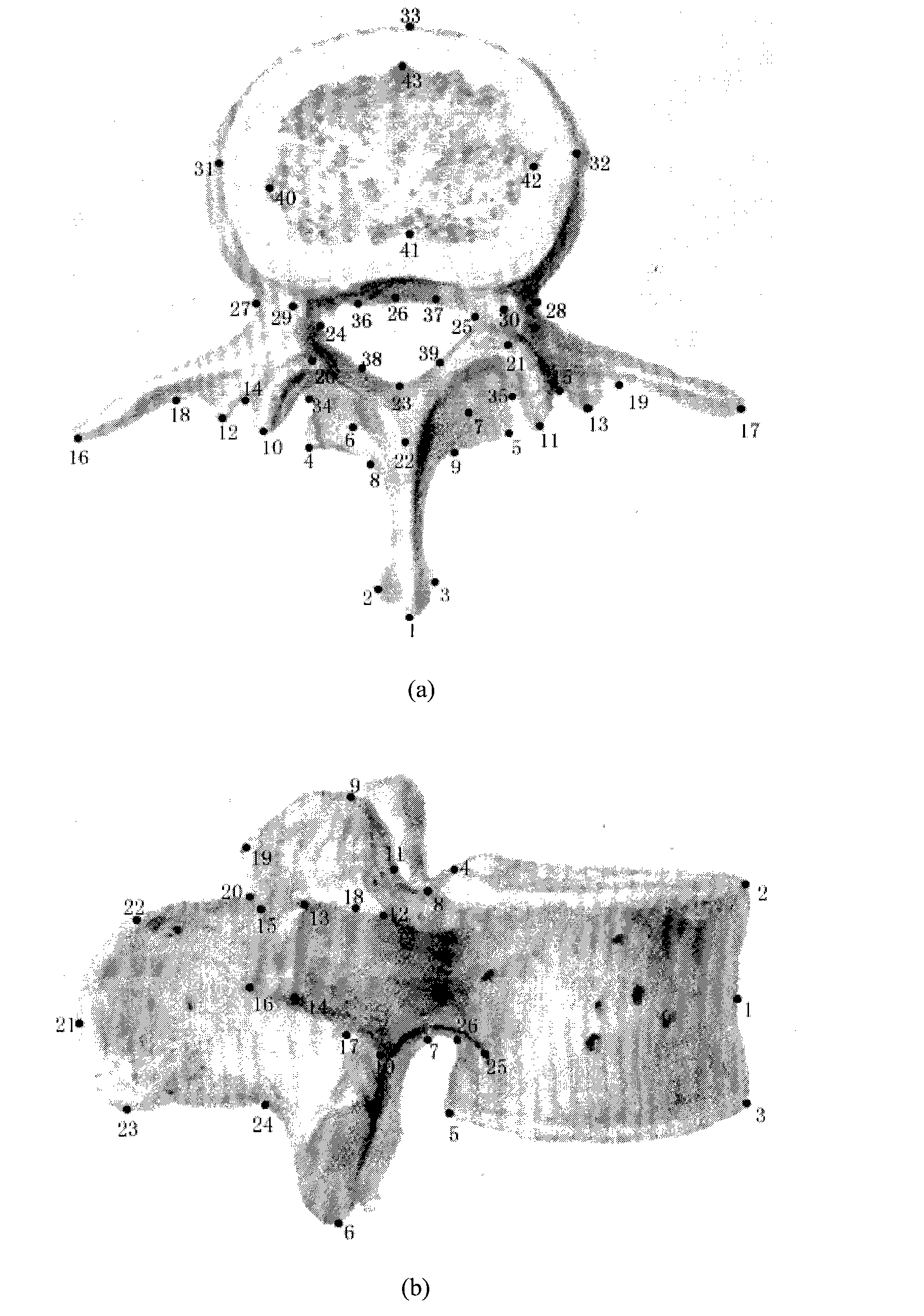Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5488 results about "Element model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
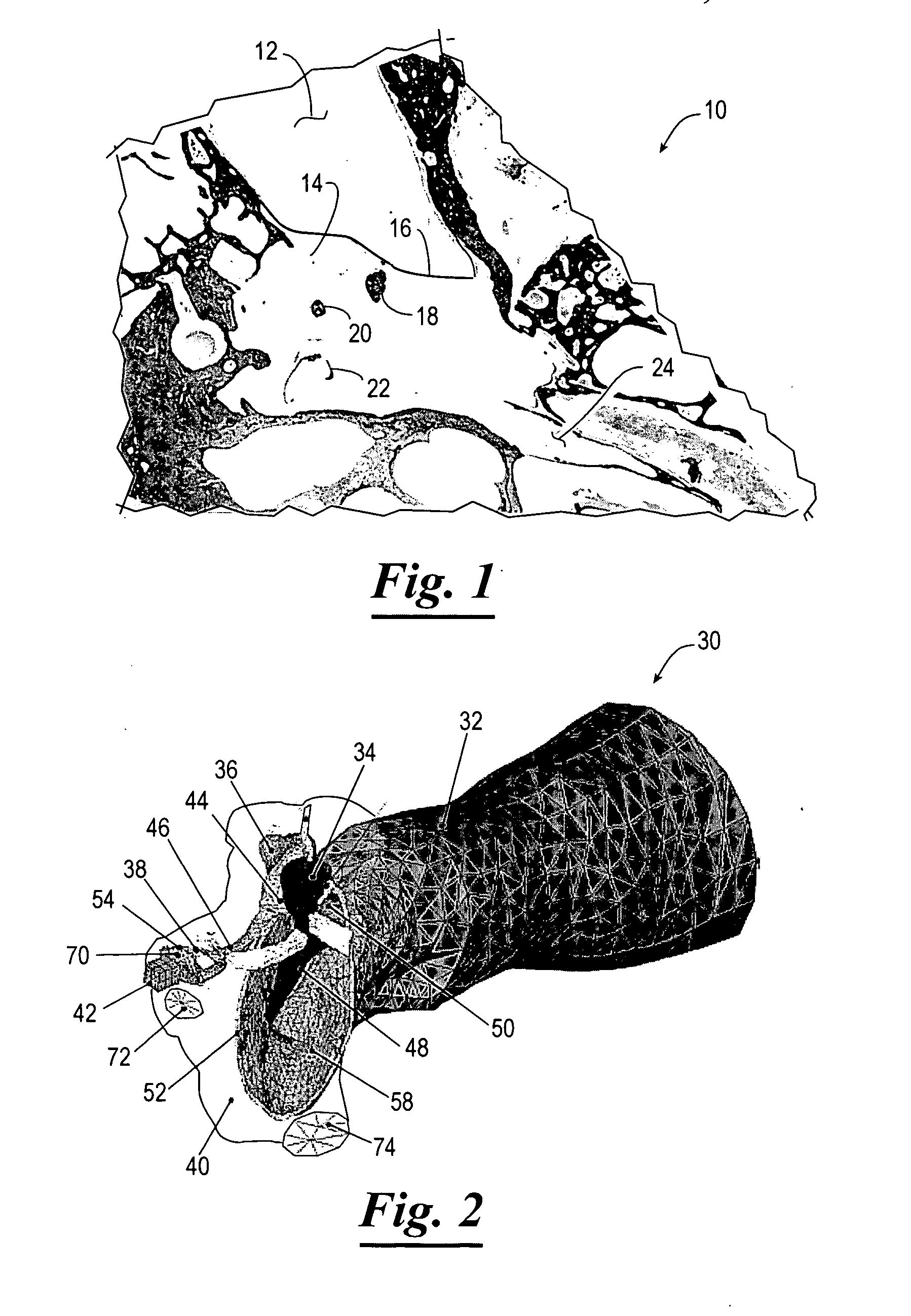
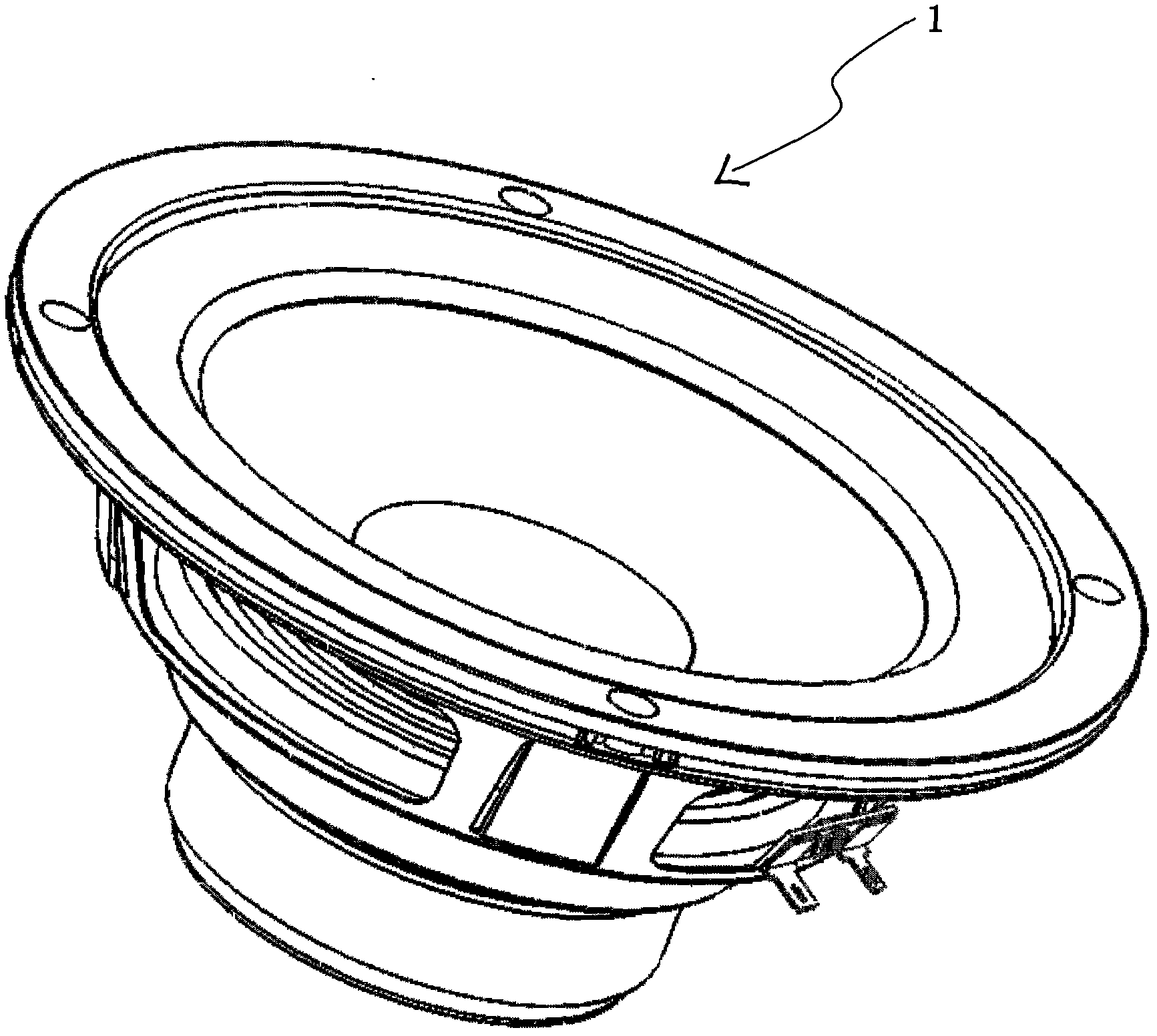
Three-dimensional finite element modeling of human ear for sound transmission
InactiveUS20060278245A1Easy to provide informationFacilitate fabricationAdditive manufacturing apparatusAudiometeringSound transmission classAnatomical structures
A finite element model of an ear stored on a computer readable medium having logic representing a three-dimensional geometric model of the ear; logic for meshing individual anatomical structures of the ear accounting for whether the anatomical structures include at least one of air, liquid material and solid material; logic for assigning material properties for each anatomical structure based on at least one physical property of each anatomical structure; logic for assigning boundary conditions for some of the anatomical structures indicative of interaction between such anatomical structures; and logic for employing acoustic-structural coupled analysis to the anatomical structures of the ear to generate data indicative of the acoustic effect on mechanical vibration transmission in the ear. Various embodiments of “one-chamber” and “two-chamber” analyses and models are described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
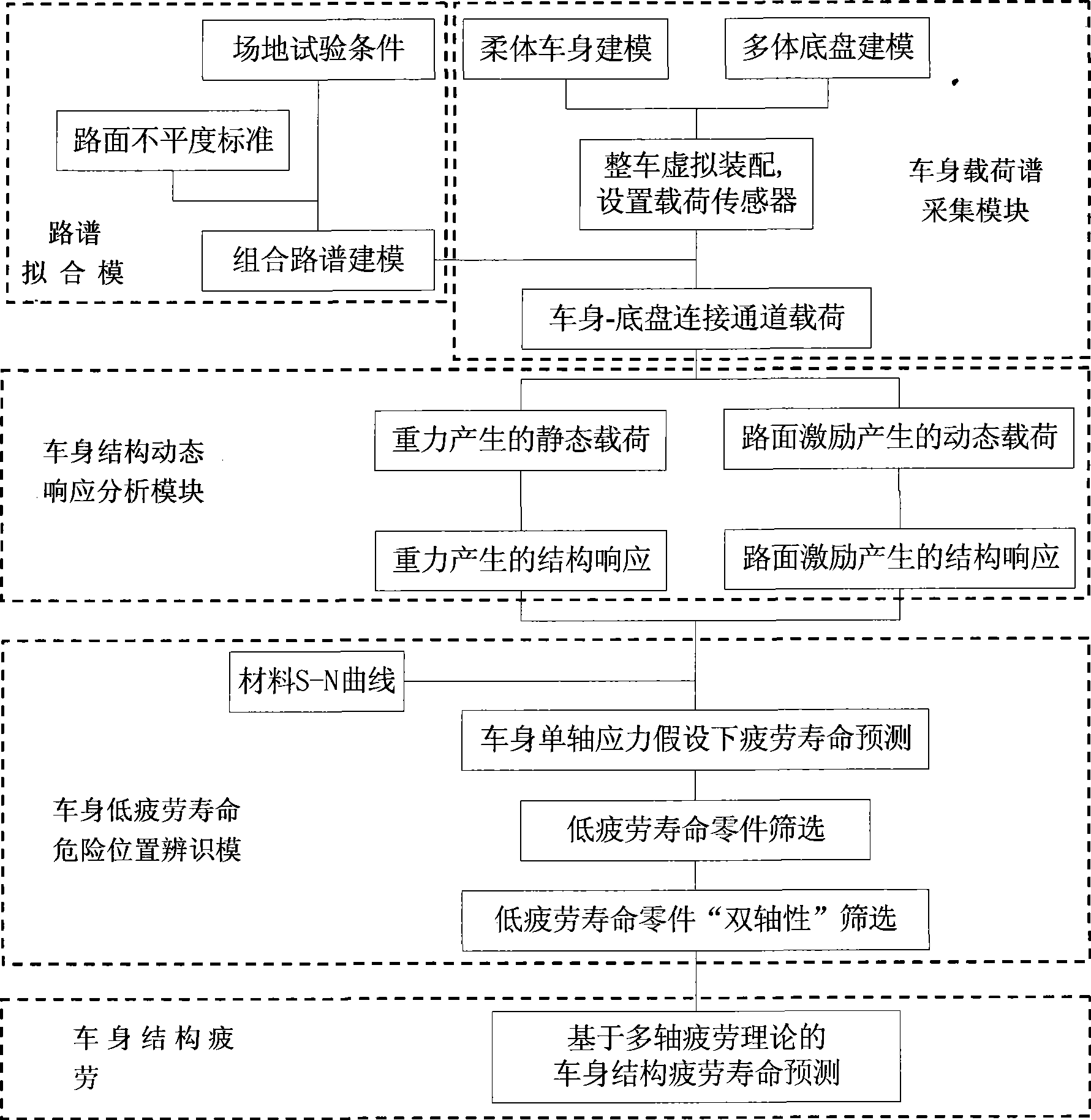
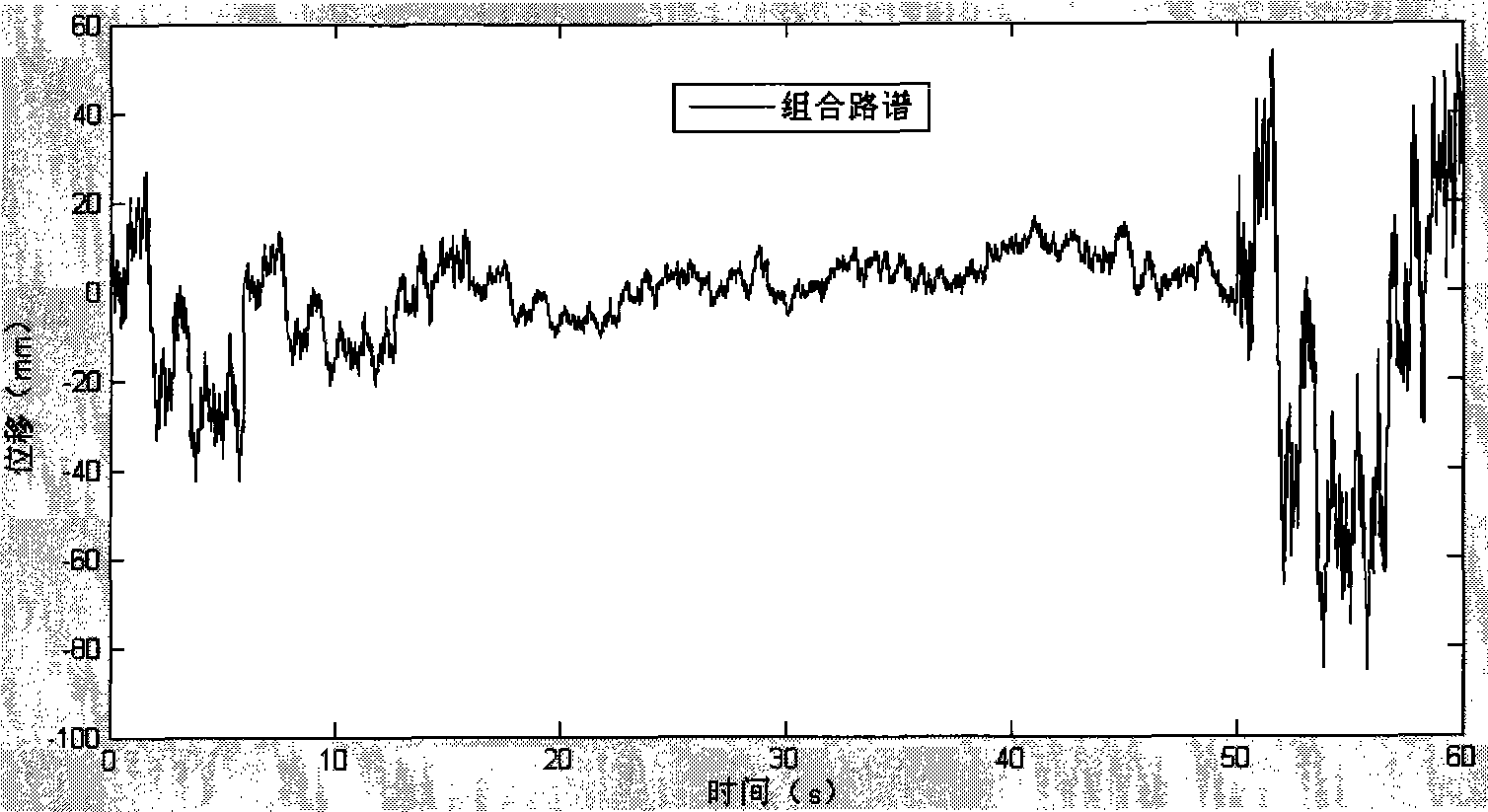
Automobile vehicle body structure fatigue life predicting system
The invention relates to a fatigue life prediction system for a vehicle body structure of a vehicle in the technical field of vehicle design. The prediction system adopts a road spectrum fitting module to establish a combined road spectrum suitable for a field test; a vehicle body loading spectrum acquisition module is adopted to establish an entire vehicle multi-body rigid-flexible coupled model so as to extract the load-time-history at a connecting passage of the vehicle body and a chassis as the input of vehicle body excitation; an automobile body structure dynamic response analysis module is adopted to establish a finite element model of the vehicle body so as to obtain the static stress history generated by gravity and the dynamic stress history generated by road surface excitation of the vehicle body when the vehicle is under the excitation of the combined road spectrum; a dangerous position identifying module of low fatigue life of the vehicle body is adopted to quickly search dangerous positions of low fatigue life through an S-N method and a Miner linear accumulated damage model, and determine the multiaxial stress state of the dangerous positions by using 'biaxiality' analysis; and a fatigue life prediction module of the vehicle body structure is adopted to predict the fatigue lives of the dangerous positions accurately. The fatigue life prediction system for the vehicle body structure can improve the speed and the precision of the fatigue life prediction for the vehicle body structure so as to provide a reference for a real vehicle test.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
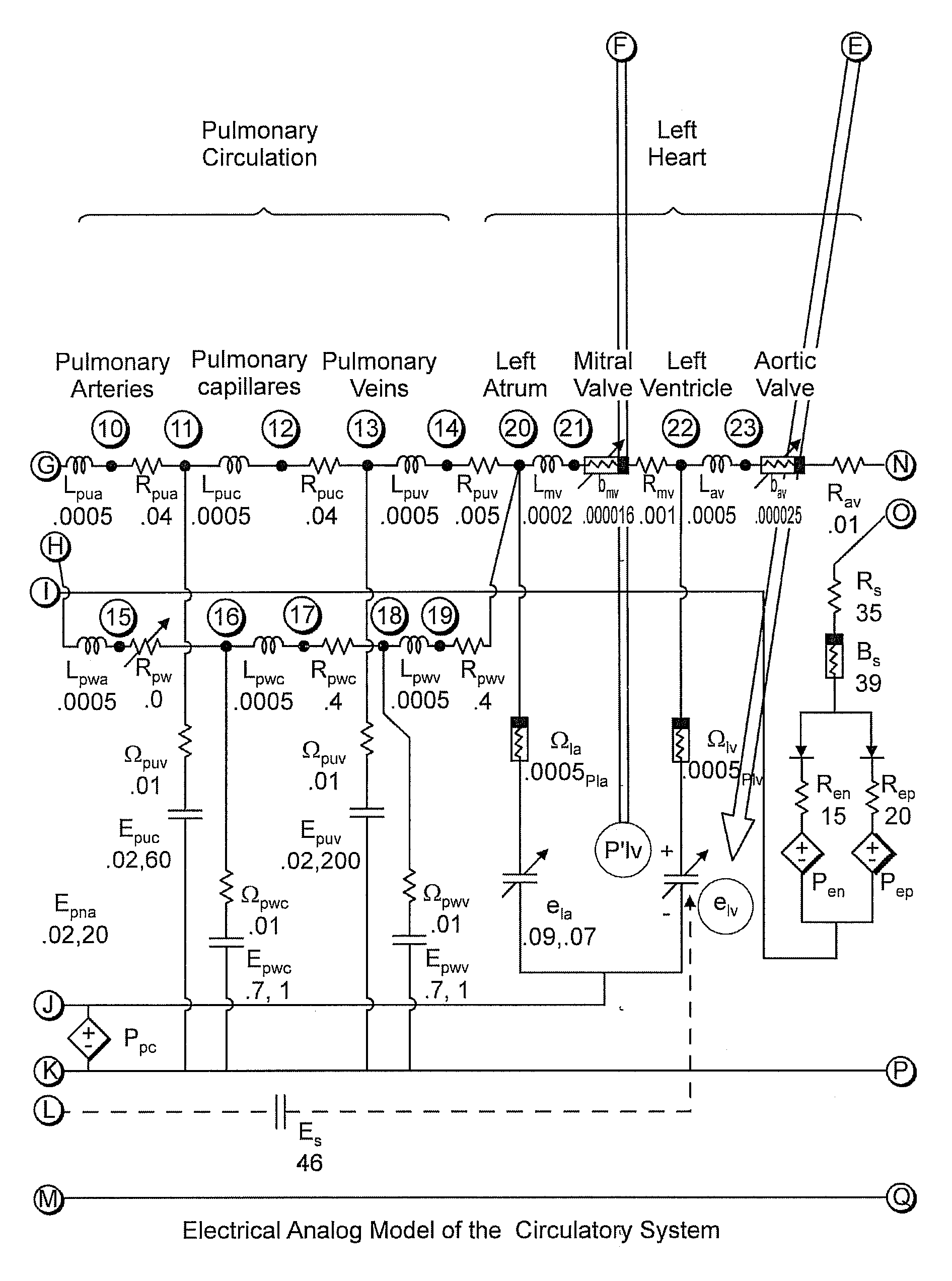
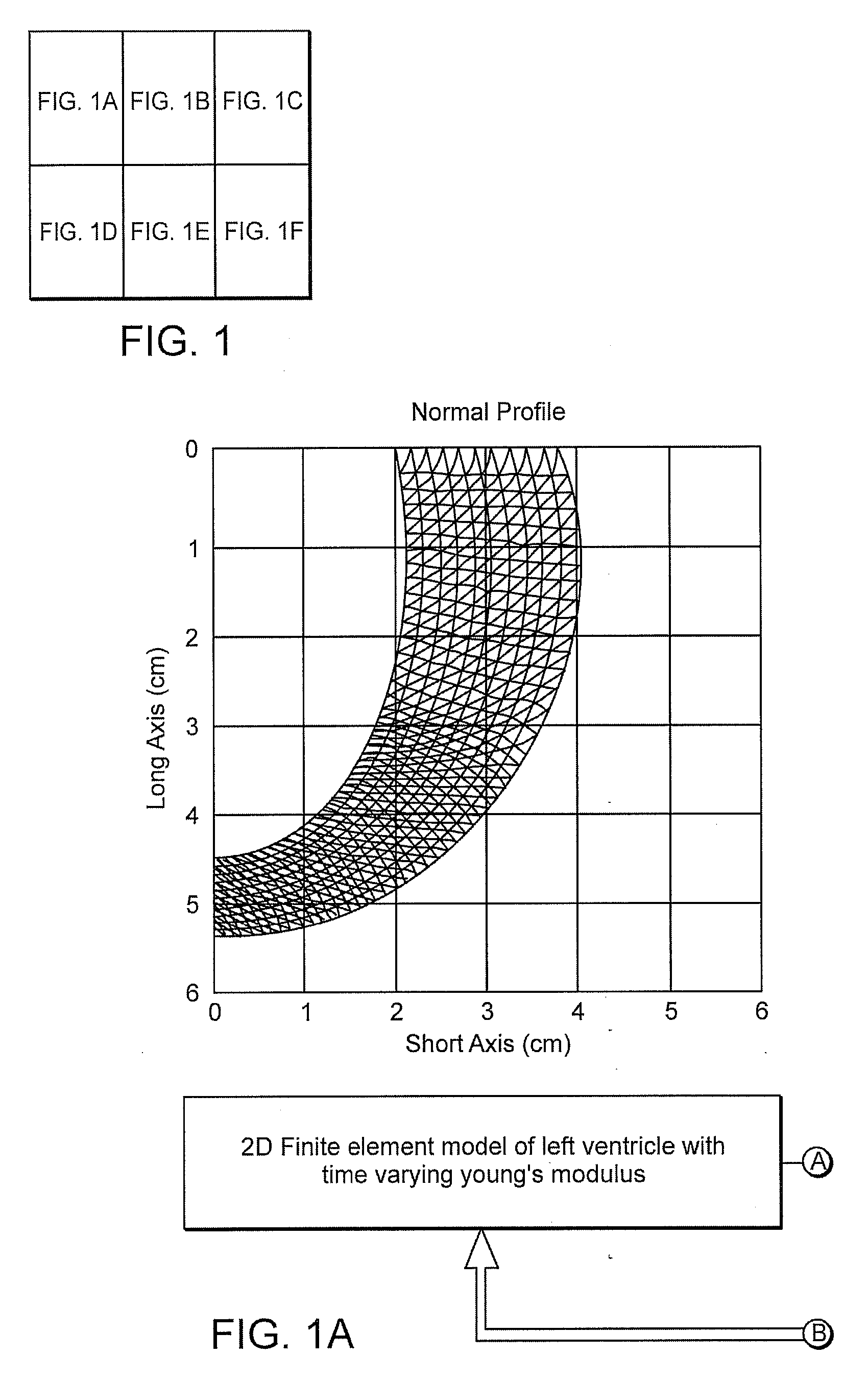
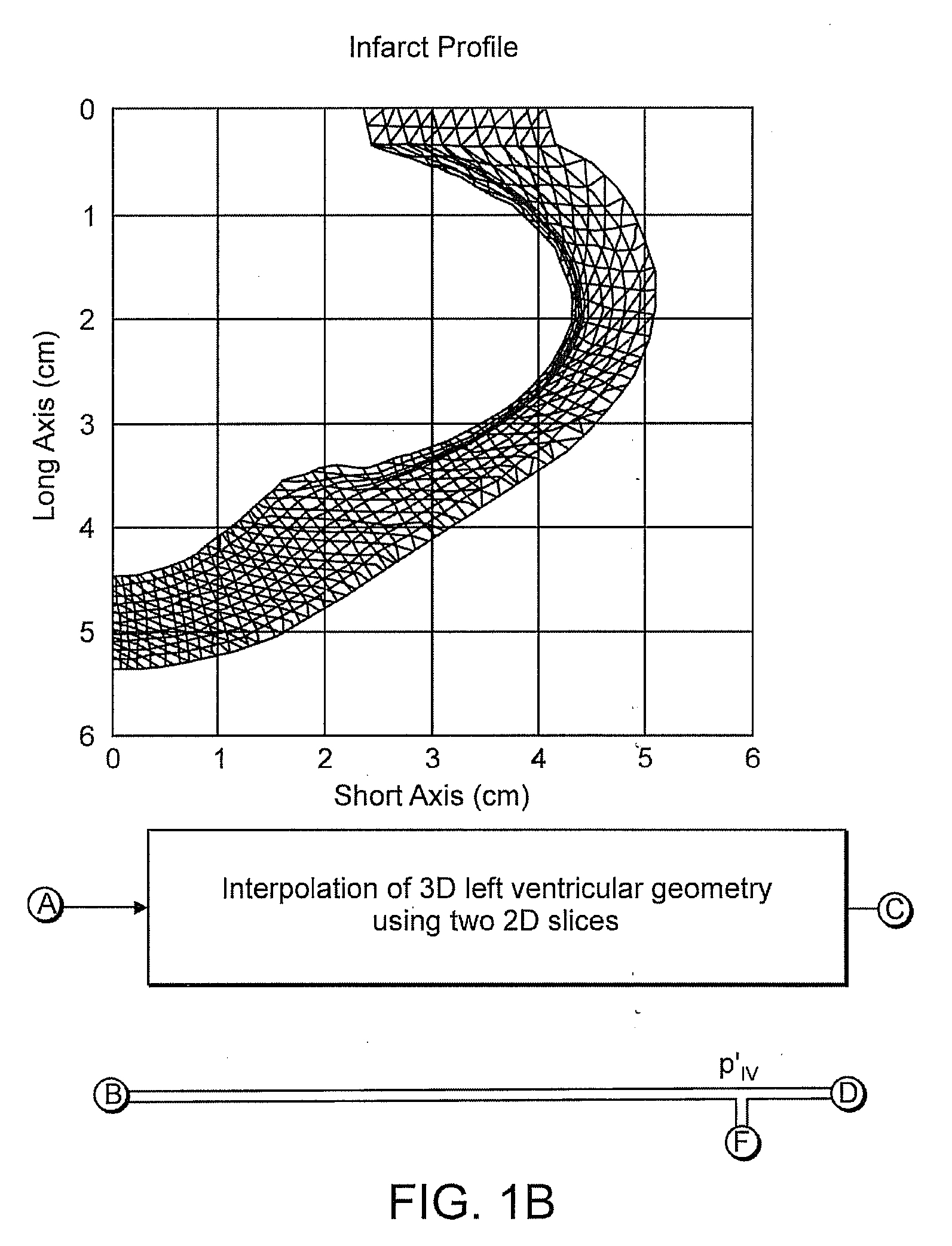
Integrated finite element and circulatory model for predicting hemodynamic effects of left ventricular impairment, resynchronization and remodeling
