Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2925 results about "Human skin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
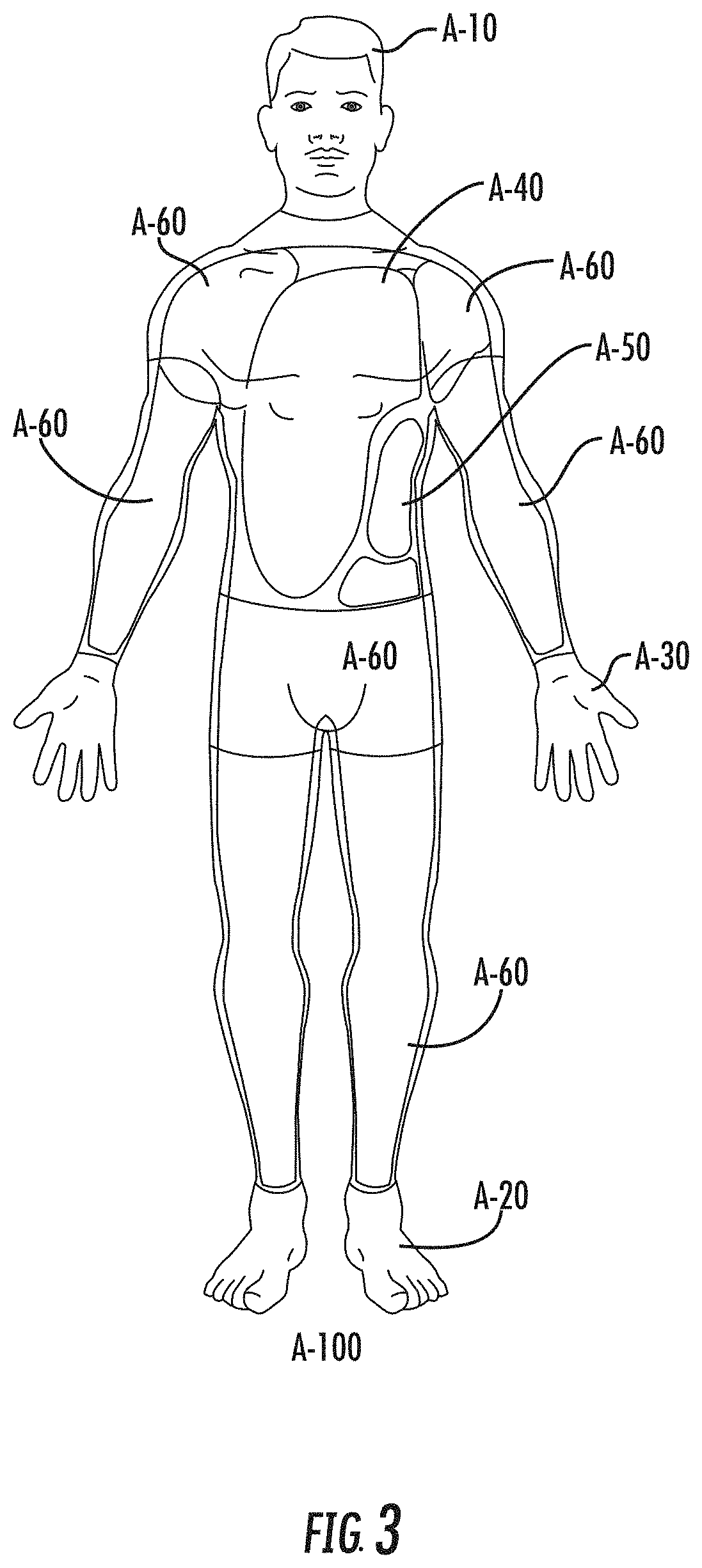
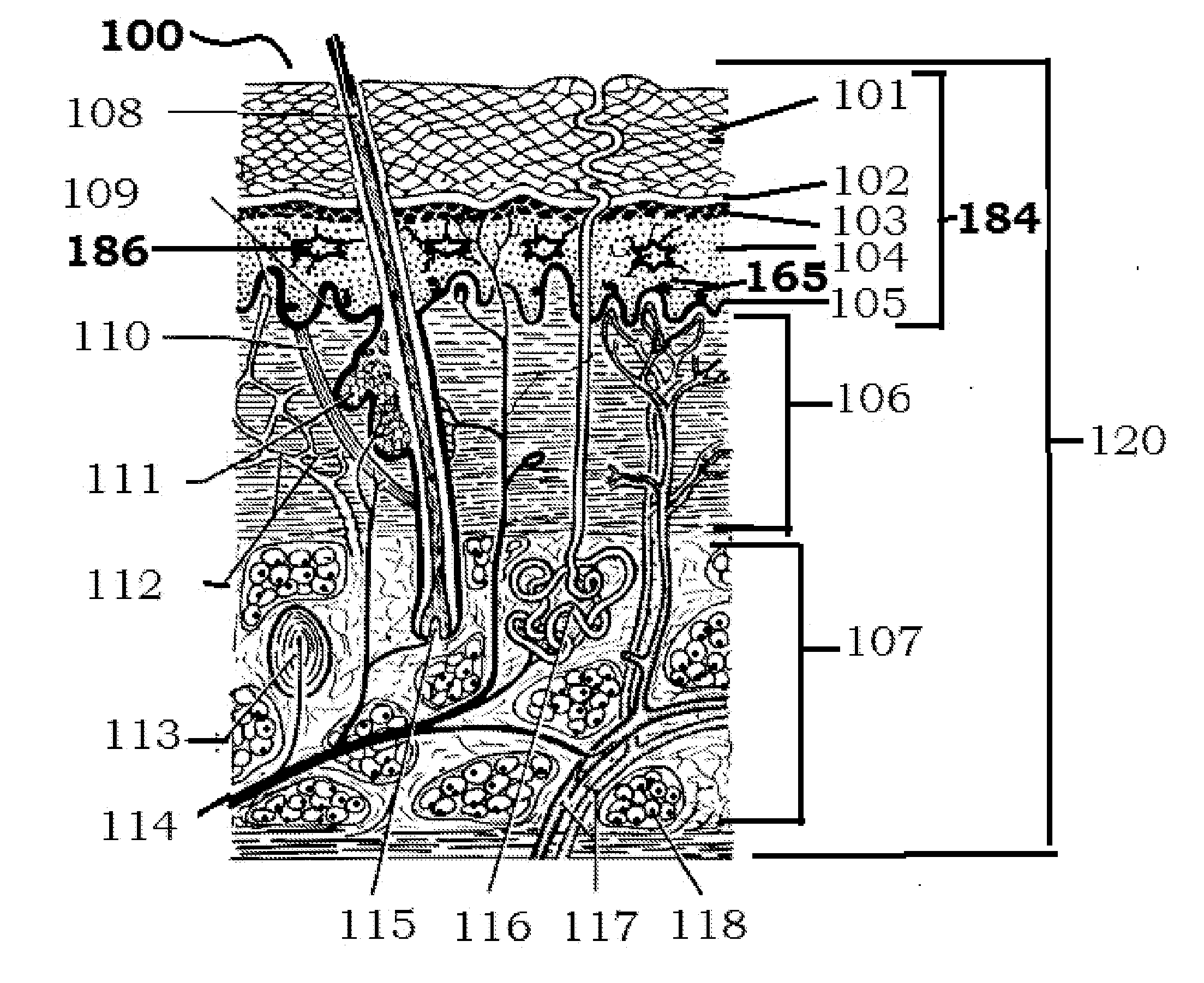
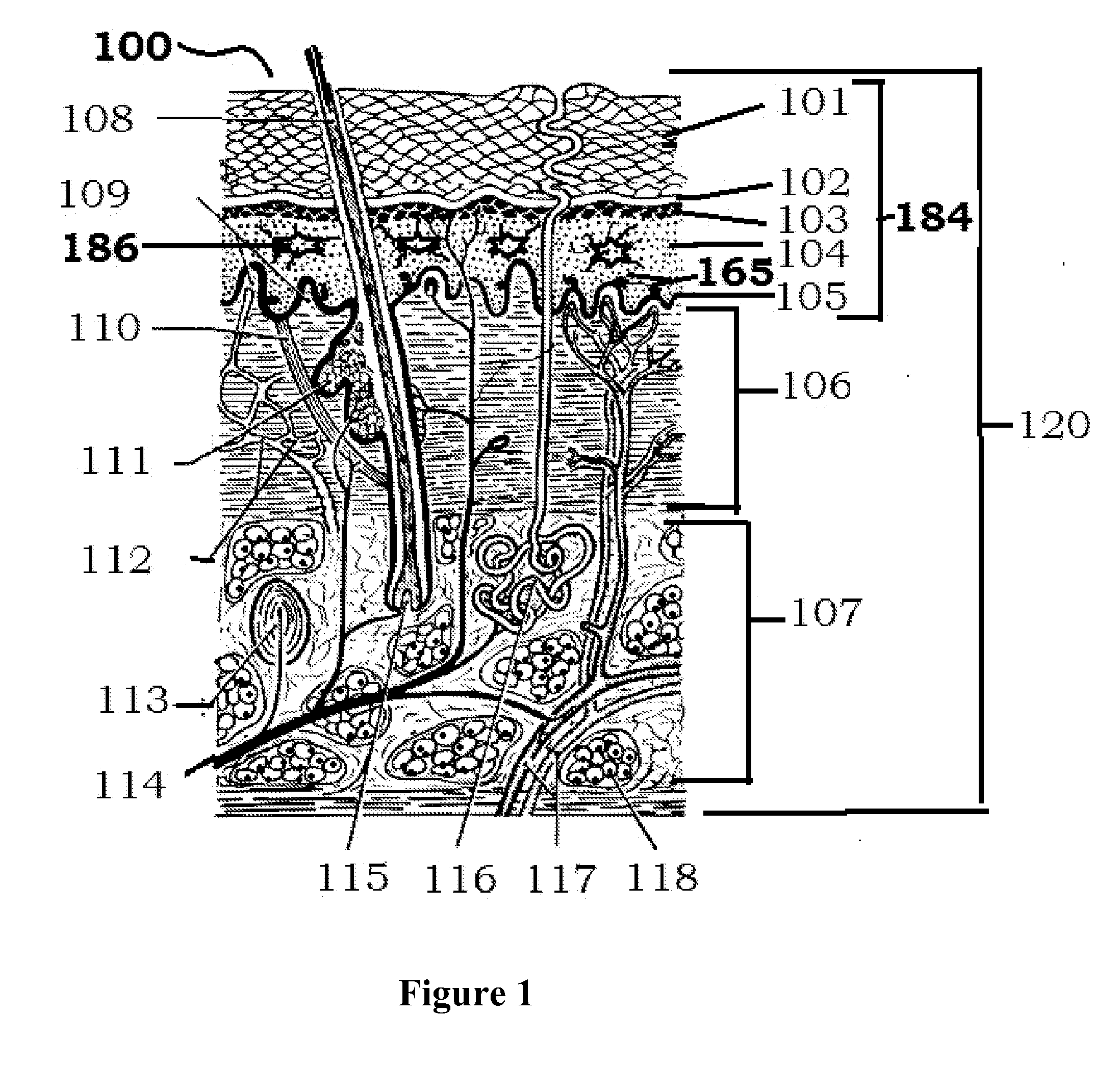
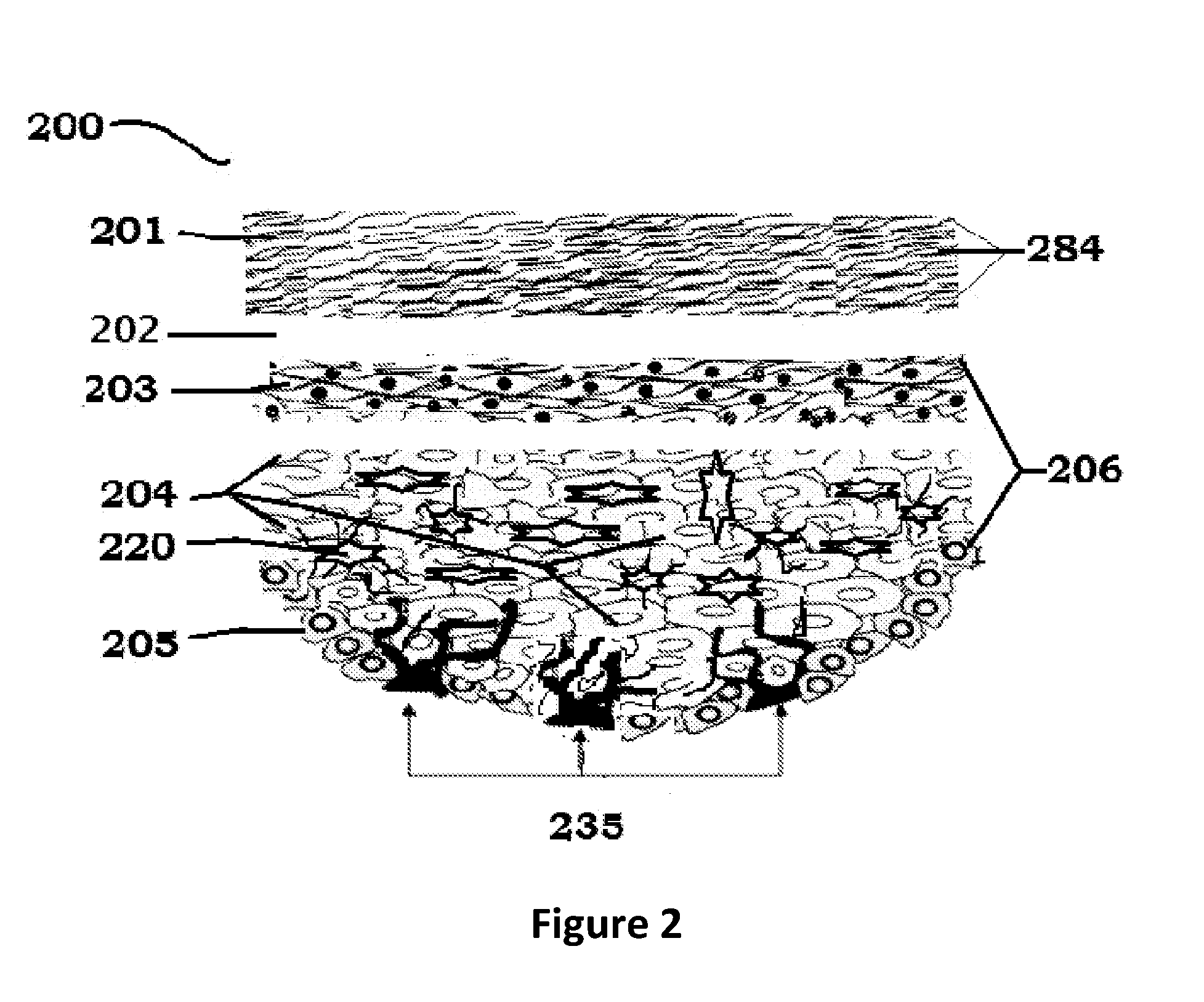
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin" (from Latin cutis, skin).
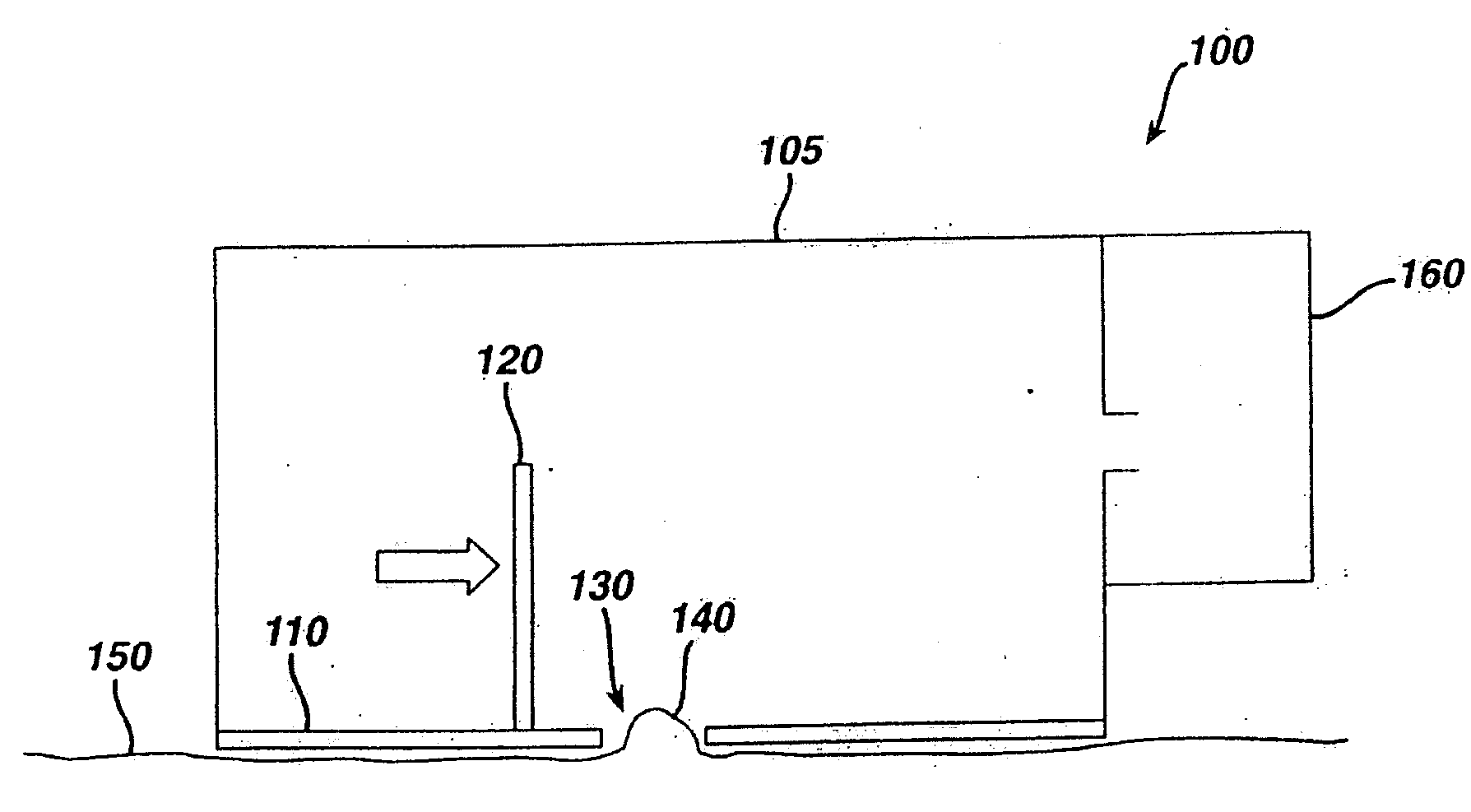
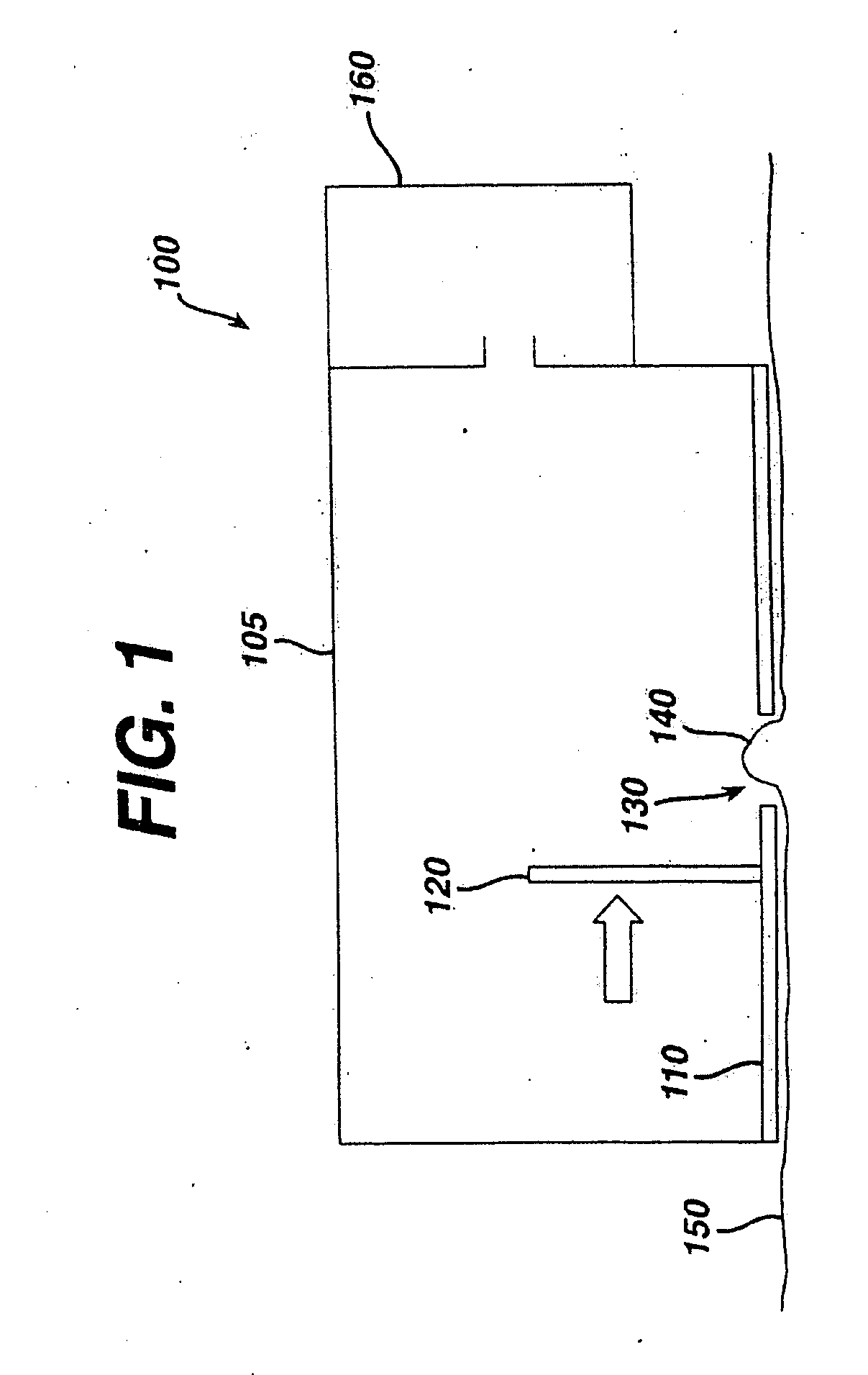
Gesture recognition apparatus, gesture recognition method, and gesture recognition program
ActiveUS7593552B2Easy to identifyInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionHuman skin
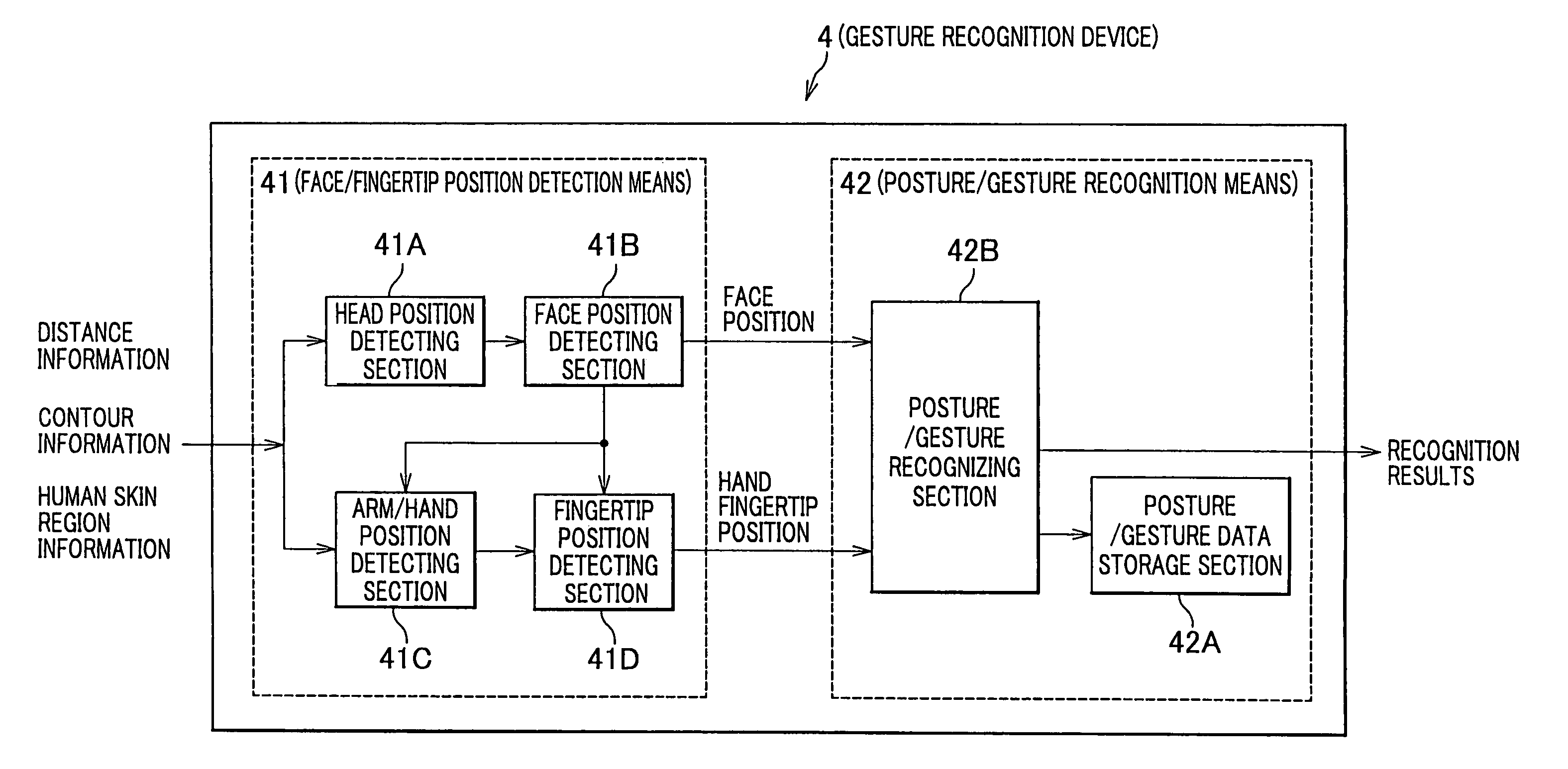
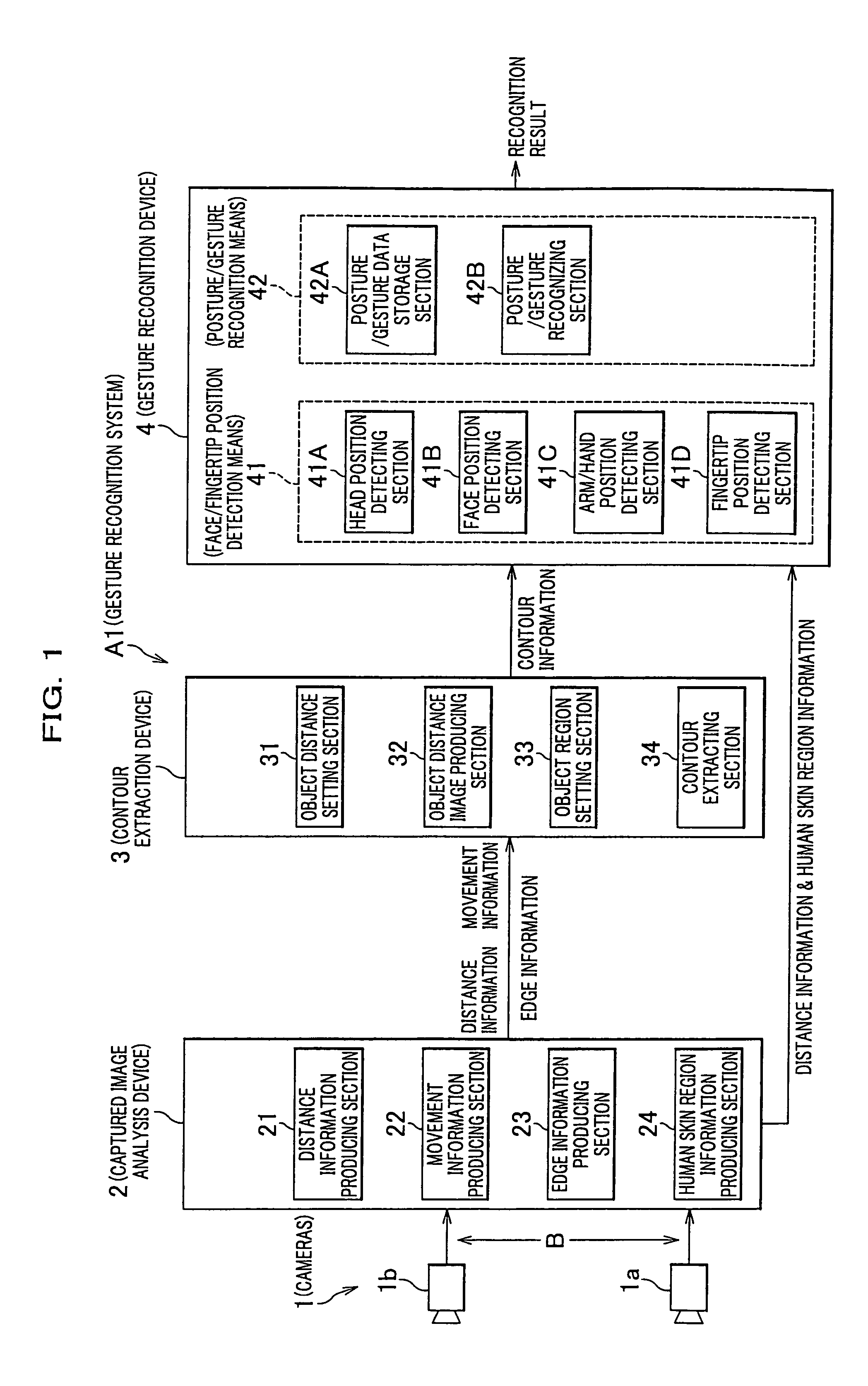
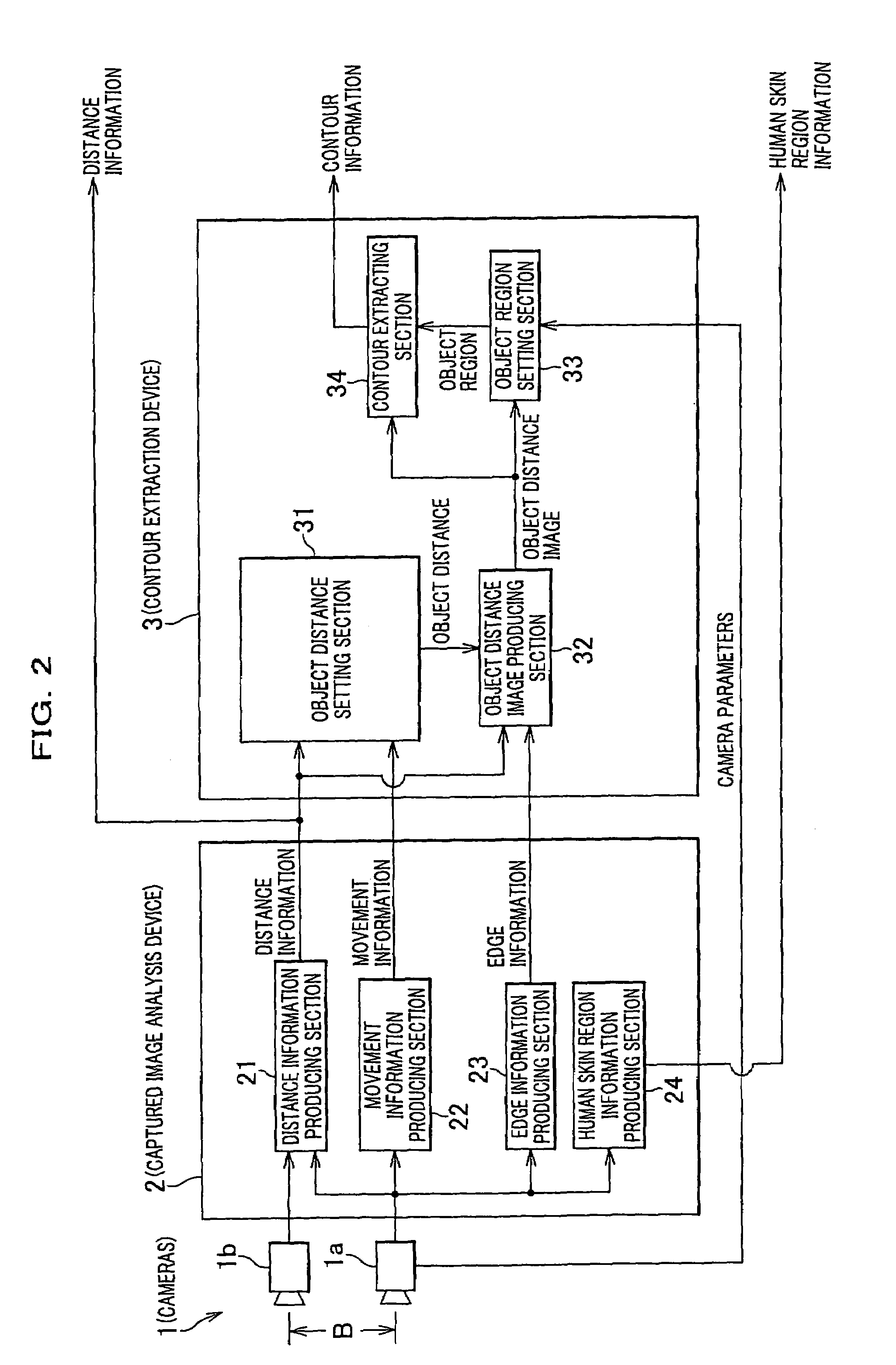
A gesture recognition apparatus for recognizing postures or gestures of an object person based on images of the object person captured by cameras. The gesture recognition apparatus includes: a face / fingertip position detection means which detects a face position and a fingertip position of the object person in three-dimensional space based on contour information and human skin region information of the object person to be produced by the images captured; and a posture / gesture recognition means which operates to detect changes of the fingertip position by a predetermined method, to process the detected results by a previously stored method, to determine a posture or a gesture of the object person, and to recognize a posture or a gesture of the object person.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Applicator for applying functional substances into human skin
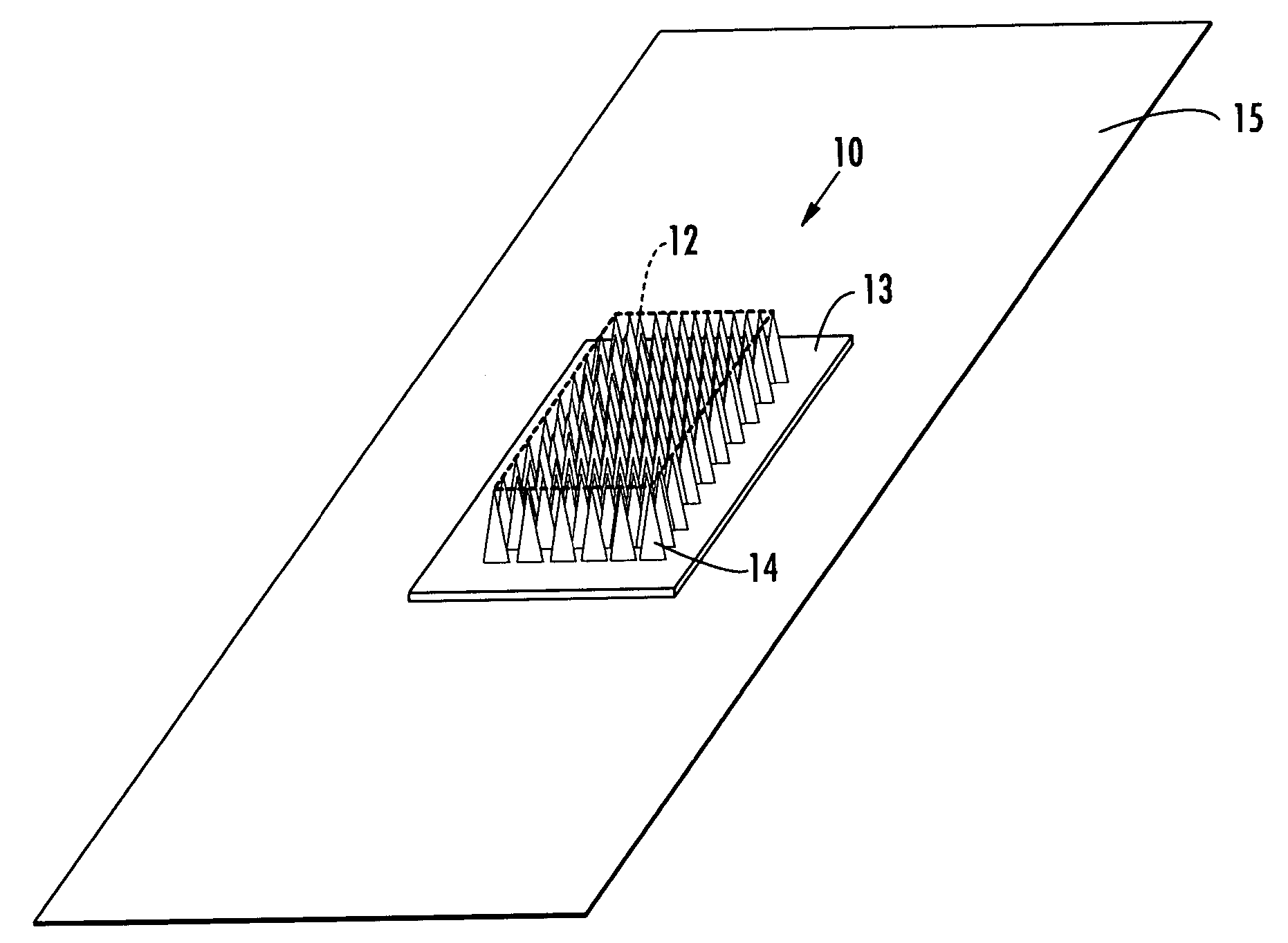
An applicator for applying functional substances, such as cosmetic powder, food color marking, India ink effect marks, or drugs into human skin, having a base, a plurality of microneedles fixed to and projecting from the base a distance only sufficient to penetrate into the stratum corneum or dermis, with the microneedles being of a material that is capable of disintegration and dispersion into the stratum corneum or dermis, such as maltose. The needles contain the functional substance for delivery into the stratum corneum or dermis. The microneedles are of a length approximately 0.5 to 500 μm when used to apply a functional substance to the stratum corneum, or are of a length of approximately 500 to 5,000 μm when used to apply a functional substance to the dermis.
Owner:TOBINAGA YOSHIKAZU +1
Methods and compositions for treatment of skin
