Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
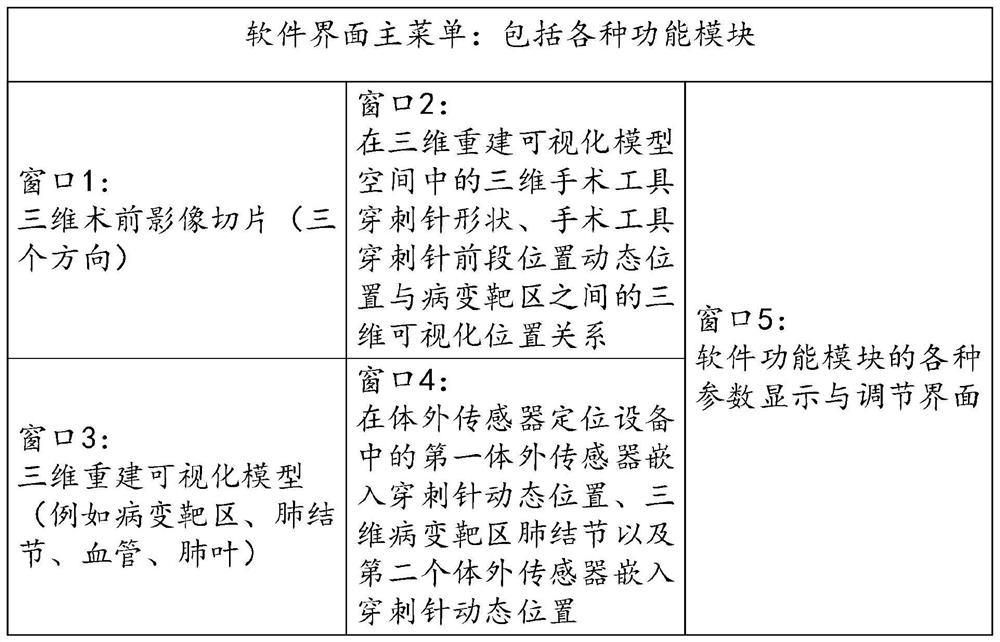
63 results about "Preoperative imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
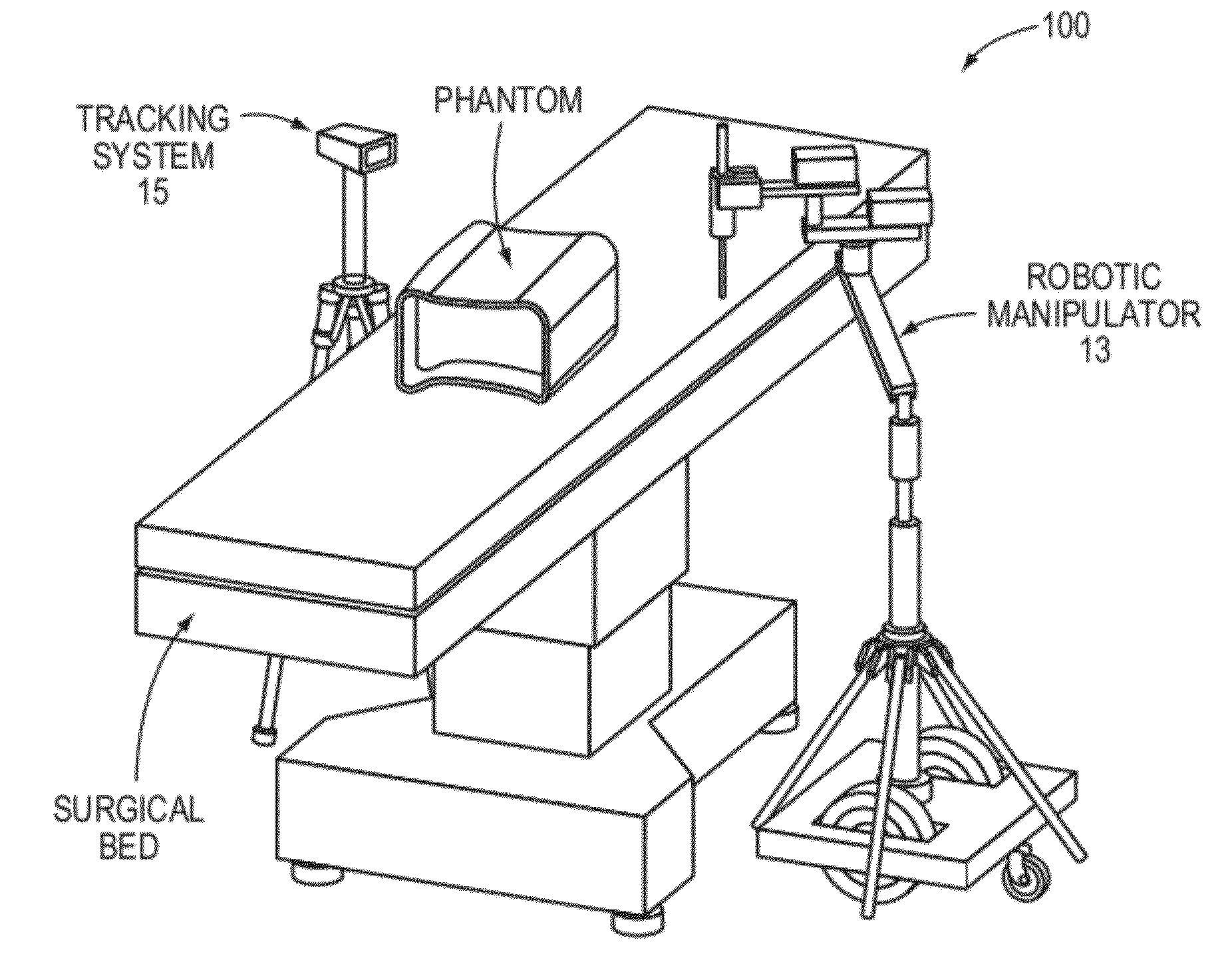
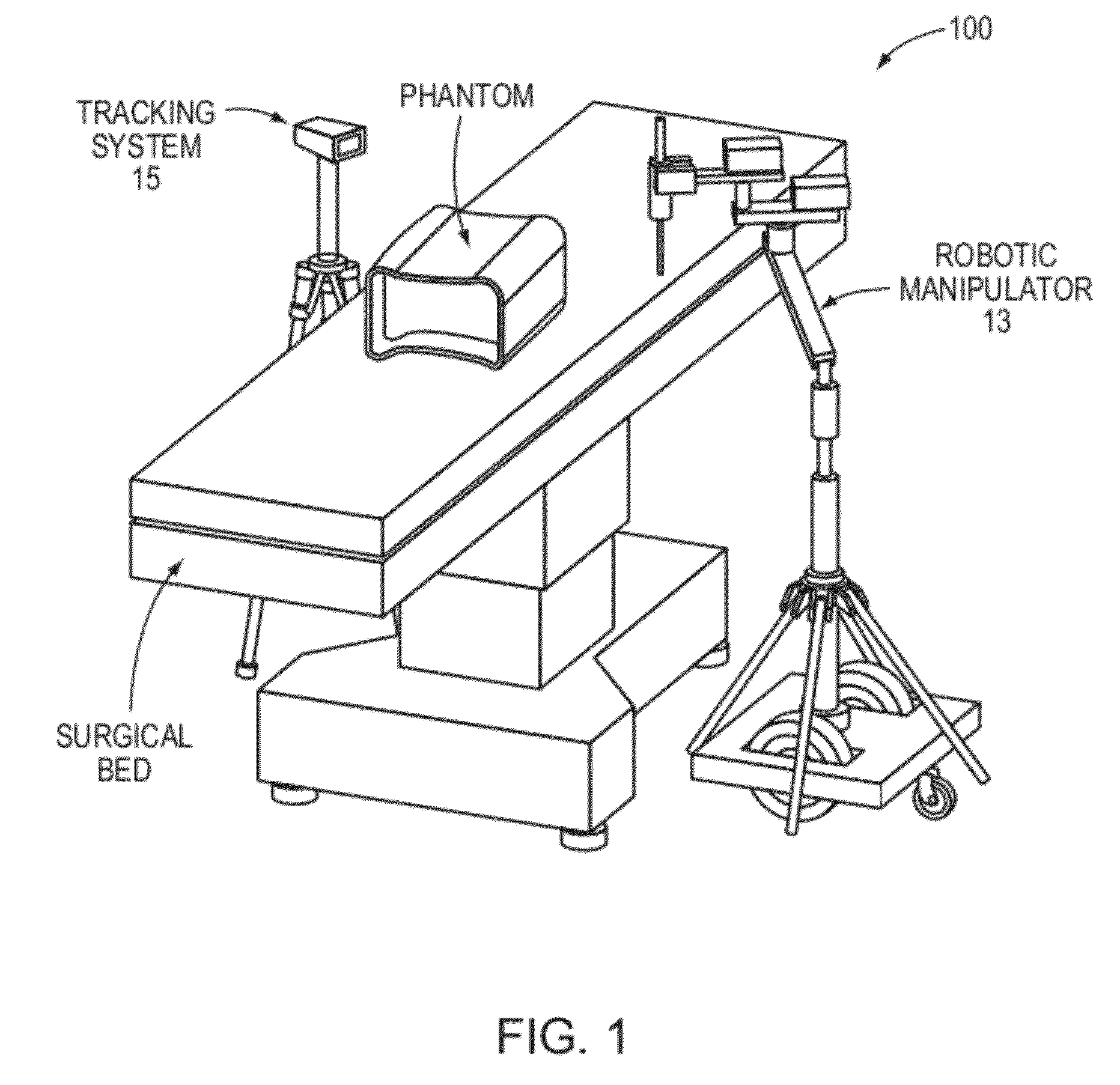
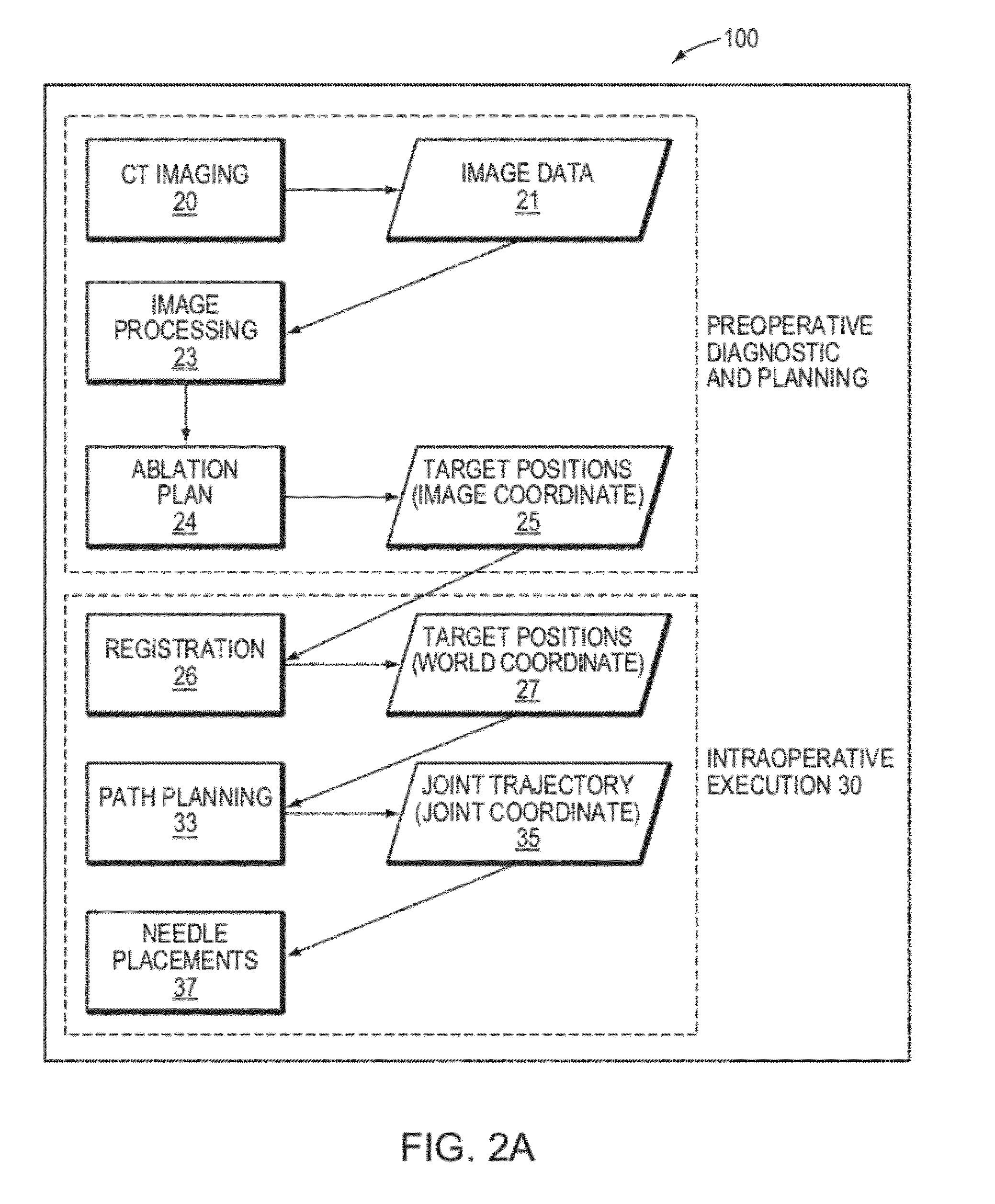
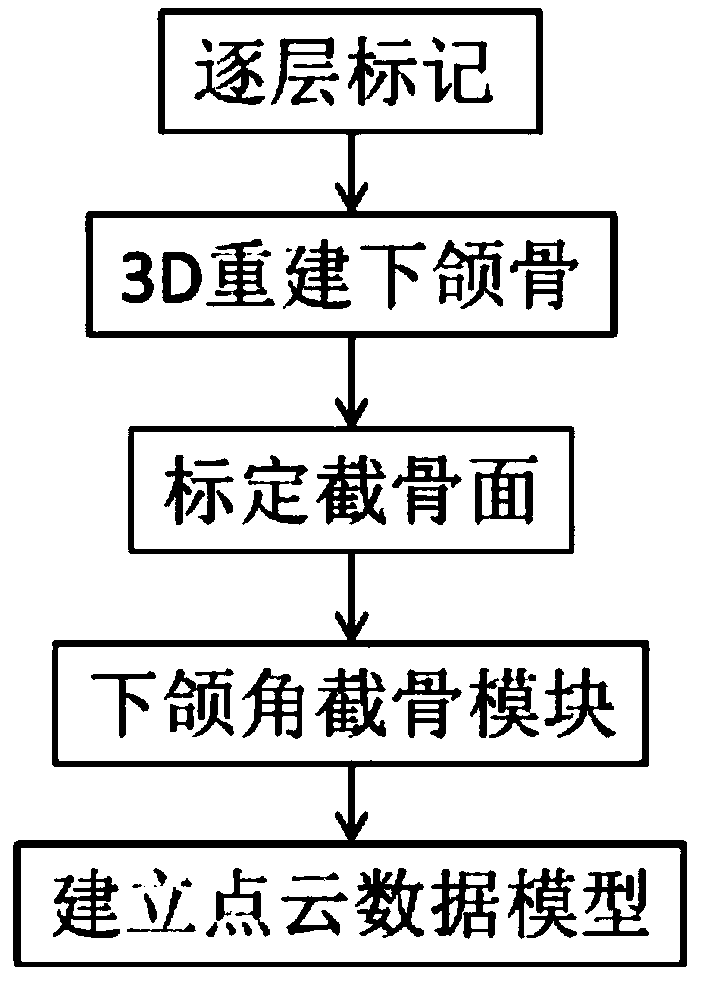
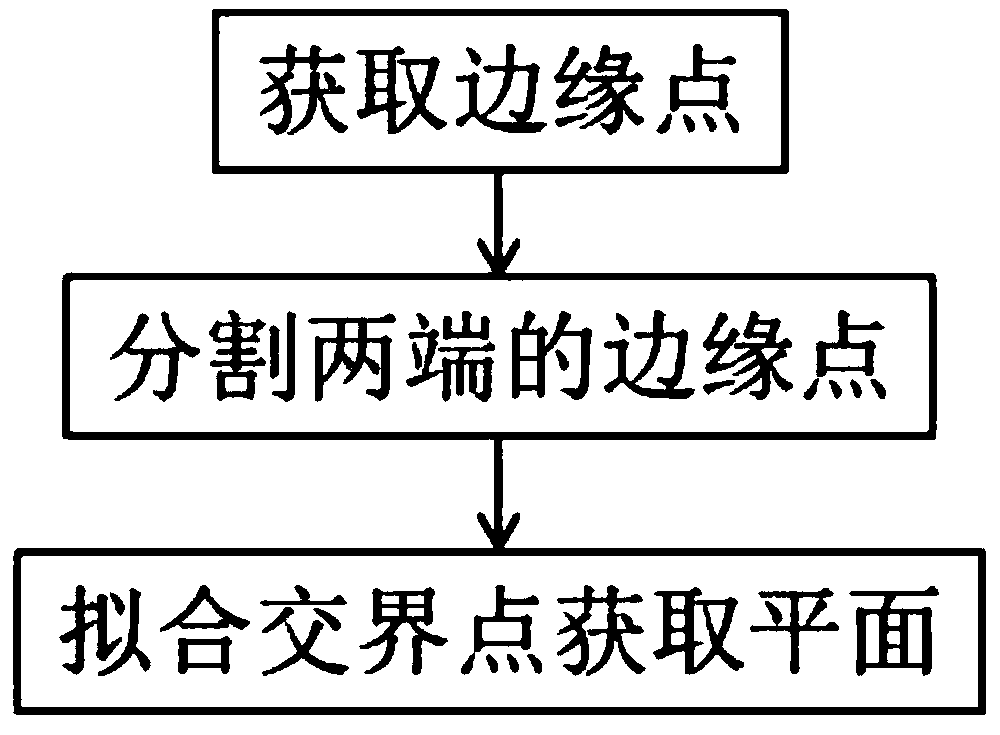
Transcutaneous robot-assisted ablation-device insertion navigation system
InactiveUS20120226145A1Easy to operateFacilitates potential expansionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesRadiofrequency ablationControl system design
A robotic system for overlapping radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in tumor treatment is disclosed. The robot assisted navigation system is formed of a robotic manipulator and a control system designed to execute preoperatively planned needle trajectories. Preoperative imaging and planning is followed by interoperative robot execution of the ablation treatment plan. The navigation system combines mechanical linkage sensory units with an optical registration system. There is no requirement for bulky hardware installation or computationally demanding software modules. Final position of the first needle placement is confirmed for validity with the plan and then is used as a reference for the subsequent needle insertions and ablations.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
System and method for association of a guiding aid with a patient tissue
A patient tissue includes a primary patient tissue area and an anatomically differentiated bordering secondary patient tissue area. An apparatus is at least partially customized responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. Means are provided for mating with the primary patient tissue area in a preselected relative orientation. Means are provided for fixing a first landmark to the primary patient tissue area in at least one of a predetermined marking location and a predetermined marking trajectory. Means are provided for fixing a second landmark to the secondary patient tissue area in at least one of a predetermined marking location and a predetermined marking trajectory. A method of associating a plurality of landmarks with a patient tissue is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
System and method for assisting with attachment of a stock implant to a patient tissue
ActiveUS20120109137A1Joint implantsComputer-aided planning/modellingProsthesisBiomedical engineering
A guide for assisting with attachment of a stock prosthetic implant to a patient tissue includes a lower guide surface configured to contact an upper implant surface of the stock prosthetic implant when a lower implant surface of the stock prosthetic implant contacts the patient tissue. An upper guide surface is accessible to a user when the lower guide surface is in contact with the upper implant surface. At least one guiding aperture extends through the guide body between the upper and lower guide surfaces at a predetermined aperture location with respect to the guide body and defines a predetermined target trajectory through the guide body. At least one of the target trajectory and the aperture location of each guiding aperture is preselected responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. A method of assisting with attachment of a stock prosthetic implant to a patient tissue is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Apparatus and method for providing a reference indication to a patient tissue
ActiveUS20120296339A1Joint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurface contourPreoperative imaging
