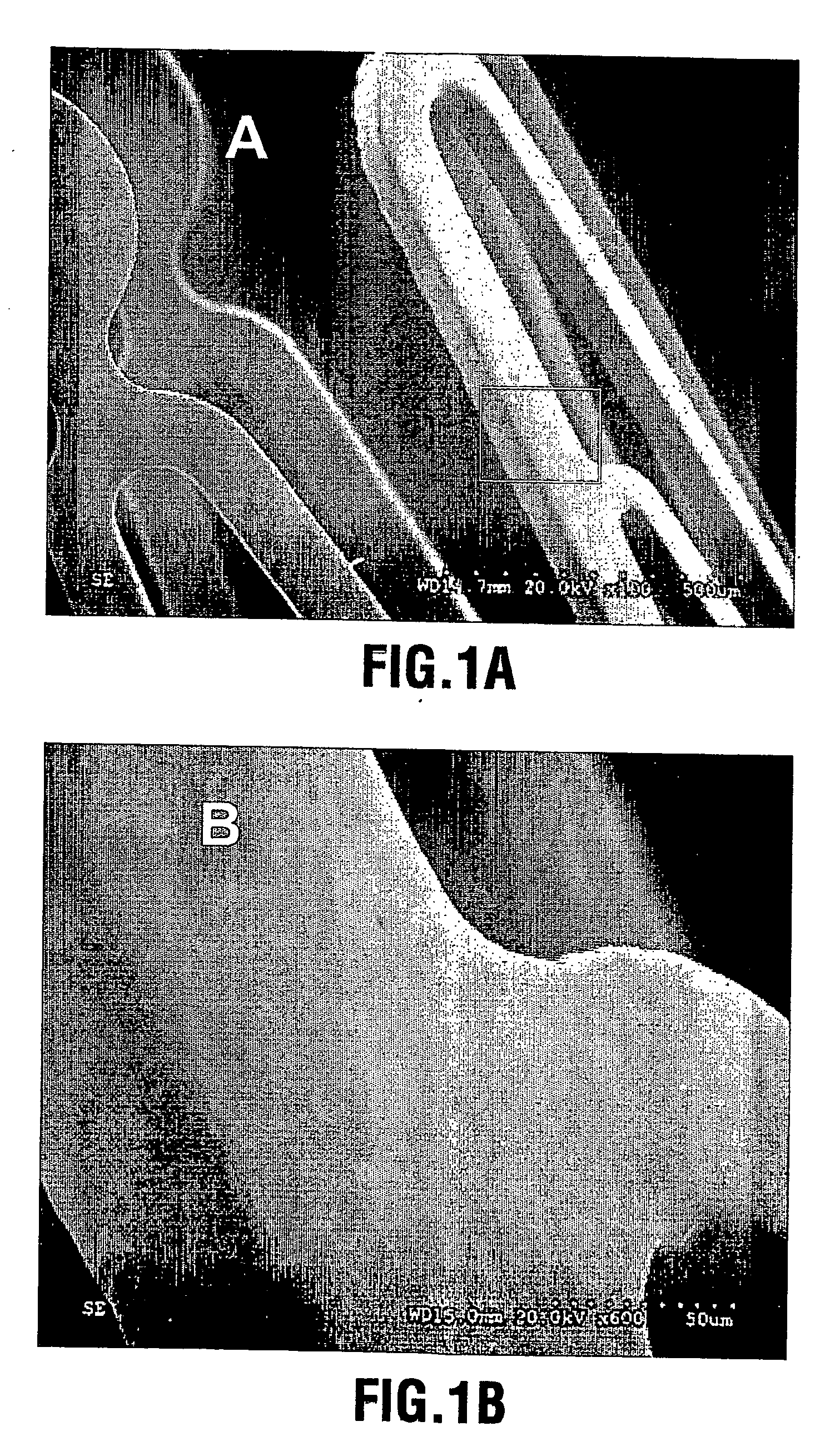
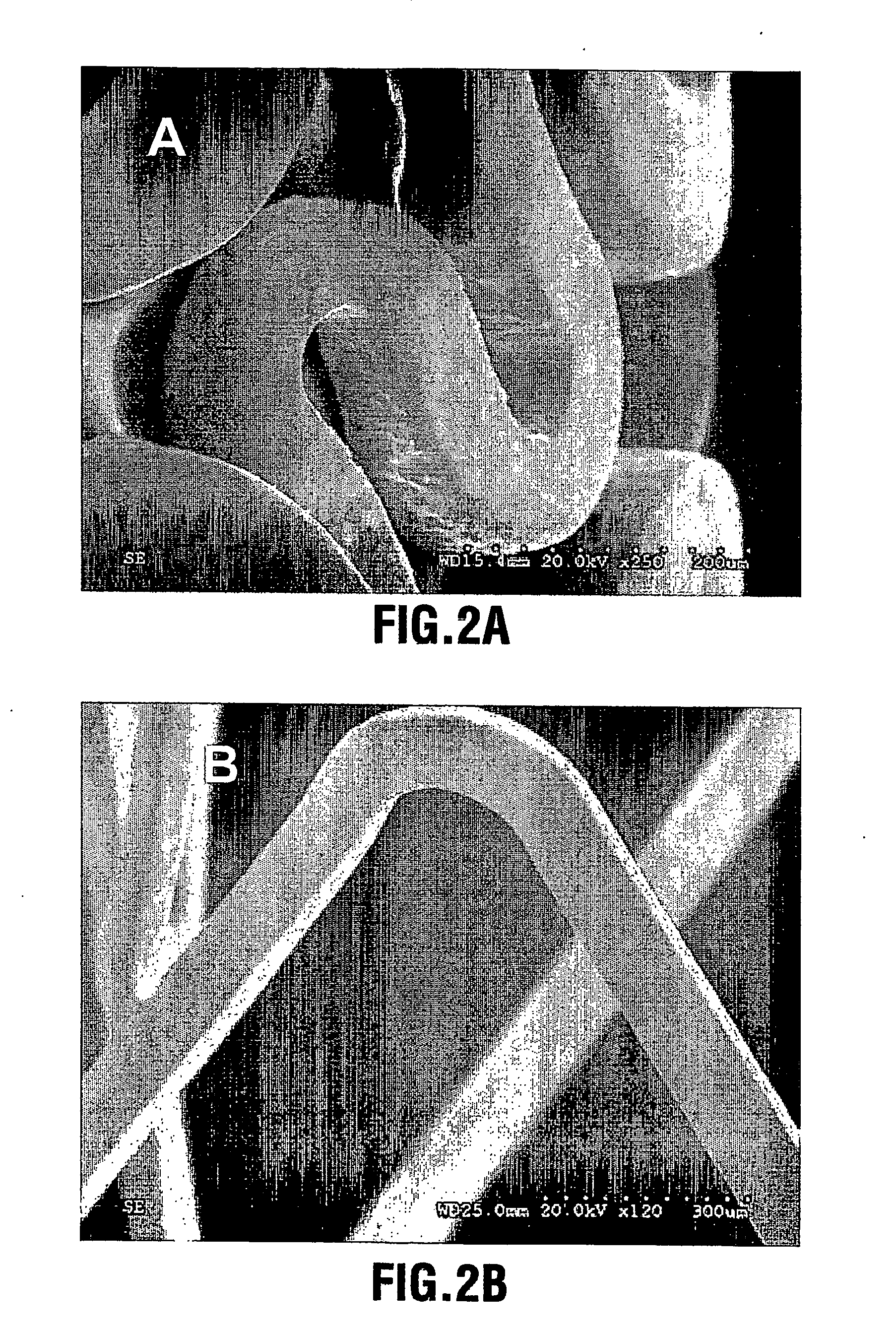
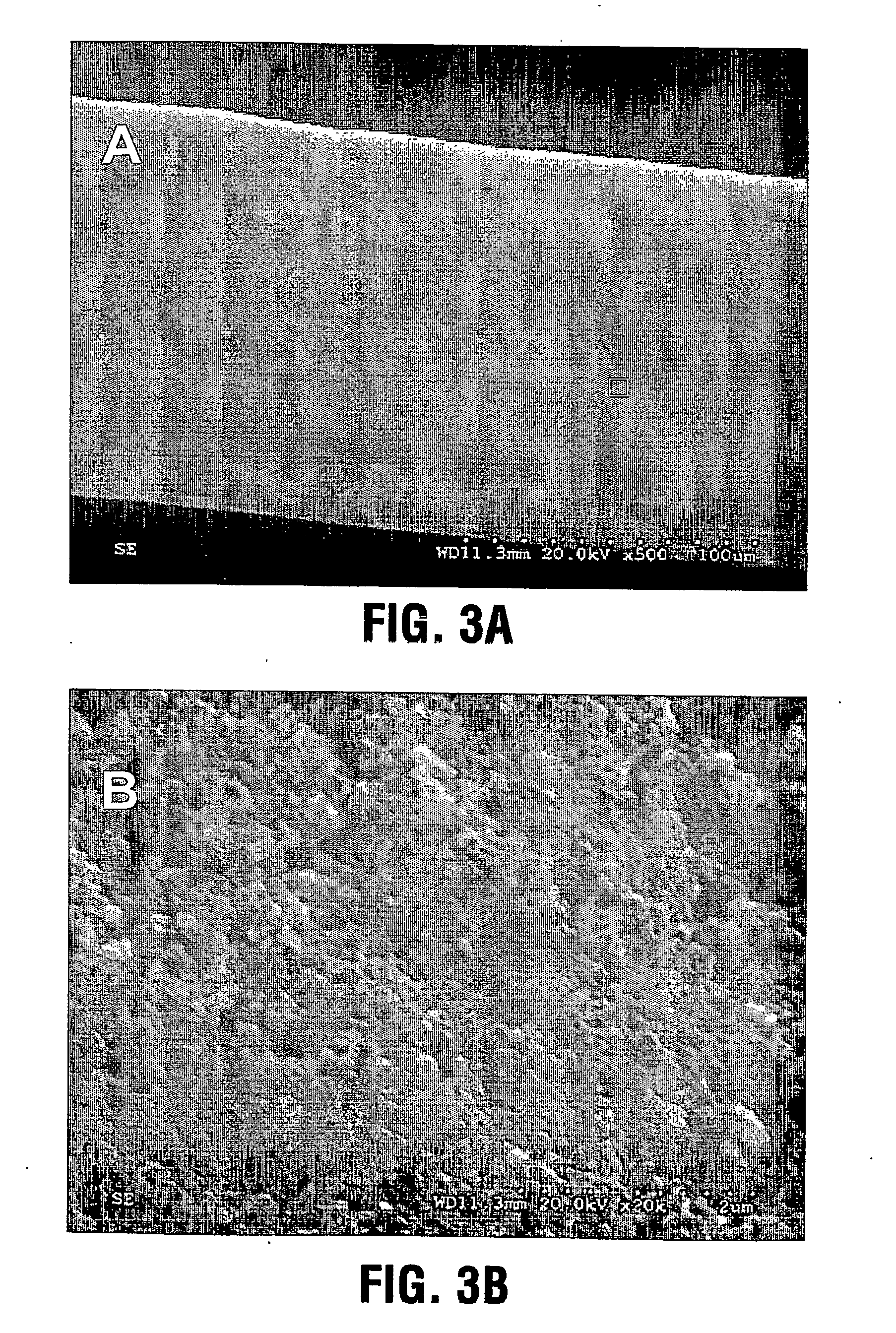
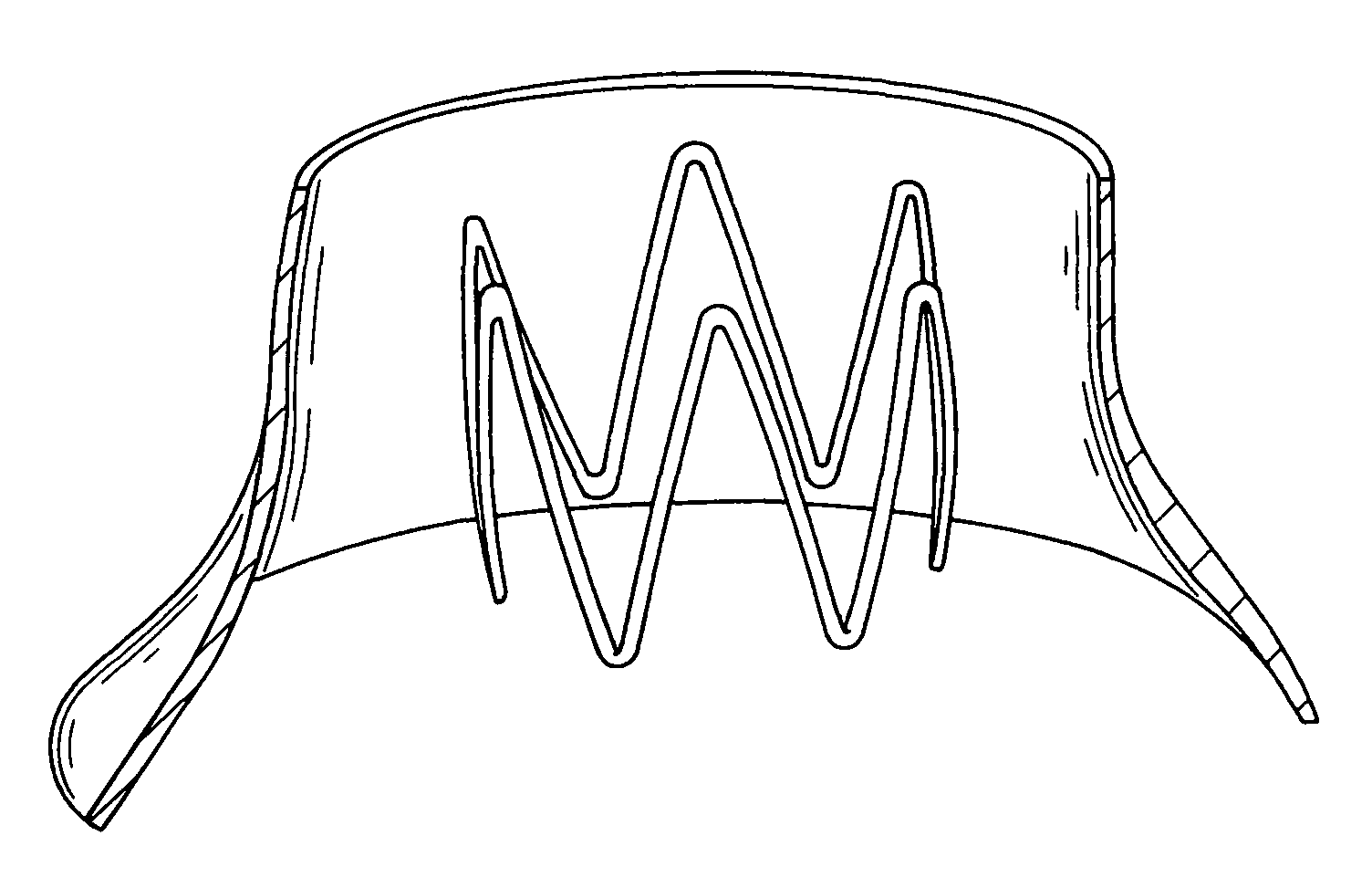
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
174 results about "Cardiovascular stent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cardiac stent is used to treat narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. It can also be used to improve blood flow immediately following a heart attack. Cardiac stents are expandable coils made of metal mesh. Your doctor can insert one during a coronary angioplasty, a nonsurgical and minimally invasive procedure.
Calcium phosphate coated implantable medical devices and processes for making same
InactiveUS20060134160A1Reduce porosityControlled release rateBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsCalcium phosphate coatingCardiovascular stent
This invention relates to novel calcium phosphate-coated implantable medical devices and processes of making same. The calcium-phosphate coatings are designed to minimize the immune response to the implant (e.g. restenosis in stenting procedures) and can be used to store and release a medicinally active agent in a controlled manner. Such coatings can be applied to any implantable medical devices and are useful for a number of medical procedures including (but not limited to) balloon angioplasty in cardiovascular stenting, ureteral stenting and catheterisation. The calcium phosphate coatings can be applied to a substrate as one or more coatings by a sol-gel deposition process, an aerosol-gel deposition process, a biomimetic deposition process, a calcium phosphate cement deposition process, an electro-phoretic deposition process or an electrochemical deposition process. The coating can contain and elude a drug in an engineered manner.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Biomedicine implant material with controllable degrading rate and its application
InactiveCN1857742AControl the rate of early degradationGuaranteed mechanical propertiesSurgeryProsthesisCardiovascular stentShort terms
The present invention relates to biomedicine metal implant material, and is especially biomedicine implant material with controllable degrading rate and its application. The biomedicine implant material with controllable degrading rate has a magnesium or magnesium alloy matrix and a coated degradable polymer layer with thickness controlled within 0.01-5 mm. The biodegradation is completed step by step so as to ensure the mechanical performance of the material during degradation and match the degradation rate with the service period of the implanted device. The biomedicine metal implant material of magnesium or magnesium alloy may be used in preparing temporary or short term implanted device, such as degradable blood rack and peripheral rack, bone fracture plate and bone nail for inner fixing, tissue engineering rack, etc.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Virtual prototyping and testing for medical device development
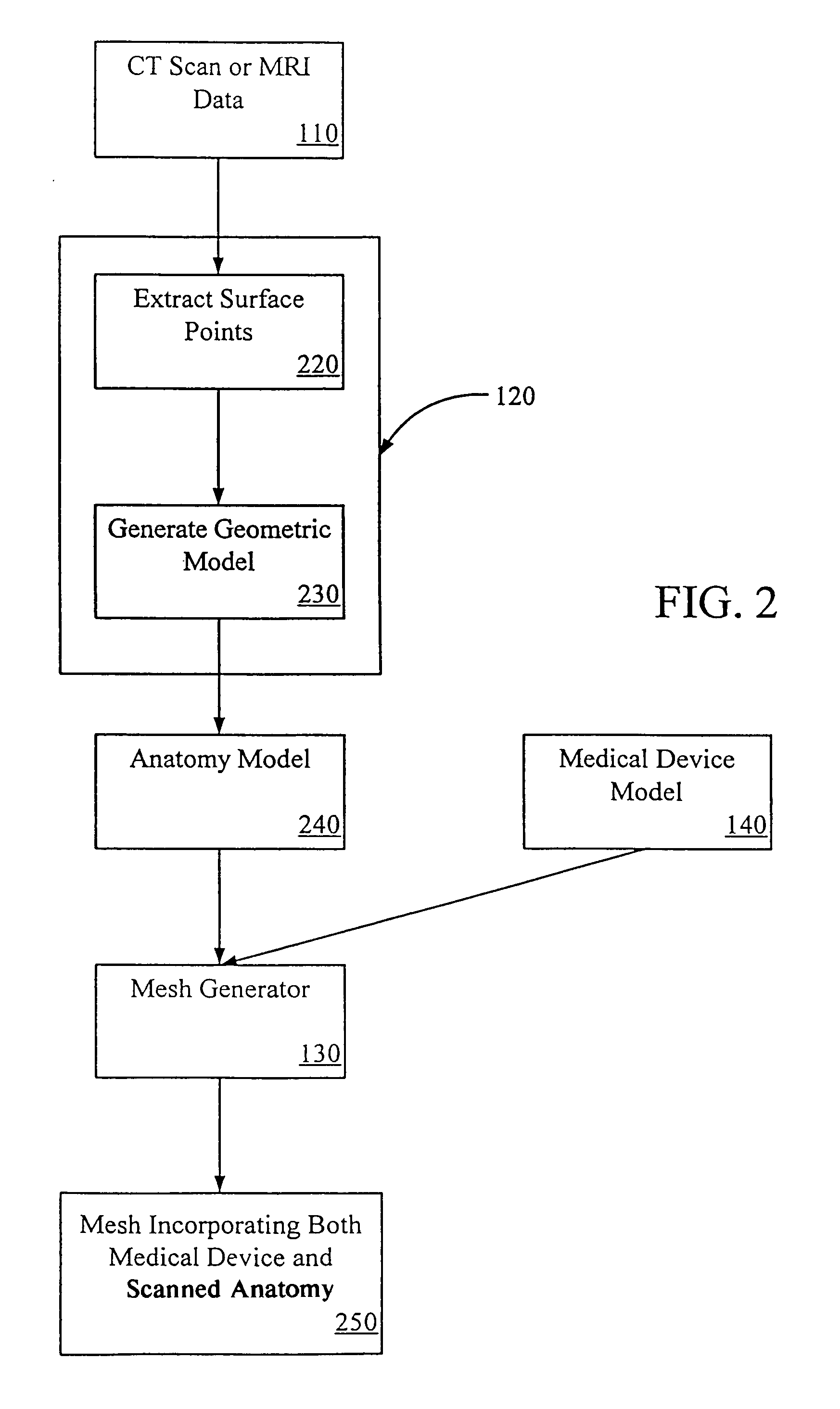
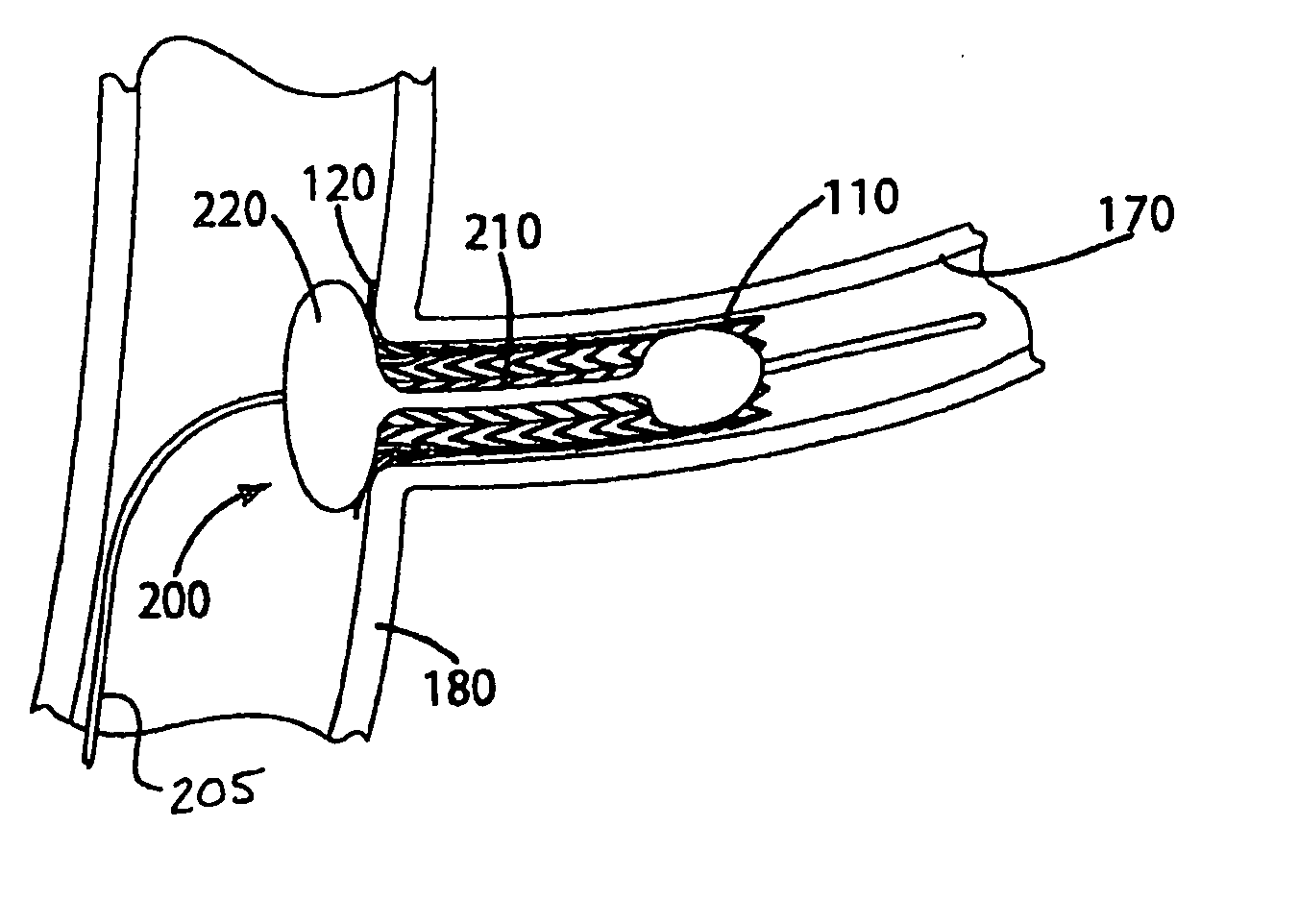
A system and method of developing better-designed medical devices, particularly cardiovascular stents and endovascular grafts. The system comprises a geometry generator, a mesh generator, a stress / strain / deformation analyzer, and a visualization tool. In one embodiment, the geometry generator receives three-dimensional volumetric data of an anatomical feature and generates a geometric model. The mesh generator then receives such geometric model of an anatomical feature or an in vitro model and a geometric model of a candidate medical device. In another embodiment, the mesh generator only receives a geometric model of the candidate medical device. Using the geometric model(s) received, the mesh generator creates or generates a mesh or a finite element model. The stress / strain / deformation analyzer then receives the mesh, and the material models and loads of that mesh. Using analysis, preferably non-linear analysis, the stress / strain / deformation analyzer determines the predicted stresses, strains, and deformations on the candidate medical device. Such stresses, strains, and deformations may optionally be simulated visually using a visualization tool.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Medicine eluted cardiovascular frame and its preparing process
