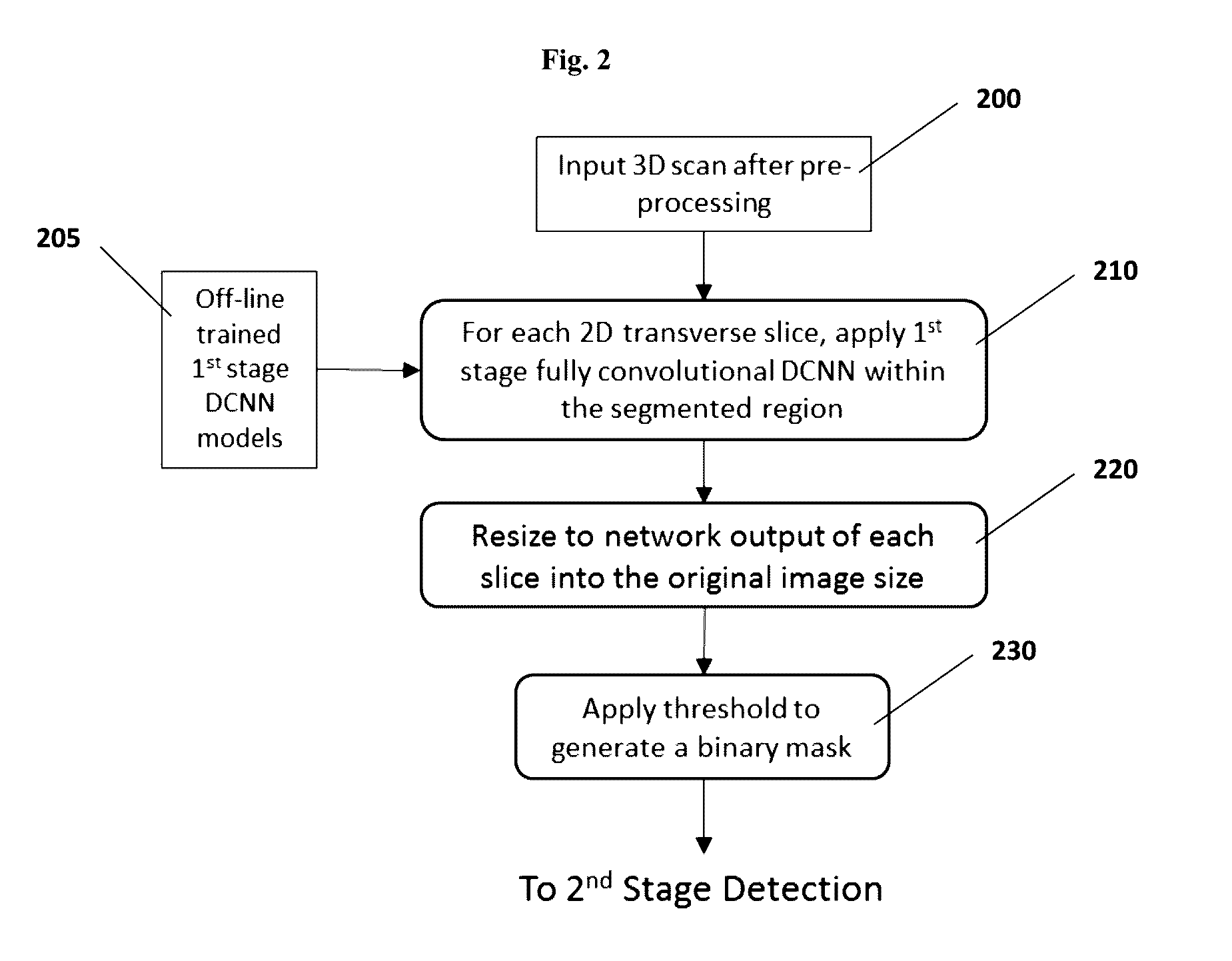
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3009results about "Medical imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
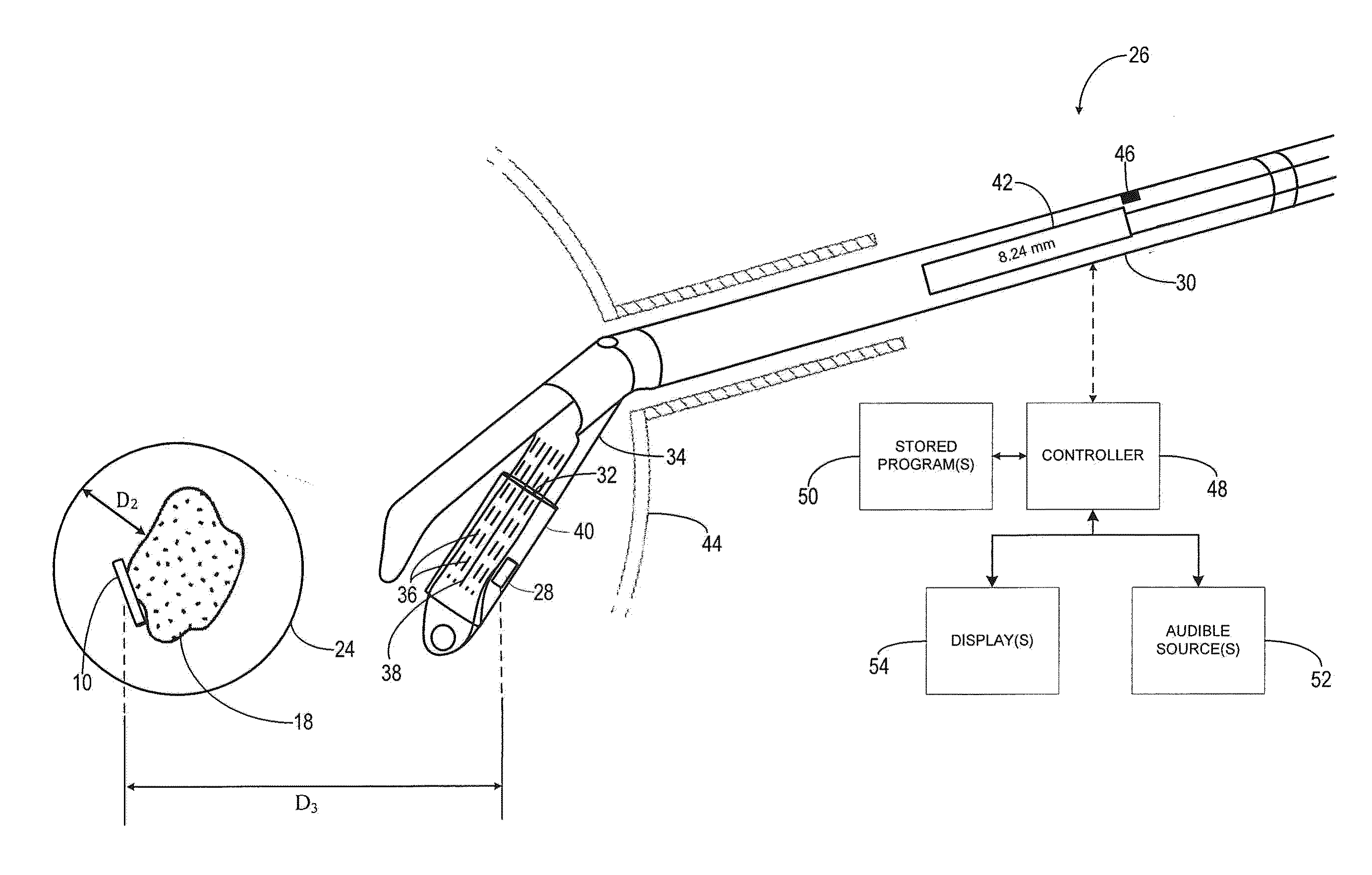
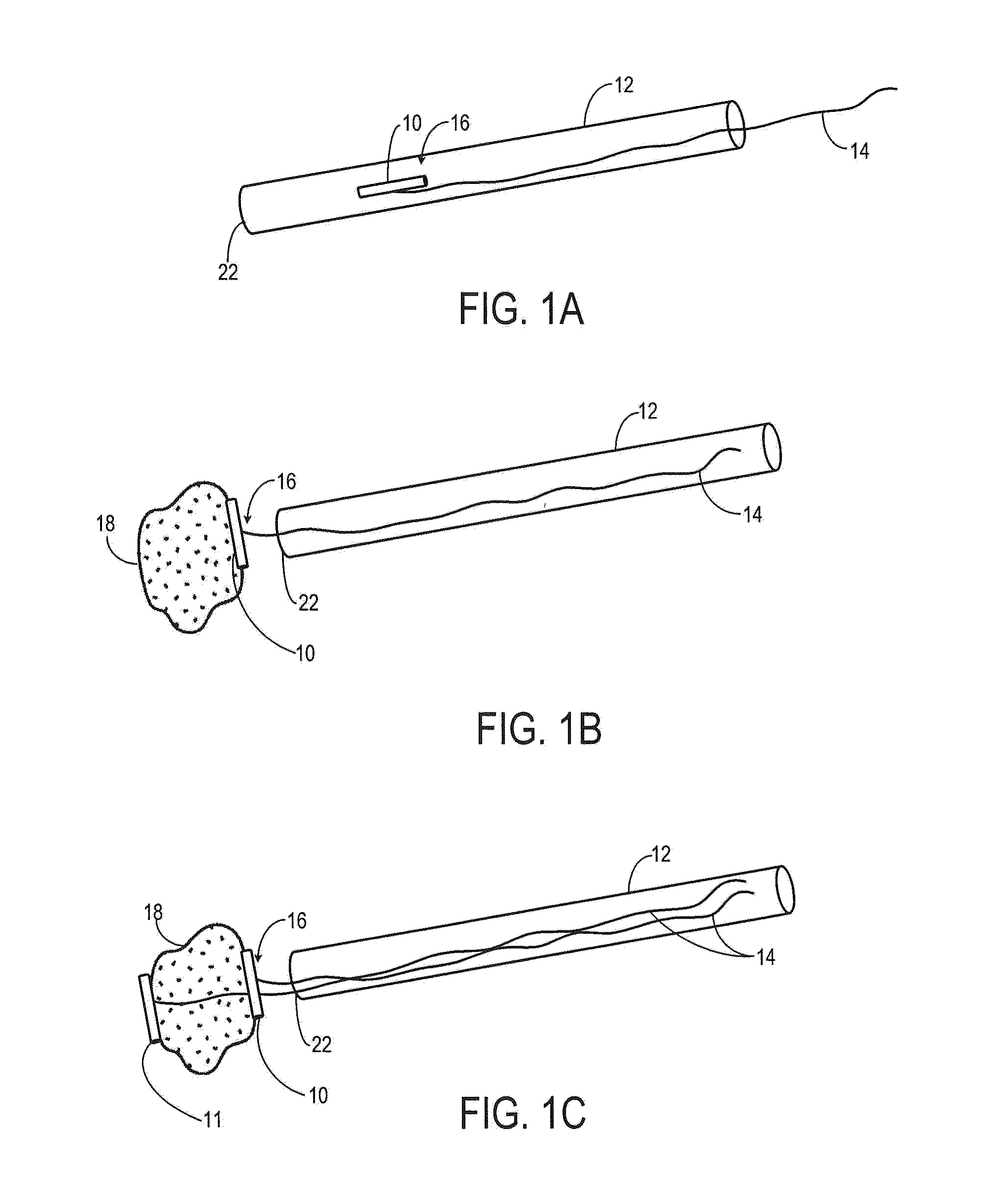
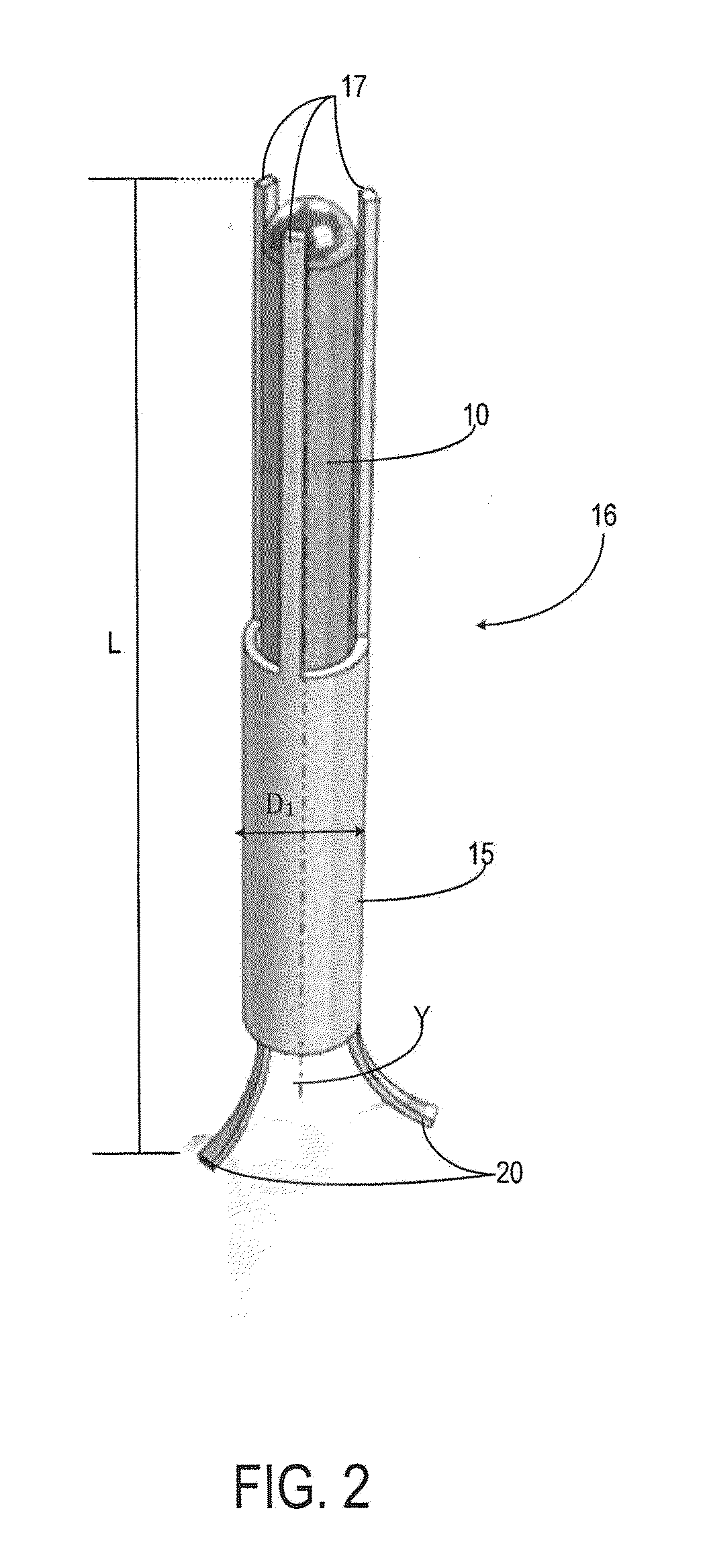
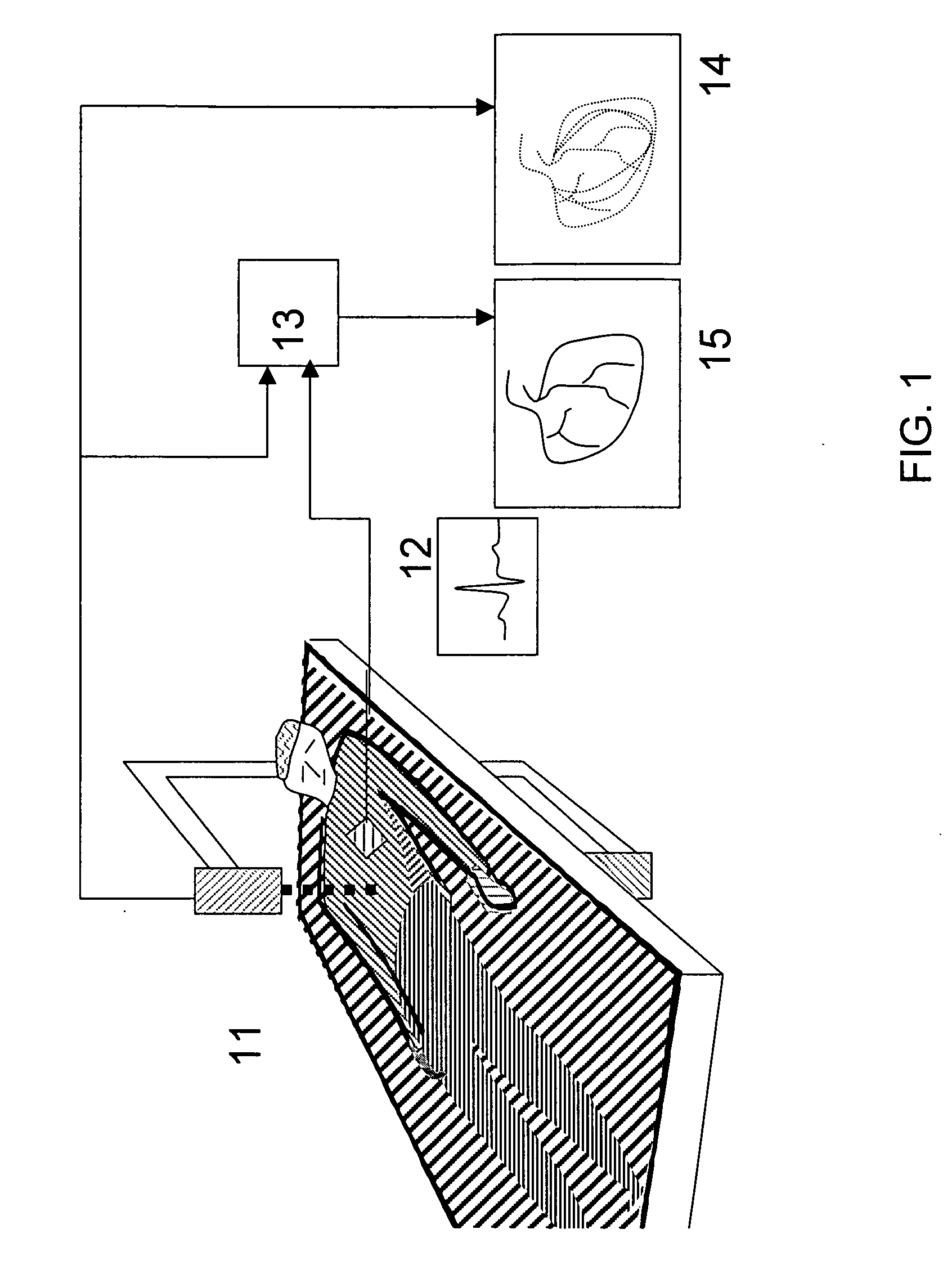
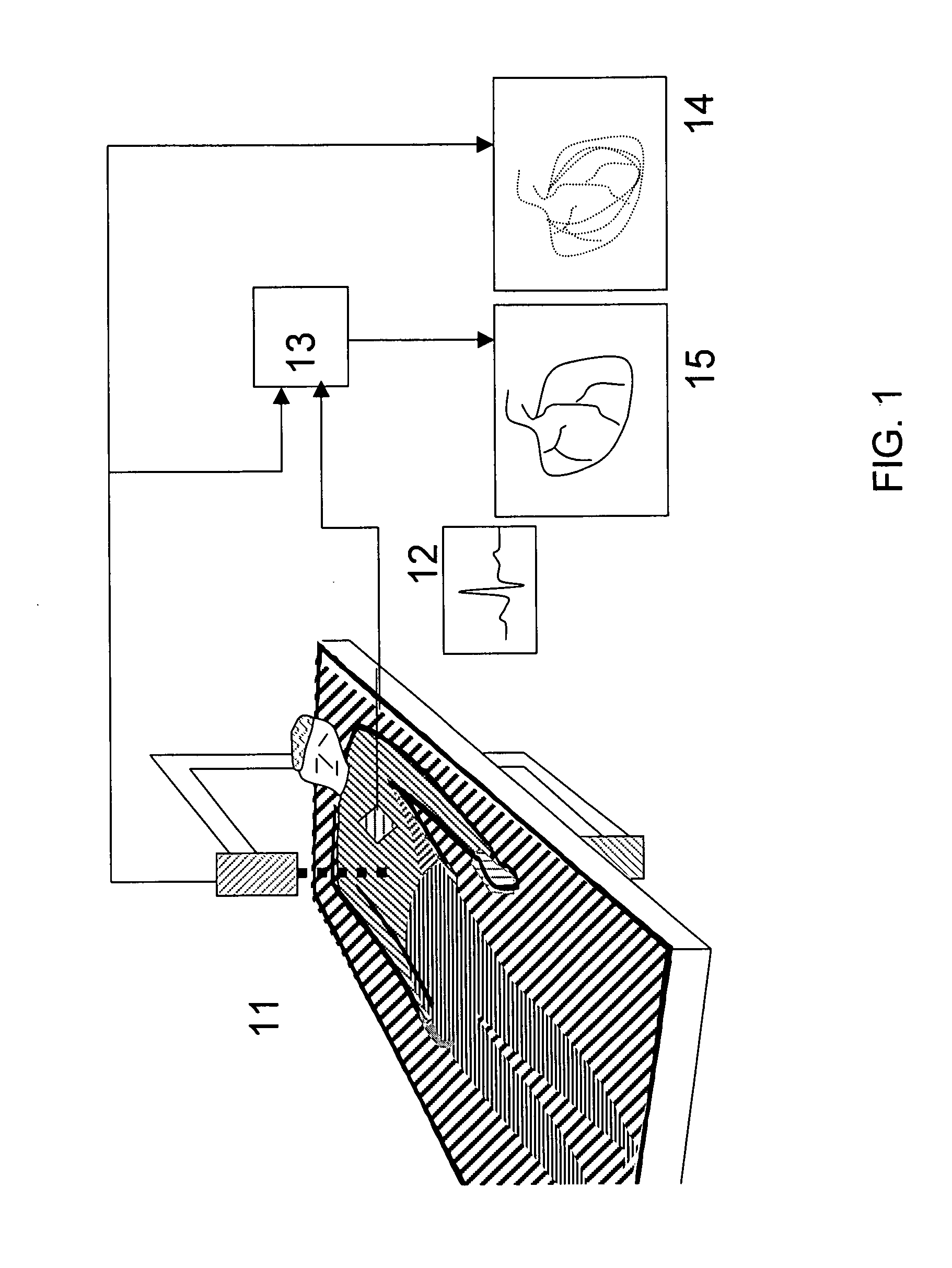
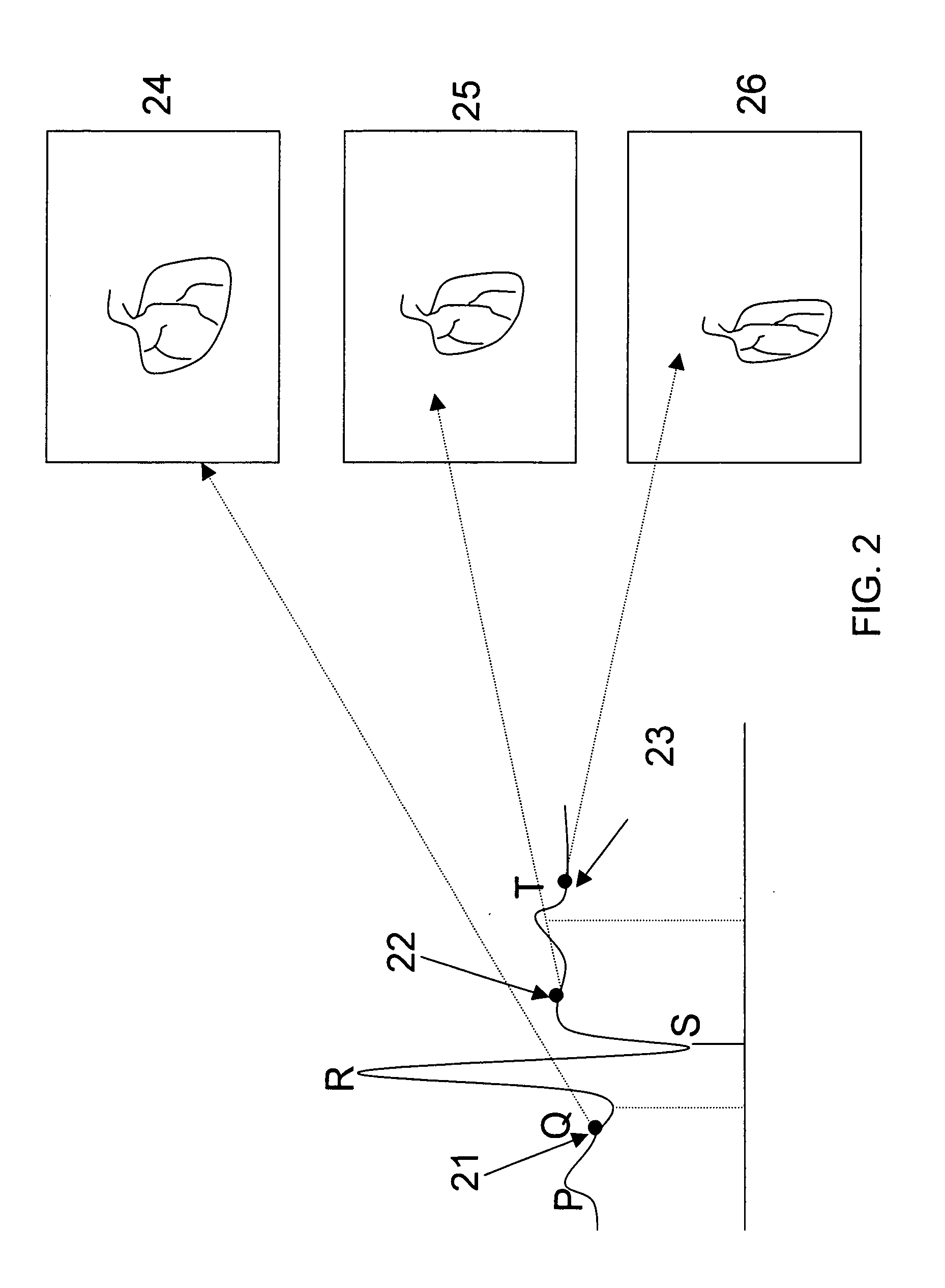
System and method for a tissue resection margin measurement device
ActiveUS20160192960A1Minimally invasiveCompensation for deformationMedical imagingSurgical needlesMeasurement deviceVisual perception
Embodiments of the invention provide a system and method for resecting a tissue mass. The system for resecting a tissue mass includes a surgical instrument and a first sensor for measuring a signal corresponding to the position and orientation of the tissue mass. The first sensor is dimensioned to fit insider or next to the tissue mass. The system also includes a second sensor attached to the surgical instrument configured to measure the position and orientation of the surgical instrument. The second sensor is configured to receive the signal from the first sensor. A controller is in communication with the first sensor and / or the second sensor, and the controller executes a stored program to calculate a distance between the first sensor and the second sensor. Accordingly, visual, auditory, haptic or other feedback is provided to the clinician to guide the surgical instrument to the surgical margin.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
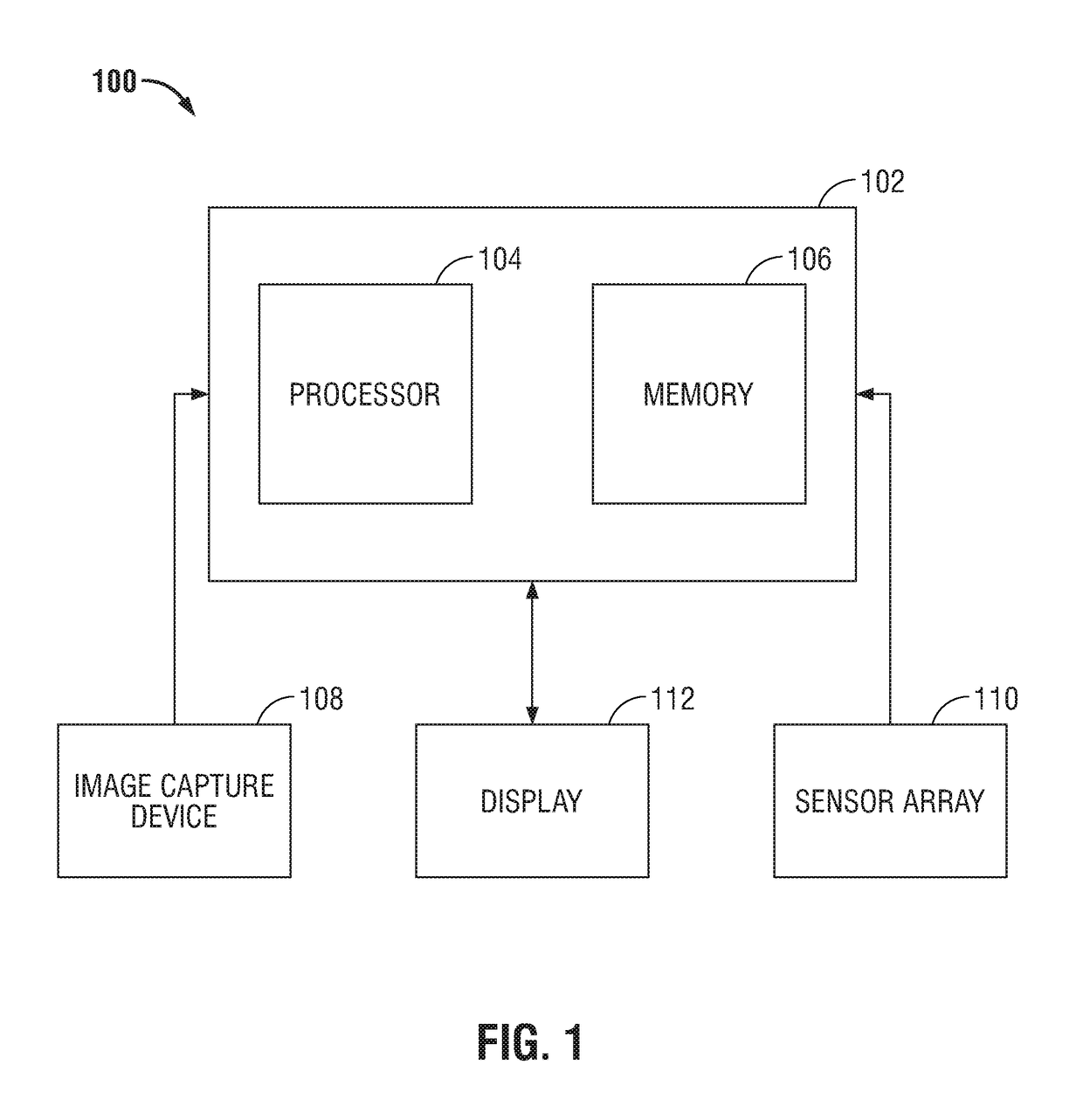
Augmented surgical reality environment
The present disclosure is directed to an augmented reality surgical system for viewing an augmented image of a region of interest during a surgical procedure. The system includes an image capture device that captures an image of the region of interest. A controller receives the image and applies at least one image processing filter to the image. The image processing filter includes a spatial decomposition filter that decomposes the image into spatial frequency bands. A temporal filter is applied to the spatial frequency bands to generate temporally filtered bands. An adder adds each band spatial frequency band to a corresponding temporally filtered band to generate augmented bands. A reconstruction filter generates an augmented image by collapsing the augmented bands. A display displays the augmented image to a user.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
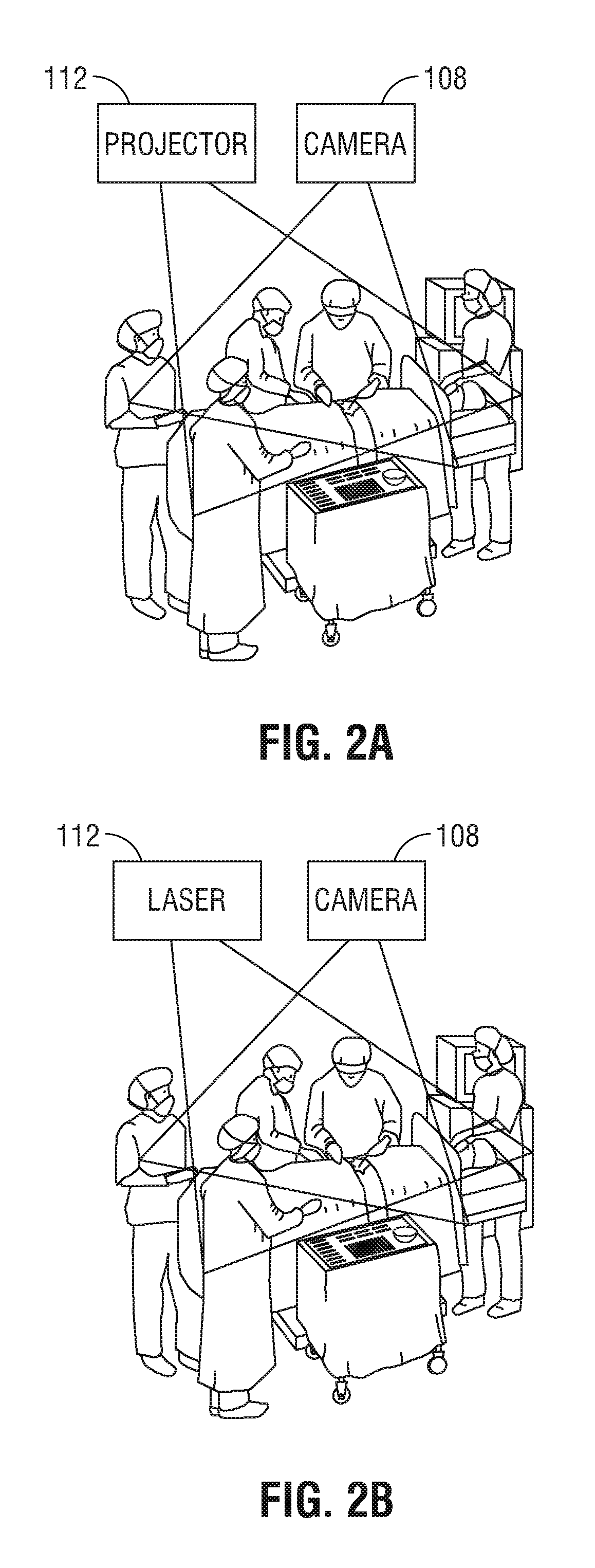
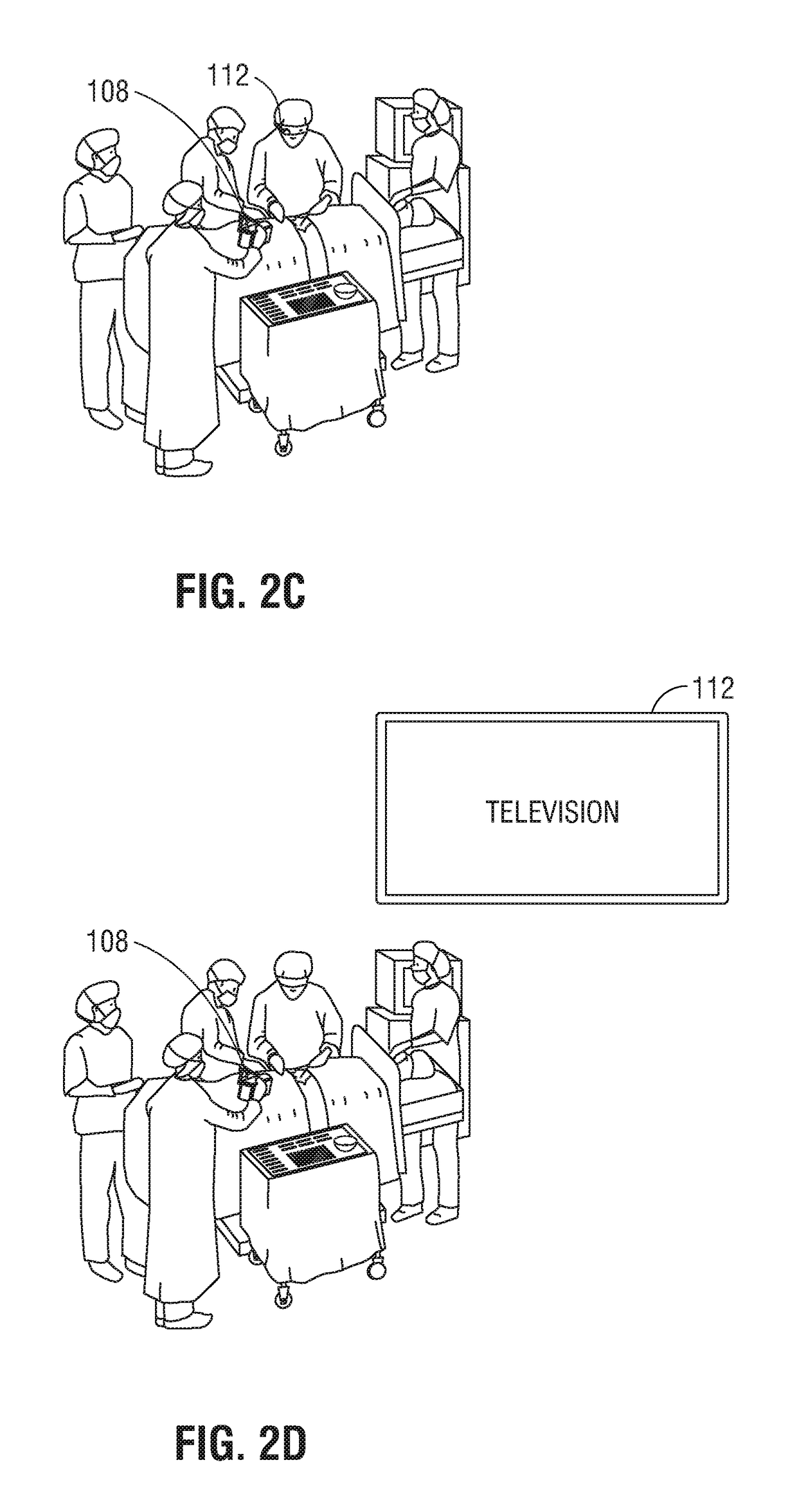
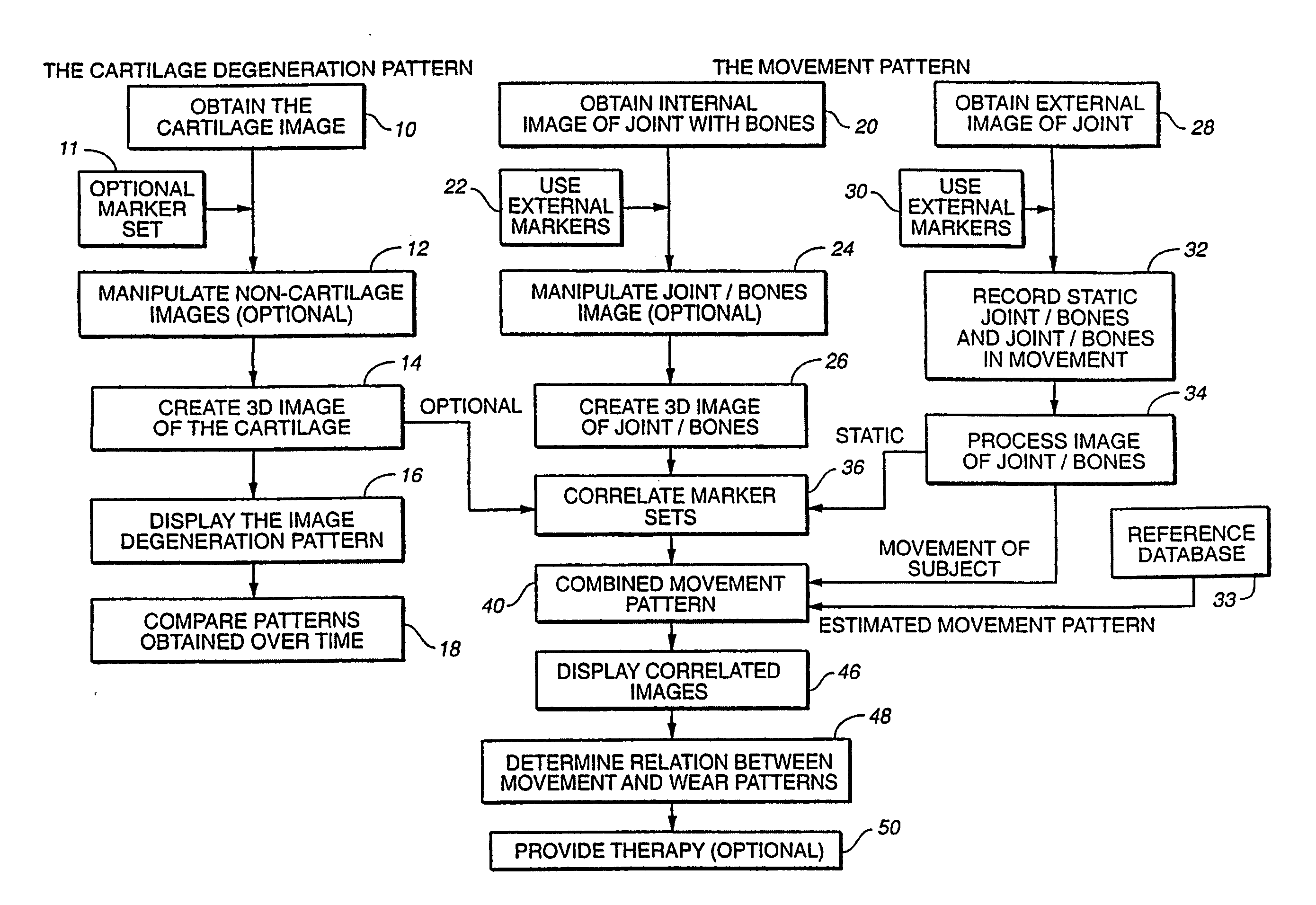
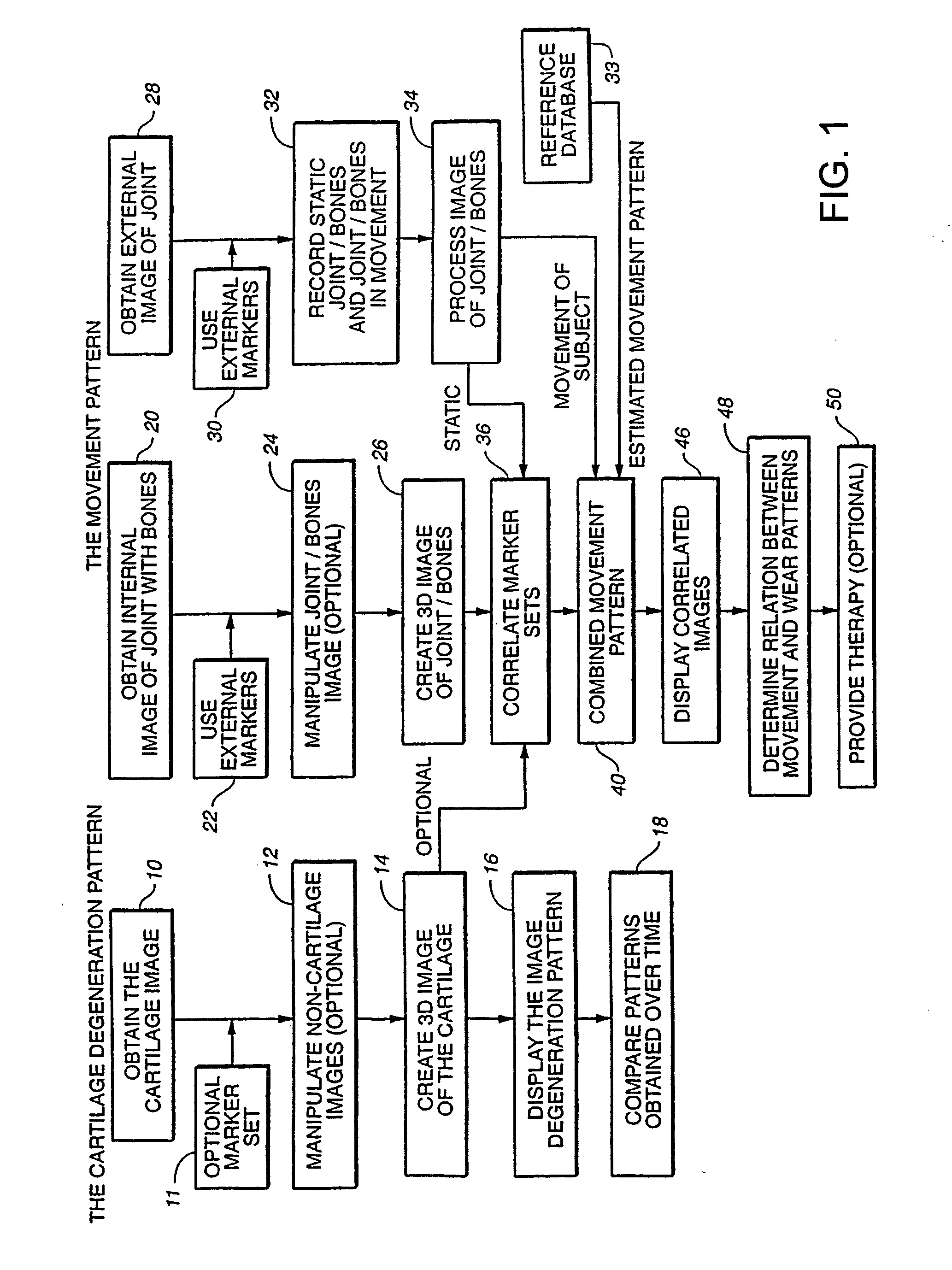
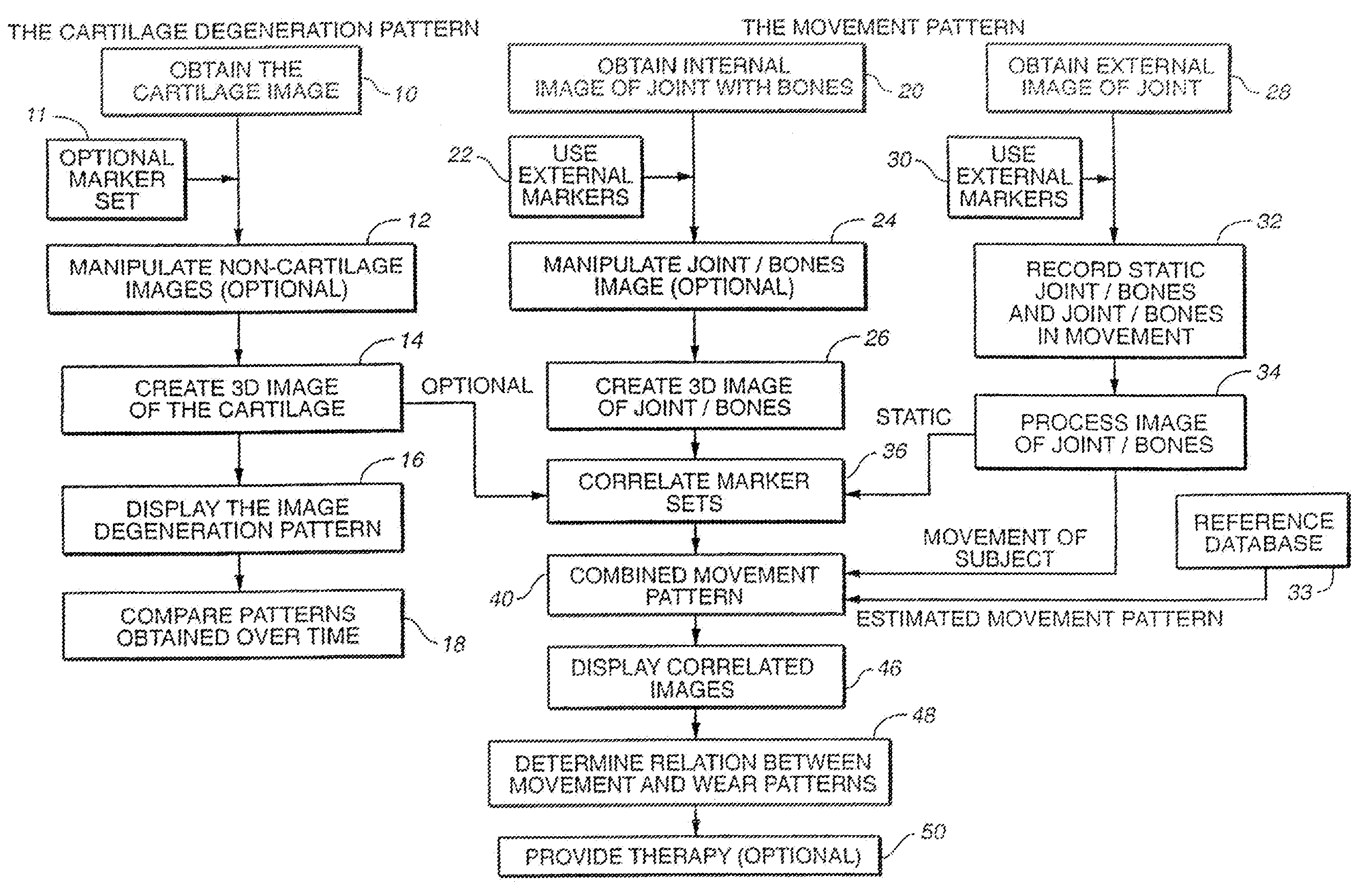
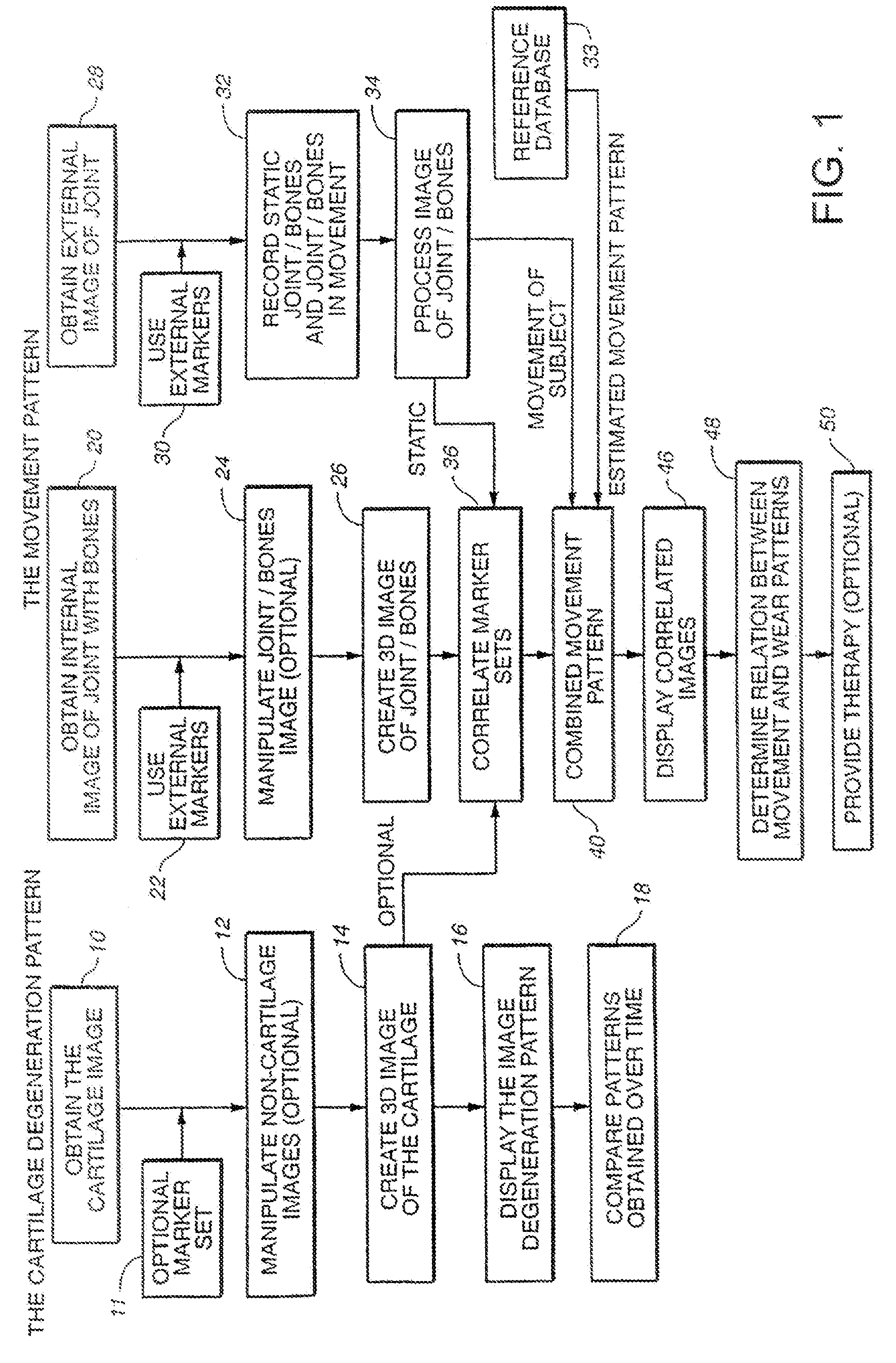
