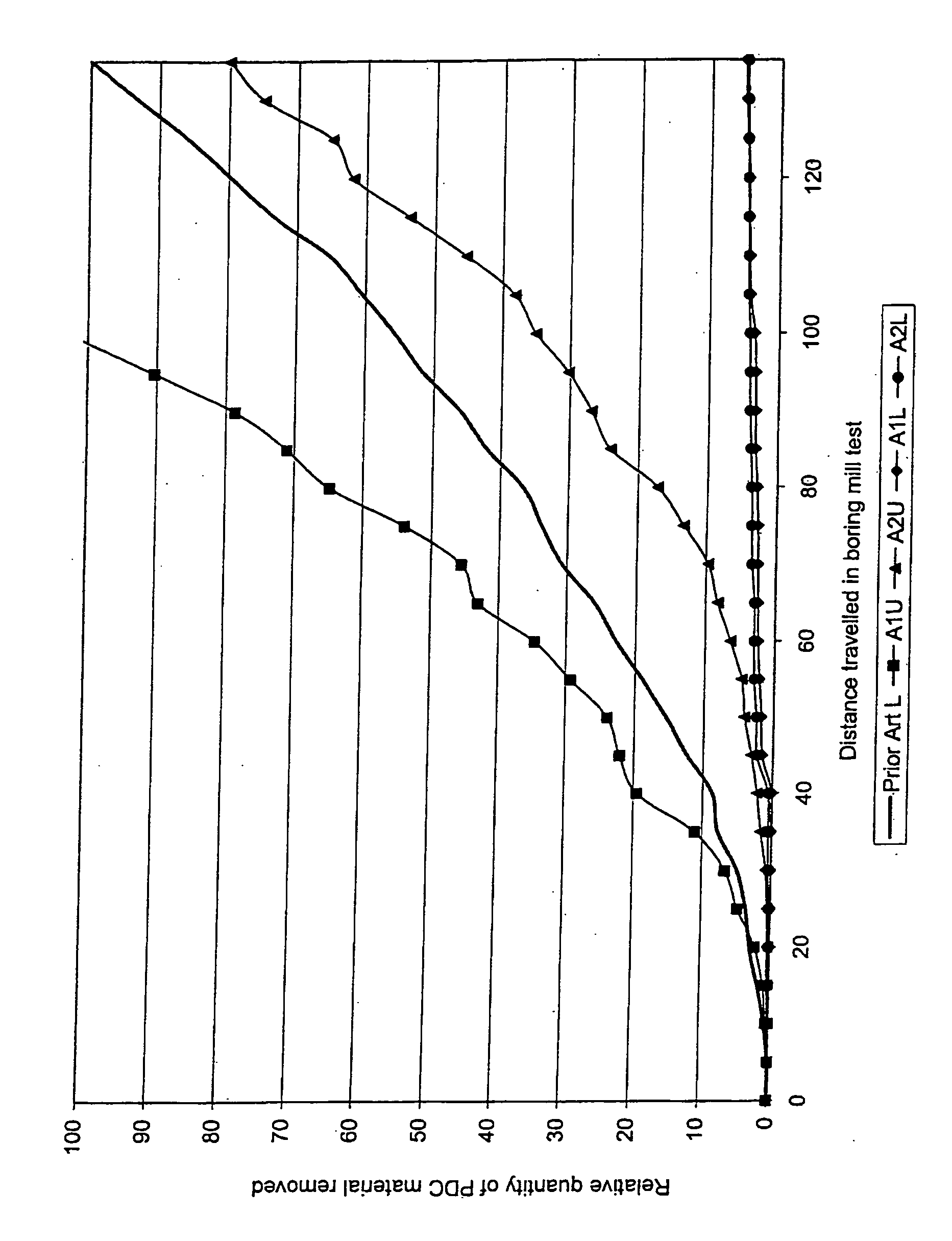
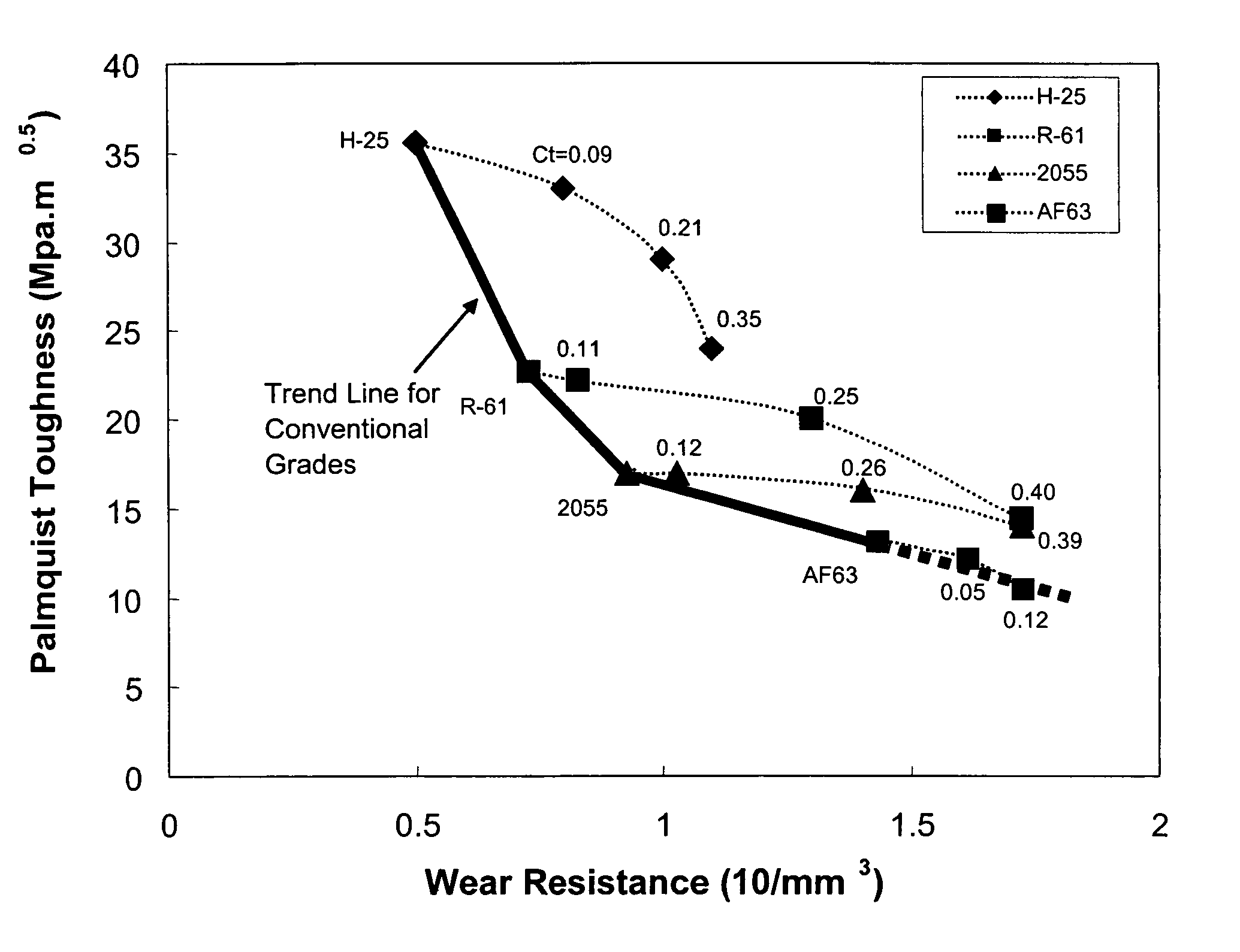
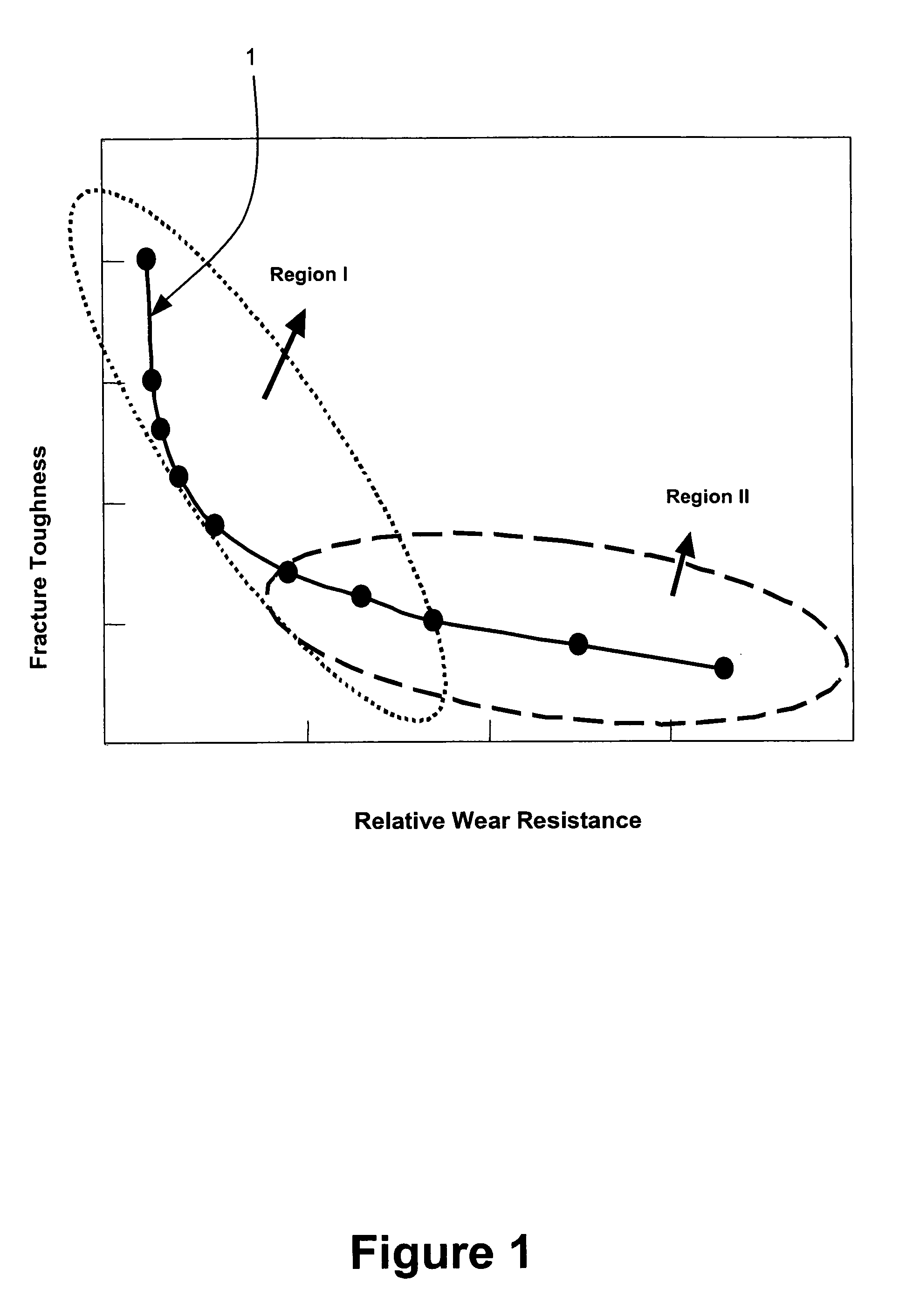
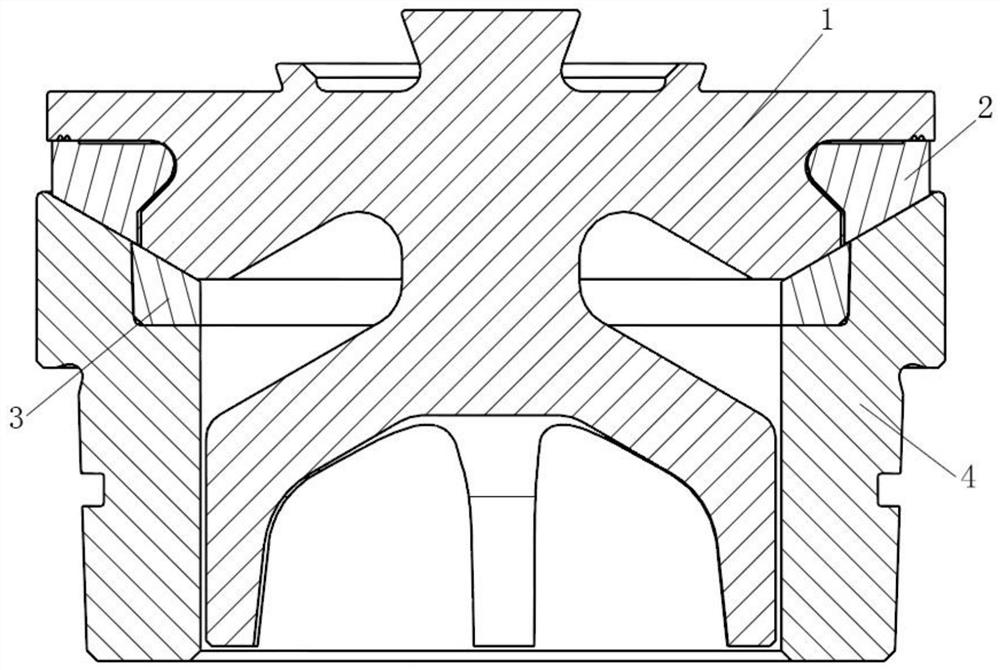
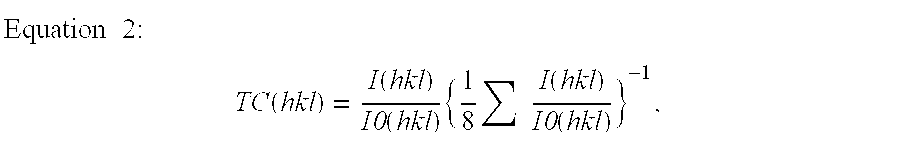Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5285 results about "Cemented carbide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
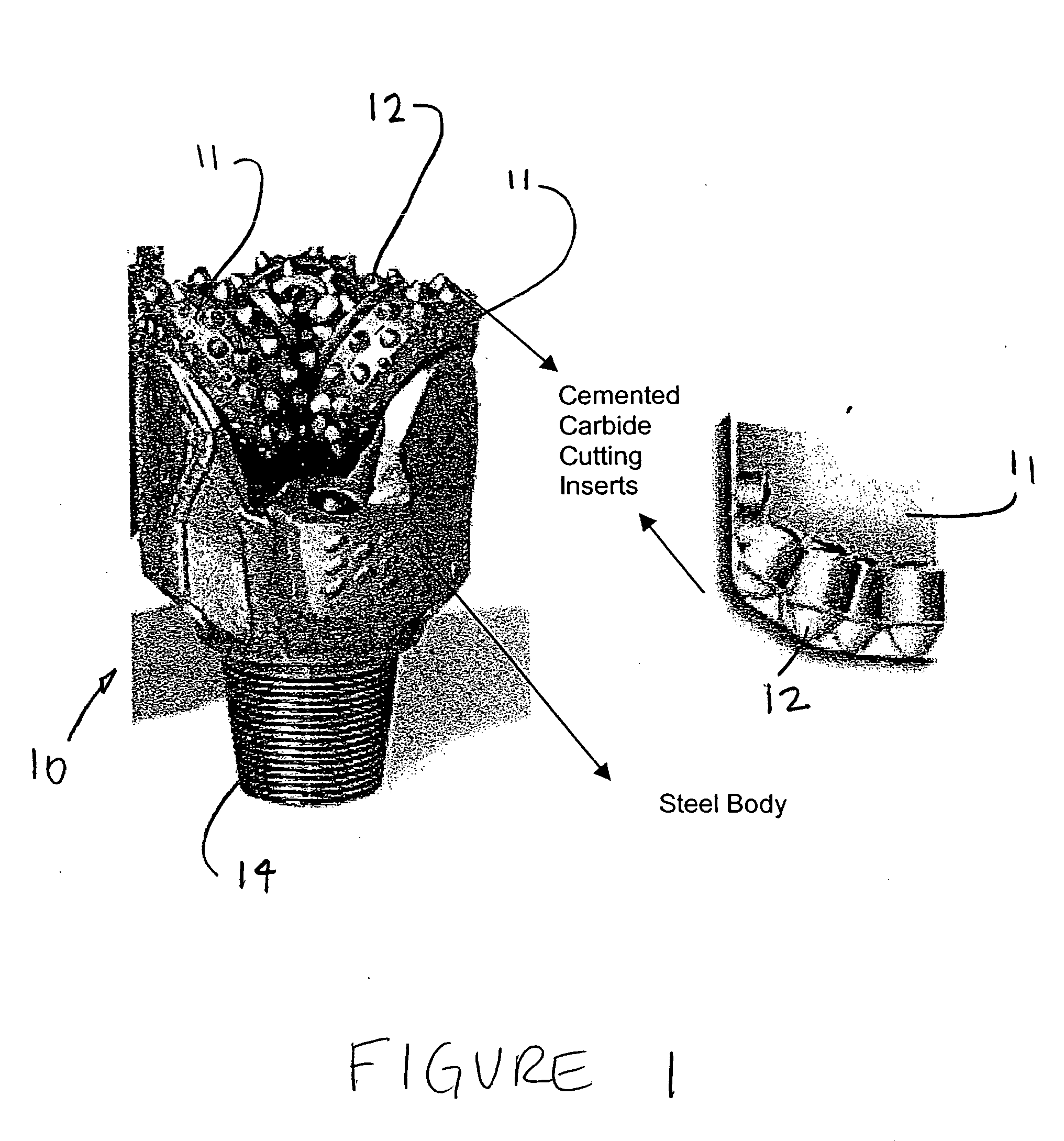
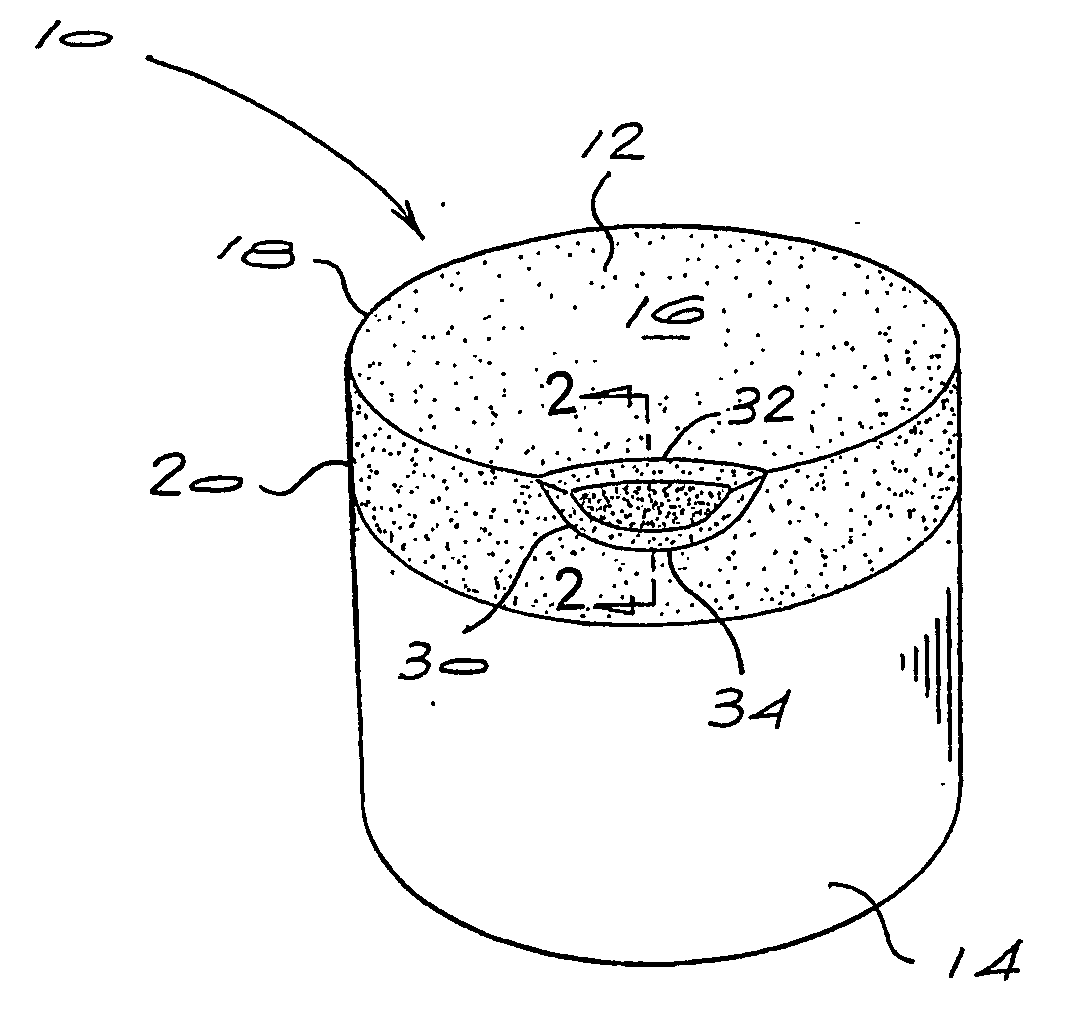
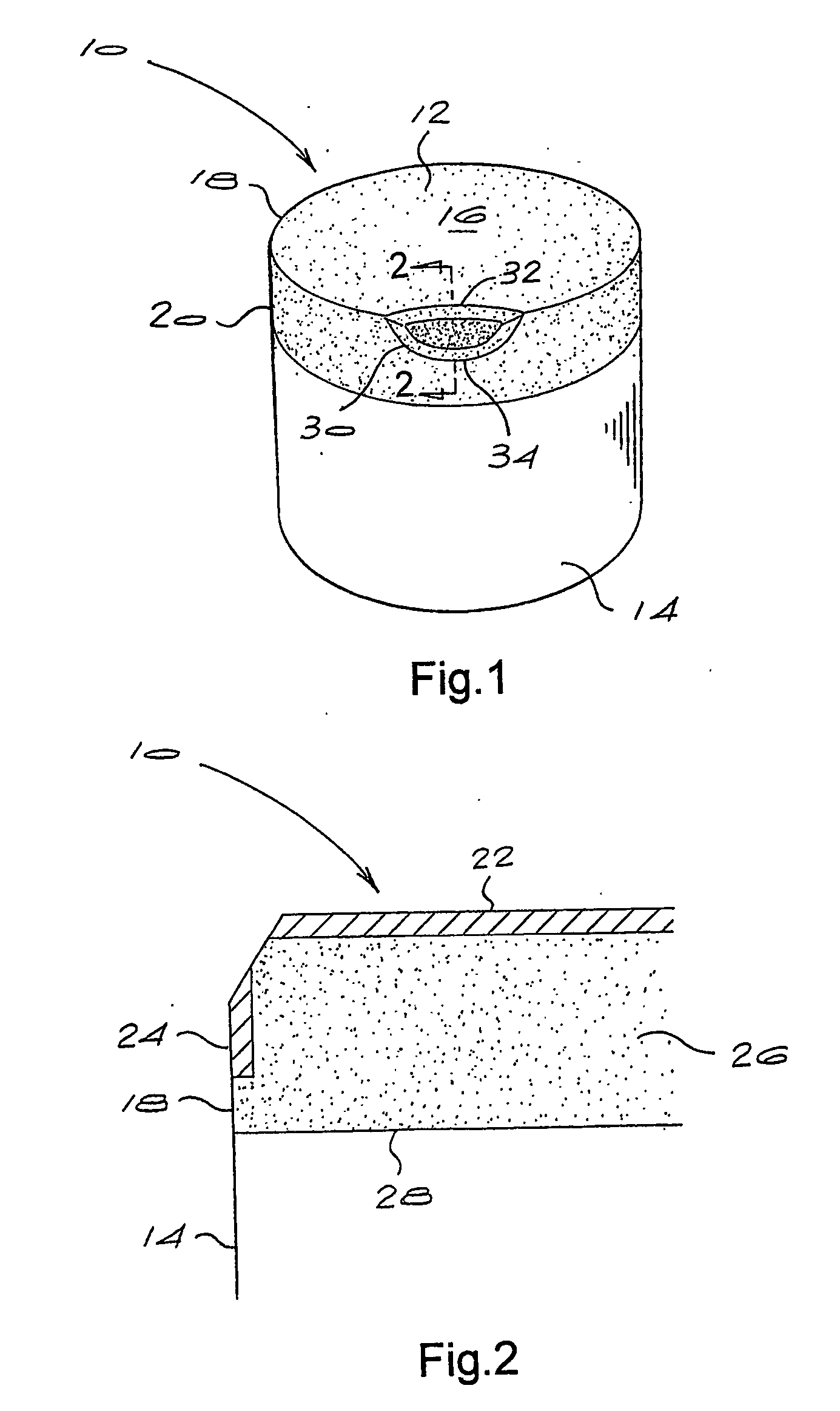
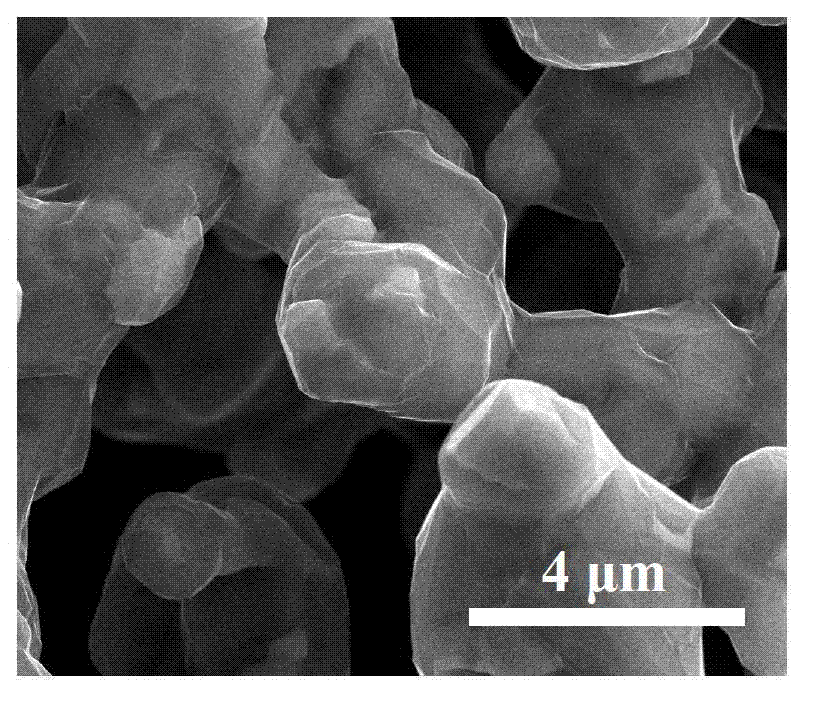