InactiveUS20080004508A1Predictable outcomeMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesElement modelCardiac cycle
A computational model which integrates a complex circulatory model and a finite element to determine the dynamics of a left ventricle continuously over consecutive cardiac cycles. The model includes determining a LV pressure (plv) using a circulatory model, using a finite element model plv as input and determining a LV volume (vlv), computing a LV elastance according to: elv=plv / vlv, driving the circulatory model with the elv; and returning to determining a LV pressure and starting the next iteration, wherein the steps continue at a sufficient time resolution for a desired number of entire cardiac cycles. The dynamic Young's modulus functions are assigned to individual finite elements, resulting in a time-varying left ventricular elastance that drives the circulatory model.
Owner:BOARD OF GOVERNORS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION STATE OF RHODE ISLAND & PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS
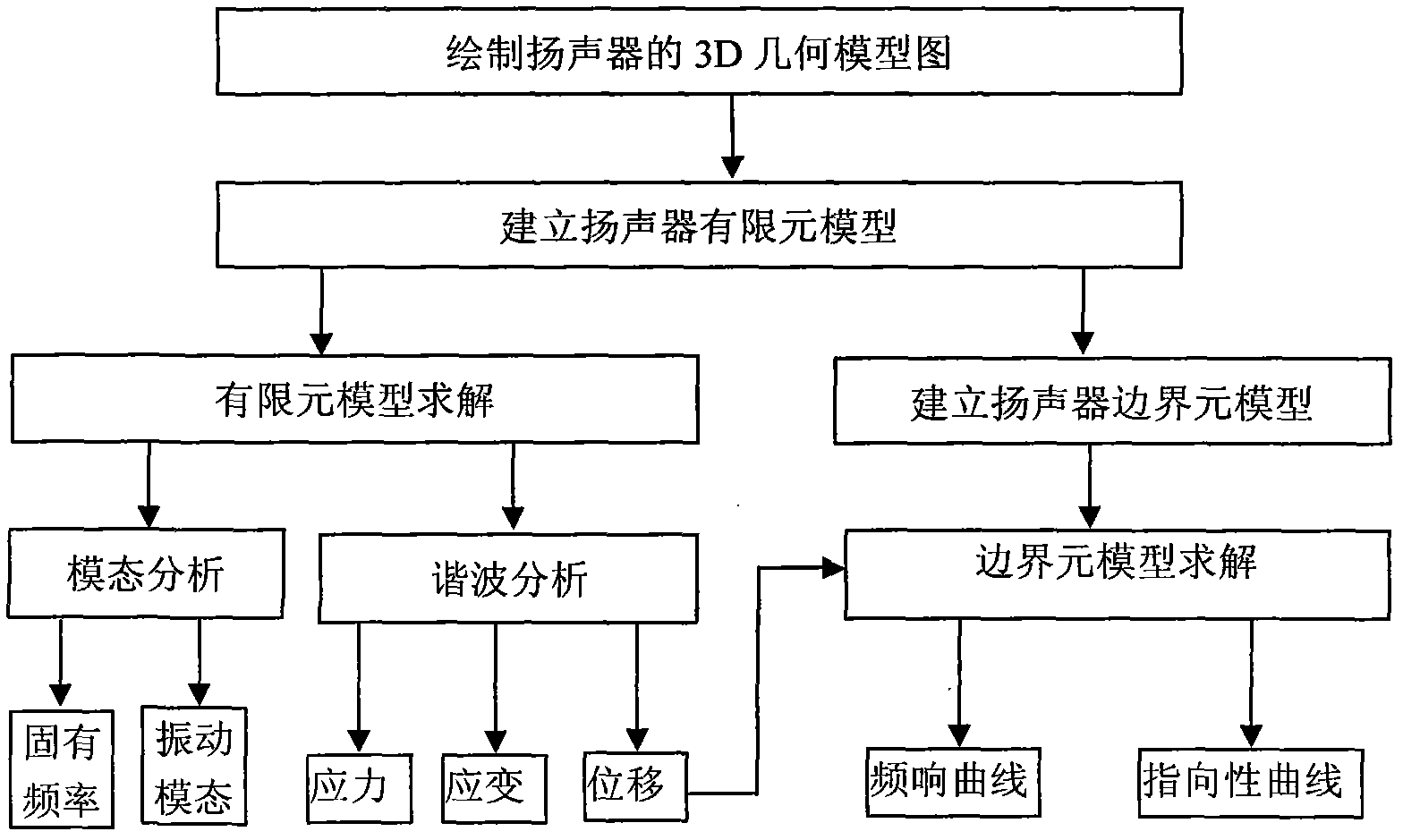
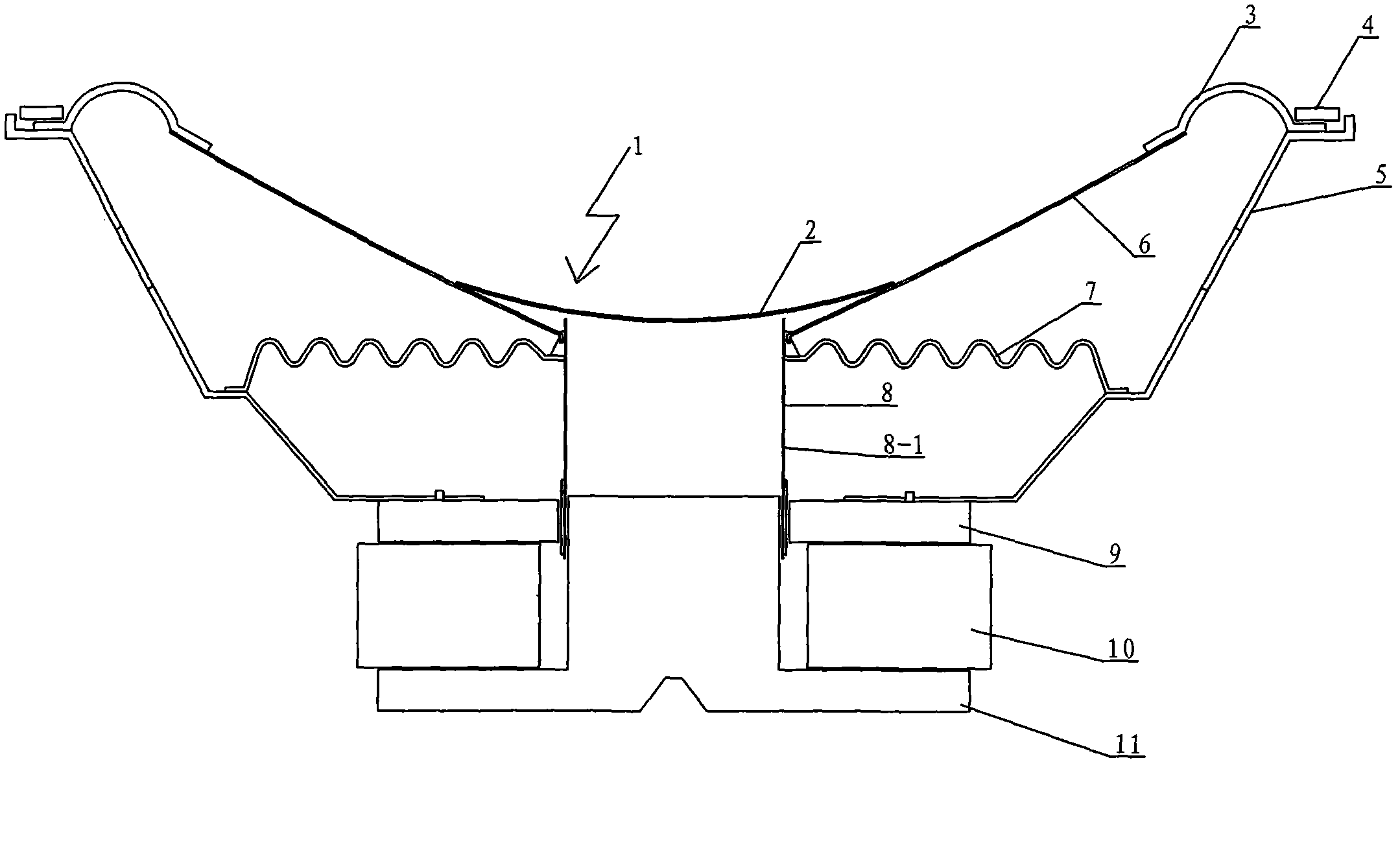
Numerical value simulation method of vibration and acoustic characteristics of speaker
ActiveCN102004823ASpeed up the design processOvercome the disadvantage of being limited to low frequenciesSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelGeometric modeling
The invention provides a numerical value simulation method of the vibration and acoustic characteristics of a speaker. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, drawing a 3D (Three-Dimensional) geometric model diagram of the speaker by using 3D drawing software; then, adding the 3D geometric model diagram of the speaker to meshing software to mesh the 3D geometric model diagram into body elements, defining element types, materials and boundary conditions and applying a load to acquire a finite element model; establishing a boundary element model matched with the finite element model; and finally, solving the finite element model with a finite element solver to acquire the vibration characteristics of the speaker, and solving the boundary element model with a boundary element solver to acquire the acoustic characteristics of the speaker, wherein the vibration characteristics include the natural frequency, the vibration mode (vibration type), the displacement, the strain and the stress, and the acoustic characteristics include a frequency response curve and a directivity curve.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ELECTRO ACOUSTIC R&D CENT CAS +1
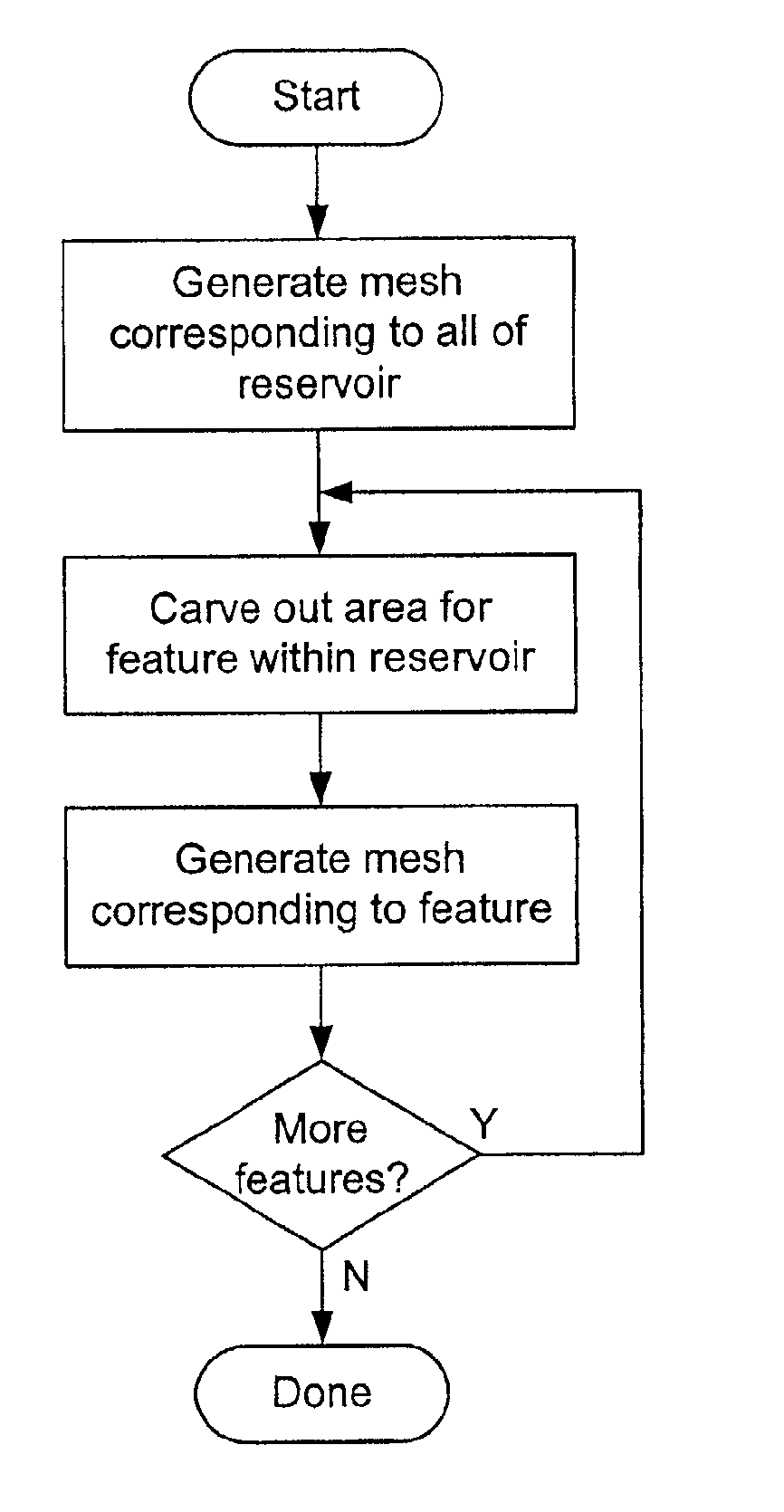
Feature modeling in a finite element model
ActiveUS6941255B2Accurate representationSmall amount of calculationGeometric CADComputation using non-contact making devicesFinite element techniqueElement model
A method for simulating a physical system using finite element techniques, wherein two or more distinct models corresponding to distinct regions within the modeled system are solved, each with a corresponding evaluator. Nodes which lie on the boundaries between the models may have different values corresponding to the different models. When a particular model is solved, the evaluator for that model is used to obtain the appropriate values for each of these common nodes. In one embodiment, a first model is defined, then a region corresponding to a particular feature within the system is carved out of it. A finite element model corresponding to the feature is then inserted into the region. The finite elements may be adapted to share nodes on the boundaries between them.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
