Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
232 results about "Angioplasty" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
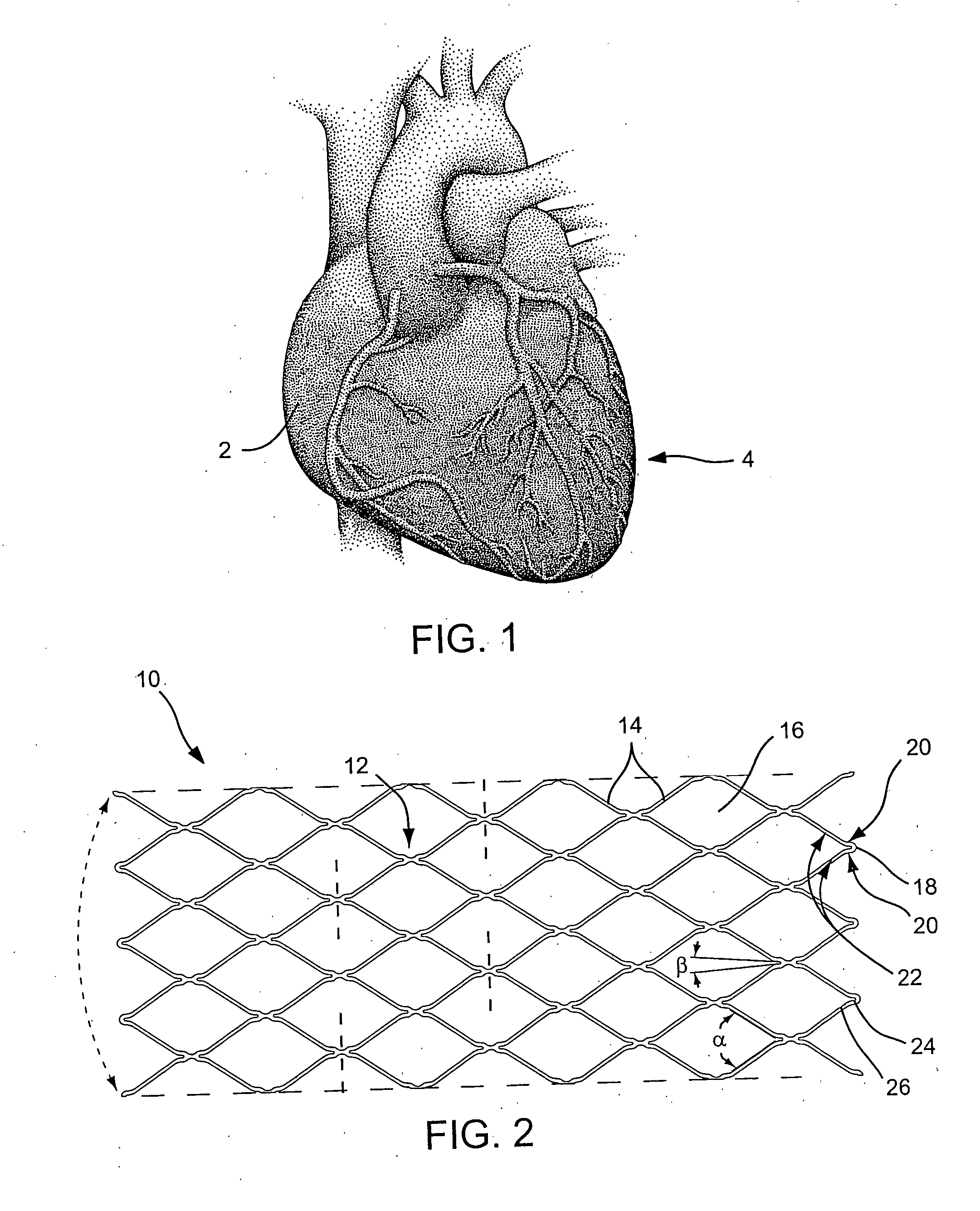
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive, endovascular procedure to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. A deflated balloon attached to a catheter (a balloon catheter) is passed over a guide-wire into the narrowed vessel and then inflated to a fixed size. The balloon forces expansion of the blood vessel and the surrounding muscular wall, allowing an improved blood flow. A stent may be inserted at the time of ballooning to ensure the vessel remains open, and the balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. Angioplasty has come to include all manner of vascular interventions that are typically performed percutaneously.
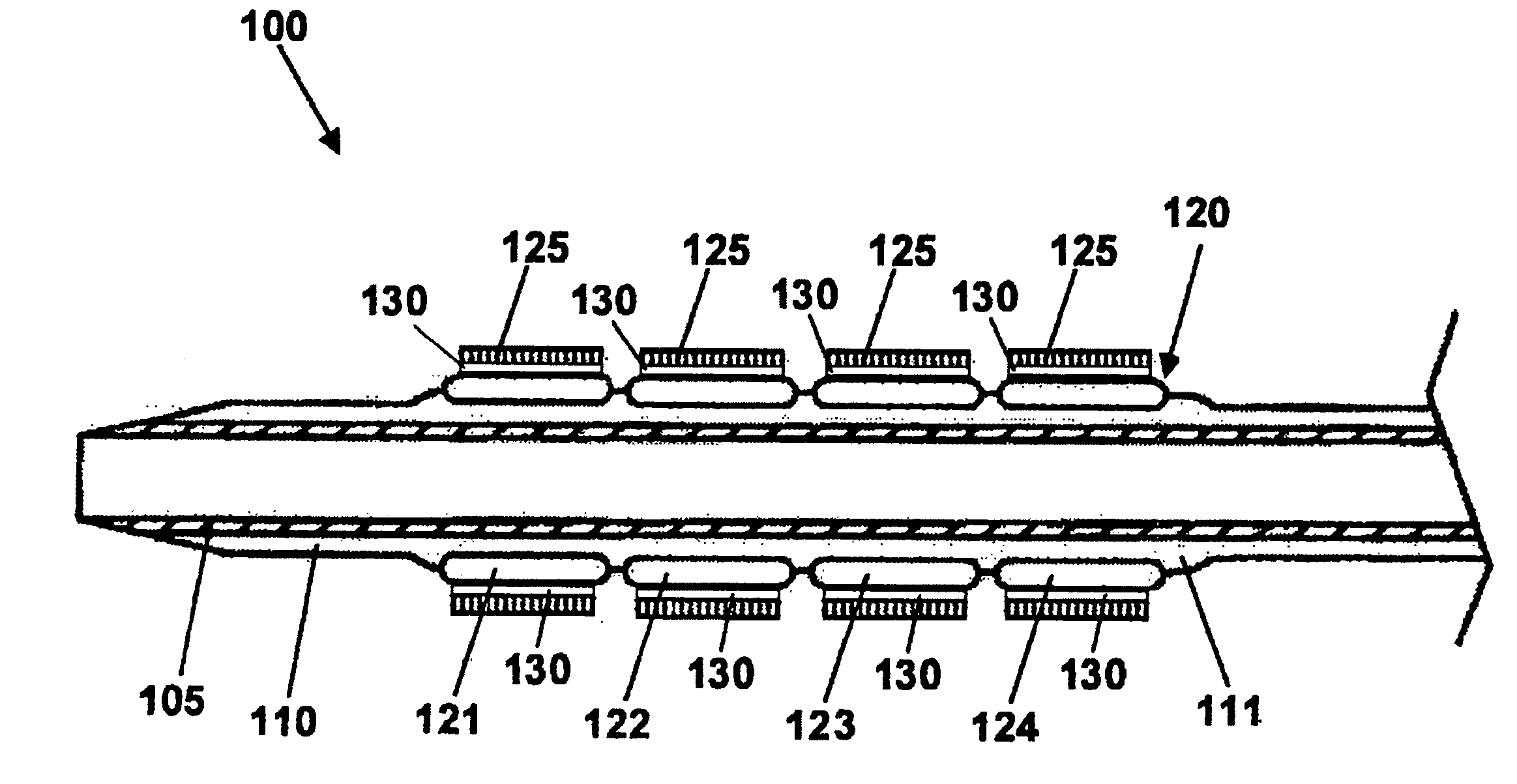
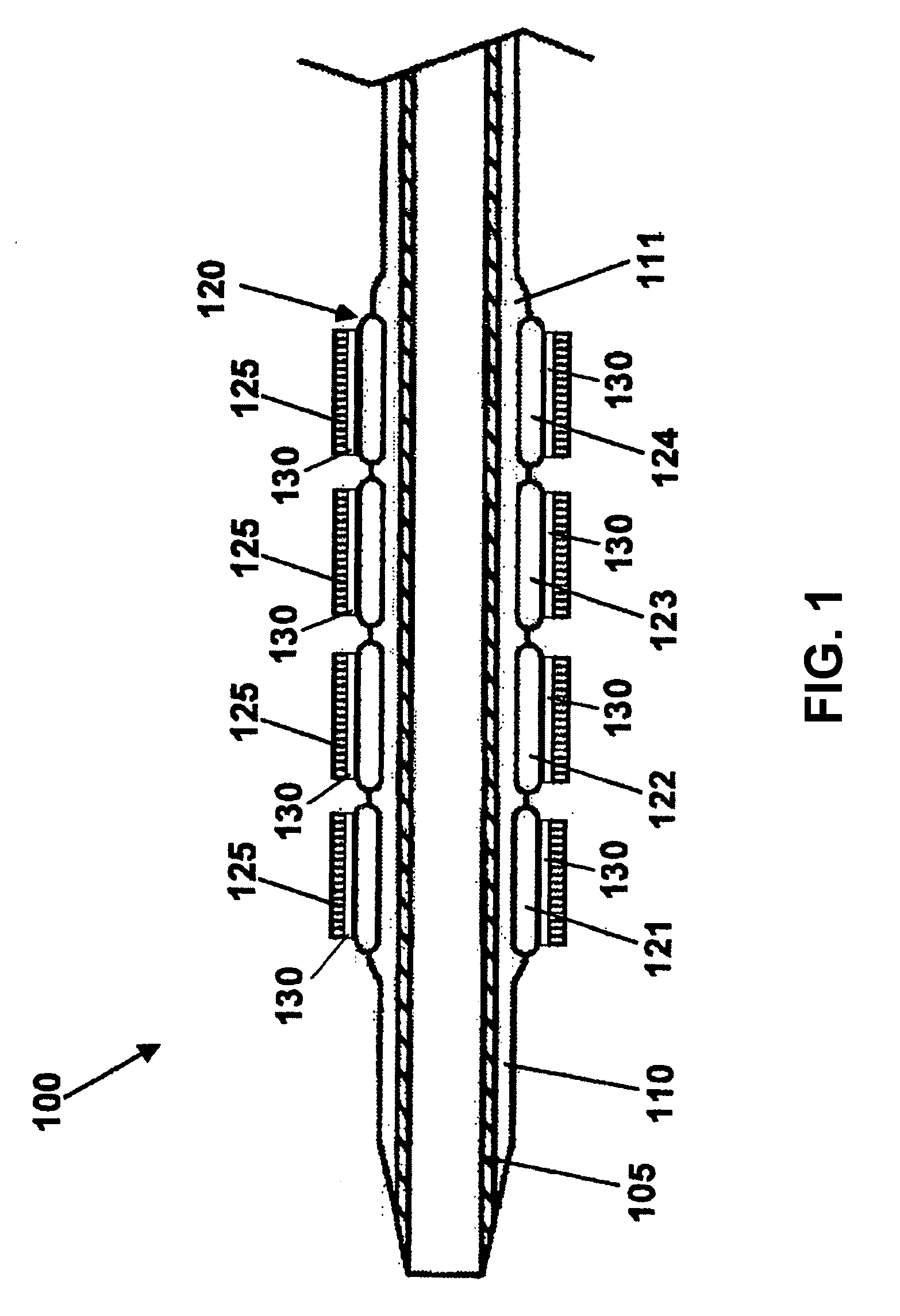
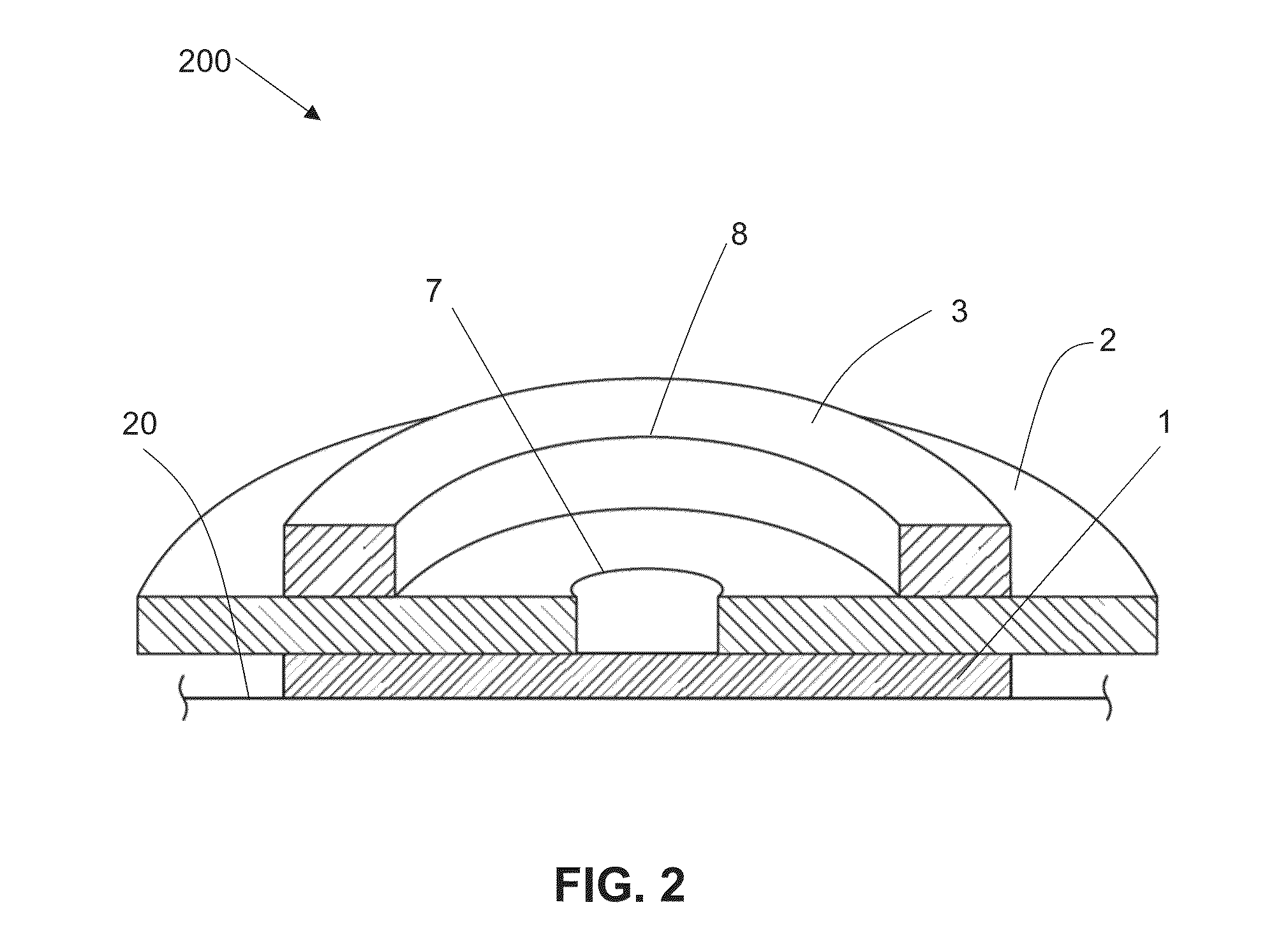
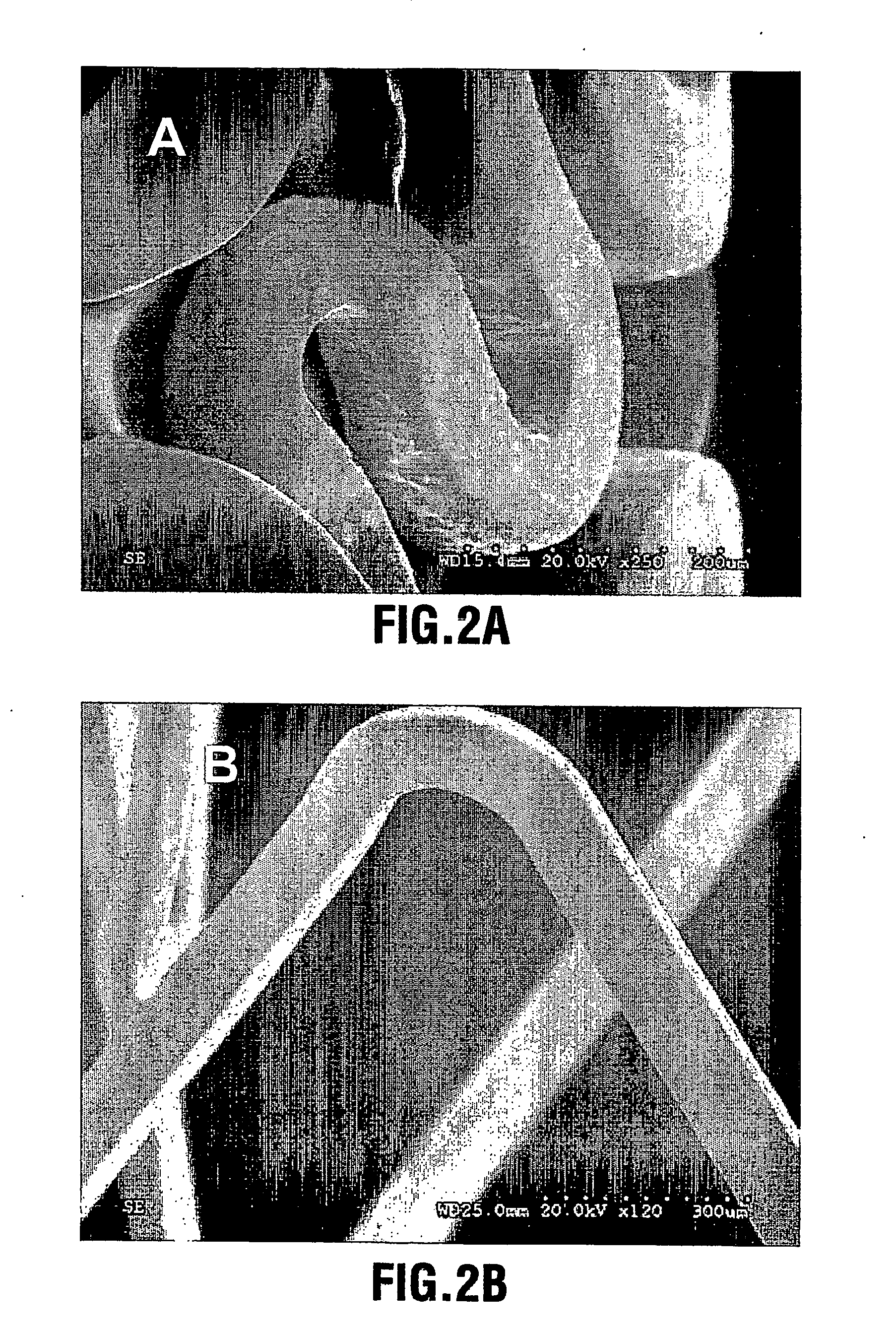
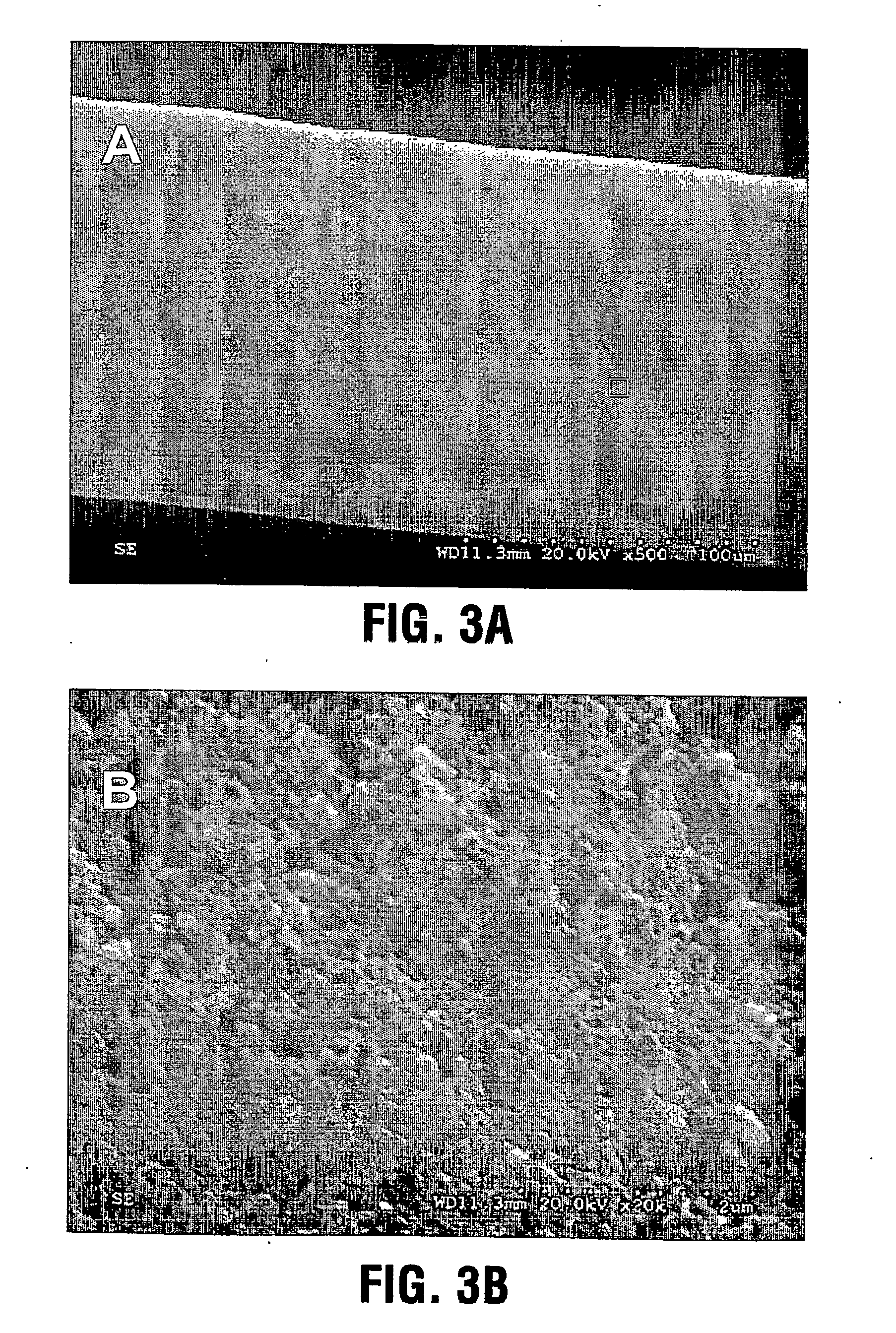
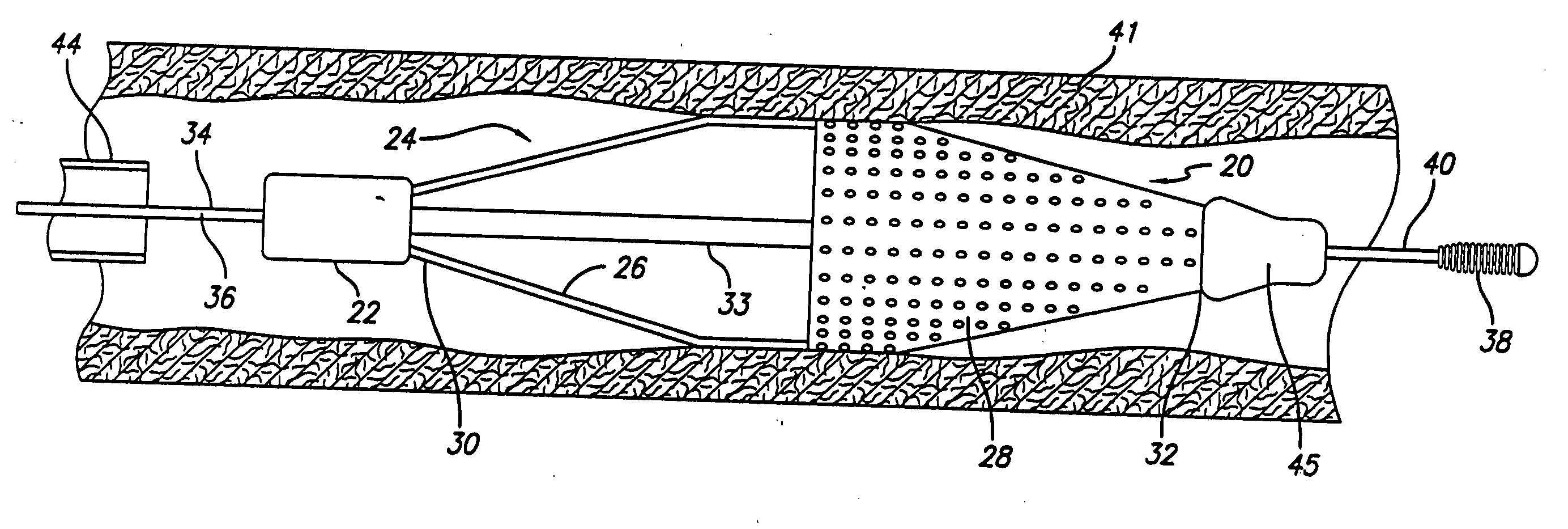
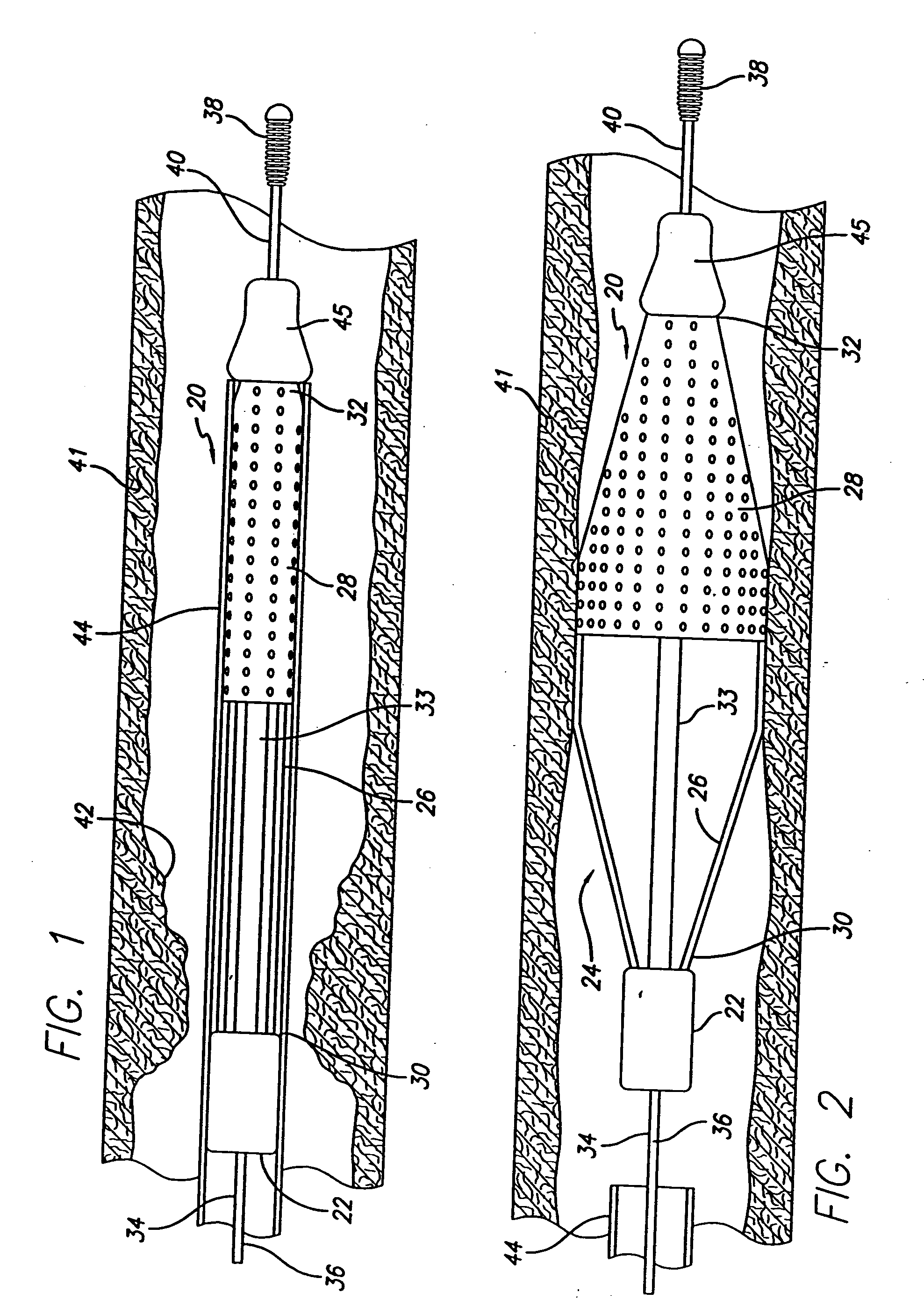
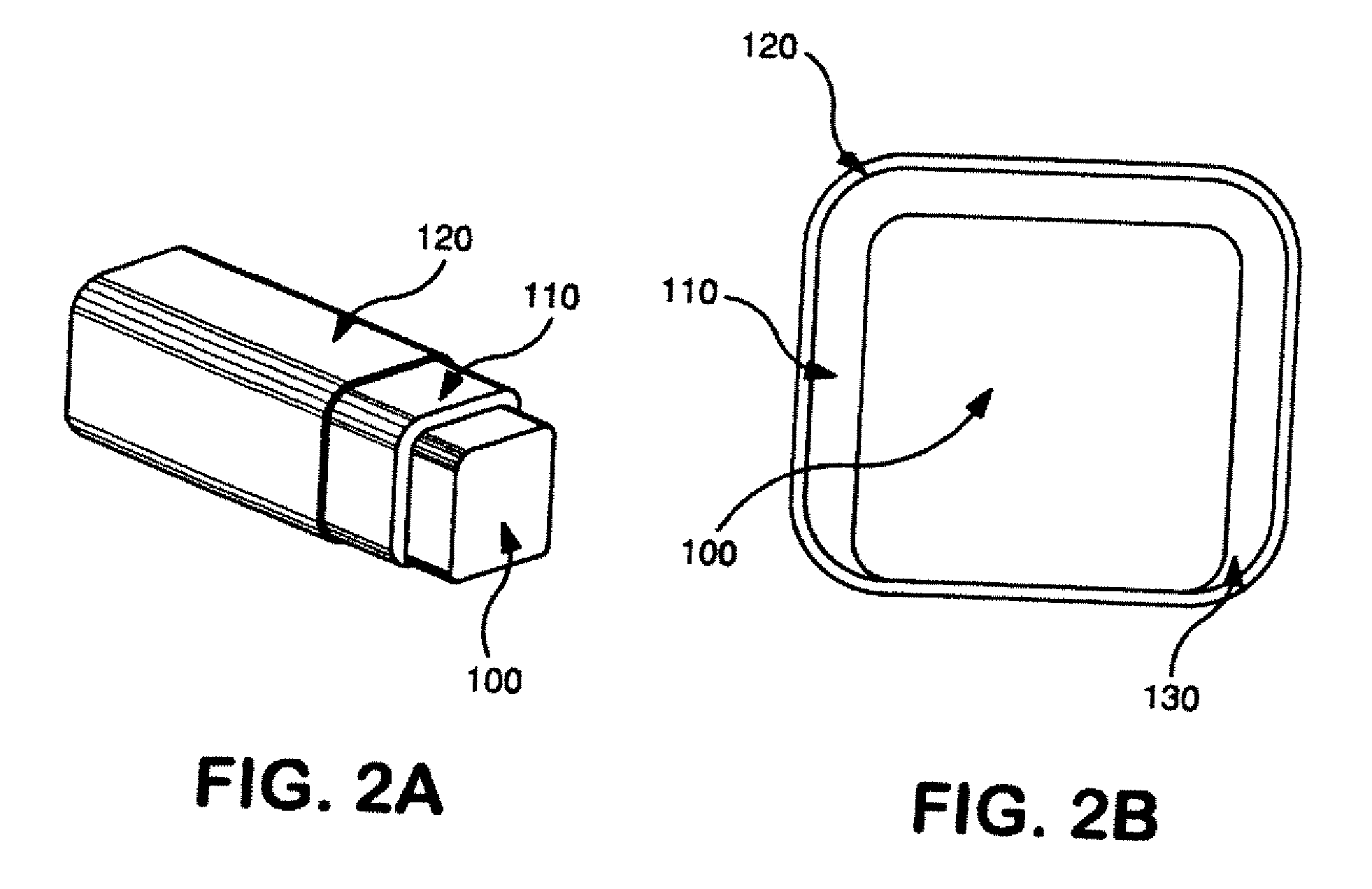
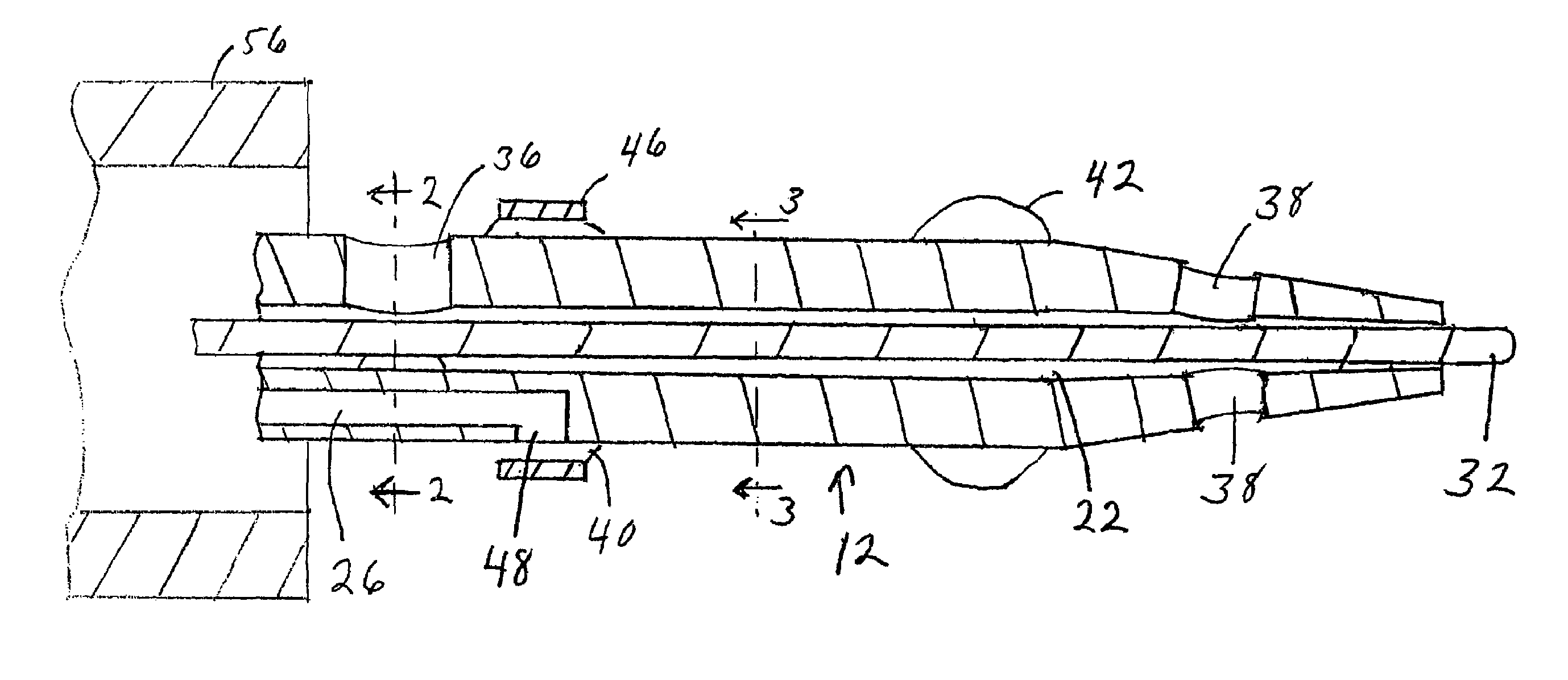
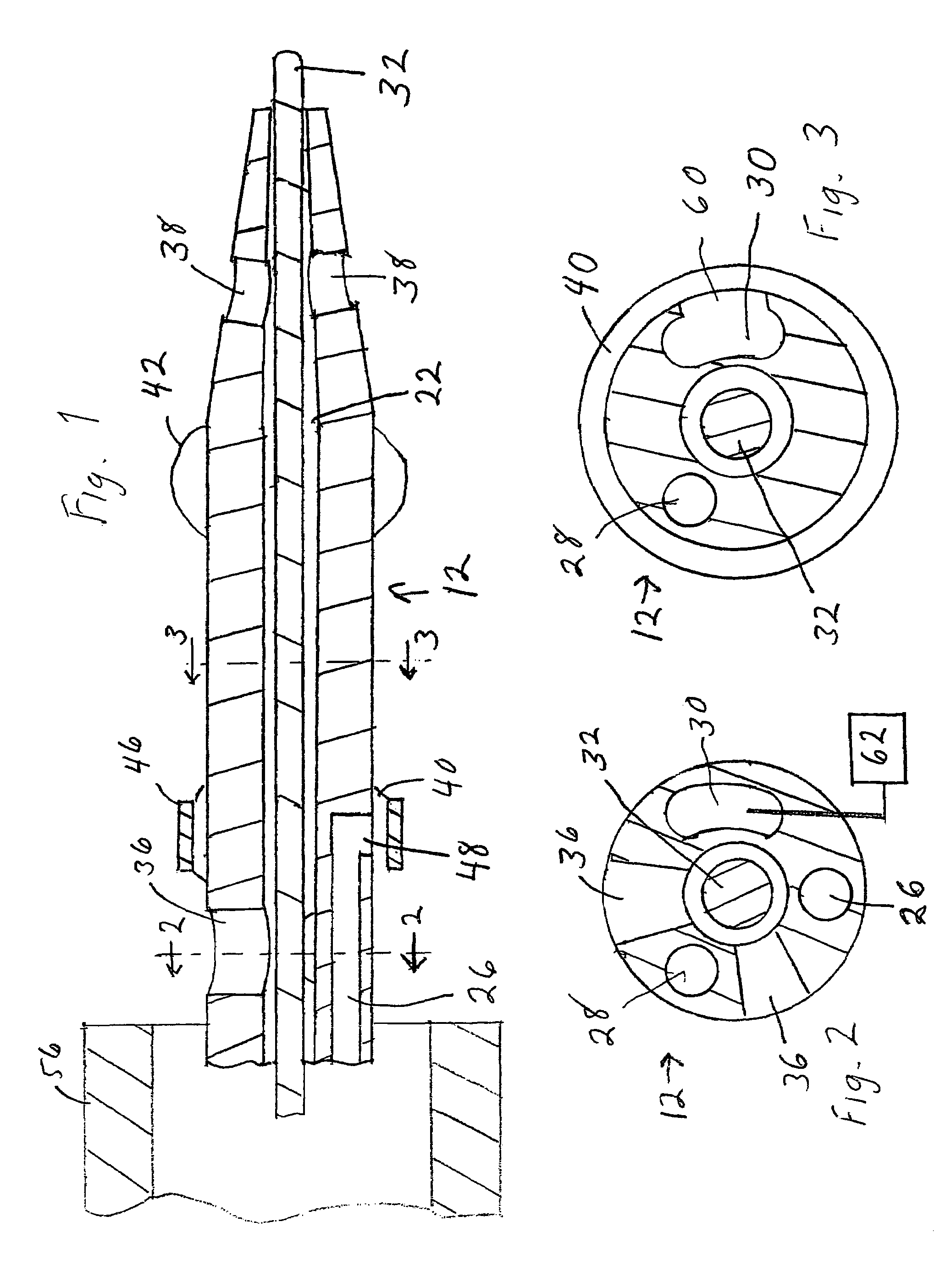
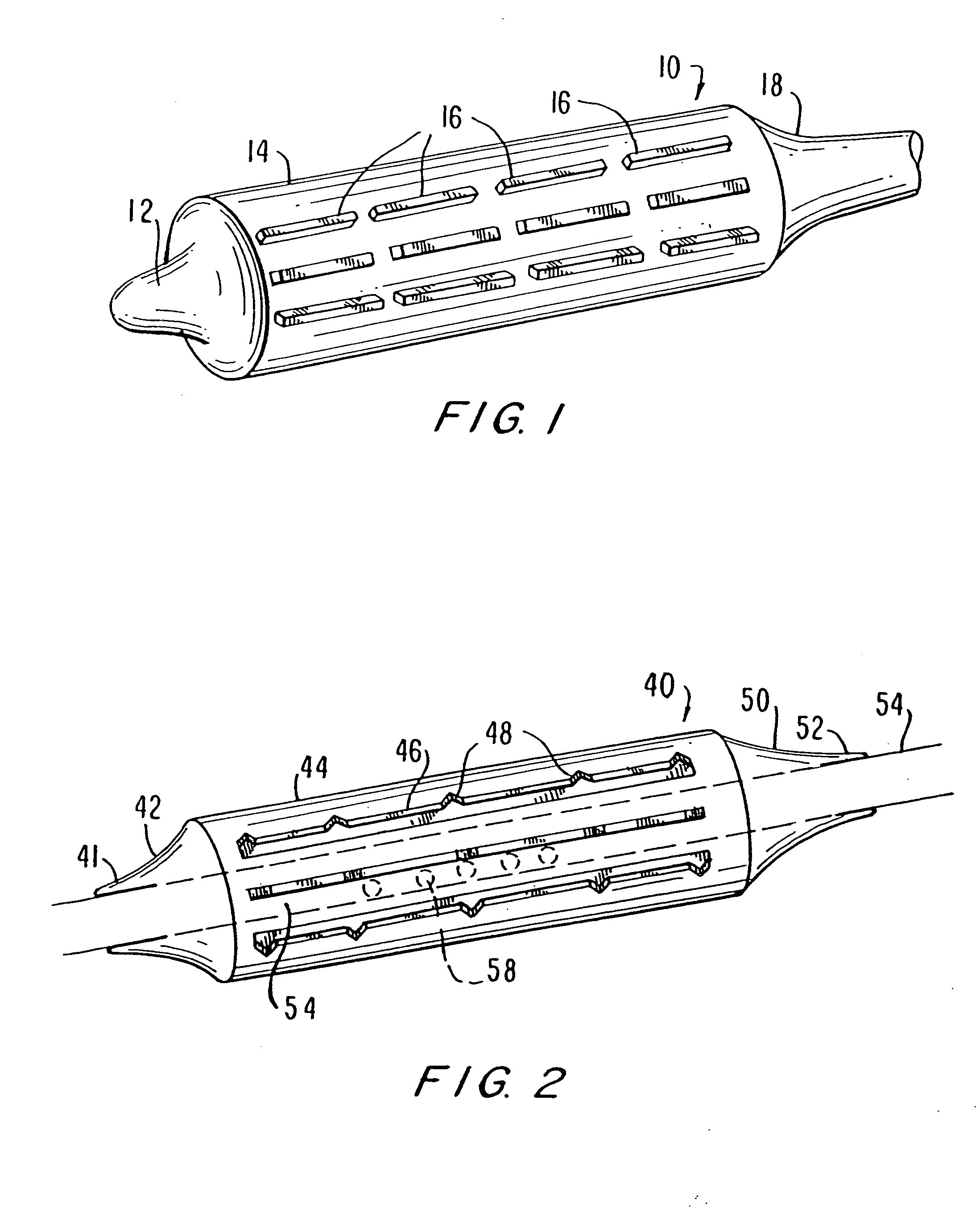
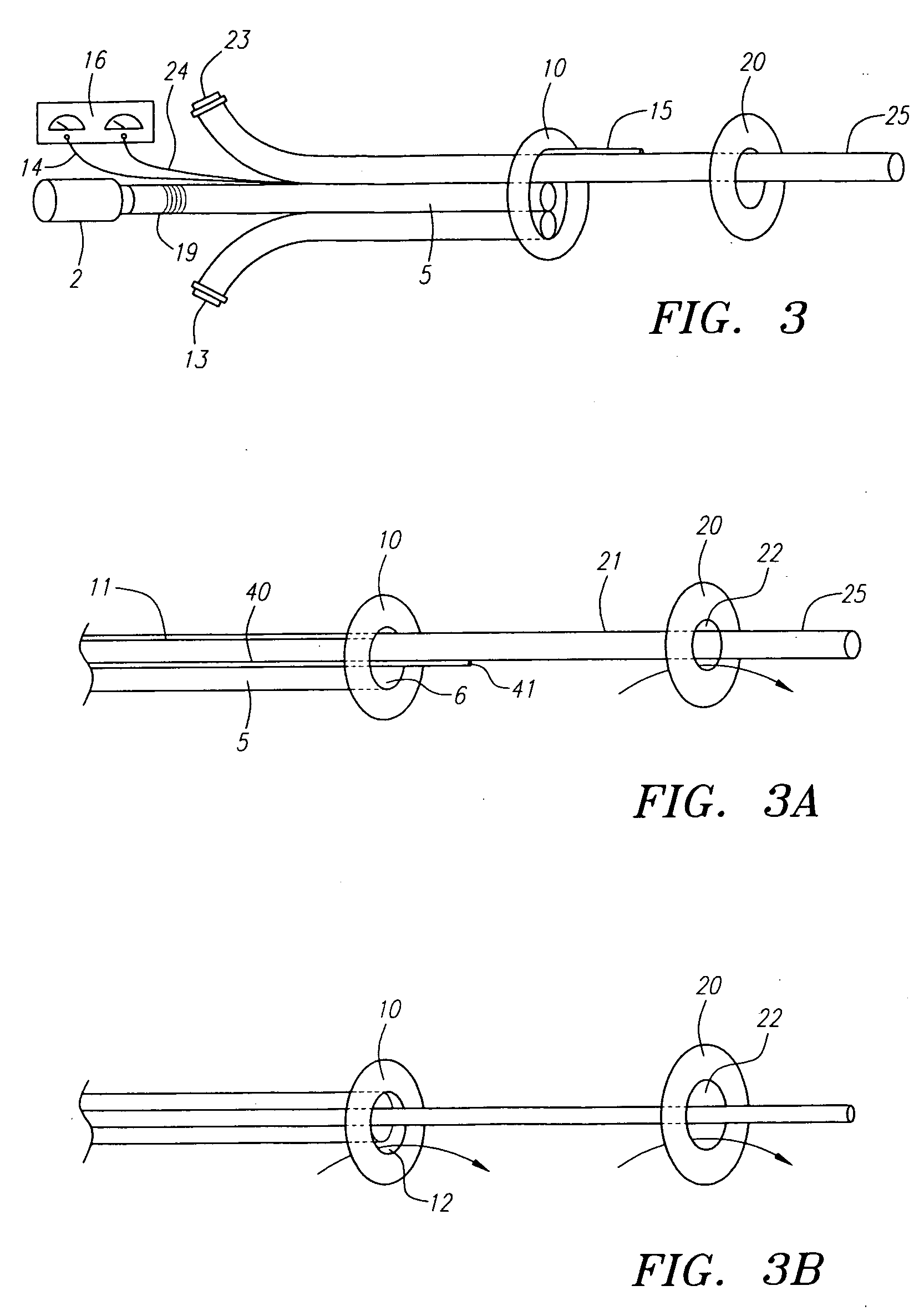
Stent with outer slough coating
The stent with an outer slough coating 125 of the present invention provides a coated stent having a permanent coating 130 disposed on the stent and a slough coating 125 disposed on the permanent coating 130. The permanent coating 130 includes an anti-proliferative agent and the slough coating 125 includes an anti-inflammatory agent. The slough coating 125 erodes shortly after stent implantation to deliver the anti-inflammatory agent, which treats tissue trauma from the angioplasty and the presence of the stent. Once the slough coating 125 has substantially eroded, the permanent coating 130 delivers the anti-proliferative agent long-term to prevent tissue growth on the stent or within the body lumen, and prevent restenosis. The permanent coating 130 can also include an anti-inflammatory agent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Balloon catheter method for reducing restenosis via irreversible electroporation
InactiveUS20090247933A1Promote resultsPrevent excessive cell lysingElectrotherapyInfusion devicesPercent Diameter StenosisIrreversible electroporation