InactiveCN1355005AContinuous and stable releasePromote healingStentsCoatingsCardiovascular stentEthylene Homopolymers
A medicine eluted cardiovascular frame is composed of expandible support and the medicine coated biodegradable layer coated on the said frame. The said biodegradable material contains one of the homopolymer and copolymer of glycollide, L-lactide or epsilon-caprolactone, and the copolymer of multi-group amino acids. The medicine can resist the cardiovascular narrowness. The process for preparing the said support includes such steps as preparing the said expandible support, immersing it in the mixture of the said medicine, biodegradable material and solvent, and drying. It can prevent thrombosis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Ostial stent and balloon
InactiveUS20070038283A1Less subject to movementLess to other complicationStentsBlood vesselsCardiovascular stentFlange
A cardiovascular stent and a stent balloon have portions that provide different degrees of expandability. A distal stent portion has a first degree of expandability to support a vessel, while a proximal stent portion has a second, higher degree of expandability so that it can be radially expanded to form a flange-like structure at an inlet to the vessel. The balloon is configured to deploy the stent and includes distal and proximal balloon portions having different diameters corresponding to the distal and proximal stent portions. The balloon portions may be individually inflated. Optionally, a first stent may be deployed through one branch of a bifurcation, and a second stent may be deployed through a wall of the first stent and into another branch of the bifurcation. The flange on the second stent may position and / or secure the second stent within the first stent.
Owner:SQUAREONE ACQUISITION
Method for preparing cardiovascular drug eluting stent
ActiveCN1569270AGood wetting and spreadingHigh bonding strengthSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCardiovascular drugCardiovascular stent
A process for preparing cardiovascular stent with a drug coating layer on its surface is disclosed. It includes the steps of: 1. pretreatment for the stent surface by plasma 2. dipping or spraying of the stent surface in routine method by hyperplasia proof drug and coating polymer containing solution The drug coated stent prepared by the present invention can endure long period washing by all kinds of stress and body fluid in the stent transportation and dilation process, with the coating layer not easy to falling off.
Owner:SHANGHAI REBONE BIOMATERIALS +1
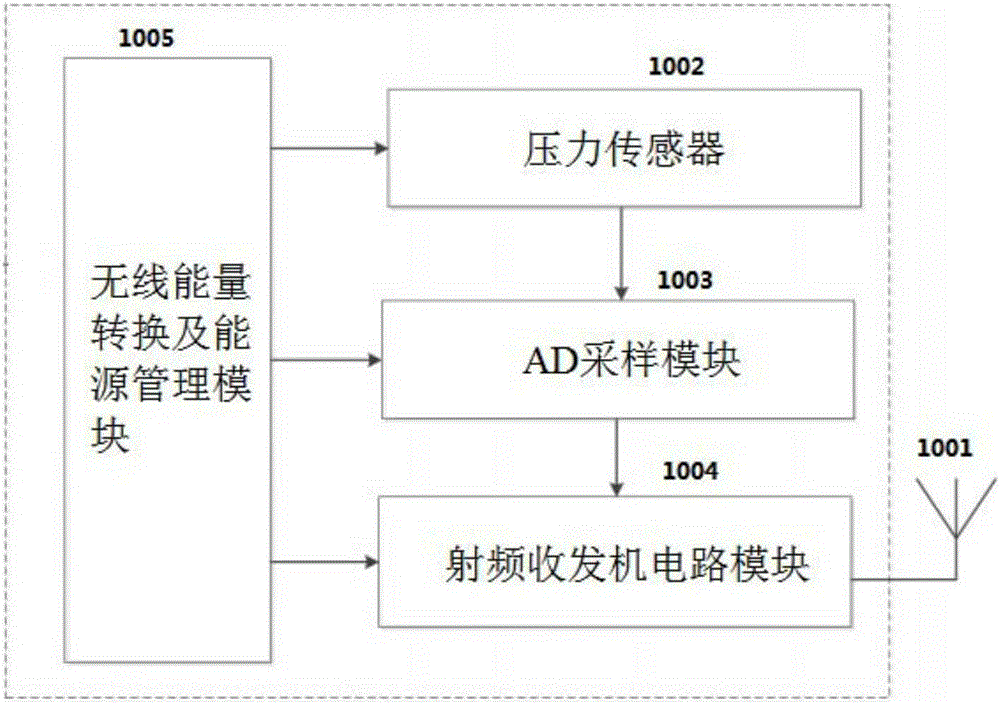
In vivo wireless sensing system based on cardiovascular stent
PendingCN105193529AEasy to implantQuick understandingStentsEvaluation of blood vesselsCardiovascular stentTransceiver
The invention discloses an in vivo wireless sensing system based on a cardiovascular stent. The in vivo wireless sensing system comprises the cardiovascular stent, a radio frequency transceiver circuit module mounted on the cardiovascular stent and a pressure sensor, wherein the cardiovascular stent is used as the vascular stent and an antenna of the system at the same time, so as to achieve energy and information interaction with the outside; the pressure sensor is used for collecting blood pressure data in blood vessels; the radio frequency transceiver circuit module codes, modulates, outputs and sends the data information obtained by the pressure sensor to the cardiovascular stent, and sends a wireless signal outwards by adopting the cardiovascular stent as the antenna; the radio frequency transceiver circuit module also receives an external signal received by the cardiovascular stent, and interprets the external signal. According to the in vivo wireless sensing system, a special antenna structure is not needed, so that the system is conveniently implanted into human bodies; besides, as real-time blood pressure monitoring is realized, patients and medical staff can quickly and timely know the blood pressure state.