Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
15589 results about "Boron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. Produced entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in the Solar system and in the Earth's crust. Boron is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known boron deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals.
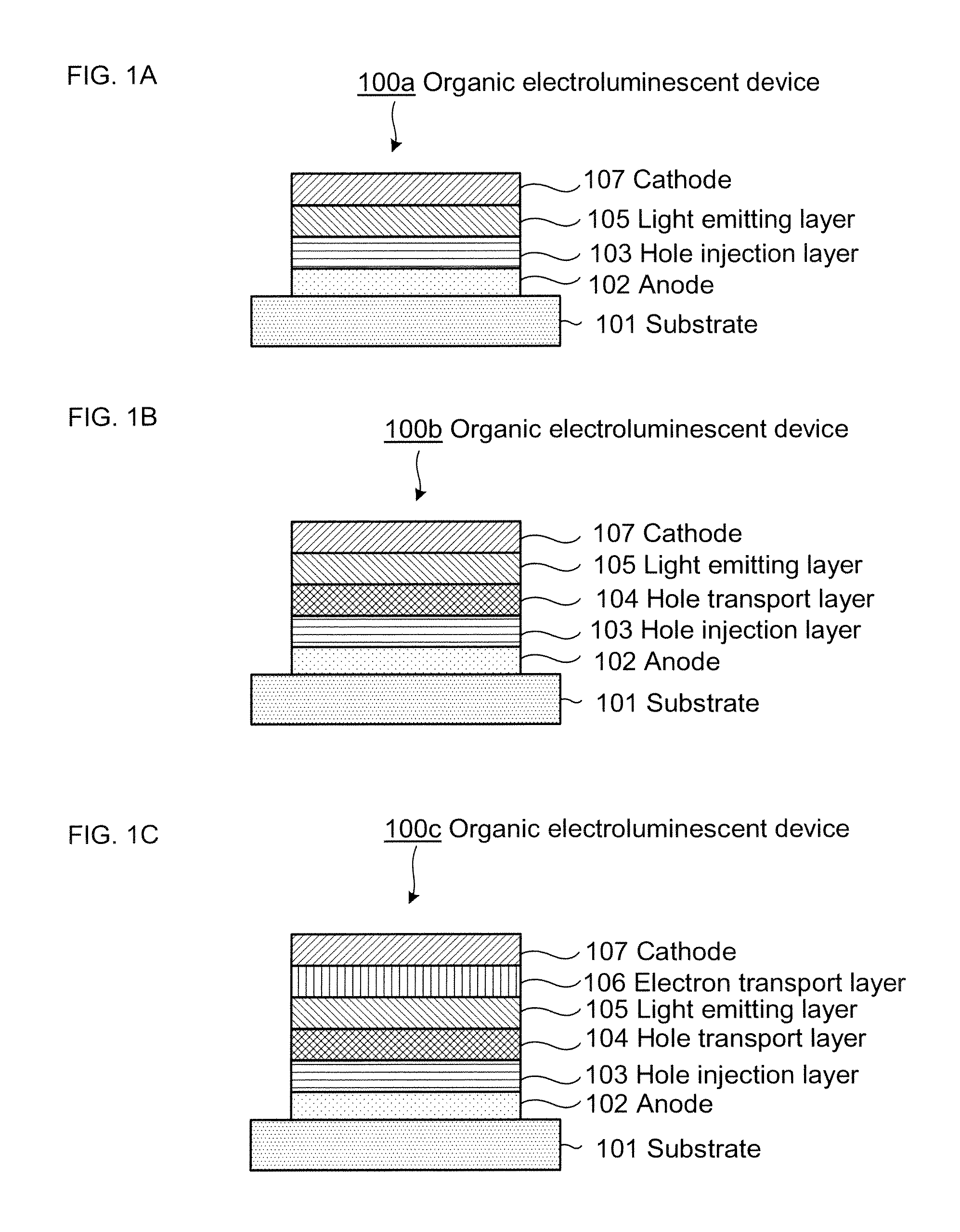
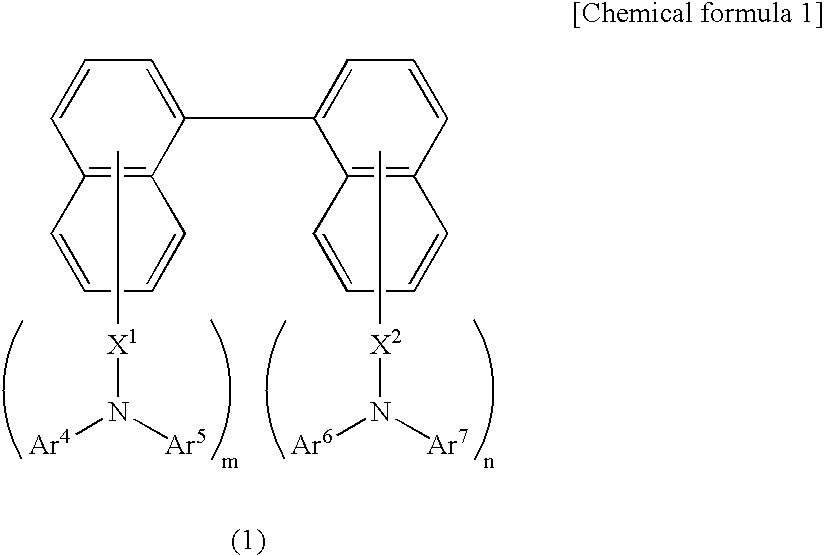
Organic electroluminescent element, illuminator, display and compound
InactiveUS20050069729A1Improve emission efficiencySolution to short lifeMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceBoron
An organic electroluminescent element comprising a light emission layer and a hole blocking layer adjacent to the light emission layer, wherein, (i) the light emission layer contains a compound having a specified partial structure and having a molecular weight of not more than 1700; and (ii) the hole blocking layer contains a derivative selected from the group consisting of a styryl derivative, a boron derivative and a carboline derivative.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
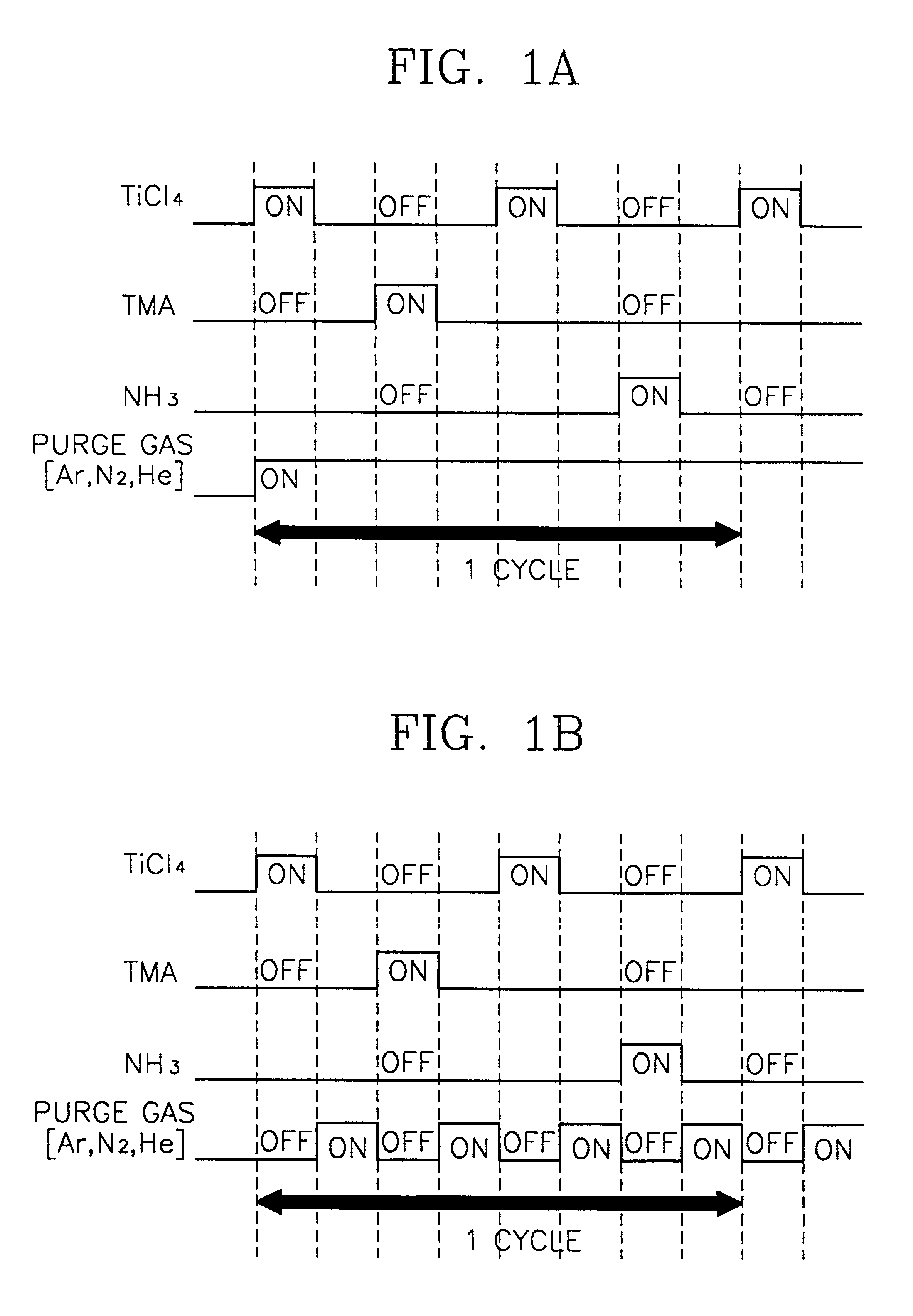
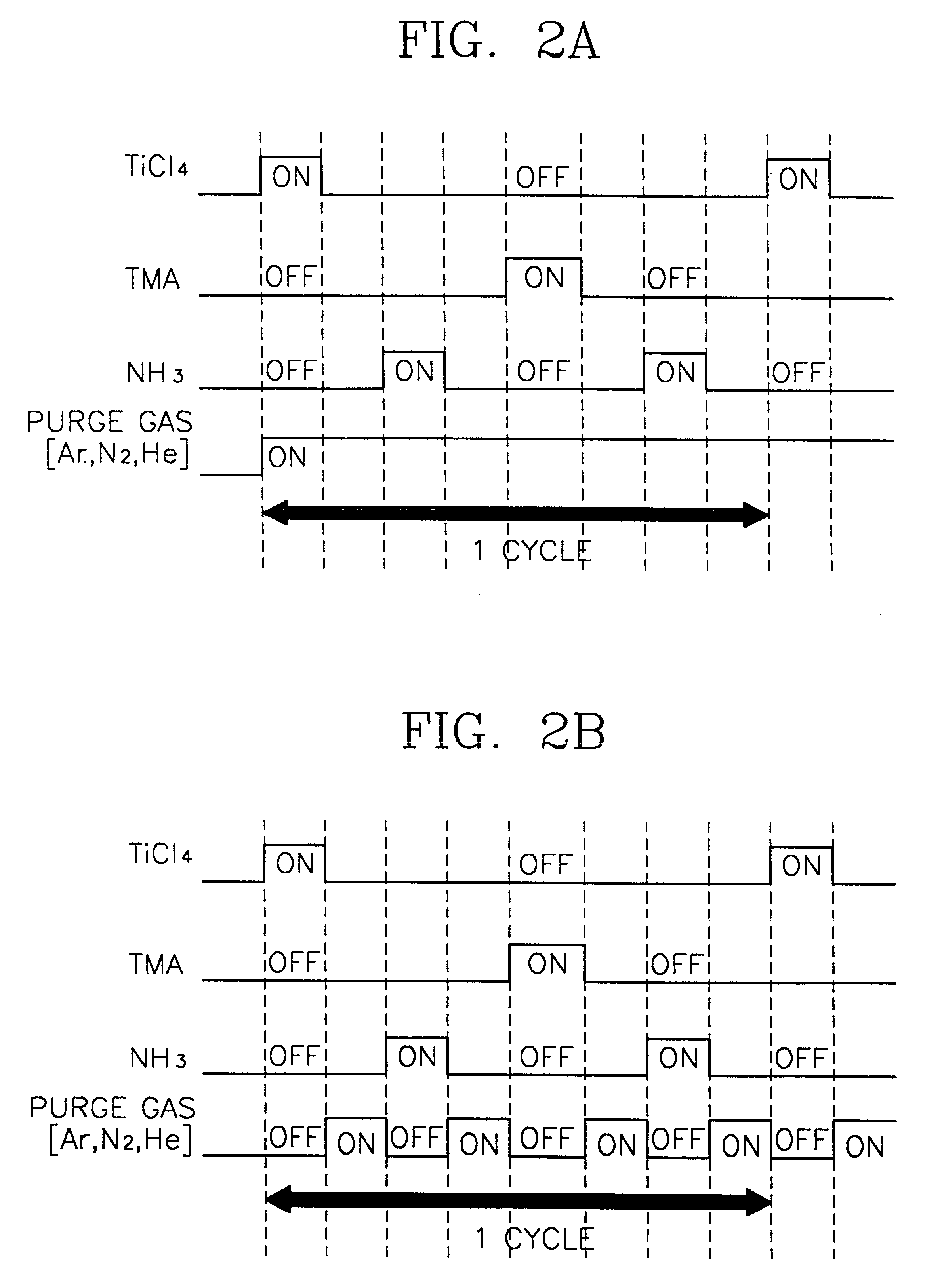
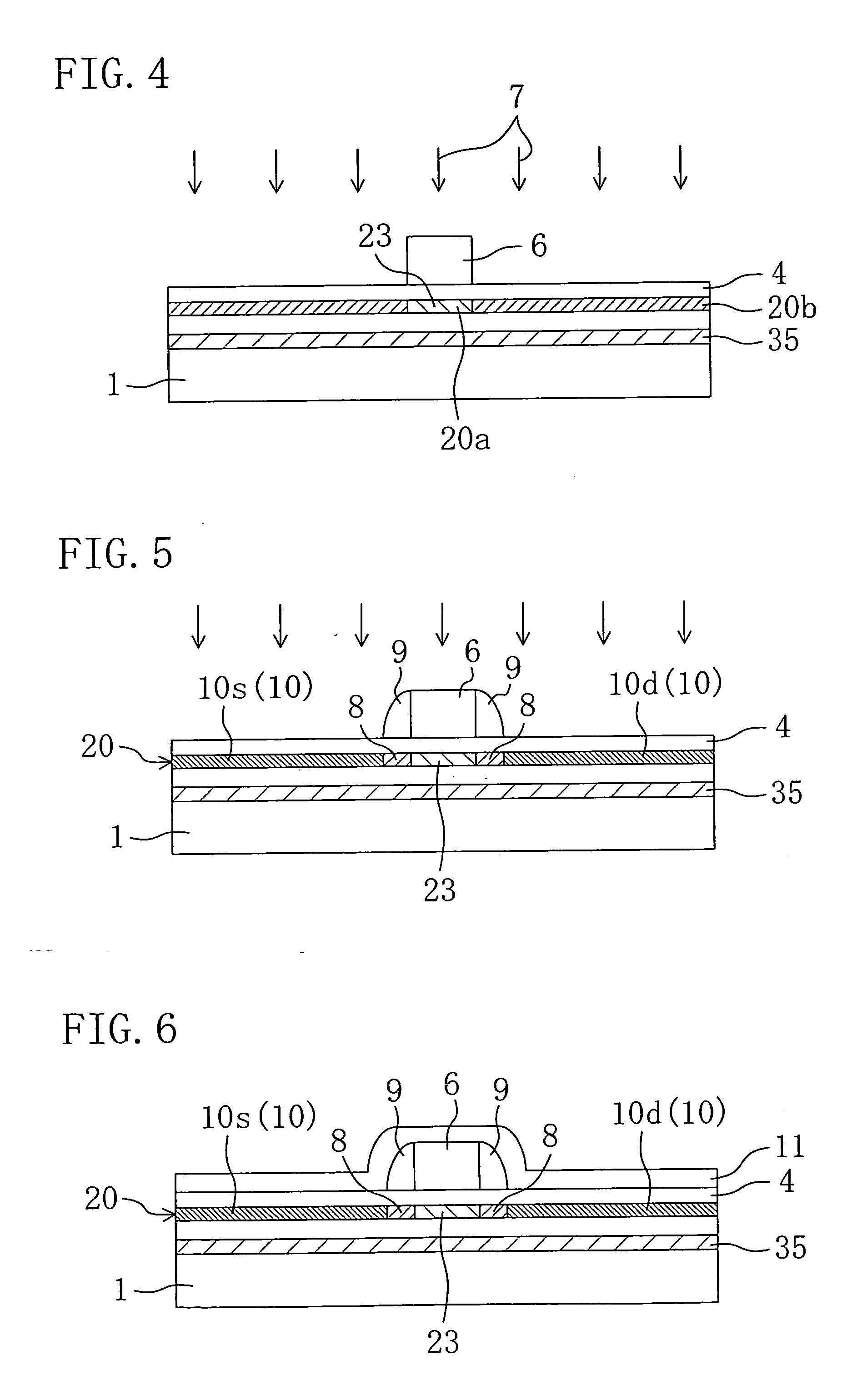
Method of forming metal layer using atomic layer deposition and semiconductor device having the metal layer as barrier metal layer or upper or lower electrode of capacitor
InactiveUS6287965B1High thermal resistantEasy to adjustSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsNiobiumDevice material
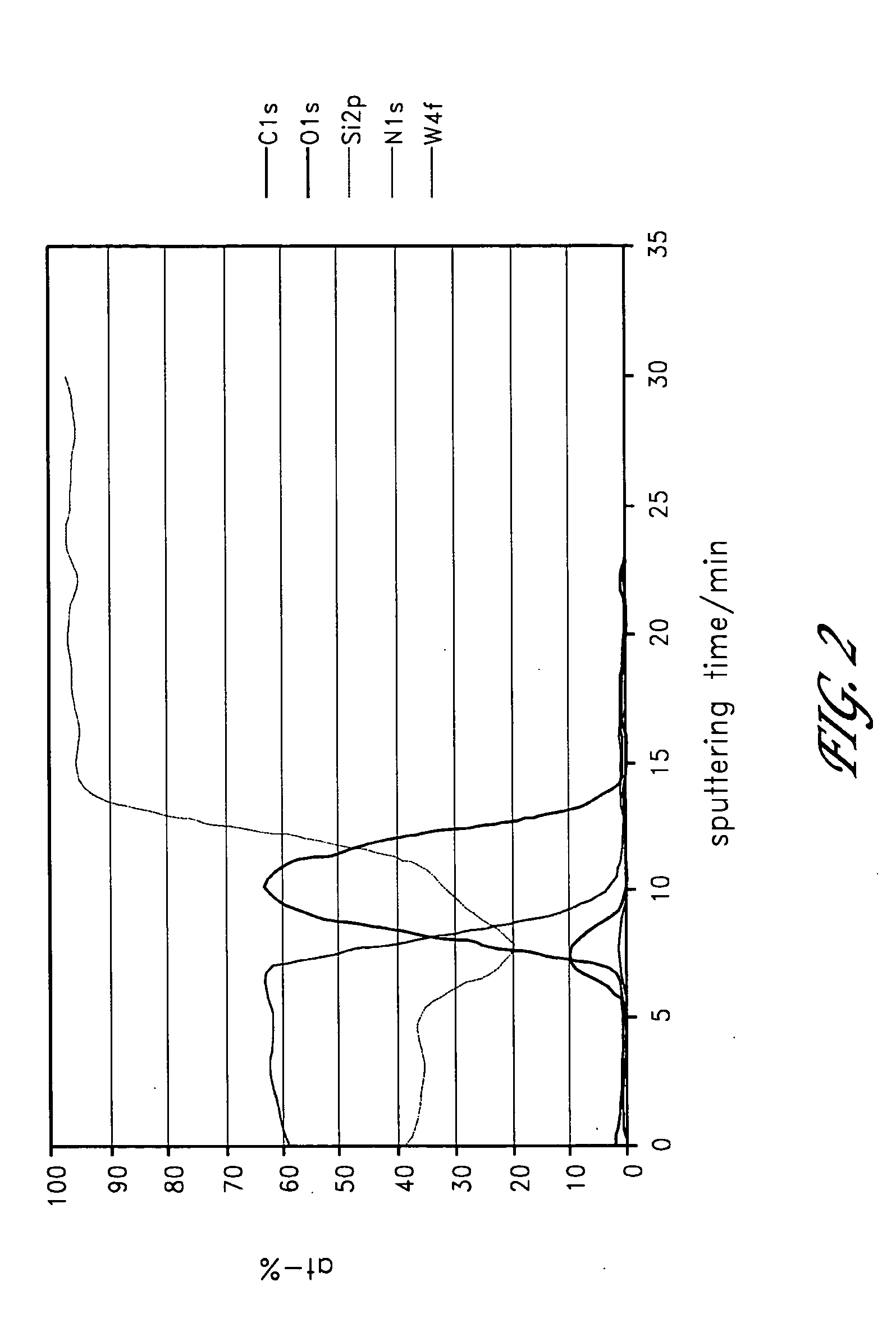
A method of forming a metal layer having excellent thermal and oxidation resistant characteristics using atomic layer deposition is provided. The metal layer includes a reactive metal (A), an element (B) for the amorphous combination between the reactive metal (A) and nitrogen (N), and nitrogen (N). The reactive metal (A) may be titanium (Ti), tantalum (Ta), tungsten (W), zirconium (Zr), hafnium (Hf), molybdenum (Mo) or niobium (Nb). The amorphous combination element (B) may be aluminum (Al), silicon (Si) or boron (B). The metal layer is formed by alternately injecting pulsed source gases for the elements (A, B and N) into a chamber according to atomic layer deposition to thereby alternately stack atomic layers. Accordingly, the composition ratio of a nitrogen compound (A-B-N) of the metal layer can be desirably adjusted just by appropriately determining the number of injection pulses of each source gas. According to the composition ratio, a desirable electrical conductivity and resistance of the metal layer can be accurately obtained. The atomic layers are individually deposited, thereby realizing excellent step coverage even in a complex and compact region. A metal layer formed by atomic layer deposition can be employed as a barrier metal layer, a lower electrode or an upper electrode in a semiconductor device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Compositions for organic electroluminescent device and organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20060182993A1Reduce inactivationChange propertiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensDuplicating/marking methodsSolubilityHole injection layer
