Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33964results about How to "Improve scalability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
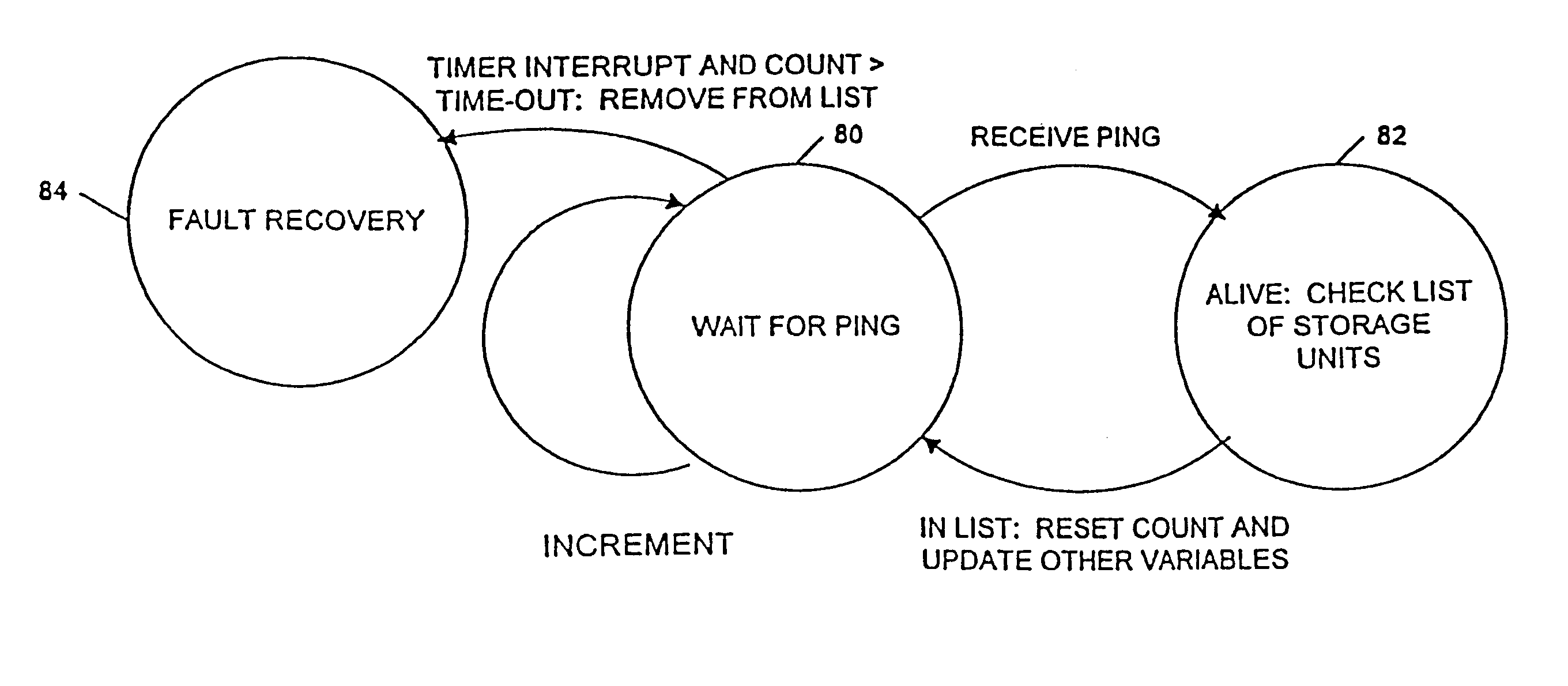
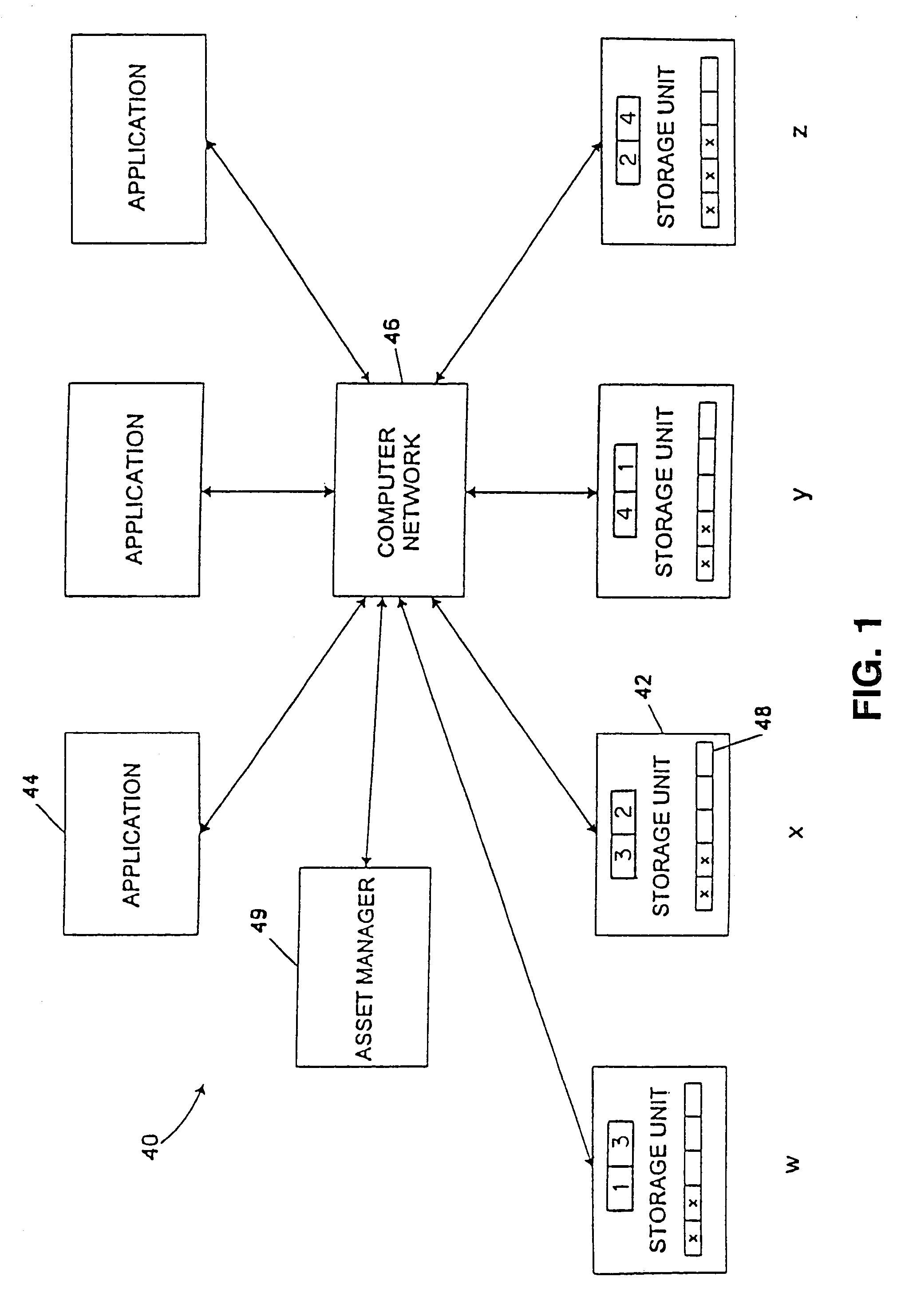
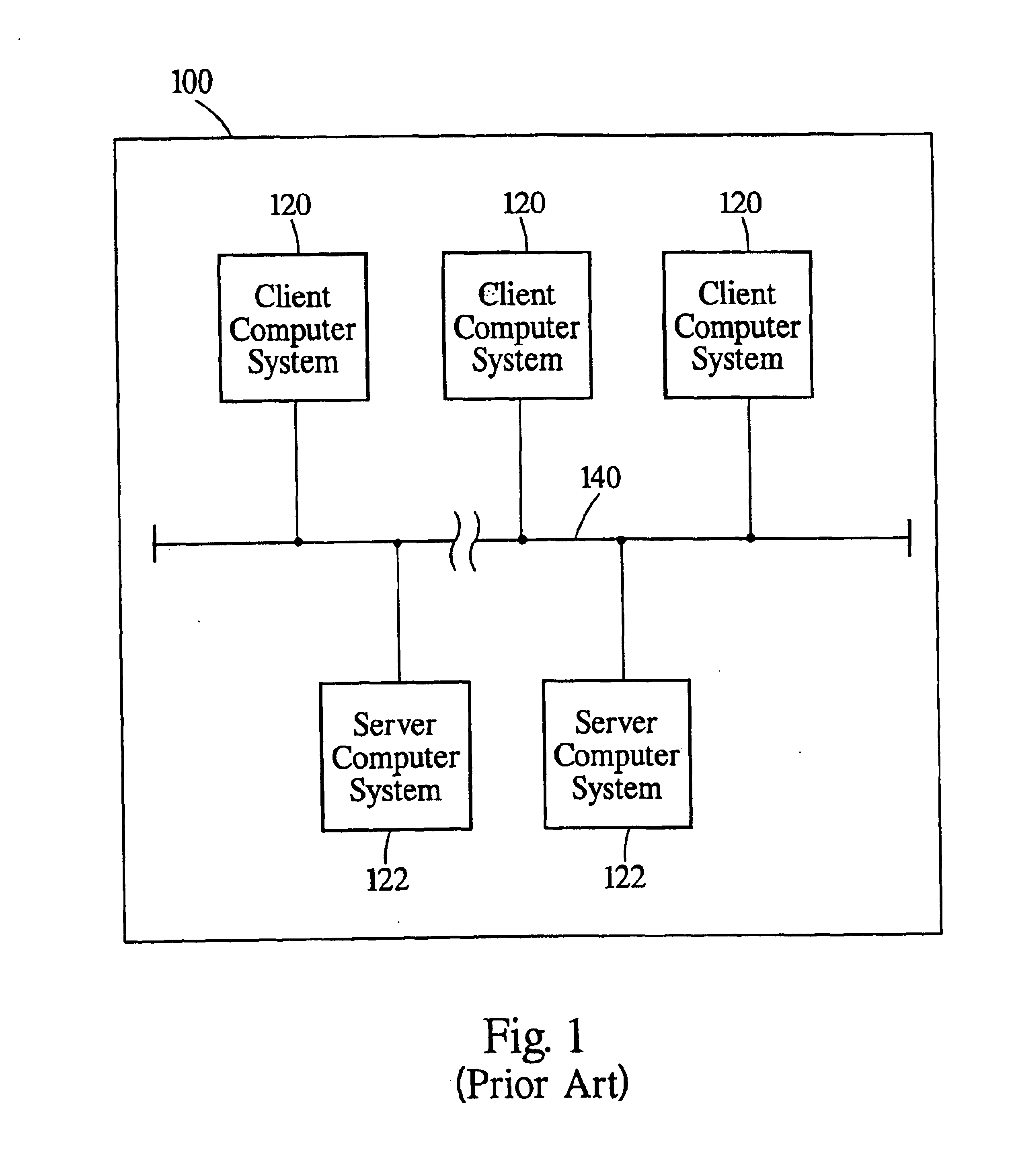
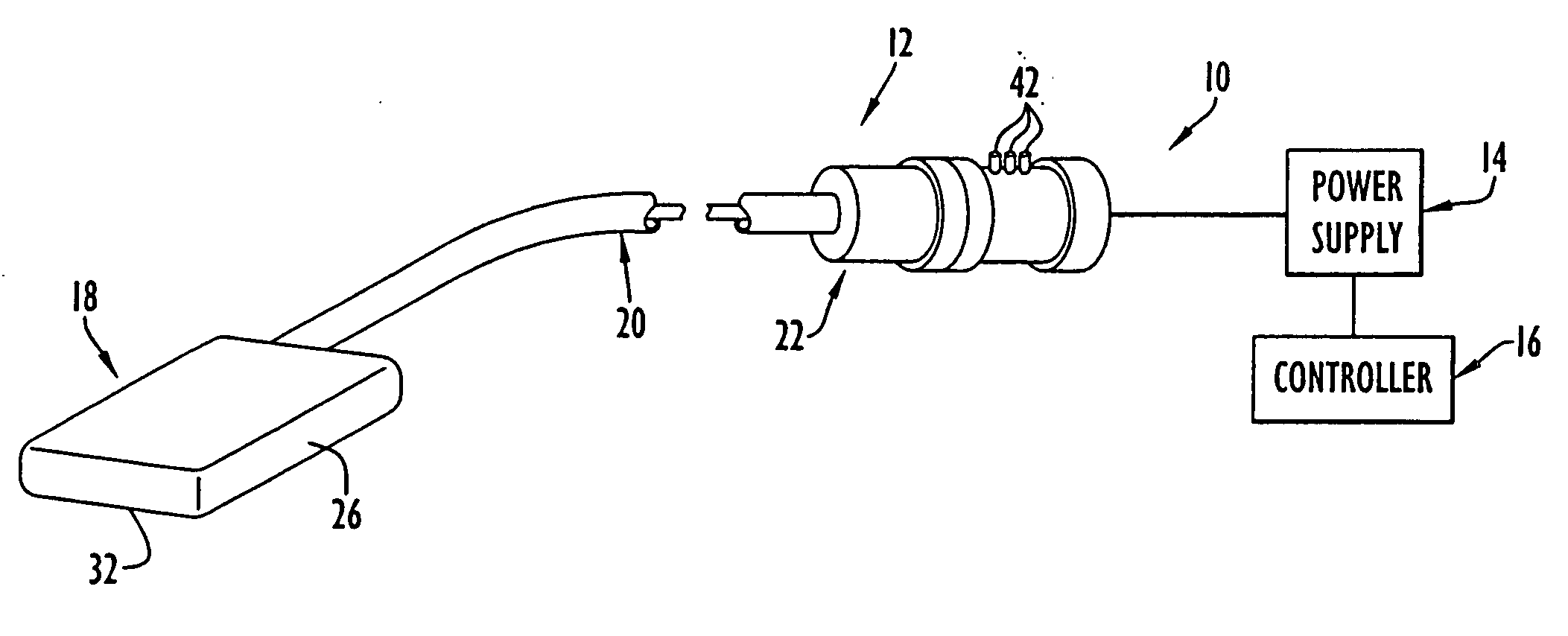
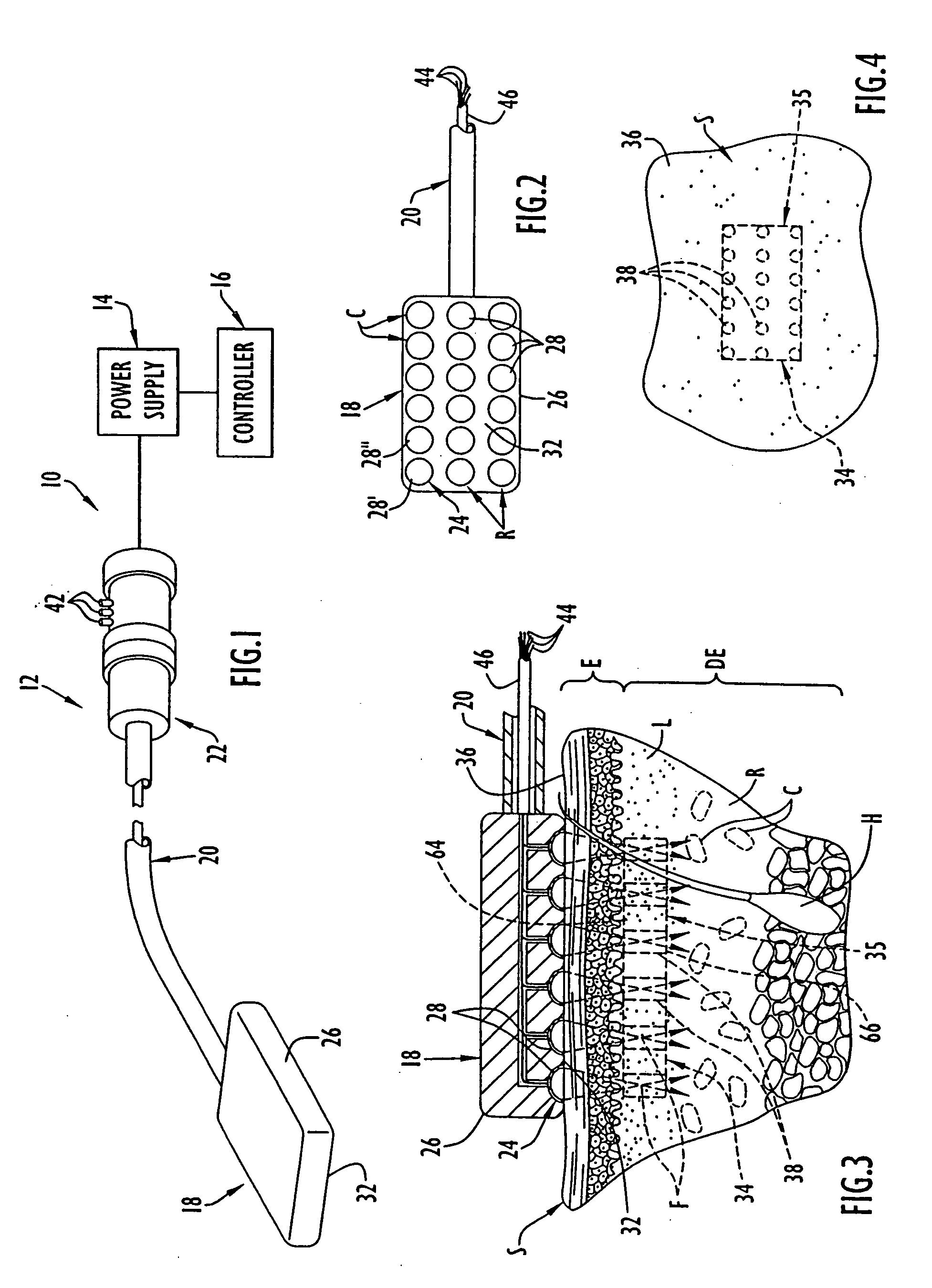
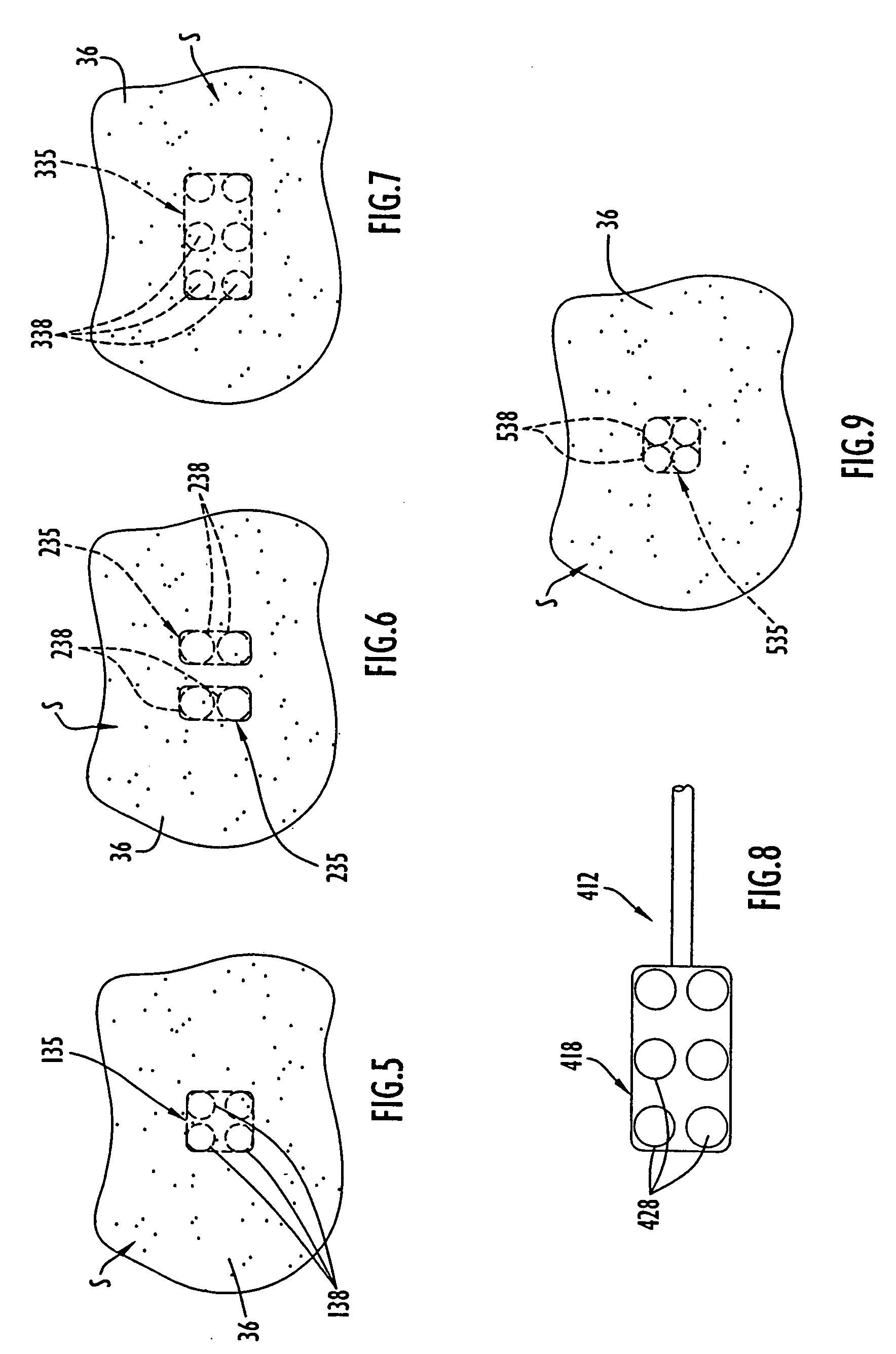
Computer system and process for transferring multiple high bandwidth streams of data between multiple storage units and multiple applications in a scalable and reliable manner
InactiveUS7111115B2Improve reliabilityImprove scalabilityInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsHigh bandwidthData segment
Multiple applications request data from multiple storage units over a computer network. The data is divided into segments and each segment is distributed randomly on one of several storage units, independent of the storage units on which other segments of the media data are stored. At least one additional copy of each segment also is distributed randomly over the storage units, such that each segment is stored on at least two storage units. This random distribution of multiple copies of segments of data improves both scalability and reliability. When an application requests a selected segment of data, the request is processed by the storage unit with the shortest queue of requests. Random fluctuations in the load applied by multiple applications on multiple storage units are balanced nearly equally over all of the storage units. This combination of techniques results in a system which can transfer multiple, independent high-bandwidth streams of data in a scalable manner in both directions between multiple applications and multiple storage units.
