Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99results about How to "High track density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
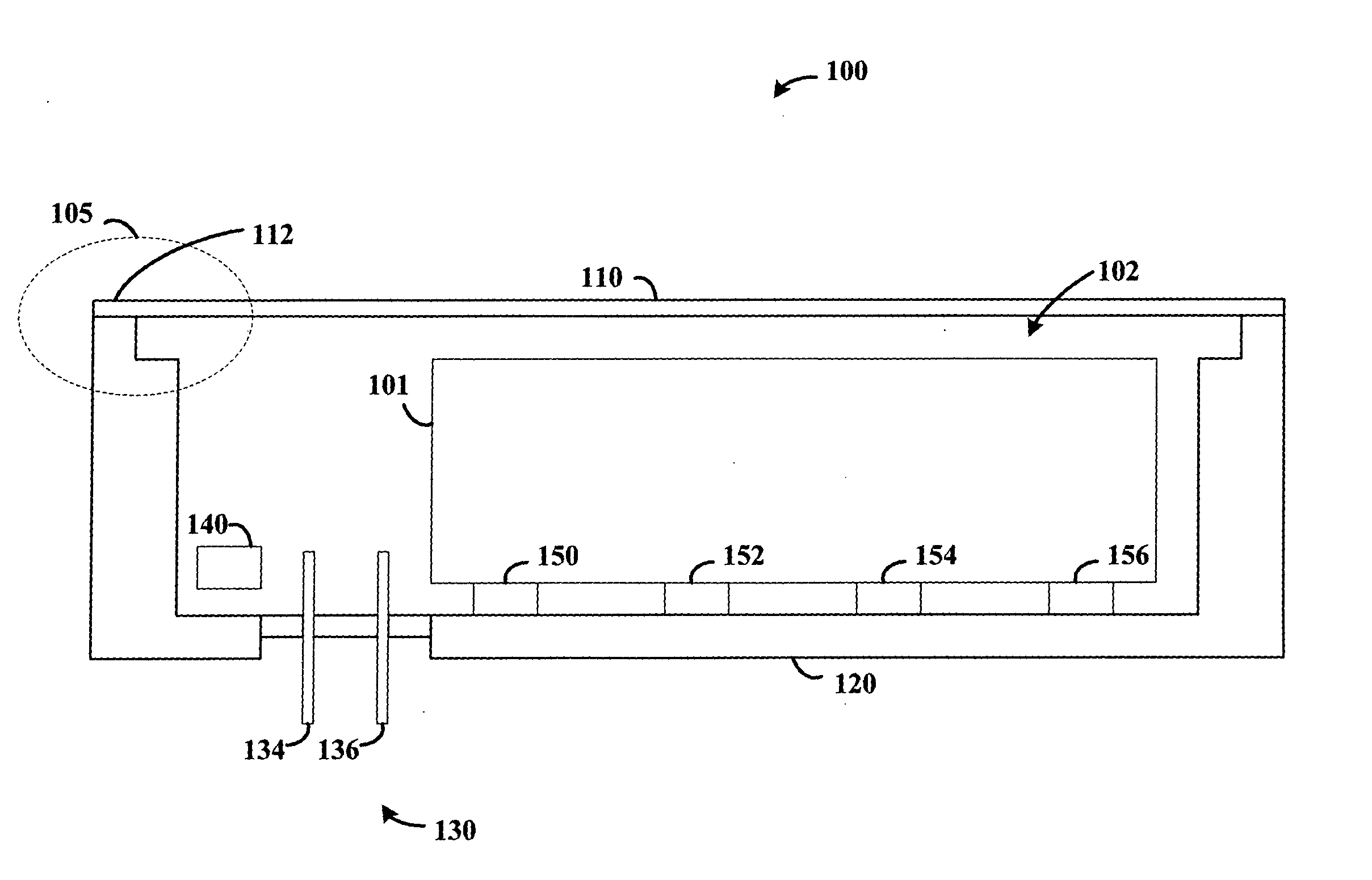
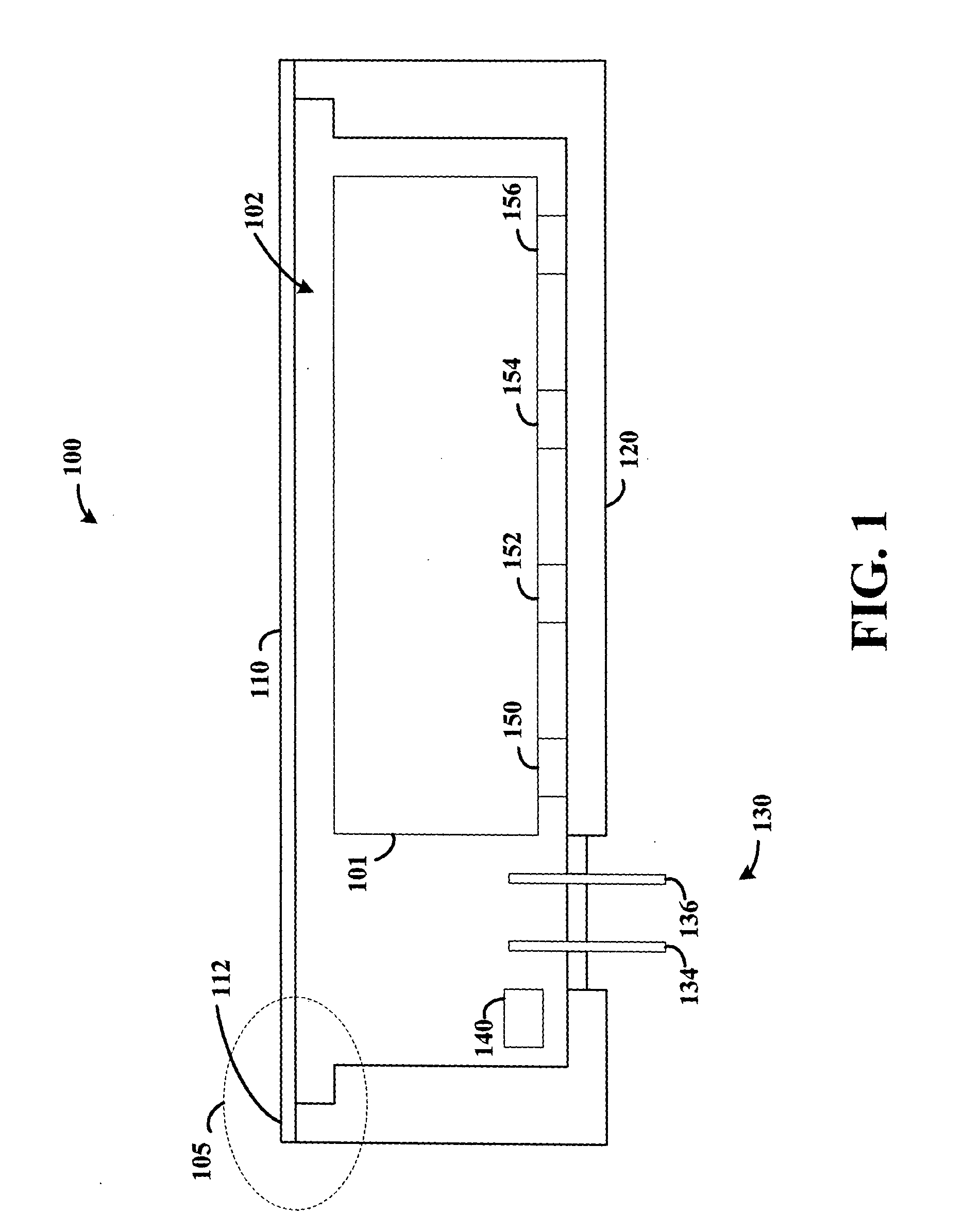
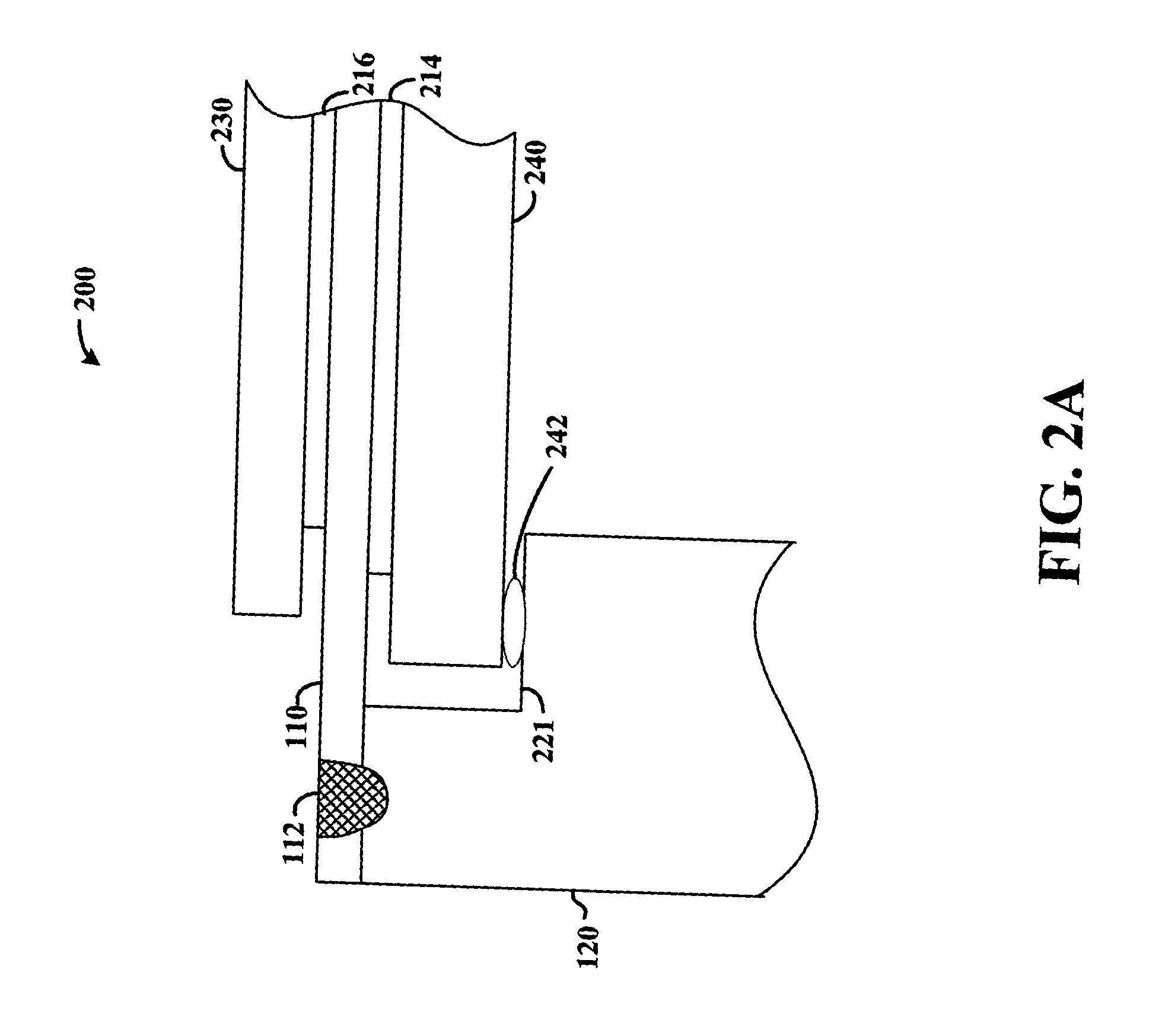
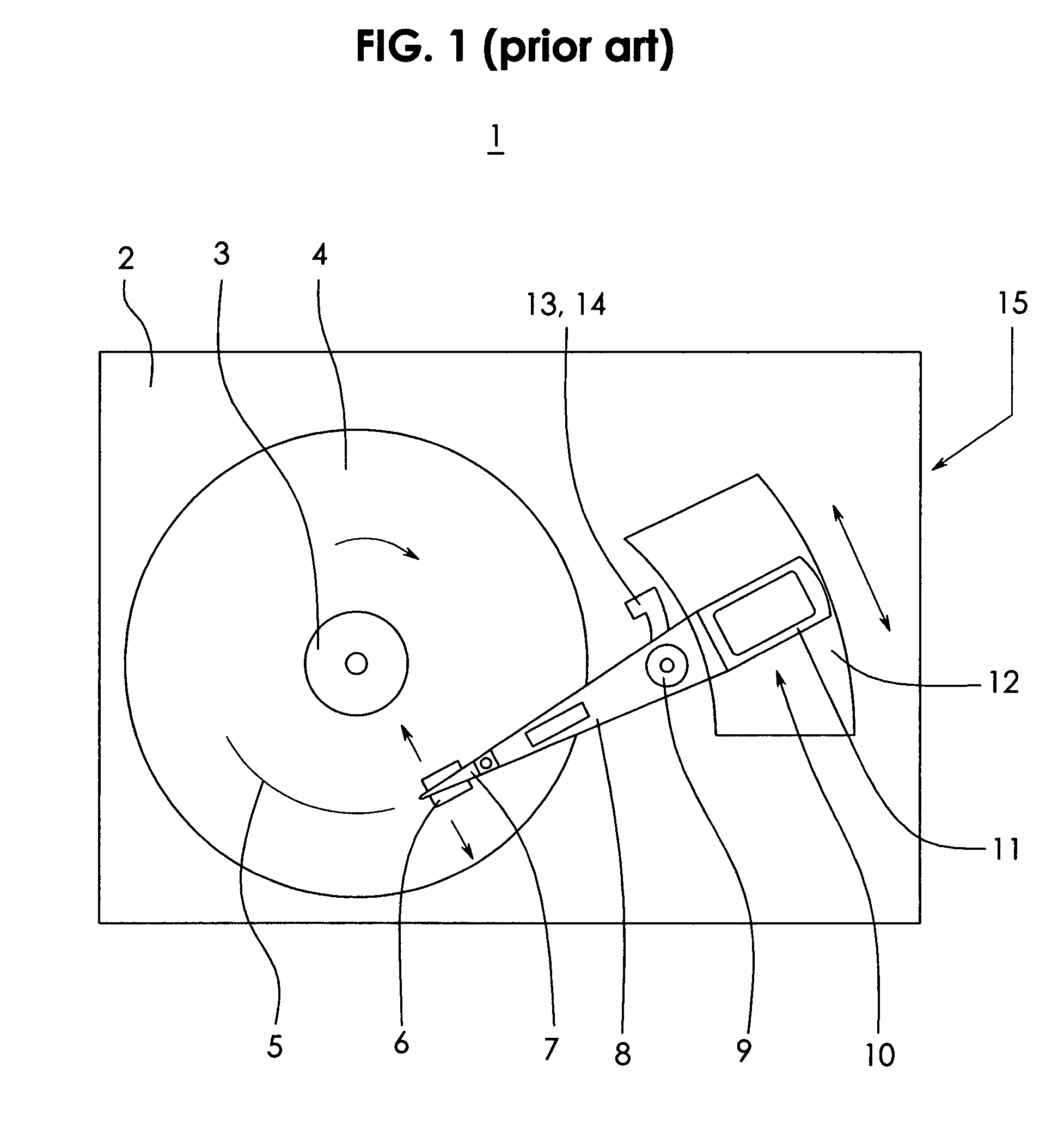
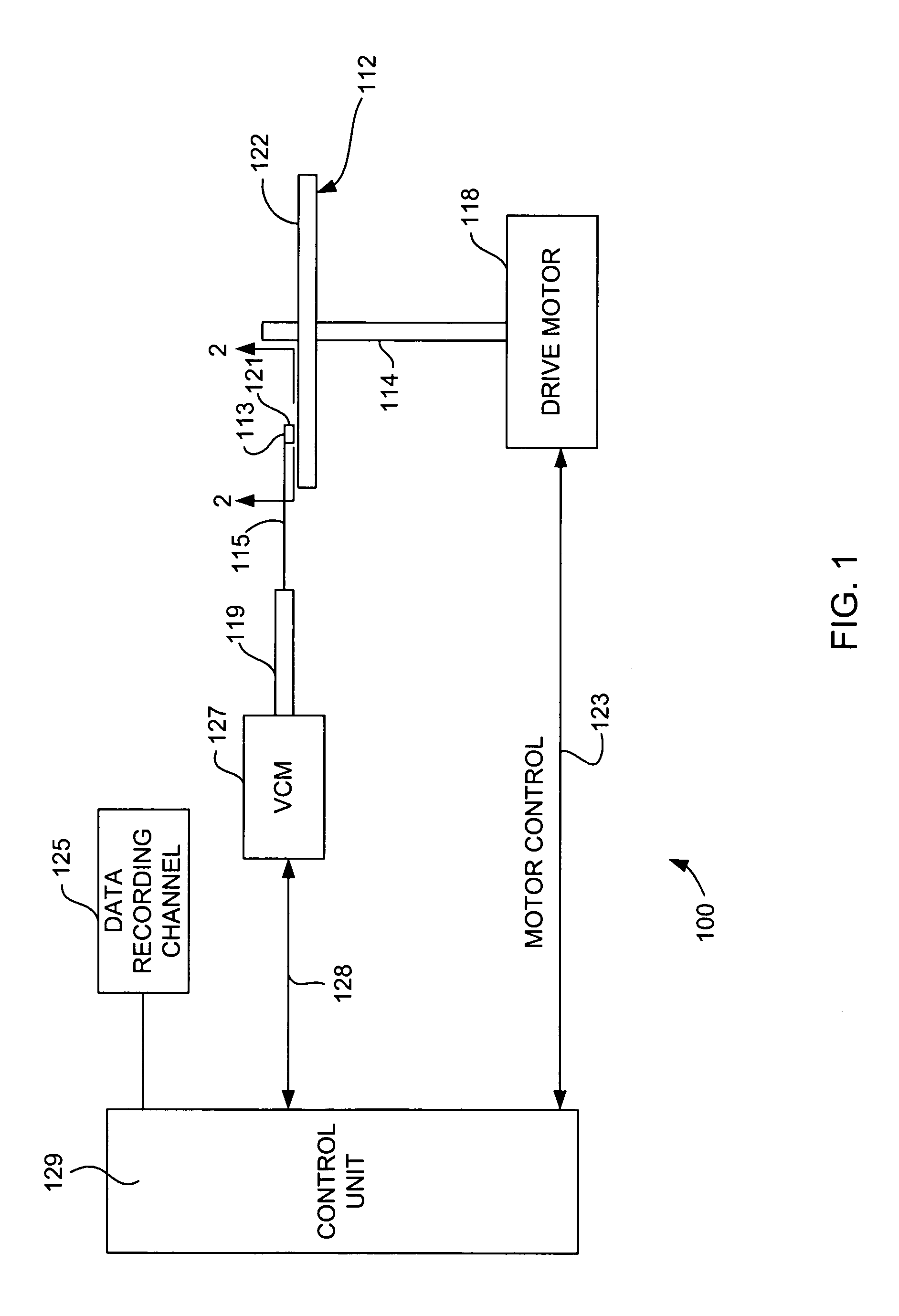
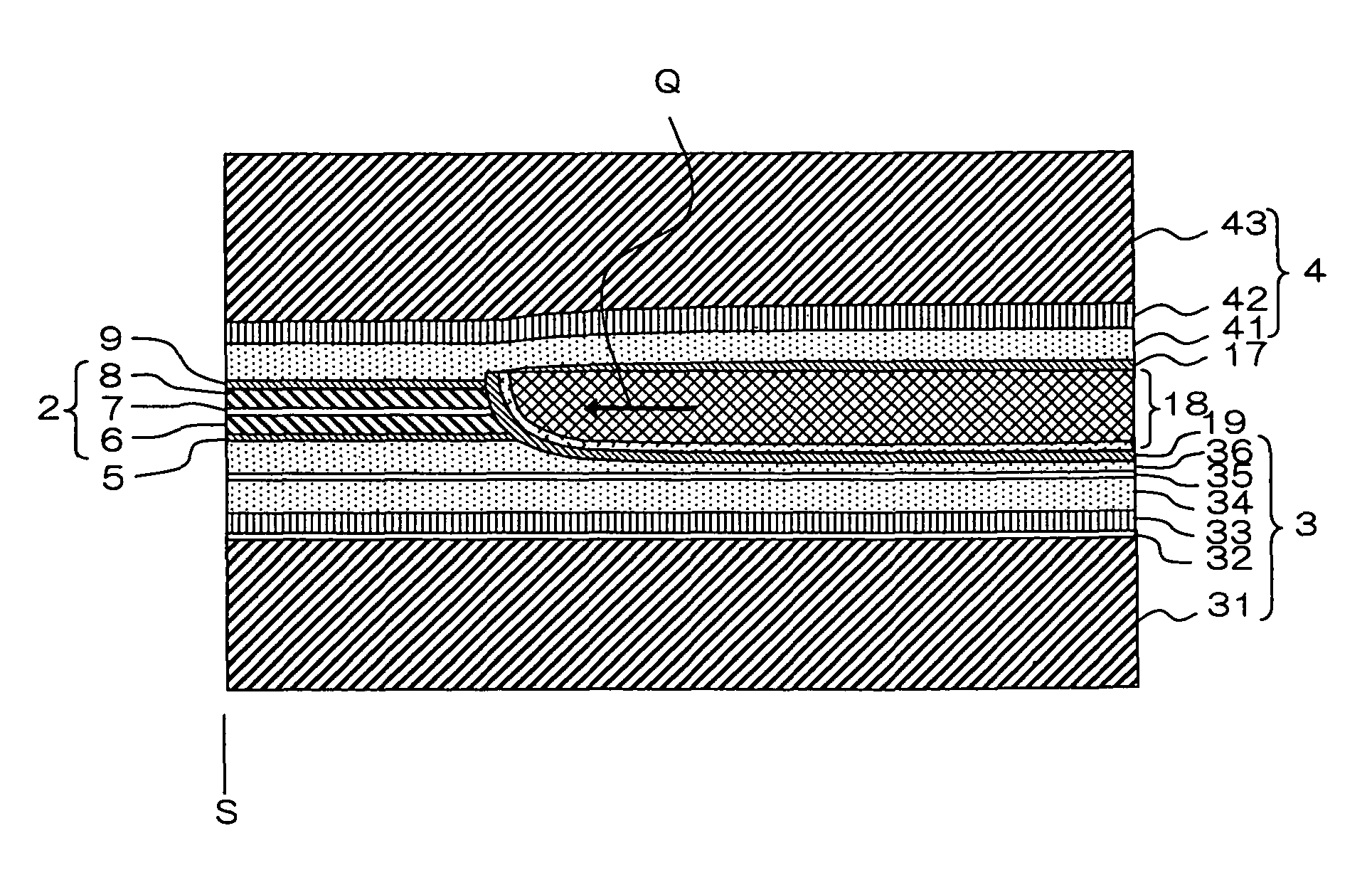
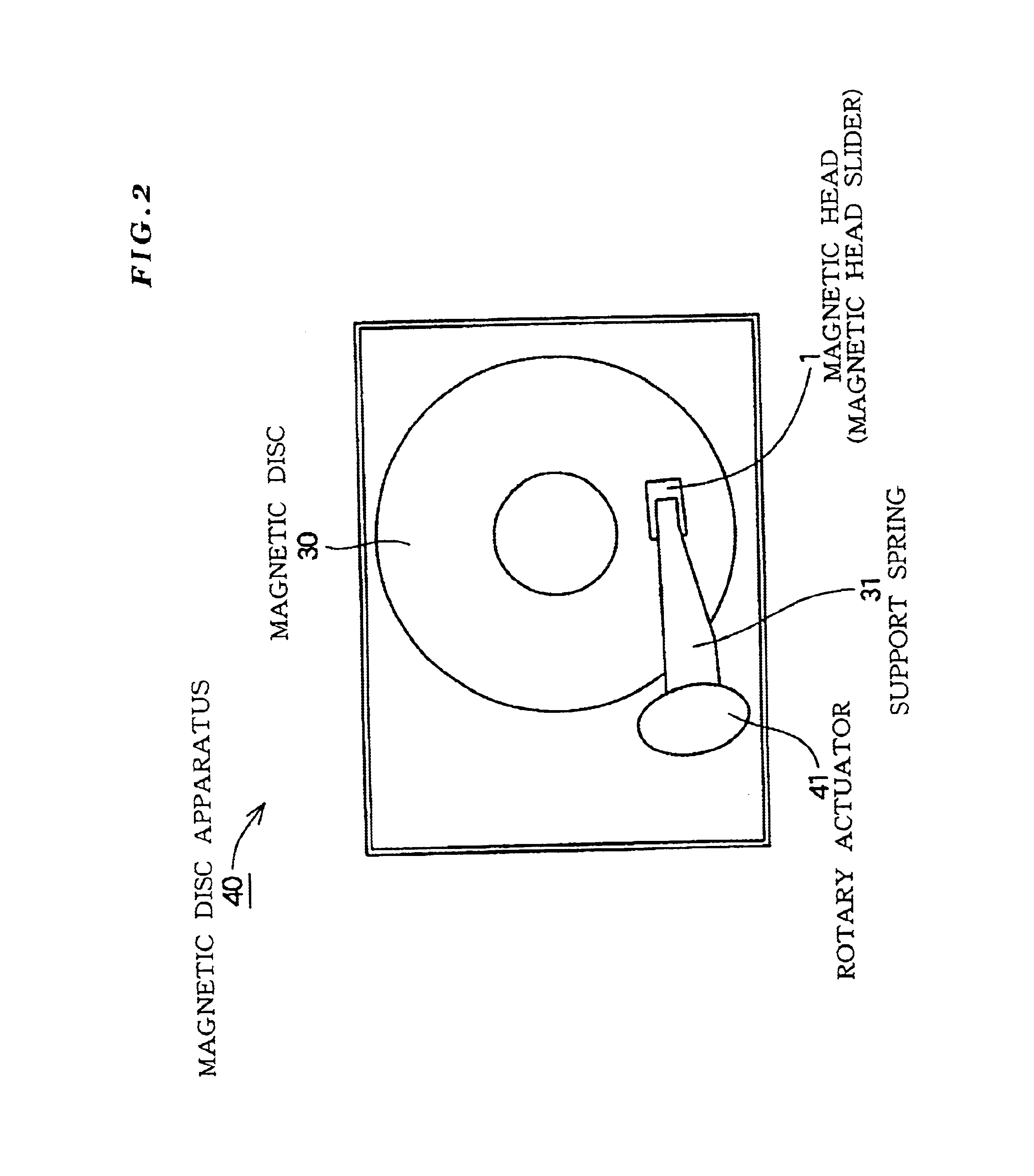
Hermetically sealed electronics arrangement and approach
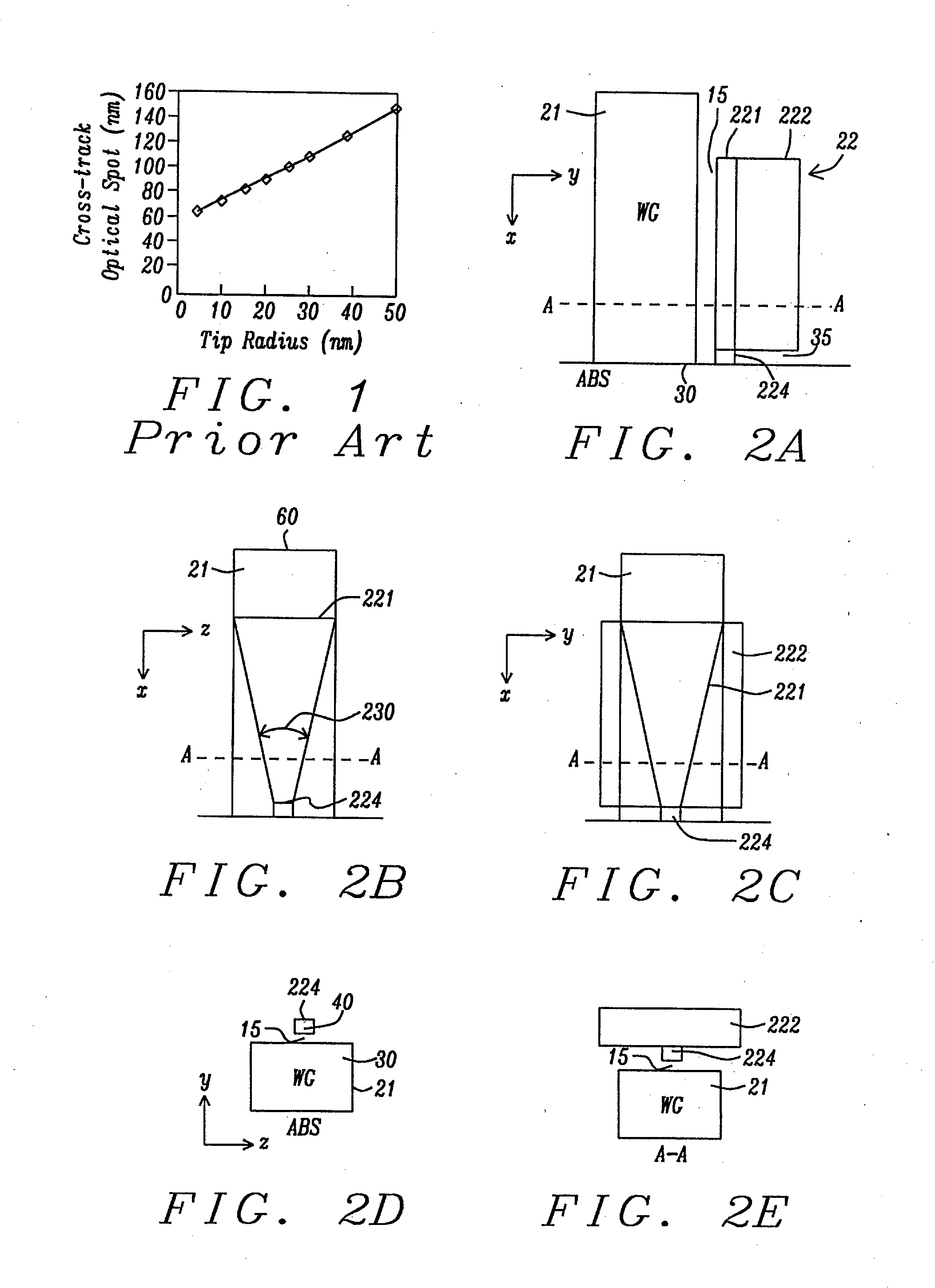
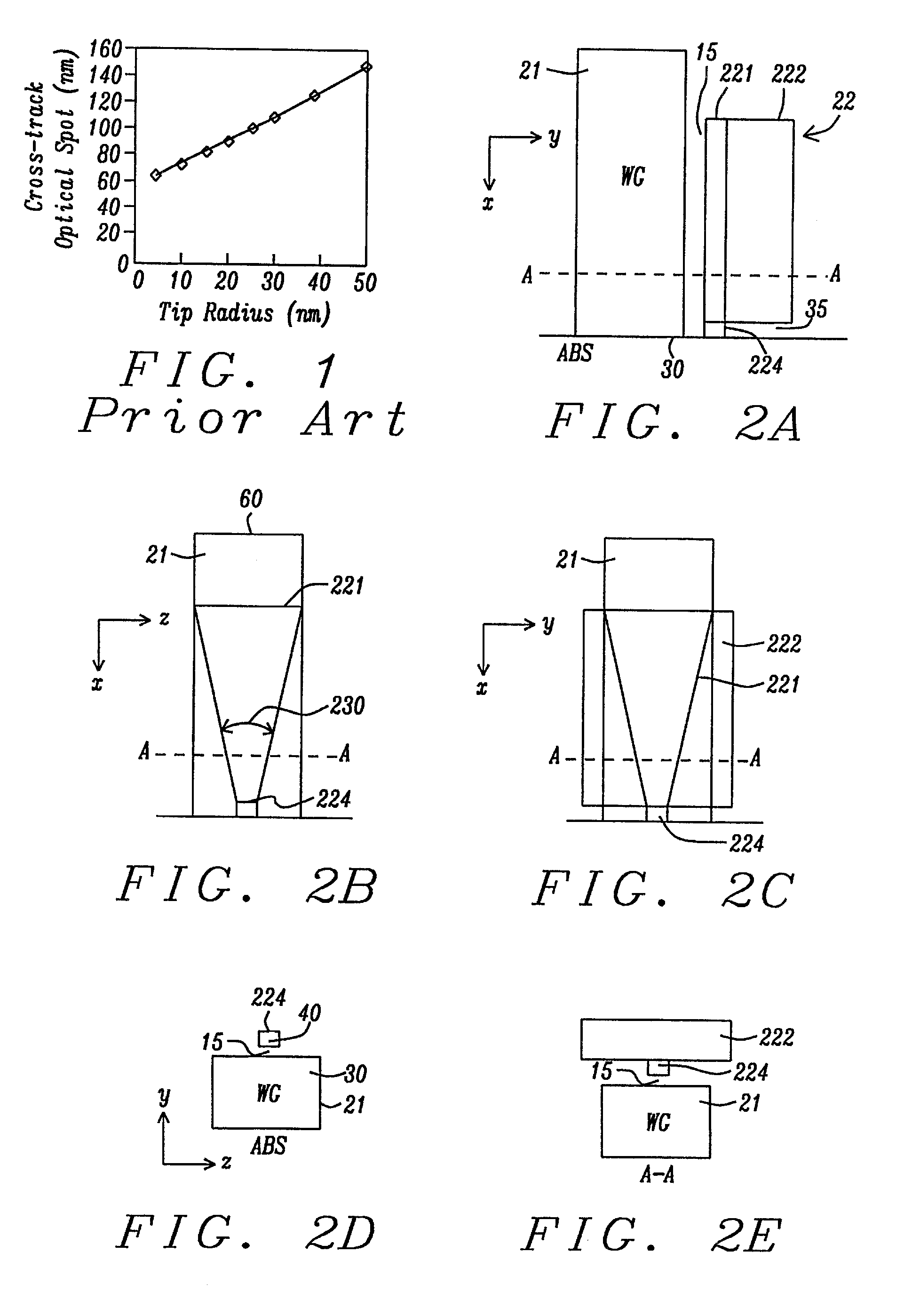
InactiveUS20050068666A1Reduction of magnetic spacingImprove performanceApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionMetallic enclosureCold formed
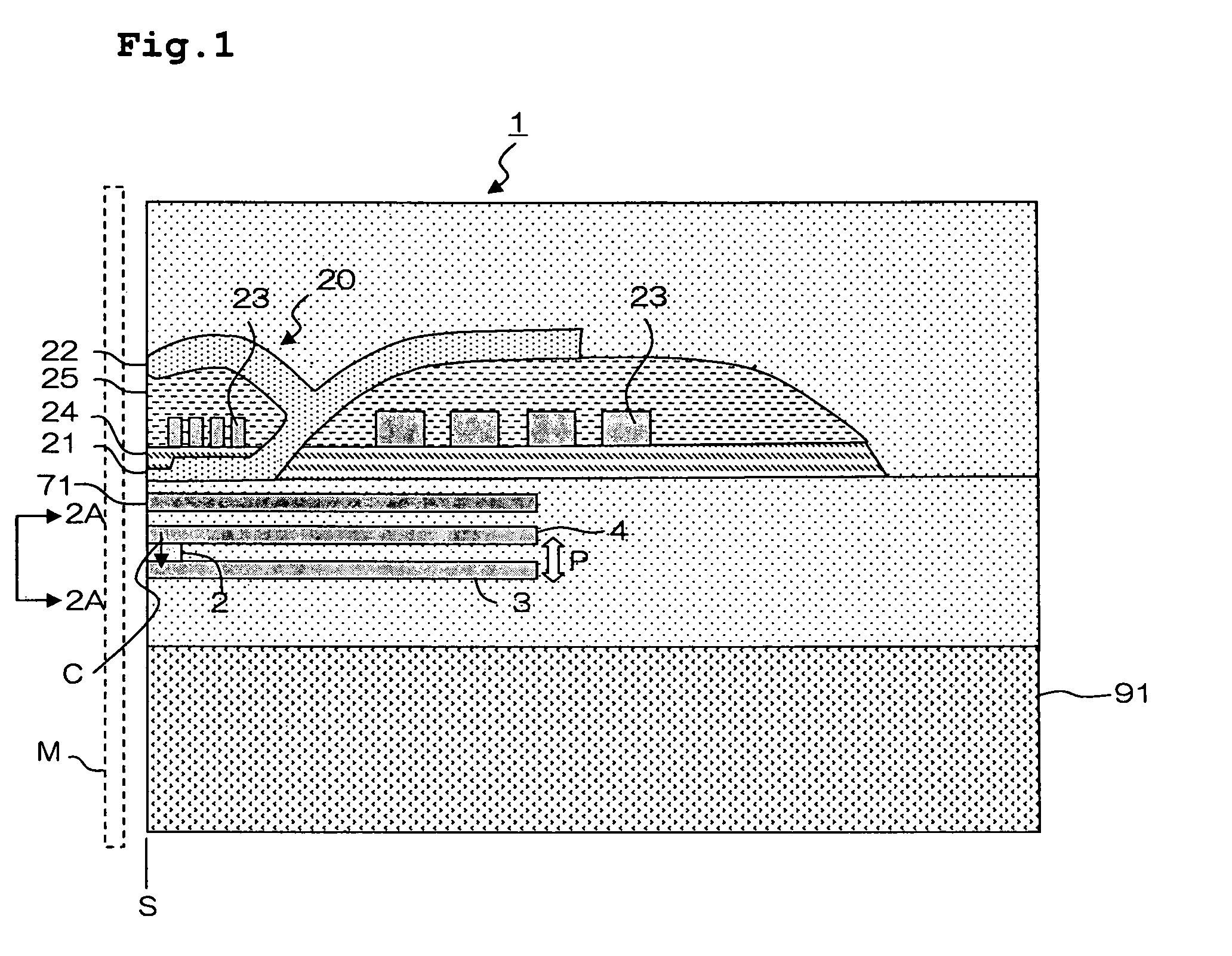
A hermetic sealing approach involves welding an Aluminum cover onto a low-cost Aluminum housing. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, a metal housing having a base and sidewalls extending upward therefrom is adapted to receive and couple to an HDD arrangement. The metal housing is formed using material and processing (e.g., cold formed or die cast Aluminum) that are relatively inexpensive. A feedthrough arrangement including a plurality of communication pins extends through an opening in the base and is coupled thereto, with the communication pins adapted to pass signals between the inside and the outside of the metal housing. A metal cover is welded to an upper portion of the sidewalls and, with the feedthrough arrangement, hermetically seals the metal housing.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
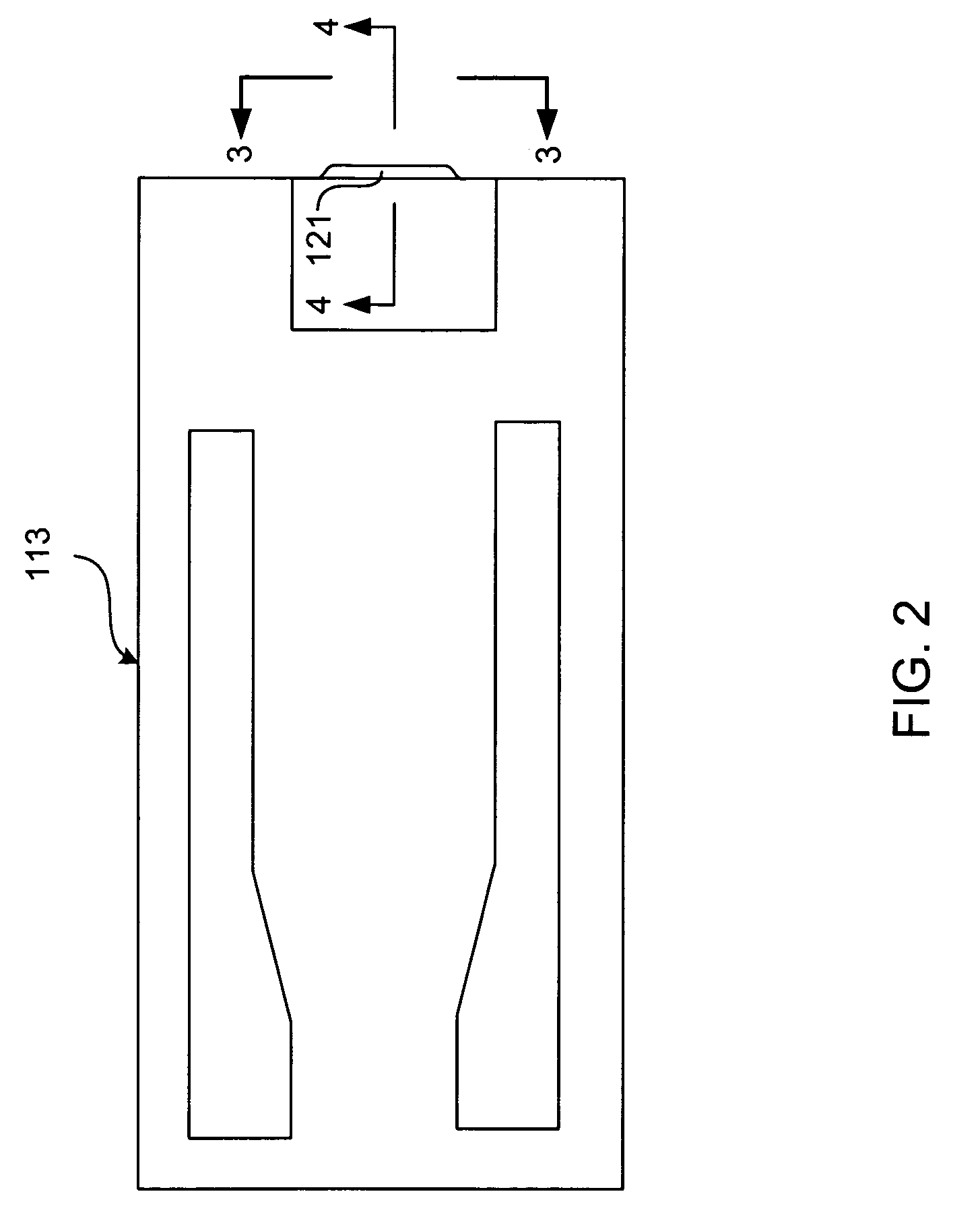
CPP-type thin film magnetic head provided with side shields
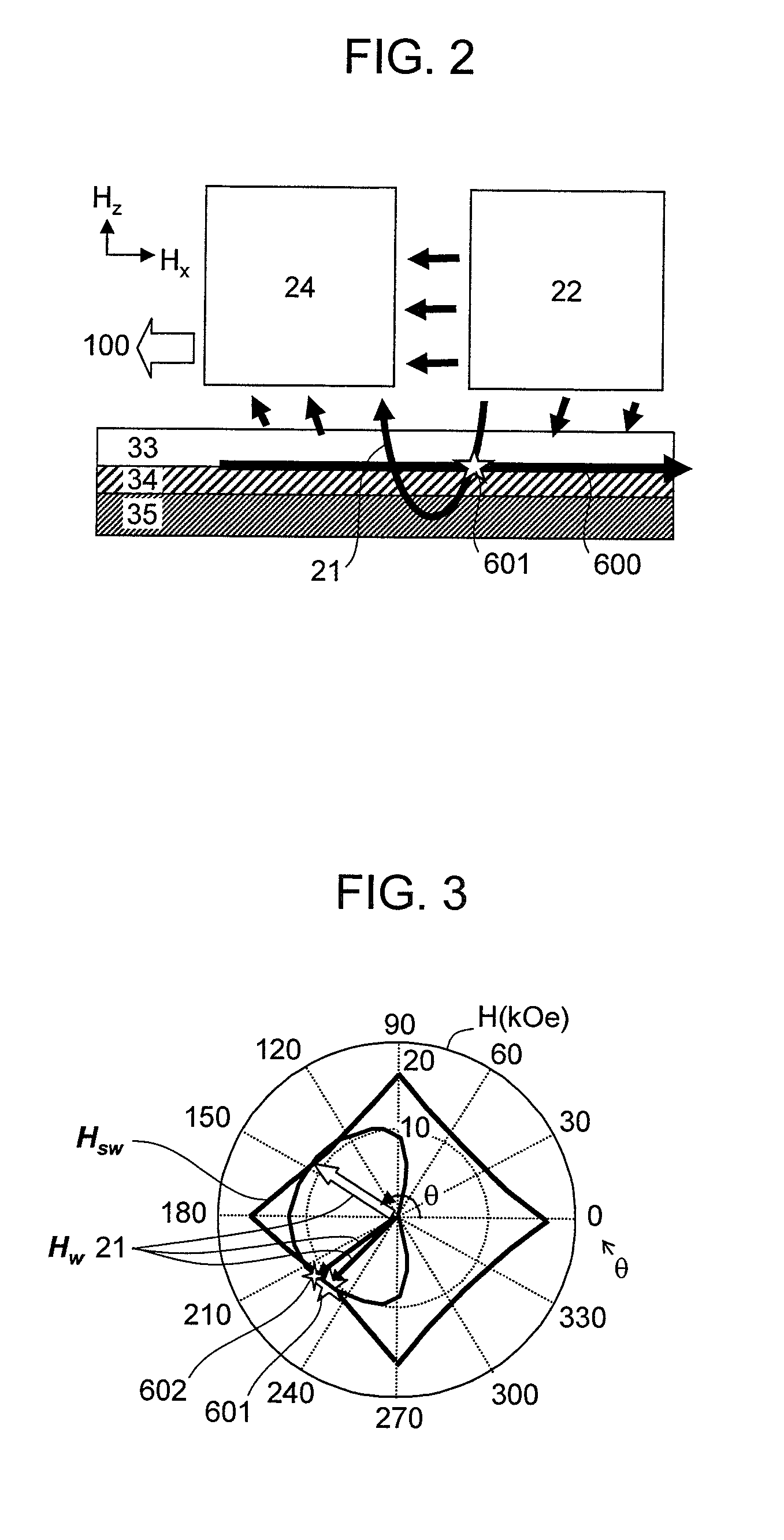
ActiveUS20110051291A1High track densityLinearityNanomagnetismDisposition/mounting of recording headsControl layerCoupling
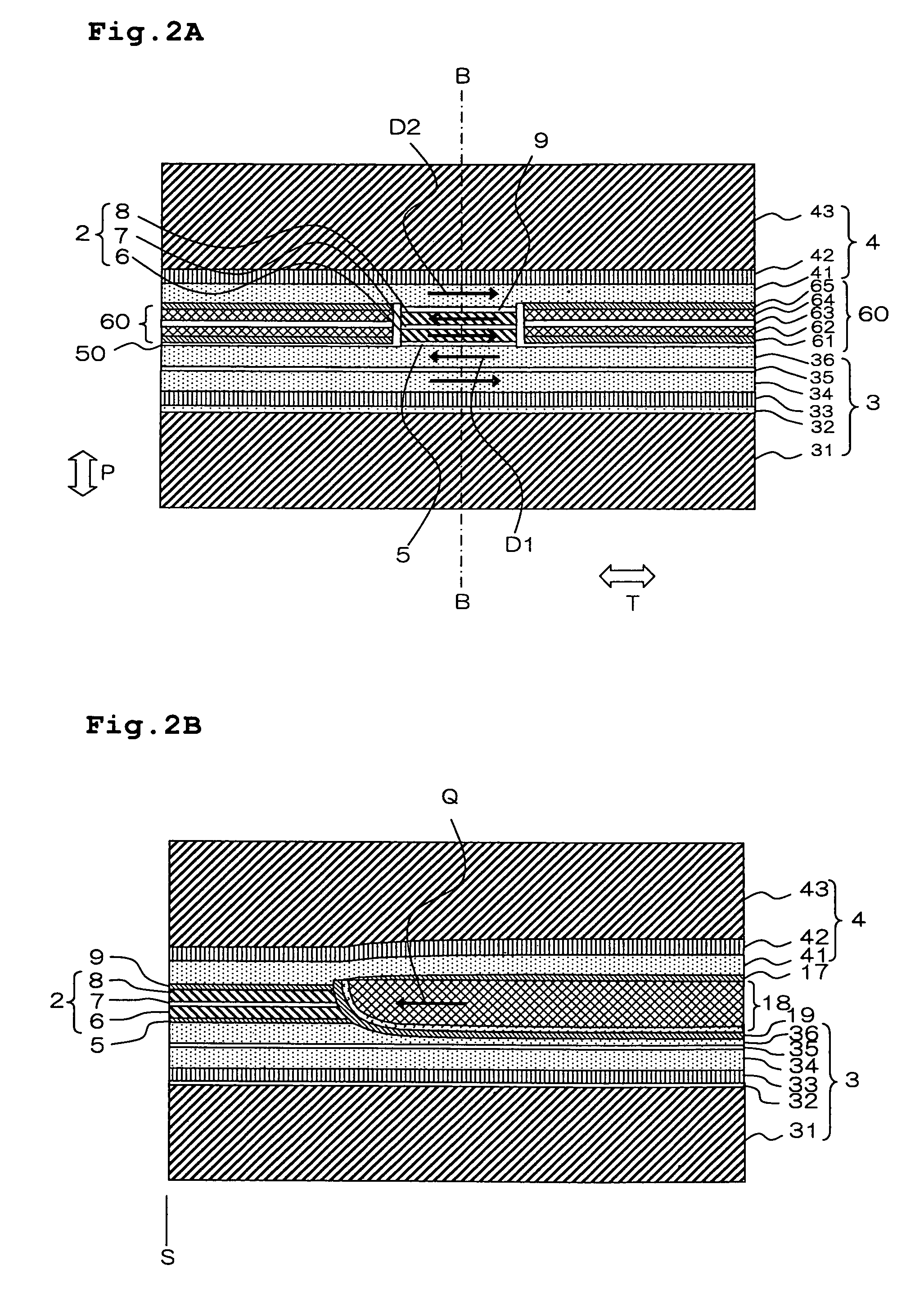
A thin film magnetic head includes first and second shield layers that are positioned on both sides of a magnetoresistive (MR) stack with respect to a film surface orthogonal direction; a first exchange-coupling layer that is positioned between the MR stack and the first shield layer and that generates an exchange-coupling between a first magnetoresistive (MR) magnetic layer and a first magnetic control layer of the first shield layer; a second exchange-coupling layer that is positioned between the MR stack and the second shield layer and that generates an exchange-coupling between a second magnetoresistive (MR) magnetic layer