Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5520 results about "Recording layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
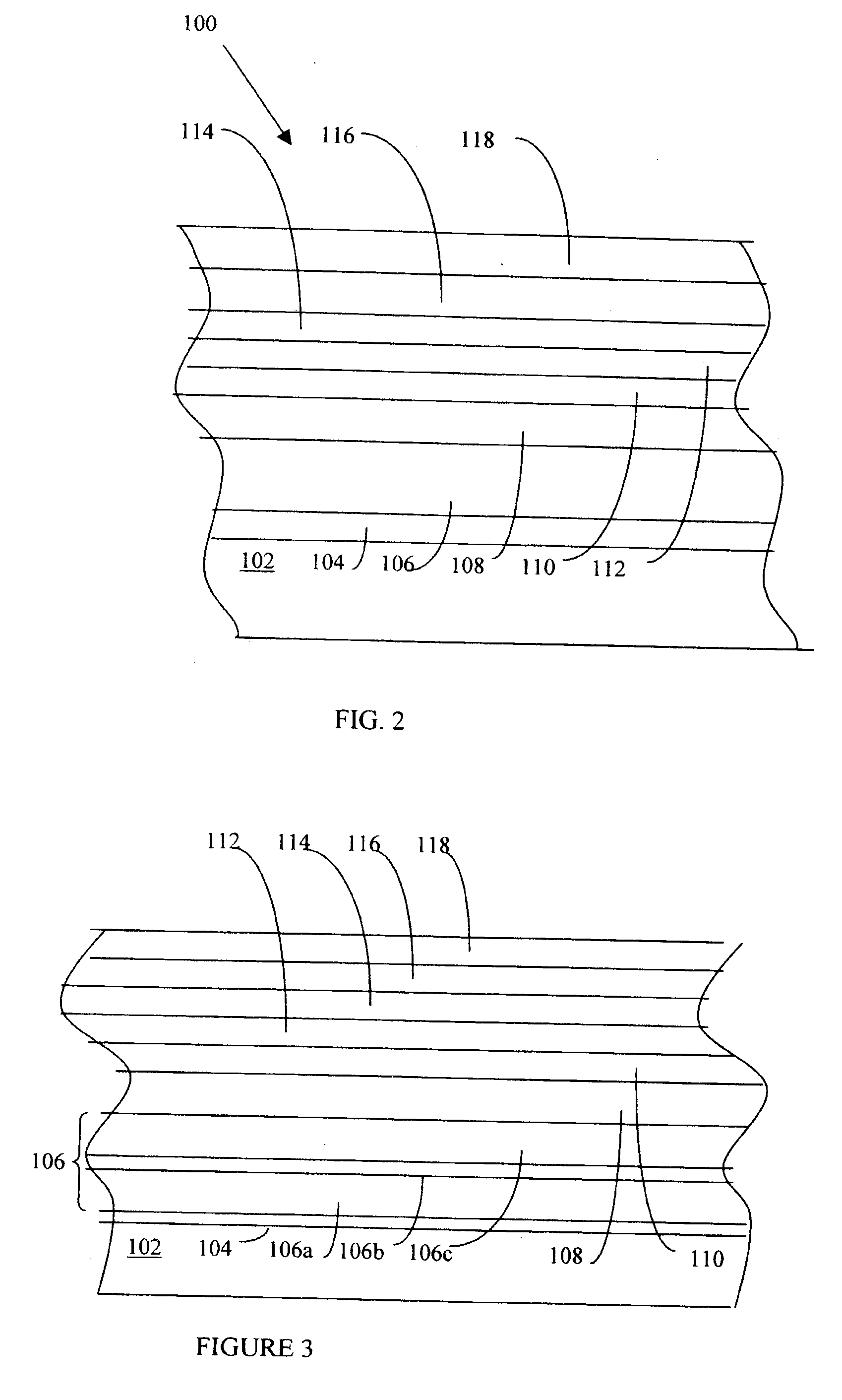
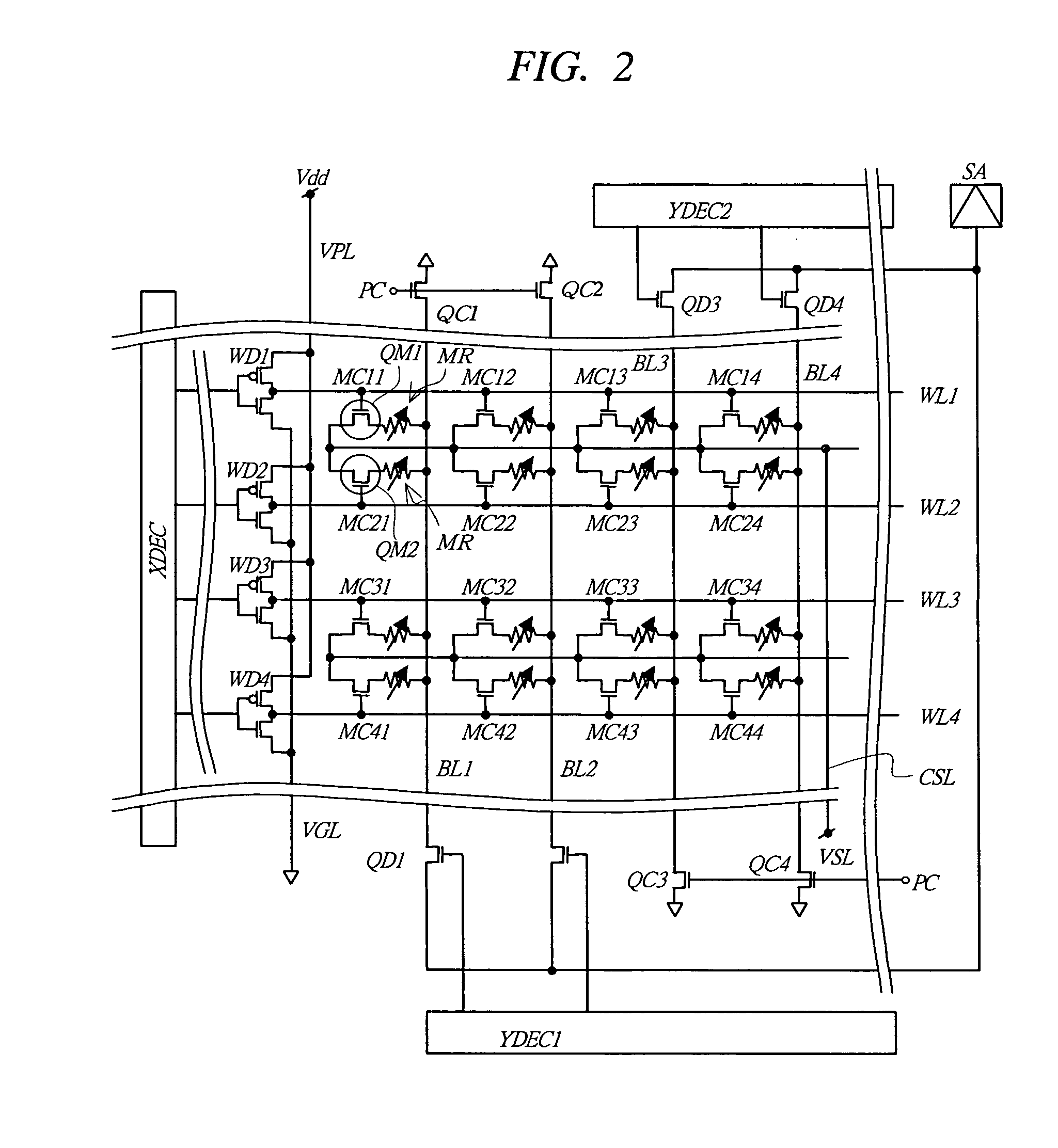
System for Fabricating a Pattern on Magnetic Recording Media
InactiveUS20120223048A1Easy to useReduce system footprintLiquid surface applicatorsDecorative surface effectsHard disc driveMagnetic media
An inline processing system for patterning magnetic recording layers on hard discs for use in a hard disc drive. Discs are processed on both sides simultaneously in a vertical orientation, in round plate-like holders called MDCs. A plurality (as many as 10) discs are held in a dial carrier of the MDC, and transferred from one process station to another. The dial carrier of the MDC may be rotated and / or angled at up to 70° from normal in each process station, so that one or a plurality of process sources may treat the discs simultaneously. This configuration provides time savings and a reduction in the number and size of process sources needed. A mask enhancement process for patterning of magnetic media, and a filling and planarizing process used therewith, are also disclosed.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
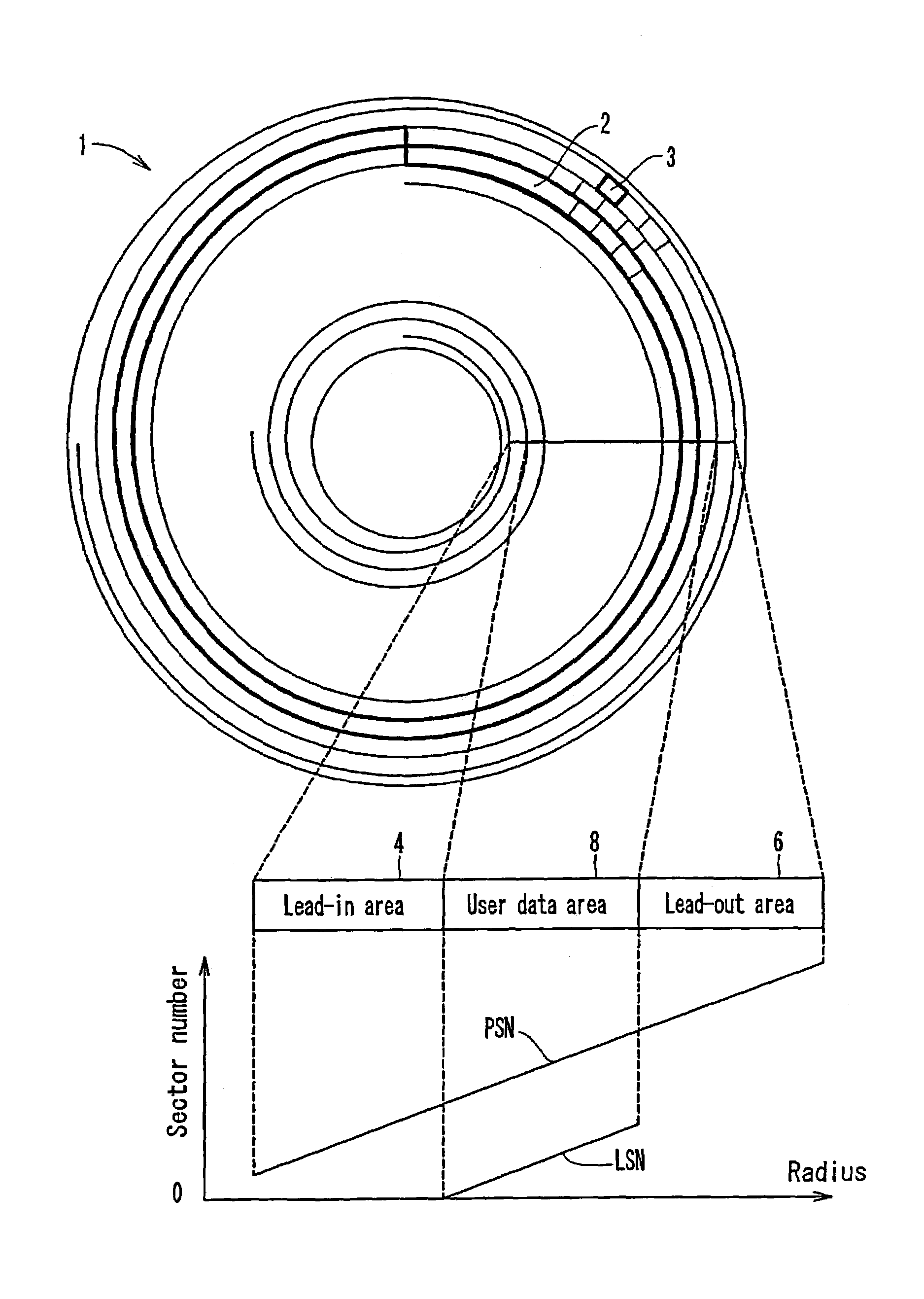
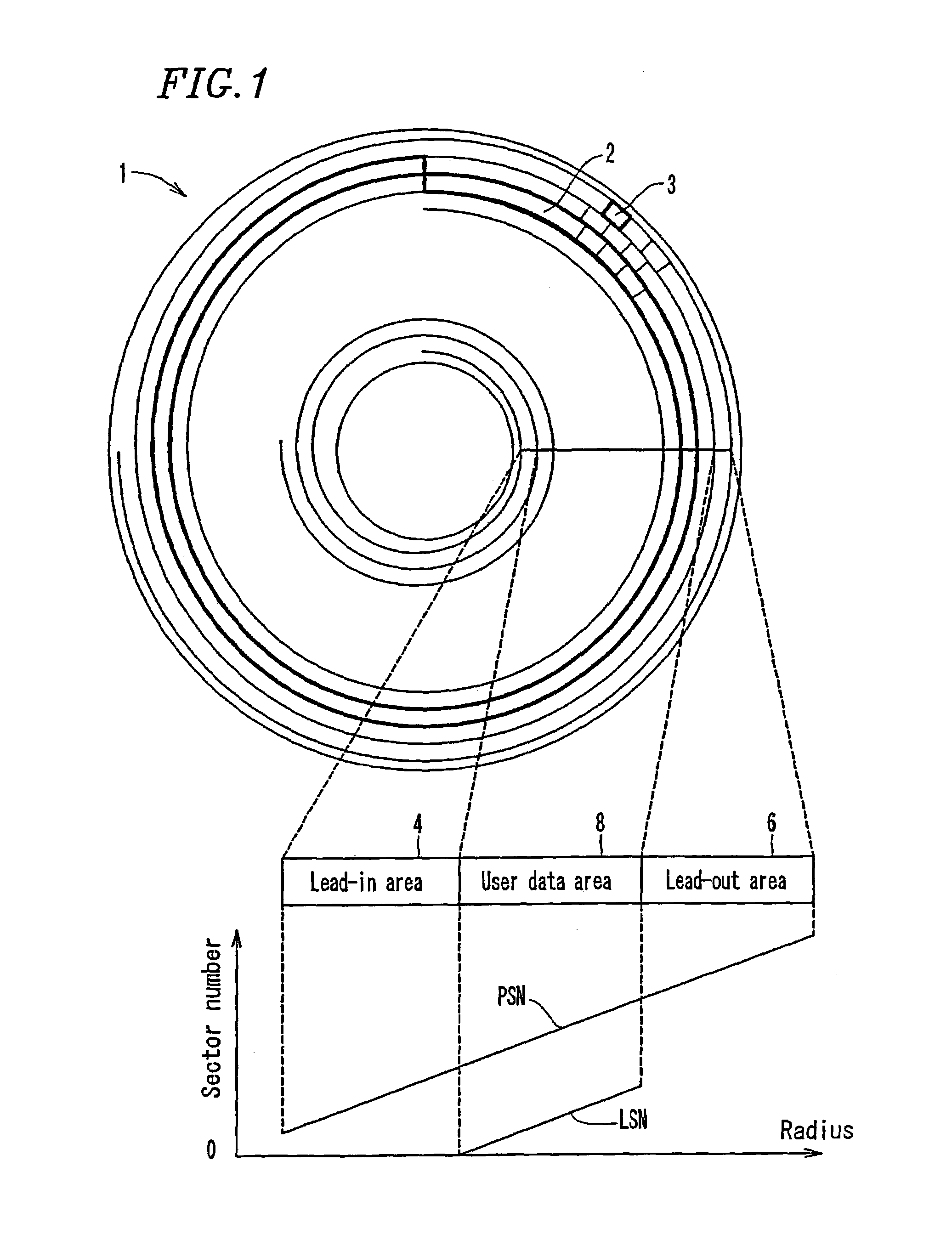
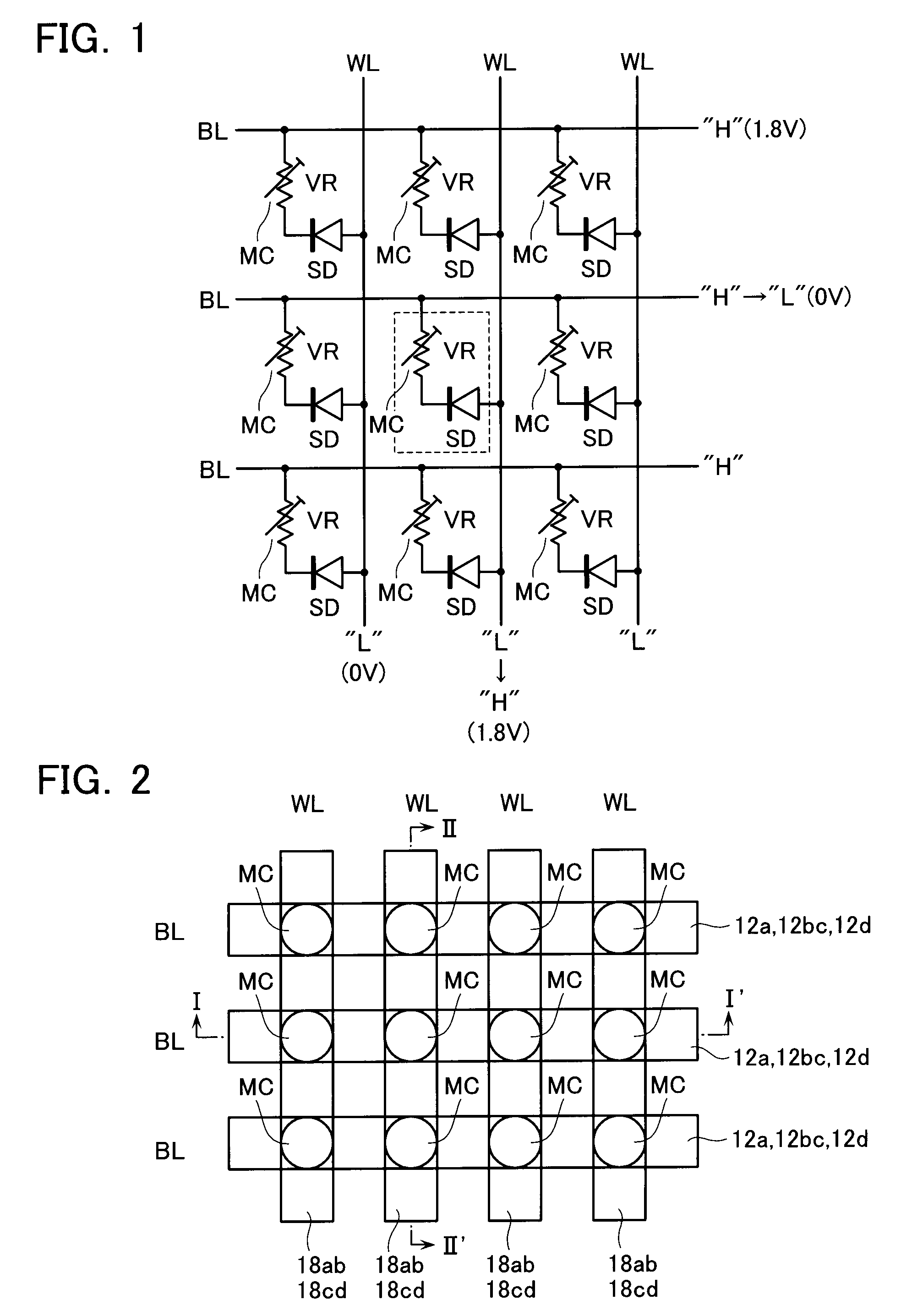
Multi-layered information recording medium, recording apparatus, and recording method
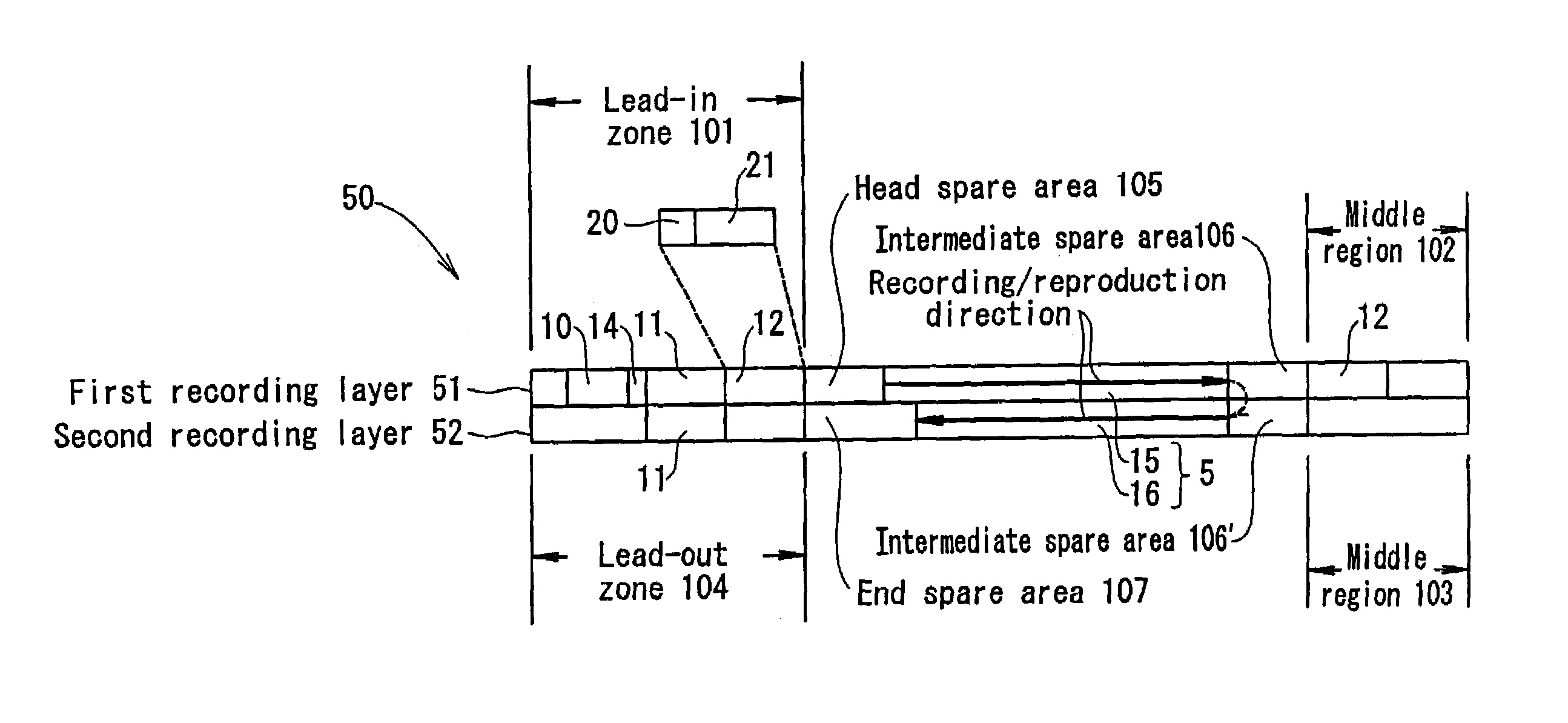
ActiveUS7184377B2Effective areaEasy accessFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesComputer hardwareRadial position
A multi-layered information recording medium including a plurality of recording layers, the multi-layered information recording medium comprising: a user data area for recording user data; and a plurality of spare areas including at least one replacement region, wherein when the user data area includes at least one defect region, the at least one replacement region may be used in place of the at least one defect region, wherein a first spare area of the plurality of spare areas is positioned so as to be contiguous to a first user data area of a first recording layer, a second spare area of the plurality of spare areas is positioned so as to be contiguous to a second user data area of a second recording layer, and the first spare area and the second spare area are positioned approximately at the same radial position on the multi-layered information recording medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
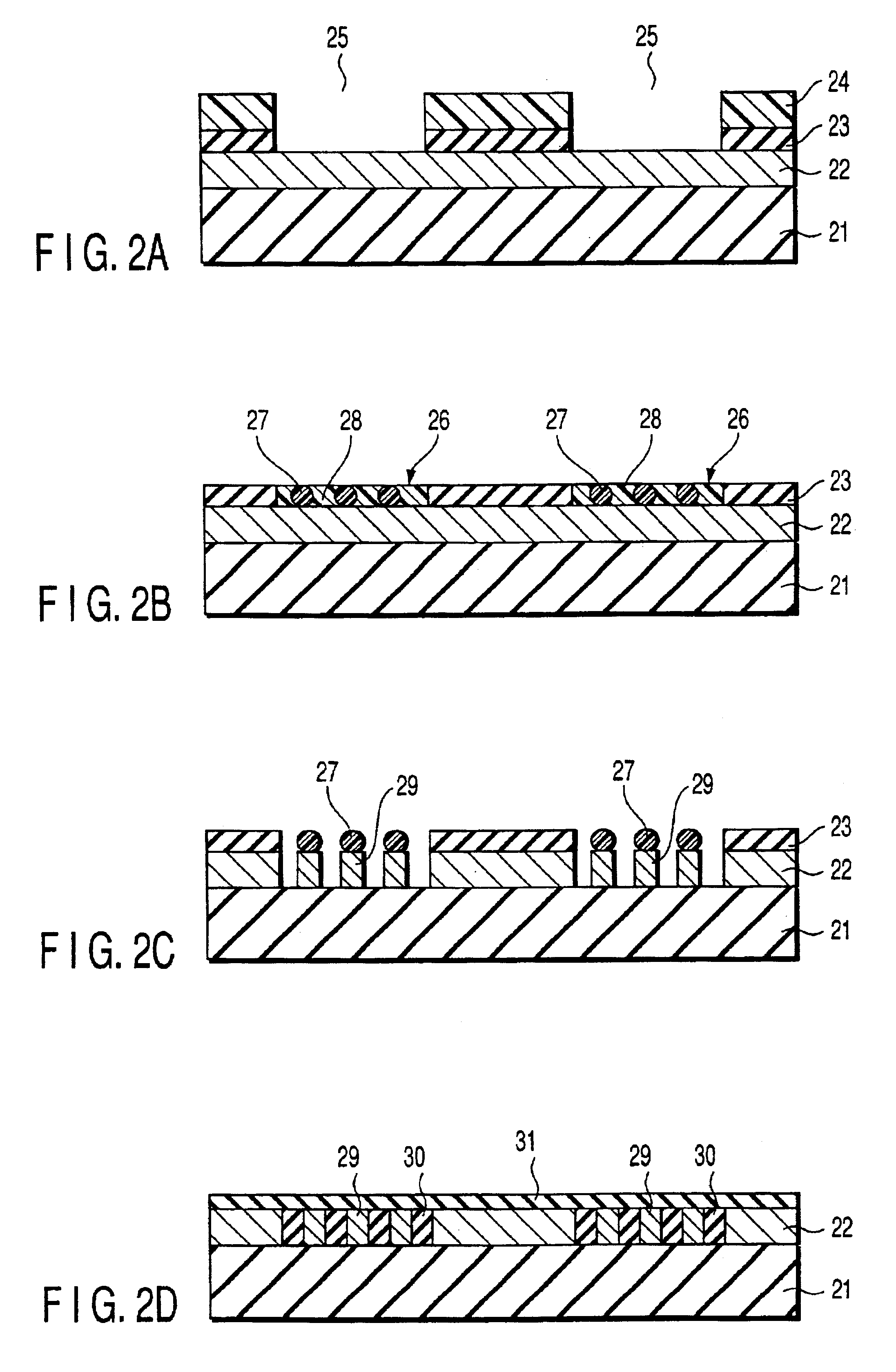
Electrically rewritable non-volatile memory element and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070063180A1Minimizing damageImprove thermal efficiencySolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesEngineeringRecording layer
