Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
355 results about "Dynamic stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic Stress. in linguistics, a stress in which a stressed syllable is distinguished, in comparison with an unstressed one, by greater tension of articulation, particularly of a vowel, and by the greater force of the expelled air.
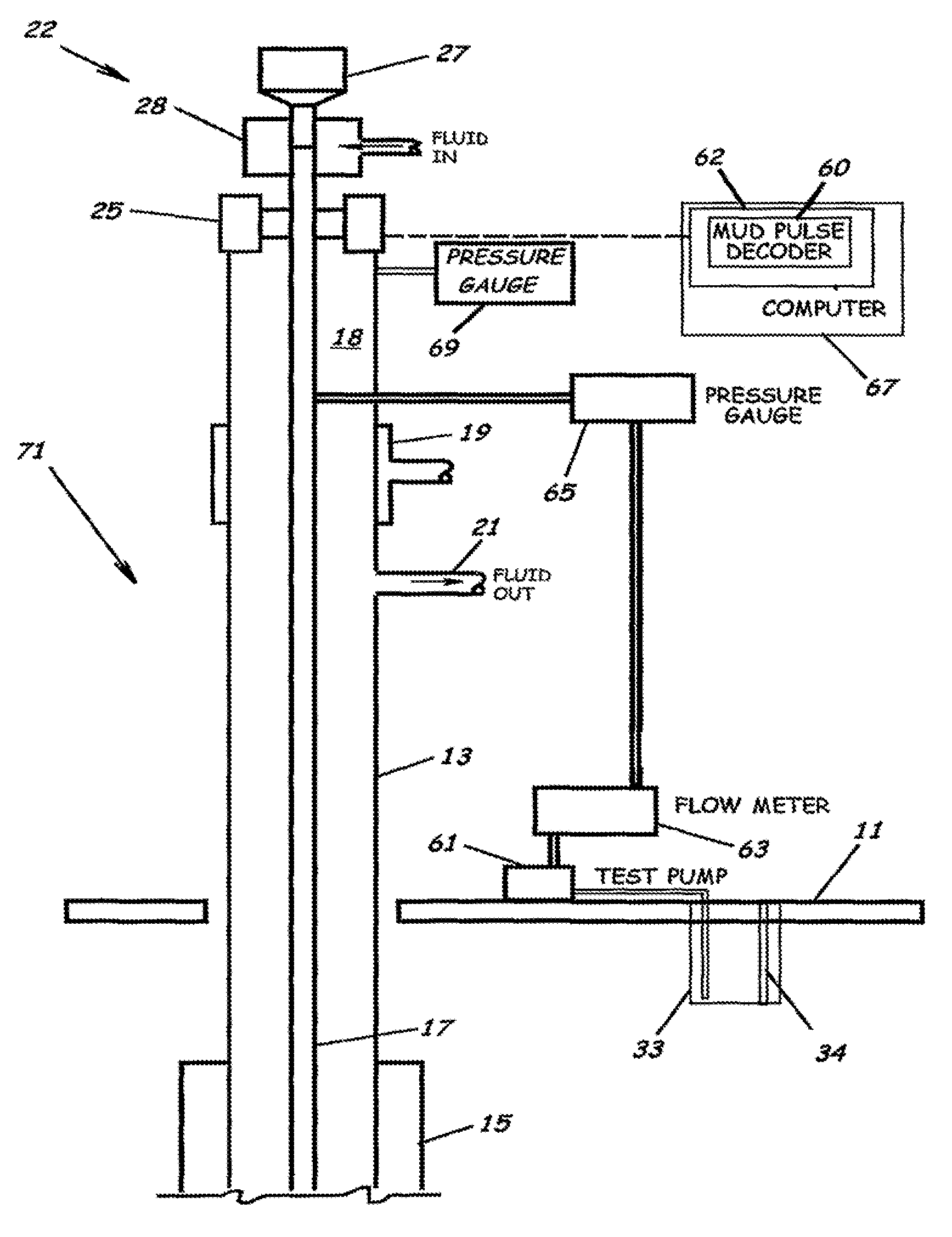
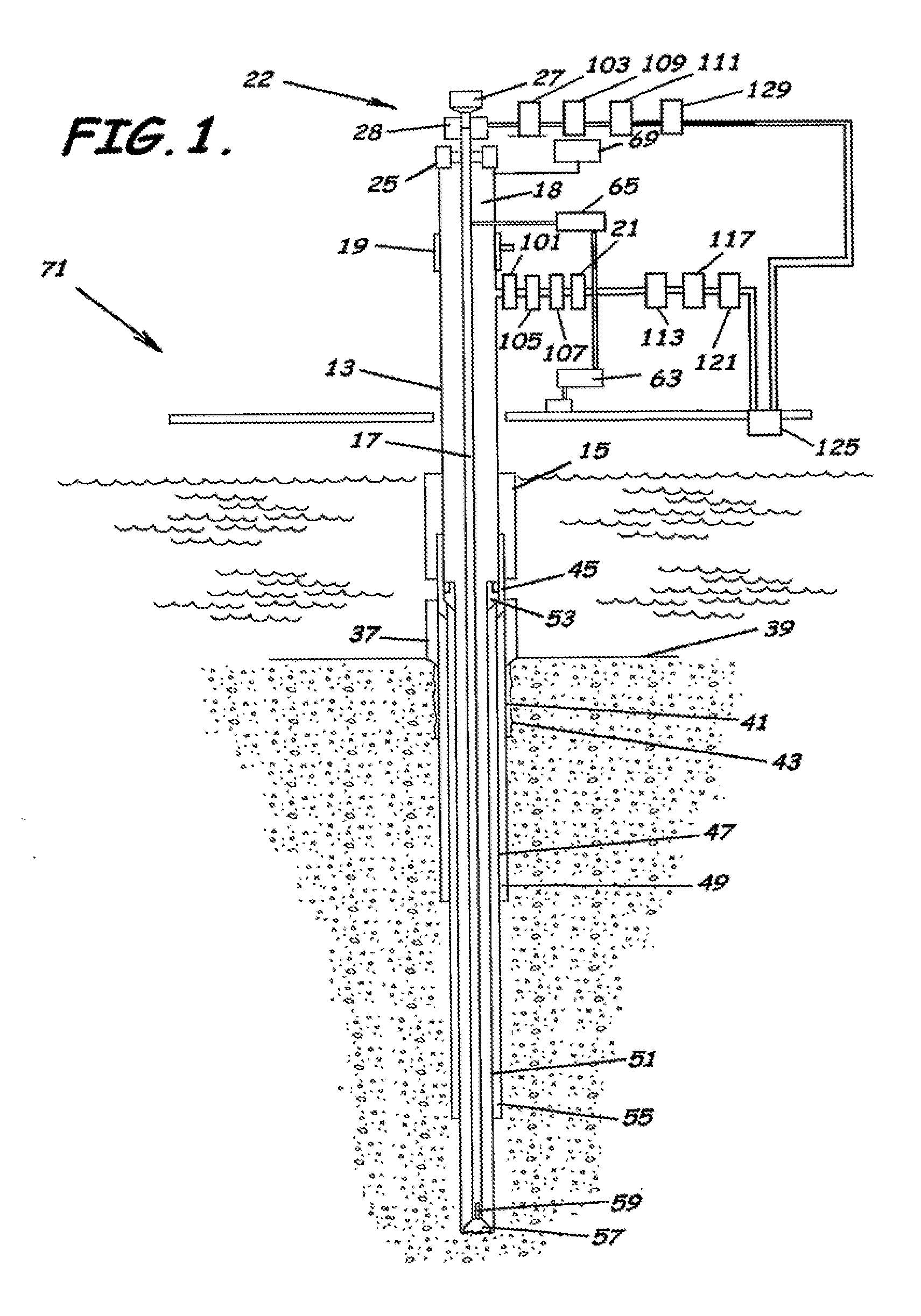
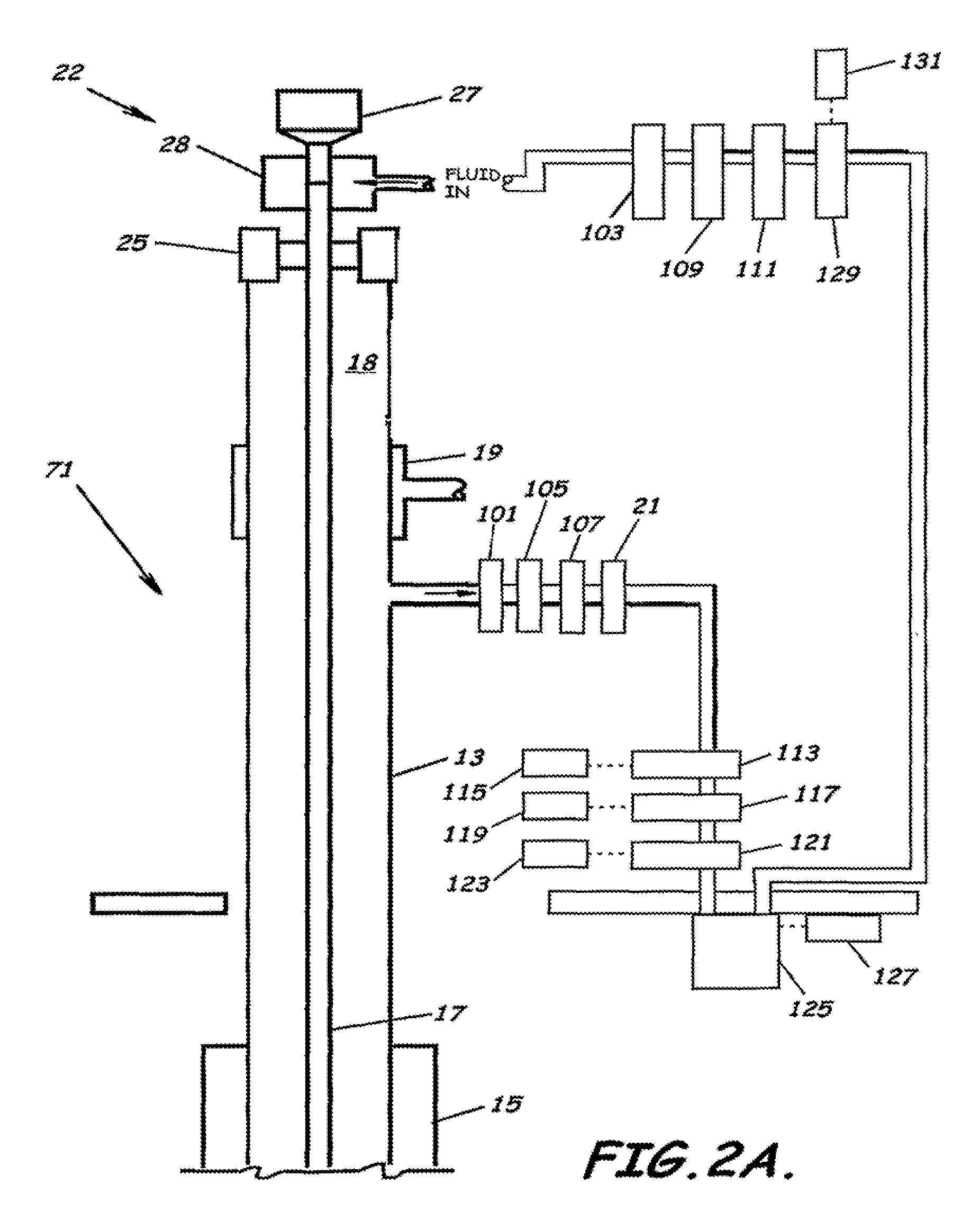
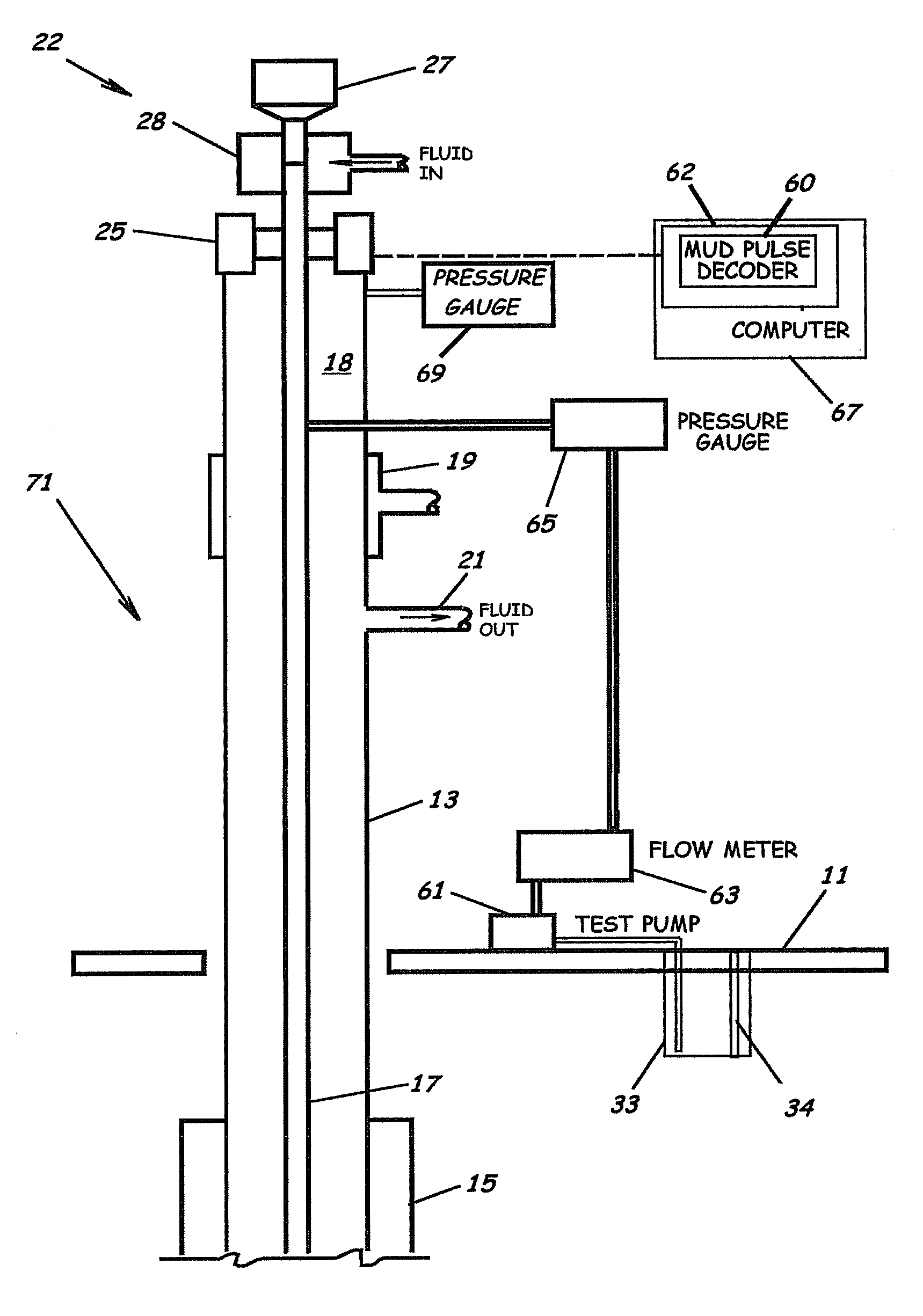
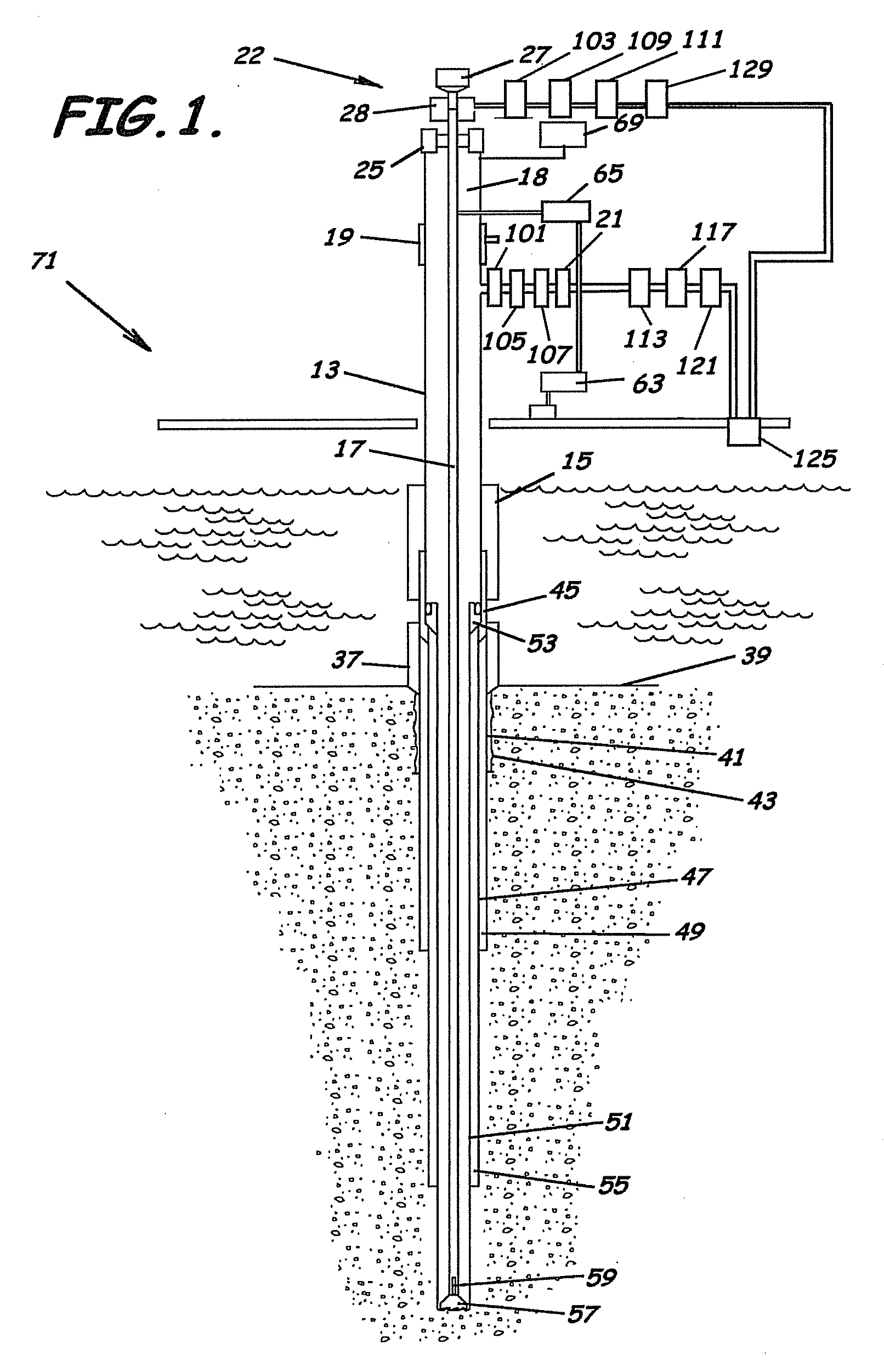
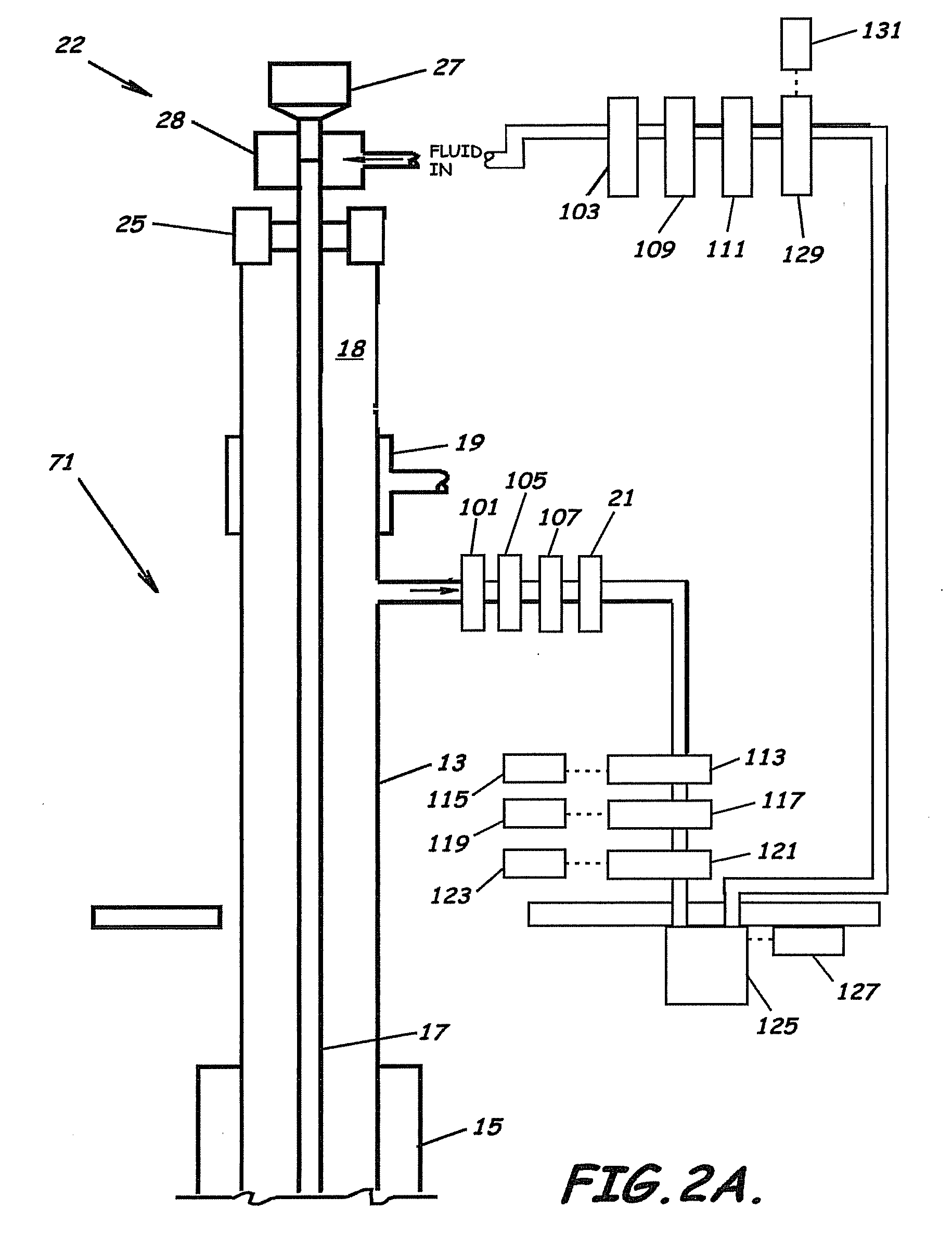
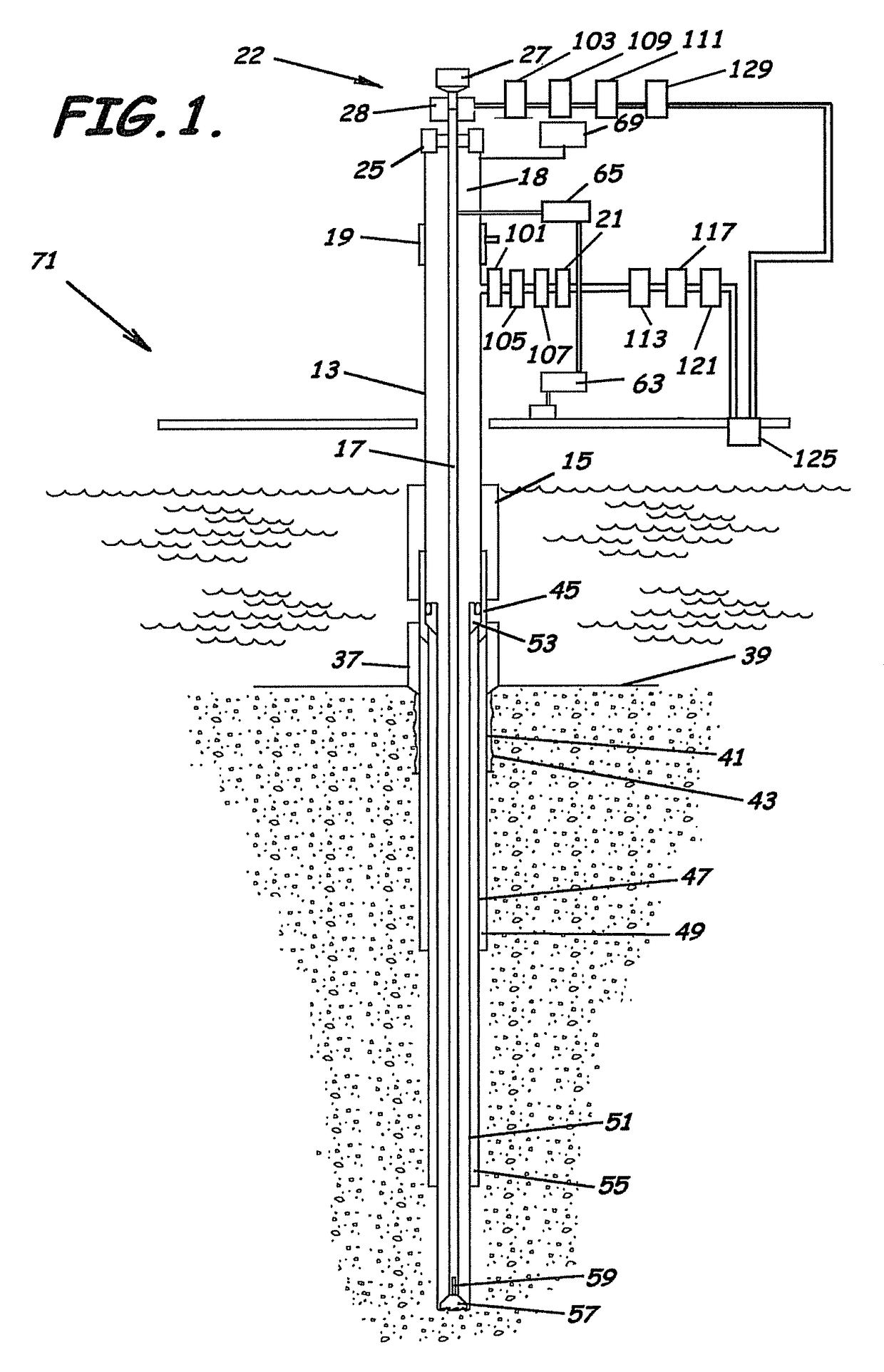
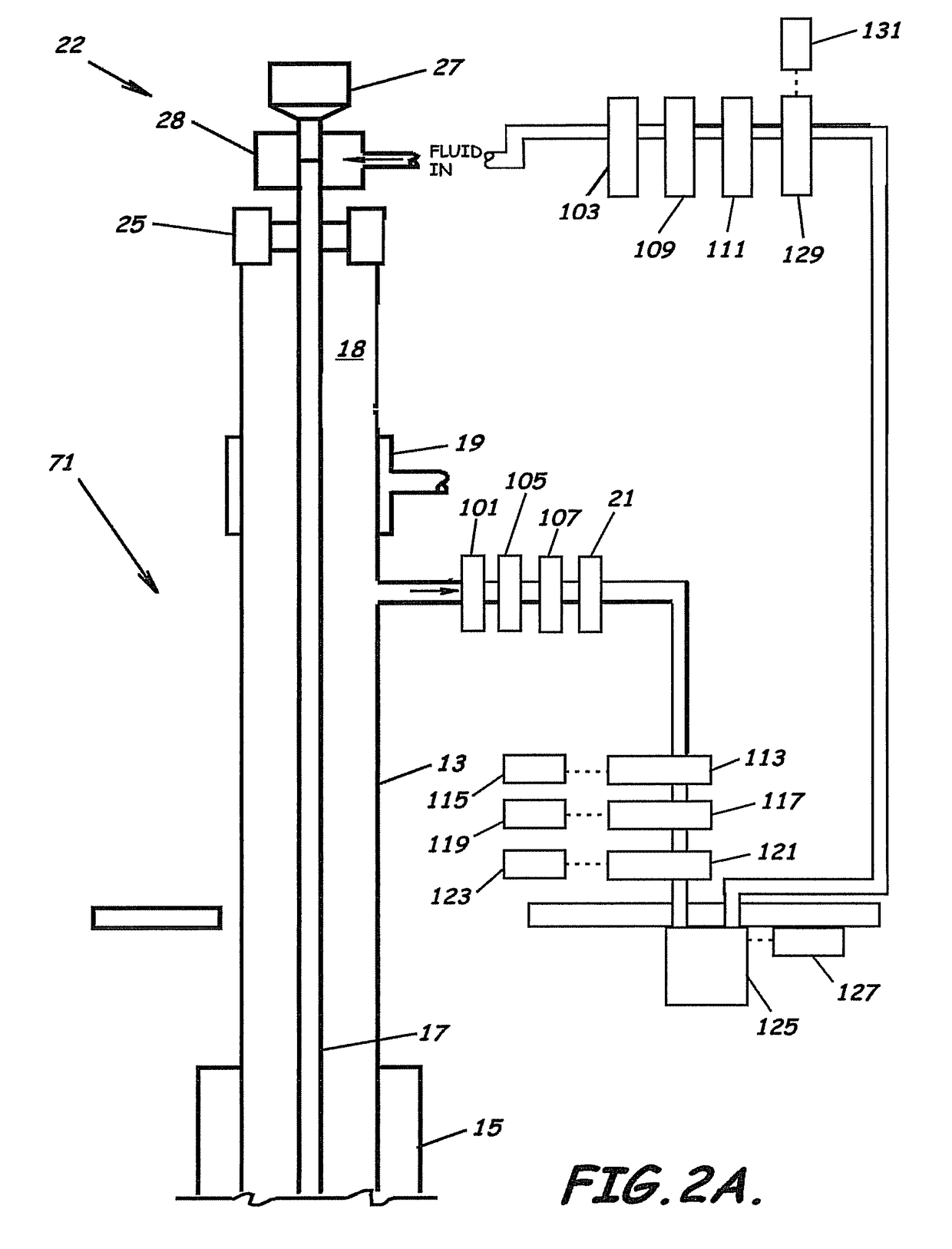
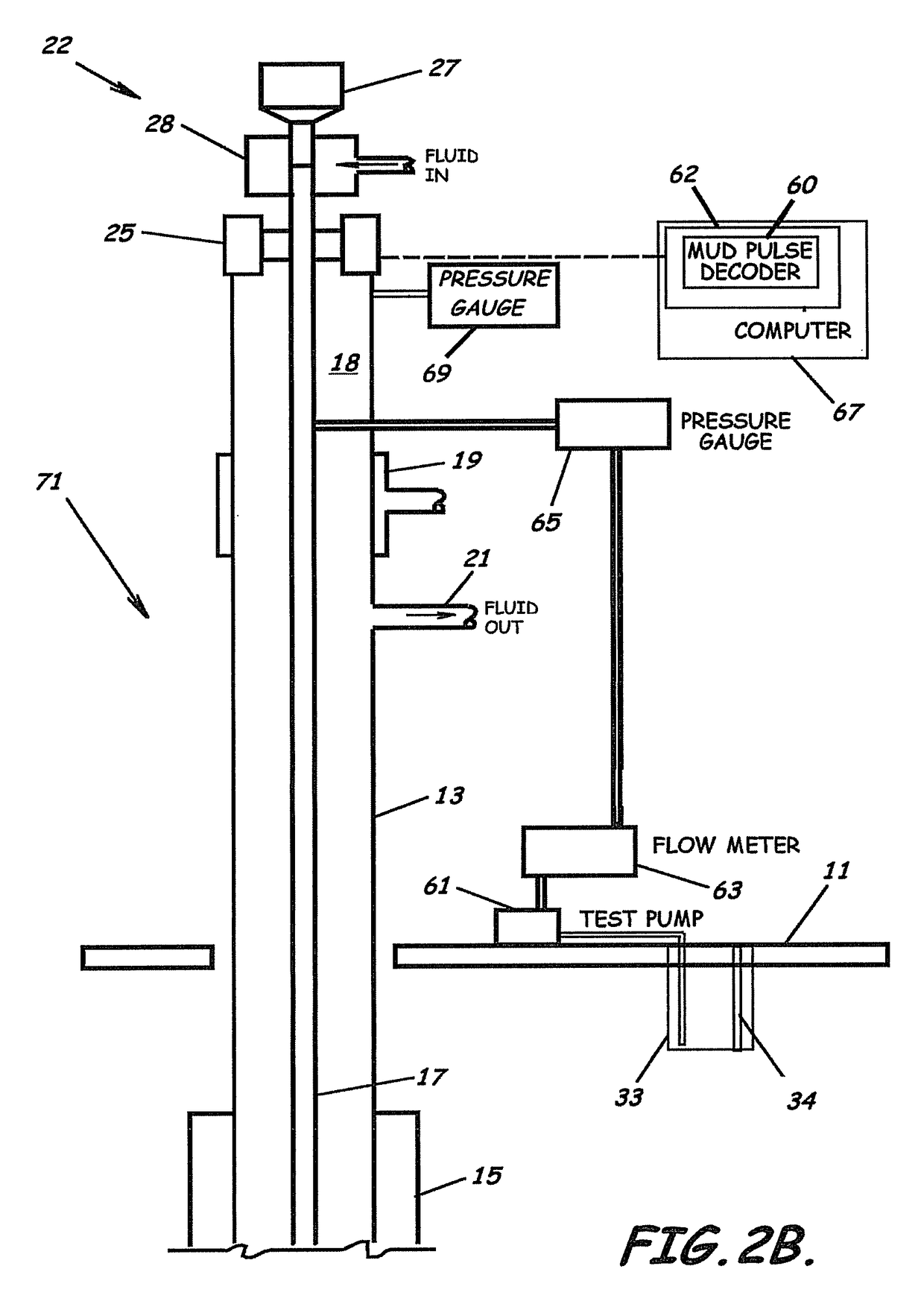
System, Program Products, and Methods For Controlling Drilling Fluid Parameters
ActiveUS20110125333A1Easy to controlEconomic securityFlushingDrilling compositionMarine engineeringSelf adaptive
Embodiments of systems, program product, and methods for controlling drilling fluid pressures are provided. These embodiments, for example, can provide dynamic density control with highly adaptive, real-time, process-control and are scalable to any rig, large or small, on land or water. Combined static and dynamic stresses and displacements can be determined continuously at strategic locations in and around the wellbore of a well so that insitu and operational induced pressure window limitations at specific weak-points or other locations of interest are controlled.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