and a second magnetic control layer of the second shield layer; a bias magnetic field application layer that is disposed at an opposite surface of the MR stack from an air bearing surface (ABS) and that applies a bias magnetic field to the MR stack in a direction orthogonal to the ABS; and pair of side shield layers that are positioned at both sides of the MR stack with respect to a track width direction. Each of the side shield layers includes a pair of magnetic layers that are antiferromagnetically exchange-coupled through a side shield ruthenium layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method and apparatus for recording information on information recording medium
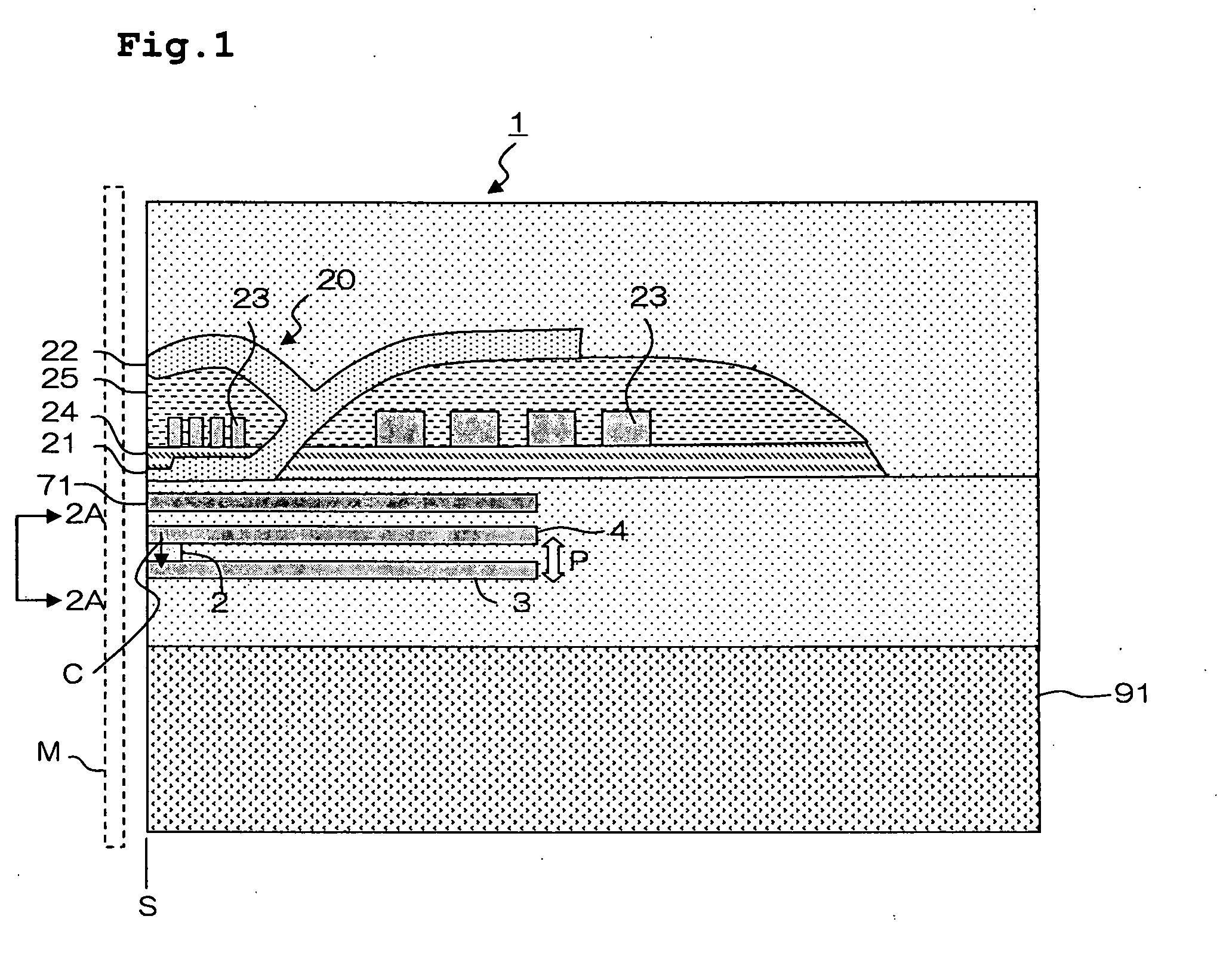
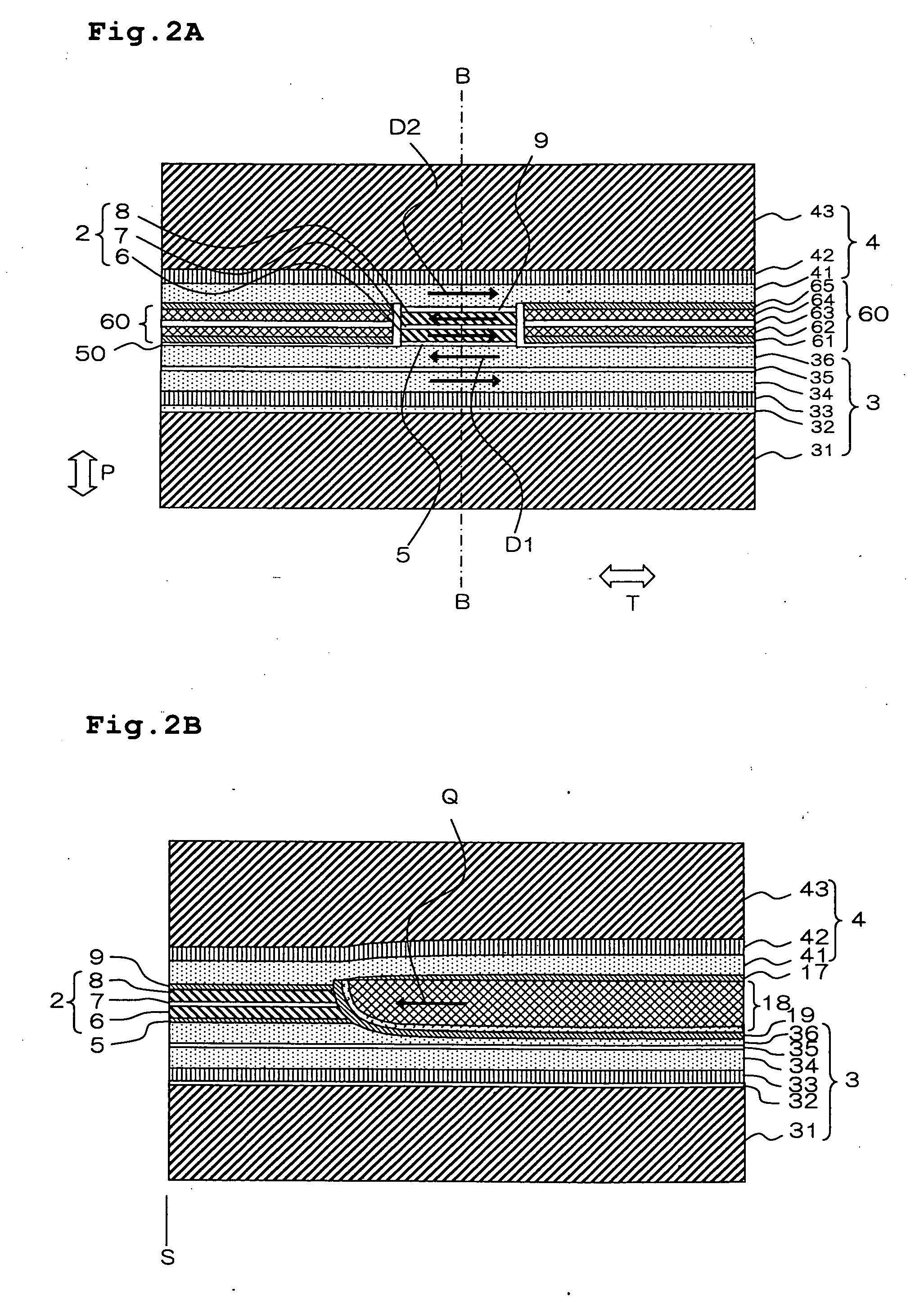
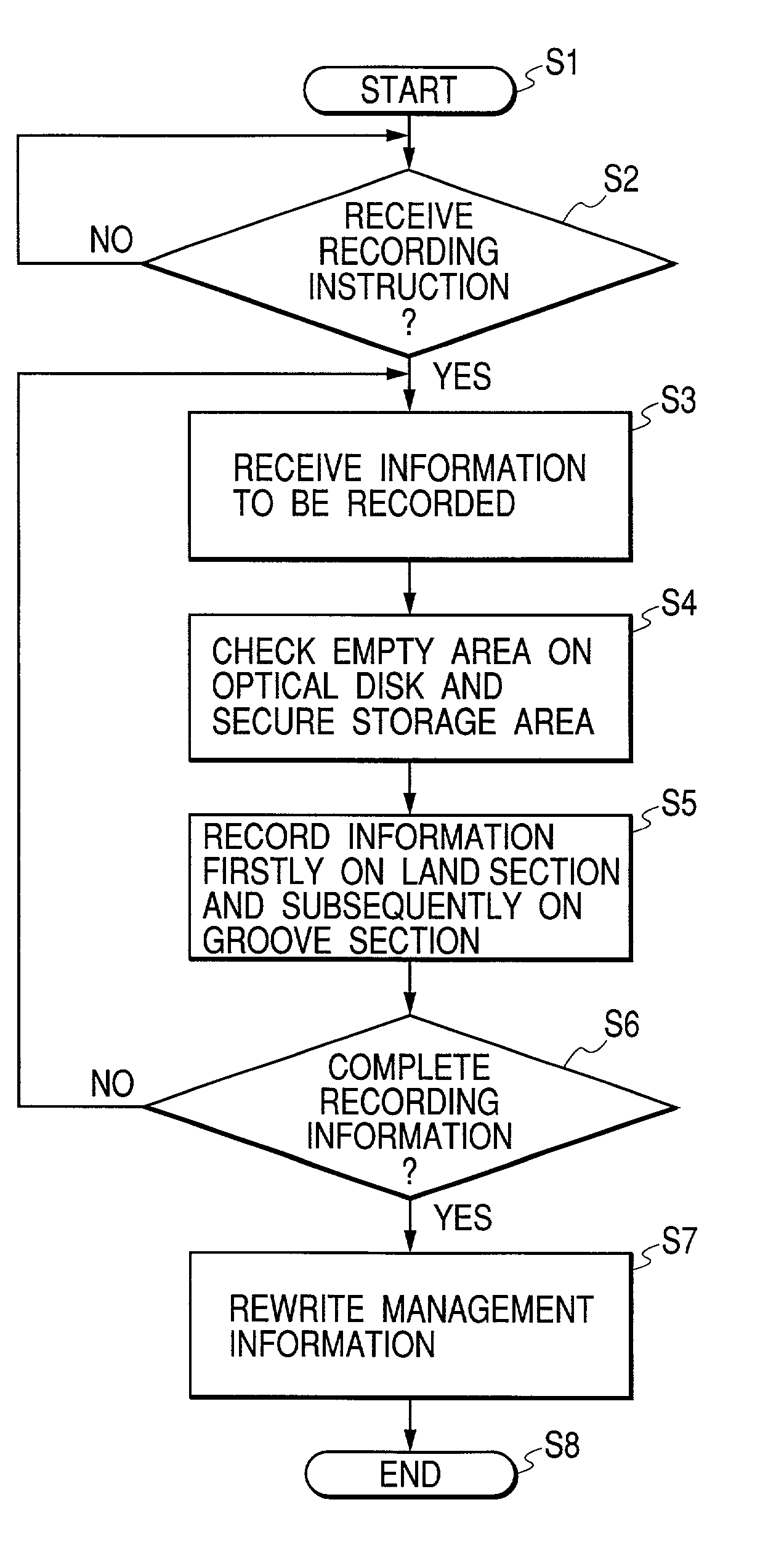
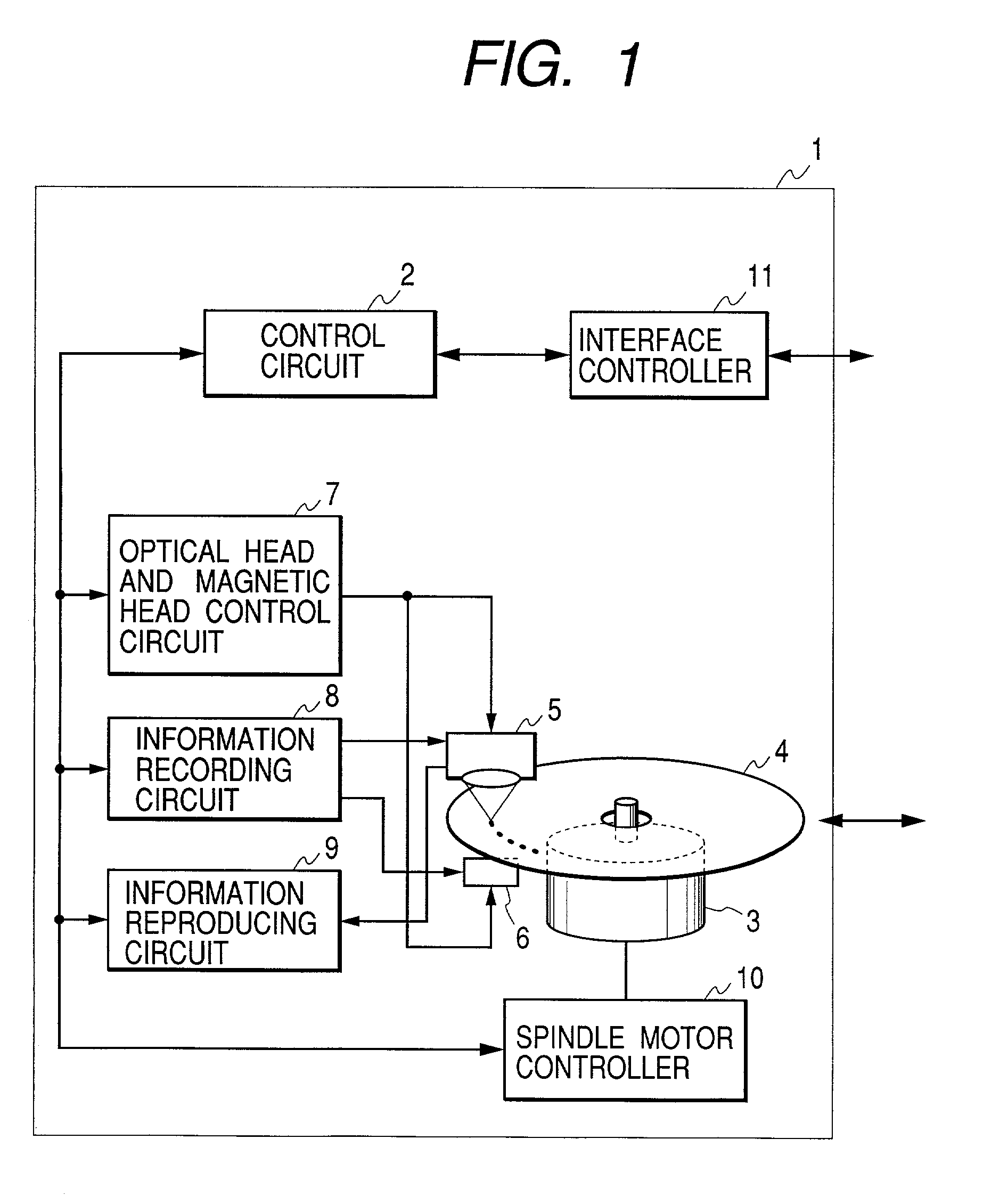
InactiveUS6999398B2Reduce decreaseHigh track densityRecord information storageLight beam reproducingComputer hardwareMagneto optical
Information is recorded on an information recording medium such as a magneto-optical recording medium, having two recording tracks arranged alternately, typically in a double spiral manner. The two recording tracks have different recording characteristics and information is firstly recorded on the recording track less liable to cross write, typically on a land section, and subsequently on the recording track more liable to cross write, typically on a groove section.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for manufacturing magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20080075845A1Raising track densityReducing edge noiseRecord information storageCoatingsPhysicsAlloy
A method for manufacturing a magnetic recording medium includes the steps of (a) forming a perpendicular magnetic recording layer and (b) applying an ion beam to regions between tracks of the perpendicular magnetic recording layer so as to form separation regions for magnetically separating the tracks from each other. In the step (a), a continuous film layer composed of a multilayer film is formed, and CoB layers and Pd layers are laminated in the multilayer film. In the step (b), the CoB layers and the Pd layers are melted by the ion beam so as to form an alloy of metals contained in the CoB layers and the Pd layers to thereby form the separation regions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic recording medium manufacturing method, and magnetic disk
ActiveUS8076013B2Reduce noiseHigh track densityPretreated surfacesRecord information storageMagnetization curveMagnetic shield
