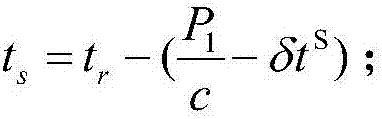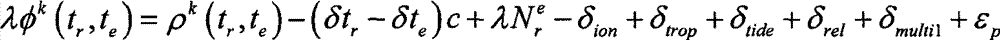Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
822 results about "Natural satellite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
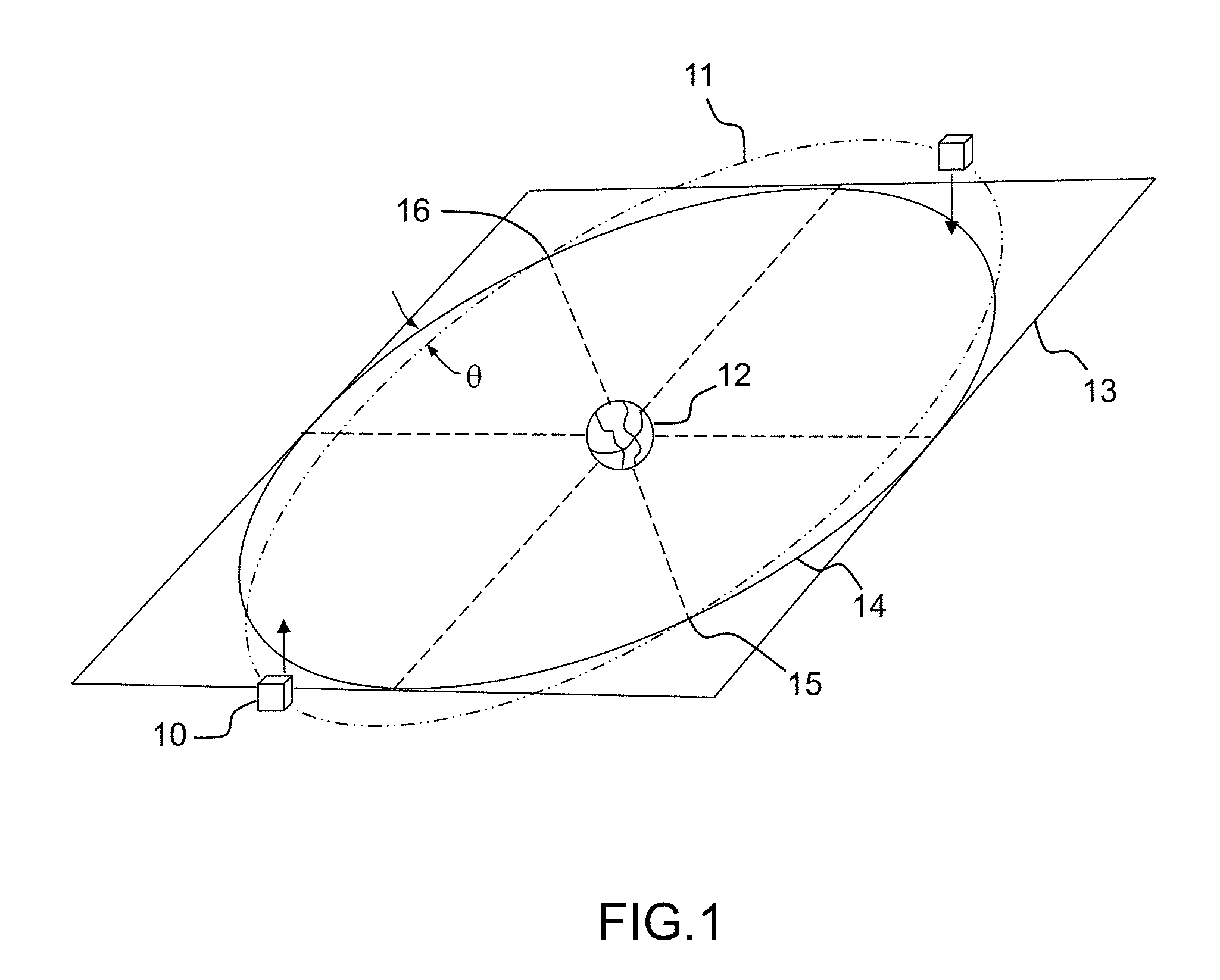
A natural satellite, or moon, is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet or minor planet (or sometimes another small Solar System body). In the Solar System there are six planetary satellite systems containing 205 known natural satellites. Four IAU-listed dwarf planets are also known to have natural satellites: Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris. As of September 2018, there are 334 other minor planets known to have moons.
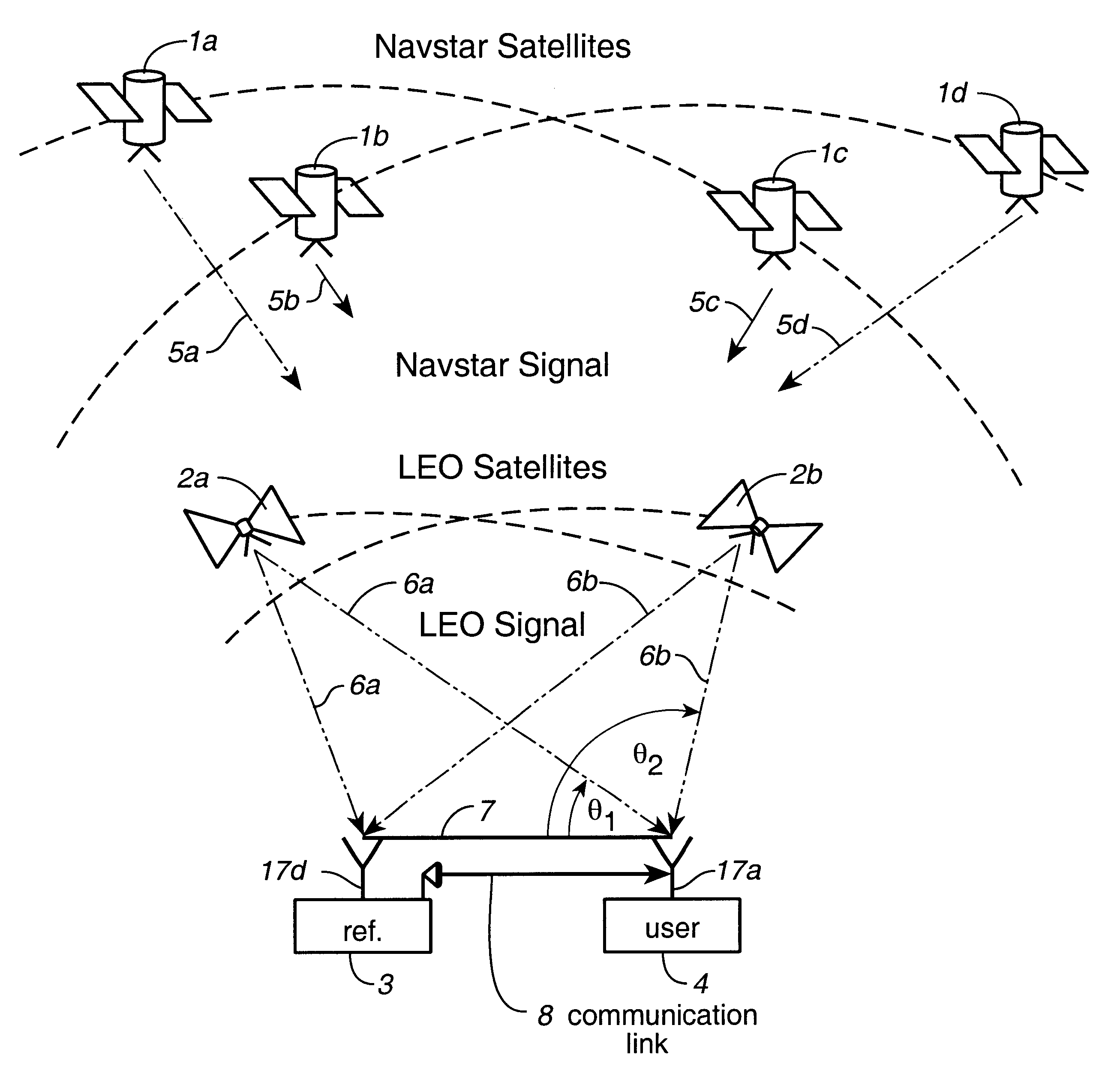
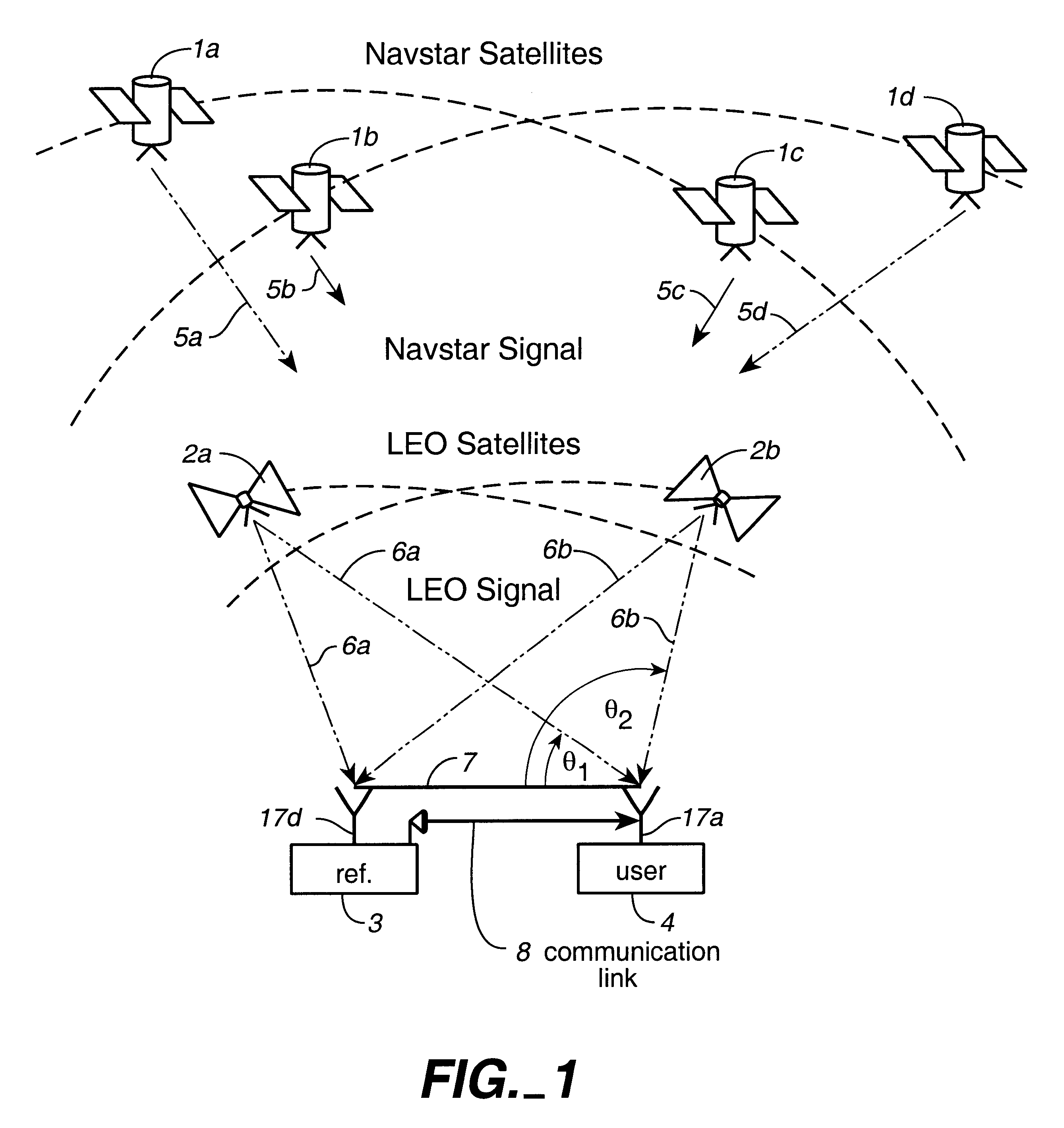
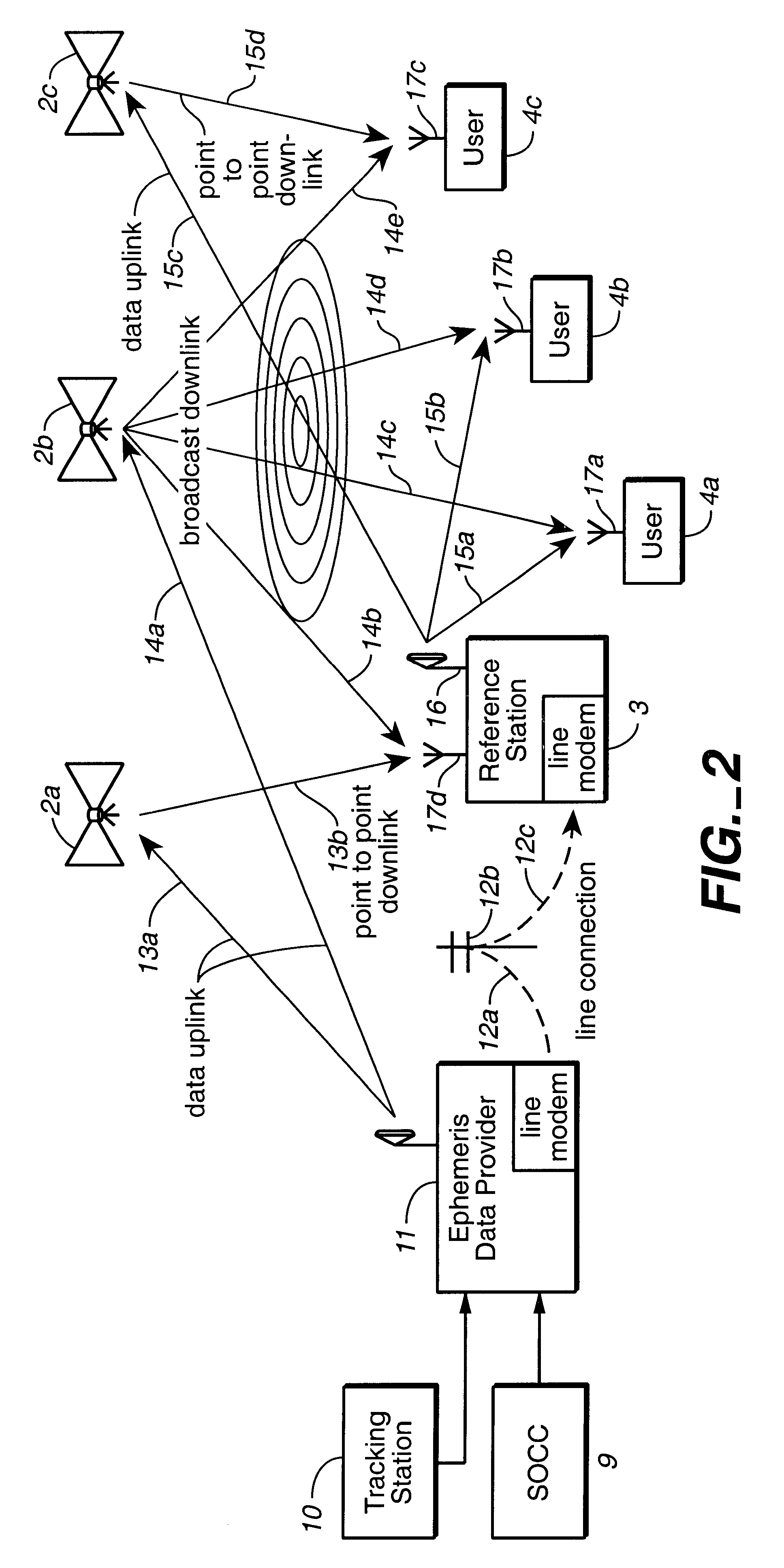
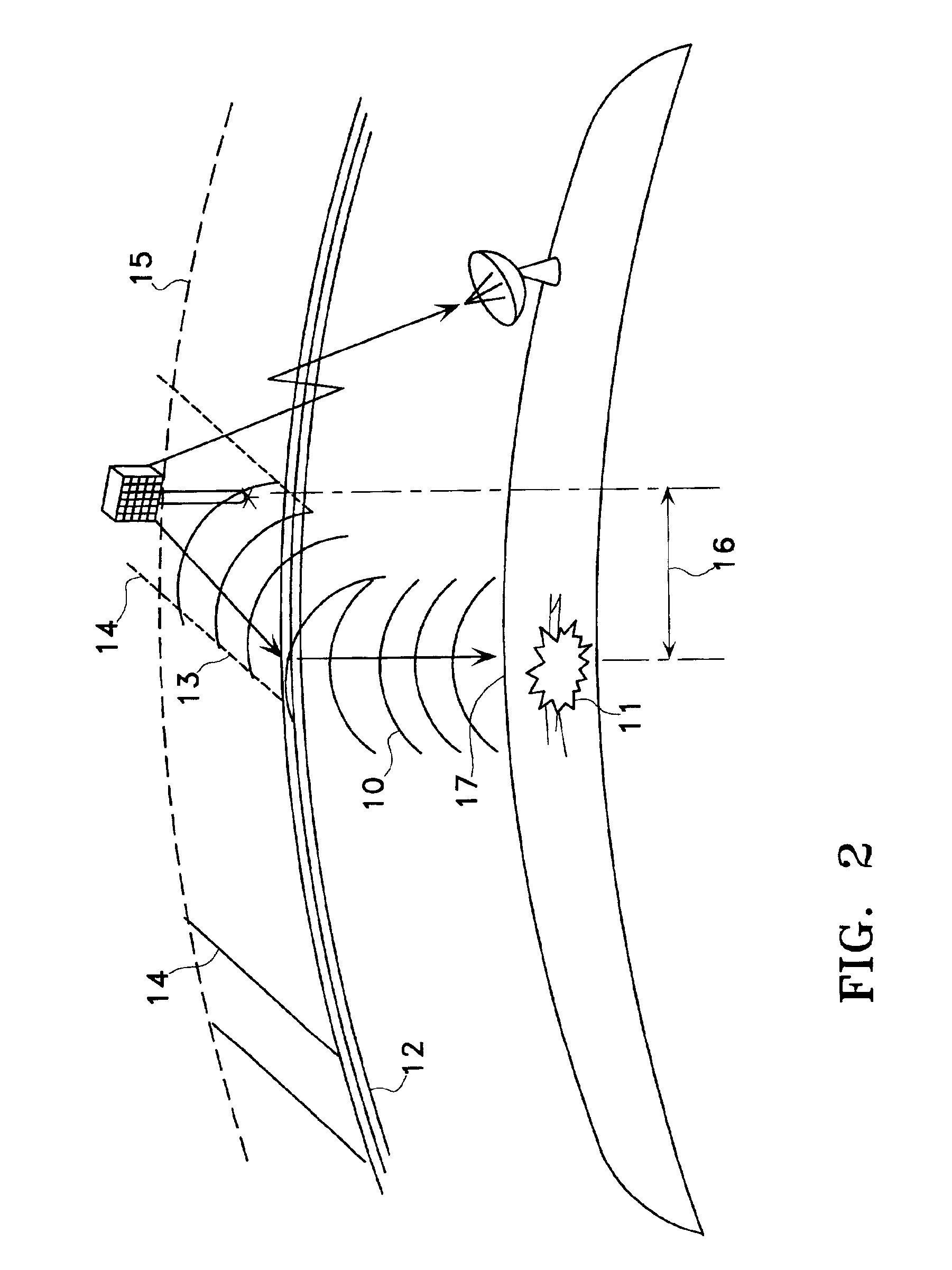
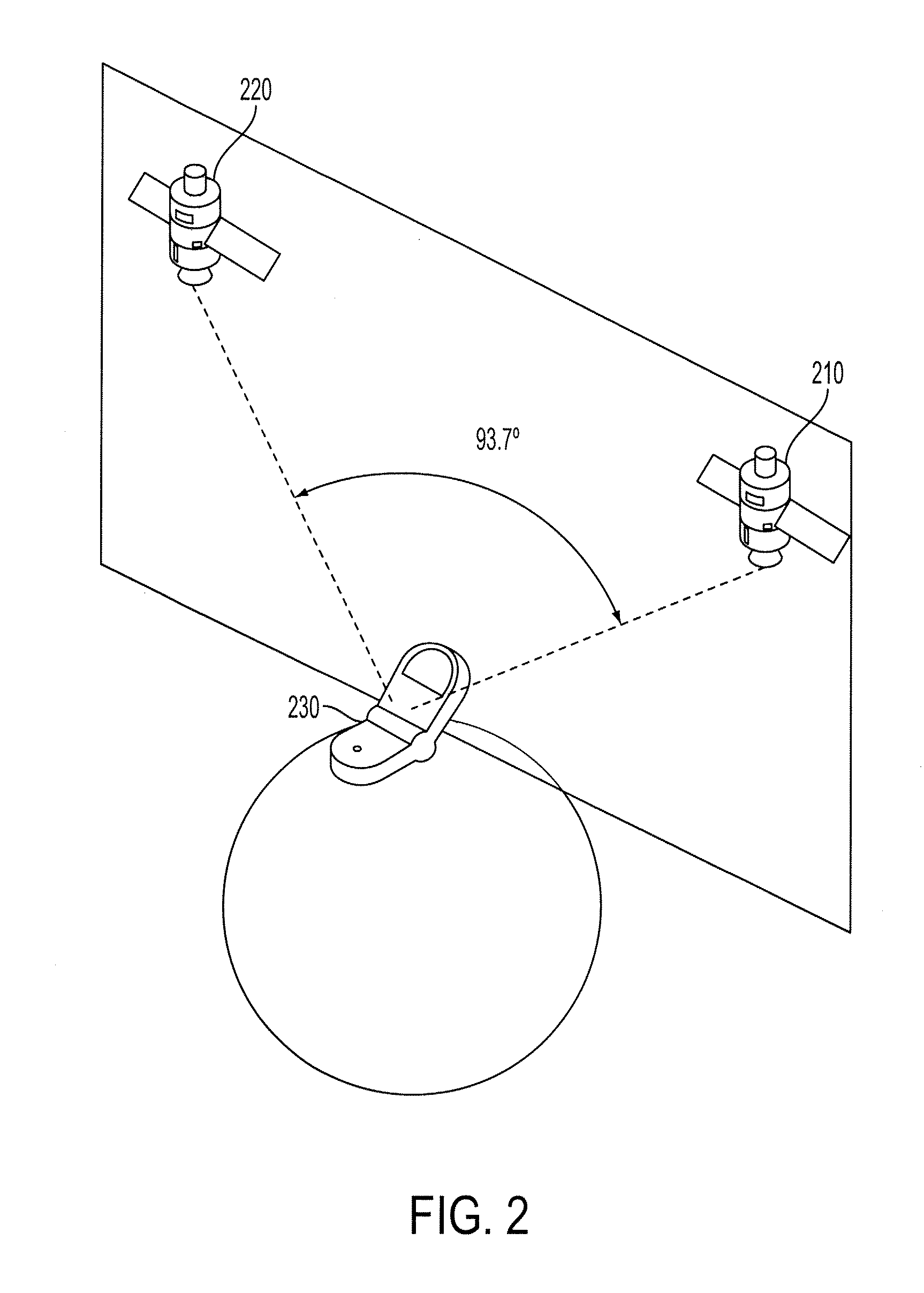
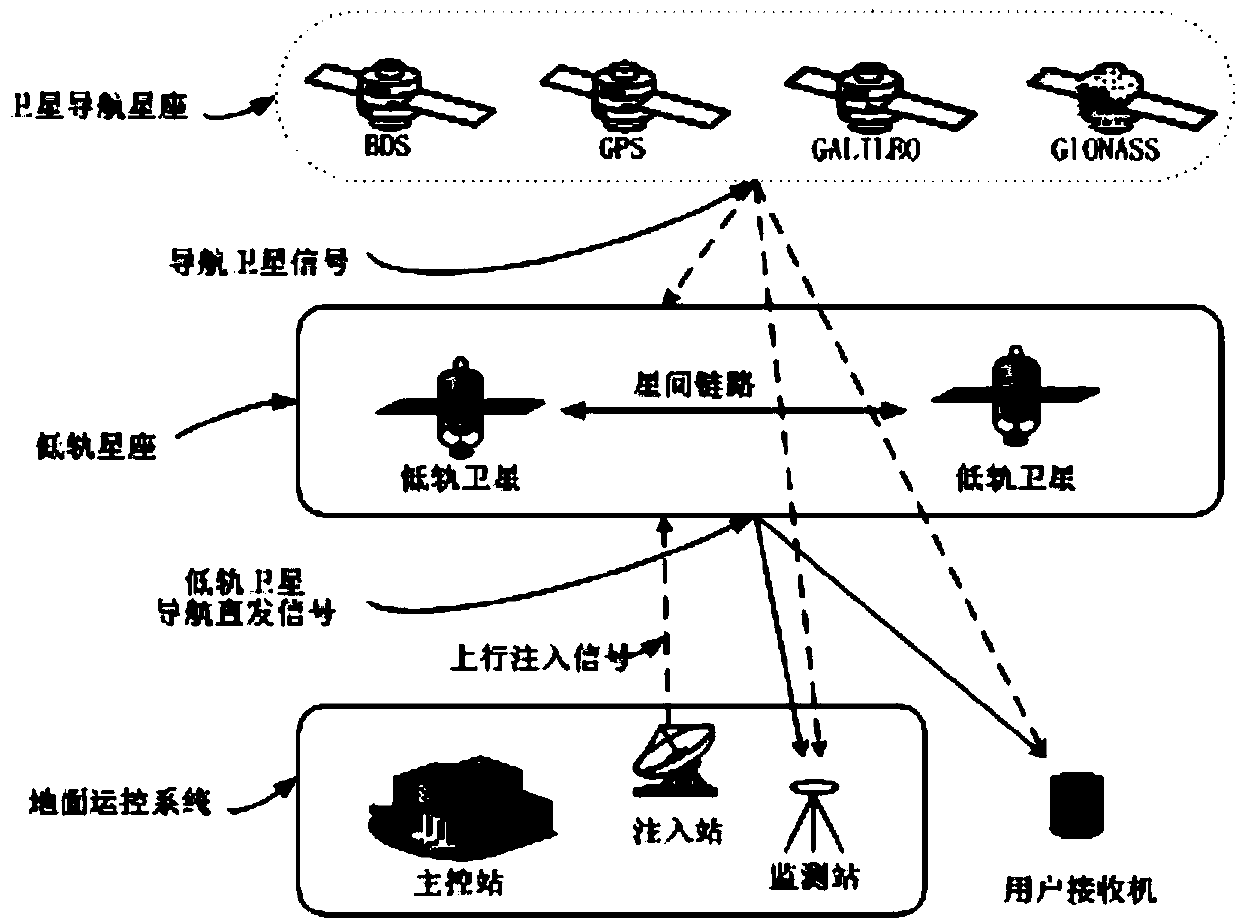
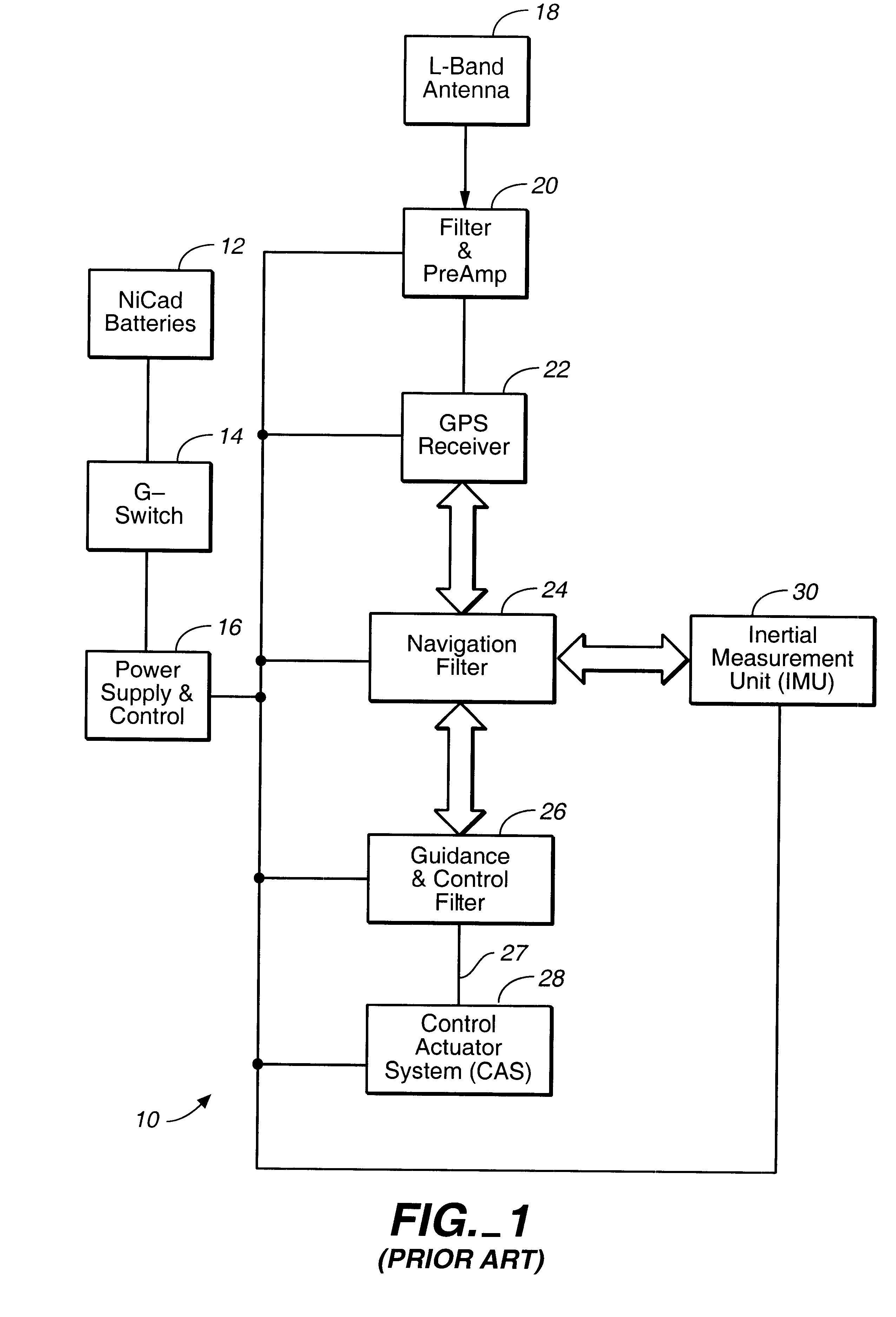
System using leo satellites for centimeter-level navigation
InactiveUS6373432B1Improve reliabilityEasy accessPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNatural satelliteAmbiguity
Disclosed herein is a system for rapidly resolving position with centimeter-level accuracy for a mobile or stationary receiver [4]. This is achieved by estimating a set of parameters that are related to the integer cycle ambiguities which arise in tracking the carrier phase of satellite downlinks [5,6]. In the preferred embodiment, the technique involves a navigation receiver [4] simultaneously tracking transmissions [6] from Low Earth Orbit Satellites (LEOS) [2] together with transmissions [5] from GPS navigation satellites [1]. The rapid change in the line-of-sight vectors from the receiver [4] to the LEO signal sources [2], due to the orbital motion of the LEOS, enables the resolution with integrity of the integer cycle ambiguities of the GPS signals [5] as well as parameters related to the integer cycle ambiguity on the LEOS signals [6]. These parameters, once identified, enable real-time centimeter-level positioning of the receiver [4]. In order to achieve high-precision position estimates without the use of specialized electronics such as atomic clocks, the technique accounts for instabilities in the crystal oscillators driving the satellite transmitters, as well as those in the reference [3] and user [4] receivers. In addition, the algorithm accommodates as well as to LEOS that receive signals from ground-based transmitters, then re-transmit frequency-converted signals to the ground.
Owner:INTEGRINAUTICS
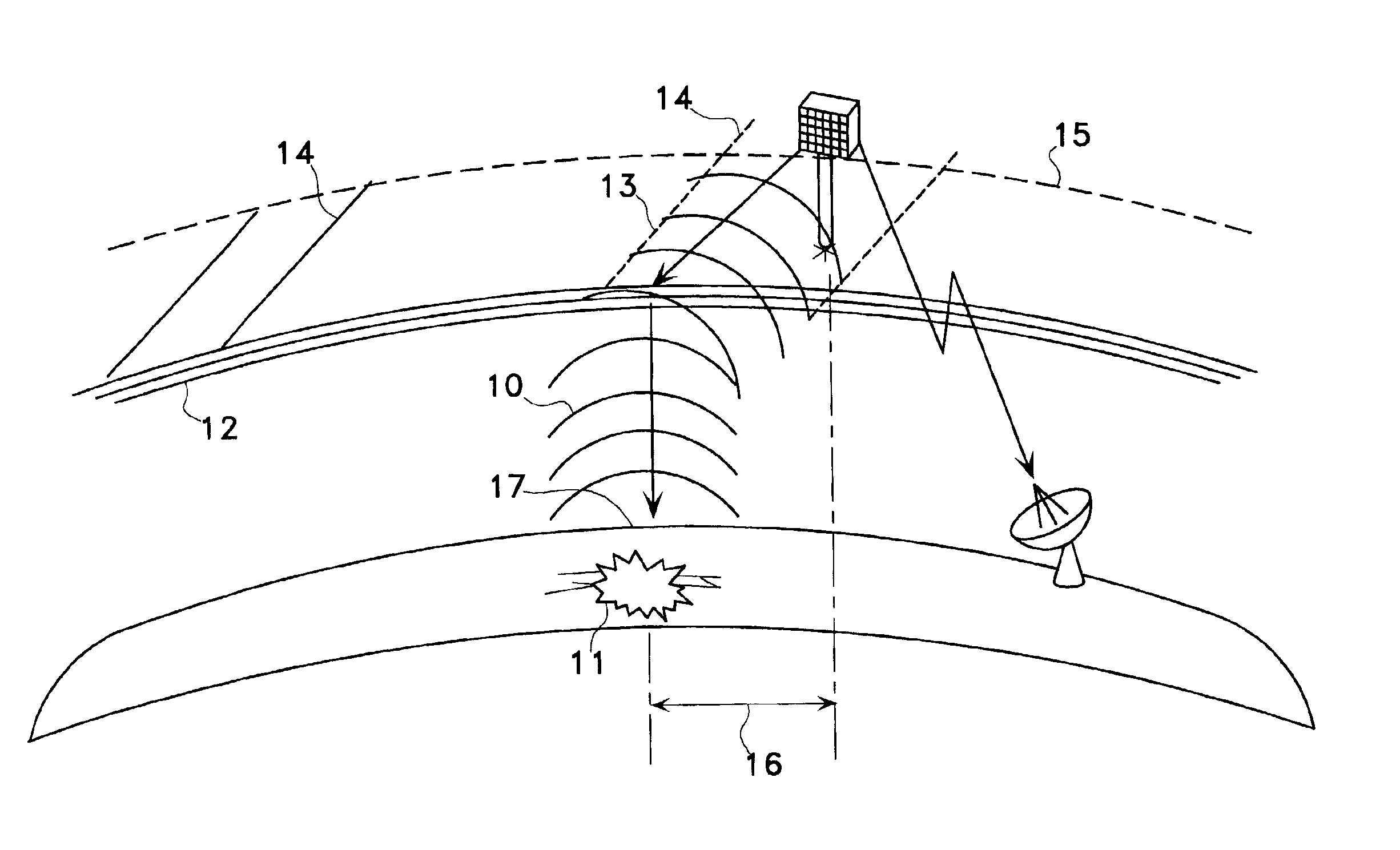
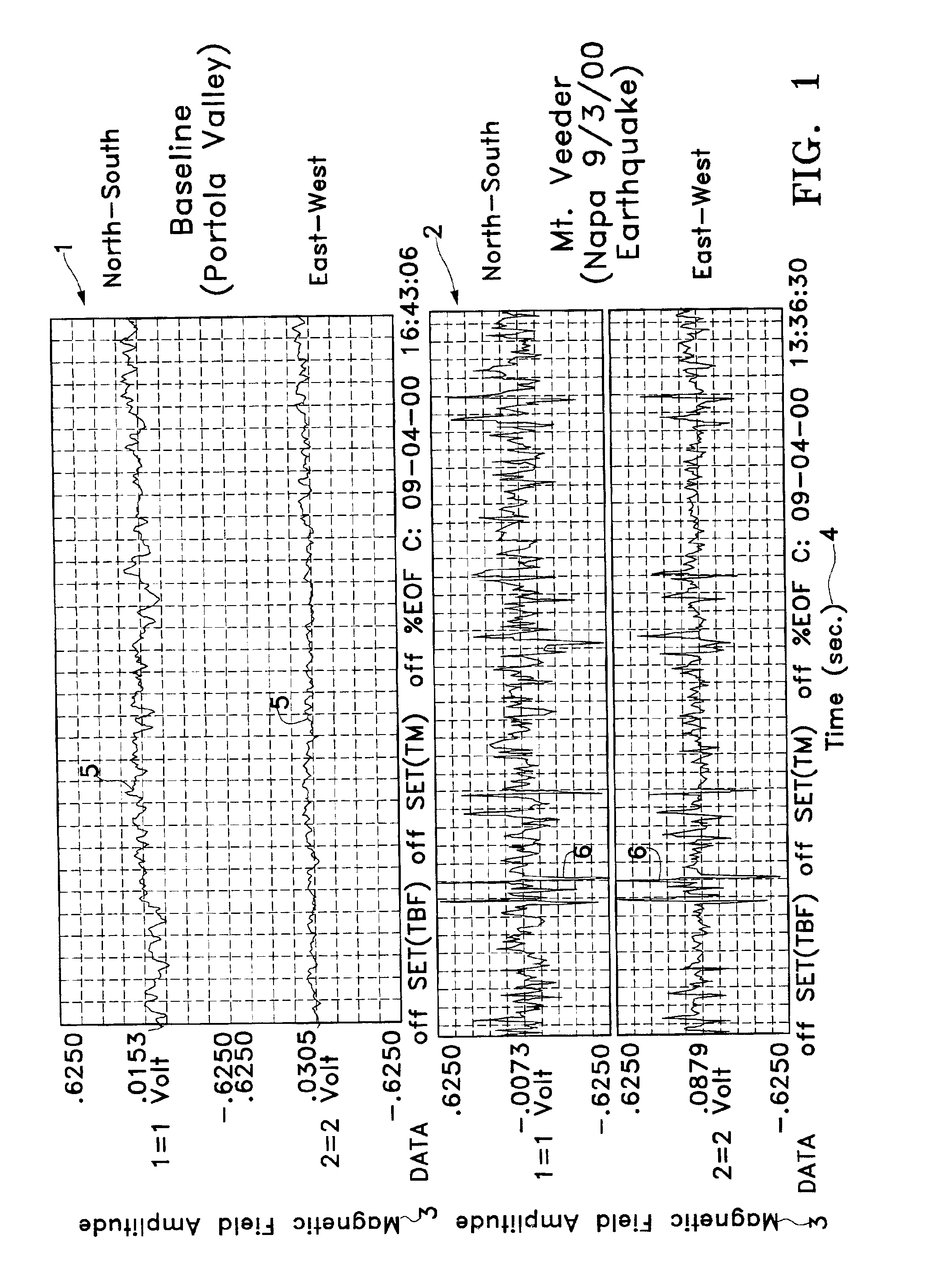
Satellite and ground system for detection and forecasting of earthquakes
InactiveUS6873265B2Low costSignificant comprehensive benefitsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementEarthquake measurementNatural satelliteWide area
