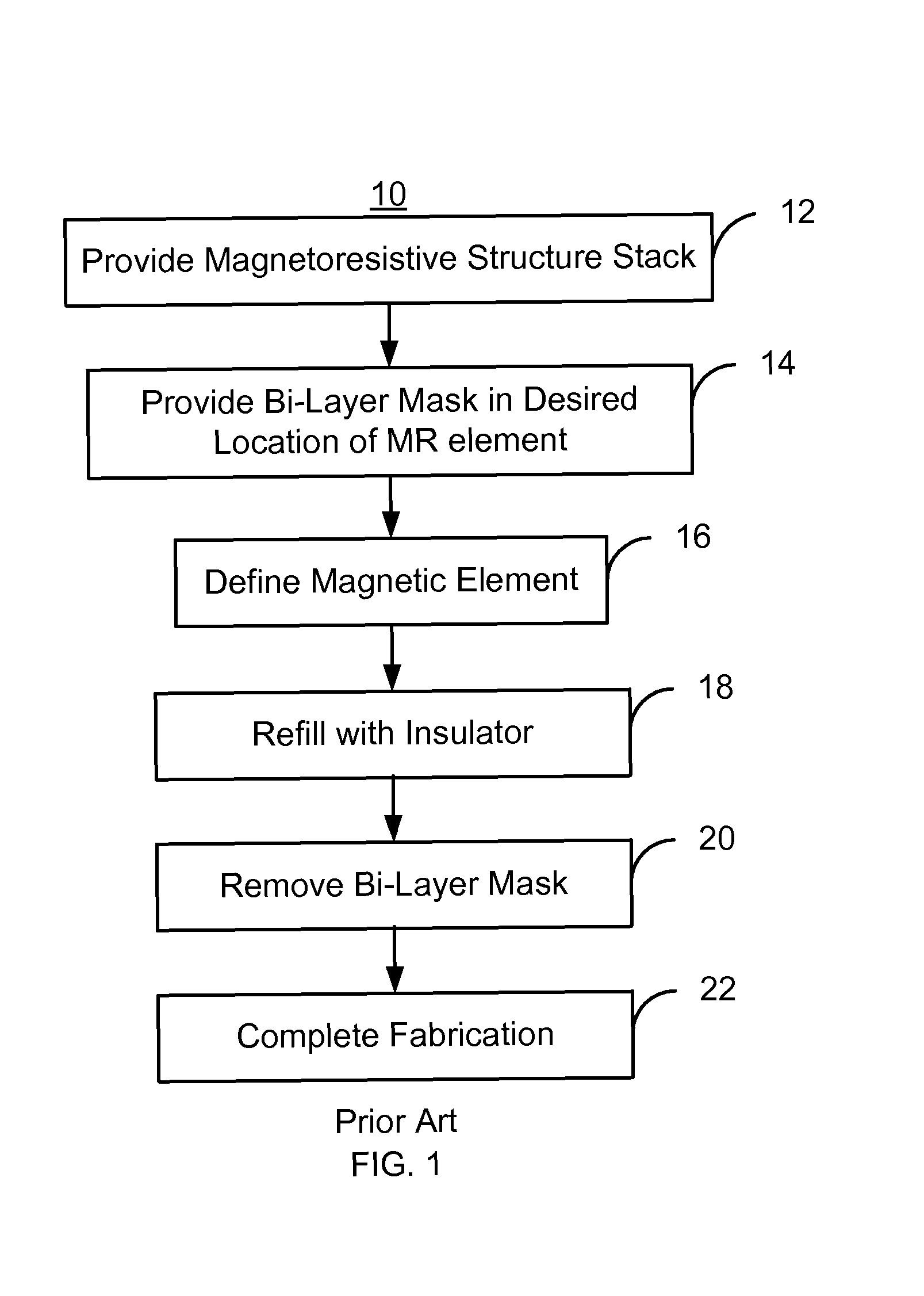
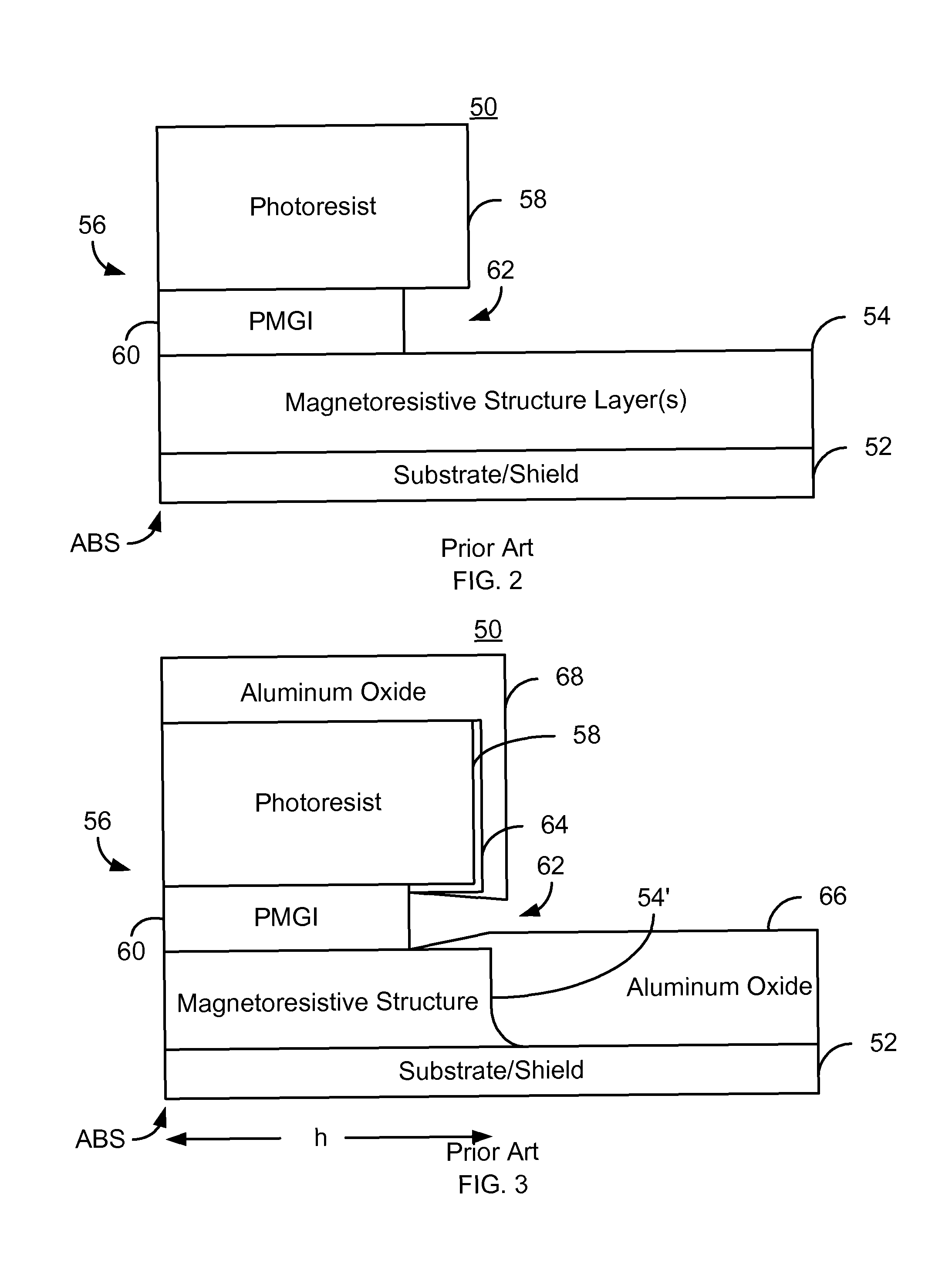
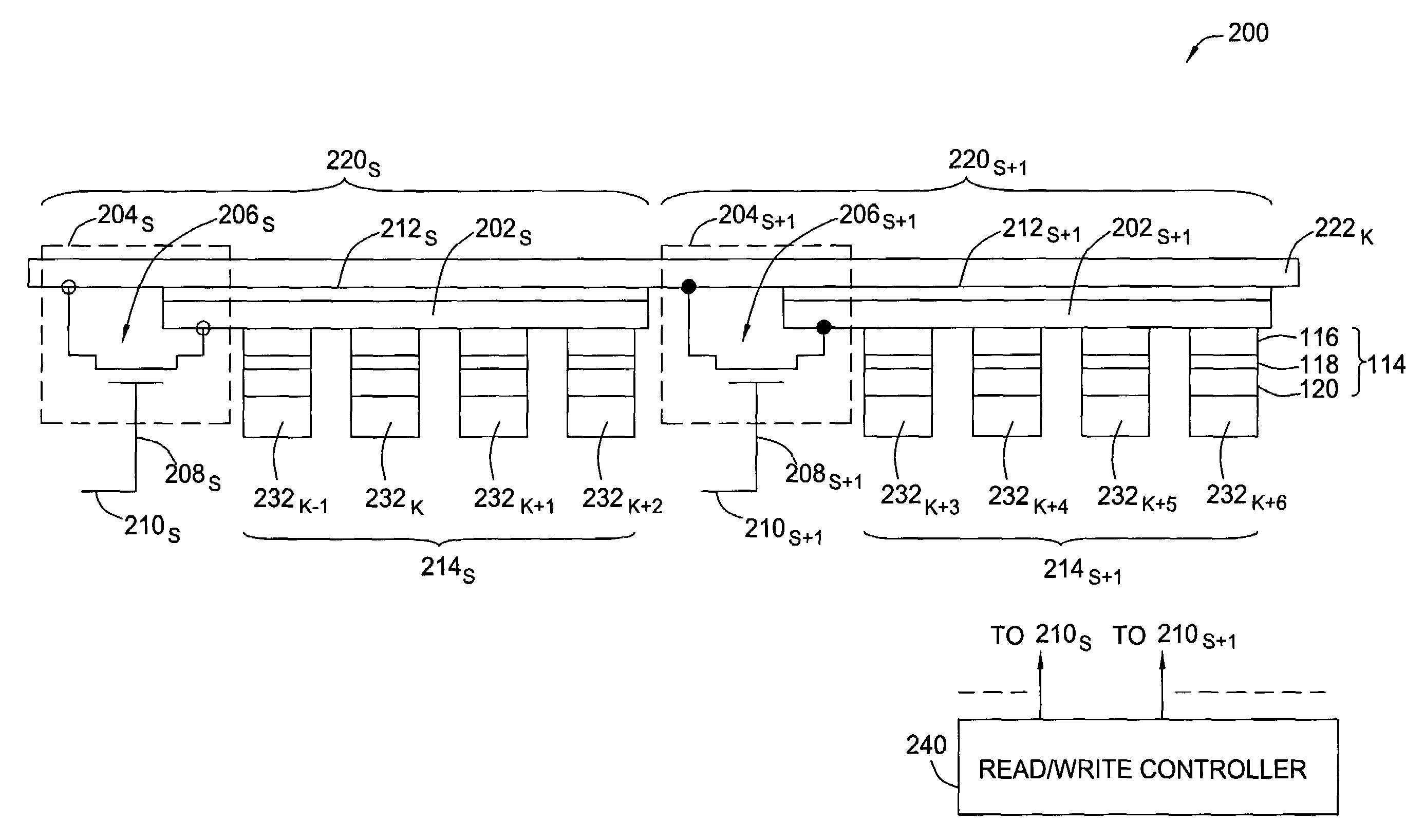
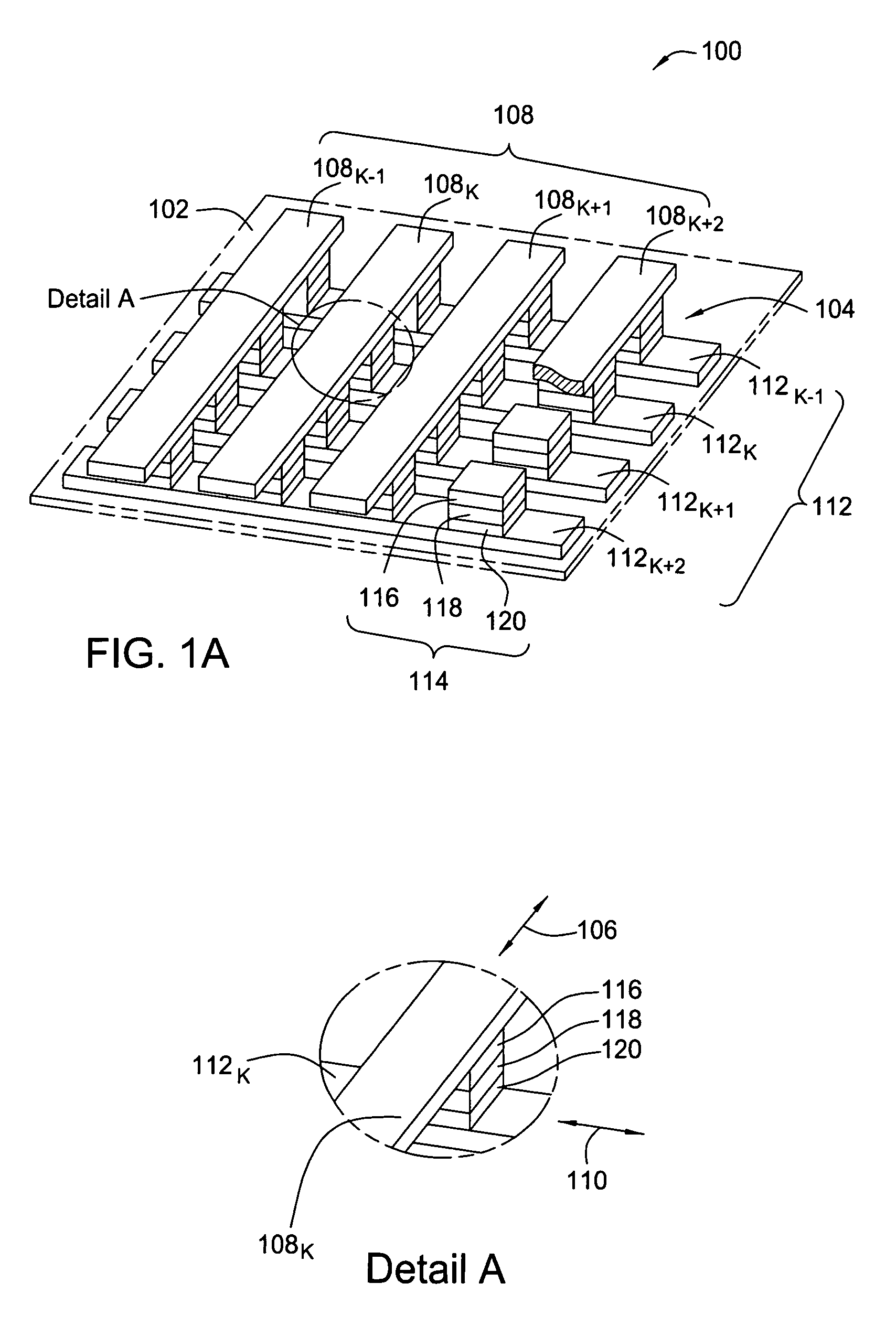
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3941 results about "Magnetic reluctance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
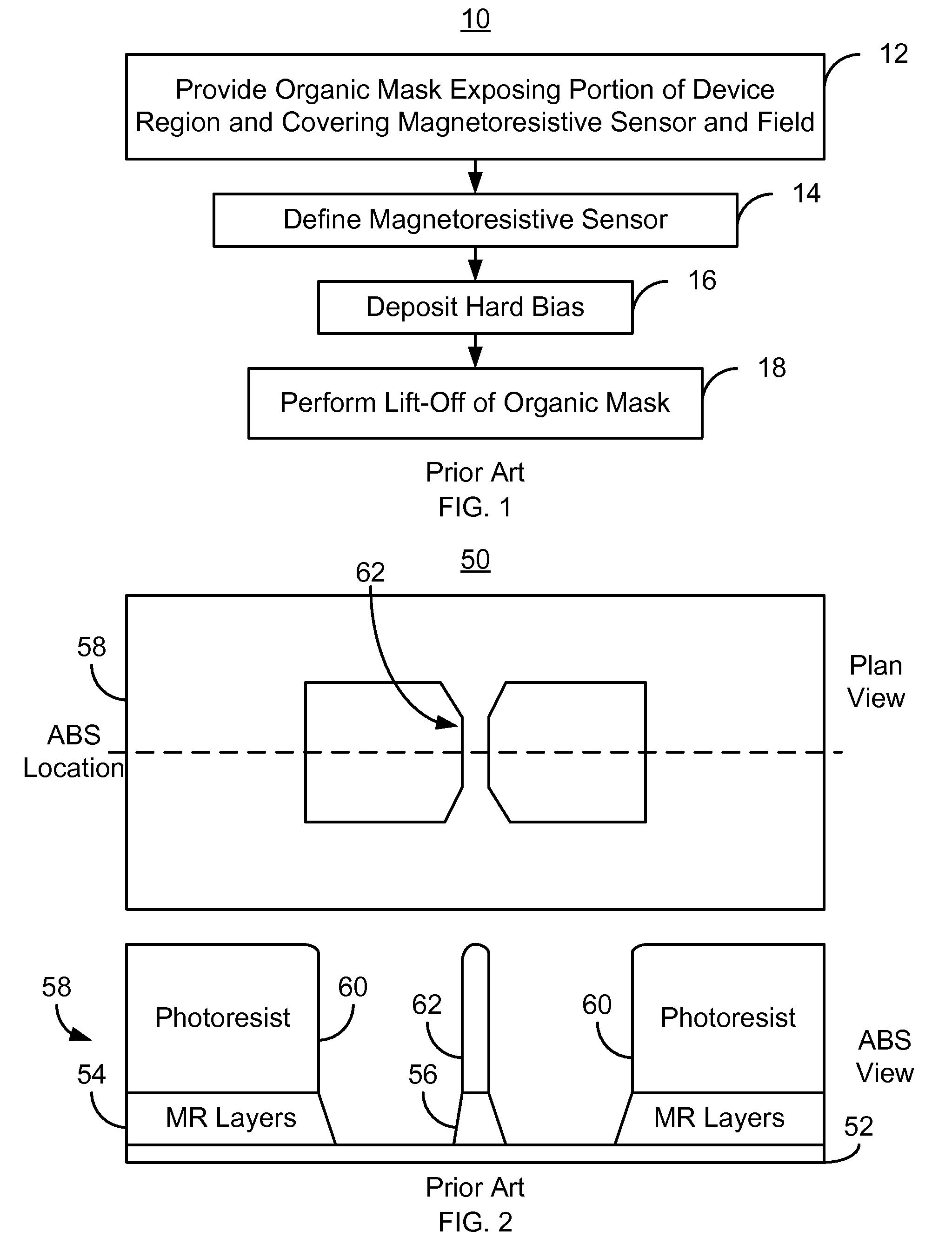
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnetic reluctance, or magnetic resistance, is a concept used in the analysis of magnetic circuits. It is defined as the ratio of magnetomotive force (mmf) to magnetic flux. It represents the opposition to magnetic flux, and depends on the geometry and composition of an object.
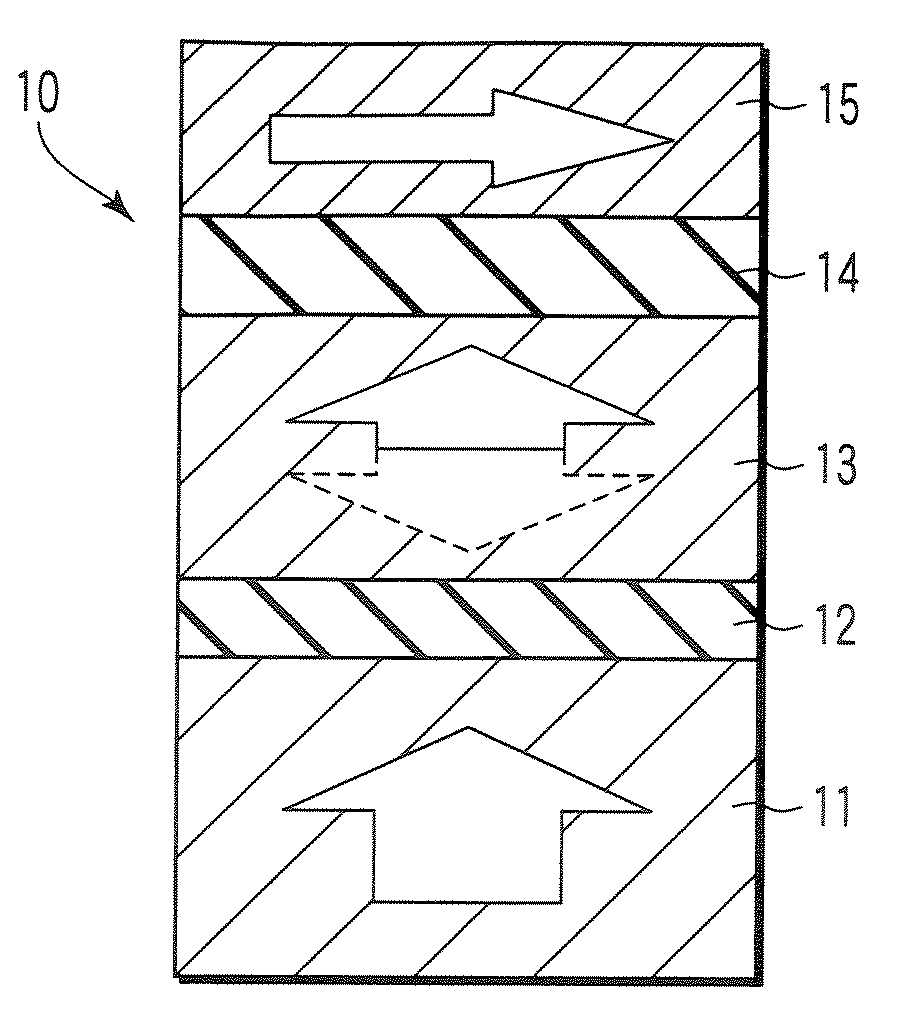
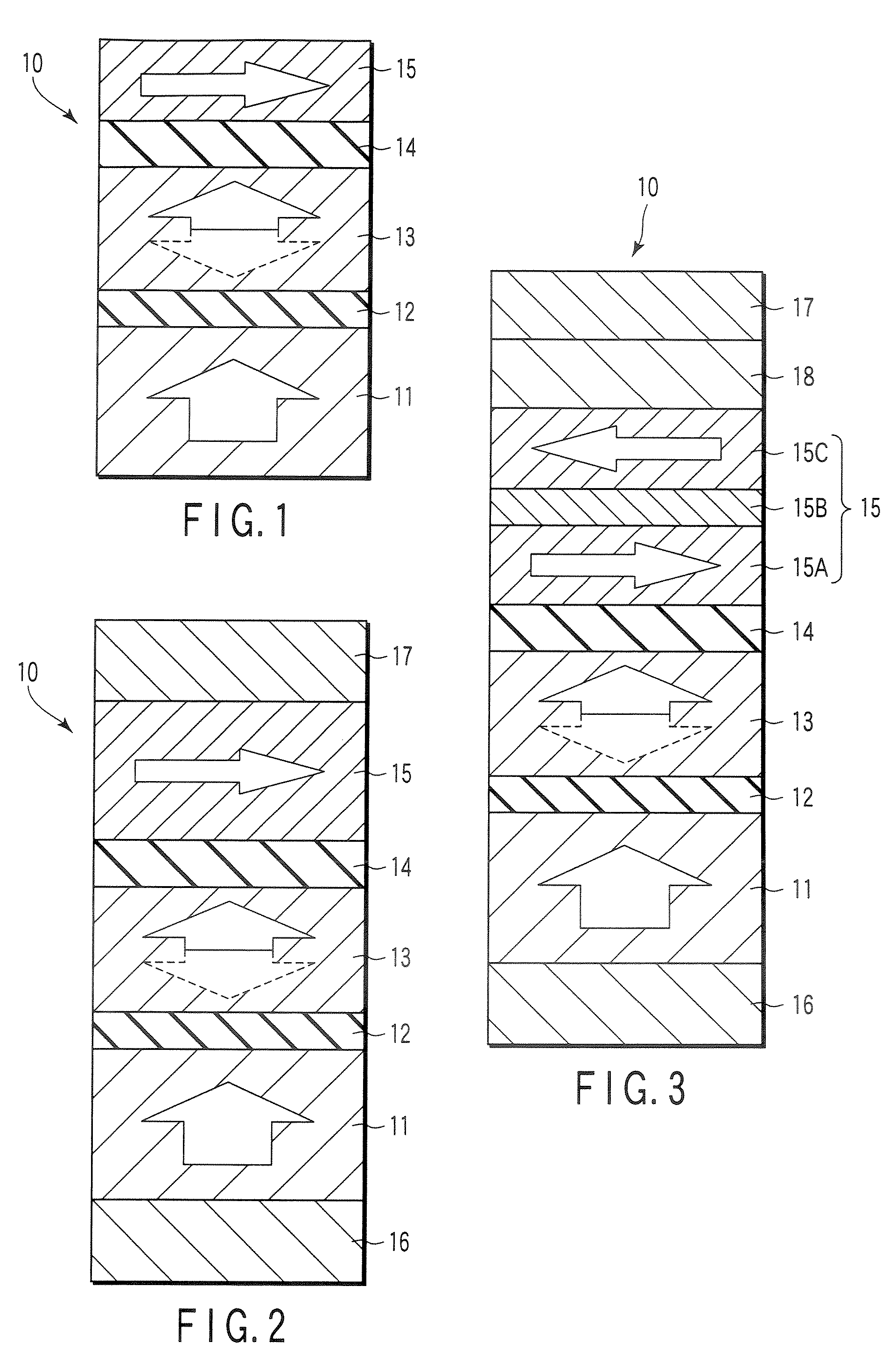
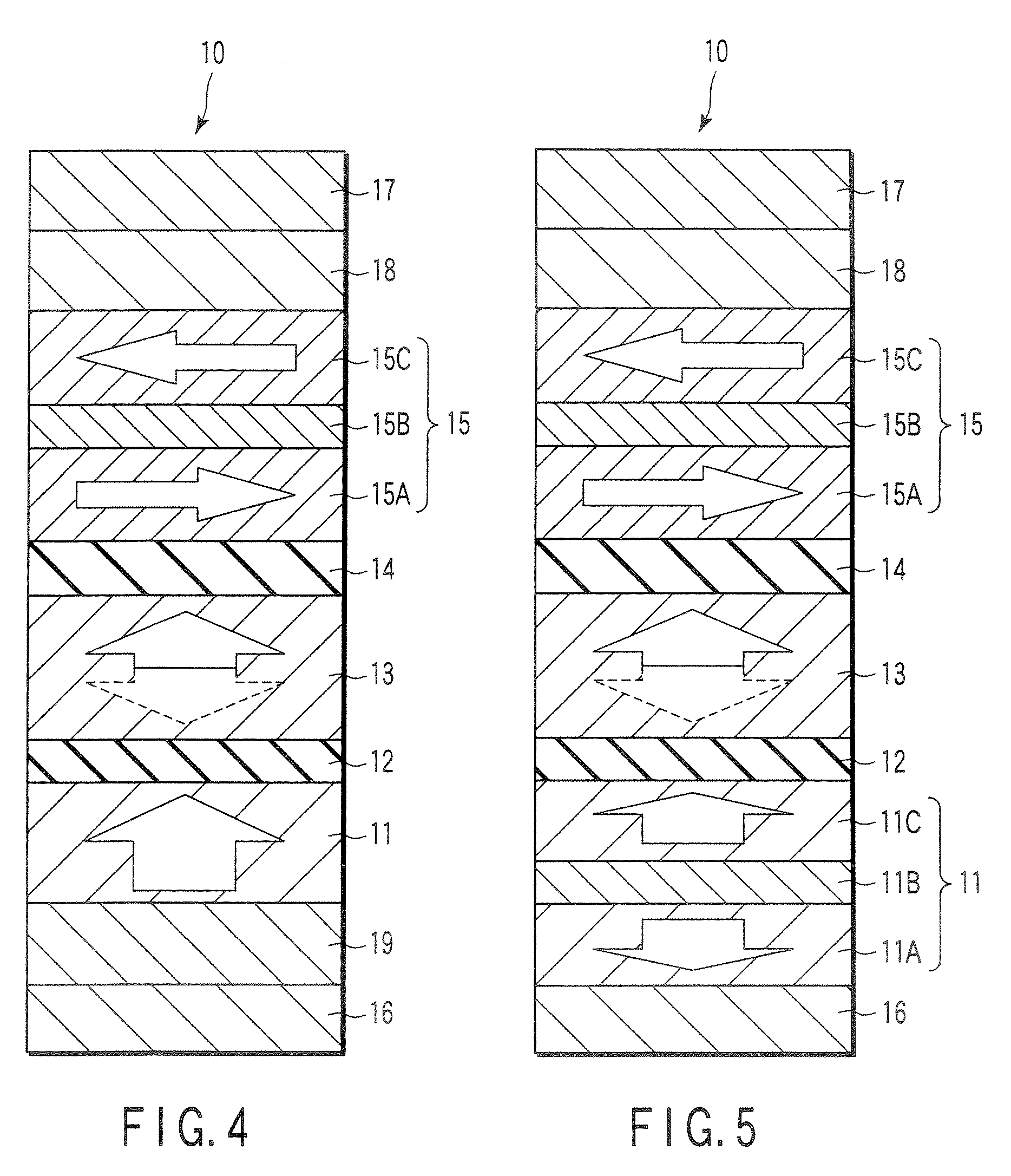
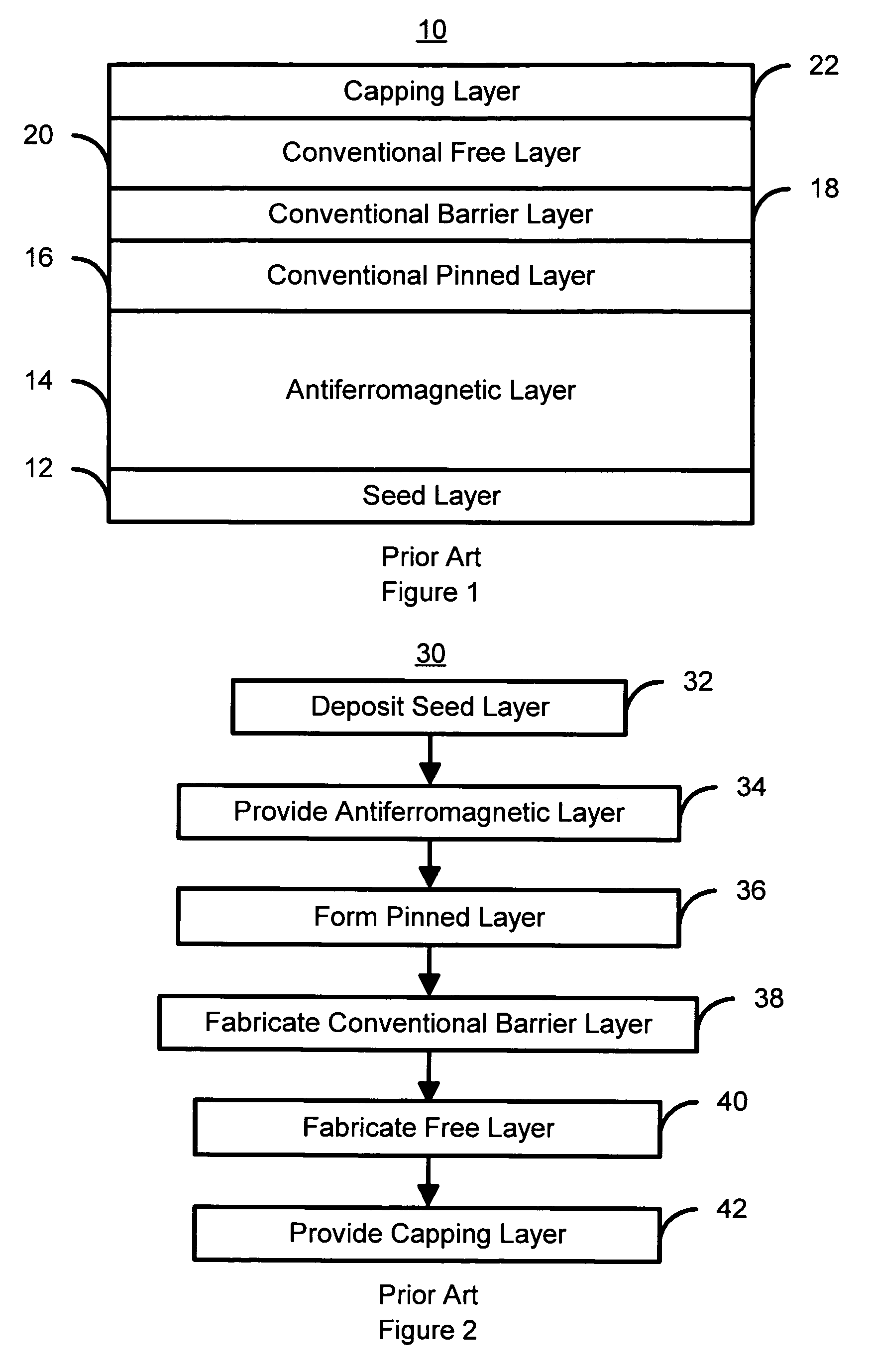
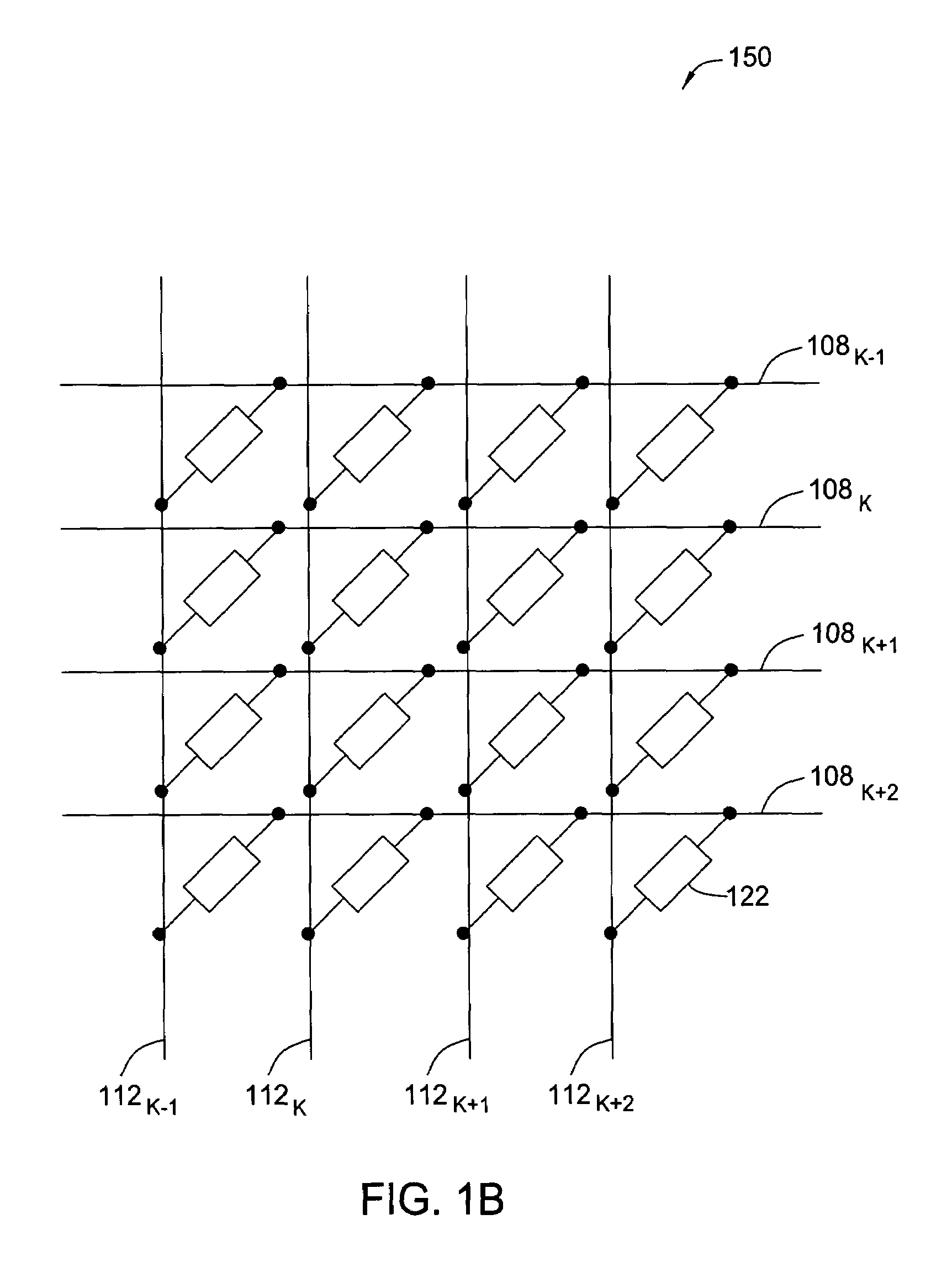
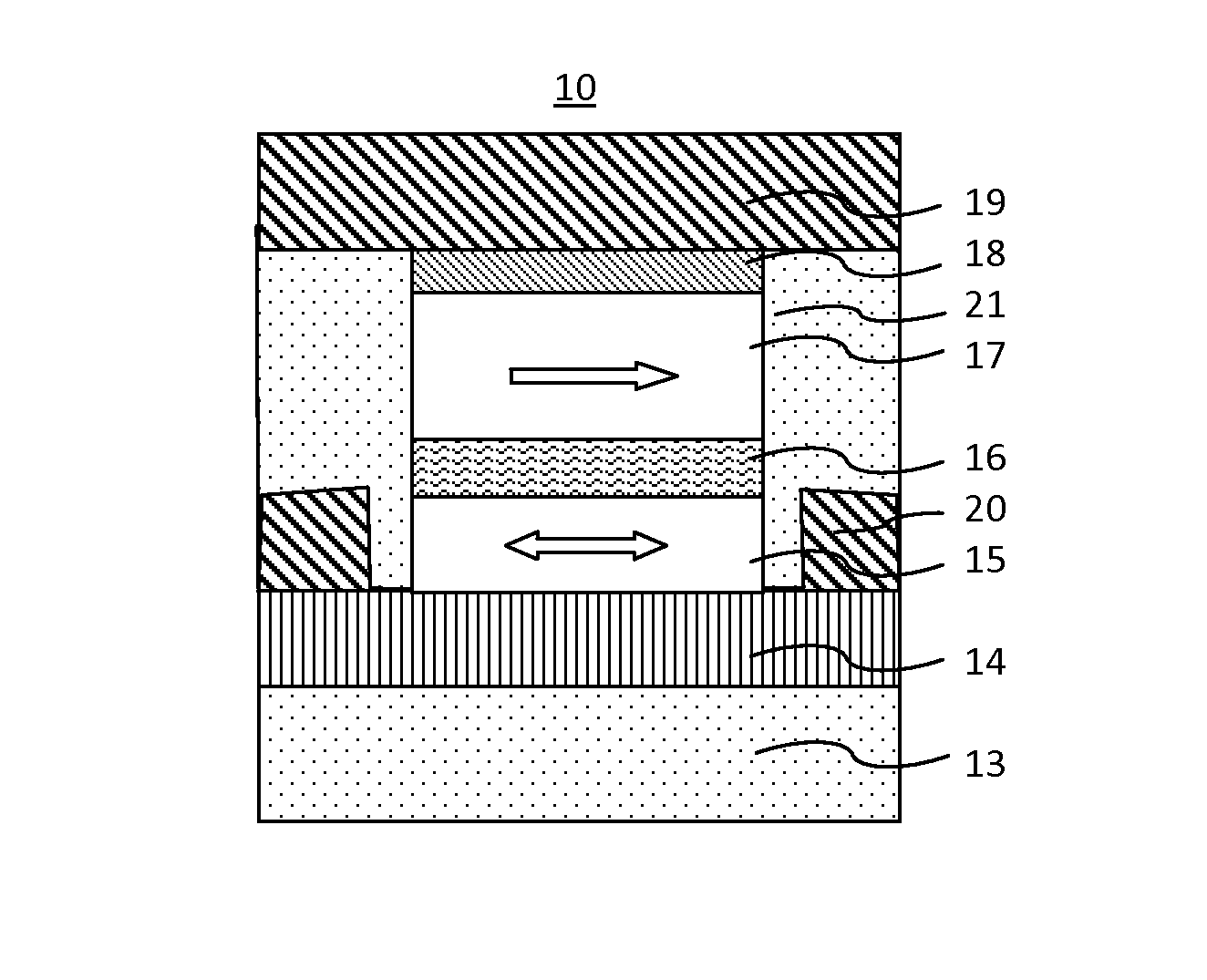
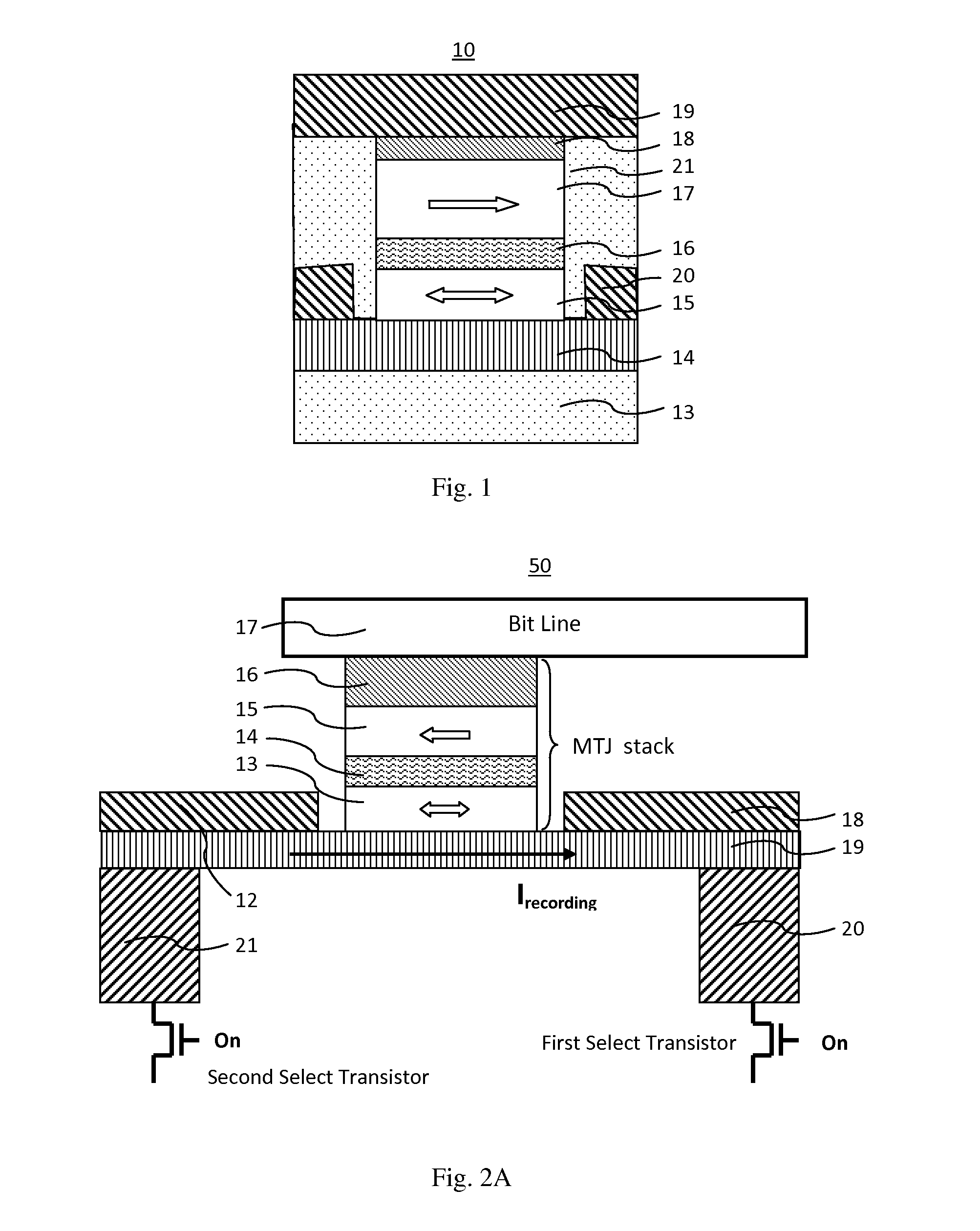
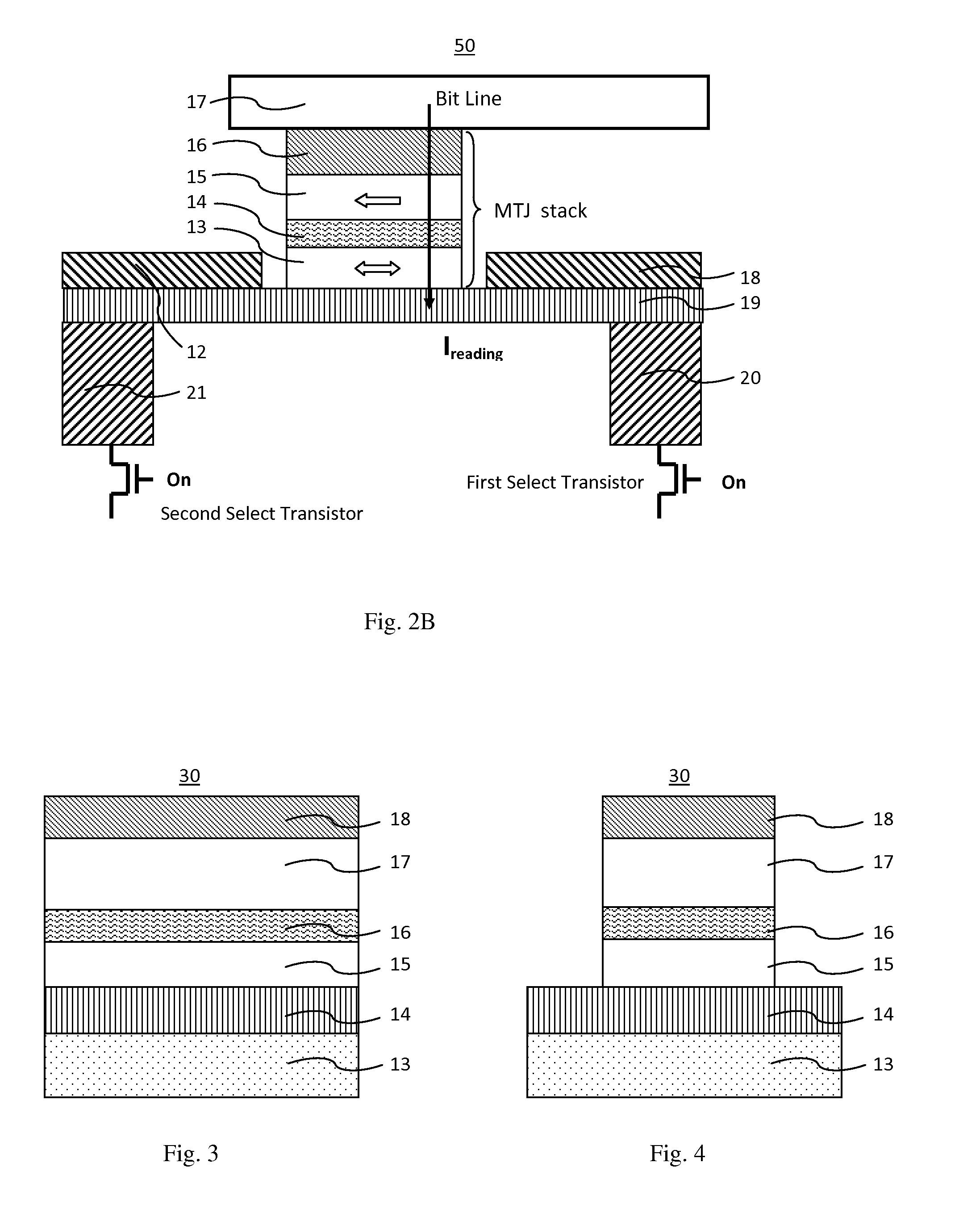
Magnetoresistive element
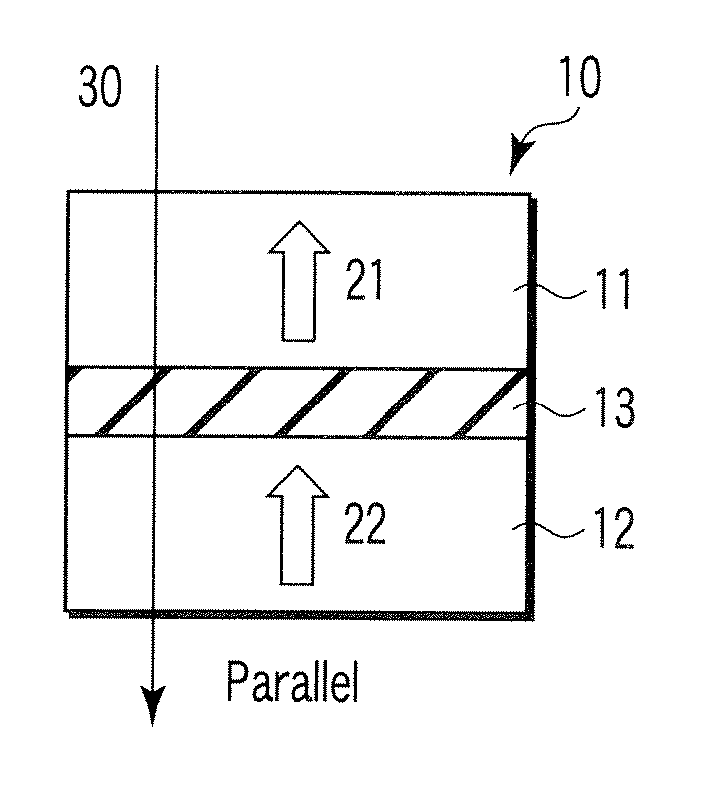
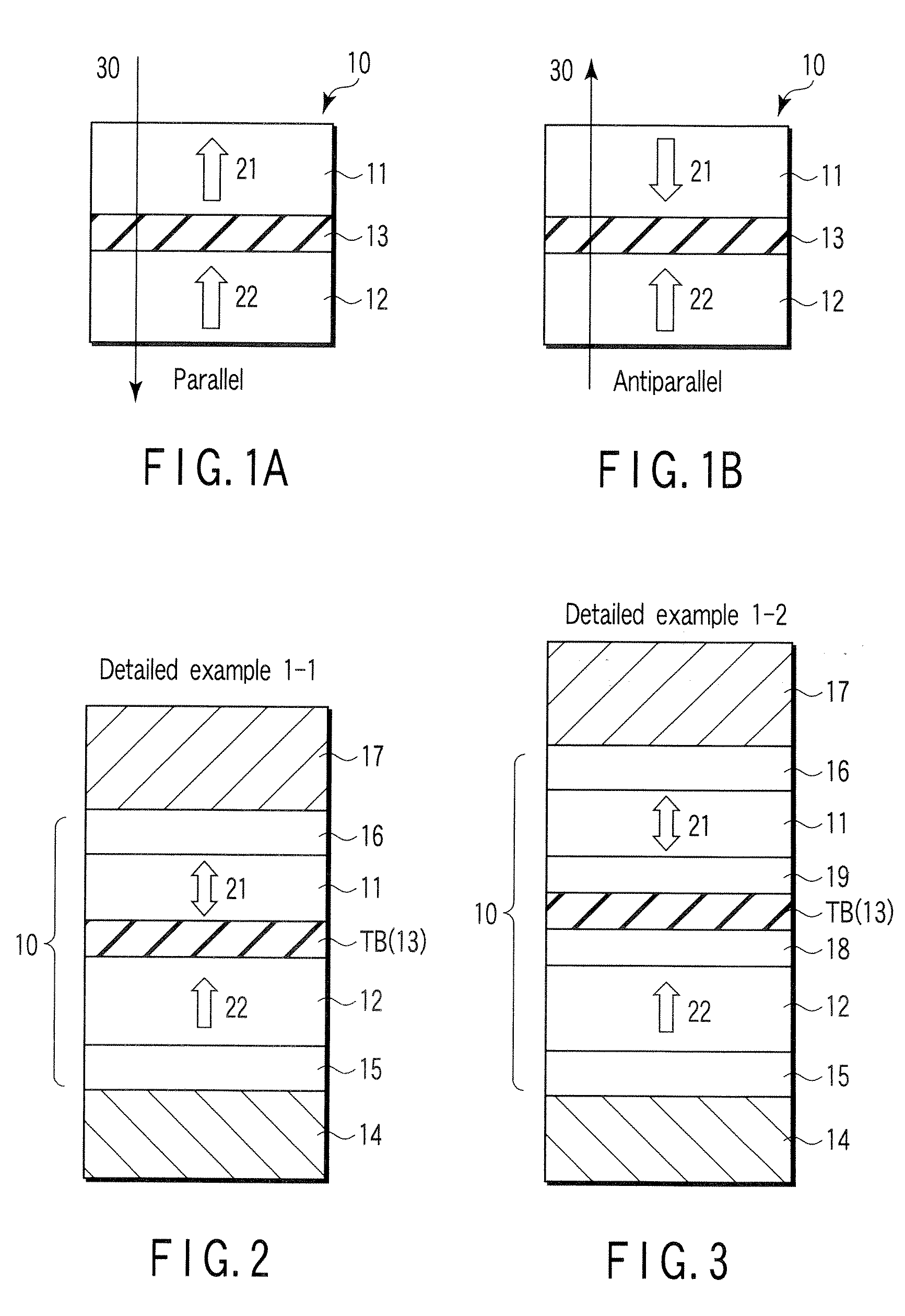
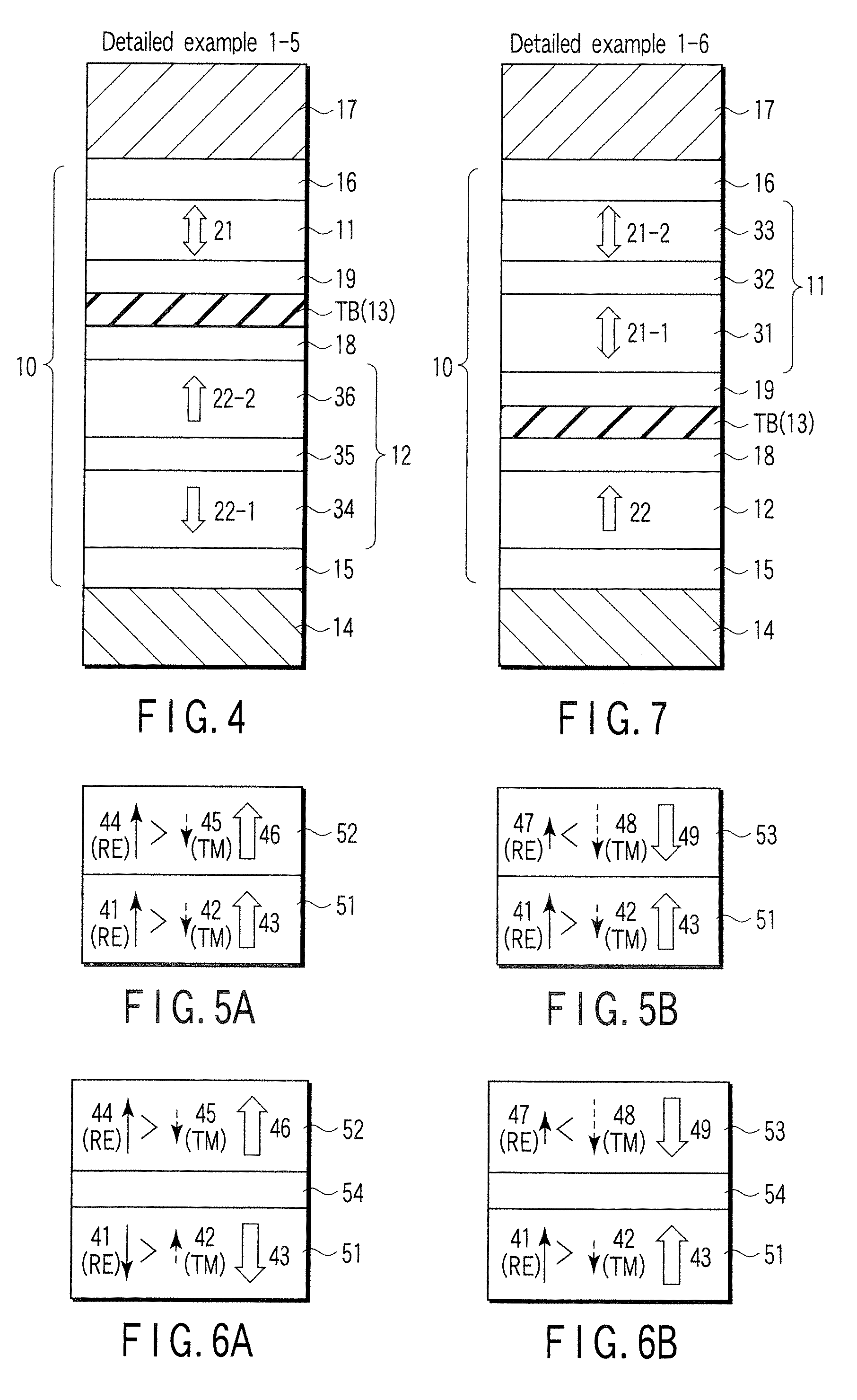
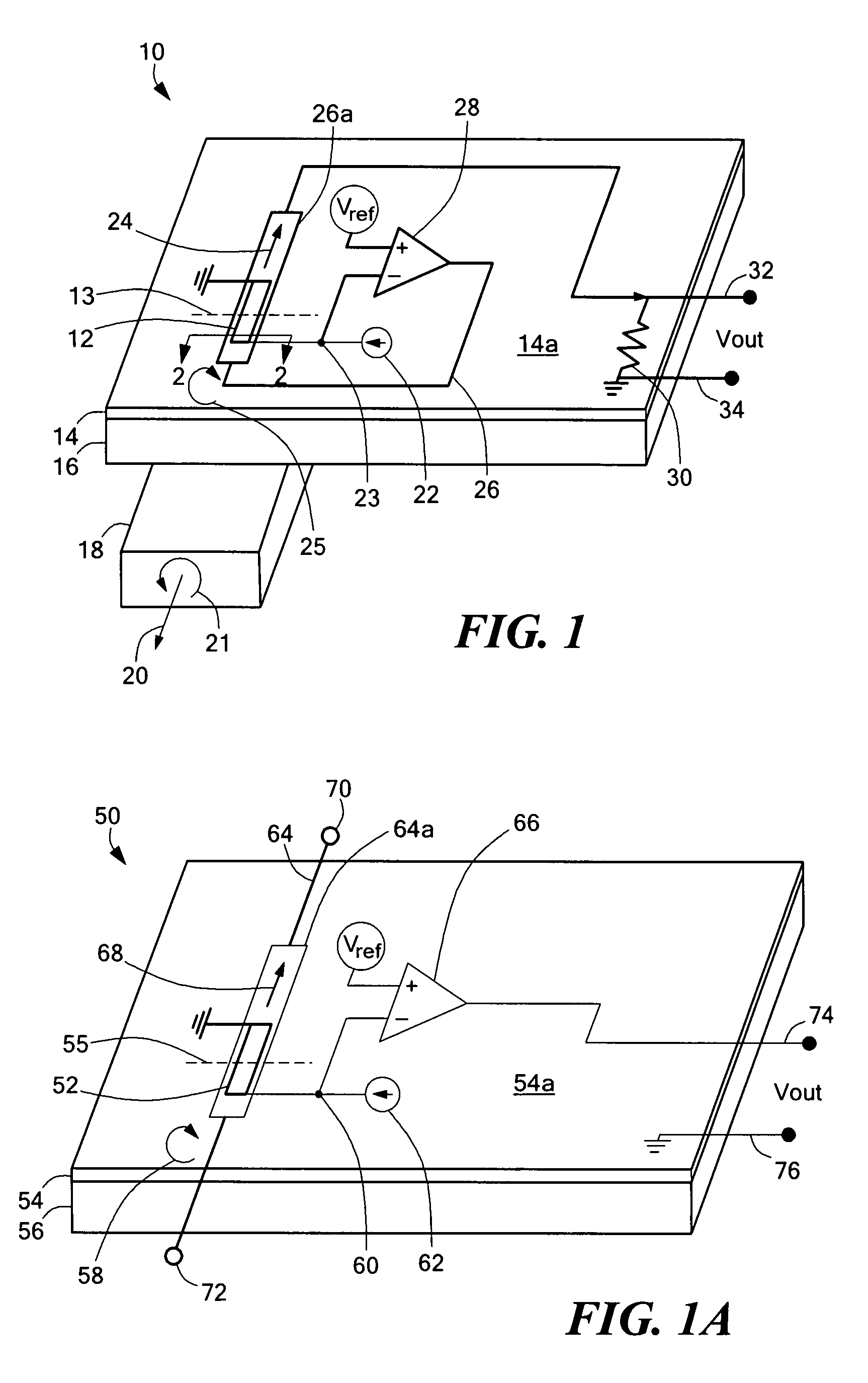
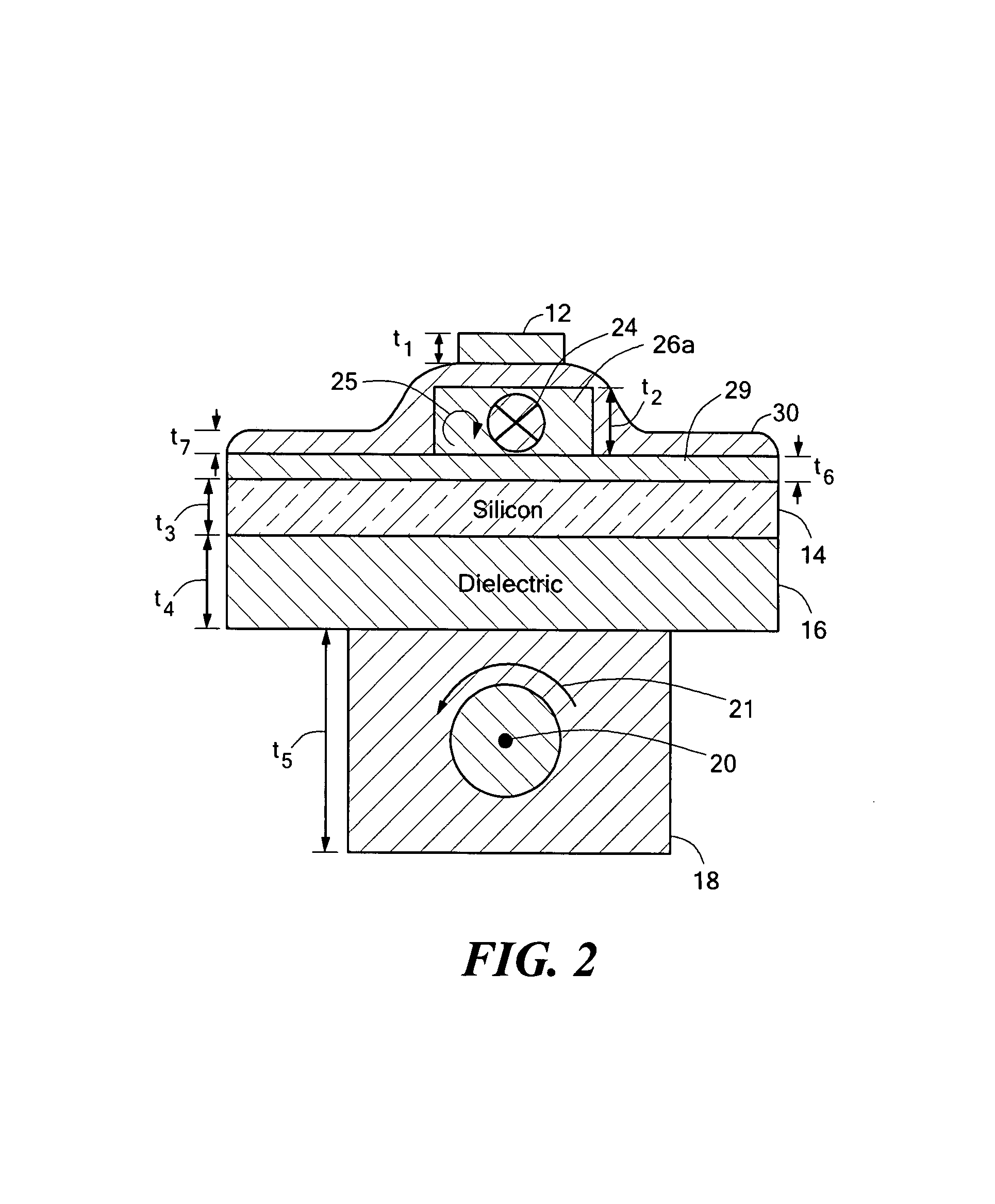
A magnetoresistive element which records information by supplying spin-polarized electrons to a magnetic material, includes a first pinned layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a first magnetization directed in a direction perpendicular to a film surface, a free layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a second magnetization directed in the direction perpendicular to the film surface, the direction of the second magnetization reversing by the spin-polarized electrons, and a first nonmagnetic layer which is provided between the first pinned layer and the free layer. A saturation magnetization Ms of the free layer satisfies a relationship 0≧Ms<√{square root over ( )}{Jw / (6nAt)}. Jw is a write current density, t is a thickness of the free layer, A is a constant.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Method of manufacturing a magnetoresistive-based device
ActiveUS8747680B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic reluctanceHard mask
A method of manufacturing a magnetoresistive-based device having magnetic material layers formed between a first electrically conductive layer and a second electrically conductive layer, the magnetic materials layers including a tunnel barrier layer formed between a first magnetic materials layer and a second magnetic materials layer, including removing the first electrically conductive layer and the first magnetic materials layer unprotected by a first hard mask, to form a first electrode and a first magnetic materials, respectively; and removing the tunnel barrier layer, second magnetic materials layer, and second electrically conductive layer unprotected by the second hard mask to form a tunnel barrier, second magnetic materials, and a second electrode.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
Structure to achieve sensitivity and linear density in tunneling GMR heads using orthogonal magnetic alignments
ActiveUS7035062B1Increase linear densityHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetization