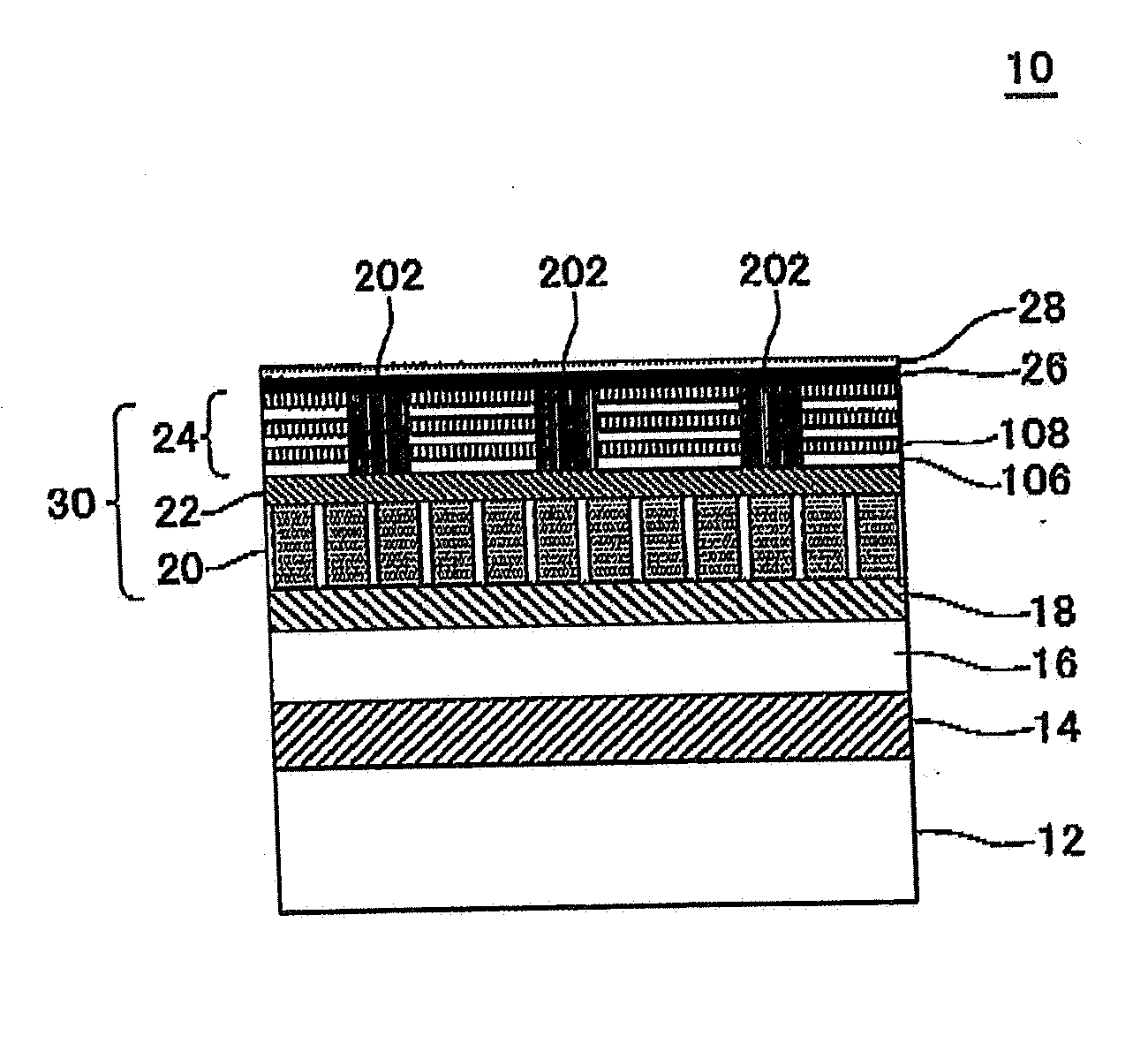
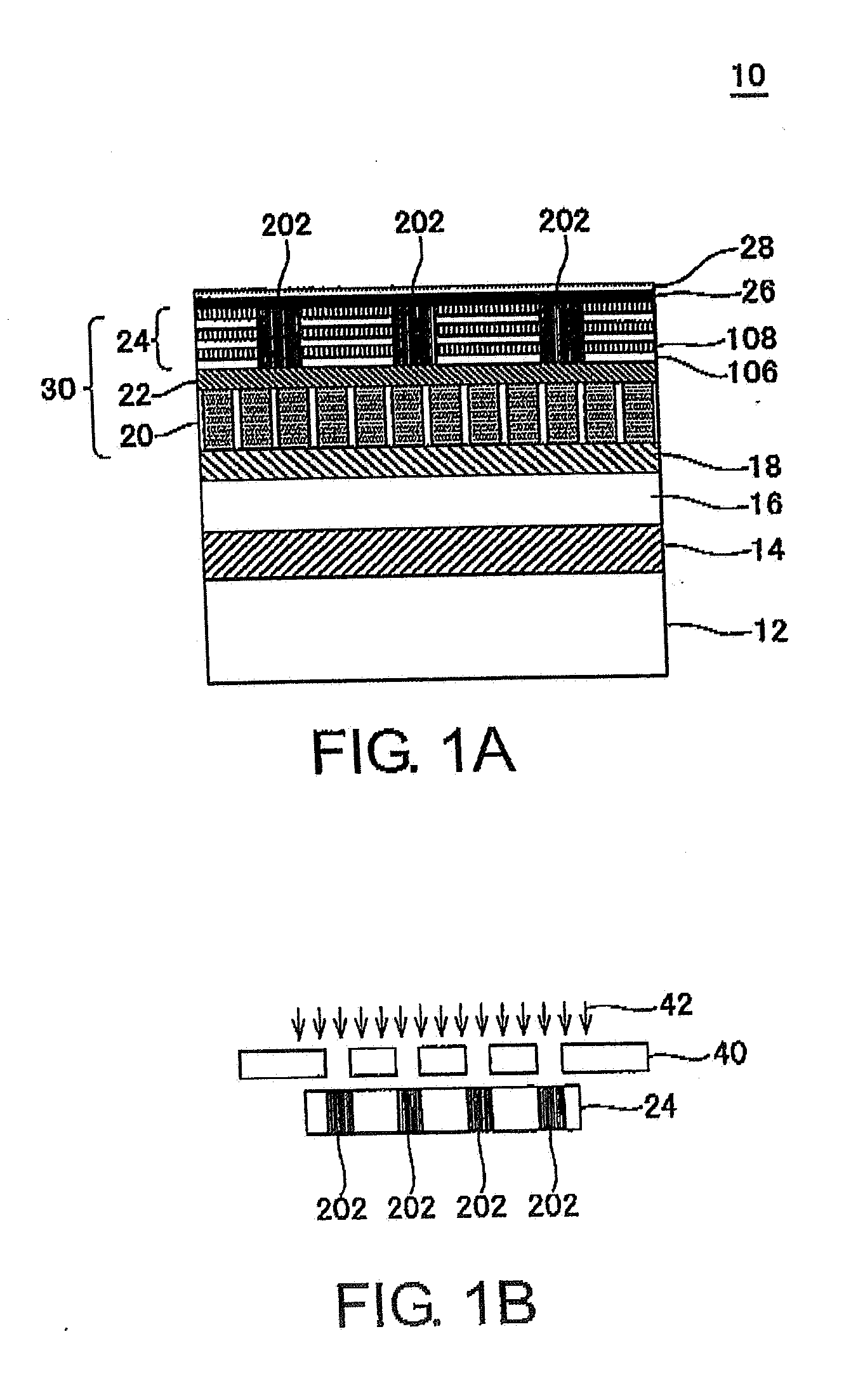
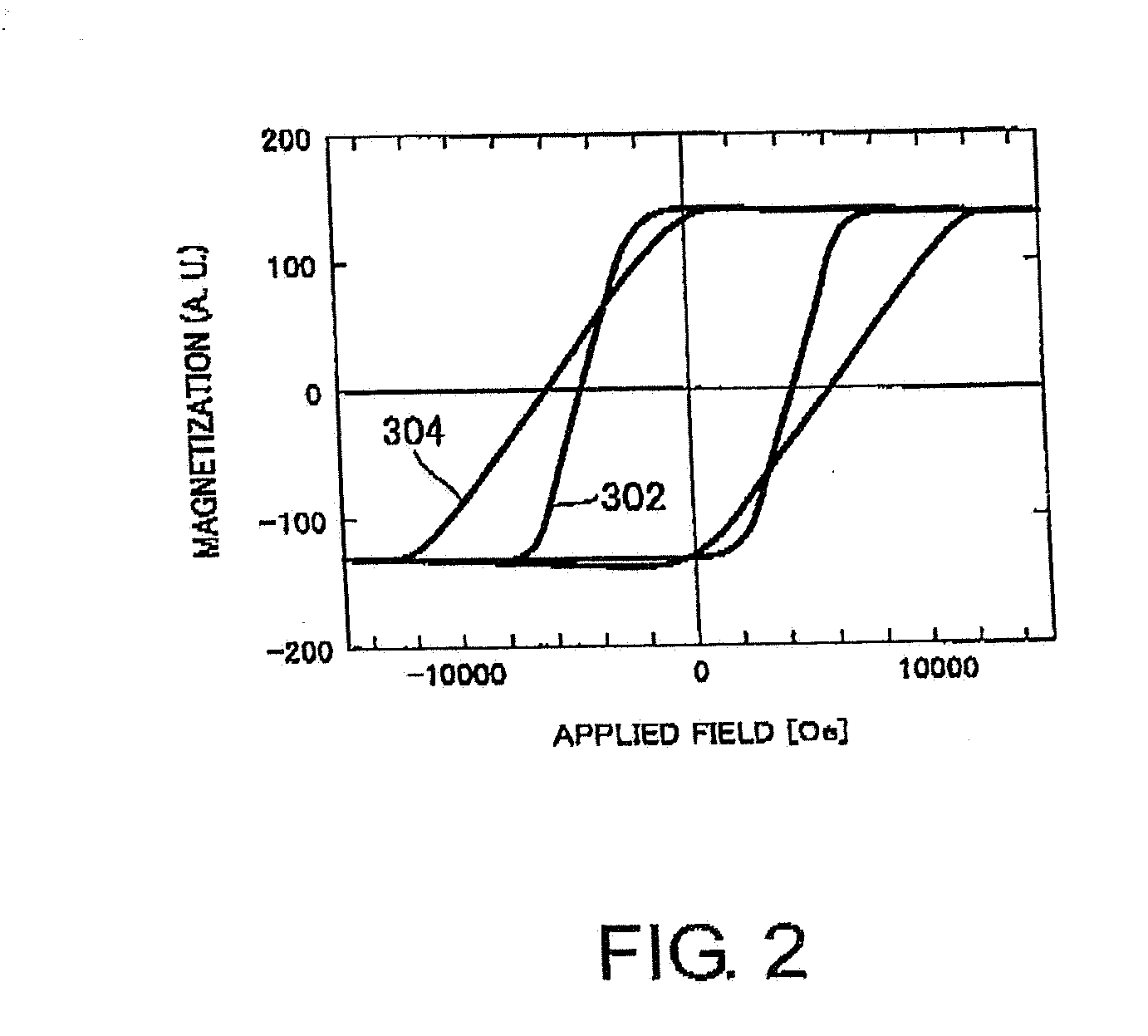
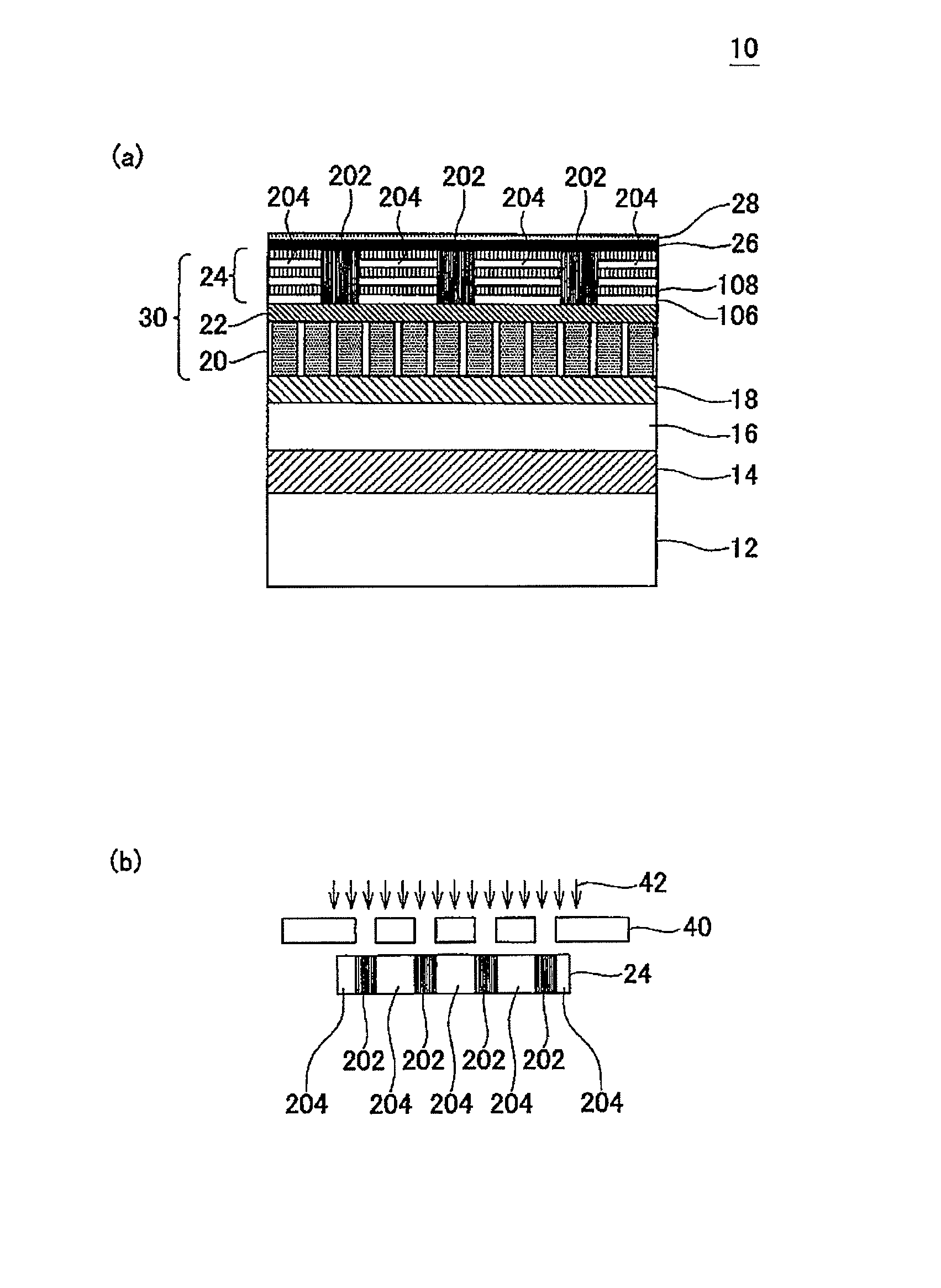
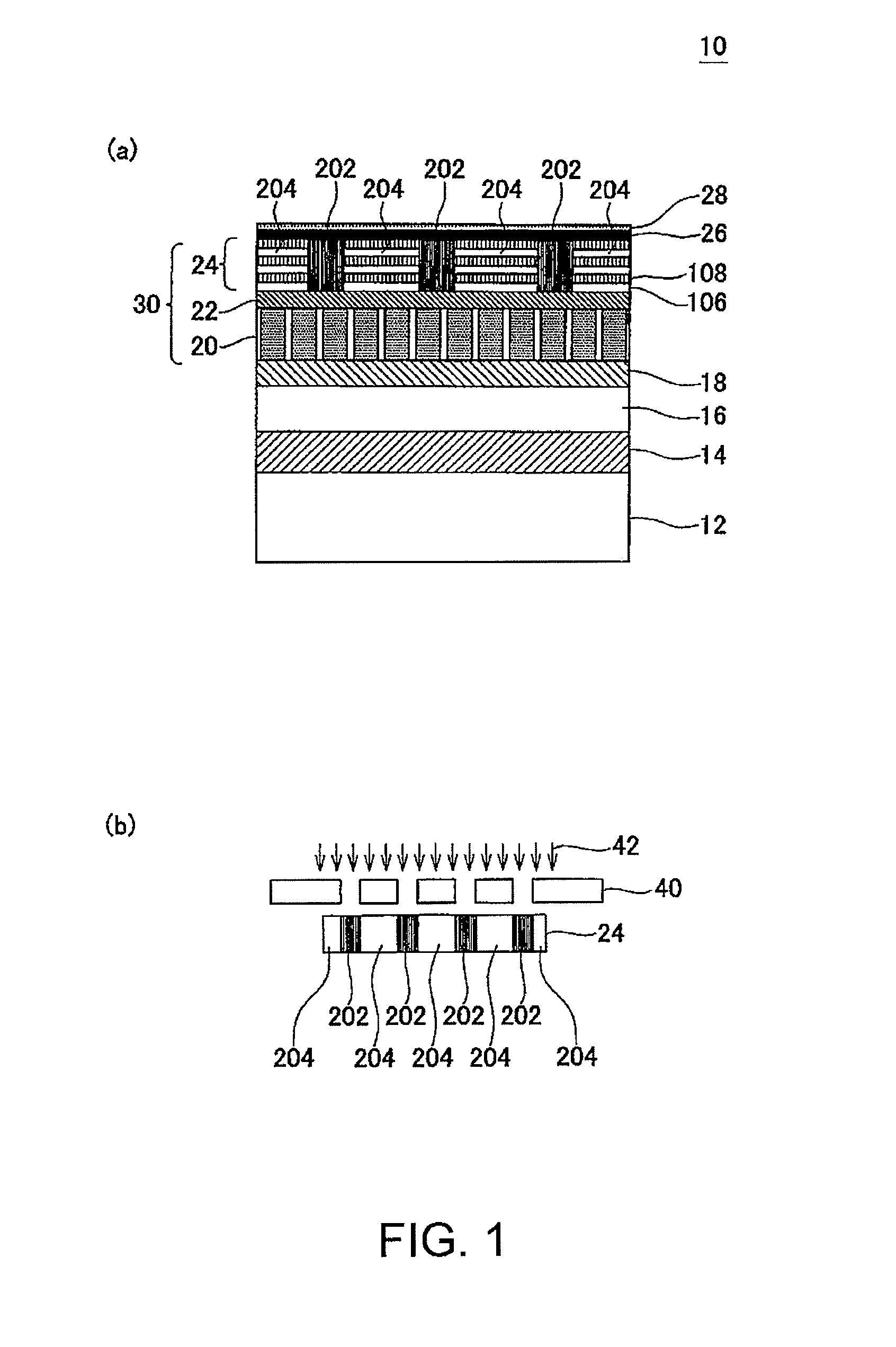
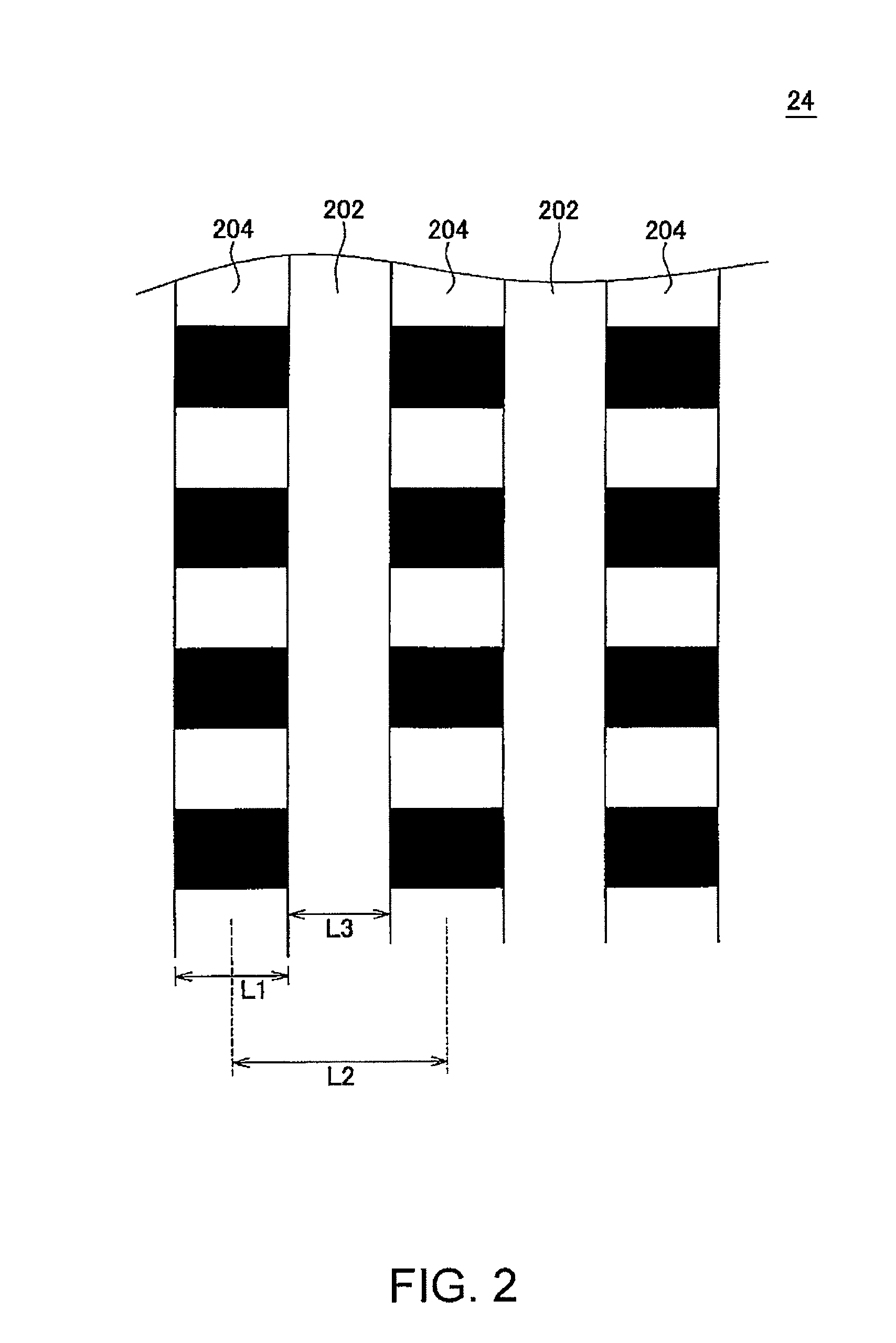
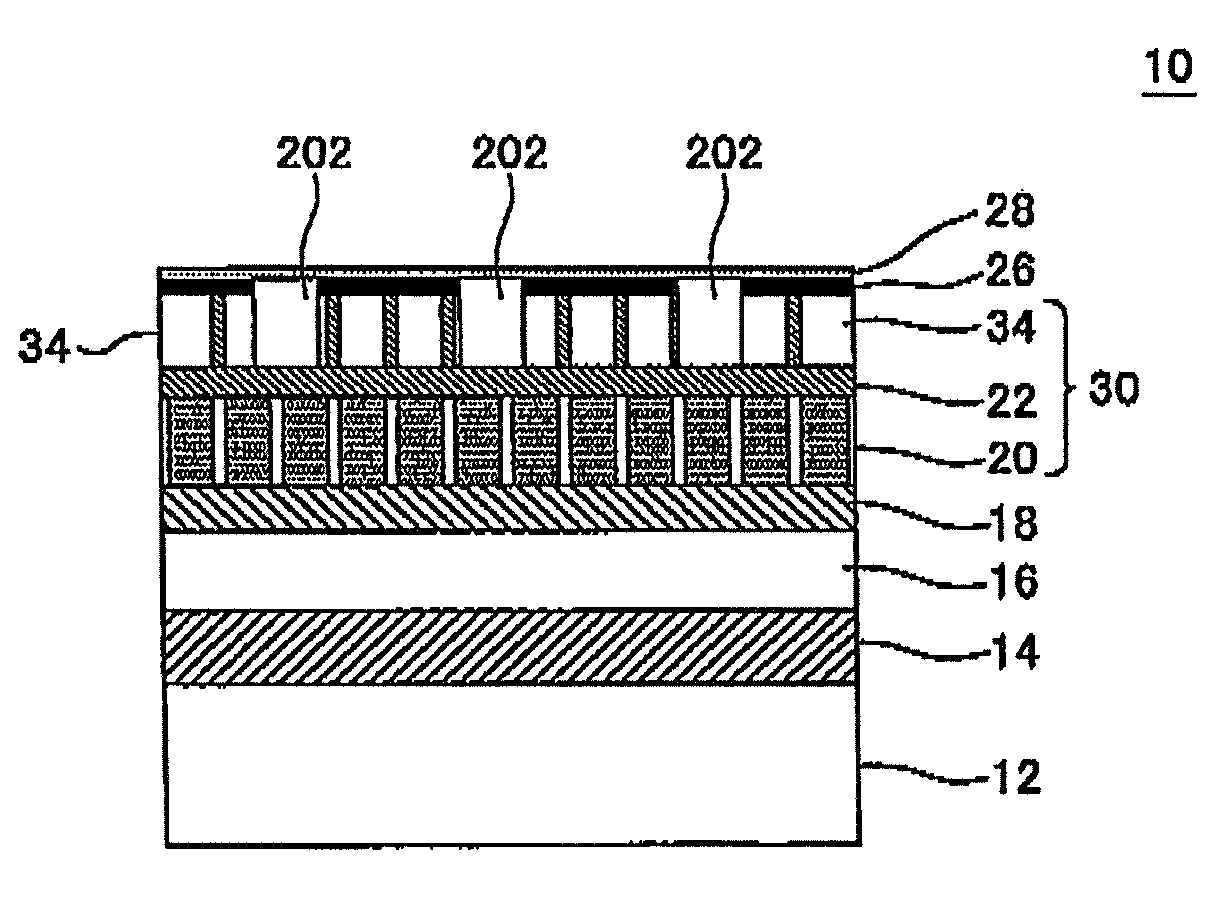
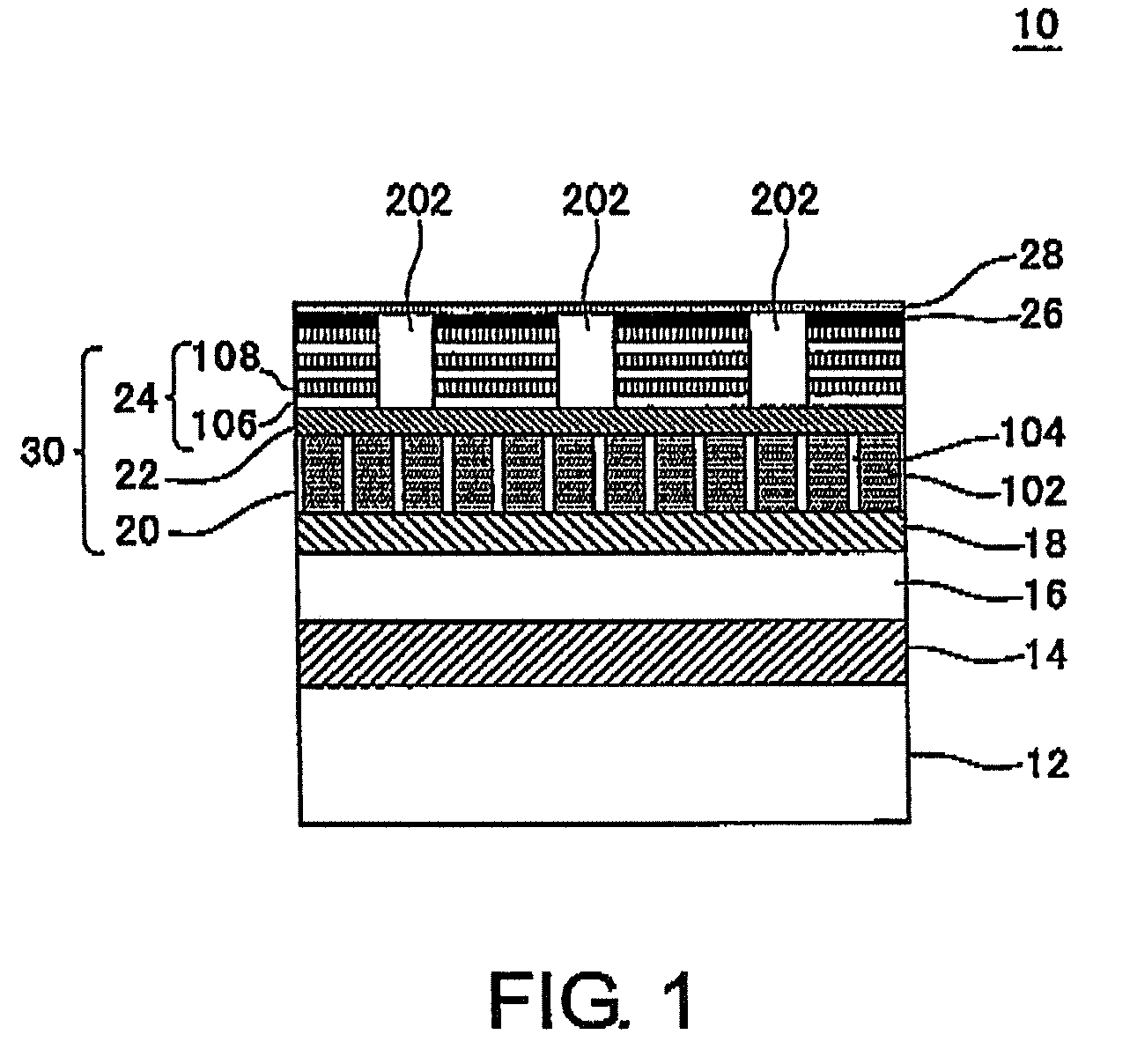
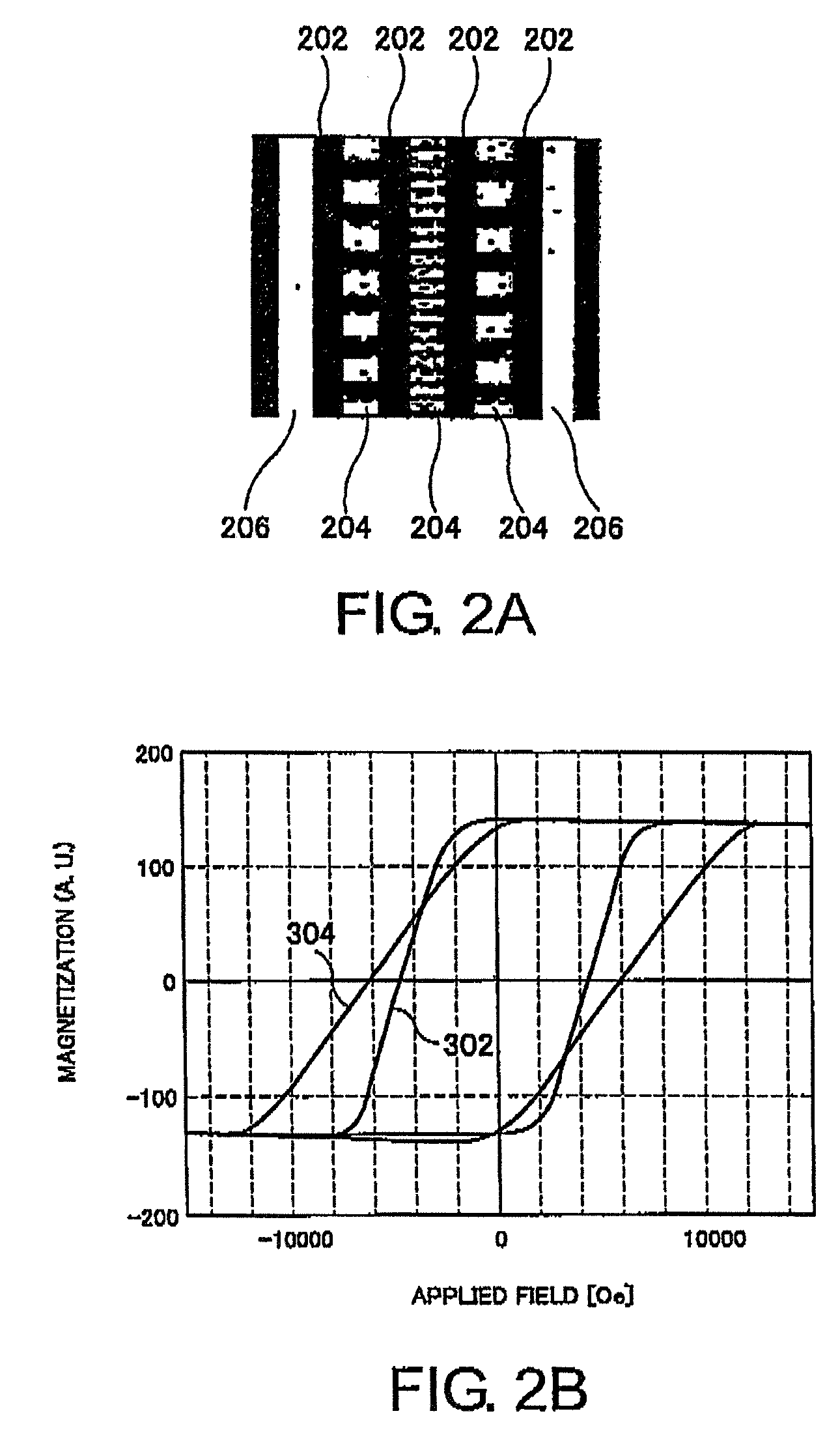
A magnetic recording medium (10) has a substrate (12) and a perpendicular magnetic recording layer (30) formed over the substrate (12). The perpendicular magnetic recording layer (30) has a granular layer (20) in which a magnetic signal is recorded and a continuous film layer (24) magnetically coupled to the granular layer (20). The continuous film layer (24) has hard magnetic portions (204) formed in positions corresponding to the recording regions where magnetic signals are recorded in the granular layer (20) and magnetic shield portions (202) formed between the hard magnetic portions (204), each having a magnetization curve whose slope is larger than those of the hard magnetic portions in the region where the applied magnetic filed is zero when the magnetization curve is measured, and each having a residual magnetic polarization smaller than those in the hard magnetic portions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic head, magnetic recording method and apparatus for controlling magnetic head with spin torque oscillator in a disk drive
ActiveUS9275672B2Improve recording densityHigh densityManufacture head surfaceDriving/moving recording headsSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
A microwave assisted magnetic recording head includes a recording magnetic pole unit that produces a recording field for writing to a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, and a high-frequency magnetic field oscillator that produces a high-frequency magnetic field. The recording magnetic pole unit includes a magnetic core with a write gap portion at which a main recording field component is concentrated, and the high-frequency magnetic field oscillator is disposed in the write gap.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic recording medium and method for manufacturing magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS7833639B2Delay transitionImprove thermal stabilityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsGrain boundaryCrystallite
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
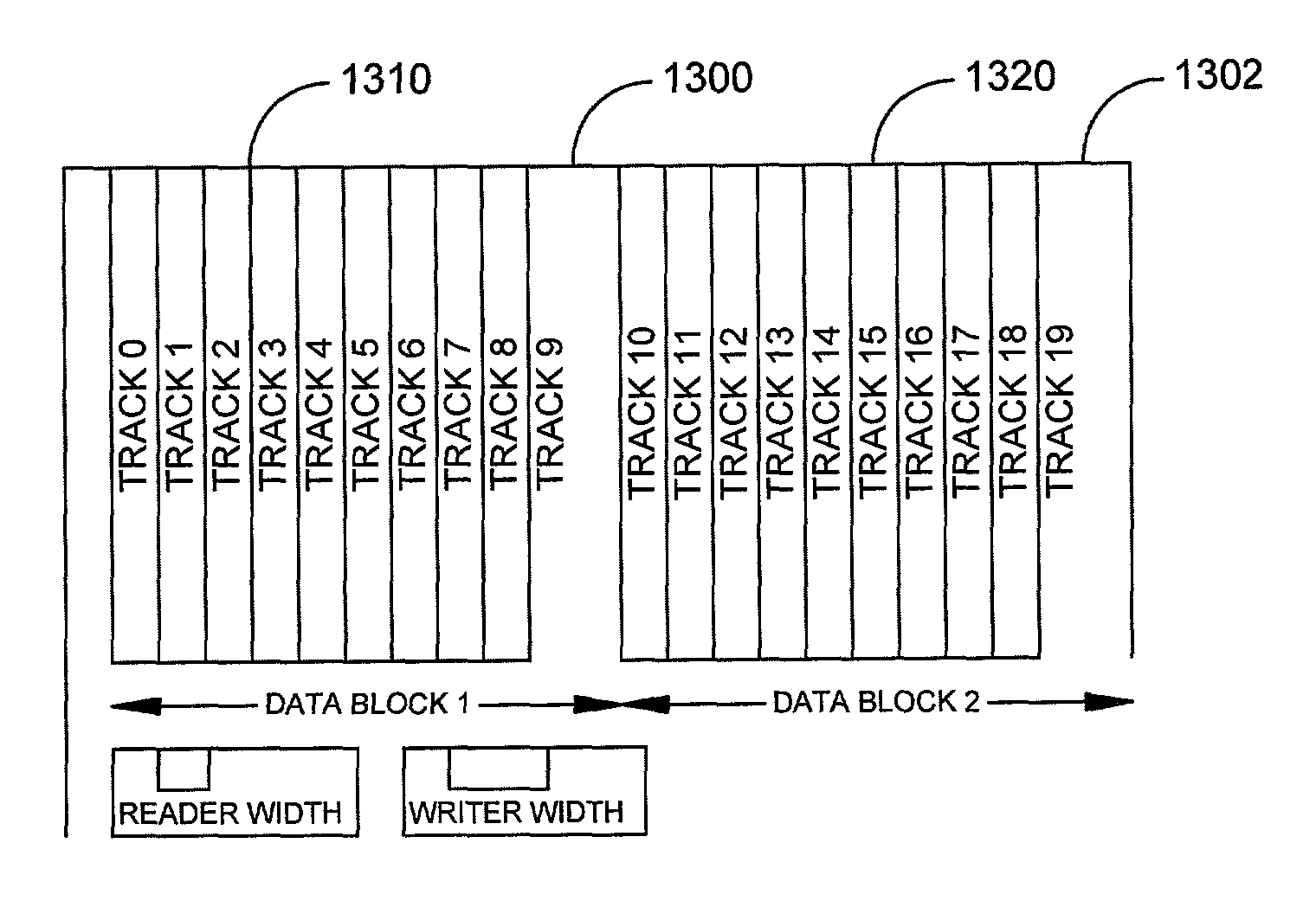
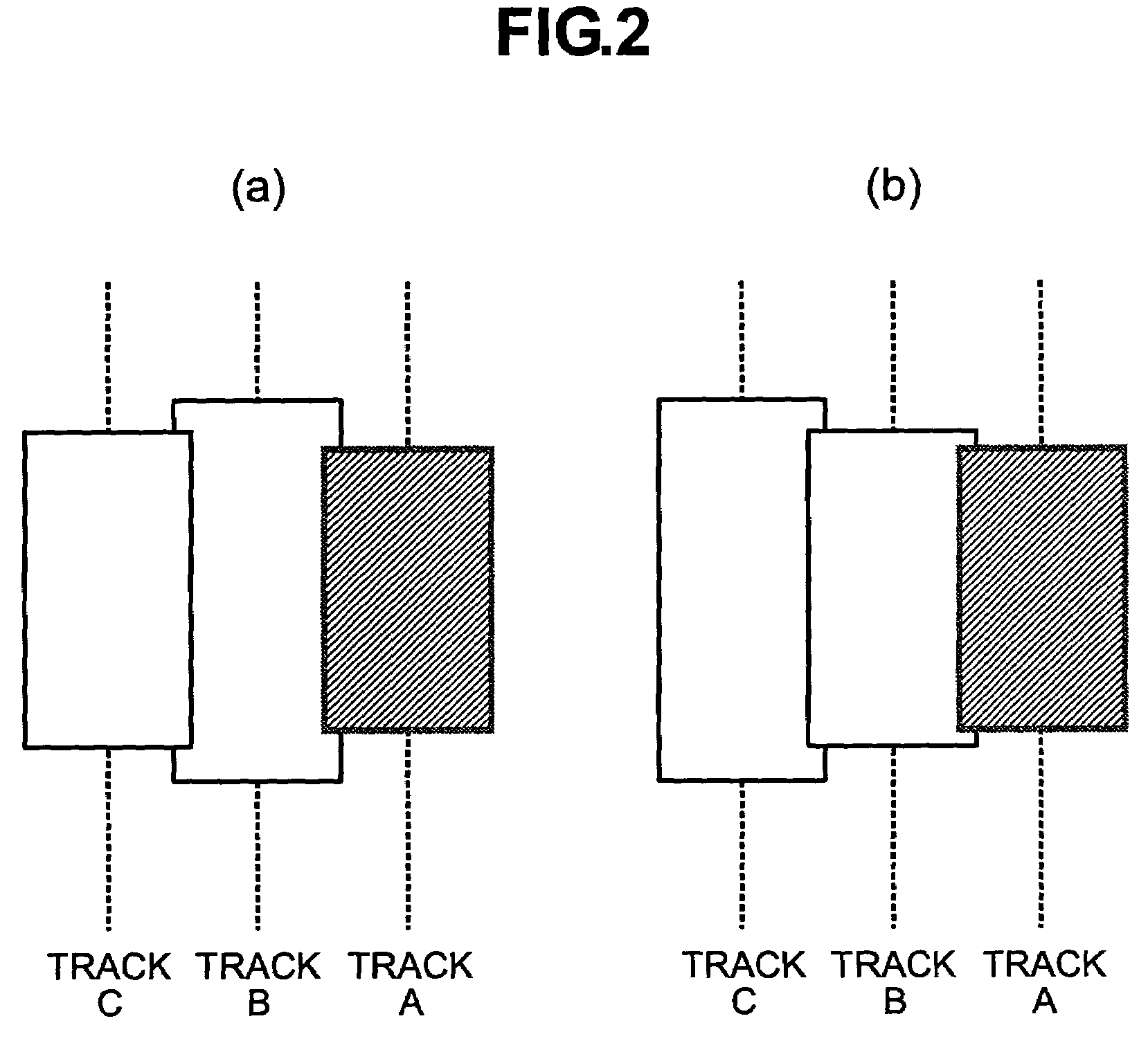