An apparatus for providing a reference indication to a patient tissue includes a primary locating block having a patient-specific primary mating surface contoured for mating contact with a portion of the patient tissue in a predetermined primary mating orientation custom-configured responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. At least one mounting feature is provided to the primary locating block. At least one secondary item is configured for selective engagement with the primary locating block. The secondary item is at least one of a noncustomized secondary item and a patient-specific secondary item. The secondary item provides a reference indication to at least a portion of the patient tissue. The mounting feature of the primary locating block is configured for engagement with at least one secondary item in a predetermined secondary mounting relationship. The secondary mounting relationship is custom-configured for the patient tissue responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
System and method for assisting with arrangement of a stock instrument with respect to a patient tissue
A stock instrument includes at least one guide interacting feature. A lower instrument surface of the stock instrument is placed into contact with the patient tissue. A guide has a lower guide surface contoured to substantially mate with at least a portion of an upper instrument surface of the stock instrument. A predetermined instrument orientation upon the patient tissue is defined, which is preselected responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. The guide and instrument are mated in a predetermined relative guide / instrument orientation wherein at least one guide interacting feature of the instrument is placed into engagement with at least one instrument guiding feature of the guide. The guide is moved into a predetermined guide orientation with respect to the patient tissue and concurrently the instrument is moved into a predetermined instrument orientation with respect to the patient tissue.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Intraoperative tissue tracking method combined with preoperative image
InactiveCN101862205AReflect spatial relationshipUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryComputer visionEndoscope
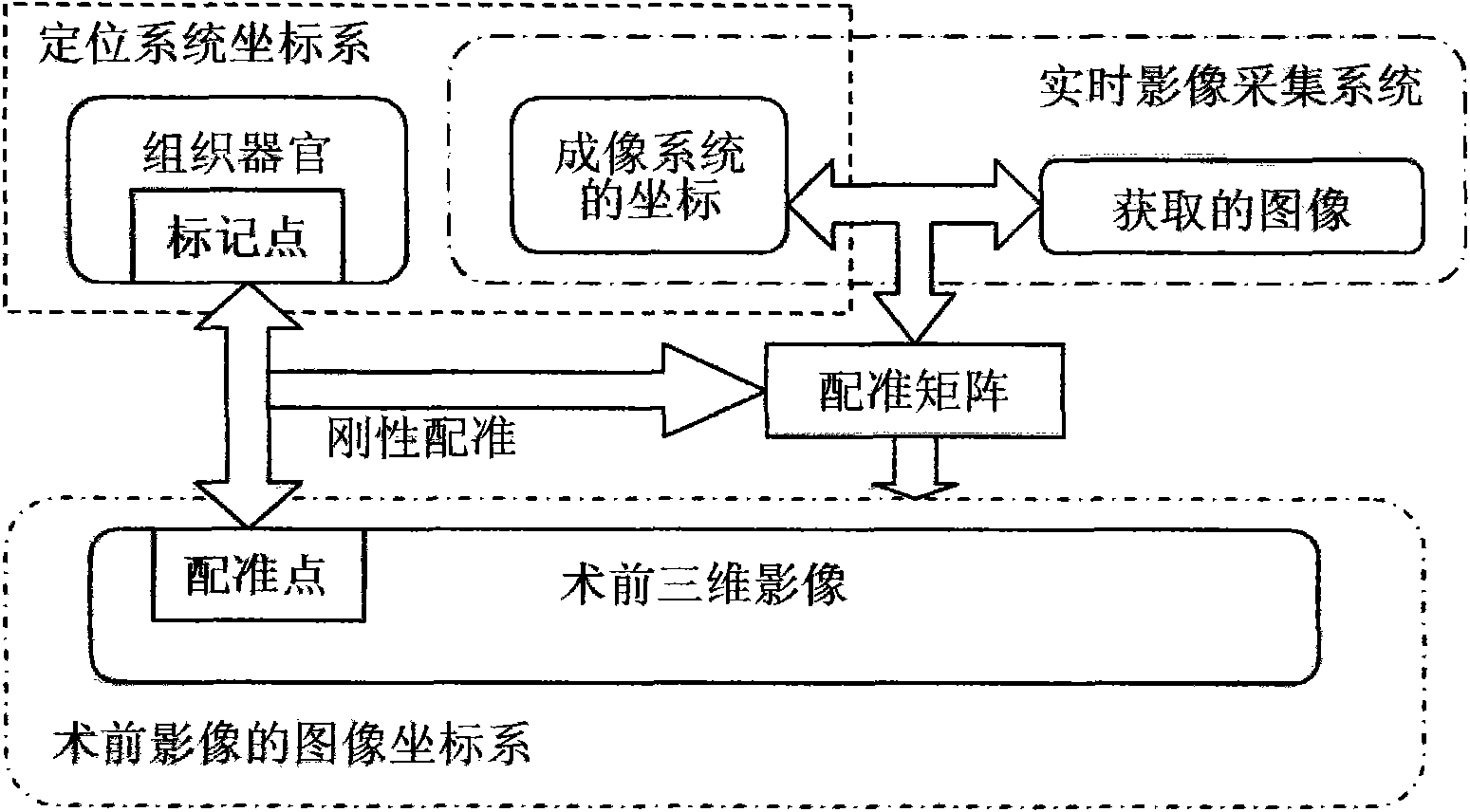
The invention provides an intraoperative tissue tracking method combined with a preoperative image, which comprises the following sequential steps: the first step: preoperative preparation, including the steps of acquiring a space position of a marking point in the preoperative image and calibration of equipment; and the second step: deformation tracking of an intraoperative tissue, including 1, coordinate system registration which is one of main parts of the invention; and 2. tissue deformation and fusion display which is also one of the main parts of the invention. By using intraoperative real-time two-dimensional ultrasound image and endoscope image and intraoperative electromagnetic or optical positioning system and using algorithm analysis and geometric registration calculation, a tissue structure of an intraoperative interest tissue can be reflected in the image.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Elastography imaging modalities for characterizing properties of tissue
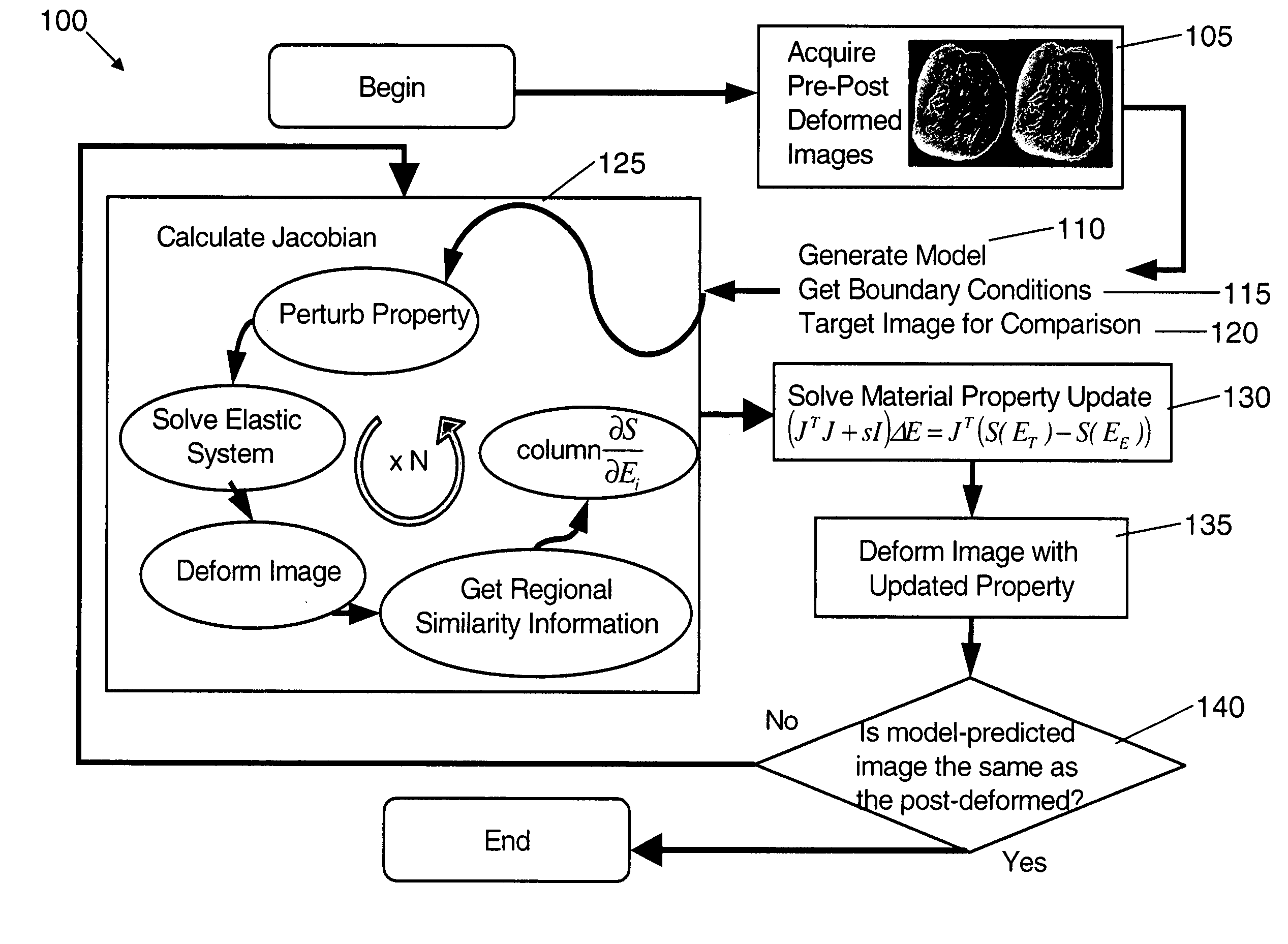
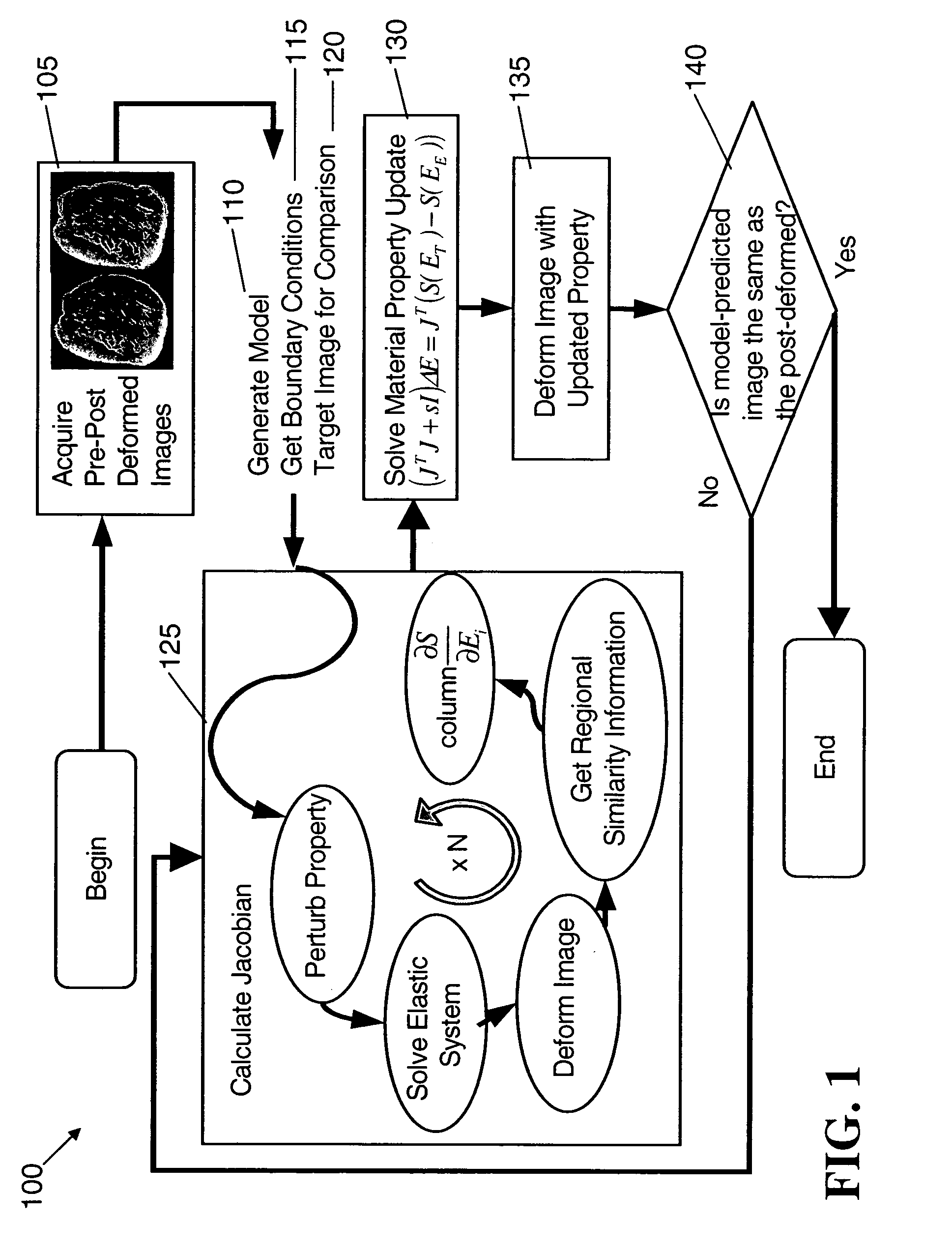
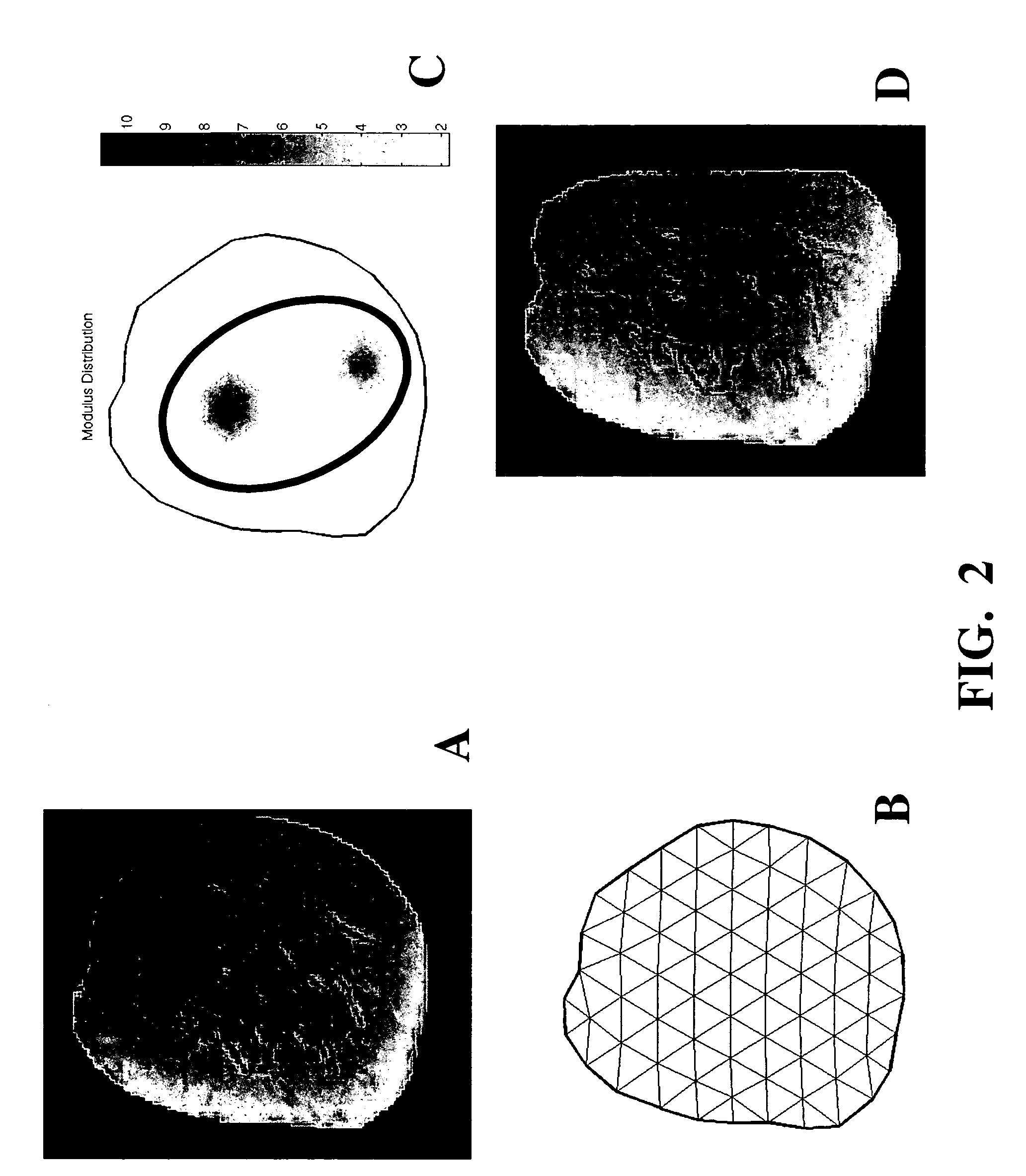
An image reconstruction algorithm begins with an initial acquisition of a preoperative imaging volume followed by a second imaging sequence subsequent to an applied deformation. A computational domain (model) is generated from the preoperative image series and boundary conditions are derived from a pre-post deformation comparison, as well as from information gathered from deformation source application (i.e., displacement and / or force). Using boundary conditions, a series of model-based image deformations is accomplished while varying model material properties. A calculation of a Jacobian matrix relating the change in regional mutual information is performed with respect to the change in material properties. Upon completion of this process, matrix regularization techniques are used to condition the system of equations and allow for inversion and subsequent delivery of model-property adjustments.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