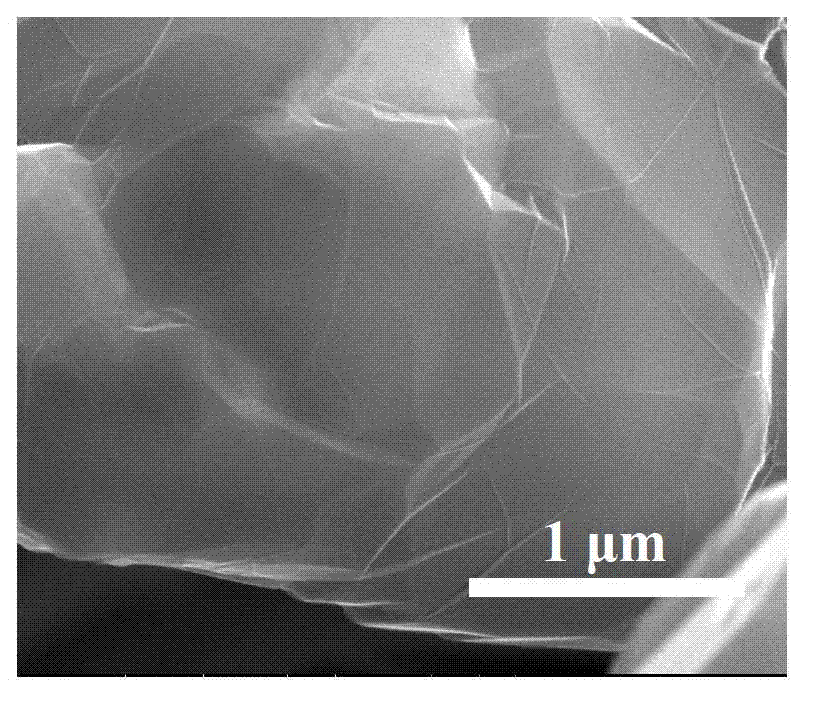
Cemented carbide is a hard material used extensively as cutting tool material, as well as other industrial applications. It consists of fine particles of carbide cemented into a composite by a binder metal. Cemented carbides commonly use tungsten carbide (WC), titanium carbide (TiC), or tantalum carbide (TaC) as the aggregate. Mentions of "carbide" or "tungsten carbide" in industrial contexts usually refer to these cemented composites.