The present invention provides a tunneling magneto-resistive read sensor structure that improves sensitivity and linear density of the sensor structure. The sensor includes first and second electrodes and a stack positioned between the electrodes. The stack includes first and second free layers with magnetization orientations that are biased relative to each other. A tunneling barrier (insulating layer) or non-magnetic metal spacer is positioned between the first and second free layers. A sense current is passed between the first and second free layers of the stack. The amount of current passing through the first and second free layer changes based upon the orientation of the first and second free layers relative to each other.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic thin film memory, method of writing information in it, and me
InactiveUS6226197B1NanoinformaticsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic reluctanceField-effect transistor
The present invention relates to a magnetic thin film memory having a hybrid element including a field effect transistor and a magnetoresistive thin film connected to the field effect transistor in parallel. In the magnetic thin film memory, the hybrid element is preferably arranged in plurality in a matrix state. The present invention also relates to a method of writing information in this magnetic thin film memory, and a method of reading the information written in this magnetic thin film memory.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20070297220A1Easily magnetizedNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeInter layer
A magnetoresistive includes a first magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a magnetic free layer having a magnetization direction which is changeable by being supplied with spin polarized electrons, a second magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a first intermediate layer provided between the first magnetic reference layer and the magnetic free layer, and a second intermediate layer provided between the magnetic free layer and the second magnetic reference layer. The magnetic free layer and the first magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular or parallel to an in-plane direction. The first magnetic reference layer and the second magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Integrated sensor
ActiveUS7259545B2Measurement using dc-ac conversionMagnetic measurementsResistive couplingElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Hybrid write mechanism for high speed and high density magnetic random access memory
A method of writing to a magnetic random access memory comprising: producing a magnetic field along a magnetically hard axis of a free layer of a magnetoresistive element; and passing current through the magnetoresistive element to change a direction of magnetization of the free layer by spin momentum transfer. A magnetic random access memory that operates in accordance with the method is also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
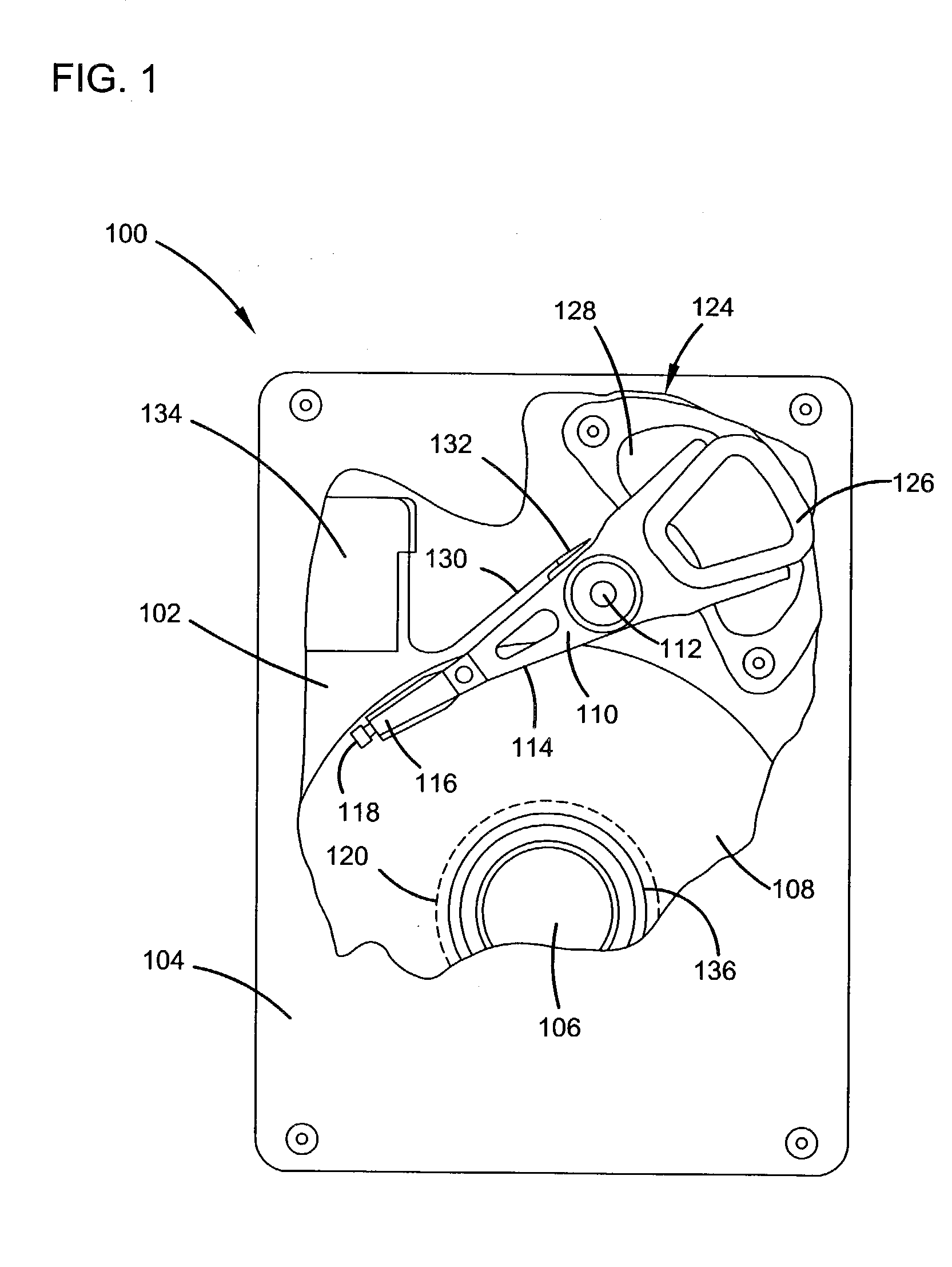
Method and devices for providing magnetoresistive heads with protection from electrostatic discharge and electric overstress events
InactiveUS6891702B1Electrical connection between head and armRecord information storageDisk packClassical mechanics
A disk drive includes a disk having a recording surface, a head stack assembly that includes a body portion, an actuator arm cantilevered from the body portion and a head gimbal assembly supported at the actuator arm. The head gimbal assembly includes a suspension having a first end and a second end, the first end being attached to the actuator arm, a slider coupled to the second end of the suspension, the slider comprising a transducer for reading from and writing to the recording surface. A gimbal is coupled to the second end of the suspension and to the slider. An array of diodes is attached to the suspension to protect the transducer from electrostatic discharge or electrical overstress events.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