System, program products, and methods for controlling drilling fluid parameters
InactiveUS20090194330A1Easy to controlEconomic securitySurveyConstructionsMarine engineeringWellbore
Embodiments of systems, program products, and methods for controlling drilling fluid parameters are provided. These embodiments, for example, provide dynamic density control with highly adaptive, real-time, process-control and are scalable to any rig, large or small, on land or water. Combined static and dynamic stresses and displacements can be determined continuously at strategic locations in and around the wellbore of a well so that insitu and operational induced pressure window limitations at specific weak-points or other locations of interest are controlled.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
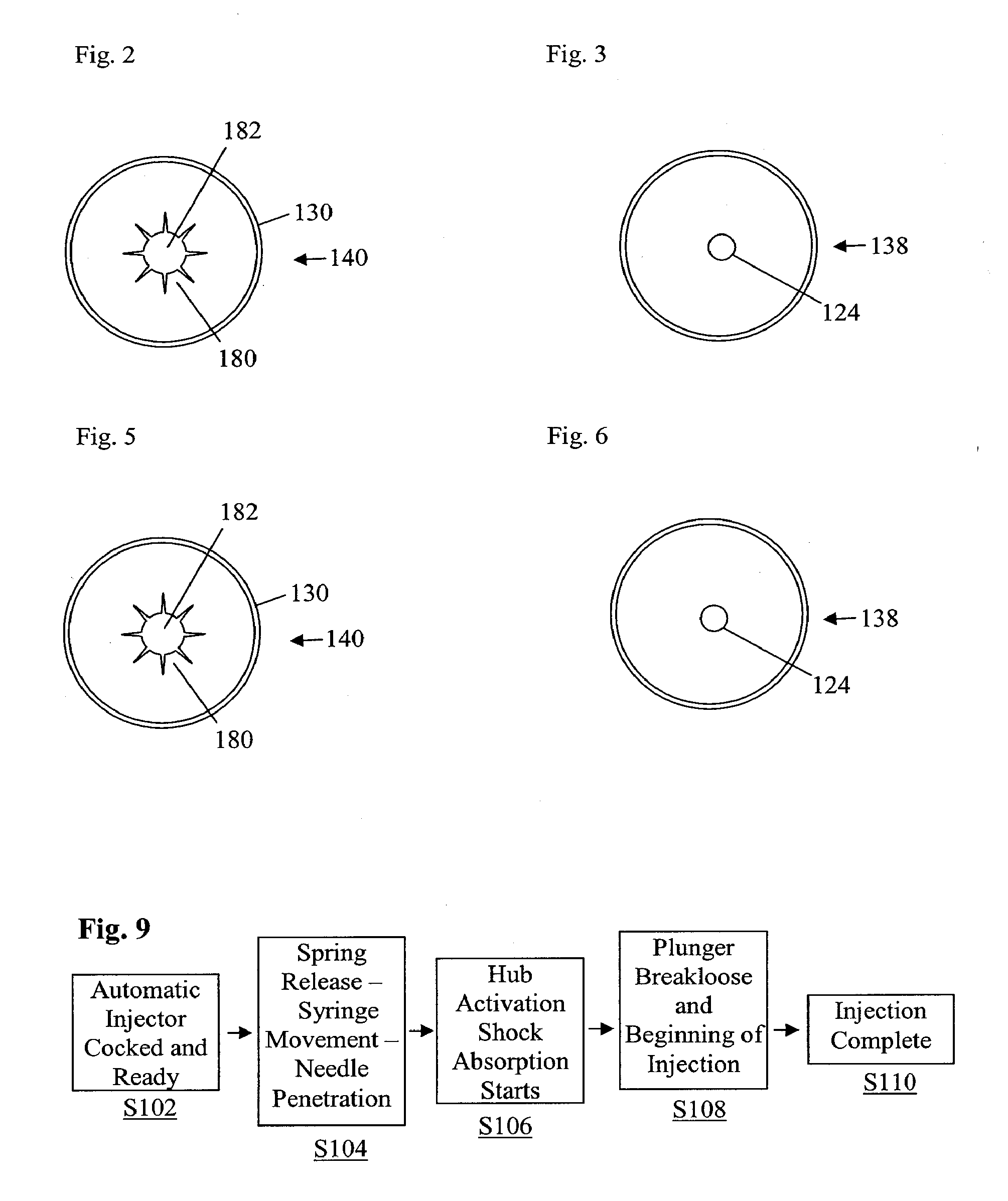
Shock absorber for automatic injector
InactiveUS20070219498A1Reduce dynamic stressRelieve pressureAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesEngineeringEnergy management system
An automatic injector comprising an improved energy management system as well as an improved shock absorber system adapted to reduce dynamic stresses on internal device components is provided. In particular, a shock absorber system comprising a stationary shock absorber is provided. In some embodiments, the stationary shock absorber is located in the nose of the automatic injector.
