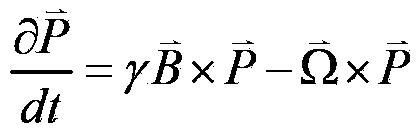Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
526 results about "Precession" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called nutation. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced.
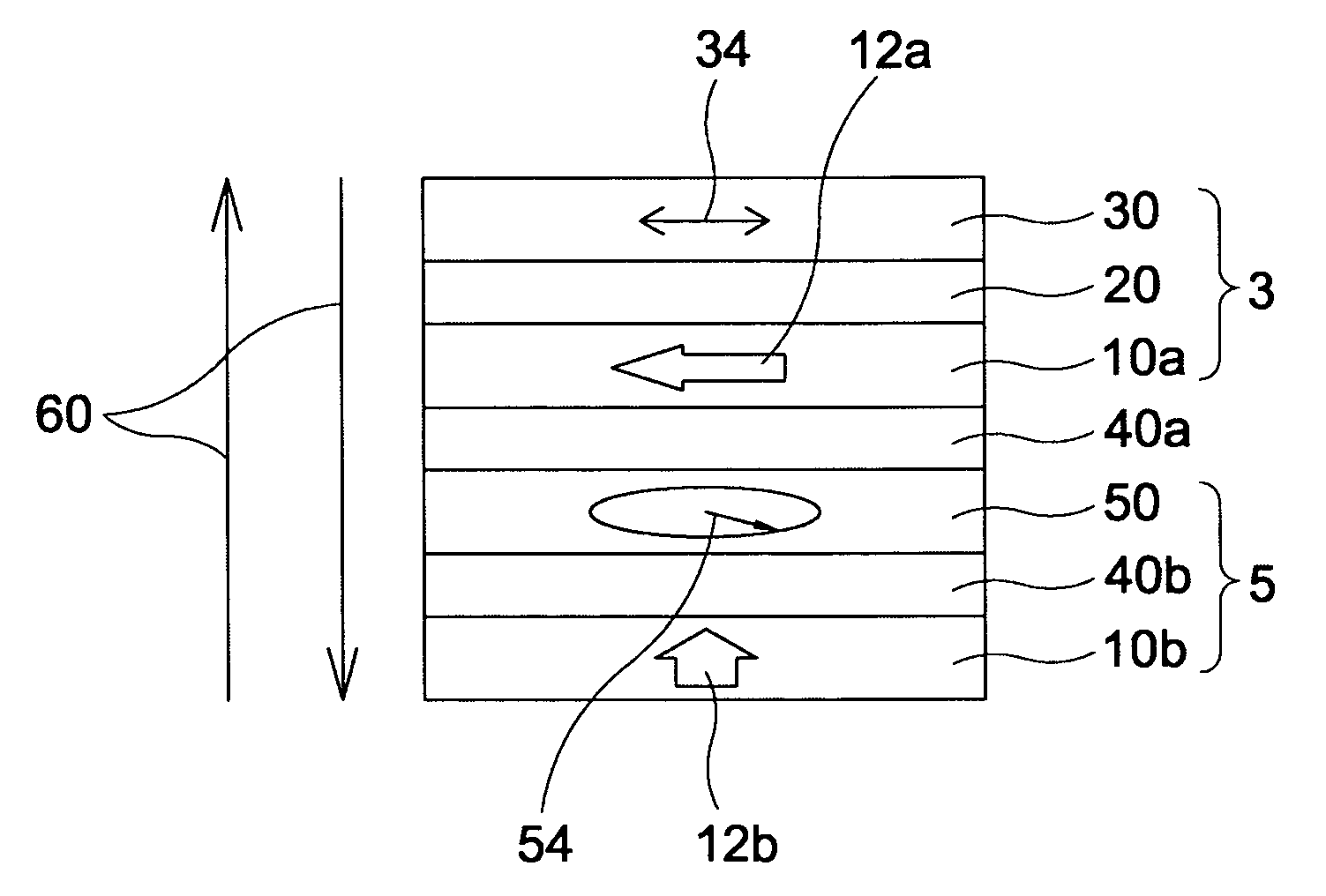
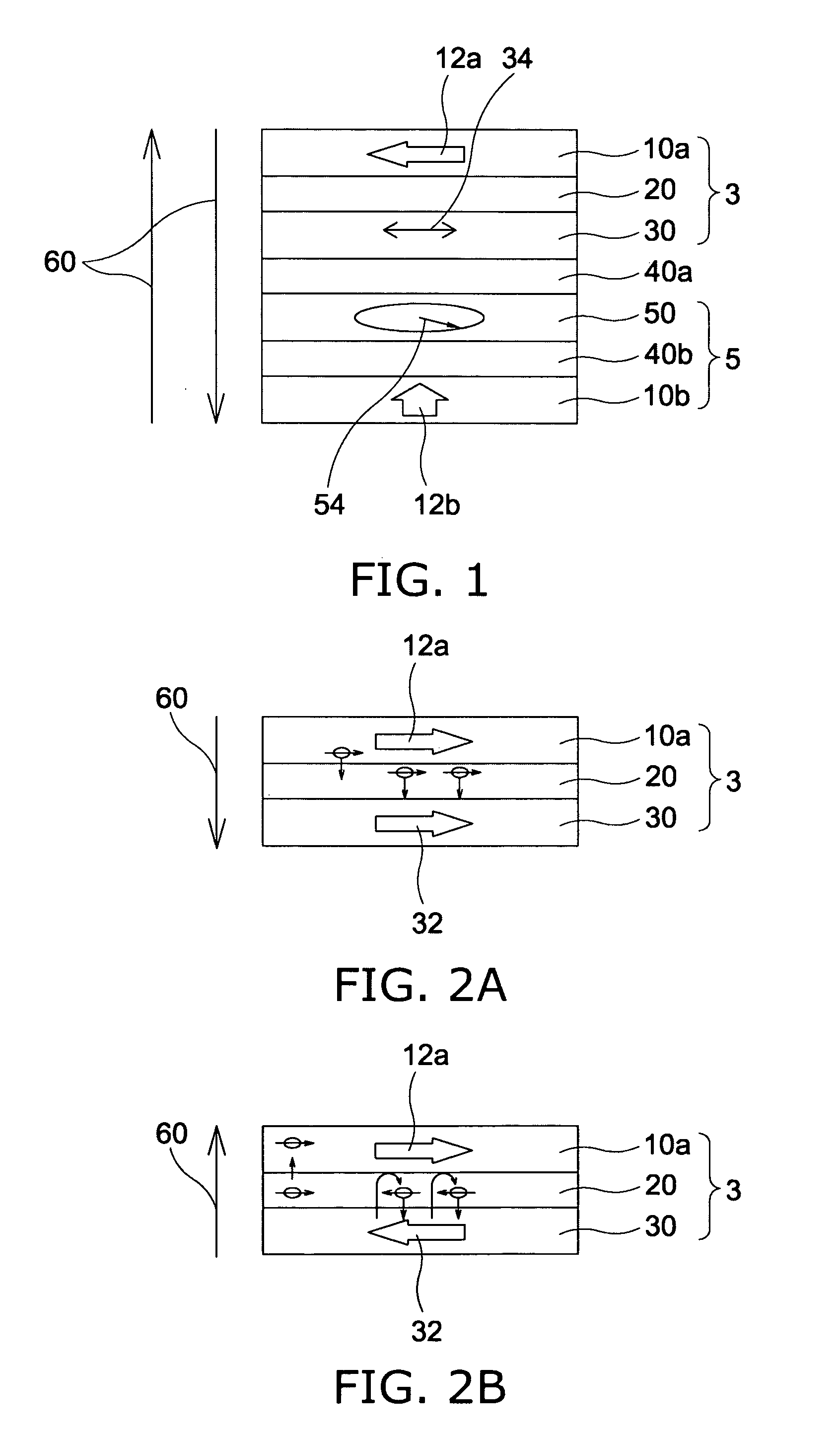
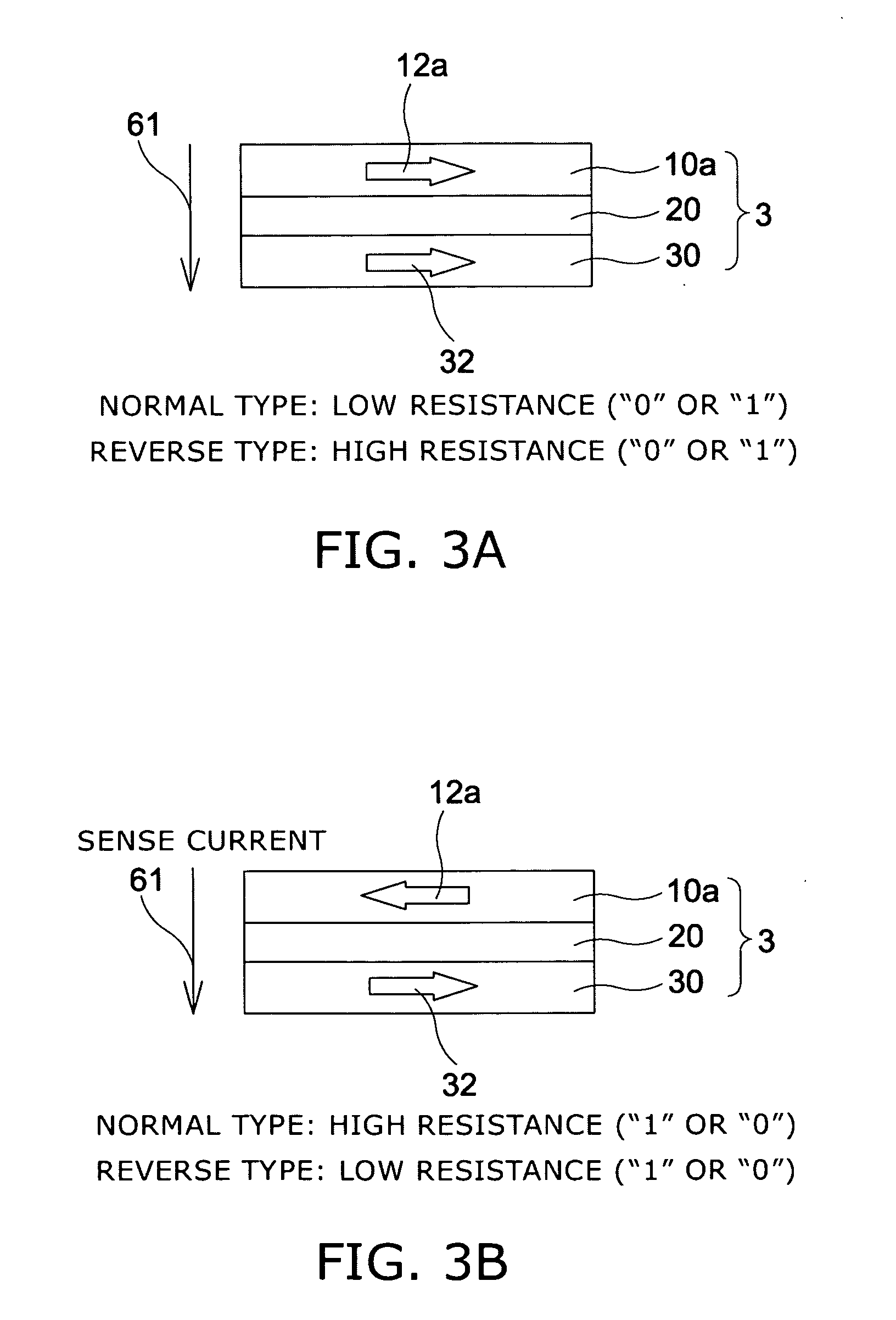
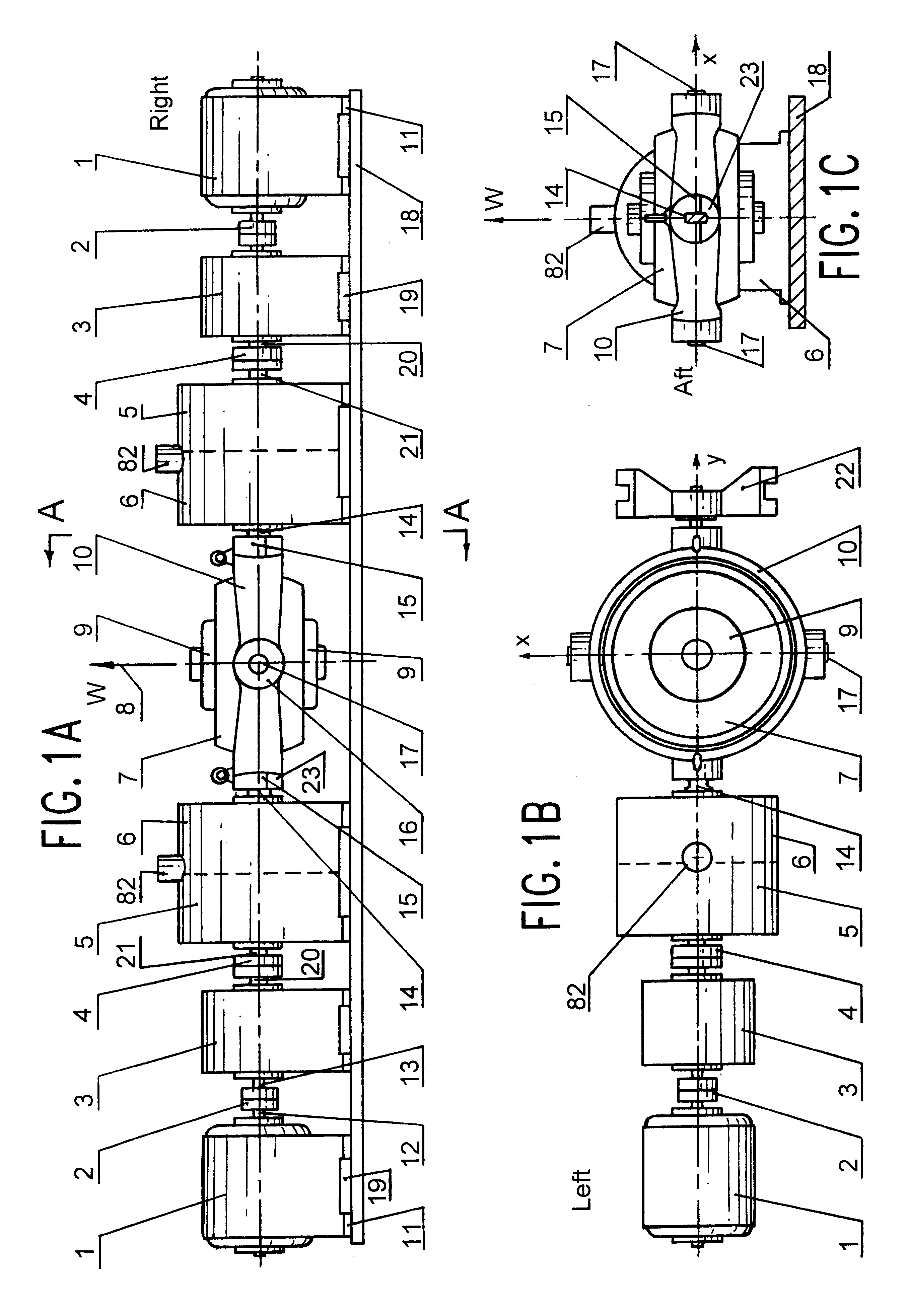
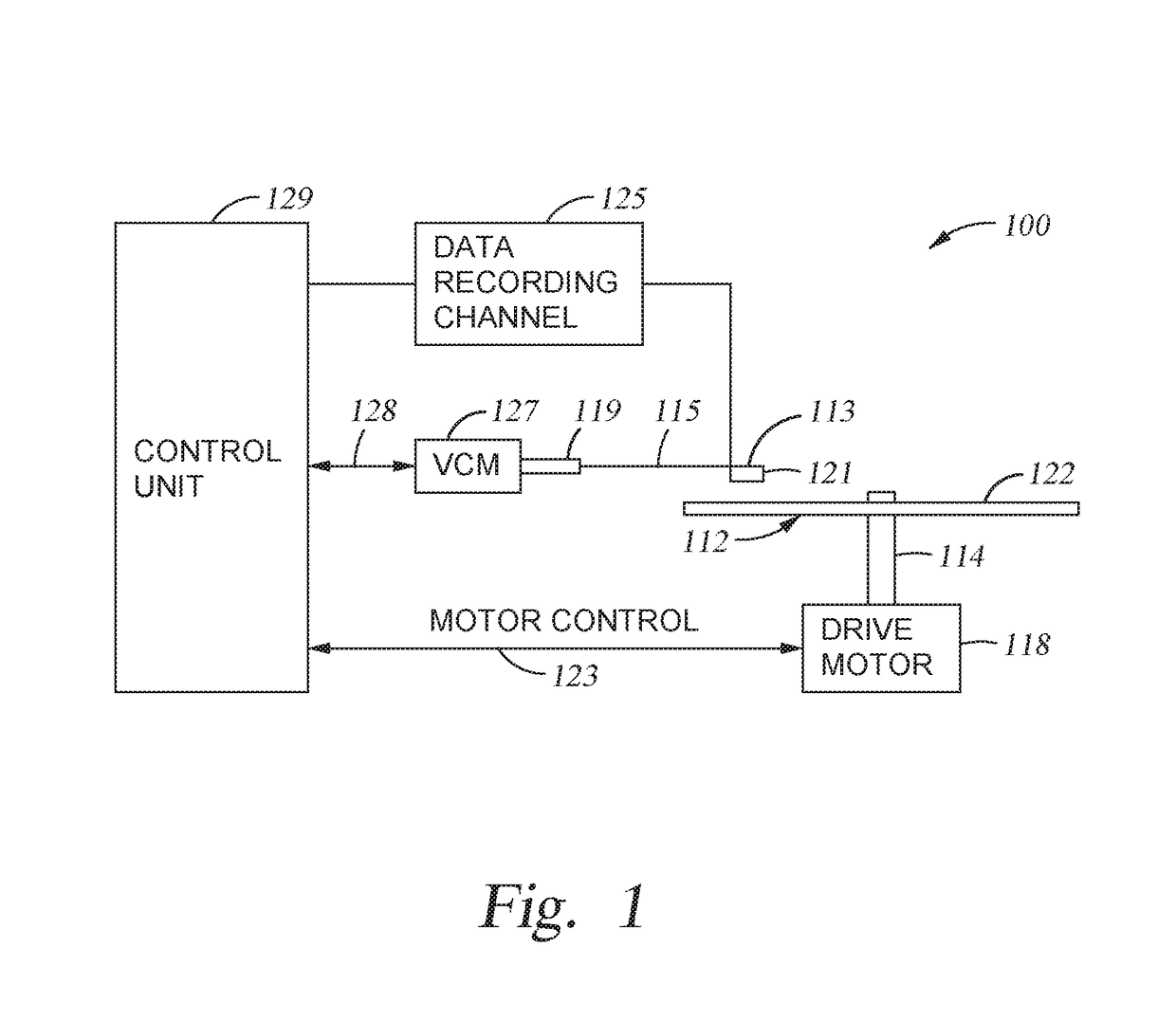
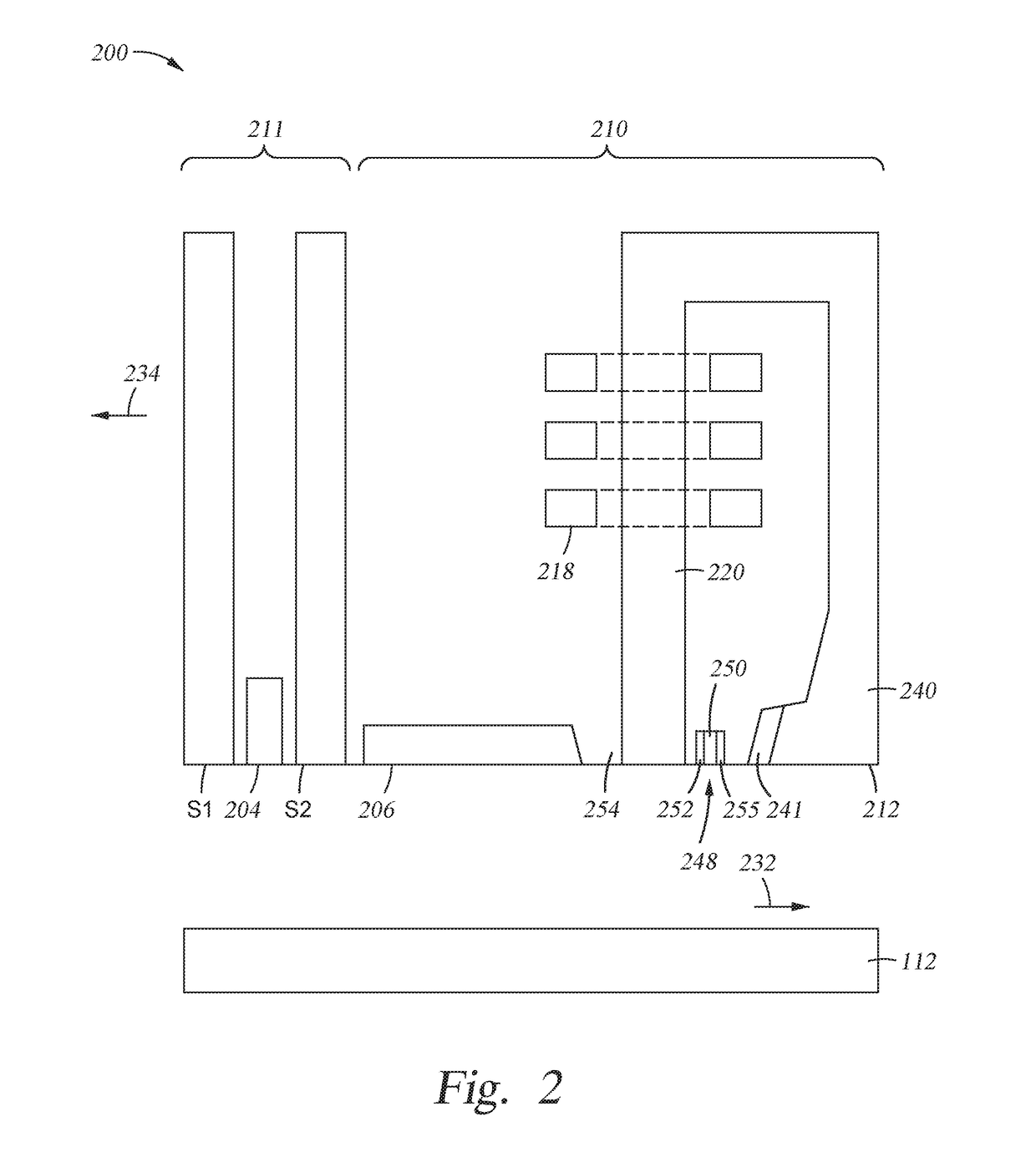
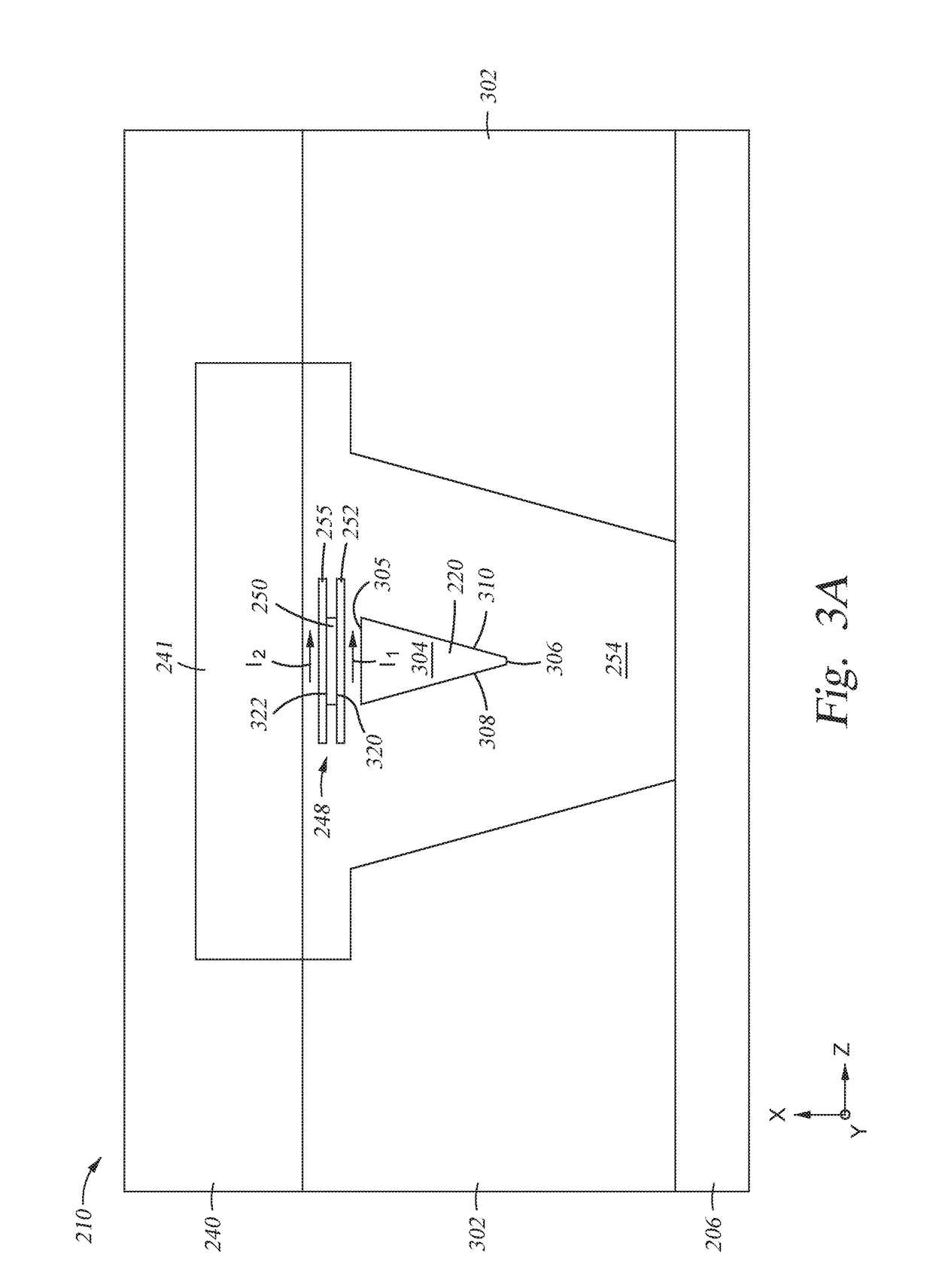
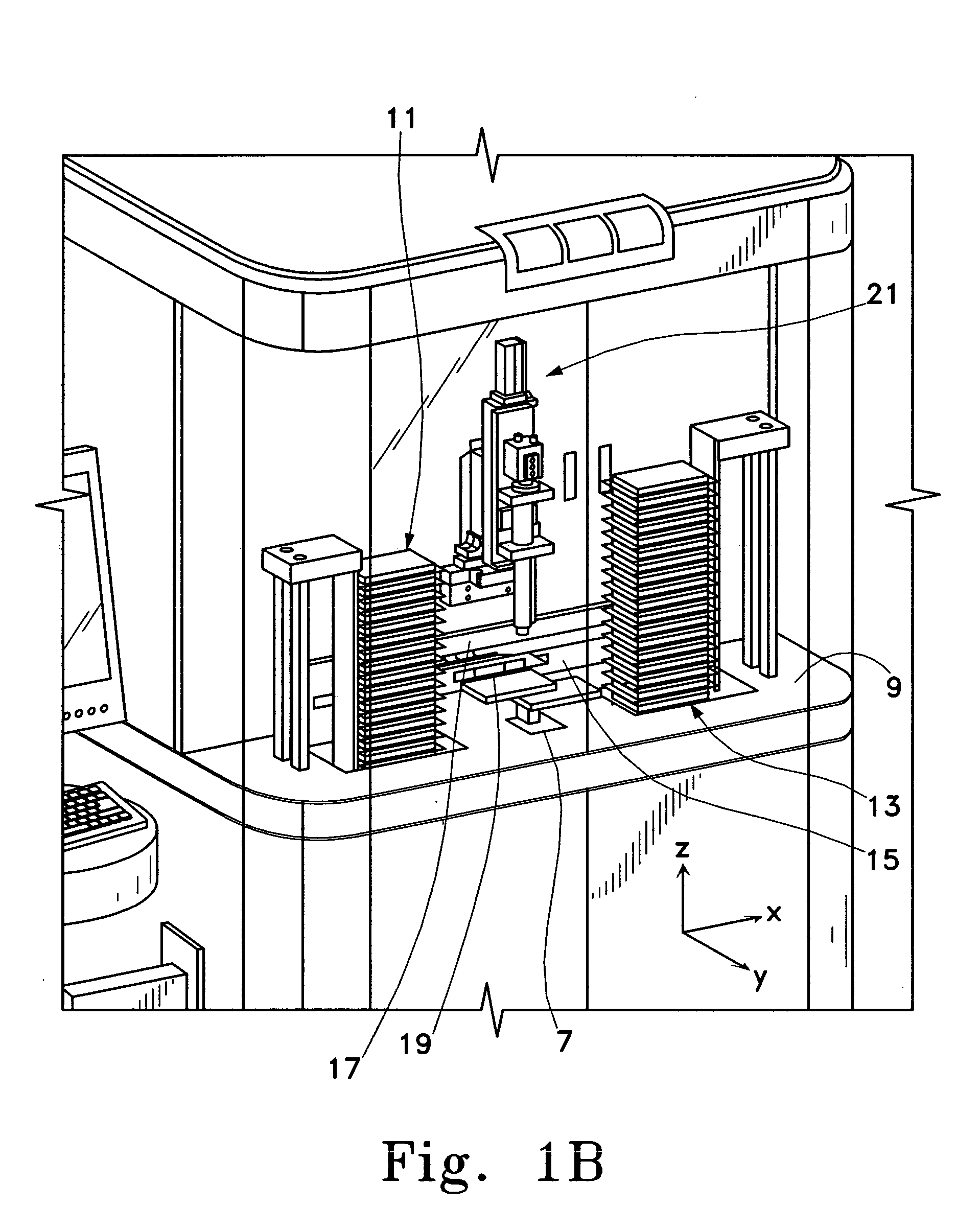
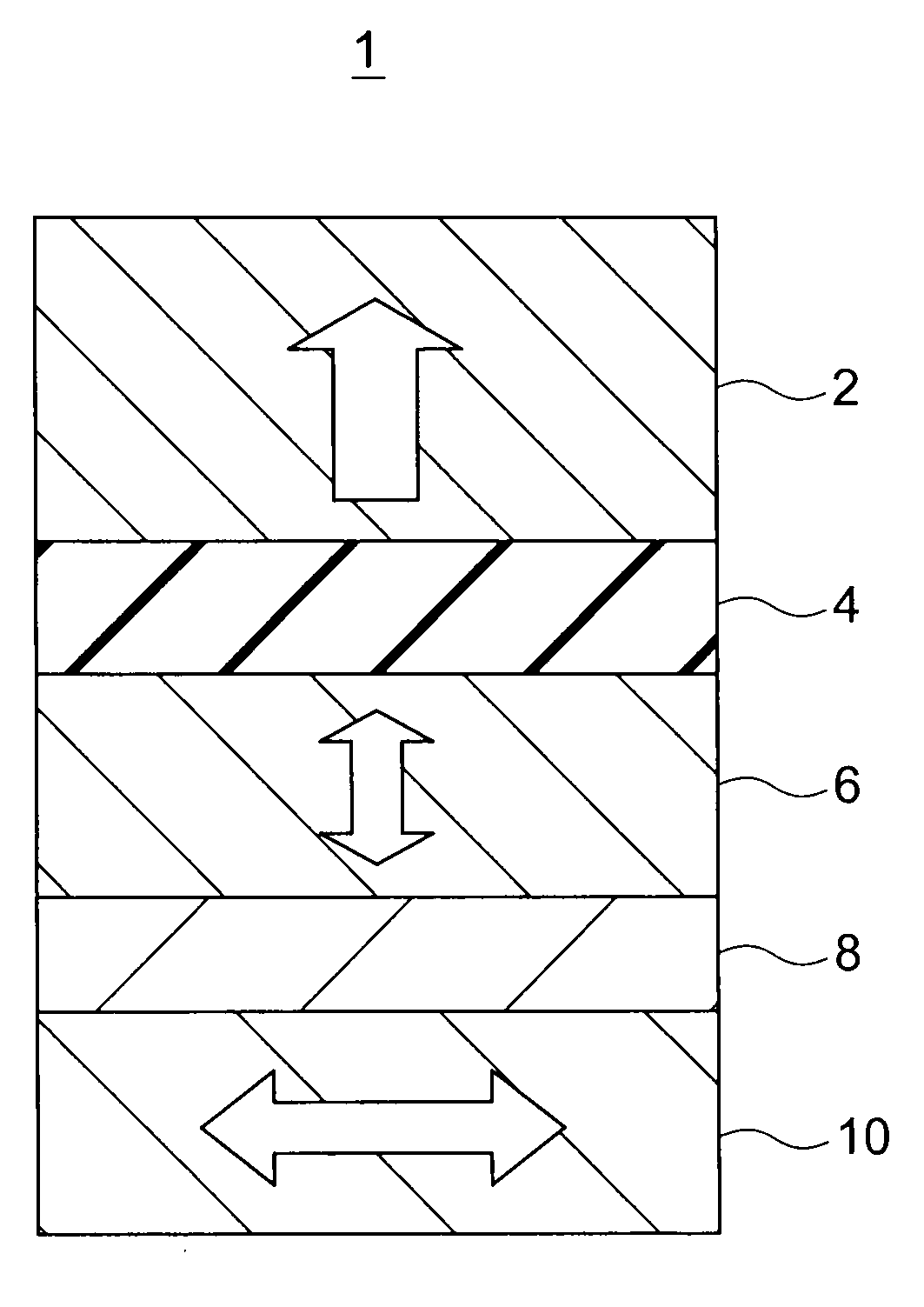
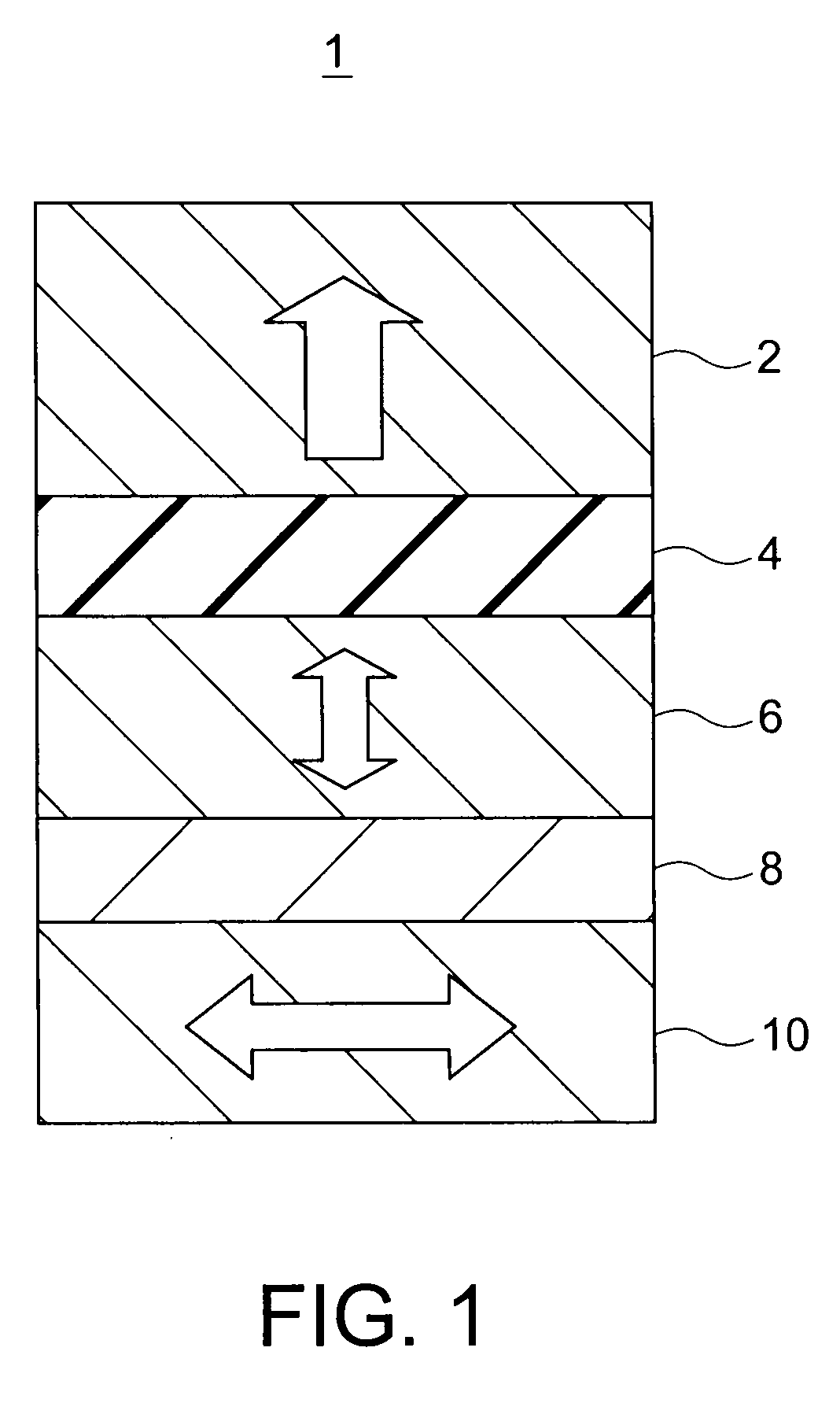
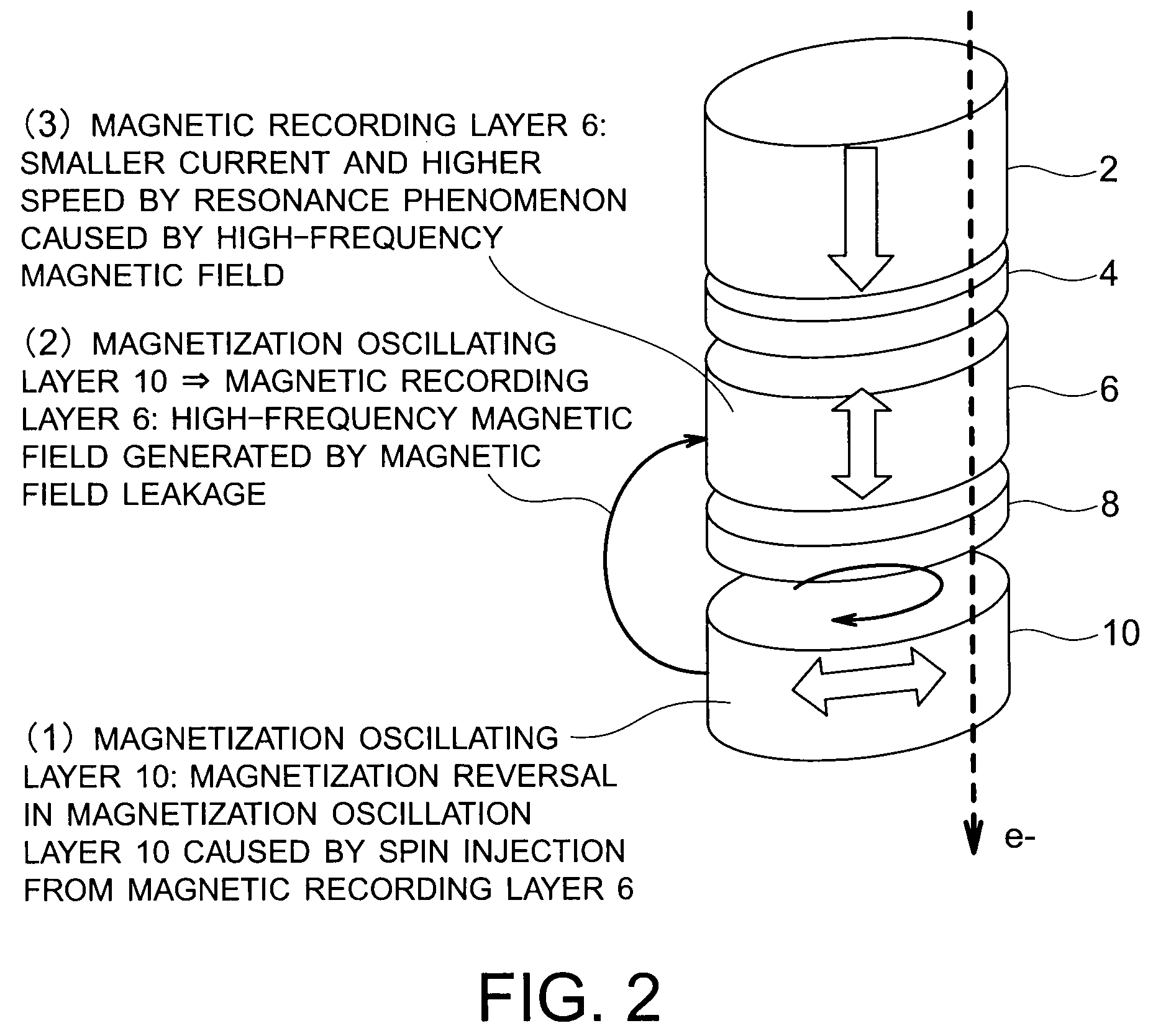
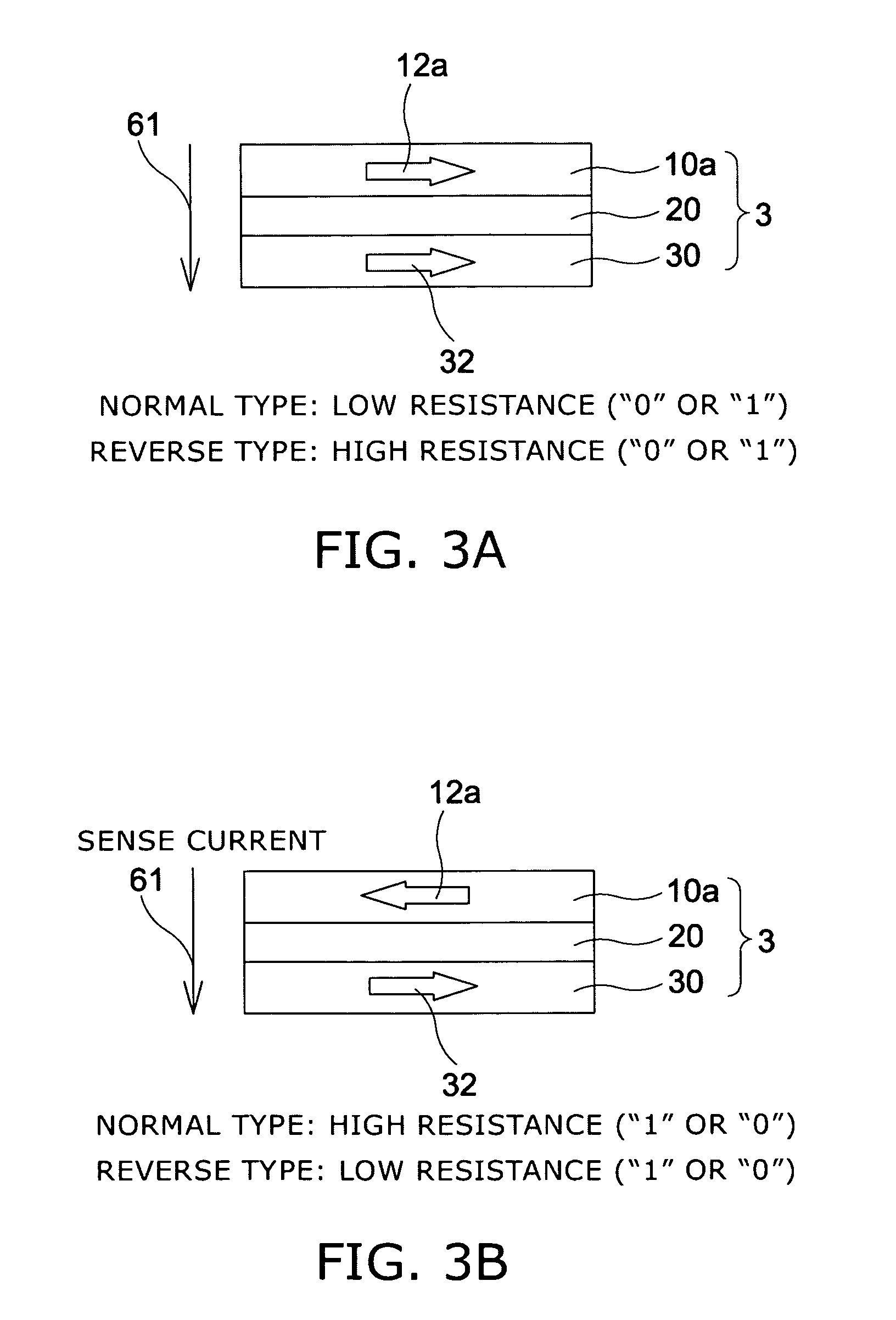
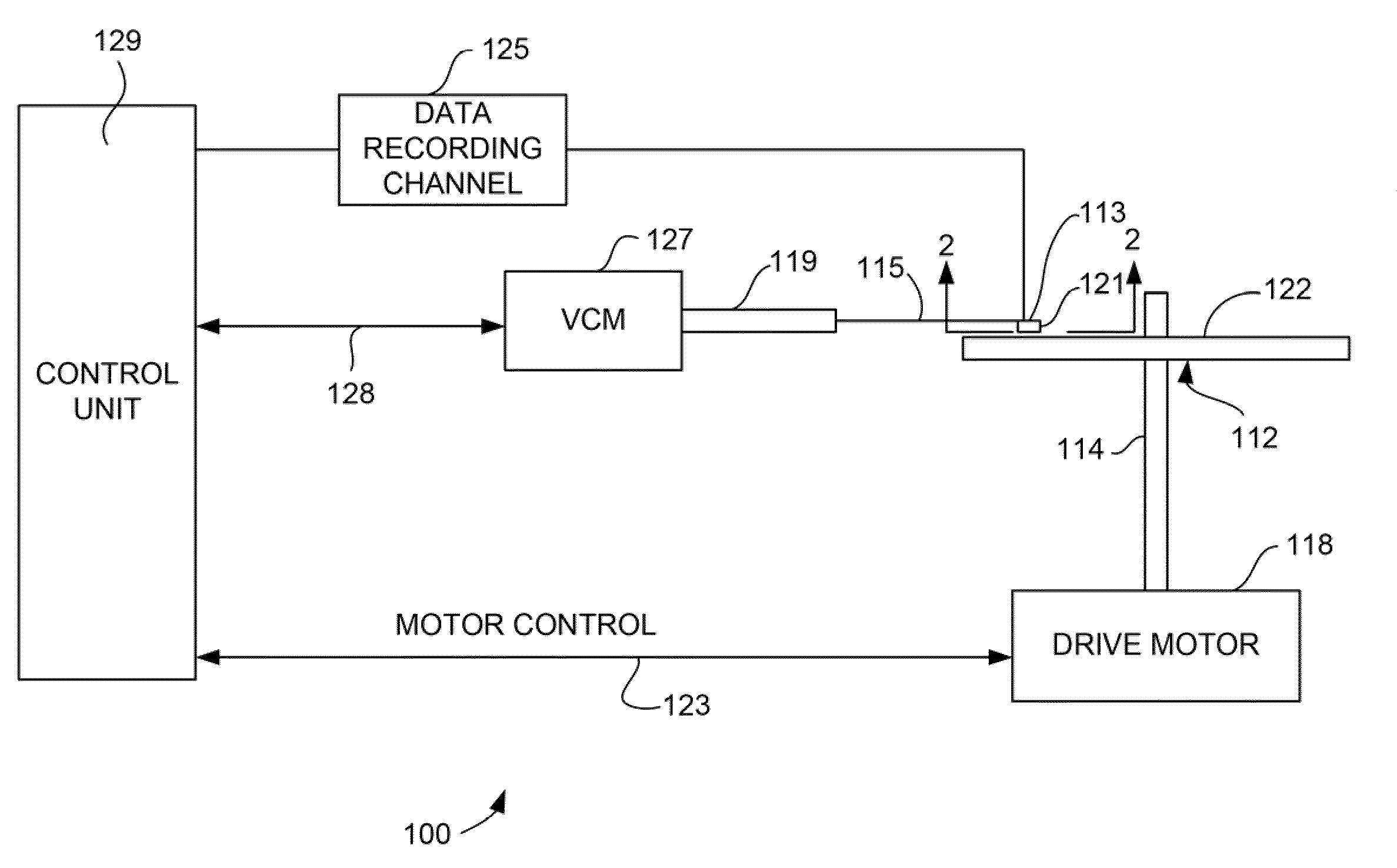
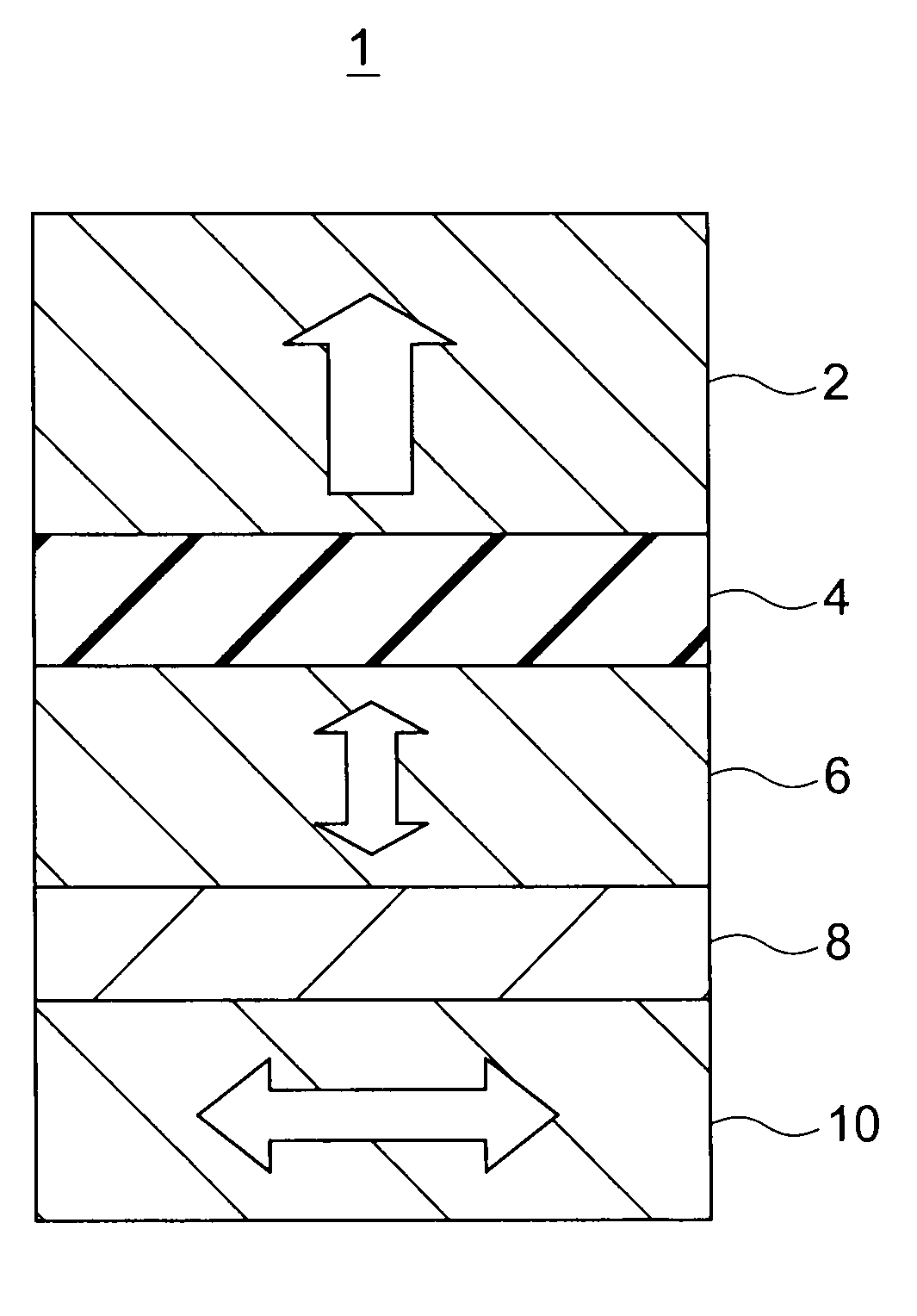
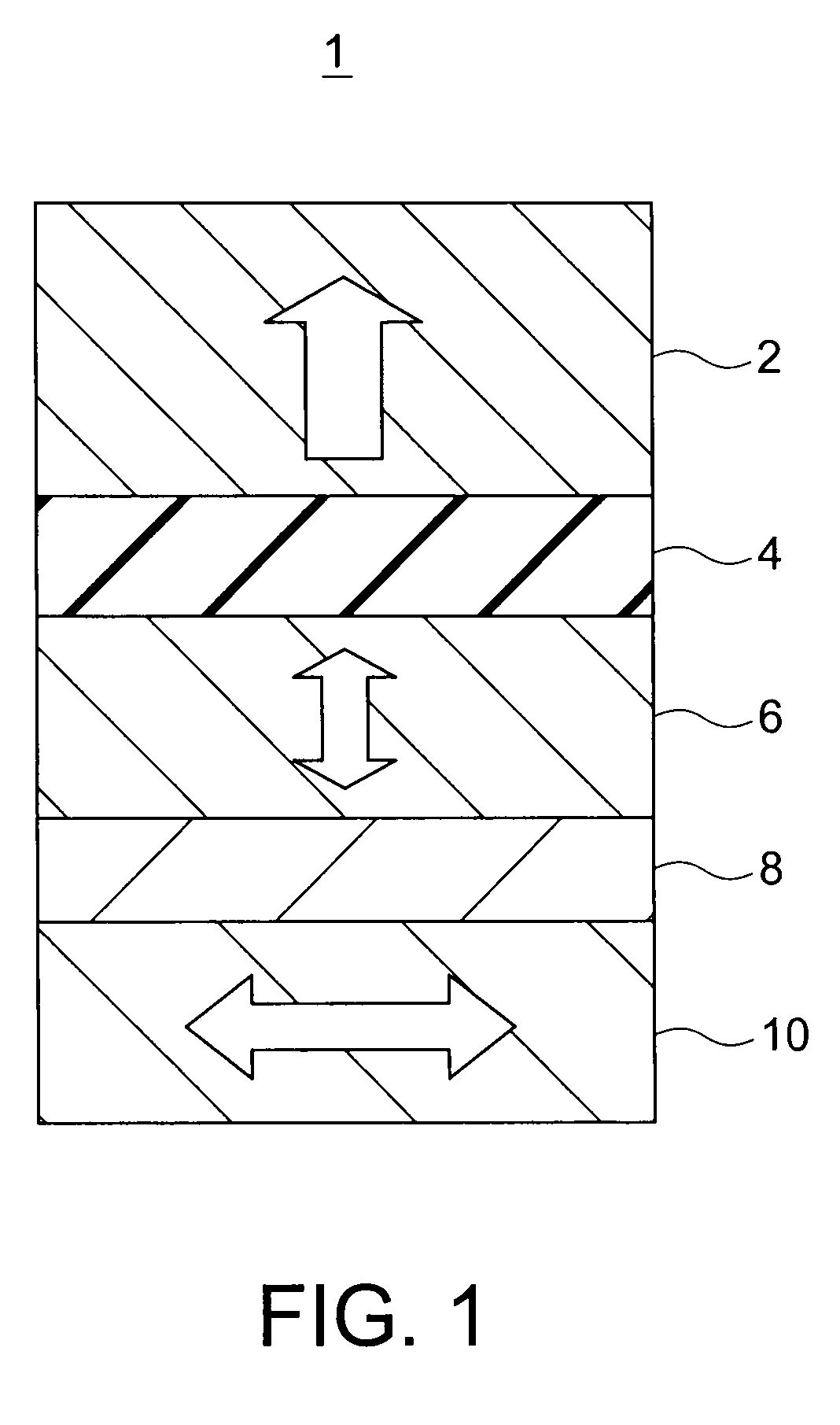
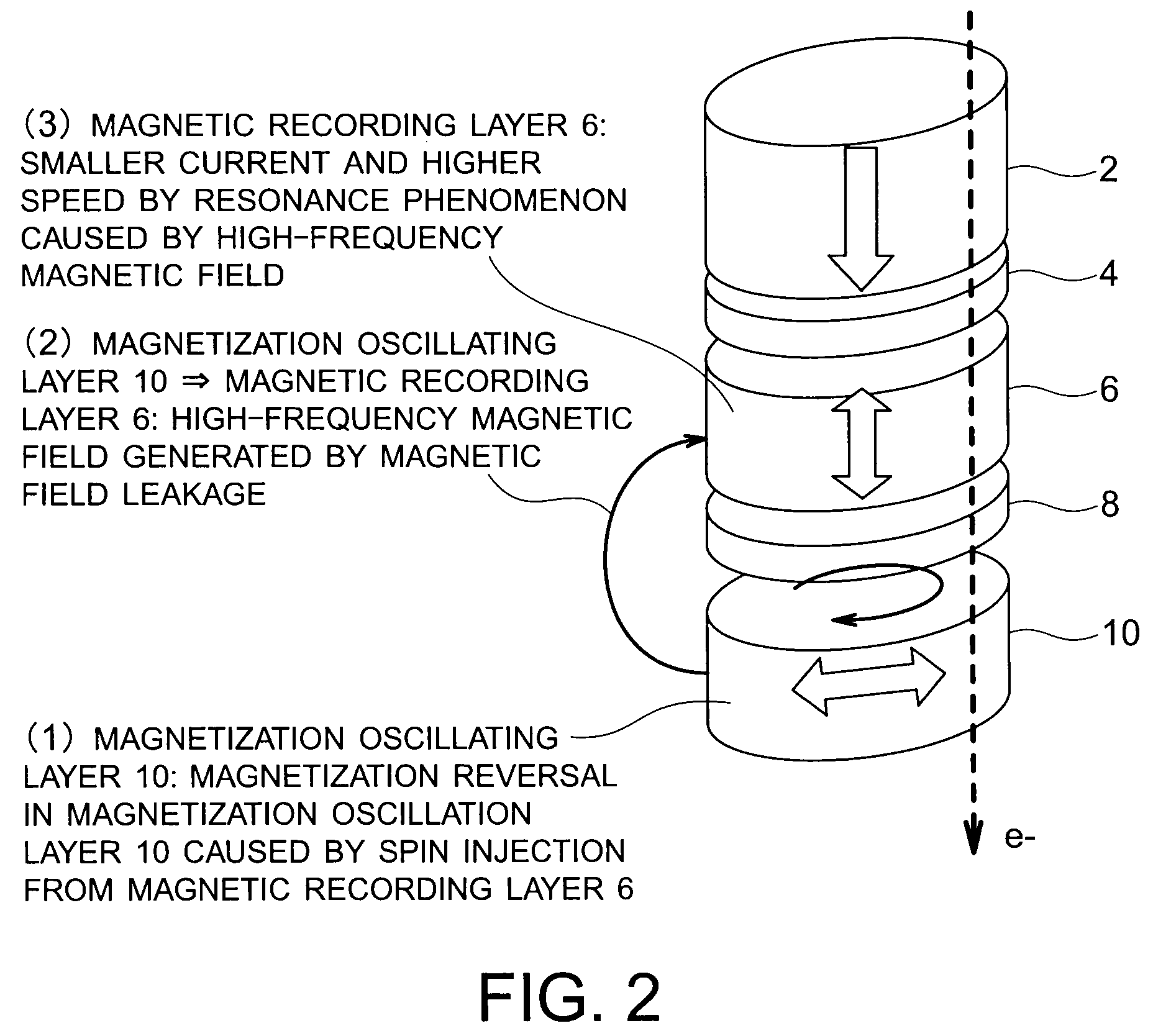
Magnetic recording device and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20090015958A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPrecessionFilm plane
A magnetic recording device includes: a laminated body including: a first ferromagnetic layer with a magnetization substantially fixed in a first direction; a second ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction; a first nonmagnetic layer disposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; and a third ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction. The magnetization direction of the second ferromagnetic layer is determinable in response to the orientation of a current, by allowing electrons spin-polarized by passing a current in a direction generally perpendicular to the film plane of the layers of the laminated body to act on the second ferromagnetic layer, and by allowing a magnetic field generated by precession of the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer to act on the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