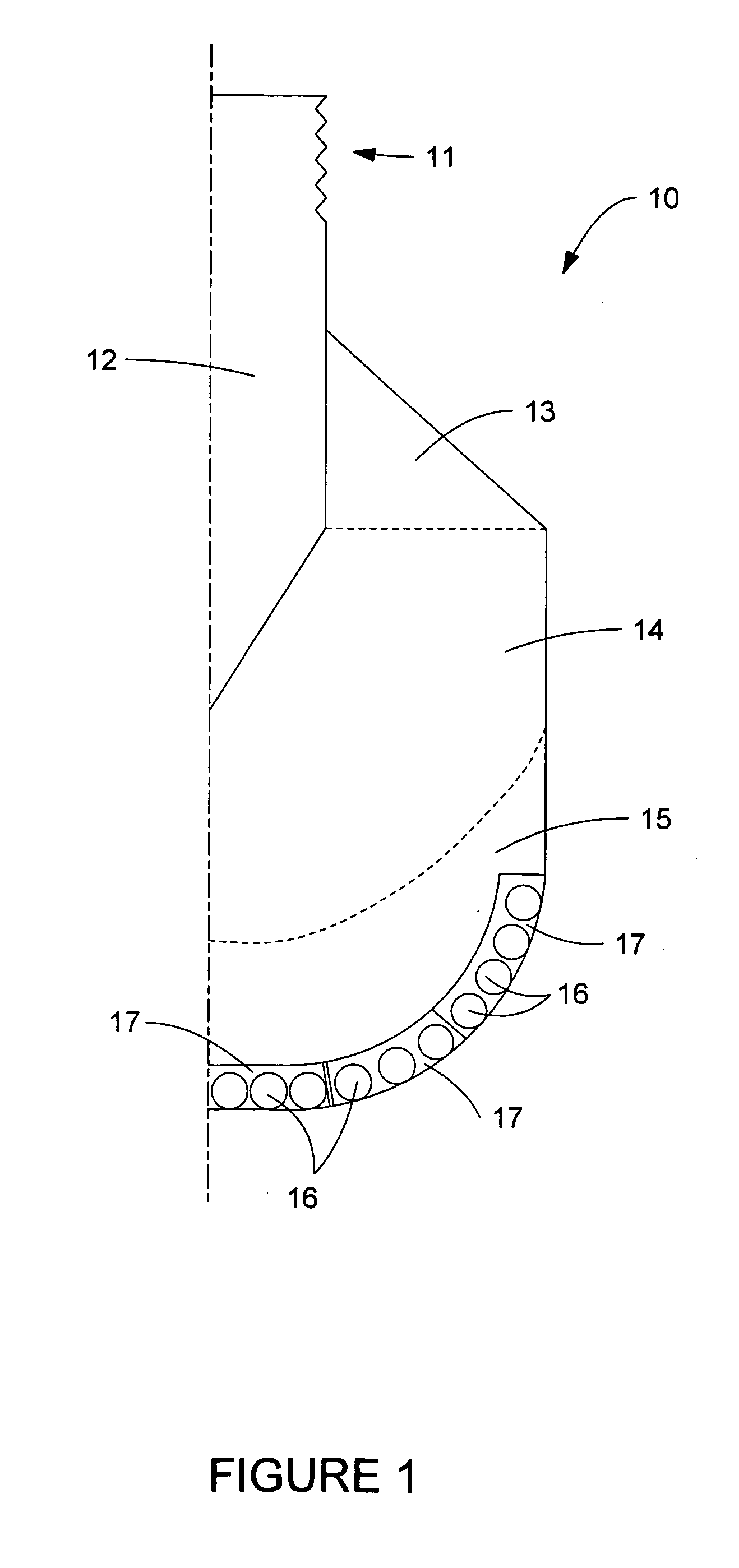
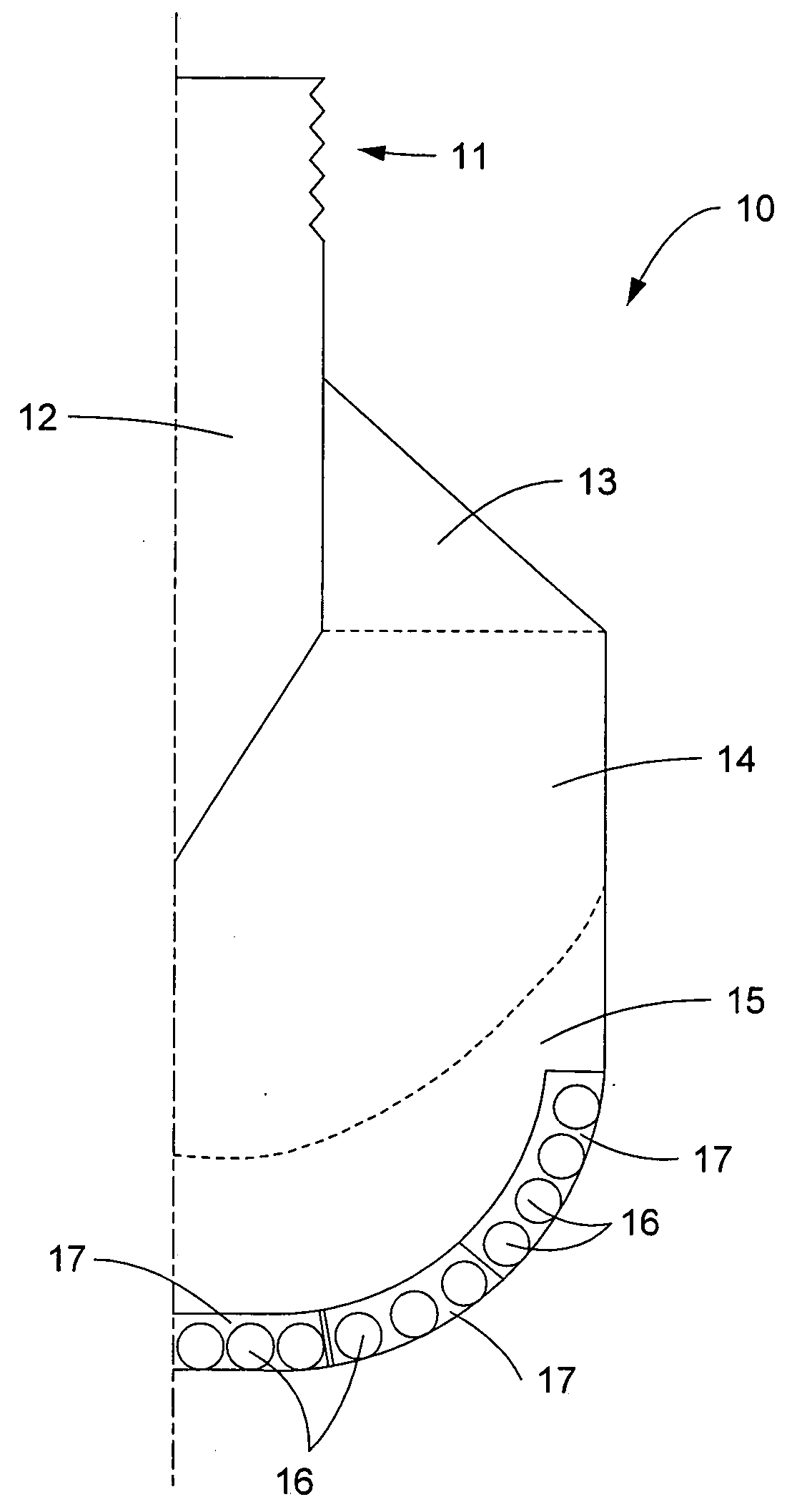
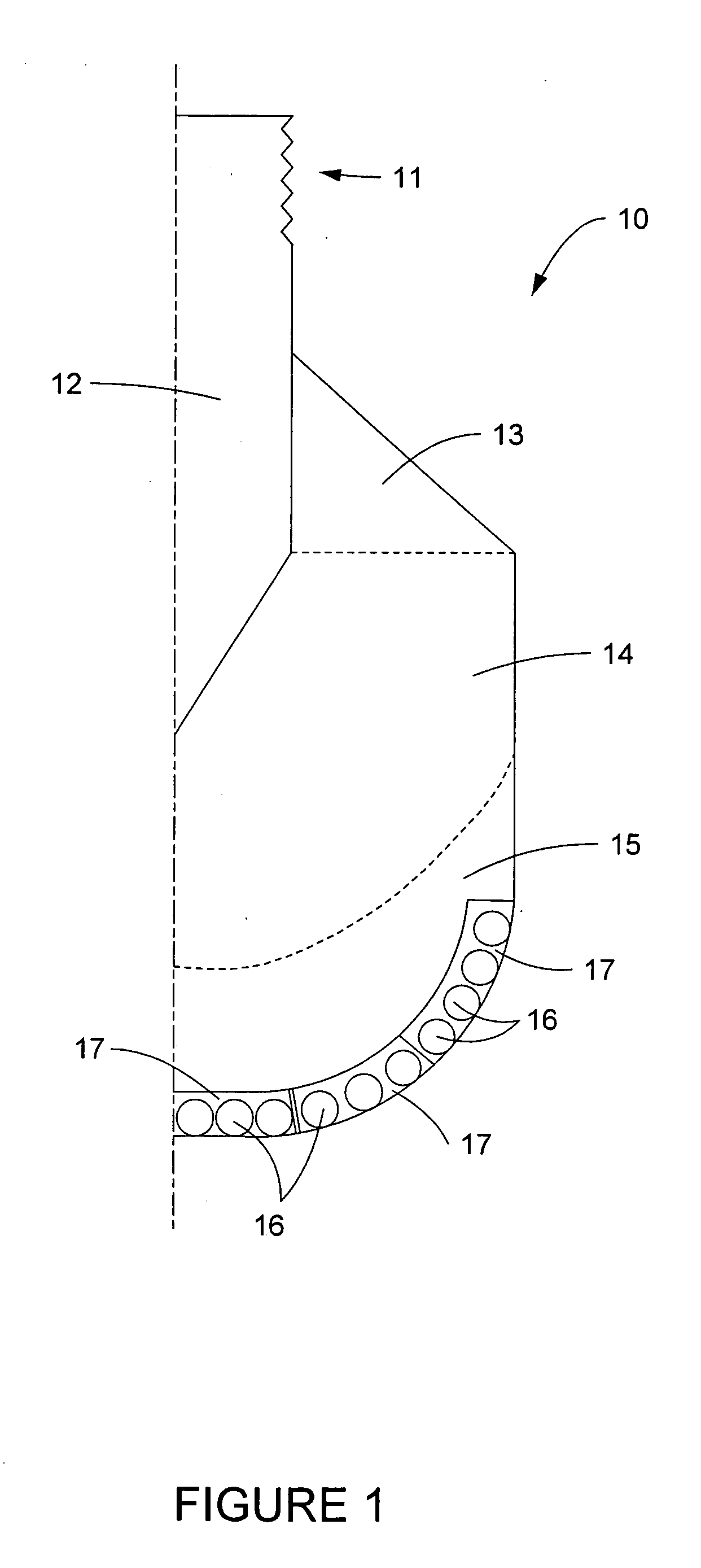
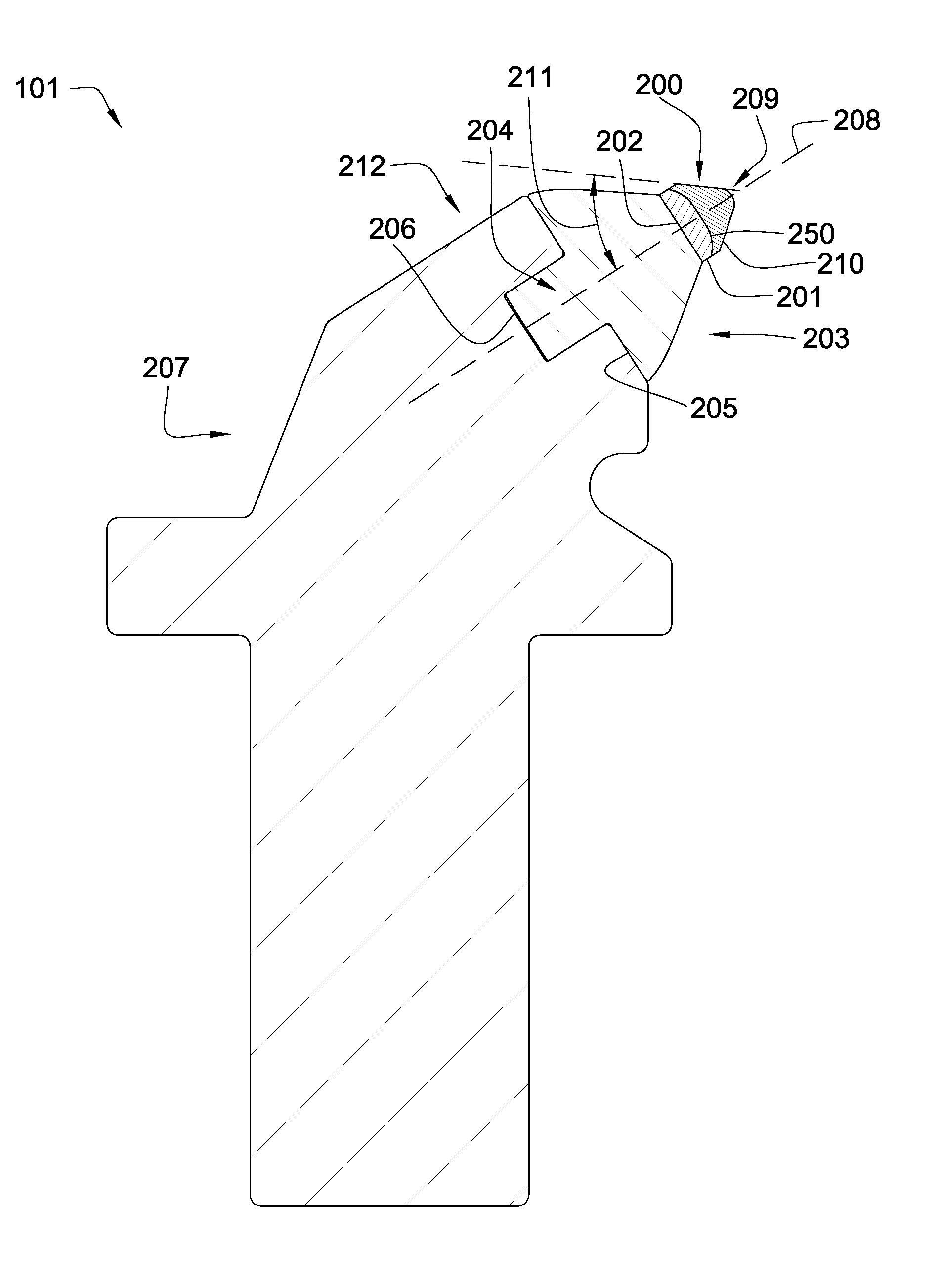
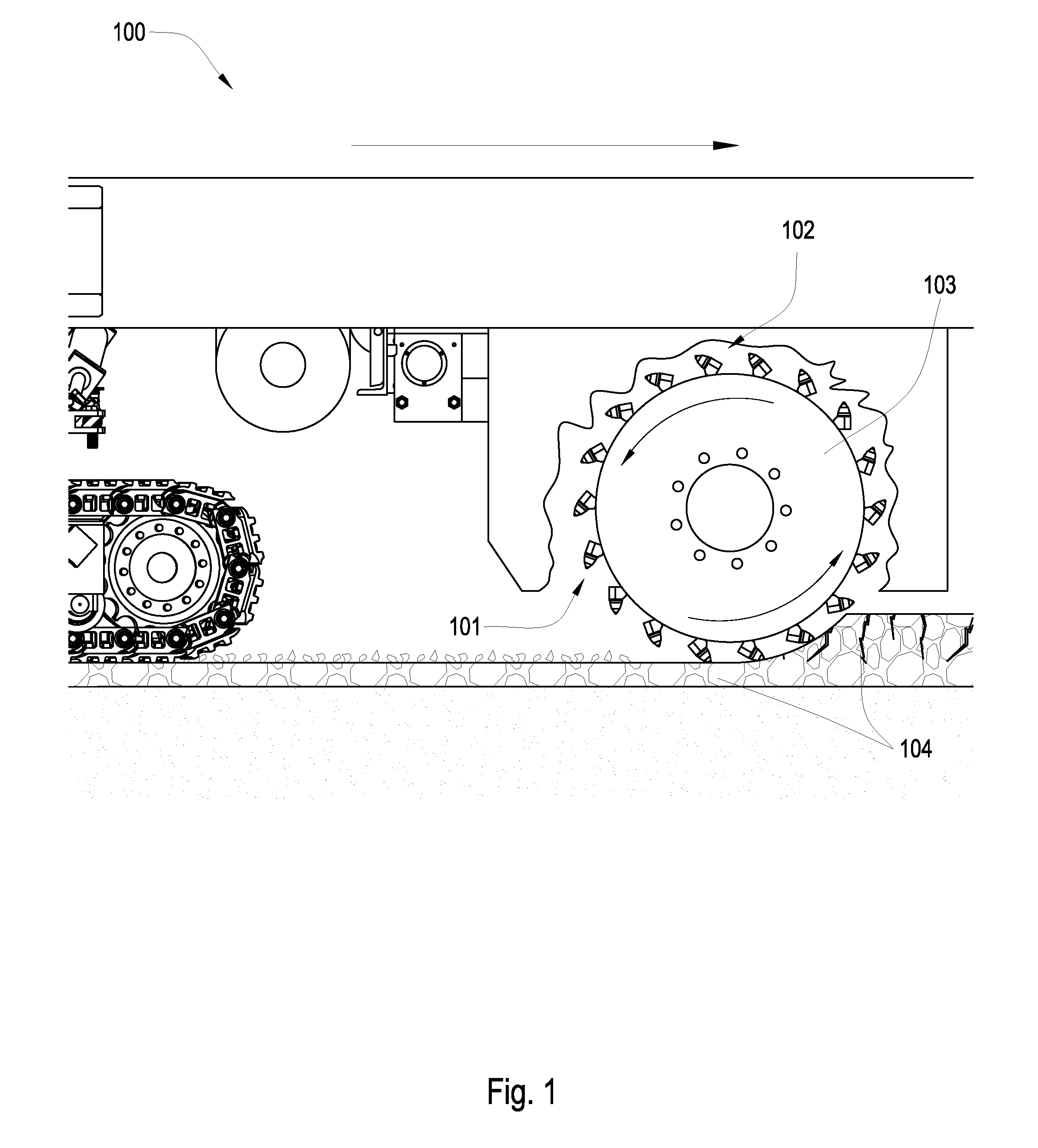
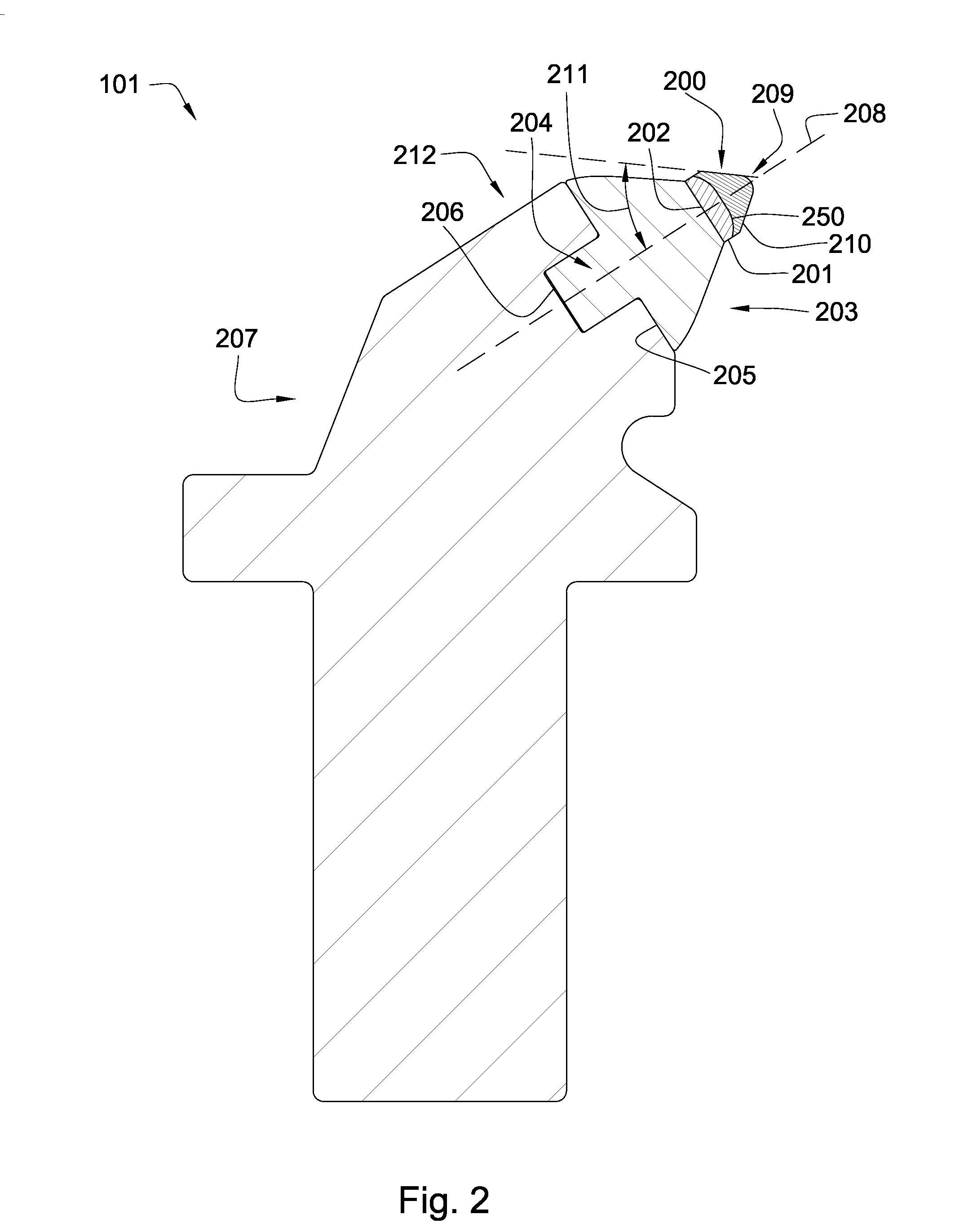
Electric drill apparatus
InactiveUS7121773B2Reduce weight and sizeLow profileDrilling/boring measurement devicesThread cutting machinesRotational axisAnnular cutter
An electric drill apparatus having a low profile is provided which comprises an annular cutter, a motor for rotating the annular cutter, a rotary shaft assembly for rotating the annular cutter attached to its leading end about a rotating, a rotation reduction mechanism disposed between the motor and rotary shaft assembly for transmitting a driving force of the motor to the annular cutter through the rotary shaft assembly, a feed mechanism responsive to an operation of a manual handle, for moving the rotary shaft assembly along with a straight line to advance or retract the annular cutter attached to the rotary shaft assembly with respect to a workpiece, and an adhesion base for securing the electric drill apparatus to the workpiece. The annular cutter has a plurality of cutting blades comprised of cemented carbide tips fixed on its lower end, thereby it is capable of rotating at a high speed. The rotary shaft assembly has a rotating shaft which rotates in a direction different from that of a rotating shaft of the motor, thereby the drill apparatus has a low profile.