The present invention describes the use of a space-based Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) magnetic field detector in conjunction with ground-based network of ELF magnetic field detectors. In particular, a space based ELF detection system can be used to perform a wide area search and find precursor earthquake signals in both known and unknown earthquake zones, and a ground-based network of ELF detectors can be used to verify that the signals are indeed earthquake generated signals. The use of this invention will minimize cost and manpower necessary to effectuate an accurate and reliable earthquake detection system.
Owner:STELLAR SOLUTIONS
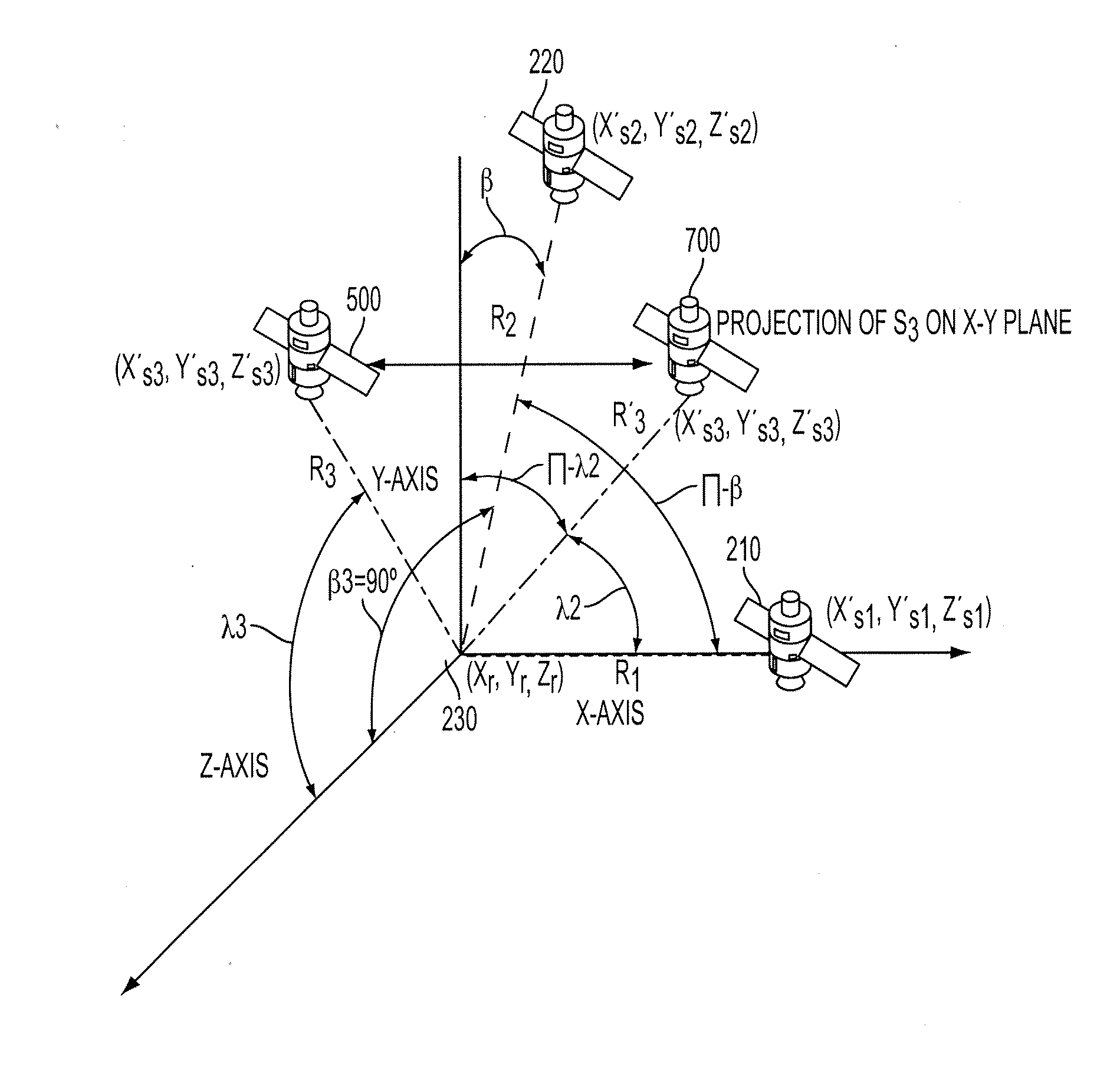
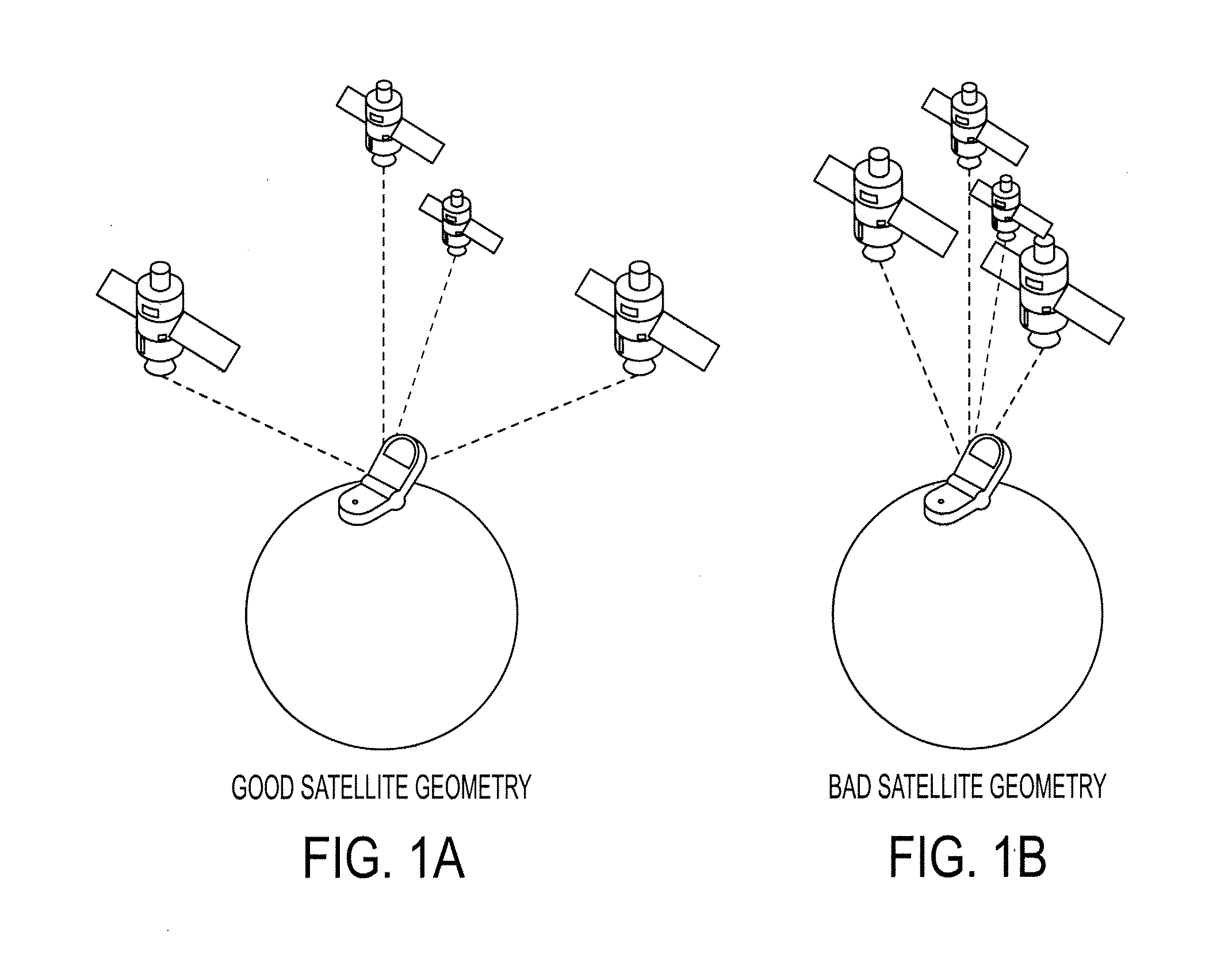
Determining A Dilution of Precision Metric Using Two or Three GPS Satellites
The disclosed subject matter relates to a method for determining a Dilution of Precision Metric (DOP) with less than four satellites in a hybrid positioning system. In some embodiments, the method includes determining an initial position estimate of a device using a non-satellite positioning system, obtaining satellite measurements from less than four satellites, wherein the measurements include each satellite's position with respect to the initial position estimate, constructing a geometry matrix corresponding to the measurements from the less than four satellites using each satellite's position and the initial position estimate, multiplying the geometry matrix by its transpose to construct an H matrix, determining an inverse of the H matrix, and determining the DOP based on a sum of the diagonal elements of the inverse H matrix. In some embodiments, the non-satellite positioning system is a WLAN positioning system.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
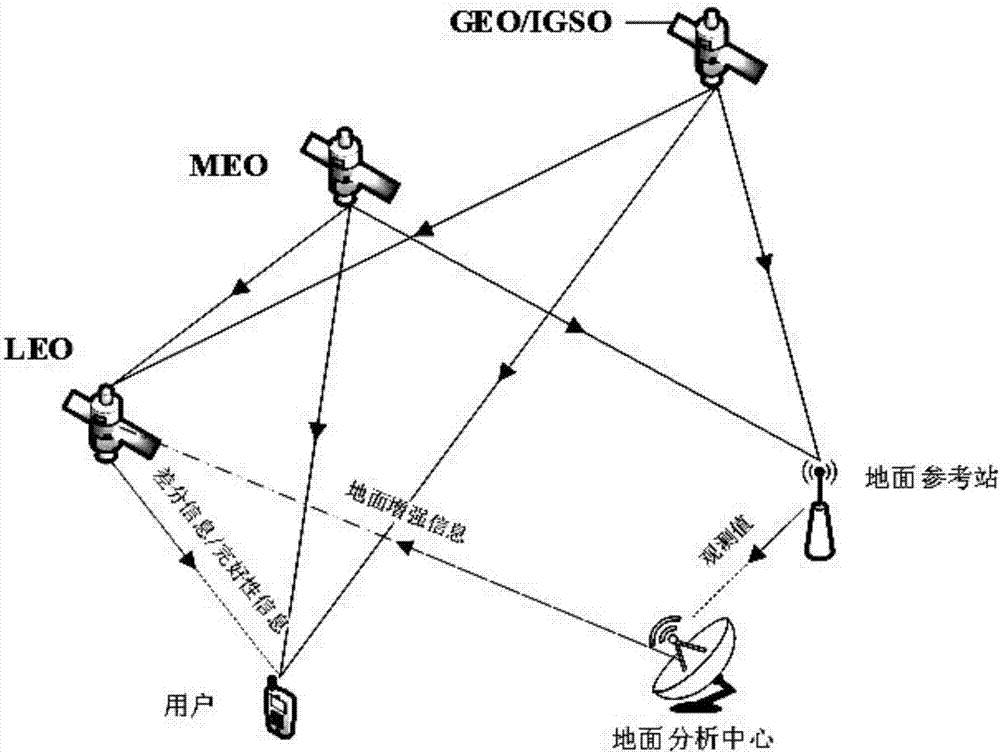
Low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method
ActiveCN107229061ARapid positioningRealize Differential Positioning ServiceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceNatural satellite
The invention belongs to the satellite navigation and positioning technical field and discloses a low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method. A low earth orbit satellite is utilized to broadcast the observation data and real-time orbit data of the satellite-borne GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver of the low earth orbit satellite to the ground; and after receiving the differential information broadcasted by the low earth orbit satellite, a ground receiver generates a double-difference observation value consisting of the differential information and a local GNSS observation value and performs pseudorange-based moving base station DGNSS (Differential Navigation Satellite System) positioning and carrier phase-based moving base station RTK (Rea-time kinematic) positioning. According to the positioning method of the invention, the global mobile low earth orbit satellite platform is adopted as a reference station, so that real-time precision differential positioning service in the whole world can be realized, and the method does not depend on the distribution of ground reference stations; and a user can realize differential real-time precise positioning just through using a single receiver, and therefore, the method is free of operating range restrictions, and data communication links are not required to be considered.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