Restenosis or neointimal formation may occur following angioplasty or other trauma to an artery such as by-pass surgery. This presents a major clinical problem which narrows the artery. The invention provides a balloon catheter with a particular electrode configuration. Also provided is a method whereby vascular cells in the area of the artery subjected to the trauma are subjected to irreversible electroporation which is a non-thermal, non-pharmaceutical method of applying electrical pulses to the cells so that substantially all of the cells in the area are ablated while leaving the structure of the vessel in place and substantially unharmed due to the non-thermal nature of the procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Methods of treatment with drug loaded polymeric materials
ActiveUS20060002971A1Increase molecular densityHigh densityPowder deliveryBiocideAntigenWound dressing
Polymeric microparticles have been developed which encapsulate therapeutic compounds such as drugs, cellular materials or components, and antigens, and can have targeting ligands directly bound to the microparticle surface. Preferred applications include use in tissue engineering matrices, wound dressings, bone repair or regeneration materials, and other applications where the microparticles are retained at the site of application or implantation. Another preferred application is in the use of microparticles to deliver anti-proliferative agents to the lining of blood vessels following angioplasty, transplantation or bypass surgery to prevent or decrease restenosis, and in cancer therapy. In still another application, the microparticles are used to treat or prevent macular degeneration when administered to the eye, where agents such as complement inhibitors are administered.
Owner:YALE UNIV
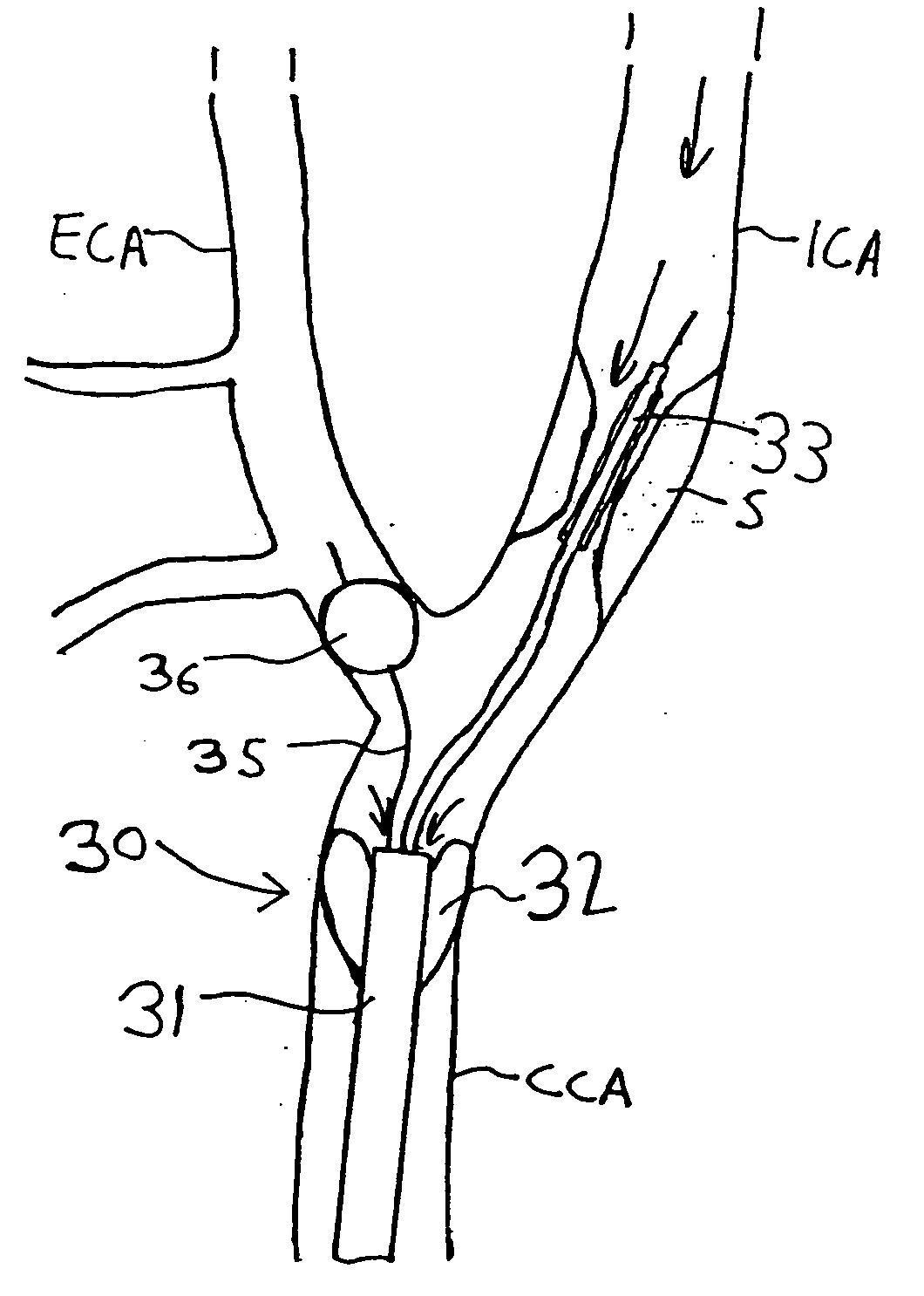
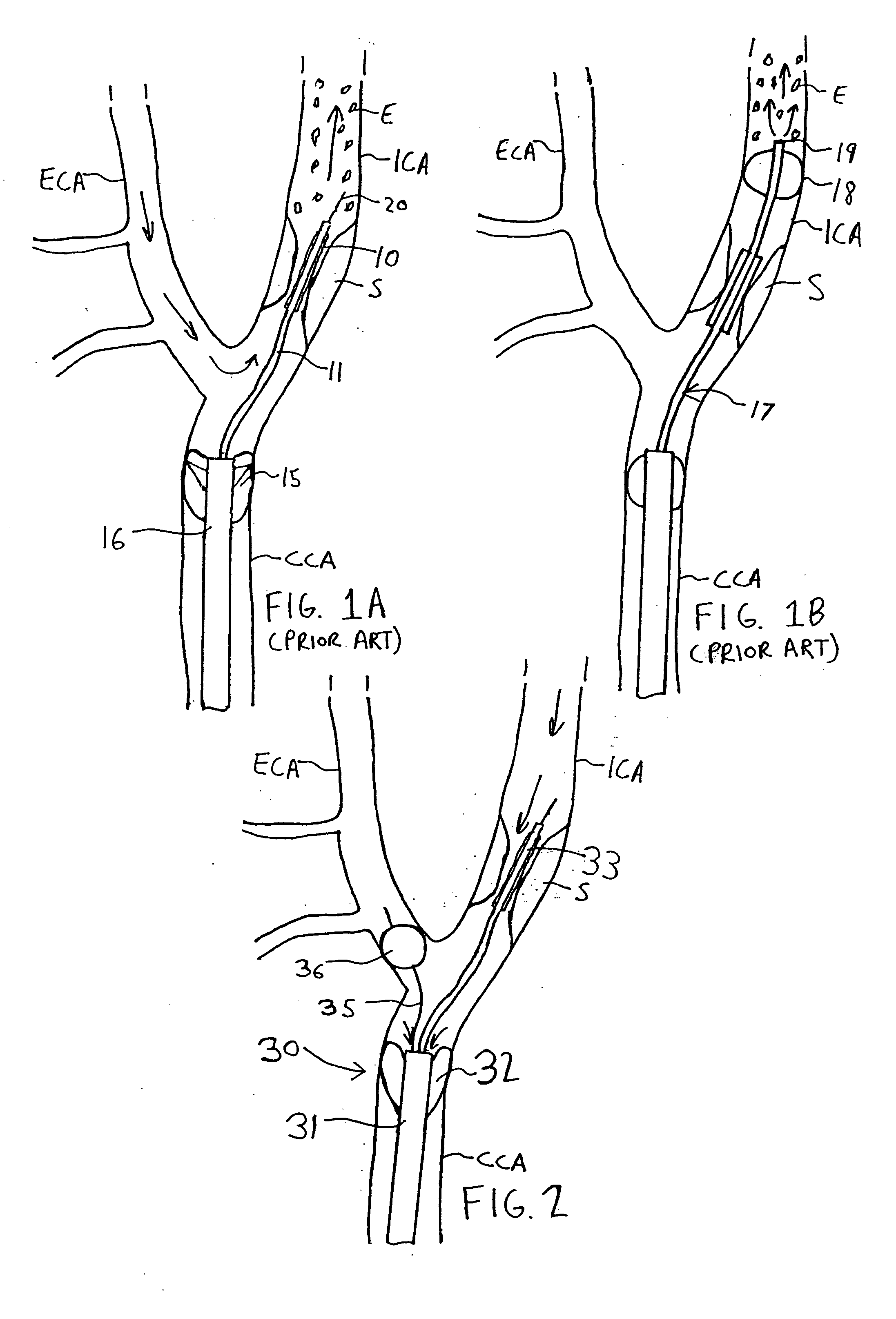
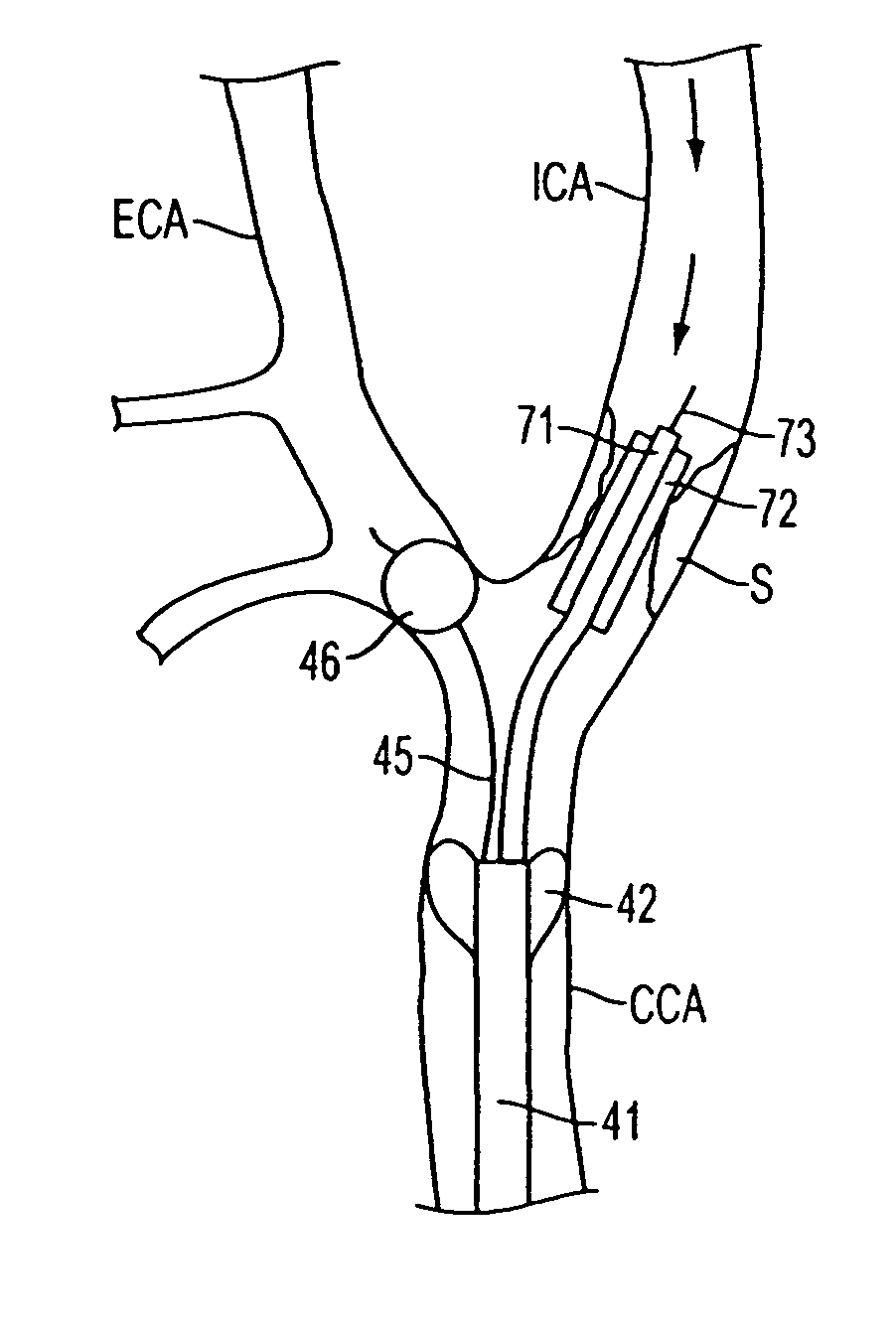
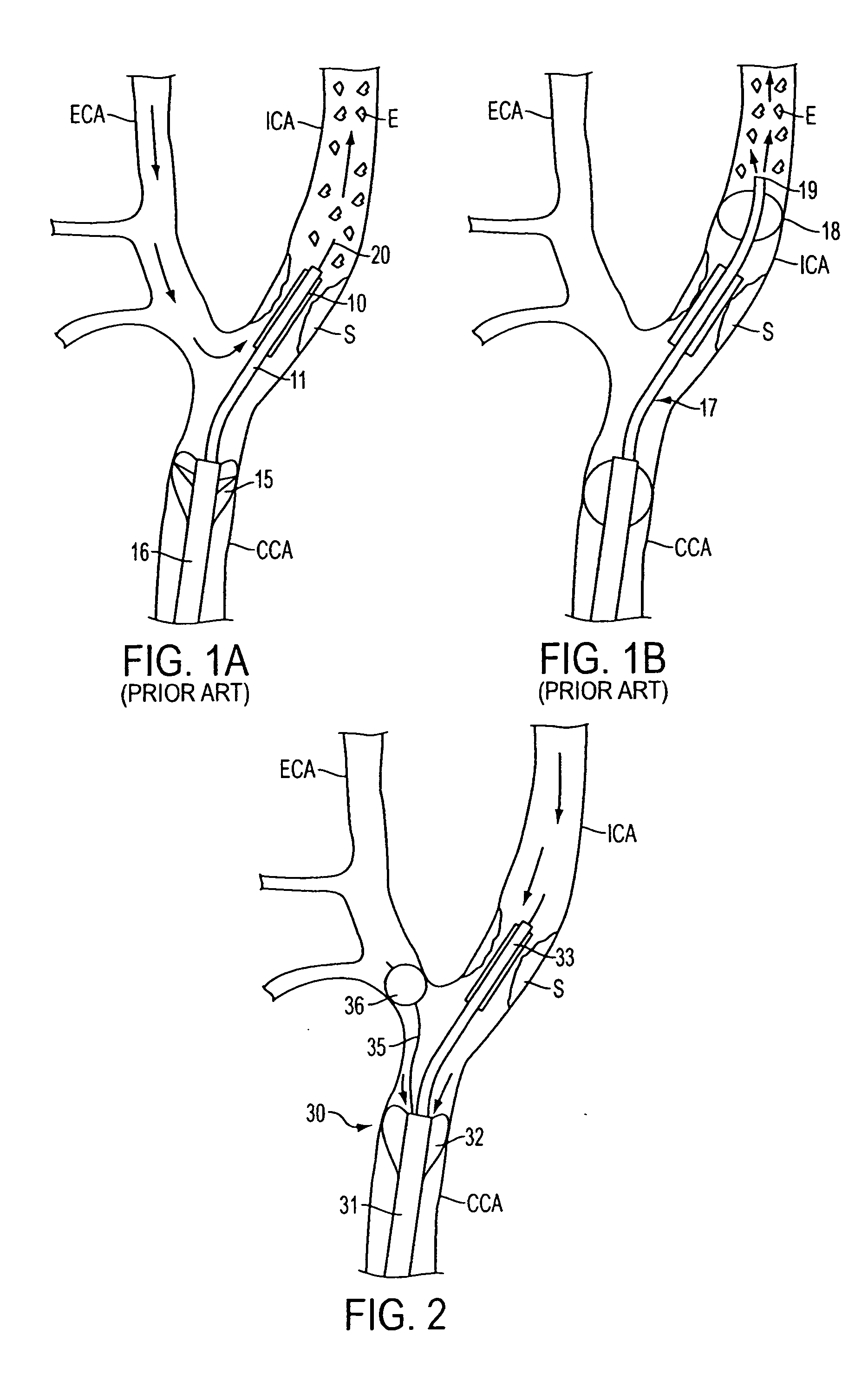
Apparatus and methods for reducing embolization during treatment of carotid artery disease
InactiveUS20050131453A1Reduce riskAvoid developmentDilatorsExcision instrumentsArterial diseaseGuide wires
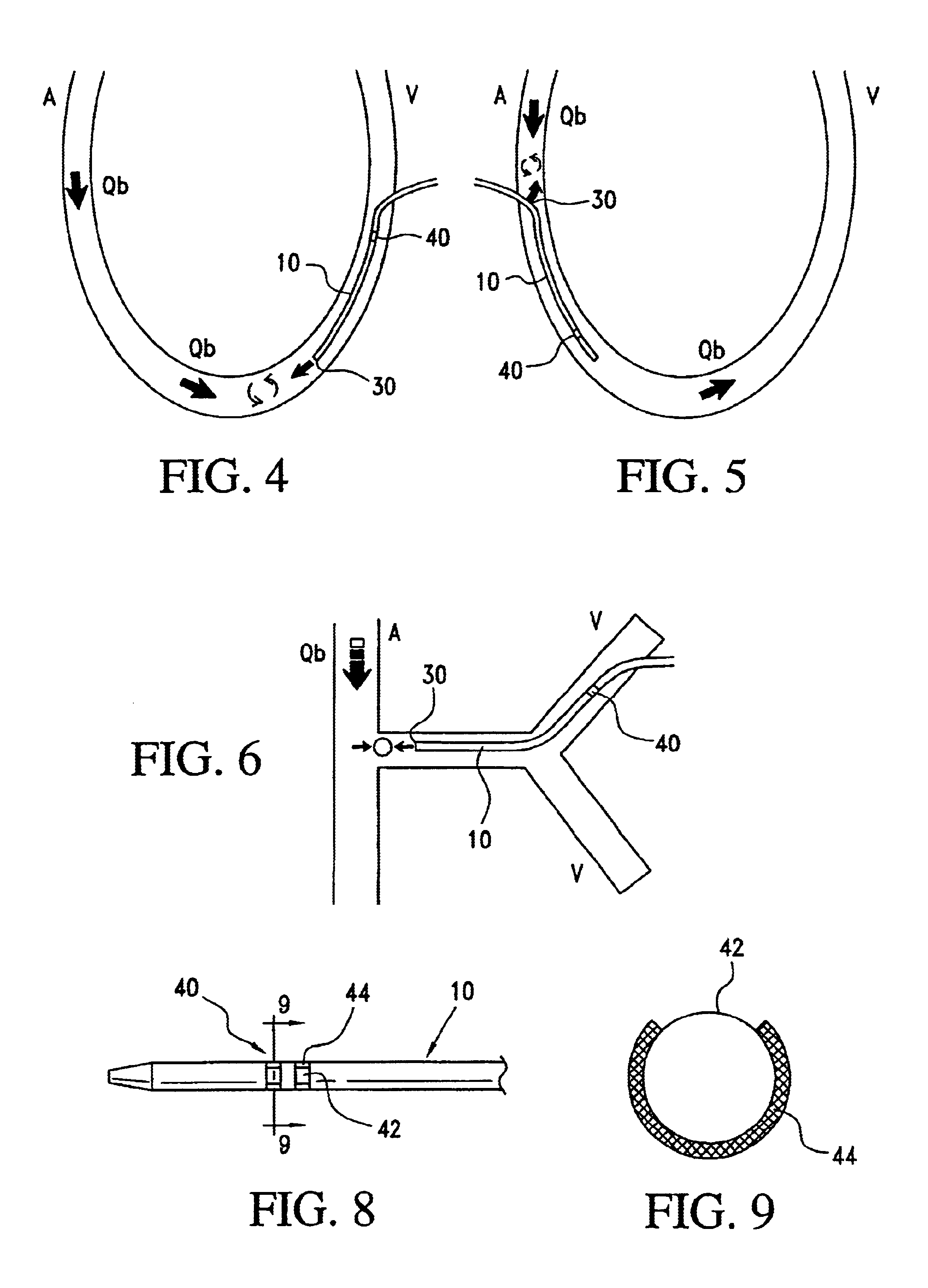
Methods and apparatus are provided for removing emboli during an angioplasty, stenting or surgical procedure comprising a catheter having an occlusion element, an aspiration lumen, and a blood outlet port in communication with the lumen, a guide wire having a balloon, a venous return catheter with a blood inlet port, and tubing that couples the blood outlet port to the blood inlet port. Apparatus is also provided for occluding the external carotid artery to prevent reversal of flow into the internal carotid artery. The pressure differential between the artery and the vein provides reverse flow through the artery, thereby flushing emboli. A blood filter may optionally be included in-line with the tubing to filter emboli from blood reperfused into the patient.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Guide catheter having selected flexural modulus segments