Owner:SCIELE PHARMA
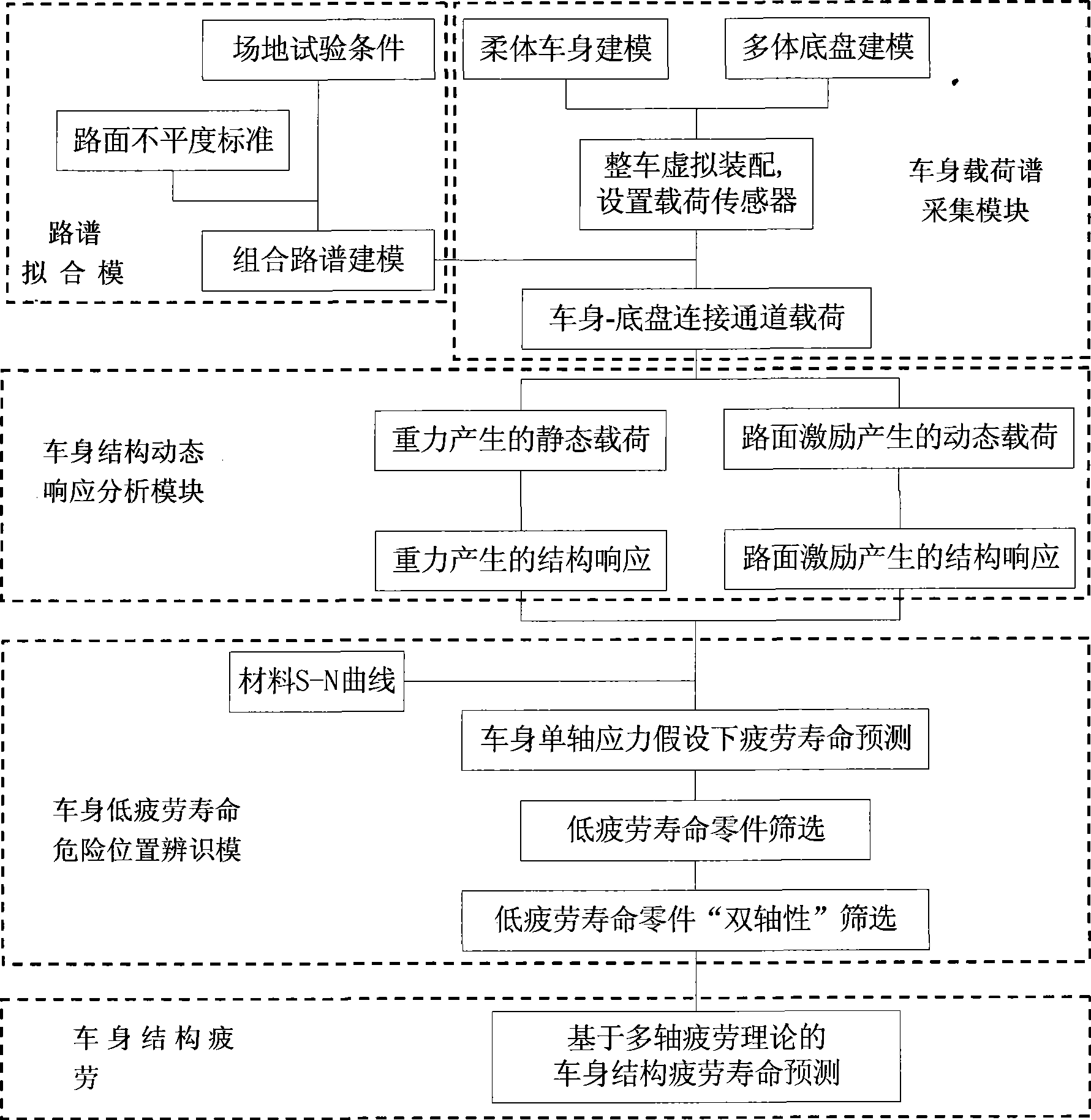
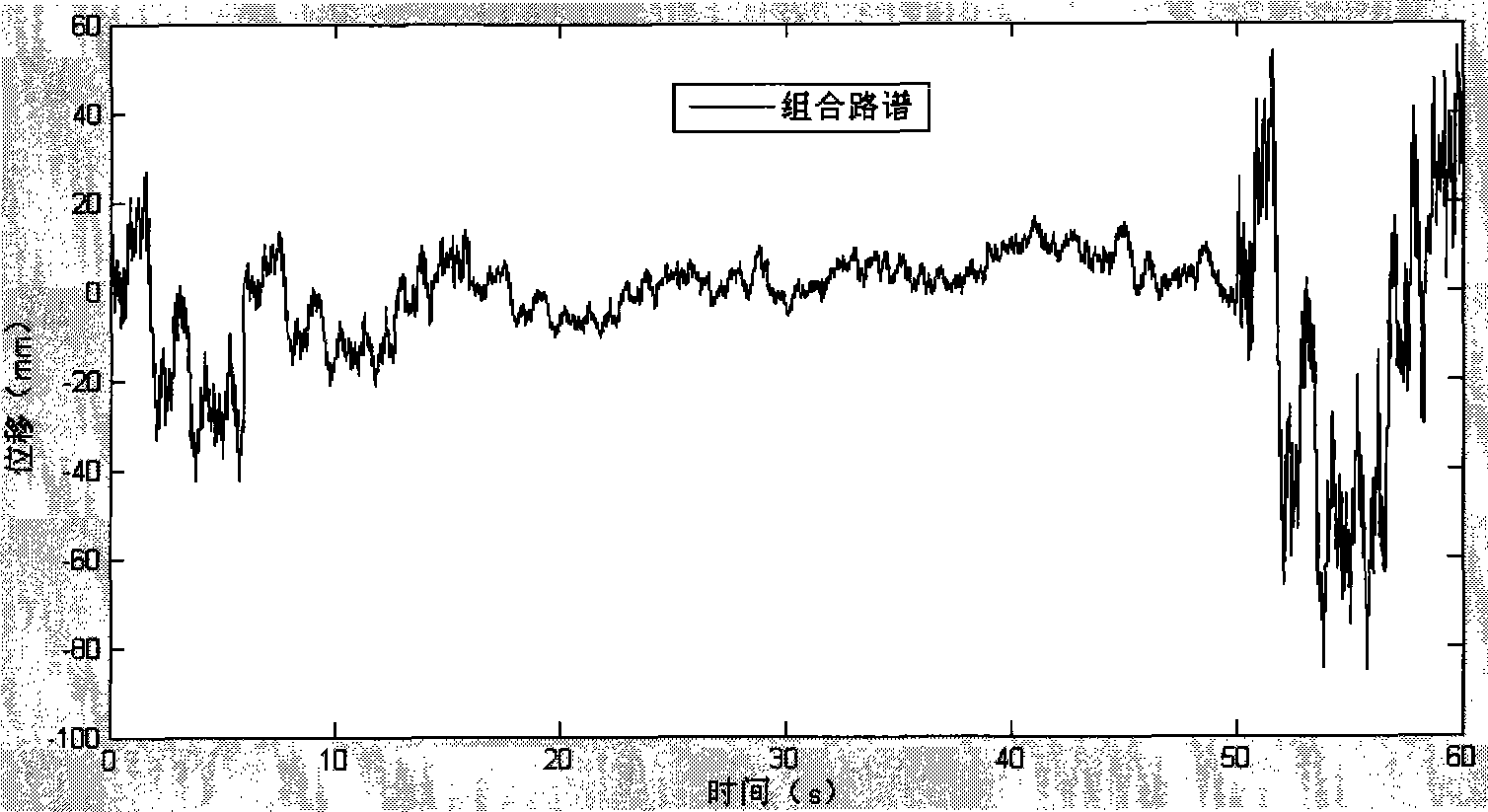
Automobile vehicle body structure fatigue life predicting system
The invention relates to a fatigue life prediction system for a vehicle body structure of a vehicle in the technical field of vehicle design. The prediction system adopts a road spectrum fitting module to establish a combined road spectrum suitable for a field test; a vehicle body loading spectrum acquisition module is adopted to establish an entire vehicle multi-body rigid-flexible coupled model so as to extract the load-time-history at a connecting passage of the vehicle body and a chassis as the input of vehicle body excitation; an automobile body structure dynamic response analysis module is adopted to establish a finite element model of the vehicle body so as to obtain the static stress history generated by gravity and the dynamic stress history generated by road surface excitation of the vehicle body when the vehicle is under the excitation of the combined road spectrum; a dangerous position identifying module of low fatigue life of the vehicle body is adopted to quickly search dangerous positions of low fatigue life through an S-N method and a Miner linear accumulated damage model, and determine the multiaxial stress state of the dangerous positions by using 'biaxiality' analysis; and a fatigue life prediction module of the vehicle body structure is adopted to predict the fatigue lives of the dangerous positions accurately. The fatigue life prediction system for the vehicle body structure can improve the speed and the precision of the fatigue life prediction for the vehicle body structure so as to provide a reference for a real vehicle test.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
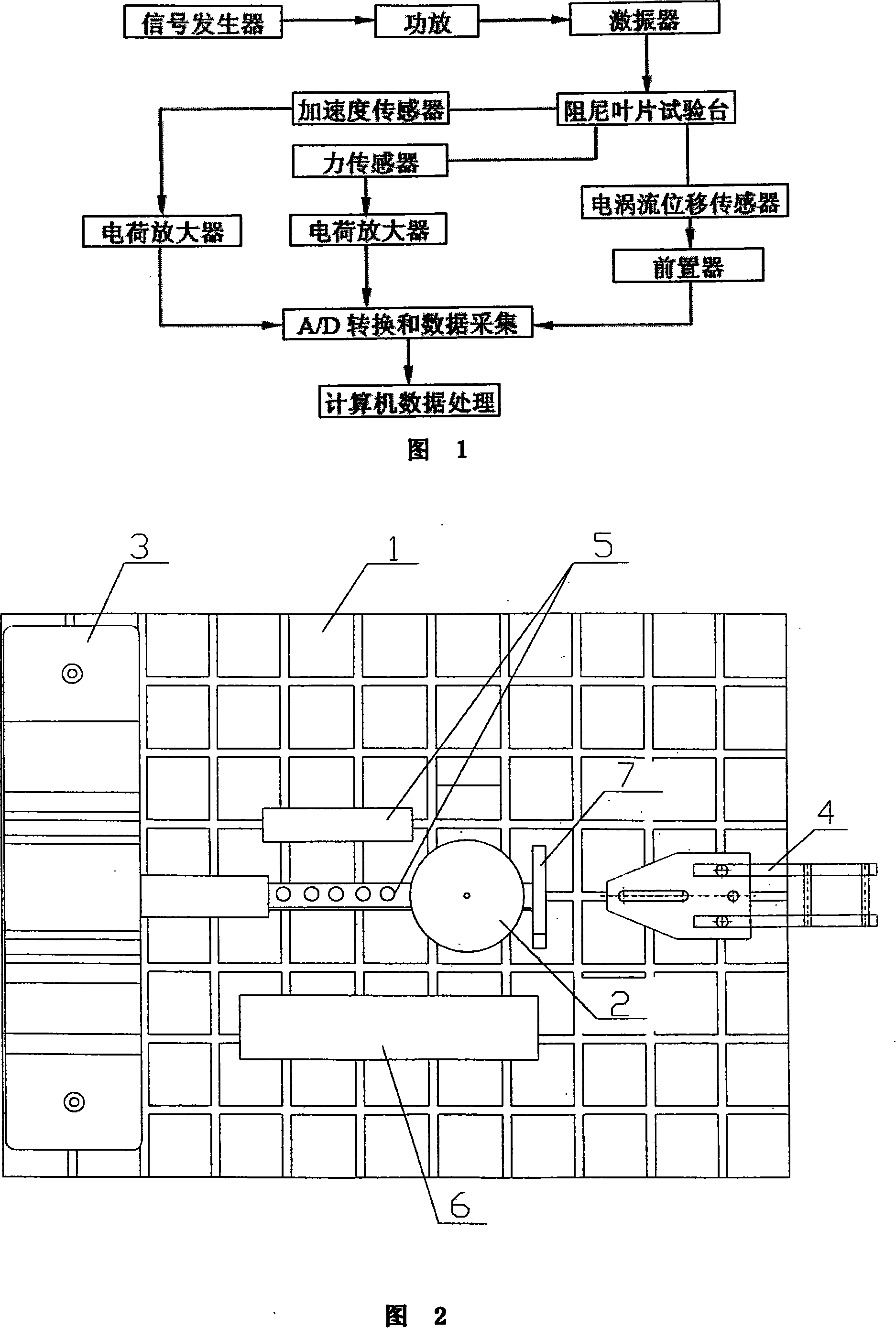
Turbine blade vibration test method and device
ActiveCN101122541AProven Vibration MechanismReasonable designVibration testingElasticity measurementMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a steam turbine blade vibration test method and device. The method steps are that firstly, a blade force vibration status is analyzed and a blade excitation force mathematical model is built. Secondly, an excitation force is imposed on the blade by a vibration source. The frequency of the excitation force is regulated until resonance is generated between the blade and the vibration source. Vibration characteristics parameters values of the blade under the excitation force are measured. Thirdly, blade damping characteristics parameters, including modal damping ratio, damper contact stiffness and blade dynamic stress, are worked out according to the vibration characteristics parameters values. The device includes a test bed, a blade clamping mechanism arranged on the test bed, an excitation generator, a vibration parameter detector and a data processing system. The excitation vibration generator is fixed on the test bed. The excitation vibration head of the excitation vibration generator is fixed with the blade. Corresponding to the blade, the vibration parameter detector transforms the vibration signals of the blade into electric signals, which are input into the data processing system. The invention proves the vibration mechanism of the damping blade. A calculation model of the damping blade is constructed through the test parameters. Experience design is terminated. The blade design is standardized to step into a scientific design orbit.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD +1
Cementing compositions and the use of such compositions for cementing wells
InactiveUS6907929B2High impact strengthGive flexibilitySolid waste managementDrilling compositionPolymer scienceWell cementing
Cementing compositions for oil wells or the like comprise between 30% and 100% (by weight of cement) of rubber particles, with grain size in the 40-60 mesh range. Adding rubber particles in accordance with the invention produces a low density slurry while keeping the cement permeability low. Compositions of the invention are particularly advantageous for cementing zones subjected to extreme dynamic stresses such as perforation zones and the junctions of branches in a multi-sidetrack well.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
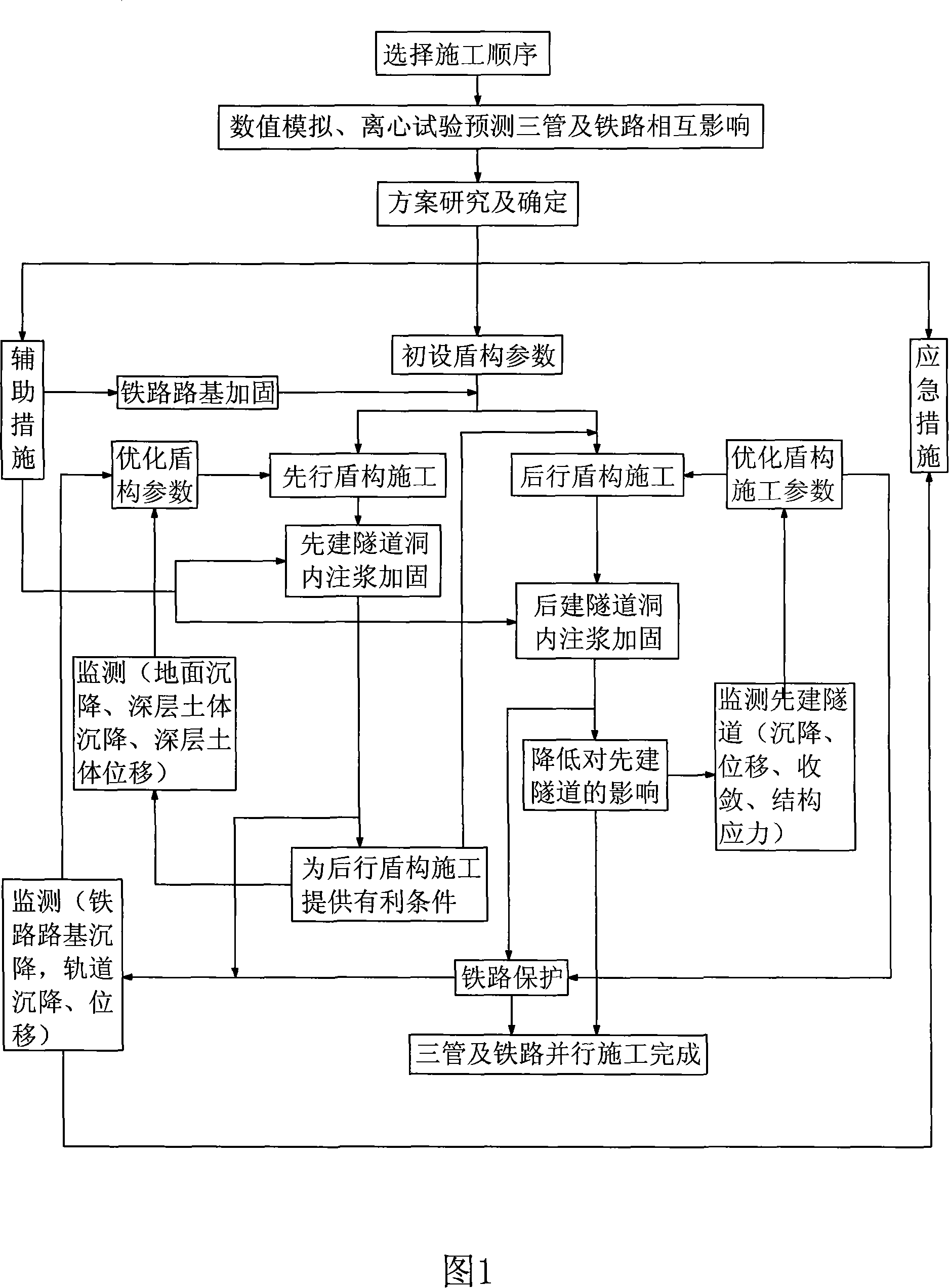
Shield construction method for three-line parallel under-passing trunk railway tunnel
ActiveCN101126318AEffective control of deformationEffective control of displacementUnderground chambersTunnel liningRailway tunnelEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a shield construction method of digging three parallel tunnels under a trunk railway, which belongs to the field of tunnel construction technology. The construction method of the invention comprises the procedure that: the model analysis on each construction sequence and method is made by a three-dimensional finite element and the shield construction sequence is selected; to select the reinforcement project of the railway bed is selected according to the influence degree of the dynamic stress, the load-carrying structural model is adopted to calculate and decide the shield area reinforcing bars enhancement project under the dynamic load of the railway train; the construction parameters are selected according to the test results and the performance of the shield machine, the front earth pressure is reasonably set , the synchronizing mortar injection is enhanced, the forward digging speed and the axis deviation are strictly controlled, the secondary mortar injection is made, the foam or mud is filled by utilizing a pre-embedded injection hole; the strict monitoring measures to monitor the shield construction process is adopted so that the construction unit can adjust the construction parameters in time and guarantee the construction safety. The invention not only guarantees the construction quality and the construction safety of the project but also creates good economic benefit.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY NO 2 ENG GRP CO LTD
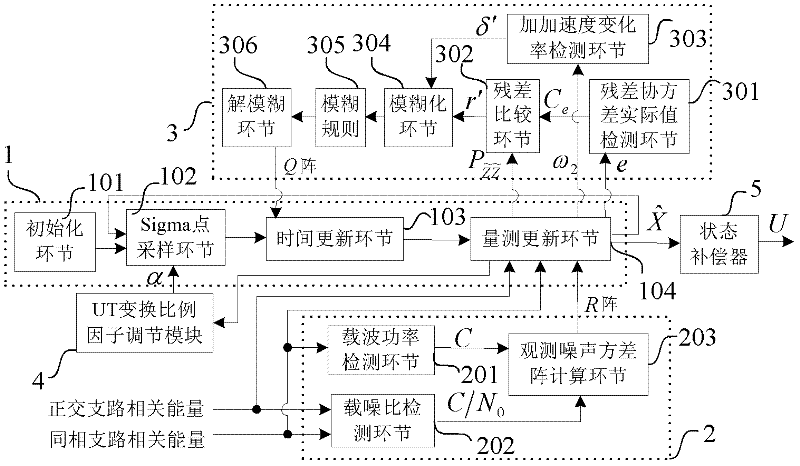
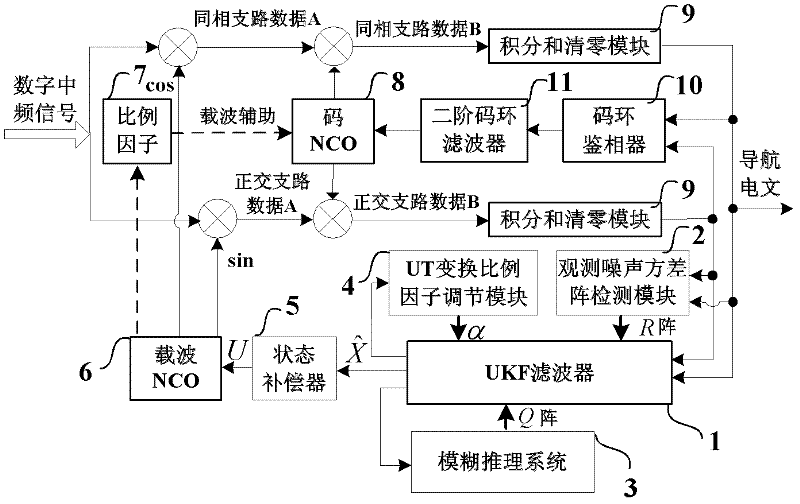
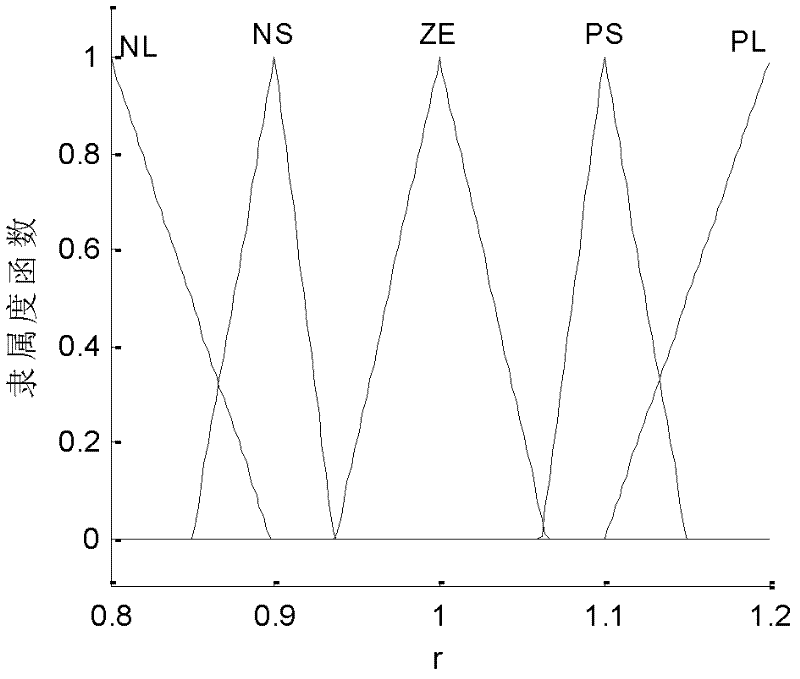
Self-adaptive tracking loop and implementation method
InactiveCN102540216AAccurate trackingSolve the noiseSatellite radio beaconingNumerical controlDiscriminator