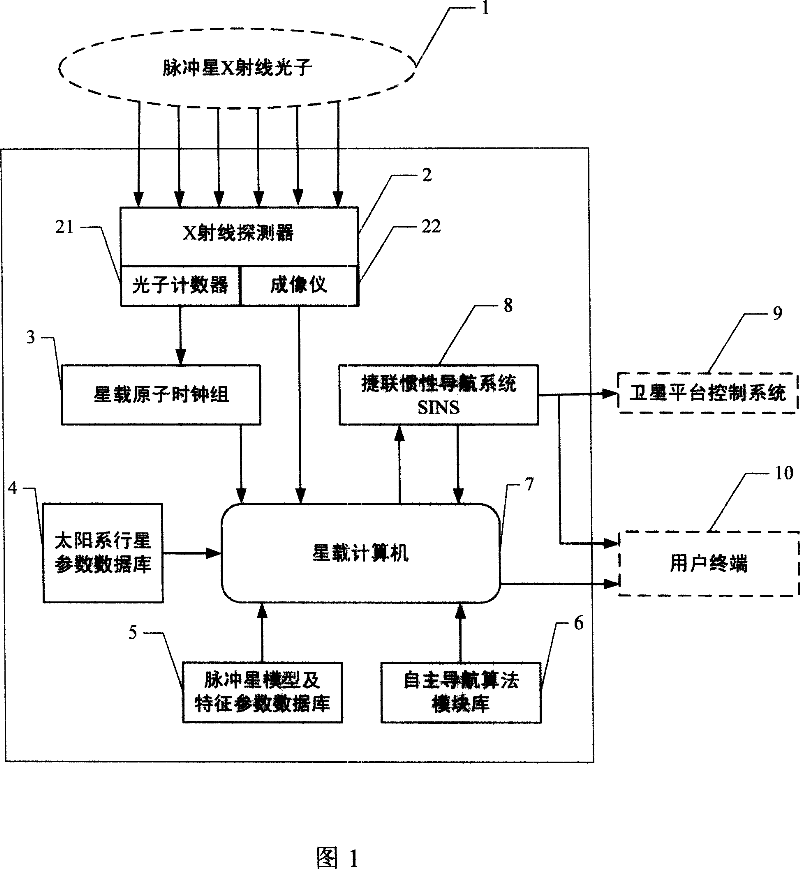
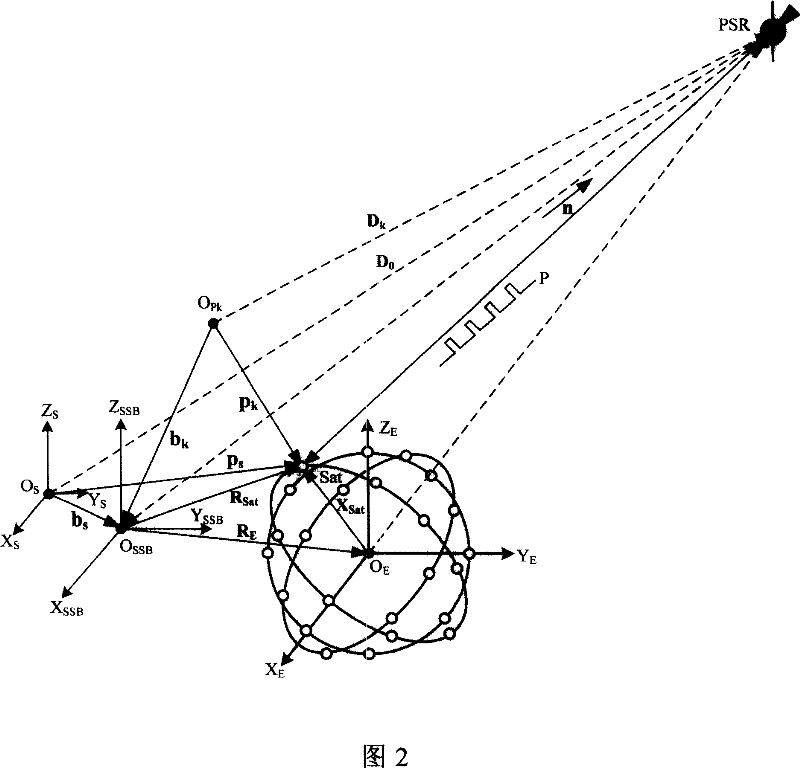
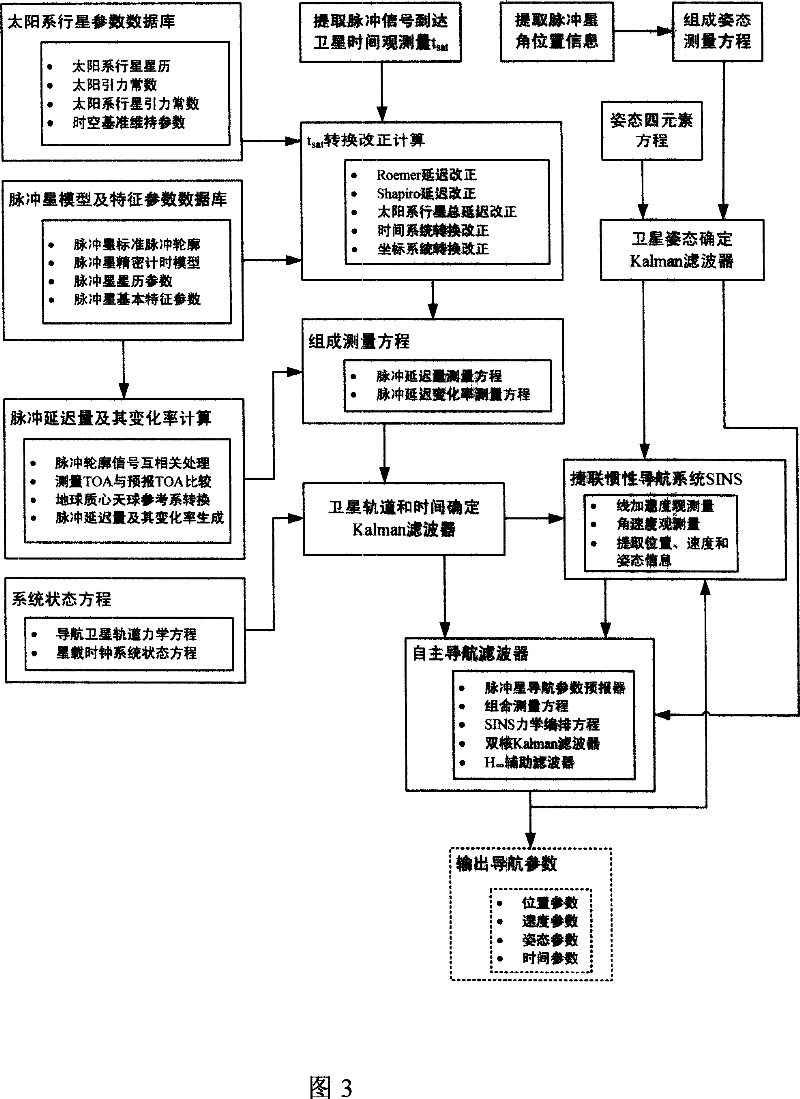
Navigation satellite autonomous navigation system and method based on X-ray pulsar
InactiveCN101038169AHigh precision autonomous navigationStable periodicityInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansFault toleranceInformation processing
A autonomous navigation system of a navigational satellite based on X radial pulse satellite includes: an X radial detector, an atomic clock group on the satellite, a planet of our solar system parameter database, an X radial pulsar module and a characteristic parameter database, a computer on the satellite, a strap-down inertial navigation system SINS and an autonomous navigation algorithm module library; in the autonomous navigation method, the X radial photons radiated from the pulsar are used as the input of the external information; the pulse arrival time TOA and the angular position information are obtained; data is processed through a autonomous navigation filter; and the navigational parameters such as the position, the speed, the time and the pose of the navigational satellite; the navigational telegraph text and the control command are generated independently, and the independent running of the navigational satellite is realized. The present invention has the advantages of providing a long time and a high degree of accuracy autonomous navigation, and providing the fault-tolerance capacity of the autonomous navigation information processing. The autonomous navigation system is also be adequate for the high degree of accuracy autonomous navigation of the near earth orbit, the deep space, the interplanetary flight space vehicle, the a celestial body lander without thickset atmosphere and the surface peripatetic machine.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
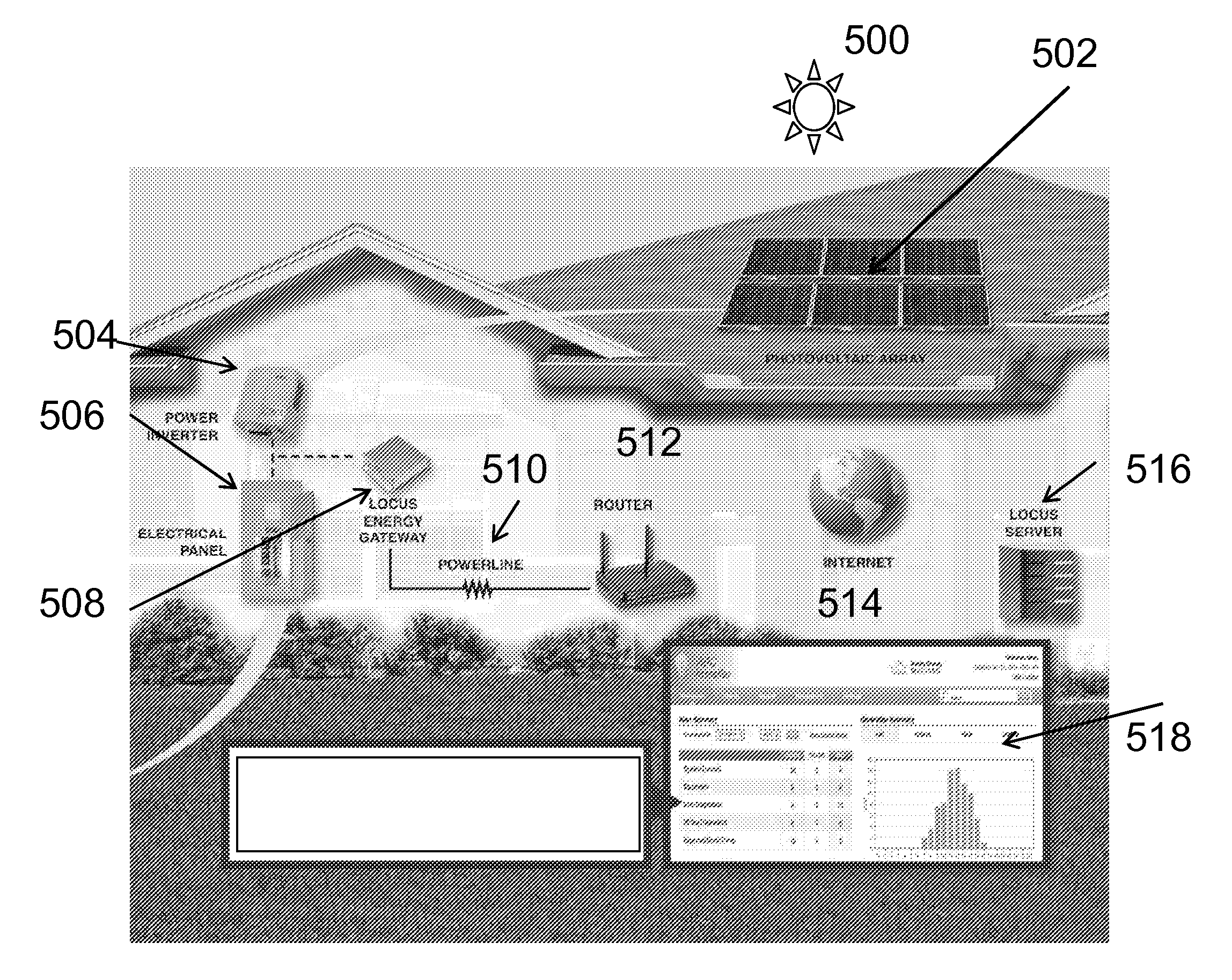
Weather and satellite model for estimating solar irradiance
ActiveUS20130166266A1Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkNatural satelliteThe Internet
Solar irradiance, the energy from the Sun's electromagnetic radiation, has a wide range of applications from meteorology to agronomy to solar power. Solar irradiance is primarily determined by a location's spatial relationship with the Sun and the atmospheric conditions that impact the transmission of the radiation. The spatial relationship between the Sun and a location on Earth is determined by established astronomical formulas. The impact of atmospheric conditions may be estimated via proxy using pixels from satellite imagery. While satellite-based irradiance estimation has proven effective, availability of the input data can be limited and the resolution is often incapable of capturing local weather phenomena. Brief qualitative descriptions of general atmospheric conditions are widely available from internet weather services at higher granularity than satellite imagery. This methodology provides logic for quantifying the impact of qualitative weather observations upon solar irradiance, and the integration of this methodology into solar irradiance estimation models.