InactiveUS6858024B1Prevent guide catheter back-outIncreasing back-out resistanceGuide needlesFlexible pipesFlexural modulusAortic arch
A guiding catheter for use in coronary angioplasty and other cardiovascular interventions which incorporates a plurality of segment of selected flexural modulus in the shaft of the device. The segments which have a different flexibility than the sections immediately proximal and distal to them, creating zones in the catheter shaft which are either more or less flexible than other zones of the shaft. The flexibility and length of the shaft in a given zone is then matched to its clinical function and role. A mid-shaft zone is significantly softer than a proximal shaft or distal secondary curve to better traverse the aortic arch shape without storing too much energy. A secondary zone section is designed to have maximum stiffness to provide optimum backup support and stability.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
System and methods for imaging within a body lumen
InactiveUS6947787B2Reduce traumaEfficient procedureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryPercutaneous angioplastyOptical image
Systems, methods and apparatus for acquiring an image from within a body lumen are provided. Systems embodying features of the invention include an intracorporeal imaging component for acquiring imaging information, an image information recording component, and an image information playback component. Methods for acquiring image information from within a body lumen include steps of acquiring imaging information, storing image information, and playing back imaging information. Imaging information may be played back as acquired, or non-sequentially, or composite images may be formed by combining, filtering, enhancing, or subtracting images and the composite images displayed. Devices embodying features of the invention include optical imaging components such as an optical IGW, an optical imaging recording component, and an optical image playback component. The systems, methods and devices are suitable for use with angiopoplasty, stent delivery, and other intracorporeal clinical procedures.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Antisense restenosis composition and method
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
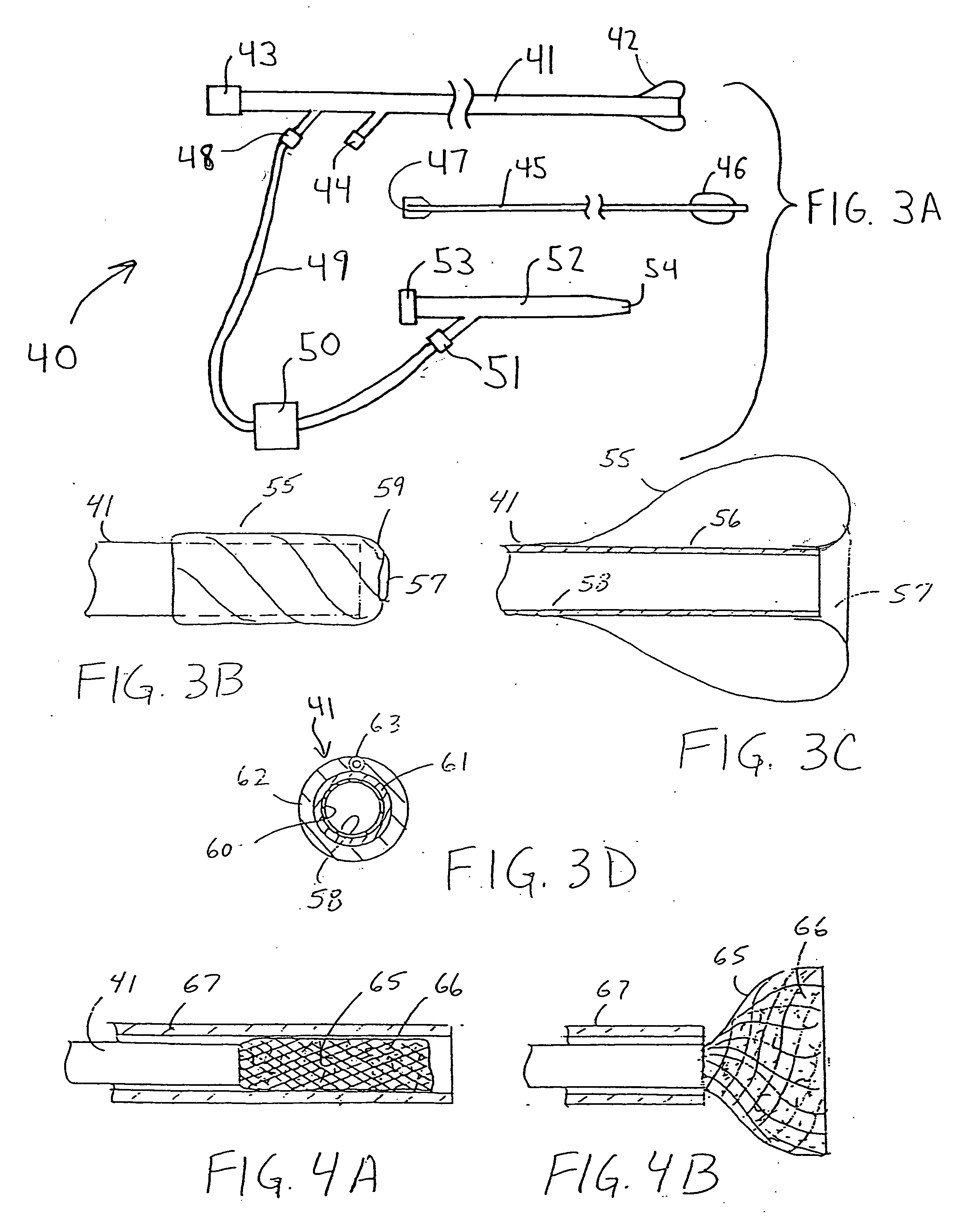
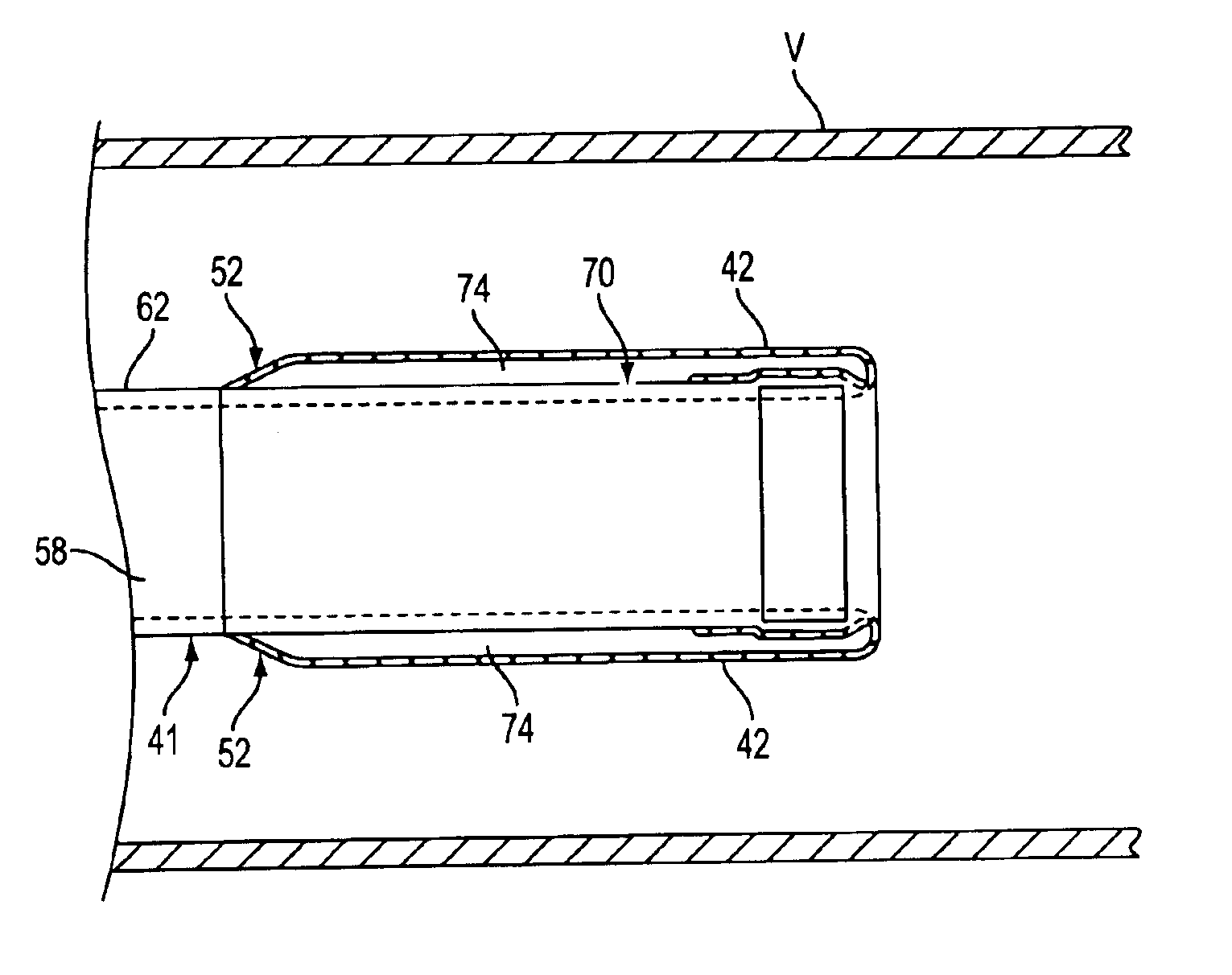
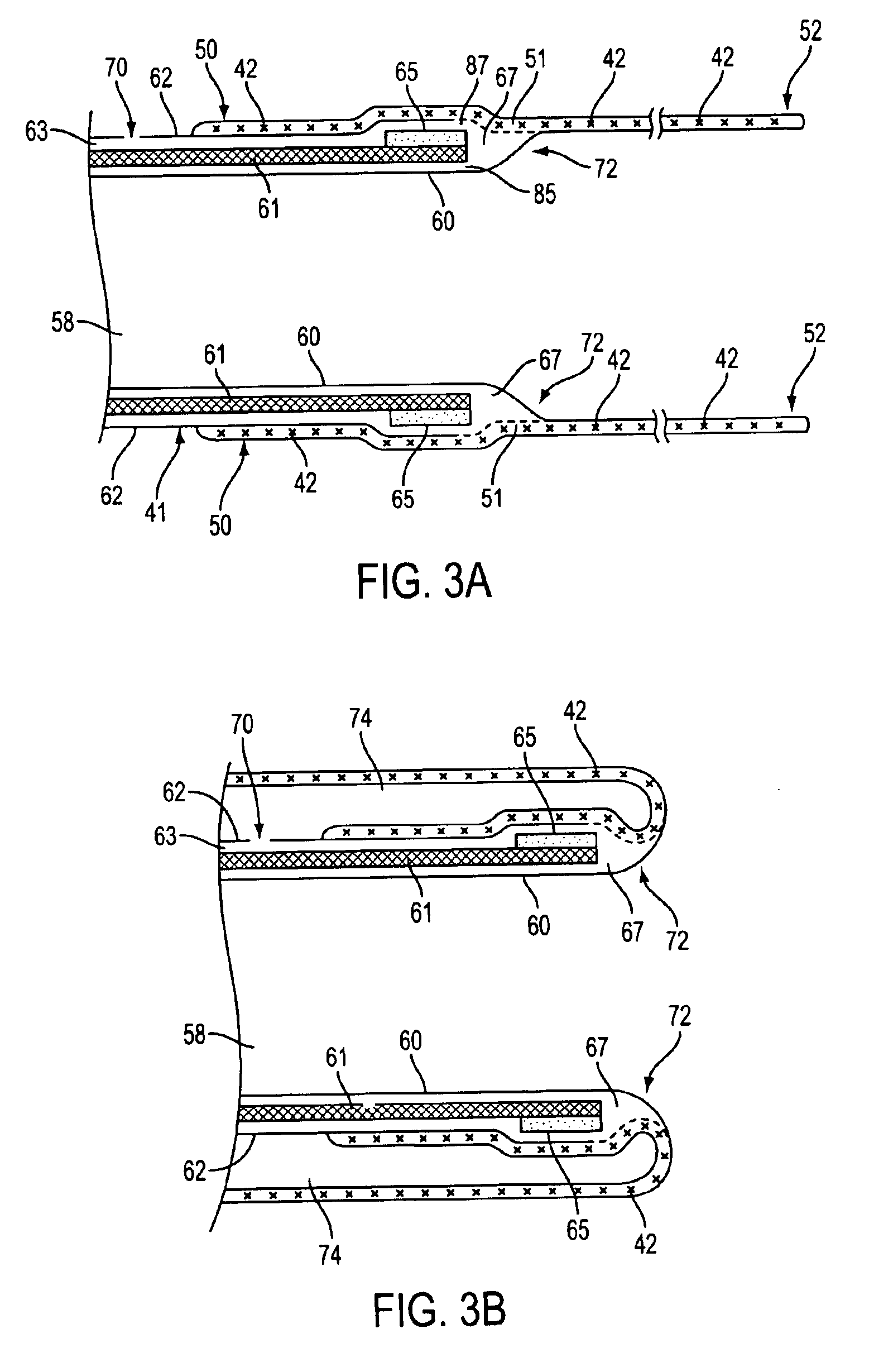