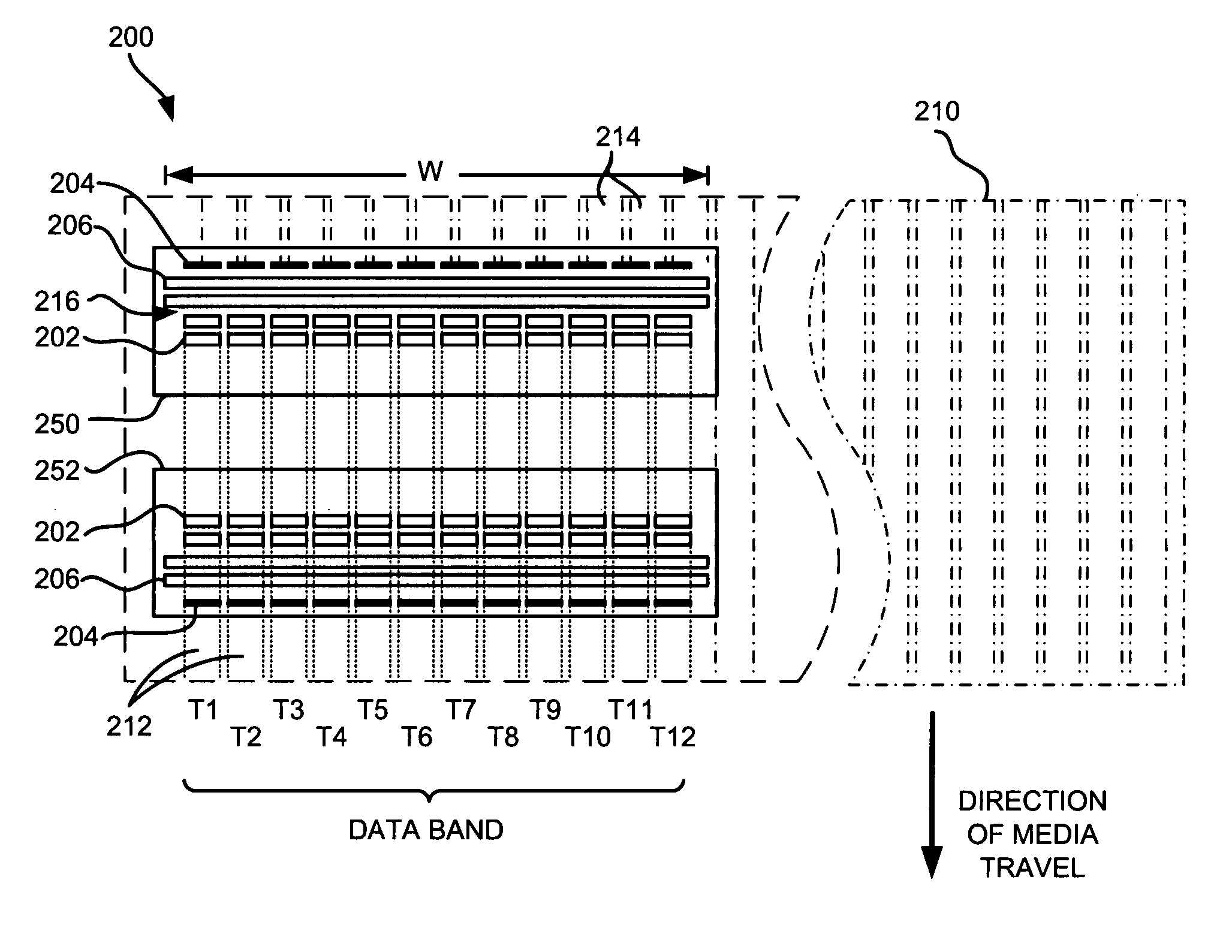
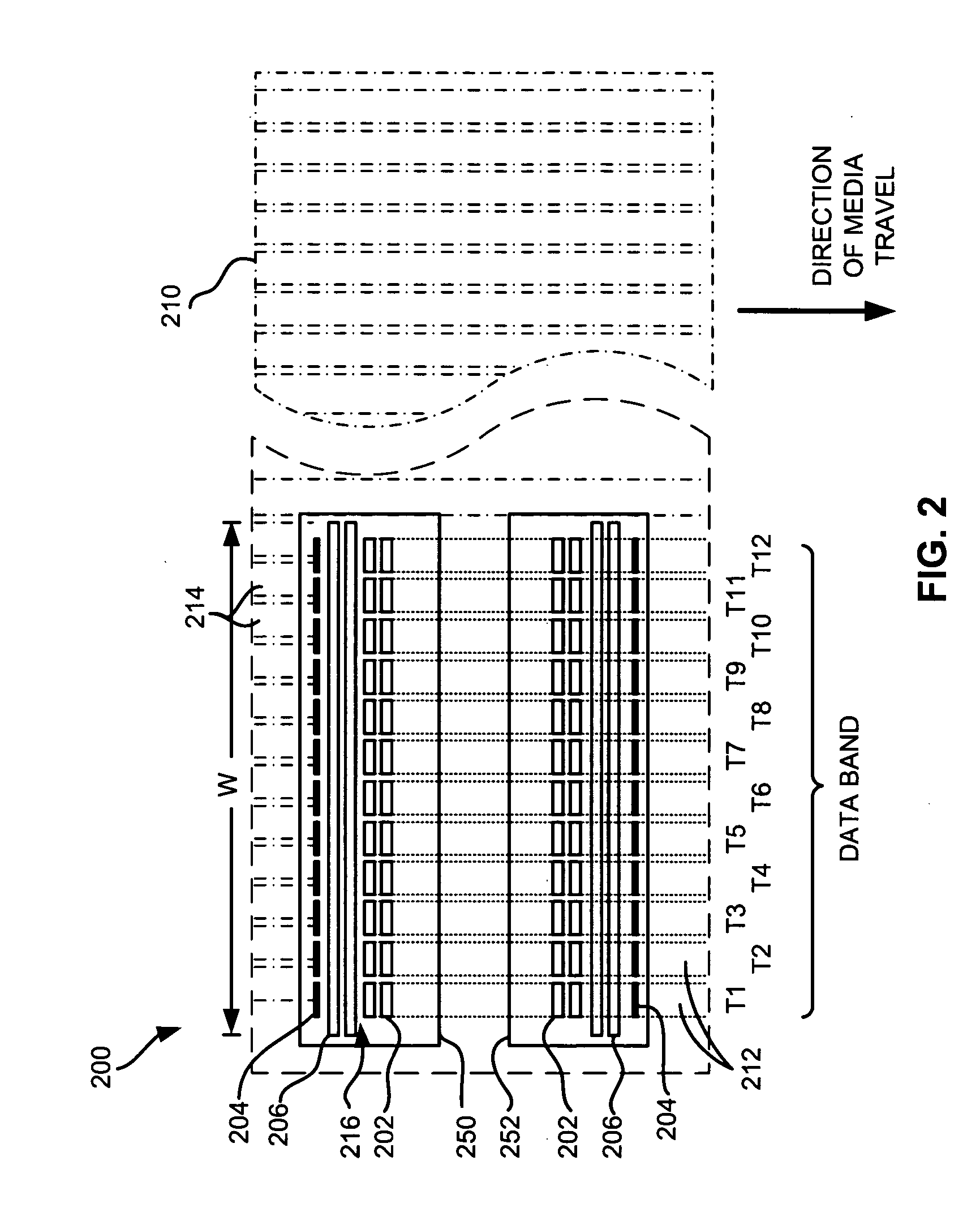
Method to achieve higher track density by allowing only one-sided track encroachment
InactiveUS7082007B2Reduced and minimized amountAccurate informationFilamentary/web carriers operation controlTrack finding/aligningTrack densityTransducer
A disc drive includes a transducer having a separate element for writing information and a separate element for reading information to and from the disc. In a disc drive designated to read and write long sequential records, the track misregistration budget is reduced to account for previously written tracks not being encroached on one side. An initial track is written. Subsequent tracks are written after a seek in one direction. The subsequent track is written so that the initially written track is overwritten to one side and leaves a track having a width substantially equal to the width of the read element. Records can be written into data bands of a selected number of tracks. A guard band is left between groups of data bands so that data on tracks in subsequent data bands are not overwritten.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
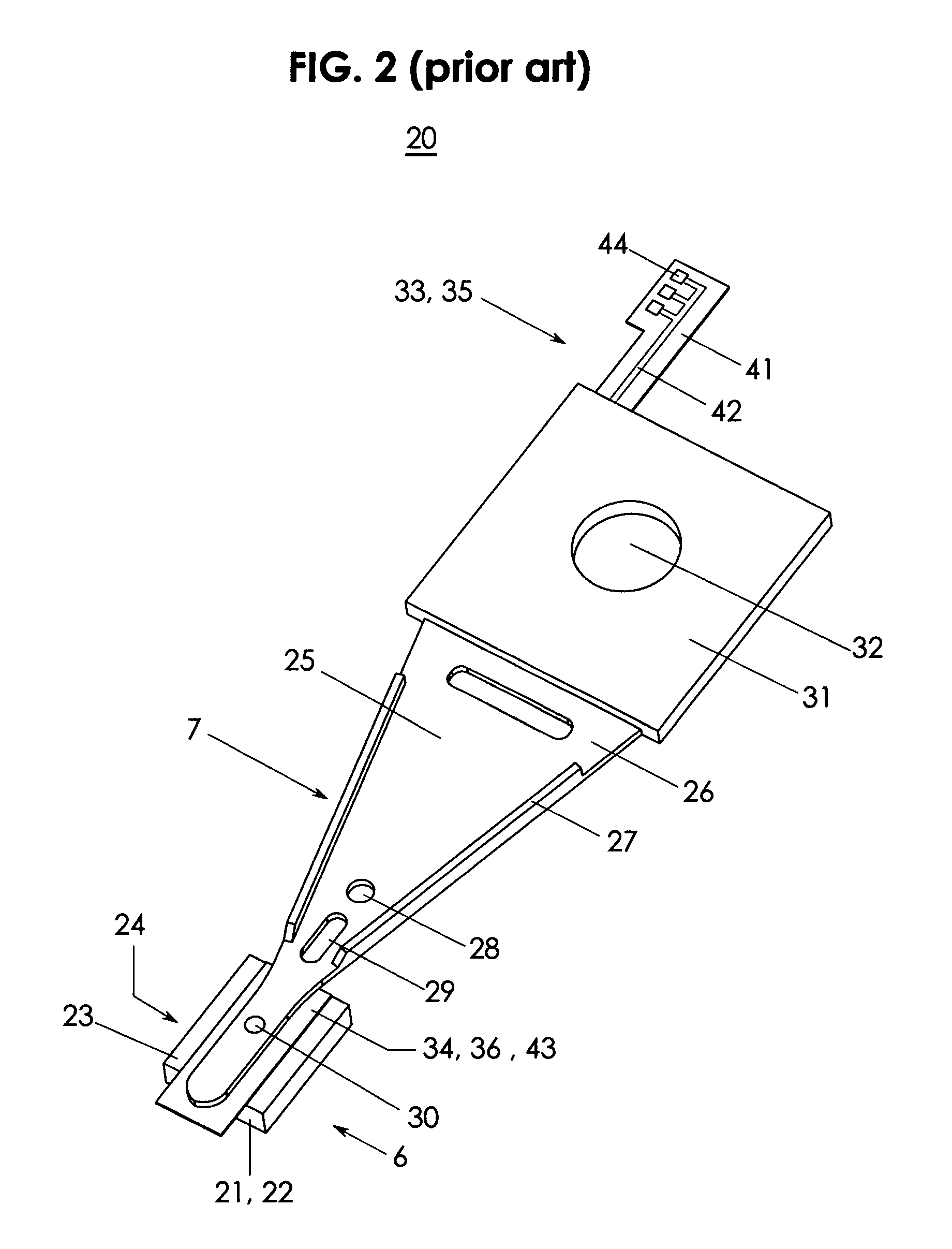
Rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor integrated into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head/gimbal assembly for improved tracking in disk drives and disk drive equipment
ActiveUS8125741B2High track densityImprove data storage capacityDriving/moving recording headsArm with actuatorsShock resistanceControl theory
A rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor is integrated with a suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) for use in disk drives and disk drive manufacturing equipment. When excited by a control voltage, the collocated, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA rotates the head enabling high frequency, high resolution track positioning of the read / write element. The motor is integrated with the head and flexure (collocation). The head rotates about a rotation axis that is ideally located at the center of mass of the head. A shear mode piezoelectric motor rotates the head. A collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA has high stiffness, high frequency response, high positioning resolution, low mass and low internal vibration for improved tracking, increased track density and greater disk drive storage capacity. Furthermore, its solid integration improves shock resistance and reduces micro-contamination.
