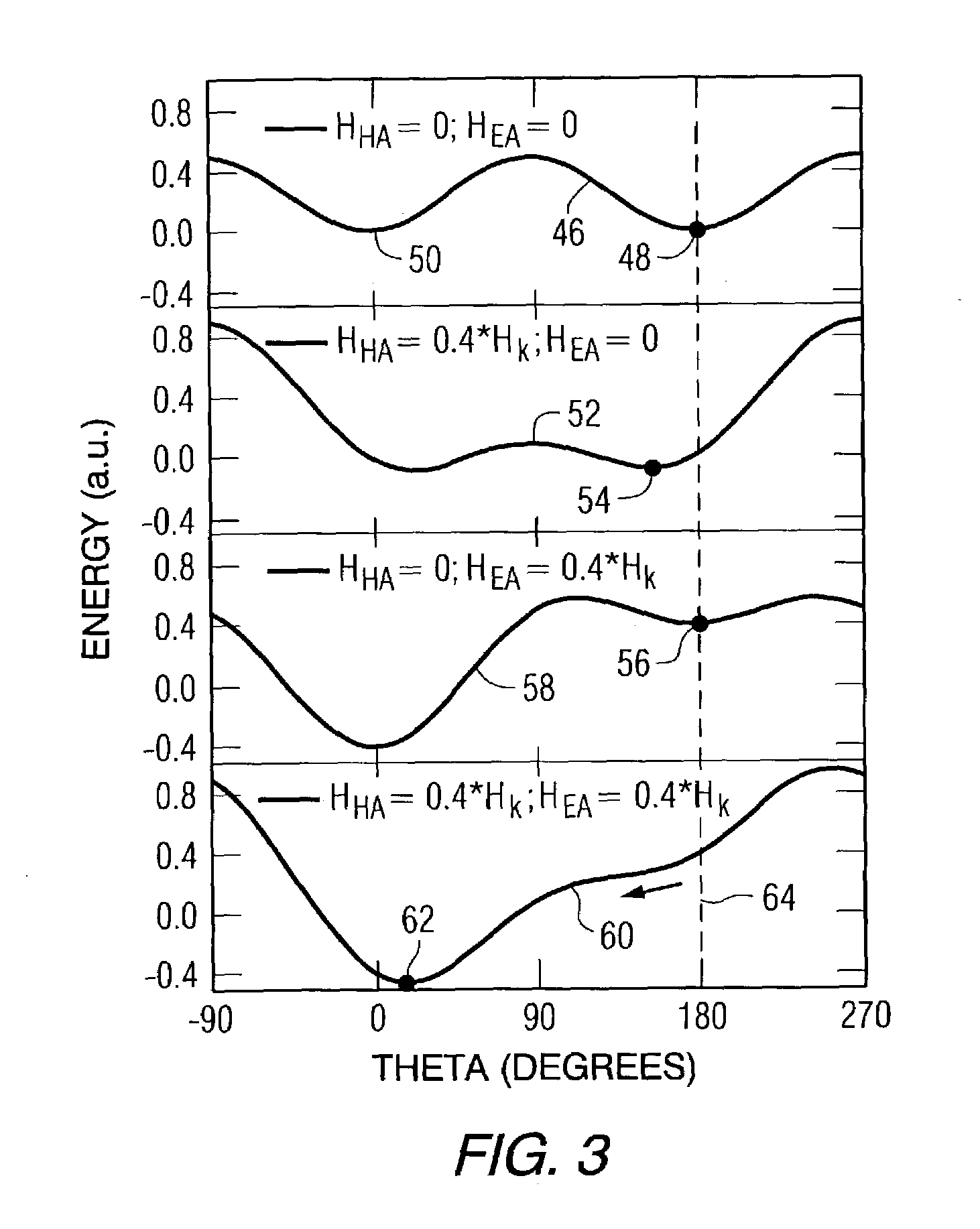
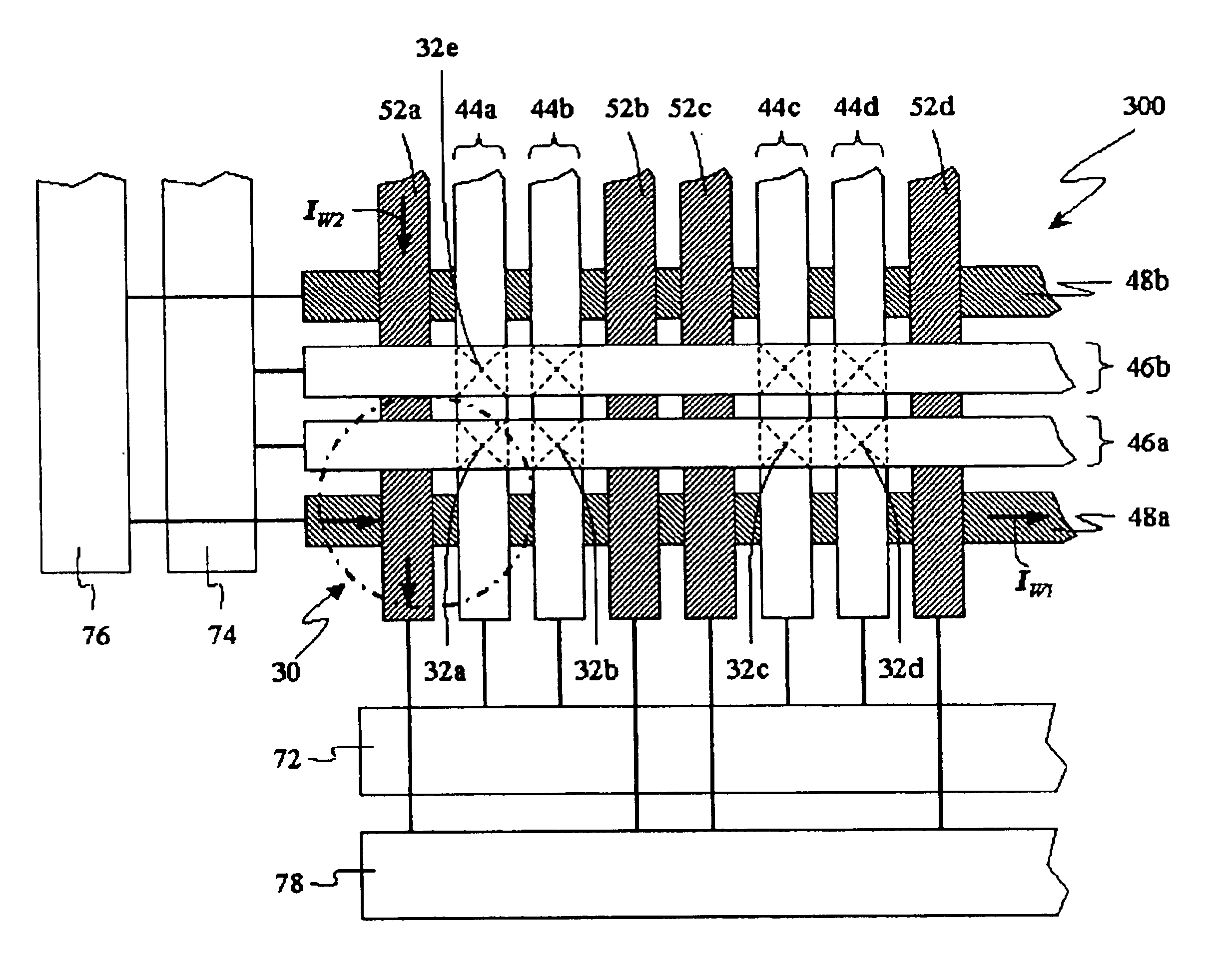
Hybrid write mechanism for high speed and high density magnetic random access memory
A method of writing to a magnetic random access memory comprising: producing a magnetic field along a magnetically hard axis of a free layer of a magnetoresistive element; and passing current through the magnetoresistive element to change a direction of magnetization of the free layer by spin momentum transfer. A magnetic random access memory that operates in accordance with the method is also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
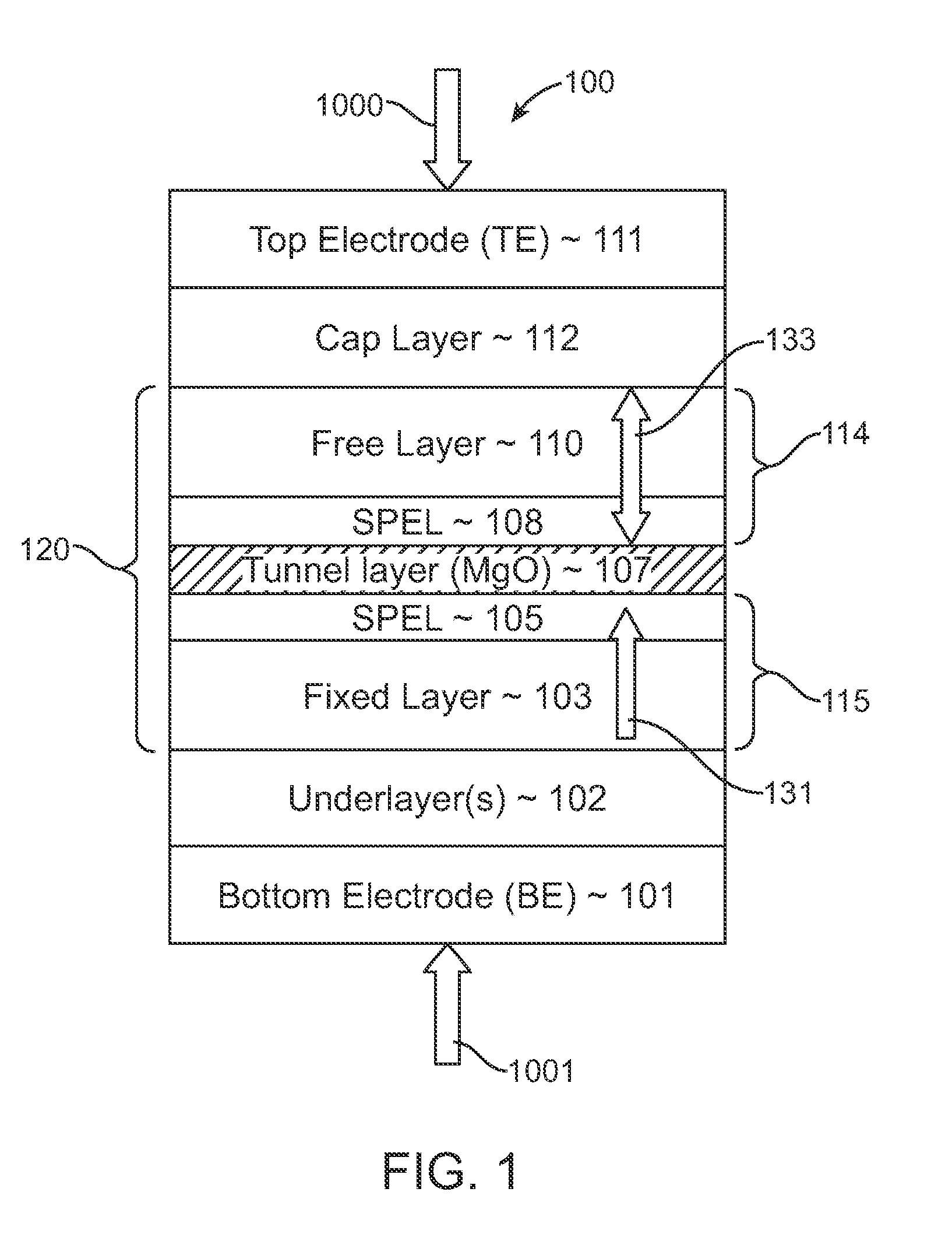
Magnetic tunnel junction memory device
InactiveUS6845038B1Improve permeabilityLow resistivityDigital storageBit linePerpendicular magnetization
A memory cell for magnetic random access memory devices based on a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) memory element with a perpendicular orientation of magnetization in pinned and free magnetic layers, and a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between the pinned and free layers. The memory cell can include the MTJ memory element, a magnetic flux guide in series with selection devices, such as a bit line, a word line, and a transistor. The magnetic flux guide can have two electrically conductive magnetic portions with the MTJ memory element positioned between the magnetic portions. The MTJ memory element is magnetically isolated from the magnetic flux guide by thin non-magnetic conductive spacers. The MTJ memory element is arranged in a vertical space between the intersecting bit and word lines at their intersection region. The memory cell also includes write and excitation lines. The write line is parallel to the bit line and the excitation line is parallel to the word line. The write and excitation lines also intersect each other and define a corner. The MTJ memory element is positioned in the corner of the intercepting write and excitation lines.