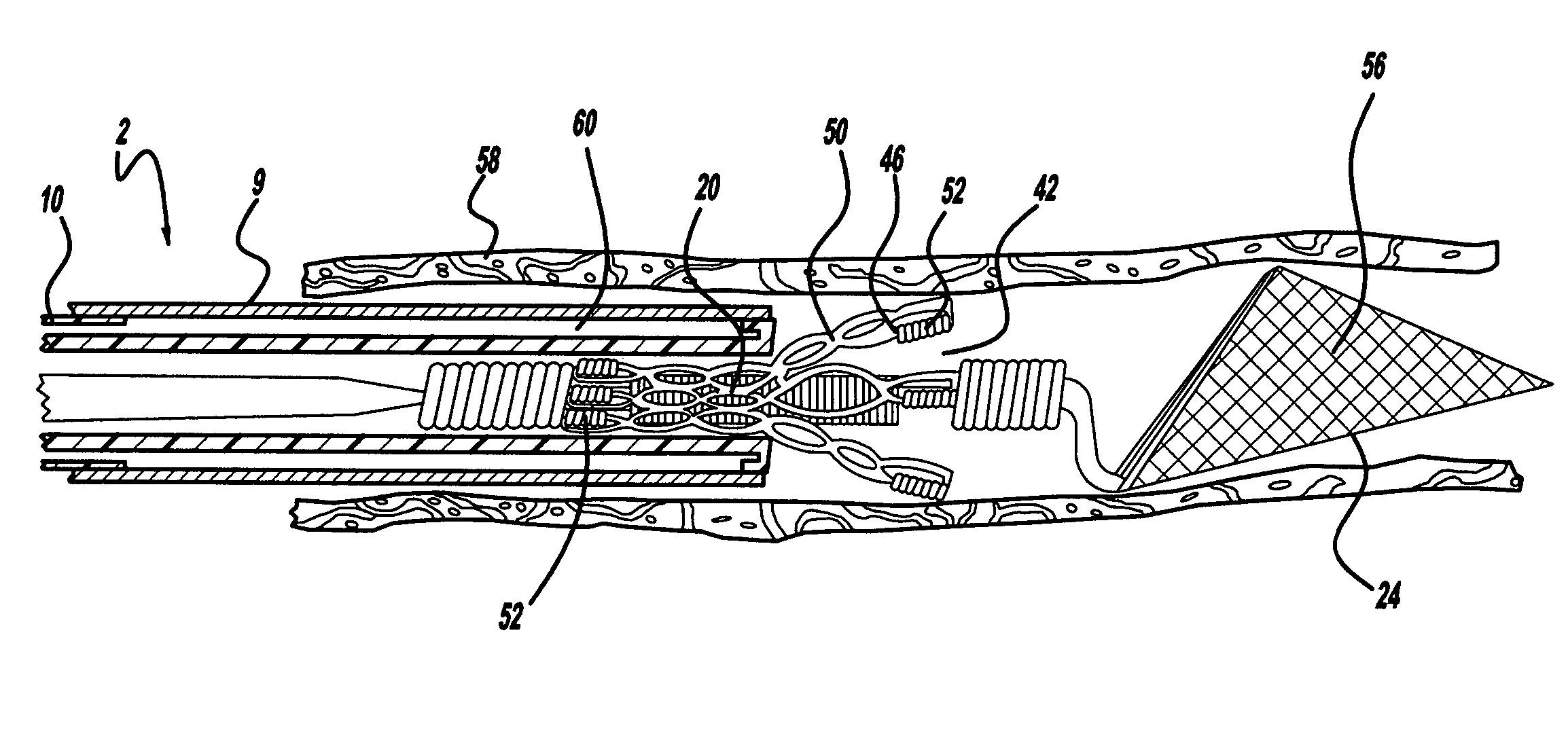
Catheter having a funnel-shaped occlusion balloon of uniform thickness and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS6960222B2Improve manufacturabilityReduce manufacturing costStentsBalloon catheterPercutaneous angioplastySurgical department
Methods and apparatus are provided for removing emboli during an angioplasty, stenting or surgical procedure comprising a catheter having a funnel-shaped occlusion balloon of uniform thickness disposed on a distal end of the catheter. The occlusion balloon is fused to the distal end so that it provides a substantially seamless flow transition into a working lumen of the catheter. Additionally, a distal edge of the occlusion balloon is configured to be in close proximity with an inner wall of a vessel to facilitate blood flow into the catheter and efficiently remove emboli.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Sliding restraint stent delivery systems
InactiveUS20050209672A1Conveniently “ lock-down ”Good locking functionStentsBlood vesselsBody organsInsertion stent
Medical device and methods for delivery or implantation of prostheses within hollow body organs and vessels or other luminal anatomy are disclosed. The subject technologies may be used in the treatment of atherosclerosis in stenting procedures. For such purposes, a self-expanding stent may be deployed in connection with an angioplasty procedure with a sliding restraint based delivery system adapted for simplified use. In the system, the sliding restraint is sized, in coordination with a fixed sleeve accepting a core wire to actuate the restraint to effect an anchoring function with the sleeve so that the stent is not inadvertently advanced during deployment.
Owner:BIOSENSORS INT GROUP
Progenitor endothelial cell capturing with a drug eluting implantable medical device
InactiveUS20050271701A1Increased formationSmooth migrationStentsHeart valvesProgenitorDrug-Coated Stents
A medical device for implantation into vessels or luminal structures within the body is provided. The medical device, such as a stent and a synthetic graft, is coated with a pharmaceutical composition consisting of a controlled-release matrix and one or more pharmaceutical substances for direct delivery of drugs to surrounding tissues. The coating on the medical device further comprises a ligand such as an antibody or a small molecule for capturing progenitor endothelial cells in the blood contacting surface of the device for restoring an endothelium at the site of injury. In particular, the drug-coated stents are for use, for example, in balloon angioplasty procedures for preventing or inhibiting restenosis.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