Owner:AVID TECHNOLOGY
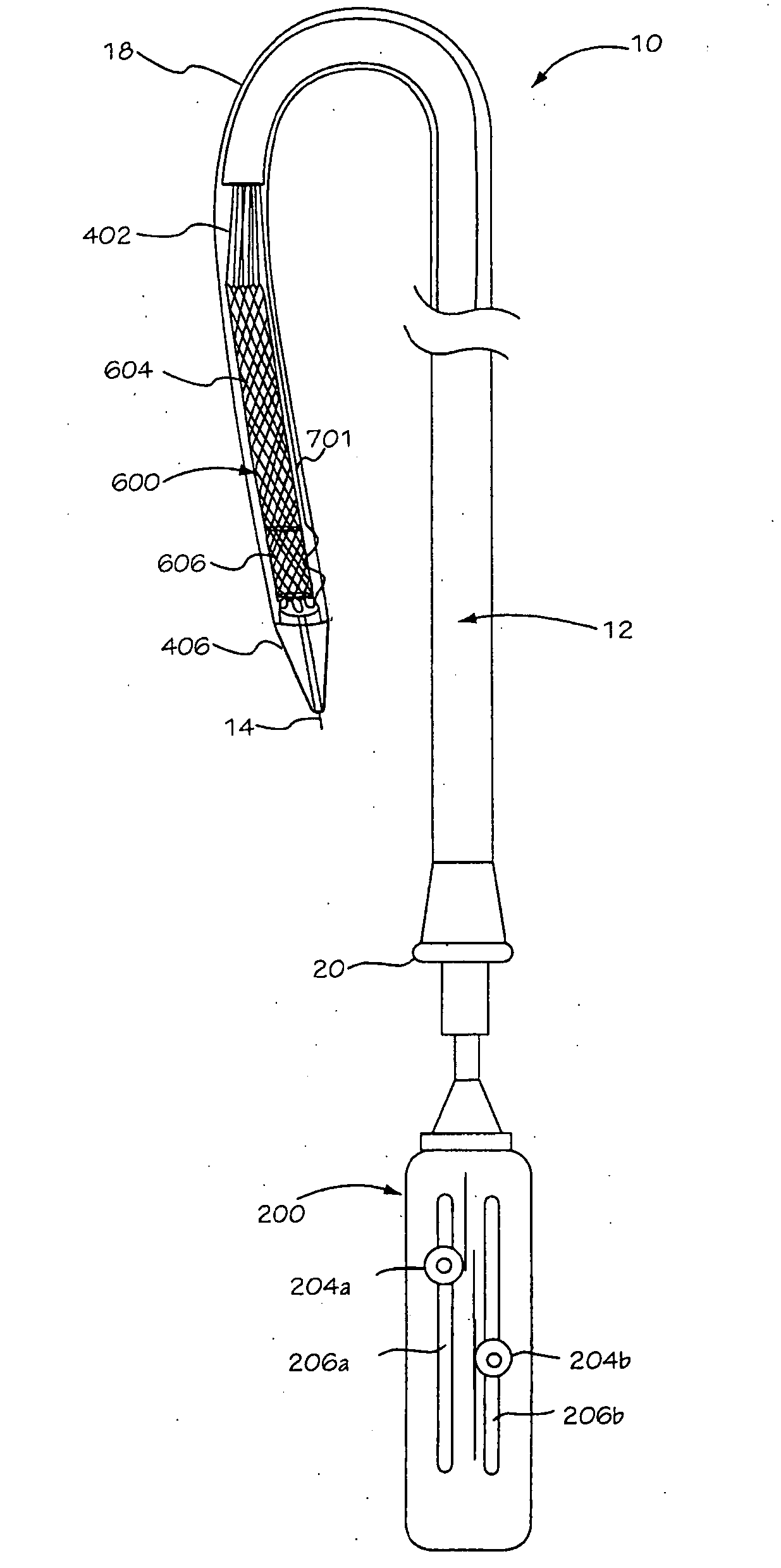
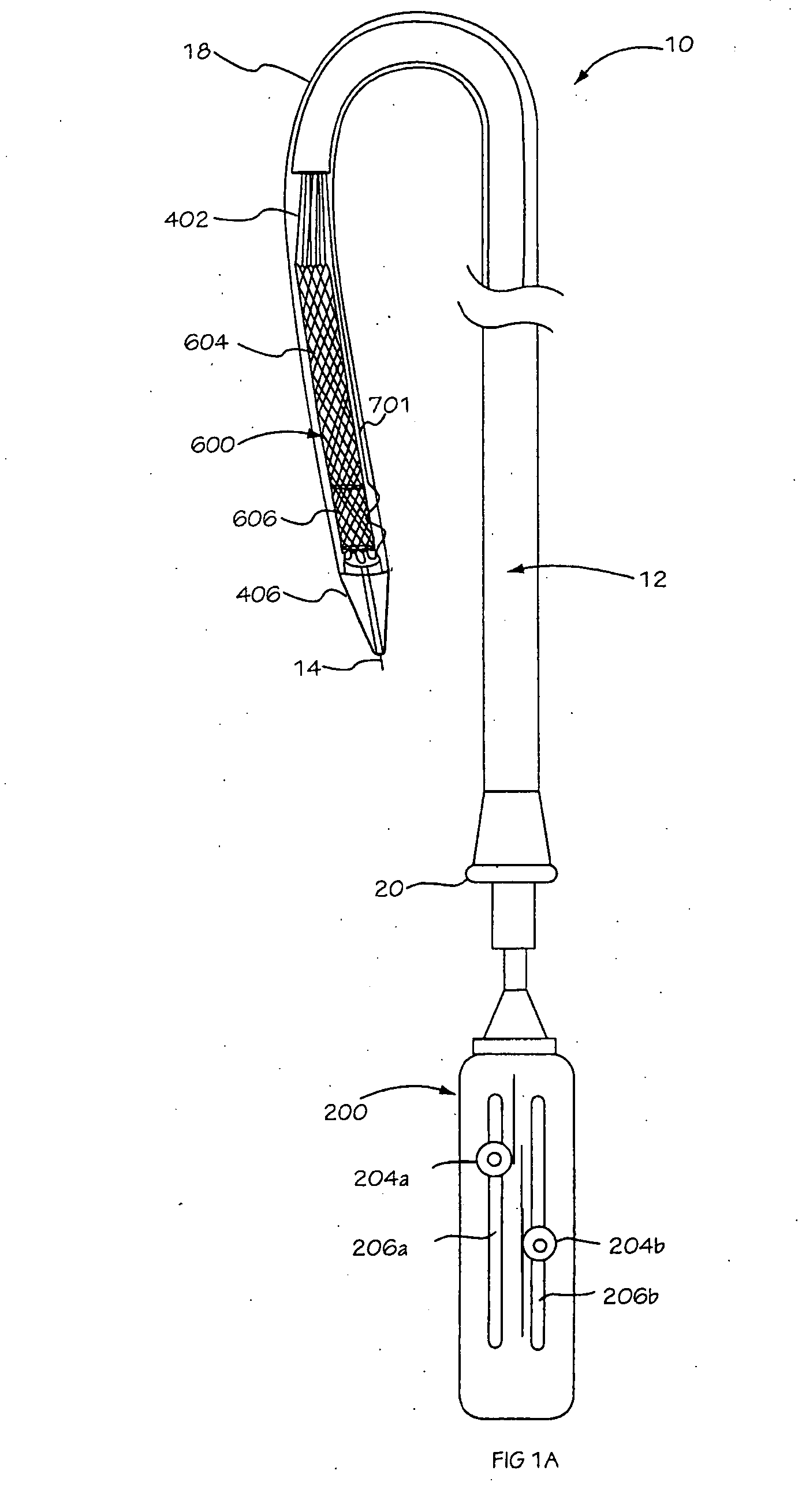
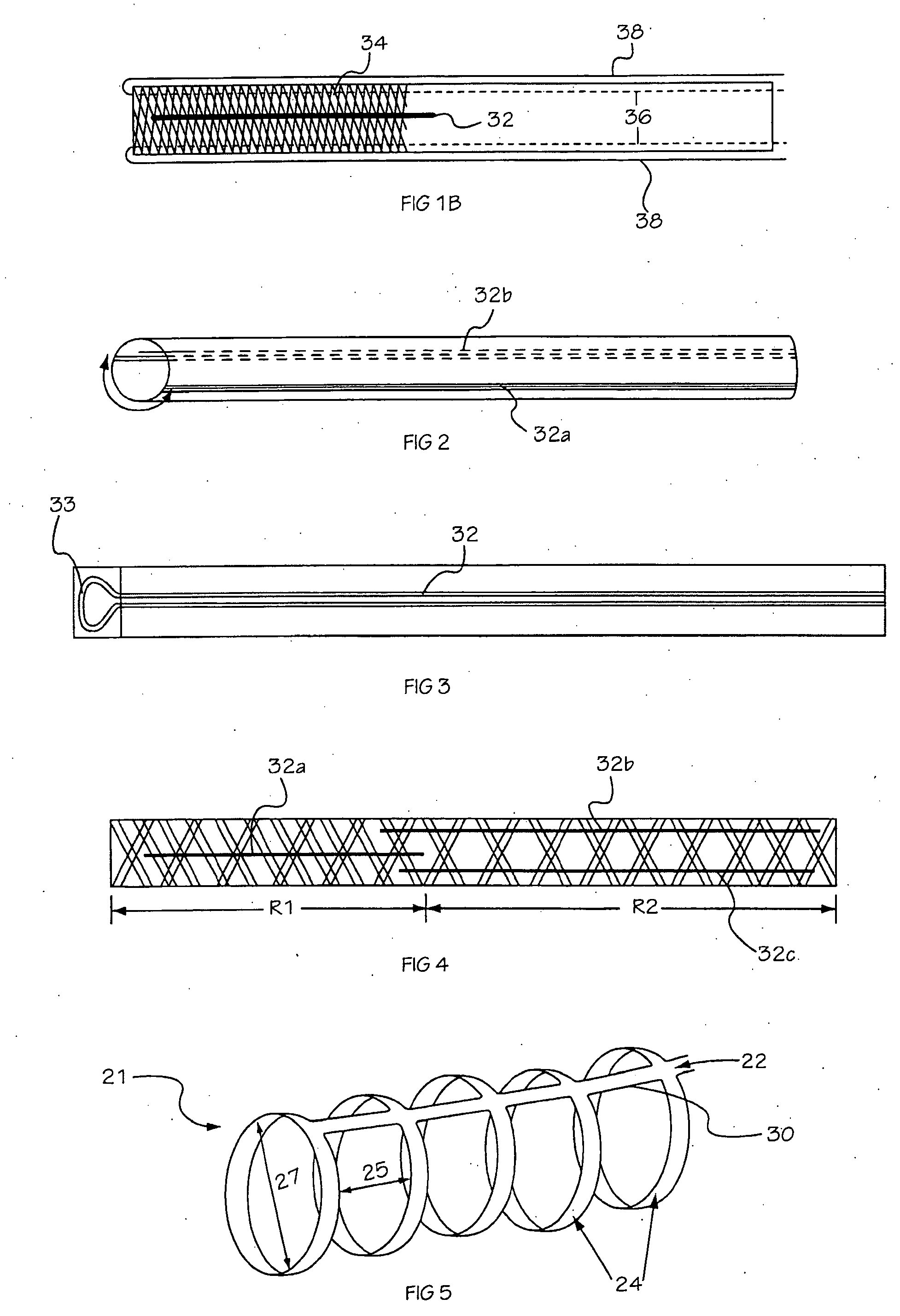
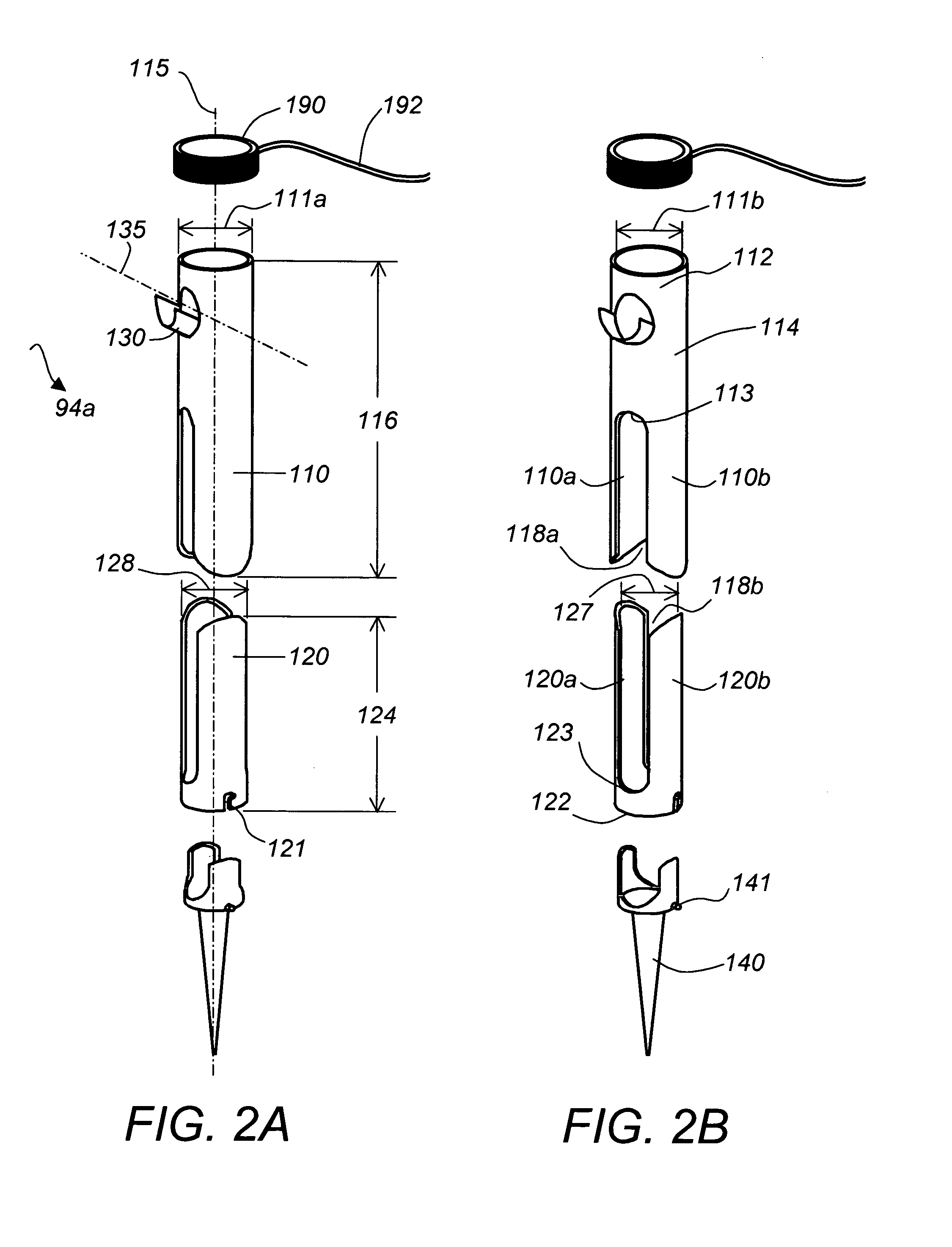
Medical device delivery sheath
InactiveUS20080188928A1Easy to collapseFacilitate resheathingStentsHeart valvesMedical deviceGuide tube
A support member for a catheter sheath is disclosed. The support member has a series of ribs with a distal member having integrated fingers for providing radial compliance. The support member provides sufficient axial stiffness to provide a desired pushability of a minimally invasive device for replacing a heart valve. Various alternative embodiments are also described.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and devices for improving percutaneous access in minimally invasive surgeries
ActiveUS20050065517A1Reduce the difficulty of operationReduce riskInternal osteosythesisCannulasLess invasive surgeryPost operative
A device for use as a portal in percutaneous minimally invasive surgery performed within a patient's body cavity includes a first elongated hollow tube having a length adjusted with a self-contained mechanism. The first elongated tube includes an inner hollow tube and an outer hollow tube and the inner tube is adapted to slide within the outer tube thereby providing the self-contained length adjusting mechanism. This length-adjustment feature is advantageous for percutaneous access surgery in any body cavity. Two or more elongated tubes with adjustable lengths can be placed into two or more adjacent body cavities, respectively. Paths are opened within the tissue areas between the two or more body cavities, and are used to transfer devices and tools between the adjacent body cavities. This system of two or more elongated tubes with adjustable lengths is particularly advantageous in percutaneous minimally invasive spinal surgeries, and provides the benefits of minimizing long incisions, recovery time and post-operative complications.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
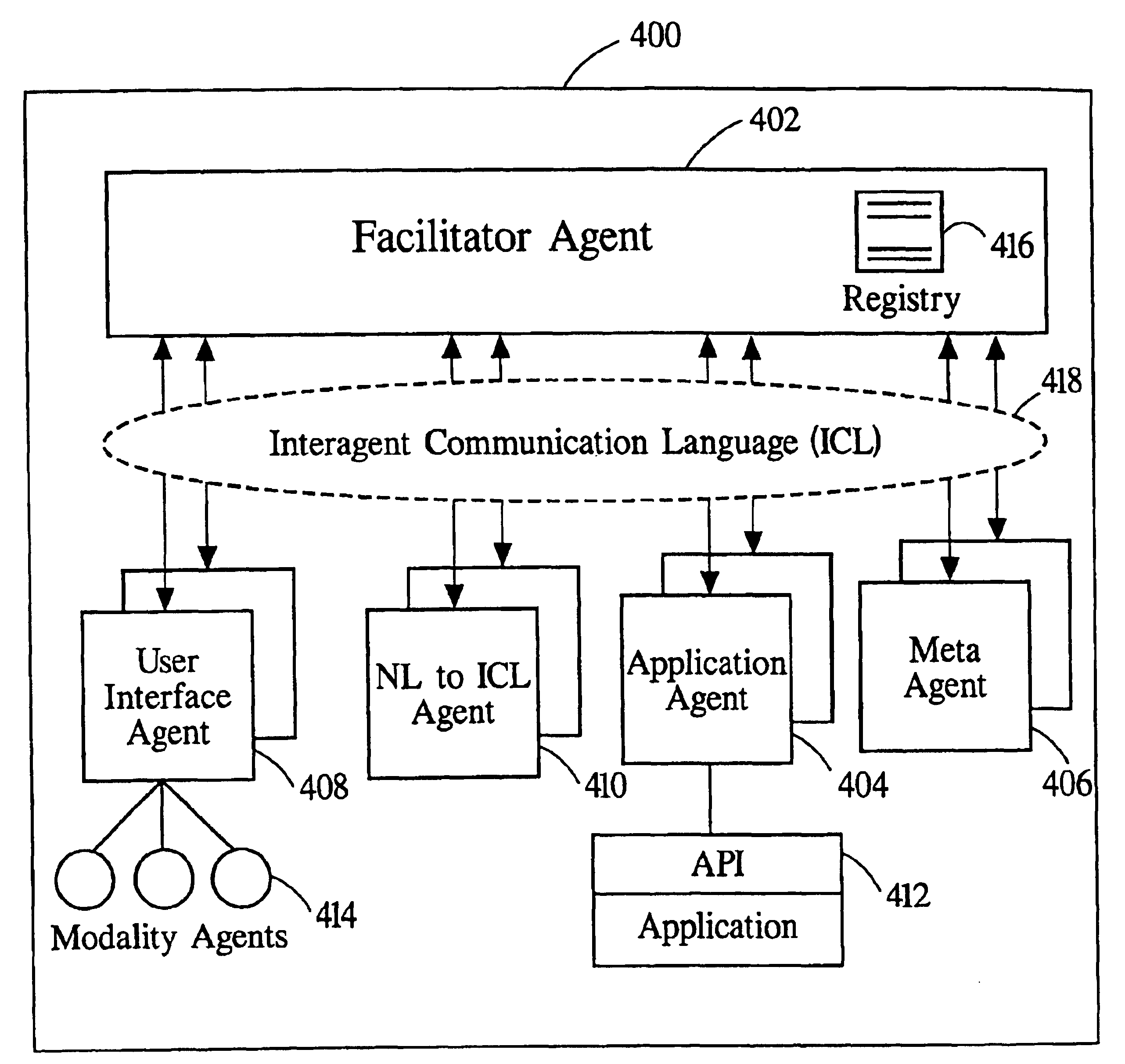
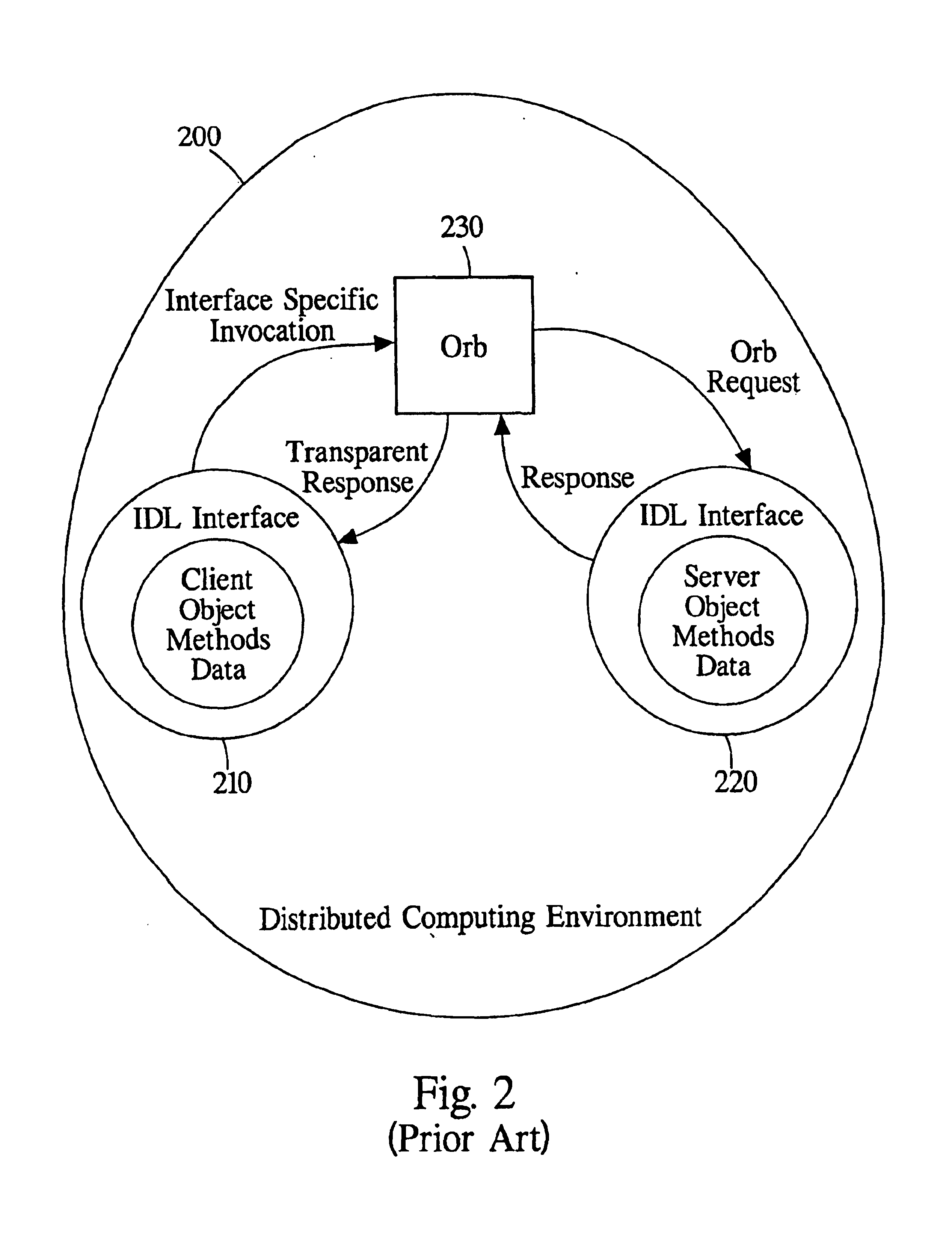
Extensible software-based architecture for communication and cooperation within and between communities of distributed agents and distributed objects
InactiveUS6859931B1Minimal effortIncrease flexibilityDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationIntelligent planningDistributed object systems
A distributed agent community is able to dynamically interact with alternative sofware technologies that manage distributed objects. The leveraging of capabilities of distributed object systems greatly expands the flexibility and capabilites of the distributed agent community. Through access to distributed object systems, the distributed agent community can draw on the capabilites of all the objects managed by the distributed object systems. The access to distributed systems by the distributed agent community allows for collaboration and intelligent planning that the distributed object systems do not themsleves provide.
Owner:IPA TECH INC
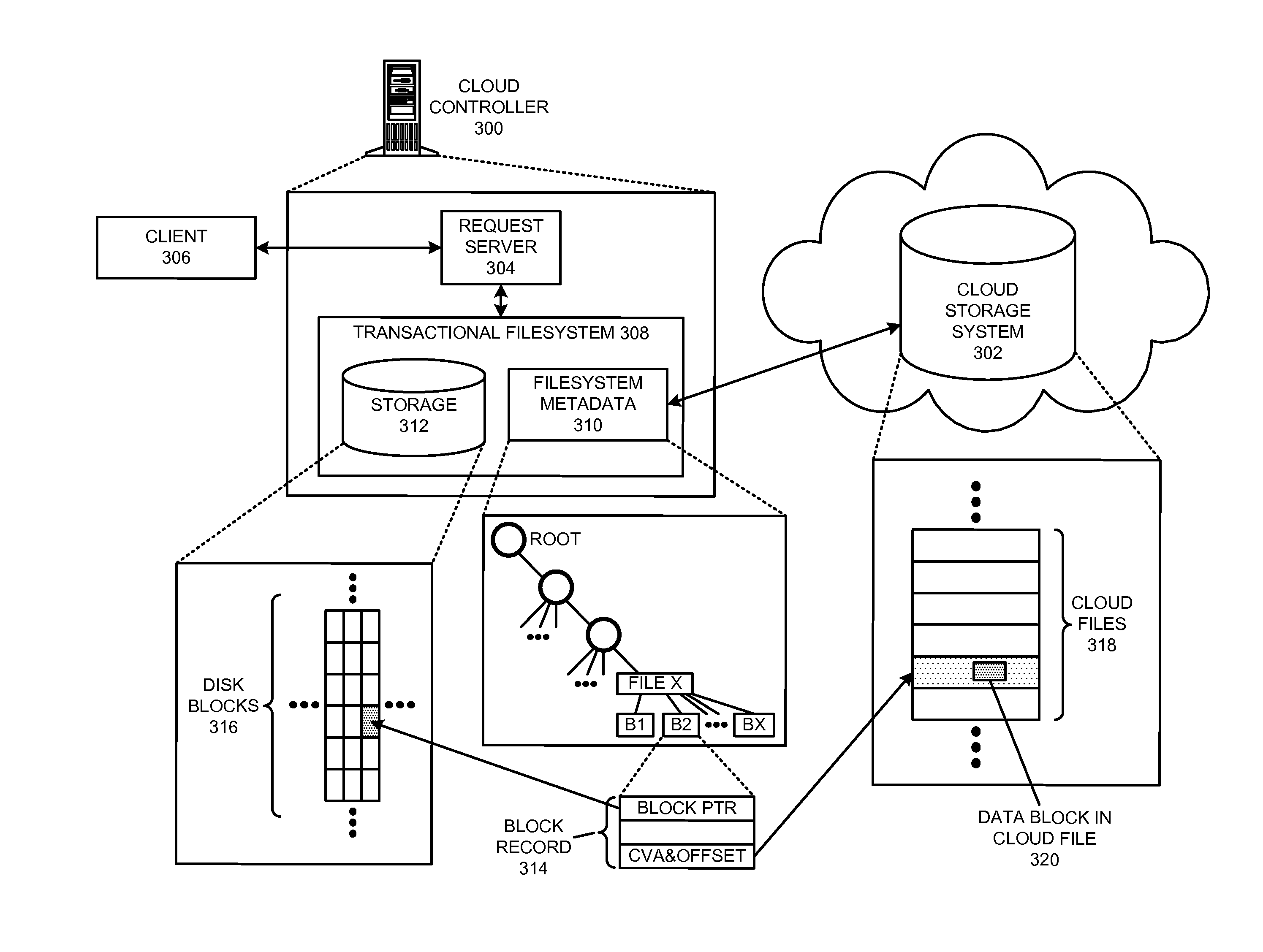
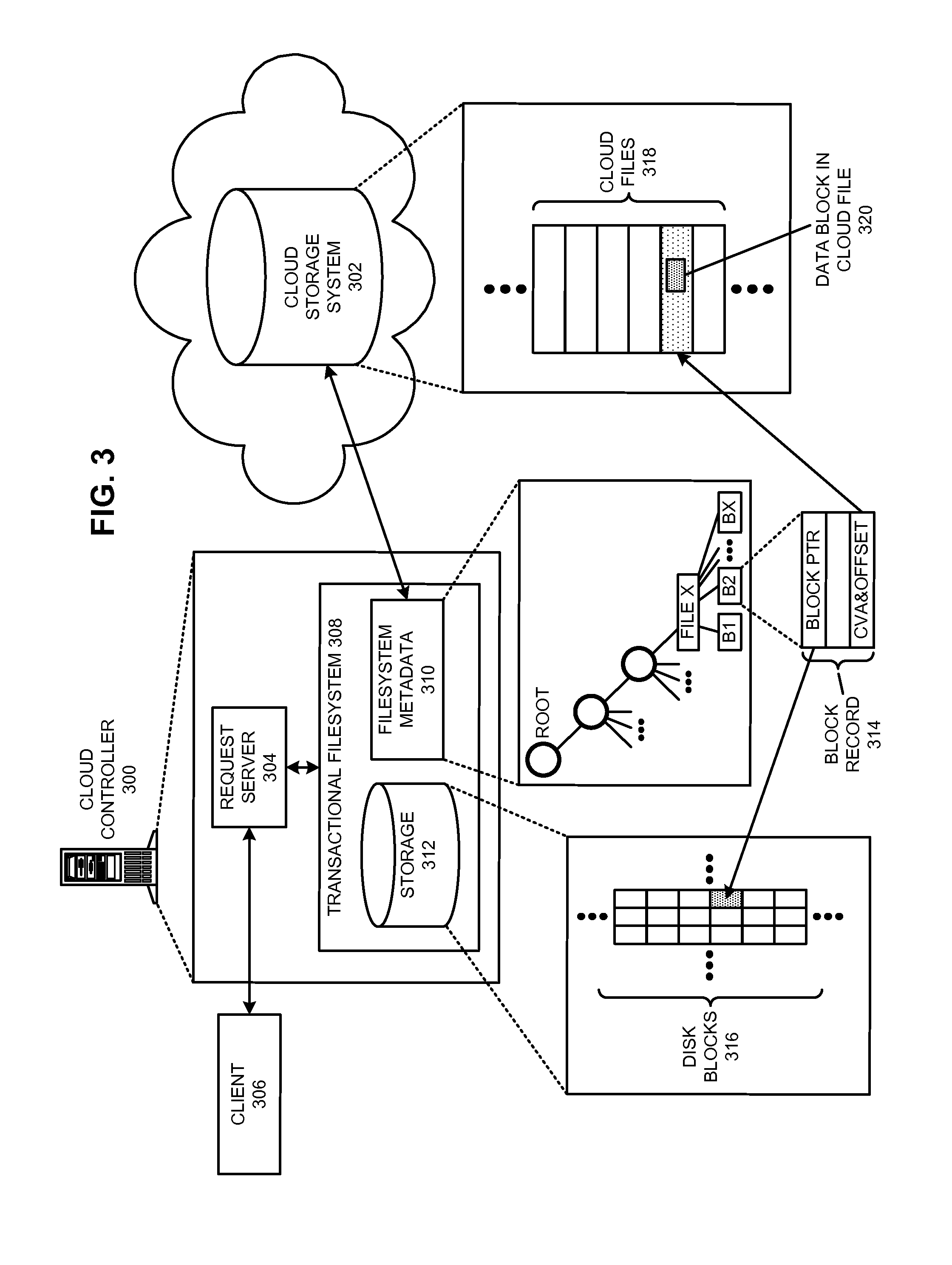
Managing a global namespace for a distributed filesystem
ActiveUS20140006465A1Outweigh additional overheadIncreasing file access performanceDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemCloud storage system
The disclosed embodiments disclose techniques for managing a global namespace for a distributed filesystem. Two or more cloud controllers collectively manage distributed filesystem data that is stored in a cloud storage system; the cloud controllers ensure data consistency for the stored data, and each cloud controller caches portions of the distributed filesystem. Furthermore, a global namespace for the distributed filesystem is also split across these cloud controllers, with each cloud controller “owning” (e.g., managing write accesses for) a distinct portion of the global namespace and maintaining a set of namespace mappings that indicate which portion of the namespace is assigned to each cloud controller. During operation, an initial cloud controller receives a request from a client system to access a target file in the distributed system. This initial cloud controller uses the namespace mappings for the global namespace to determine a preferred cloud controller that will handle the request.
Owner:PANZURA LLC
Software-based architecture for communication and cooperation among distributed electronic agents
InactiveUS6851115B1Minimal effortImprove scalabilityDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationNatural languageSoftware
A highly flexible, software-based architecture is disclosed for constructing distributed systems. The architecture supports cooperative task completion by flexible and autonomous electronic agents. One or more facilitators are used to broker communication and cooperation among the agents. The architecture provides for the construction of arbitrarily complex goals by users and service-requesting agents. Additional features include agent-based provision of multi modal interfaces, including natural language.