The invention discloses a self-adaptive tracking loop, which comprises an unscented Kalman filter (UKF), an observation noise variance matrix detection module, a fuzzy inference system, an unscented transformation (UT) scale factor regulation module, a state compensator, a carrier wave numerical controlled oscillator (NCO), scale factors, a code NCO, an integration and zero-clearing module, a code loop phase discriminator and a second order code loop filter, and additionally discloses an implementation method for the self-adaptive tracking loop. The implementation method comprises a step 1 ofsignal correlation, integration and zero clearing; a step 2 of code phase tracking; a step 3 of UKF modeling; a step 4 of observation noise variance matrix estimation; a step 5 of process noise variance matrix estimation; a step 6 of UT scale factor regulation; a step 7 of state estimation deviation compensation; and a step 8 of assistance of the carrier wave NCO in the code NCO. According to theself-adaptive tracking loop, the UKF, the observation noise variance matrix detection module and the fuzzy inference system are designed in the carrier tracking loop, so not only can a contradiction between thermal noise vibration in the tracking loop and a dynamic stress error be solved, but a process noise variance matrix and an observation noise variance matrix can be regulated in a self-adaptive manner according to changes of the external environment, and thereby the self-adaptive ability of the tracking loop under complex changeable environments of high dynamic, strong interference, and the like is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for predicting cycle life of battery pack for electric car
InactiveCN104714189AAccelerated agingEvaluate Cycle Life PerformanceElectrical testingCyclic testPredictive methods
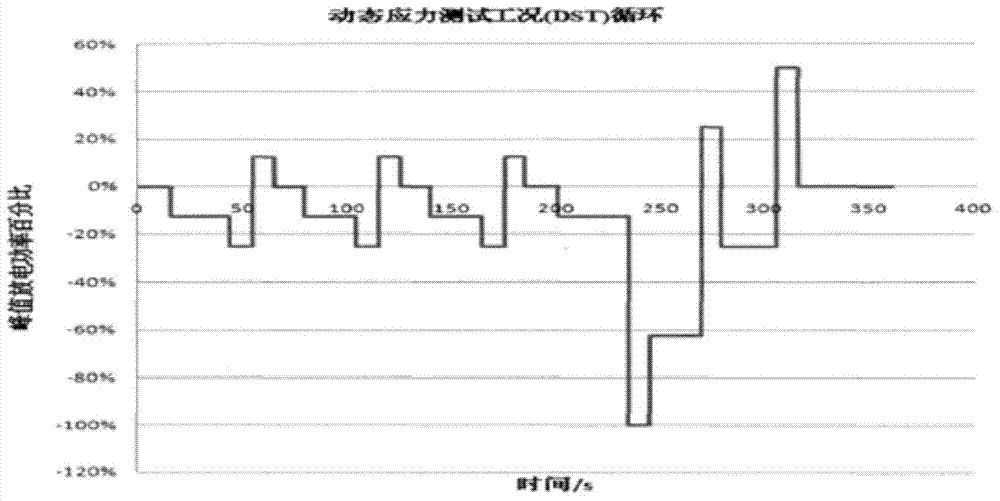
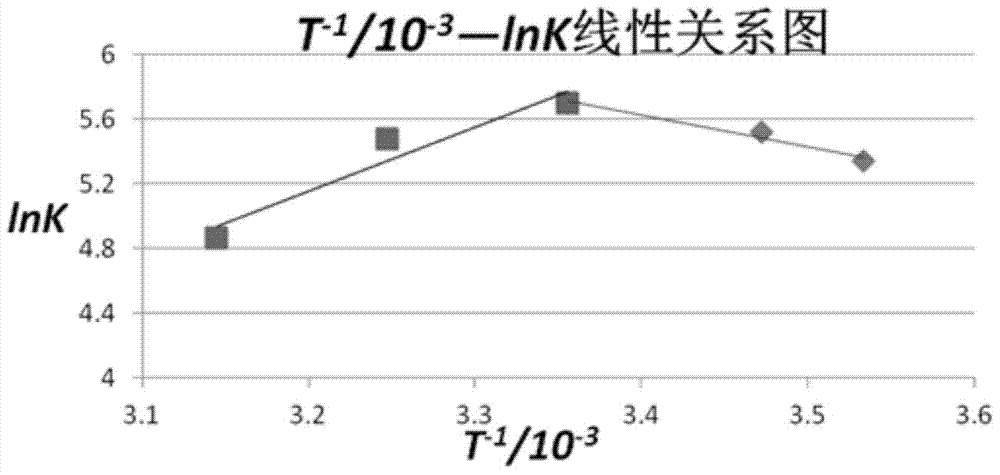
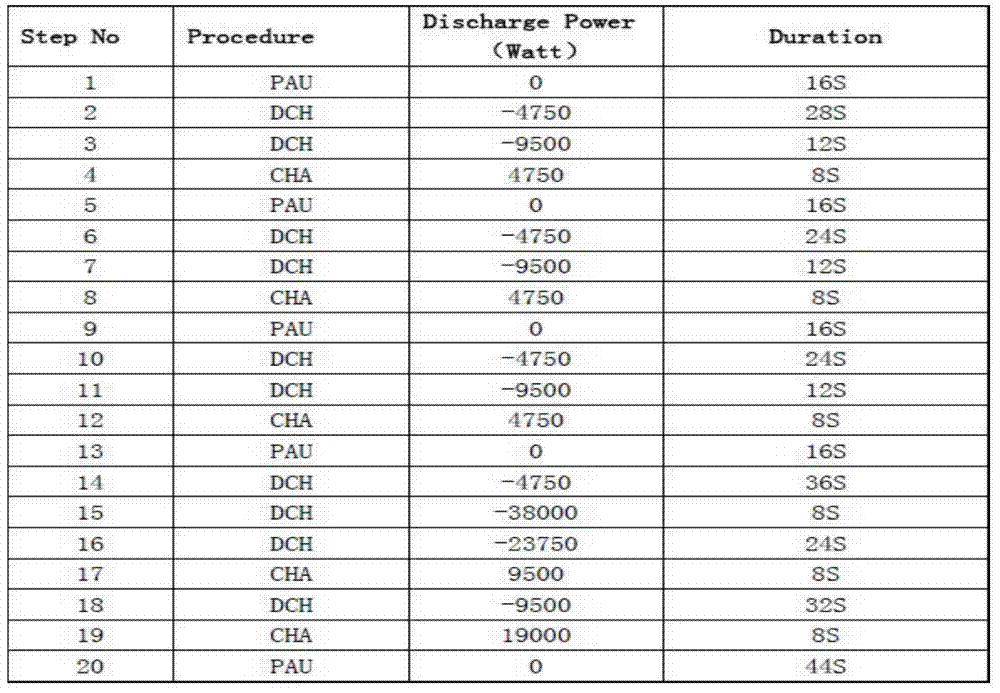
The invention relates to a method for predicting the cycle life of a battery pack for an electric car. The method comprises the following steps: step I, carrying out standard capacity test on the battery pack at normal temperature, and recording a real standard capacity of the battery pack; step II, carrying out dynamic stress working condition circulating test on the battery pack, returning to the step I after multiple times of working condition circulating test is ended, recording the test times of the standard capacity, ending the circulating test at the temperature if the real capacity of the standard capacity test for continuous 4 to 6 times is less than 80 percent of the rated capacity, wherein the test times of the standard capacity indicate the cycle life of the battery pack; step III, repeating the step I and the step II, and testing the cycle life of the battery pack under multiple temperature points. According to the method, the battery pack cycle life data at the grouped time is collected, a fitted equation is obtained by virtue of data processing, and the cycle life of a lithium ion battery at present can be predicted.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
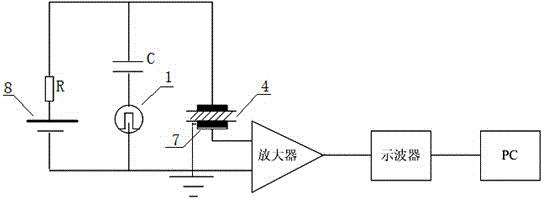
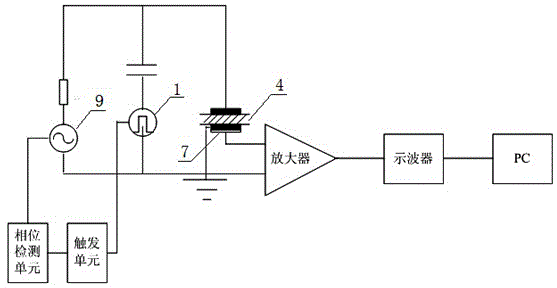
System and method for measuring high voltage cable space charges based on electroacoustic pulse method
InactiveCN103605008ARealize space charge distribution measurementReliable data baseElectrostatic field measurementsCapacitanceHigh voltage capacitors
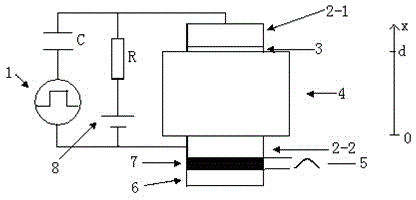
The invention relates to a system and a method for measuring high voltage cable space charges based on an electroacoustic pulse method. A high voltage pulse source and a high voltage capacitor are connected in series and are then connected with measuring electrodes at two ends of a tested piece, a high voltage power source is further connected with the measuring electrodes at two ends of the tested piece through a current limit resistor, a piezoelectric sensor closely clings to the lower measuring electrode, the piezoelectric sensor acquires a stress wave signal and sends the processed signal to a computer to form the measuring system, the high voltage power source can be a direct current high voltage power source and further can be an alternating current high voltage power source, the alternating current high voltage power source is connected with a phase detection unit, and a phase detection circuit outputs a synchronous control signal to a pulse generation unit of the high voltage pulse source. The high voltage power source forms space charges in an insulation layer of an electric power cable through electrodes, disturbance of the charges in the insulation layer of the electric power cable is realized through the high voltage pulse source to form dynamic stress waves, the measuring system acquires a signal of a pressure sensor, and a distribution state of the space charges of the electric power cable is analyzed. Through the system and the method, measurement on the distribution state of the space charges in the insulation layer of the electric power cable under the alternating current state is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
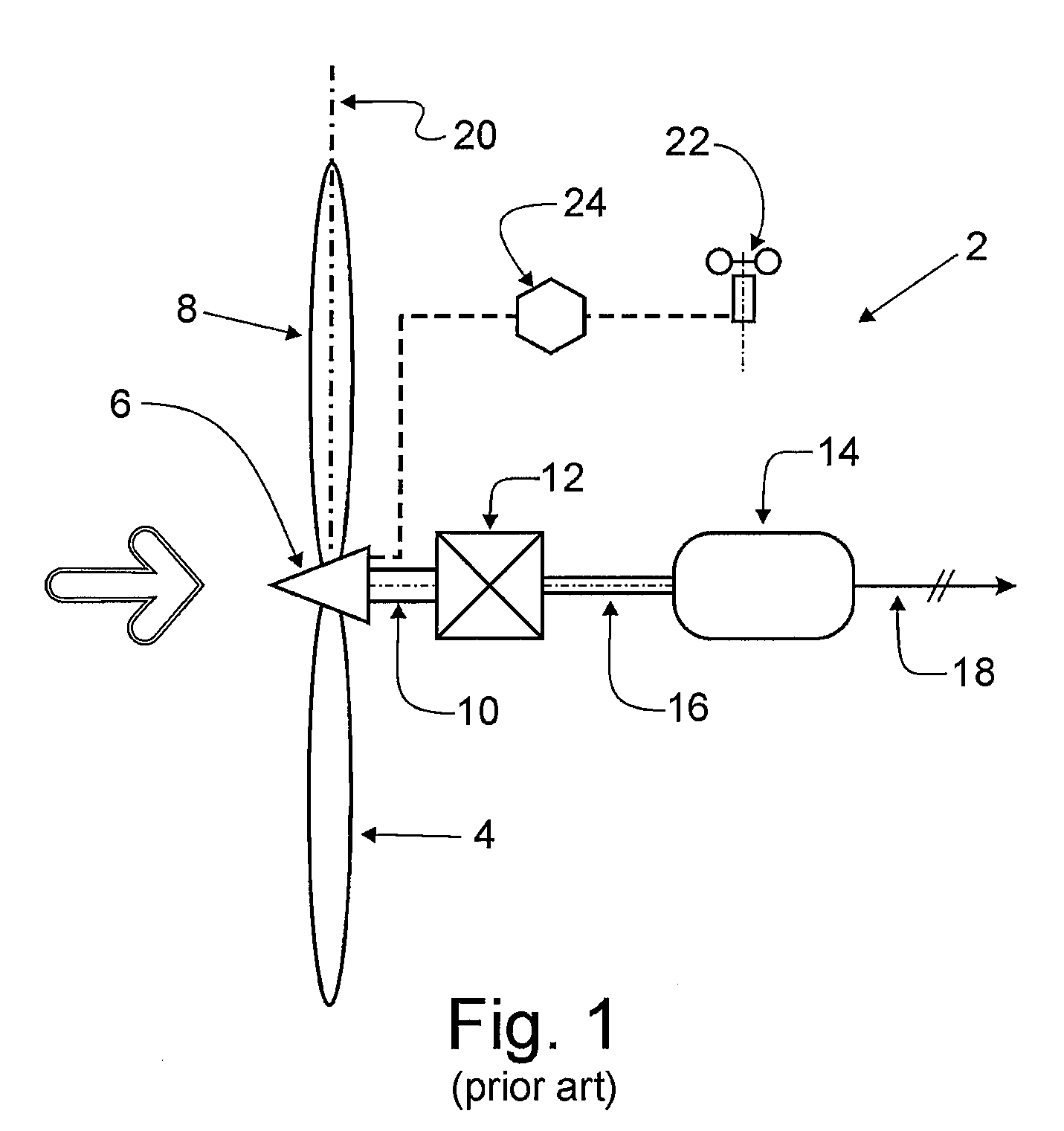
Variable speed wind turbine having a constant speed generator
InactiveUS20100230966A1Limit rotor speedEngine fuctionsWind motor combinationsVariable speed wind turbineMoment of inertia
A variable speed wind turbine including a variable speed rotor, a large constant speed generator, and a small variable speed generator is characterized by a three-shaft variable ratio gearbox connecting the shaft of the rotor with the two generator shafts. The variable ratio gearbox is an epicyclic gearbox which enables the combination of the high performance of a variable speed rotor with the low cost of a large constant speed generator. The torque of the small variable speed generator controls the rotor speed. Variable frequency power conditioning cost is less than that of a prior art variable speed wind turbine, reduced by the ratio of the rated capacity of the small generator to total rated capacity. Also, the small generator enables efficient low wind velocity energy capture. The low rotational inertia of the small variable speed generator further reduces drive train dynamic stress.