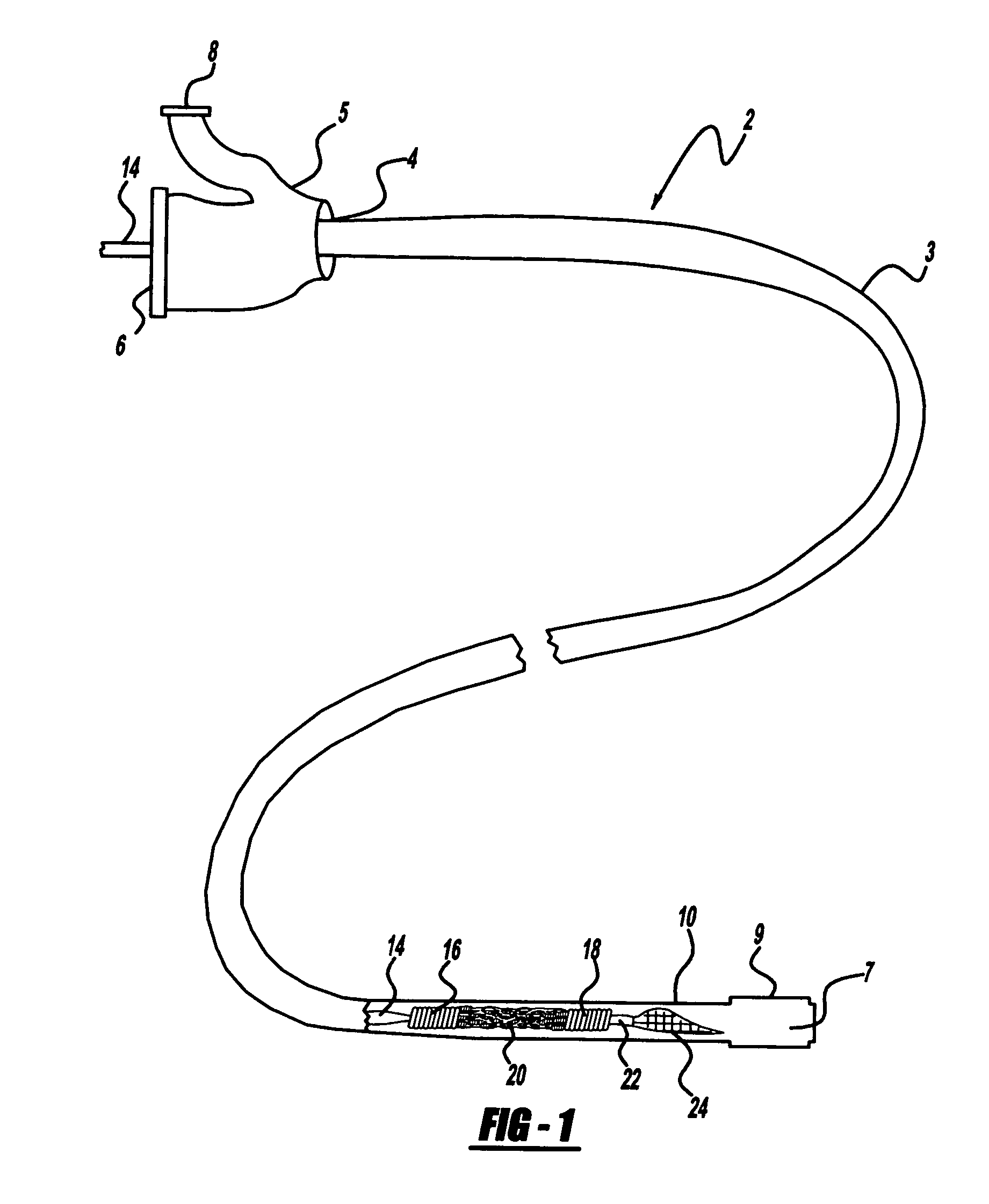
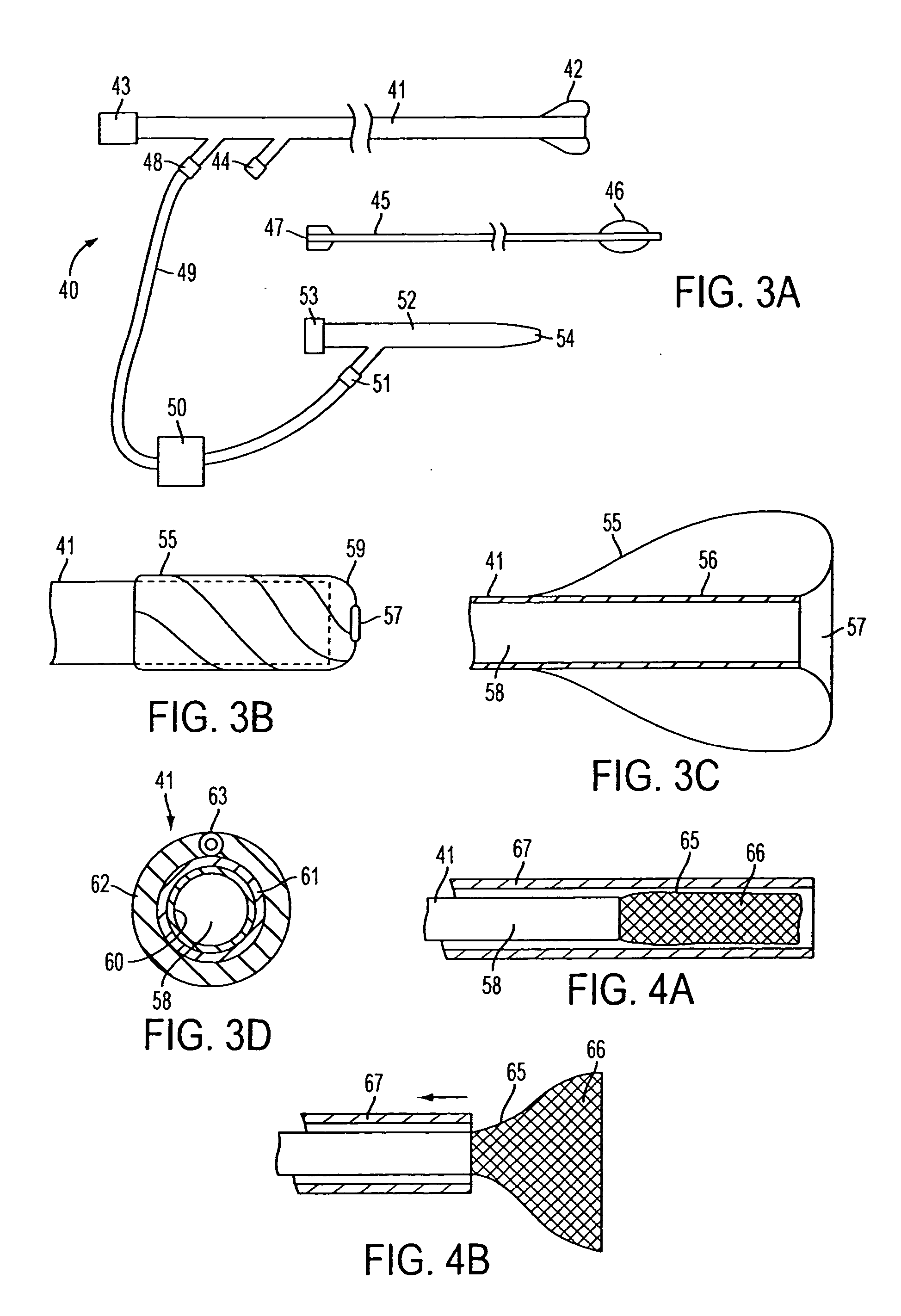
Steerable distal protection guidewire and methods of use
A steerable guidewire apparatus for use during percutaneous catheter interventions such as angioplasty or stent deployment. A protection element comprising a filter or an occluder is mounted near the distal end of the steerable guidewire, which guides a therapeutic catheter. The guidewire comprises a hollow shaft movably disposed about a core wire. The shaft and core wire control separation of the ends of the protection element, causing transformation of the protection element from a deployed configuration to a collapsed configuration. Farther separation of the ends of the protection element, after it has been collapsed, causes deflection in a distal region of the apparatus.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Composition and/or method for preventing onset and/or recurrence of cardiovascular events
ActiveUS20070021504A1Preventing onsetPrevent recurrenceBiocideMetabolism disorderSecondary hyperlipidemiaSurgery
Provided are composition and / or methods useful in preventing onset and / or recurrence of cardiovascular events, especially in patients who have escaped the unstable period after cardiovascular angioplasty or in hyperlipidemia patients who have been treated with HMG-CoA RI.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Self-expanding stent and stent delivery system with distal protection
A self-expanding stent and stent delivery system are provided for treating vascular diseases such as partially occluded blood vessels within the brain. The self-expanding stent is preferably mounted on an elongated core wire including proximal, intermediate and distal cylindrical members disposed about the core wire. The proximal, intermediate, and distal cylindrical members are spaced apart such that first and second gaps are formed. The stent, which includes anchor members, is mounted on the intermediate cylindrical member such that the anchor members interlock within the gaps between the cylindrical members. The self-expanding stent and elongated core wire are disposed within a delivery lumen of a balloon catheter such that the balloon catheter compresses and constrains the stent about the intermediate cylindrical member to thereby interlock the stent onto the core wire. The elongated core wire further includes an expandable capture basket attached to the distal end of the elongated core wire in order to capture embolic debris released during the angioplasty of the blood vessel and the deployment of the self-expanding stent.