Owner:MAGNECOMP +1
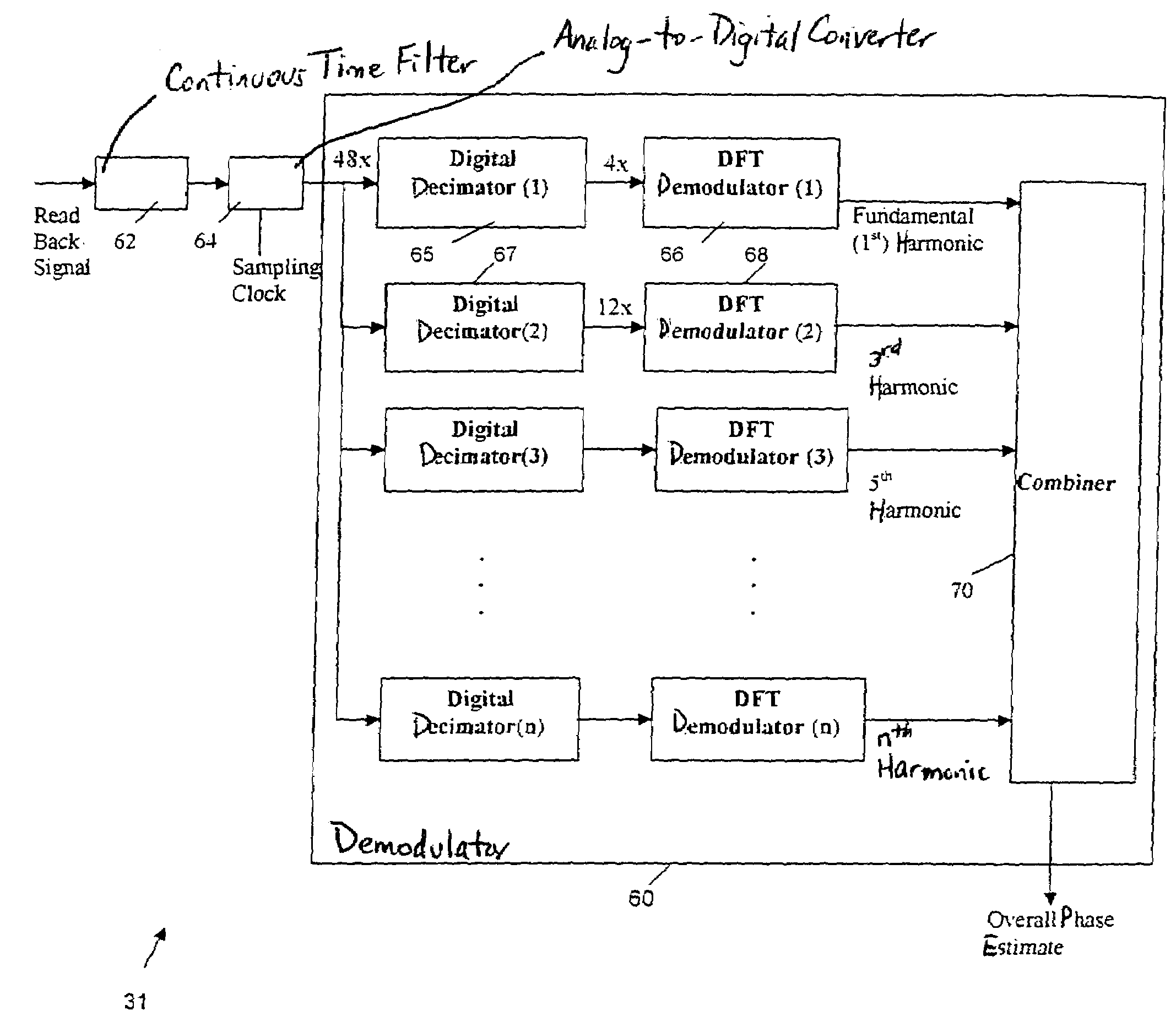
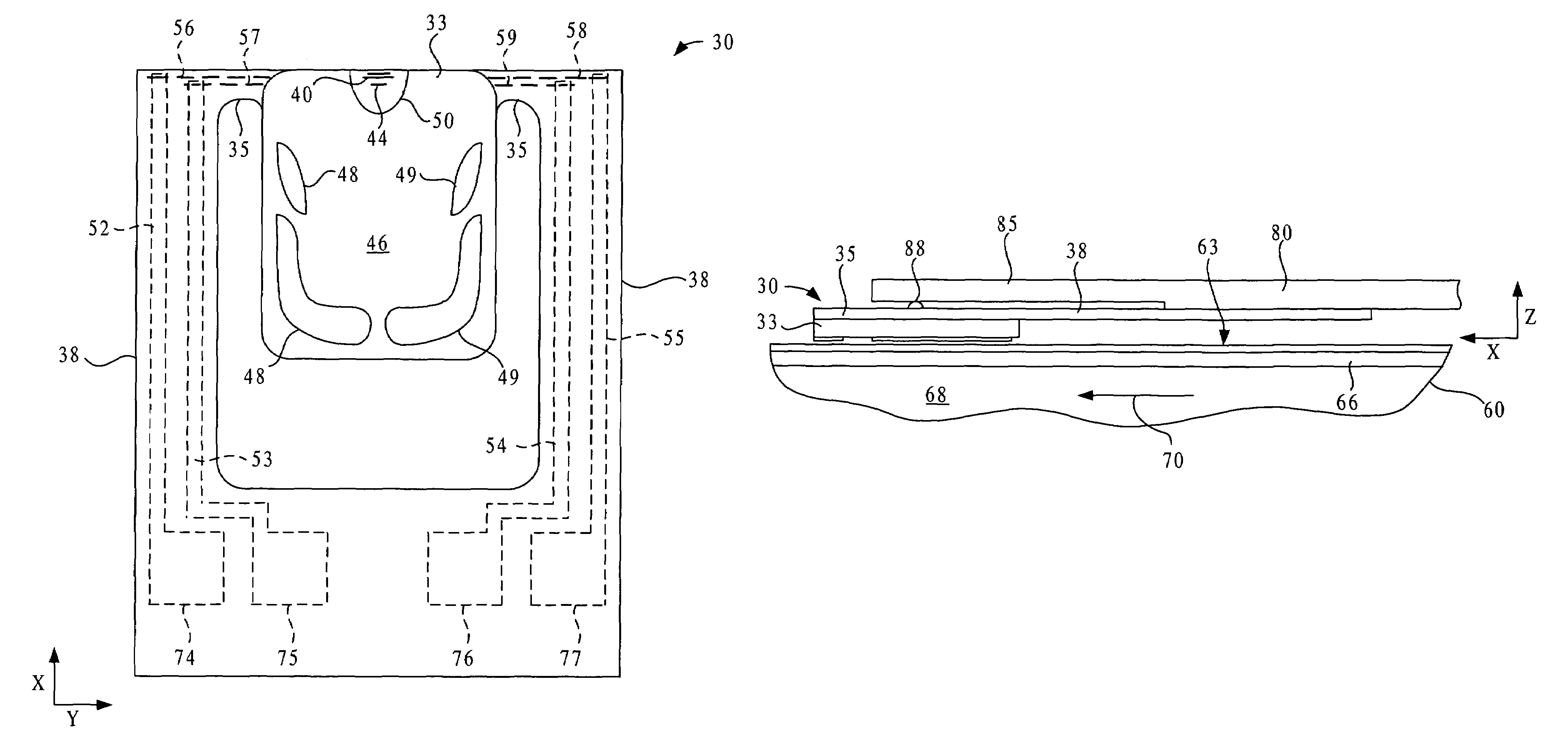
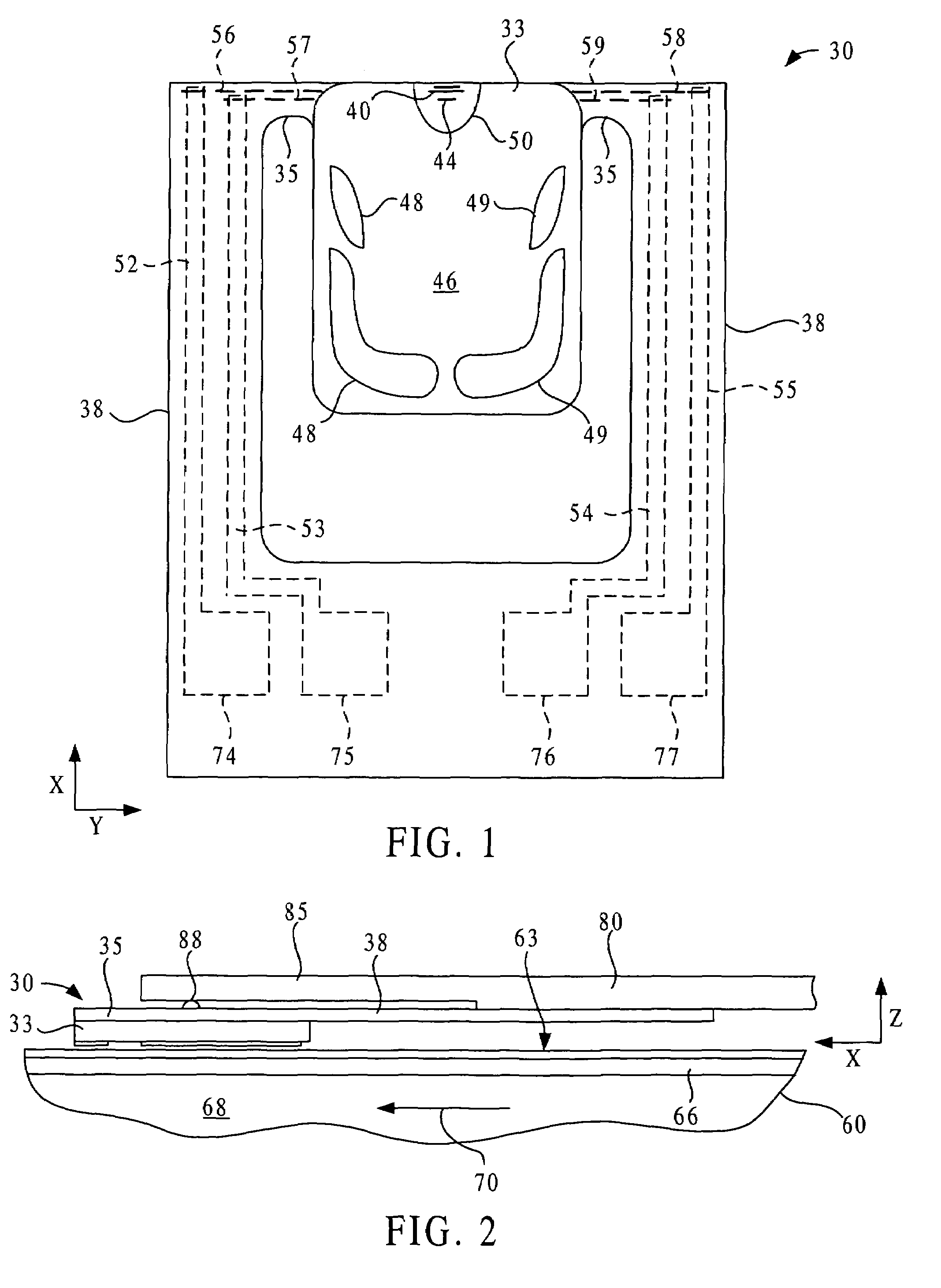
Disk drive self-servo writing using fundamental and higher harmonics of a printed reference pattern
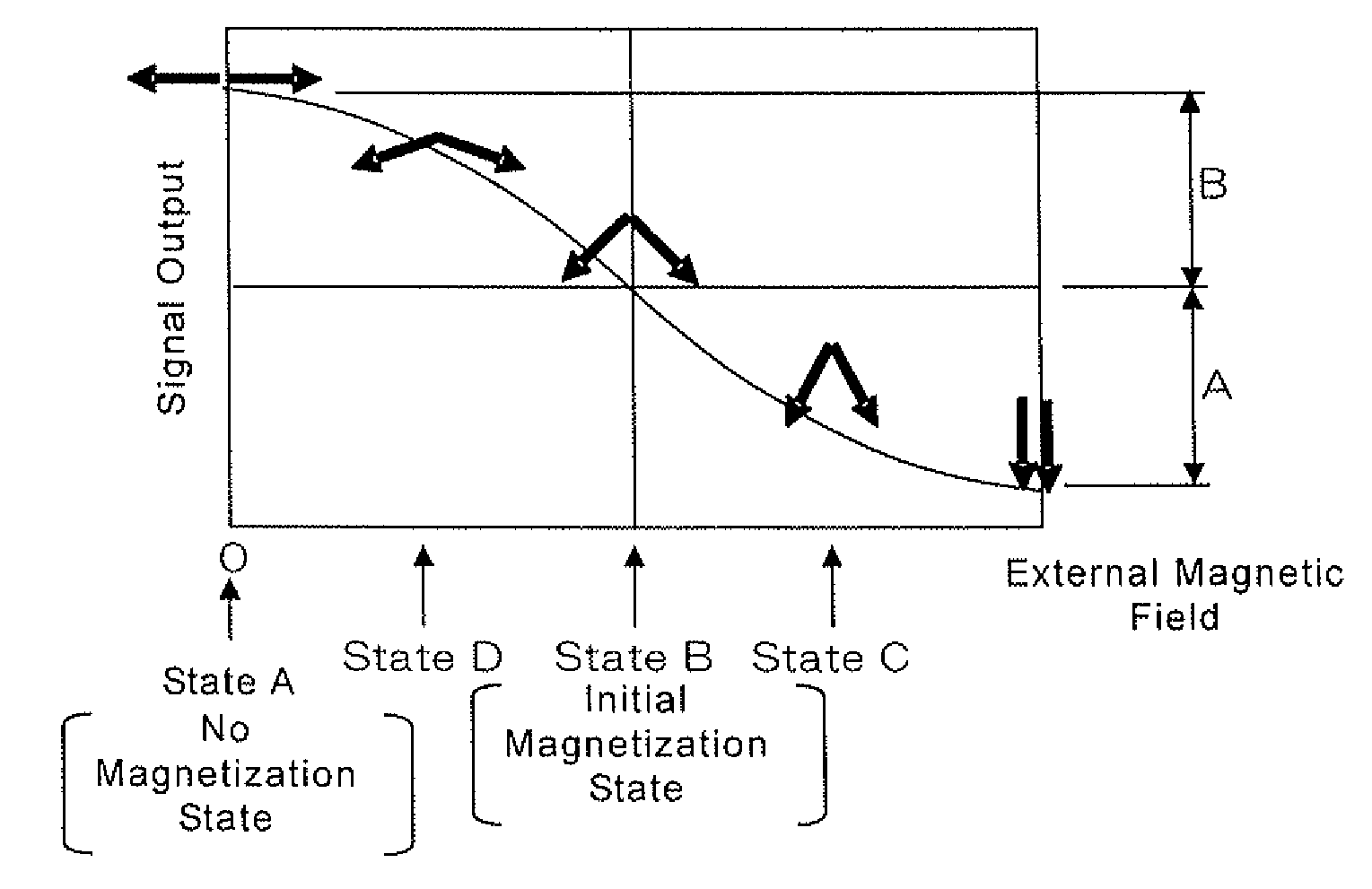
InactiveUS7199956B1Extended service lifeImprove signal-to-noise ratioDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageGraphicsFrequency spectrum
Disk drive self-servo writing includes transferring a reference pattern by magnetic printing onto a reference disk, wherein the resulting printed reference pattern includes embedded servo information that provides servo timing and head position information, installing the reference disk and a head into the disk drive, reading the printed reference pattern using the head to generate a readback signal, sampling the readback signal at a sampling rate to generate a sampled signal, processing the sampled signal waveform spectrum to generate a recovered signal including the embedded servo information and fundamental and higher harmonics of the sampled signal, using the embedded servo information from the recovered signal to precisely position and maintain the head at concentric tracks of the reference disk, and self-writing servo patterns onto the tracks with the head.
Owner:MAXTOR
Magnetic head, magnetic recording method and apparatus for controlling magnetic head with spin torque oscillator in a disk drive
ActiveUS20130229895A1Improve recording densityThe implementation process is simpleManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
A microwave assisted magnetic recording head includes a recording magnetic pole unit that produces a recording field for writing to a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, and a high-frequency magnetic field oscillator that produces a high-frequency magnetic field. The recording magnetic pole unit includes a magnetic core with a write gap portion at which a main recording field component is concentrated, and the high-frequency magnetic field oscillator is disposed in the write gap.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic heads for perpendicular recording and magnetic recording disk apparatus using the same
InactiveUS6891697B2Suppression amountHigh track densityManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsLeading edgeTrailing edge
A magnetic head having at least a main pole having a profile on a magnetic head air bearing surface composed of a first portion having a length in a cross-track direction which continuously increases from a leading edge to a trailing edge, and a second portion located on the side of the trailing edge of the first portion. A length of the second portion in the cross-track direction at the trailing edge is substantially equal to a length in the cross-track direction at the point of contact between the first and second portions. A rate of change in the length of the second portion in the cross-track direction from the leading edge to the trailing edge is different from a rate of increase in the length of the first portion in the cross-track direction.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
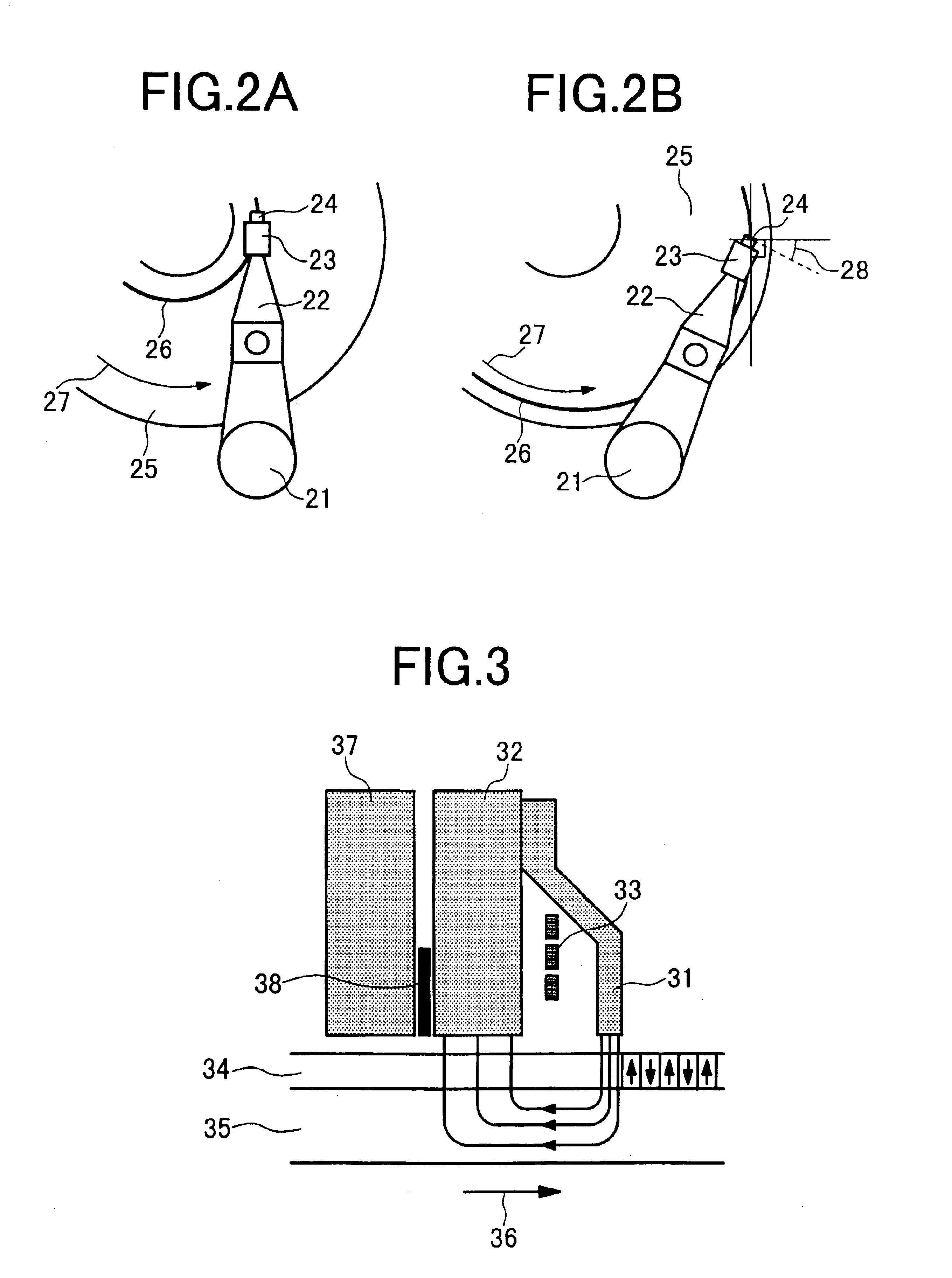
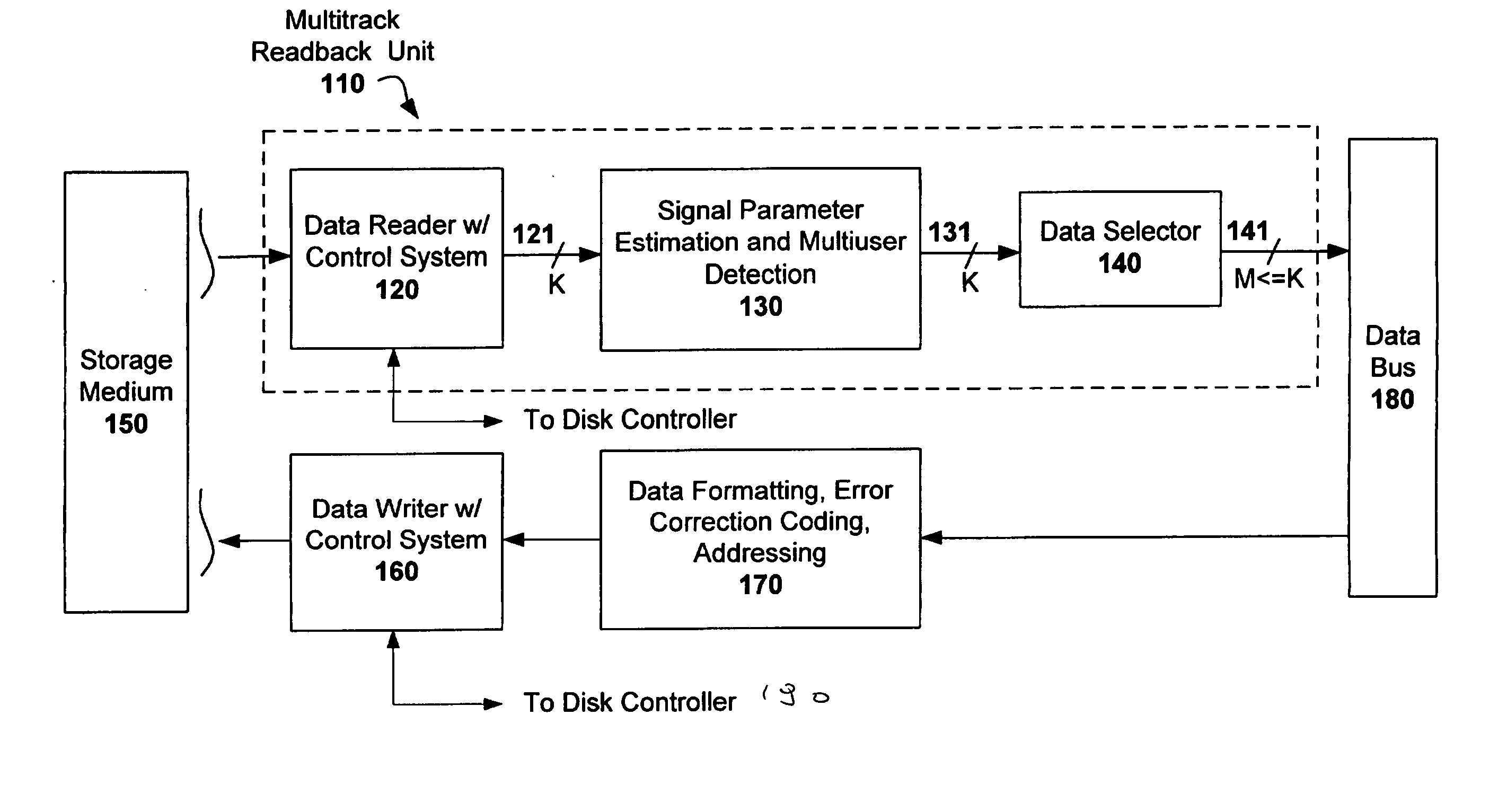
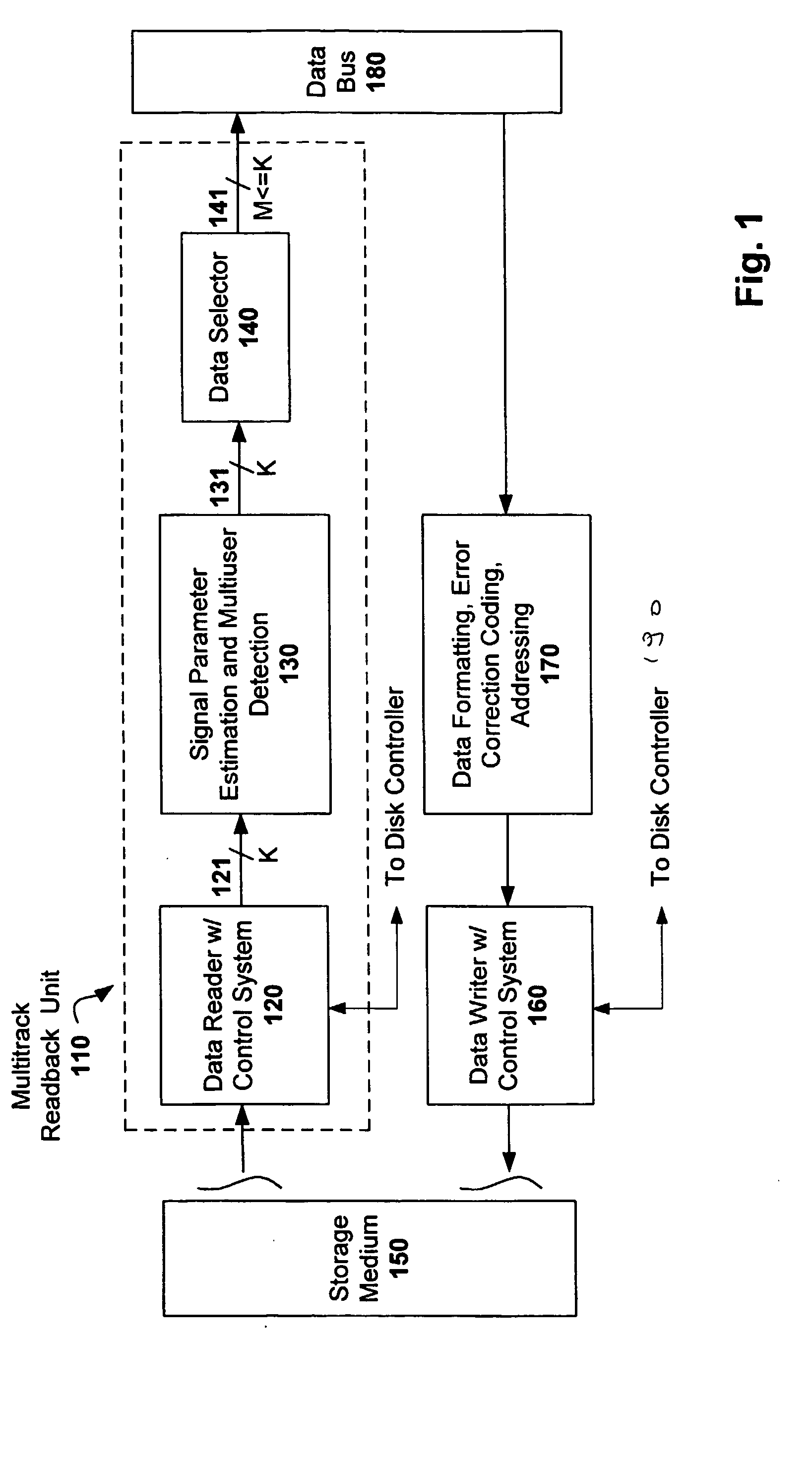
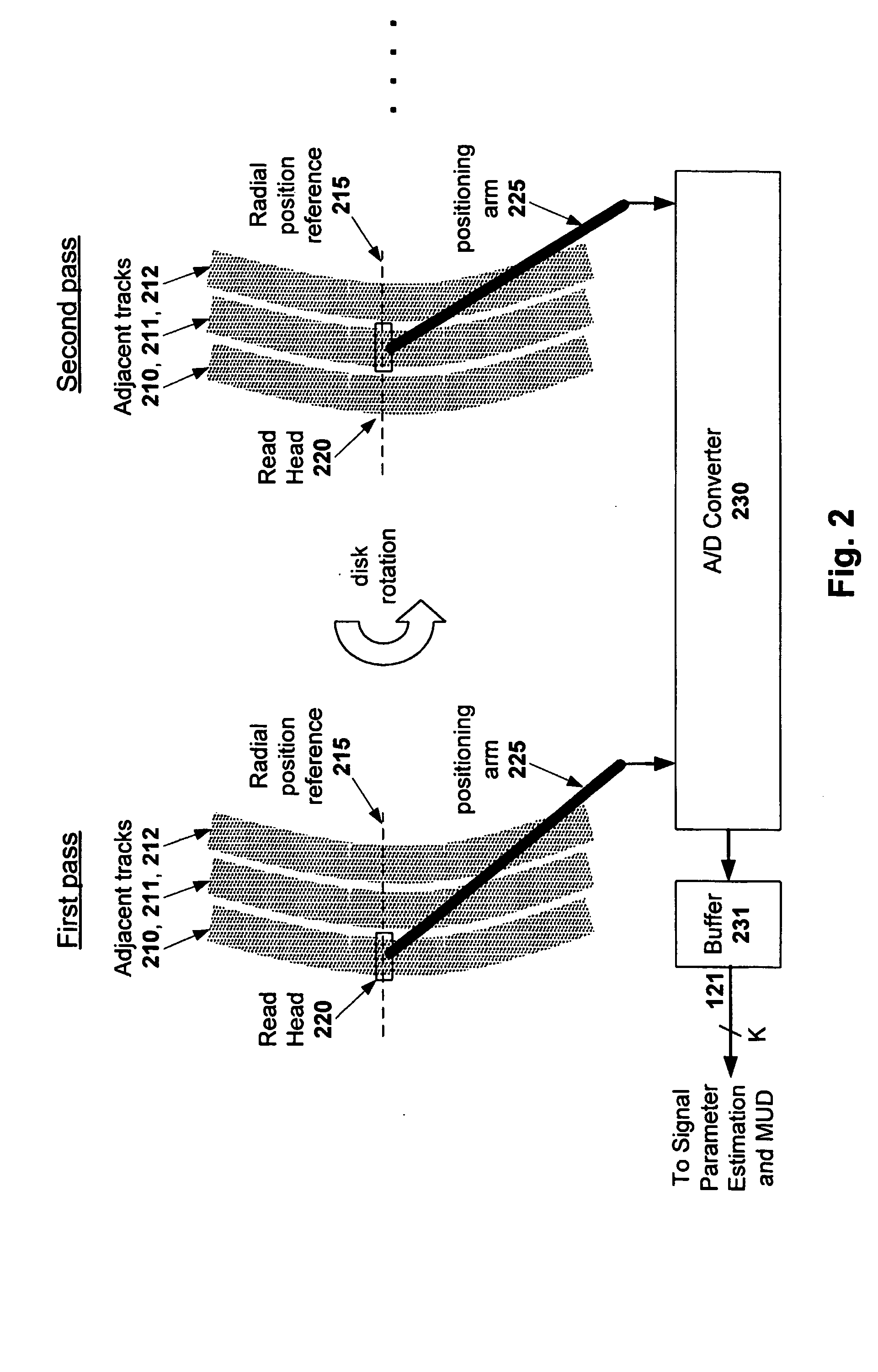
Multitrack readback and multiuser detection for disk drives
ActiveUS20050036437A1High track densityCombination recordingRecord information storageTrack densityMultiuser detection
Techniques for reading data from a storage medium (150) having a high track density prone to adjacent track interference are disclosed. One or more sensing elements (120) are used to extract data stored on adjacent tracks. Multiuser detection (130) is then used to detect / decode a single track that is closely spaced to its neighboring tracks, resolve interference from adjacent tracks, or to simultaneously detect / decode multiple adjacent closely packed tracks.