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Degradable magnesium alloy bio-implantation material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104498790ANo toxicityImprove corrosion resistanceProsthesisCardiovascular stentInsertion stent
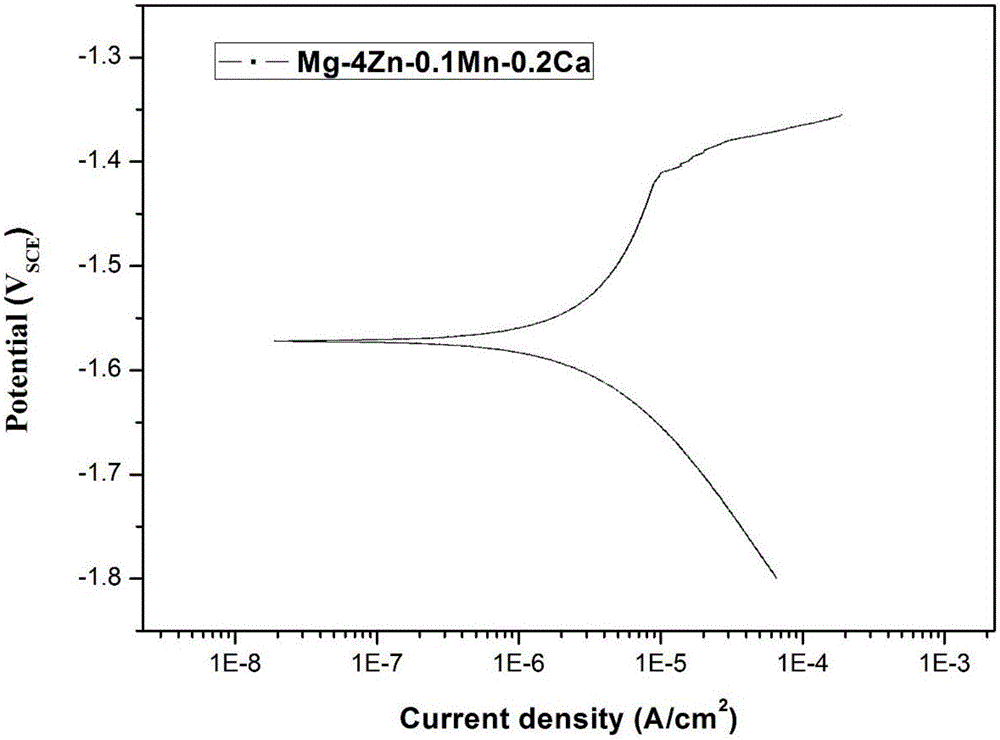
The invention relates to a degradable magnesium alloy bio-implantation material which is characterized by consisting of the following components in percentage by mass: 0-12% of Zn, 0-10.5% of Ca and the balance of Mg and unavoidable impurities carried by the raw materials, wherein the total content of Zn and Ca is higher than or equal to 1.0%; the total content of unavoidable impurities is higher than or equal to 0.005%; in the unavoidable impurities, the content of Fe is lower than or equal to 0.0005%, the content of Ni is lower than or equal to 0.0005%, and the content of Cu is lower than or equal to 0.001%; and the invention also relates to a preparation method of the degradable magnesium alloy bio-implantation material. The degradable magnesium alloy bio-implantation material provided by the invention is non-toxic to a human body, has good corrosion resistance and good strength, and is suitable to be used for preparing magnesium alloy bio-implantation devices such as bone nails, bone plates and cardiovascular stents.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON SCI ACADEMY NINGBO BRANCH
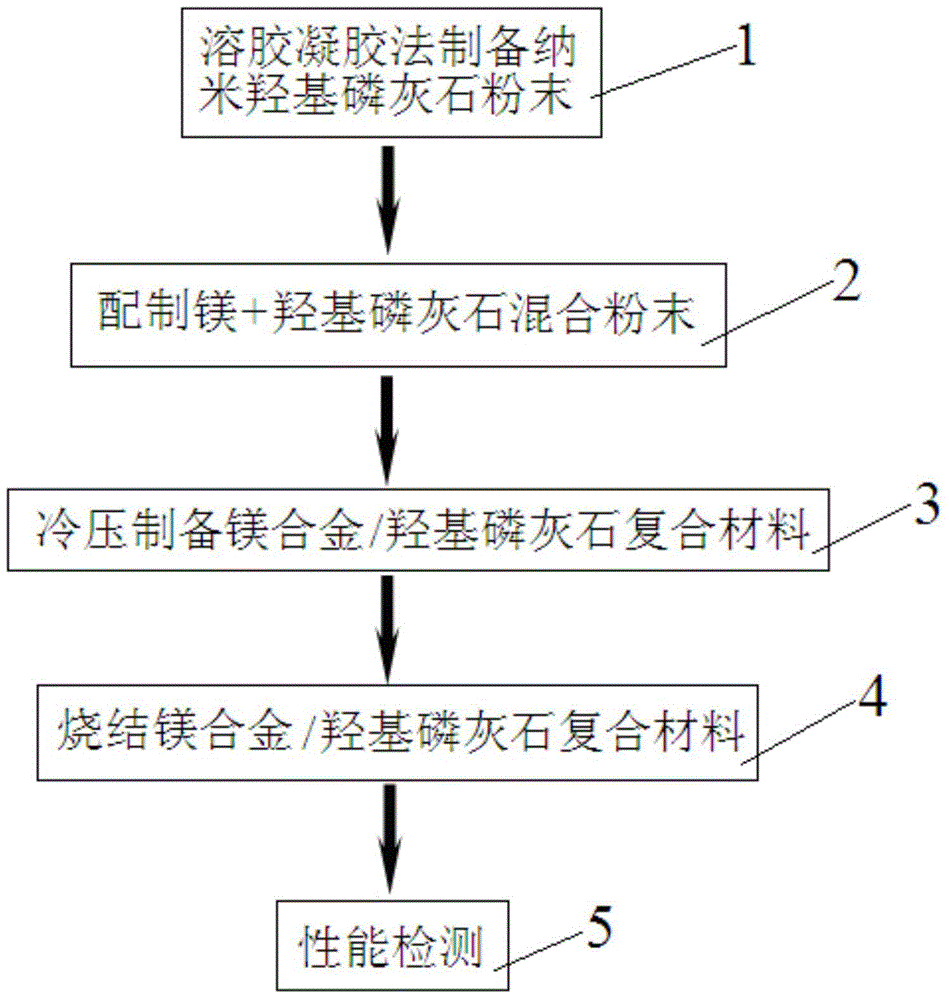
Preparation method of magnesium alloy/hydroxyapatite composite
InactiveCN103599561ADegradability adjustableDegradative regulationSurgical adhesivesProsthesisSolubilityCardiovascular stent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a magnesium alloy / hydroxyapatite composite, which comprises the steps of firstly preparing nano hydroxyapatite powder by a sol-gel process, and then uniformly mixing the magnesium powder with the nano hydroxyapatite powder; putting the mixture into a mould and performing cold pressing; putting the cold-pressing formed sample into a vacuum heat treatment furnace for sintering to obtain the magnesium alloy / hydroxyapatite composite. Compared with the prior art, in the method provided by the invention, the magnesium alloy is used as a metal matrix, the hydroxyapatite with the same chemical composition as the human skeleton and having low solubility in the human body environment is used as a reinforcing body, and the method aims at preparing a magnesium alloy / calcium phosphate composite biomedical material by use of a powder metallurgical process; the material is mainly applied to clinical medicine as a degradable endosteal fixing material, a porous bone repair material, a dental implantation material, an oral repair material, a cardiovascular stent and the like, and has broad prospects in terms of bone tissue defect repair.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method and devices for preventing restenosis in cardiovascular stents
Described herein are devices and methods fabricating devices having nanostructures that allow adhesion or growth of one cell type, such as endothelial cells, more than another cell type, such as smooth muscle cells. In particular, stent covers having such nanostructures are described, and methods for fabricating these stent covers. Also described herein are methods for optimizing the nanostructures forming the devices.
Owner:MONARCH BIOSCI INC
Drug coating-spraying method for drug eluting stent and spraying apparatus therefor