Owner:CORDIS NEUROVASCULAR
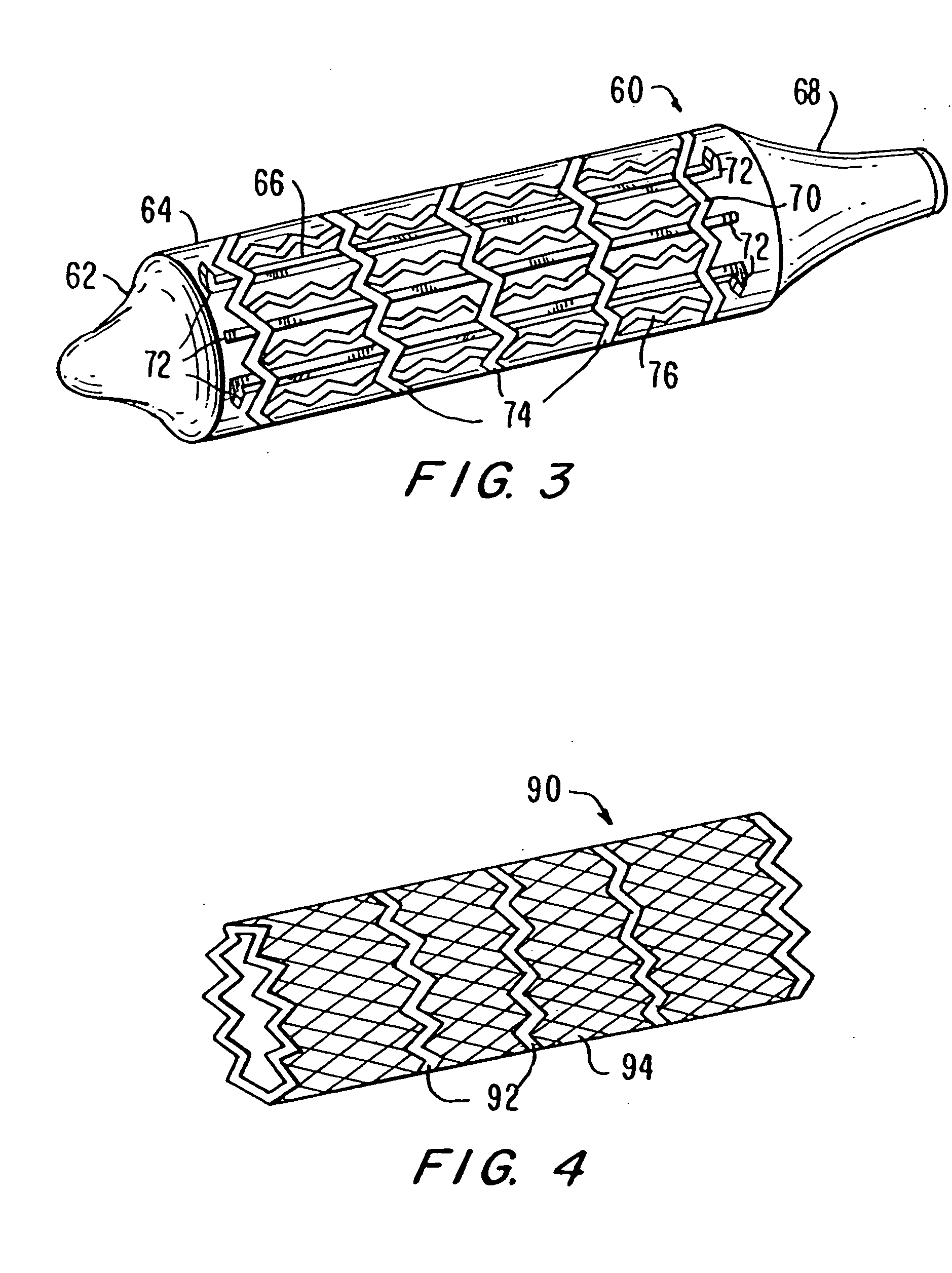
Low profile electrodes for an angioplasty shock wave catheter
Described herein are low-profile electrodes for use with an angioplasty shockwave catheter. A low-profile electrode assembly may have an inner electrode, an insulating layer disposed over the inner electrode such that an opening in the insulating layer is aligned with the inner electrode, and an outer electrode sheath disposed over the insulating layer such that an opening in the outer electrode sheath is coaxially aligned with the opening in the insulating layer. This layered configuration allows for the generation of shockwaves that propagate outward from the side of the catheter. In some variations, the electrode assembly has a second inner electrode, and the insulating layer and outer electrode may each have a second opening that are coaxially aligned with the second inner electrode. An angioplasty shockwave catheter may have a plurality of such low-profile electrode assemblies along its length to break up calcified plaques along a length of a vessel.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
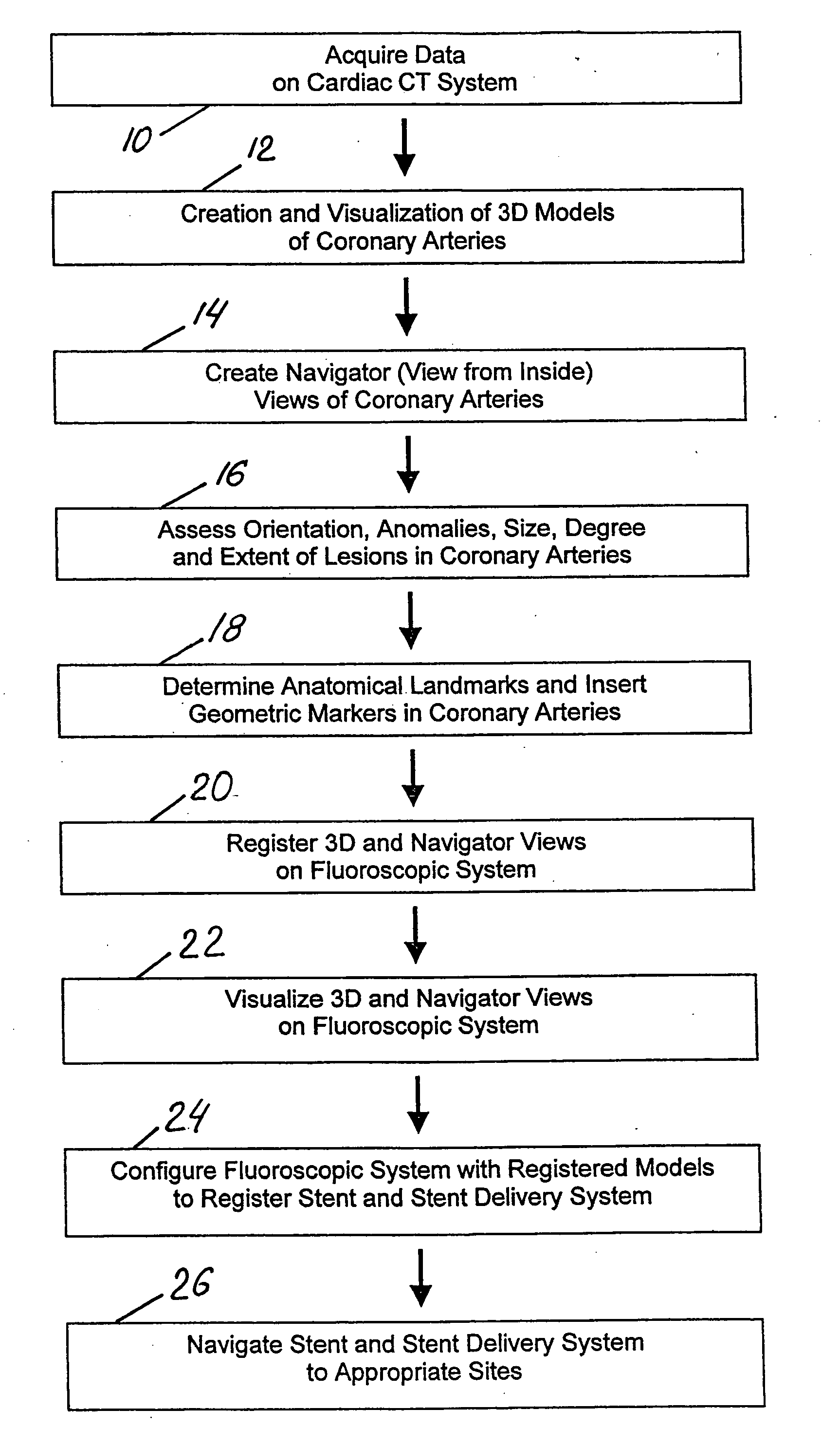
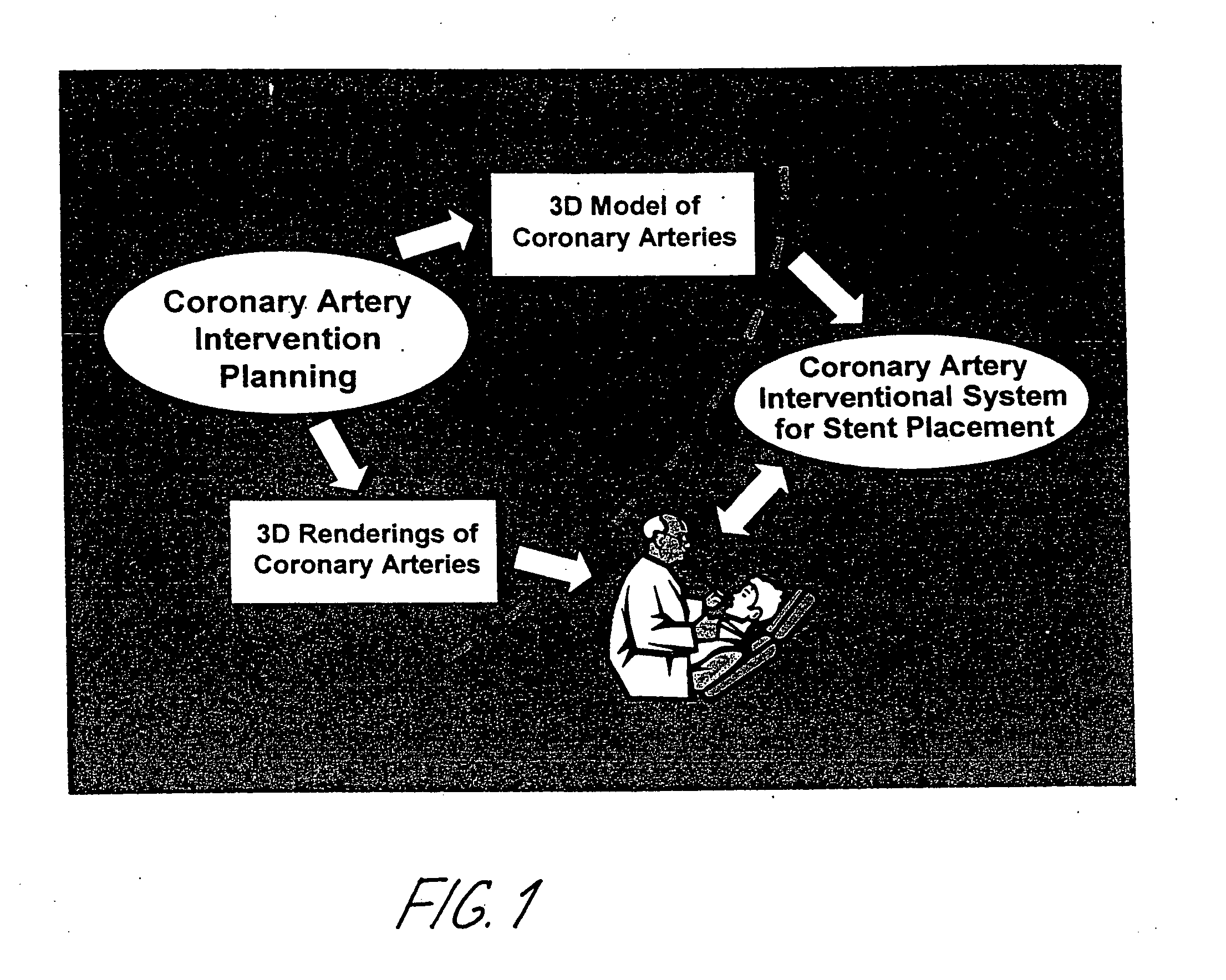
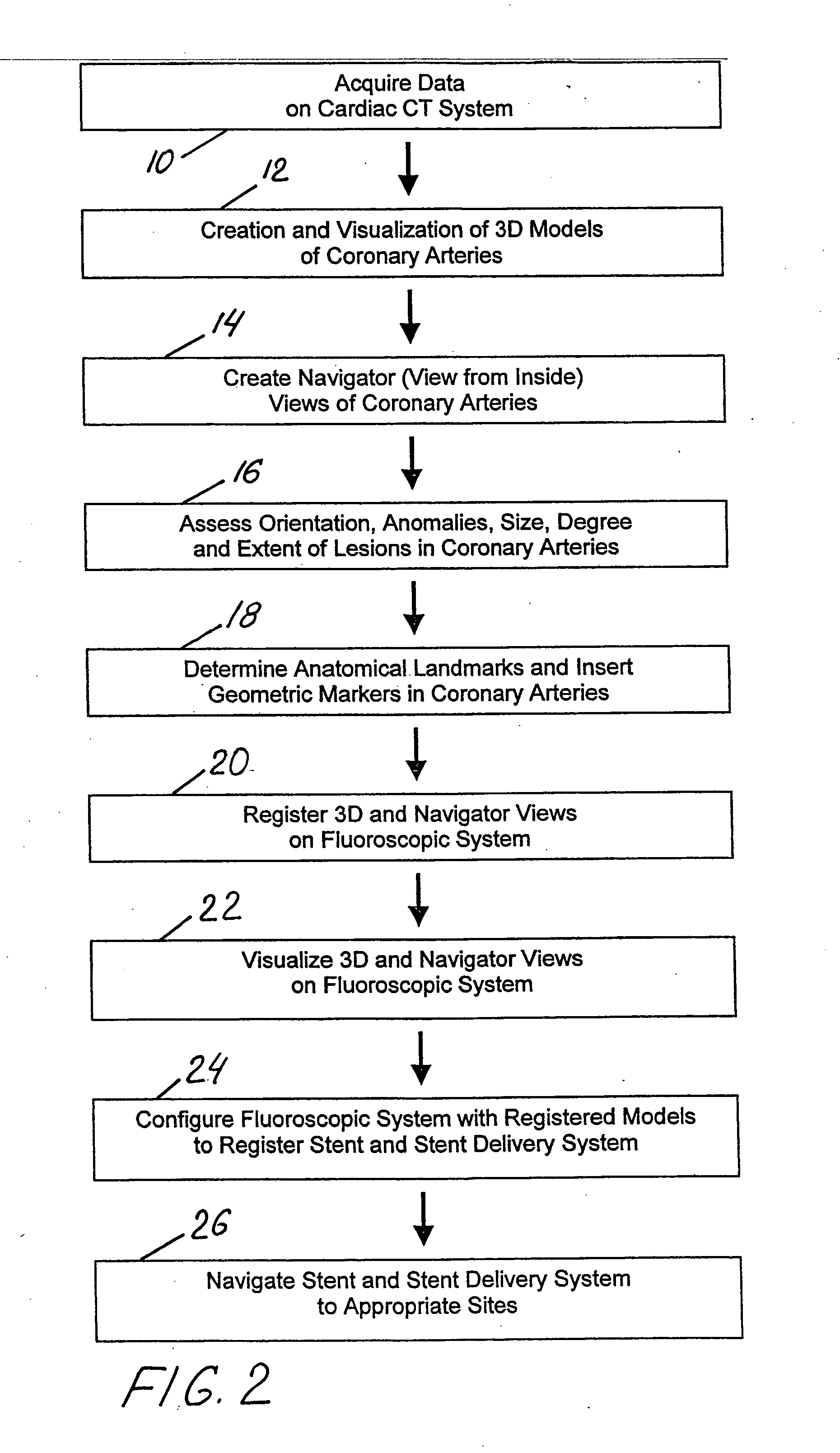
Method and system for Coronary arterial intervention
A method is provided for arterial intervention on a patient that has the steps of obtaining digital image data of the patient's artery from a medical imaging system where the artery has lesions arising from arterial disease, generating a 3D model from this image data, registering the 3D model to an image of the artery that has been visualized in real-time upon an interventional system, navigating an angioplasty delivery system to the artery utilizing this registered 3D model, and using the angioplasty delivery system to treat the artery. Preferably, the digital image data is cardiac image data, the artery is a coronary artery, and the angioplasty delivery system is a stent and stent delivery system. In another aspect of this invention, it provides a system for arterial intervention that has a medical imaging system for obtaining digital image data of at least one of the patient's arteries, an image generation system for generating a 3D model from the image data, an interventional system for visualizing an image of the artery in real-time, a workstation for registering the 3D model to this image, and an angioplasty delivery system that can be navigated to the artery utilizing the registered 3D model.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Medical wire device
InactiveUS20060161198A1Easy to confirmIncrease flexibilityDilatorsOcculdersWire rodSurgical department
Disclosed herein is a novel medical wire device which is equipped with a filter unit, capable of surely capturing free embolismic debris upon angioplasty of a constriction lesion in a lumen, capable of easily confirming a developed state of a filter under radiography by a surgeon, and thus improved in function of the filter unit. The medical wire device of the present invention comprises a filter unit which is to be located, upon angioplasty of a constriction lesion in a lumen, on a distal side from the constriction lesion for capturing free embolismic debris separated from an inner wall of the constriction lesion, and a wire provided with the filter unit at its distal-side end. A filter is made up of a metal having radiopaque property.
Owner:KANEKA MEDIX
Progenitor Endothelial Cell Capturing with a Drug Eluting Implantable Medical Device
InactiveUS20070123977A1Stimulating positive blood vessel remodelingEnhance and accelerate formationStentsSurgeryProgenitorDrug-Coated Stents
A medical device for implantation into vessels or luminal structures within the body is provided, which stimulates positive blood vessel remodeling. The medical device, such as a stent and a synthetic graft, is provided with a coating with a pharmaceutical composition containing a controlled-release matrix and one or more pharmaceutical substances for direct delivery of drugs to surrounding tissues. The coating on the medical device further comprises one or more barrier layers, and a ligand such as a peptide, an antibody or a small molecule for capturing progenitor endothelial cells in the blood contacting surface of the device for restoring an endothelium at the site of injury. In particular, the drug-coated stents are for use, for example, in balloon angioplasty procedures for preventing or inhibiting restenosis.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for determining blood flow during a vascular corrective procedure
InactiveUS6986744B1Correct effectivenessMinimize wall effectSurgeryDilatorsMedicinePercutaneous angioplasty
A method and apparatus for determining an angioplasty induced blood flow changes, wherein the apparatus includes the catheter having a port for introducing a blood property change in a downstream sensor. The downstream sensor and the catheter are configured to space the sensor from an adjacent vessel wall so as to minimize effects of the vessel wall during sensing of the blood property change.