A non-volatile memory element includes a recording layer that includes a phase change material, a lower electrode provided in contact with the recording layer, an upper electrode provided in contact with a portion of the upper surface of the recording layer, a protective insulation film provided in contact with the other portion of the upper surface of the recording layer, and an interlayer insulation film provided on the protective insulation film. High thermal efficiency can thereby be obtained because the size of the area of contact between the recording layer and the upper electrode is reduced. Providing the protective insulation film between the interlayer insulation film and the upper surface of the recording layer makes it possible to reduce damage sustained by the recording layer during patterning of the recording layer or during formation of the through-hole for exposing a portion of the recording layer.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
MRAM having spin hall effect writing and method of making the same
InactiveUS20140252439A1Easy to switchEasy to reverseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic reluctanceRecording layer
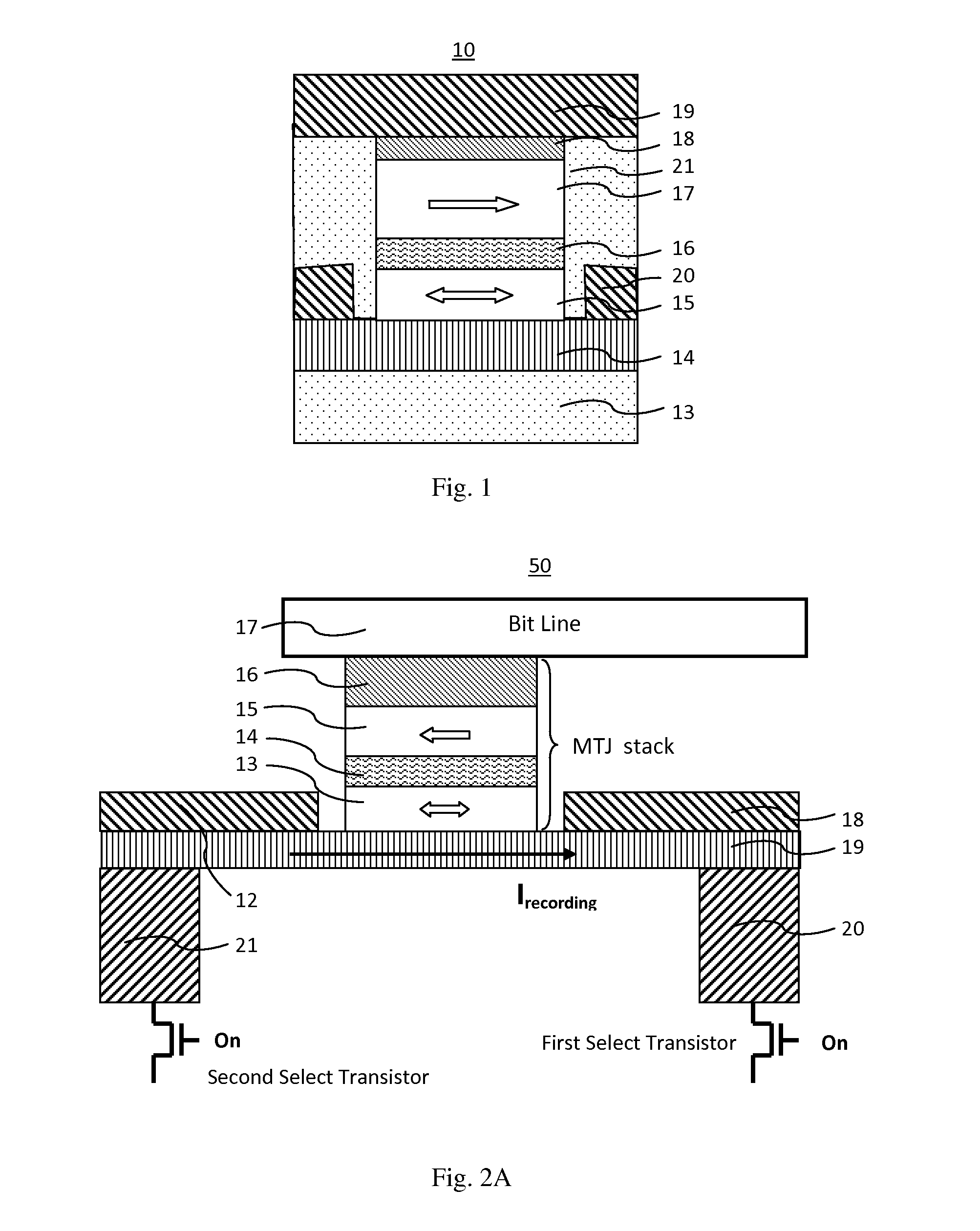
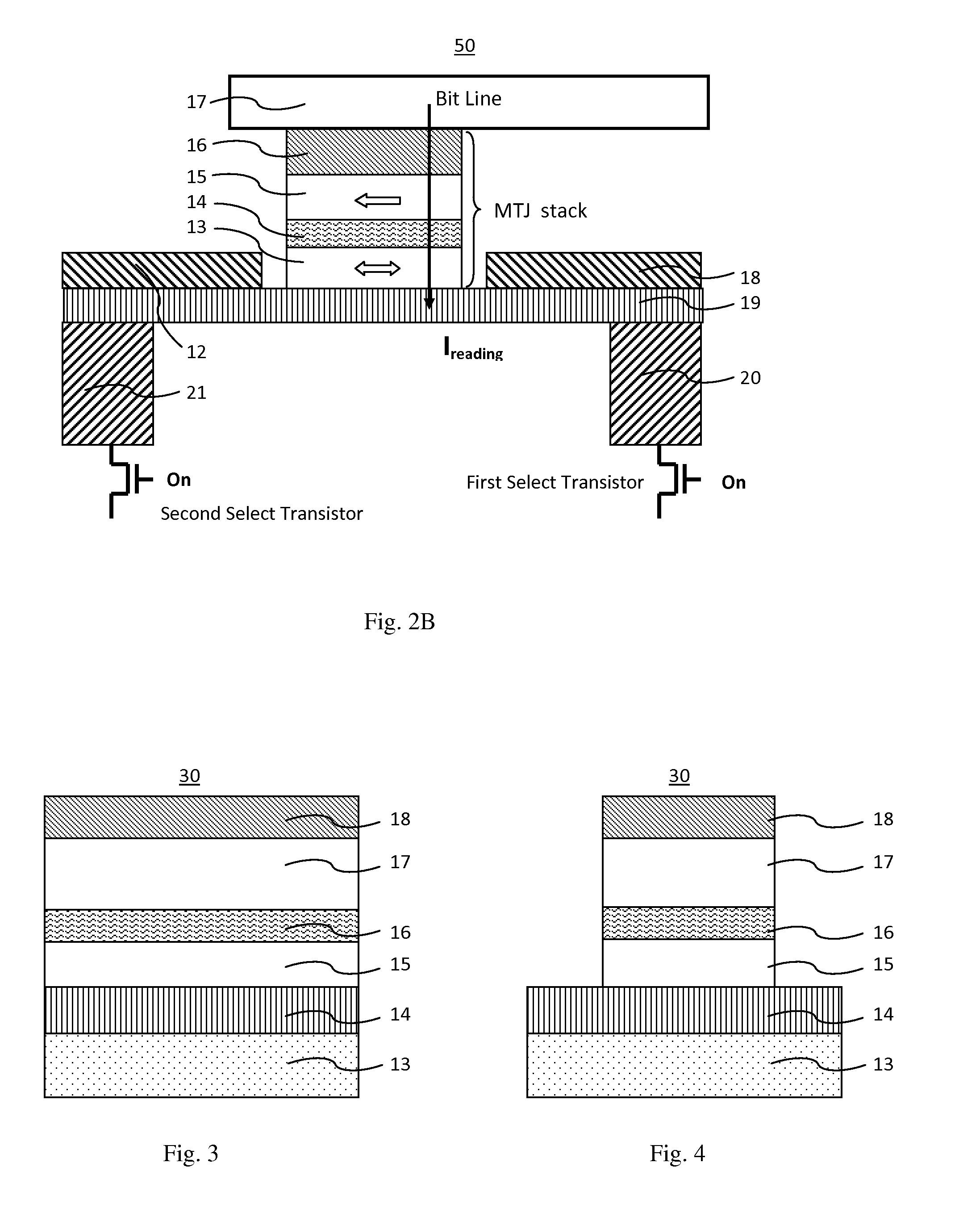
A spin-transfer-torque magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus and method of manufacturing a three terminal magnetoresistive memory element having highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid on top of a SHE-metal layer in the regions outside of an MTJ stack. The memory cell comprises a bit line positioned adjacent to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid and electrically contacting on top of a SHE-metal layer in the outside of an MTJ region and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to switch the magnetization of the recording layer. Thus magnetization of a recording layer can be readily switched or reversed to the direction in accordance with a direction of a current along the SHE-metal layer by applying a low write current.
Owner:T3MEMORY
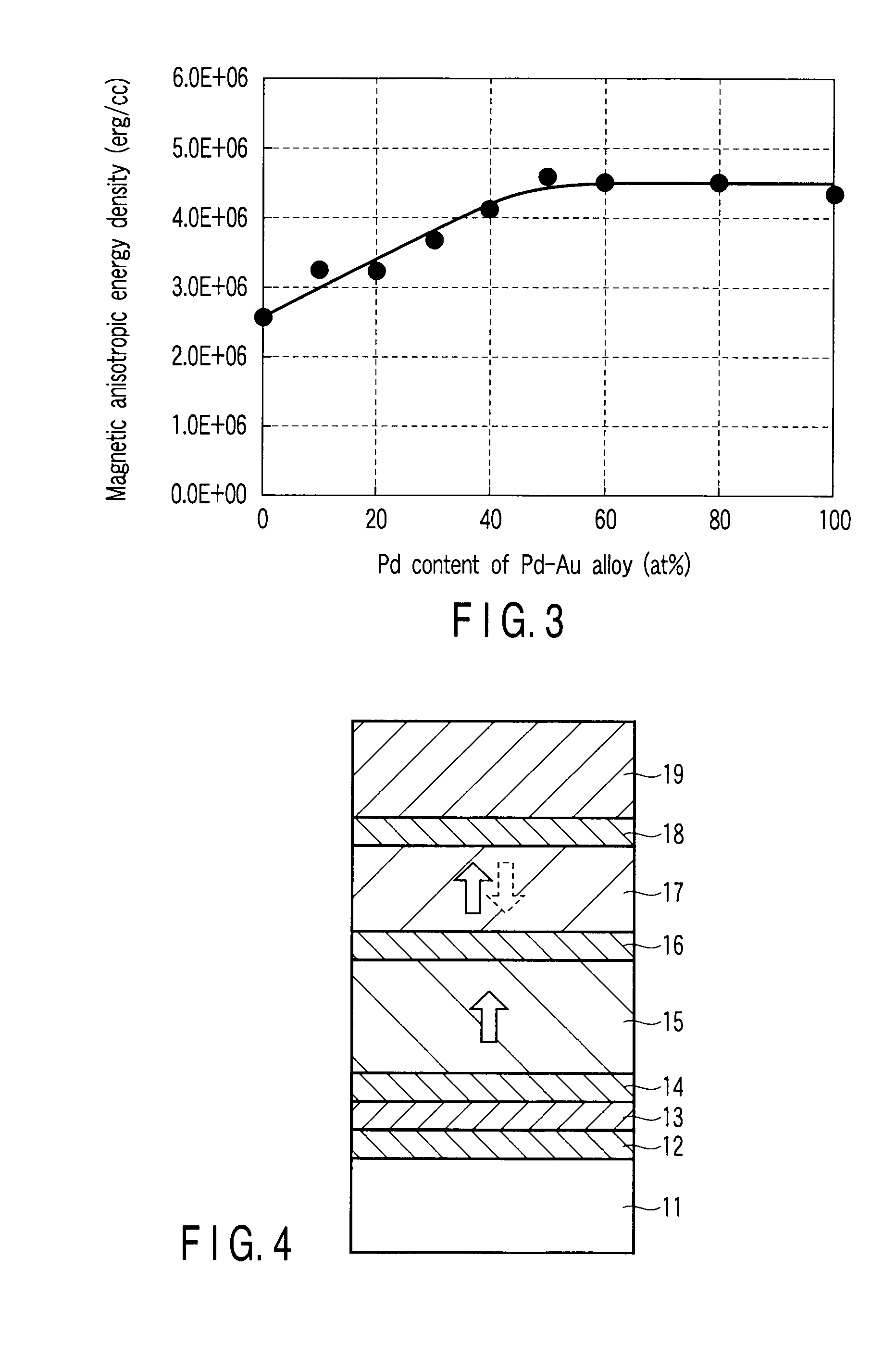
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium with improved magnetic anisotropy field
InactiveUS20100035085A1High HcExcellent crystallographic C axis orientationMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic anisotropyAlloy
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium comprising a substrate, a soft underlayer, a seed layer, a non-magnetic FCC NiW alloy underlayer, a non-magnetic HCP underlayer, and a magnetic layer. We have discovered that the combination of a seed layer comprising Ta and a NiW alloy underlayer uniquely improves media recording performance and thermal stability by achieving excellent coercivity of the thin bottom magnetic recording layer and narrow C axis orientation distribution.
Owner:WD MEDIA
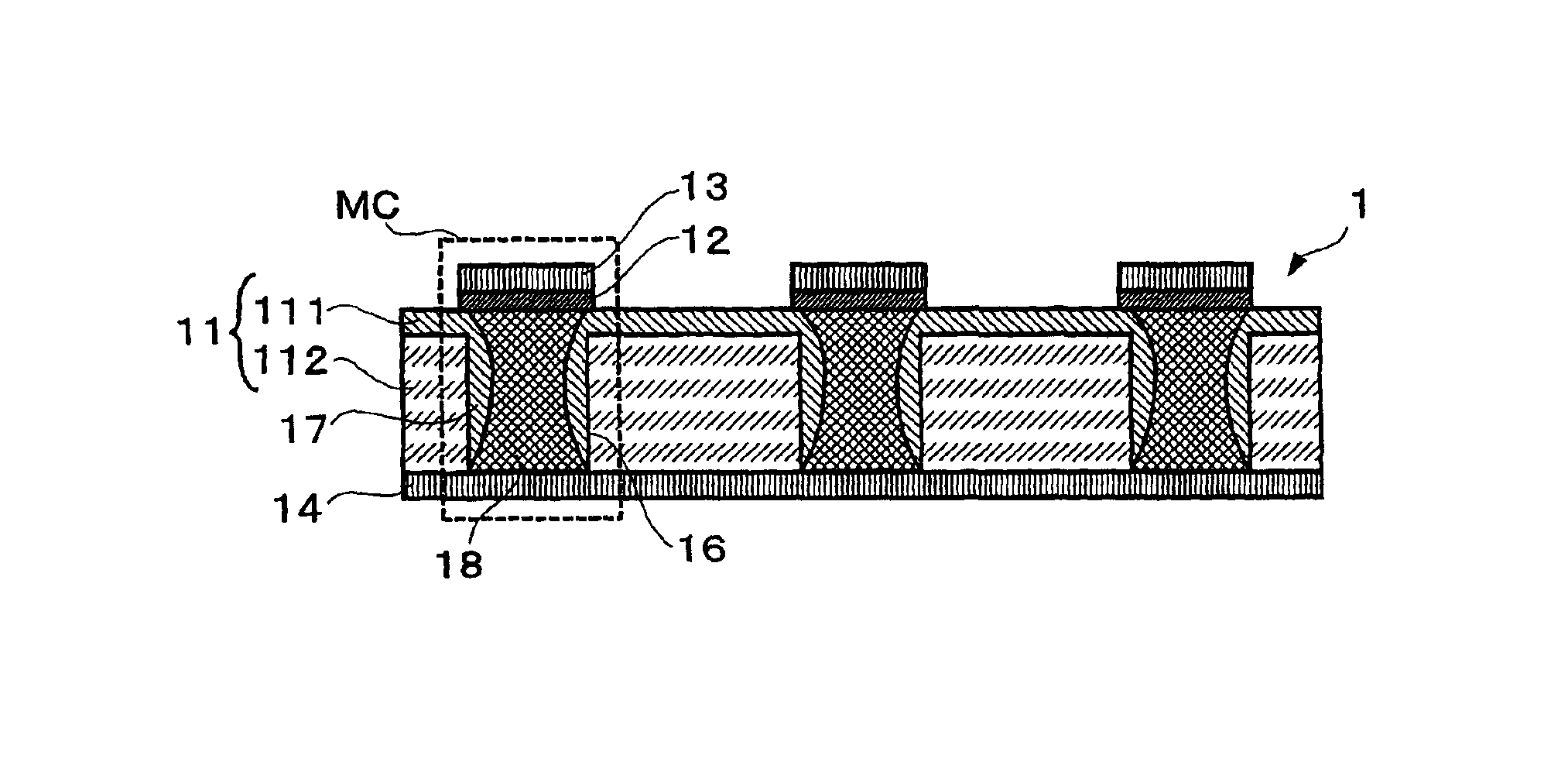
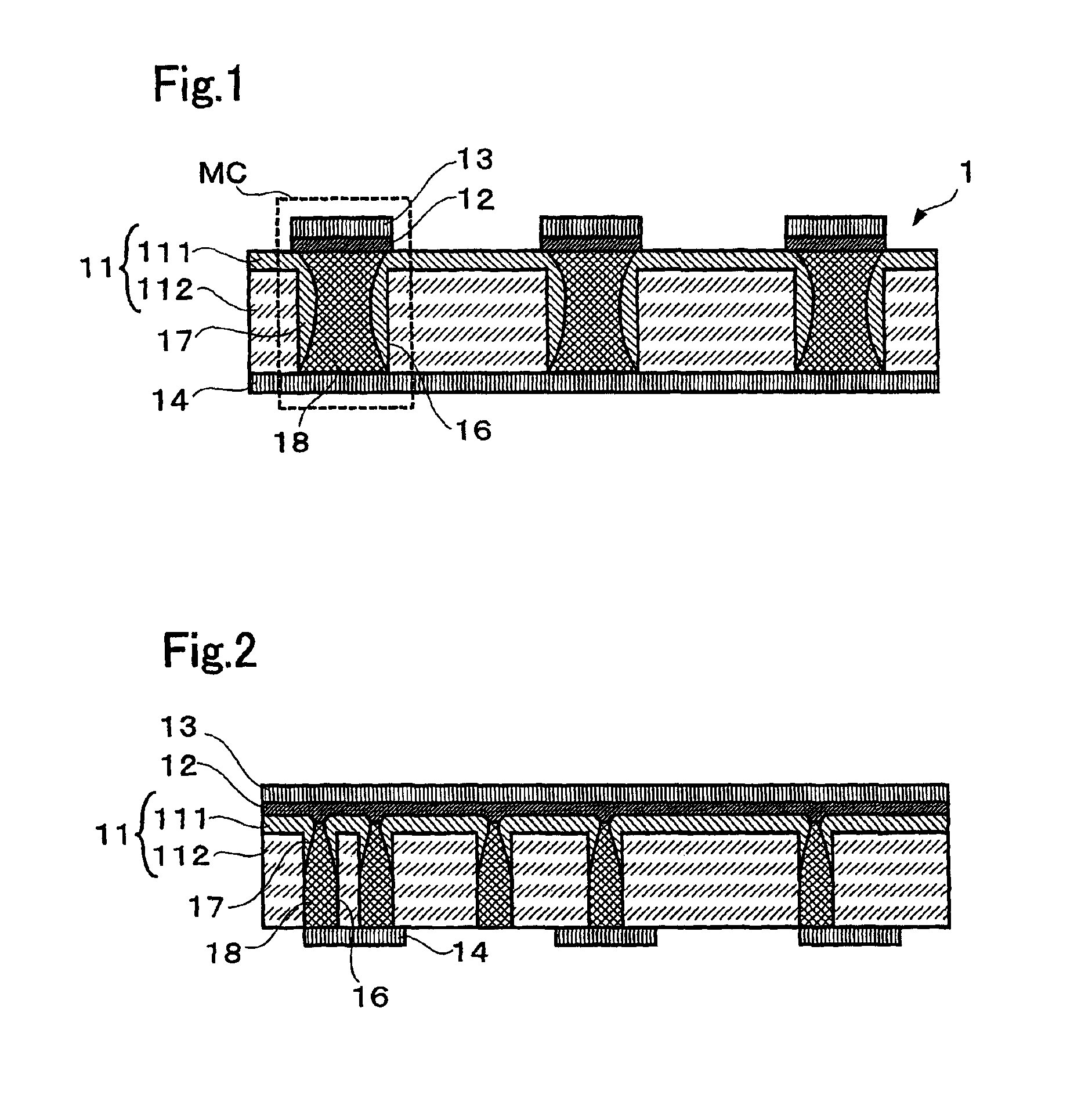
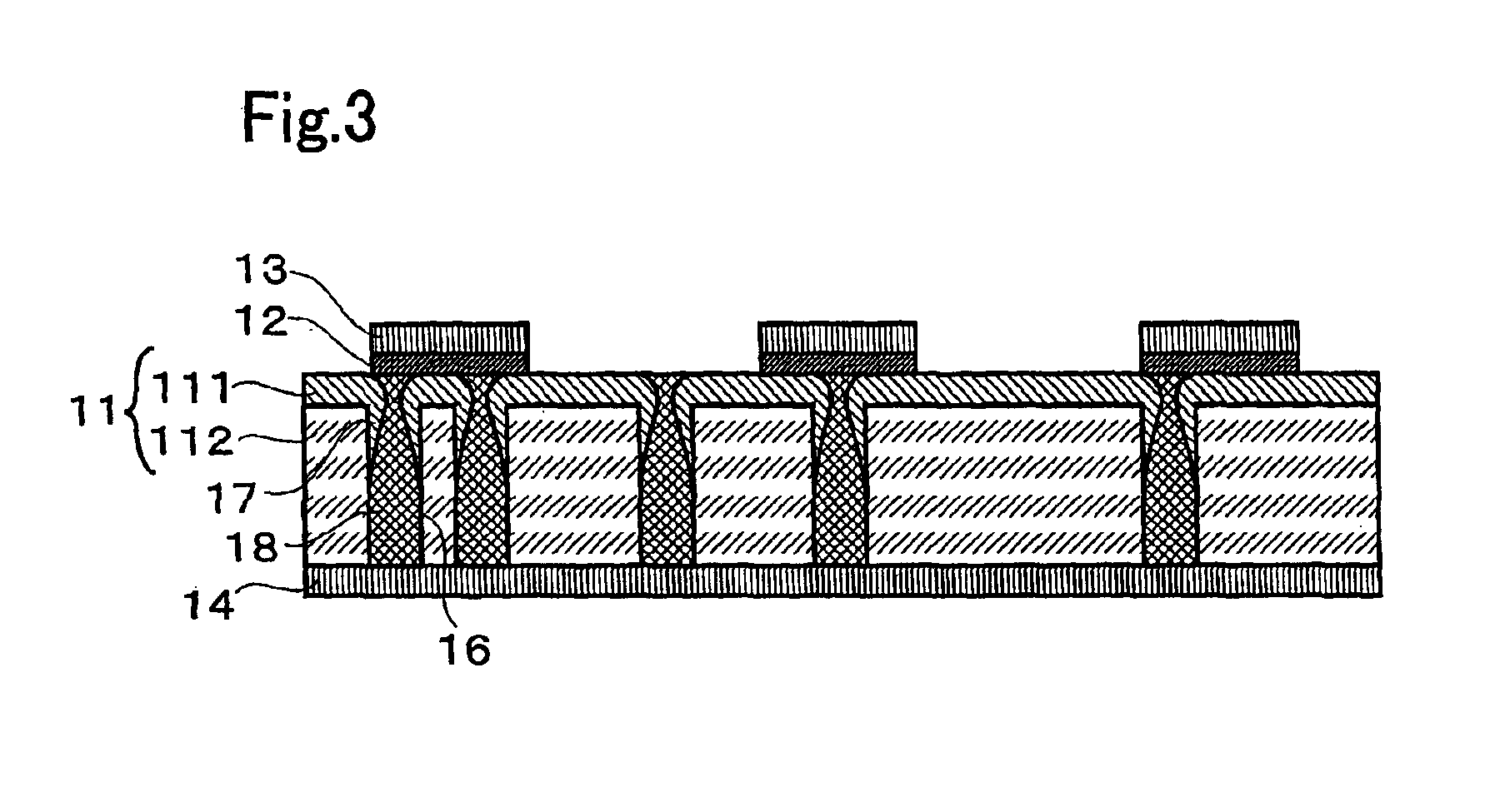
Non-volatile memory with phase-change recording layer
InactiveUS6900517B2Increase possible numberReduce power consumptionTransistorVariable resistance carrier recordingElectrical impulseEngineering
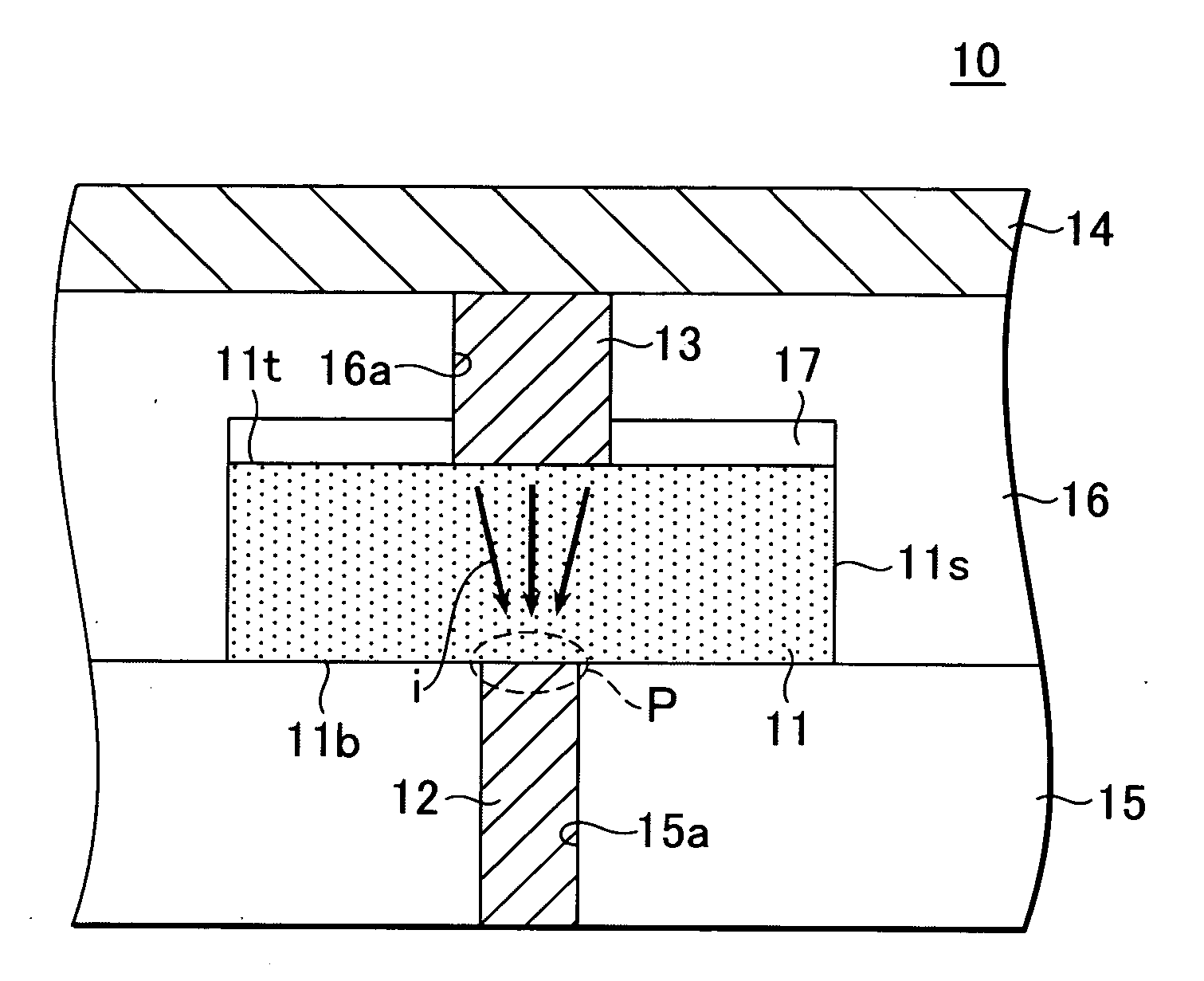
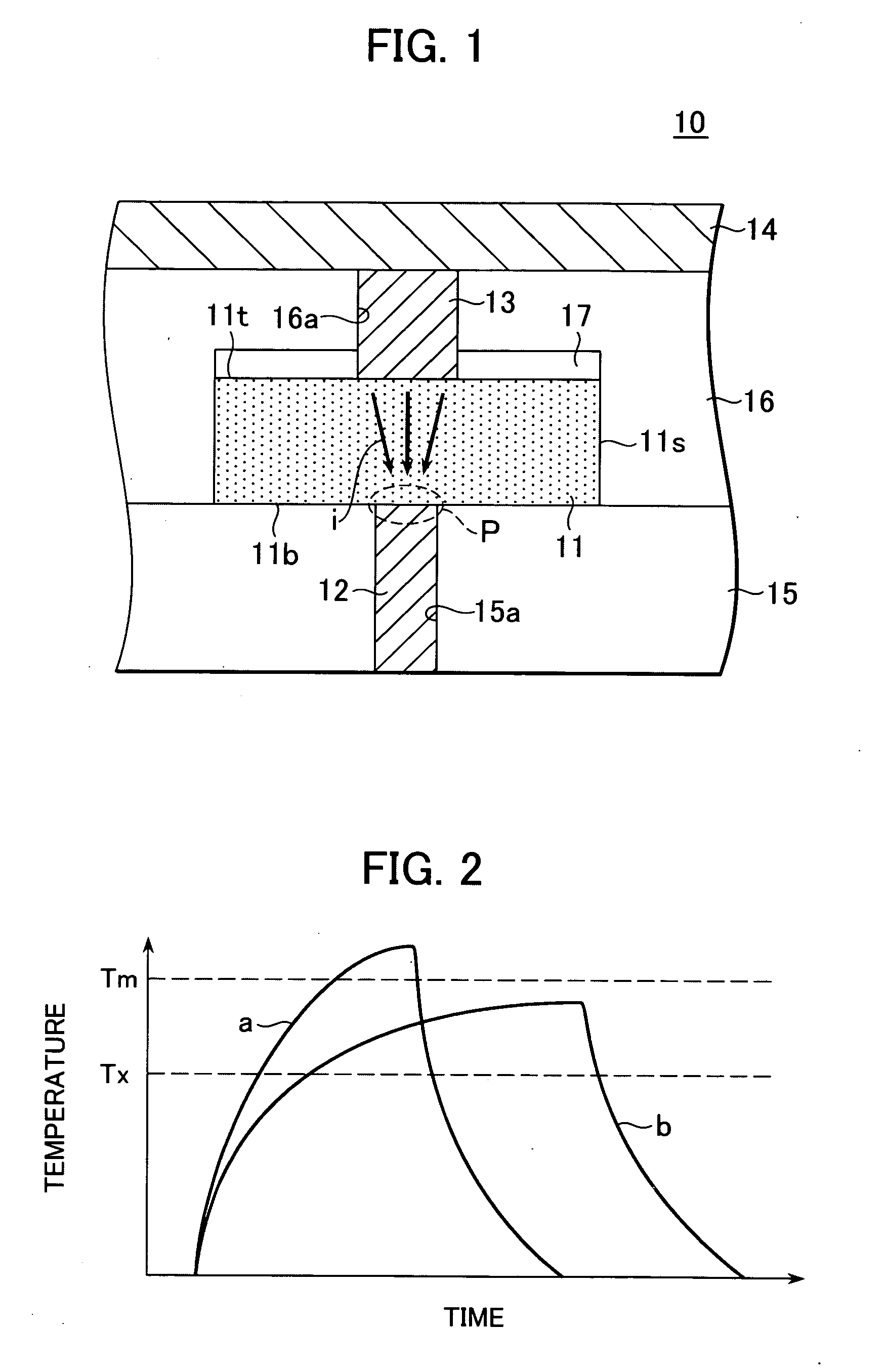
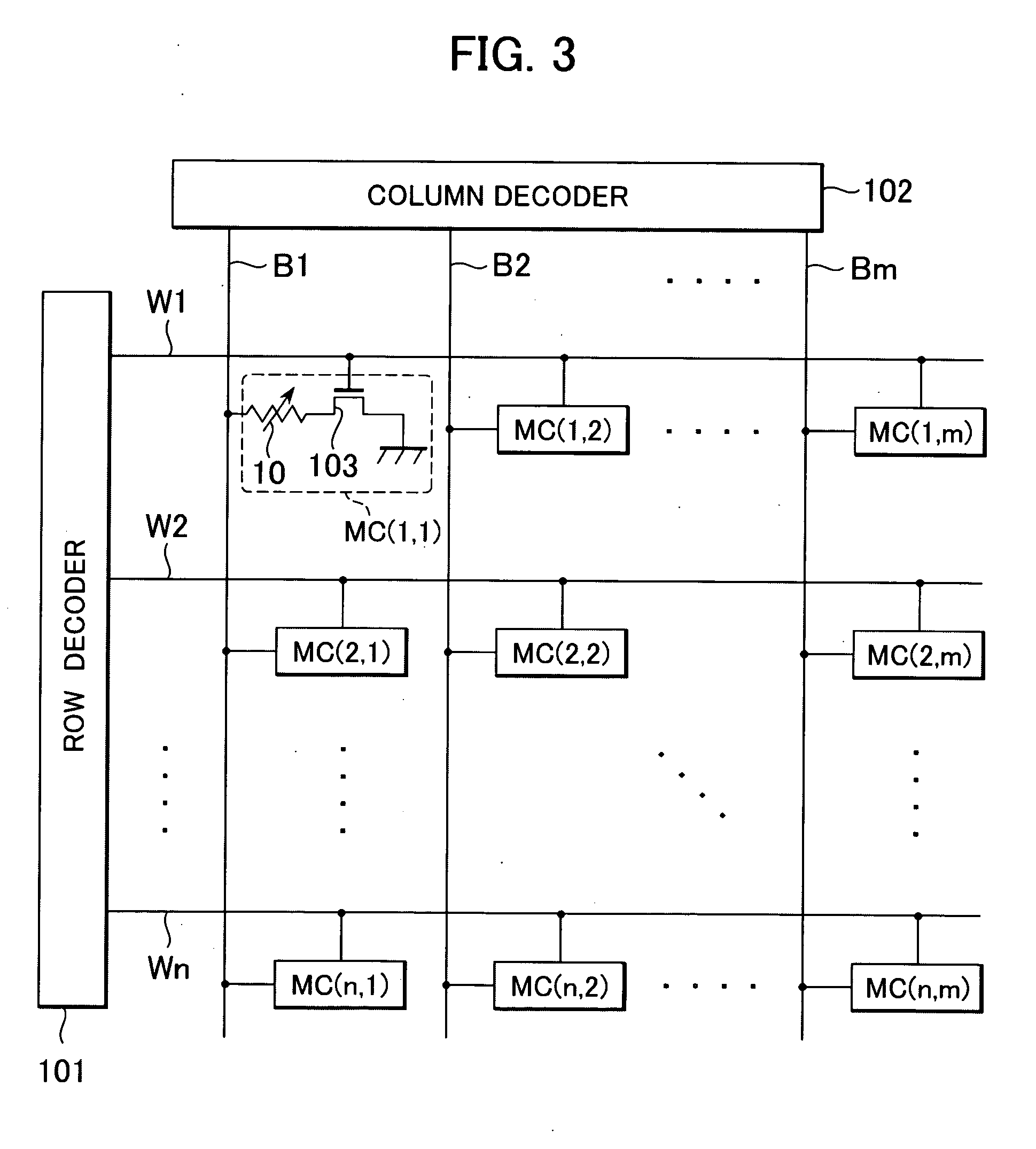