Disclosed are compositions for an organic electroluminescent device favorably used for forming a hole injection layer and a hole transport layer of the organic electroluminescent device by a wet film forming method. The compositions for the organic electroluminescent device, which are composite solutions prepared by dissolving hole transport materials such as aromatic diamine compounds and an electron acceptor such as tri(pentafluorophenyl)boron in a solvent that contains an ether solvent and / or an ester solvent whose water solubility at 25° C. is 1 weight % or less in the solvent, with a concentration of 10 weight % or higher in the compositions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Enhanced thin film deposition
ActiveUS20070148350A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilanesNitrogen
Methods of producing metal-containing thin films with low impurity contents on a substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD) are provided. The methods preferably comprise contacting a substrate with alternating and sequential pulses of a metal source chemical, a second source chemical and a deposition enhancing agent. The deposition enhancing agent is preferably selected from the group consisting of hydrocarbons, hydrogen, hydrogen plasma, hydrogen radicals, silanes, germanium compounds, nitrogen compounds, and boron compounds. In some embodiments, the deposition-enhancing agent reacts with halide contaminants in the growing thin film, improving film properties.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method for forming a thin film and method for fabricating a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050070123A1Improve mobility and reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricHafnium
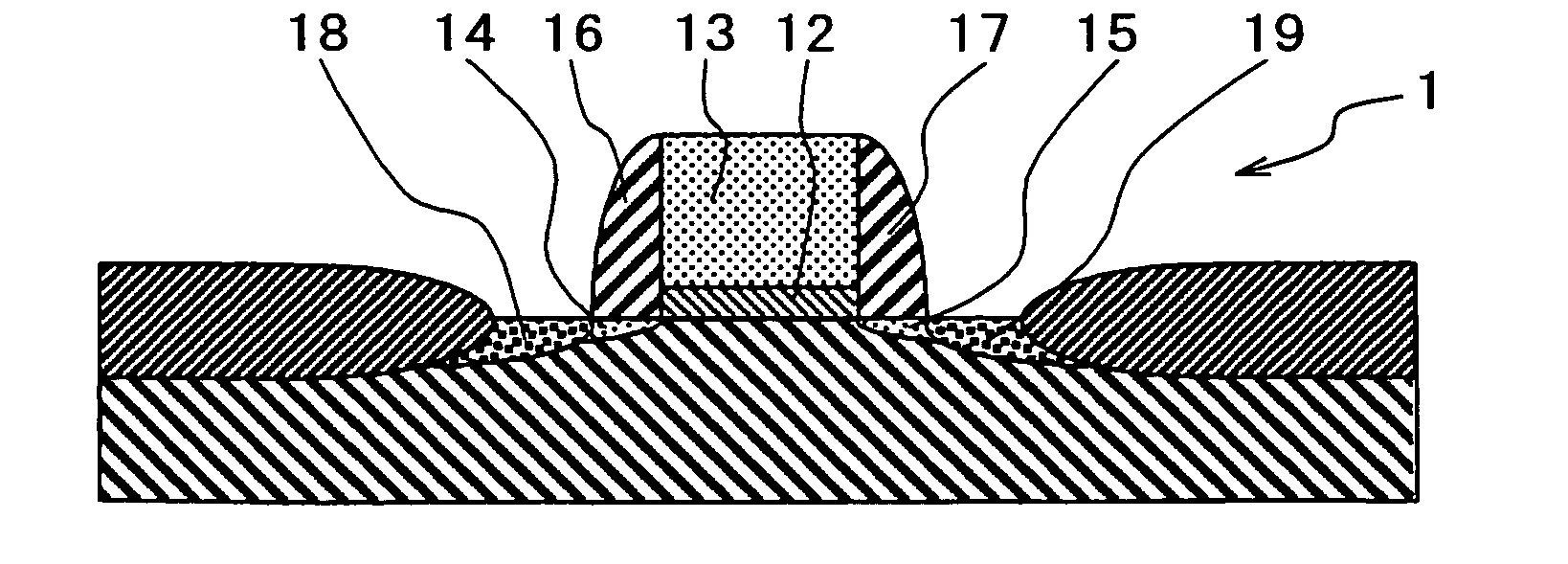
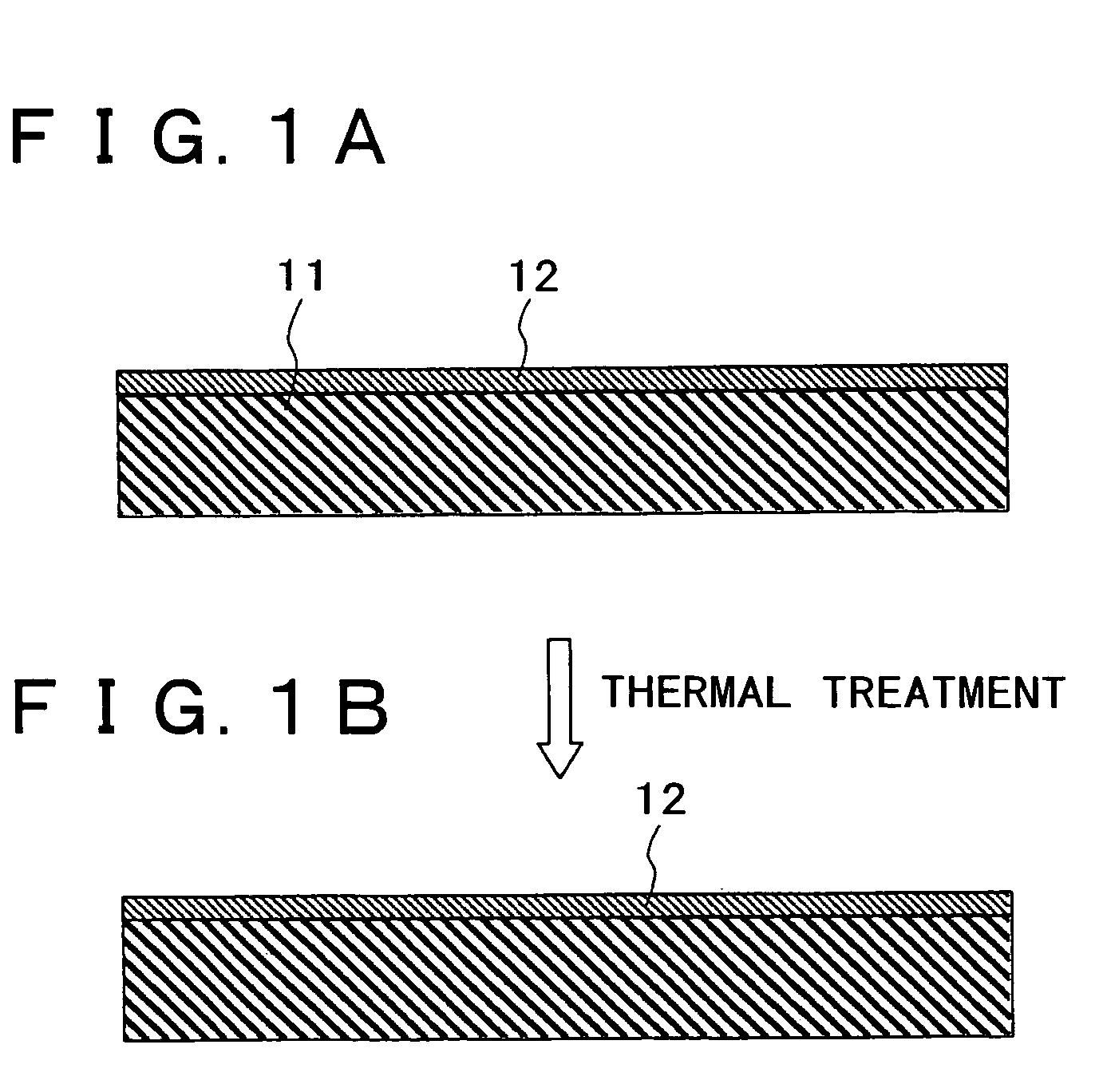
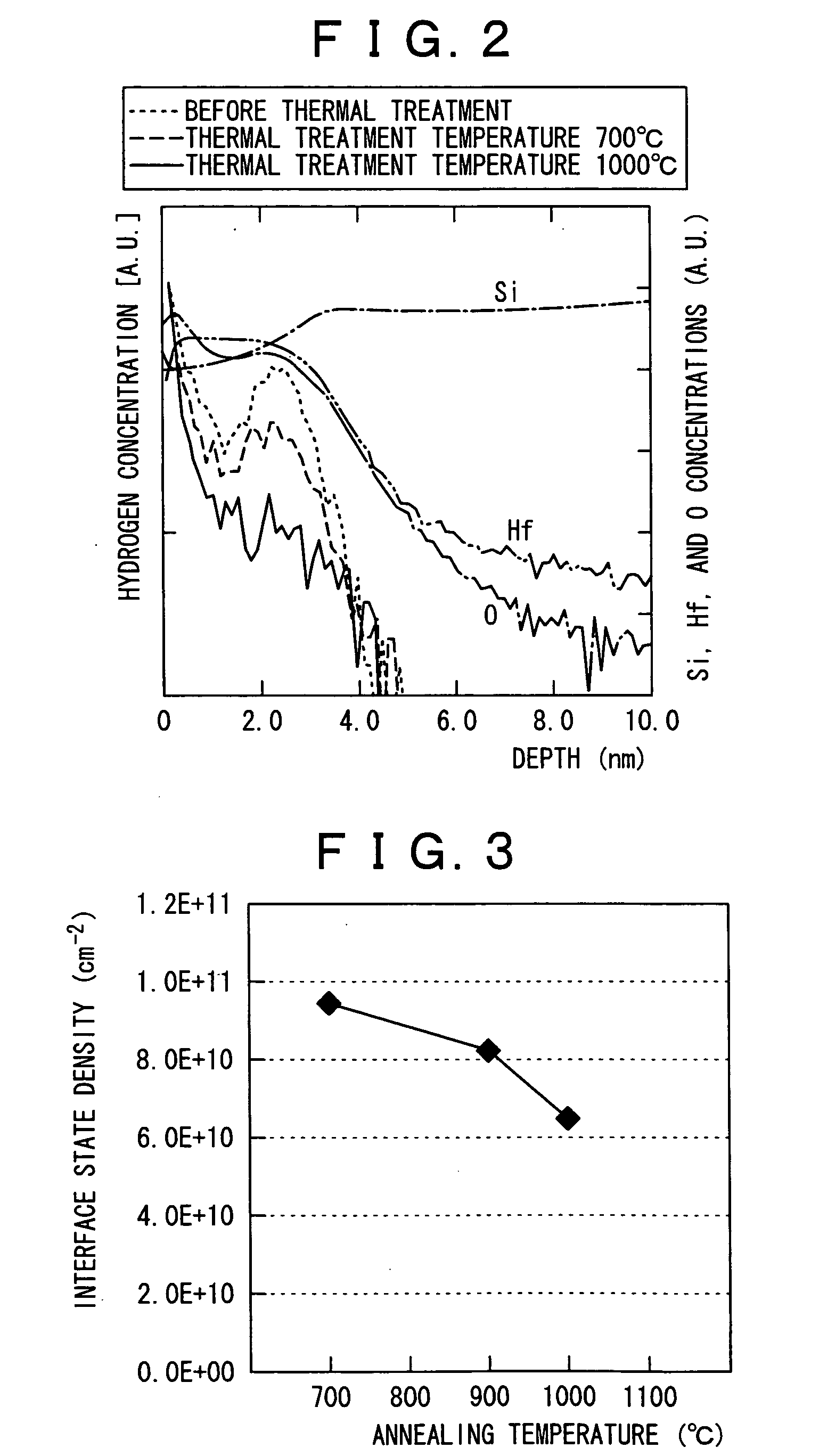
By conducting a high temperature annealing in a nitrogen atmosphere at a temperature at which a hafnium silicate film undergoes no phase separation, hydrogen contained in the film is removed and prevention of boron penetration is made possible. The present invention provides a method for forming a thin film including a step of forming a hafnium silicate film on a substrate by an atomic layer deposition method and a step of carrying out thermal treatment on the hafnium silicate film at a thermal treatment temperature equal to or higher than a temperature at which hydrogen contained in the hafnium silicate film is removed and lower than a temperature at which the hafnium silicate film undergoes no phase separation, and a method for fabricating a semiconductor device for forming a gate dielectric film using the method for forming a thin film.
Owner:SONY CORP
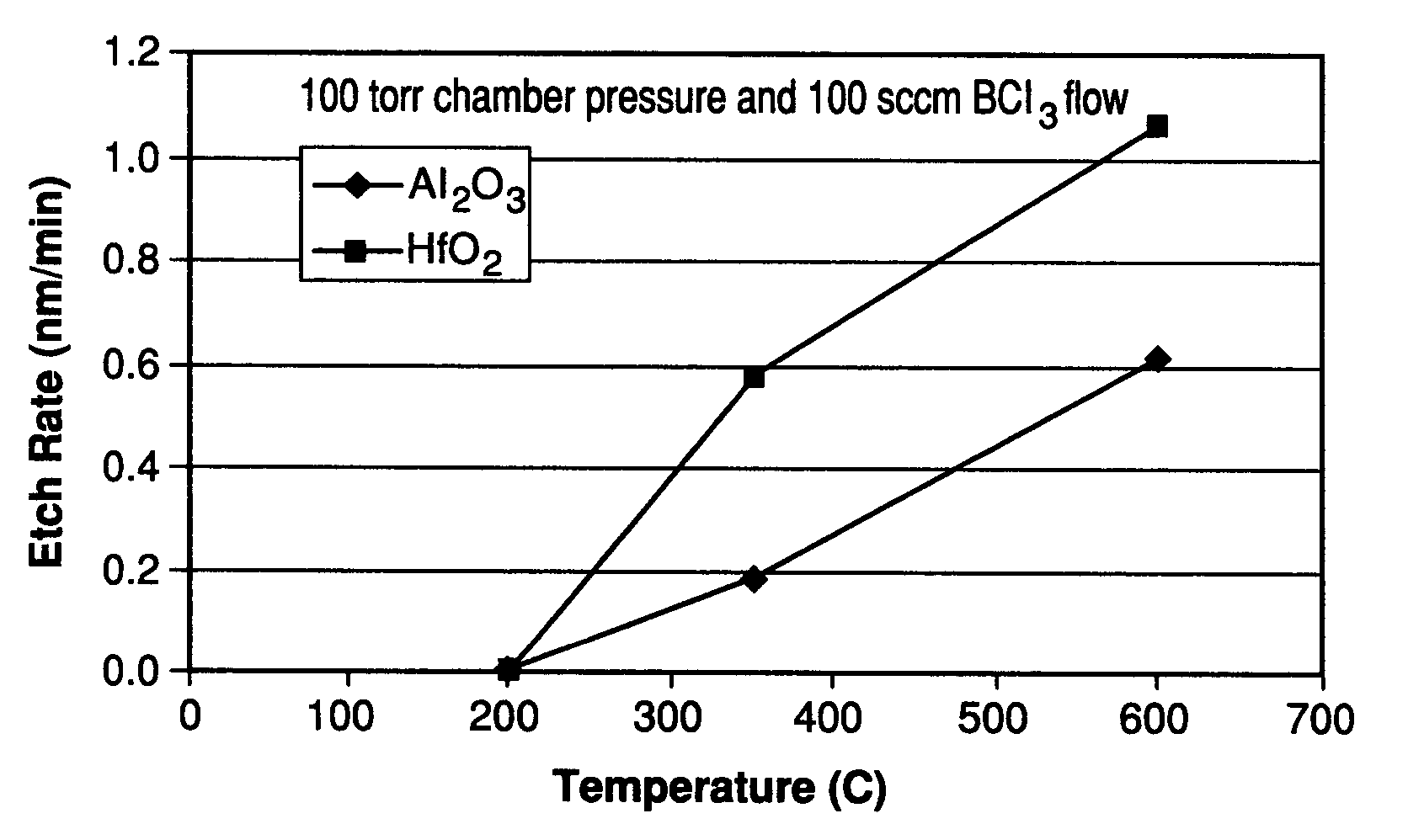
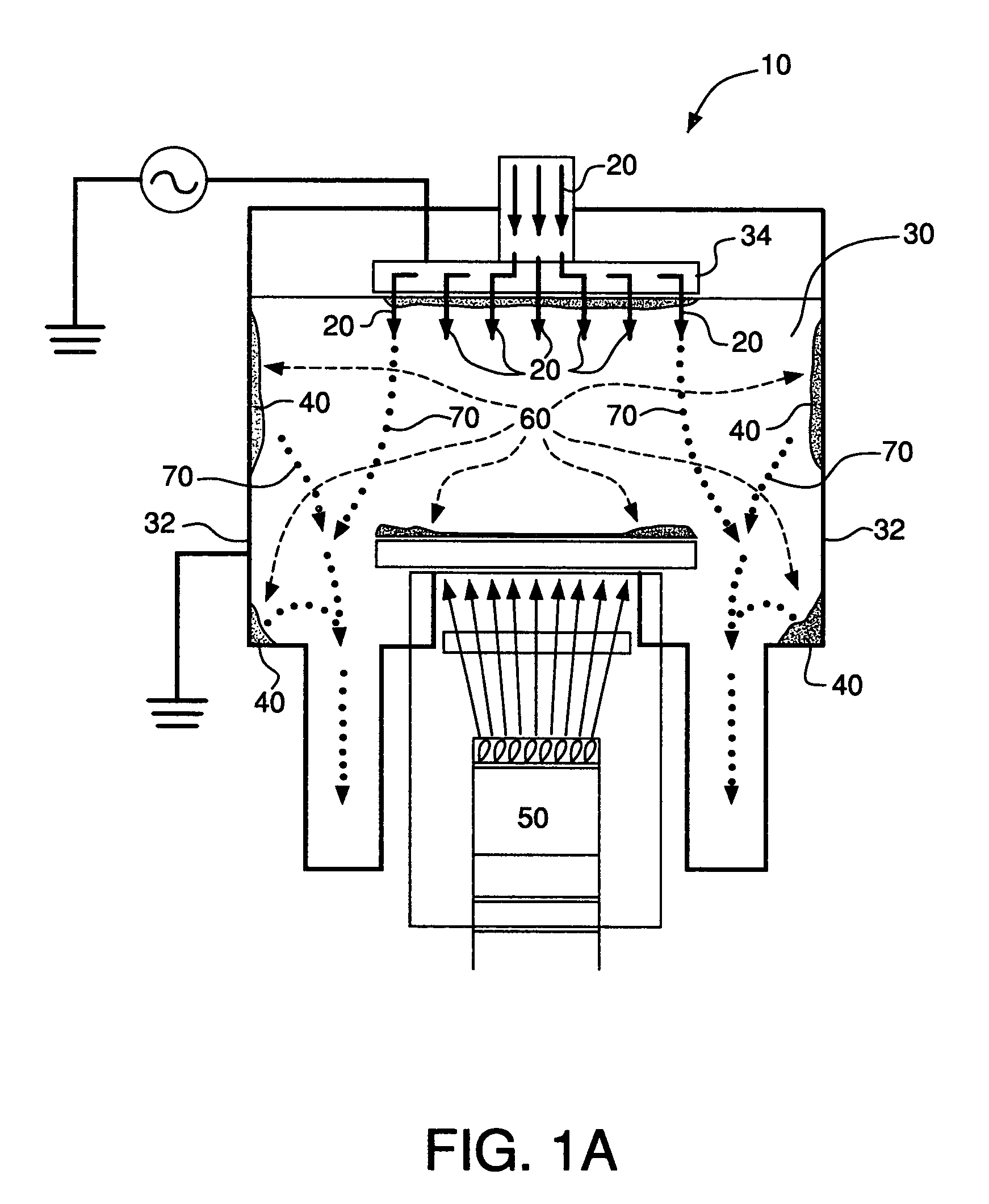
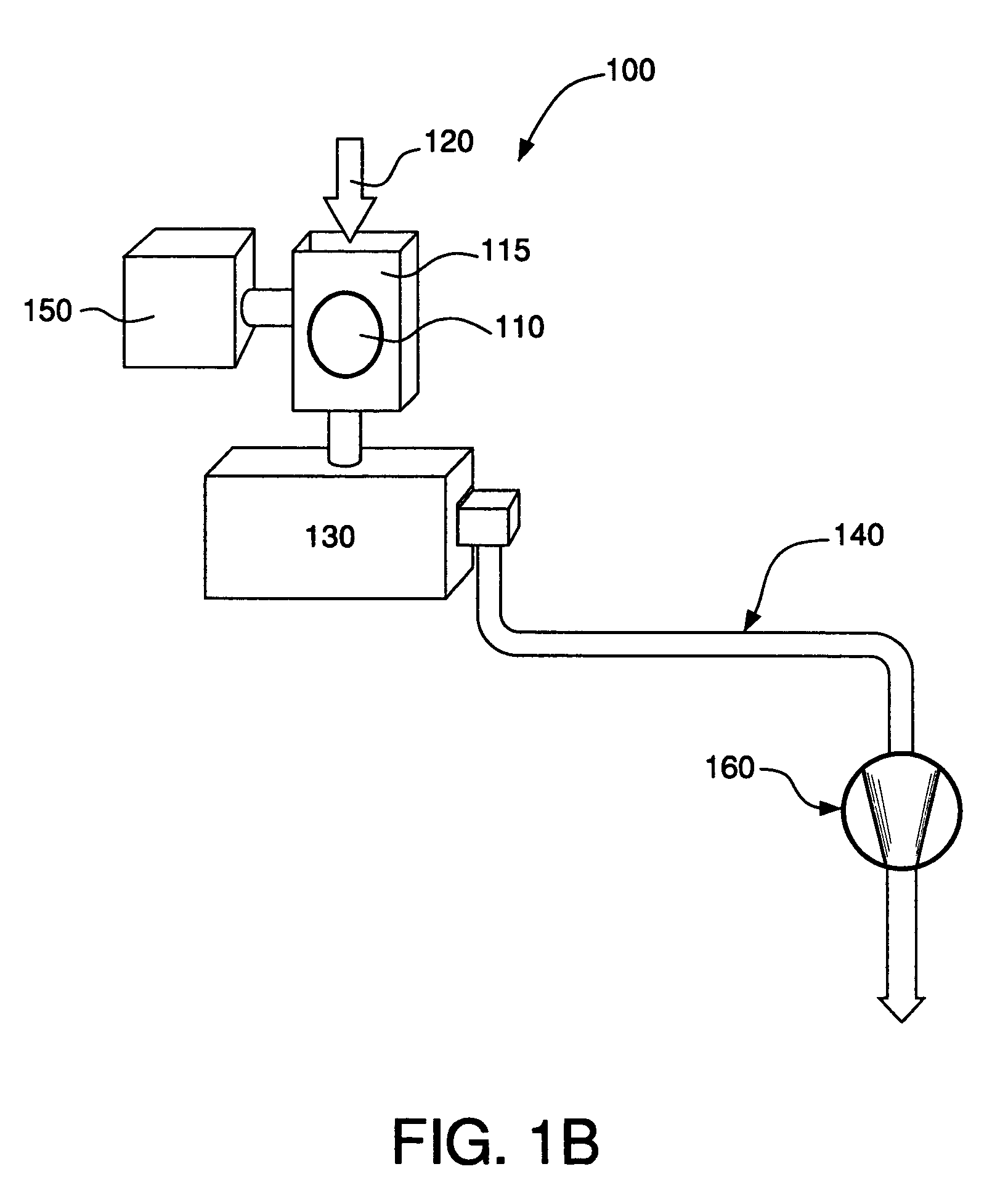
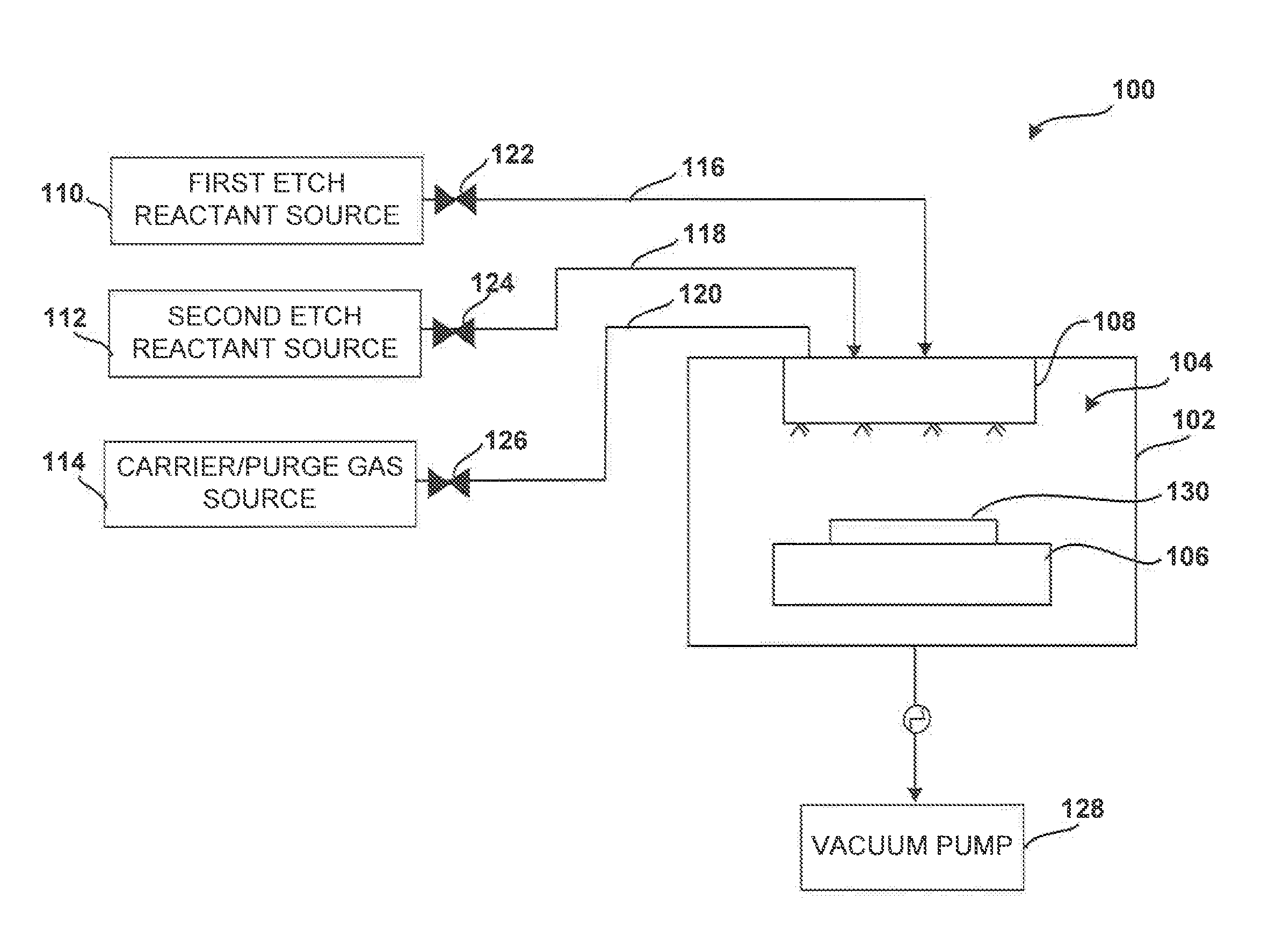
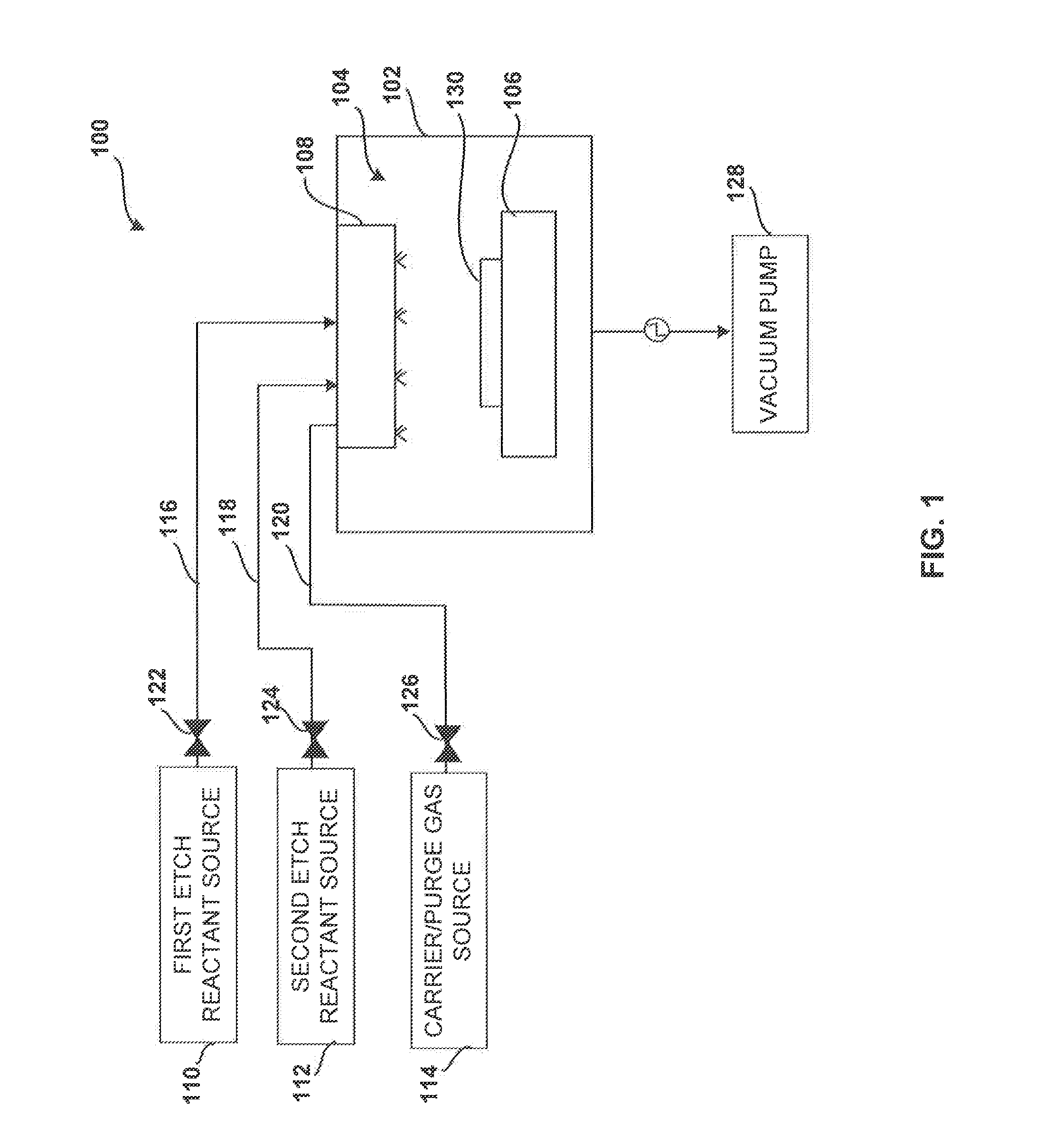