Owner:IPA TECH INC
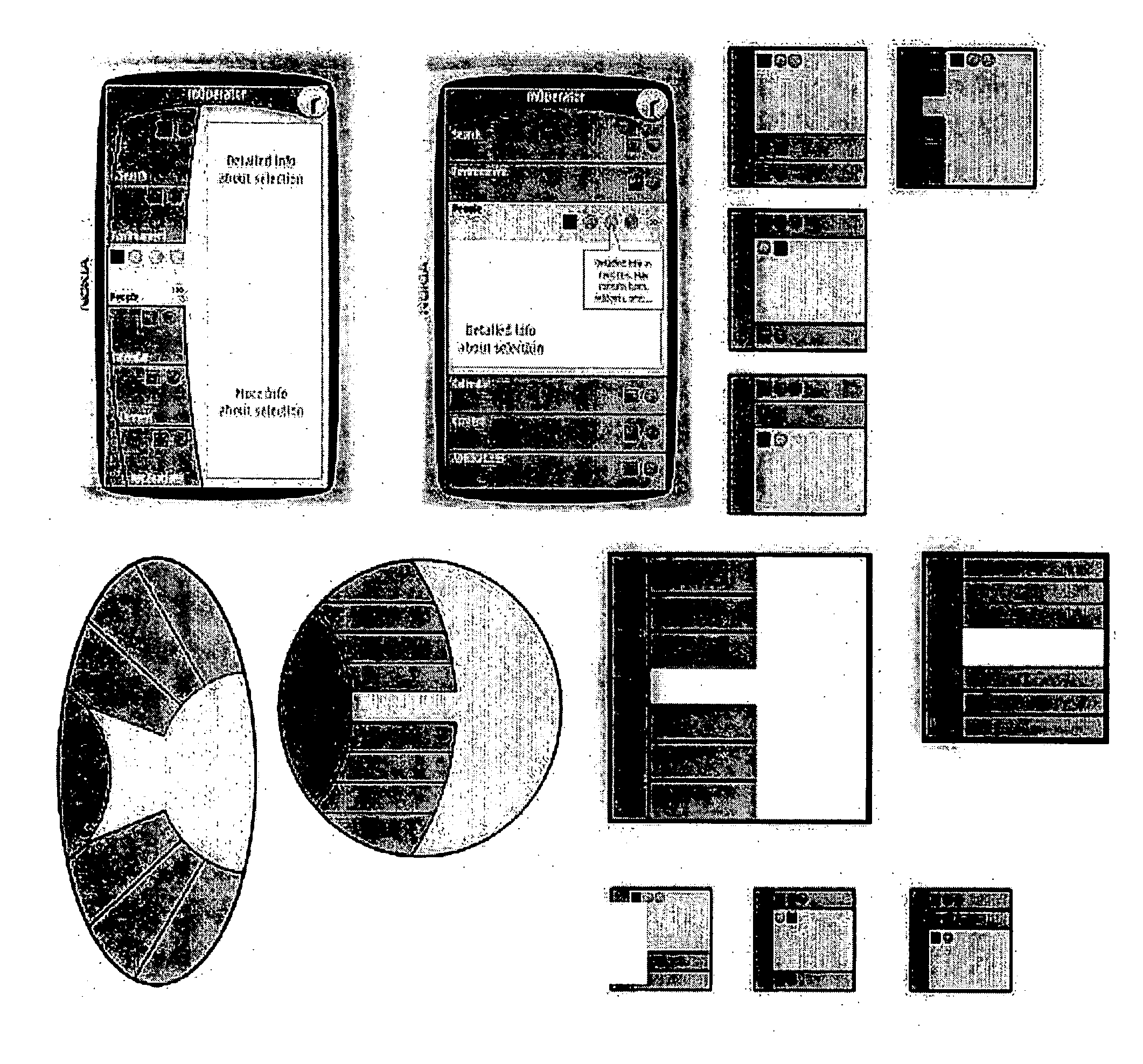
Stripe user interface
InactiveUS20060020904A1Easy to customizeImprove scalabilitySubstation equipmentInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method for navigating information in a mobile terminal. The method includes displaying, on a graphical user interface of the mobile terminal, a plurality of window regions, wherein each region is a container for objects and provides an overview of features and functions of the terminal and a status of the terminal. A first user input selects of one of the regions and in response to the first user input, displaying at least one object corresponding to a selected region in a portion of the selected region.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area containing a plurality of lesions
InactiveUS6936046B2High and great intensityEnhance resilienceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyHigh-intensity focused ultrasoundThermal ablation
A method of thermal ablation using high intensity focused ultrasound energy includes the steps of positioning an ultrasound emitting member, emitting ultrasound energy from the ultrasound emitting member, focusing the ultrasound energy, ablating with the focused ultrasound energy to form an ablated tissue area and removing the ultrasound emitting member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area containing a plurality of lesions
InactiveUS20050267454A1Improve the level ofWithout impairingUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesHigh intensityHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
A method of thermal ablation using high intensity focused ultrasound energy includes the steps of positioning an ultrasound emitting member, emitting ultrasound energy from the ultrasound emitting member, focusing the ultrasound energy, ablating with the focused ultrasound energy to form an ablated tissue area and removing the ultrasound emitting member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
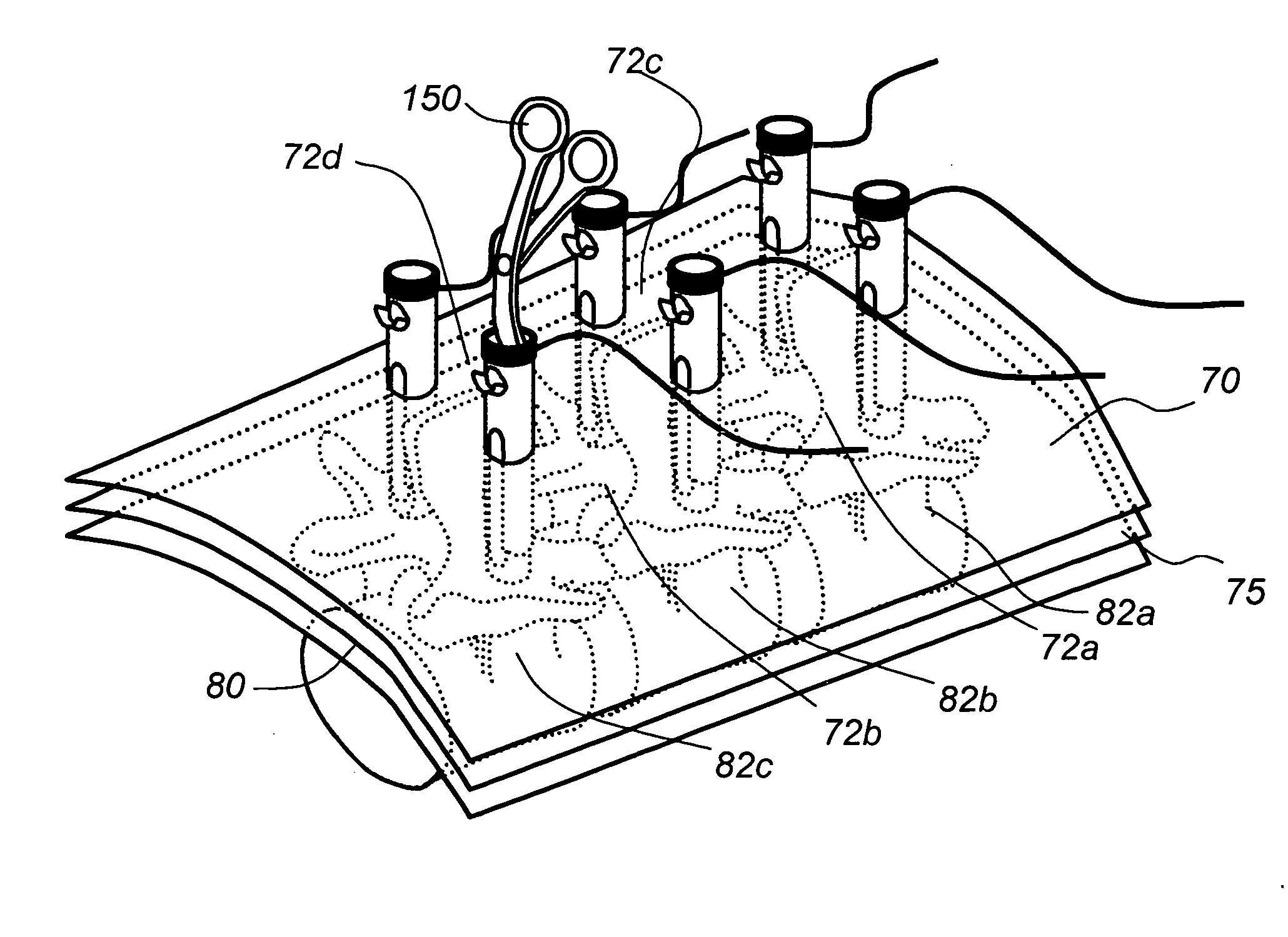
Axially compressible flared stents and apparatus and methods for delivering them
A stent includes a flaring portion and a main portion connected to the flaring portion. The main portion includes a plurality of bands of cells spaced apart axially from one another, adjacent bands of cells being intermittently connected to one another. During use, the stent is introduced into a main vessel in a contracted condition and positioned with the flaring portion adjacent an ostium. The flaring portion is flared, and the stent is advanced at least partially into the ostium. The stent is expanded further such that the main portion expands within the branch body lumen and / or the flaring portion expands adjacent the ostium. The main portion compresses axially during at least one of the steps when the stent is expanded, which may enhance conformance of the stent relative to the ostium and / or enhance reinforcement of the ostium.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
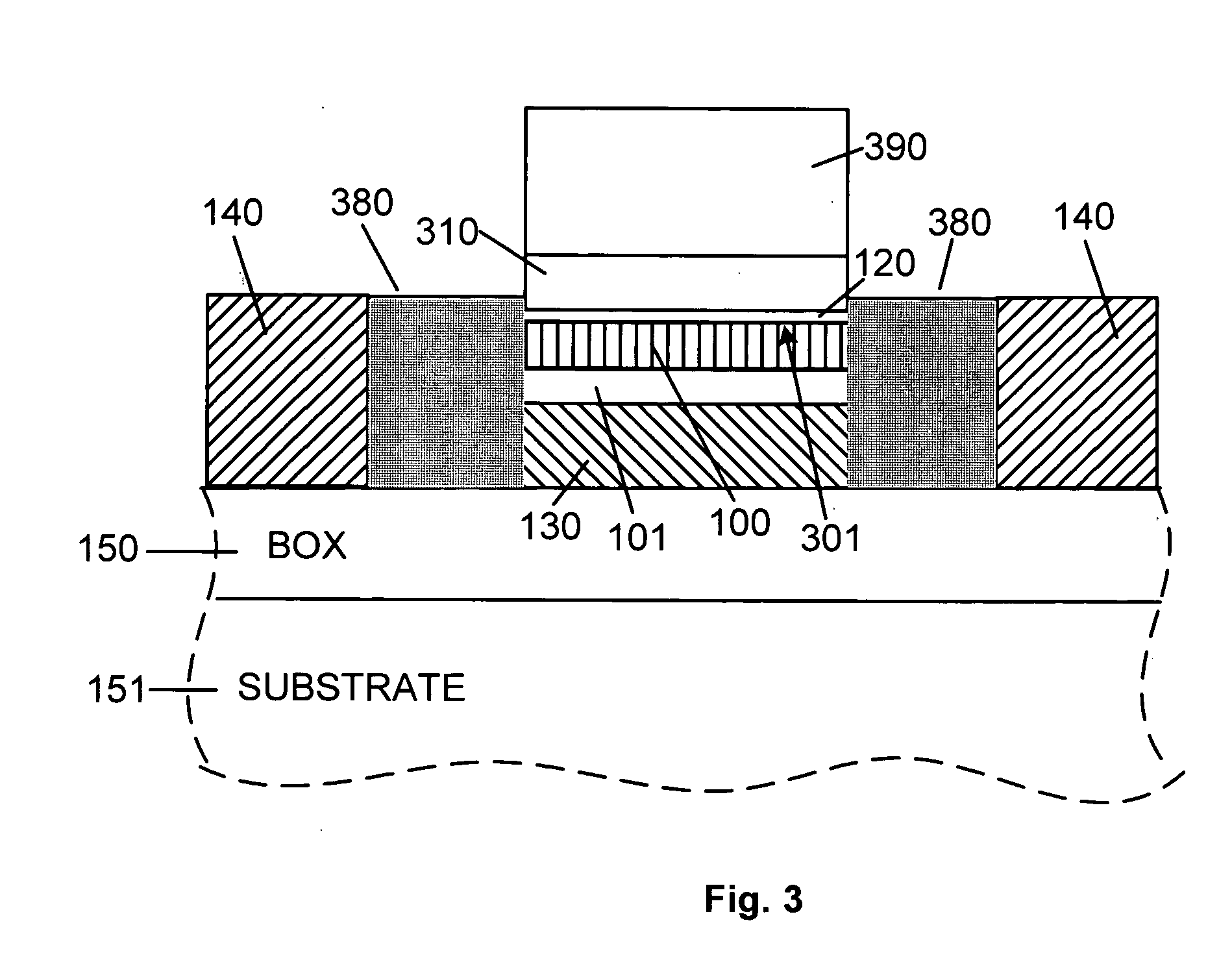
Integration of strained Ge into advanced CMOS technology
InactiveUS20050285097A1Improve mobilityImprove scalabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
A structure and method of fabrication for PFET devices in a compressively strained Ge layer is disclosed. The fabrication method of such devices is compatible with standard CMOS technology and it is fully scalable. The processing includes selective epitaxial depositions of an over 50% Ge content buffer layer, a pure Ge layer, and a SiGe top layer. Fabricated buried channel PMOS devices hosted in the compressively strained Ge layer show superior device characteristics relative to similar Si devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
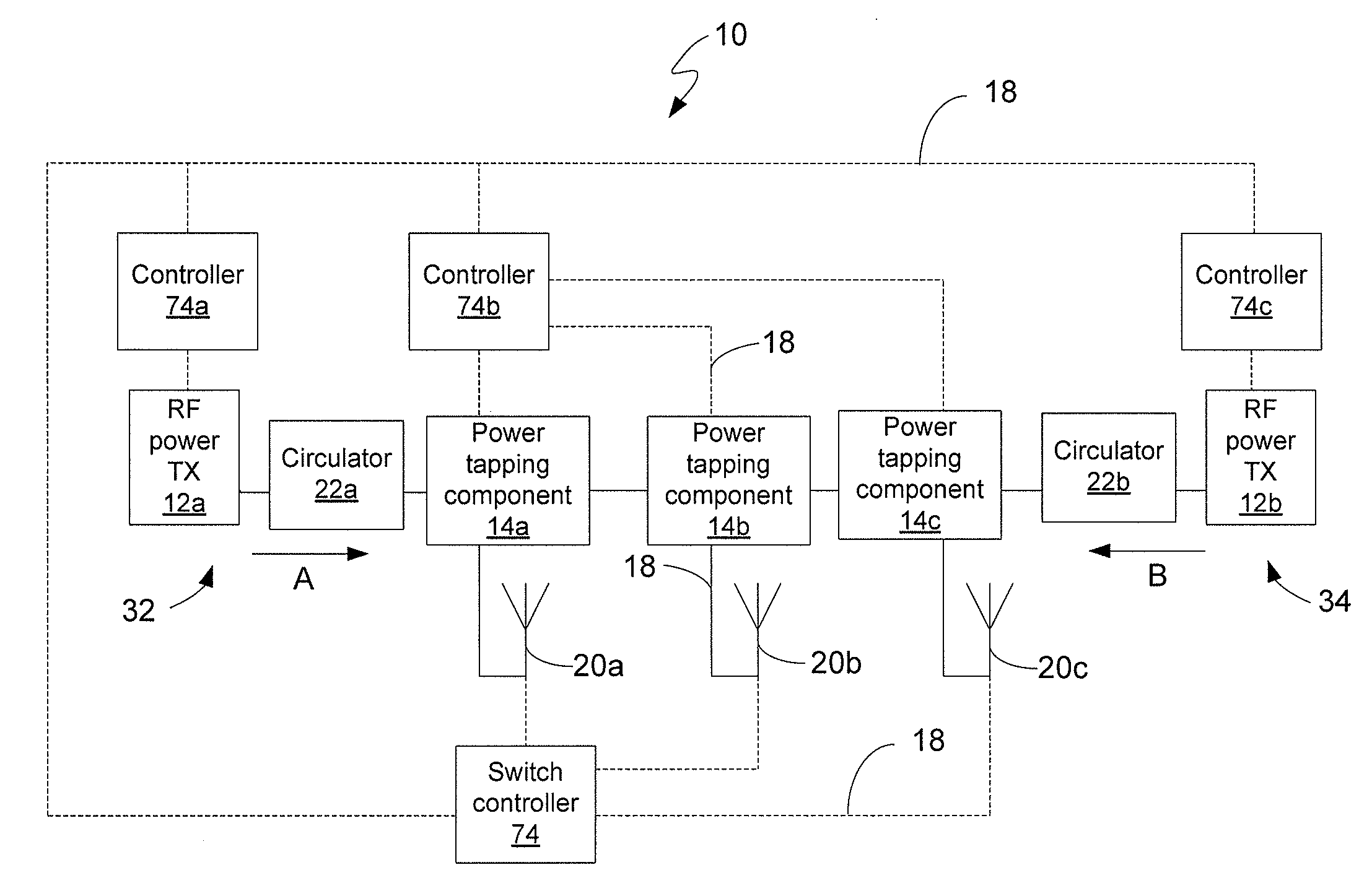
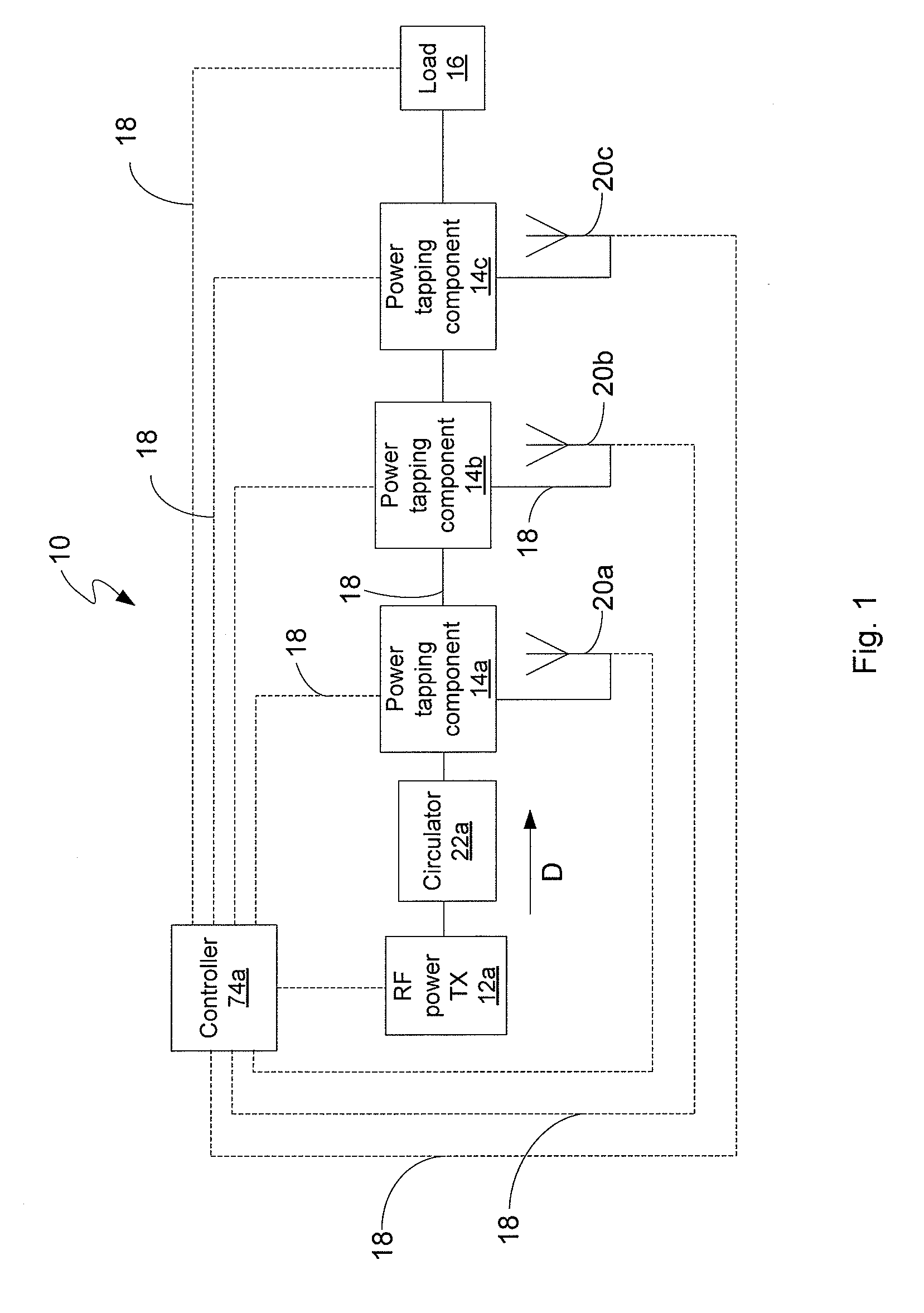
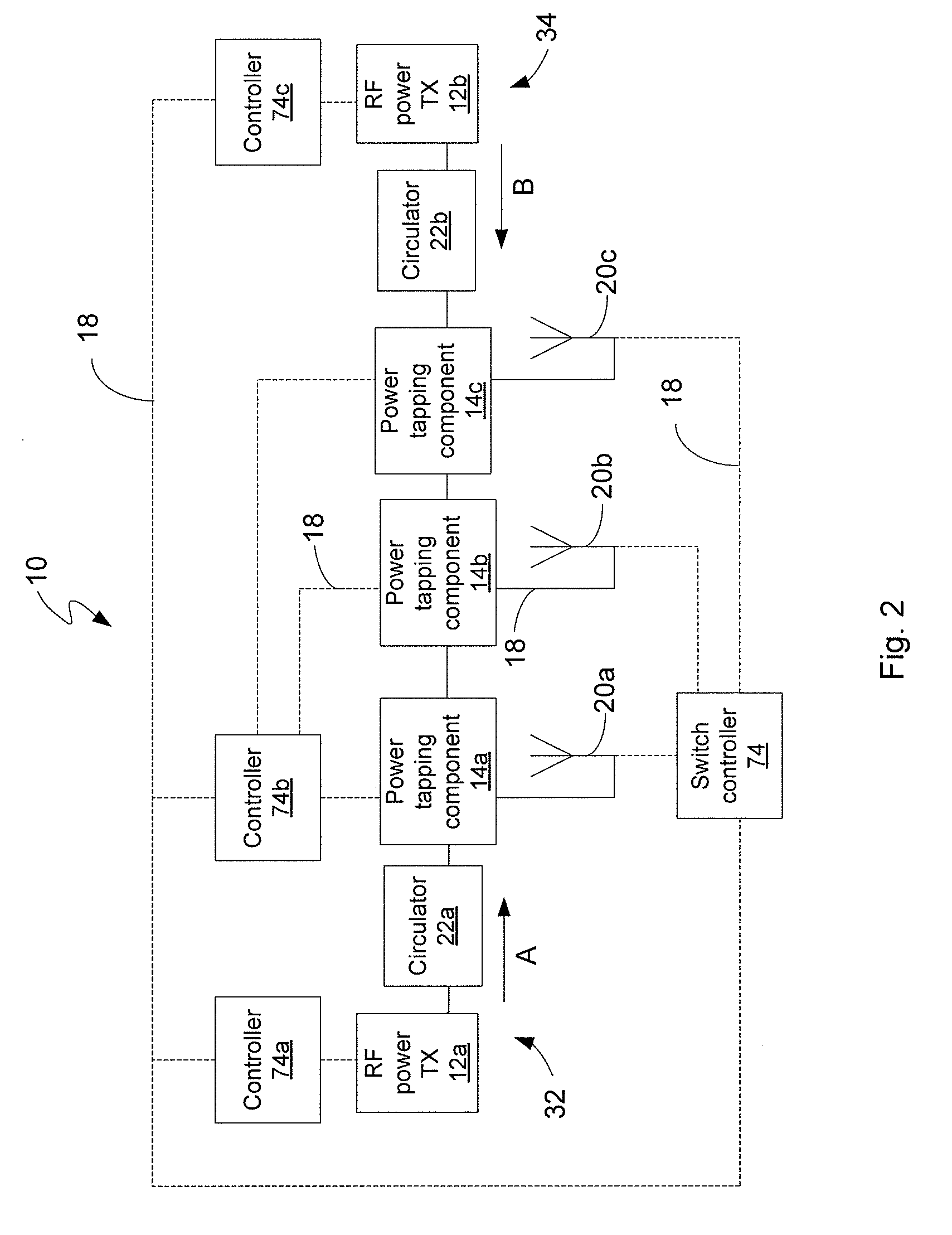
RF power transmission network and method
ActiveUS7639994B2Improve scalabilityIncrease the lengthResonant long antennasRepeater circuitsElectric powerRadio frequency power transmission
Disclosed is an RF power transmission network. The network includes at least one RF power transmitter, at least one power tapping component, and at least one load. The at least one RF power transmitter, the at least one power tapping component, and the at least one load are connected in series. The RF power transmitter sends power through the network. The power is radiated from the network to be received by a device to be charged, re-charged, or directly powered by the power.