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
Attitude control system for small satellites
Various embodiments of the present invention include an attitude control system for use with small satellites. According to various embodiments, the system allows rapid retargeting (e.g., high slew rates) and full three-axis attitude control of small satellites using a compact actuation system. In certain embodiments, the compact actuation system includes a plurality of single-gimbaled control moment gyroscopes (SGCMG) arranged in a pyramidal configuration that are disposed within a small satellite.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
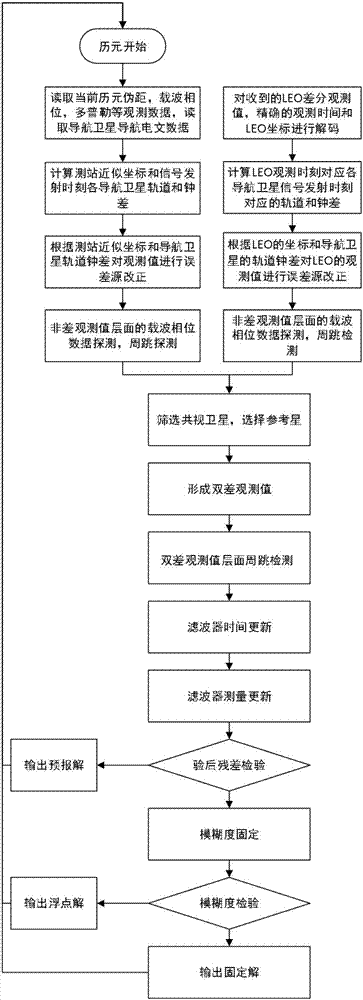
Real-time precise orbit determining method of short orbit arc low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellite
ActiveCN107153209AError Effect CompensationLow priceSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteData center
The invention discloses a real-time precise orbit determining method of a short orbit arc low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellite. The method is characterized in that four or more ground receivers are used for tracking navigation signals of a plurality of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) navigation satellites and LEO navigation satellites, and transmitting the navigation signals to a data center in real time. The method comprises the following steps: I, acquiring and preprocessing observing data; II, performing precise time synchronization on the receivers; III, calculating tropospheric delay in an LEO gazing direction by using tropospheric delay in a vertical direction and a projection function; IV, correcting hardware delay of the receivers to build an LEO determining geometric observing equation; V, solving an LEO precise orbit and a precise clock error through a dynamical model and the geometric equation of the LEO; VI, distributing the LEO precise orbit and the precise clock error in real time. By adopting the method, the problem of need of post-processing due to incapability of calculating the precise orbit of a low earth orbit satellite can be solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
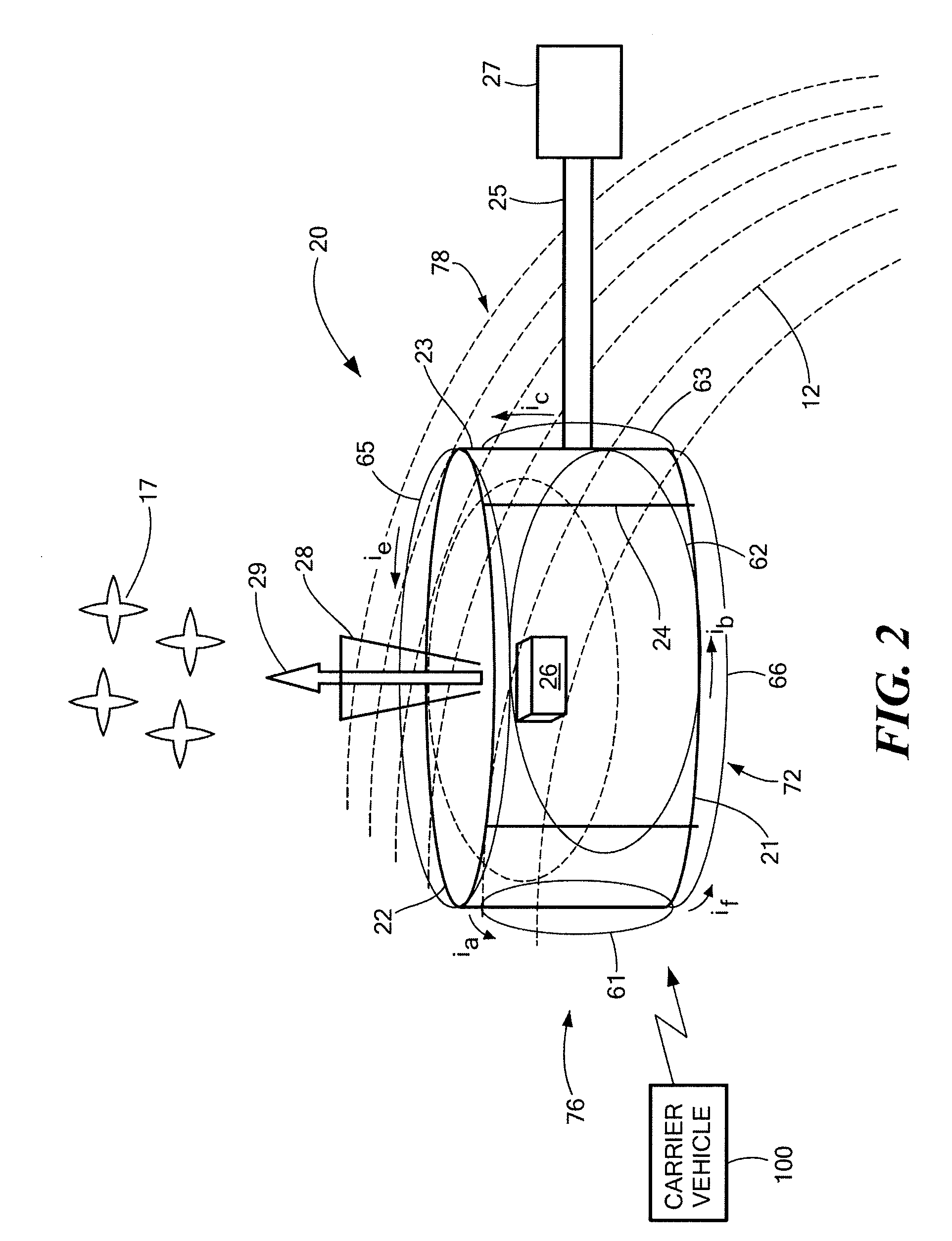
In orbit space transportation and recovery system
InactiveUS7070151B2Low costCosmonautic radiation protectionLaunch systemsNatural satelliteNuclear reactor
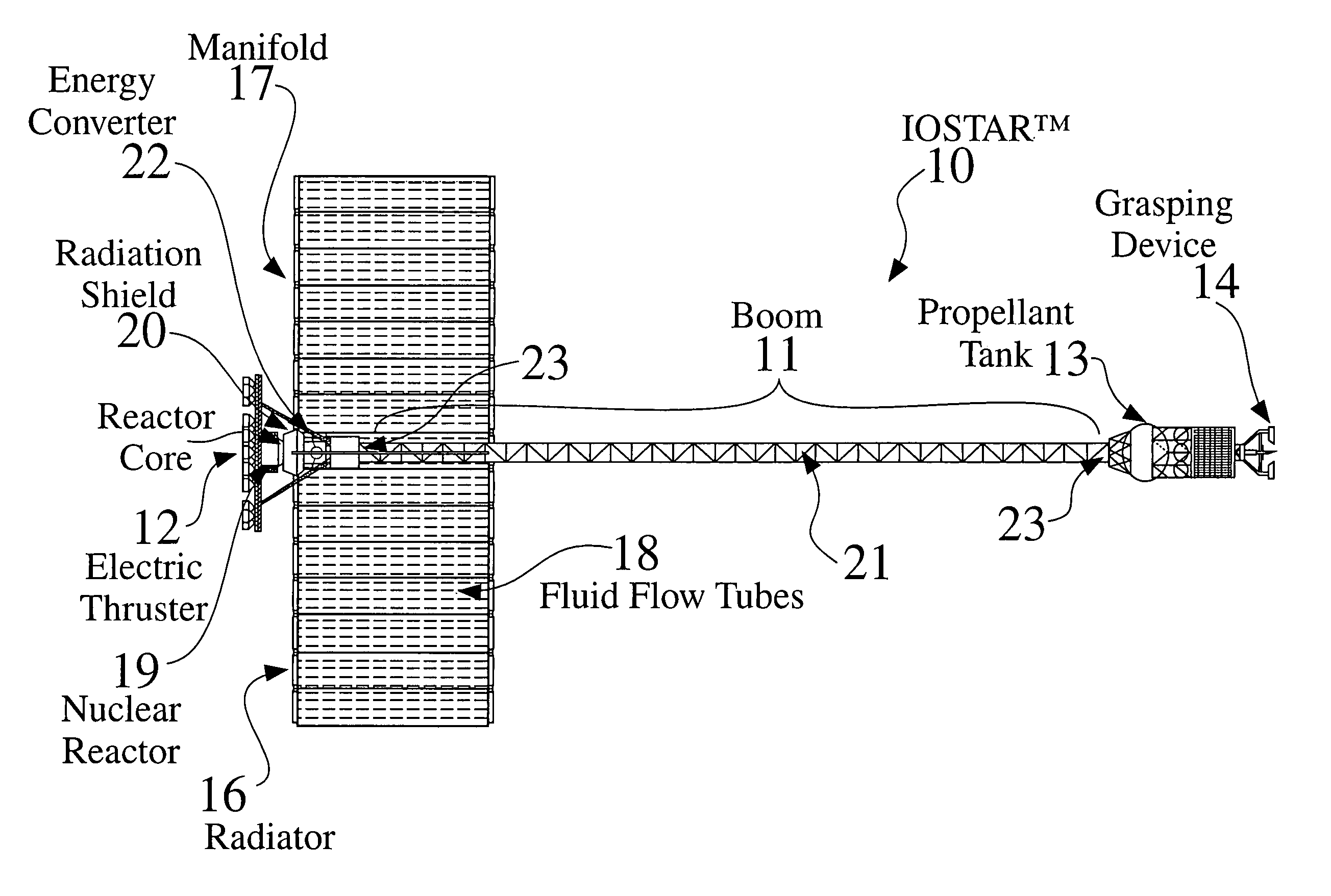
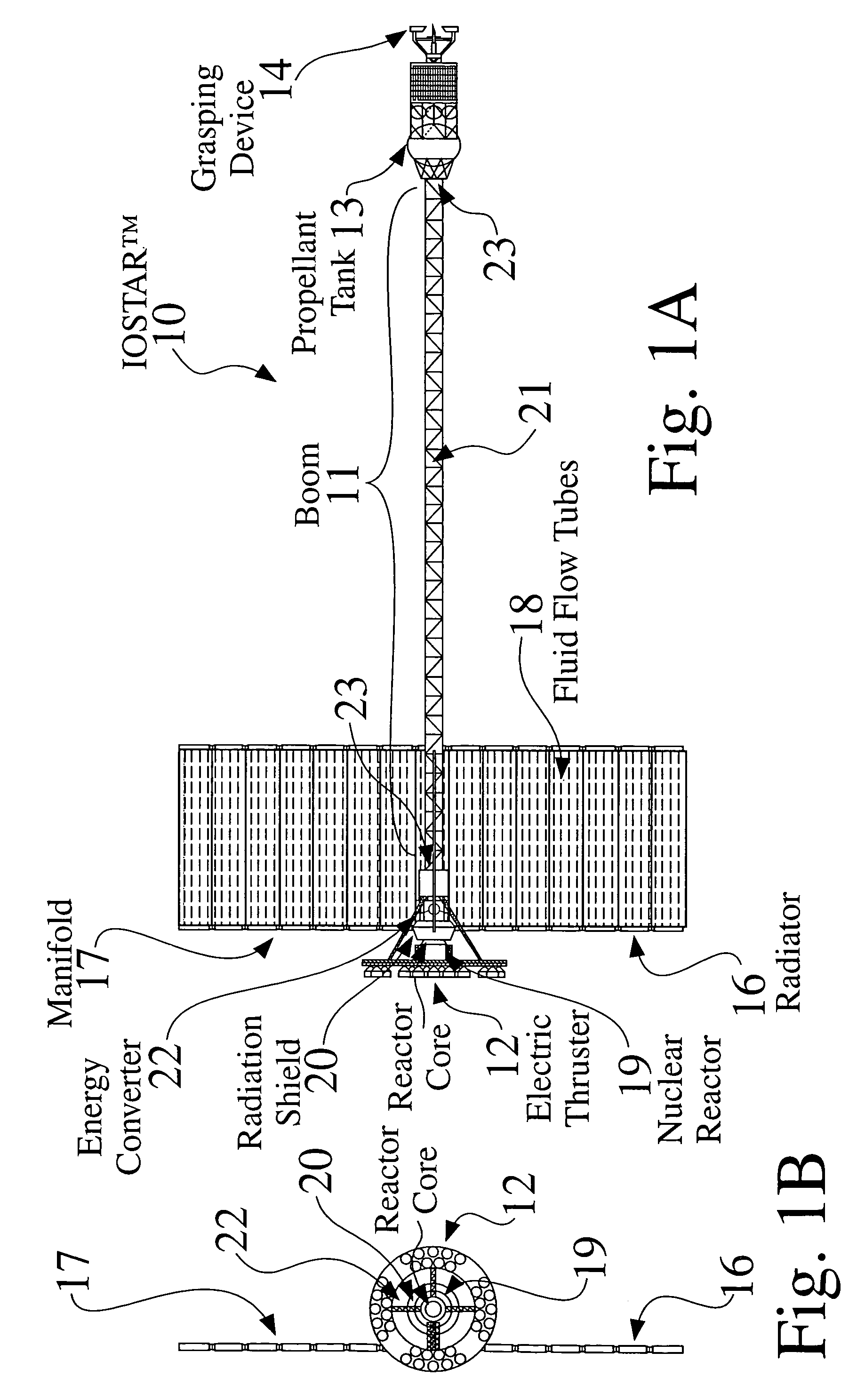
An In Orbit Transportation & Recovery System (IOSTAR™) (10) One preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a space tug powered by a nuclear reactor (19). The IOSTAR™ includes a collapsible boom (11) connected at one end to a propellant tank (13) which stores fuel for an electric propulsion system (12). This end of the boom (11) is equipped with docking hardware (14) that is able to grasp and hold a satellite (15) and as a means to refill the tank (13). Radiator panels (16) mounted on the boom (11) dissipate heat from the reactor (19). A radiation shield (20) is situated next to the reactor (19) to protect the satellite payload (15) at the far end of the boom (11). The IOSTAR™ (10) will be capable of accomplishing rendezvous and docking maneuvers which will enable it to move spacecraft between a low Earth parking orbit and positions in higher orbits or to other locations in our Solar System.
Owner:IOSTAR CORP
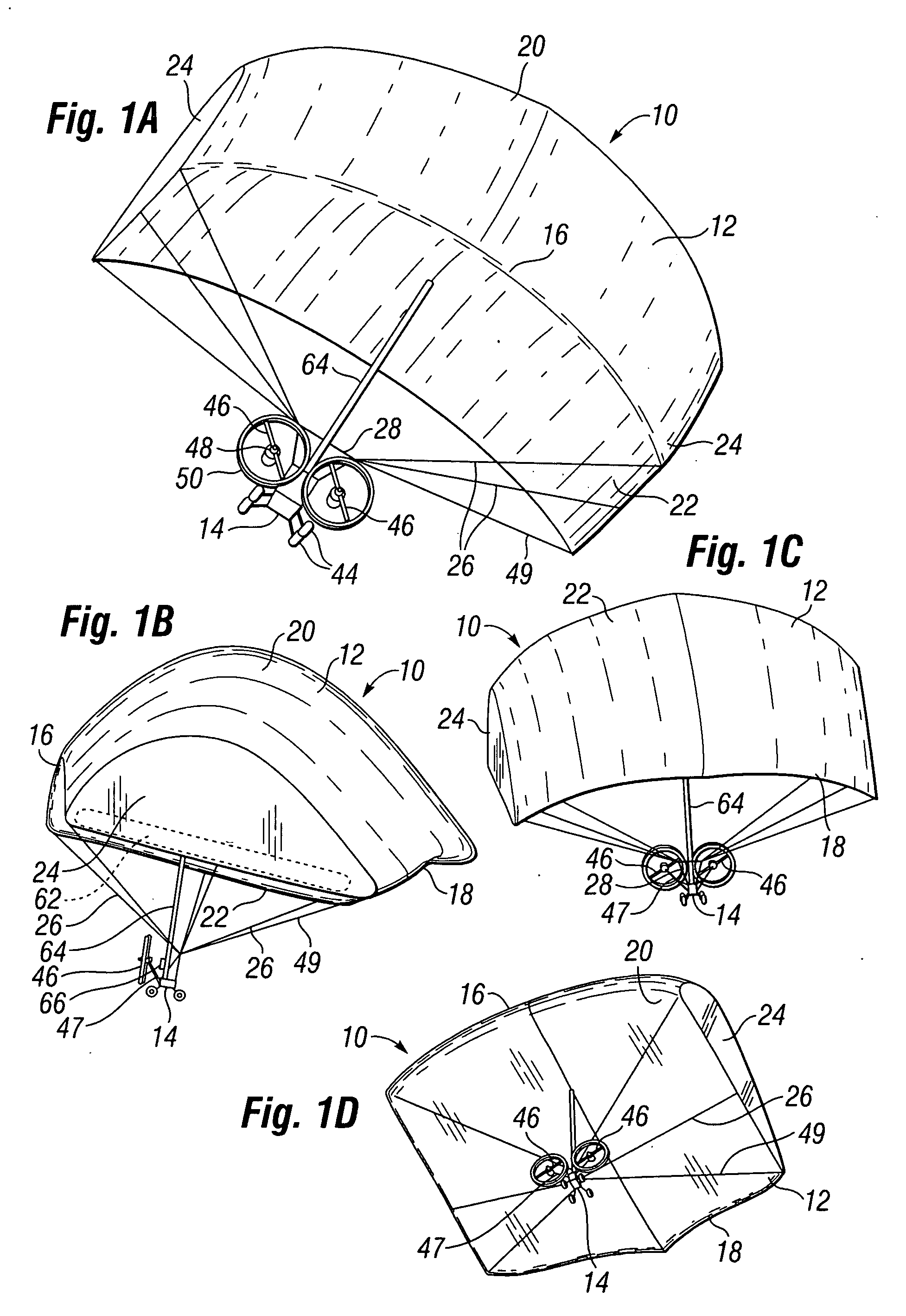
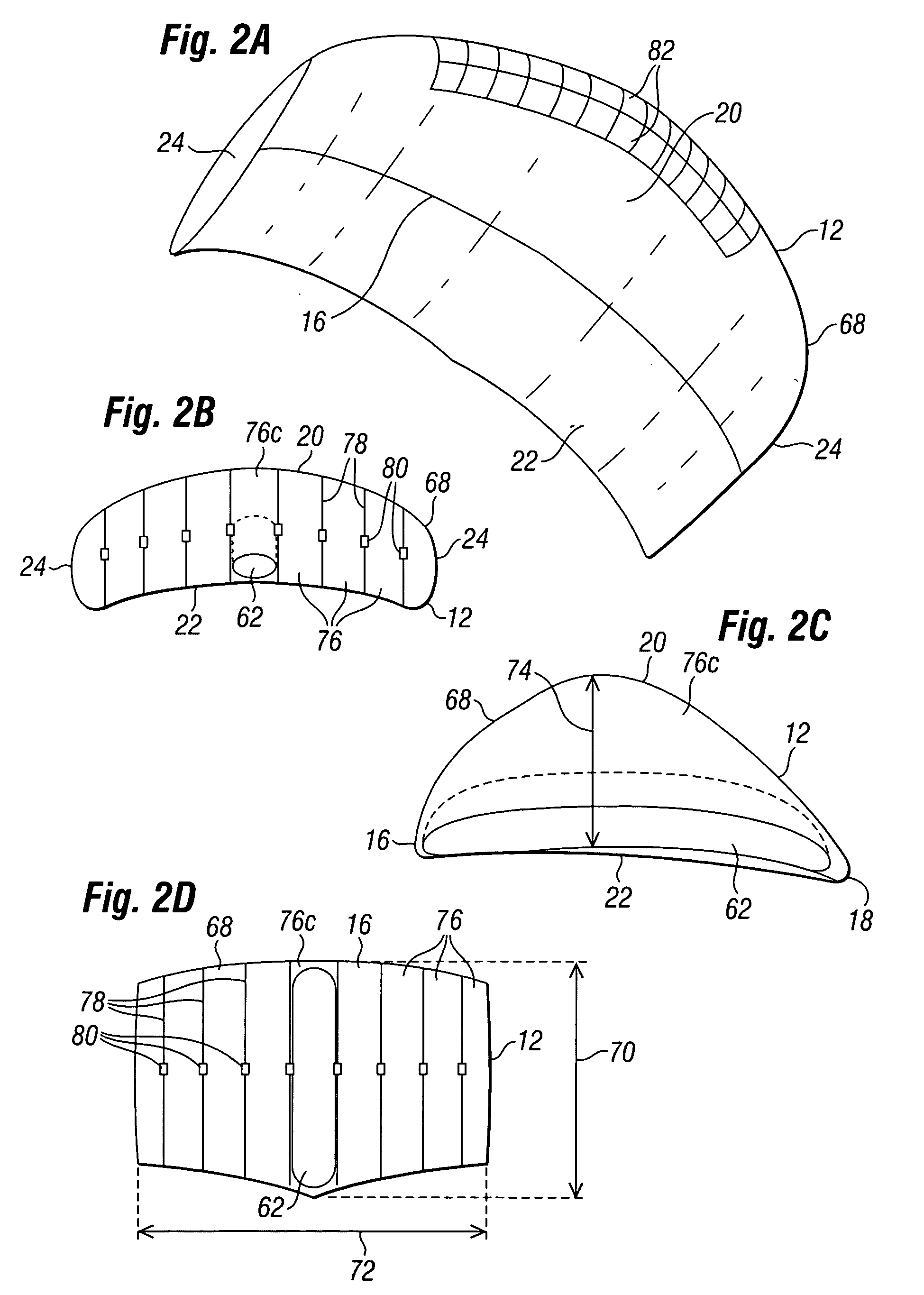
Inflatable wing flight vehicle
InactiveUS20090108135A1Improved lift characteristicThin atmosphereCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsNatural satelliteLow speed
The invention is an aircraft having an inflatable wing connected to a base unit, with the inflatable wing inflated with a lifting gas such as helium. The inflatable wing has a series of cell structures, and may be configured with ballonets to selectively introduce and expel outside air within the inflatable wing to vary the buoyancy and / or airfoil properties of the inflatable wing. The aircraft is particularly useful at low speeds and in thin atmospheres (such as at high Earth altitudes and on Mars), and can be used for interplanetary missions to explore planetary bodies, such as moons and planets, having atmospheres.
Owner:SHAW DONALD ORVAL
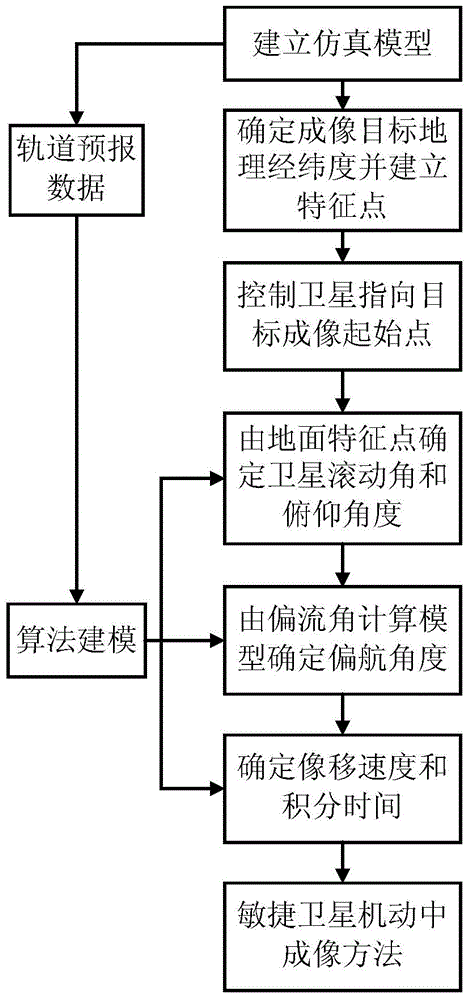
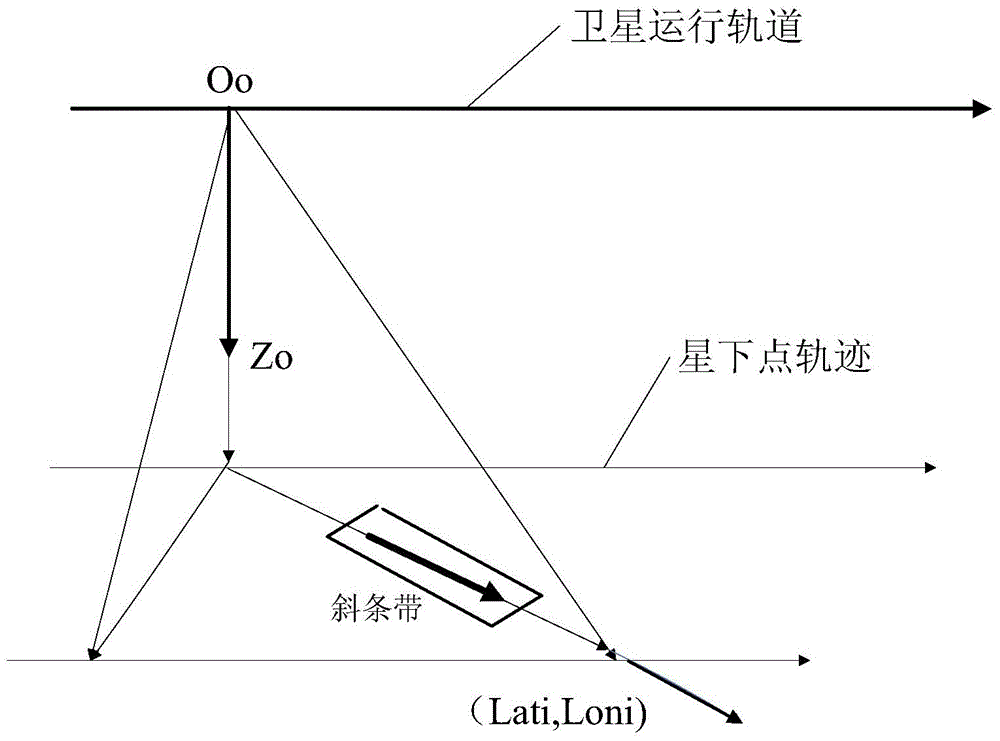
Novel imaging method in agile satellite maneuvering
ActiveCN103983254AExtended Imaging TasksGuaranteed Image Processing RequirementsPicture taking arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsNatural satelliteOn board
The invention relates to a novel imaging method in agile satellite maneuvering, which is capable of realizing imaging of satellite during a posture adjustment process. The method comprises the following steps: according to geographic latitude and longitude of on-board orbit forecast data and imaging object point, a triaxial attitude angle directional target imaging start point of satellite is arranged; a roll angle and a pitch angle are obtained through a modeling algorithm for determining the satellite optical axis directional target imaging point; establishing a CCD image plane in a satellite model, performing calculation to obtain image motion velocity vector and a drift angle through projection calculating, and yaw angle of the satellite is controlled for correcting the drift angle, calculating the image motion velocity vector to obtain TDICCD integration time for image motion compensation, and satisfying the image processing requirement of imaging in maneuvering. The design method is capable of using in a triaxial attitude maneuvering process of the satellite for starting optical payload for a dynamic imaging technology for imaging, so that target directional requirement and image processing requirement during an imaging process can be realized.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
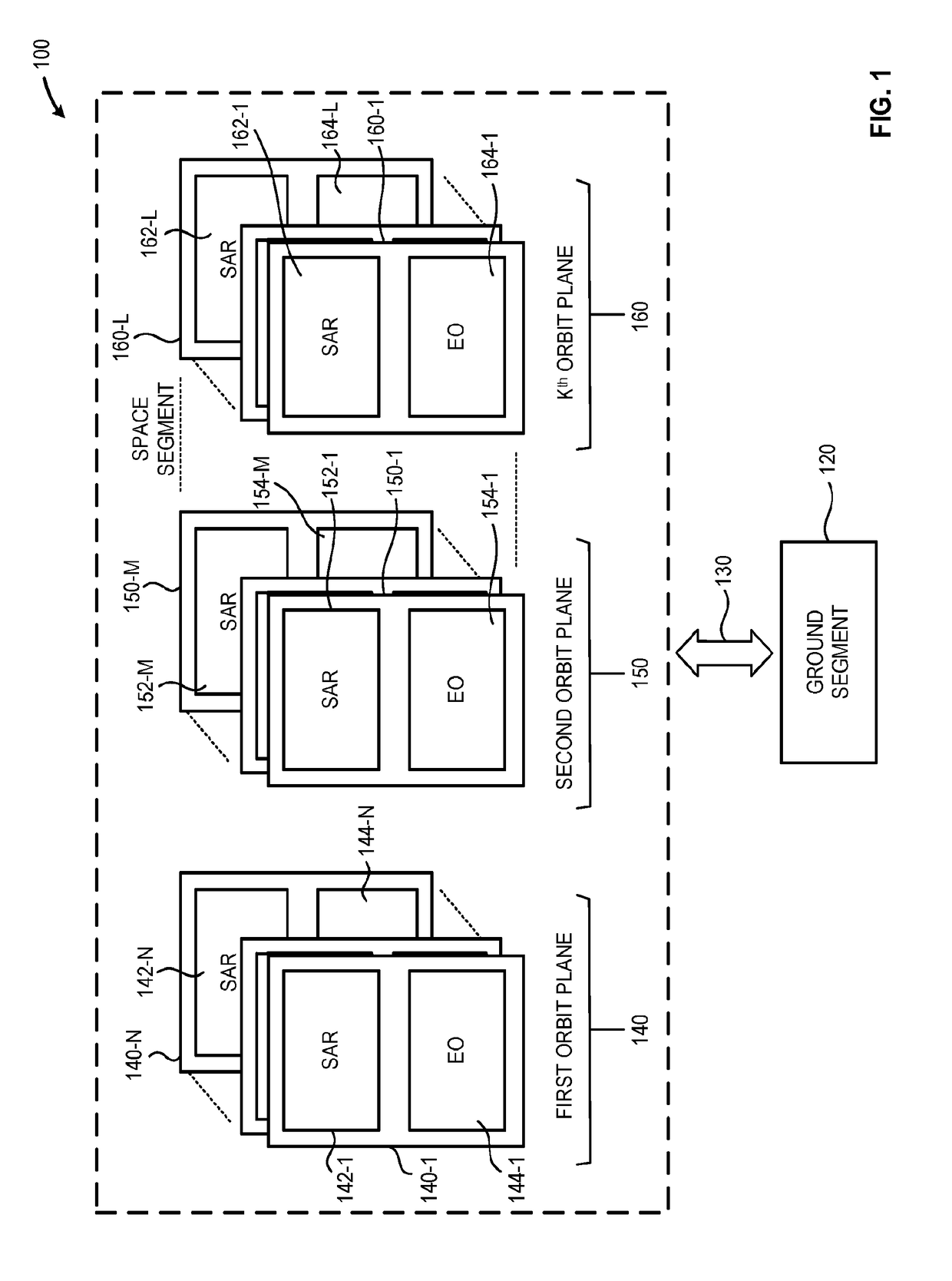
Constellation Configuration for Constellations having a Large Number of LEO Satellites
ActiveUS20180022474A1Improve the level ofOptimizationCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesNatural satelliteSatellite constellation
A configuration for a satellite constellation has a plurality of planes, each plane including a plurality of satellites therein, at least some of the planes situated at a different altitude than other of the planes. In some embodiments, all planes contain the same number of satellites; in some other embodiments, at least one plane includes a different number of satellites than the other planes in the constellation. In some embodiments, the satellites in each plane are evenly spaced.