Owner:NITTO KOHKI CO LTD
Tool with a molybdenum sulfide containing coating and method for its production
InactiveUS6528171B1Improve wear resistanceRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMetallic materialsMonolayer
The invention relates to a tool, especially a cutting insert for cutting metallic materials, which consist of a hard metal, cermet ceramics or steel base, especially of a high speed steel base, and at least one layer deposited thereon. The single layer, or in the case of several layers the outer layer or the layer underneath the outer layer, contains molybdenum sulfide. The aim of the invention is to improve the resistance to wear of the friction-reducing, molybdenum sulfide containing layer even at high pressures. To this end, the molybdenum sulfide containing layer consists of an alternating sequence of two layer that are different from one another. The first layer contains 51 to 100% by weight of metallic molybdenum and the second layer contains 21 to 100% by weight of MoS2 which substantially consists of hexagonal crystals that are at least substantially oriented in a plane parallel to the tool surface.
Owner:WIDIA
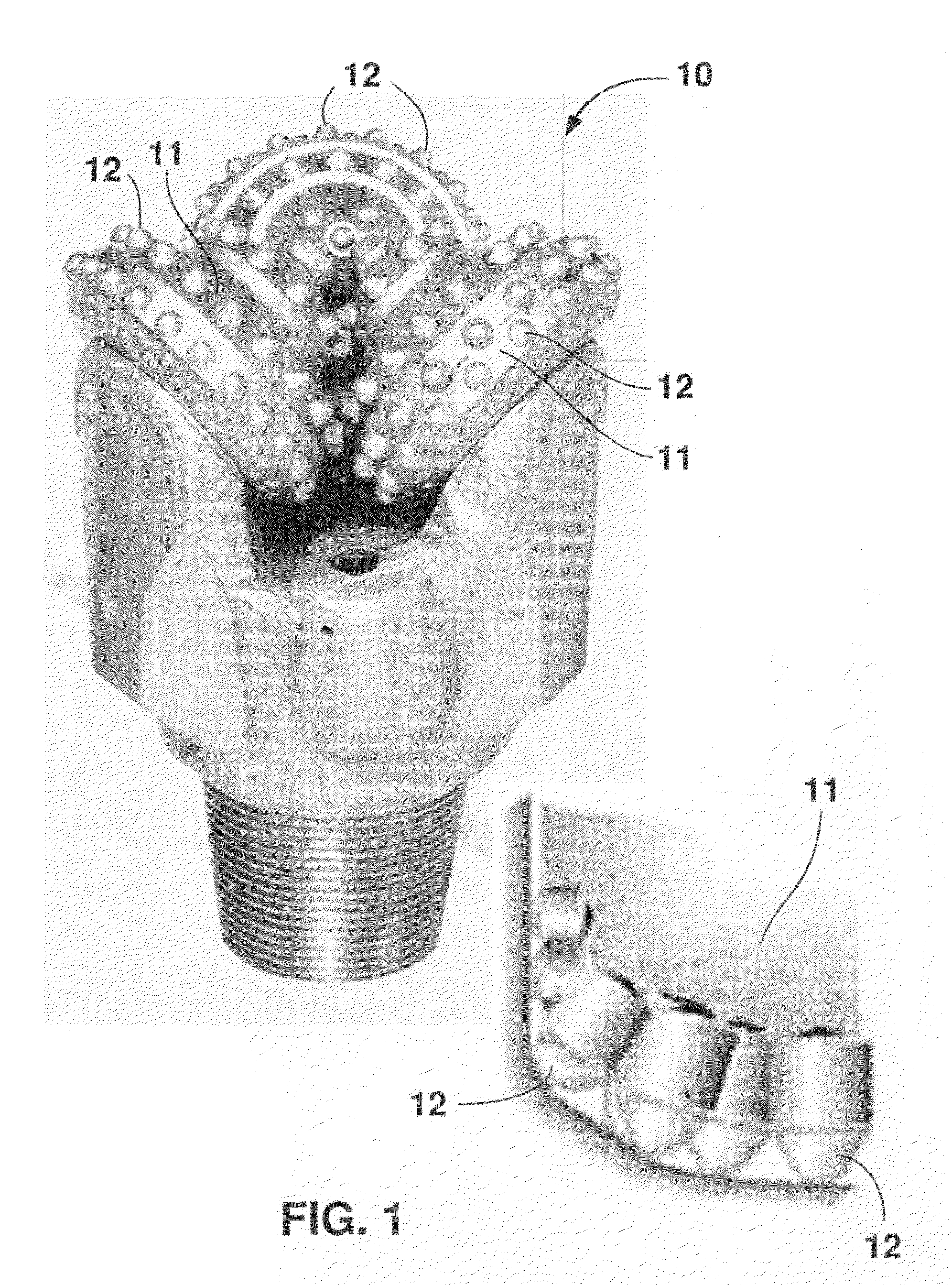
Earth-boring bits
ActiveUS20050247491A1Low melting pointLowered melting point of the binder facilitates proper infiltration of the massDrill bitsCutting machinesBorideNiobium
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for forming a bit body for an earth-boring bit. The bit body may comprise hard particles, wherein the hard particles comprise at least one carbide, nitride, boride, and oxide and solid solutions thereof, and a binder binding together the hard particles. The binder may comprise at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, and iron, and, optionally, at least one melting point reducing constituent selected from a transition metal carbide in the range of 30 to 60 weight percent, boron up to 10 weight percent, silicon up to 20 weight percent, chromium up to 20 weight percent, and manganese up to 25 weight percent, wherein the weight percentages are based on the total weight of the binder. In addition, the hard particles may comprise at least one of (i) cast carbide (WC+W2C) particles, (ii) transition metal carbide particles selected from the carbides of titanium, chromium, vanadium, zirconium, hafnium, tantalum, molybdenum, niobium, and tungsten, and (iii) sintered cemented carbide particles.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC +1
Earth-boring bits
InactiveUS20050211475A1Low melting pointLowered melting point of the binder facilitates proper infiltration of the massDrill bitsMetal-working drilling toolsBorideNiobium
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for forming a bit body for an earth-boring bit. The bit body may comprise hard particles, wherein the hard particles comprise at least one carbide, nitride, boride, and oxide and solid solutions thereof, and a binder binding together the hard particles. The binder may comprise at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, and iron, and at least one melting point reducing constituent selected from a transition metal carbide in the range of 30 to 60 weight percent, boron up to 10 weight percent, silicon up to 20 weight percent, chromium up to 20 weight percent, and manganese up to 25 weight percent, wherein the weight percentages are based on the total weight of the binder. In addition, the hard particles may comprise at least one of (i) cast carbide (WC+W2C) particles, (ii) transition metal carbide particles selected from the carbides of titanium, chromium, vanadium, zirconium, hafnium, tantalum, molybdenum, niobium, and tungsten, and (iii) sintered cemented carbide particles.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES +1
Multilayered coated cutting tool
The present invention relates to a cutting tool comprising a body of sintered cemented carbide or cermet, ceramic or high speed steel on which at least one of the functioning parts of the surface of the body, a thin, adherent, hard and wear resistant coating is applied. The coating comprises a laminar, multilayered structure of refractory compounds in polycrystalline, non-repetitive form, MX / NX / MX / NX where the alternating layers MX and NX are metal nitrides or carbides with the metal elements M and N selected from the group consisting of Ti, Nb, Hf, V, Ta, Mo, Zr, Cr, Al and W. The sequence of individual layer thicknesses is essentially aperiodic throughout the entire multilayered structure, and layer thicknesses are larger than 0.1 nanometer but smaller than 30 nanometer, preferably smaller than 20 nanometer. The total thickness of said multilayered coating is larger than 0.5 mu m but smaller than 20 mu m.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Polycrystalline diamond abrasive elements
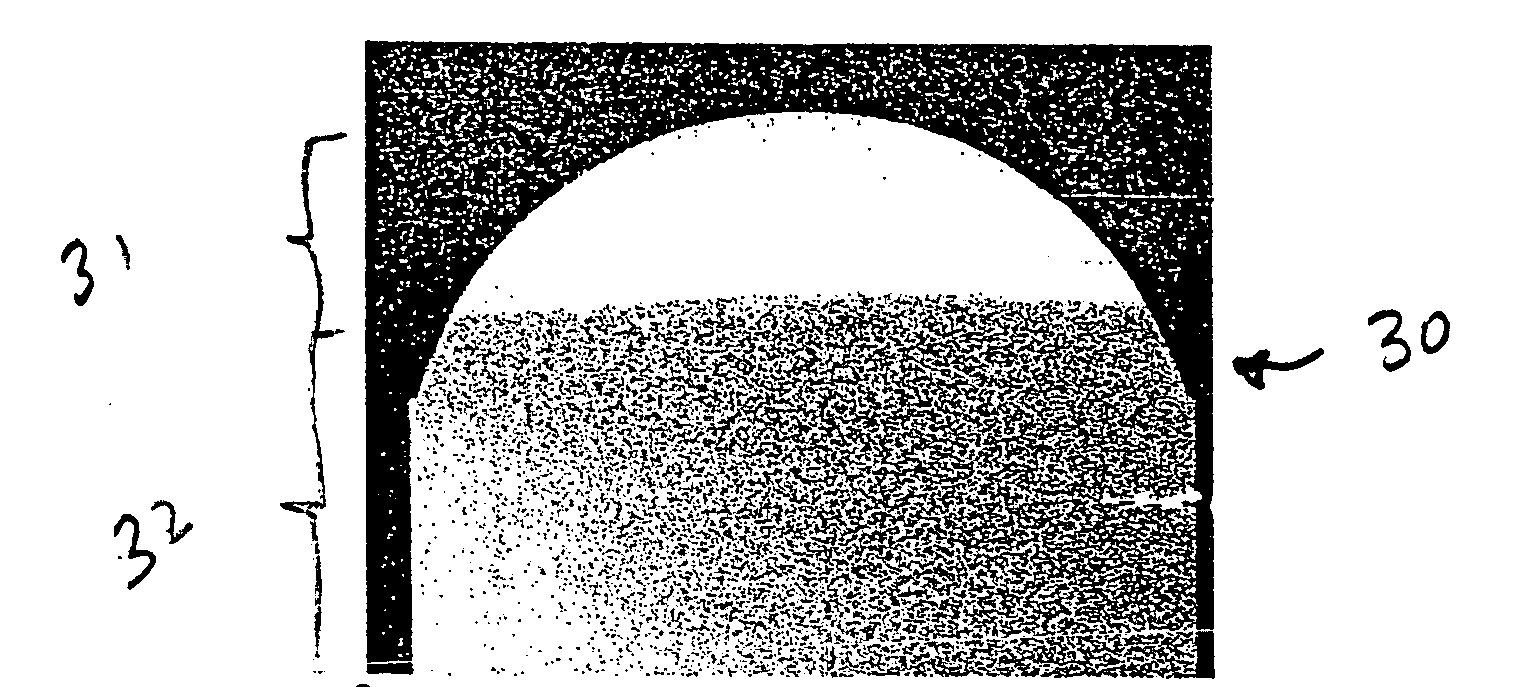
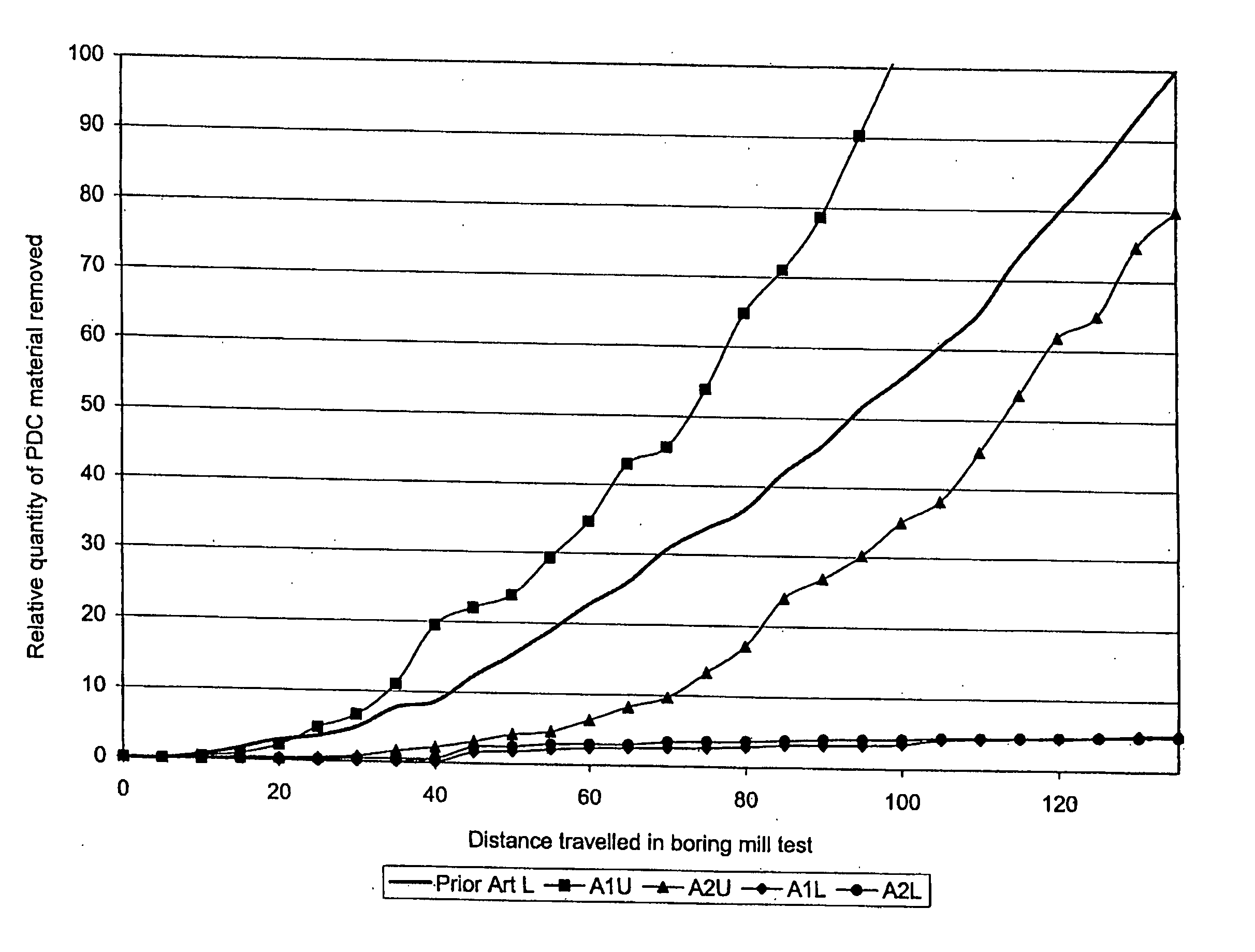
A polycrystalline diamond abrasive element, particularly a cutting element, comprises a table of polycrystalline diamond bonded to a substrate, particularly a cemented carbide substrate, along a non-planar interface. The non-planar interface typically has a cruciform configuration. The polycrystalline diamond has a high wear-resistance, and has a region adjacent the working surface lean in catalysing material and a region rich in catalysing material. The region lean in catalysing material extends to a depth of 40 to 90 microns, which is much shallower than in the prior art. Notwithstanding the shallow region lean in catalysing material, the polycrystalline diamond cutters have a wear resistance, impact strength and cutter life comparable to that of prior art cutter, but requiring only 20% of the treatment times of the prior art cutters.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
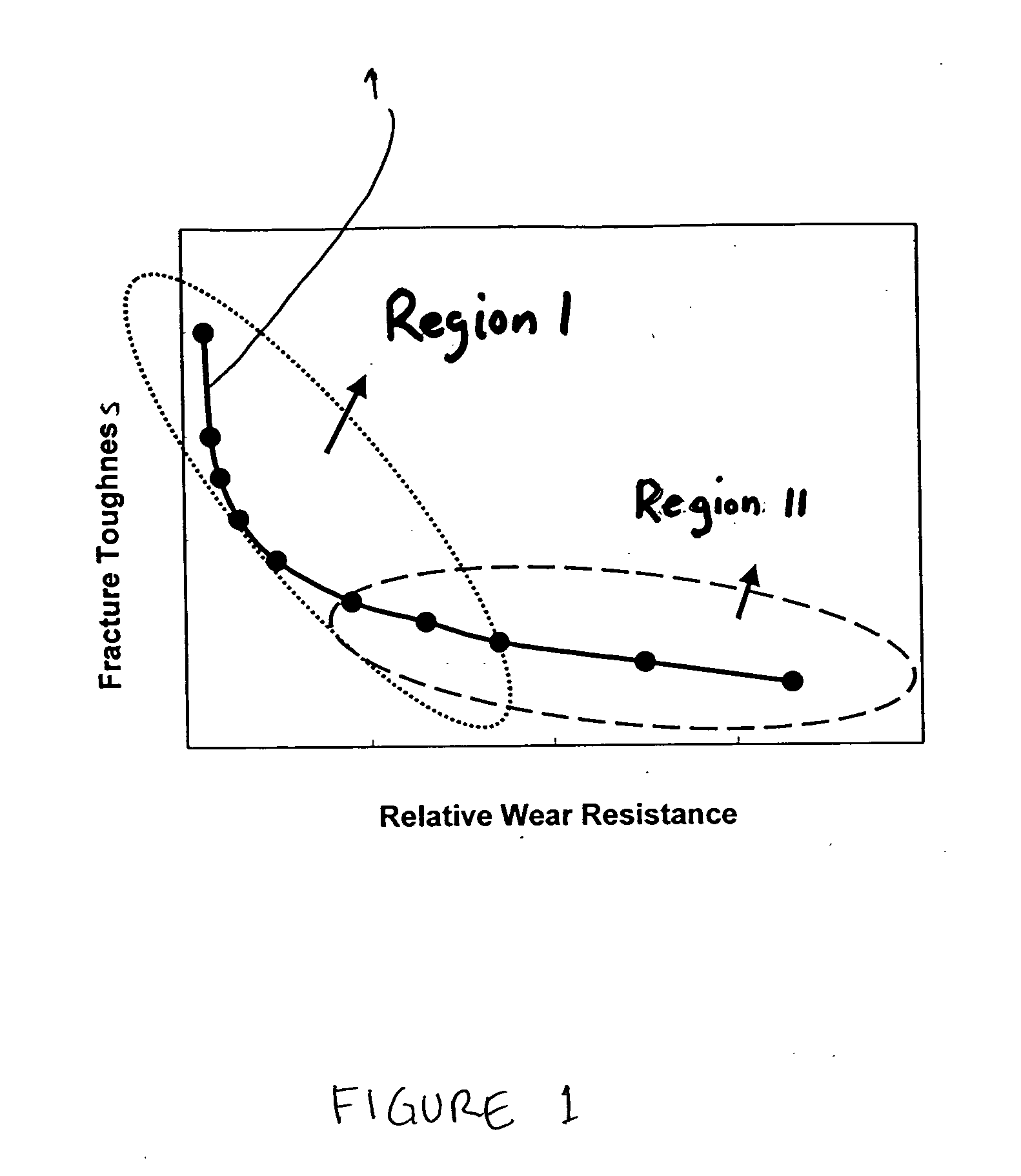
Hybrid cemented carbide composites
Embodiments of the present invention include hybrid composite materials comprising a cemented carbide dispersed phase and a cemented carbide continuous phase. The contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase of embodiments may be less than or equal to 0.48. The hybrid composite material may have a hardness of the dispersed phase that is greater than the hardness of the continuous phase. For example, in certain embodiments of the hybrid composite material, the hardness of the dispersed phase is greater than or equal to 88 HRA and less than or equal to 95 HRA and the hardness of the continuous phase is greater than or equal to 78 and less than or equal to 91 HRA. Additional embodiments may include hybrid composite materials comprising a first cemented carbide dispersed phase wherein the volume fraction of the dispersed phase is less than 50 volume percent and a second cemented carbide continuous phase, wherein the contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase is less than or equal to 1.5 times the volume fraction of the dispersed phase in the composite material. The present invention also includes a method of making a hybrid cemented carbide composite by blending partially and / or fully sintered granules of the dispersed cemented carbide grade with “green” and / or unsintered granules of the continuous cemented carbide grade to provide a blend. The blend may then be consolidated to form a compact. Finally, the compact may be sintered to form a hybrid cemented carbide.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Cemented carbide inserts for earth-boring bits