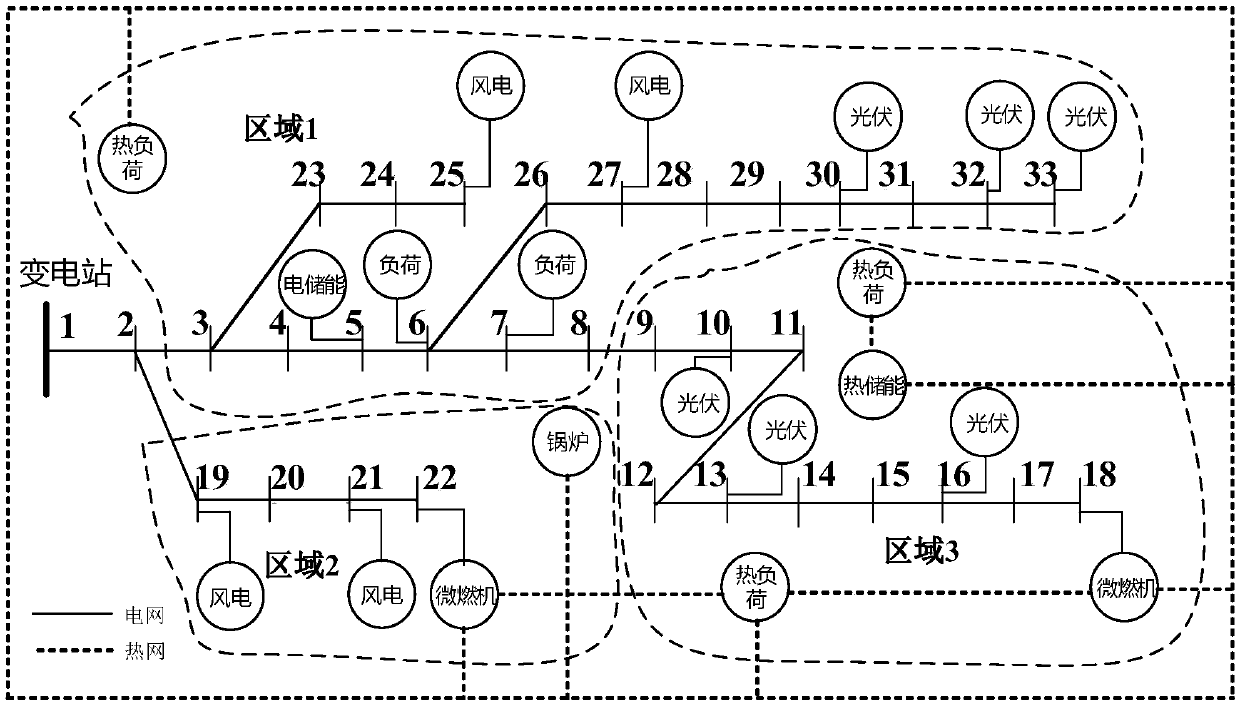
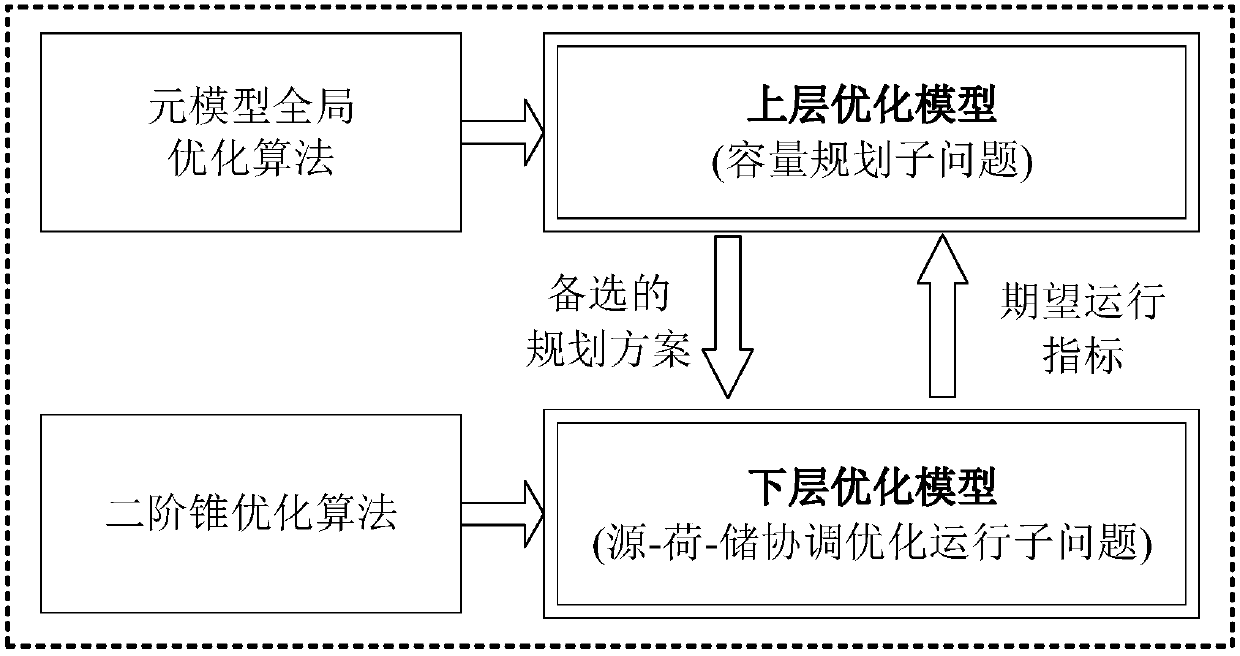
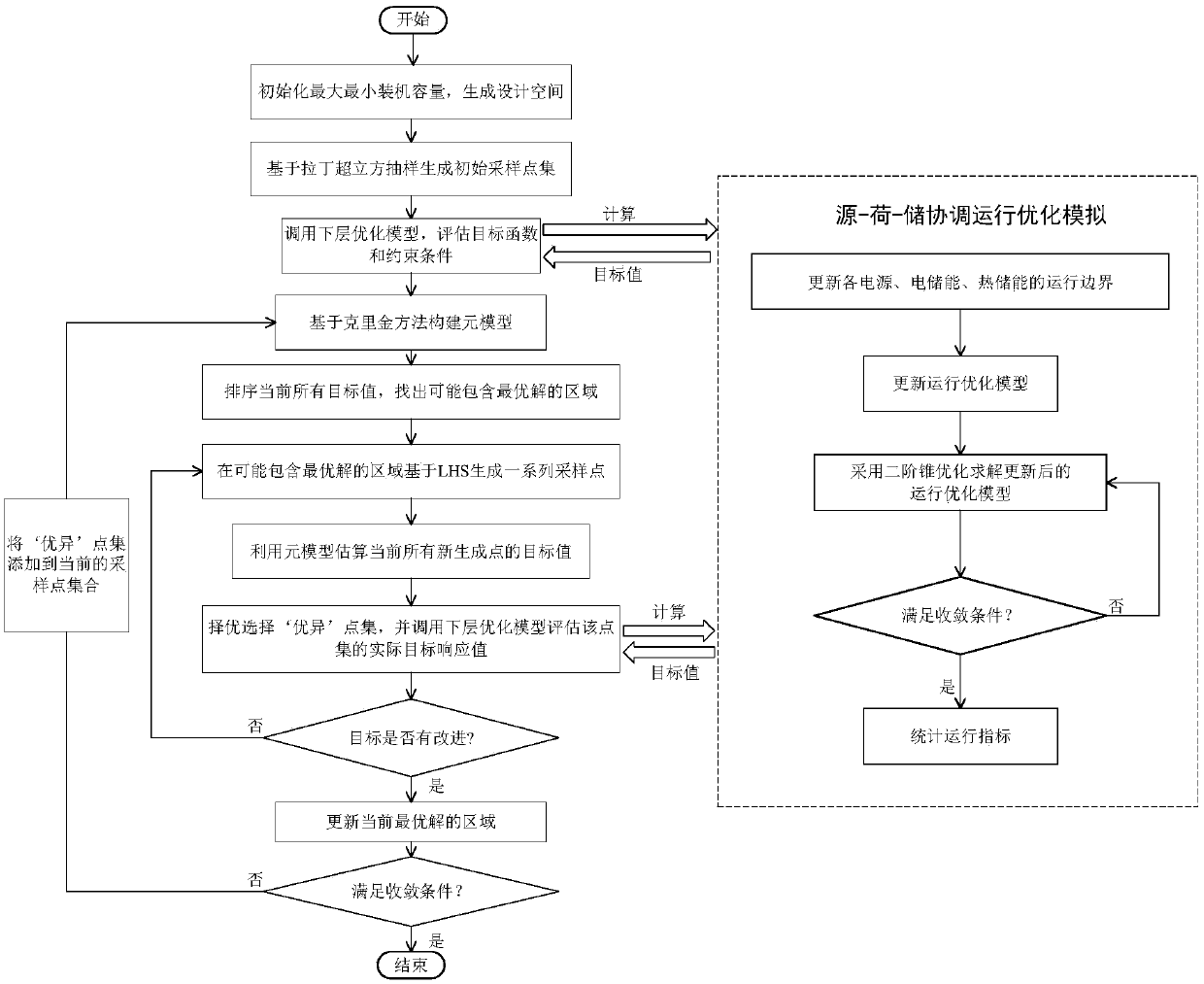
Design method for integrated energy system with source-load-storage coordination and interaction
ActiveCN108494015APreserve the properties of uncertain probability distributionsReduce computational complexitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingElement modelIntegrated energy system
The invention relates to a design method for an integrated energy system with source-load-storage coordination and interaction. A lot of source-load output scenes are generated via Latin hypercube sampling, and a few of specific probability of planning scenes in which original scene characteristics are reserved are obtained via cluster analysis combined with a scene reduction method. An installedcost model and an operation cost model are established for each piece of equipment, an upper-level optimization model is optimized to minimize the sum of the annual investment conversion cost and theannual operation cost in different probability scenes, a lower-level optimization model is optimized to minimize the annual operation cost in different probability scenes a double-layer planning modelof the integrated energy system with source-load-storage coordination and interaction is established, and different reliable and safe operation constraints are met. The upper-level and lower-level optimization models are solved by an element model global optimization algorithm and a second-order conic optimization method respectively, solving is carried out by interactive iteration till convergence, and the installed capacity and optimal operation scheme of each piece of equipment of the integrated energy system are obtained by optimization. The method can be applied to capacity planning andoptimized design of the multiple energy complementary integrated energy system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
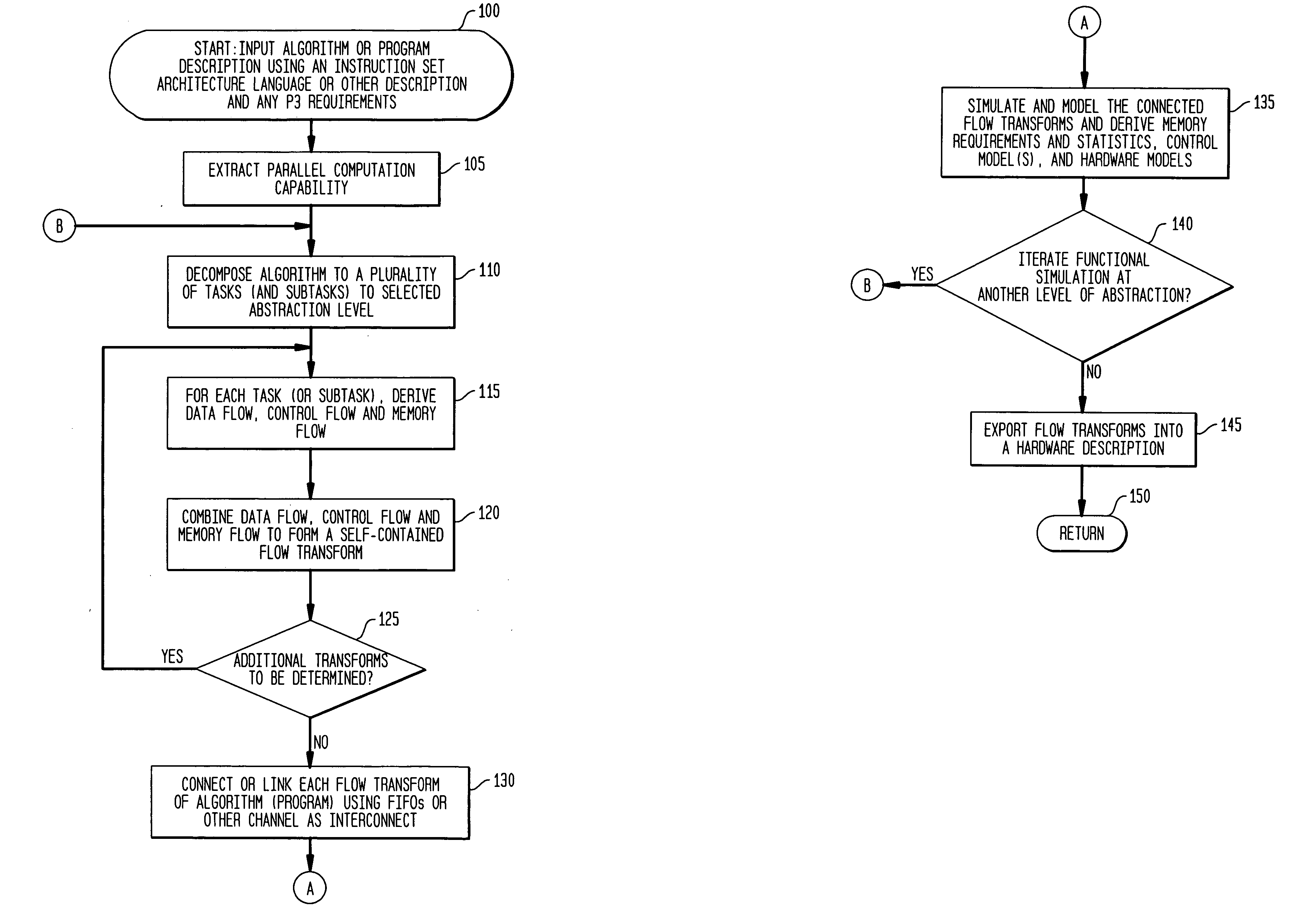
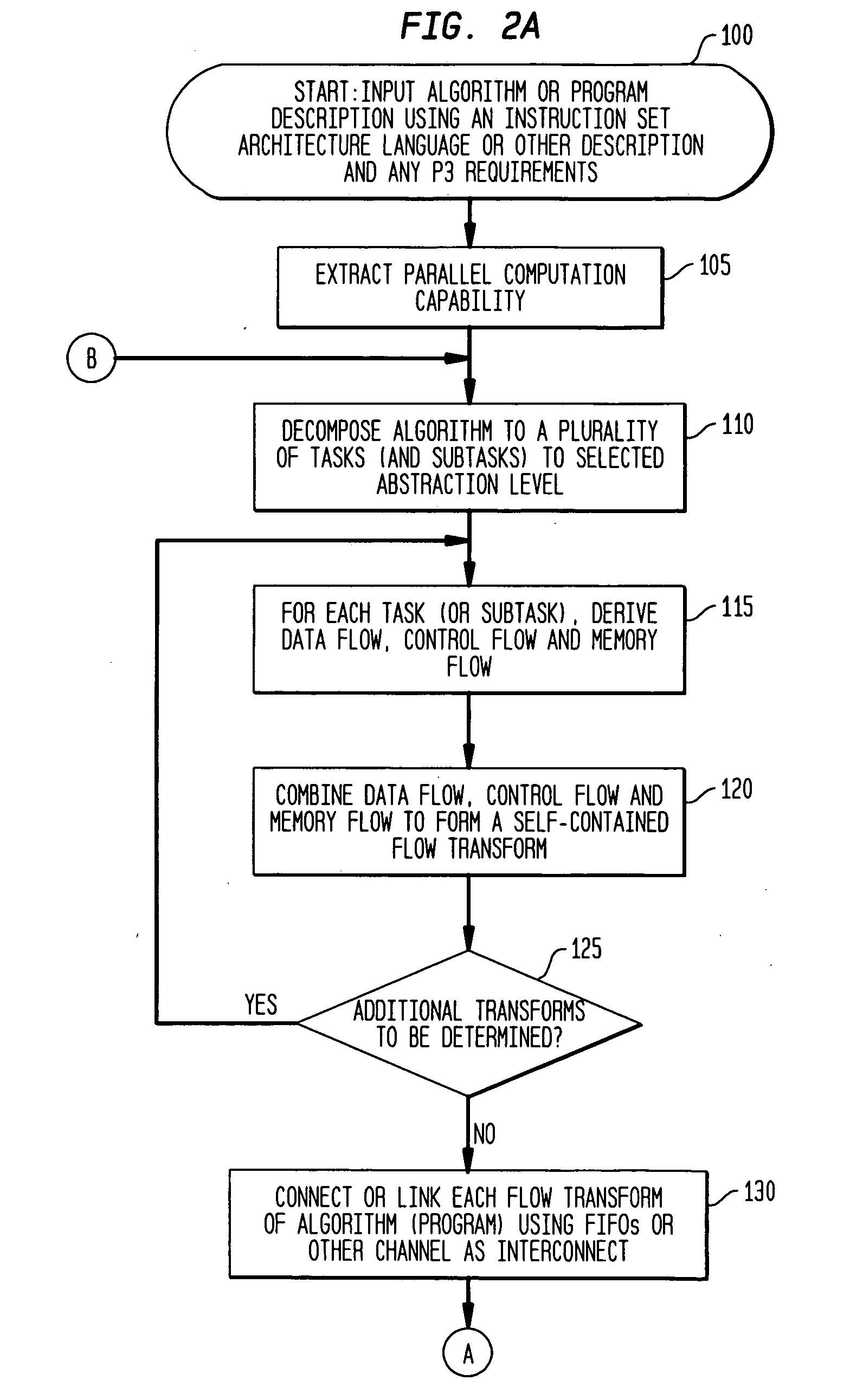
Algorithmic electronic system level design platform
InactiveUS20070162268A1CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelComputer architecture
A computing system and method are provided for algorithmic electronic system level design. An exemplary system comprises a plurality of databases for storing a plurality of functional models, a plurality of computational element models, and a plurality of hardware definition representations. An application design processor is adapted to perform a first functional simulation of an algorithm using a plurality of computational element architecture definitions to generate a first selection of a plurality of computational elements and corresponding control code for an implementation of the algorithm. A control and memory modeling processor is adapted to generate a plurality of flow transforms from the algorithm and to convert the plurality of flow transforms into the plurality of plurality of computational element models. A system simulation processor is adapted to convert the plurality of computational element models into the plurality of hardware definition representations and to perform a second functional simulation of the algorithm using the plurality of computational element models corresponding to the first selection and the corresponding control code.
