Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8049 results about "Spacecraft" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket).
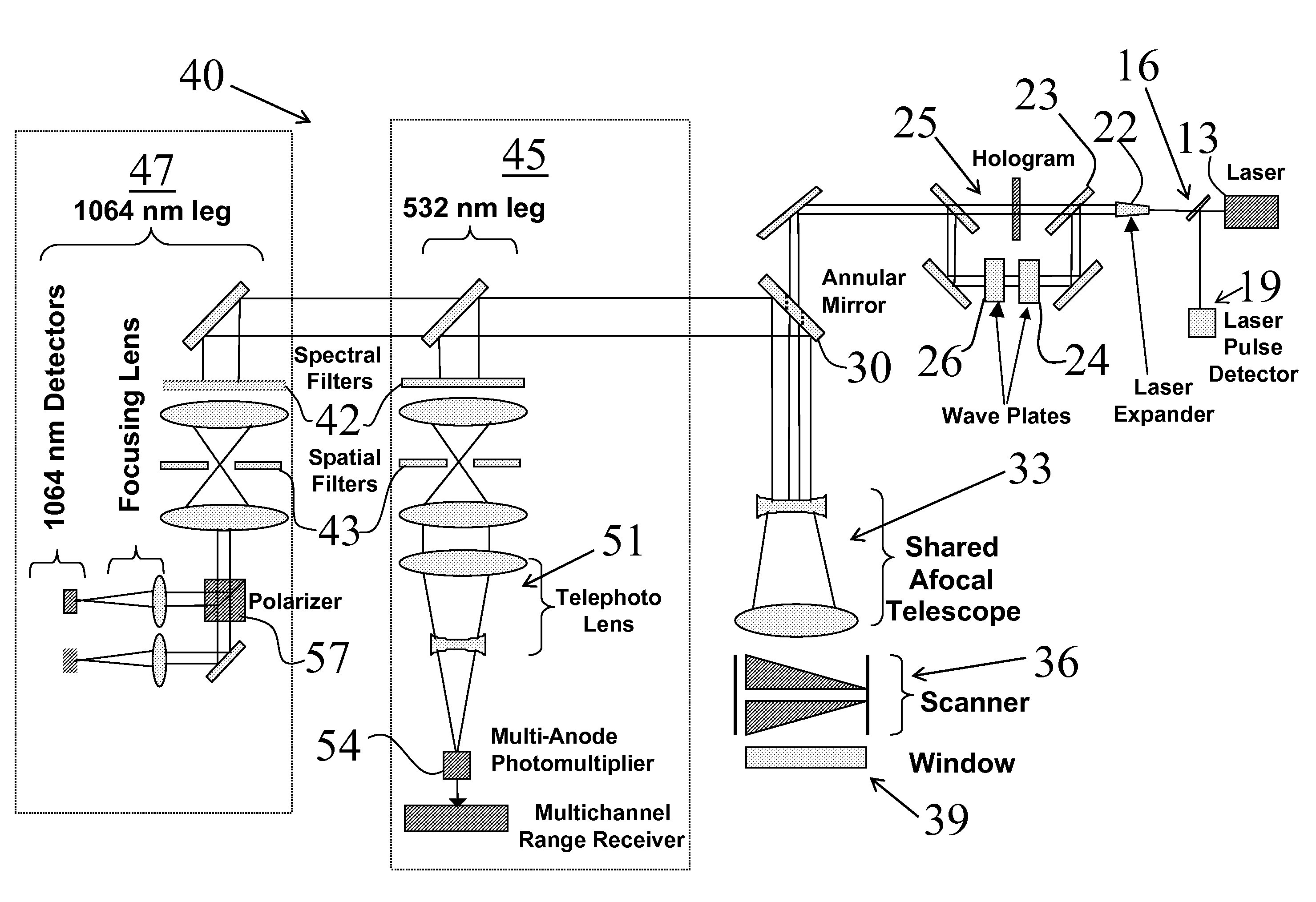
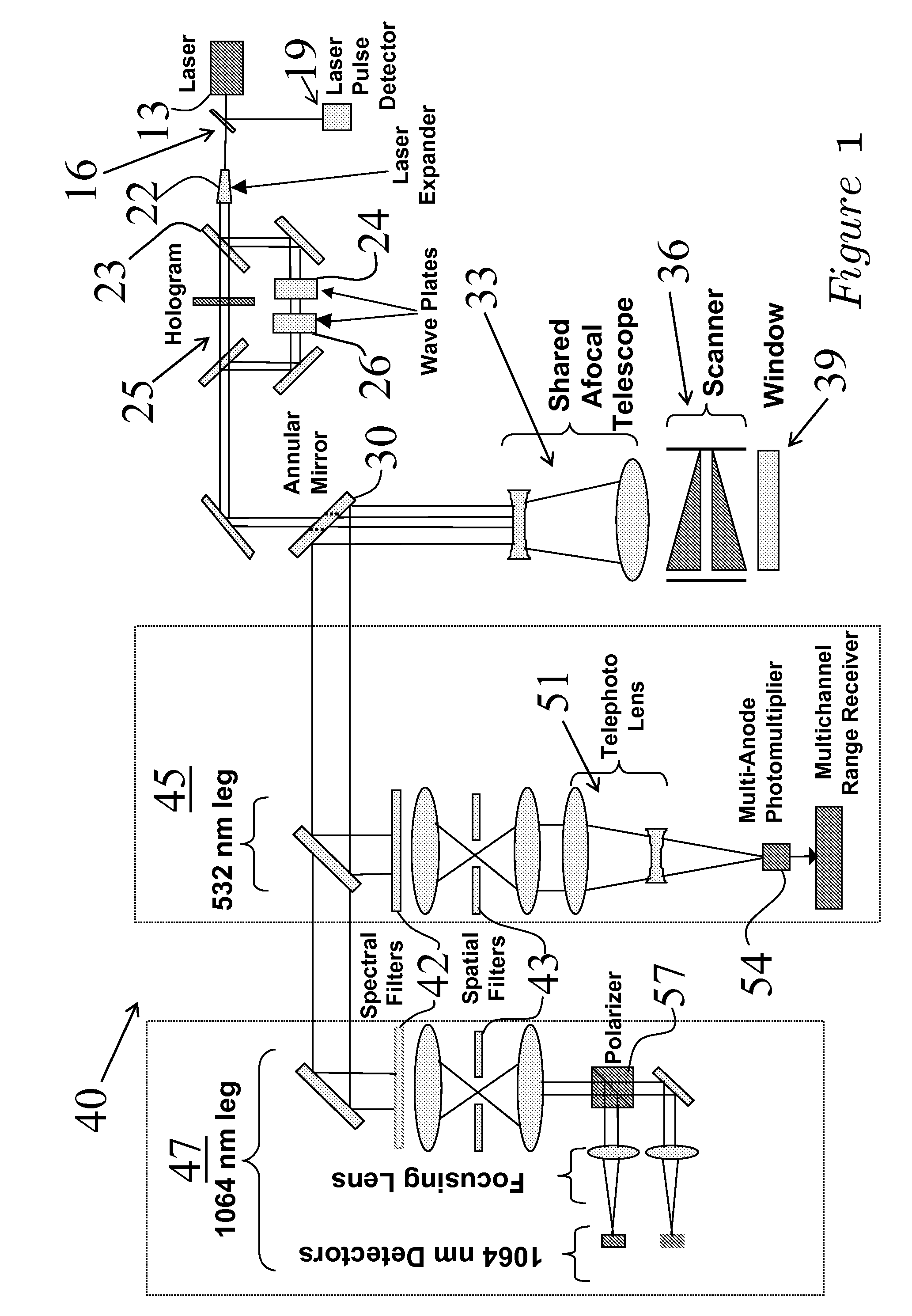
Three-dimension imaging lidar
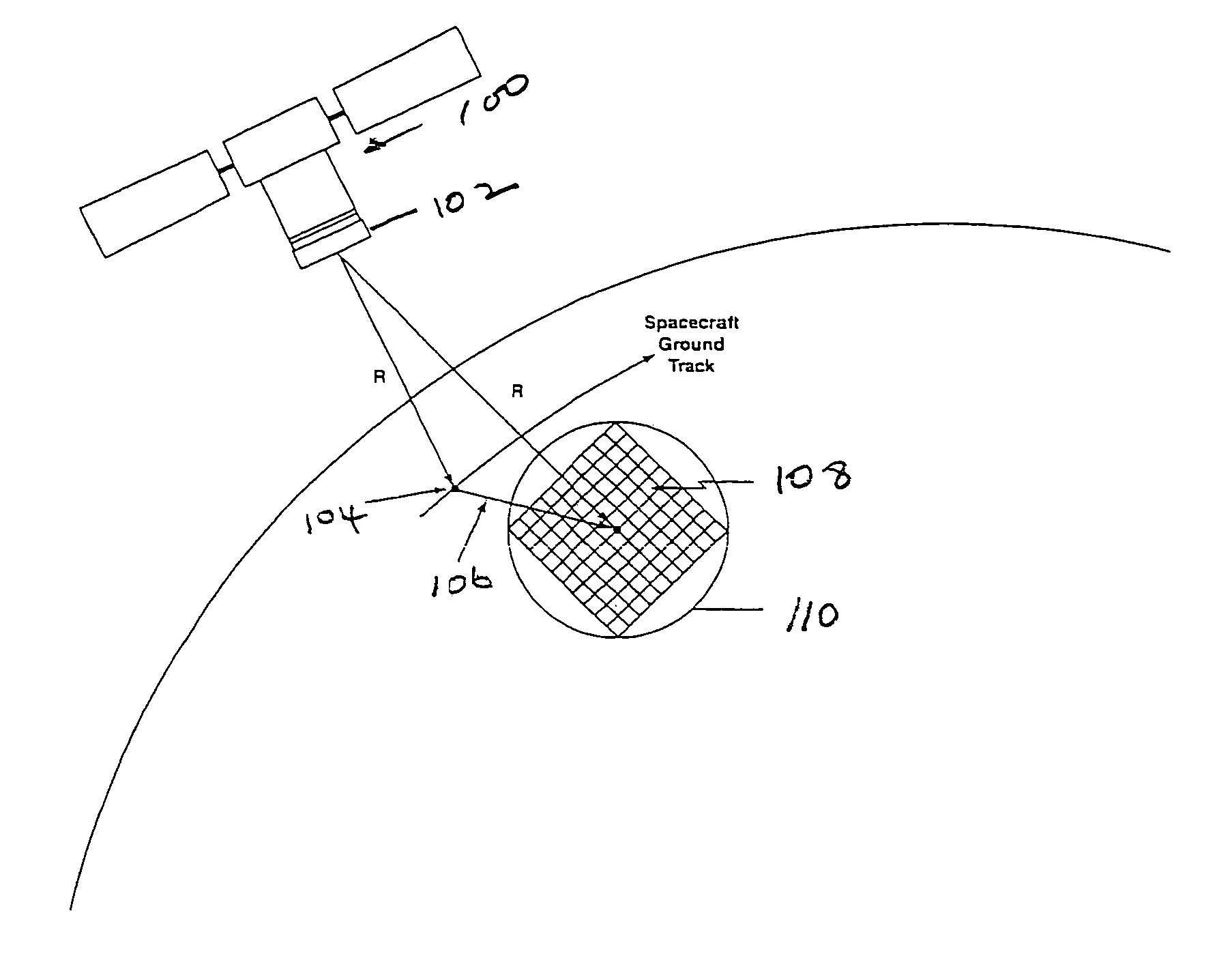
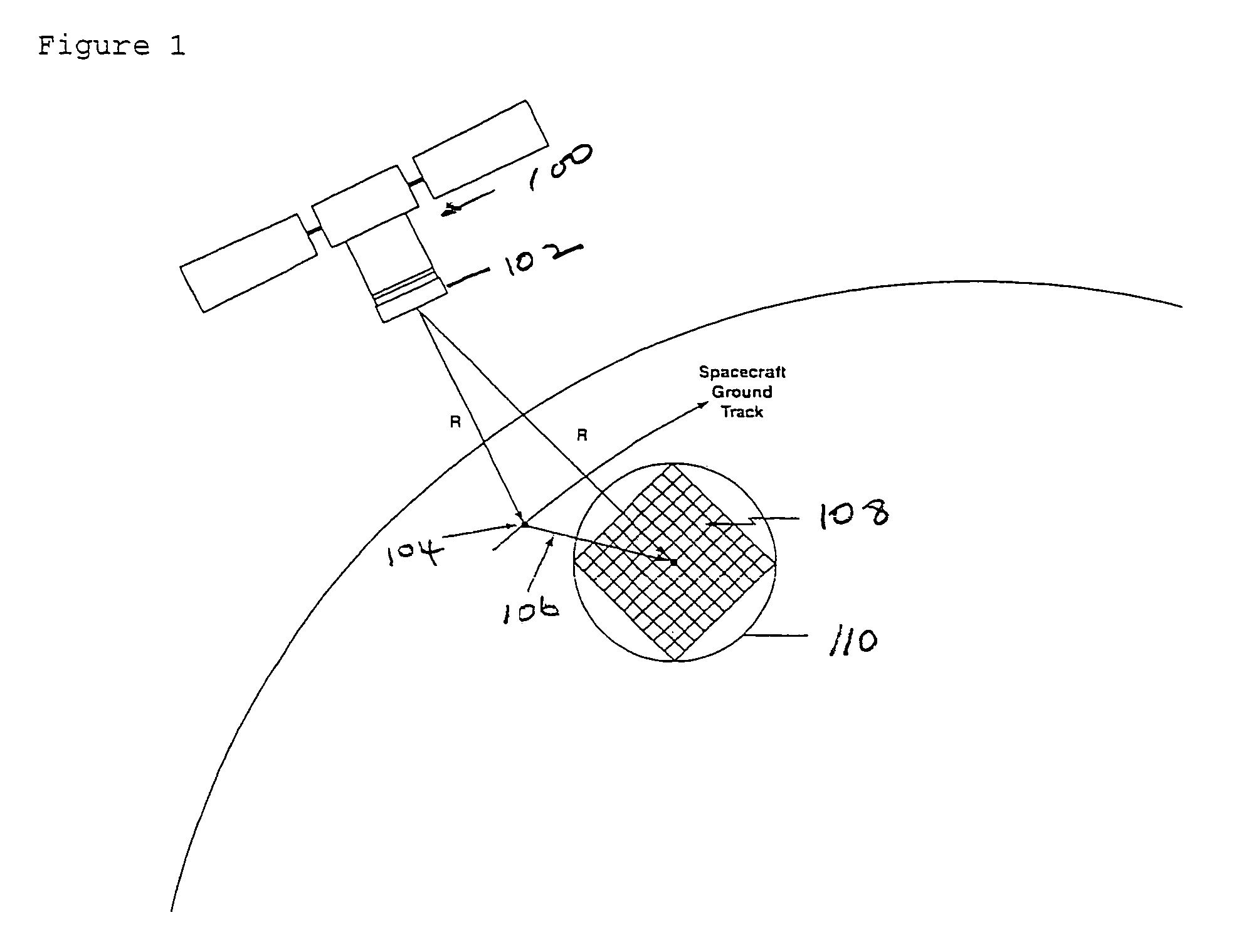
This invention is directed to a 3-dimensional imaging lidar, which utilizes modest power kHz rate lasers, array detectors, photon-counting multi-channel timing receivers, and dual wedge optical scanners with transmitter point-ahead correction to provide contiguous high spatial resolution mapping of surface features including ground, water, man-made objects, vegetation and submerged surfaces from an aircraft or a spacecraft.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE NAT AERONAUTICS SPACE ADMINISTATION