This invention relates to cutting inserts for earth boring bits comprising a cutting zone, wherein the cutting zone comprises first cemented hard particles and a body zone, wherein the body zone comprises second cemented hard particles. The first cemented hard particles may differ in at least one property from the second cemented hard particles. As used herein, the cemented hard particles means a material comprising hard particles in a binder. The hard particles may be at least one of a carbide, a nitride, a boride, a silicide, an oxide, and solid solutions thereof and the binder may be at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, iron and alloys of cobalt, nickel or iron.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Polycrystalline diamond abrasive elements
ActiveUS20050139397A1Improved wear behaviorImprove wear resistanceDrill bitsConstructionsMetallurgyPolycrystalline diamond
A polycrystalline diamond abrasive element, particularly a cutting element, comprises a layer of polycrystalline diamond having a working surface and bonded to a substrate, particularly a cemented carbide substrate, along an interface. The polycrystalline diamond abrasive element is characterised by using a binder phase that is homogeneously distributed through the polycrystalline diamond layer and that is of a fine scale. The polycrystalline diamond also has a region adjacent the working surface lean in catalysing material and a region rich in catalysing material.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX PRODION +2
Hybrid cemented carbide composites
Embodiments of the present invention include hybrid composite materials comprising a cemented carbide dispersed phase and a cemented carbide continuous phase. The contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase of embodiments may be less than or equal to 0.48. The hybrid composite material may have a hardness of the dispersed phase that is greater than the hardness of the continuous phase. For example, in certain embodiments of the hybrid composite material, the hardness of the dispersed phase is greater than or equal to 88 HRA and less than or equal to 95 HRA and the hardness of the continuous phase is greater than or equal to 78 and less than or equal to 91 HRA.Additional embodiments may include hybrid composite materials comprising a first cemented carbide dispersed phase wherein the volume fraction of the dispersed phase is less than 50 volume percent and a second cemented carbide continuous phase, wherein the contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase is less than or equal to 1.5 times the volume fraction of the dispersed phase in the composite material.The present invention also includes a method of making a hybrid cemented carbide composite by blending partially and / or fully sintered granules of the dispersed cemented carbide grade with “green” and / or unsintered granules of the continuous cemented carbide grade to provide a blend. The blend may then be consolidated to form a compact. Finally, the compact may be sintered to form a hybrid cemented carbide.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Long-service-life split type valve seat
PendingCN111664087AExtended service lifeHigh hardnessPositive displacement pump componentsLiquid fuel engine componentsWorking pressureStructural engineering
The invention discloses a long-service-life split type valve seat. The long-service-life split type valve seat comprises linings and bases. The linings are embedded into the outlet ends of the bases.The linings are matched with a valve body for use. Each lining is a tungsten carbide alloy. The long-service-life split type valve seat has the beneficial effects that the valve seat is composed of the linings and the bases, the linings are made of a hard alloy material, the hardness, the strength, the wear resistance and the corrosion resistance of the linings are improved, and the service life of the valve seat is greatly prolonged; the valve seat is of a split structure, once abrasion occurs, only the linings or the bases need to be replaced, integral replacement is not needed, maintenanceis convenient, the time and labor are saved, and meanwhile the production cost of an oil and gas field is reduced; the appropriate diameter sizes of the linings can be selected according to the working pressure, the conveying medium, the degree of abrasion of the valve body to the valve seat and the like in actual working conditions, and the application range is wide; the linings and the bases arein various shapes and can be combined according to actual working condition requirements, and the applicability is high.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH CO LTD
Superfine WC-Co cemented carbide containing rare-earth elements and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101760685AChange processSteady improvement in overall performanceRare-earth elementChemical reaction
The invention discloses a superfine WC-Co cemented carbide containing rare-earth elements and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of cemented carbide. In the cemented carbide, the weight of WC rigid phase accounts for 85-94% of that of the cemented carbide, the weight of Co binder phase accounts for 5-14% of that of the cemented carbide, the weight of grain growth inhibitor accounts for 0.3-2.0% of that of the cemented carbide, and the weight of the thulium in the rare earth addition accounts for 0.2-1.2% of that of the Co binder phase. The method comprises the following steps: weighing various powder stocks, ball-milling, drying and pelletizing to form a compound; and suppressing and shaping the compound, sintering and cooling to obtain the cemented carbide. The adding mode of nano rare earth oxide or Co-RE composite powder can be implemented easily and conveniently, and the rare earth is diffusely and evenly distributed, thereby facilitating to perform physo-chemical reactions; and the cemented carbide has the advantages of low production cost, stable and enhanced performance and easy implementation, production and application.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Sintered bodies for earth-boring rotary drill bits and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20080101977A1Low melting pointLowered melting point of the binder facilitates proper infiltration of the massDrill bitsBorideNiobium
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for forming a bit body for an earth-boring bit. The bit body may comprise hard particles, wherein the hard particles comprise at least one carbide, nitride, boride, and oxide and solid solutions thereof, and a binder binding together the hard particles. The binder may comprise at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, and iron, and, optionally, at least one melting point reducing constituent selected from a transition metal carbide in the range of 30 to 60 weight percent, boron up to 10 weight percent, silicon up to 20 weight percent, chromium up to 20 weight percent, and manganese up to 25 weight percent, wherein the weight percentages are based on the total weight of the binder. In addition, the hard particles may comprise at least one of (i) cast carbide (WC+W2C) particles, (ii) transition metal carbide particles selected from the carbides of titanium, chromium, vanadium, zirconium, hafnium, tantalum, molybdenum, niobium, and tungsten, and (iii) sintered cemented carbide particles.