A non-volatile memory, which comprises an insulating substrate (11) that has a first electrode (18) that extends through the substrate from the front surface to the rear surface thereof; a second electrode (13) that is formed on one side of the insulating substrate (11); and a recording layer (12) that is clamped between the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13) and whose resistance value varies when an electric pulse is applied across the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13); wherein the insulating substrate (11) has a layered structure composed of an organic dielectric thin film (112) and an inorganic dielectric layer (111) that is thinner than the organic dielectric thin film (112); with the recording layer (12) being formed on the side on which the inorganic dielectric layer is formed. Use of this non-volatile memory increases the possible number of data writing cycles while saving power.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
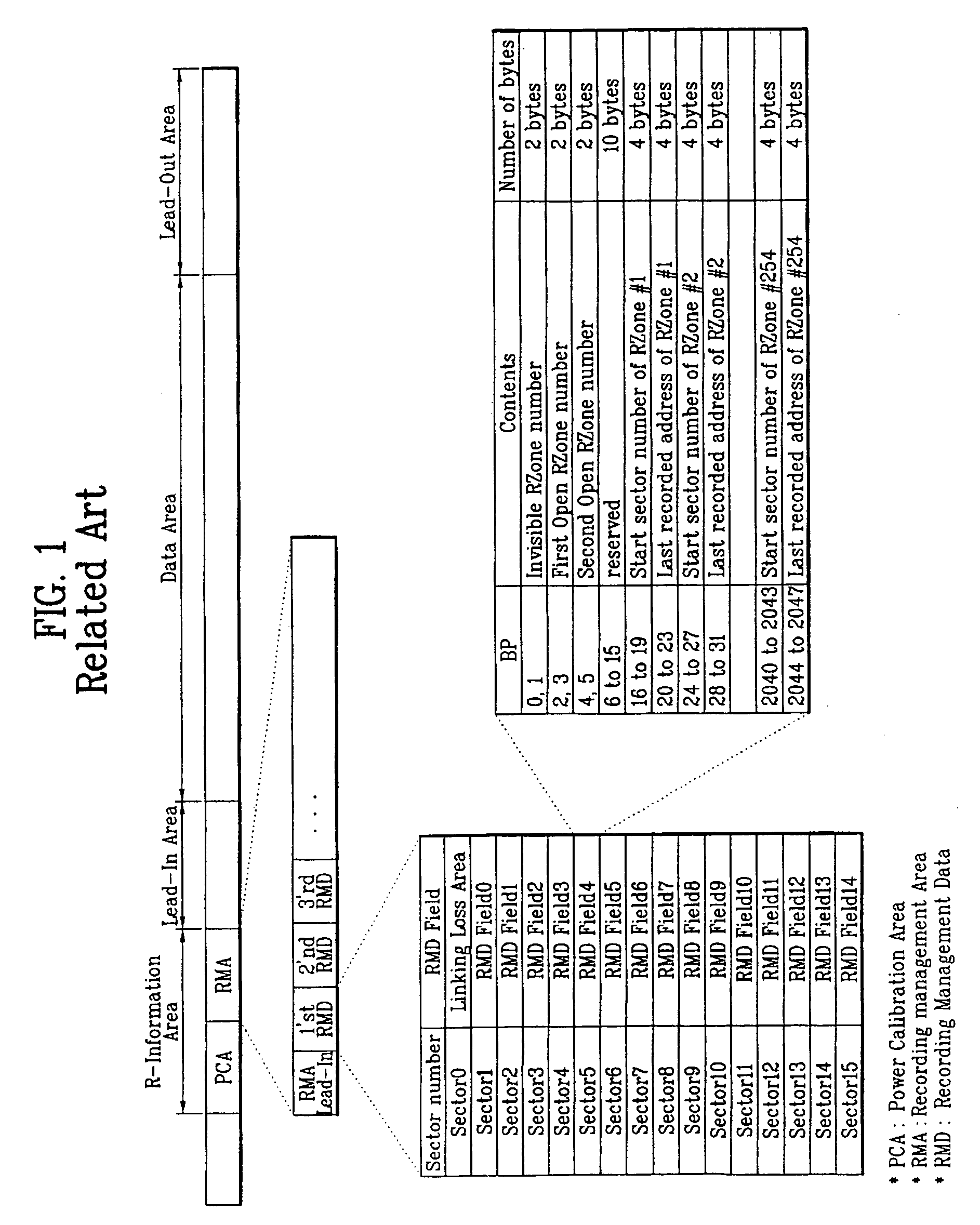
Write-once optical disc, method and apparatus for recording management information on write-once optical disc
InactiveUS20050060489A1Efficiently recording and managing this recording status informationFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageRecord statusRecording layer
A write-once optical disc, and a method and apparatus for recording management information on the write-once optical disc, are provided. The optical disc includes at least one recording layer, and at least one SRR entry. Each SRR entry corresponds to an SRR and includes at least one status field for indicating a recording status of the corresponding SRR. The status field includes a session start flag for indicating whether the corresponding SRR is a start of a session, the session being formed by a group of the SRRs. Each SRR entry further includes a start address field indicating where the corresponding SRR starts, and a last address field indicating the last recorded address of the corresponding SRR.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
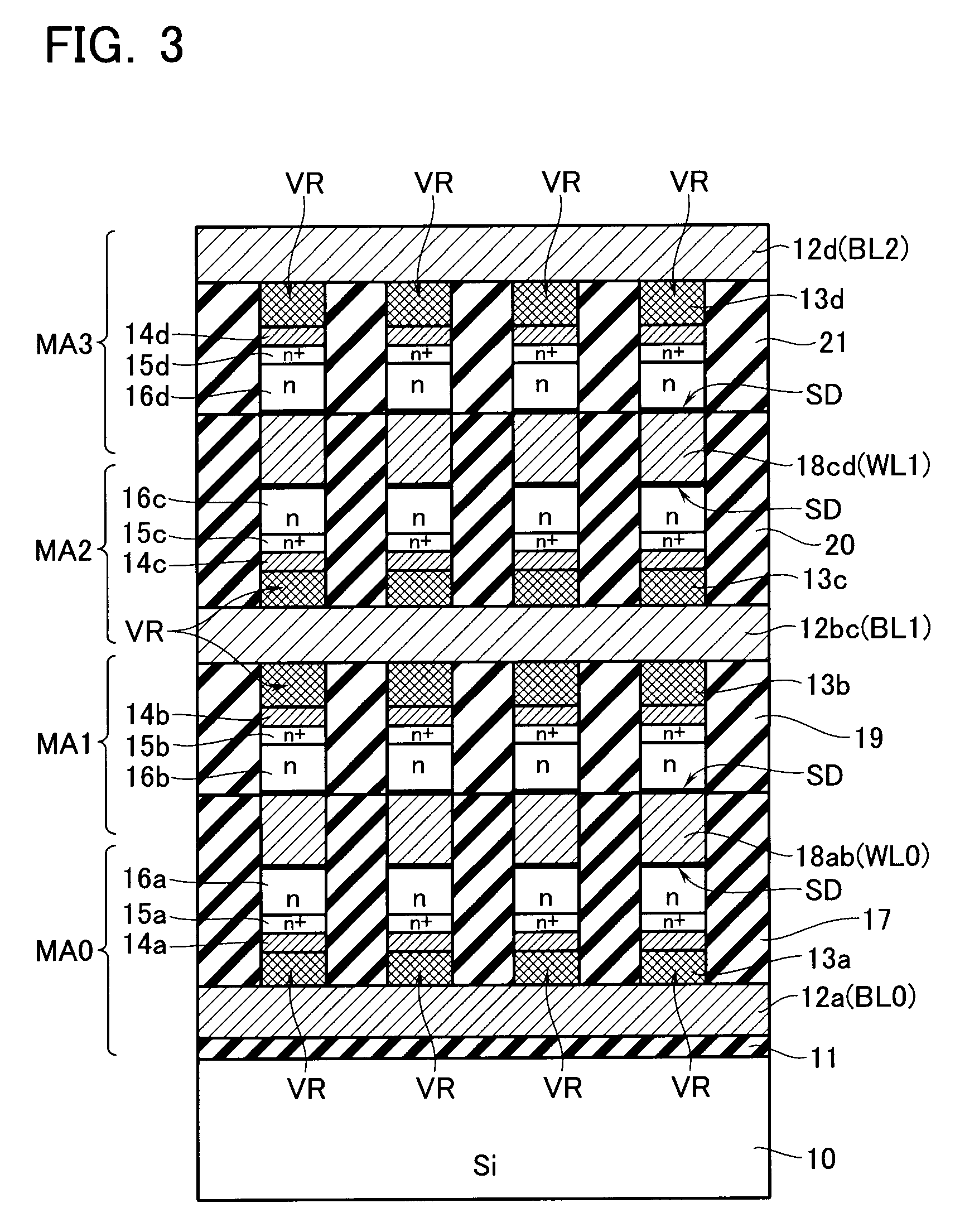
Multi-layered information recording medium with spare defect management areas
ActiveUS7123556B2Shorten the timeEfficient managementInput/output to record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareRecording layer
A multi-layered information recording medium comprising a plurality of recording layers, a user data area for recording user data, provided in at least two of the plurality of recording layers, and a defect list storing area for storing a defect list. When at least one defective area is detected in the user data area, the defect list is used to manage the at least one defective area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
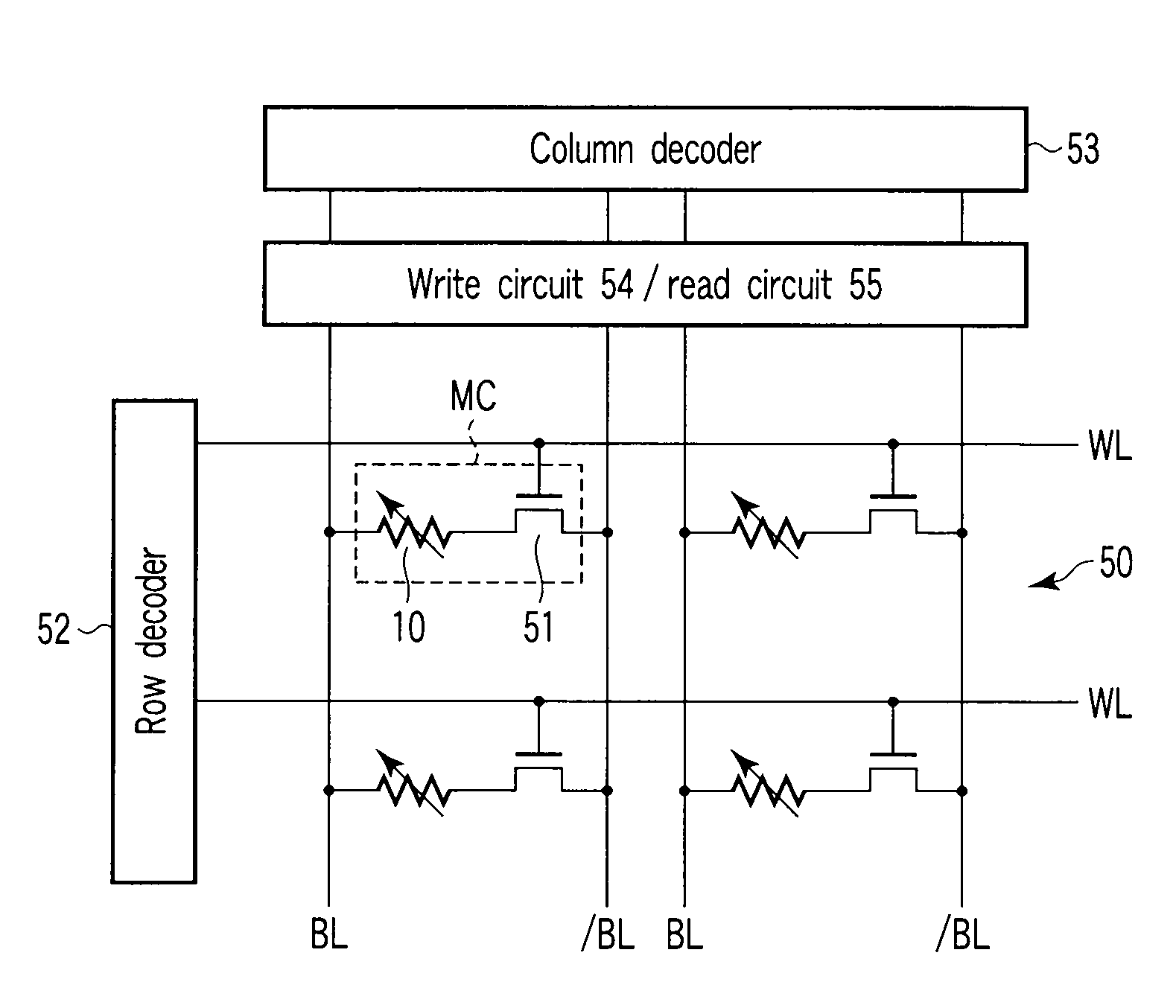
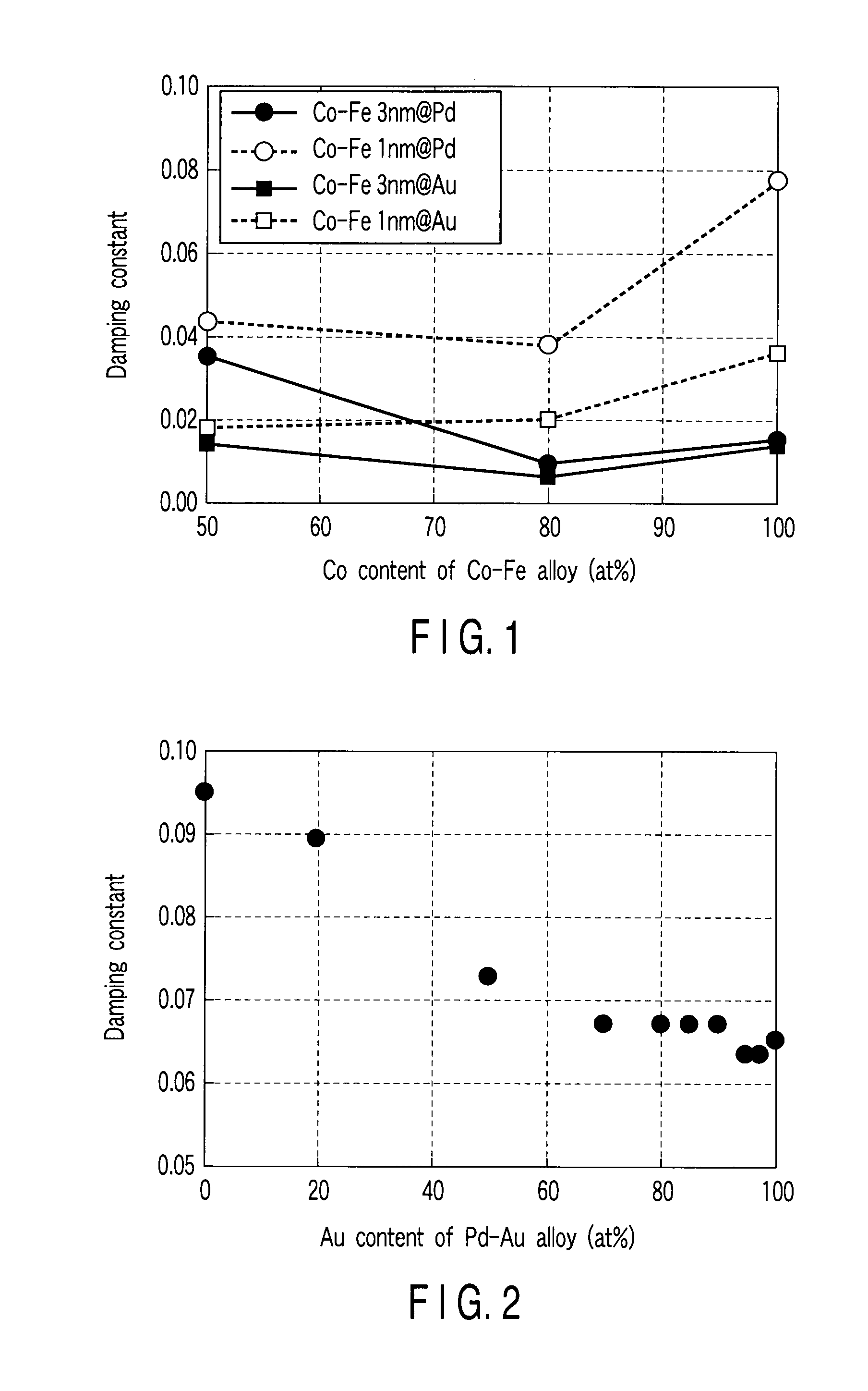
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
A magnetoresistive element includes a first reference layer having magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to a film surface, and an invariable magnetization, a recording layer having a stacked structure formed by alternately stacking magnetic layers and nonmagnetic layers, magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to a film surface, and a variable magnetization, and an intermediate layer provided between the first reference layer and the recording layer, and containing a nonmagnetic material. The magnetic layers include a first magnetic layer being in contact with the intermediate layer and a second magnetic layer being not in contact with the intermediate layer. The first magnetic layer contains an alloy containing cobalt (Co) and iron (Fe), and has a film thickness larger than that of the second magnetic layer.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Recording medium including patterned tracks and isolation regions