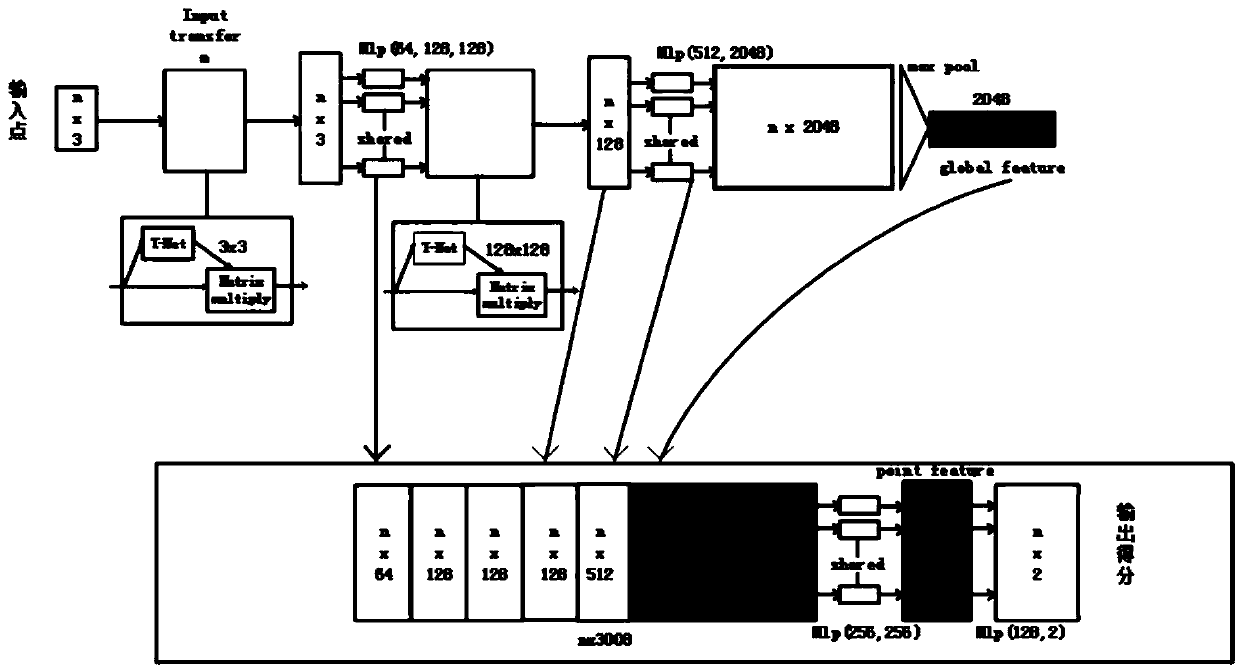
Cranio-maxillo-facial surgery robot auxiliary system adopting artificial intelligence technology
ActiveCN109567942ASurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingHuman bodyAnatomical structures
The invention relates to a cranio-maxillo-facial surgery robot auxiliary system adopting an artificial intelligence technology. The cranio-maxillo-facial surgery robot auxiliary system comprises a preoperative surgical program planning subsystem, an intraoperative navigation positioning subsystem and a robot control subsystem; the preoperative surgical program planning subsystem utilizes preoperative imaging data to design an osteotomy surgical program; the intraoperative navigation positioning subsystem conducts real-time obstacle avoidance on an anatomical structure and an instrument human body in a surgical area under assistance of a machine vision technology so as to automatically reach a designed navigation area; and the robot control subsystem optimizes a motion trajectory of a mechanical arm according to the obtained navigation area. According to the cranio-maxillo-facial surgery robot auxiliary system, the corresponding surgical osteotomy program can be generated before surgery, and an anatomical area and a working area which needing obstacle avoidance are identified in real time during the surgery.
Owner:南通罗伯特医疗科技有限公司
Virtual fiducial markers
Embodiments of the invention introduce the concept of a virtual fiducial marker (VFM). This marker will not be placed prior to preoperative imaging. It will therefore not initially appear in the preoperative 3D image. Instead, the marker will be virtually placed in the 3D data set prior to surgery, and as such the marker does not even need to be attached to the patient, if the patient is not expected to move during surgery. The idea behind such a VFM comes from the observation that there is a big variation in the difficulty of an image based registration depending on the quality of the images and their field of view. However, provided two initial registrations to high quality wide field of view images can be carried out, it then becomes possible to use these registrations to insert a virtual fiducial marker within the 3D preoperative image. Once inserted it may then be used to obtain a starting position for a registration procedure, and particularly to obtain in-plane translations. It may also be used at the end of a registration to provide a measure of registration accuracy, to verify the registration and detect mis-registrations.
Owner:CYDAR LTD
Orthopedic navigation positioning system and method
InactiveCN112603538AMaximum operating precisionTraumaSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modelling3d imageMachine
The invention discloses an orthopaedic navigation and positioning system and method, and the system comprises a mechanical arm which is provided with an actuator and a tracer at the tail end; a precision verification device which is used for cooperating with the C-arm machine and the optical tracker to verify and optimize the navigation precision of the system; an optical tracker which is used for collecting the position of the tracer on each device and obtaining the position information of the corresponding device; a C-arm machine which is used for scanning to generate a preoperative 3D image and registering the preoperative 3D image with the intraoperative 2D perspective image; and an upper computer which is used for planning a path according to the preoperative 3D image, controlling the mechanical arm to move to a target position after the preoperative 3D image is registered with the intraoperative 2D perspective image, and carrying out an operation. By means of precise positioning, the operation precision of a person and a mechanical arm can be maximized, wounds of a patient are reduced, meanwhile, the operation process can be accelerated, and radiation borne by doctors and the patient is reduced.
