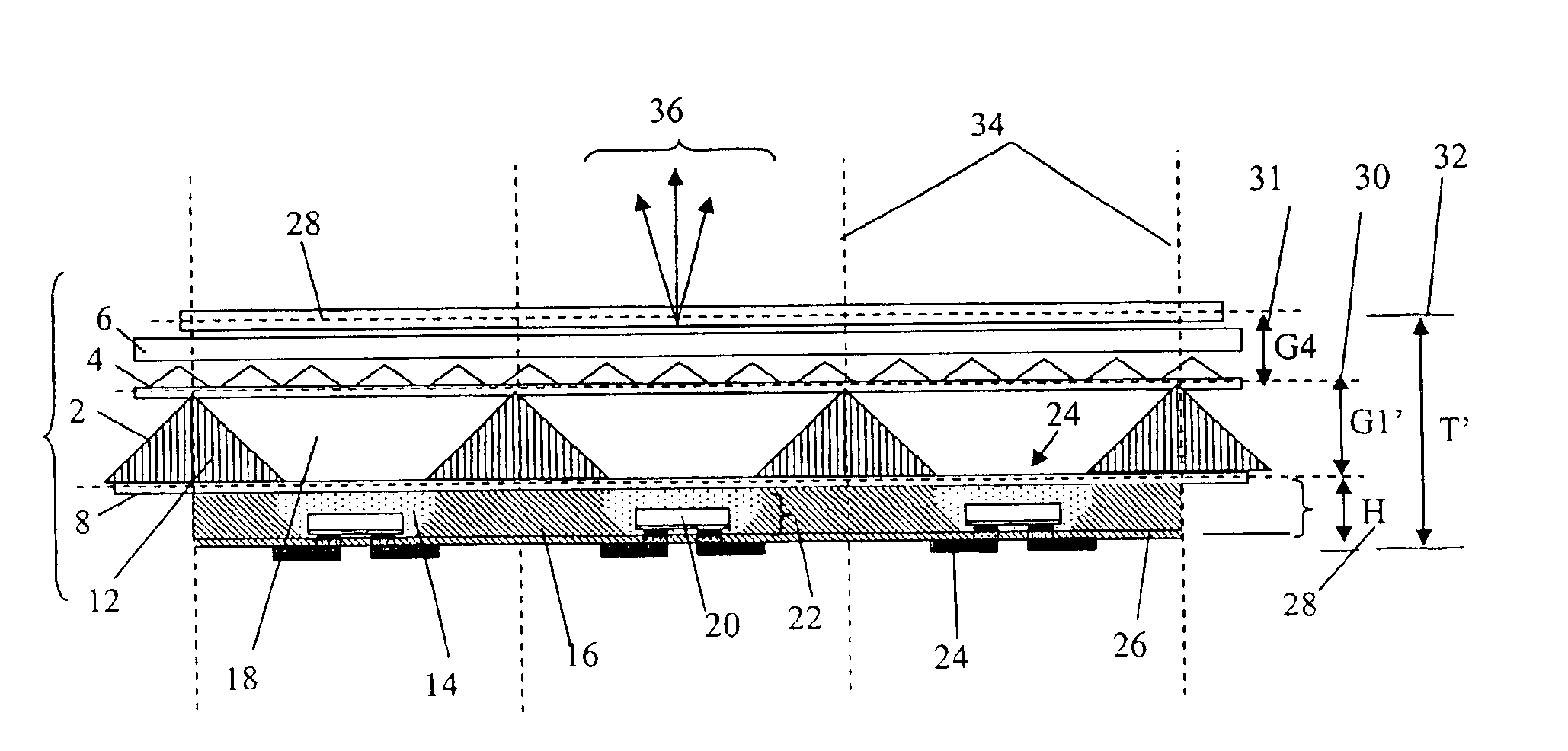
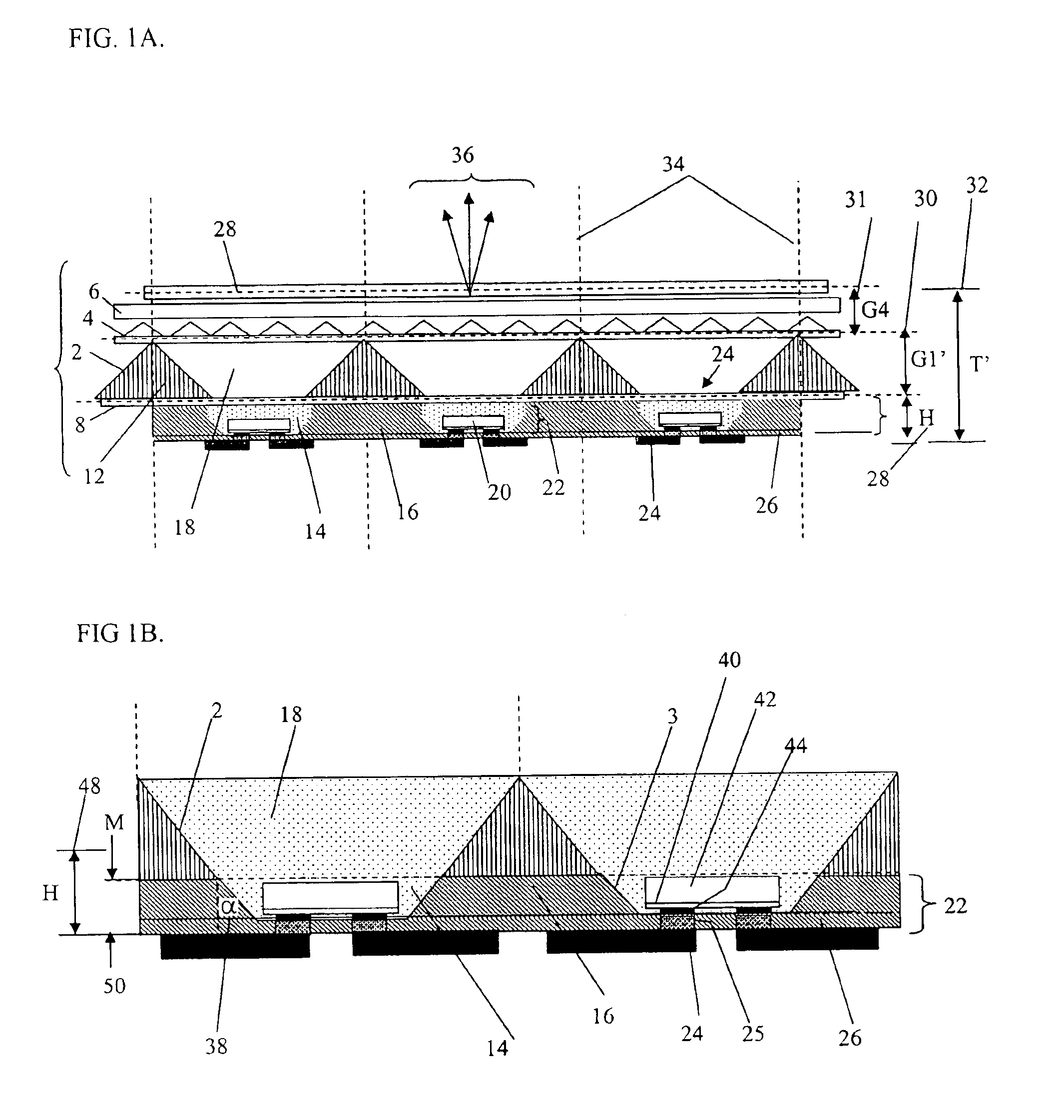
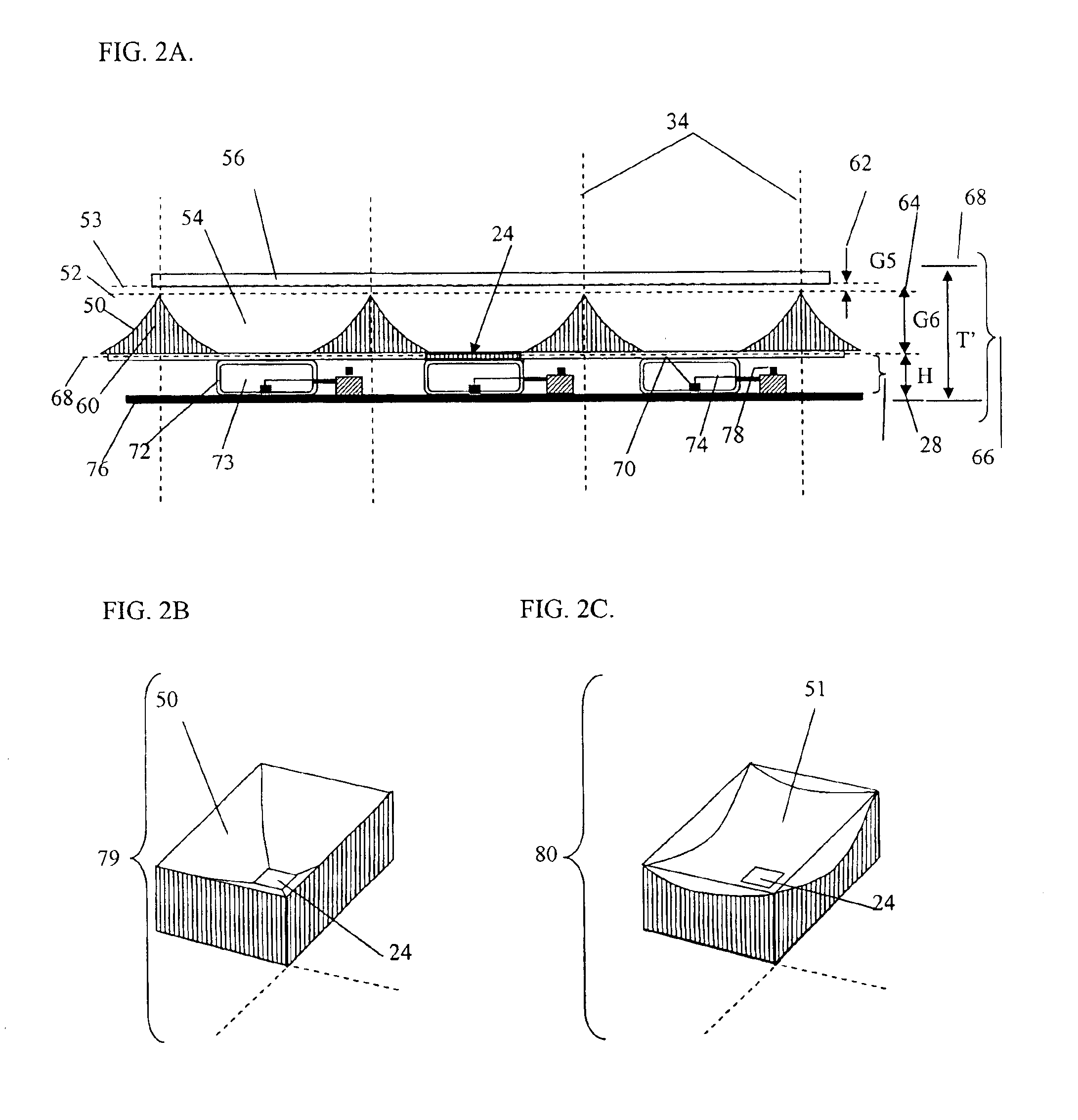
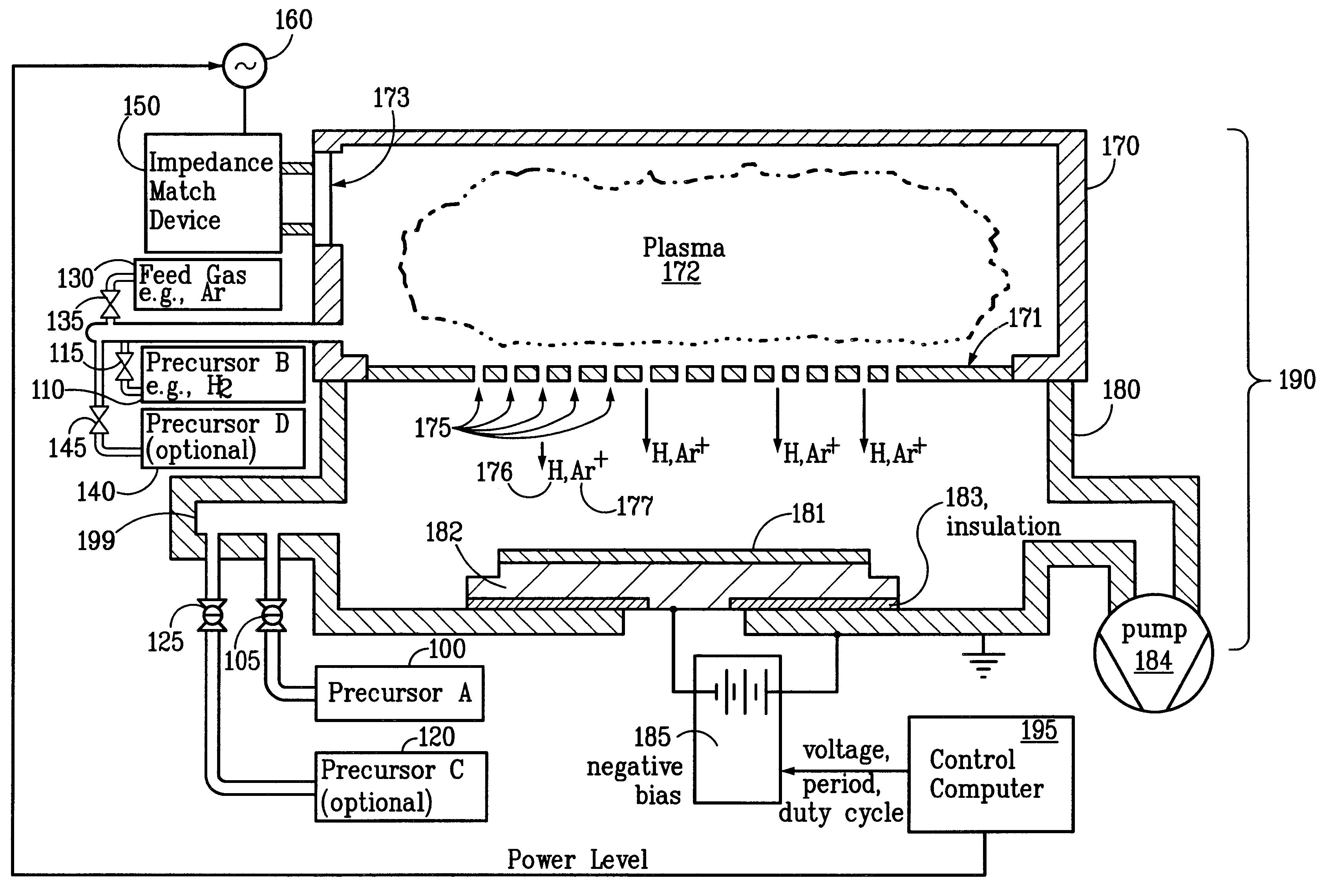
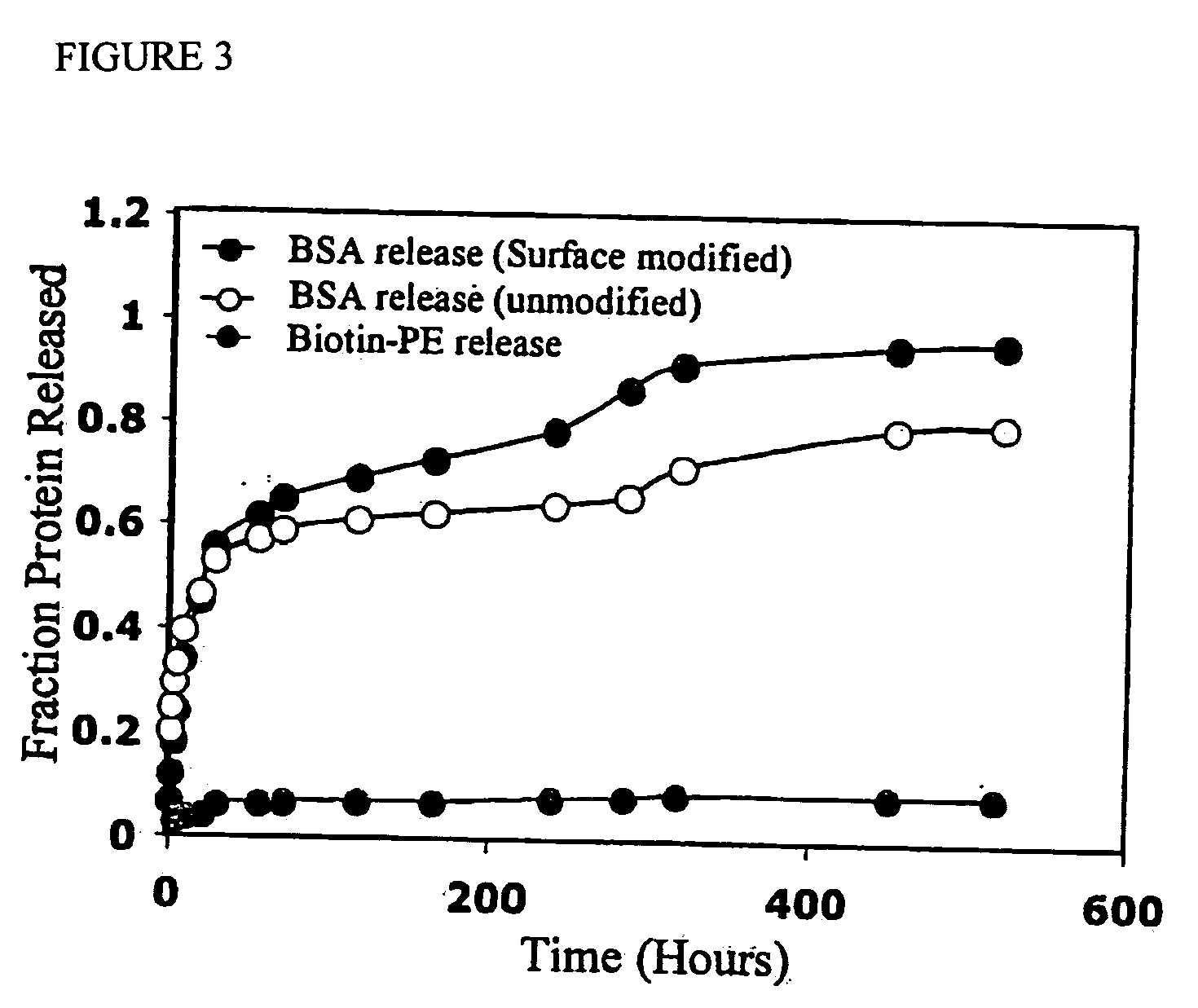
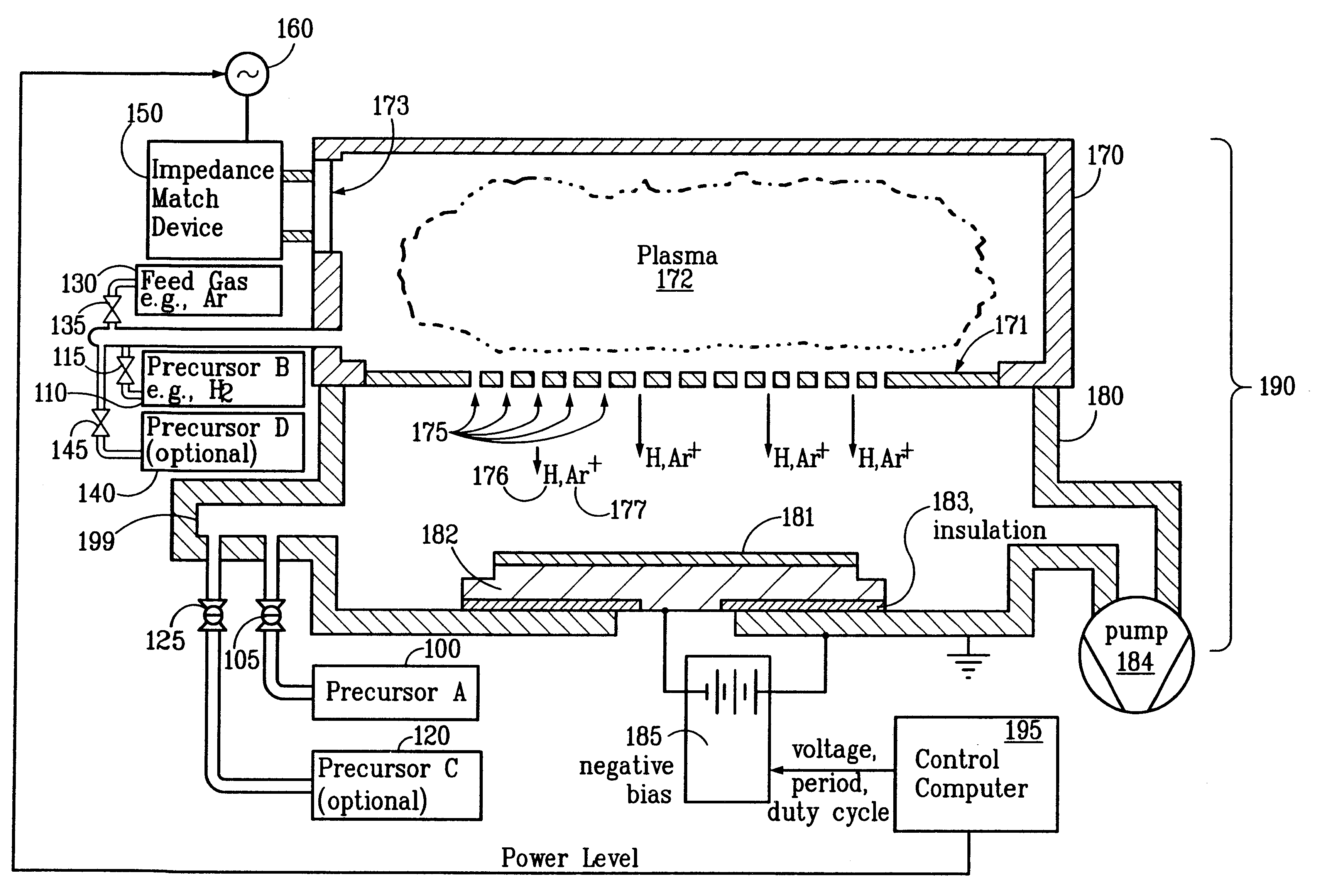
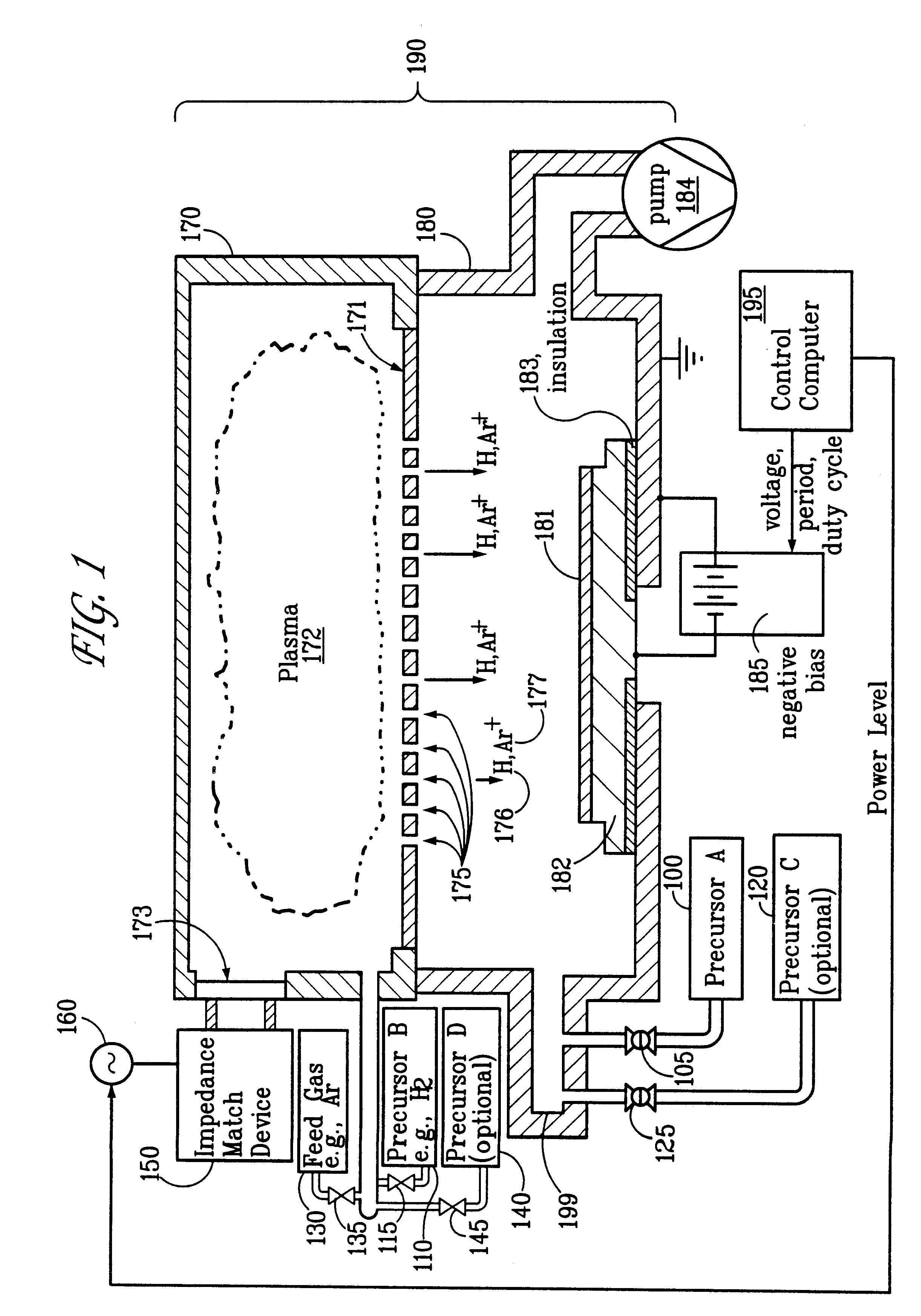
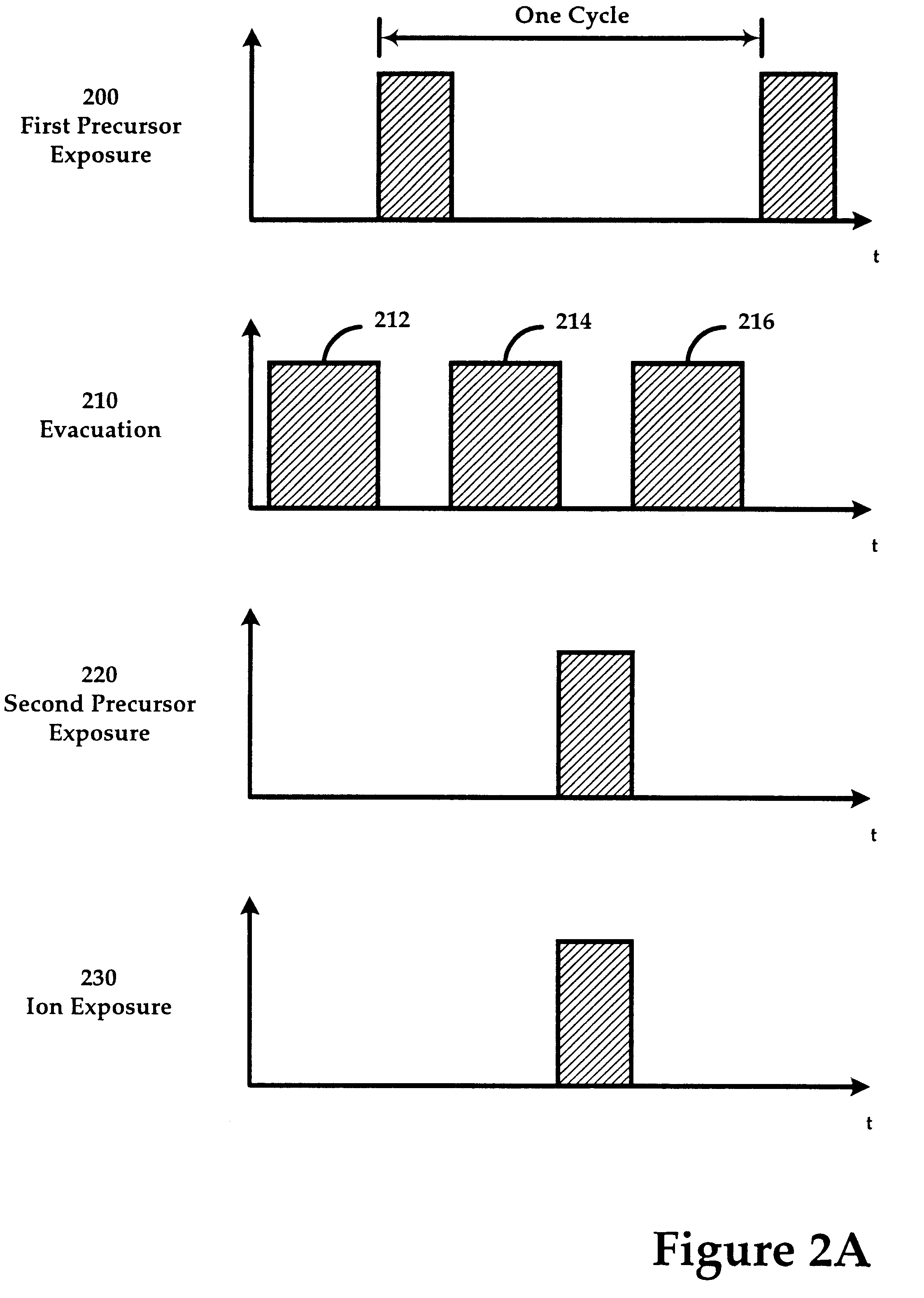
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32010 results about "High density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
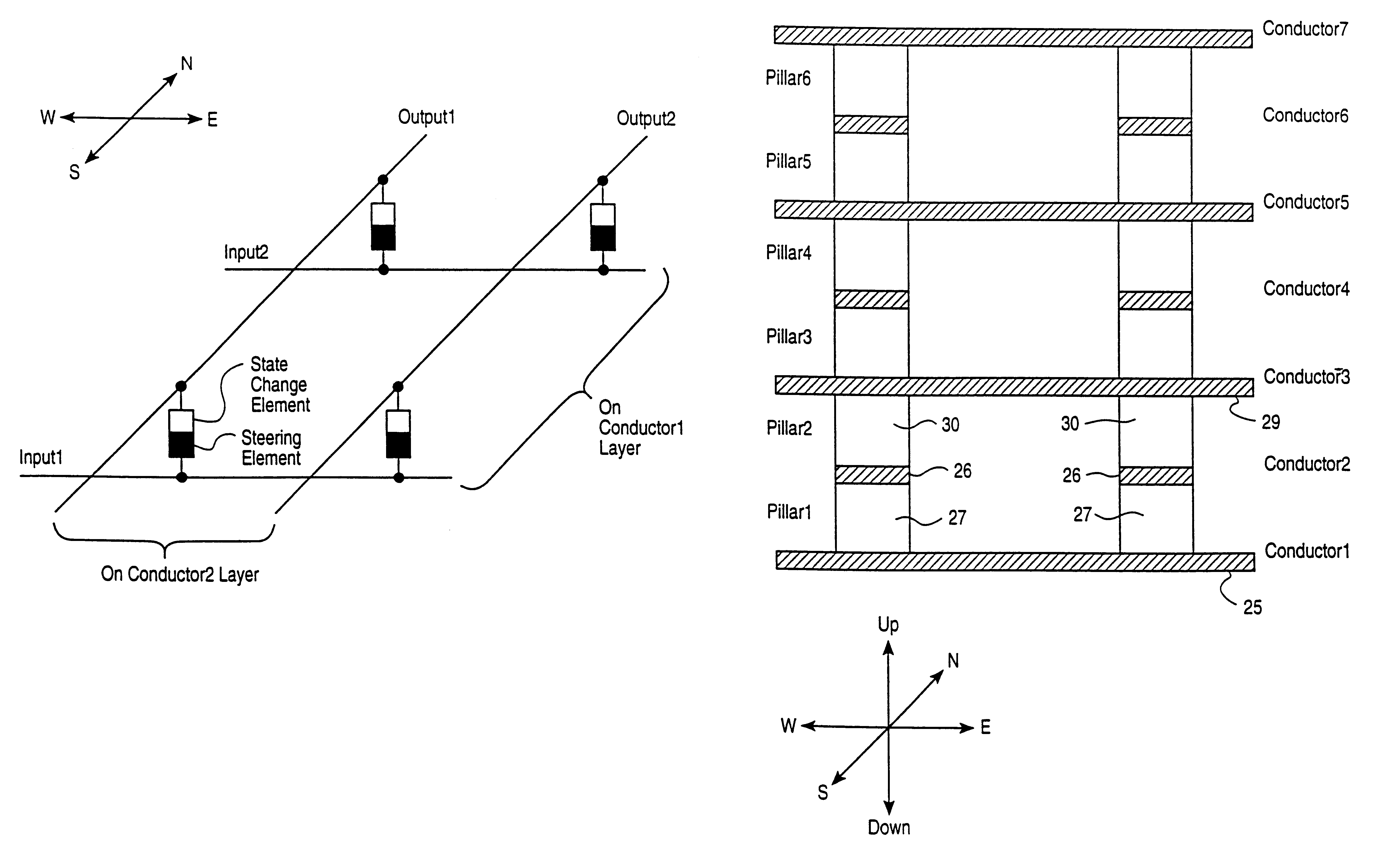
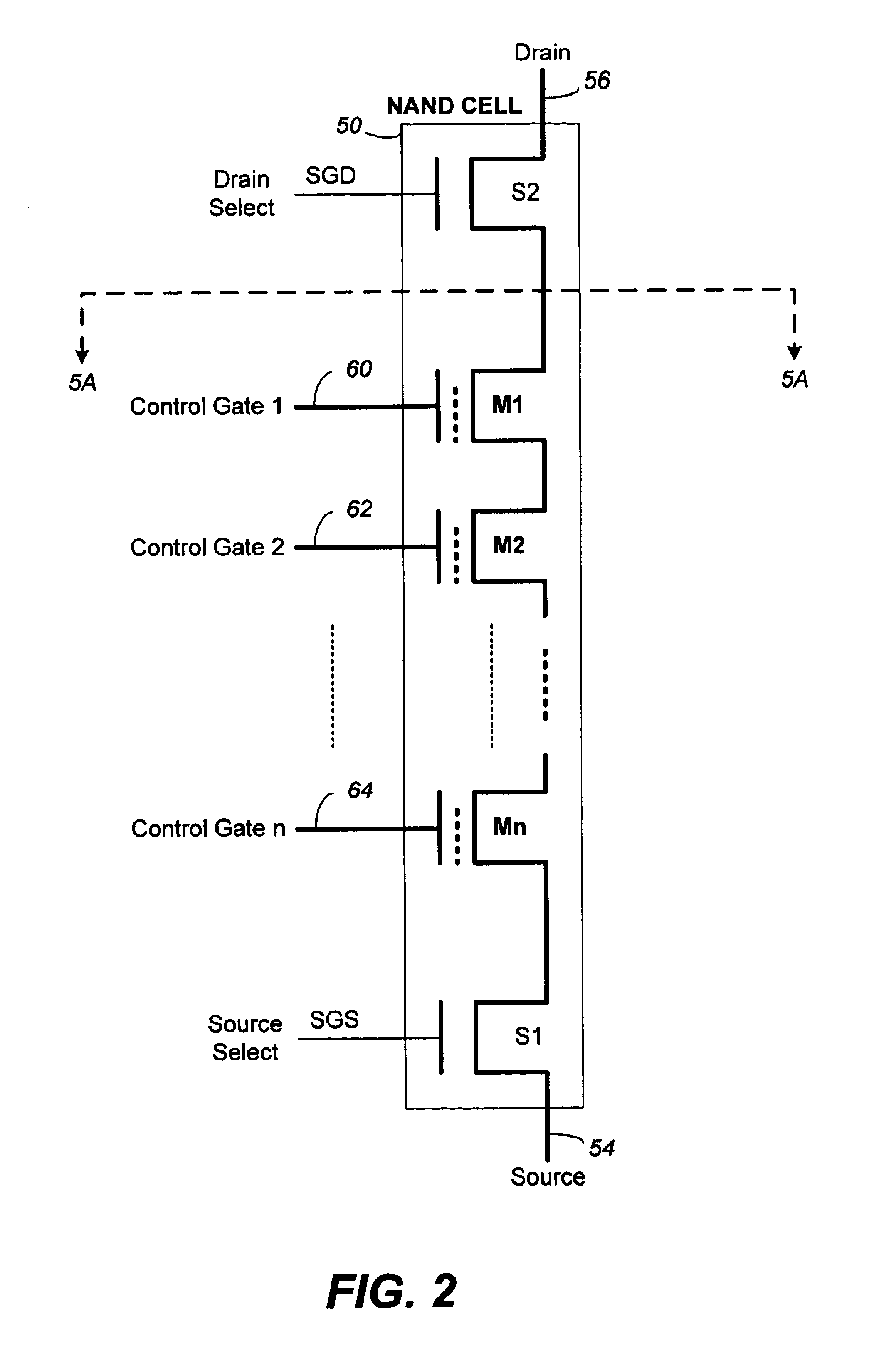
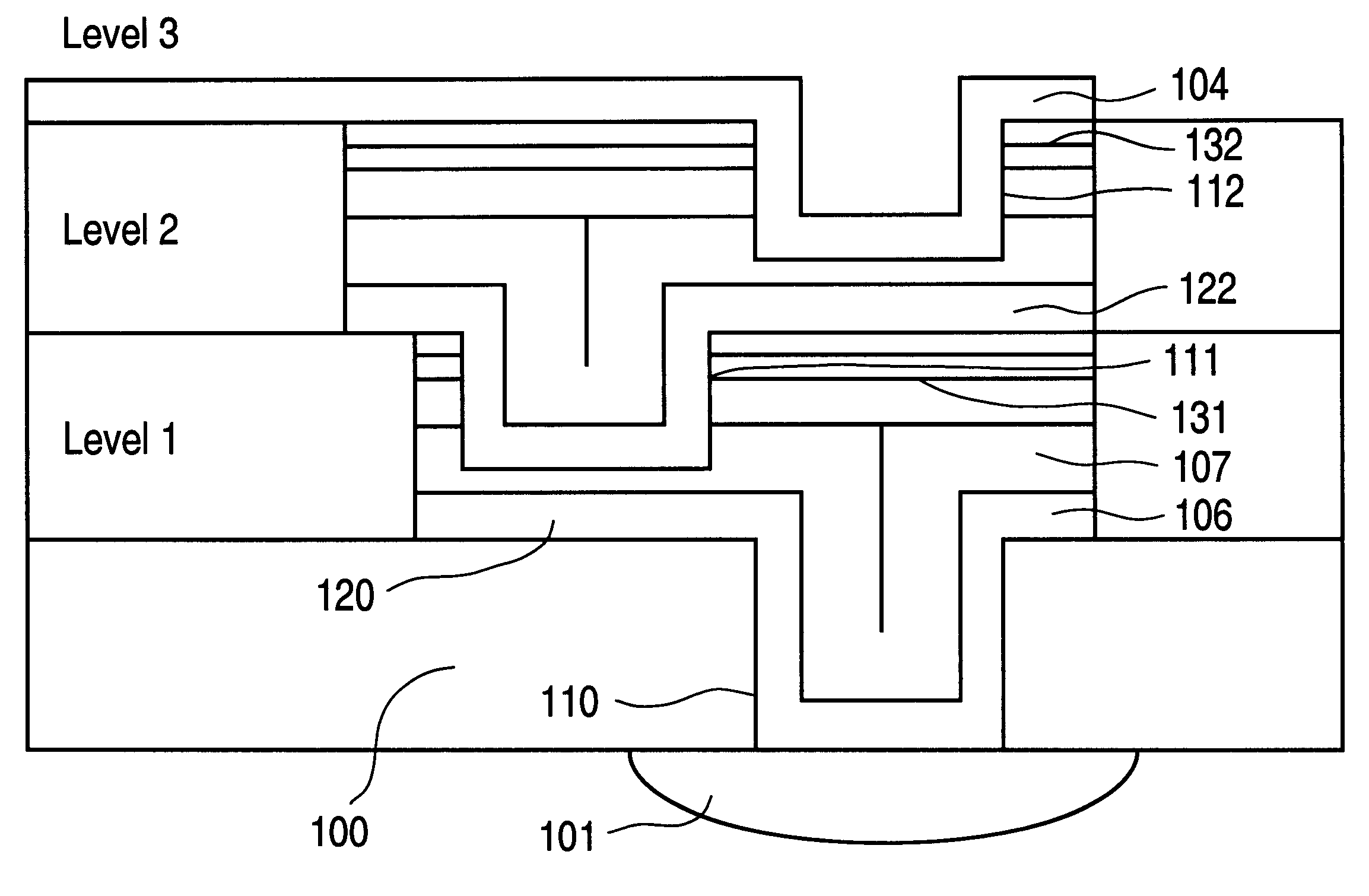
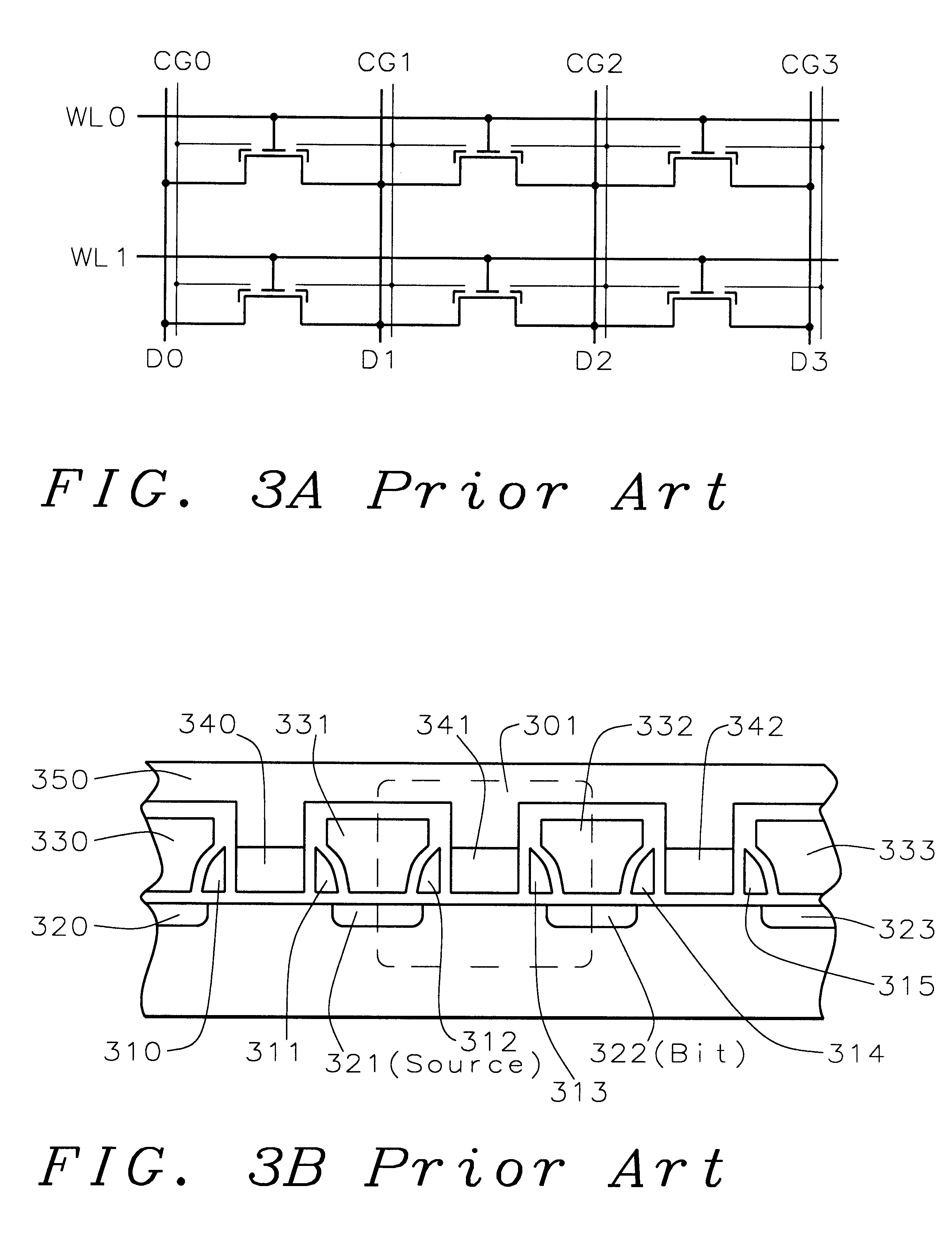
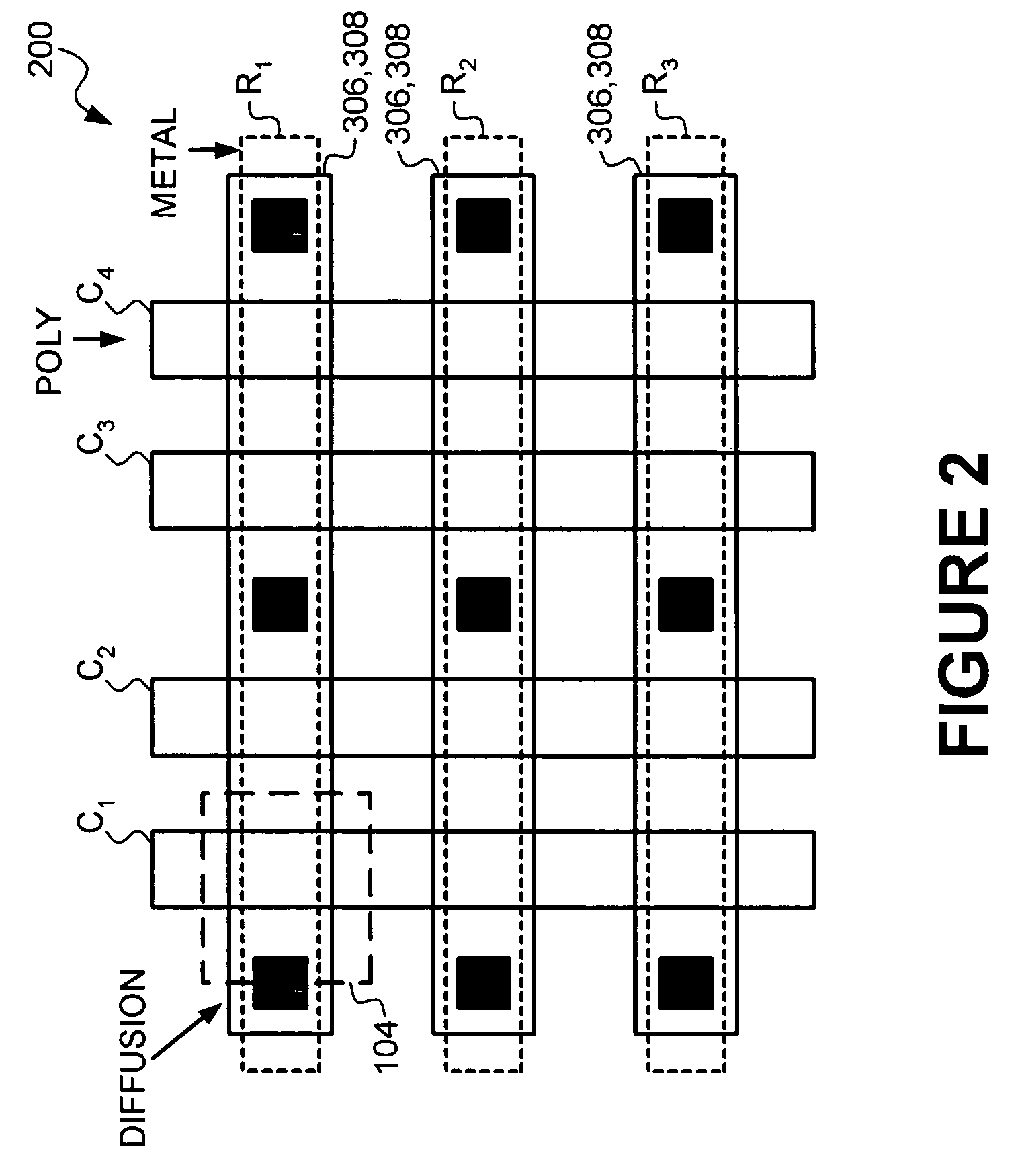
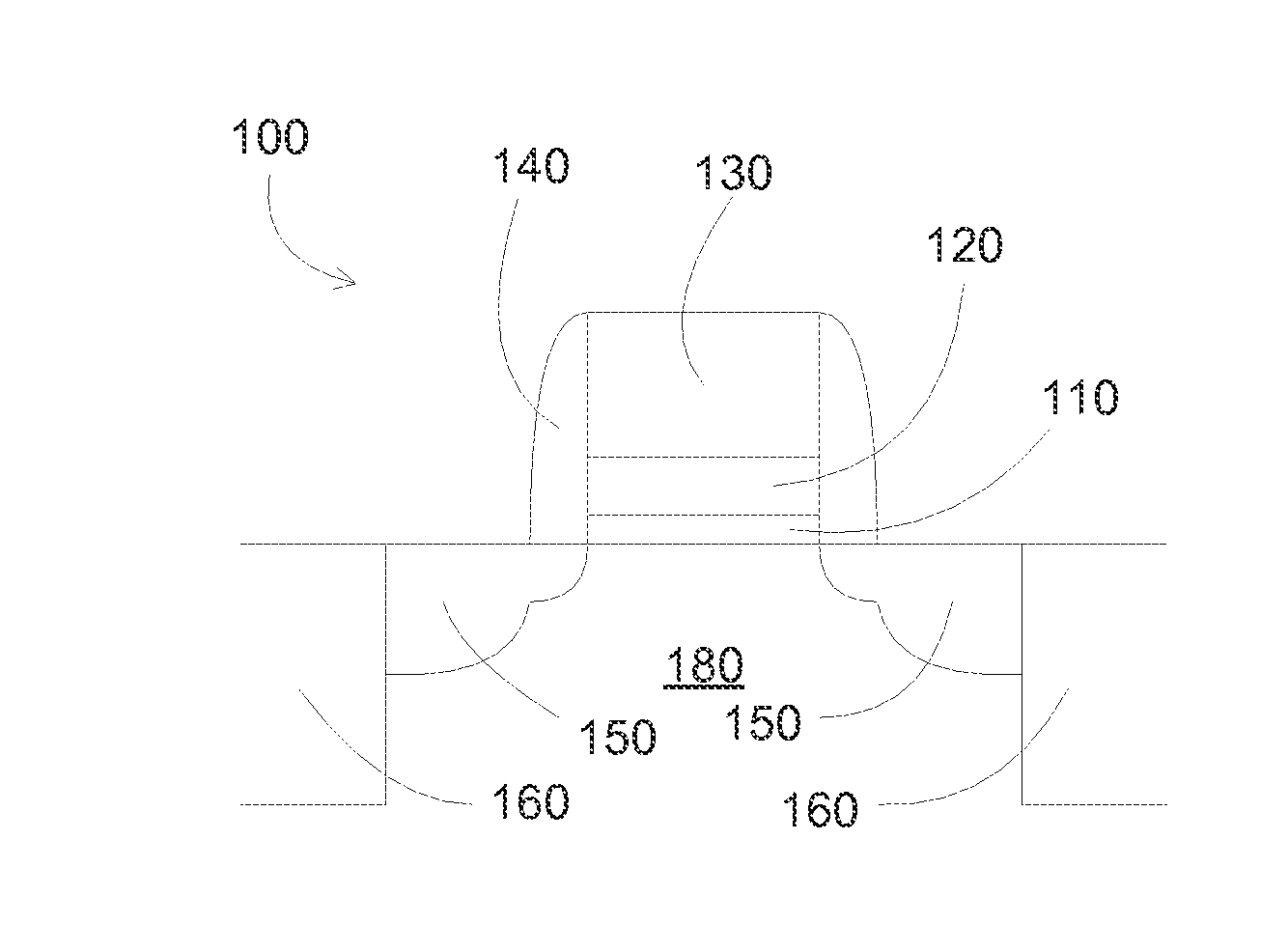
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:RHOMBUS
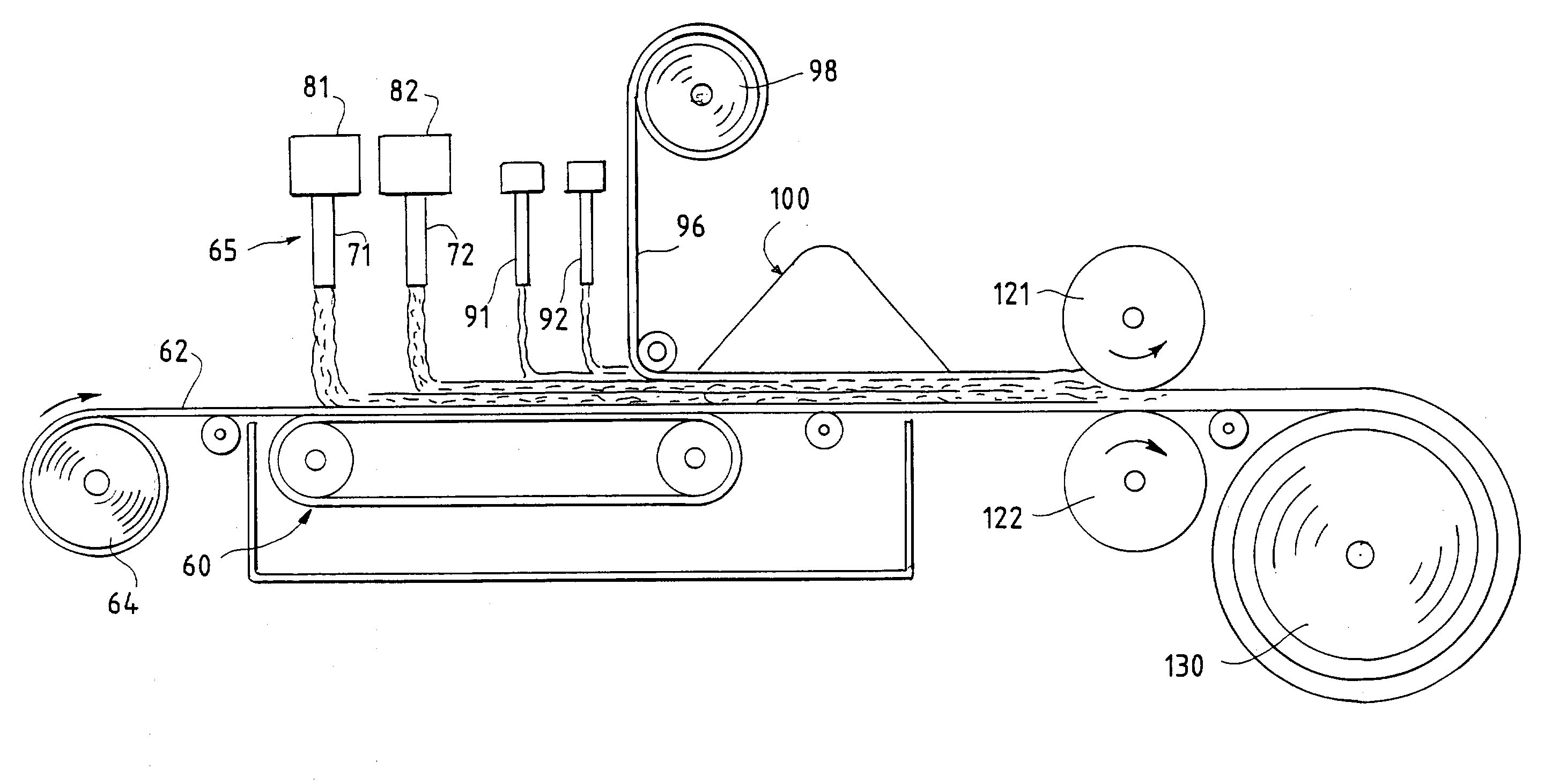