InactiveUS6977108B2Easy to manufactureIncrease speedTrack finding/aligningMagnetic materials for record carriersEngineeringRecording layer
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
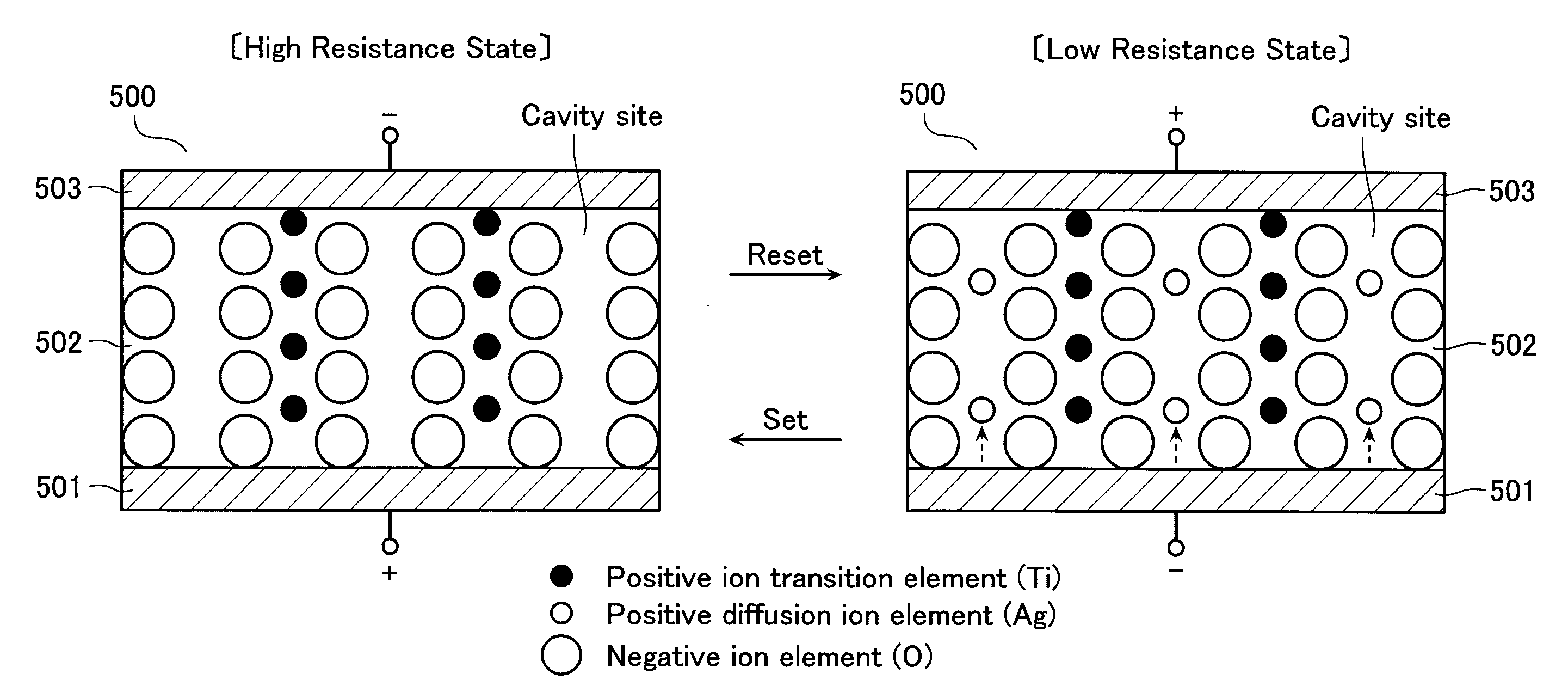
Resistance change memory device having a variable resistance element with a recording layer electrode served as a cation source in a write or erase mode
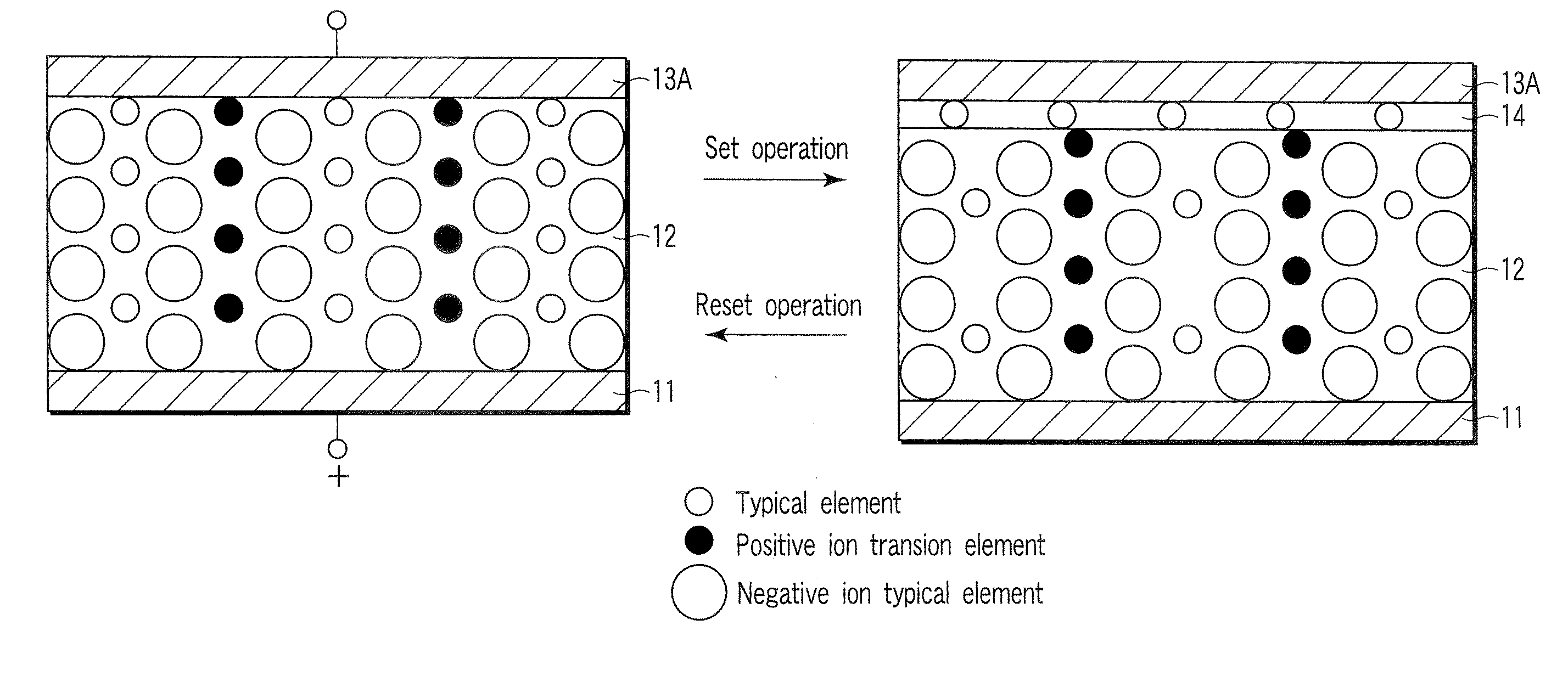
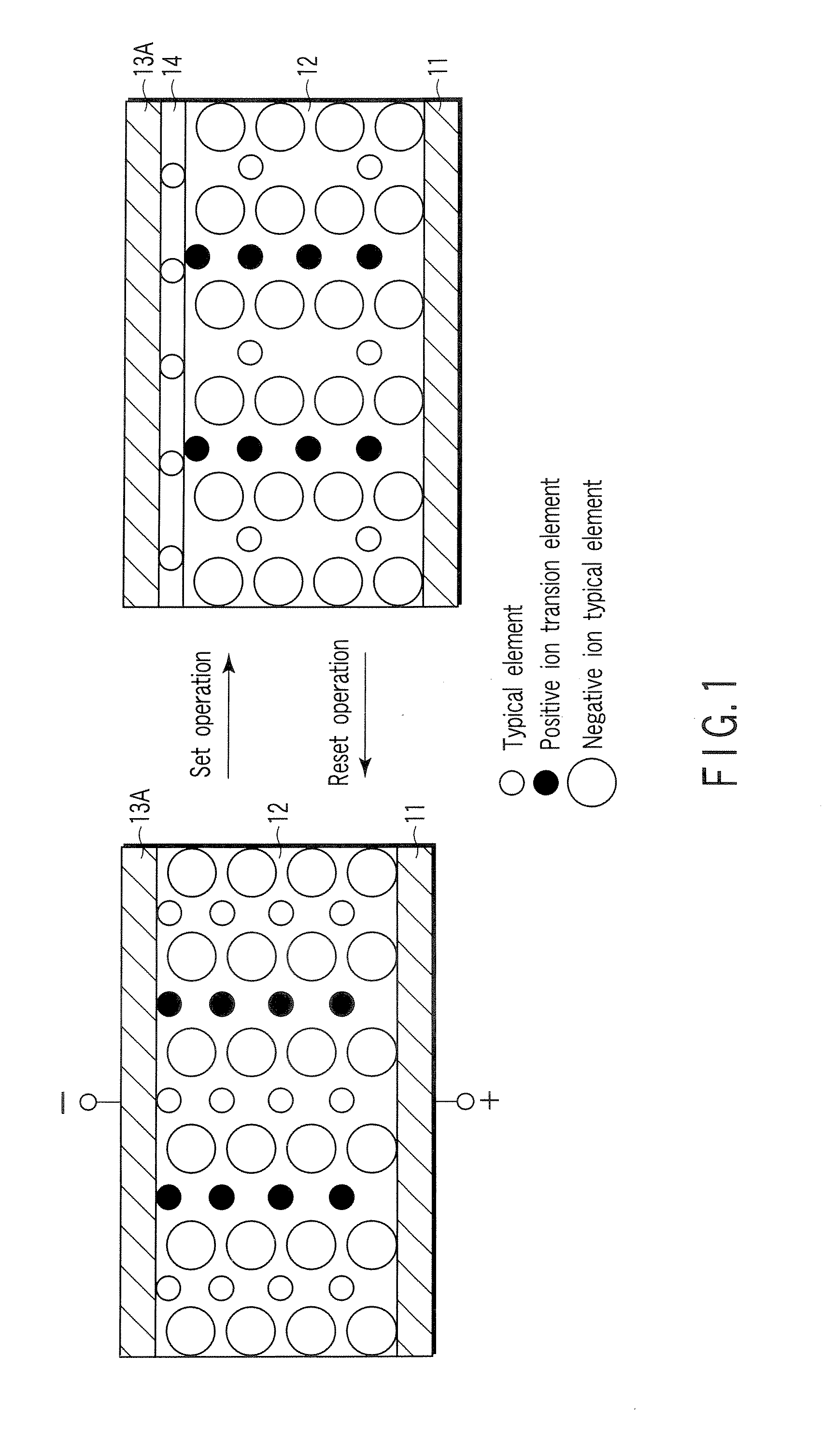
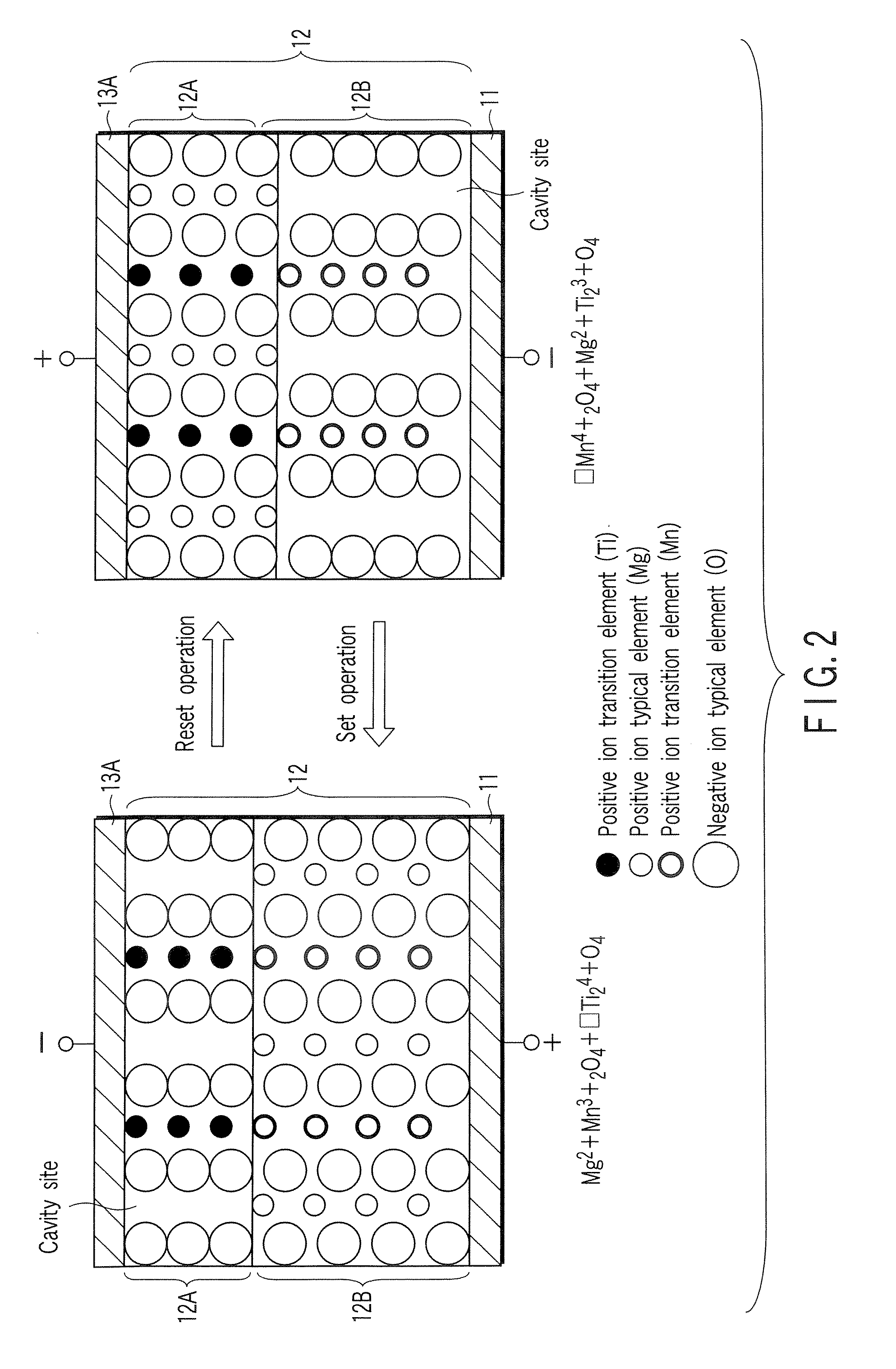
A resistance change memory device including: a semiconductor substrate; at least one cell array formed above the semiconductor substrate to have a stack structure of a variable resistance element and an access element, the variable resistance element storing a high resistance state or a low resistance state in a non-volatile manner, the access element having such an off-state resistance value in a certain voltage range that is ten times or more as high as that in a select state; and a read / write circuit formed on the semiconductor substrate, wherein the variable resistance element includes: a recording layer formed of a composite compound containing at least one transition element and a cavity site for housing a cation ion; and electrodes formed on the opposite sides of the recording layer, one of the electrodes serving as a cation source in a write or erase mode for supplying a cation to the recording layer to be housed in the cavity site.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Method of manufacturing magnetic recording medium
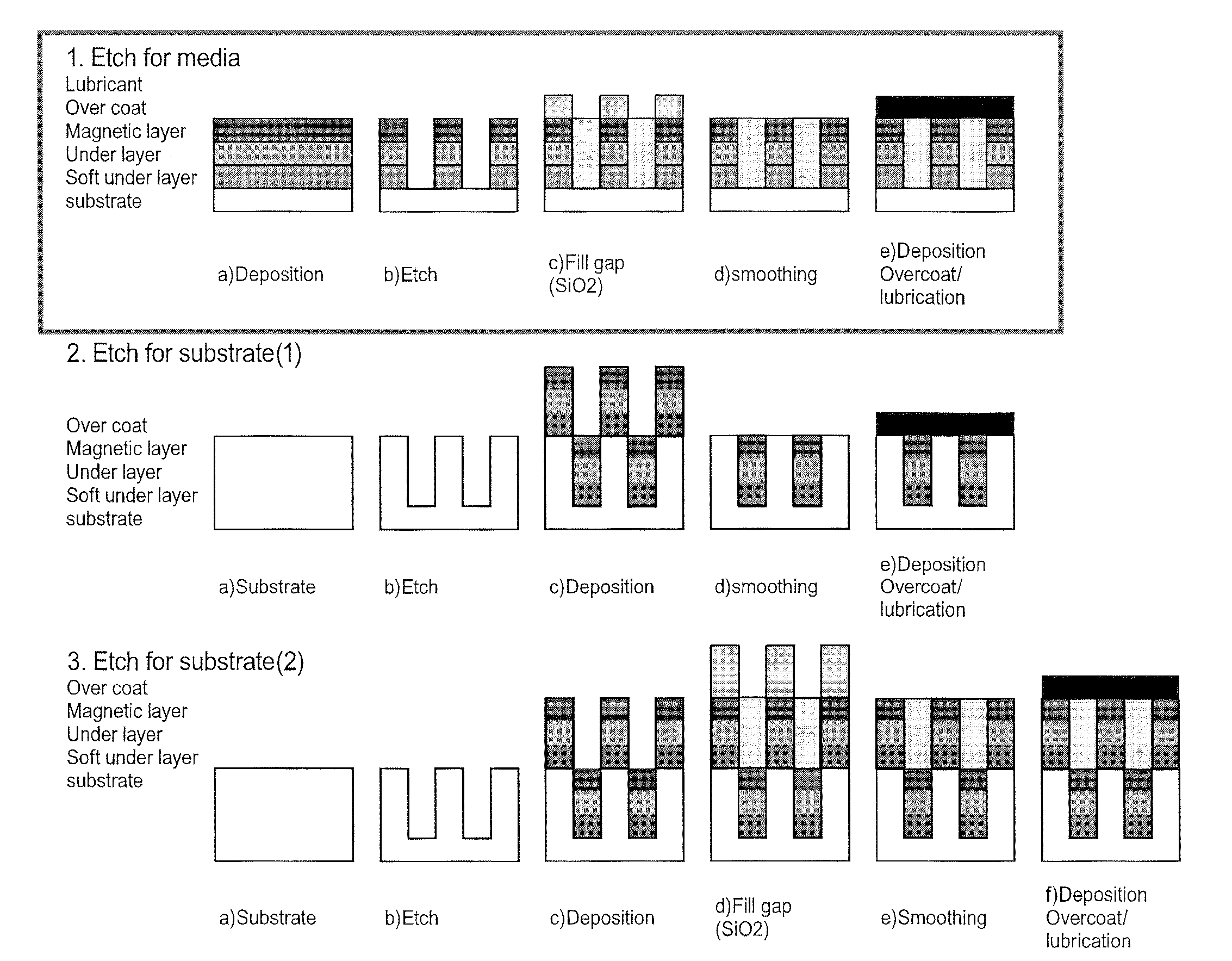
InactiveUS20100000966A1Excellent magnetic propertiesLow positioning accuracy requirementsDecorative surface effectsConductive/insulating/magnetic material on magnetic film applicationEngineeringRecording layer
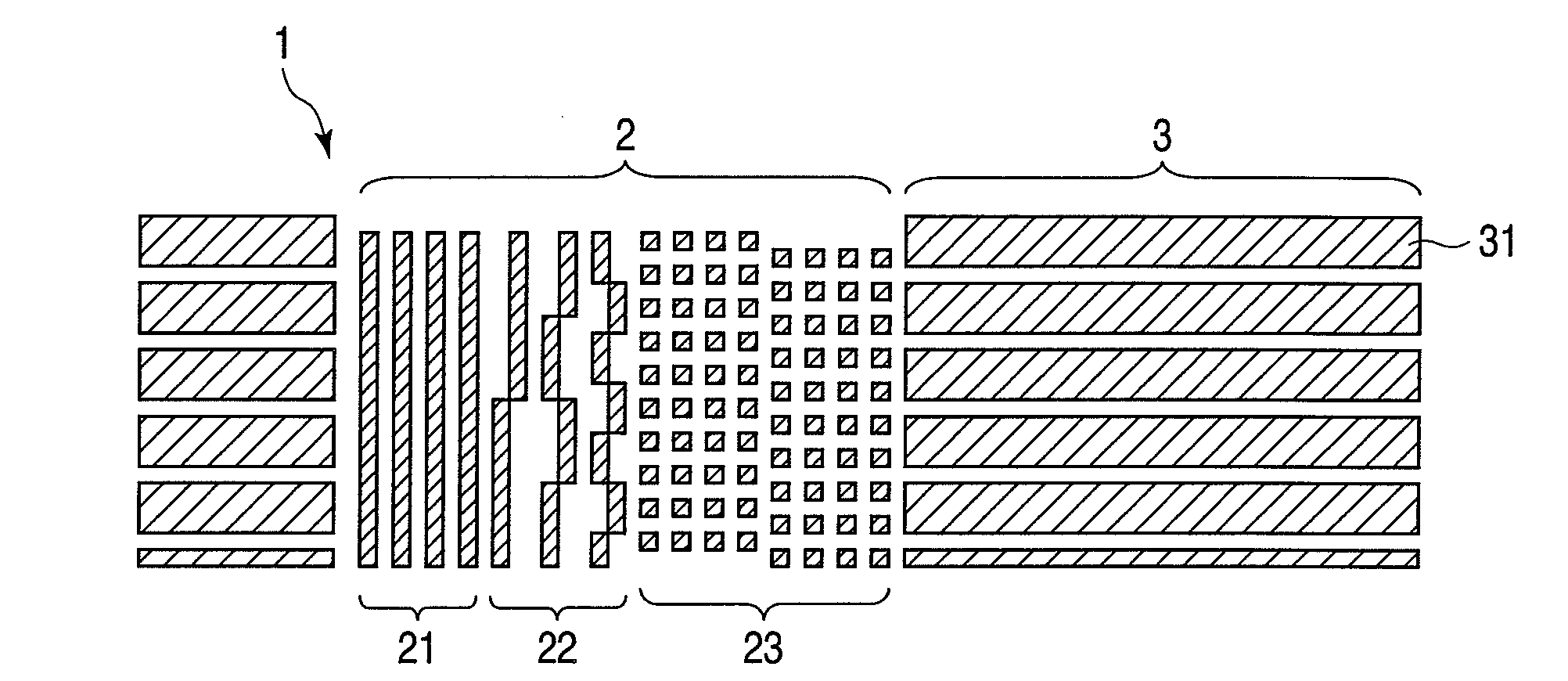
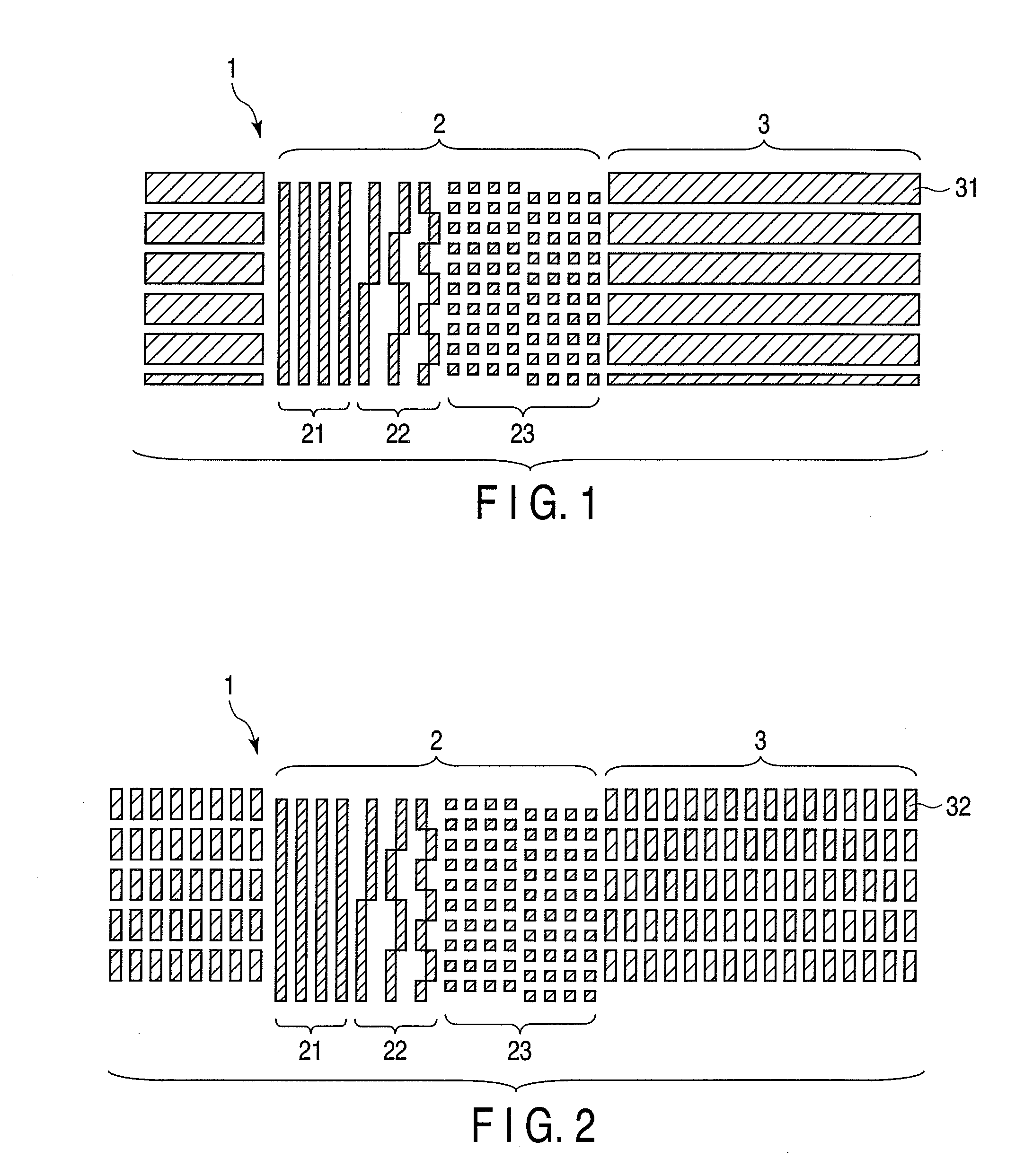
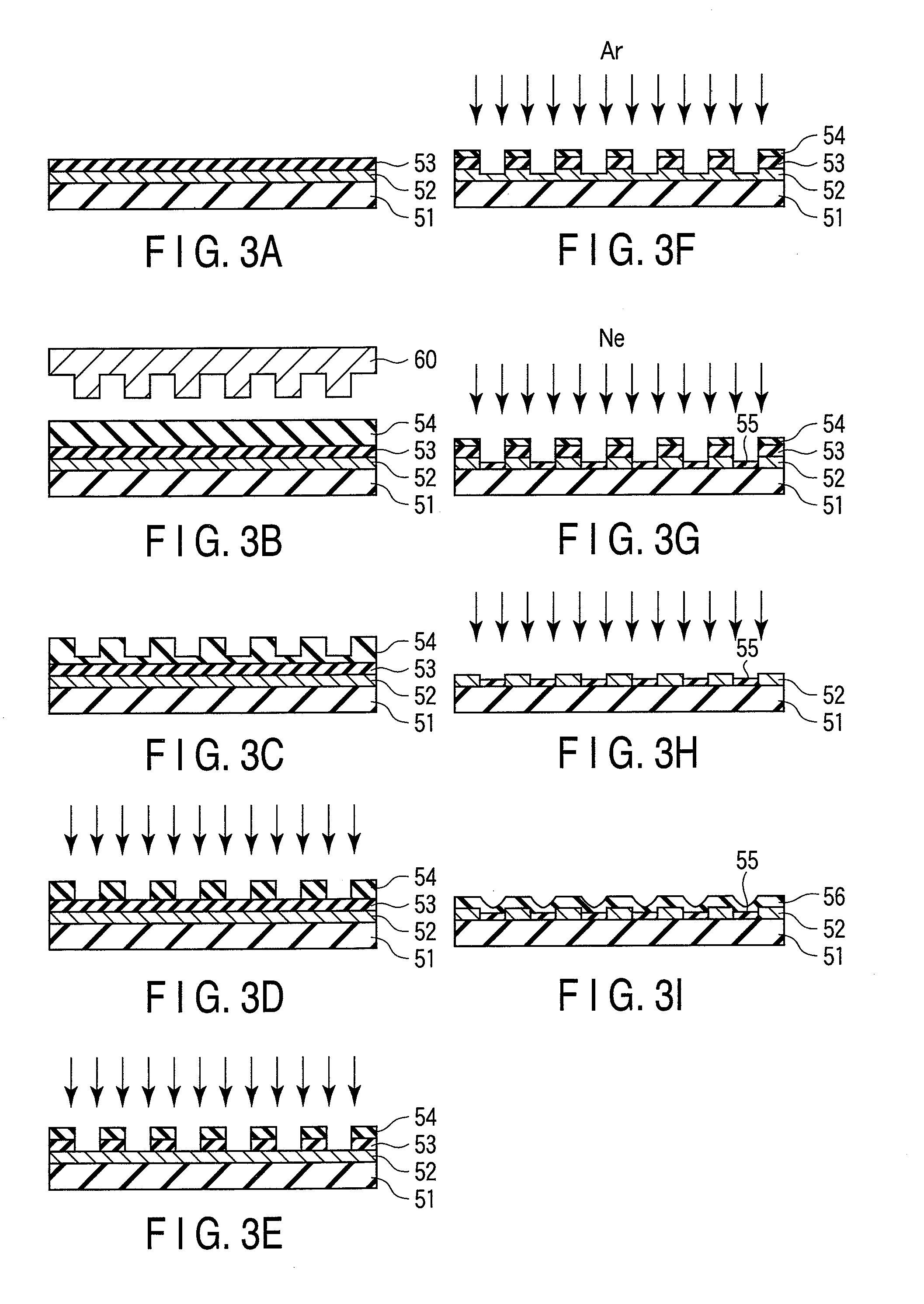
According to one embodiment, a method of manufacturing a magnetic recording medium includes depositing a magnetic recording layer on a substrate, forming masks on areas corresponding to recording regions of the magnetic recording layer, partially etching the magnetic recording layer in areas not covered with the masks with an etching gas to form protrusions and recesses on the magnetic recording layer, modifying the magnetic recording layer remaining in the recesses with Ne gas to form non-recording regions, and forming a protecting film on an entire surface.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Temperature indicating display device
A temperature indicating display device capable of displaying a thermo-history above a predetermined temperature reliably and irreversibly. Moreover, it is possible to provide a laminated body having a temperature detecting layer and an information recording film layer. When the temperature indicating display device is exposed to a predetermined temperature, an irreversible shift is caused and the temperature history can be displayed. Moreover, the temperature indicating display device includes an information recording film layer containing information, an information record holding layer for holding the information, and a temperature