This invention is about a process for painting drug elution vas internal support and the painting apparatus. It is a process for painting cardiovascular support and the painting apparatus. This invention solves the problem of heterogeneous painting and great material consumption in current support. The painting preparation processes mainly contain cleaning, drying and spraying to prepare drug coating. The painting apparatus mainly contain: support, nozzle, solution bottle, plastic hose, flow instrument, high-pressure tank, nozzle, ultrasonic atomizer, adjustable rotary table and flume. The downside of the support strut connects with the adjustable rotary table; the solution bottle connects with high-pressure tank by the flow instrument, the ultrasonic atomizer, whose top connects with the solution bottle, is installed in the flume. The uniform drug coating is formed by painting ultrasonic nebulized aerosol fogdrop on the surface of the support of certain movement state. This invention can not only paint heterogeneously and decrease surface roughness of support, but also can greatly save painting material.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Full-degradable magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105671391AGood biocompatibilityControllable degradation rateSurgeryCardiovascular stentBiocompatibility Testing
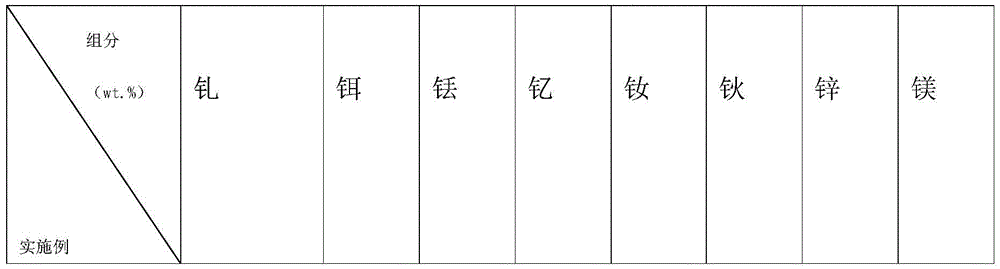
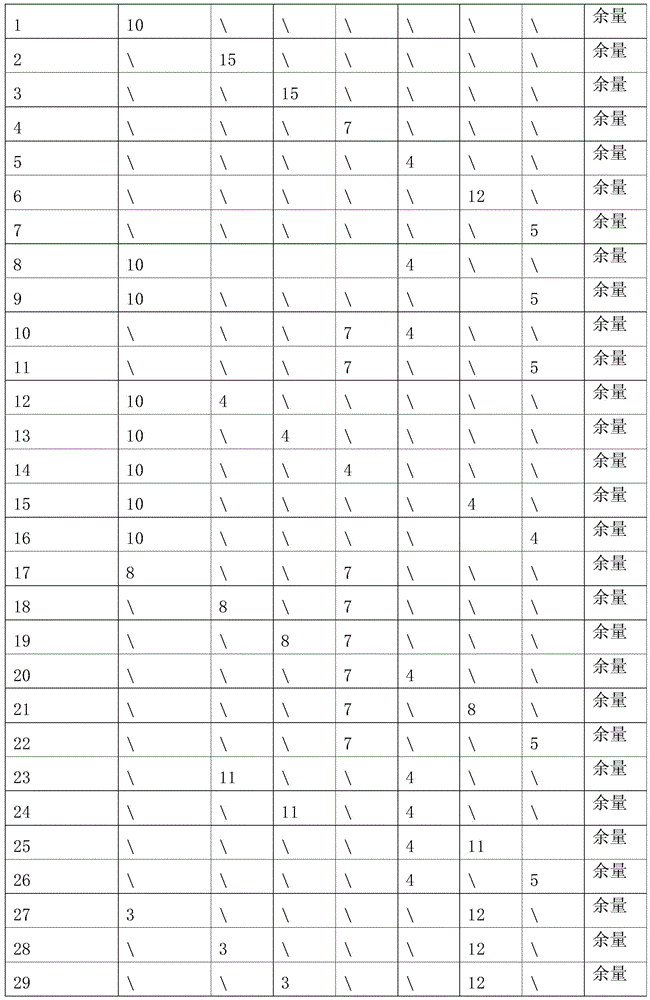
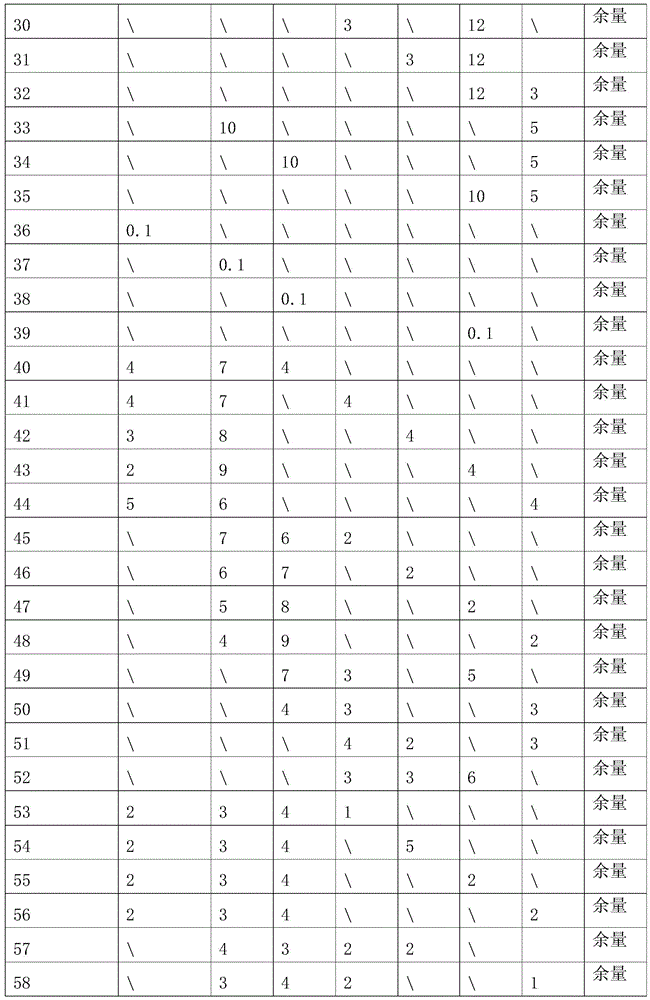
The invention discloses a novel full-degradable magnesium alloy cardiovascular stent material. A full-degradable magnesium alloy comprises magnesium and alloy elements, wherein the weight ratio of the magnesium is not smaller than 85%, and the alloy elements include a combination of one or more of gadolinium, erbium, thulium, yttrium, neodymium, holmium and zinc. Mechanical properties of the full-degradable magnesium alloy can meet requirements of cardiovascular biological stents, in-vitro immersion corrosion tests and electrochemical corrosion tests prove that the in-vitro corrosion resistance of the full-degradable magnesium alloy is good, in-vitro cytotoxicity tests of the full-degradable magnesium alloy indicate the good biocompatibility, the degradation velocity is controllable, and the biocompatibility is good.
Owner:周倩 +1
Bioabsorbable polymeric medical device
In embodiments there is described a cardiovascular tube-shaped lockable and expandable bioabsorbable scaffold having a low immunogenicity manufactured from a crystallizable bioabsorbable polymer composition or blend.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL INC
Manufacturing method of magnesium alloy cardiovascular stent, stent and perform of stent
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a magnesium alloy cardiovascular stent, the stent and a perform of the stent, aiming at solving the technical problems of an existing magnesium alloy stent manufacturing method which is complex in process and high in cost. The method comprises the following steps: manufacturing the perform of the magnesium alloy cardiovascular stent; sputtering a magnesium alloy target material on the surface of the perform through magnetron sputtering; and immersing the perform which is sputtered with the magnesium alloy target material in an alcohol solution or water solution, so that the perform is dissolved to obtain the magnesium alloy cardiovascular stent, wherein the perform is prepared by printing on the basis of a 3D printing technology, and the perform comprises a stent main body and a liner; the stent main body is a tubular body of a meshed structure; the meshed structure of the tubular body is composed of axial ribs and beam ribs; the cross sections of the axial ribs are of trapezoidal structures; the side faces of the beam ribs are inclined inwards the tubular body; and the liner is of a tubular structure which is arranged on the inner side of the tubular body. The design of the trapezoidal cross sections of the axial ribs and the liner is conducive to the dissolving and peeling of the perform, and the appearance of burrs during magnetron sputtering is avoided, the process is simplified and the cost is reduced.
