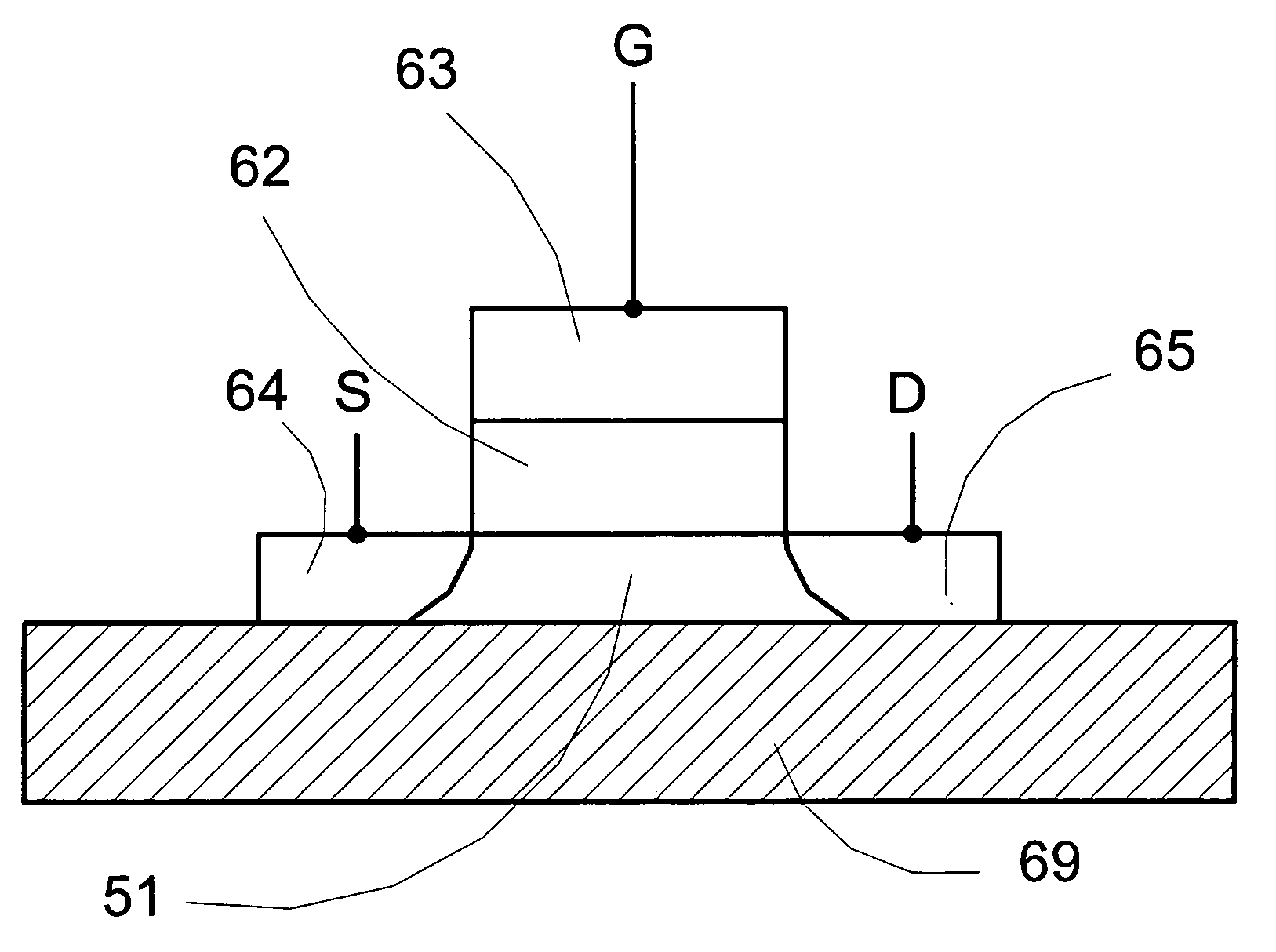
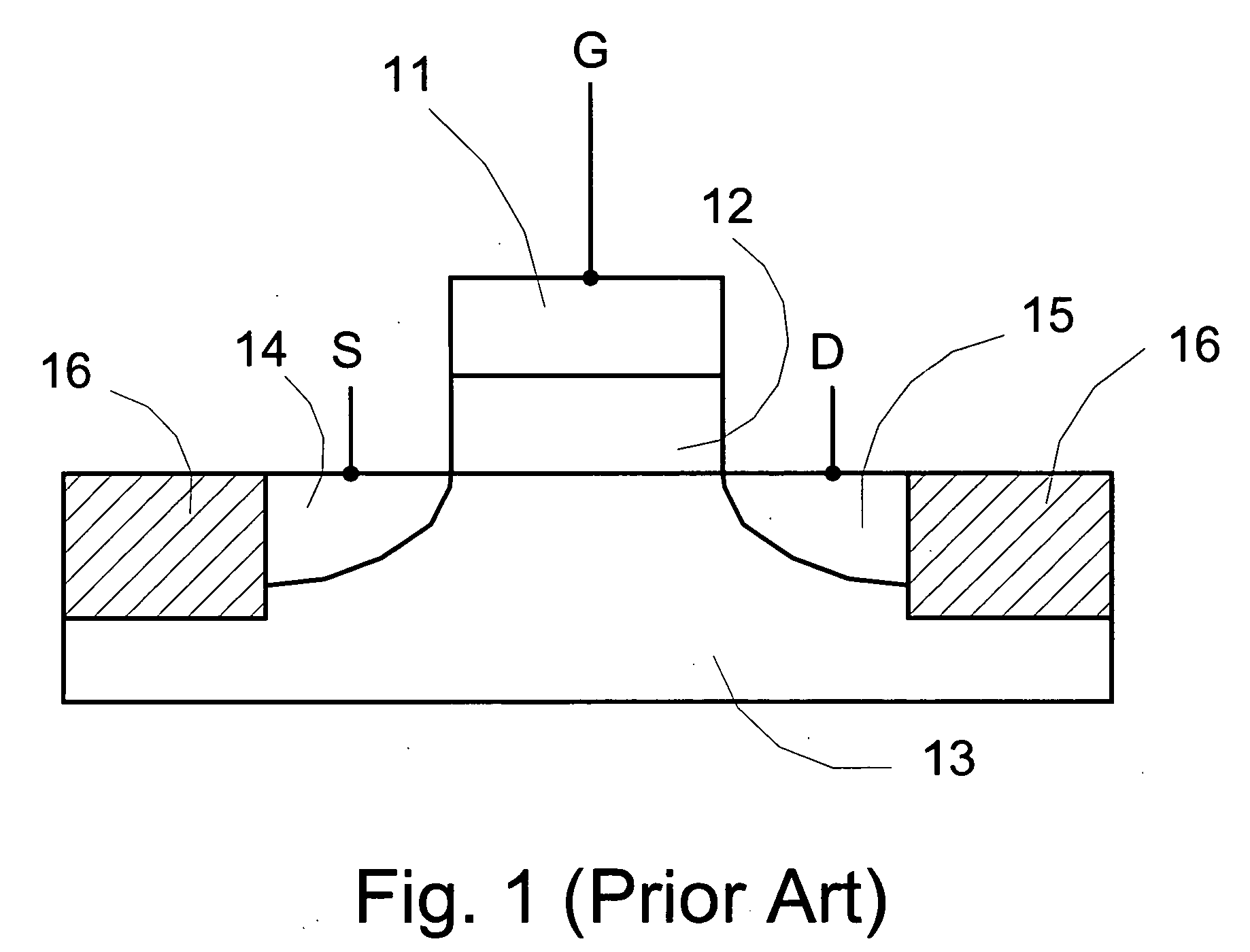
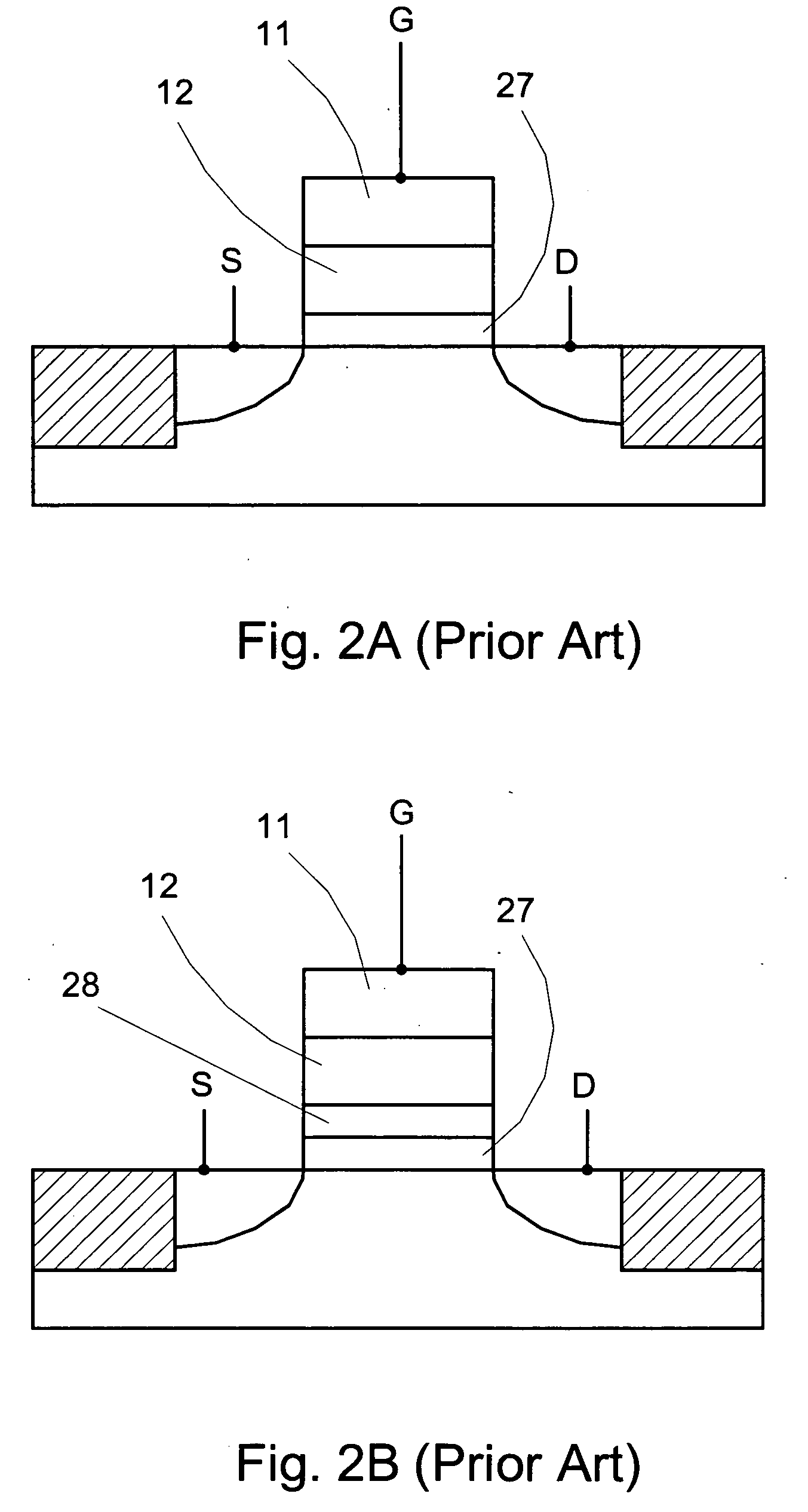
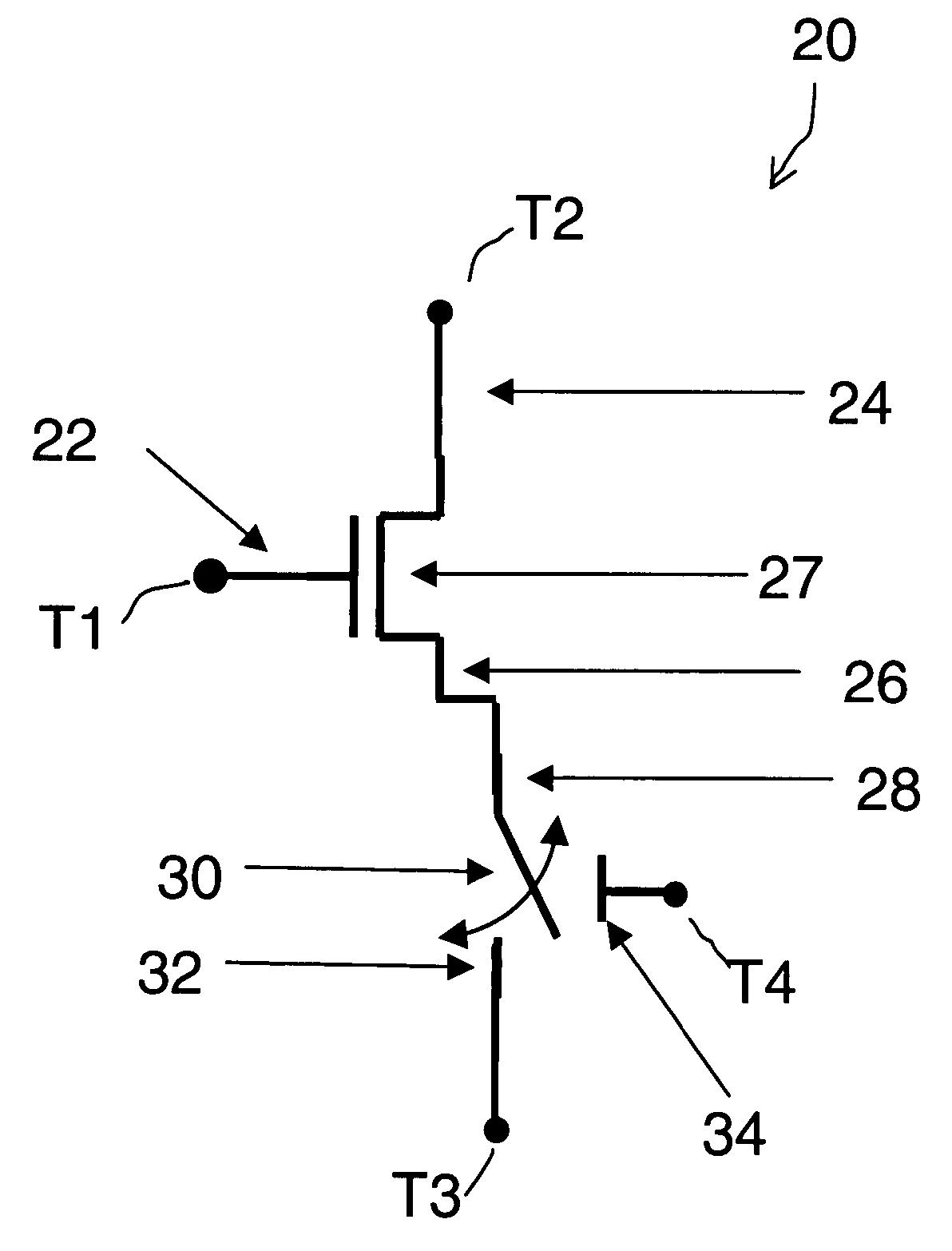
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5551 results about "AND gate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
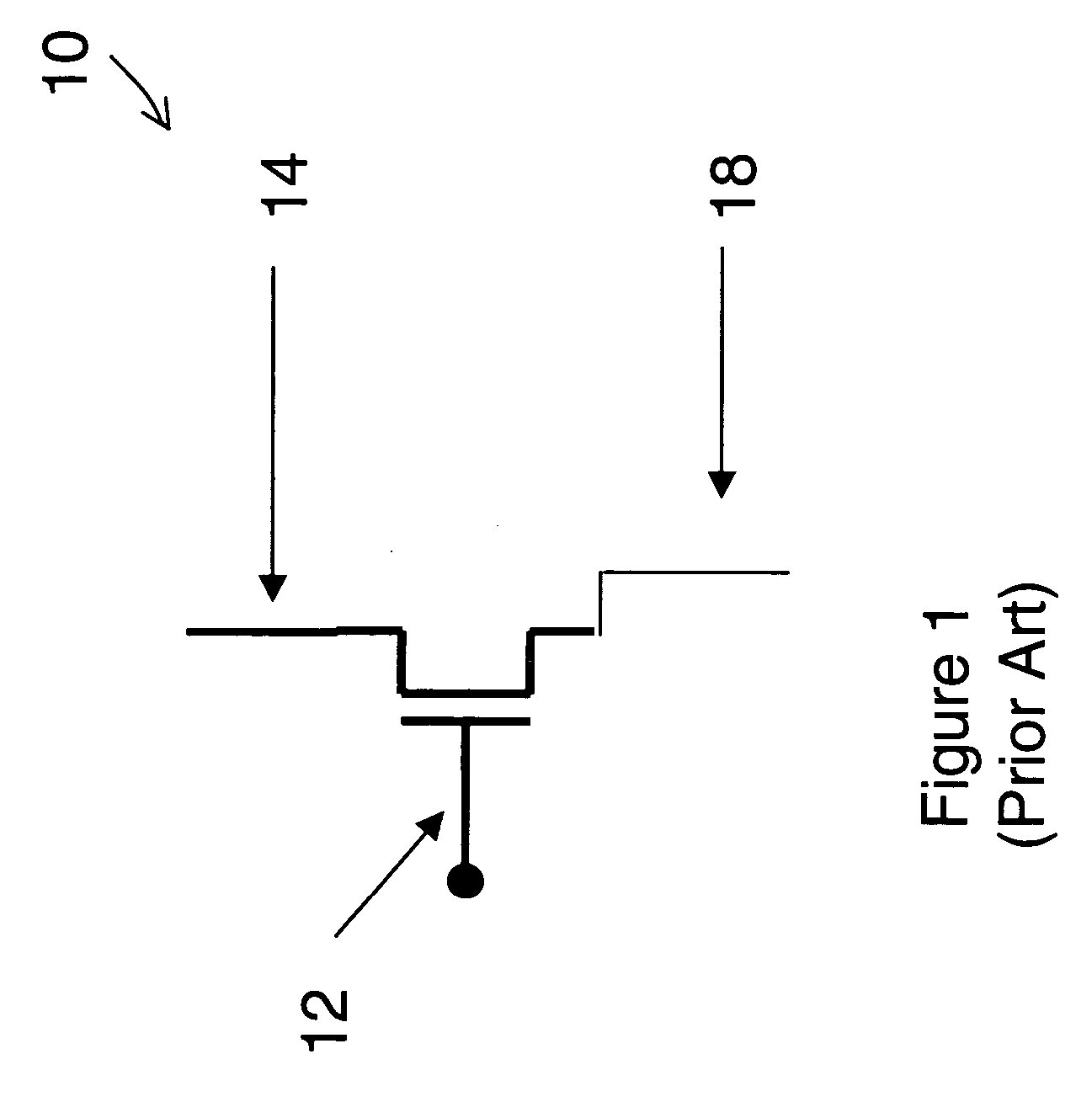
The AND gate is a basic digital logic gate that implements logical conjunction - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results only if all the inputs to the AND gate are HIGH (1). If none or not all inputs to the AND gate are HIGH, a LOW output results. The function can be extended to any number of inputs.