ActiveUS20090214628A1Good lookingGood conditionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideHormonal imbalanceActive agent
Owner:SPECIAL WATER PATENTS
Communication Unit for a Person's Skin
InactiveUS20080021519A1Preserve sleeping timeLow costAcoustic time signalsOral administration deviceHuman skinCommunication unit
Electric communication unit to be placed on a person's skin, comprising a support element (3), a series of body contacts (7), a pulse generator (6) provided for generating a series of pulses and for transmitting the series of pulses to said series of body contacts (7), said series of body contacts (7) being provided to transmit said series of pulses onto the skin of said person. The electric communication unit is in the form of a patch.
Owner:THERASOLVE NV
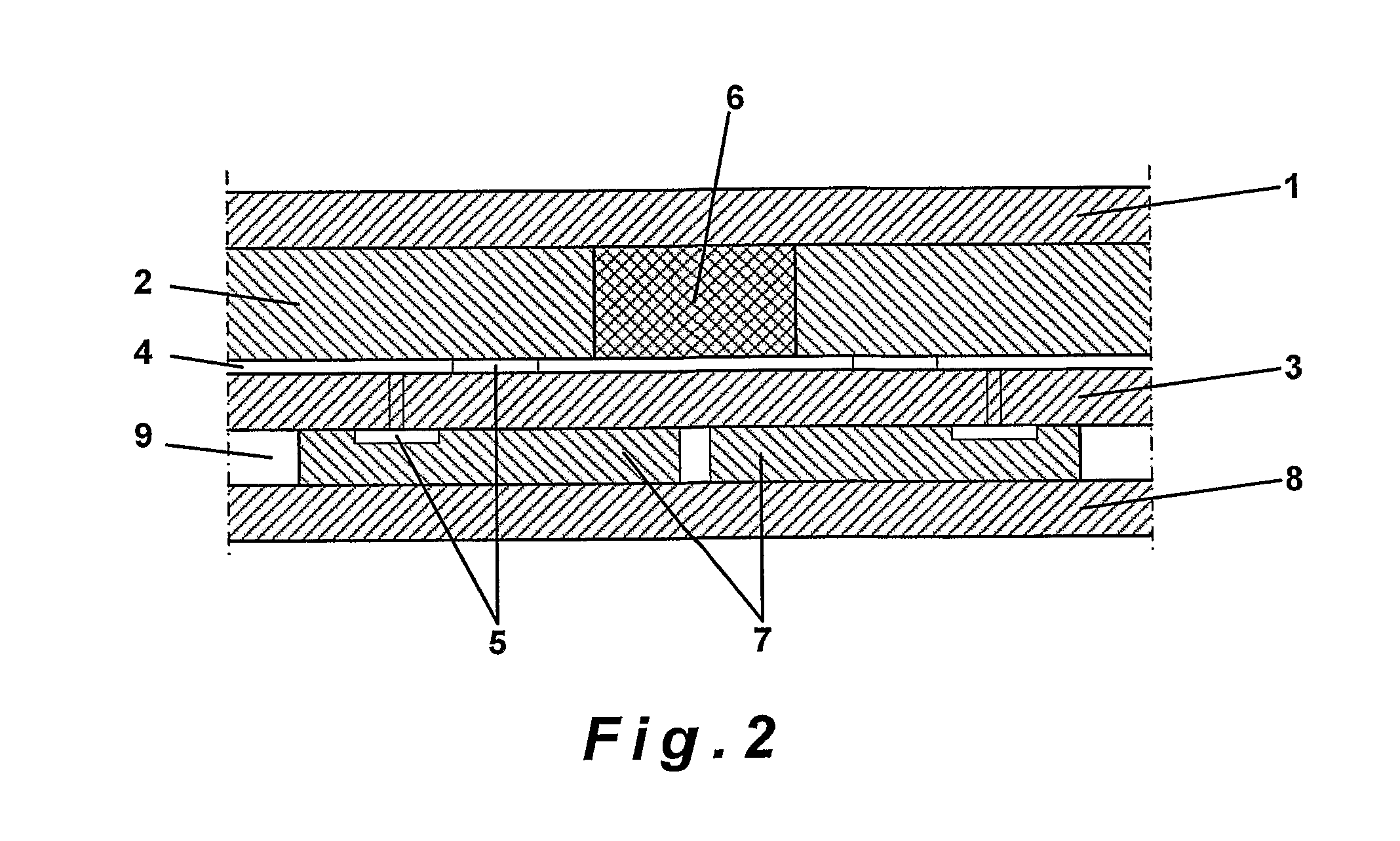
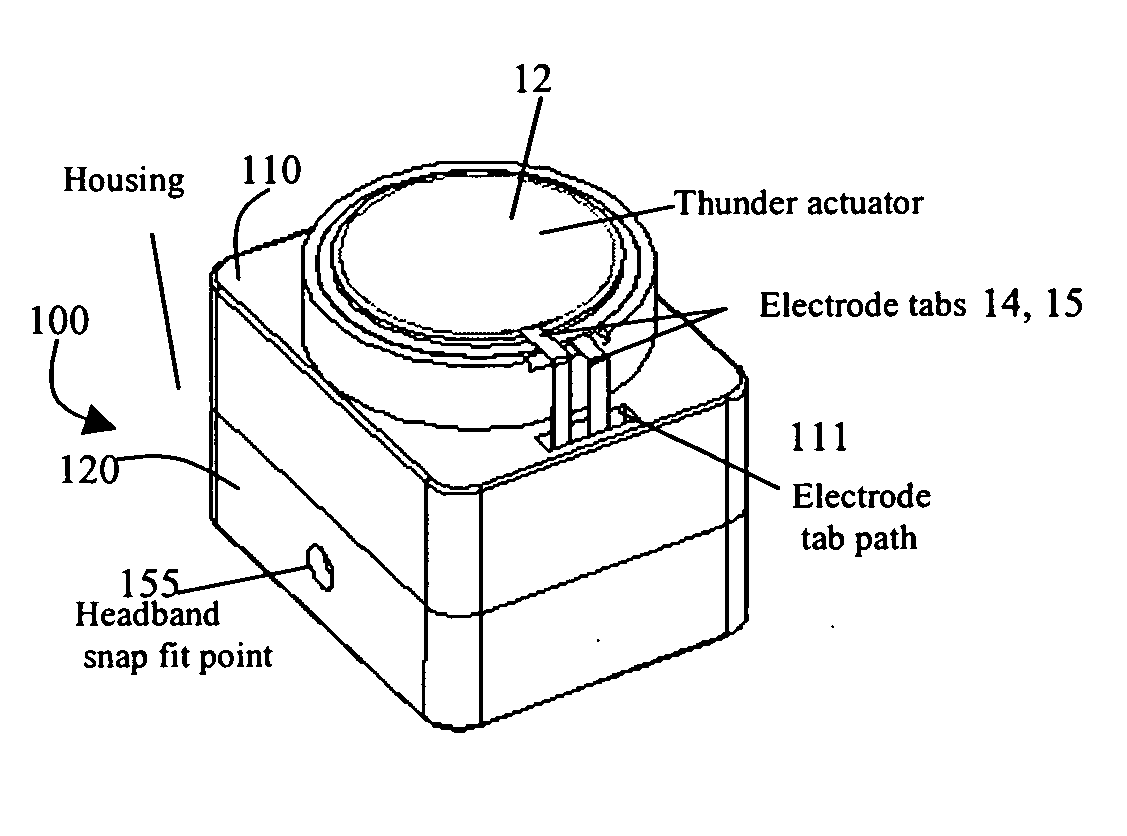
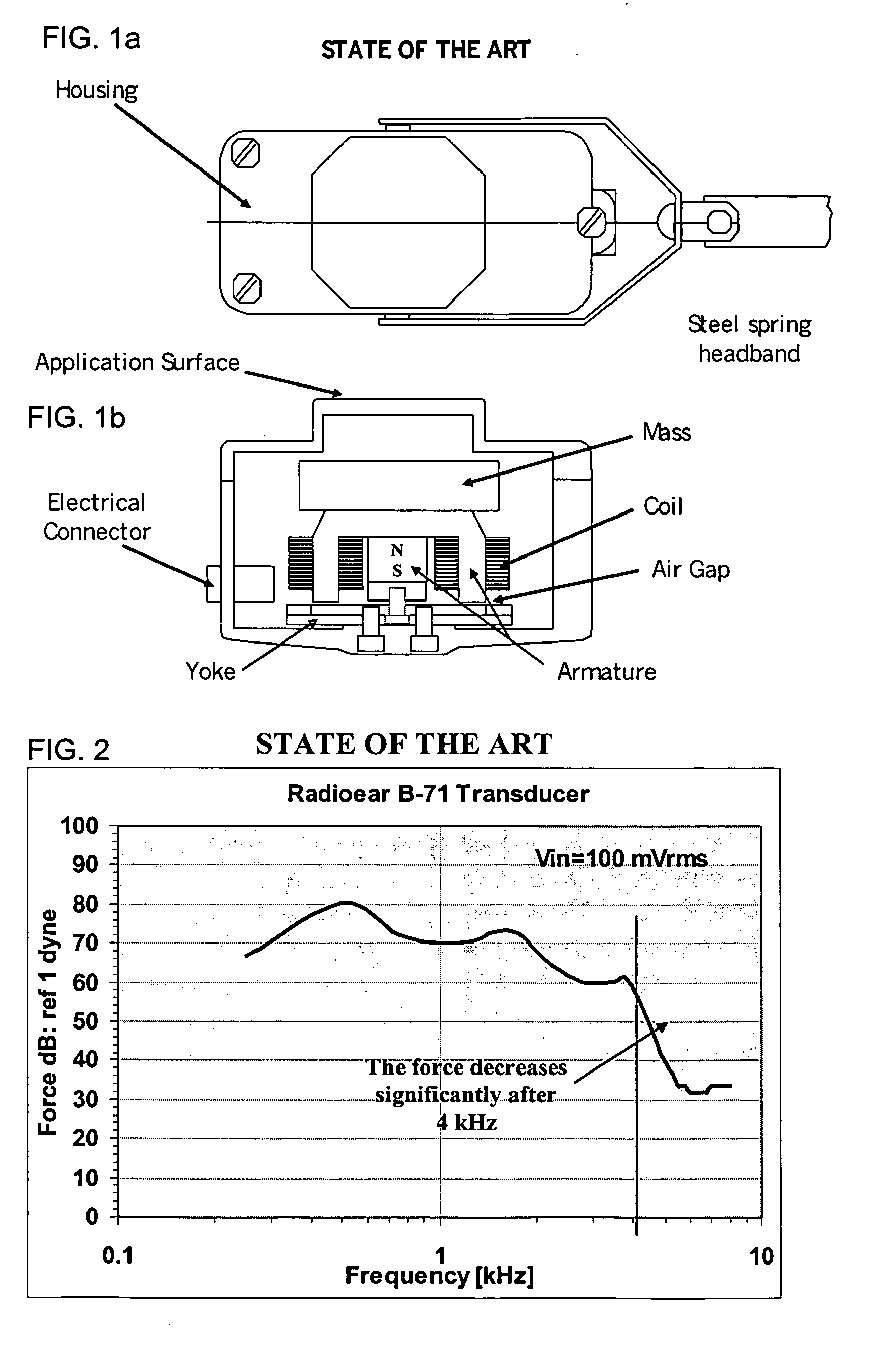
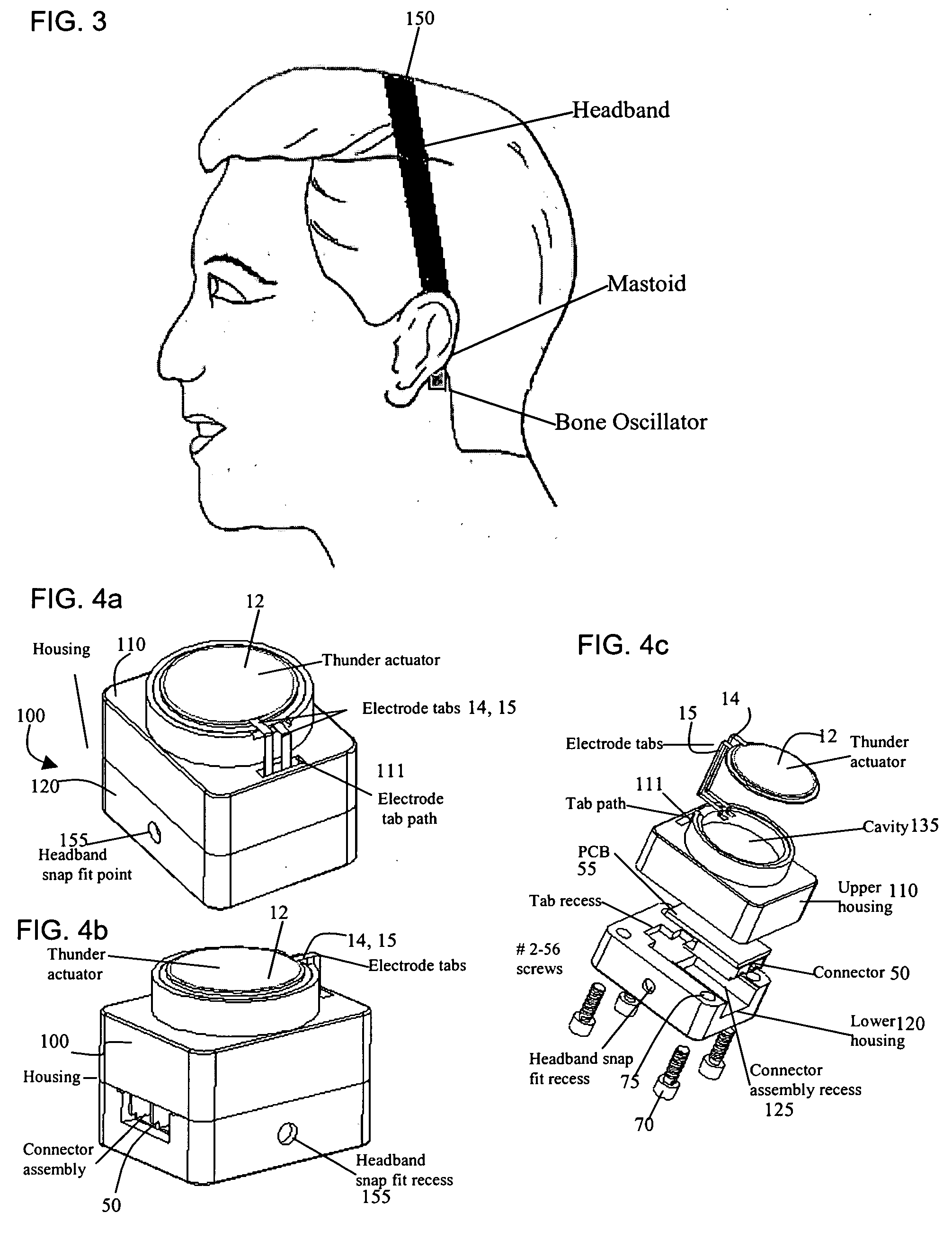
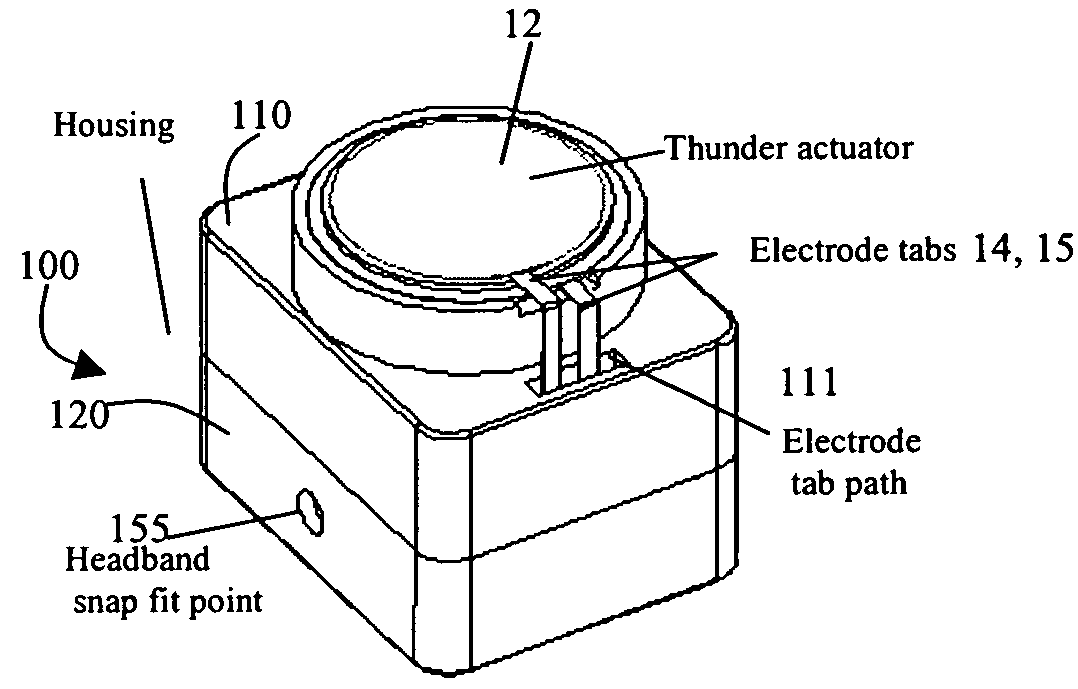
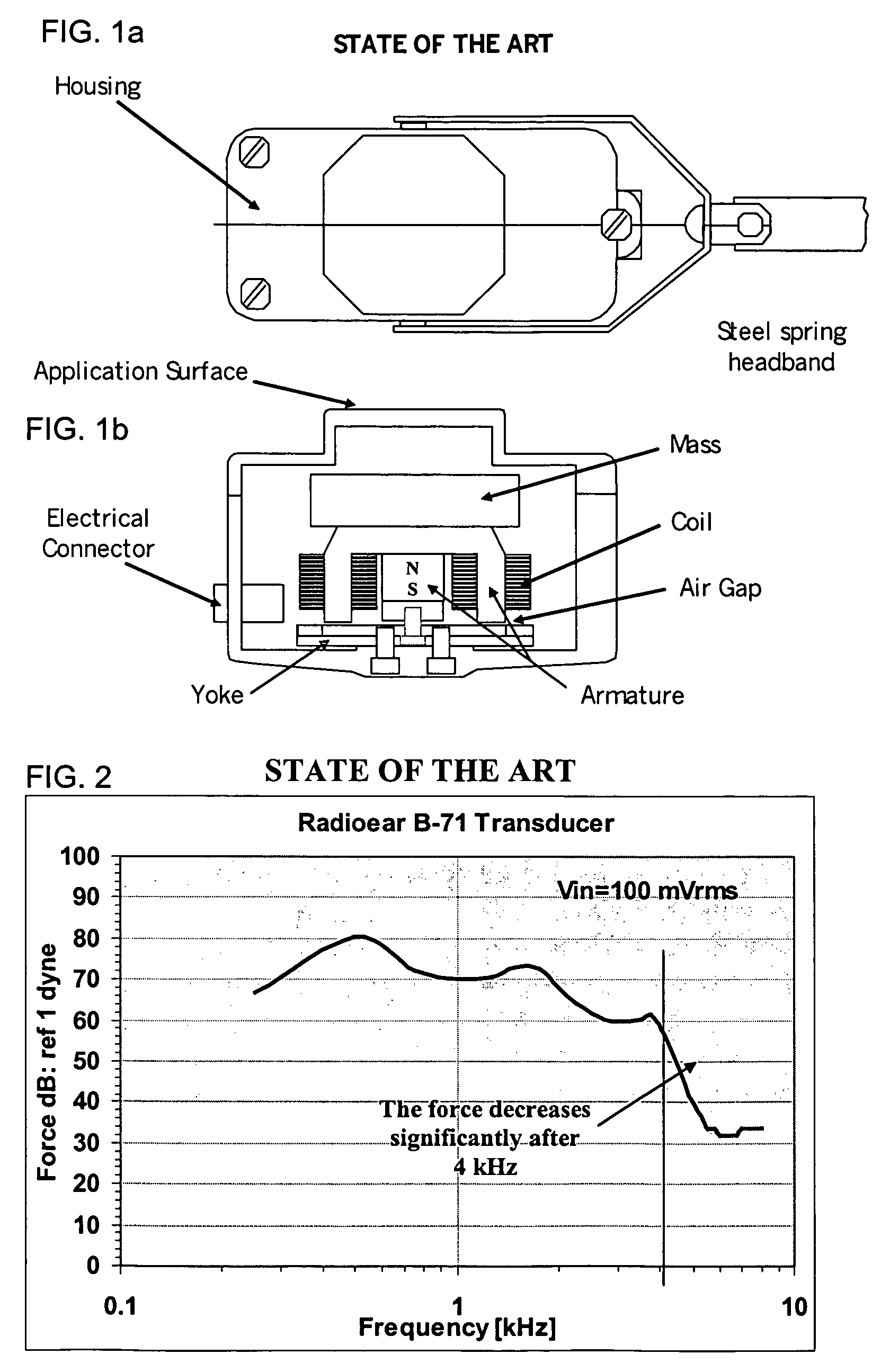
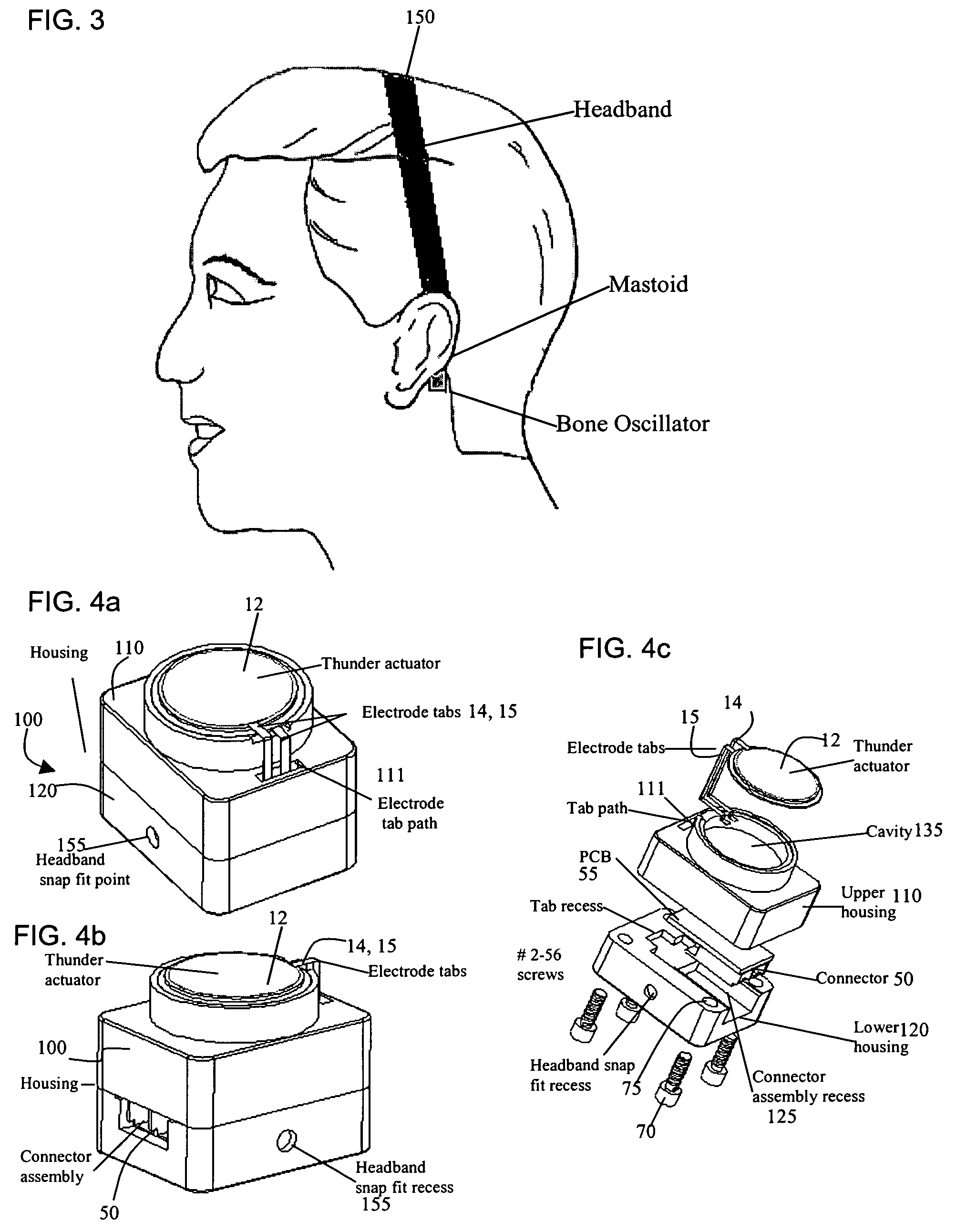
Bone-conduction hearing-aid transducer having improved frequency response
InactiveUS20070041595A1Eliminates soldering wireEliminate useRecord carriersPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersFrequency spectrumBone structure
A hearing-aid device and a method for transmitting sound through bone conduction are disclosed. The hearing-aid device comprises a piezoelectric-type actuator, housing and connector. The piezoelectric actuator is preferably a circular flextensional-type actuator mounted along its peripheral edge in a specifically designed circular structure of the housing. During operation, the bone-conduction transducer is placed against the mastoid area behind the ear of the patient. When the device is energized with an alternating electrical voltage, it flexes back and forth like a circular membrane sustained along its periphery and thus, vibrates as a consequence of the inverse piezoelectric effect. Due to the specific and unique designs proposed, these vibrations are directly transferred trough the human skin to the bone structure (the skull) and provide a means for the sound to be transmitted for patients with hearing malfunctions. The housing acts as a holder for the actuators, as a pre-stress application platform, and as a mass which tailors the frequency spectrum of the device. The apparatus exhibits a performance with a very flat response in the frequency spectrum 200 Hz to 10 kHz, which is a greater spectrum range than any other prior art devices disclosed for bone-conduction transduction which are typically limited to less than 4 kHz.