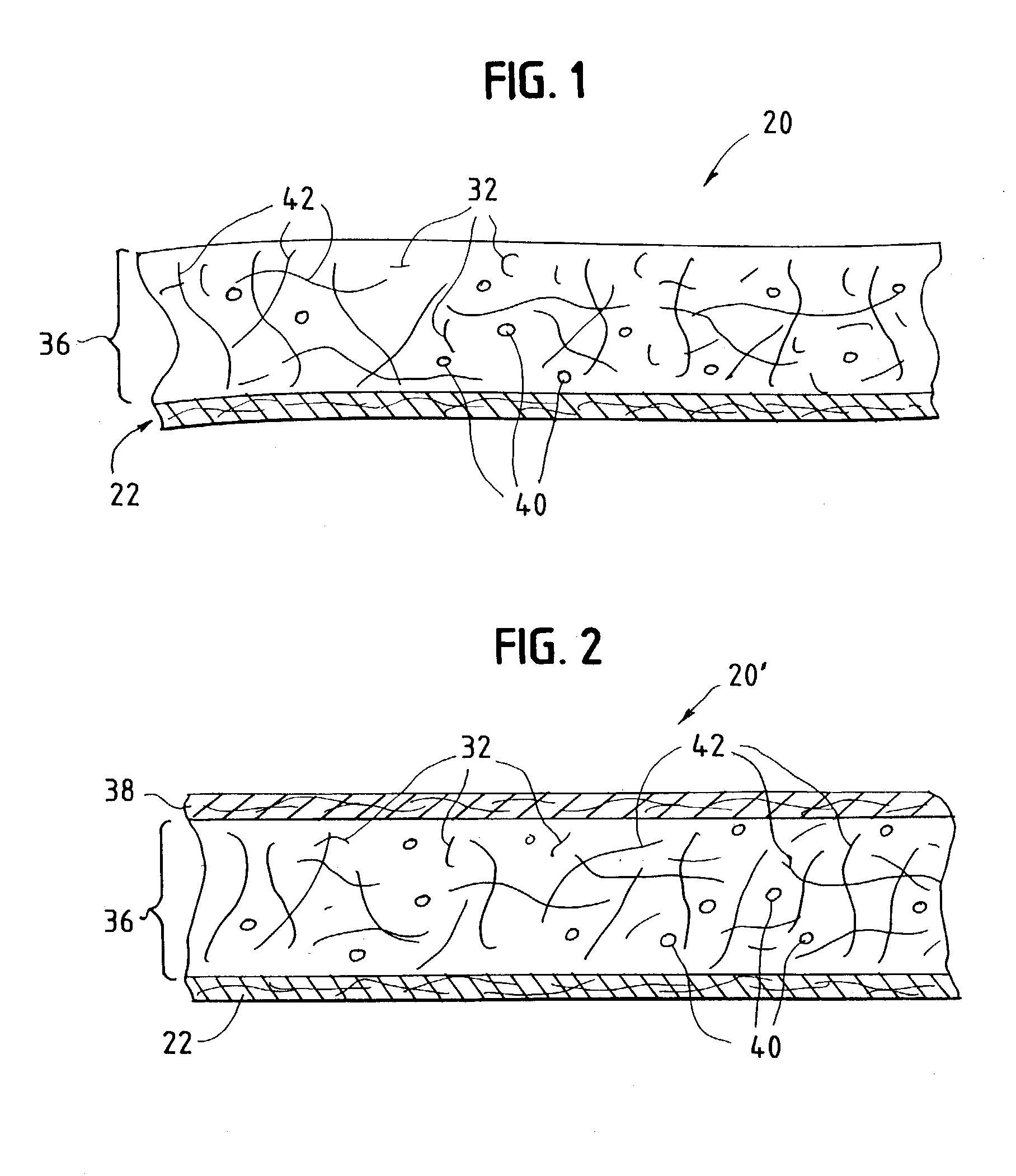
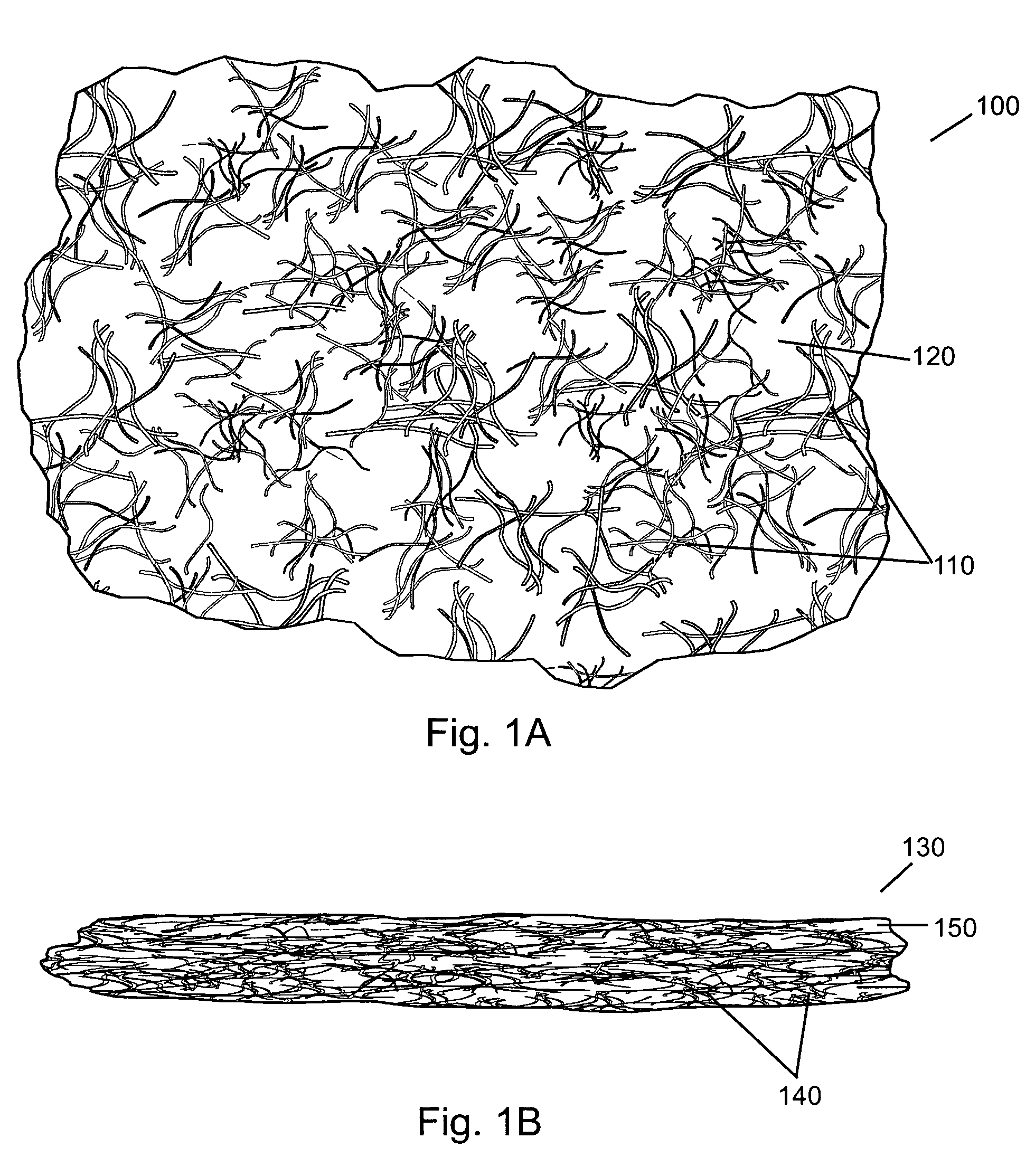
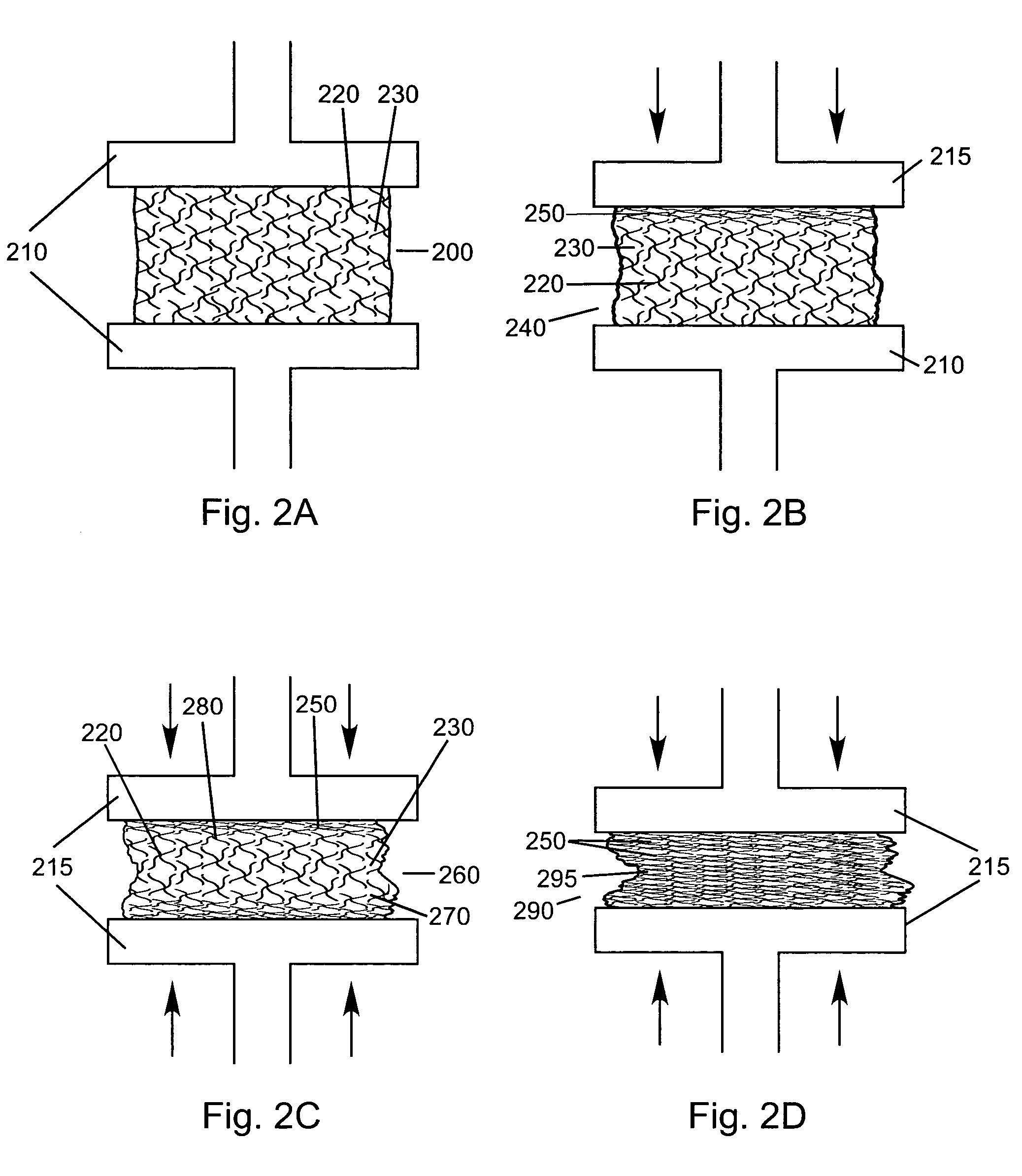
Absorbent material incorporating synthetic fibers and process for making the material
InactiveUS20030084983A1Reduce leakageWidespread acceptanceLayered productsBaby linensPolymer scienceHigh density
A process is provided for making a soft, high density, absorbent material with improved characteristics. A web is formed from material that includes a mixture of cellulosic fibers and synthetic polymer fibers. Then, the web is preferably compacted and embossed at an elevated temperature to further increase the web density and preferably to also create liquid-stable bonds between the synthetic polymer fibers and the cellulosic fibers in spaced-apart regions of the web.