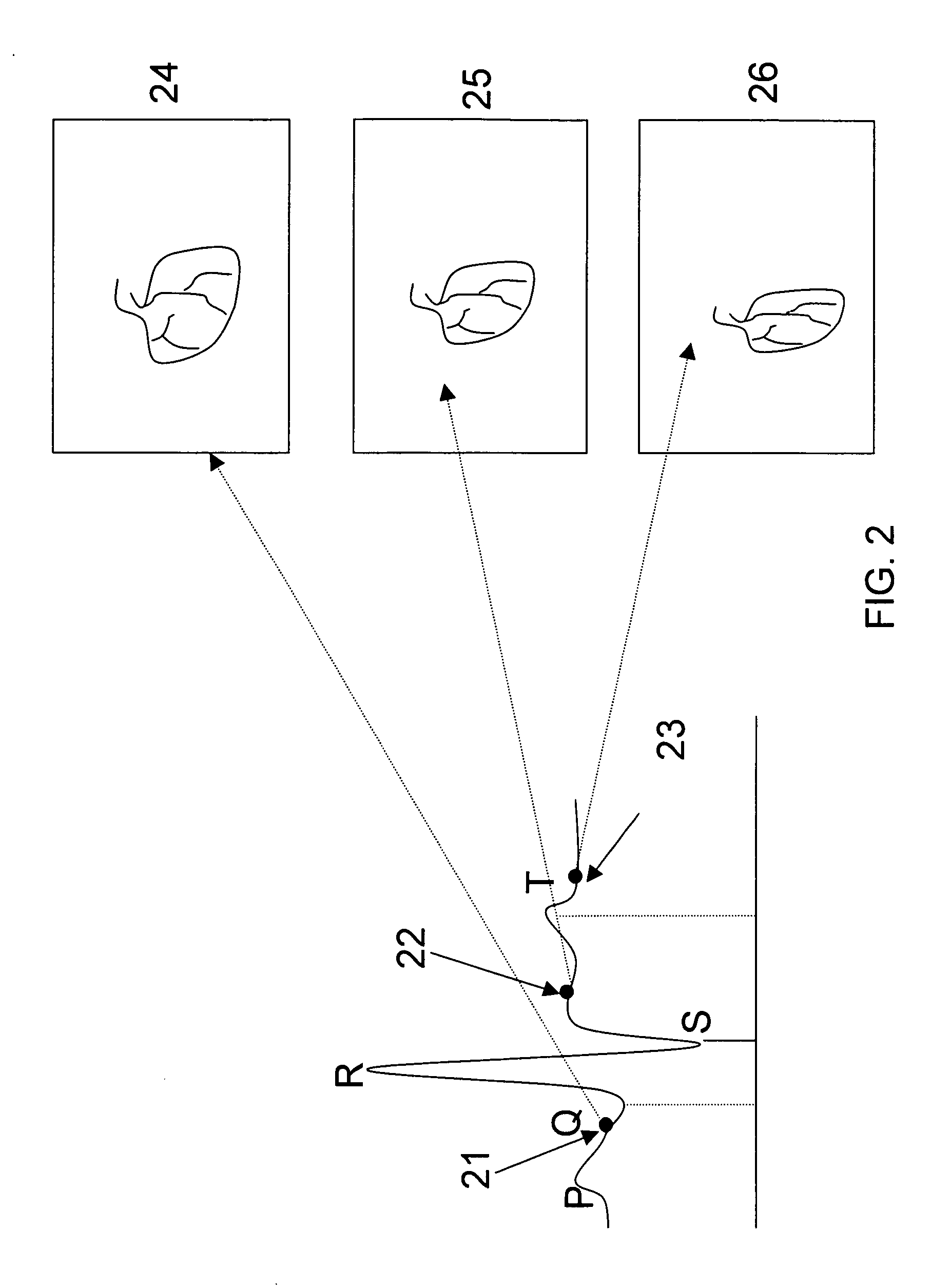
Joint and cartilage diagnosis, assessment and modeling
Methods are disclosed for assessing the condition of a cartilage in a joint and assessing cartilage loss, particularly in a human knee. The methods include converting an image such as an MRI to a three dimensional map of the cartilage. The cartilage map can be correlated to a movement pattern of the joint to assess the affect of movement on cartilage wear. Changes in the thickness of cartilage over time can be determined so that therapies can be provided. The amount of cartilage tissue that has been lost, for example as a result of arthritis, can be estimated.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and system for measurement of physiological parameters
InactiveUS20110251493A1Improve consistencyAdvancing personal healthcareMedical imagingCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionRegion of interest
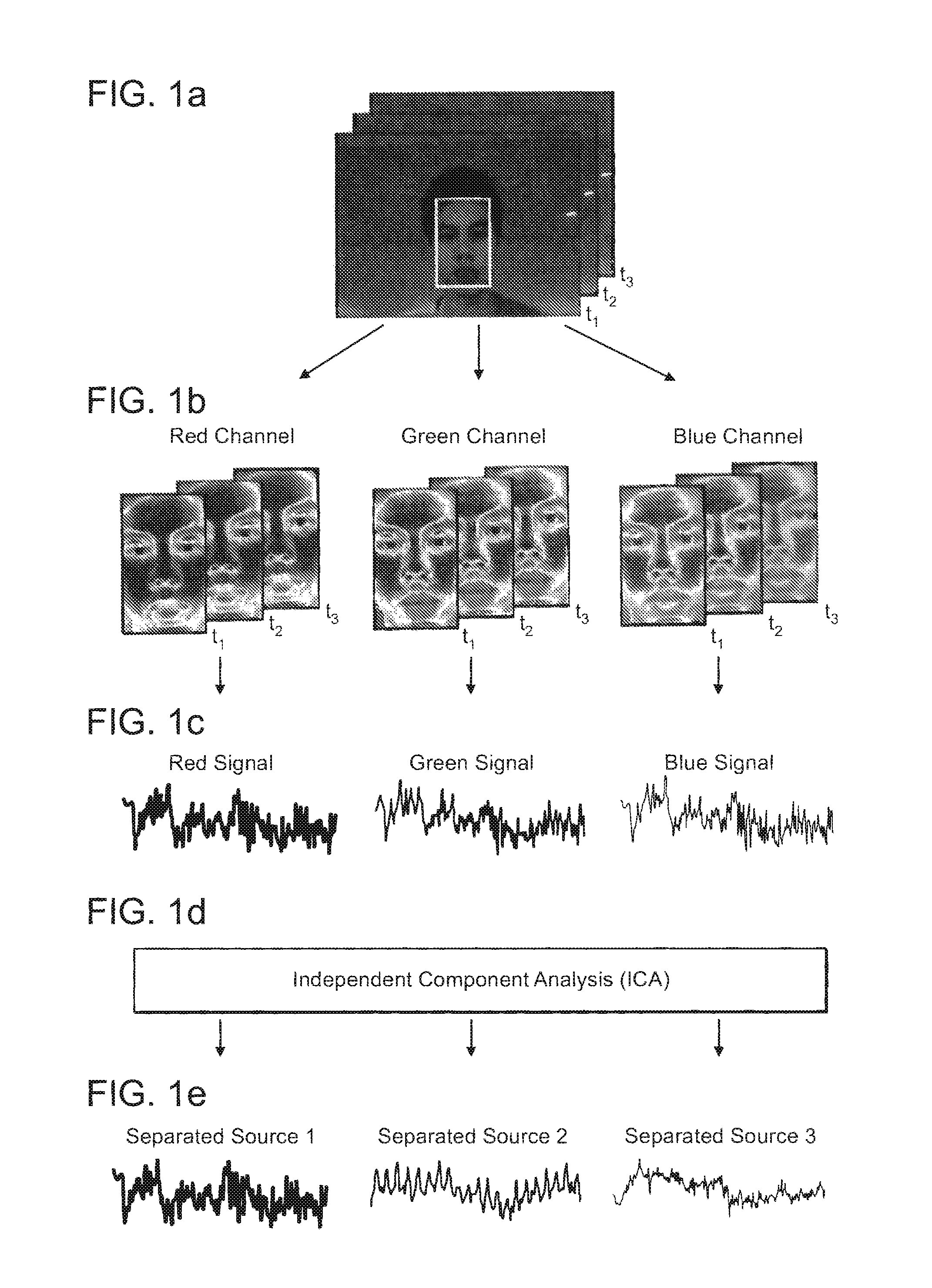
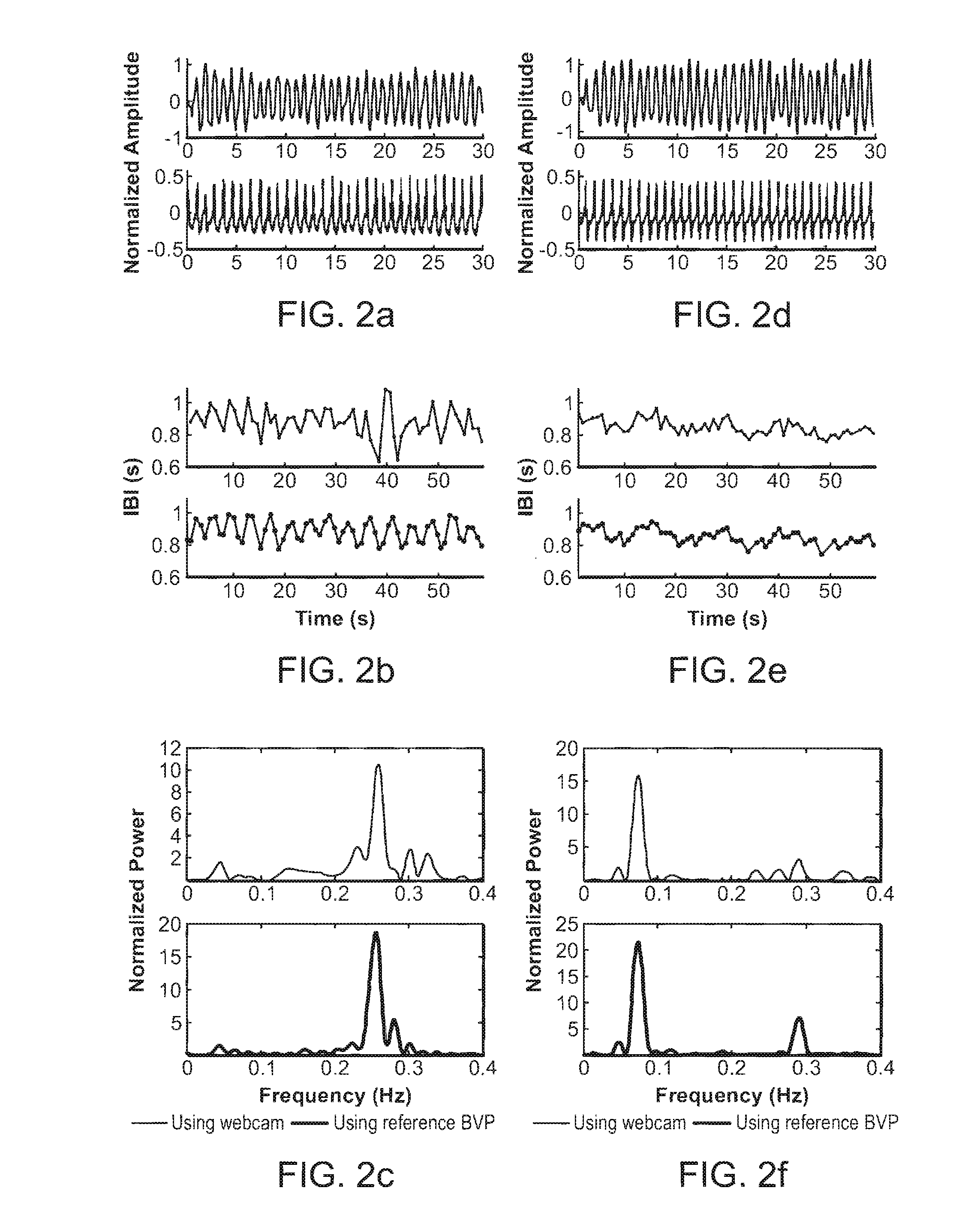
Method and system for measuring physiological parameters. The method includes capturing a sequence of images of a human face and identifying the location of the face in a frame of the video and establishing a region of interest including the face. Pixels are separated in the region of interest in a frame into at least two channel values forming raw traces over time. The raw traces are decomposed into at least two independent source signals. At least one of the source signals is processed to obtain a physiological parameter.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Joint and Cartilage Diagnosis, Assessment and Modeling
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods, apparatuses, and systems useful in conducting image guided interventions
Methods, apparatuses, and systems relating to image guided interventions on dynamic tissue. One embodiment is a method that includes creating a dataset that includes images, one of the images depicting a non-tissue internal reference marker, being linked to non-tissue internal reference marker positional information, and being at least 2-dimensional. Another embodiment is a method that includes receiving a position of an instrument reference marker coupled to an instrument; transforming the position into image space using a position of a non-tissue internal reference marker implanted in a patient; and superimposing a representation of the instrument on an image in which the non-tissue internal reference marker appears. Computer readable media that include machine readable instructions for carrying out the steps of the disclosed methods. Apparatuses, such as integrated circuits, configured to carry out the steps of the disclosed methods. Systems that include devices configured to carry out steps of the disclosed methods.