Owner:NANJING TUODAO MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Guide for assisting with arrangement of a stock instrument with respect to a patient tissue
A stock instrument includes at least one guide interacting feature. A lower instrument surface of the stock instrument is placed into contact with the patient tissue. A guide has a lower guide surface contoured to substantially mate with at least a portion of an upper instrument surface of the stock instrument. A predetermined instrument orientation upon the patient tissue is defined, which is preselected responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. The guide and instrument are mated in a predetermined relative guide / instrument orientation wherein at least one guide interacting feature of the instrument is placed into engagement with at least one instrument guiding feature of the guide. The guide is moved into a predetermined guide orientation with respect to the patient tissue and concurrently the instrument is moved into a predetermined instrument orientation with respect to the patient tissue.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Cancer prognosis model construction method combining global weighted LBP and texture analysis
ActiveCN111340770AHighlight tumor featuresThe build result is validMedical simulationImage enhancementComputed tomographyImaging data
The invention discloses a cancer prognosis model construction method combining global weighted LBP (Local Binary Pattern) and texture analysis. The cancer prognosis model construction method comprisesthe following steps: acquiring original preoperative CT (Computed Tomography) image data of a cancer patient, marks of focus parts and survival data; calculating a three-dimensional global weighted LBP for the original CT data, and reconstructing new image data, namely global weighted LBP data; for the obtained global weighted LBP data, using GLSZM texture analysis to extract texture features. Texture analysis characteristics extracted by the method provided by the invention highlight tumor characteristics of a patient, and a prognosis model construction result is more effective; GLSZM is used for representing texture features, the effects in the aspects of texture consistency, rotation invariance and aperiodicity are remarkable, and the method has better performance than a co-occurrencematrix and a travel matrix in the aspect of cell nucleus and CT image texture.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
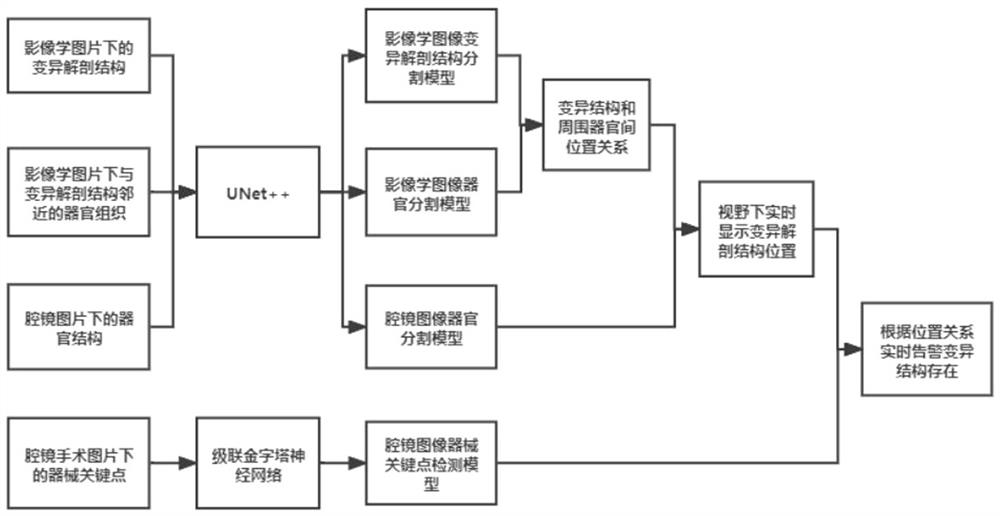
Anatomical variation recognition prompting method and system based on artificial intelligence
ActiveCN114299072AAvoid variant structural damageAvoid bad consequencesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesImage analysisSurgical operationAnatomical structures
The invention relates to an artificial intelligence-based anatomical variation recognition prompting method and system, and the method comprises the steps: collecting an endoscope image in real time, and obtaining real-time organ segmentation data and instrument key point data according to an endoscope organ segmentation model and an instrument key point detection model; acquiring a position relationship between the variation structure and the surrounding organs by analyzing the preoperative iconography image, extracting the tissue segmentation data of the surrounding organs of the variation structure of the iconography image for comparison, and judging the position of the variation structure; detecting the position information of the key points of the instrument and the variation structure in real time, prompting the variation anatomical structure area when the instrument operates in the variation anatomical structure area, and operating according to the prompt. According to the method, by establishing the corresponding relation between the imaging examination and the endoscopic surgery visual field, the vein pipeline structure of the key operation in the surgery is accurately and effectively positioned, and important conditions are provided for more accurate operation of the surgical operation.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV +1
System and method for association of a guiding aid with a patient tissue
A patient tissue includes a primary patient tissue area and an anatomically differentiated bordering secondary patient tissue area. An apparatus is at least partially customized responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. Means are provided for mating with the primary patient tissue area in a preselected relative orientation. Means are provided for fixing a first landmark to the primary patient tissue area in at least one of a predetermined marking location and a predetermined marking trajectory. Means are provided for fixing a second landmark to the secondary patient tissue area in at least one of a predetermined marking location and a predetermined marking trajectory. A method of associating a plurality of landmarks with a patient tissue is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Apparatus and method for providing a reference indication to a patient tissue
An apparatus for providing a reference indication to a patient tissue includes a primary locating block having a patient-specific primary mating surface contoured for mating contact with a portion of the patient tissue in a predetermined primary mating orientation custom-configured responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. At least one mounting feature is provided to the primary locating block. At least one secondary item is configured for selective engagement with the primary locating block. The secondary item is at least one of a noncustomized secondary item and a patient-specific secondary item. The secondary item provides a reference indication to at least a portion of the patient tissue. The mounting feature of the primary locating block is configured for engagement with at least one secondary item in a predetermined secondary mounting relationship. The secondary mounting relationship is custom-configured for the patient tissue responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
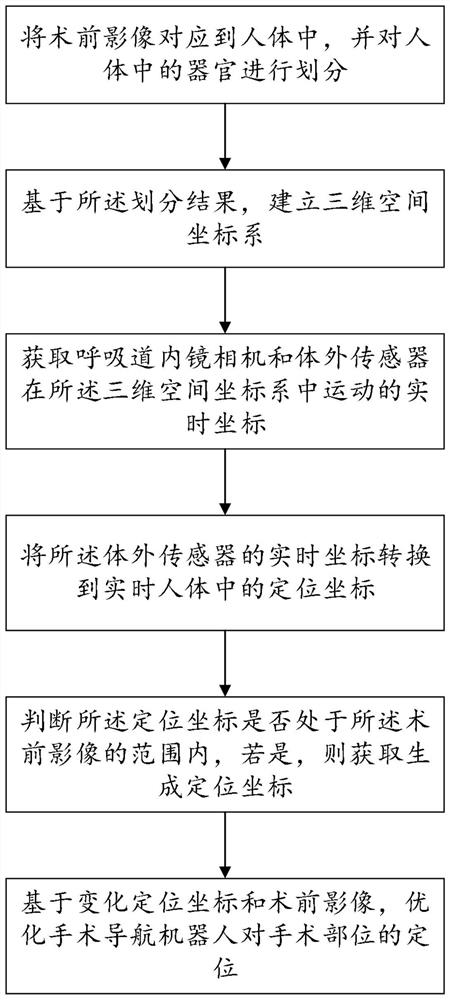
Positioning method and device for minimally invasive surgery navigation robot