Owner:EAM
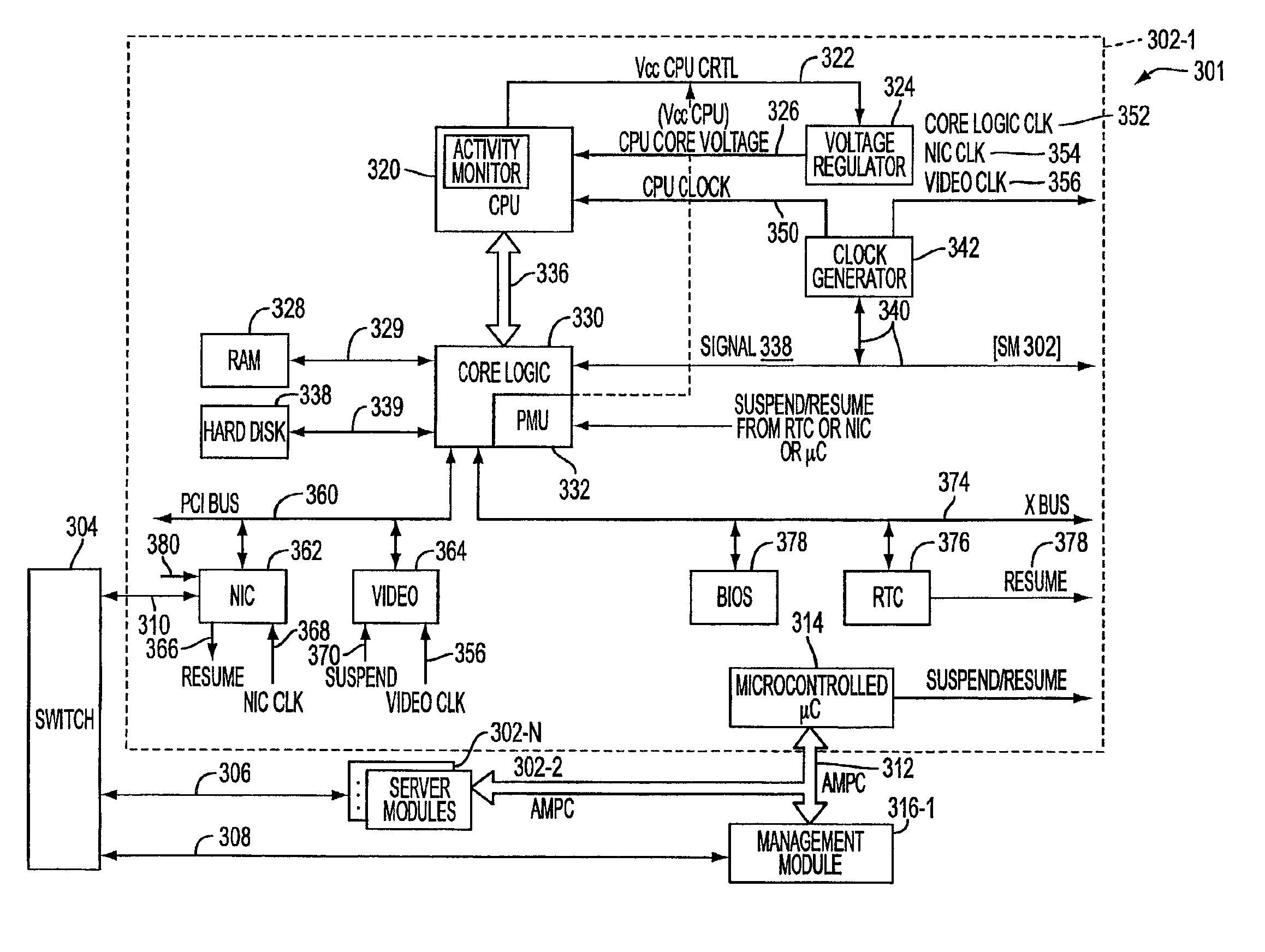
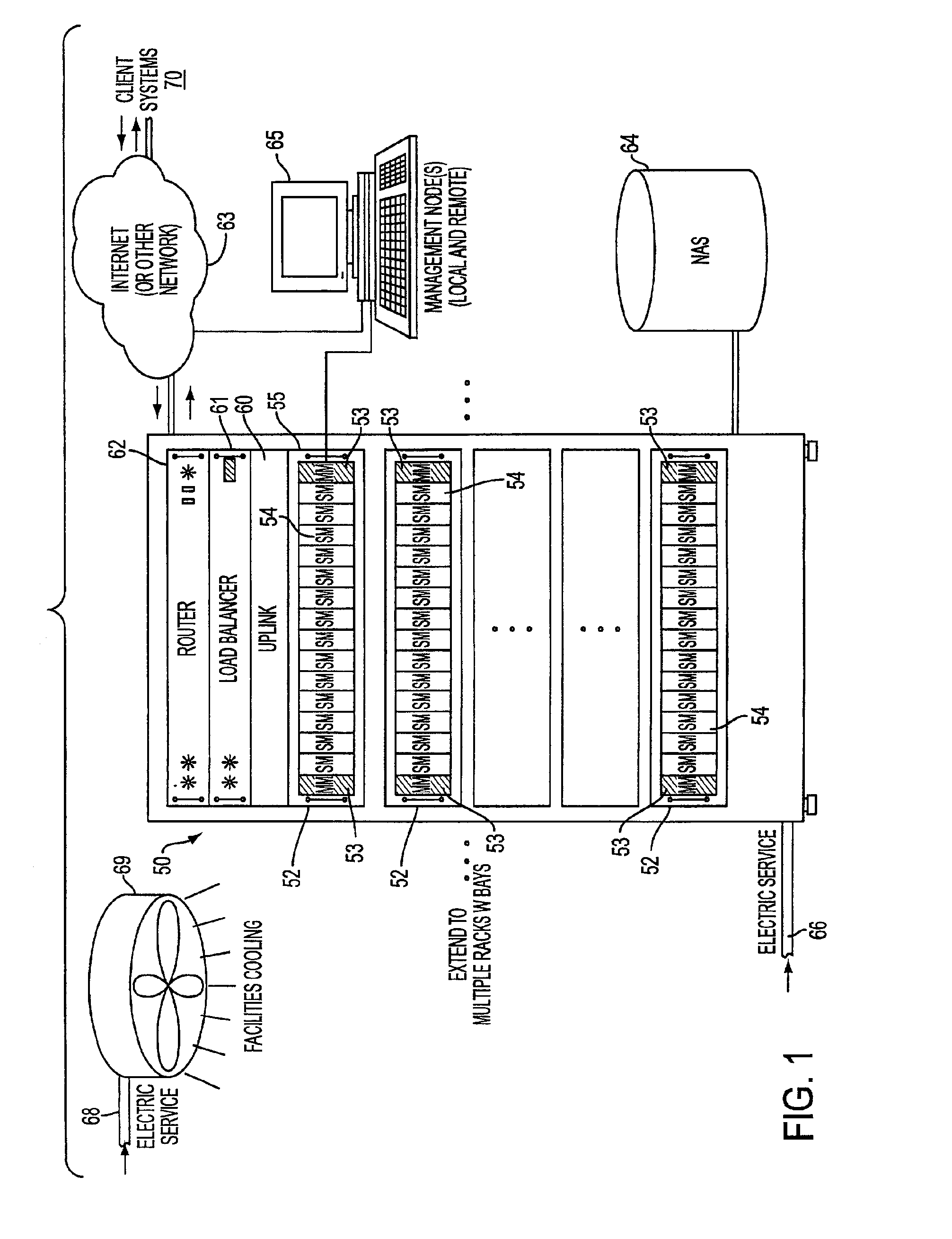
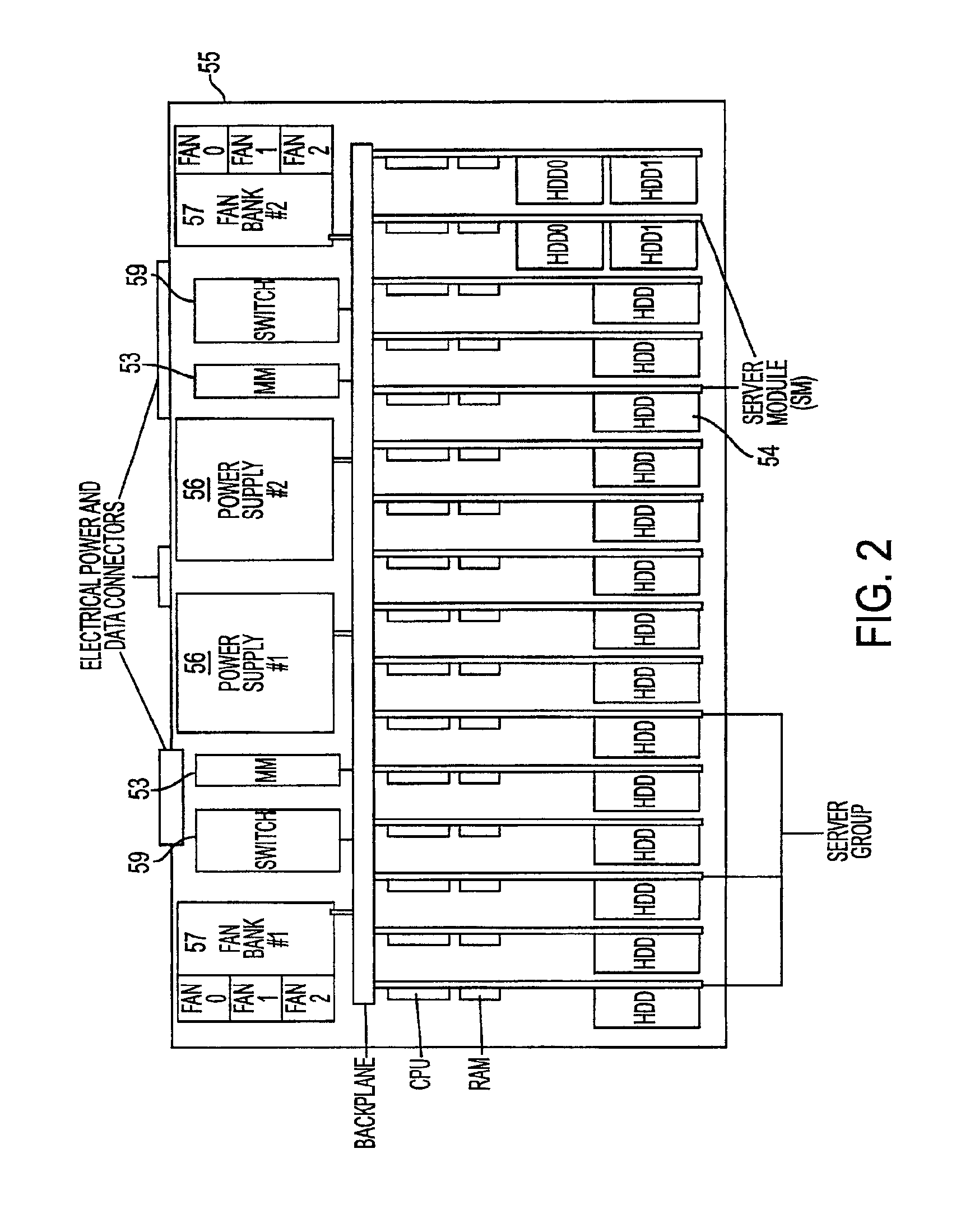
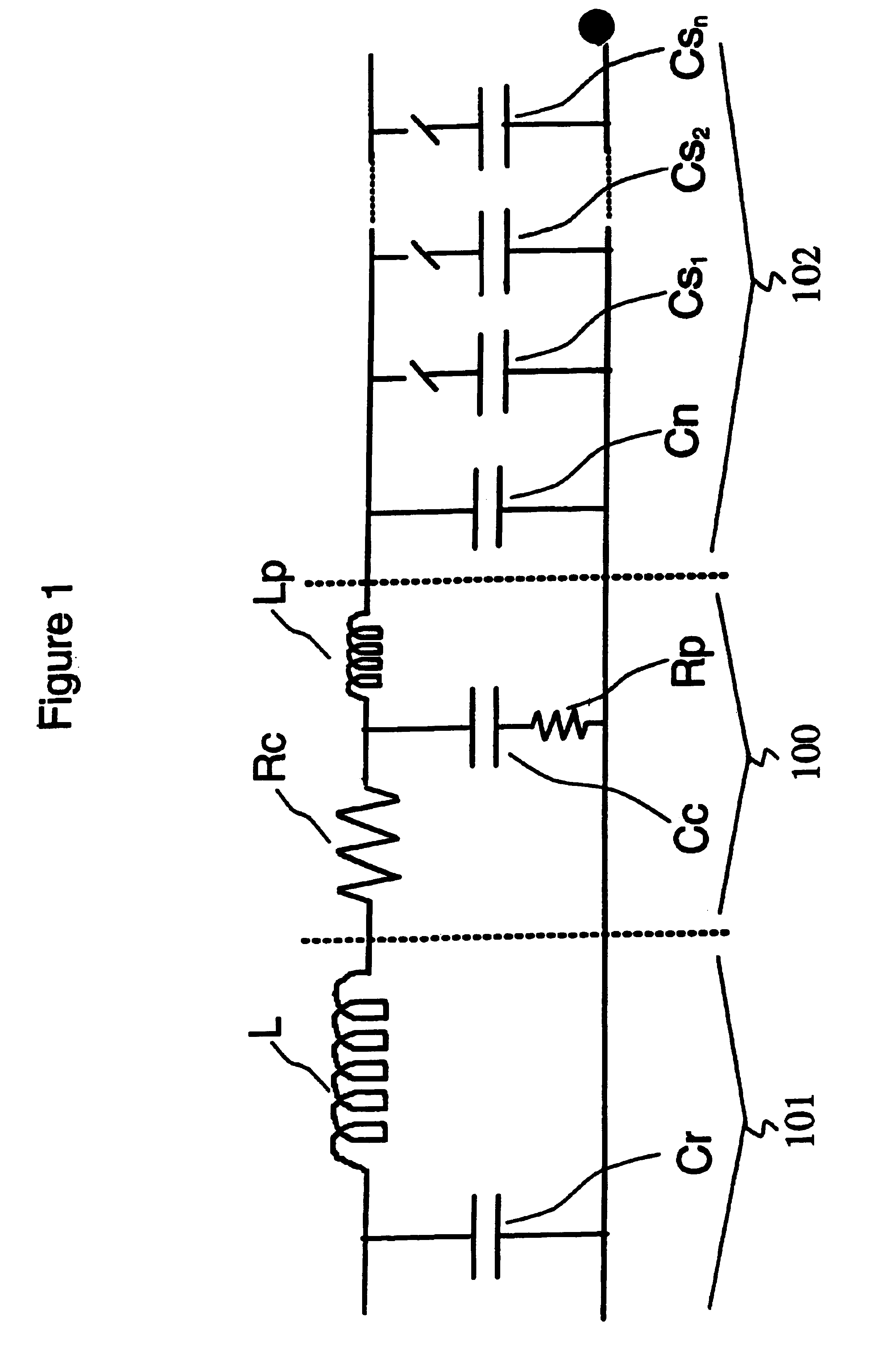
System, method, and architecture for dynamic server power management and dynamic workload management for multi-server environment
InactiveUS6859882B2Save energyConserving methodEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementNetwork architectureWorkload management
Network architecture, computer system and / or server, circuit, device, apparatus, method, and computer program and control mechanism for managing power consumption and workload in computer system and data and information servers. Further provides power and energy consumption and workload management and control systems and architectures for high-density and modular multi-server computer systems that maintain performance while conserving energy and method for power management and workload management. Dynamic server power management and optional dynamic workload management for multi-server environments is provided by aspects of the invention. Modular network devices and integrated server system, including modular servers, management units, switches and switching fabrics, modular power supplies and modular fans and a special backplane architecture are provided as well as dynamically reconfigurable multi-purpose modules and servers. Backplane architecture, structure, and method that has no active components and separate power supply lines and protection to provide high reliability in server environment.
Owner:HURON IP
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
High-Density Self-Retaining Sutures, Manufacturing Equipment and Methods
InactiveUS20130238021A1Improve abilitiesImprove retentionSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesHigh densityEngineering
A self-retaining suture has a suture thread less than 1 millimeter nominal diameter. A plurality of retainers is cut into the suture thread using a high accuracy retainer cutting machine. The retainer cutting machine has sufficient accuracy and repeatability to cut consistent and effective retainers at high density on suture threads less than 1 mm nominal diameter.
Owner:ETHICON INC +1
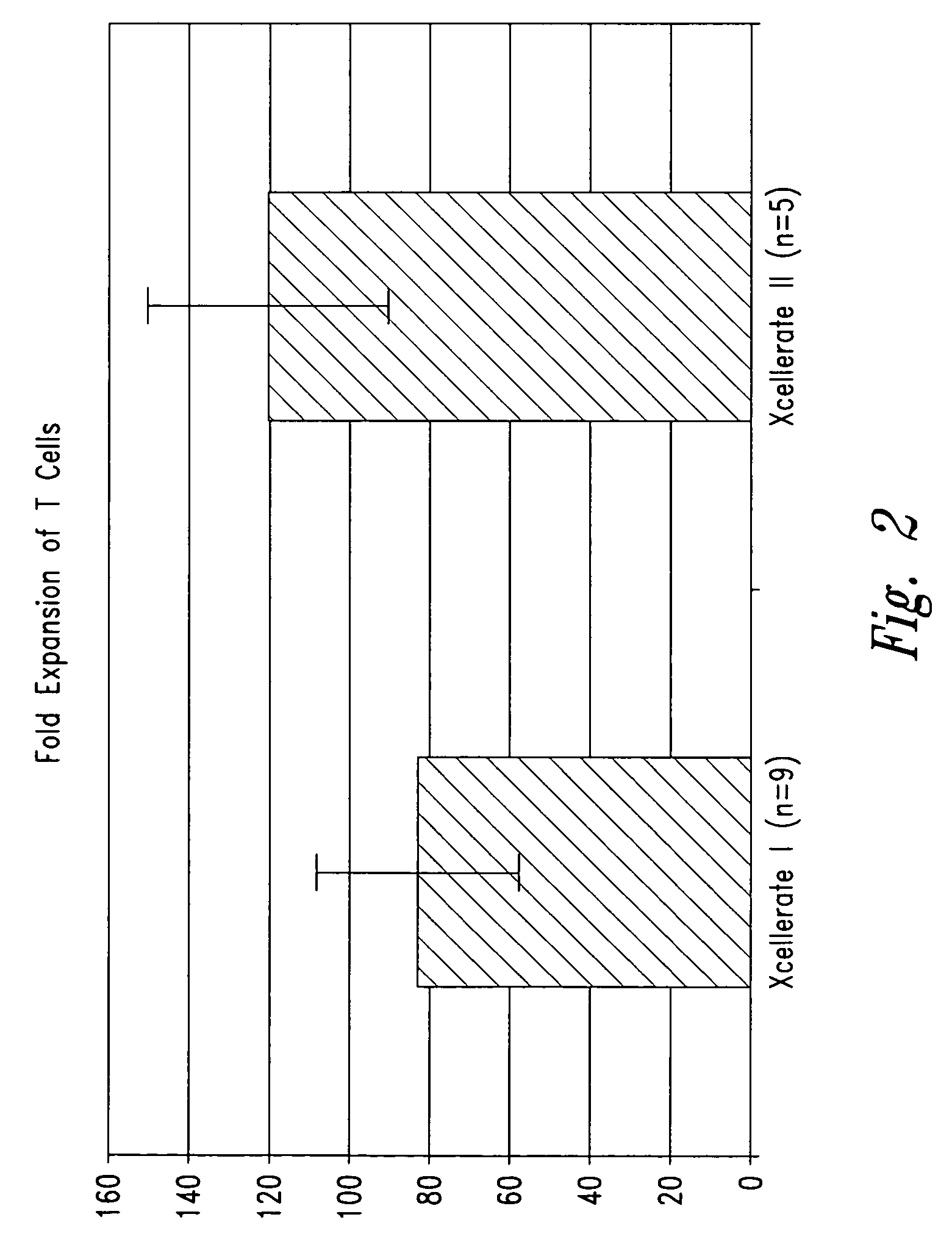
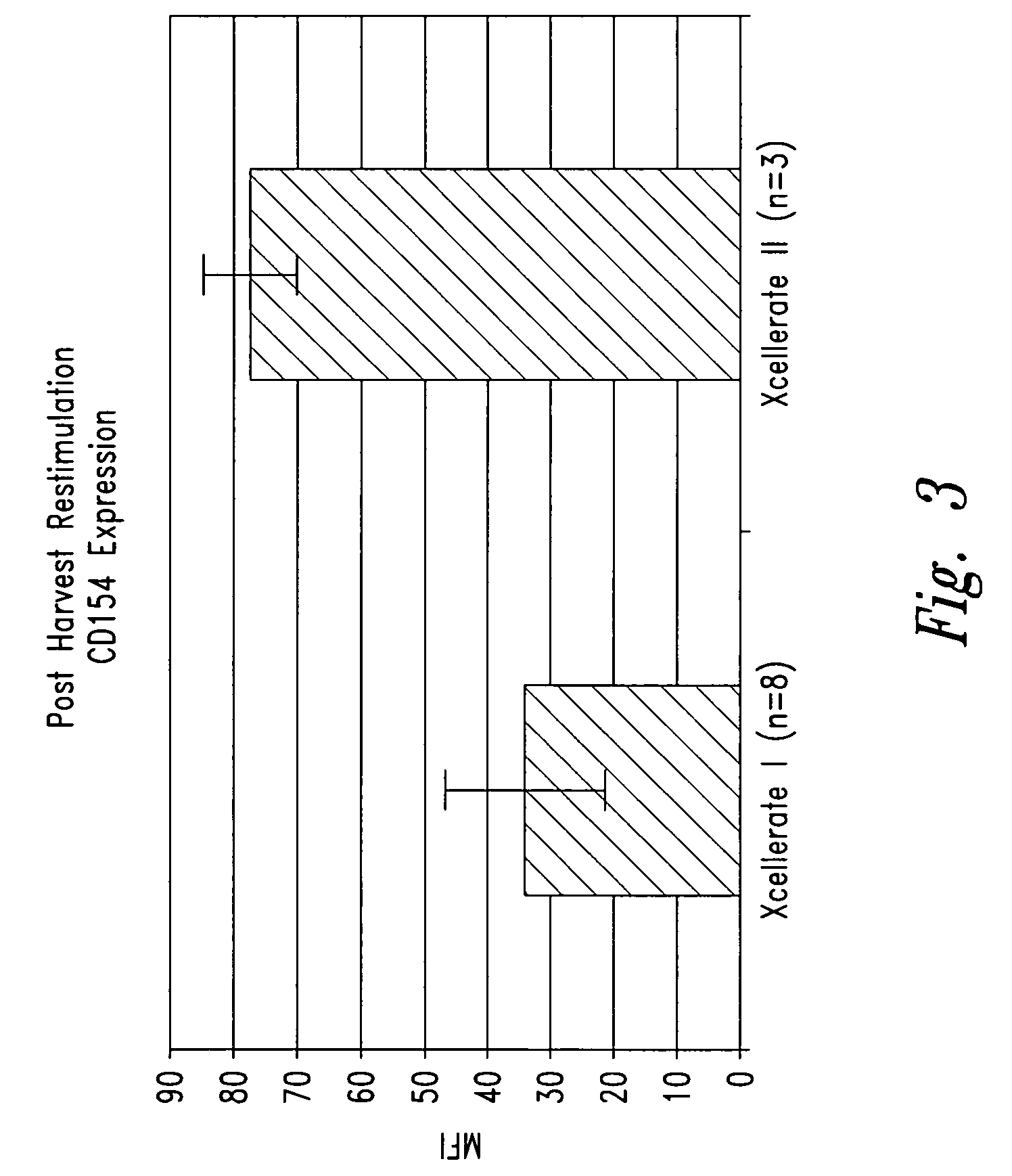
Activation and expansion of cells
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
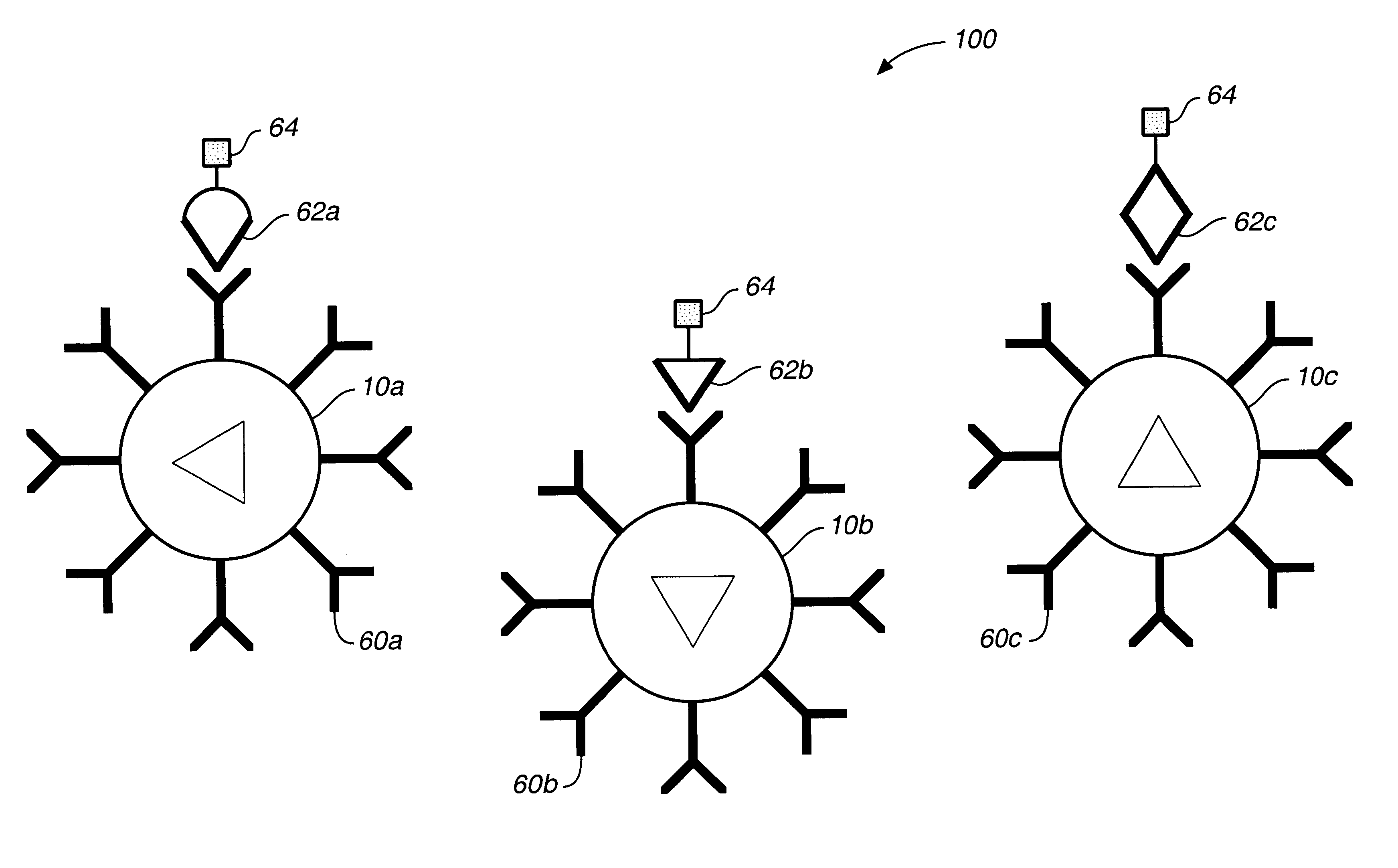
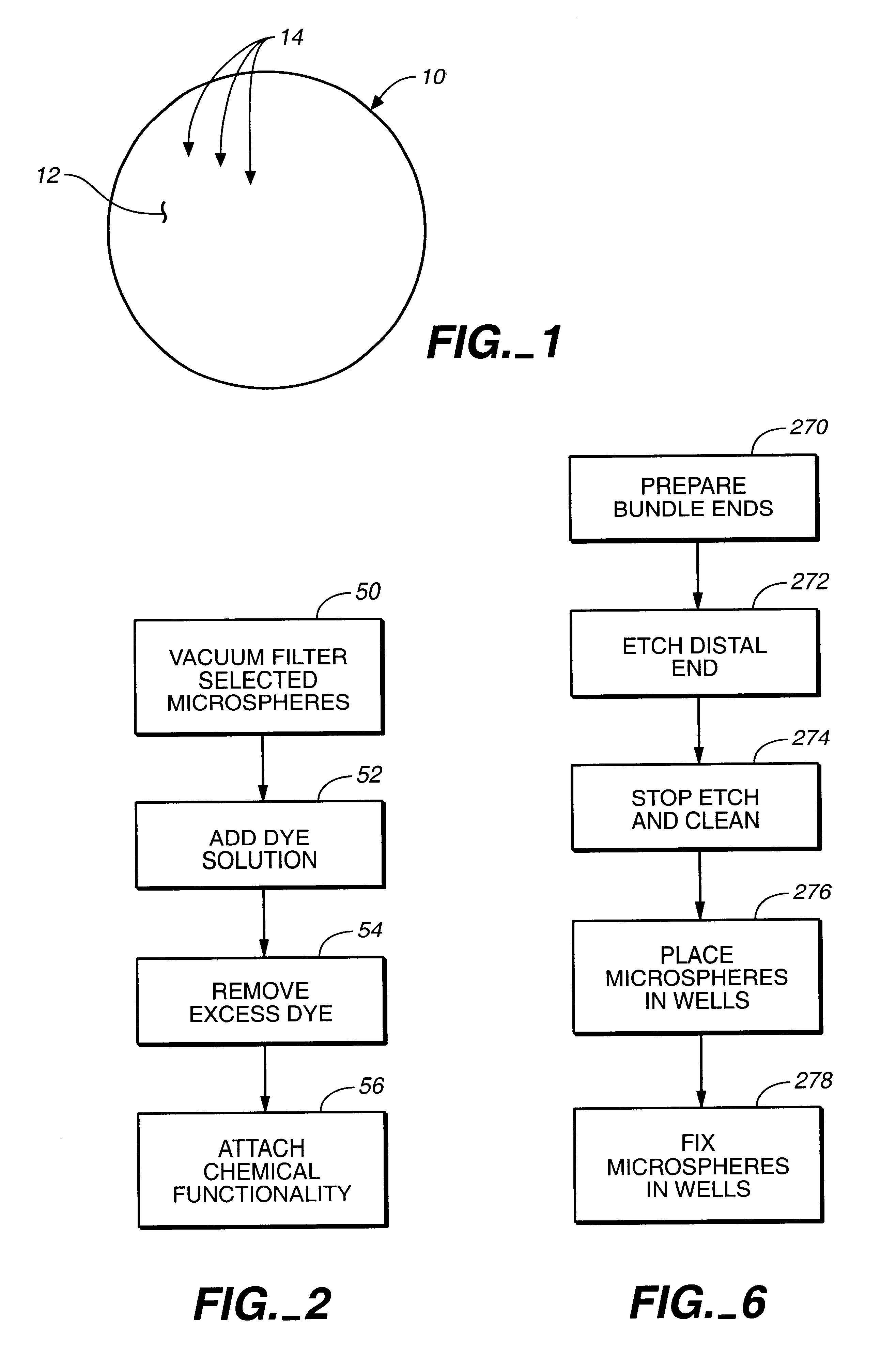
Target analyte sensors utilizing microspheres
A microsphere-based analytic chemistry system and method for making the same is disclosed in which microspheres or particles carrying bioactive agents may be combined randomly or in ordered fashion and dispersed on a substrate to form an array while maintaining the ability to identify the location of bioactive agents and particles within the array using an optically interrogatable, optical signature encoding scheme. A wide variety of modified substrates may be employed which provide either discrete or non-discrete sites for accommodating the microspheres in either random or patterned distributions. The substrates may be constructed from a variety of materials to form either two-dimensional or three-dimensional configurations. In a preferred embodiment, a modified fiber optic bundle or array is employed as a substrate to produce a high density array. The disclosed system and method have utility for detecting target analytes and screening large libraries of bioactive agents.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGETHE
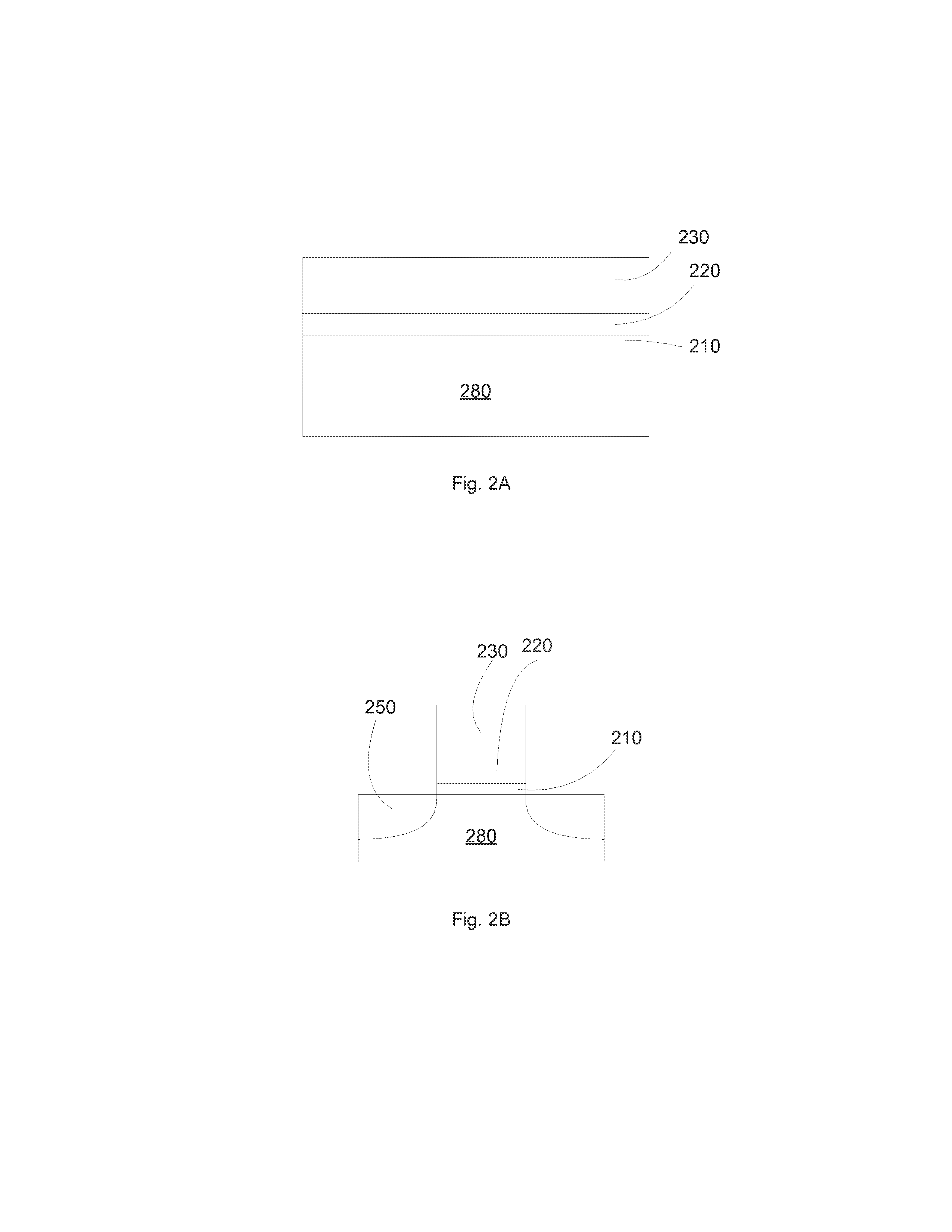
High-density three-dimensional memory cell
InactiveUS6952030B2High densityReduce the overall heightTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorHigh density