Owner:VERAN MEDICAL TECH
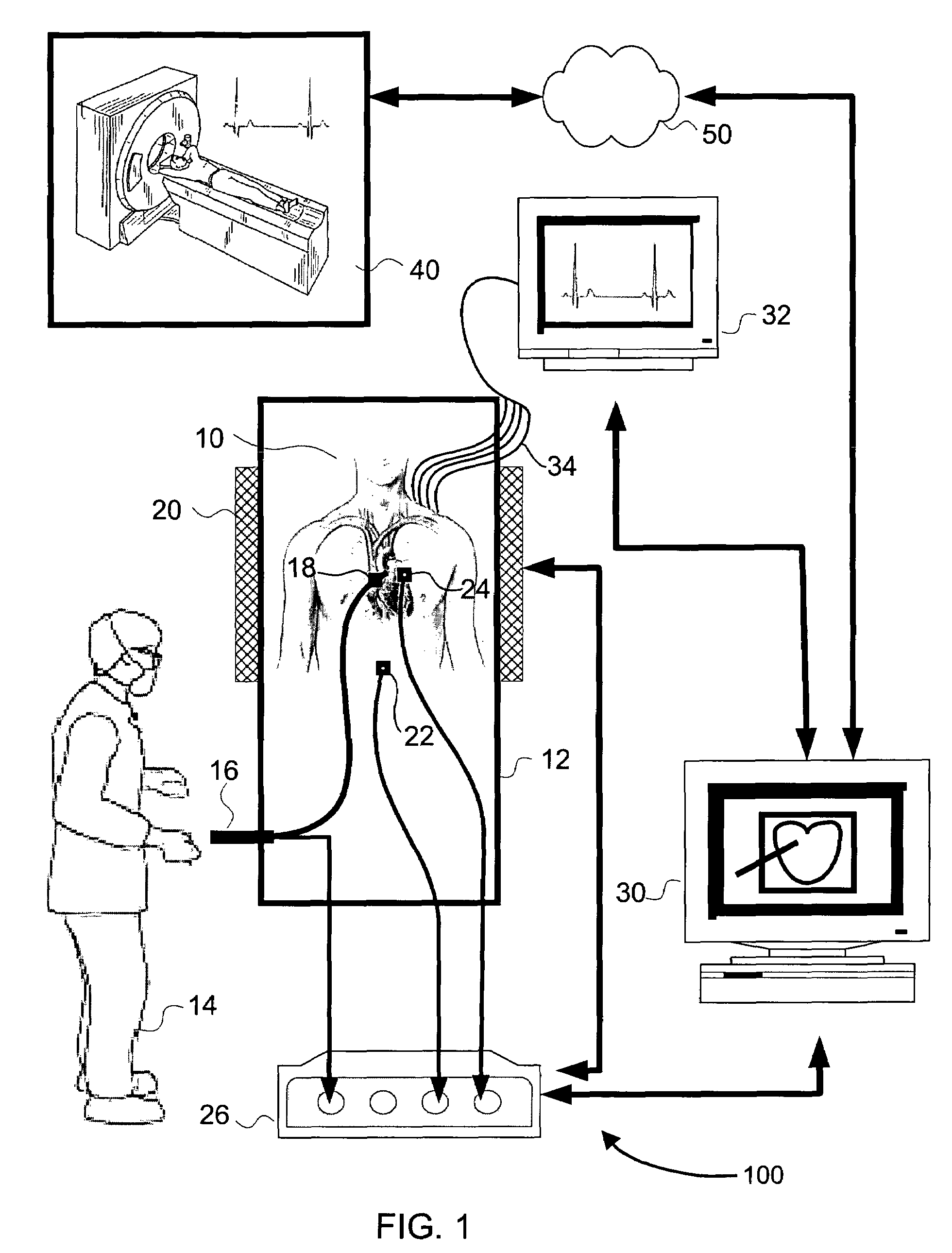
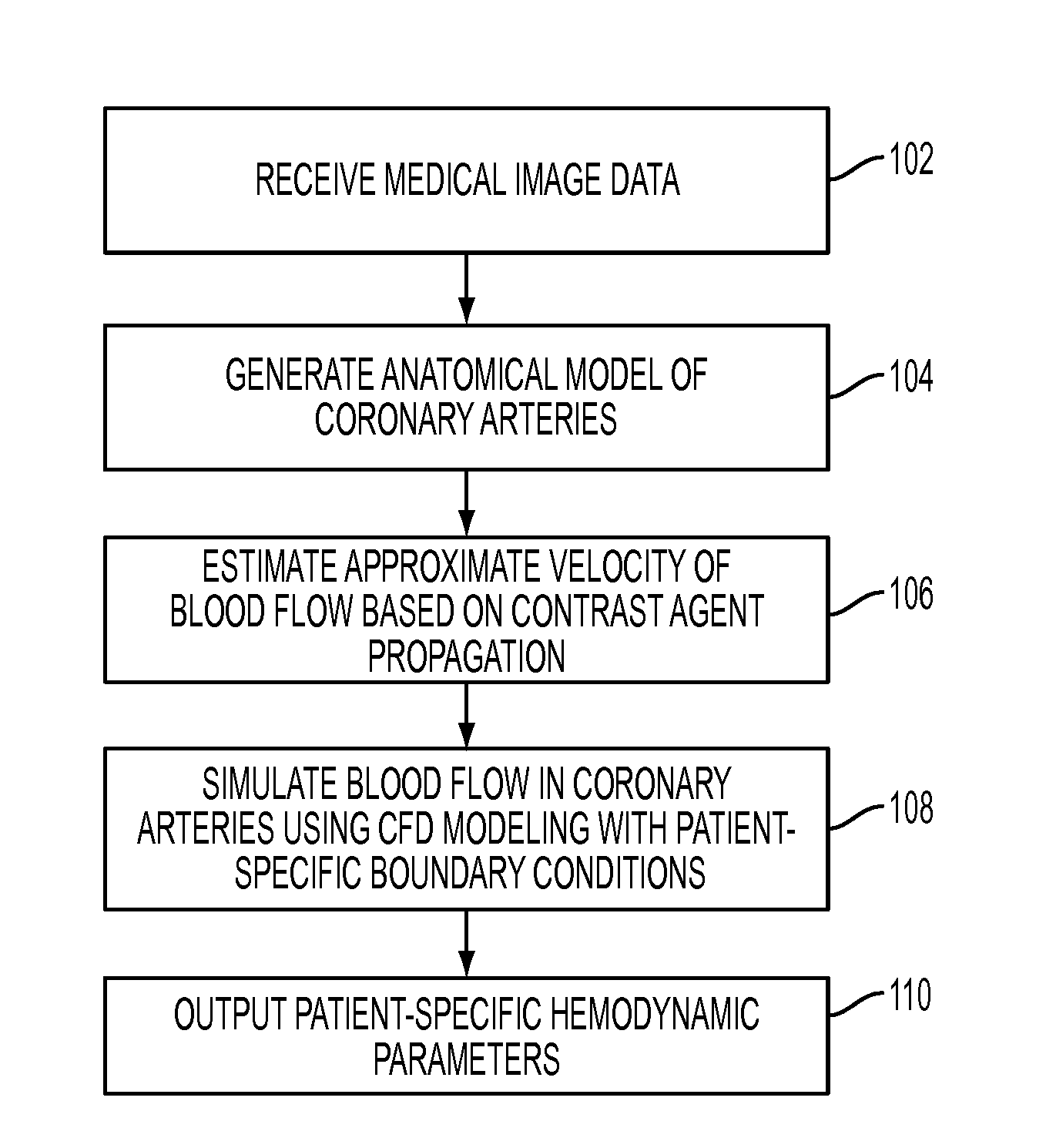
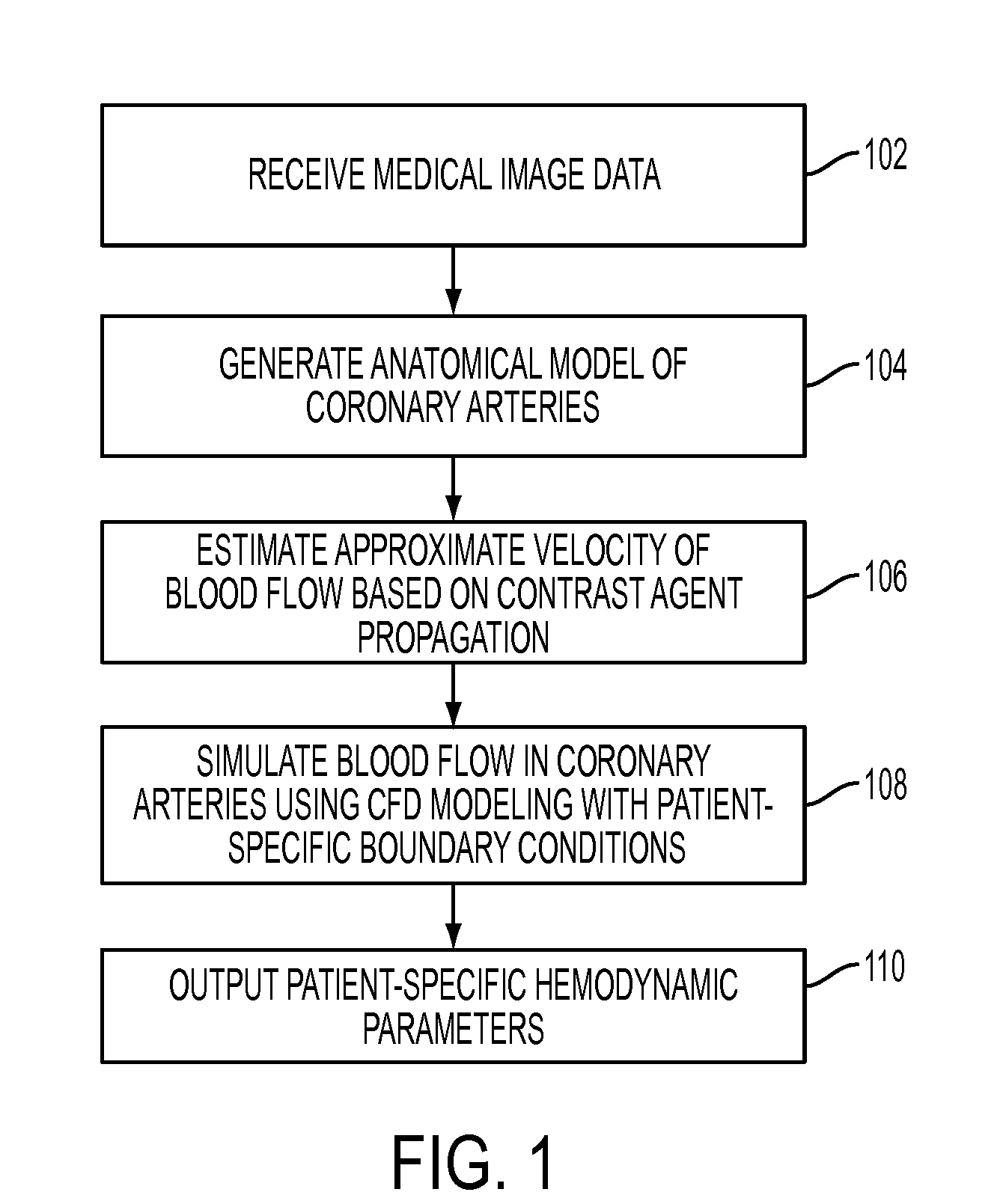
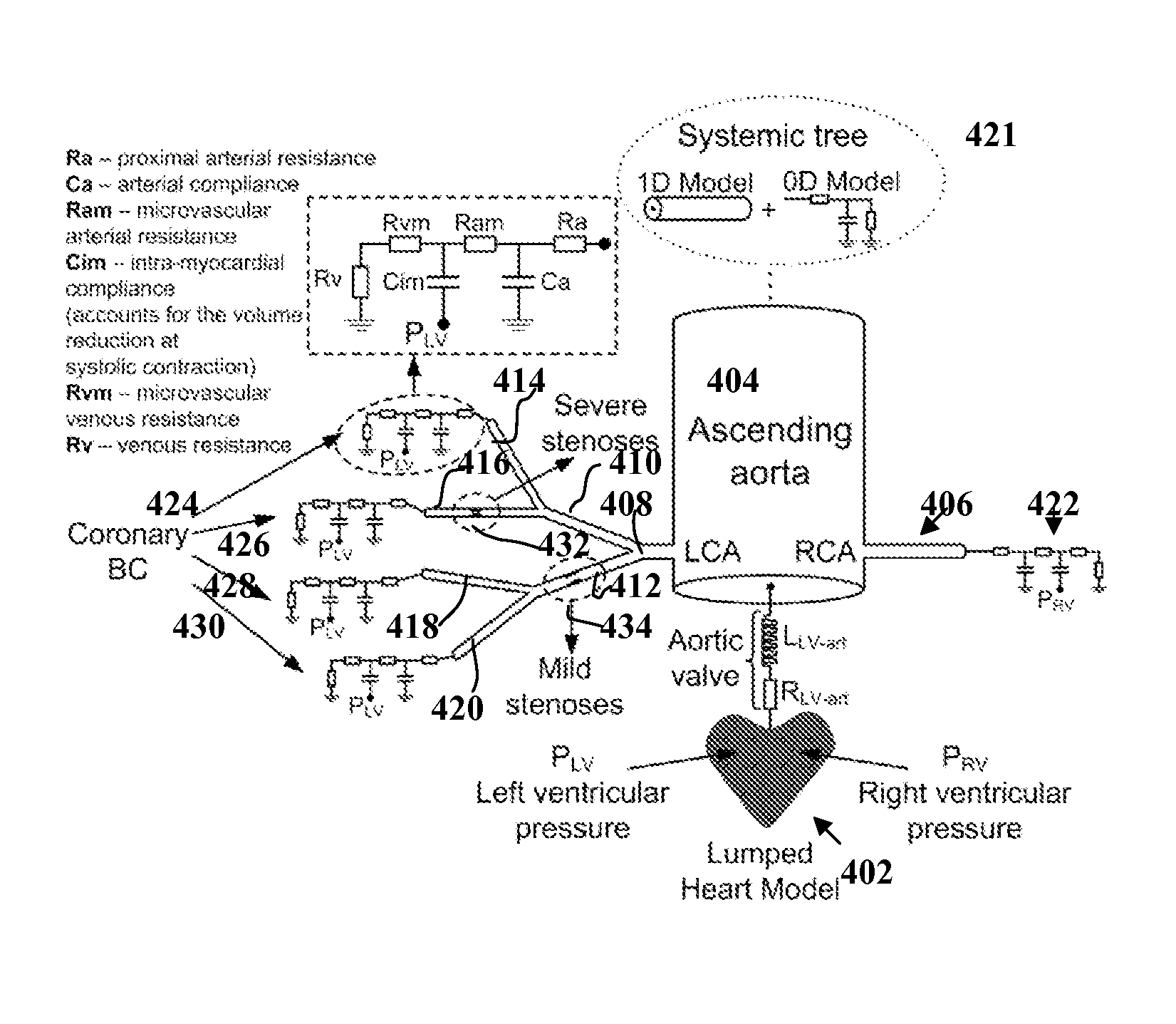
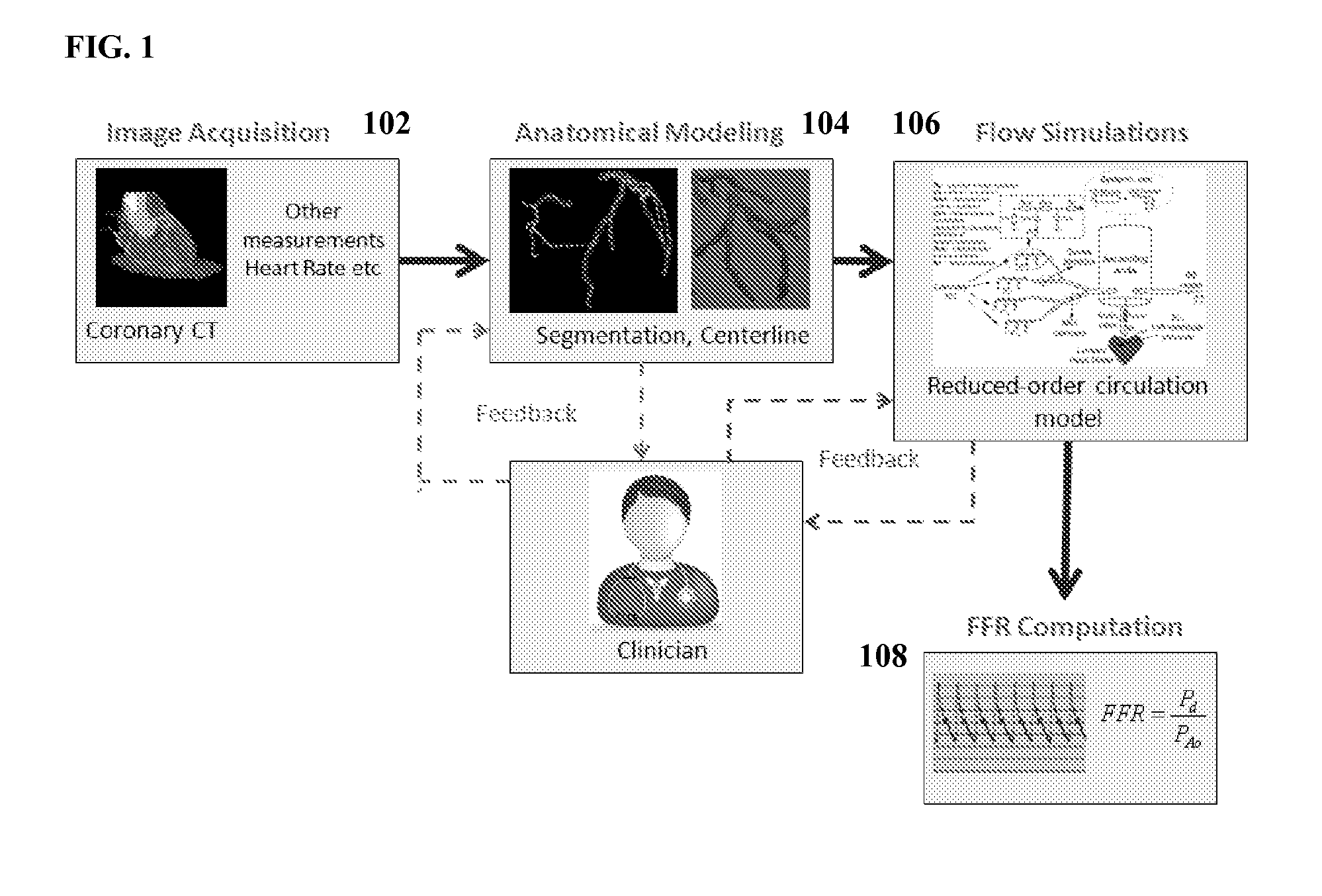
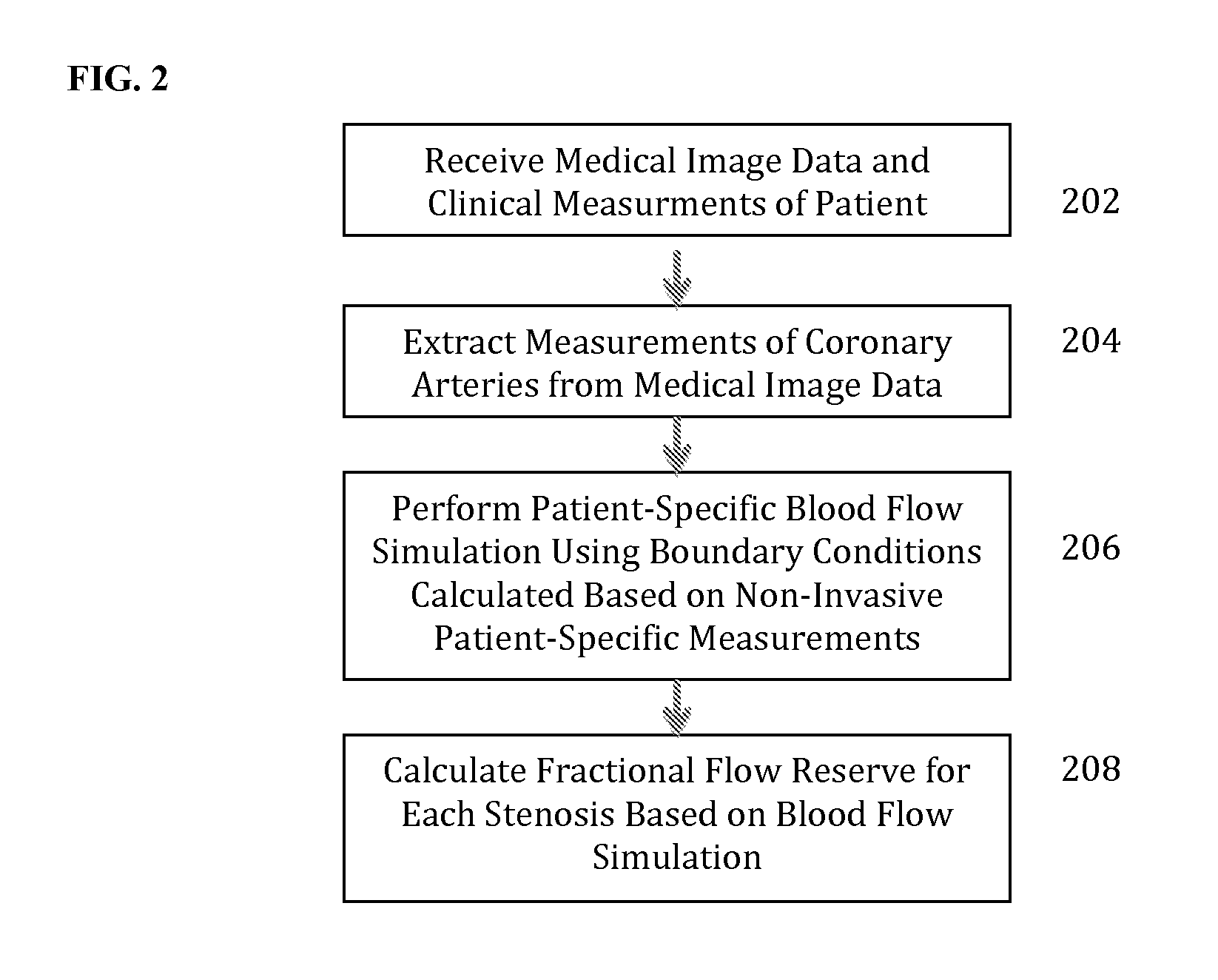
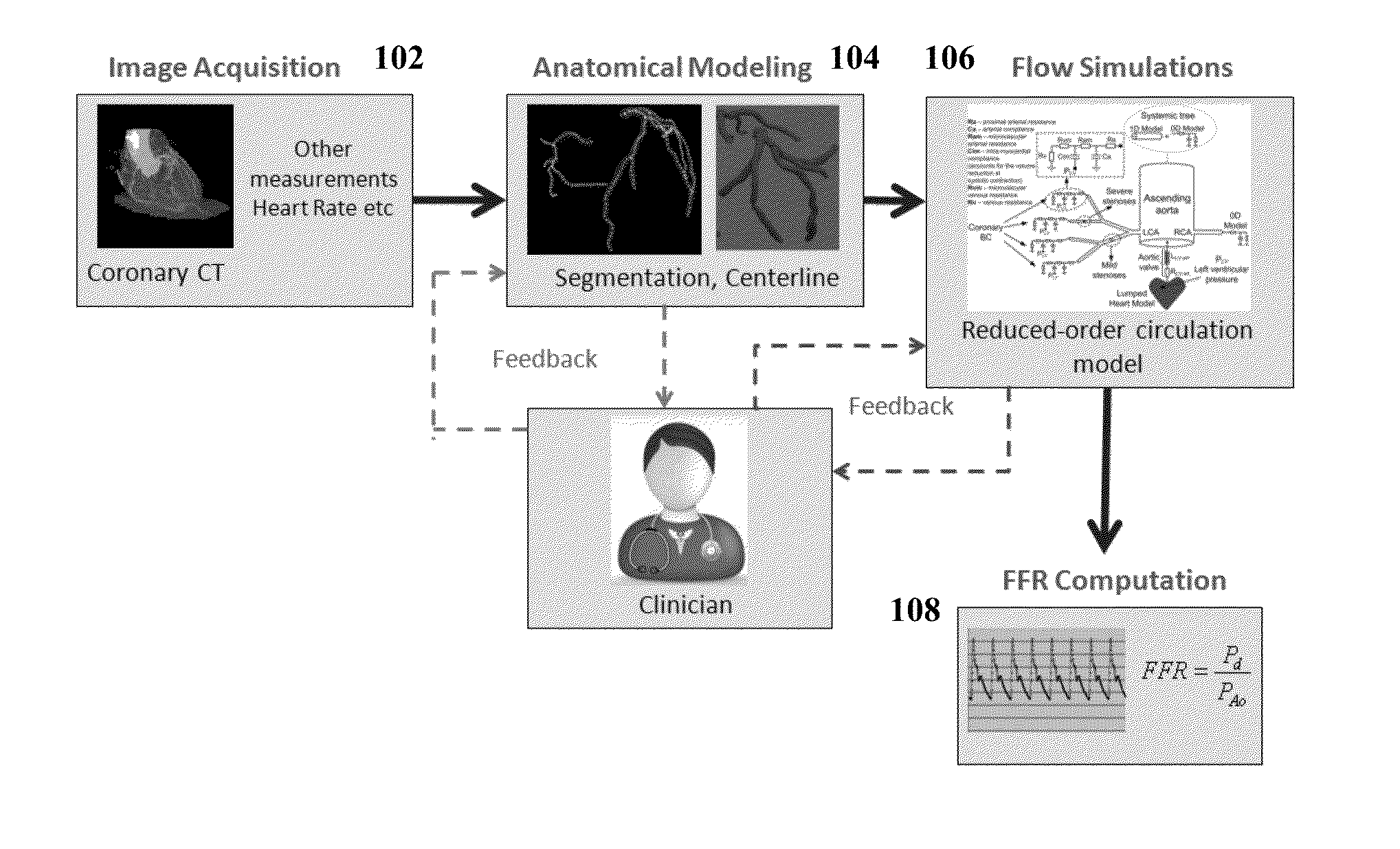
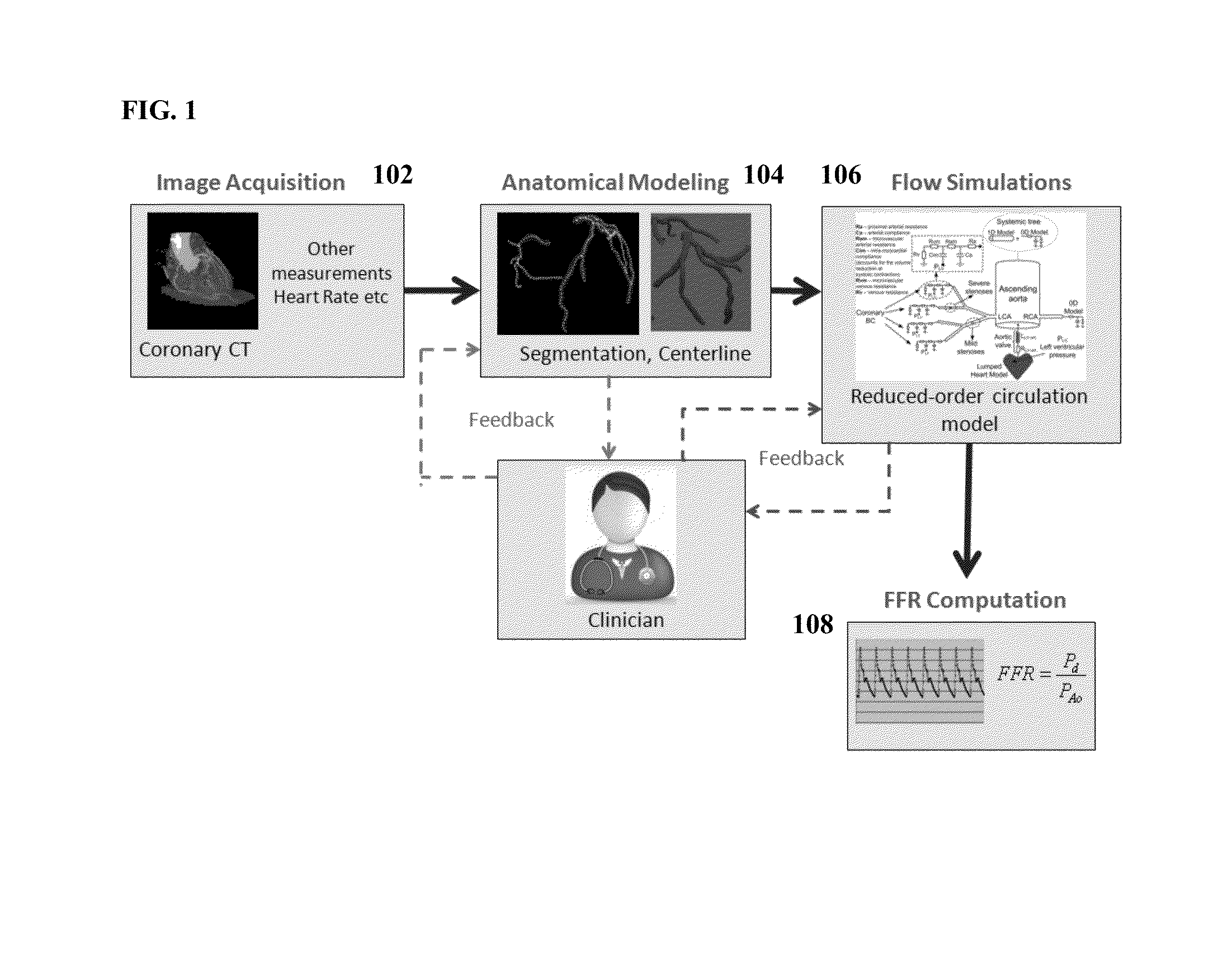
Method and System for Non-Invasive Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease
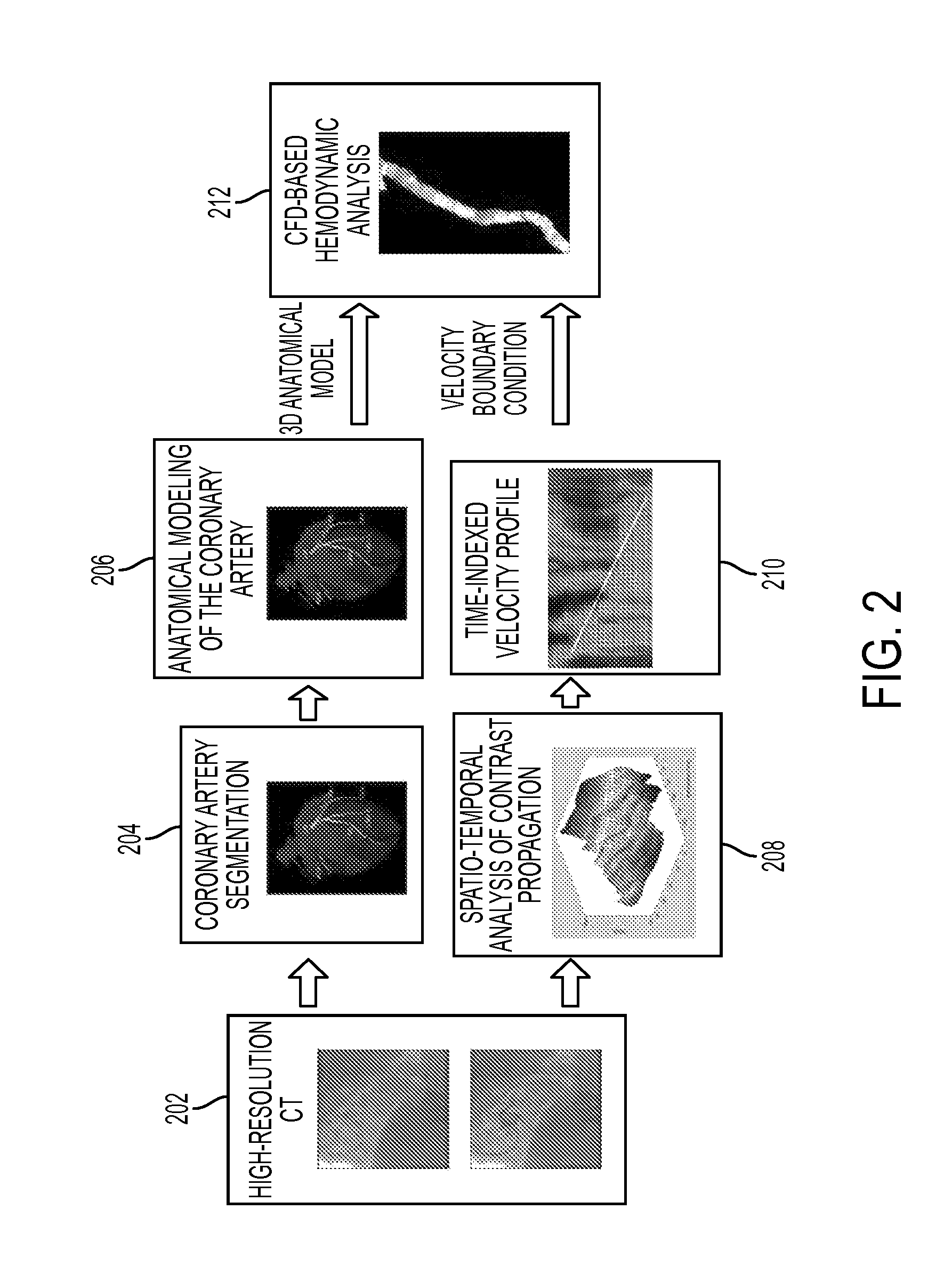
A method and system for non-invasive patient-specific assessment of coronary artery disease is disclosed. An anatomical model of a coronary artery is generated from medical image data. A velocity of blood in the coronary artery is estimated based on a spatio-temporal representation of contrast agent propagation in the medical