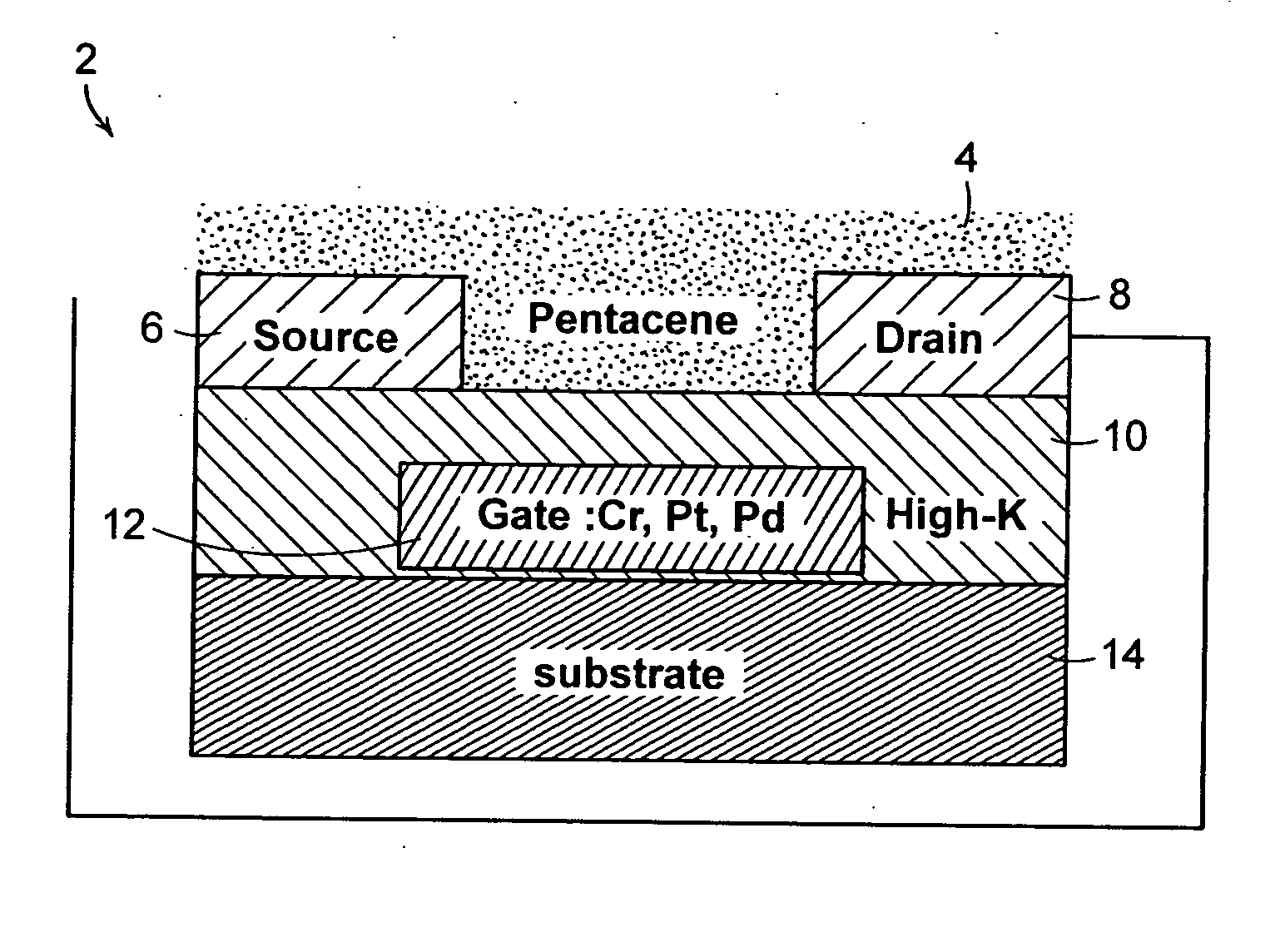
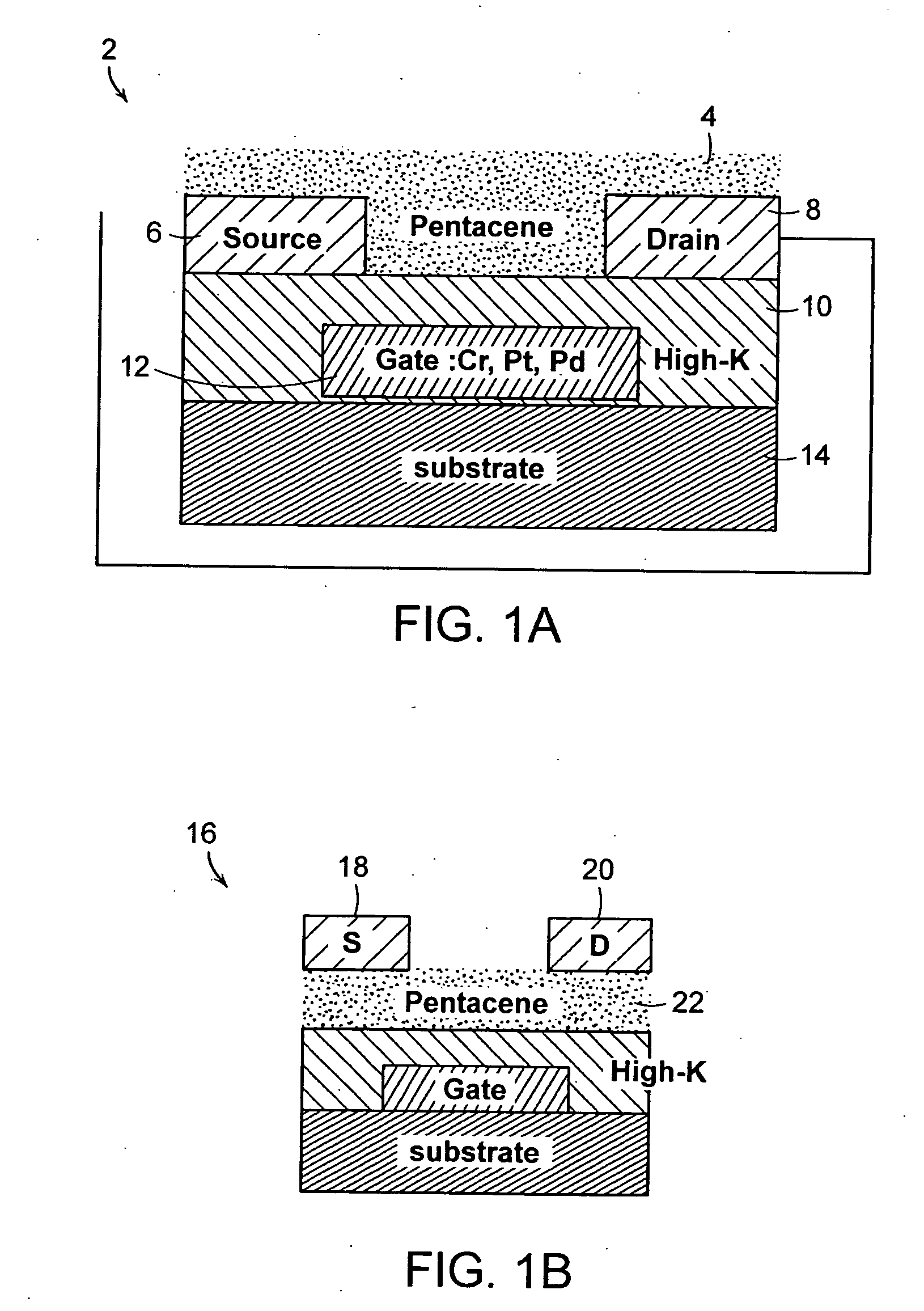
Low voltage flexible organic/transparent transistor for selective gas sensing, photodetecting and CMOS device applications
A thin film transistor (TFT) includes a source electrode, a drain electrode, and a gate electrode. A gate insulator is coupled to the source electrode, drain electrode, and gate electrode. The gate insulator includes room temperature deposited high-K materials so as to allow said thin film transistor to operate at low operating voltage.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
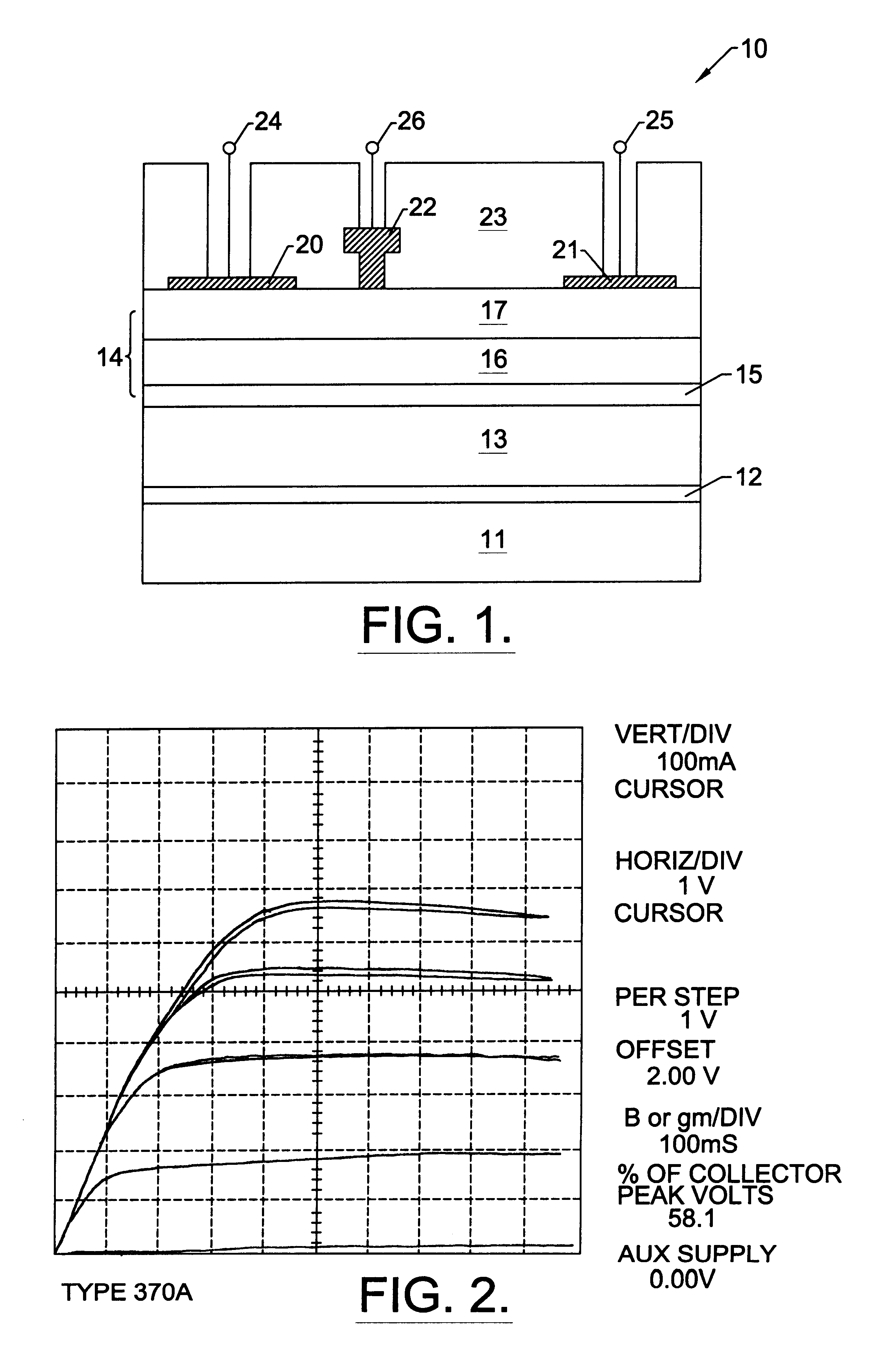
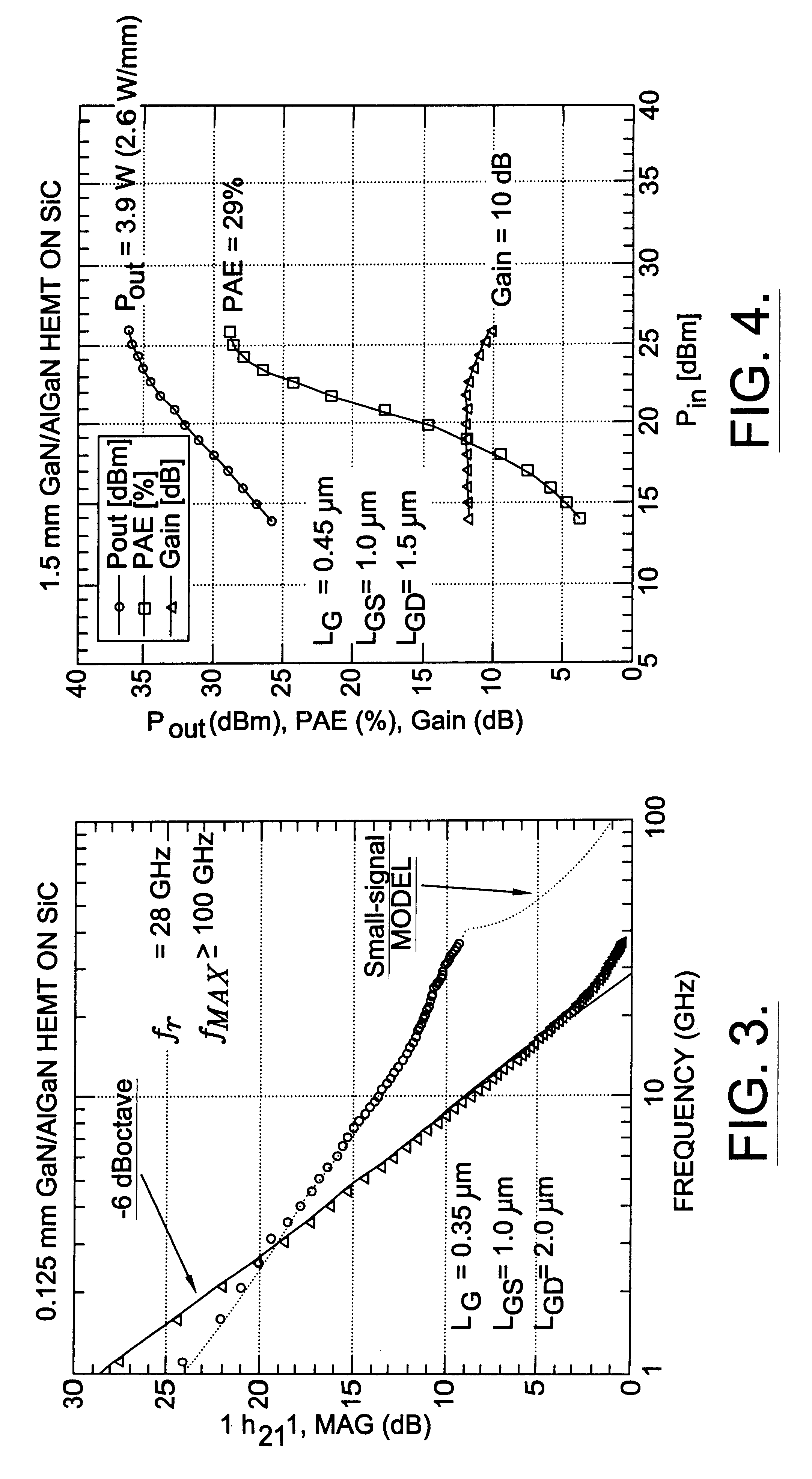
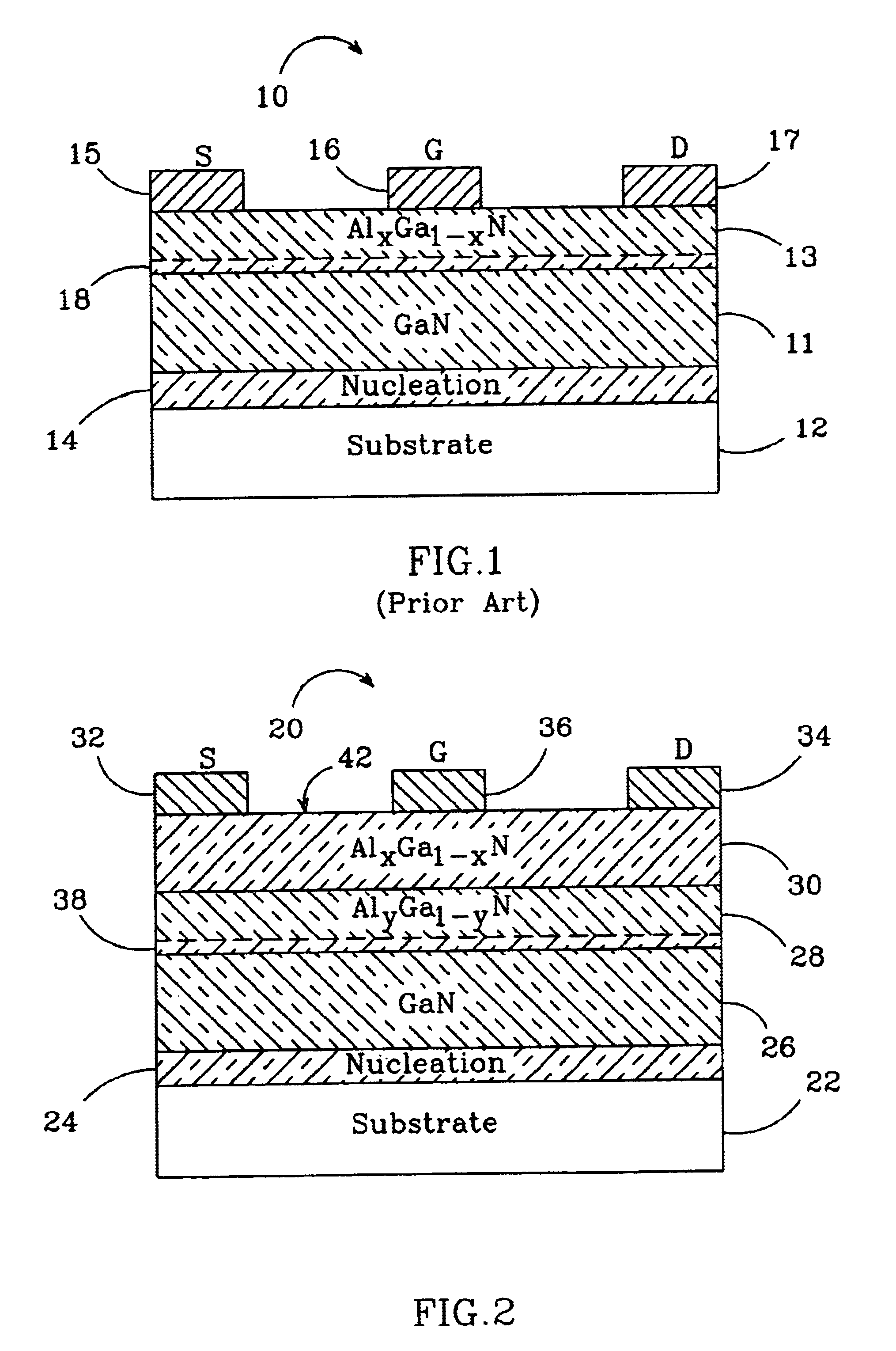
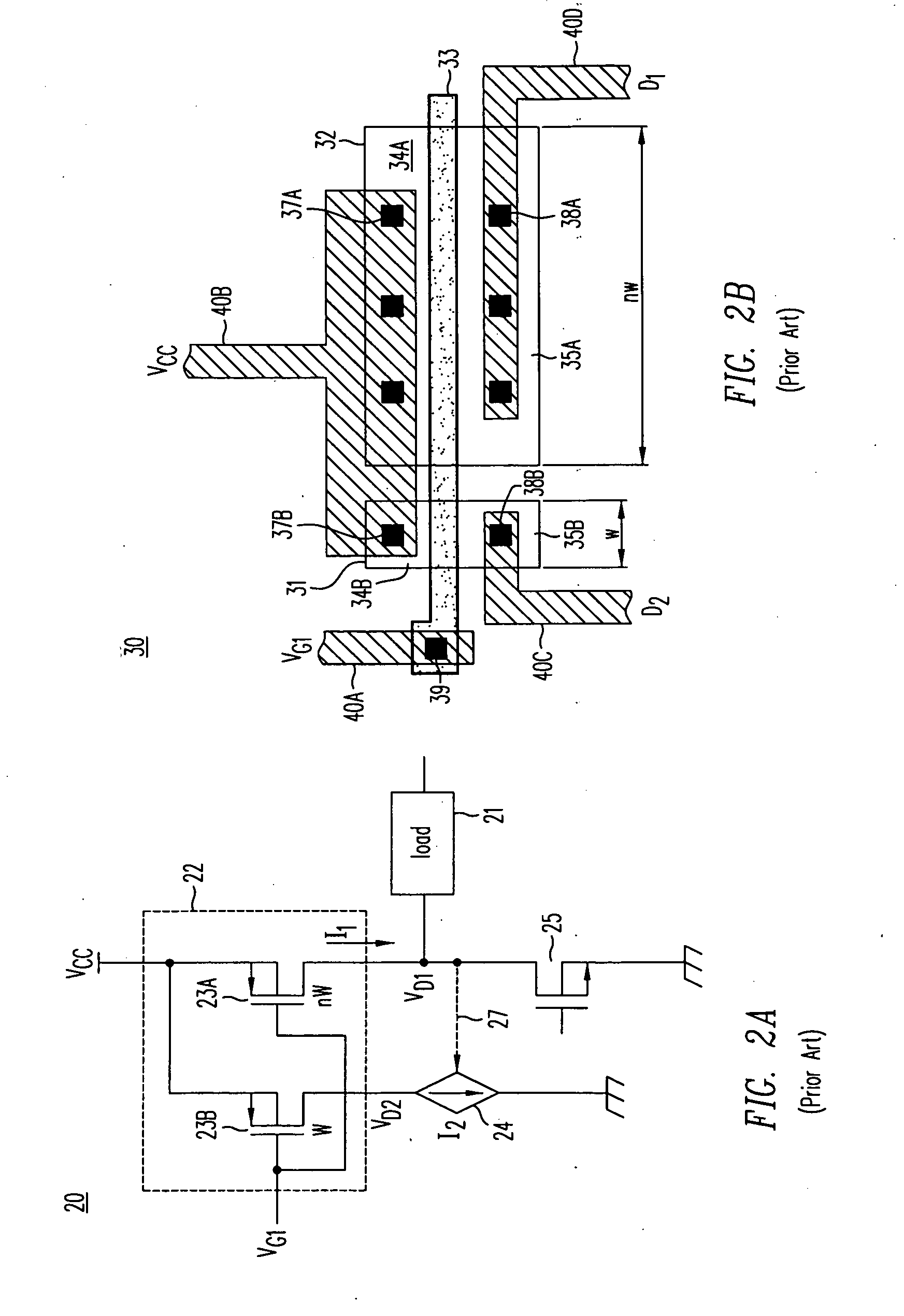
Nitride based transistors on semi-insulating silicon carbide substrates
InactiveUS6316793B1Quality improvementImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideMaterials science
A high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) is disclosed that includes a semi-insulating silicon carbide substrate, an aluminum nitride buffer layer on the substrate, an insulating gallium nitride layer on the buffer layer, an active structure of aluminum gallium nitride on the gallium nitride layer, a passivation layer on the aluminum gallium nitride active structure, and respective source, drain and gate contacts to the aluminum gallium nitride active structure.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
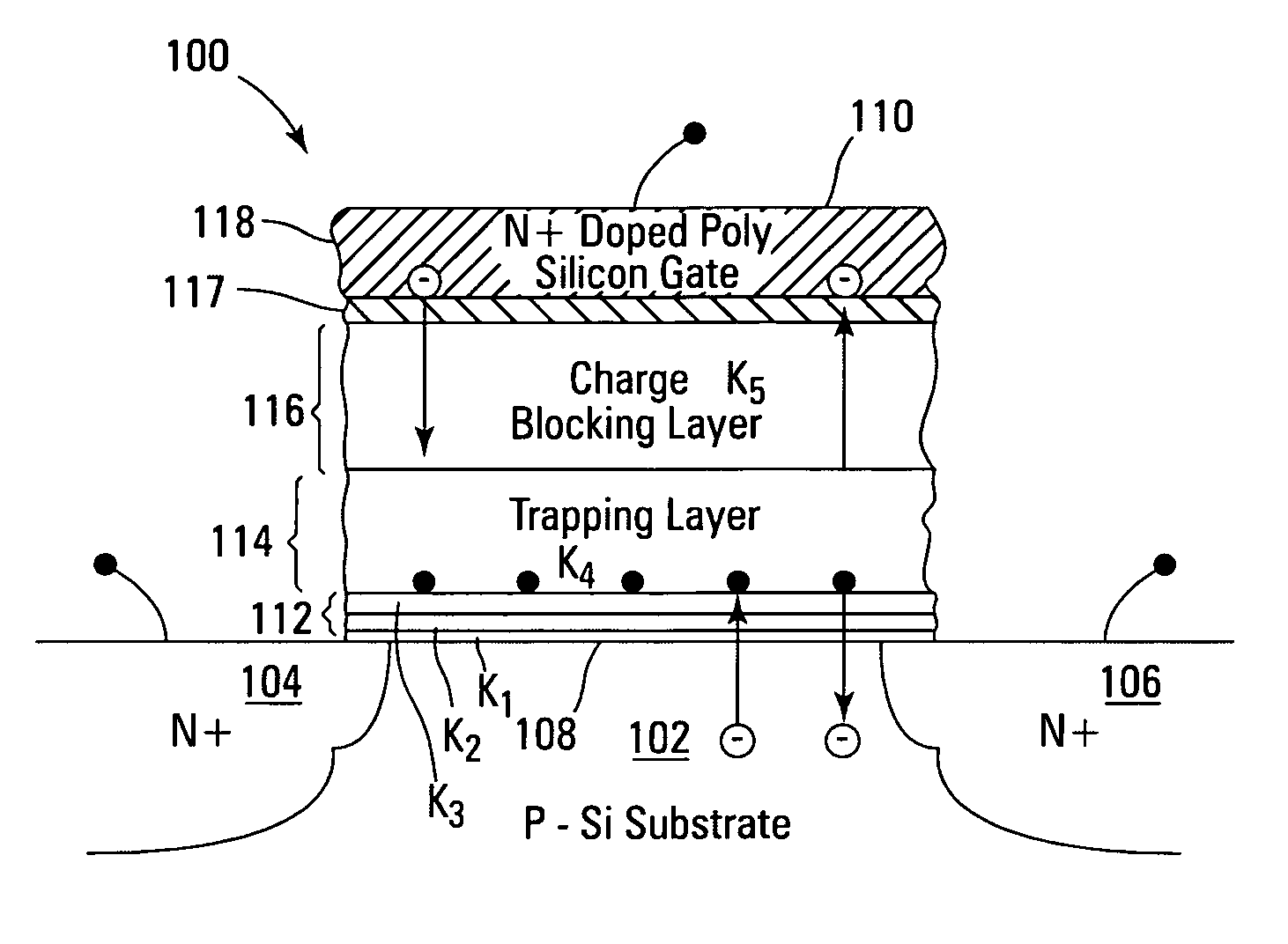
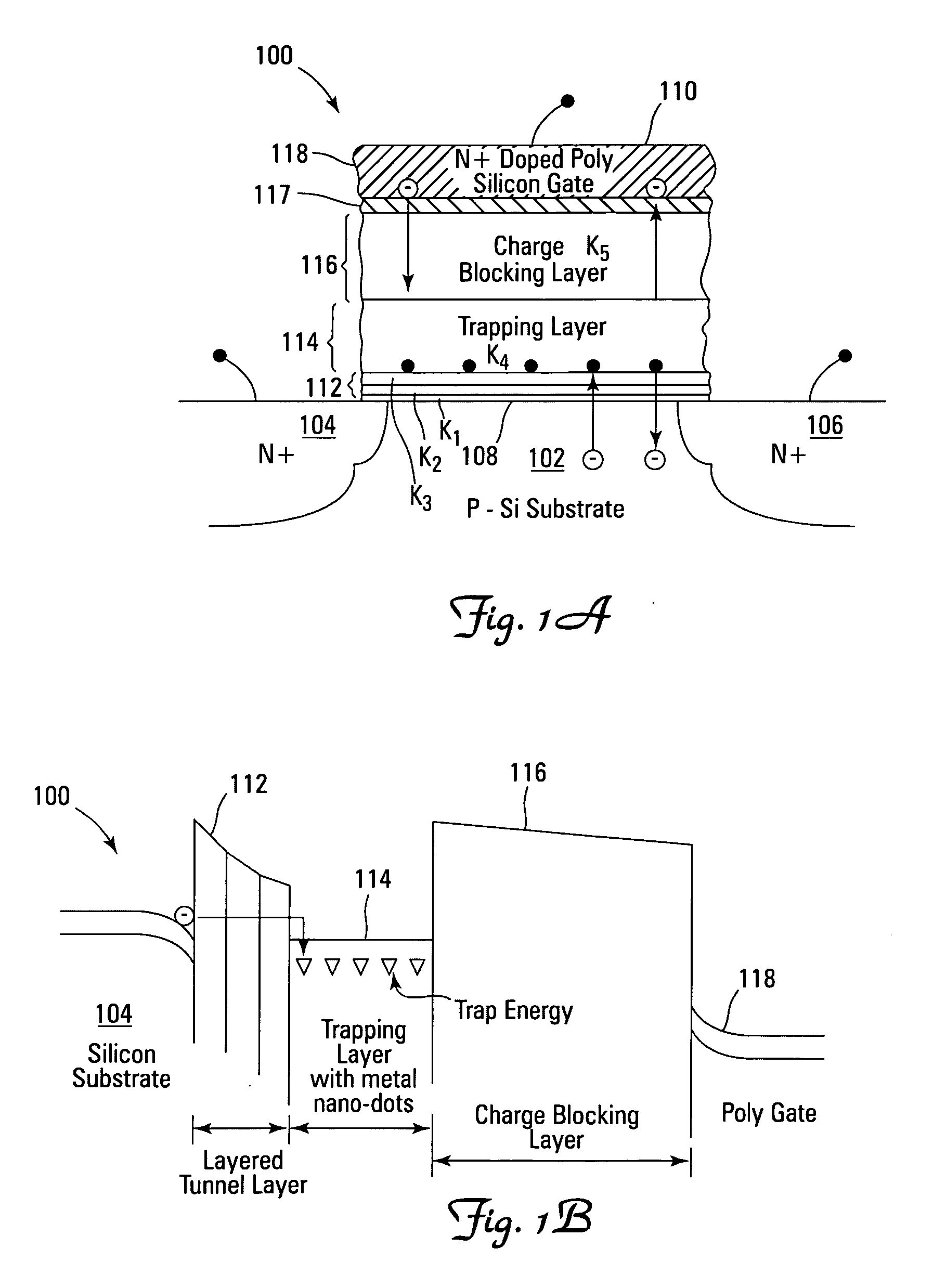
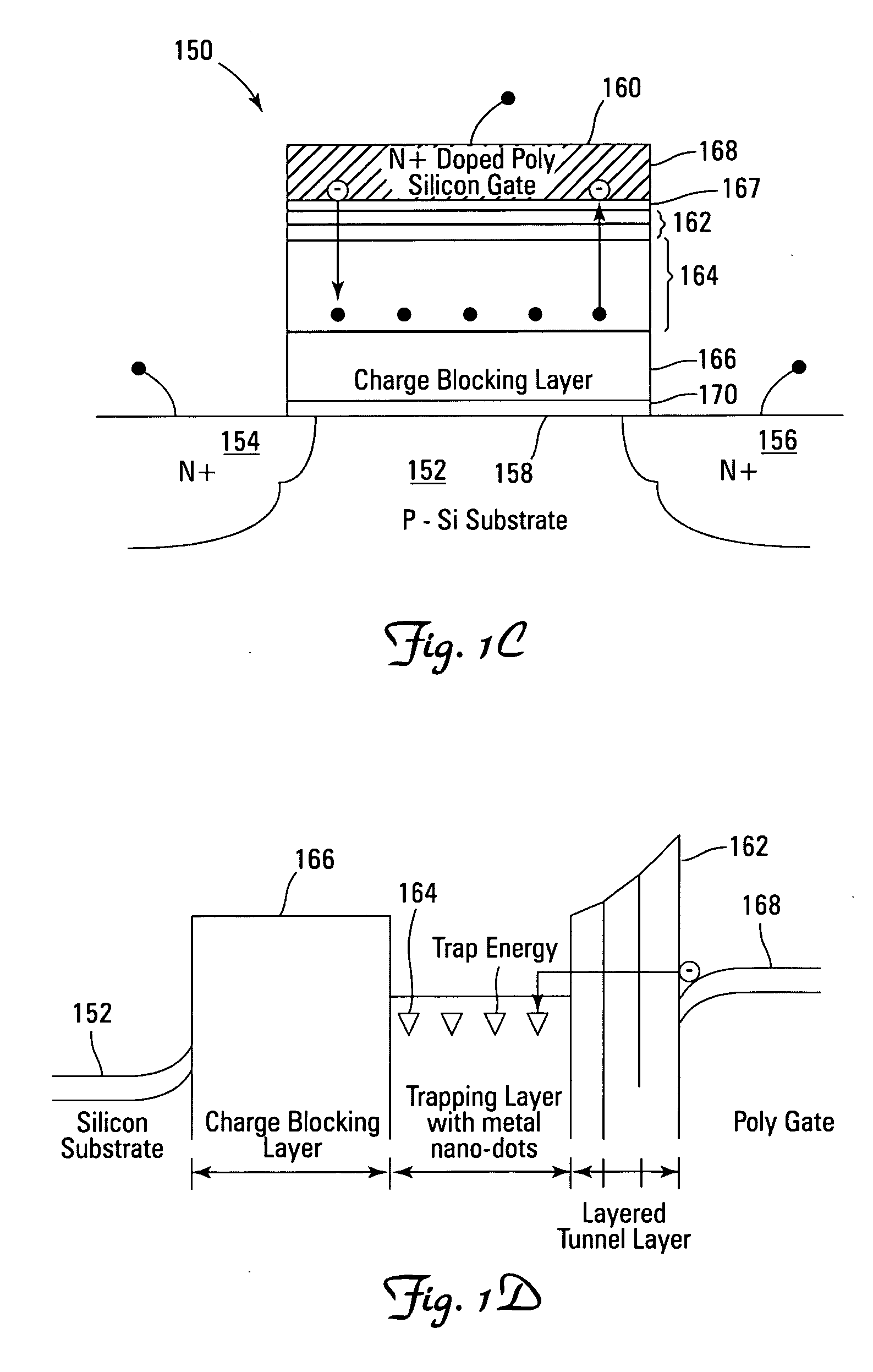
Novel low power non-volatile memory and gate stack
ActiveUS20060261401A1High charge blocking barrierExcellent charge retentionTransistorNanoinformaticsCharge retentionLow voltage
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers in reverse and normal mode floating node memory cells in NOR or NAND memory architectures that allow for direct tunnel programming and erase, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The low voltage direct tunneling program and erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and enhancing device lifespan. The low voltage direct tunnel program and erase capability also enables size reduction through low voltage design and further device feature scaling. Memory cells of the present invention also allow multiple bit storage. These characteristics allow memory device embodiments of the present invention to operate within the definition of a universal memory, capable of replacing both DRAM and ROM in a system.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
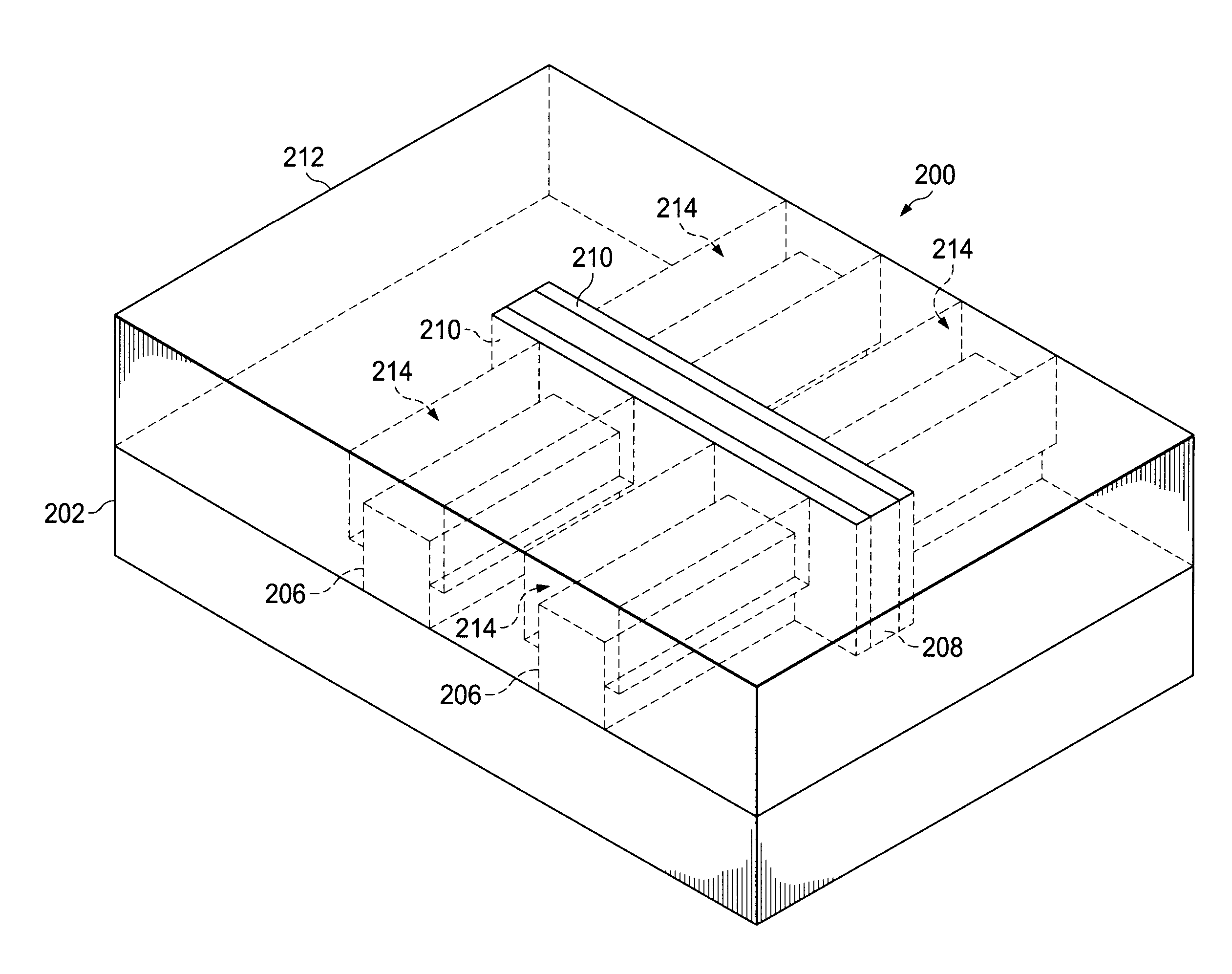
Method for fabricating a FinFET device
ActiveUS8652894B2Improve device densityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
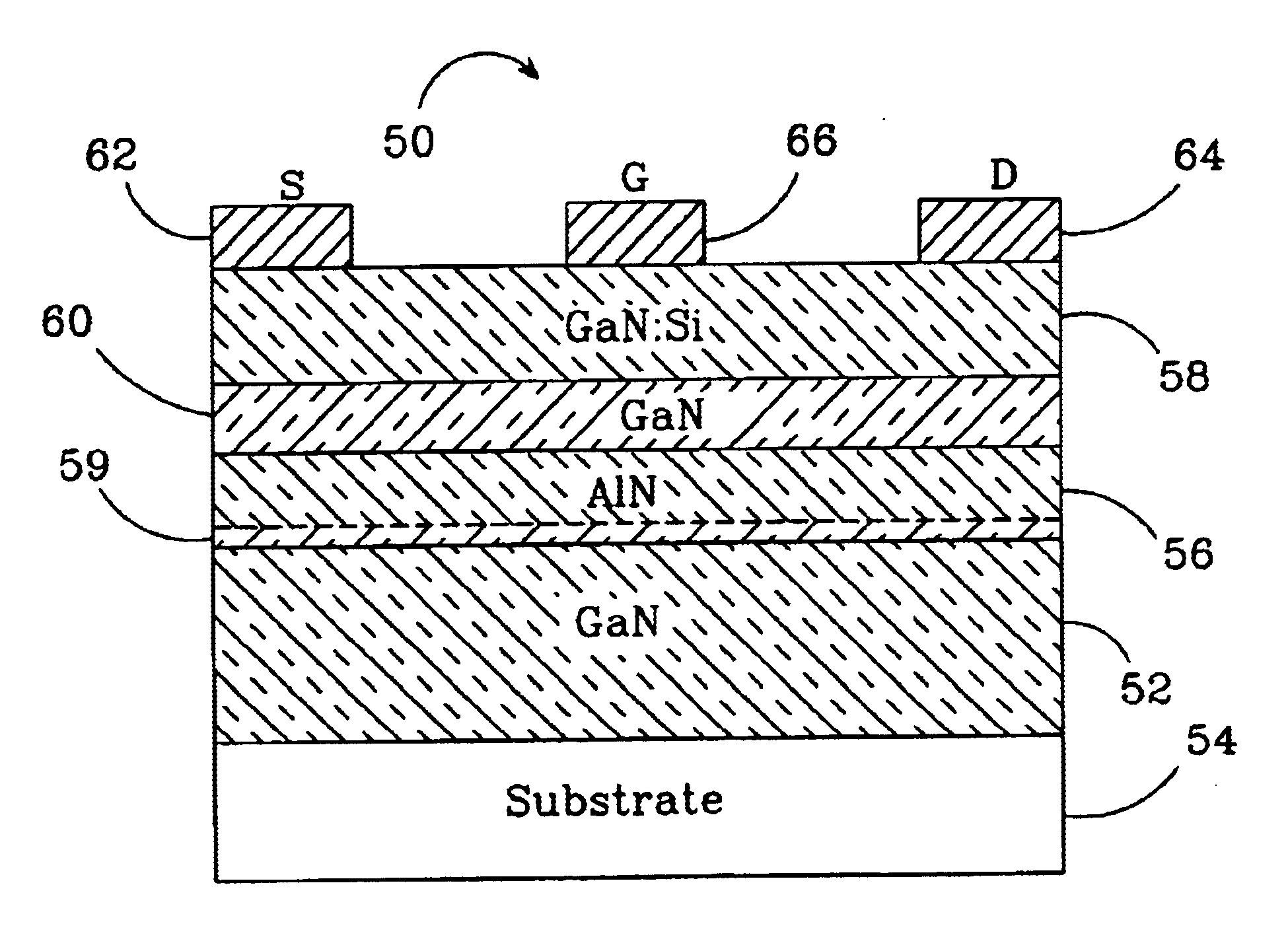
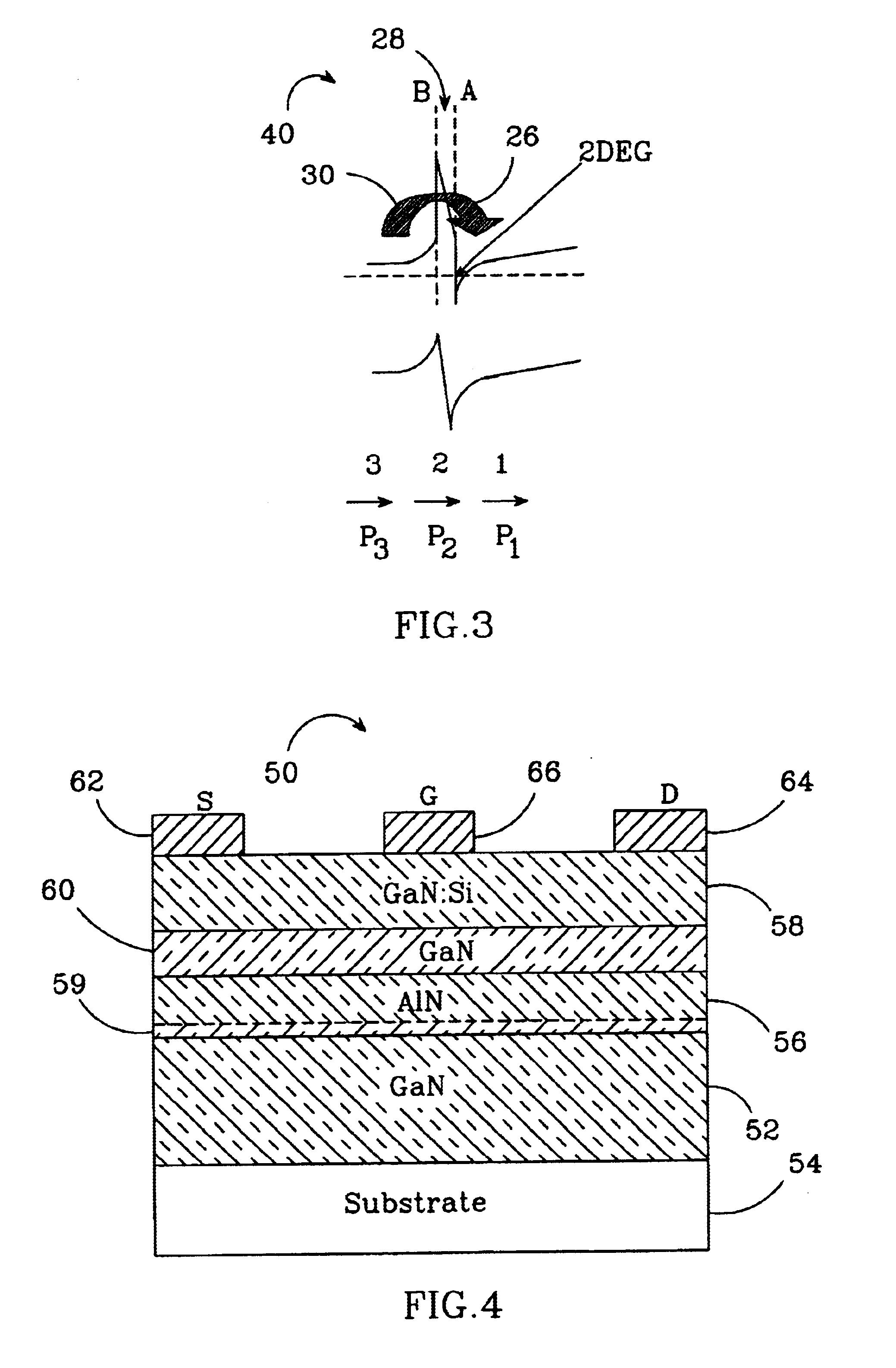
Group-III nitride based high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) with barrier/spacer layer
InactiveUS6849882B2High piezoelectric chargeReduction in piezoelectric scatteringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh electronNucleation
A Group III nitride based high electron mobility transistors (HEMT) is disclosed that provides improved high frequency performance. One embodiment of the HEMT comprises a GaN buffer layer, with an AlyGa1−yN (y=1 or y 1) layer on the GaN buffer layer. An AlxGa1−xN (0≦x≦0.5) barrier layer on to the AlyGa1−yN layer, opposite the GaN buffer layer, AlyGa1−yN layer having a higher Al concentration than that of the AlxGa1−xN barrier layer. A preferred AlyGa1−yN layer has y=1 or y˜1 and a preferred AlxGa1−xN barrier layer has 0≦x≦0.5. A 2DEG forms at the interface between the GaN buffer layer and the AlyGa1−yN layer. Respective source, drain and gate contacts are formed on the AlxGa1−xN barrier layer. The HEMT can also comprising a substrate adjacent to the buffer layer, opposite the AlyGa1−yN layer and a nucleation layer between the AlxGa1−xN buffer layer and the substrate.
Owner:CREE INC +1
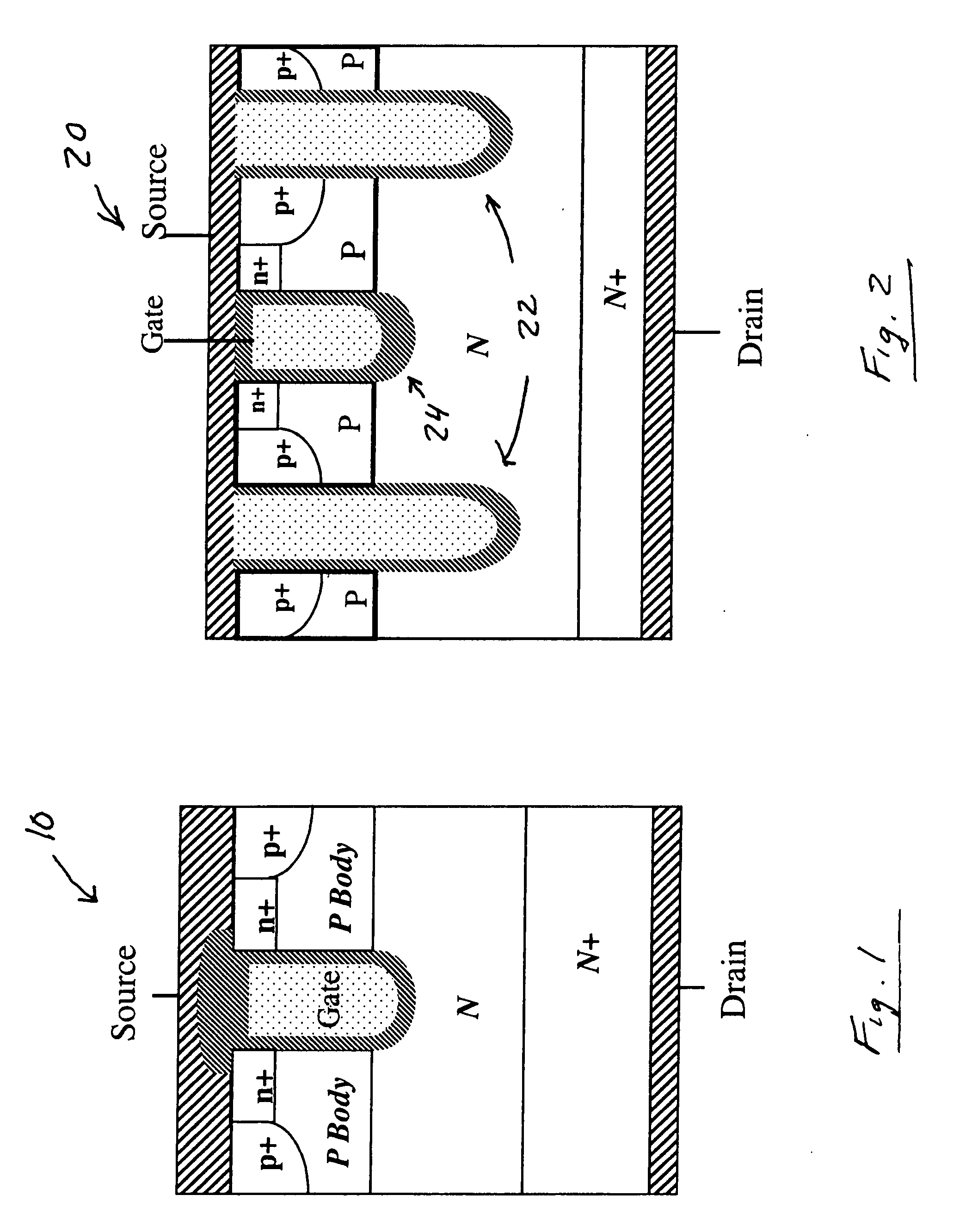
FET channel having a strained lattice structure along multiple surfaces
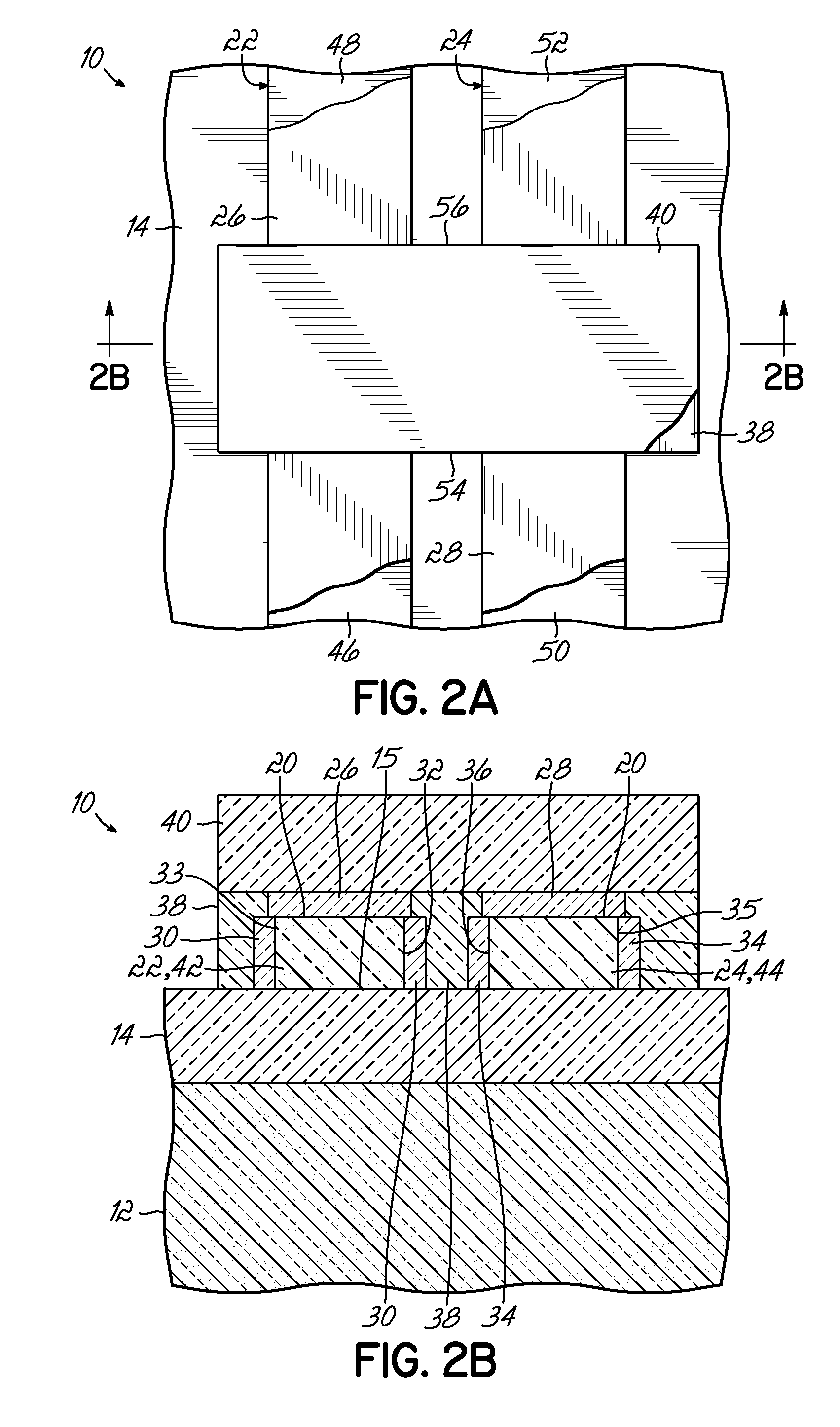
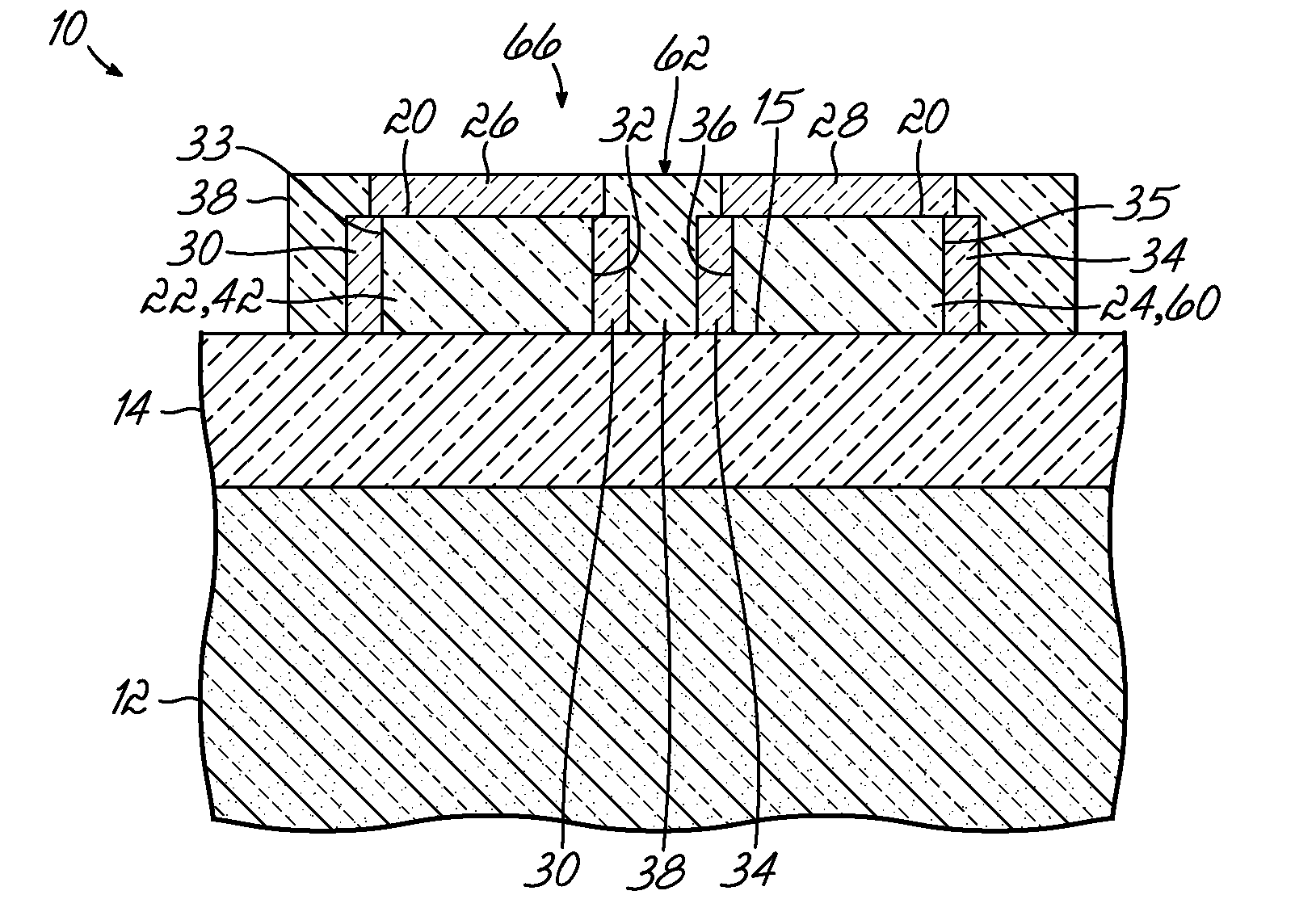
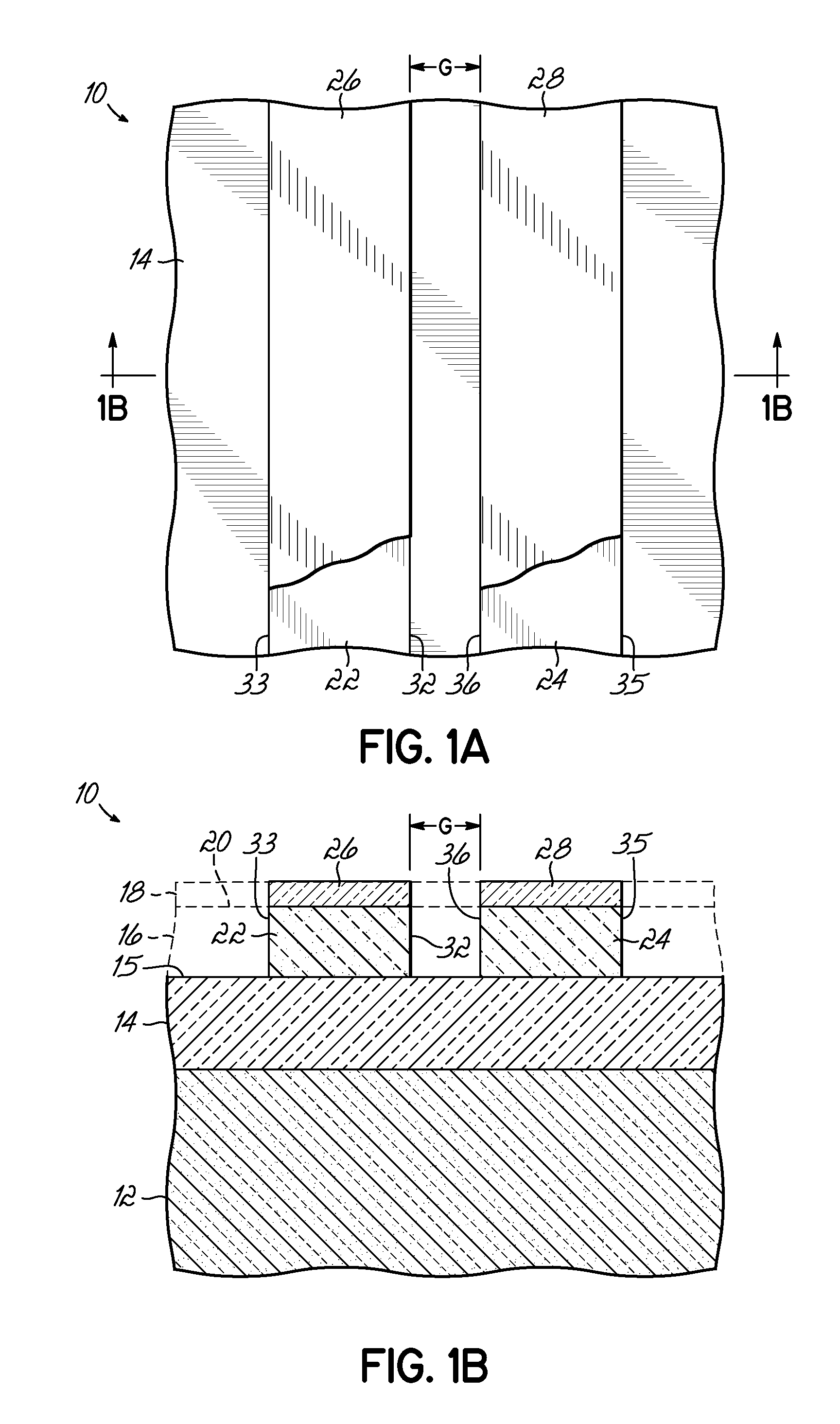
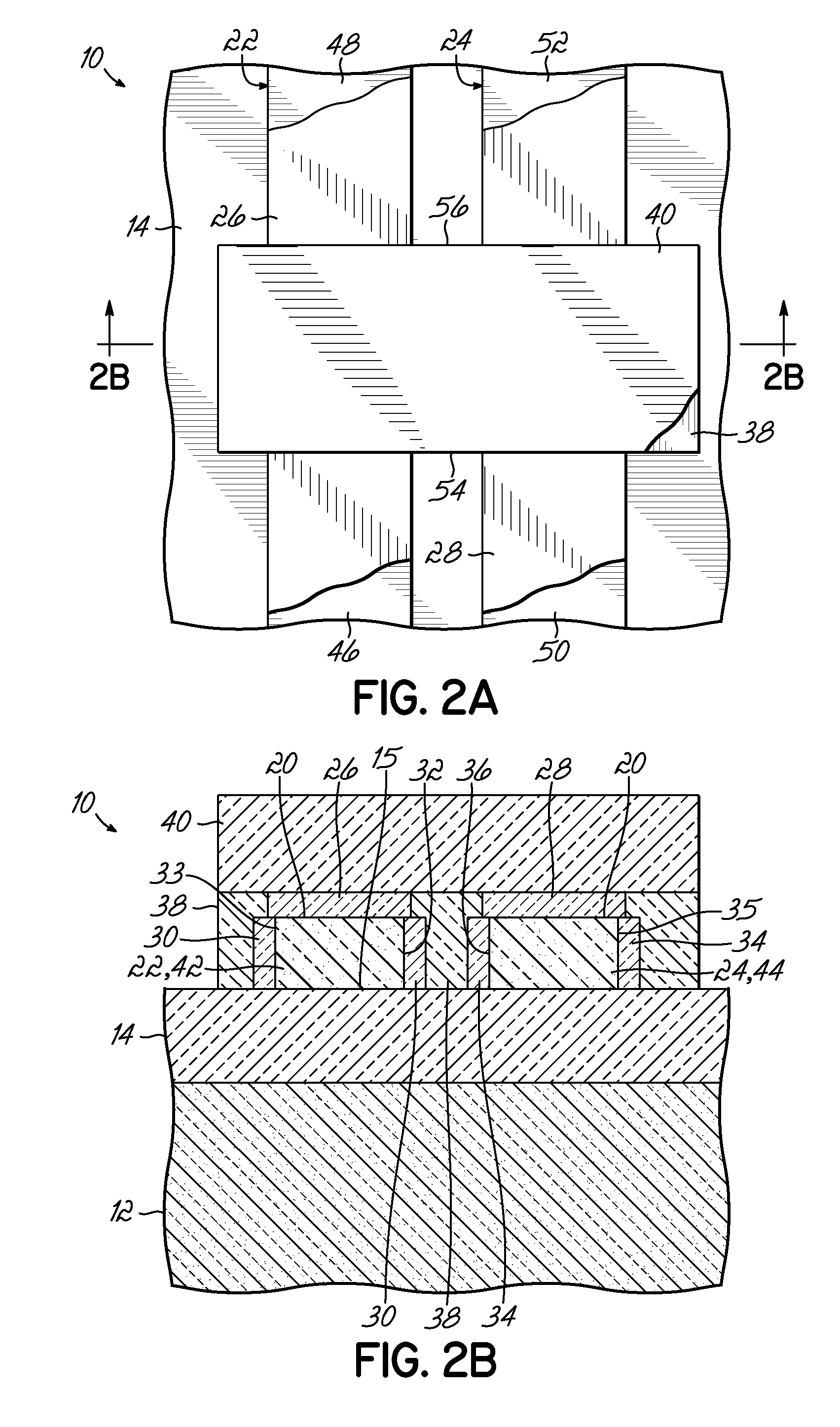
InactiveUS6921982B2Improve conductivityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricSemiconductor materials
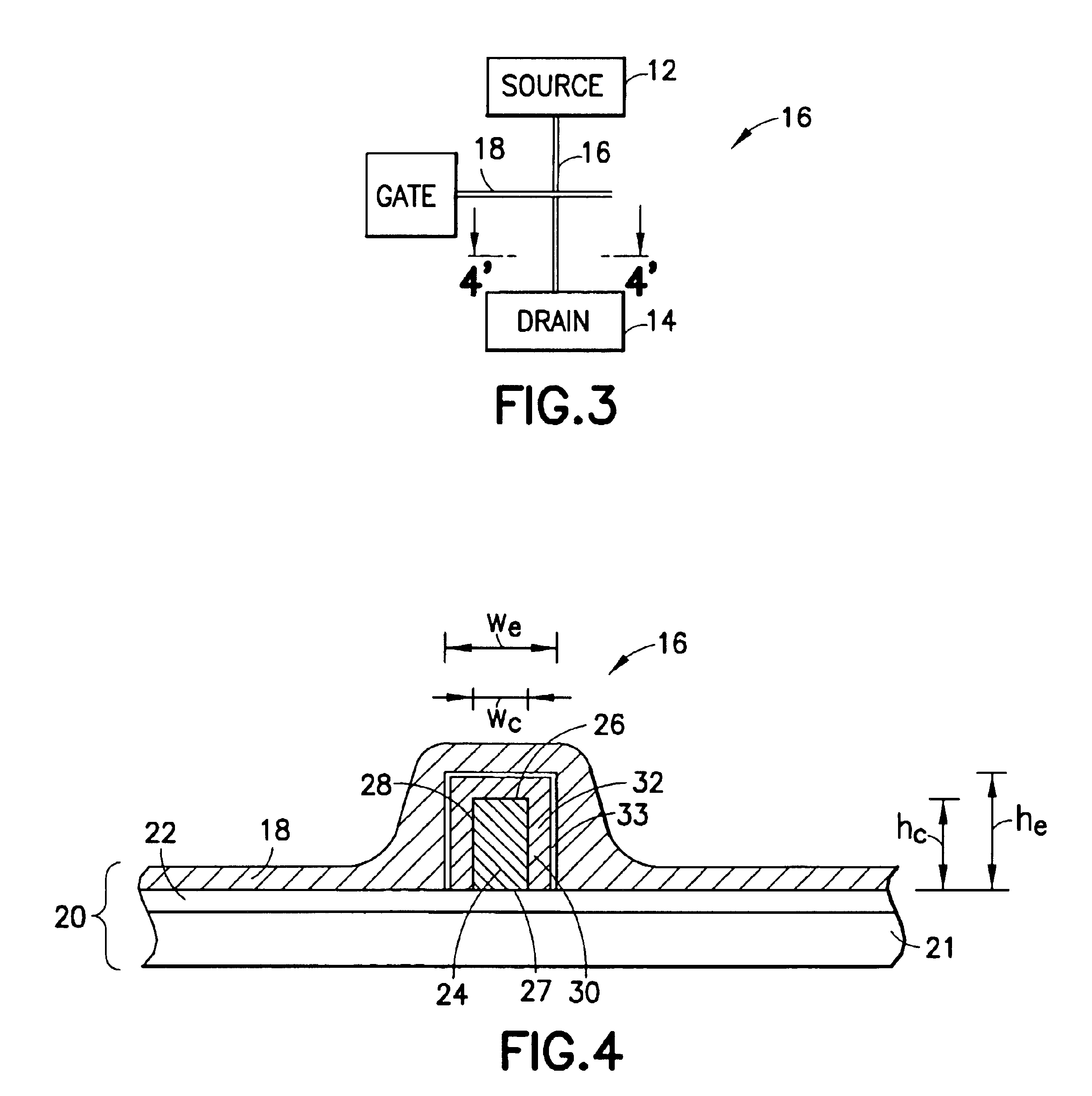