Owner:深圳尤尼智康医疗科技有限公司
Iron-based composite material used for full-degradation cardiovascular support and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102961787AFulfil requirementsIncrease corrosion rateSurgeryCoatingsCardiovascular stentCarbon nanotube
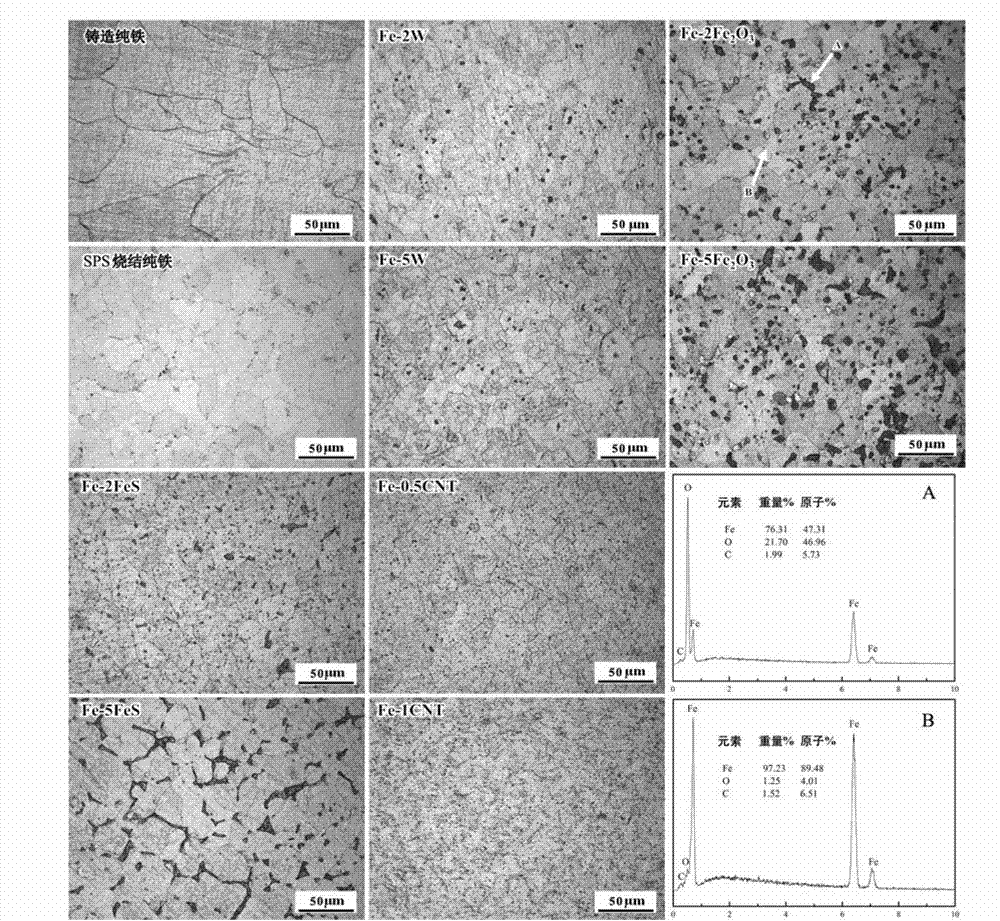
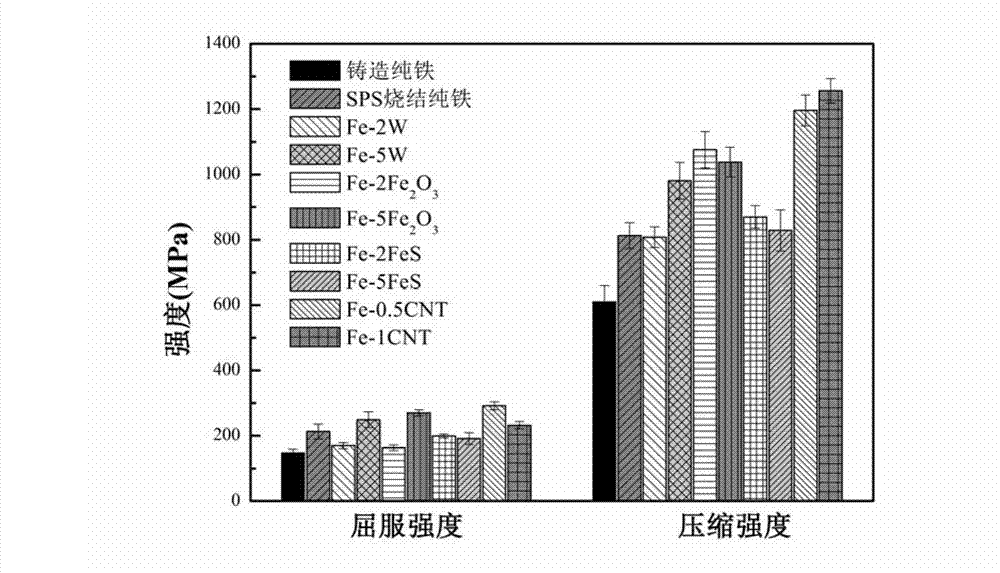
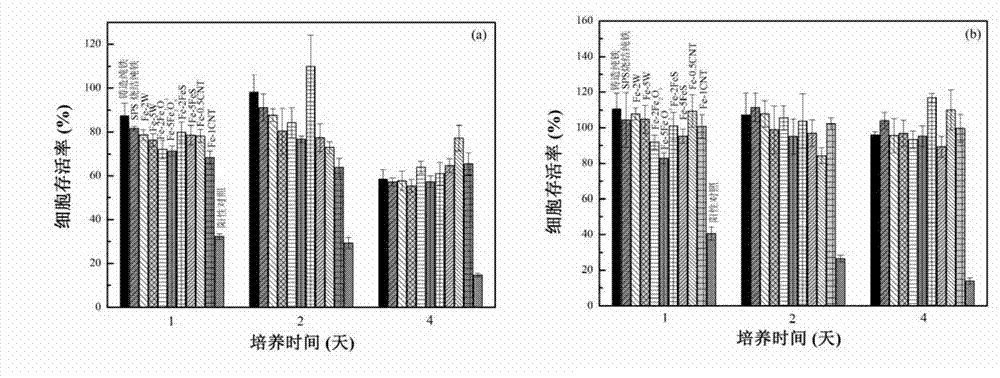
The invention discloses an iron-based composite material used for a full-degradation cardiovascular support and a preparation method thereof. The iron-based composite material comprises Fe and any one of W, Fe2O3, FeS and carbon nano tube, wherein the content of any one of W, Fe2O3, FeS and carbon nano tube is 0-10% and more than 0% in the iron-based composite material in percent by weight. The preparation method of the iron-based composite material comprises the following steps of: mixing iron powder with any one of tungsten powder, Fe2O3 powder, FeS powder and carbon nano tube powder, then carrying out spark plasma sintering or sintering by virtue of powder metallurgy, and cooling, so that the iron-based composite material is obtained. The iron-based composite material used for full-degradation cardiovascular support disclosed by the invention overcomes the defects of the traditional inert metal support such as late thrombosis and restenosis; and a secondary phase harmless to a human body is selected as a strengthening phase of the composite material, so that corrosion rate of an iron base in a body fluid environment is increased, and corrosion of the iron base is more uniform.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Degradable multi-layer Mg/Zn composite material for medical use and preparation method thereof
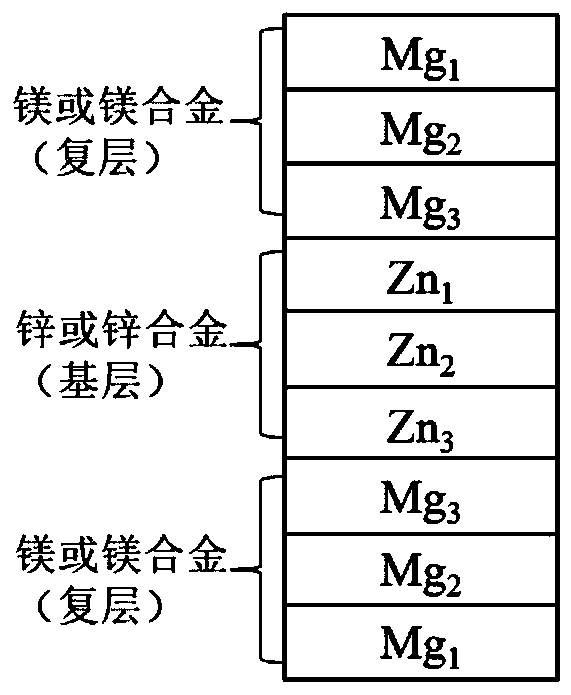
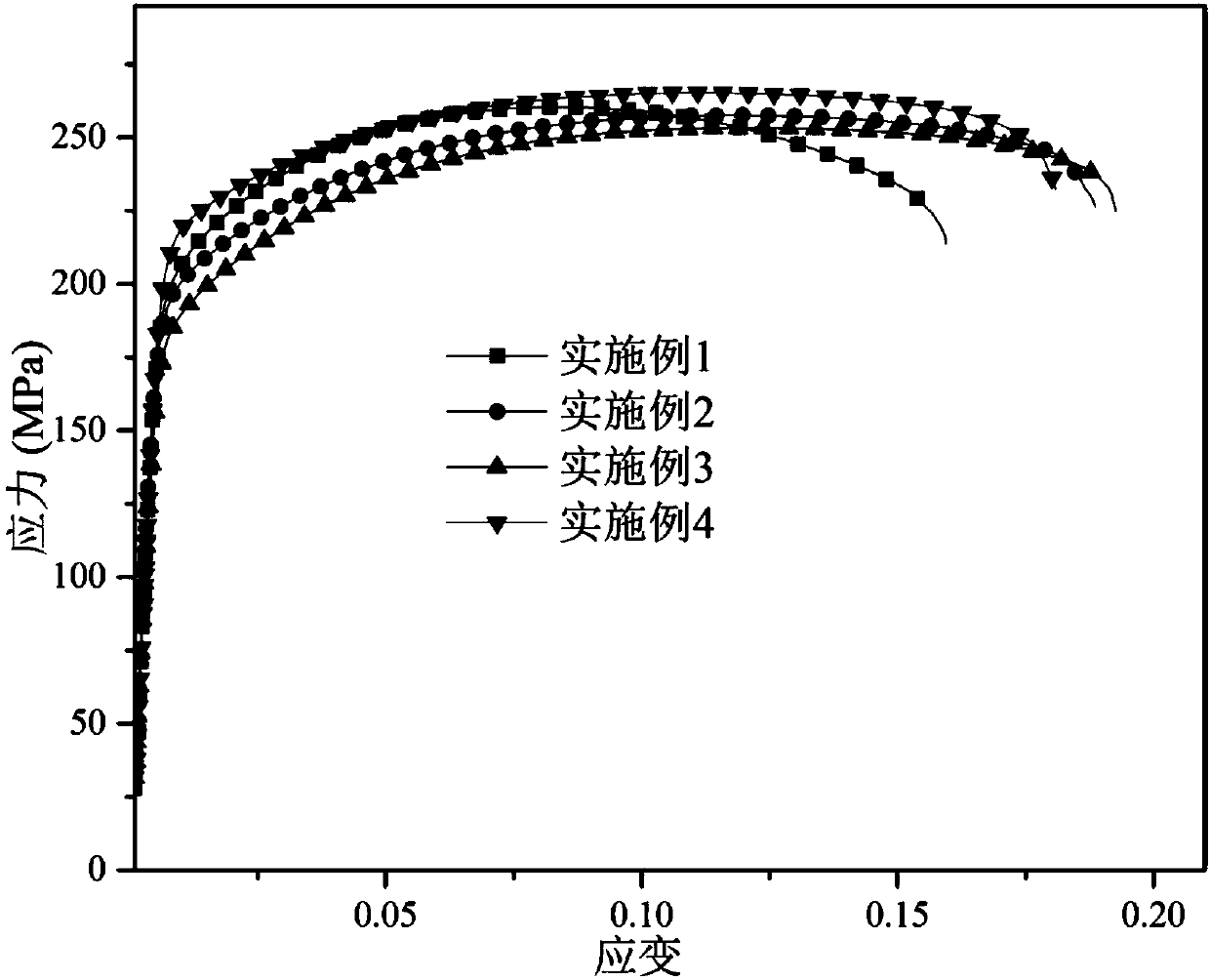
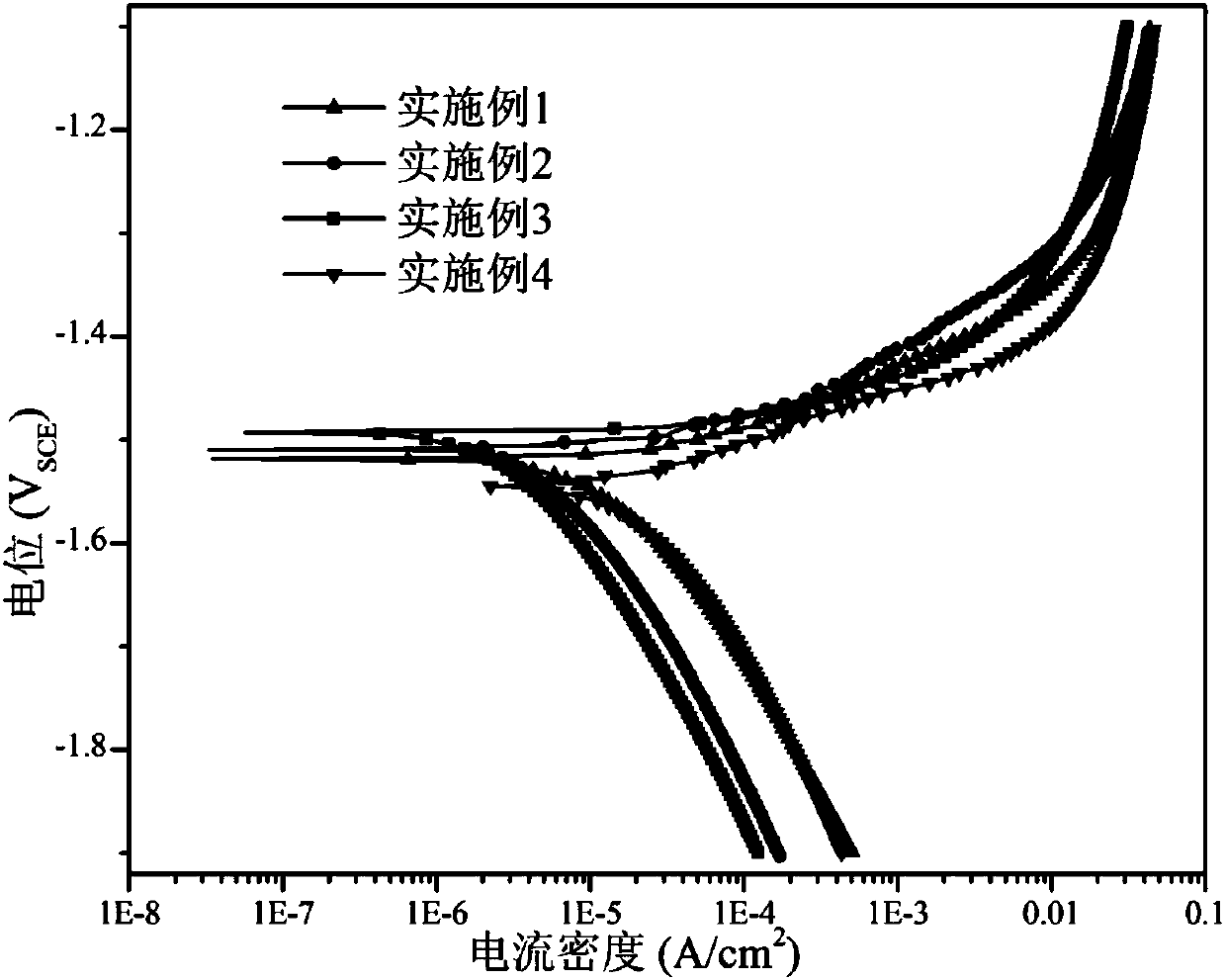
ActiveCN111450322ALow elastic modulusGood biocompatibilitySurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCardiovascular stentMg alloys
The invention provides a multi-layer Mg / Zn laminated composite material for medical use and a preparation method thereof. The composite material comprises composite layers and base layers, wherein thecomposite layers are made of pure magnesium or magnesium alloy; and the base layers are made of a corrosion-resistant, high-strength and high-plasticity zinc alloy for medical use. The magnesium composite layers are arranged in an ordered manner according to self-corrosion potential, so that corrosion laterally develops layer by layer and strong galvanic corrosion between the magnesium layers andthe zinc layers is prevented. In addition, through the magnesium composite layers, the composite material has a lower elasticity modulus than zinc, and the stress shielding effect is effectively mitigated. The composite material has good biocompatibility of the magnesium and excellent mechanical property of the zinc. When implants, such as a bone screw, a bone plate and a stent prepared from thecomposite material play a medical role after being implanted, the zinc base layer bears more than 50% of load. In the early stage after implantation, the magnesium composite layers are in direct contact with bone tissues and promote the growth and healing of the bone tissues or recirculate blood as cardiovascular stents. Finally, the composite material is completely degraded in vivo, and the complete degradation time is 8-18 months.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Metal implant material with controllable corrosion and degradation and its application
InactiveCN1857744AHigh strengthIncrease stiffnessSurgeryPharmaceutical containersCardiovascular stentImplanted device
The present invention relates to biomedicine metal implant material, and is especially metal implant material with controllable erosion and degrading rate and its application. The metal implant material with controllable erosion and degrading rate is magnesium or magnesium alloy with poor anticorrosive property. The metal implant material with controllable erosion and degrading rate of magnesium or magnesium alloy may be used in preparing temporary or short term implanted device, such as degradable blood rack and peripheral rack, bone fracture plate and bone nail for inner fixing, tissue engineering rack, etc.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Degradable biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Nd alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a degradable biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Nd alloy material and a preparation method thereof. Magnesium alloy comprises, by mass, 1-3% of Zn, 0.5-1% of Zr, 0.1-1.5% of Nd, and the balance Mg and inevitable impurities. The preparation method comprises the specific steps of raw material smelting, casting forming, homogenizing treatment, hot extrusion and artificial ageing treatment, and the biomedical magnesium alloy bar material meeting the service requirements under the biological fluid environment is obtained. According to the degradable biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Nd alloy material and the preparation method thereof, the alloy elements harmless to human bodies are added into the magnesium alloy, the alloy is non-poisonous to the human bodies after being degraded in the human bodies, is excellent in mechanical property, has good mechanical performance and machining performance, is good in corrosion resistance, can be completely degraded in the biological fluid environment and can also ensure the appropriate corrosion rate so that early failure can be avoided. The degradable biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Nd alloy material is simple in preparation method, low in production cost and suitable for being made into a cardiovascular stent, a bone nail and other medical materials.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Three-dimensional vector expansion cardiovascular stent with memory effect based on 4D printing and manufacturing method
ActiveCN108403256ASufficient expansion forceReduce harmStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusFlagellar basal bodyCardiovascular stent