Method for etching high dielectric constant materials and for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A process for the removal of a substance from a substrate for etching and / or cleaning applications is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, there is provided a process for removing a substance having a dielectric constant greater than silicon dioxide from a substrate by reacting the substance with a reactive agent that comprises at least one member from the group consisting a halogen-containing compound, a boron-containing compound, a hydrogen-containing compound, nitrogen-containing compound, a chelating compound, a carbon-containing compound, a chlorosilane, a hydrochlorosilane, or an organochlorosilane to form a volatile product and removing the volatile product from the substrate to thereby remove the substance from the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Multi-step method and apparatus for etching compounds containing a metal
ActiveUS20140217065A1Reduce harmReduce formationDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfurChemical compound
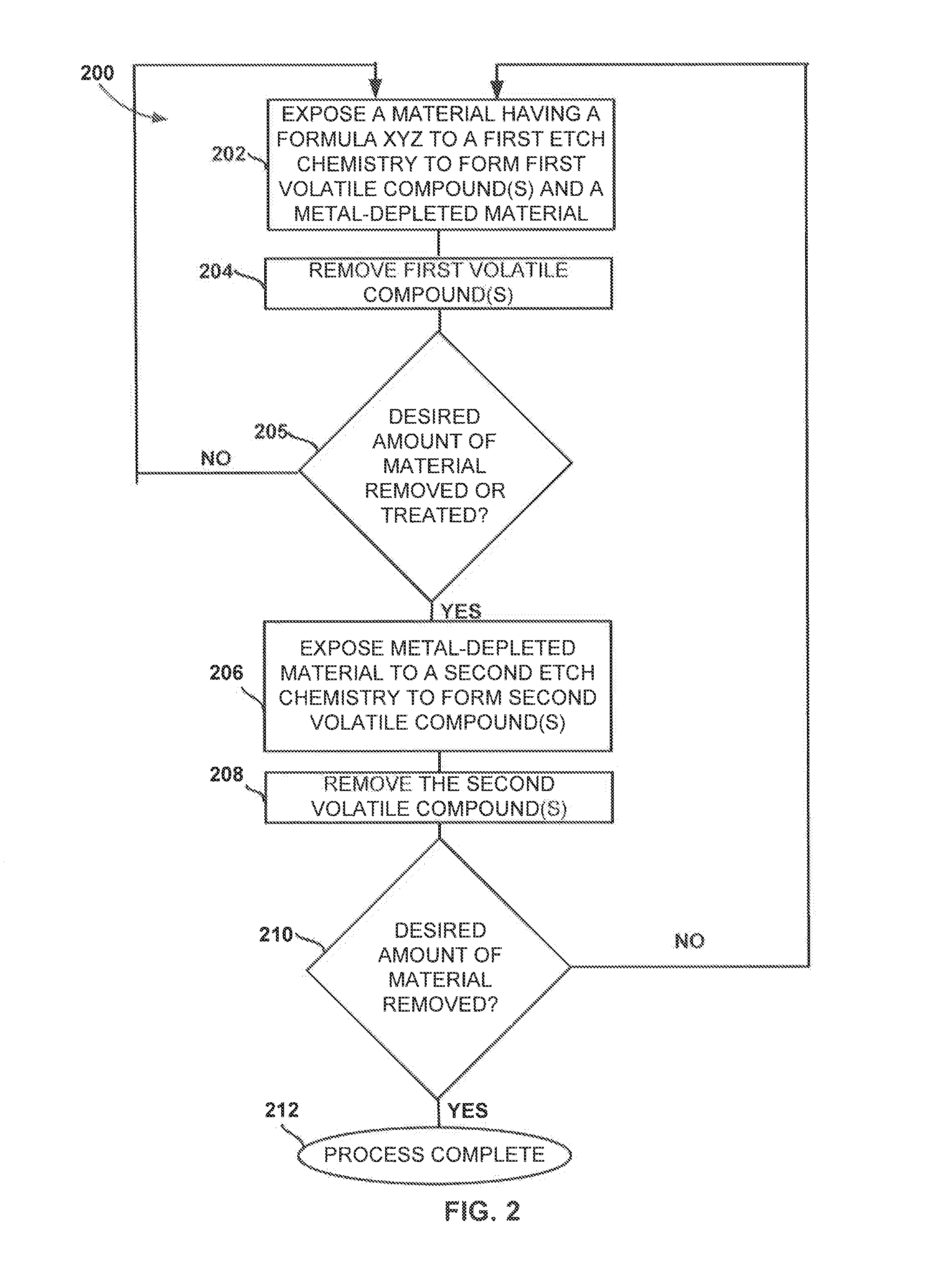
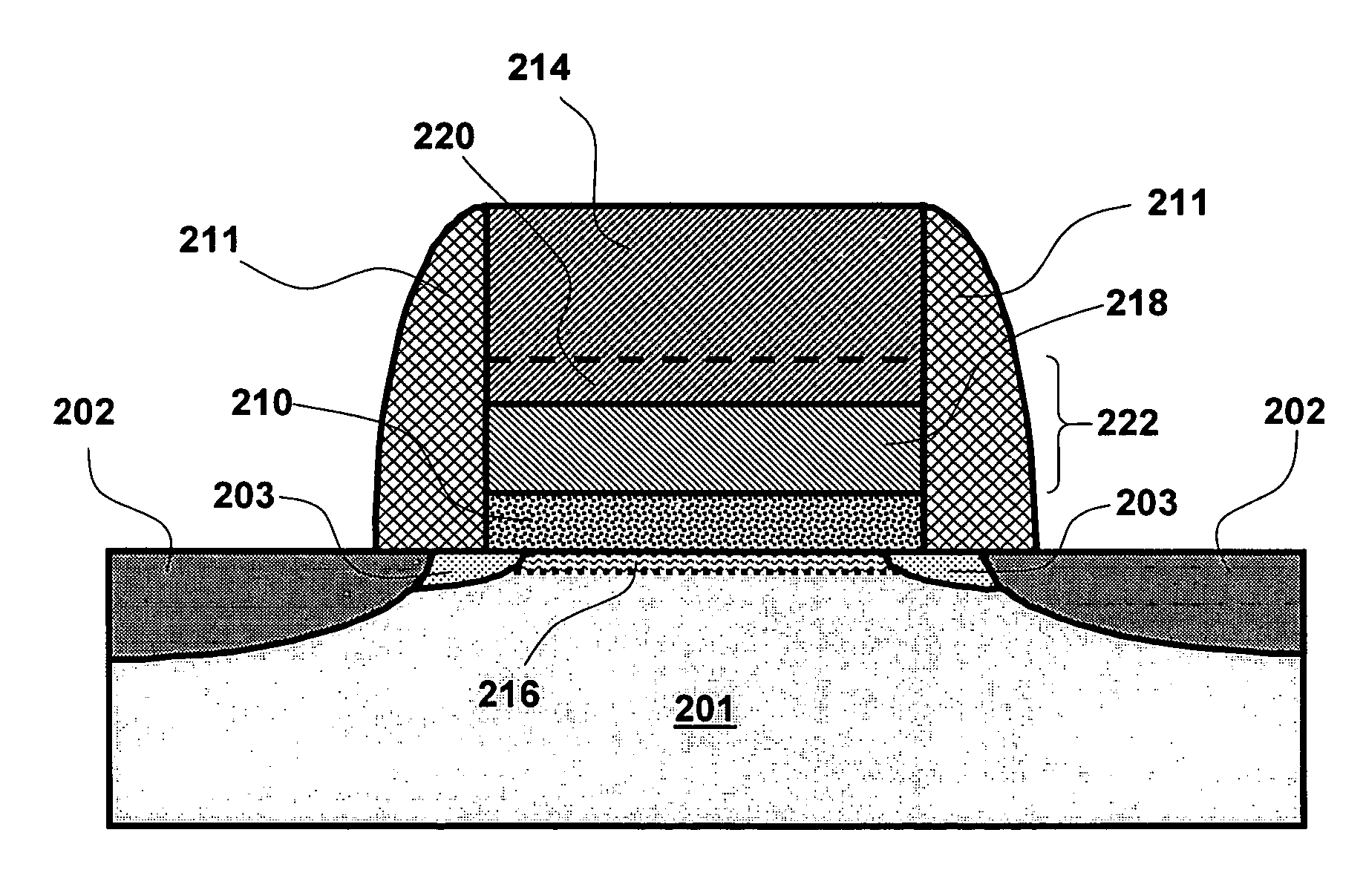
A system and method for etching a material, including a compound having a formulation of XYZ, wherein X and Y are one or more metals and Z is selected from one or more Group 13-16 elements, such as carbon, nitrogen, boron, silicon, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium, are disclosed. The method includes a first etch process to form one or more first volatile compounds and a metal-depleted layer and a second etch process to remove at least a portion of the metal-depleted layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of producing thin films
ActiveUS7563715B2Lower work functionReduce crystallinityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWork functionMetal electrodes
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Formation of boron-doped titanium metal films with high work function
ActiveUS10083836B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHalogenTitanium metal
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Methods for Selective and Conformal Epitaxy of Highly Doped Si-containing Materials for Three Dimensional Structures
InactiveUS20140120678A1Improve crystal qualityIncreased junctionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantPhosphate
The present invention addresses the key challenges in FinFET fabrication, that is, the fabrications of thin, uniform fins and also reducing the source / drain series resistance. More particularly, this application relates to FinFET fabrication techniques utilizing tetrasilane to enable conformal deposition with high doping using phosphate, arsenic and boron as dopants thereby creating thin fins having uniform thickness (uniformity across devices) as well as smooth, vertical sidewalls, while simultaneously reducing the parasitic series resistance.
Owner:MATHESON TRI GAS INC
Method of producing thin films
ActiveUS20070128858A1Lower work functionReduce crystallinityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWork functionMetal electrodes
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Formation of boron-doped titanium metal films with high work function
ActiveUS20170025280A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium metalWork function
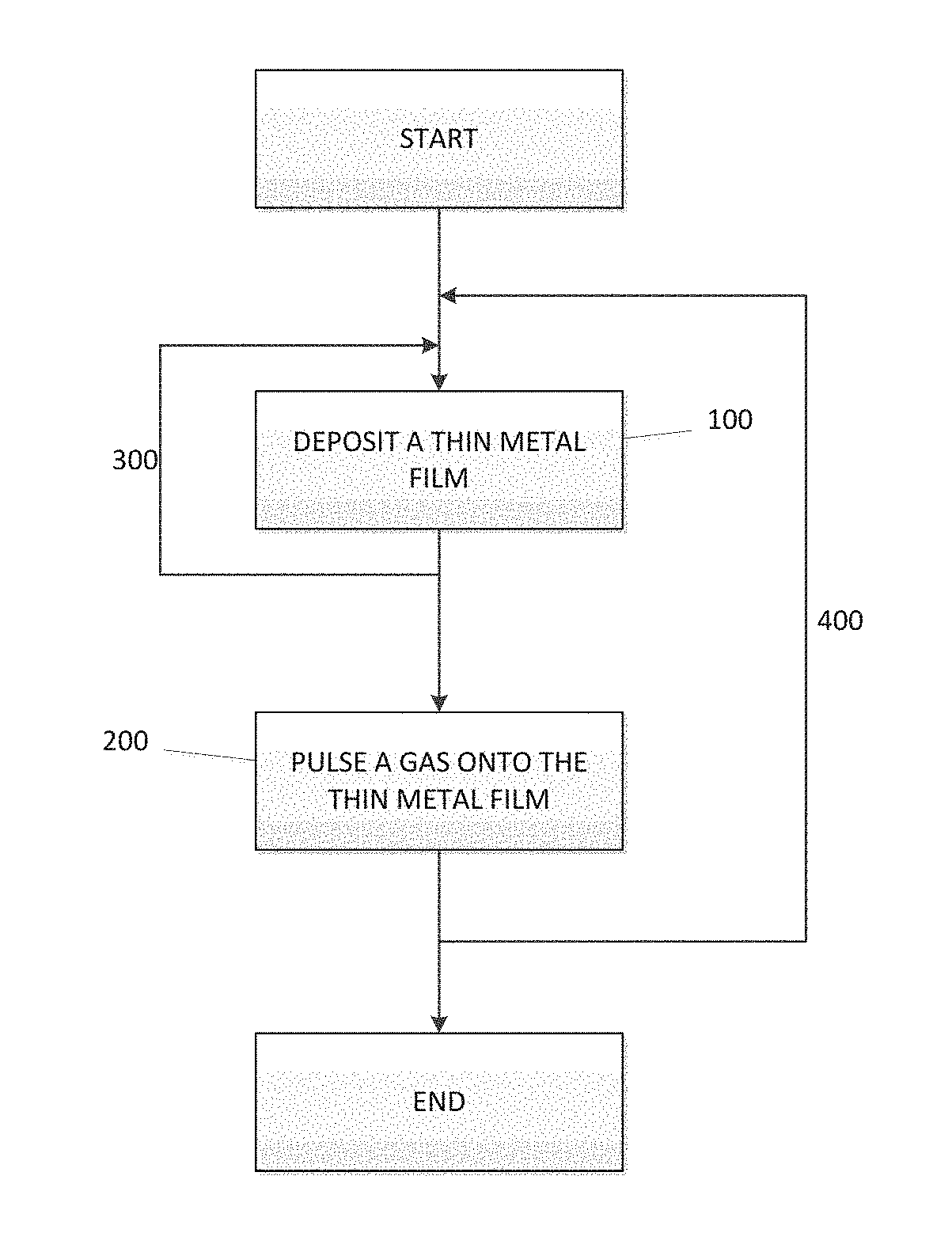
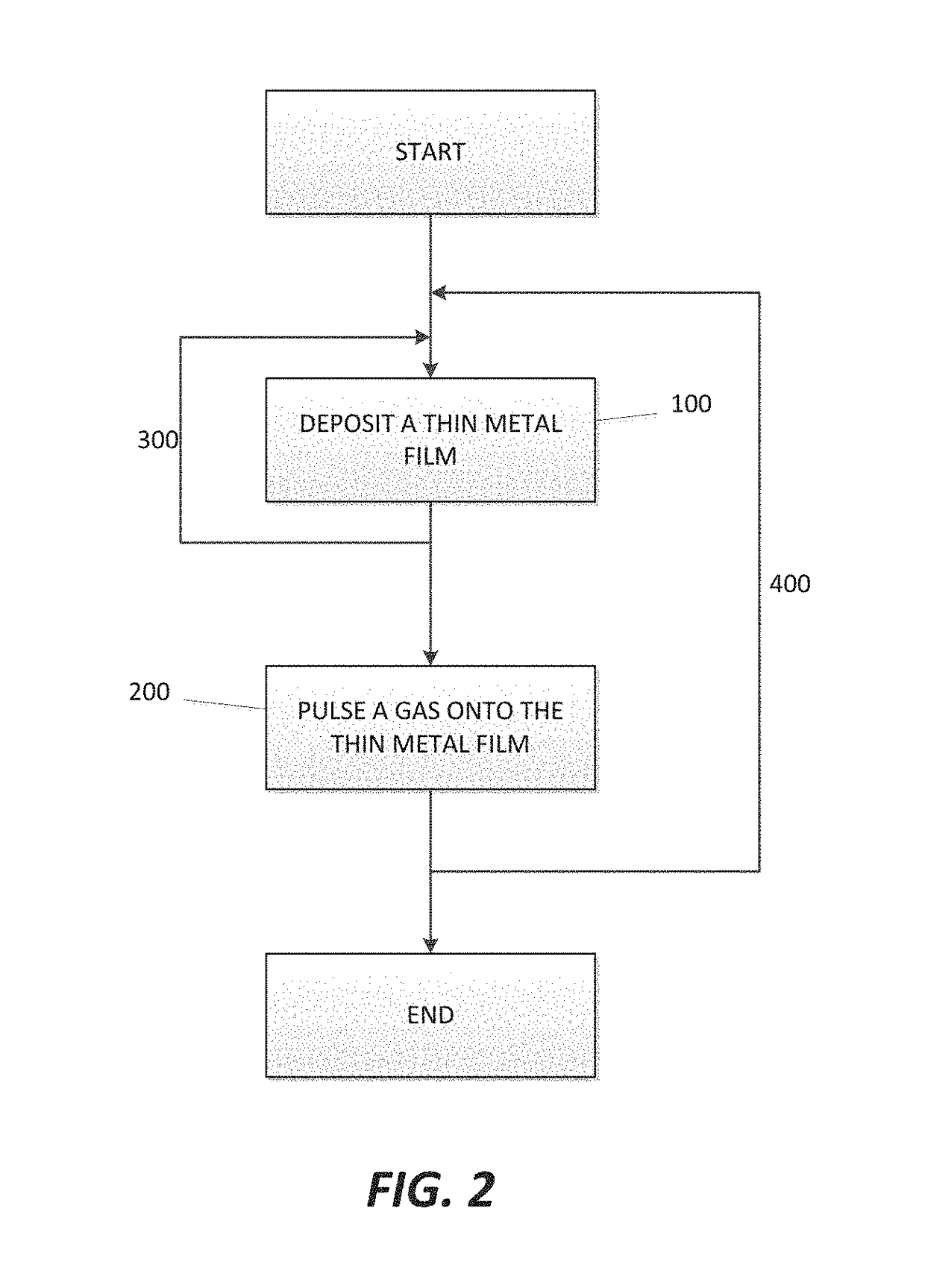