A three dimensional monolithic memory comprising a memory cell allowing for increased density is disclosed. In the memory cell of the present invention, a bottom conductor preferably comprising tungsten is formed. Above the bottom conductor a semiconductor element preferably comprises two diode portions and an antifuse. Above the semiconductor element are additional conductors and semiconductor elements in multiple stones of memories. The arrangement of processing steps and the choice of materials decreases aspect ratio of each memory cell, improving the reliability of gap fill and preventing etch undercut.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
High-density illumination system
ActiveUS6871982B2Valid conversionIncrease Lumen DensityPrismsMechanical apparatusHigh densityLed array
A compact and efficient optical illumination system featuring planar multi-layered LED light source arrays concentrating their polarized or un-polarized output within a limited angular range. The optical system manipulates light emitted by a planar array of electrically-interconnected LED chips positioned within the input apertures of a corresponding array of shaped metallic reflecting bins using at least one of elevated prismatic films, polarization converting films, micro-lens arrays and external hemispherical or ellipsoidal reflecting elements. Practical applications of the LED array illumination systems include compact LCD or DMD video image projectors, as well as general lighting, automotive lighting, and LCD backlighting.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
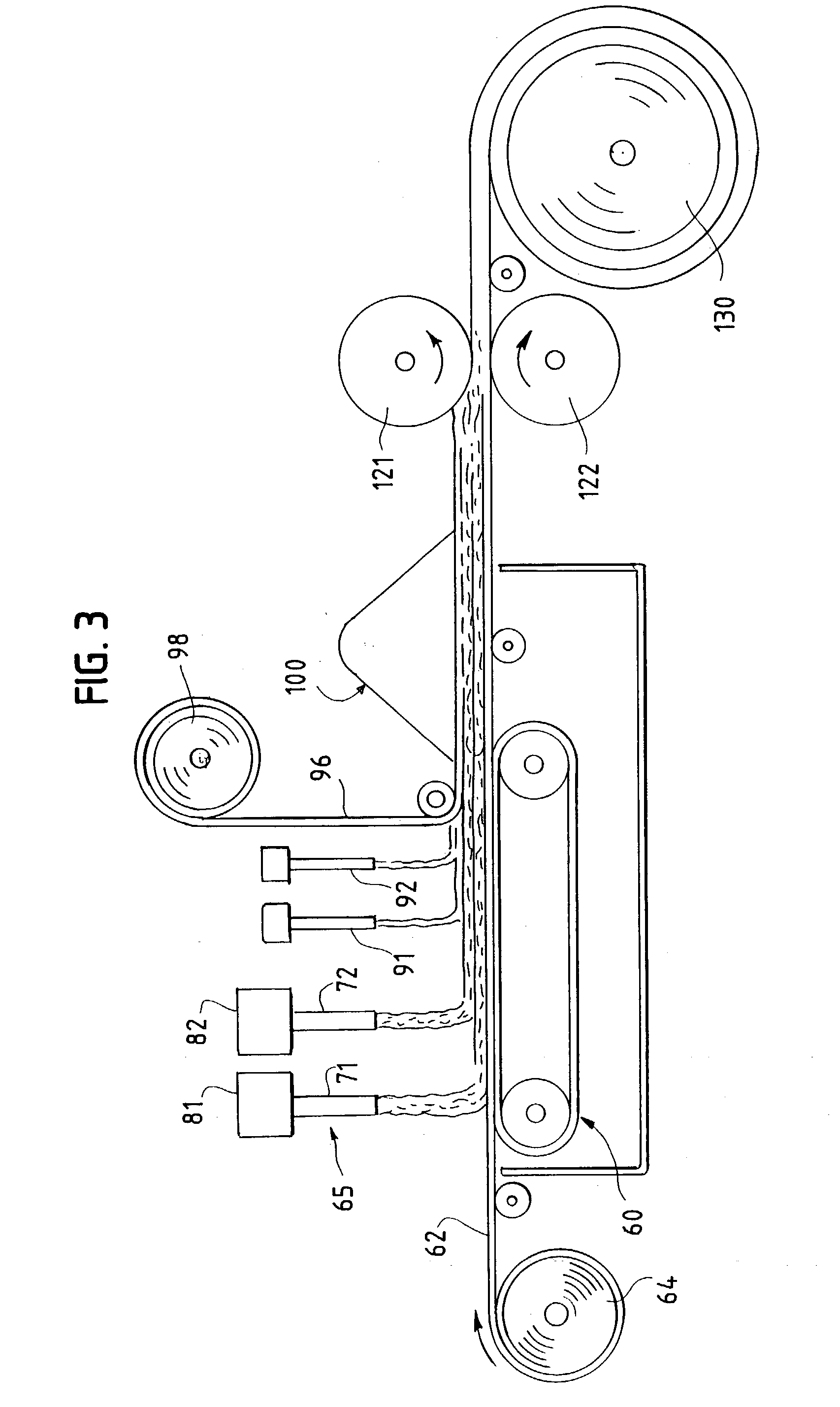
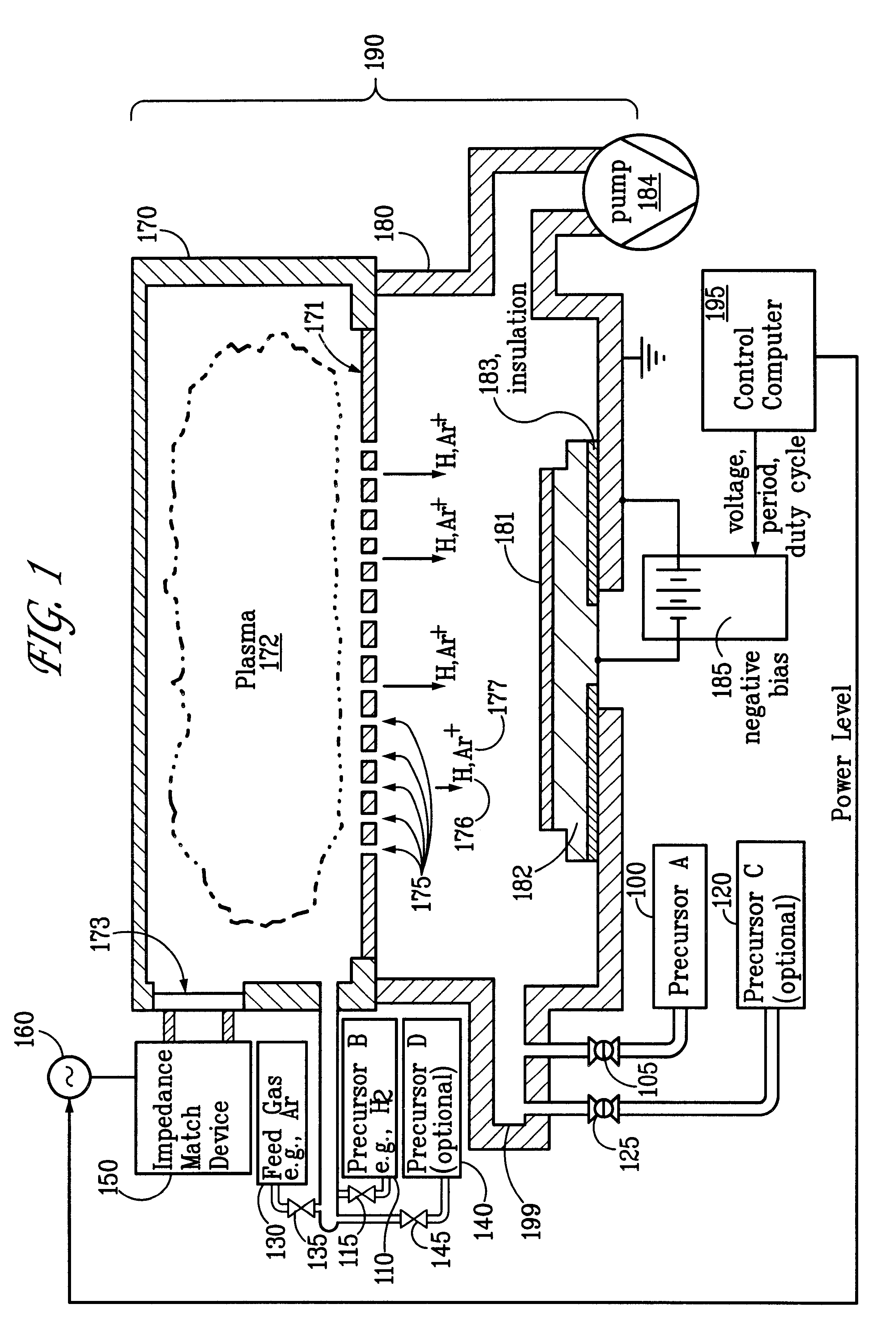
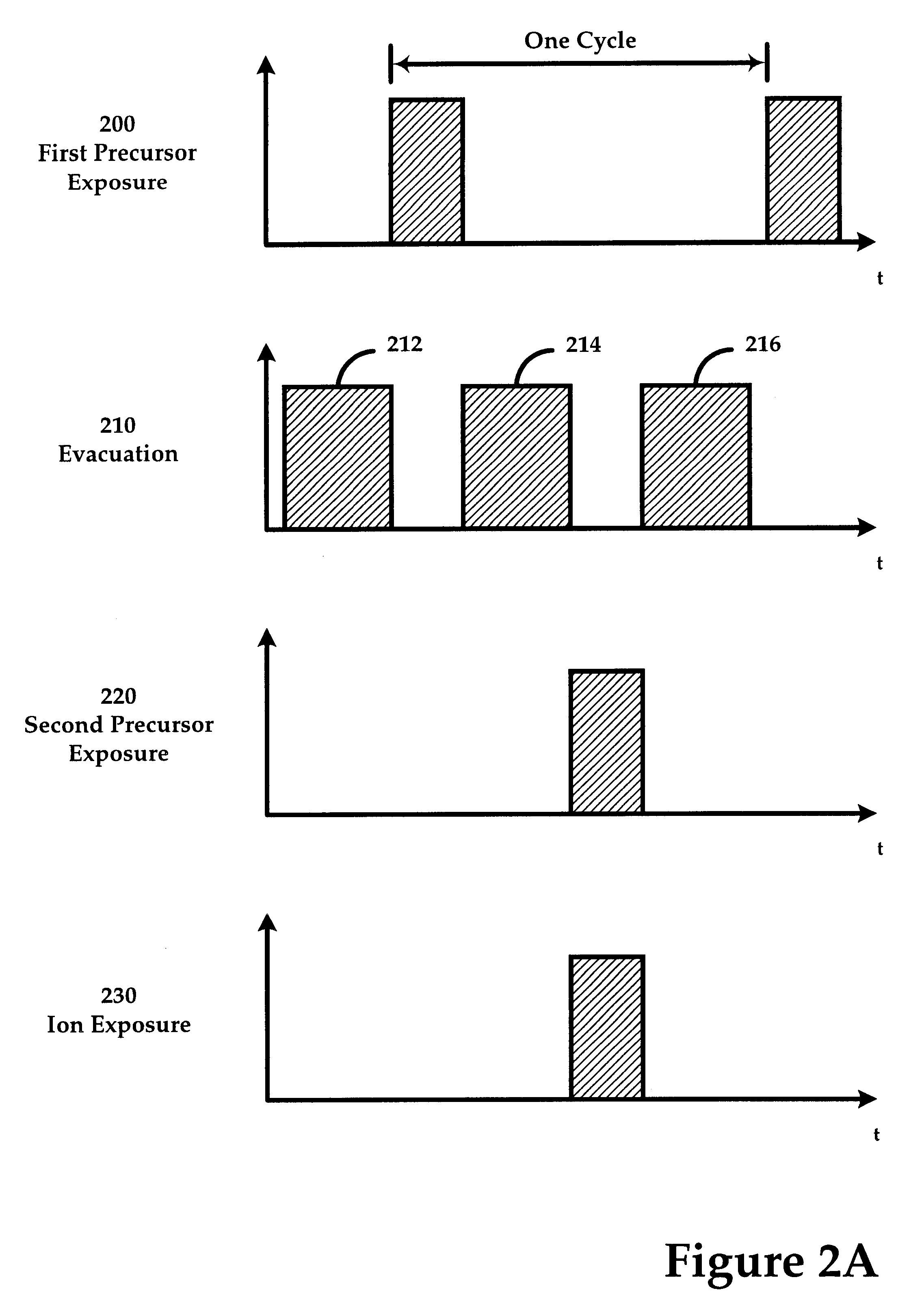
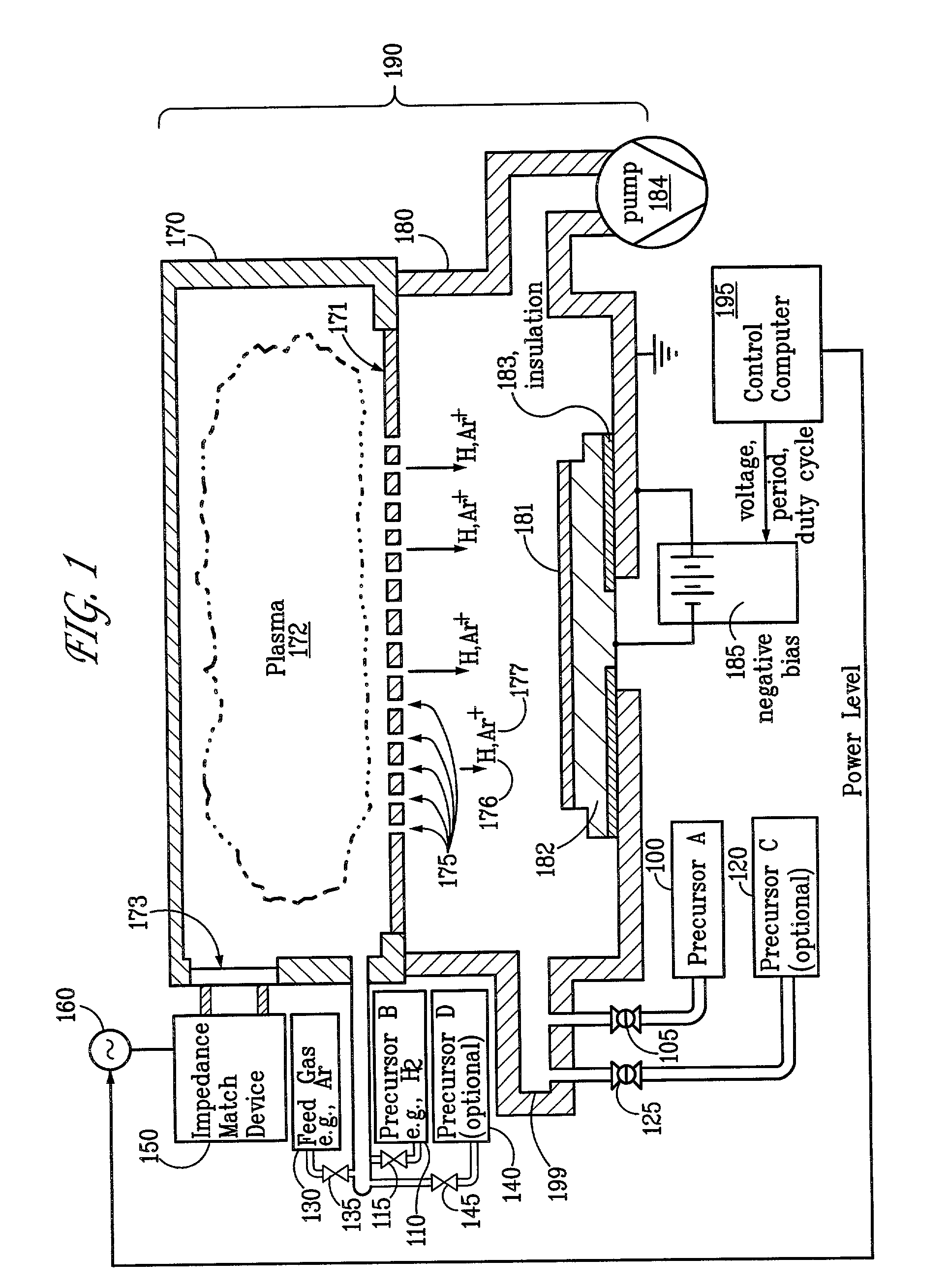
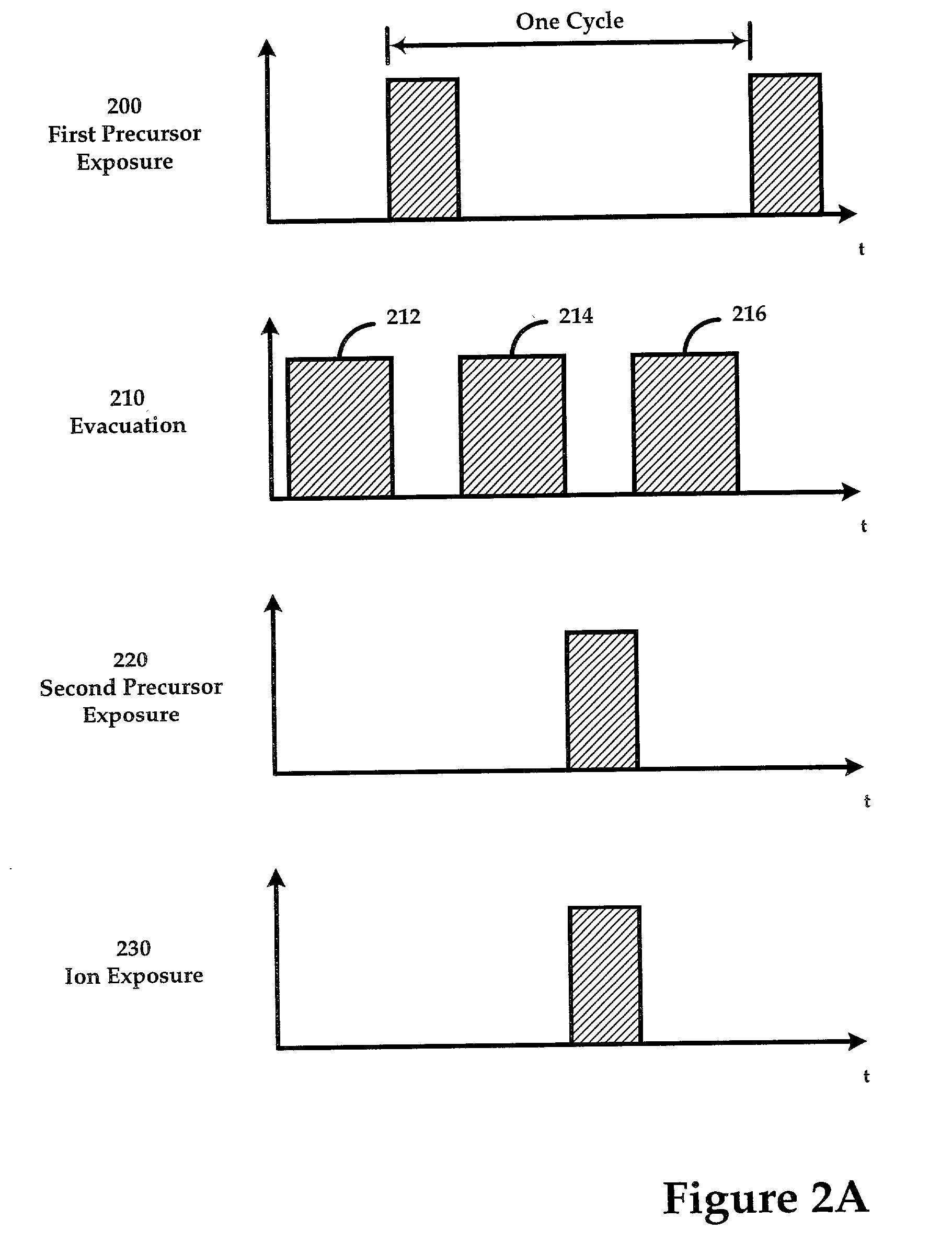
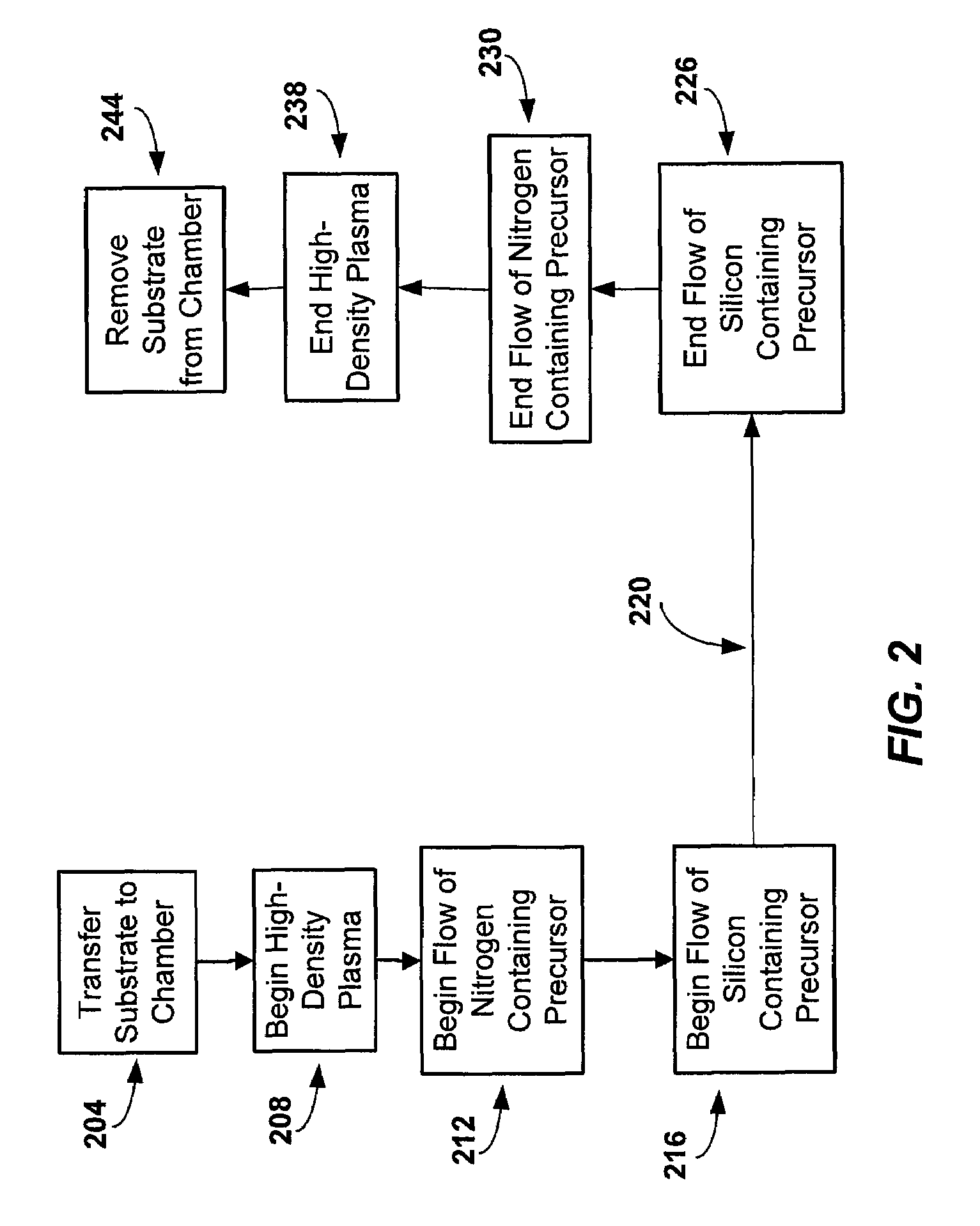
Sequential method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6428859B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSequential methodHigh density
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Compressed high density fibrous polymers suitable for implant
An embodiment of the present invention may be made by the following steps: providing a mixture comprising a plurality of fibers, a lubricant, and a suspension fluid, with the suspension fluid filling a void space between said fibers and subjecting said mixture to at least one compressive force. The compressive force causes the migration and alignment of said fibers; and may remove substantially all of the suspension fluid from said mixture. The mixture may further comprise a biologically active agent, or a reinforcing agent.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
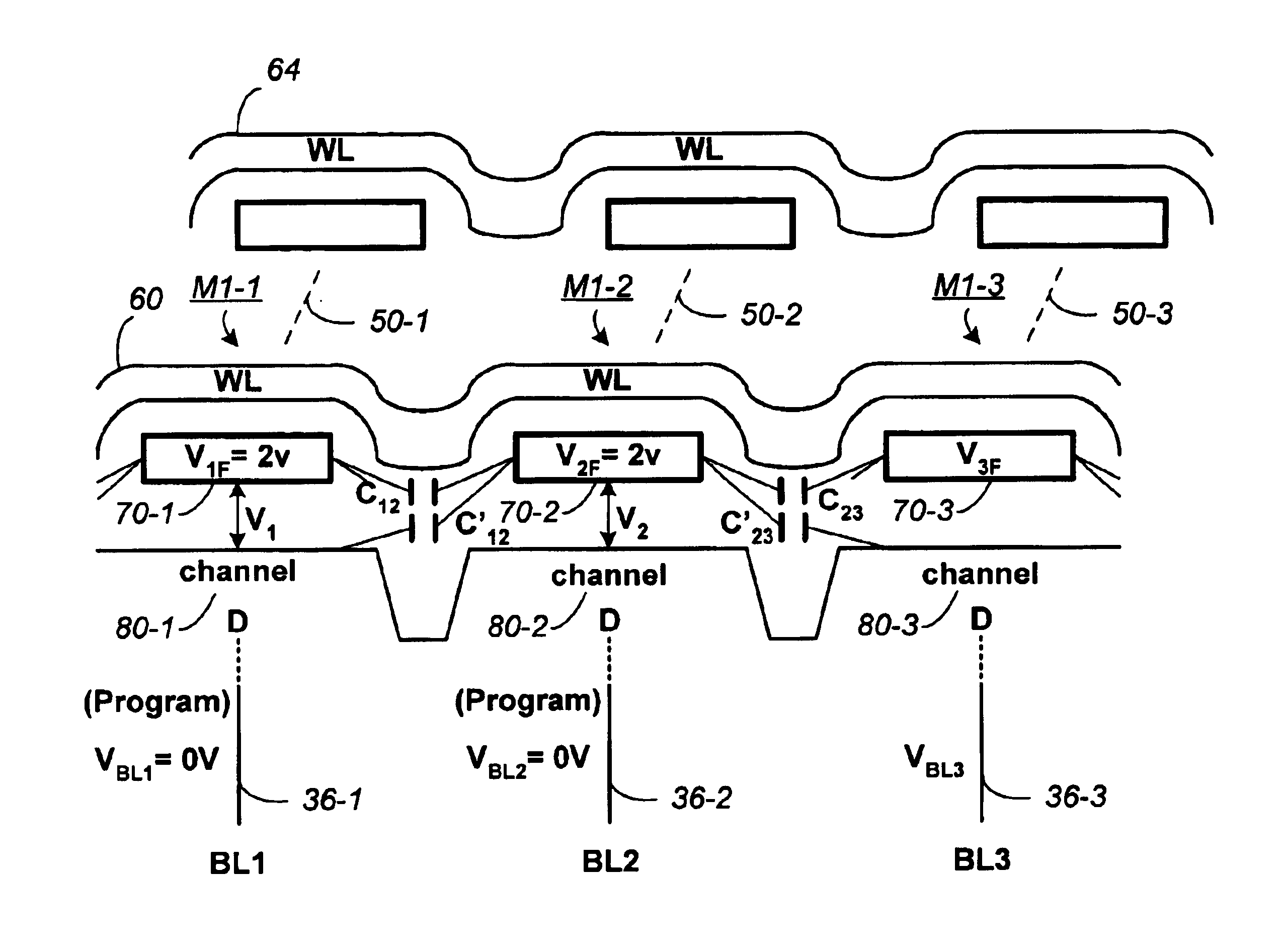
Non-volatile memory and method with bit line compensation dependent on neighboring operating modes
ActiveUS6956770B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineHigh density
When programming a contiguous page of memory storage units, every time a memory storage unit has reached its targeted state and is program-inhibited or locked out from further programming, it creates a perturbation on an adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The present invention provides as part of a programming circuit and method in which an offset to the perturbation is added to the adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The offset is added as voltage offset to a bit line of a storage unit under programming. The voltage offset is a predetermined function of whether none or one or both of its neighbors are in a mode that creates perturbation, such as in a program inhibit mode. In this way, an error inherent in programming in parallel high-density memory storage units is eliminated or minimized.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
System and method for modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS20020104481A1Faster efficient meanSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh densitySubject matter
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential or non-sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) apparatus and technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method; and, 4) providing a means of improved radical generation and delivery. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. [37 C.F.R. § 1.72(b)].