image data. Blood flow is simulated in the anatomical model of the coronary artery using a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation using the estimated velocity of the blood in the coronary artery as a boundary condition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
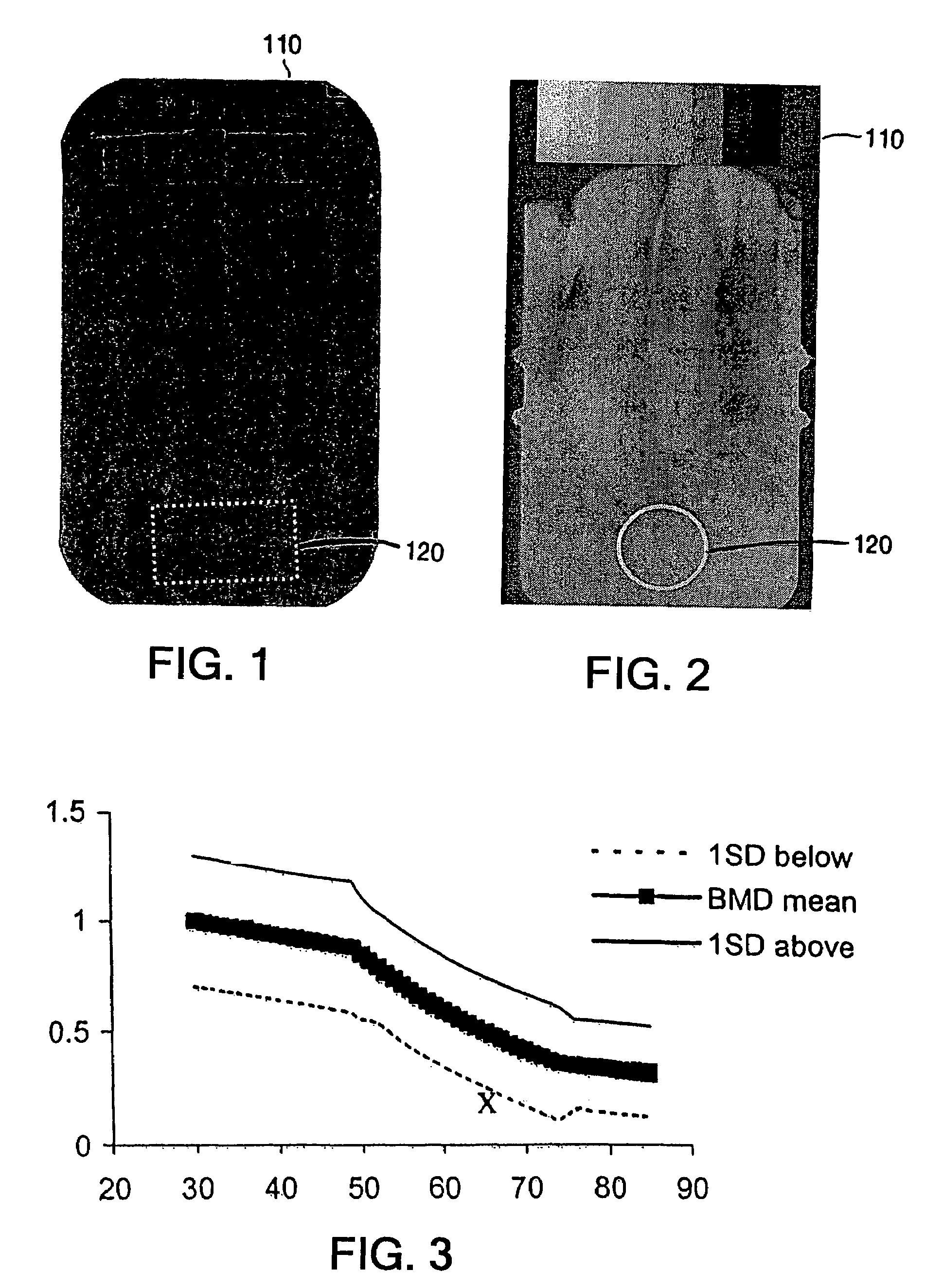
Methods for the compensation of imaging technique in the processing of radiographic images
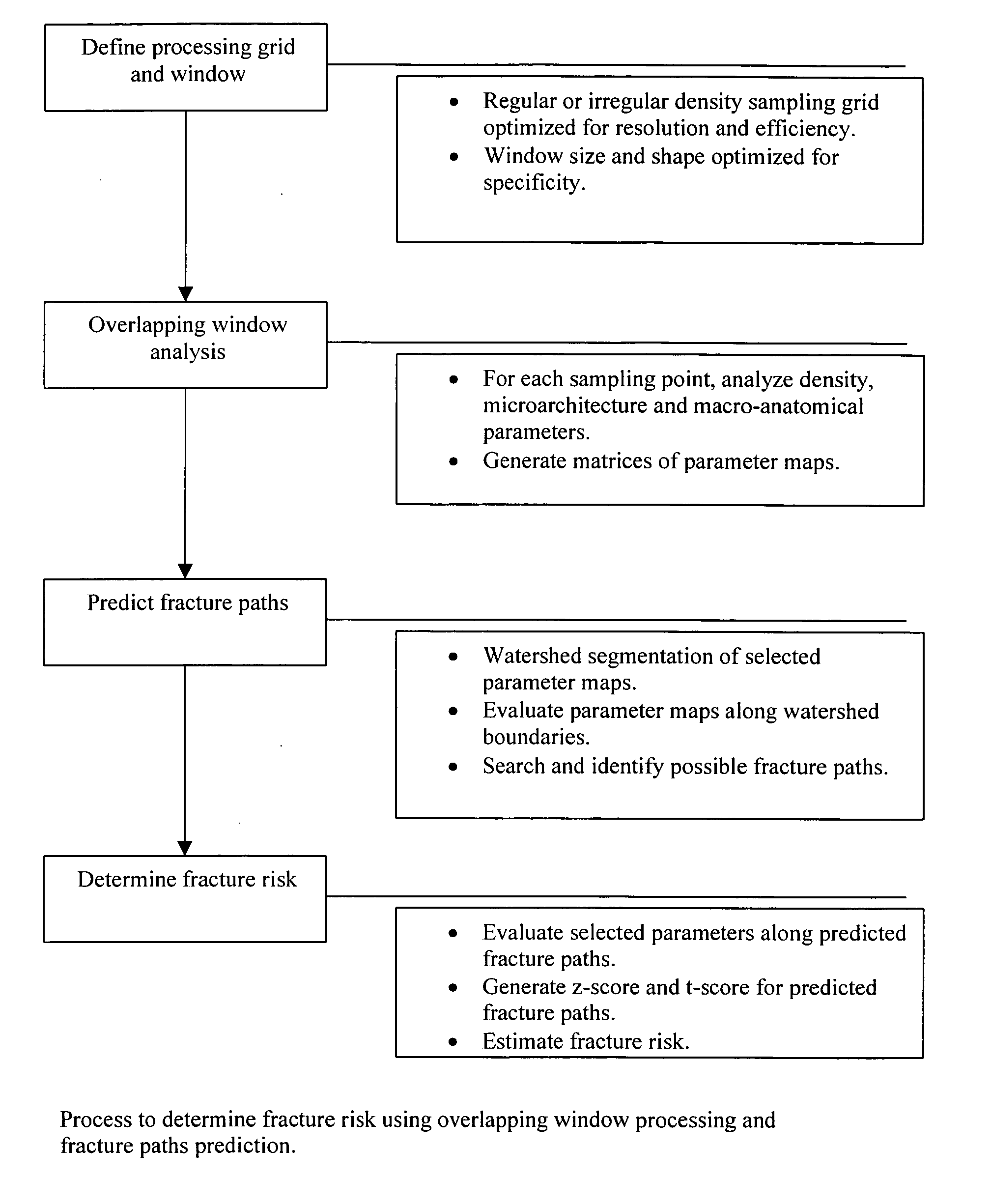
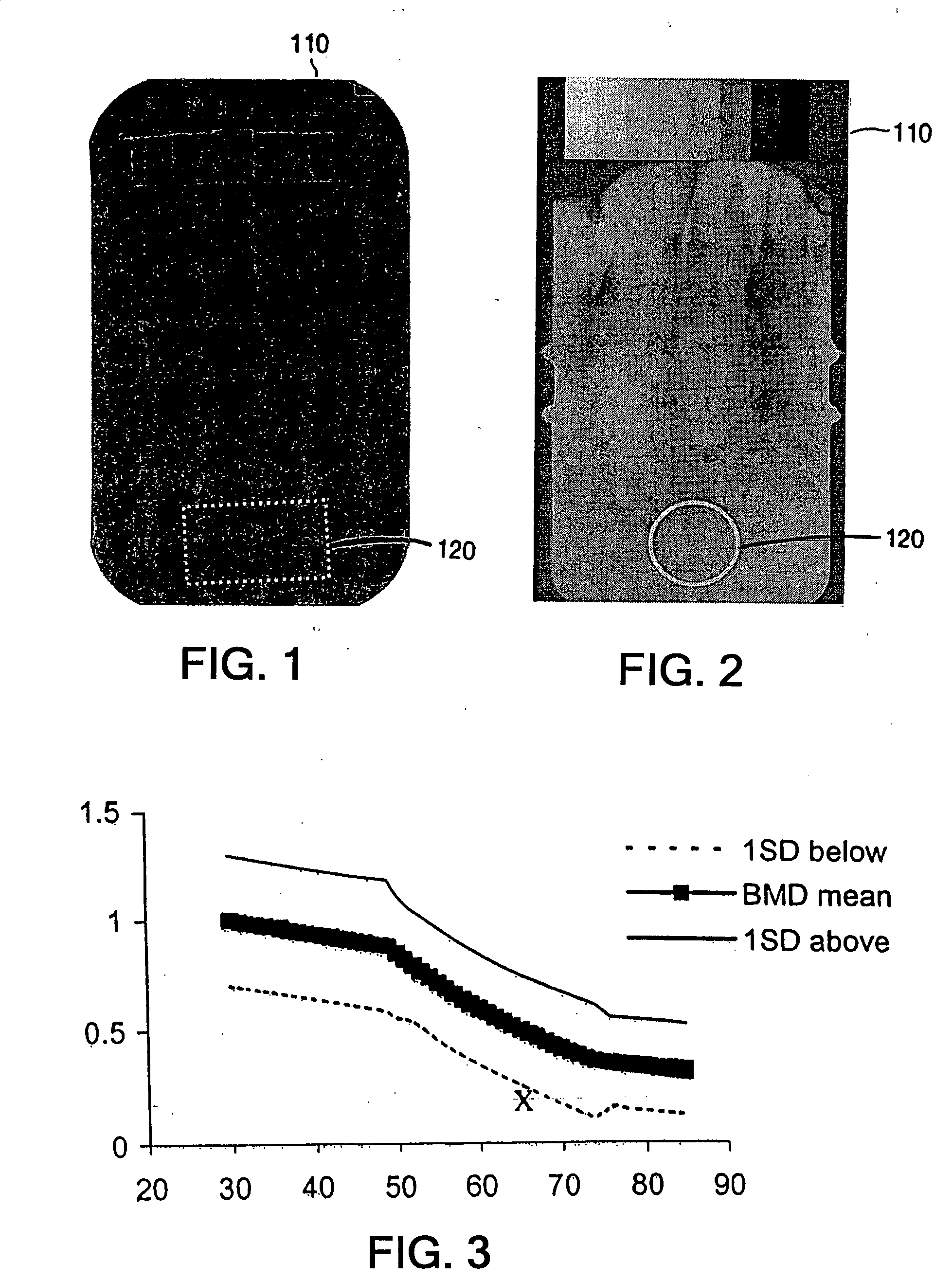
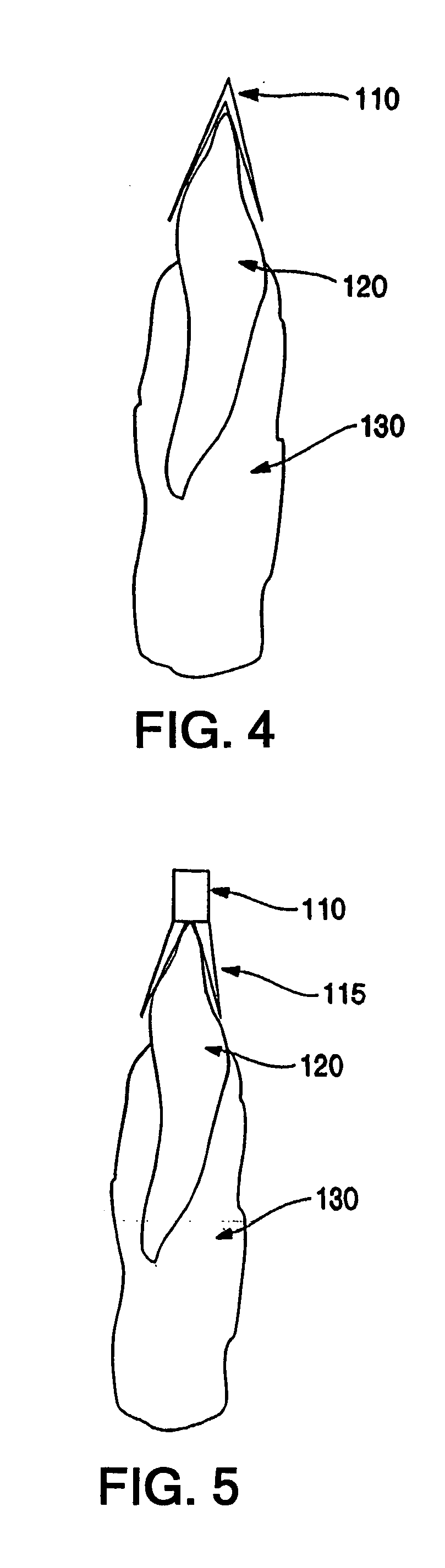
The present invention relates to methods and devices for analyzing x-ray images. In particular, devices, methods and algorithms are provided that allow for the accurate and reliable evaluation of bone structure and macro-anatomical parameters from x-ray images.