Owner:KOTA BHASKAR +3
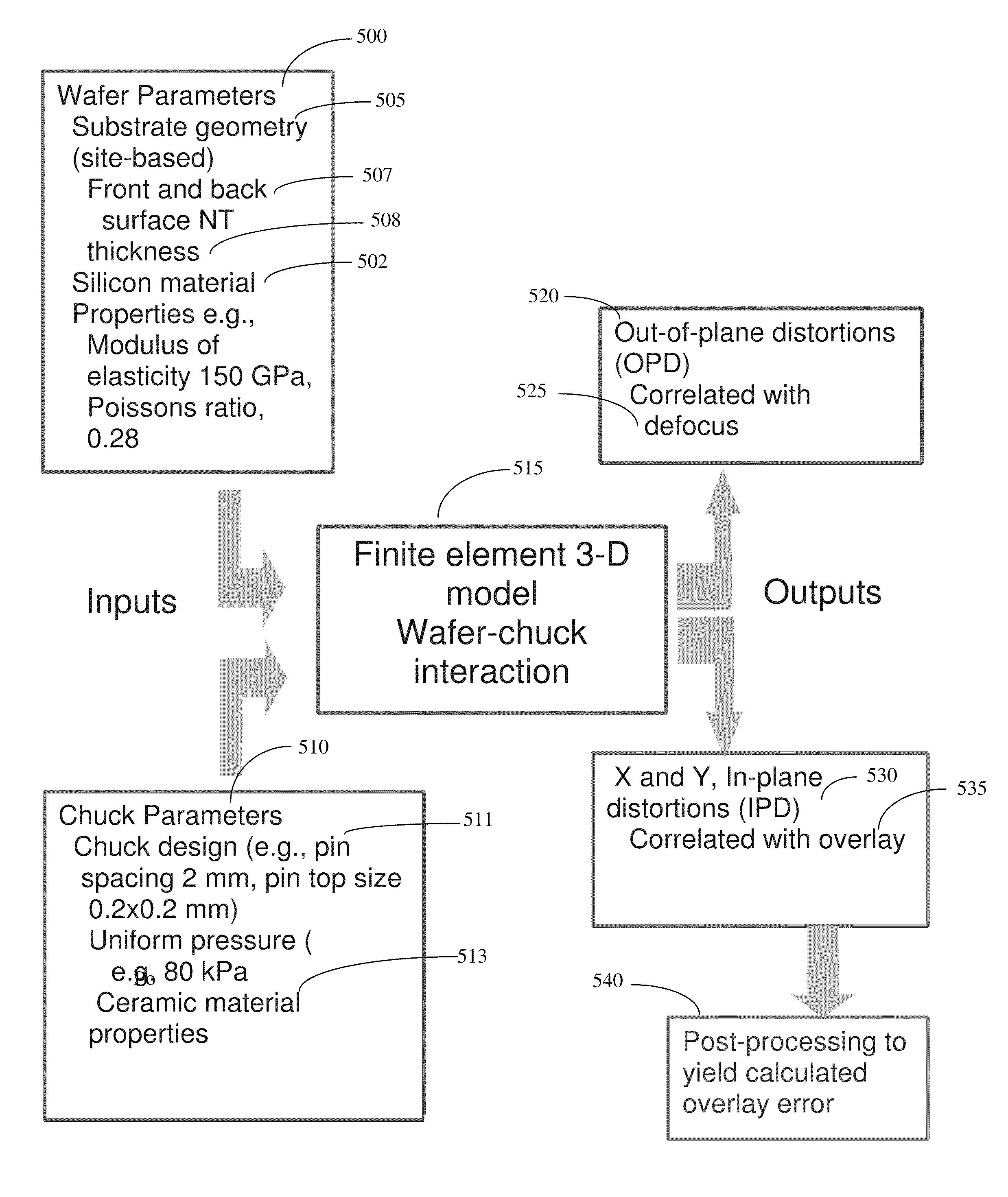
Site based quantification of substrate topography and its relation to lithography defocus and overlay
ActiveUS20110172982A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAnalogue computers for electric apparatusElement modelLithographic artist
A method and system for modeling and analyzing wafer nanotopography data utilizes a nonlinear contact finite element model. Inputs to the model include lithography chuck parameters and site-based geometry data. Outputs from the model include in-plane distortions and out-of-plane distortions, from which defocus and overlay can be derived.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
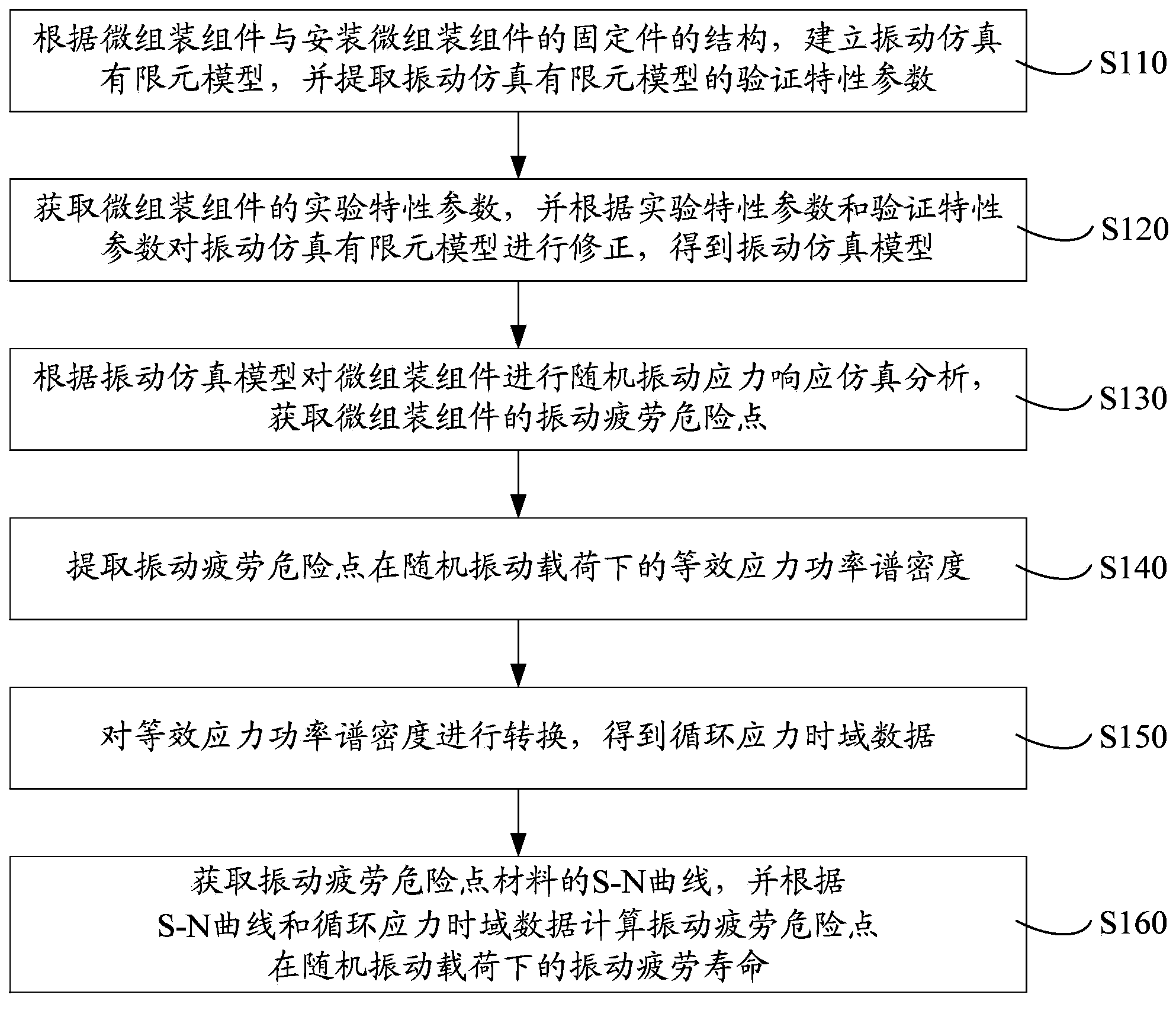
Vibration fatigue life predication method and system for micro-packaging assembly
ActiveCN104268335ASolving the Difficulty of Vibration Fatigue Life PredictionAvoid data difficultiesSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainElement model
The invention provides a vibration fatigue life predication method and system for a micro-packaging assembly. The method comprises the following steps: creating a vibration simulating finite element model according to the structures of the micro-packaging assembly and a fixing part; extracting the verification characteristics parameters; modifying the vibration simulating finite element model according to the verification characteristics parameters and the experimental characteristics parameters of the micro-packaging assembly to obtain a vibration simulating model; performing random vibration stress response simulation analysis for the micro-packaging assembly according to the vibration simulation model to obtain a dangerous vibration fatigue point; extracting equivalent stress power spectrum density of the dangerous vibration fatigue point under the random vibration load; converting the equivalent stress power spectrum density to obtain cyclic stress time domain data; calculating the vibration fatigue life of the dangerous vibration fatigue point under the random vibration load according to an S-N curve and the cyclic stress time domain data of the dangerous vibration fatigue point; predicating the vibration fatigue life of the micro-packaging assembly by the method of synchronously extracting the response data of the fixing part and the micro-packaging assembly. With the adoption of the method and system, the testing accuracy is improved.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
Computer process for prescribing second-order tetrahedral elements during deformation simulation in the design analysis of structures
InactiveUS6044210AComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelEngineering
A computer implemented process prescribes second-order tetrahedral elements during simulation in the design analysis of structure. The computer implemented process includes the steps of defining a finite element model for an element including at least one tetrahedral element, and defining the at least one tetrahedral element as a combination of hexahedral sub-elements. The computer implemented process also includes the steps of executing the simulation, and evaluating the structure for structural integrity responsive thereto.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES SIMULIA CORP
Numerical simulation method for selective laser melting process
InactiveCN108062432APrevent cracks and other phenomenaOptimize printing parametersDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSelective laser meltingElement model
The invention discloses a numerical simulation method for a selective laser melting process. The method comprises a first step of establishment of a finite element model of additive manufacturing process simulation; a second step of meshing on the finite element model of the additive manufacturing process, wherein full-hexahedron meshing is adopted; a third step of definition of printing powder material properties and thermal physical performance parameters which must be determined for temperature field analysis in the additive manufacturing process; a fourth step of loading of a control equation of a mobile heat source; and a fifth step of analysis of thermal stress field and total deformation changes in the additive manufacturing process and after sintering is finished. Through the numerical simulation method for the selective laser melting process, printing parameters can be optimized, and warping and deformation of parts can be prevented; and the method provides effective guidancefor supporting structural design and a printing strategy (speed and direction), lowering the rejection rate and realizing ''success at a time''.
Owner:XIAN BRIGHT ADDTIVE TECH CO LTD
Method for optimally designing dynamic property of complete machine tool
ActiveCN102063548ASimple structureAssembly precisionSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelResonance
The invention discloses a method for optimally designing dynamic property of a complete machine tool, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a complete machine tool entity parameterized model, simplifying the structure according to the analysis requirement on the dynamics and the structure characteristic of the machine tool; and guiding the simplified entity model into a finite element analyzing software ANSYS / Workbench for grid division to obtain a complete machine finite element model. The statics analysis is carried out through the ANSYS / Workbench to obtain a complete machine prestress field, and the mode of the complete machine tool under the prestress field is obtained through the mode analysis. The complete machine tool dynamics response of a main shaft, caused by a cutting force, under different rotating speeds is obtained through resonance response analysis on the complete machine tool, and the reference is provided for the searching of the dynamics thin link and the optimization design. Finally, by using the parameterized analysis method, the rule of influencing the complete machine tool dynamic property by the structure quality and the rigidity parameter is obtained, and the dynamic rigidity thin link is obtained and optimally designed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
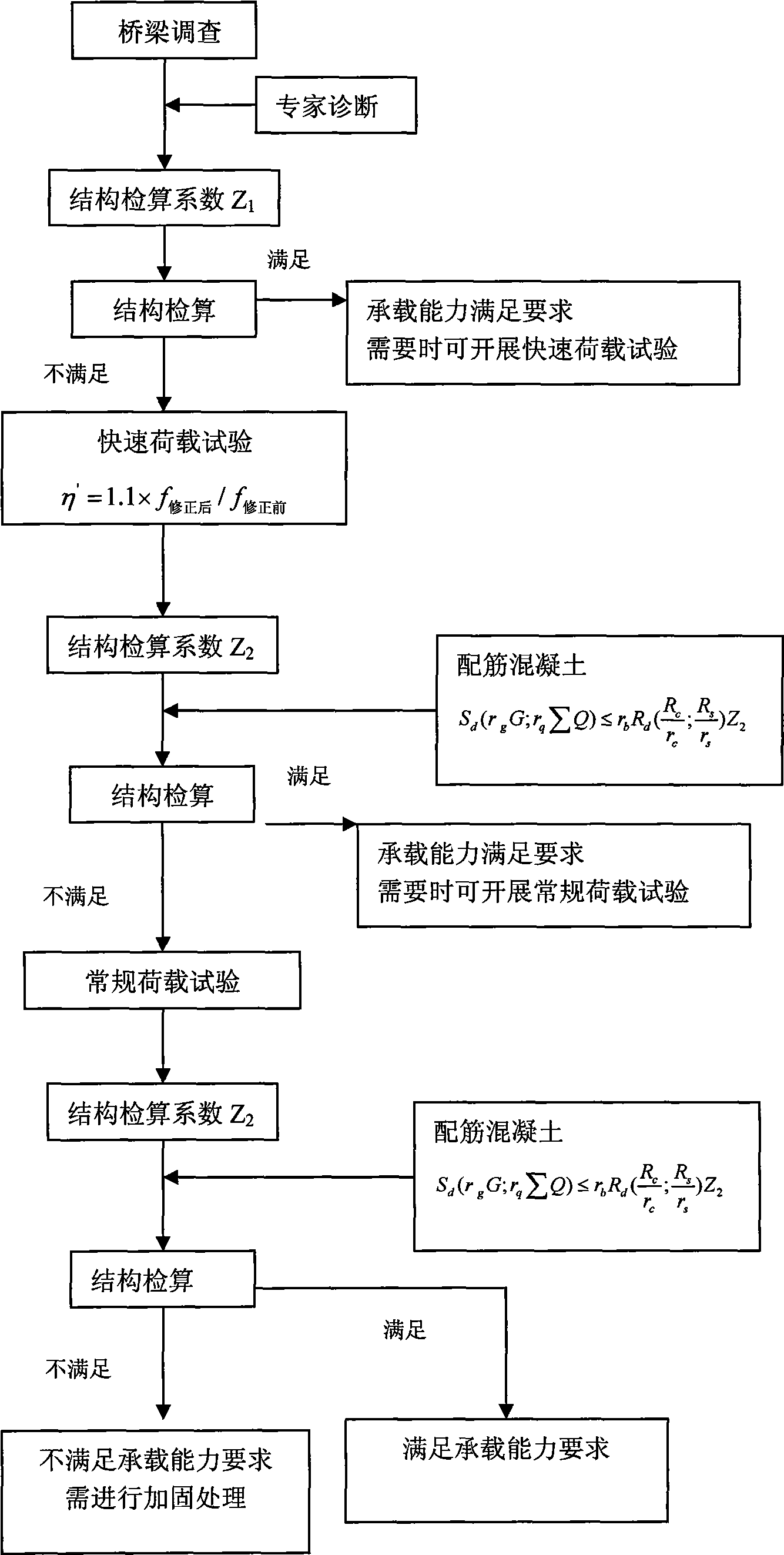
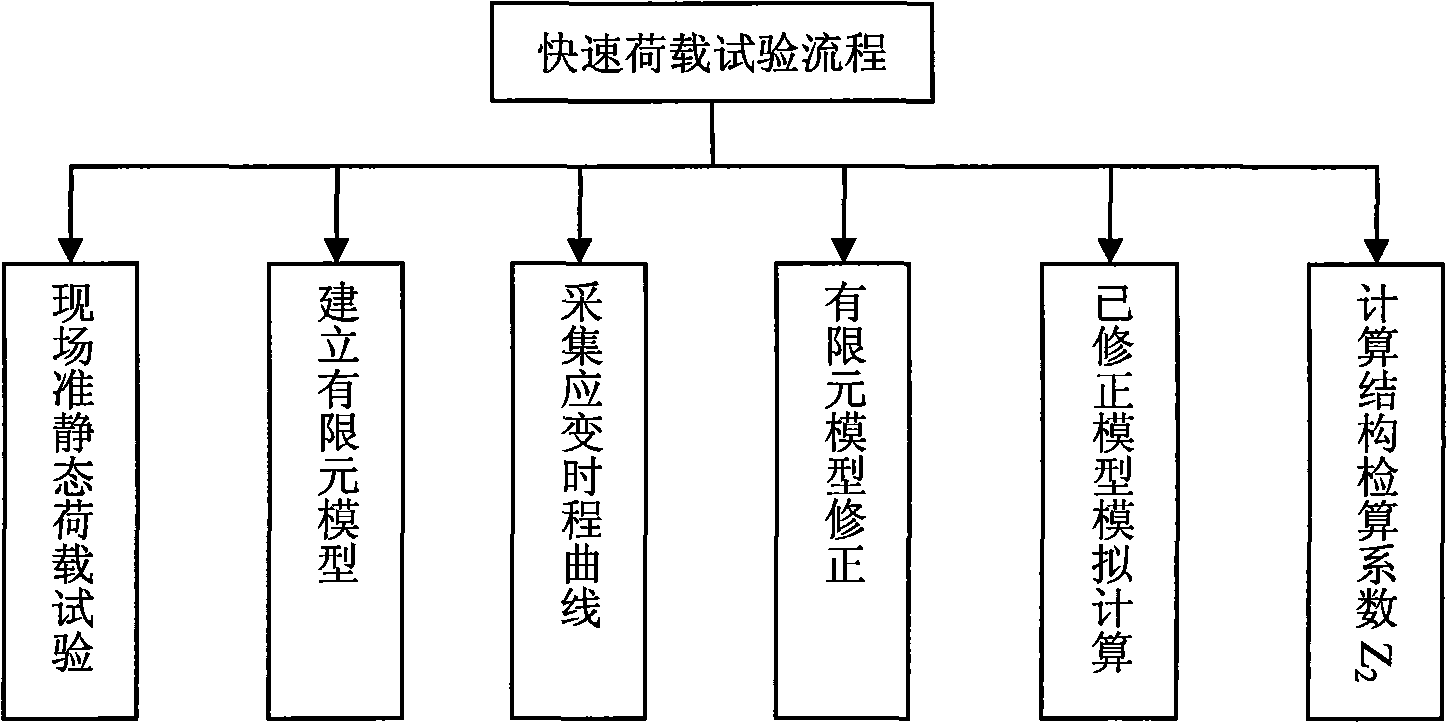
Quick load test method for bridge carrying capacity
ActiveCN101532917AAvoid the influence of human factorsHigh precisionStructural/machines measurementInfluence lineCarrying capacity
The invention relates to a quick load test method for bridge carrying capacity, and aims to provide a quick and accurate bridge carrying capacity evaluating method. The method comprises the following steps: performing a bridge quasi-static load test; establishing an initial finite element model; correcting the model by a control measuring point strain influence line obtained through actual measurement of the quasi-static load test; respectively distributing loads on the model before and after the correction according to the load test requirement, and calculating to obtain control measuring point flexivity values f before the correction and f after the correction; and defining that eta'=1.1*f after the correction / f before the correction, obtaining a check-calculation coefficient Z2 of a structure according to the efficiency coefficient eta', and performing check calculation on the structure through Z2.