Owner:WORLDVU SATELLITES
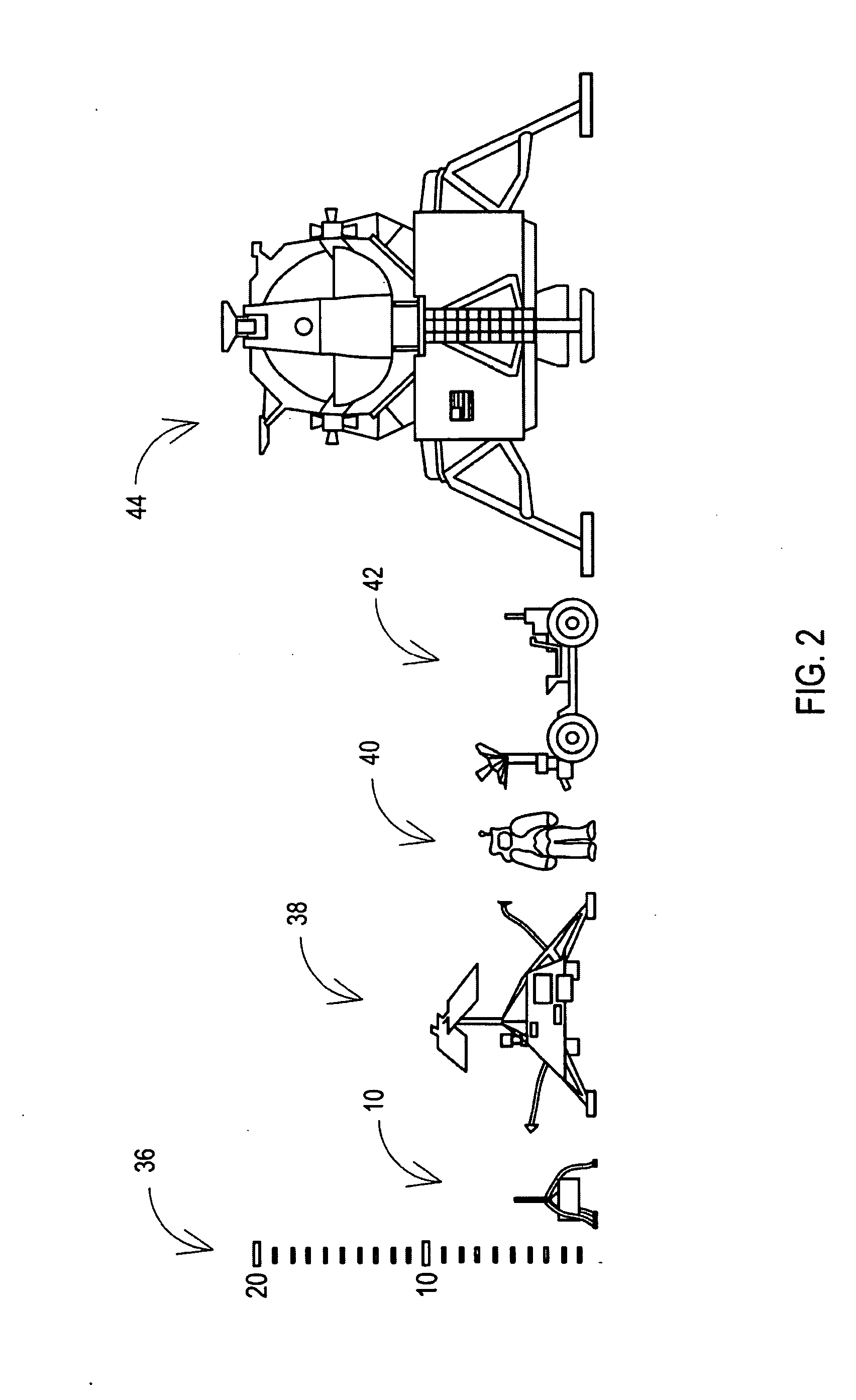
Spin-stabilized lander
InactiveUS20090206204A1Low costAdditive manufacturing apparatusCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusNatural satelliteCelestial body
The invention provides a novel, low-cost, spin-stabilized lander architecture capable (with appropriate system scaling tailored to the attributes of the target) of performing a soft-landing on a solar-system body such as Earth's Moon, Mars, Venus, the moons of Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, selected near-Earth and main-belt asteroids, comets and Kuiper belt objects and even large human-made objects, and also moving about on the surface of the target solar-system body after the initial landing in movement akin to hopping.
Owner:ECLIPTIC ENTERPRISES CORP
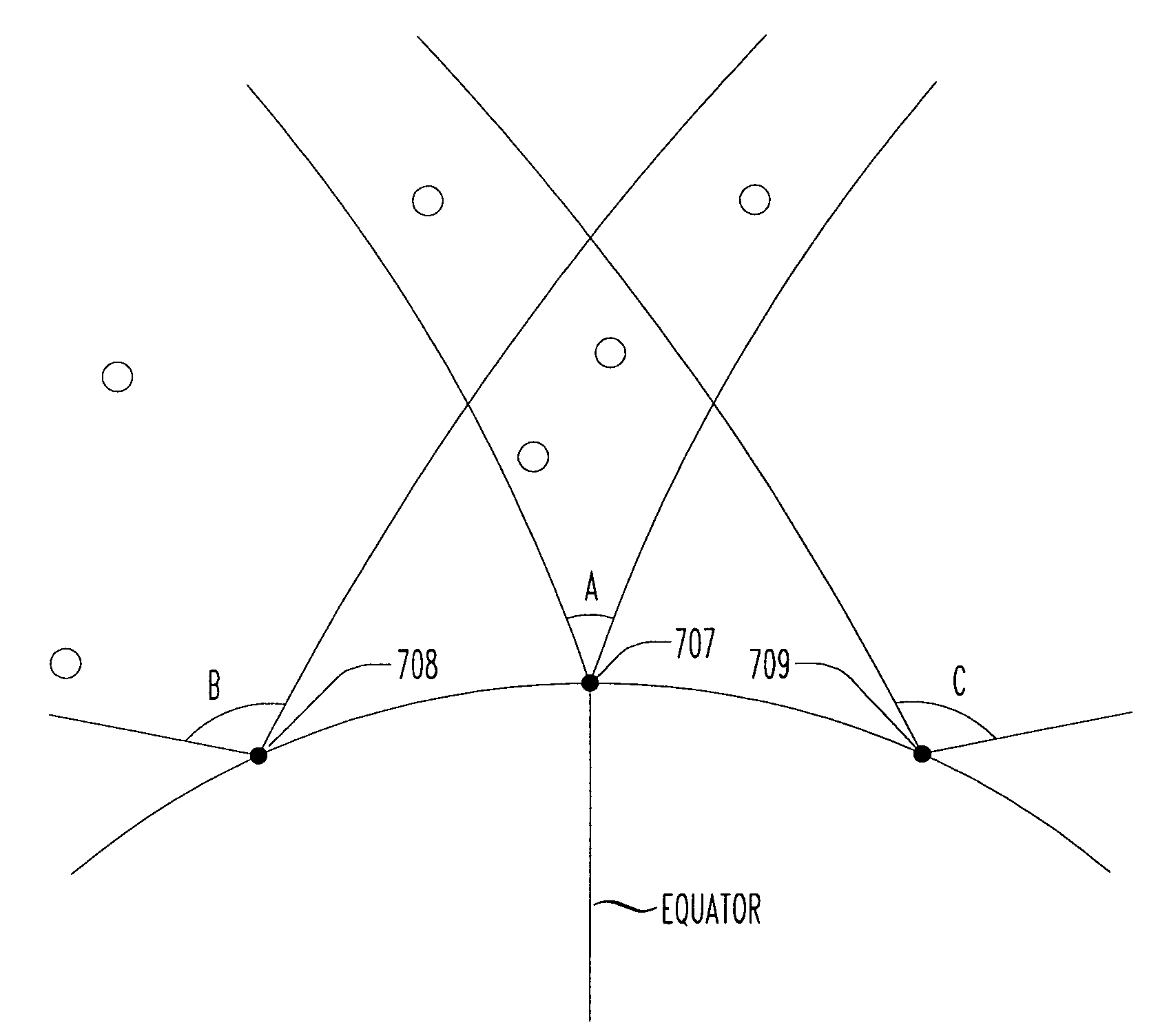
Culled satellite ephemeris information based on limiting a span of an inverted cone for locating satellite in-range determinations
Locating satellites (e.g., GPS) are culled into a sub-plurality based largely on dwell time within an inverted cone above a relevant site in communication with a wireless device. A first inverted cone having a first base angle is defined above a first site, a second inverted cone having a second base angle is defined above a second site. If the second site is farther from an equator of Earth than the first site, then the second inverted cone is made to have a base angle larger than a base angle of the first inverted cone. If the first site is farther from the equator of Earth than the second site, then the first inverted cone is made to have a base angle larger than a base angle of the second inverted cone. The span of the inverted cone over the site closest to the equator may be limited.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Time slot optimization-based double-layer satellite network routing method
ActiveCN104821844AReduce overheadImprove reliabilityRadio transmissionData switching networksNatural satelliteRouting table
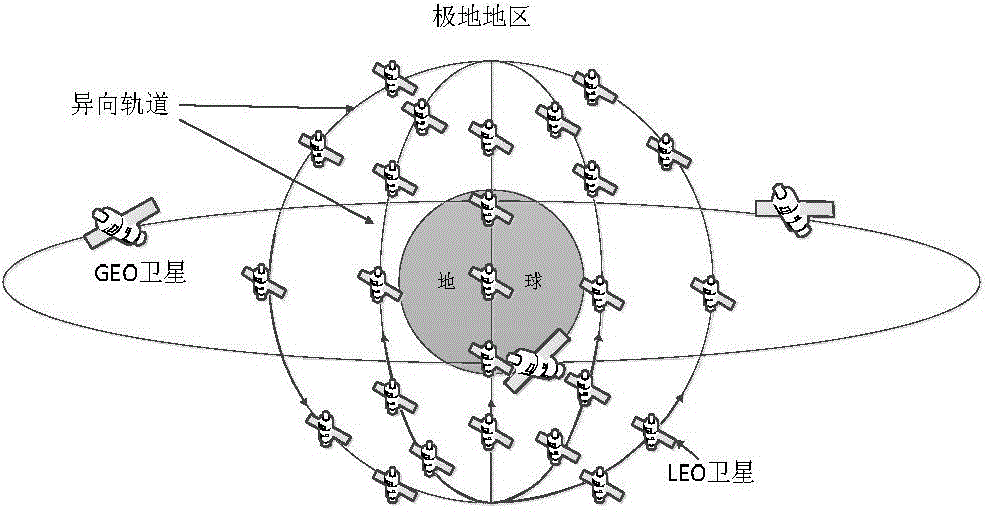
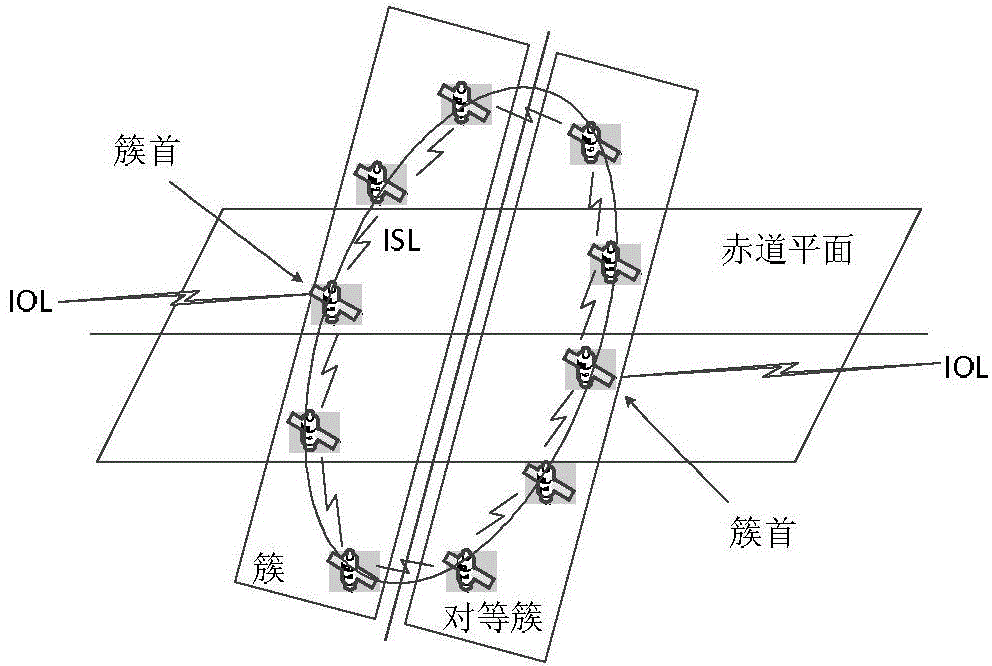
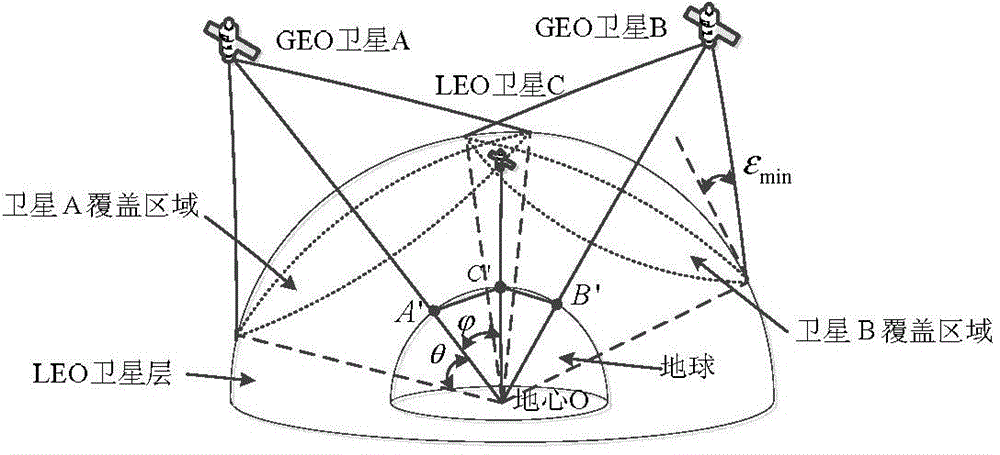
The invention relates to a time slot optimization-based double-layer satellite network routing method, so as to solve the problems that routing protocol overhead in the traditional method is large, an LEO satellite is hard to be connected with a GEO satellite in a polar region, and temporary link breaking of a polar orbit satellite between polar region orbits is not considered. The method comprises steps: (1) a 3GEO+66LEO double-layer satellite network model is built; (2) a covering domain grouping + orbit plane clustering-based satellite grouping management method is applied to determine a control relationship between an upper layer of satellites and a lower layer of satellites; (3) according to the control relationship between the upper layer of satellites and the lower layer of satellites, time slot division and optimization are carried out on a satellite operation cycle; (4) on the basis of location prediction routing algorithm, the GEO satellites calculate a routing table for the LEO satellites; and (5) the first step to the fourth step are combined, and routing updating is carried out when each time slice starts. The method belongs to the field of satellite communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
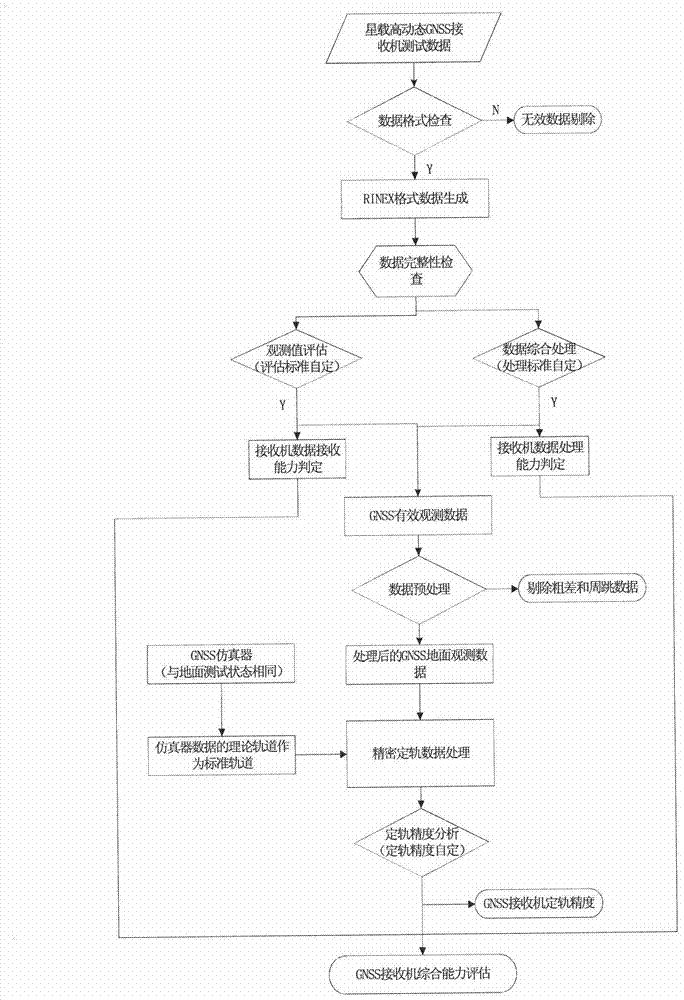
Method for performing ground check and performance evaluation on satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver
ActiveCN103076618AImprove the scope of performance assessmentImprove verification capabilitiesSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteSource Data Verification
The invention provides a method for performing ground check and performance evaluation on a satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly performing observation data verification on observation data generated by the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver; and after verification is finished, further performing orbit determination performance test on the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver by utilizing a geometrical orbit determination method. The process of performing data verification on the observation data mainly comprises four links, namely observation data standard format treatment, observation data type integrity checking, observation