Owner:PAVLAK ALEXANDER J
System, program products, and methods for controlling drilling fluid parameters
Embodiments of systems, program products, and methods for controlling drilling fluid parameters are provided. These embodiments, for example, provide dynamic density control with highly adaptive, real-time, process-control and are scalable to any rig, large or small, on land or water. Combined static and dynamic stresses and displacements can be determined continuously at strategic locations in and around the wellbore of a well so that insitu and operational induced pressure window limitations at specific weak-points or other locations of interest are controlled.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
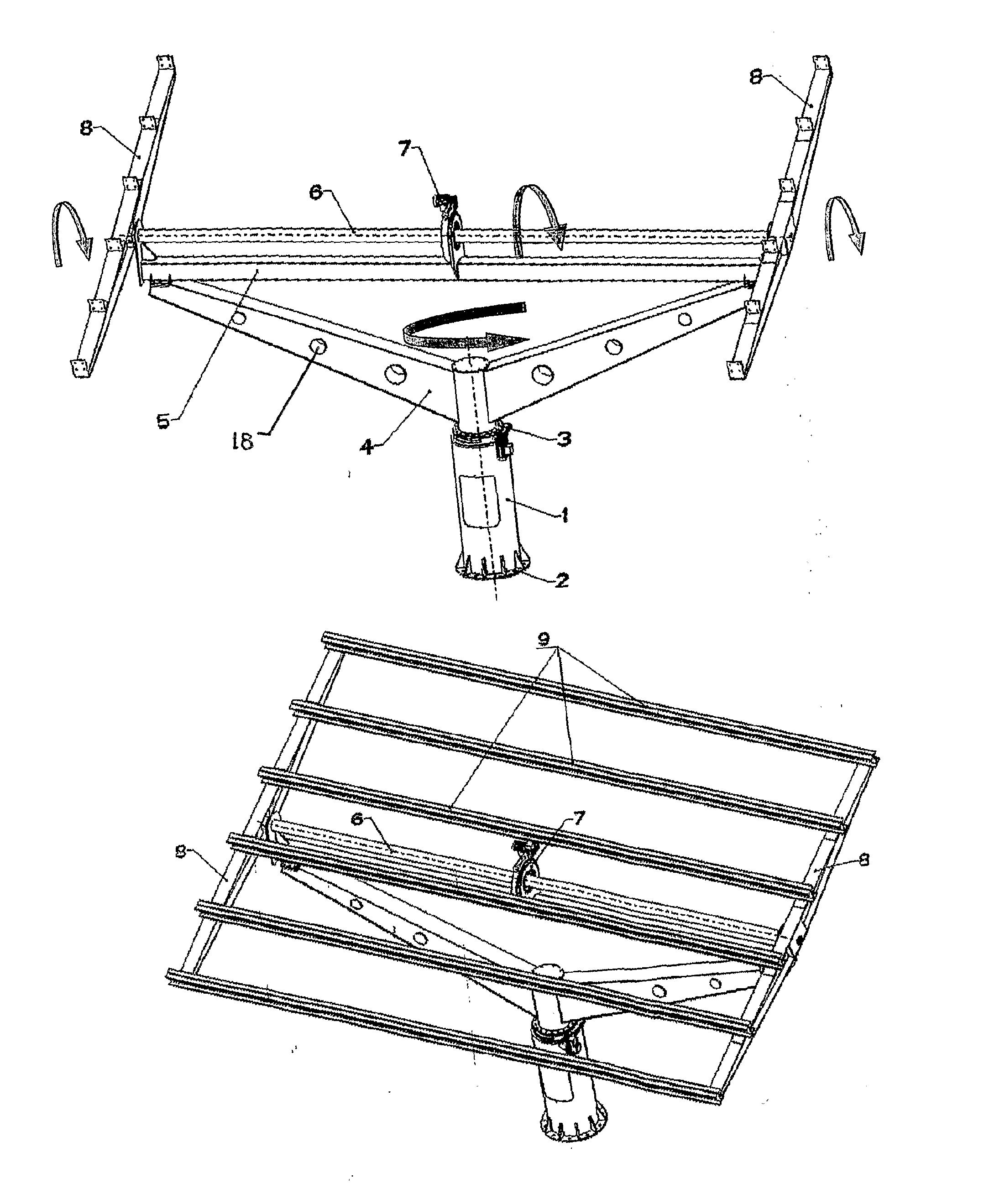
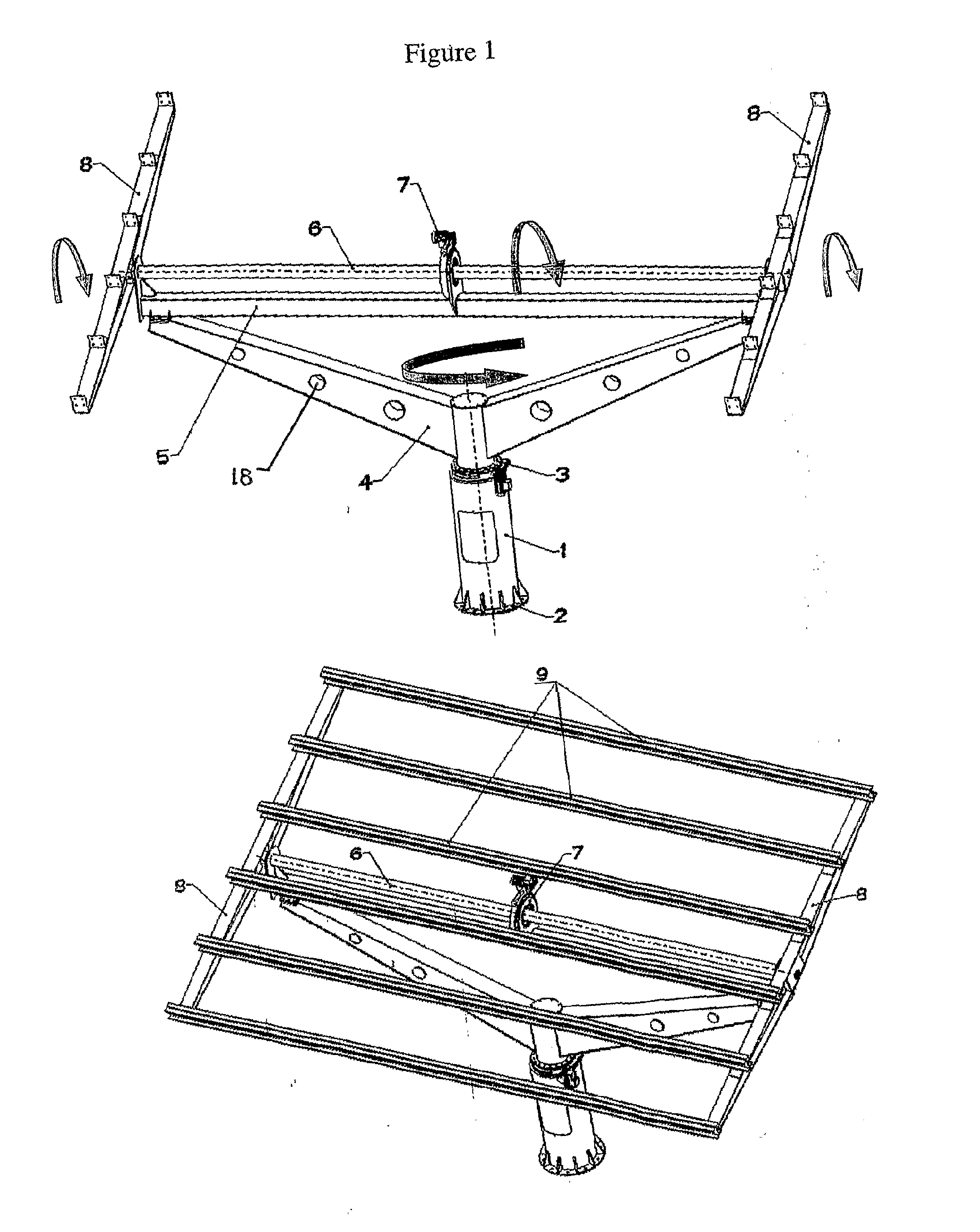
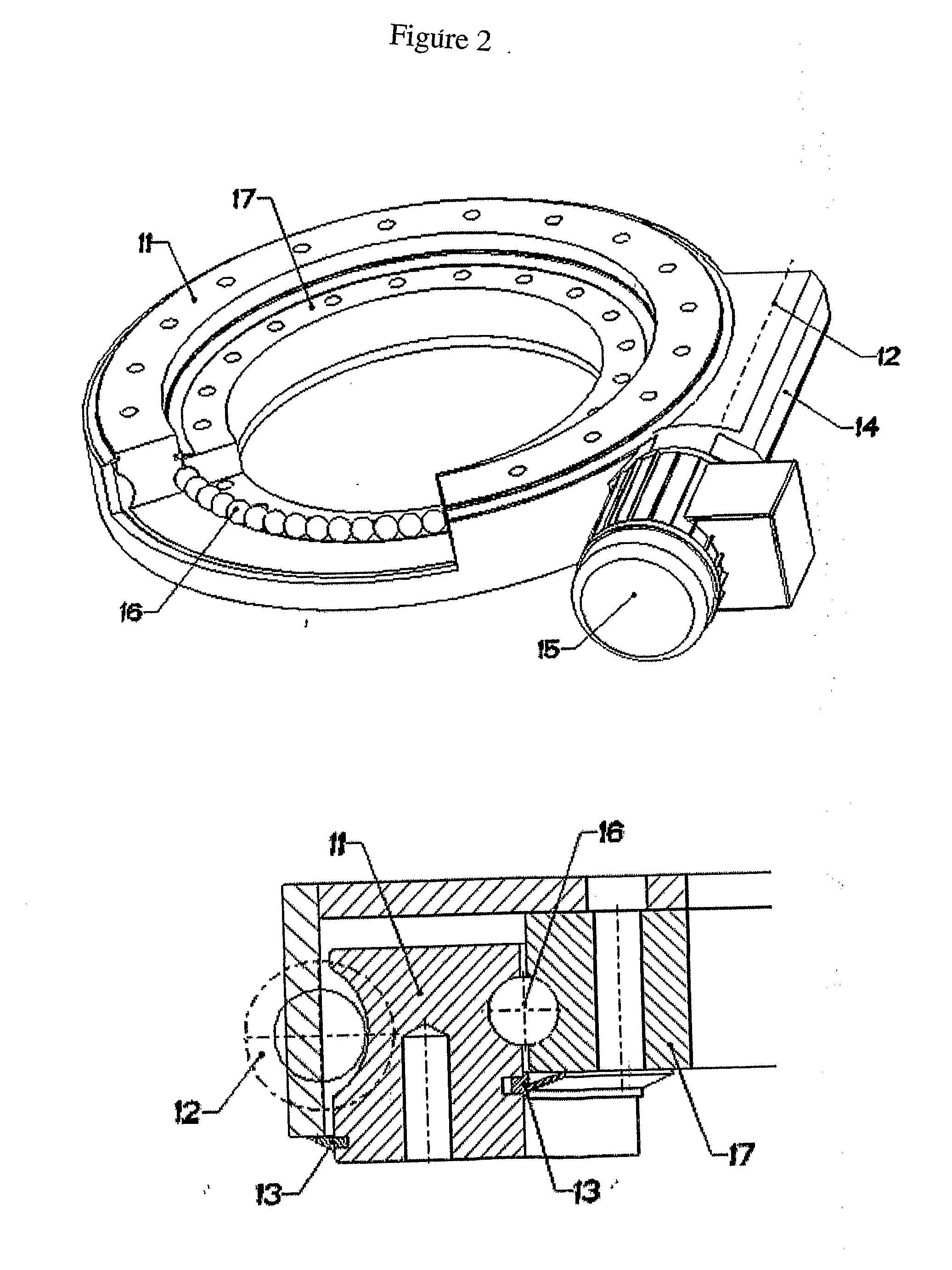
Photovoltaic panel support base rotating simultaneously around a horizontal and a vertical axis
InactiveUS20110126884A1Guaranteed smooth receptionPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyBall bearingShaped beam
A Photovoltaic panel support base rotating simultaneously around two axes, i.e. around an horizontal axis (North-South direction) for the continuous correction of the swivel angle (β), and around a vertical axis (East-West direction) for the continuous correction of the hour angle (ω), the solar deviation (δ) and the azimuthal surface (γ). The assembly comprises the tower (1), the base (2) with round profile, used for the anchorage and the seat of the assembly, the first drive mechanism (3) with ball bearings (16) for the rotation of the upper part around a vertical axis, the cantilevers' support assembly (4) of V shape, the rod (5), the second mechanism (7) for the rotation of the photovoltaic panels plane around an horizontal axis, the rotation axis (6) of the photovoltaic panels plane, the beams (8) of changing thin walled profile H and the series of transverse thin walled beams (9) of U profile. The frames of the photovoltaic panels rest on the frame formed by the U-shaped beams. The strong wind which falls at the photovoltaic panel plane is received and transmitted to the inner part of the construction, from one hand by the beams assembly (8) of shape H and from the other by the V-shaped assembly of the cantilevers (4). The strong forces' flow to the increasing profiles of the two assemblies (8) and (4) significantly decreases their strength to the inner part of the construction and as a result the two rotating drive mechanisms (3) and (7) substantially receive minimum dynamic stressing having the form of contact voltages (Hertz) created to their ball bearings (16). The electric motors of the two rotation mechanisms are driven by means of satellite control in order for the combination of β, ω, δ and γ to provide the instantly desired result cos θ=1 or Θ=0, i.e. the incident solar radiation to always be vertical with regard to the panels plane.
Owner:DRITSAS VASILEIOS
Hybrid resonant structure
ActiveUS20070040473A1Improve the coupling effectUnwanted effectImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCouplingTransducer
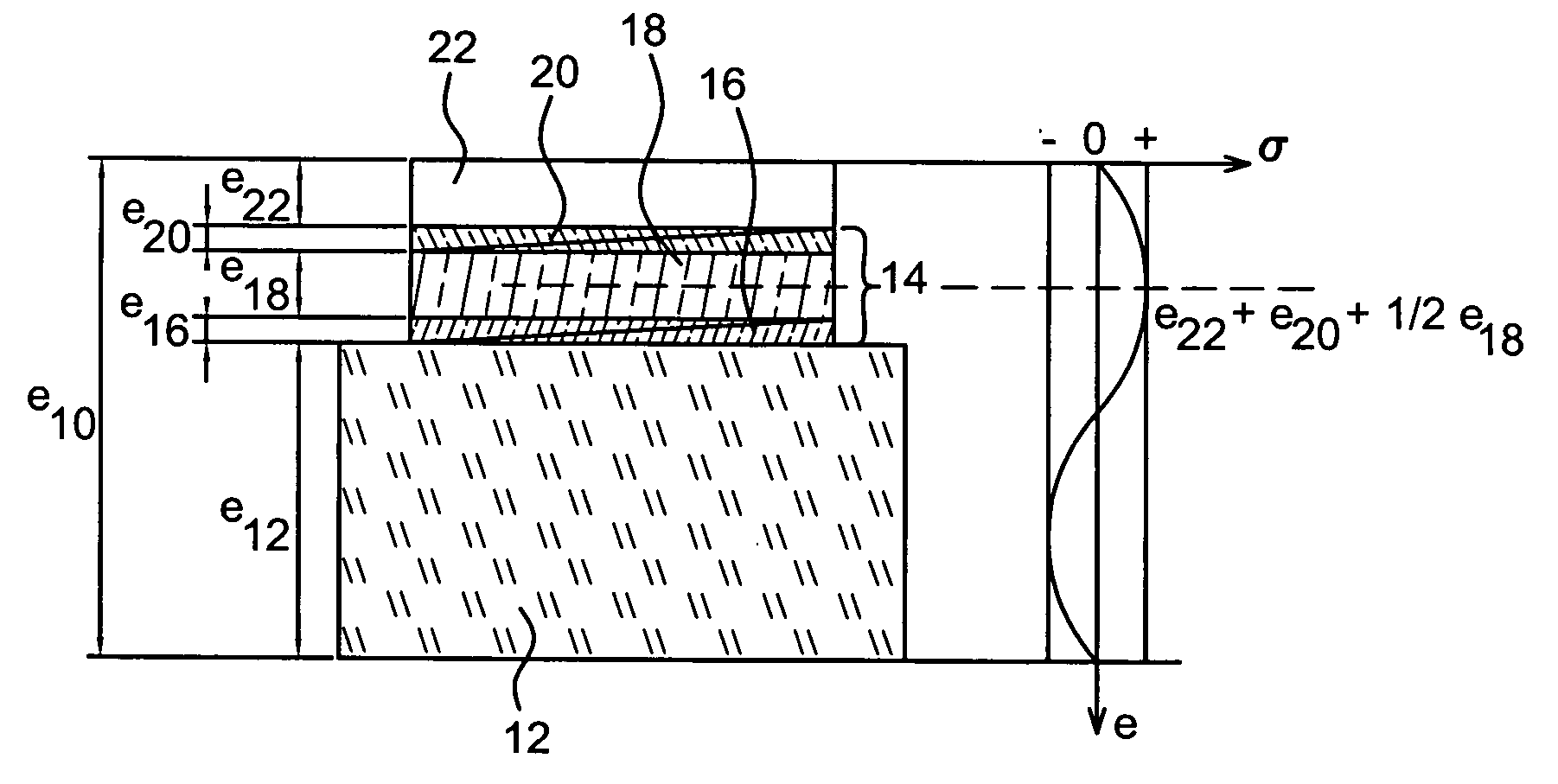
A bulk wave acoustic resonant structure which is in accordance with the invention allows the difficulties encountered at high frequency, the impossibility of working at low frequency on simple structures and the absence of an adequate coupling level to be overcome. The invention therefore proposes the use of an additional layer of material which covers the upper electrode of a piezoelectric transducer in order to localize the position of maximum intensity of the dynamic stress close to the centre of the piezoelectric layer through the effect of propagation. The structure that is in accordance with the invention may be associated with Bragg mirrors and various uses are presented.