Owner:JSTI GRP CO LTD
Aeroelastic stability fluid-structure interaction prediction method of turbo-machine changed interblade phase angles
InactiveCN101882177AReduce computing costCoupling calculation simplificationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelPredictive methods
The invention relates to an aeroelastic stability fluid-structure interaction prediction method of turbo-machine changed interblade phase angles, which predicts the aeroelastic stability of a turbo-machine through the modal pneumatic damping ratio of different interblade phase angles by adopting an energy method. The method adopts the modal analysis containing prestress on established single-sector finite element models, realizes the vibration displacement transfer on the fluid-structure interaction interface through a data transfer method, adopts the dynamic mesh technology for obtaining mesh files taking the interblade phase angles into consideration, is used for unsteady computation fluid mechanic analysis of Junction Box modules in CFX, further obtains the modal pneumatic damping ratio of each interblade phase angle, and is used for predicting the aeroelastic stability. The method based on the fluid-structure interaction fully utilizes the cutting edge technology of the computational structural mechanics and the computation fluid mechanics, ensures the computation precision in each sub system, and improves the computation efficiency through the division of a fixed region and a movable region. The invention has good practical value and wide application prospects in the technical field of turbo-machine simulation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
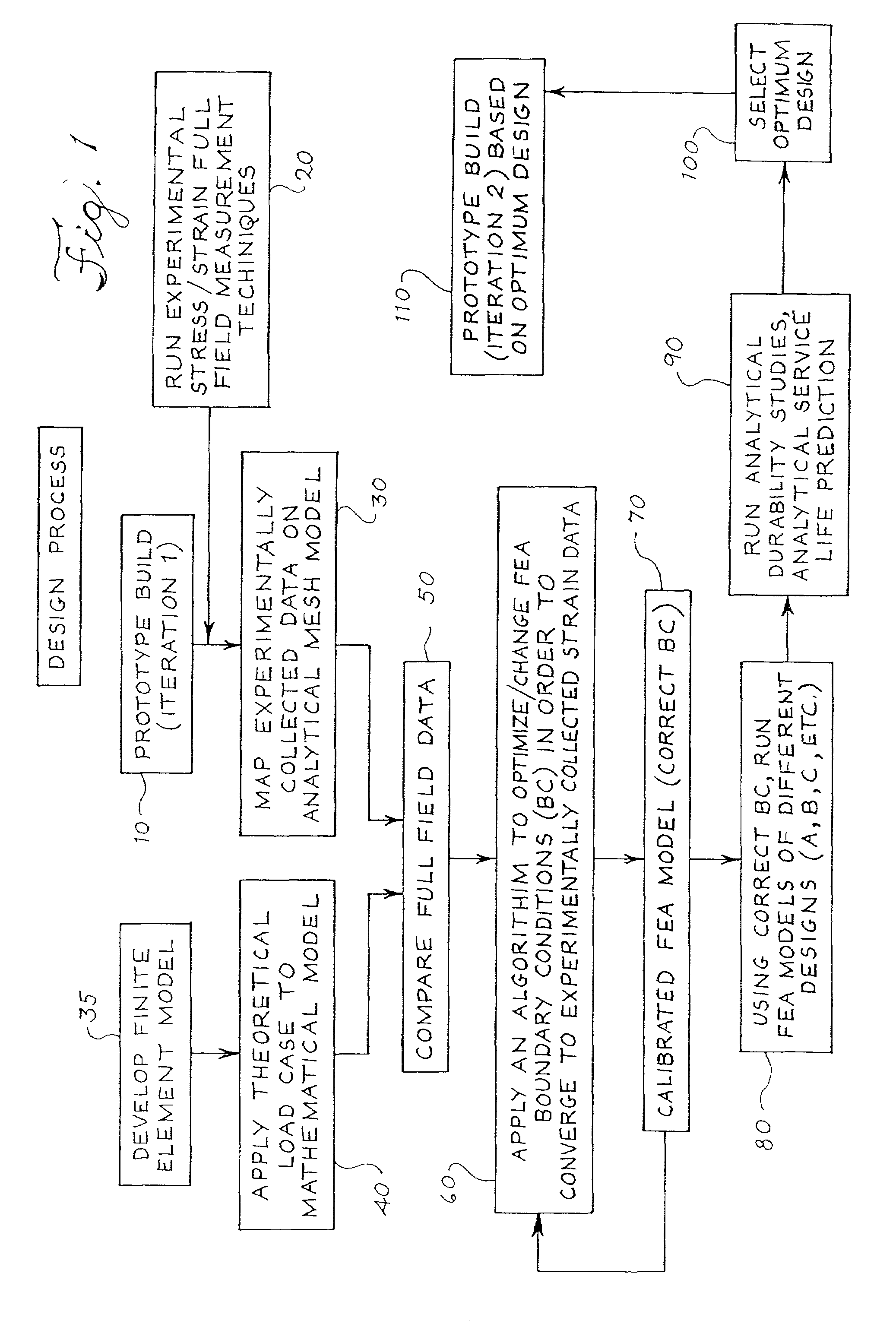
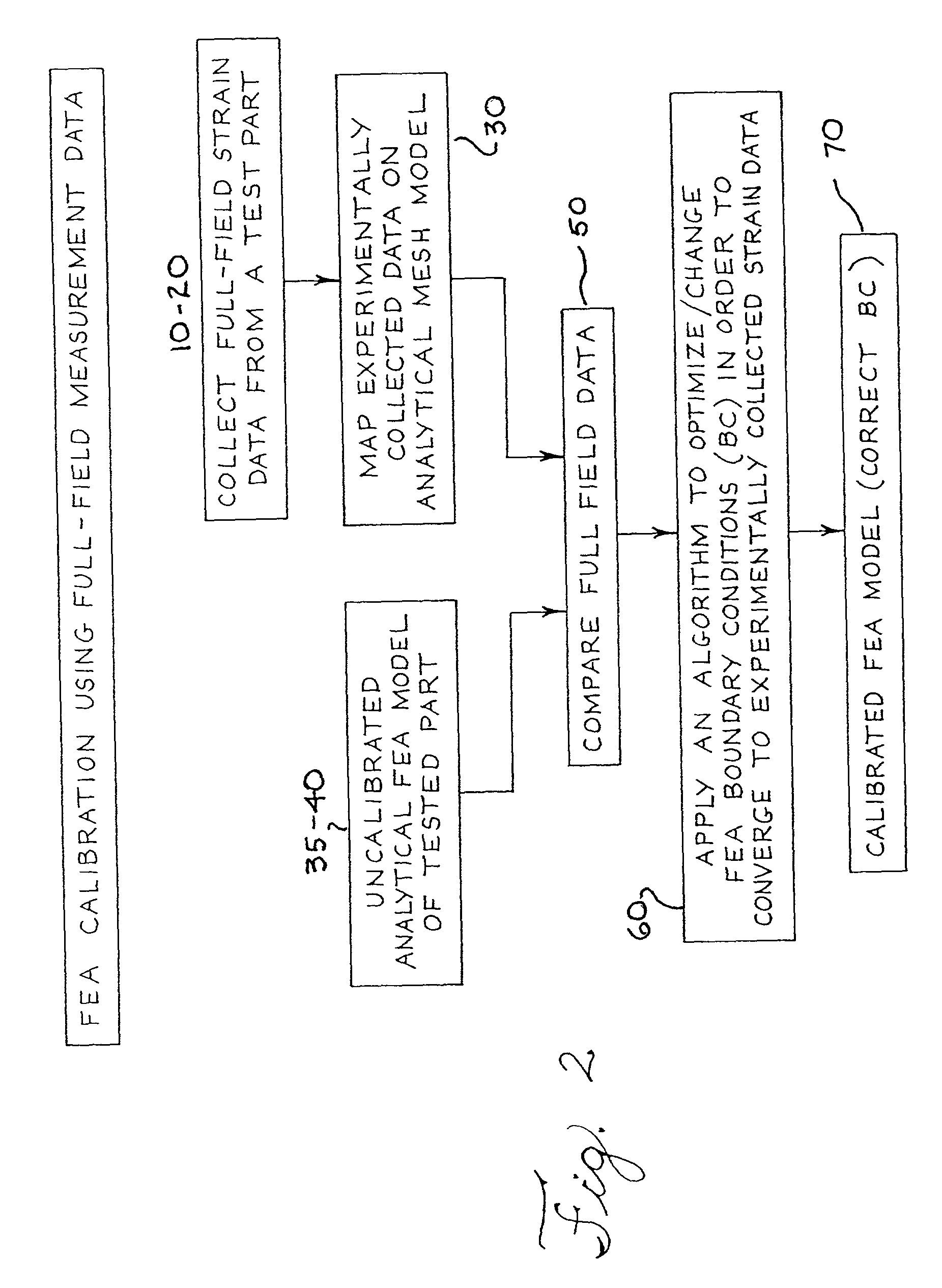
Method for calibrating a mathematical model
InactiveUS7024343B2Overcome disadvantagesAccurately modeling the characteristics of a componentComputation using non-denominational number representationUsing optical meansElement modelFull field
A method is disclosed for calibrating a mathematical model of a component using prototype full-field experimentally collected deformation / strain data. Specifically, the method involves obtaining actual experimental field data using strain sensitive coating material and then mapping said data on a CAD mesh model. The analytical mesh model is then compared to a finite element model that is based on theoretical values referred to as boundary conditions. The finite element model boundary conditions are then calibrated to reflect the values derived from the experimental field measurements. Once calibrated, the model can be used to optimize design of components.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
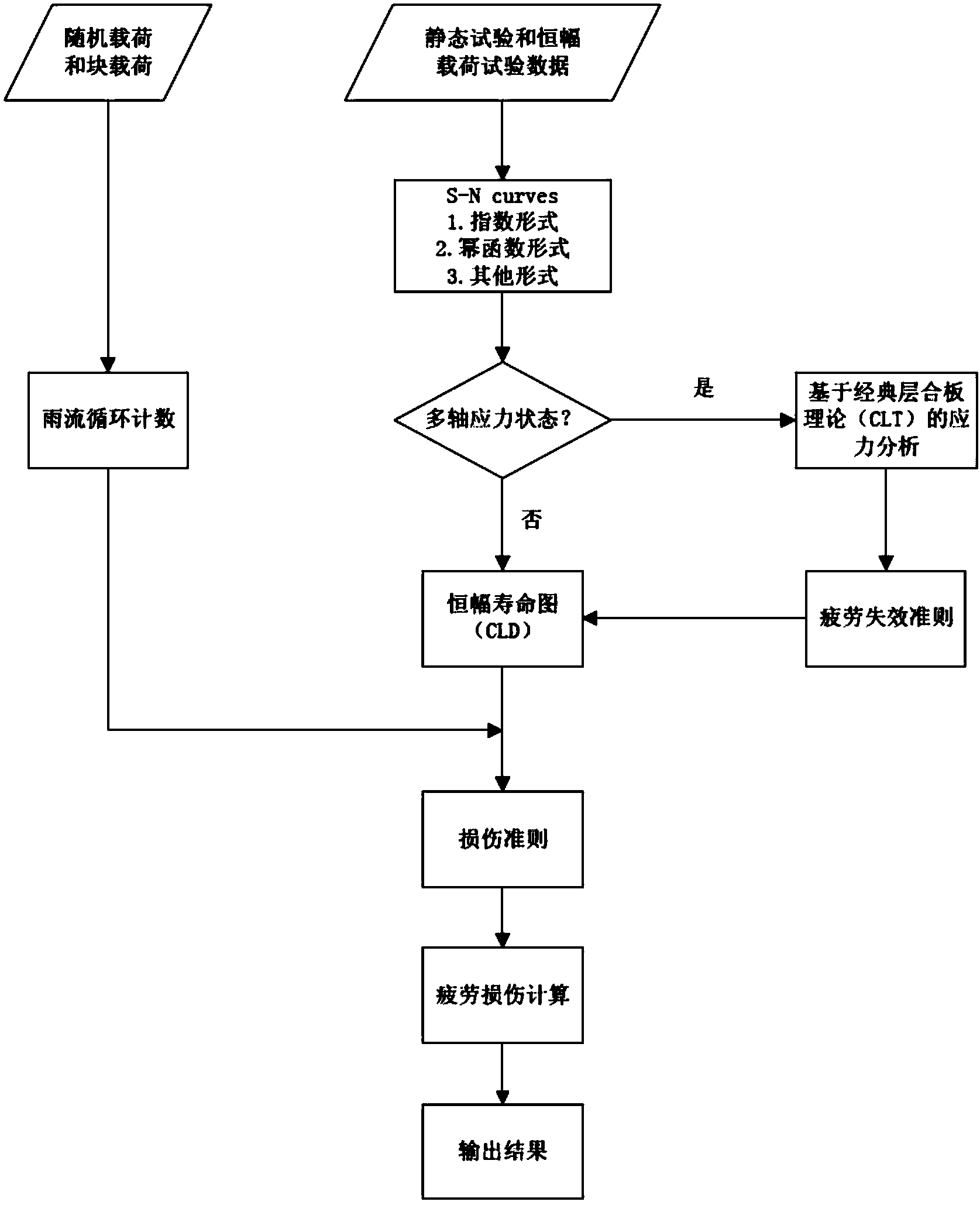
Carbon fiber composite material fatigue life estimating method based on stress ratio influences
InactiveCN103942441AAccurate lifeAccurate Damage AssessmentSpecial data processing applicationsStrength propertiesFinite element techniqueDispersity
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite materials, and discloses a carbon fiber composite material fatigue life estimating method based on stress ratio influences. Structural response calculation is carried out by means of a finite element technology. A finite element model is based on a classical laminate plate theory, and a umat subprogram taking tension and compression asymmetry into consideration is built. By carrying out constant-amplitude fatigue tests under different stress ratios, an equation of an influence mechanism of average stress on prediction of the service life of a carbon fiber composite material structure is built and is popularized to a block load and a spectrum load. A service life estimating model built through the method is based on the classical laminate plate theory and takes influences of the average stress and a variable-amplitude load into consideration, dispersity of a prediction result is little, accuracy is high, theoretical guidance is provided for reliability design of parts made of carbon fiber composite materials, and the technical problems that existing carbon fiber composite material structure fatigue life is only estimated through a test method, and accordingly cost is high and consumed time is long are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for simulating manufacturing, electrical and physical characteristics of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6826517B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsDetecting faulty computer hardwareElement modelMaterial Design
An electronic device simulator includes a three-dimensional lumped device model, a three-dimensional visco-elastic process simulation model and a material design model that are interlinked with each other. The three-dimensional lumped device element model comprises a Poisson's equation model, an electron continuity equation model, a hole continuity equation model, a Maxwell's equations model, an eddy current equation model, and an Ohm's law equation model. The simulator accounts for the three dimensional characteristics of the circuit to determine circuit performance.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment
ActiveCN104133933AGuaranteed continuitySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a pneumatic elastic analytical method, and provides a pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of a hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment. According to the method, the piston theory is used for carrying out frequency domain nonsteady aerodynamic calculation on a full-aircraft finite element model of the hypersonic speed aircraft; on the basis, the pneumatic thermal effect on the model in the hypersonic speed thermal environment is considered; the weak coupling effect of pneumatic thermal input in aerodynamic input and elastic force input is ignored; only the structure temperature steady-state characteristics under the pneumatic thermal load effect are considered; after the steady aerodynamic calculation, the thermal flux density on the surface of the aircraft is obtained by adopting a reference enthalpy method; further, the steady temperature distribution on the surface of the aircraft is calculated; the practical equivalent rigidity matrix of the structure at the moment is obtained; and the critical flutter speed is calculated by an engineering method. The pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method has the advantages that the pneumatic elastic analytical problem of the hypersonic speed aircraft in the pneumatic thermal environment is solved, and the pneumatic elastic performance of the hypersonic speed aircraft is improved through flutter speed analysis.