ActiveCN111887988AAccurate locationConvenient treatmentSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsHuman bodyRectangular coordinates
The invention relates to a positioning method and device for a minimally invasive surgery navigation robot. The positioning method comprises following steps: a preoperative image is mapped to a real-time human body, and organs in the real-time human body are divided; a three-dimensional space rectangular coordinate system is established on the basis of the dividing result; real-time movement coordinates of a respiratory tract endoscope camera and an in-vitro sensor in the three-dimensional space rectangular coordinate system are acquired; the real-time coordinates of the in-vitro sensor are converted into positioning coordinates of the real-time human body; whether the positioning coordinates are located in the range of the preoperative image or not is judged, and if yes, variable positioning coordinates are generated; and on the basis of the variable positioning coordinates and the preoperative image, the positioning of the surgery navigation robot for a surgical site is optimized. By means of mutual binding process of the preoperative image, the in-vitro sensor and the respiratory tract endoscope camera, the preoperative image is enabled to accurately correspond to the real-timehuman body.
Owner:罗雄彪 +2
Puncture positioning method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113610826AReduce the number of image capturesAvoid multiple exposuresImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a puncture positioning method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps that: a preoperative image is obtained according to an intra-operative image, wherein the intra-operative image is composed of a part of the preoperative image; based on a puncture needle in a coordinate system of navigation equipment, a simulation puncture needle is generated in a coordinate system of the preoperative image, wherein the coordinate system of the preoperative image is the same as the coordinate system of the intraoperative image; and the simulation puncture needle located in the coordinate system of the intraoperative image is sent to front-end equipment, so that the front-end equipment can conveniently position the simulation puncture needle, the number of times of image shooting on a patient in the operation can be reduced, and multiple times of radiation on the patient is avoided.
Owner:武汉推想医疗科技有限公司 +1
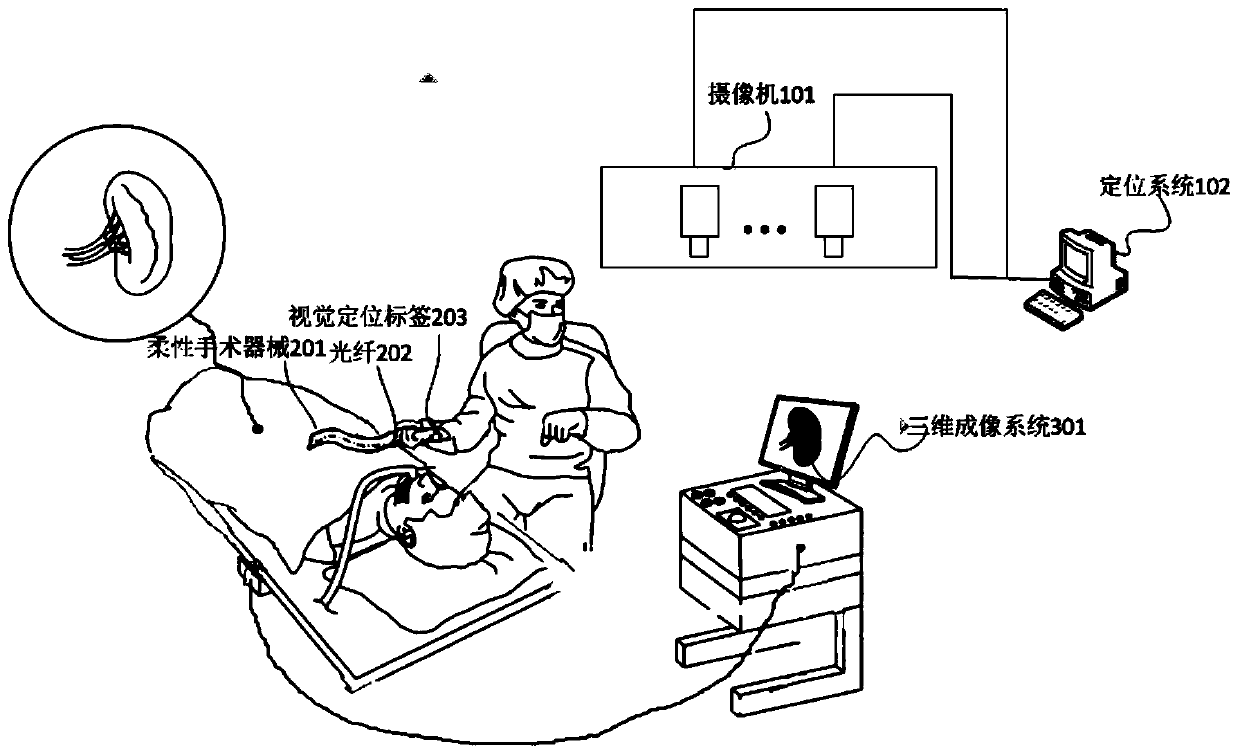
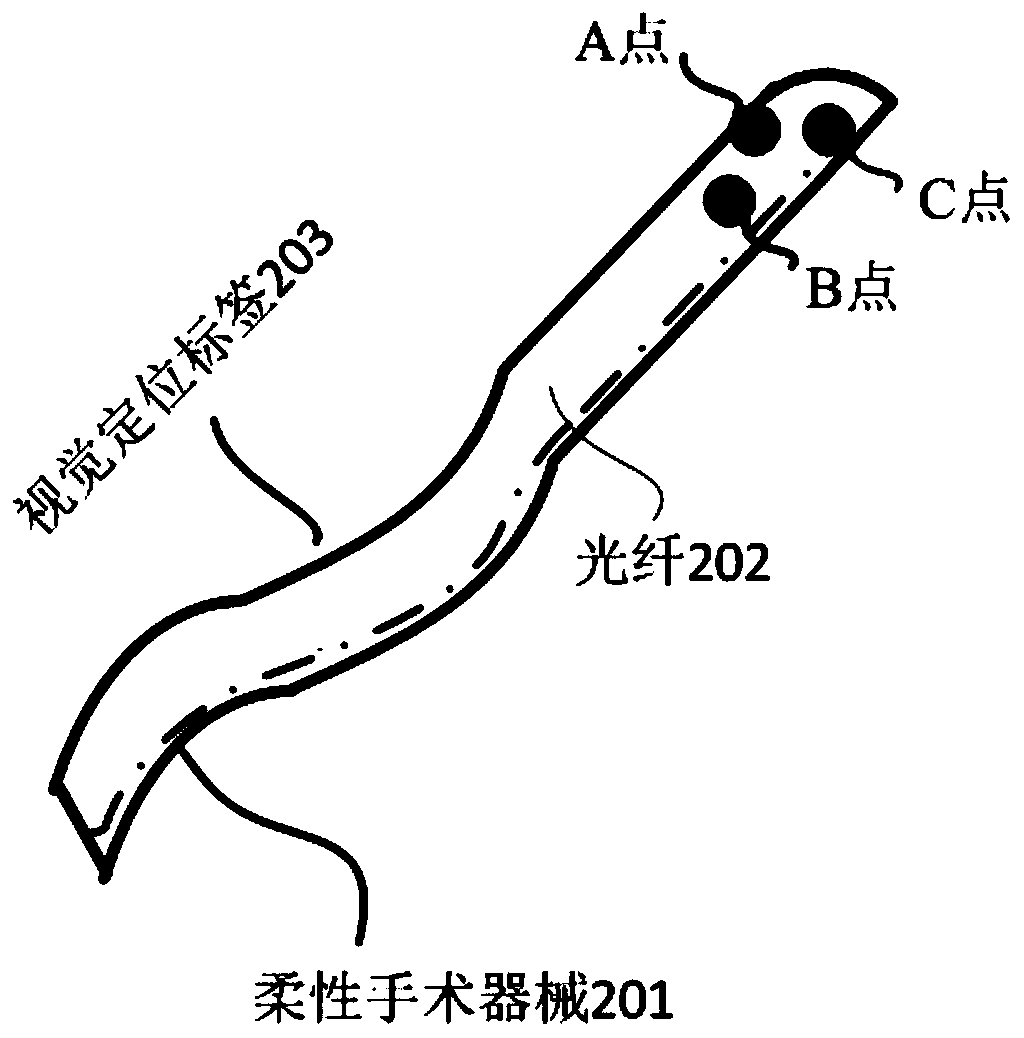
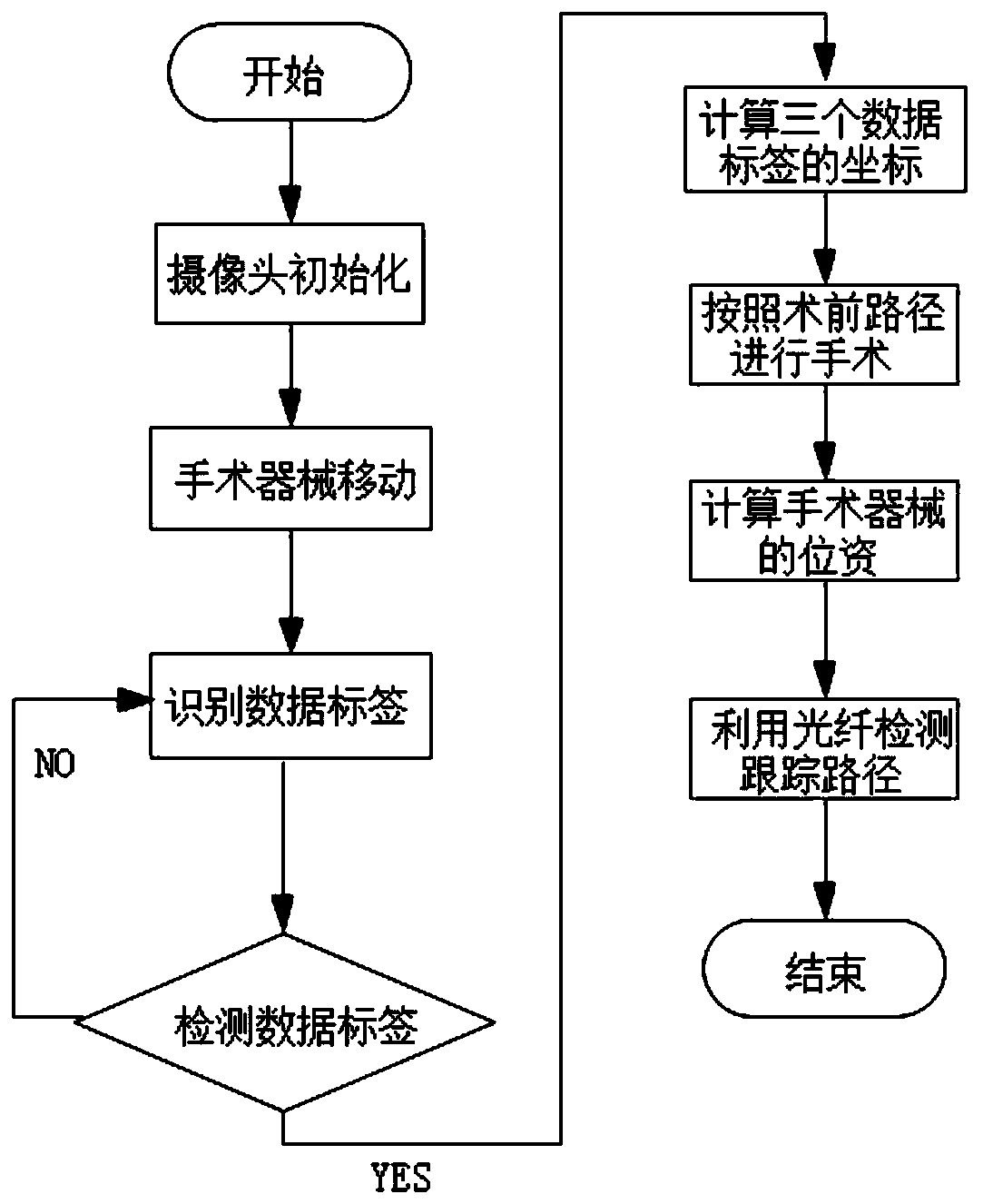
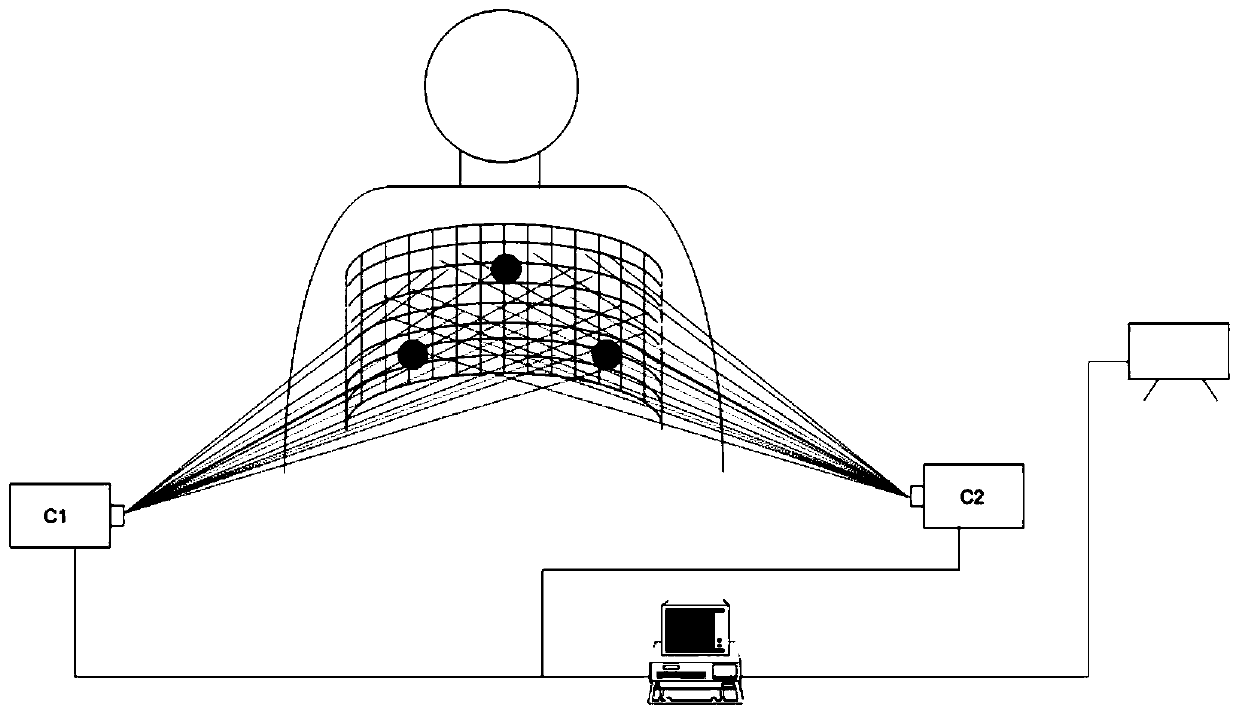
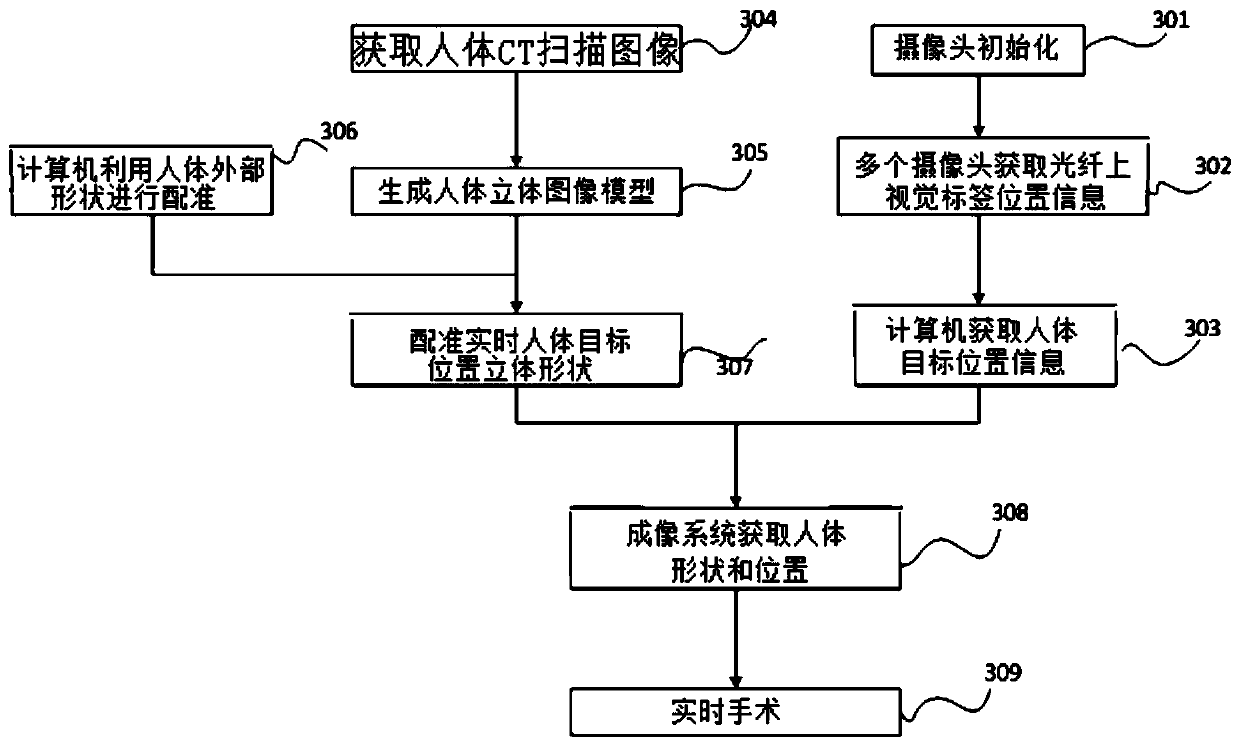
Surgical navigation method based on optical fiber shape sensing
The invention relates to a surgical navigation method based on optical fiber shape sensing. A stereoscopic vision label is installed at the outer tail end of a flexible surgical instrument body of theinner auxiliary optical fiber, the position and posture of the outer tail end of the flexible surgical instrument body are measured through a binocular camera or a multi-view camera, and meanwhile the overall shape of the flexible surgical instrument body is measured through the optical fiber. Then, a positioning system calculates the spatial position and posture of the inner tail end of the flexible surgical instrument body in combination with the position and posture of the outer tail end of the flexible surgical instrument body and the overall shape. A three-dimensional imaging system displays a three-dimensional visual virtual human body on a computer by using a preoperative image; the real posture of the flexible surgical instrument body entering the human body is obtained by combining the position and posture of the flexible surgical instrument, and a surgeon observes the specific position and posture of the flexible surgical instrument through a display screen and operates theflexible surgical instrument to perform an operation, thereby navigating the surgeon in real time during the operation. The method has the advantages of high precision, high reliability and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for association of a guiding aid with a patient tissue
A patient tissue includes a primary patient tissue area and an anatomically differentiated bordering secondary patient tissue area. An apparatus is at least partially customized responsive to preoperative imaging of the patient tissue. Means are provided for mating with the primary patient tissue area in a preselected relative orientation. Means are provided for fixing a first landmark to the primary patient tissue area in at least one of a predetermined marking location and a predetermined marking trajectory. Means are provided for fixing a second landmark to the secondary patient tissue area in at least one of a predetermined marking location and a predetermined marking trajectory. A method of associating a plurality of landmarks with a patient tissue is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Mouth prop facilitating oral cavity observation
PendingCN112043228AAdjust the size of the openingAdjust the size of the stretchComputerised tomographsSomatoscopeOral cavity observationPre-operative evaluation
The invention discloses a mouth prop facilitating oral cavity observation, and belongs to the field of medical instruments. According to the technical scheme, the mouth prop utilizes a length-adjustable telescopic part and an angle-adjustable connecting rod part, so that the length and the width of the mouth prop, namely the opening size, can be conveniently adjusted, the applicability is good, lip and cheek soft tissues can be effectively separated, the boundary of gingiva and mucous membrane tissues can be clearly displayed on a CT or cone beam CT image, the thickness of gingiva and mucous membrane tissues can be measured, information provided by preoperative images is increased, preoperative evaluation and treatment of doctors are facilitated, a tongue fixing frame is detachably mountedinside, tongue soft tissues can be effectively separated, and soft tissue mucous membranes in the oral cavity can be effectively observed. The telescopic part adopts two different structures, the opening size of the mouth prop can be conveniently adjusted, and the mouth prop is simple in structure and convenient and fast to use.