Owner:IMATX
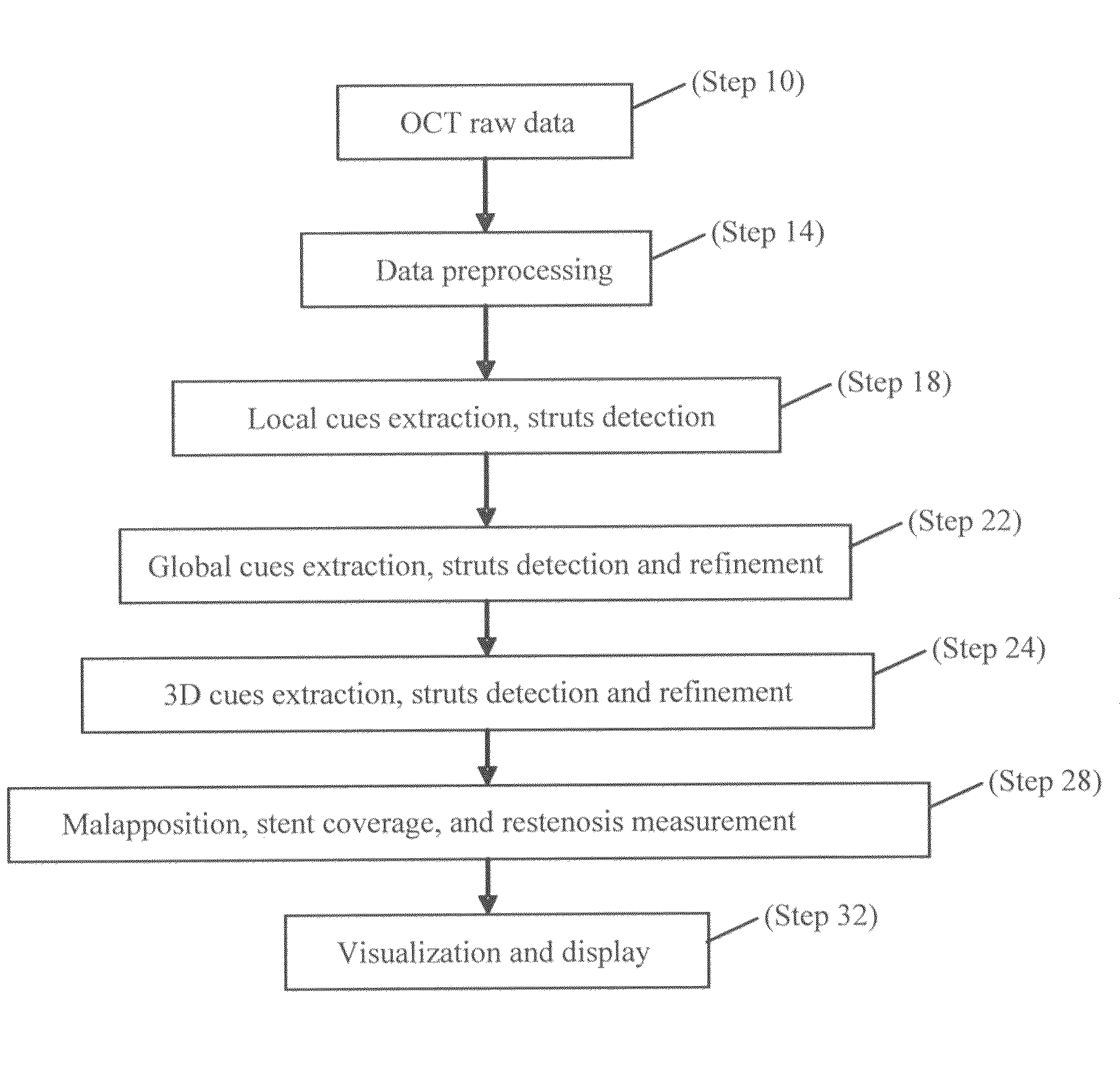
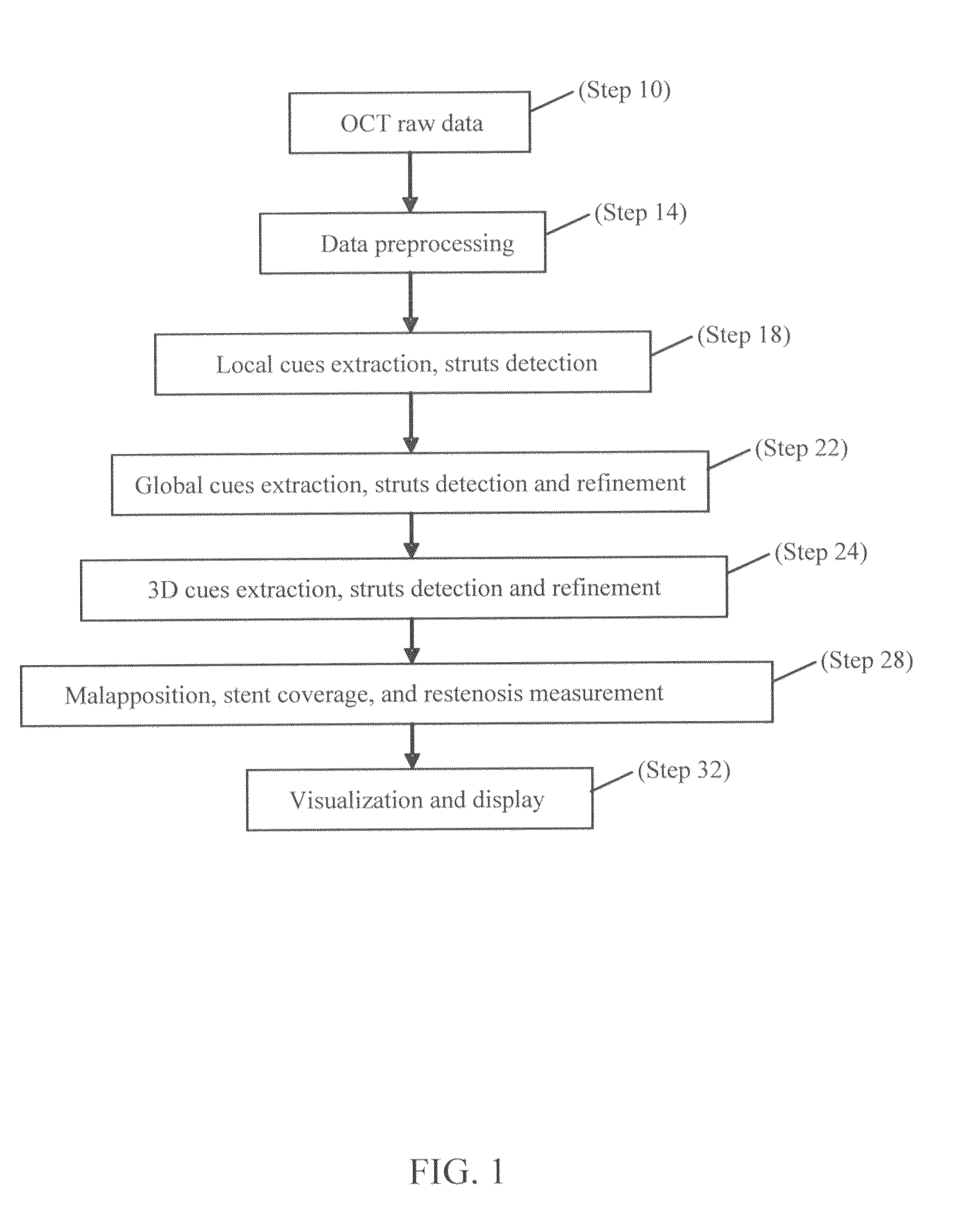
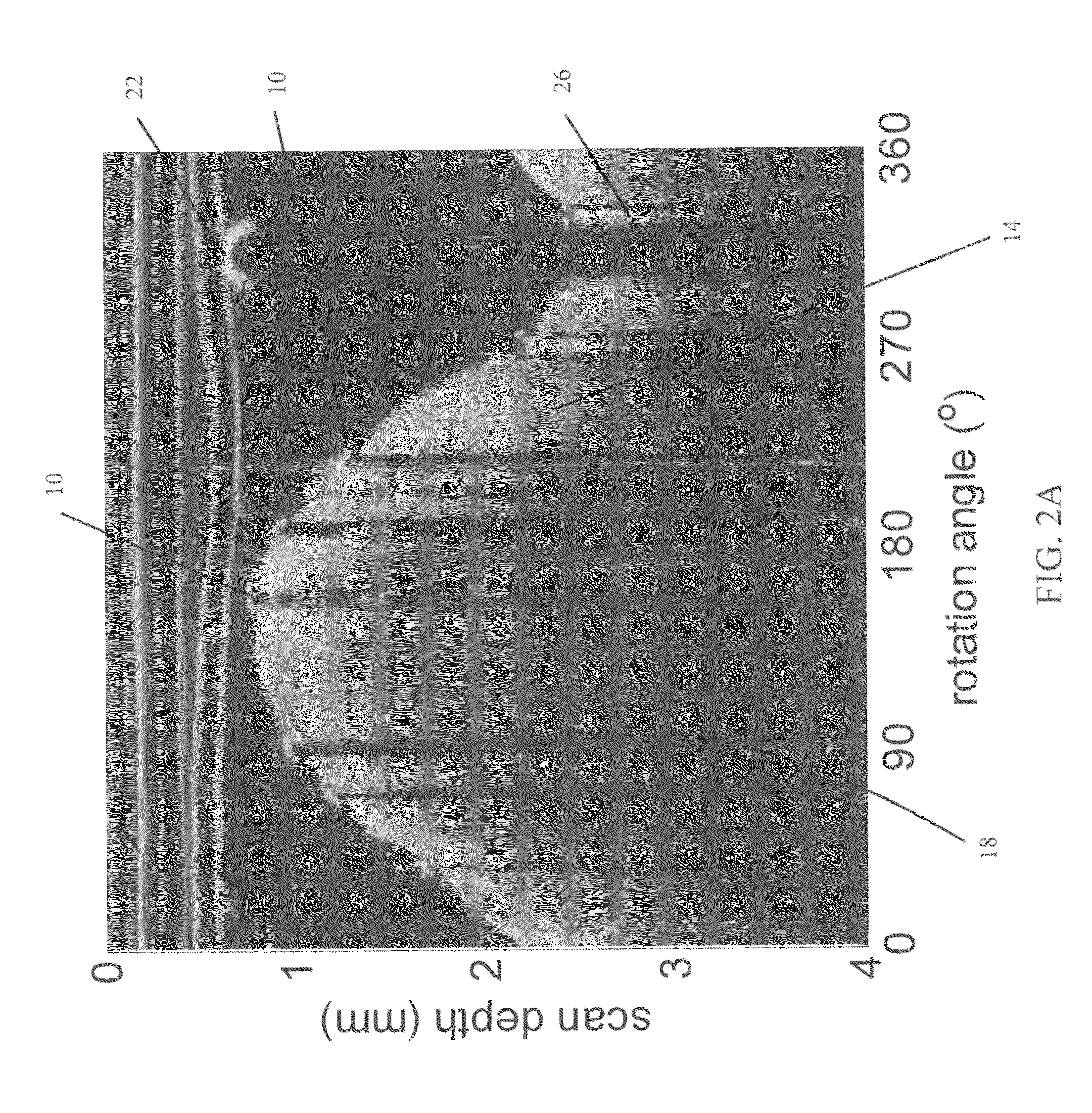
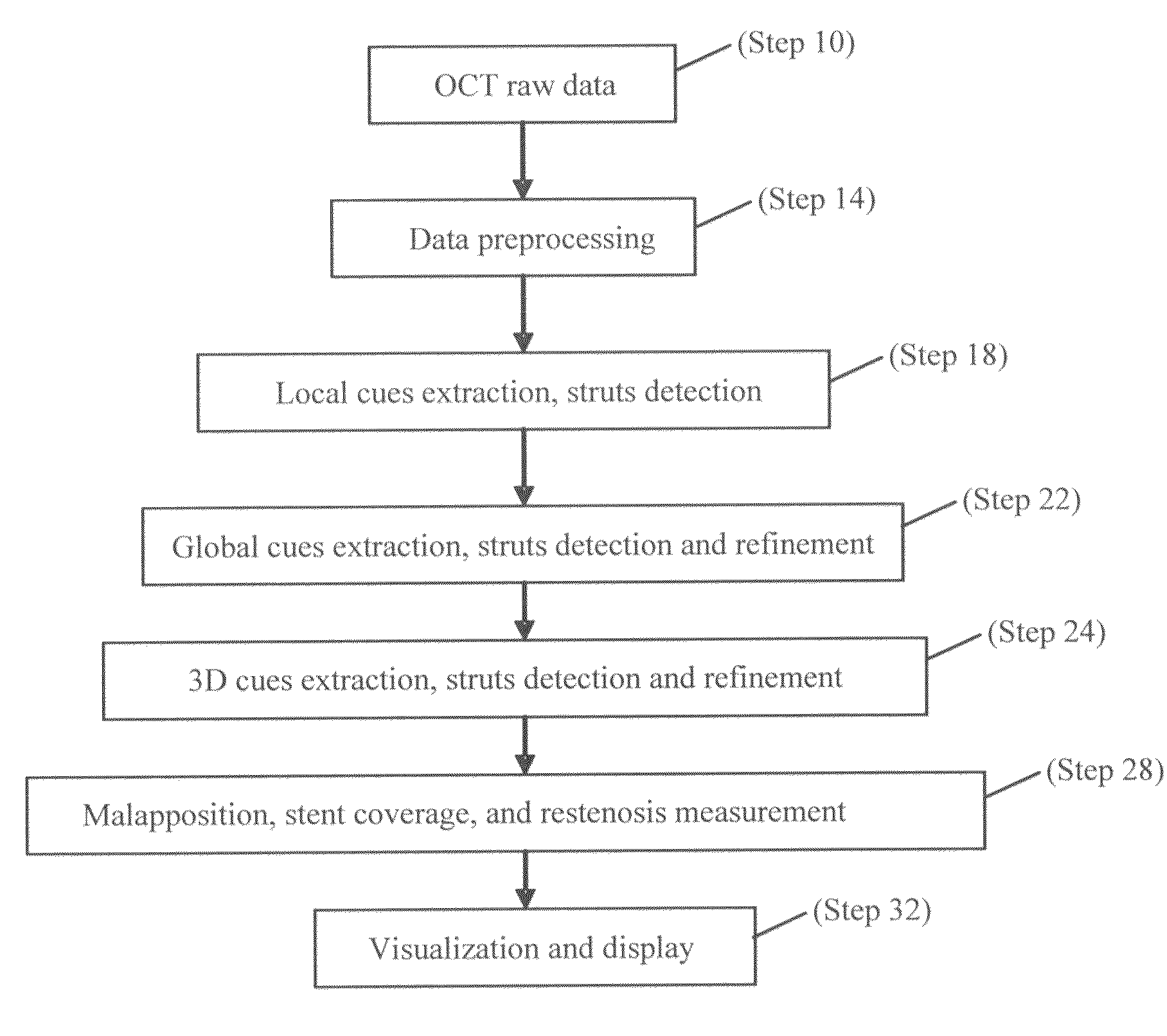
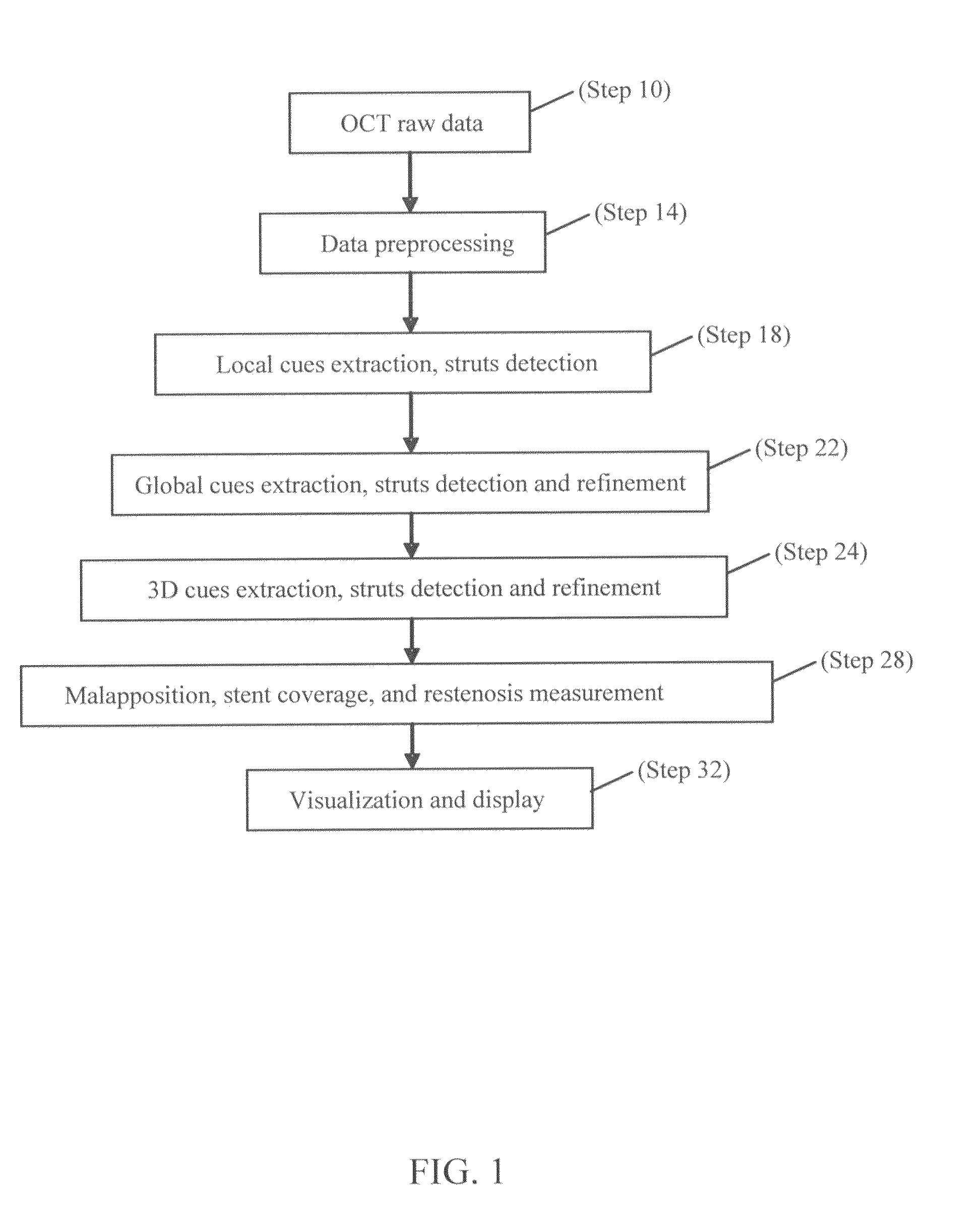
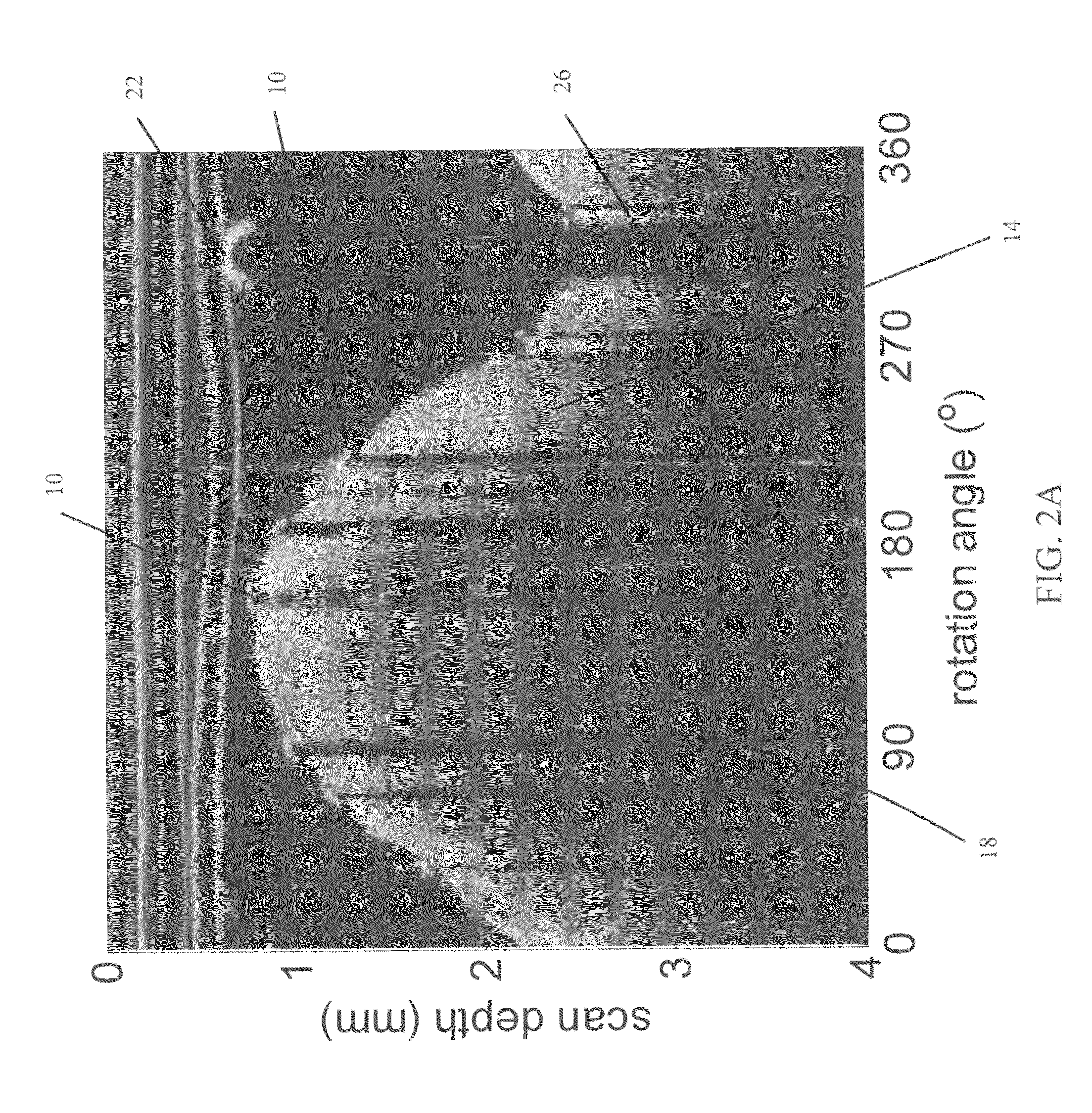
Methods for stent strut detection and related measurement and display using optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20100094127A1High resolutionIncrease contrastImage enhancementMedical imagingData setInsertion stent
In one embodiment, the invention relates to a processor based method for generating positional and other information relating to a stent in the lumen of a vessel using a computer. The method includes the steps of generating an optical coherence image data set in response to an OCT scan of a sample containing at least one stent; and identifying at least one one-dimensional local cue in the image data set relating to the position of the stent.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Interface for viewing video from cameras on a surgical visualization system
ActiveUS8882662B2Medical imagingIncision instrumentsComputer graphics (images)Electromagnetic interference
A surgical device includes a plurality of cameras integrated therein. The view of each of the plurality of cameras can be integrated together to provide a composite image. A surgical tool that includes an integrated camera may be used in conjunction with the surgical device. The image produced by the camera integrated with the surgical tool may be associated with the composite image generated by the plurality of cameras integrated in the surgical device. The position and orientation of the cameras and / or the surgical tool can be tracked, and the surgical tool can be rendered as transparent on the composite image. A surgical device may be powered by a hydraulic system, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference with tracking devices.
Owner:CAMPLEX
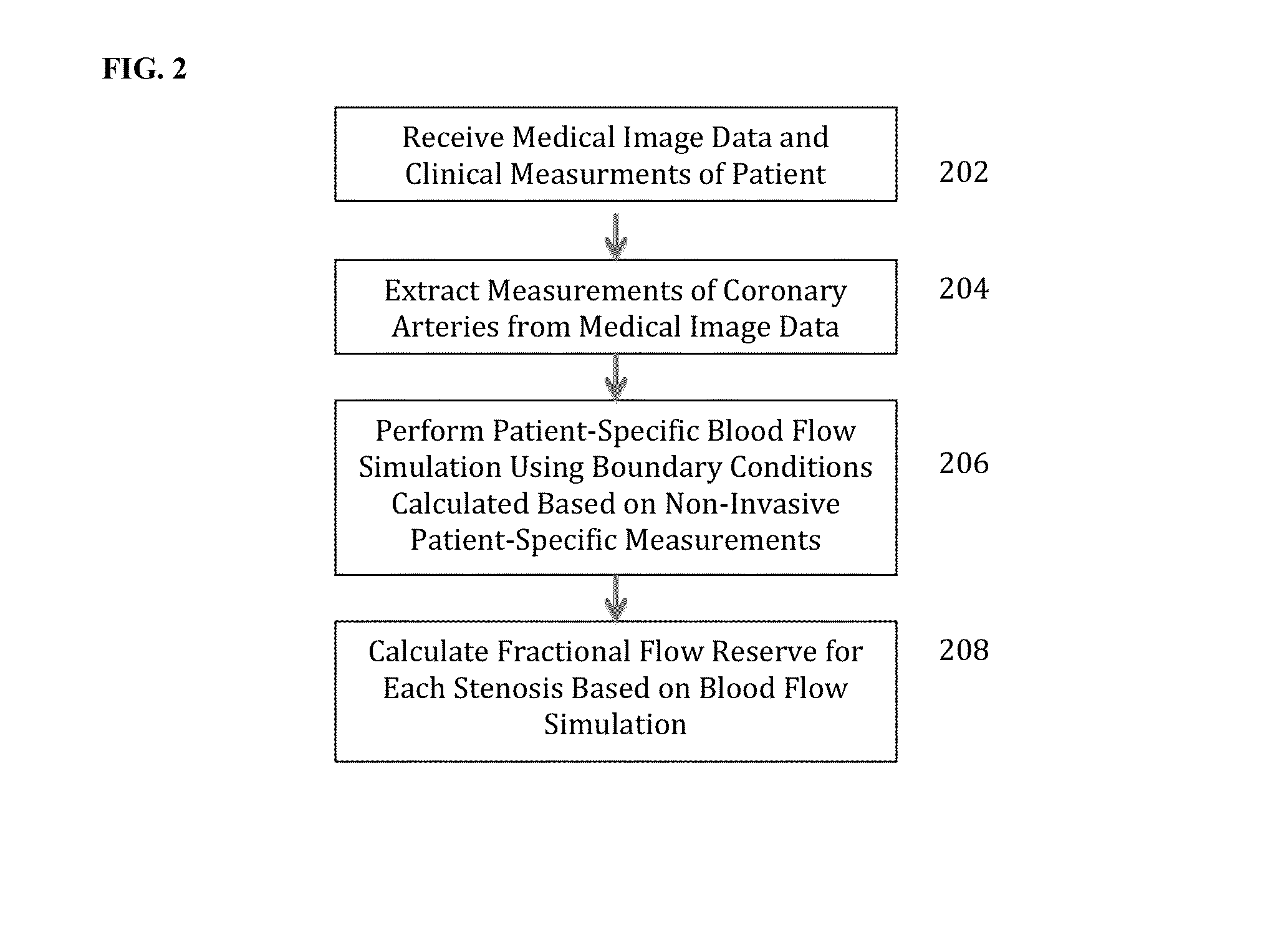
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
InactiveUS20130246034A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Imaging for use with moving organs
InactiveUS20080221442A1Reduce imaged motionWeaken the visual effectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingImage trackingBody system
Apparatus is described for imaging a portion of a body of a subject that moves as a result of cyclic activity of a body system of the subject and that also undergoes additional motion. An imaging device acquires a plurality of image frames of the portion. A sensor senses a phase of the cyclic activity of the body system. A control unit generates a stabilized set of image frames of the portion by identifying a given phase of the cyclic activity, and outputting a set of the image frames corresponding to image frames of the portion acquired during the given phase, and by image tracking at least the set of image frames to reduce imaged motion of the portion associated with the additional motion. A display displays the stabilized set of image frames of the portion. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:SYNC RX
Physiologic data acquisition and analysis
InactiveUS20140378810A1Lower cost of careImage enhancementMedical imagingPattern recognitionImaging analysis
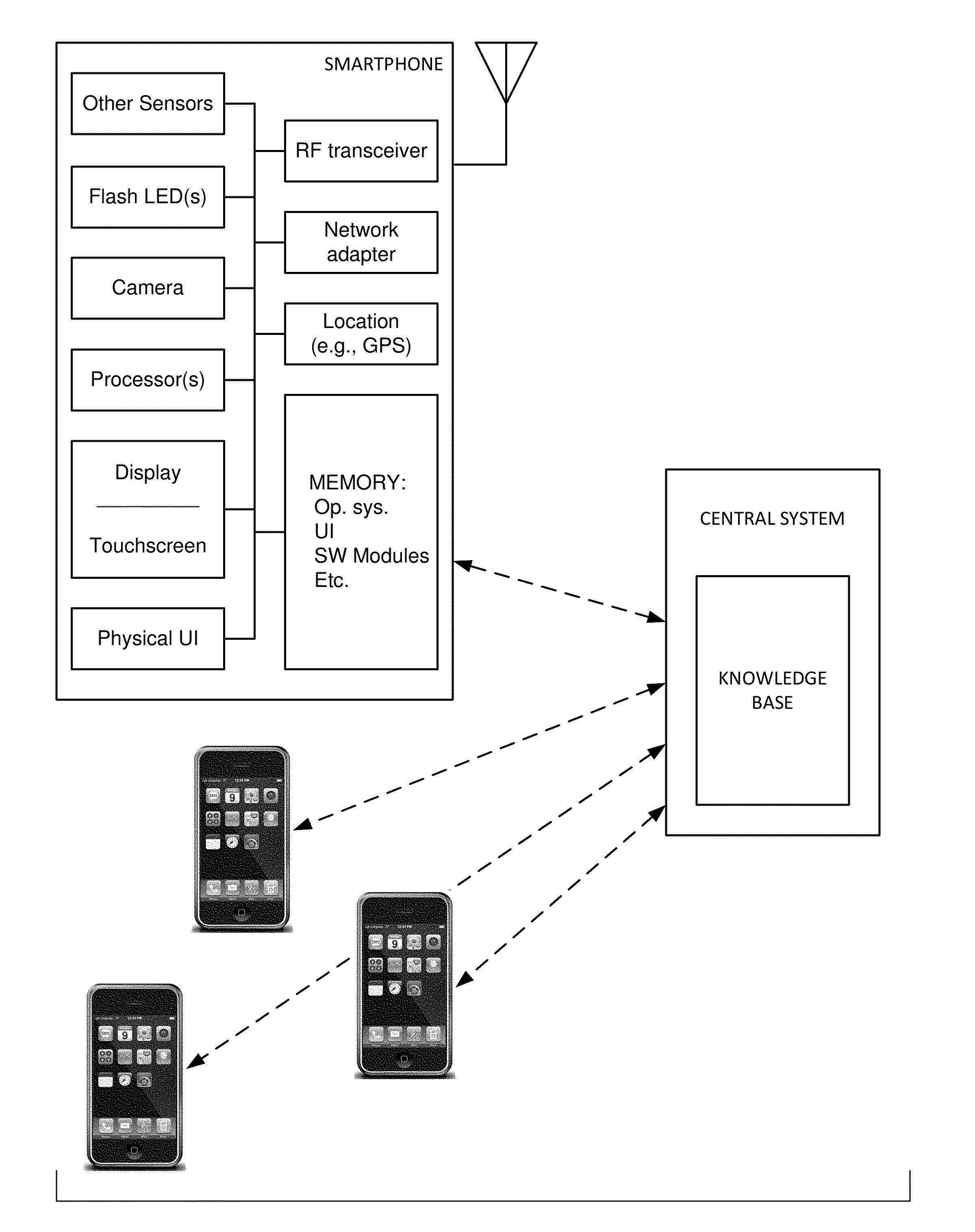
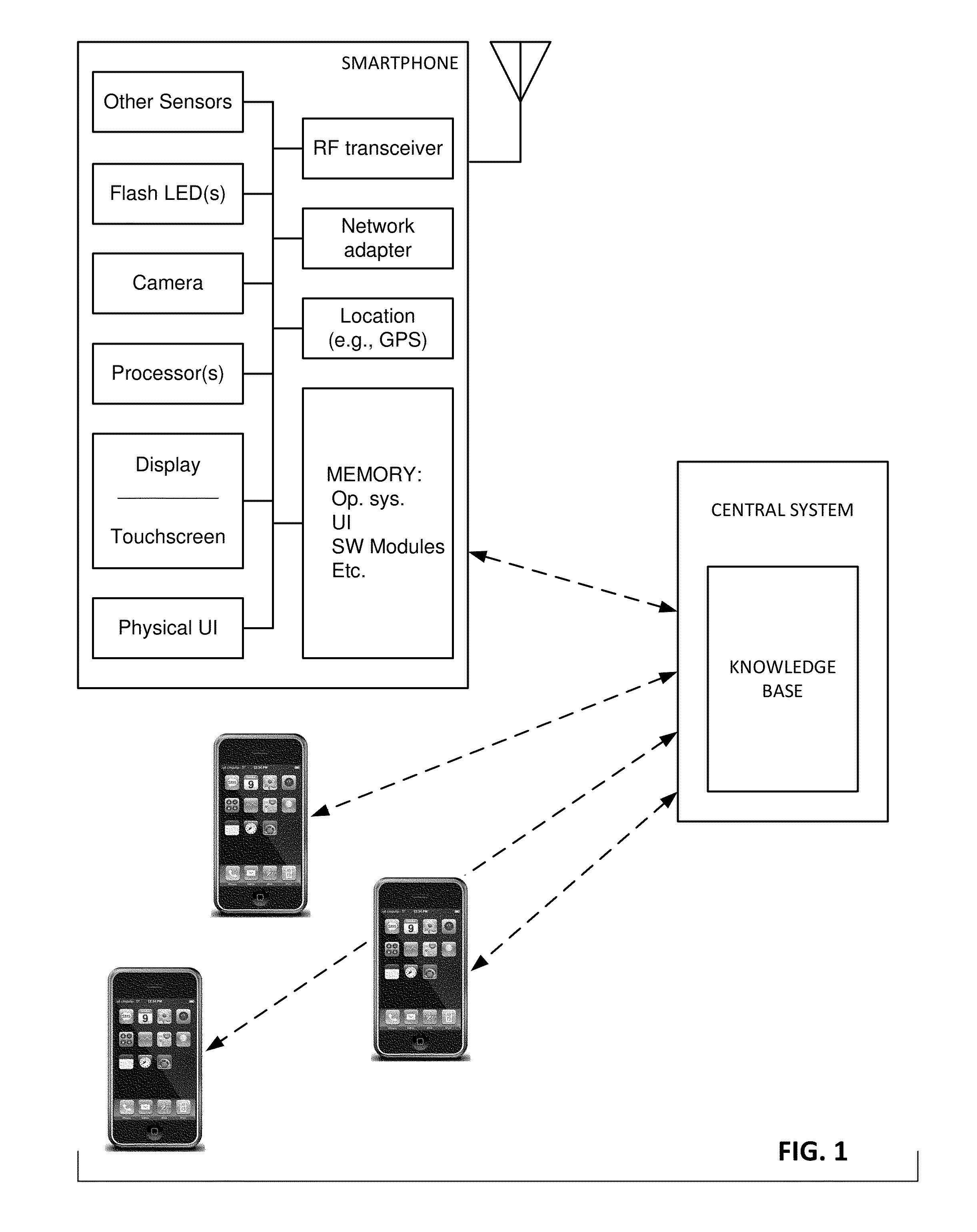
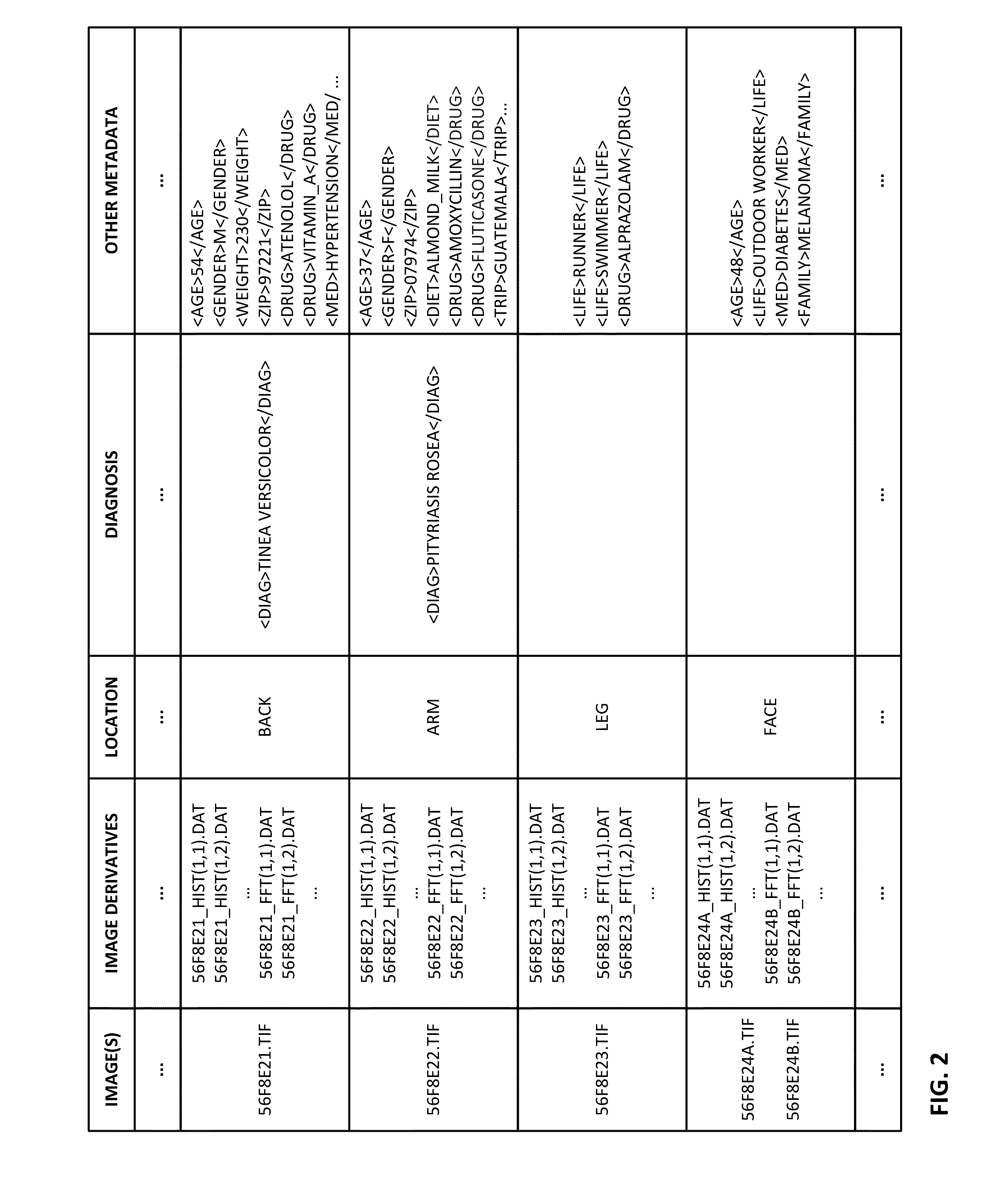
The availability of high quality imagers on smartphones and other portable devices facilitates creation of a large, crowd-sourced, image reference library that depicts skin rashes and other dermatological conditions. Some of the images are uploaded with, or later annotated with, associated diagnoses or other information (e.g., “this rash went away when I stopped drinking milk”). A user uploads a new image of an unknown skin condition to the library. Image analysis techniques are employed to identify salient similarities between features of the uploaded image, and features of images in this reference library. Given the large dataset, statistically relevant correlations emerge that identify to the user certain diagnoses that may be considered, other diagnoses that may likely be ruled-out, and / or anecdotal information about similar skin conditions from other users. Similar arrangements can employ audio and / or other physiologically-derived signals. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Interface for viewing video from cameras on a surgical visualization system
ActiveUS20140005484A1Different stiffnessMedical imagingSurgical furnitureRadiologyReoperative surgery
A surgical device includes a plurality of cameras integrated therein. The view of each of the plurality of cameras can be integrated together to provide a composite image. A surgical tool that includes an integrated camera may be used in conjunction with the surgical device. The image produced by the camera integrated with the surgical tool may be associated with the composite image generated by the plurality of cameras integrated in the surgical device. The position and orientation of the cameras and / or the surgical tool can be tracked, and the surgical tool can be rendered as transparent on the composite image. A surgical device may be powered by a hydraulic system, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference with tracking devices.