Owner:POWERCAST
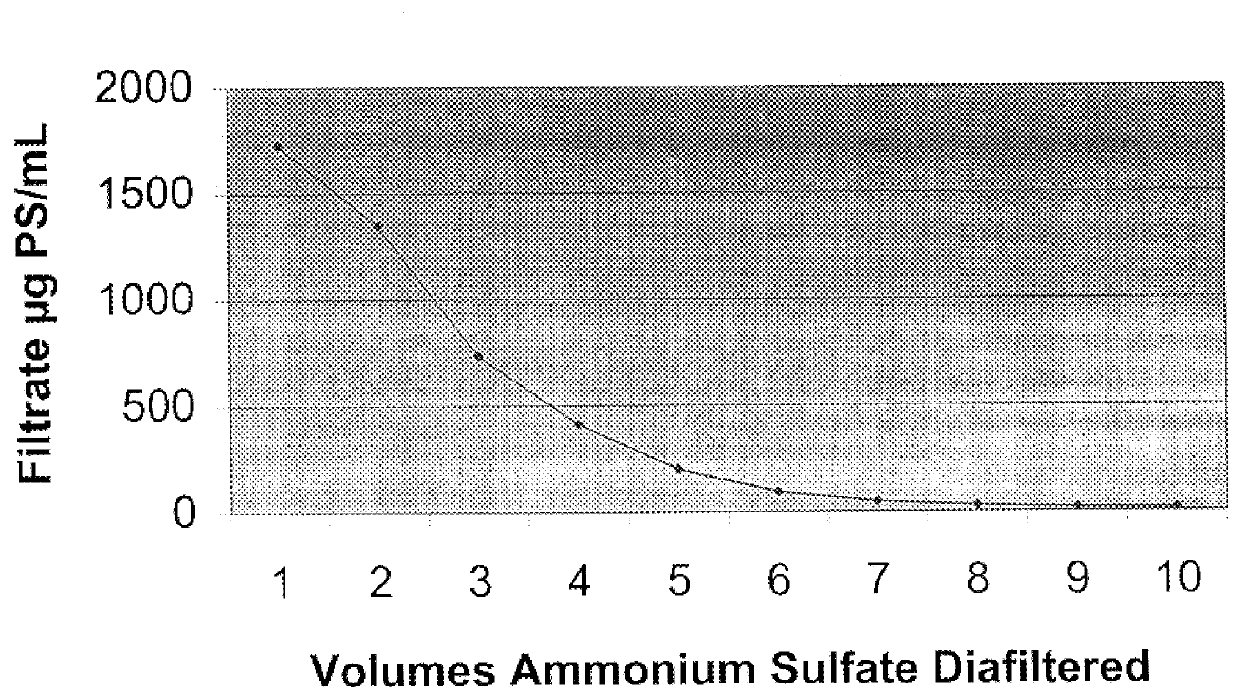
Purification of polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines by ultrafiltration with ammonium sulfate solutions
InactiveUS6146902AImprove scalabilityLevel of purityAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesConjugate vaccineUltrafiltration
Disclosed and claimed are a method for the purification of polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines by ultrafiltration in a saturated solution of ammonium sulfate. The ultrafiltration method of the present invention provides an efficient, readily scalable method for removal of unbound polysaccharides from polysaccharide-protein vaccines, thereby improving the purity and consistency of the polysaccharide-protein vaccines.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
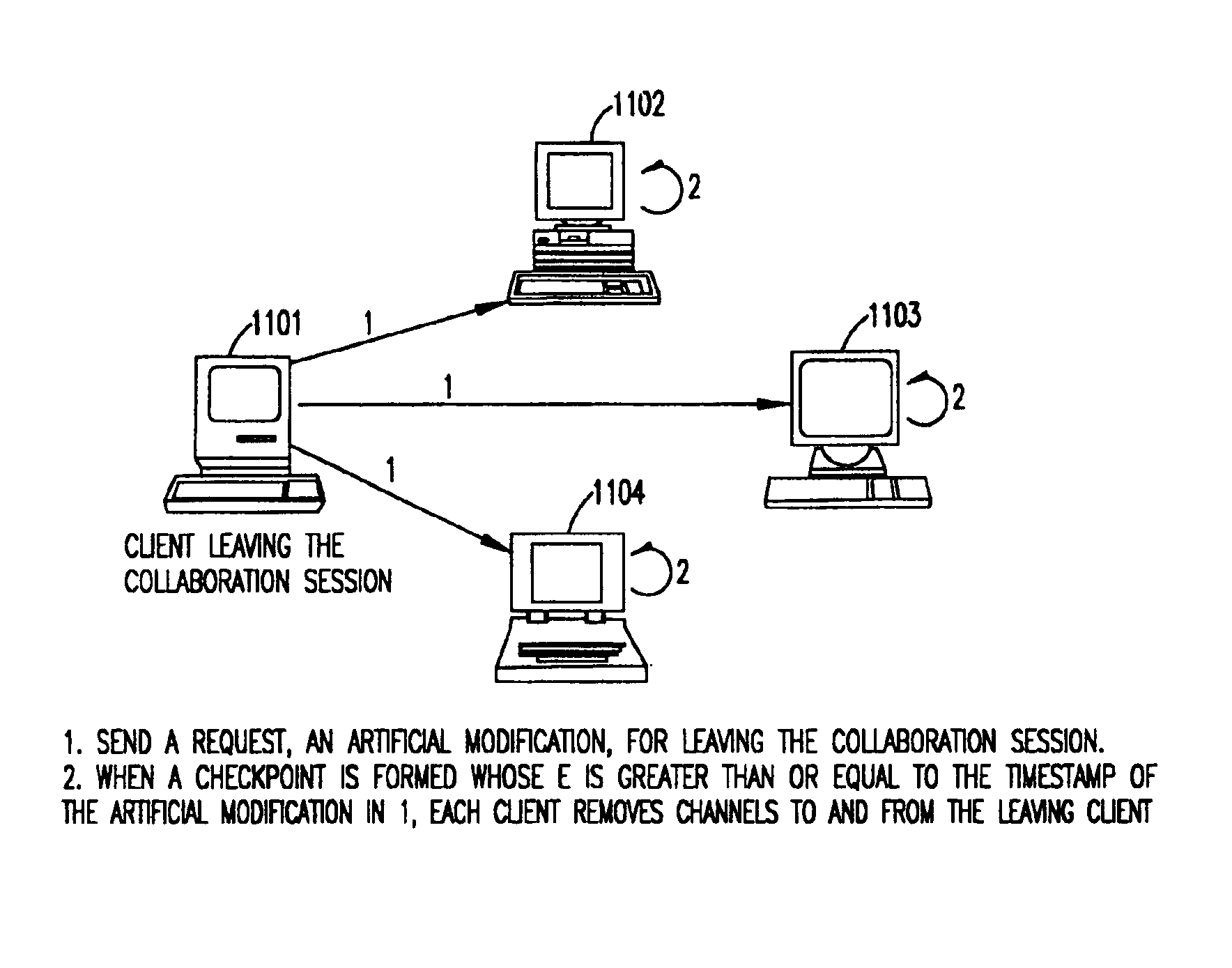
Synchronous collaboration based on peer-to-peer communication
InactiveUS6898642B2Eliminate useFully treatDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampWorkspace
A peer-to-peer protocol is based on the use of global timestamps and client priorities in serializing modifications to a shared workspace of real-time collaboration. The method caters to dynamic clients wherein a client can leave or join an ongoing collaboration session as long as there is always at least one client present / remaining in the collaboration session. The method can support multiple definitions of a modification, including partitioning-based definitions, wherein the method provides full support for locking of partitions, and a full treatment of inter-partition synchronization via a modification definition over multiple partitions. The method is capable of utilizing the many standard methods of creating a global, distributed, synchronized clock for the global timestamps utilized by it. The method is rollback-based for correcting tentative but incorrect serializations, and provides additional backup in terms of checkpoints for additional safety and for the support of lightweight, pervasive clients. The method includes many optimizations for efficiency, and includes a method of switching to and back from distributed server-based serialization for the periods when the network response is better suited to a distributed server than the peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Internet-of-things and android system based intelligent home system and control method
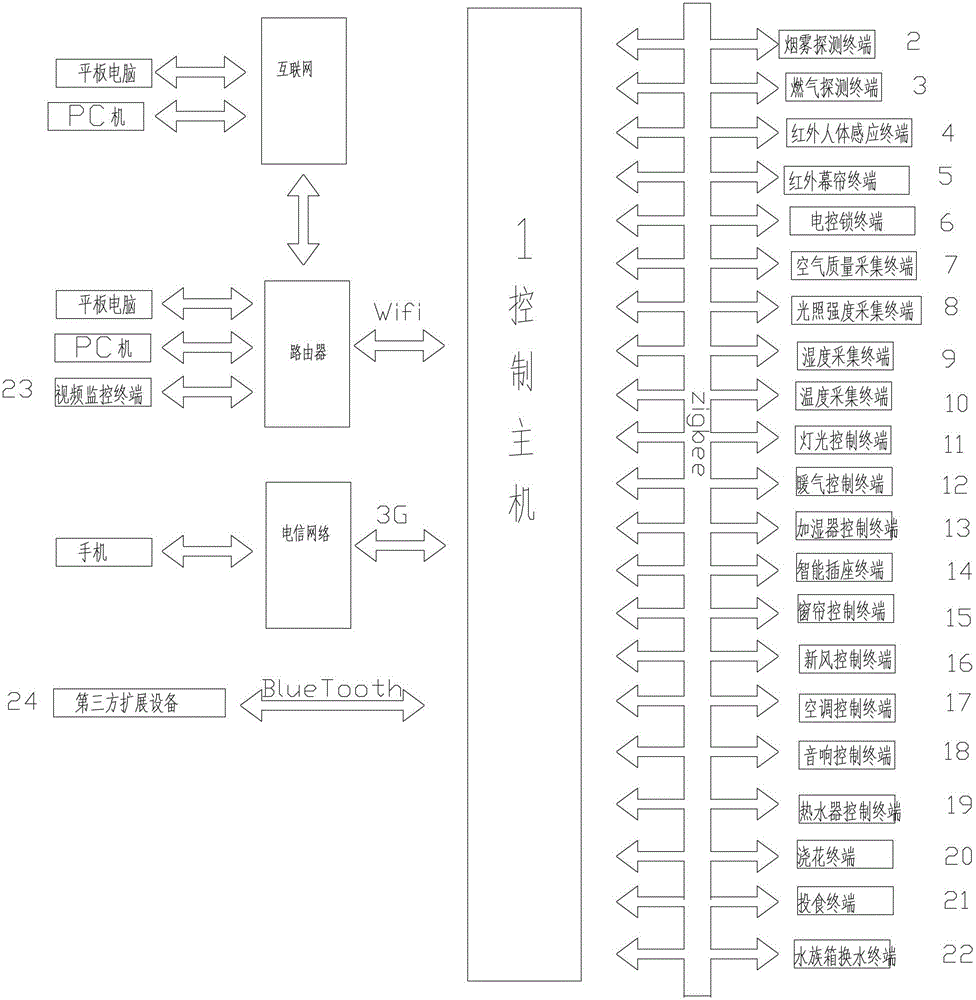
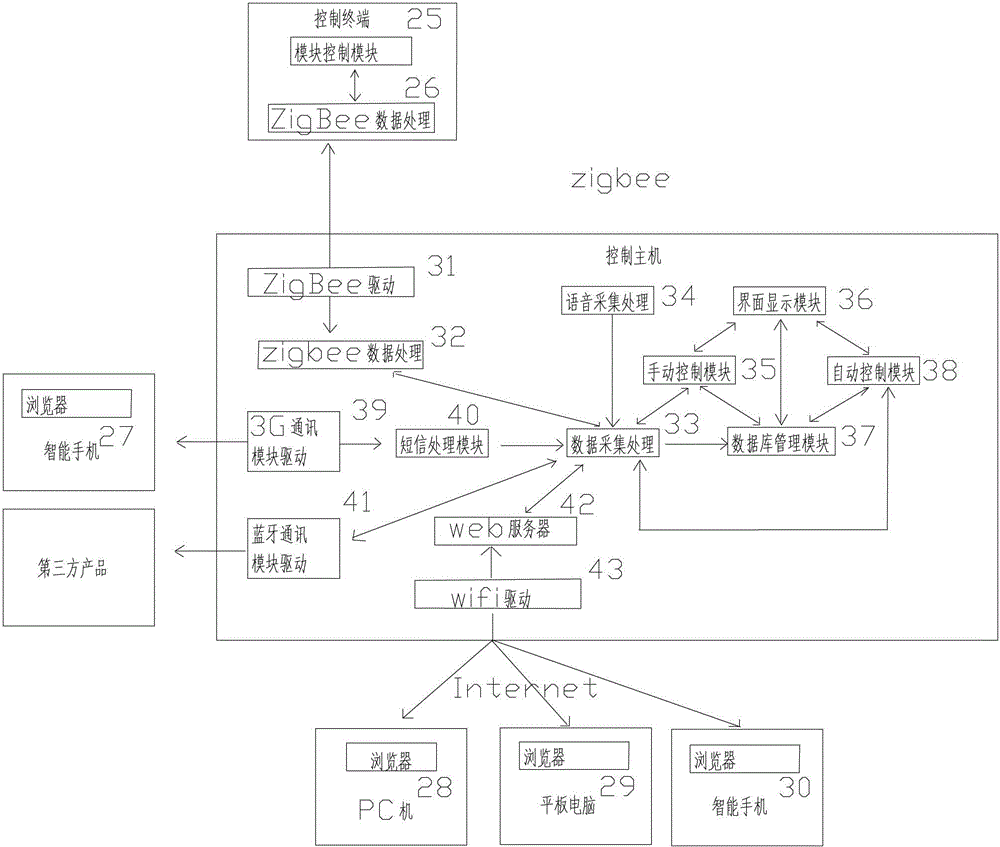
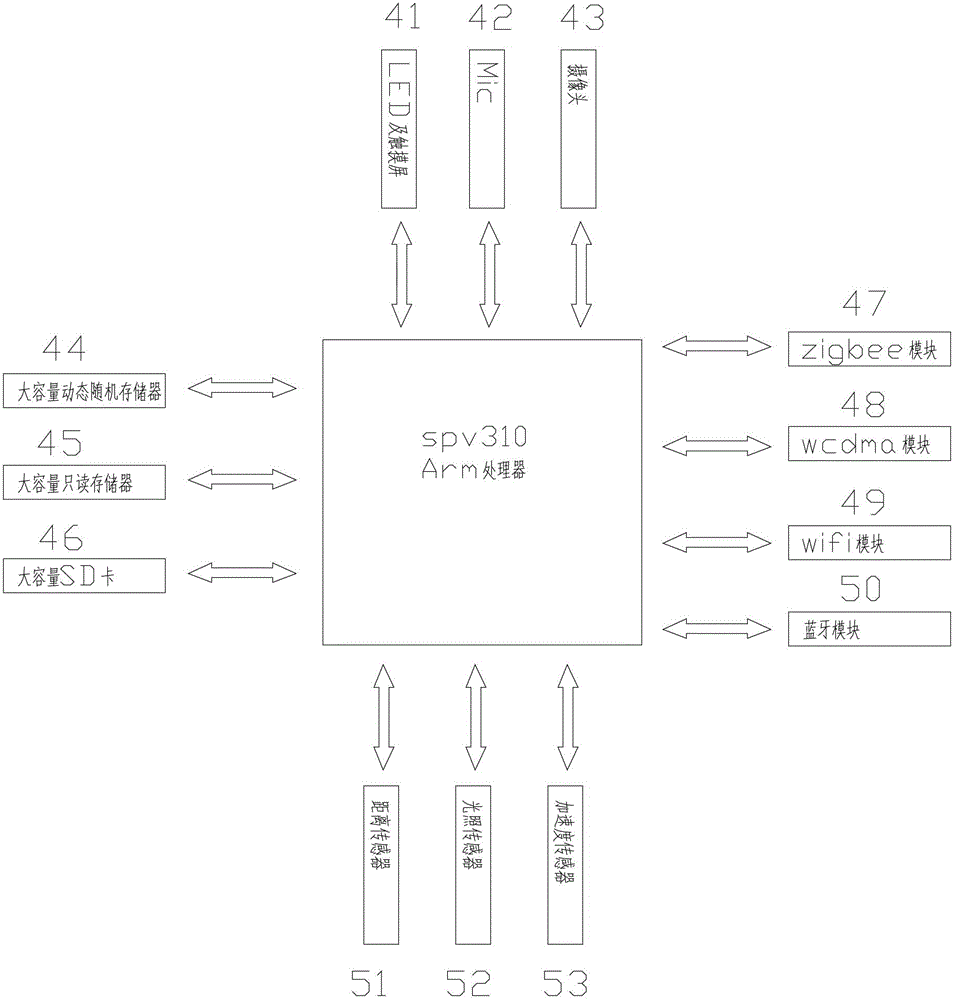
InactiveCN102882752ARealize automatic arming and disarmingReduce complexityData switching by path configurationAutomatic controlWeb service
The invention discloses an internet-of-things and android system based intelligent home system which comprises a control host and a plurality of terminal devices. The control host is provided with a high-performance arm processor, a touch screen and an android operation system, supports zigbee, blueTooth, wifi (wireless fidelity), 3G (the third generation) communication, is provided with a built-in web server and a built-in database, has functions of display, operation, control data storage, server, energy management, and particularly has functions of automatic control, hand-operated control, voice control and remote control. The terminal devices include a sensor terminal, a security terminal and a control terminal, are provided with independent processors and network addresses, have functions of data acquisition, data transmission, instruction receiving, transmitting and processing and IO (input / output) control, and support one or multiple wireless communication manners of zigbee, blueTooth, wifi and 3G.
Owner:TIANJIN GUANGHONG TECH
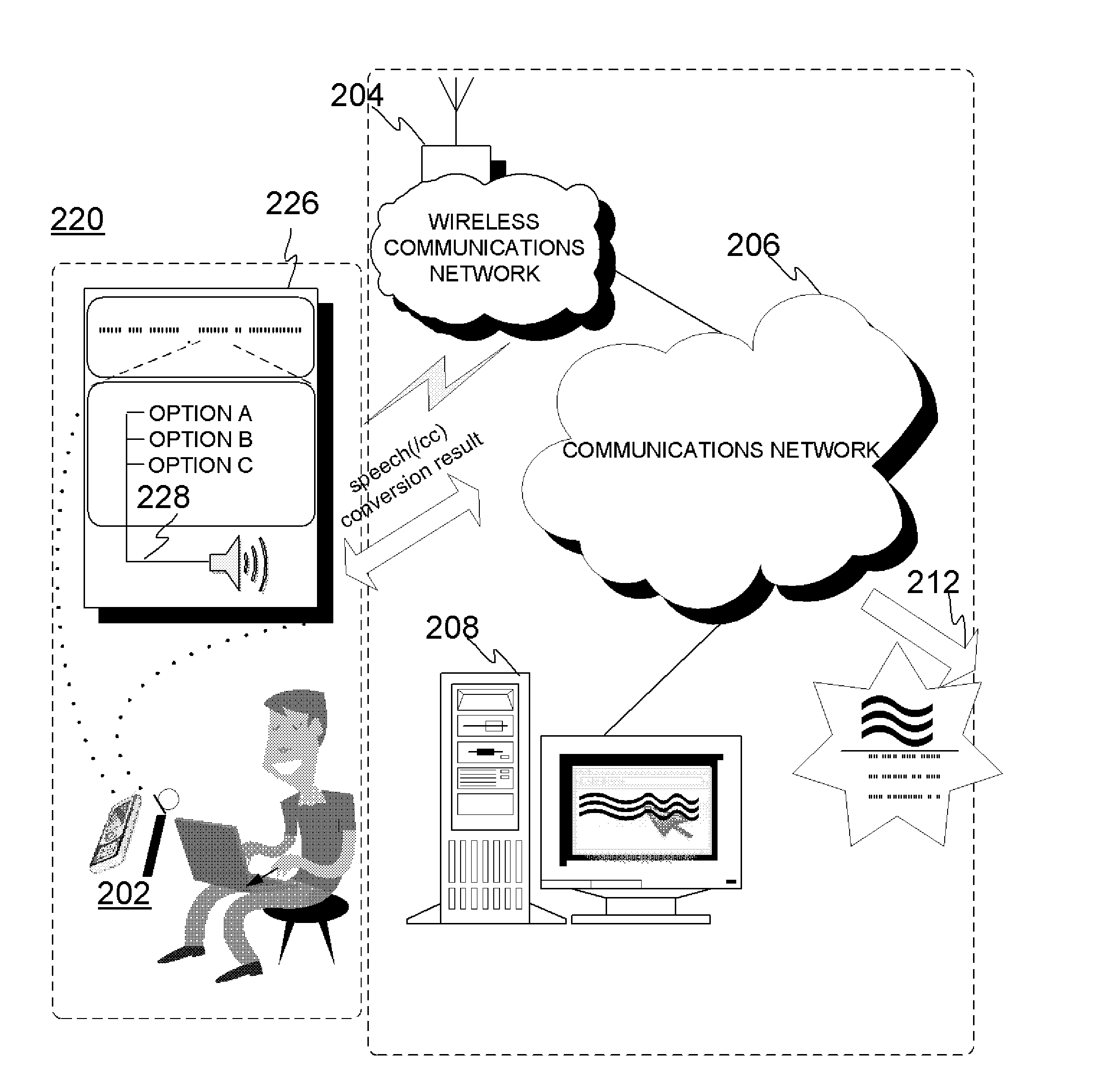
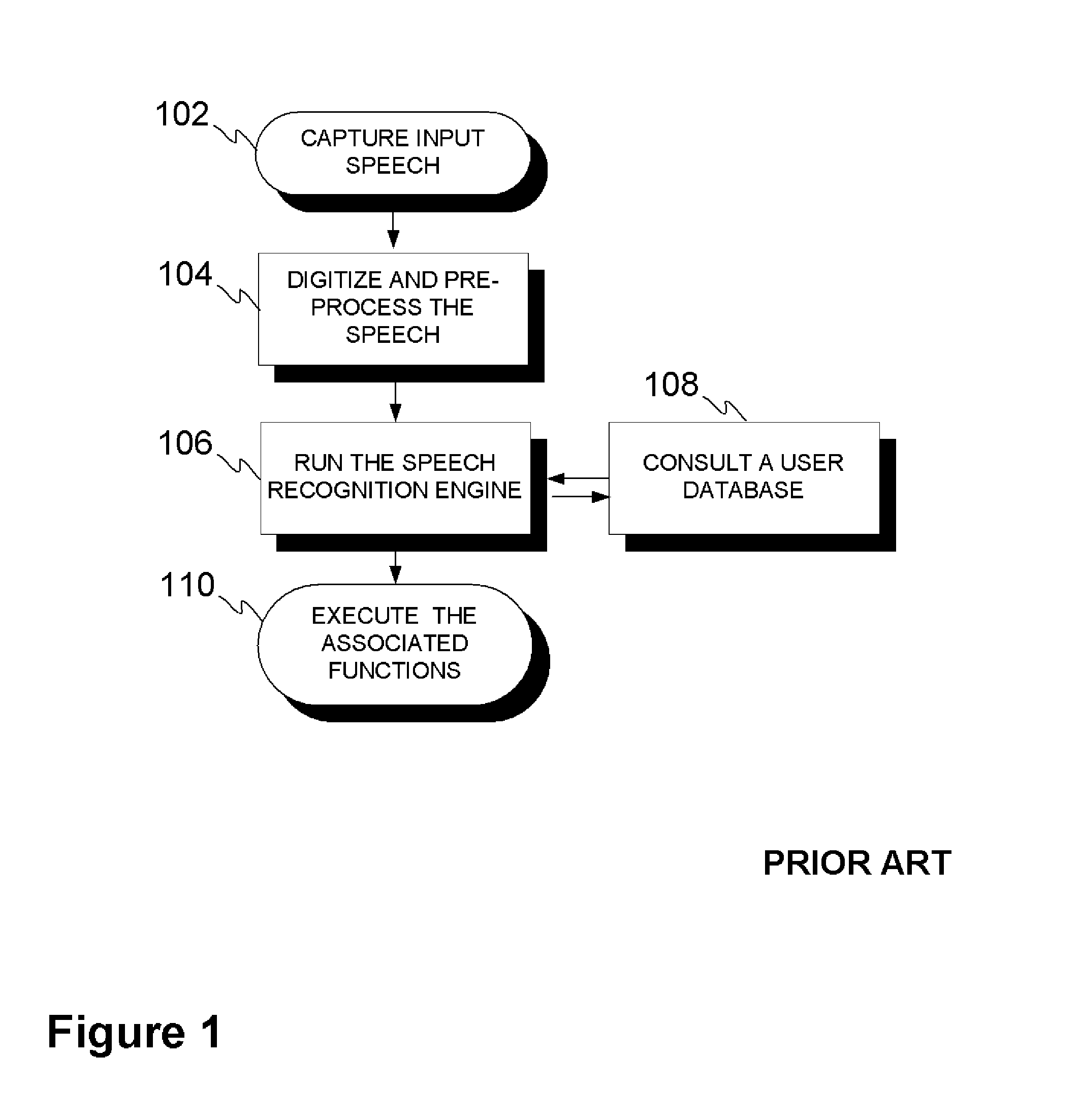
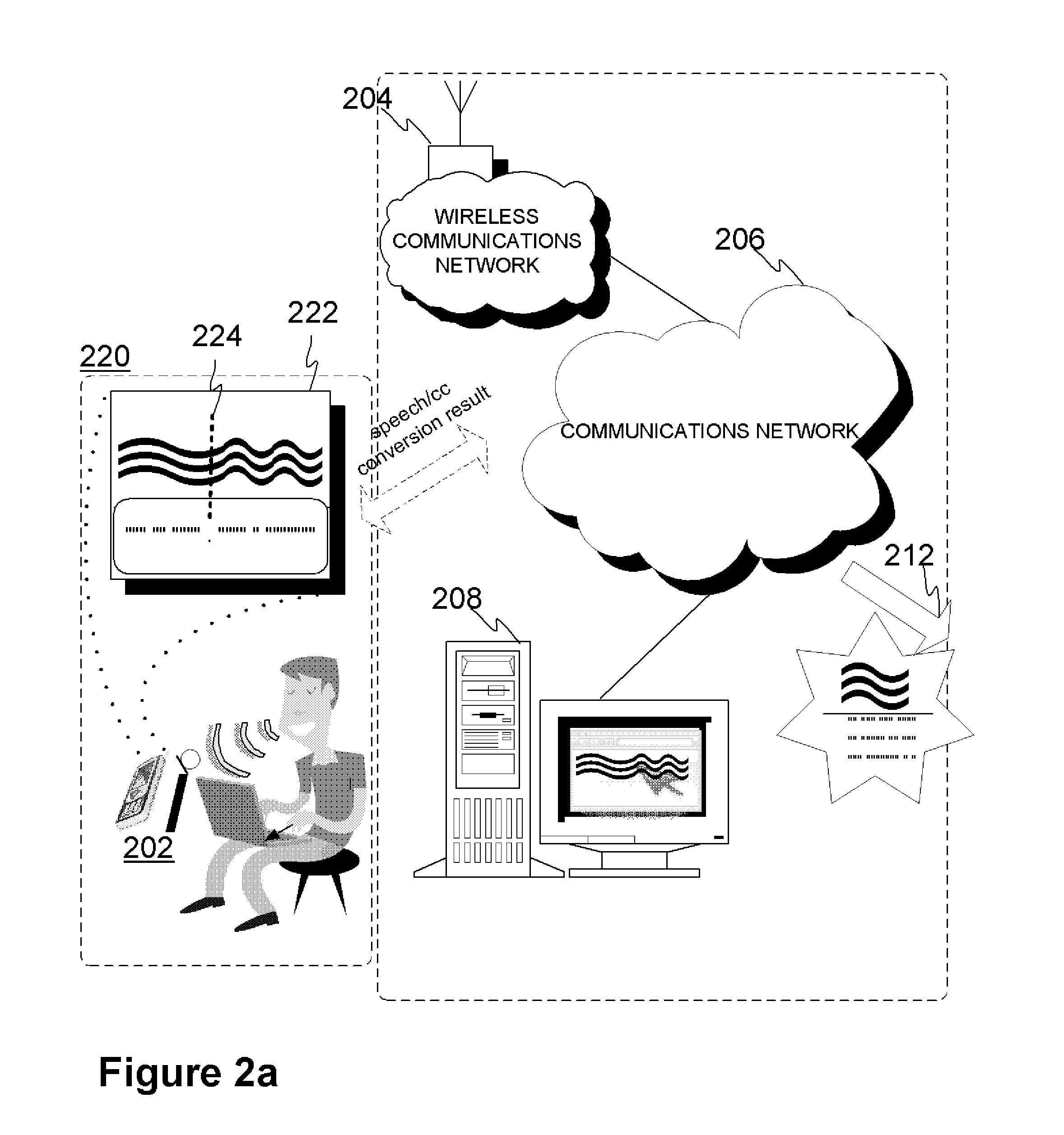
Method and device for converting speech
InactiveUS20110112837A1Reduce defectsImprove accuracySpeech recognitionTransformation of textVoice transformation
Electronic device and method for speech to text conversion procedure, wherein the overall conversion result may include smaller portions with multiple conversion options that are audibly and optionally visually or tactilely reproduced for user confirmation, thereby resulting enhanced conversion accuracy with minimal additional effort by the user.