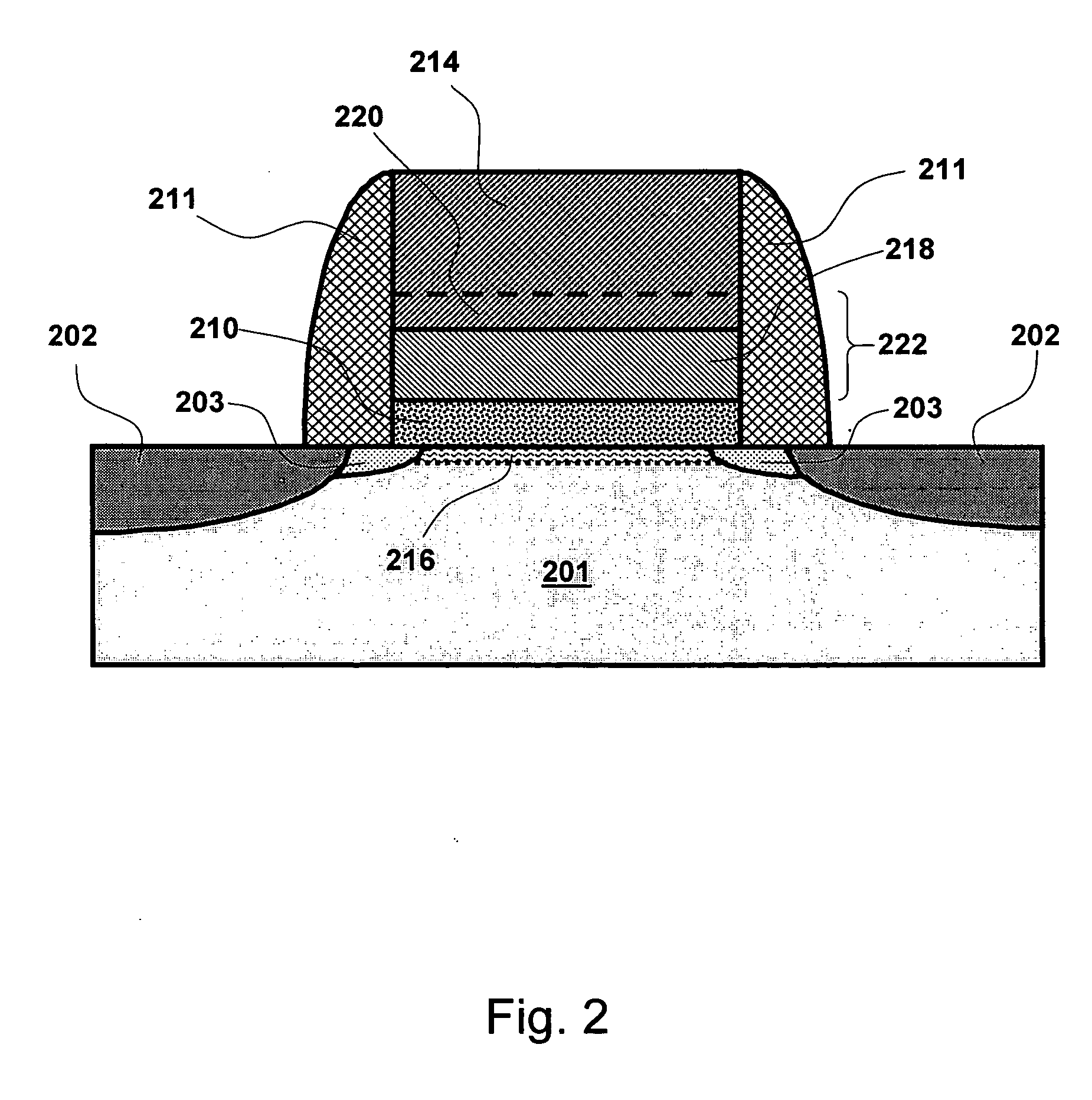
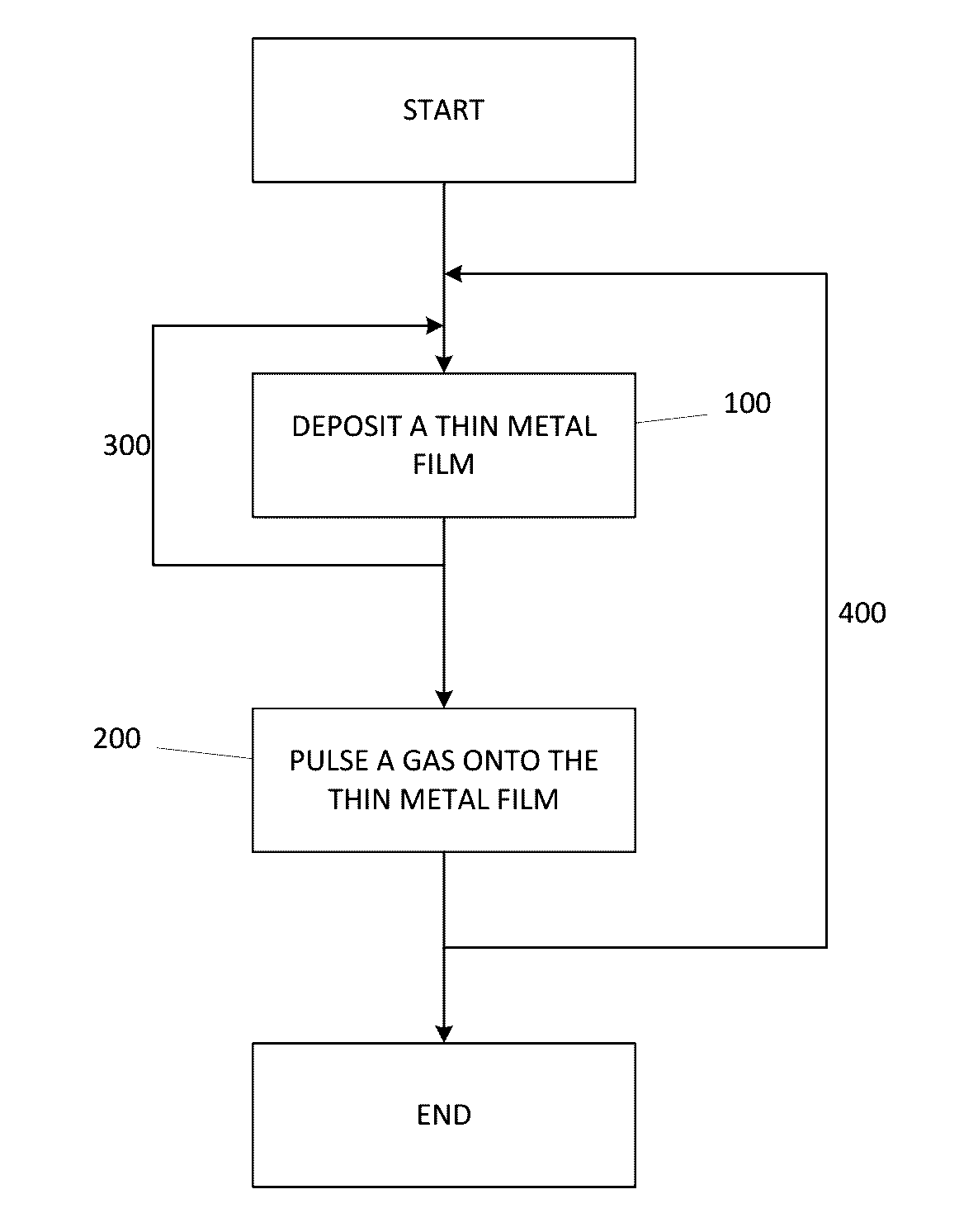
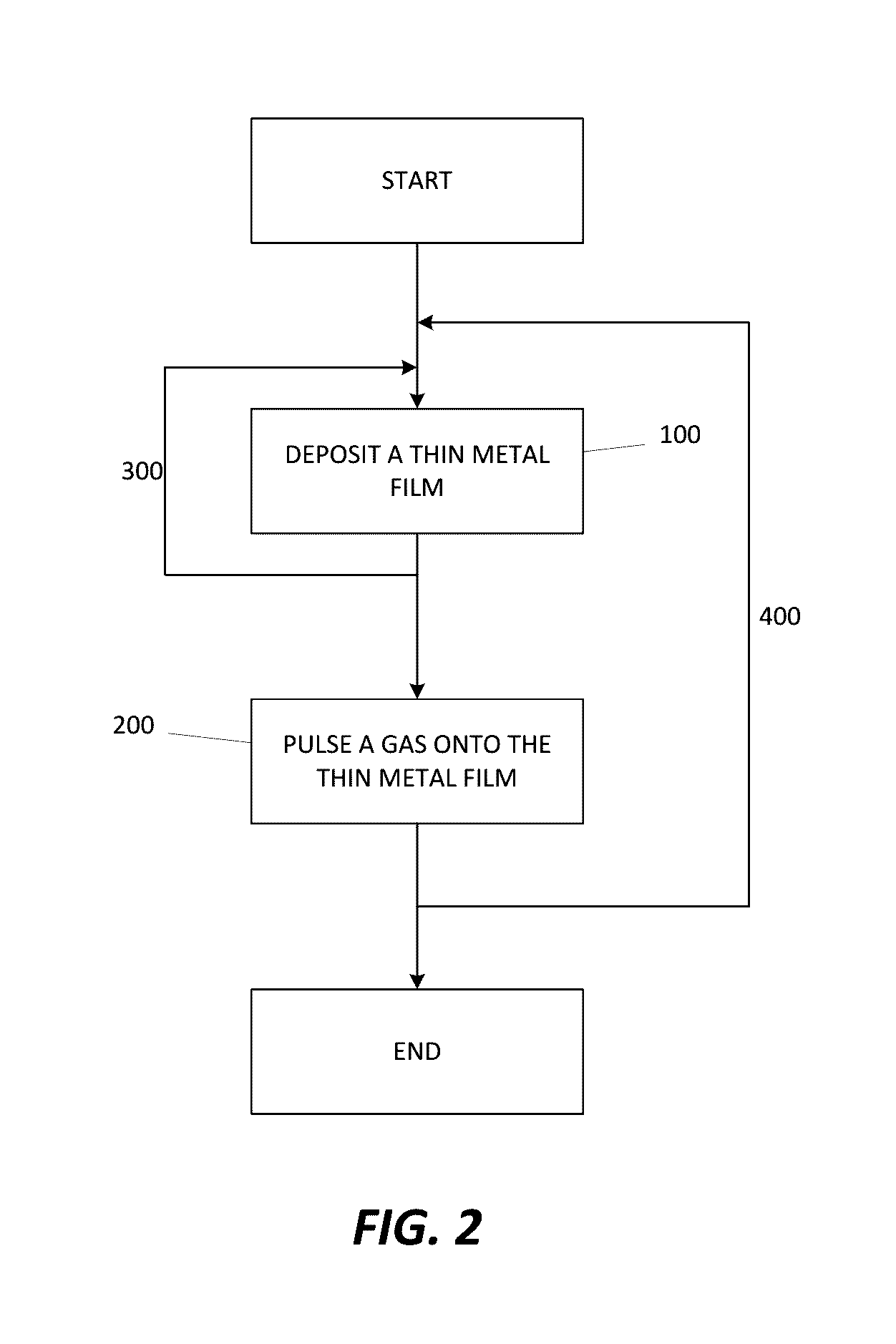
A method for forming a Boron doped metallic film, such as Titanium Boron Nitride, is disclosed. The method allows for creation of the metallic film with a high work function and low resistivity, while limiting the increase in effective oxide thickness. The method comprises a thin metallic layer deposition step as well as a Boron-based gas pulse step. The Boron-based gas pulse deposits Boron and allows for the removal of excess halogens within the metallic film. The steps may be repeated in order to achieve a desired thickness of the metallic film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
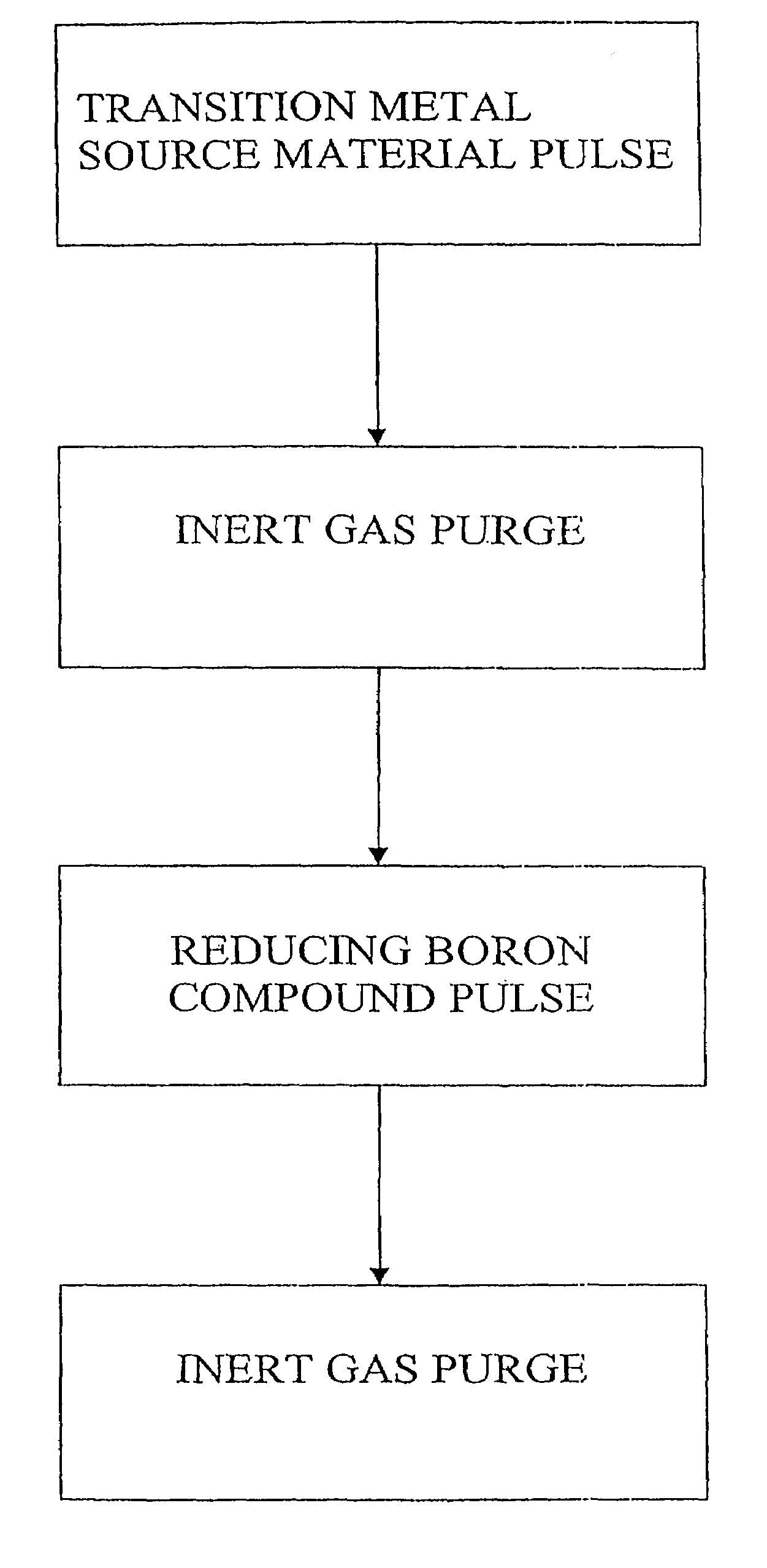
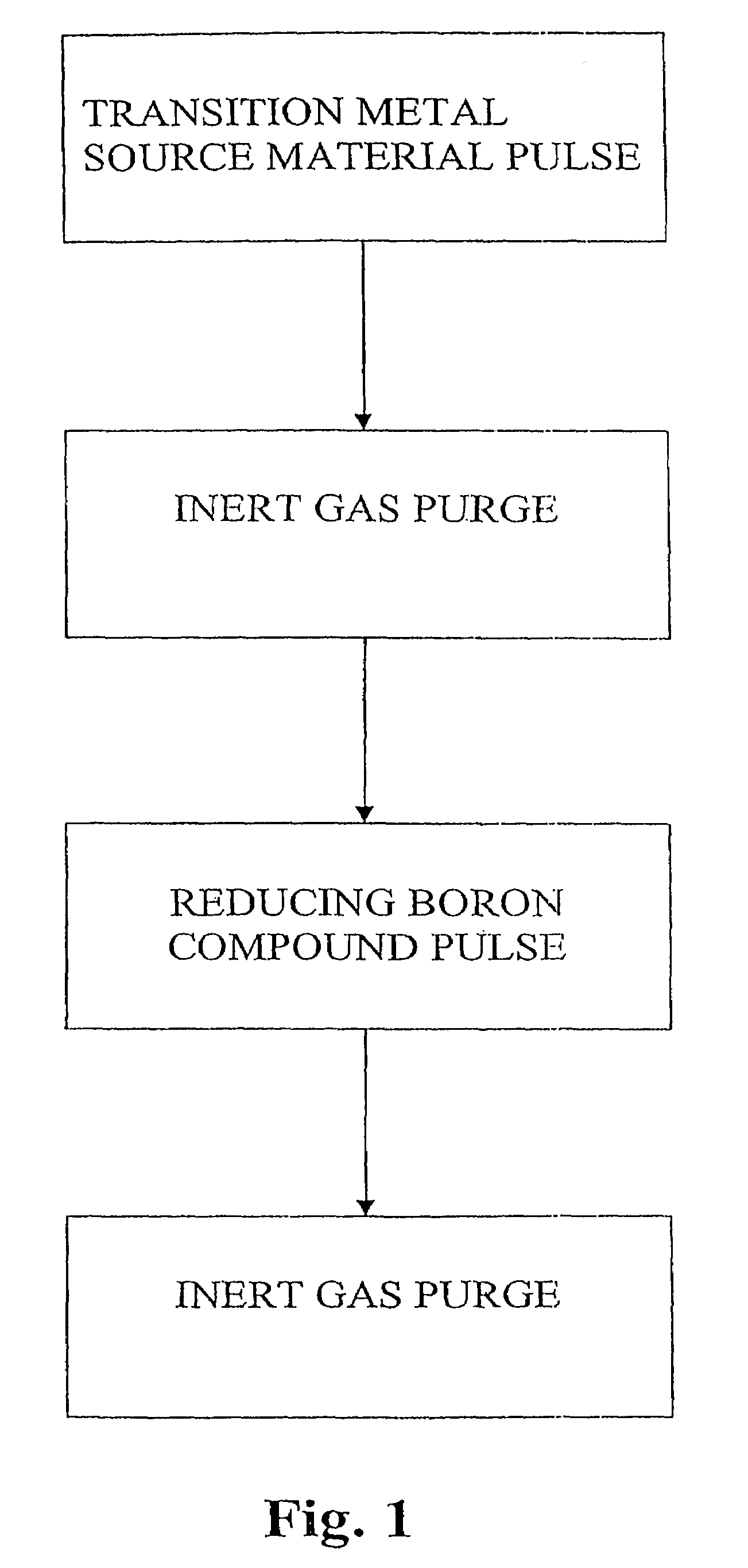
Production of elemental films using a boron-containing reducing agent
InactiveUS7144809B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityGas phase
The present invention relates generally to depositing elemental thin films. In particular, the invention concerns a method of growing elemental metal thin films by Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) using a boron compound as a reducing agent. In a preferred embodiment the method comprises introducing vapor phase pulses of at least one metal source compound and at least one boron source compound into a reaction space that contains a substrate on which the metal thin film is to be deposited. Preferably the boron compound is capable of reducing the adsorbed portion of the metal source compound into its elemental electrical state.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
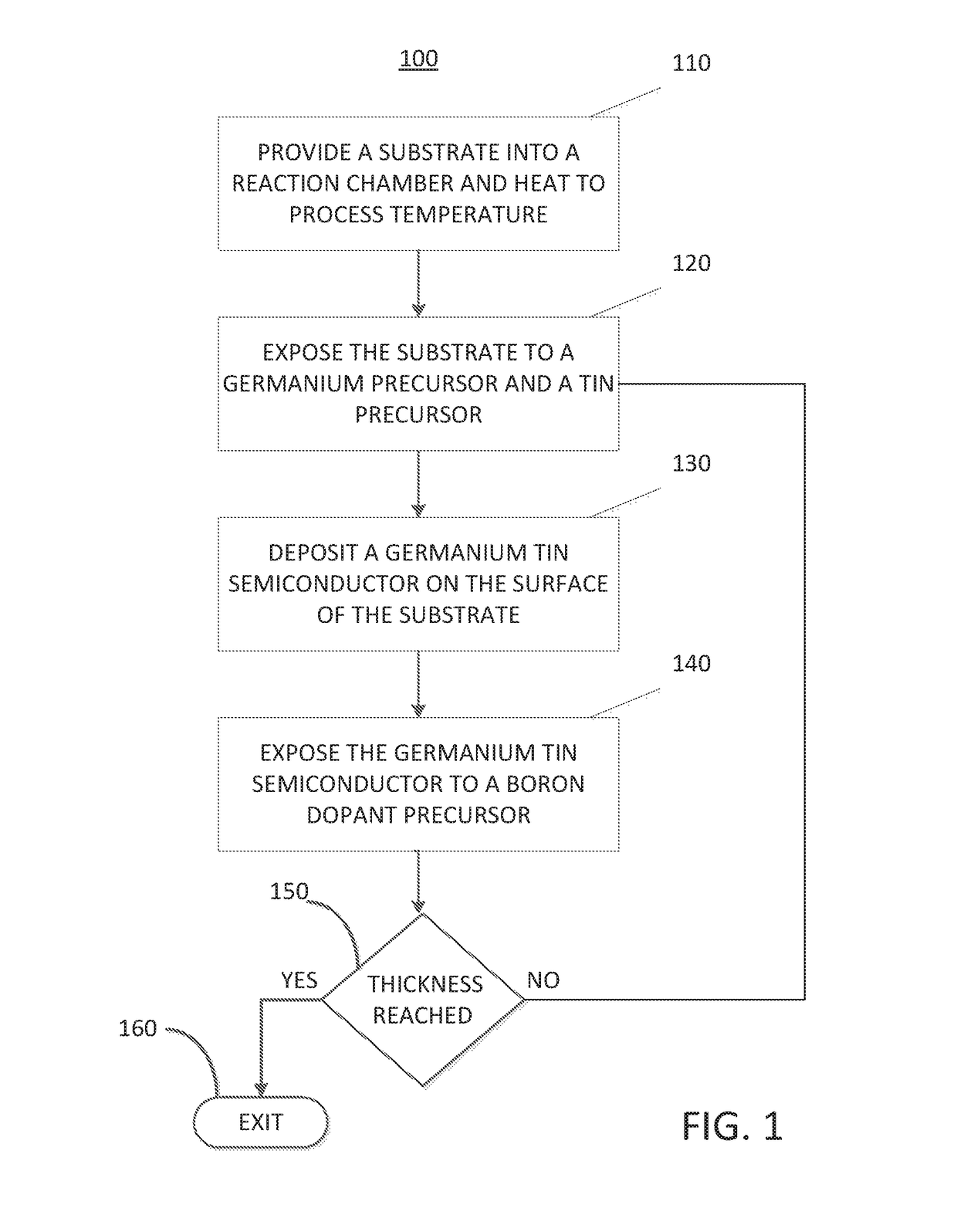
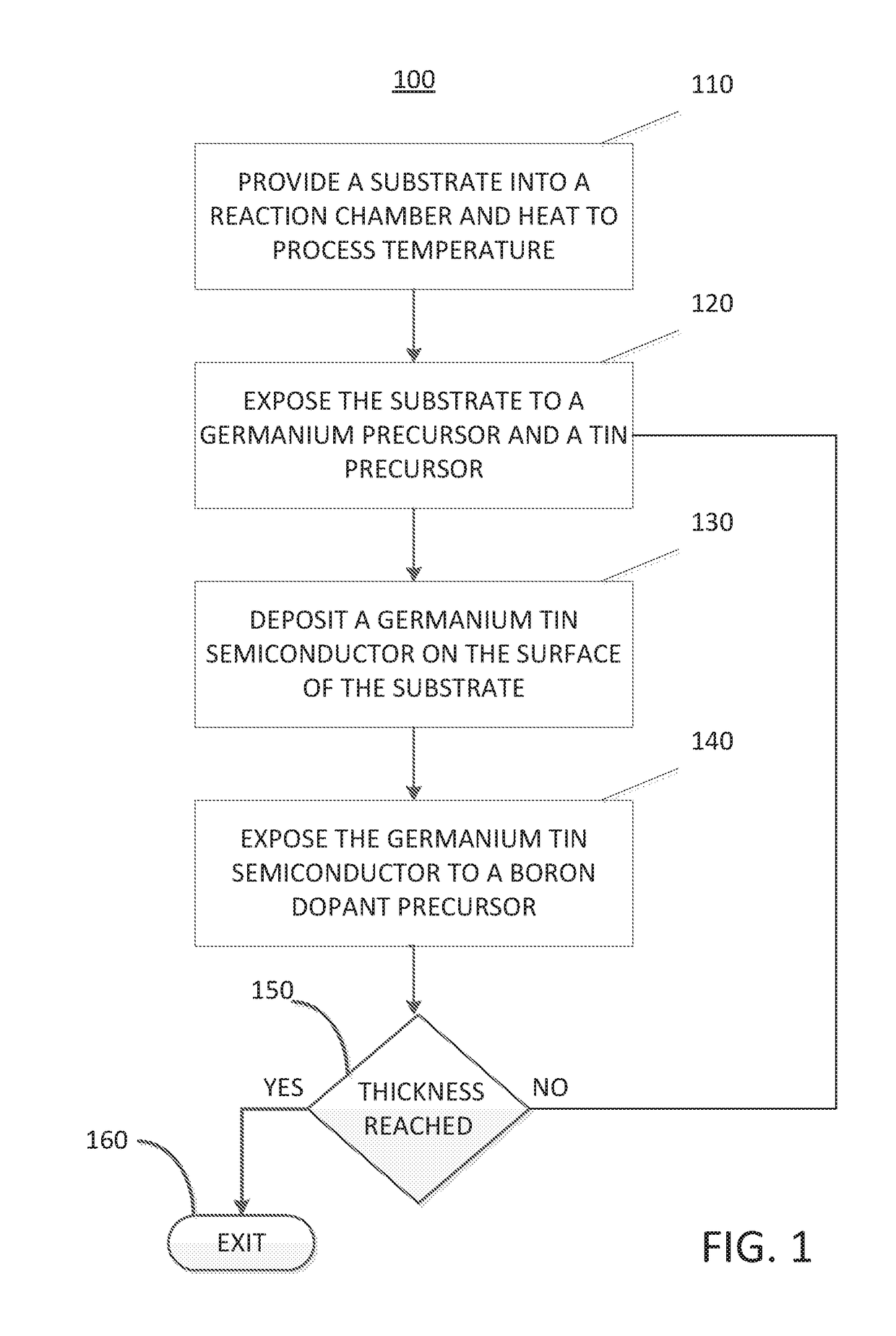
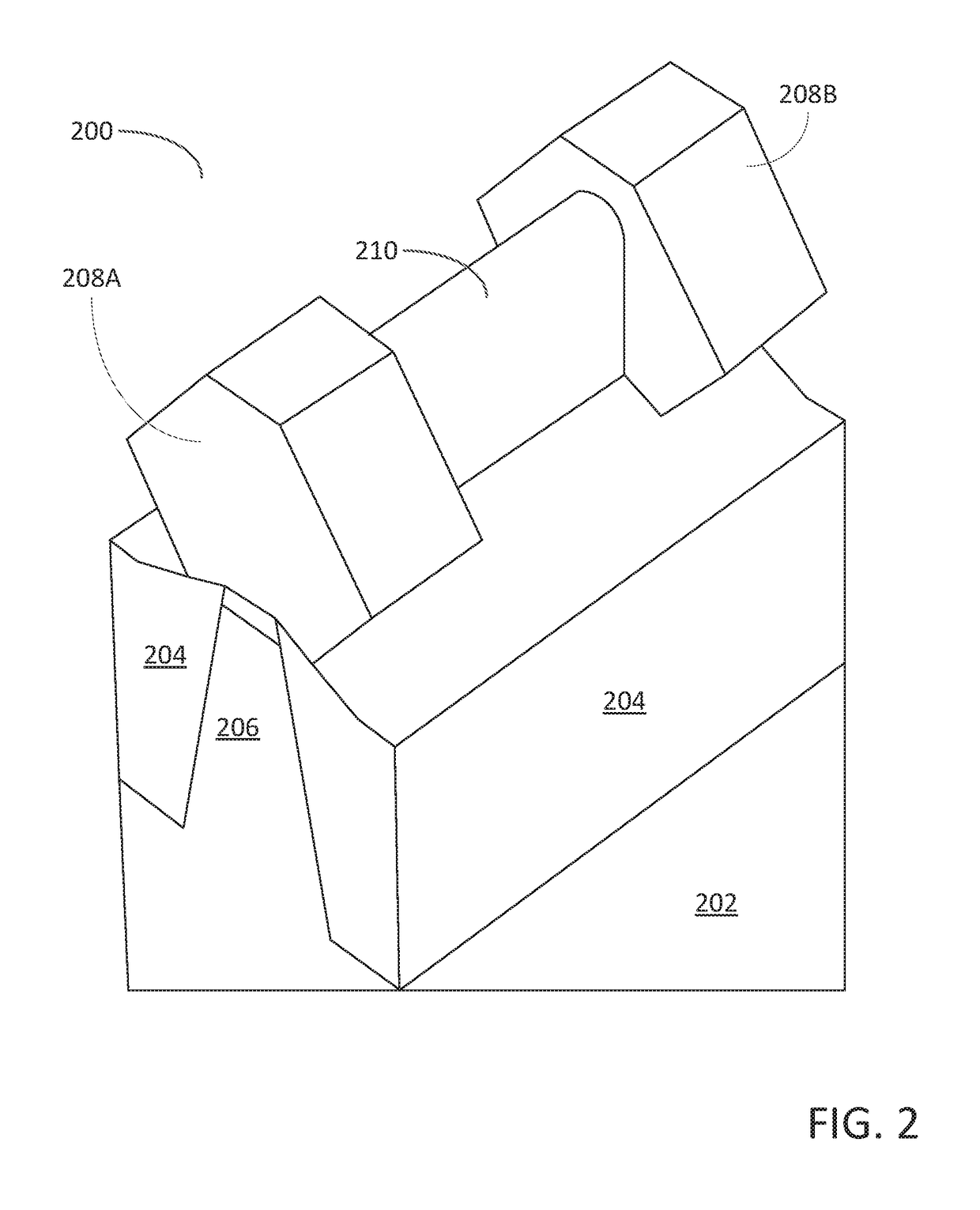
Methods for depositing a doped germanium tin semiconductor and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS10236177B1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantDeposition temperature
A method for depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor is disclosed. The method may include; providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature and exposing the substrate to a germanium precursor and a tin precursor. The method may further include; depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor on the surface of the substrate, and exposing the germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor to a boron dopant precursor. Semiconductor device structures including a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor formed by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method and apparatus for germanium tin alloy formation by thermal CVD
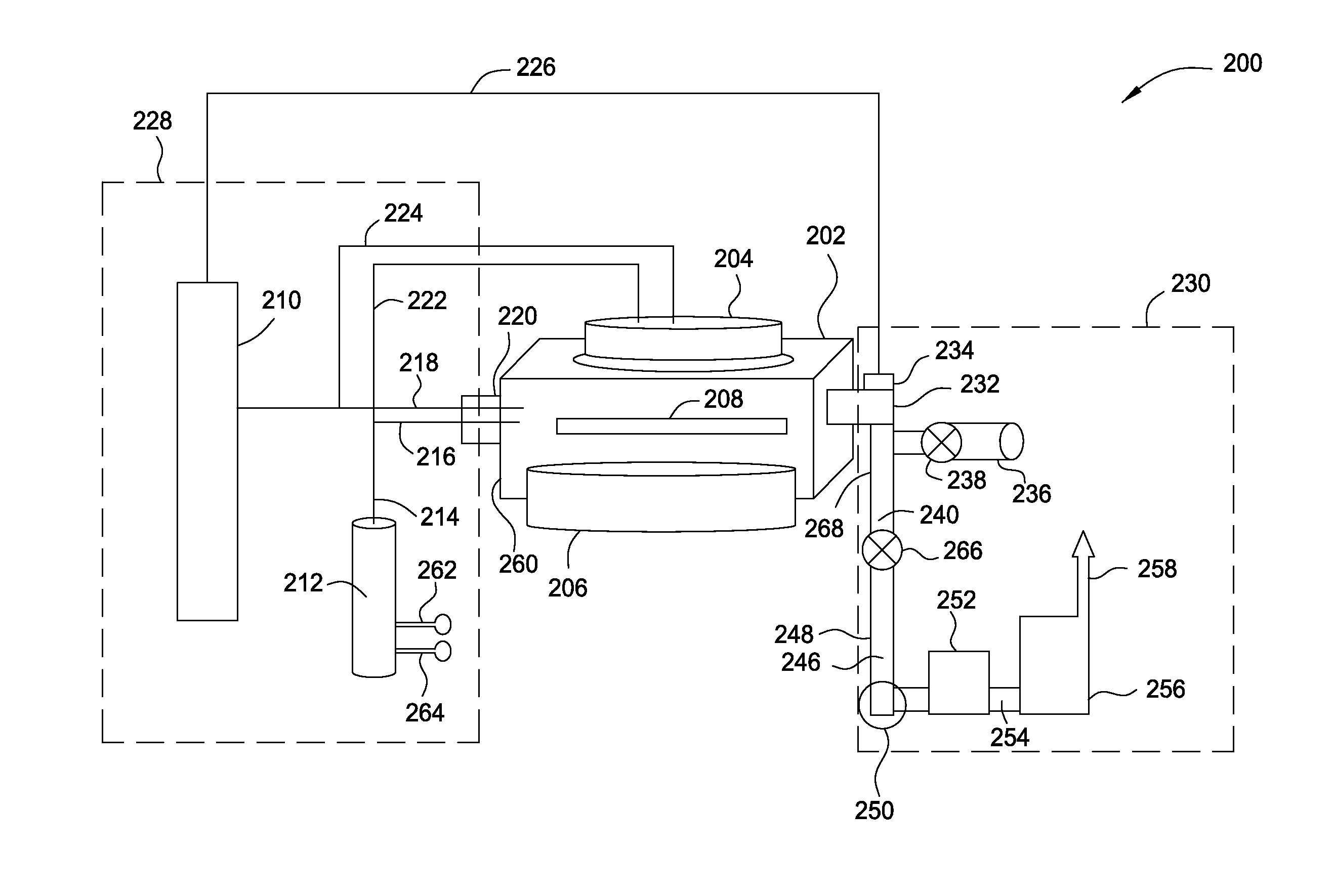
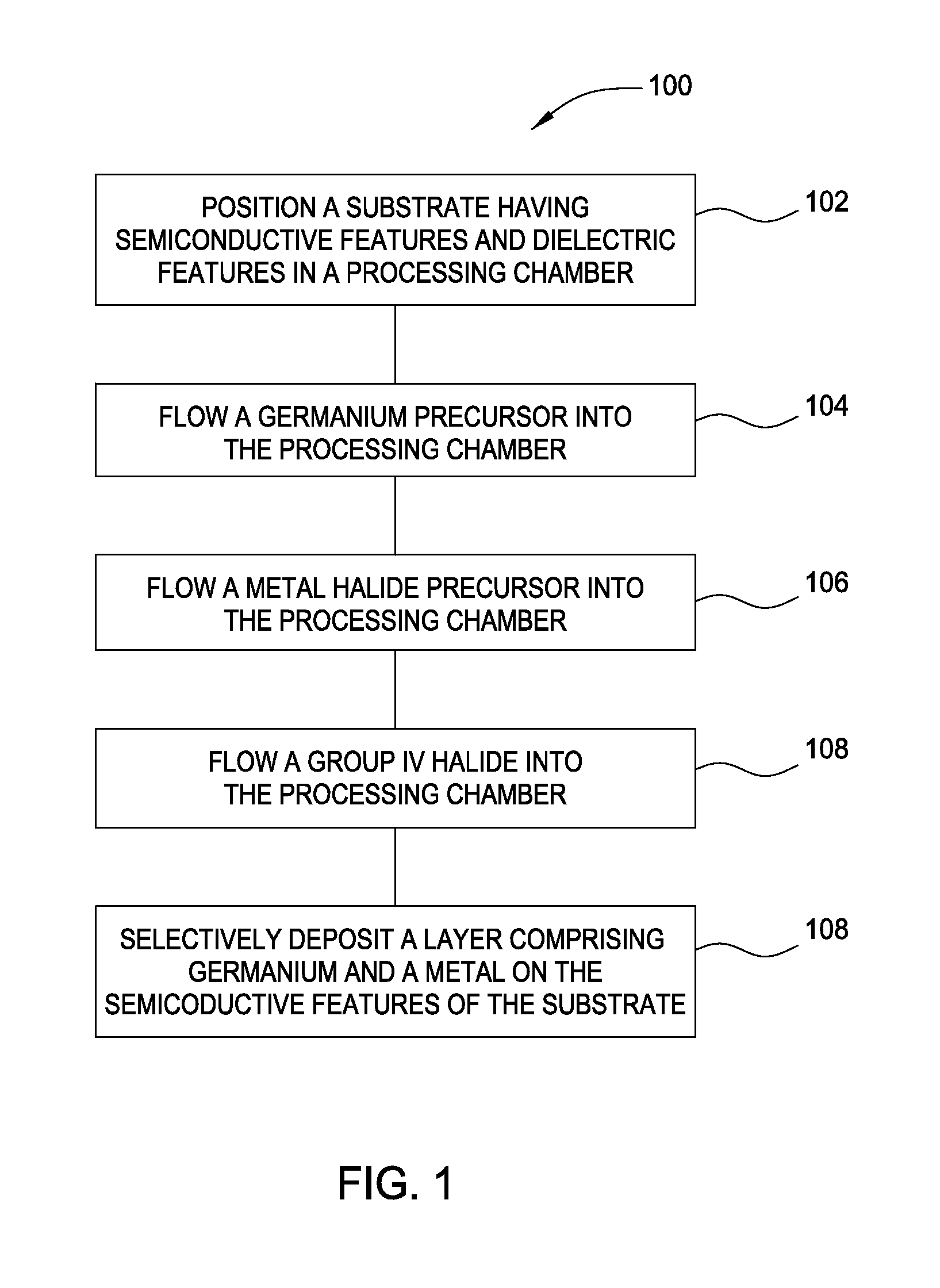
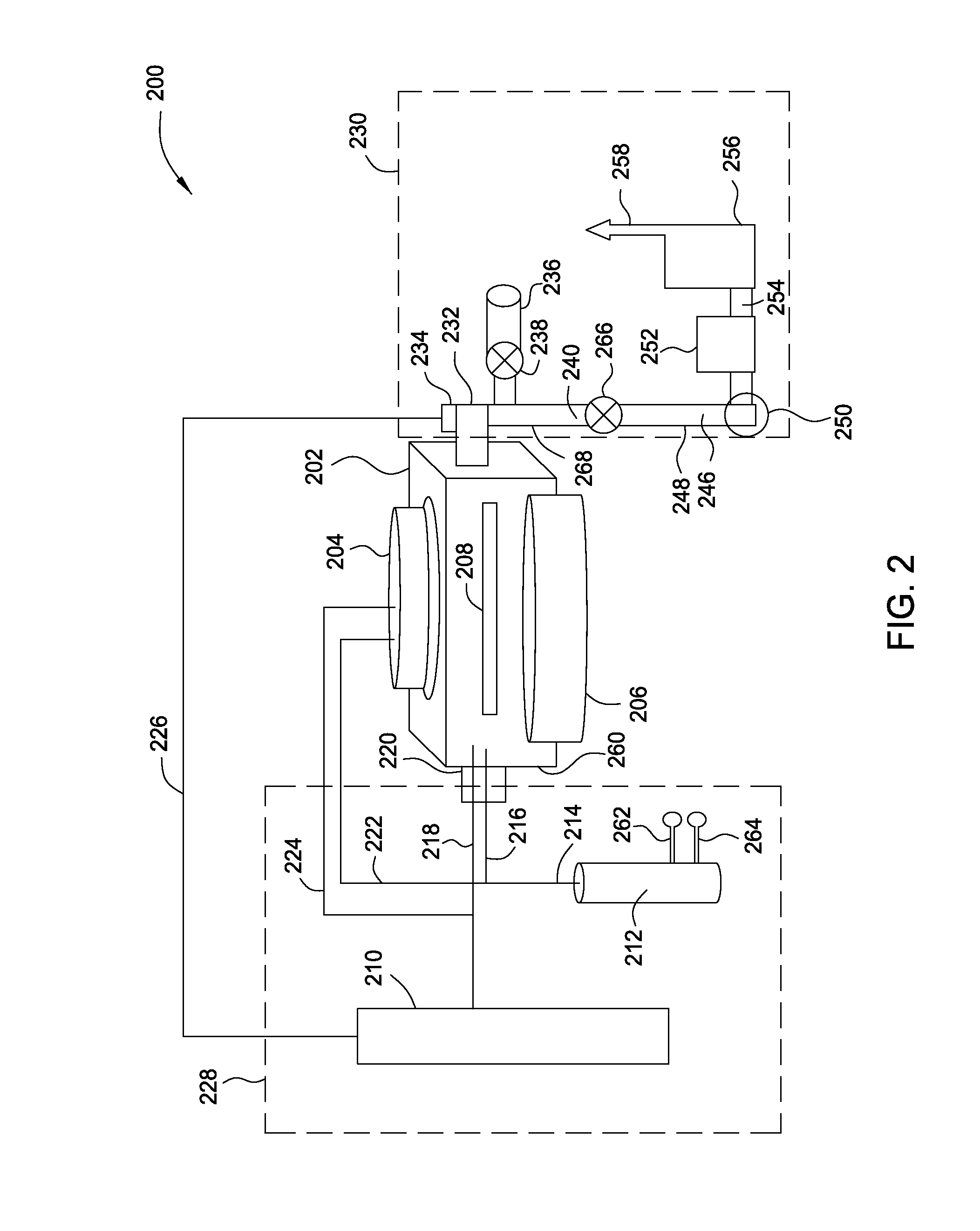
InactiveUS20130280891A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelective depositionLiquid metal