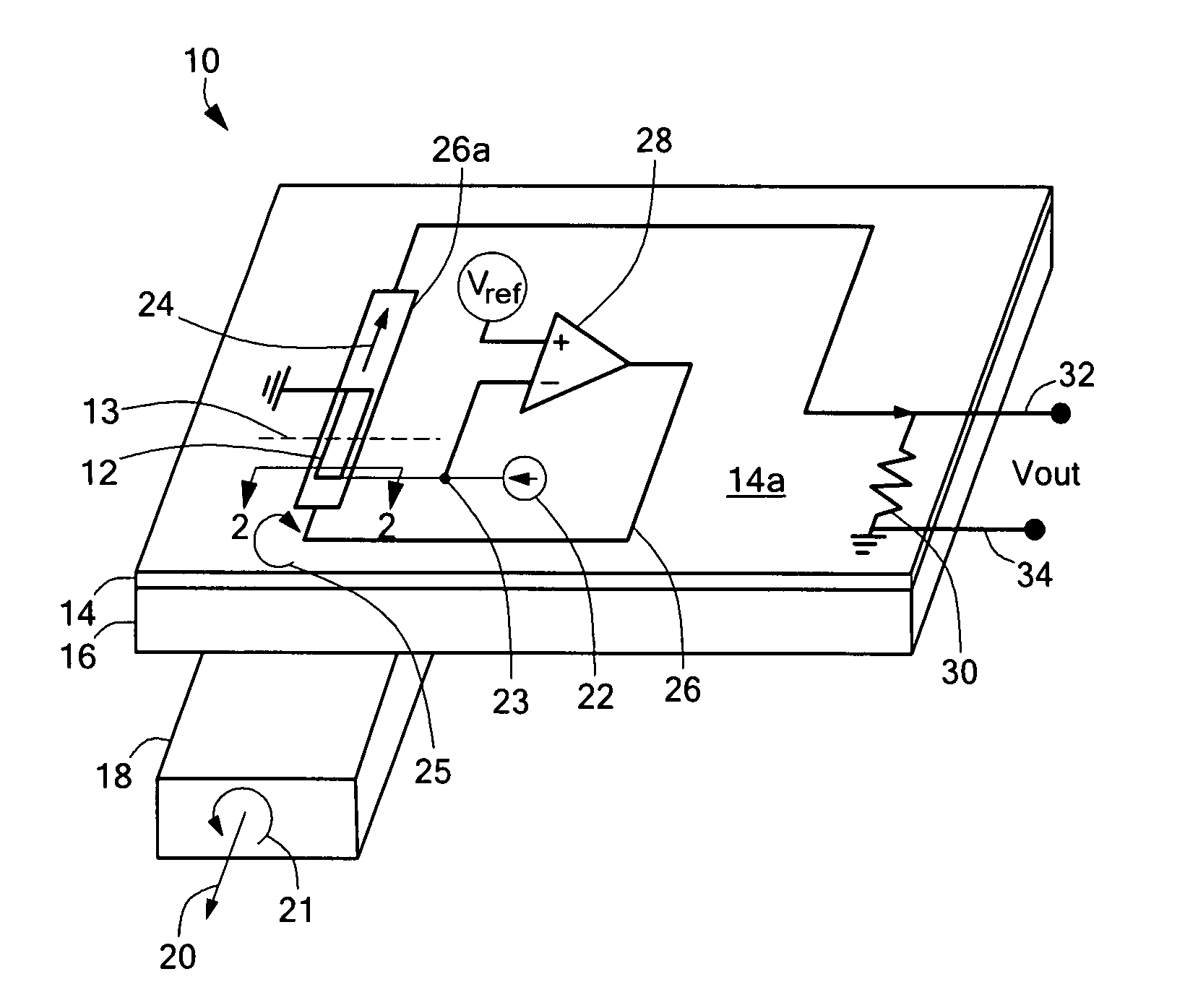
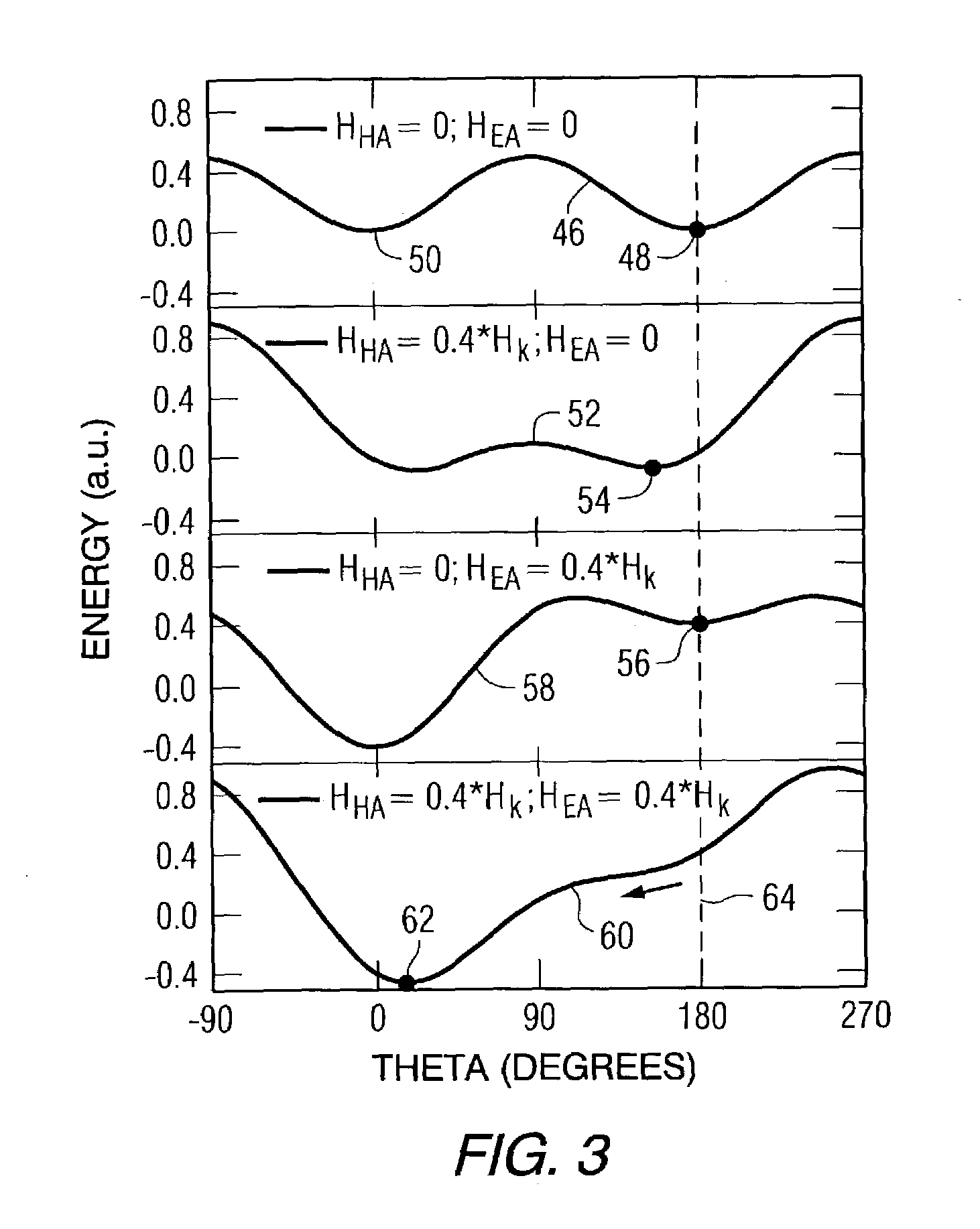
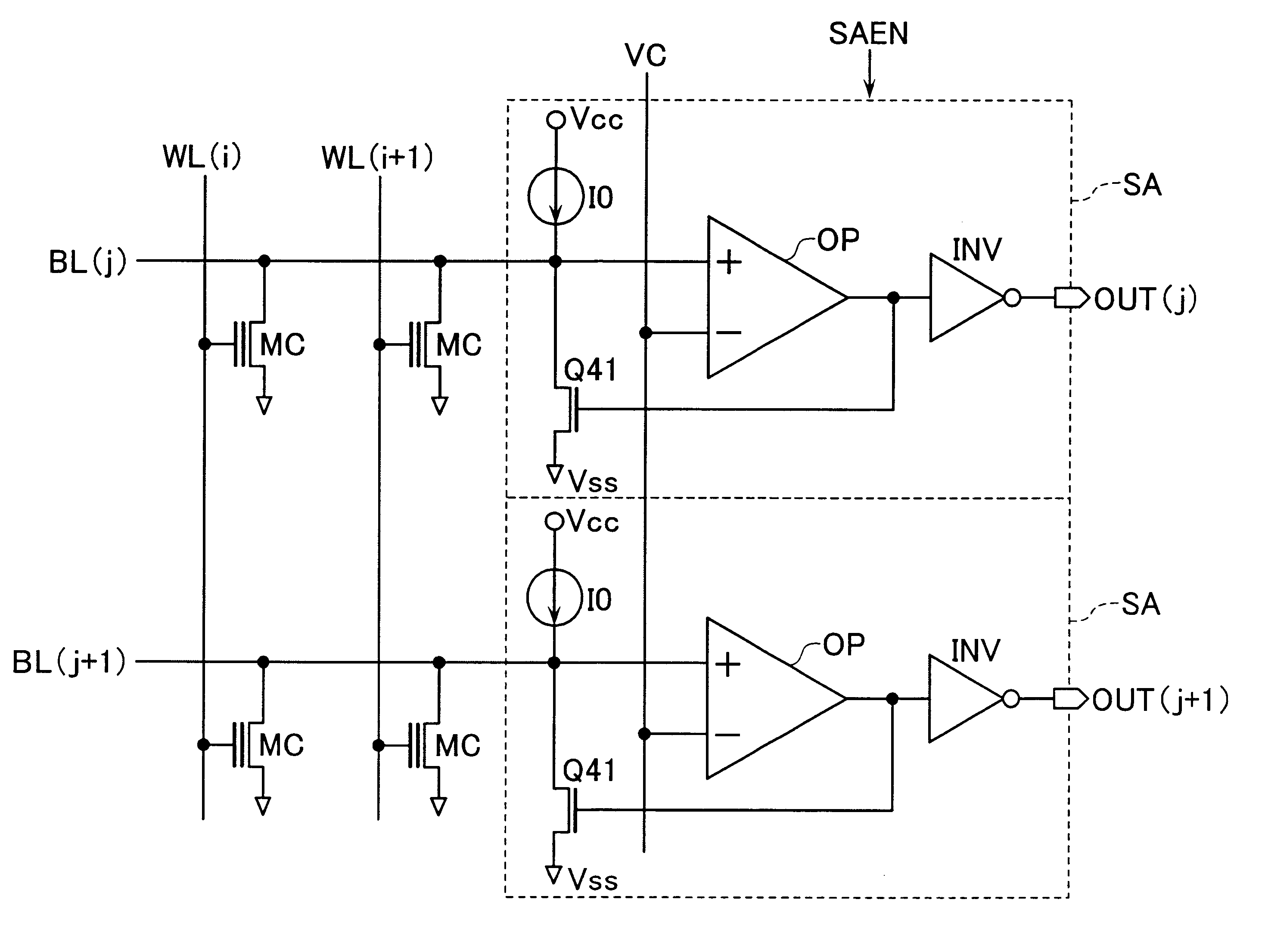
Magnetoresistive memory device
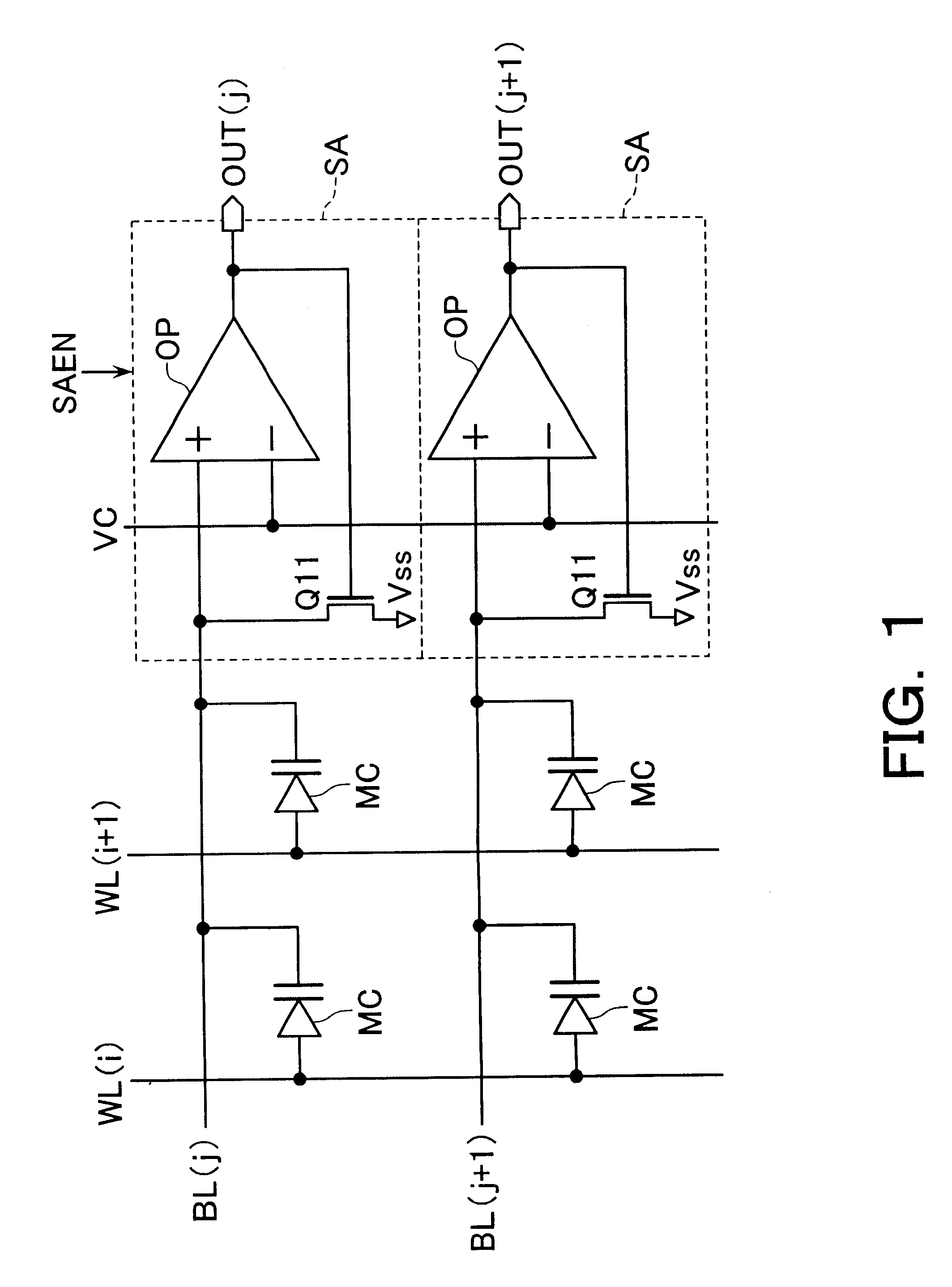
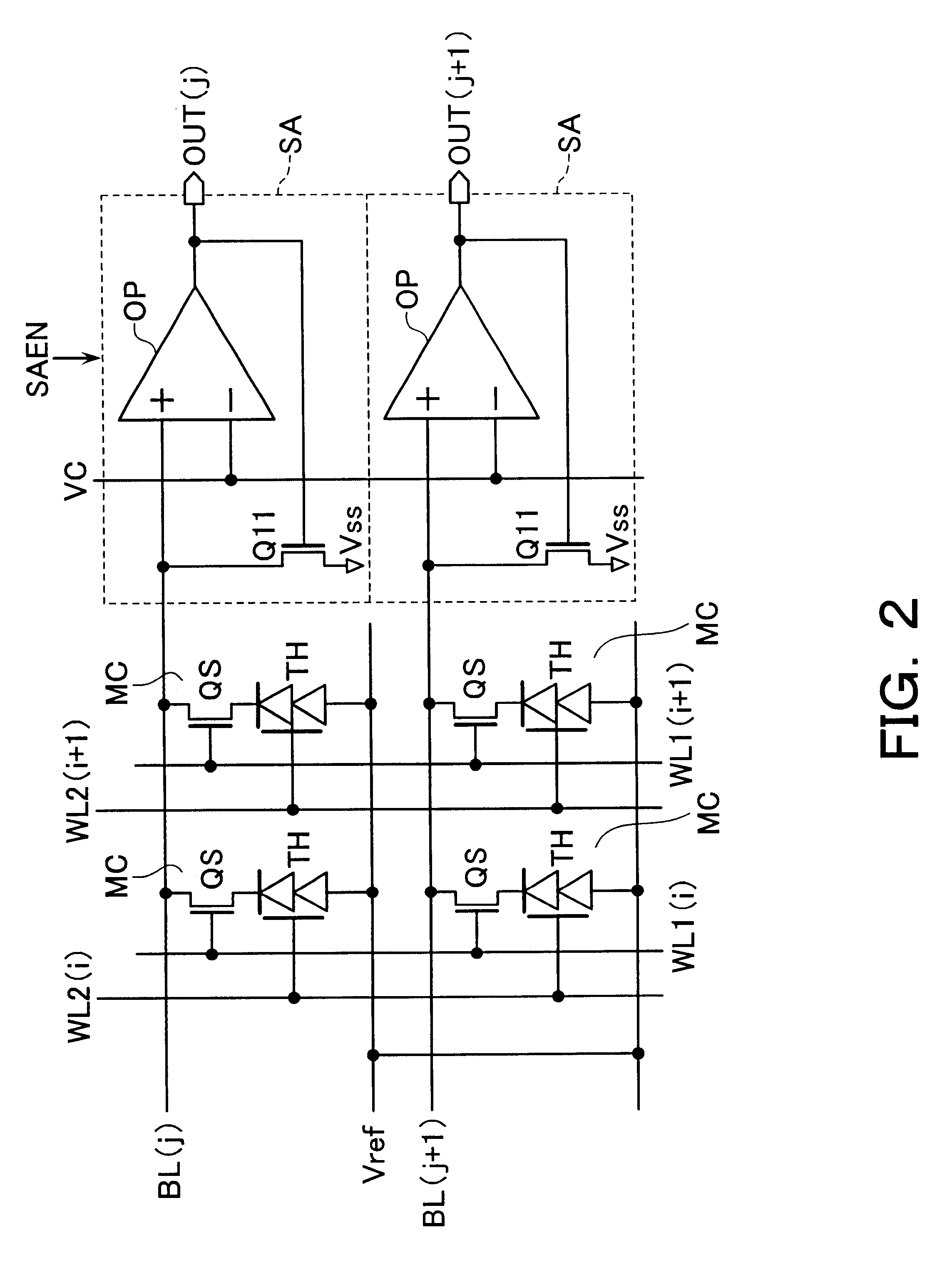
An integrated semiconductor memory device with an array of memory cells MC using magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cells is disclosed. A sense amplifier SA that is connected to a bit line BL for data readout of a selected memory cell MC is arranged using an operational amplifier OP. The operational amplifier OP has an inverting input terminal which is connected to the bit line BL and a non-inverting input terminal, to which a potentially fixed constant voltage VC is given. A PMOS transistor Q31 is provided, which can also do double-duty as a current source load. This PMOS transistor has its drain and gate that are connected to the inverting input terminal, and a source as connected to an output terminal of the operational amplifier OP whereby the transistor is under feedback control in response to an output of the operational amplifier OP so that a clamped voltage potential of the bit lime BL is fixed to the voltage VC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
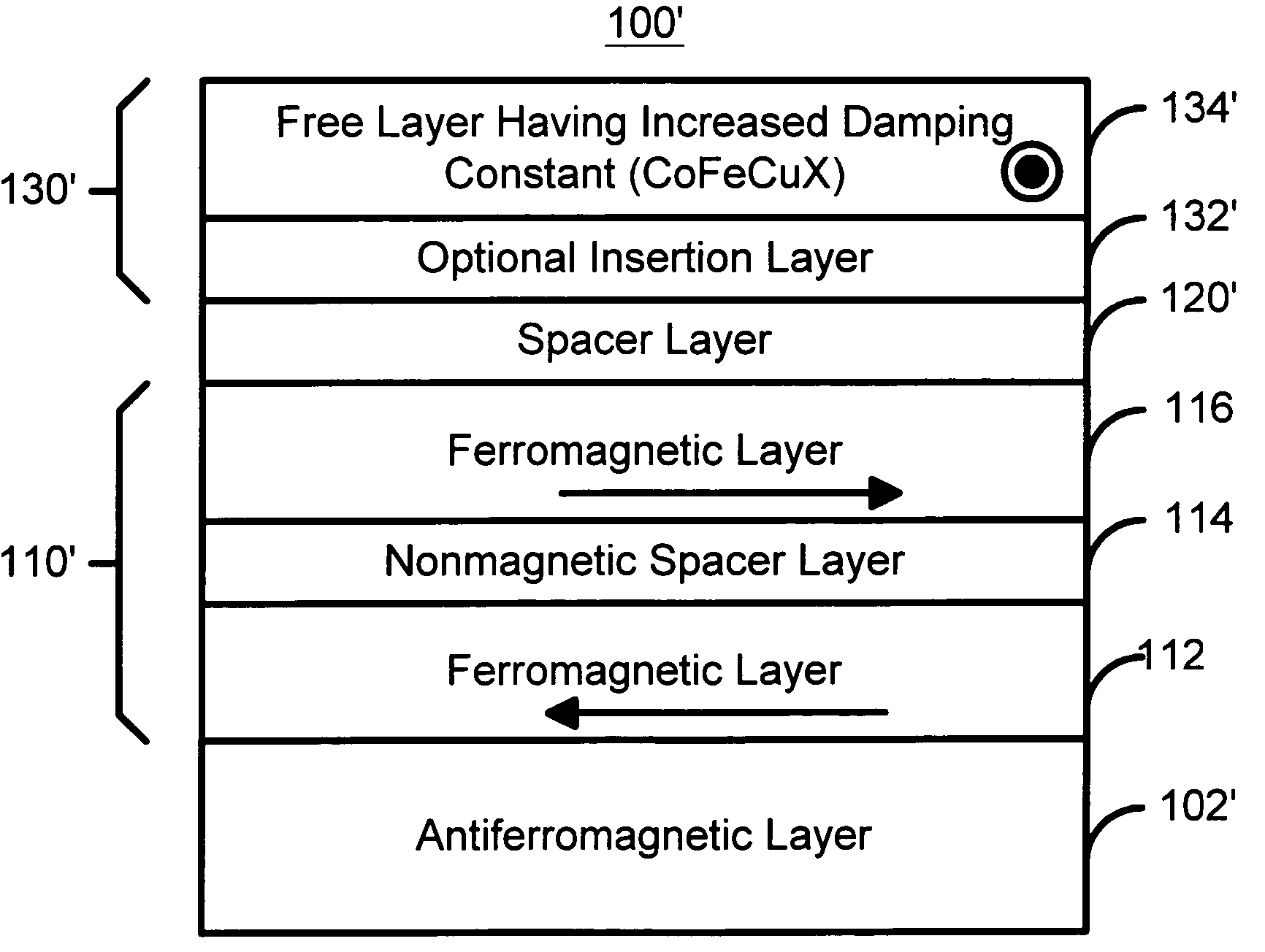
Magnetoresistive element having reduced spin transfer induced noise
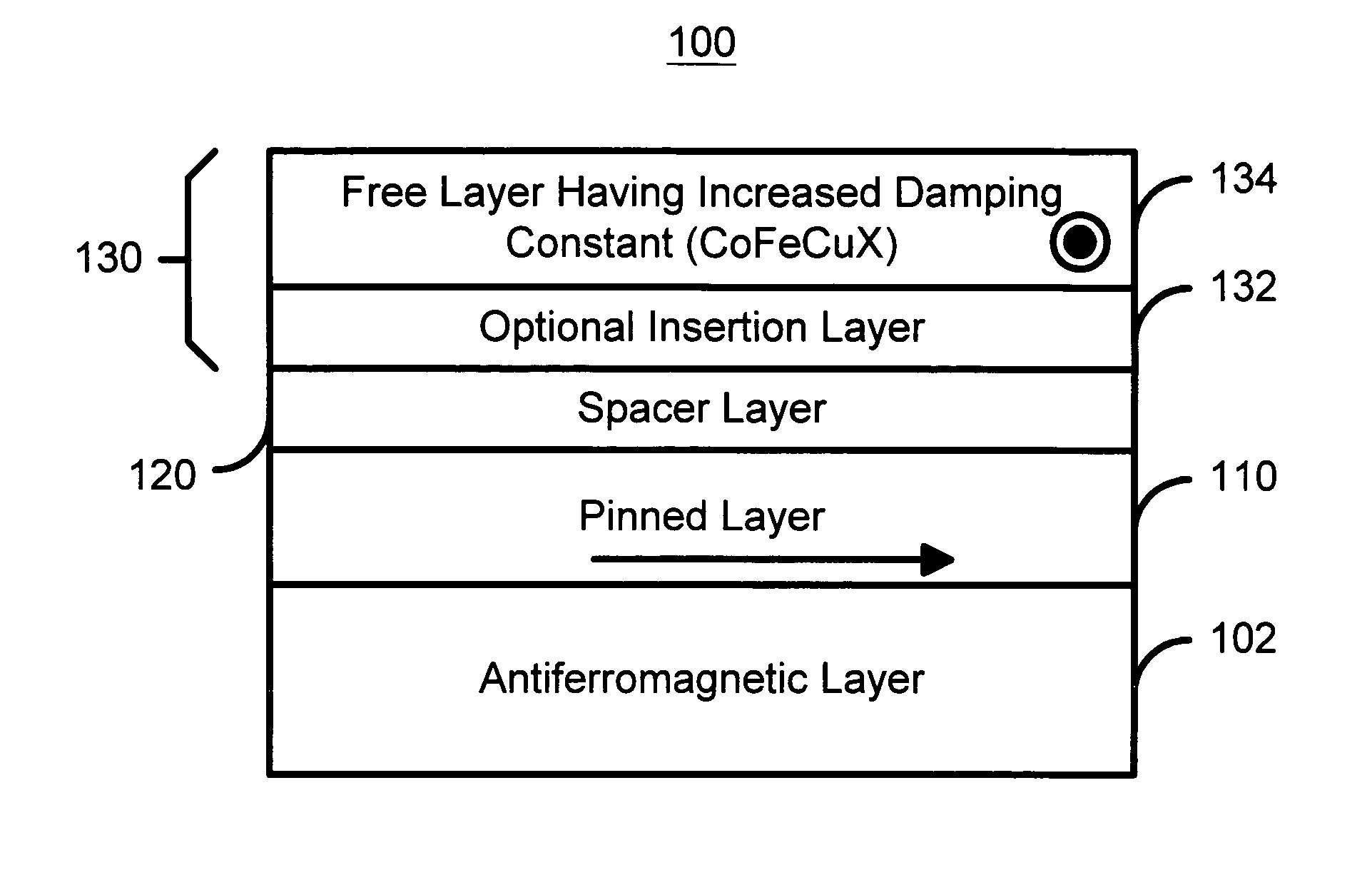
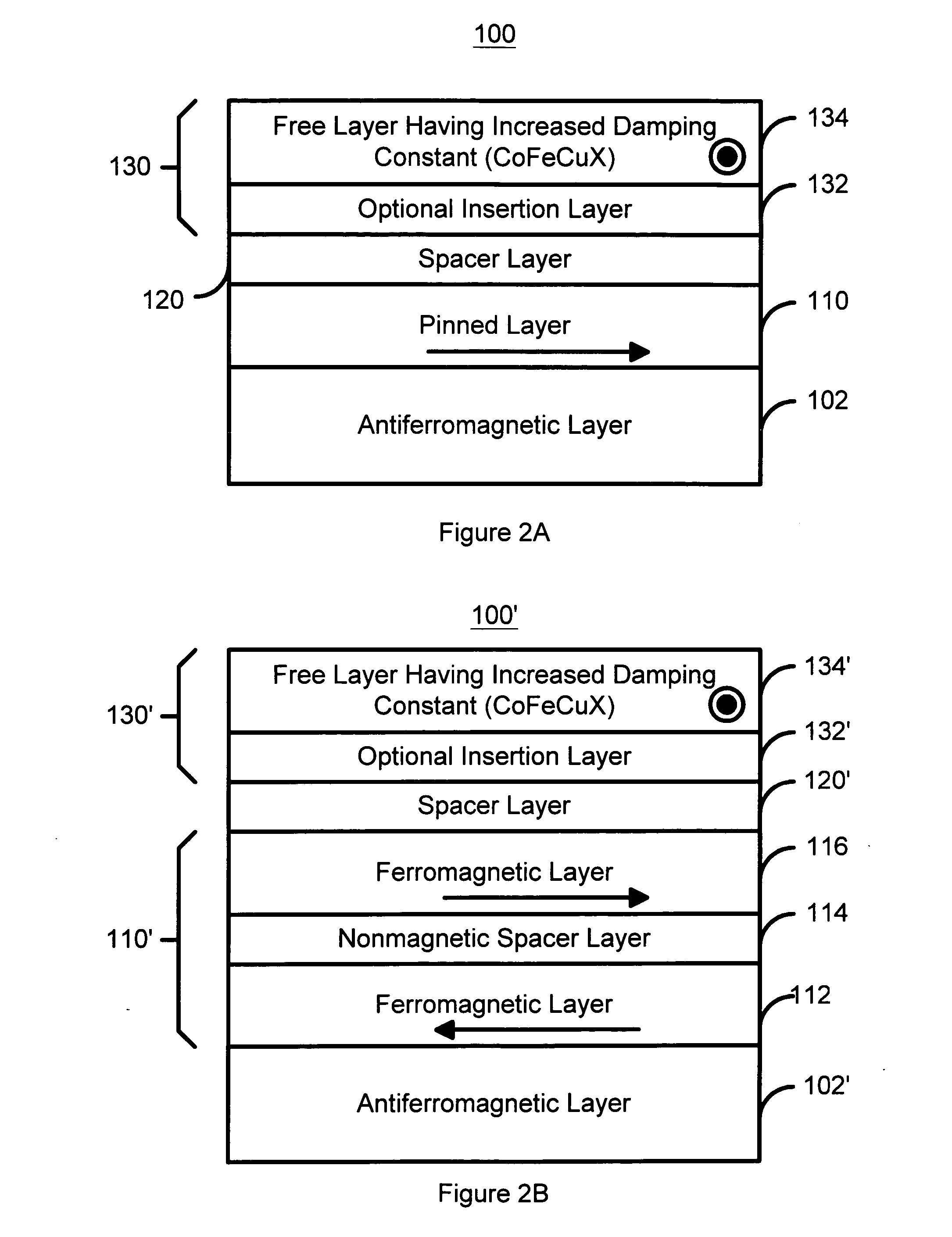
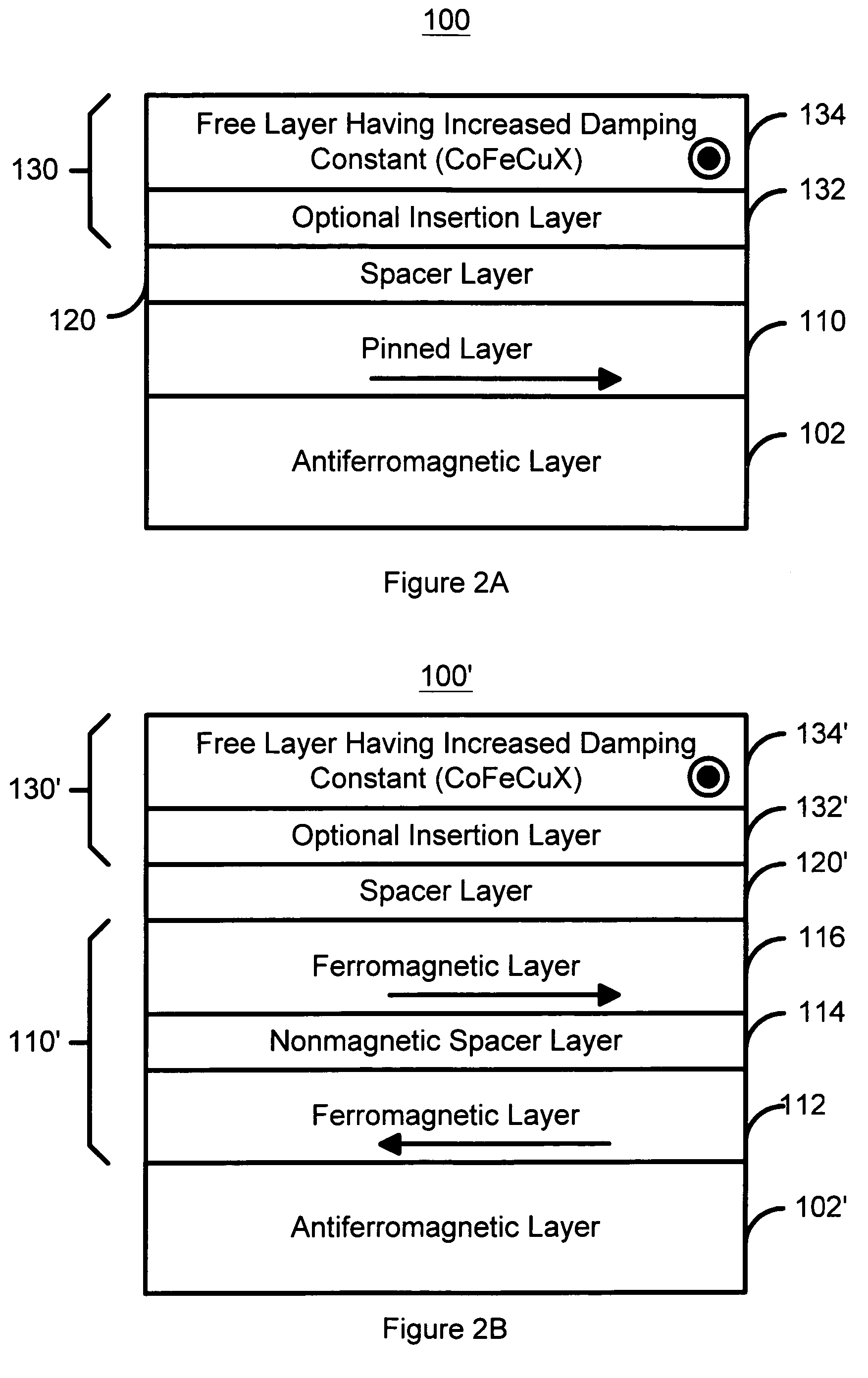
InactiveUS20050041342A1Increased magnetic damping constantNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceSpin transfer
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The method and system include providing a ferromagnetic pinned layer, providing a free layer, and providing a spacer layer between the pinned layer and the free layer. The pinned layer and free layer are ferromagnetic and have a pinned layer magnetization and a free layer magnetization, respectively. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic. In one aspect, the free layer is configured to have an increased magnetic damping constant. In another aspect, the method and system also include providing a second pinned layer and a second spacer layer between the free layer and the second pinned layer. In this aspect, the first pinned layer and / or the second pinned layer are configured such that a forward torque and a reflected torque due to a current driven through the magnetic element in a current-perpendicular-to-plane configuration are substantially equal and opposite.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Magnetic elements with ballistic magnetoresistance utilizing spin-transfer and an MRAM device using such magnetic elements
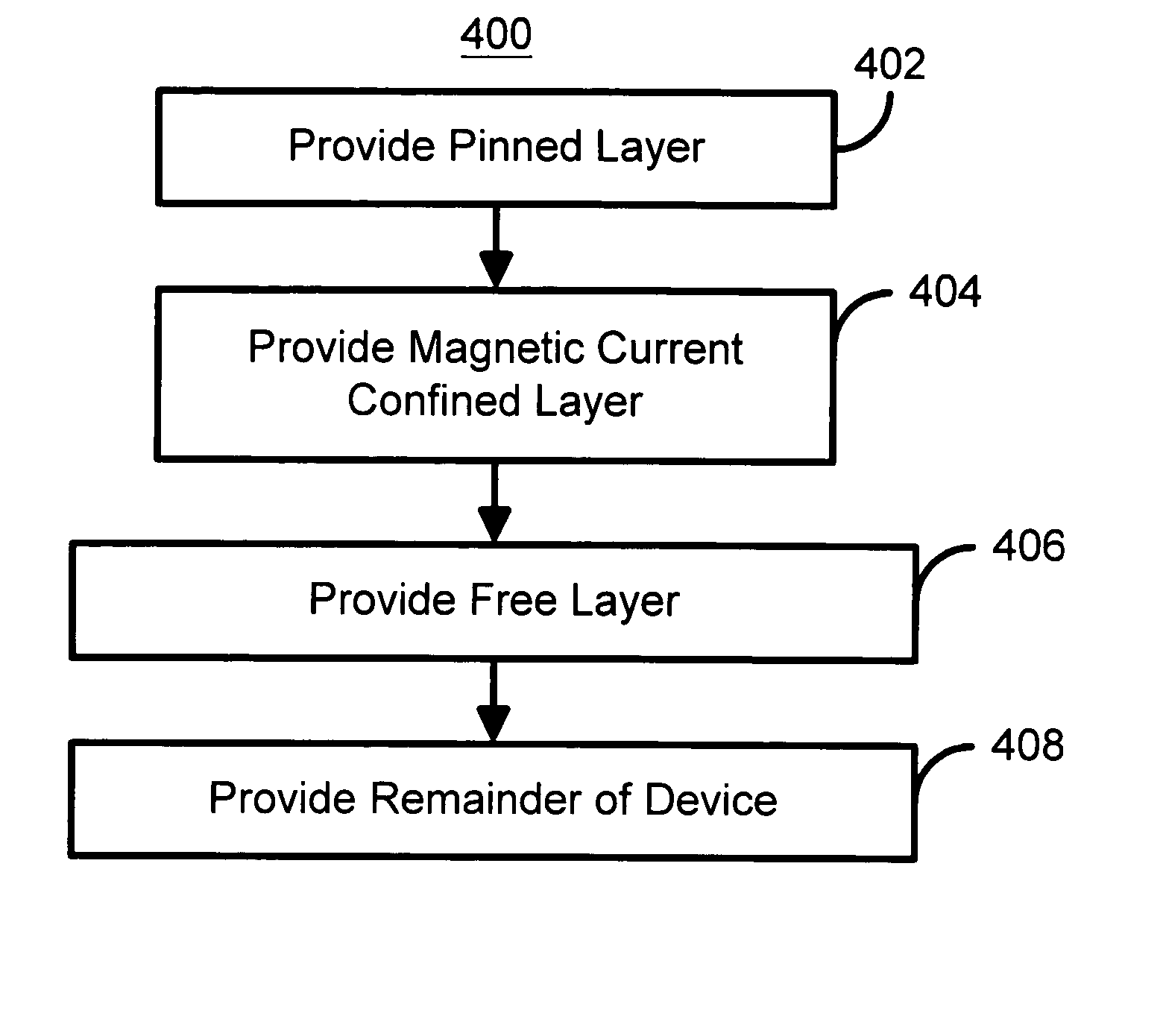
InactiveUS20050136600A1Improve signal outputTransistorNanostructure applicationMagnetic currentCharge carrier
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The method and system include providing a pinned layer, a magnetic current confined layer, and a free layer. The pinned layer is ferromagnetic and has a first pinned layer magnetization. The magnetic current confined layer has at least one channel in an insulating matrix and resides between the pinned layer and the free layer. The channel(s) are ferromagnetic, conductive, and extend through the insulating matrix between the free layer and the pinned layer. The size(s) of the channel(s) are sufficiently small that charge carriers can give rise to ballistic magnetoresistance in the magnetic current confined layer. The free layer is ferromagnetic and has a free layer magnetization. Preferably, the method and system also include providing a second pinned layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the second pinned layer and the free layer. In this aspect, the magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer magnetization to be switched using spin transfer.