Owner:MOBITER DICTA
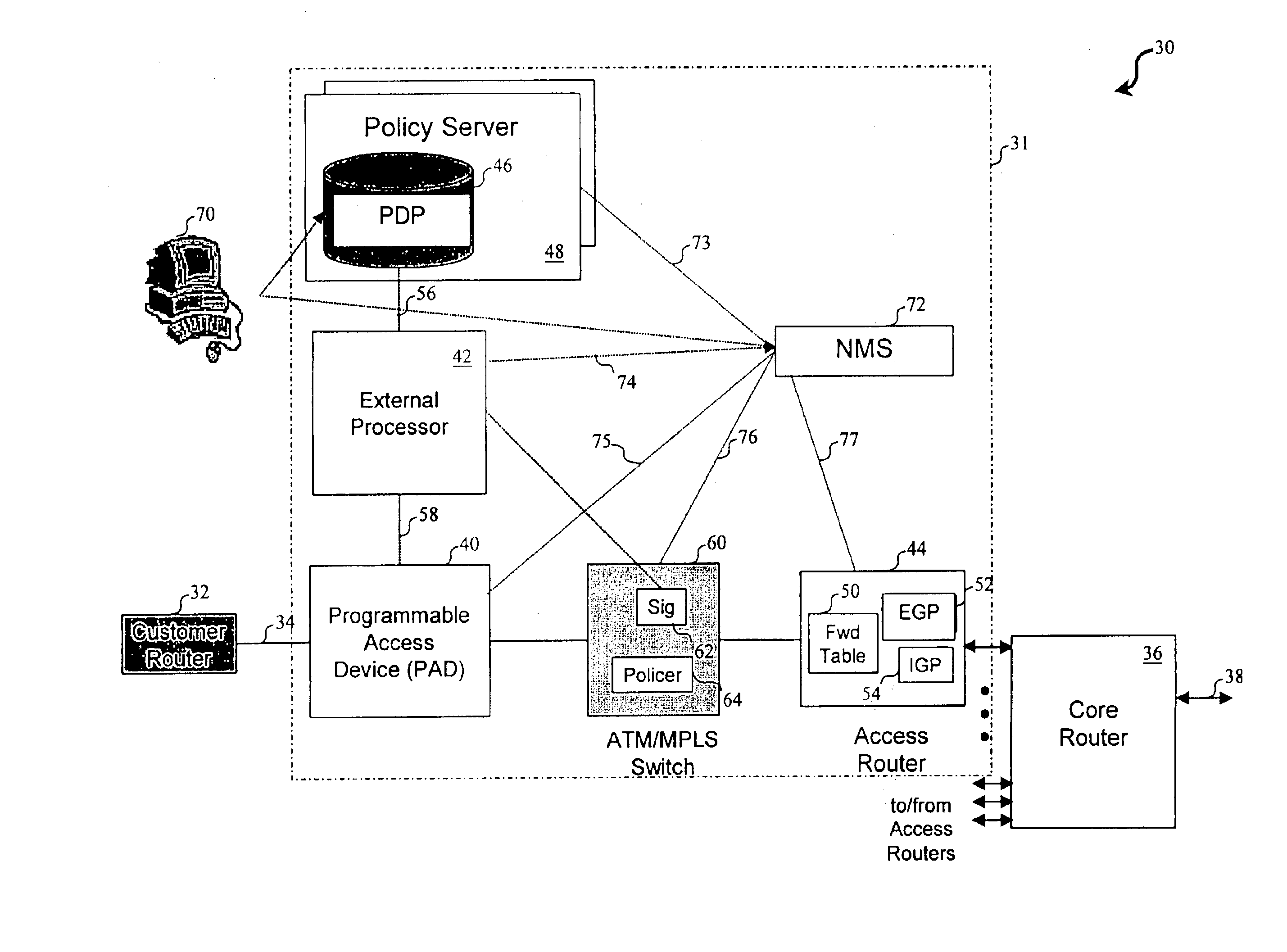
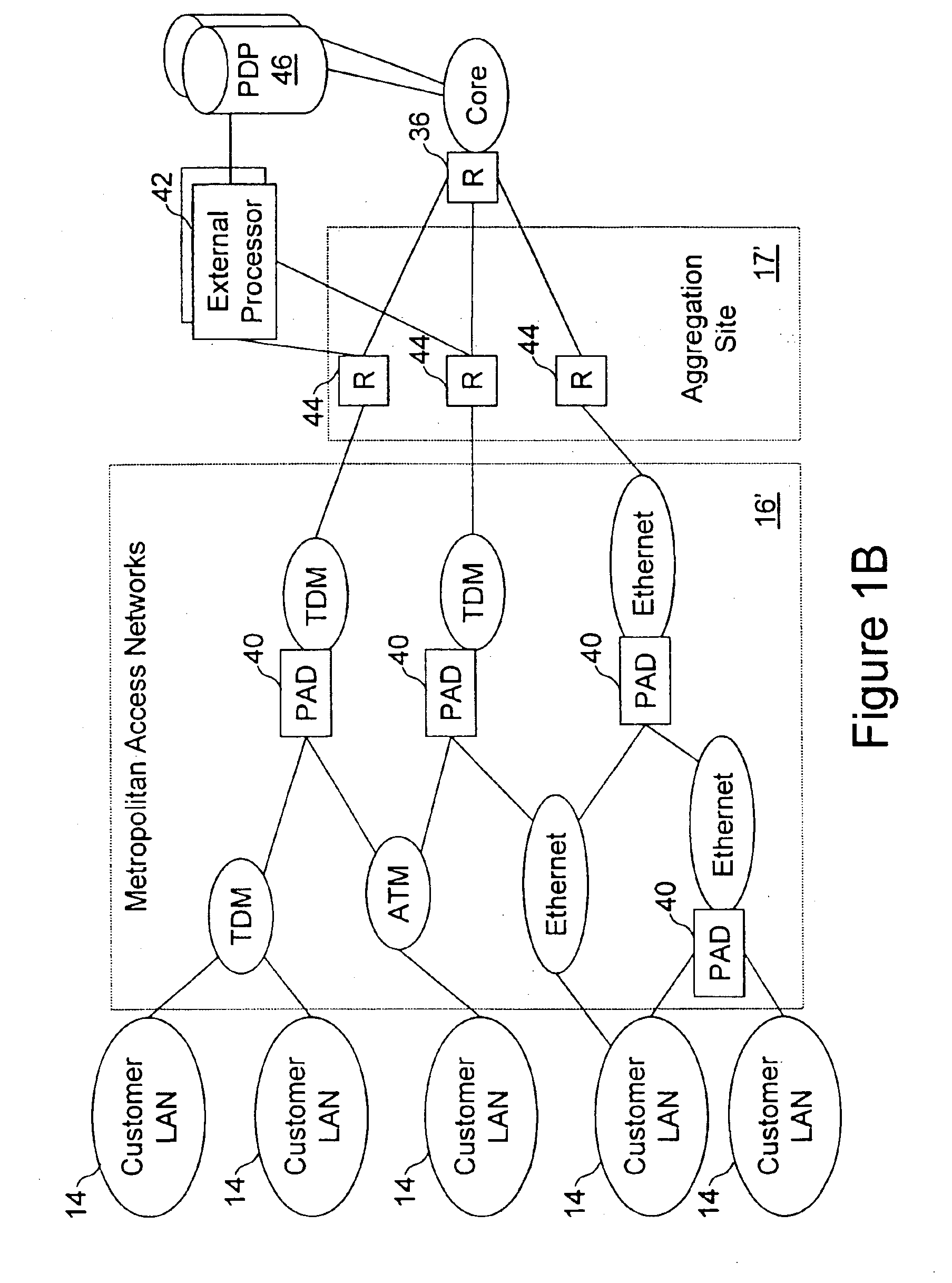
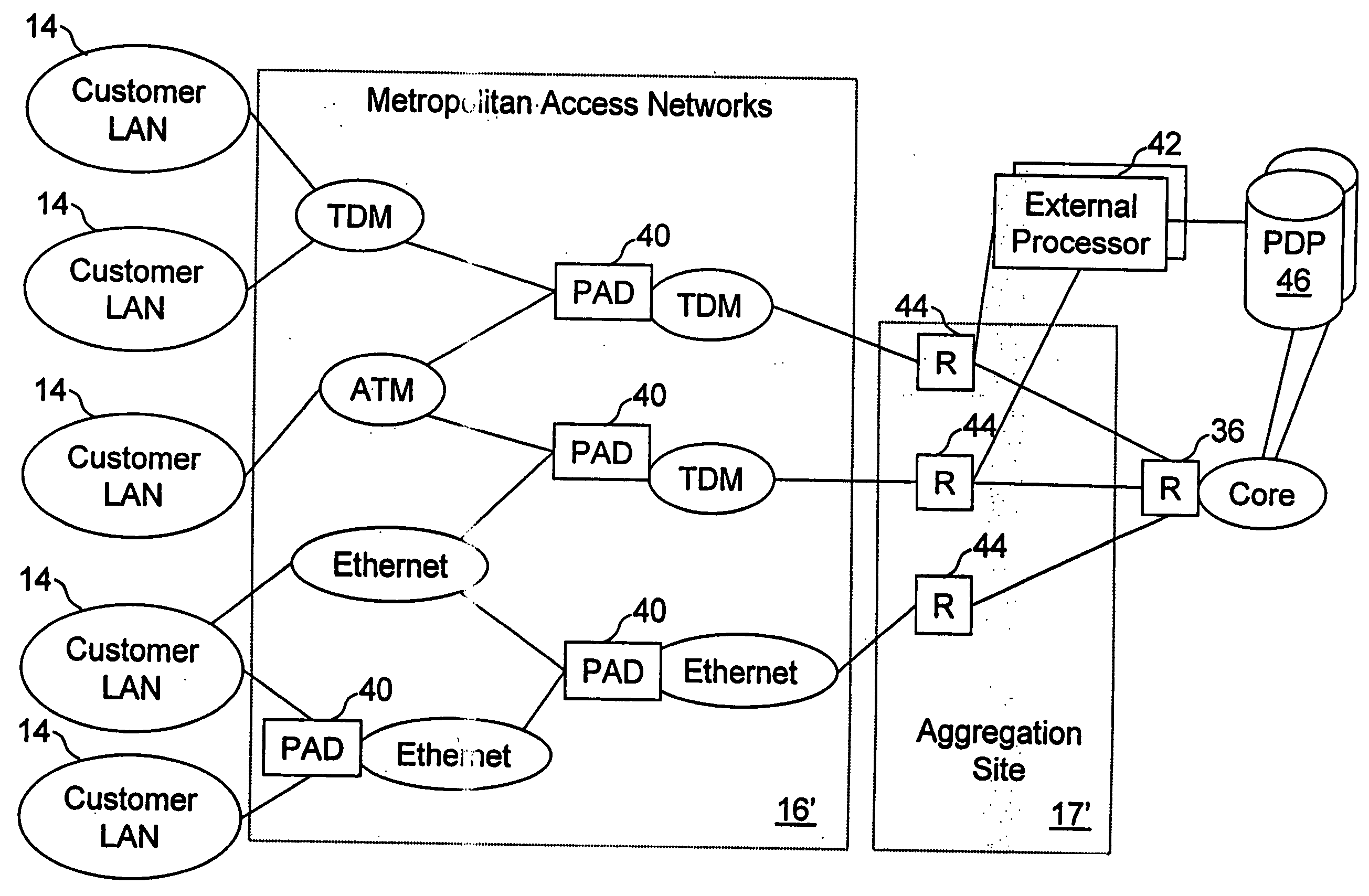
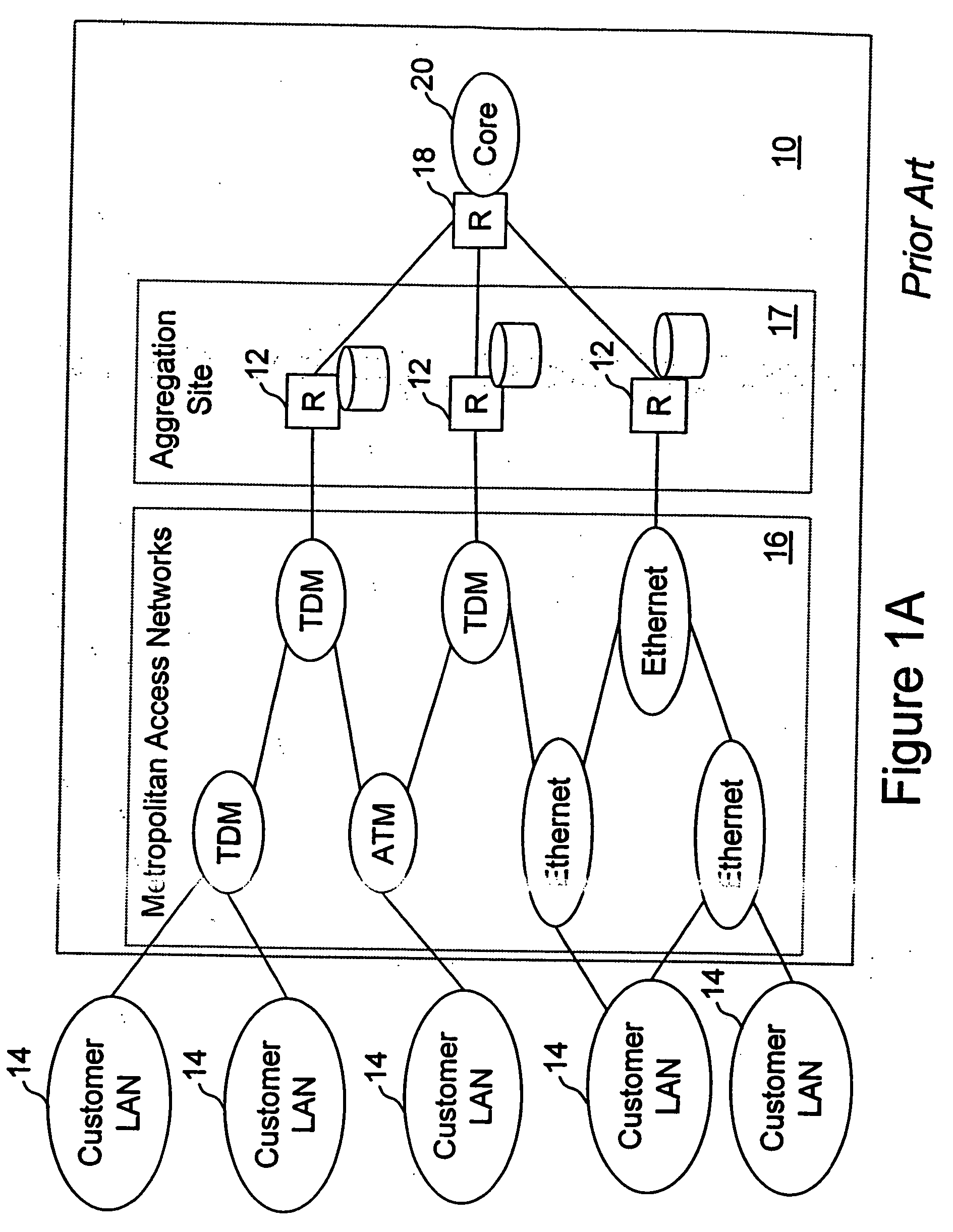
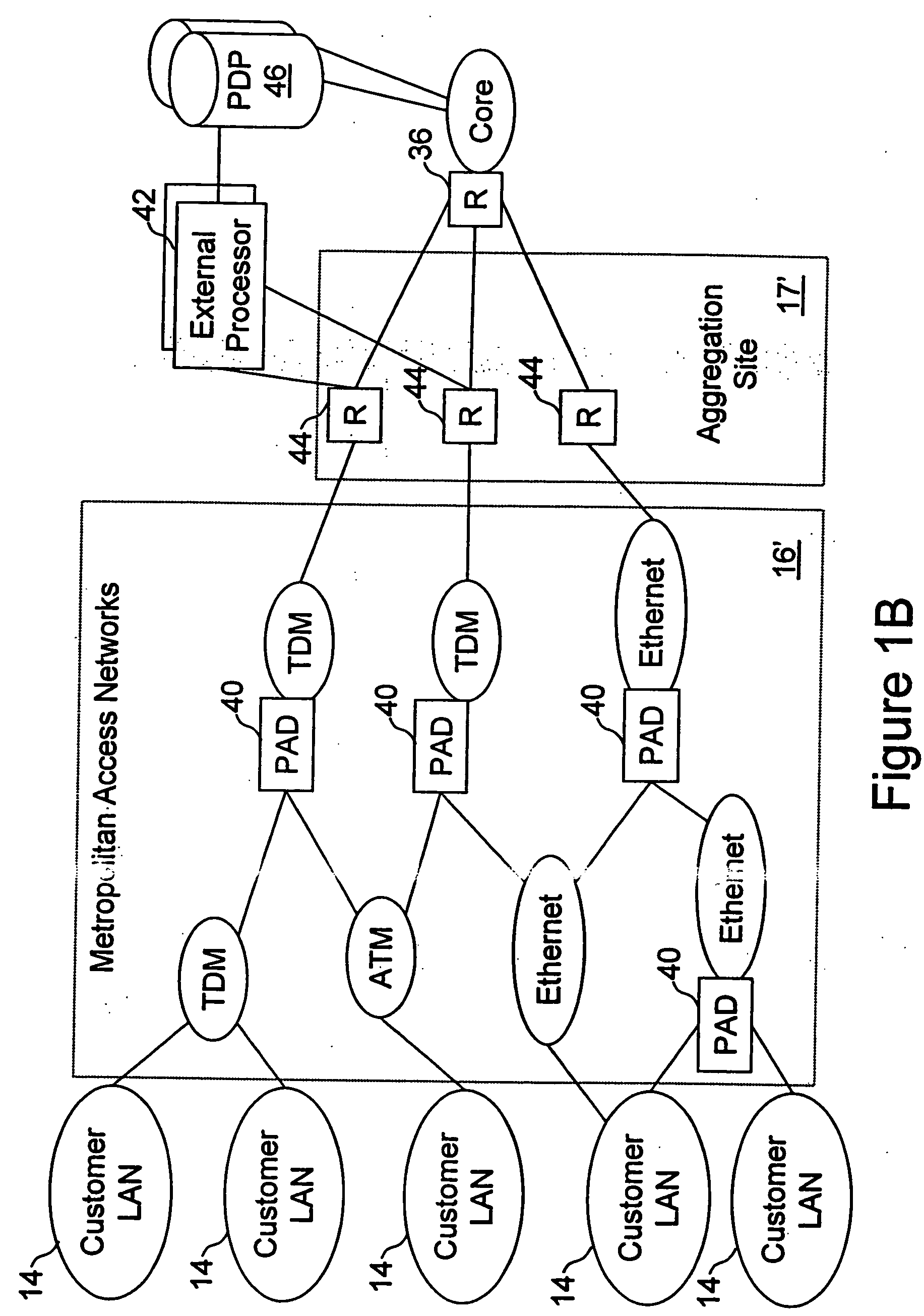
Network access system including a programmable access device having distributed service control
InactiveUS7046680B1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilityData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgrammable logic deviceMessage Passing Interface
A distributed network access system in accordance with the present invention includes at least an external processor and a programmable access device. The programmable access device has a message interface coupled to the external processor and first and second network interfaces through which packets are communicated with a network. The programmable access device includes a packet header filter and a forwarding table that is utilized to route packets communicated between the first and second network interfaces. In response to receipt of a series of packets, the packet header filter in the programmable access device identifies messages in the series of messages upon which policy-based services are to be implemented and passes identified messages via the message interface to the external processor for processing. In response to receipt of a message, the external processor invokes service control on the message and may also invoke policy control on the message.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Network access system including a programmable access device having distributed service control
InactiveUS20050117576A1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilityData switching by path configurationPacket communicationService control
A distributed network access system in accordance with the present invention includes at least an external processor and a programmable access device. The programmable access device has a message interface coupled to the external processor and first and second network interfaces through which packets are communicated with a network The programmable access device includes a packet header filter and a forwarding table that is utilized to route packets communication between the first and second network interfaces. In response to receipt of a series of packets, the packet header filter in the programmable access device identifies messages in the series of messages upon which policy-based services are to be implemented and passes identified messages via the message interface to the external processor for processing. In response to receipt of a message, the external processor invokes service control on the message and may also invoke policy control on the message.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Herbicide tolerant rice plants and methods for identifying same
ActiveUS20080289060A1Superior agronomic phenotypeImprove scalabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRice plantsGenetically modified rice
The invention provides specific transgenic rice plants, plant material and seeds, characterized in that these products harbor a specific transformation event at a specific location in the rice genome. Tools are also provided which allow rapid and unequivocal identification of the event in biological samples.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
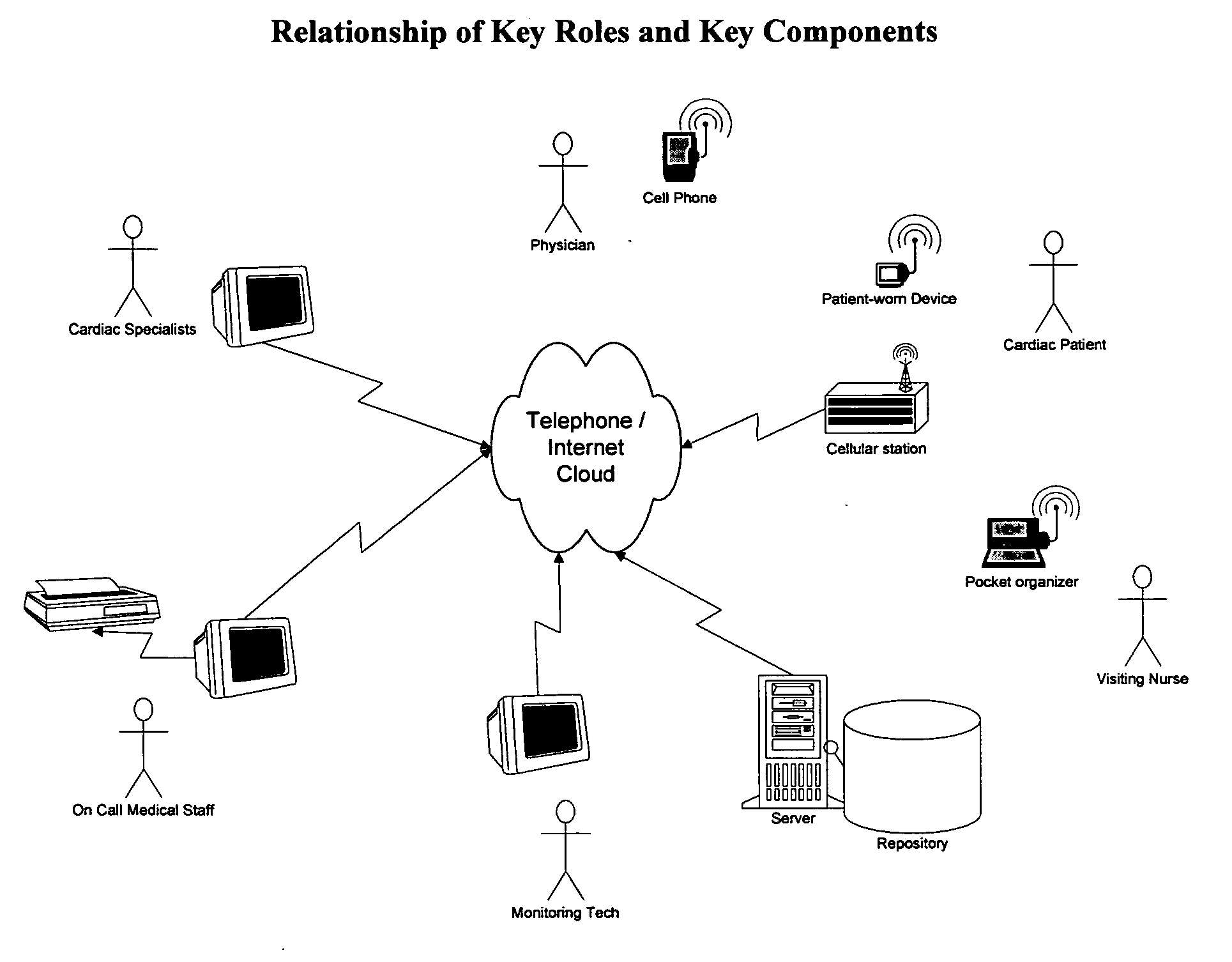
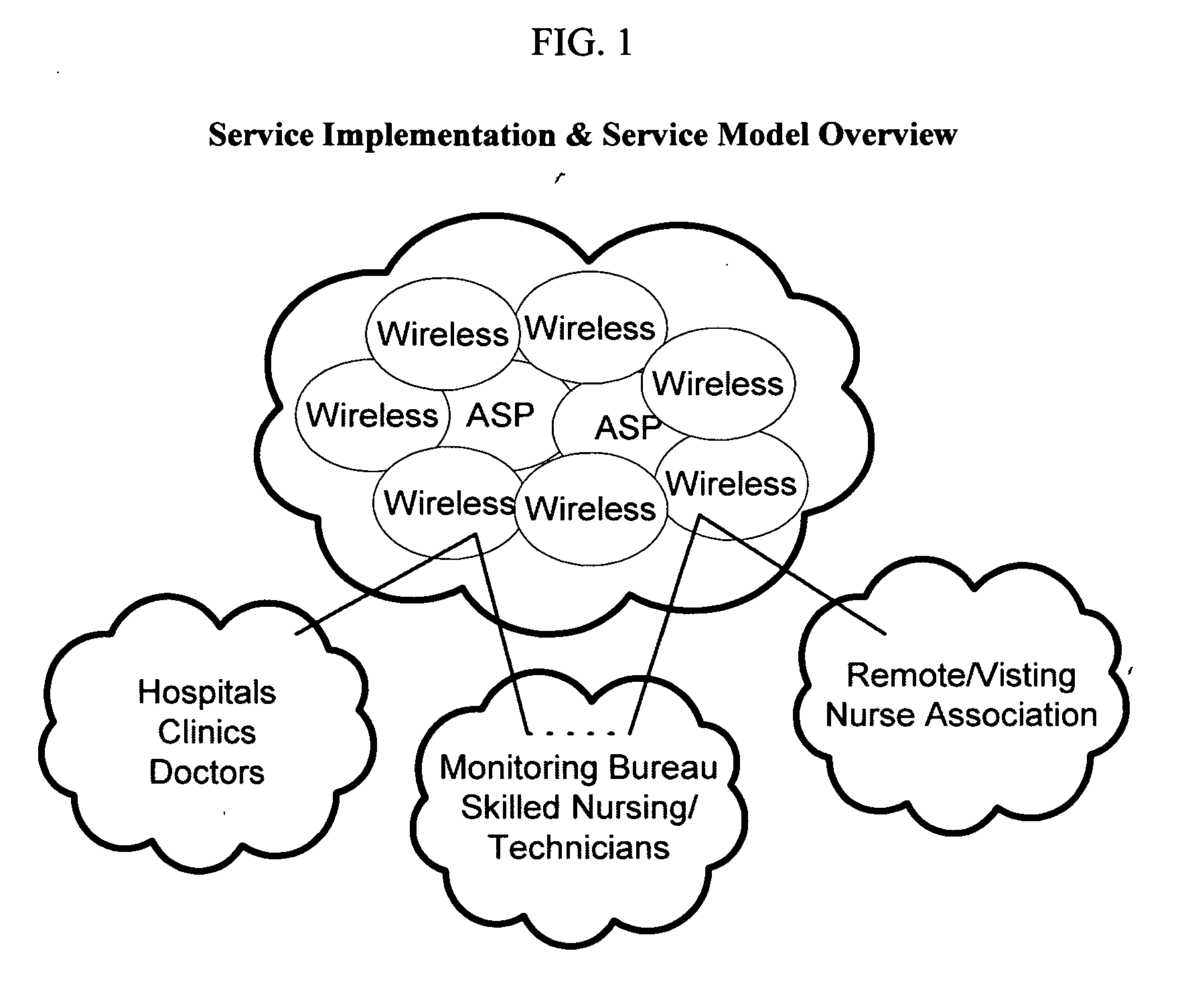
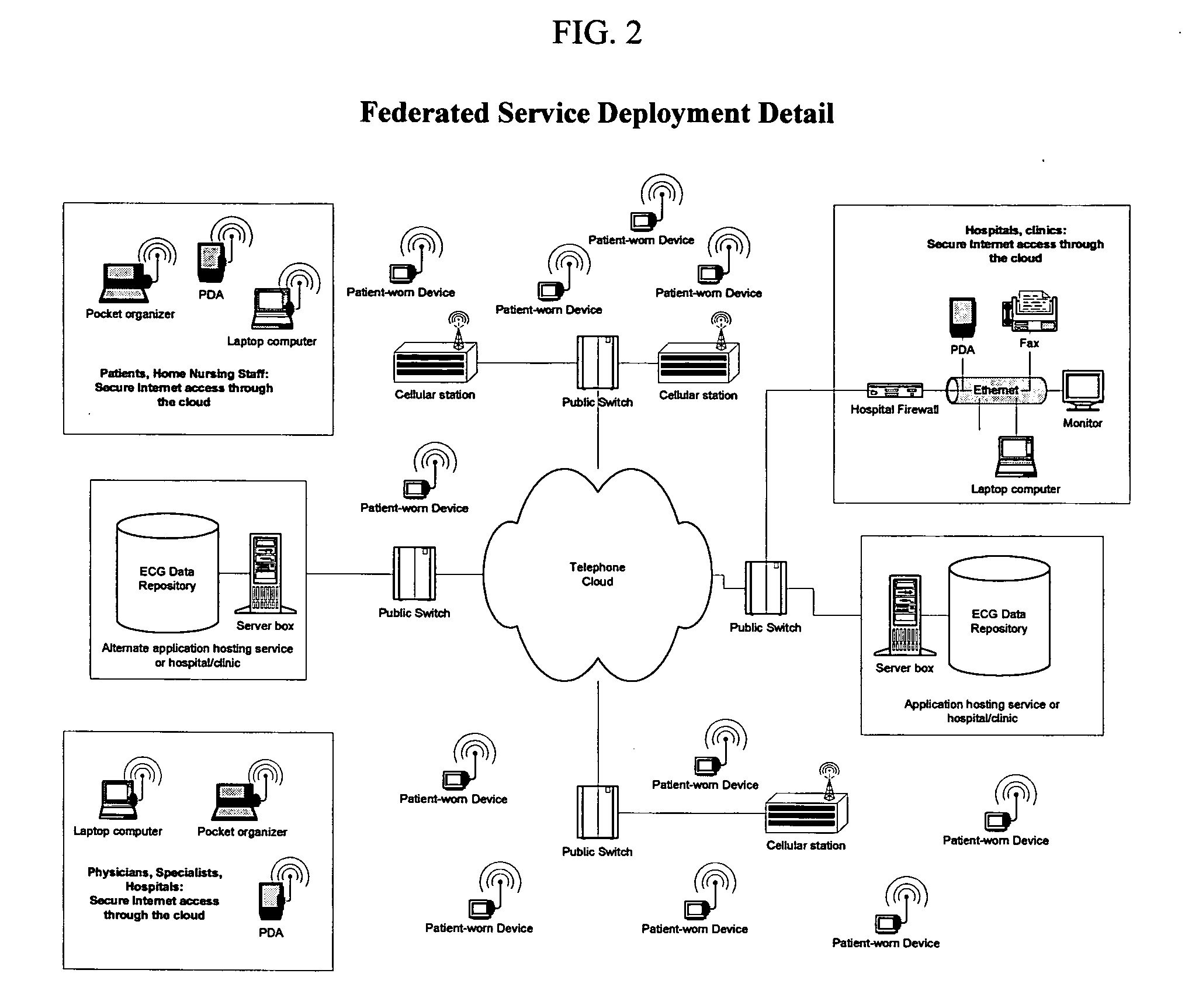
Remote medical monitoring system
InactiveUS20060122469A1Improve scalabilityEffective step-down patient careSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMonitoring systemEmergency medicine
A medical monitoring system that brings the hospital-campus telemetry experience to the patient home. This system is designed to enable effective step-down patient care in the home setting while providing the patient with the freedom to go anywhere and remain “logically” tethered to the system. The system achieves this by being distributed in nature, globally accessible, highly scalable, with near real-time concurrent reporting and analysis of multiple physiological parameters, and making this information real-time accessible to healthcare practitioners.