Owner:CAMPLEX
System and Method for Diagnosing Arrhythmias and Directing Catheter Therapies
An efficient system for diagnosing arrhythmias and directing catheter therapies may allow for measuring, classifying, analyzing, and mapping spatial electrophysiological (EP) patterns within a body. The efficient system may further guide arrhythmia therapy and update maps as treatment is delivered. The efficient system may use a medical device having a high density of sensors with a known spatial configuration for collecting EP data and positioning data. Further, the efficient system may also use an electronic control system (ECU) for computing and providing the user with a variety of metrics, derivative metrics, high definition (HD) maps, HD composite maps, and general visual aids for association with a geometrical anatomical model shown on a display device.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
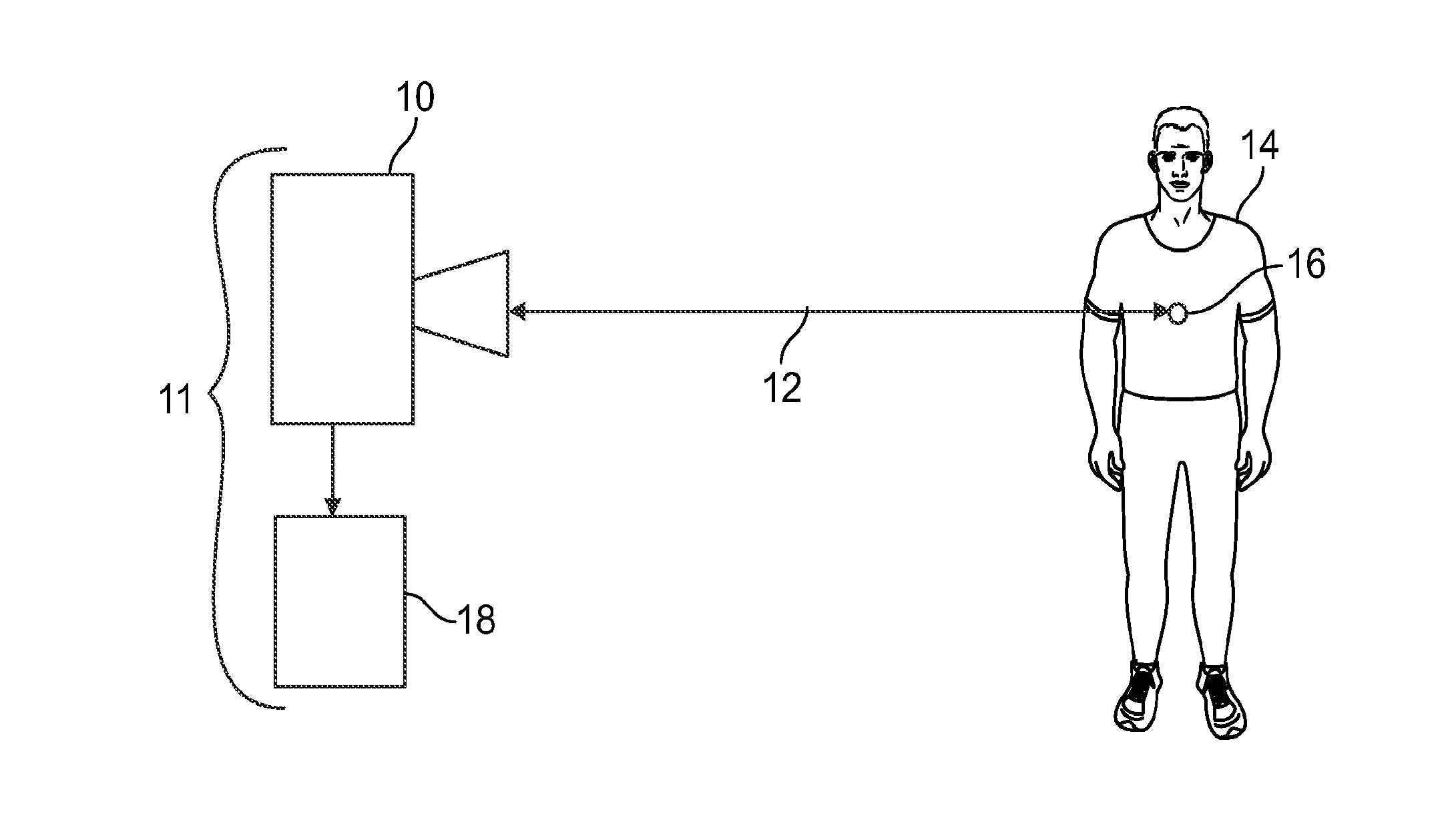
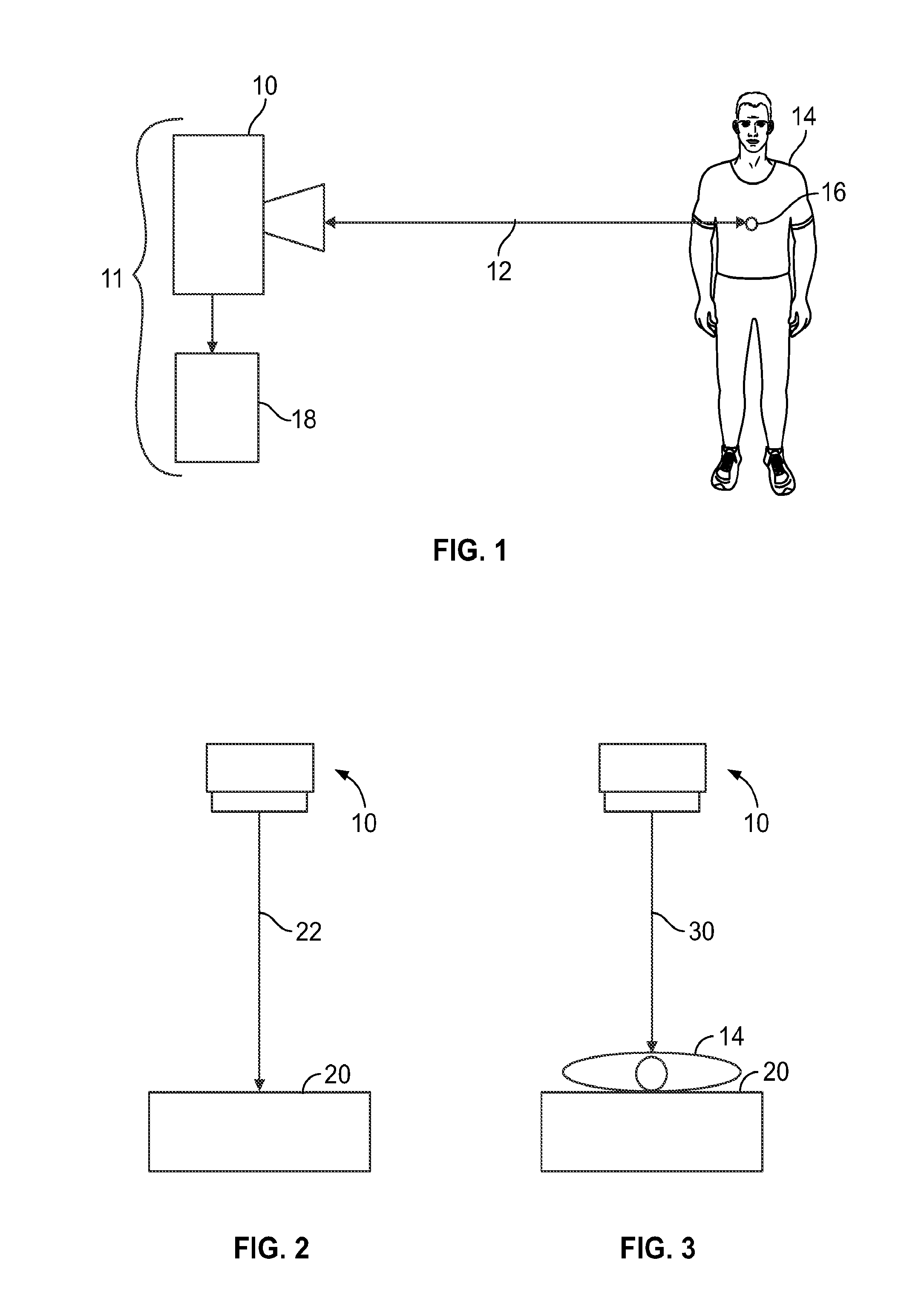
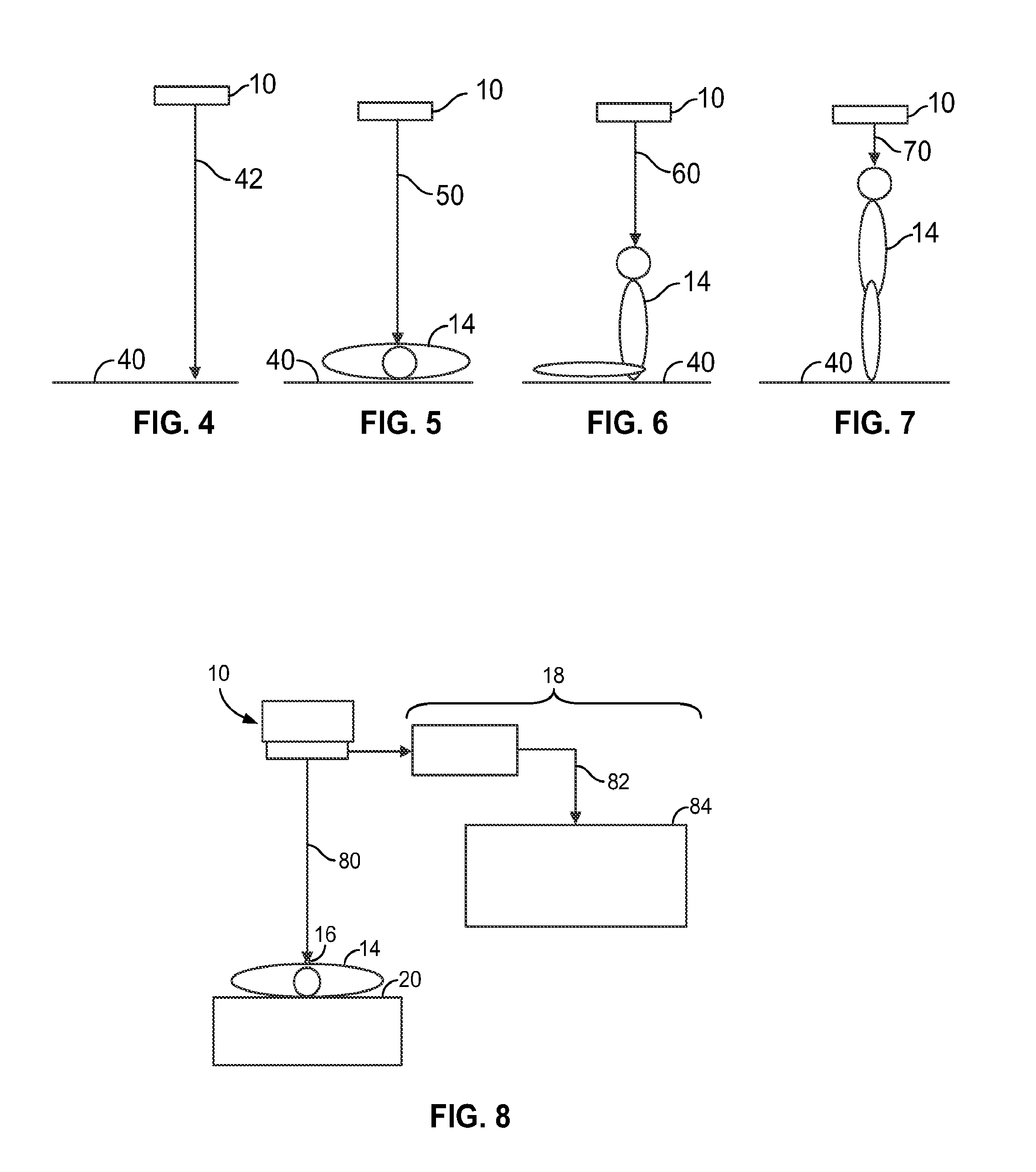
Systems and methods for high resolution distance sensing and applications
A sensing system (11) includes a first radar sensing assembly (10; 3104, 3106; 4100, 4200) and an analysis system (18). The first radar sensing assembly (10; 3104, 3106; 4100, 4200) measures plural distances (12; 22, 30; 42, 50, 60, 70, 80; 4102, 4202) to a first target location (16) at different times using radar. The analysis system (18) receives the plural distances (12; 22, 30; 42, 50, 60, 70, 80; 4102, 4202) from the first radar sensing assembly (10; 3104, 3106; 4100, 4200) and quantifies movements of a target object (14) at the first target location (16) at the different times by calculating differences in the plural distances (10; 3104, 3106; 4100, 4200) measured by the first radar sensing assembly (10; 3104, 3106; 4100, 4200). The analysis system (18) generates one or more first quantified activity level values indicative of the movements of the target object (14) at the first target location (16) using the differences in the plural distances (12; 22, 30; 42, 50, 60, 70, 80; 4102, 4202) that are calculated.
Owner:TRANSROBOTICS INC
Health diagnostic systems and methods
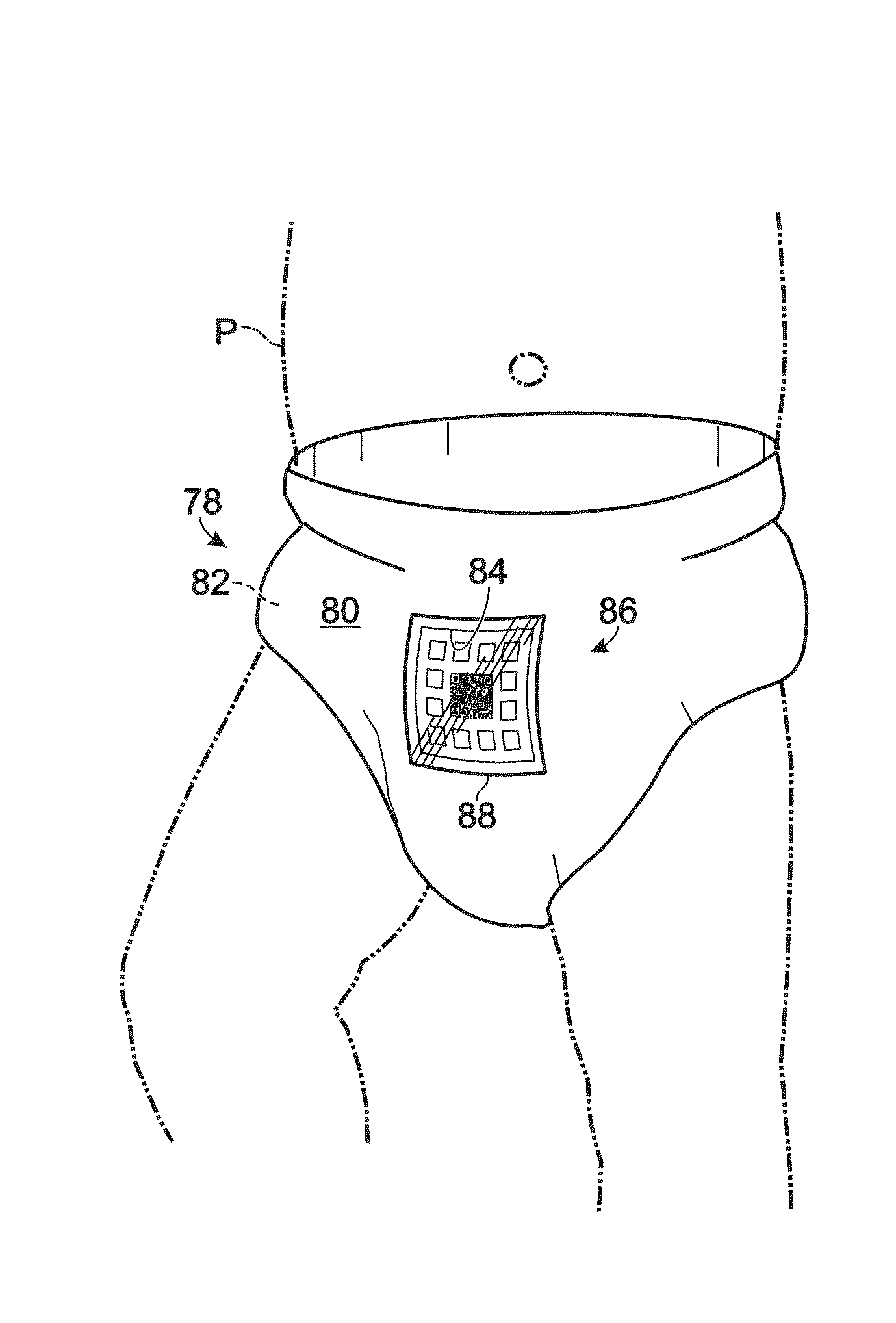
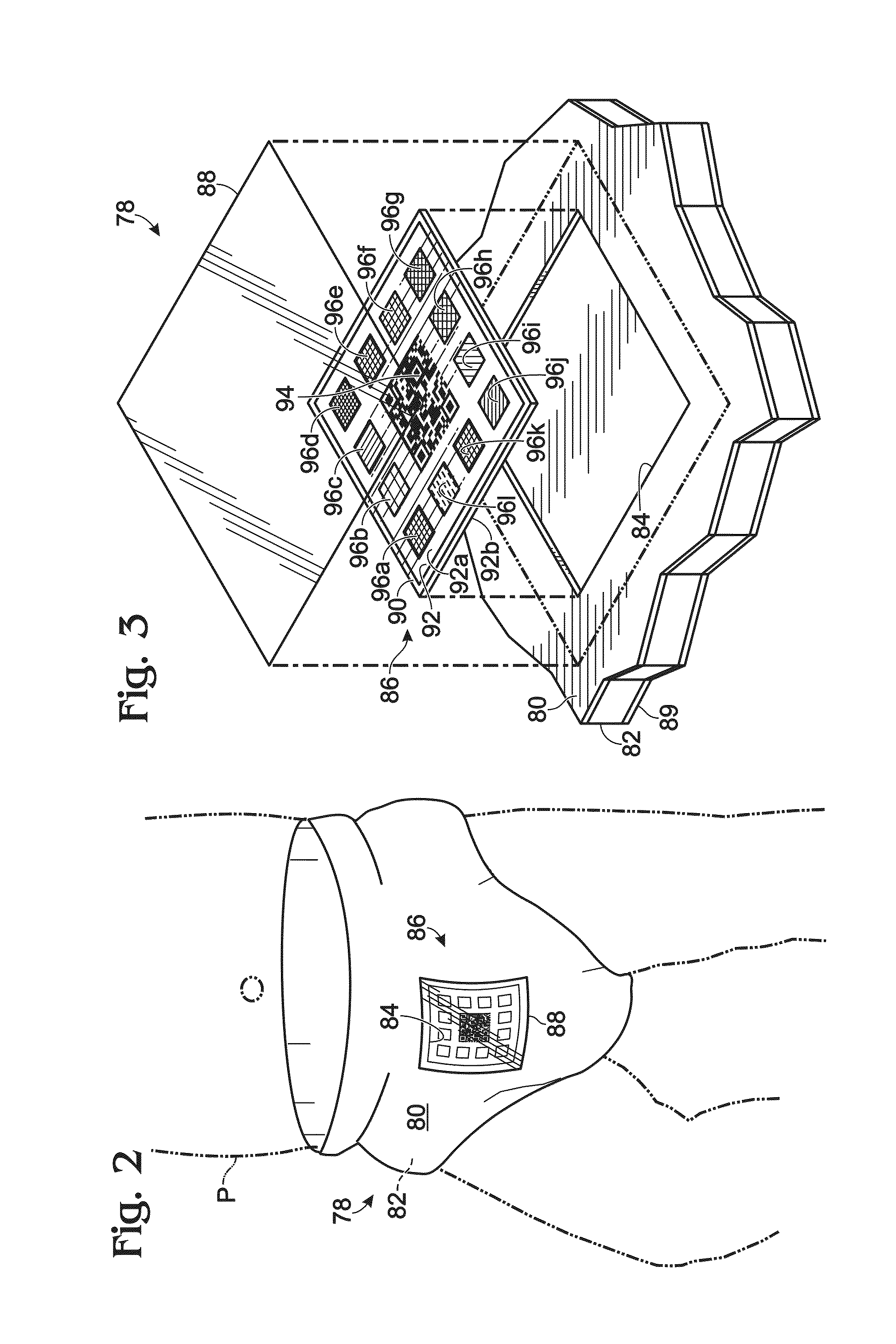
A health monitoring system, and methods of use and manufacture thereof are disclosed. The health monitoring system may include a computing system and a diagnostic test coupled to a diaper. The diagnostic test may include one or more sensors configured to produce a visual indication of one or more analytes contained in a sample produced by a subject. The diagnostic test may include a machine-readable code. The computing system may be configured to read the machine-readable code to allow an application running on the computing system to automatically perform at least one task related to a production of a data point based on the visual indication. The health monitoring system may aid in identifying a potential abnormal health condition of the subject by providing automatic longitudinal analysis of analytes contained in samples produced by the subject over a period of time.