Owner:TRANSONIC SYST
Progenitor Endothelial Cell Capturing with a Drug Eluting Implantable Medical Device
InactiveUS20070129789A1Stimulating positive blood vessel remodelingEnhance and accelerate formationOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryProgenitorDrug-Coated Stents
A medical device for implantation into vessels or luminal structures within the body is provided, which stimulates positive blood vessel remodeling. The medical device, such as a stent and a synthetic graft, is coated with a pharmaceutical composition consisting of a controlled-release matrix and one or more pharmaceutical substances for direct delivery of drugs to surrounding tissues. The coating on the medical device further comprises a ligand such as a peptide, an antibody or a small molecule for capturing progenitor endothelial cells in the blood contacting surface of the device for restoring an endothelium at the site of injury. In particular, the drug-coated stents are for use, for example, in balloon angioplasty procedures for preventing or inhibiting restenosis.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Catheter with cryogenic and electrical heating ablation
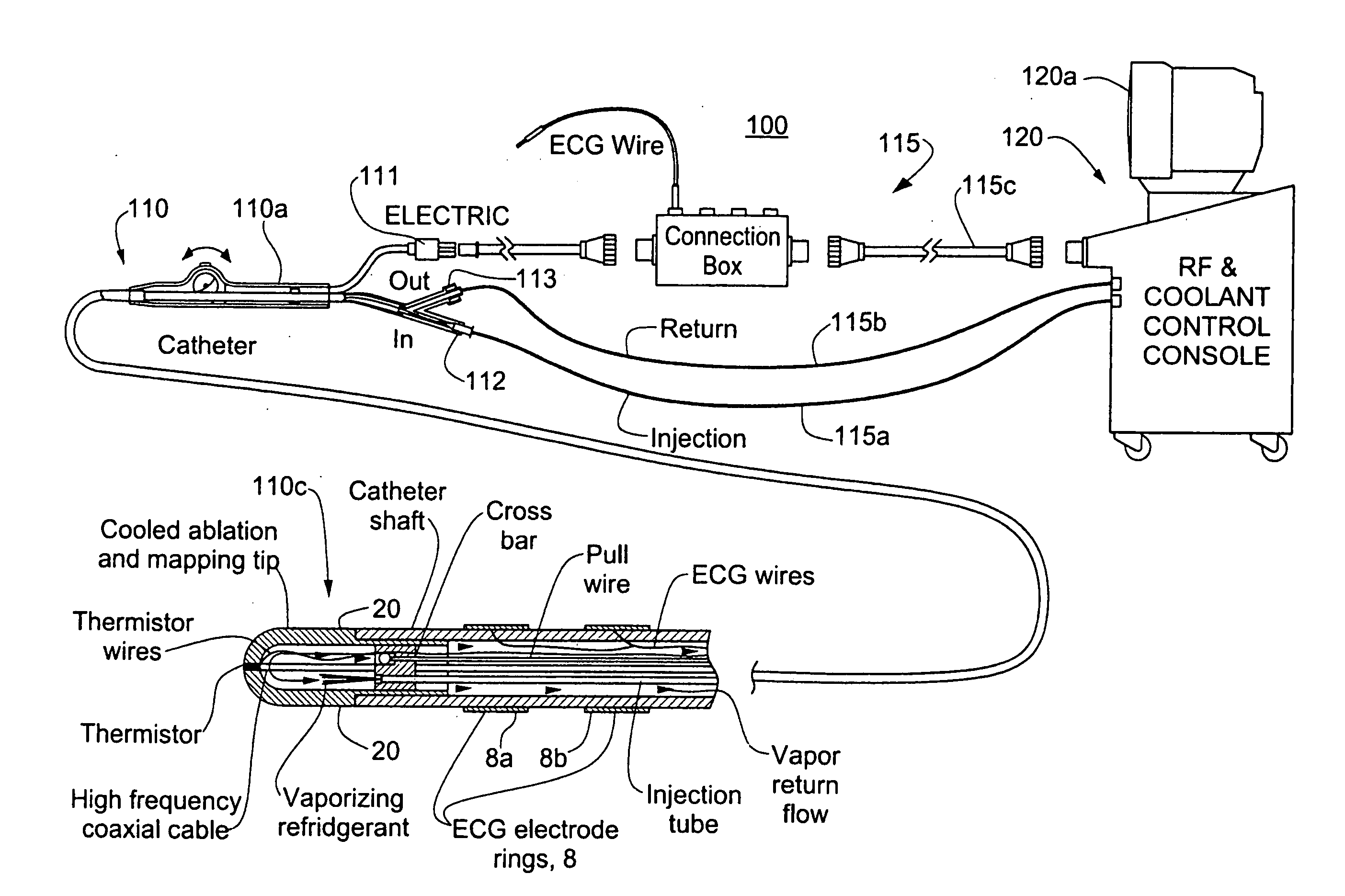
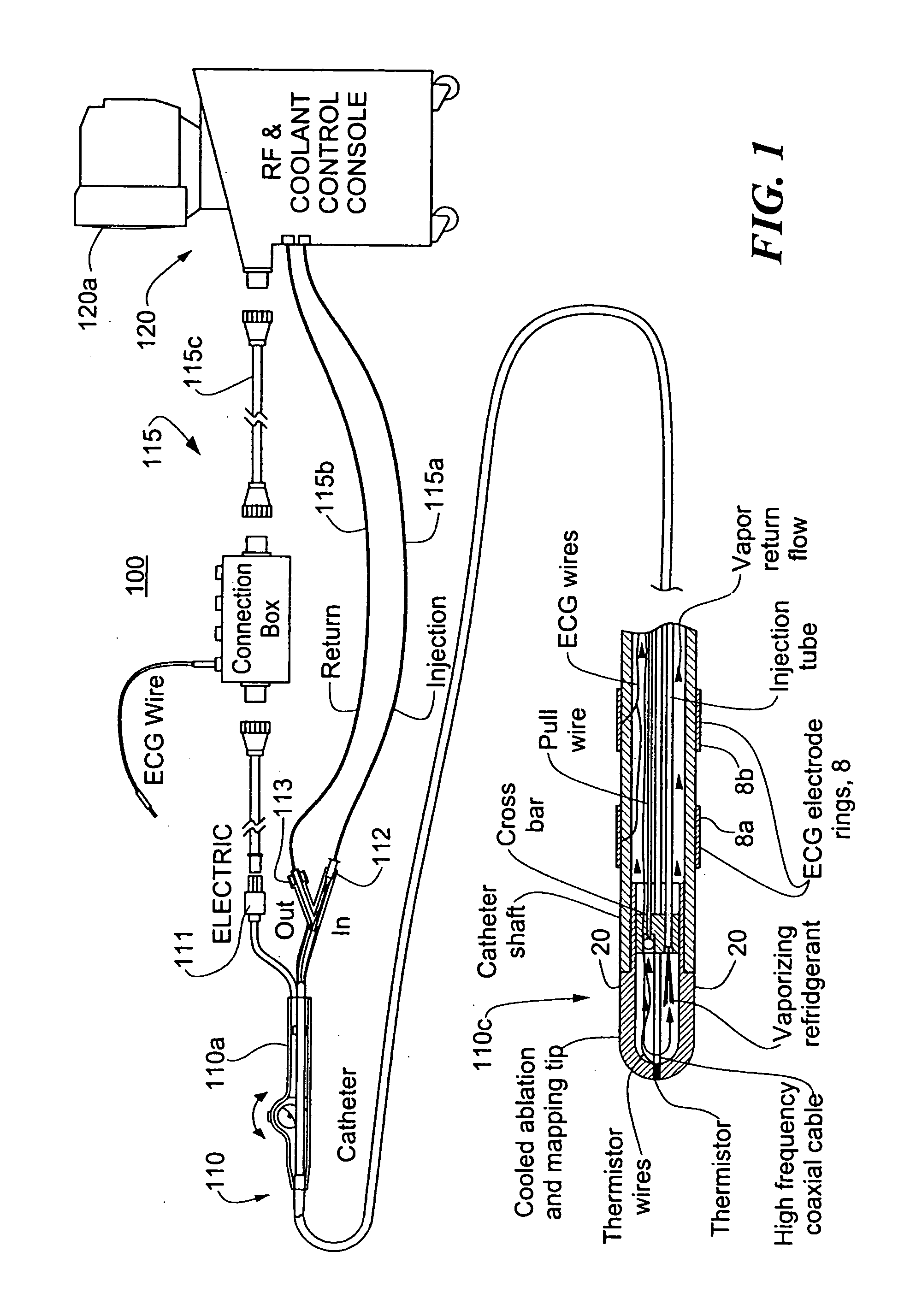
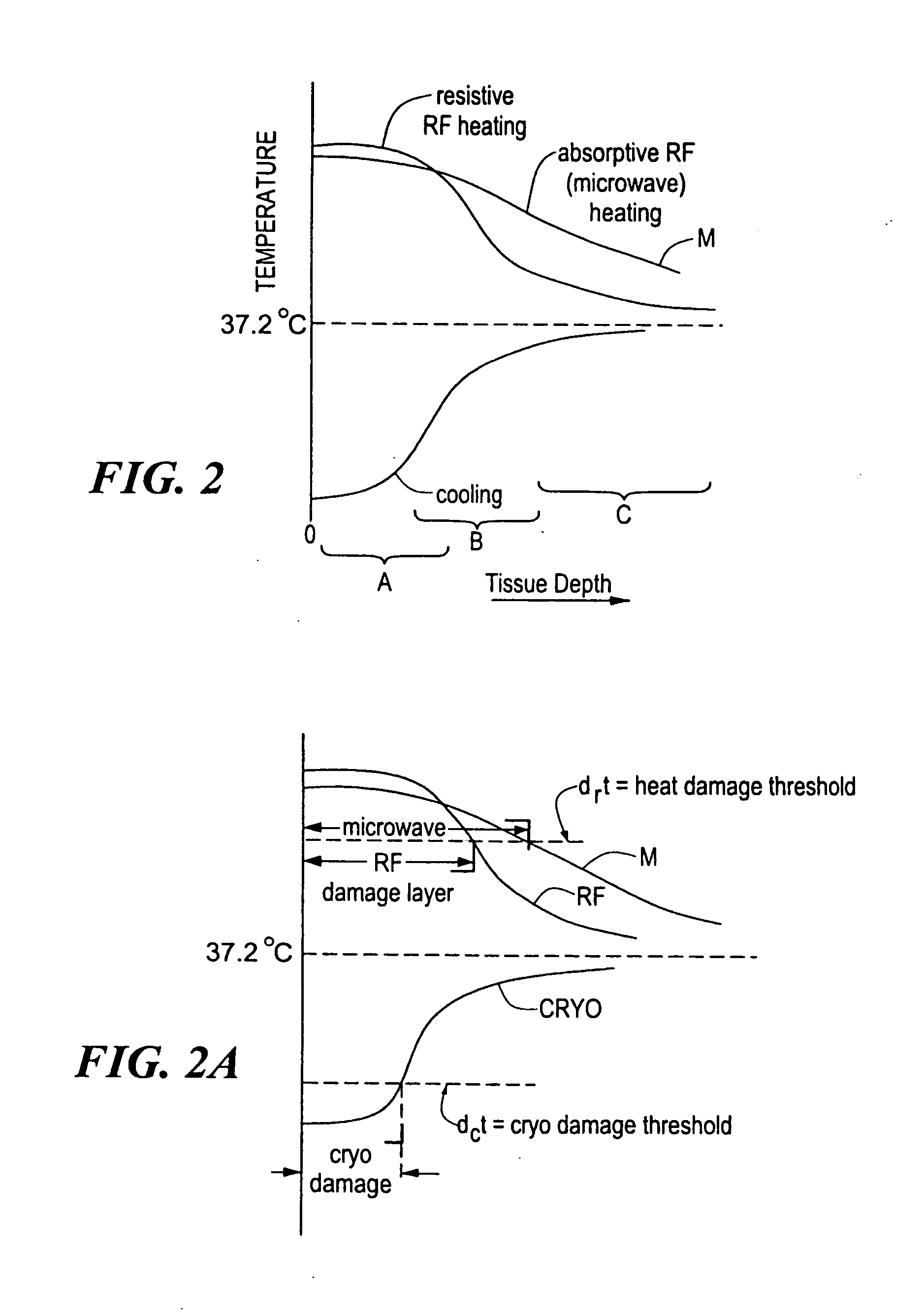
InactiveUS20060004351A1Reduce tip temperatureReduce movement sequenceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTissue remodelingCelsius Degree
A catheter includes a cryoablation tip with an electrically-driven ablation assembly for heating tissue. The cryoablation tip may be implemented with a cooling chamber through which a controllably injected coolant circulates to lower the tip temperature, and having an RF electrode at its distal end. The RF electrode may be operated to warm cryogenically-cooled tissue, or the coolant may be controlled to conductively cool the tissue in coordination with an RF treatment regimen, allowing greater versatility of operation and enhancing the lesion size, speed or placement of multi-lesion treatment or single lesion re-treatment cycles. In one embodiment a microwave energy source operates at a frequency to extend beyond the thermal conduction depth, or to penetrate the cryogenic ice ball and be absorbed in tissue beyond an ice boundary, thus extending the depth and / or width of a single treatment locus. In another embodiment, the cooling and the application of RF energy are both controlled to position the ablation region away from the surface contacted by the electrode, for example to leave surface tissue unharmed while ablating at depth or to provide an ablation band of greater uniformity with increasing depth. The driver or RF energy source may supply microwave energy at a frequency effective to penetrate the ice ball which develops on a cryocatheter, and different frequencies may be selected for preferential absorption in a layer of defined thickness at depth in the nearby tissue. The catheter may operate between 70 and minus 70 degrees Celsius for different tissue applications, such as angioplasty, cardiac ablation and tissue remodeling, and may preset the temperature of the tip or adjacent tissue, and otherwise overlay or delay the two different profiles to tailor the shape or position where ablation occurs or to speed up a treatment cycle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Calcium phosphate coated implantable medical devices and processes for making same
InactiveUS20060134160A1Reduce porosityControlled release rateBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsCalcium phosphate coatingCardiovascular stent
This invention relates to novel calcium phosphate-coated implantable medical devices and processes of making same. The calcium-phosphate coatings are designed to minimize the immune response to the implant (e.g. restenosis in stenting procedures) and can be used to store and release a medicinally active agent in a controlled manner. Such coatings can be applied to any implantable medical devices and are useful for a number of medical procedures including (but not limited to) balloon angioplasty in cardiovascular stenting, ureteral stenting and catheterisation. The calcium phosphate coatings can be applied to a substrate as one or more coatings by a sol-gel deposition process, an aerosol-gel deposition process, a biomimetic deposition process, a calcium phosphate cement deposition process, an electro-phoretic deposition process or an electrochemical deposition process. The coating can contain and elude a drug in an engineered manner.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
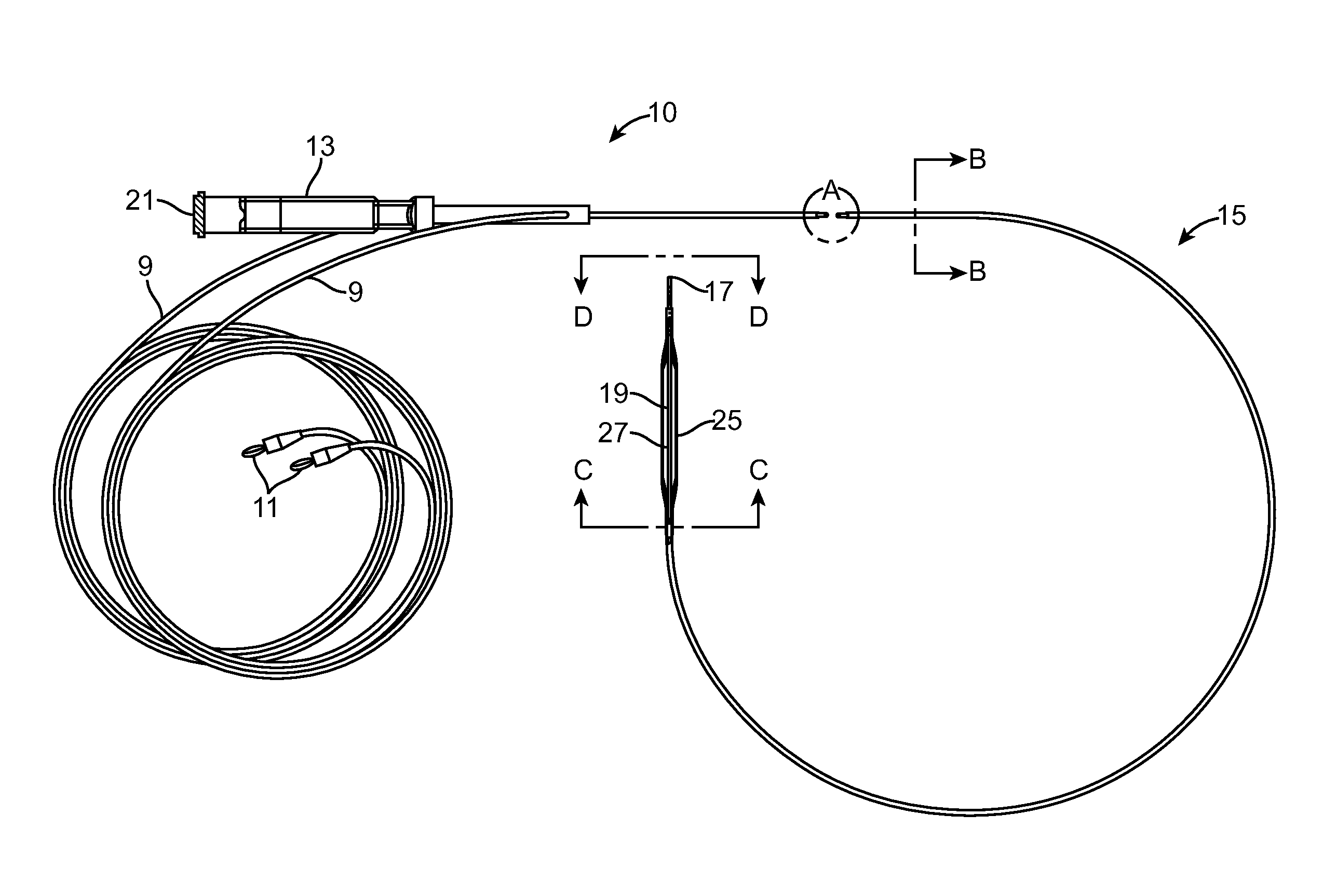
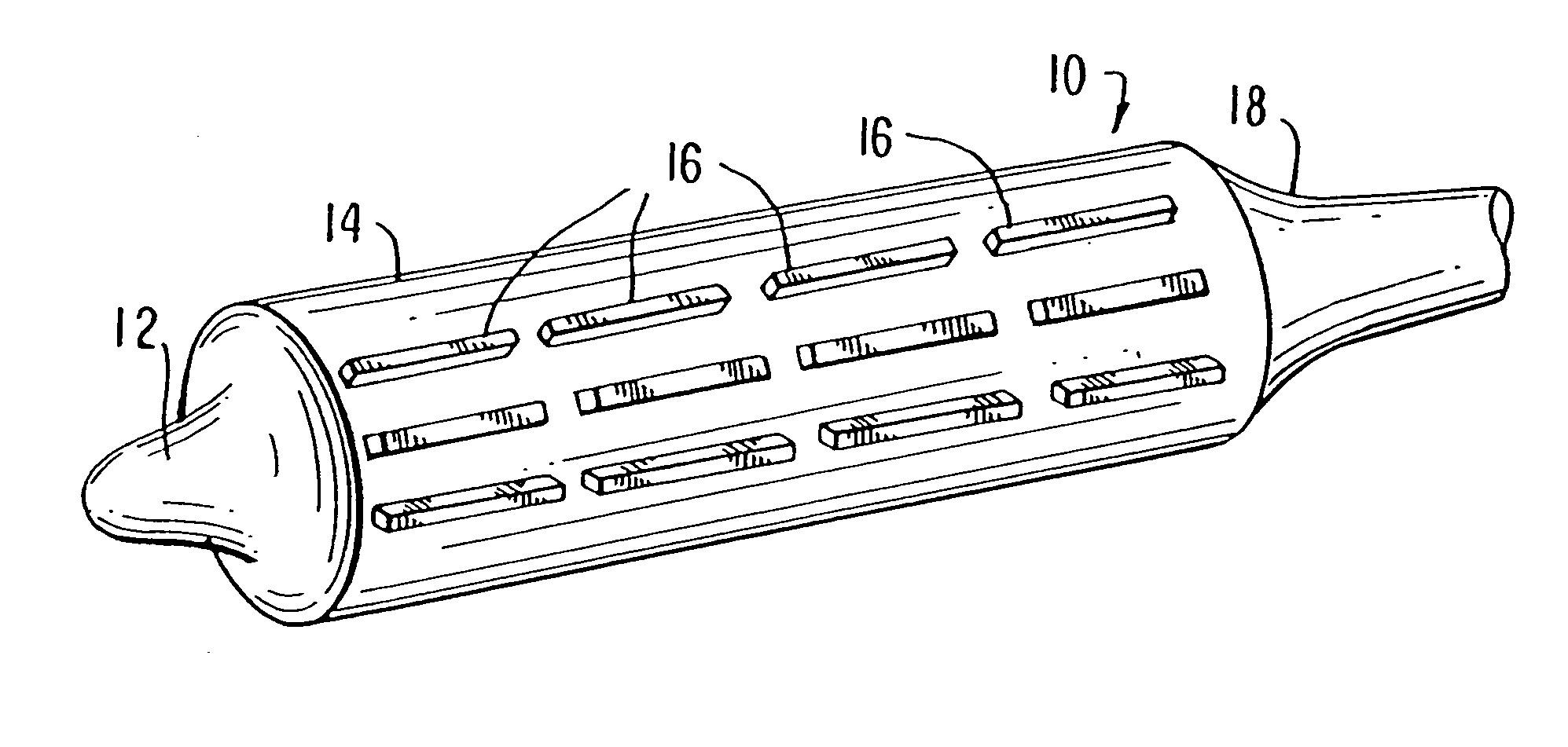
Locking component for an embolic filter assembly
A locking component for locking a medical device onto a guide wire. Such medical devices include, for example, an embolic filter assembly used to capture embolic material that may be created and released into a patient's vasculature during a stenting or angioplasty procedure. The embolic filter assembly tracks along the guide wire, and is delivered to a treatment site where it is locked in place and deployed. The locking component enables the filter assembly to lock onto any standard guide wire, and does not require a modified guide wire that has a specially-designed fitting or stop to accomplish the locking function.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Stent delivery system with diameter adaptive restraint
InactiveUS20050209670A1Improve space efficiencyWide applicabilityStentsBlood vesselsBody organsInsertion stent
Medical device and methods for delivery or implantation of prostheses within hollow body organs and vessels or other luminal anatomy are disclosed. The subject technologies may be used in the treatment of atherosclerosis in stenting procedures. For such purposes, a self-expanding stent may be deployed in connection with an angioplasty procedure with a stent delivery system having a diameter adaptive restraint. Upon withdrawal of the restraint, the stent is freed, while the restraint or connections thereto assumes a reduced diameter within a tubular body of the delivery guide.