Owner:EASON JIMMY W +2
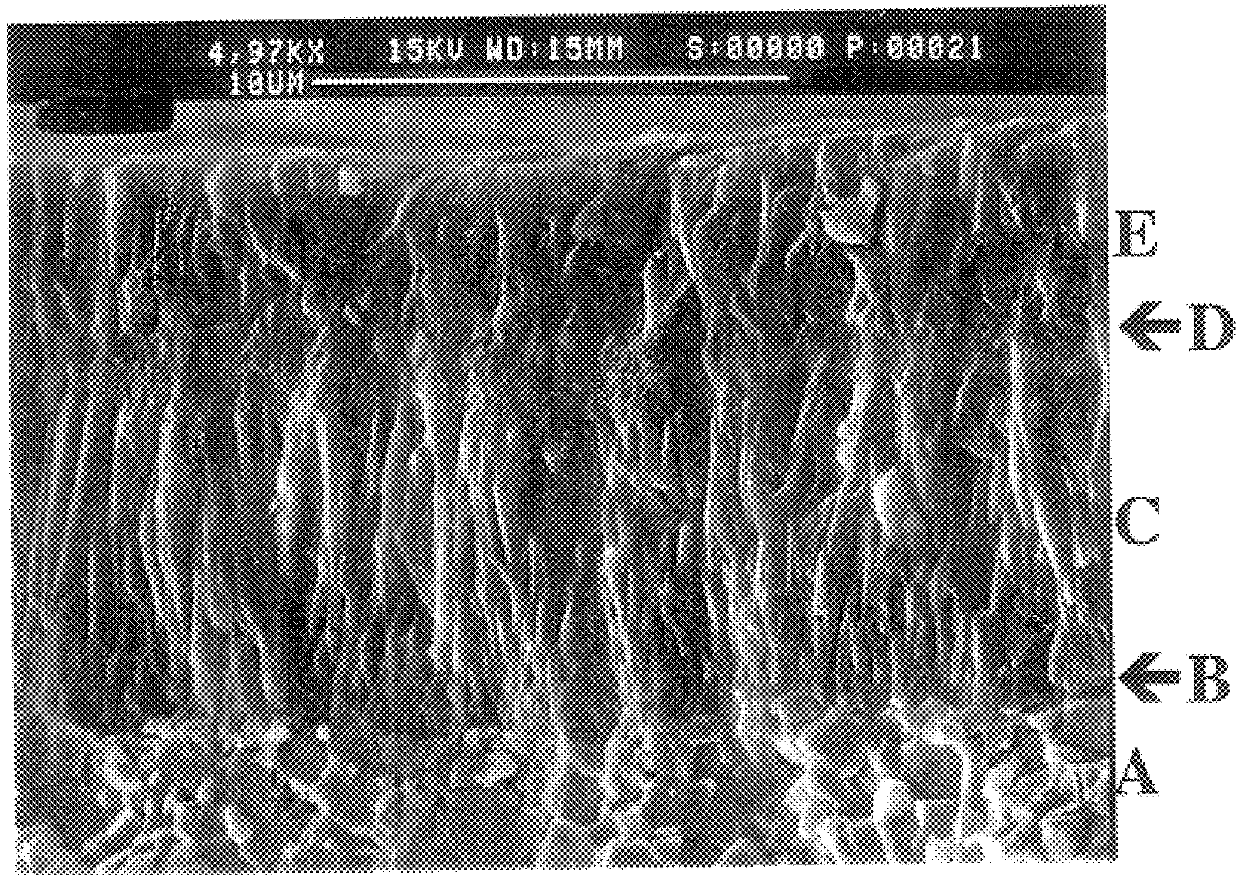
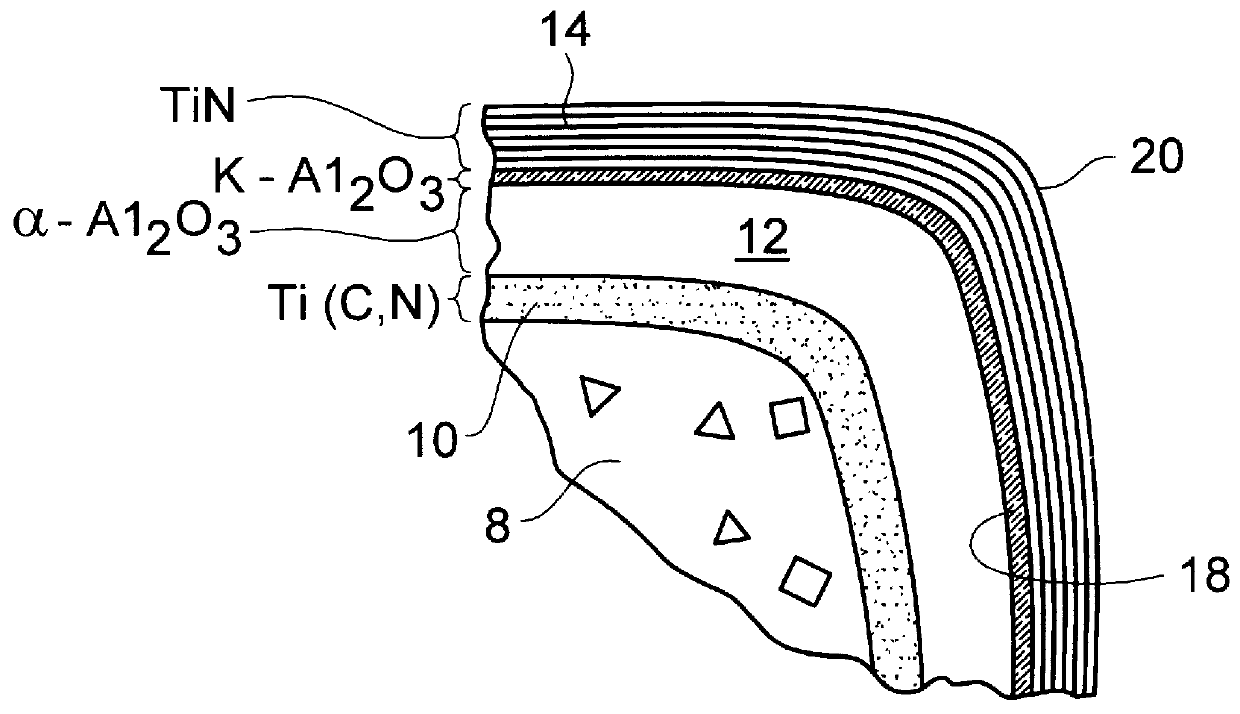
Coated cutting insert and method of making it
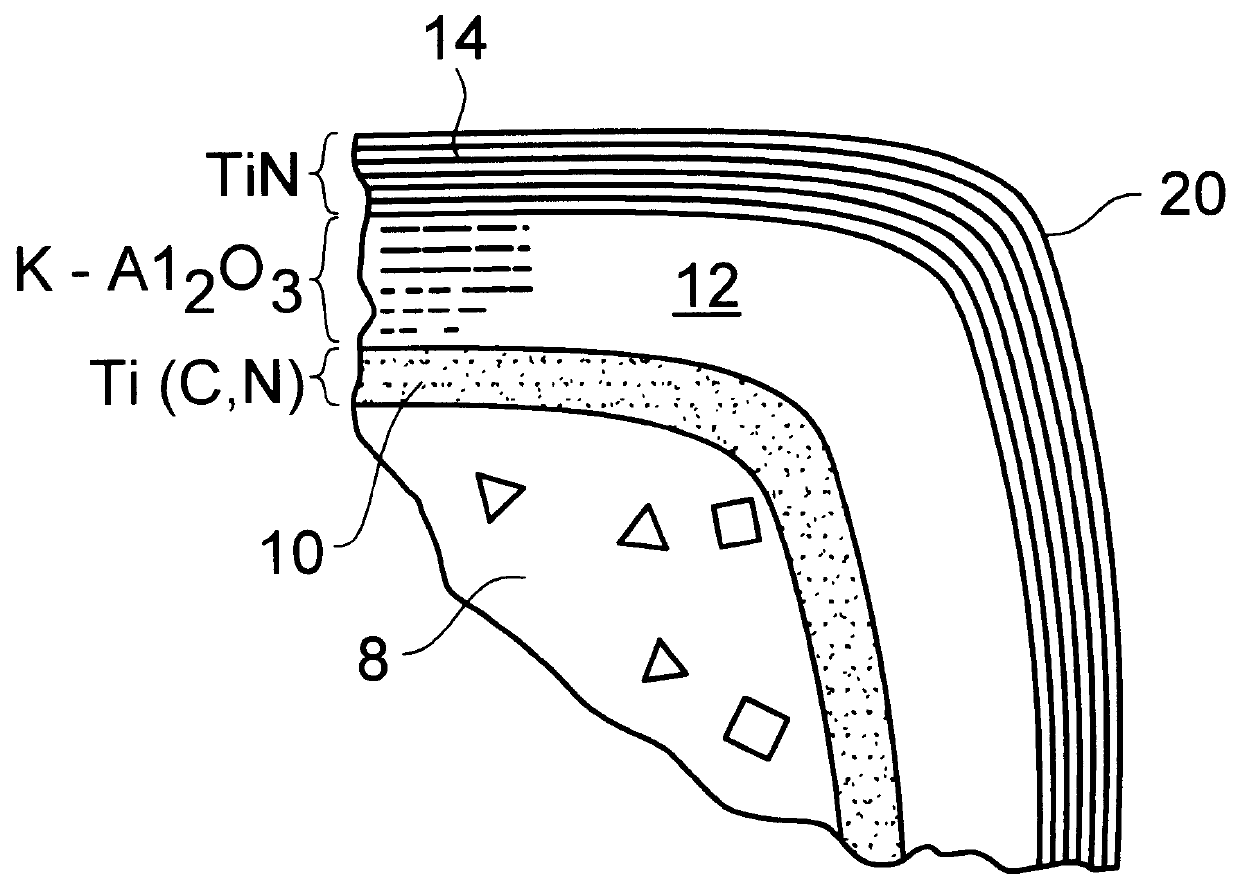
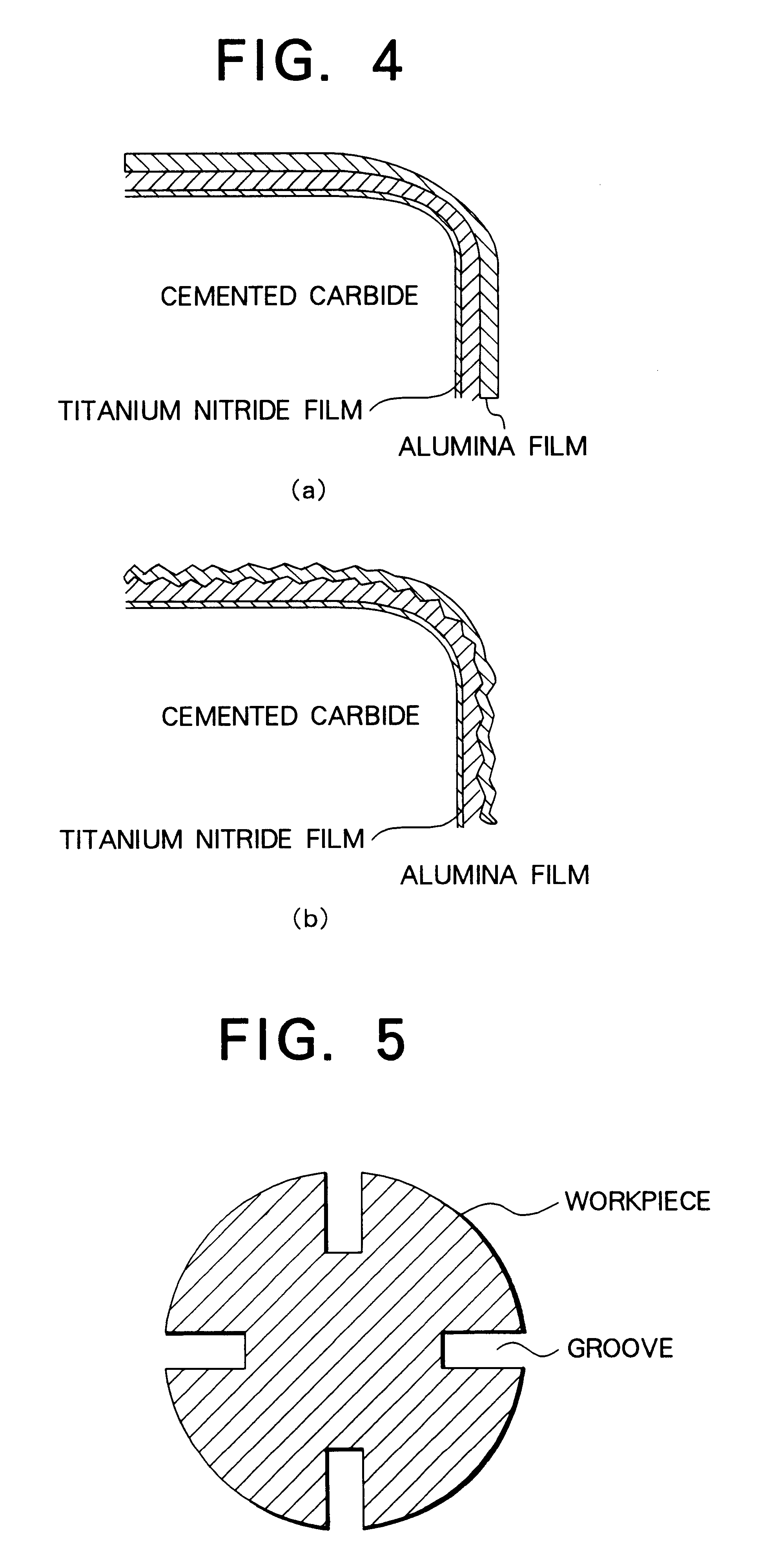
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 01579 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 1, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 1, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 29, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 20083 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 5, 1997A coated turning insert particularly useful for dry and wet machining in low and medium alloyed steels, stainless steels, with or without raw surface zones under severe conditions such as vibrations, long overhang and recutting of chips. The insert is characterized by a WC-Co cemented carbide with a low content of cubic carbides and a rather low W-alloyed binder phase and a coating including an innermost layer of TiCxNyOz with columnar grains and a top layer of TiN and an intermediate layer of kappa -Al2O3. The layers are deposited by using CVD-methods.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Cutting tool insert
ActiveUS20070039762A1Reducing and preferably eliminating and spalling and chipping typeImproved wear behaviorDrill bitsWorkpiecesLeading edgeMetallurgy
A polycrystalline diamond abrasive cutting element consists generally of a layer of high grade polycrystalline diamond bonded to a cemented carbide substrate. The polycrystalline diamond layer has a working surface and an outer peripheral surface and is characterized by having an annular region or a portion thereof adjacent the peripheral surface that is lean in catalysing material. A region adjacent the working surface is also lean in catalysing material such that in use, as a wear scar develops, both the leading edge and the trailing edge thereof are located in a region lean in catalysing material.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Coated cutting insert
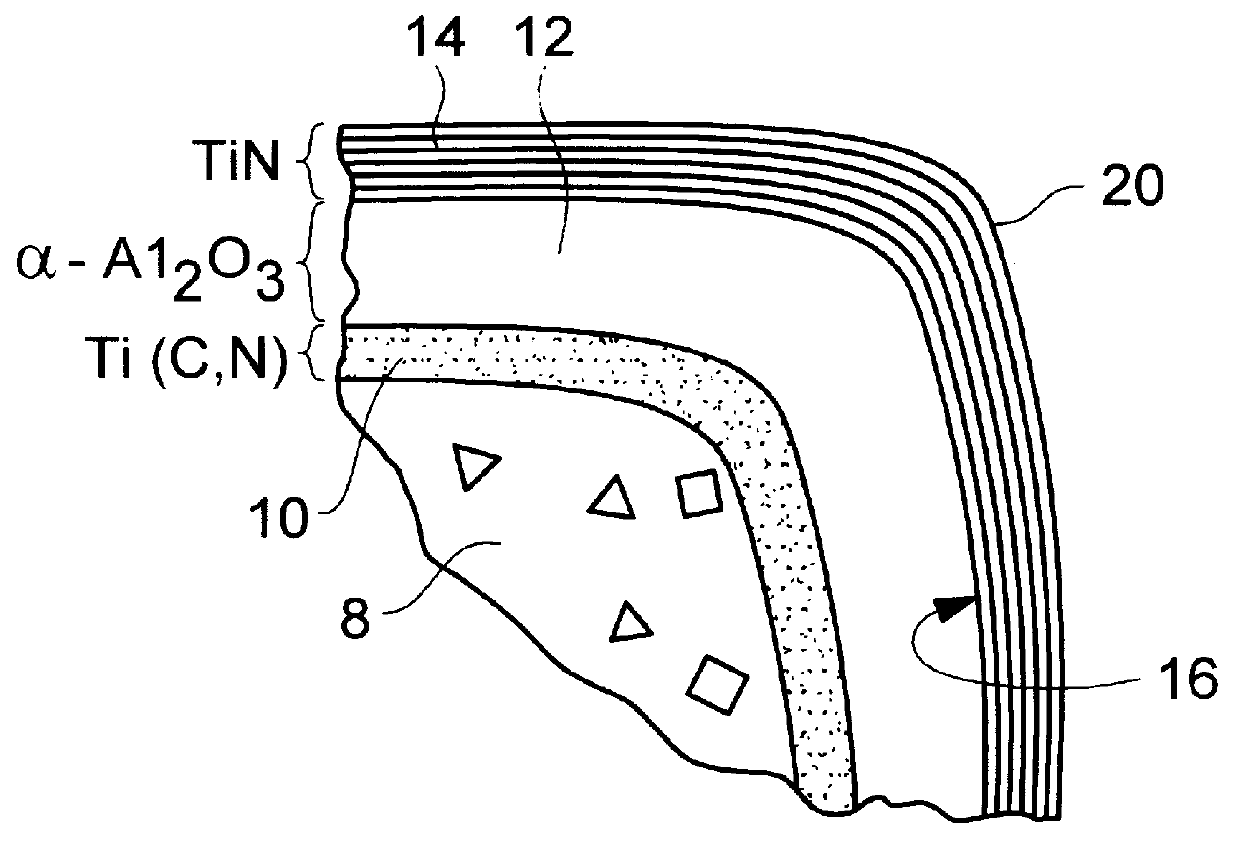
The present invention discloses a coated cutting insert particularly useful for dry milling of grey cast iron. The insert is characterized by a WC-Co cemented carbide substrate and a coating including an innermost layer of TiCxNyOz with columnar grains and a top coating of a fine grained alpha-Al2O3 layer.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Cemented carbide body with high wear resistance and extra tough behavior
InactiveUS6015614AImprove wear resistanceExtra tough behaviorSynthetic resin layered productsTurning toolsWear resistantAlloy
There is provided an Al2O3-TiN coated cemented carbide insert intended for turning of steels and especially Ca-treated steels. The alumina layer is protected by an extra thick and multilayered coating of TiN. The TiN coating is wet blasted and, for this purpose, (Ti,Al)(C,O,N) bonded to the underlying Al2O3 layer which preferably consists of alpha -Al2O3. The extra tough behavior together with increased wear resistance can be obtained by optimizing the TiN layer thickness, structure and adhesion and wet blasting the said TiN coating. This invention is characterized by the fact that the coating layers are not missing at the cutting edge of the insert.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
Carbide stem press fit into a steel body of a pick
In one aspect of the present invention, a high impact resistant tool, having a super hard material is bonded to a cemented metal carbide substrate at a non-planar interface. The cemented metal carbide substrate is bonded to a front end of a cemented metal carbide segment. A stem is formed in the base end of the carbide segment opposite the front end and the carbide stem is press fitted into bore of a steel body.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
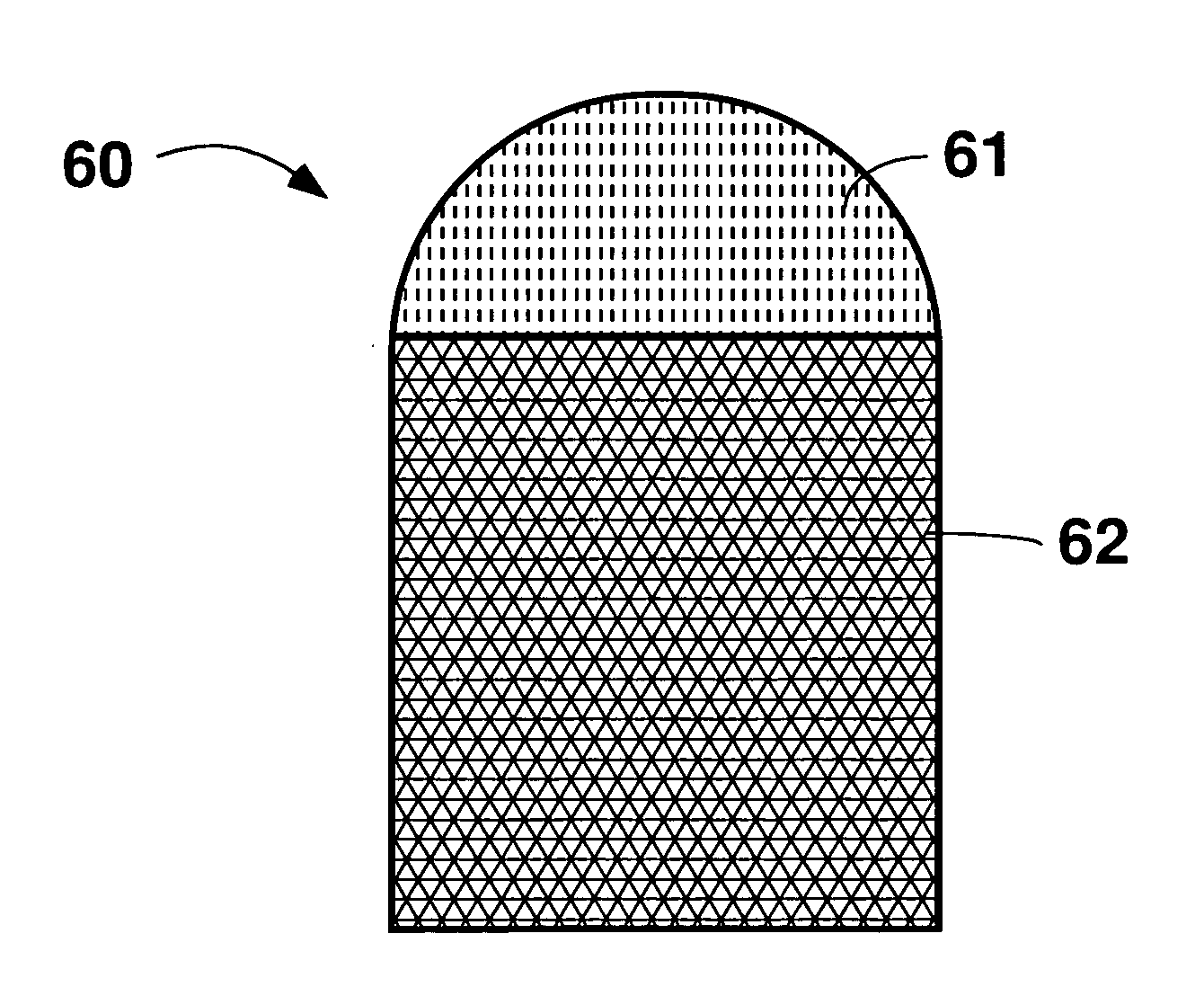
Tool with a large volume of a superhard material
In one aspect of the invention, a tool has a wear-resistant base suitable for attachment to a driving mechanism and also a hard tip attached to an interfacial surface of the base. The tip has a first cemented metal carbide segment bonded to a superhard material at a non-planar interface. The tip has a height between 4 and 10 mm and also has a curved working surface opposite the interfacial surface. A volume of the superhard material is about 75% to 150% of a volume of the first cemented metal carbide segment.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Non-rotating Pick with a Pressed in Carbide Segment
ActiveUS20080035383A1Improve impact resistanceDrill bitsSlitting machinesSuperhard materialCemented carbide
In one aspect of the present invention, a high impact resistant tool has a superhard material bonded to a cemented metal carbide substrate at a non-planar interface. The cemented metal carbide substrate is bonded to a front end of a cemented metal carbide segment. A stem formed in the base end of the carbide segment opposite the front end is press fit into a bore of a steel body. The steel body is rotationally fixed to a drum adapted to rotate about its axis.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Coated cemented carbide cutting tool
InactiveUS6293739B1Extended service lifeImproving flaking resistance of coating layerLayered productsTurning toolsCrystal structureAlloy