detection agent layer composed of a material whose state is shifted according to a temperature and is characterized in that when a predetermined temperature is detected, the material of the temperature detection agent layer is changed so as to change the display state of information recorded in the information recording layer. A laminated body using the temperature indicating display device, a vessel containing the device, and a labeled temperature indicating display device are also disclosed. Furthermore, the present invention provides a side-type temperature indicating display device in which a conventional information display member can be used as it is.
Owner:CHROMIC +1
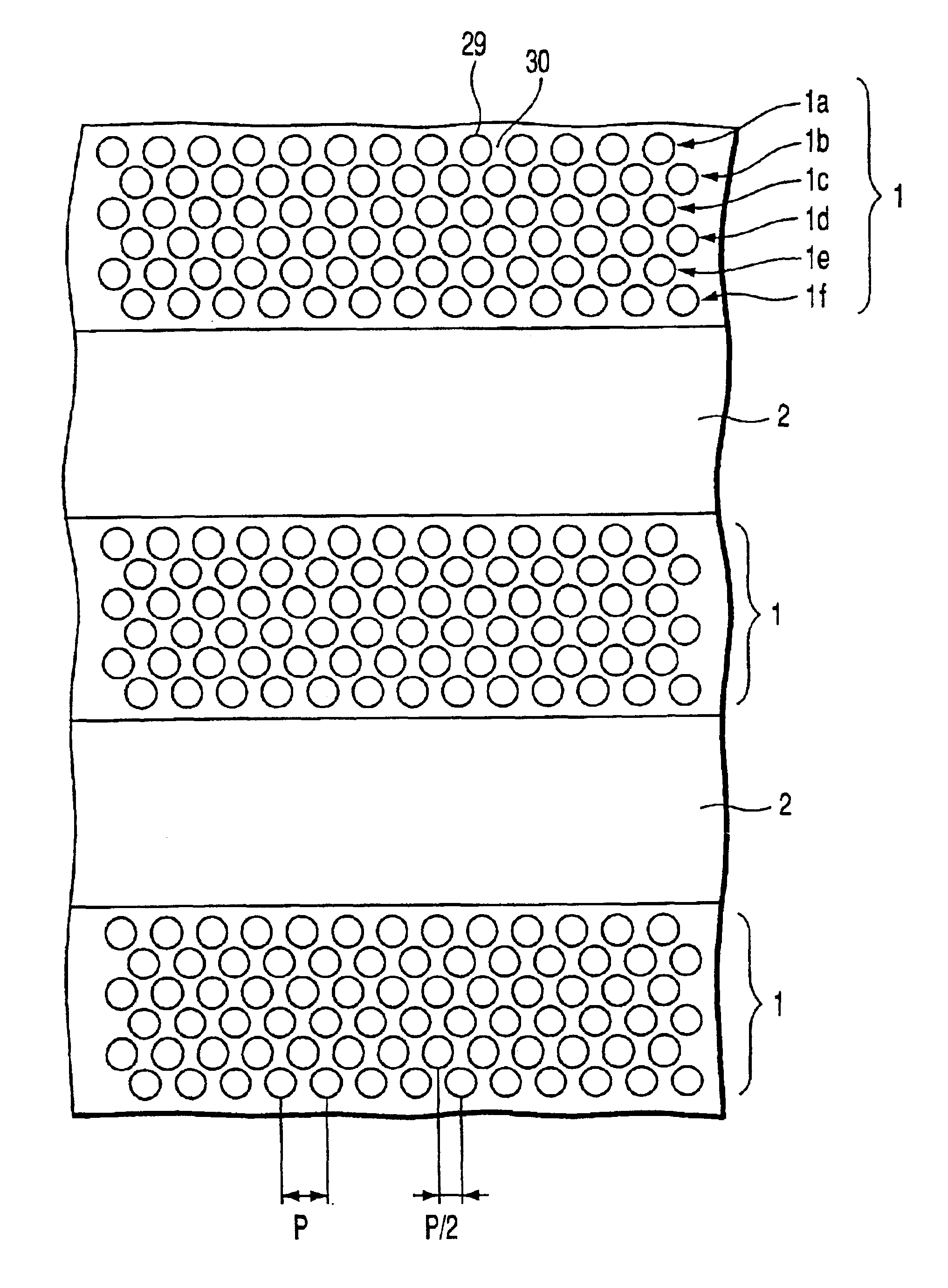
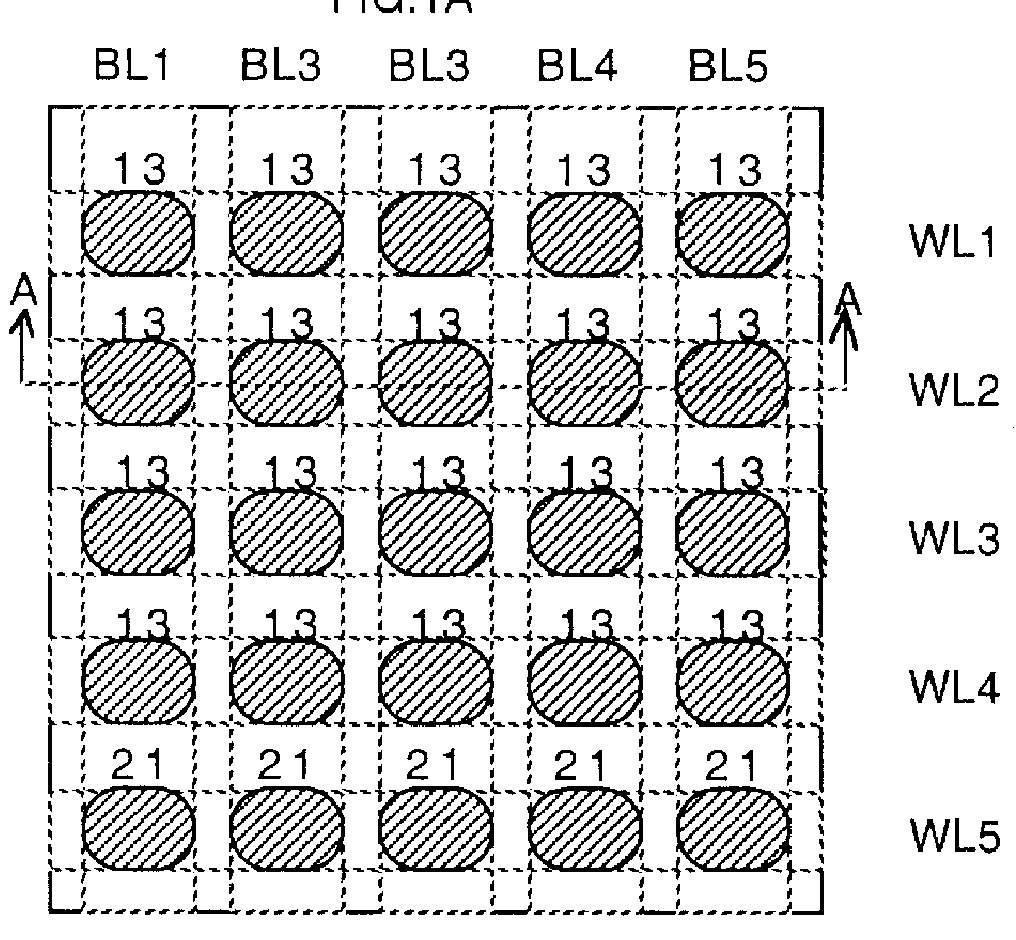
Dot-patterned structure magnetic recording medium and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20090098413A1Function increaseHigh crystallinityRecord information storageDisk carriersCrystallinityRecording layer
Disclosed herein are a dot-patterned structure for magnetic recording bits and a magnetic recording medium provided therewith. The former exhibits high functionality and high performance owing to good crystallinity. The dot-patterned structure is composed of a first layer, which is continuous, and a second layer, which is discrete. The magnetic recording medium having a dot-patterned recording layer is formed by the steps of treating an underlying layer by lithography, thereby forming grooves, filling the grooves by epitaxial growth with the same material as the underlying layer, removing the photoresist used for lithography in a solvent, thereby forming pits, and filling the pits by epitaxial growth with a magnetic film as the recording layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
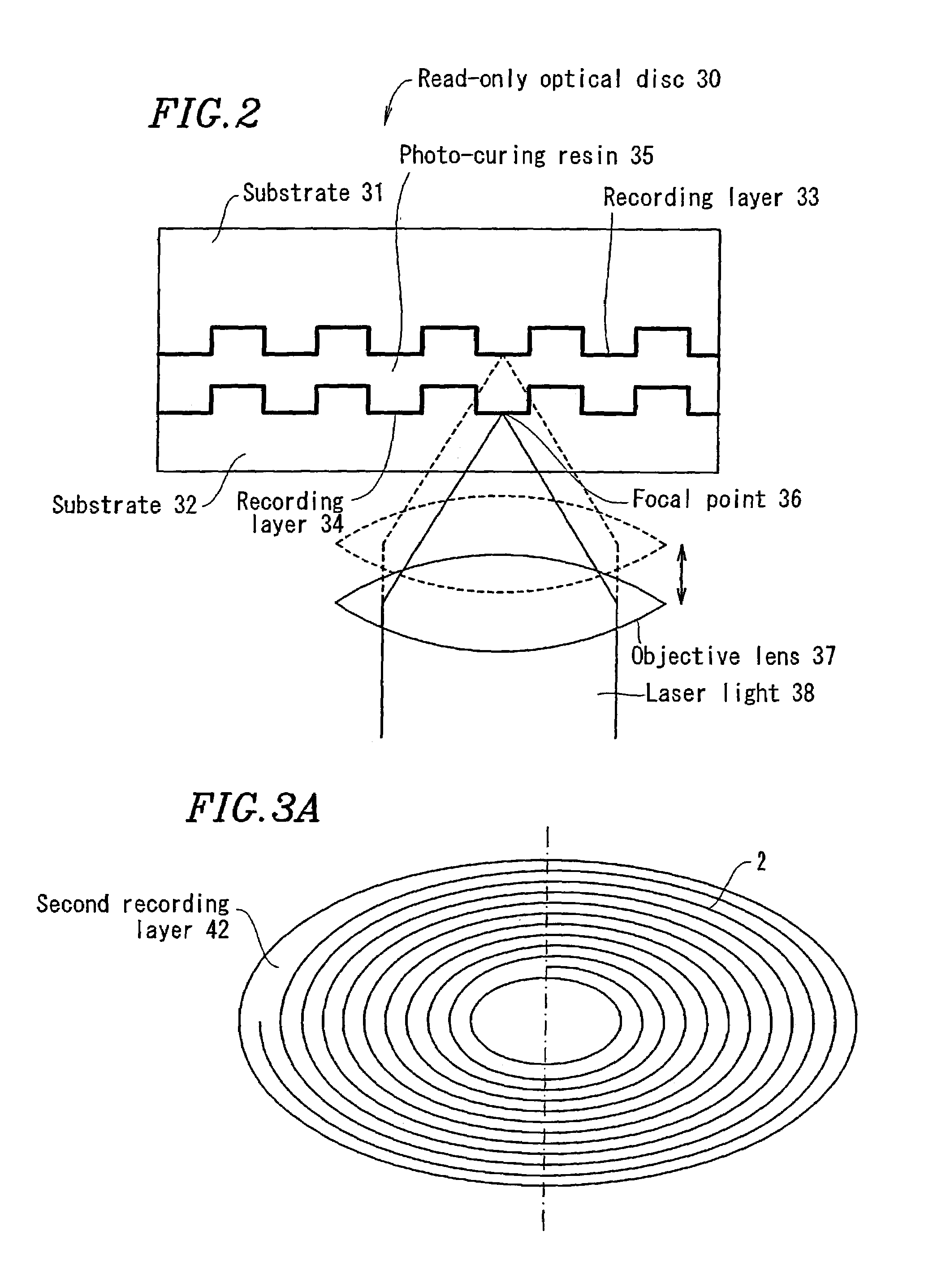
Optical recording medium and method for recording optical information
The present invention provides an optical recording medium which incorporates an inorganic based recording layer which has a high reflectance, sufficient for reproduction compatibility on devices such as CD-ROM drives, as well as a high degree of modulation between the state prior to recording and that after recording, as well as an information recording method therefor. Accordingly, an optical recording medium comprises a substrate (2) which is substantially transparent with respect to a recording light beam and a reproduction light beam, a first recording layer (3) which is layered on top of the substrate (2) and which incorporates as the main constituent a metal which has a low melting point and a high reflectance, and a second recording layer (4) which is layered on top of the first recording layer (3) and which will, due to heat generated from irradiation of a light beam through the substrate (2), either mix, or alternatively react, with the first recording layer (3) to form an alloy of low reflectance as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby enabling the recording of information. Due to the heat generated from irradiation of a recording light beam through the substrate (2) the first recording layer (3) and the second recording layer (4) are either mixed, or alternatively reacted to form an alloy as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby recording information.