Owner:SNAPTRACK +1
Novel test structure for automatic dynamic negative-bias temperature instability testing
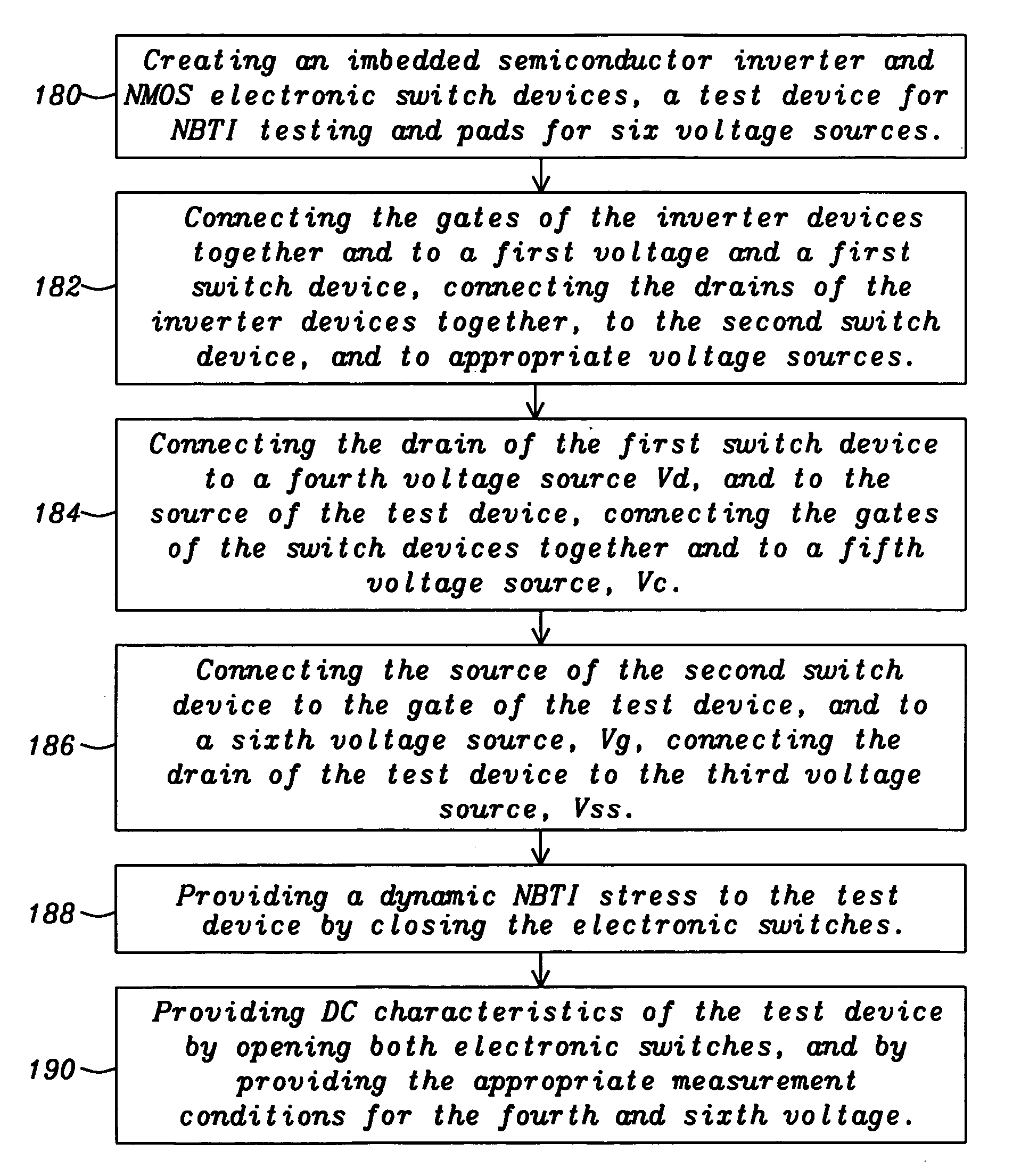
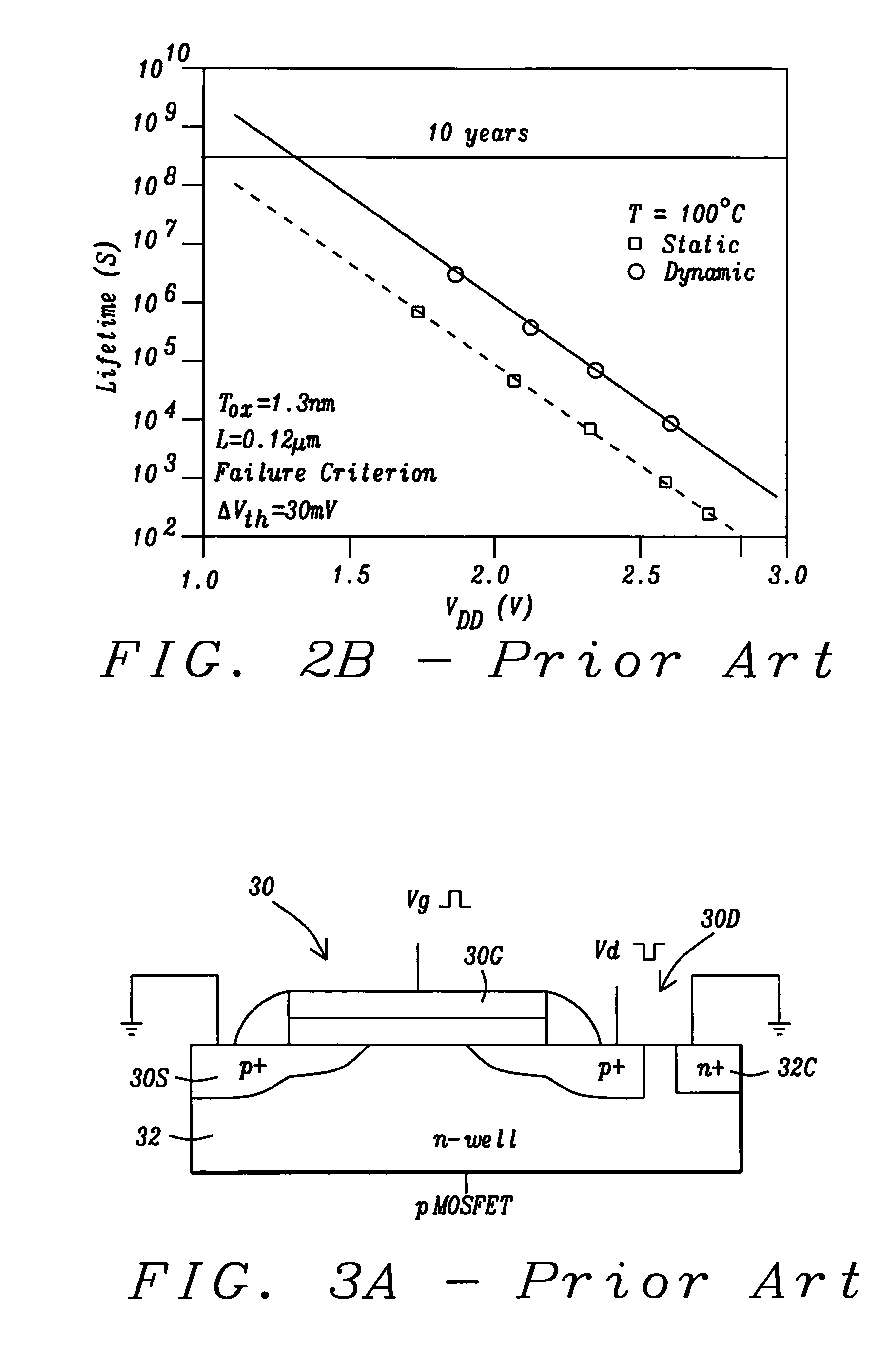
InactiveUS20050278677A1Minimize parasitic capacitanceMinimizes parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectronic switchEngineering
The invention describes a novel test structure and process to create the structure for performing automatic dynamic stress testing of PMOS devices for Negative Bias Temperature Instability (NBTI). The invention consists of an integrated inverter, two integrated electronic switches for switching from stress mode to device DC characterization measurement mode, and a PMOS FET device under test (DUT). The inverter assures the proper 180 degree phase relationship between the test device source and gate voltage while the imbedded electronic switches provide isolation of the test device during DC characterization testing. Another embodiment of the invention enables the testing of multiple devices under test (DUT's).
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Suspension type monorail vehicle coupling dynamic simulation system and method
ActiveCN108256278ASolve decouplingReduce simulation errorSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationVehicle dynamicsDynamic models
The invention discloses a suspension type monorail vehicle dynamic model and a vehicle-bridge coupling power simulation method, belongs to the technical field of rail traffic and aims to solve the technical problem that an existing suspension type monorail dynamics simulation device is large in simulation result errors during rail beam local vibration research. By providing the suspension type monorail vehicle system dynamic model, a rubber wheel-rail surface contact mechanical model, a rail beam bottom plate and web equivalent surface force application method and a vehicle and rail beam coupling dynamic model building method, a suspension type monorail vehicle-rail beam coupling dynamic simulation system is built. By the model, the system and the method, suspension type monorail vehicle system suspension mechanism decoupling and equivalent treatment are achieved, and the technical problems that the existing suspension type monorail dynamics simulation device is large in simulation result errors during the rail beam local vibration research, rail beam dynamic stress and strain results are hard to extract, rail beam local strength destroying cannot be evaluated accurately and the like are solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Vibration aging method and device employing electric vibratory test system
ActiveCN101492766AEfficient and fast processingSimple processMechanical vibrations separationVibration testingVibration controlAge method
The invention relates to a vibration stress relief method using an electric vibration experimental system and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: residual stress in a workpiece is measured, and dynamic stress level applied during vibration stress relief for the workpiece is determined; frequency spectrum analysis for the workpiece is carried out by an electric vibration table to preferably choose a plurality of harmonic frequencies; the exciting force of sinusoidal fixed-frequency or frequency sweep is randomly applied on the workpiece, the dynamic stress level of the workpiece is detected in real time in the process of force application, and proper exciting force is chosen according to parameters adjusting the exciting force of vibration table; under proper exciting force, continuous ageing treatment for the workpiece is carried out till the operation is finished after reaching the set time. The device comprises the electric vibration table, a dynamic stress measuring system and a vibration controller. The invention has simple technique and low operation cost, and is suitable for workpieces with different sizes; the process is high-efficient and fast, and saves energy and protects environment; furthermore, the device has simple structure and convenient operation, small occupying space and low energy consumption, and is widely applied to the technical field of machining.
Owner:苏州长菱测试技术有限公司
Dynamic concrete stress sensor and calibrating method based on piezoelectric ceramics
ActiveCN102401707AProtection from damageGood compatibilityForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingEpoxyElectricity
The invention relates to a dynamic concrete stress sensor and a calibrating method based on piezoelectric ceramics. The sensor comprises piezoelectric ceramic sheets subject to waterproof insulation processing, shielded conductors, a connector and two capsulation force transmission blocks; a groove is arranged at the middle part of each of the opposite sides of the two capsulation force transmission blocks; the piezoelectric ceramic sheets are arranged in the grooves; the two capsulation force transmission blocks are bonded and fixed with the piezoelectric ceramic sheets into a whole through epoxy resin mixed with dry cement powder with the weight percentage of 6-14%; and the piezoelectric ceramic sheets are connected with the connector through the shielded conductors. The invention further comprises the dynamic concrete stress sensor calibrating method and an internal dynamic stress measurement system for a concrete structure using the dynamic concrete stress sensor. The dynamic stress sensor and calibrating equipment are simple in structure; the dynamic stress sensor is small in size; the manufacture technology is simple and convenient; the cost performance is high; and the sensor is suitable for volume production.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Engine crankshaft dynamic analysis method
The invention discloses an analysis method of motor crank dynamics, which includes that: in Hypermesh software, a crank system is divided by finite element mesh generation into a crank, a flywheel, a belt pulley, a timing gear and a main bearing seat etc.; use Nastran software to execute the reduction solving of a finite element substructure; in EXCITE software, construct a model of the crank system dynamics, and exert the corresponding boundary condition on elements to implement simulation calculation; use the Nastran software to implement restoration solving of dynamic stress on the crank, perform post-processing and execute fatigue analysis on dangerous points; reasonably evaluate the crank system according to the results, and if the structure is not reasonable, the structure optimization is still needed. The method uses EXCITE calculation technique to execute dynamics analysis on the motor crank, obtains the strength and the fatigue parameters of the motor crank, and further evaluates the structure parameters of the crank and the related parts of the motor reasonably, therefore, making the improvement thereof.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Method of vibration aging and strain detection for workpiece
InactiveCN1546973ARealization of vibration agingDetect strainVibration testingEngineeringStrain sensor
The present invention discloses a method for vibration aging and strain detection for workpieces. There is involved a vibration aging equipment. After the vibration aging equipment is located by the workpiece to be treated, the exciter and the acceleration sensor in the vibration aging equipment are located respectively at the workpiece to be treated and are connected respectively to the control box in the vibration aging equipment through conducting wires, the strain sensor is positioned at the workpiece to be treated and is connected with the control box equipped with a strain detection and analysis circuit and of the vibration aging equipment through conducting wires, the control box directly detects the dynamic strain amplitude values, phase, strain detection drop-away values, equivalent dynamic stress values and residual stress drop-away values of the workpiece to be treated through the strain sensor. It can resolve the problems, existing in the prior art, that the same one vibration aging equipment is unable to directly detect the dynamic strain amplitude values, phase, strain detection drop-away values, equivalent dynamic stress values and residual stress drop-away values, and the like, of a workpiece to be treated.
Owner:汤小牛 +1
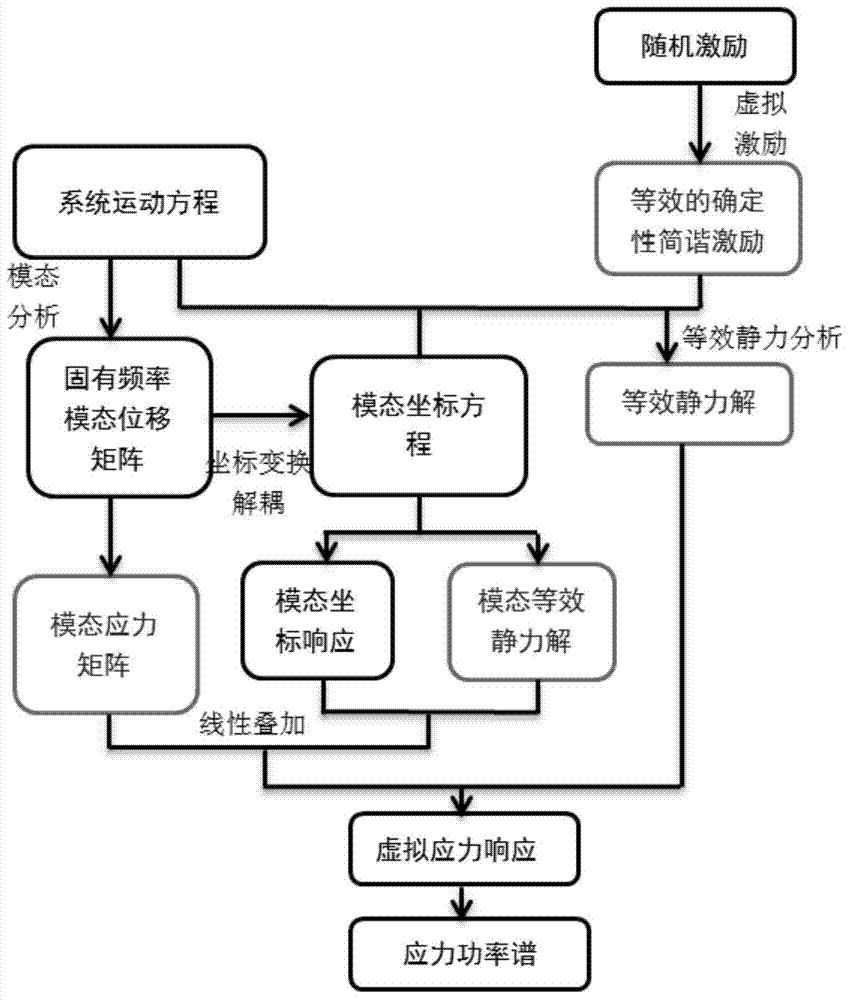
High-precision calculating method of random vibration dynamic stress of mechanical structure
InactiveCN104850713AImprove calculation accuracyImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRandom vibrationStress mode
The invention discloses a high-precision calculating method of a random vibration dynamic stress of a mechanical structure. The random excitation is converted into certainty excitation, and calculation efficiency is improved when mode-coupling effect is completely taken into consideration. By the mode stress coefficient calculation, precision reduction during stress calculation by displacement derivation is avoided; static force is corrected, neglected influence of high-order modes in mode interception is considered, and calculation accuracy of random dynamic stress is improved. Cross-correlation terms among all vibration-involved modes are included during calculation, and exact solution is obtained. For large-scale and complex projects, the high-precision calculating method is easy to operate and implement and is higher in calculation efficiency than a conventional algorithm. In addition, calculation accuracy is improved by introducing a stress mode matrix and static force correction terms of the high-order modes.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method of Stressing Static Random Access Memories for Pass Transistor Defects
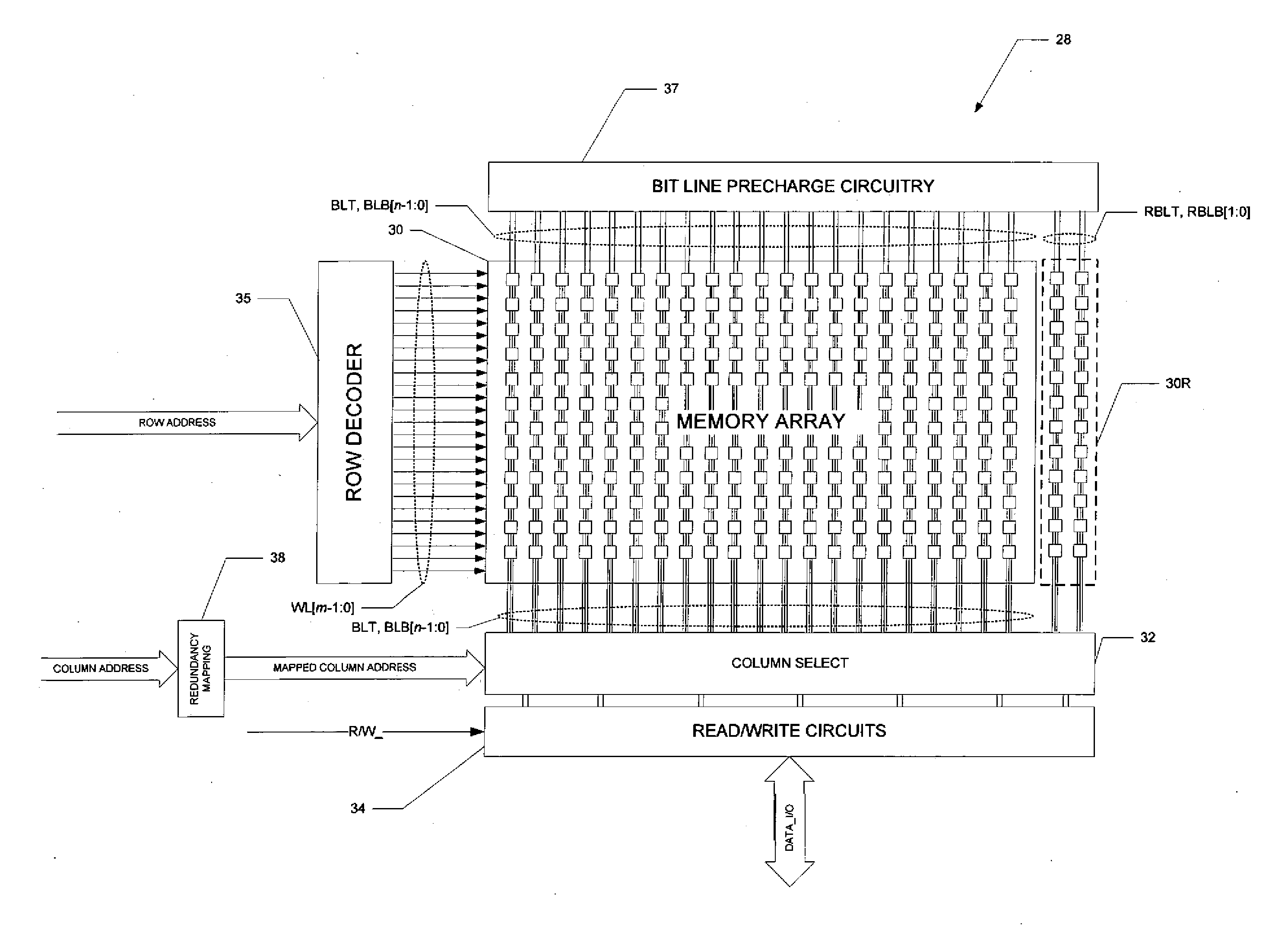
ActiveUS20130039139A1Effective distinctionWithout yield lossDigital storageBit lineStatic random-access memory
A method of stressing and screening static random access memory (SRAM) arrays to identify memory cells with bit line side pass transistor defects. After writing initial data states into the memory array under nominal bias conditions, an elevated bias voltage is applied to the memory array, for example to its power supply node. Under the elevated bias voltage, alternating data patterns are written into and read from the memory array for a selected duration. The elevated bias voltage is reduced, and a write screen is performed to identify defective memory cells. The dynamic stress of the repeated writes and reads accelerates early life failures, facilitating the write screen.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Novel vibration aging method
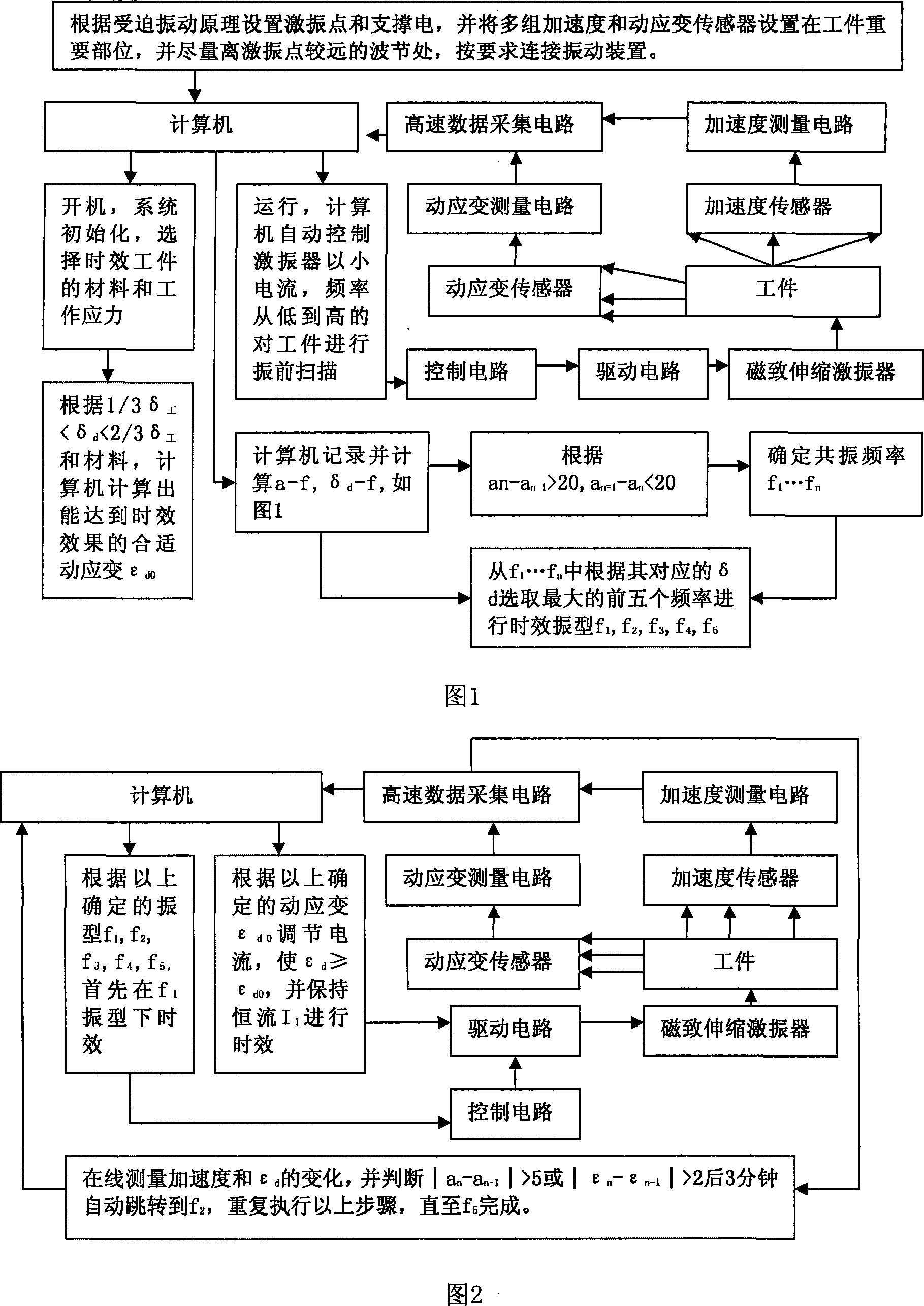
InactiveCN101225466ASolve the problem that manual adjustment affects real-time performanceMeet the requirements of dynamic stressMechanical vibrations separationAge methodStress variation
The invention discloses a vibration aging method, comprising a computer, a magnetostrictive vibration exciter, an acceleration sensor and a dynamic strain sensor. The vibration aging method is characterized in that the vibration exciter loads on the workpiece and exerts a cyclist exciting force, two sensors are respectively positioned on the easily cracking and deforming area of the workpiece, the sensors are analyzed and different frequency, the corresponding relationship between the dynamic strains and sorting are done by the computer, selecting the frequencies corresponding to the first biggest dynamic strains as the typical vibration, adjusting the working current and time of the vibration exciter, making the vibration exciter to vibrate at the above frequency till the aging is finished. The vibration aging method has the advantages of using the magnetostrictive vibration exciter as a vibration source, regulating the exciting force by the computer, timely responding the vibration variation to meet the dynamic stress, controlling the vibration source to vibrate at the resonation frequency by the computer, timely tuning the output current of the vibration exciter, analyzing and judging the vibration mode and the vibration time of the vibration aging, lively measuring the dynamic stress variation, and outputting the correct remaining stress variation as the prove for the experiment.