data quality evaluation based on calculation on observed value dual difference of different navigational satellites at a same frequency and observed value single difference of a same navigational satellite at different frequencies, and evaluation on pseudo range and carrier noise based on simulation data observation in a zero / short base line under the condition of no satellite; and during orbit determination performance test, by virtue of solving a linearized observation equation and comparing the linearized observation equation with a theoretical value, the orbit determination accuracy of the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver is obtained. The method provided by the invention can be used for directly and comprehensively evaluating the performance of the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
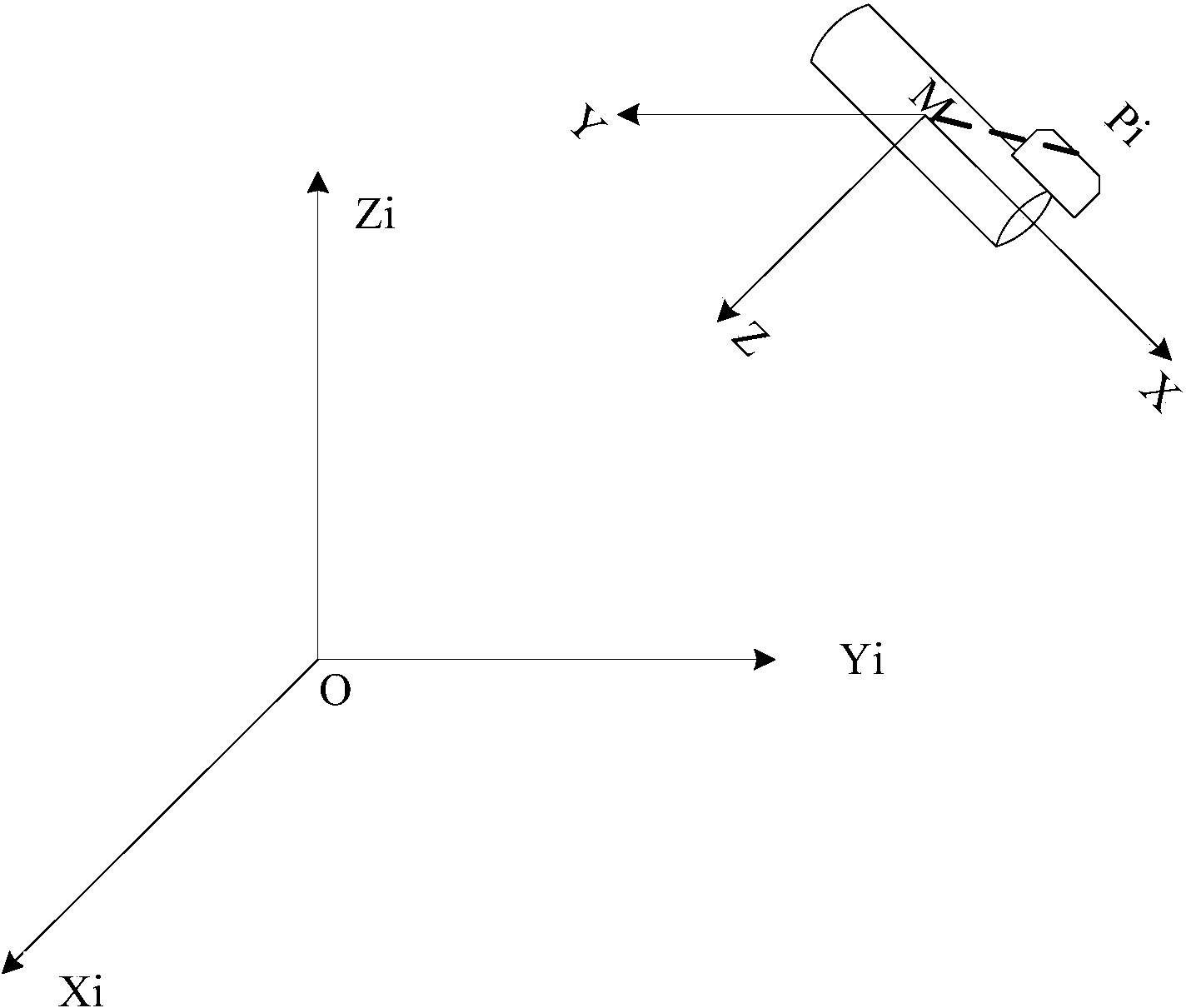
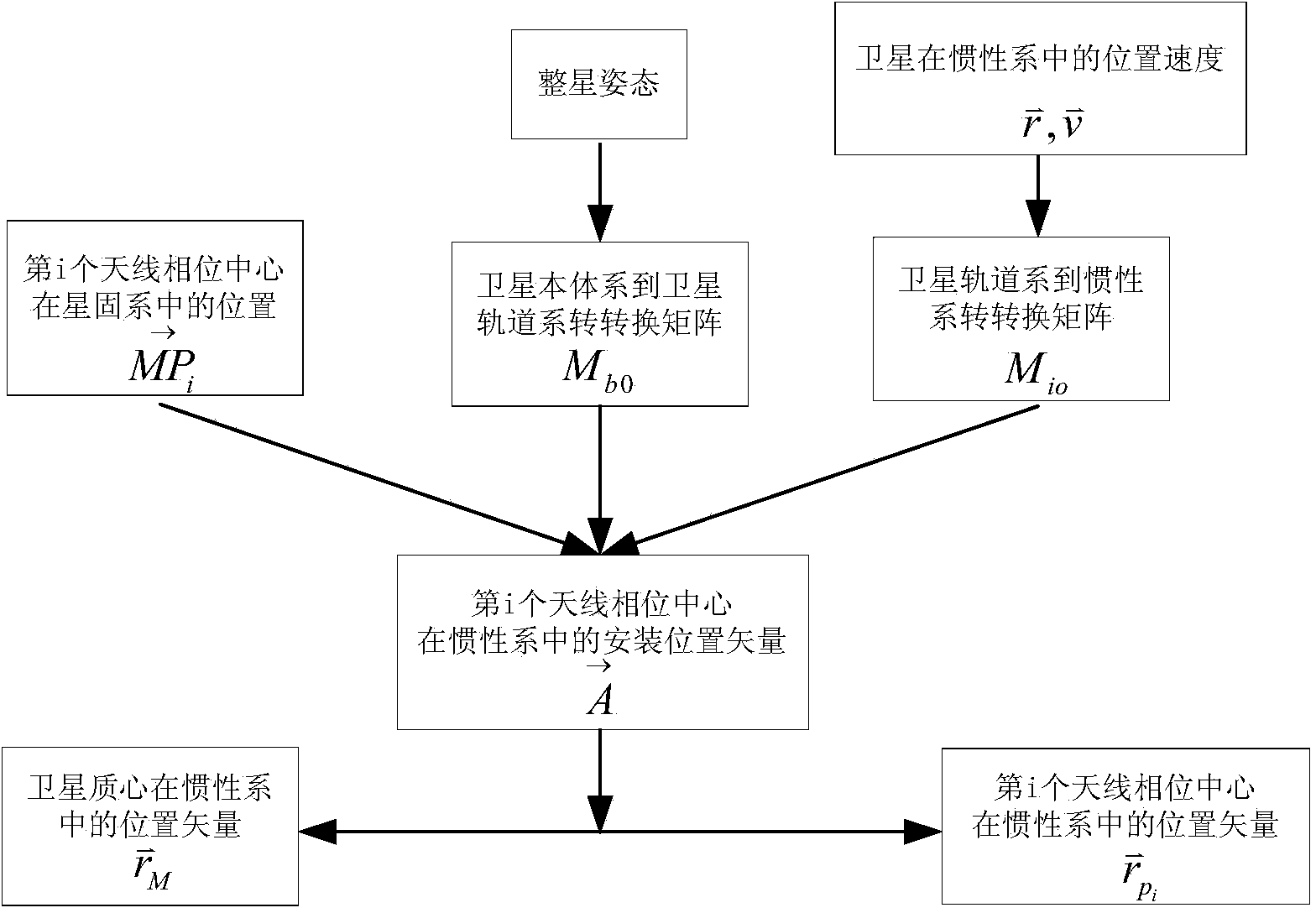
Satellite autonomous orbit determination method based on satellite-borne GNSS multiple antennas
ActiveCN103675861AExcellent data fusion resultsImprove the accuracy of orbit determinationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteKaiman filter
A satellite autonomous orbit determination method based on satellite-borne GNSS multiple antennas. According to the method, a Kalman filter is extended; multiple GNSS antennas measured pseudorange observation values are made full use of to carry out real-time filtering correction of an orbit prediction value using a high precision mechanical model; and high precision satellite orbit information is obtained. According to the invention, the problems of the high precision orbit determination in a complex posture maneuver can be solved. In the invention, the orbit determination result is high in precision, good in stability, and highly real-time, can meet the orbit determination demand of the low orbit satellite and high precision satellite, can be widely applied to the high precision orbit determination of the space station, high resolution earth observation satellite and other space missions, and has a wide promotion and application prospect.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
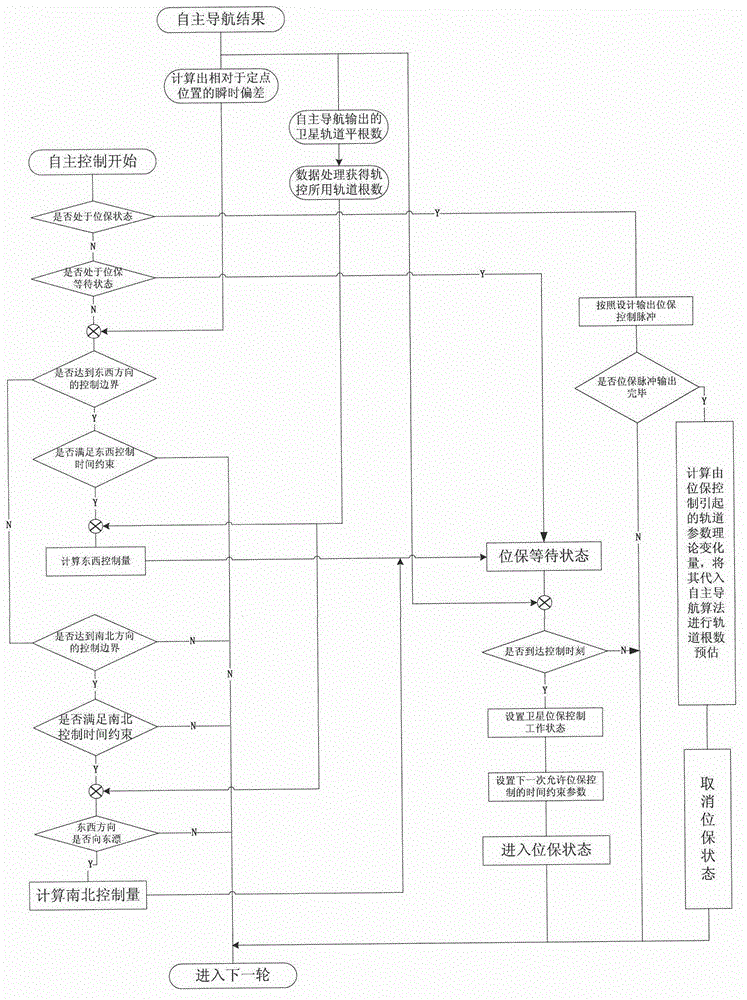
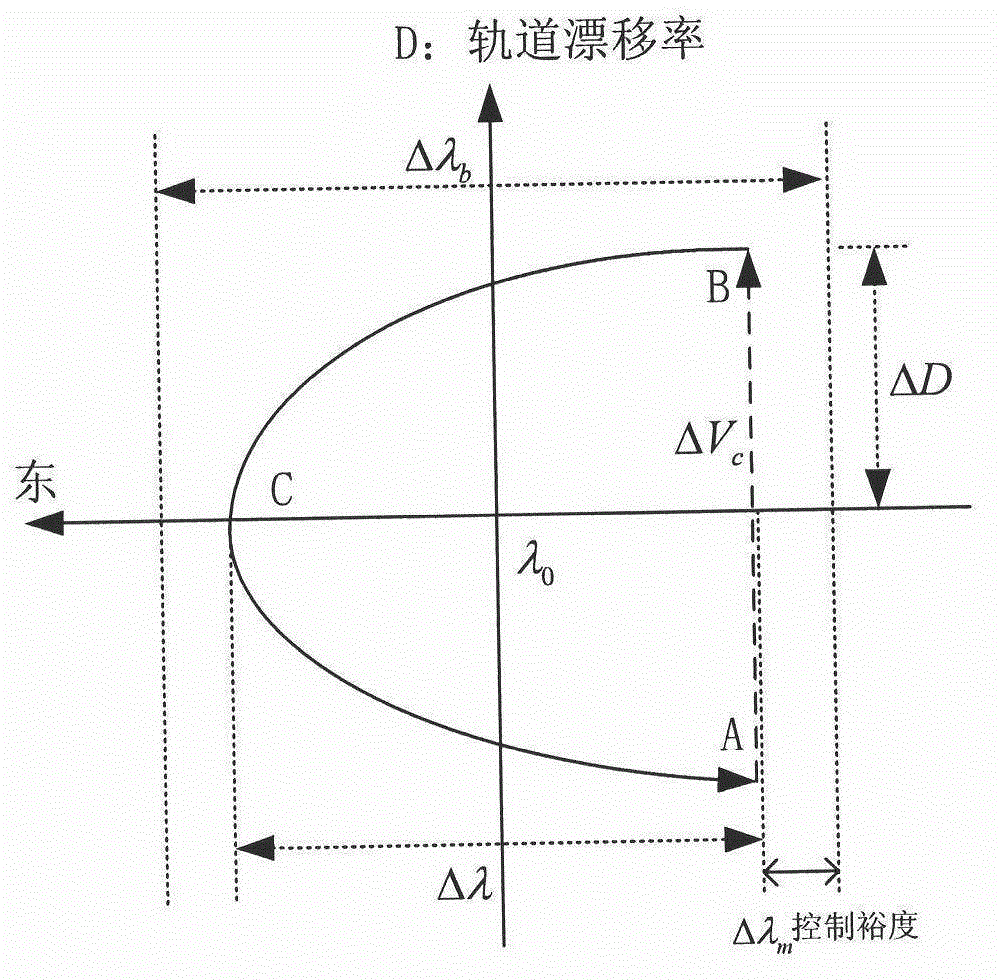
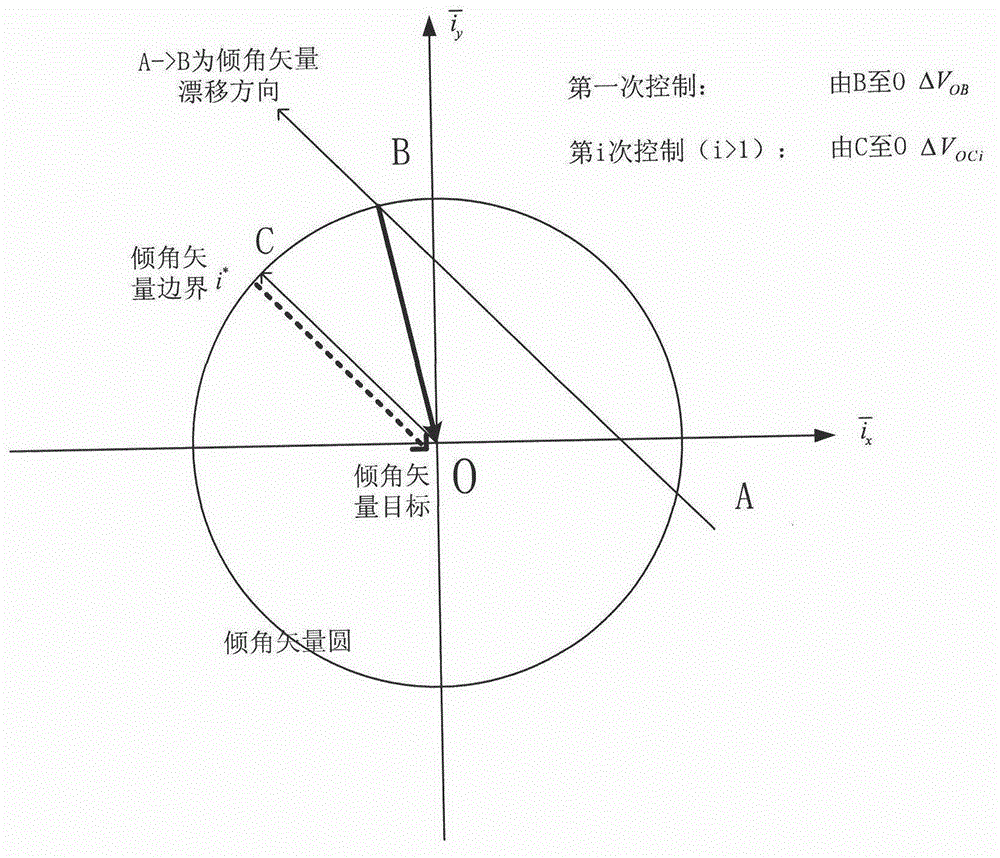
Autonomous orbit control method for stationary orbit satellite
ActiveCN102880184AStable controlReduce mistakesAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsNatural satelliteGeostationary orbit
The invention relates to an autonomous orbit control method for a stationary orbit satellite, belonging to the technical field of autonomous orbit control of the satellite. The autonomous orbit control method can be applied to a long-term operation management task of the stationary orbit satellite. After the satellite goes beyond a specified error box in east-west direction or south-north direction, corresponding autonomous orbit maintenance is required to be performed; and meanwhile, by considering the regularity for drift of the satellite along a stationary orbit and error of an autonomous navigation result, the effectiveness of control quantity and the rationality of time interval between every two control processes are required to be judged at each time when the orbit control quantity of the autonomous orbit, i.e., control impulses in the south-north direction and the east-west direction which are delta VNS and delta VEW respectively, are calculated. The method has been successfully applied to china satellites; a remote sensing result shows that the autonomous control strategy of the satellite is correct; and the method can be widely applied to all geostationary orbit satellites required to have the autonomous function.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
System and method for observing a satellite using a satellite in retrograde orbit
ActiveUS20080081556A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionNatural satelliteRadar systems