The invention discloses a three-dimensional vector expansion cardiovascular stent with a memory effect based on a 4D printing and manufacturing method. The stent is made by metalprinting a metal material with a vector expansion effect and comprises multiple net annular wires uniformly arranged in the axial direction and composed of inwards concave hexahedral grid basic units, multiple layers of the net annular wires are arranged in an array to constitute a stent main body, and an upper supporting ring and a lower supporting ring are connected to the net annular wires at the two ends of the stent main body respectively and fix the stent main body. The manufacturing method of the three-dimensional vector expansion cardiovascular stent comprises the steps of controlling the energy density oflaser area selecting melting, adjusting austenite-martensite phase change temperature, using different energy densities to form different parts of a basal body structure and achieving deformation adjustability of a formed cardiovascular stent based on temperature dependence change. Thus different parts of the stent have different expansion coefficients based on temperatures, so that the stent better adapts to the specificity and the thermal expansion of the shape of the blood vessel.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of polymer drug-laden coating on cardiovascular stent
The invention provides the preparation of polymer drug-laden coating on cardiovascular stent, which comprises carrying out surface chemical oxidation treatment to the steel stent, coating methacrylate ester cross linking agent onto the surface and performing optical solidification treatment, then immersing the stent into the mixed solution of polymer carrier and medicament, finally taking out and vacuum drying.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
High-potential super-hydrophilic polypeptide monolayer film and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111840661AGood adhesionIncreased proliferationSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseCardiovascular stent
The invention provides a high-potential super-hydrophilic polypeptide monolayer film and preparation method and application thereof. The polypeptide is composed of polypeptide molecules with the molecular weight of (1.48 + / - 0.2)*10 < 5 >g / mol, the thickness of a single-layer film is 13.8-14.9 nm, the exposure amount of primary amino groups on the surface of the film is 12-14%, the Zeta potentialof the polypeptide single-layer film is -1-5 mV, and the contact angle of the film is 10 + / - 1 degrees. As a surface coating material of a cardiovascular stent, the material is applied to treatment ofcardiovascular diseases, and the super-hydrophilic property can enable a layer of hydration film to be formed on the surface of the material so as to effectively prevent protein adsorption. The surface high potential can improve the cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation capacity.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
High-power femtosecond fiber laser device
ActiveCN105428975AGuaranteed to keep the state of polarization unchangedImprove stabilityActive medium shape and constructionCardiovascular stentAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a high-power femtosecond fiber laser device, which comprises a circuit and a light path, wherein the circuit comprises a circuit board, an acousto-optic modulation driver and a plurality of semiconductor diodes as pumps; the light path comprises an oscillator, a first coupler, a first-stage preamplifier, an acousto-optic modulator, a second coupler, a second-stage preamplifier, a separated pulse amplifier, a first pulse compressor, a main amplifier and a second pulse compressor; and the devices of the light path are sequentially connected with one another along the light path. The high-power femtosecond fiber laser device has irreplaceable advantages in the aspects of high-precision laser cutting, high-precision laser deep welding, special material surface treatment and the like; and the specific application comprises sapphire and toughened glass cutting, cardiovascular stent construction, high-precision machining of a thin-film solar cell and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPU INTELLIGENT EQUIP CO LTD
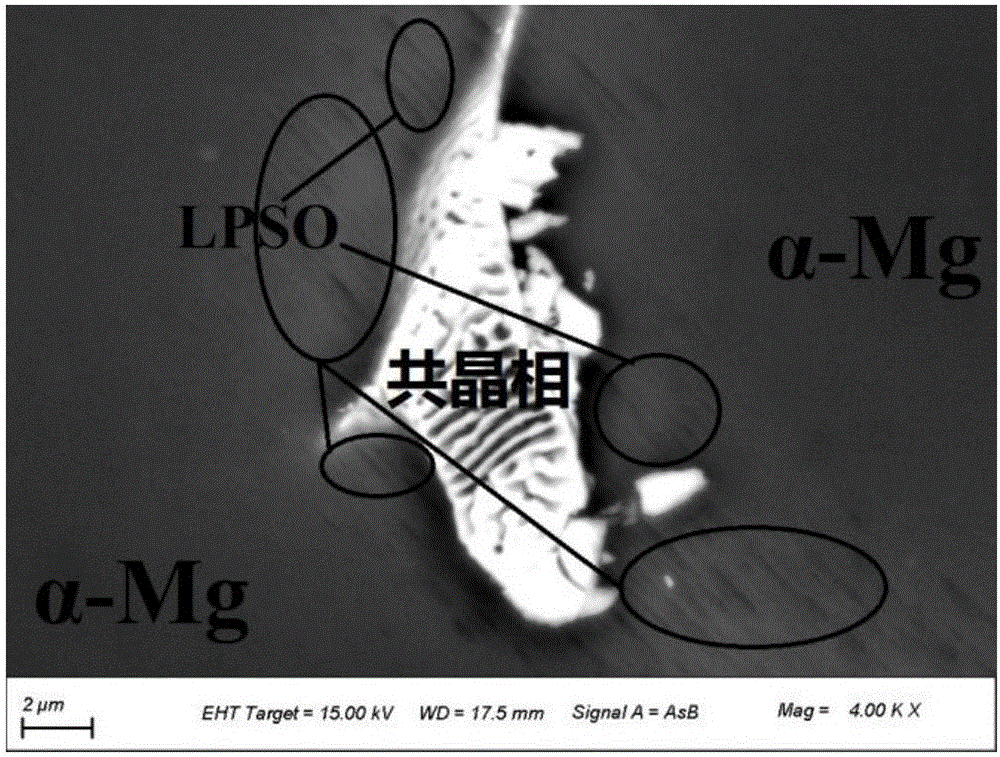
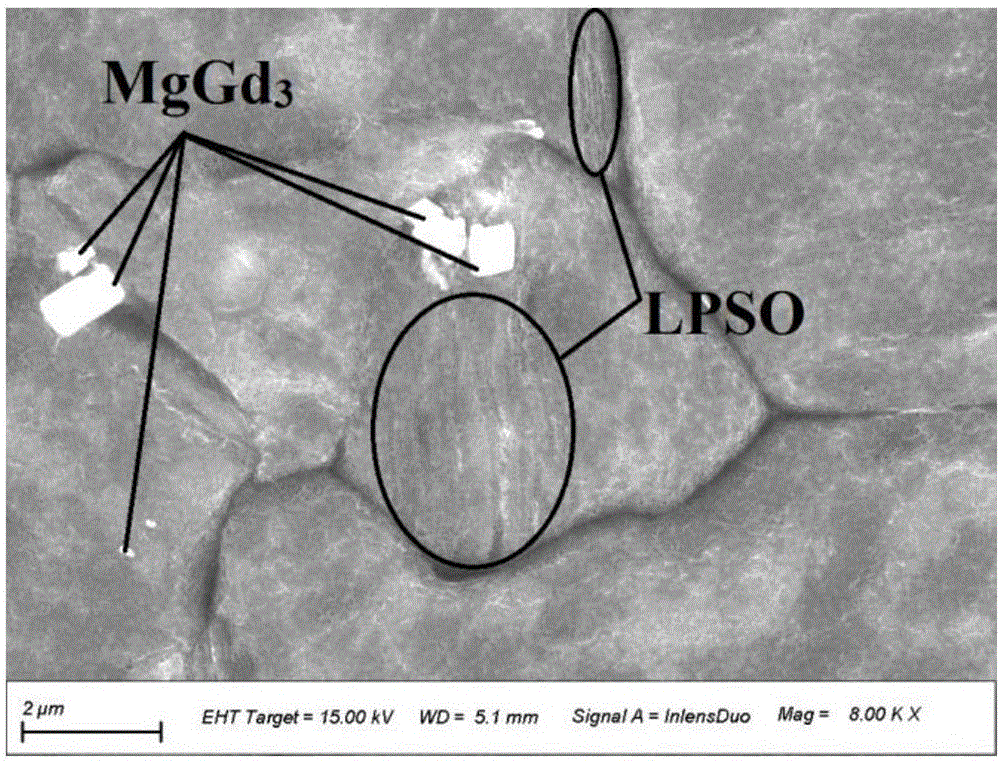
Medical Mg-Gd-Zn (-Ca) magnesium alloy with LPSO structure and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a medical Mg-Gd-Zn (-Ca) magnesium alloy with an LPSO structure and a preparation method of the medical Mg-Gd-Zn (-Ca) magnesium alloy with the LPSO structure and belongs to the field of medical magnesium alloy preparation. The medical Mg-Gd-Zn (-Ca) magnesium alloy with the LPSO structure comprises, by mass, 1.0%-3.5% of Gd, 0.3%-1.2% of Zn and 0-1.0% of Ca. The preparation method of the medical Mg-Gd-Zn (-Ca) magnesium alloy with the LPSO structure comprises the steps that raw materials which are in an appropriate ratio are placed in a crucible containing mixed protective gases of CO2 and SF6 in sequence for melting, stirring, standing and casting, wherein during casting, the solidification rate is controlled; and a cast ingot is placed in a resistance furnace with a protective atmosphere for heat treatment, and then rod materials are formed through extrusion. The medical Mg-Gd-Zn (-Ca) magnesium alloy with the LPSO structure has the advantages that the contents of the Gd element and the Zn element are low, the biological safety is high, the cost is low, and the technology is simple. Cast alloy tissue and extrusion alloy tissue both have the LPSO structure. Besides, after Ca is added, a divorced eutectic (Mg, Zn, Ca) 3Gd phase is formed in the cast alloy and is beneficial for the abrasion resistance performance of the alloy, the microstructure is adjustable, and the corrosion resistance of a material can be effectively improved. The medical Mg-Gd-Zn (-Ca) magnesium alloy with the LPSO structure has broad application prospect in the biomedical fields of orthopedics and cardiovascular stent implantation.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for making biodegradable structures