Owner:FACE INT
Face detection in color images with complex background
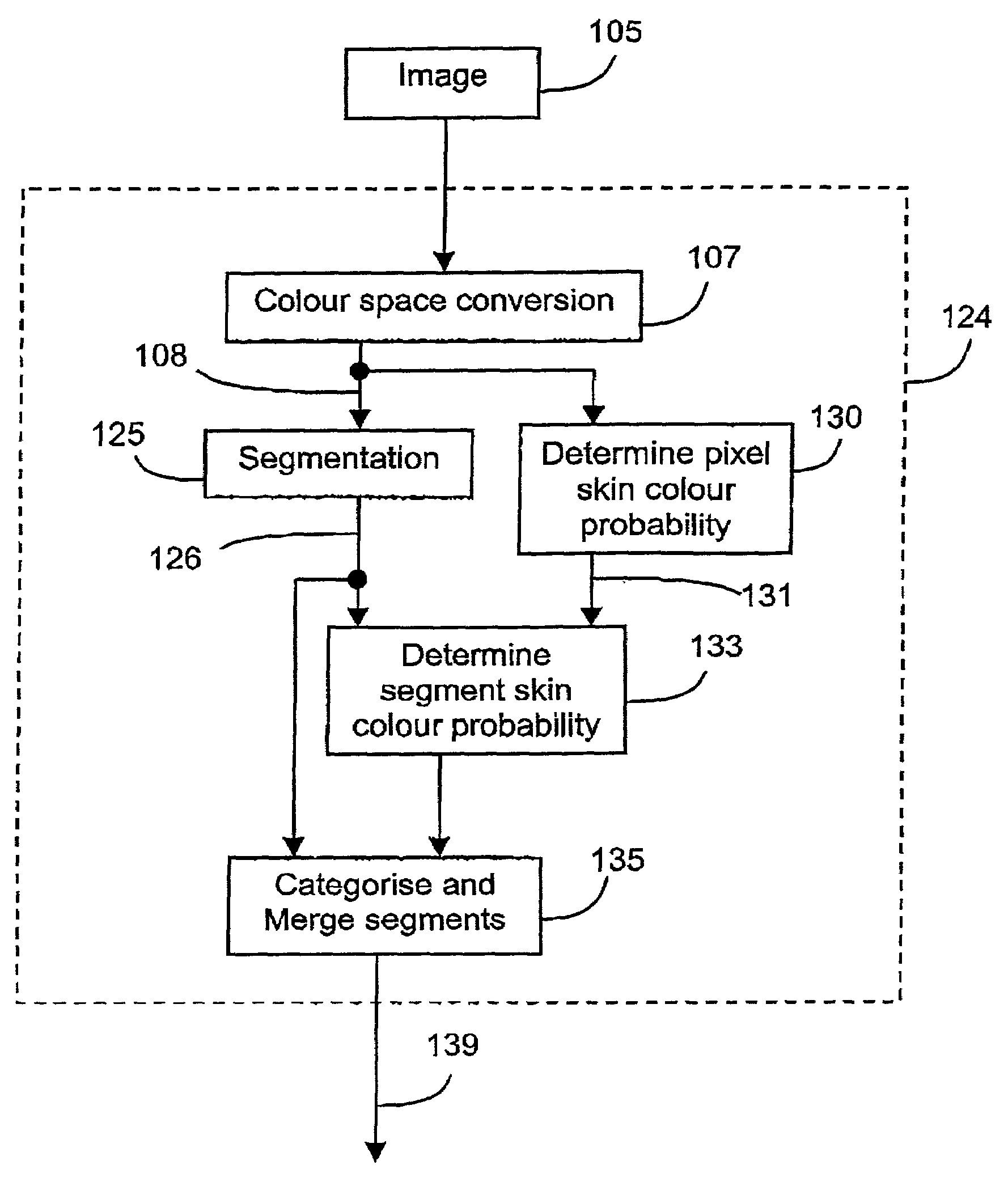
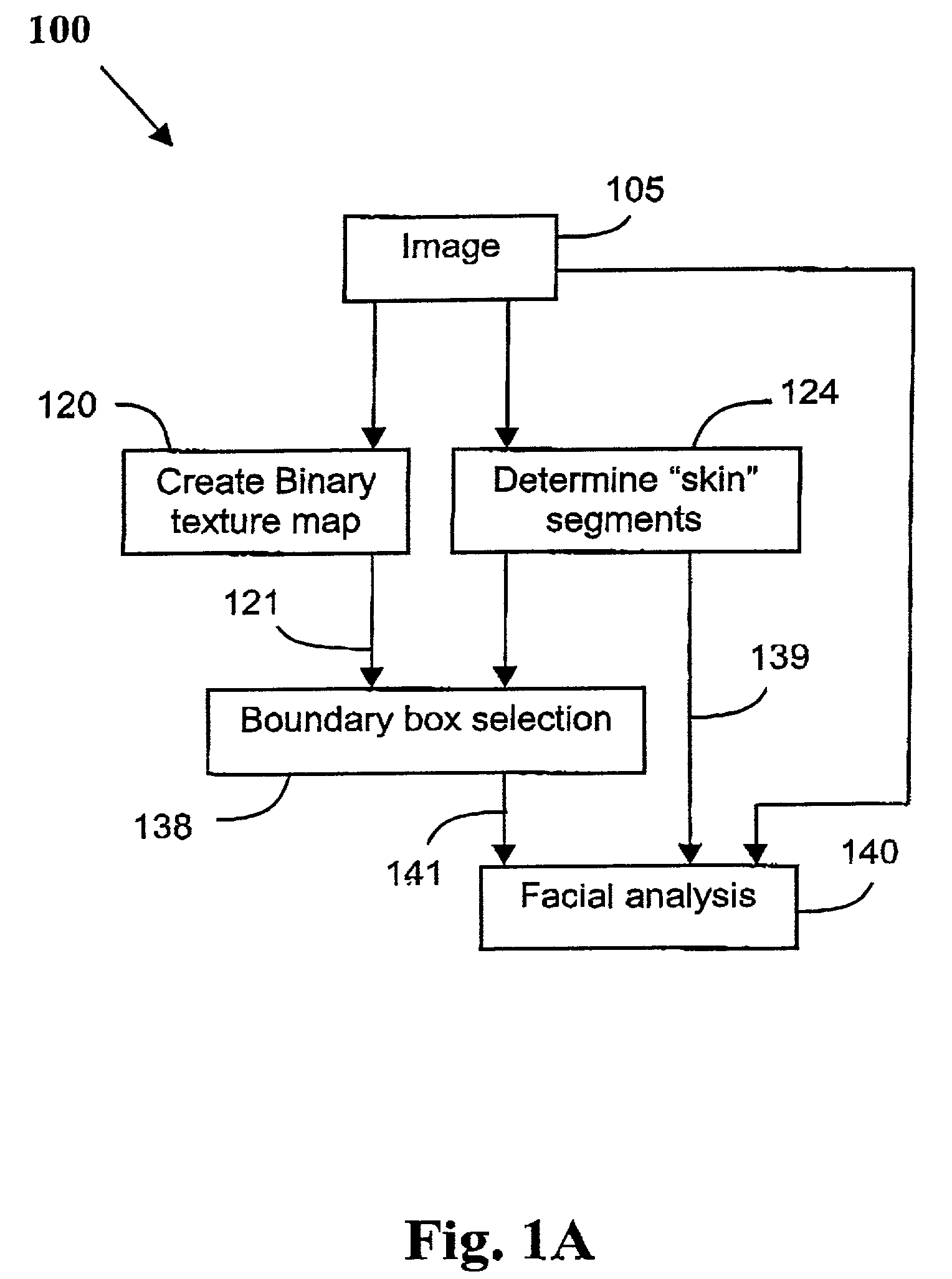
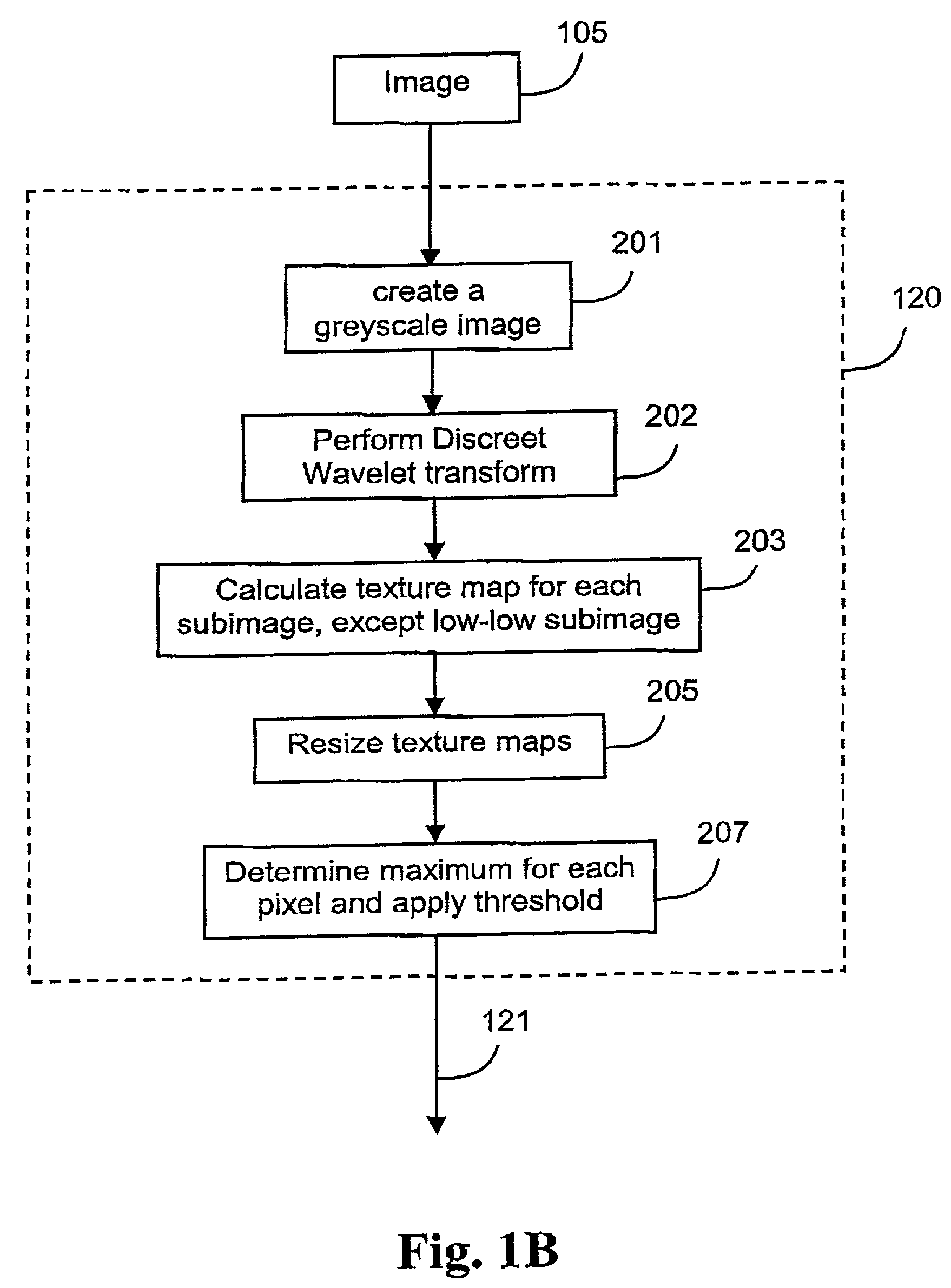
A method (100) of locating human faces, if present, in a cluttered scene captured on a digital image (105) is disclosed. The method (100) relies on a two step process, the first being the detection of segments with a high probability of being human skin in the color image (105), and to then determine a bounday box, or other boundary indication, to border each of those segments. The second step (140) is the analysis of features within each of those boundary boxes to determine which of the segments are likely to be a human face. As human skin is not highly textured, in order to detect segments with a high probability of being human skin, a binary texture map (121) is formed from the image (105), and segments having high texture are discarded.
Owner:CANON KK
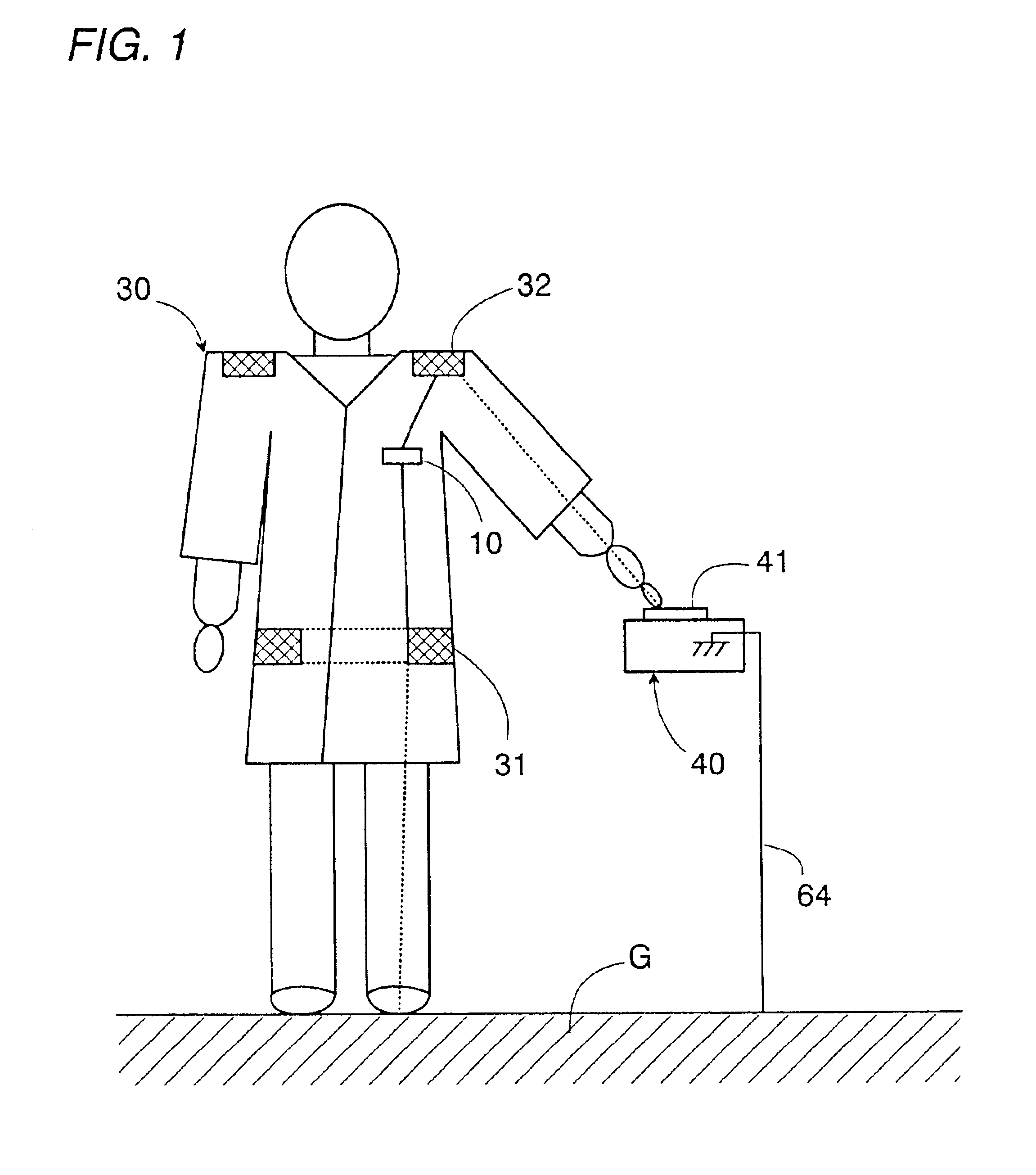
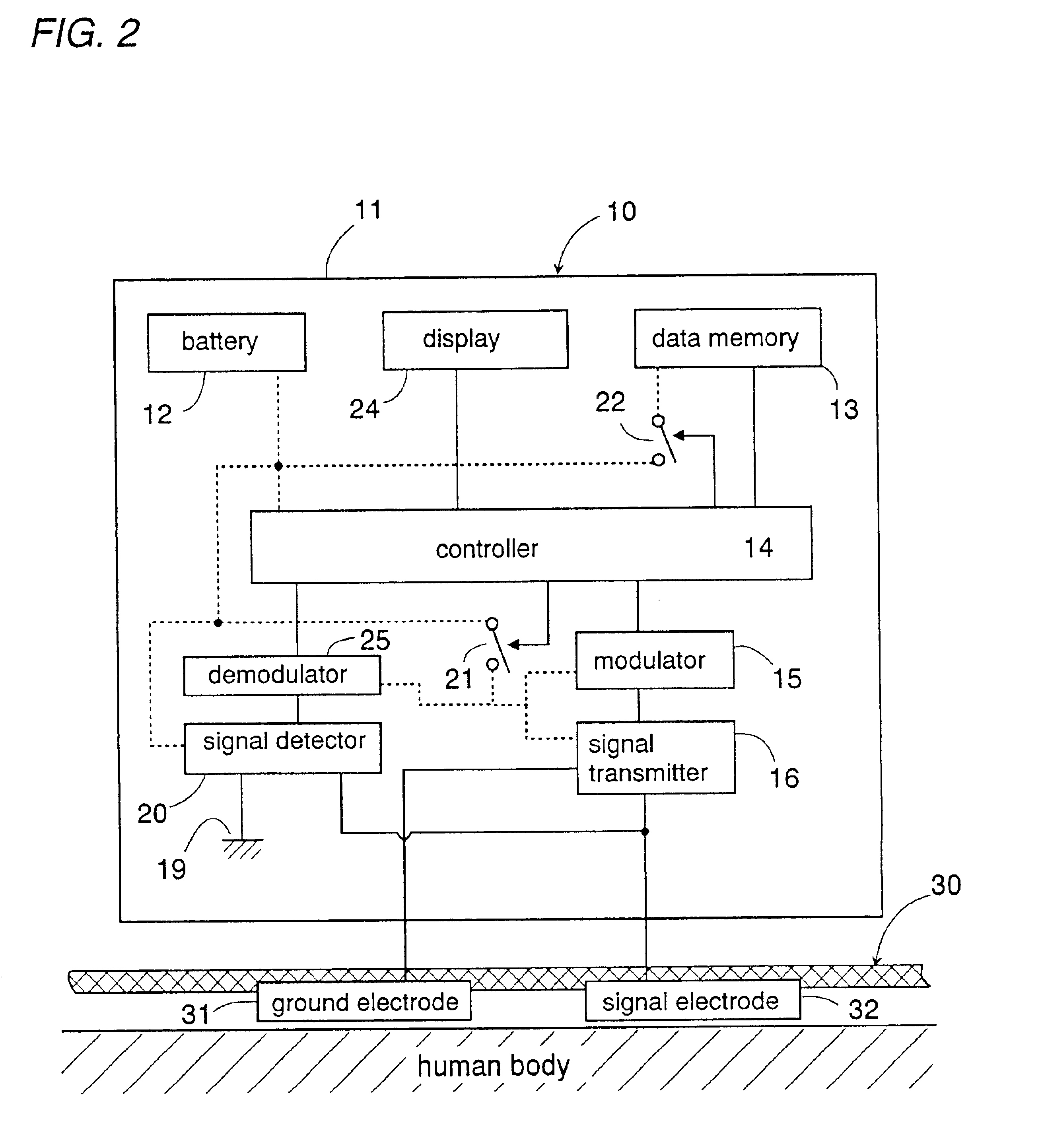
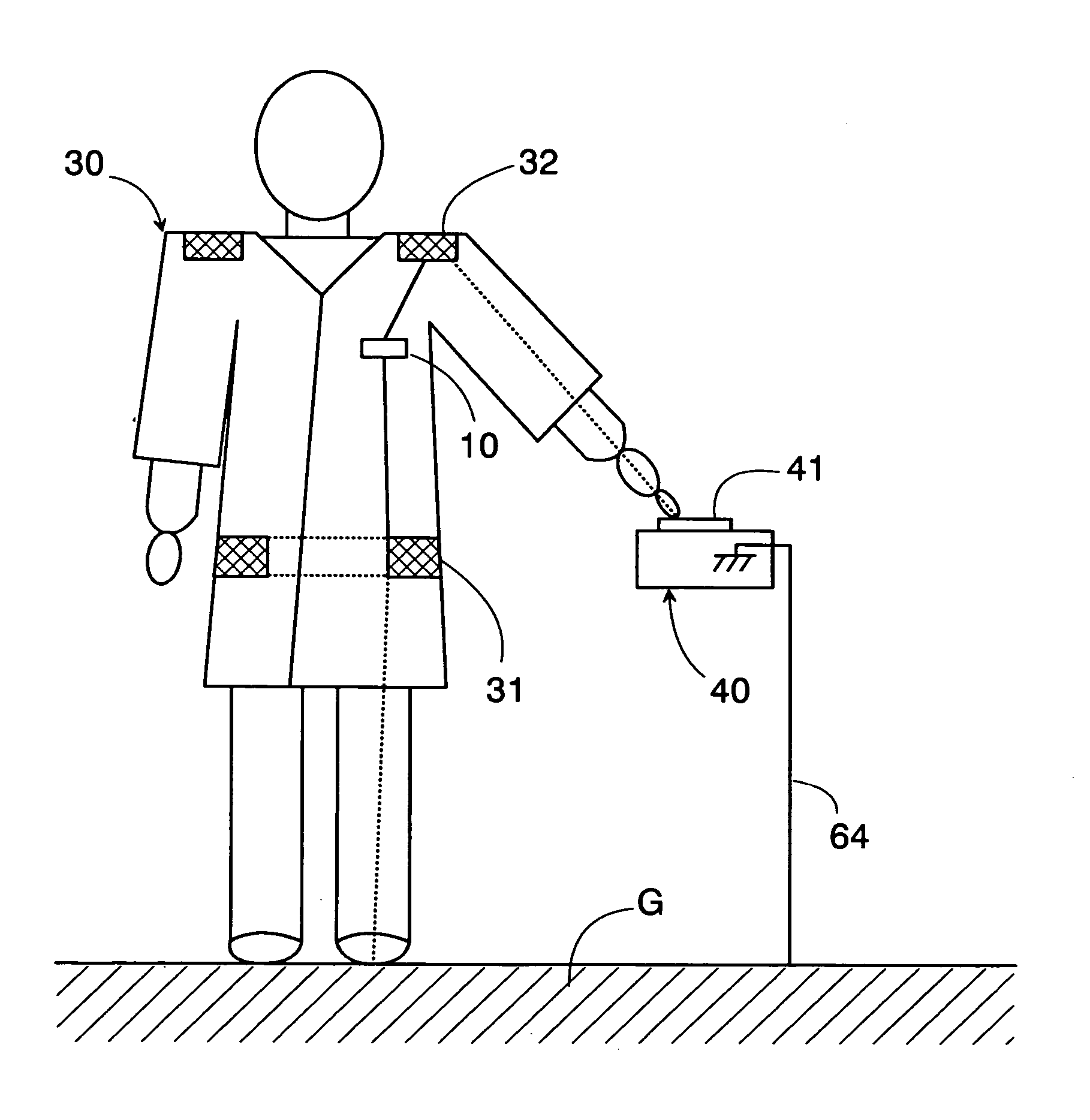
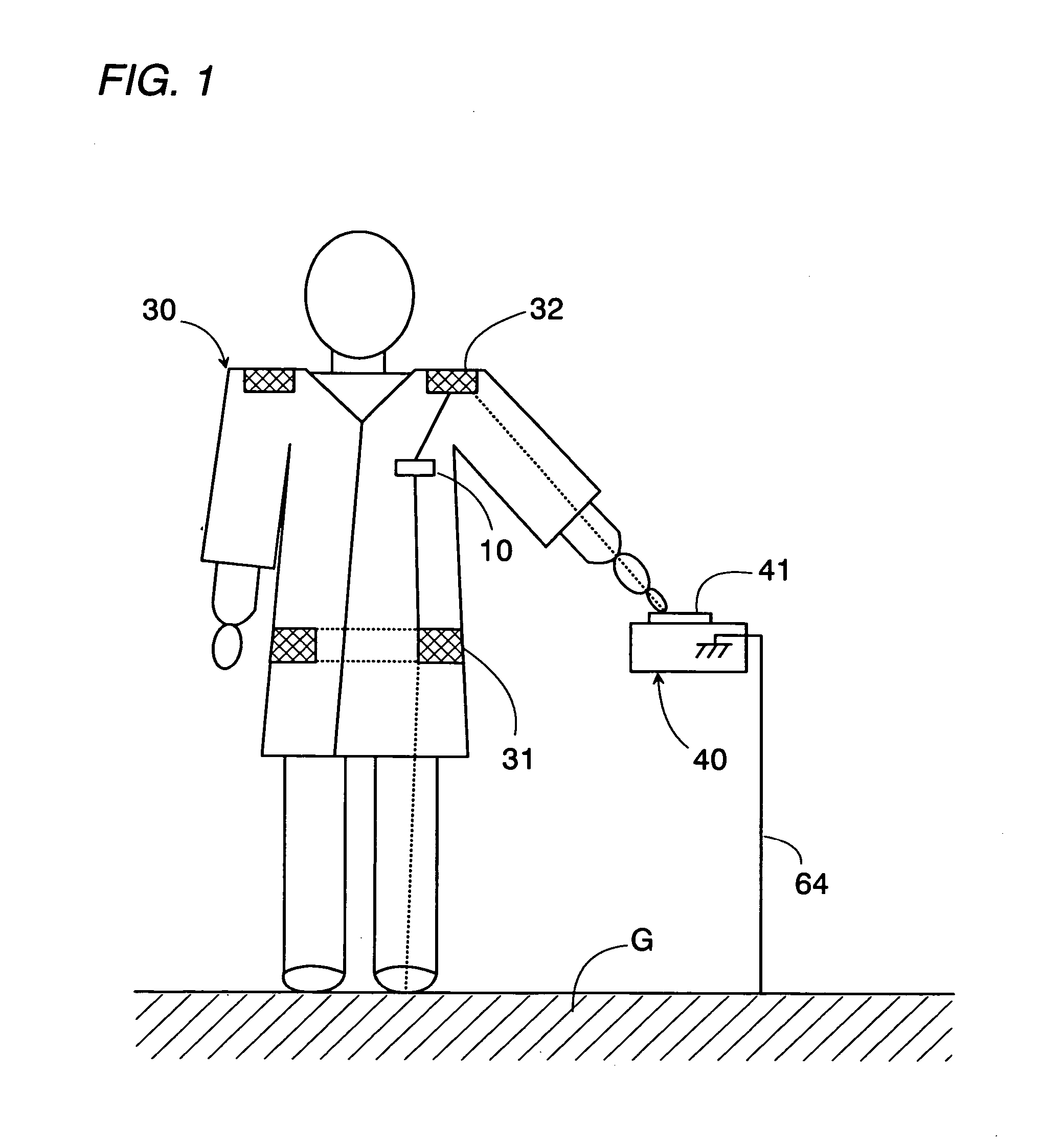
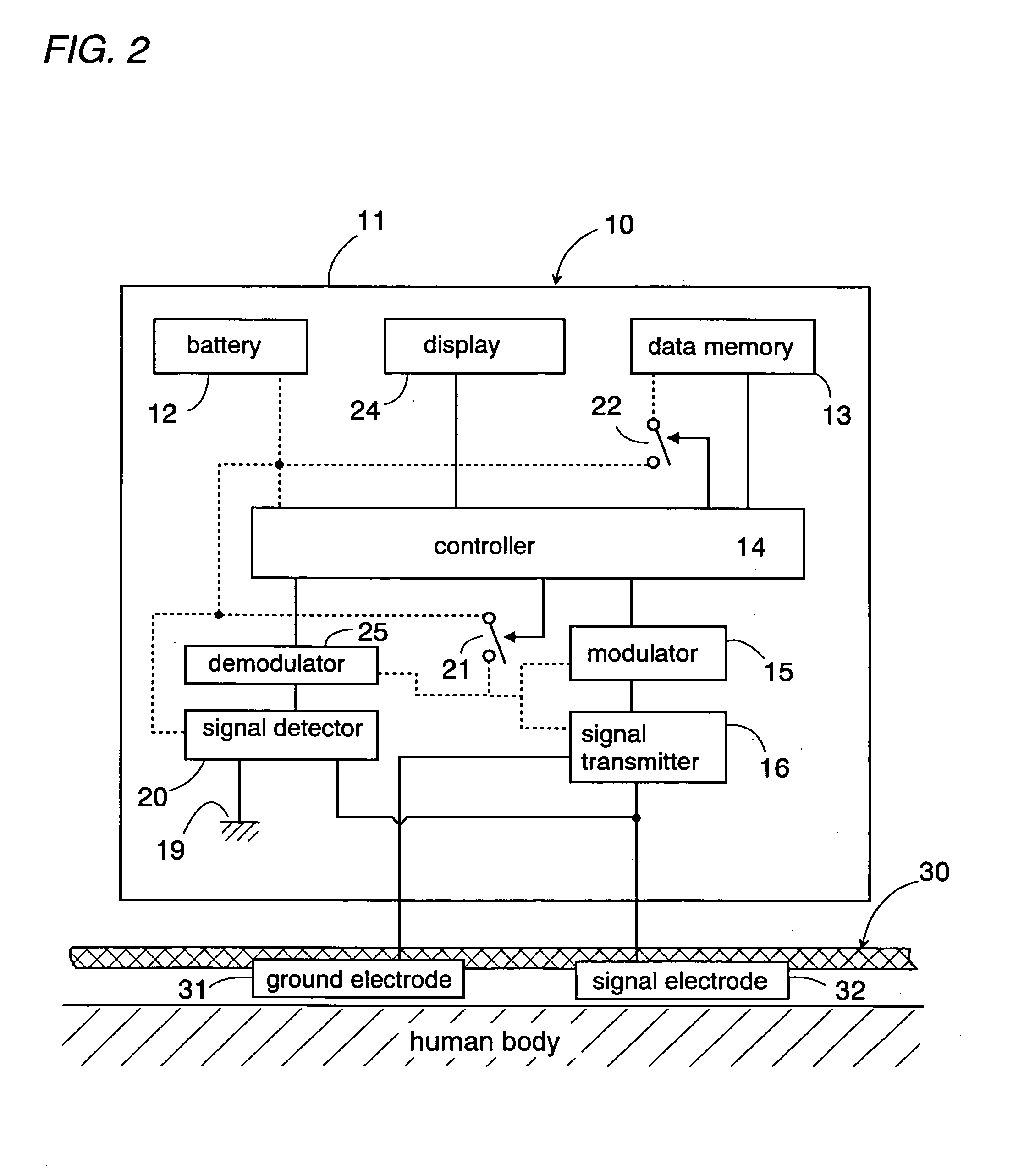
Data transmission system using a human body as a signal transmission path
InactiveUS6864780B2Easy to carryGuaranteed normal transmissionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsHuman bodySuccessful transmission
A data transmission system using a human body as a signal transmission path includes a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter uses a pair of electrodes which are held in close proximity to the skin of the human body. The transmitter transmits data to the receiver through the signal transmission path partly extending through the human body when a user carrying the transmitter touches a touch electrode of the receiver. The electrodes are integrated into a garment worn by the user in such a manner that the electrodes are kept in a closely facing relation to the skin of the user, thereby establishing the electrical path extending through the human body. With the integration of the two electrodes into the garment, the user wearing the garment as an everyday clothes or uniform can be easy and convenient to carry the transmitter for successful transmission of the data.
Owner:PANASONIC ELECTRIC WORKS CO LTD
Methods and devices for improving delivery of a substance to skin
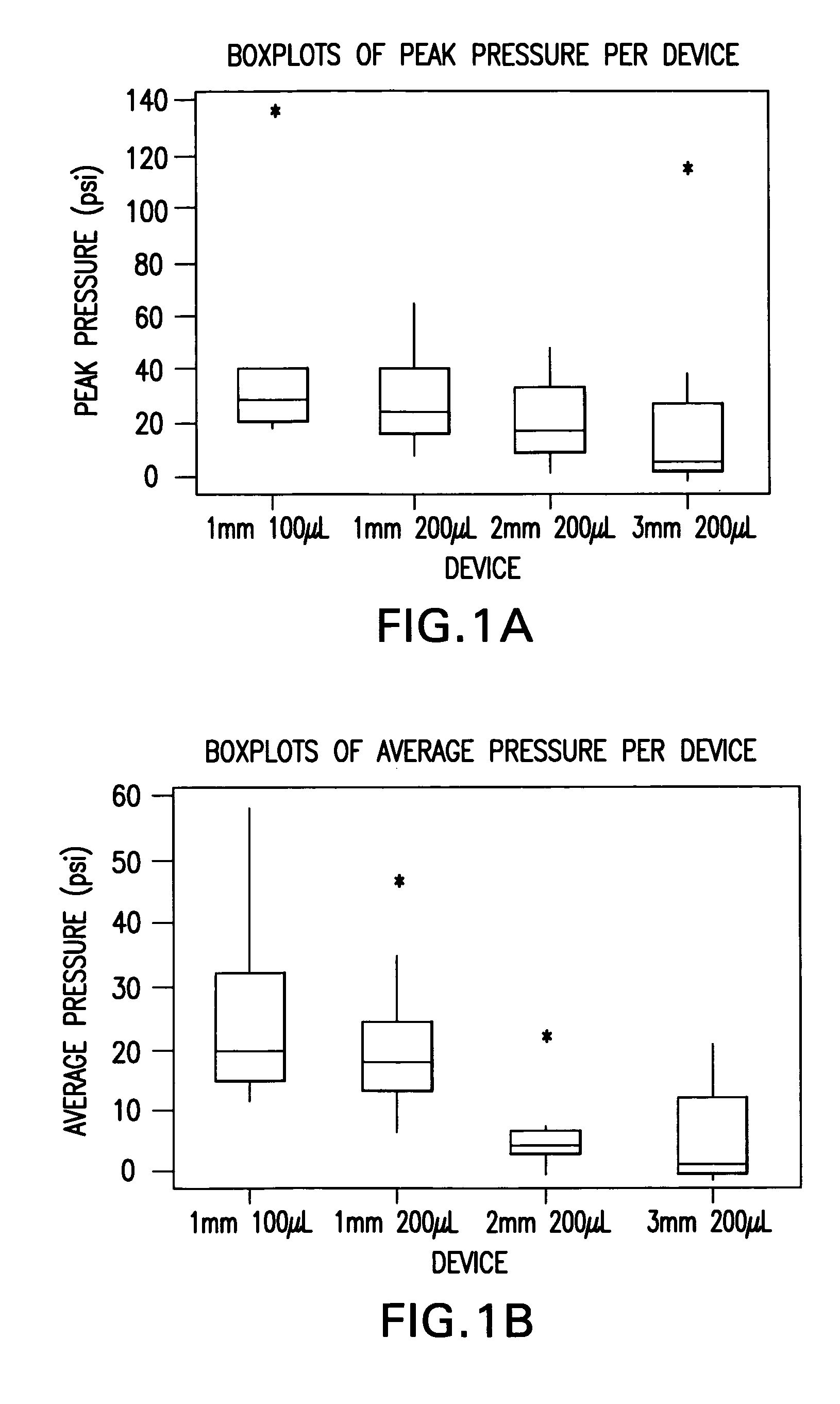
InactiveUS20050256499A1Efficacy is alteredImprove delivery capabilitiesMedical devicesPressure infusionDelivery PerformanceInjection site
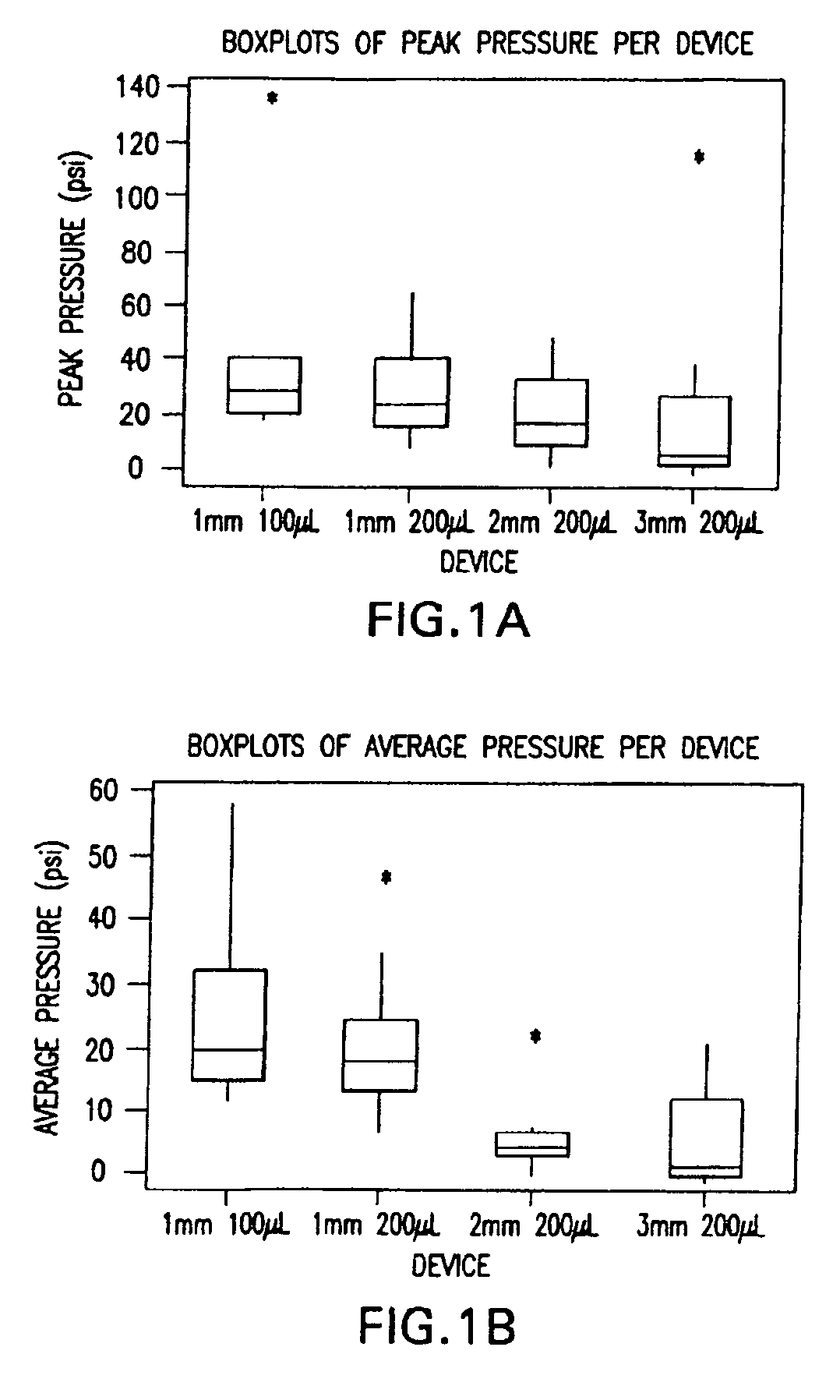
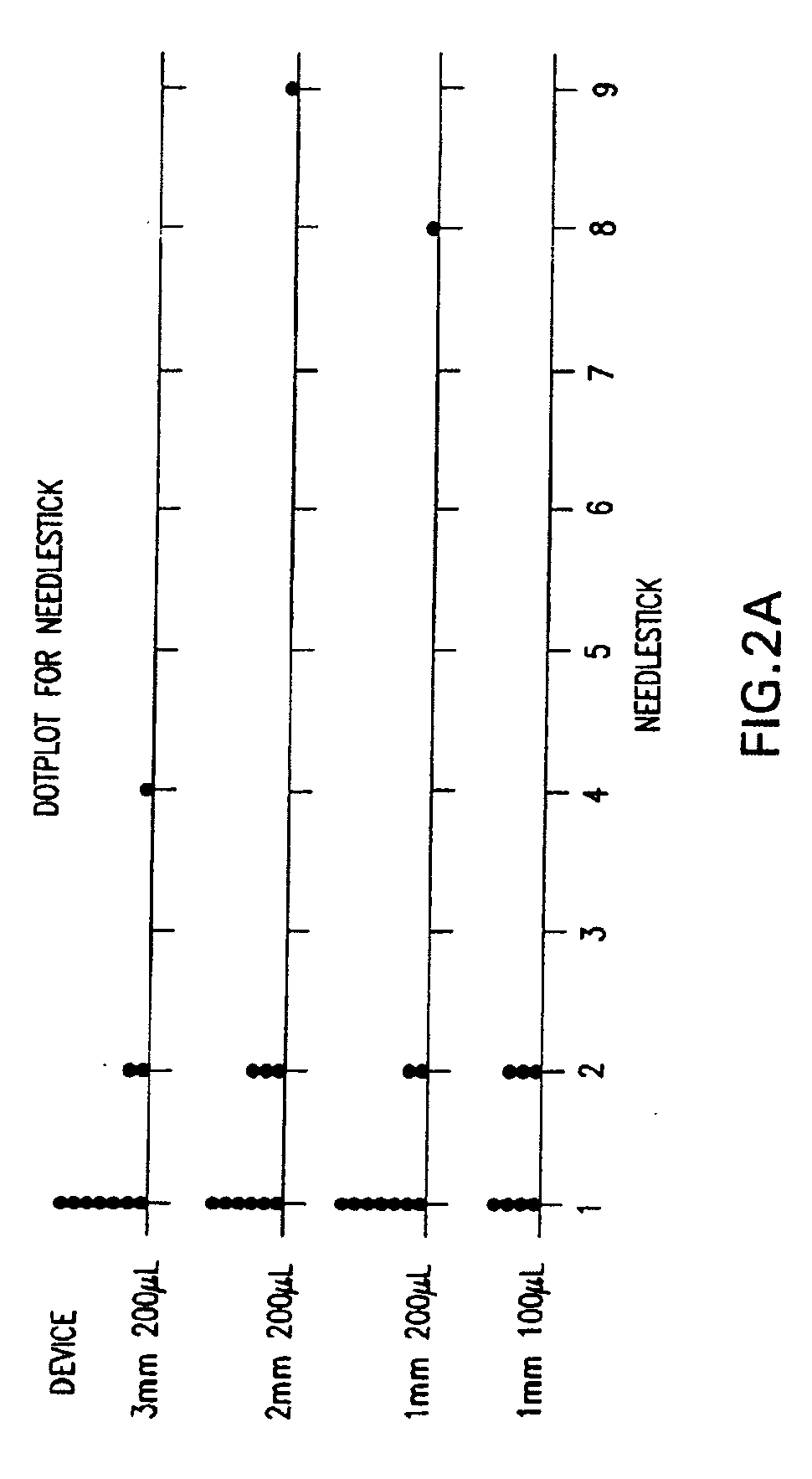
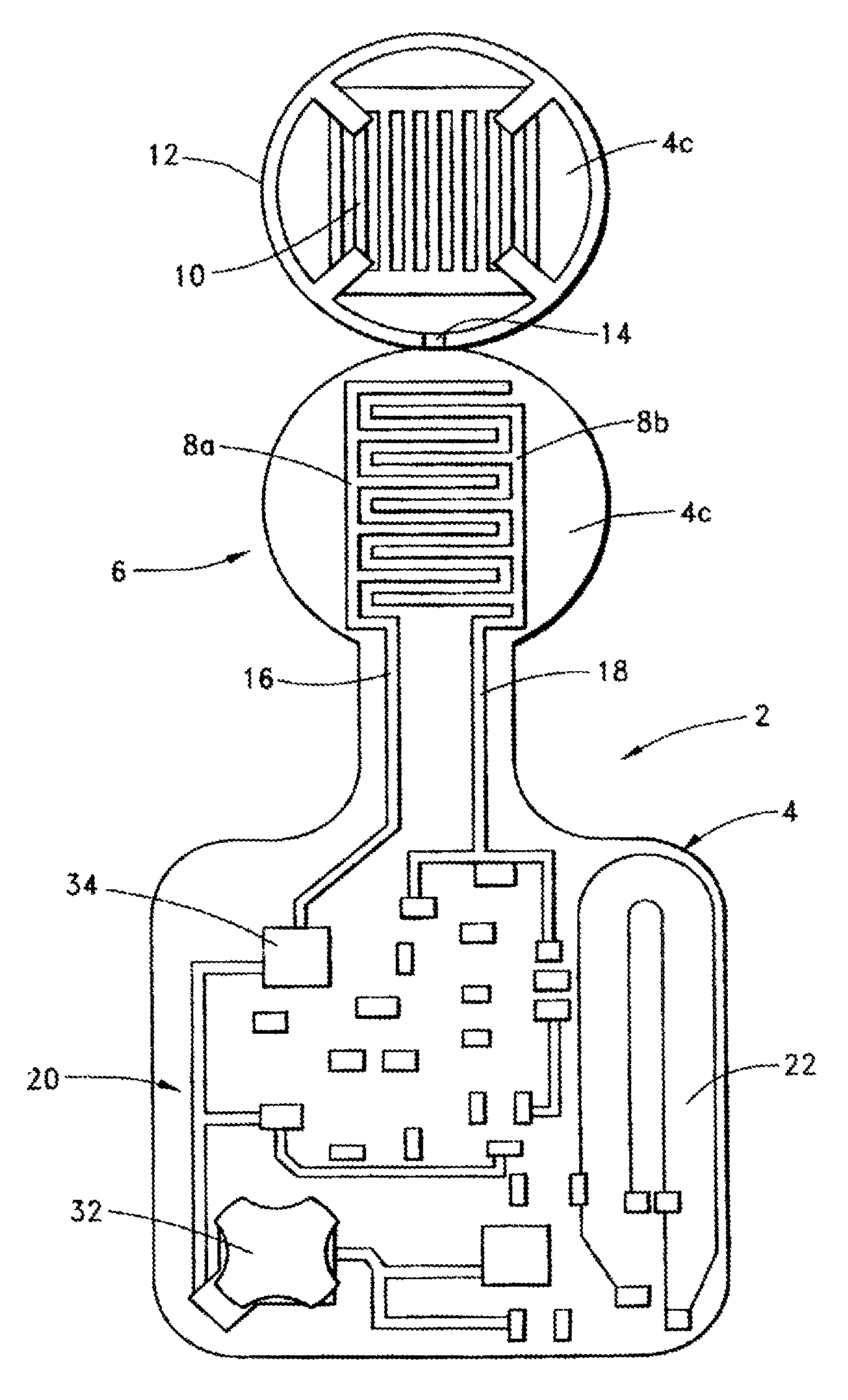
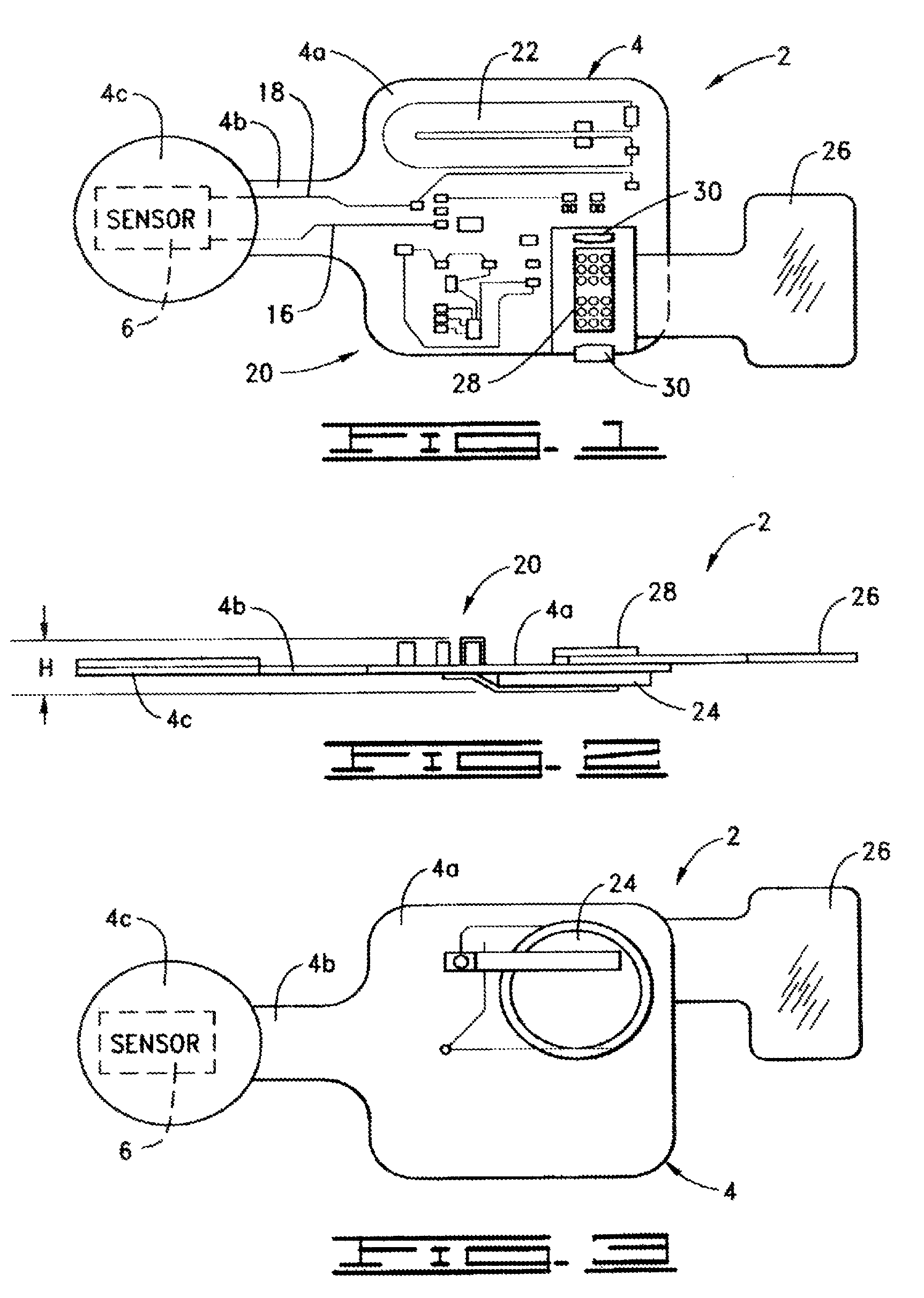