The invention is to prolong the life time of tools dramatically by (1) considerably improving the flaking resistance of the coating layer at the time of cutting, (2) increasing the wear resistance and crater resistance of the coating layer itself, and (3) enhancing the breakage strength of the coating layer in comparison with the conventional coating cutting tools. In order to achieve the object, the coated cemented carbide of the invention has the following structure in the coating layer on the surface of the cemented carbides: The outer layer has an Al2O3 layer practically having an alpha-type crystal structure. The Al2O3 layer has a region where alpha-type and kappa-type crystal grains coexist in the first row of the crystal grains that grow on the inner layer. In addition to that, the crystal grains of alpha-Al2O3 in the region include no pores.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Biocompatible cemented carbide articles and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20070082229A1Eliminate and minimize toxic effectReduce concentrationSurgeryJewelleryBiocompatibility TestingAlloy
This invention relates to cemented carbide articles that are characterized by substantially improved biocompatibility with human skin, tissue, organs, etc., compared with articles made from conventional cemented carbides. The essential feature of these improved biocompatible cemented carbide articles is a binder-depleted zone at and near the exposed surfaces of the articles. By depleting the binder (which mainly consists of Co and / or Ni, as well as their alloys) at and near the surface, the toxic effects of Co and Ni (known carcinogens), as well as the allergic reactions that these metals can cause when in contact with human skin, are eliminated. By depleting the binder only at and near the surface, the bulk properties of the cemented carbide article are not compromised or altered in any manner. Applications of these binder-depleted cemented carbides could include articles that human skin may experience prolonged exposure to, for example, jewelry articles such as rings, bracelets, bangles, chains, necklaces, pendants, watches, watch cases, watch straps, etc. In addition, the cemented carbides of this invention may be used in applications where the article comes directly in contact with human skin, tissue, organs, etc. such as surgical and other medical instruments, razor blades, etc. Also, other applications could include knives, tools, dies, and other wear components that are used to process and handle, and hence, come into direct contact with materials meant for human consumption and / or ingestion. Examples of such materials include foodstuffs and pharmaceuticals.
Owner:MIRCHANDANI RAJINI P +1
Coated tool of cemented carbide
InactiveUS6187421B1Improve propertiesImprove tool lifePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCoated membraneCarbide coating
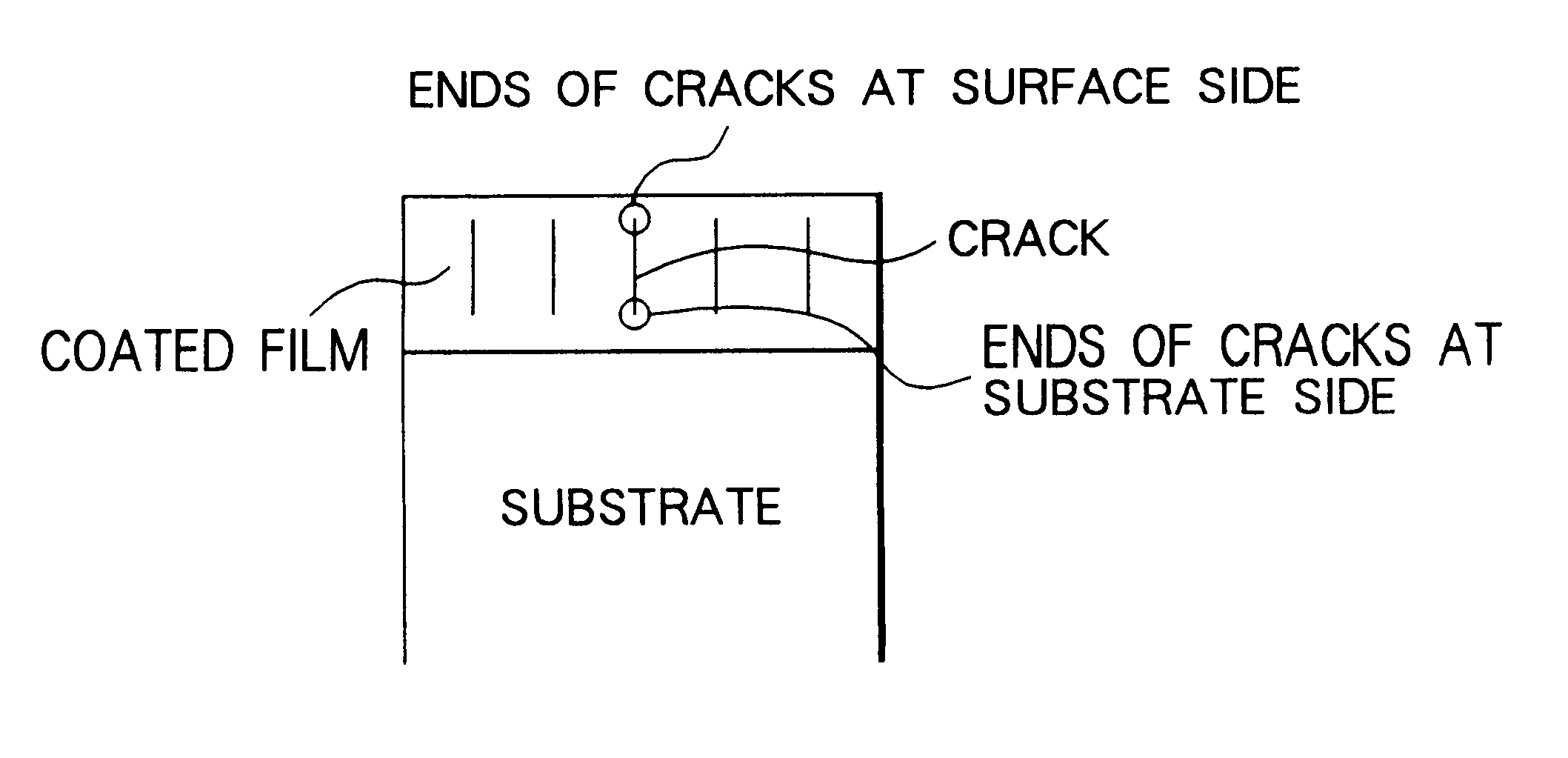
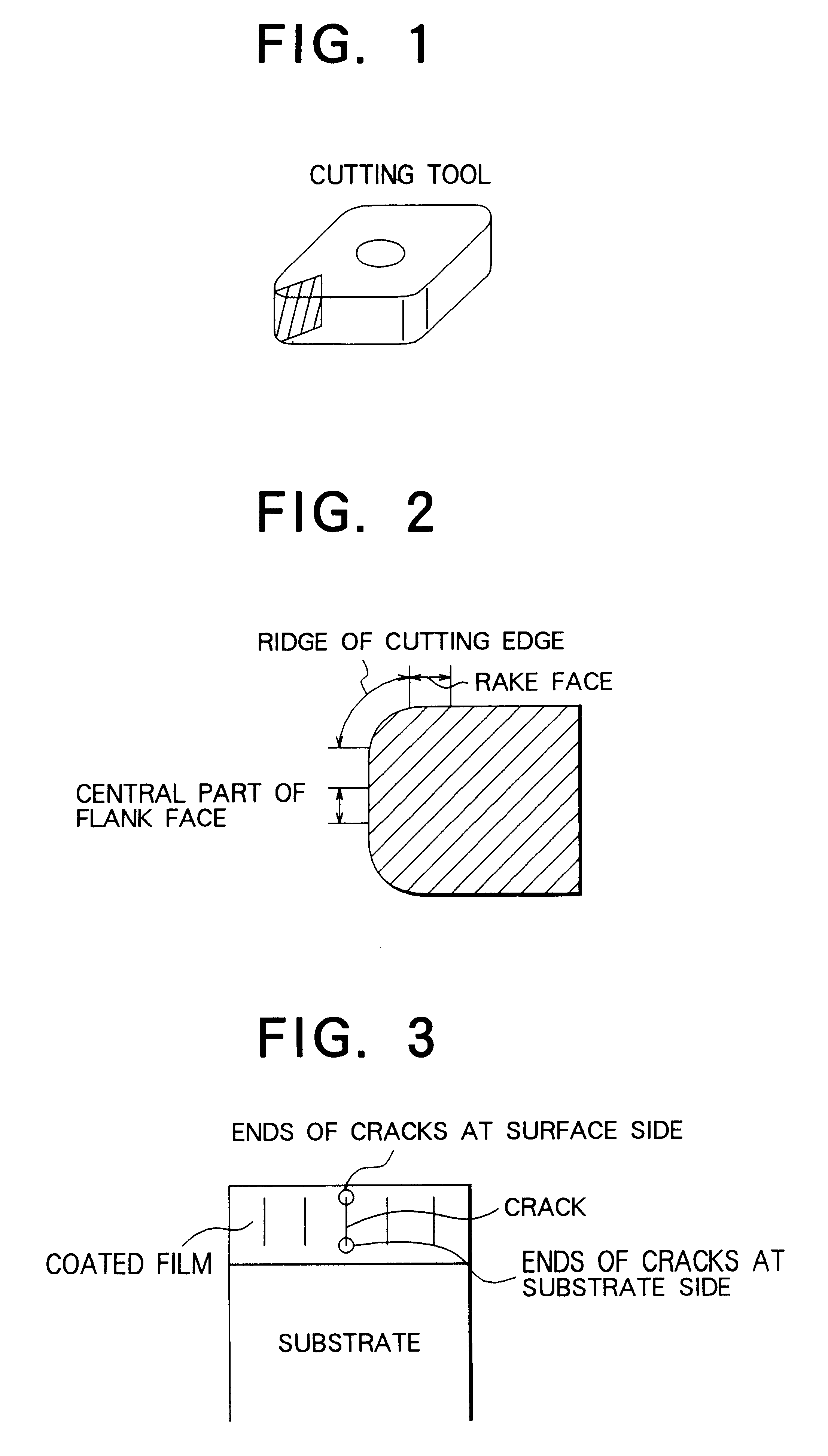
The principal object of the present invention is to provide a coated cemented carbide tool whose both properties of breakage resistance and wear resistance are improved and whose life is lengthened.The present invention has been made to achieve this object and is related with a coated cemented carbide cutting tool comprising a substrate consisting of a matrix of WC and a binder phase of an iron group metal and a plurality of coated layers provided on a surface of the substrate, in which (a) an innermost layer, adjacent to the substrate, of the coated layers consists essentially of titanium nitride having a thickness of 0.1 to 3 mum, (b) on a mirror-polished cross-sectional microstructure of the said tool, an average crack interval in the coated film on a ridge of a cutting edge and / or rake face is smaller than an average crack interval in the coated layer on a flank face, (c) at least 50% of the cracks in the coated film on the said ridge of the cutting edge and / or rake face have ends of the cracks in the said innermost titanium nitride layer, in a layer above the titanium nitride layer or in an interface between these layers and (d) an average crack length in the coated film on the said ridge of the cutting edge and / or rake face is shorter than an average film thickness on the flank face.According to the present invention, quantitatively specifying the crack intervals and positions of the ends of the cracks in the coated layer results in excellent breakage resistance as well as wear resistance.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Cemented carbide insert for turning, milling and drilling
InactiveUS6221479B1Improve cutting performancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesAlloyCemented carbide
There is disclosed a cemented carbide insert with excellent properties for machining of steels and stainless steels. The cemented carbide comprises WC and 4-25 wt-% Co. The WC-grains have an average grain size in the range 0.2-3.5 mum and a narrow grain size distribution in the range 0-4.5 mum.According to the method of the invention a cemented carbide cutting tool insert is made by mixing powders of WC, TiC, TaC and / or NbC, binder metal and pressing agent, drying preferably by spray drying, pressing to inserts and sintering. The method characterised inthat a deagglomerated WC-powder with a narrow grain size distribution is used,that the powders of TiC, TaC and / or NbC are deagglomerated andthat the mixing is wet mixing with no change in grain size or grain size distribution.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Non-rotating pick with a pressed in carbide segment
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
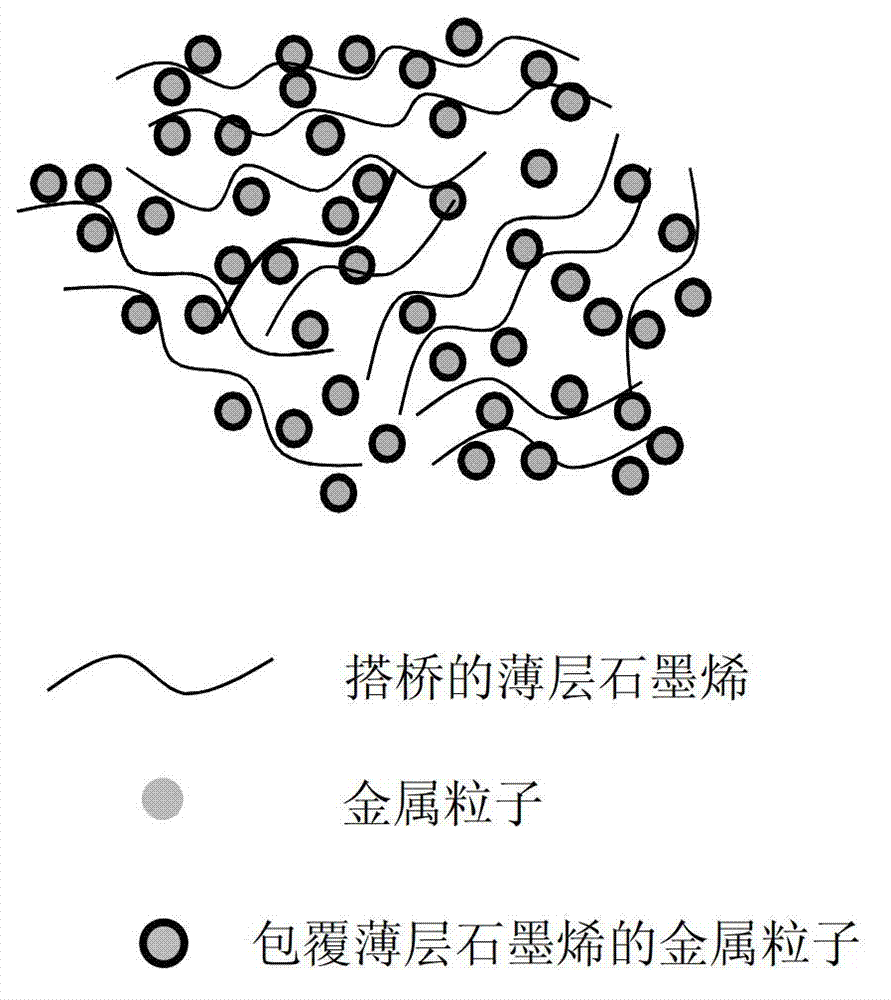
Material adopting thin graphene and metal powder composite structure, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103192072AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove corrosion resistanceCarbon compoundsGas phaseSlurry