Owner:ANAVAH HEALTH LLC
Imaging and tools for use with moving organs
InactiveUS20080221440A1Reduce imaged motionWeaken the visual effectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingDisplay deviceComputer science
Apparatus is described for use with a portion of a subject's body that moves as a result of cyclic activity of a body system. An imaging device acquires a plurality of image frames of the portion. A sensor senses a phase of the cyclic activity. A medical tool performs a function with respect to the portion. A control unit generates a stabilized set of image frames of the medical tool disposed within the portion, actuates the tool to perform the function or move, in response to the sensor sensing that the cyclic activity is at a given phase thereof, and inhibits the tool from performing the action or moving in response to the sensor sensing that the cyclic activity is not at the given phase. A display facilitates use of the tool by displaying the stabilized set of image frames. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:SYNC RX
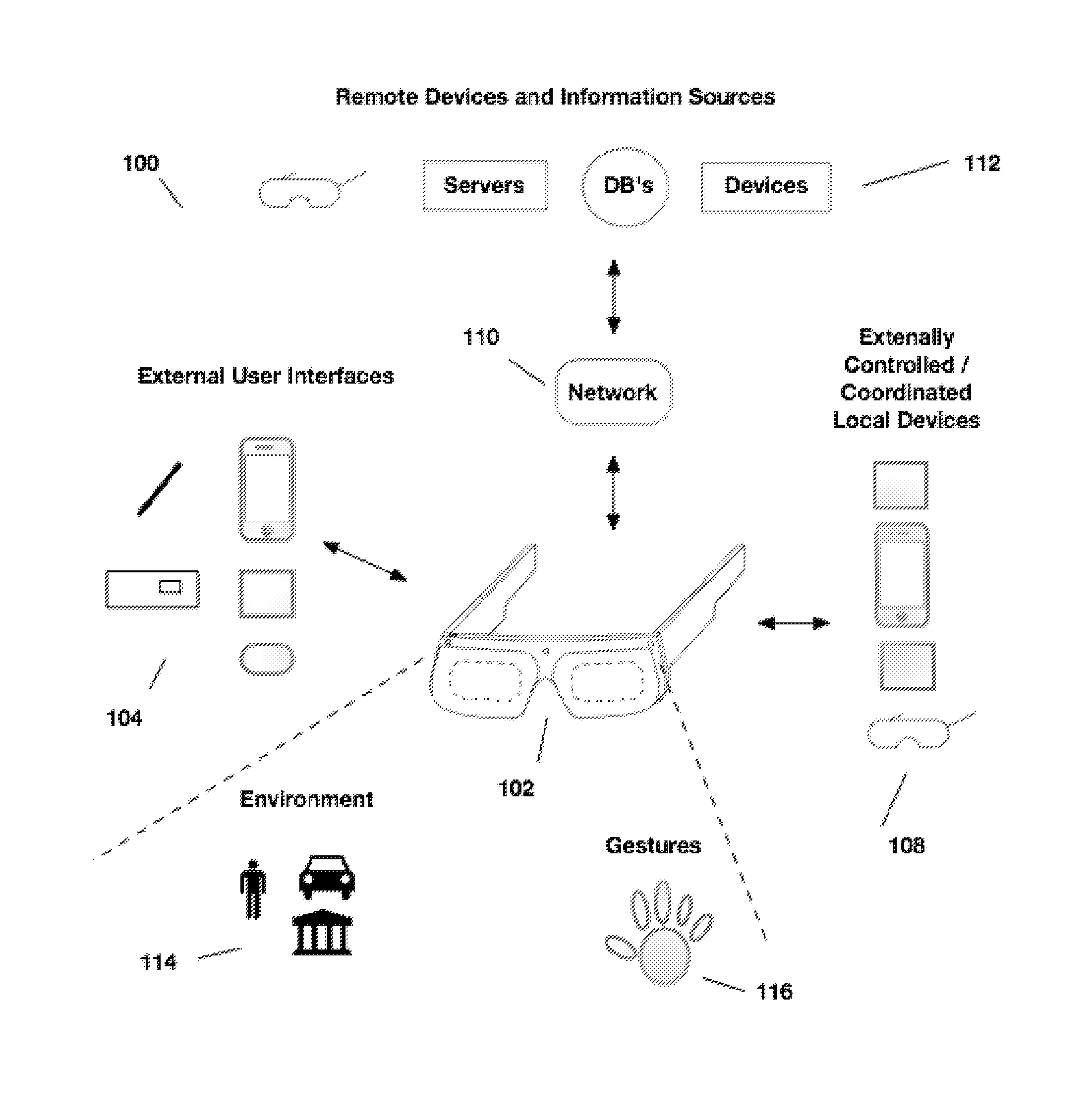
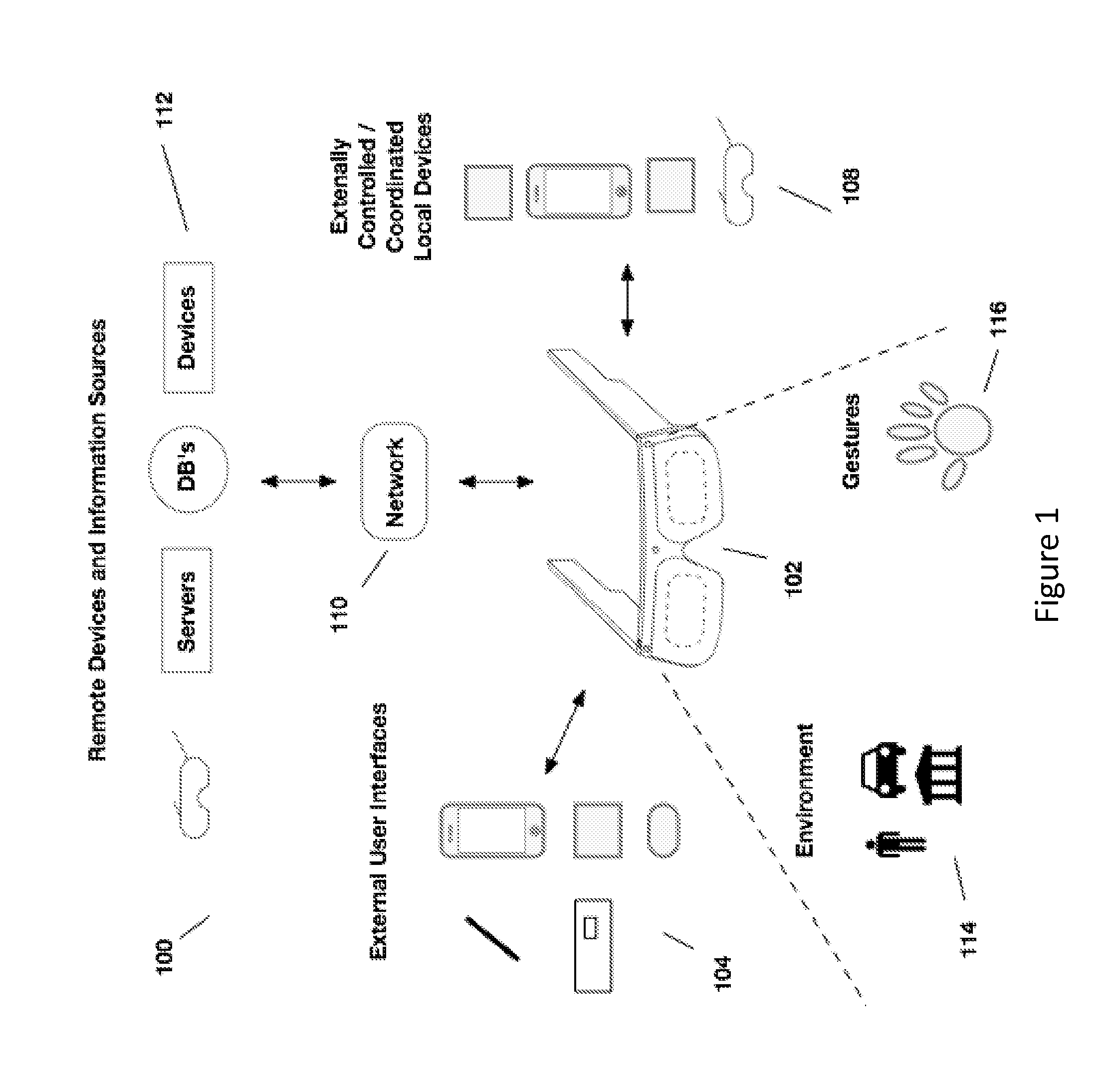
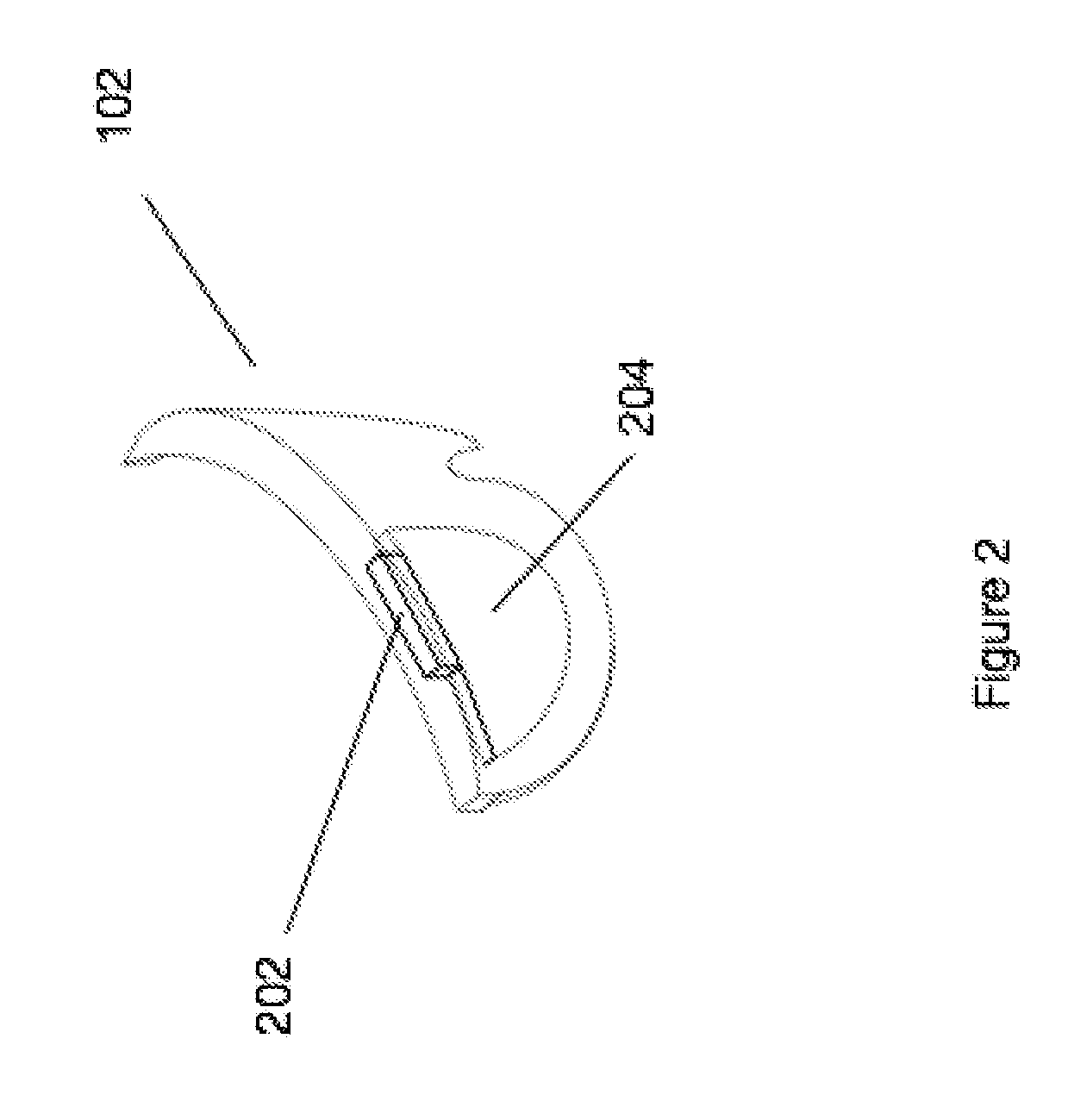
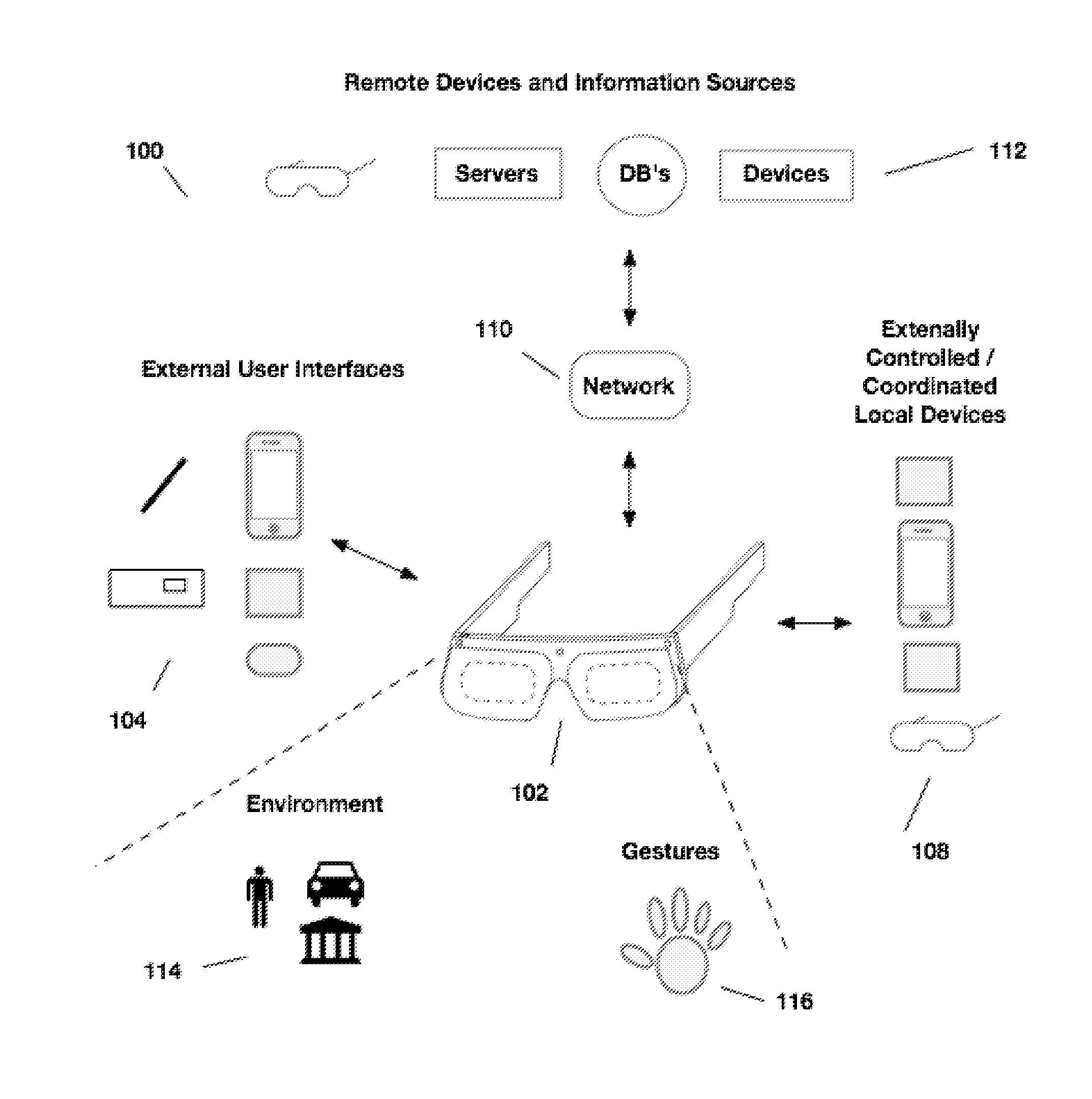
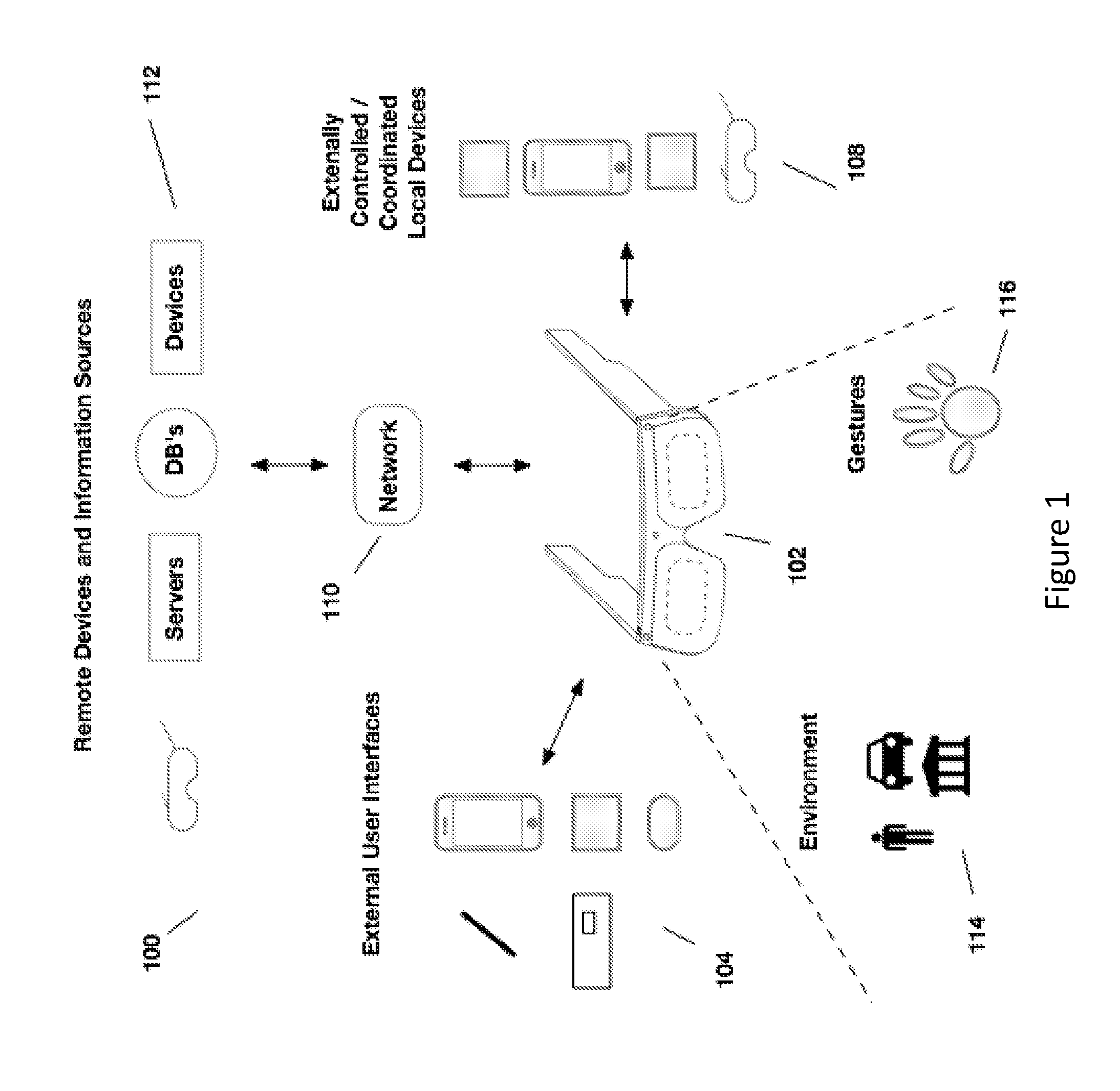
Content presentation in head worn computing
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Nmr systems for in vivo detection of analytes
ActiveUS20100072994A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingAnalyteNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
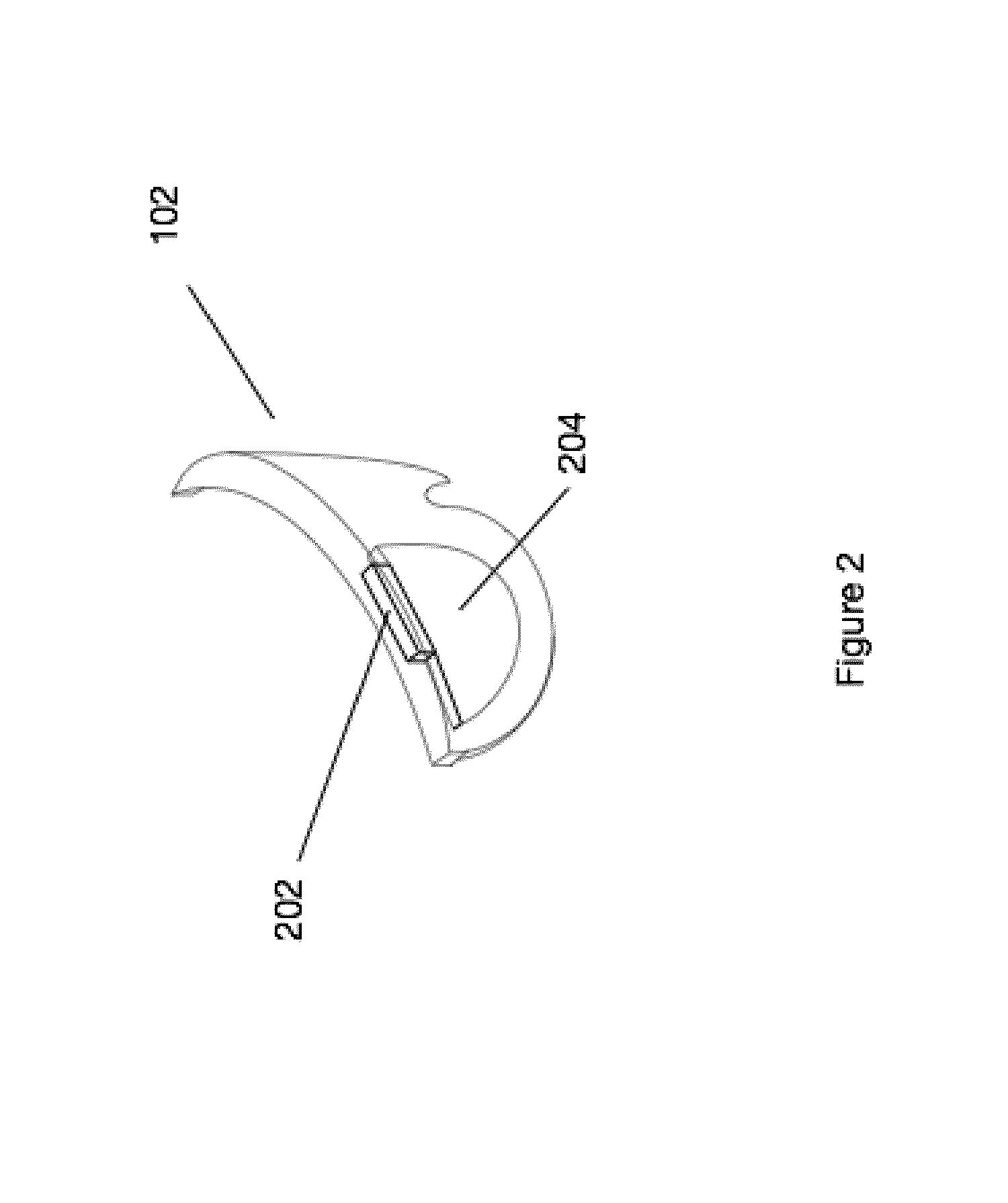
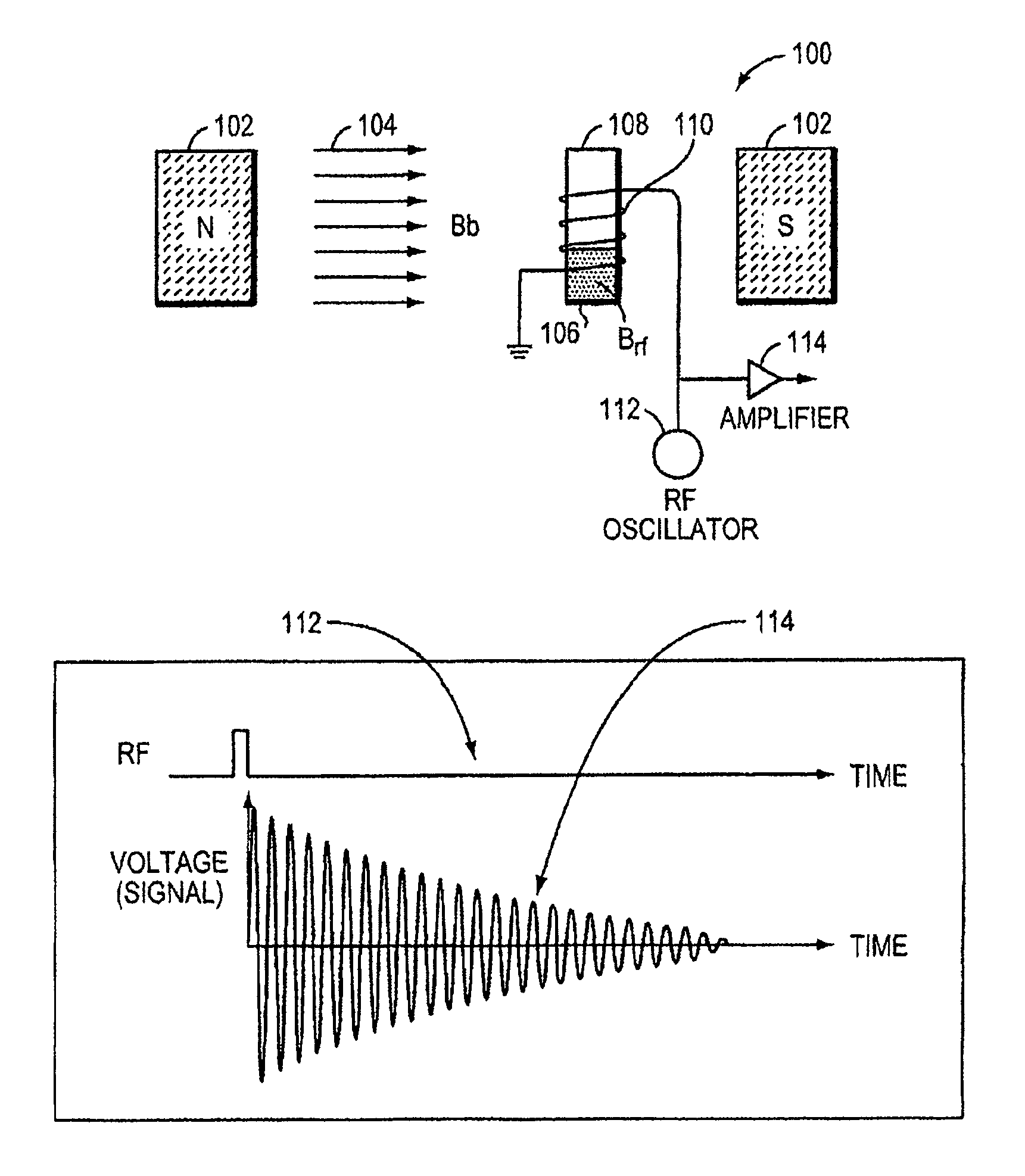
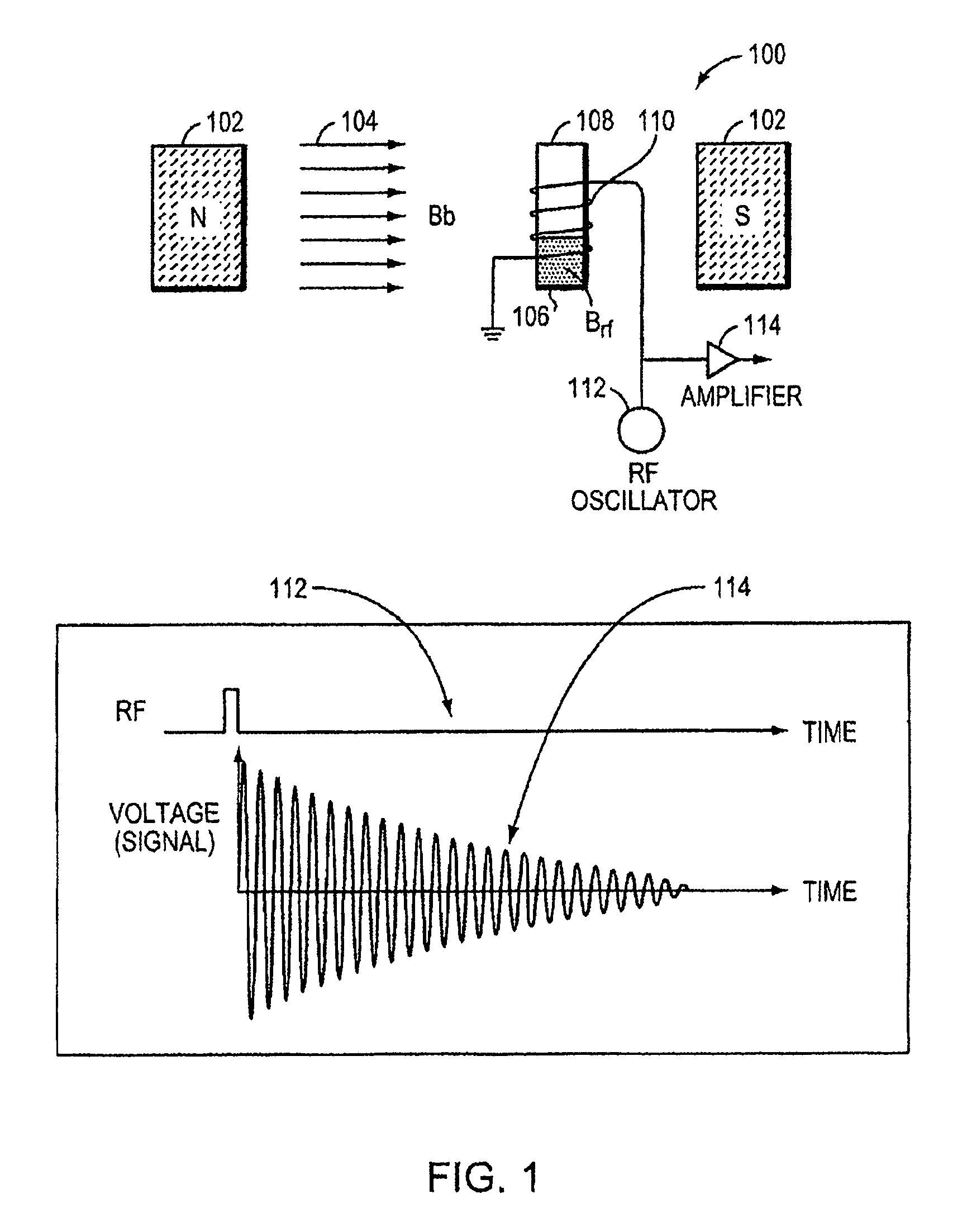
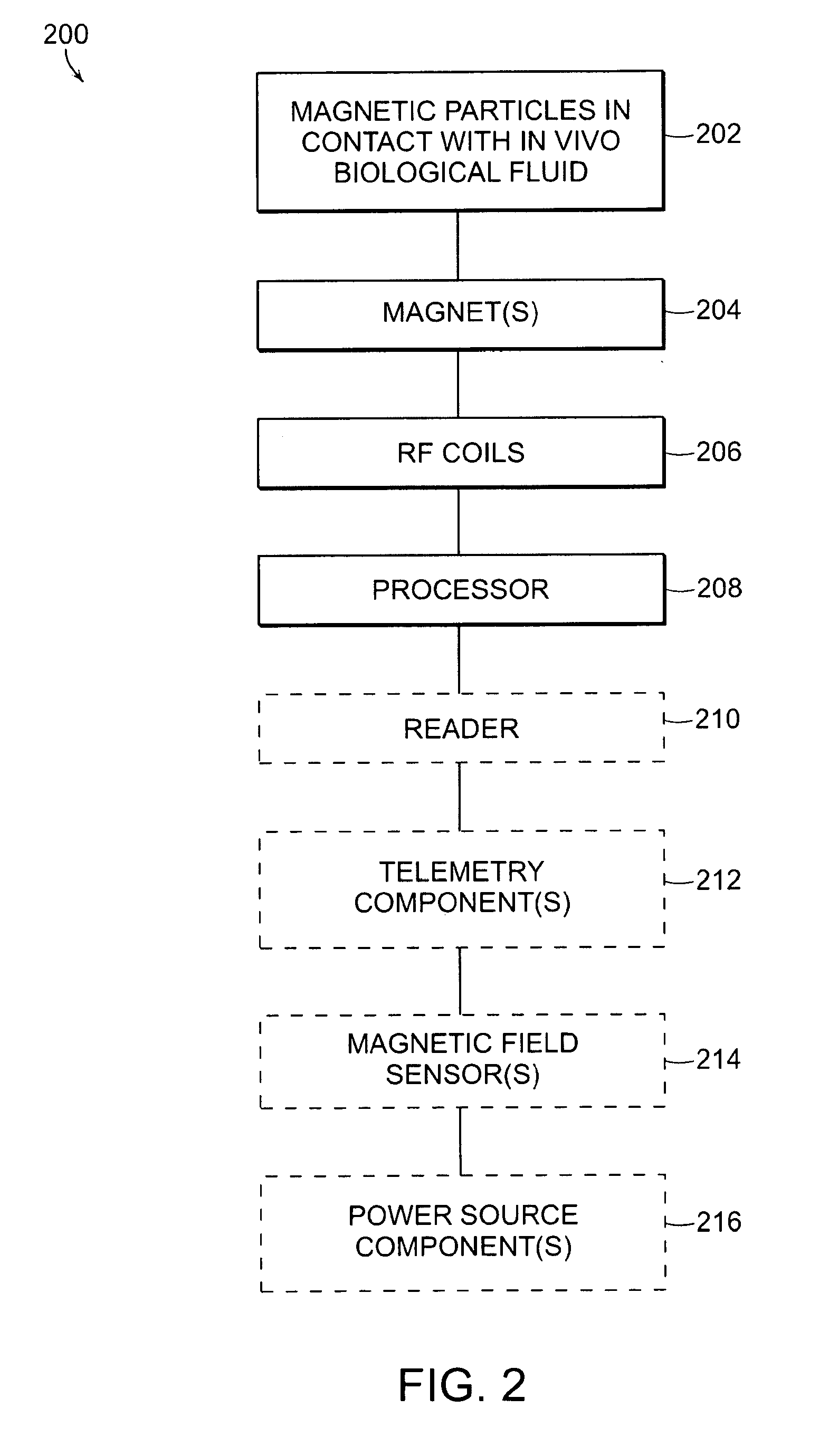
This invention relates generally to NMR systems for in vivo detection of analytes. More particularly, in certain embodiments, the invention relates to systems in which superparamagnetic nanoparticles are exposed to a magnetic field and radio frequency (RF) excitation at or near the Larmor frequency, such that the aggregation and / or disaggregation of the nanoparticles caused by the presence and / or concentration of a given analyte in a biological fluid is detected in vivo from a monitored RF echo response.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
Content presentation in head worn computing
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Content presentation in head worn computing
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
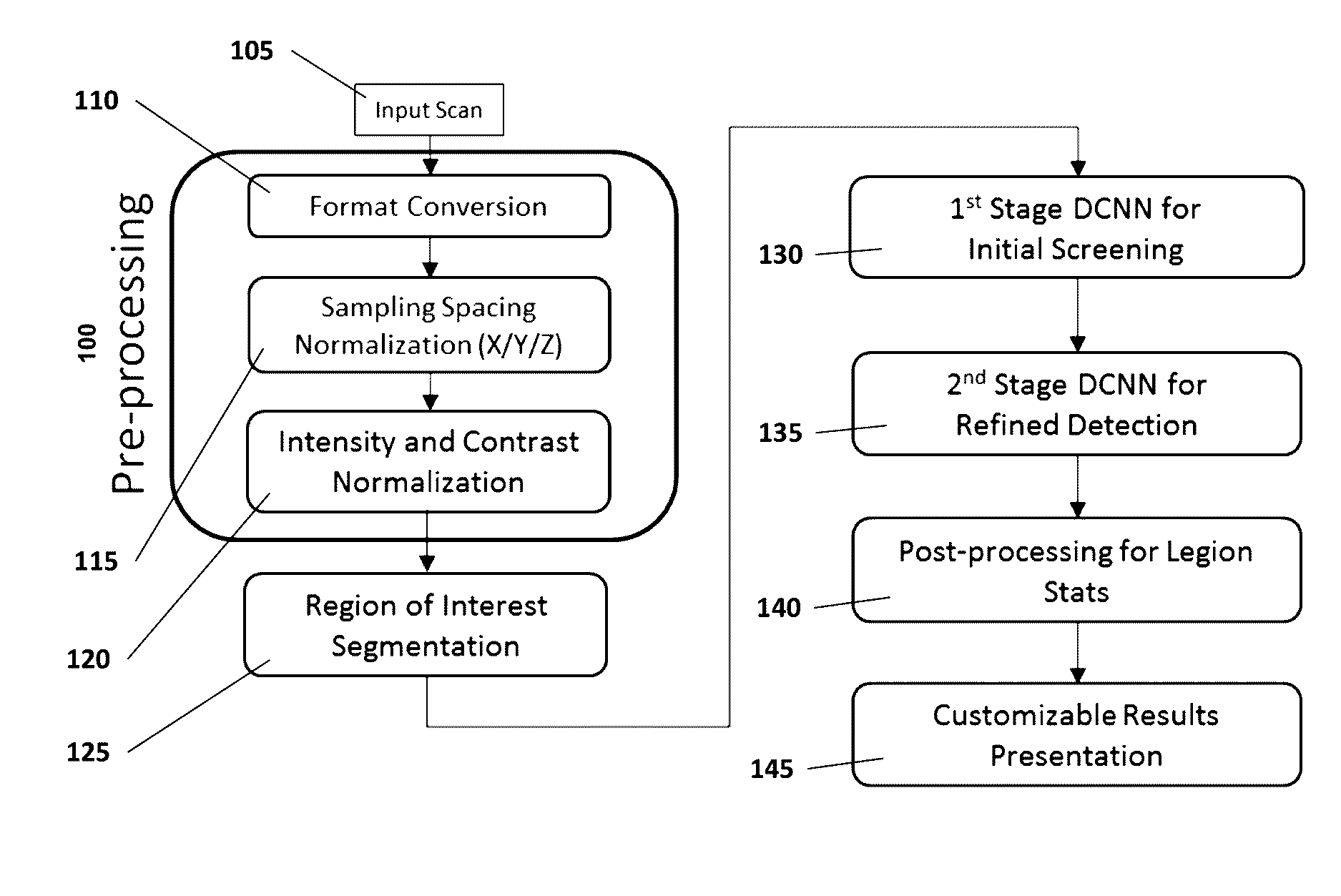
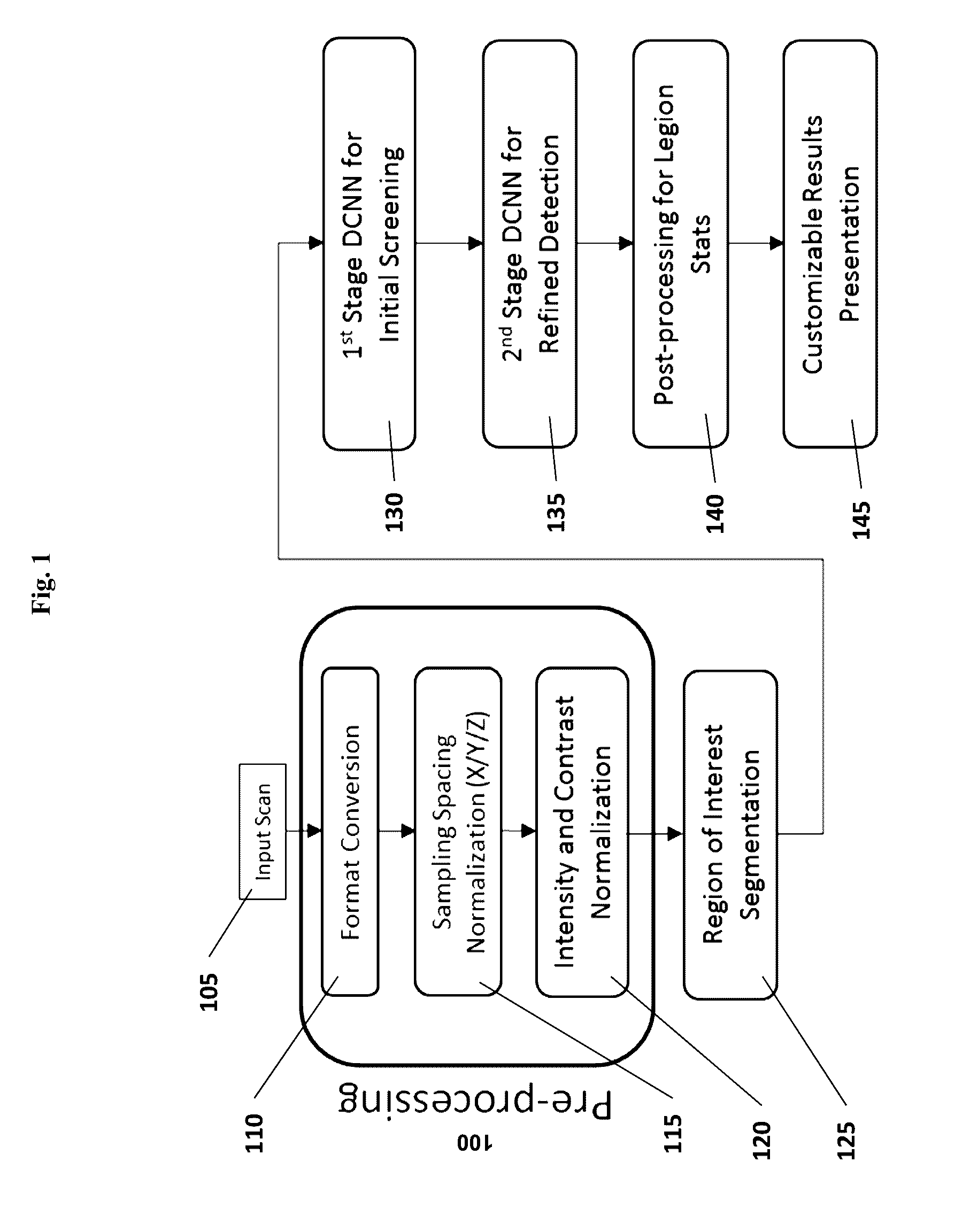
Computer-aided diagnosis system for medical images using deep convolutional neural networks
InactiveUS9589374B1Examination time can be shortenedImprove diagnostic accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer visionAided diagnosis
Owner:12 SIGMA TECH
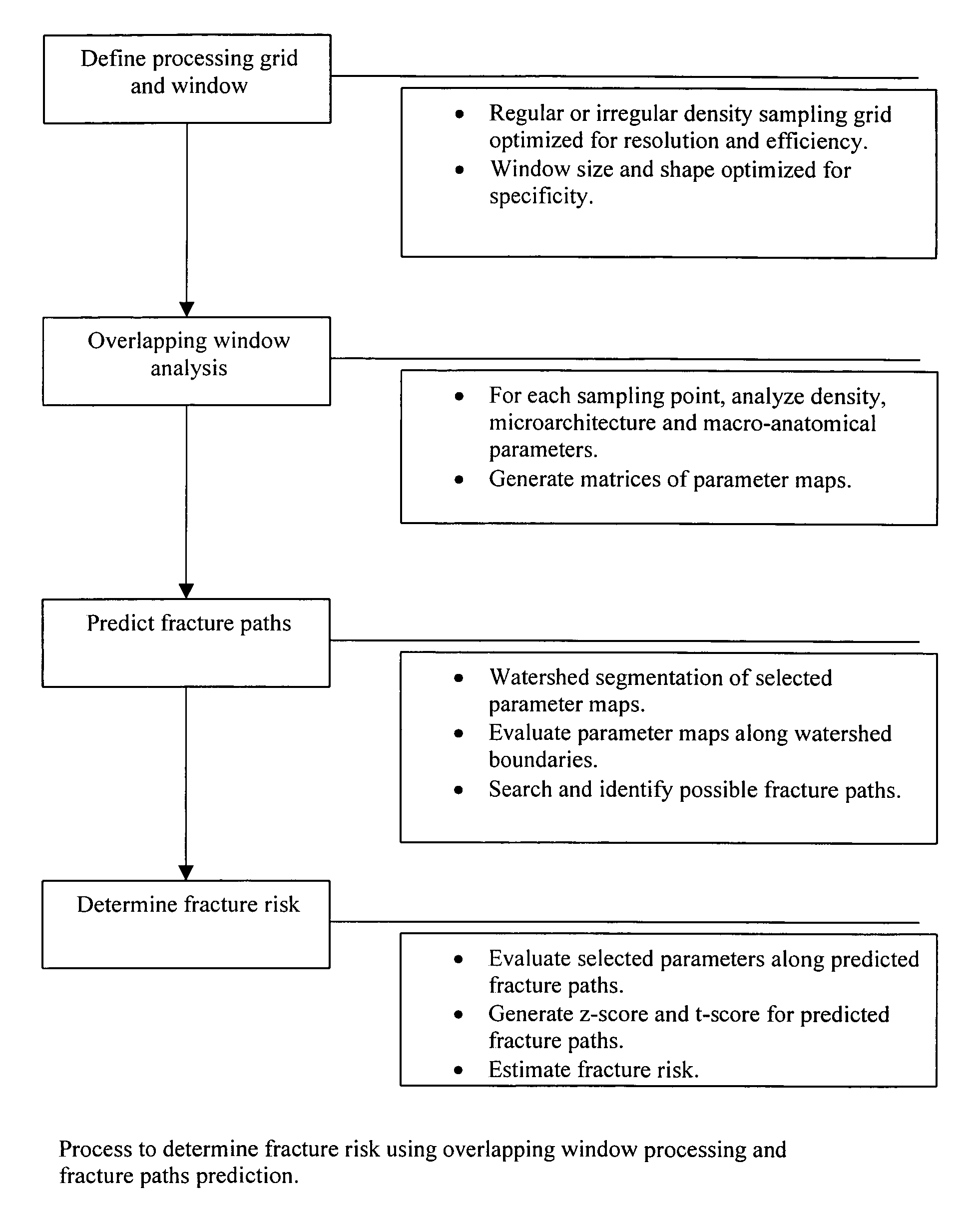
System and method of predicting future fractures
Methods of predicting fracture risk of a patient include: obtaining an image of a bone of the patient; determining one or more bone structure parameters; predicting a fracture line with the bone structure parameter; predicting a fracture load at which a fracture will happen; estimating body habitus of the patient; calculating a peak impact force on the bone when the patient falls; and predicting a fracture risk by calculating the ratio between the peak impact force and the fracture load. Inventive methods also includes determining the effect of a candidate agent on any subject's risk of fracture.
Owner:IMATX
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
ActiveUS20140058715A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Laser Optoacoustic Ultrasonic Imaging System (LOUIS) and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20130190595A1Increase contrastImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingHelical computed tomographyContrast resolution