Owner:MARTEL NORMAND M
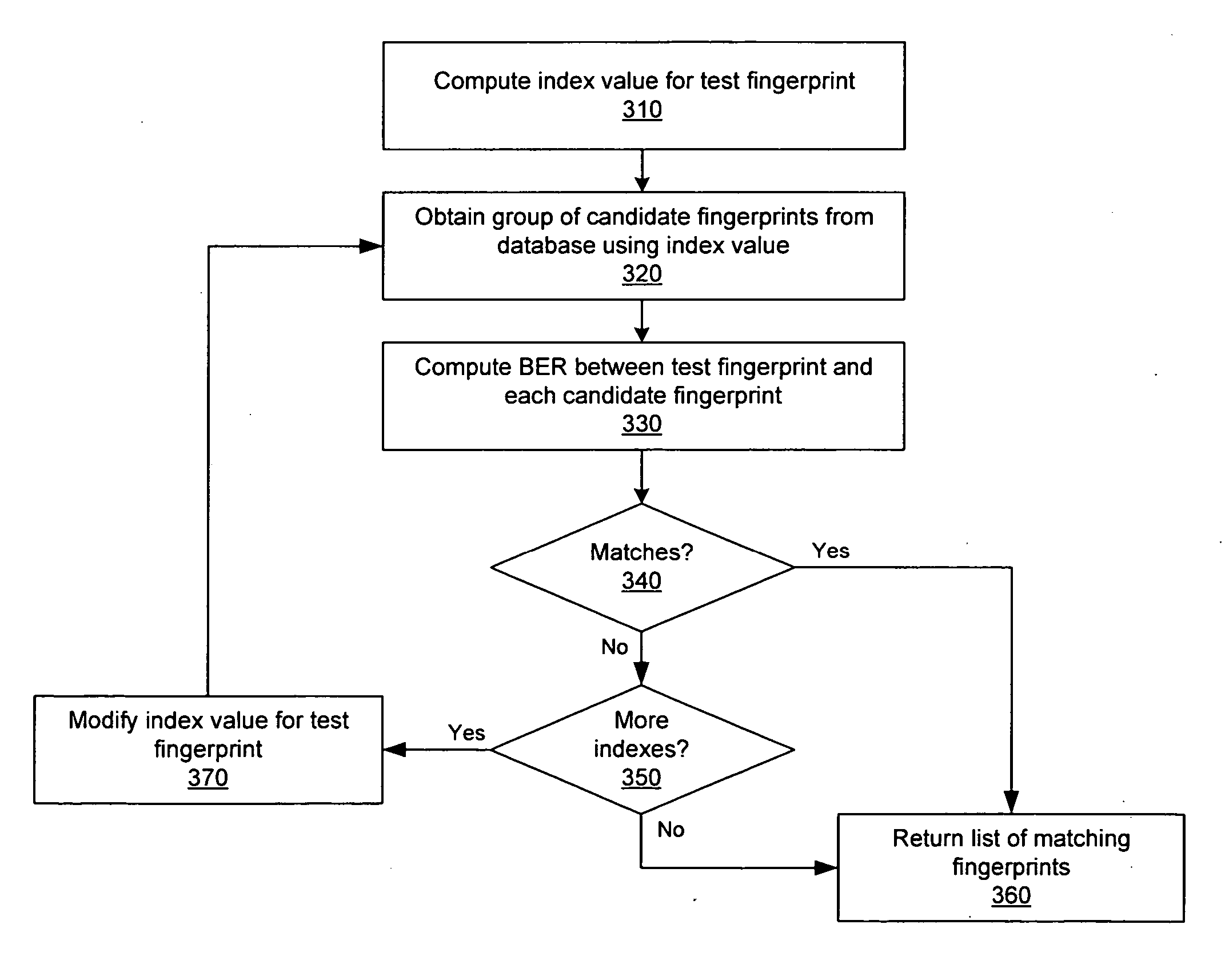
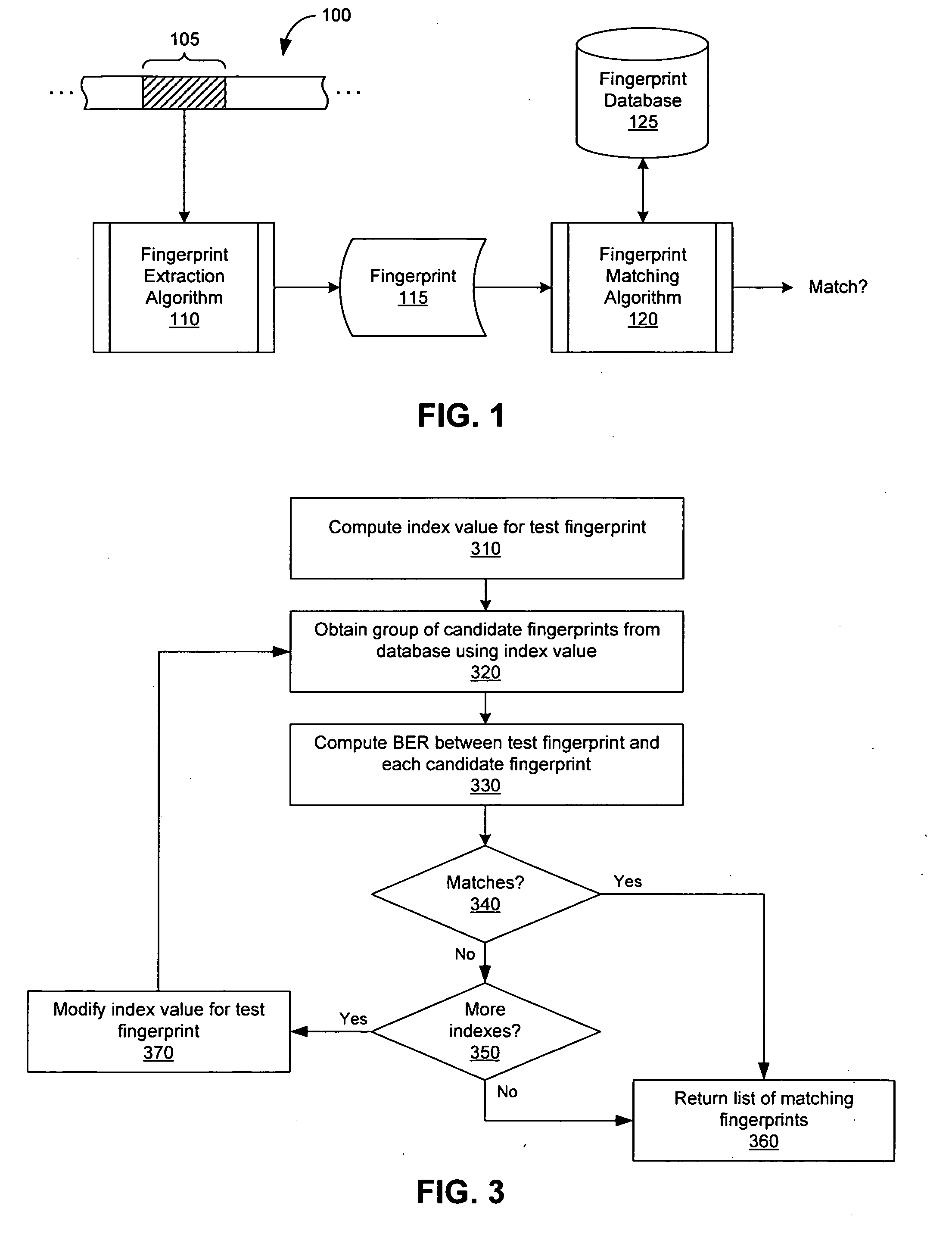
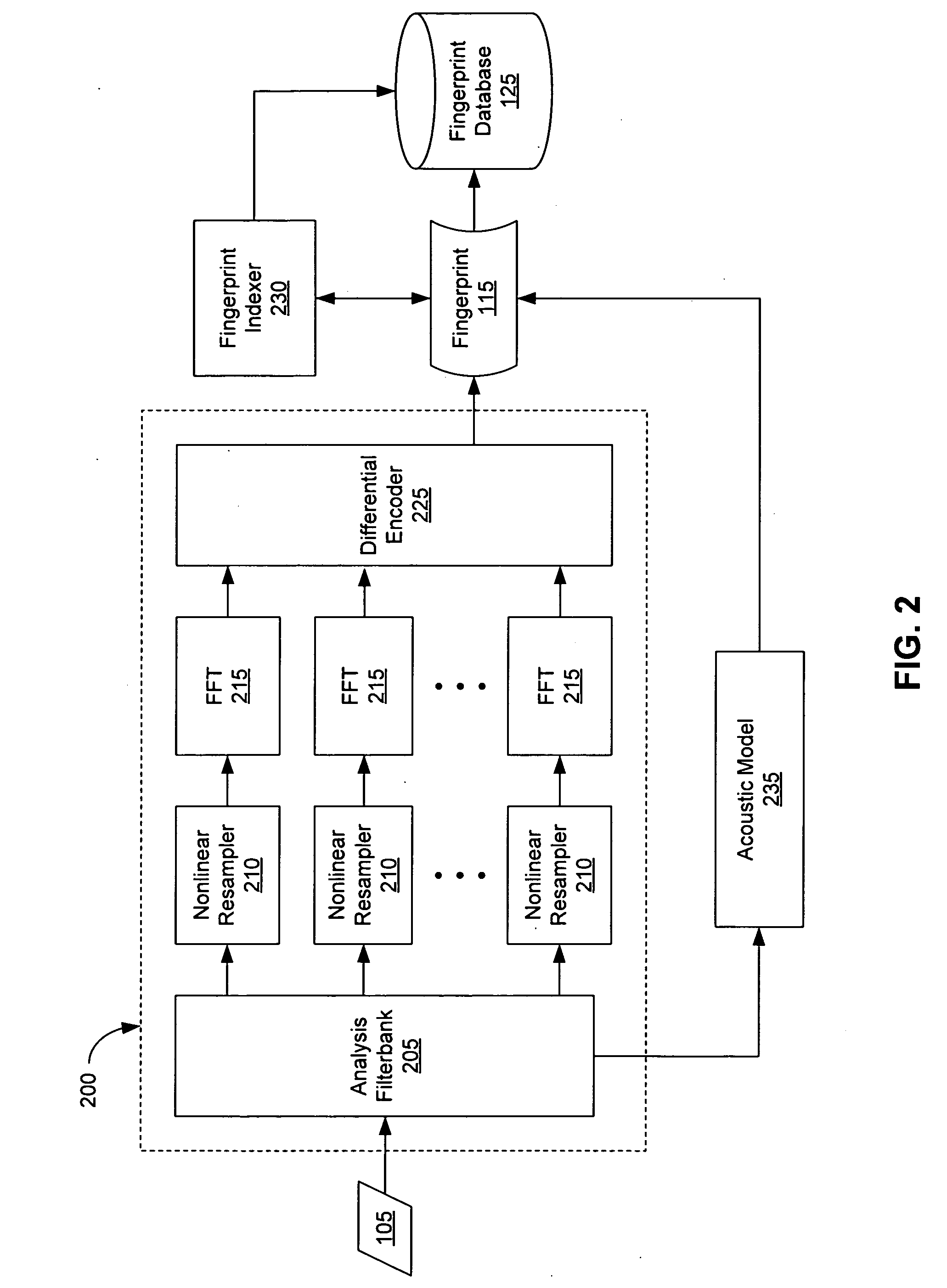
Extraction and matching of characteristic fingerprints from audio signals
InactiveUS20070055500A1Efficient and real-time medium content auditingEfficient and real-time and other reportingDigital data information retrievalSpeech analysisFeature vectorDifferential coding
An audio fingerprint is extracted from an audio sample, where the fingerprint contains information that is characteristic of the content in the sample. The fingerprint may be generated by computing an energy spectrum for the audio sample, resampling the energy spectrum logarithmically in the time dimension, transforming the resampled energy spectrum to produce a series of feature vectors, and computing the fingerprint using differential coding of the feature vectors. The generated fingerprint can be compared to a set of reference fingerprints in a database to identify the original audio content.
Owner:AUDITUDE COM +1
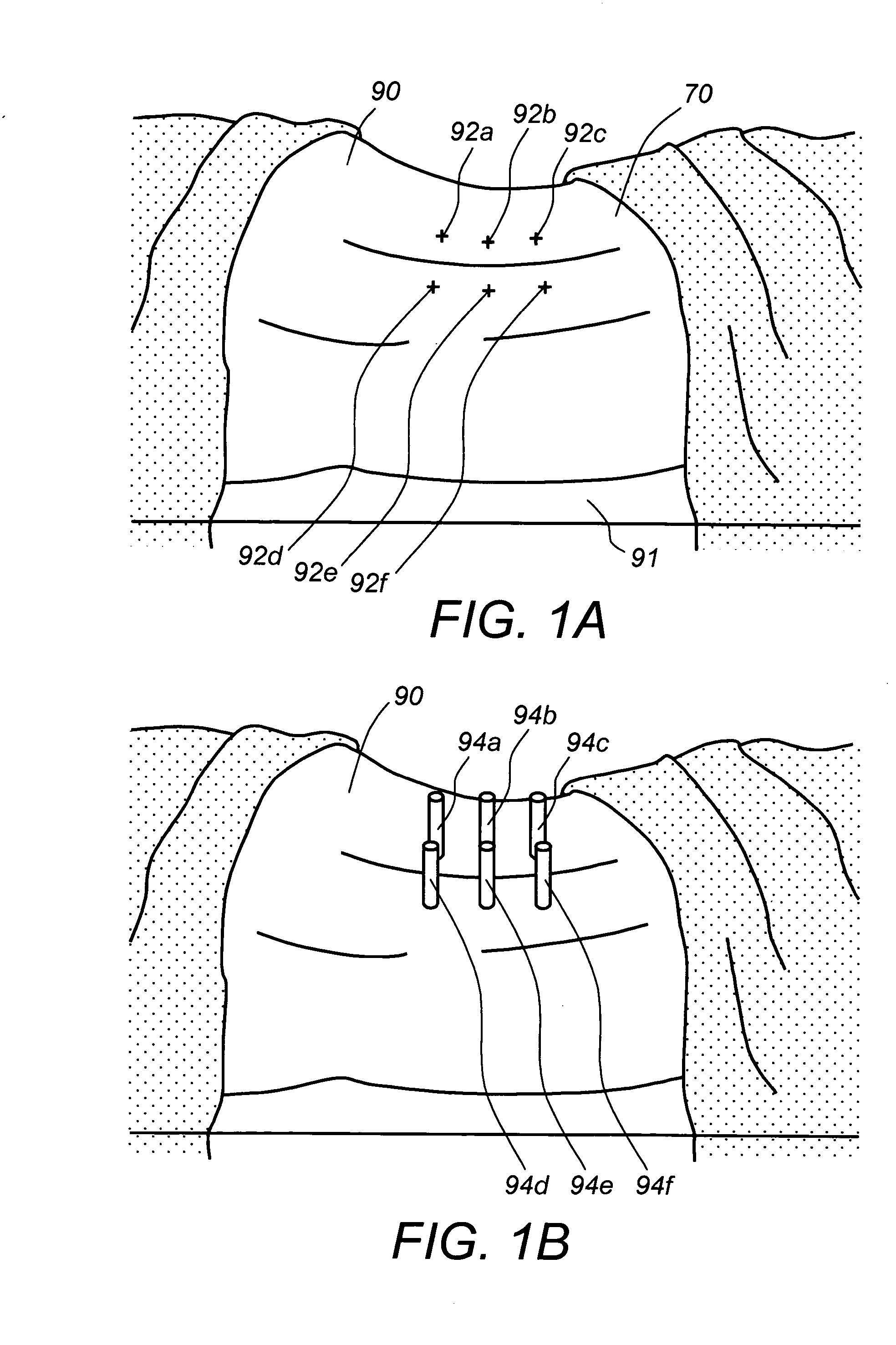
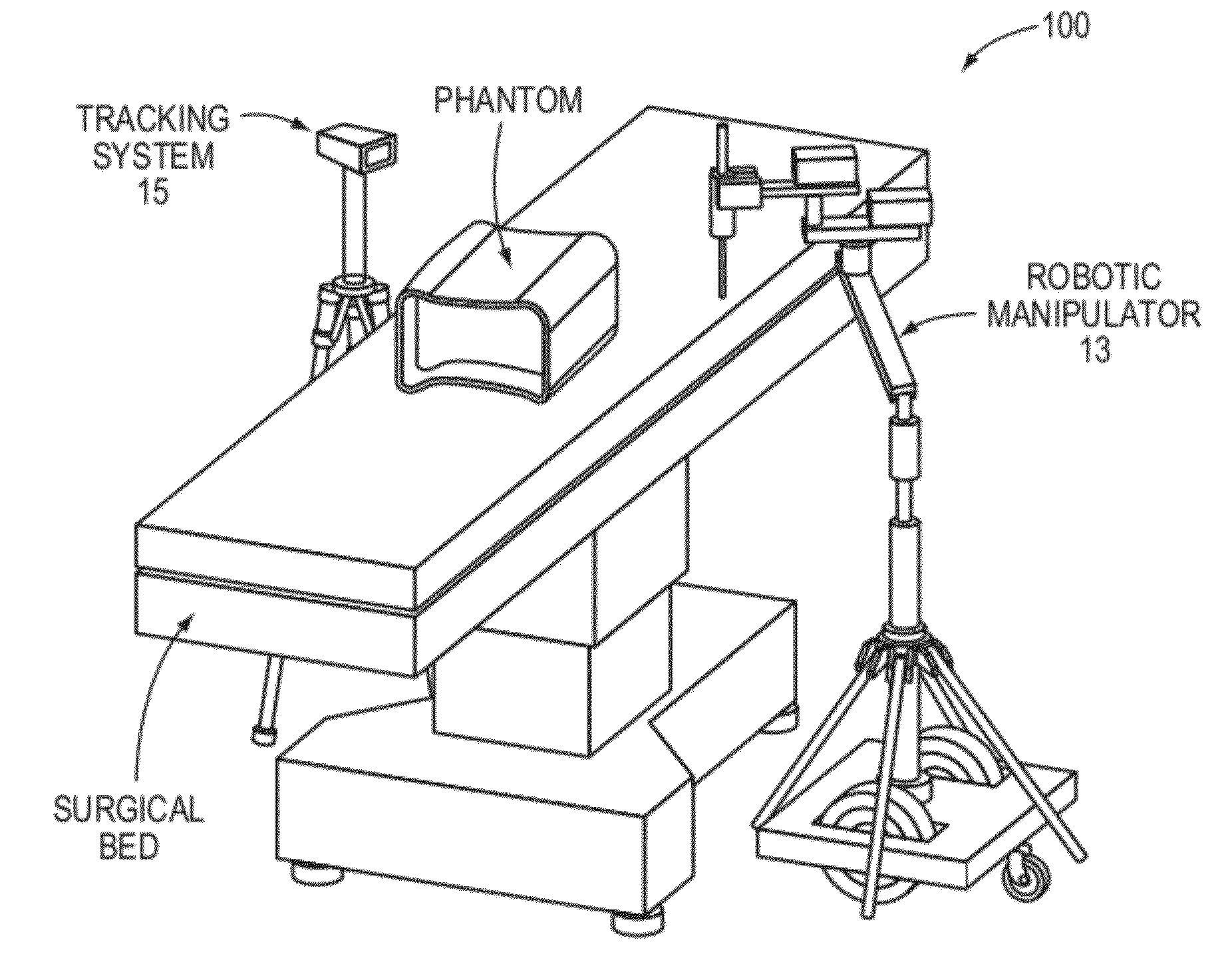
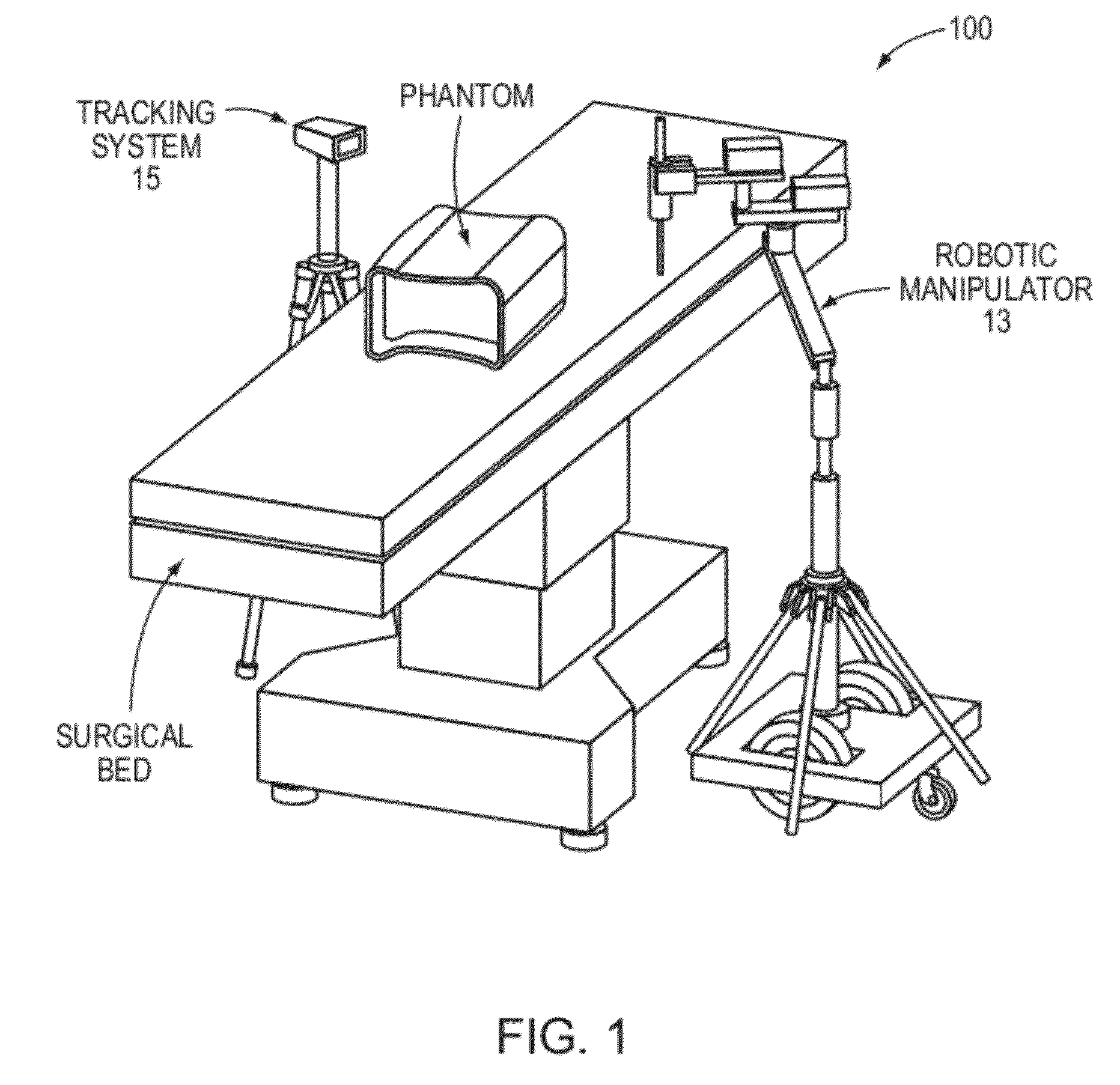
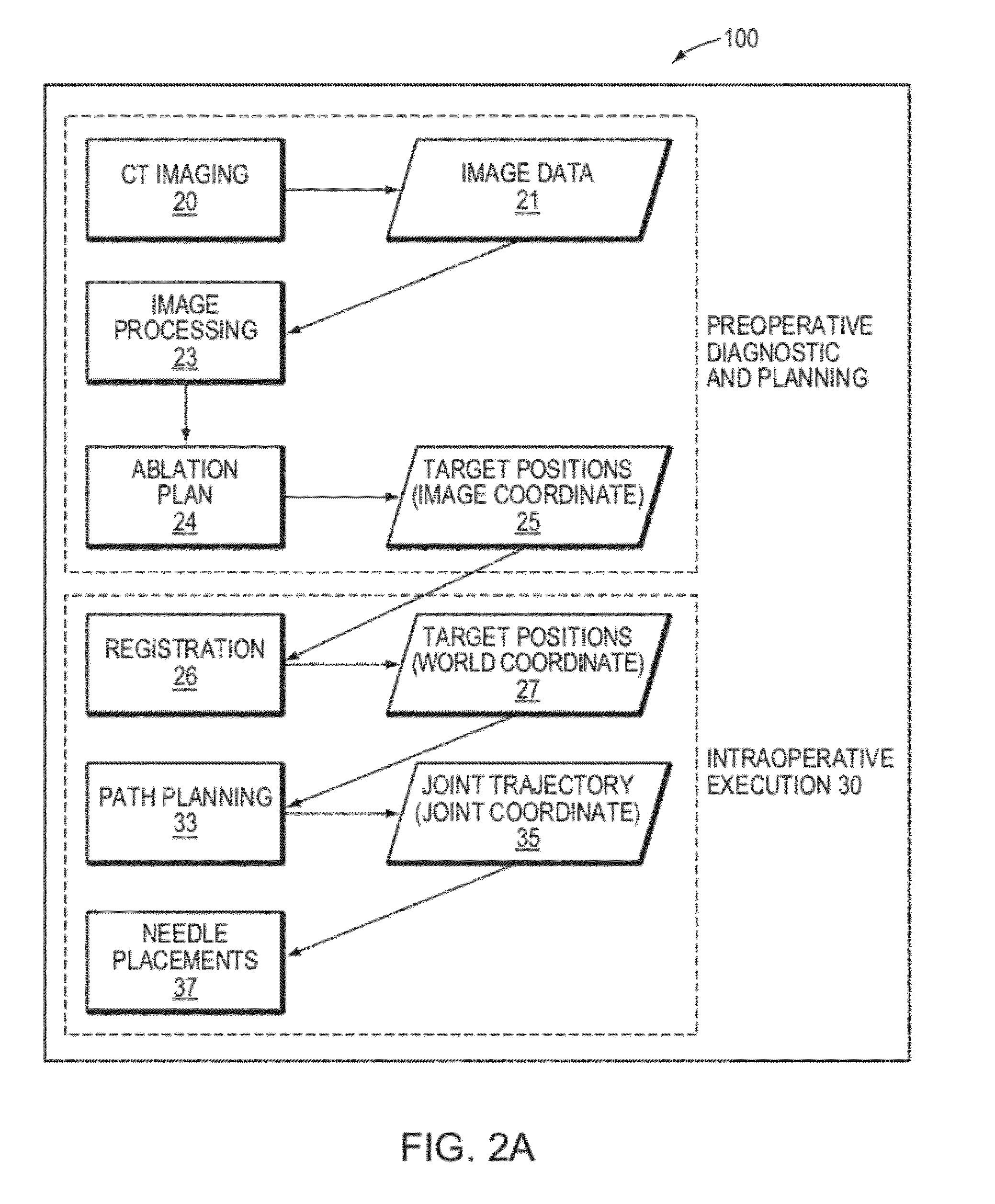
Transcutaneous robot-assisted ablation-device insertion navigation system
InactiveUS20120226145A1Easy to operateFacilitates potential expansionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesRadiofrequency ablationControl system design
A robotic system for overlapping radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in tumor treatment is disclosed. The robot assisted navigation system is formed of a robotic manipulator and a control system designed to execute preoperatively planned needle trajectories. Preoperative imaging and planning is followed by interoperative robot execution of the ablation treatment plan. The navigation system combines mechanical linkage sensory units with an optical registration system. There is no requirement for bulky hardware installation or computationally demanding software modules. Final position of the first needle placement is confirmed for validity with the plan and then is used as a reference for the subsequent needle insertions and ablations.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
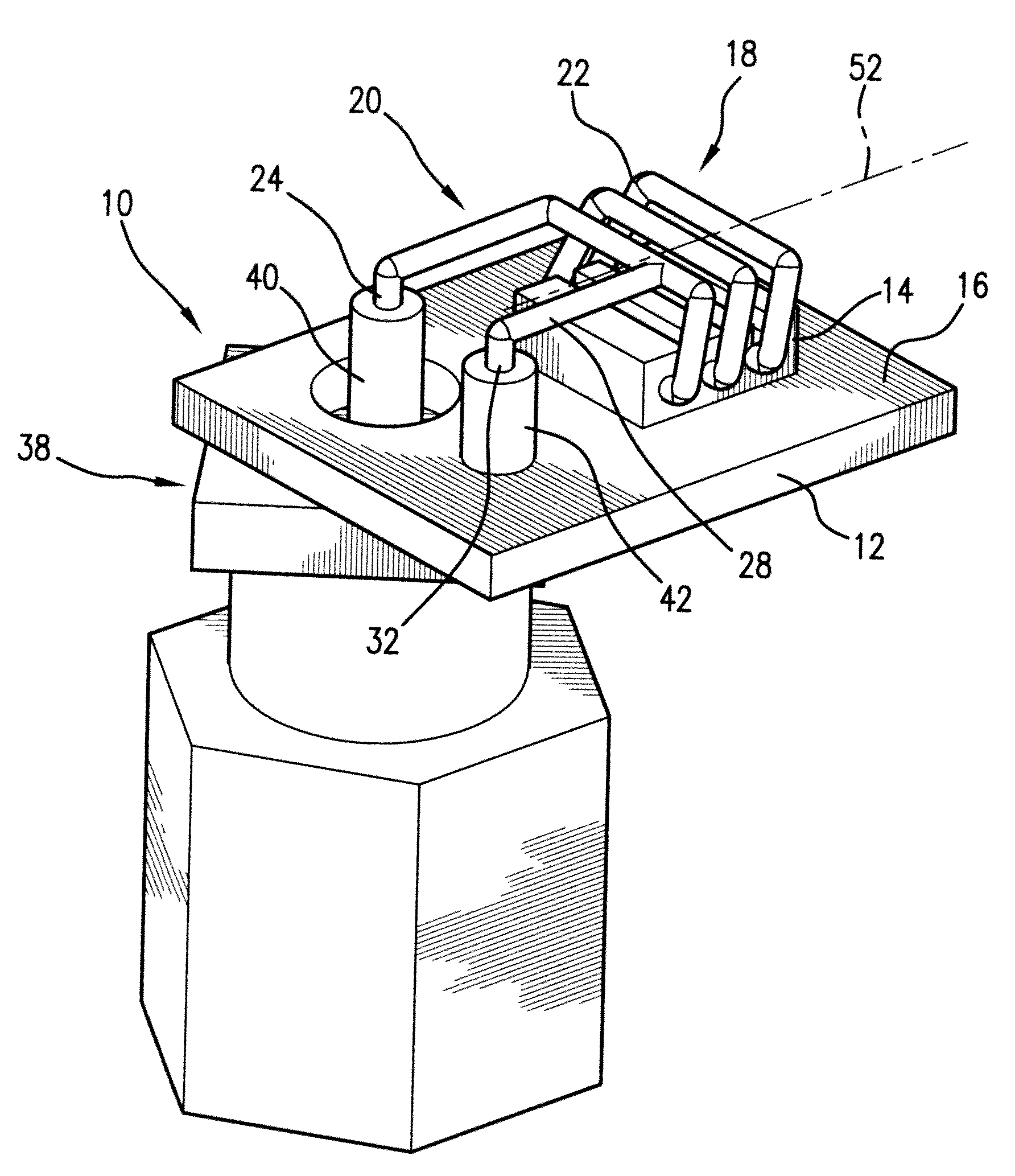
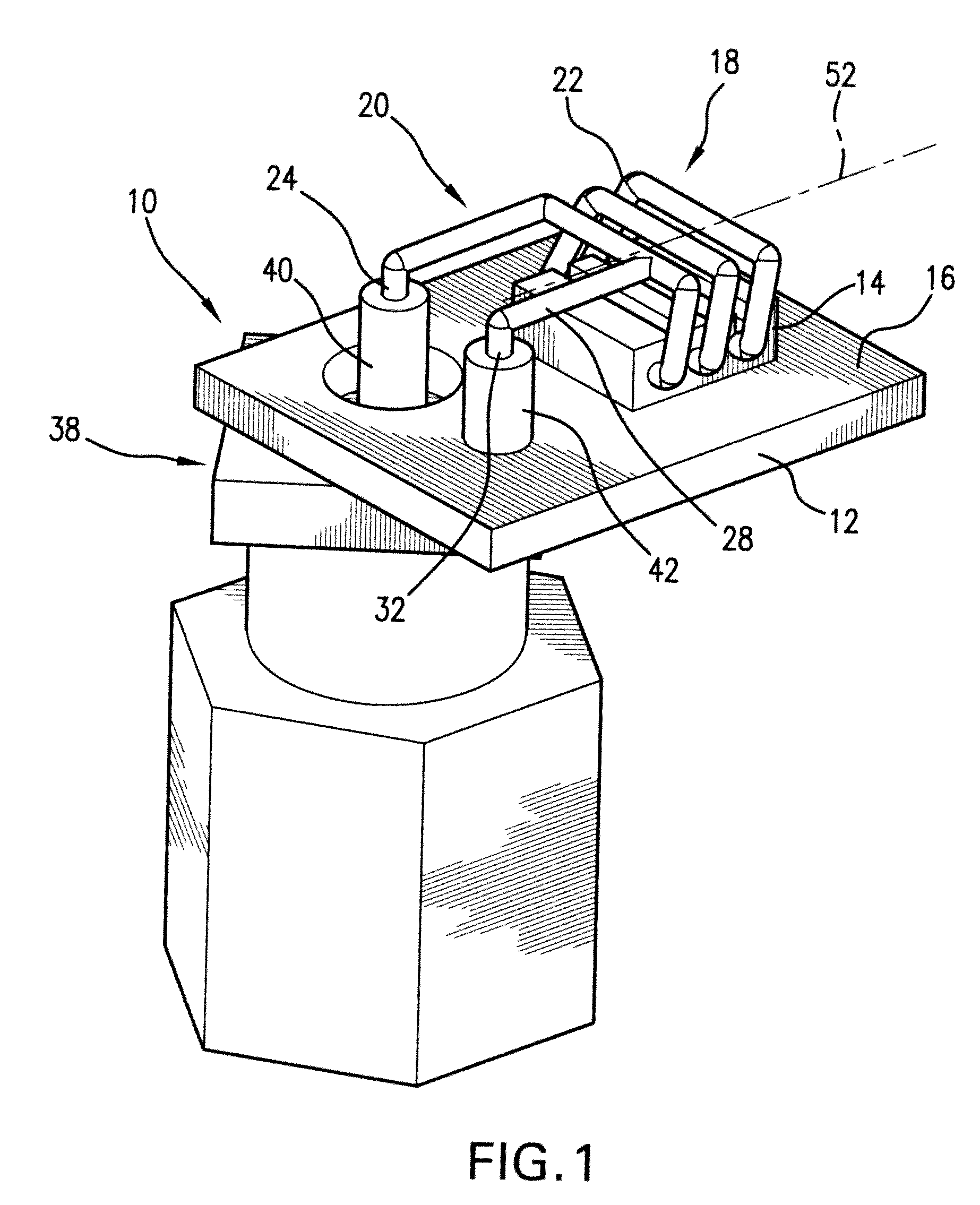
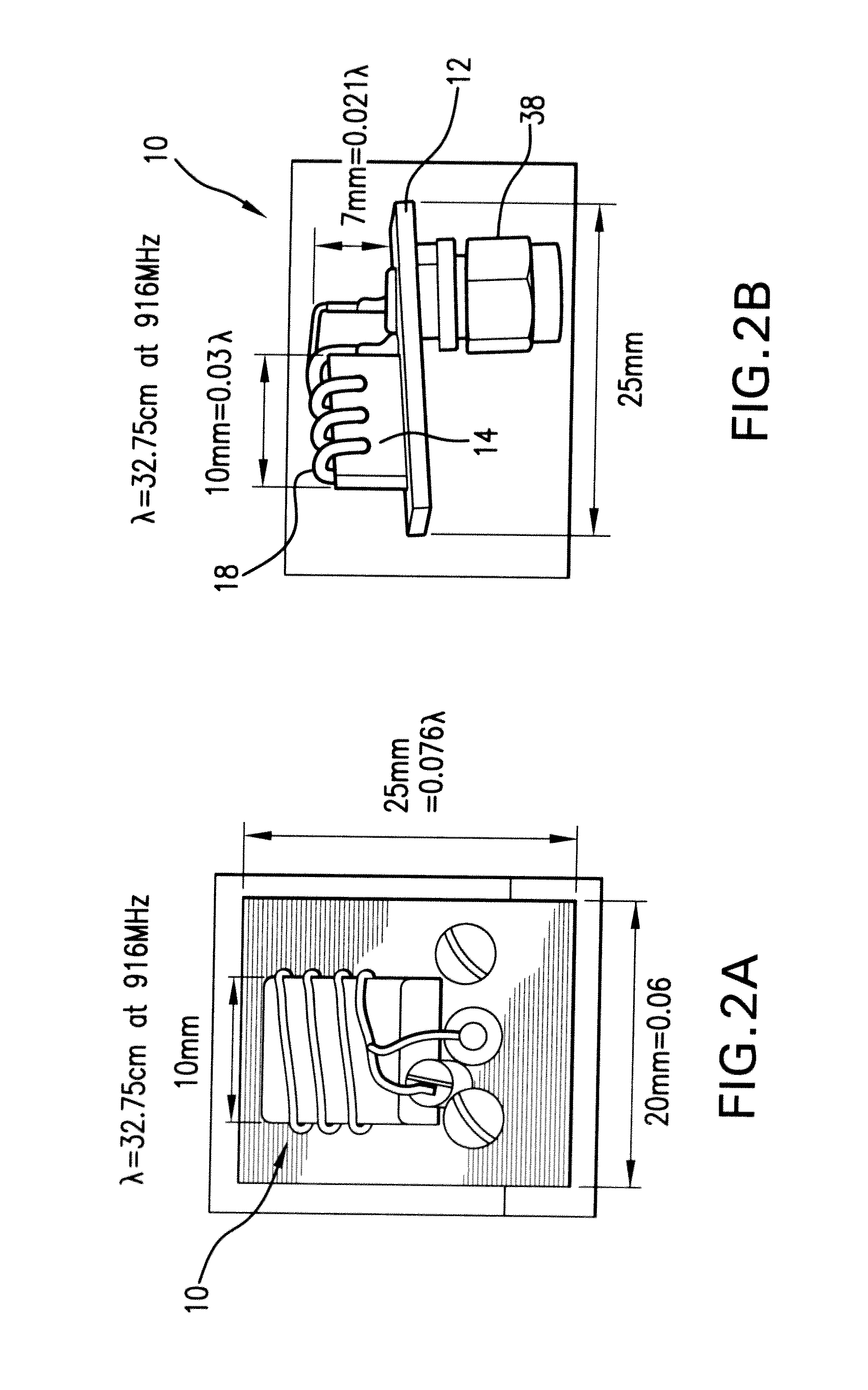
F-inverted compact antenna for wireless sensor networks and manufacturing method
InactiveUS20100026605A1Effective bandwidthLow profileRadiating elements structural formsHelical antennasDielectricCopper wire
An F-inverted compact antenna for ultra-low volume Wireless Sensor Networks is developed with a volume of 0.024λ×0.06λ×0.076λ, ground plane included, where λ is a resonating frequency of the antenna. The radiation efficiency attained is 48.53% and the peak gain is −1.38 dB. The antenna is easily scaled to higher operating frequencies up to 2500 MHz bands with comparable performance. The antenna successfully transmits and receives signals with tolerable errors. It includes a standard PCB board with dielectric block thereon and helically contoured antenna wound from a copper wire attached to the dielectric block and oriented with the helix axis parallel to the PCB. The antenna demonstrates omnidirectional radiation patterns and is highly integratable with WSN, specifically in Smart Dust sensors. The antenna balances the trade offs between performance and overall size and may be manufactured with the use of milling technique and laser cutters.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