Temperature measurement and calibration platform in space vacuum environment
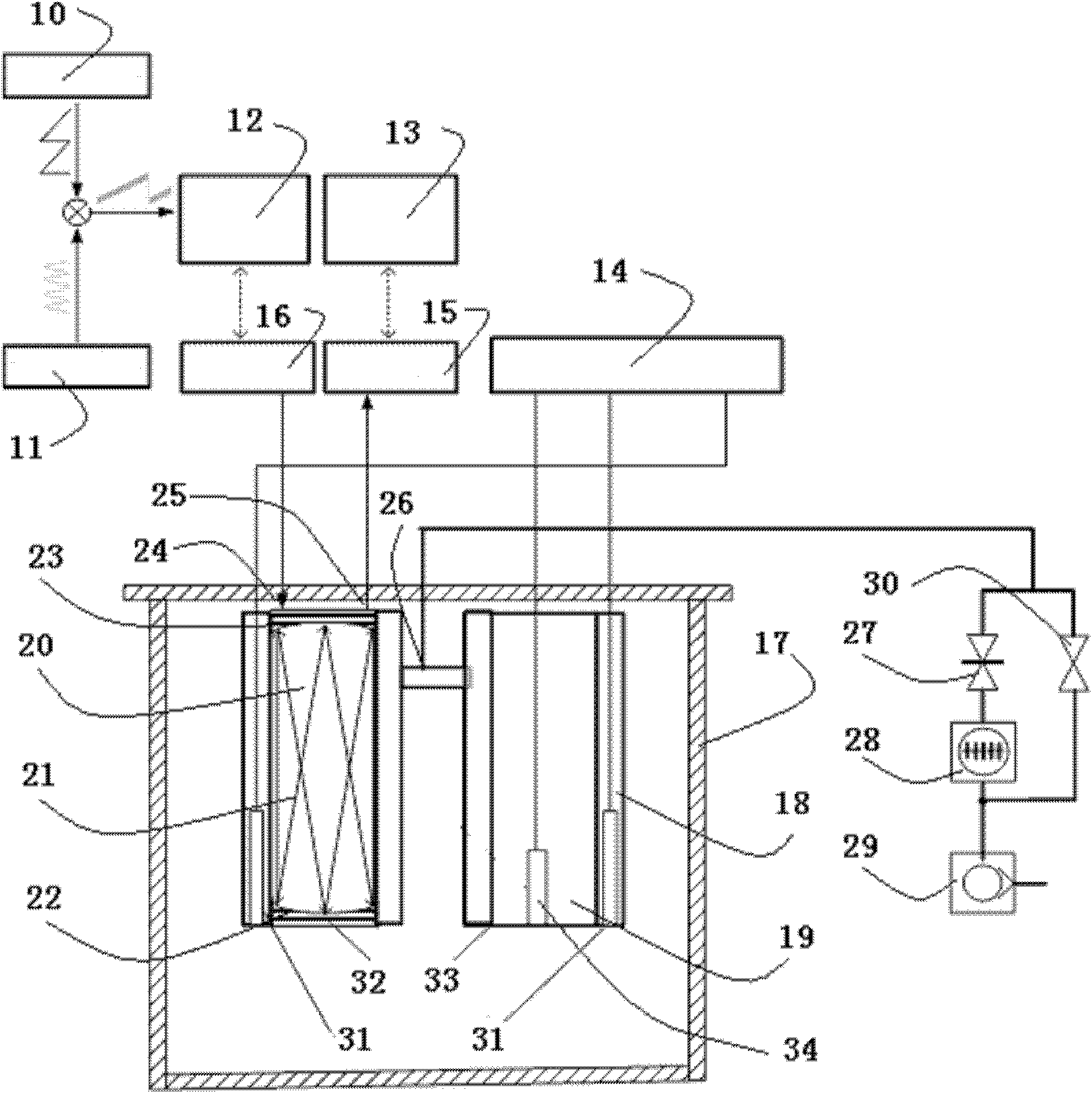
ActiveCN102539019ASolve the problem of large differences in measurement resultsSolve the traceability problemThermometer testing/calibrationVacuum pumpingSpace environment
The invention relates to a temperature measurement and calibration platform in space vacuum environment. The temperature measurement and calibration platform is favorable for realizing the simultaneous calibration of contact type temperature measurement and non-contact type temperature measurement, so the temperature measurement and calibration