Owner:郝俊山
Tensile impact apparatus
InactiveUS7320242B2Increase ratingsHigh strain rateAcceleration measurementMaterial testing goodsEngineeringImpact loading
The present invention generally relates to a tensile impact apparatus that is designed to give dynamic stress-strain curves and fracture characteristics for a rubber specimen undergoing tensile impact loading. More particularly, this invention relates to a tensile impact apparatus that is capable of achieving strains of up to fracture. The apparatus is also capable of visually recording fracture phenomena.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
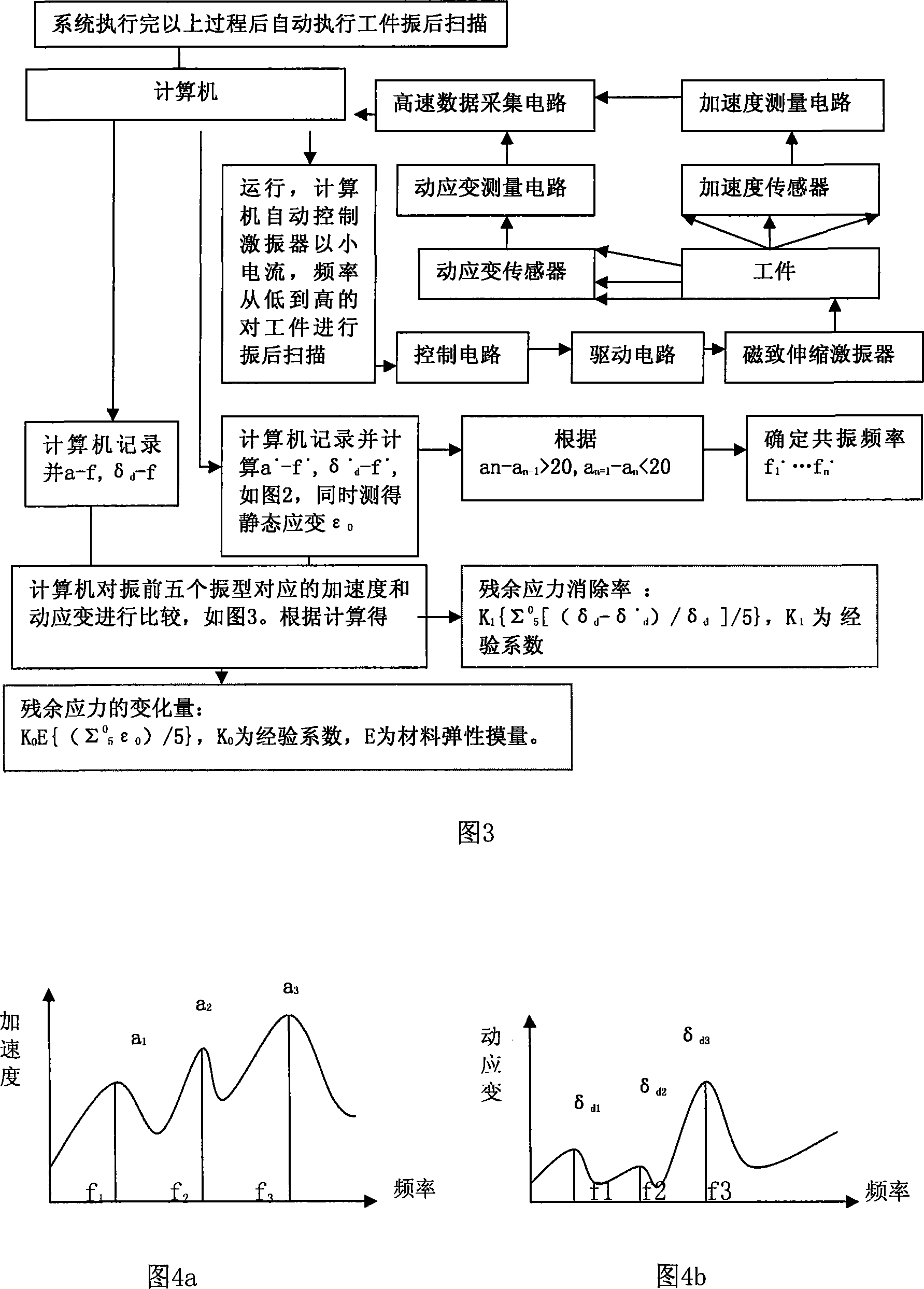
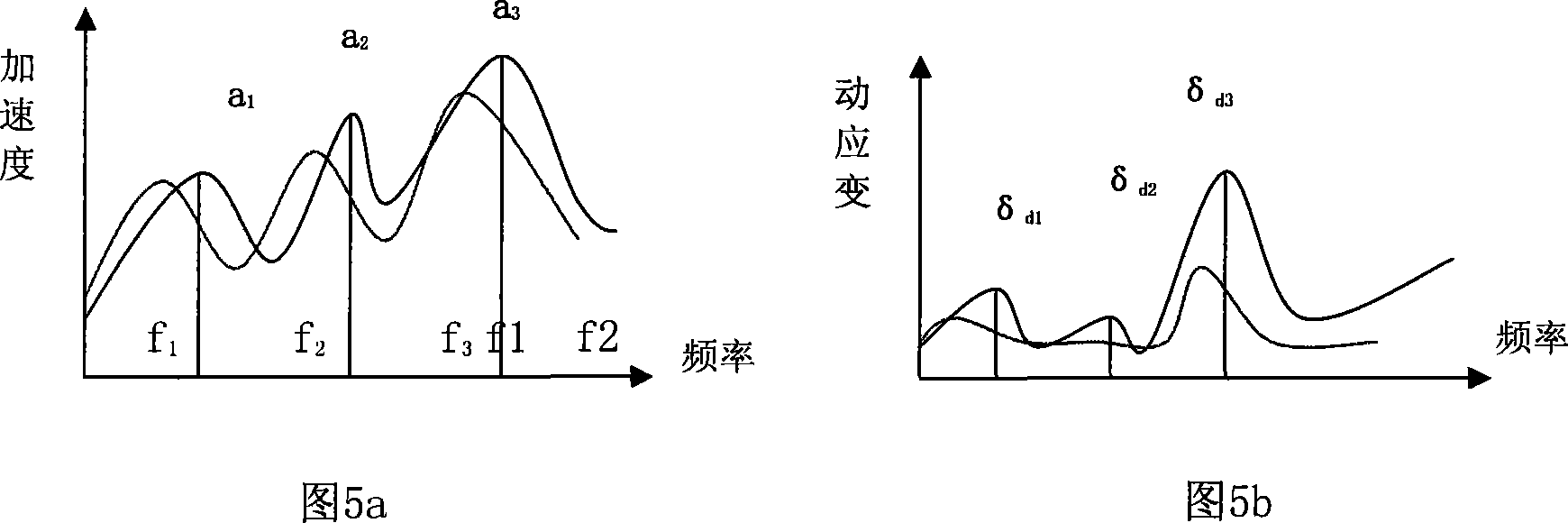
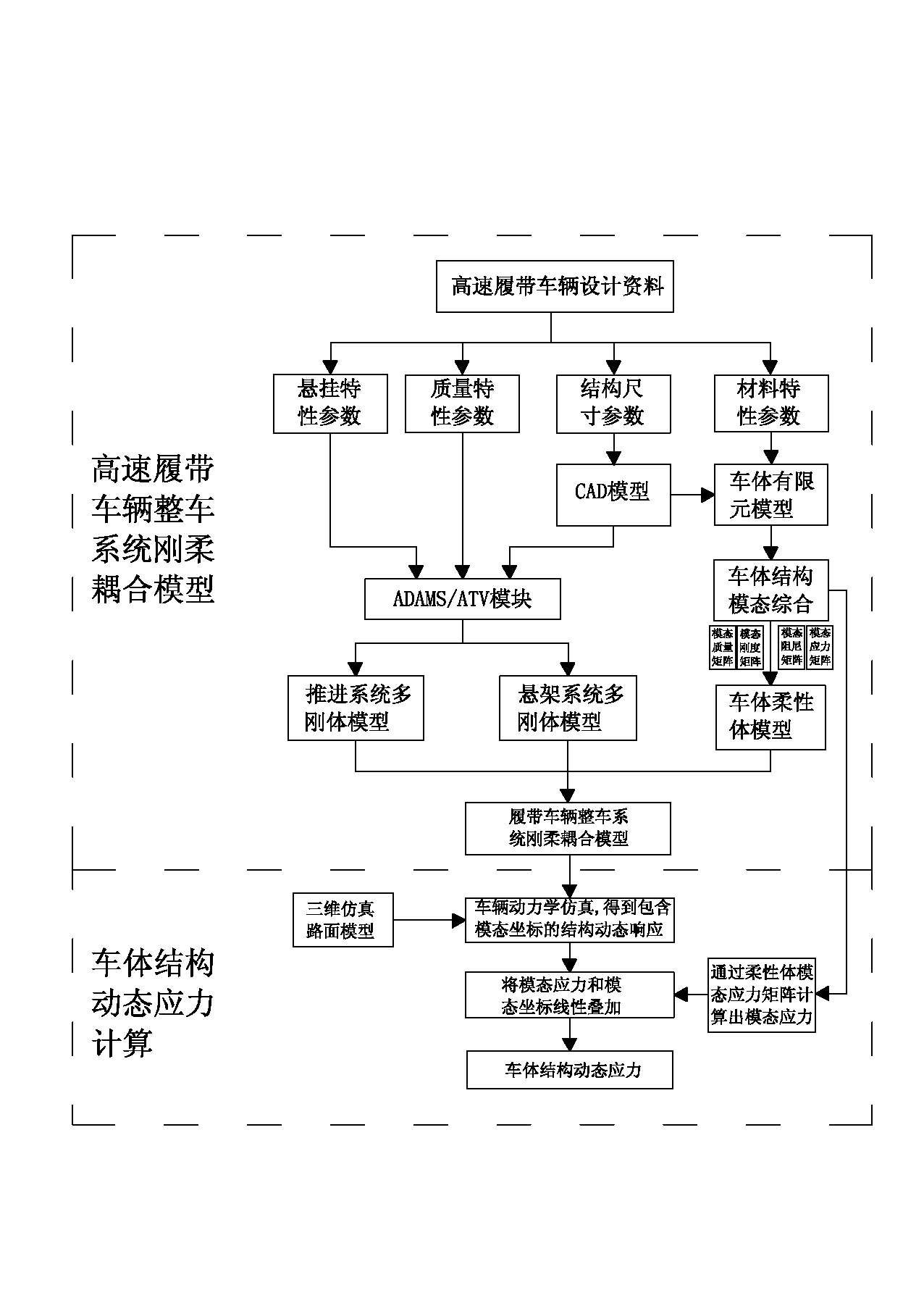
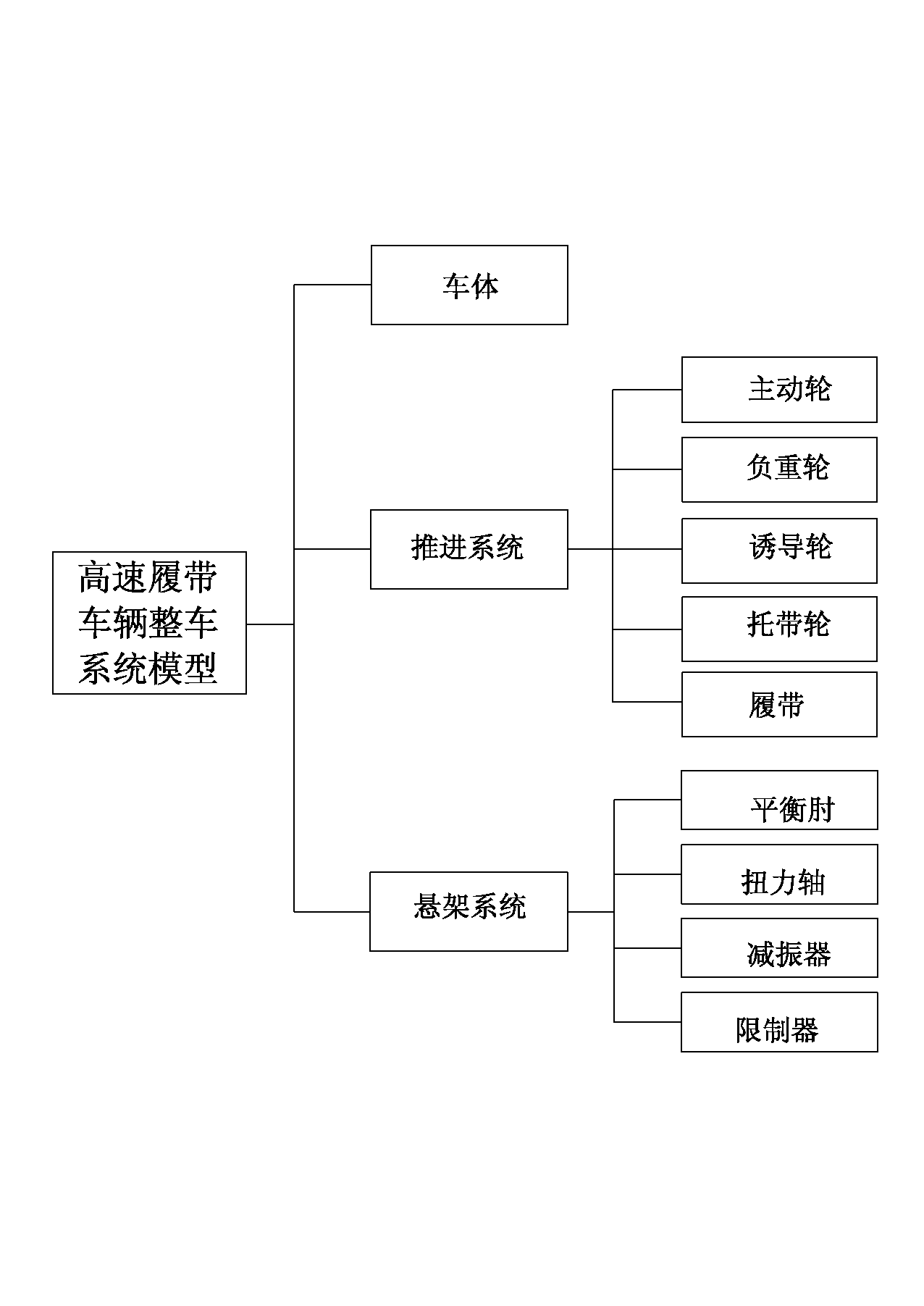
Method for simulating and calculating dynamic stress of a vehicle body structure of high-speed tracked vehicle
InactiveCN102855363AAccurately reflect coupling dynamicsSpecial data processing applicationsStructural dynamicsElement model
The invention relates to the technical field of calculation, simulation and estimation of dynamic stress of a bearing structure of a high-speed tracked vehicle, in particular to a method for simulating and calculating dynamic stress of a vehicle body structure of the high-speed tracked vehicle. The method comprises two implementation steps of constructing a finished high-speed tracked vehicle system rigid-flexible coupling model based on a modal comprehensive method and calculating the dynamic stress of the vehicle body structure based on a modal stress recovering method. An integrated rigid body suspension system model, a propelling system model and a high-speed tracked vehicle rigid-flexible coupling complex dynamics model with a vehicle body structure finite element model are built by adopting a modal comprehensive technology, and the characteristics of the coupling dynamics between the vehicle system dynamics and the structure dynamics are accurately reflected. The method can obtain structural edge load at a designing and development stage of the high-speed tracked vehicle and simultaneously obtain structure dynamic stress, and provides effective means for design and improvement of a system structure of the high-speed tracked vehicle.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
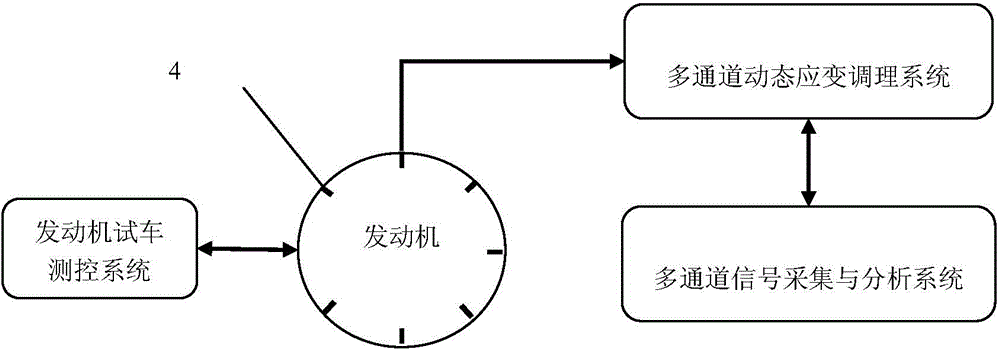
Dynamic stress testing method for stator vane under operating state of gas turbine engine
The invention belongs to the technology for testing aircraft engines and relates to an engine vane surface dynamic stress testing method. A dynamic stress testing method for a stator vane under the operating state of a gas turbine engine allows a dynamic stress test to be conducted on a guide vane and the stator vane of the engine under the operating state of the engine. Due to the fact that strain gages are directly stuck to the vanes of the engine to conduct dynamic testing, test data are real and accurate, information is complete, quantitative analysis is easy, and bases can be provided for analysis of faults such as vane cracking and chip off-falling, and meanwhile reliable data are provided for the further mastering of the distribution of charges on the surfaces of the engine vanes.