Owner:SHUKH ALLA MIKHAILOVNA
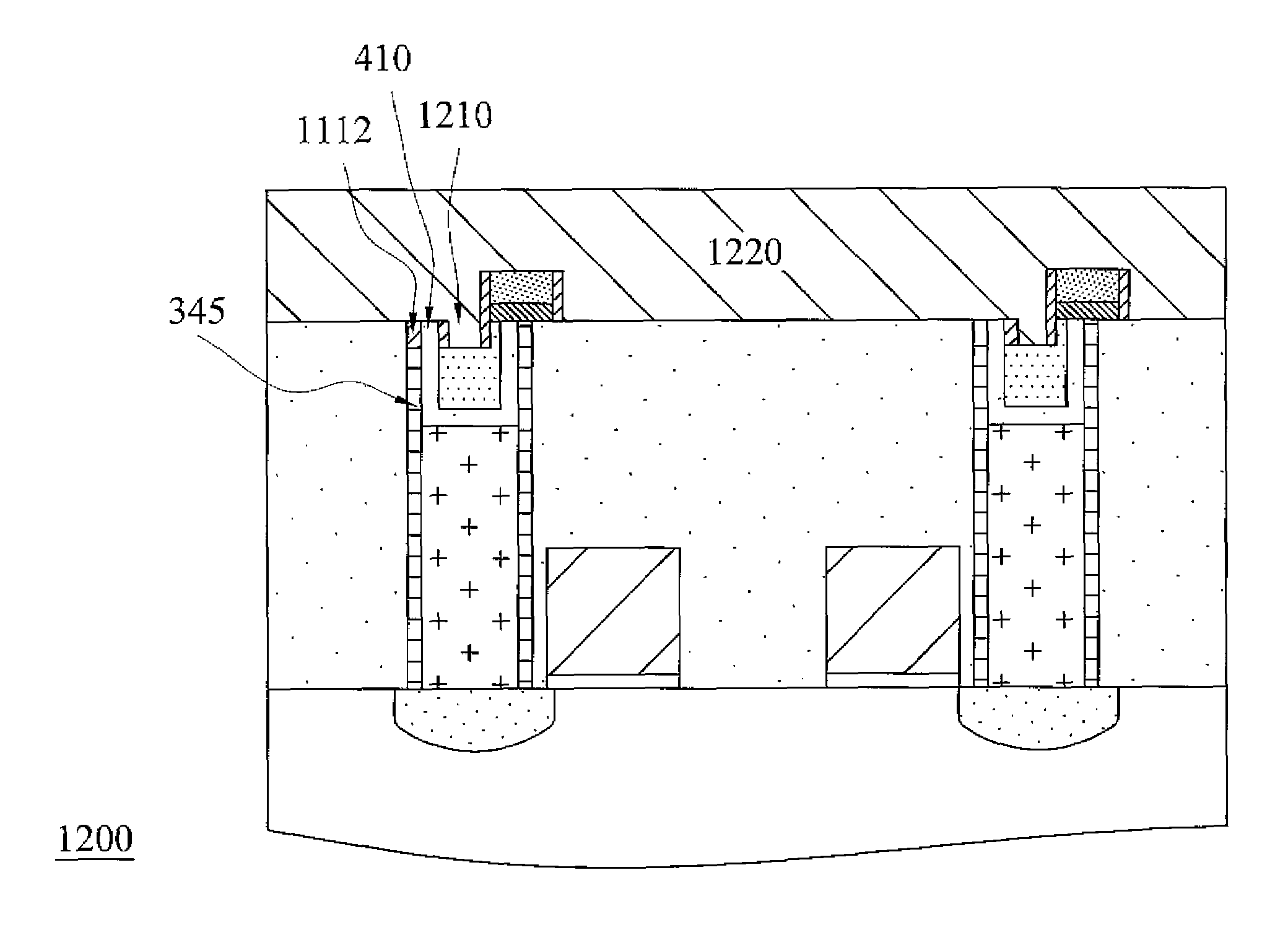
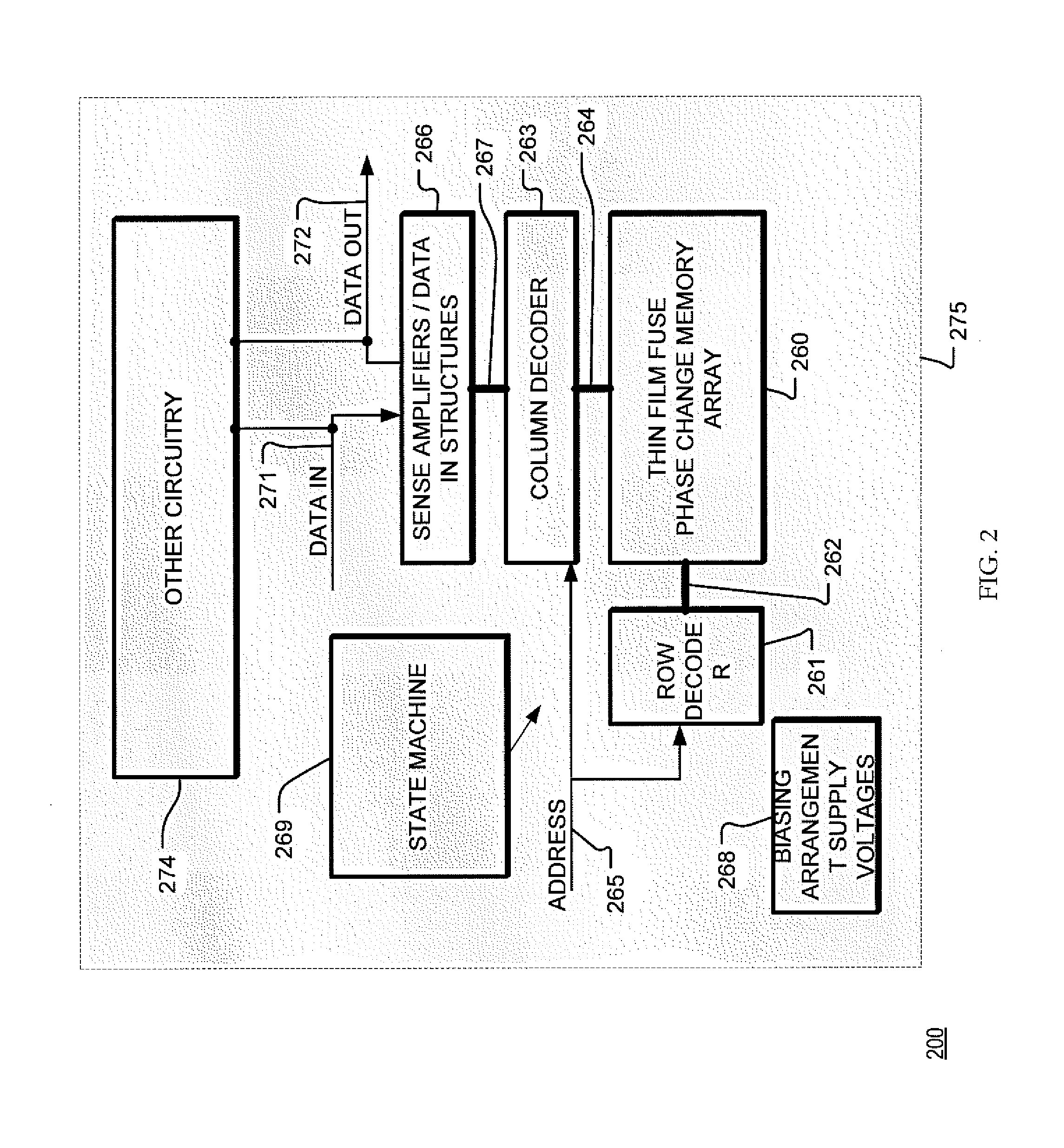
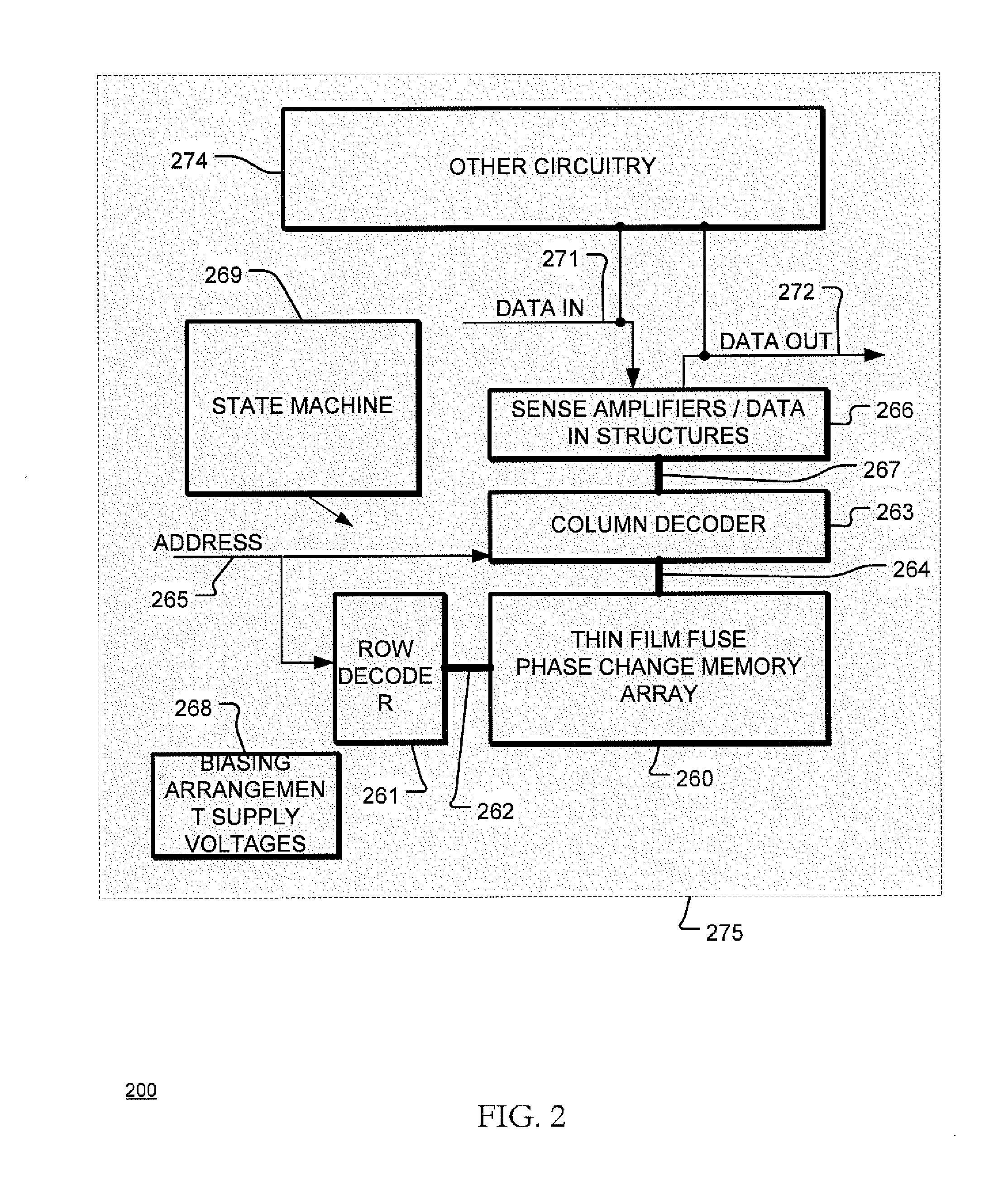
Self-align planerized bottom electrode phase change memory and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20070158645A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryRandom access memory
A method is described for self-aligning a bottom electrode in a phase change random access memory PCRAM device where a top electrode serves as a mask for self-aligning etching of the bottom electrode. The bottom electrode has a top surface that is planarized by chemical mechanical polishing. The top electrode also has a top surface that is planarized by chemical mechanical polishing. A bottom electrode layer like TiN is formed over a substrate and prior to the formation of a via during subsequent process steps. A first dielectric layer is formed over the bottom electrode layer, and a second dielectric layer is formed over the first dielectric layer. A via is formed at a selected section that extends through the first and second dielectric layers.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
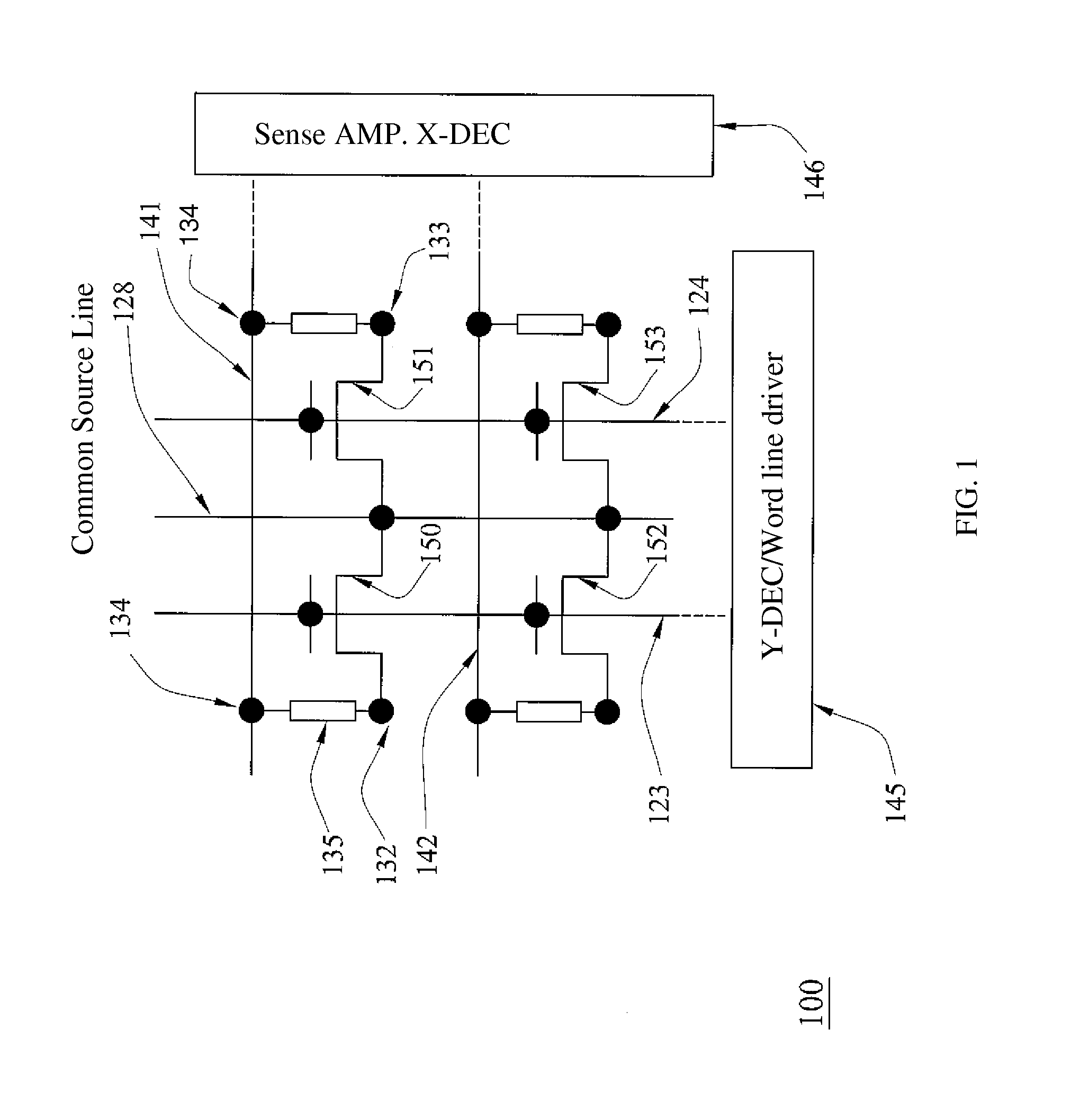