Owner:GRANDIS
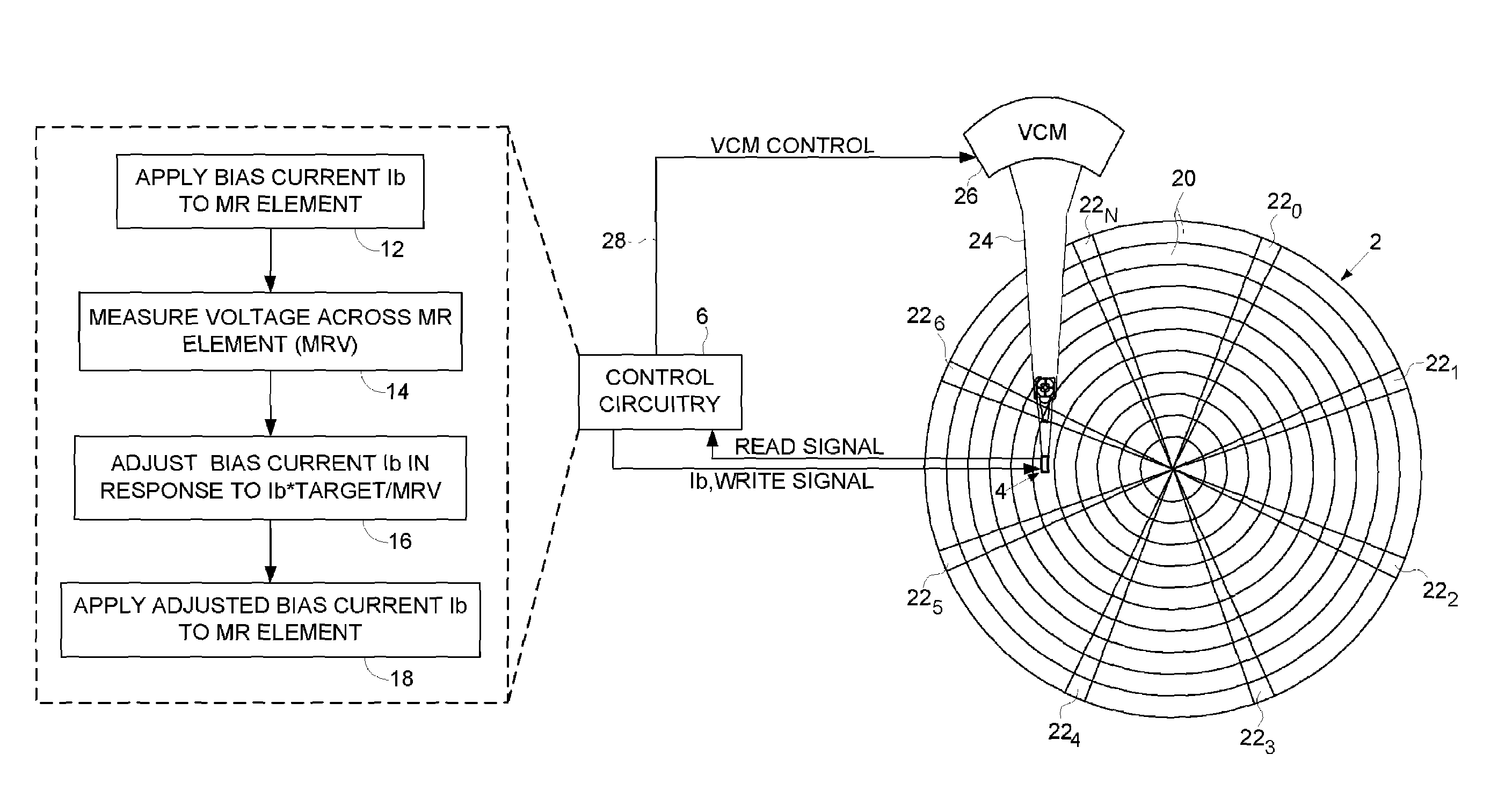
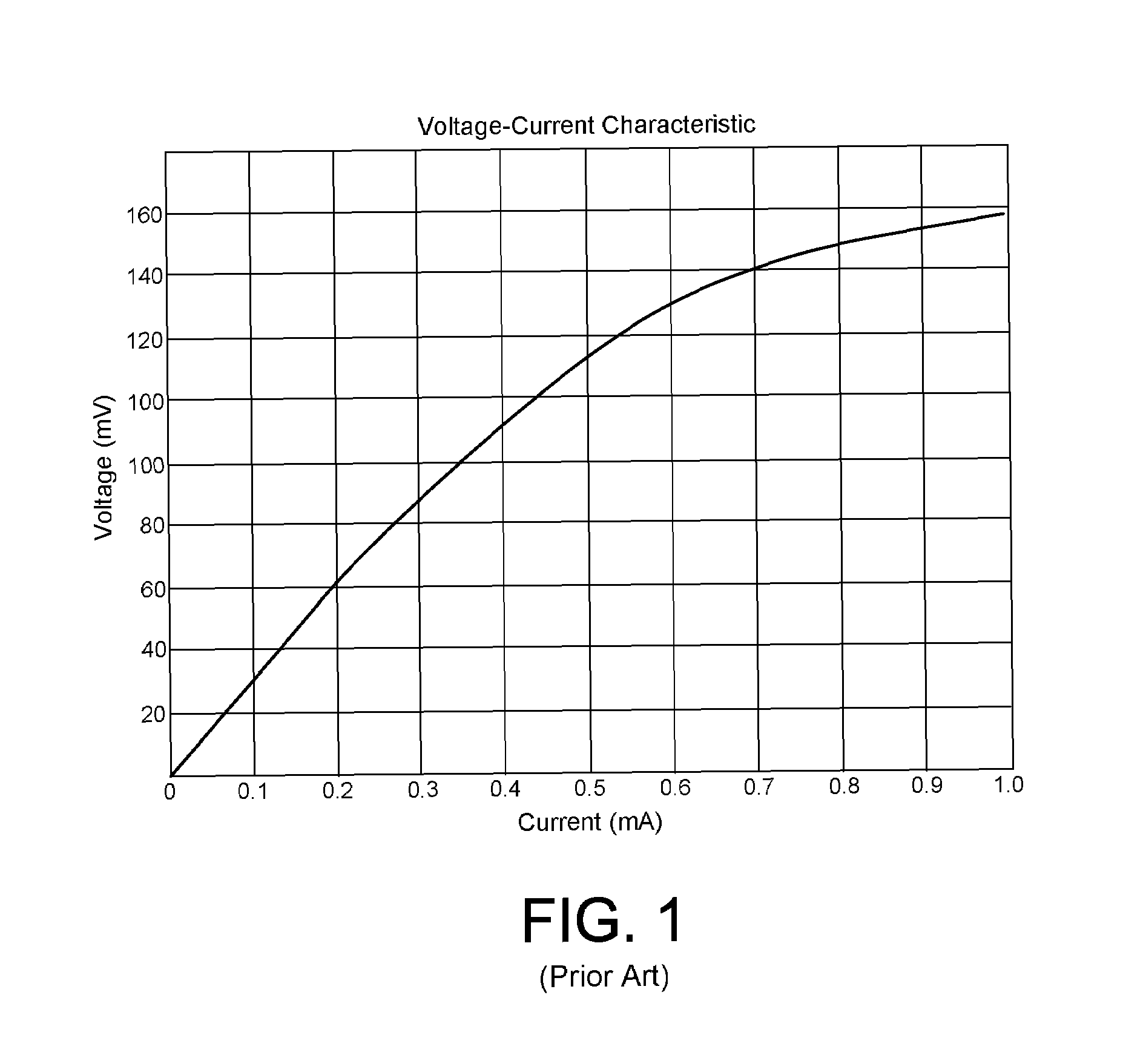
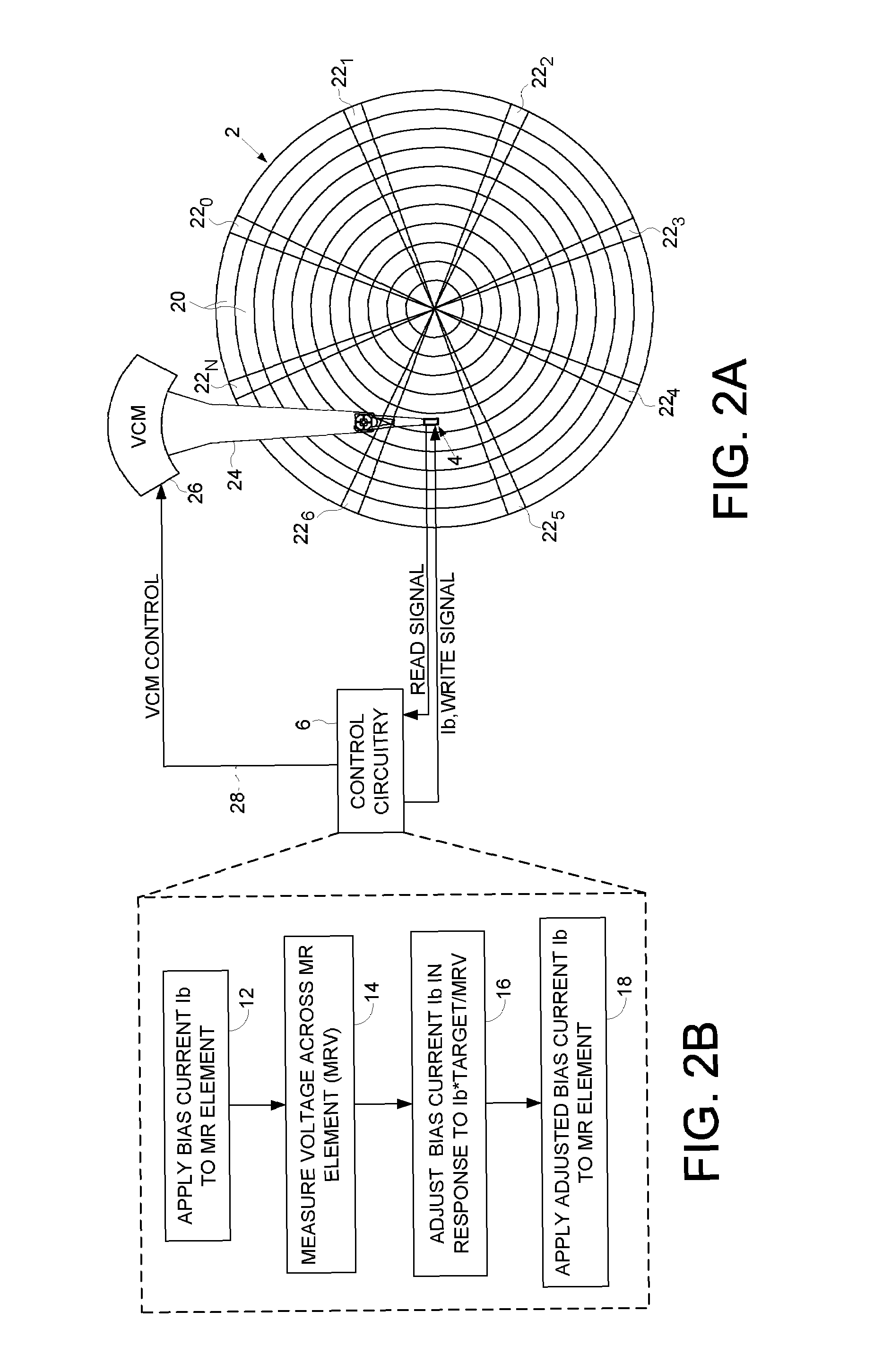
Setting an operating bias current for a magnetoresistive head using ratio of target voltage and measured voltage
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
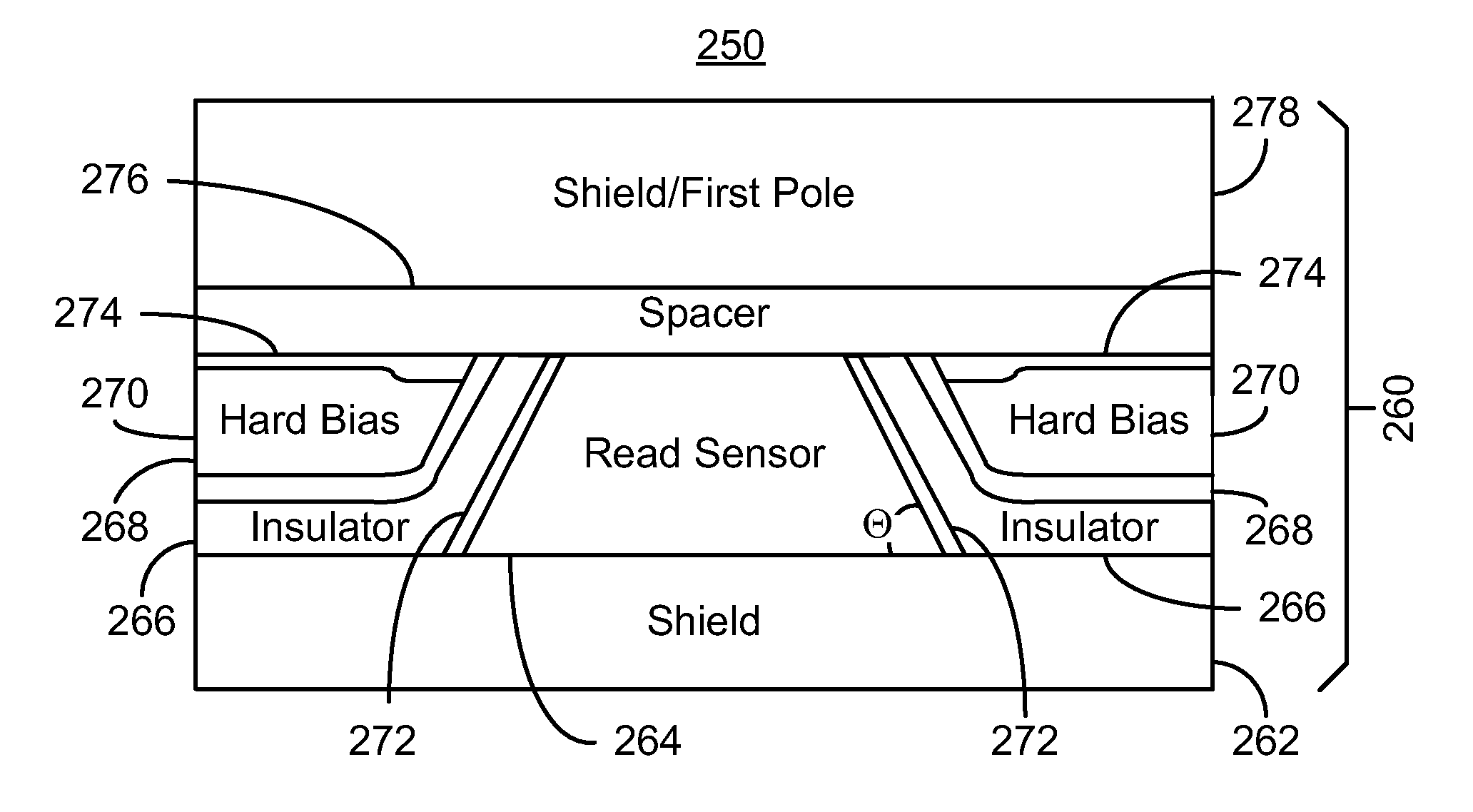
Magnetoresistive read sensor with reduced effective shield-to-shield spacing
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
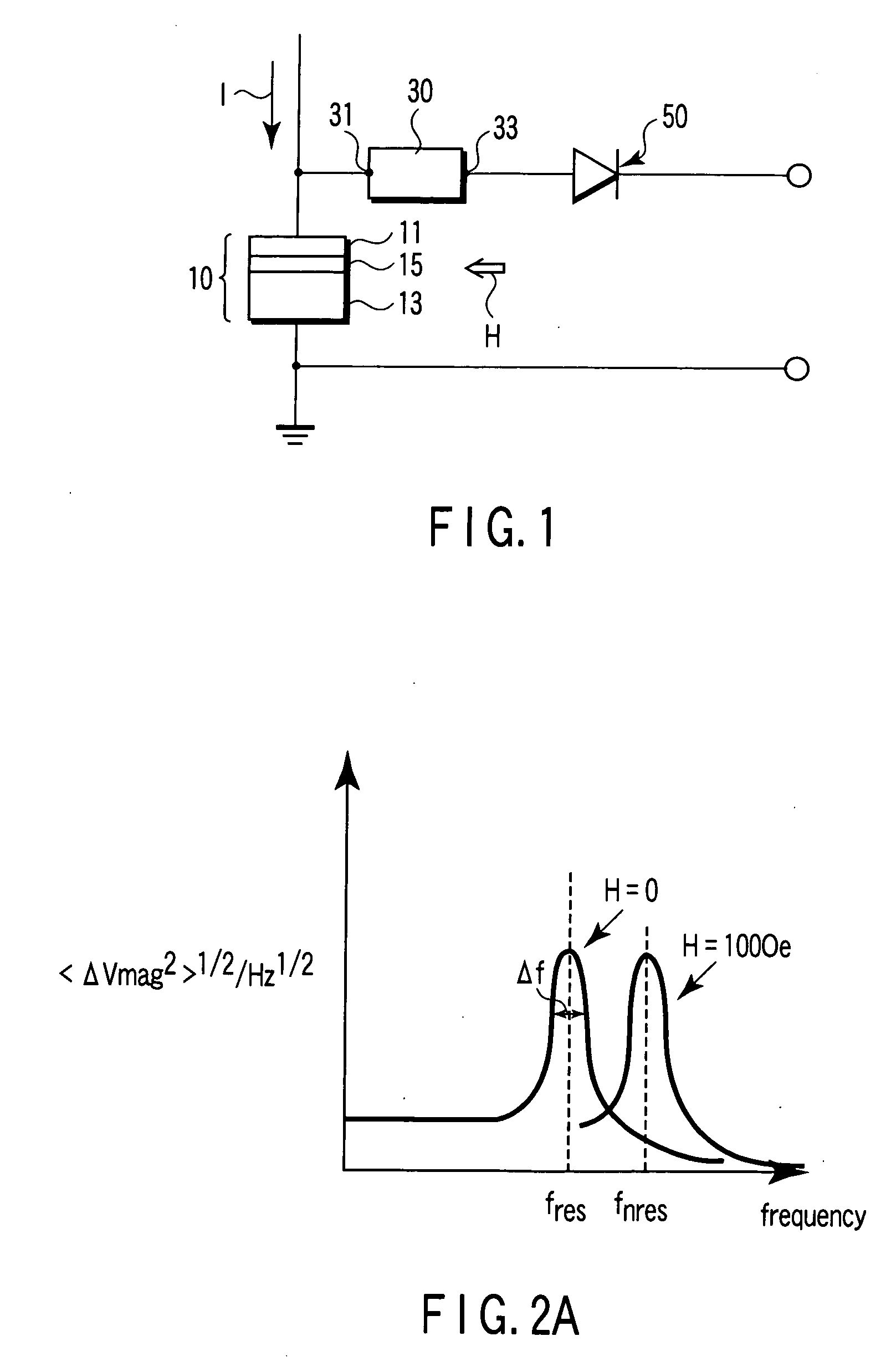
Magnetic sensor, magnetic field sensing method, semagnetic recording head, and magnetic memory device
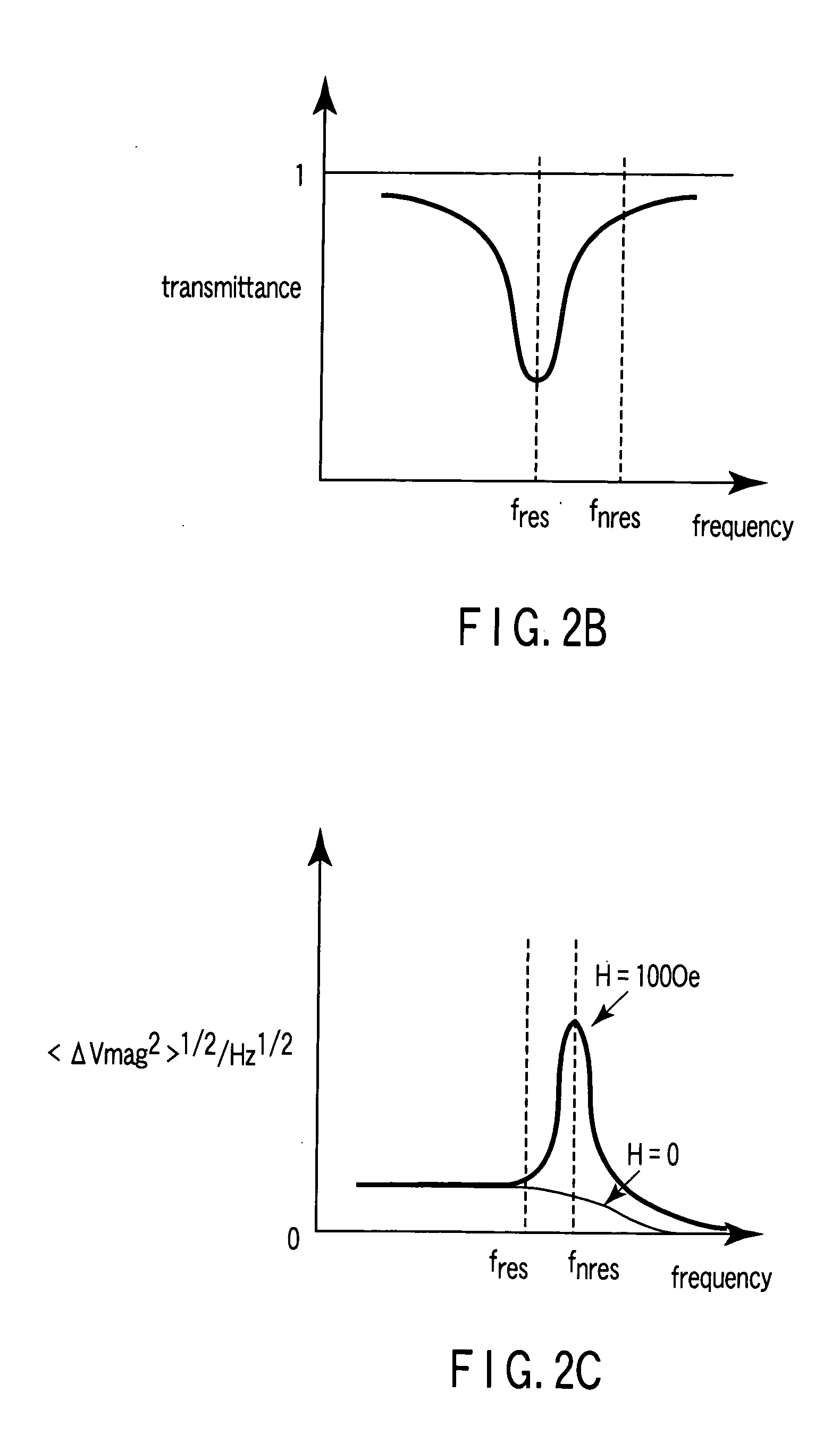
ActiveUS20050219771A1Modification of read/write signalsNanomagnetismFrequency filteringMagnetization
A magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistance element having a peak of a thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization under a magnetic field having a certain frequency, a frequency filter connected to the magnetoresistance element and having its transmittance decreased or increased in substantially the frequency of the magnetic field to output a signal corresponding substantially to the peak of the thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization, and a detector connected to the frequency filter to detect the magnetic field based on the signal of the frequency filter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
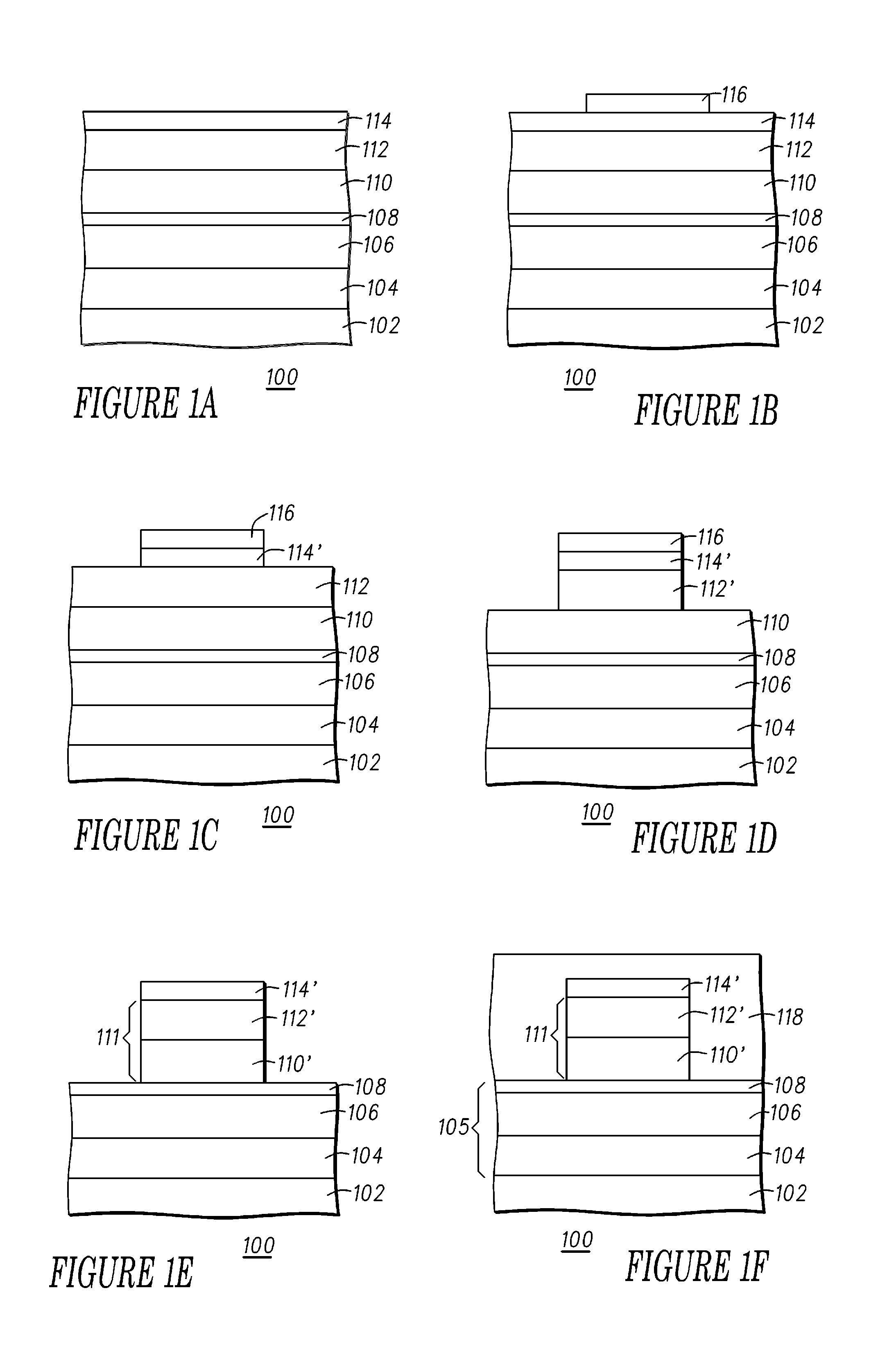
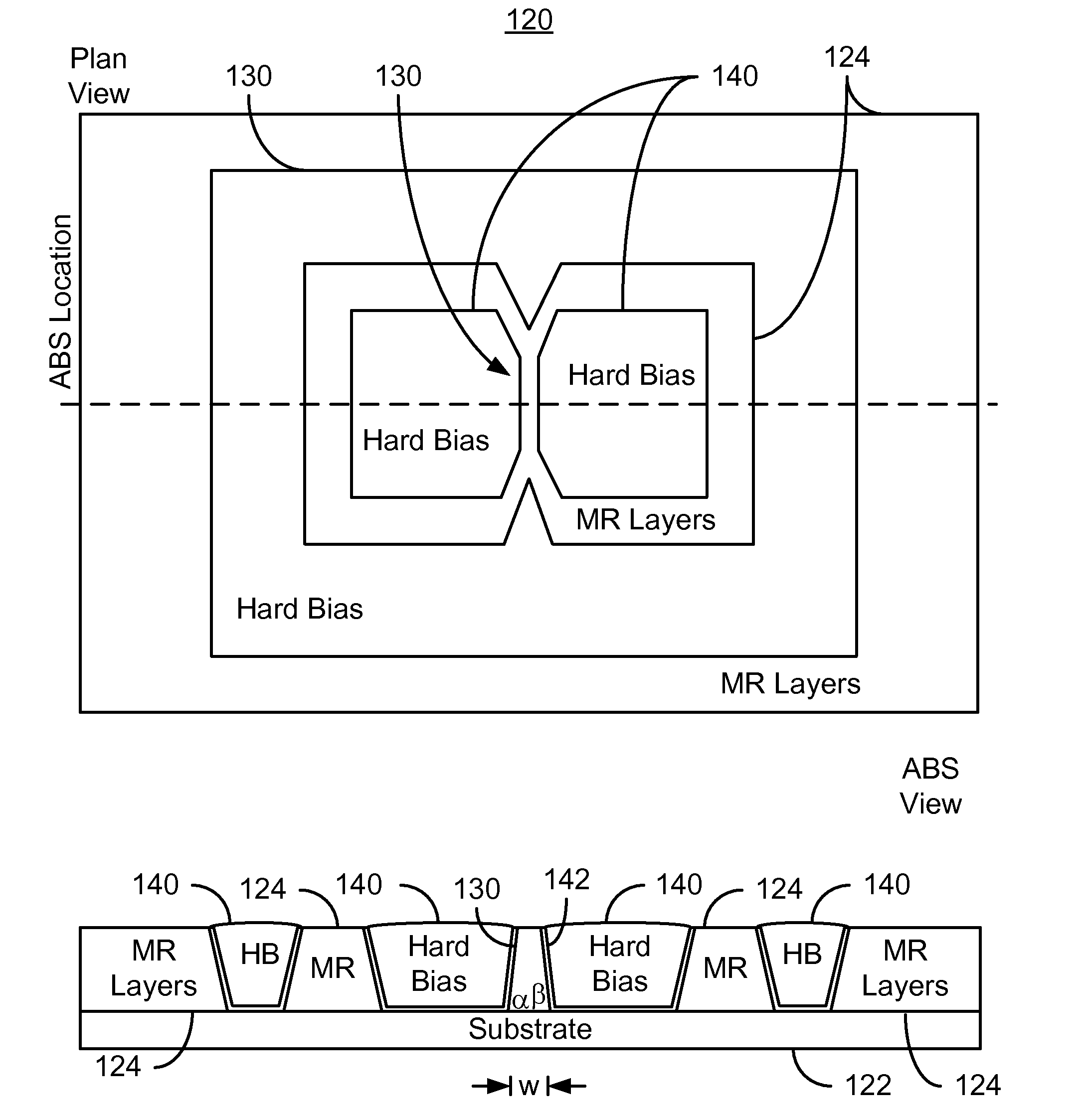
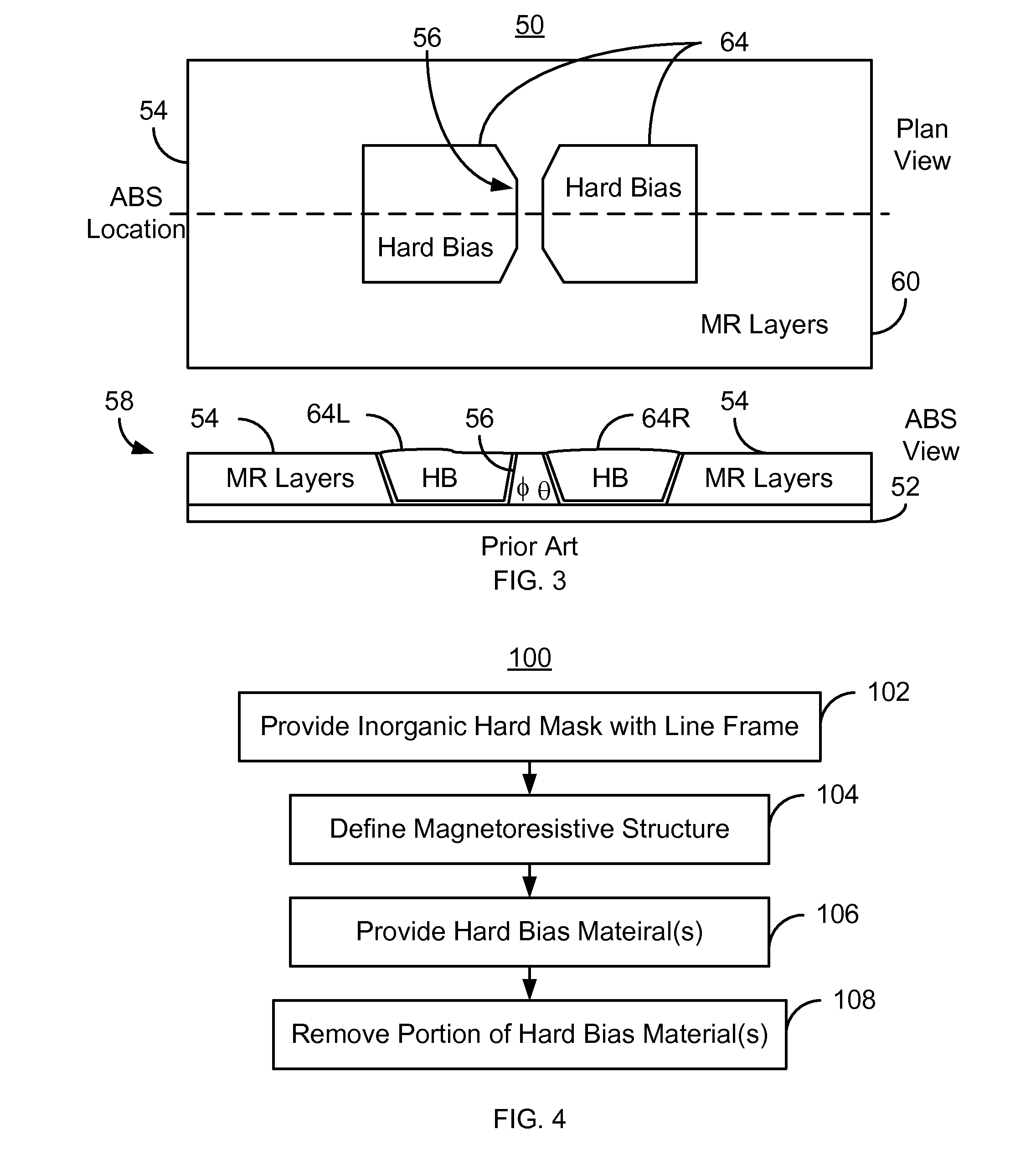
Method and system for providing a magnetic recording transducer using a line hard mask
InactiveUS8233248B1Electrical transducersMagnetic measurementsMagnetic transducersMagnetic reluctance
A method and system for fabricating a magnetic transducer is described. The transducer has a device region, a field region, and a magnetoresistive stack. The method and system include providing a hard mask on the magnetoresistive stack. The hard mask is inorganic and includes a sensor portion and a line frame. The sensor portion covers a first portion of the magnetoresistive stack corresponding to a magnetoresistive structure. The line frame covers a second portion of the magnetoresistive stack in the device region. The method and system include defining the magnetoresistive structure in a track width direction using the hard mask and providing at least one hard bias material after the magnetoresistive structure is defined. A first portion of the hard bias material(s) is substantially adjacent to the magnetoresistive structure in the track width direction. The method and system also include removing a second portion of the hard bias material(s).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
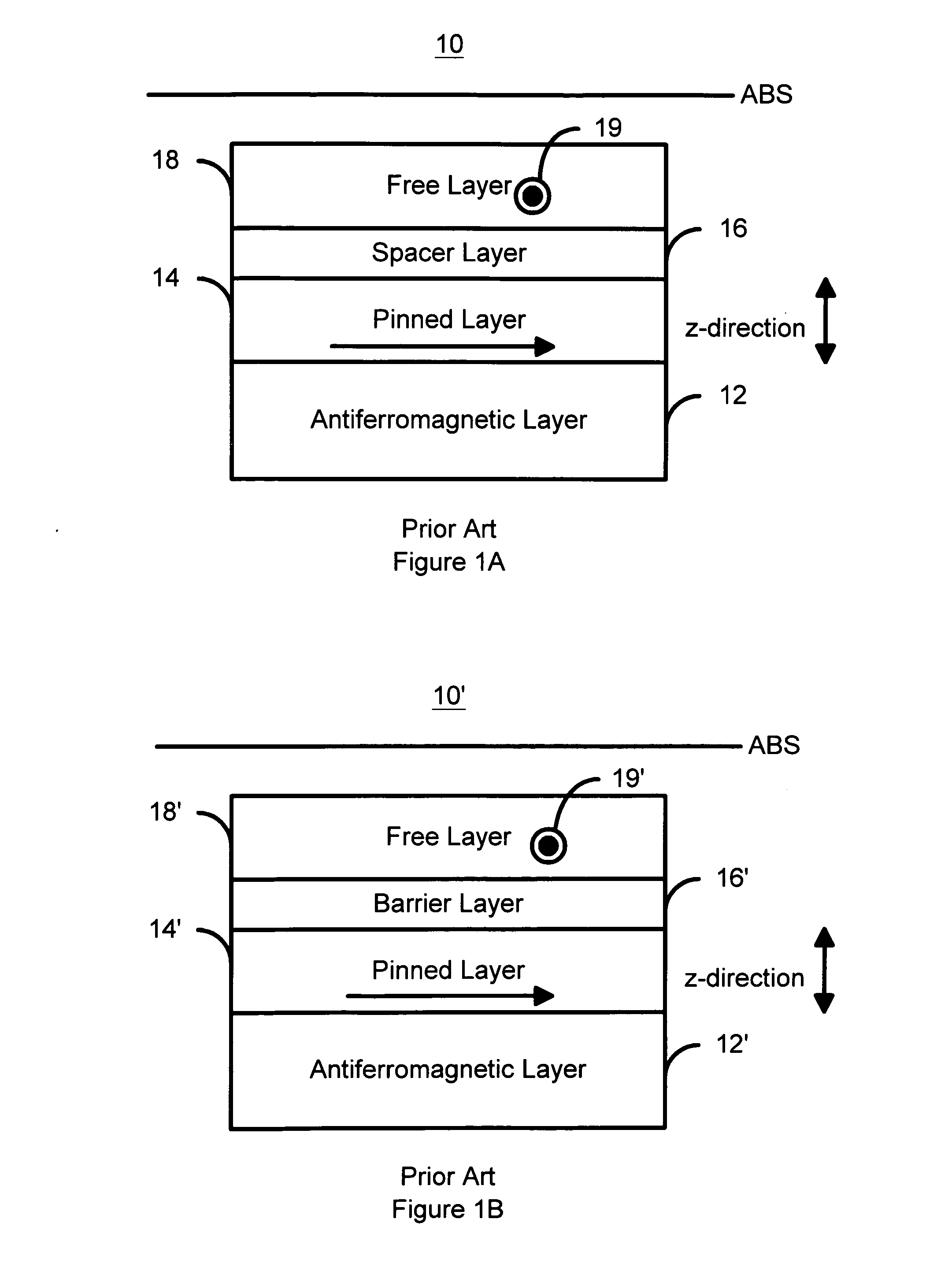
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic head
A magnetic transducing element in which a ferromagnetic tunneling junction film, including first and second ferromagnetic layers and an insulating layer are enclosed between the ferromagnetic layers, and a nonmagnetic metal thin film is inserted between the second ferromagnetic layer and the insulating layer, is formed on a substrate.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