ActiveUS20160136326A1Additive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsCardiovascular stentPhotoinitiator
A composition including PPF or a PPF copolymer that can be used to fabricate biodegradable structures. The composition can be used in 3-D patterning (e.g., 3-D printing and sterolighography) methods. For example, 3-D patternable compositions include PPF or a PPF copolymer, a photoinitiator or photoinitiators, and a resolution control inhibitor or inhibitors. The compositions can be used to make biodegradable structures (such as cardivascular scaffolds). The biodegradable structures can be surface functionalized. The biodegradable structures can be used in methods of blood delivery in an individual.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Anti-infection medical stainless steel
InactiveCN102234739AHas broad-spectrum antibacterial propertiesExcellent anti-bacterial infection functionProsthesisChemical compositionCardiovascular stent
The invention relates to the field of stainless steel materials, in particular to medical anti-infection stainless steel. The stainless steel comprises the following chemical compositions in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.08 percent of C, less than or equal to 1.00 percent of Si, less than or equal to 2.00 percent of Mn, 8-16 percent of Ni, 16-20 percent of Cr, 3.0-5.0 percent of Cu, 0-4.0 percent of Mo and the balance of Fe. The content of impurity elements in steel is consistent with a corresponding requirement in a medical stainless steel national standard. After special thermal treatment on the stainless steel, bar-shaped or particulate copper-rich precipitated phases are uniformly dispersed and distributed in a stainless steel substrate, so that the stainless steel is endowed with an anti-bacterial-infection function. The medical anti-infection stainless steel has a unique anti-bacterial-infection function and can be widely applied to various stainless steel medical instruments used in the medical clinical fields of the department of orthopedics, the department of stomatology, cardiovascular brackets and the like; and the problems of bacterial infection and the like caused by medical instruments such as medical stainless steel and the like in the prior art are solved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biomedical magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106498251AGood biocompatibilityControllable degradation rateRare-earth elementCardiovascular stent
The invention provides a biomedical magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of biomedical metal materials. The alloy is composed of, by mass percentage, 0.05%-0.2% of Mn, 1%-4% of Zn, 0.05%-1% of Ca and the balance Mg, wherein the molar ratio of Zn to Ca is larger than 1.5. The novel human body biodegradable medical alloy is prepared through certain key technical parameters, such as a melting process and the alloy component ratio. The alloy does not contain rare earth elements and mainly contains the Mg-Zn-Ca phase, the alloy is mainly distributed in the crystal boundary, and less of the alloy is distributed inside a matrix. The alloy has excellent biocompatibility, prominent mechanical properties and excellent plastic processing properties and is controllable in degradation rate. According to the application characteristic of the alloy, the alloy can be used for preparing biodegradable cardiovascular stent materials, orthopaedic implants, bone plates, bone nails and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Anticoagulant hydrogel coating capable of catalyzing release of nitric oxide and preparation method of anticoagulant hydrogel coating capable of catalyzing release of nitric oxide
ActiveCN108969805ACompact structureImprove stabilitySurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCardiovascular stentBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses an anticoagulant hydrogel coating capable of catalyzing the release of nitric oxide and a preparation method of the anticoagulant hydrogel coating capable of catalyzing releaseof nitric oxide. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating a substrate material; (2) sequentially placing the pretreated substrate material in a polycation electrolyte, a mixed solution of polyphenol and a compound A, and a polyanion electrolyte at room temperature to react for 20 minutes, and washing for 3 to 5 times; (3) using a product obtained in step (2) as a substrate at room temperature, repeating the operation of step (2) for 5 to 20 times, after drying by nitrogen, obtaining the anticoagulant hydrogel coating capable of catalyzing the release of nitric oxide. The hydrogel coating prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple method, stable structure, and good biocompatibility, can stably catalyze NO to release for a long time to protect endothelial cells and has an anticoagulant effect. The coating can be used for surface modification of cardiovascular stent materials and heart valves.
Owner:JILIN VENUS HAOYUE MEDICAL LTD
Medicine eluted cardiovascular support
InactiveCN1669595APromote healingInhibition of intimal hyperplasiaSurgeryDilatorsCardiovascular stentThrombus
A kind of medicinal elution cardiovascular frame, comprises frame and biological degradation layer, which is made of biological degradation material that embeds the drug and covered in the frame. The characteristic is: the biological degradation material includes glycolide, L-lactide, homopolymers or one of the copolymer and the copolymer with polyfunctional group amino acid of Epsilon-caprolactone; the biological degradation layer contains the drug is a kind of macromolecule graft heparin. After the frame is implanted, the drug is deliveried to limit the endometrial hyperplasia sufficiently, and the heparin is exist continuously and steadily. It can prevent the occurrence of acute or subacute thrombus, and can promote the healing of the injury vessel wall, prevent the occurrence of late thrombus. Compare to the traditional heparin frame, it overcomes the defects like intolerance by the humor erosion and interceding poison substance in the progress of chemical binding.