A method and apparatus for forming semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers is described. A germanium precursor and a metal precursor are provided to a chamber, and an epitaxial layer of germanium-metal alloy, optionally including silicon, is formed on the substrate. The metal precursor is typically a metal halide, which may be provided by evaporating a liquid metal halide, subliming a solid metal halide, or by contacting a pure metal with a halogen gas. A group IV halide deposition control agent is used to provide selective deposition on semiconductive regions of the substrate relative to dielectric regions. The semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers may be doped, for example with boron, phosphorus, and / or arsenic. The precursors may be provided through a showerhead or through a side entry point, and an exhaust system coupled to the chamber may be separately heated to manage condensation of exhaust components.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
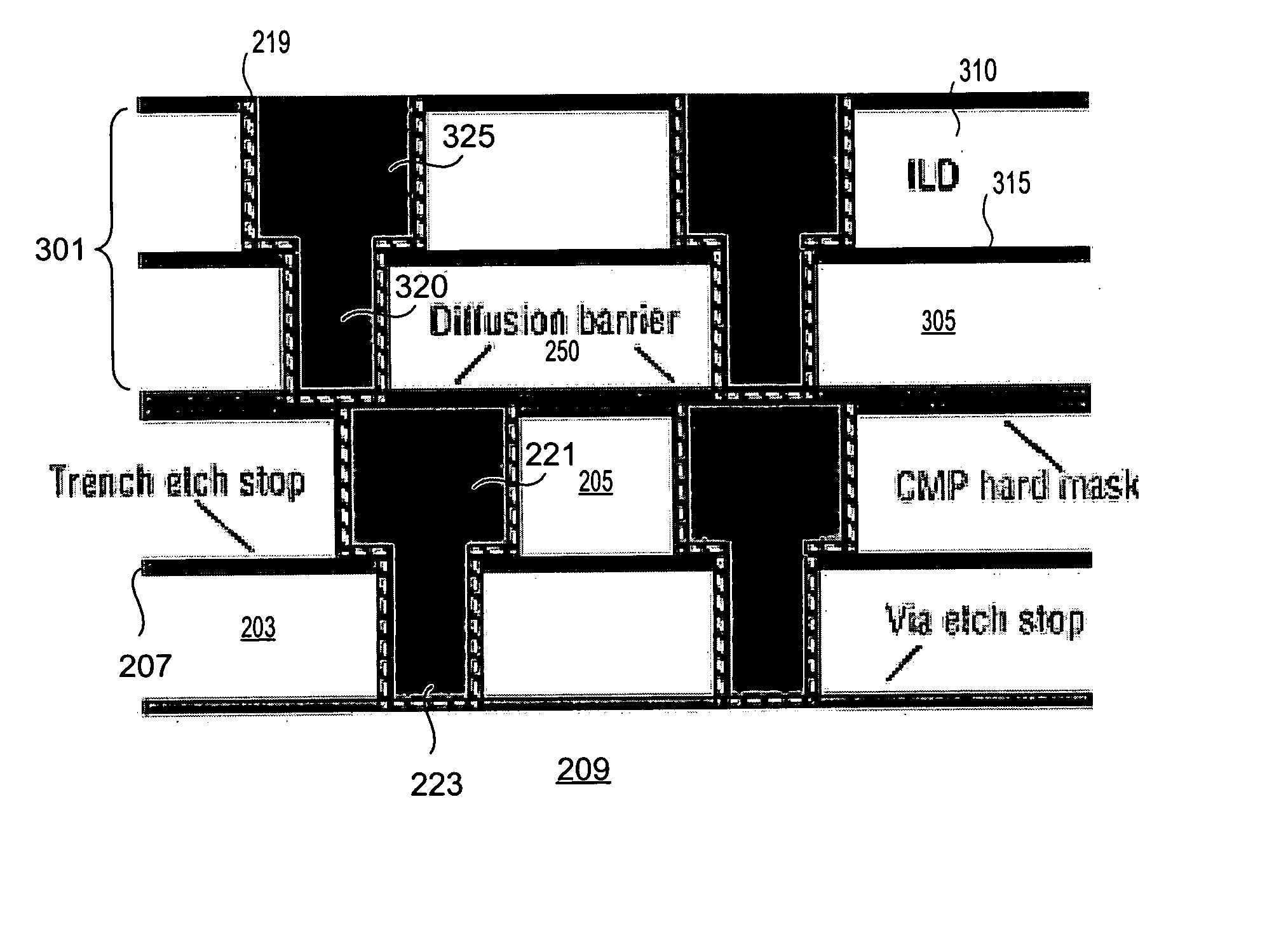
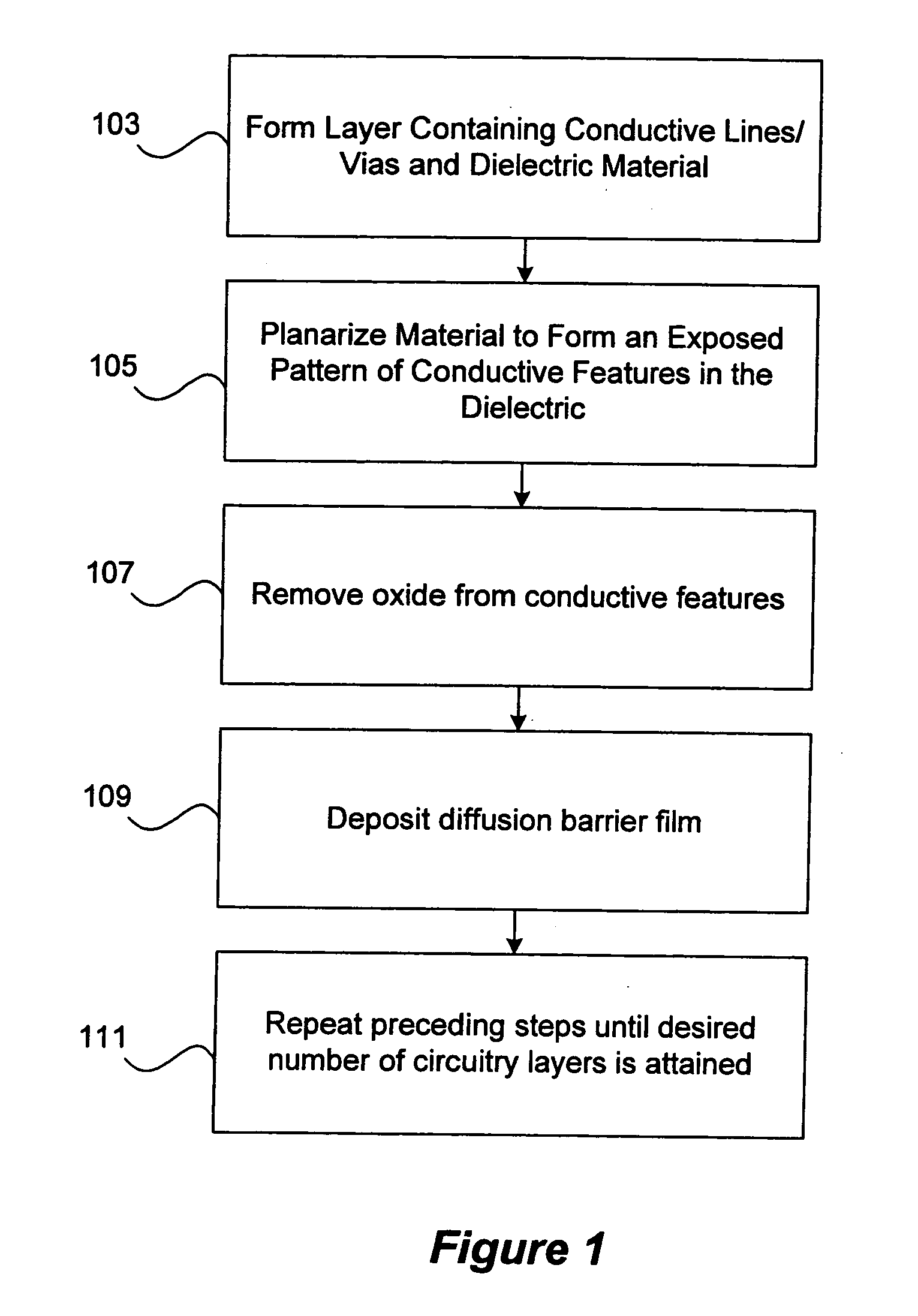
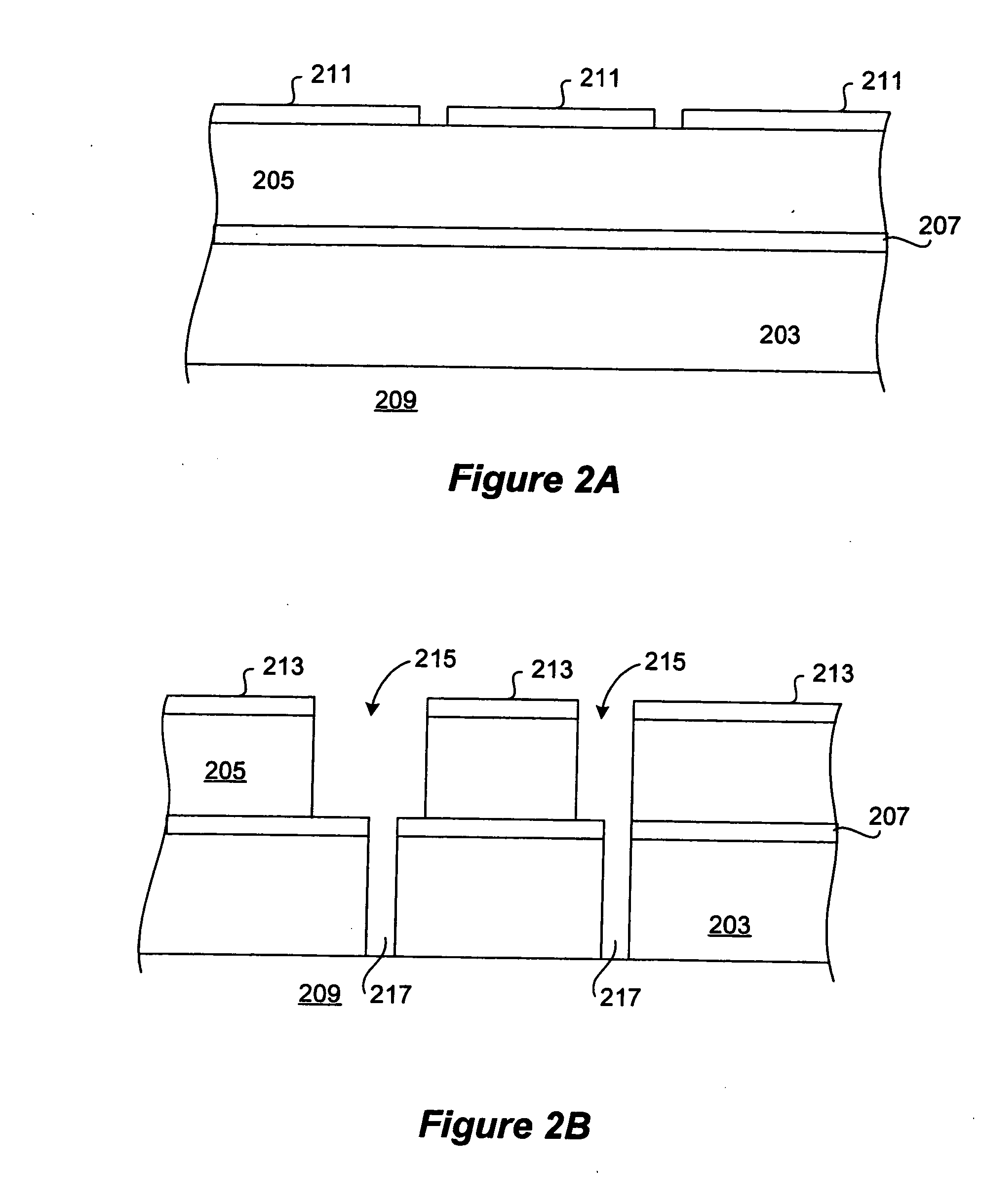
Novel film for copper diffusion barrier
InactiveUS20060019486A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAtmospheric airBoron nitride
The present invention provides a low dielectric constant copper diffusion barrier film suitable for use in a semiconductor device and methods for fabricating such a film. Some embodiments of the film are formed of a silicon-based material doped with boron. Other embodiments are formed, at least in part, of boron nitride. Some such embodiments include a moisture barrier film that includes oxygen and / or carbon. Preferred embodiments of the copper diffusion barrier maintain a stable dielectric constant of less than 4.5 in the presence of atmospheric moisture.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods for depositing a doped germanium tin semiconductor and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20190067004A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantDeposition temperature
A method for depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor is disclosed. The method may include; providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature and exposing the substrate to a germanium precursor and a tin precursor. The method may further include; depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor on the surface of the substrate, and exposing the germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor to a boron dopant precursor. Semiconductor device structures including a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor formed by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Fire retardant compositions and methods for preserving wood products
Wood preservative compositions are disclosed. Treatment of lumber, plywood, and other wood products with a novel composition comprising the boron source composition, a melamine binder resin, and a urea casein activator resin protects lumber, plywood, and other wood products from attack by termites, fungi, fire and flame. The preservative can be formed by combining a source of boron such as boric acid and the water-soluble salts thereof, a melamine binder resin, and a urea casein resin. A wood preservative is characterized by a weight ratio of the urea casing activator resin to the melamine binder resin ranging from about 1:20 to 1:4 and a weight ratio of the boron source composition to the melamine binder resin ranging from about 1.3:1 to 9.6:1.