A method of delivery of a substance to a human subject's skin comprising deposition into a specific compartment of the skin, wherein the delivery occurs at a controlled rate and pressure. The methods of the invention provide accurate deposition of s pre-selected volume of the substance, e.g., greater than 90% of the pre-selected volume. The methods of the invention encompass varying one or more parameters including but not limited to configurations of the delivery device, volume, pressure, and flow rate of delivery, to enhance the efficacy of delivery of the substance to the human skin. Substances delivered in accordance with the methods of the invention result in a more efficacious deposition of the substance into the targeted compartment, improved delivery performance, i.e., completeness of delivery as measured by quantification of the substance not delivered or the amount of the substance leaked out from the injection site, and enhanced safety as measured by the occurrence of minimal adverse cutaneous events at the site of injection.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Data transmission system using a human body as a signal transmission path
InactiveUS20050017841A1Easy to carryEasily integrated into garmentElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsHuman bodyElectricity
A data transmission system using a human body as a signal transmission path includes a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter uses a pair of electrodes which are held in close proximity to the skin of the human body. The transmitter transmits data to the receiver through the signal transmission path partly extending through the human body when a user carrying the transmitter touches a touch electrode of the receiver. The electrodes are integrated into a garment worn by the user in such a manner that the electrodes are kept in a closely facing relation to the skin of the user, thereby establishing the electrical path extending through the human body. With the integration of the two electrodes into the garment, the user wearing the garment as an everyday clothes or uniform can be easy and convenient to carry the transmitter for successful transmission of the data.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
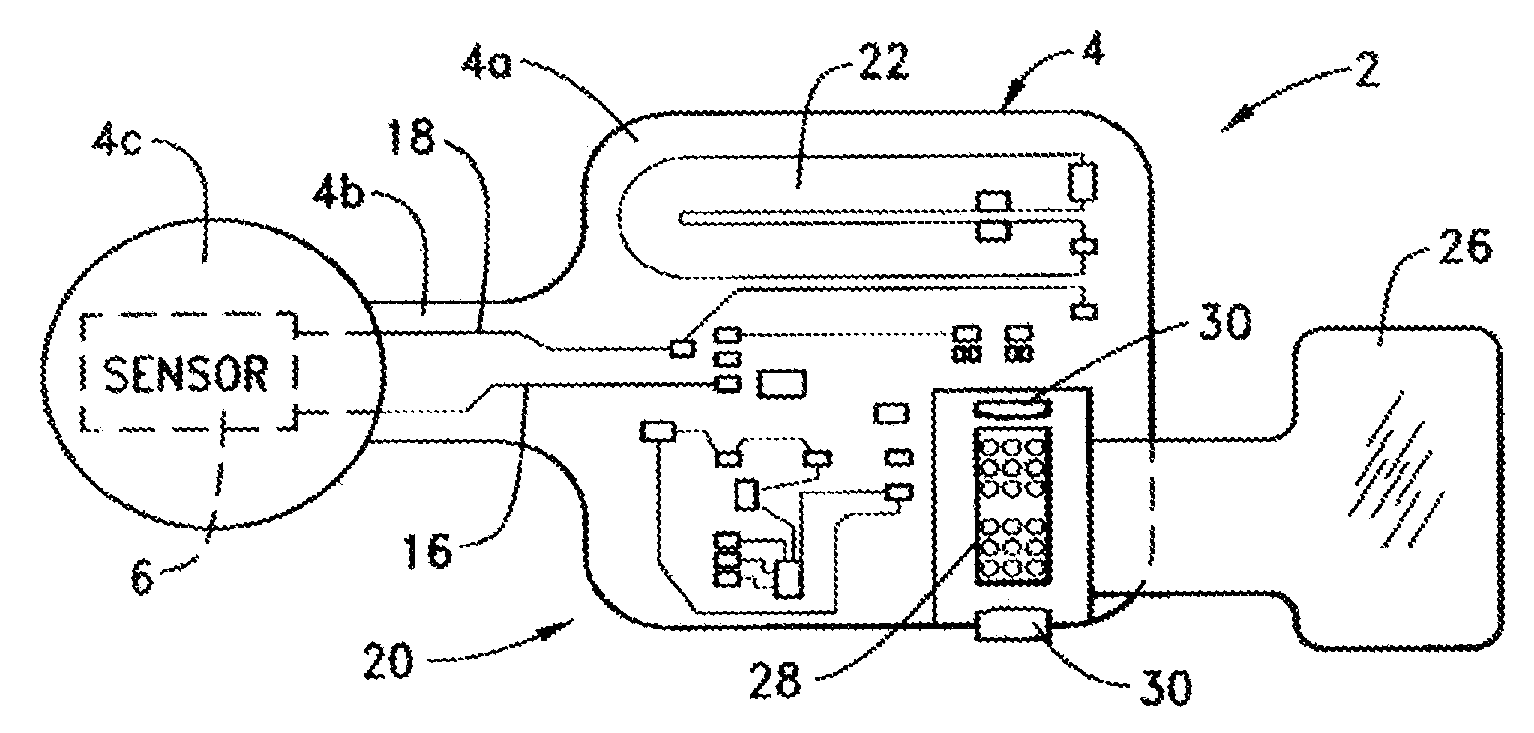
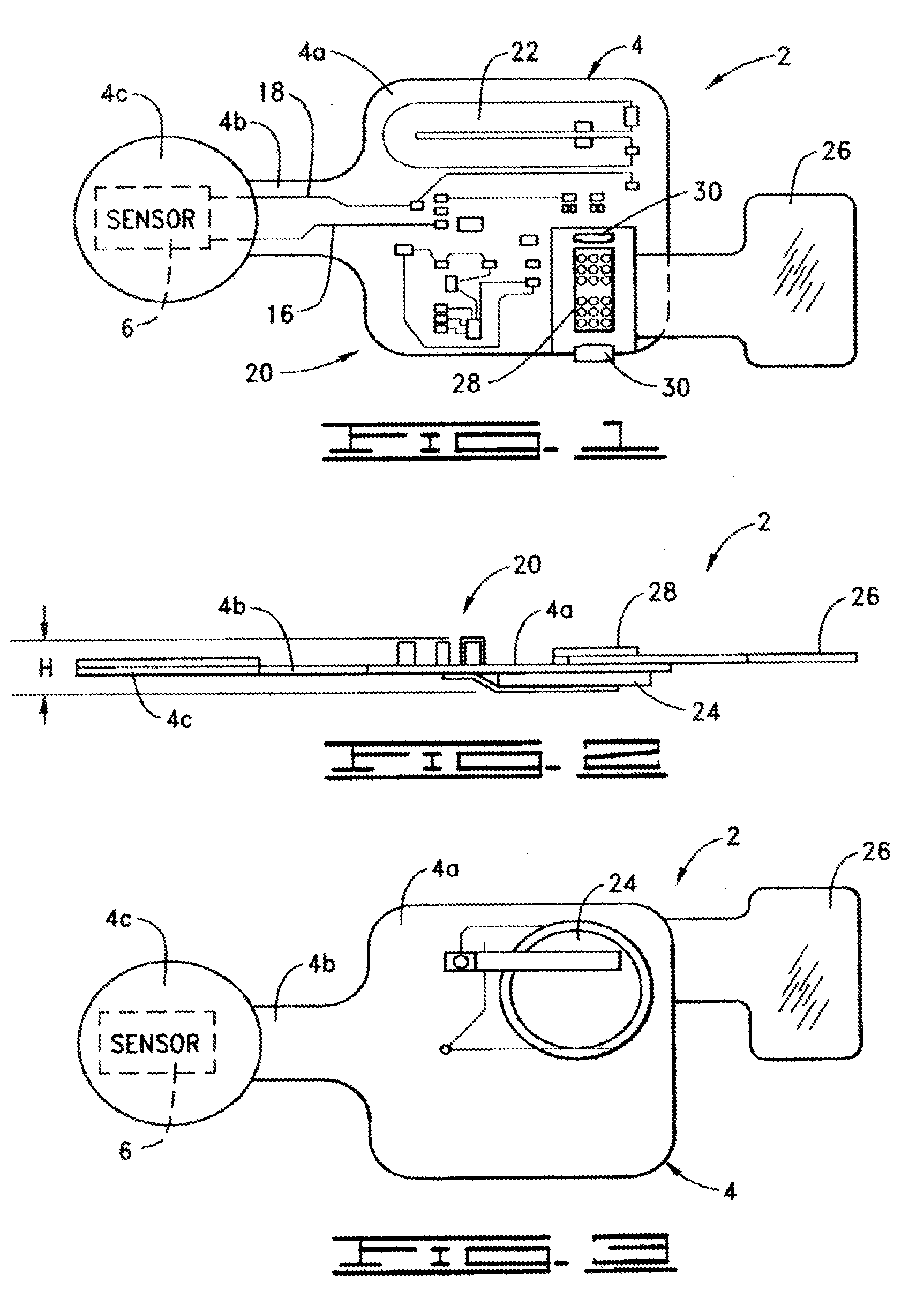
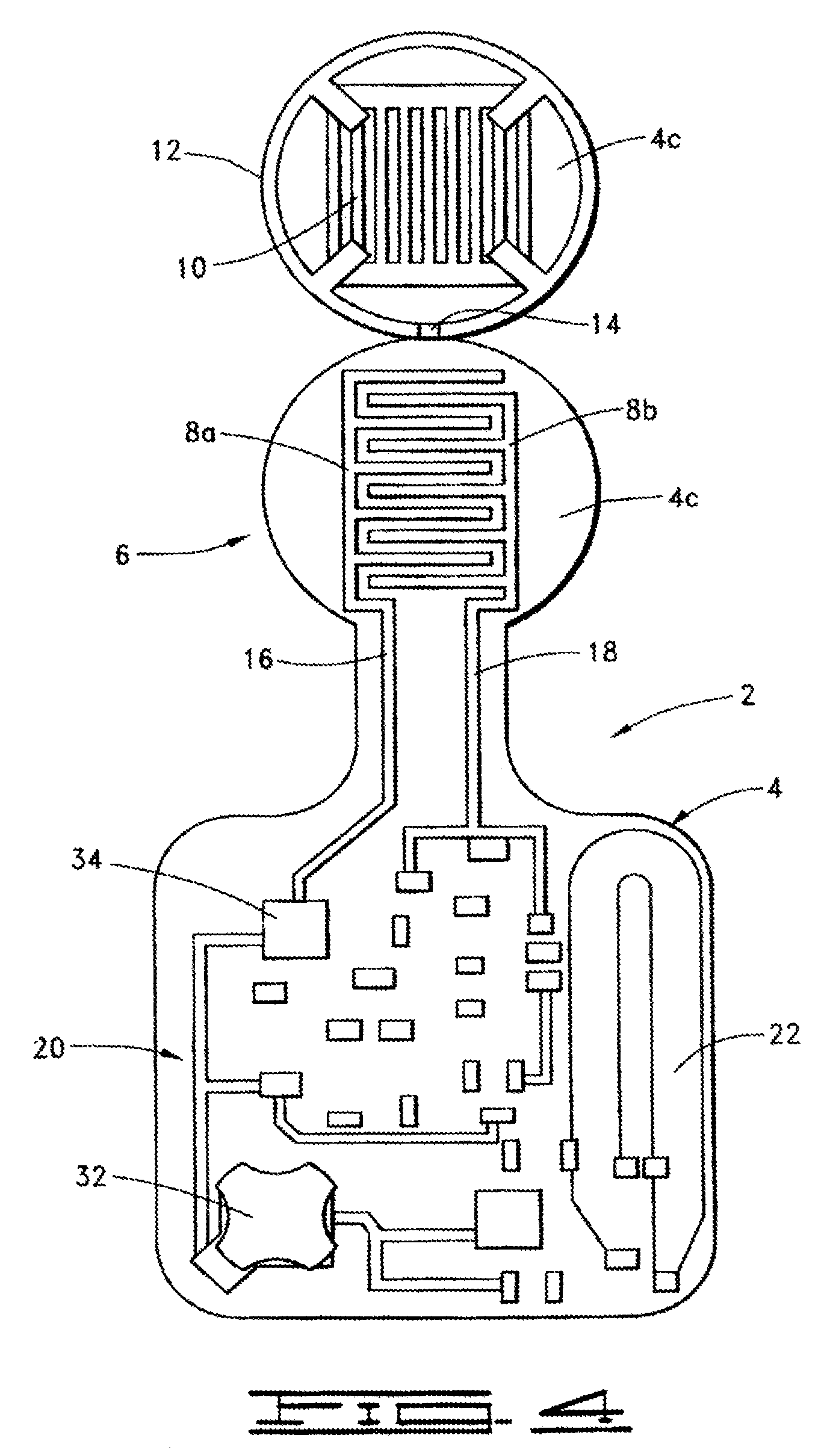
Active on-patient sensor, method and system