Owner:ANGSTRON SYST
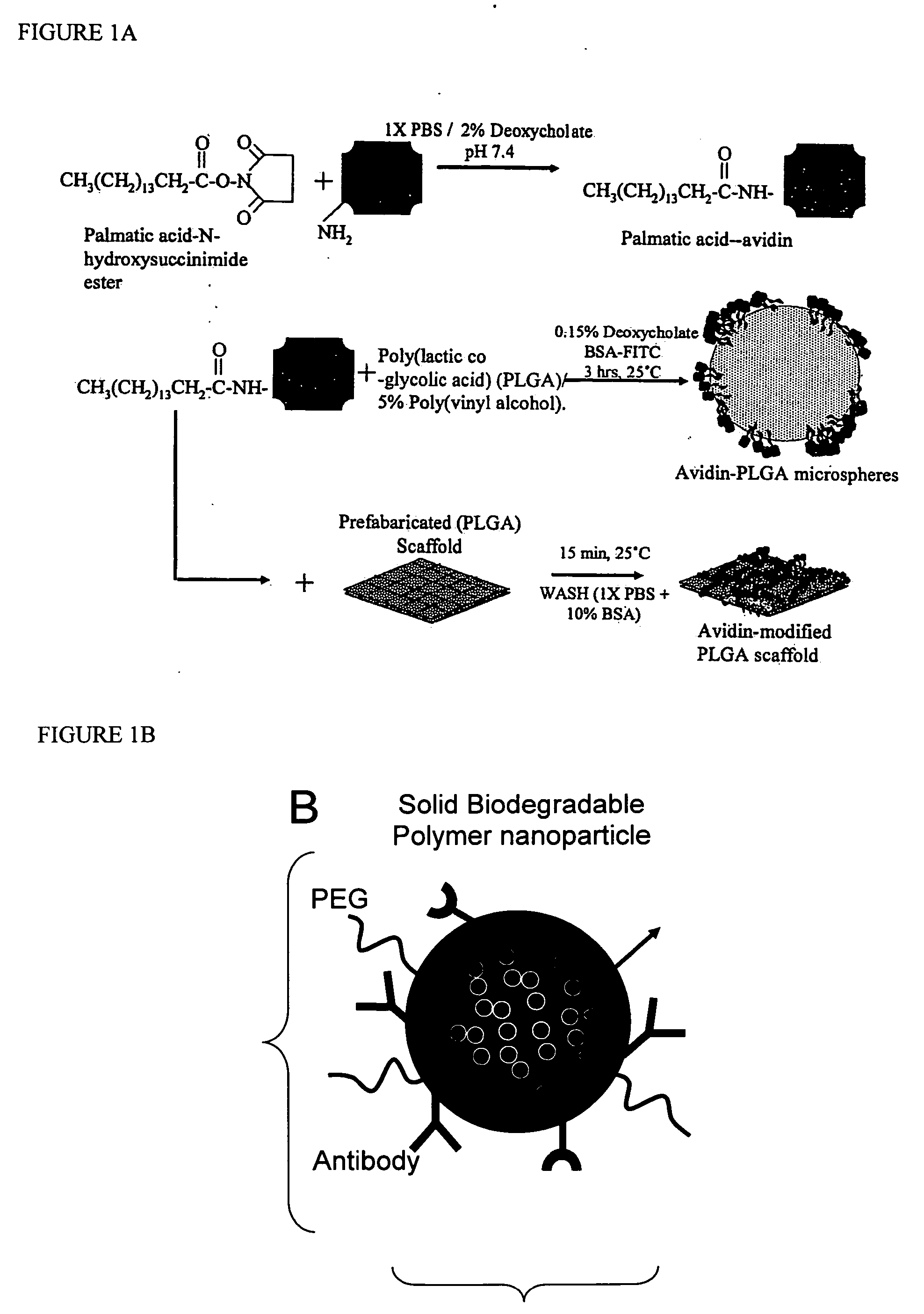
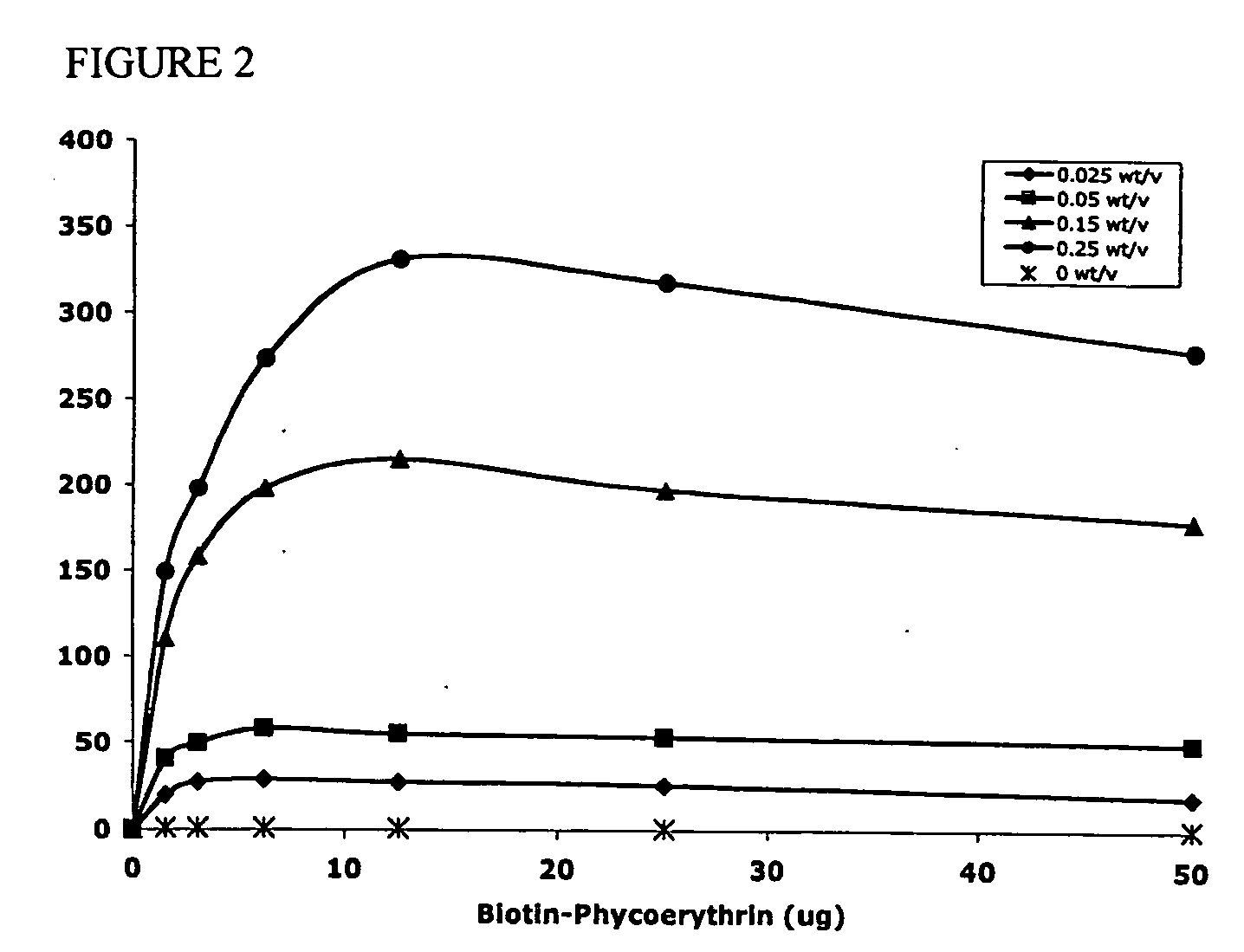
Targeted and high density drug loaded polymeric materials
ActiveUS20060002852A1Increase molecular densityHigh densityPowder deliveryBiocideAntigenWound dressing
Polymeric delivery devices have been developed which combine high loading / high density of molecules to be delivered with the option of targeting. As used herein, “high density” refers to microparticles having a high density of ligands or coupling agents, which is in the range of 1000-10,000,000, more preferably between 10,000 and 1,000,000 ligands per square micron of microparticle surface area. A general method for incorporating molecules into the surface of biocompatible polymers using materials with an HLB of less than 10, more preferably less than 5, such as fatty acids, has been developed. Because of its ease, generality and flexibility, this method has widespread utility in modifying the surface of polymeric materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering, as well other other fields. Targeted polymeric microparticles have also been developed which encapsulate therapeutic compounds such as drugs, cellular materials or components, and antigens, and have targeting ligands directly bound to the microparticle surface. Preferred applications include use in tissue engineering matrices, wound dressings, bone repair or regeneration materials, and other applications where the microparticles are retained at the site of application or implantation. Another preferred application is in the use of microparticles to deliver anti-proliferative agents to the lining of blood vessels following angioplasty, transplantation or bypass surgery to prevent or decrease restenosis, and in cancer therapy. In still another application, the microparticles are used to treat or prevent macular degeneration when administered to the eye, where agents such as complement inhibitors are administered.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Continuous method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6416822B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to an enhanced non-sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
High-density cable distribution frame
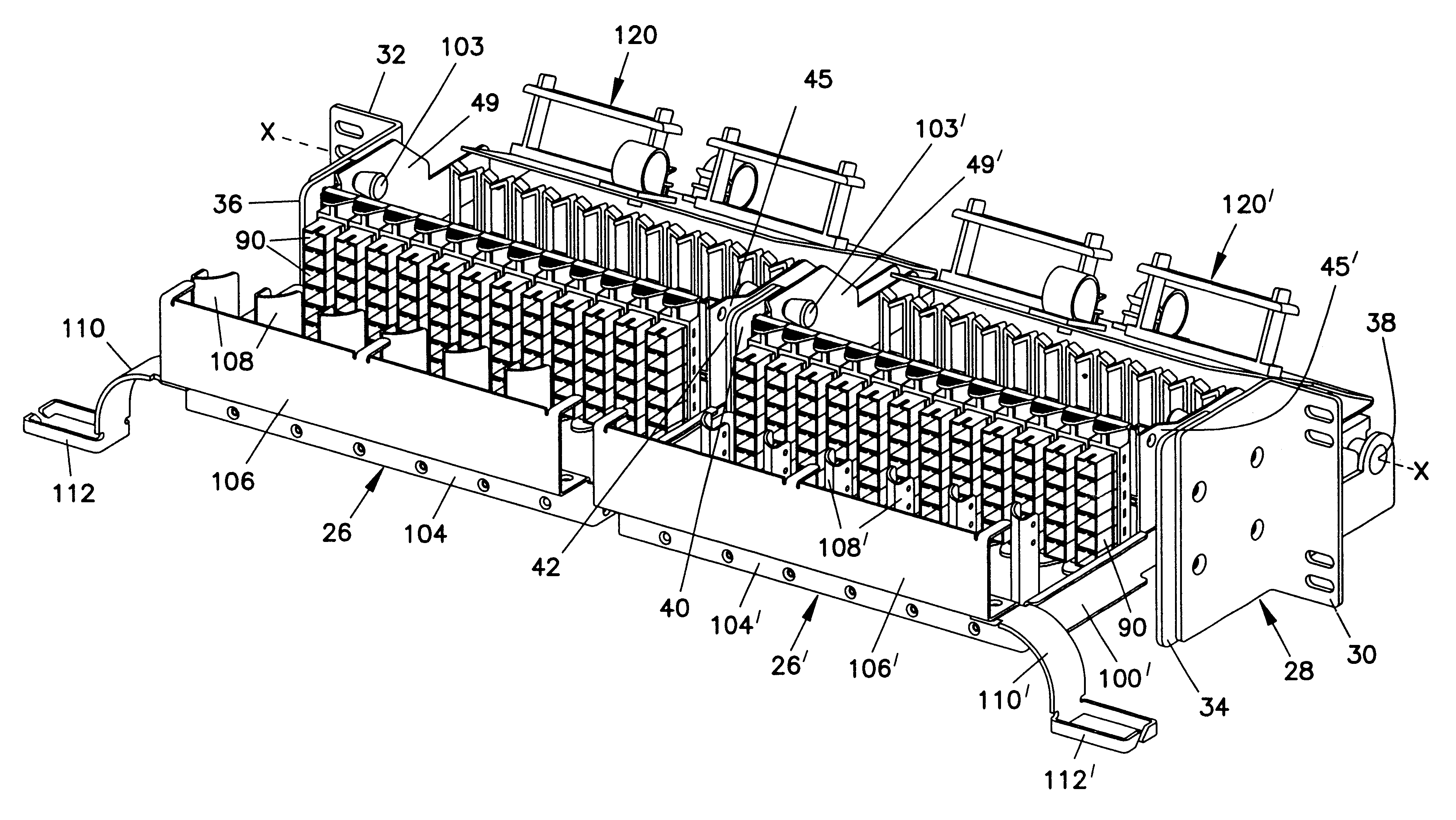
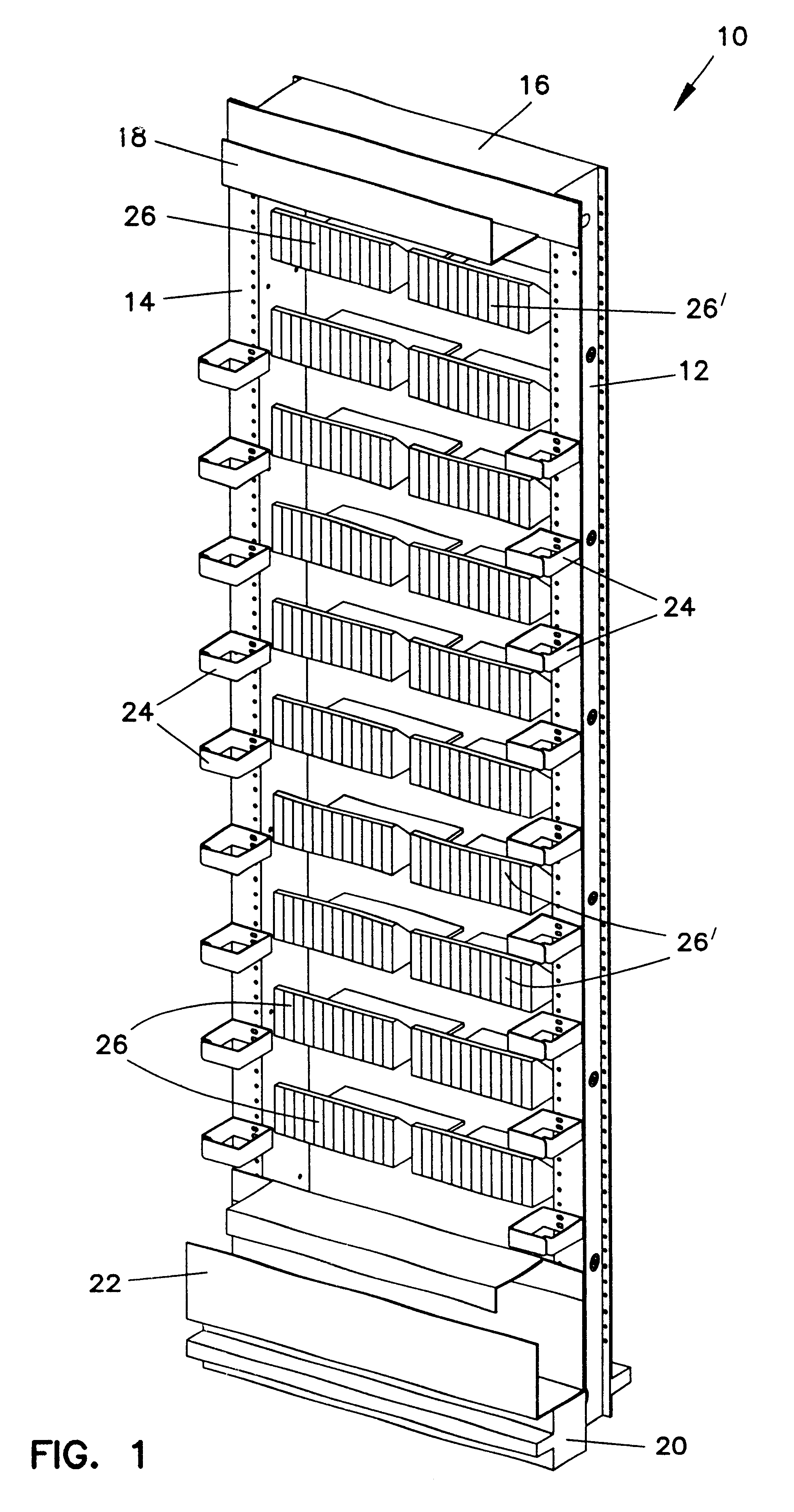
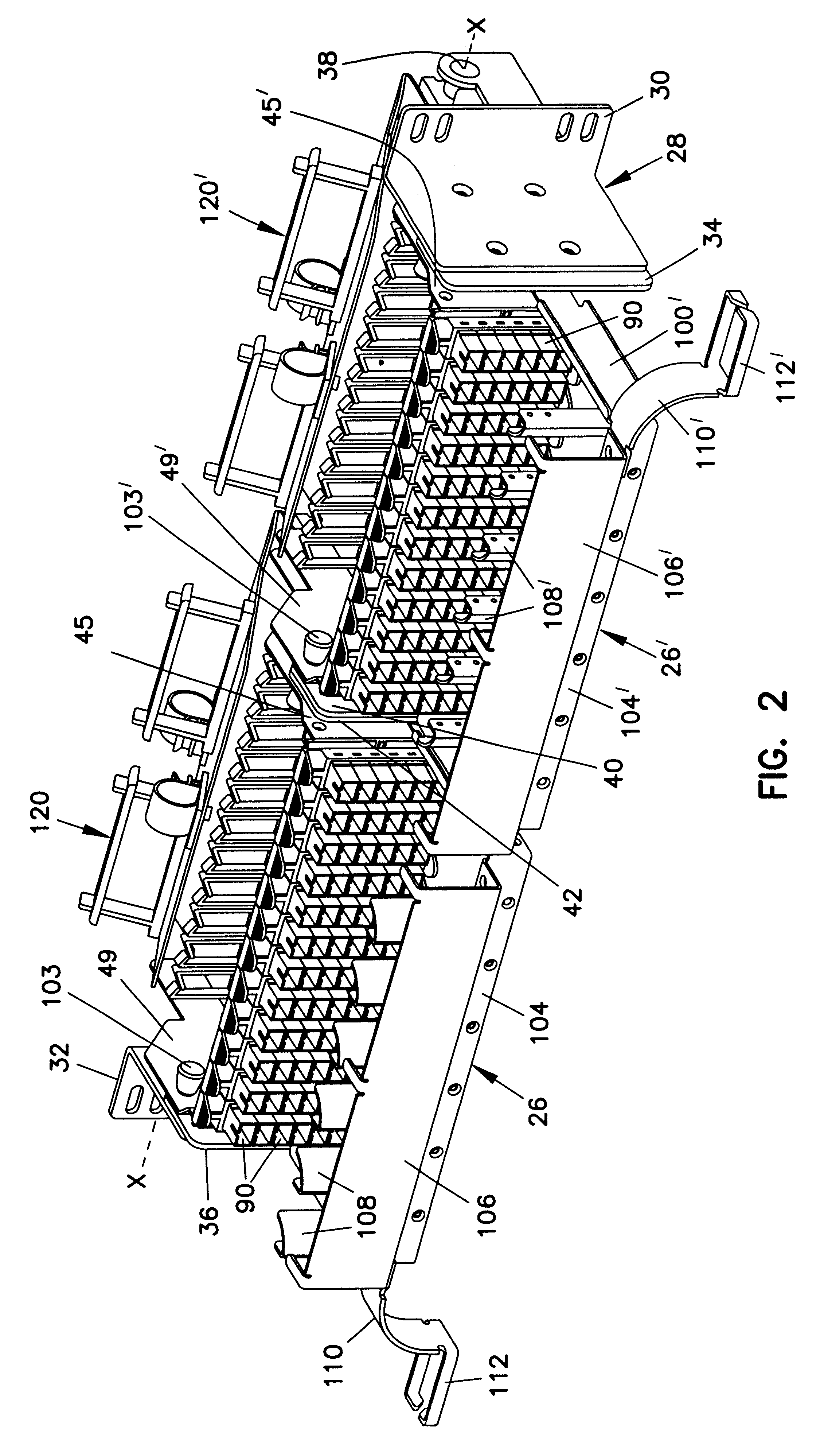
InactiveUSRE38311E1Control displacementSmall movementCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresDistribution frameFiber
A fiber distribution frame (10) includes a fixture (26) having a plurality of modules (58) mounted side-by-side within said fixture with each of the modules being individually mounted in a line of travel. Each of the modules (58) can be locked in any one of a plurality of discrete positions within the line of travel. Each of the modules (58) contains a plurality of adapters (90) for receiving and retaining fiber optic connectors. Further, the fixture (26) may be tilted downwardly to provide access to the rear of the fixture.