Owner:LOPEZ RICHARD A
Faceted structure, article, sensor device, and method
A faceted structure is provided that includes a crystalline composition comprising a metal nitride. The metal comprises one or more of aluminum, boron, indium, or gallium. The crystalline composition has at least one exposed surface that is a grain boundary, an etched surface, or a naturally formed facet, and the surface has the same crystallographic orientation of a substrate on which the crystalline composition is grown. A sensor device is provided that includes a faceted structure. Associated methods of making and using the faceted structure in a sensor device are provided.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
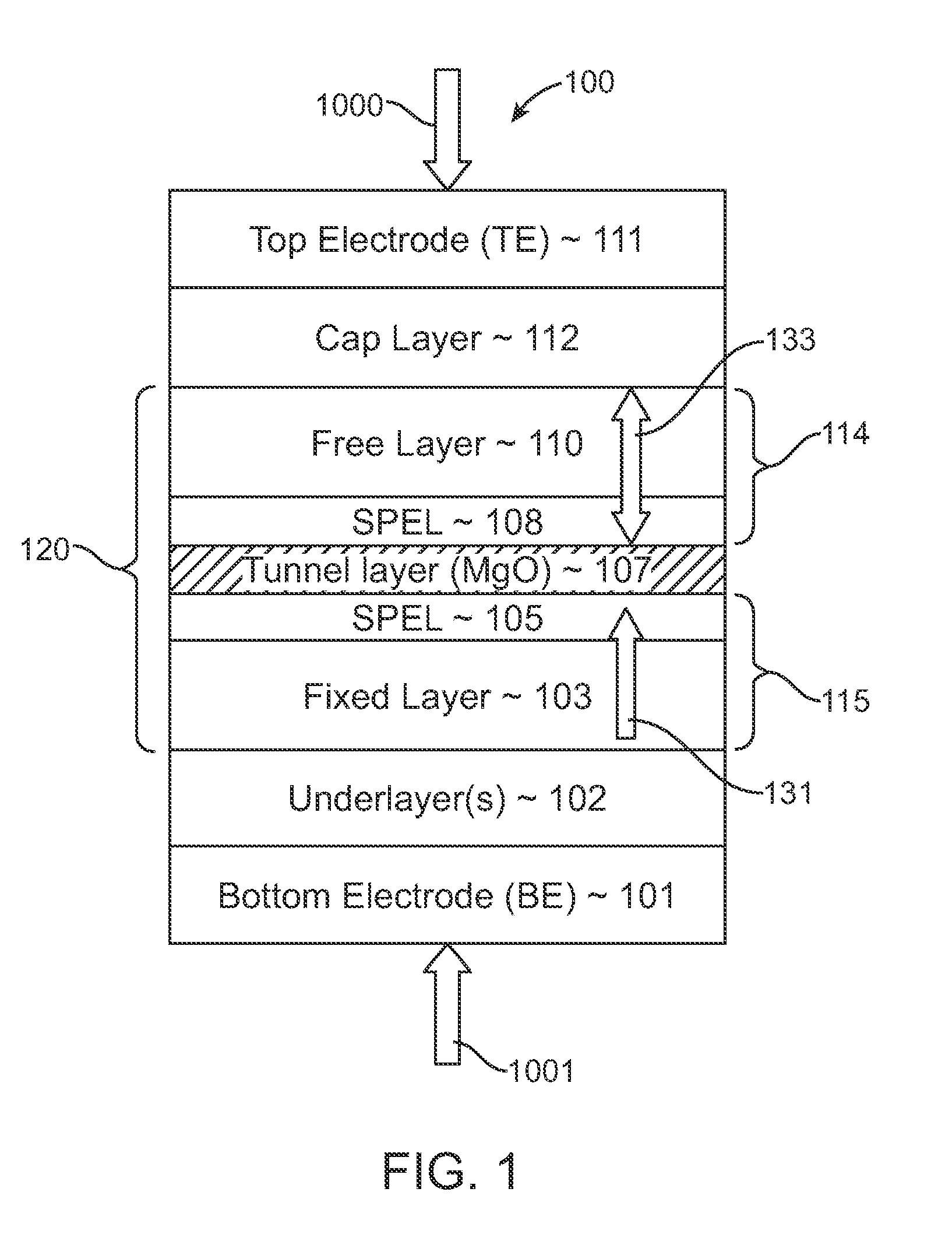
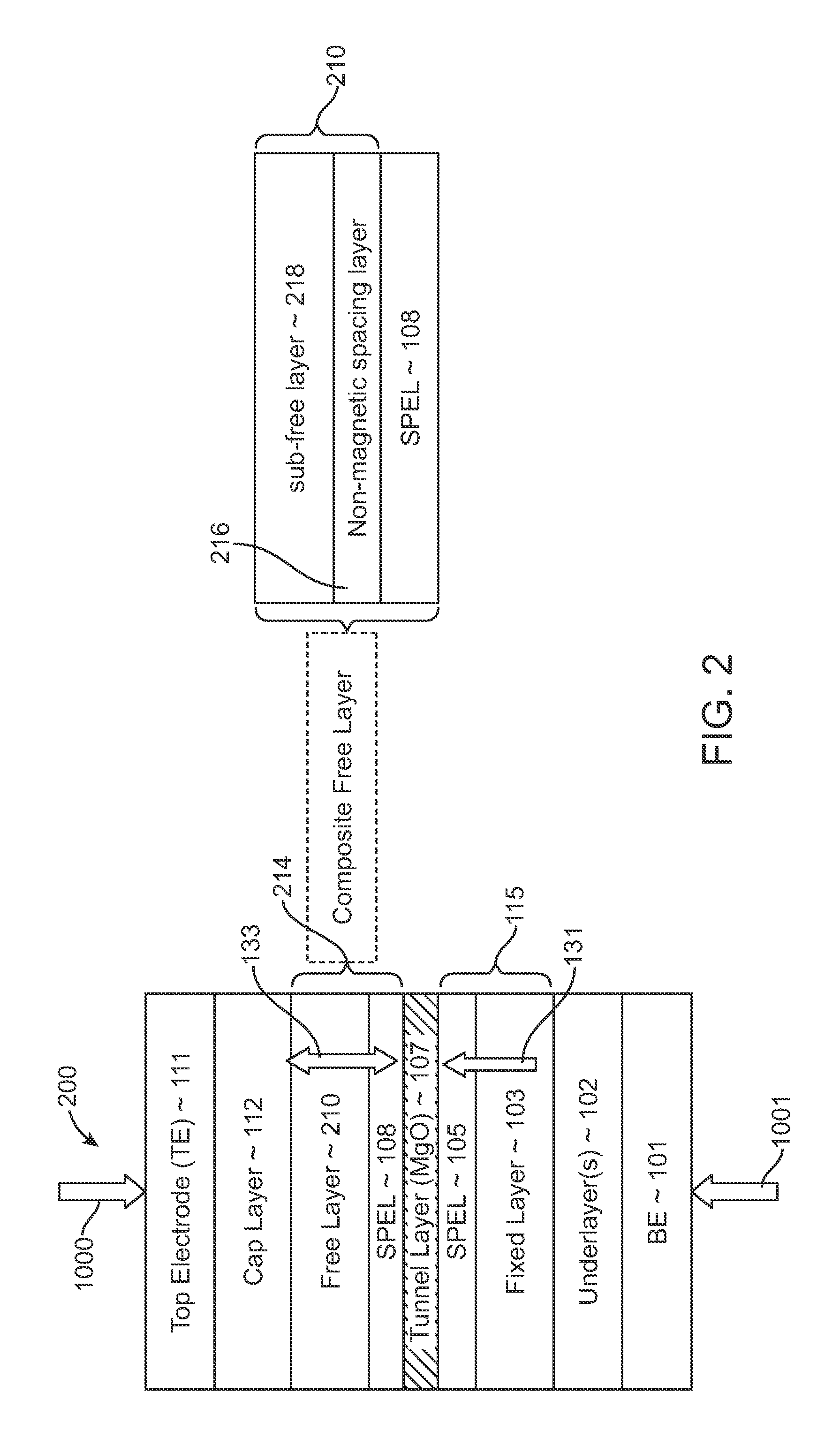
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
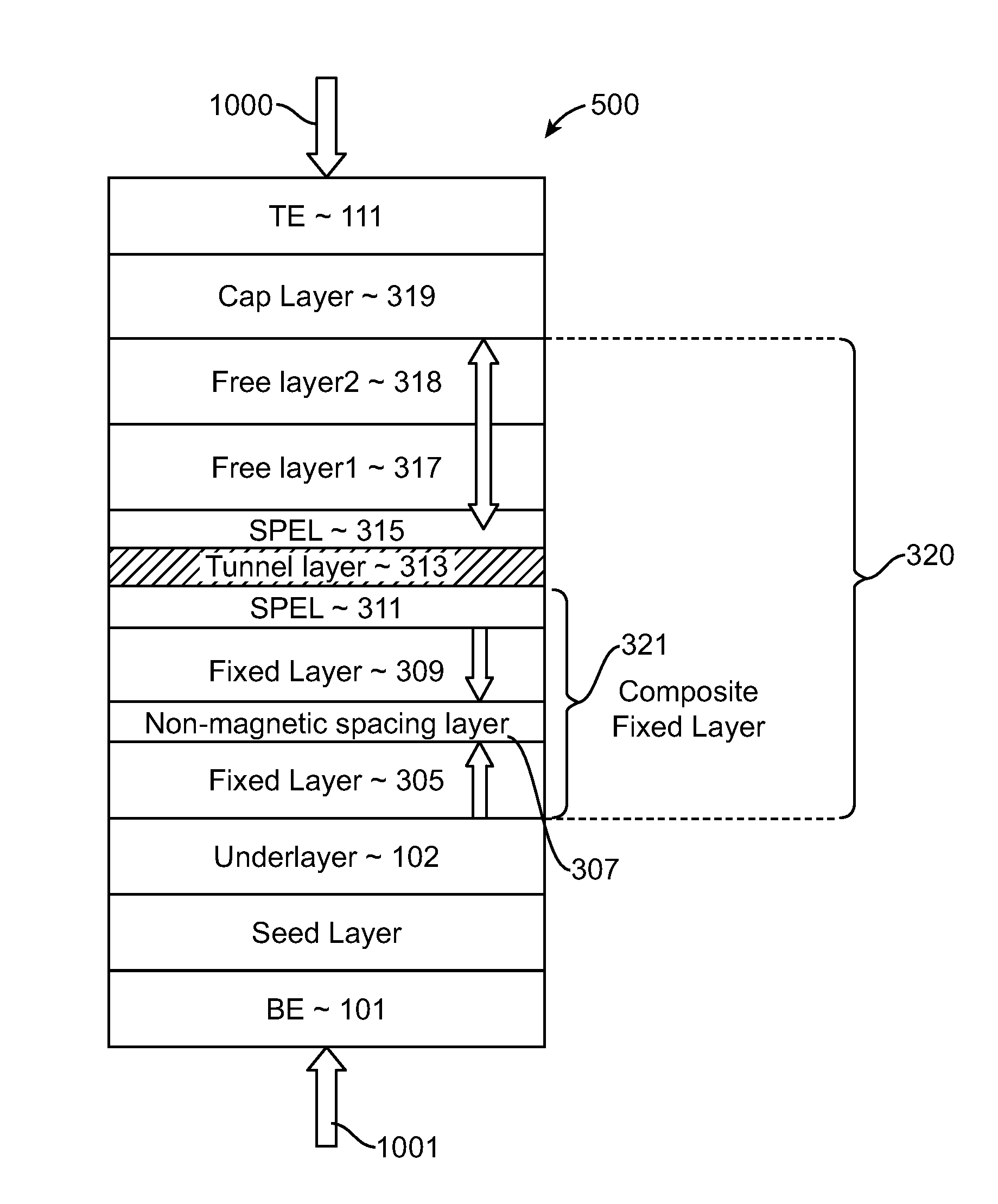
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Method for manufacturing semiconductor substrate and semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS20050282019A1Reduce adverse effectsInhibit migrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenGate oxide
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor substrate comprises the steps of: forming a gate oxide film as an insulating layer on the surface of a semiconductor substrate; implanting boron ions for inhibiting the migration of a peeling substance in the semiconductor substrate to form an anti-diffusion layer in the semiconductor substrate; activating boron in the anti-diffusion layer by heat treatment; implanting hydrogen ions into the semiconductor substrate to form a peel layer in part of the semiconductor substrate at a side of the anti-diffusion layer opposite to the gate oxide film; bonding a glass substrate to the surface of the semiconductor substrate where the gate oxide film has been formed; and heat-treating the semiconductor substrate to separate part of the semiconductor substrate along the peel layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
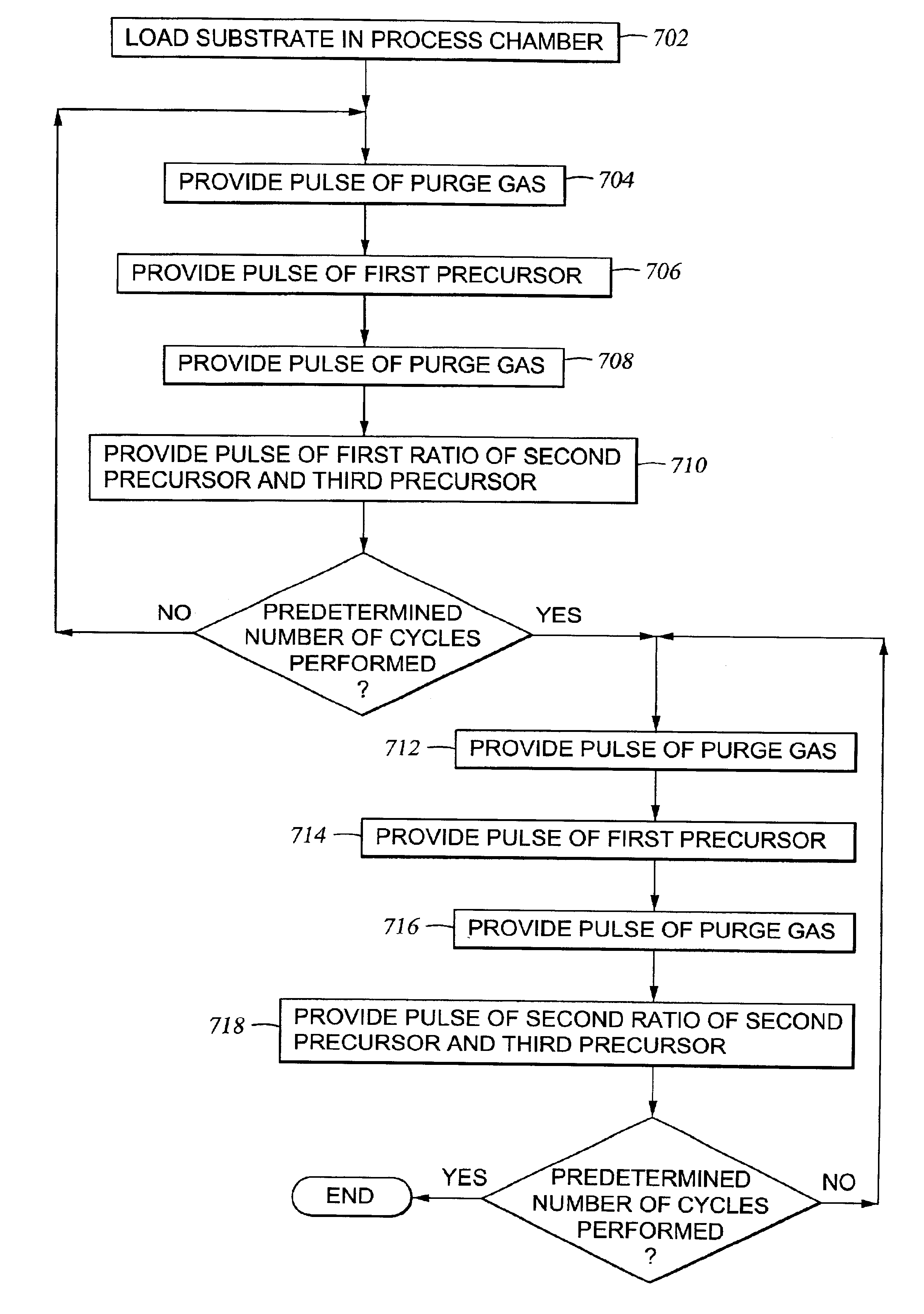
Multiple precursor cyclical deposition system
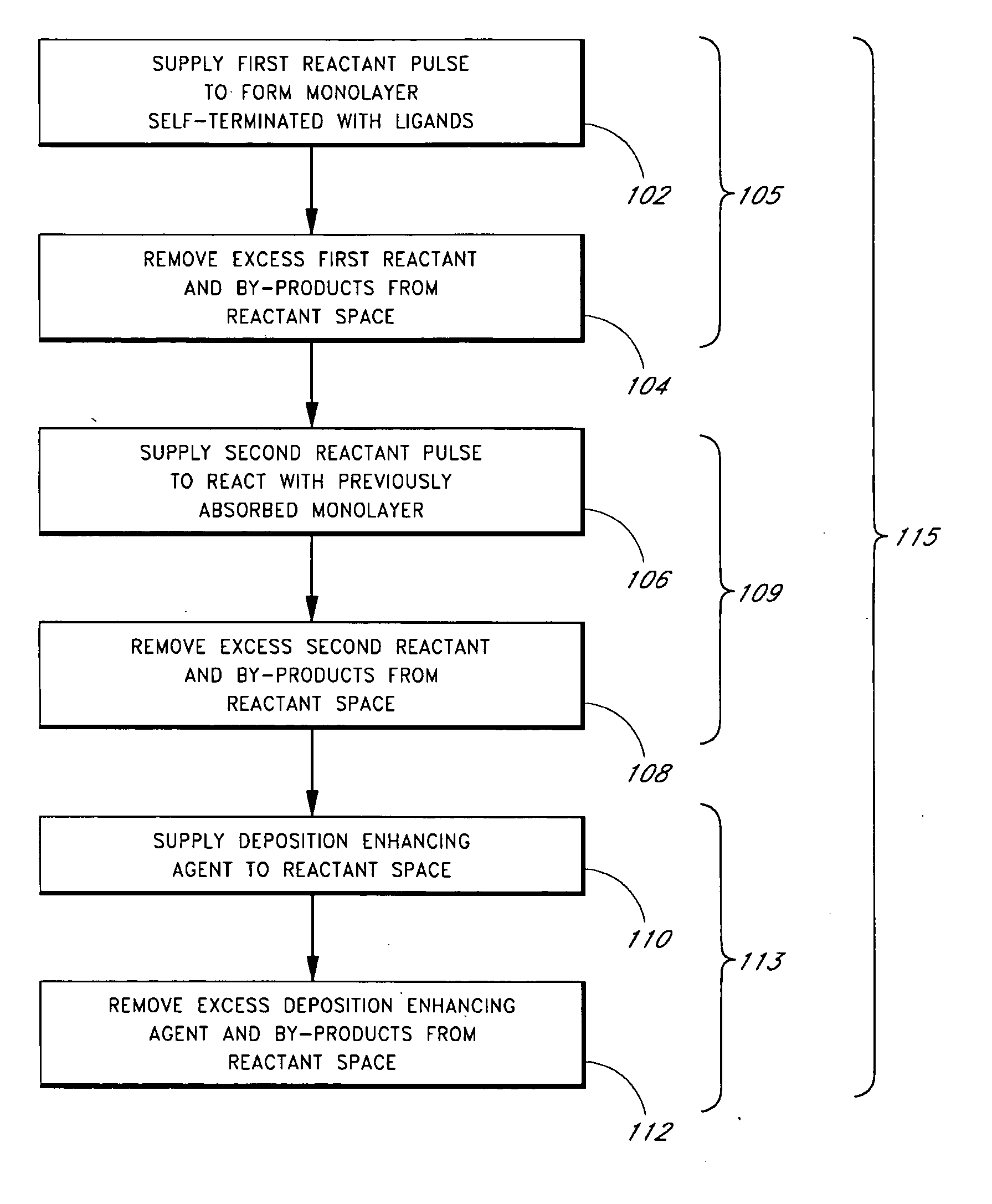
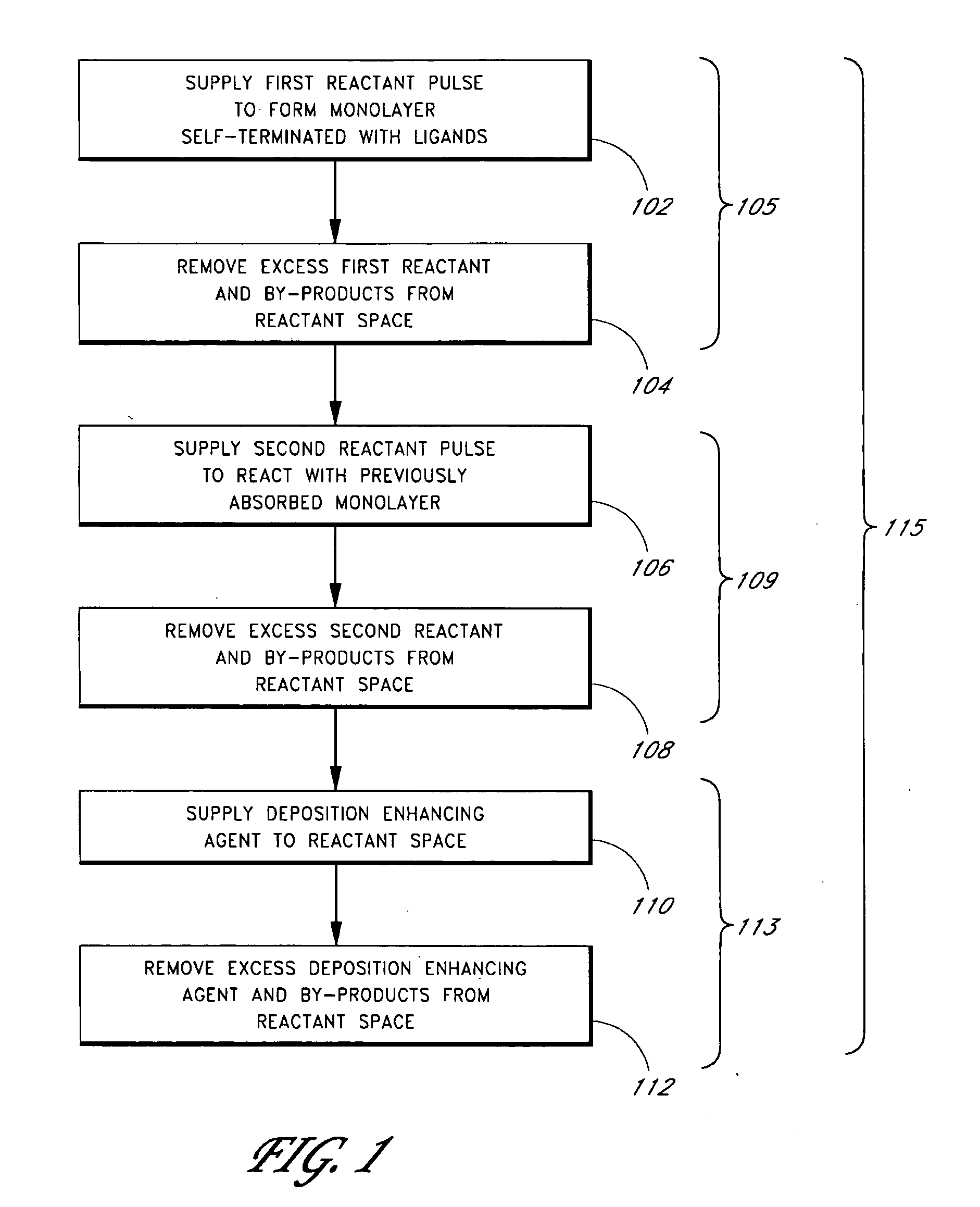
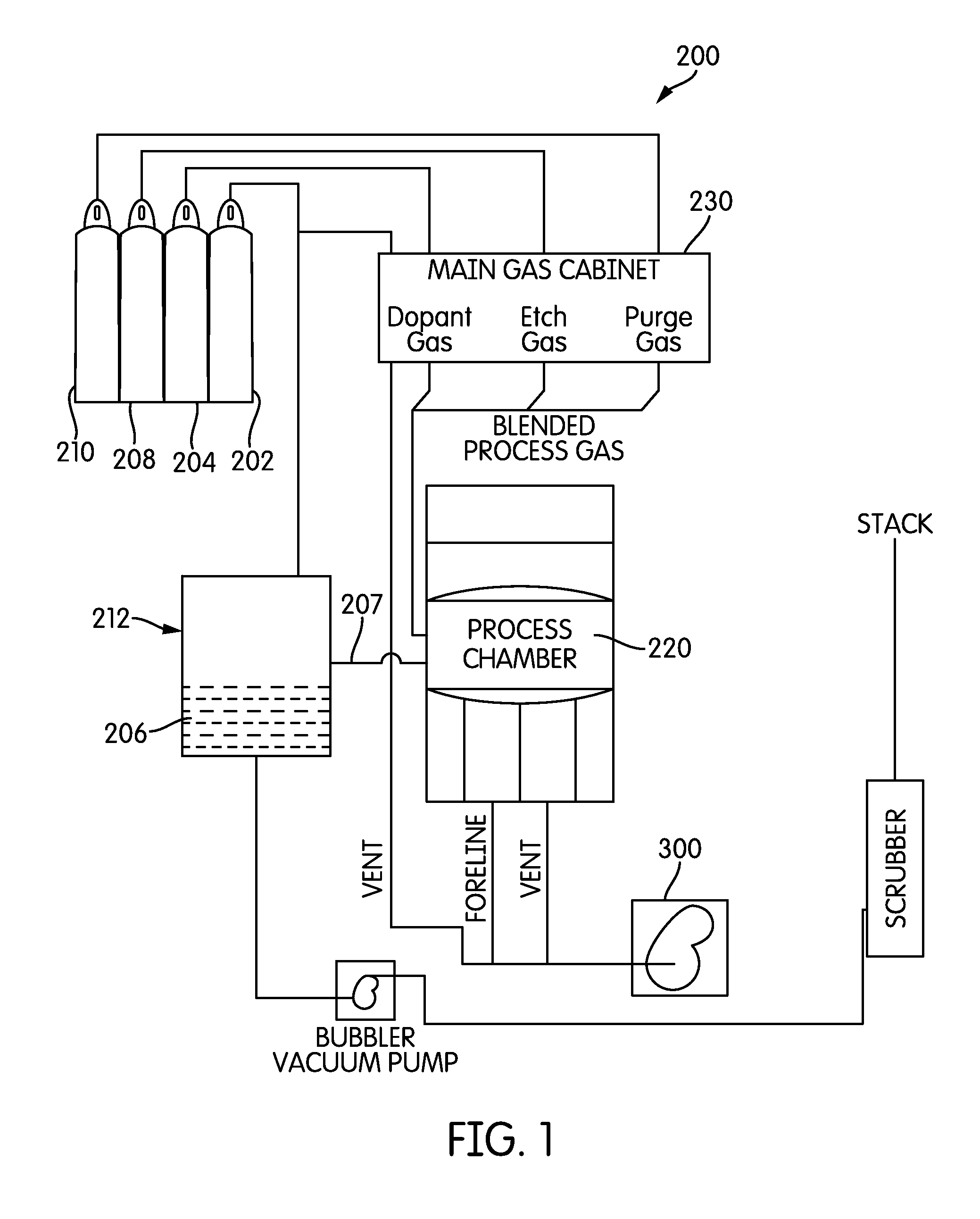
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an apparatus and method of cyclical deposition utilizing three or more precursors in which delivery of at least two of the precursors to a substrate structure at least partially overlap. One embodiment of depositing a ternary material layer over a substrate structure comprises providing at least one cycle of gases to deposit a ternary material layer. One cycle comprises introducing a pulse of a first precursor, introducing a pulse of a second precursor, and introducing a pulse of a third precursor in which the pulse of the second precursor and the pulse of the third precursor at least partially overlap. In one aspect, the ternary material layer includes, but is not limited to, tungsten boron silicon (WBxSiy), titanium silicon nitride (TiSixNy), tantalum silicon nitride (TaSixNy), silicon oxynitride (SiOxNy), and hafnium silicon oxide (HfSixOy). In one aspect, the composition of the ternary material layer may be tuned by changing the flow ratio of the second precursor to the third precursor between cycles.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
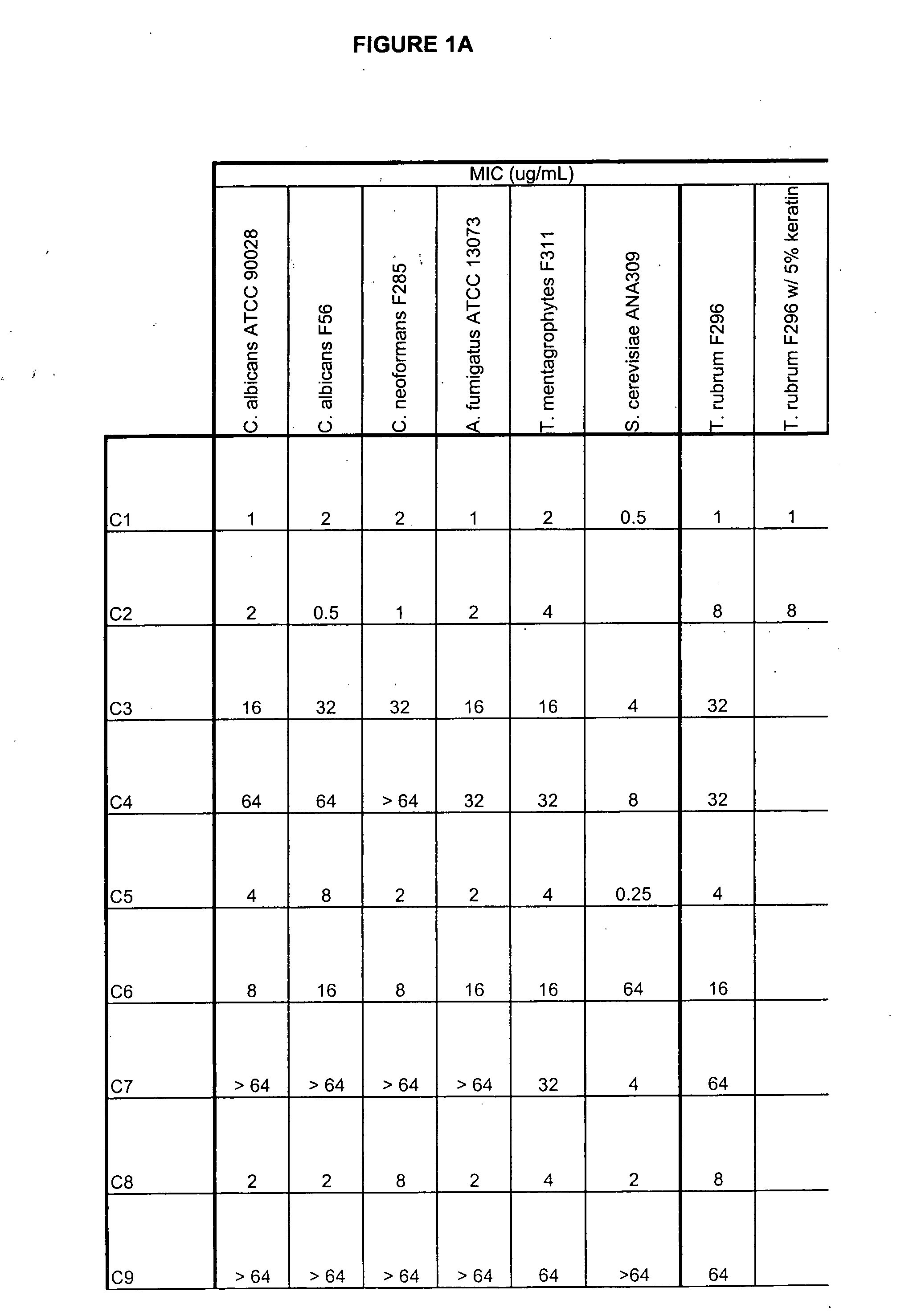
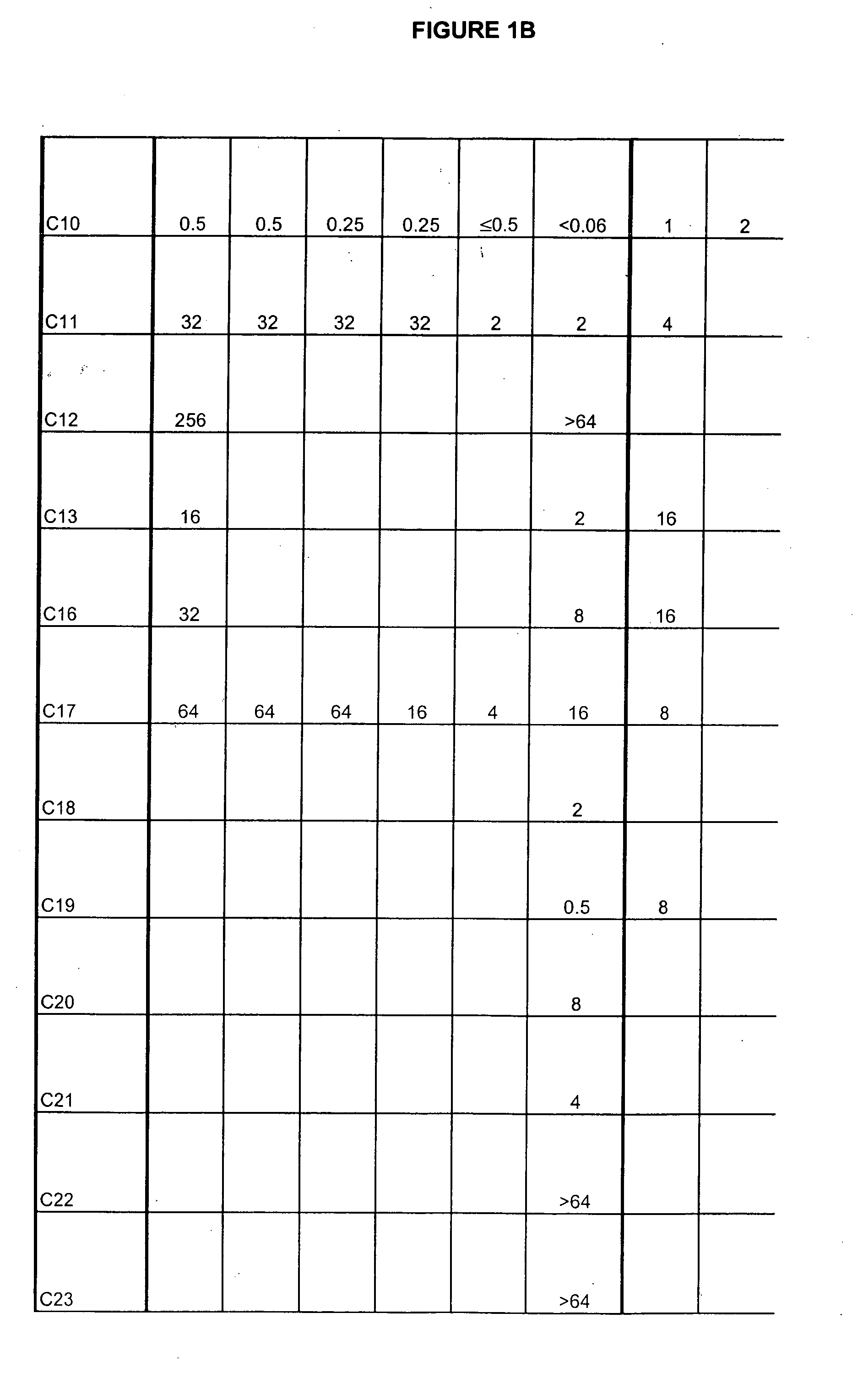
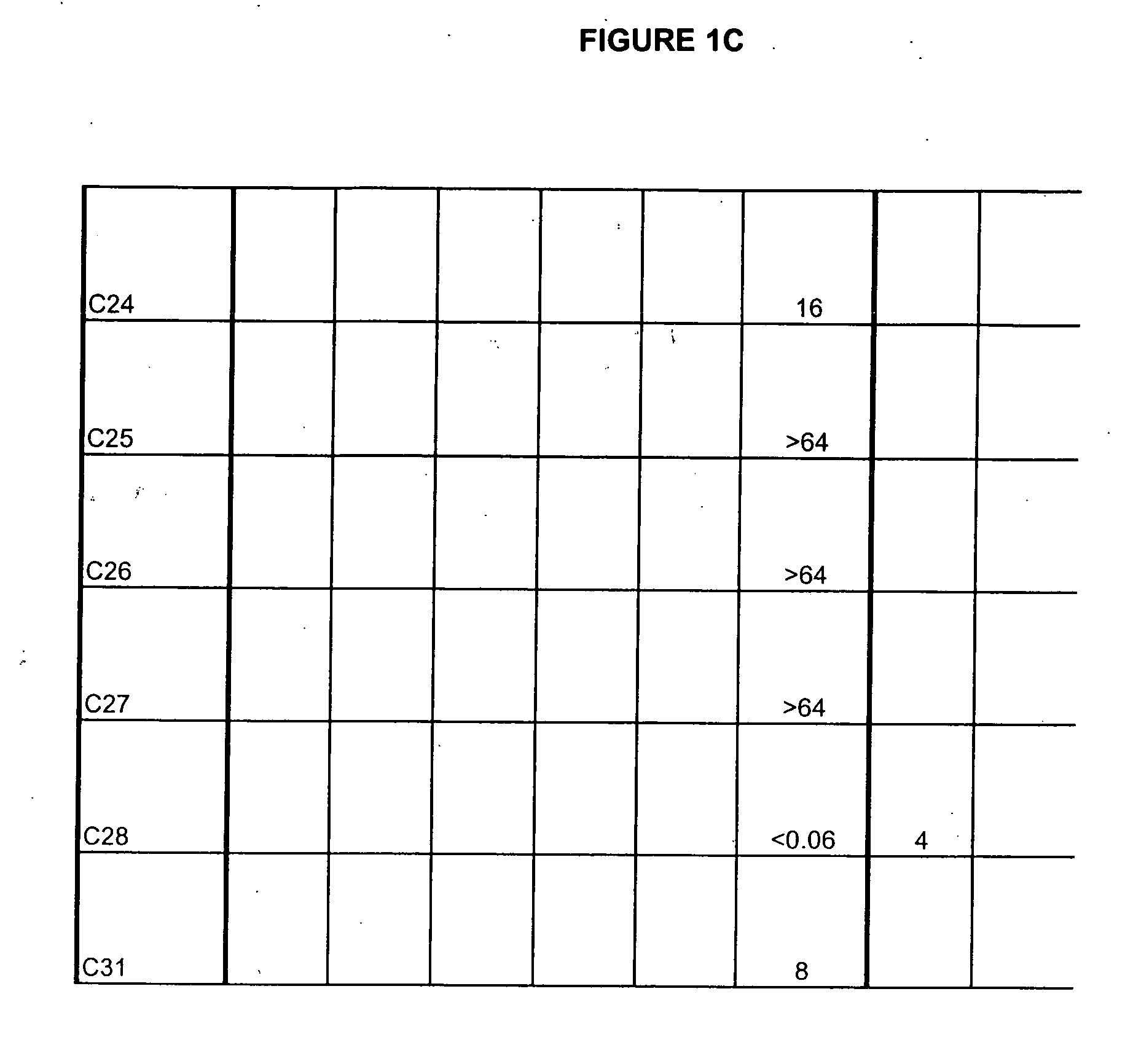
Boron-containing small molecules
ActiveUS20060234981A1Growth inhibitionAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsBiocideFungal microorganismsTopical treatment