A channel 16 of a FinFET 10 has a channel core 24 and a channel envelope 32, each made from a semiconductor material defining a different lattice structure to exploit strained silicon properties. A gate is coupled to the channel envelope through a gate dielectric. Exemplary materials are Si and SixGe1-x, wherein 78<x<92. The channel core 24 has a top surface 26 of width wc and an upstanding surface 28, 30 of height hc, preferably oriented 90° to one another. The channel envelope 32 is in contact with the top 26 and upstanding surfaces 28, 30 so that the area of interface is increased as compared to contact only along the top surface 26, improving electrical conductivity and gate 18 control over the channel 16. The height hc can be tailored to enable a smaller scale FET 10 within a stabilized SRAM. Various methods of making the channel 16 are disclosed, including a mask and etch method, a handle wafer / carrier wafer method, and a shallow trench method. Embodiments and methods for FinFETs with one to four gates are disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method to form a contact hole
InactiveUS20050181588A1Reduce duplicationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound (substance)Fluorocarbon
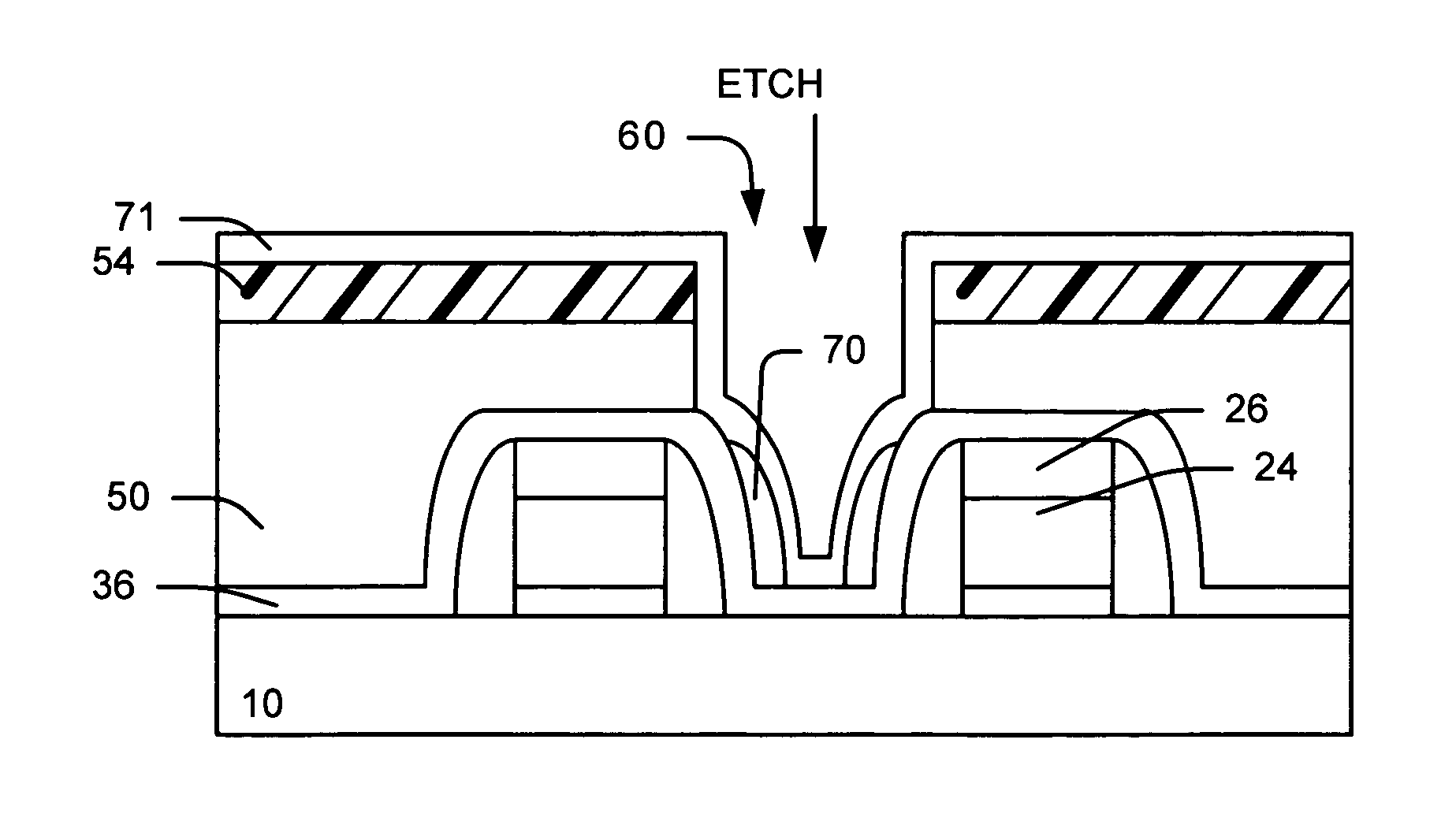
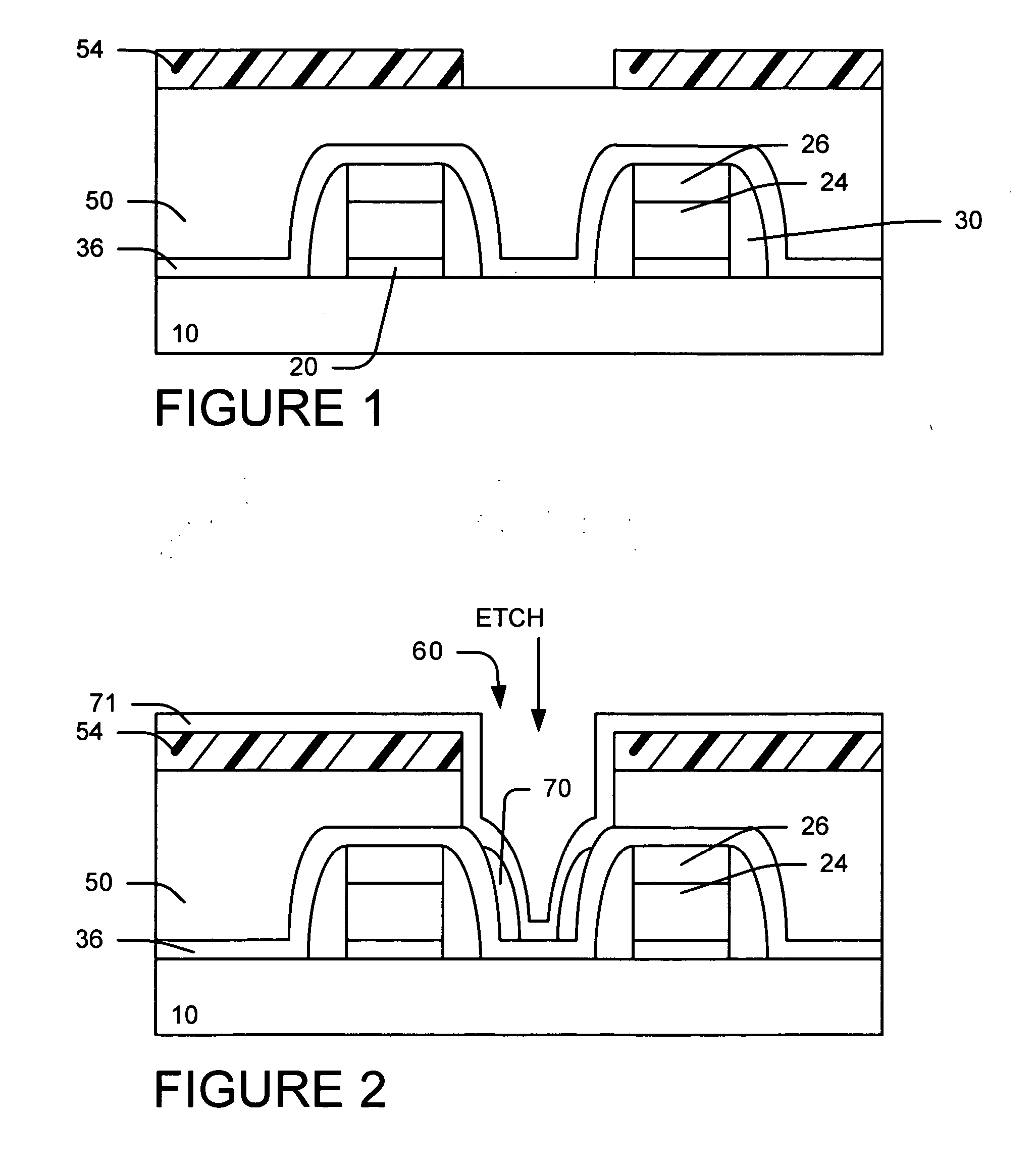
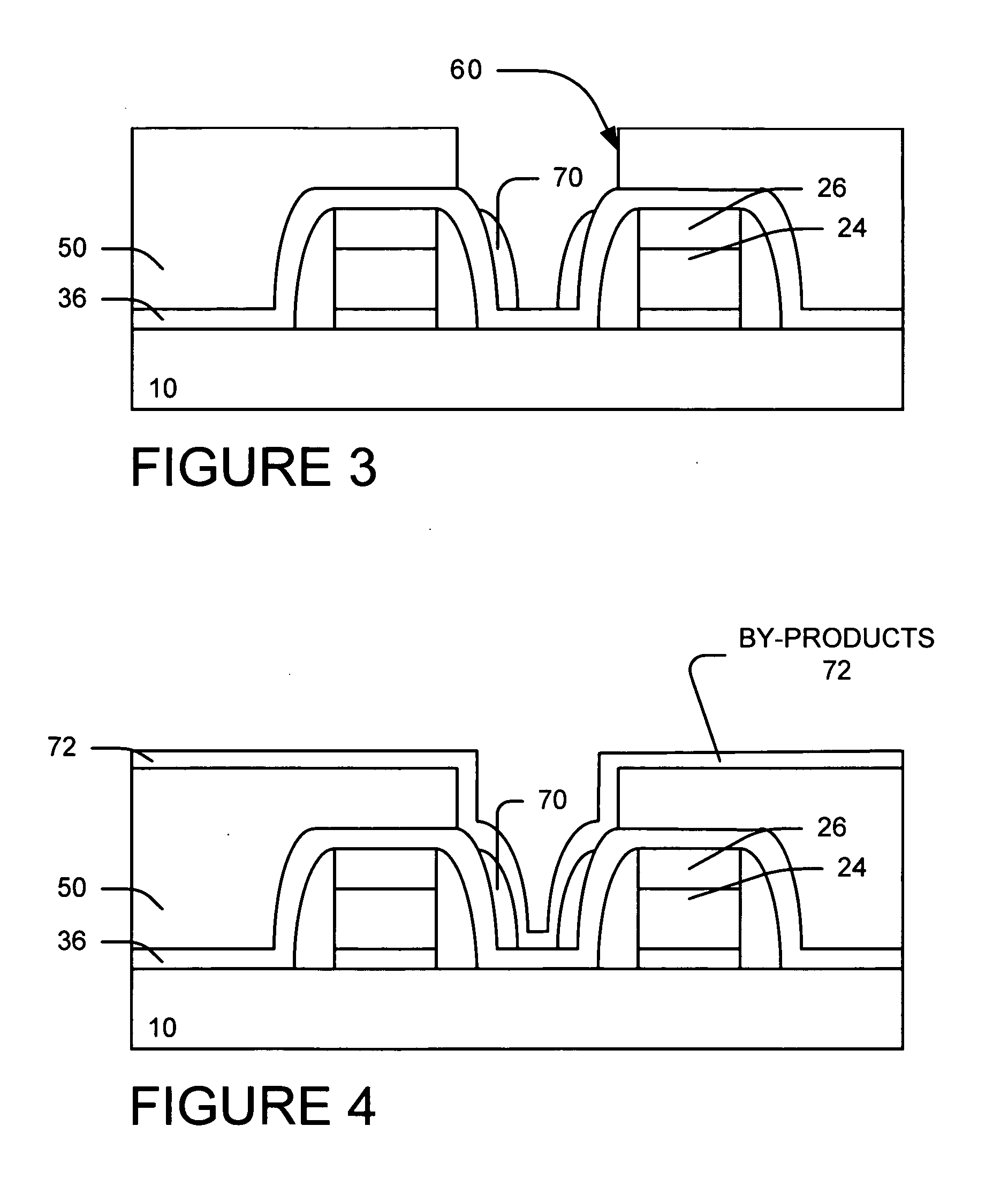
A example method of forming of a contact hole by removing residue and oxide spacer beside a nitride spacer after a CF containing etch. We provide a gate structure with nitride spacers on the sidewalls of the gate. We provide a dielectric layer (oxide) over the substrate and gate structure. We form a contact photoresist pattern over the oxide dielectric layer. We etch the oxide dielectric layer using fluorocarbons (CxFy) to form contact openings and residual spacer. The photoresist is striped. Preferably, a NF3 and N2 and H2 plasma treatment is performed to deposit a byproducts layer over the residual spacer. The byproducts layer and residual spacer are removed preferably using one of the following processes: (1) heat (2) DI rinse or (3) IR or UV radiation.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Hexagonal architecture
InactiveUS6407434B1Reduce total wirelength interconnect congestionReduce the numberTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Several inventions are disclosed. A cell architecture using hexagonal shaped cells is disclosed. The architecture is not limited to hexagonal shaped cells. Cells may be defined by clusters of two or more hexagons, by triangles, by parallelograms, and by other polygons enabling a variety of cell shapes to be accommodated. Polydirectional non-orthogonal three layer metal routing is disclosed. The architecture may be combined with the tri-directional routing for a particularly advantageous design. In the tri-directional routing arraingement, electrical conductors for interconnecting terminals of microelectronic cells of an integrated circuit preferrably extend in three directions that are angularly displaced from each other by 60°. The conductors that extend in the three directions are preferrably formed in three different layers. A method of minimizing wire length in a semiconductor device is disclosed. A method of minimizing intermetal capacitance in a semiconductor device is disclosed. A novel device called a "tri-ister" is disclosed. Triangular devices are disclosed, including triangular NAND gates, triangular AND gates, and triangular OR gates. A triangular op amp and triode are disclosed. A triangular sense amplifier is disclosed. A DRAM memory array and an SRAM memory array, based upon triangular or parallelogram shaped cells, are disclosed, including a method of interconnecting such arrays. A programmable variable drive transistor is disclosed. CAD algorithms and methods are disclosed for designing and making semiconductor devices, which are particularly applicable to the disclosed architecture and tri-directional three metal layer routing.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Power MOSFET having laterally three-layered structure formed among element isolation regions
A semiconductor apparatus has an NPN (or PNP) laterally three-layered pillar formed in a mesh form among a plurality of trench type element isolation regions, and having a source and gate on an upper surface of the three-layered pillar, and a drain on a lower surface thereof. A depth DT and minimum planar width WTmin of the element isolation region and a width WP of the three-layered pillar are configured to satisfy a relation of 3.75<=DT / WP<=60 or 5.5<=DT / WTmin<=14.3. The above configuration realizes a high breakdown voltage and low on-resistance are realized.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS6925006B2Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