Owner:KAO CORP
Data read/ write device
ActiveUS20070133358A1Variable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsComputer hardwareShortest distance
A data read / write device according to an example of the present invention includes a recording layer, and means for applying a voltage to the recording layer, generating a resistance change in the recording layer, and recording data. The recording layer is composed of a composite compound having at least two types of cation elements, at least one type of the cation element is a transition element having a “d” orbit in which electrons have been incompletely filled, and the shortest distance between the adjacent cation elements is 0.32 nm or less.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
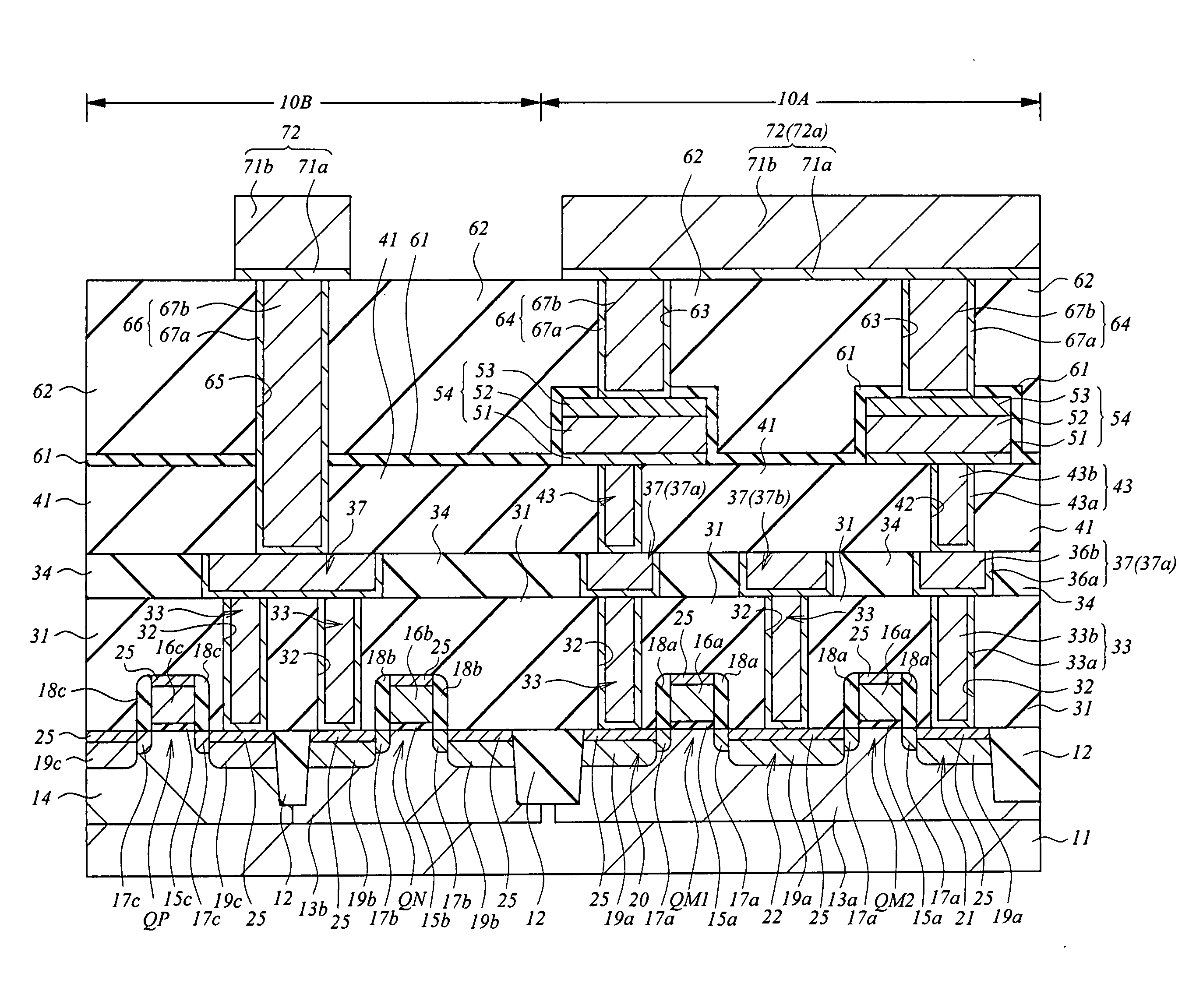
InactiveUS20070029676A1Improve reliabilityImprove manufacturing yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialElectrical connection
A resistor element formed of a peel-preventive film, a recording layer made of chalcogenide, and an upper electrode film is formed on a semiconductor substrate, first and second insulation films are formed so as to cover the resistor element, a via hole for exposing the upper electrode film is formed through the first and second insulation films, and a plug for electrical connection to the upper electrode film is formed in the via hole. To form the via hole, the first insulation film made of silicon nitride is used as an etching stopper to perform dry etching on the second insulation film. Then, dry etching is performed on the first insulation film to expose the upper electrode film from the via hole.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
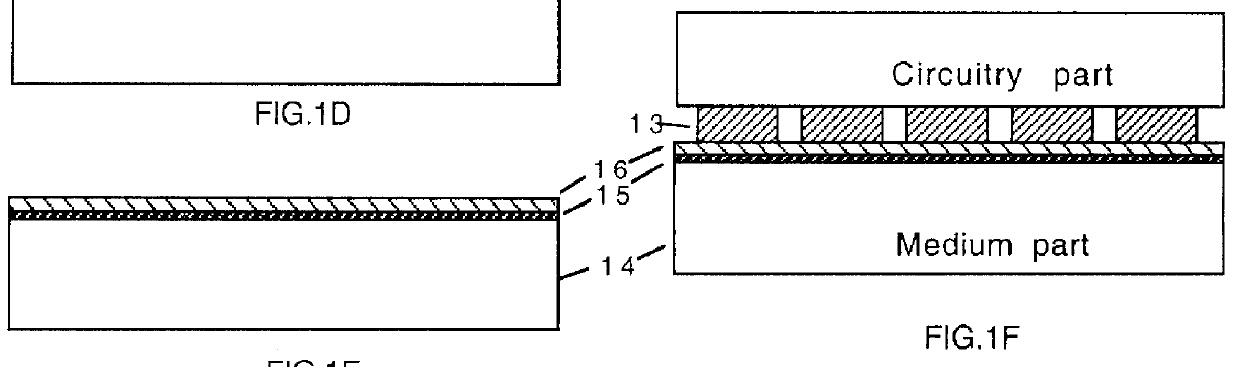
Two-parts ferroelectric RAM
InactiveUS6025618AEasy to manufactureEasy constructionPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical connectionData recording
A method of fabricating a complex IC in two parts and making the electrical connections between them afterwards is described. By this method, a ferroelectric RAM is fabricated in two parts, where the first part has an array of unit cells each of those has a transistor or a group of transistors serving the purpose of selecting one address for data recording and has an array of electrically conductive pads facing upward, protruding out from the surface of the first part, where the second part consists of a data-recording layer on another substrate. The data-recording layer consists of ferroelectric material and is pressed on the first part during data writing and reading.
Owner:CHEN ZHI QUAN
Resistance change memory device
A resistance change memory device including: a semiconductor substrate; cell arrays stacked above the substrate, each having memory cells, bit lines and word lines; a read / write circuit formed on the semiconductor substrate; first and second vertical wirings disposed to connect the bit lines to the read / write circuit; and third vertical wirings disposed the word lines to the read / write circuit. The memory cell includes a variable resistance element for storing as information a resistance value, which has a recording layer composed of a composite compound containing at least two types of cation elements, at least one type of the cation element being a transition element having “d” orbit, in which electrons are incompletely filled, the shortest distance between adjacent cation elements being 0.32 nm or less.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Resistance change memory device
A resistance change memory device including: a semiconductor substrate; cell arrays stacked above the substrate, bit lines word lines; a read / write circuit formed on the semiconductor substrate; first and second vertical wirings disposed to connect the bit lines to the read / write circuit; and third vertical wirings disposed to connect the word lines to the read / write circuit, wherein the memory cell includes a variable resistance element for storing as information a resistance value, which has a recording layer formed of a first composite compound expressed by AxMyOz (where “A” and “M” are cation elements different from each other; “O” oxygen; and 0.5≦x≦1.5, 0.5≦y≦2.5 and 1.5≦z≦4.5) and a second composite compound containing at least one transition element and a cavity site for housing a cation ion.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Digital content kiosk and associated methods for delivering selected digital content to a user
InactiveUS20050049931A1Low priceSufficient protectionRecord information storagePayment architectureComputer hardwareDigital content
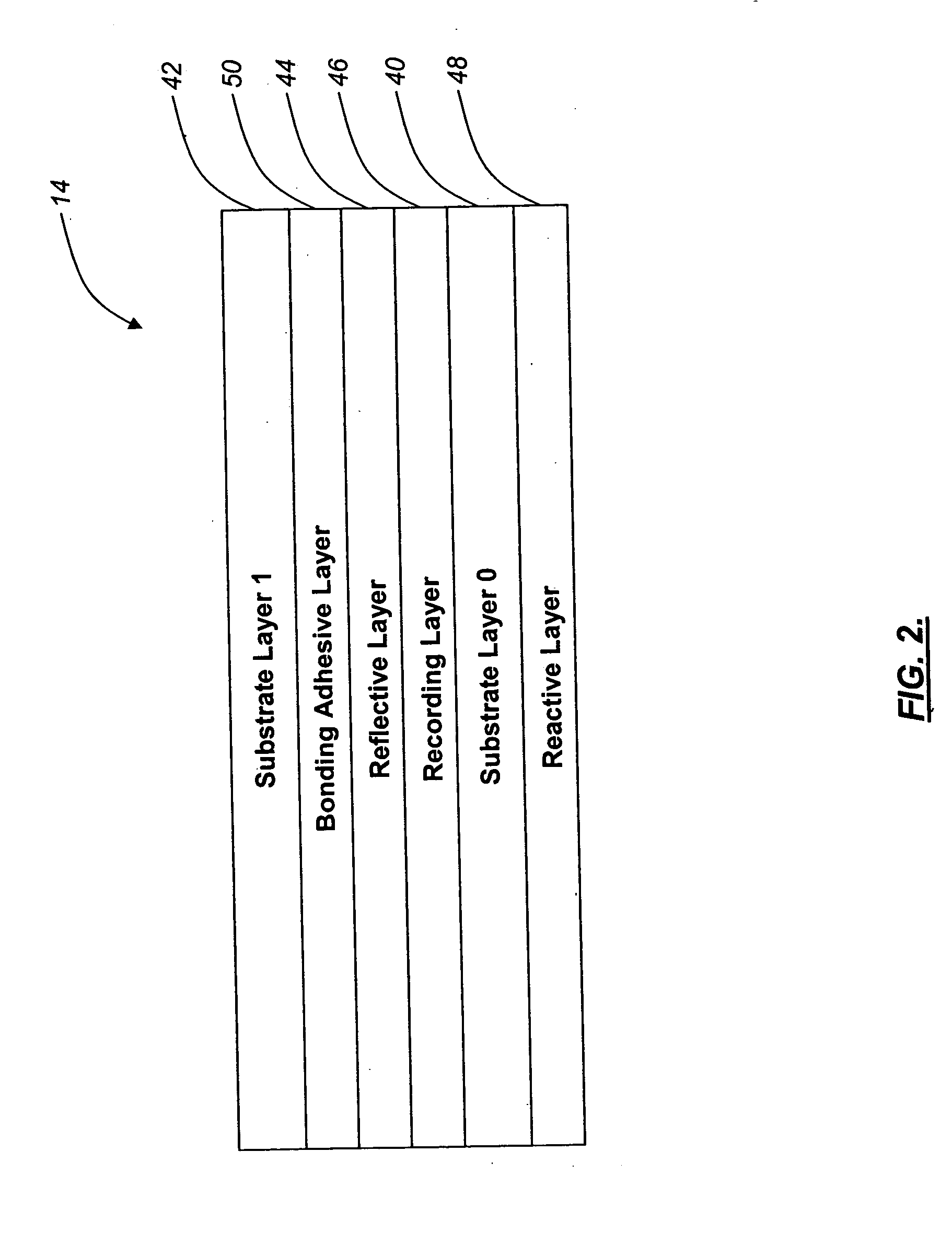
The present invention provides a digital content kiosk system operable for delivering selected digital content to a user. The digital content kiosk system of the present invention includes a limited-play recordable data storage medium configured to receive selected digital content and a data storage media recording device operable for recording the selected digital content on the limited-play recordable data storage medium at the request of a user. The limited-play recordable data storage medium of the present invention includes a reflective layer, a recording layer disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the reflective layer, and at least one of a reactive layer and a reactive bonding adhesive layer disposed between the data storage media recording device and at least one of the reflective layer and the recording layer.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Nonvolatile magnetic memory device
InactiveUS20100176472A1Reduce polarizabilitySmall MRNanomagnetismGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetizationMagnetic memory
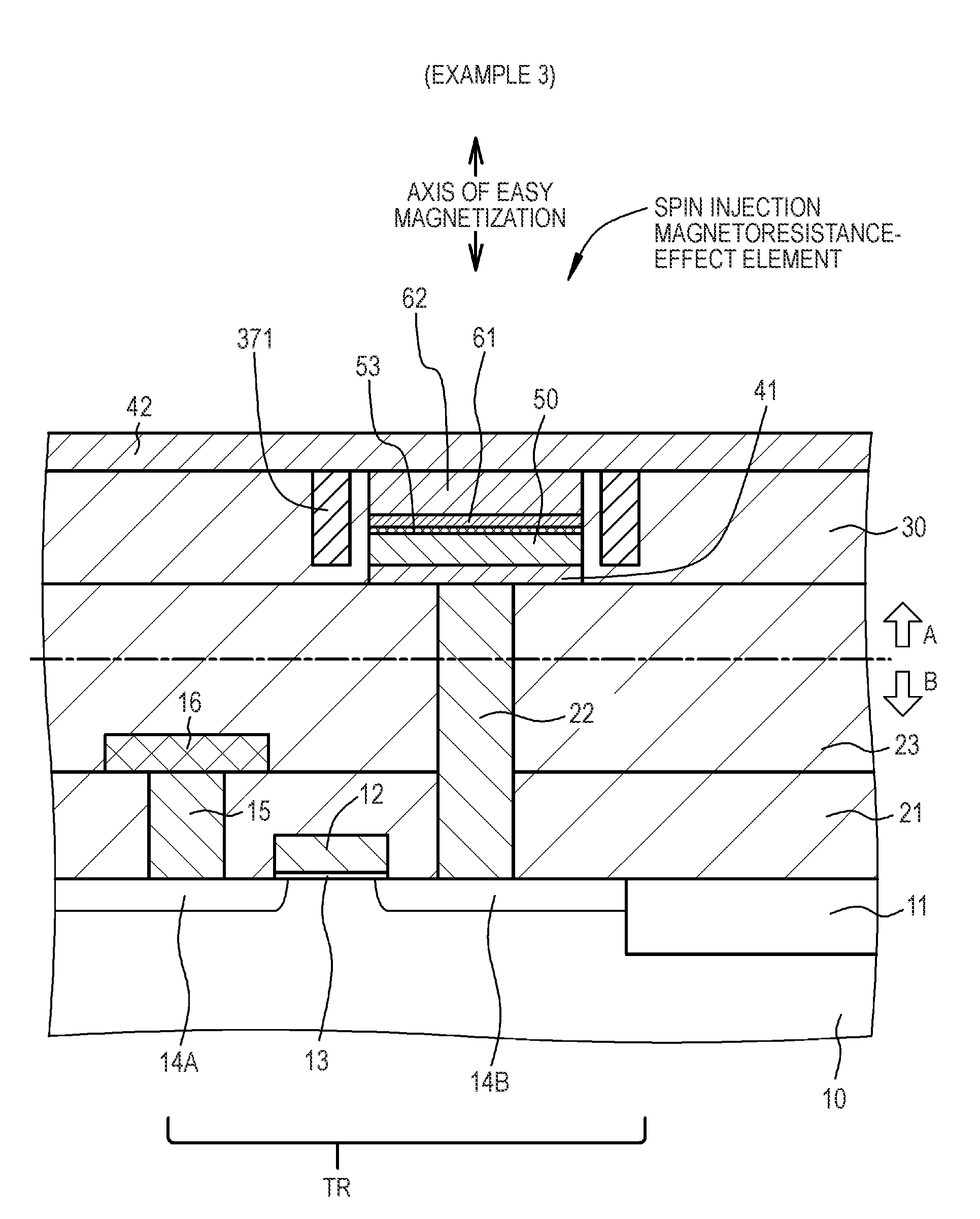
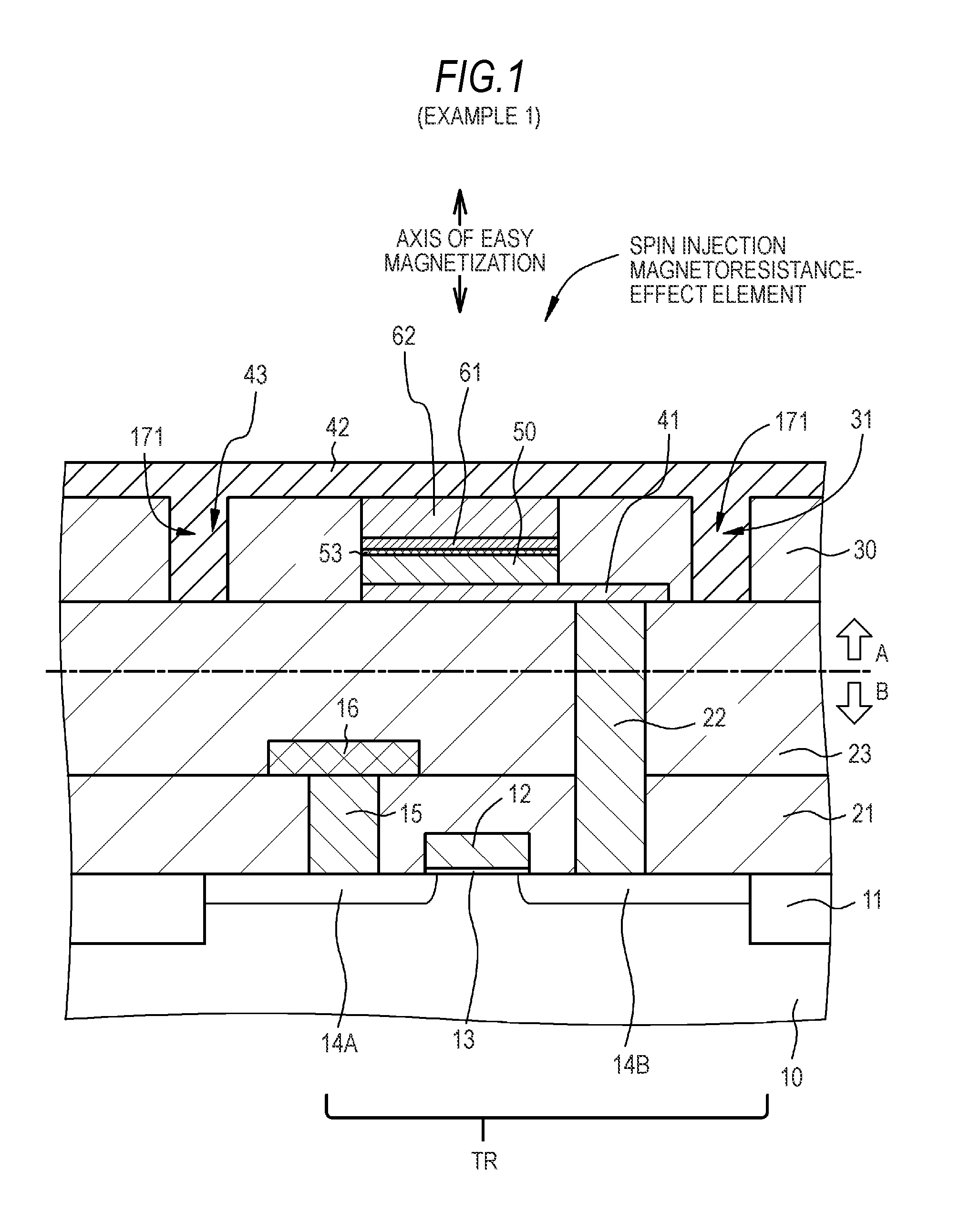
A nonvolatile magnetic memory device having a magnetoresistance-effect element includes: (A) a laminated structure having a recording layer in which an axis of easy magnetization is oriented in a perpendicular direction; (B) a first wiring line electrically connected to a lower part of the laminated structure; and (C) a second wiring line electrically connected to an upper part of the laminated structure, wherein a high Young's modulus region having a Young's modulus of a higher value than that of a Young's modulus of a material forming the recording layer is provided close to a side surface of the laminated structure.
Owner:SONY CORP
Stable write trial process with respect to optical record medium
InactiveUS20050025013A1The method is simple and reliableStable write trial processTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersEngineeringRecording layer
Provision is made to perform a write trial process in a stable manner at all times in a write trial area for the purpose of determining optimum recording power. Sub-areas of the write trial area are used successively from an inner circumference side of the medium to an outer circumference side of the medium with respect to the spiral direction that extends from the outer circumference side of the medium to the inner circumference side of the medium, and the sub-areas of the write trial area are used successively from the outer circumference side of the medium to the inner circumference side of the medium with respect to the spiral direction that extends from the inner circumference side of the medium to the outer circumference side of the medium With this provision, the write trial process is performed by accessing a sub-area portion of interest without accessing the sub-area portion having undergone the write trial, no matter which record layer is used. Servo control and address read can thus be stabilized. As a result, a seek operation toward the sub-area of interest is also stabilized, thereby achieving a stable write trial process.