This invention relates to compounds useful for treating fungal infections, more specifically topical treatment of onychomycosis and / or cutaneous fungal infections. This invention is directed to compounds that are active against fungi and have properties that allow the compound, when placed in contact with a patient, to reach the particular part of the skin, nail, hair, claw or hoof infected by the fungus. In particular the present compounds have physiochemical properties that facilitate penetration of the nail plate.
Owner:ANACOR PHARMA INC
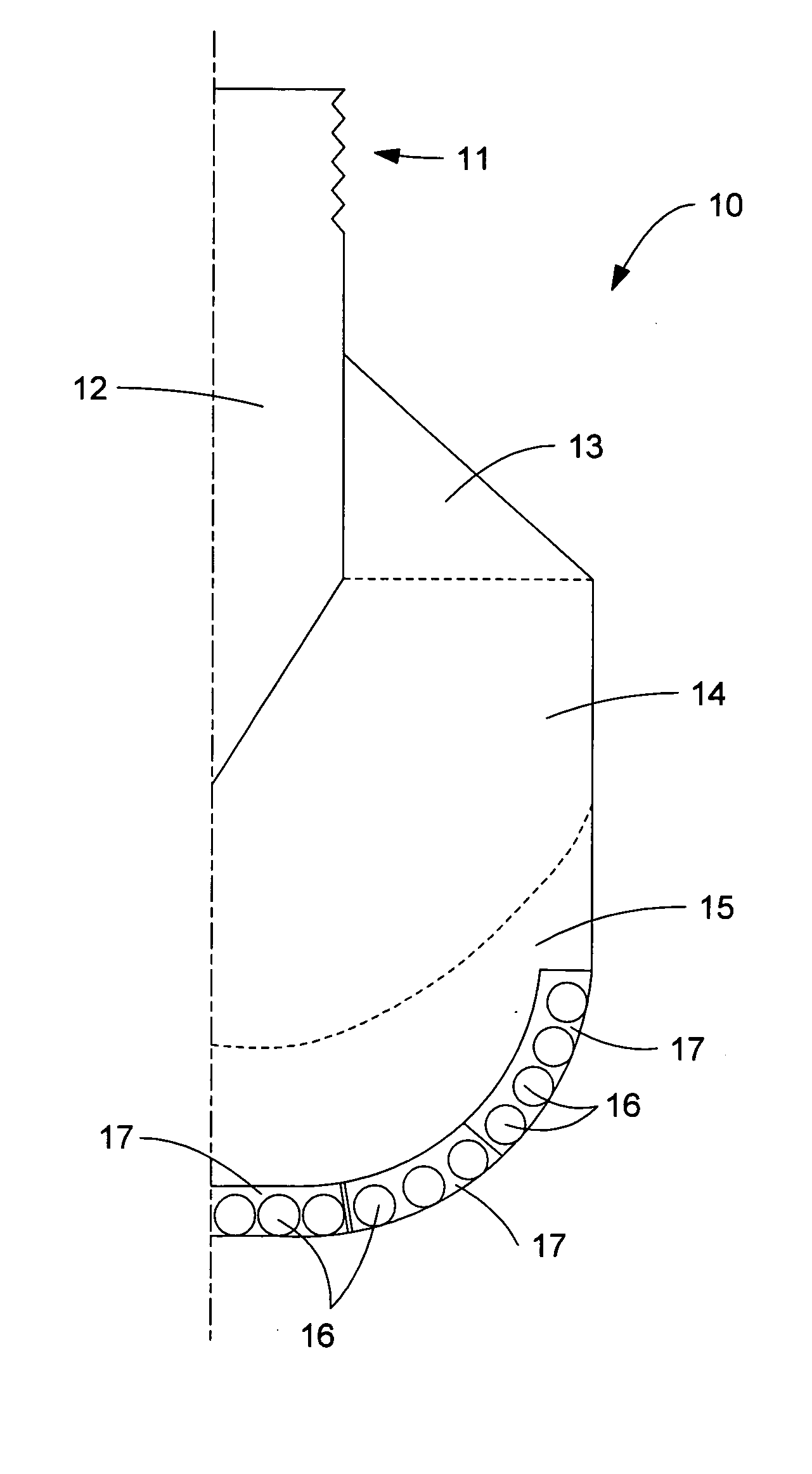
Earth-boring bits
ActiveUS20050247491A1Low melting pointLowered melting point of the binder facilitates proper infiltration of the massDrill bitsCutting machinesBorideNiobium
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for forming a bit body for an earth-boring bit. The bit body may comprise hard particles, wherein the hard particles comprise at least one carbide, nitride, boride, and oxide and solid solutions thereof, and a binder binding together the hard particles. The binder may comprise at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, and iron, and, optionally, at least one melting point reducing constituent selected from a transition metal carbide in the range of 30 to 60 weight percent, boron up to 10 weight percent, silicon up to 20 weight percent, chromium up to 20 weight percent, and manganese up to 25 weight percent, wherein the weight percentages are based on the total weight of the binder. In addition, the hard particles may comprise at least one of (i) cast carbide (WC+W2C) particles, (ii) transition metal carbide particles selected from the carbides of titanium, chromium, vanadium, zirconium, hafnium, tantalum, molybdenum, niobium, and tungsten, and (iii) sintered cemented carbide particles.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC +1
Tunable dielectric compositions including low loss glass
InactiveUS6905989B2Lower sintering temperatureIncrease varietyFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic layered productsBreakdown strengthStrontium titanate
Tunable dielectric materials including an electronically tunable dielectric ceramic and a low loss glass additive are disclosed. The tunable dielectric may comprise a ferroelectric perskovite material such as barium strontium titanate. The glass additive may comprise boron, barium, calcium, lithium, manganese, silicon, zinc and / or aluminum-containing glasses having dielectric losses of less than 0.003 at 2 GHz. The materials may further include other additives such as non-tunable metal oxides and silicates. The low loss glass additive enables the materials to be sintered at relatively low temperatures while providing improved properties such as low microwave losses and high breakdown strengths.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Earth-boring bits
InactiveUS20050211475A1Low melting pointLowered melting point of the binder facilitates proper infiltration of the massDrill bitsMetal-working drilling toolsBorideNiobium
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for forming a bit body for an earth-boring bit. The bit body may comprise hard particles, wherein the hard particles comprise at least one carbide, nitride, boride, and oxide and solid solutions thereof, and a binder binding together the hard particles. The binder may comprise at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, and iron, and at least one melting point reducing constituent selected from a transition metal carbide in the range of 30 to 60 weight percent, boron up to 10 weight percent, silicon up to 20 weight percent, chromium up to 20 weight percent, and manganese up to 25 weight percent, wherein the weight percentages are based on the total weight of the binder. In addition, the hard particles may comprise at least one of (i) cast carbide (WC+W2C) particles, (ii) transition metal carbide particles selected from the carbides of titanium, chromium, vanadium, zirconium, hafnium, tantalum, molybdenum, niobium, and tungsten, and (iii) sintered cemented carbide particles.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES +1