Owner:ADC TELECOMMUNICATIONS +1
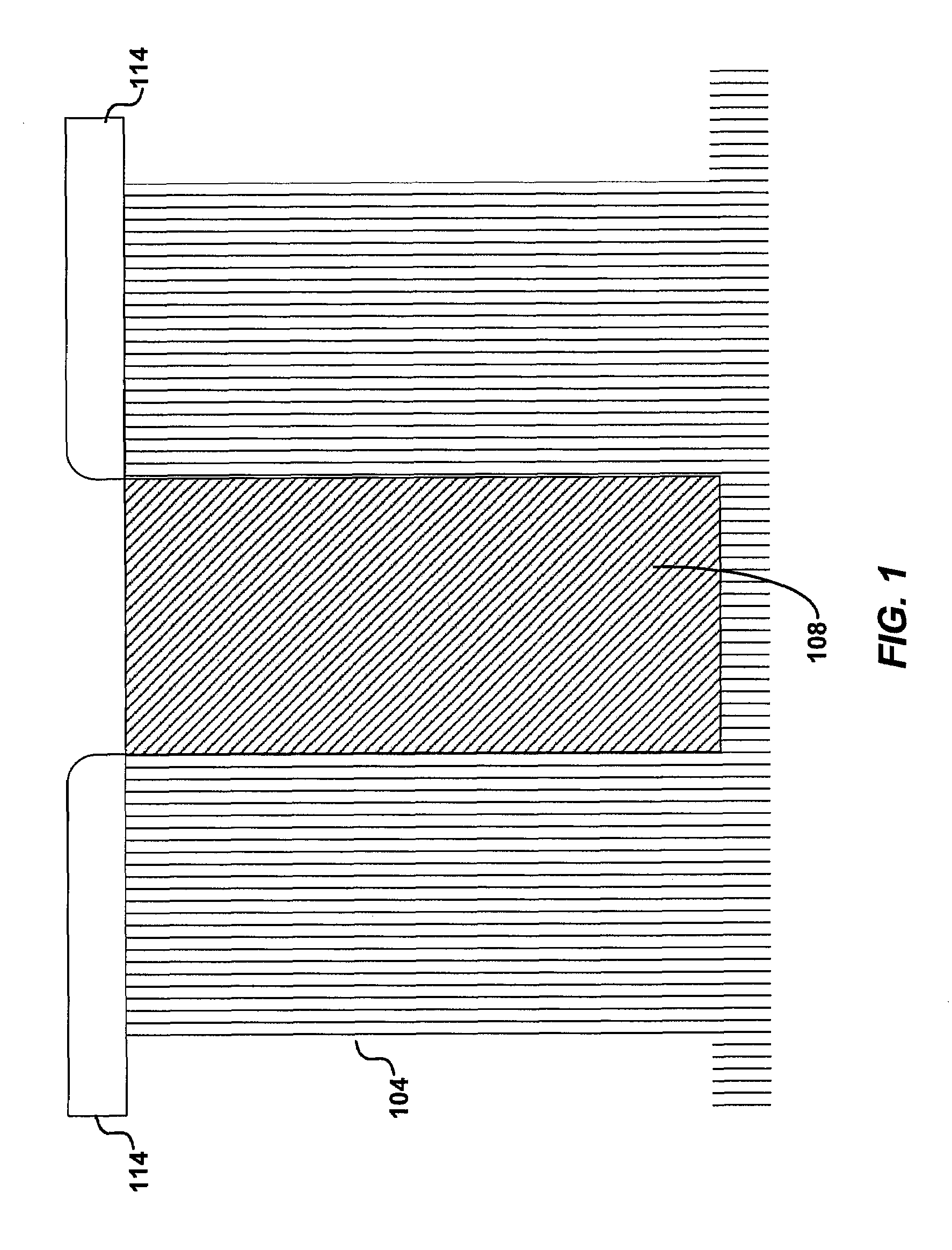
Low wet etch rate silicon nitride film
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
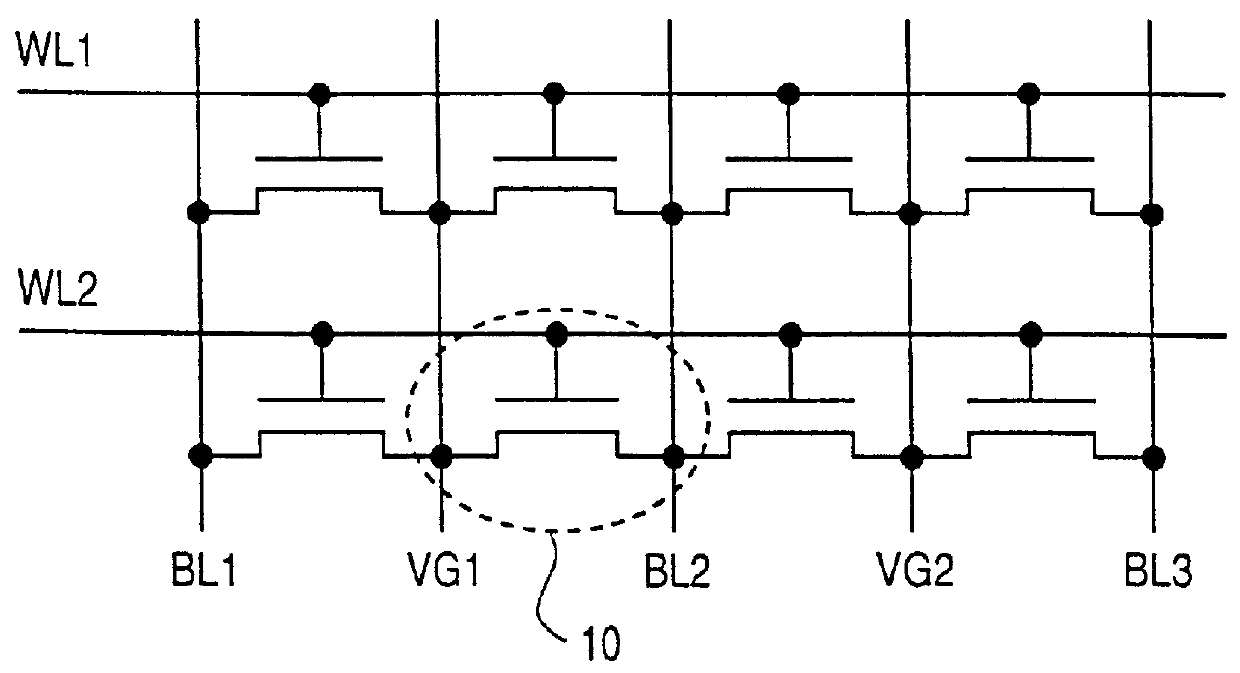
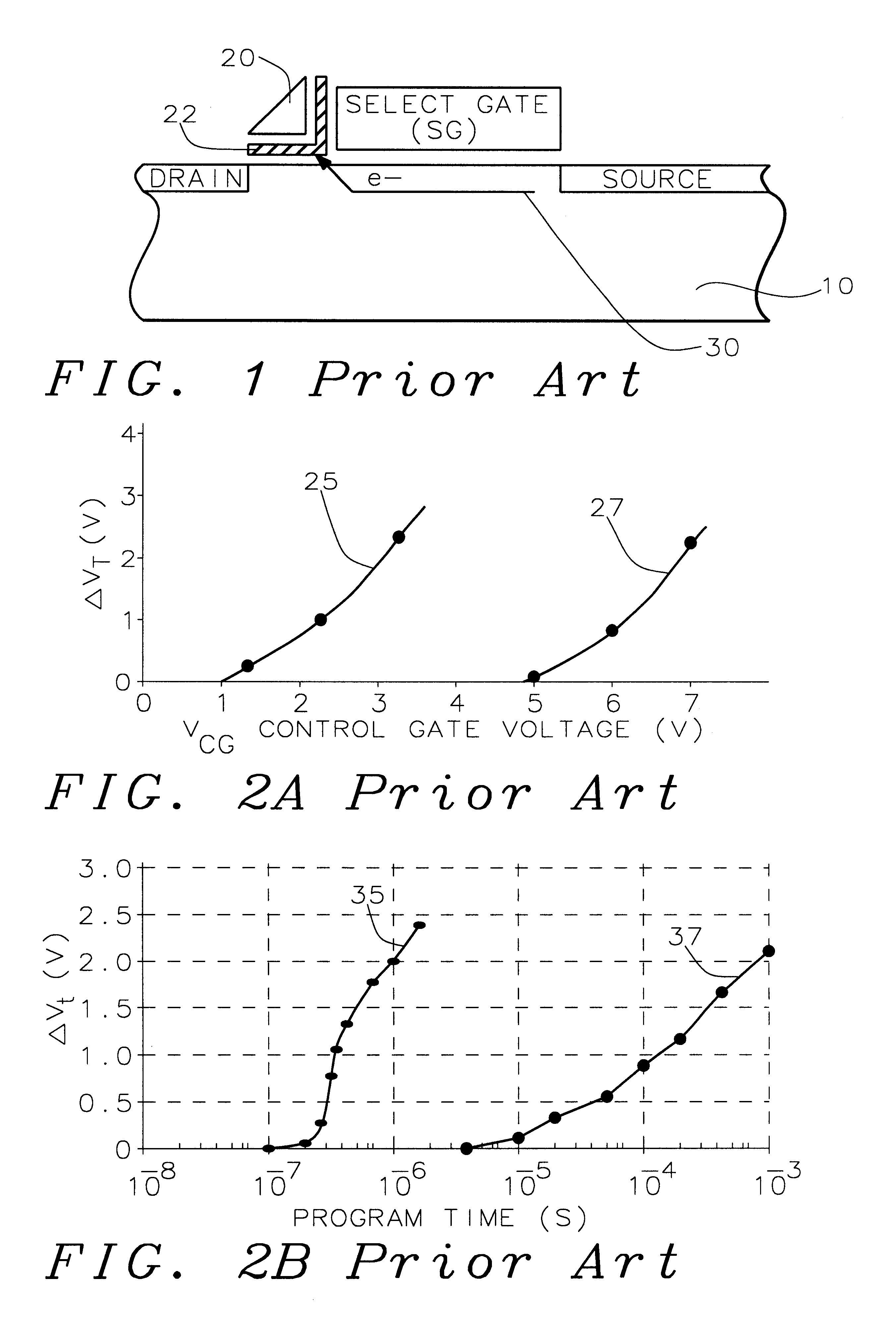
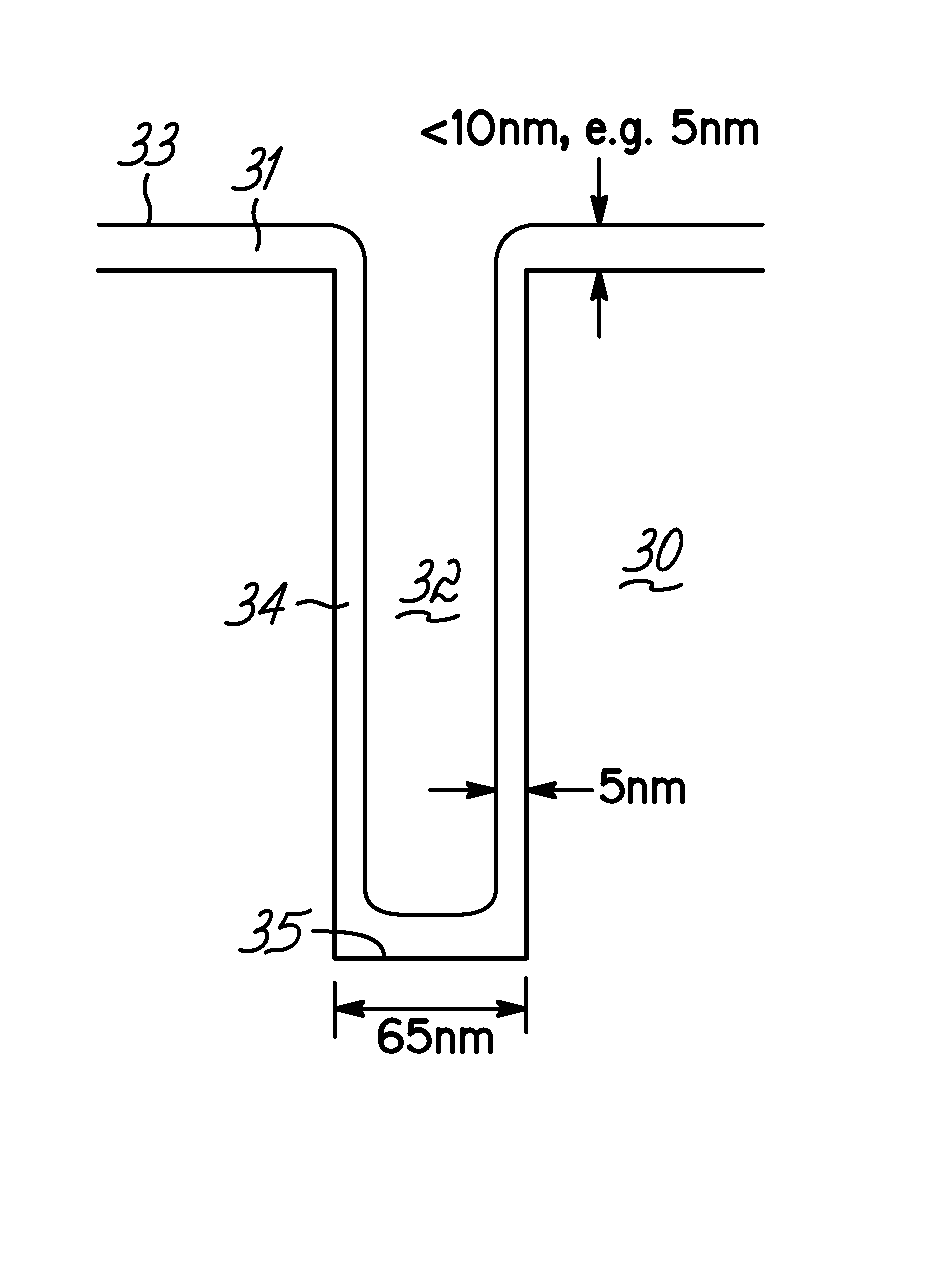
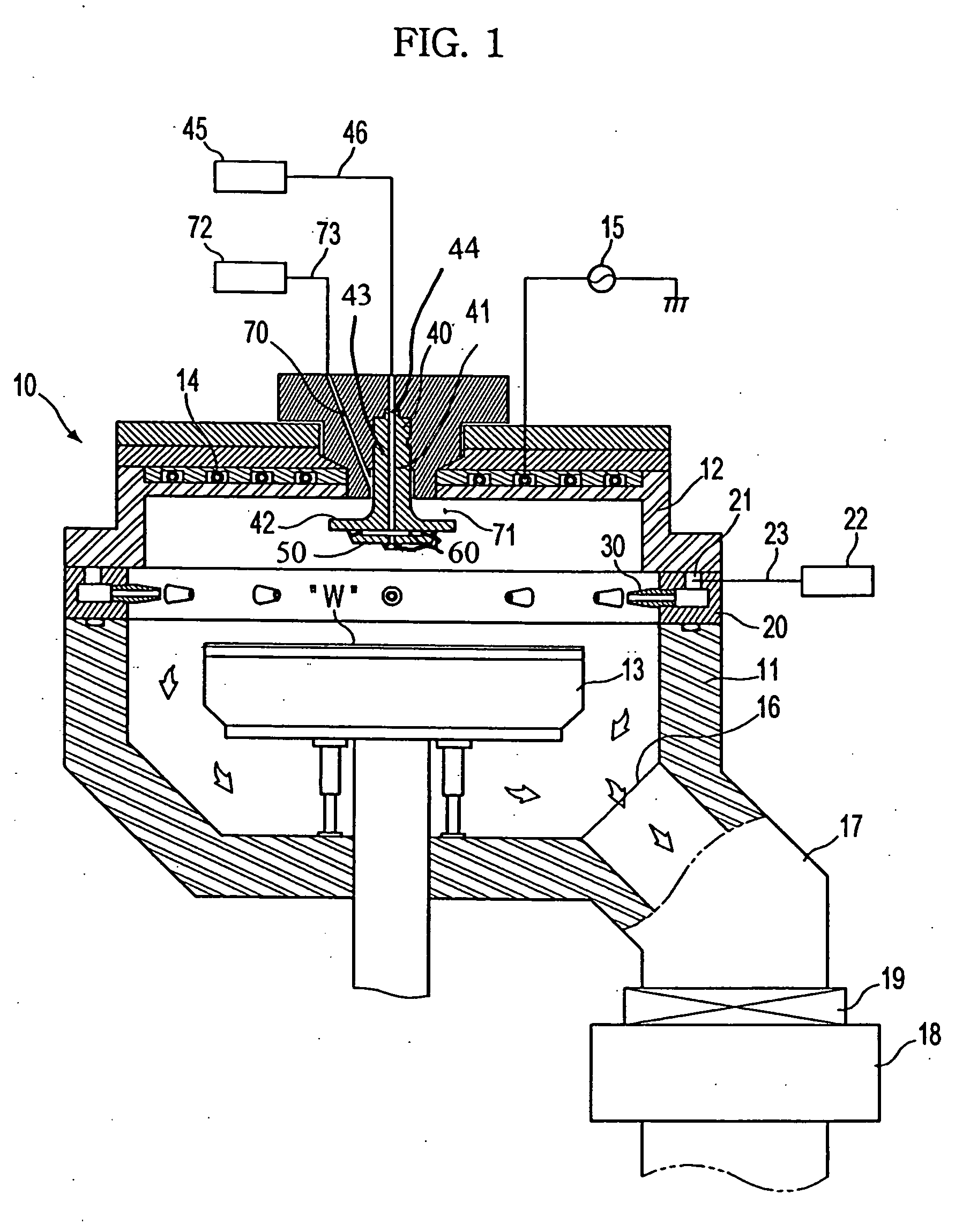
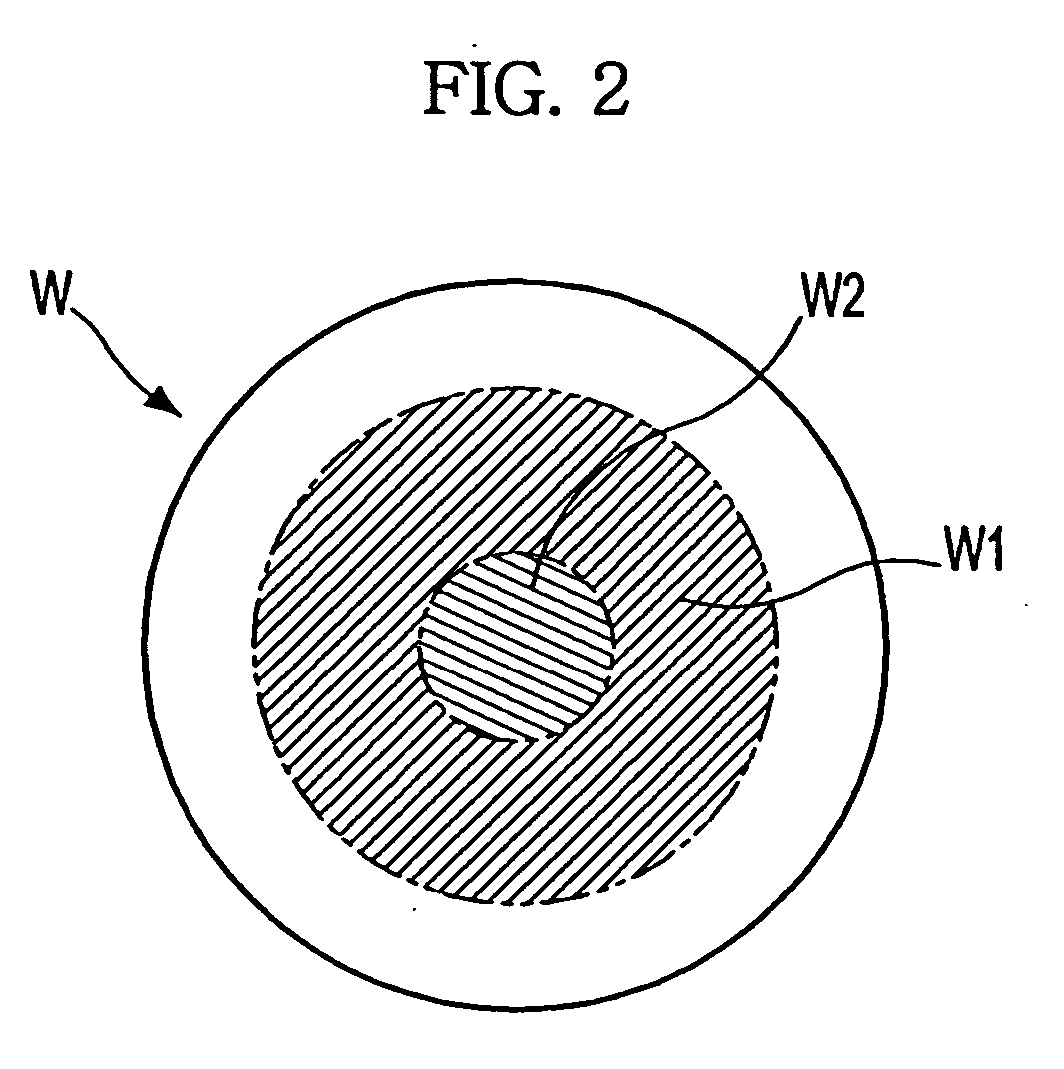
Process for making and programming and operating a dual-bit multi-level ballistic MONOS memory
A fast low voltage ballistic program, ultra-short channel, ultra-high density, dual-bit multi-level flash memory is described with a two or three polysilicon split gate side wall process. The structure and operation of this invention is enabled by a twin MONOS cell structure having an ultra-short control gate channel of less than 40nm, with ballistic injection which provides high electron injection efficiency and very fast program at low program voltages of 3~5V. The cell structure is realized by (i) placing side wall control gates over a composite of Oxide-Nitride-Oxide (ONO) on both sides of the word gate, and (ii) forming the control gates and bit diffusion by self-alignment and sharing the control gates and bit diffusions between memory cells for high density. Key elements used in this process are: 1) Disposable side wall process to fabricate the ultra short channel and the side wall control gate with or without a step structure, and 2) Self-aligned definition of the control gate over the storage nitride and the bit line diffusion, which also runs in the same direction as the control gate. The features of fast program, low voltage, ultra-high density, dual-bit, multi-level MONOS NVRAM of the present invention include: 1) Electron memory storage in nitride regions within an ONO layer underlying the control gates, 2) high density dual-bit cell in which there are two nitride memory storage elements per cell, 3) high density dual-bit cell can store multi-levels in each of the nitride regions, 4) low current program controlled by the word gate and control gate, 5) fast, low voltage program by ballistic injection utilizing the controllable ultra-short channel MONOS, and 6) side wall control poly gates to program and read multi-levels while masking out memory storage state effects of the unselected adjacent nitride regions and memory cells. The ballistic MONOS memory cell is arranged in the following array: each memory cell contains two nitride regions for one word gate, and ½ a source diffusion and ½ a bit diffusion. Control gates can be defined separately or shared together over the same diffusion. Diffusions are shared between cells and run in parallel to the side wall control gates, and perpendicular to the word line.
Owner:HALO LSI INC
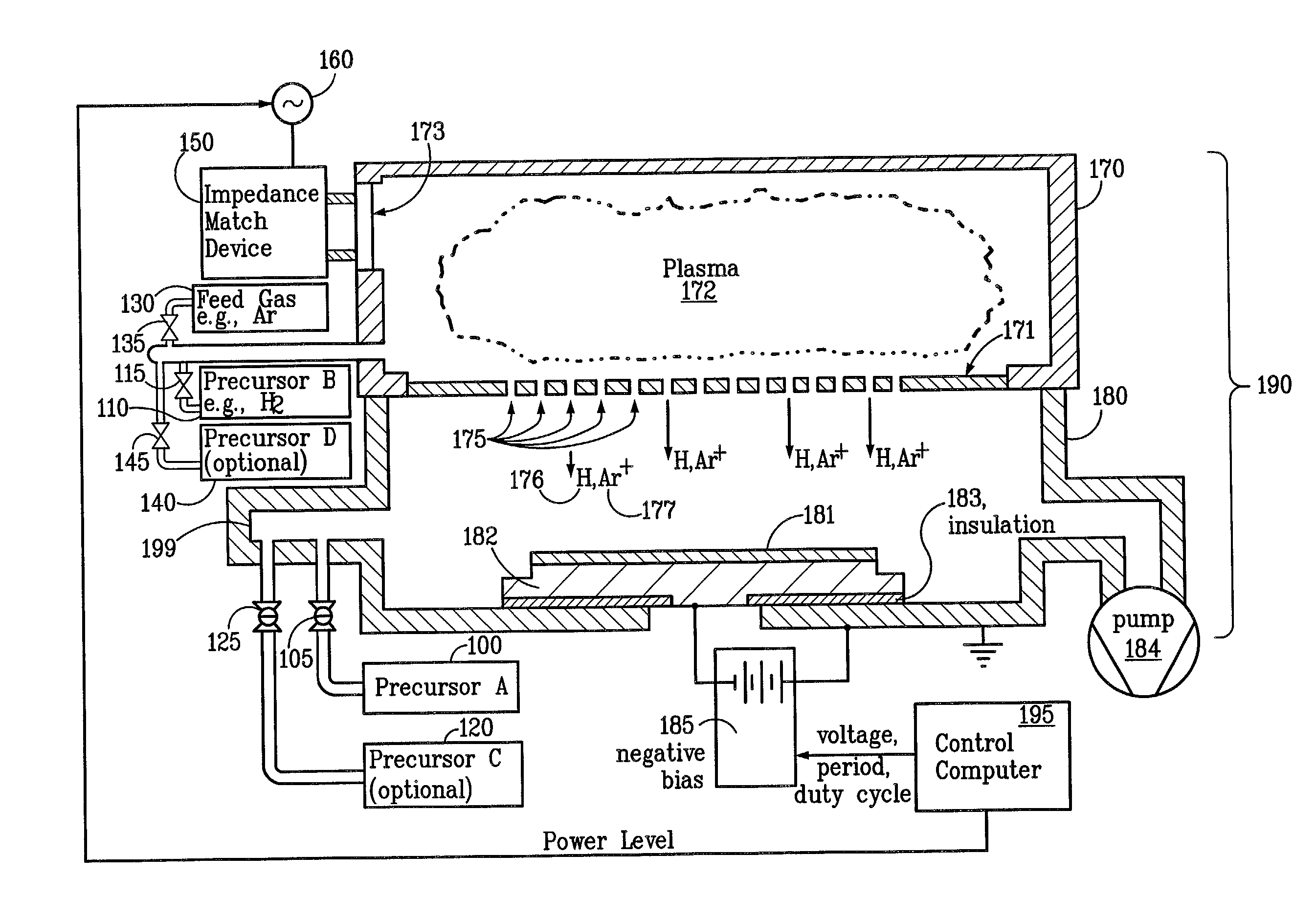
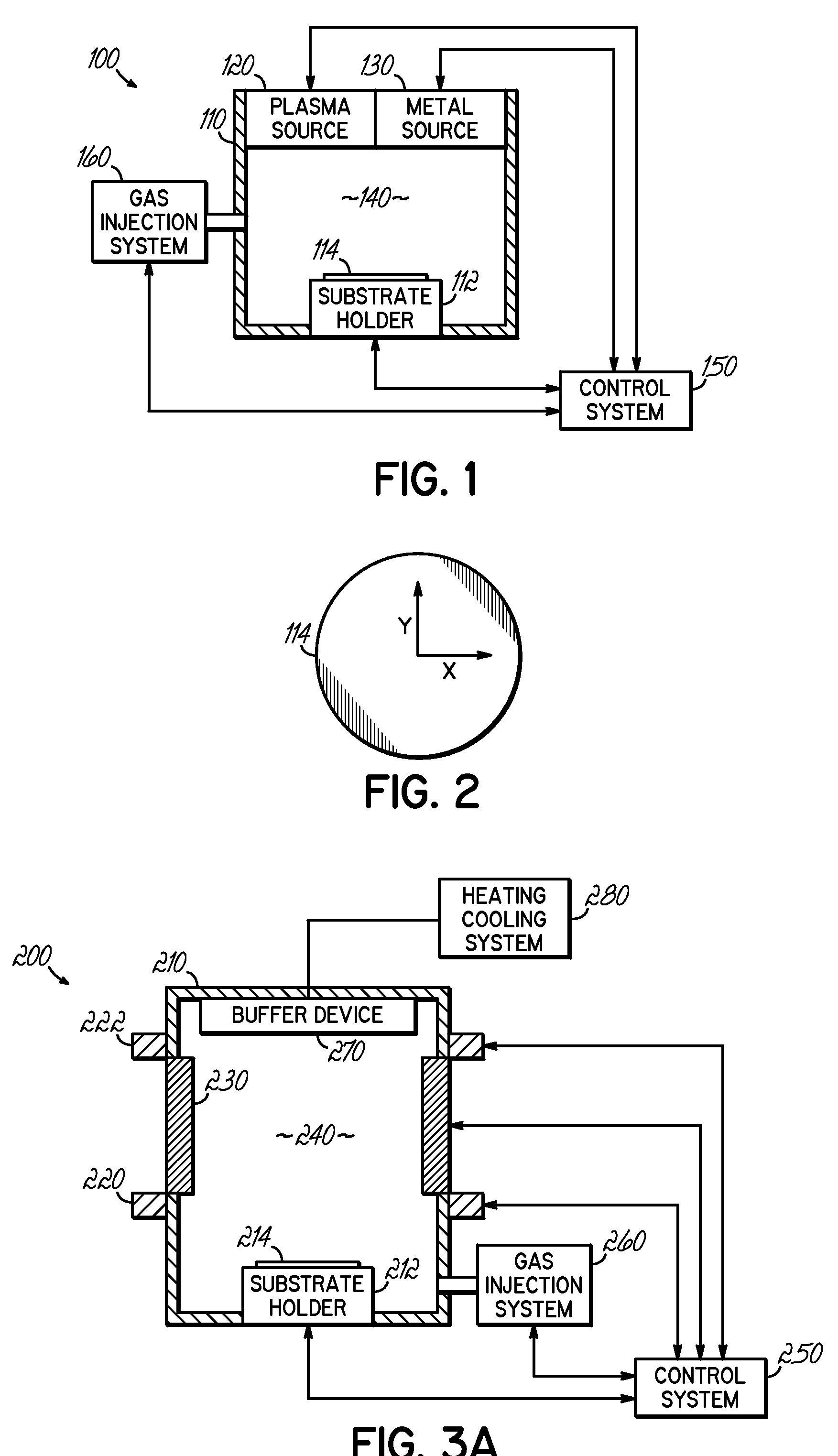
Method and apparatus of distributed plasma processing system for conformal ion stimulated nanoscale deposition process
InactiveUS20080026574A1Good coverageHigh aspect ratio (HAR) featuresVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPlasma densityHigh density
A deposition system and method of operating thereof is described for depositing a conformal metal or other similarly responsive coating material film in a high aspect ratio feature using a high density plasma is described. The deposition system includes a plasma source, and a distributed metal source for forming plasma and introducing metal vapor to the deposition system, respectively. The deposition system is configured to form a plasma having a plasma density and generate metal vapor having a metal density, wherein the ratio of the metal density to the plasma density proximate the substrate is less than or equal to unity. This ratio should exist at least within a distance from the surface of the substrate that is about twenty percent of the diameter of the substrate. A ratio that is uniform within plus or minus twenty-five percent substantially across the surface of said substrate is desirable. The ratio is particularly effective for plasma density exceeding 1012 cm−3, and for depositing film on substrates having nanoscale features with maximum film thickness less than half of the feature width, for example, at ten percent of the feature width.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
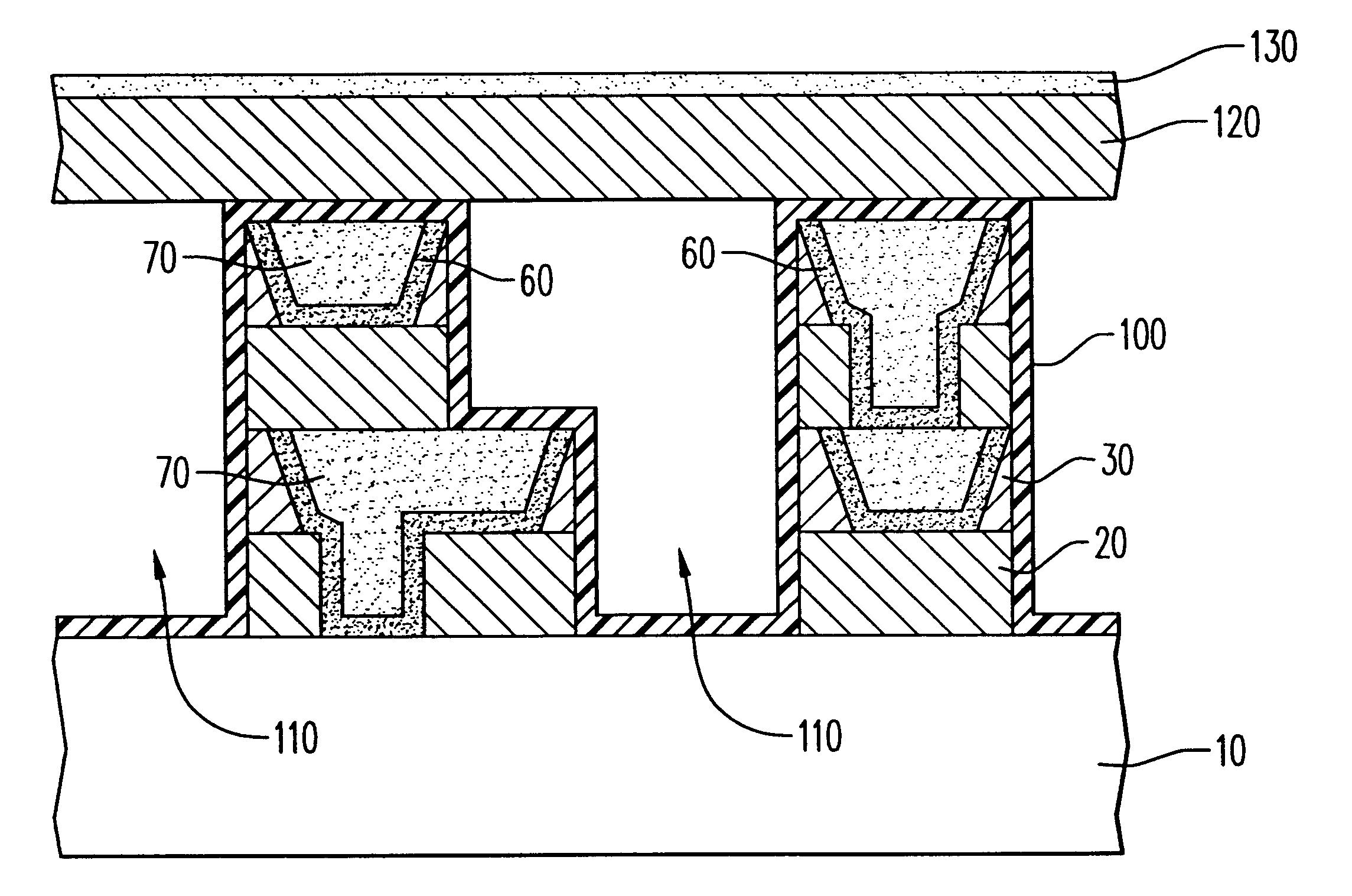
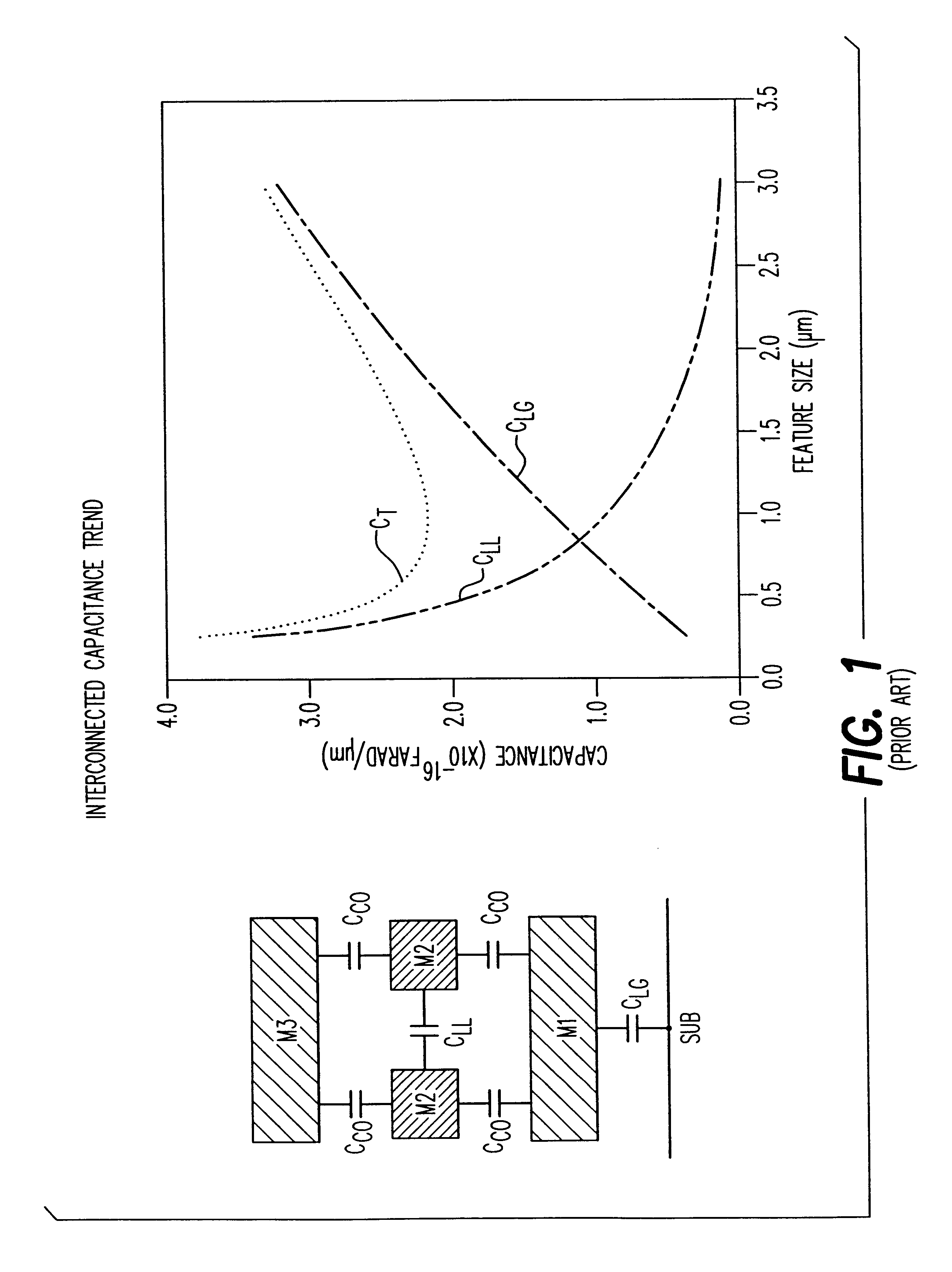
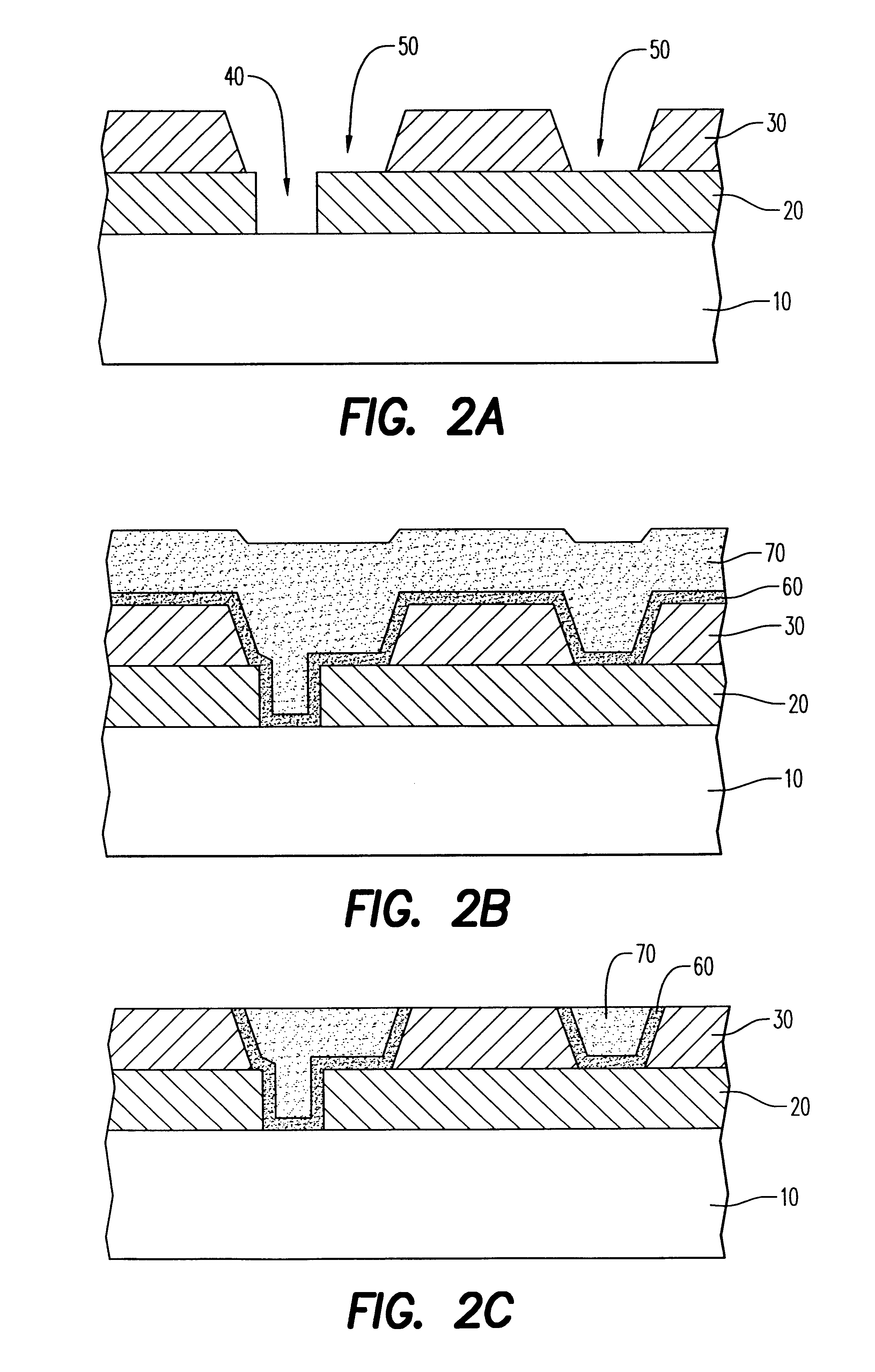
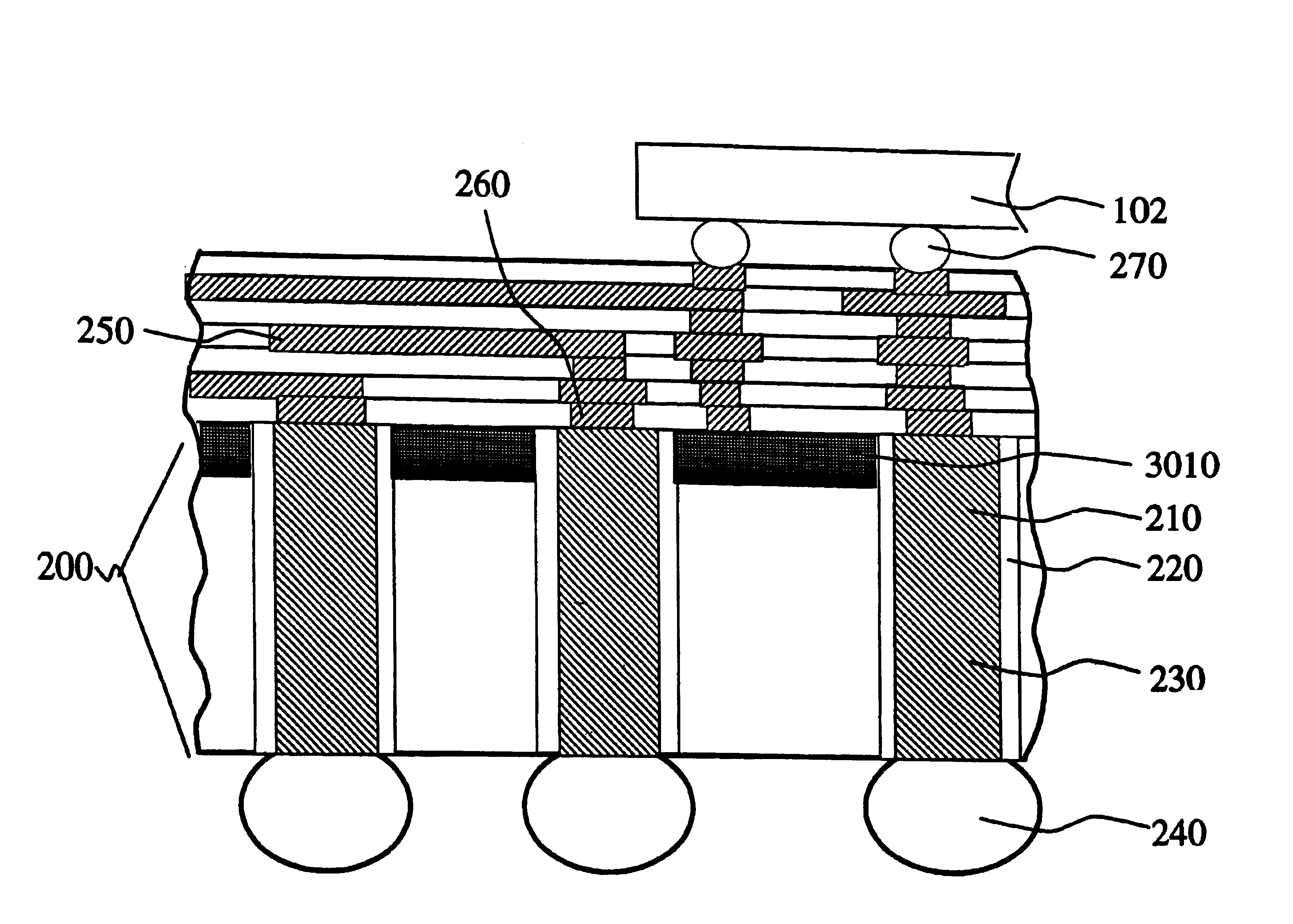
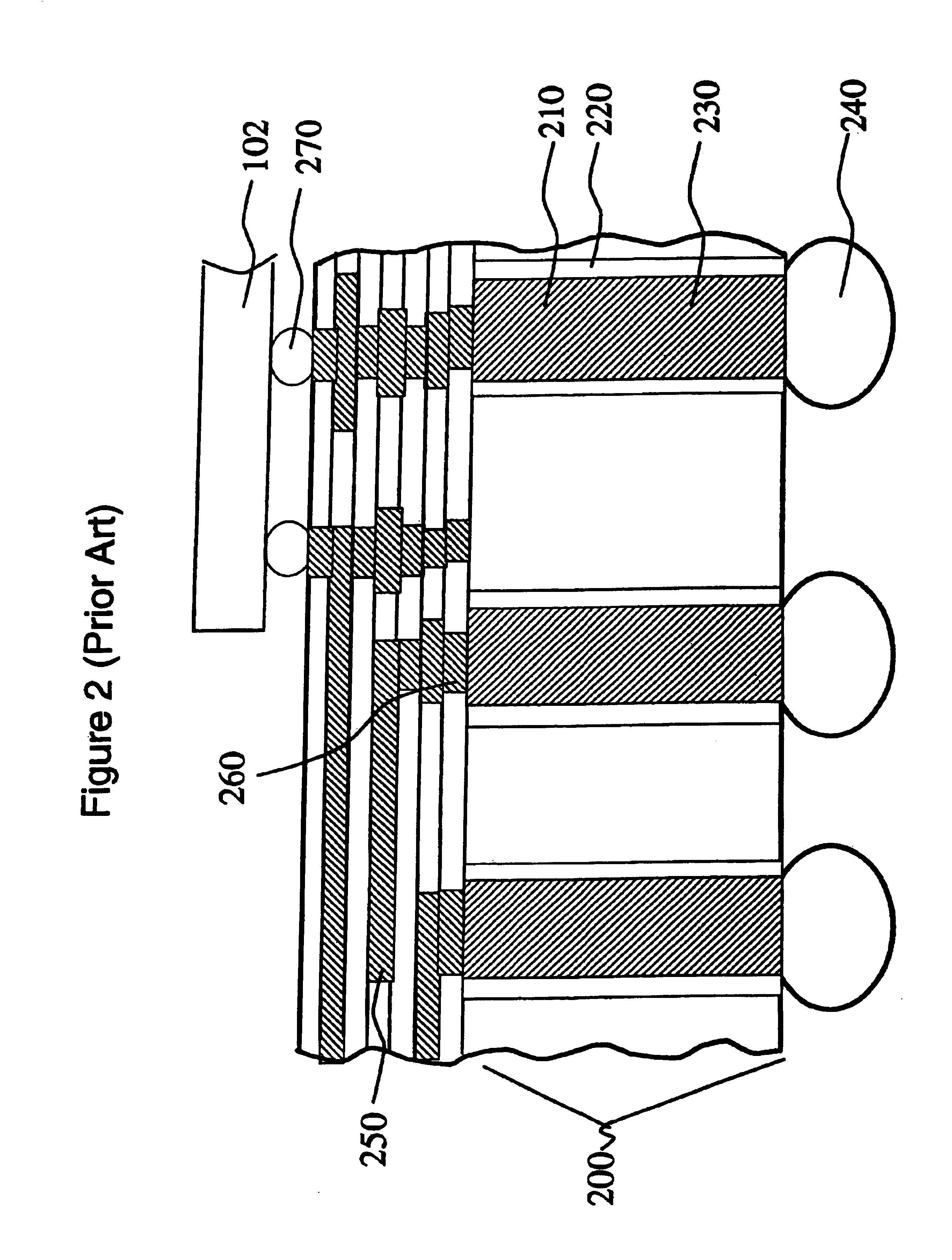
Chip interconnect wiring structure with low dielectric constant insulator and methods for fabricating the same