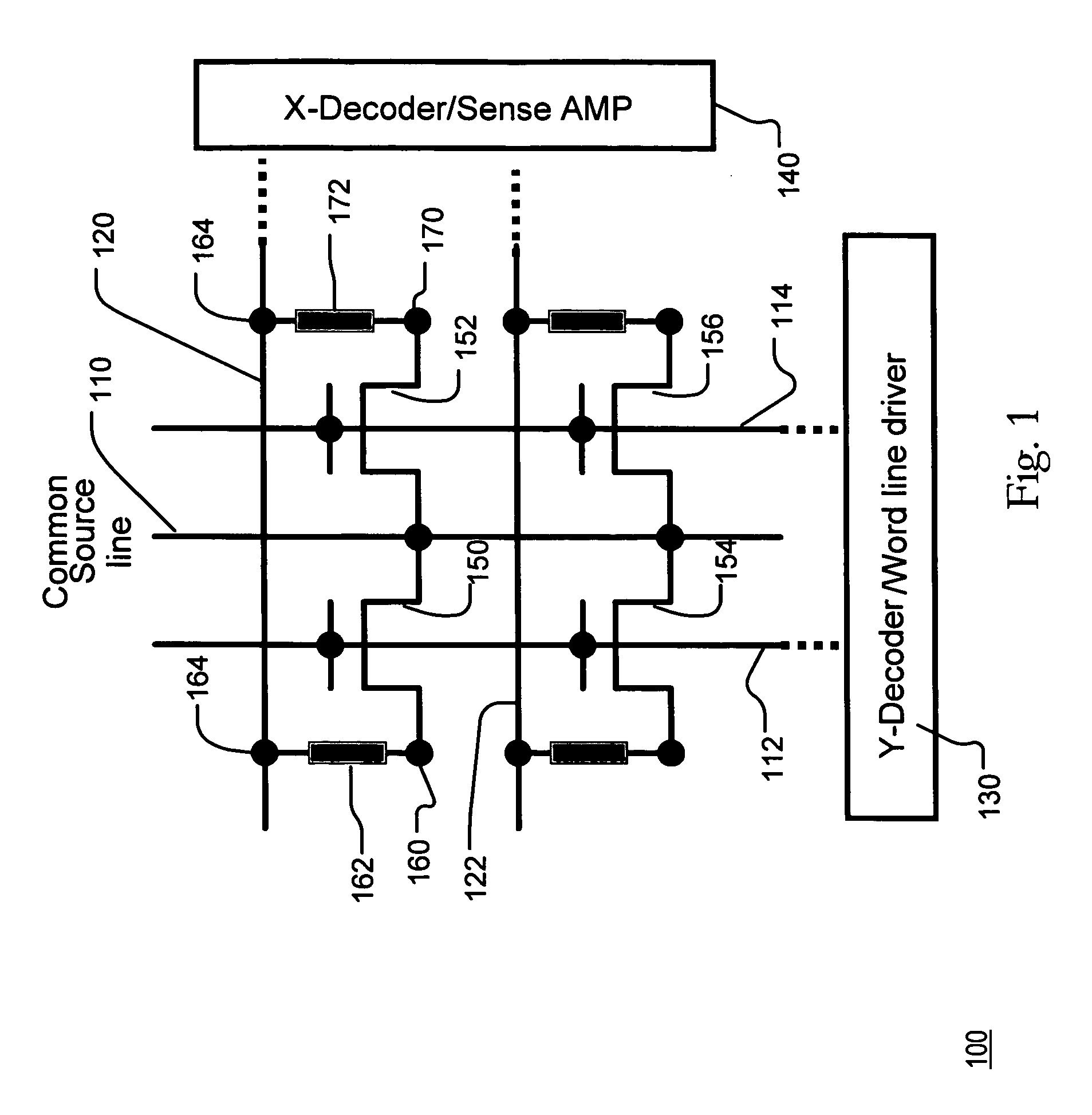
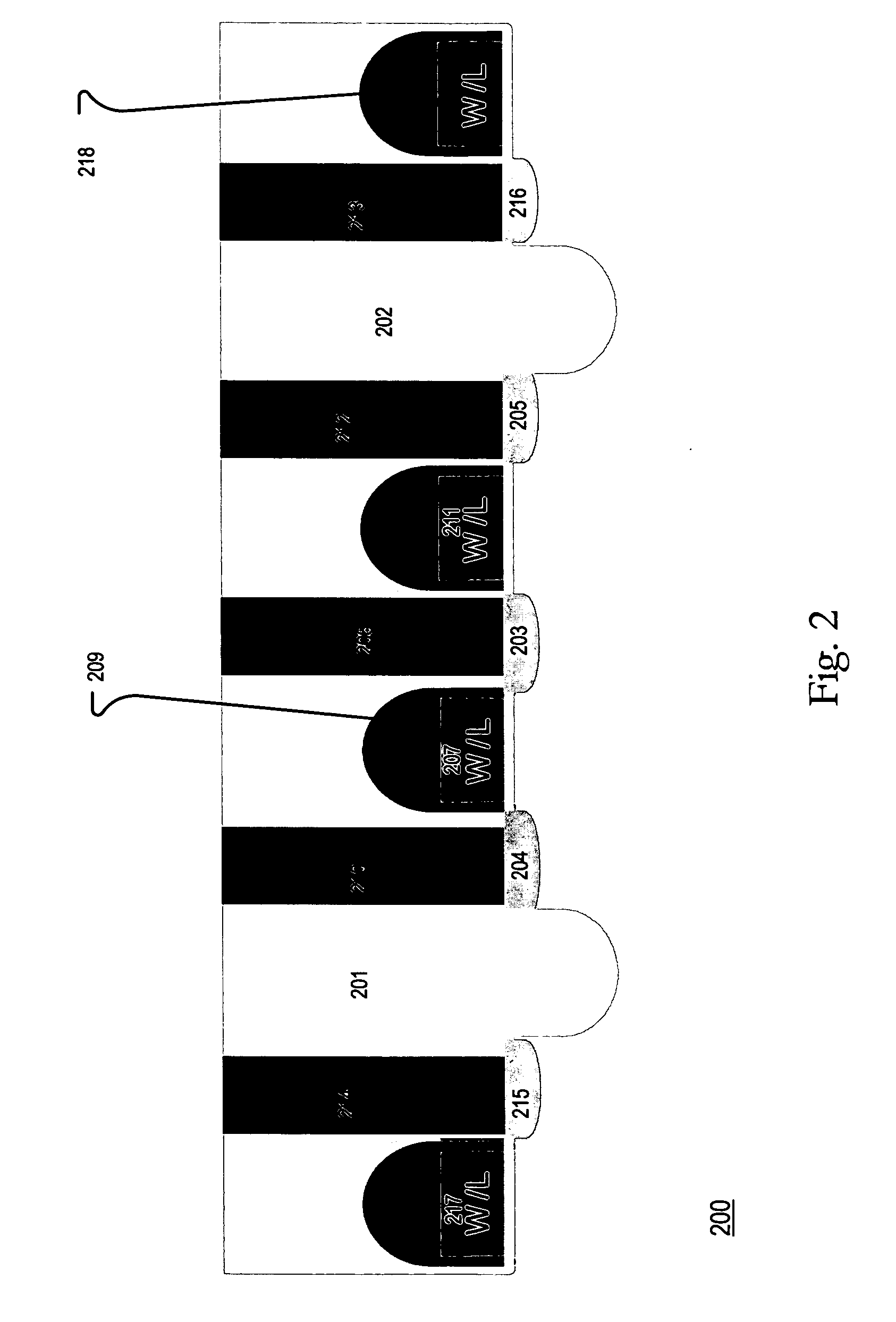
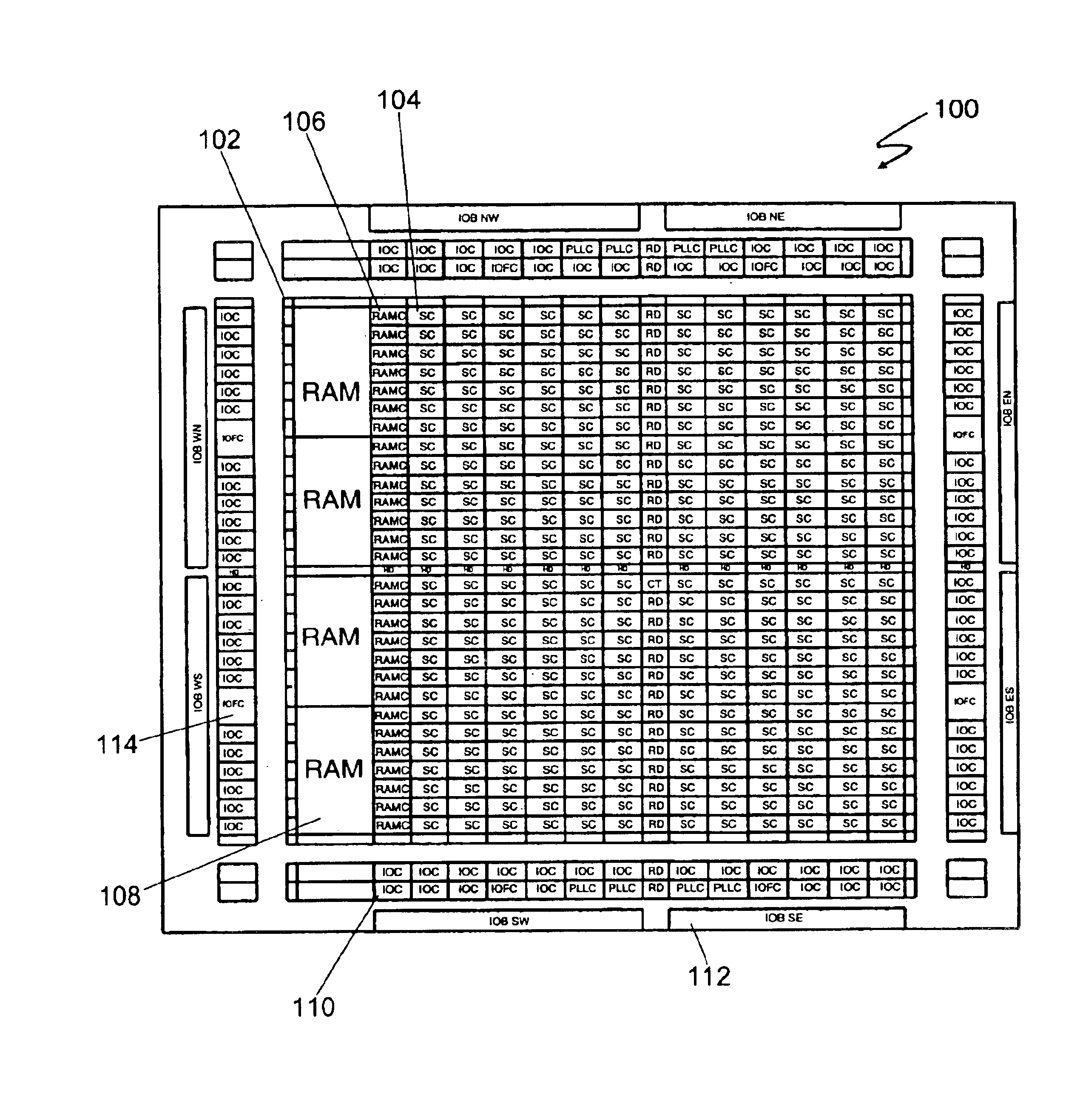
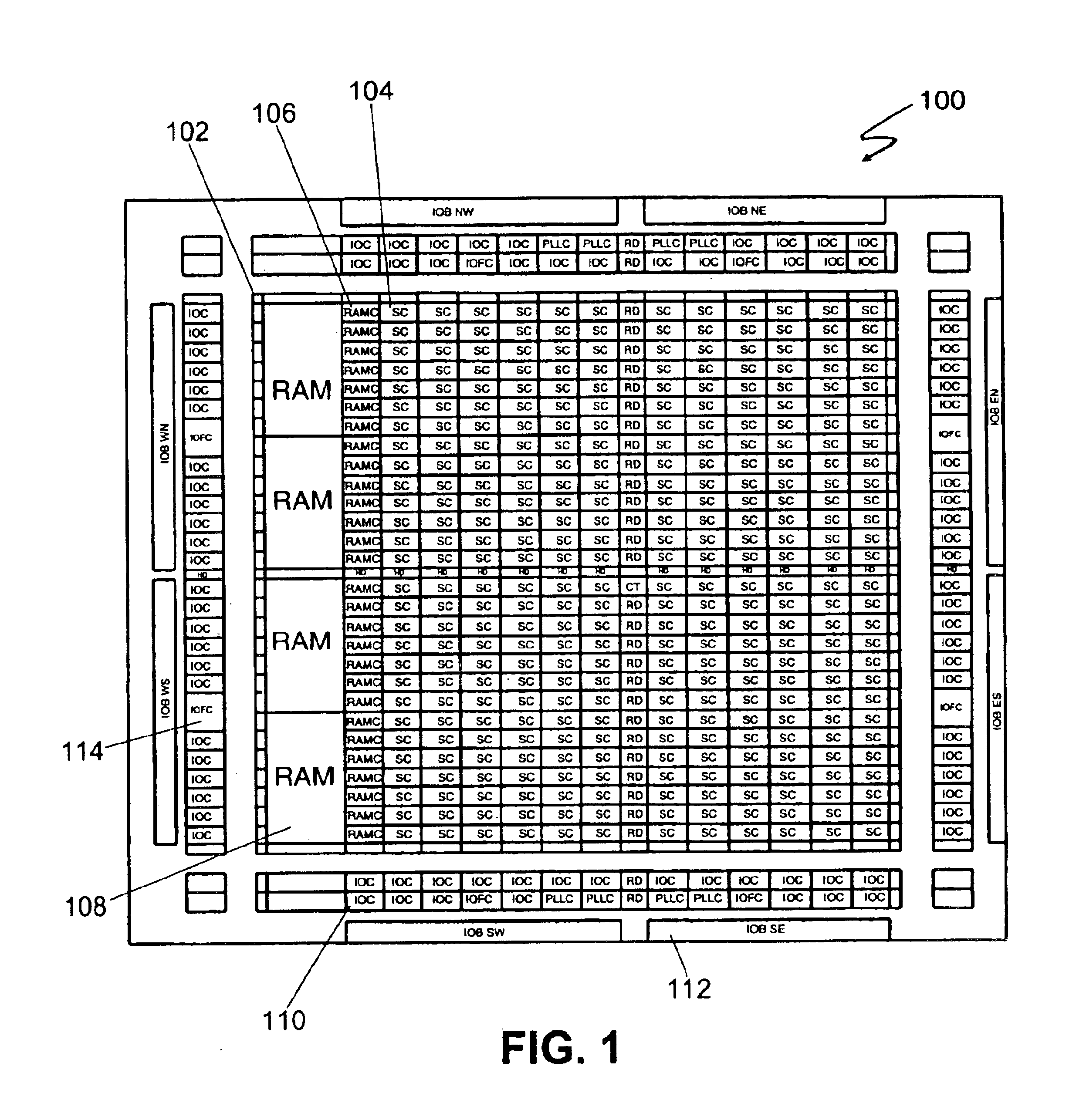
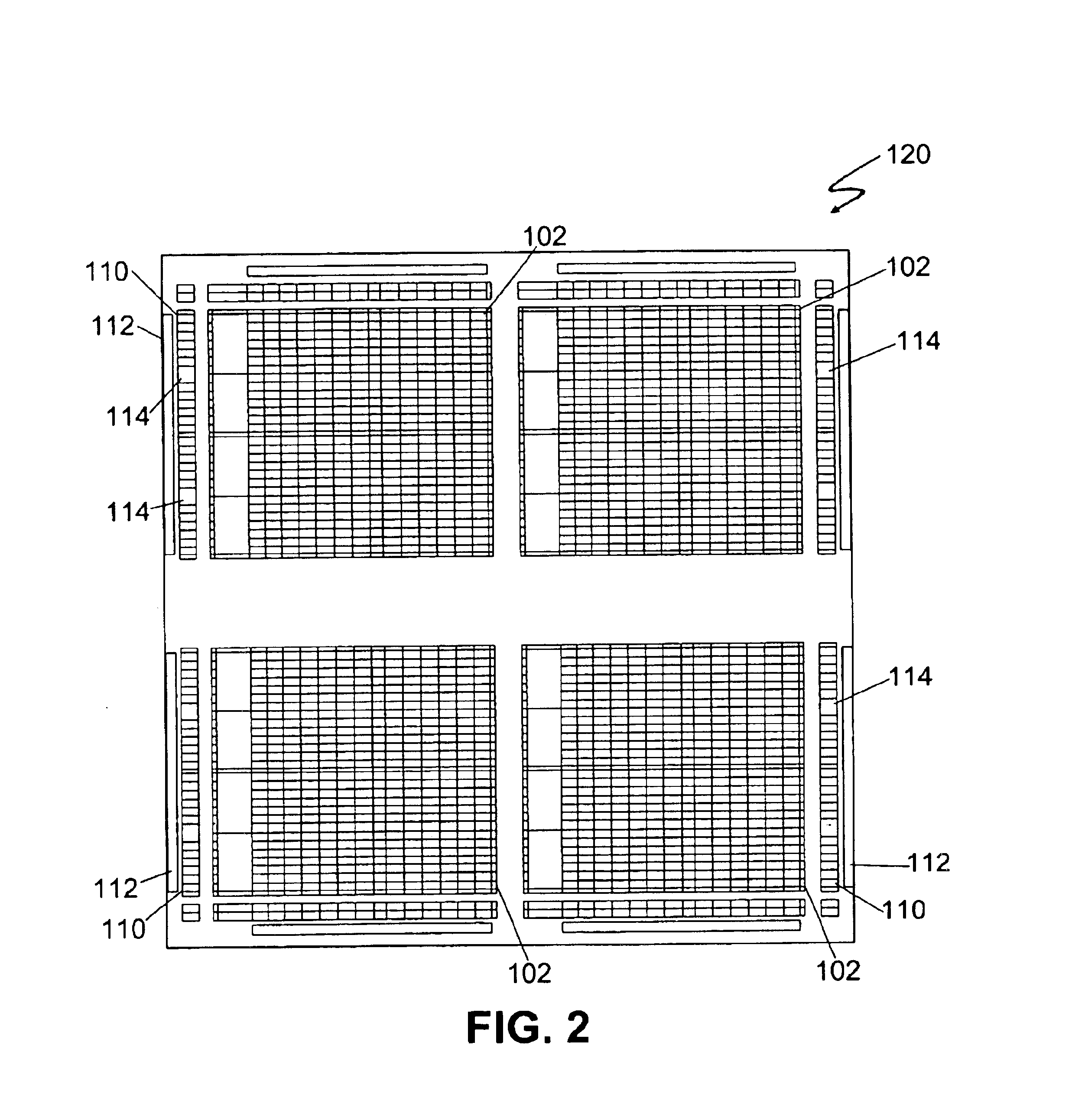
Synchronous first-in/first-out block memory for a field programmable gate array
The present invention comprises a field programmable gate array that has a plurality of dedicated first-in / first-out memory logic components. The field programmable gate array includes a plurality of synchronous random access memory blocks that are coupled to a plurality of dedicated first-in / first-out memory logic components and a plurality of random access memory clusters that are programmably coupled to the plurality of dedicated first-in / first-out memory logic components and to the plurality of synchronous random access memory blocks.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
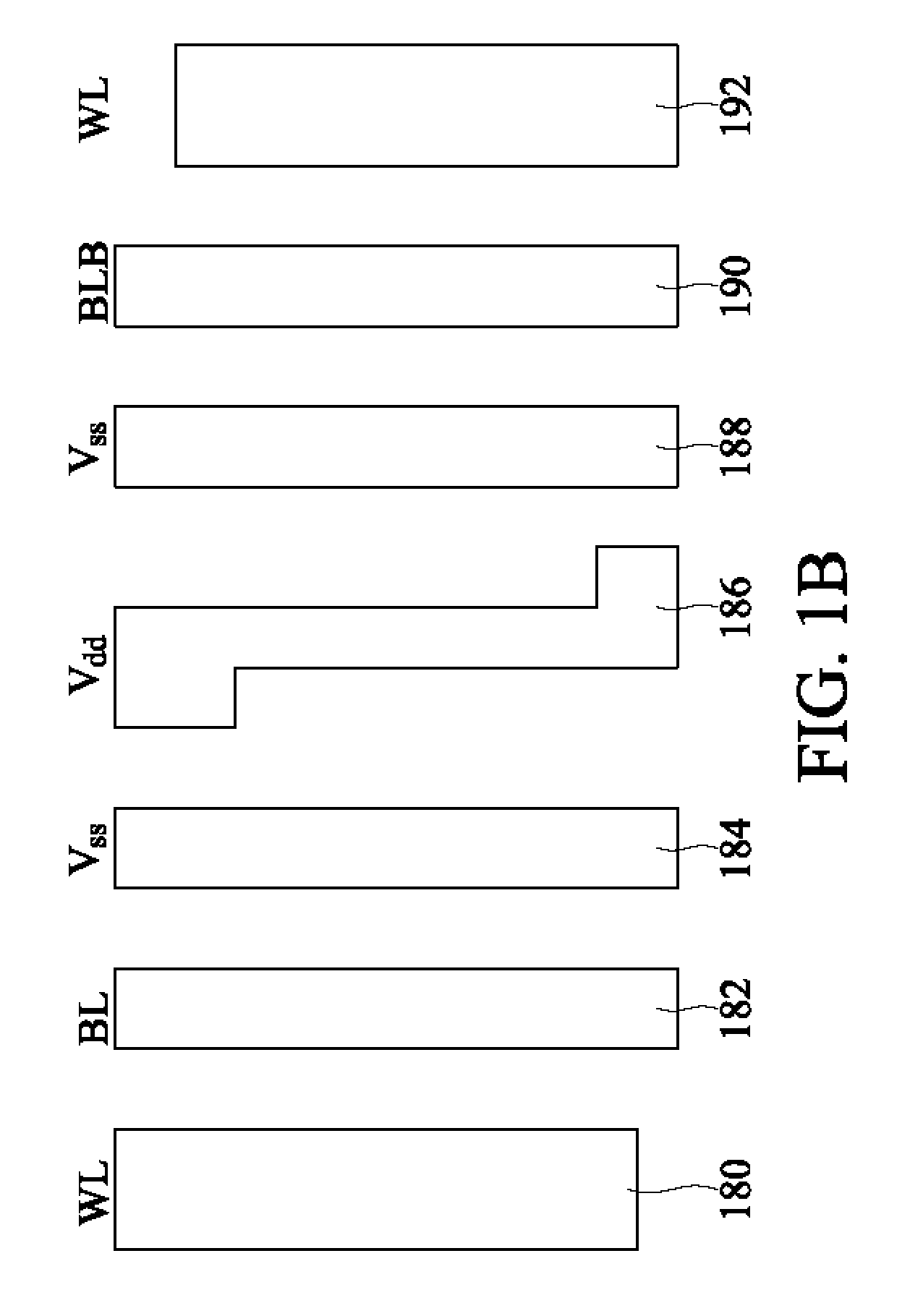
Static random access memory architecture
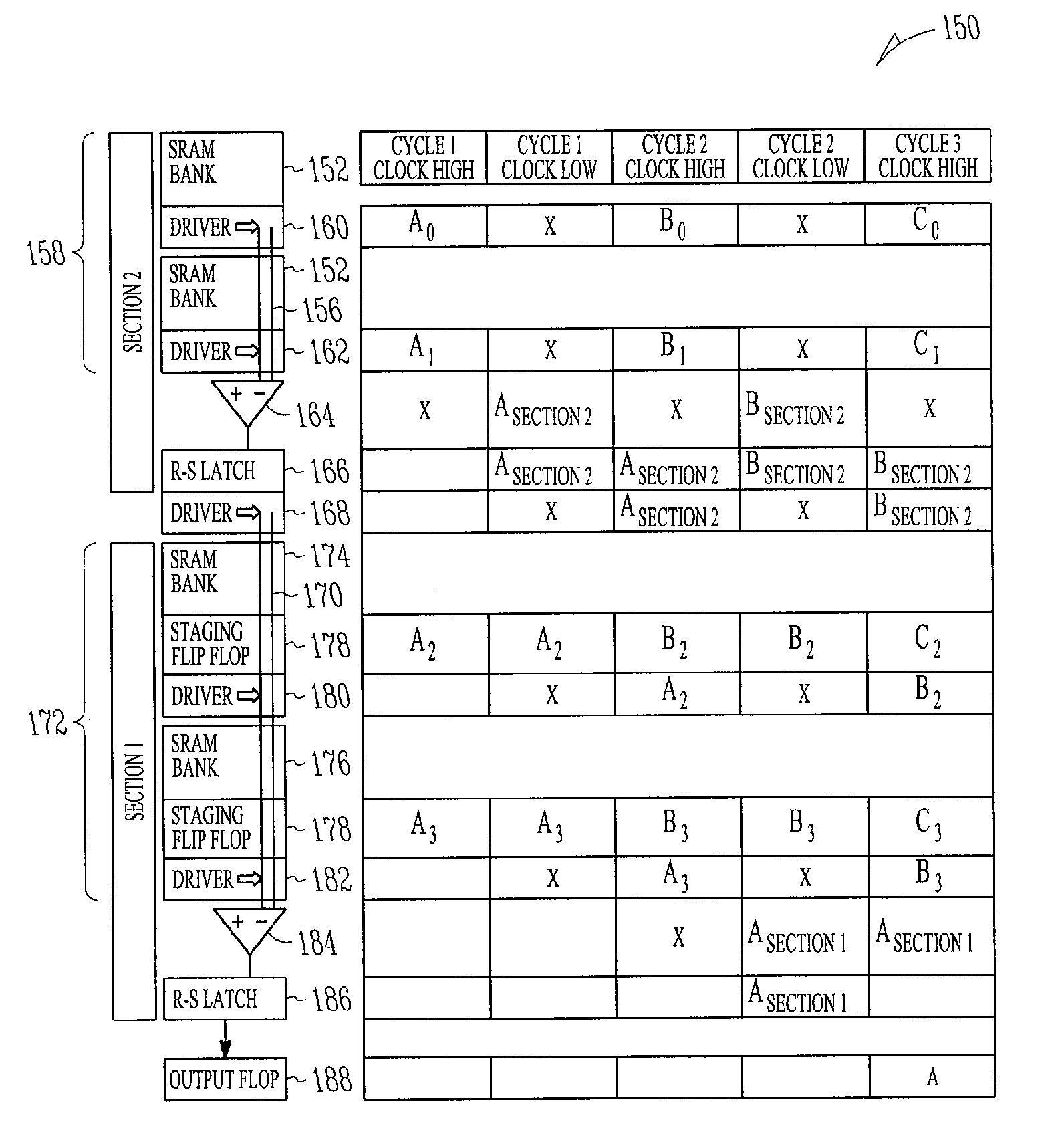