Owner:胡慧
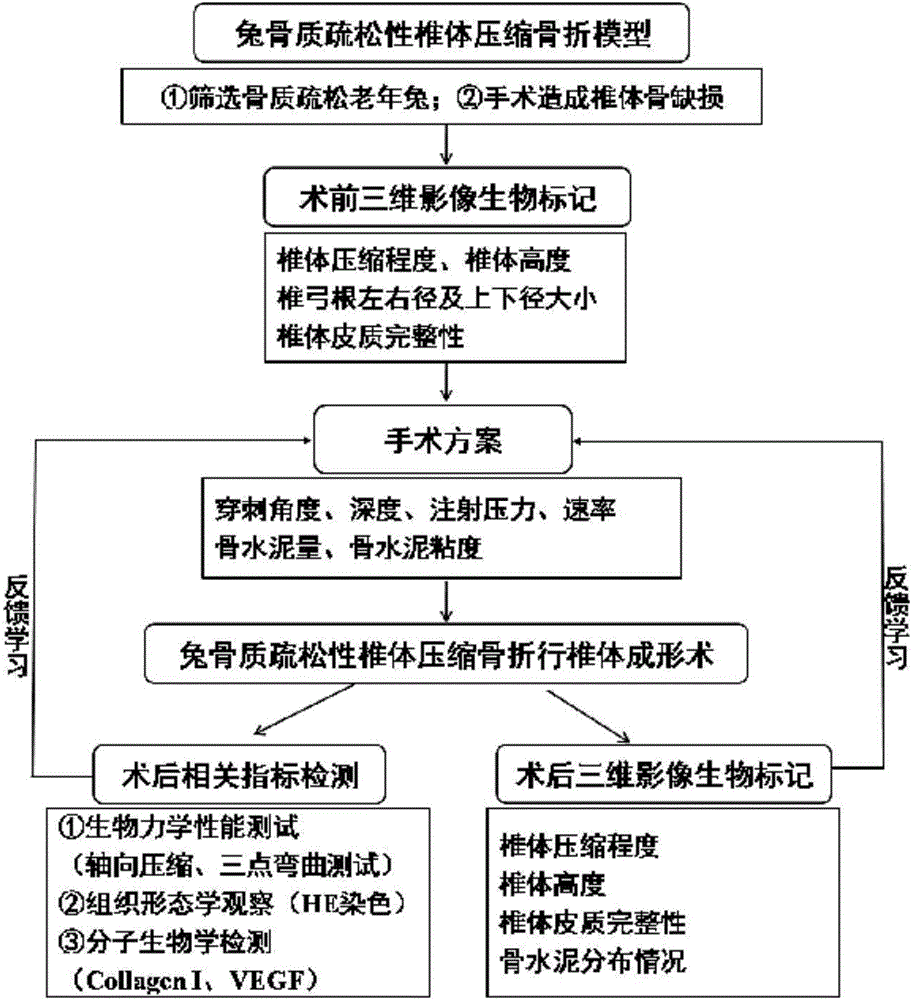
Imaging biomarker for guiding percutaneous vertebroplasty and application of imaging biomarker for guiding percutaneous vertebroplasty
InactiveCN106420051AReduce exposureReduce serious complicationsMedical imagingComputerised tomographsVertebral heightImaging biomarker
The invention relates to a marker in medicine and application of the marker, in particular to an imaging biomarker for guiding percutaneous vertebroplasty and application of the imaging biomarker for guiding percutaneous vertebroplasty. The imaging biomarker comprises a preoperative imaging biomarker and a postoperative imaging biomarker, wherein the preoperative imaging biomarker involves vertebral compression degree, a vertebral height, a vertebral pedicle transversal diameter, a vertebral pedicle vertical diameter and vertebral cortex integrity, and the postoperative imaging biomarker involves vertebral compression degree, a vertebral height, vertebral cortex integrity and bone cement distribution conditions. The imaging biomarker provides quantitative bases for operation plans and lays a firm foundation for precise standardized vertebroplasty plans.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
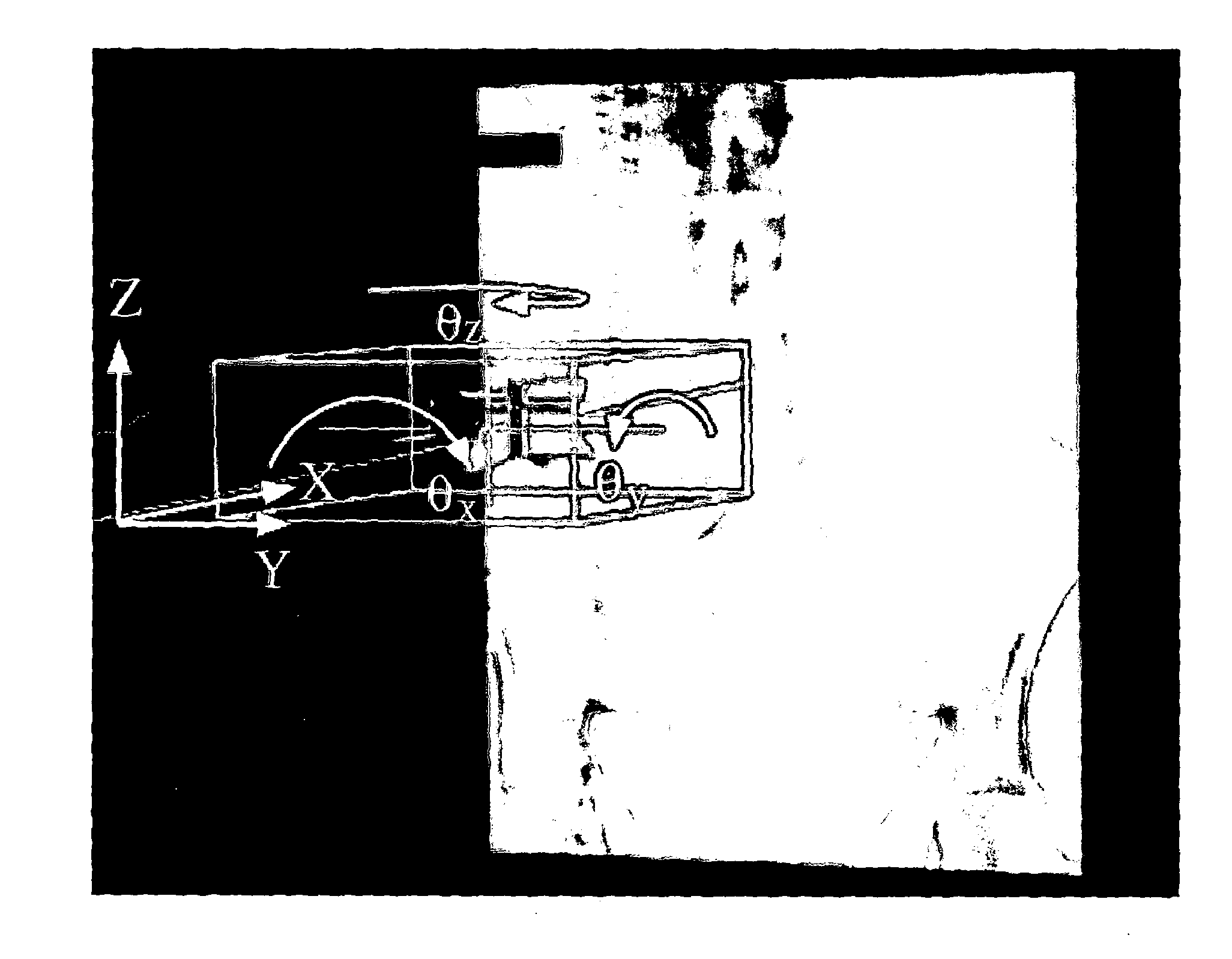
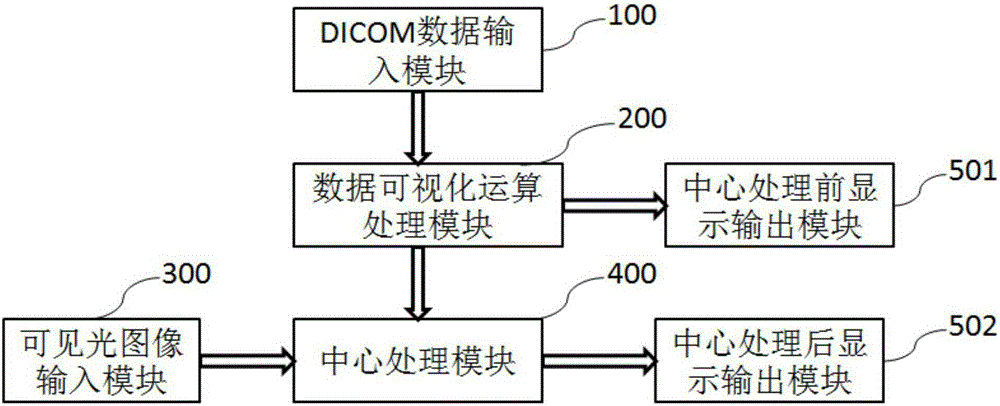
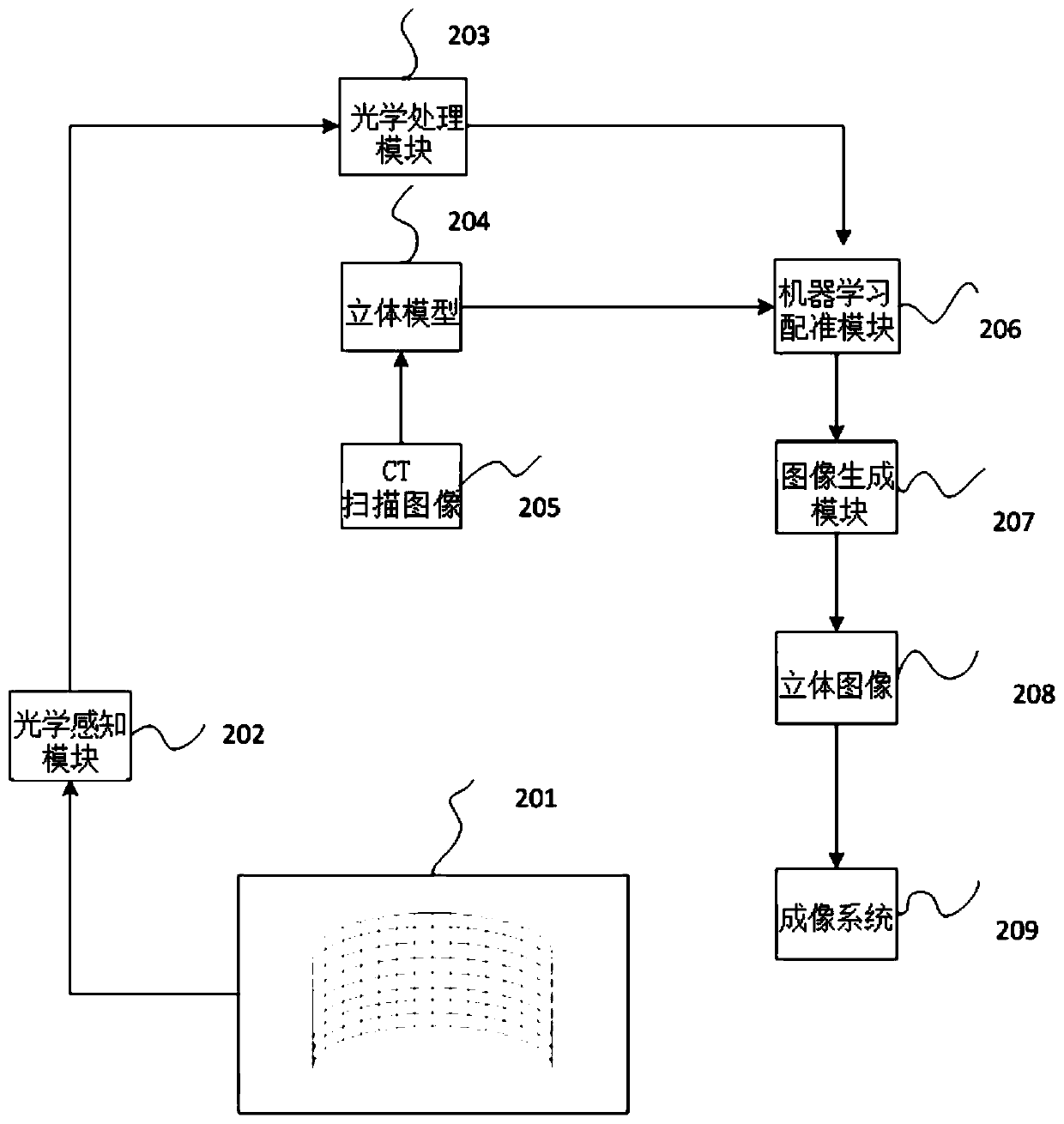
Operative positioning system
ActiveCN105213032ALower requirementMandatory useDiagnosticsSurgeryAnatomical structuresDigital imaging
The invention discloses an operative positioning system. The operative positioning system completes positioning through direct comparison between real-time visible light images and non-real-time imageology images. The operative positioning system comprises a DICOM (digital imaging and communications in medicine) data input module, a data visualization operation processing module, a visible light image input module, a central processing module and an image display output module. The operative positioning system has the advantages that on the basis of imageology data, a preoperative 3D (three-dimensional) non-real-time image model is generated and then is fused with an intra-operative real-time camera image, so that requirements on intra-operative equipment can be lowered, for example, special laparoscopy ultrasonic equipment or endoscope ultrasonic equipment is unneeded, and only routine preoperative imaging results need to be used; according to the method, theoretically, a 100% lesion part can be displayed on the 3D model surely, and a camera only needs to focus on corresponding positions of operative instruments and symbolic anatomical structures on a 3D map.