A sensor (which could be detachable) to sense a condition (including pressure from body weight or moisture from incontinence; applied by adhering to skin of a human body or by putting a diaper on the human body, for example), a signal processing circuit, a periodic or continuous transmitter, and a power supply (typically including a battery) are associated with a flexible substrate in low profile enabling disposition adjacent the human body. A transmitter antenna is on the substrate. Insulator film between battery contacts and a switch-and-transistor combination are two power-on techniques. A bedside monitor, a transceiver configured to receive signals from and transmit signals to the bedside monitor, and a computer connected with the transceiver can be included. Other features include: notification signaling; differently responsive antennas; unique identification; low battery detection; anti-collision transmission; patient protocol scheduling; local data transfer from the bedside monitor; and out-of-range transmission detection.
Owner:ORTHOCARE INNOVATIONS
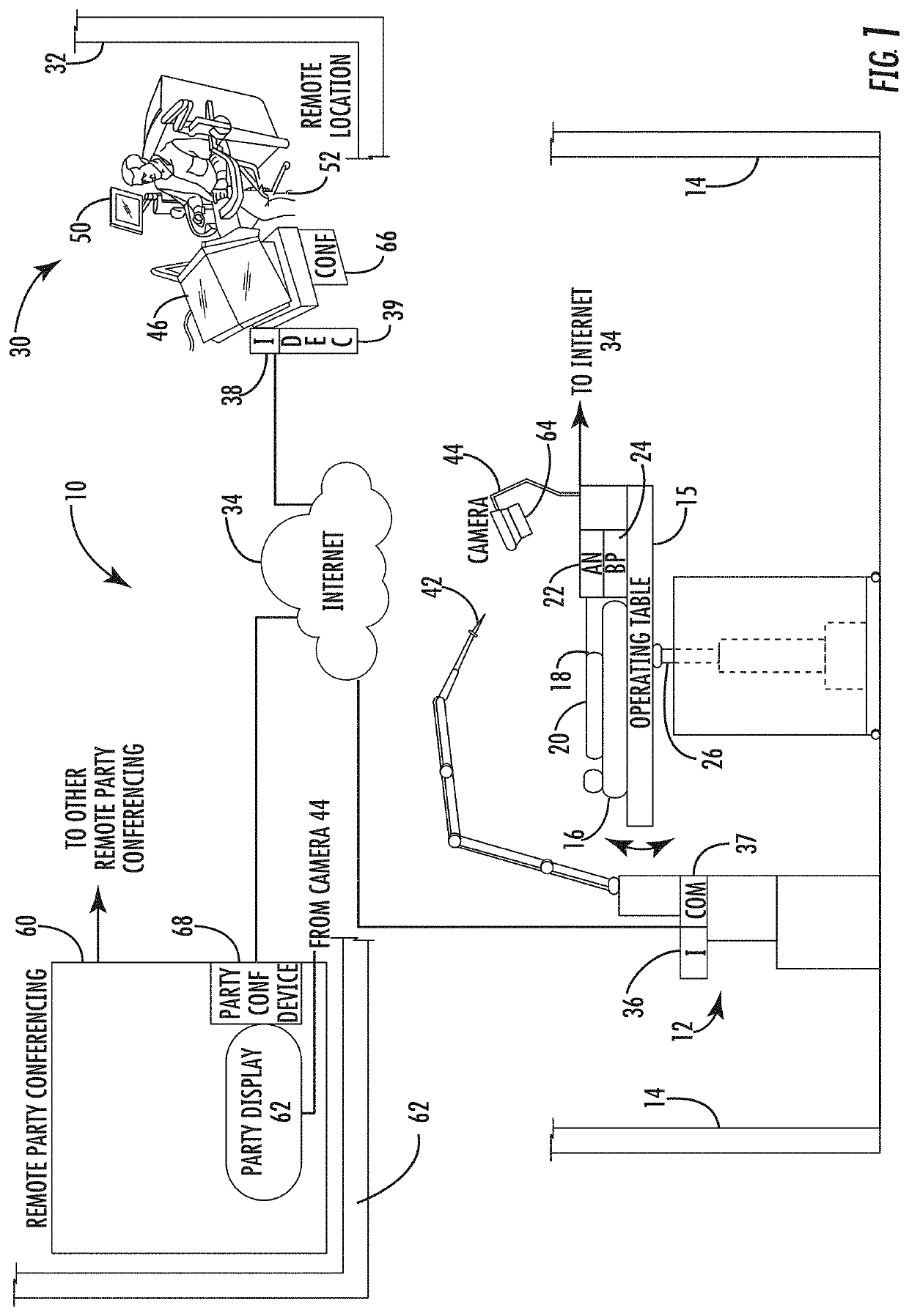
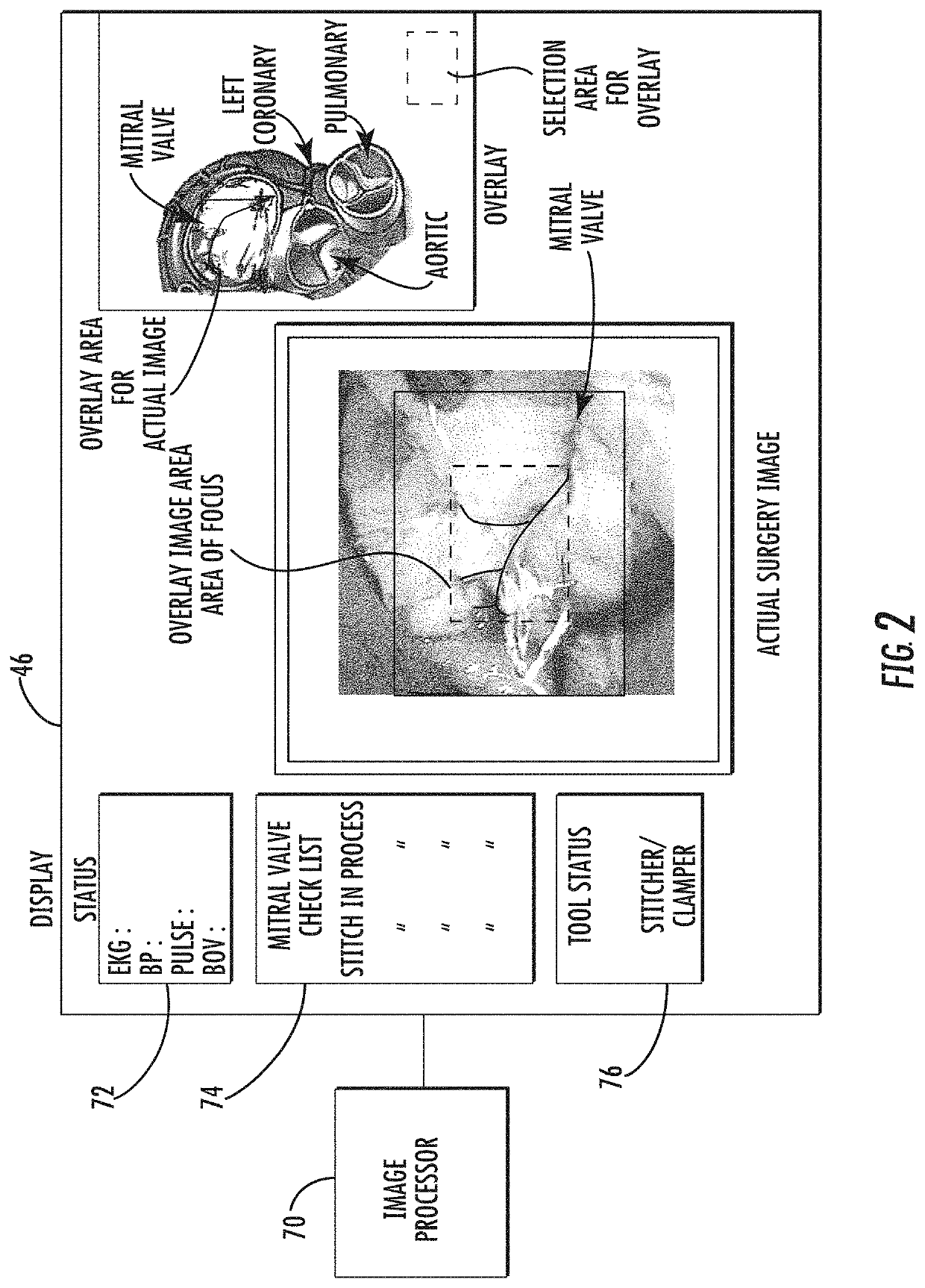
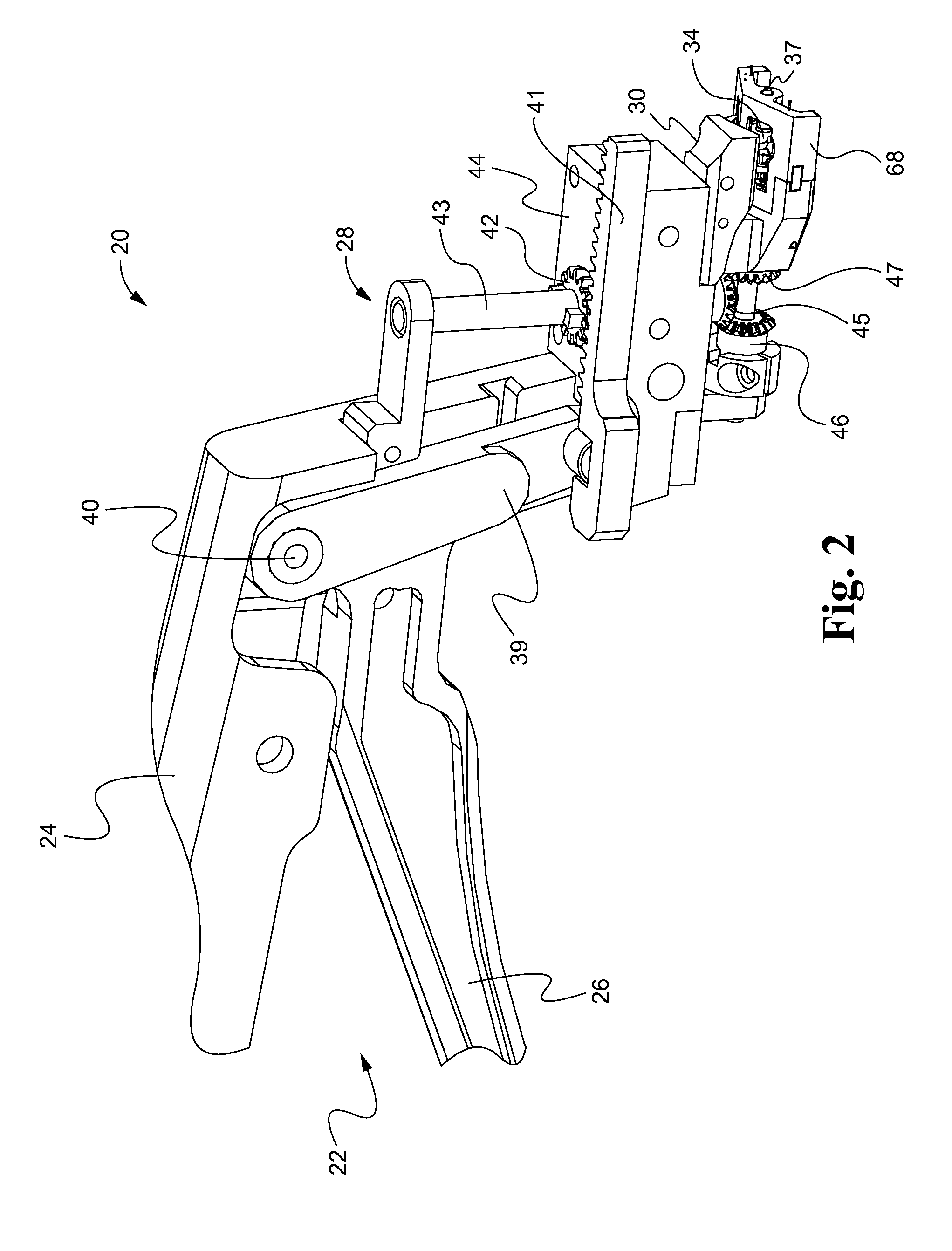
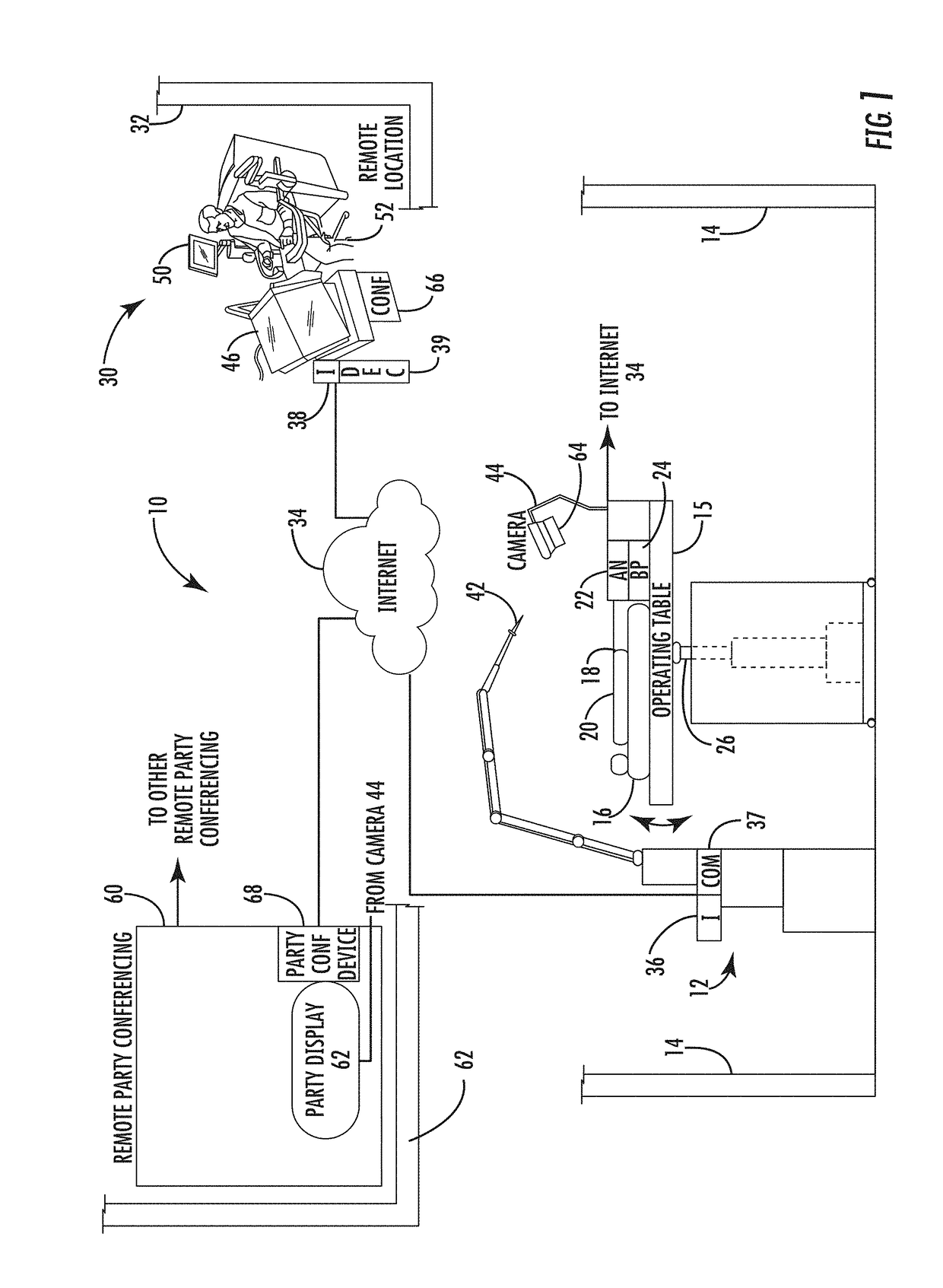
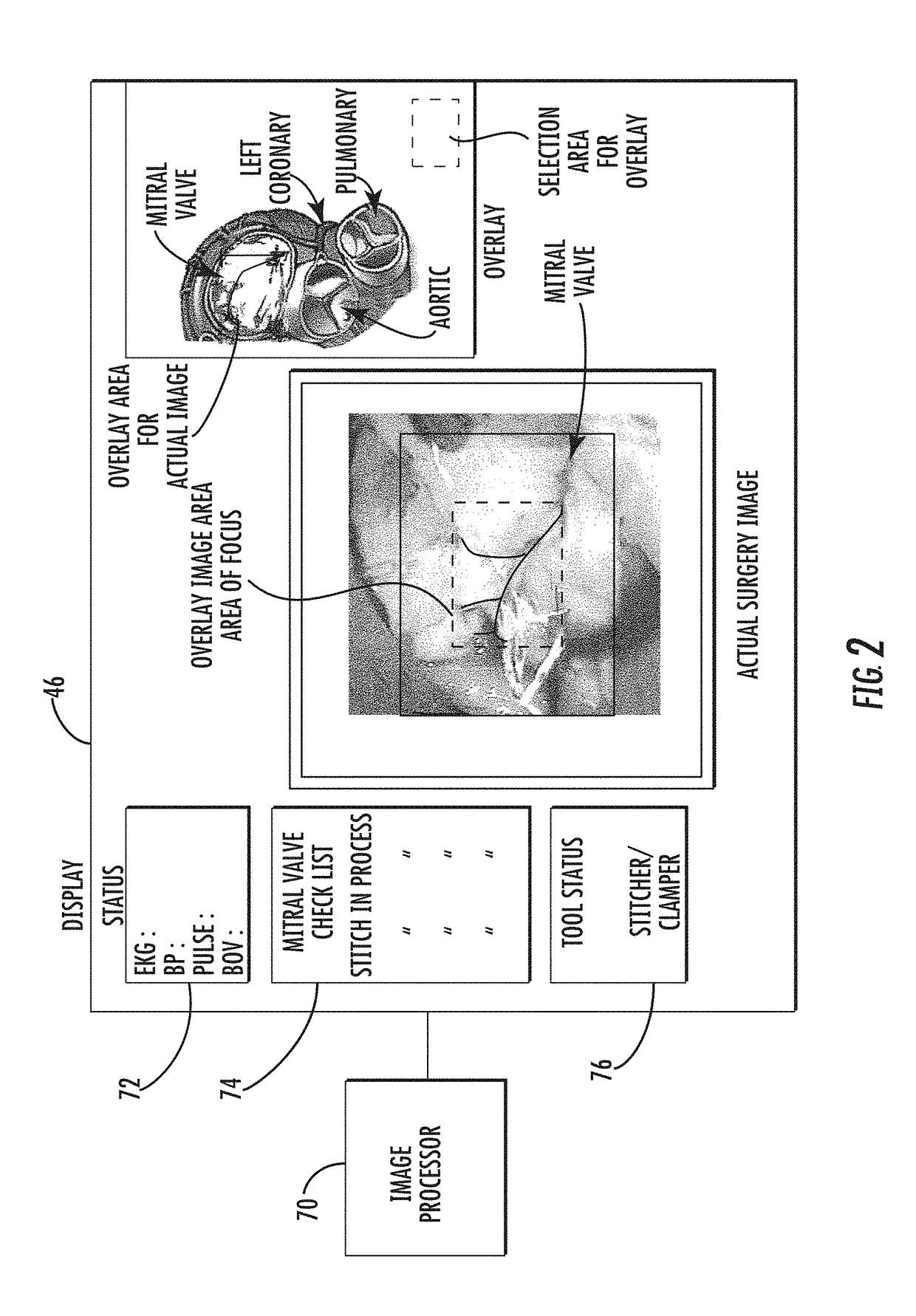
Surgical simulation system using force sensing and optical tracking and robotic surgery system
A surgical simulation device includes a support structure and animal tissue carried in a tray. A simulated human skeleton is carried by the support structure above the animal tissue and includes simulated human skin. A camera images the animal tissue and an image processor receives images of markers positioned on the ribs and animal tissue and forms a three-dimensional wireframe image. An operating table is adjacent a local robotic surgery station as part of a robotic surgery station and includes at least one patient support configured to support the patient during robotic surgery. At least one patient force / torque sensor is coupled to the at least one patient support and configured to sense at least one of force and torque experienced by the patient during robotic surgery.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Feminine undergarment
An undergarment comprises a strapless, coreless web sized and configured between an anterior end and a posterior end to cover, in use, at least the vulva of an adult female wearer. The undergarment is pre-adherent to the wearer, e.g., having pre-applied adhesive or pre-applied suction material on the body side of the web, suitable for contact with human skin and sufficiently adherent to removably hold the undergarment in place during use. In another aspect, a feminine undergarment comprises such pre-adherent strapless, coreless web with a removable protective cover over at least the adhesive. In another aspect, a package of feminine undergarments comprises outer packaging containing at least multiple of such feminine undergarments and optionally inner packaging for each of the undergarments individually.