Owner:程树军
Method for implanting functional biological coating on surface of implant
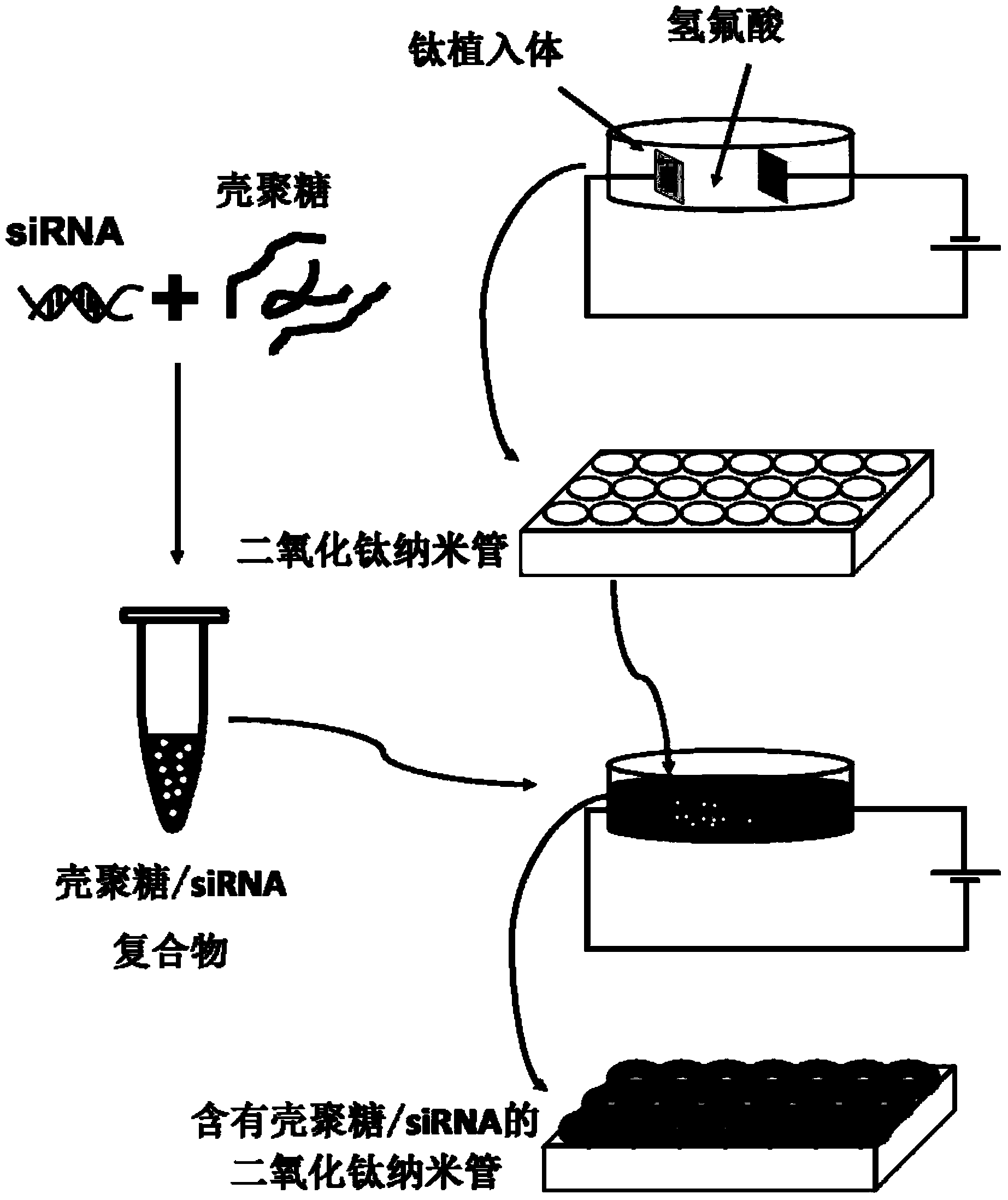
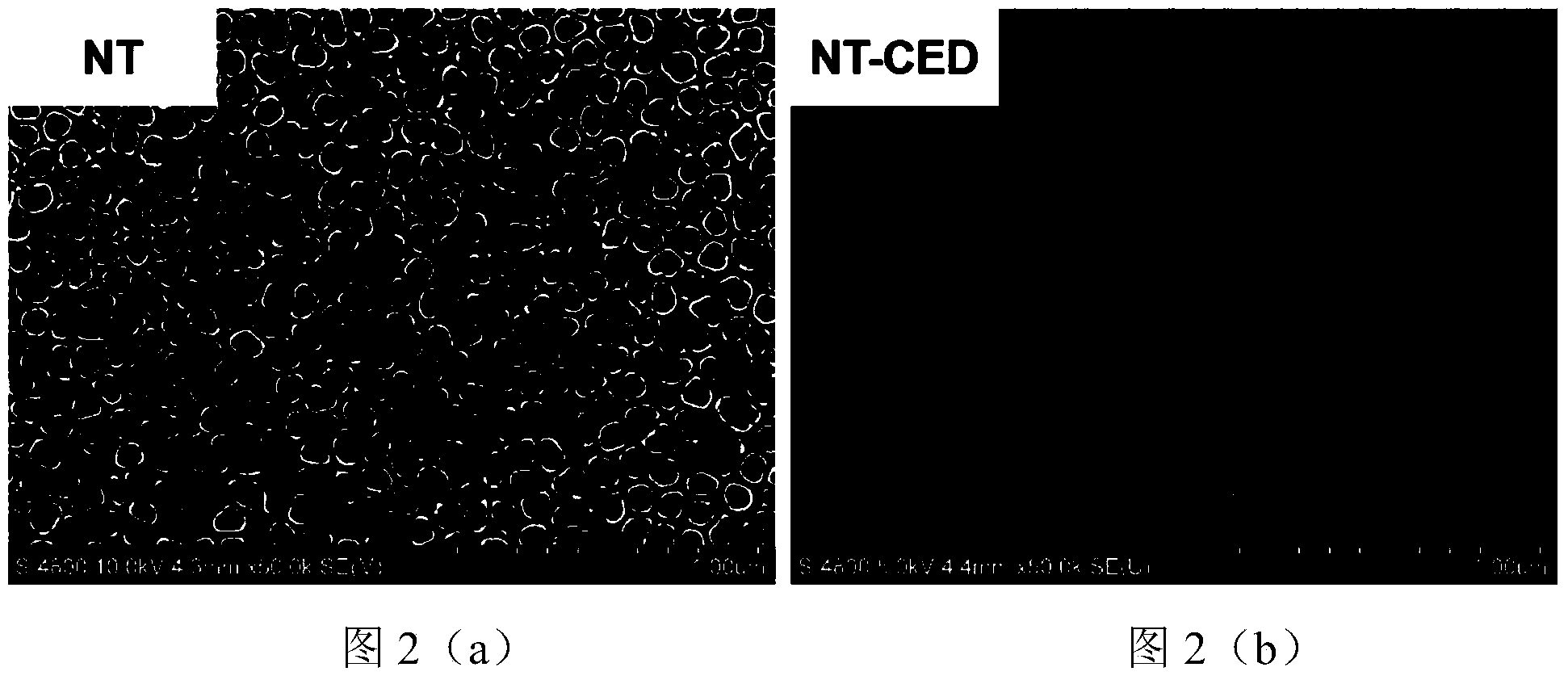
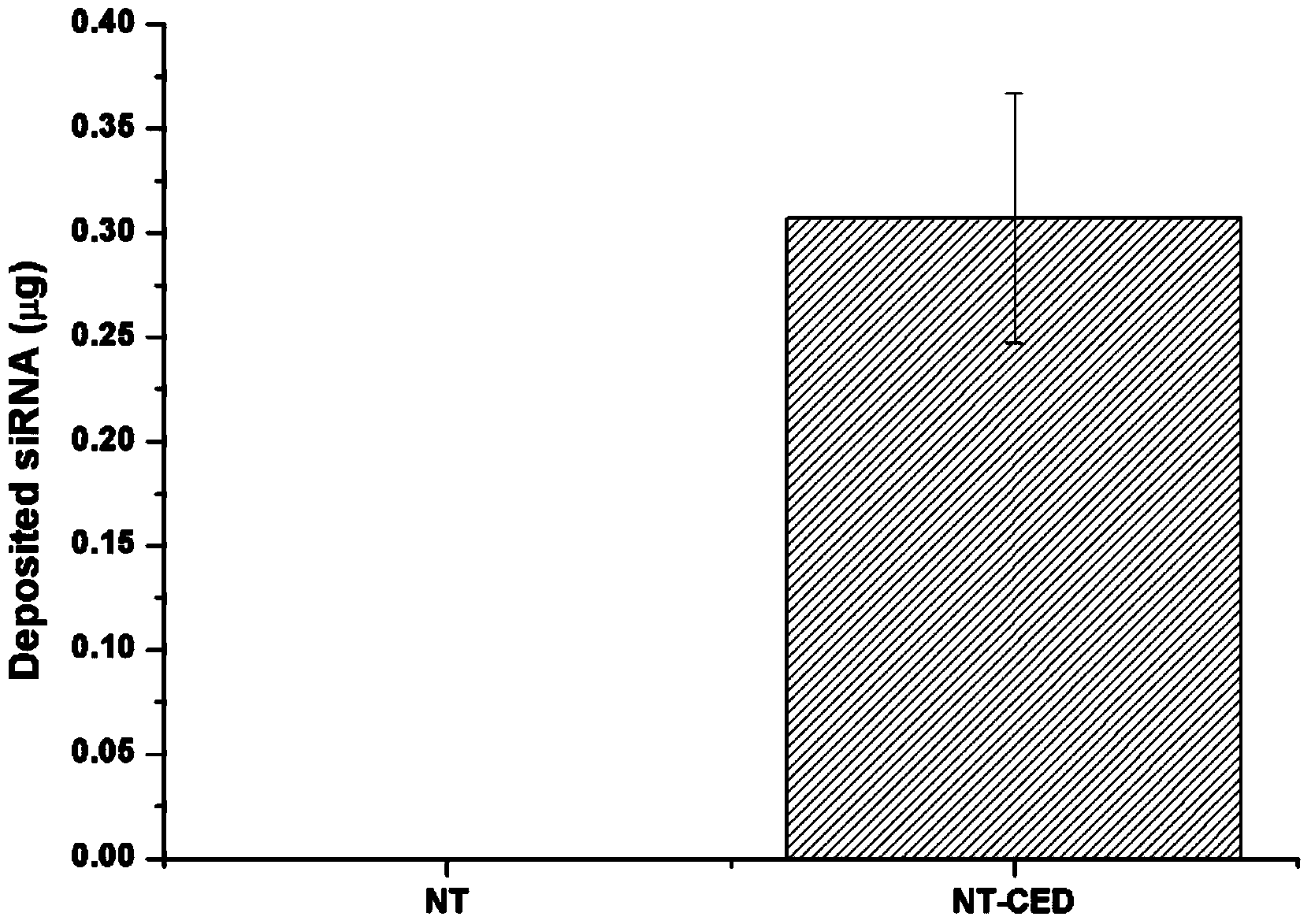
ActiveCN104018199ALow equipment requirementsImprove loading efficiencySurgerySurface reaction electrolytic coatingControlled releaseCardiovascular stent
The invention relates to a method for implanting a functional biological coating on the surface of an implant. The method is characterized in that a functional biological coating is implanted on surface of the implant in an electrolytic deposition manner, the implant is a dental implant, a bone implant or a cardiovascular stent, and the functional biological coating is a siRAN coating, a miRNA coating or a DNA coating. The method has the advantages that chitosan and a functional biological material are jointly deposited on the surface of a titanium dioxide nanotube array on the basis that chitosan has a characteristic of cathodic electrodeposition and has a transfer effect on the functional biological material, and as the pH value of chitosan changes after electrodeposition, the dissolution rate of the chitosan slows down, and the controlled-release characteristic of the functional biological material can be realized to a certain degree.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing and using vascular stent
InactiveCN106366285ACause damageSafe and Stable StayAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryMemory typeVitrification
The invention relates to a method for preparing and using a vascular stent. A cardiovascular stent is prepared by using a self-made thermosensitive memory polymer and a 3D printing technology. The self-made thermosensitive memory polymer is a thermosensitive memory type polyurethane material with a molecular weight of 8000-200000 Dalton and a vitrification conversion temperature of 35-45 DEG C. The preparation method of the vascular stent is simple, the product can be controlled, the prepared thermosensitive memory type polyurethane material has the vitrification conversion temperature larger than the temperature of a body, and meets the use requirements; the use of the 3D printing technology can provide a customized vascular stent for a patient under the condition of a subfebrile temperature according to the needs of an operation, the use method is simple, and the storage is convenient.
Owner:福州维亚多国际贸易有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com