A satellite and an arrangement for placing the satellite in a retrograde orbit, i.e. inclined at approximately 180° to the equator. Multiple satellites may be used and the orbits thereof may be circular or elliptical. The invention is well-suited for an illustrative satellite inspection application. In this embodiment, the system includes one or more satellites; means disposed on each satellite for receiving electromagnetic energy from objects (e.g. satellites) within a field-of-view thereof; and an arrangement for placing the inspection satellites in a retrograde orbit. The satellites may be equally spaced in a single orbit or disposed in equally spaced orbits. The satellites may include a variety of instruments including radar, infrared, visible, etc. In a radar implementation, the satellite may include a bistatic or (with a transmitter) monostatic radar system. In the bistatic case, the signal may be transmitted from a ground-based or space based platform.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
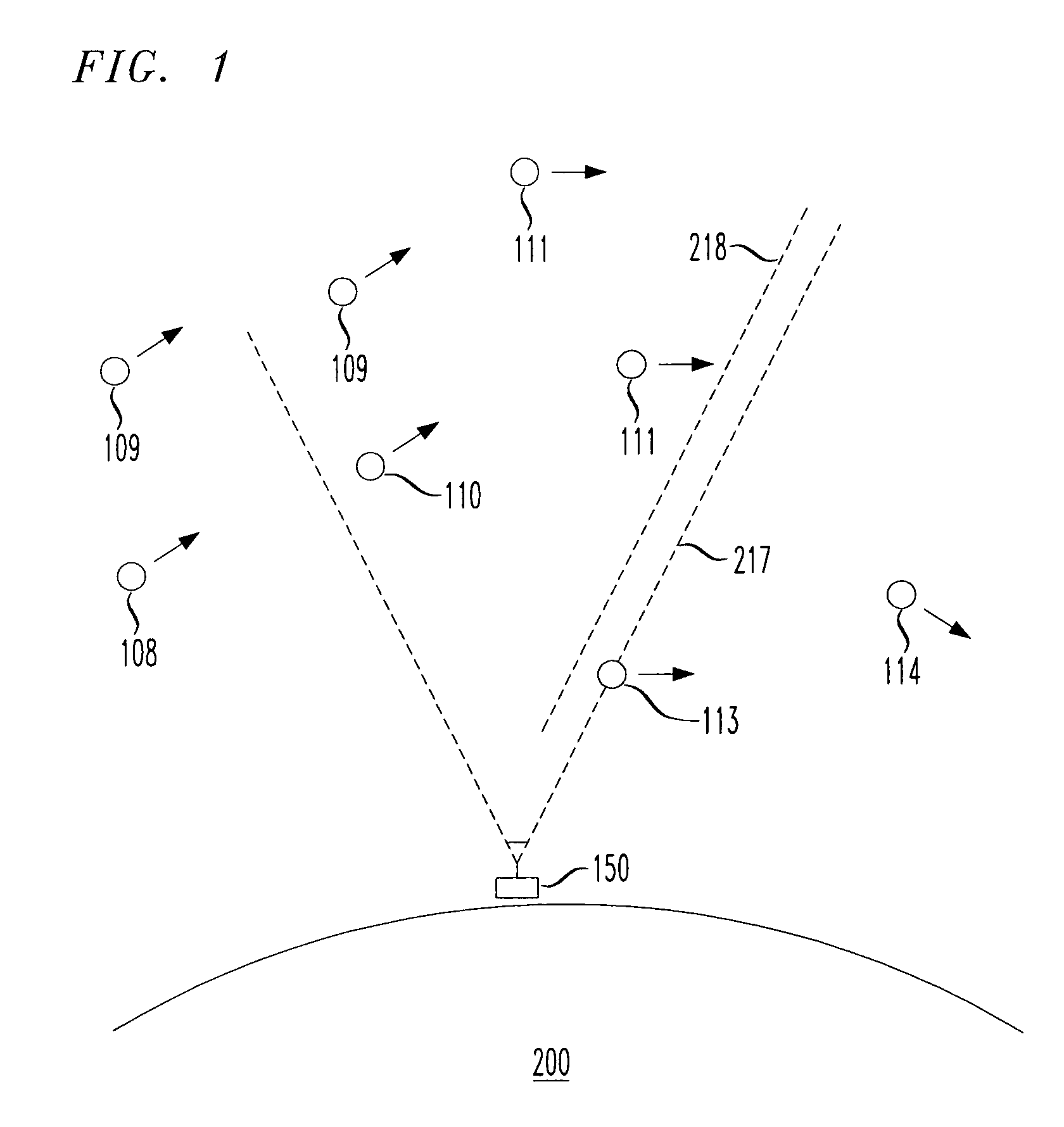
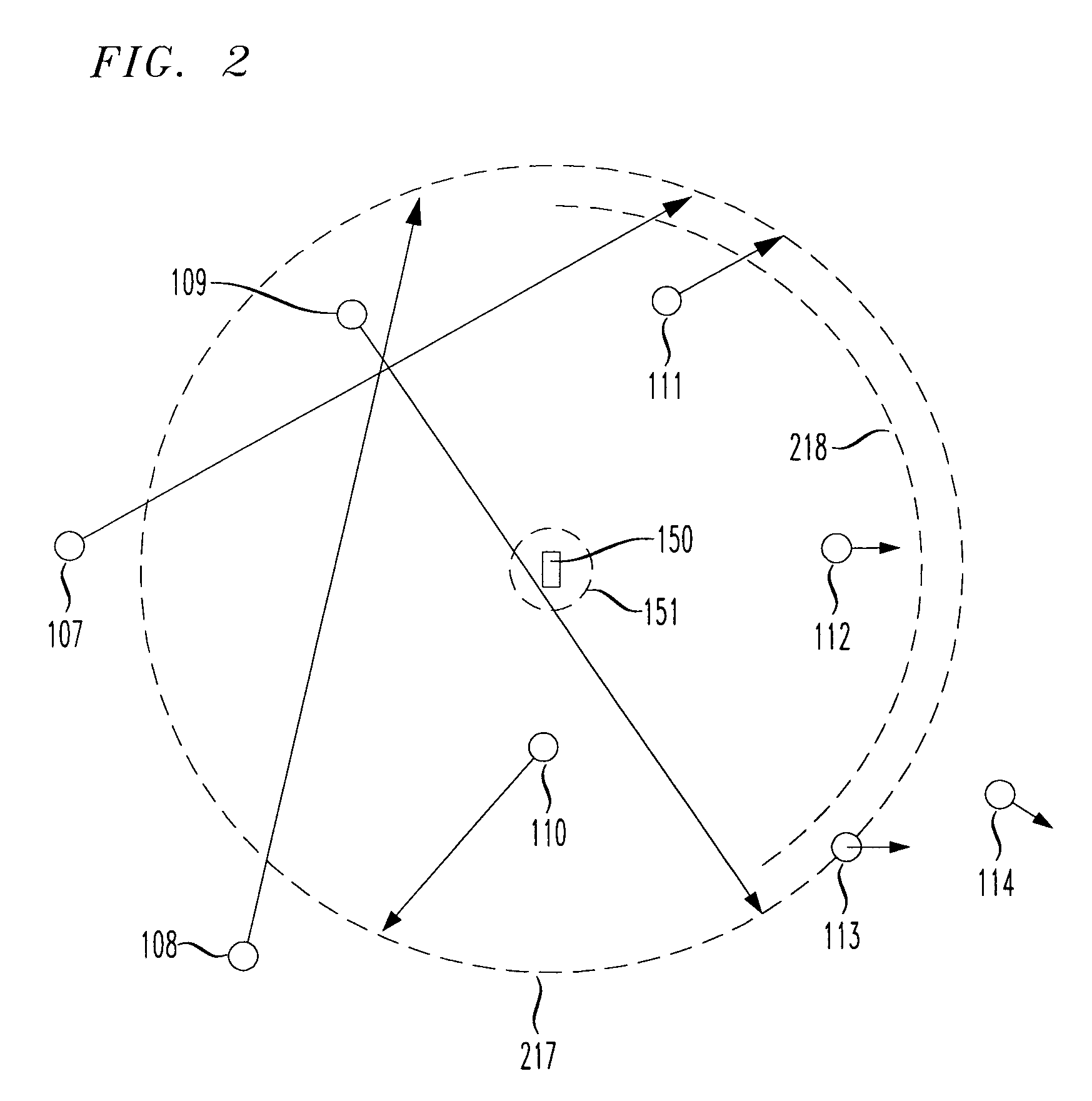
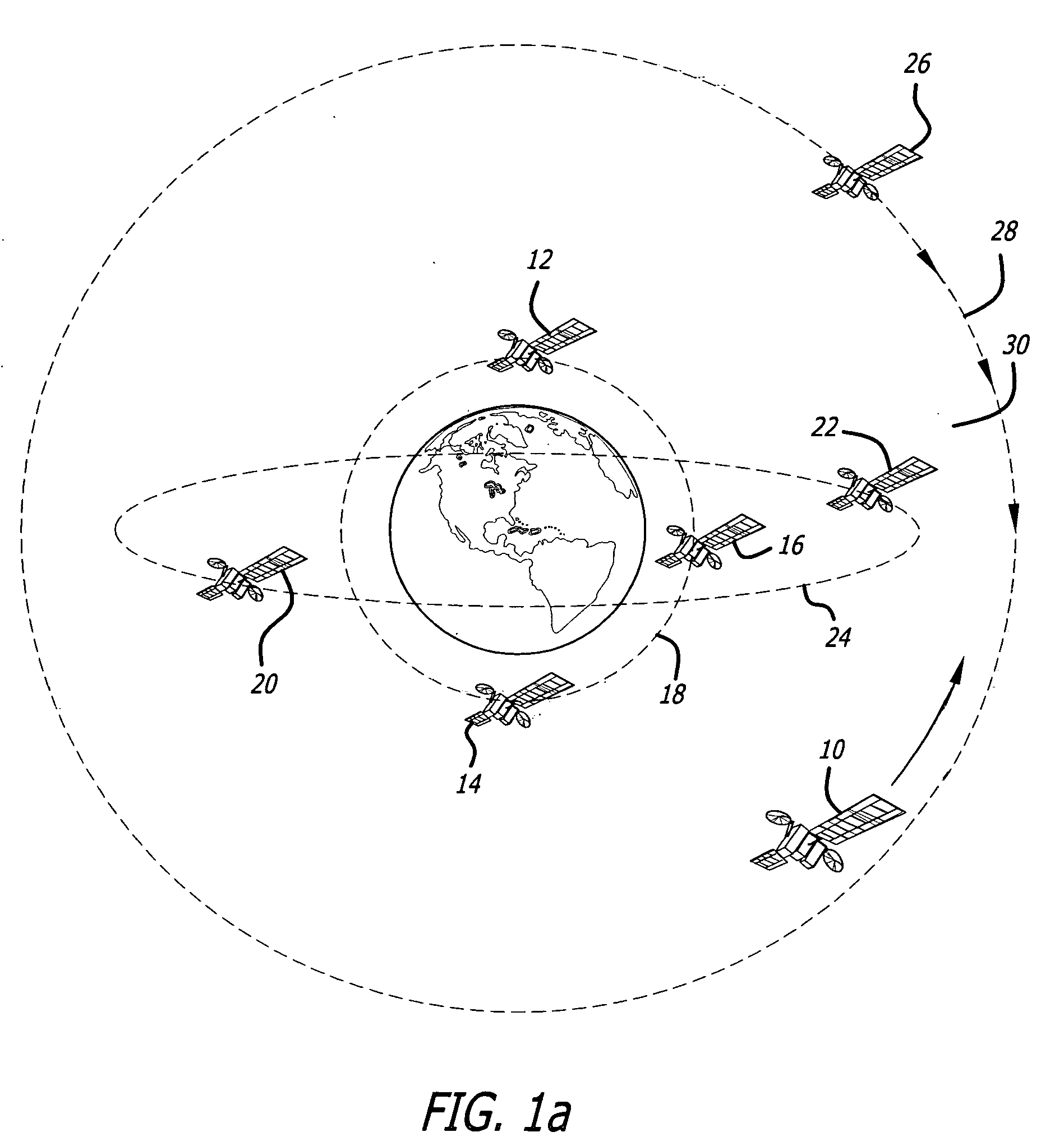
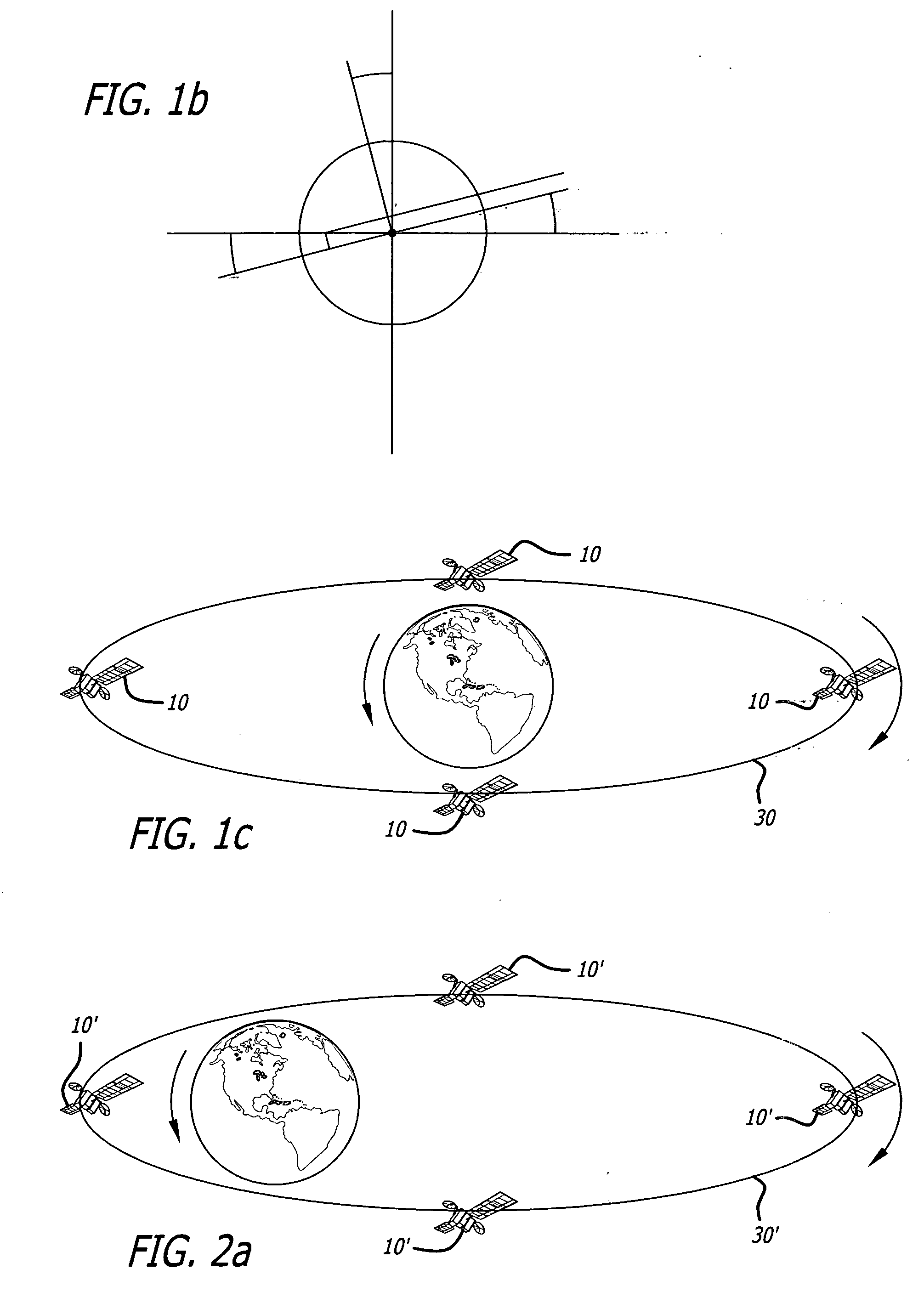
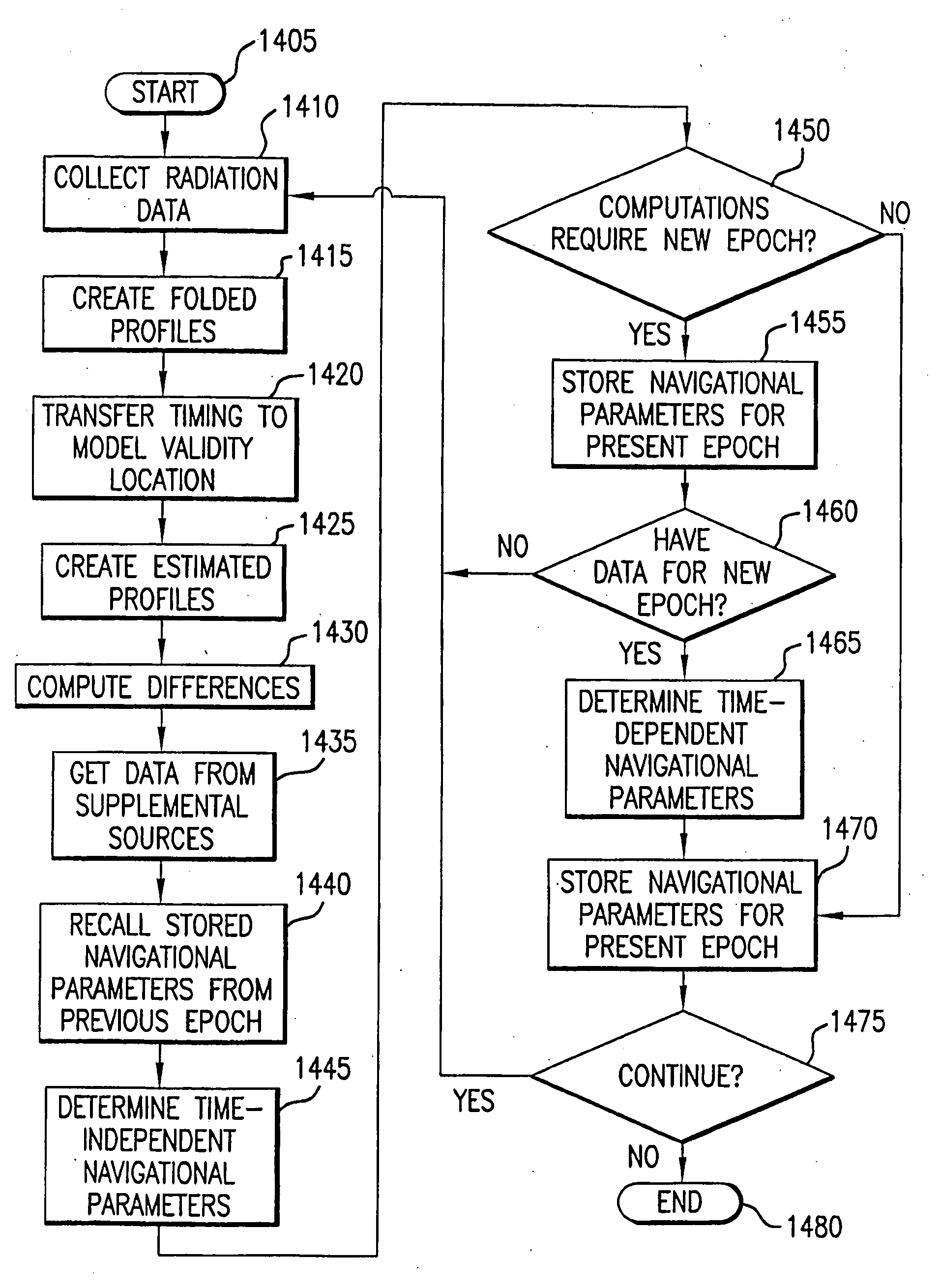
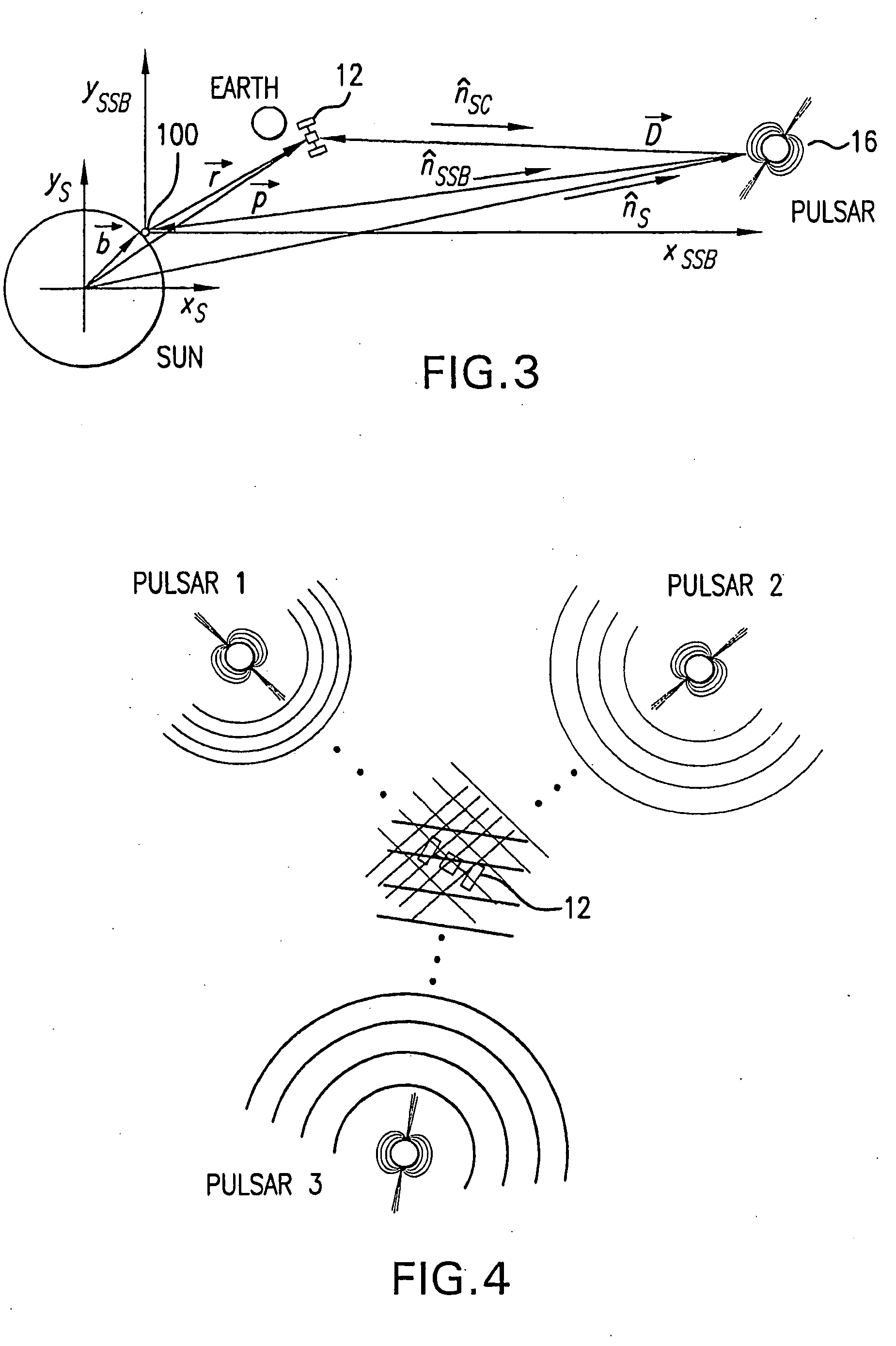
Navigation system and method using modulated celestial radiation sources
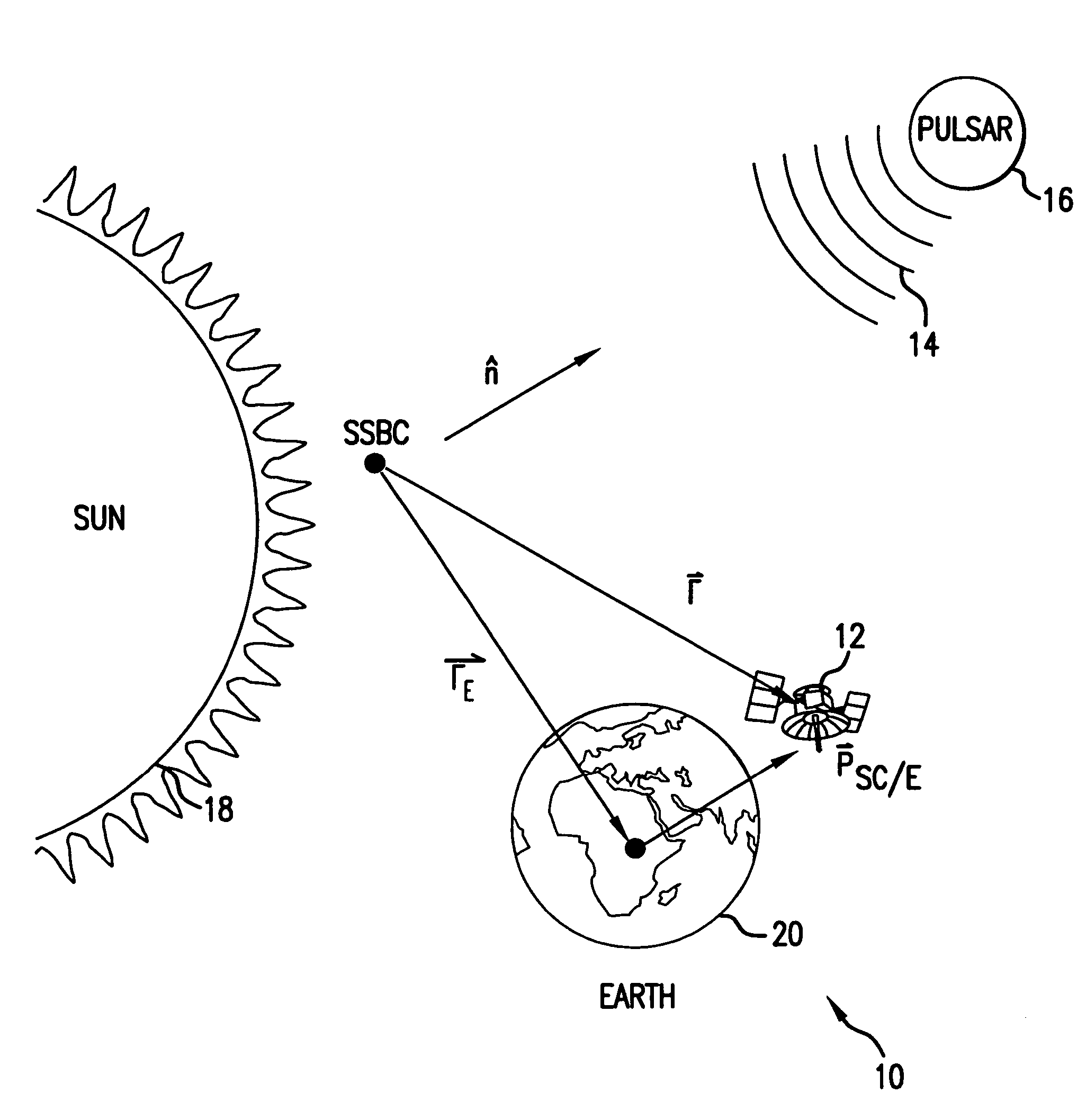
A system and method for navigation utilizes sources of modulated celestial radiation. A spacecraft, satellite, or other vehicle (12) has one or more modulated radiation sensors (22a-22x) mounted thereto for detecting a modulated signal (14) generated by one or more pulsars or other celestial objects (16). A timer (24) measures the pulse time of arrival at a respective pulse sensor (22a-22x) by comparing the pulse signal (14) with a known pulse profile, and a processor (30) calculates a timing difference between the measured pulse time of arrival at sensor (22a-22x) with a calculated pulse time of arrival at a selected reference point (100). The positions and pulse profile characteristics of the pulsars (16) are stored in a digital memory (34) and combining the calculated time difference with the known positions of pulsars (16), the navigational parameters, such as position, velocity, and attitude, for spacecraft (12) with respect to the selected localized reference point (100) can be calculated.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Navigational system and method utilizing sources of pulsed celestial radiation
A system and method for navigation utilizing sources of pulsed celestial radiation are provided. A spacecraft, satellite, or other vehicle (12) has a pulse sensor (22) mounted thereto for detecting signal pulses (14) generated by a plurality of pulsars or other celestial objects (16). The detected signal pulses (14) are synchronously averaged at the known period of the pulsar or other celestial object (16) with respect to a timer (24). Timer (24) measures the pulse time of arrival at the pulse sensor (22) by comparing the pulse signal (14) with a pulse shape template (52), and a processing means (30) calculates the offset time between the measured pulse time of arrival at sensor (22) with a calculated pulse time of arrival at the solar system barycenter (SSBC). The positions and pulse profile characteristics of the pulsars (16) are stored in a digital memory (34) and combining the calculated time offset with the known positions of pulsars (16), the navigational position, velocity, attitude and time of spacecraft (12) with respect to the SSBC can be calculated.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Systems and methods for remote sensing of the earth from space
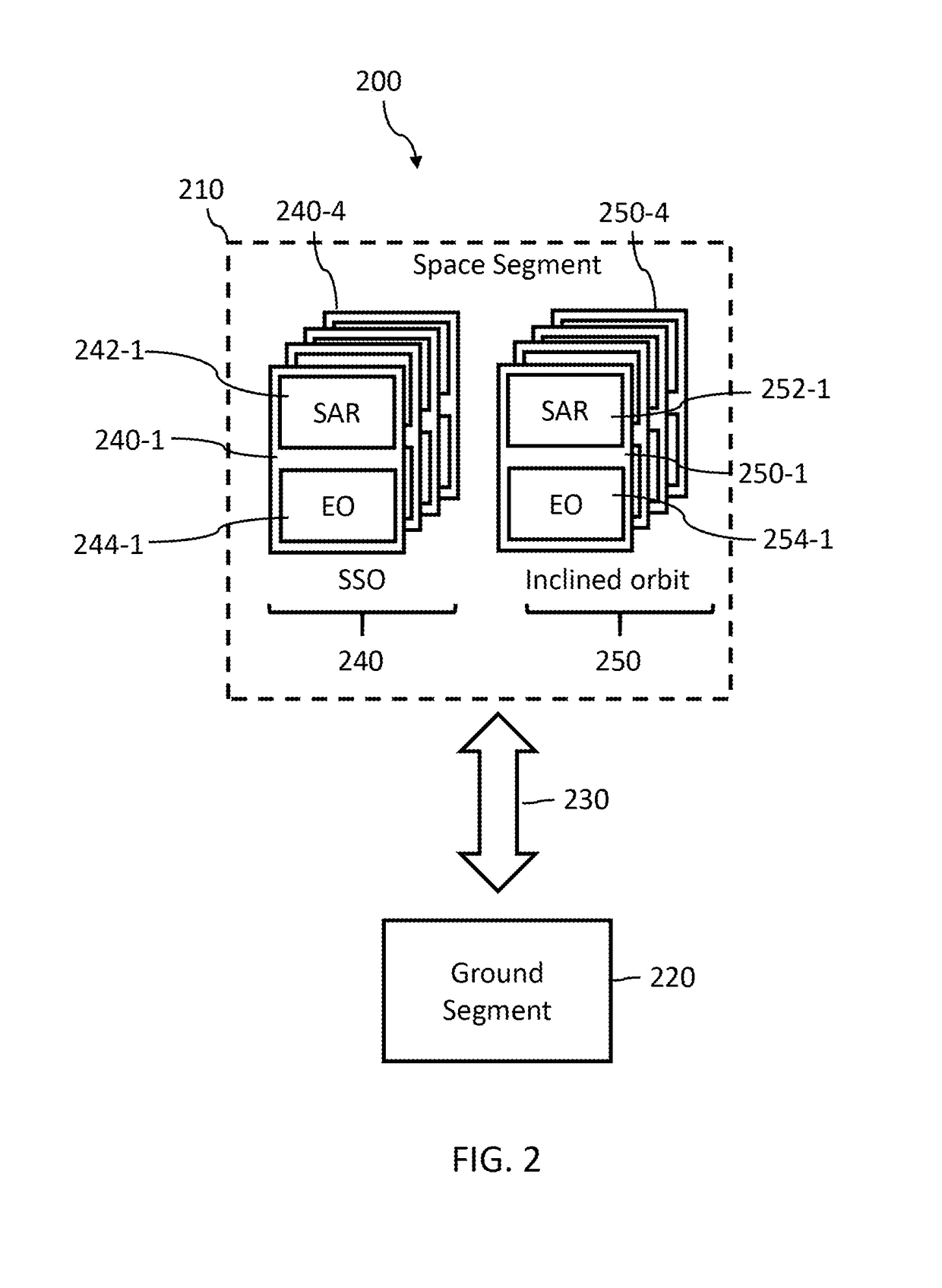
InactiveUS20180172823A1More opportunityIncrease opportunitiesCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsNatural satelliteGround station
A constellation of satellites may include a plurality of satellites in each of two or more different orbits. Satellites in a given orbit may operate in pairs, flying in tandem, one satellite leading, the other trailing closely behind, to be positioned to image the same target(s) of interest with substantially the same orientation (geographical coincident) at substantially the same time (temporally coincident). The first satellite may acquire SAR data, determine a location of a target of interest, assess cloud cover, and based on an extent of cloud cover, can acquire additional SAR data or cause the second satellite to capture optical imaging data (e.g., cross-cueing). Selection of orbits can provide a relatively high revisit rate may be obtained, allowing frequent opportunities to image given locations on a planet (e.g., Earth). One or more ground stations communicate with the constellation of satellites, and inter-satellite communications may be employed.