Provided herein are the systems, methods, components for a three-dimensional tomography system. The system is a dual-modality imaging system incorporates a laser ultrasonic system and a laser optoacoustic system. The dual-modality imaging system has means for generate tomographic images of a volume of interest in a subject body based on speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation and / or ultrasound backscattering and for generating optoacoustic tomographic images of distribution of the optical absorption coefficient in the subject body based on absorbed optical energy density or various quantitative parameters derivable therefrom. Also provided is a method for increasing contrast, resolution and accuracy of quantitative information obtained within a subject utilizing the dual-modality imaging system. The method comprises producing an image of an outline boundary of a volume of interest and generating spatially or temporally coregistered images based on speed of sound and / or ultrasonic attenuation and on absorbed optical energy within the outlined volume.
Owner:TOMOWAVE LAB INC
Methods for the compensation of imaging technique in the processing of radiographic images
The present invention relates to methods and devices for analyzing x-ray images. In particular, devices, methods and algorithms are provided that allow for the accurate and reliable evaluation of bone structure and macro-anatomical parameters from x-ray images.
Owner:IMATX INC
Integrated patient bed system
InactiveUS20090275808A1Easy to monitorImprove treatmentRadiation diagnosis data transmissionMedical imagingTherapeutic DevicesComputer science
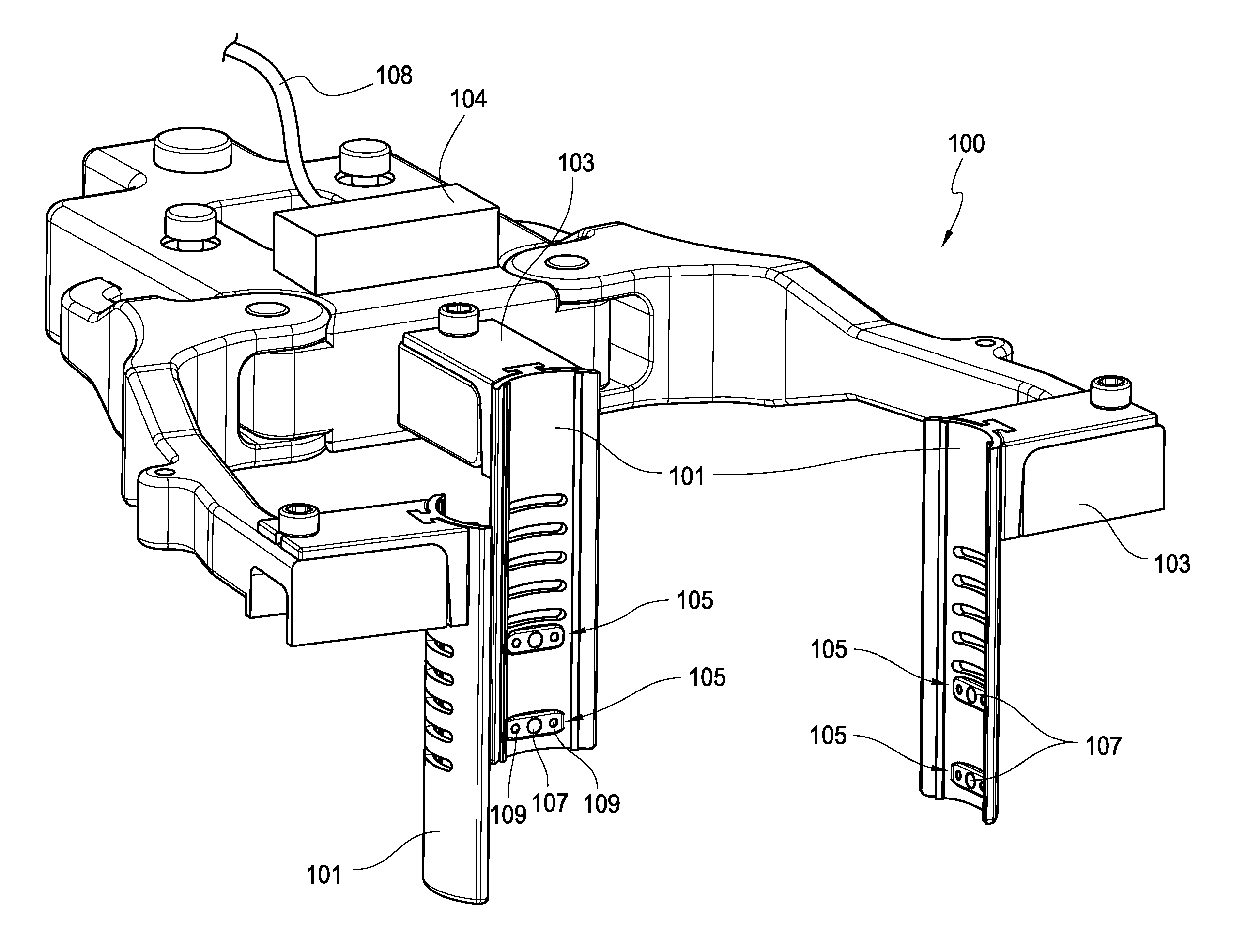
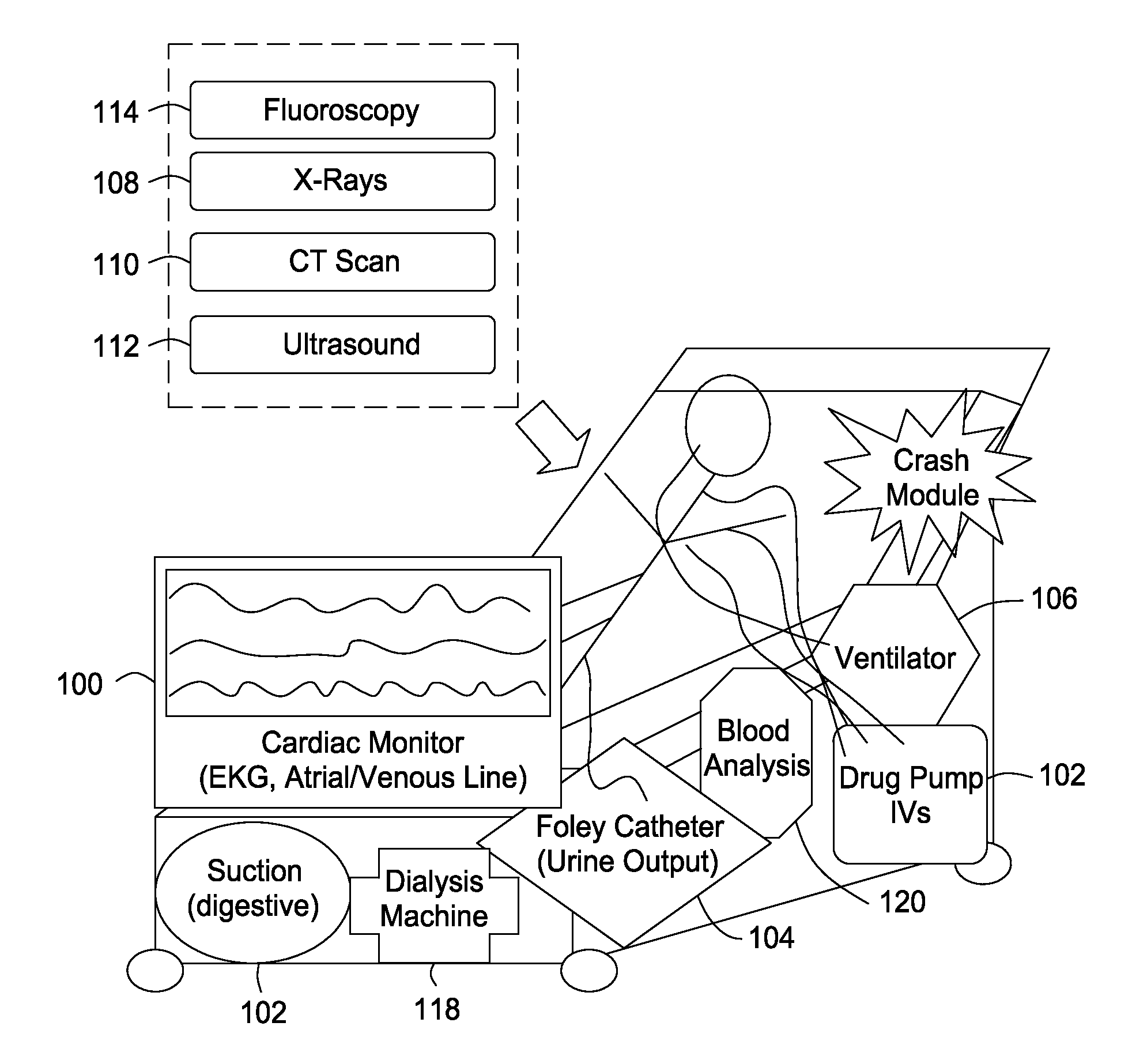
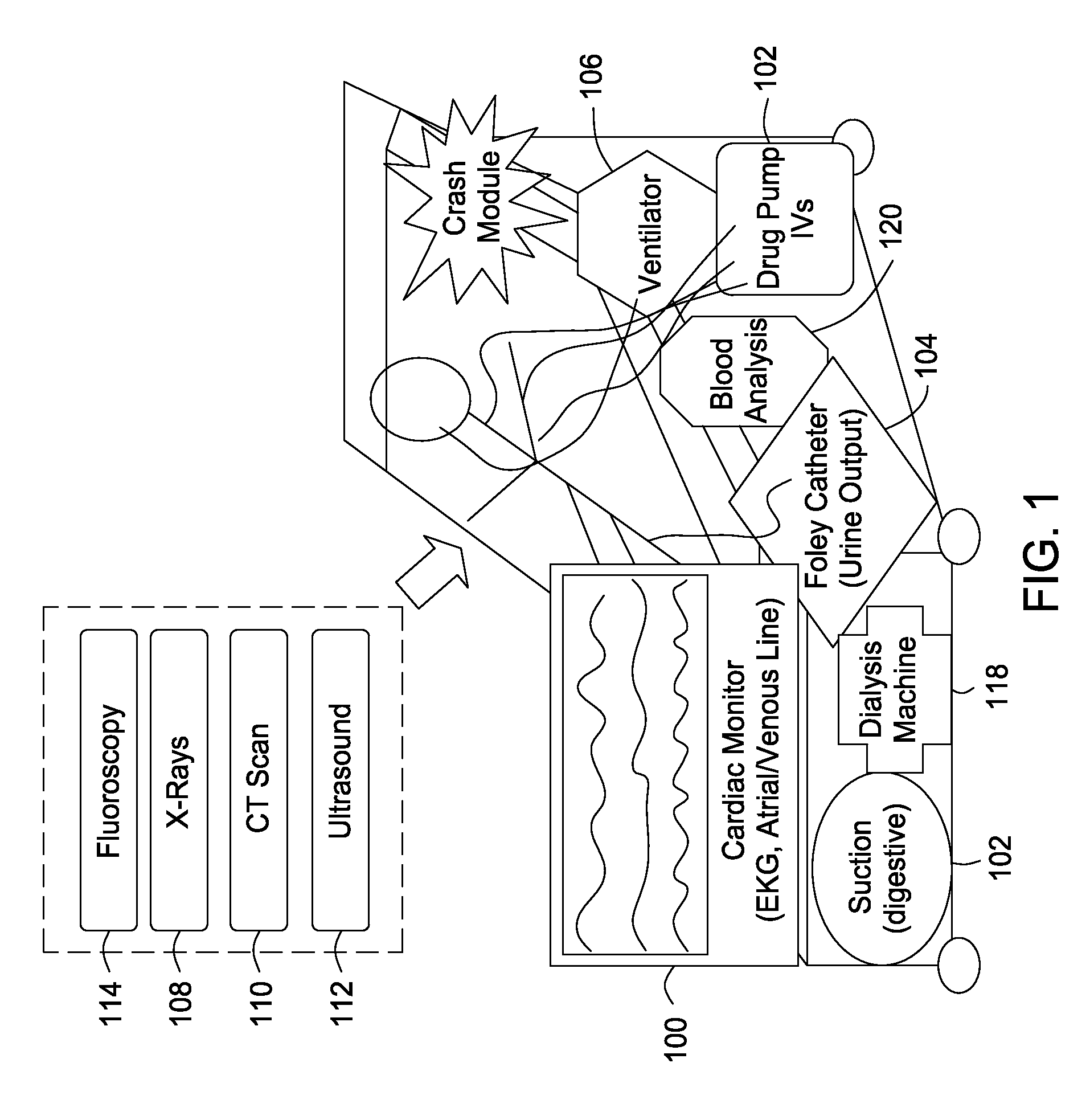
The present invention includes an integrated system and methods for patient treatment, the system includes a hospital bed; a plurality of patient diagnostic and treatment devices connected to a network, wherein each of the devices can communicate to a network and exchange information with the network about the care of a patient; and a processor accessible adjacent to the bed and connected to the network to integrate information obtained from the devices through the network with one or more additional sources of information databases, wherein the processor can communicate to one or more patient treatment devices either directly or via the network and the processor directs the one or more patient treatment devices to change the treatment of the patient.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for stent strut detection and related measurement and display using optical coherence tomography
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Tools for use with moving organs
InactiveUS20080221439A1Reduce imaged motionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingControl engineeringControl cell
A sensor senses a phase of cyclic activity of a portion of a subject's body. A control unit, in a first cycle of the cyclic activity, moves a portion of a tool, in a given direction, in response to the sensor sensing that the cyclic activity is at a first given phase thereof. The control unit, following the given phase and prior to an occurrence of the given phase in a subsequent cycle, inhibits the tool's movement. The control unit in a second cycle, subsequent to the inhibiting, moves the tool in the given direction, in response to the sensor sensing that the second cycle is at the given phase, without moving the tool in an opposite direction, between (a) moving the tool in the given direction in the first cycle, and (b) moving the tool in the given direction in the second cycle. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:SYNC RX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com