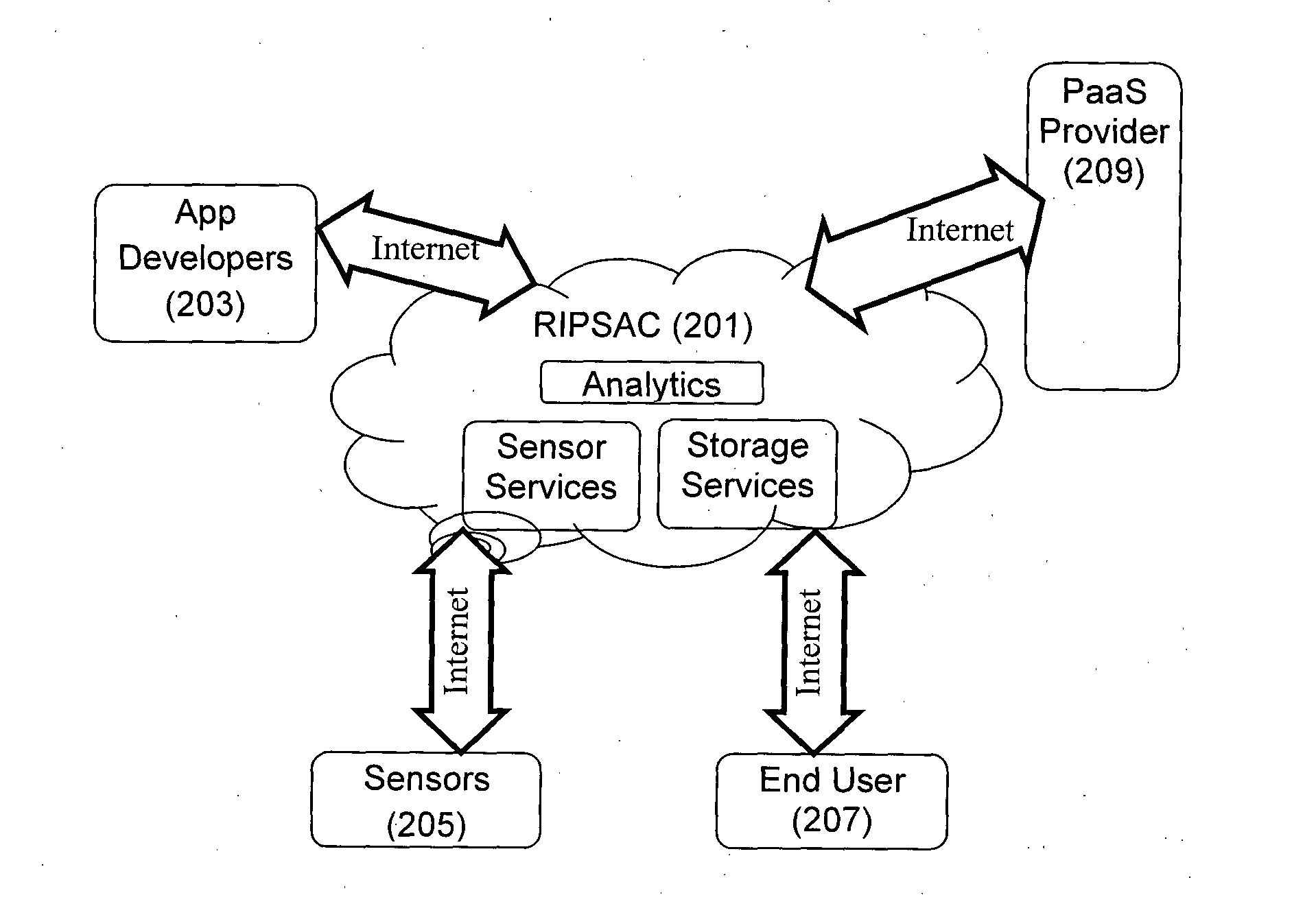
Computer Platform for Development and Deployment of Sensor Data Based Applications and Services
ActiveUS20140359552A1Facilitating crowd sourcing application developmentFacilitates and easy developmentError detection/correctionSoftware reuseReal time analysisCloud base
A method and system for real-time analytics of sensor-based data is disclosed. Also disclosed is a Cloud-based Paltform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering for sensor driven applications with services and features for their complete life-cycle management including prompt development, testing, deployment and so forth. The method of the present disclosure enables real-time tracking of various physical parameters and attributes related to smart-spaces using sensor devices implemented in the premises of the smart-space environment and using crowd-sourced user input data. Further, the parameters obtained are sent to the cloud-computing server, wherein the analytics are performed in real-time based on the obtained parameters.
Owner:TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD
Flash memory device using semiconductor fin and method thereof
ActiveUS7285820B2Improve scalabilityProgramming and erasing efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesCoupling ratioCrystal plane
A flash memory device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor fin including a top surface and a side surface originated from different crystal planes. The flash memory device comprises: insulating layers having different thicknesses formed on a side surface and a top surface of the semiconductor fin, a storage electrode, a gate insulating layer and a control gate electrode sequentially formed on the insulating layers. A thin insulating layer enables charges to be injected or emitted through it, and a thick insulating layer increases a coupling ratio. Accordingly, it is possible to increase an efficiency of a programming or an erase operation of a flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
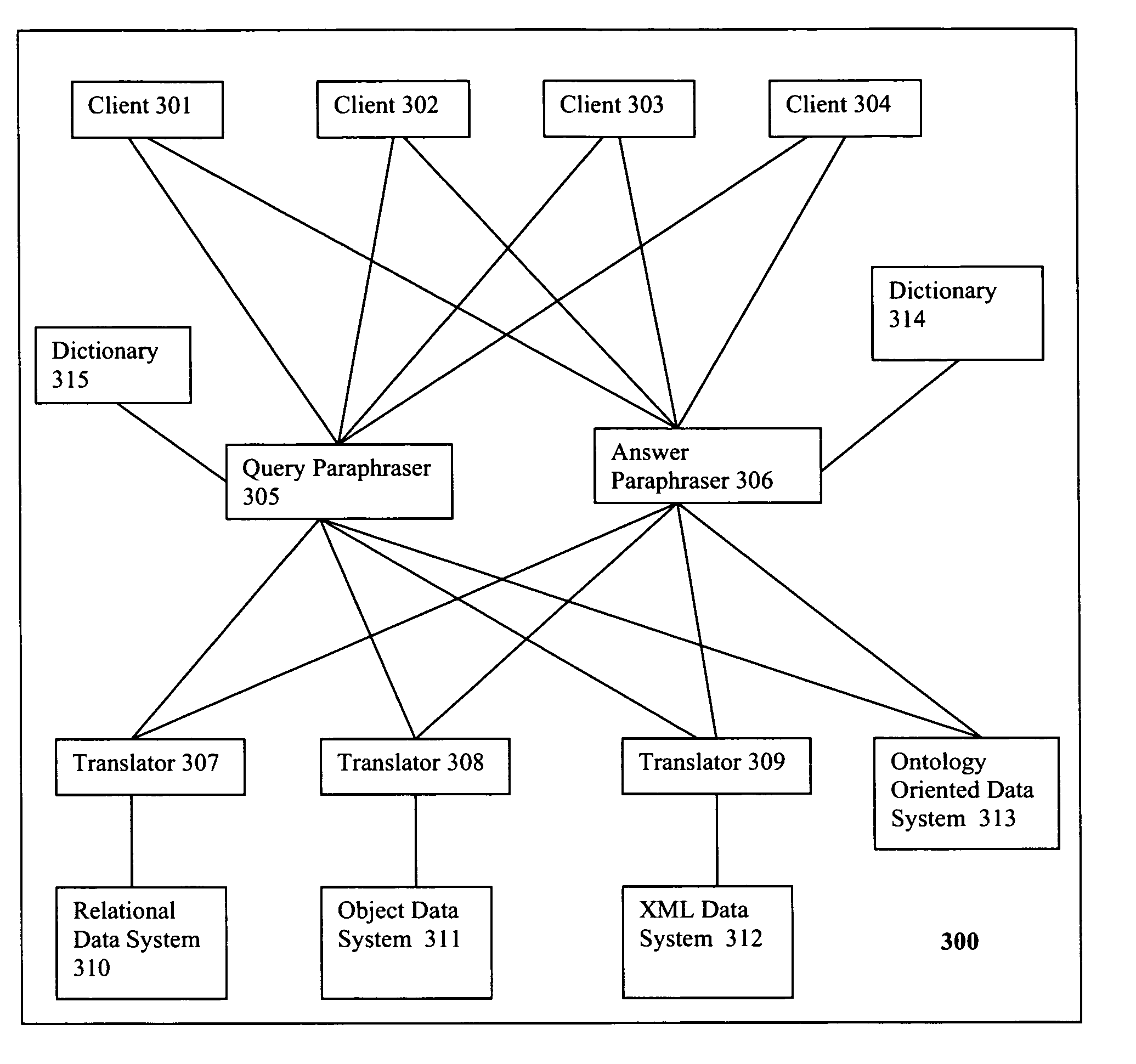
System and method of query paraphrasing
InactiveUS20070038609A1Simple processAvoid programmingDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData retrievalData system
A platform-independent process for data retrieval from ontology-oriented data systems over computer networks through a flexible system and method of query paraphrasing. The present invention uses a “common ontology” that is not tied to any particular data system. Thus, each client computer issues queries to a target data system in the common ontology. Of course, the target data system will not be able to directly process the query (as it is not in its local ontology). Instead, the query is first paraphrased back from the common ontology into local ontology by taking the semantic query, passing it through a query paraphraser, and then sending the paraphrased query to the data system. Once it is paraphrased successfully, the target data system can process it and produce a result using local ontology. The result may then be sent from the data system to an answer paraphraser for paraphrasing, and the paraphrased answer may be returned to its original query issuer and on to the client.