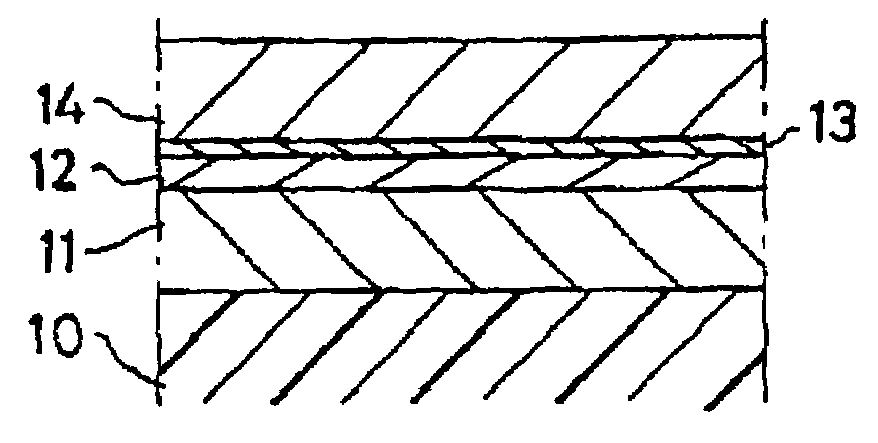
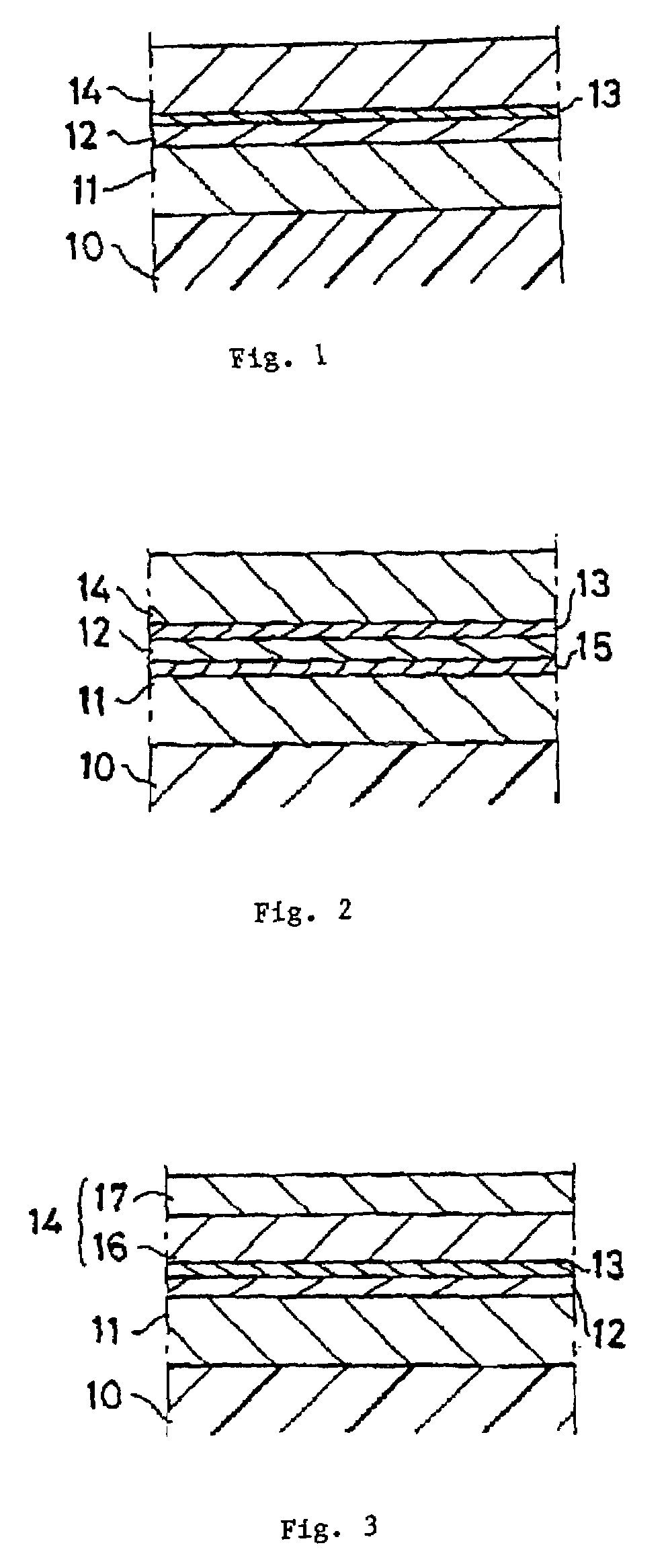
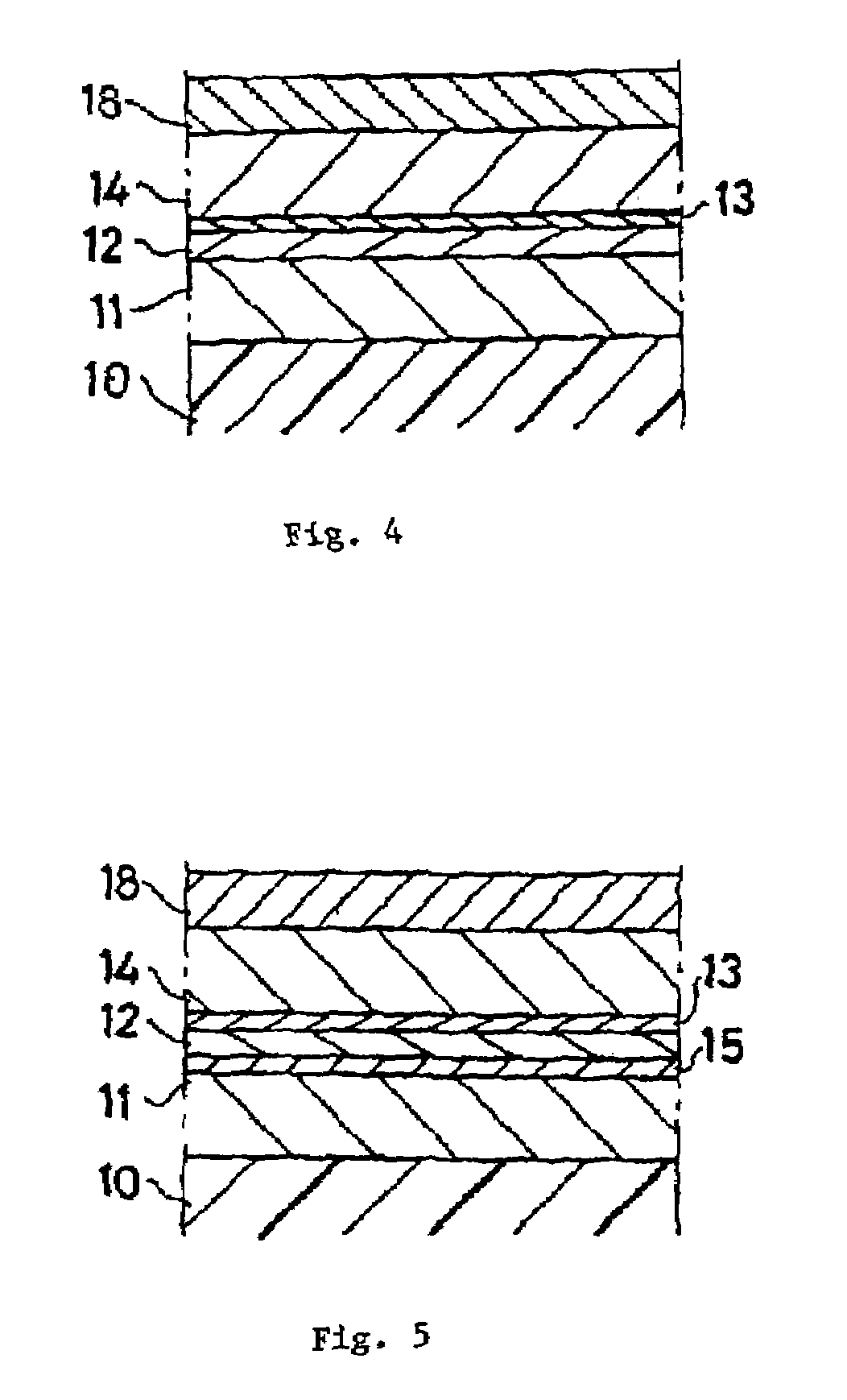
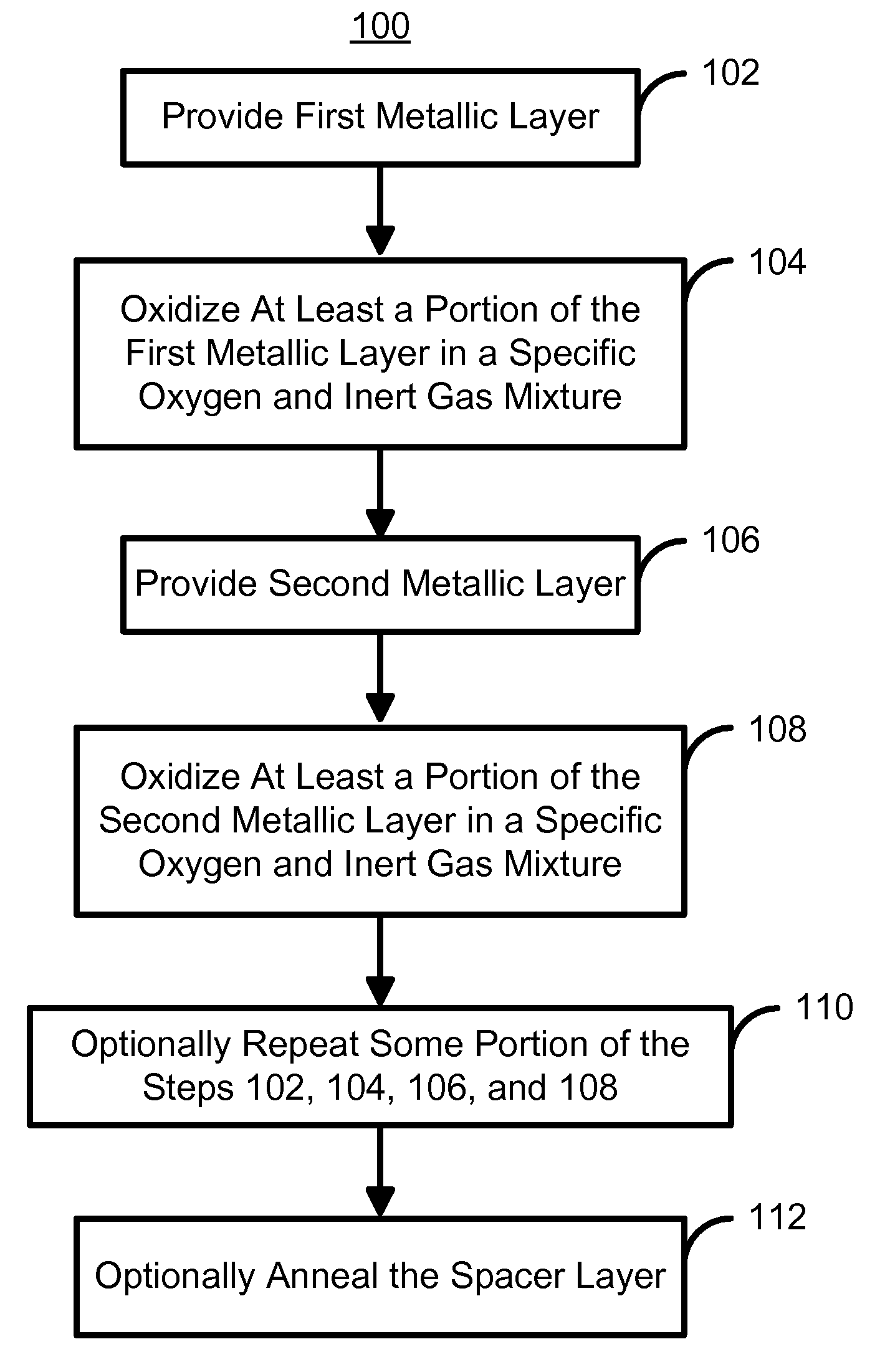
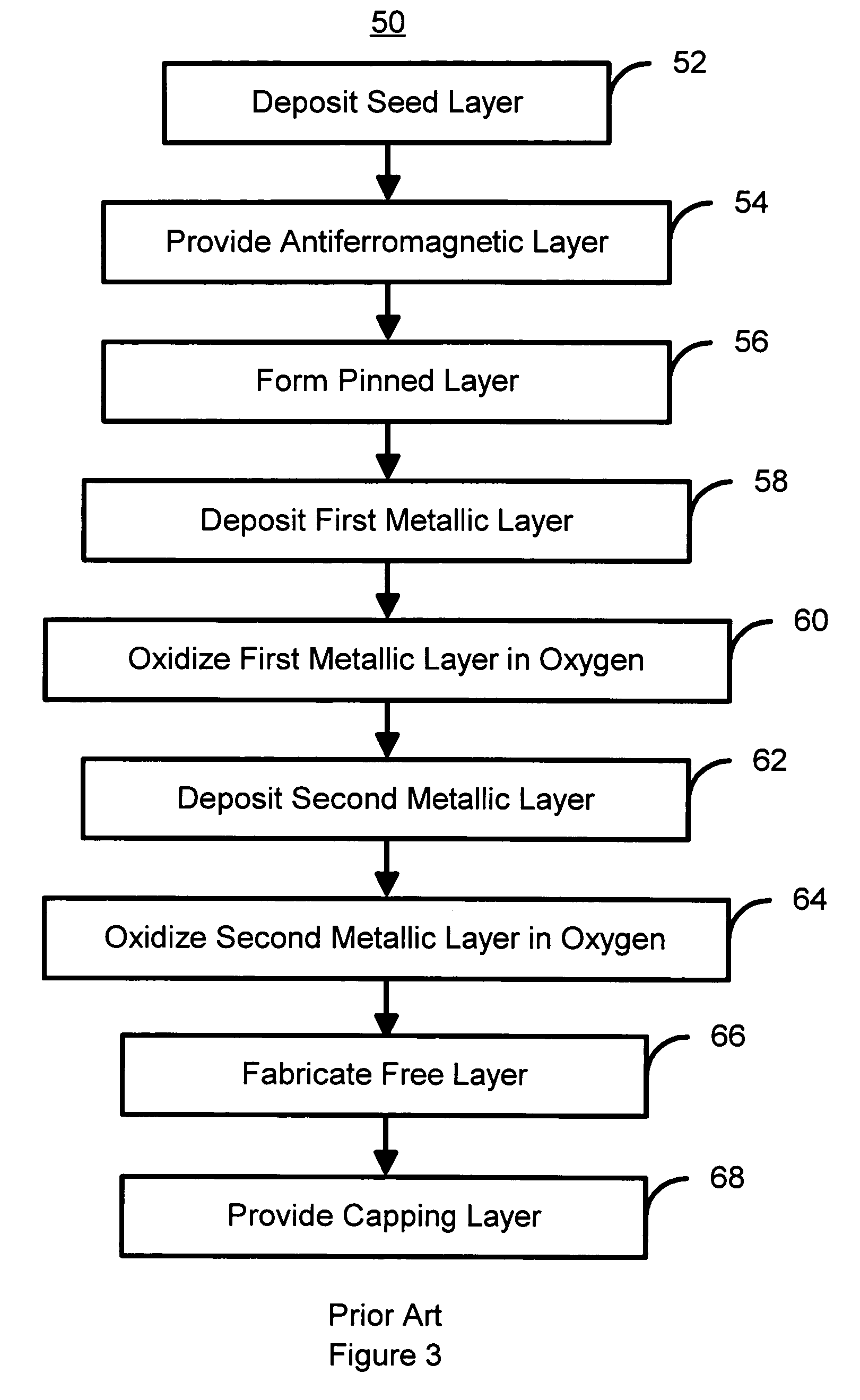
Method for fabricating a spacer layer for a magnetoresistive element
InactiveUS7595967B1Reduce magnetostrictionElectrical transducersNanomagnetismMagnetic reluctanceOptoelectronics
A method and system for manufacturing a spacer layer in a magnetoresistive element are described. The spacer layer resides between a free layer and a pinned layer. The method and system include providing a first metallic layer and oxidizing the first metallic layer in a first environment including at least oxygen and a first gas inert with respect to the first metallic layer. The method and system further include providing a second metallic layer and oxidizing the second metallic layer in a second environment including at least oxygen and a first gas inert with respect to the first metallic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetoresistive element having reduced spin transfer induced noise
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The method and system include providing a ferromagnetic pinned layer, providing a free layer, and providing a spacer layer between the pinned layer and the free layer. The pinned layer and free layer are ferromagnetic and have a pinned layer magnetization and a free layer magnetization, respectively. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic. In one aspect, the free layer is configured to have an increased magnetic damping constant. In another aspect, the method and system also include providing a second pinned layer and a second spacer layer between the free layer and the second pinned layer. In this aspect, the first pinned layer and / or the second pinned layer are configured such that a forward torque and a reflected torque due to a current driven through the magnetic element in a current-perpendicular-to-plane configuration are substantially equal and opposite.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Dual axis magnetic sensor
A two-axis magnetic field sensor includes a substrate, a first sensor having at least one magnetoresistive element formed of GMR material on the substrate has a free layer having an easy axis of effective anisotropy field in a first direction. The first sensor is sensitive to magnetic field components perpendicular to the first direction. A current is caused to flow through the first sensor and variations in the resistivity of the first sensor due to the first magnetic field components are sensed. A second sensor having at least one magnetoresistive element formed of GMR material on the substrate has a free layer having an easy axis of effective anisotropy field in a direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction. The second sensor is sensitive to second magnetic field components perpendicular to its easy axis of effective anisotropy. A current is caused to flow through the second sensor and variations in the resistivity of the second sensor due to second magnetic field components are sensed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
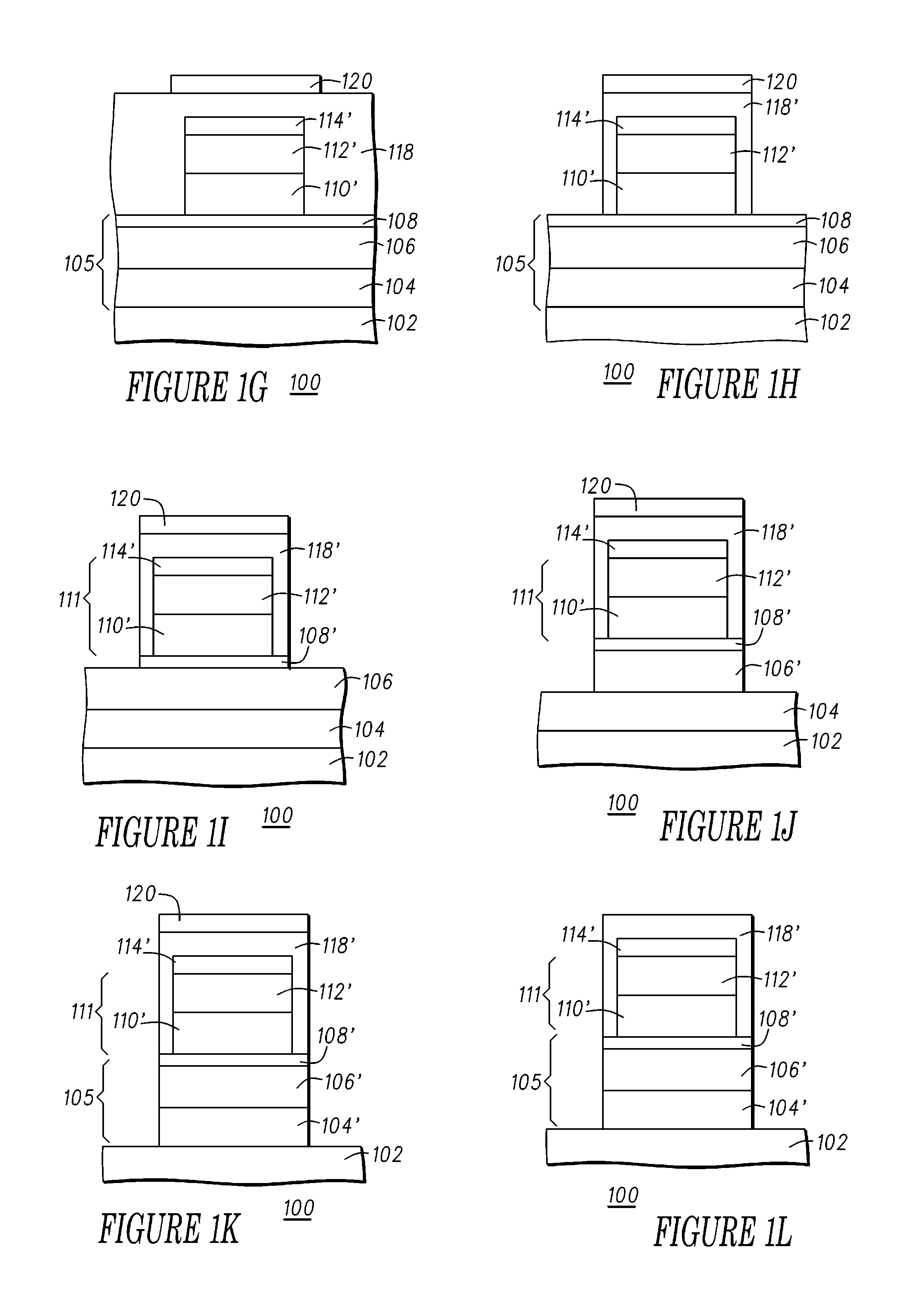
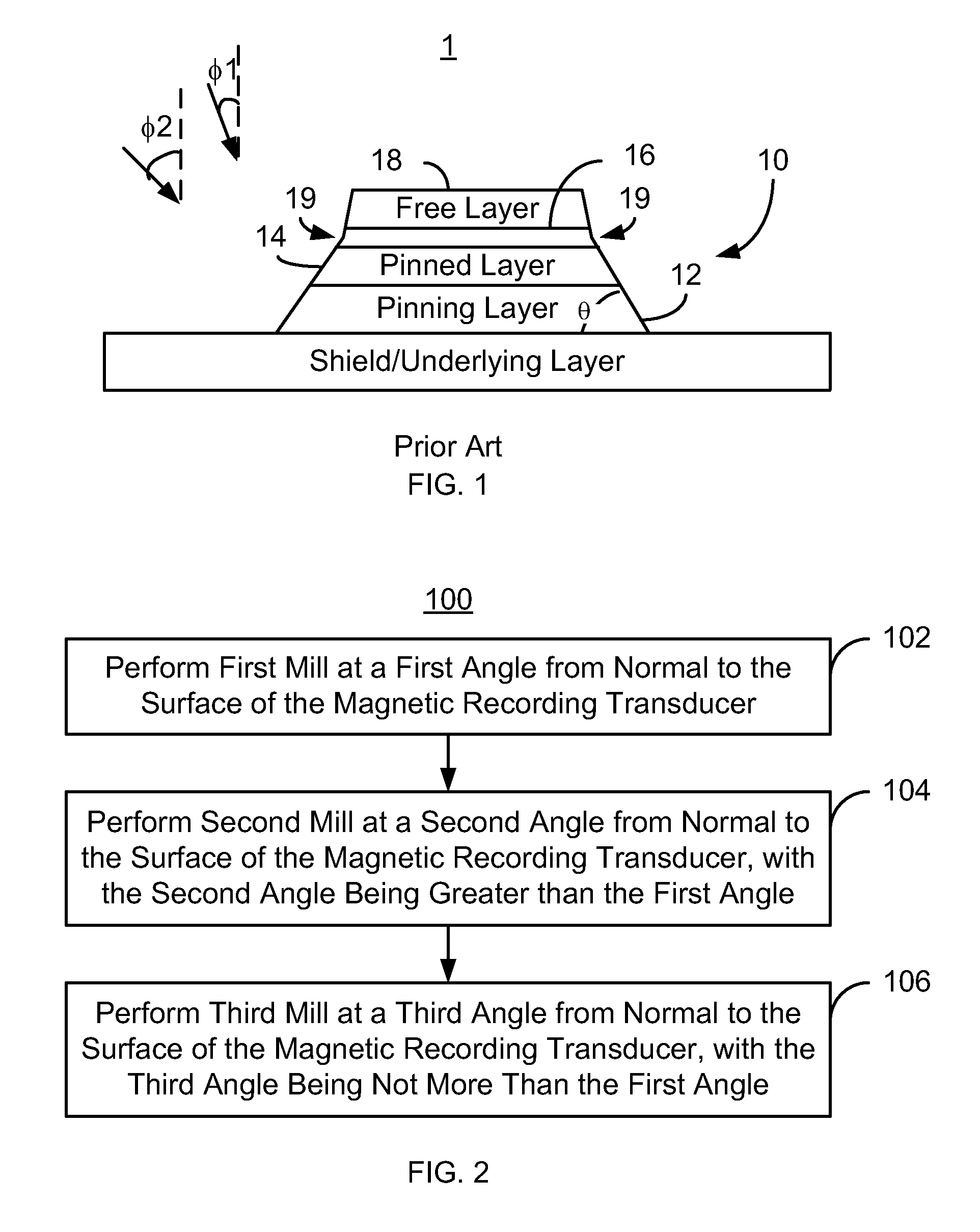
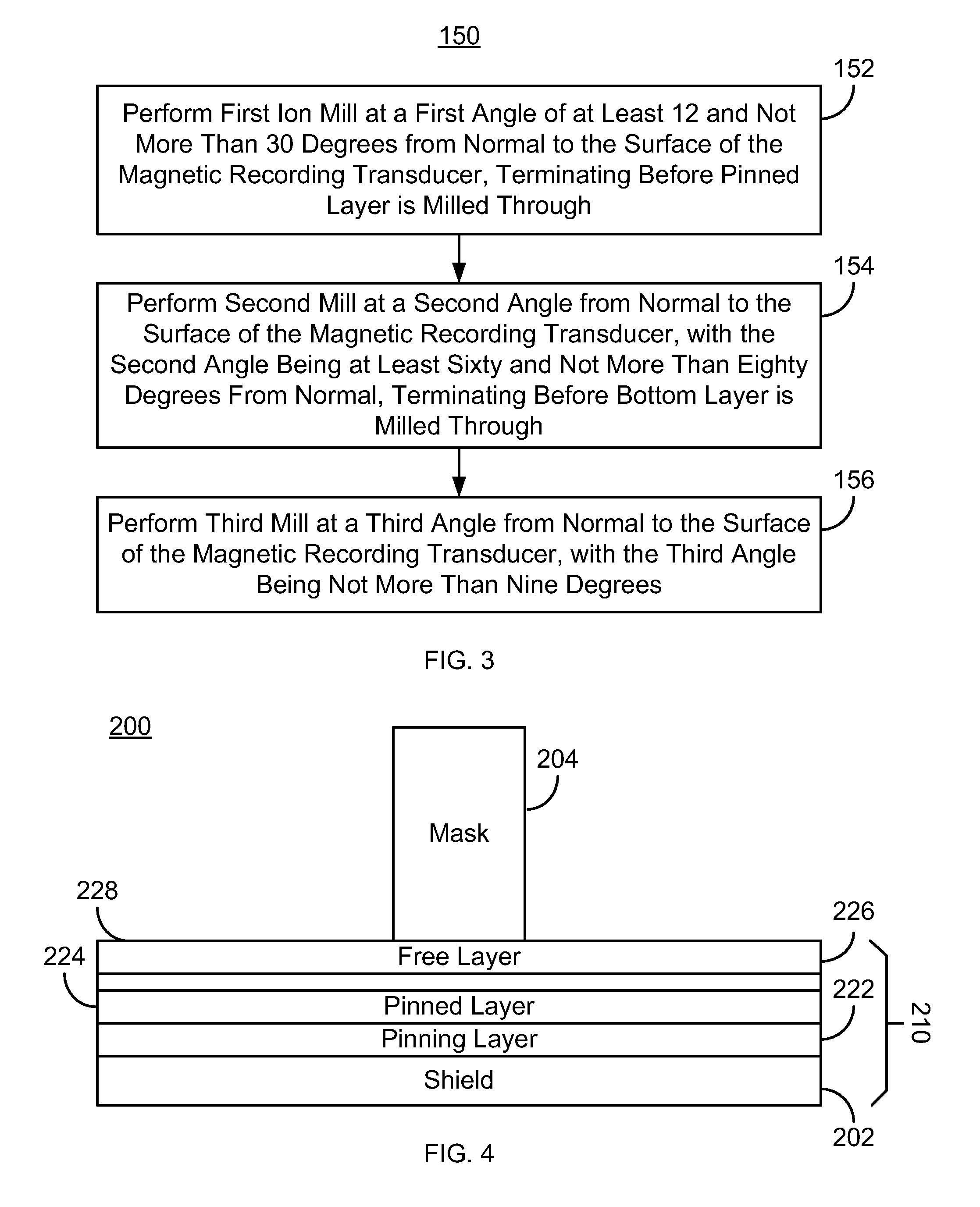
Method and system for defining a magnetoresistive junction