Owner:ANHUI JINSANHUAN METAL SCI & TECH
Bridge field static load test evaluation method
ActiveCN104933285AEffective and comprehensive assessmentImprove securitySpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEvaluation Interval
The present invention relates to a bridge field static load test evaluation method, which is mainly a method for evaluating the bearing capacity and adaptation performance of a bridge by means of a field static load test. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining specific content and method for collecting relevant data for early stage preparation work; (2) establishing a reasonable and accurate bridge structure finite element model according to the collected data; (3) calculating and analyzing a result according to an endogenous force and a stress of the bridge under dead and live loads, and determining theoretical force bearing safety and live load force bearing characteristics; (4) in combination with a traditional key section of the bridge, determining a bridge test section and completing static load test solution designing; (5) performing the field static test for the bridge and processing the test data; (6) studying an evaluation interval corresponding to a preset test evaluation indicator; and (7) making a reasonable and comprehensive assessment on the structural performance of the bridge. The evaluation method and indicator according to the present invention can more effectively indicate the practical bearing capacity and applicability of the bridge in a refined manner, and improving the reasonability and accuracy of the evaluation result.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of identifying critical elements in fatigue analysis with von mises stress bounding and filtering modal displacement history using dynamic windowing
InactiveUS6212486B1Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationTransient analysisElement model
A method of dynamic durability analysis and fatigue area identification using modal techniques for a structure includes the steps of simulating a finite element model of the structure to determine modal stresses and modal displacements for an element of the structure and performing a modal transient analysis using the modal displacements. The method also includes the steps of determining a stress bound for the element from the modal stresses and modal transient analysis, determining if a stress bound for the element is greater than a predetermined value and identifying the element as a critical element if the stress bound for the element is greater than the predetermined value. The method further includes the steps of determining a stress time history for the critical element and using the stress time history to perform a fatigue analysis to identify an area of fatigue within the structure.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
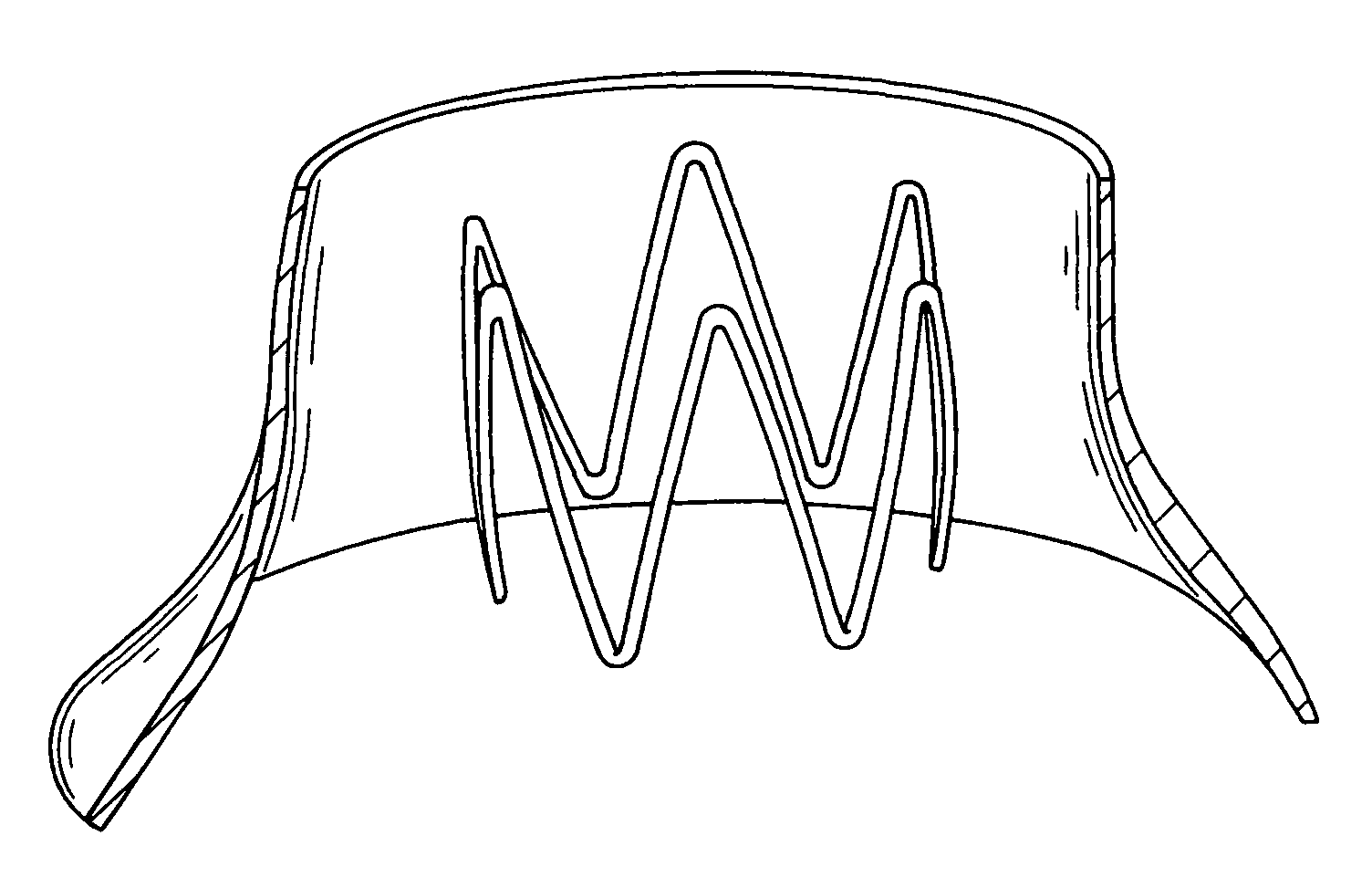
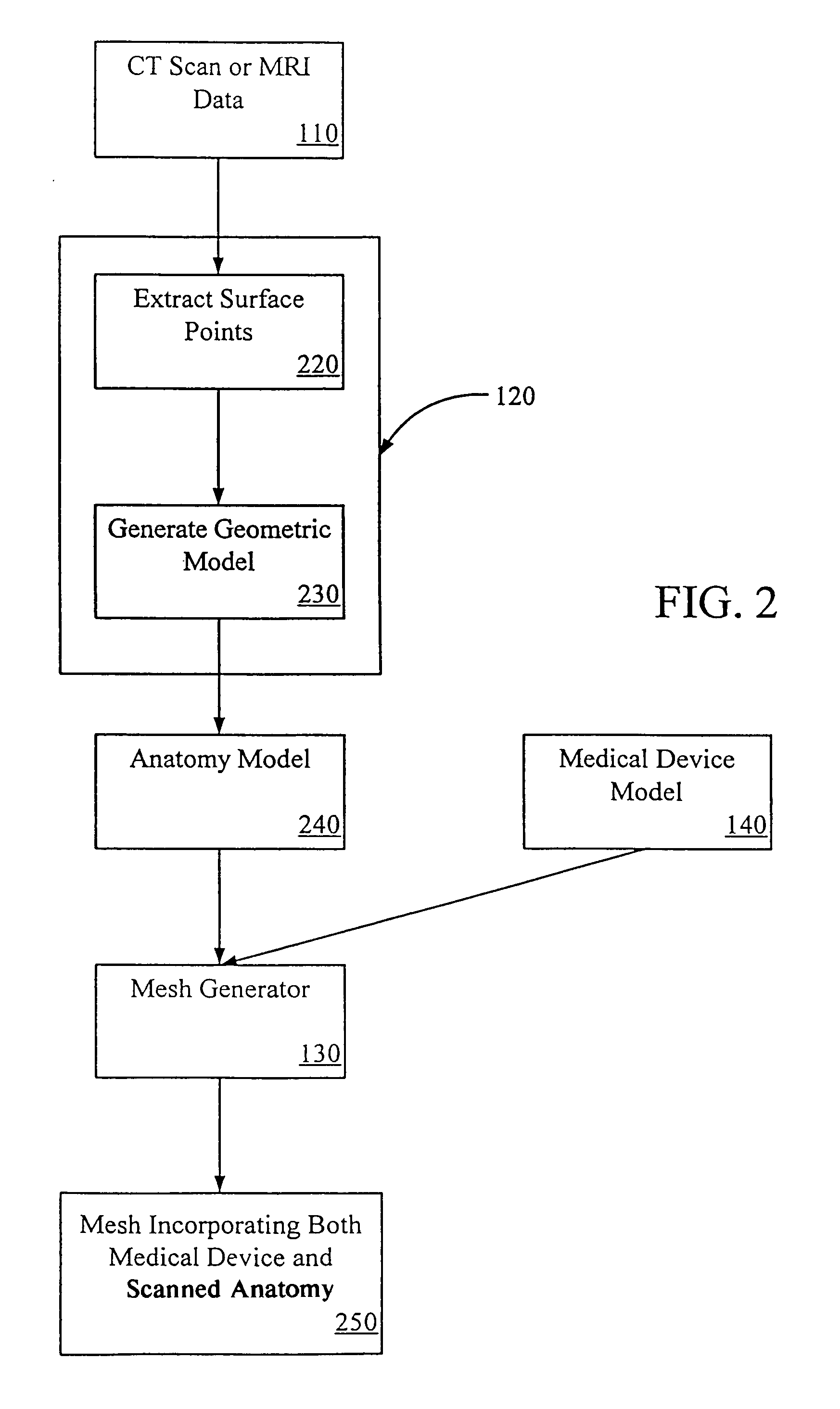
Virtual prototyping and testing for medical device development
A system and method of developing better-designed medical devices, particularly cardiovascular stents and endovascular grafts. The system comprises a geometry generator, a mesh generator, a stress / strain / deformation analyzer, and a visualization tool. In one embodiment, the geometry generator receives three-dimensional volumetric data of an anatomical feature and generates a geometric model. The mesh generator then receives such geometric model of an anatomical feature or an in vitro model and a geometric model of a candidate medical device. In another embodiment, the mesh generator only receives a geometric model of the candidate medical device. Using the geometric model(s) received, the mesh generator creates or generates a mesh or a finite element model. The stress / strain / deformation analyzer then receives the mesh, and the material models and loads of that mesh. Using analysis, preferably non-linear analysis, the stress / strain / deformation analyzer determines the predicted stresses, strains, and deformations on the candidate medical device. Such stresses, strains, and deformations may optionally be simulated visually using a visualization tool.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
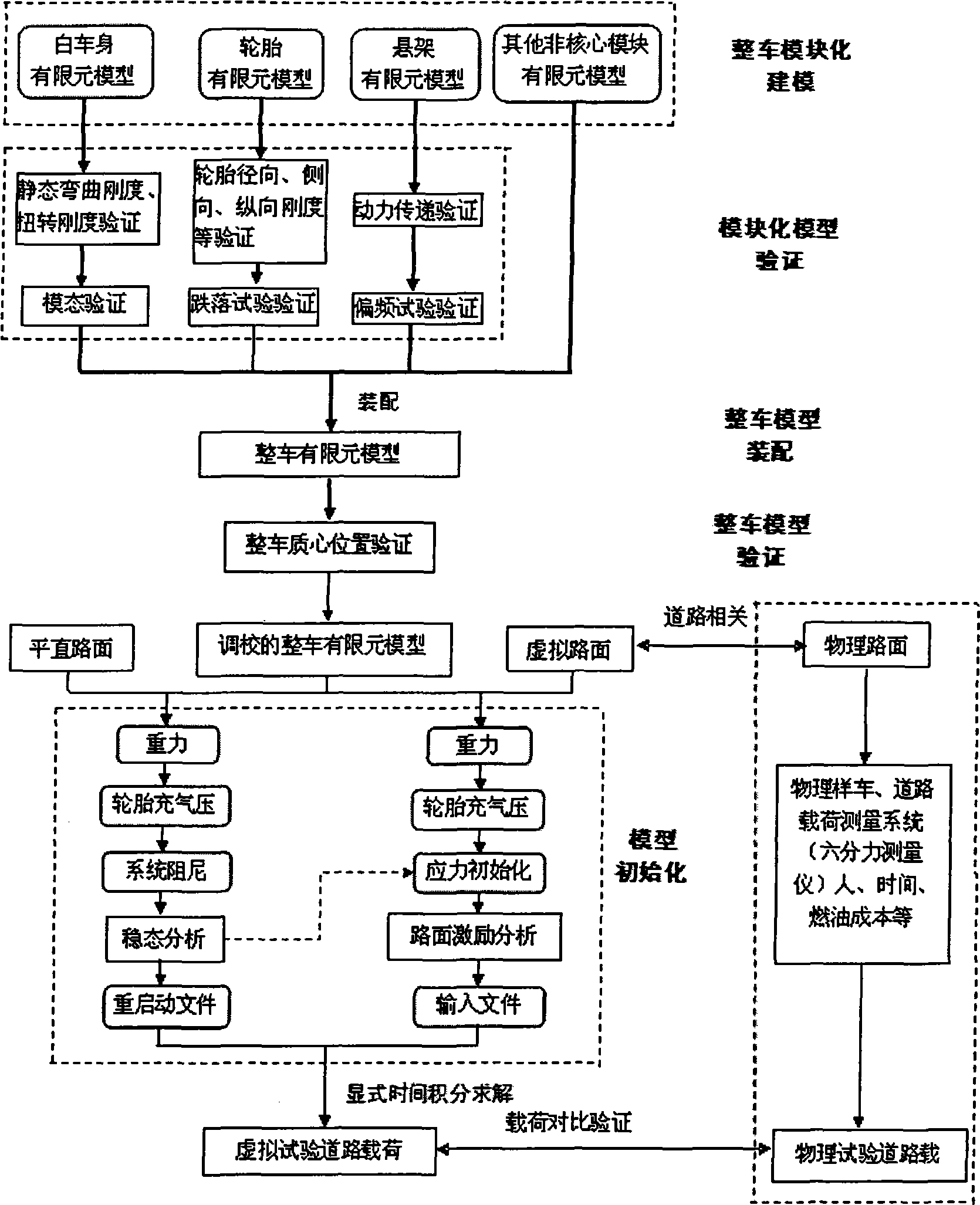
Vehicle road load emulation method
InactiveCN101510230AAvoid the difficulty of determining the force relationshipAvoid undetermined difficultiesSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelModularity
The invention provides a vehicle road load simulation method which comprises the following steps of: 1) complete vehicle modular modeling; 2) complete vehicle modular model validation; 3) complete vehicle model assembly; 4) complete vehicle model validation; 5) establishment of finite element models of enhanced durable roads; 6) model initialization; 7) obtaining of virtual road load result; and 8) comparative validation with physical road load. The invention has the advantages of shortening development time and reducing costs, which is of great significance to vehicle development during the conceptual design phase. During the conceptual design phase of new models, fatigue analysis can be carried out before the design and manufacture process by using a virtual prototype to predict road load so as to truly predict the life of the product, thus greatly reducing great expenses caused by producing prototype machines and testing the fatigue life.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
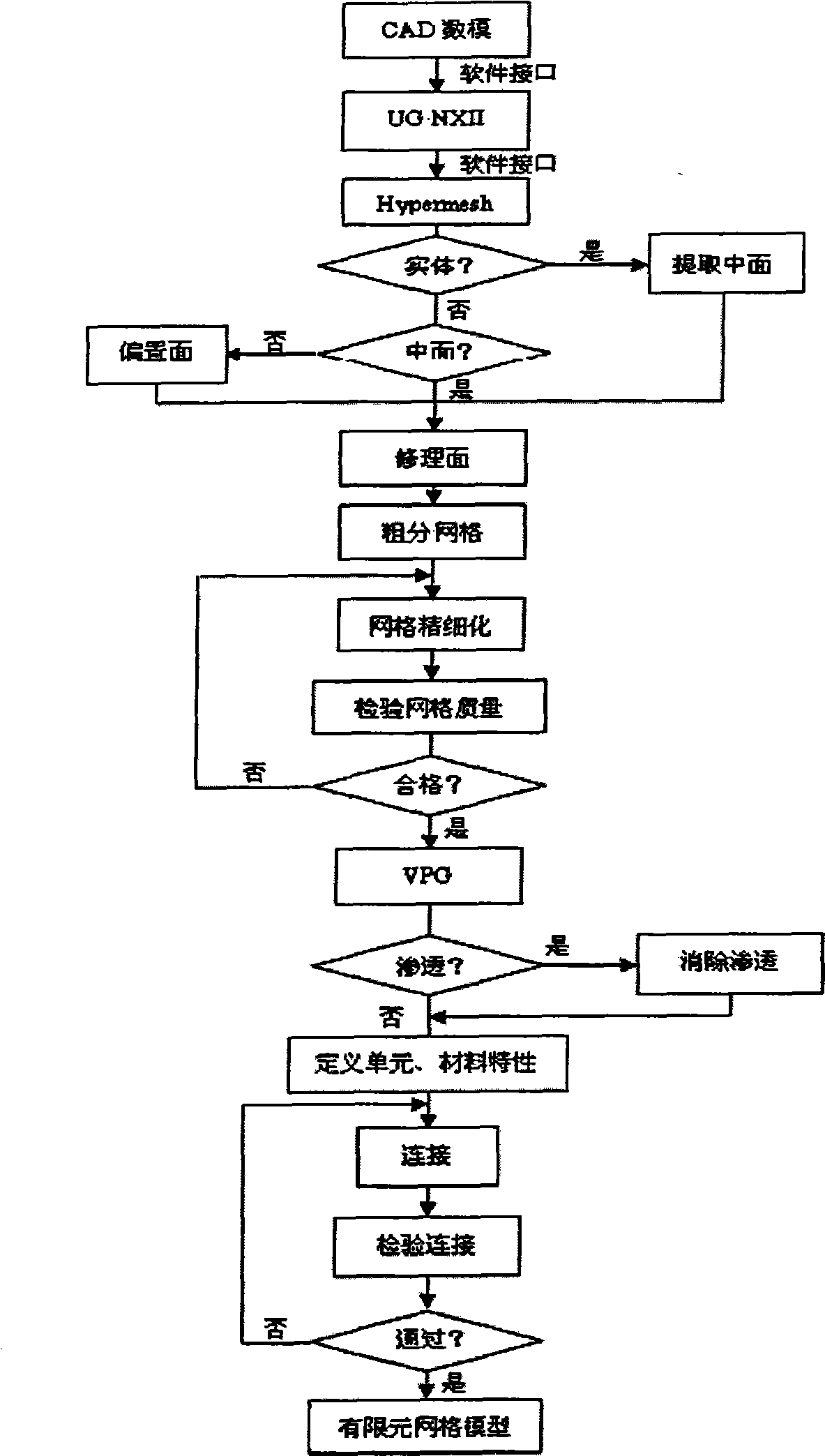
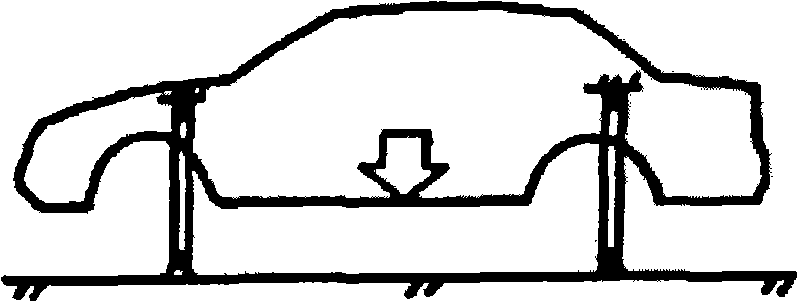
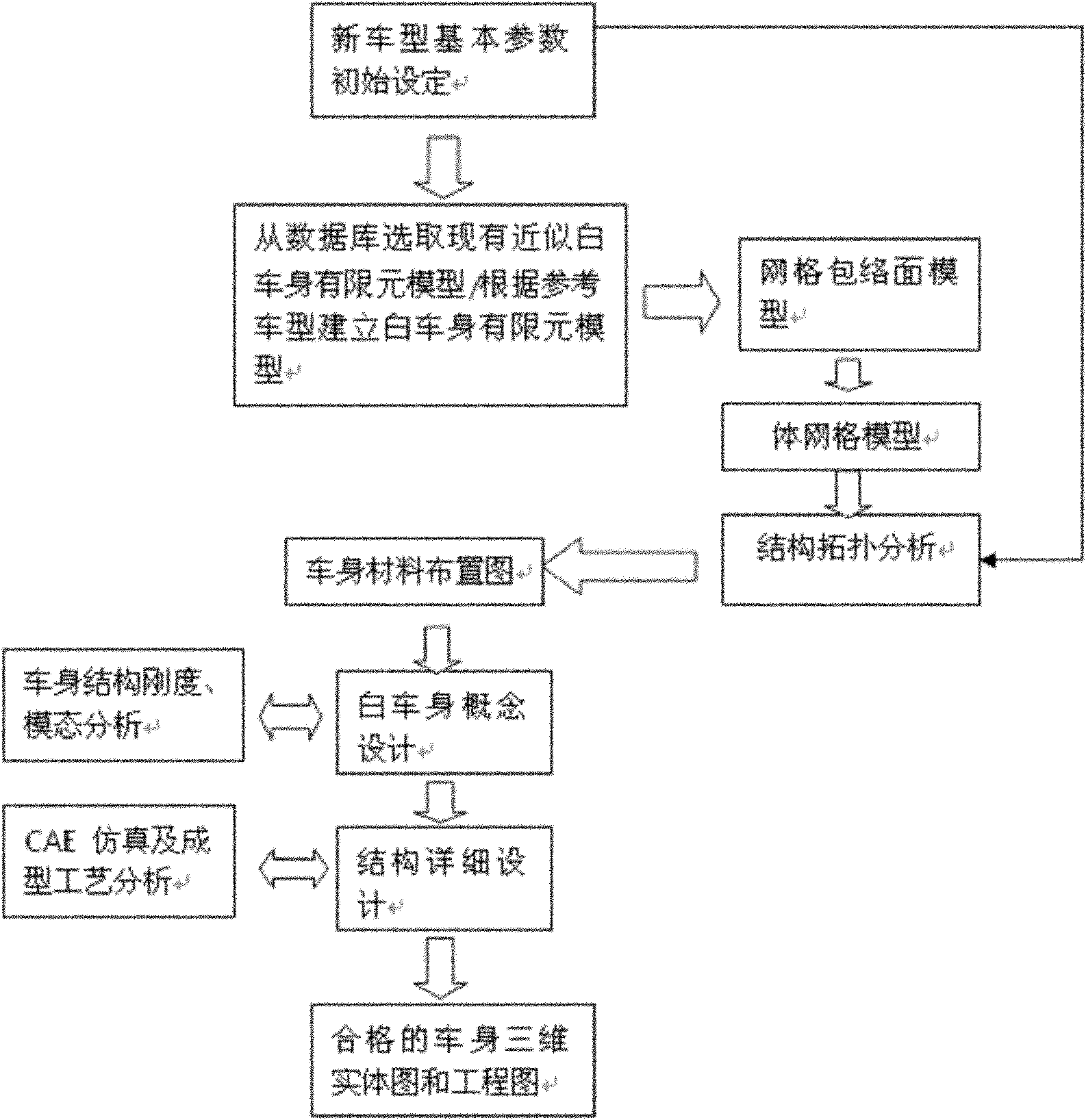
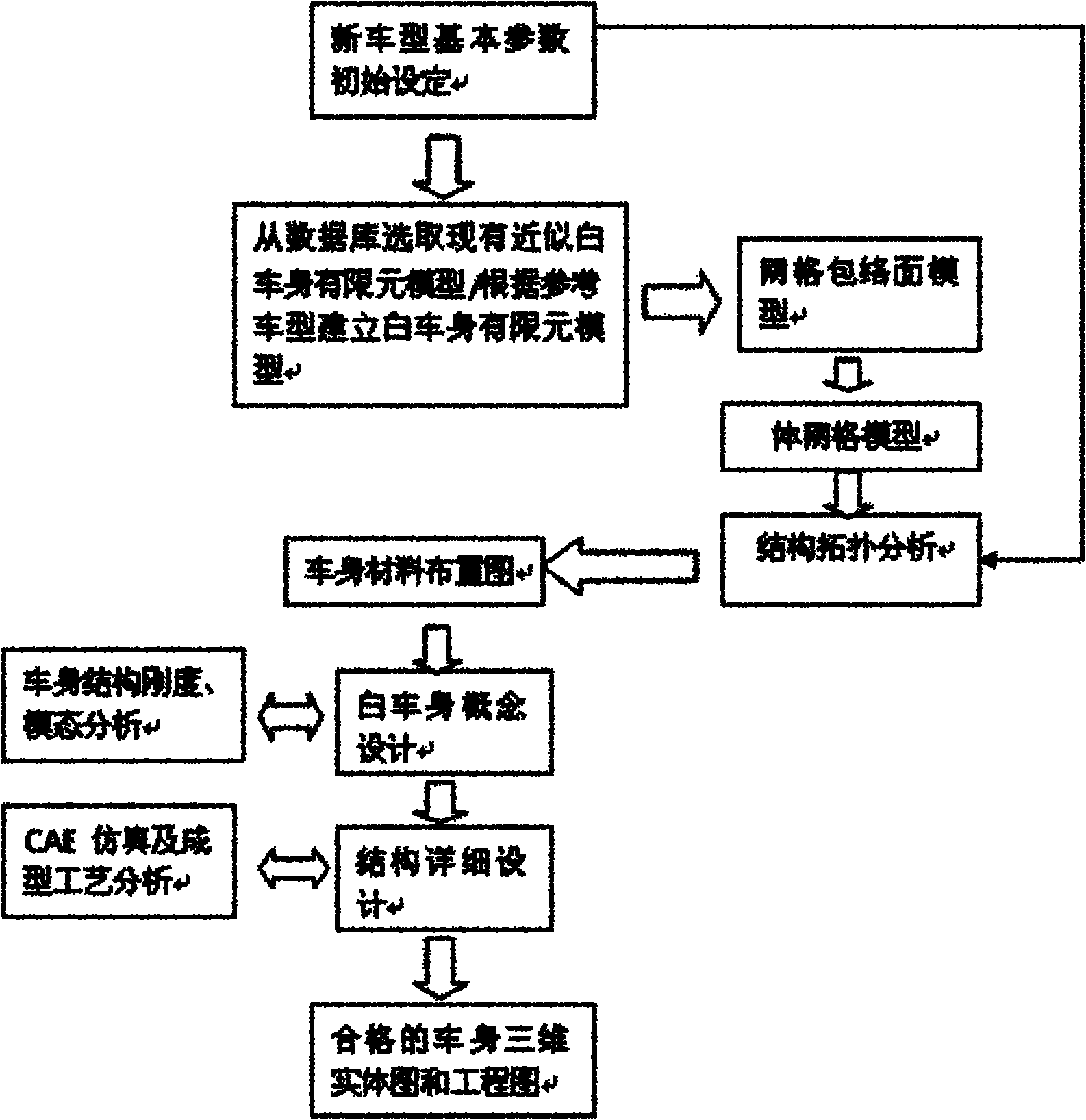
Method for designing automobile body structure layout
InactiveCN102012958AImprove guidanceShorten the development cycleAerodynamics improvementSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelTopology optimization