Owner:AECC AVIATION POWER CO LTD
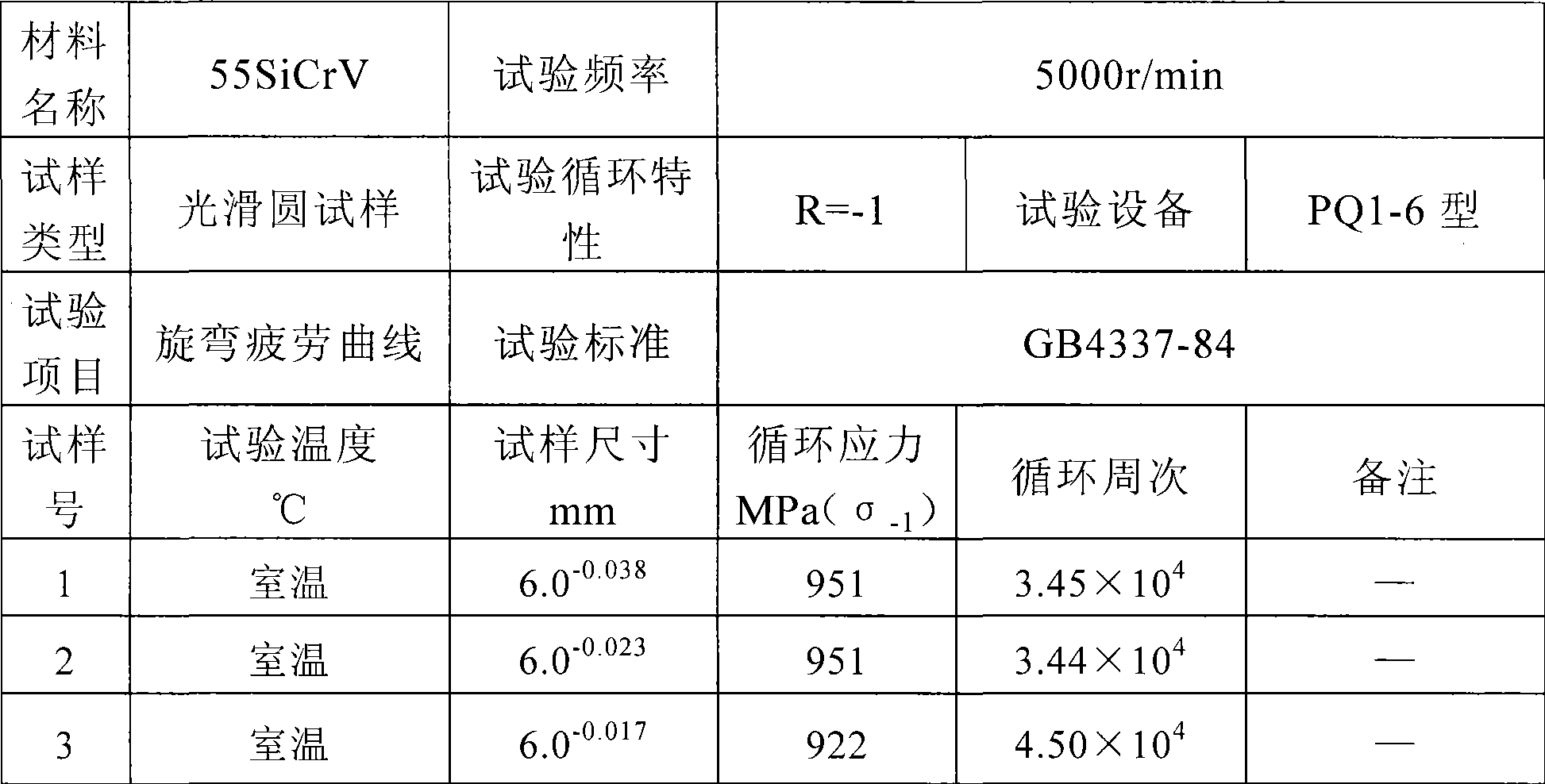
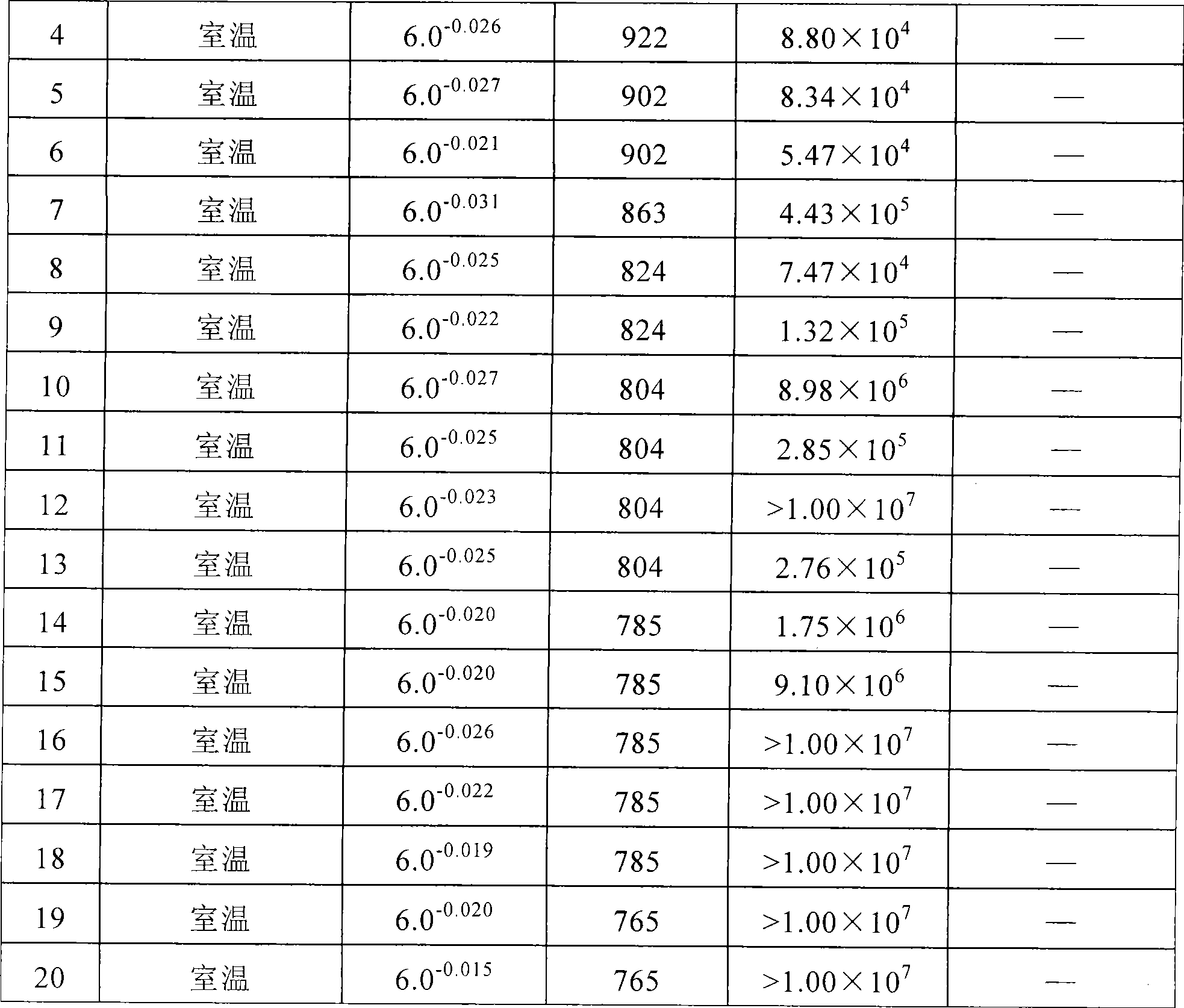
Method for controlling non-metallic impurities in structural alloy steel
ActiveCN101519710AAvoid it happening againFully float to removeProcess efficiency improvementFatigue loadingNon-metallic inclusions
A method for controlling non-metallic impurities in structural alloy steel includes the following steps of: step one: pre-smelting molten steel: (1) batching; (2) slagging in advance in the melting stage; (3) tapping, tapping conditions: (P) is less than or equal to 0.005 percent; (S) is less than or equal to 0.005 percent; and tapping temperature is 1640 DEG C to 1660 DEG C; step two: external refining: at the time of one third of the tapping of a primary smelting furnace, fluxing medium is added into ladles; the heating station of an external refining furnace adopts Si-Fe powder and SiC powder to conduct diffusive deoxidation; oxygen is determined before the ladles enter vacuum degassing, and deoxidizing agent is added; step three: vacuum refining: the vacuum process is kept for longer than or equal to 20min under less than or equal to 66.7Pa; the post-vacuum soft argon blowing time is longer than or equal to 15min; the soft argon blowing intensity is less than or equal to 0.10Mpa; and the post-vacuum crane ladle temperature is 1530 DEG C to 1540 DEG C; and step four: continuous casting. The method improves the purity of steel by improving the composition and size of the non-metallic impurities in steel so as to further meet the requirement on pure steel under high dynamic stress and high cycle fatigue loading.
Owner:宝武特种冶金有限公司
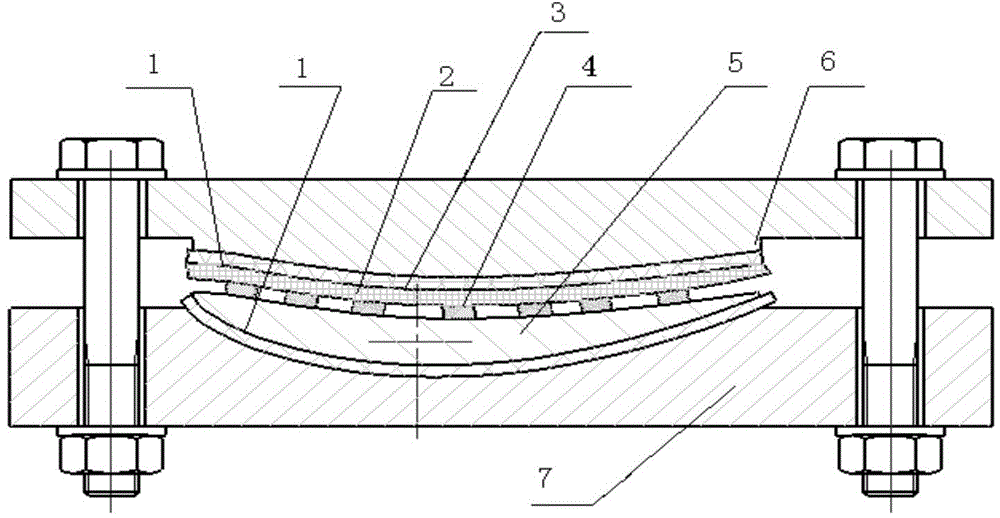
Vibratory stress relief apparatus for medium frequency and low frequency shaft type parts, and use method thereof
InactiveCN102321793AAddress effectivenessAddress stressFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMedium frequencyEngineering
The invention relates to a vibratory stress relief apparatus for medium frequency and low frequency shaft type parts, and a use method thereof. The apparatus comprises a vibration exciter, a support block for clamping and supporting a workpiece, and a support mechanism connected with the support block. The support mechanism comprises a pair of support frames comprising a left support frame and a right support frame, and a support seat for installing the left support frame and the right support frame, wherein the left support frame and the right support frame right are arranged relatively. Thesupport block respectively forms rotatable connections with the left support frame of the support mechanism and the right support frame of the support mechanism. The apparatus further comprises a vibration exciter base for installing the vibration exciter, wherein the vibration exciter base is arranged on the middle portion of the workpiece, the vibration exciter, the vibration exciter base and the workpiece synchronously vibrate during vibratory stress relief. According to the present invention, a simply supported beam form is adopted, the flexural vibration type primary resonance is generated by the shaft type parts under the excitation of the vibration exciter at the natural frequency adopted for shaft flexural vibration; in the prior art, the dynamic stress generated by the apparatus does not reach the requirement of residual stress decreasing, with the apparatus provided by the present invention, the problem in the prior art is solved; the deformation amounts on both ends of the shaft are substantially improved; the dynamic stress distribution of the shaft is uniform so as to effectively reduce the residual stress of the shaft part.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Simple instrument method for test of internal stress of soil mass under cyclic loading
ActiveCN105181498AMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesAutomatic controlData acquisition
The invention relates to a soil dynamic characteristic test technique for geotechnical engineering and especially relates to a simple instrument and a method for test of an internal stress of a soil mass under cyclic loading. A large quantity of researches and reports record that the roadbed soil under the cyclic loading is suffered from dynamic stress accumulation, but the academics does not pay attention to the phenomenon. The simple instrument can be mainly used for measuring the response conditions of the internal stress in the soil on factors such as different cyclic loading magnitudes, loading waveforms, loading frequencies and soil compaction rate, and acquiring the parameters, such as settlement curve, dynamic elastic modulus, total deformation modulus, static elastic modulus, of the soil mass under the cyclic loading effect. The method provided by the invention belongs to an innovative technology which is simple in laboratory test and convenient in soil dynamic characteristic acquisition; with the help of a lever pressure meter, the instrument can realize 10-times load output and can save instrument consumable materials and power sources; a computer system can be utilized to realize the automatic control on the instrument control and the data collection.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Electromagnetic impact dynamic tensile test method and device
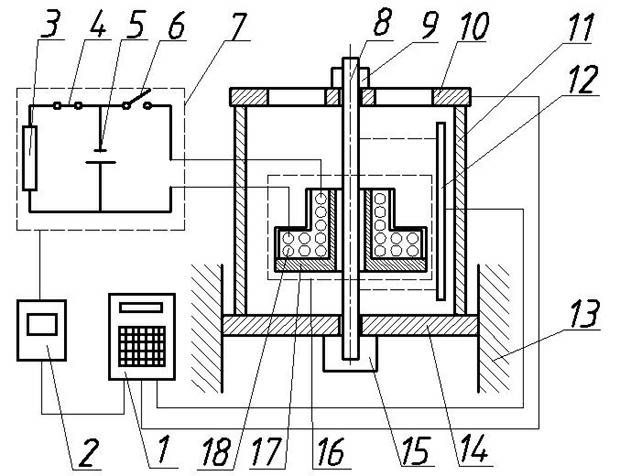
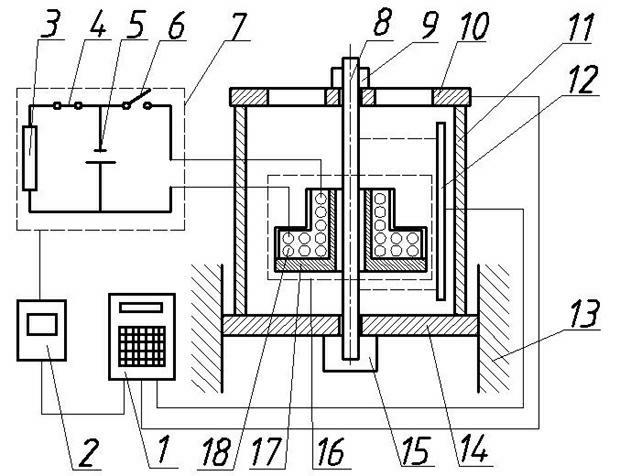
ActiveCN102109436AAchieving Dynamic StretchEasy to controlMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStrong pulseElectromagnetic pulse
The invention relates to an electromagnetic impact dynamic tensile test method and a device, and belongs to the technical field of dynamic tensile mechanical property test of materials. The device adopts an electromagnetic pulse to load; a tensile test piece (8) passes through a central hole of an electromagnetic pulse device (16); the electromagnetic pulse device (16) is used for arousing a strong-pulse magnetic field; the action of electromagnetic force is generated between a target (14) and an electromagnetic pulse coil (18), so that the tensile test piece (8) mounted between the target (14) and a bracket (10) obtains direct instantaneous tensile force to finish the dynamic tensile test of the tensile test piece (8). The method and the device are used for measuring the dynamic stress and strain relationship of the materials in a high strain state; and the device has simple structure and simple test process, can be used for carrying out direct dynamic tensile test as well as the dynamic tensile test of the materials under the conditions of different high strain rates and ultrahigh strain rates, and has low cost and good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com