Owner:URTHECAST CORP +1
Navigation enhancement method and system based on low-orbit constellation
ActiveCN109001763AReduce fine positioning initialization timeReduce complexityActive radio relay systemsPosition fixationNatural satelliteTelecommunications link
The invention provides a navigation enhancement method and system based on a low-orbit constellation. The method comprises the following steps: (a) broadcasting a navigation direct transmission signaland navigation enhancement information by using a low-orbit constellation satellite; (b) comprehensively utilizing the navigation direct transmission signals of the navigation satellite and the low-orbit satellite, and the navigation enhancement information to carry out precision location, speed measurement and timing by a user. The method can enhance the observation space geometrical configuration of the user by using the low-orbit satellite fast-moving feature and shorten the precise positioning initialization time of the user. The user receiver has the same hardware configuration as the universal satellite navigation receiver. Only needing to receive the direct transmission signals of the navigation satellite and the low-orbit satellite in one direction can rapid precise positioning beachieved, without needing to consider other data communication links. The navigation enhancement system comprises a low-orbit constellation, a ground control system and a user receiver. The system can achieve global coverage and provide the user with real-time precision positioning, speed measurement and timing services with high precision and high integrity.
Owner:BEIJING FUTURE NAVIGATION TECH CO LTD
Satellite constellation system
InactiveUS6868316B1Increase continuous access timeExtended access timeDigital data processing detailsArtificial satellitesNatural satelliteAccess time
A satellite constellation system, including a plurality of satellites in relatively close proximity to each other so that line-of-sight communications can be maintained at all times between adjacent satellites. The satellites are in closely-spaced orbits with incremental offsets in their starting true anomalies to create a pattern of the satellites which is serpentine in nature, moving north and south through latitudes covered as a result of the selected inclination angle while moving also in a longitudinal direction so that the serpentine pattern moves across most ground regions of interest. The constellation is asymmetric in nature in order to maximize the continuous access time. It is also possible to have multiple symmetrically-located constellations of this type.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
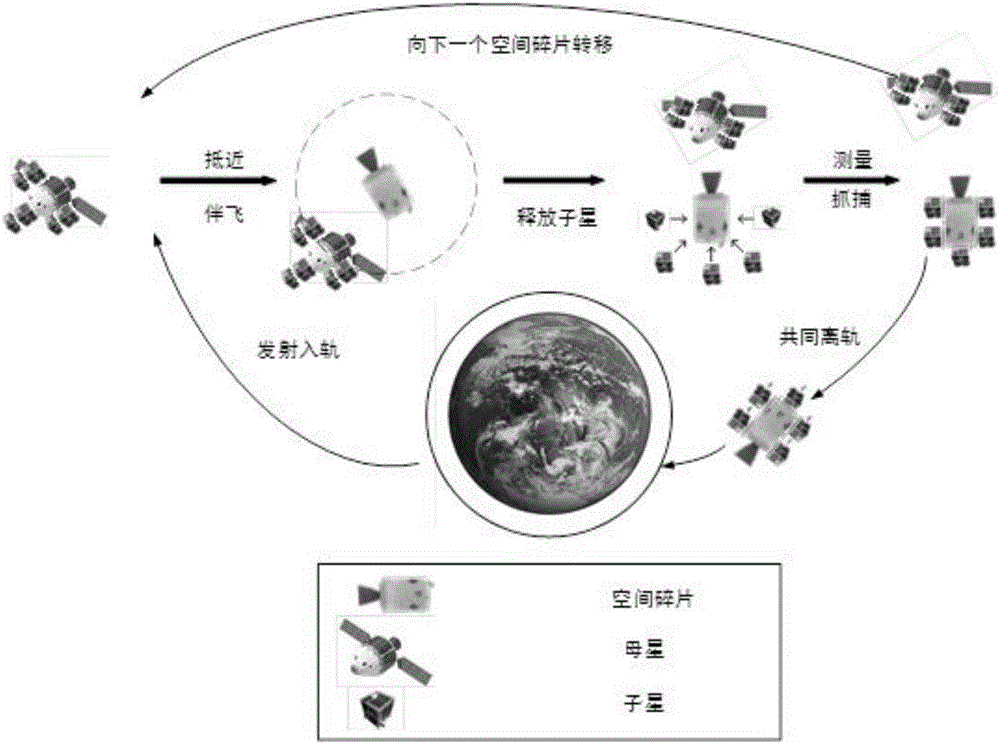
Child-mother satellite space debris clearing platform and clearing method
InactiveCN106809405AImprove removal efficiencyExtended service lifeArtificial satellitesToolsMicro nanoNatural satellite
The invention discloses a child-mother satellite space debris clearing platform. The child-mother satellite space debris clearing platform includes a plurality of child satellites for clearing space debris; each child satellite is detachably connected the same mother satellite; the mother satellite is used for driving the child satellites to move among a multiple pieces of space debris; a space debris clearing device is arranged on each child satellite; and each space debris clearing device includes a child measurement device for measuring a pose of the space debris and a child satellite capturing device. A microsatellite is used as the mother satellite, and a plurality of micro-nano satellites are used as the child satellites; operations such as orbit transferring, closing and detailed survey, and capturing and de-orbiting can be completed coordinately; the child-mother satellite space debris clearing platform is low in cost, is fast in response speed, and is high in reliability; after the child satellites are released, the combined space debris observation network can acquire accurate debris pose information through coordinate observation; and the child satellites can independently complete de-orbiting operations, the mother satellite can directly go to next space debris to be cleared, time and energy can be saved, the benefits of space debris clearing can be increased, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Satellite positioning-based guidance system that utilizes simulated inertial navigation system
InactiveUS6456906B1Cosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsNatural satelliteGuidance system
A satellite positioning-based guidance system and method that utilize a simulated inertial navigation system are disclosed. The trajectory of the body of a non-thrusted flight vehicle is used instead of a conventional inertial navigation system. The attitude of the flight vehicle is determined using a satellite receiver, and the Extended Kalman filter is used to implement the navigation function.
Owner:HUA CUONG TU +1
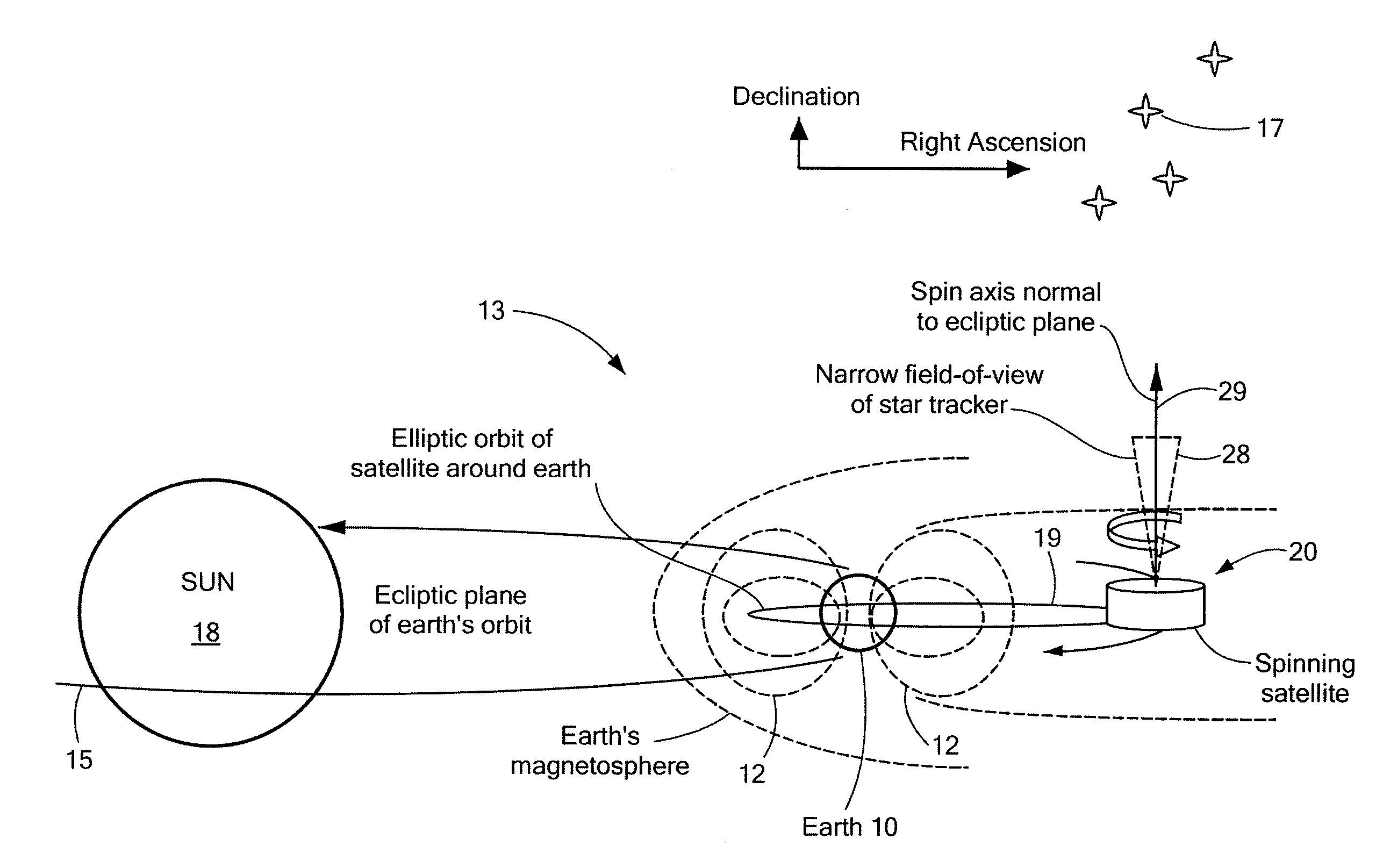
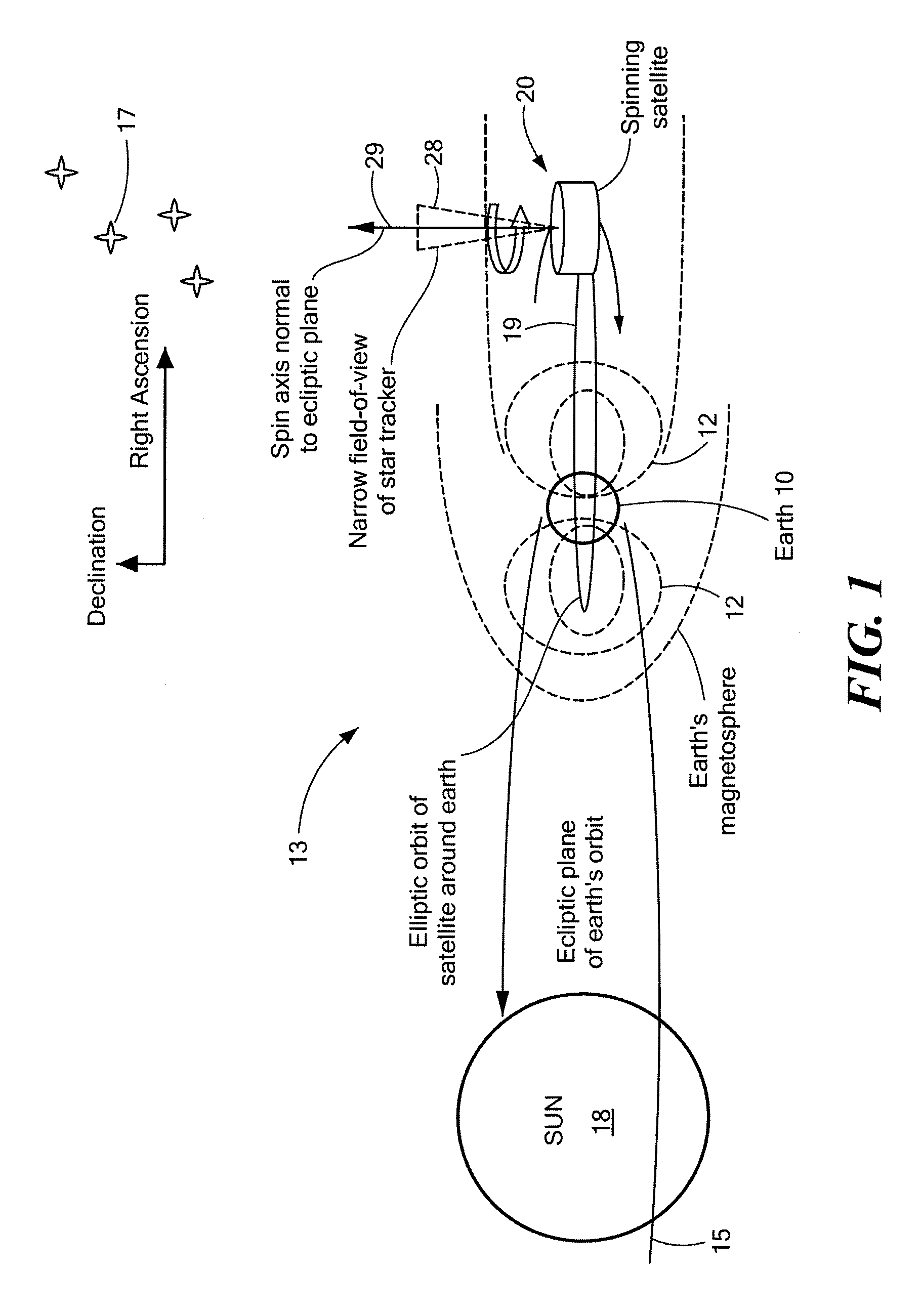
Method of determining and controlling the inertial attitude of a spinning, artificial satellite and systems therefor
InactiveUS20090222153A1Reduce material volumeHigh gainCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationNatural satelliteGyroscope
A method of and apparatus for determining and controlling the inertial attitude of a spinning artificial satellite without using a suite of inertial gyroscopes. The method and apparatus operate by tracking three astronomical objects near the Earth's ecliptic pole and the satellite's and / or star tracker's spin axis and processing the track information. The method and apparatus include steps and means for selecting preferably three astronomical objects using a histogram method and determining a square of a first radius (R12) of a track of a first astronomical object; determining a square of a second radius (R22) of a track of a second astronomical object; determining a square of a third radius (R32) of a track of a third astronomical object; determining the inertial attitude of the spin axis using the squares of the first, second, and third radii (R12, R22, and R32) to calculate pitch, yaw, and roll rate; determining a change in the pitch and yaw of the artificial satellite; and controlling on-board generated current flow to various orthogonally-disposed current-carrying loops to act against the Earth's magnetic field and to apply gyroscopic precession to the spinning satellite to correct and maintain its optimum inertial attitude.
Owner:JOHNSON KARA WHITNEY +1
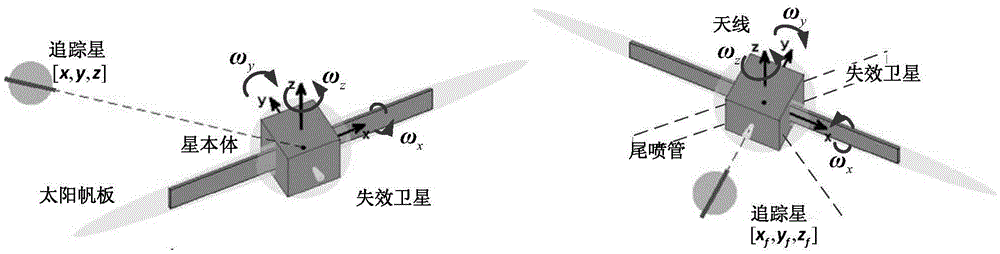
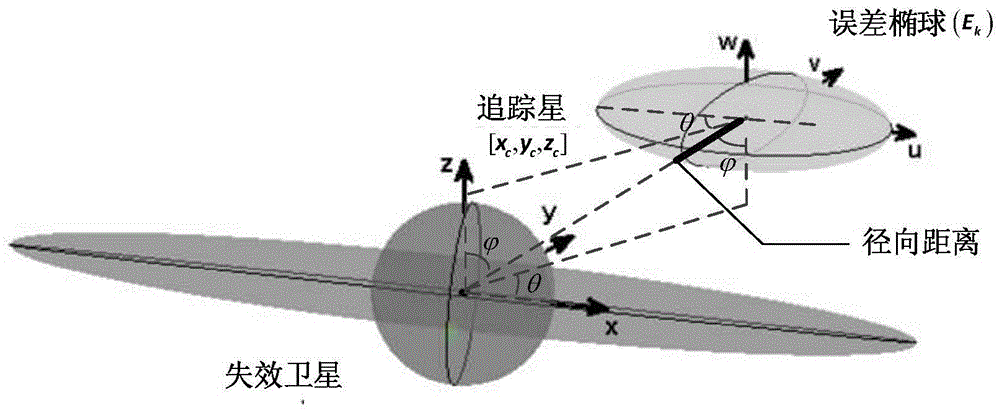
Super-close optimized collision-avoidance proximity method for failure satellite
ActiveCN105549606AMeet space constraintsEnsuring safety and collision-free mission requirementsAttitude controlNatural satelliteClosed loop feedback
The invention relates to a super-close optimized collision-avoidance proximity method for a failure satellite, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft encounter. An object, namely the failure satellite, is designed into an envelope model in the sphere and ellipsoid combined form to simplify configuration of the object; posture rolling of the object is considered, a relative dynamic model of the object and a tracked star as well as constraints of the path of the tracked star are derived in the dynamic object system; positional nondeterminacy caused by navigation and measurement errors is considered, and the flight forbidden area of the tracked start is further broadened by combining the collision possibility problem; and a safe collision avoidance path is planned on the basis of the Gauss pseudospectral method, and closed-loop feedback control is carried out. According to the invention, spatial limitation in super-close proximity are considered, and requirements for a safe collision free task can be met; and the posture coupling feature of a close proximity spacecraft is emphasized, and whether the distance between the aircrafts satisfies the constraints can be directly determined.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Propulsion system with four modules for satellite orbit control and attitude control
ActiveUS20140361124A1Cosmonautic propulsion system apparatusArtificial satellitesNatural satelliteAttitude control
A propulsion system for the orbital control of a satellite with terrestrial orbit travelling with a speed of displacement along an axis V tangential to the orbit comprises two propulsion assemblies, fixed to the satellite facing one another with respect to the plane of the orbit, each of the propulsion assemblies comprising two propulsion modules; each of the propulsion modules successively comprising: a motorized link for rotation about an axis parallel to the axis V, an offset arm, and a platen supporting a propulsion unit able to deliver a thrust oriented along an axis perpendicular to the axis V; the two propulsion modules of each propulsion assembly being linked to the satellite on either side and substantially at equal distances from a plane perpendicular to the axis V passing through a centre of mass of the satellite.
Owner:THALES SA
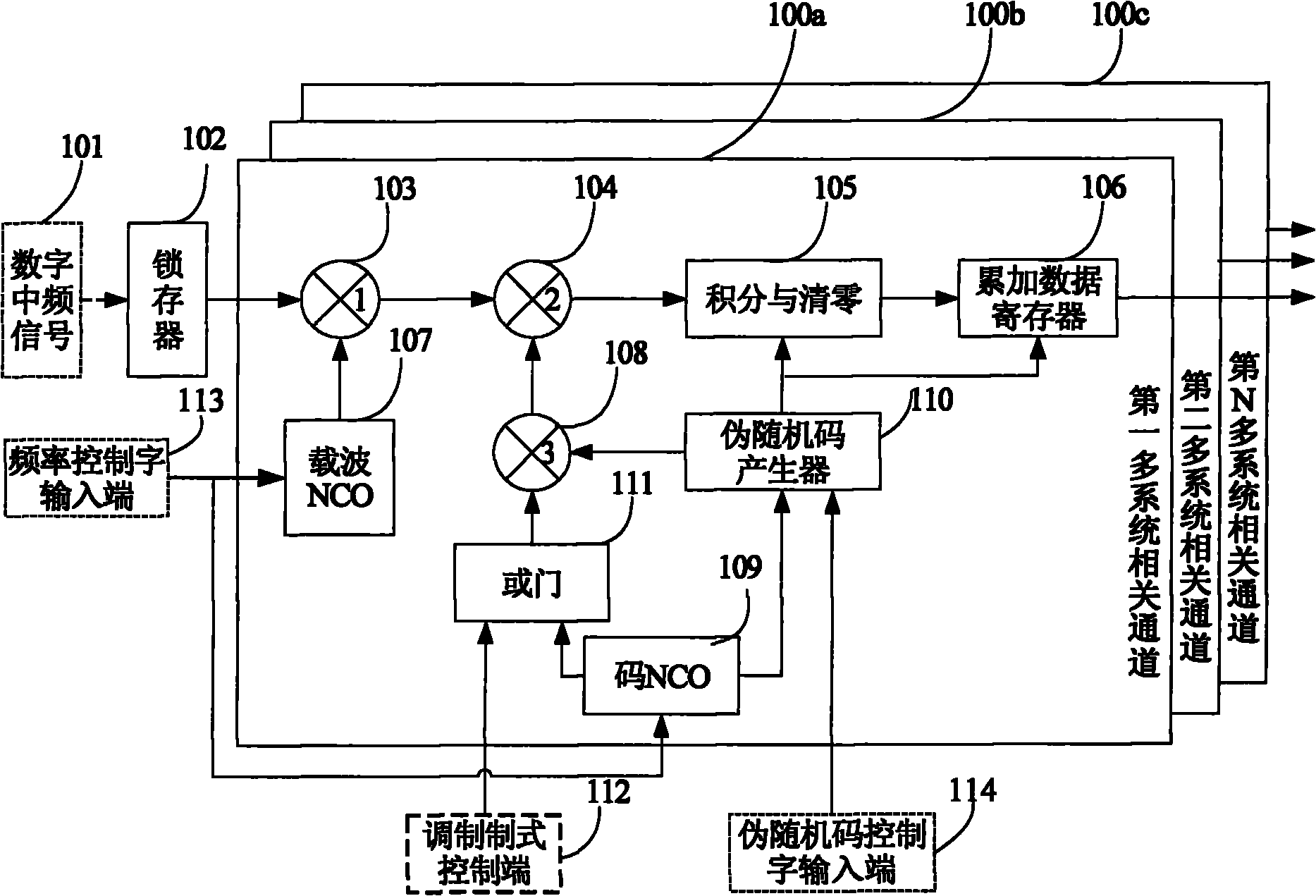
Multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signal receiving method and correlator thereof
ActiveCN102096078AFix compatibility issuesImprove continuitySatellite radio beaconingNumerical controlNatural satellite
The invention provides a multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signal receiving method which supports the receiving of satellite signals of a GPS (Global Position System), a GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System), a Big Dipper navigation system and a Galileo satellite navigation system at present. The invention also discloses a multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS signal receiving correlator which comprises N multi-system correlated channels, wherein each multi-system correlated channel mainly comprises a carrier numerical controlled oscillator (NCO), a code NCO, a pseudo-random code generator and an integrating and zero clearing module; each code NCO is used for outputting a pulse sequence for triggering the pseudo-random code generator and also generating square signals with the same rate as subcarrier signals in a BOC (1, 1) signal demodulation mode; each pseudo-random code generator can generate 14 grades of pseudo-random codes at most; and each integrating and zero clearing module has an overflow protection function and improves the reliability. The multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS correlator can be compatible with four satellite systems, effectively improves the reliability and the continuity of navigation and positioning and obviously reduces the use risk of single-system navigation.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com