Owner:BEIJING YIQIANCHUANG TECH CO LTD
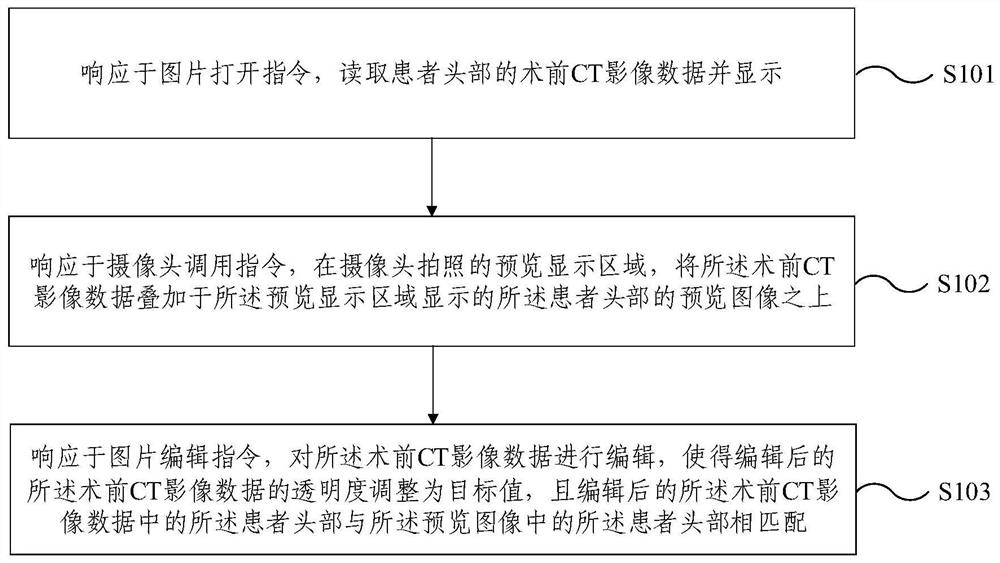
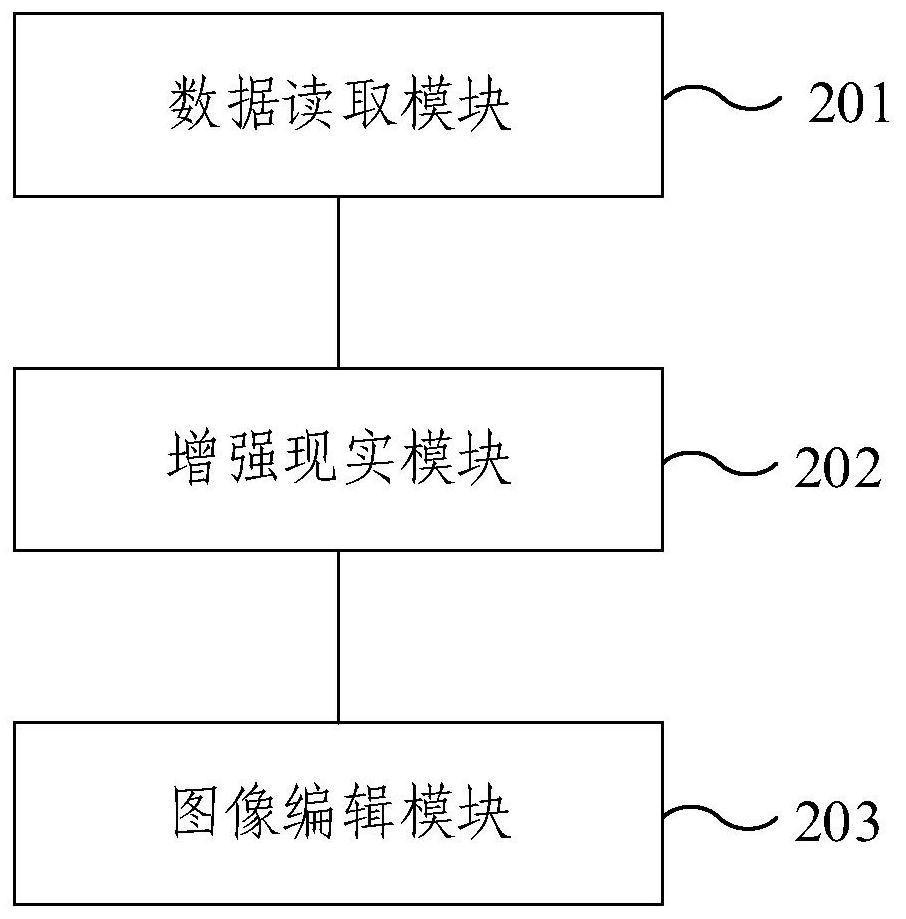
Positioning assisting method and device for intracranial hematoma operation
ActiveCN111789675AEasy to operateLow costComputer-aided planning/modellingBone drill guidesPositioning aidsComputer vision
An embodiment of the invention provides a positioning assisting method and device for intracranial hematoma operation. The method comprises the following steps: in response to a picture opening instruction, reading and displaying preoperative CT image data of the head of a patient; in response to a camera call instruction, superimposing the preoperative CT image data on a preview image, displayedby a preview display area, of the head of the patient in the preview display area shot by a camera; and in response to a picture editing instruction, editing the preoperative CT image data so that thetransparency of the edited preoperative CT image data is adjusted to a target value, and the head of the patient in the edited preoperative CT image data is matched with the head of the patient in the preview image. According to the positioning assisting method and device for intracranial hematoma operation provided by the embodiment of the invention, enhanced display is performed by superimposing and aligning the preoperative CT image data on the preview image of the head of the patient, preoperative body surface marking can be assisted, and the positioning assisting method and device are simpler to operate, lower in cost and wider in appliance range.
Owner:BEIJING TIANTAN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV +1
Virtual fiducial markers
Embodiments of the invention introduce the concept of a virtual fiducial marker (VFM). This marker will not be placed prior to preoperative imaging. It will therefore not initially appear in the preoperative 3D image. Instead, the marker will be virtually placed in the 3D data set prior to surgery, and as such the marker does not even need to be attached to the patient, if the patient is not expected to move during surgery. The idea behind such a VFM comes from the observation that there is a big variation in the difficulty of an image based registration depending on the quality of the images and their field of view. However, provided two initial registrations to high quality wide field of view images can be carried out, it then becomes possible to use these registrations to insert a virtual fiducial marker within the 3D preoperative image. Once inserted it may then be used to obtain a starting position for a registration procedure, and particularly to obtain in-plane translations. It may also be used at the end of a registration to provide a measure of registration accuracy, to verify the registration and detect mis-registrations.
Owner:CYDAR LTD
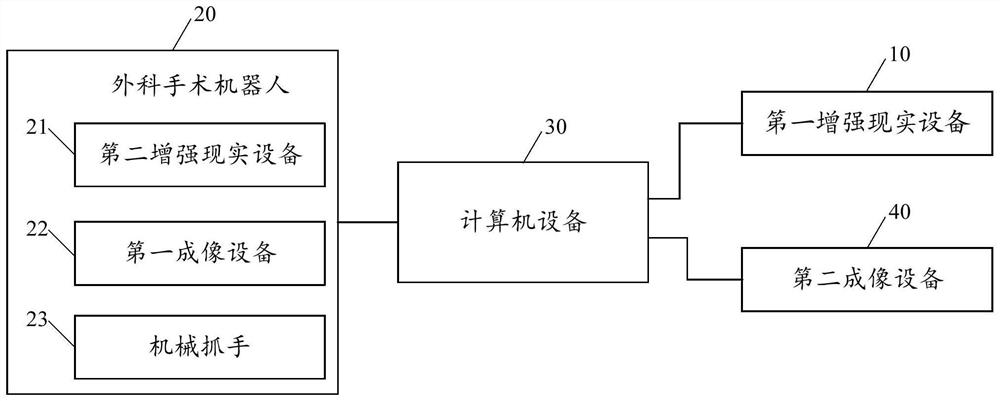
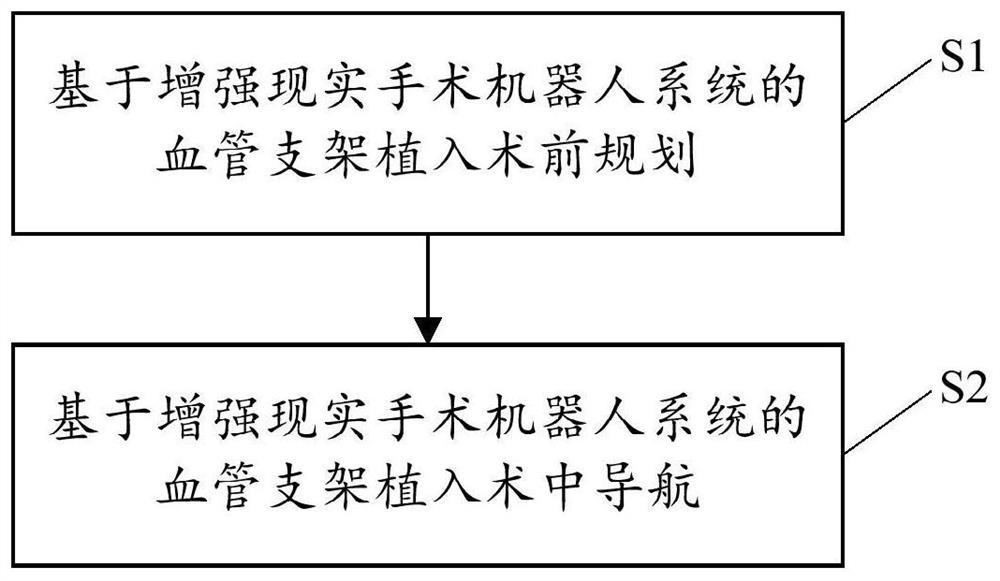
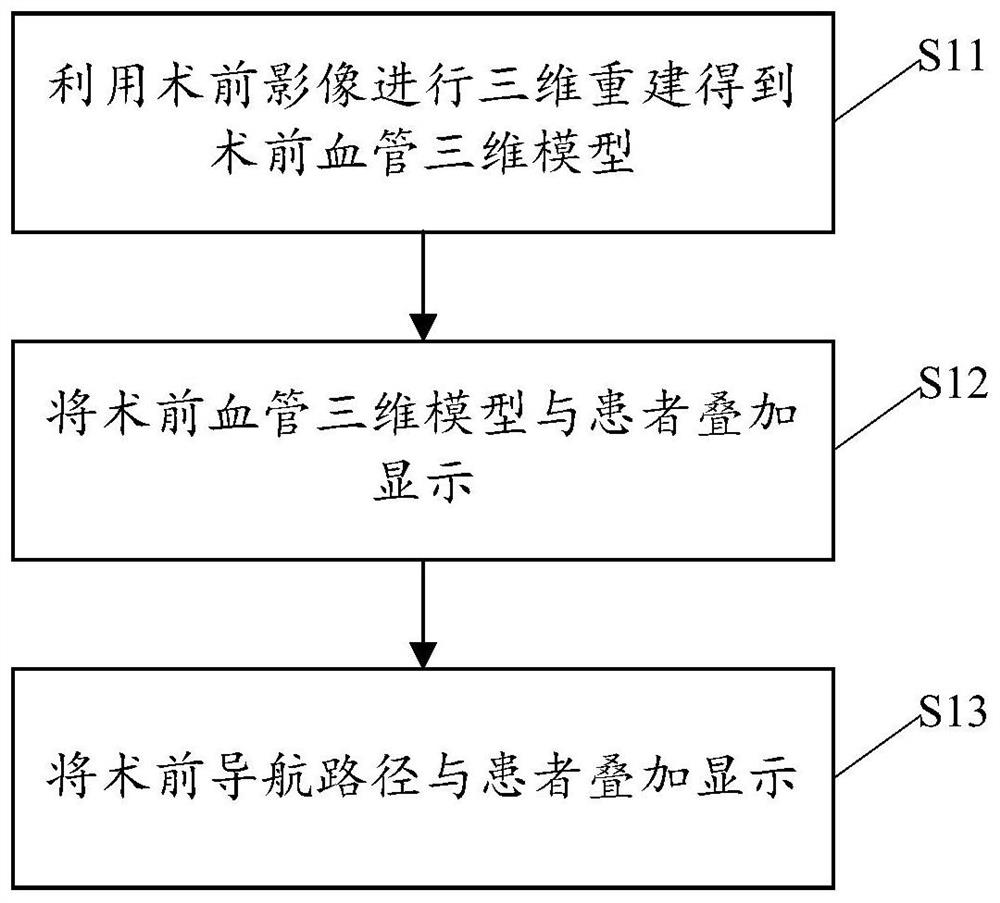
Augmented reality surgical robot system and augmented reality equipment
ActiveCN113317877AEasy to assistImprove the success rate of surgerySurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingSimulationTarget tissue
The invention provides an augmented reality surgical robot system and augmented reality equipment. The augmented reality surgical robot system comprises first augmented reality equipment and a surgical robot, wherein the surgical robot comprises second augmented reality equipment. The first augmented reality equipment is in communication connection with the second augmented reality equipment, a first virtual three-dimensional model of a target tissue of an entity object is established according to a preoperative image before an implantation operation is carried out, and the second augmented reality equipment obtains the first virtual three-dimensional model; the first virtual three-dimensional model is superposed and registered on the entity object by using an augmented reality technology, so that a doctor wearing the first augmented reality equipment can visually see the effect of superposing the first virtual three-dimensional model of the entity object on the entity object, and the doctor can be well assisted in performing surgical operation; and the operation success rate is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT PROPHECY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method and system for realizing surgical navigation by using real-time structured light technology
InactiveCN113229937AReduce one space conversionReduce mistakesSurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceEngineeringComputer-aided
The invention relates to a surgical navigation method and system, in particular to a method and a system for realizing surgical navigation by using a real-time structured light technology. According to the method, real-time structured light is used for scanning a structured light coverage area of an operation area in real time to obtain three-dimensional point cloud data, and then registration is carried out through unmarked registration and preoperative images; meanwhile, the surgical instrument in the space is recognized through structured light, then the surgical instrument in the space is positioned, real-time 3D point cloud reconstruction and preoperative image superposition are synchronously carried out, and finally the purpose of precise navigation surgery is achieved. The invention further provides the system for implementing the method. The system comprises a DICOM module, a preoperative planning module, a three-dimensional scanning module, an unmarked registration module, a display module, a computer aided design (CAD) module and a computer vision enhancement module. According to the method and the system, the space relation between the focus and the operation instrument can be directly obtained, one-time space conversion is reduced, errors are reduced, and accurate positioning is achieved.