An architecture for a semiconductor static random access memory (SRAM) is described. In one example, a first set or group or stage of SRAM banks are coupled to a first data bus formed using bit line pairs, and a second set or group or stage of SRAM banks are coupled to a second data bus formed using other bit line pairs. The number of banks coupled to each bit line pair is determined by the SRAM's operating frequency and size. Each data bus is coupled to a sense amplifier. The output from the sense amplifier is then coupled to the bit line pair of a group of SRAM banks. This adjacent group has staging logic coupled to each SRAM bank to store the output of the SRAM bank until the contents from the first group is placed on the bit line of the adjacent stage of SRAM banks. The output from either the first stage or from one of the SRAM banks in the adjacent stage's SRAM banks, which had been stored in the adjacent stage's staging logic, is driven to the sense amplifier coupled to the adjacent stage. Successive stages of SRAM banks can be coupled together until an arbitrary number of stages of SRAM banks have been coupled together.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Microfluidic large scale integration
ActiveUS7143785B2Easy to handleDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesHigh densityRandom access memory
High-density microfluidic chips contain plumbing networks with thousands of micromechanical valves and hundreds of individually addressable chambers. These fluidic devices are analogous to electronic integrated circuits fabricated using large scale integration (LSI). A component of these networks is the fluidic multiplexor, which is a combinatorial array of binary valve patterns that exponentially increases the processing power of a network by allowing complex fluid manipulations with a minimal number of inputs. These integrated microfluidic networks can be used to construct a variety of highly complex microfluidic devices, for example the microfluidic analog of a comparator array, and a microfluidic memory storage device resembling electronic random access memories.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC +1
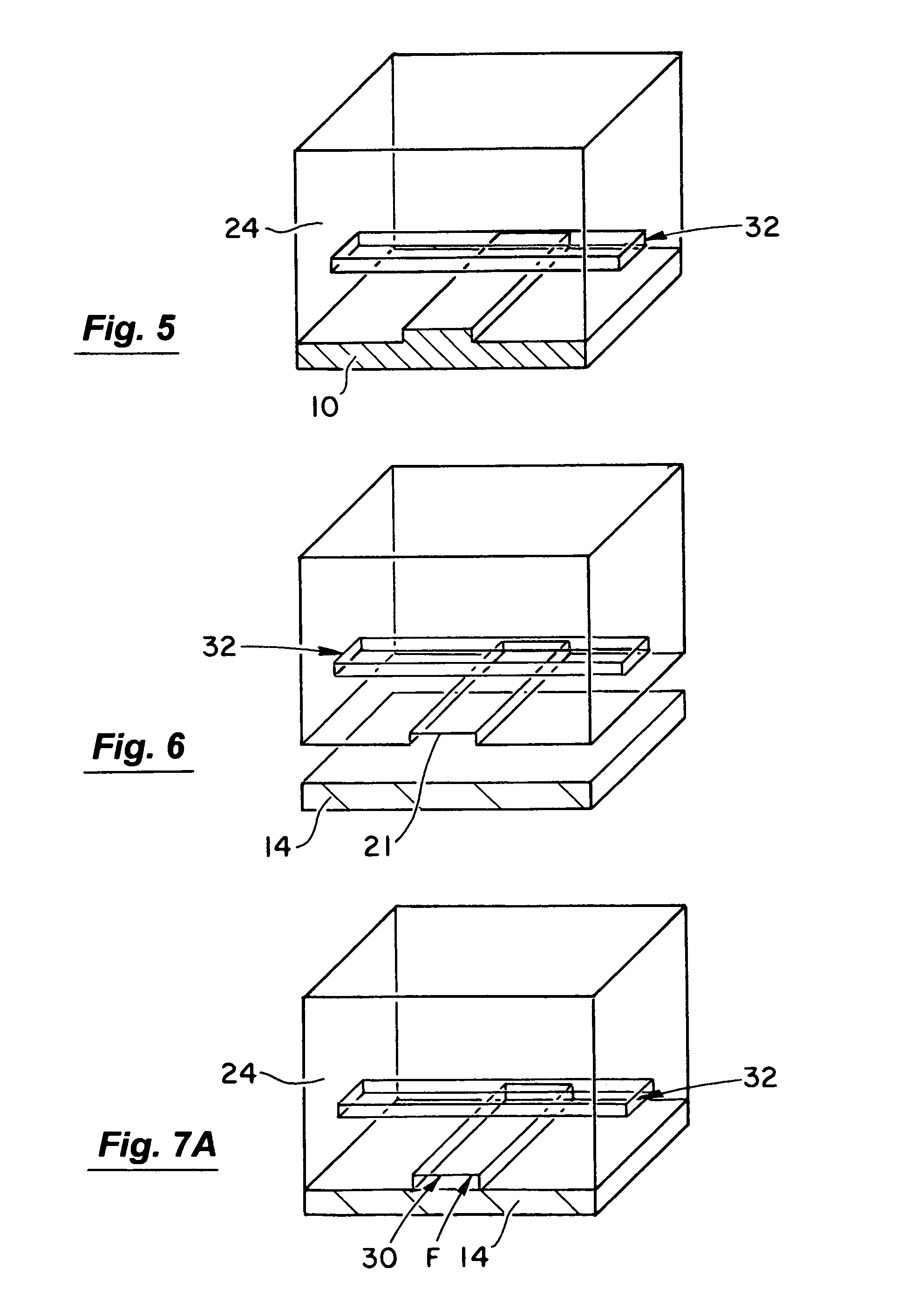
Thermally-assisted magnetic writing using an oxide layer and current-induced heating
InactiveUS6771534B2Increase in sizeIncrease in coercivityNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