Owner:COLLISION COMM
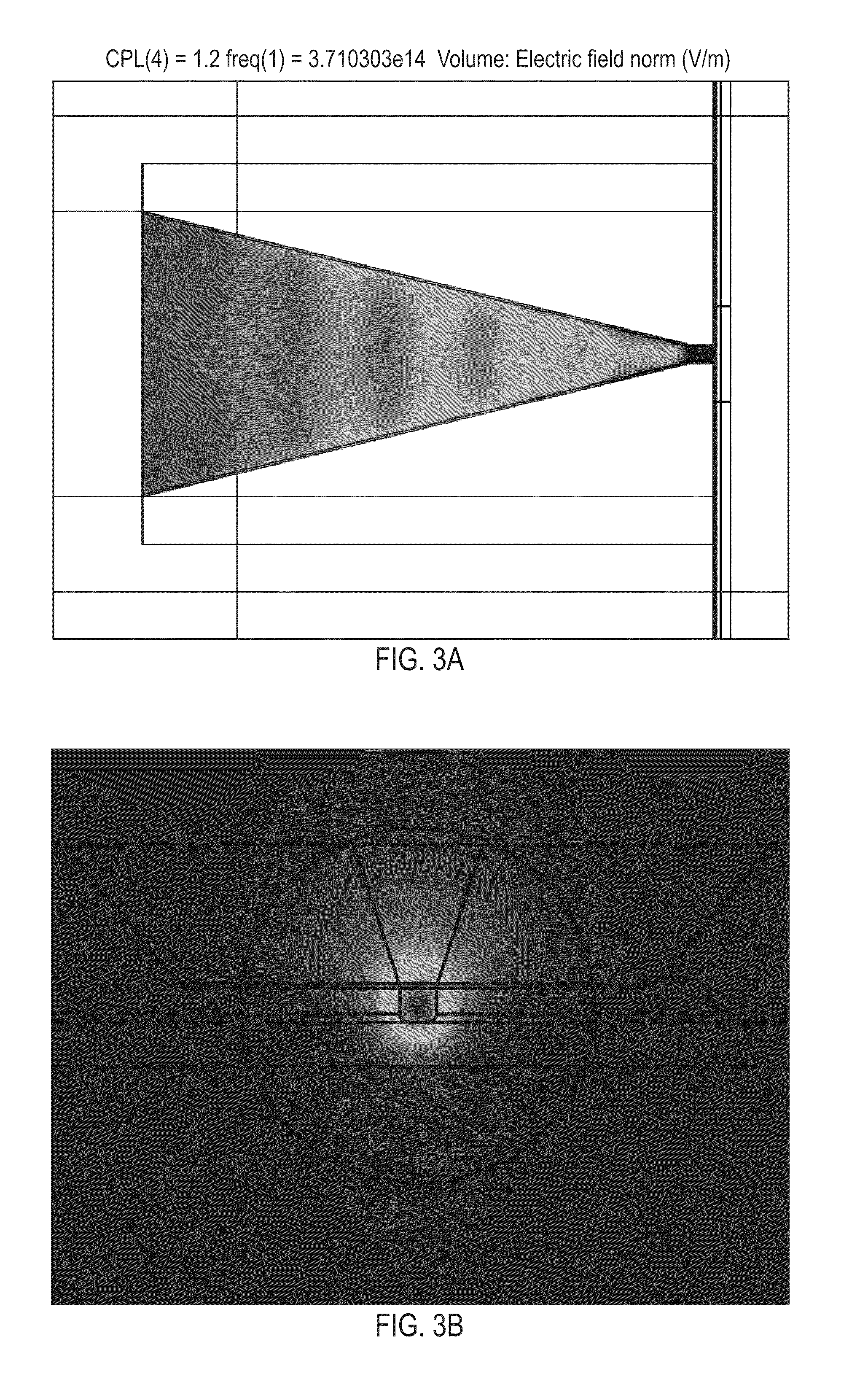
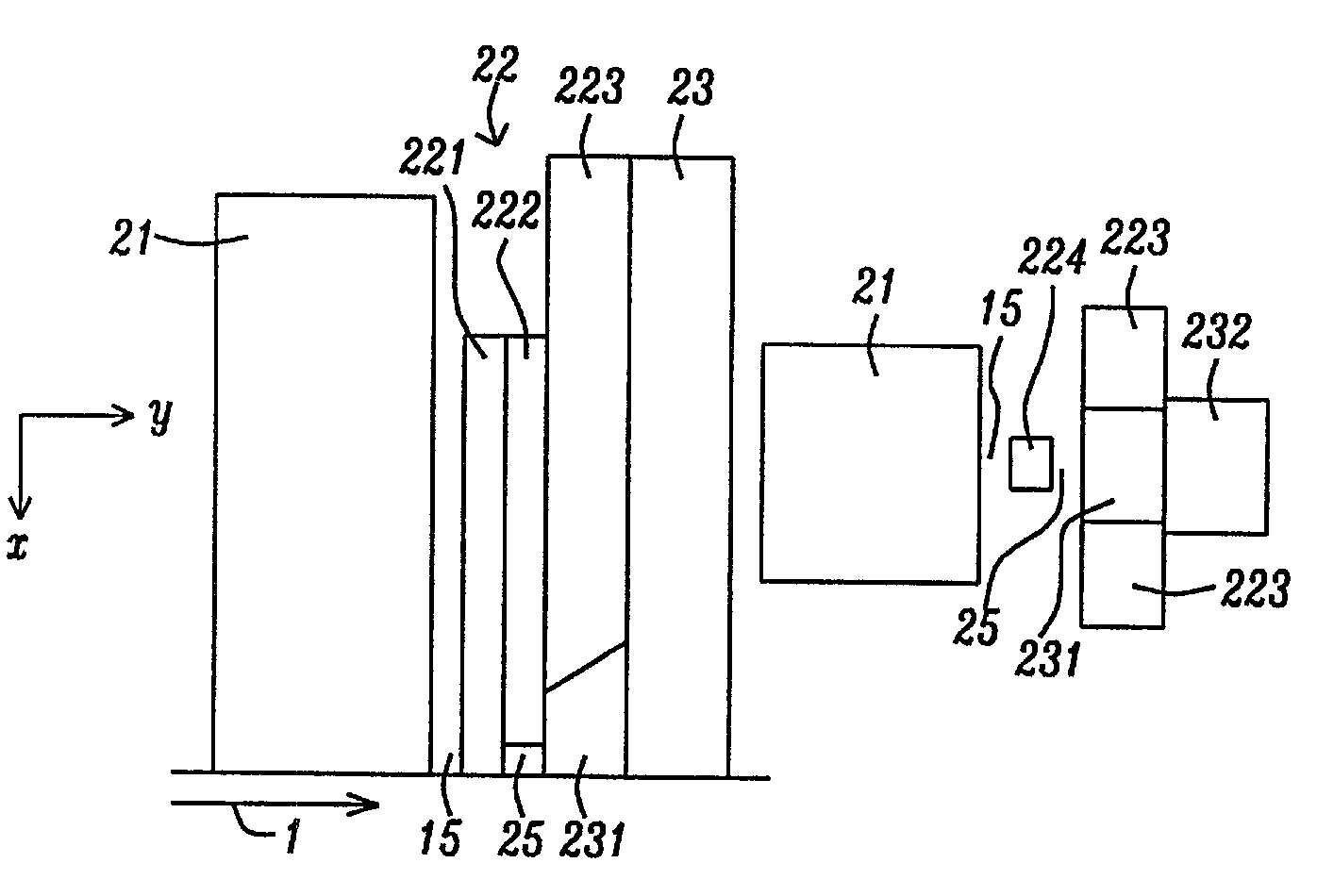
Planar Plasmon Generator with a Scalable Feature for TAMR
ActiveUS20130148485A1Reduce spot sizeReduce widthRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMagnetic anisotropyHeat-assisted magnetic recording
A TAMR (Thermal Assisted Magnetic Recording) write head uses the energy of optical-laser excited surface plasmons in a scalable planar plasmon generator to locally heat a magnetic recording medium and reduce its coercivity and magnetic anisotropy. The planar plasmon generator is formed as a multi-layered structure in which one planar layer supports a propagating surface plasmon mode that is excited by evanescent coupling to an optical mode in an adjacent waveguide. A peg, which can be a free-standing element or an integral projection from one of the layers, is positioned between the ABS end of the generator and the surface of the recording medium, confines and concentrates the near field of the plasmon mode immediately around and beneath it.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Planar plasmon generator with a scalable feature for TAMR
ActiveUS8599656B2Reduce spot sizeReduce widthCombination recordingRecord information storageMagnetic anisotropyHeat-assisted magnetic recording
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
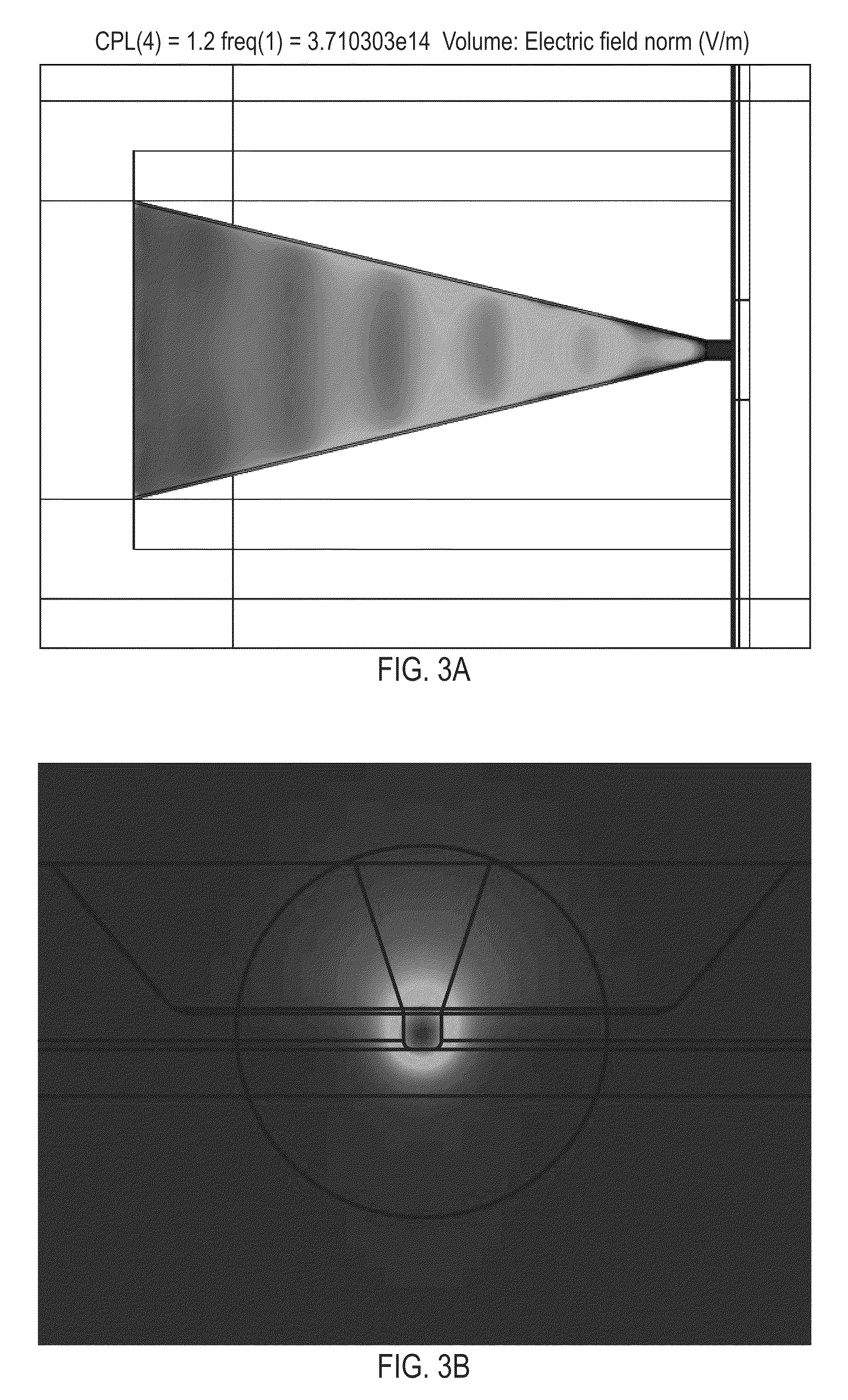
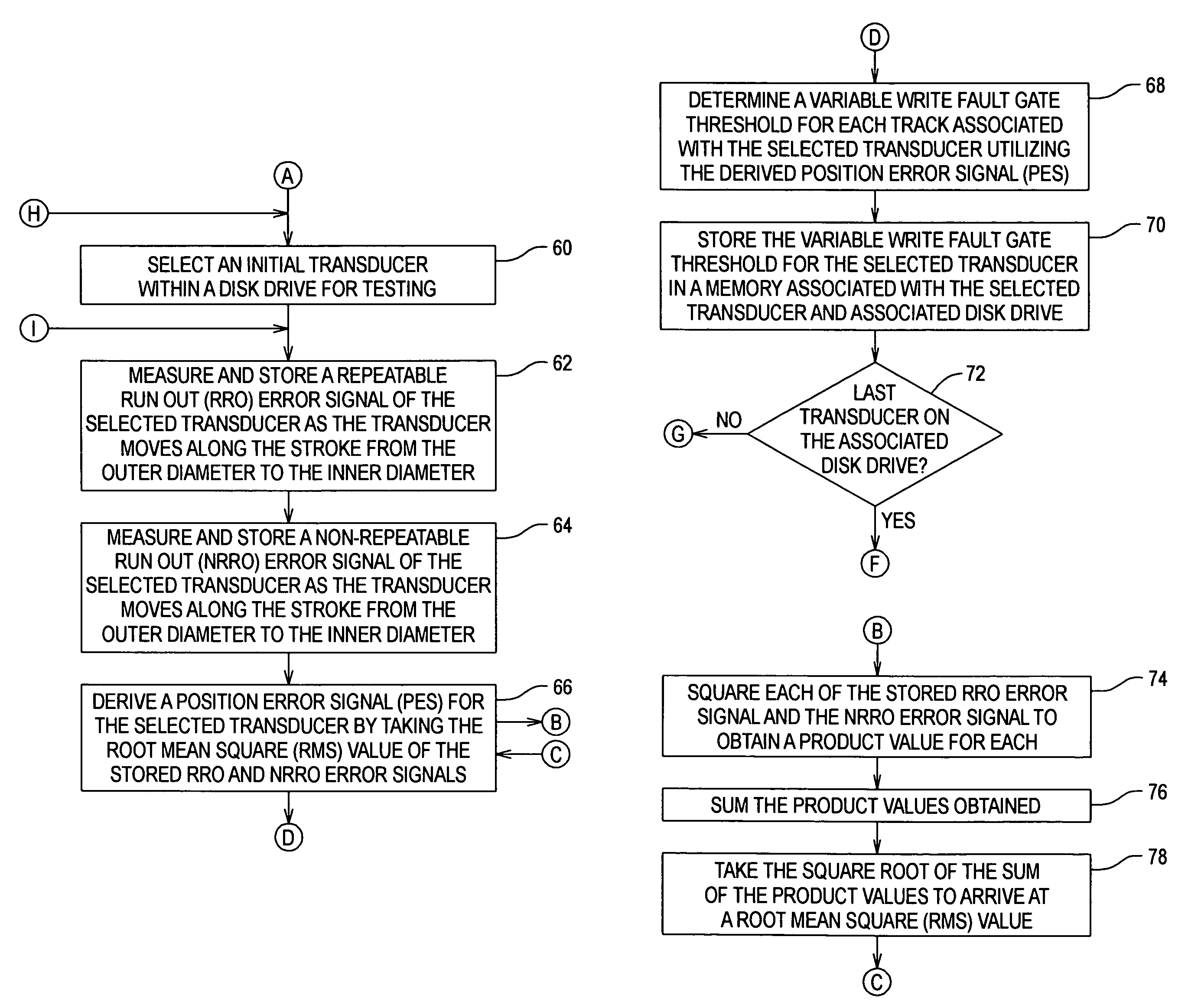
Method and apparatus for increasing track density by adapting write fault gate to position error signal as it varies from ID to OD
InactiveUS6940679B1Increasing capacity of diskHigh track densityRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksTrack densityEngineering
A disk drive utilizes a track dependent variable write fault gate for each of the transducers within the drive. By deriving a 3 sigma distribution across the repeatable run out (RRO) and the non-repeatable run out (NRRO), a position error signal (PES) is derived which varies in magnitude across the stroke of the transducers and which has a slope used to derive variable write fault gate thresholds for the tracks associated with each transducer. As the stroke of the transducer moves from the outer diameter (OD) to the inner diameter (ID), the magnitude of the write fault gate thresholds may be decreased relative to the PES, and track density and capacity may increase where PES and write fault gate thresholds are low. The invention thus maintains a constant hard error recovery margin across the stroke.
Owner:MAXTOR
Tape recording system and head device
ActiveUS20050007700A1Reduce overlap areaImprove recording densityManufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsSignal onMagnetic tape
There is provided a tape recording system and head device. A tape recording system and head device include a plurality of recording sections for recording data signals on a recording medium wherein one recording section of the plurality of recording sections and another recording section arranged so as to adjoin the one recording section are disposed such that the one recording section and the another recording section are shifted from each other in a running direction and a width direction of the recording medium, and wherein the one recording section and another recording section simultaneously record a data signal on adjacent recording tracks on the recording medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
CPP sensor having hard bias stabilization placed at back edge of the stripe
InactiveUS7333304B2Easy to trackHigh track densityNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsEngineeringMagnetic shield
A current perpendicular to plane (CPP) having hard magnetic bias layers located at the back of the sensor, opposite the air bearing surface. The bias layer is magnetostatically coupled with the free layer to bias the free layer in a desired direction parallel with the ABS. First and second magnetic shield layers may be provided at either lateral side of the sensor to provide exceptional track width definition. The placement of the bias layer at the back of the sensor makes possible the addition of magnetic shields at the sides of the sensor.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Asymmetric type perpendicular magnetic recording head and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070206323A1Reduce the amount requiredHigh track densityManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageData recordingRecording layer
An asymmetric perpendicular magnetic recording head and a method of manufacturing the same, wherein the perpendicular magnetic recording head includes a read head for reading data from a magnetic recording layer and a write head for writing data on the magnetic recording layer. A main pole of the write head has a first surface facing toward the inside of the magnetic recording layer, a second surface opposing a data recording surface of the magnetic recording layer, and a third surface facing toward the outside of the magnetic recording layer and the first surface is asymmetric to the third surface. An angle between one of the first and third surfaces and the second surface may be greater than 90°.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Areal density capability improvement with spin-orbit torque based structures surrounding main pole tip
ActiveUS10157632B1High track densityImproves write-abilityHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageTrack densityMagnetic media
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a heavy metal structure surrounding at least a portion of the main pole at a media facing surface (MFS), and two magnetic structures sandwiching the heavy metal structure. Spin-orbit torque (SOT) is generated from the heavy metal structure, inducing magnetization switching (or precession) in the magnetic structures. The SOT reduces the magnetic flux shunting from the main pole to the trailing shield, and the magnetization switching sharpens the write field profile in the cross-track direction. The SOT based head with the magnetic structures sandwiching the heavy metal structure increases both track density (tracks per inch) and linear density (bit per inch), which in turn increases the areal density capability (ADC), which is the product of tracks per inch and bit per inch.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
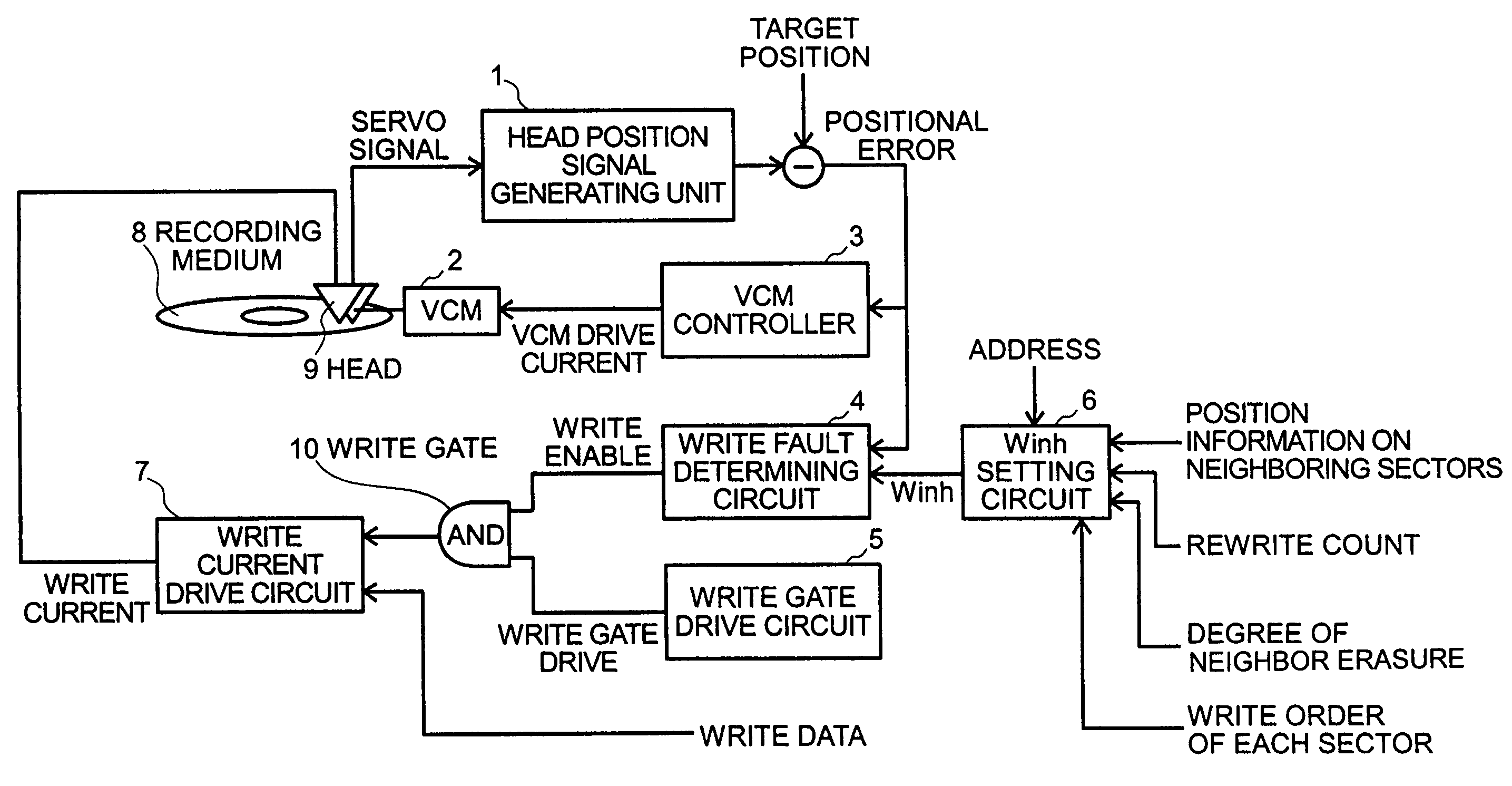
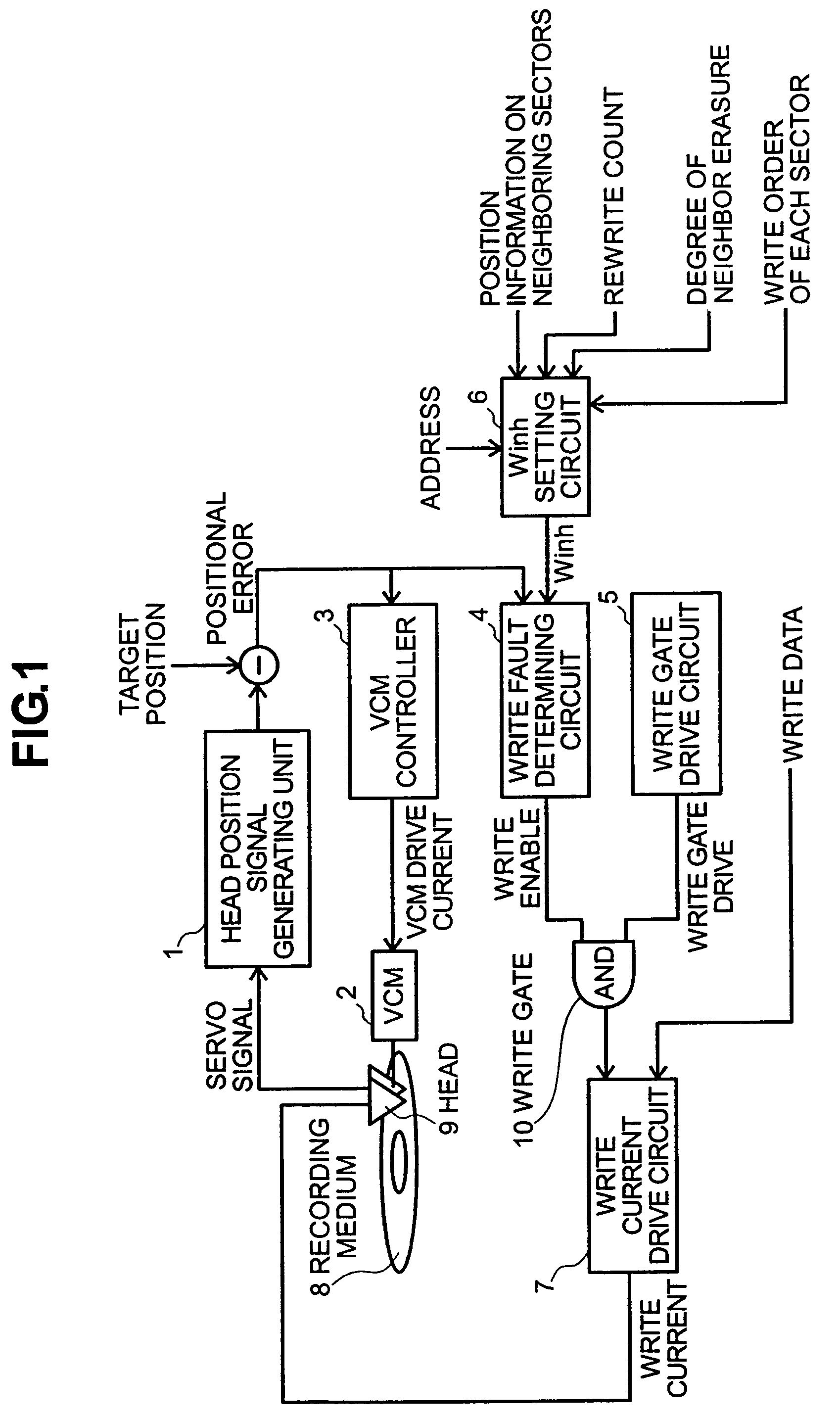
Magnetic read/write apparatus having a write inhibit slice setting circuit
InactiveUS7245447B2High track densityAvoid erasureRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksRecord statusComputer science
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
CPP-type thin film magnetic head provided with side shields including a pair of antimagnetically exchanged-coupled side shield magnetic layers
ActiveUS8369048B2High track densityLinearityNanomagnetismDisposition/mounting of recording headsCouplingProtocol Application
A thin film magnetic head includes a magnetoresistive (MR) stack disposed between first and second shield layers in a direction orthogonal to the film surface; a first exchange-coupling layer that is positioned between the MR stack and the first shield layer; a second exchange-coupling layer that is positioned between the MR stack and the second shield layer; a bias magnetic field application layer that is disposed at an opposite surface of the MR stack from an air bearing surface (ABS); and pair of side shield layers that are positioned at both sides of the MR stack with respect to a track width direction. Each of the side shield layers includes a pair of magnetic layers that are antiferromagnetically exchange-coupled through a side shield ruthenium layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multi-channel head position controlling apparatus and method of controlling position of multi-channel head
InactiveUS20040120070A1Easy alignmentHigh track densityAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageControl signalRecording media
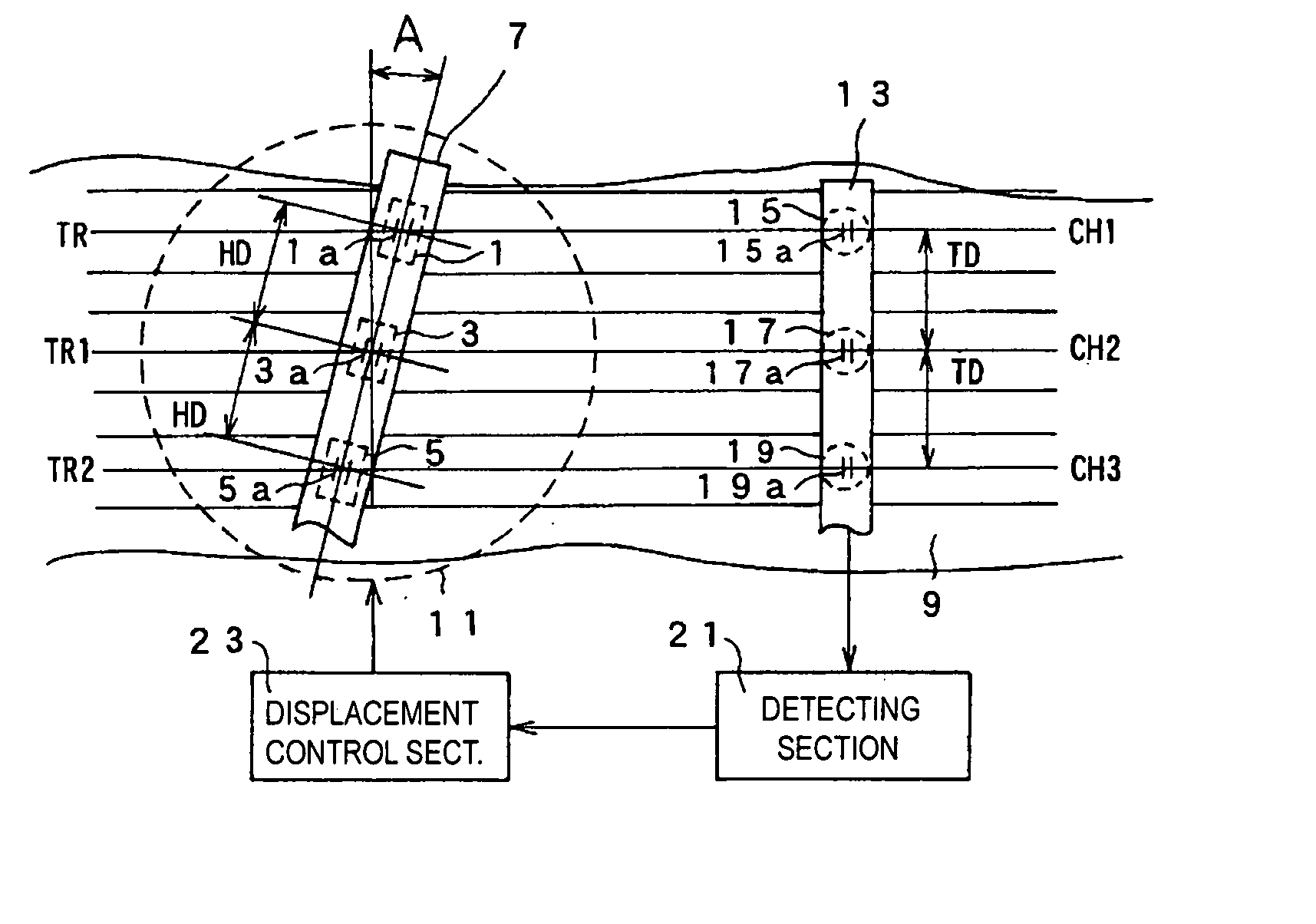
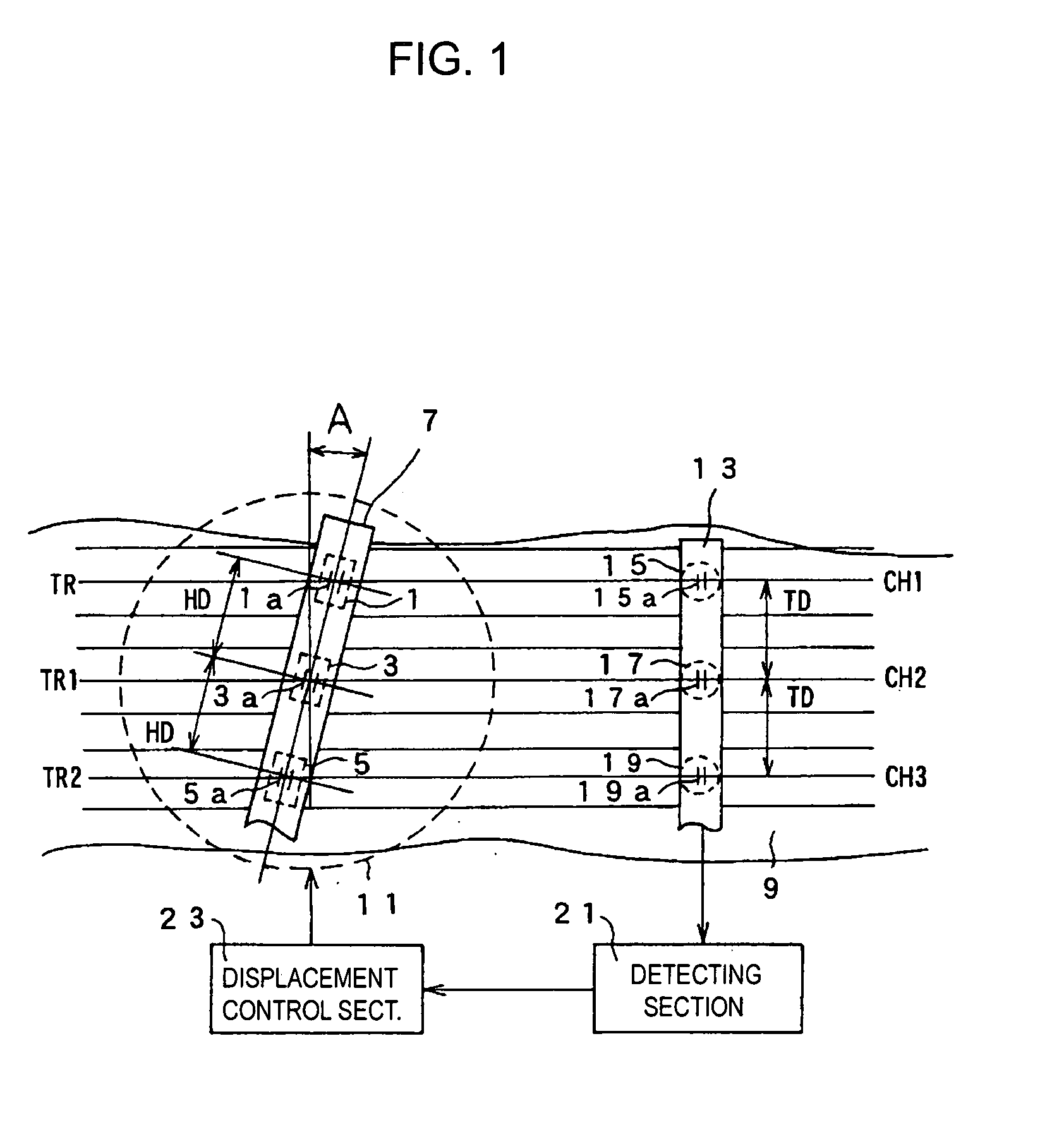
A multi-channel head position control apparatus and a method of controlling the position of the multi-channel head in which even if the width of a tape-like recording medium is changed, each of unit recording heads constituting a multi-channel head can be aligned with corresponding track centers. The multi-channel head having a plurality of unit recording heads arrayed in the longitudinal direction is disposed so that the alignment direction of the unit recording heads forms an azimuth angle relative to the running direction of the tape-like recording medium. The position of the multi-channel head is controlled by a supporting section in accordance with a control signal recorded on the tape-like recording medium and detected by a detecting section so that the alignment between each of the unit recording heads and corresponding track center is maintained.