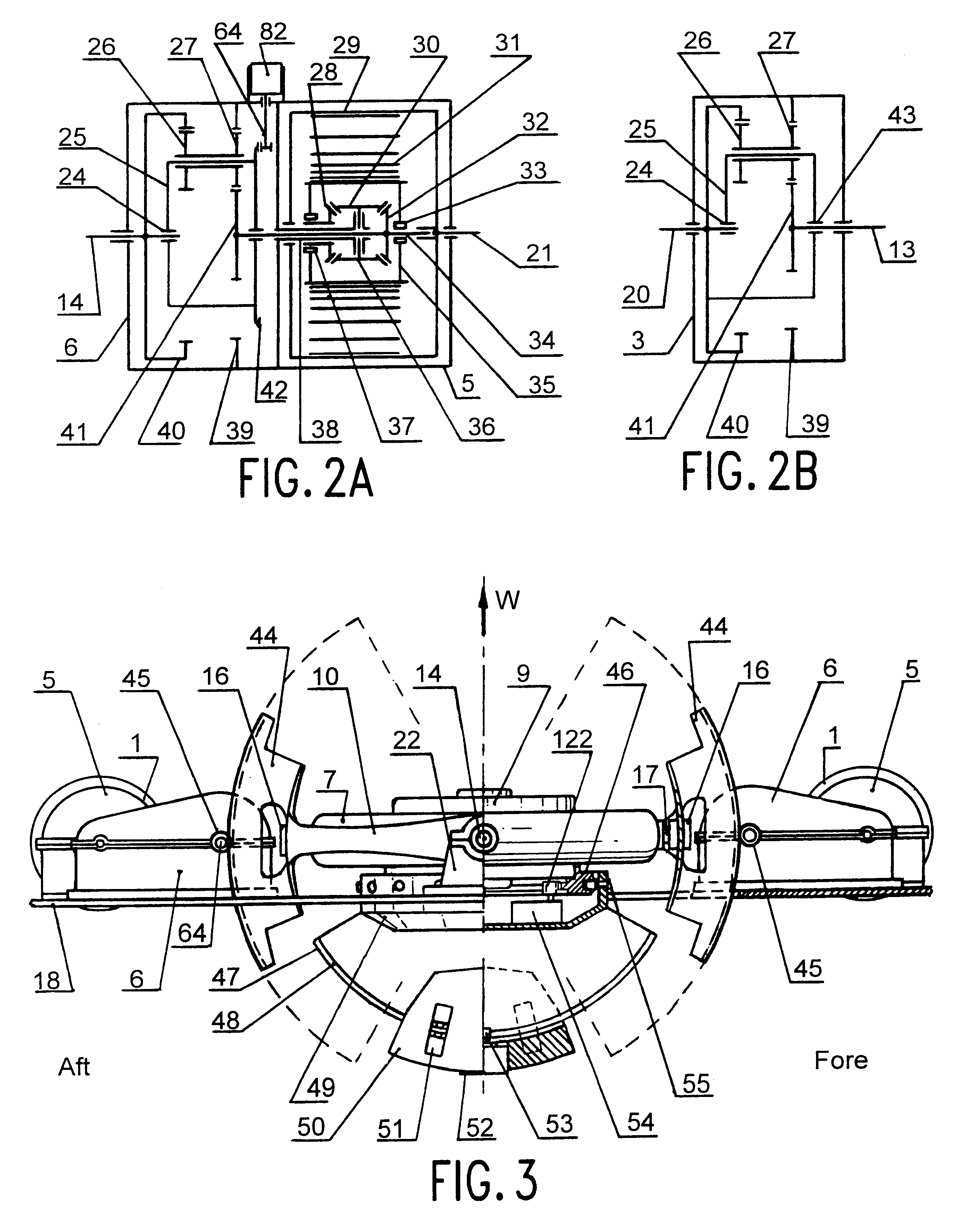
Power floating production and ship propulsion supported by gyroscope and energized by seas
InactiveUS6561856B1Enough timePropulsion based emission reductionPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeGyroscopePower station
To access the inexhaustible energy source like seas and oceans we need to learn how to convert its wave motion to the customized power for our ships, for our existing littoral settlements and our future ocean settlements. Here is an attempt to develop method of the conversion the wave energy to power with floating means based on a gyroscope strong capability to resist against the outer force moment trying to tilt it to any side.The gyroscope is used as the fulcrum torque dynamic supporting instead traditional static base used in the issued devices. Alternate force moment created by the waves and transmitted to the gyroscope (via the floating body and the wave energy converter) inducts alternative gyro precession so as the gyroscope axis hesitates about mean position. This is important because it allows the gyroscope to keep dynamic fulcrum torque in unlimited time.The few gyroscope precession control devices and methods have been developed to compensate other reasons enforcing the mean gyro axis to drift from initial plumb.Also here are developed the new ship architecture with the separated floating gyro section. The wagging propulsor driven by the pitching and with strokes amplified by the fulcrum gyro section, the spring moment generator for the gyroscope drift compensation, non gyroscope floating power station able to derive, convert, accumulate and transmit wave energy to consumer also have been developed here.