A method and system define a magnetoresistive junction in a magnetic recording transducer. The method and system include performing a first mill at a first angle from a normal to the surface of the magnetic recording transducer. A second mill is performed at a second angle from the normal to the surface. The second angle is larger than the first angle. A third mill is performed at a third angle from the normal to the surface. The third angle is not larger than the first angle.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
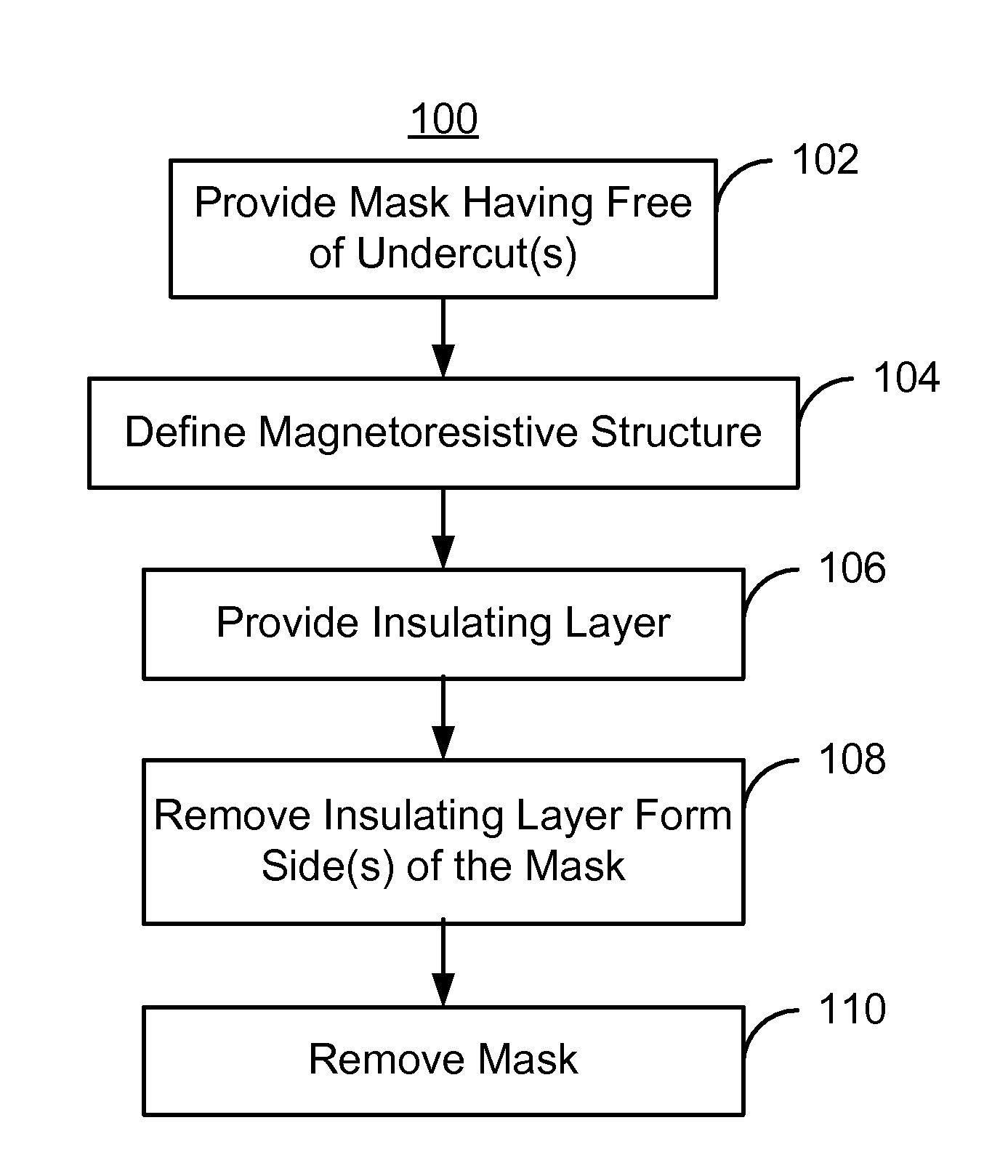
Method and system for providing a magnetoresistive structure using undercut free mask
A method and system provide a magnetoresistive structure from a magnetoresistive stack that includes a plurality of layers. The method and system include providing a mask that exposes a portion of the magnetoresistive stack. The mask has at least one side, a top, and a base at least as wide as the top. The method and system also include removing the portion of the magnetoresistive stack to define the magnetoresistive structure. The method and system further include providing an insulating layer. A portion of the insulating layer resides on the at least one side of the mask. The method and system further include removing the portion of the insulating layer on the at least one side of the mask and removing the mask.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
MRAM array having a segmented bit line
InactiveUS6982902B2Reduce leakage currentRaise the ratioDigital storageBit lineStatic random-access memory
A magneto-resistive random access memory (MRAM) array comprises global bit lines segmented using a plurality of local bit lines. A read / write controller is connected to the switches. Switches couple the global bit line to the local bit lines. The MRAM array has low leakage currents and facilitates a high signal-to-noise (S / N) ratio of read and write operations.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
MRAM having spin hall effect writing and method of making the same
InactiveUS20140252439A1Easy to switchEasy to reverseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic reluctanceRecording layer
A spin-transfer-torque magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus and method of manufacturing a three terminal magnetoresistive memory element having highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid on top of a SHE-metal layer in the regions outside of an MTJ stack. The memory cell comprises a bit line positioned adjacent to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid and electrically contacting on top of a SHE-metal layer in the outside of an MTJ region and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to switch the magnetization of the recording layer. Thus magnetization of a recording layer can be readily switched or reversed to the direction in accordance with a direction of a current along the SHE-metal layer by applying a low write current.
Owner:T3MEMORY
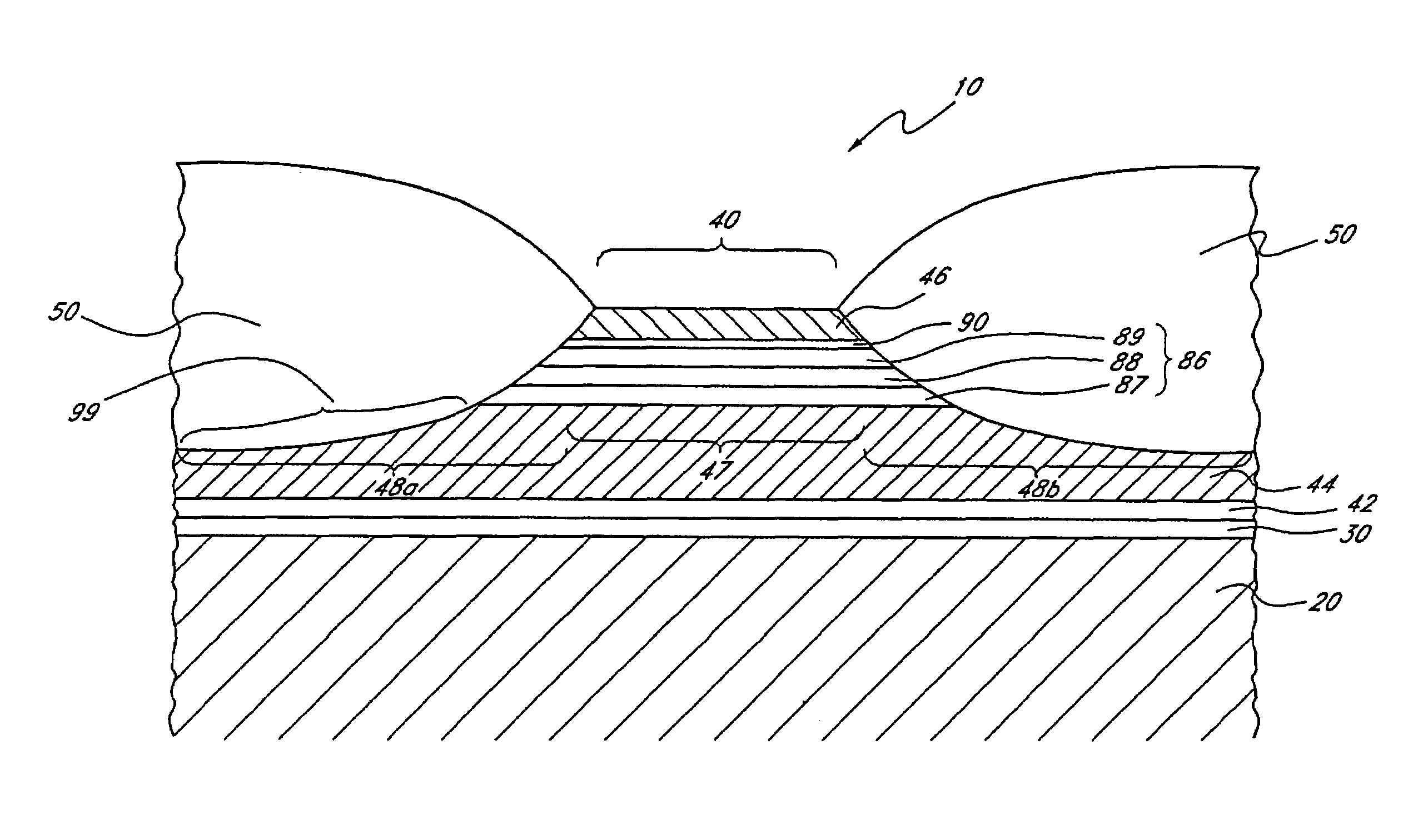
Method for fabricating magnetoresistive read head having a bias structure with at least one dusting layer
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
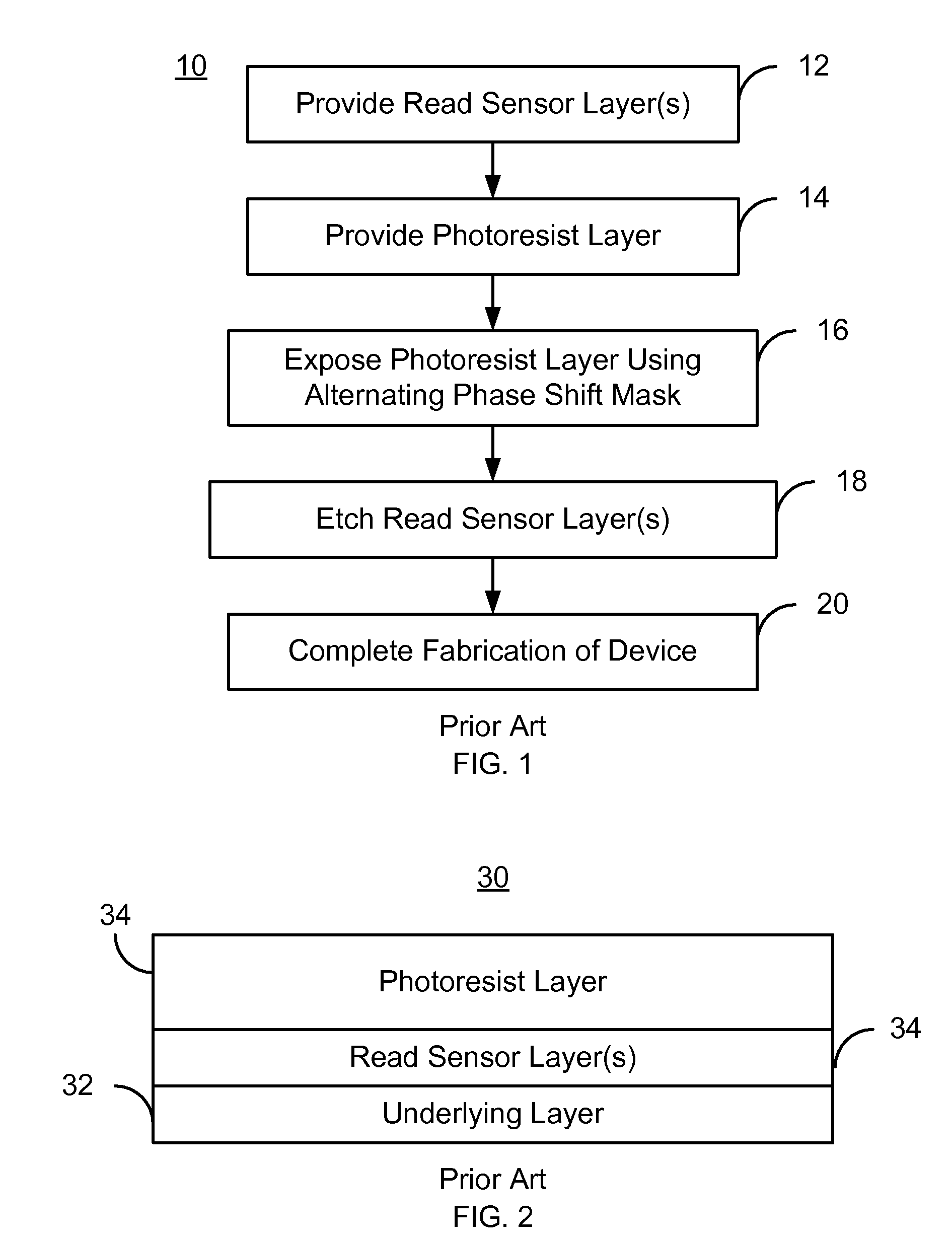
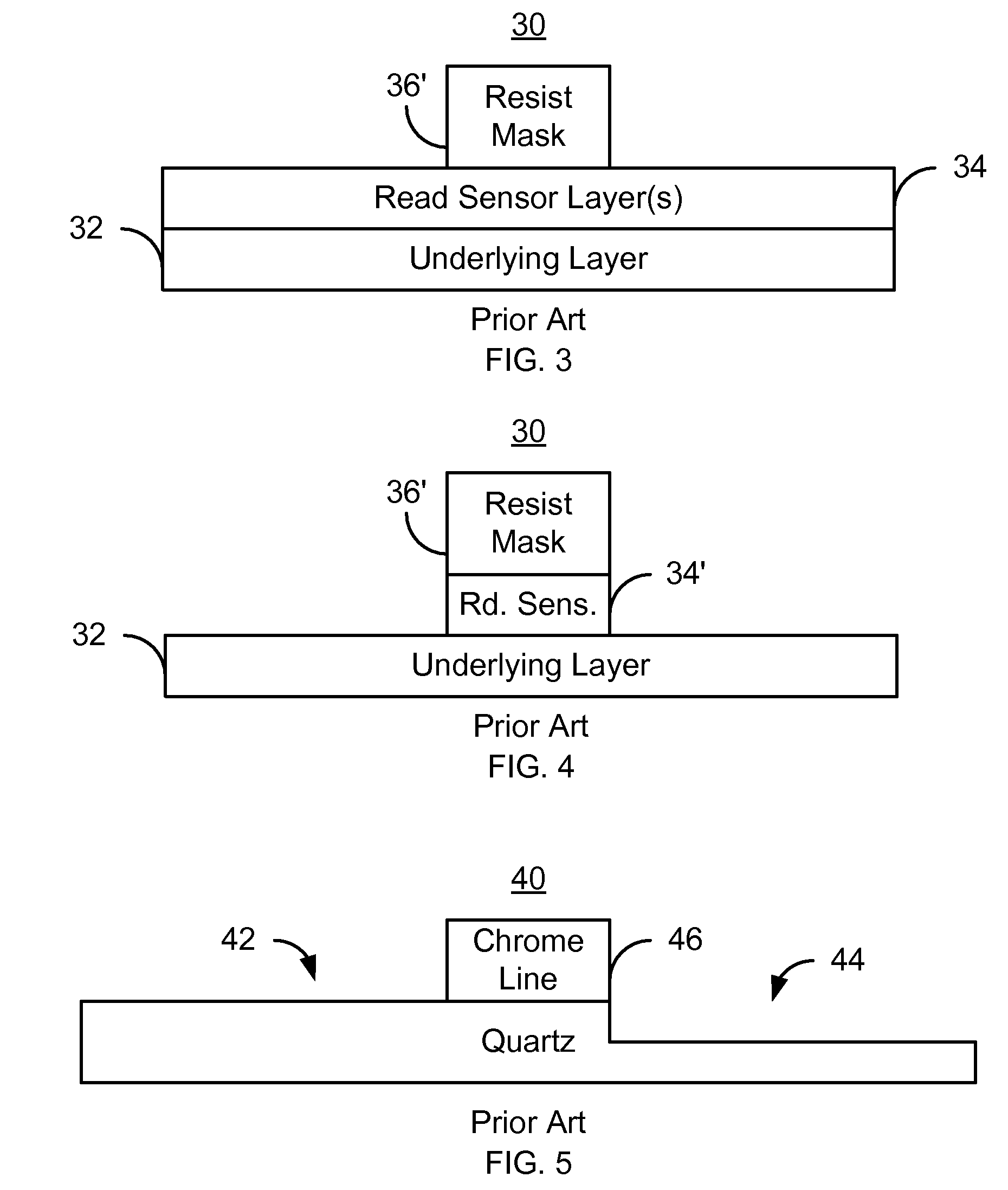
Method and system for providing a structure in a microelectronic device using a chromeless alternating phase shift mask