A method and structure for a non-volatile magnetic random access memory (MRAM) device that has a stable magnetic electrode, an oxide layer adjacent the stable magnetic electrode, and a free magnetic electrode. The oxide layer is between the stable magnetic electrode and the free magnetic electrode. In the invention, a conductor is connected to a stable magnetic electrode. The oxide layer has a resistance at levels to allow sufficient power dissipation to lower the anisotropy of the free magnetic electrode through current induced heating. Current-induced heating is used in combination with spin-transfer torque or a magnetic field to switch the free magnetic electrode.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
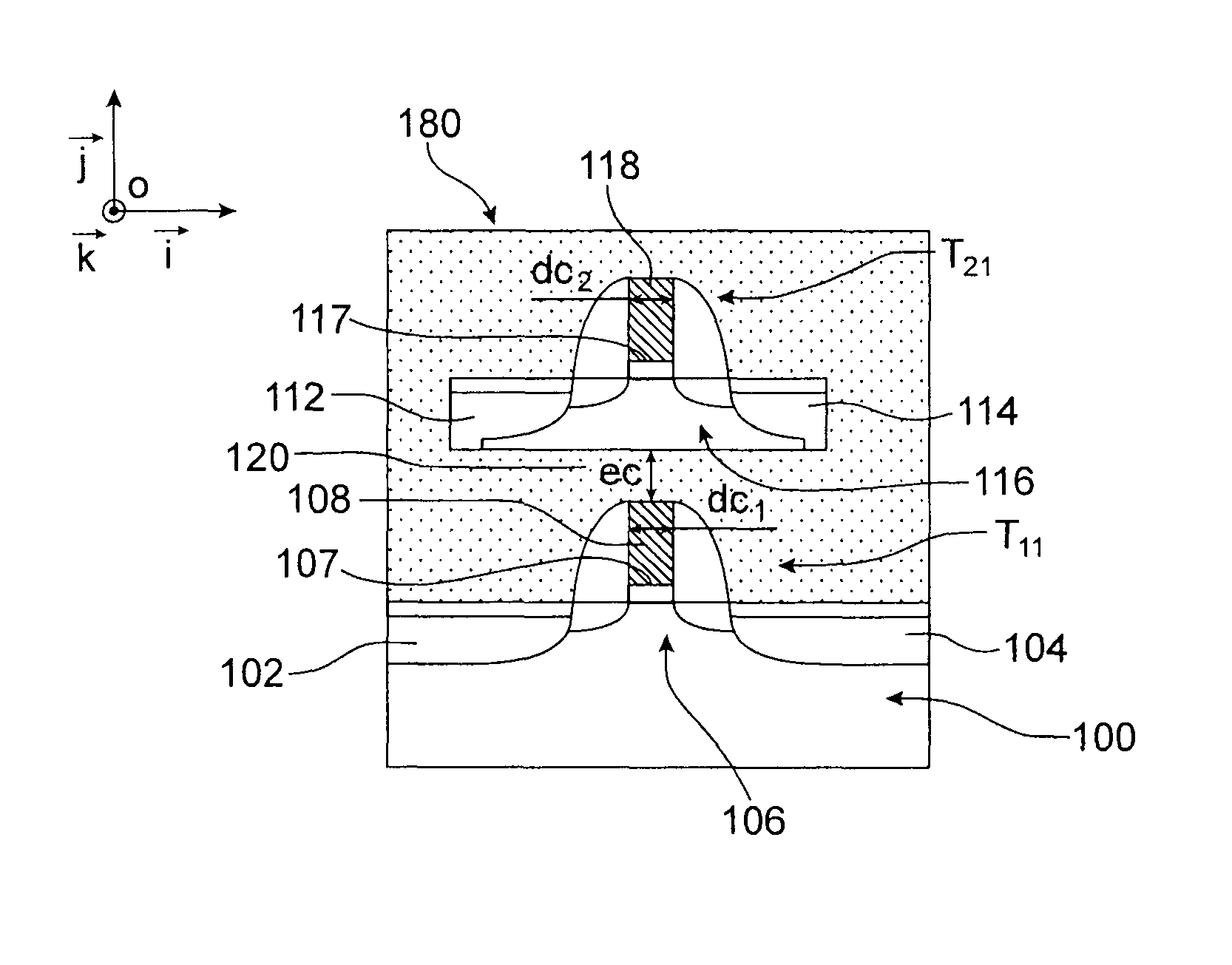
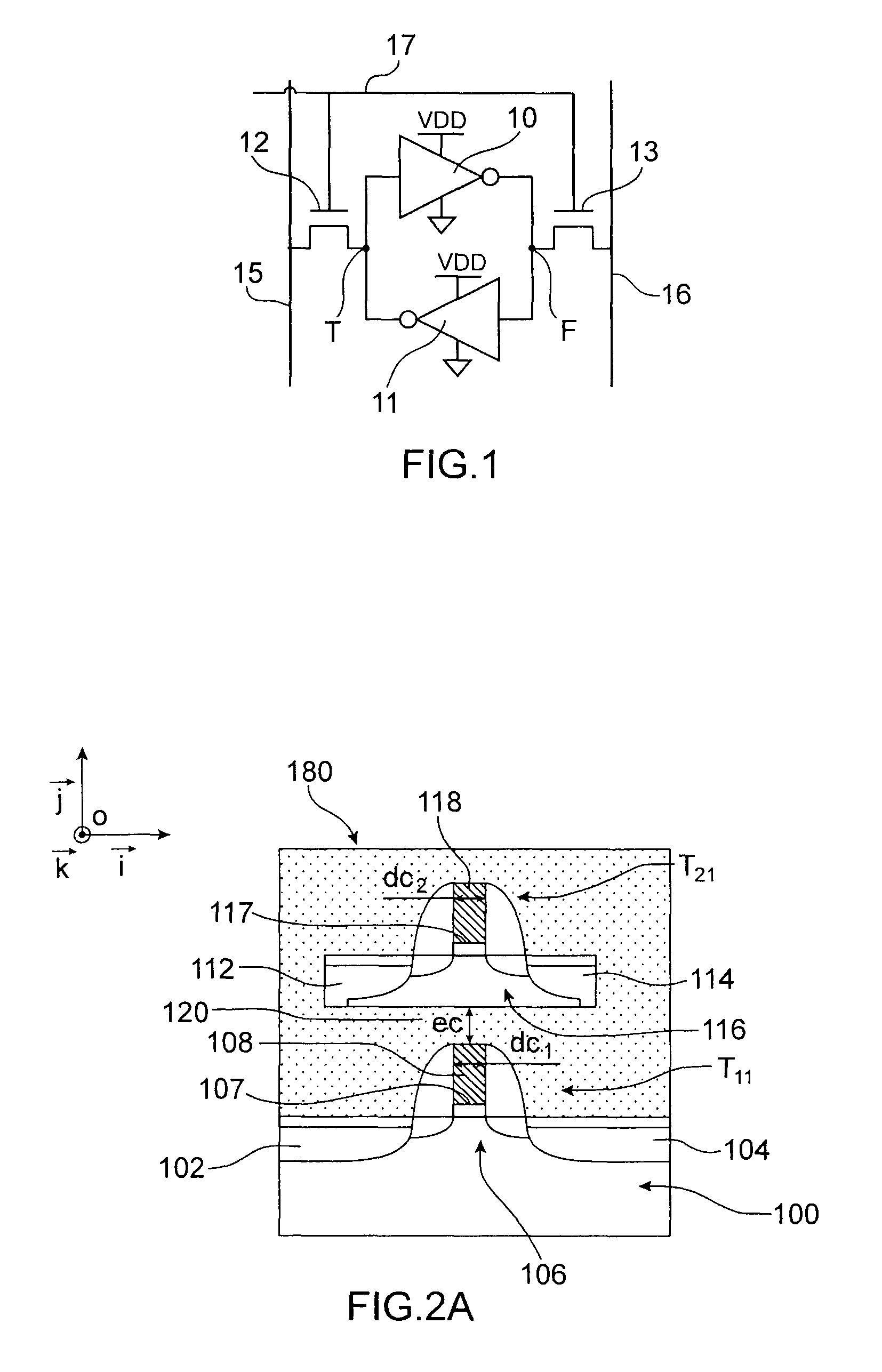
Static random access memory (SRAM) cell and method for forming same
InactiveUS8004042B2High densitySmall sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
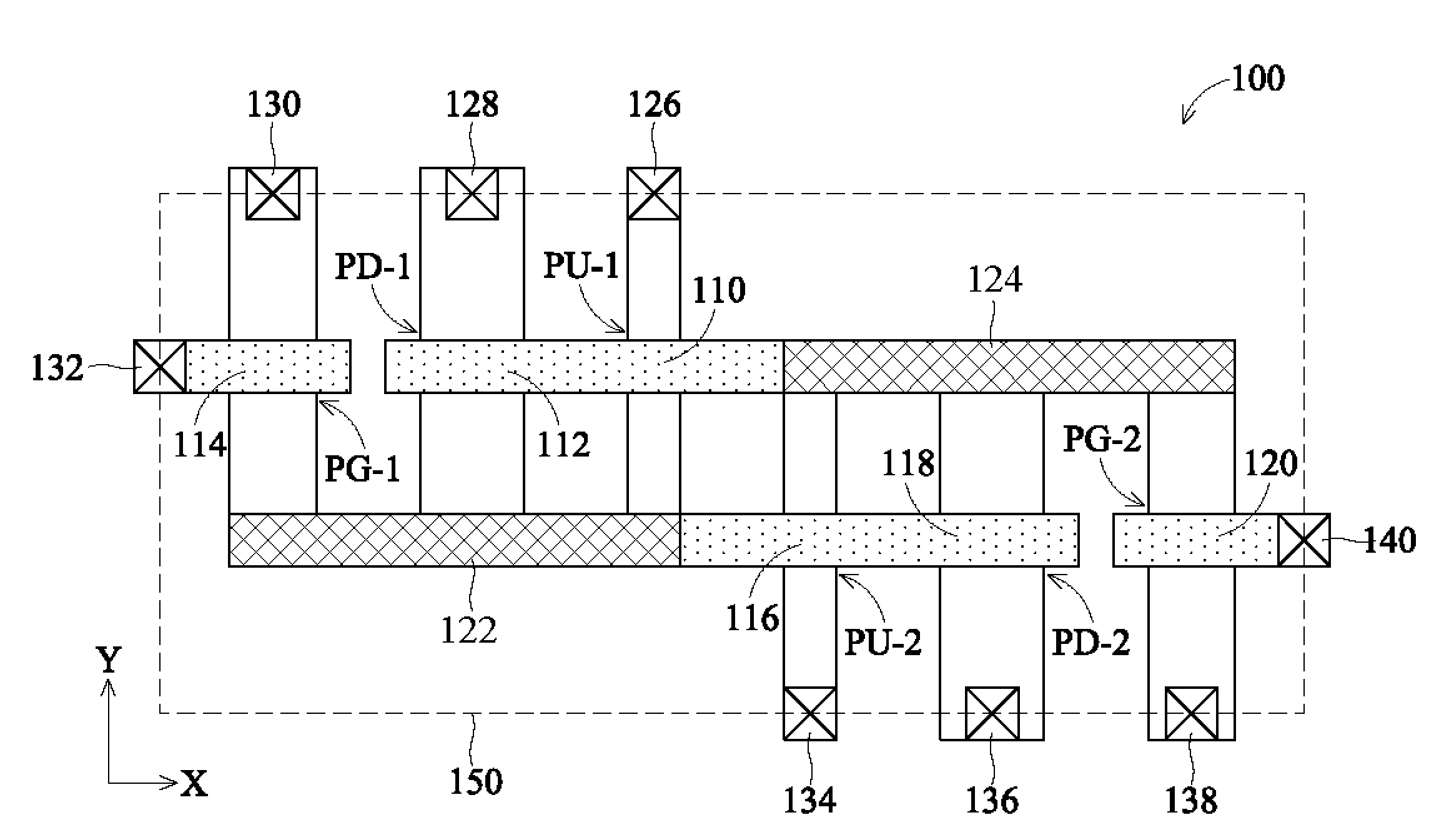
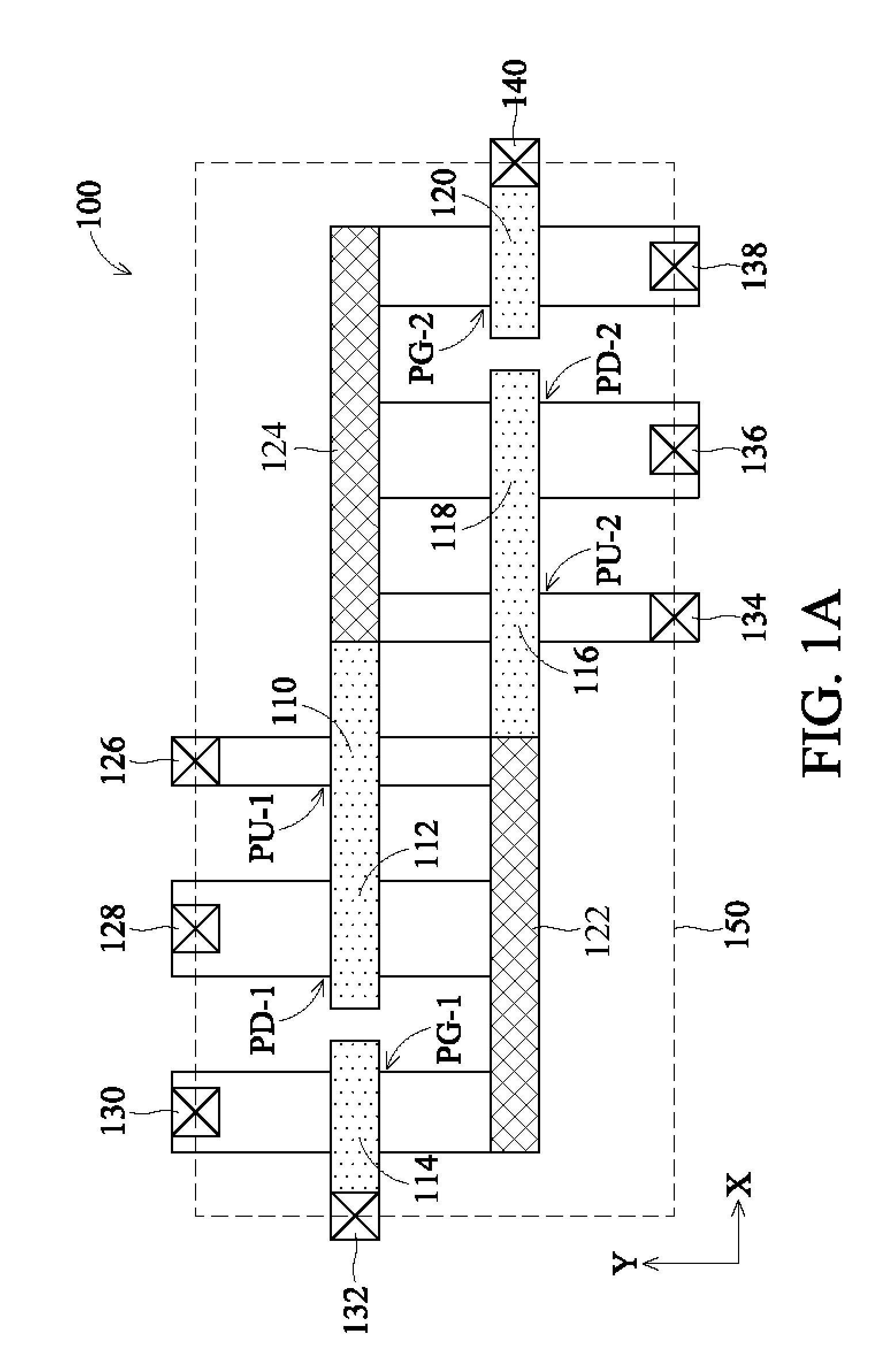
In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a static random access memory (SRAM) cell comprises a first pull-down transistor, a first pull-up transistor, a first pass-gate transistor, a second pull-down transistor, a second pull-up transistor, a second pass-gate transistor, a first