The invention relates to a method for designing automobile body structure layout. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) initially setting the parameters of a new type automobile, 2) choosing the white automobile body finite element models having similar structures and sizes, or directly building a white automobile body finite element model, 3) generating a grid enveloped model according to the white automobile body finite element model, 4) generating a body grid model according to the grid enveloped model, 5) topologically optimizing and analyzing according to a target parameter based on the body grid model, 6) according to an analyzed result and drawing an automobile body material layout diagram, 7) designing conception according to the layout diagram, and 8) designing the layout structure in detail according to the data of the conception design, performing simulating analysis of strength, NVH and impact performance CAE and formability process analysis according to the data of the detailed design of the layout structure, and modifying so as to acquire a three-dimensional digitized product model fit for volume production. The automobile body structure layout has the advantages of shortened developing period and lowered researching and developing cost.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
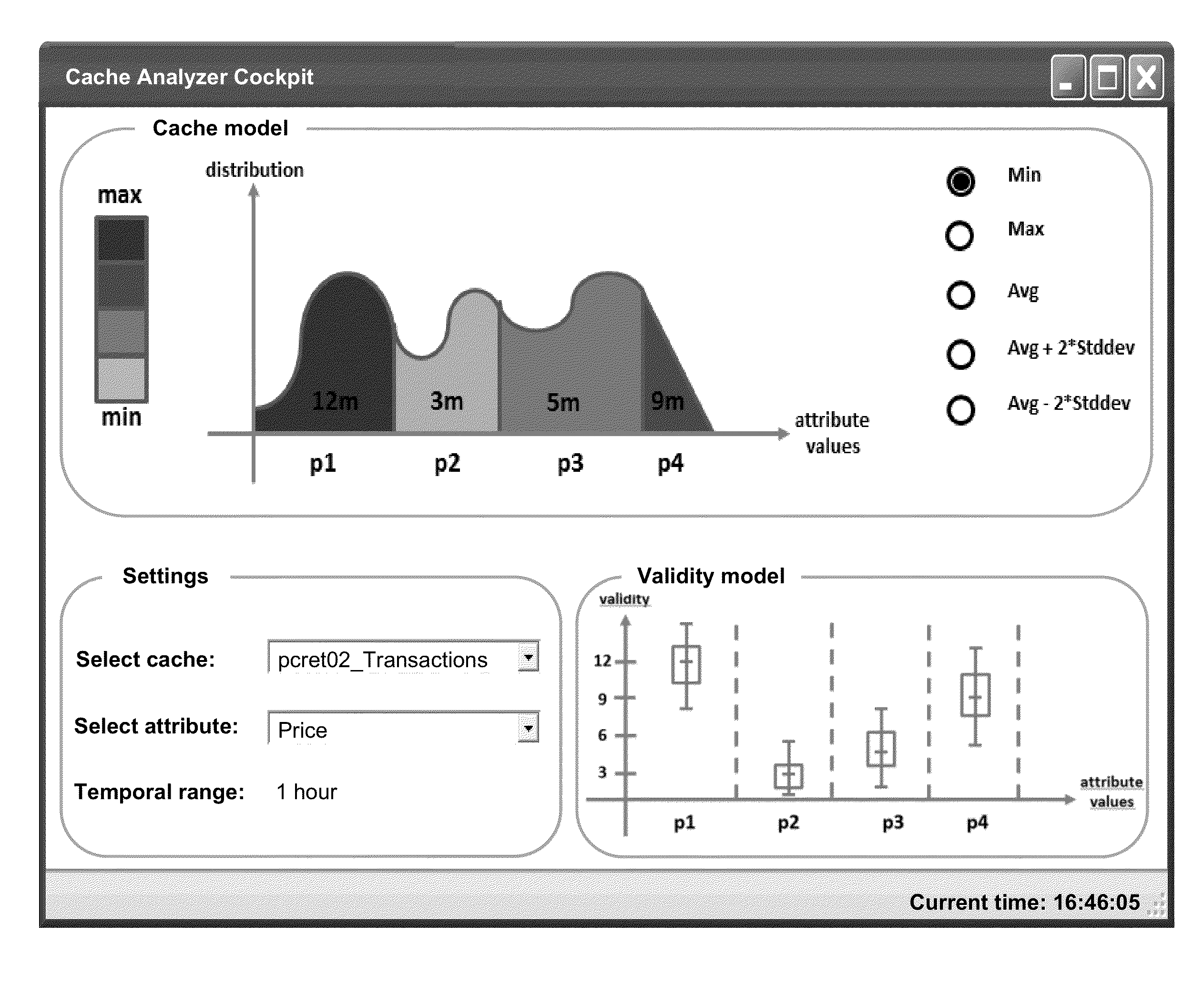
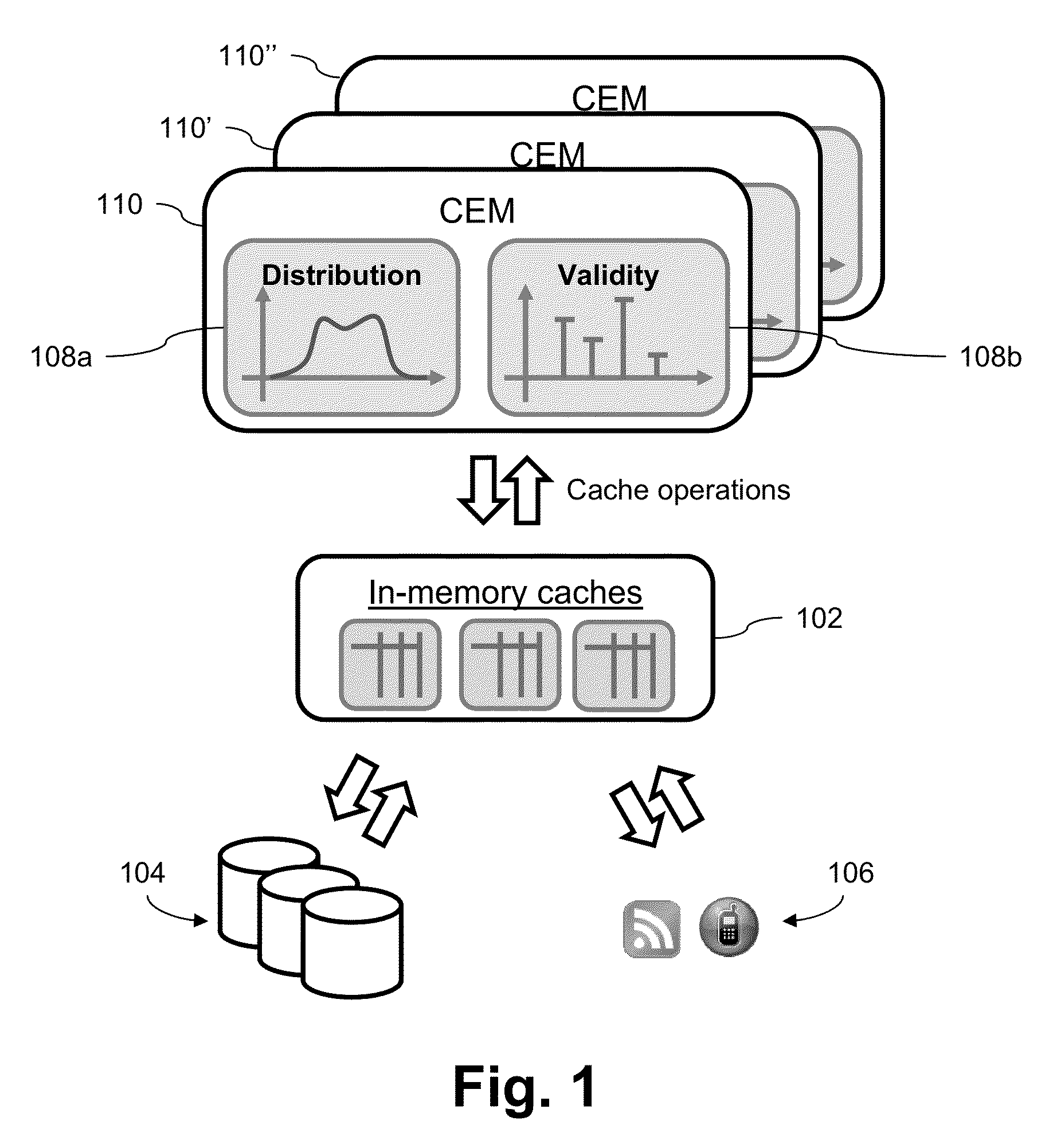
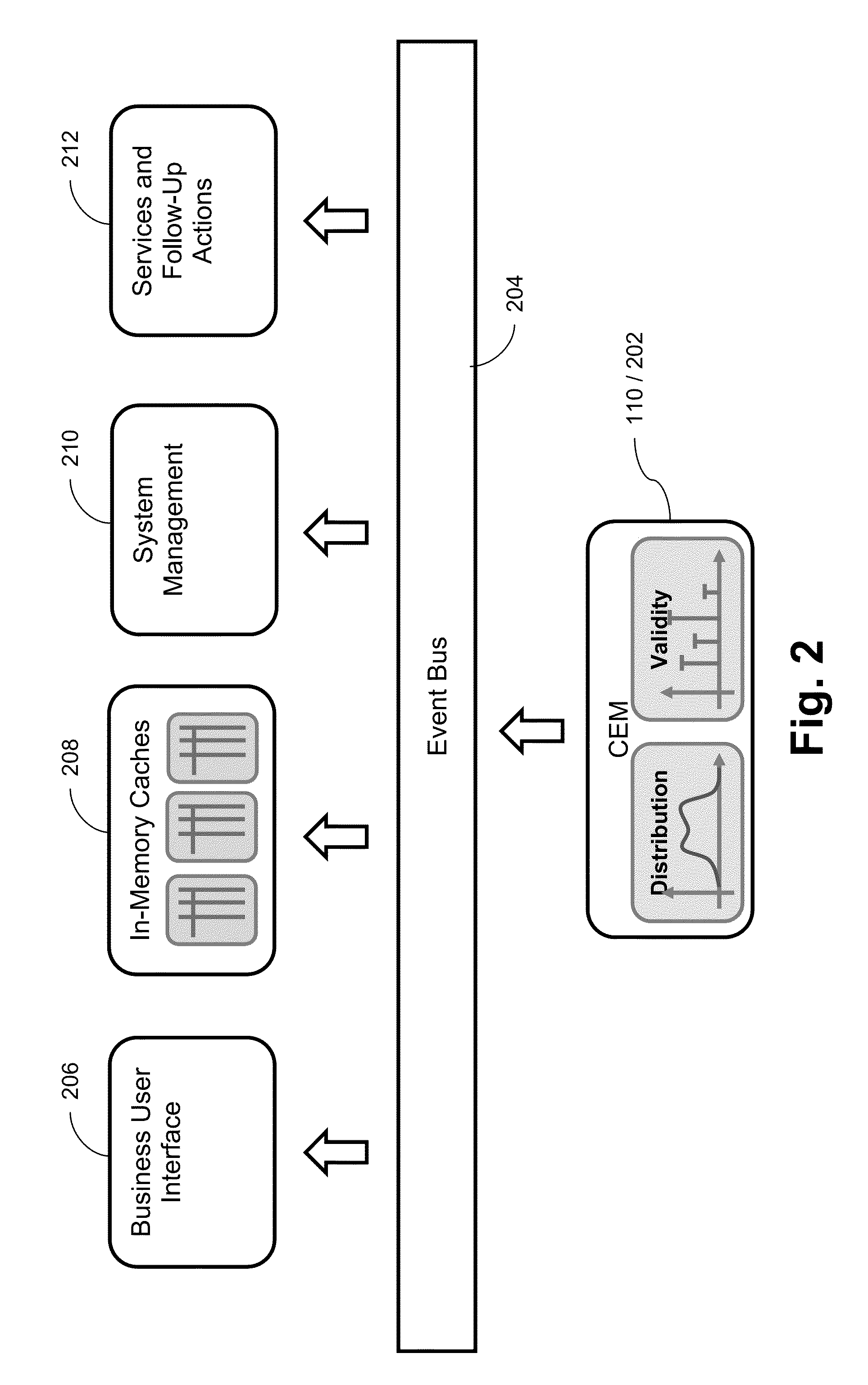
Systems and/or methods for statistical online analysis of large and potentially heterogeneous data sets
ActiveUS9122786B2Enhanced interactionImprove responsivenessDigital data information retrievalHardware monitoringAnalytic modelElement model
Certain example embodiments relate to using Complex Event Processing (CEP) techniques for statistical analysis of cache behavior and parameters, e.g., in connection with large, potentially heterogeneous data sets (e.g., “Big Data”). A dedicated stream mining operator registers a listener to a cache and receives notifications on cache operations. For selected element attributes, a first model estimates the probability density functions of the attribute values, delivering well-defined estimates of the attribute value distributions. A second model analyzes the time elements stay in the cache (“validity”). Validity is combined with the attribute value distribution. A meaningful analysis model (Cache Element Model) can be derived by combining additional summary statistics for the validity with the attribute value distribution, describing how long elements stay in the cache for attribute values of a specific region, and how the values are distributed. It may be used to inform administrative tasks such as, optimization of cache parameters.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
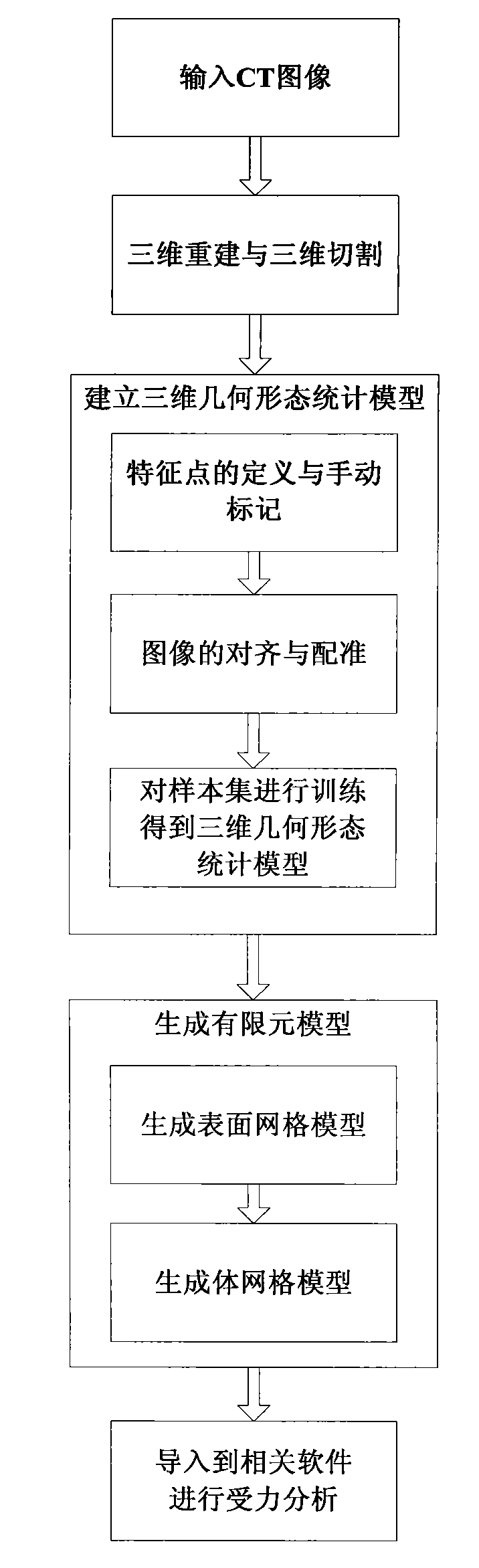
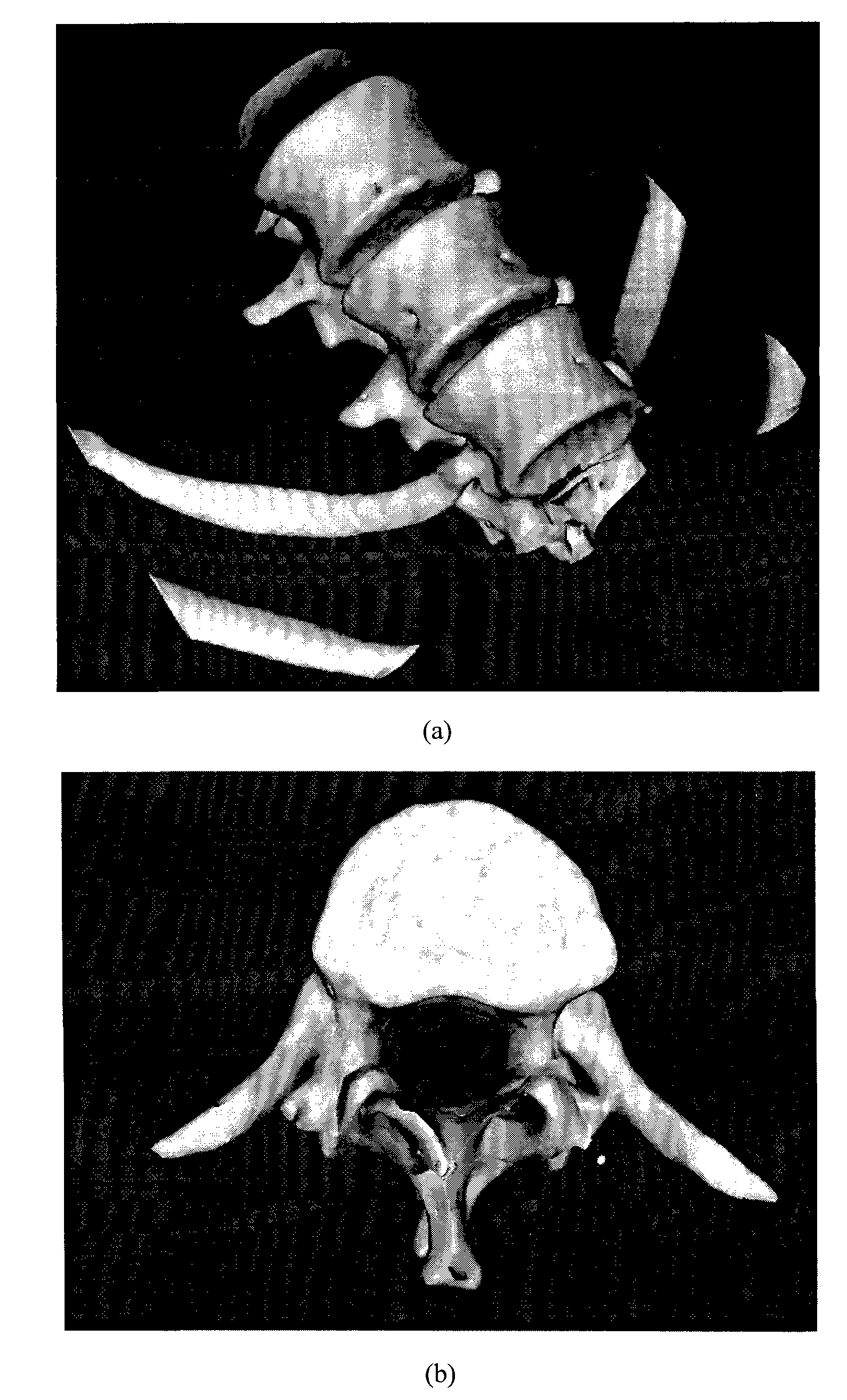
Method for constructing vertebral three-dimensional geometry and finite element mixture model
The invention provides a method for constructing a vertebral three-dimensional geometry and finite element mixture model, which belongs to the technical field of processing of medical images. The method comprises the following construction processes of: inputting a vertebral computer tomography (CT) image; performing three-dimensional reconstruction and three-dimensional cutting on the CT image to acquire a vertebral three-dimensional image set; establishing a three-dimensional geometric statistical model, namely defining and manually calibrating vertebral characteristic points, aligning and registering vertebral images, and training a sample set to acquire the statistical model; and generating a finite element model, importing the statistical model, generating a surface mesh model, and generating a volume mesh model, wherein the model can be directly imported into finite element analysis software for biomechanics analysis. By the method, a vertebral geometrical shape can be precisely described, the accuracy of finite element analysis results can be ensured, and the precision of vertebral models can be improved. The method is convenient to use, facilitates the scientific measurement of the shapes and the stress of vertebras and can be used for researches related to vertebral columns and the vertebras in the field of surgical medicine.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
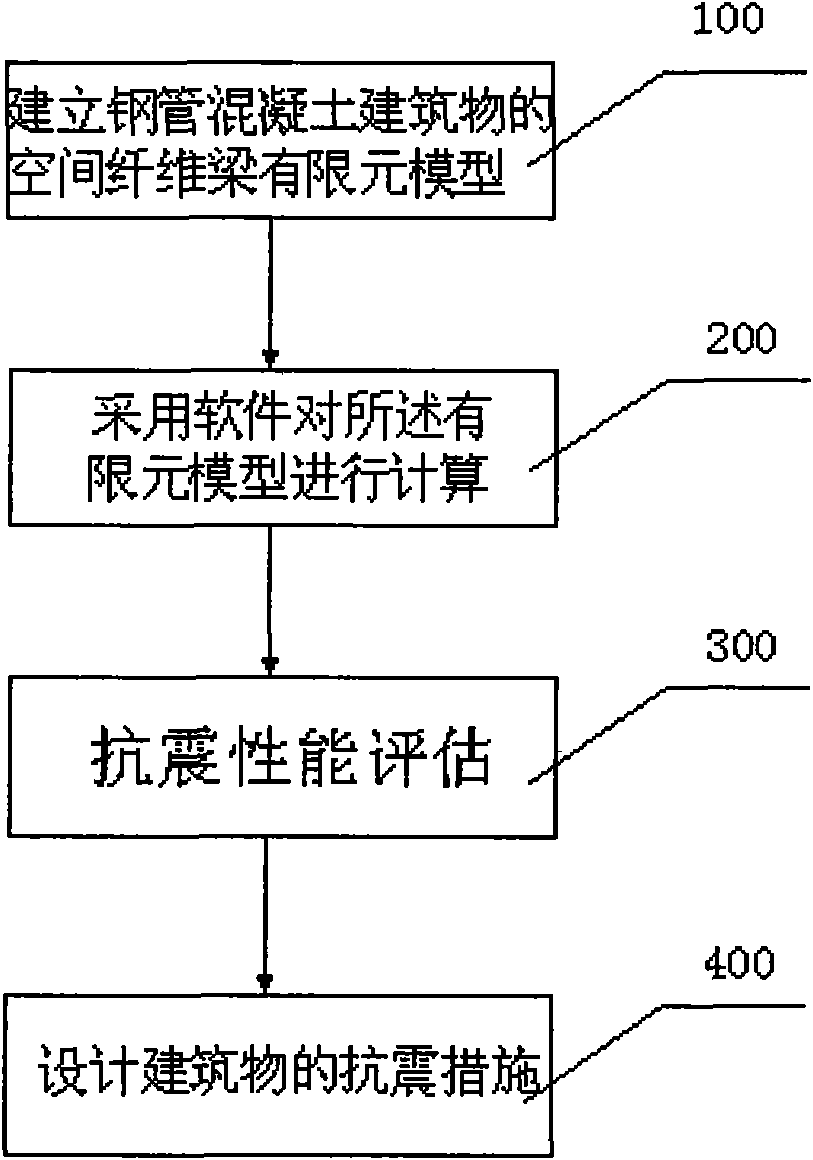
Evaluation method of earthquake resistant performance of steel tube concrete building and application
The invention relates to an evaluation method of earthquake resistant performance of a steel tube concrete building. A building support component is formed by steel tube concrete. The evaluation method comprises the following steps of establishing a space fiber beam finite element model of the steel tube concrete building, developing an analysis method suitable for a fiber beam, considering that the confinement effect and the material characteristic of the elasto-plasticity under earthquake cyclic loading damage a constitutive model and a corresponding subprogram, calculating the finite element model by adopting a software and combining with the material subprogram, evaluating the earthquake resistant performance, and designing the earthquake resistant measure of the building. In the provided evaluation method of the earthquake resistant performance of the steel tube concrete building, the earthquake resistant performance of the building is evaluated on the basis of the maximum inter-story displacement angle limit value required by a steel tube concrete structure by establishing the space fiber beam finite element model of the steel tube concrete building, developing the analysis method suitable for the fiber beam, considering that the confinement effect and the material characteristic of the elasto-plasticity under earthquake cyclic loading damage the constitutive model, calculating the finite element model by adopting the software and obtaining the maximum inter-story displacement angle of the building, and building earthquake resistant measures are planed according to the evaluation result of the earthquake resistant performance of the building.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
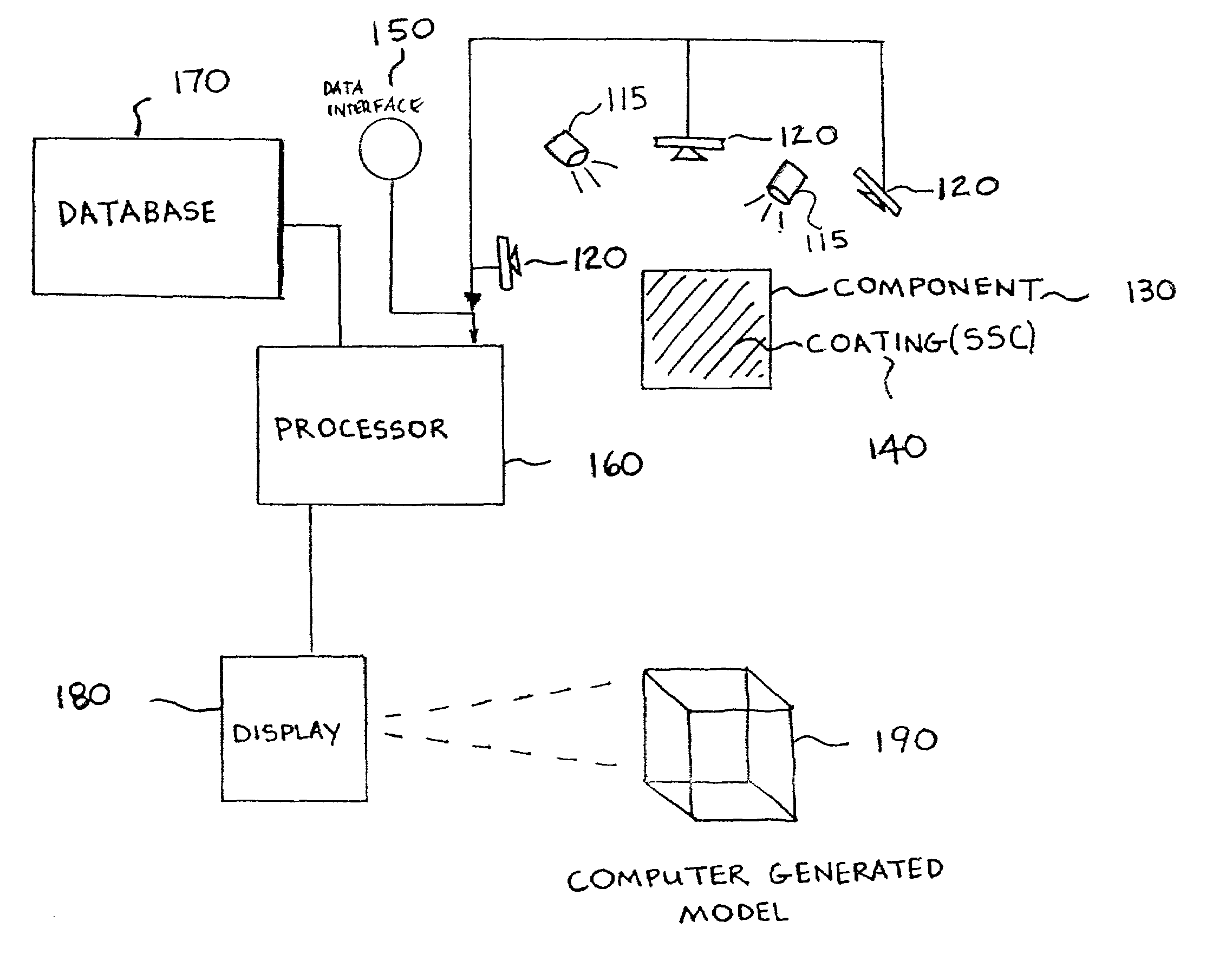
Capture and display of image of three-dimensional object