A method and system for providing a microelectric device, such as a magnetoresistive read sensor are described. The method and system include providing a mask layer on the microelectric device. The method and system further include exposing the mask layer to provide a mask. A portion of the mask covers a portion of the microelectric device. The step of exposing the mask layer further includes utilizing a chromeless alt-phase shift mask for providing the portion of the mask.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
A magnetoresistive element includes a free layer which contains a magnetic material and has an fct crystal structure with a (001) plane oriented, the free layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a direction to be changeable by spin-polarized electrons, a first nonmagnetic layer and a second nonmagnetic layer which sandwich the free layer and have one of a tetragonal crystal structure and a cubic crystal structure, and a fixed layer which is provided on only one side of the free layer and on a surface of the first nonmagnetic layer opposite to a surface with the free layer and contains a magnetic material, the fixed layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a fixed direction.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
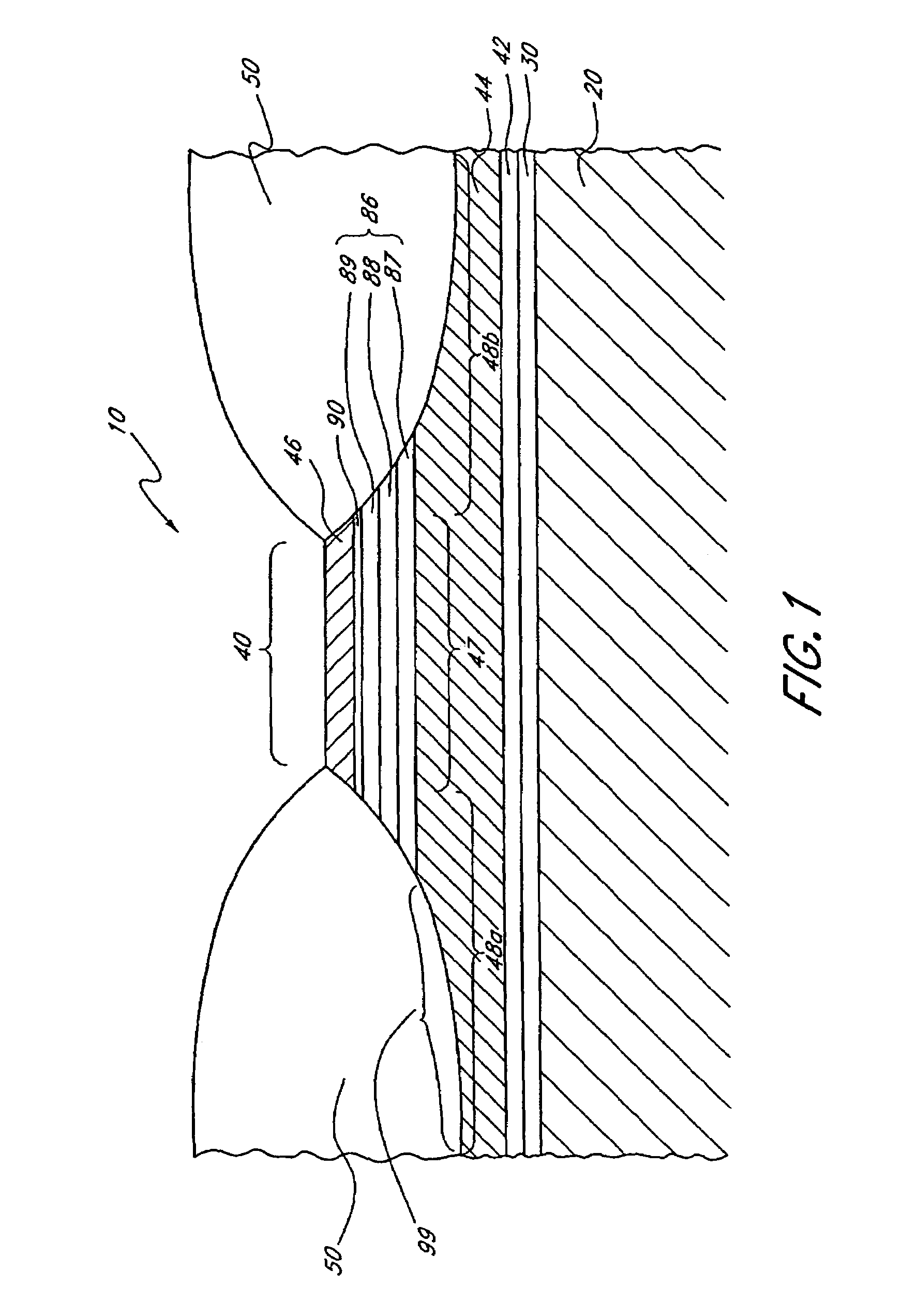
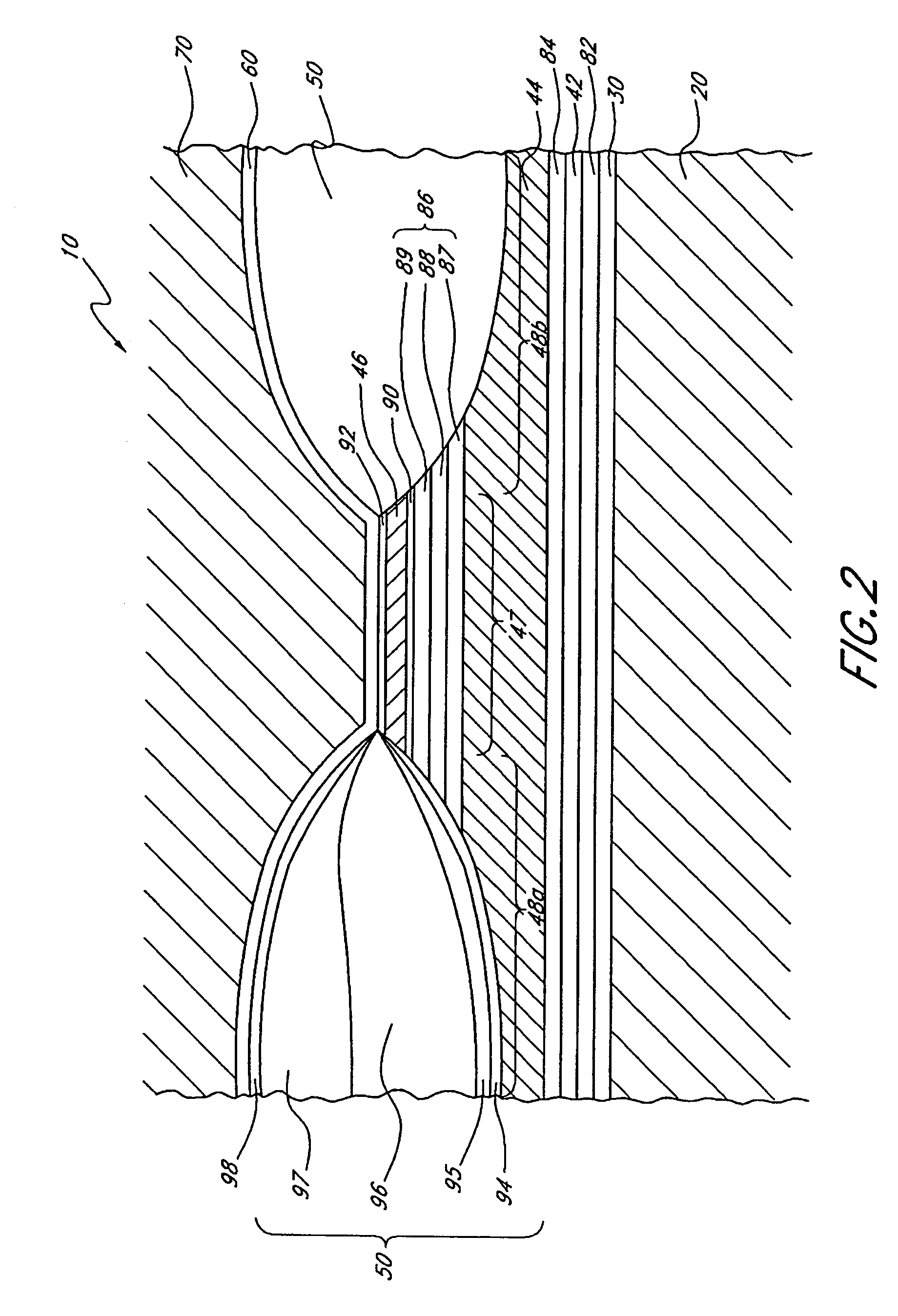
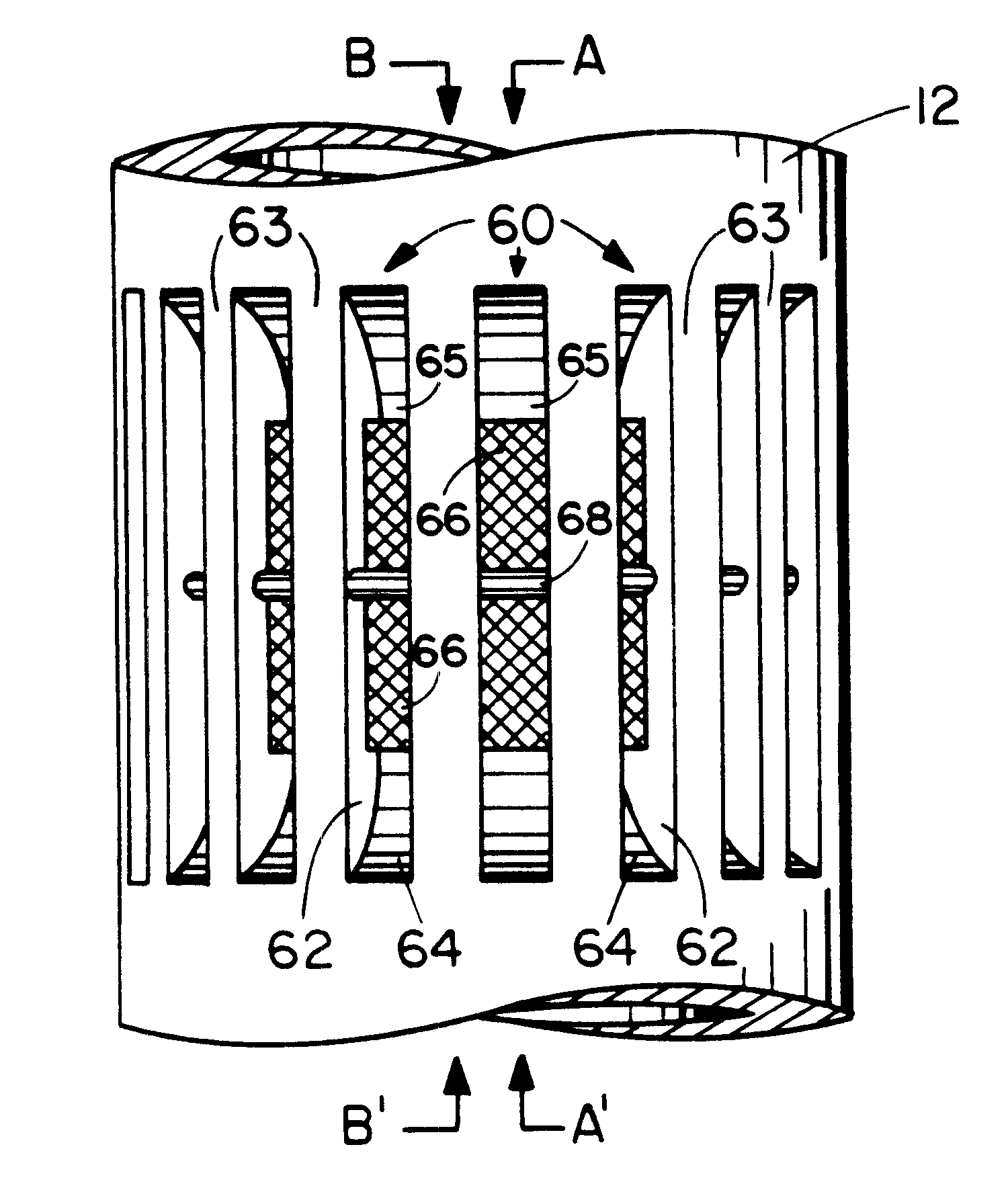
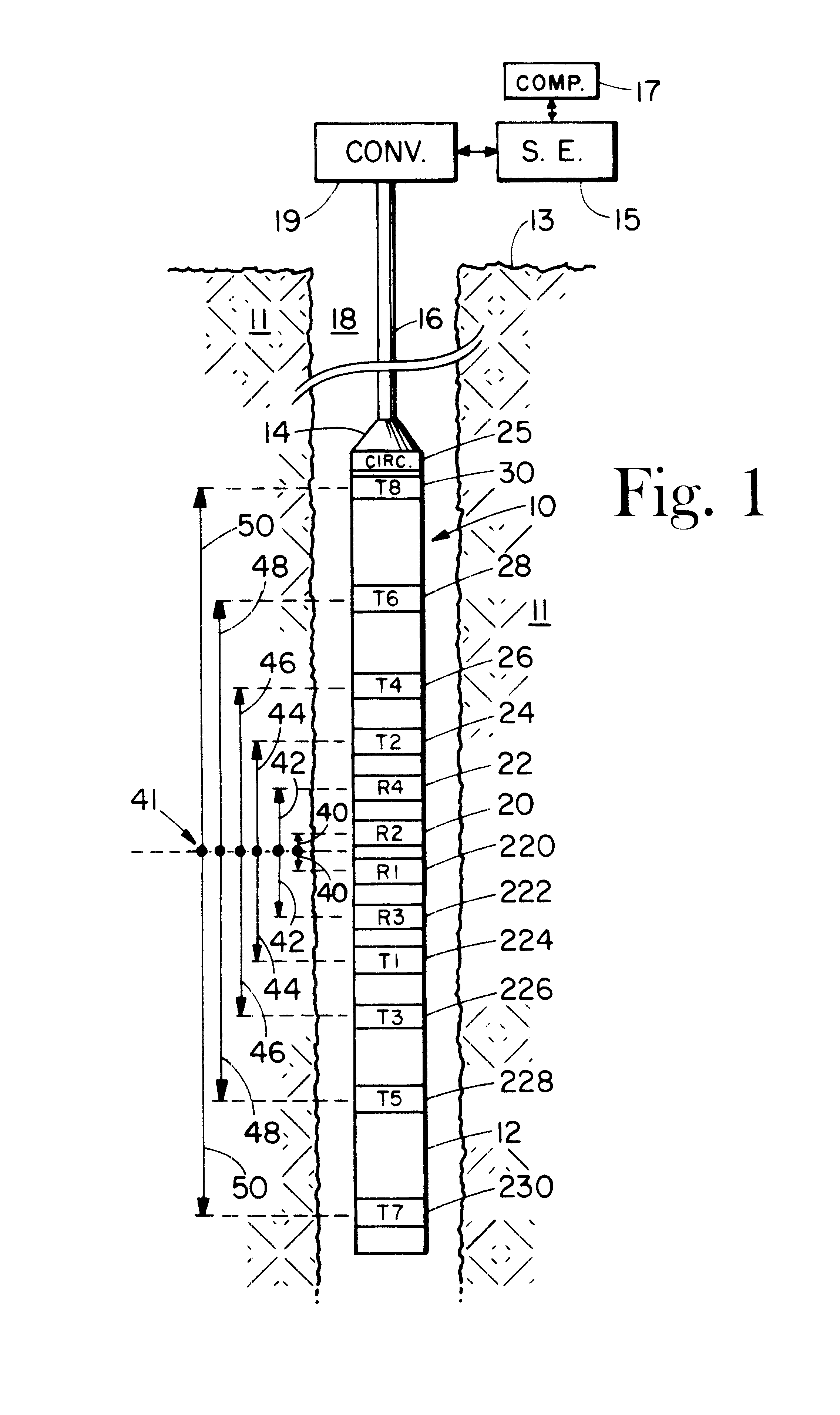
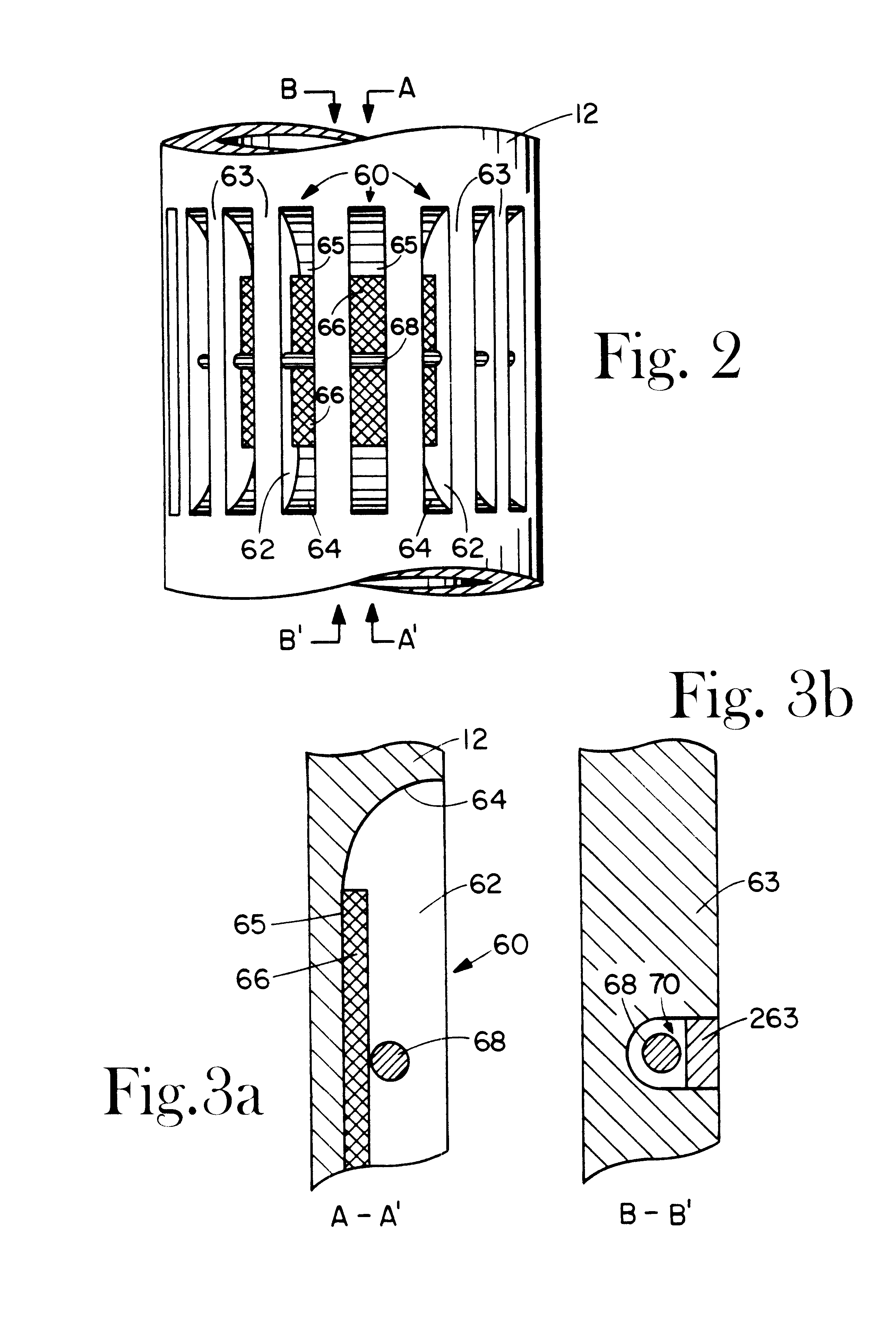
Well logging system for determining directional resistivity using multiple transmitter-receiver groups focused with magnetic reluctance material
InactiveUS6577129B1Improve antenna efficiencyHigh gainElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSubaqueous/subterranean adaptionWell loggingMagnetic reluctance
An electromagnetic wave propagation resistivity borehole logging system comprising multiple groups of electromagnetic transmitter-receiver arrays operating at three frequencies. The borehole logging tool component of the system employs eight transmitters and four receivers. The transmitters and receivers are disposed axially and symmetrically along the major axis of the tool to form four group pairs. Each group pair consists of a transmitter-receiver groups axially and symmetrically on opposing sides of a reference point on the tool. Each, transmitter-receiver group consists of one transmitter assembly and two receiver assemblies. Each transmitter-receiver group is operated at two of three operating frequencies which are 100 kHz, 400 kHz and 2 MHz. Some of the transmitter and receiver assemblies are fabricated to yield azimuthally focused resistivity measurements, and to yield vertical and horizontal resistivity in anisotropic dipping beds. The system can be embodied as a logging-while-drilling system or as a wireline logging system.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Rdma-ssd dual-port unified memory and network controller
ActiveUS20150254003A1Increase storage capacityLower latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersMagnetic reluctanceData memory
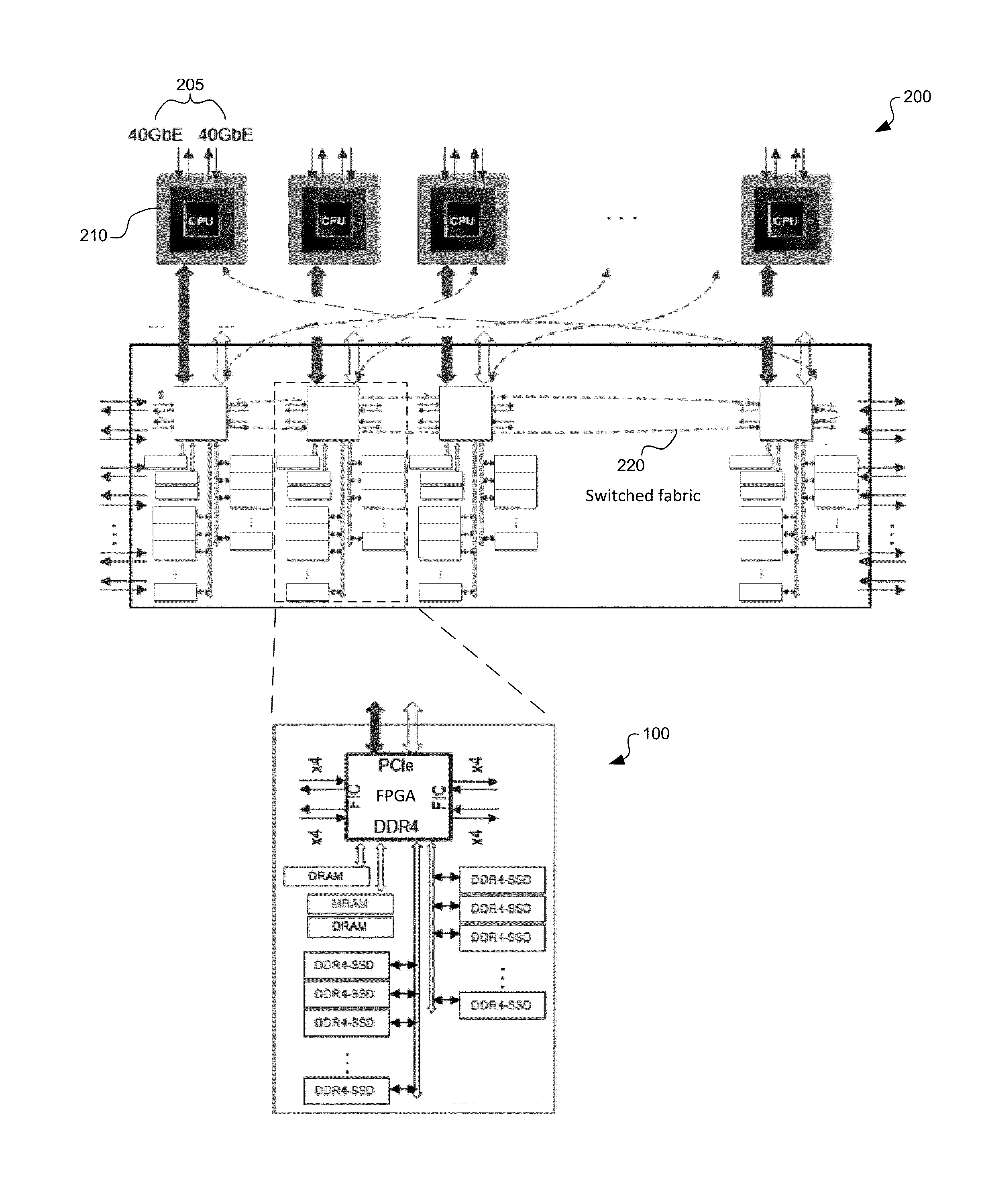
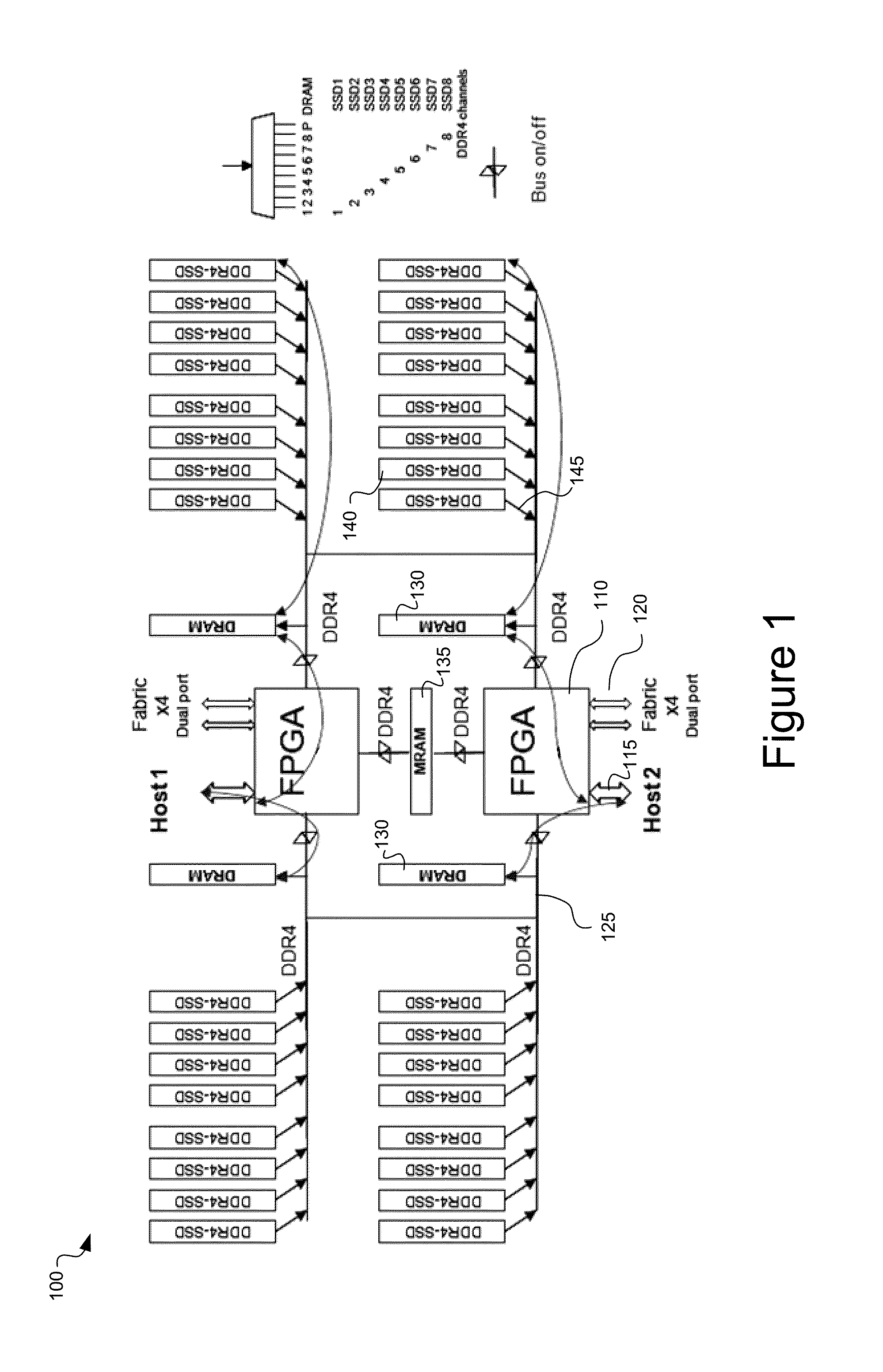
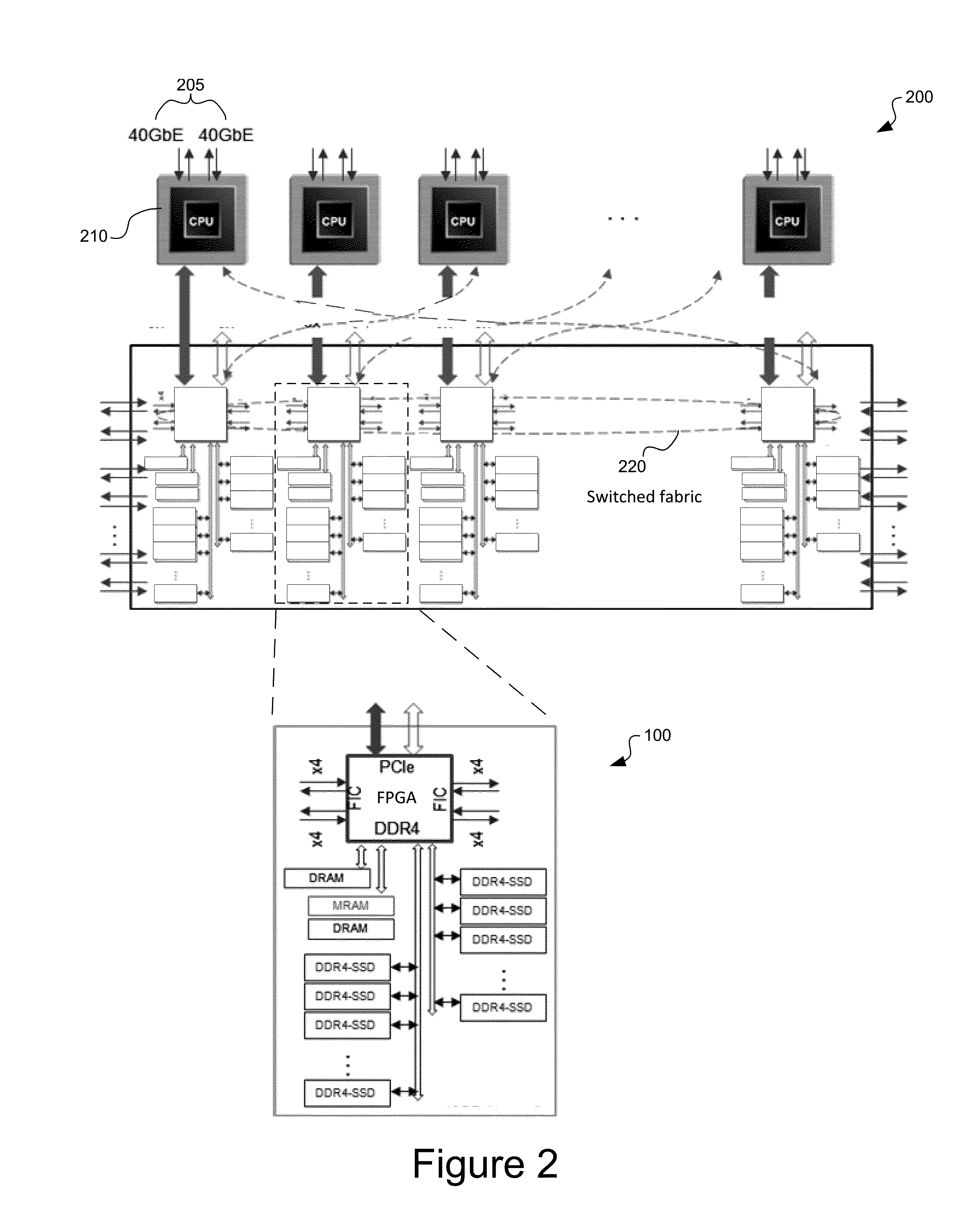
System and method for a unified memory and network controller for an all-flash array (AFA) storage blade in a distributed flash storage clusters over a fabric network. The unified memory and network controller has 3-way control functions including unified memory buses to cache memories and DDR4-AFA controllers, a dual-port PCIE interconnection to two host processors of gateway clusters, and four switch fabric ports for interconnections with peer controllers (e.g., AFA blades and / or chassis) in the distributed flash storage network. The AFA storage blade includes dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) and magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) configured as data read / write cache buffers, and flash memory DIMM devices as primary storage. Remote data memory access (RDMA) for clients via the data caching buffers is enabled and controlled by the host processor interconnection(s), the switch fabric ports, and a unified memory bus from the unified controller to the data buffer and the flash SSDs.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