Owner:李珍珠
Surgical registration system using shape sensing optical fiber grids
PendingCN111329587AAccurate operationImprove anti-interference abilitySurgical navigation systemsUsing optical meansSurgical operationHuman body
The invention relates to a surgical registration system using shape sensing optical fiber grids. Due to different postures, pulse beating and spontaneous breathing movements, the actual shape of a target organ of a patient during surgery can be inconsistent with a shape obtained by preoperative image measurement, a surgical navigation system needs to register the preoperative image with a real human body in real time, and performs surgical operation based on the registered image, and human body surface shape information is an important source of information for registration. The system uses shape sensing optical fibers to weave a mesh surface, and the mesh surface is attached to the surface of a human body for real-time shape measurement of the human body surface; and the obtained result is input into a registration system of a surgical navigation device, and a computer generates a real-time stereoscopic image of the human body according to a CT scan image obtained by preoperative human body scanning to guide a doctor to perform more accurate surgical operation.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
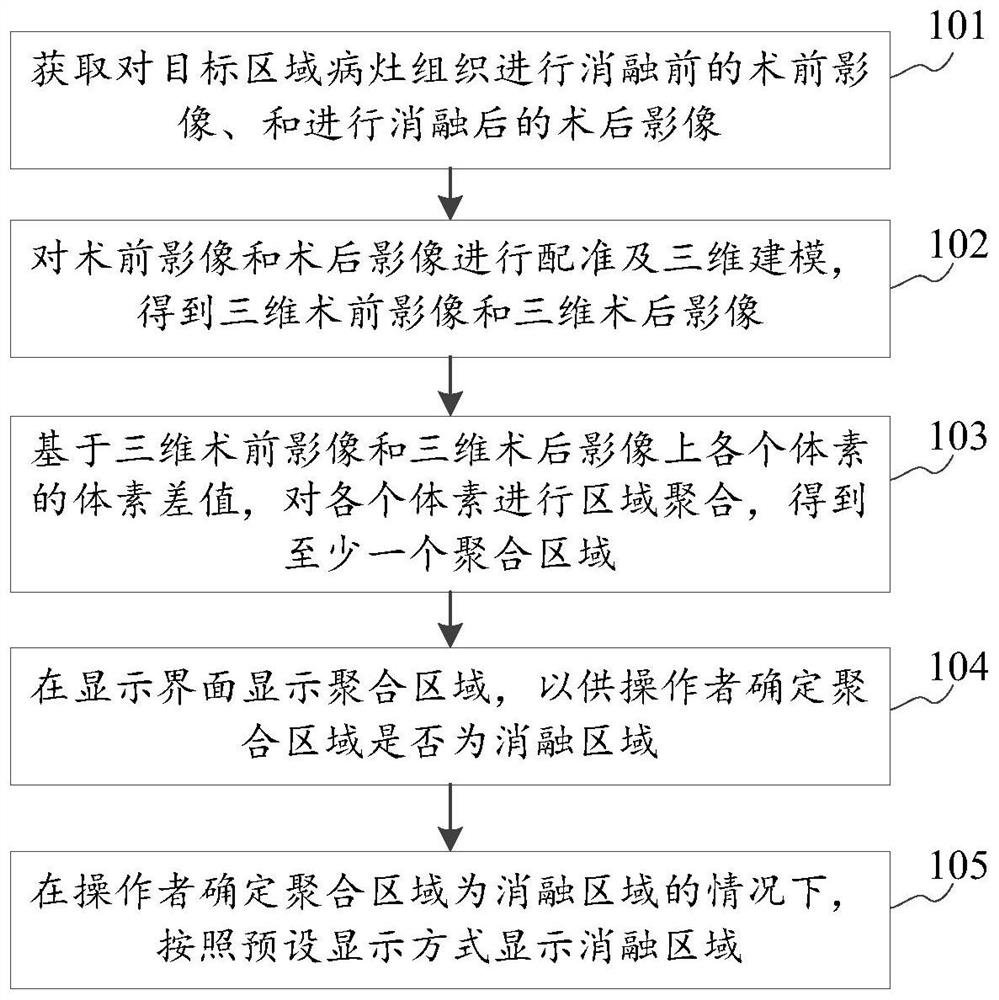
Ablation area determination method and device based on medical image and storage medium
PendingCN114299009AImprove accuracySolve the problem that the recognition result may be inaccurateImage analysisImaging processingVoxel
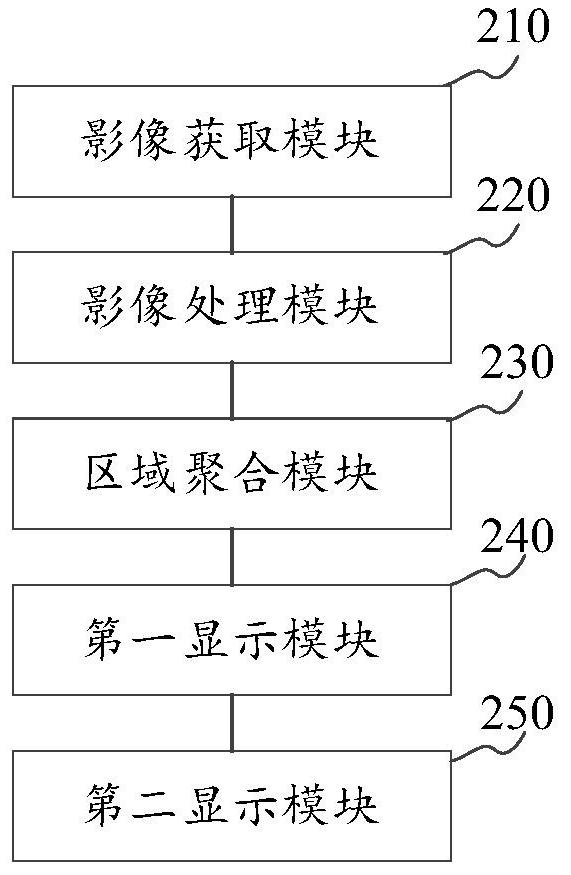
The invention discloses an ablation area determination method and device based on a medical image and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a preoperative image before ablation of focus tissue in a target area and a postoperative image after ablation; performing registration and three-dimensional modeling on the preoperative image and the postoperative image to obtain a three-dimensional preoperative image and a three-dimensional postoperative image; based on the voxel difference value of each voxel on the three-dimensional preoperative image and the three-dimensional postoperative image, performing regional aggregation on each voxel to obtain at least one aggregation region; displaying the aggregation area on a display interface so that an operator can determine whether the aggregation area is an ablation area or not; under the condition that the operator determines that the aggregation area is an ablation area, displaying the ablation area according to a preset display mode; the problem that the recognition result is possibly inaccurate when a machine recognizes the ablation area can be solved; the accuracy of ablation area identification can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU GENLIGHT MEDTECH CO LTD
A design and fabrication method for individualized 3D printed implants
The invention discloses a design and production method of an individualized 3D printing implant, which divides the aperture of the porous grid body into n1 grades on average, the porosity into n2 grades on average, and the thickness into n3 grades on average, n1 ×n2×n3 The elastic modulus corresponding to the porous grid body is divided into n4 grades, so as to correspond to n4 kinds of bone density; preoperative quantitative CT of the jaw is taken for the patient, and the three-dimensional reconstruction software and empirical formula are used to calculate Find the average bone elastic modulus E, and select the thickest porous grid body among the implants with similar elastic modulus range; 3D printing is carried out on the implant, and the head and body are integrally formed. The pore diameter, porosity and thickness of the porous network frame body of the present invention are set in stages, so that the implant can reach elastic modulus of different sizes, and is suitable for people with different bone densities.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System and method for pretreatment of a volume of tissue slated for treatment
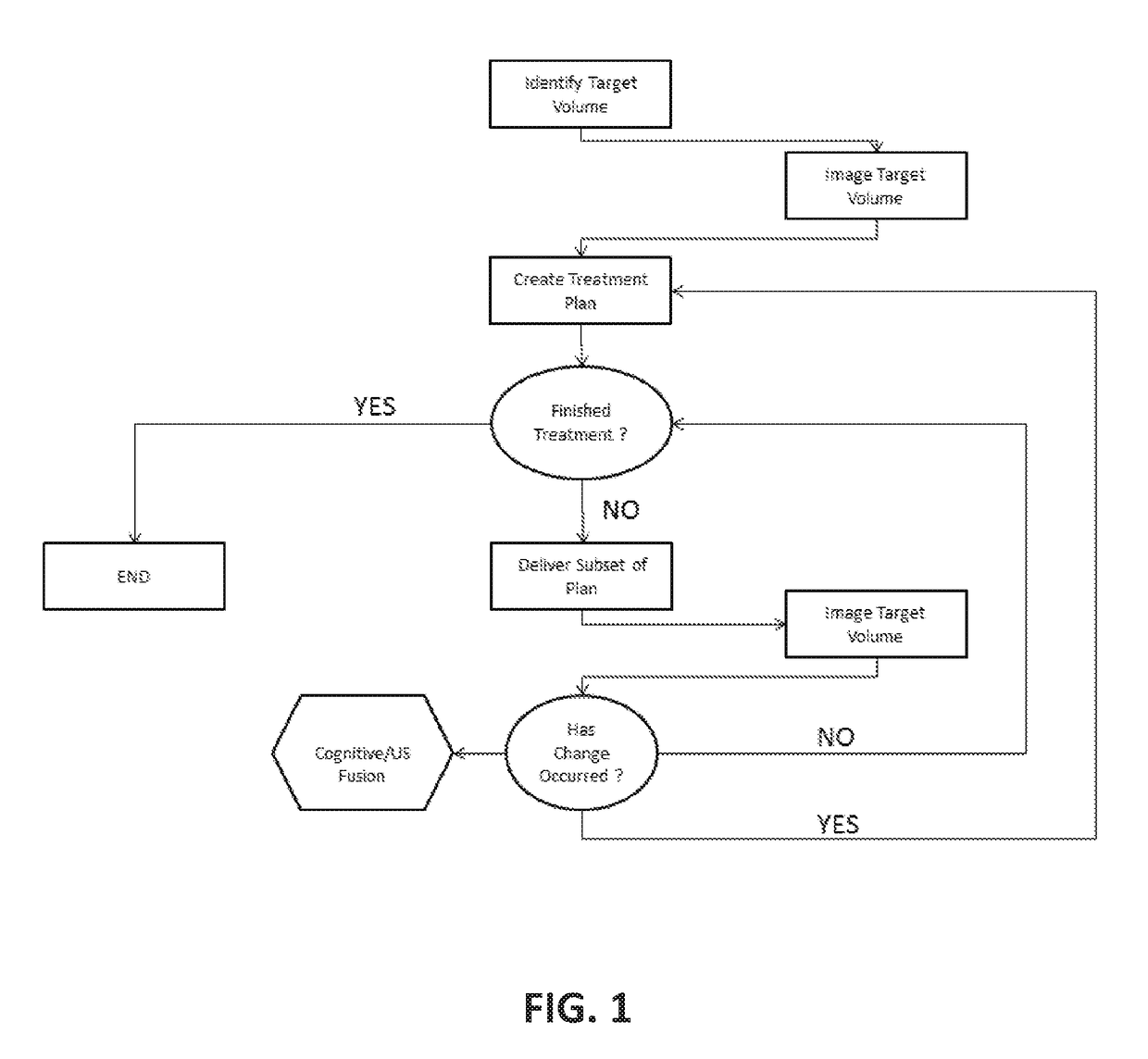
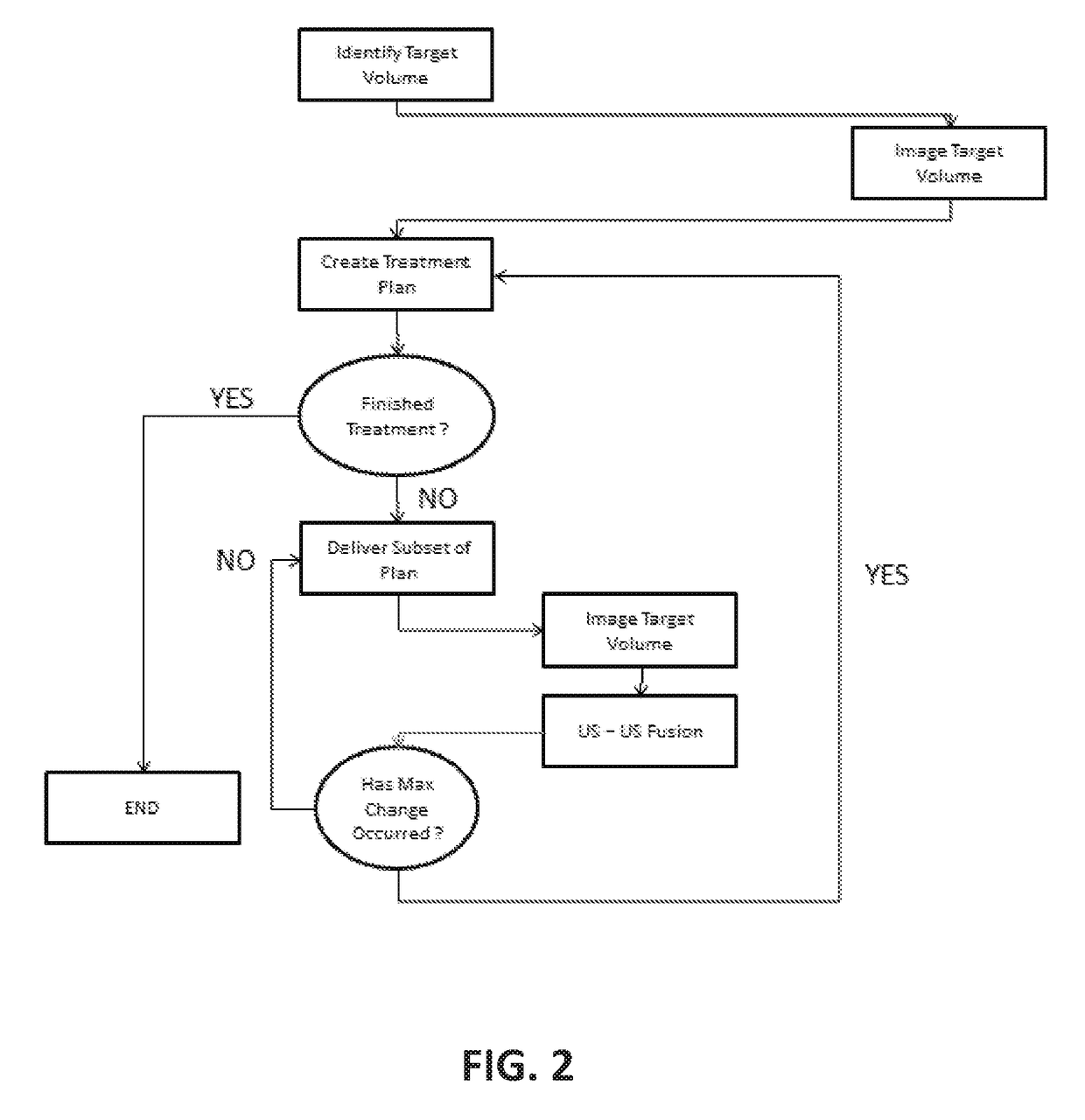
InactiveUS20170319875A1Promote resultsLocation minimalImage enhancementUltrasound therapyDistal portionPre treatment
A method for delivering therapeutic ultrasound to a patient to ensure full treatment of targeted tissue can include performing preoperative imaging of a first volume of targeted tissue of a patient using an ultrasound probe and creating a first treatment plan. Energy can be delivered into at least a distal portion of the first volume. The amount of energy delivered can be sufficient to produce swelling of tissue in the first volume. The first volume can be reimaged to identify if any changes have occurred in at least one of a size, shape and location of the first volume of the targeted tissue. A second treatment plan can be designed to treat a second volume of tissue equivalent to the changed first volume of targeted tissue. Energy can be delivered into the second volume of the targeted tissue.
Owner:SONACARE MEDICAL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com