InactiveUS20060066877A1Realistic viewing experienceSimple modelInvestigating jewelsUsing optical meansElement modelMultiple perspective
A system and method for modeling three-dimensional objects such as diamonds and other gemstones. A three-dimensional finite-element model obtained by, for example, analysis of boundaries of the object in photographs taken from multiple perspectives with frontal lighting or silhouette lighting, or by analysis of structured-light photographs of the object taken from multiple perspectives, is combined with color or grayscale information obtained from photographs of the object. Enhanced or “false” color can be used to improve the viewing experience or to emphasize particular features of the object. A computer can rotate the model about arbitrary axes according to the desires of a viewer.
Owner:BENZANO DANIEL
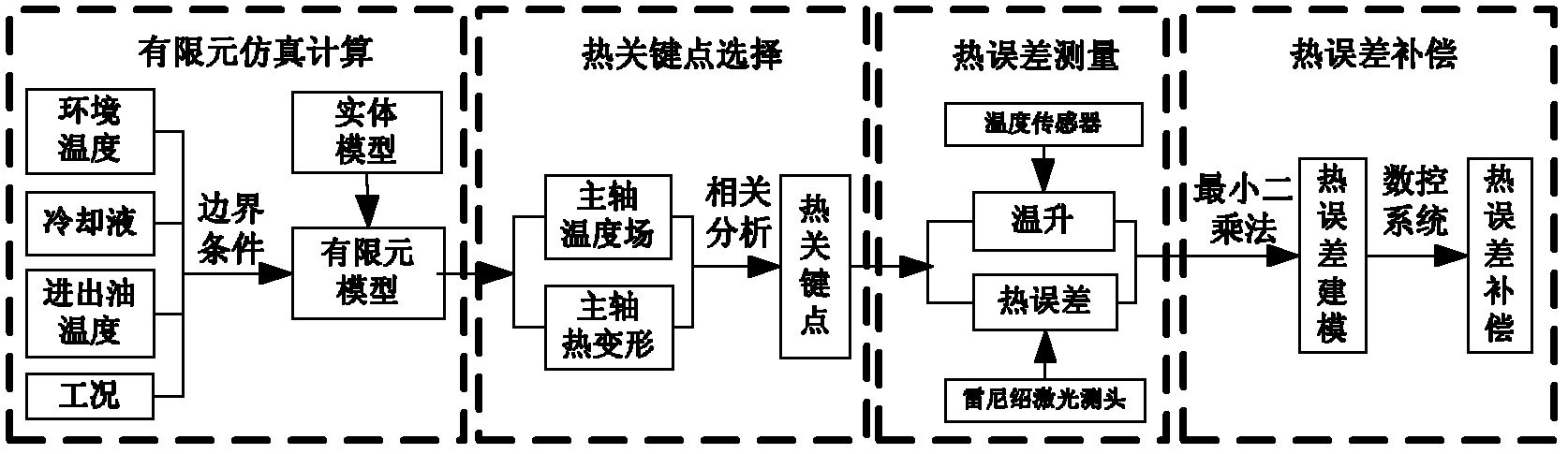
Spindle thermal distortion compensation method for precision horizontal machining center
InactiveCN102658499AReduce thermal errorsMeasurement/indication equipmentsMaintainance and safety accessoriesElement modelEngineering
A spindle thermal distortion compensation method for a precision horizontal machining center comprises the steps as follows: a spindle model of a machine tool is simplified structurally; an ANSYS (finite element analysis software)-Workbench is utilized to perform mesh generation on a spindle entity model that is simplified, so as to obtain a spindle finite element model; and boundary conditions are calculated by combining with the practical spindle rotational speed, the environmental temperature, the coolant velocity, the flow rate, the inlet and outlet oil temperature and the like, and configuration is performed. Thermodynamics analysis and statics analysis are carried out in the ANSYS-Workbench to obtain more accurate spindle temperature field distribution and thermal deformation. Based on a finite element emulation result, the spindle temperatures in different positions and the spindle thermal deformations are analyzed at different rotational speeds by utilizing the Spearman rank correlation analysis, and spindle thermal key points are found out, so that references are provided to spindle thermal error tests and thermal error compensation. Finally, a thermal error compensation model is built up by utilizing a least squares method according to the key point temperature of the spindle and the thermal errors in the practical tests. Based on the thermal error compensation model, the spindle thermal error compensation is carried out by combining with thermal error compensation strategies of a numerical control system of the machine tool.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
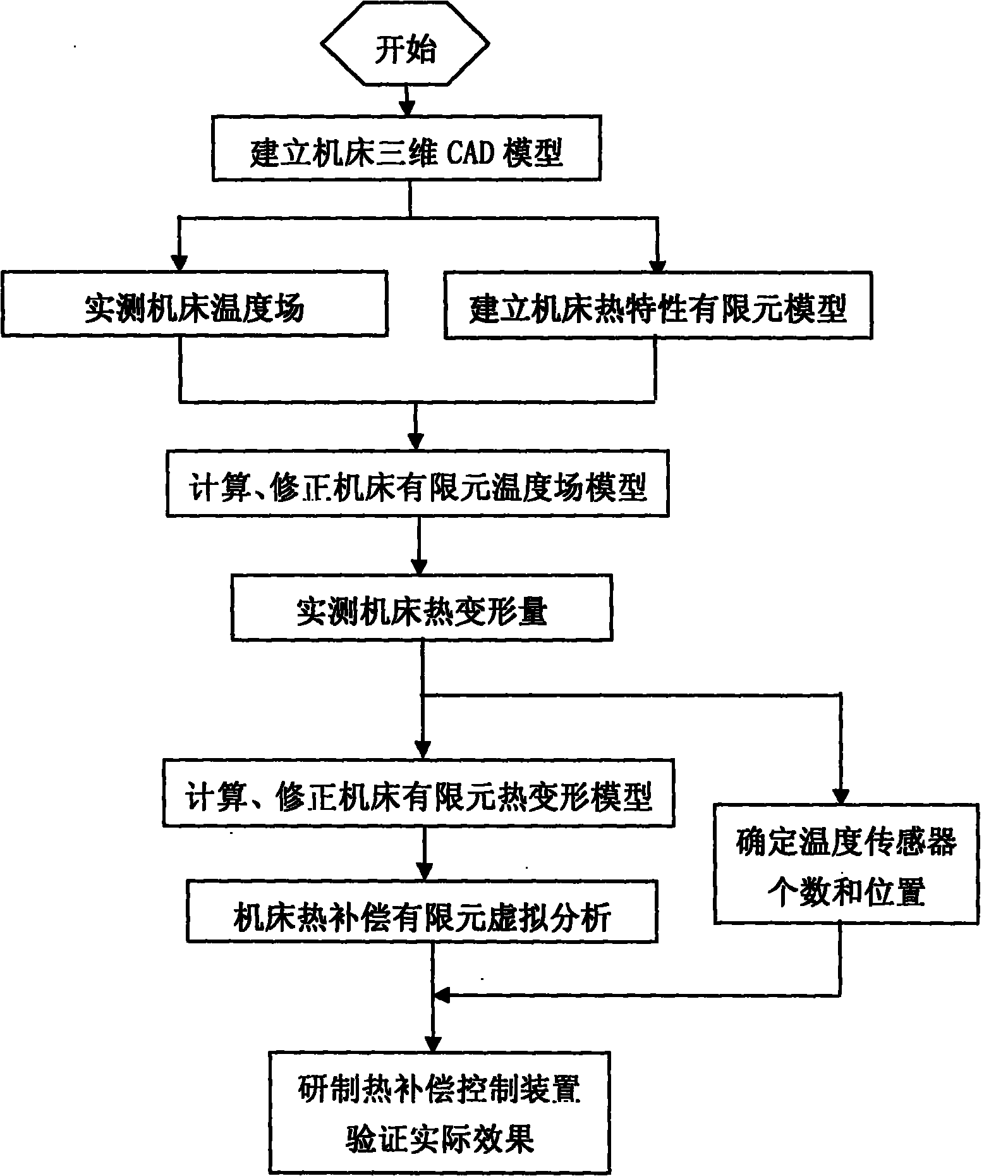
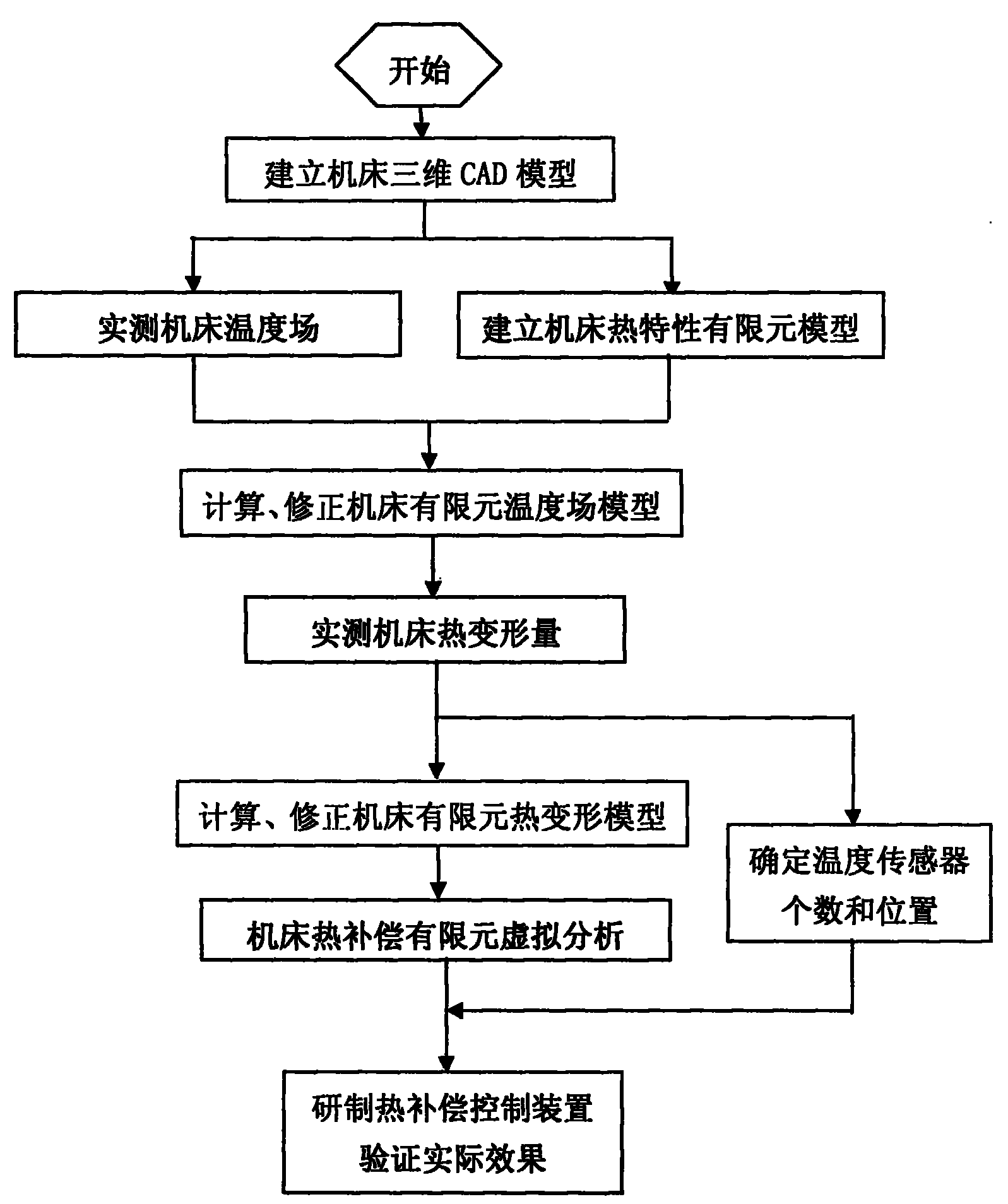
Implementation method of automatic compensation for thermal deformation of machine tool
InactiveCN101804581AShorten the development cycleHigh compensation accuracyAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusElement modelThermal deformation
The invention discloses an implementation method of automatic compensation for thermal deformation of a machine tool, which comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a three-dimensional CAD model of the machine tool; (2) actually measuring the temperature field of the machine tool; (3) establishing a thermal characteristic finite element model of the machine tool; (4) calculating and correcting a finite element temperature field model; (5) actually measuring the thermal deformation of the machine tool; (6) determining the number and positions of temperature sensors; (7) calculating and correcting a finite element thermal deformation model of the machine tool; and (8) virtually analyzing the thermal compensation finite element of the machine tool. The method corrects the finite element temperature field and the thermal deformation model of the machine tool, so that the established finite element model of the machine tool can truly reflect the practical situation of the thermal deformation of the machine tool; and thus, the invention has the advantages of high compensation precision and good stability. In the method, multiple thermal compensation testing processes on the machine tool are completed by a computer through virtual analysis, thereby shortening the development cycle and reducing the development cost.
Owner:四川普什宁江机床有限公司
Pre-stressed continuous concrete beam design method based on BIM technology
ActiveCN106354968AAchieve integrationRealize automatic generationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelContinuous beam
The invention discloses a pre-stressed continuous concrete beam design method based on the BIM technology. The pre-stressed continuous concrete beam design method includes the following steps that according to a file format, pre-stressed continuous beam design information is input; a finite element model is formed, and the structure size is analyzed and determined through the numerical value; an information-model parameterization cross section library is built; according to the structure size, a cross section is automatically instantiated to generate a continuous beam three-dimensional model containing user information; according to the characteristics of the cross section of the continuous beam, a reinforcing-steel-bar-net space node coordinate database is automatically built; instantiation data is sequentially comprises all parts of arrangement space reinforcing steel bars of the continuous beam, and user information is added; according to an information module, two-dimensional drawings are automatically established, quantity statistics is automatically completed. By means of the pre-stressed continuous concrete beam design method based on the BIM technology, rapid forming of universal data, the three-dimensional information model and the reinforcing-steel-bar drawings is achieved, and the pre-stressed continuous concrete beam design method has good popularization value and the good application value.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY DESIGN GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com