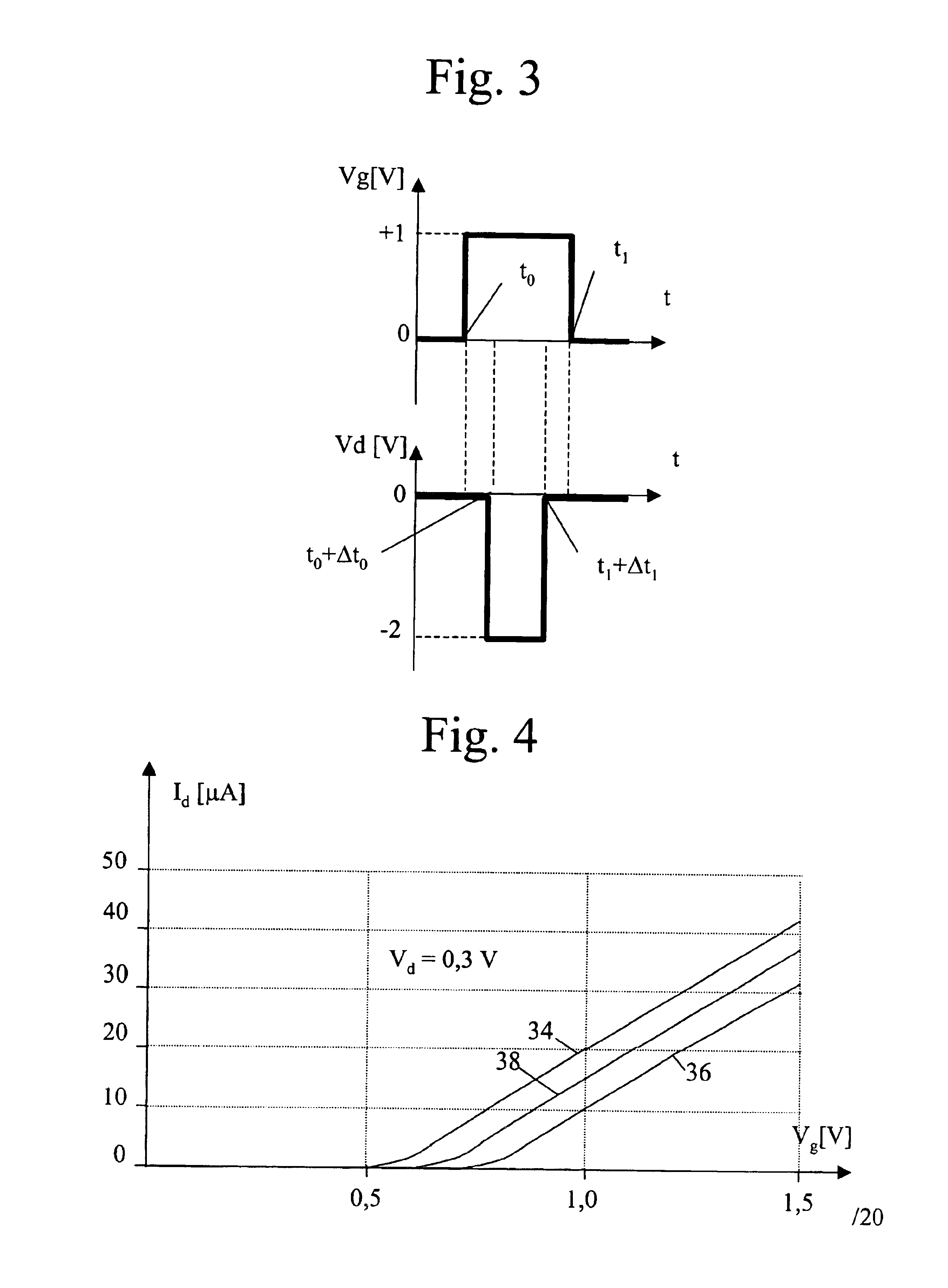
Method of driving electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS7535449B2Shorten the timeLower display costsElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesElectricityControl signal
The invention provides a method of driving an electro-optical device and an electronic apparatus which are capable of reducing the time for writing data without providing special circuits. In the electro-optical device pixel circuits having reset transistors for controlling an electric connection between drains and gates of driving transistors between the drains and the gates of the driving transistors are arranged on a display panel in a matrix. The pixel circuits arranged in a matrix are electrically connected to a scanning line driving circuit via scanning lines. The scanning line driving circuit sequentially switches on the reset transistors from the pixel circuit connected to first scanning lines in accordance with scanning line control signals supplied from a control circuit and then lets organic EL elements emit light.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
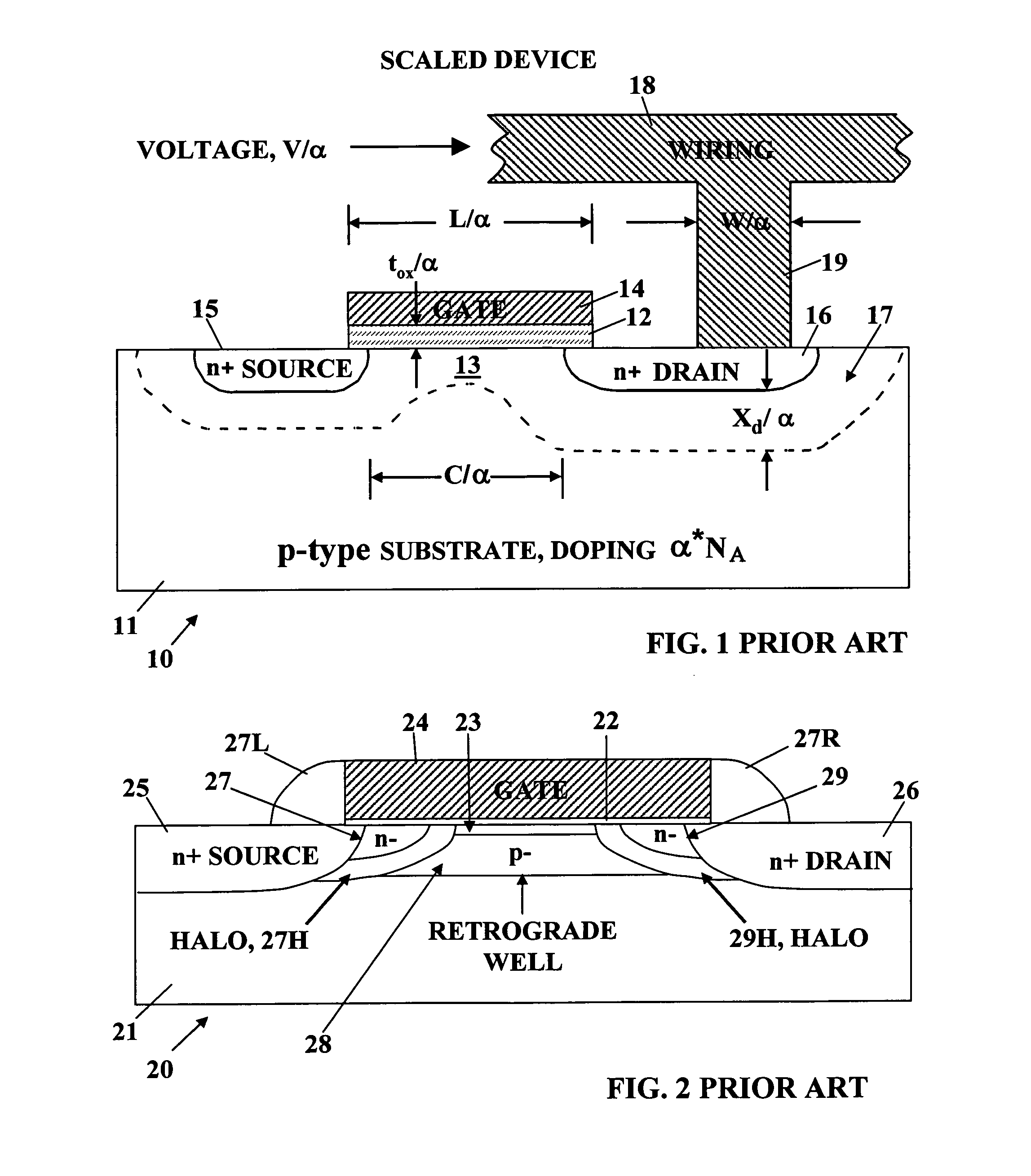
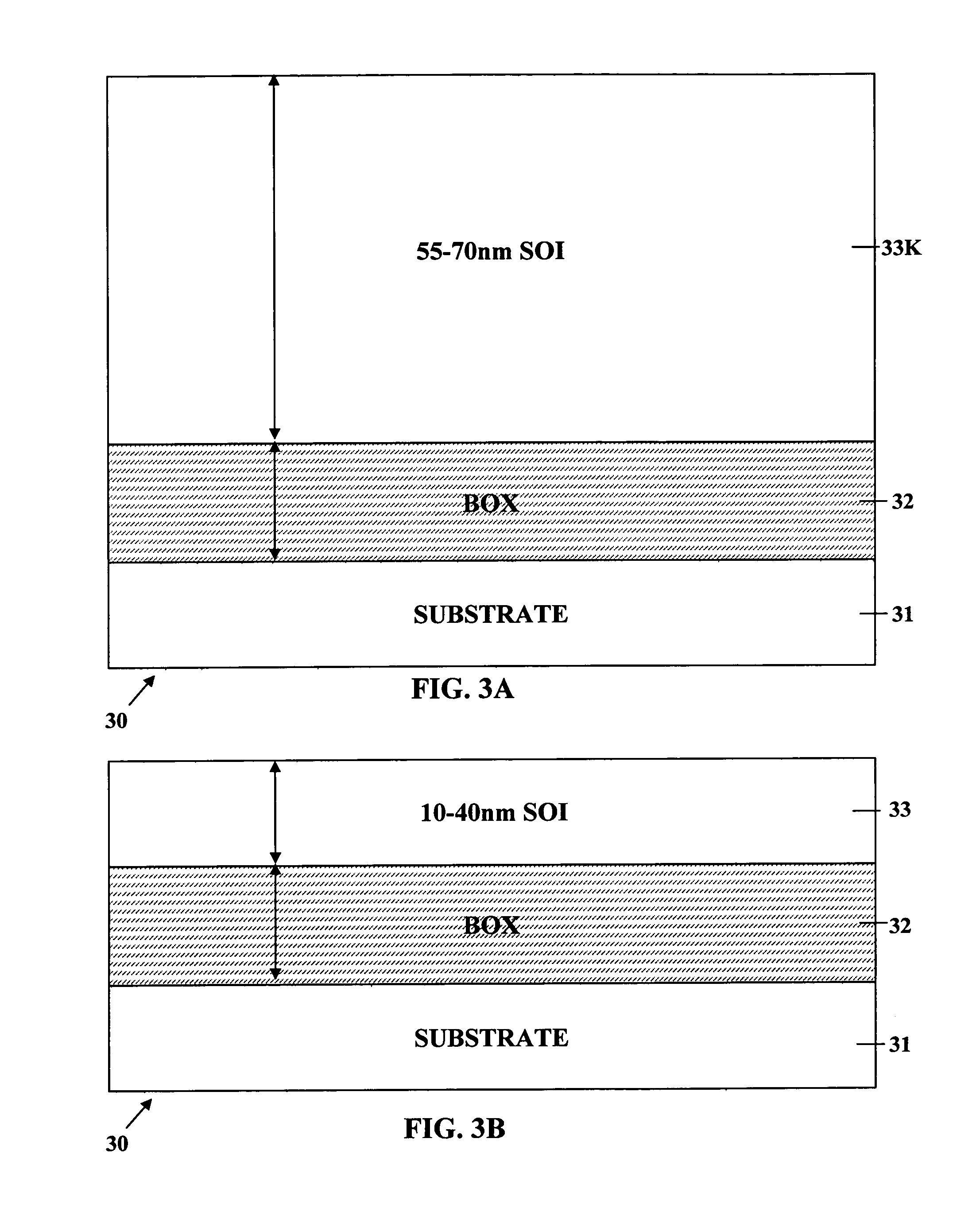
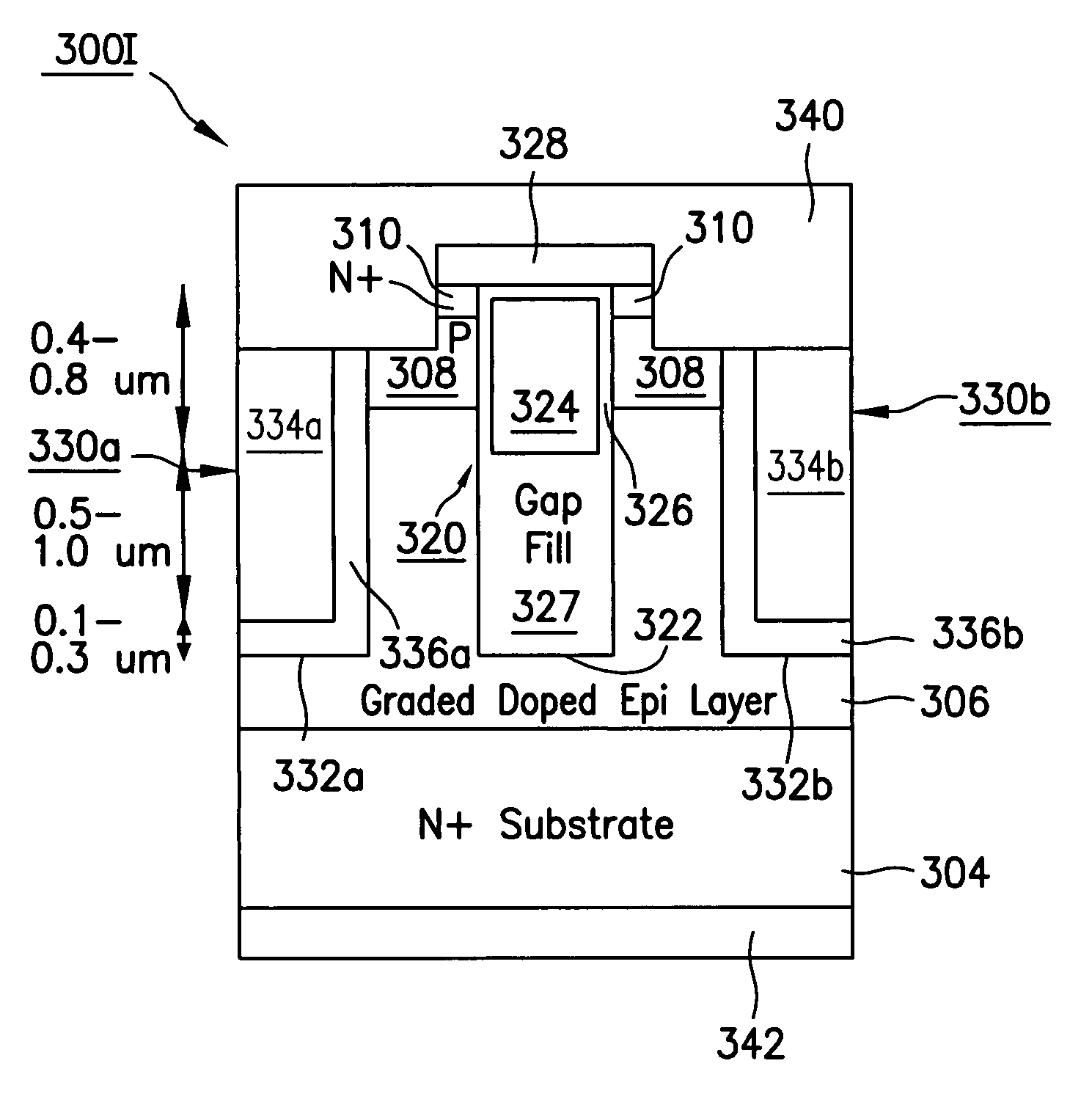
Ultra-thin body super-steep retrograde well (SSRW) FET devices
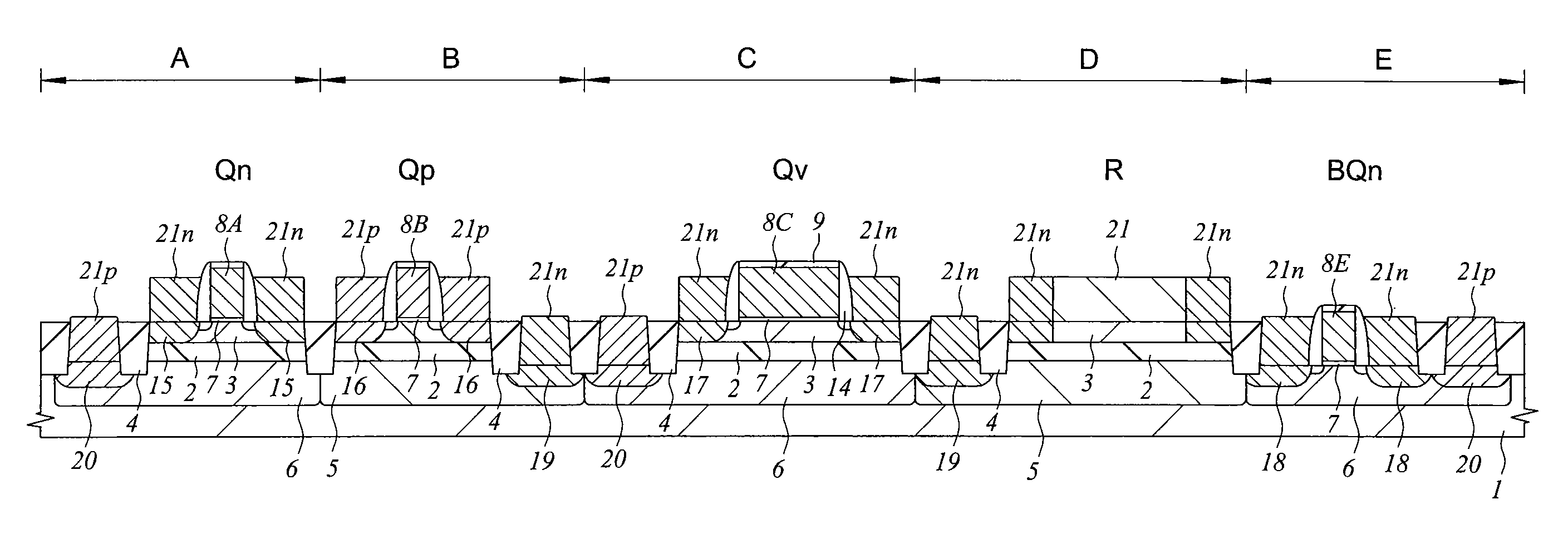
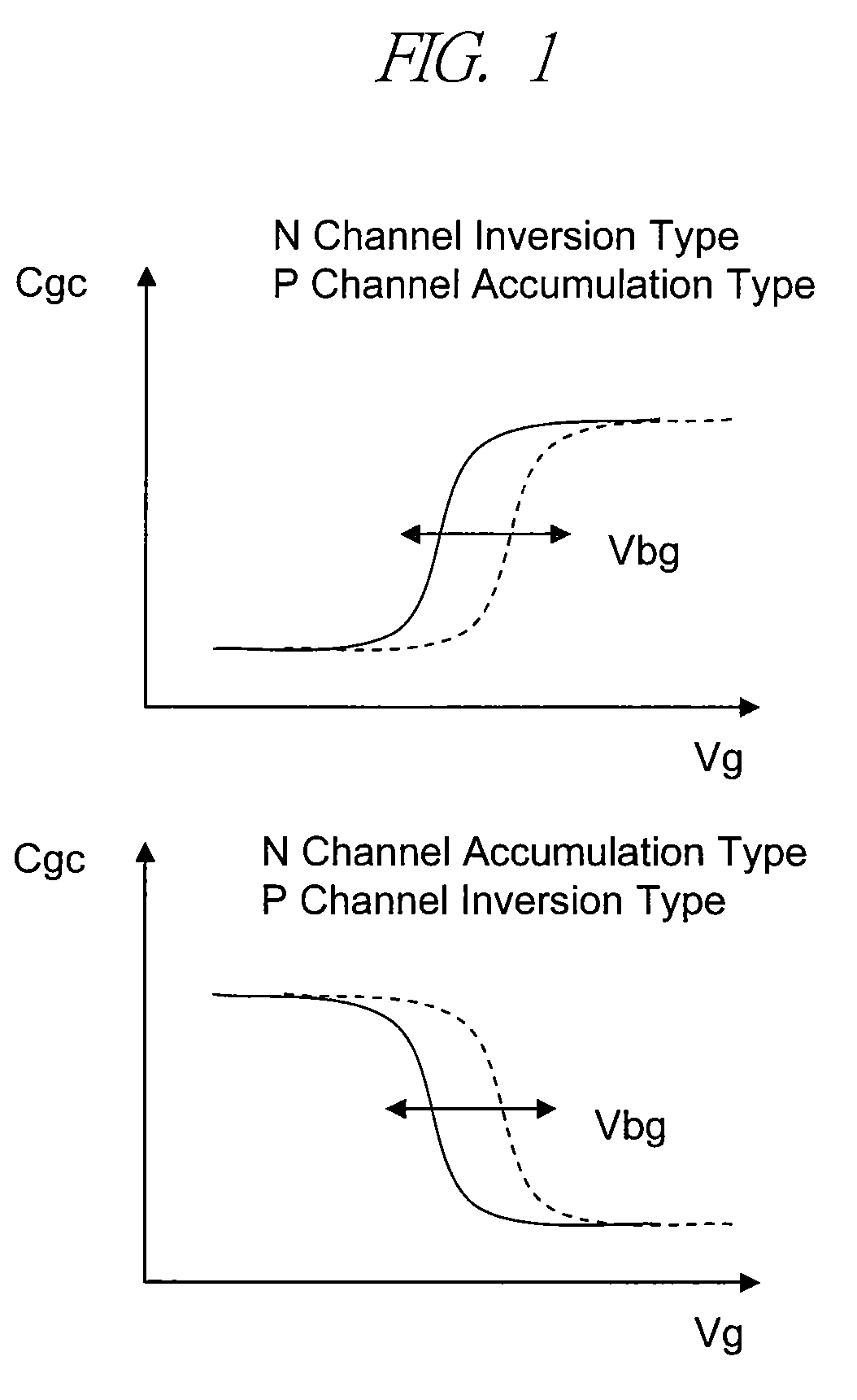
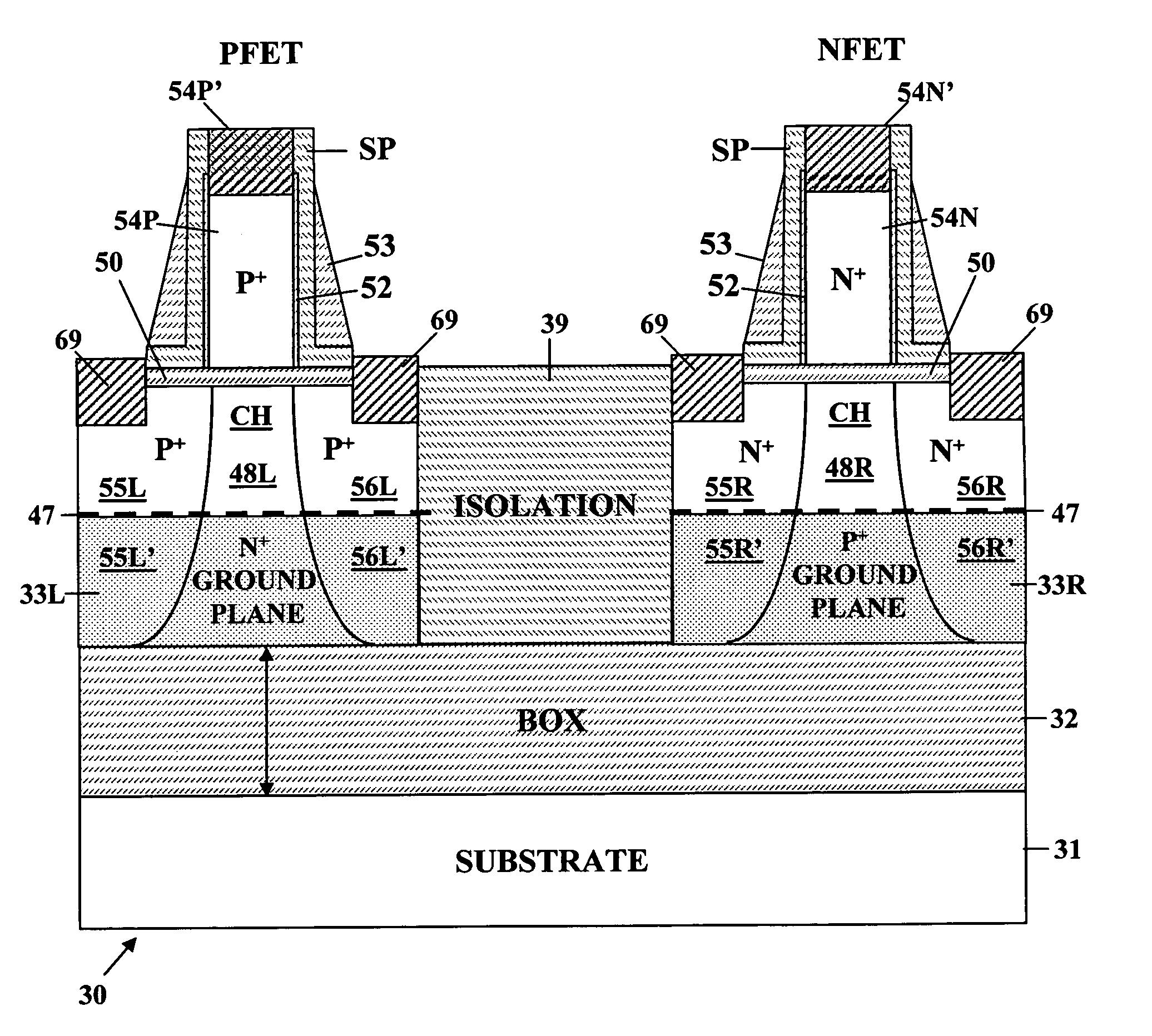
ActiveUS20060022270A1Minimize space-charge related fluctuationReduce capacitanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGround plane
A method of manufacture of a Super Steep Retrograde Well Field Effect Transistor device starts with an SOI layer formed on a substrate, e.g. a buried oxide layer. Thin the SOI layer to form an ultra-thin SOI layer. Form an isolation trench separating the SOI layer into N and P ground plane regions. Dope the N and P ground plane regions formed from the SOI layer with high levels of N-type and P-type dopant. Form semiconductor channel regions above the N and P ground plane regions. Form FET source and drain regions and gate electrode stacks above the channel regions. Optionally form a diffusion retarding layer between the SOI ground plane regions and the channel regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
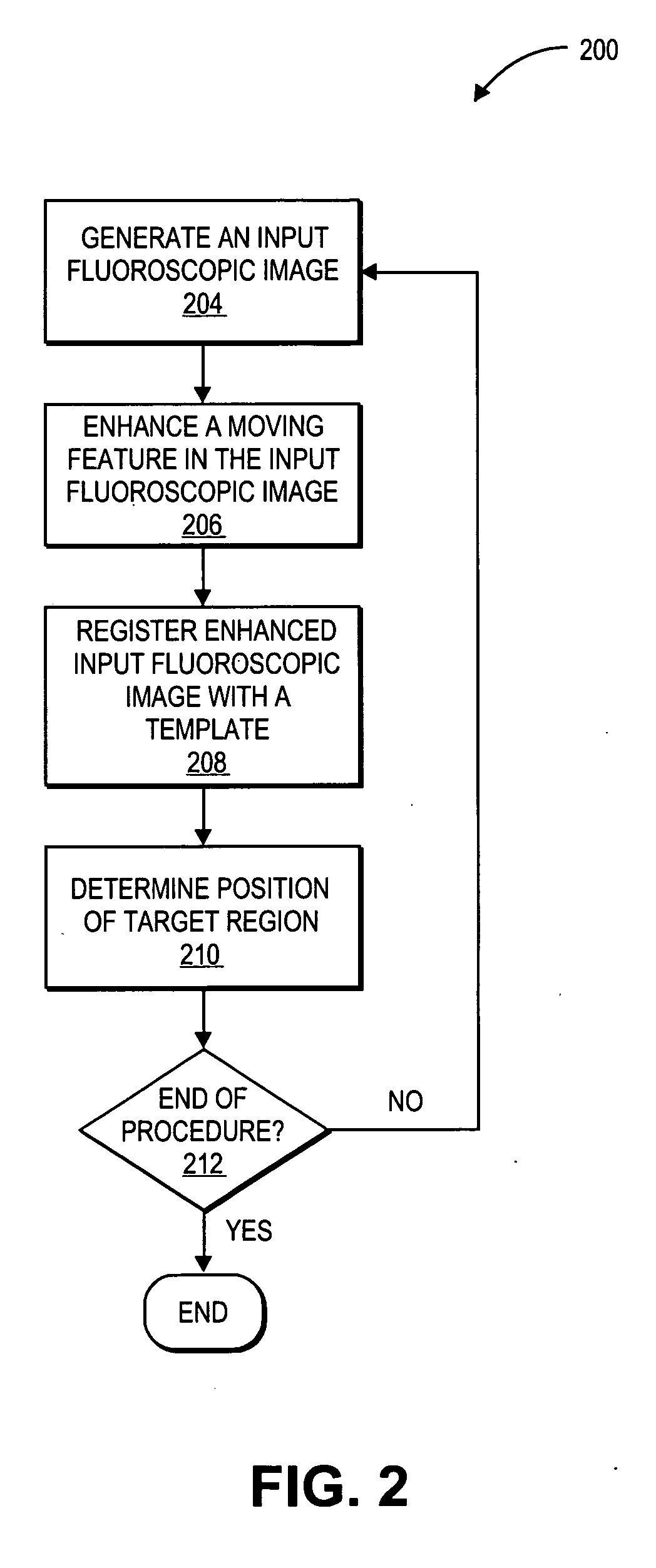
Systems and methods for gating medical procedures
ActiveUS20050054916A1Easy to implementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedical procedureMedical treatment
A method of performing physiological gating in a medical procedure includes acquiring a sequence of images having at least a first image and a second image of a target region, determining a first composite image based on the first and second images, and gating a medical procedure based on the composite image. A method of performing a medical procedure includes providing a plurality of templates, each of the templates having an image and treatment data, acquiring an input image, registering the input image with one of the templates, and performing a medical procedure based on the treatment data of the one of the templates that is registered with the input image.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Wellbore circulation system
InactiveUS6412554B1Fast connection timeNot to damageDrilling rodsConstructionsLine tubingCoiled tubing
A system for continuously circulating fluid to and through a tubular string either of coiled tubing or made up of a plurality of tubulars connected end-to-end while an upper tubular is added to or removed from a top tubular of the plurality of tubulars, all tubulars having a top-to-bottom fluid flow channel therethrough, the system having an upper chamber with a bottom opening, a top opening, and an upper sealing apparatus for sealingly encompassing a portion of the upper tubular, a lower chamber with a bottom opening, a top opening and a lower sealing apparatus for sealingly encompassing a portion of the top tubular, one of the upper chamber and the lower chamber sized for accommodating connection and disconnection therein of the upper tubular and the top tubular, and gate apparatus between and in fluid communication with the upper chamber and the lower chamber. Such a system may have apparatus for isolating a tubular therein from an axial load imposed by fluid pressure in a chamber; at least one of the lower chamber and the upper chamber with inner