Owner:RICOH KK
Heatsink films for magnetic recording media
ActiveUS20070026263A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove mechanical propertiesRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMetal alloy
Metal alloy heatsink films for magnetic recording media are disclosed. The metal alloy heatsink films possess both high thermal conductivity and improved mechanical properties such as relatively high hardness. The metal alloy heatsink films also have controlled microstructures which are compatible with subsequently deposited crystalline magnetic recording layers. The films may comprise single phase CuZr or AgPd alloys having a selected crystal structure and orientation. The combination of high thermal conductivity, good mechanical properties and controlled microstructures makes the metal alloy heatsink films suitable for various applications including heat assisted magnetic recording systems.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic disk and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20110311841A1Reduce noiseImprove recording densityMagnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingOxygenRecording layer
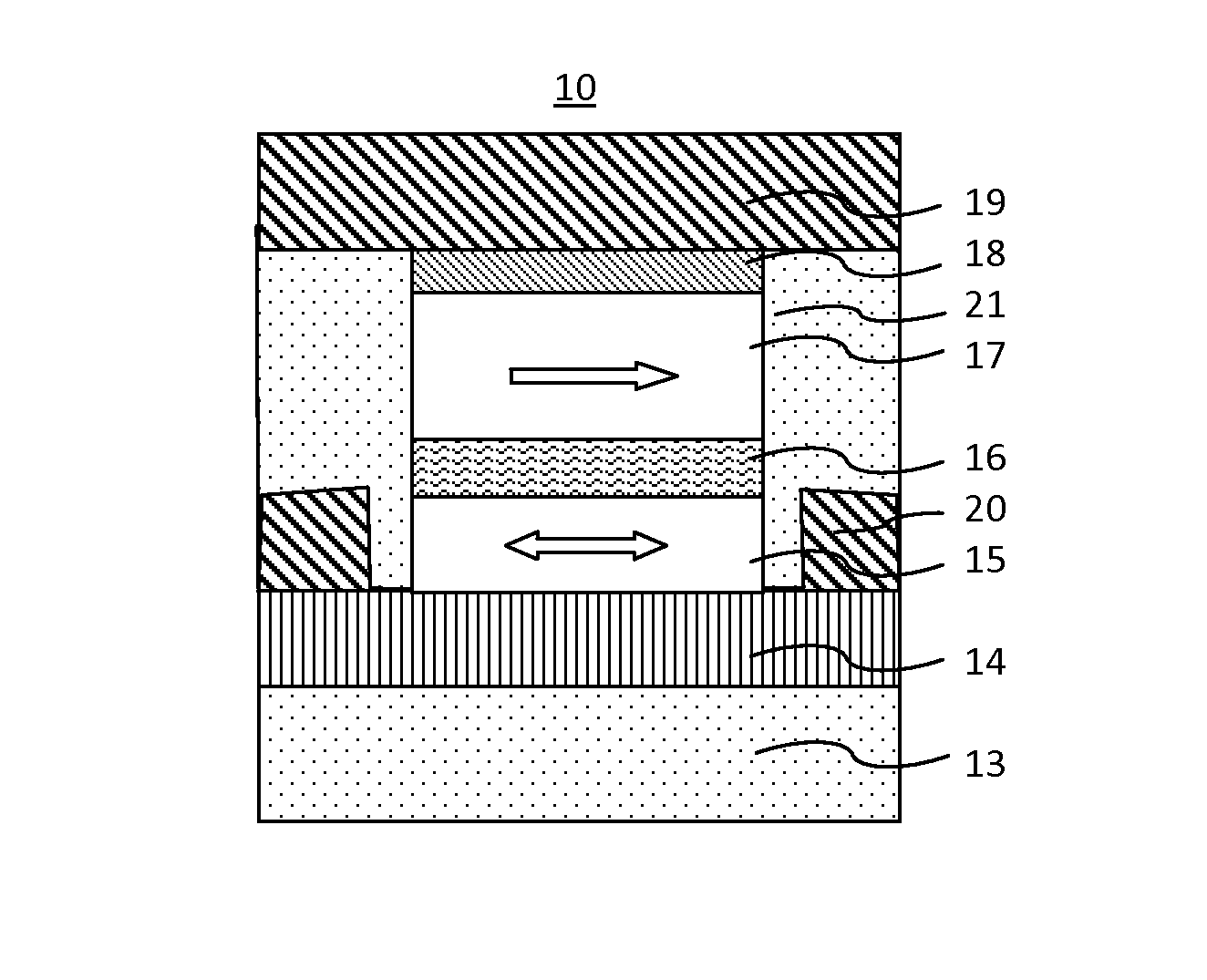
Provided are a magnetic disk comprising a granular magnetic recording layer which causes less noise even with a recording capacity thereof of 250 G or more bits per square inch; and a method for manufacturing the same. The magnetic disk according to the present invention comprises: a granular magnetic recording layer (20) which is formed on a disk substrate 10 directly or via an intermediate layer and which has non-magnetic regions between granular columnar particles; and an auxiliary recording layer (22) which is formed on the granular magnetic recording layer 20 and which causes exchange interaction among the granular columnar particles, wherein the auxiliary recording layer (22) contains 0.1 to 3 moles of oxygen.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Information recording mediums, supporter used in the mediums, manufacture methods of the supporter, manufacturing apparatus of the supporter and stampers for producing the mediums
InactiveUS6254966B1Magnetic materials for record carriersLayered productsHigh densityManufactured apparatus
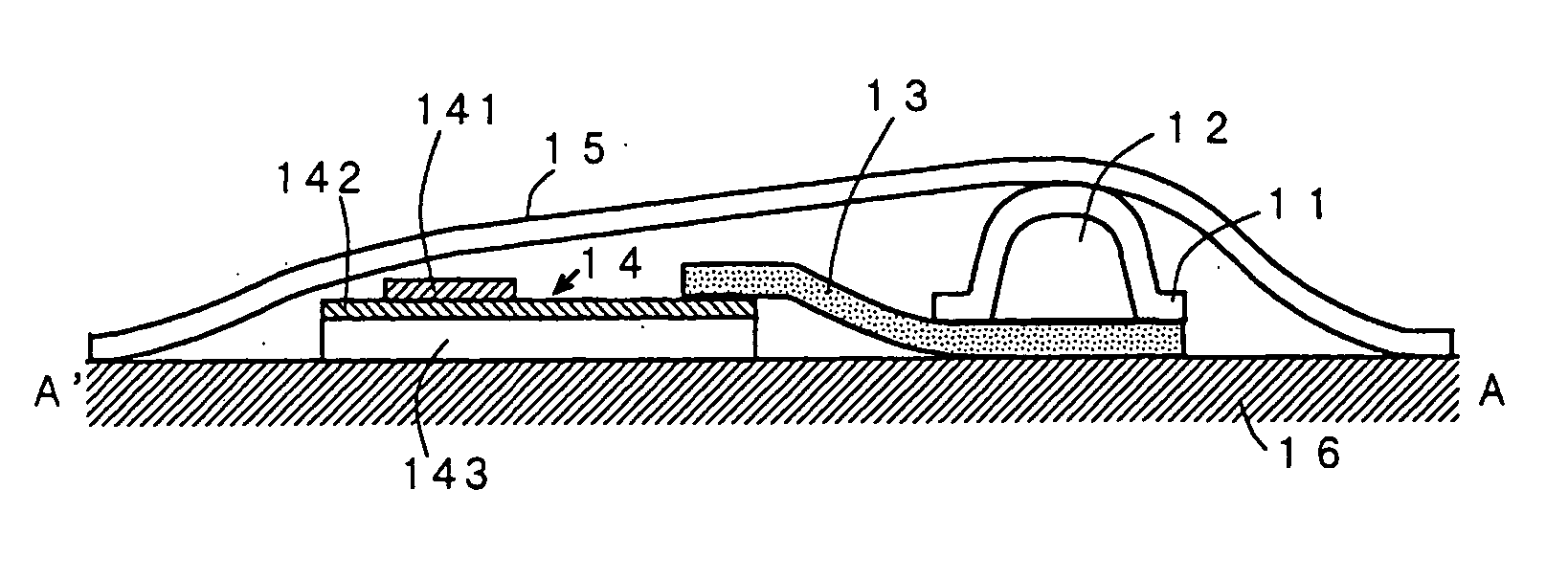
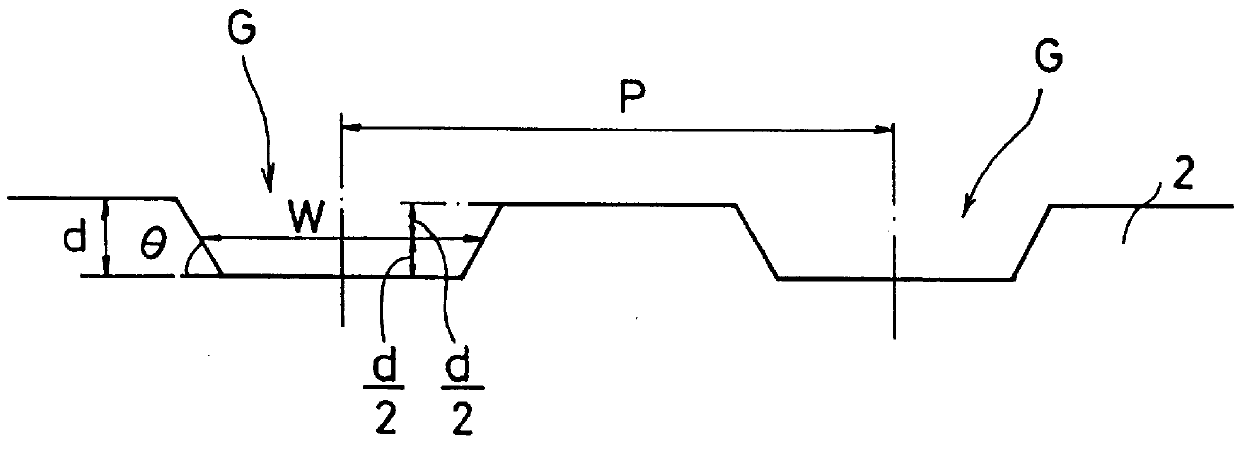
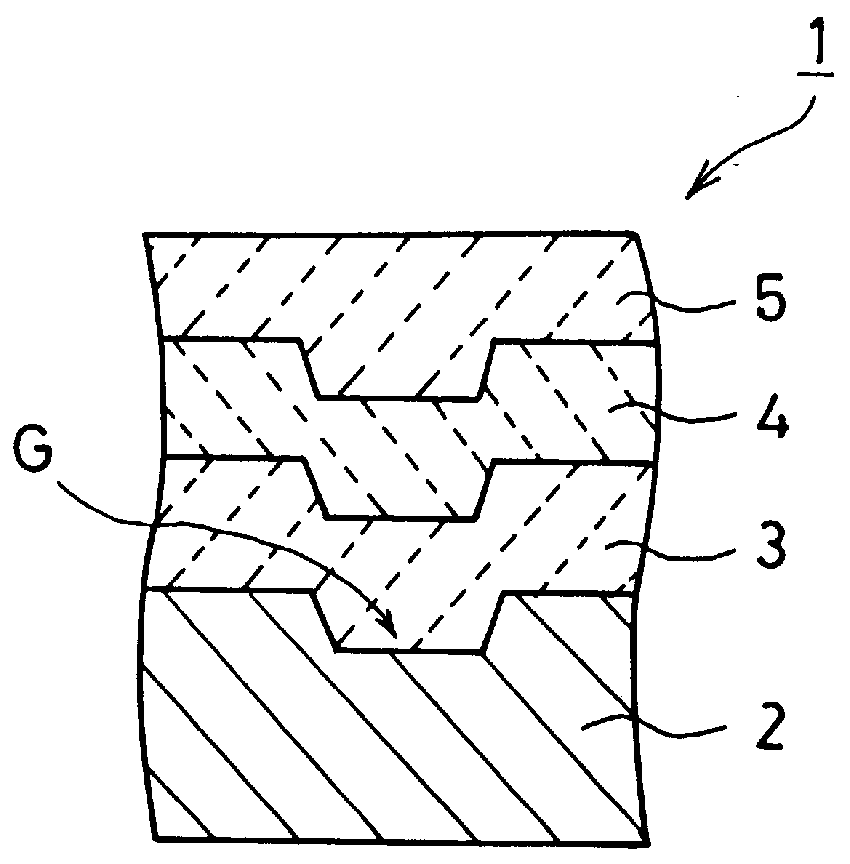
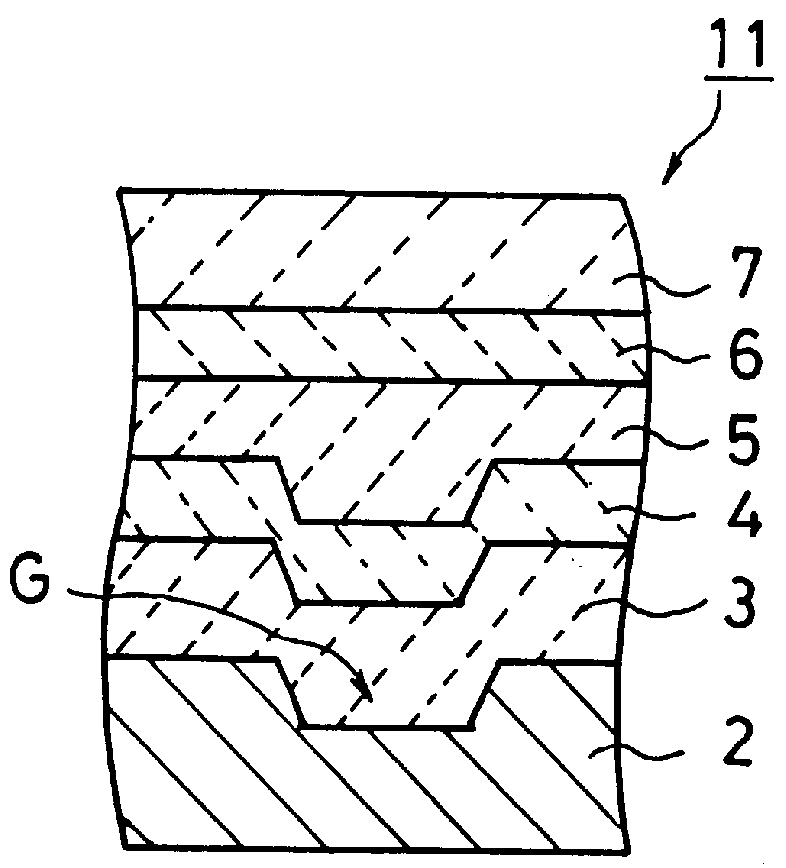
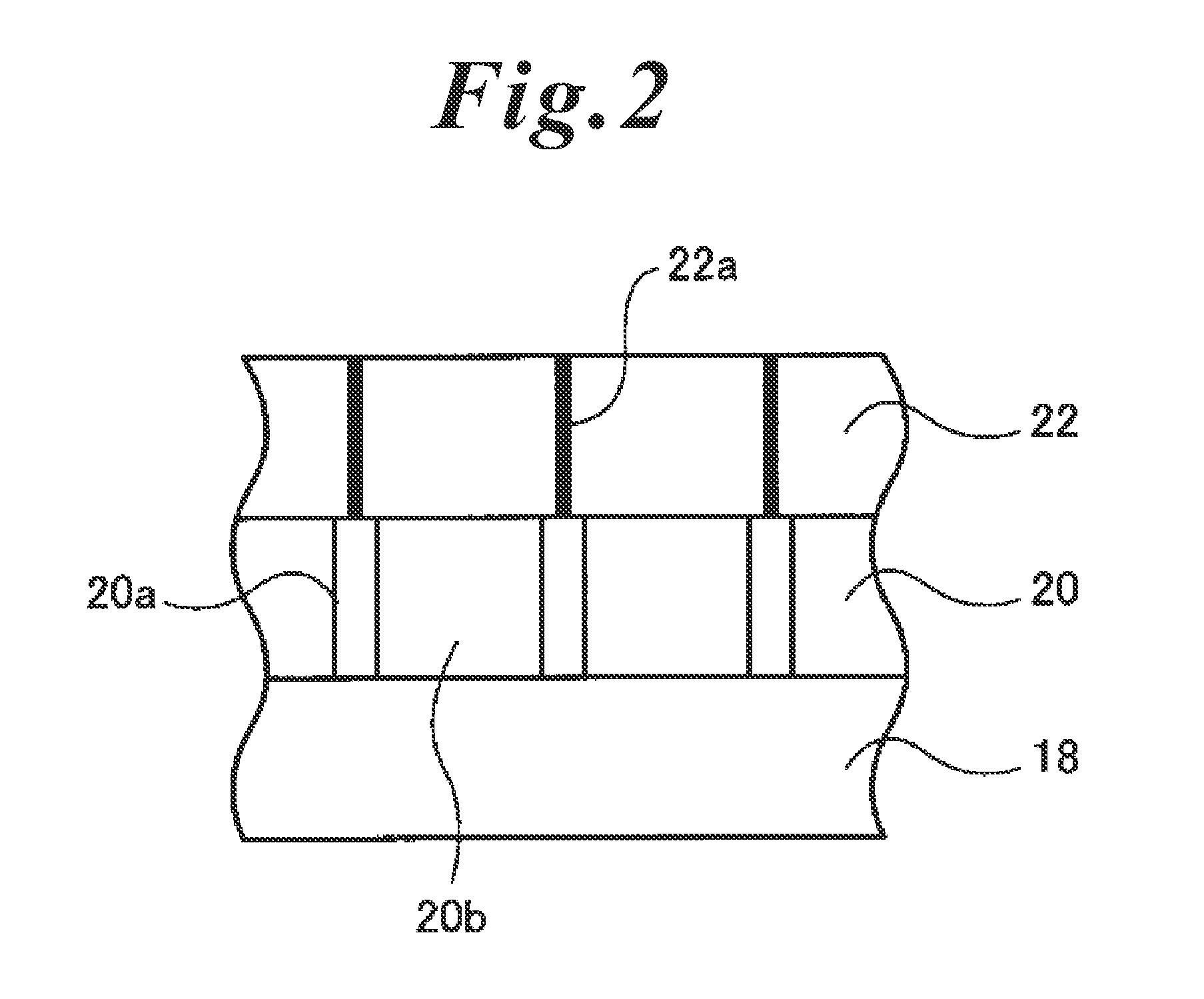
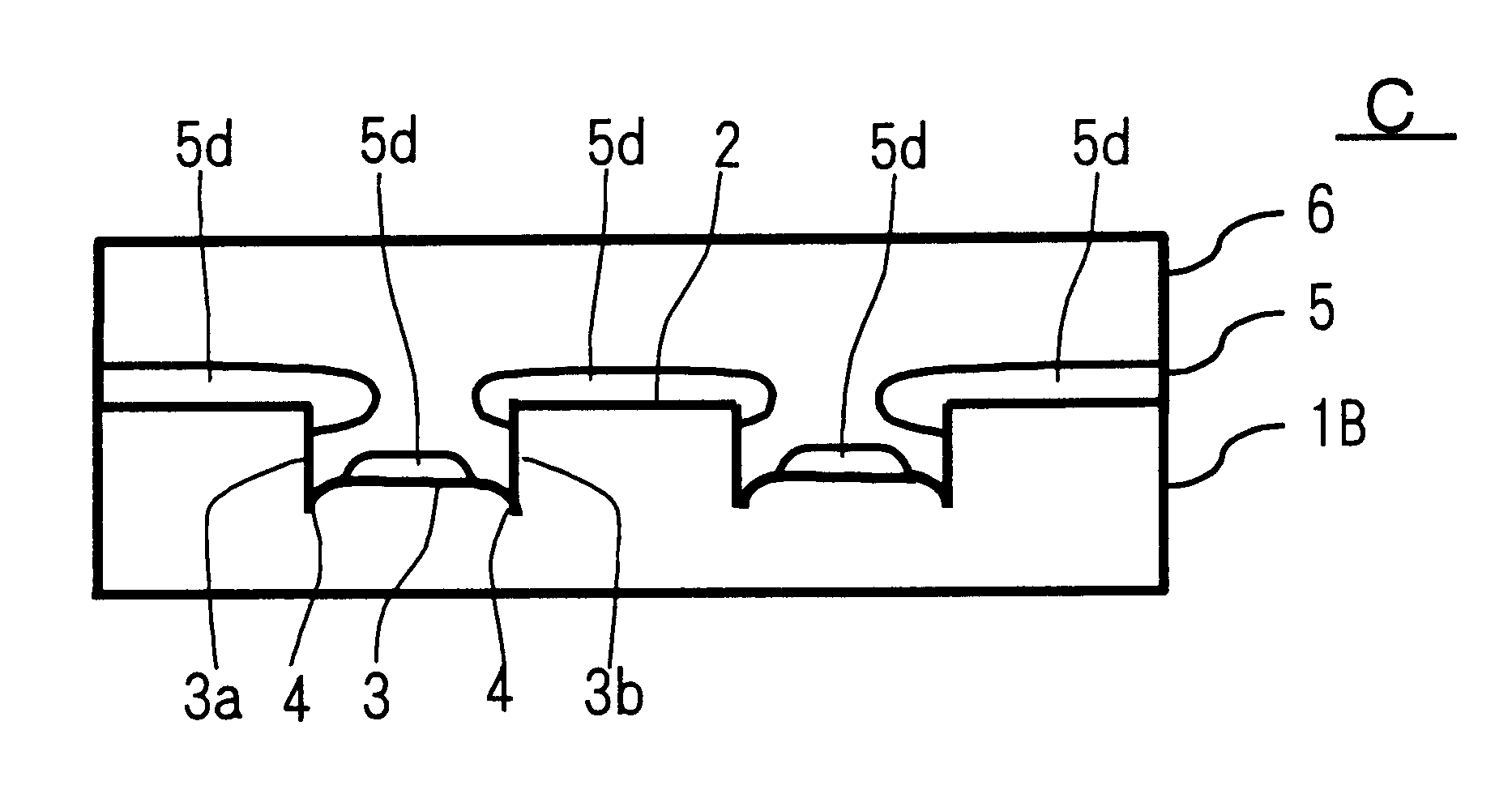
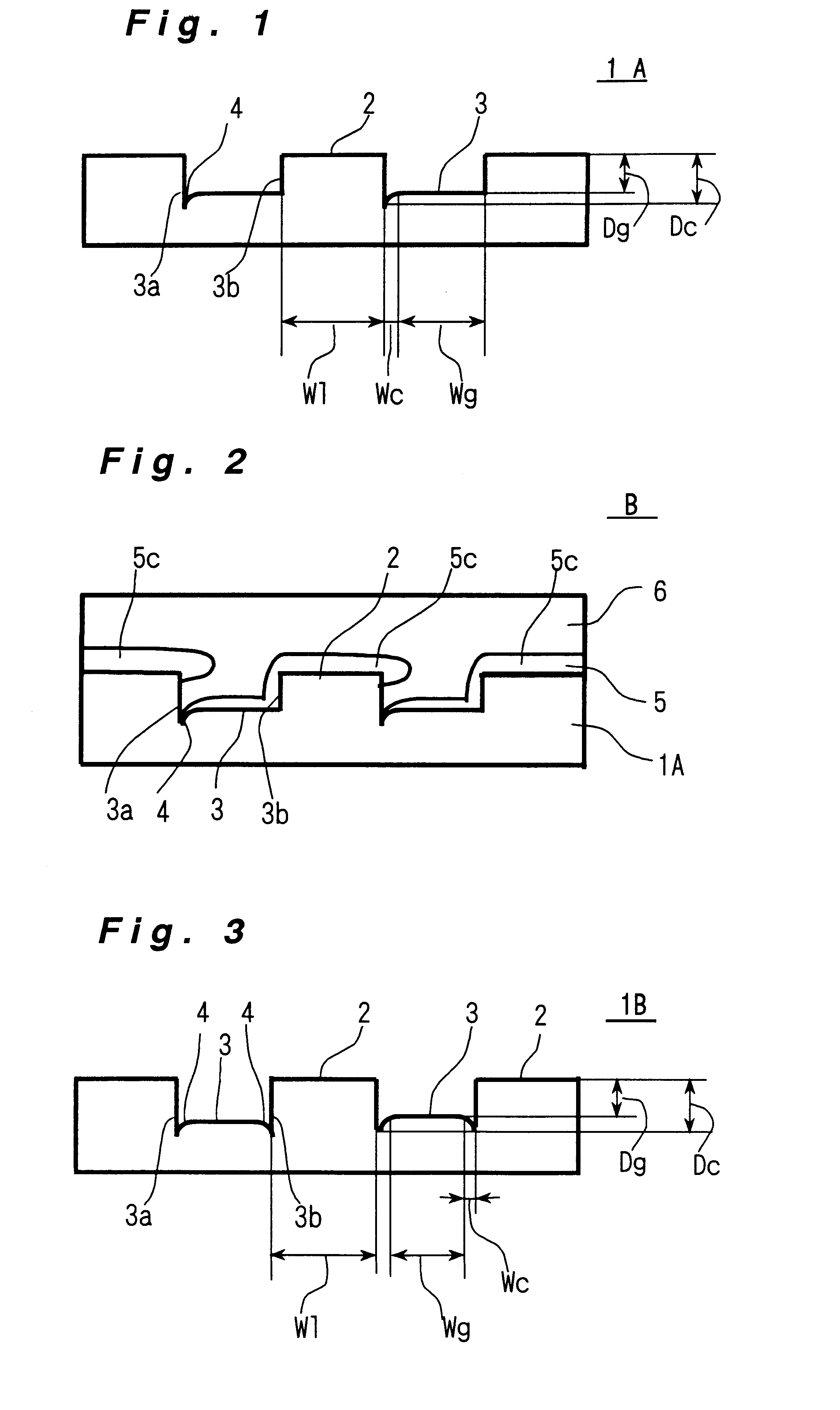
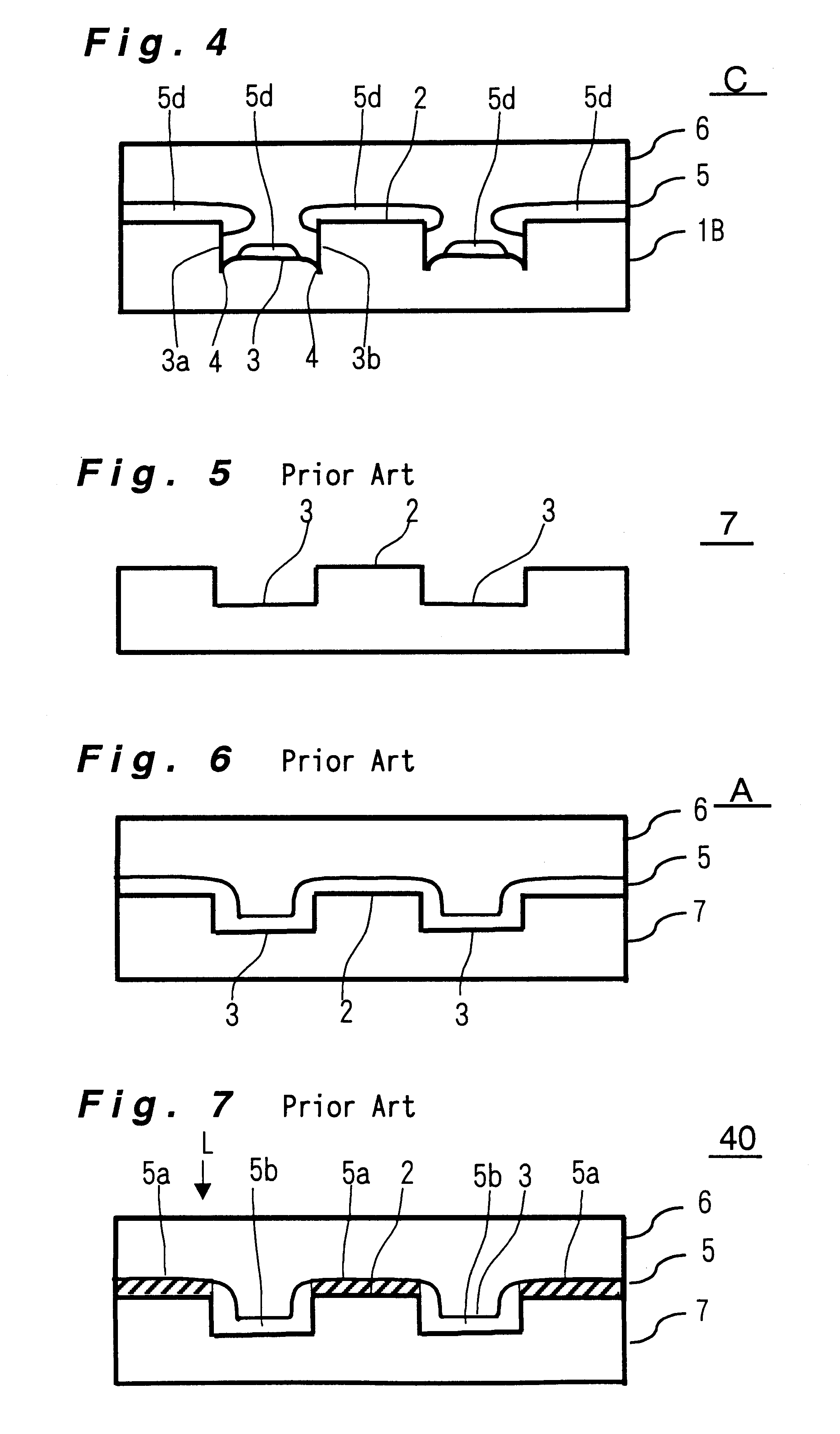
An information recording medium and a supporter used for the information recording medium capable of recording a land / groove recording by using a high density recording technique such as a super-resolution, resulting in a high density recording. An information recording medium B has a supporter 1A, on which a recording layer 5 is formed. On the supporter 1A, lands 2 and groove 3 are alternately formed as a minute track pattern. A crevice 4 having a depth Dc larger than a depth Dg of the respective grooves 3 is formed in the respective grooves 3 at one end of the respective grooves 3 in a width direction of the respective grooves.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
In a phase-change recording medium, a recording medium is provided with a barrier layer including Ge-N, Ge-N-O between a recording layer and a dielectric protective layer in order to prevent a chemical reaction and an atom diffusion between the recording layer and the dielectric protective layer. A barrier material can be also applied to the protective layer itself. Thereby, it is possible to considerably suppress a reduction of a reflectivity and a reduction of a signal amplitude due to the repeat of recording and erasing, such reductions being observed in a conventional phase-change optical information recording medium, and thereby the number of overwriting times can be increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Resistance change memory device