Owner:CARLOZZI ANTONELLA F
Tissue Ablation by Shear Force for Sampling Biological Fluids and Delivering Active Agents
A shear device for use in transporting a molecule through a mammal's mammalian barrier membrane of at least one layer of cells includes a sheet containing an opening(s) and a shear member(s). The sheet is configured for contacting the mammalian barrier membrane (e.g., human skin) and the shear member is configured for ablating a portion of the mammalian barrier membrane forced through the opening(s). This ablating is accomplished by movement of the shear member(s) over the sheet and the opening(s). The ablation of the portion of the mammalian barrier membrane is such that a driving force can be employed to transport the molecule therethrough.
Owner:KOLLIAS NIKIFOROS +2
Methods and devices for improving delivery of a substance to skin
InactiveUS20090124997A1Efficacy is alteredImprove delivery capabilitiesMedical devicesPressure infusionDelivery PerformanceHuman skin
A method of delivery of a substance to a human subject's skin comprising deposition into a specific compartment of the skin, wherein the delivery occurs at a controlled rate and pressure. The methods of the invention provide accurate deposition of s pre-selected volume of the substance, e.g., greater than 90% of the pre-selected volume. The methods of the invention encompass varying one or more parameters including but not limited to configurations of the delivery device, volume, pressure, and flow rate of delivery, to enhance the efficacy of delivery of the substance to the human skin. Substances delivered in accordance with the methods of the invention result in a more efficacious deposition of the substance into the targeted compartment, improved delivery performance, i.e., completeness of delivery as measured by quantification of the substance not delivered or the amount of the substance leaked out from the injection site, and enhanced safety as measured by the occurrence of minimal adverse cutaneous events at the site of injection.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Active on-patient sensor, method and system
Owner:ORTHOCARE INNOVATIONS LLC
Surgery practice kit
A simple to use, inexpensive and readily portable surgical practice and teaching kit is described that includes in portfolio form a two layer practice suturing pad including a latex rubber layer simulating human skin attached to a plastic foam layer that simulates underlying human tissue, the foam layer having incorporated therein simulated subcutaneous growths or lesions such as simulated lipomas or sebaceous cysts. The practice pad is mounted on a folder or portfolio for convenient access and use by the student or practitioner, the portfolio also including pictorial illustrations showing various proper suturing techniques as a visual guide to the user in practicing suturing procedures.
Owner:PALAKODETI RATNA K
Skin Suturing Device Using Rotating Needles
A medical device for installing sutures to close an incision in tissue or human skin is disclosed. The suturing device may provide first and second arcuate needles. Once properly positioned, the first and second arcuate needles are driven through the sub-dermal layer, or alternatively through a superficial surface, of two sections of skin to be joined. This is done in arcuate fashion and at identical and symmetrical rates of angular displacement. During the driving or retraction process of the first and second arcuate needles, a suture is positioned within both the first and second sections of skin and transformed from a planar or a multi-planar serpentine orientation to a helical orientation. The resulting suturing process is thus much faster than conventional or manual suturing and results in superior wound approximation / alignment that will lead to decreased scarring compared to prior art devices.
Owner:SURGIMATIX
Surgical simulation system using force sensing and optical tracking and robotic surgery system
A surgical simulation device includes a support structure and animal tissue carried in a tray. A simulated human skeleton is carried by the support structure above the animal tissue and includes simulated human skin. A camera images the animal tissue and an image processor receives images of markers positioned on the ribs and animal tissue and forms a three-dimensional wireframe image. An operating table is adjacent a local robotic surgery station as part of a robotic surgery station and includes at least one patient support configured to support the patient during robotic surgery. At least one patient force / torque sensor is coupled to the at least one patient support and configured to sense at least one of force and torque experienced by the patient during robotic surgery.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Intra-serum and intra-gel for modeling human skin tissue
InactiveUS6475800B1Diagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsConfocalCrosslinking reagent
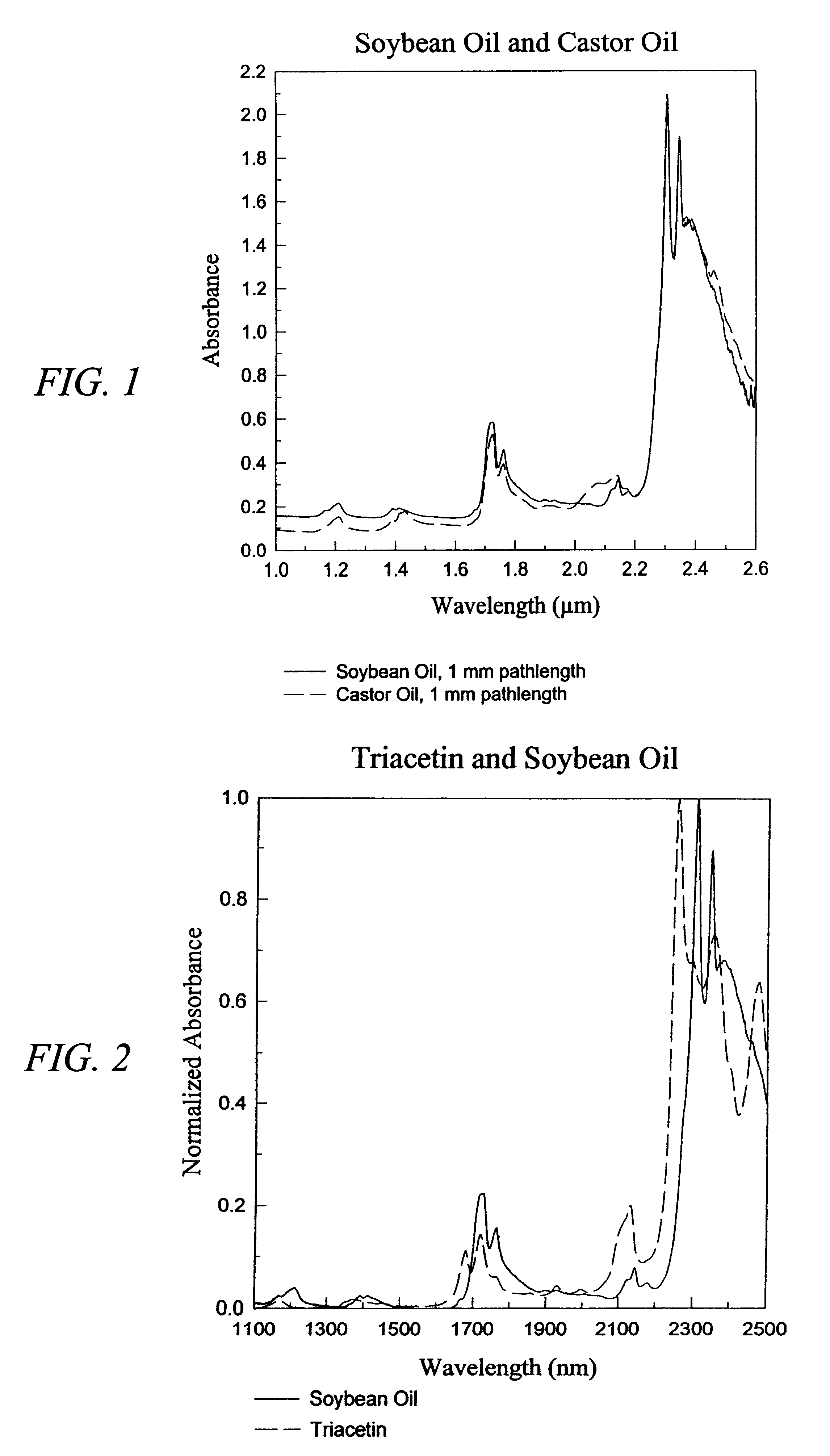
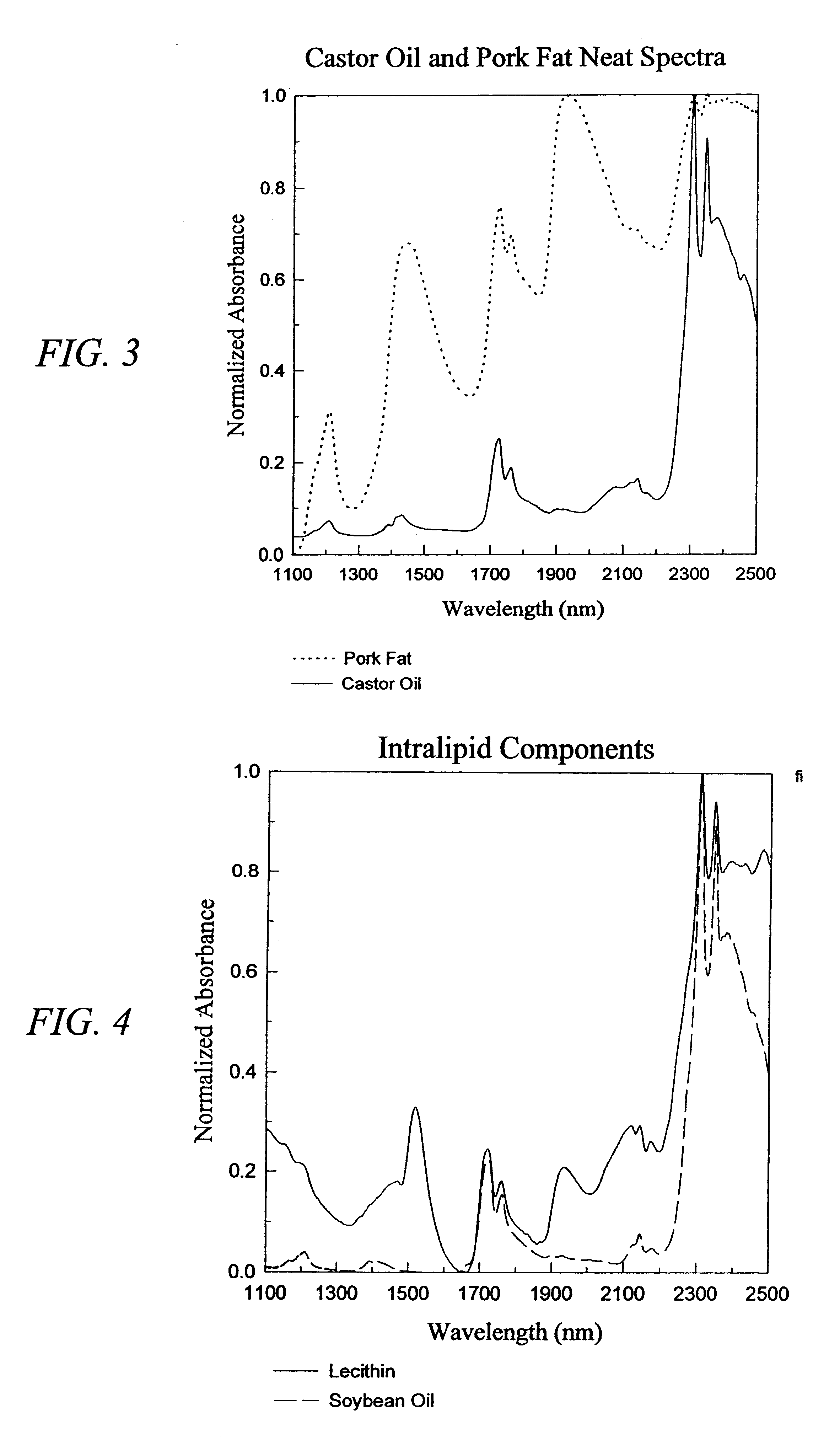
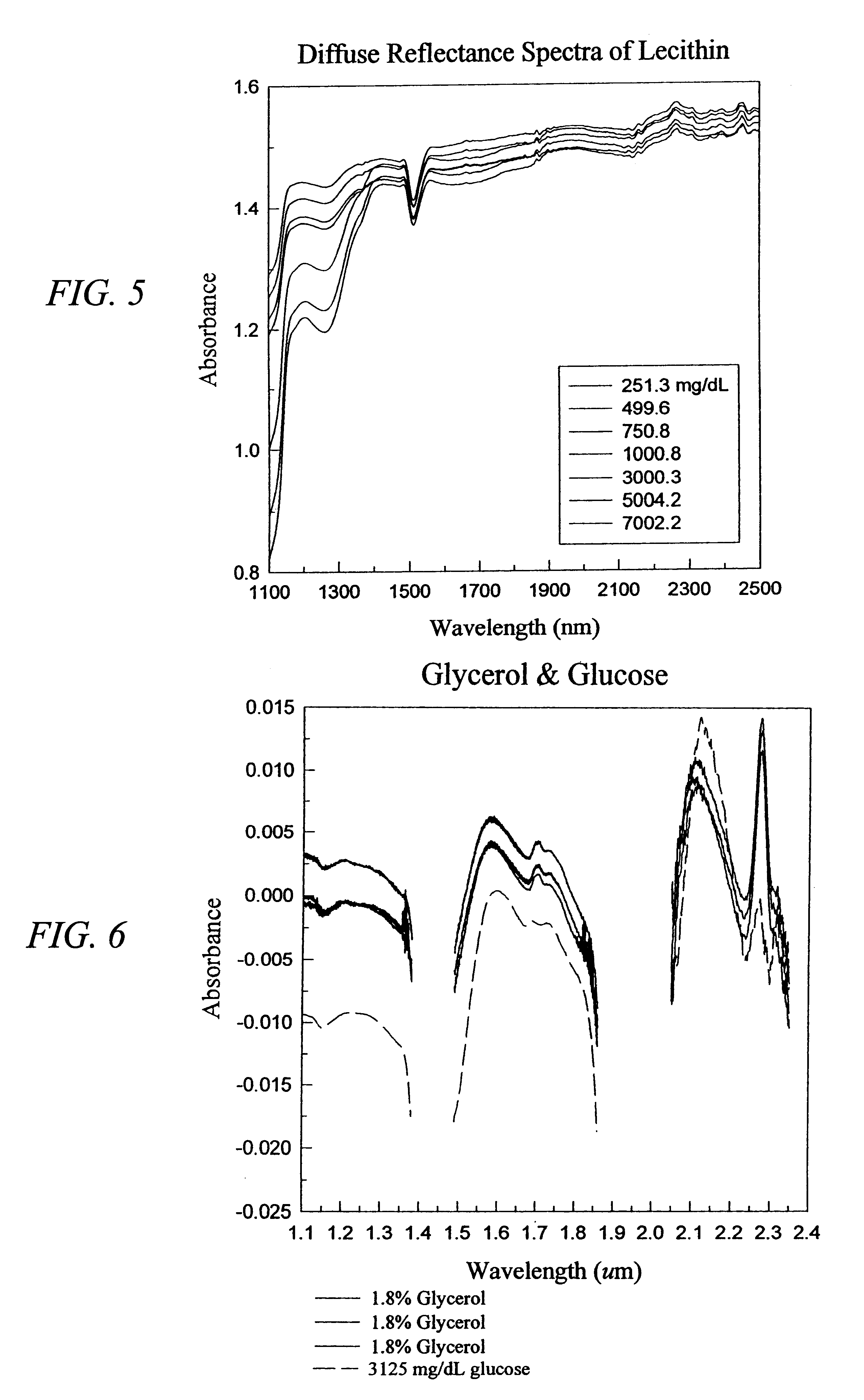
The invention provides a class of samples that model the human body. This family of samples is based upon emulsions of oil in water with lecithin acting as the emulsifier. These solutions that have varying particle sizes may be spiked with basis set components (albumin, urea and glucose) to simulate skin tissues further. The family of samples is such that other organic compounds such as collagen, elastin, globulin and bilirubin may be added, as can salts such as Na+, K+ and Cl-. Layers of varying thickness with known index of refraction and particle size distributions may be generated using simple crosslinking reagents, such as collagen (gelatin). The resulting samples are flexible in each analyte's concentration and match the skin layers of the body in terms of the samples reduced scattering and absorption coefficients, mums and muma. This family of samples is provided for use in the medical field where lasers and spectroscopy based analyzers are used in treatment of the body. In particular, knowledge may be gained on net analyte signal, photon depth of penetration, photon radial diffusion, photon interaction between tissue layers, photon density (all as a function of frequency) and on instrument parameter specifications such as resolution and required dynamic range (A / D bits required). In particular, applications to delineate such parameters have been developed for the application of noninvasive glucose determination in the near-IR region from 700 to 2500 nm with an emphasis on the region 1000 to 2500 nm (10,000 to 4,000 cm-1).
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
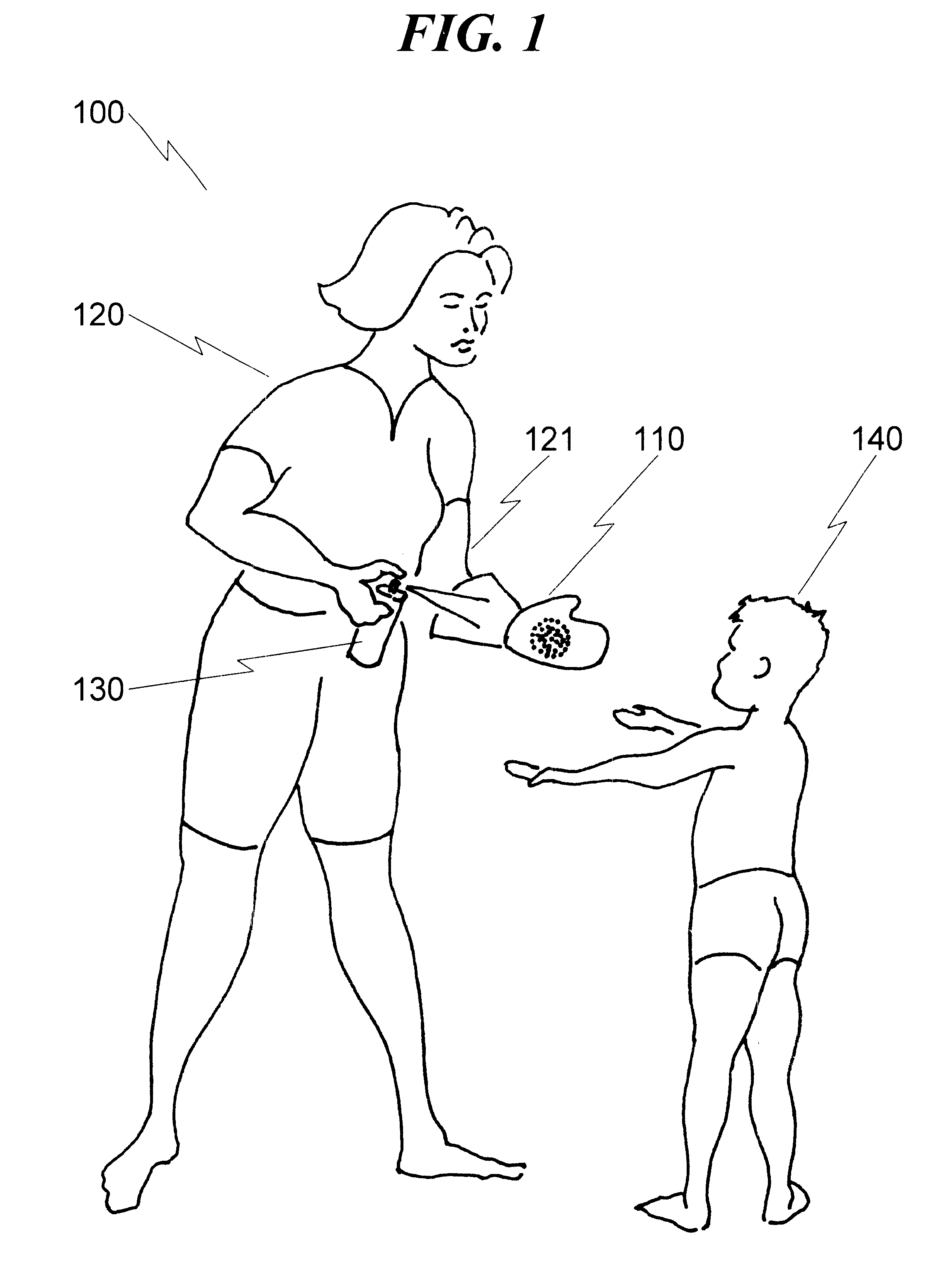
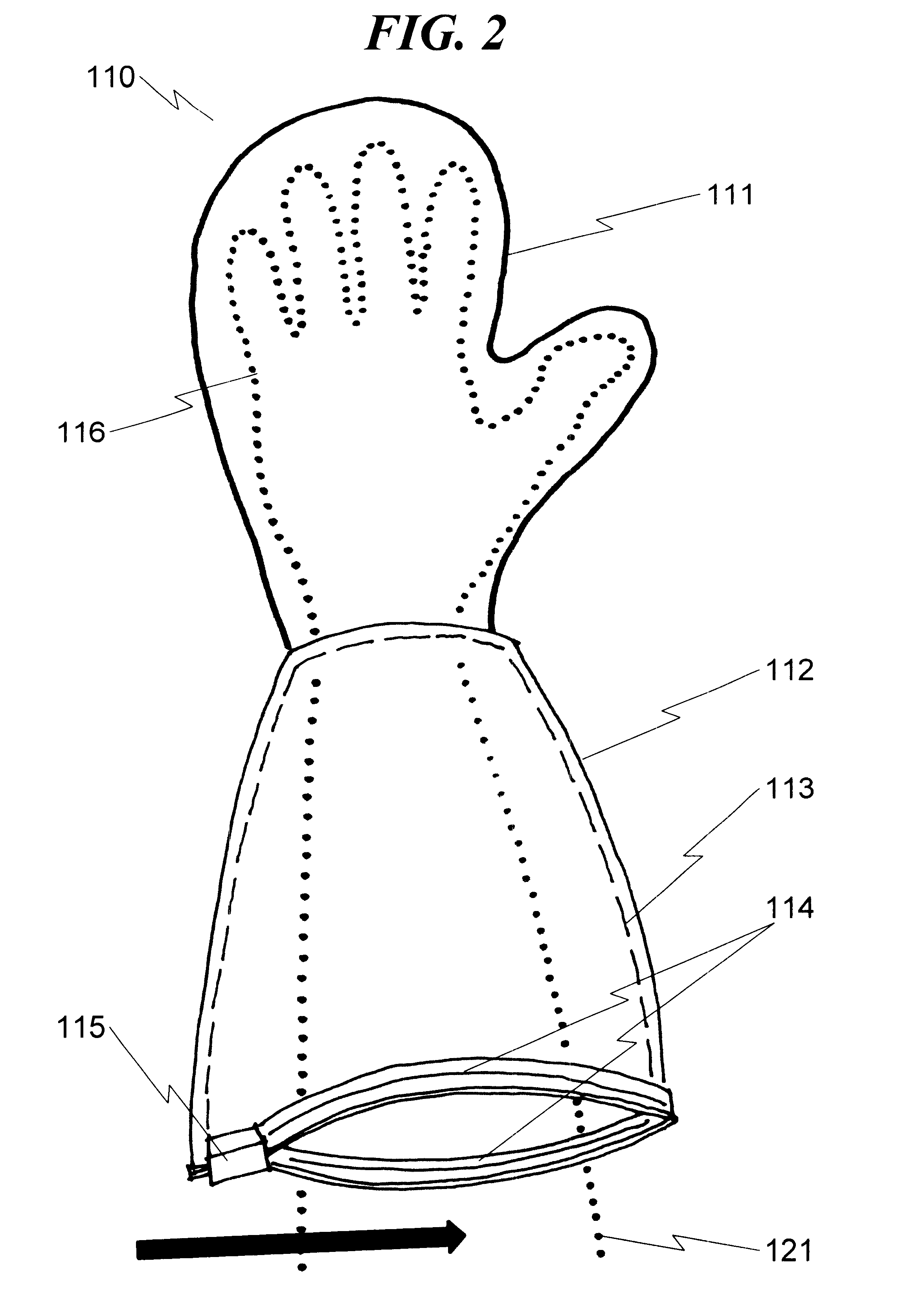
Safety applicator glove system and method
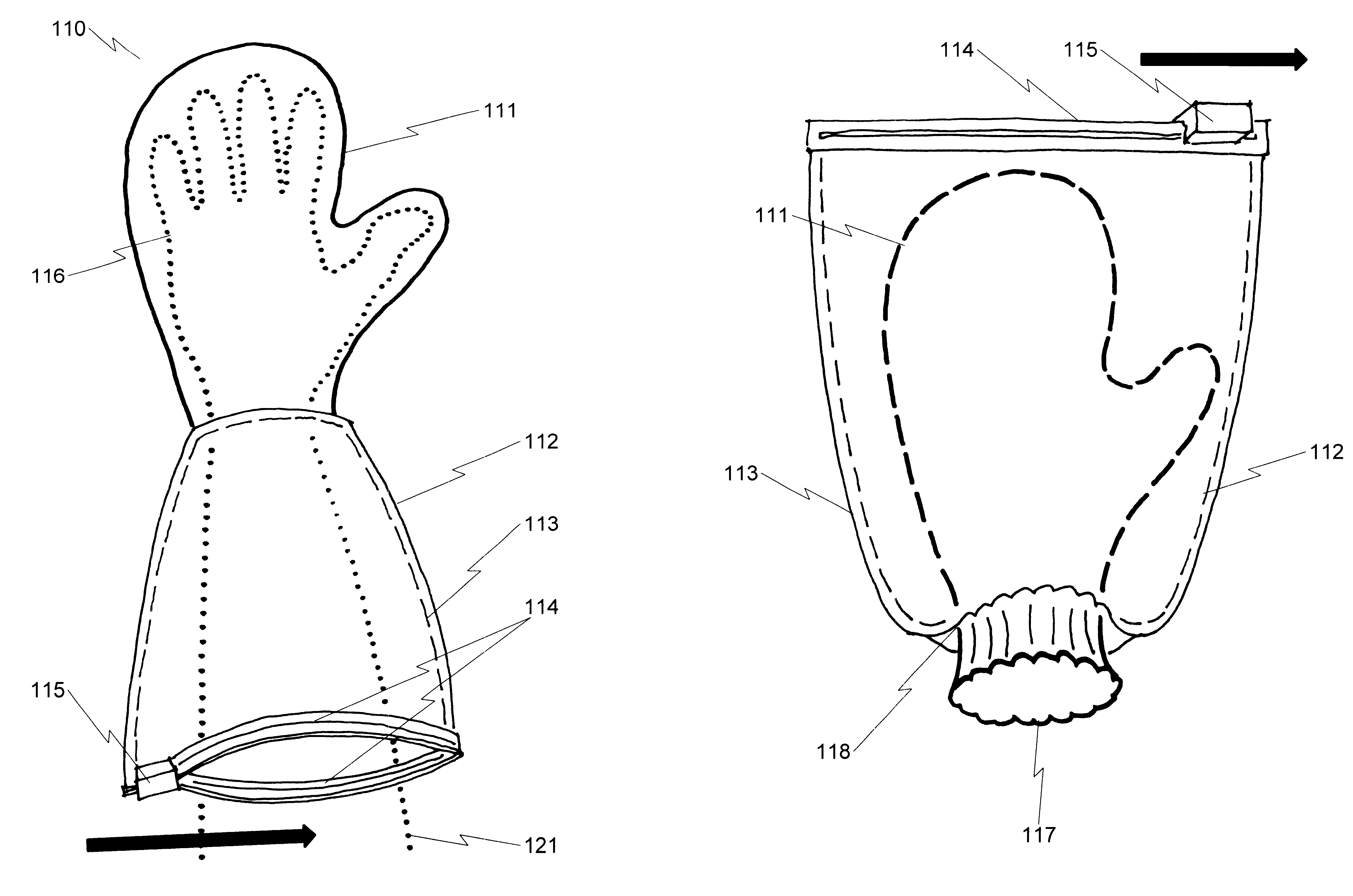
A safety applicator glove system and method is disclosed that is particularly suitable for use in situations where insect repellent and the like must be applied to human skin without contaminating the hands of the person applying the insect repellent. The basic system disclosed includes a glove or mitten with an absorbent outer surface and an internal barrier lining to prevent penetration of liquid on the outer surface of the glove with the person's hand that has been inserted into the glove / mitten. Attached to the glove / mitten proximally to the hand entry point is a protective sleeve / gauntlet that may be extended over the surface of the glove and sealed to act as a containment vessel for the liquid-soaked glove. When retracted, this protective sleeve / gauntlet serves to prevent contamination of the person making use of the glove / mitten system. Various embodiments of the present invention may also be applied with advantage to the control of contamination associated with biohazardous waste, including but not limited to use with surgical gloves and the like.