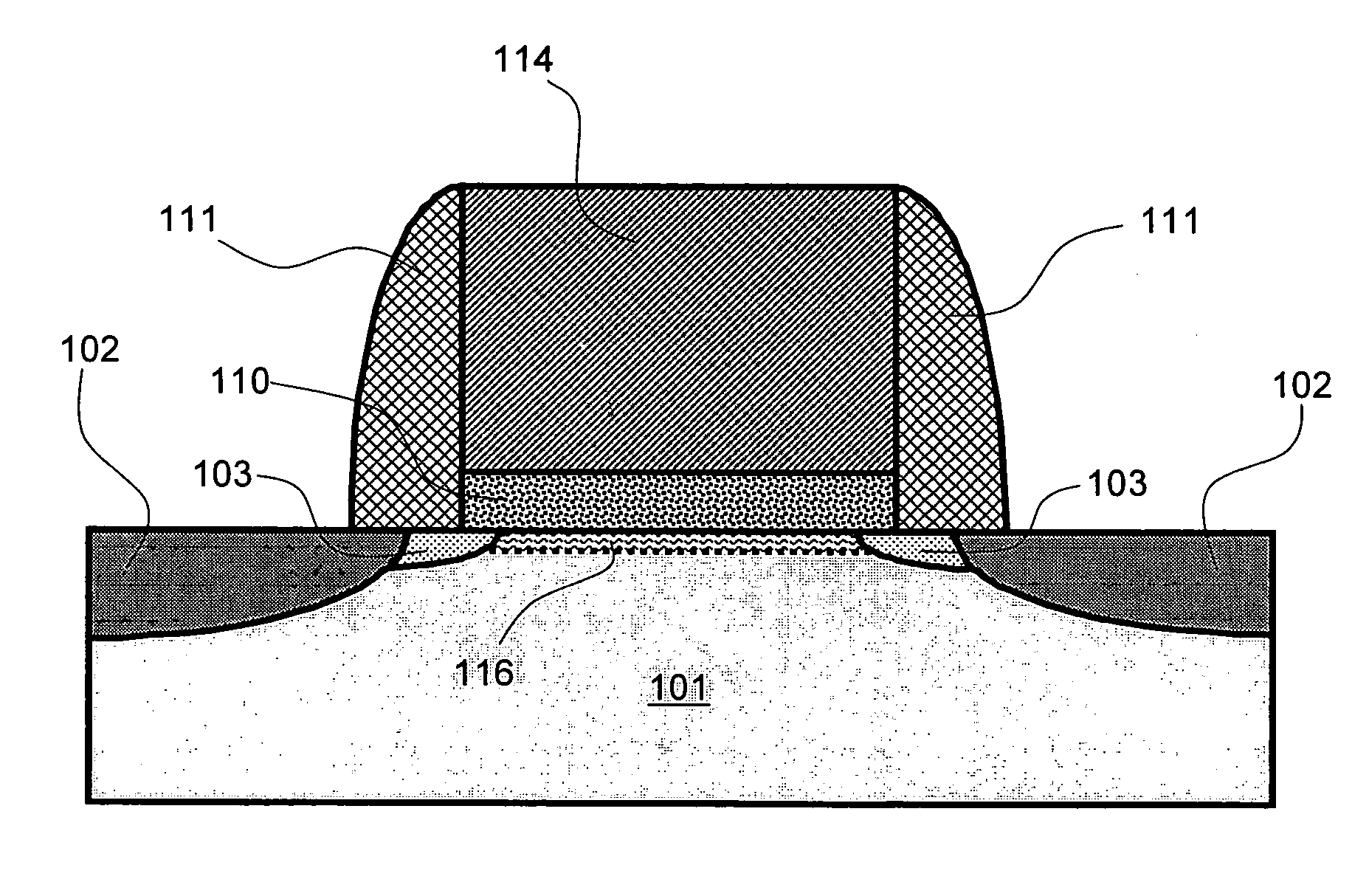
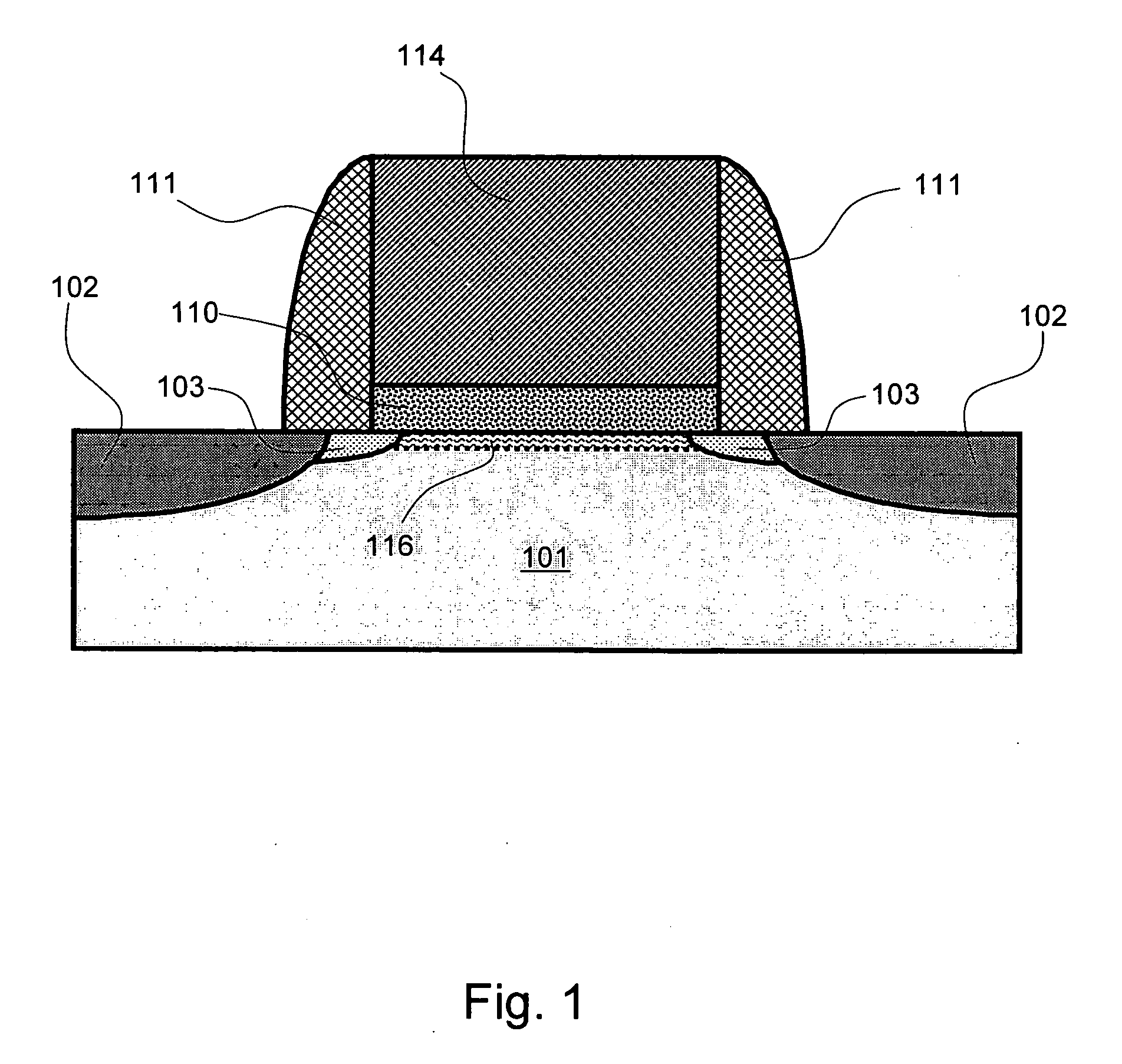
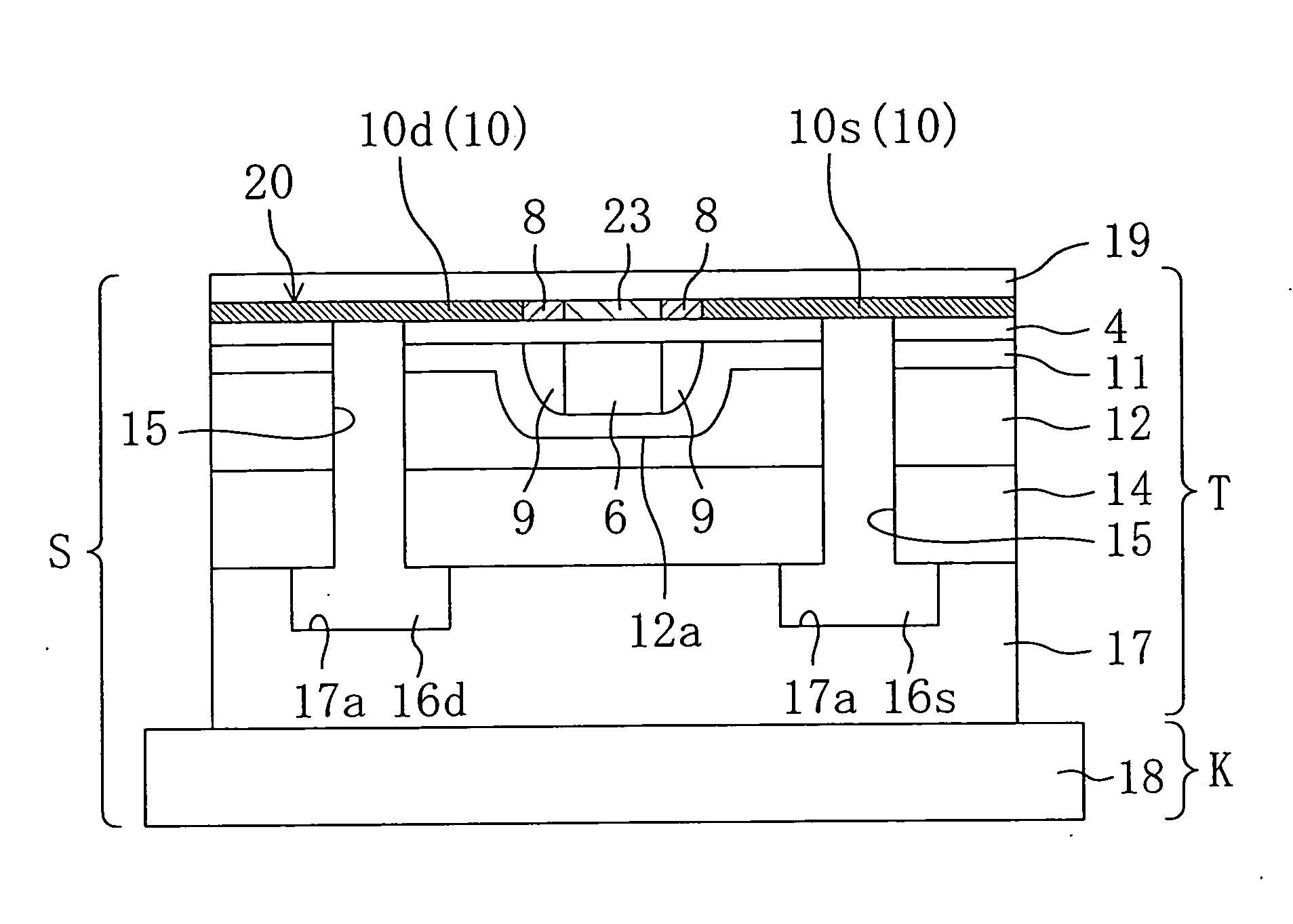
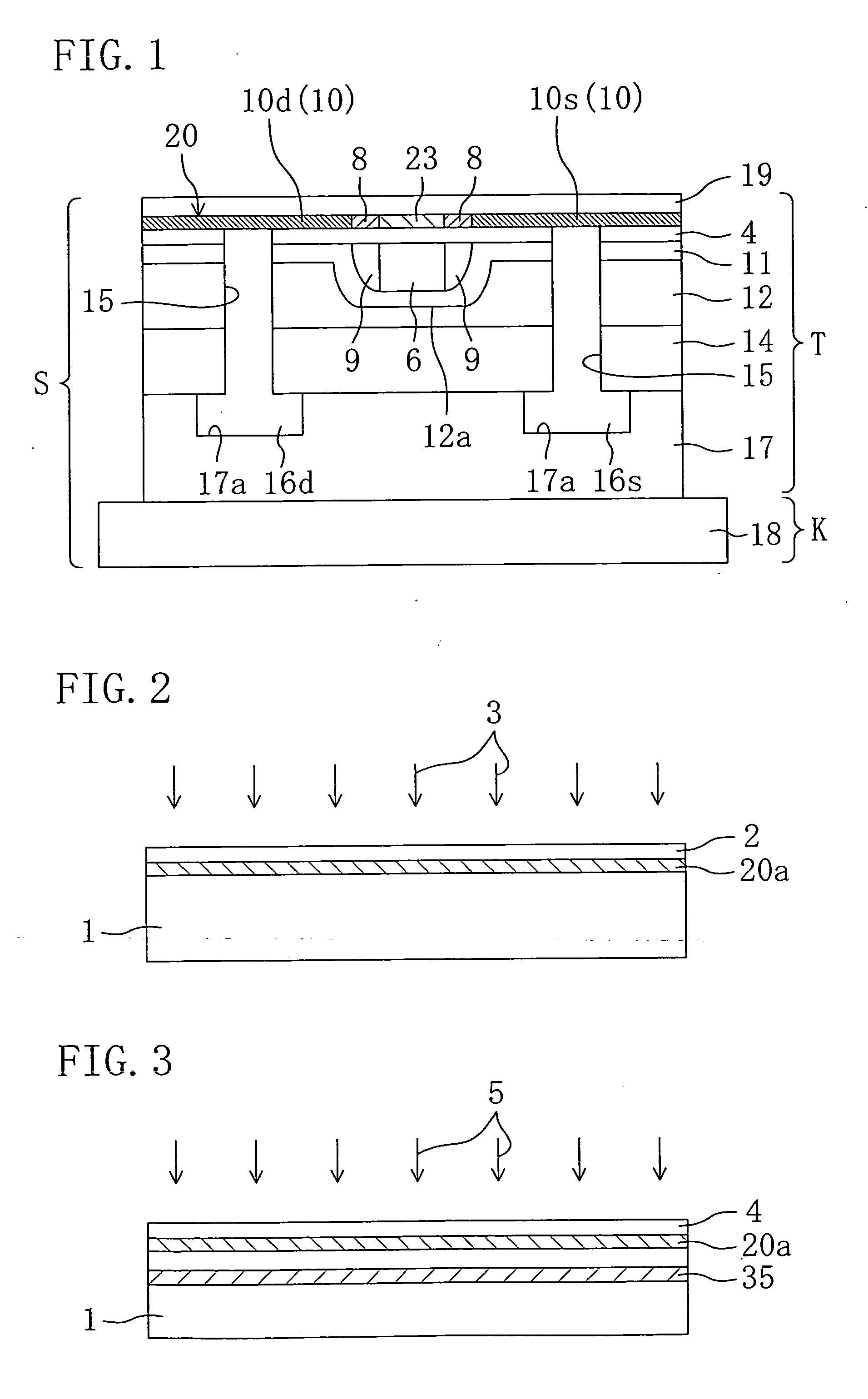
Thin-film transistor, method of manufacturing the same, and display device
A thin film transistor is provided. The thin film transistor includes an oxide semiconductor layer including a source region, a drain region, and a channel region wherein a portion of the source and drain regions has an oxygen concentration less than the channel region. Further provided is a thin film transistor that includes an oxide semiconductor layer including a source region, a drain region, and a channel region, wherein a portion of the source and drain regions includes a dopant selected from the group consisting of aluminum, boron, gallium, indium, titanium, silicon, germanium, tin, lead, and combinations thereof.
Owner:JOLED INC
Methods of Forming Integrated Circuit Devices Having Ion-Cured Electrically Insulating Layers Therein
ActiveUS20090098706A1Quality improvementDegree of reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic orderEngineering
Methods of forming integrated circuit devices include forming a trench in a surface of semiconductor substrate and filling the trench with an electrically insulating region having a seam therein. The trench may be filled by depositing a sufficiently thick electrically insulating layer on sidewalls and a bottom of the trench. Curing ions are then implanted into the electrically insulating region at a sufficient energy and dose to reduce a degree of atomic order therein. The curing ions may be ones selected from a group consisting of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), boron (B), arsenic (As), carbon (C), argon (Ar), germanium (Ge), helium (He), neon (Ne) and xenon (Xe). These curing ions may be implanted at an energy of at least about 80 KeV and a dose of at least about 5×1014 ions / cm2. The electrically insulating region is then annealed at a sufficient temperature and for a sufficient duration to increase a degree of atomic order within the electrically insulating region.
Owner:IBM CORP +2
Boron-containing small molecules
This invention relates to compounds useful for treating fungal infections, more specifically topical treatment of onychomycosis and / or cutaneous fungal infections. This invention is directed to compounds that are active against fungi and have properties that allow the compound, when placed in contact with a patient, to reach the particular part of the skin, nail, hair, claw or hoof infected by the fungus. In particular the present compounds have physiochemical properties that facilitate penetration of the nail plate.
Owner:ANACOR PHARMA LLC
Method and system for providing a magnetoresistive structure
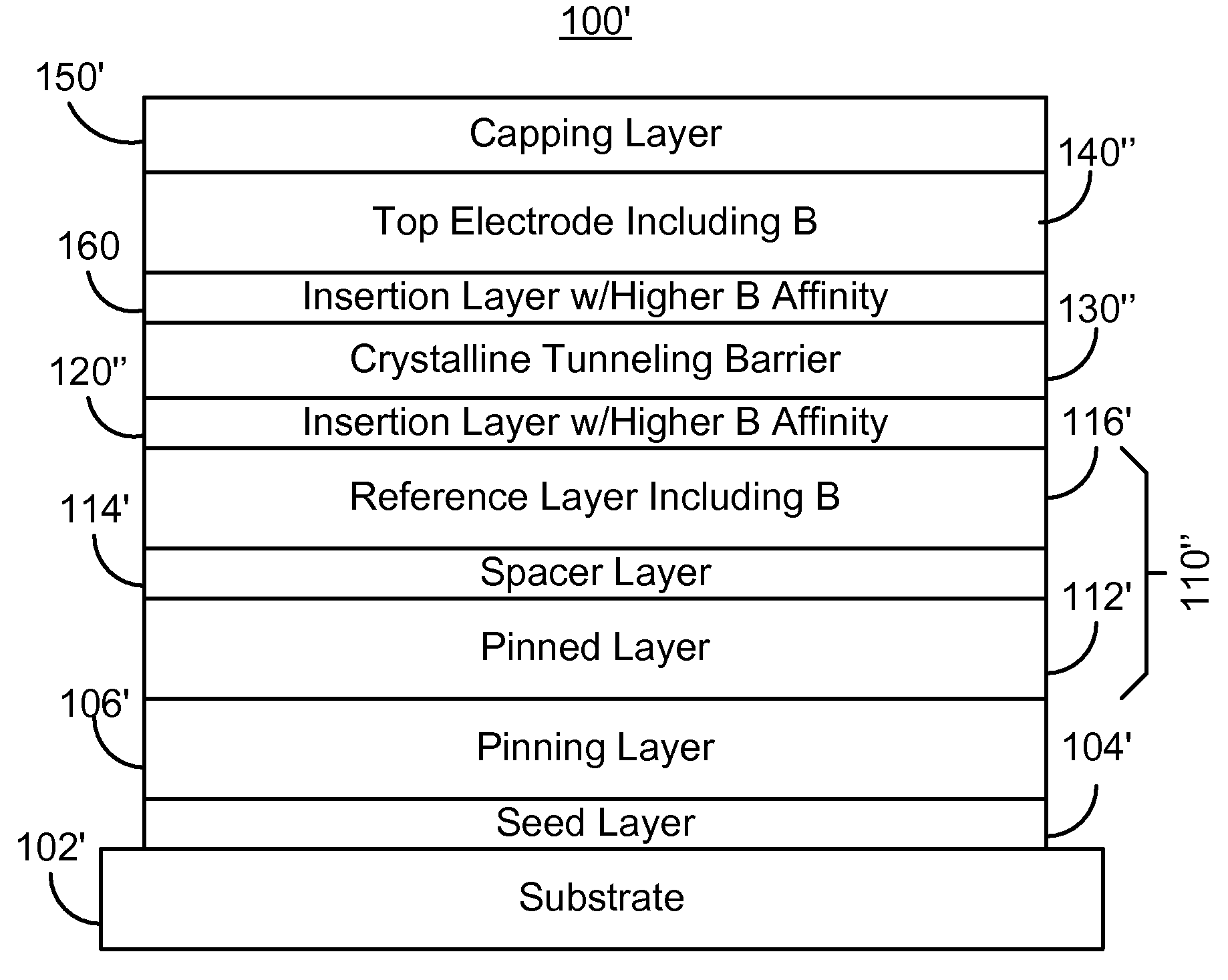
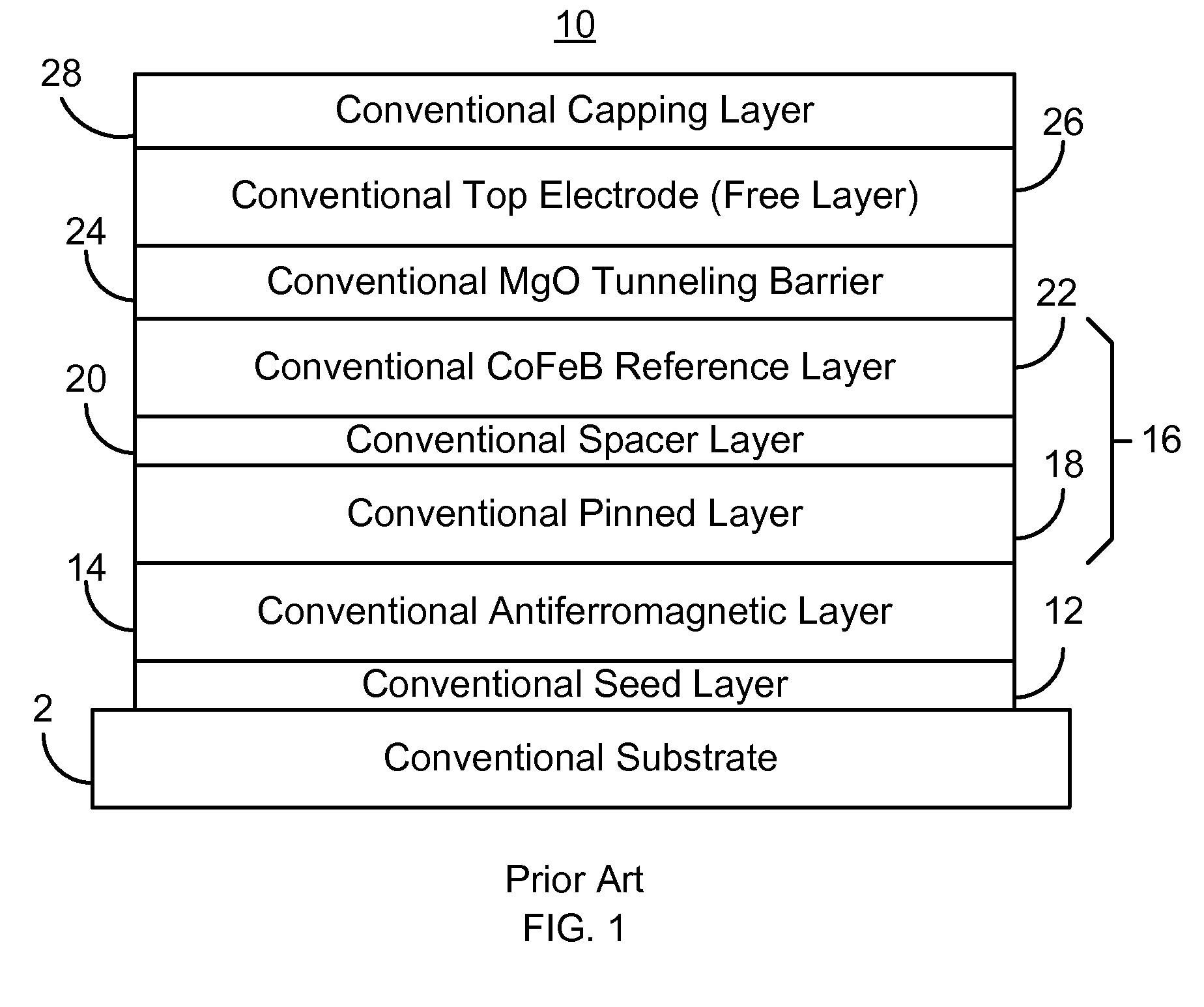
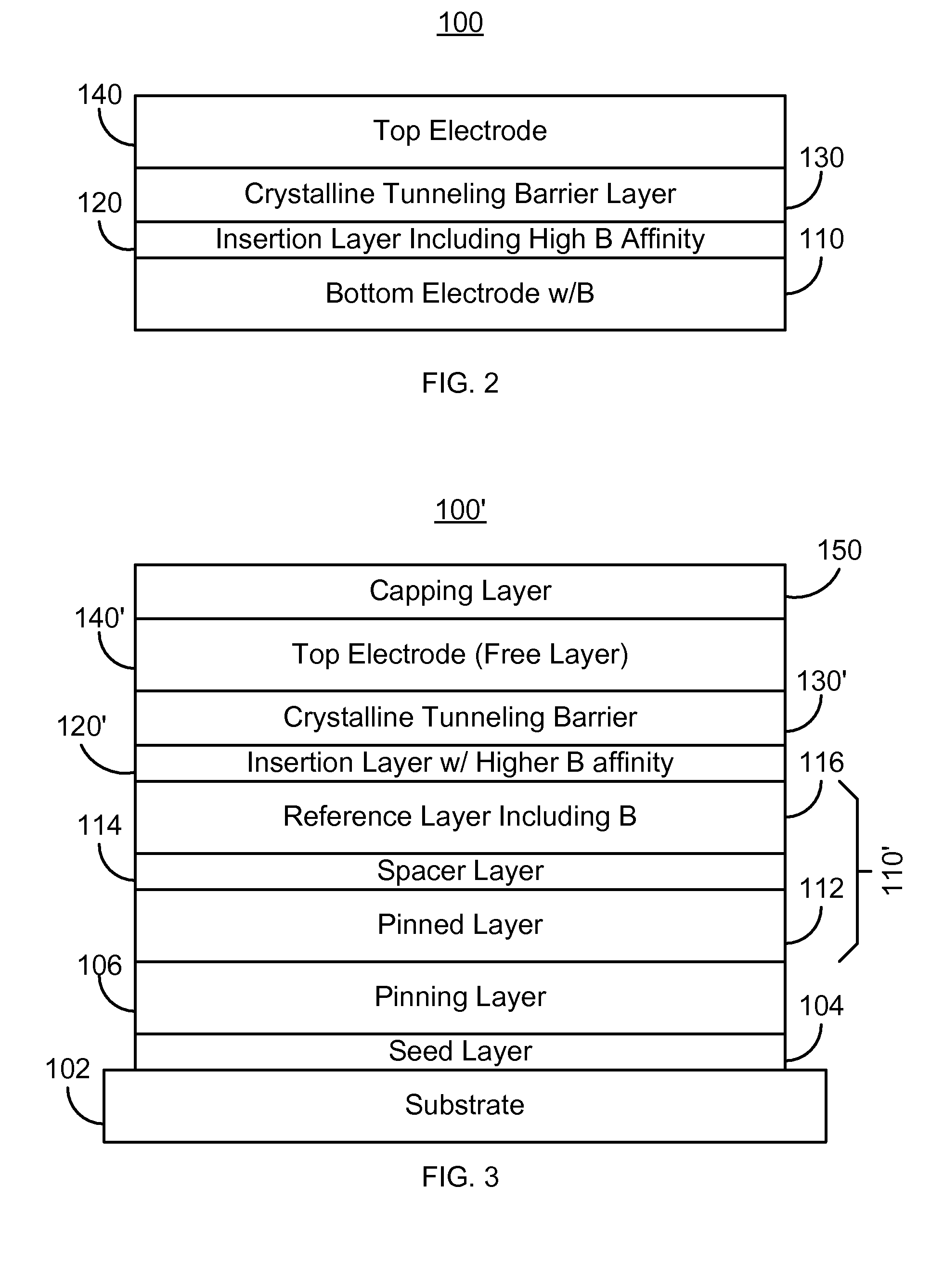
A method and system for providing a magnetoresistive structure are described. The magnetoresistive structure includes a first electrode, an insertion layer, a crystalline tunneling barrier layer, and a second electrode. The first electrode includes at least a first magnetic material and boron. The crystalline tunneling barrier layer includes at least one constituent. The insertion layer has a first boron affinity. The at least one constituent of the crystalline tunneling barrier layer has at least a second boron affinity that is less than the first boron affinity. The second electrode includes at least a second magnetic material.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com