bushing apparatus with a portion thereof movably disposable within the chamber's sealing apparatus for facilitating movement of a tubular with respect to the chamber's sealing apparatus, and the system connectible to and rotatable by a rotating system for rotating the tubular string; and / or heave compensation interconnections for interconnecting the system to an offshore rig's heave compensation system. The system in certain aspects including fluid flow lines to each of the top and bottom chambers, a supply of fluid for circulating through the tubular string and through the upper and lower chambers, apparatus for continuously moving circulating fluid from the supply through the system into the tubular string.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090317950A1Reduce parasitic resistanceImprove leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor packageSoi substrate
A semiconductor device manufacturing method which sequentially forms a gate oxide film and gate electrode material over a semiconductor layer of an SOI substrate and patterns the material into gate electrodes. The method further comprises the steps of forming sidewalls made of an insulator to cover side surfaces of the gate electrode; ion-implanting into the semiconductor layer on both sides of the gate electrode to form drain / source regions; partially etching the sidewalls to expose upper parts of the side surfaces of the gate electrode; depositing a metal film to cover the tops of the drain / source regions and of the gate electrode and the exposed upper parts of the side surfaces of the gate electrode; and performing heat treatment on the SOI substrate to form silicide layers respectively in the surfaces of the gate electrode and of the drain / source regions.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
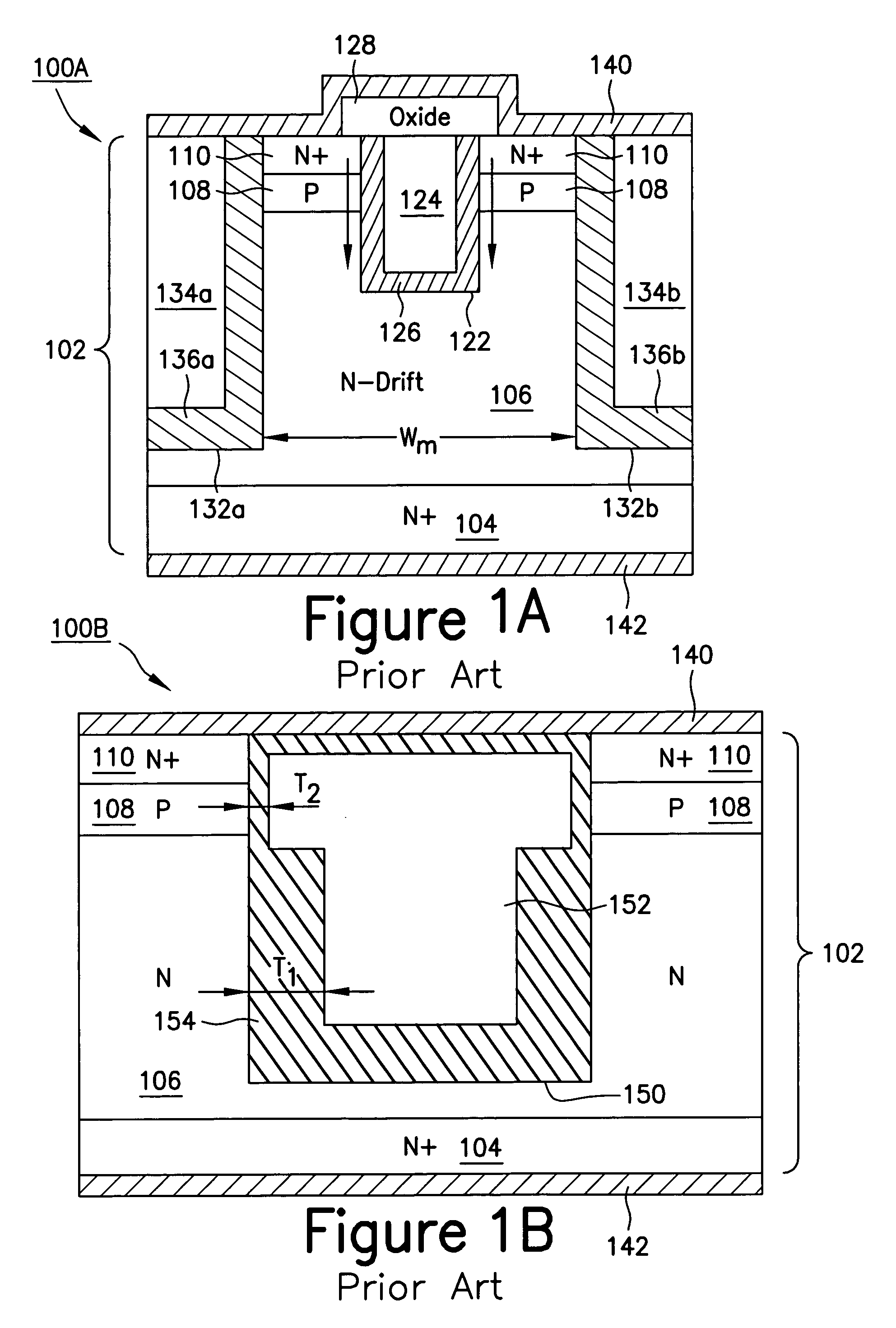
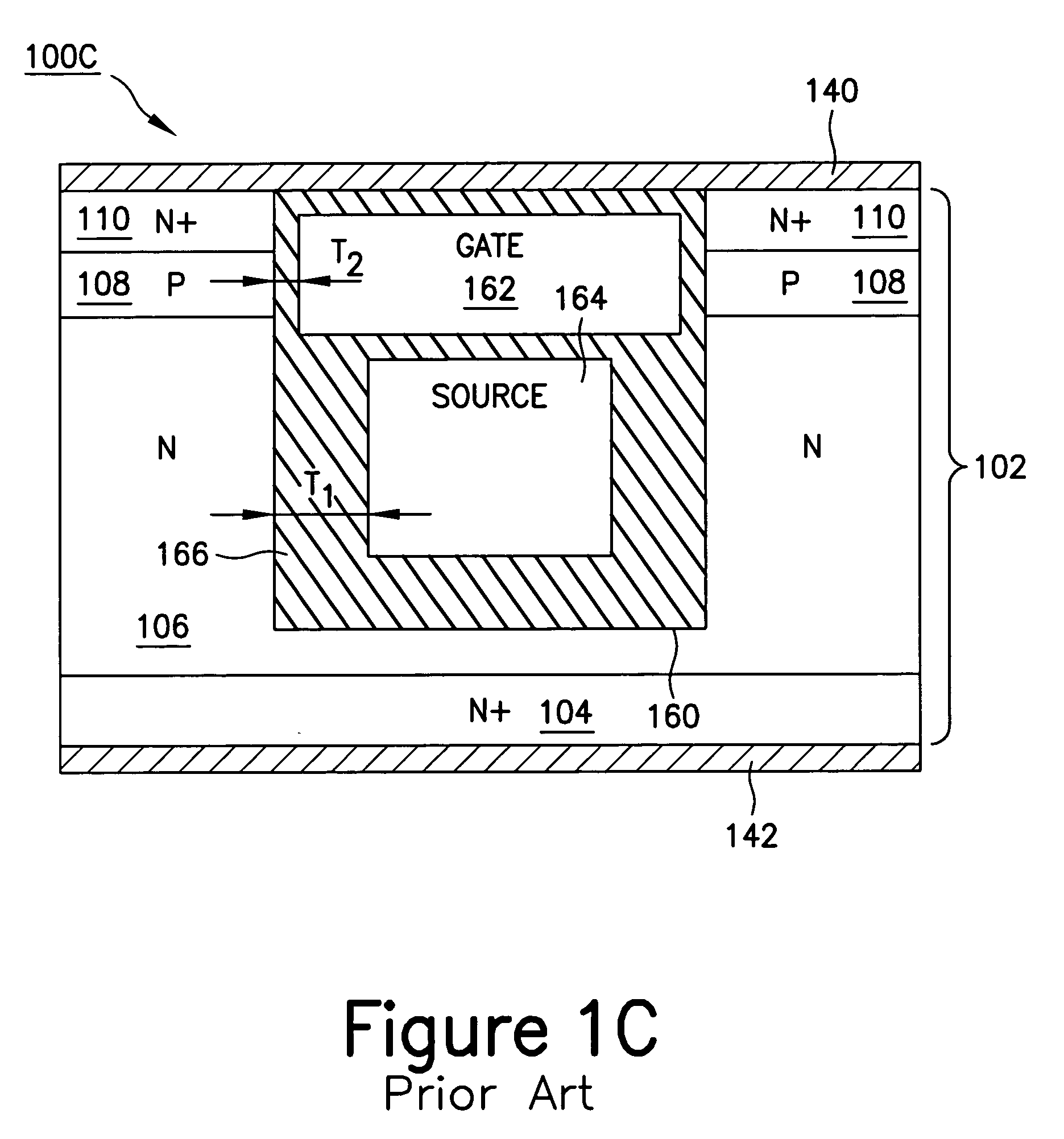
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor and methods of fabricating such device structures
InactiveUS7790543B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETGate dielectric
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) that is suitable for operation at relatively high voltages and methods of forming same. The MOSFET, which is formed using a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate, includes a channel in a semiconductor body that is self-aligned with a gate electrode. The gate electrode and semiconductor body, which are both formed from the monocrystalline SOI layer of the SOI substrate, are separated by a gap that is filled by a gate dielectric layer. The gate dielectric layer may be composed of thermal oxide layers grown on adjacent sidewalls of the semiconductor body and gate electrode, in combination with an optional deposited dielectric material that fills the remaining gap between the thermal oxide layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor and methods of fabricating such device structures
InactiveUS20090179266A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETGate dielectric
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) that is suitable for operation at relatively high voltages and methods of forming same. The MOSFET, which is formed using a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate, includes a channel in a semiconductor body that is self-aligned with a gate electrode. The gate electrode and semiconductor body, which are both formed from the monocrystalline SOI layer of the SOI substrate, are separated by a gap that is filled by a gate dielectric layer. The gate dielectric layer may be composed of thermal oxide layers grown on adjacent sidewalls of the semiconductor body and gate electrode, in combination with an optional deposited dielectric material that fills the remaining gap between the thermal oxide layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
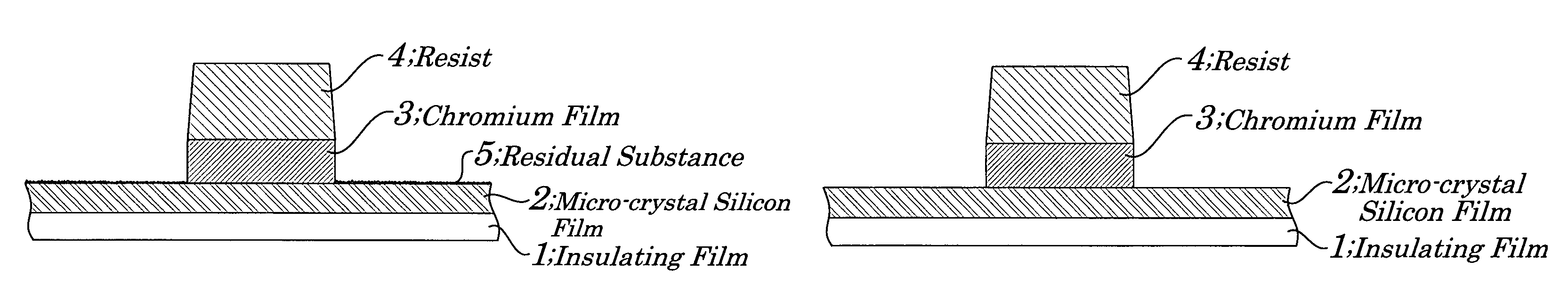
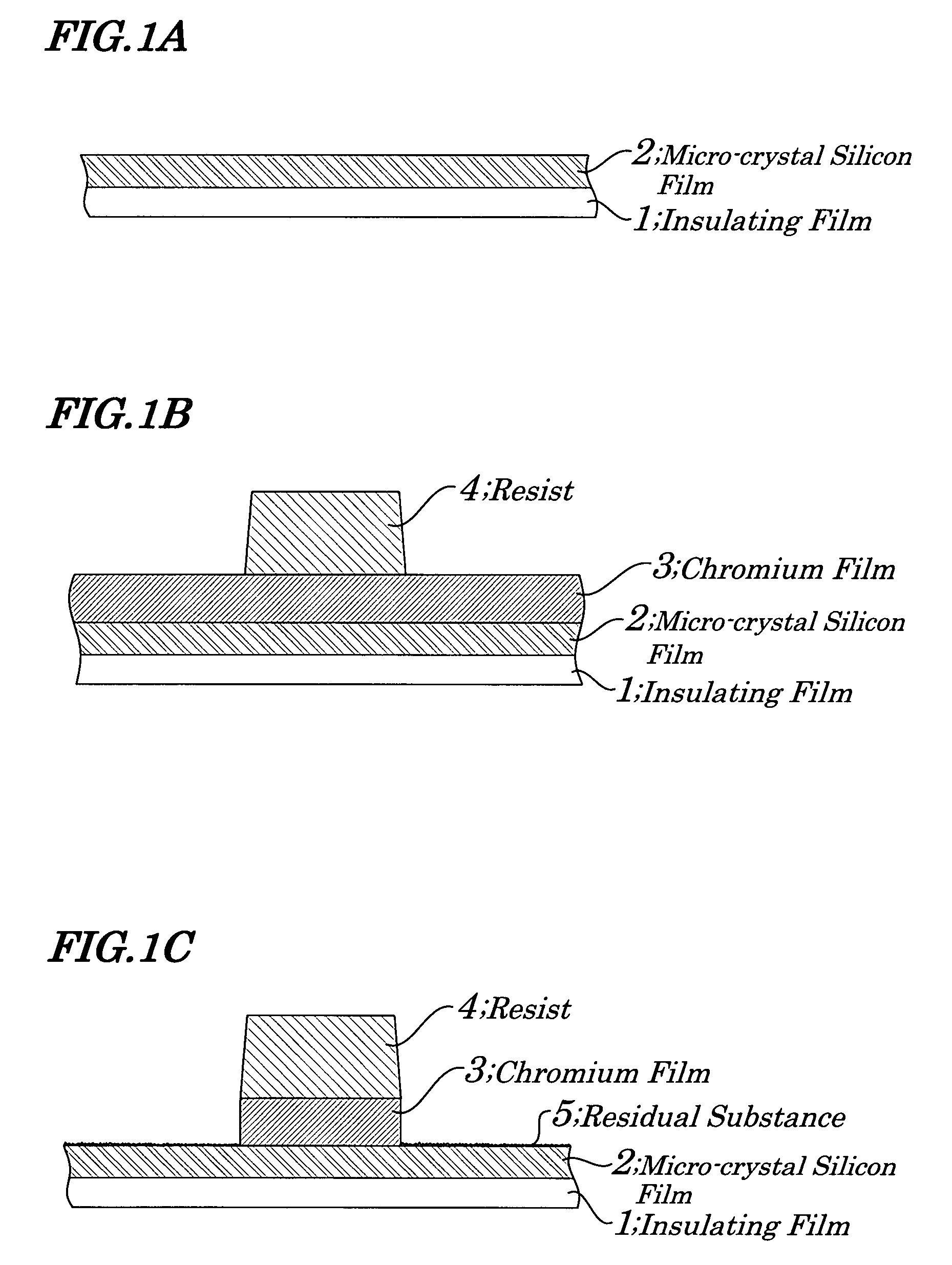
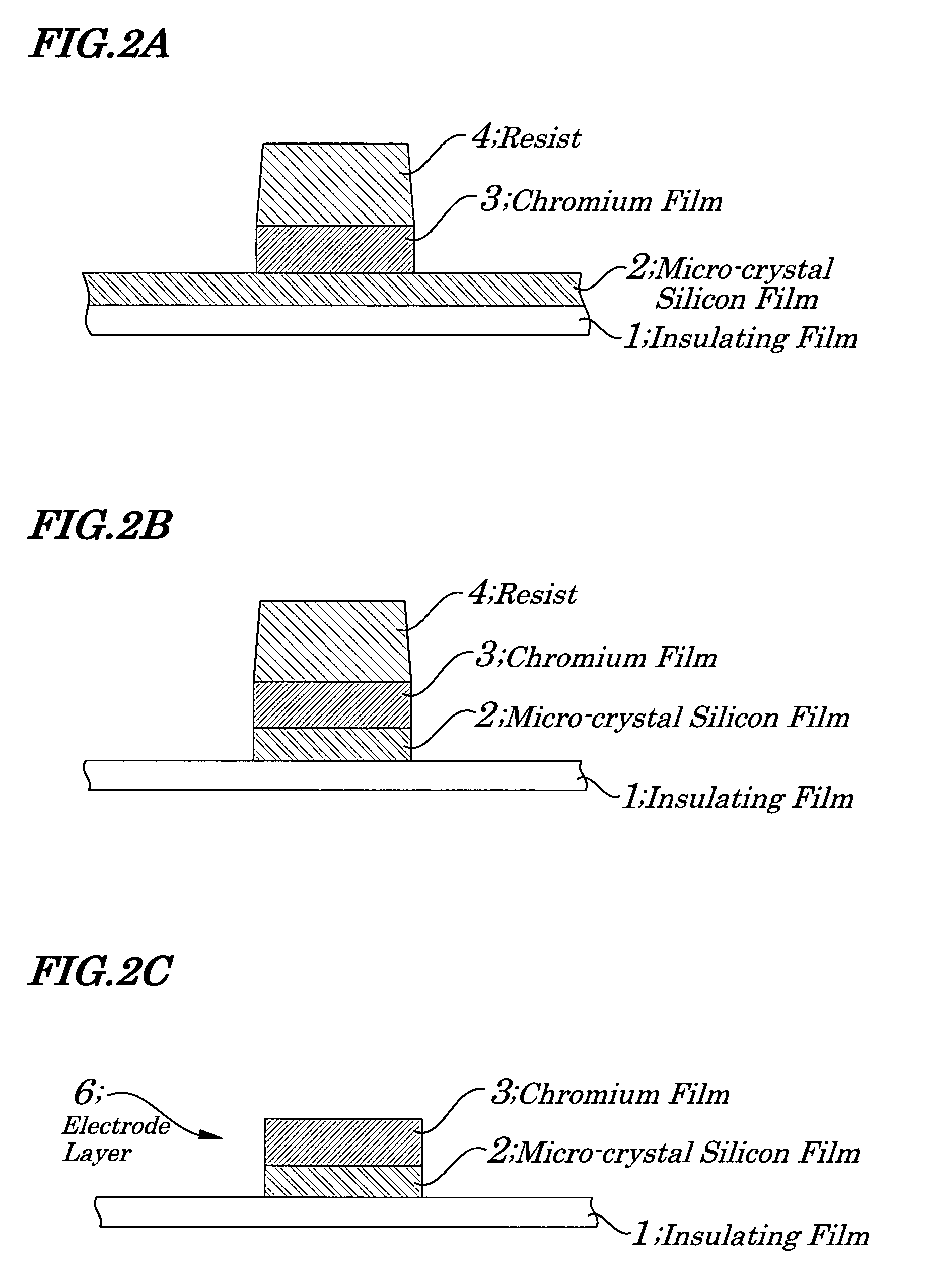
Stacked film patterning method and gate electrode forming method
InactiveUS7723221B2Improve uniformityAvoid it happening againSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistMixed gas