Owner:GORSHKOV VLADISLAV VASILYEVICH
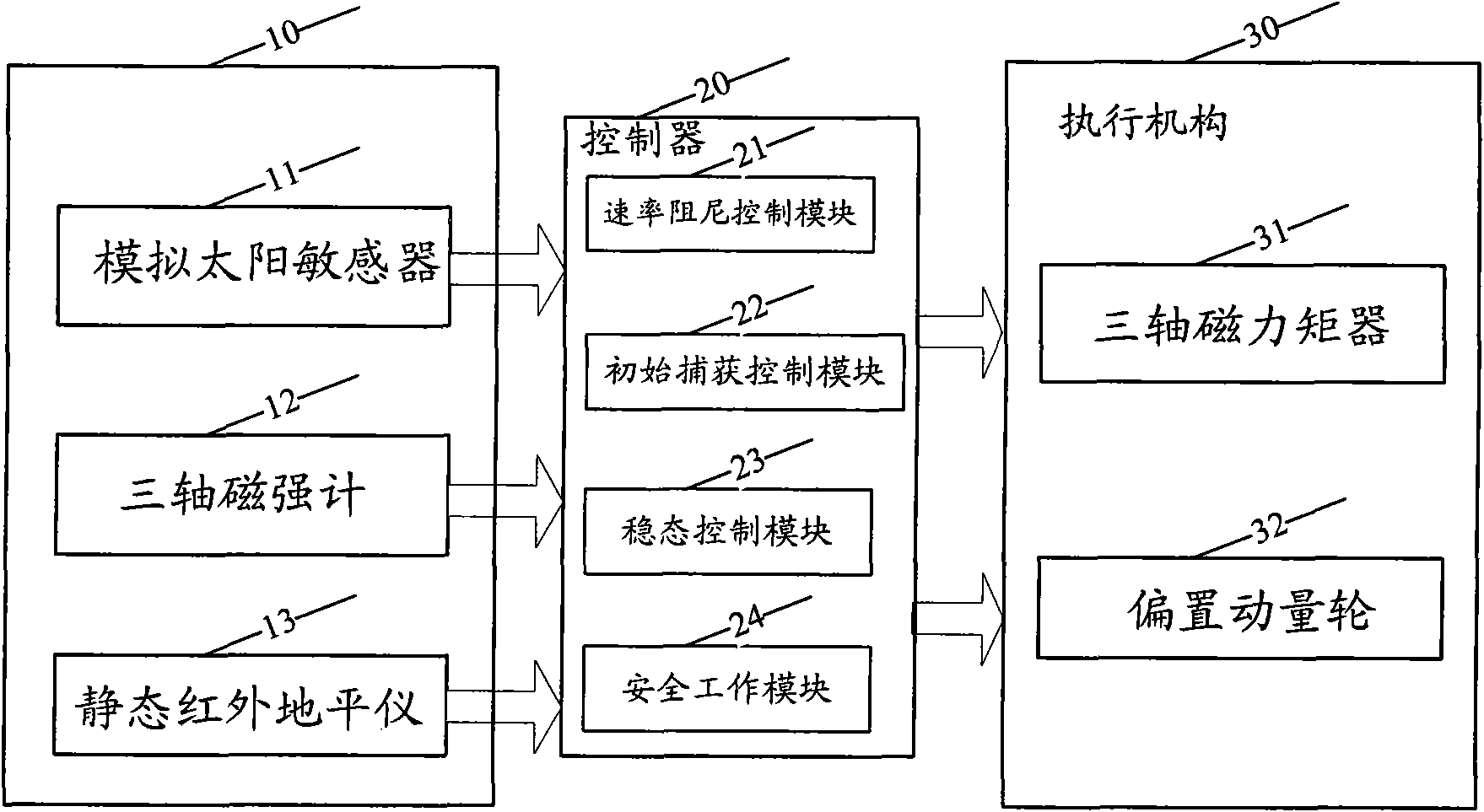
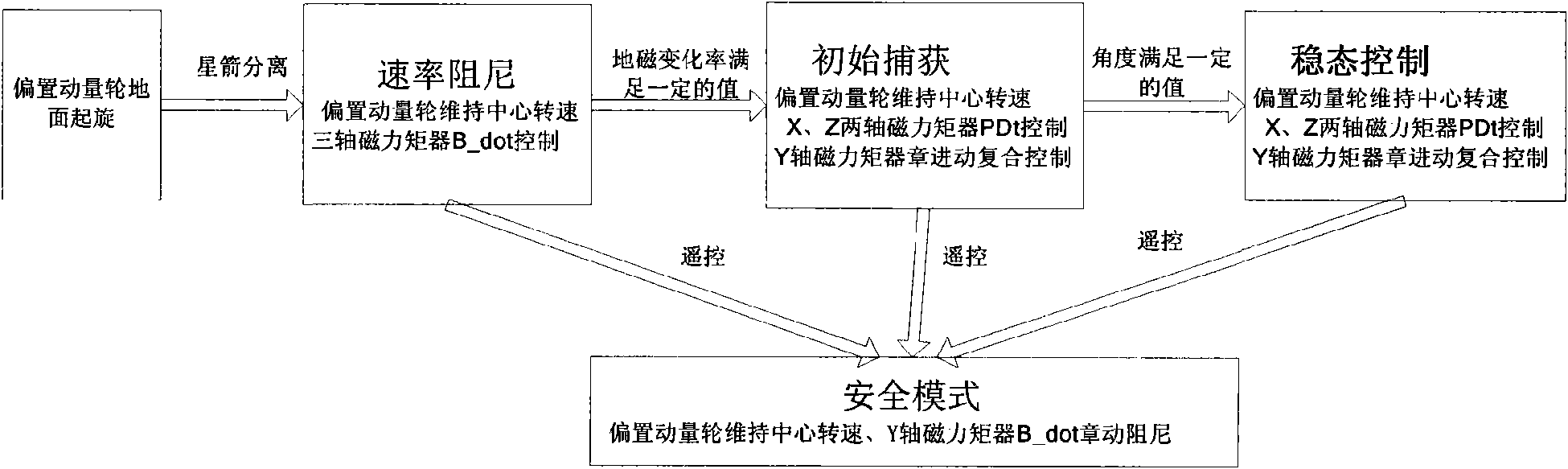
Attitude control system for space vehicle and method thereof
InactiveCN101554926AStable separationStable Initial Rate DampingSpacecraft guiding apparatusMagnetic tension forceNutation
The invention discloses an attitude control system for space vehicle and a method thereof. The control system has only one biased momentum wheel, one set of tri-axial magnetic torquer and one attitude controller loaded with algorithm. The method comprises a step of rate damping controlling, a step of initially capturing controlling and a step of stationarity controlling. At the rate damping stage, geomagnetism change is used to control the magnetic control of three passages of a satellite by B-dot; at the initially capturing stage, the magnetic control is realized, PD control is performed by pitching and the passages are rolled and yawed to carry out nutation and precession composite control; at the stationarity controlling stage, the magnetic control is realized, PD control is performed by pitching and the passages are rolled and yawed to carry out nutation and precession composite control. The capturing stage and the stationarity controlling stage fully depend on magnetic torquer to perform positive magnetic control, thereby changing which a satellite only uses a magnetic torquer to carry out unload of the momentum wheel or auxiliary magnetic control, so as to refine system configuration to further improve reliability of the system. Momentum of a satellite is biased to rotate on the ground, so as to ensure stable separation of the satellite without performing air injection control. Therefore, the magnetic torquer can be used for realizing fast and stable initial rate damping.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
Dual spin-orbit torque oscillator in magnetic recording
ActiveUS10210888B1Reduce critical currentQuality improvementMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsHeads using thin filmsIn planeMagnetic media
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a trailing shield, and an oscillator located between the main pole and the trailing shield. The oscillator is disposed at a media facing surface (MFS). The oscillator includes a spin-torque layer sandwiched between two distinct spin Hall layers. The two distinct spin Hall layers generate spin-orbit torque (SOT) that induces in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer, and both in-plane precessions are in the same direction. The same-direction in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer reduce the critical current of the oscillation of the oscillator, leading to high quality recording.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
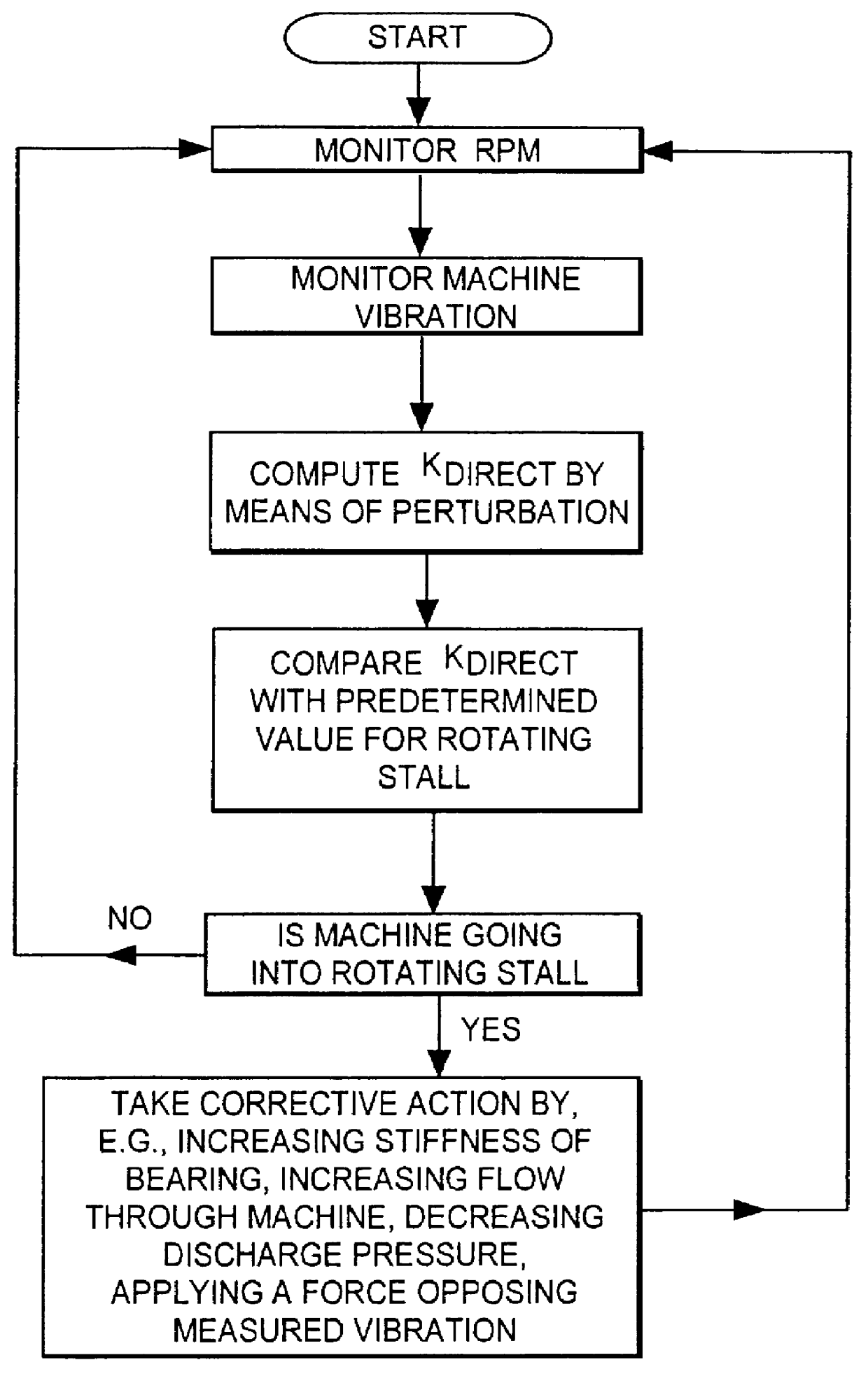
Method and apparatus for diagnosing and controlling rotating stall and surge in rotating machinery
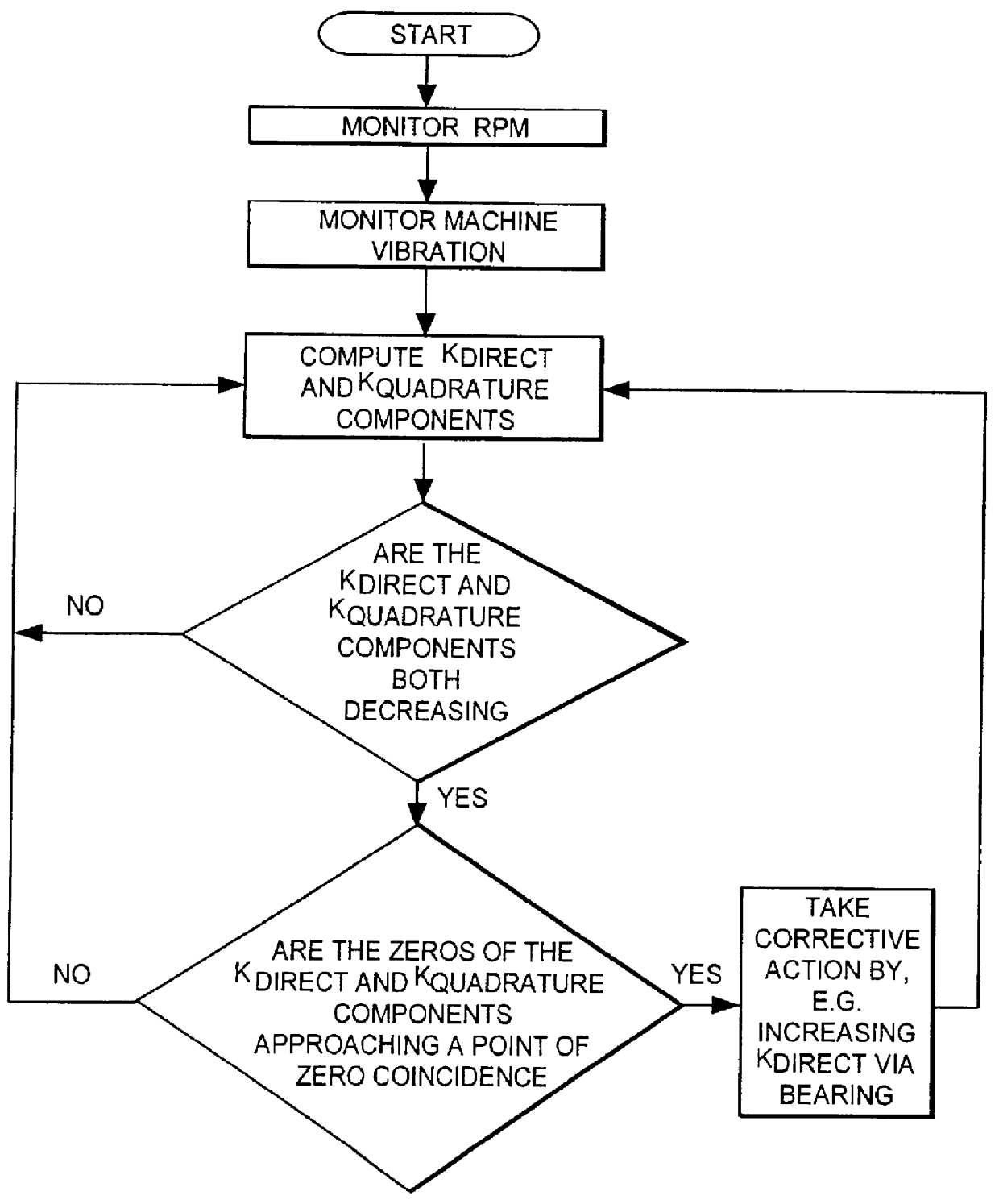
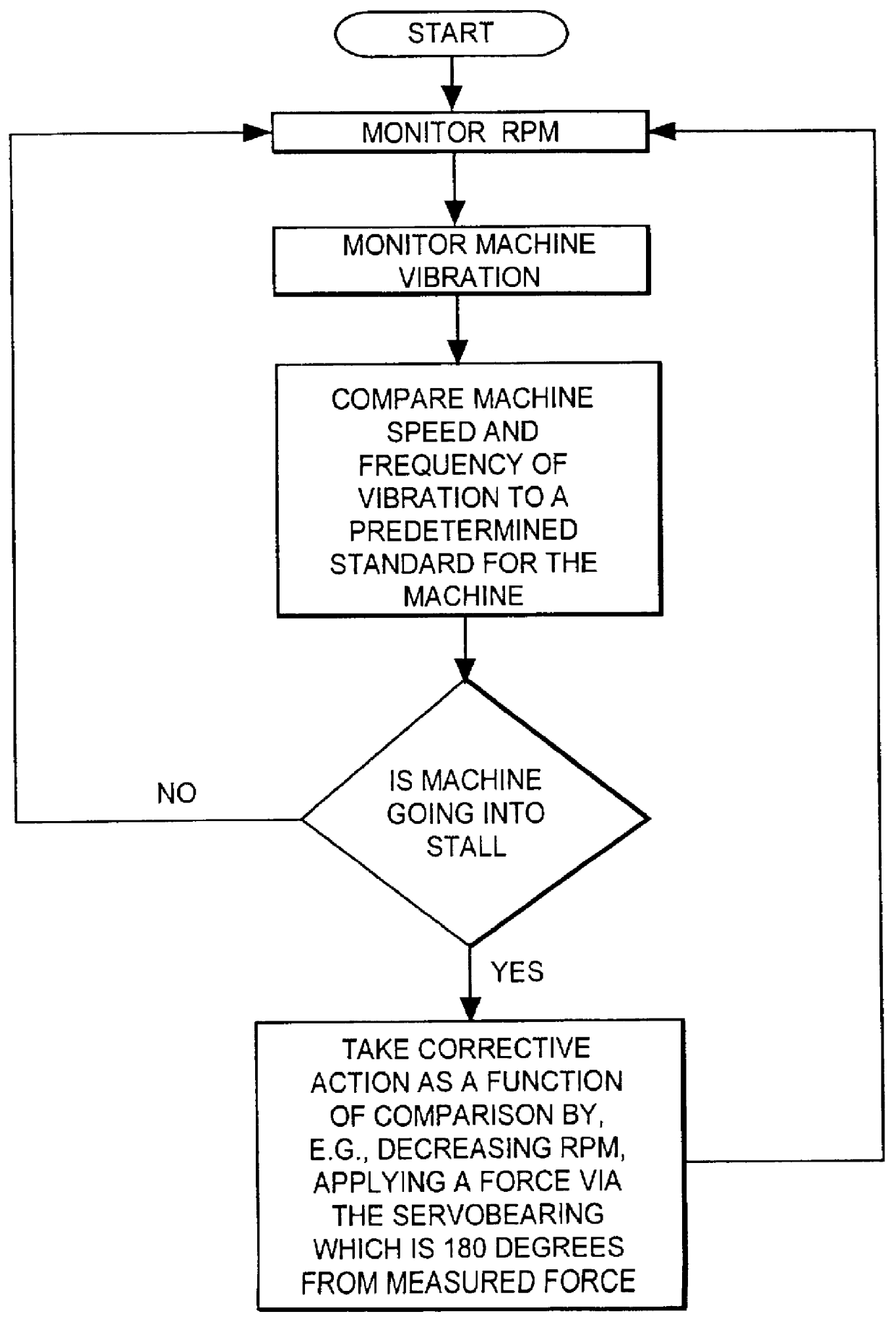
InactiveUS6092029AProtection from damageMachine bearings testingFlow propertiesDynamic stiffnessPrecession
A method and apparatus is provided for diagnosing and correcting rotating stall and surge in rotating machines by monitoring dynamic shaft precession and comparing this precession with a standard and altering the precession as the machine approaches a destabilizing condition when indicated by the comparison step. Axial vibration monitoring means is also provided for monitoring and comparing a dynamic axial vibration of the machine with a standard and altering the axial vibration as the machine approaches a destabilizing condition. Furthermore, the instant invention measures the complex dynamic stiffness of the machine and computes the direct dynamic stiffness and the quadrature dynamic stiffness for use as a destabilizing warning device by monitoring for a drop in direct dynamic stiffness and / or a coincidence of zero crossing of both the direct dynamic stiffness and the quadrature dynamic stiffness components. One embodiment for altering the rotating stall and / or surge is by a controlled active servobearing.
Owner:BENTLY NEVADA CORP
Source and target management system for high throughput transfer of liquids
InactiveUS20040120855A1Spray nozzlesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPrecession
An apparatus for high-throughput screening and generation of chemical libraries. The apparatus comprises computer controlled mechanical displacement devices and storage queues capable of managing a large number of source well plates and target well plates. In one aspect of the invention, precession alignment mechanisms are provided for efficient transfer of liquid from source well plates to target well plates. The apparatus may be configured such that any source fluid in any of the source well plates may be transferred to any target location within any of the target well plates in any sequence defined by the user. The computer controller may track the location of all the source well plates and target well plates and allow user defined association of any source well with any target well in any order defined by the user, thus providing an effective platform for chemical and biochemical synthesis and screening.