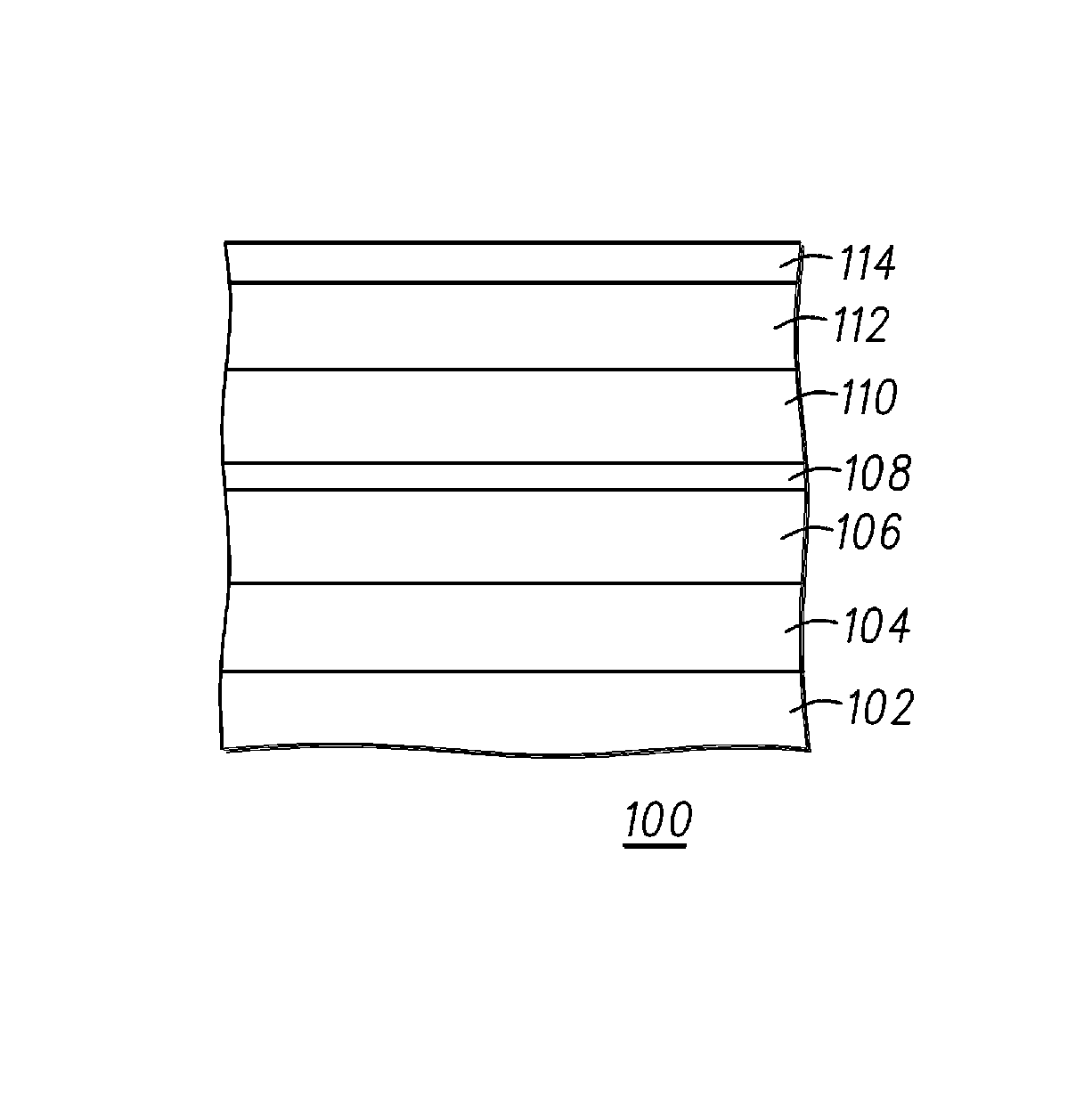
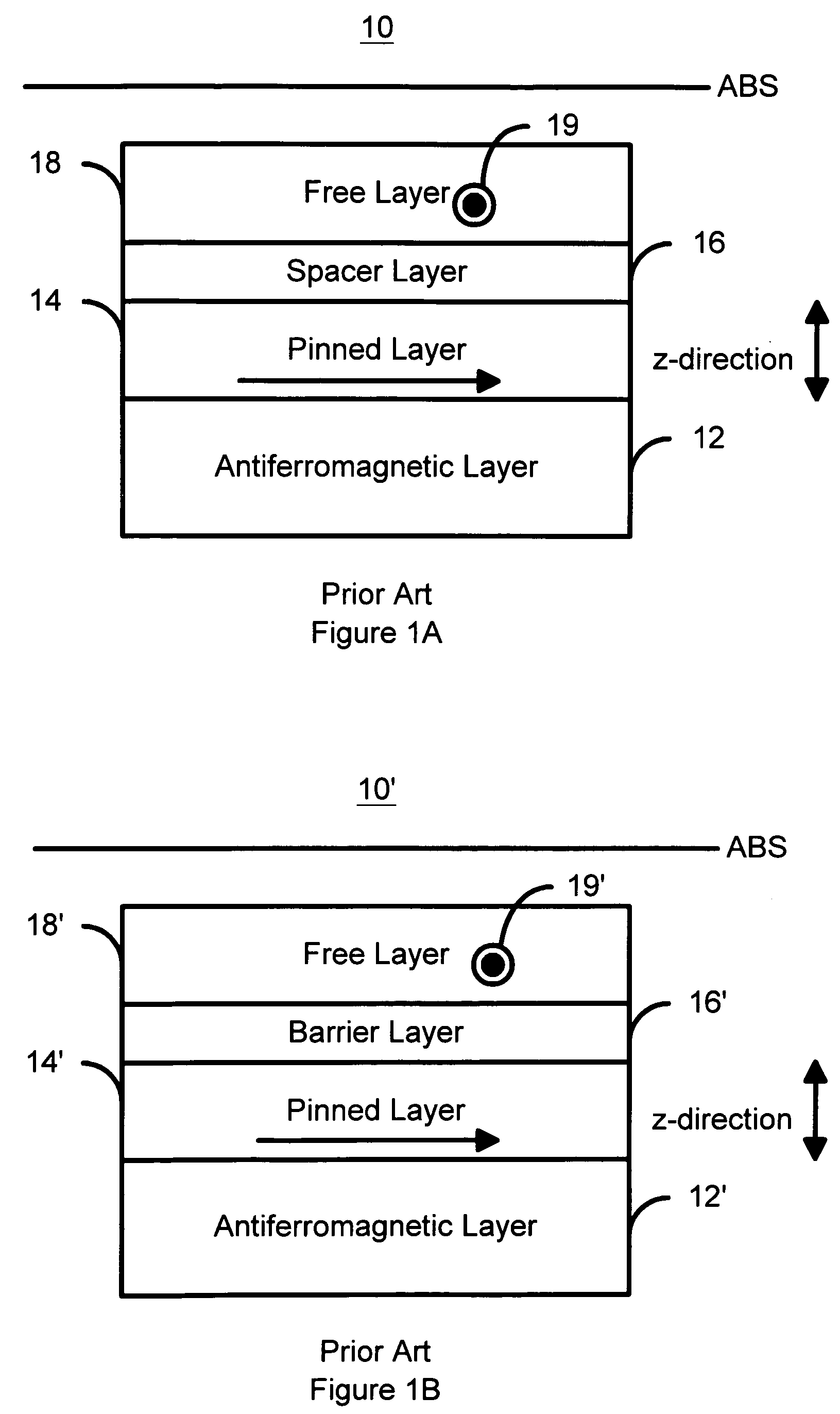
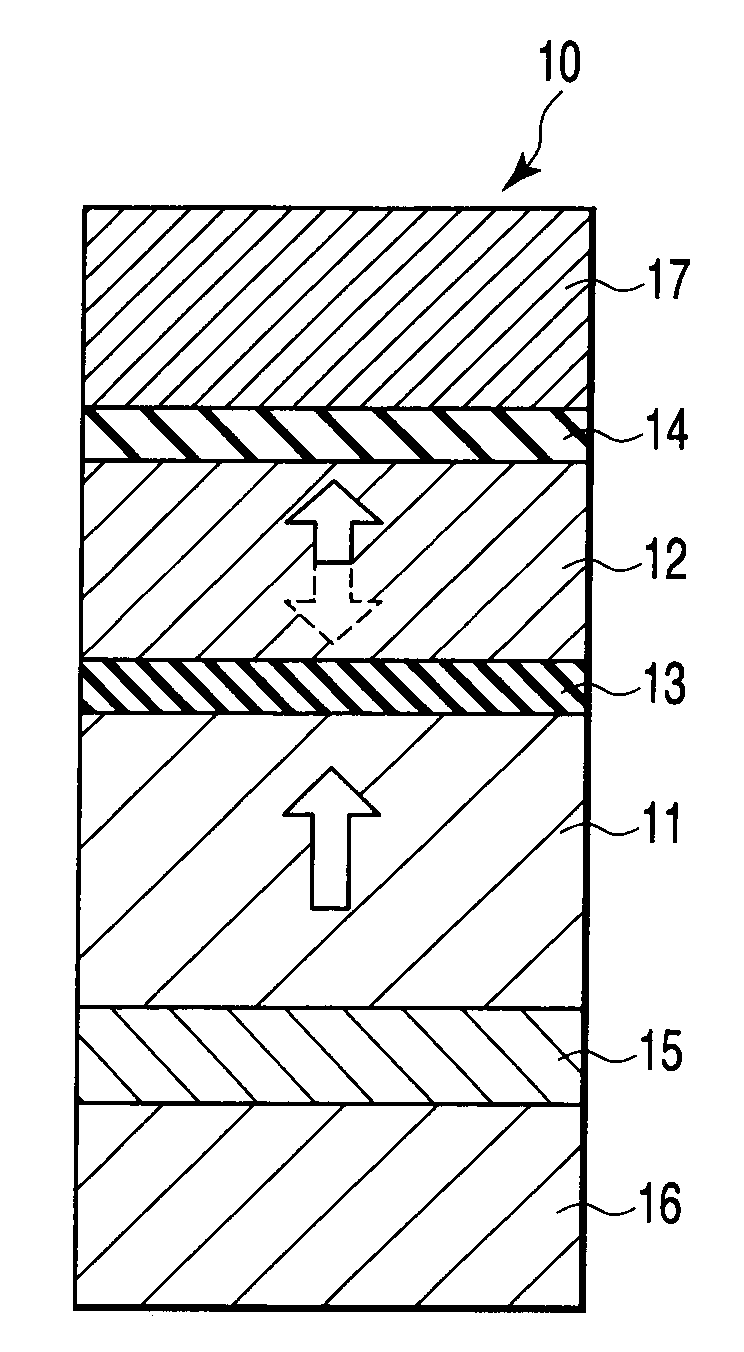
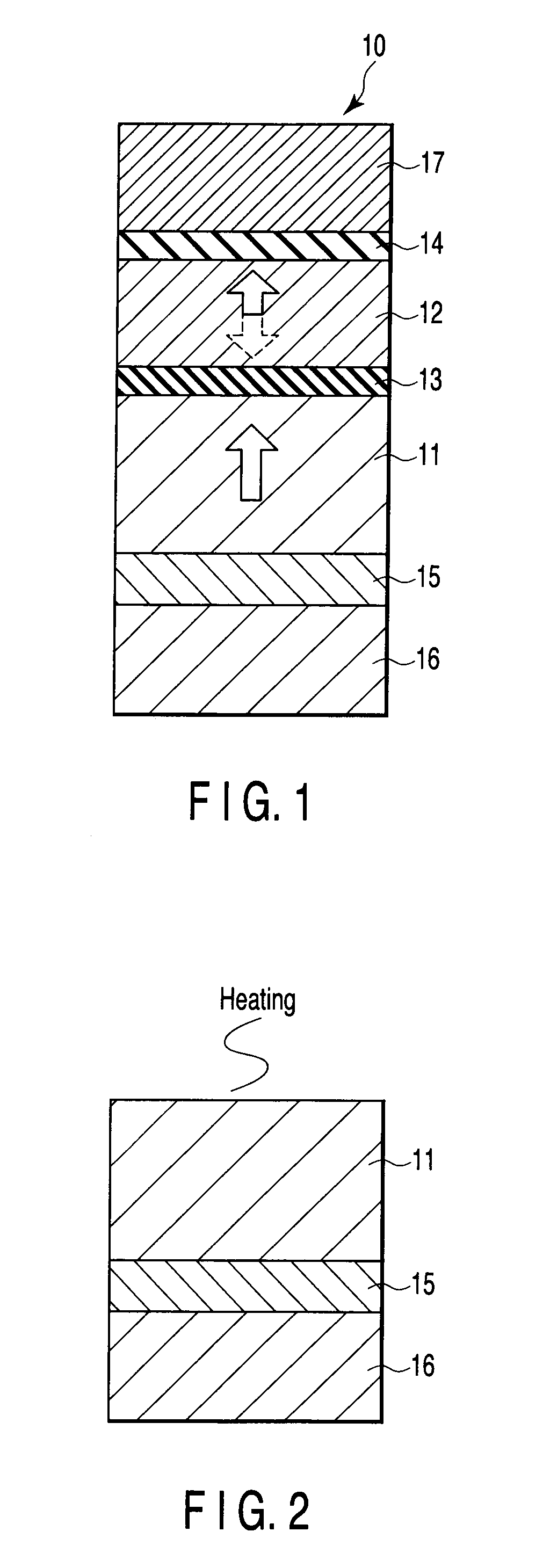
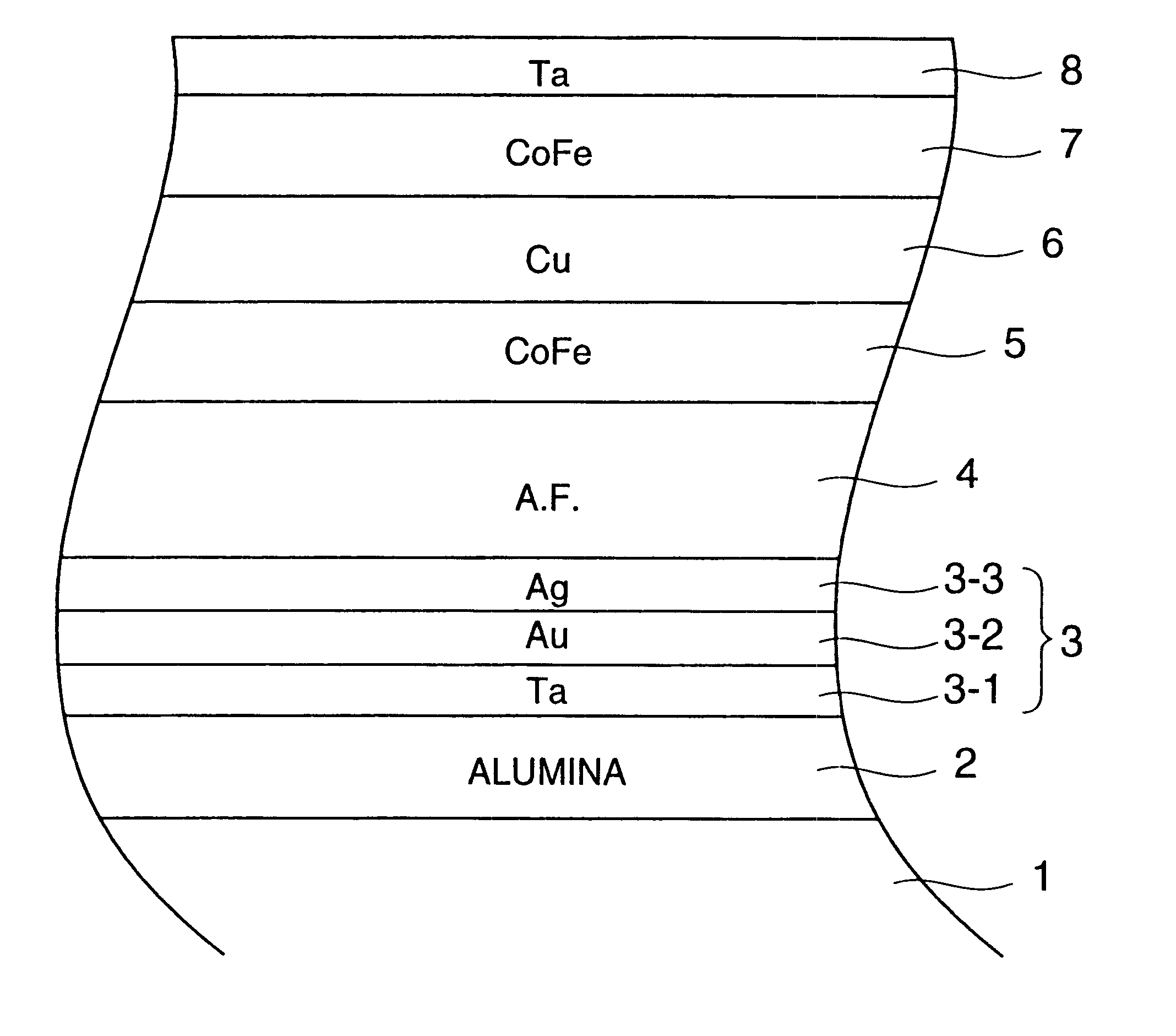
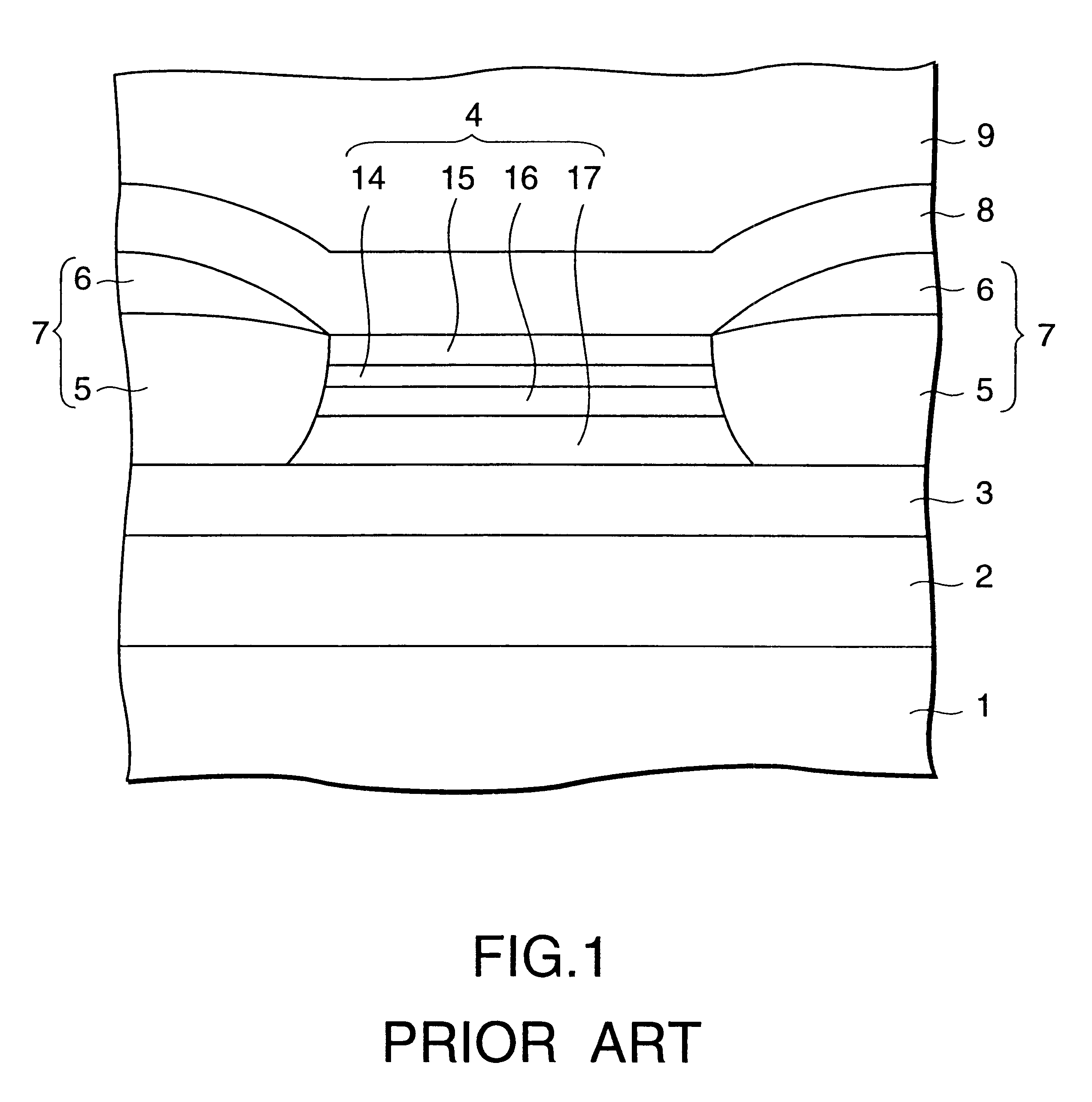
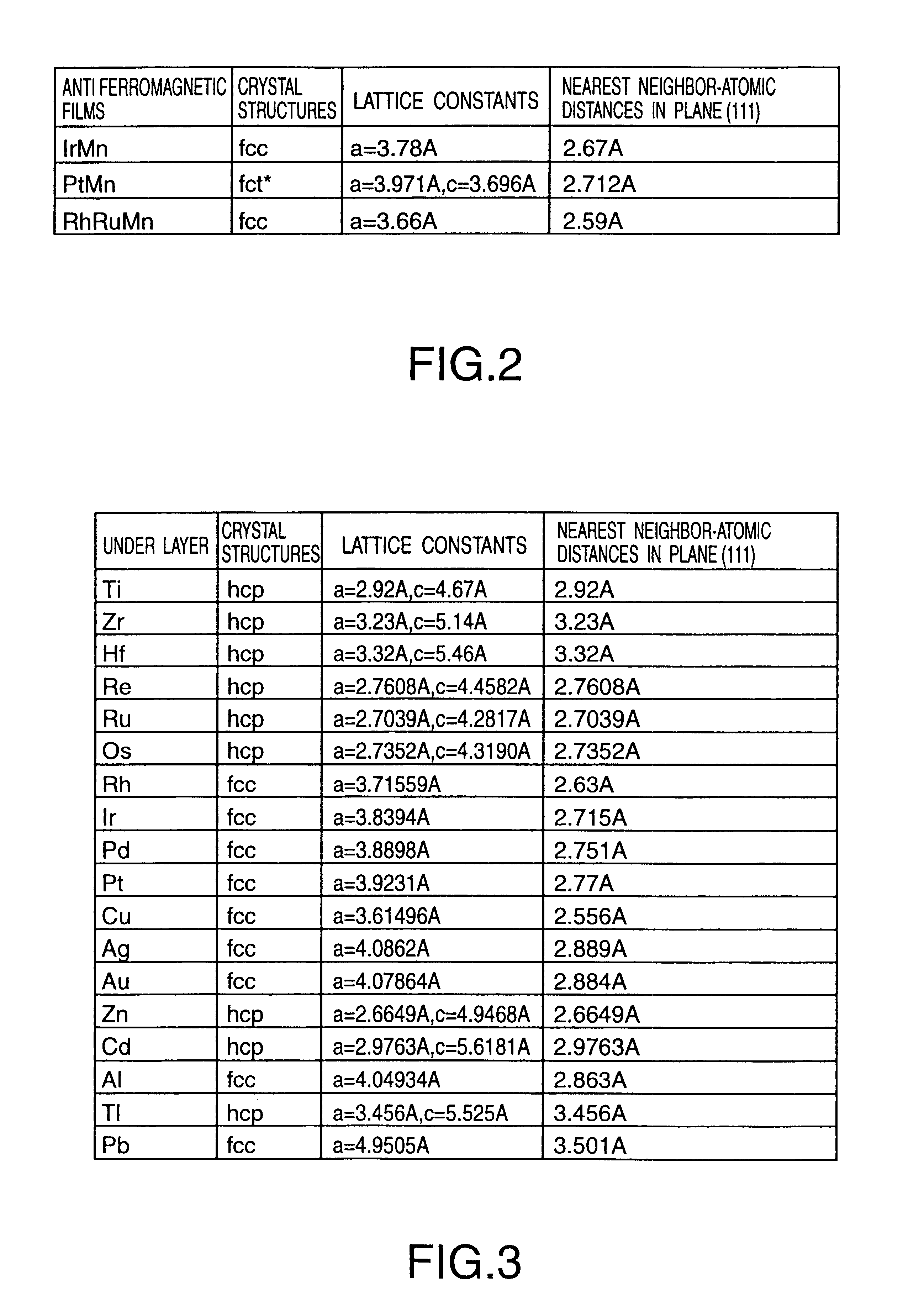
Laminated magnetorestrictive element of an exchange coupling film, an antiferromagnetic film and a ferromagnetic film and a magnetic disk drive using same
InactiveUS6313973B1Stable output voltageRaise the ratioNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsGiant magnetoresistanceCoupling
A magnetoresistive element comprises an exchange coupling film having a under layer, an antiferromagnetic film and a ferromagnetic film, which are laminated in that order, the under layer including a metal having a face centered cubic crystal structure or hexagonal closest packing crystal structure which have a longer nearest neighbor atomic distance than that of the antiferromagnetic film. With this construction, it is possible to improve the exchange coupling field and to satisfy a stable output over a long period of time. A magnetoresistive element having a dual spin valve structure has a magnetization adjusting layer, which is antiferromagnetically connected to a pinned layer via an anti-parallel connection layer, to adjust the value of the product of the saturation magnetization of each of the magnetization adjusting layer and the pinned layer by the thickness thereof. Moreover, a magnetoresistance head use a giant magnetoresistance effect, and has at least one pair of pinned layer and free layer arranged via a non-magnetic spacer layer. The pinned layer has a pair of ferromagnetic layers which have different compositions and different coercive forces and which are antiferromagnetically connected to each other via a connection layer, so that the effective exchange coupling field of the pinned layer is 200 Oe or more.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
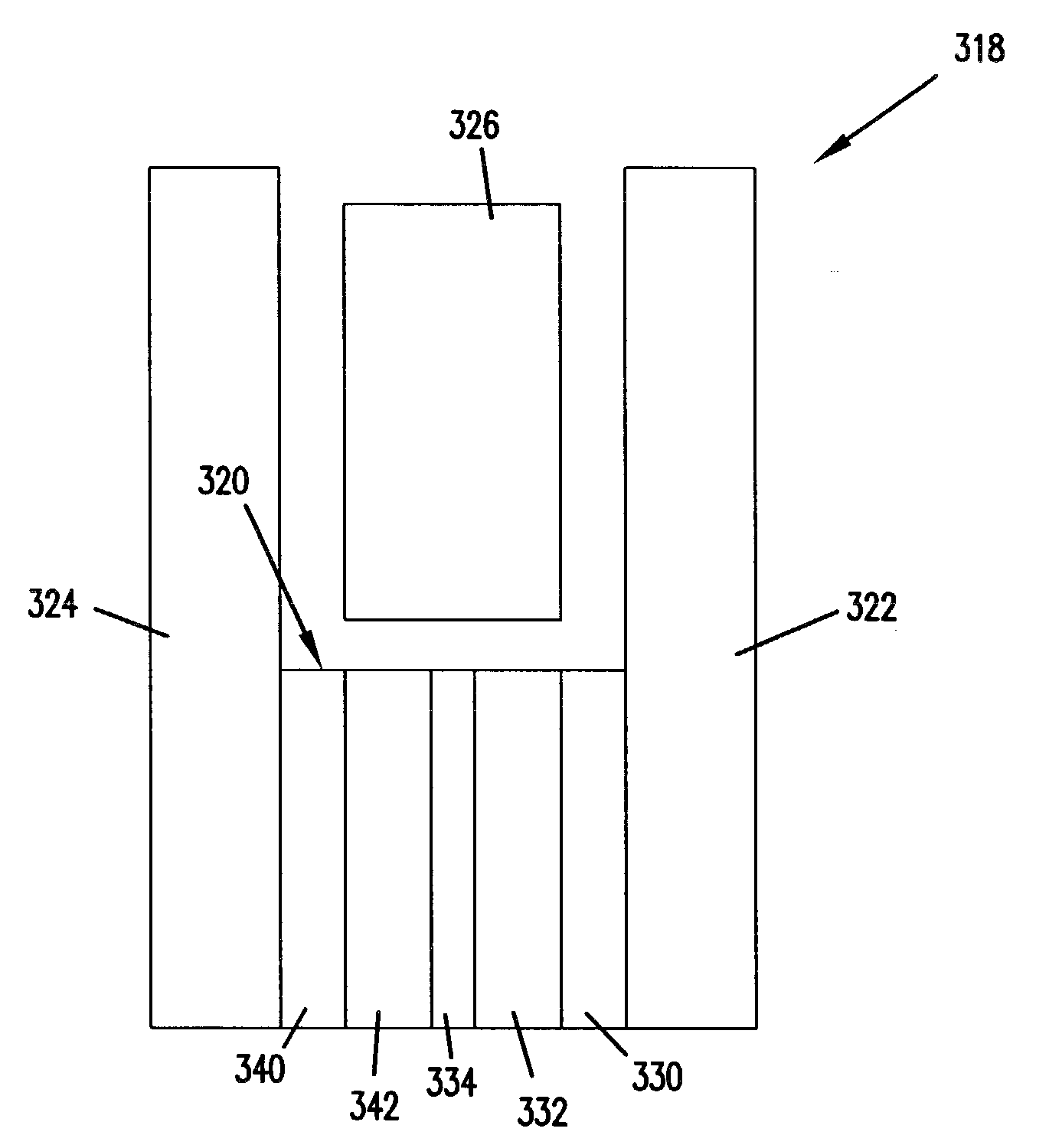
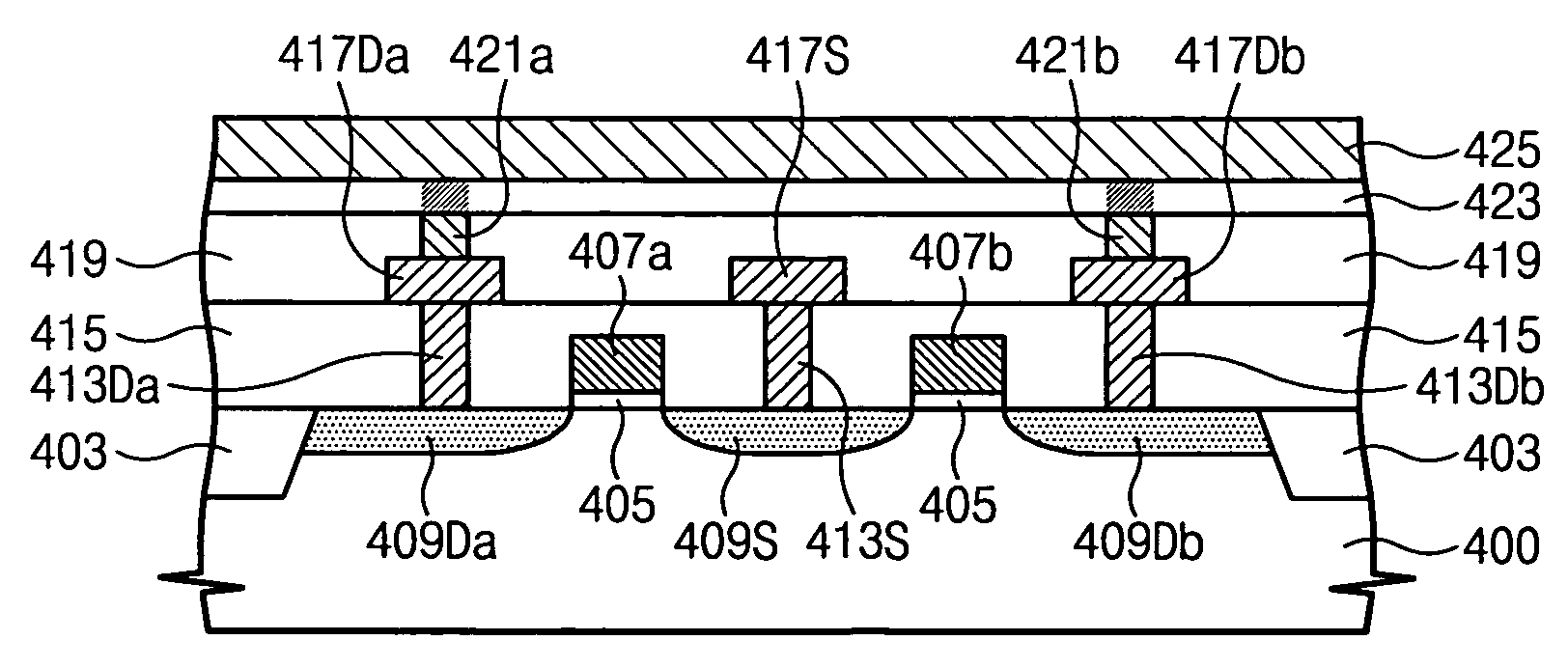
Magneto-resistive memory cells and devices having asymmetrical contacts and methods of fabrication therefor
ActiveUS20060215445A1Good switching operation characteristicEasy to implementSolid-state devicesDigital storageMagnetic reluctanceEngineering
A memory cell includes a plug-type first electrode in a substrate, a magneto-resistive memory element disposed on the first electrode, and a second electrode disposed on the magneto-resistive memory element opposite the first electrode. The second electrode has an area of overlap with the magneto-resistive memory element that is greater than an area of overlap of the first electrode and the magneto-resistive memory element. The first surface may, for example, be substantially circular and have a diameter less than a minimum planar dimension (e.g., width) of the second surface. The magneto-resistive memory element may include a colossal magneto-resistive material, such as an insulating material with a perovskite phase and / or a transition metal oxide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com