Owner:BIOSENSORS INT GROUP
Progenitor Endothelial Cell Capturing with a Drug Eluting Implantable Medical Device
InactiveUS20070141107A1Stimulating positive blood vessel remodelingEnhance and accelerate formationStentsSurgeryProgenitorDrug-Coated Stents
A medical device for implantation into vessels or luminal structures within the body is provided, which stimulates positive blood vessel remodeling. The medical device, such as a stent and a synthetic graft, is provided with a coating with a pharmaceutical composition containing a controlled-release matrix and one or more pharmaceutical substances for direct delivery of drugs to surrounding tissues. The coating on the medical device further comprises one or more barrier layers, and a ligand such as a peptide, an antibody or a small molecule for capturing progenitor endothelial cells in the blood contacting surface of the device for restoring an endothelium at the site of injury. In particular, the drug-coated stents are for use, for example, in balloon angioplasty procedures for preventing or inhibiting restenosis.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Guidewire apparatus for temporary distal embolic protection
A guidewire apparatus for use during percutaneous catheter interventions, such as angioplasty or stent deployment. A protection element comprising a filter or an occluder is mounted near the distal end of a steerable guidewire, which guides a therapeutic catheter. The guidewire apparatus comprises a hollow shaft movably disposed about a core wire and, optionally, a slippery liner interfitted there between. The shaft and core wire control relative displacement of the ends of the protection element, causing transformation of the protection element between a deployed configuration and a collapsed configuration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Arterial obstruction treatment kit
A kit for performing angioplasty or stenting in a blood vessel, composed of at least two components. One of the components includes a first catheter providing a blood bypass flow path and carrying a blocking balloon and a blood vessel dilation device. Another one of the components includes a second catheter having an imperforate wall enclosing an axial lumen and having an open distal end, a hollow tube surrounding, and movable longitudinally with respect to, the second catheter, and a second blocking balloon carried by the hollow tube.
Owner:DON MICHAEL INT +1
Stiffened balloon catheter for dilatation and stenting
InactiveUS20050102020A1Improved stiffening memberStentsBalloon catheterStent graftingInsertion stent
The present invention pertains to a stiffened balloon which can be used in angioplasty, endovascular, and valvuloplasty procedures or as a delivery balloon to deliver a stent or a stent-graft. Longitudinally discontinuous stiffening members connected to the expandable balloon stiffen the balloon but allow it to be navigated through curved passages. Projections on the stiffening members may engage, incise, crush, fracture, or pierce occlusions or retain a stent or stent-graft. Radio-opaque portions may be referenced to determine orientation. Longitudinally continuous stiffening members bearing projections and connected to the balloon perform in a similar manner.
Owner:GRAYZEL JEFFREY +1
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal in arteries having collateral blood flow
InactiveUS20050149112A1Preventing ischemia and infarctionMinimizing embolizationStentsBalloon catheterAtherectomyBlood flow
The invention provides a medical device having a catheter and one or more expandable constricting / occluding members. The catheter is adapted for use with therapeutic or diagnostic devices, including an angioplasty / stent catheter and an atherectomy catheter. The constrictor / occluder is mounted at the distal end of the catheter. Manometers may be mounted distal to one or more constrictors for measuring pressure distal to the constrictor(s). Methods of using the devices are disclosed for preventing distal embolization during extracranial or intracranial carotid artery, vertebral artery, or coronary artery procedures, or procedures involving any vessel having collateral flow by reversing flow in the diseased vessel.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Apparatus and methods for reducing embolization during treatment of carotid artery disease
InactiveUS20050228432A1Reduce riskAvoid developmentGuide needlesBalloon catheterArterial diseaseGuide wires
Methods and apparatus are provided for removing emboli during an angioplasty, stenting or surgical procedure comprising a catheter having an occlusion element, an aspiration lumen, and a blood outlet port in communication with the lumen, a guide wire having a balloon, a venous return sheath with a blood inlet port, and tubing that couples the blood outlet port to the blood inlet port. Apparatus is also provided for occluding the external carotid artery to prevent reversal of flow into the internal carotid artery. The pressure differential between the artery and the vein provides reverse flow through the artery, thereby flushing emboli. A blood filter may optionally be included in-line with the tubing to filter emboli from blood reperfused into the patient.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Intravascular stent device
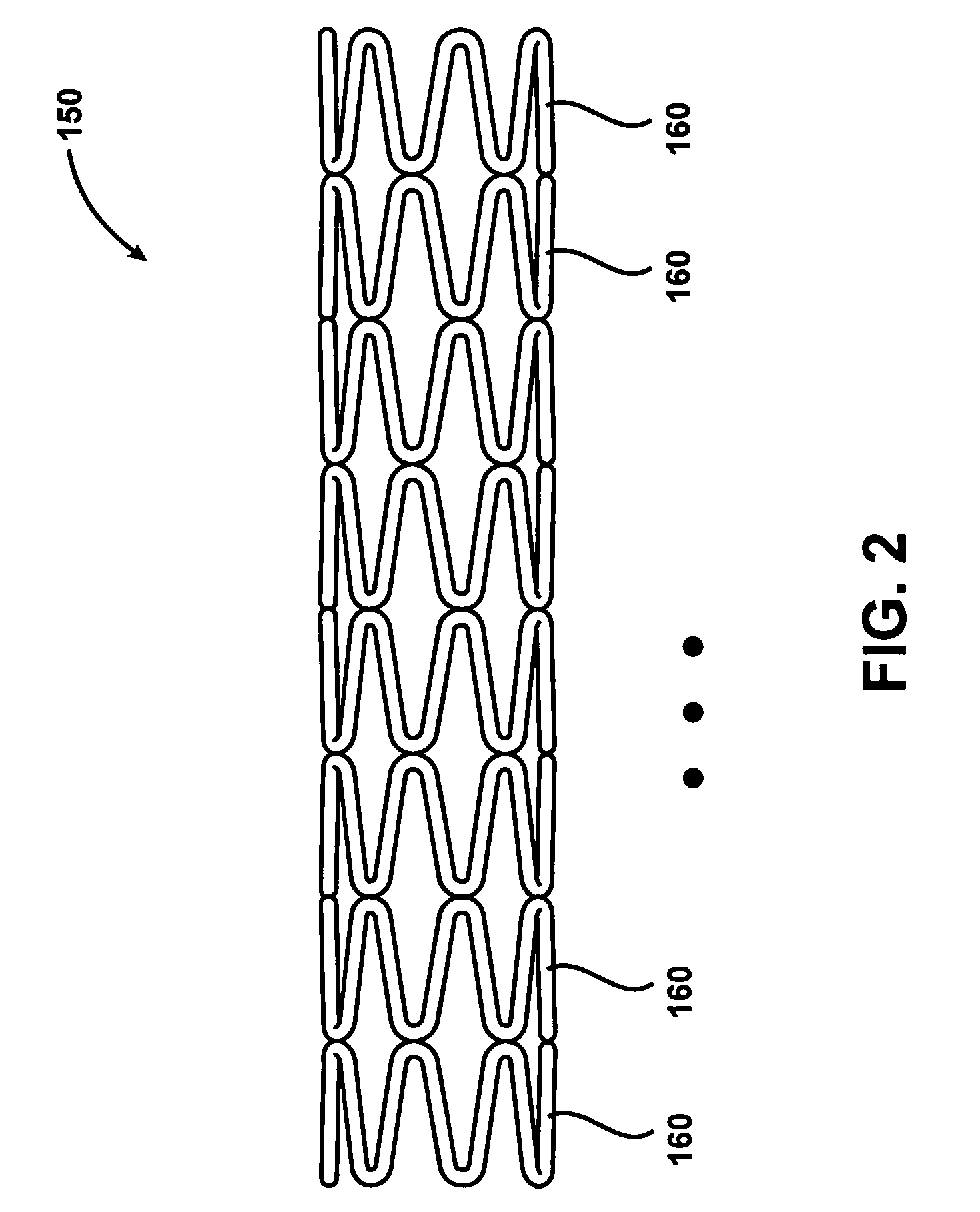
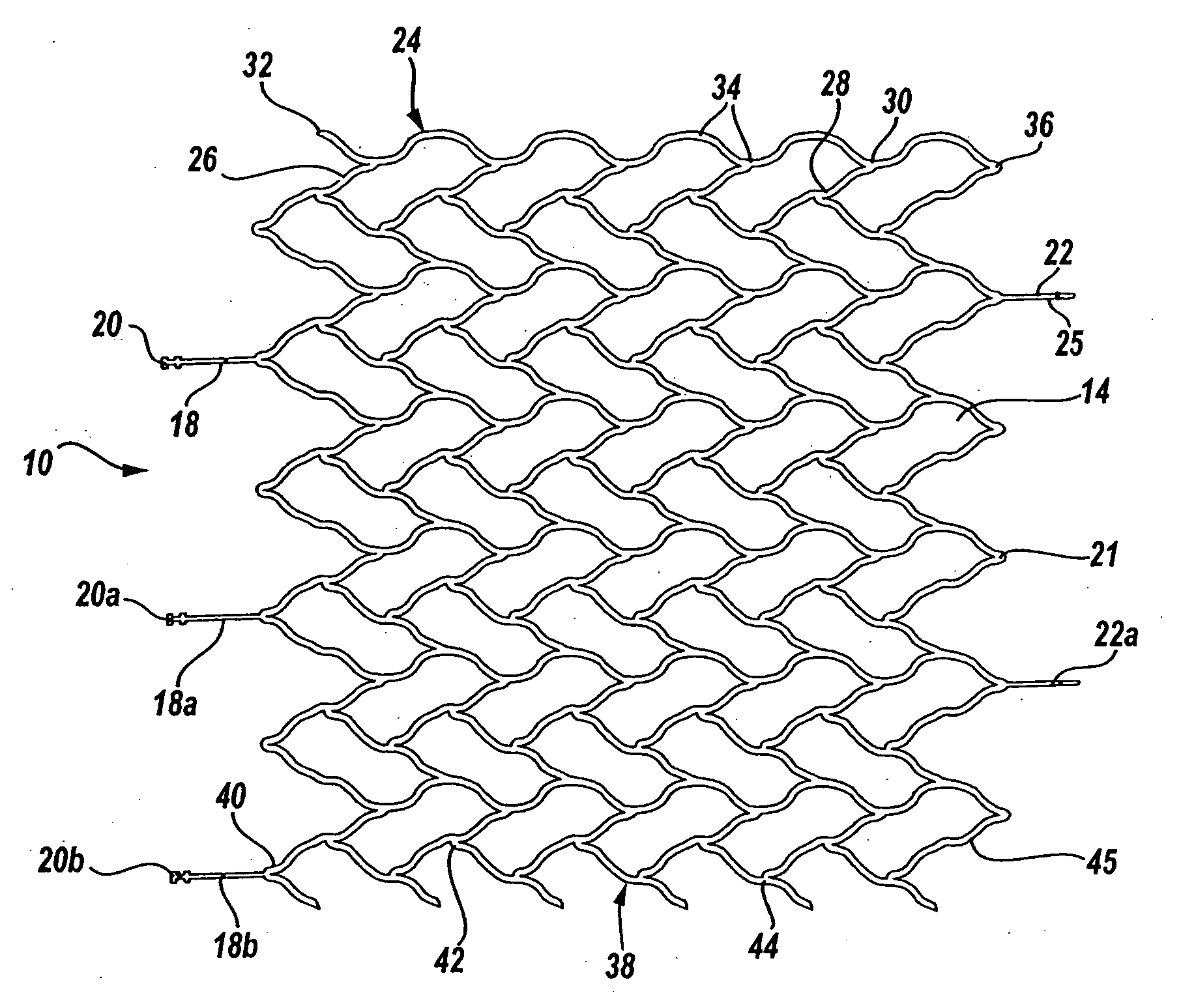
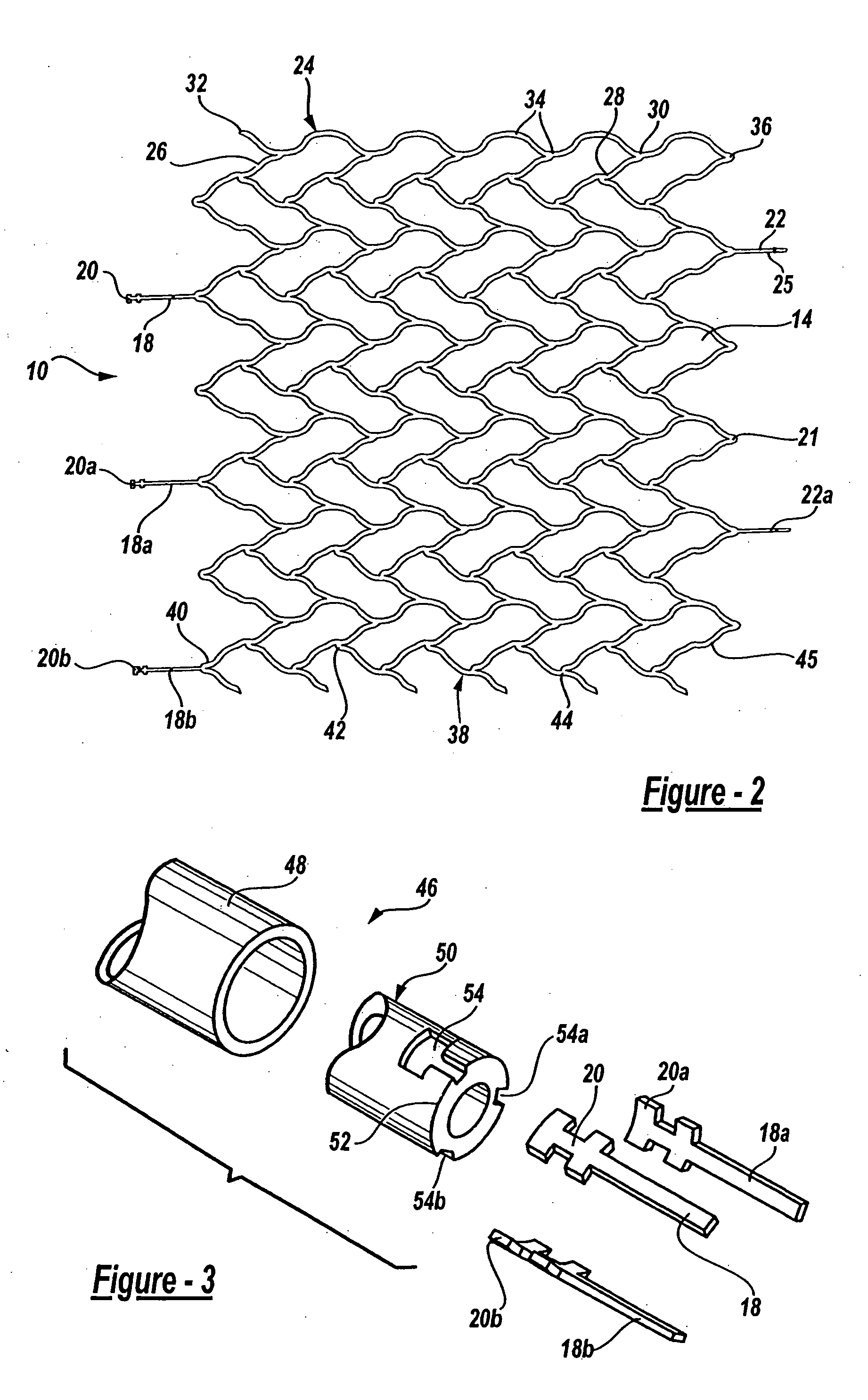
A very small diameter intravascular stent device which may be used in balloon angioplasty or in the treatment of an aneurysm in the human brain, which is comprised of a thin-walled skeletal cylindrical tube formed of undulating or sinusoidal elements which, when compressed, nest tightly with each other.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com