A resistance change memory device including: a semiconductor substrate; cell arrays stacked above the substrate, bit lines word lines; a read / write circuit formed on the semiconductor substrate; first and second vertical wirings disposed to connect the bit lines to the read / write circuit; and third vertical wirings disposed to connect the word lines to the read / write circuit, wherein the memory cell includes a variable resistance element for storing as information a resistance value, which has a recording layer formed of a first composite compound expressed by AxMyOz (where “A” and “M” are cation elements different from each other; “O” oxygen; and 0.5≦x≦1.5, 0.5≦y≦2.5 and 1.5≦z≦4.5) and a second composite compound containing at least one transition element and a cavity site for housing a cation ion.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
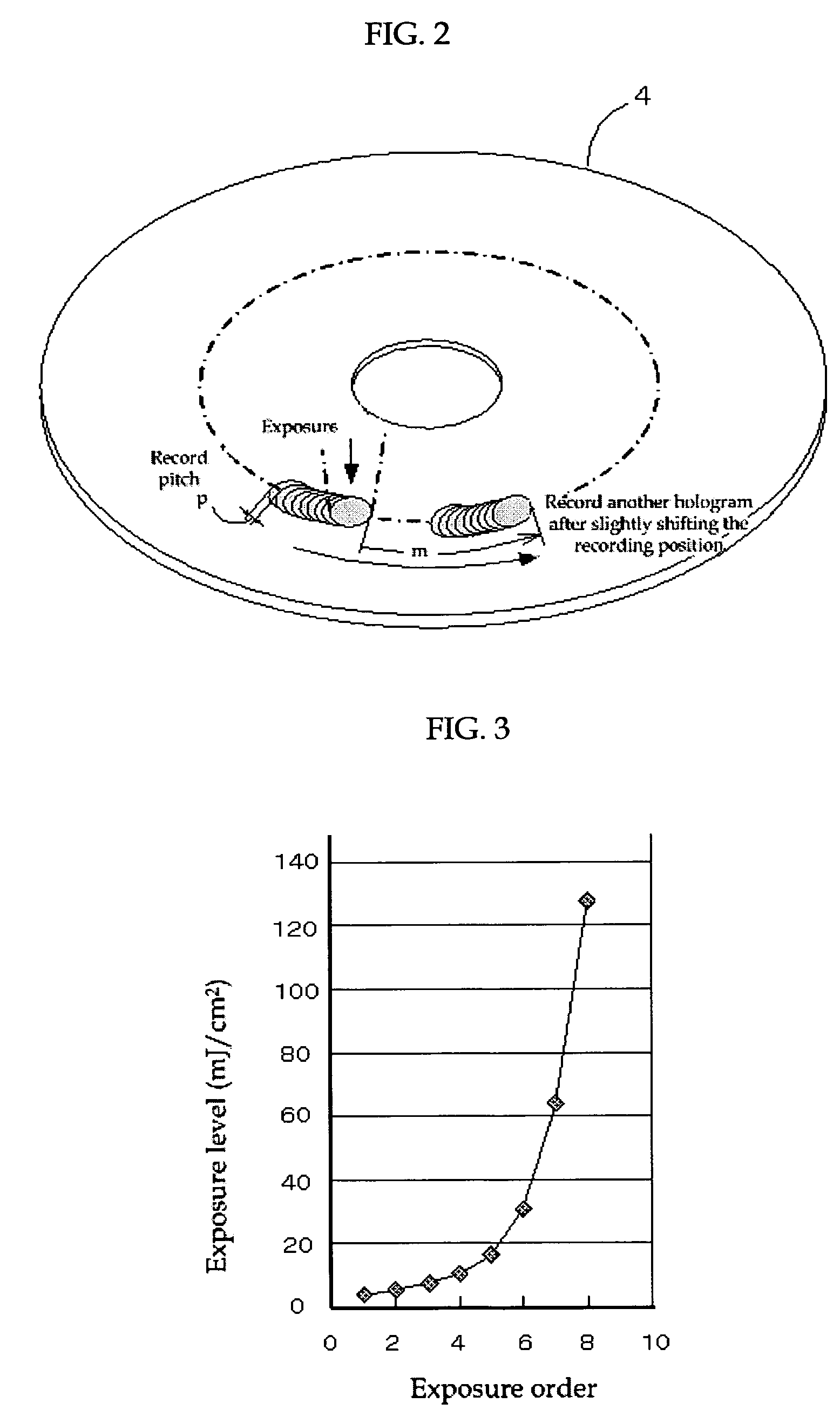
Optical information recording method, optical information recording apparatus and optical information recording medium
InactiveUS7626913B2Reduce sensitivitySufficient informationRecord information storageInstrumental componentsLight beamRecording layer
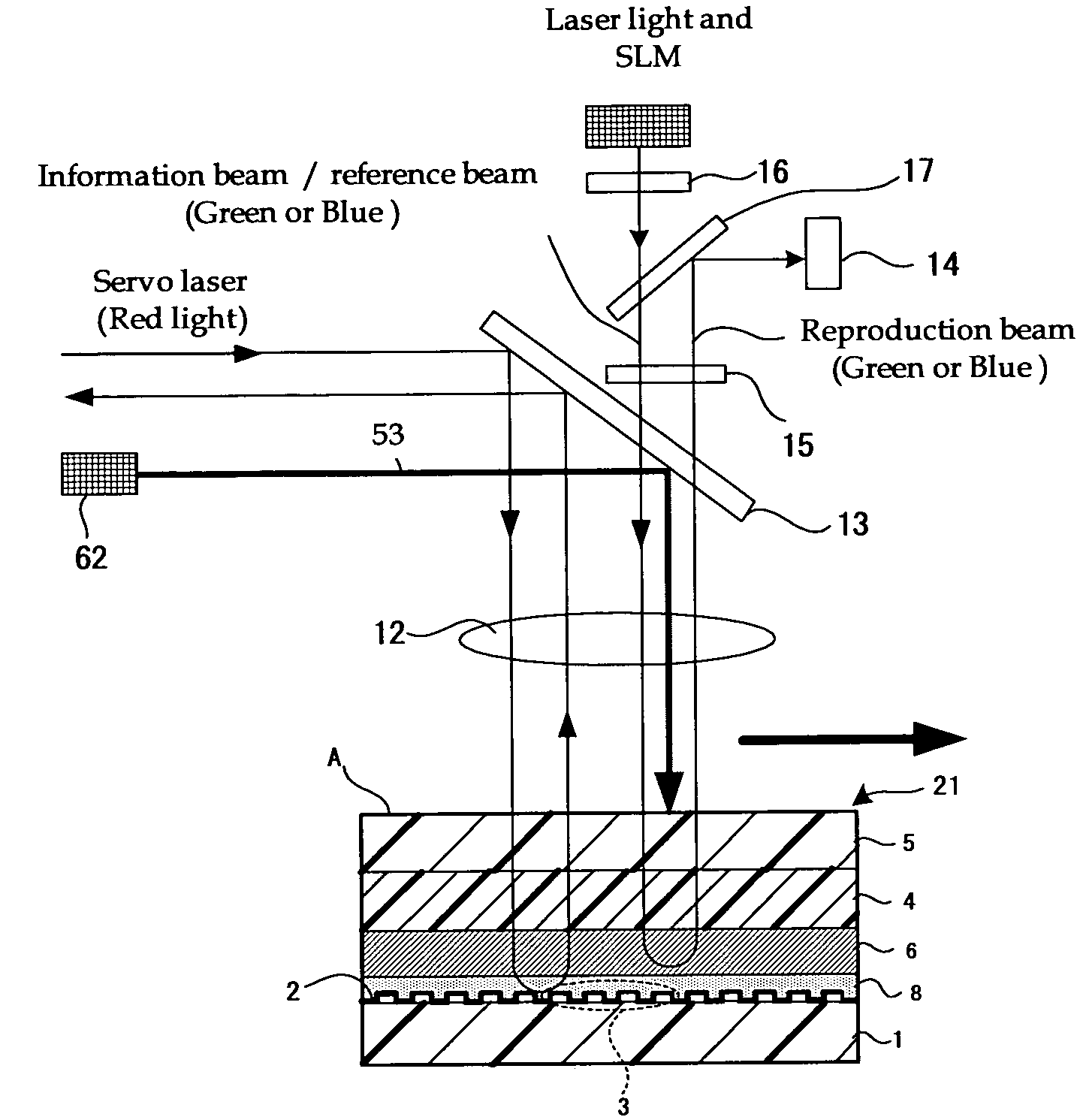
To provide an excellent optical information recording method, optical information recording medium and optical information recording apparatus both of which use the method. The method generates no excessively-exposed region, can sufficiently fix recorded information, and never reduce the sensitivity of non-recorded regions. This is achieved because the method applies a fixing beam onto at least a portion of an exposed region of a recording layer of the optical information recording medium, the recording layer recording information by holography, at an exposure level T (mJ / cm2) that satisfies the condition H<(S+T)<2H (where S is an integrated exposure level (mJ / cm2), which is the total of the exposure level in each predetermined region that constitutes the exposed region where an interference image has been recorded by irradiating the recording layer with an information beam and a reference beam, and H is a minimum fixing exposure level (mJ / cm2) required to fix the interference image).
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
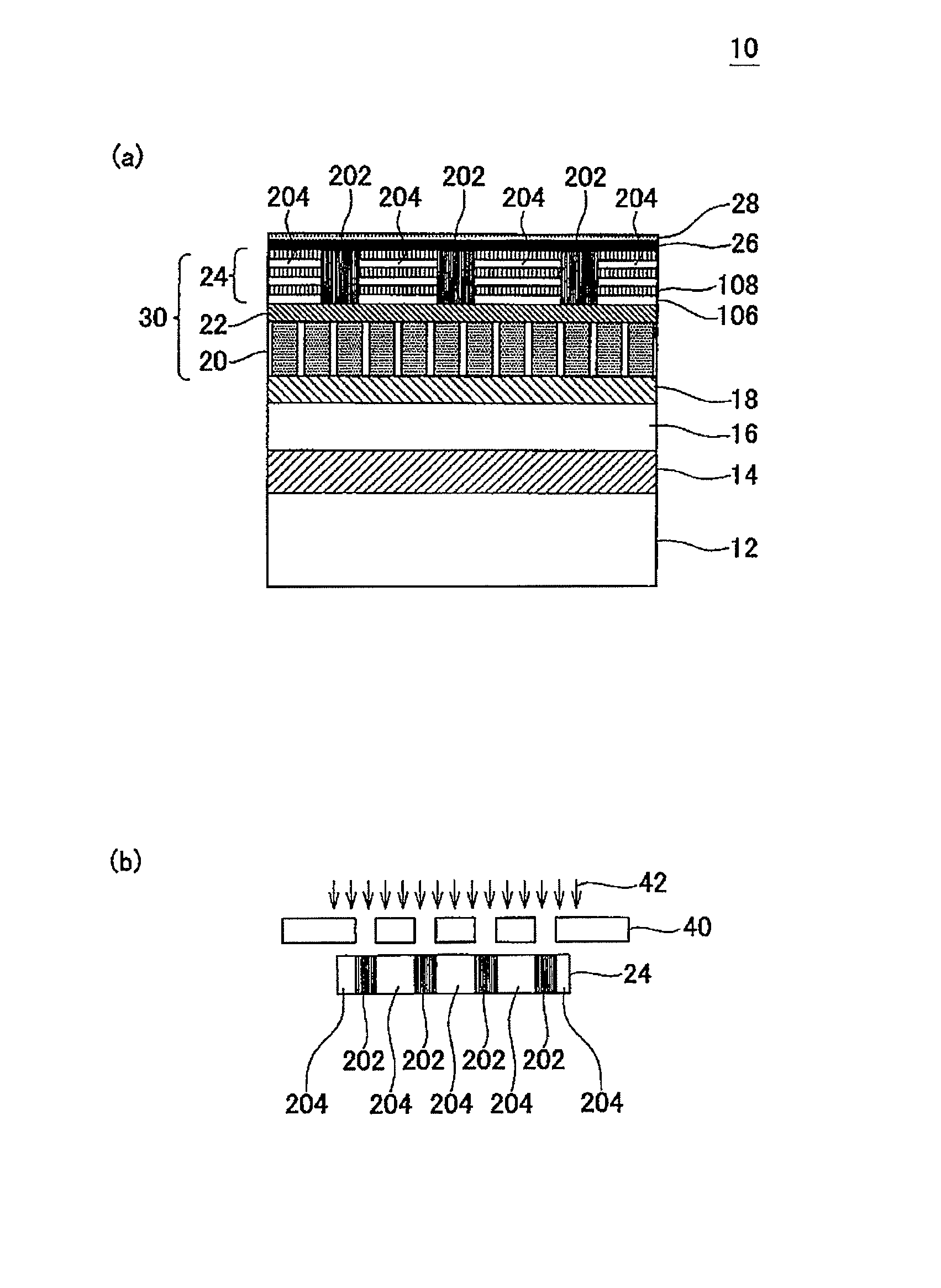
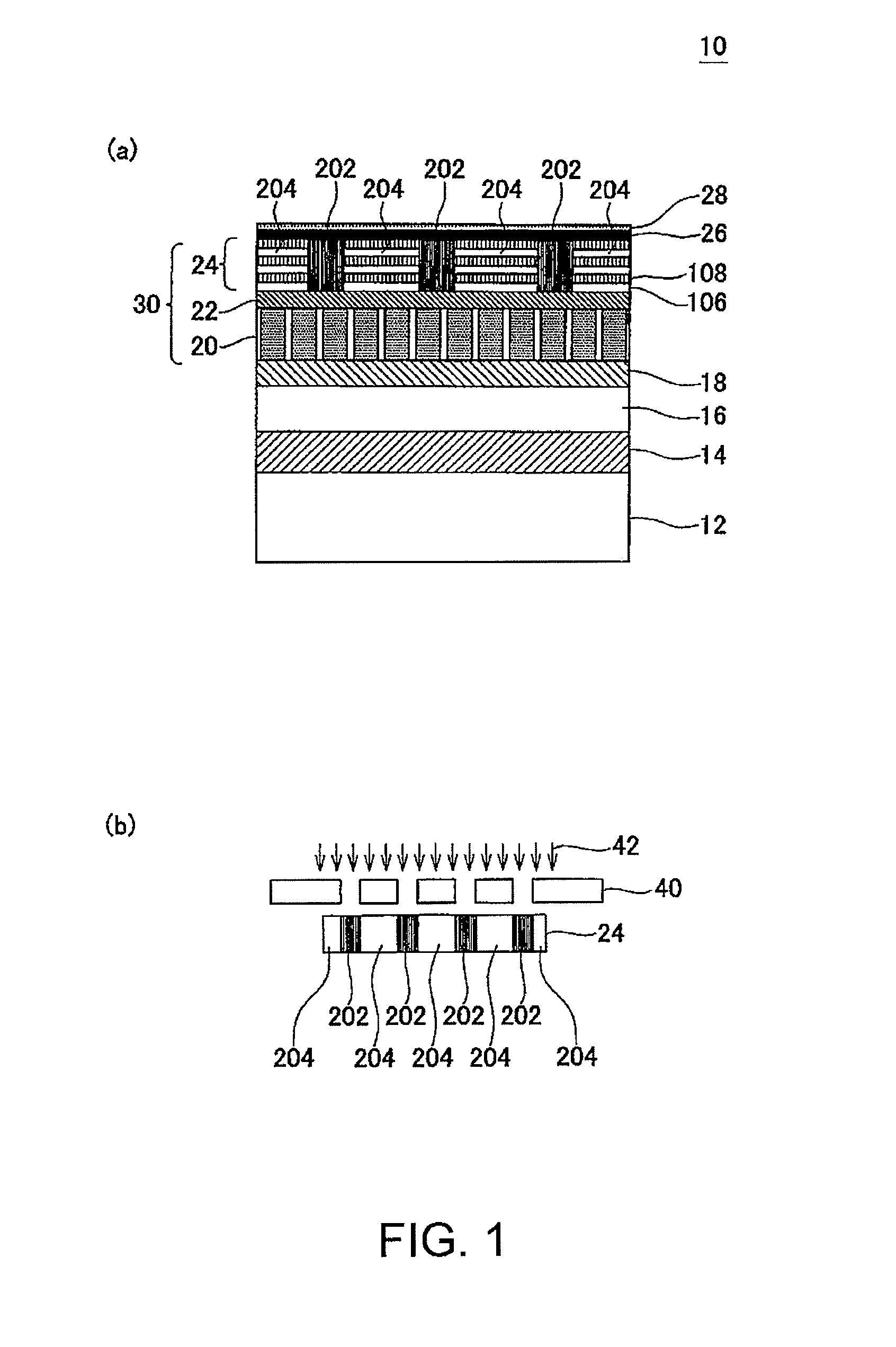
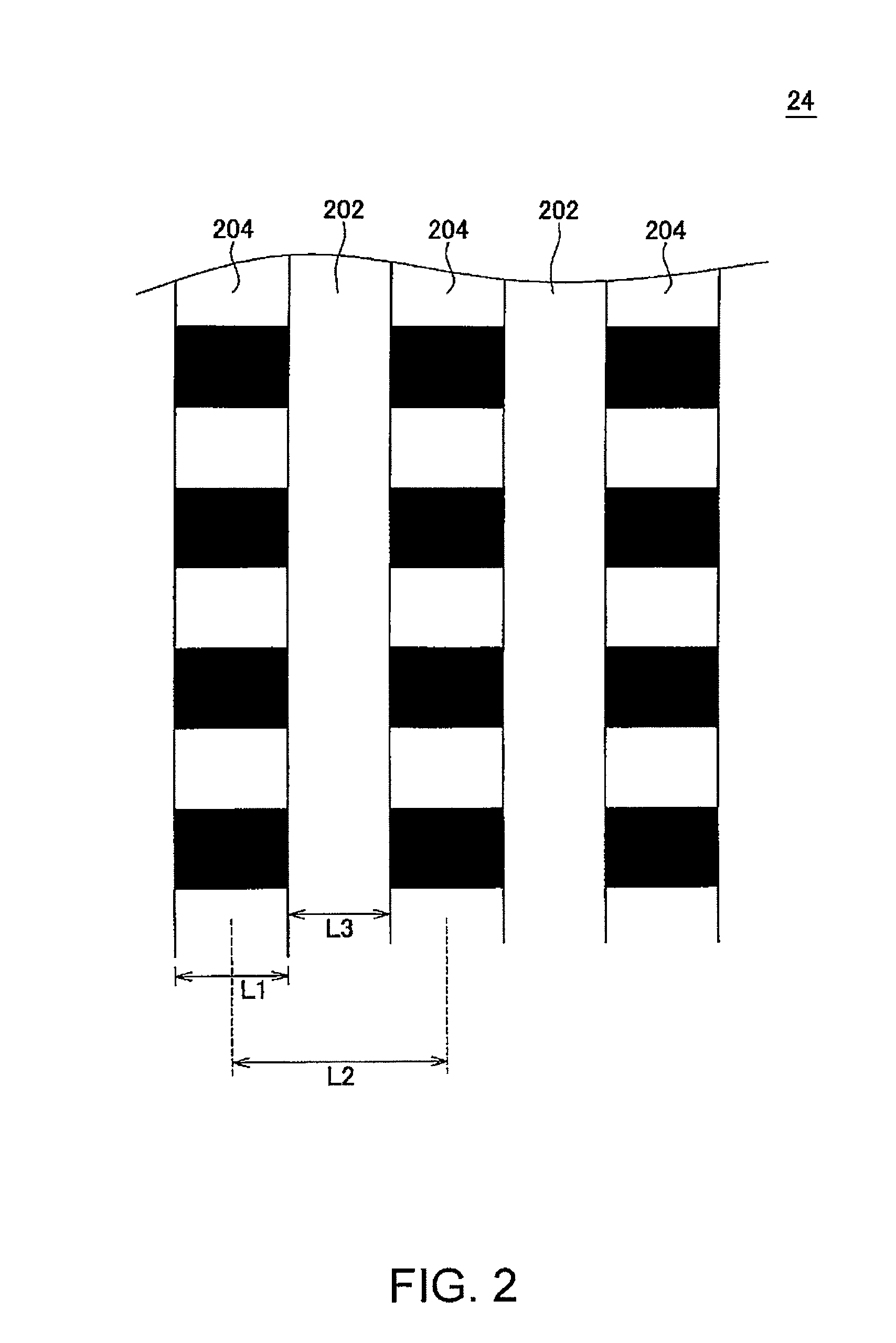
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic recording medium manufacturing method, and magnetic disk
ActiveUS8076013B2Reduce noiseHigh track densityPretreated surfacesRecord information storageMagnetization curveMagnetic shield
A magnetic recording medium (10) has a substrate (12) and a perpendicular magnetic recording layer (30) formed over the substrate (12). The perpendicular magnetic recording layer (30) has a granular layer (20) in which a magnetic signal is recorded and a continuous film layer (24) magnetically coupled to the granular layer (20). The continuous film layer (24) has hard magnetic portions (204) formed in positions corresponding to the recording regions where magnetic signals are recorded in the granular layer (20) and magnetic shield portions (202) formed between the hard magnetic portions (204), each having a magnetization curve whose slope is larger than those of the hard magnetic portions in the region where the applied magnetic filed is zero when the magnetization curve is measured, and each having a residual magnetic polarization smaller than those in the hard magnetic portions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com