Owner:LABCYTE
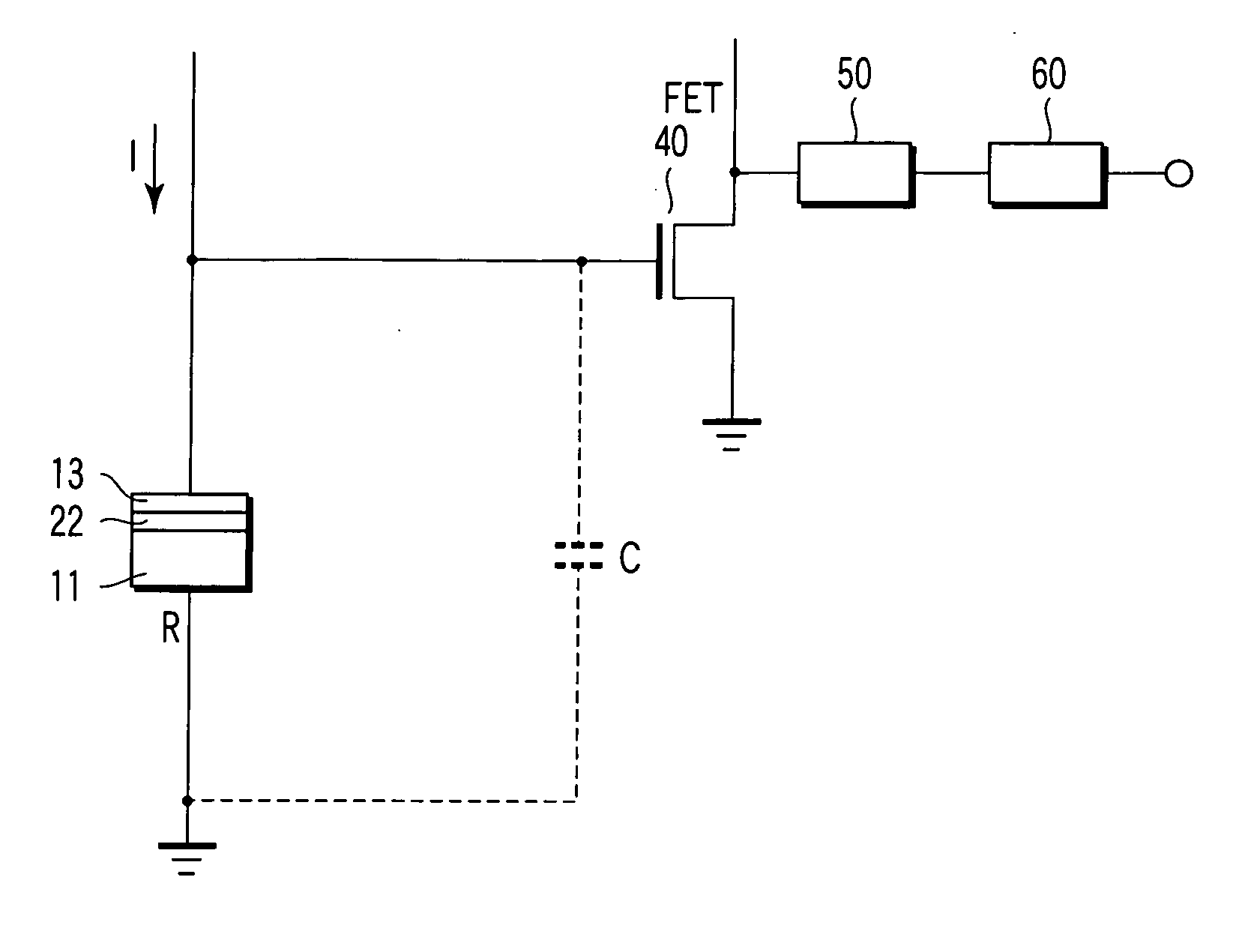
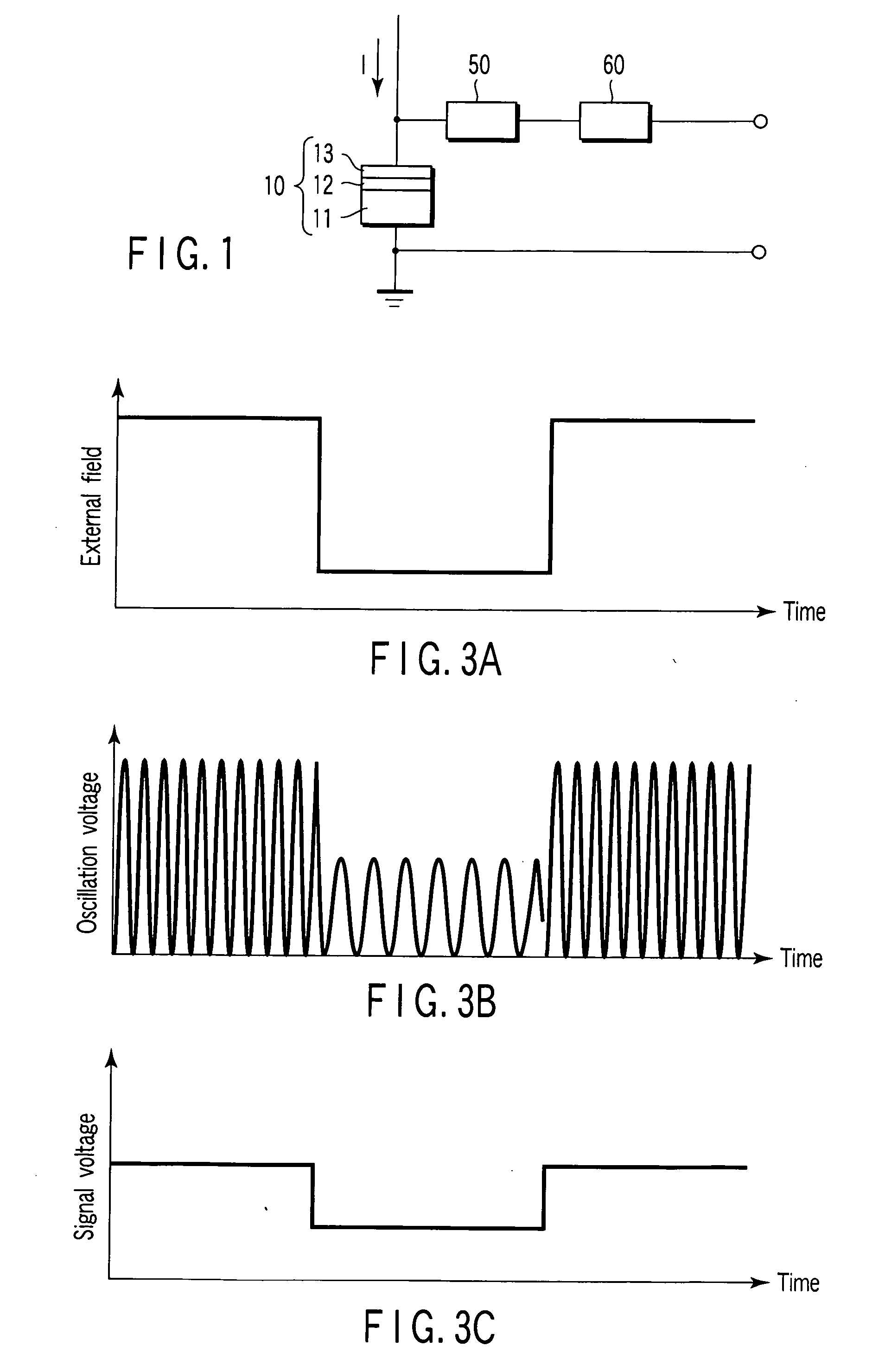
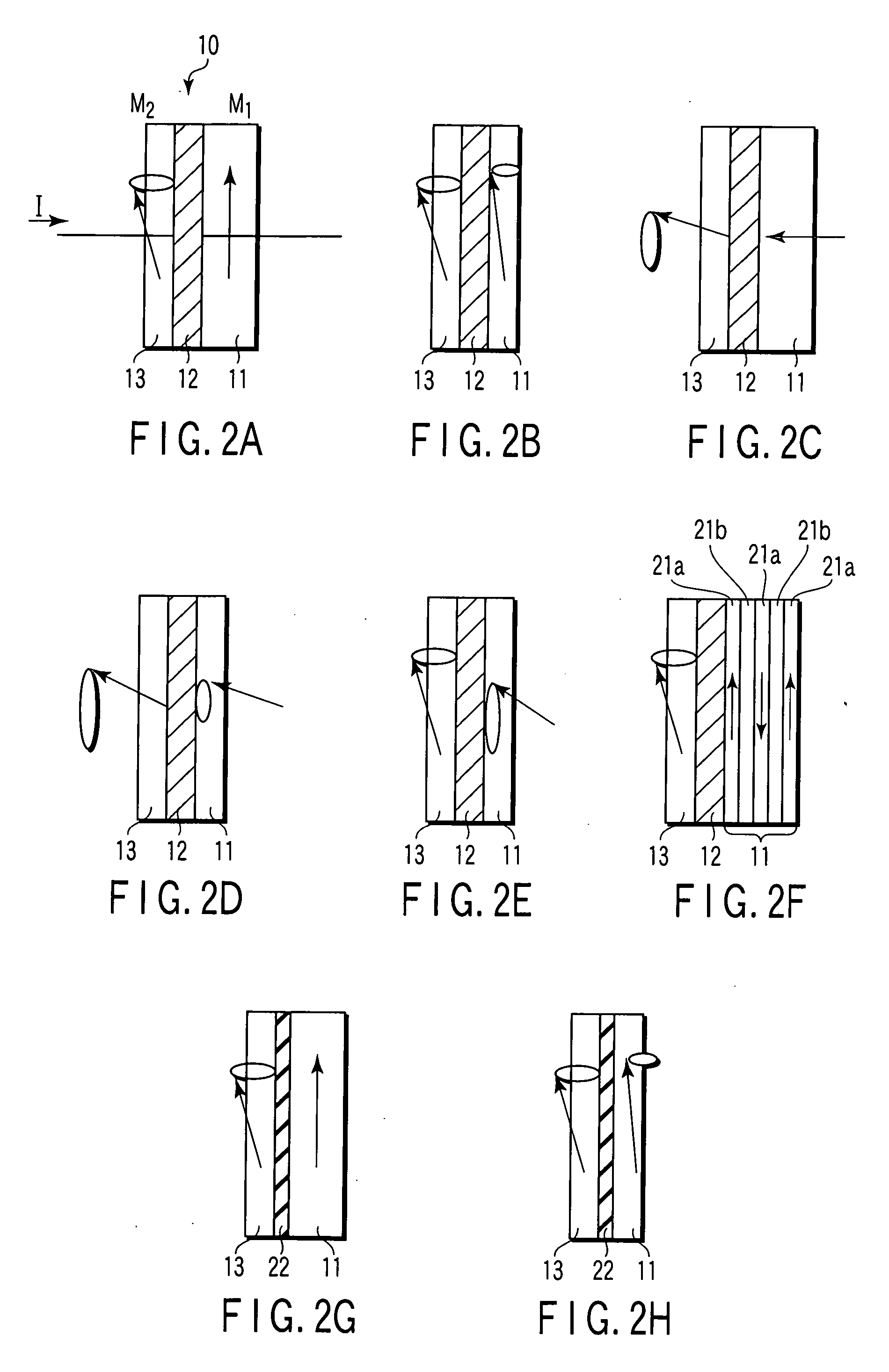
Magnetic sensor
A magnetic sensor has a magnetic oscillation element including a first magnetic resonance layer, a second magnetic resonance layer, a nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the first and second magnetic resonance layers, and a pair of electrodes which supply a current perpendicularly to planes of the first resonance layer, the nonmagnetic layer and the second magnetic resonance layer, and a monitor monitoring a change dependent on an external magnetic field in a change of a high-frequency oscillation voltage generated across the magnetic oscillation element due to precession of magnetization in at least one of the first and second magnetic resonance layers caused by supplying the current.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
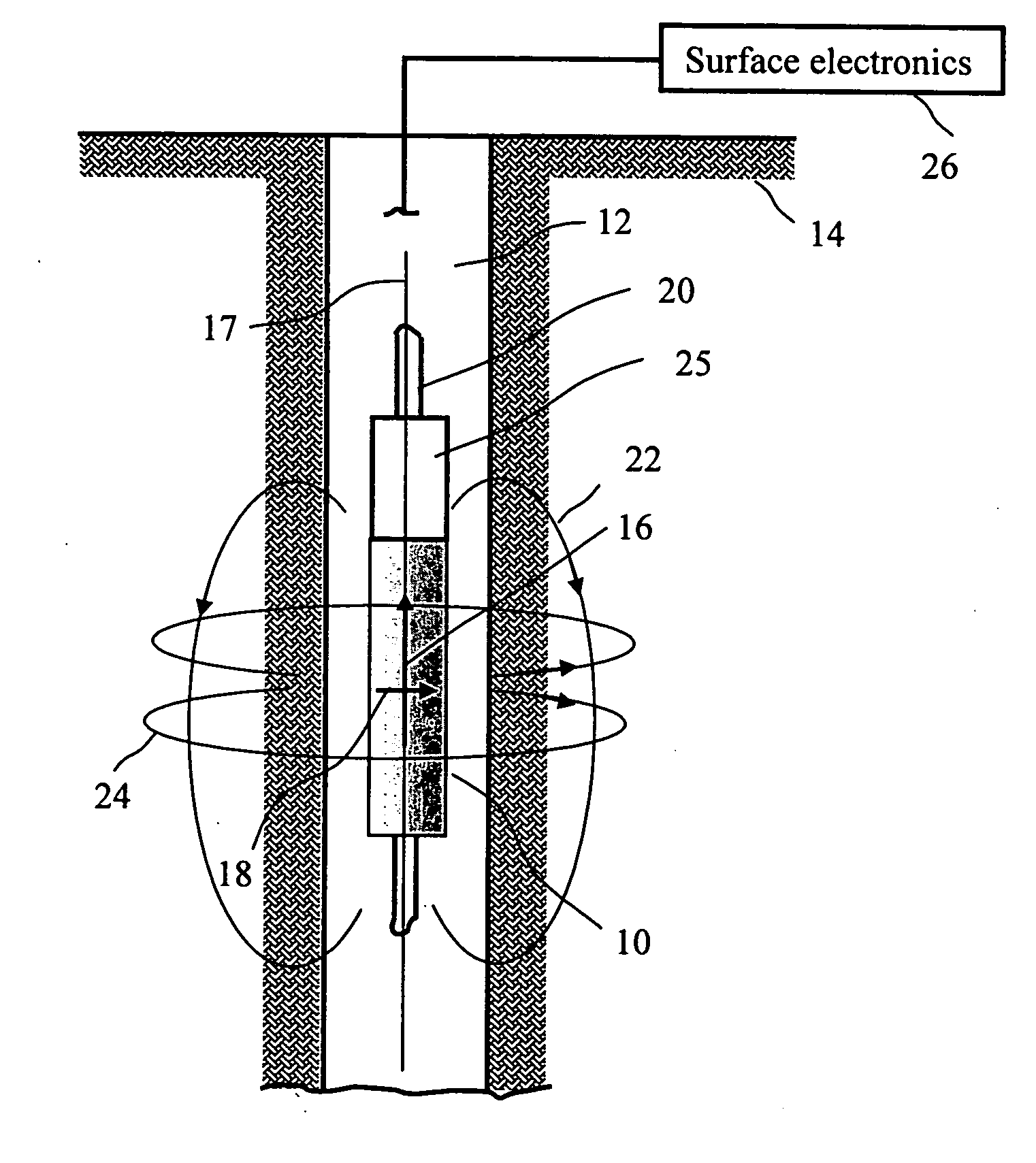
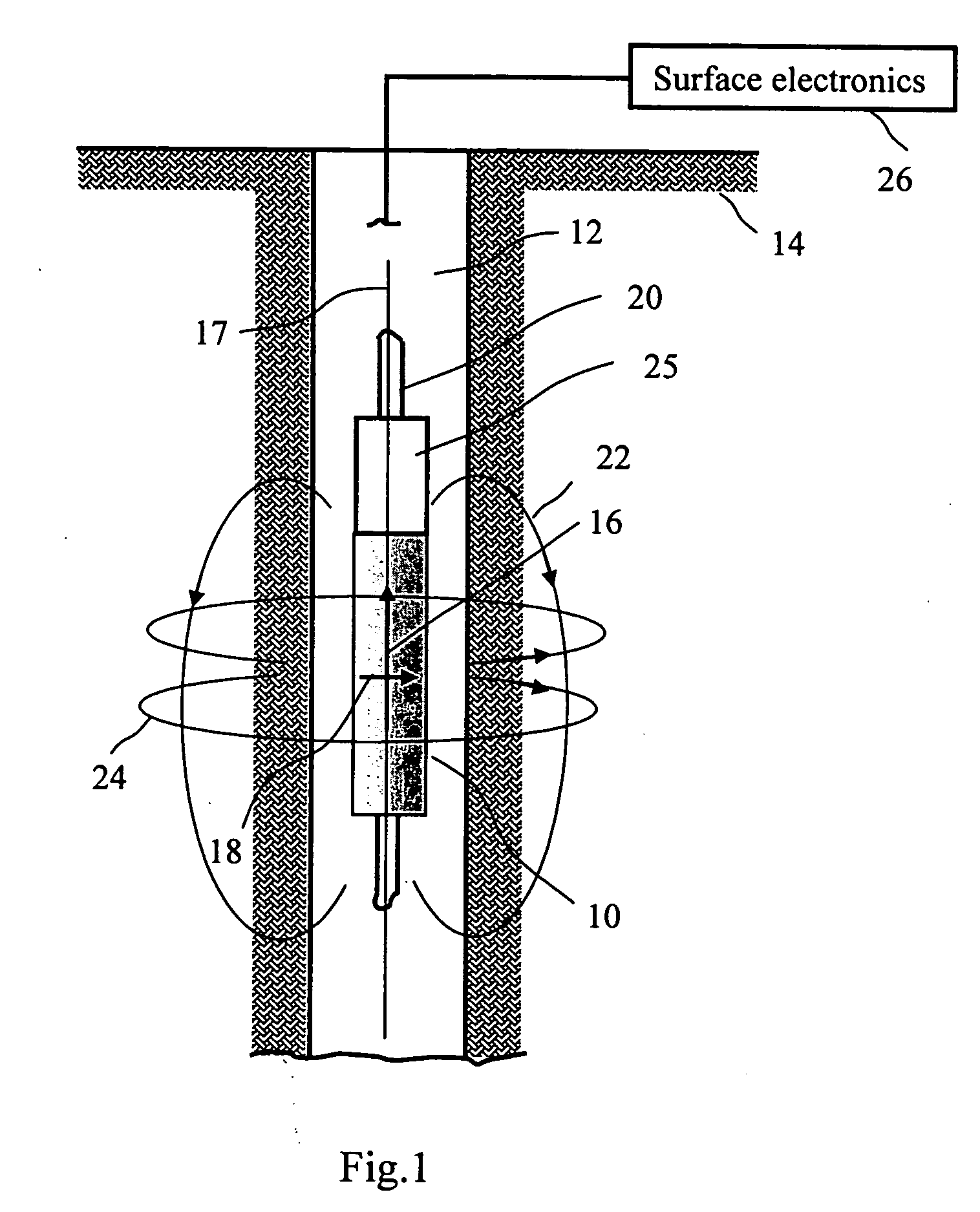
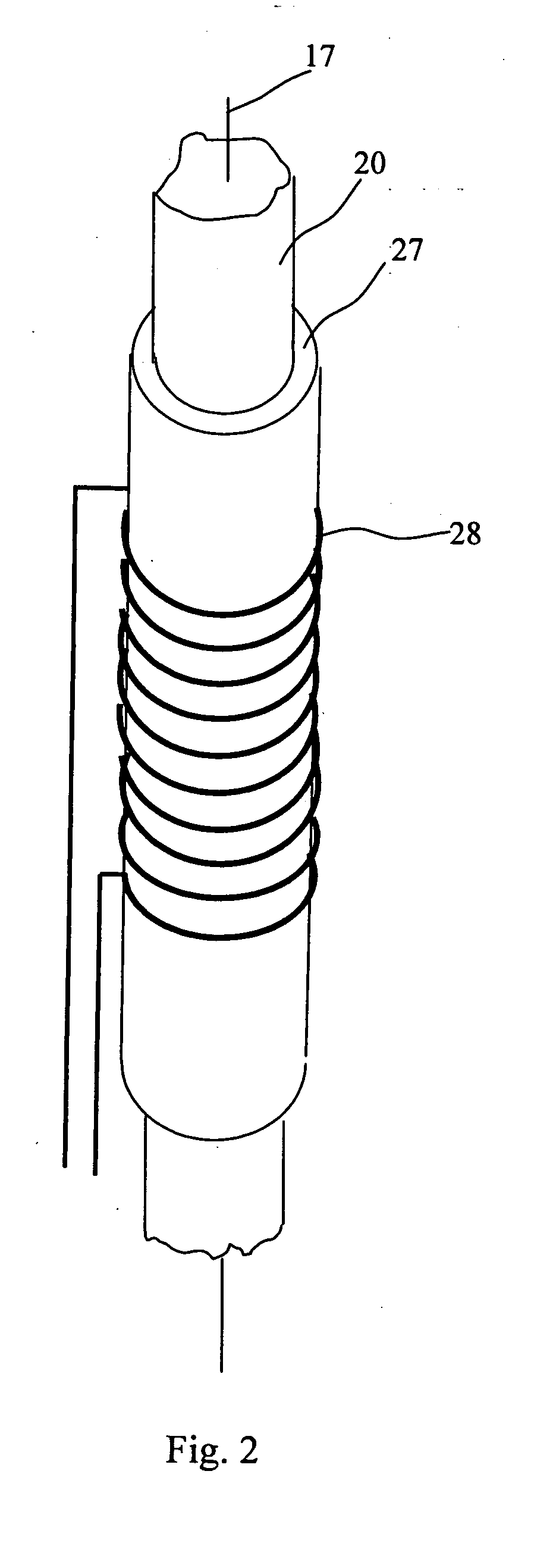
Nuclear magnetic resonance tool using switchable source of static magnetic field
ActiveUS20060255799A1Effective permeability of magneticElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceSpin magnetic moment
A nuclear magnetic resonance sensing apparatus and method for operating in an earth borehole comprises a source of switchable magnetic field to polarize nuclei in the region of interest, said source comprising a coil wound on a magnetic core having controllable residual magnetization. Maintaining the magnetization of the core during a polarization interval does not require steady current in the coil. Switching intensity and polarity of magnetization of the core causes precession of spin magnetic moments of the nuclei; the precession induces a signal indicative of nuclear magnetic resonance properties of earth formations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
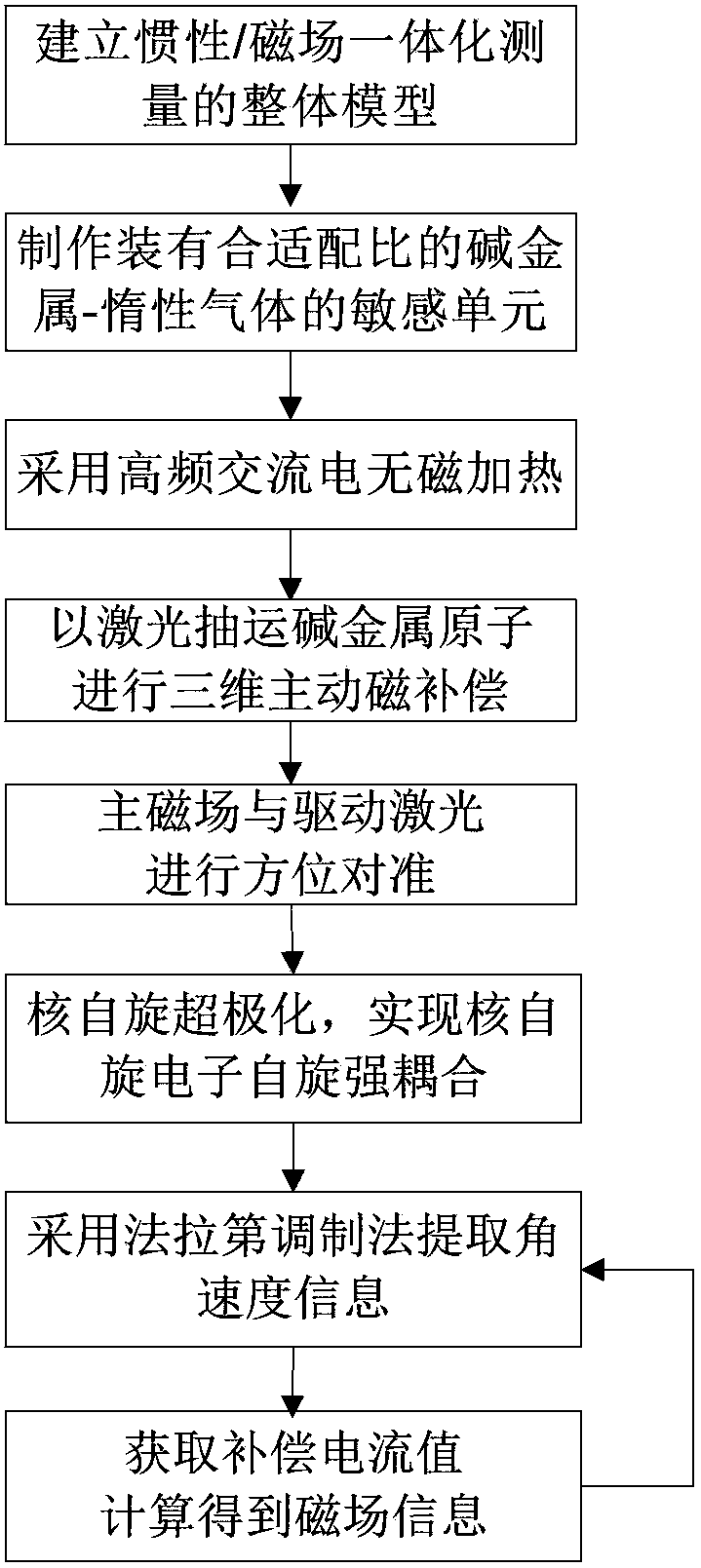
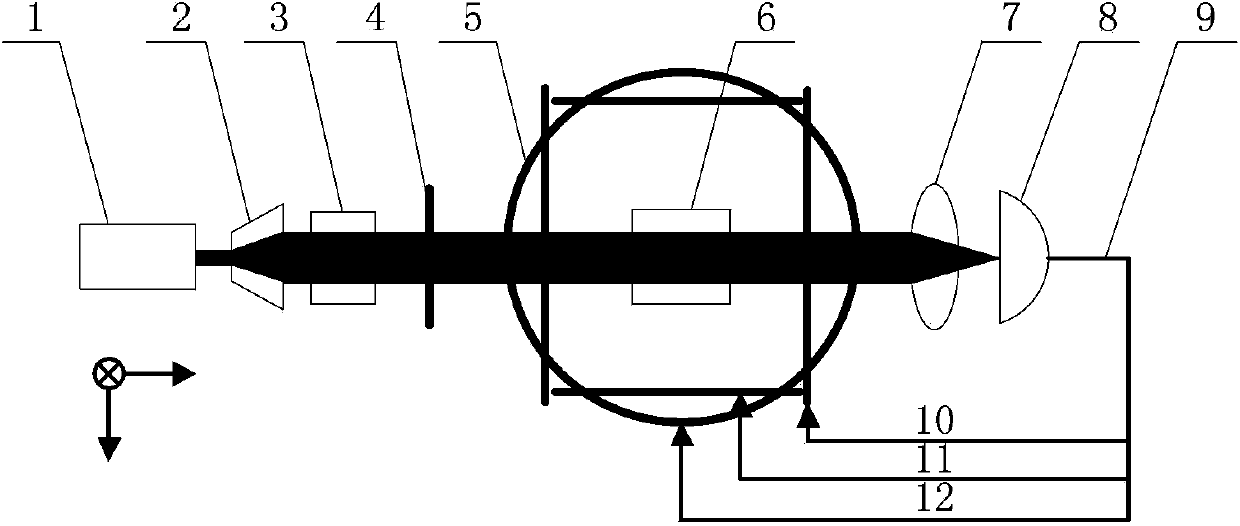
Inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on SERF (spin-exchange-relaxation-free) atomic spin effect
ActiveCN103438877AHigh measurement accuracyStrong autonomyRotary gyroscopesMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsSpin effectClosed loop
The invention provides an inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on an SERF (spin-exchange-relaxation-free) atomic spin effect. The inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on the SERF atomic spin effect comprises the following steps: firstly establishing an overall model for the inertia and magnetic field integration measurement; secondly, manufacturing a measurement sensing unit, and carrying out high-frequency alternating current non-magnetic electric heating; starting a driving laser (z-axis) for carrying out optical pumping on the sensing unit; and emitting a detection laser (x-axis) in a direction vertical to the z-axis; thirdly, carrying out driving magnetic compensation through a three-dimensional magnetic compensation coil so as to counteract a magnetic field of the outside world; fourthly, carrying out azimuth alignment on a main magnetic field and the driving laser and hyperpolarization nucleon self-spin so as to realize the nuclear spin-electron spin strong coupling; fifthly, extracting the information of the atomic spin precession movement in the detection laser by adopting a closed-loop faraday modulation detection method, and obtaining inertia angular speed information; and finally, obtaining the current value of a compensation signal of the magnetic field, and calculating to obtain the information of the current magnetic field. The inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on the SERF atomic spin effect has the characteristics of high measurement accuracy and strong autonomy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
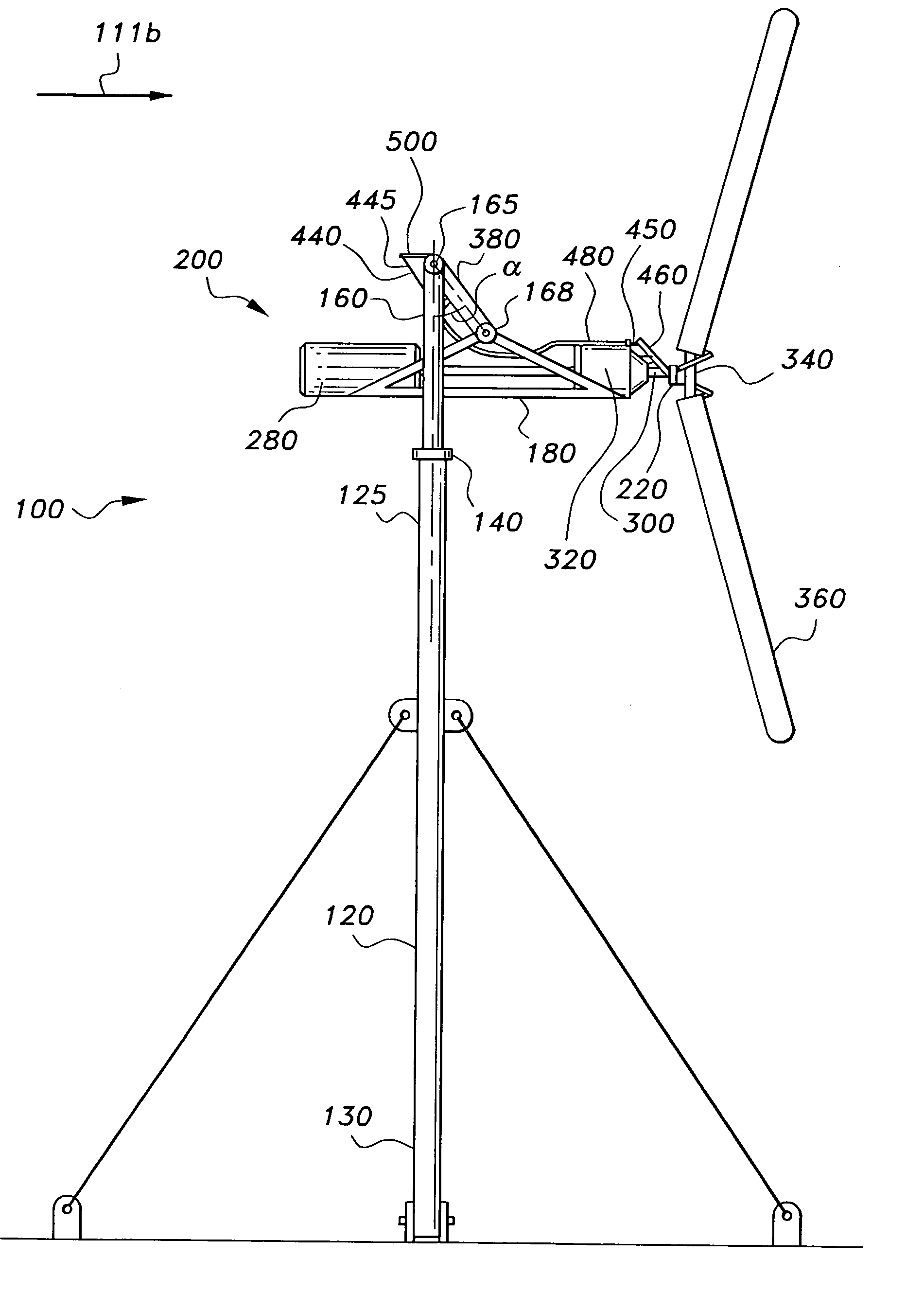
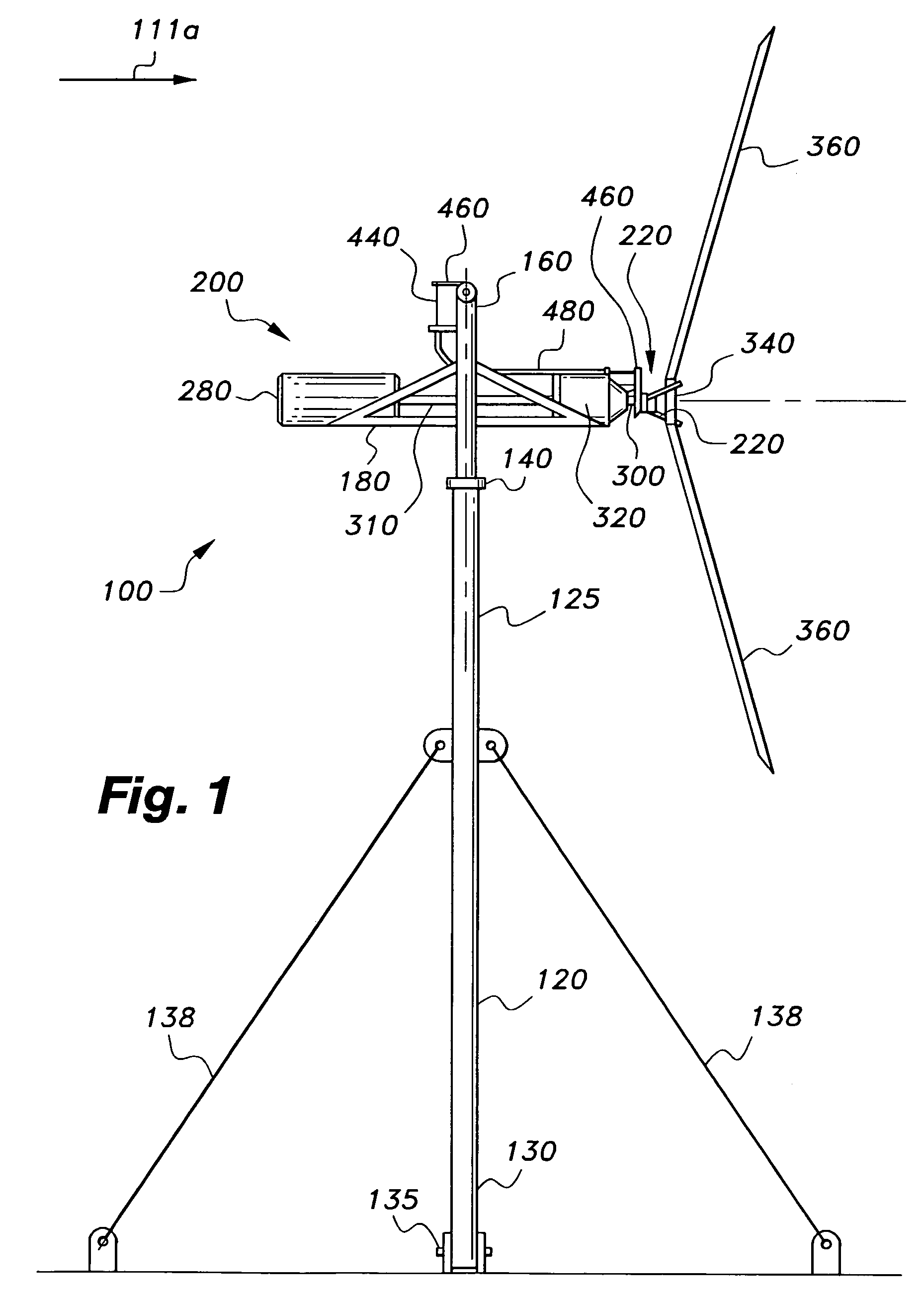
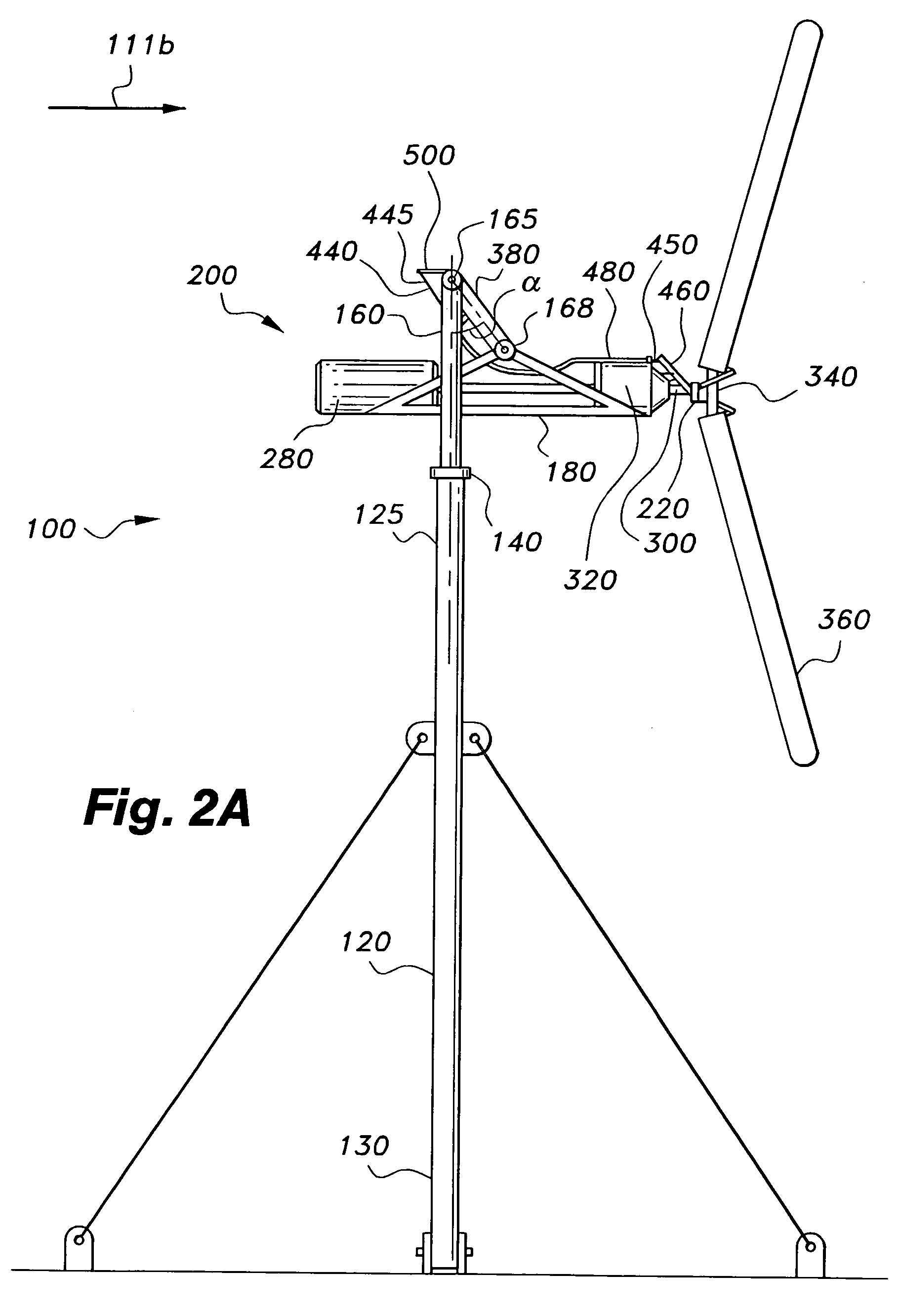
Downstream wind turbine
A downstream wind turbine for converting wind energy into electrical energy. In a preferred embodiment the downstream wind turbine adapted to respond to high winds and gyroscopic precession. The downstream wind turbine comprises a support tower; a yaw bearing attached to the support tower; a support frame operably linked to the bearing; at least one swing arm with one end pivotally attached to the support frame; an elongated carry member pivotally attached to the other end of the swing arm; a wind driven energy conversion system balanced on and attached to the carry member so that the carry member is biased to maintain an approximately horizontal orientation with respect to the support frame and in response to wind proportionally swings downstream, and which responds to gyroscopic precession forces by tilting up or down; and a governor device for modifying at least one dynamic characteristic of the turbine.