Owner:SONY CORP
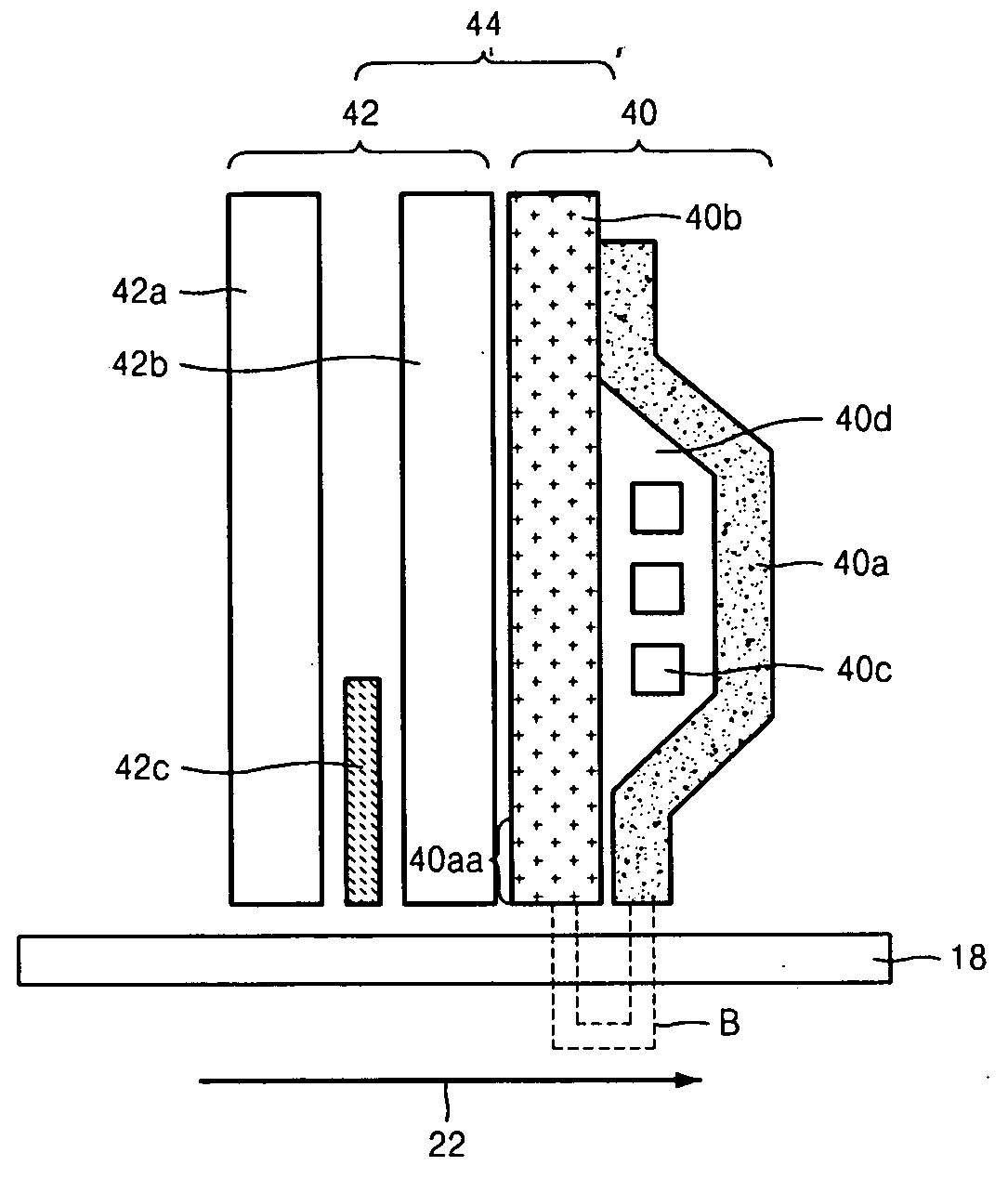
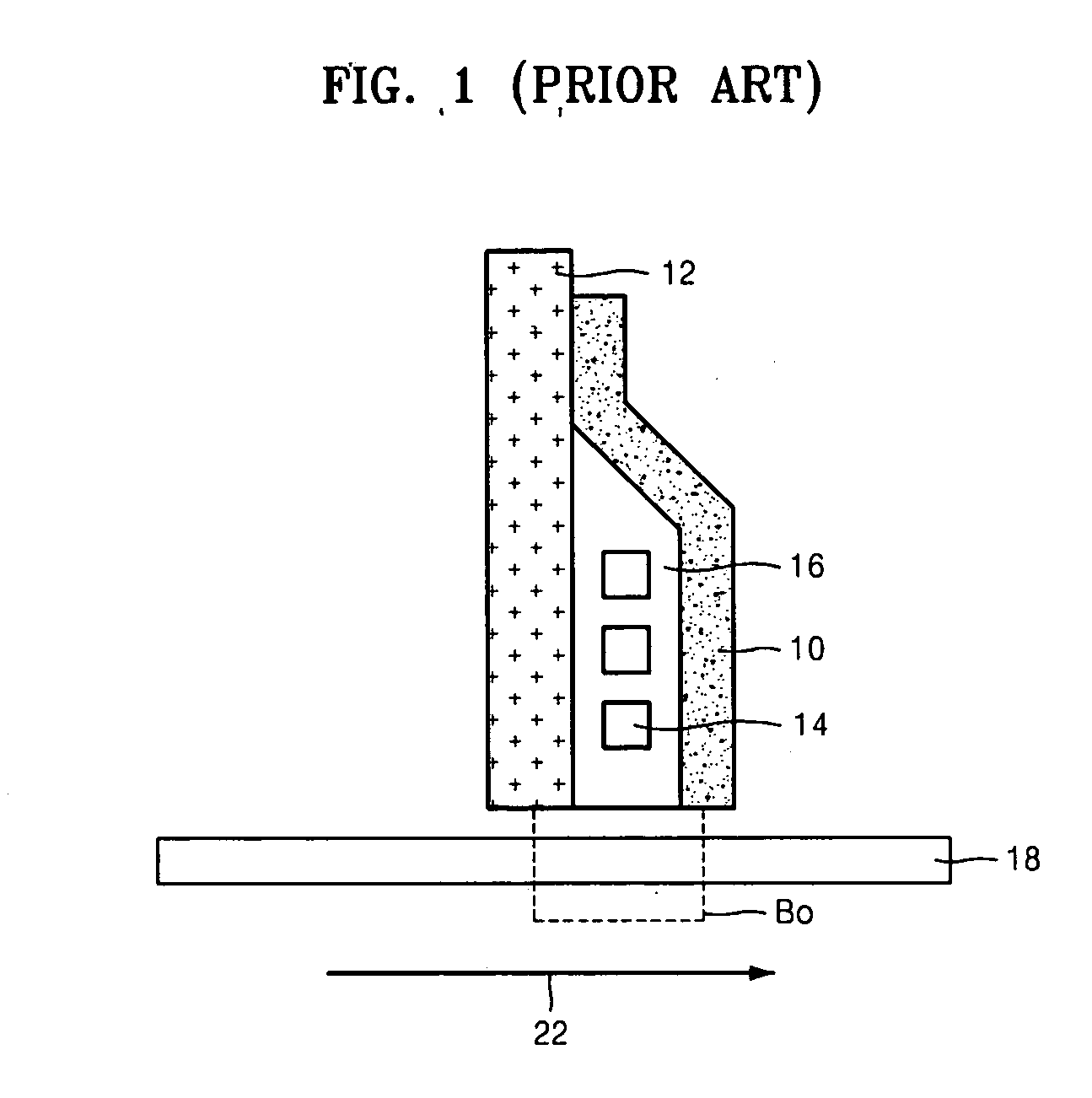
Magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing same
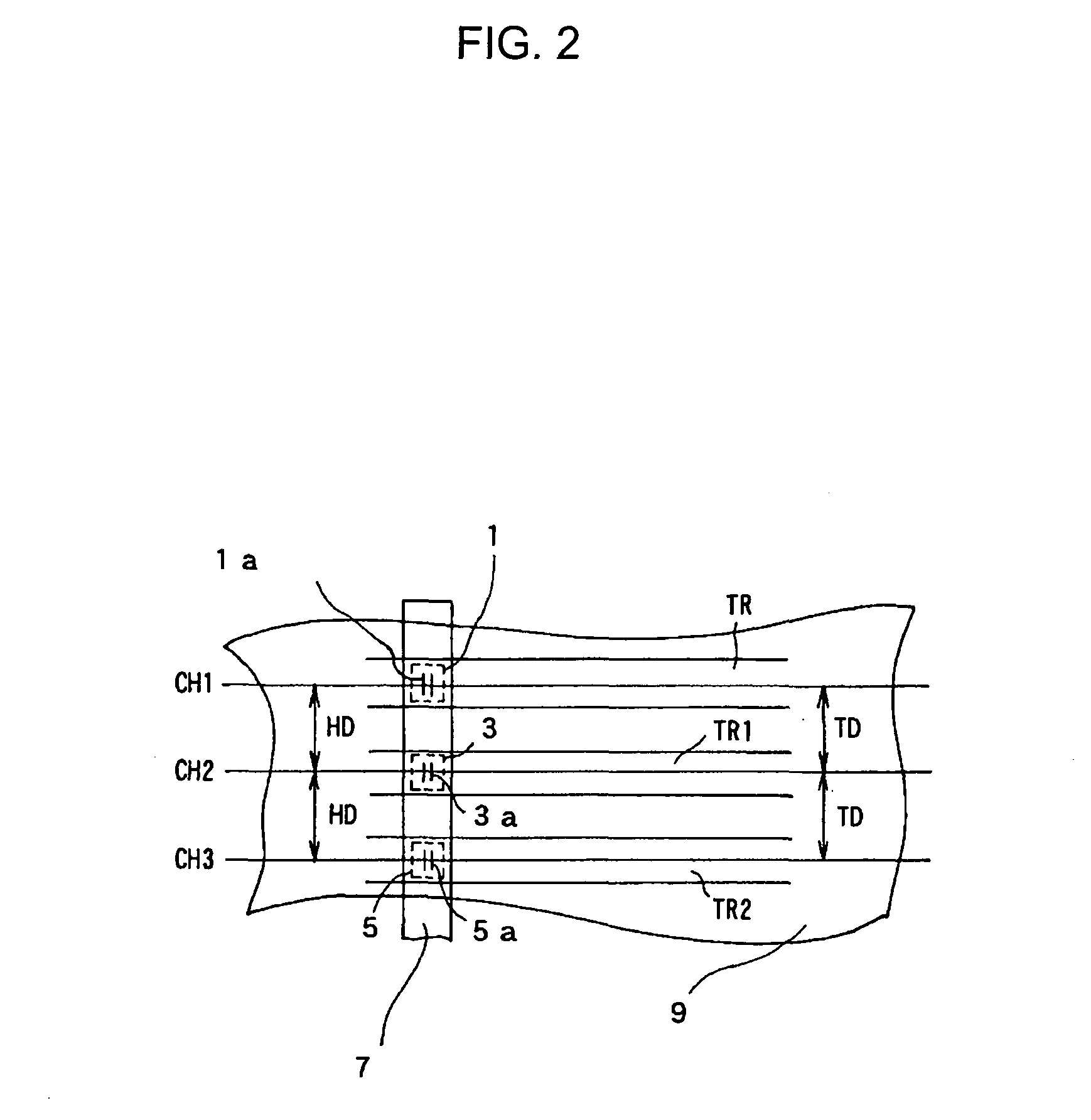
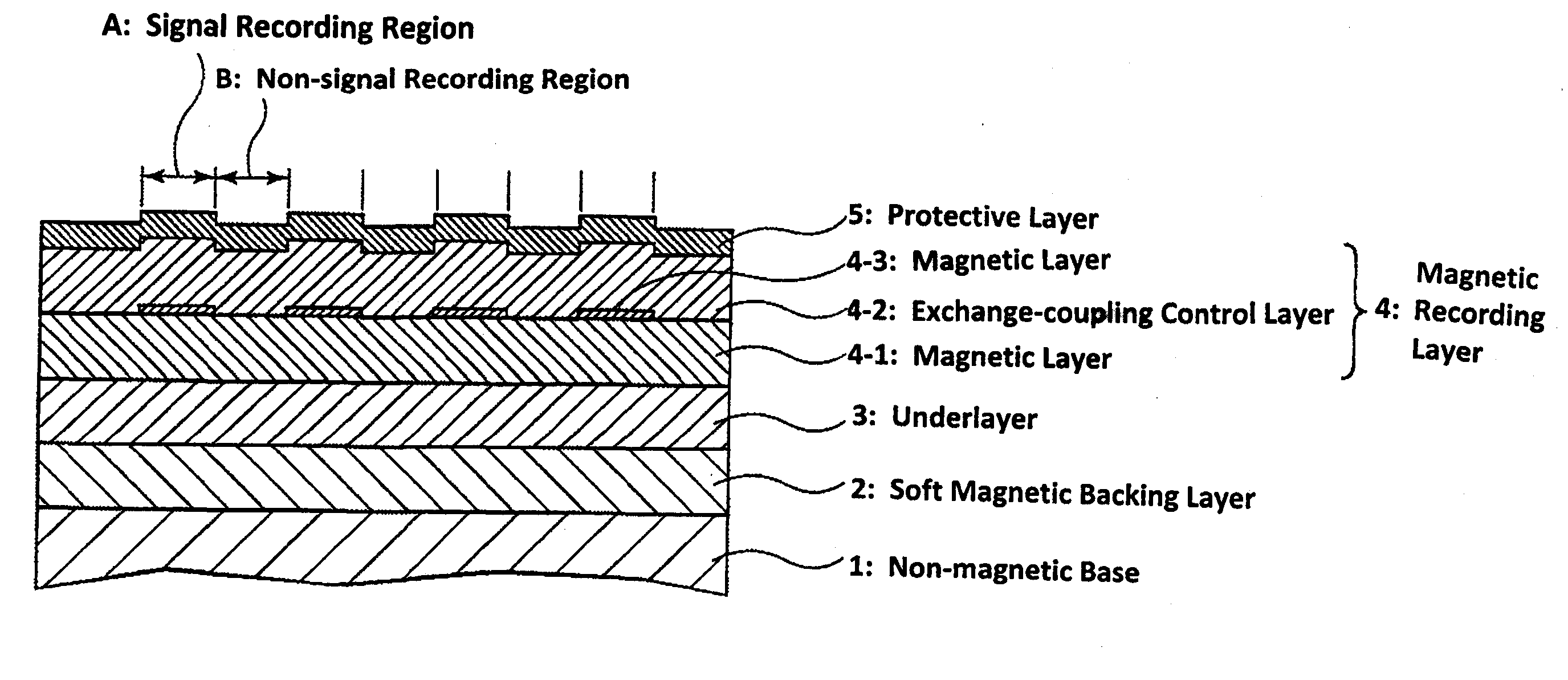
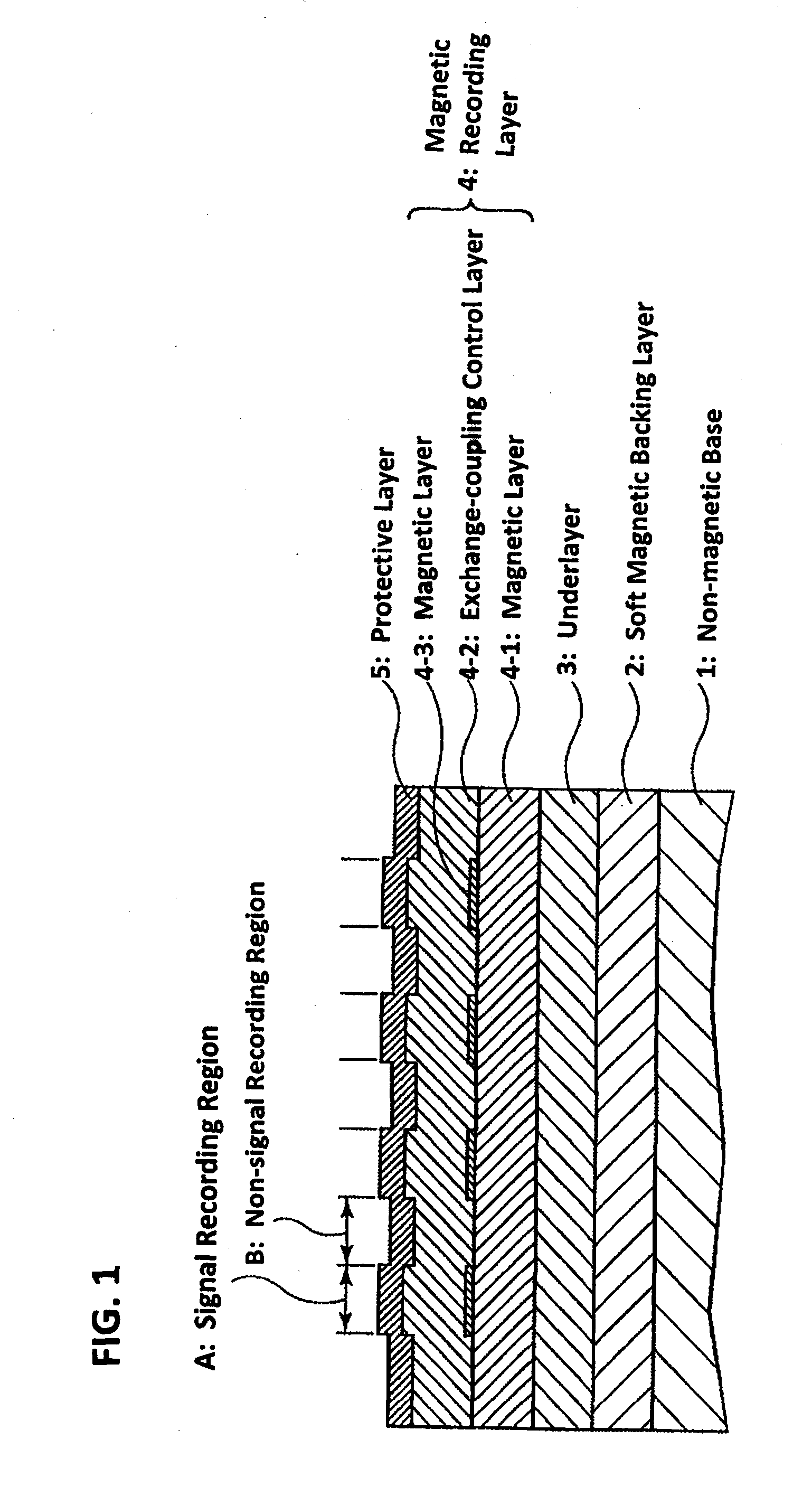
InactiveUS20090239100A1High-density recordingSimple manufacturing methodDifferent record carrier formsRecord information storageControl layerEngineering
A magnetic recording medium is formed by stacking in order, on a nonmagnetic base, at least an underlayer, magnetic recording layer, and protective layer. The magnetic recording layer includes a plurality of magnetic layers and an exchange-coupling control layer, and the magnetic recording medium is characterized in that a physical pattern is formed in the exchange-coupling control layer. The exchange-coupling control layer is located between the magnetic layers of the magnetic recording layer.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
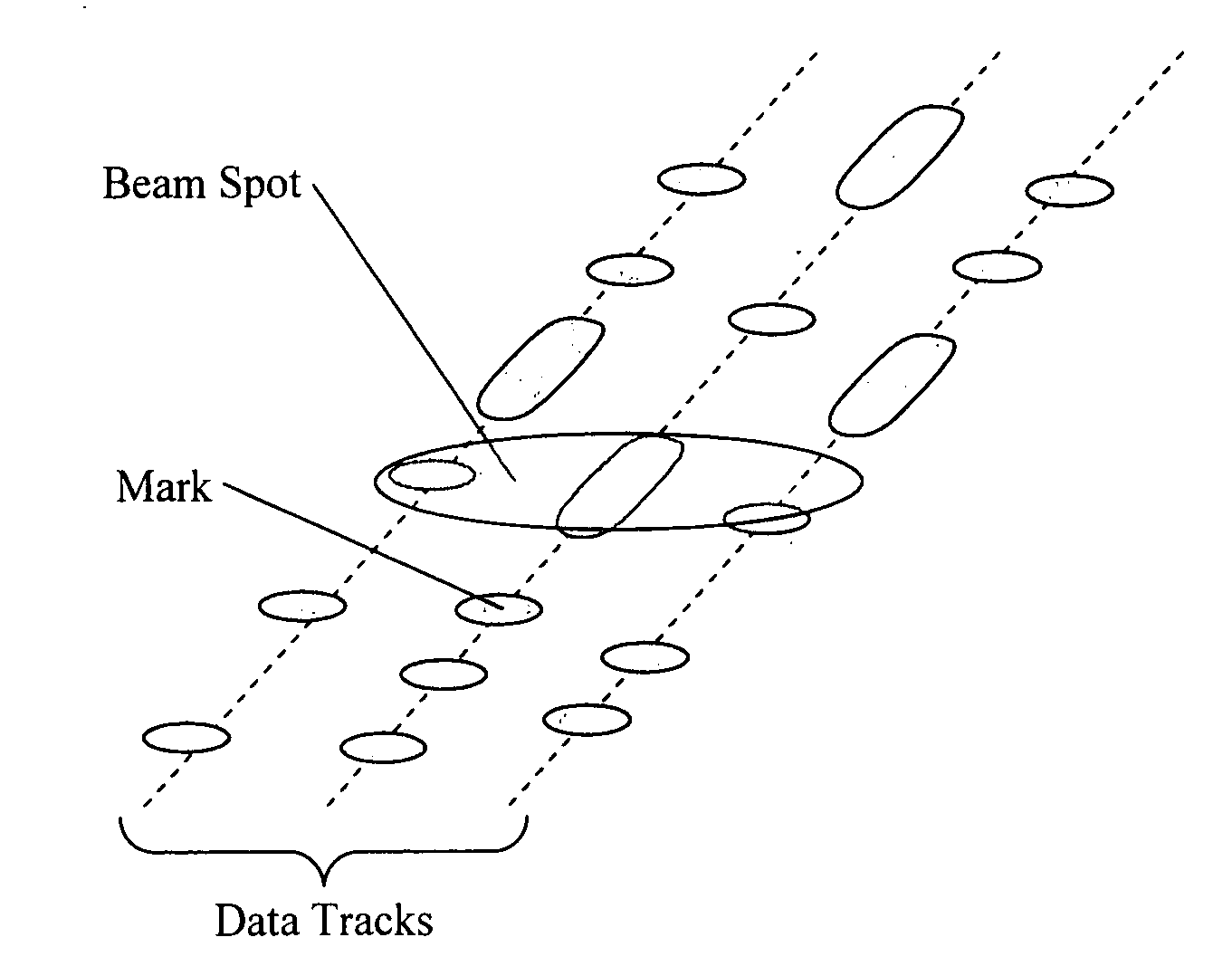
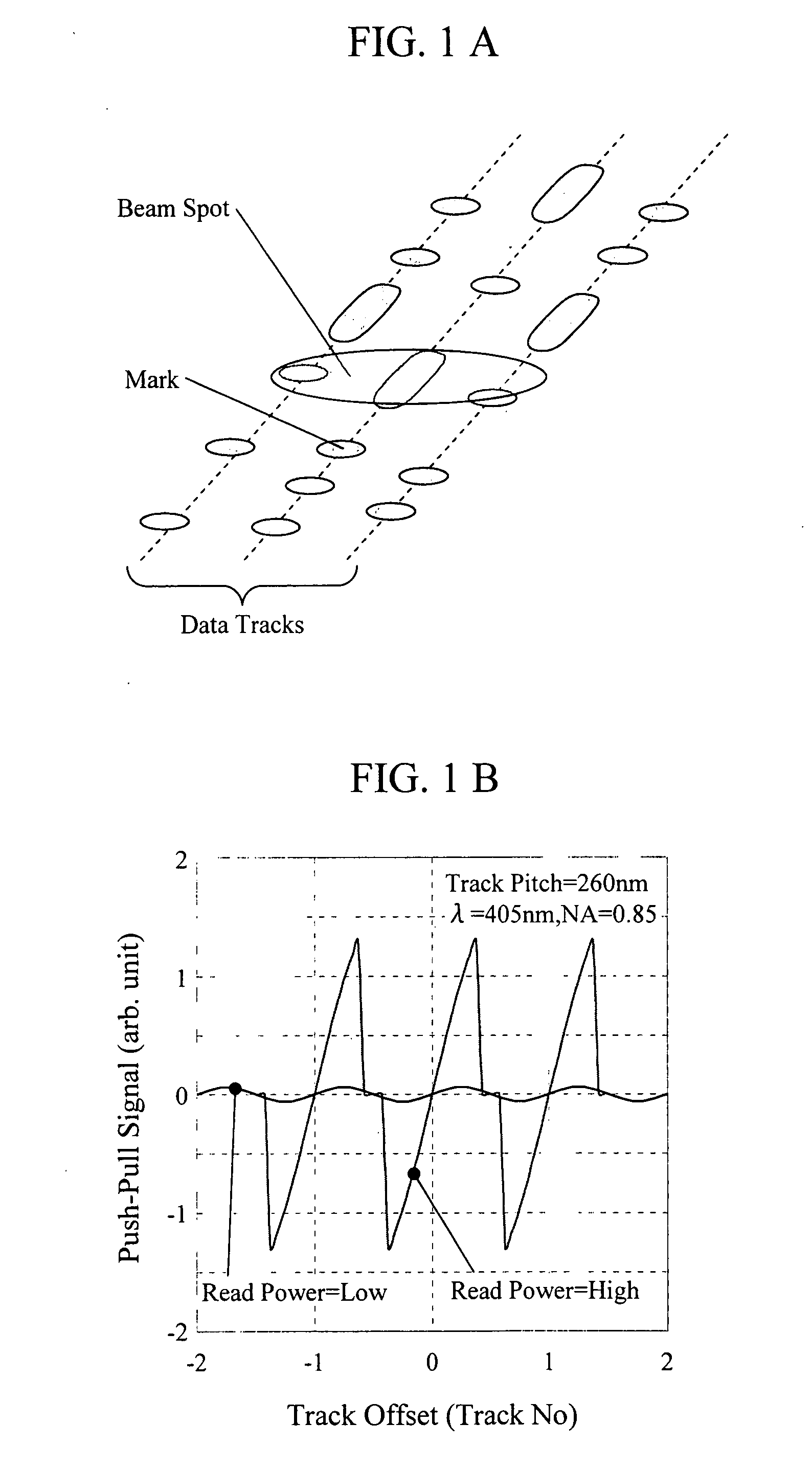
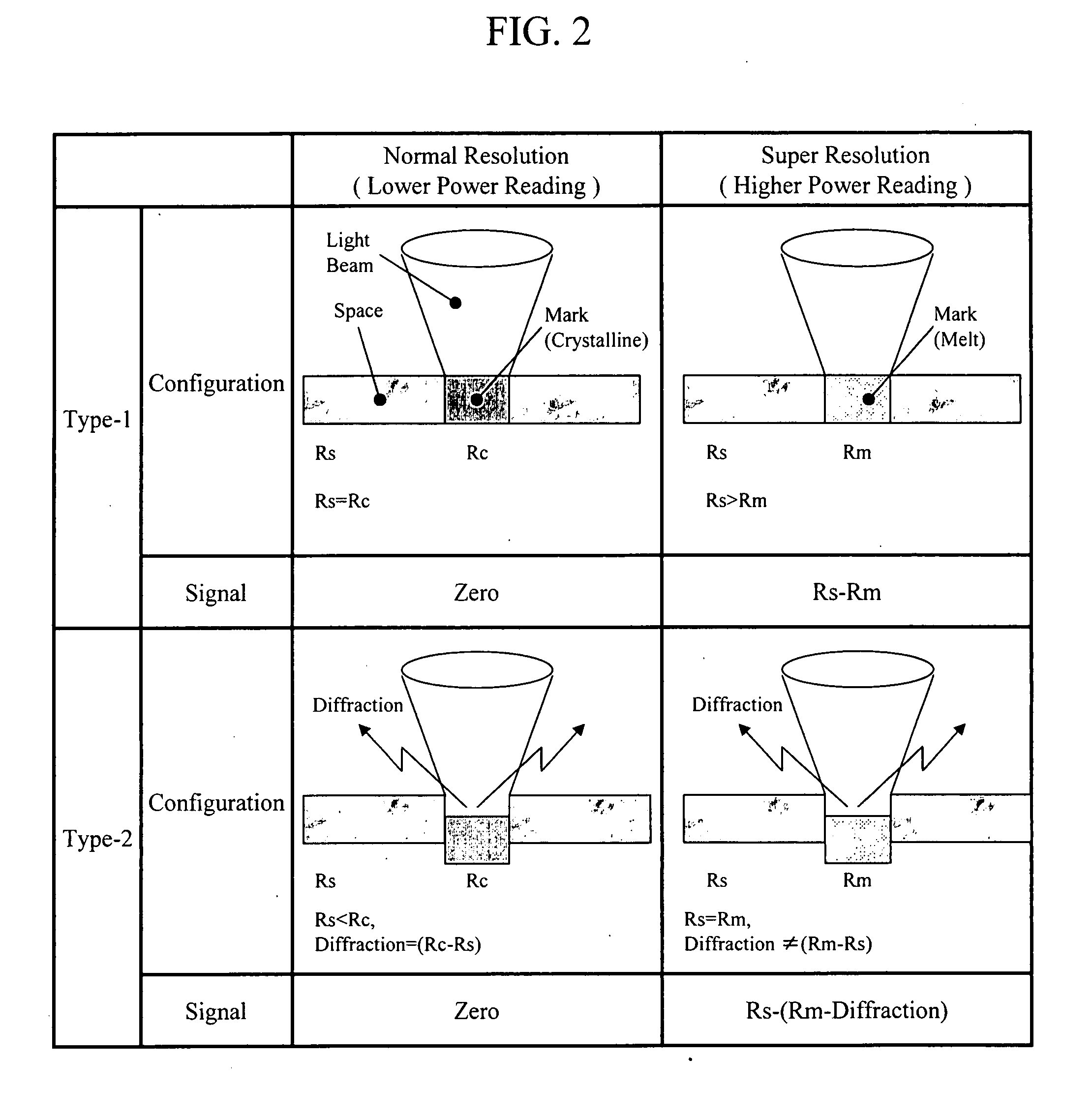
Optical disk medium and tracking method
InactiveUS20080285431A1Stable controlHigh track densityMechanical record carriersRecord information storagePhase differencePush pull
A super-resolution material is formed in only a data pit, in a low temperature state of the super-resolution material, reflectivity of each of a pit portion and a space portion and an optical phase difference therebetween are set to be sufficiently small, in a high temperature state, and at least the optical phase difference between the pit and the space is set to be larger than the aforementioned value in an absolute value. Accordingly, by conducting irradiation with an appropriate read power by which substantially only one data track width can be heated to a high temperature state, a good push-pull signal can be obtained even with a track pitch being less than a diffraction limit. At the same time, by an optical device having functions such as a switching means with a DPP type, an offset correcting means of the push-pull signal due to lens shift, a shaping means of the push-pull signal, a learning means of read power, and the like, there is provided an optical disk device that corresponds to the optical disk medium of the present invention and achieves an increase in capacity.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
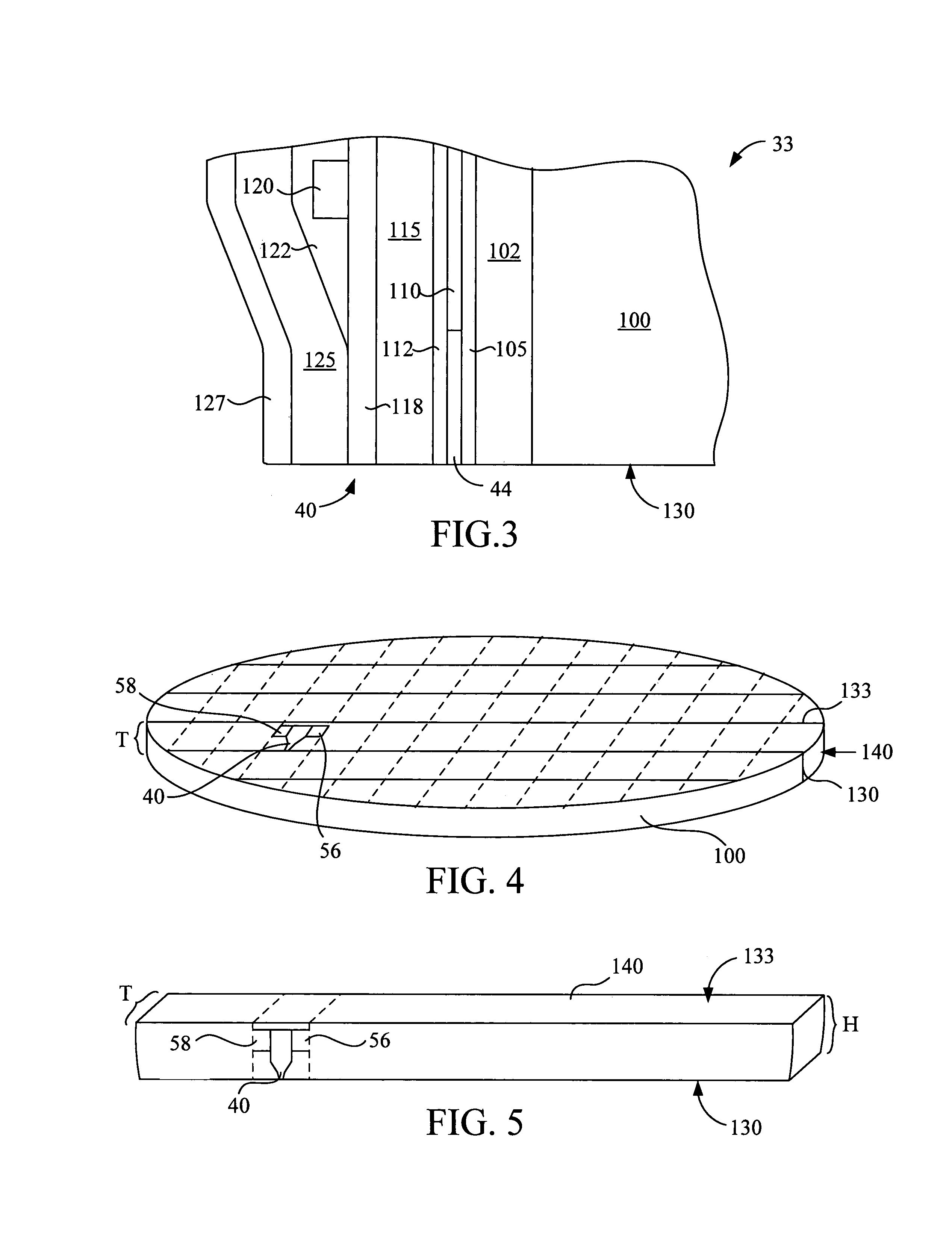
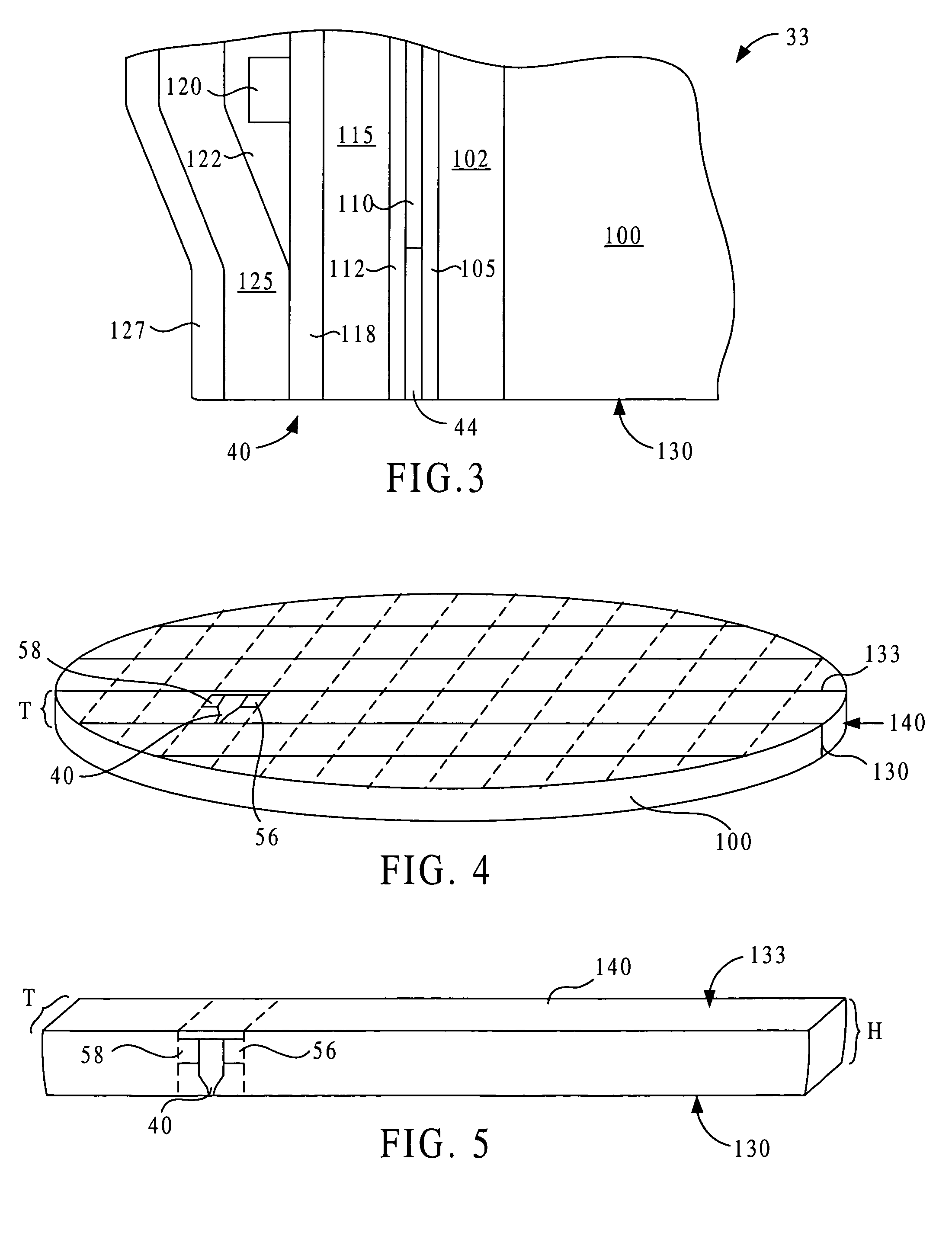
Electromagnetic heads, flexures, gimbals and actuators formed on and from a wafer substrate
InactiveUS7684158B1Improve accuracyHigh track densityElectrical connection between head and armRecord information storageAccess timePiezoelectric actuators
Devices for reading or writing electromagnetic information include a wafer substrate piece disposed between an electromagnetic transducer and an electrostrictive or piezoelectric actuator. The substrate piece is shaped as a rigid body adjoining the transducer and as a flexible element connecting the body and the actuator. To fabricate, at least one electrostrictive layer and many transducers are formed on opposite sides of a wafer that is then cut into rows containing plural transducers. The rows are processed from directions generally normal to the wafer surface upon which the transducers were formed, by removing material to form a head, flexures and a media-facing surface on the head. Conductive leads are formed on a back surface of flexures connecting the transducer with drive electronics. The flexures are aligned with forces arising from interaction with the media surface and from seeking various tracks, reducing torque and dynamic instabilities and increasing actuator access time.
Owner:LAUER MARK A
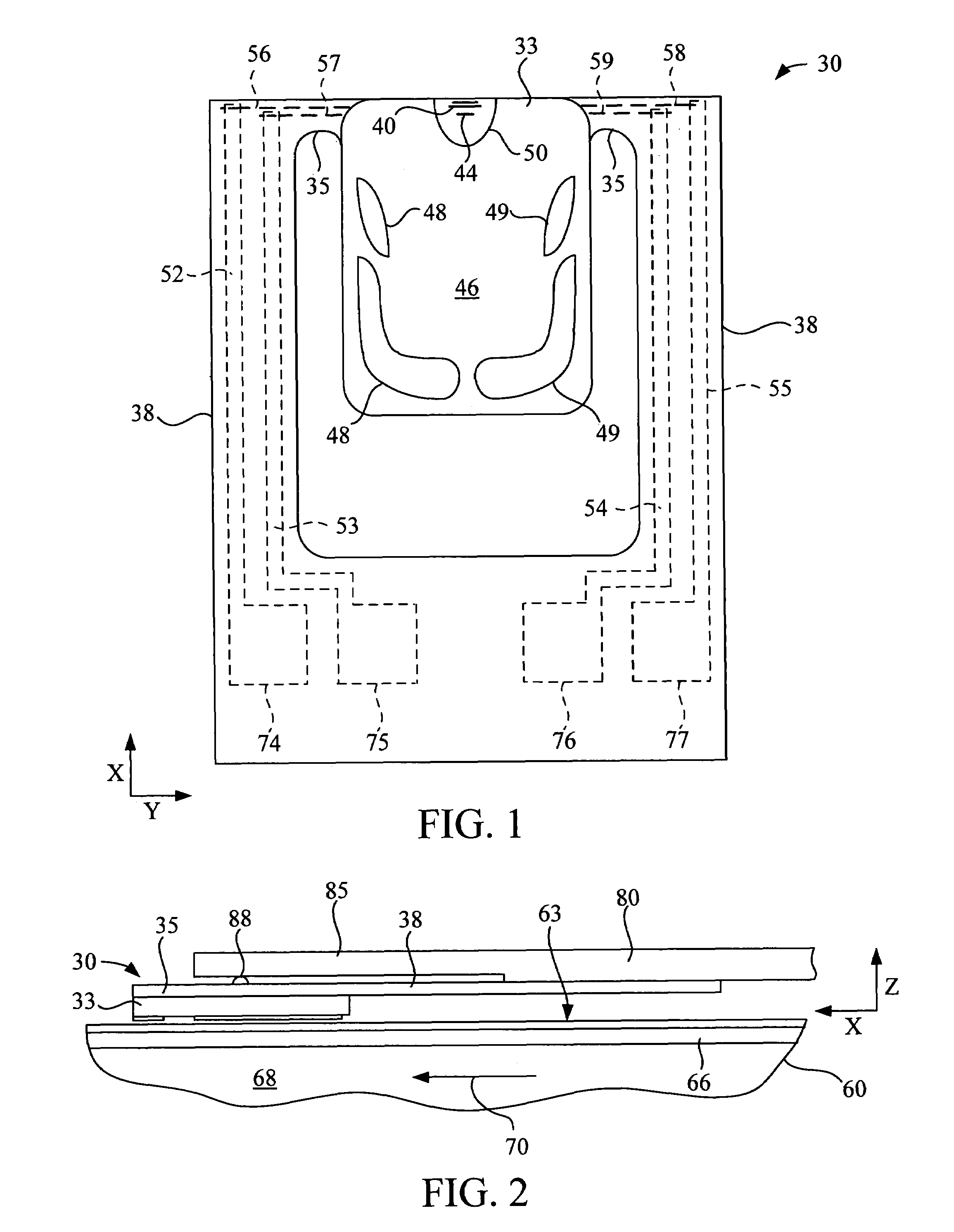
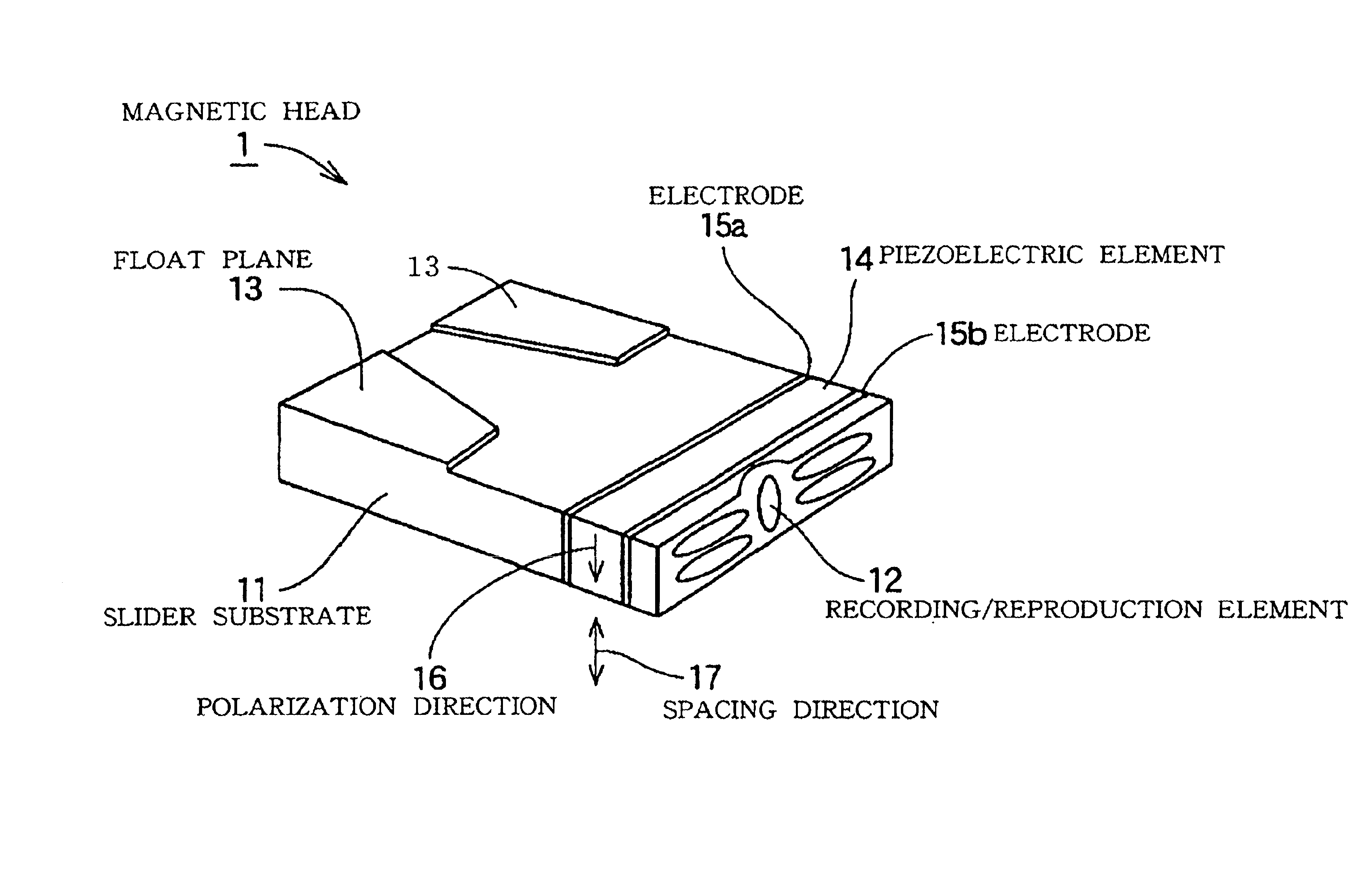
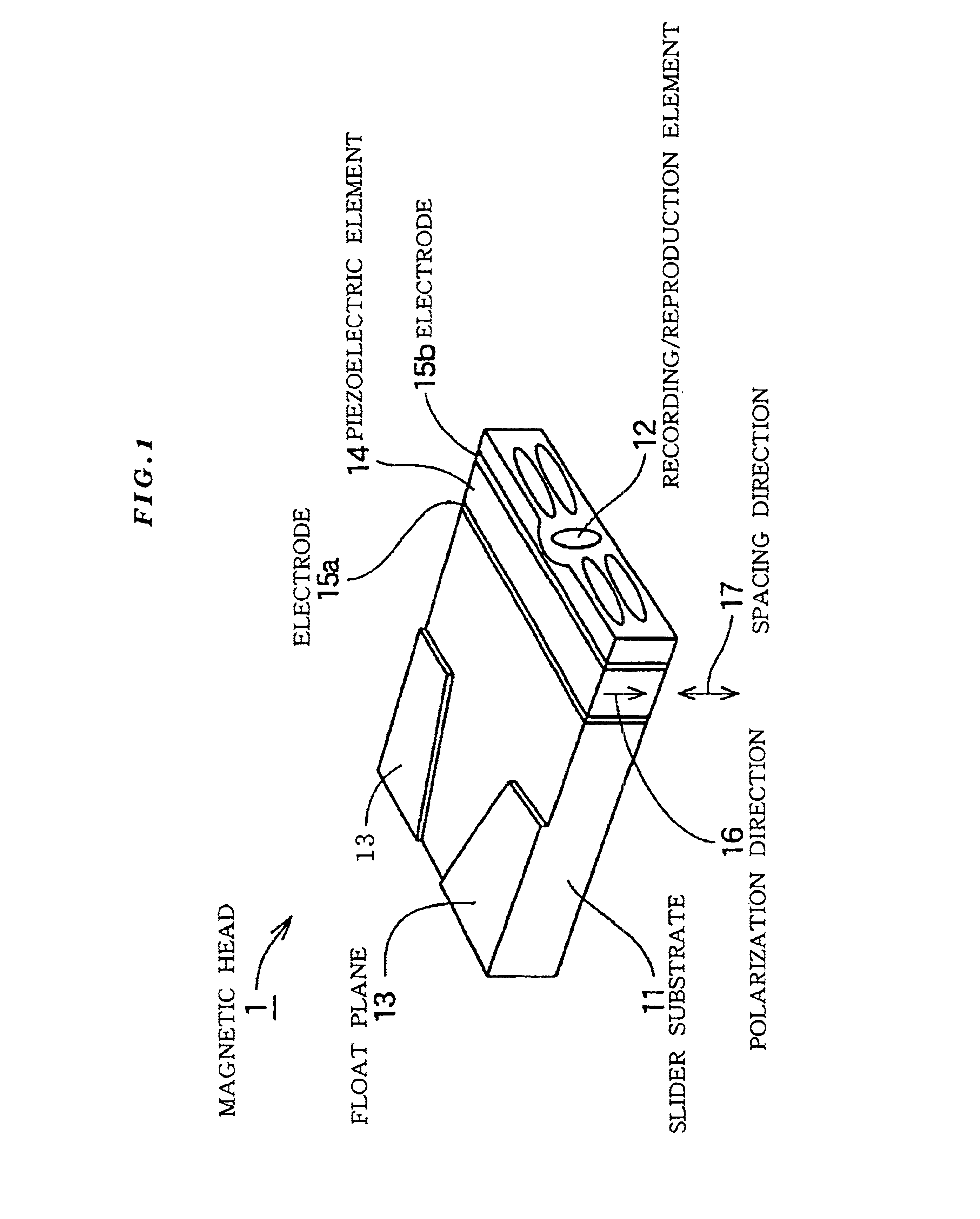
Magnetic disc apparatus and magnetic head in which a recording/reproduction element is mounted on a slider via a piezoelectric element
InactiveUS6928722B2Improve accuracySpace minimizationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyTrack finding/aligningTrack densityElectricity