A method to achieve a very low effective dielectric constant in high performance back end of the line chip interconnect wiring and the resulting multilayer structure are disclosed. The process involves fabricating the multilayer interconnect wiring structure by methods and materials currently known in the state of the art of semiconductor processing; removing the intralevel dielectric between the adjacent metal features by a suitable etching process; applying a thin passivation coating over the exposed etched structure; annealing the etched structure to remove plasma damage; laminating an insulating cover layer to the top surface of the passivated metal features; optionally depositing an insulating environmental barrier layer on top of the cover layer; etching vias in the environmental barrier layer, cover layer and the thin passivation layer for terminal pad contacts; and completing the device by fabricating terminal input / output pads. The method obviates issues such as processability and thermal stability associated with low dielectric constant materials by avoiding their use. Since air, which has the lowest dielectric constant, is used as the intralevel dielectric the structure created by this method would possess a very low capacitance and hence fast propagation speeds. Such structure is ideally suitable for high density interconnects required in high performance microelectronic device chips.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
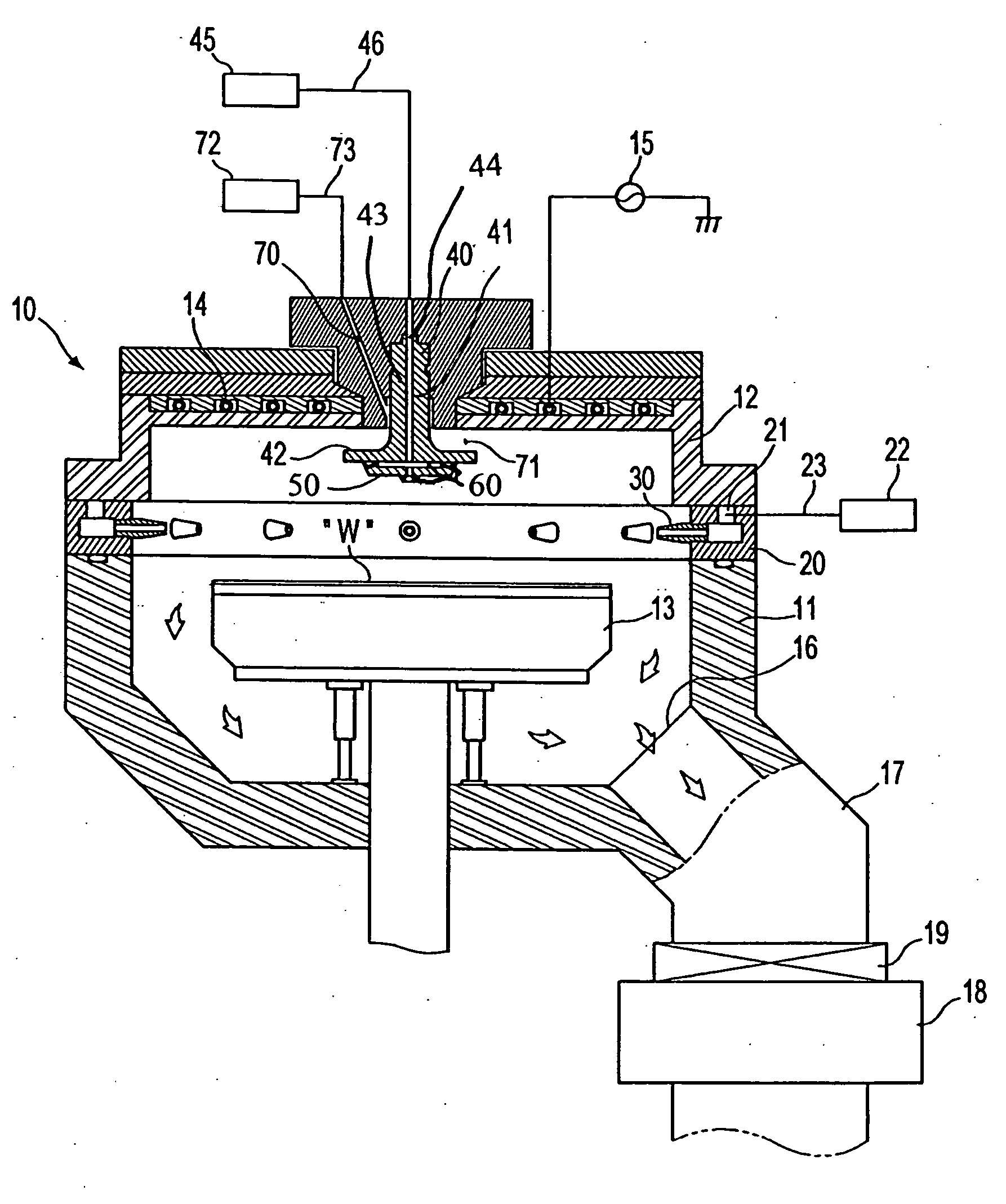
High density plasma chemical vapor deposition apparatus
InactiveUS20060196420A1Unified performanceEasy to handleElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingHigh densityEngineering
A high density plasma chemical vapor deposition apparatus includes an upper gas supply nozzle which includes a nozzle body, a gas supply passage formed vertically in the nozzle body, a nozzle cover attached to a lower surface of the horizontal portion of the nozzle body, and a plurality of gas inlets formed through the nozzle cover to uniformly supply the processing gas towards a semiconductor wafer within the processing chamber.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
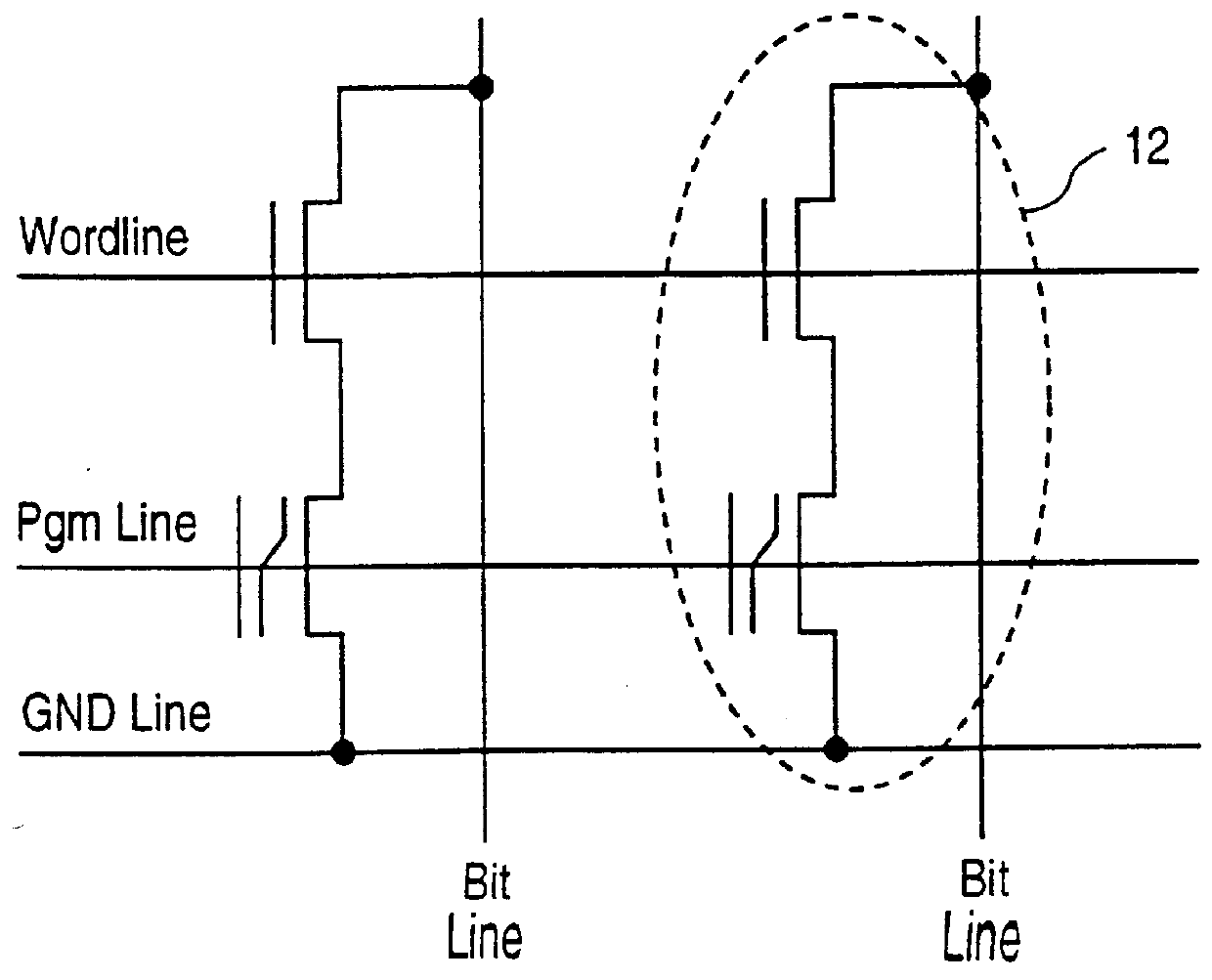
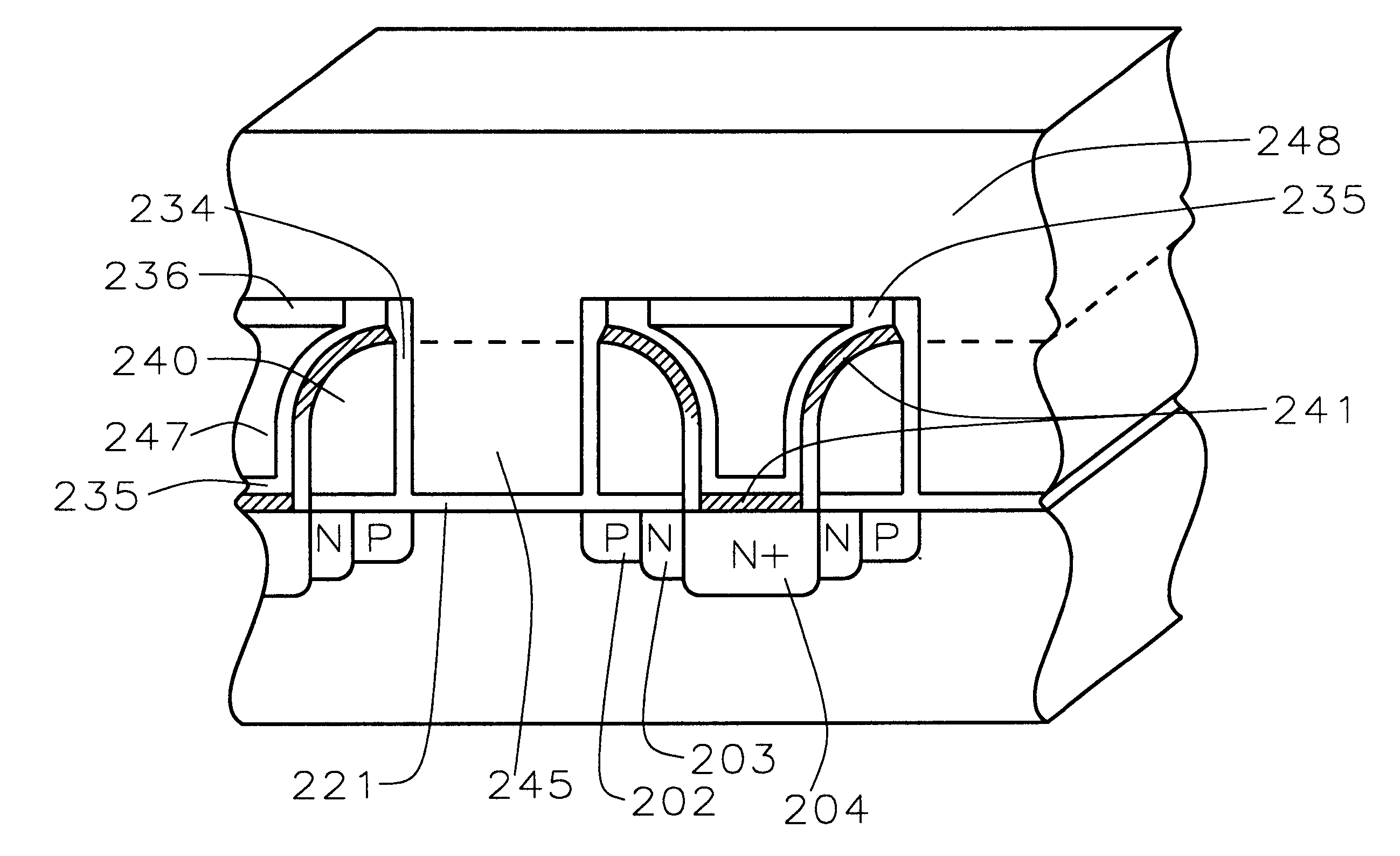
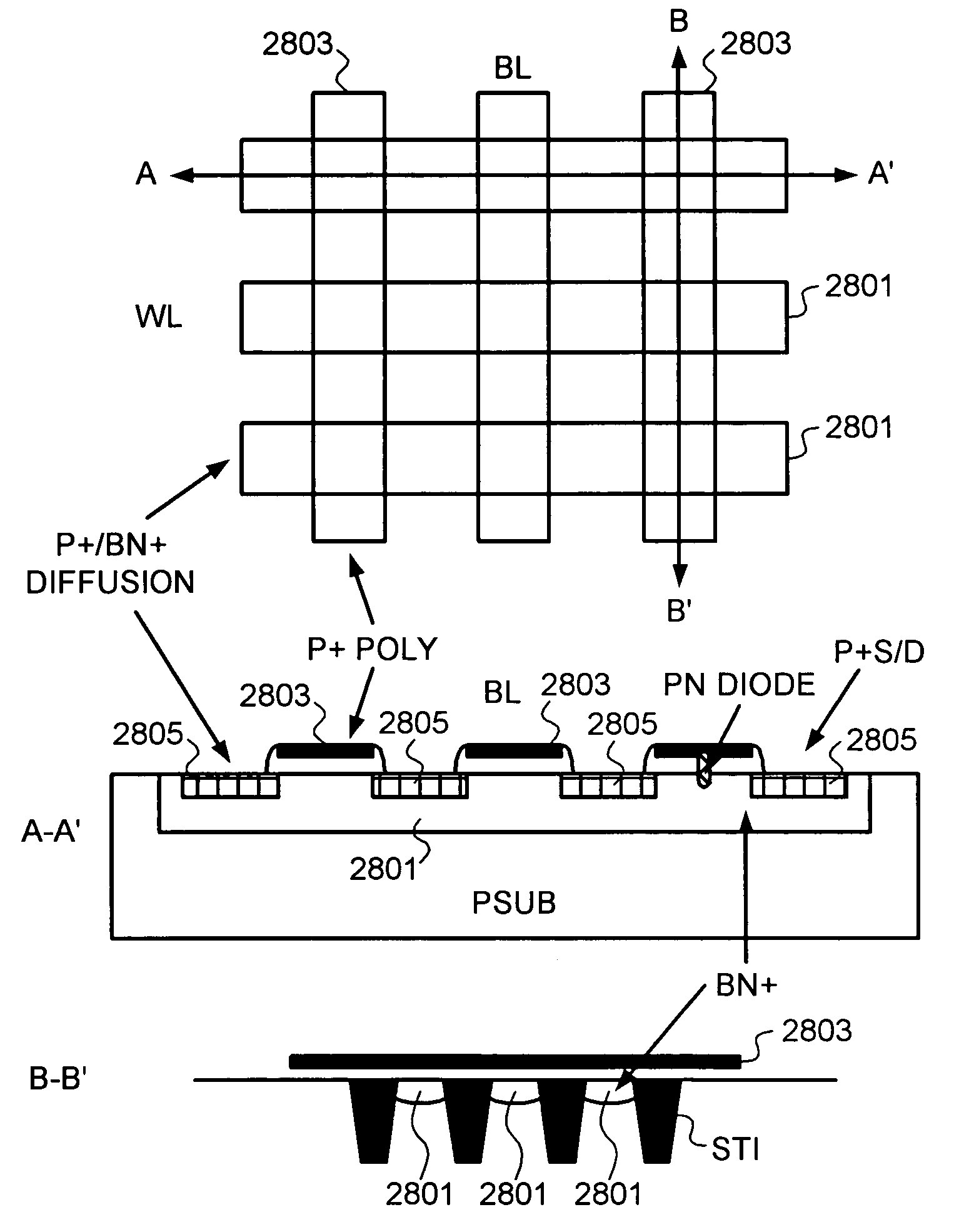
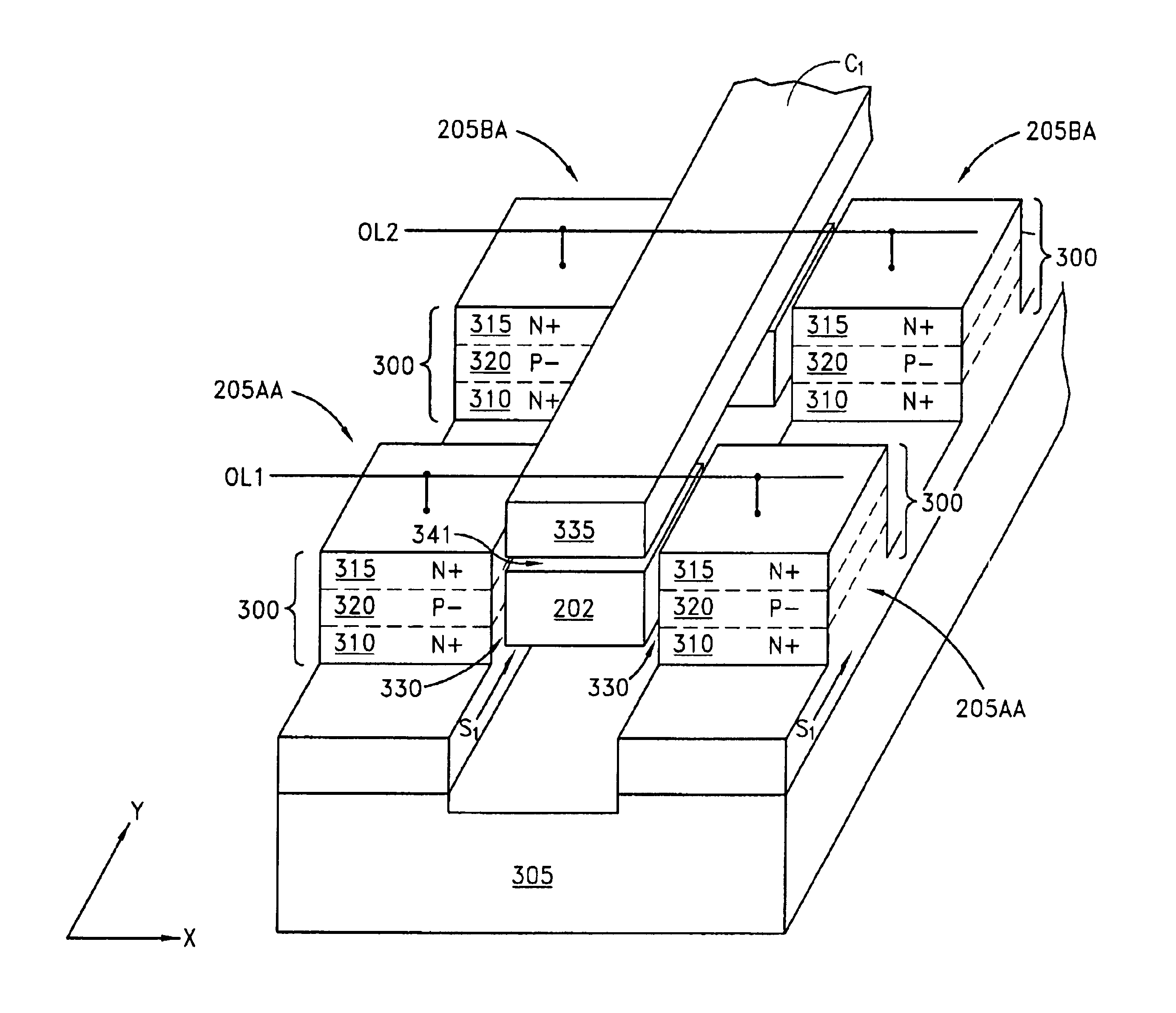
High density semiconductor memory cell and memory array using a single transistor and having counter-doped poly and buried diffusion wordline
A programmable memory cell comprised of a transistor located at the crosspoint of a column bitline and a row wordline is disclosed. The transistor has its gate formed from the column bitline and its source connected to the row wordline. The memory cell is programmed by applying a voltage potential between the column bitline and the row wordline to produce a programmed p+ region to form a p-n diode in the substrate underlying the gate of the transistor. Further, the wordline is formed from a buried diffusion N+ layer while the column bitline is formed from a counterdoped polysilicon layer.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
High density chip carrier with integrated passive devices
InactiveUS6962872B2Reduce inductanceEasy accessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsHigh densityEngineering
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
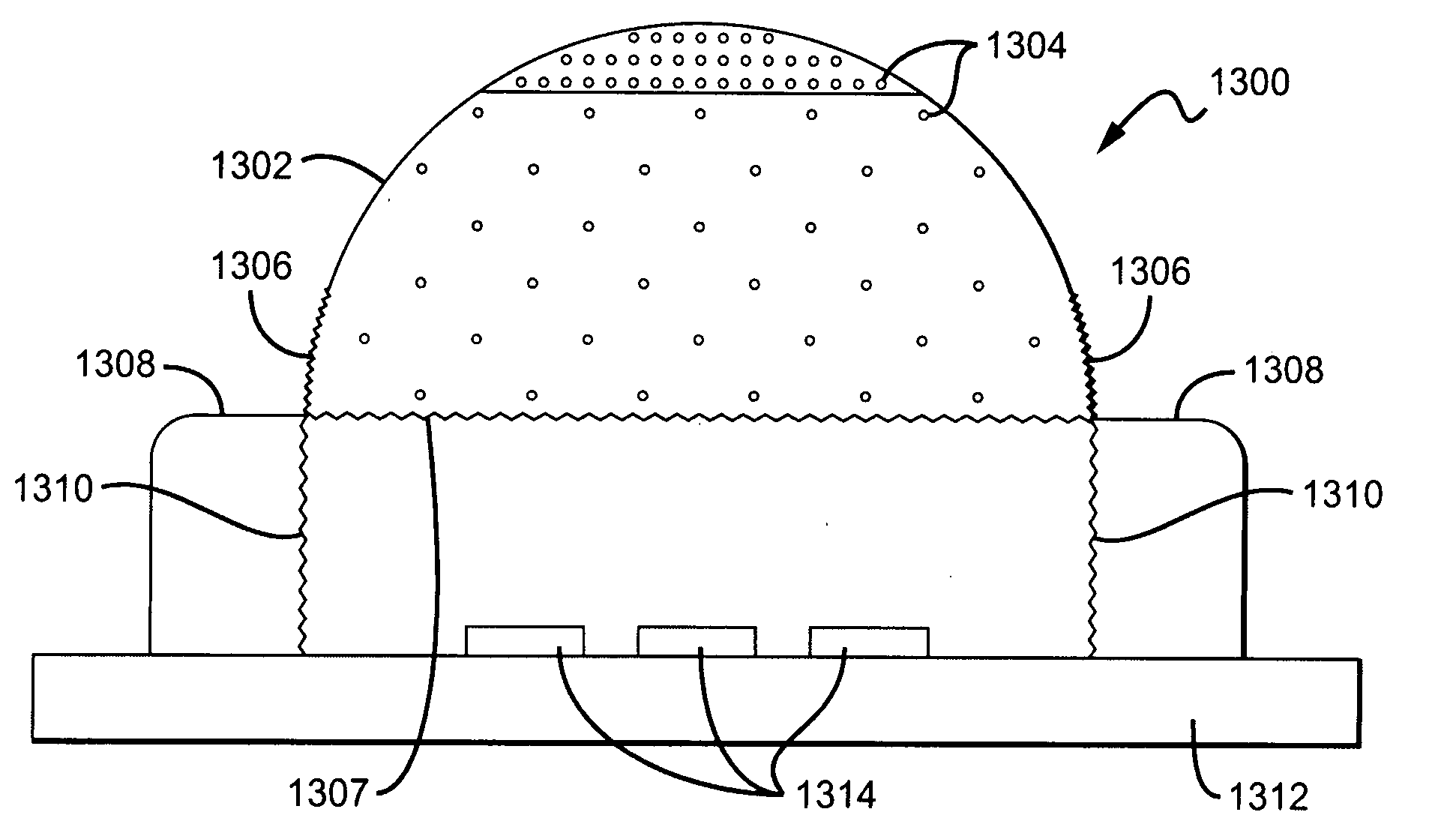
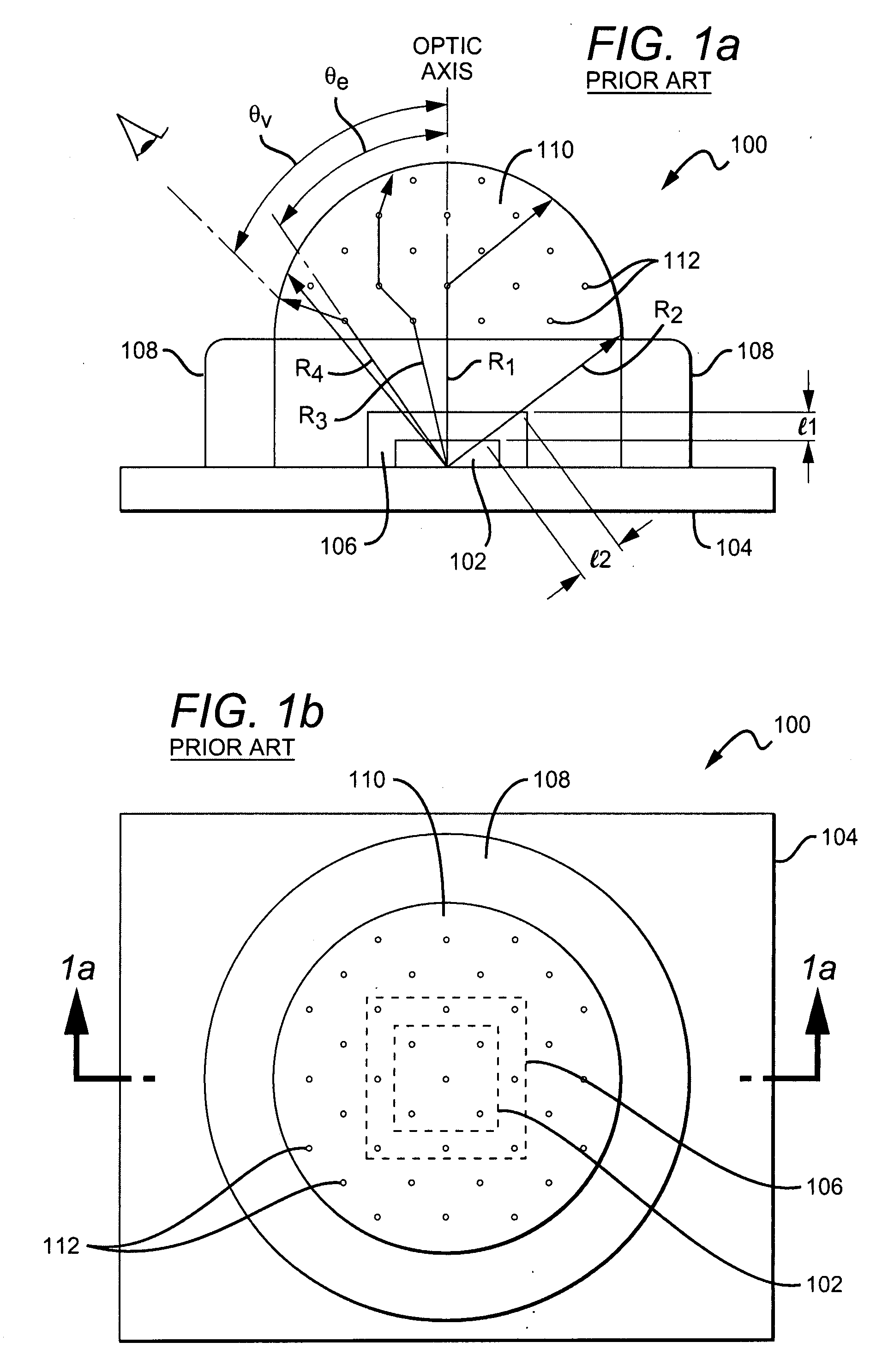
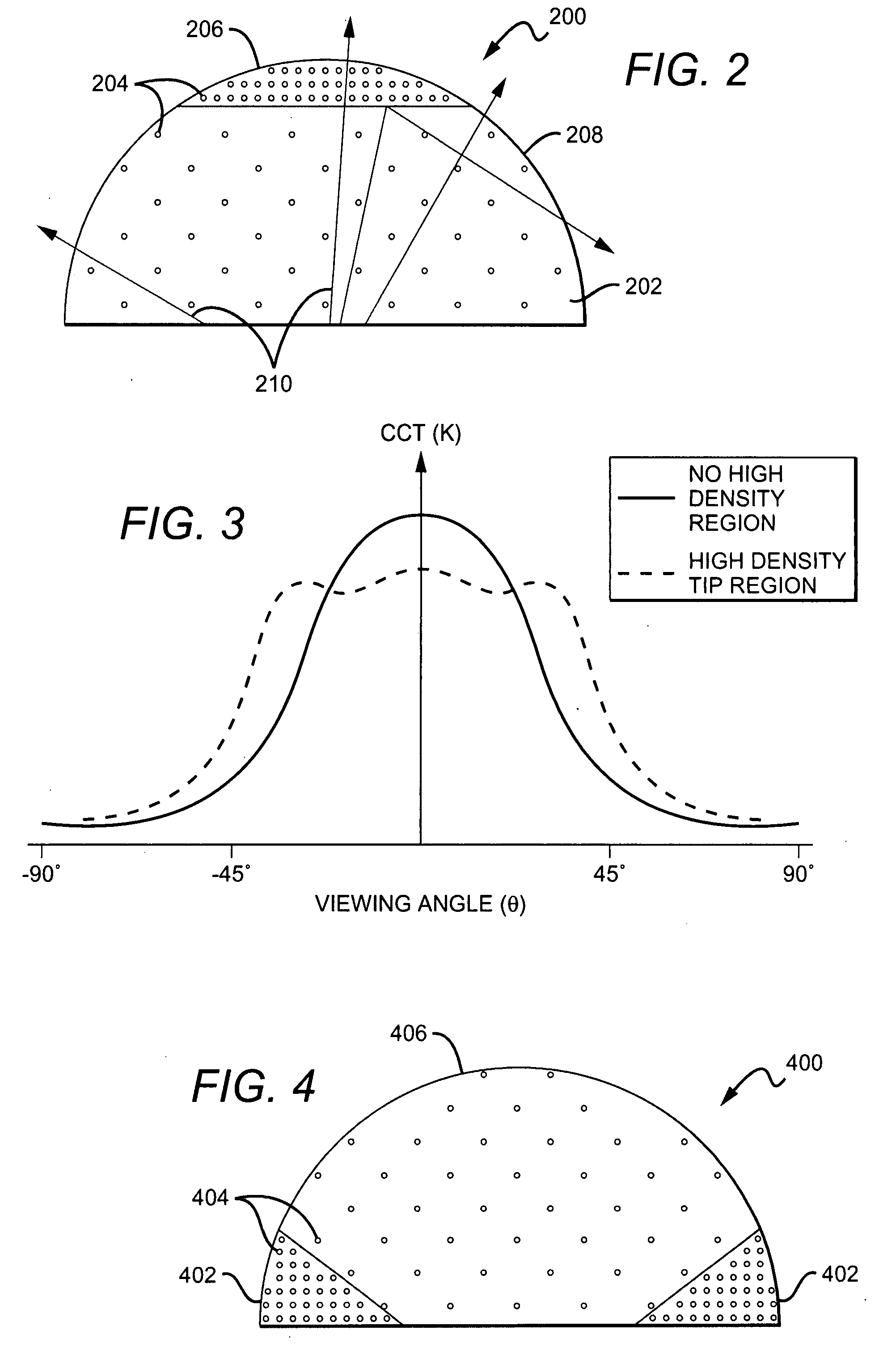
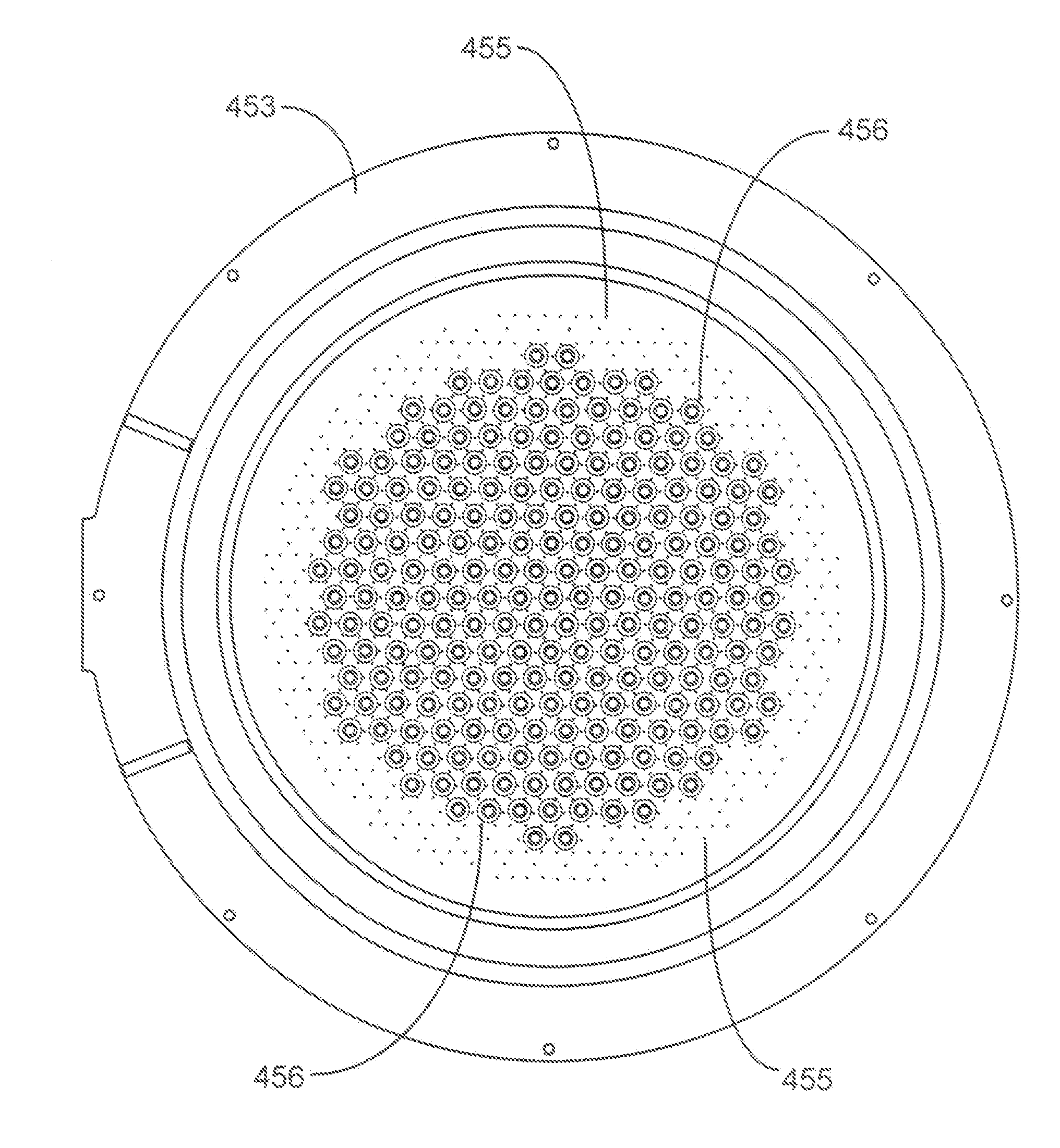
Encapsulant with scatterer to tailor spatial emission pattern and color uniformity in light emitting diodes
ActiveUS20080308825A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityLight beam
A light emitting device having an encapsulant with scattering features to tailor the spatial emission pattern and color temperature uniformity of the output profile. The encapsulant is formed with materials having light scattering properties. The concentration of these light scatterers is varied spatially within the encapsulant and / or on the surface of the encapsulant. The regions having a high density of scatterers are arranged in the encapsulant to interact with light entering the encapsulant over a desired range of source emission angles. By increasing the probability that light from a particular range of emission angles will experience at least one scattering event, both the intensity and color temperature profiles of the output light beam can be tuned.
Owner:CREELED INC
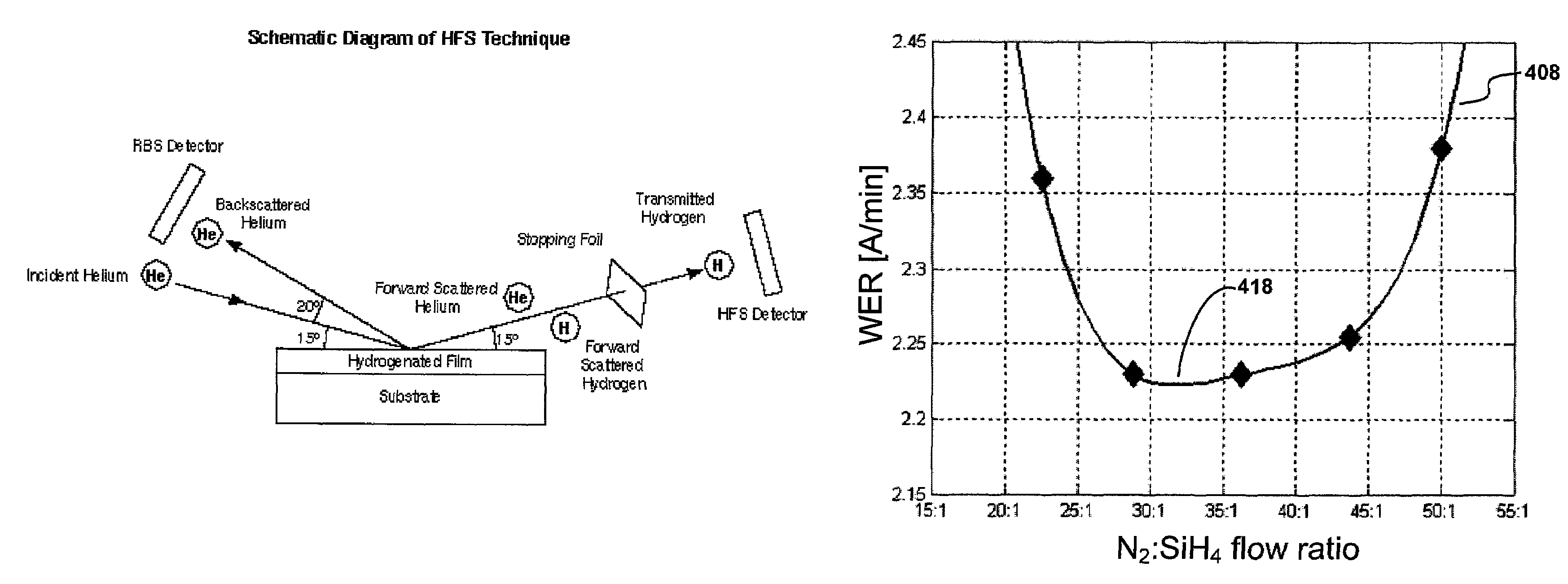
Densification for flowable films
InactiveUS20130288485A1Increase etch toleranceImprove toleranceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityDielectric layer