Owner:WU WILLIAM
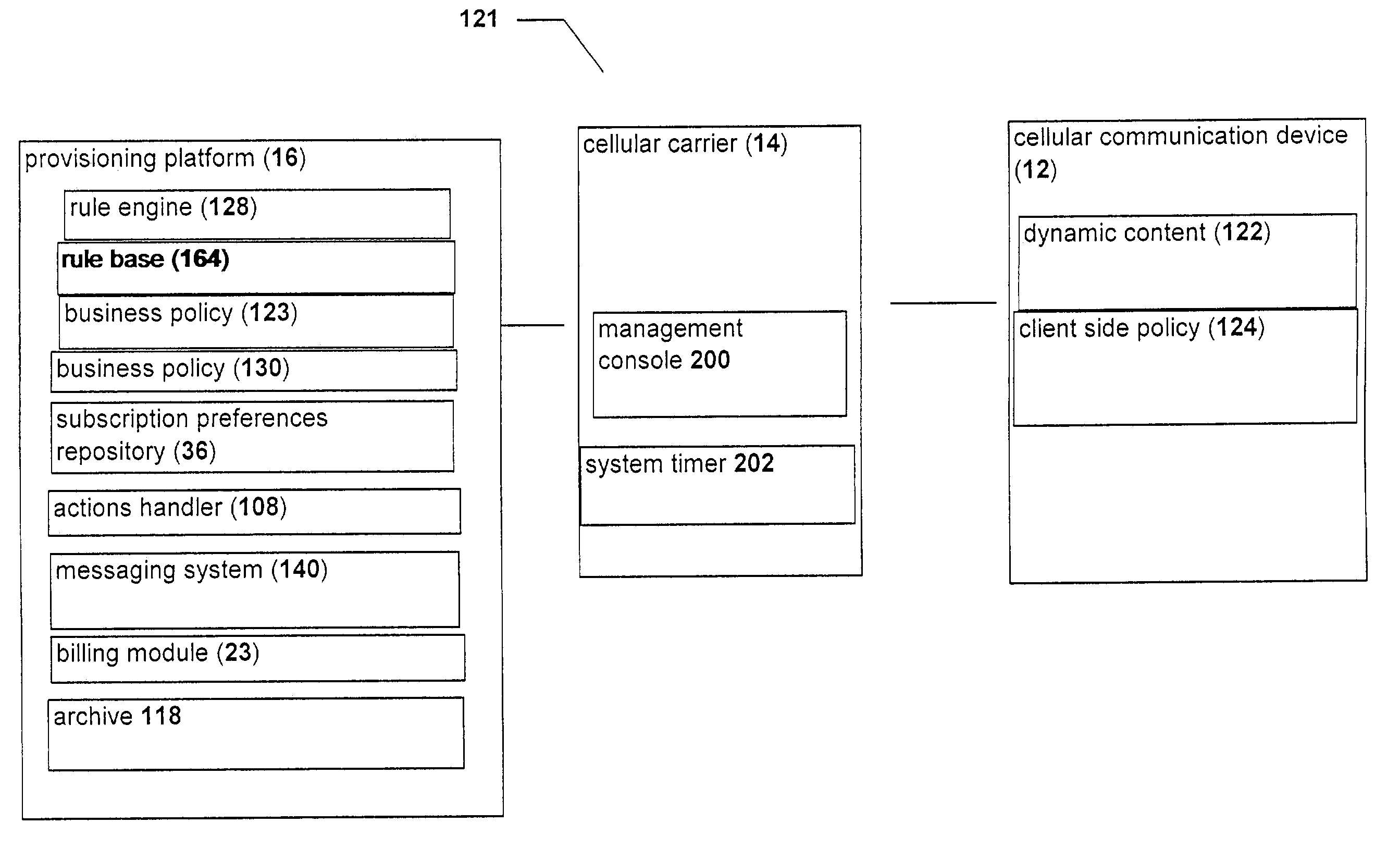
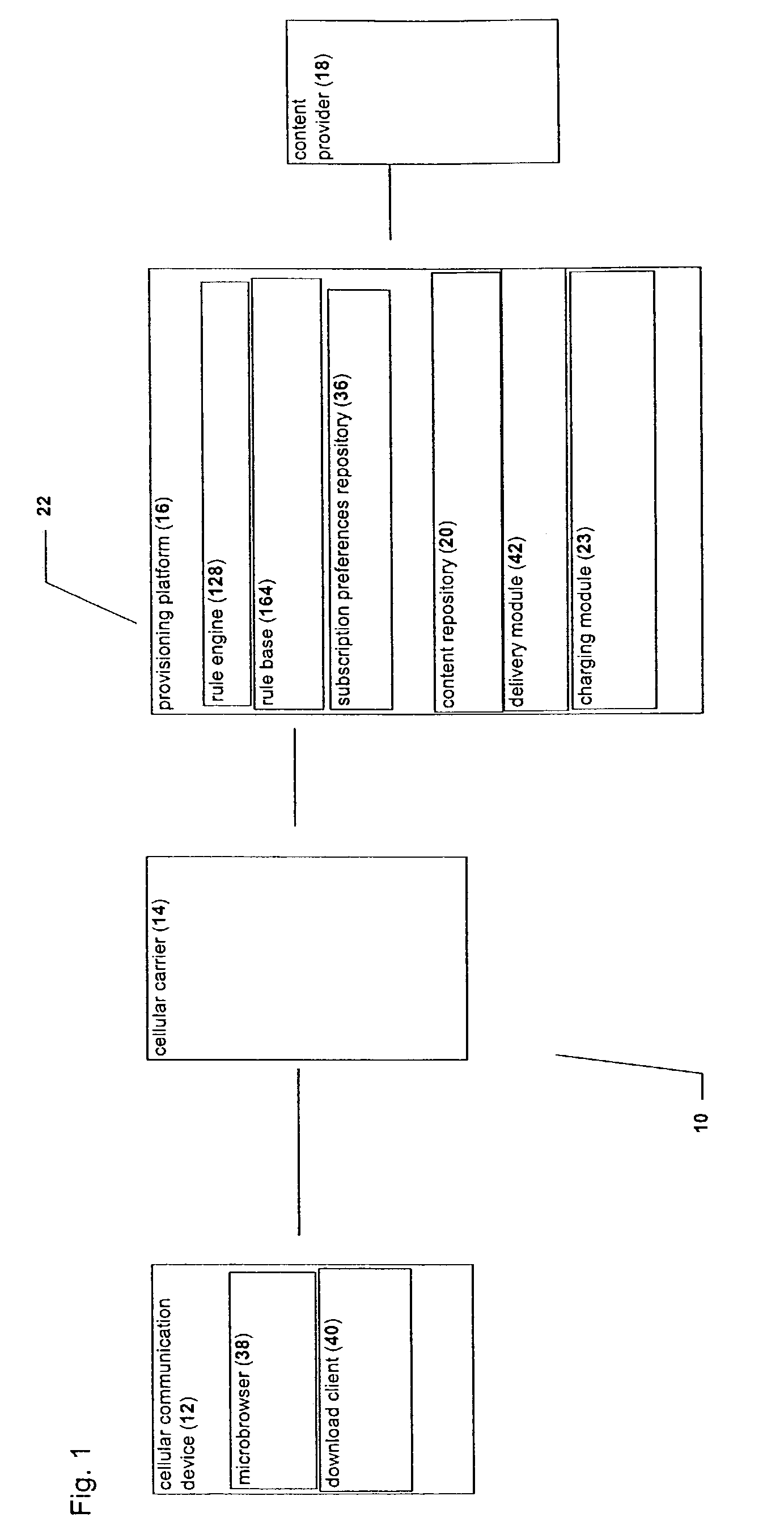
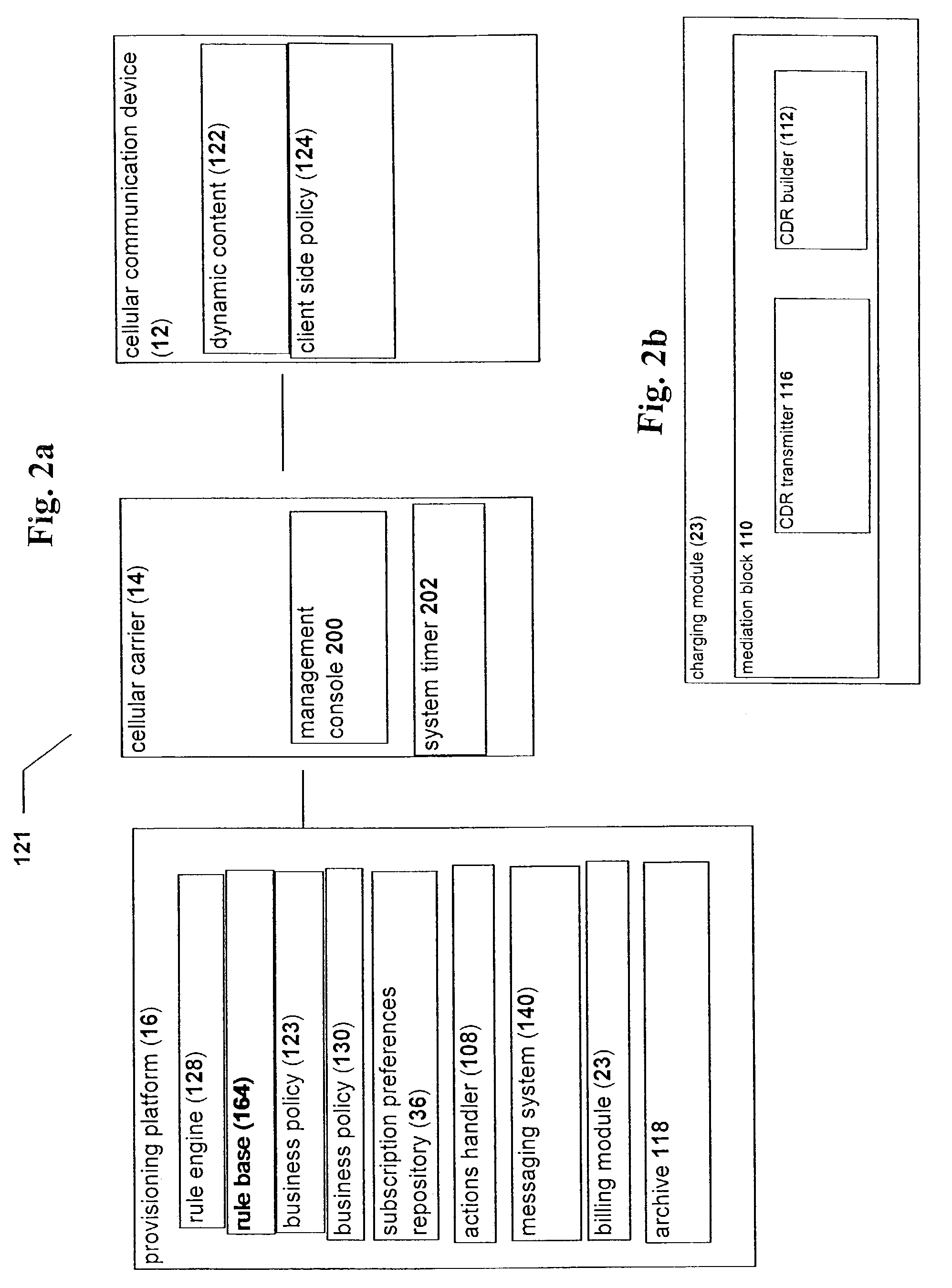
Rule-based system and method for managing the provisioning of user applications on limited-resource and/or wireless devices
InactiveUS7330717B2Suppress actionCapacity to connectAccounting/billing servicesSpecial service for subscribersLimited resourcesIntegration platform
A system and a method for charging for directed provisioning and using of dynamic content to limited resource devices, through an integrated platform which handles all aspects of aggregation and management of such dynamic content. The integrated platform features a billing system for performing billing actions. The billing system of the present invention interacts with other components of the integrated platform in order to be able to determine the charge for particular triggering events, such as downloading dynamic content, and / or events which are actually triggered by the application itself. The charge is preferably determined according to one of a plurality of rules, as applied by a rules engine of the billing system. These rules are part of a charging policy, which may optionally be determined by the content provider.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
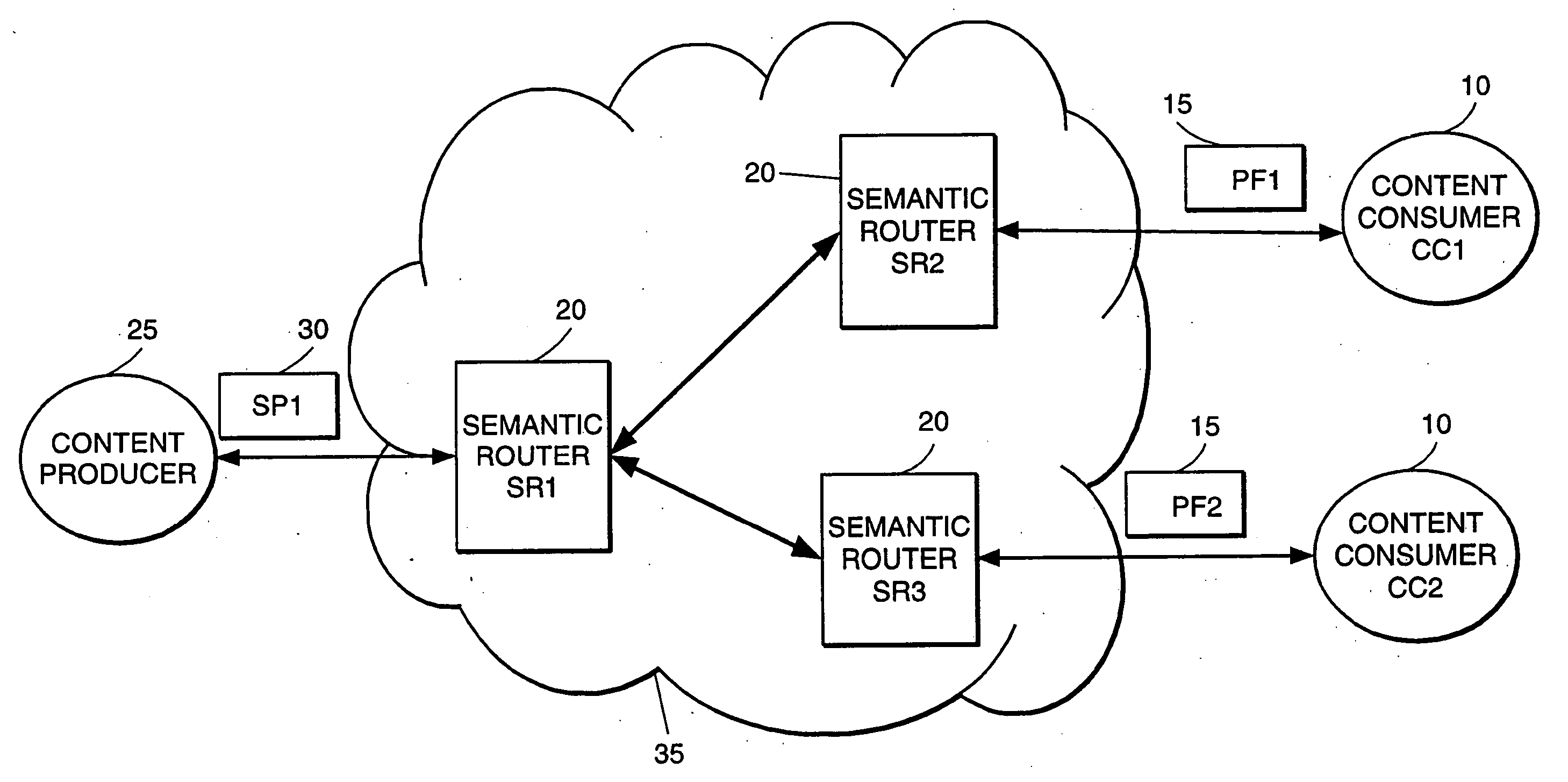
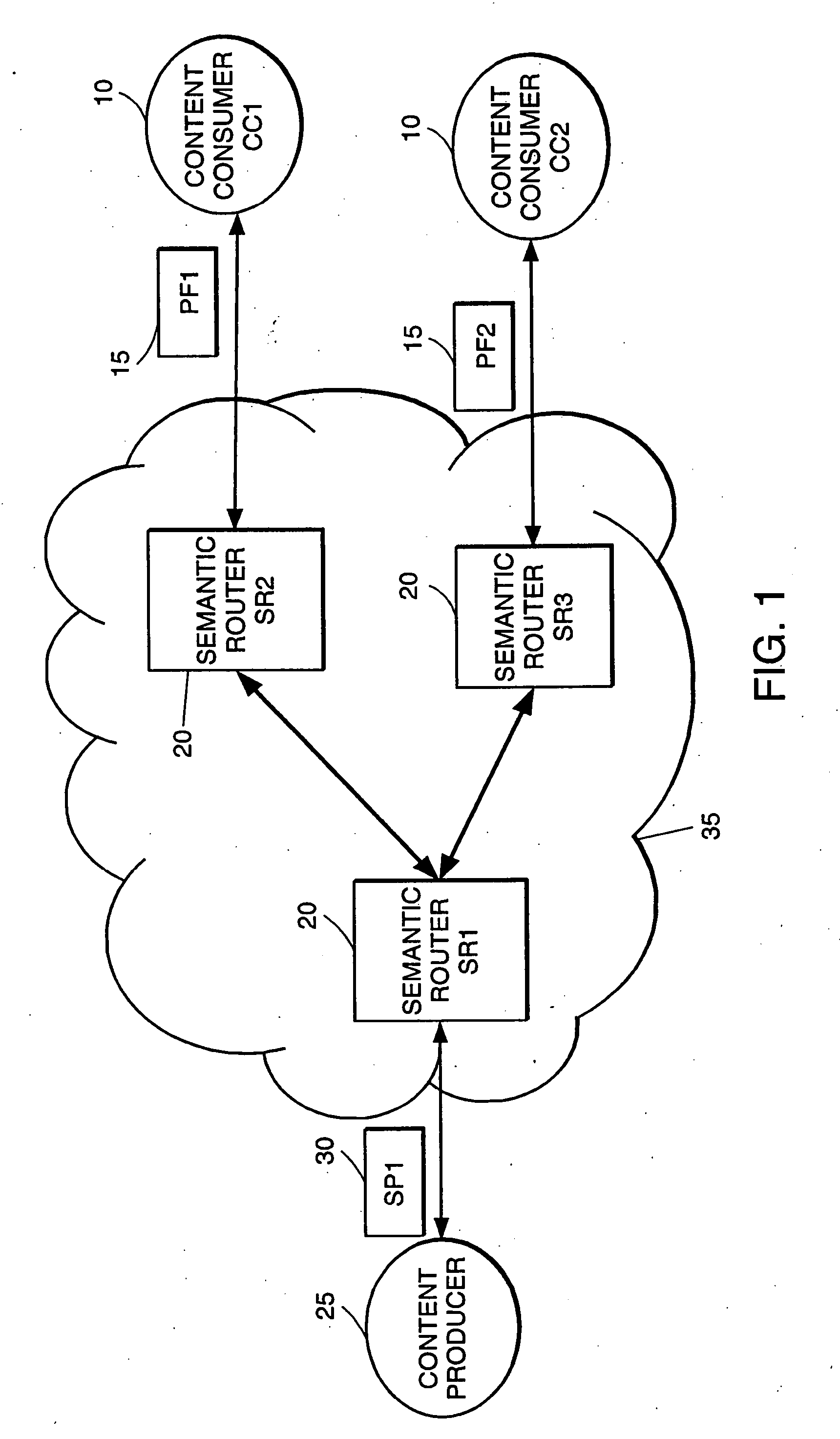
High-performance addressing and routing of data packets with semantically descriptive labels in a computer network
InactiveUS20070239892A1Reduce storageEasy to operateDigital computer detailsData switching networksRouting tableNetwork packet
A method, system and apparatus for routing data through a network based on the content or semantics of the data. Semantic routing engines route the data through the network based upon information maintained in routing tables. The routing tables used to route the content through the network are derived by aggregating information about either content consumers or content producers into ontological
Owner:SEMANDEX NETWORKS
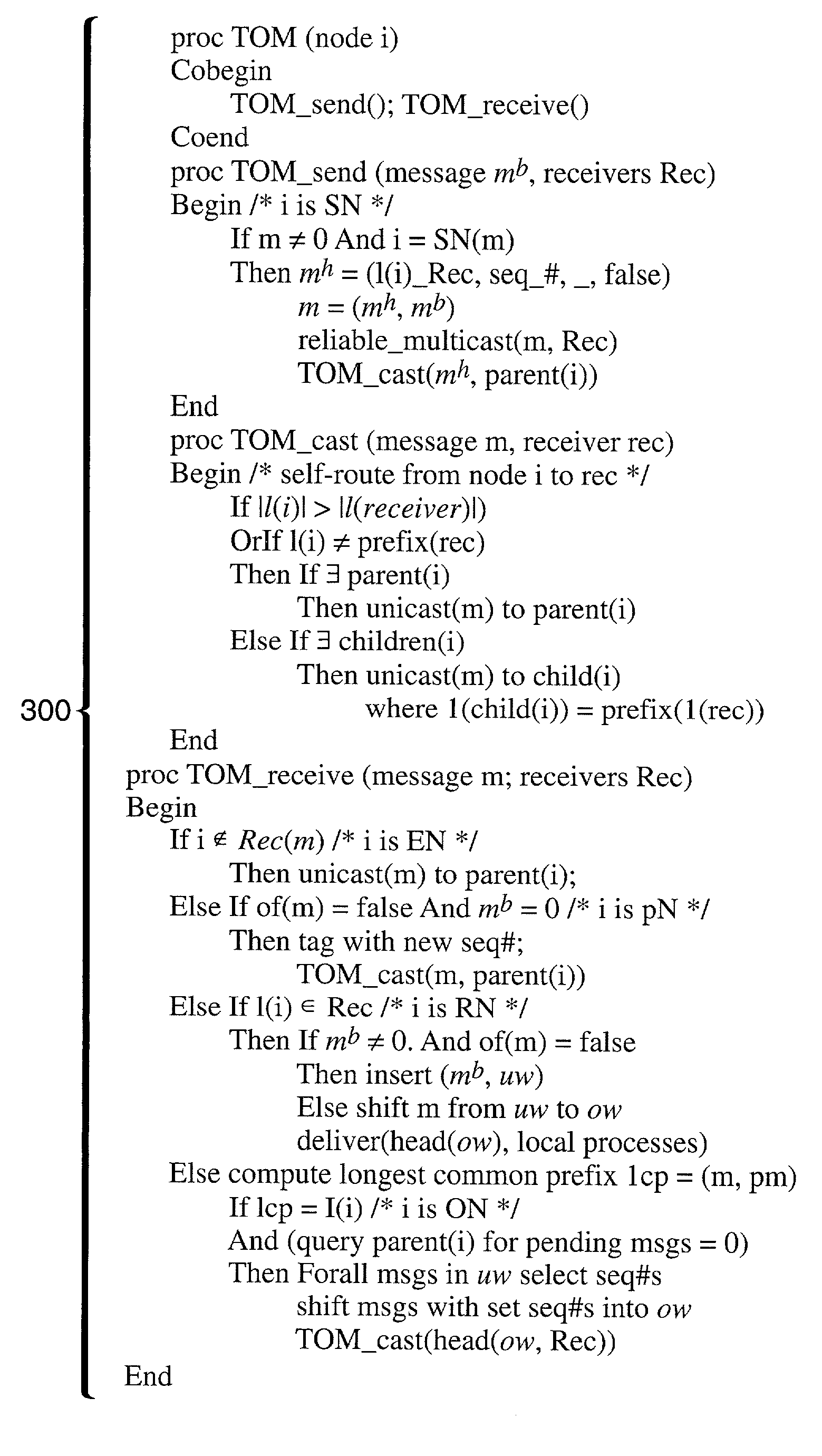
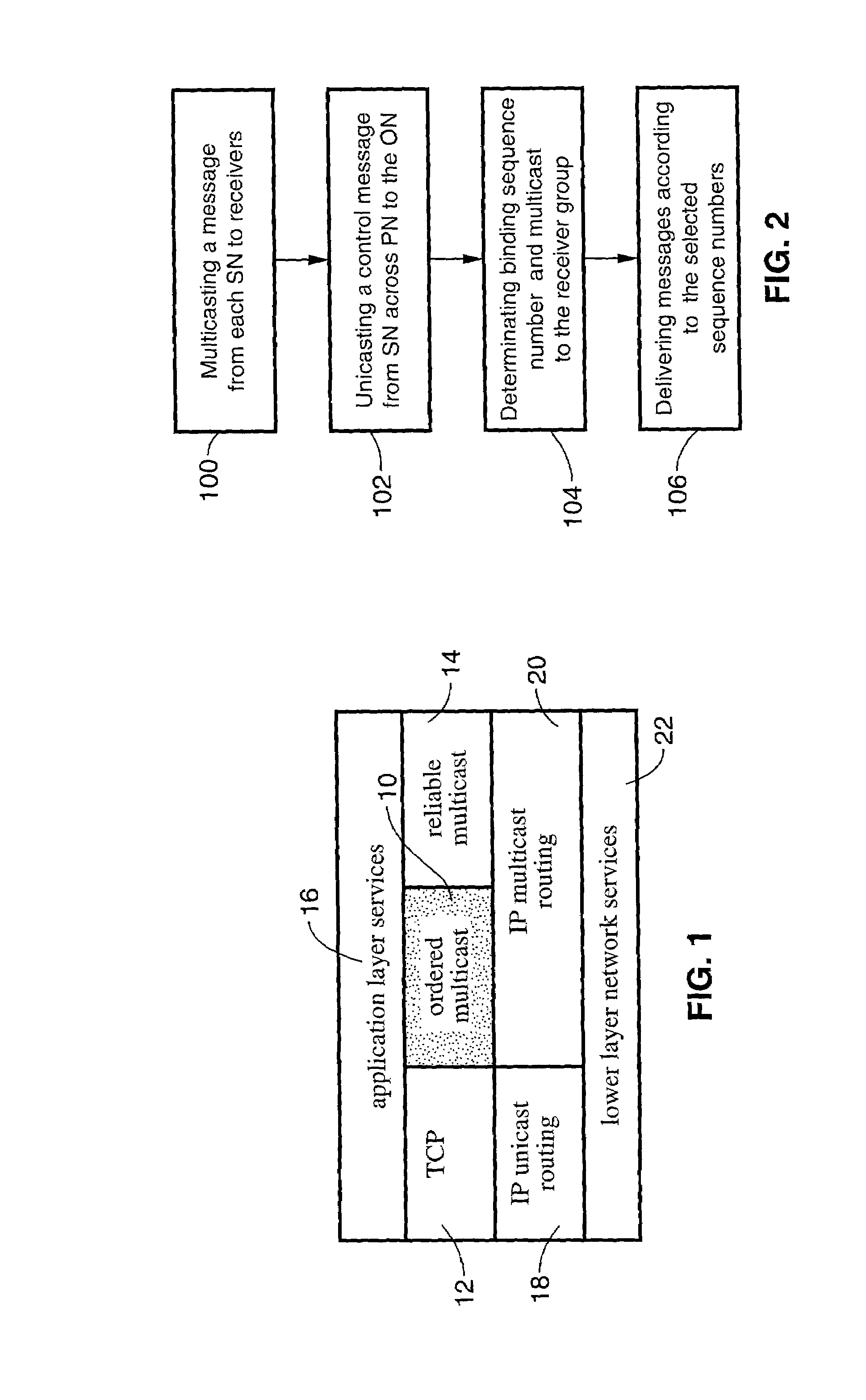
Tree-based ordered multicasting method
ActiveUS7031308B2Improve efficiencyImprove scalabilitySpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessMulticast
A method for performing end-to-end “tree-based ordered multicasting” (TOM) which ensures collective integrity and consistency of distributed operations, and which is applicable to distributed multiparty collaboration and other multipoint applications. The TOM protocol performs cascaded total ordering of messages among on-tree hosts en route from senders to receivers, and does not require the building of a separate propagation graph to compute ordering information. TOM elects sequencer nodes dynamically based on address extensions of the multicast tree. Message ordering is performed by multicasting a message from each source node to receivers, unicasting a control message from a source node across a primary node to an ordering node for the designated multicast group or transmission in the tree, determining a binding sequence number for the message and a multicast to the receiver group, and delivering messages at end hosts according to the agreed-upon sequence numbers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
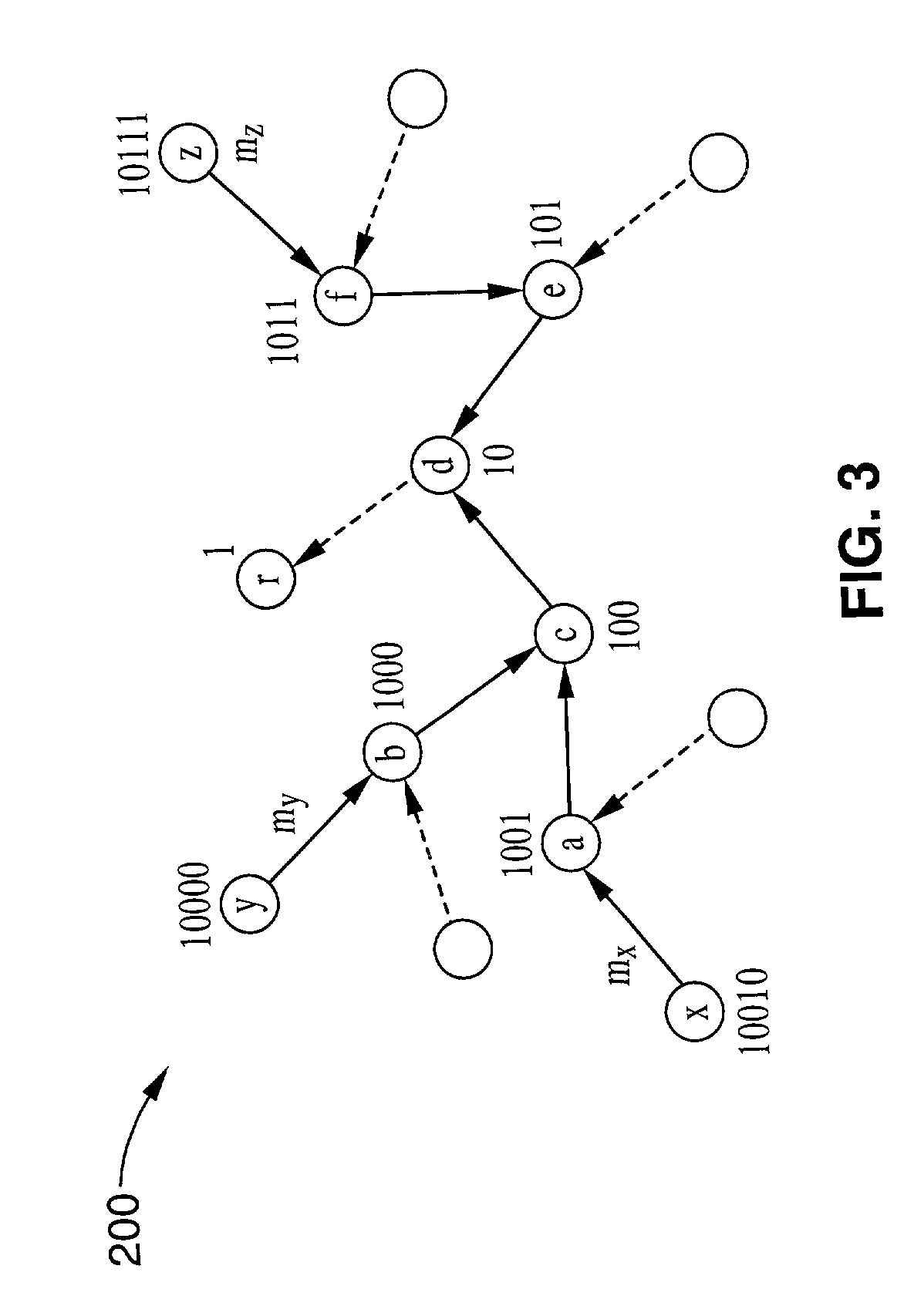
Implementation of serverless applications over wireless networks
InactiveUS20060030339A1Facilitates display of and selectionFacilitates associationPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsHandsetTelephony
Owner:CELLITITUDE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com