A stacked film patterning method is provided which is capable of reliably removing residual substances remaining after etching of a metal film, improving etching uniformity of a silicon film, and preventing an occurrence of etching residues. A micro-crystal film and a chromium film are sequentially formed on an insulating film serving as a front-end film and the chromium film is etched to be patterned by using a resist as a mask. Next, a micro-crystal silicon film on which the residual substances exist is exposed to plasma of a mixed gas including chlorine gas and oxygen gas to selectively etch the residual substances on a surface of the micro-crystal silicon film. After that, the micro-crystal silicon film is dry etched.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
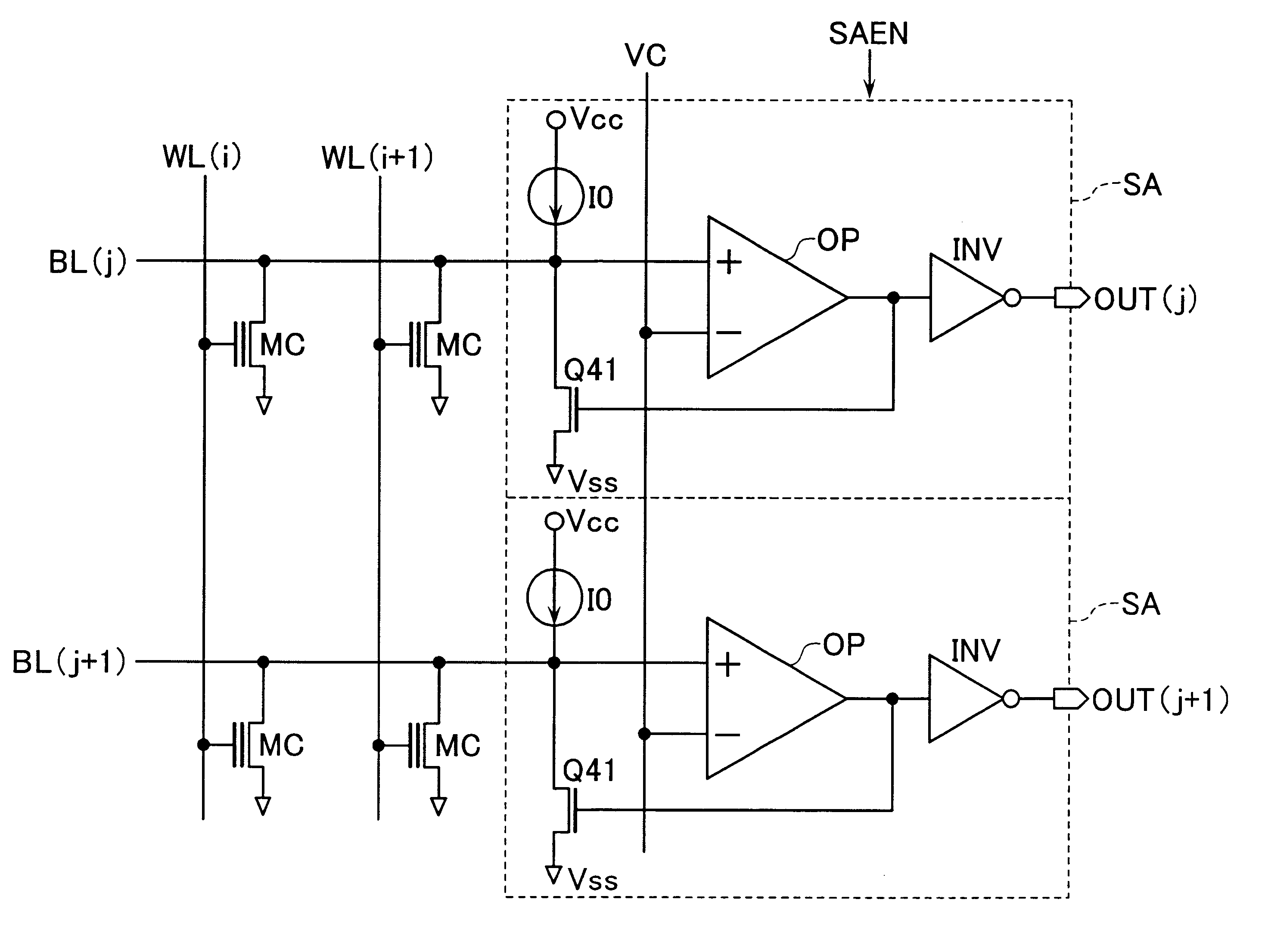
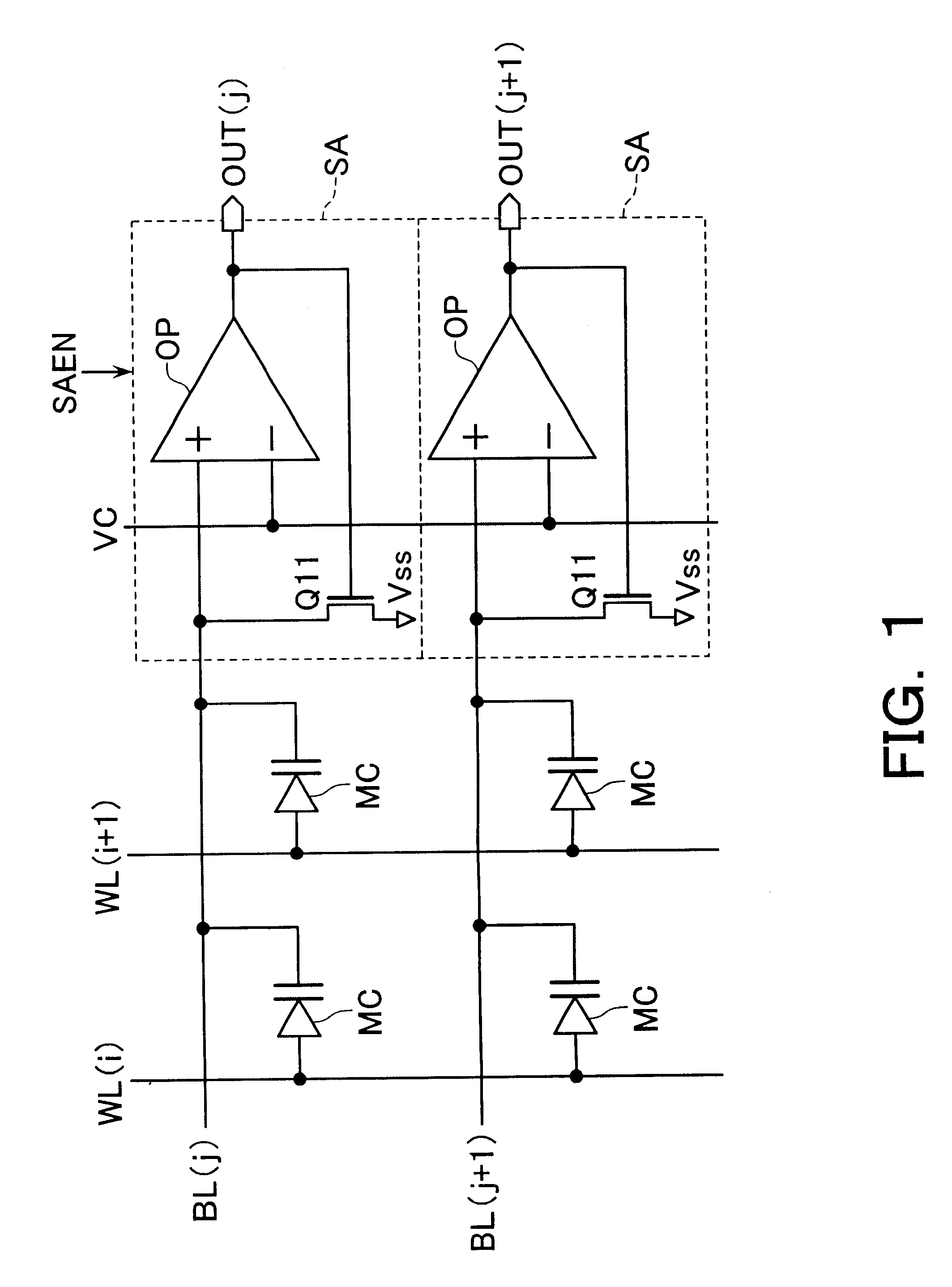
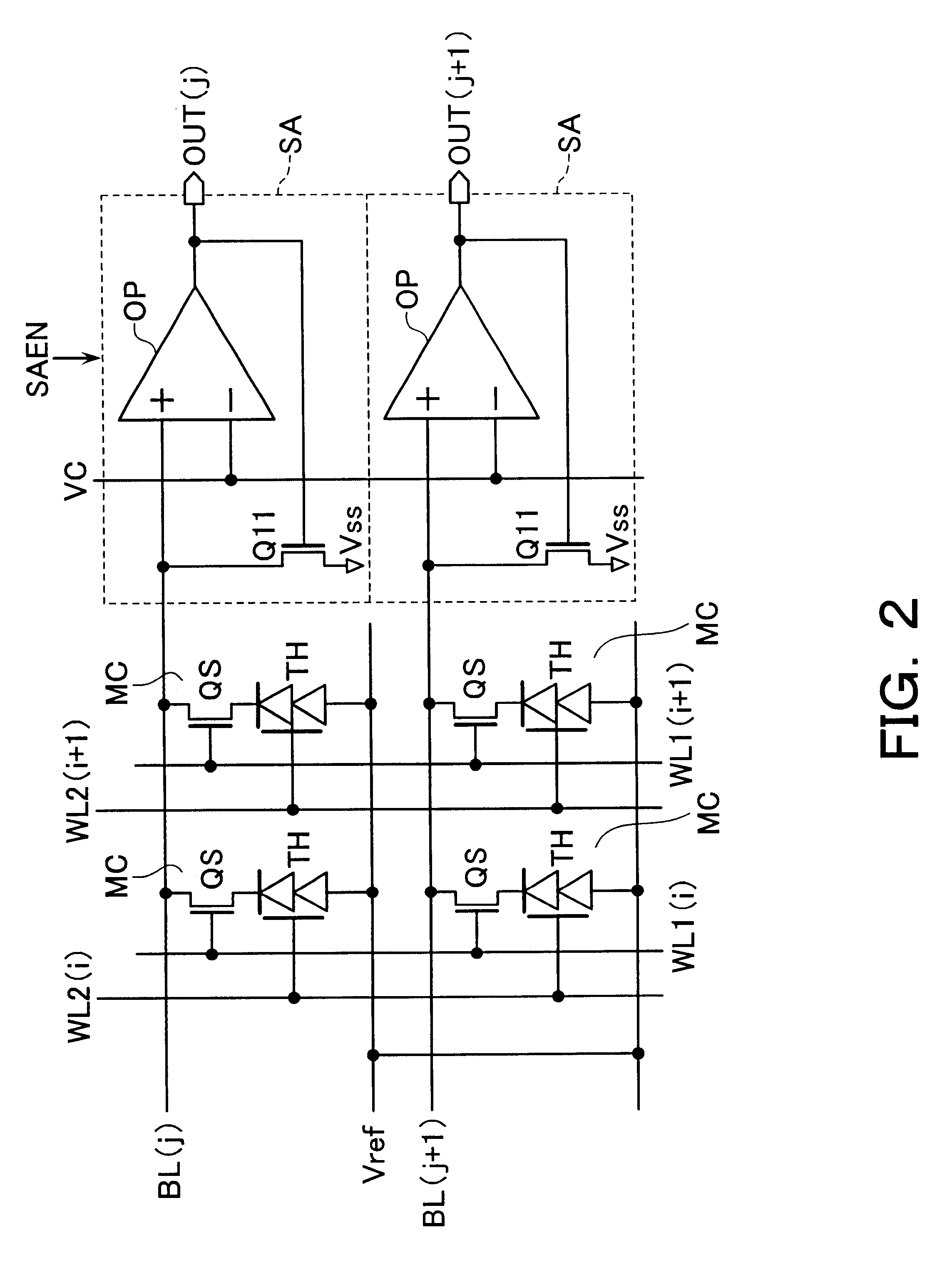
Magnetoresistive memory device
An integrated semiconductor memory device with an array of memory cells MC using magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cells is disclosed. A sense amplifier SA that is connected to a bit line BL for data readout of a selected memory cell MC is arranged using an operational amplifier OP. The operational amplifier OP has an inverting input terminal which is connected to the bit line BL and a non-inverting input terminal, to which a potentially fixed constant voltage VC is given. A PMOS transistor Q31 is provided, which can also do double-duty as a current source load. This PMOS transistor has its drain and gate that are connected to the inverting input terminal, and a source as connected to an output terminal of the operational amplifier OP whereby the transistor is under feedback control in response to an output of the operational amplifier OP so that a clamped voltage potential of the bit lime BL is fixed to the voltage VC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
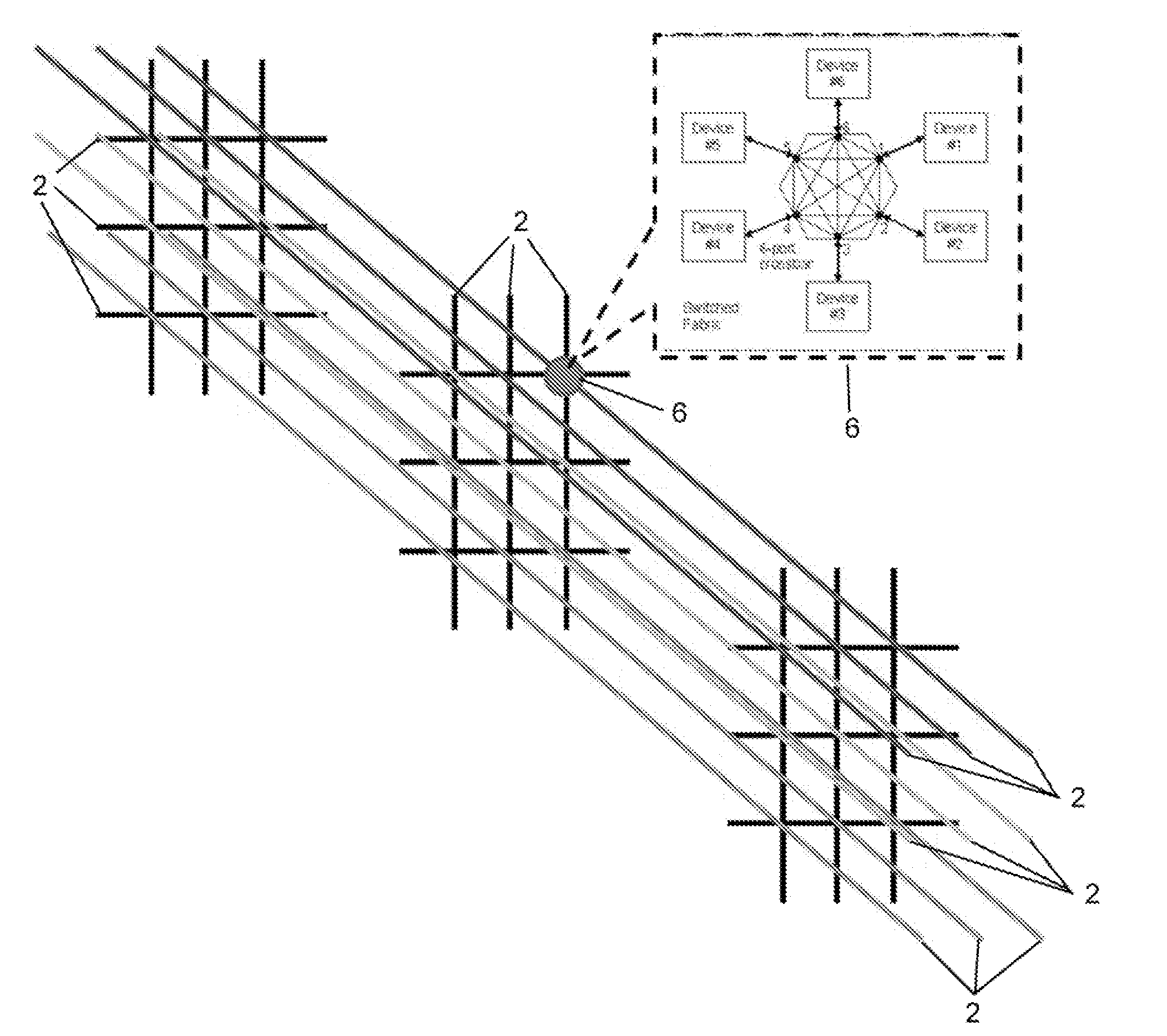
Programmable logic device with embedded switch fabric
InactiveUS20080278197A1Telephonic communicationBootstrappingCrossbar switchProgrammable logic device
The invention in the simplest form is a programmable logic device consisting of gate arrays, external I / O endpoints, and an embedded switch fabric configurable for connecting gates to gates, endpoints to endpoints and gates to endpoints. The architecture may employ a fabric interface of non-blocking crossbar switches for making complex bus connections of multiple devices to facilitate high speed processing.
Owner:TECNICA
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090057746A1High Q valueSmall parasitic capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceGate dielectric
A semiconductor device having a passive element whose characteristic is adjustable even after manufacture by applying back bias voltage is provided. Formed on a main surface of a SOI substrate comprising a supporting substrate, a BOX layer, and an SOI layer is a MOS varactor comprising a gate dielectric formed on a surface of the SOI layer, a gate electrode formed on the gate dielectric, and a n+ type semiconductor region formed in the SOI layer located on both sides of the gate electrode. The MOS varactor, is configured so that capacitance formed by the SOI layer, gate dielectric, and gate electrode is varied by applying bias voltage to the supporting substrate (p type well) under the gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Ultra-thin body super-steep retrograde well (SSRW) FET devices
ActiveUS7002214B1Reduce capacitanceReduce junctionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGround plane
A method of manufacture of a Super Steep Retrograde Well Field Effect Transistor device starts with an SOI layer formed on a substrate, e.g. a buried oxide layer. Thin the SOI layer to form an ultra-thin SOI layer. Form an isolation trench separating the SOI layer into N and P ground plane regions. Dope the N and P ground plane regions formed from the SOI layer with high levels of N-type and P-type dopant. Form semiconductor channel regions above the N and P ground plane regions. Form FET source and drain regions and gate electrode stacks above the channel regions. Optionally form a diffusion retarding layer between the SOI ground plane regions and the channel regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
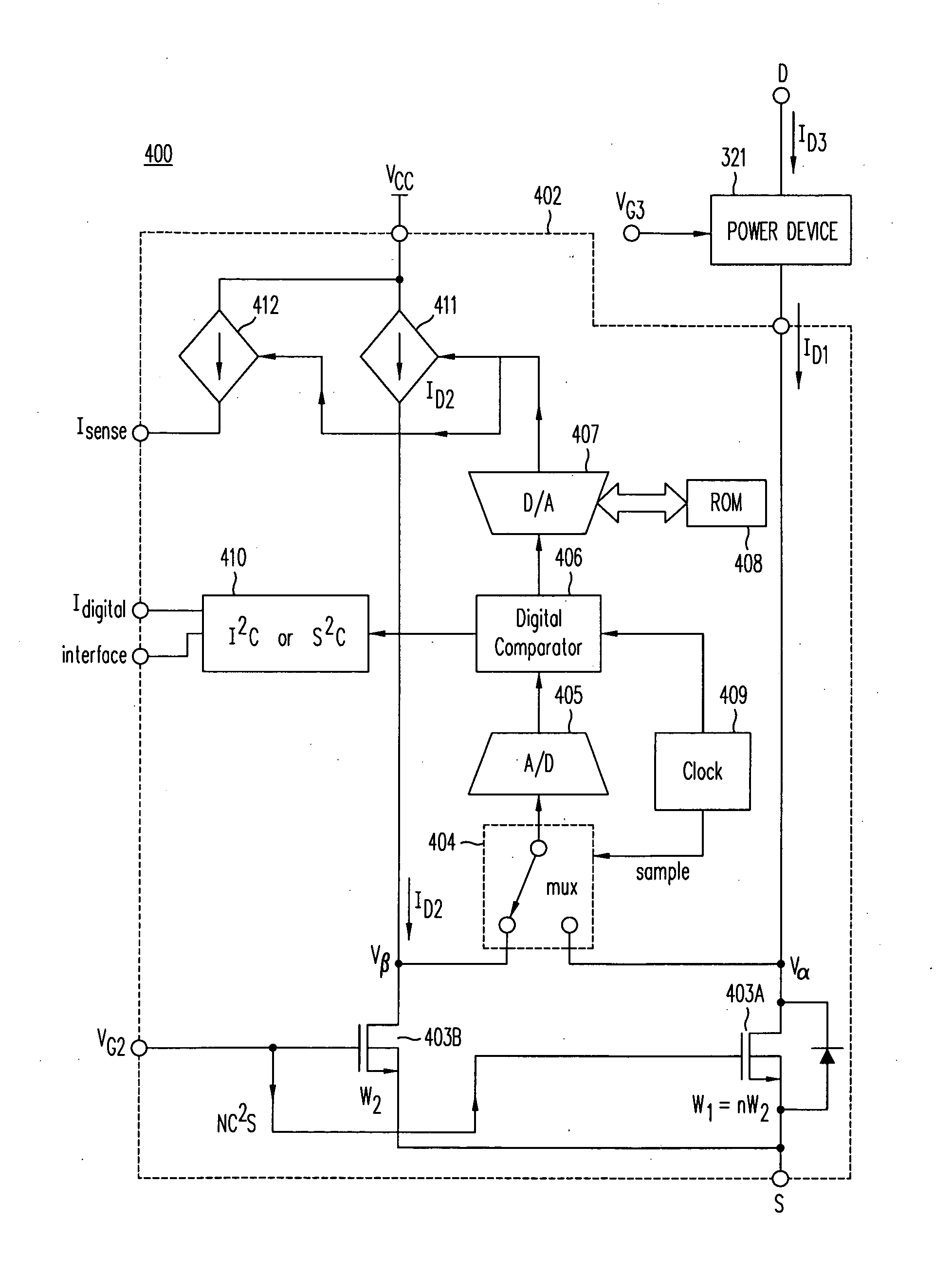
Cascode Current Sensor For Discrete Power Semiconductor Devices
InactiveUS20090039869A1Accurate detectionTransistorElectrical measurement instrument detailsMOSFETCascode