Owner:DRAKE DEVON GLEN
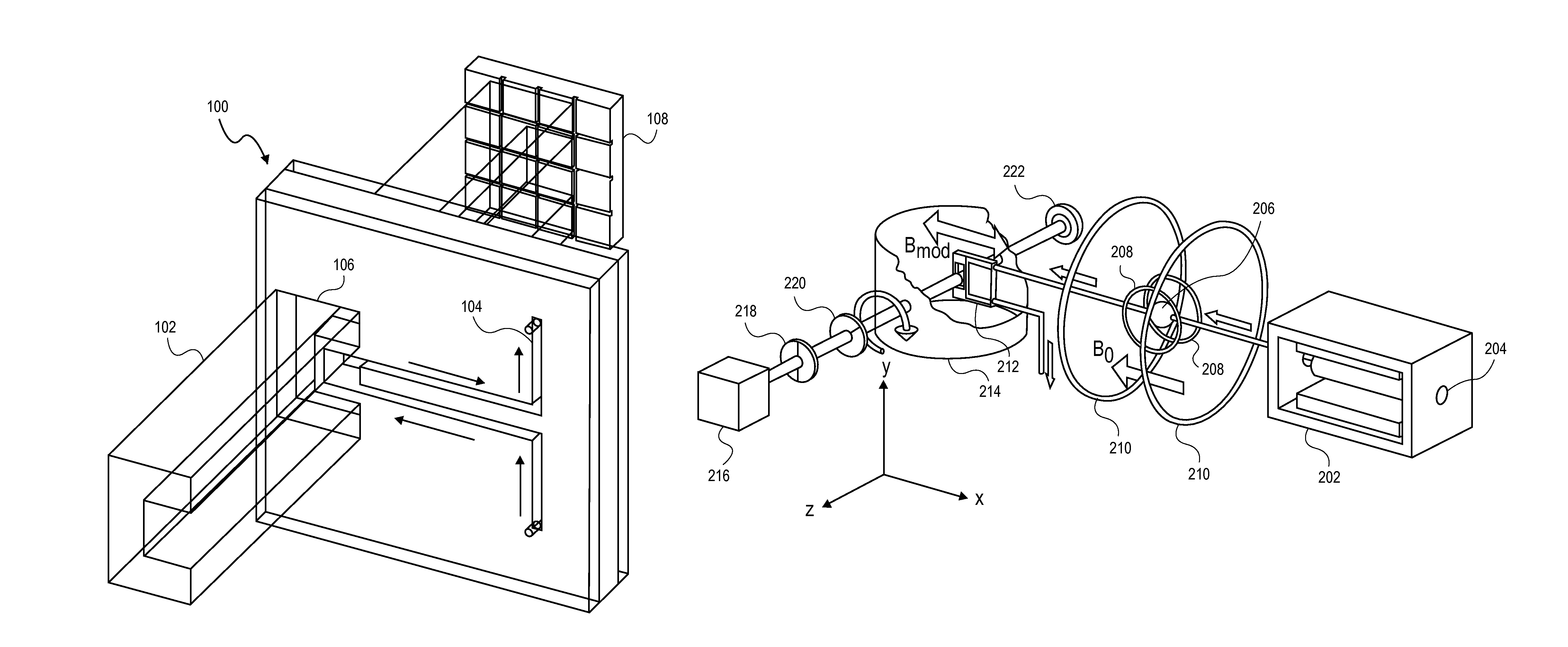
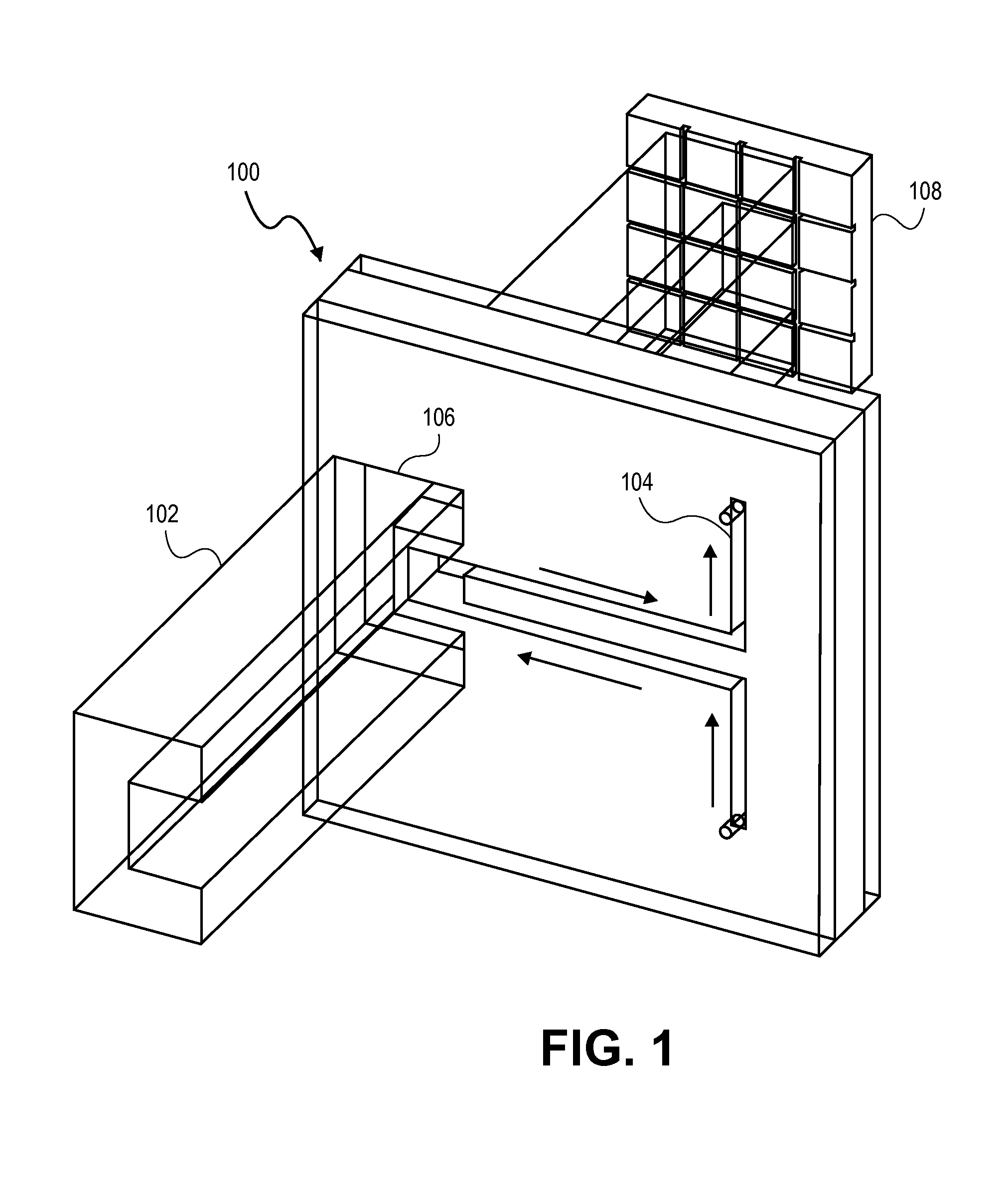
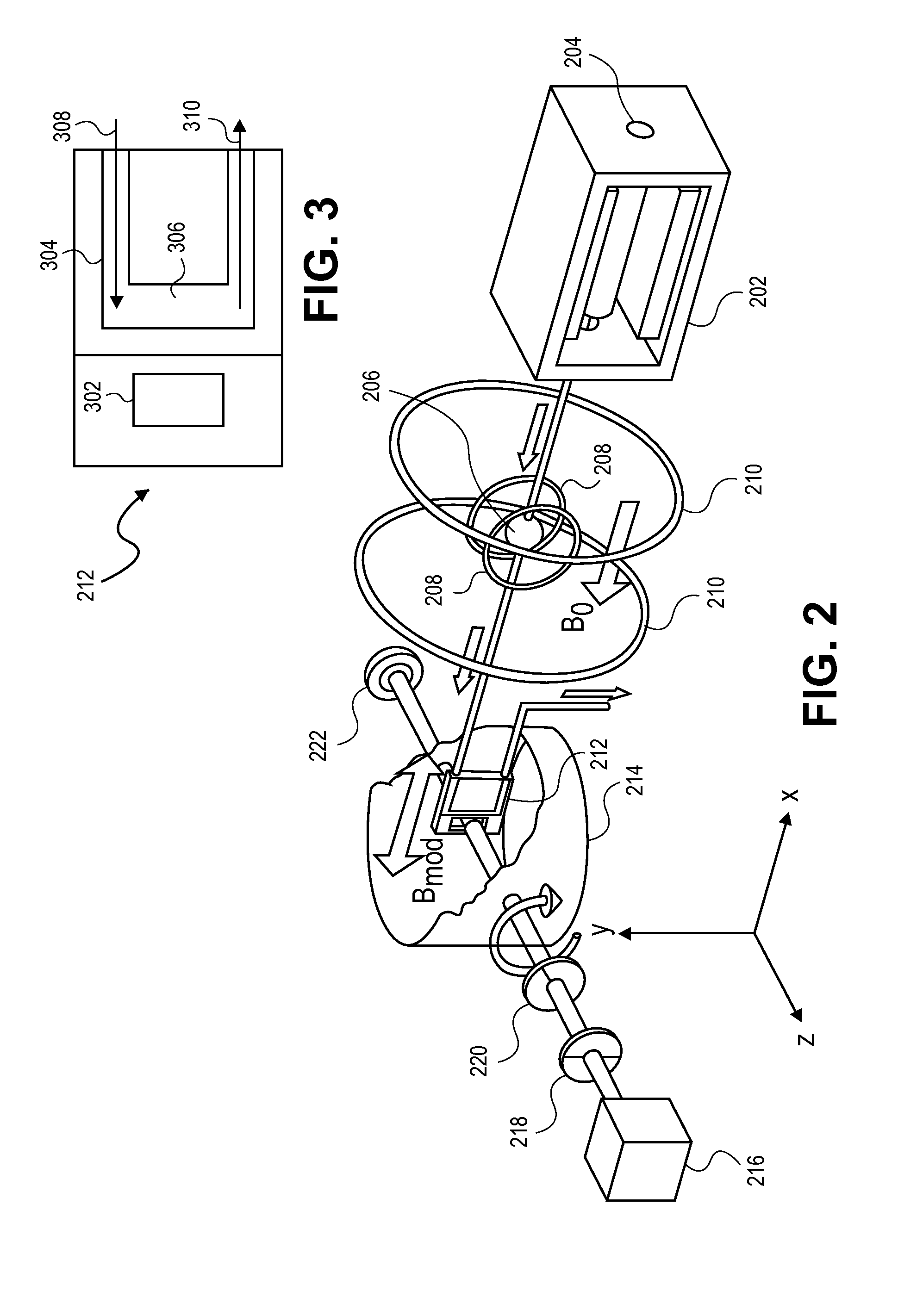
Integrated microchip incorporating atomic magnetometer and microfluidic channel for NMR and MRI
ActiveUS7994783B2Improve scalabilityLow costElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMicrofluidic channel
An integral microfluidic device includes an alkali vapor cell and microfluidic channel, which can be used to detect magnetism for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Small magnetic fields in the vicinity of the vapor cell can be measured by optically polarizing and probing the spin precession in the small magnetic field. This can then be used to detect the magnetic field of in encoded analyte in the adjacent microfluidic channel. The magnetism in the microfluidic channel can be modulated by applying an appropriate series of radio or audio frequency pulses upstream from the microfluidic chip (the remote detection modality) to yield a sensitive means of detecting NMR and MRI.
Owner:GOVERNMNET OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TECH +1
Magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS20090244792A1Minimize current required for writingHigh-speed writingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryMicrowave
A magnetoresistance effect element includes: a first ferromagnetic layer having invariable magnetization perpendicular to a film plane; a second ferromagnetic layer having variable magnetization perpendicular to the film plane; a first nonmagnetic layer interposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; a third ferromagnetic layer provided on an opposite side of the second ferromagnetic layer from the first nonmagnetic layer, and having variable magnetization parallel to the film plane; and a second nonmagnetic layer interposed between the second and third ferromagnetic layers. Spin-polarized electrons are injected into the second ferromagnetic layer by flowing a current in the direction perpendicular to the film planes between the first and third ferromagnetic layers, precession movement is induced in the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer by injecting the spin-polarized electrons, and a microwave magnetic field of a frequency corresponding to the precession movement is applied to the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
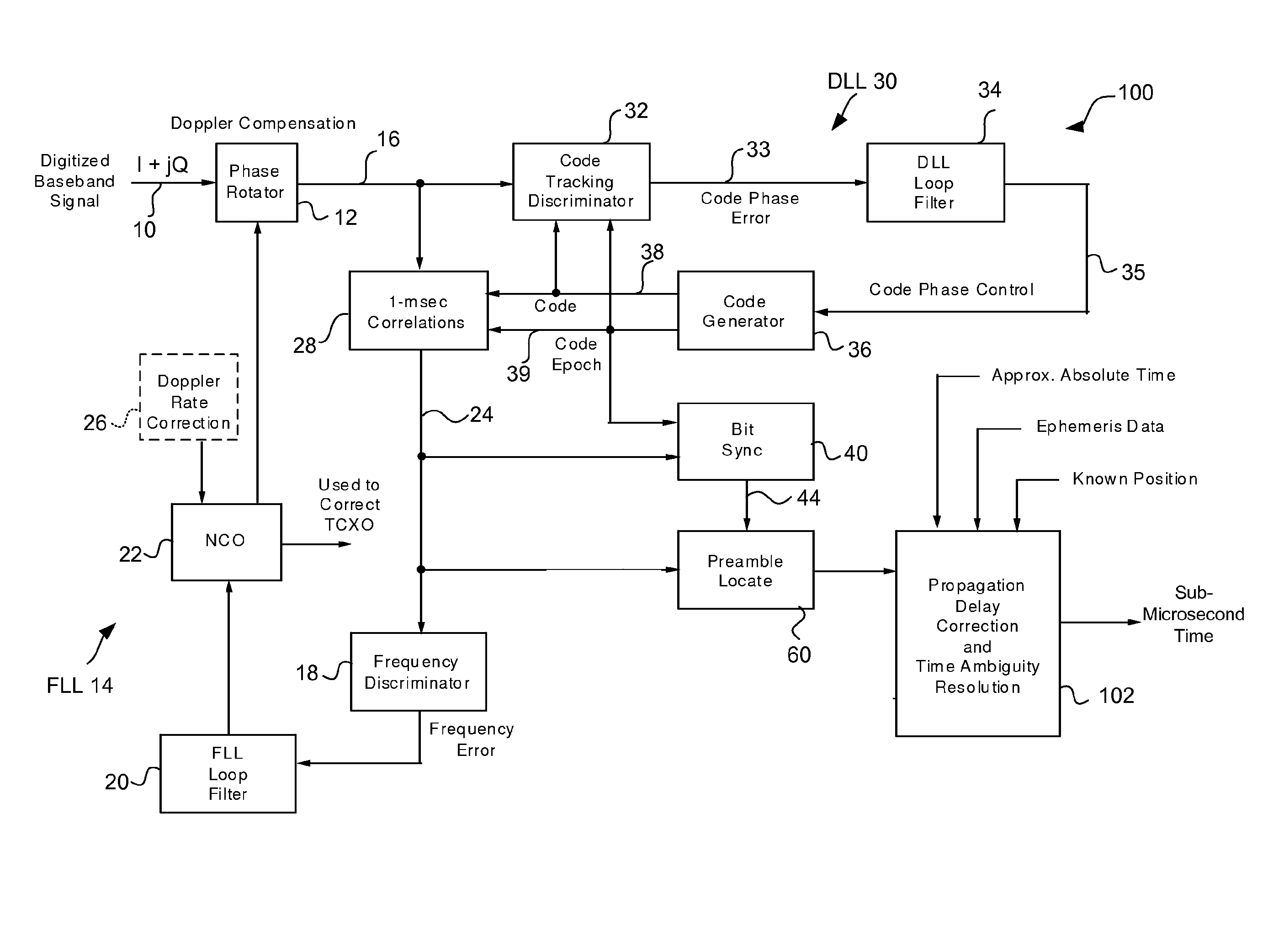
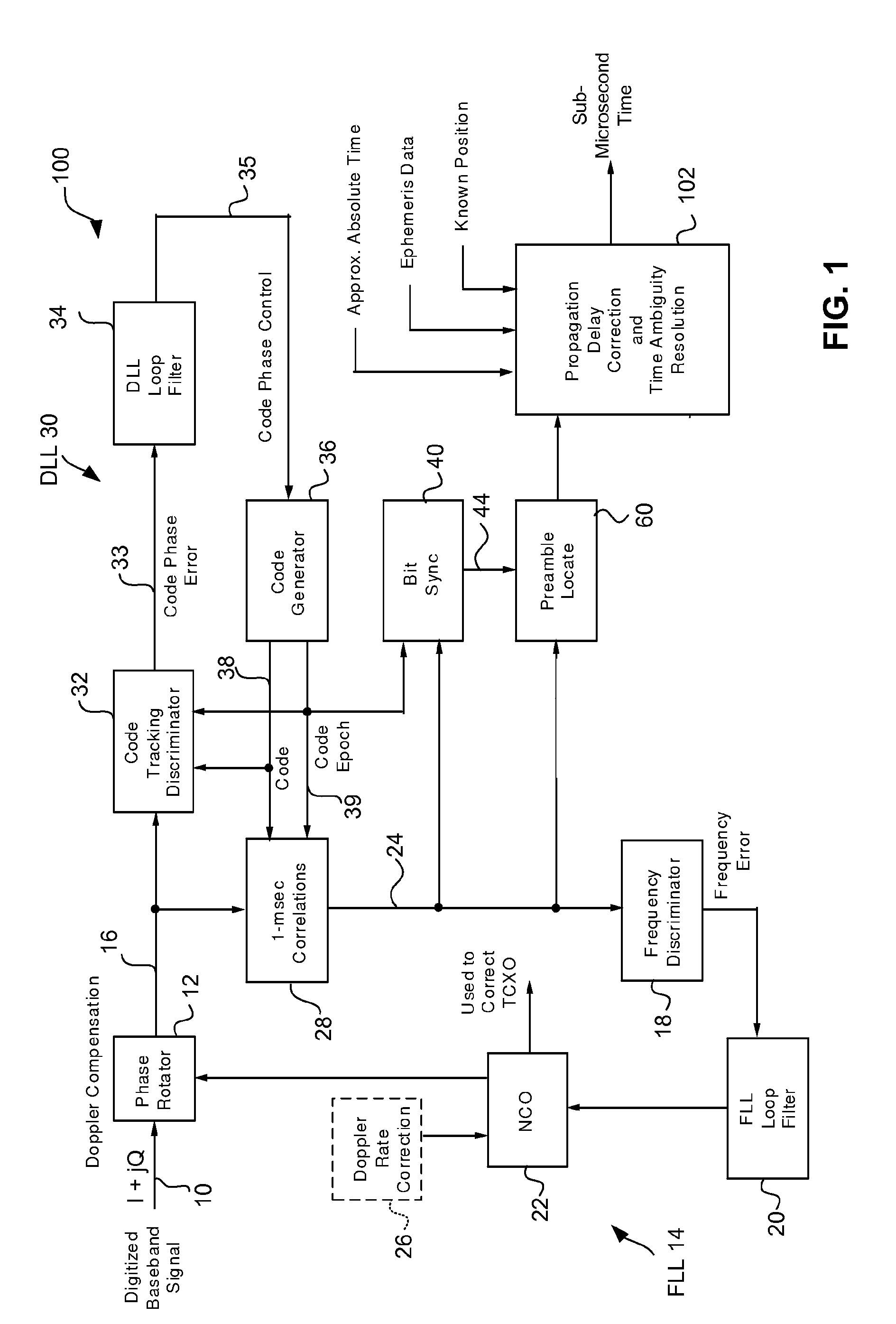
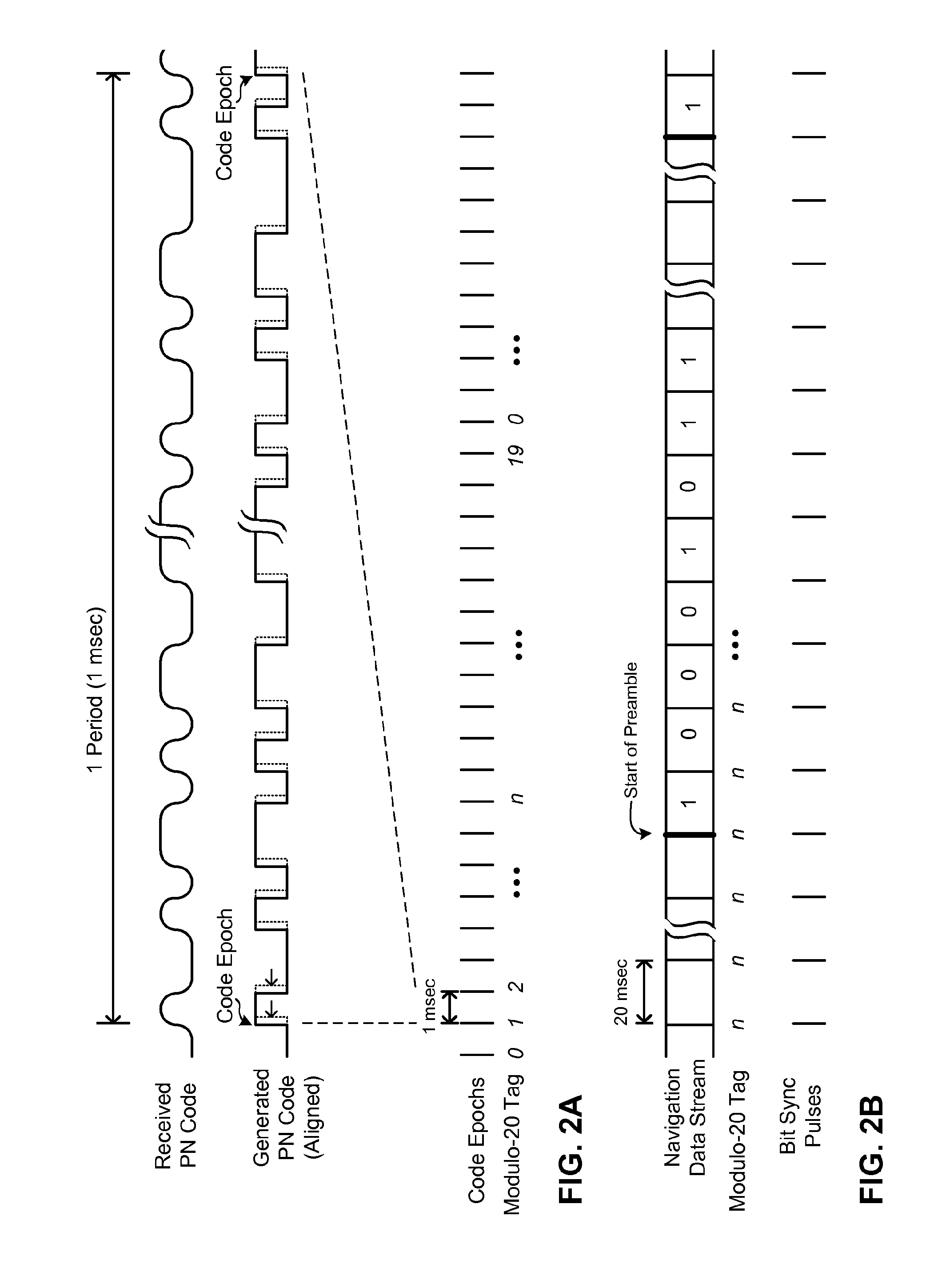
Method and apparatus for acquisition, tracking, and sub-microsecond time transfer using weak gps/gnss signals
ActiveUS20110007783A1Reduce time uncertaintySatellite radio beaconingTransmissionPrecessionTime transfer
A method and apparatus provide high-sensitivity GPS / GNSS signal acquisition in a stationary GPS / GNSS receiver. The uncertainty in frequency due to apparent Doppler shift is partitioned into a plurality of contiguous frequency bins, and the uncertainty in location of navigation data bit boundaries is partitioned into equally spaced trial bit boundary locations. For each combination of the trial bit boundary location and the frequency bin, a signal block of captured complex baseband signal is Doppler-compensated using a phase rotator, and then synchronously summed with a periodicity of one period of C / A code so as to produce a compressed sample block having N samples. Each compressed sample block is cross-correlated with one period of reference C / A code to produce an N-value correlation function. A predetermined number of magnitudes of the N-value correlation functions are stack-accumulated into an array with precession compensation so as to find a correlation peak having the largest value.