A method of forming a dielectric layer is described. The method first deposits an initially-flowable layer on a substrate. The initially-flowable layer is then densified by exposing the substrate to a high-density plasma (HDP). Essentially no additional material is deposited on the initially-flowable layer, in embodiments, but the impact of the accelerated ionic species serves to condense the layer and increase the etch tolerance of the processed layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods of filling trenches using high-density plasma deposition (HDP)
ActiveUS20050037610A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh densityPlasma deposition
Methods of filling trenches / gaps defined by circuit elements on an integrated circuit substrate are provided. The methods include forming a first high-density plasma layer on an integrated circuit substrate including at least one trench thereon using a first reaction gas. The first high-density plasma layer is etched using an etch gas including nitrogen fluoride gas (NF3). A second high-density plasma layer is formed on the etched first high-density plasma layer using a second reaction gas including nitrogen fluoride.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Atomic Layer Deposition of Oxides Using Krypton as an Ion Generating Feeding Gas
InactiveUS20070281105A1Improve abilitiesImprove efficiencyChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueKryptonHigh density
An atomic layer deposition system and method utilizing radicals generated from a high-density mixed plasma for deposition is disclosed. A high-quality oxide or oxynitride can be deposited by exposing a substrate to a first precursor which is adsorbed onto the substrate during a first phase of one deposition cycle. After purging the deposition chamber, the substrate is exposed to a second precursor which includes oxygen radicals and krypton ions formed from the high-density mixed plasma. The ions and radicals are formed by introducing a radical generating feed gas (e.g., O2) and an ion generating feed gas into a plasma chamber and exciting the gases to form the high-density mixed plasma. The radicals and ions are then introduced to the substrate where they react with the first precursor to deposit a layer of the desired film. Krypton is preferably used as the ion generating feed gas because the metastable states of krypton lead to an efficient dissociation of oxygen into oxygen radicals when compared with other inert gases.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Methods of atomic layer deposition of hafnium oxide / erbium oxide bi-layer as advanced gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20130313656A1Improve electrical performanceFew defectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricHafnium
Provided is a two-step ALD deposition process for forming a gate dielectric involving an erbium oxide layer deposition followed by a hafnium oxide layer deposition. Hafnium oxide can provide a high dielectric constant, high density, large bandgap and good thermal stability. Erbium oxide can act as a barrier against oxygen diffusion, which can lead to increasing an effective oxide thickness of the gate dielectric and preventing hafnium-silicon reactions that may lead to higher leakage current.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Floating gate transistor with horizontal gate layers stacked next to vertical body
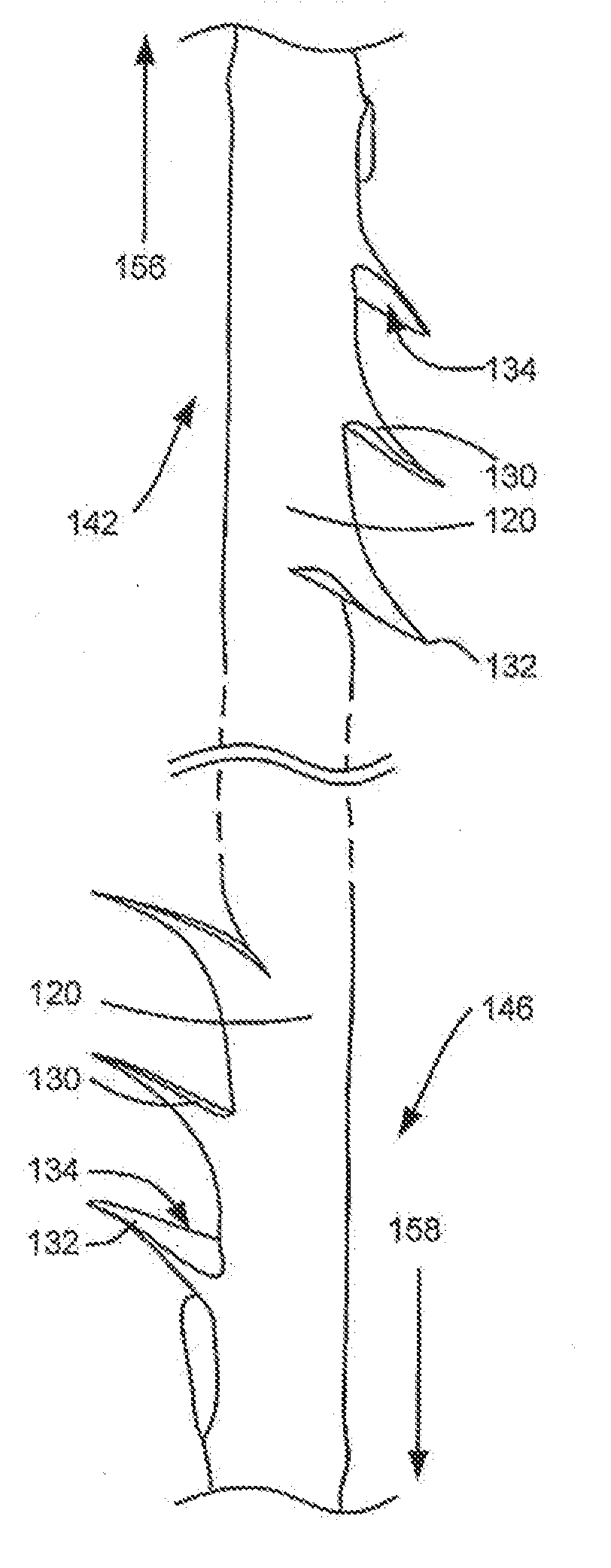
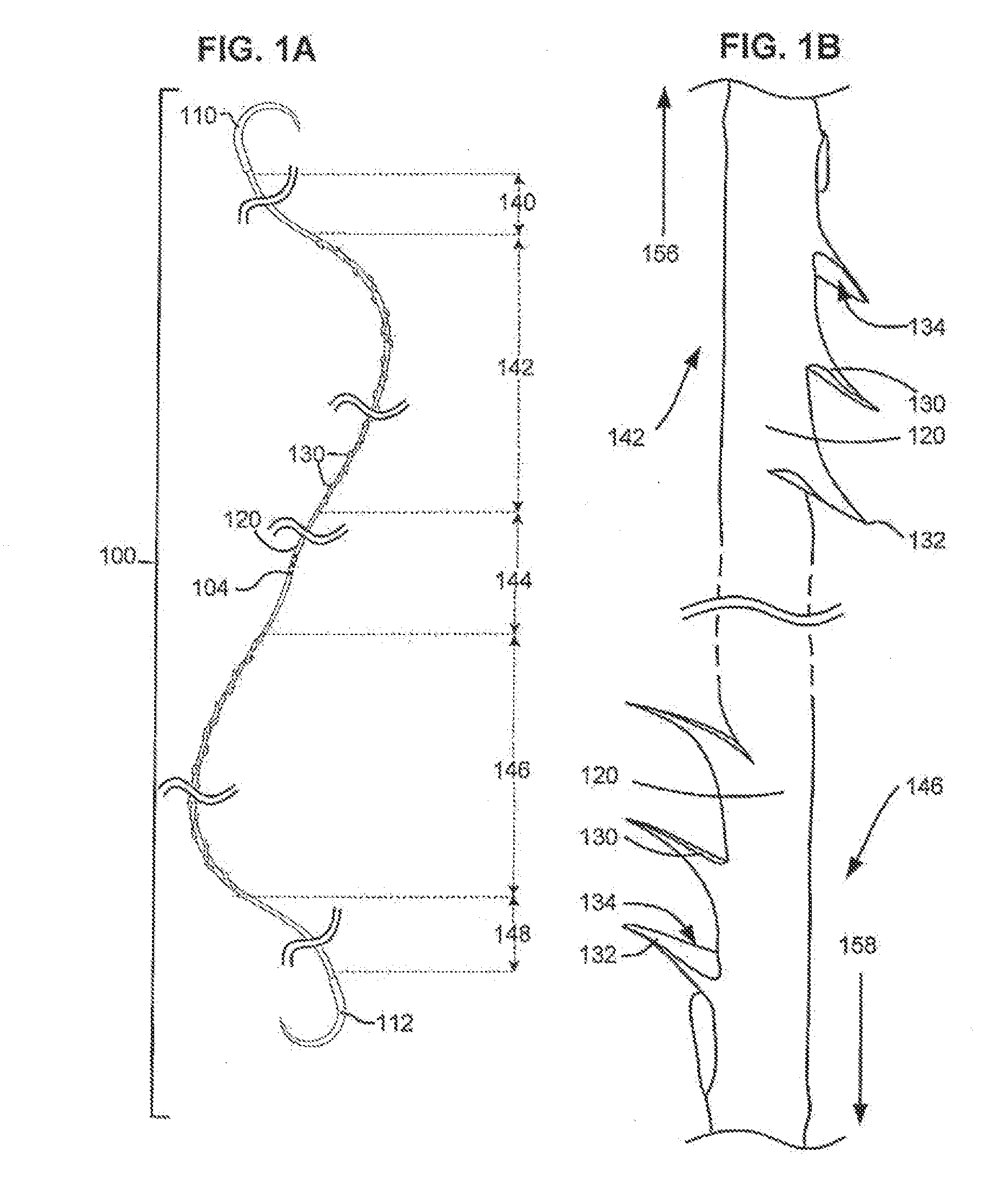
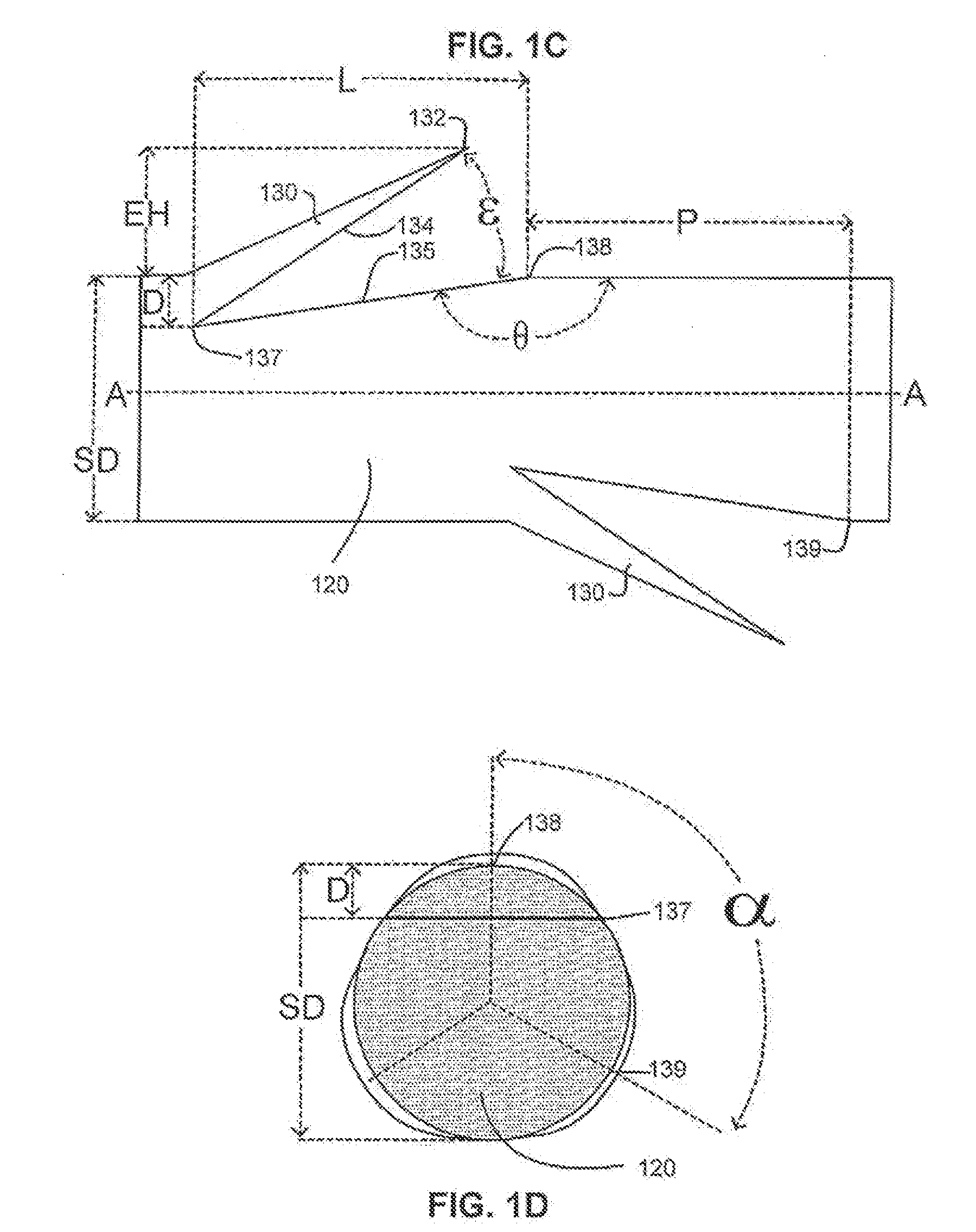
Vertical body transistors with adjacent horizontal gate layers are used to form a memory array in a high density flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (EEPROM) or a logic array in a high density field programmable logic array (FPLA). The transistor is a field-effect transistor (FET) having an electrically isolated (floating) gate that controls electrical conduction between source regions and drain regions. If a particular floating gate is charged with stored electrons, then the transistor will not turn on and will provide an indication of the stored data at this location in the memory array within the EEPROM or will act as the absence of a transistor at this location in the logic array within the FPLA. The memory array or the logic array includes densely packed cells, each cell having a semiconductor pillar providing shared source and drain regions for two vertical body transistors that have control gates overlaying floating gates distributed on opposing sides of the semiconductor pillar. Both bulk semiconductor and silicon-on-insulator embodiments are provided. If a floating gate transistor is used to store a single bit of data or to represent a logic function, an area of only 2F<2 >is needed per respective bit of data or bit of logic, where F is the minimum lithographic feature size.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com