Owner:PETERS JR GEORGE A
Therapy patch
Therapy patches are disclosed which are designed to deliver vibration and heat (or cold) to human skin so as to provide muscle relief. These patches have a chemical pouch that generates heat or cold upon initiation. They also have a motor and battery to provide a vibration source. Forms of the invention have an adhesive so that the patch can be attached to the skin (and thus need not be manually held in place during use). Kits are also provided in which the motor and battery can be used with a string of linked, severable replacement pouches. Methods of using these patches are also disclosed.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
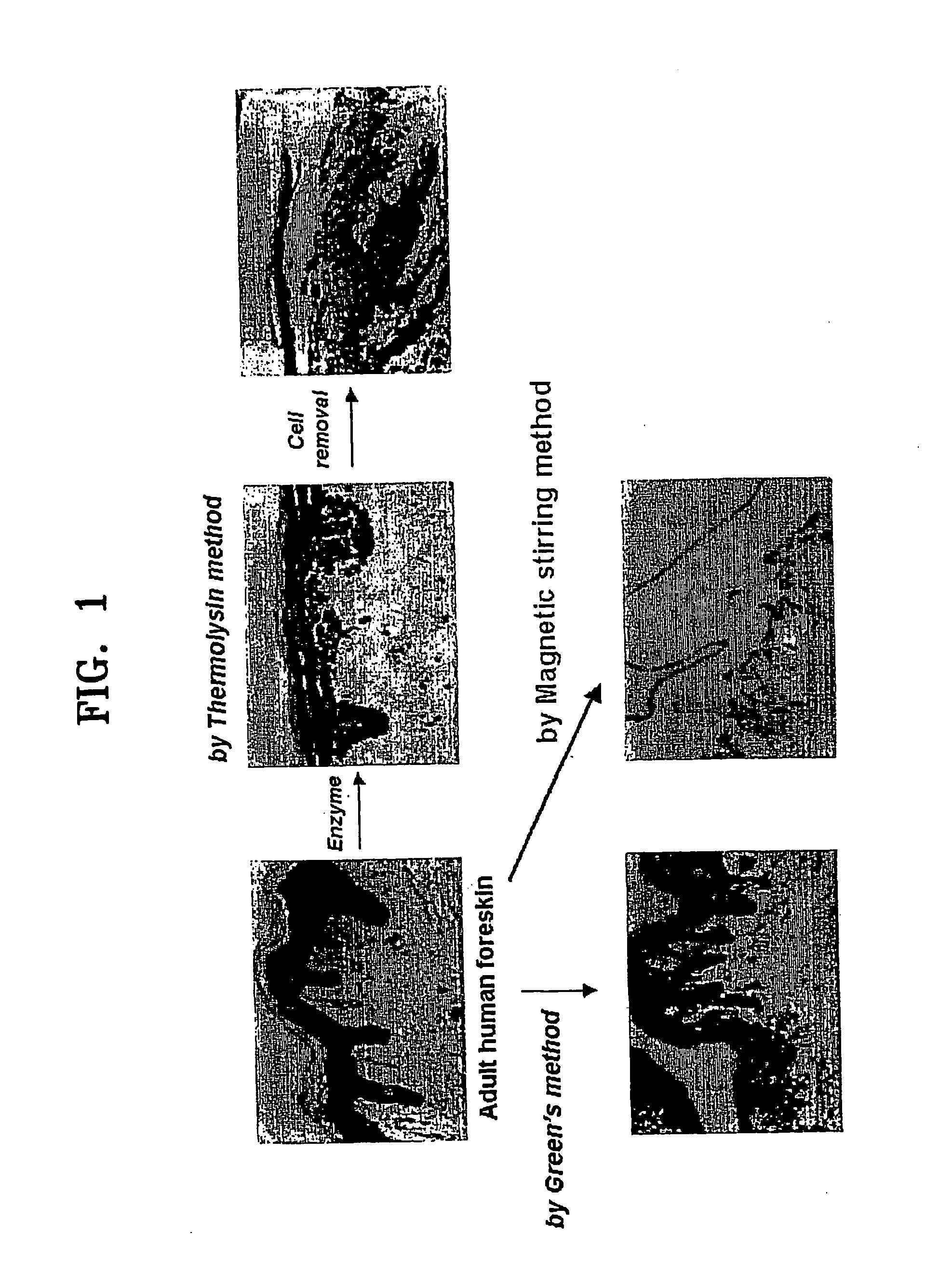
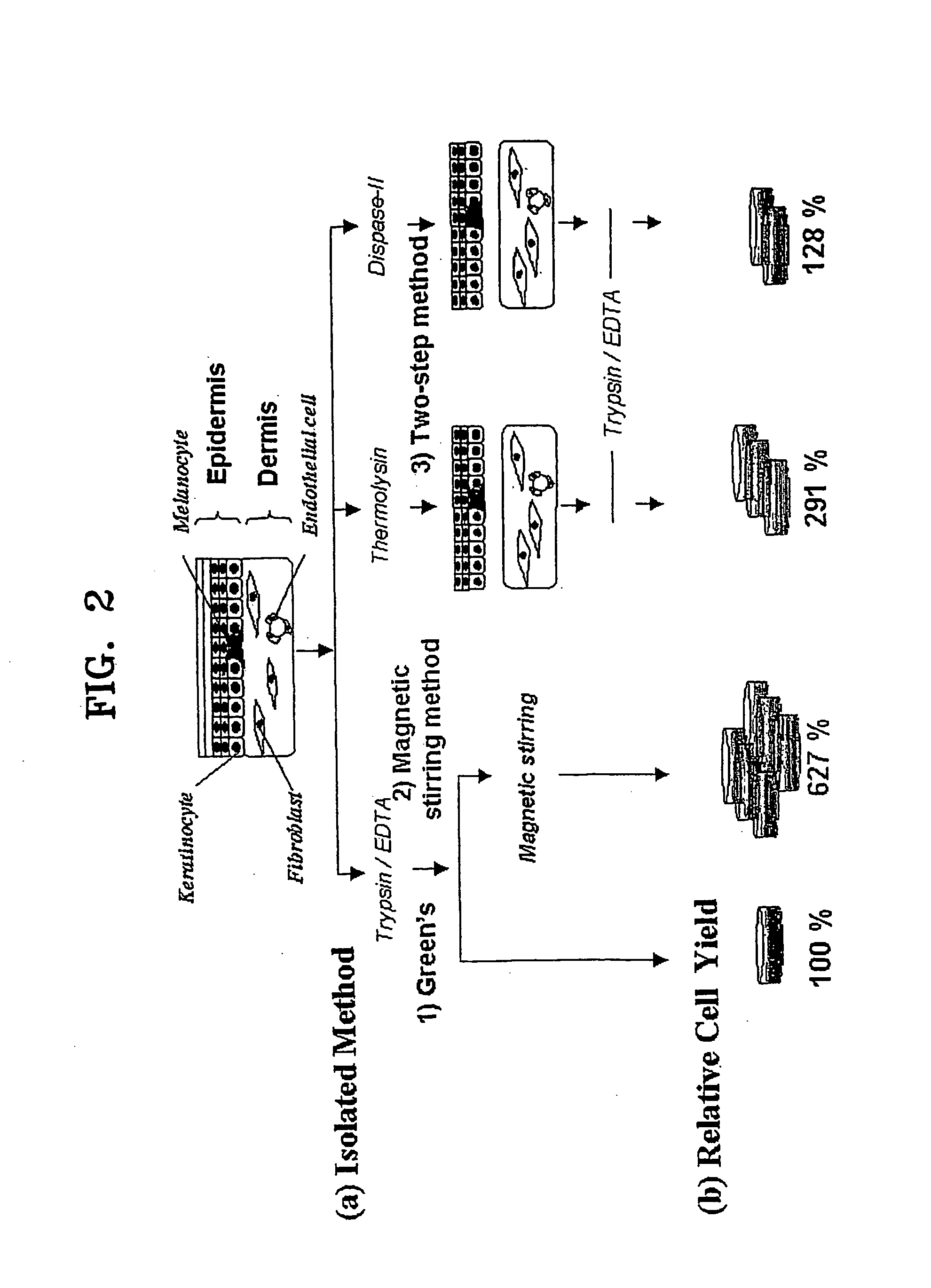
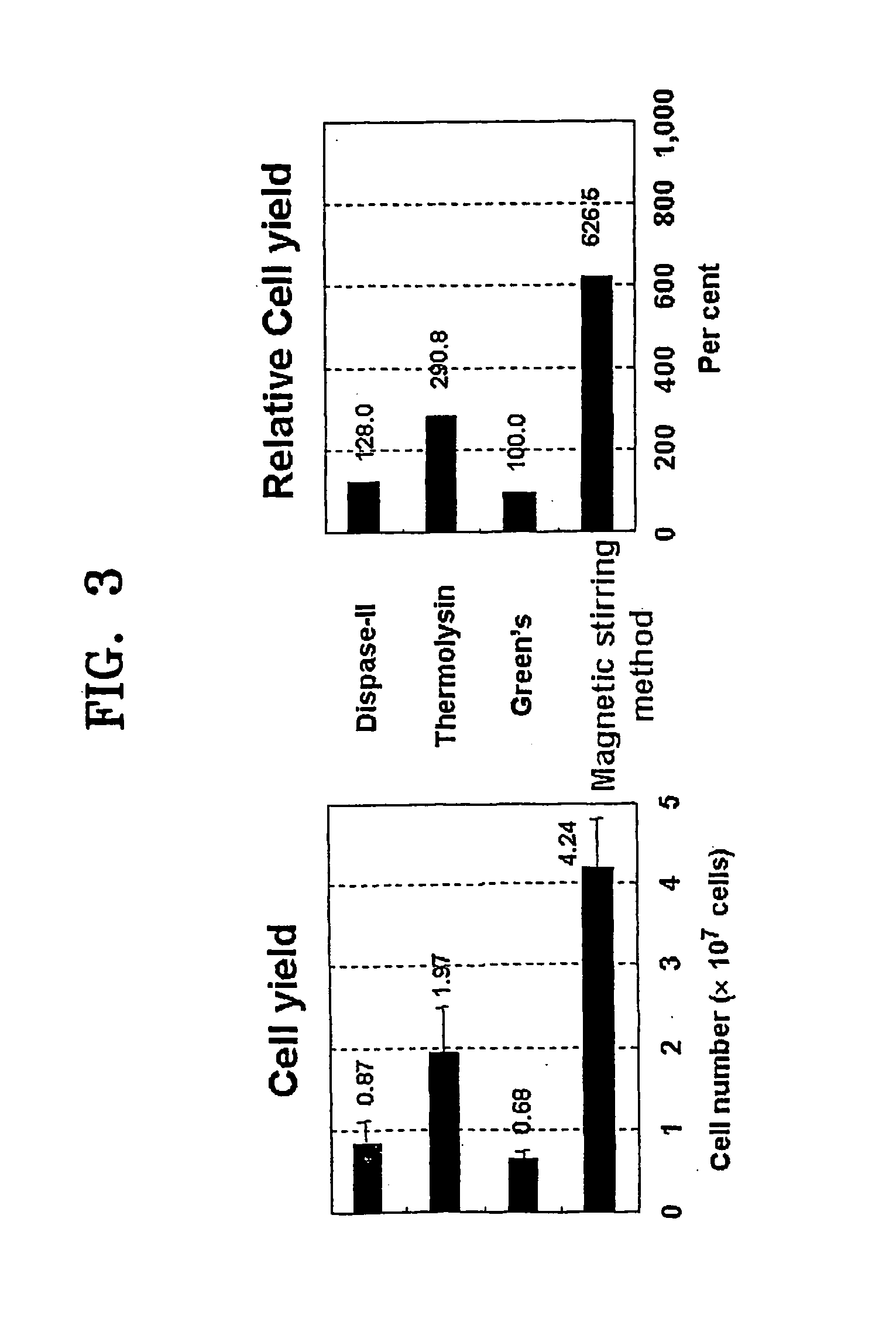
Method of isolating epithelial cells, method of preconditioning cells, and methods of preparing bioartificial skin and dermis with the epithelial cells or the preconditioned cells
InactiveUS20060105454A1Increased cell yieldEasy to implantCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsDamages tissueTrypsin
A method of isolating epithelial cells from a human skin tissue or internal organ tissue using trypsin and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) simultaneously with the application of magnetic stirring, a method of preconditioning isolated biological cells by the application of physical stimulus, i.e., strain, are provided. Epithelial cells can be isolated by the method with increased yield, colony forming efficiency (CFE), and colony size. Also, the increased percentage of stem cells in isolated cells is advantageous in therapeutic tissue implantation by autologous or allogeneic transplantation. In skin cells preconditioned by the application of strain, cell division is facilitated, and the secretion of extracellular matrix components and growth factors and the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are improved. When preconditioned cells are implanted by autologous or allogeneic transplantation to heal a damaged tissue, the improved cell adhesion, mobility, and viability provides a biological adjustment effect against a variety of stresses or physical stimuli which the cells would undergo after implantation, with improved capability of integration into host tissue, thereby markedly improving the probability of success in skin grafting.
Owner:KOREA INST OF RADIOLOGICAL & MEDICAL SCI
Biocompatible cemented carbide articles and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20070082229A1Eliminate and minimize toxic effectReduce concentrationSurgeryJewelleryBiocompatibility TestingAlloy
This invention relates to cemented carbide articles that are characterized by substantially improved biocompatibility with human skin, tissue, organs, etc., compared with articles made from conventional cemented carbides. The essential feature of these improved biocompatible cemented carbide articles is a binder-depleted zone at and near the exposed surfaces of the articles. By depleting the binder (which mainly consists of Co and / or Ni, as well as their alloys) at and near the surface, the toxic effects of Co and Ni (known carcinogens), as well as the allergic reactions that these metals can cause when in contact with human skin, are eliminated. By depleting the binder only at and near the surface, the bulk properties of the cemented carbide article are not compromised or altered in any manner. Applications of these binder-depleted cemented carbides could include articles that human skin may experience prolonged exposure to, for example, jewelry articles such as rings, bracelets, bangles, chains, necklaces, pendants, watches, watch cases, watch straps, etc. In addition, the cemented carbides of this invention may be used in applications where the article comes directly in contact with human skin, tissue, organs, etc. such as surgical and other medical instruments, razor blades, etc. Also, other applications could include knives, tools, dies, and other wear components that are used to process and handle, and hence, come into direct contact with materials meant for human consumption and / or ingestion. Examples of such materials include foodstuffs and pharmaceuticals.
Owner:MIRCHANDANI RAJINI P +1
Electronic skin based on three-dimensional flexible substrate graphene and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN104359597AExcellent detection characteristicsUltra-light and ultra-thinForce measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceShape change
The invention relates to electronic skin based on three-dimensional flexible substrate graphene and a preparing method thereof. The graphene electronic skin comprises two flexible substrates and graphene films covering the inner surfaces of the flexible substrates. When the three-dimensional flexible substrates are subjected to external action force such as squeezing and stretching, the contact area of the upper graphene layer and the lower graphene layer is changed, so that change of the contact resistance between the two layers is caused directly, and then the shape change of the electronic skin under external force is reflected by reading a voltage or current signal. The electronic skin based on the three-dimensional flexible substrate graphene is transparent and has the advantages of being ultralight, ultrathin, capable of saving energy and the like. The graphene is environmentally friendly, poisonless and compatible with the human body and can be used on the human skin in a more healthy way.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
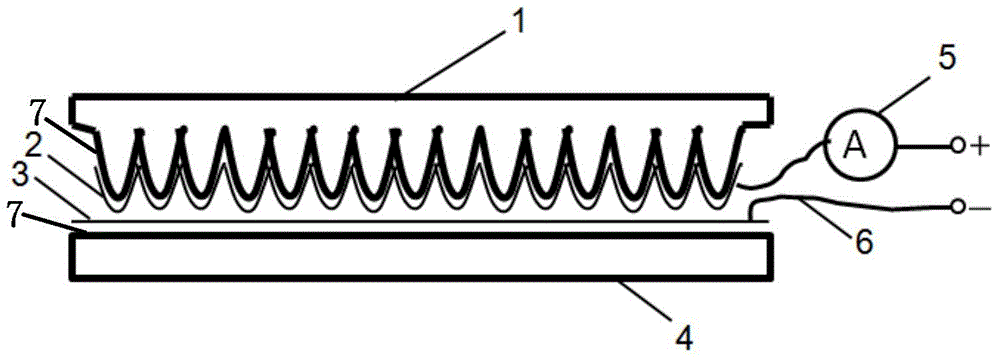
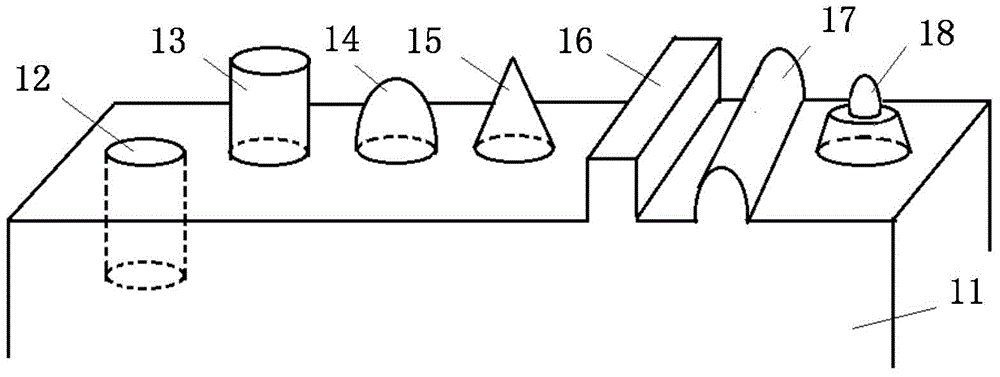
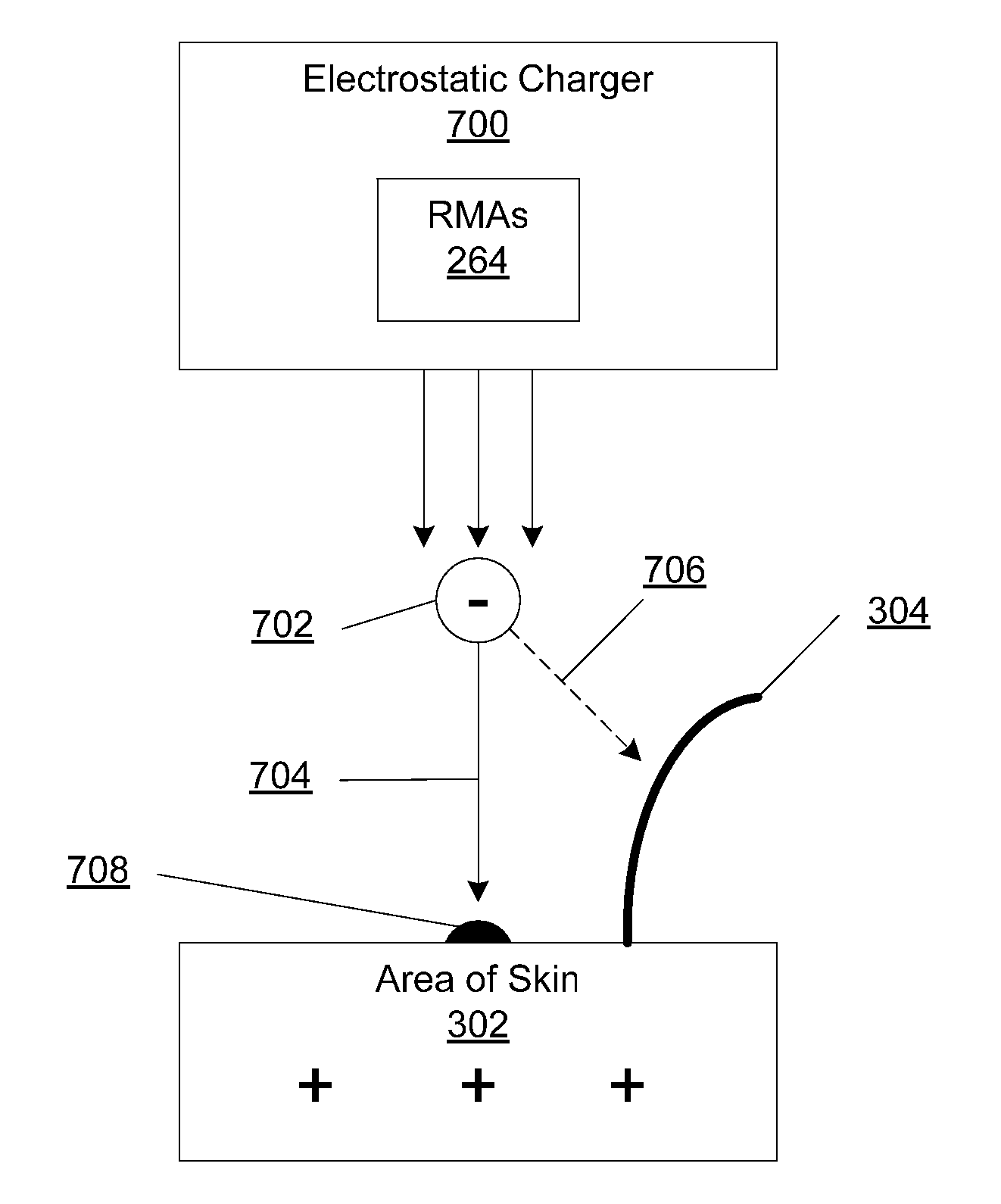
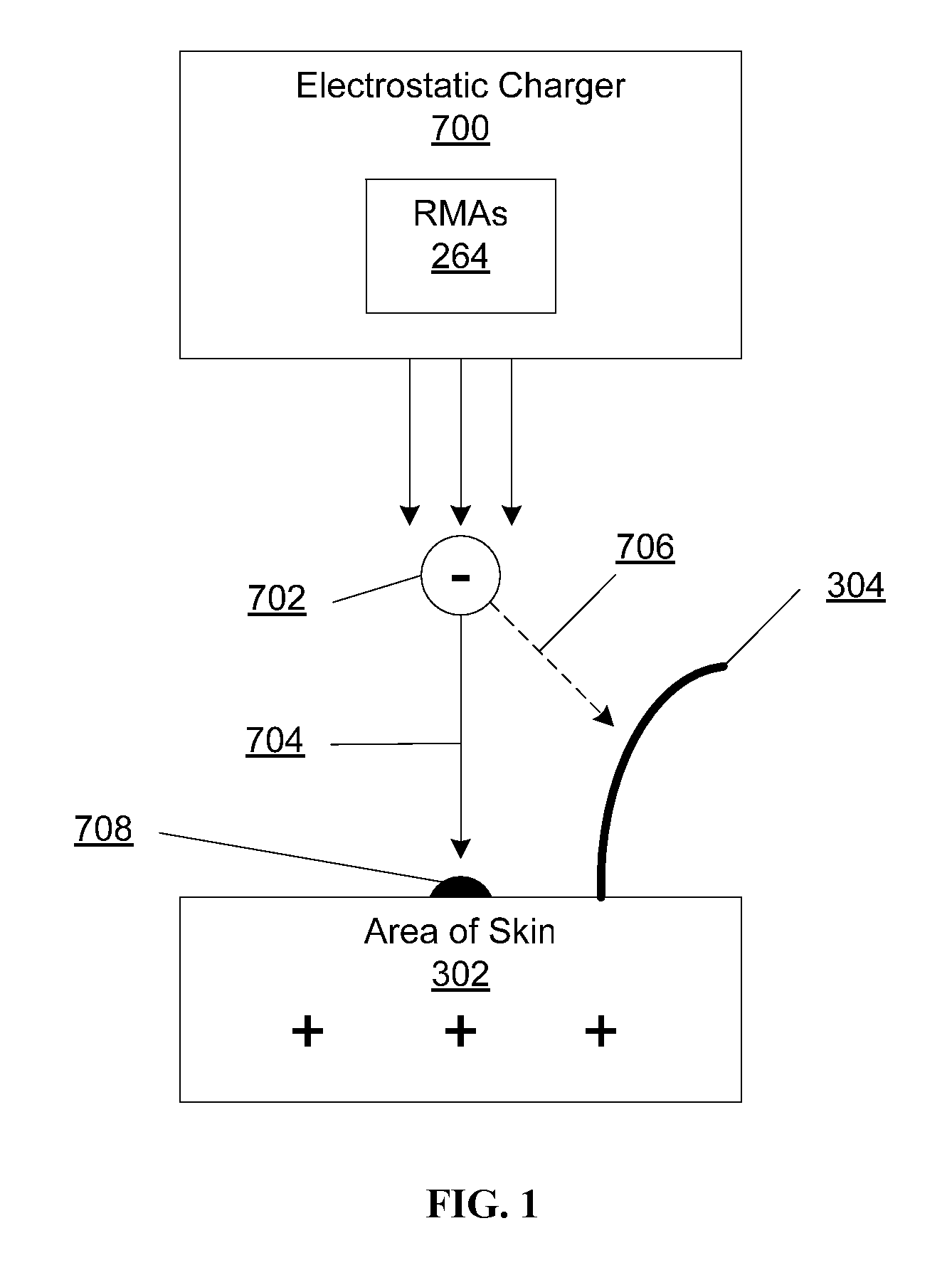
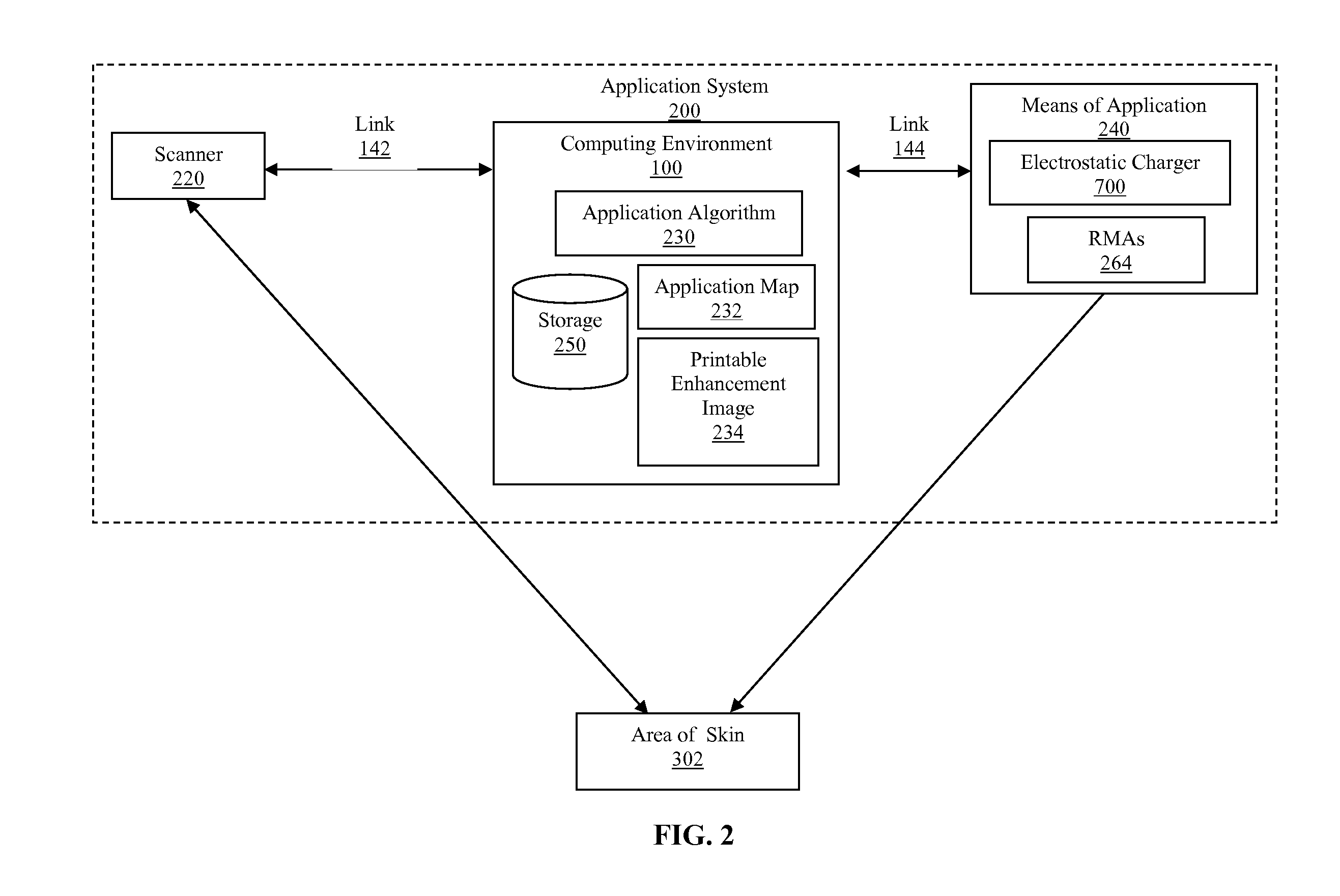
System and method for applying a reflectance modifying agent electrostatically to improve the visual attractiveness of human skin
ActiveUS20080194971A1Enhanced surface irregularityTypewritersMedical applicatorsComputer control systemHuman skin
Owner:TCMS TRANSPARENT BEAUTY LLC
Bone-conduction hearing-aid transducer having improved frequency response
InactiveUS7822215B2Simplified component countRecord carriersBone conduction transducer hearing devicesBone structureFrequency spectrum
A hearing-aid device and a method for transmitting sound through bone conduction are disclosed. The hearing-aid device comprises a piezoelectric-type actuator, housing and connector. The piezoelectric actuator is preferably a circular flextensional-type actuator mounted along its peripheral edge in a specifically designed circular structure of the housing. During operation, the bone-conduction transducer is placed against the mastoid area behind the ear of the patient. When the device is energized with an alternating electrical voltage, it flexes back and forth like a circular membrane sustained along its periphery and thus, vibrates as a consequence of the inverse piezoelectric effect. Due to the specific and unique designs proposed, these vibrations are directly transferred through the human skin to the bone structure (the skull) and provide a means for the sound to be transmitted for patients with hearing malfunctions. The housing acts as a holder for the actuators, as a pre-stress application platform, and as a mass which tailors the frequency spectrum of the device. The apparatus exhibits a performance with a very flat response in the frequency spectrum 200 Hz to 10 kHz, which is a greater spectrum range than any other prior art devices disclosed for bone-conduction transduction which are typically limited to less than 4 kHz.