Owner:MAGELLAN SYST JAPAN
Magnetic recording device and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS8085582B2Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsFilm planePrecession
A magnetic recording device includes: a laminated body including: a first ferromagnetic layer with a magnetization substantially fixed in a first direction; a second ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction; a first nonmagnetic layer disposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; and a third ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction. The magnetization direction of the second ferromagnetic layer is determinable in response to the orientation of a current, by allowing electrons spin-polarized by passing a current in a direction generally perpendicular to the film plane of the layers of the laminated body to act on the second ferromagnetic layer, and by allowing a magnetic field generated by precession of the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer to act on the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS20110309418A1Minimise currentHigh-speed writingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryMicrowave
A magnetoresistance effect element includes: a first ferromagnetic layer having invariable magnetization perpendicular to a film plane; a second ferromagnetic layer having variable magnetization perpendicular to the film plane; a first nonmagnetic layer interposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; a third ferromagnetic layer provided on an opposite side of the second ferromagnetic layer from the first nonmagnetic layer, and having variable magnetization parallel to the film plane; and a second nonmagnetic layer interposed between the second and third ferromagnetic layers. Spin-polarized electrons are injected into the second ferromagnetic layer by flowing a current in the direction perpendicular to the film planes between the first and third ferromagnetic layers, precession movement is induced in the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer by injecting the spin-polarized electrons, and a microwave magnetic field of a frequency corresponding to the precession movement is applied to the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Spin Torque Oscillator Sensor
ActiveUS20100328799A1Save spaceHigh data densityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPrecessionSpin torque oscillators
A spin torque oscillation magnetoresistive sensor for measuring a magnetic field. The sensor uses a change in precessional oscillation frequency of a magnetization of a magnetic layer to determine the magnitude of a magnetic field. The sensor can include a magnetic free layer, a magnetic pinned layer and a non-magnetic layer sandwiched therebetween. Circuitry is connected with these layers to induce an electrical current through the layers. Spin polarization of electrons traveling through the device causes a spin torque induced precession of the magnetization of one or more of the layers. The frequency of this oscillation modulates in response to a magnetic field. The modulation of the oscillation frequency can be measured to detect the presence of the magnetic field, and determine its magnitude.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
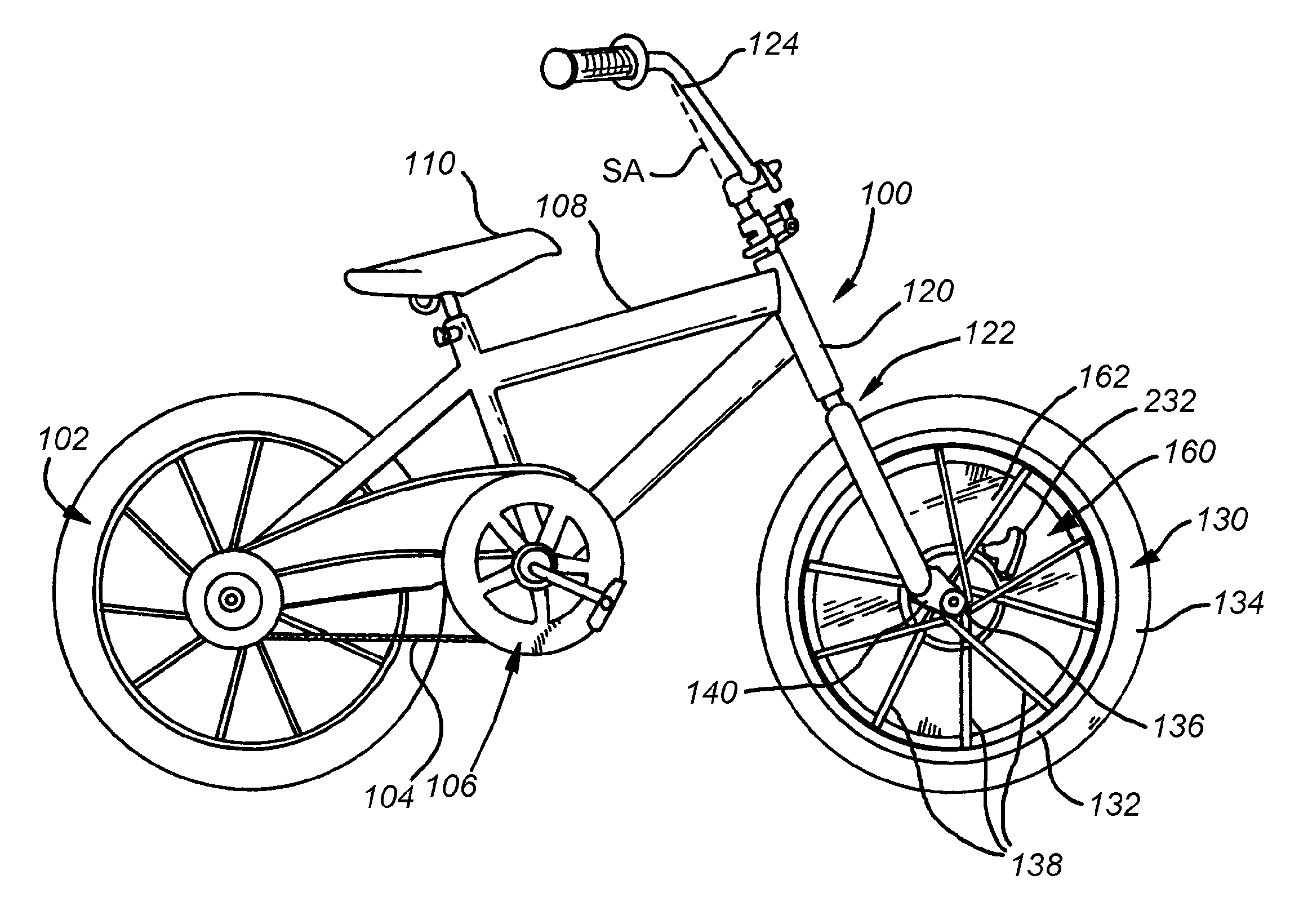
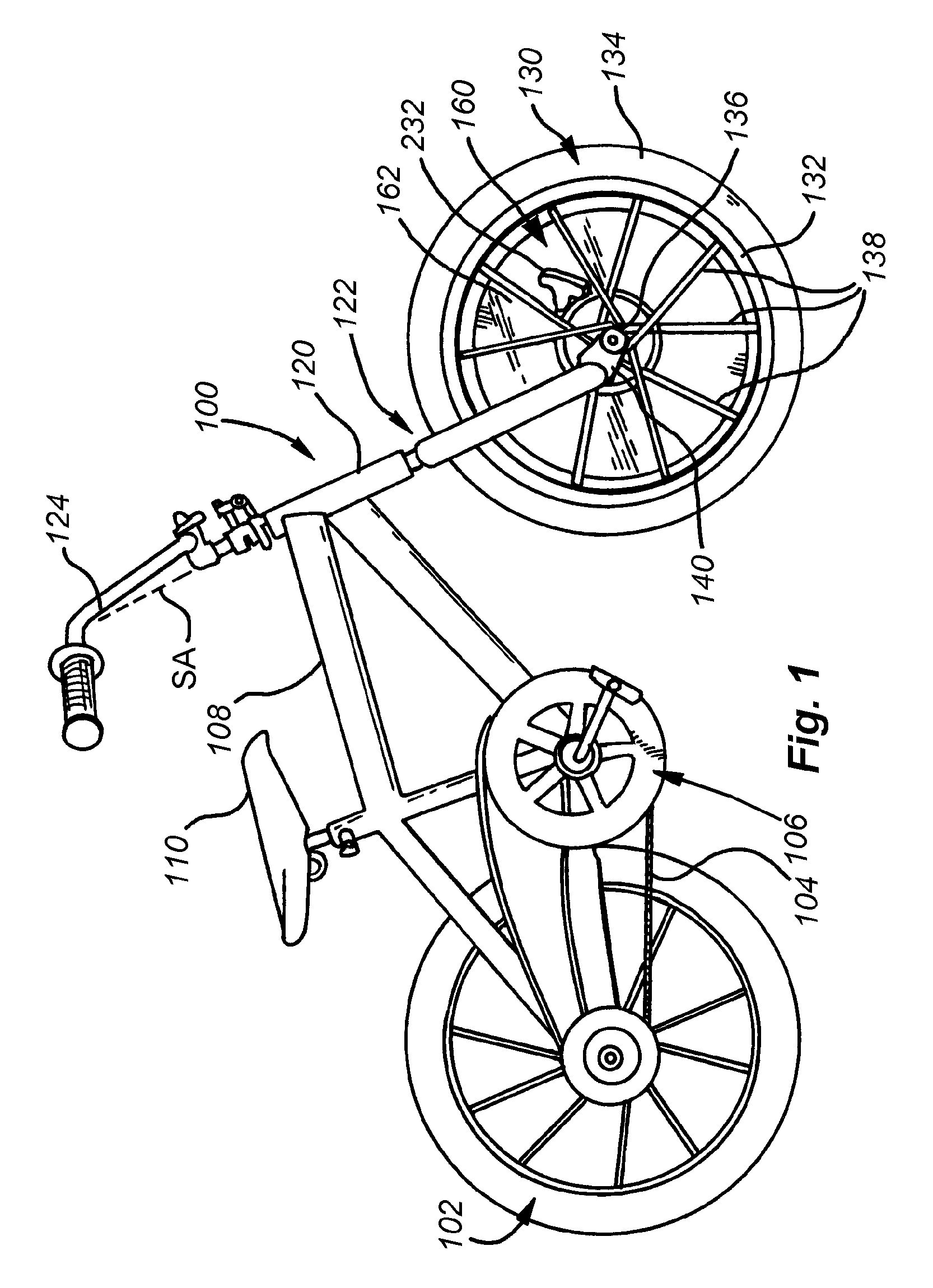
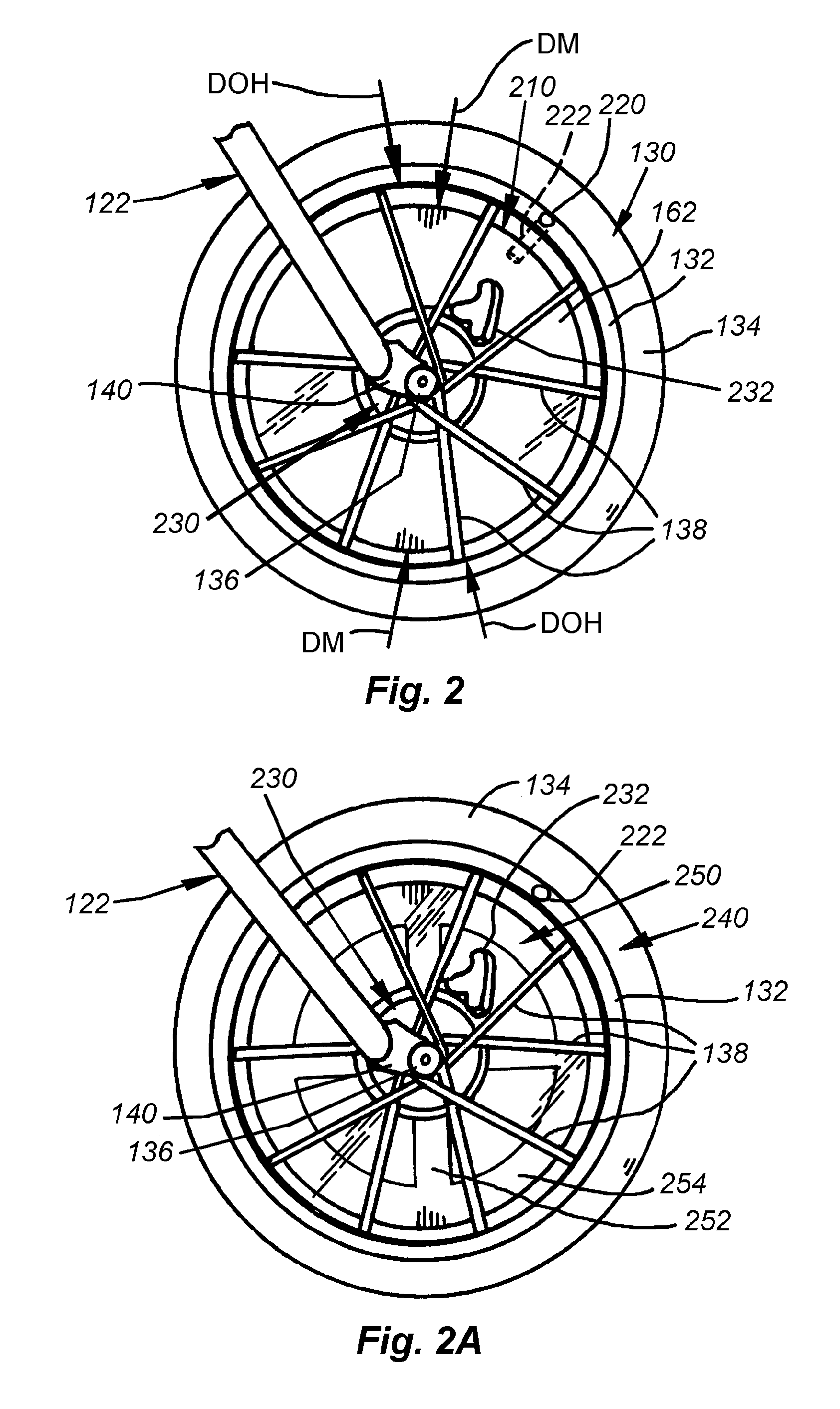
System and method for providing gyroscopic stabilization to a wheeled vehicle
InactiveUS20100090440A1Improve stabilityLimited abilityRider propulsionOther supporting devicesControl systemPrecession
This invention provides a stabilizing system and method for two-wheeled vehicles that affords the rider no restriction on the full range of movements (banks, leans, etc.) common to bicycles, but that provides greater stability during turns and other maneuvers so that an unintentional bank or tilt (potentially causing a fall) is less likely, even at relatively slow speeds and startup. A rotating mass of predetermined mass-value and radial mass-distribution is provided coaxially with the front axle. The mass is supported on bearings so as to freewheel with respect to the rotation of the front wheel. As such it can be induced to spin significantly faster than the front wheel thereby generating a gyroscopic effect at the front wheel about the axle. This gyroscopic effect influences the steering of the wheel by the rider. Due to precession, the wheel tends to follow any excessive bank by the vehicle, ensuring that the rider can “steer-out-of” an unintended tilt or bank. Likewise, the gyroscopic effect limits the rider's ability to execute excessive steering, thereby preventing jackknife movements. The mass can be an electric-motor-driven flywheel within a shell housing that includes a battery, control system and drive motor. The drive motor engages a surface of the flywheel with a drive tire in a resilient manner to reduce potential damage to the motor.
Owner:THE GYROBIKE
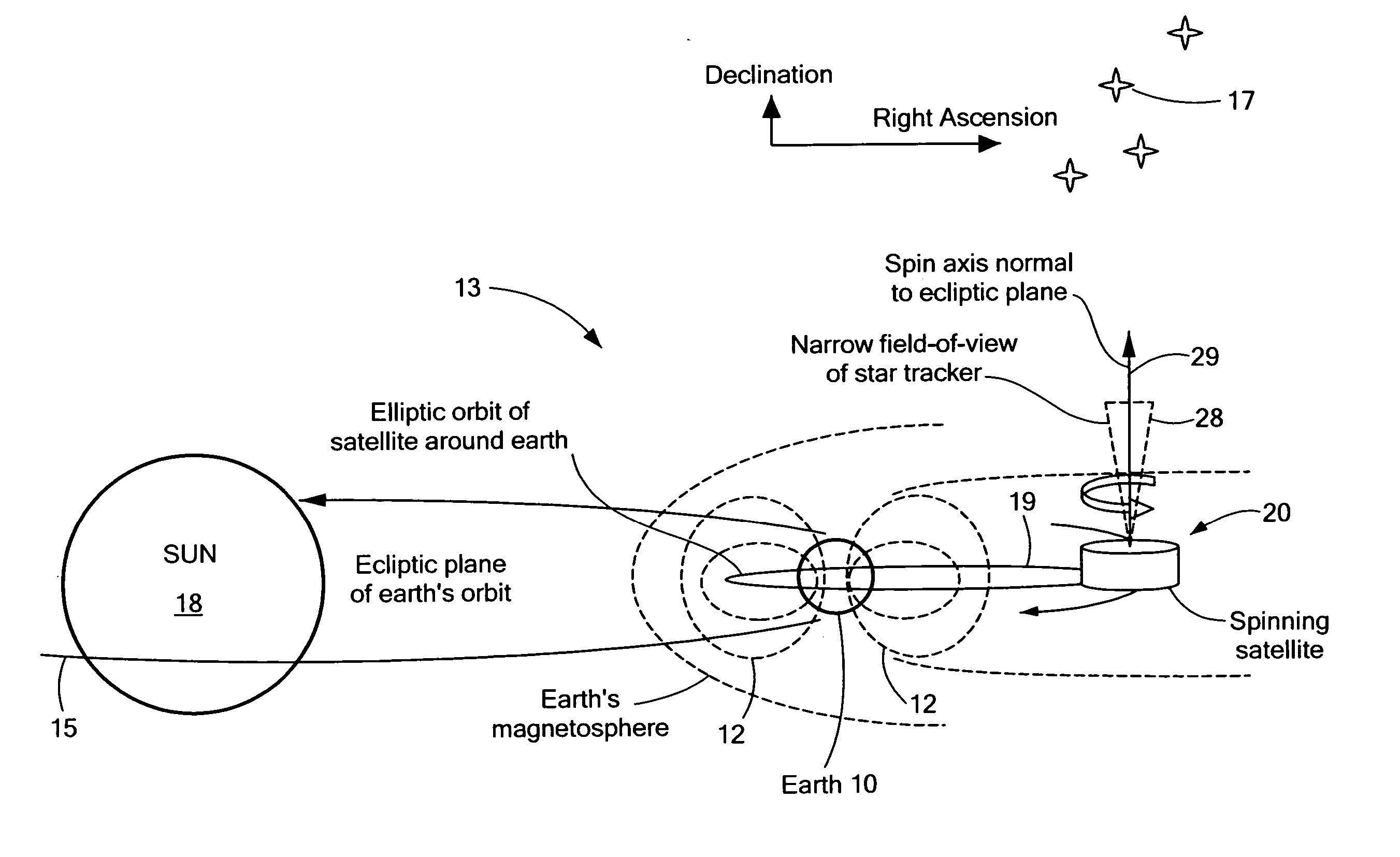
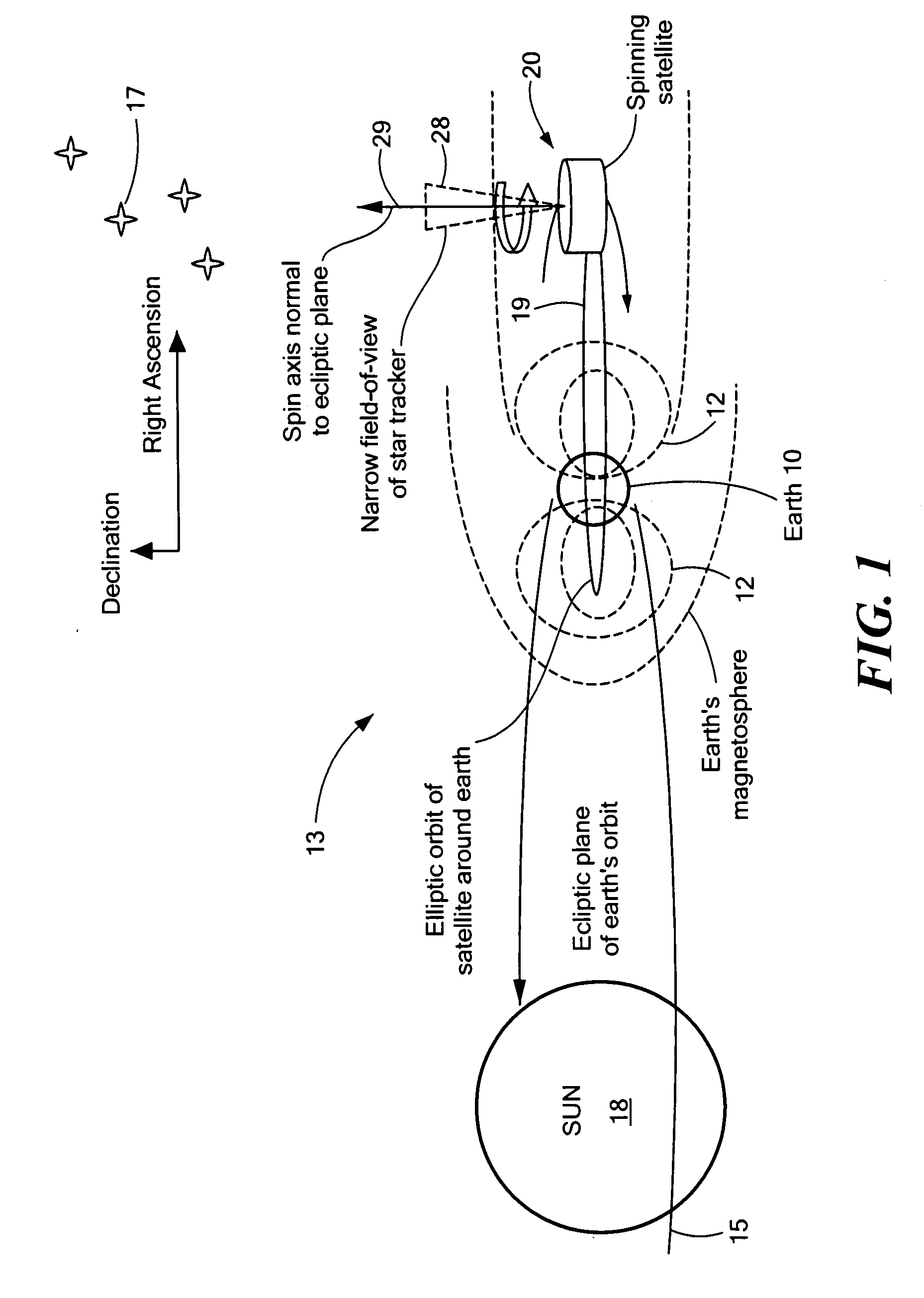
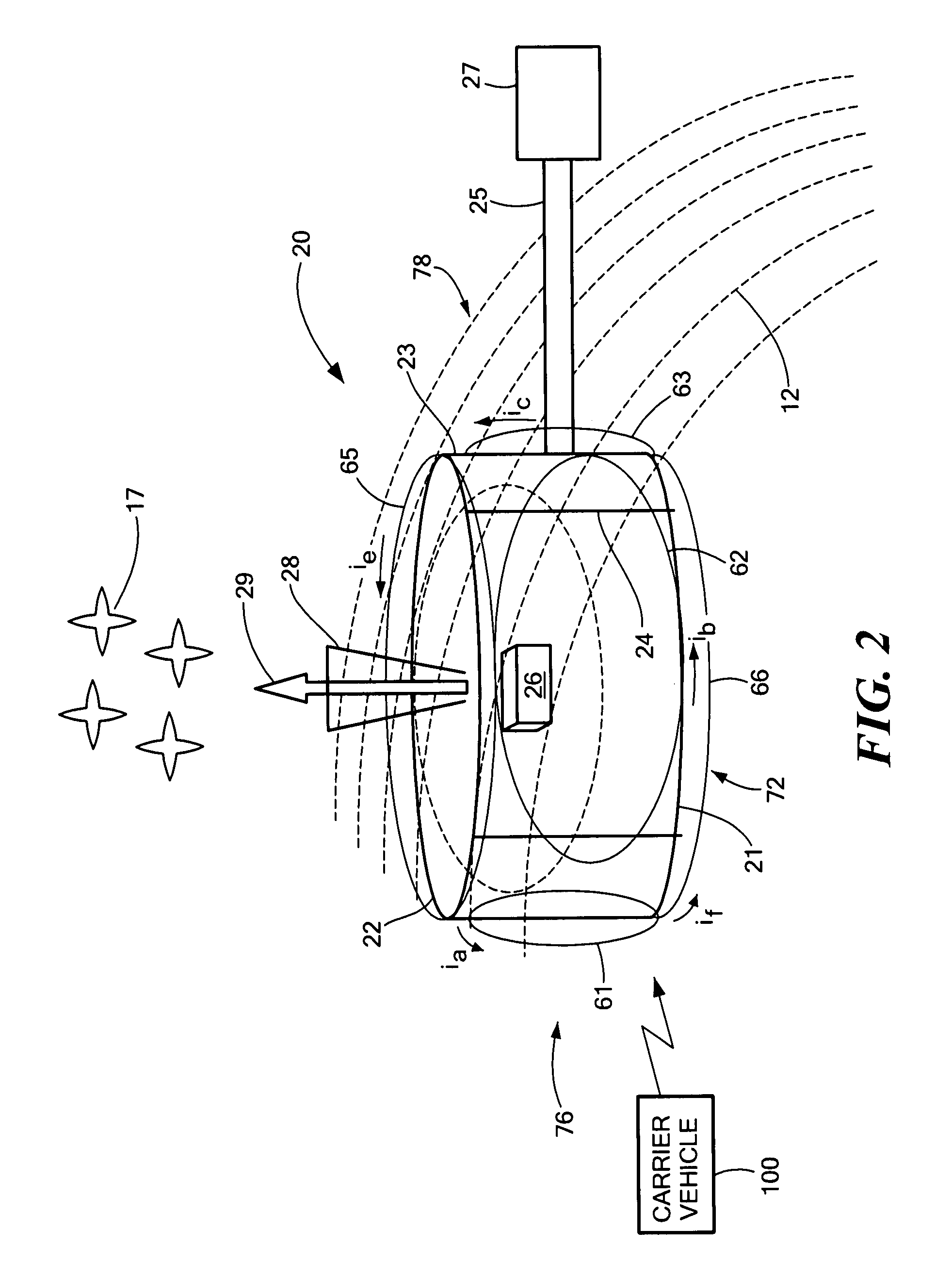
Method of determining and controlling the inertial attitude of a spinning, artificial satellite and systems therefor
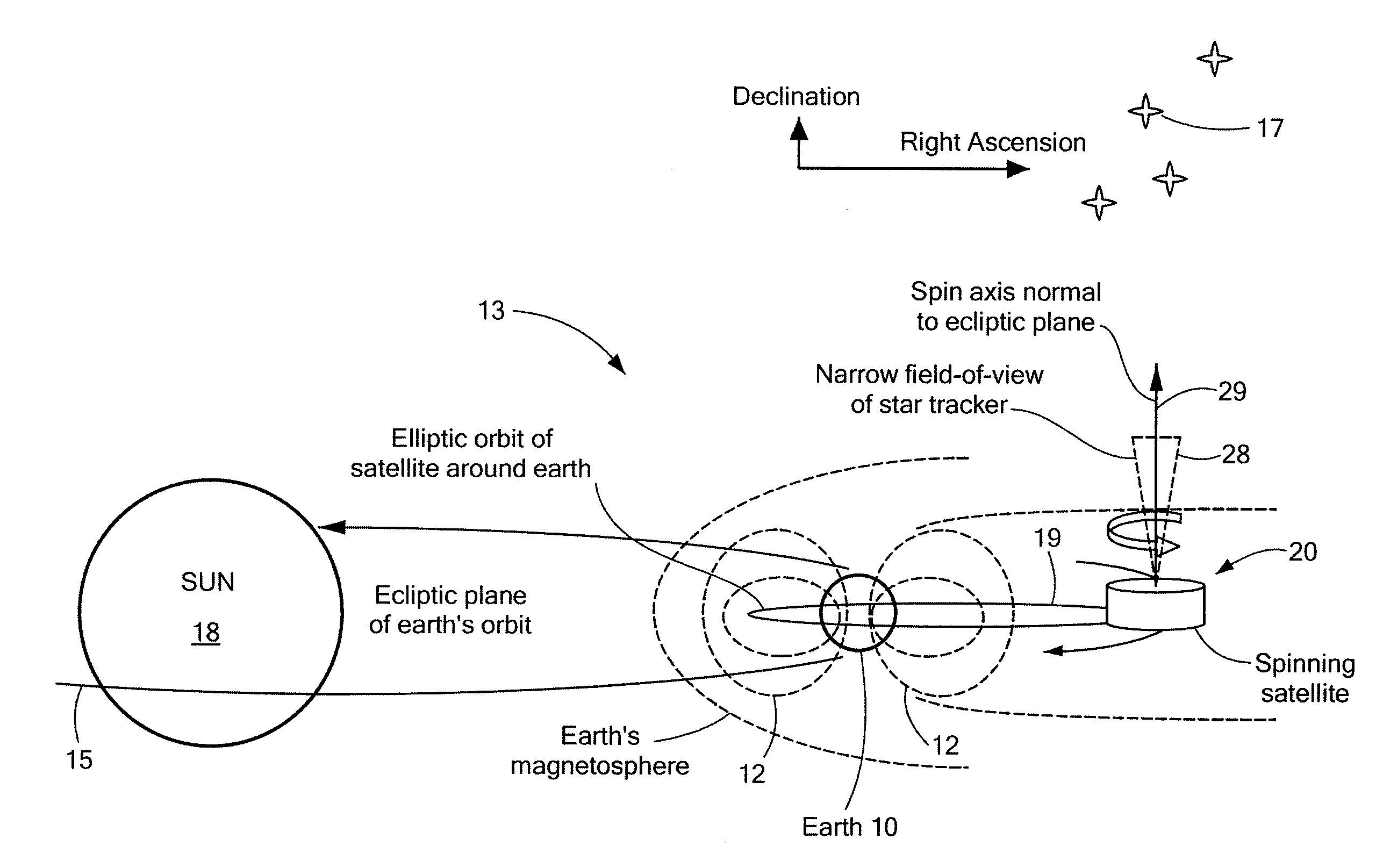
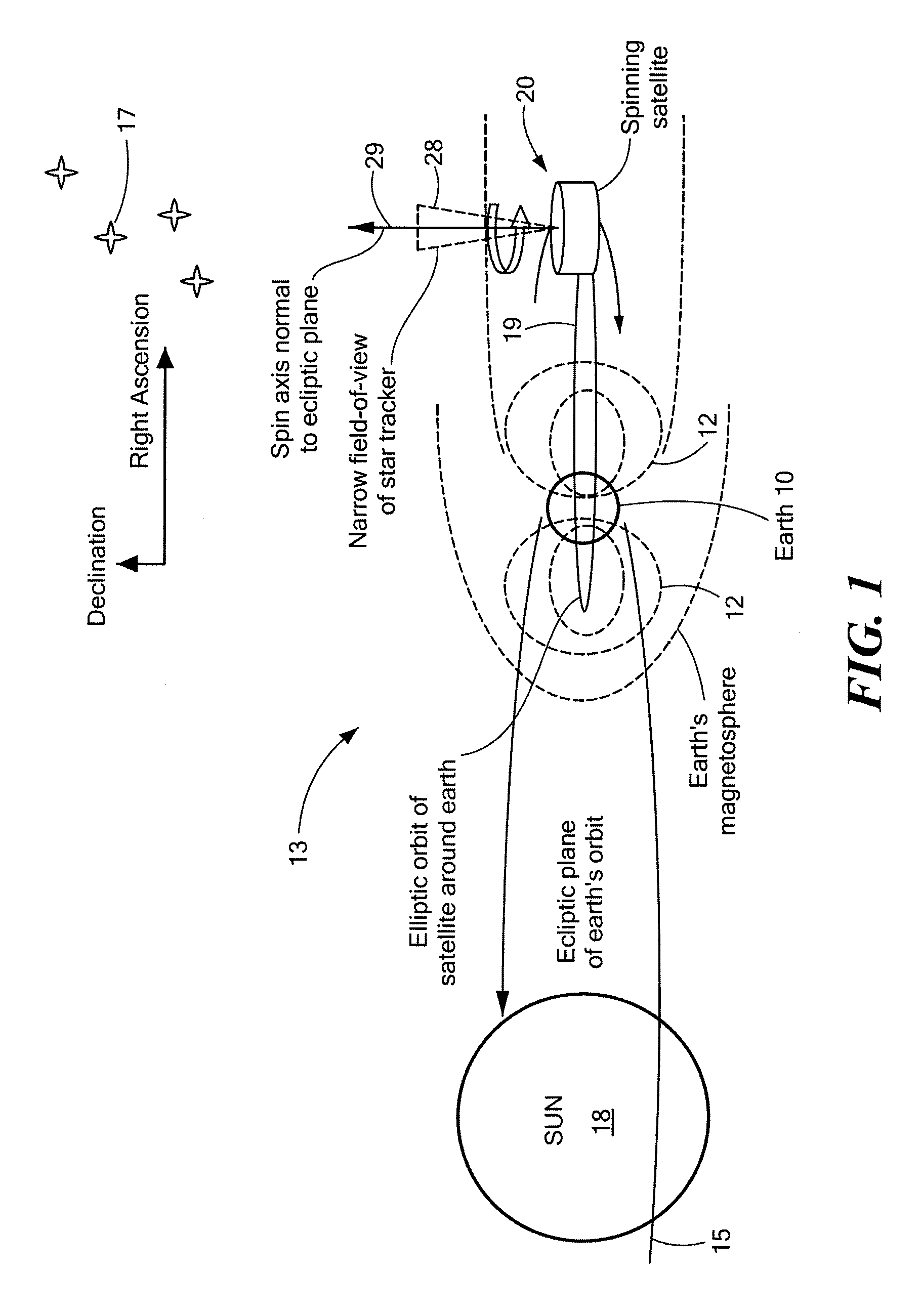
InactiveUS20080087769A1Reduce material volumeHigh gainCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsGyroscopeOn board
A method of and apparatus for determining and controlling the inertial attitude of a spinning artificial satellite without using a suite of inertial gyroscopes. The method and apparatus operate by tracking three astronomical objects near the Earth's ecliptic pole and the satellite's and / or star tracker's spin axis and processing the track information. The method and apparatus include steps and means for selecting preferably three astronomical objects using a histogram method and determining a square of a first radius (R12) of a track of a first astronomical object; determining a square of a second radius (R22) of a track of a second astronomical object; determining a square of a third radius (R32) of a track of a third astronomical object; determining the inertial attitude of the spin axis using the squares of the first, second, and third radii (R12, R22, and R32) to calculate pitch, yaw, and roll rate; determining a change in the pitch and yaw of the artificial satellite; and controlling on-board generated current flow to various orthogonally-disposed current-carrying loops to act against the Earth's magnetic field and to apply gyroscopic precession to the spinning satellite to correct and maintain its optimum inertial attitude.