A cascode current sensor includes a main MOSFET and a sense MOSFET. The drain terminal of the main MOSFET is connected to a power device whose current is to be monitored, and the source and gate terminals of the main MOSFET are connected to the source and gate terminals, respectively, of the sense MOSFET. The drain voltages of the main and sense MOSFETs are equalized, in one embodiment by using a variable current source and negative feedback. The gate width of the main MOSFET is typically larger than the gate width of the sense MOSFET. Using the size ratio of the gate widths, the current in the main MOSFET is measured by sensing the magnitude of the current in the sense MOSFET. Inserting the relatively large MOSFET in the power circuit minimizes power loss.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
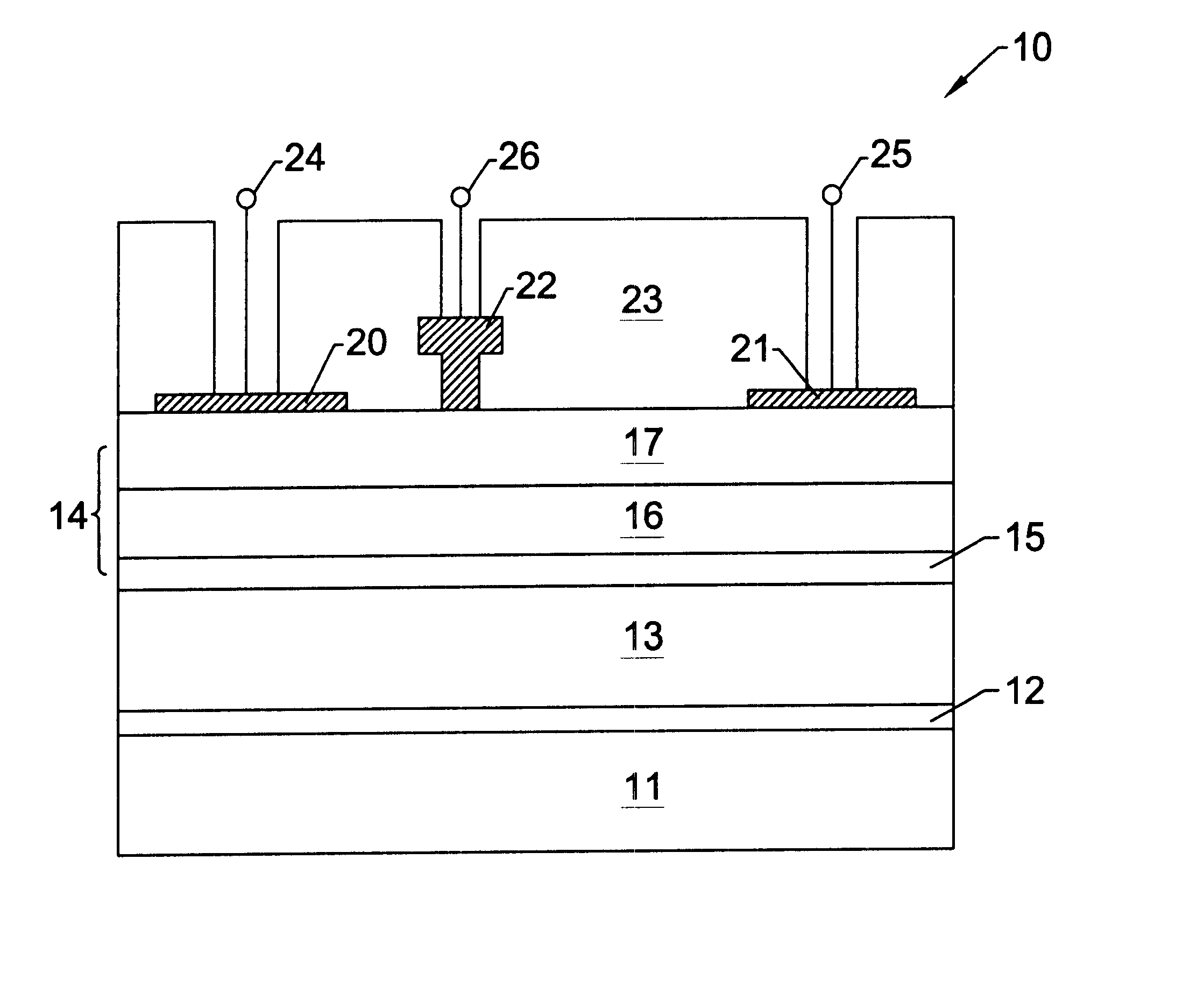
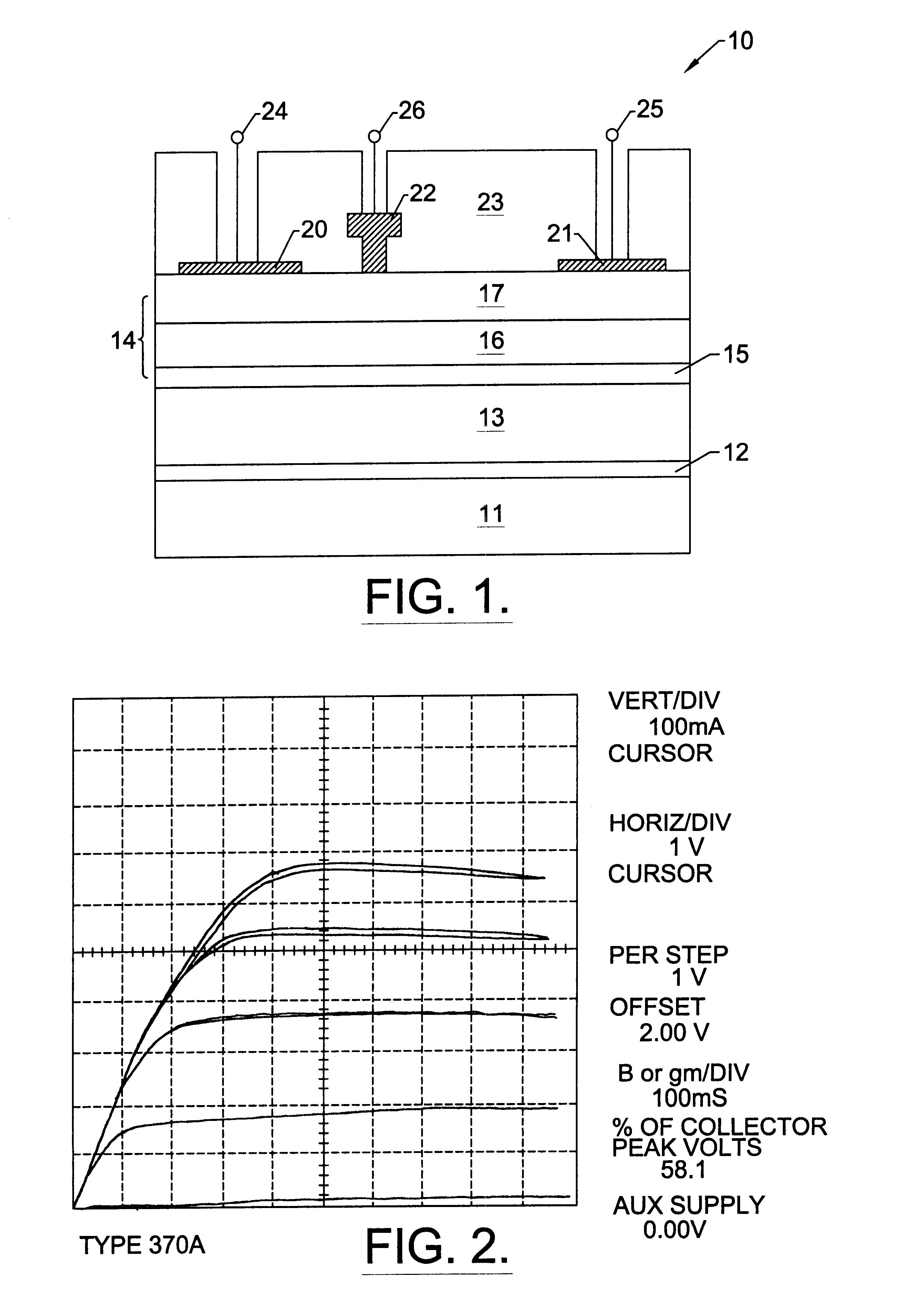
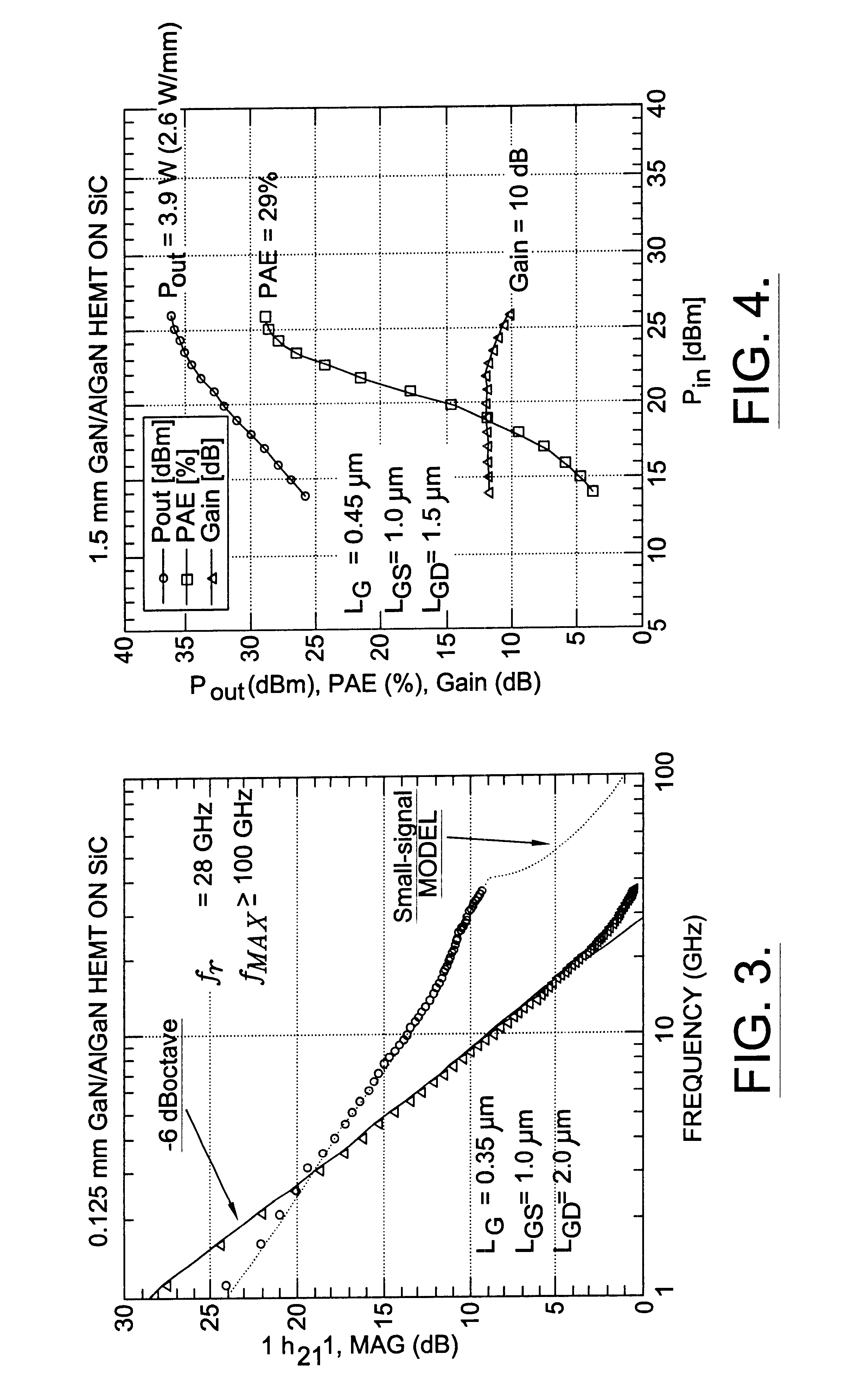
Nitride based transistors on semi-insulating silicon carbide substrates
InactiveUS6486502B1Quality improvementImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideNitride
A high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) (10) is disclosed that includes a semi-insulating silicon carbide substrate (11), an aluminum nitride buffer layer (12) on the substrate, an insulating gallium nitride layer (13) on the buffer layer, an active structure of aluminum gallium nitride (14) on the gallium nitride layer, a passivation layer (23) on the aluminum gallium nitride active structure, and respective source, drain and gate contacts (21, 22, 23) to the aluminum gallium nitride active structure.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Replacement Metal Gate Structures Providing Independent Control On Work Function and Gate Leakage Current
The thickness and composition of a gate dielectric can be selected for different types of field effect transistors through a planar high dielectric constant material portion, which can be provided only for selected types of field effect transistors. Further, the work function of field effect transistors can be tuned independent of selection of the material stack for the gate dielectric. A stack of a barrier metal layer and a first-type work function metal layer is deposited on a gate dielectric layer within recessed gate cavities after removal of disposable gate material portions. After patterning the first-type work function metal layer, a second-type work function metal layer is deposited directly on the barrier metal layer in the regions of the second type field effect transistor. A conductive material fills the gate cavities, and a subsequent planarization process forms dual work function metal gate structures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
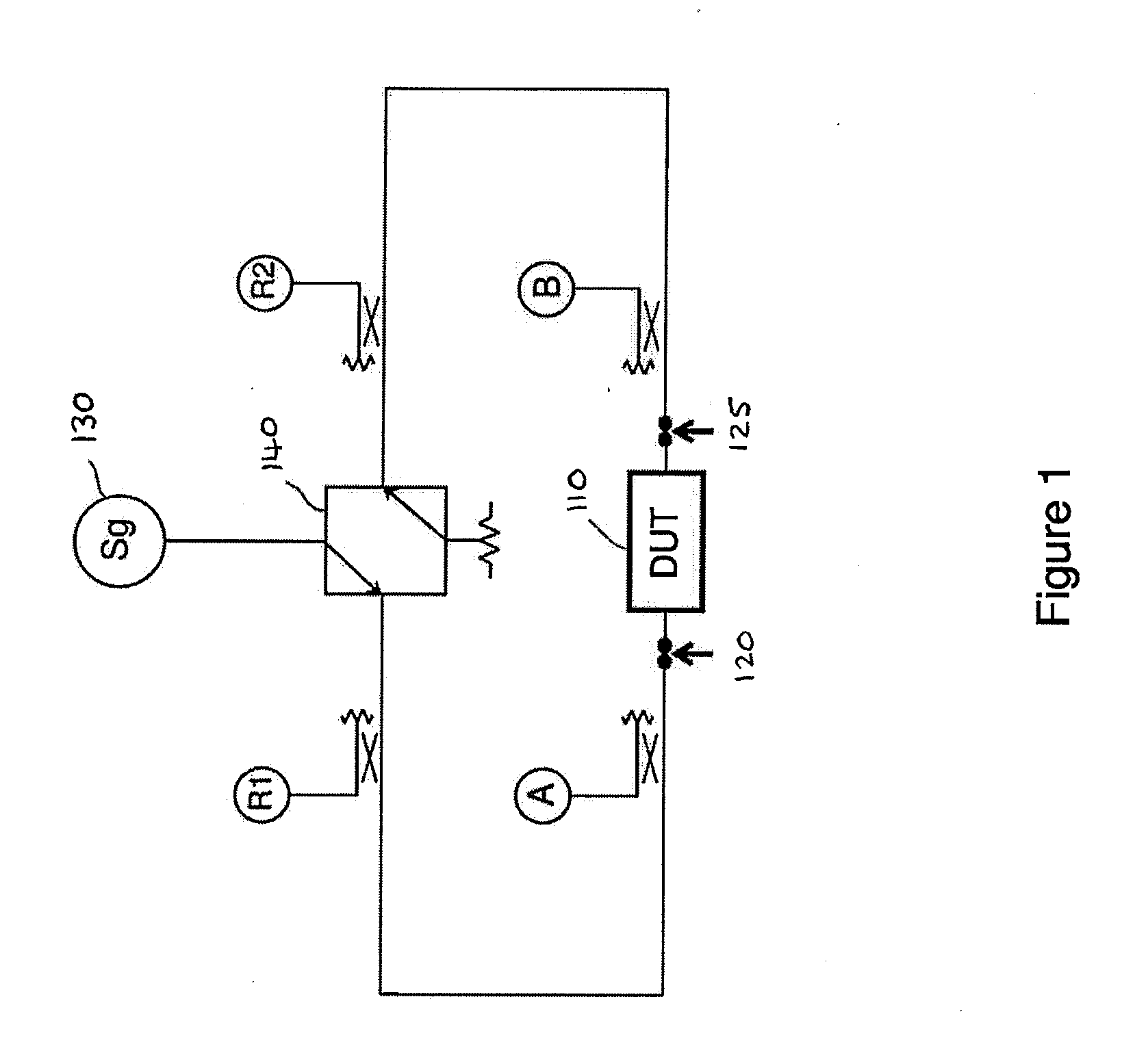
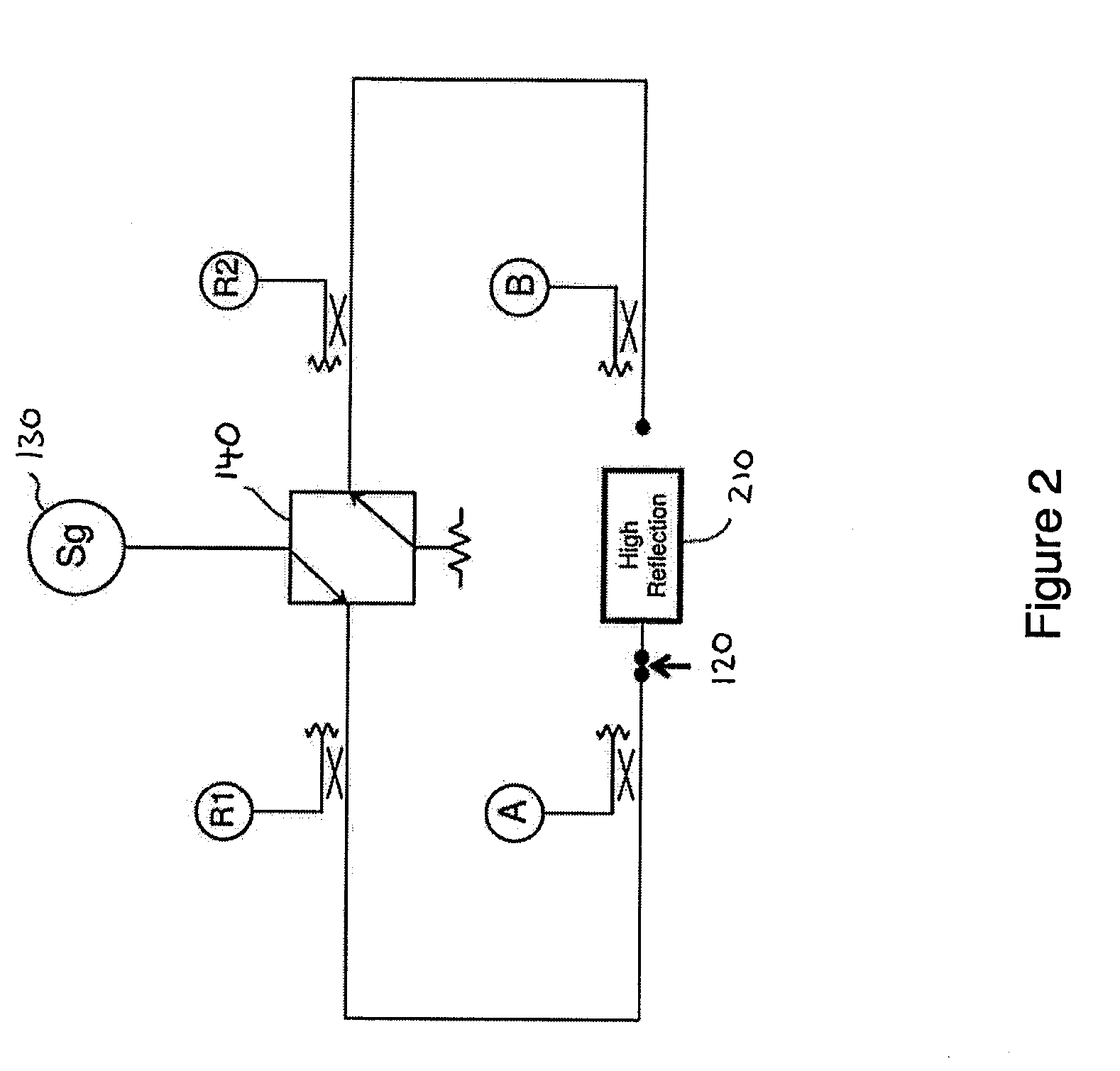
Method and apparatus for calibrating a test system for measuring a device under test
InactiveUS20120109566A1High precisionResistance/reactance/impedenceSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainImpulse response
A calibration method for a two-port VNA includes presenting a high reflection calibration standard and measuring reflection data for each of the two ports, calculating a location of the high reflection calibration standard at each of the two ports, presenting a load calibration standard and measuring the reflection characteristic for each of the two ports to provide load data, converting the load data to the time domain to provide time domain impulse response load data, and gating the time domain impulse response load data based on the locations of the high reflection calibration standard at each of two ports. The method further includes reconstructing frequency domain load data from the gated time domain data, connecting the two ports together and determining forward and reverse transmission characteristics, and calculating systematic error coefficients for the VNA based on the reconstructed frequency domain data and the forward and reverse transmission characteristics.
Owner:ATE SYST
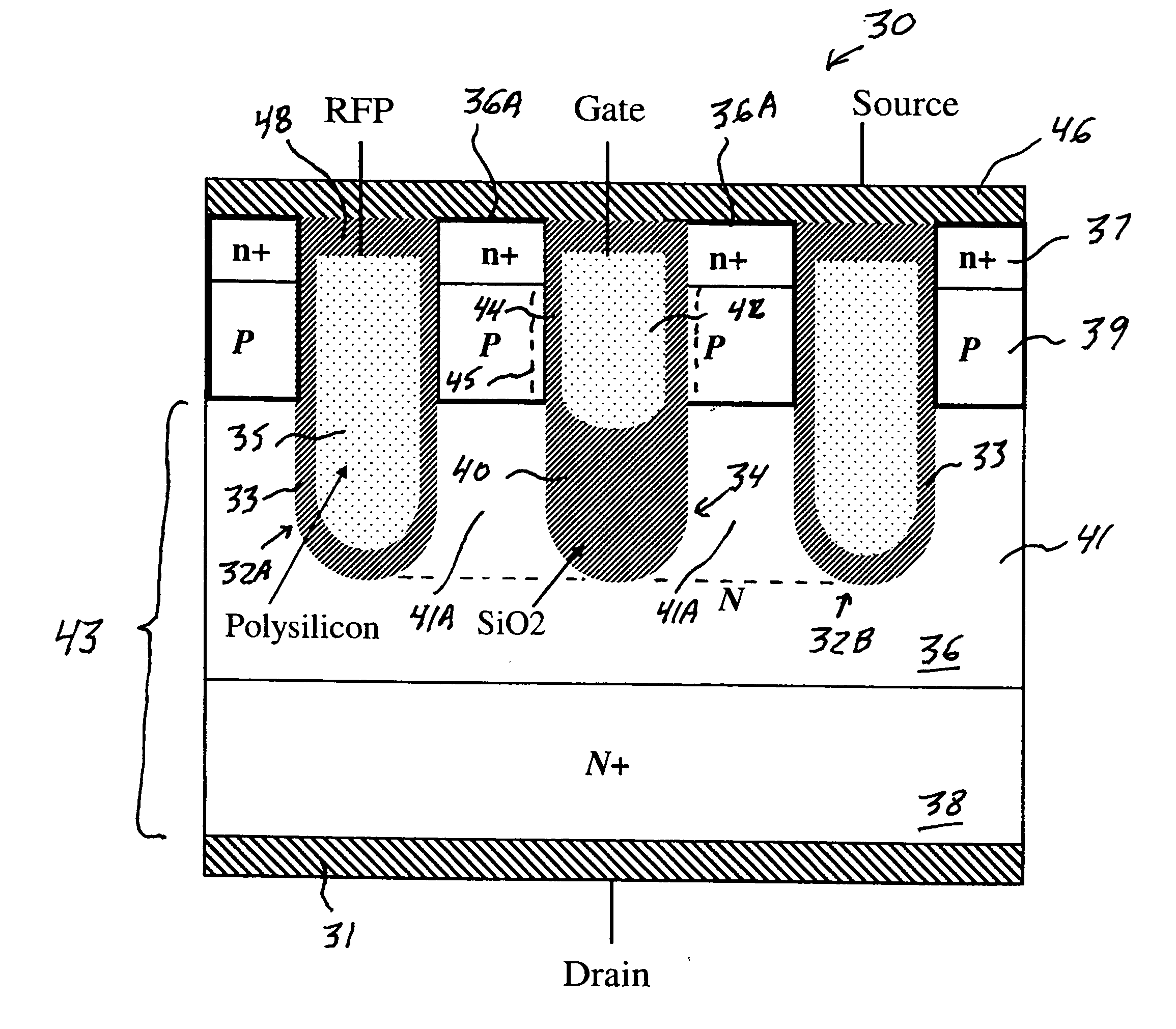
Power MOSFET with recessed field plate
ActiveUS20080073707A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench mosfetReverse recovery
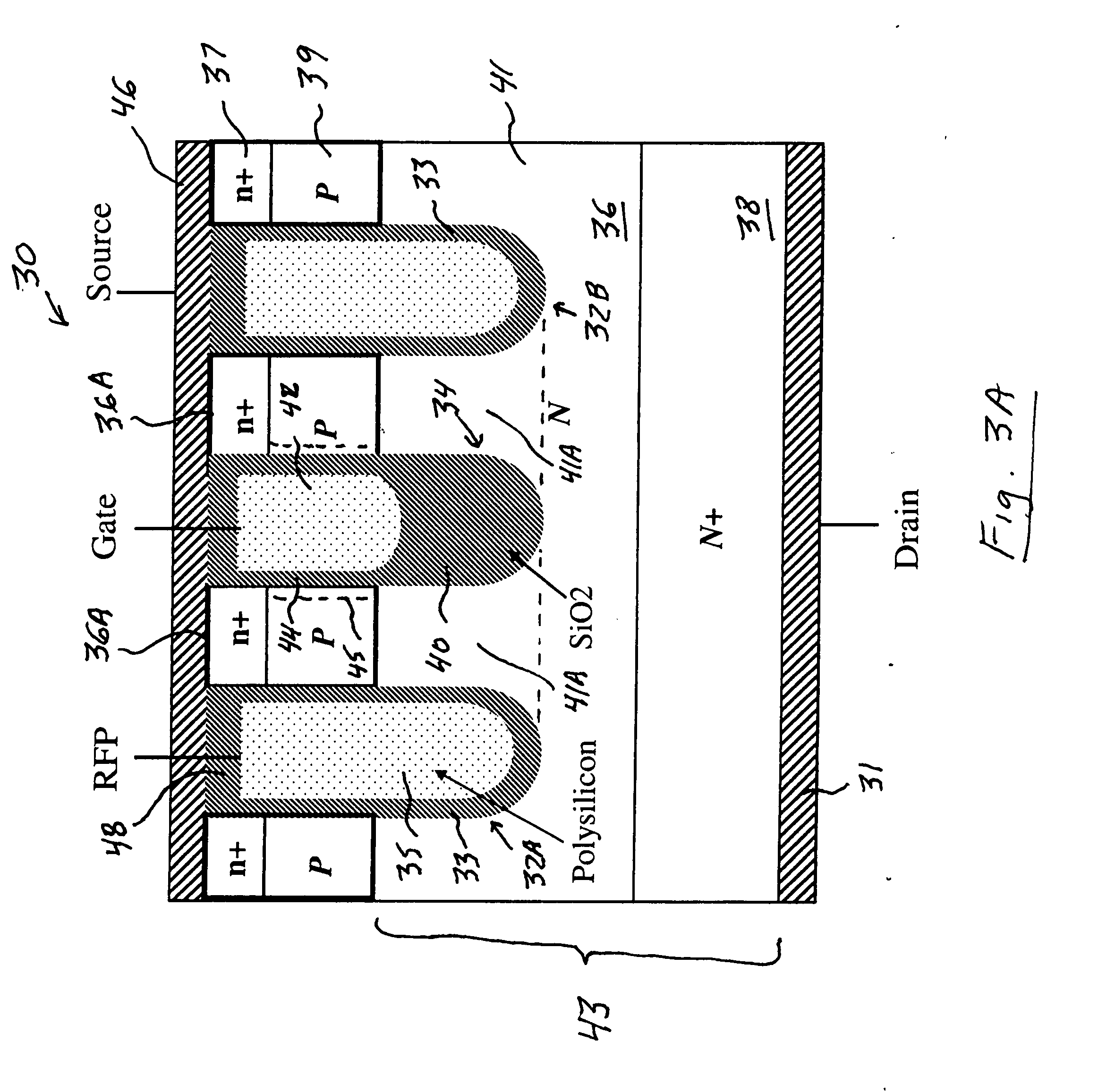
A trench MOSFET contains a recessed field plate (RFP) trench adjacent the gate trench. The RFP trench contains an RFP electrode insulated from the die by a dielectric layer along the walls of the RFP trench. The gate trench has a thick bottom oxide layer, and the gate and RFP trenches are preferably formed in the same processing step and are of substantially the same depth. When the MOSFET operates in the third quadrant (with the source / body-to-drain junction forward-biased), the combined effect of the RFP and gate electrodes significantly reduces in the minority carrier diffusion current and reverse-recovery charge. The RFP electrode also functions as a recessed field plates to reduce the electric field in the channel regions when the MOSFET source / body to-drain junction reverse-biased.