linear intra-cell connection, and a second linear intra-cell connection. Active areas of the transistors are disposed in a substrate, and longitudinal axes of the active areas of the transistors are all parallel. The first linear intra-cell connection electrically couples the active area of the first pull-down transistor, the active area of the first pull-up transistor, and the active area of the first pass-gate transistor to a gate electrode of the second pull-down transistor and a gate electrode of the second pull-up transistor. The second linear intra-cell connection electrically couples the active area of the second pull-down transistor, the active area of the second pull-up transistor, and the active area of the second pass-gate transistor to a gate electrode of the first pull-down transistor and a gate electrode of the first pull-up transistor.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Resistive random accress memory containing a conformal titanium aluminum carbide film and method of making
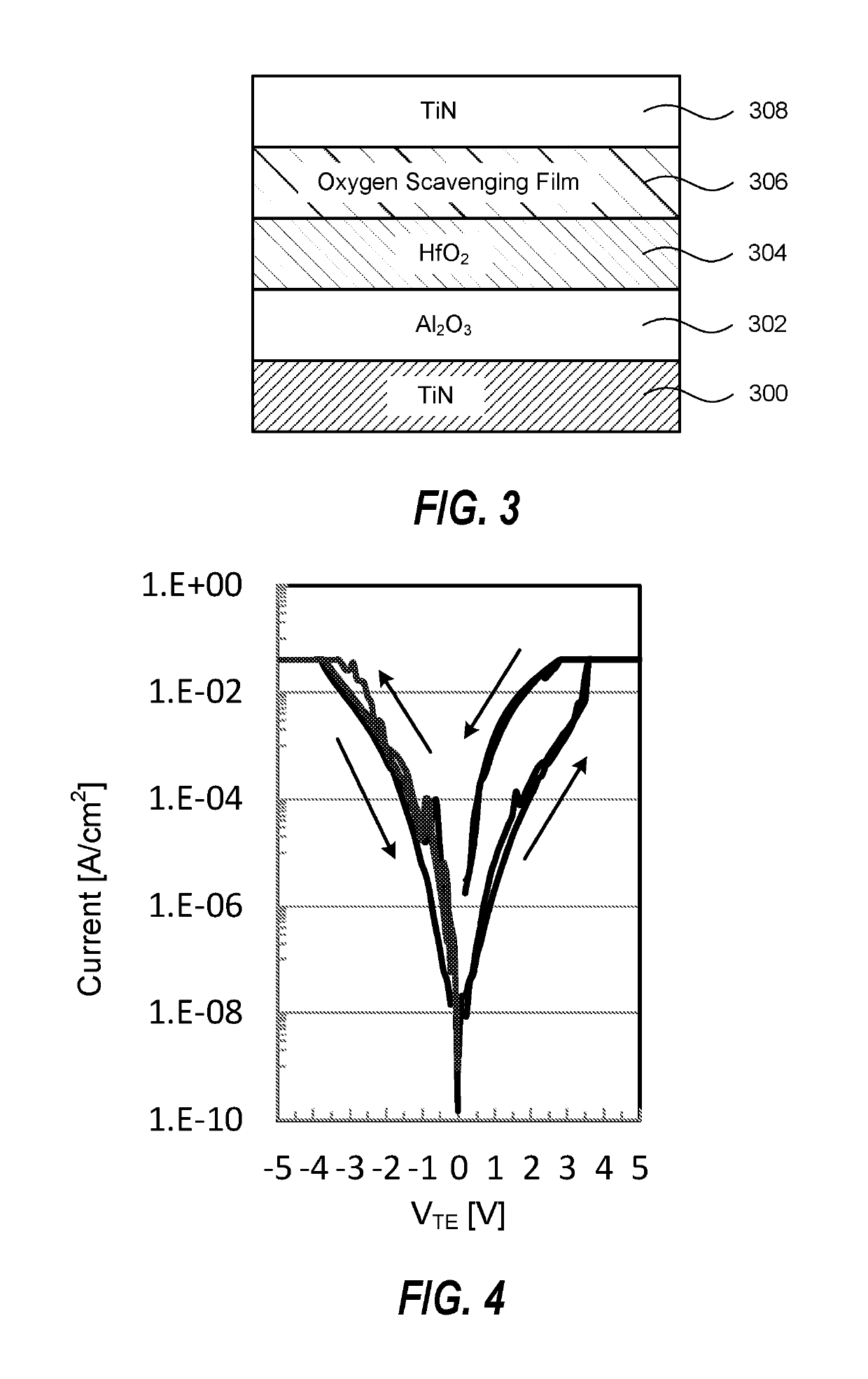
ActiveUS10361366B2Digital storagePiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesOxygen vacancyRandom access memory
A plurality of embodiments for ReRAM devices and method of making are described. According to one embodiment, the ReRAM device includes a first electrode film formed on a substrate, a metal oxide film with oxygen vacancies formed on a first electrode film, a conformal TiAlC film, oxidized by diffused oxygen atoms from the metal oxide film, formed on the metal oxide film, and a second electrode film formed on the TiAlC film. According to another embodiment, the ReRAM device includes a pair of vertical metal oxide films, a pair of vertical conformal TiAlC films formed on the pair of vertical metal oxide films, the pair of vertical conformal TiAlC films oxidized by diffused oxygen atoms from the pair of vertical metal oxide films, and an electrode film formed between the pair of vertical conformal TiAlC films.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
SRAM memory cell having transistors integrated at several levels and the threshold voltage VT of which is dynamically adjustable
InactiveUS8013399B2Improved integration density and electrical performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineStatic random-access memory
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com