Owner:FACE INT
Microphone and communication interface system
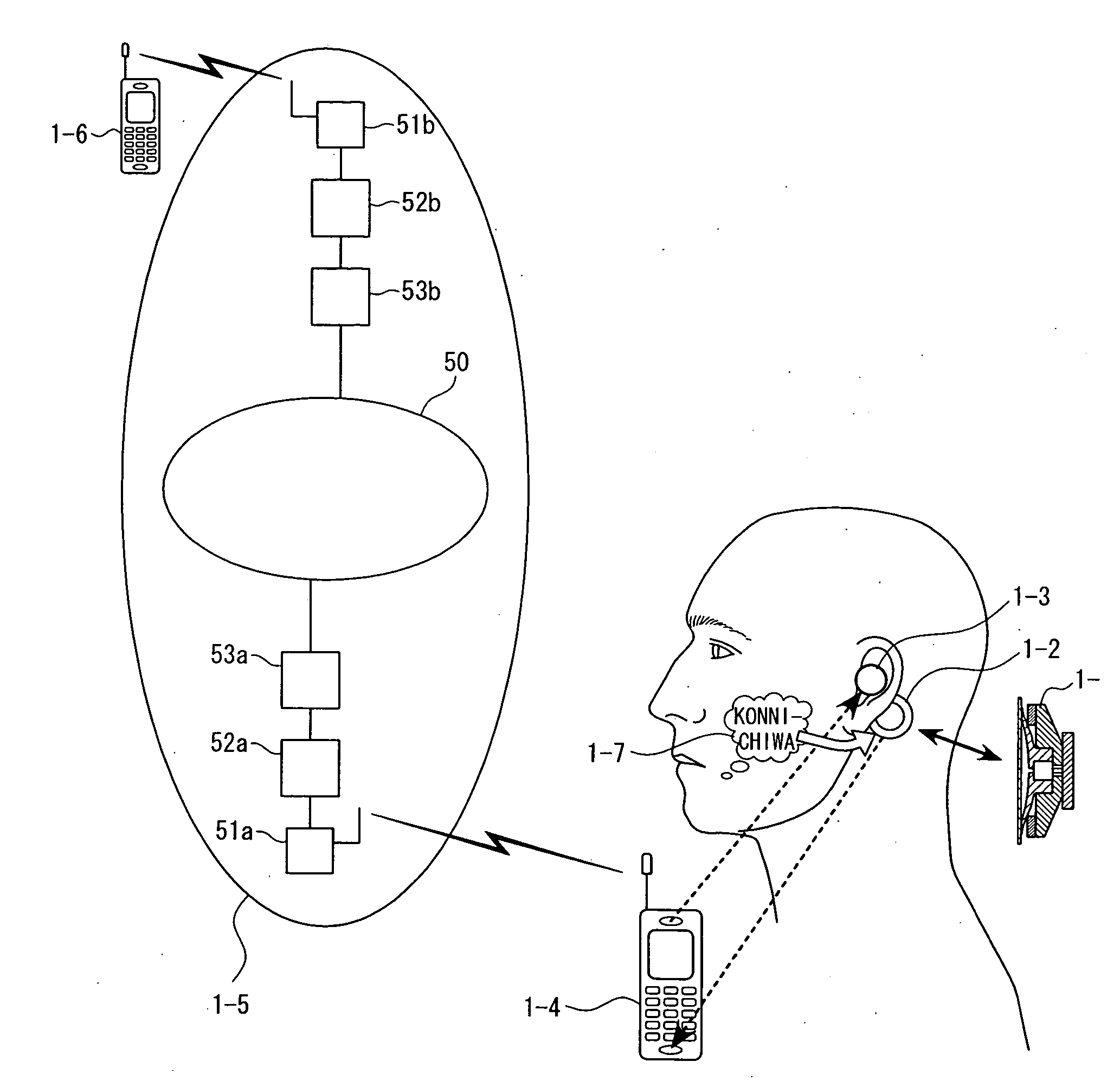
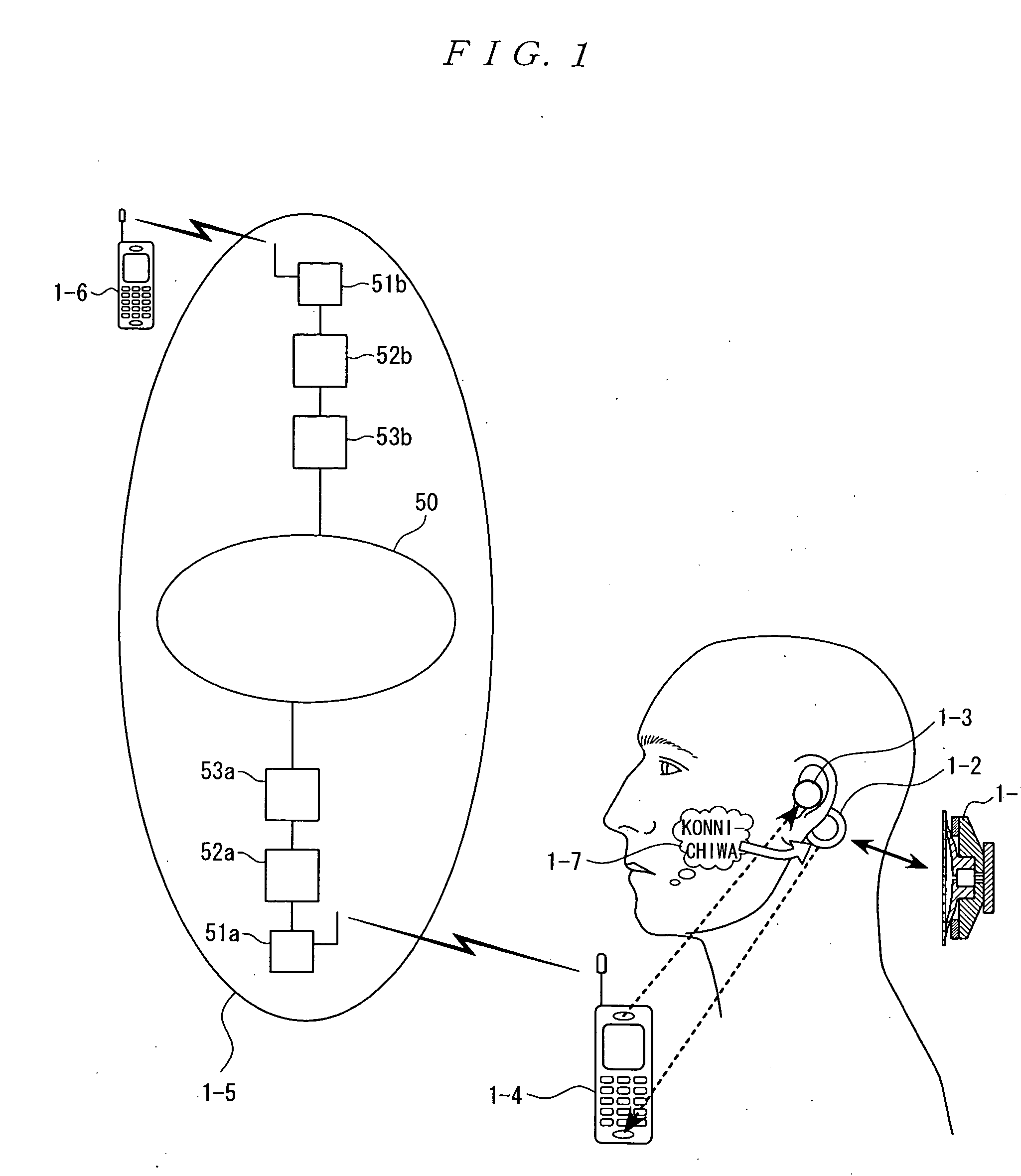
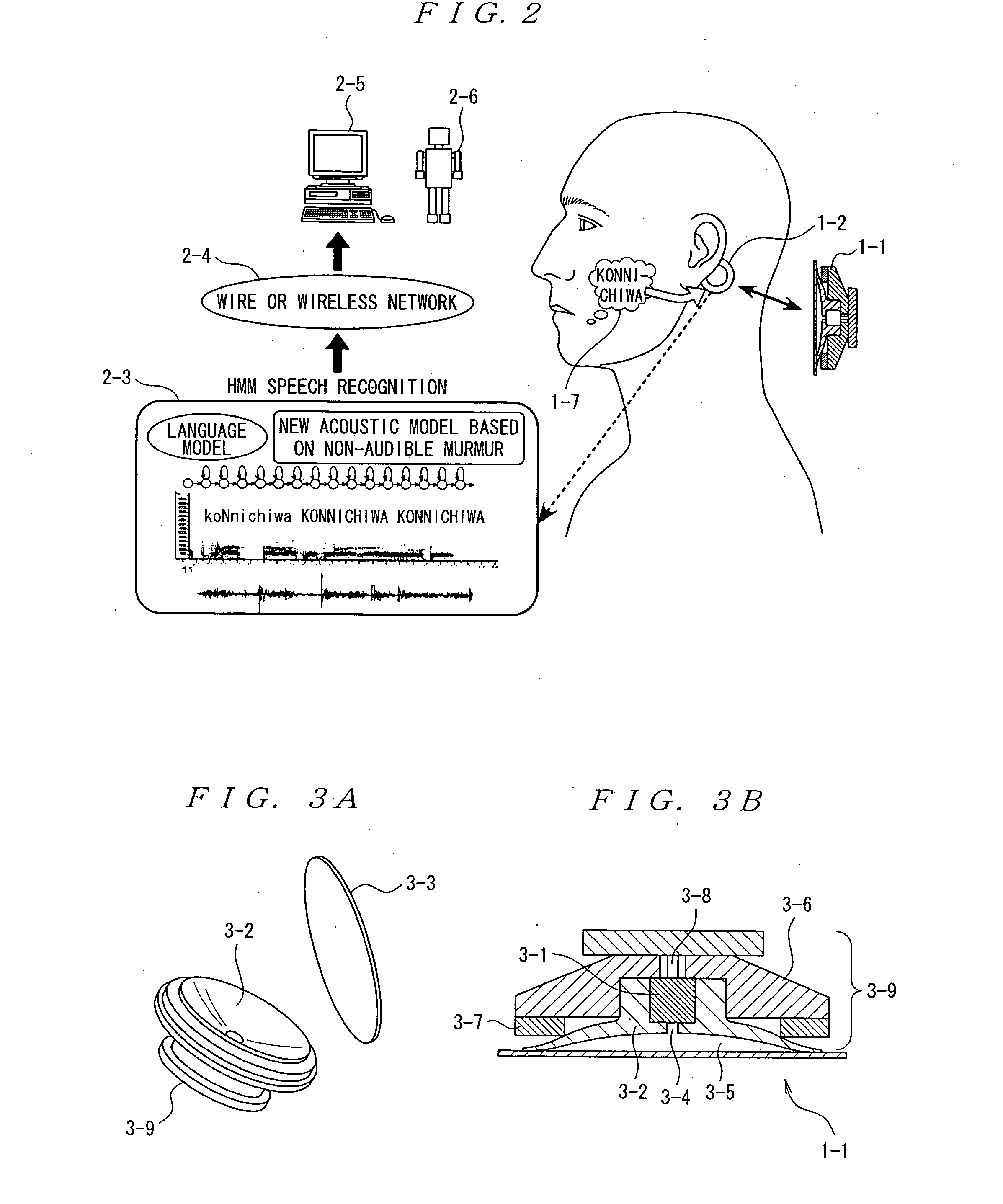
InactiveUS20050244020A1Avoid damaging the environmentHigh expiratoryMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsSpeech recognitionCultural practiceHuman body
The present invention eliminates the disadvantages of an analysis target used by a cellular phone and speech recognition, that is, a normal sound which is transmitted through the air and which is externally sampled through a microphone, and improves the disadvantages that noise may be mixed or occur in the target, that information may leak, and that corrections are difficult. The present invention also provides a personal portable information terminal realizing new portable terminal communications which do not require training and which conform to the cultural practice of human beings. In the present invention, no apparatus that obtains an analysis target is put off human body, and a normal sound is not an analysis target. A stethoscope-type microphone is installed on the surface of the human skin. Then, a vibration sound is sampled which is obtained when a non-audible murmur articulated in association with speech action (the motion of the mouth) not using the regular vibration of the vocal cords is transmitted through the flesh. A vibration sound obtained when a non-audible murmur amplified is transmitted through the flesh is similar to a whisper. The vibration sound can thus be heard and understood by human beings. Accordingly, the vibration sound can be used for a speech over the cellular phone as it is. Further, when the vibration sound obtained when the non-audible murmur is transmitted through the flesh is analyzed and converted into parameters, a kind of soundless recognition is realized. The present invention replaces the HMM model, conventionally used for speech recognition by an acoustic model created on the basis of a vibration sound obtained when a non-audible murmur is transmitted through the flesh. Therefore, the present invention provides a new method of inputting data to the personal portable information terminal.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method of long lasting human skin tanning
InactiveUS20110020252A1Durable UVRAvoid repeated contactCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHuman skinDermatology
The invention relates to the use of Rifampin and its related compound as a method of producing long-lasting, effective skin tanning for human and animal. The invention relates to methods of accelerating and facilitating the tanning of the skin using Rifampin along with use of the other tanning facilitators and accelerants with or without UVR.
Owner:SHANTHA TOTADA R +2
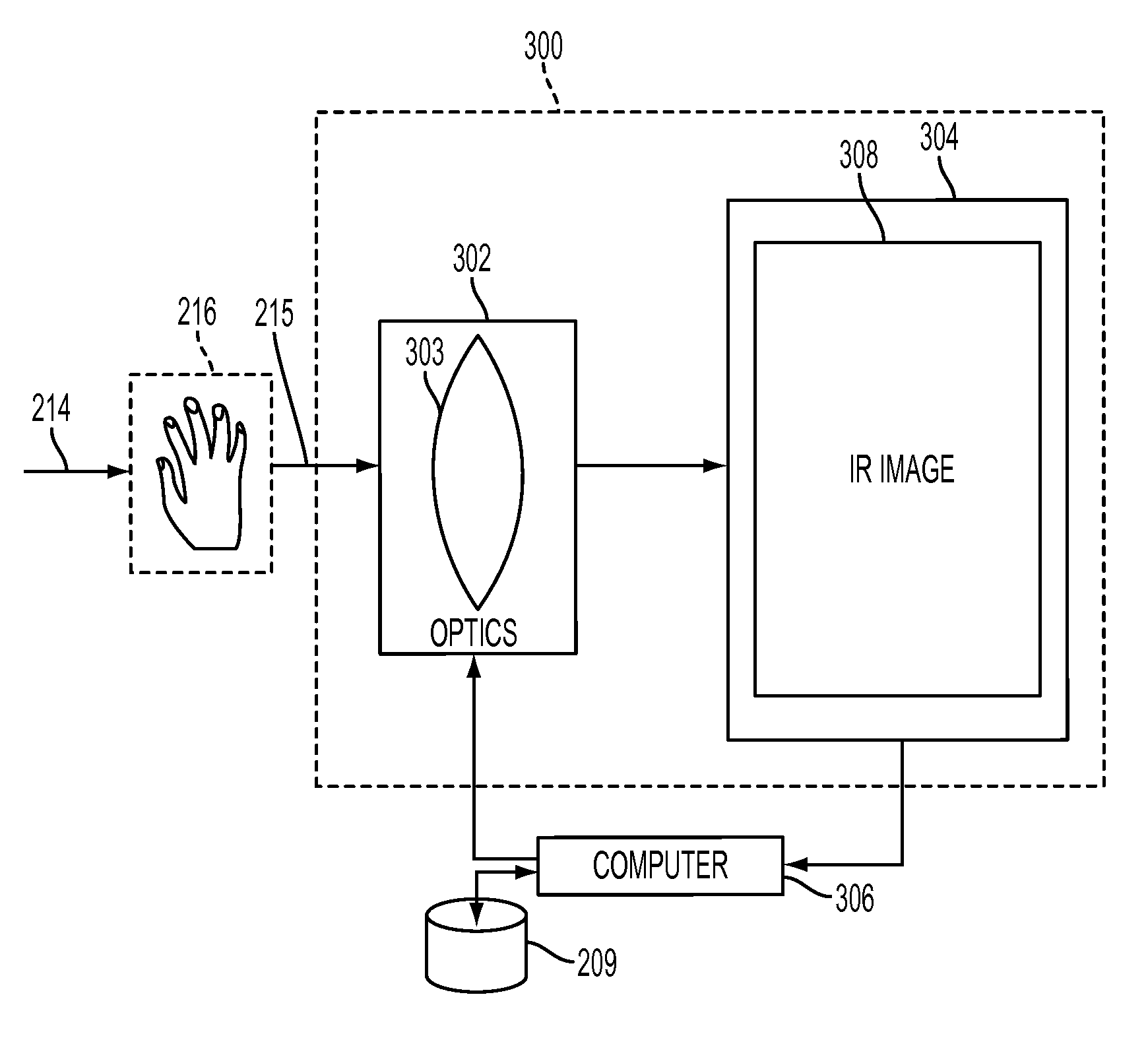
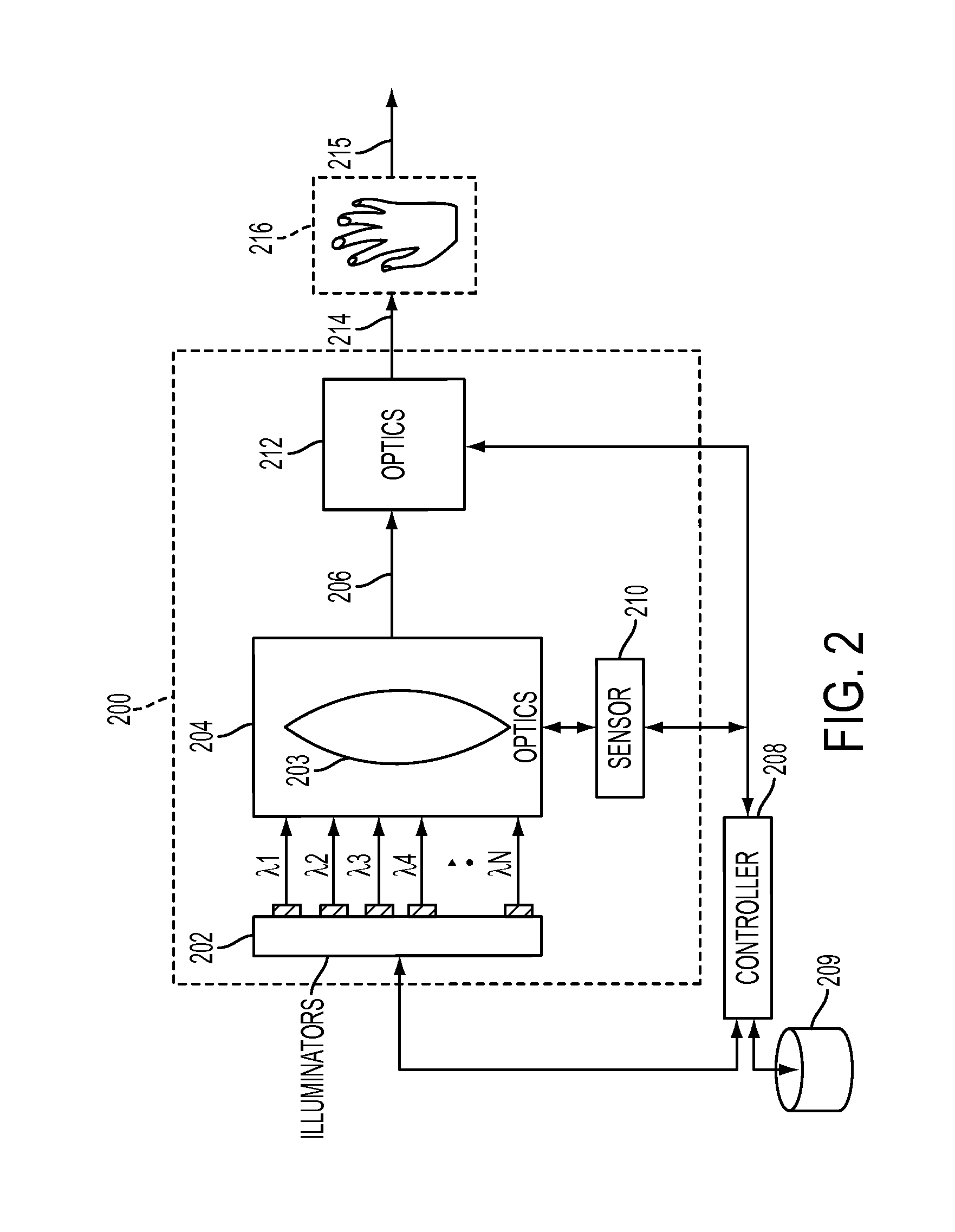
Subcutaneous vein pattern detection via multi-spectral IR imaging in an identity verification system
InactiveUS8509495B2Quick configurationImprove scalabilitySubcutaneous biometric featuresVerifying markings correctnessPattern recognitionVideo based
What is disclosed is a novel system and method for identifying an individual in an IR image involves the following. Intensity values are collected at N wavelengths for each pixel in an IR video-based image. The intensity values are collected using an IR imaging system having an IR detector and an IR Illuminator. The intensity values are then used to identify pixels of human skin in the IR image. If human skin is identified in the IR image then, the human hand is identified in the IR image from the human skin to distinguish the hand from the background. Vein patterns in the hand are then located and extracted. A reference vein pattern is retrieved from a database of known vein patterns for individuals, and a comparison is made to determine a match. If a match is determined, then the individual in the captured IR image can be identified.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Transdermal delivery of drugs based on crystal size
ActiveUS20060078603A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureHigh drug loadingNervous disorderAdhesive dressingsSkin surfacesPolymer
A blend of at least two polymers in combination with a drug provides a pressure-sensitive adhesive composition for a transdermal drug delivery system in which the drug is delivered from the pressure-sensitive adhesive composition and through dermis when the pressure-sensitive adhesive composition is in contact with human skin. According to the invention, providing drug having differing crystal sizes as well as drug which is solublized in the pressure-sensitive adhesive composition controls the rate of drug delivery from the pressure-sensitive adhesive composition.
Owner:NOVEN PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com