Owner:JOHNSON KARA WHITNEY +1
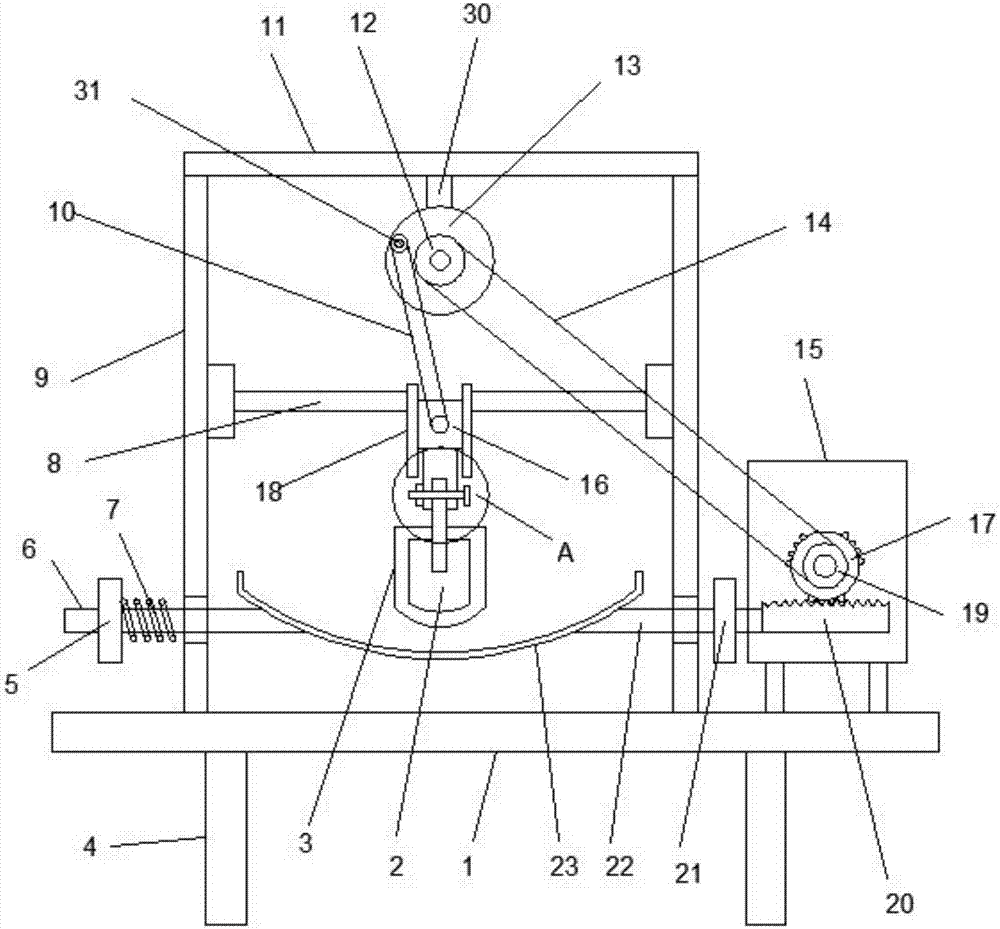
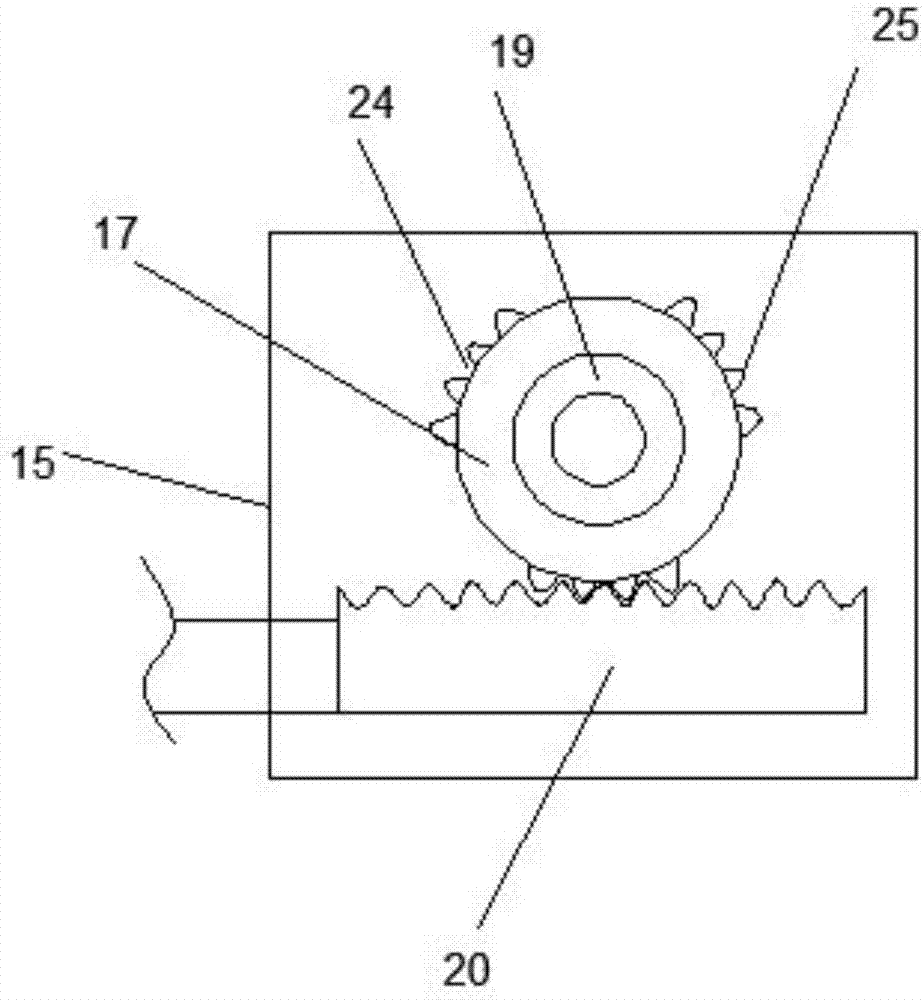
Quick medicine mashing device for Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturing
InactiveCN107008526AImprove the efficiency of pounding medicineImprove the quality of pounding medicineGrain treatmentsGear wheelReciprocating motion
The invention discloses a rapid pounding device for traditional Chinese medicine, which comprises a support base and a drive box. Support columns are connected to both sides of the upper end of the support base. The upper end of the support column is connected to a top plate. The middle part is connected with a rotating wheel, and the front end of the middle part of the rotating wheel is connected with a connecting rod. The shaft position is connected with a driven pulley, the driven pulley is connected with a driving belt, the other end of the driving belt is connected with a driving pulley, the rear end of the driving pulley is connected with a rotating gear at the coaxial position, and the lower end of the rotating gear is meshed with a rack and a gear. The left end of the bar is connected with a right moving rod, the middle part of the right end of the right moving rod is connected with a right limit block, and the left end of the right moving rod is connected with a pounding medicine groove. The present invention realizes the up and down reciprocating motion of the tamping hammer and the left and right reciprocating motion of the ramming trough, greatly improving the ramming quality and ramming efficiency.
Owner:六安市我罗生工业设计有限公司
Inertial propulsion device to move an object up and down
ActiveUS20110219893A1Process controlImprove efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsGyroscopePrecession
Disclosed herein are two separate processes that do not require a propellant and do not produce an equal and opposite reaction against any external form of matter in the Local Inertial Reference Frame and do not violate Newton's Laws in the Universal Reference Frame. The first process produces horizontal motion, relies on the earth's gravitational field as an external force, and has been successfully tested. The second process produces vertical motion and relies only on the aether. It has been successfully tested considering the effect of the earth's gravity. Due to the law of conservation of angular momentum, the first process is considered by some to not be possible, but with the proper use of an external field (for example, gravity) and the phenomenon of precession, it is clearly possible. A clear distinction is made between a simple rotor and a gyroscope which is a far more complex device.
Owner:FIALA HARVEY E +2
Magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS8014193B2Minimise currentHigh-speed writingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryMicrowave
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Three-dimensional wafer-scale batch-micromachined sensor and method of fabrication for the same
ActiveUS20110239763A1Improve performanceReduce roughnessAcceleration measurement using interia forcesLamination ancillary operationsPrecessionEngineering
A vibratory sensor is fabricated as a three-dimensional batch-micromachined shell adapted to vibrate and support elastic wave propagation and wave precession in the shell or membrane and at least one driving electrode and preferably a plurality of driving electrodes directly or indirectly coupled to the shell to excite and sustain the elastic waves in the shell. The pattern of elastic waves is determined by the configuration of the driving electrode(s). At least one sensing electrode and preferably a plurality of sensing electrodes are provided to detect the precession of the elastic wave pattern in the shell. The rotation of the shell induces precession of the elastic wave pattern in the shell which is usable to measure the rotation angle or rate of the vibratory sensor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Spin torque oscillator sensor
ActiveUS8259409B2Save spaceHigh data densityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsSpin torque oscillatorsPrecession
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
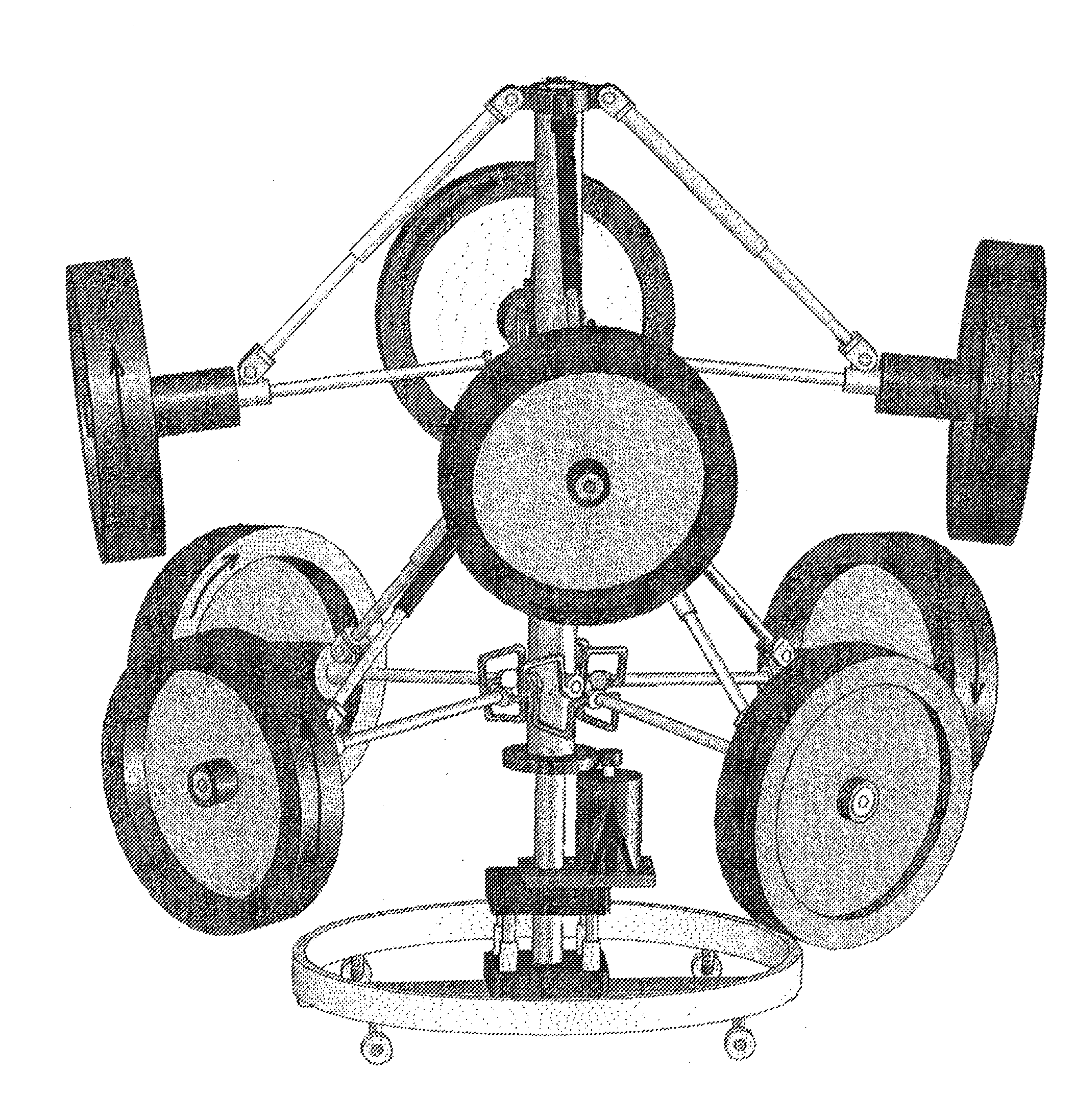
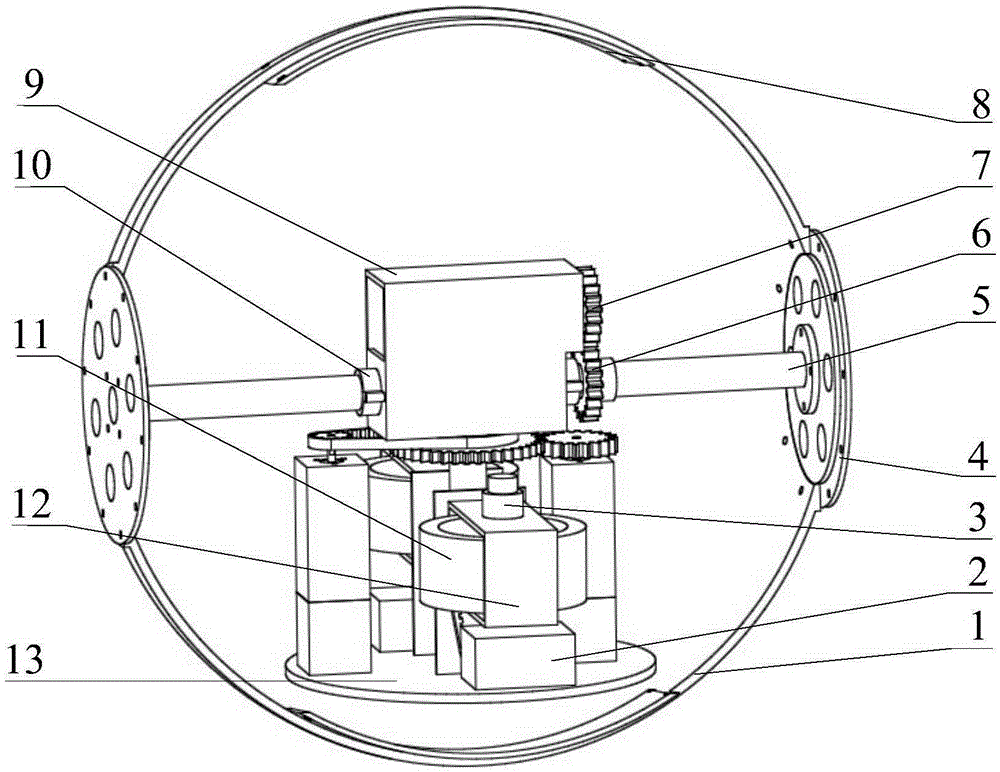
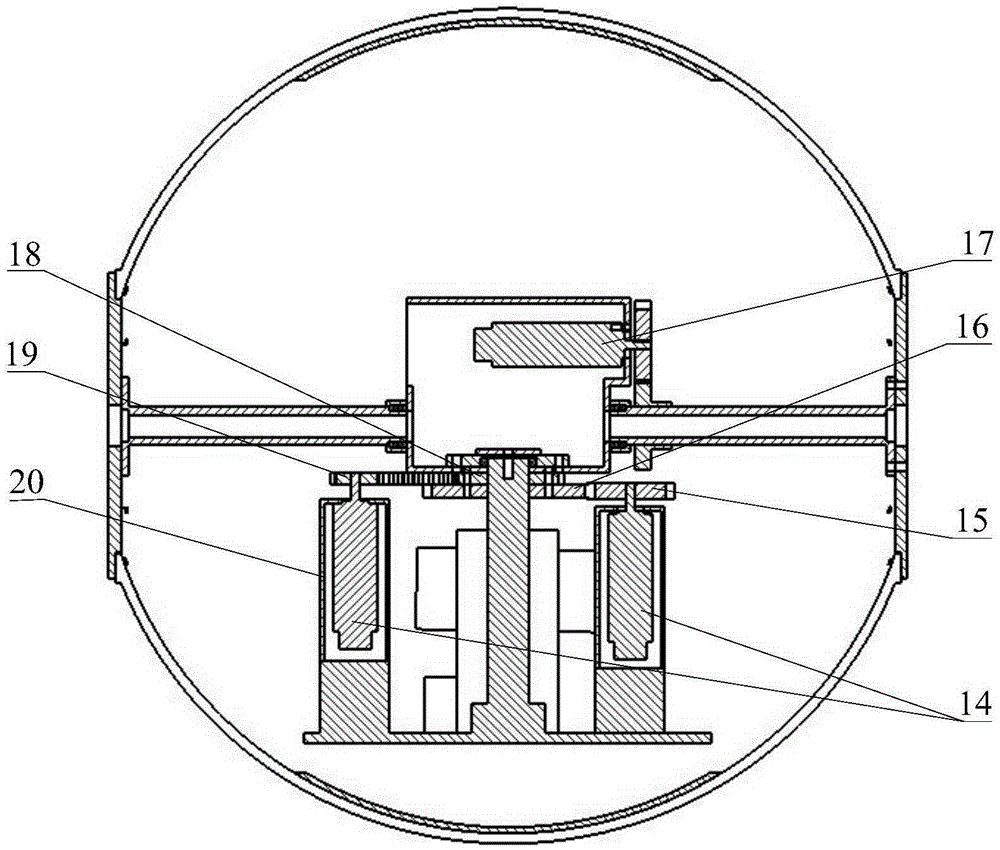
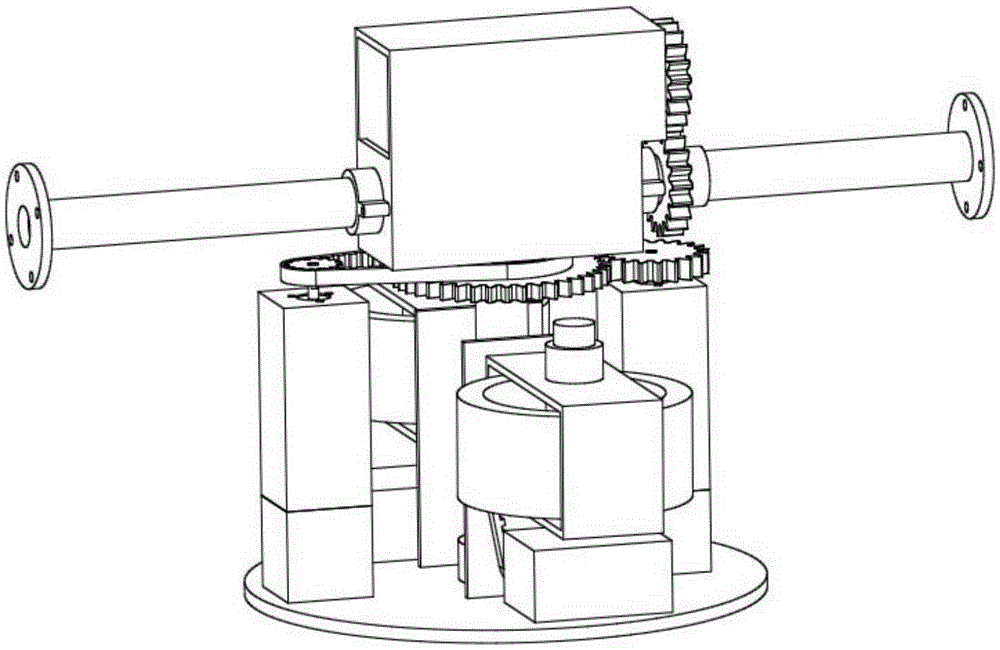
Spherical robot with in-situ rotation function carried with control moment gyro
The invention discloses a spherical robot with an in-situ rotation function carried with a control moment gyro. The robot is mainly composed of a homogeneous spherical shell, an advance driving mechanism, a steering mechanism, a control moment gyro mechanism, a heavy pendulum and the like. The steering mechanism is composed of two steering motors, a steering gear mechanism, a toothed belt wheel mechanism and the like. In-situ steering of the sphere is achieved through the cooperation of output torques of the two motors. Meanwhile, the robot is carried with the control moment gyro mechanism, and the control moment gyro mechanism is mainly composed of a flywheel, a flywheel rotation motor, a flywheel fixing frame, a frame rotation steering engine, the toothed belt wheel mechanism and the like; extra precession moment is provided through the precession effect of a gyro rotor which rotates at a high speed, so that the operation speed of the robot is higher, and the climbing and obstacle crossing capacity is improved. The spherical robot can steer in-situ and is high in operation speed, the movement rapidity and flexibility of the spherical robot are greatly improved, and the spherical robot has great application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
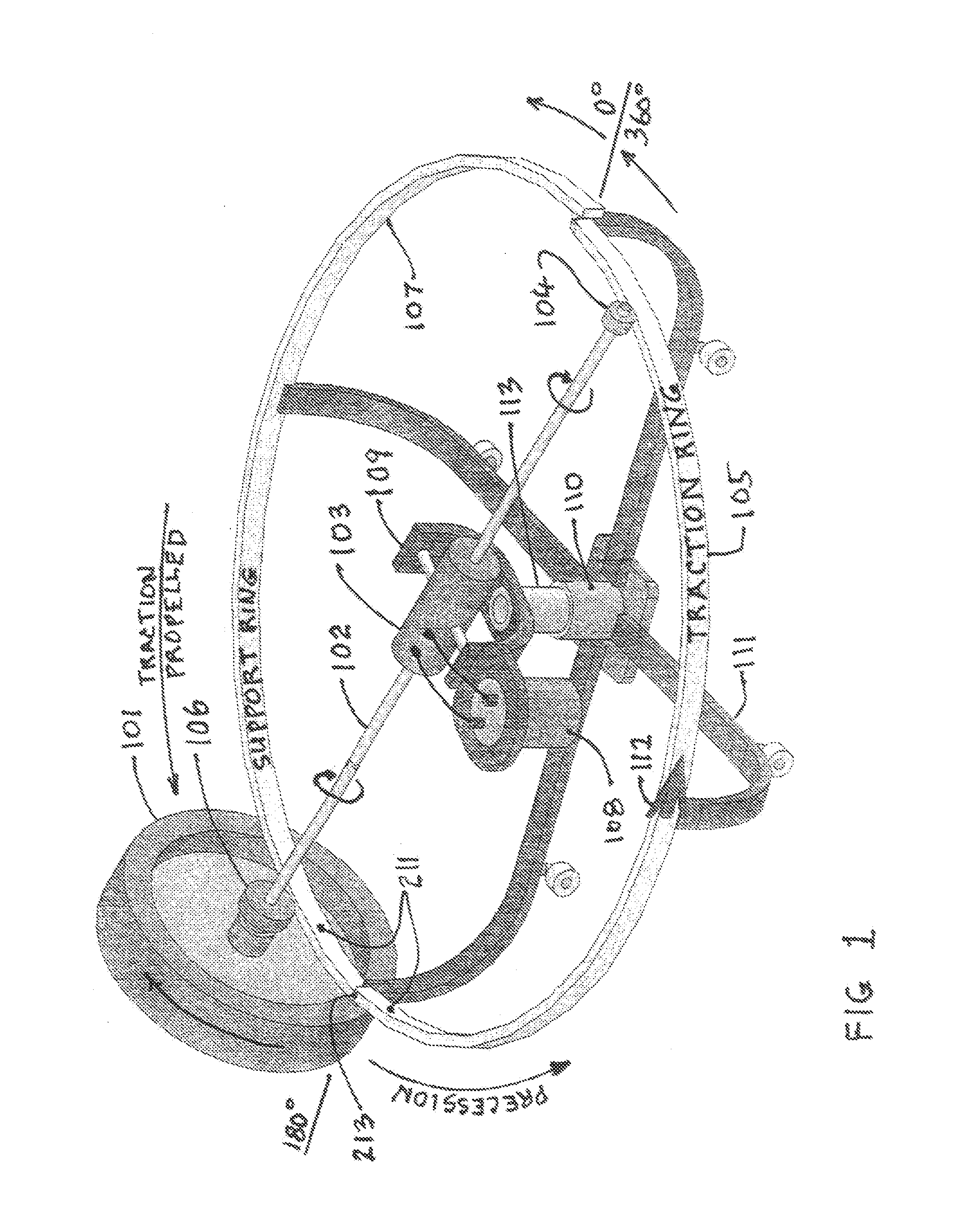
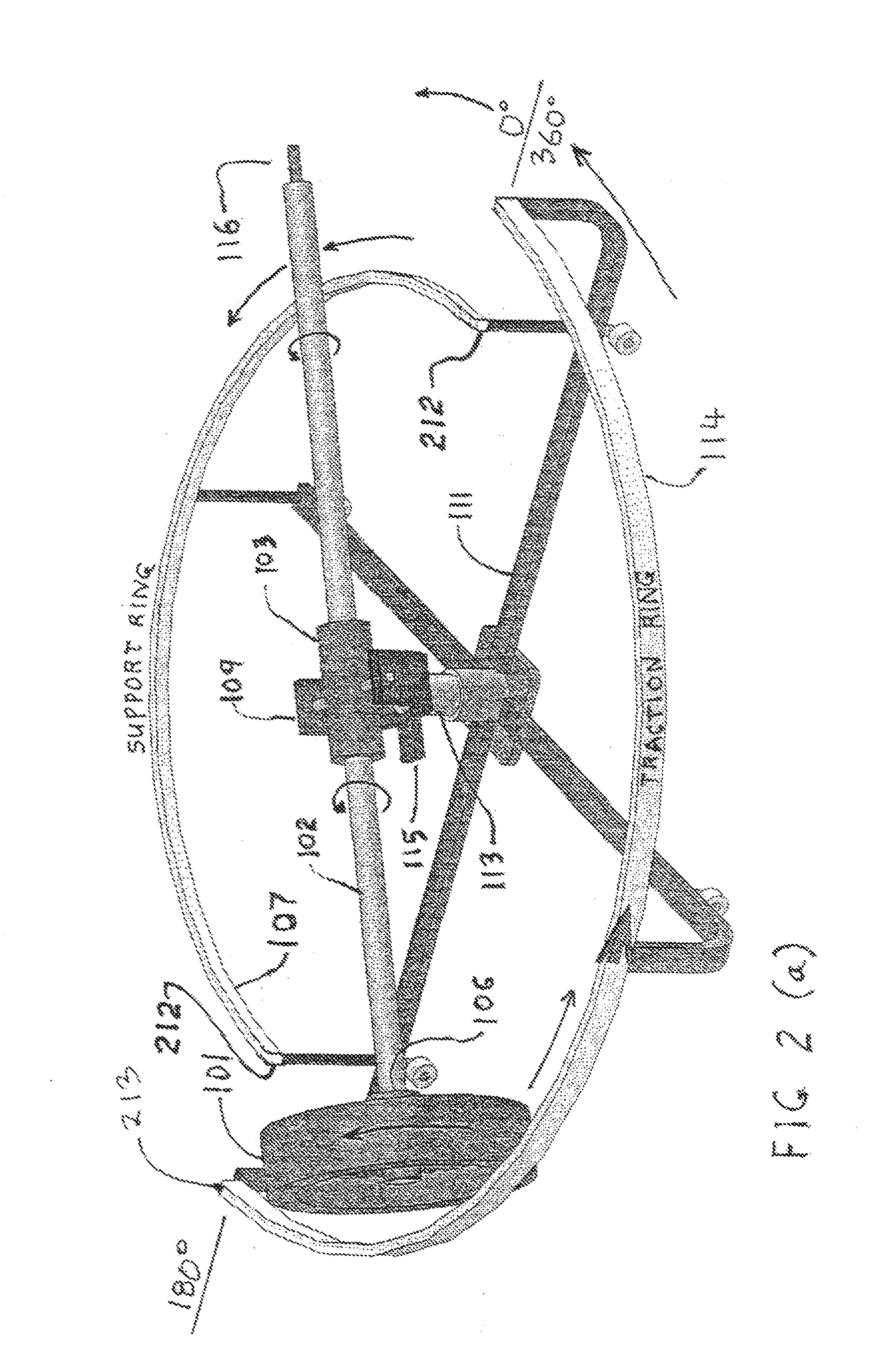
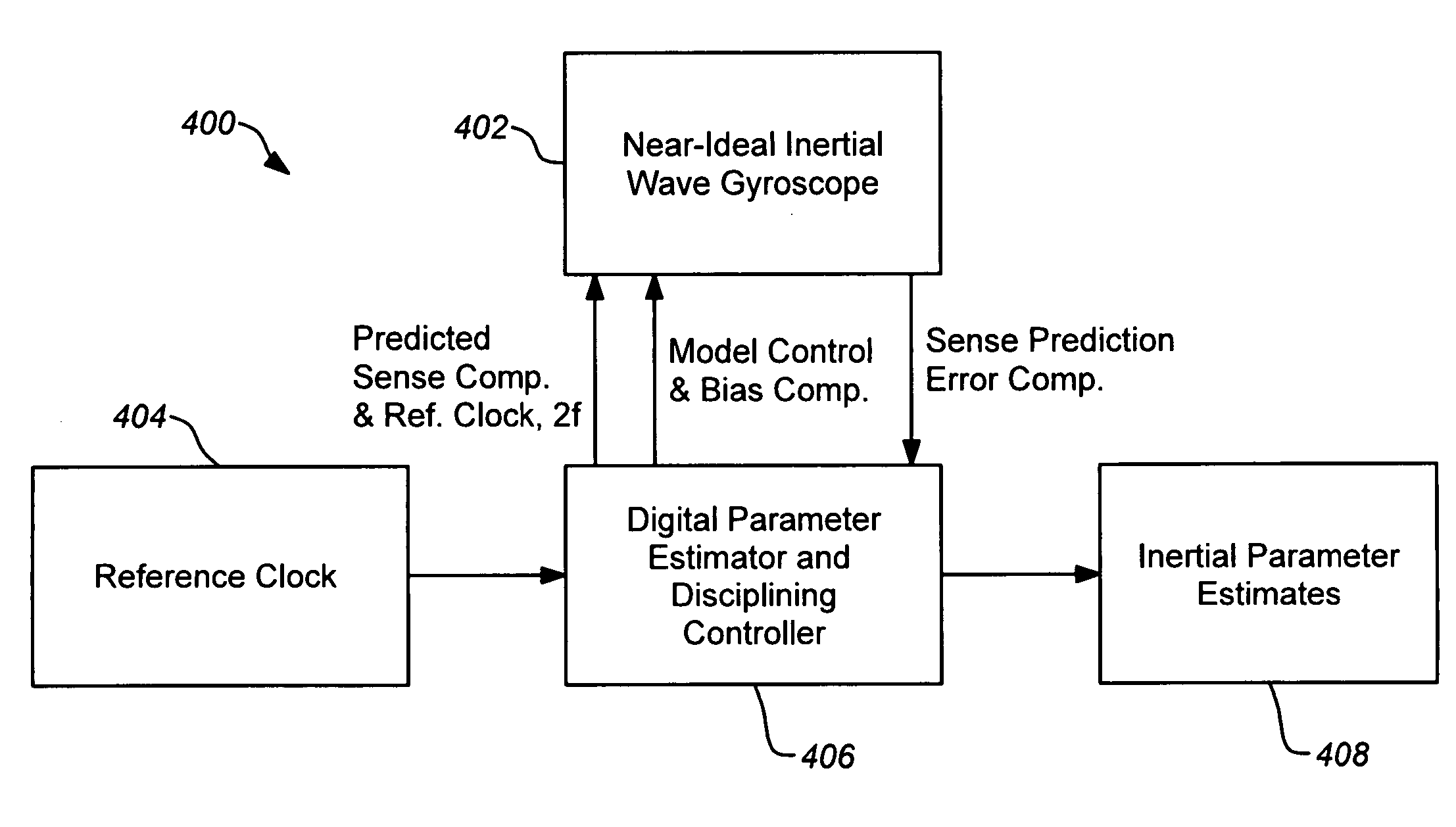
Parametrically disciplined operation of a vibratory gyroscope
ActiveUS20060037417A1Facilitate complete disciplineExcellent characteristicsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMechanical apparatusGyroscopePrecession
Parametrically disciplined operation of a symmetric nearly degenerate mode vibratory gyroscope is disclosed. A parametrically-disciplined inertial wave gyroscope having a natural oscillation frequency in the neighborhood of a sub-harmonic of an external stable clock reference is produced by driving an electrostatic bias electrode at approximately twice this sub-harmonic frequency to achieve disciplined frequency and phase operation of the resonator. A nearly symmetric parametrically-disciplined inertial wave gyroscope that can oscillate in any transverse direction and has more than one bias electrostatic electrode that can be independently driven at twice its oscillation frequency at an amplitude and phase that disciplines its damping to zero in any vibration direction. In addition, operation of a parametrically-disciplined inertial wave gyroscope is taught in which the precession rate of the driven vibration pattern is digitally disciplined to a prescribed non-zero reference value.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Rotor bearing system failure perfect information analytical method and apparatus
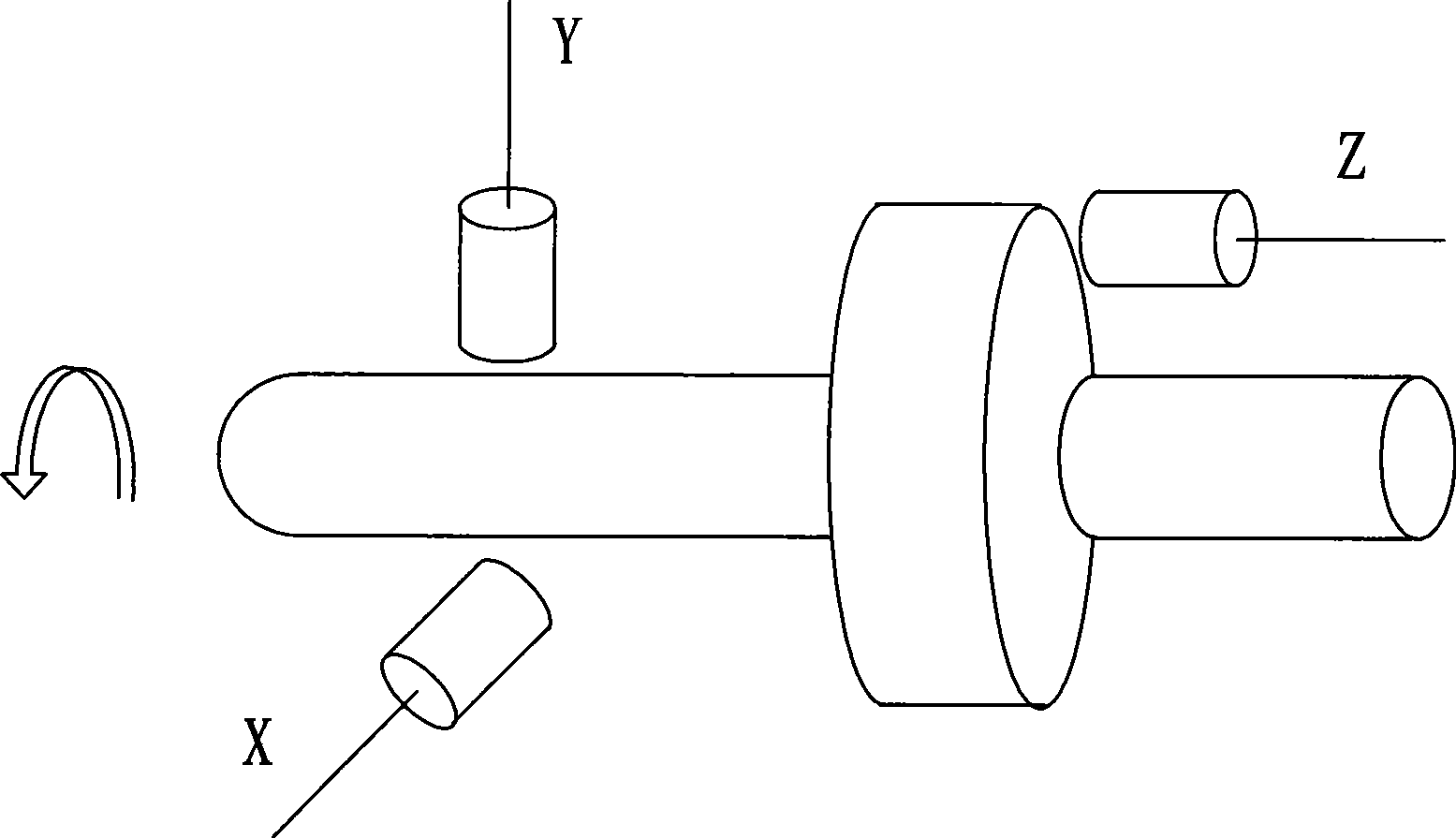
InactiveCN101387575AComprehensive descriptionAccurate descriptionMachine bearings testingInformation analysisPrecession
The invention discloses a rotor bearing system accident comprehensive information analysis method and a device thereof, wherein one section of a rotor is radial and vertically mounted with two sensors X, Y, the axle end of the rotor is axially mounted with a sensor Z, the radial and axial information of the rotor motion transmitted by the sensors are fused to analyze the motion state of the rotor bearing system, the axis center line position and the axis center track of the rotor in the X-Y, Y-Z and Z-X planes of a dimension space are described and displayed visibly to completely and accurately describe the spatial motion information of the rotor, and the information contains the unique diagnosis information as dimension space eccentricity, an attitude angle, a precession direction and vibration vector direction and the like, thereby improving the ability for visually recognizing the accidents of a rotary machine.