The invention discloses a material adopting a thin graphene and metal powder composite structure, a preparation method and an application thereof. The material adopting the composite structure comprises metal powder bridged by and coated with thin graphene. The preparation technology of the material comprises the steps as follows: mixing transition metal powder or reduced transition metal powder with the thin graphene, and growing the thin graphene on the surface of the transition metal powder through CVD (chemical vapor deposition) and coating the surface of the transition metal powder with the thin graphene, so as to obtain the metal powder bridged by and coated with the thin graphene; or growing the thin graphene on the surface of the transition metal powder through the CVD, and then compositing the metal powder with the thin graphene to obtain a target product. The invention has the advantages that the technology is simple; the oxidation resistance and the corrosion prevention of the metal powder can be enhanced, meanwhile, the metal powder has good heat conduction, antistatic and electromagnetic shielding properties, the service life of the metal powder can be prolonged, and the cost can be reduced; and besides, the material has a wide application prospect in antistatic performance, thermal management, heat conduction and radiation, electromagnetic shielding, catalysts, sintering activators, electro-conduction slurry, batteries, cemented carbide and the like.
Owner:苏州格瑞丰纳米科技有限公司
Tool for chip removing machining as well as a solid indexable cutting insert and a solid basic body therefor
ActiveUS20100329800A1Reduce manufacturing costGood precisionMilling cuttersCutting insertsHardnessEngineering
A tool for chip removing machining, including a basic body having an insert seat, and an indexable cutting insert fixed in the seat. The insert includes an upperside, an underside, a pair of side contact surfaces, two cutting edges that individually extend along a chip surface included in one of the upperside and underside, at least two heads that are spaced-apart via an intermediate part and individually include a front portion having at least one cutting edge and a rear portion along which the pair of side contact surfaces are formed. The insert seat of the basic body includes a central hollow space, and a front cavity and at least one rear cavity in which the heads of the cutting insert are housed, the front cavity including a pair of side support surfaces against which the pair of side contact surfaces of the cutting insert are pressed when a tightening element pulls the head rearward toward the side support surfaces. The basic body is solid by being formed integrally of steel material. The seat is countersunk in the basic body such that the side support surfaces are integrated in the steel material. The cutting insert is formed integrally from a second, hard-wearing material having at least the same hardness as cemented carbide, the pair of side contact surfaces of the insert being integrated in the second material.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Articles Having Improved Resistance to Thermal Cracking
An article includes a working portion including cemented carbide, and a heat sink portion in thermal communication with the working portion. The heat sink portion includes a heat sink material having a thermal conductivity greater than a thermal conductivity of the cemented carbide. Also disclosed are methods of making an article including a working portion comprising cemented carbide, and a heat sink portion in thermal communication with the working portion and including a heat sink material having a thermal conductivity that is greater than a thermal conductivity of the cemented carbide. The heat sink portion conducts heat from the working portion.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Coated cemented carbide insert
ActiveUS7153562B2Eliminate deficienciesImprove performancePigmenting treatmentCutting insertsAlloyCemented carbide
The present invention relates to a cutting tool insert particularly for turning of steel comprising a cemented carbide body, a coating with a post treatment witha first, innermost layer system of one or several layers of TiCxNyOz with x+y+z≦1 with a total thickness of 0.7–4.5 μma second multilayer system consisting of a totally 5–31 alternating Al2O3 and TiCxNyOz (x+y+z≦1), preferably κ-Al2O3 and TiN, the Al2O3-layers having an individual layer thickness of <0.5 μm and the TiCxNyOz-layers 0.01–0.2 μm with a total thickness of the multilayer of 1.0–4.0 μm. The multilayer is exposed along the edge line and into the rake and flank face, at least 0.02 mm, from the edge line on the rake face, preferably the contact length of the chip at most 0.9 mm, and 0.02–0.20 mm on the flank face.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
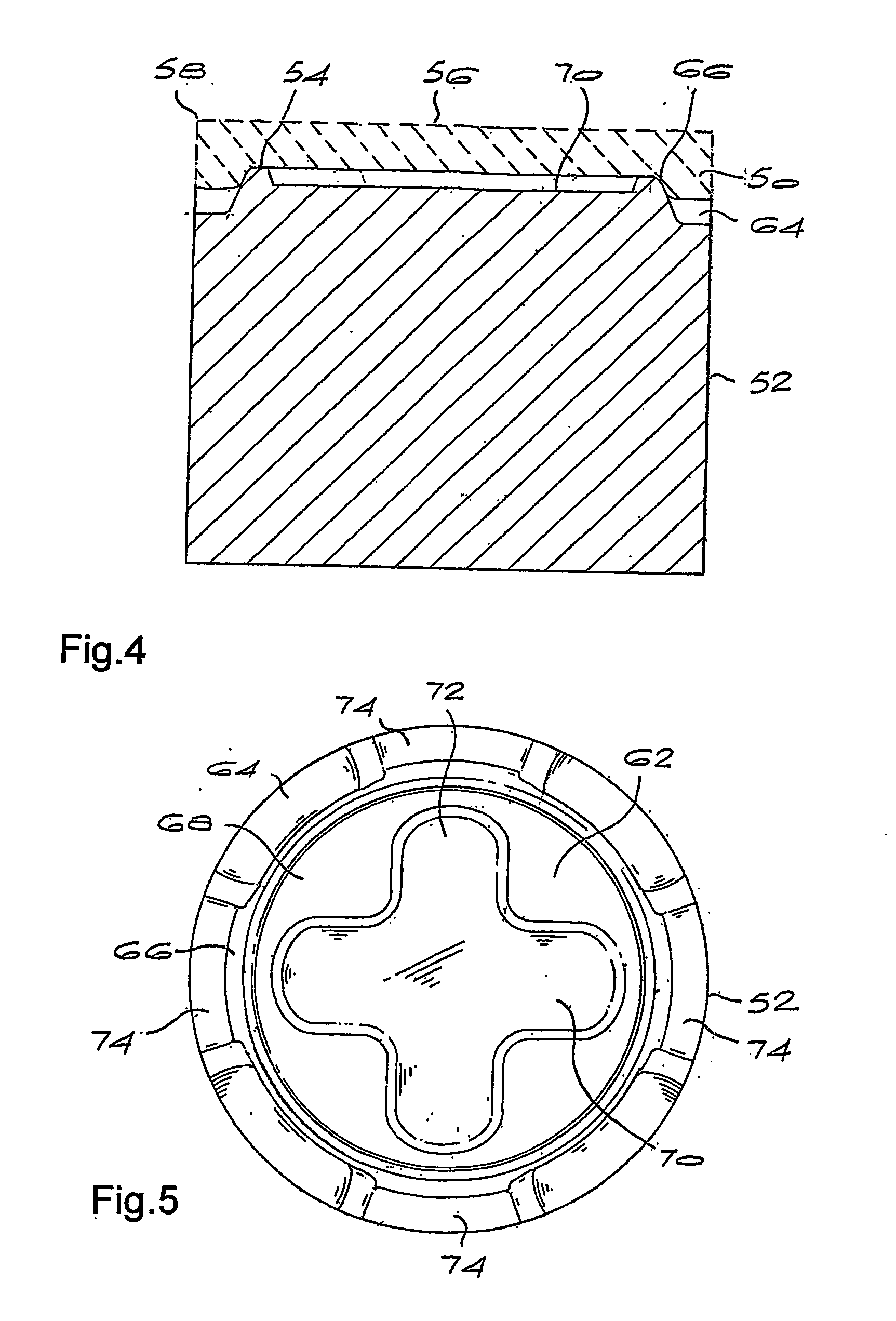
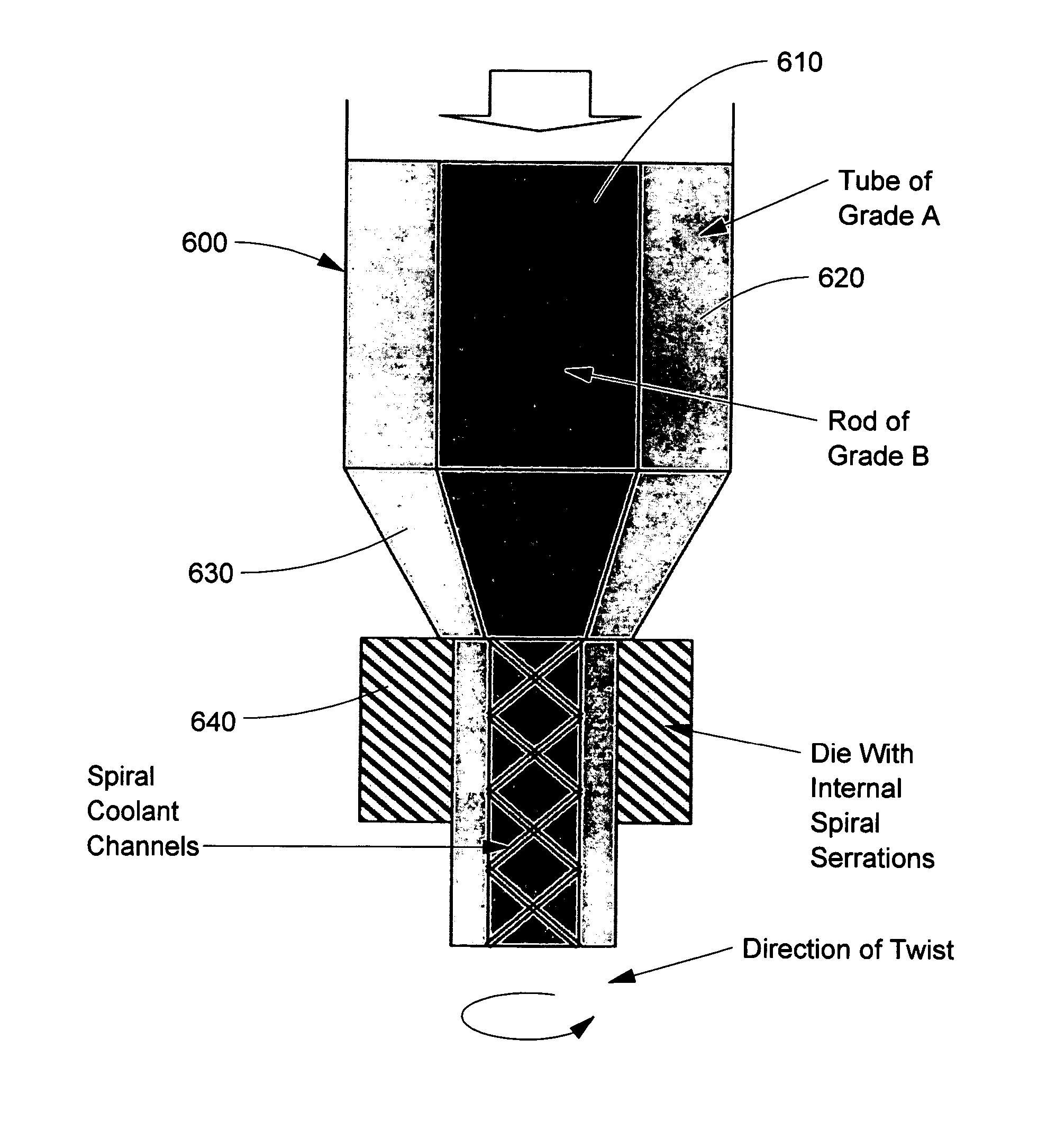
Composite article with coolant channels and tool fabrication method
Embodiments of the present invention include composite articles comprising at least a first region and a second region and methods of making such articles. The first region may comprise a first composite material, wherein the first region comprises less than 5 wt. % cubic carbides by weight, and the second region may comprise a second composite material, wherein the second composite material differs from the first composite material in at least one characteristic. The composite article may additionally comprise at least one coolant channel. In certain embodiments, the first and second composite material may individually comprise hard particles in a binder, wherein the hard particles independently comprise at least one of a carbide, a nitride, a boride, a silicide, an oxide, and solid solutions thereof and the binder comprises at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, iron and alloys thereof. In specific embodiments, the first composite material and the second composite material may individually comprise metal carbides in a binder, such as a cemented carbide.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com