A recording / reproduction element is mounted on a magnetic head slider via a piezoelectric element so that a displacement of the piezoelectric element performs fine control of the position of the recording / reproduction, thus enabling fine spacing and high track positioning accuracy. This improves linear recording density and track density. A pair of electrodes are formed on both sides of a piezoelectric element to constitute a piezoelectric actuator. One electrode is arranged opposite the rear surface (air flow out end) of a magnetic head slider 11. A recording / reproduction element is arranged on and electrically insulated from the other electrode. The piezoelectric element includes a piezoelectric element displaced in a spacing direction, enabling fine spacing control, a piezoelectric element displaced in the track direction, enabling a fine track position control, and a piezoelectric element displaced in a magnetic disc rotation direction, enabling reduction of jitter of a reproduction signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Electromagnetic heads, flexures, gimbals and actuators formed on and from a wafer substrate
InactiveUS7248444B1Improve accuracyHigh track densityElectrical connection between head and armRecord information storageAccess timePiezoelectric actuators
Devices for reading or writing electromagnetic information include a wafer substrate piece disposed between an electromagnetic transducer and an electrostrictive or piezoelectric actuator. The substrate piece is shaped as a rigid body adjoining the transducer and as a flexible element connecting the body and the actuator. To fabricate, at least one electrostrictive layer and many transducers are formed on opposite sides of a wafer that is then cut into rows containing plural transducers. The rows are processed from directions generally normal to the wafer surface upon which the transducers were formed, by removing material to form a head, flexures and a media-facing surface on the head. Conductive leads are formed on a back surface of flexures connecting the transducer with drive electronics. The flexures are aligned with forces arising from interaction with the media surface and from seeking various tracks, reducing torque and dynamic instabilities and increasing actuator access time.
Owner:LAUER MARK A
Tape head having write devices and narrower read devices
InactiveUS20070047122A1Feature size of to decreaseHigh track densityRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsMagnetic mediaComputer science
A magnetic head, such as a tape head, according to one embodiment includes an array of data writers for writing to multiple data tracks on a magnetic medium, a width of the array being defined between the data writers positioned farthest apart. An erase writer having a width at least about as wide as the width of the array is present for erasing at least part of the magnetic medium prior to the writing by the data writers. A plurality of readers may also be present. Preferably, the data writers and erase writer are formed on the same substrate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic head for perpendicular recording including a main pole having a pole tip with three tapered sides
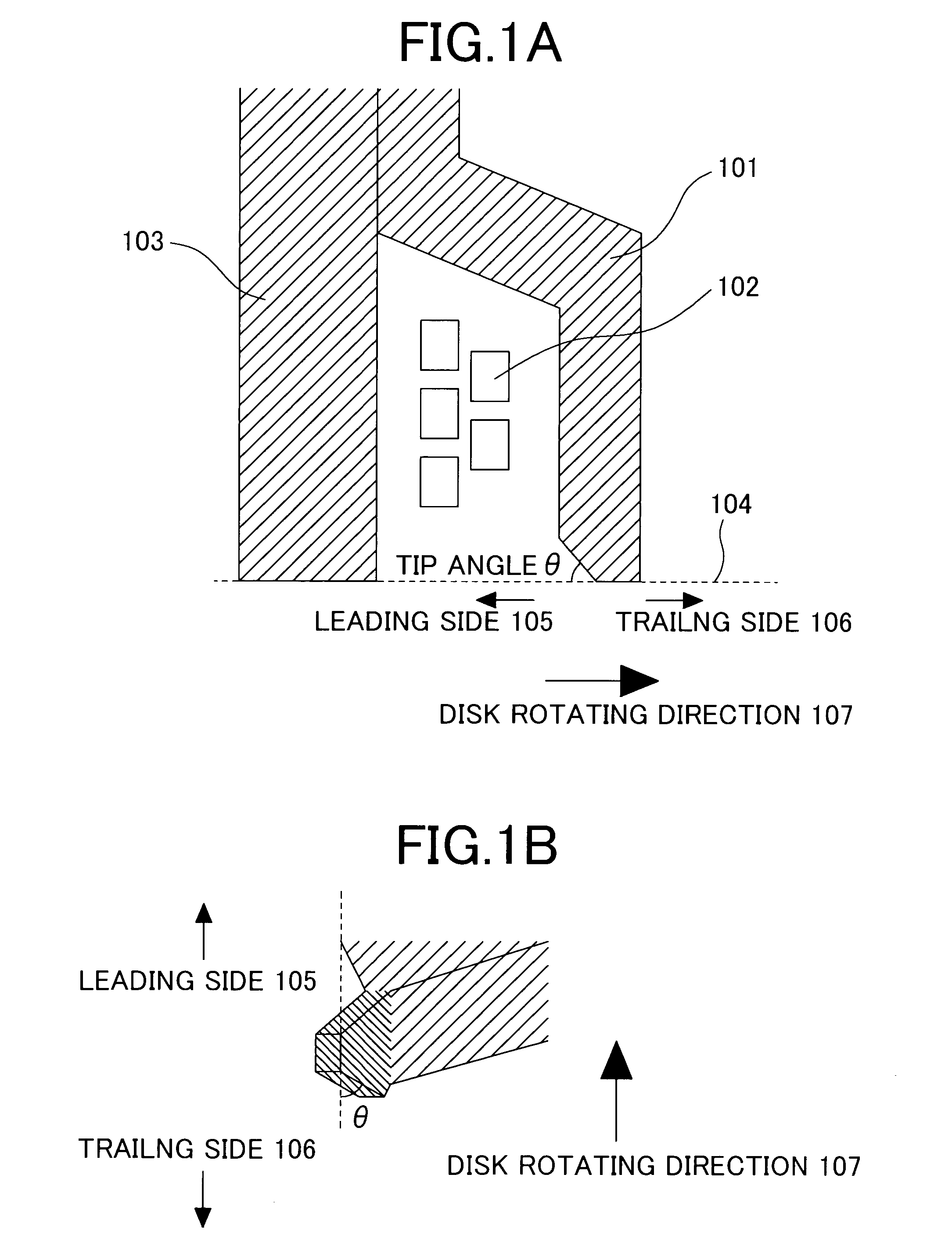
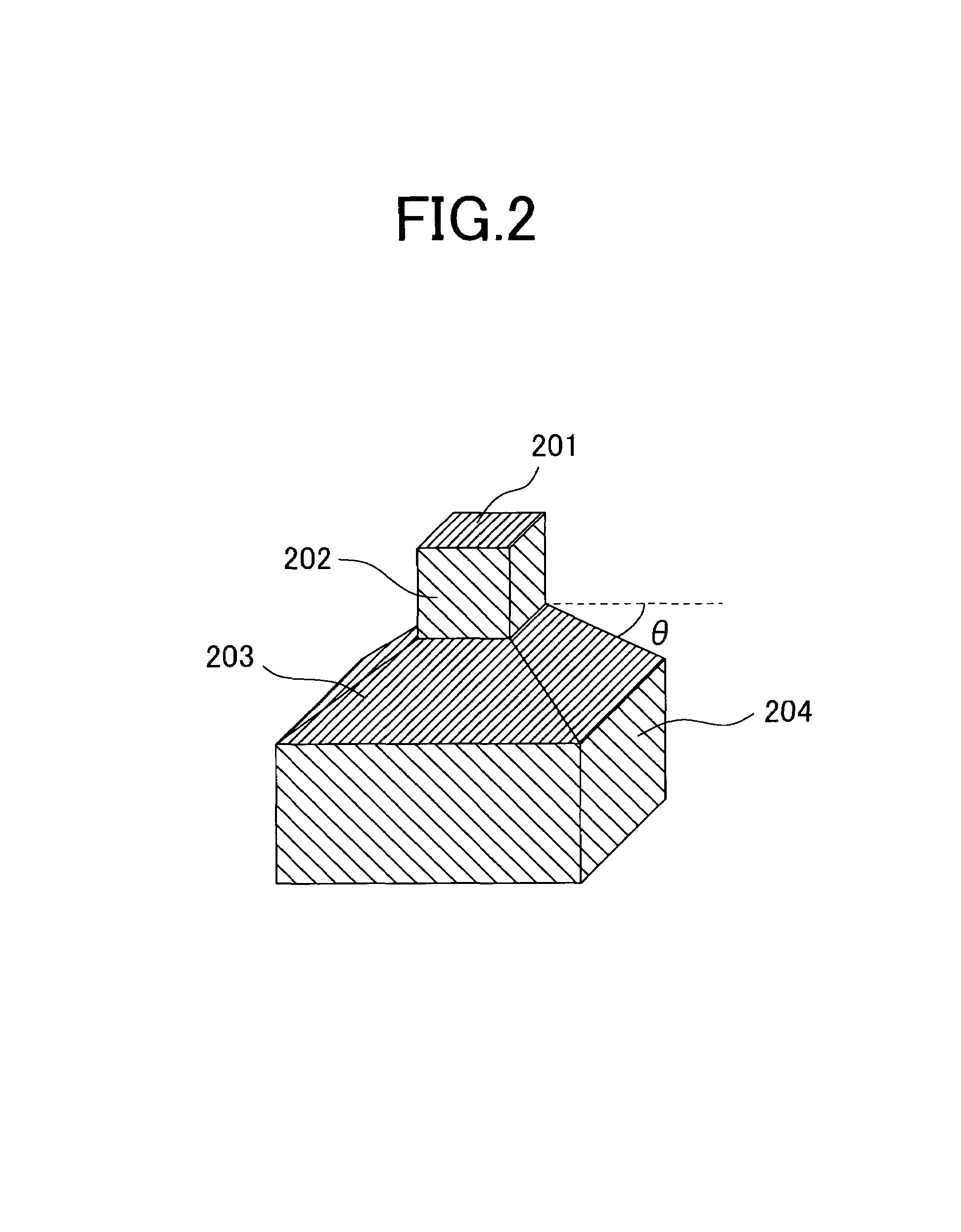
InactiveUS7038881B2High linear recording densityHigh track densityManufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersMagnetic disksRecording density
The invention provides a magnetic head for perpendicular recording capable of recording with high linear recording density and high track density, and a magnetic disk drive incorporating the same. In order to achieve this, one or more sides of the main pole of the magnetic head for perpendicular recording except for the trailing side are formed in a taper with an appropriate angle against the tip surface of the main pole, and the yoke whose widest principal plane is in parallel to the tip surface is provided on the bottom of the main pole.Thereby, the invention achieves the magnetic head for perpendicular recording that generates a sufficiently high magnetic field, and assumes a sharp gradient of magnetic field on the trailing side. By incorporating this magnetic head, a magnetic disk drive capable of handling high linear recording density can be produced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com