Owner:MAXPOWER SEMICON INC
Power devices having trench-based source and gate electrodes
ActiveUS20060060916A1Improve breakdown voltageIncrease the on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodePower semiconductor deviceDevice material
A power semiconductor device includes a plurality of trenches formed within a semiconductor body, each trench including one or more electrodes formed therein. In particular, according to embodiments of the invention, the plurality of trenches of a semiconductor device may include one or more gate electrodes, may include one or more gate electrodes or one or more source electrodes, or may include a combination of both gate and source electrodes formed therein. The trenches and electrodes may have varying depths within the semiconductor body.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Semiconductive metal oxide thin film ferroelectric memory transistor
InactiveUS20060038242A1Simplify the manufacturing processHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention discloses a novel transistor structure employing semiconductive metal oxide as the transistor conductive channel. By replacing the silicon conductive channel with a semiconductive metal oxide channel, the transistors can achieve simpler fabrication process and could realize 3D structure to increase circuit density. The disclosed semiconductive metal oxide transistor can have great potential in ferroelectric non volatile memory device with the further advantages of good interfacial properties with the ferroelectric materials, possible lattice matching with the ferroelectric layer, reducing or eliminating the oxygen diffusion problem to improve the reliability of the ferroelectric memory transistor. The semiconductive metal oxide film is preferably a metal oxide exhibiting semiconducting properties at the transistor operating conditions, for example, In2O3 or RuO2. The present invention ferroelectric transistor can be a metal-ferroelectric-semiconductive metal oxide FET having a gate stack of a top metal electrode disposed on a ferroelectric layer disposed on a semiconductive metal oxide channel on a substrate. Using additional layer of bottom electrode and gate dielectric, the present invention ferroelectric transistor can also be a metal-ferroelectric-metal (optional)-gate dielectric (optional)-semiconductive metal oxide FET.
Owner:SHARP KK
Non-volatile electromechanical field effect devices and circuits using same and methods of forming same
Non-volatile field effect devices and circuits using same. A non-volatile field effect device includes a source, drain and gate with a field-modulatable channel between the source and drain. Each of the source, drain, and gate have a corresponding terminal. An electromechanically-deflectable, nanotube switching element is electrically positioned between one of the source, drain and gate and its corresponding terminal. The others of the source, drain and gate are directly connected to their corresponding terminals. The nanotube switching element is electromechanically-deflectable in response to electrical stimulation at two control terminals to create one of a non-volatile open and non-volatile closed electrical communication state between the one of the source, drain and gate and its corresponding terminal. Under one embodiment, one of the two control terminals has a dielectric surface for contact with the nanotube switching element when creating a non-volatile open state. Under one embodiment, the source, drain and gate may be stimulated at any voltage level from ground to supply voltage, and wherein the two control terminals are stimulated at any voltage level from ground to a switching threshold voltage larger in magnitude than the supply voltage. Under one embodiment, the nanotube switching element includes an article made from nanofabric that is positioned between the two control terminals. Under one embodiment, one of the two control terminals is a release electrode for electrostatically pulling the nanotube article out of contact with the one of the source, drain and gate so as to form a non-volatile open state. Under one embodiment, the other of the two control terminals is a set electrode for electrostatically pulling the nanotube article into contact with the one of the source, drain and gate so as to form a non-volatile closed state.
Owner:NANTERO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com