Owner:YANCON CATHAY COAL CHEM +2
Implantable artificial ventricular assist device
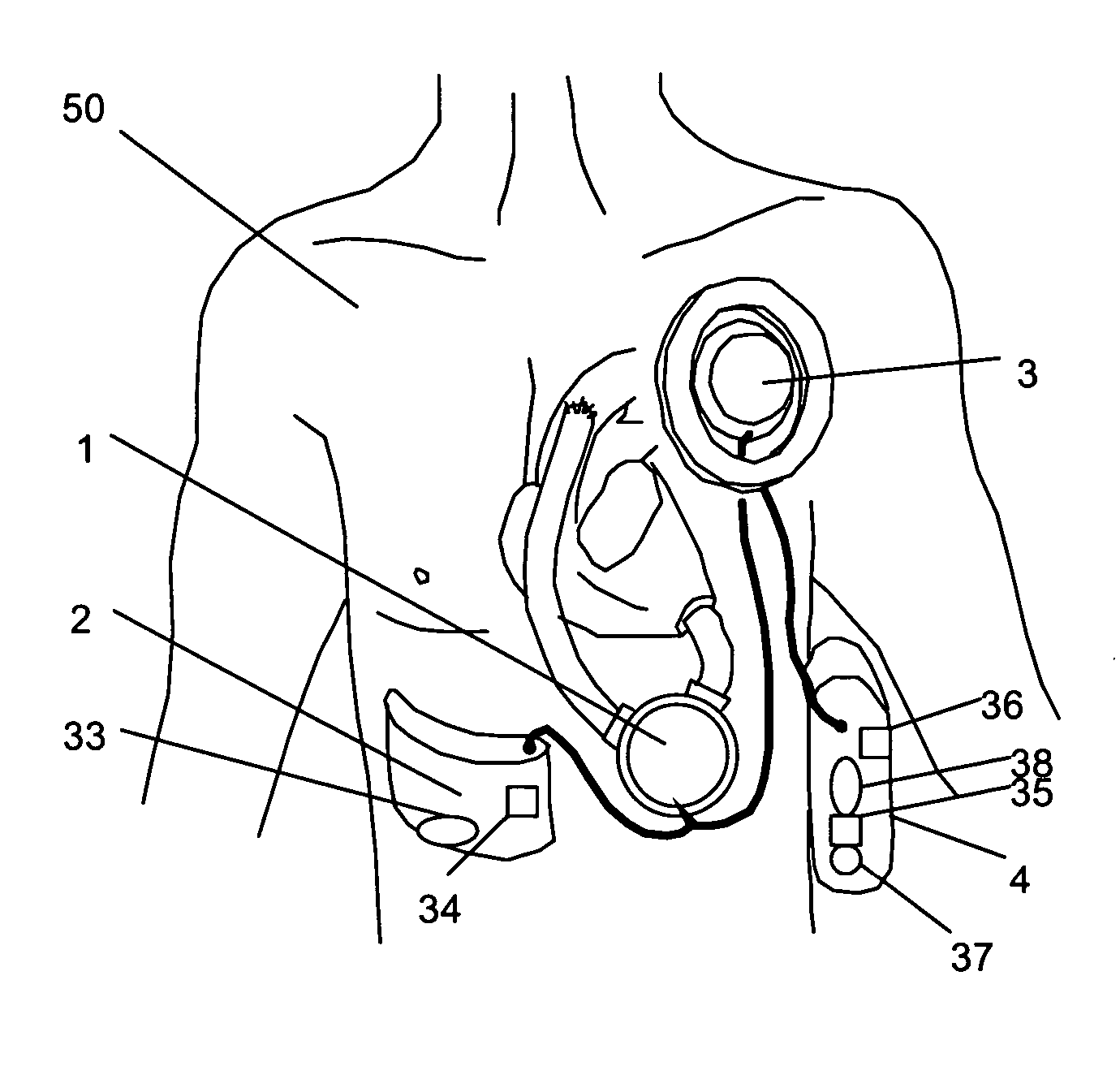
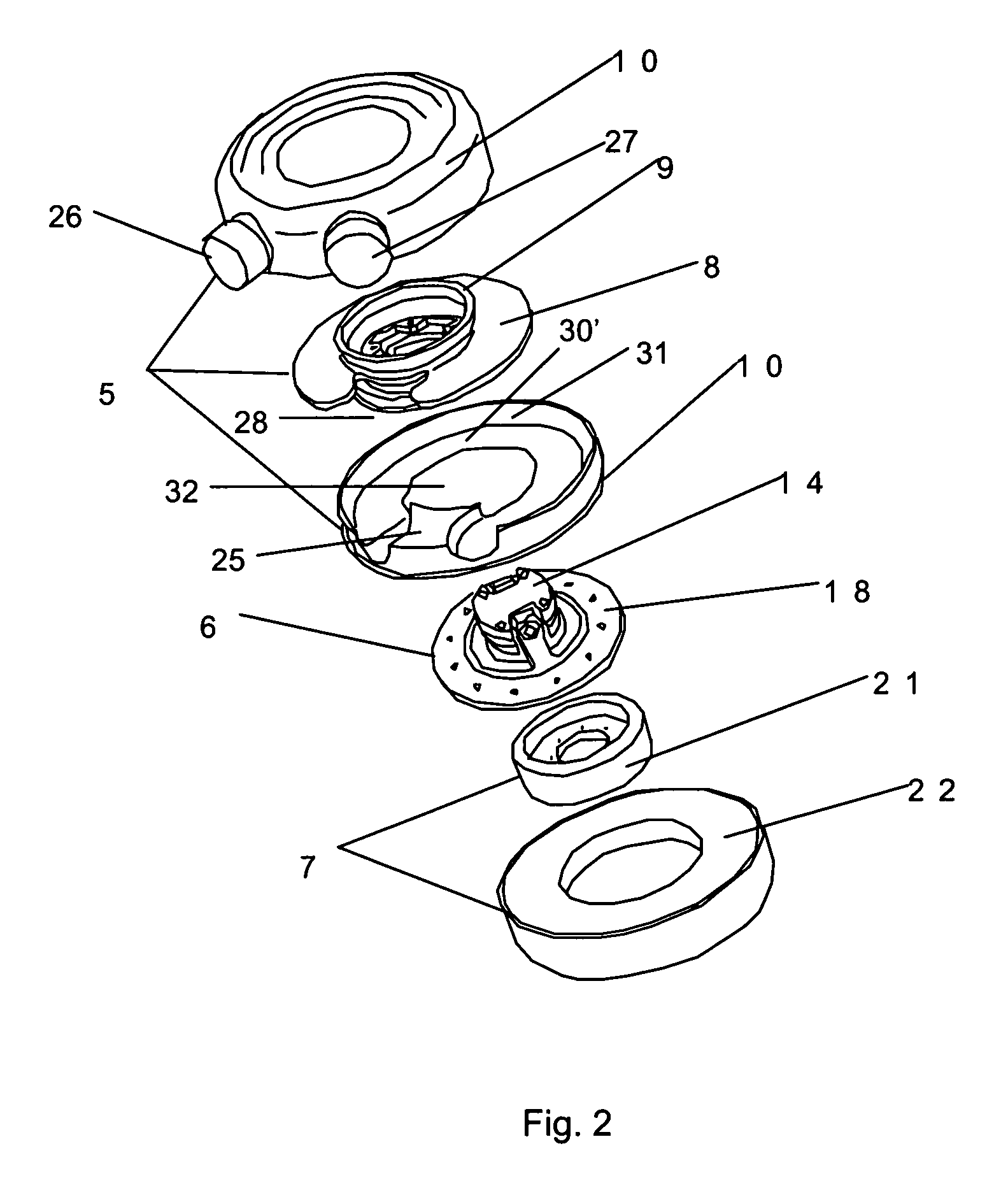
InactiveUS20050261543A1Improve securityIncreased durabilityFlexible member pumpsBlood pumpsPrecessionBiomedical engineering
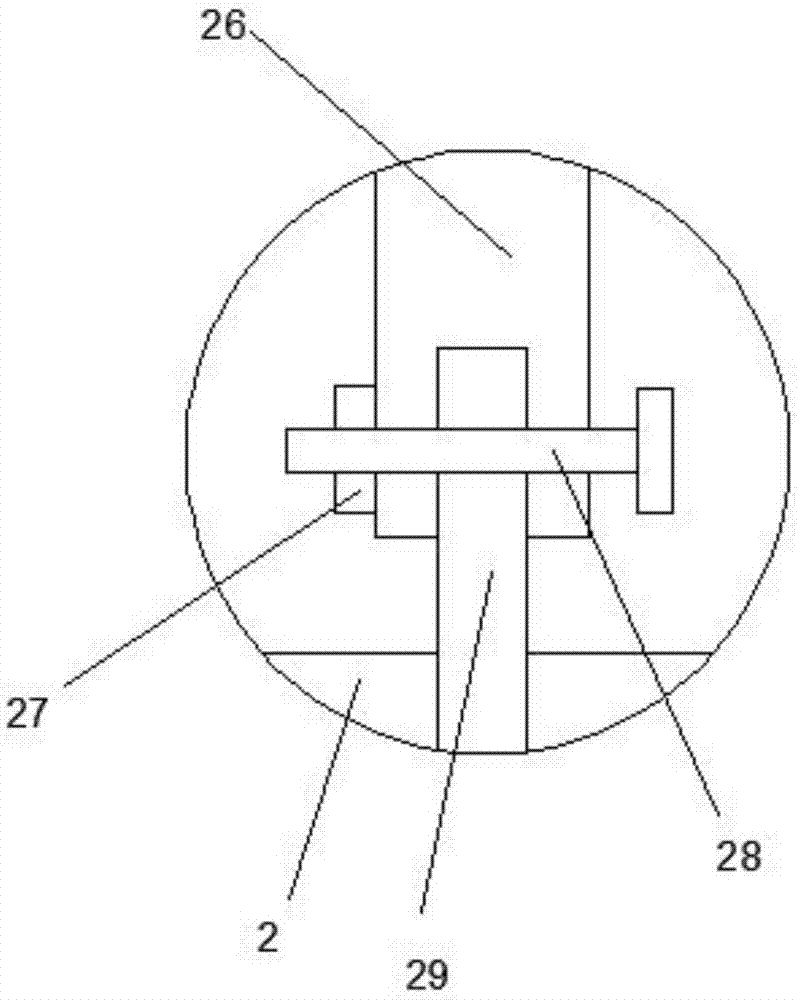
The present invention provides an implantable, artificial ventricular assist device and system employing an undulation pump and methods for the use thereof. The undulation pump has a toroidal-shaped pump chamber with two angled side walls, an arc-shaped outer wall, an inlet port, an outlet port, and an inner circumferential opening and an undulation disk with a diameter that extends to about the arc-shaped outer wall of the pump chamber. The device includes a circumferential, flexible inner wall membrane covering the inner circumferential opening and least one surface of the undulation disk and forming liquid-tight seals to the pump chamber, or alternatively a precession assembly with inner bearings connected in series with an anti-rotation assembly, the anti-rotation assembly disposed within the pump and connected to the undulation disk, and preferably both, and a motor in connected communication with the precession assembly so that the disk undulates when motive force is applied.
Owner:ABE YUSUKE +2
Method of determining and controlling the inertial attitude of a spinning, artificial satellite and systems therefor
InactiveUS20090222153A1Reduce material volumeHigh gainCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationNatural satelliteGyroscope
A method of and apparatus for determining and controlling the inertial attitude of a spinning artificial satellite without using a suite of inertial gyroscopes. The method and apparatus operate by tracking three astronomical objects near the Earth's ecliptic pole and the satellite's and / or star tracker's spin axis and processing the track information. The method and apparatus include steps and means for selecting preferably three astronomical objects using a histogram method and determining a square of a first radius (R12) of a track of a first astronomical object; determining a square of a second radius (R22) of a track of a second astronomical object; determining a square of a third radius (R32) of a track of a third astronomical object; determining the inertial attitude of the spin axis using the squares of the first, second, and third radii (R12, R22, and R32) to calculate pitch, yaw, and roll rate; determining a change in the pitch and yaw of the artificial satellite; and controlling on-board generated current flow to various orthogonally-disposed current-carrying loops to act against the Earth's magnetic field and to apply gyroscopic precession to the spinning satellite to correct and maintain its optimum inertial attitude.
Owner:JOHNSON KARA WHITNEY +1
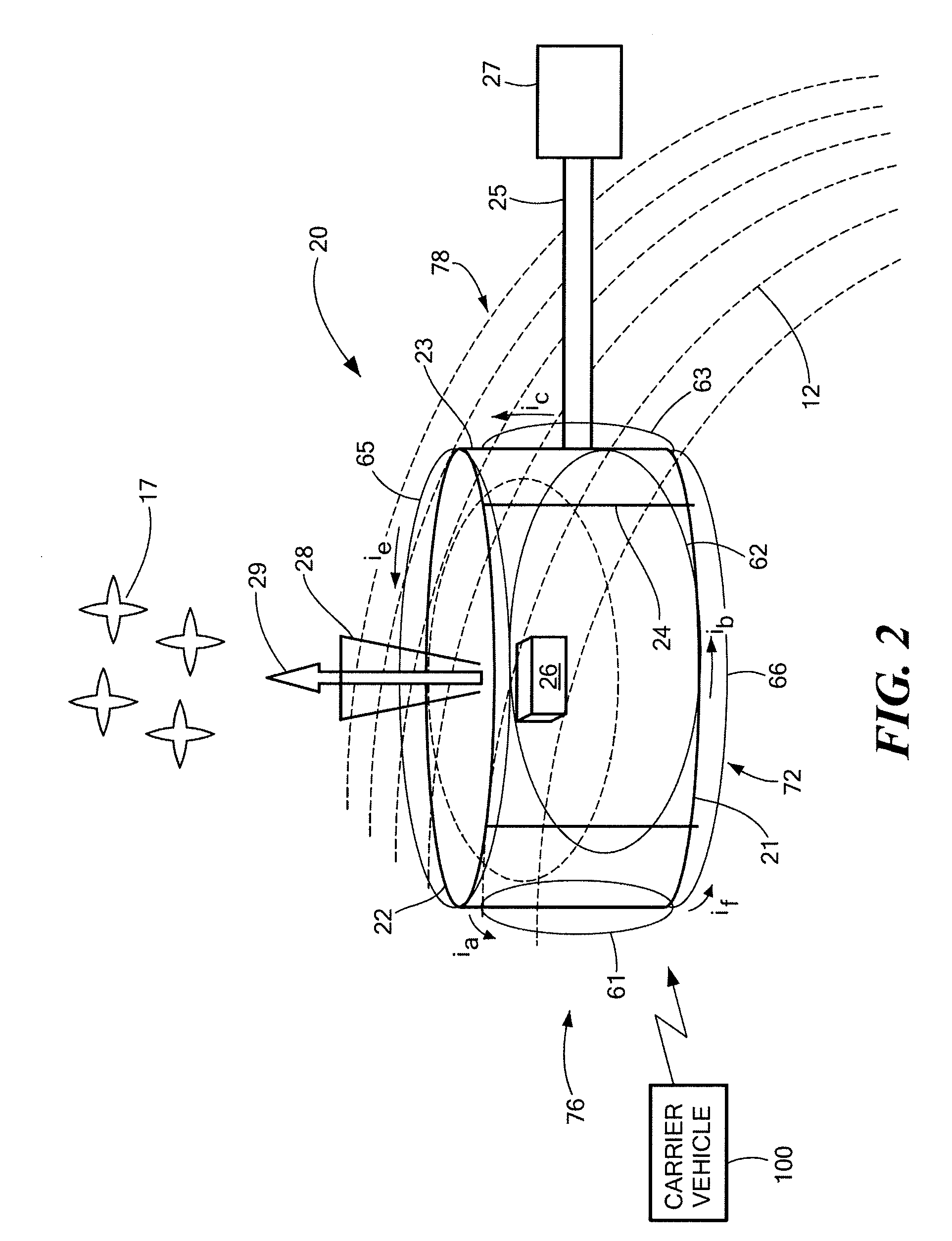
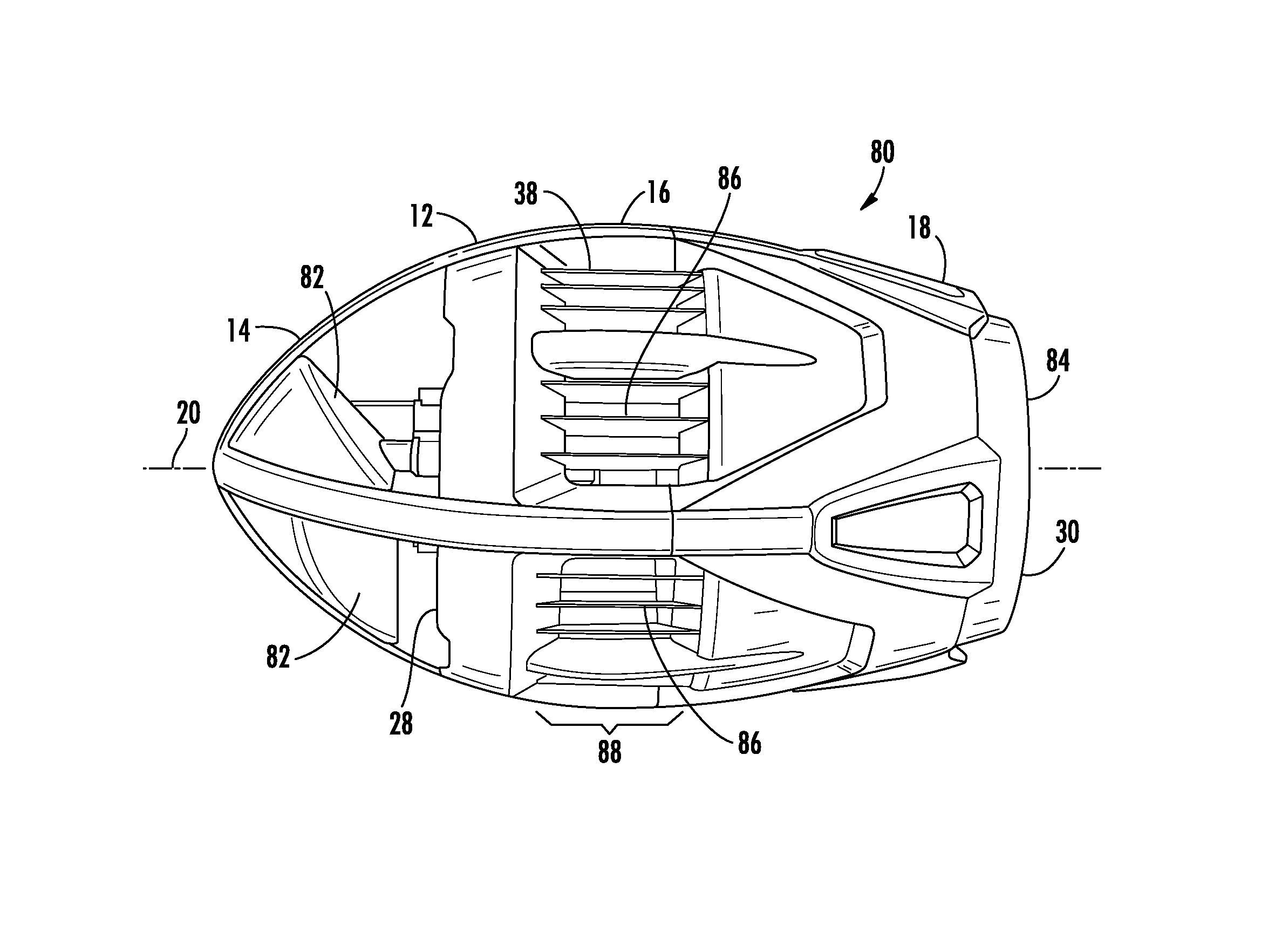
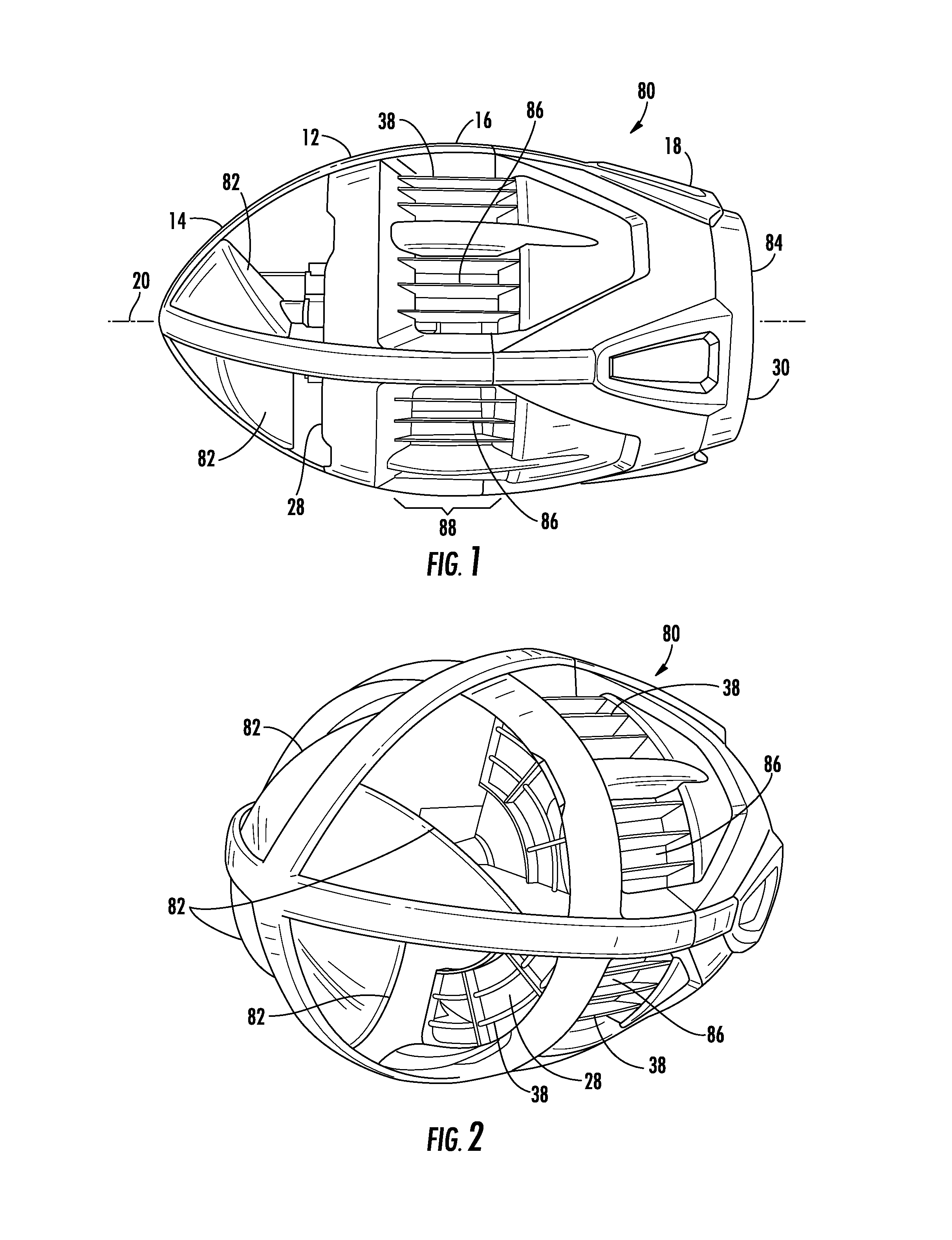
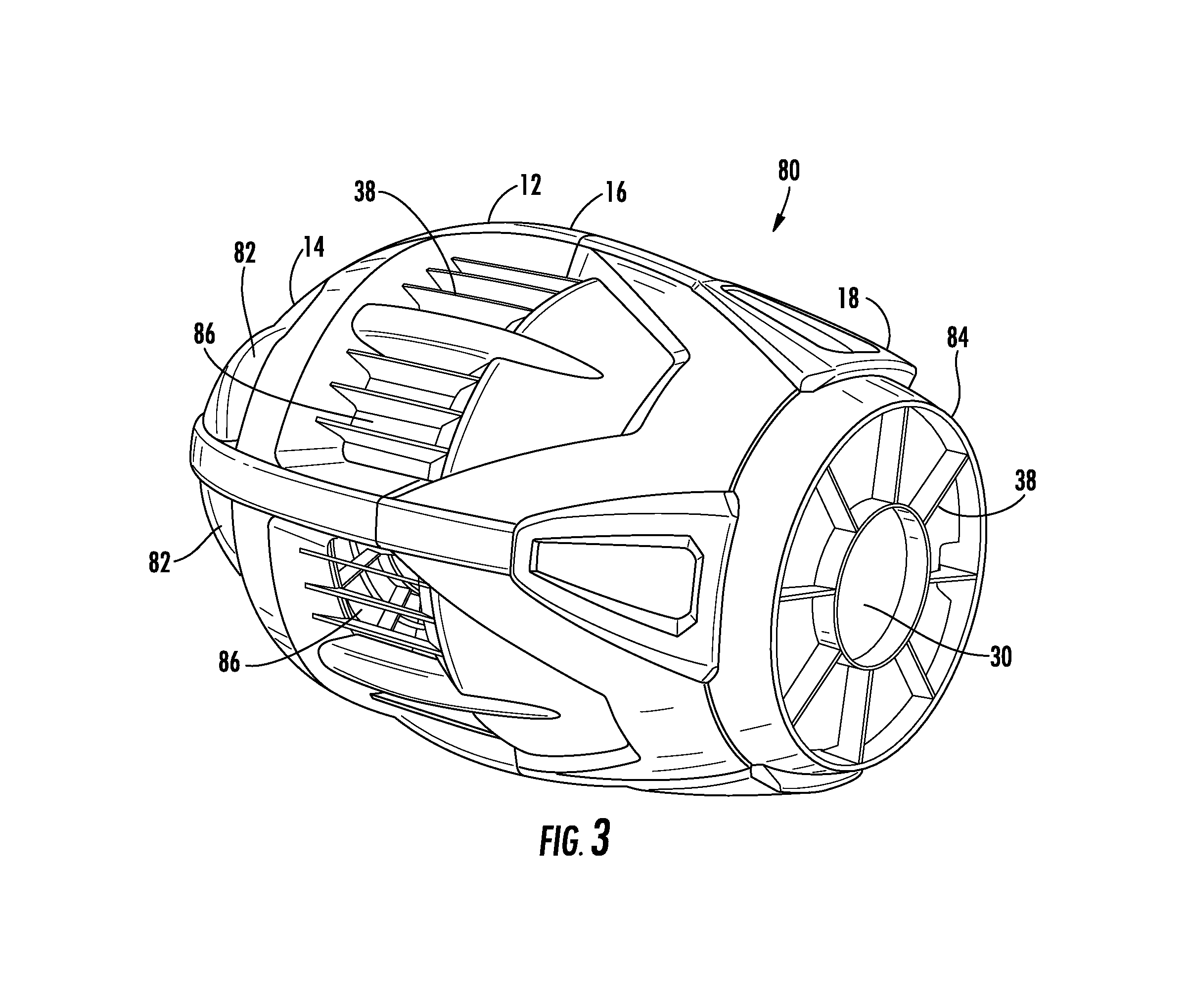
Self-propelled football with gyroscopic precession countermeasures
A self-propelled flying toy includes a body defined as having a front section, a center section and a back section each along a longitudinal axis. A ducted fan is located within the body substantially centered about the longitudinal axis. A motor is mechanically coupled to the ducted fan and a power source is coupled to the motor. An air-inlet is located substantially within the front section in airflow communication with the ducted fan. An air-outlet is located substantially within the back section in airflow communication with the ducted fan. At least two angled surfaces are fixed relative to the body and located substantially within the front section. Each of the at least two angled surfaces are evenly centered about the longitudinal axis and facing an opposite thrust-generating rotational direction relative to the ducted fan.
Owner:MARTINO MARC GREGORY
Atomic spin precession detection method and device based on circular polarization detection light
ActiveCN104677508AEffectively isolate the influence of light intensityIsolate the effect of light intensityOptical measurementsPrecessionPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention discloses an atomic spin precession detection method and device based on circular polarization detection light. The atomic spin precession detection method is based on spinning light characteristics of polarized atoms of an atom air chamber, left circular polarization light and right circular polarization light are formed through double refracted light paths, the left circular polarization light and the right circular polarization light are fed into the atom air chamber, phase position difference in direct proportion to atomic spin precession is generated from left spinning circular polarization light and right spinning circular polarization light of the air chamber, outgoing circular polarization light is fed back along the original path by using a reflection mirror, the left and right spinning directions of the left spinning circular polarization light and the right spinning circular polarization light are switched, the phase position difference is multiplied, the left spinning circular polarization light and the right spinning circular polarization light are interfered according to a circular polarization light interference technique, and thus phase position difference measurement and high-sensitivity detection on atomic spin precession detection are achieved. Atomic spin precession detection can be achieved, and the atomic spin precession detection device is high in precision, sensitivity, and anti-interference capability and small in size. The method and the device are practical, and super high in sensitivity and precision when provided for an atomic spin precession sensor based on atomic spin precession detection.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com