platform is served for heat vacuum and heat balance experiments of spacecrafts such as satellites, spaceship and the like. The temperature measurement and calibration platform comprises a constant temperature bath, wherein a double-sub-cavity vacuum cavity, the double-sub-cavity vacuum cavity comprises a first vacuum cavity body and a second vacuum cavity body, the first vacuum cavity body and the second vacuum cavity body are connected with a vacuum pumping device through a three-way valve, standard temperature indicator sensors are respectively arranged on the outer wall of the first vacuum cavity body and on the outer wall of the second vacuum cavity body, the standard temperature indicator sensors are connected with a temperature secondary meter, a laser light path reflecting device is arranged in the vacuum cavity of the first vacuum cavity body for calibrating a non-contact type temperature measuring system based on the tunable diode laser absorption spectrum technology, and the vacuum cavity of the second vacuum cavity body is used for accommodating a temperature sensor for calibrating a contact type temperature measuring system adopting the temperature sensor.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG MEASUREMENT & TEST INST
Spacecraft docking mechanism
The present invention provides a docking mechanism that is capable of interfacing with Apogee Boost Motors (ABM) including Liquid Apogee Motors (LAM) of the satellite being captured to allow a servicing spacecraft to dock with a satellite that has no special docking features. The docking mechanism includes a compliant probe with spring-loaded fingers at its tip which is inserted into the LAM by the approach motion of the servicer spacecraft. When the probe tip has passed beyond the throat of the LAM the finger extend to trap the LAM on the probe thus achieving capture. The rigidization stage of docking is achieved by retracting the probe to pull the two spacecraft together. The docking mechanism includes abutment pads which interface with the launcher interface ring of the client spacecraft. With the preload applied by the probe retraction mechanism reacted through these pads, the docking mechanism can maintain a rigid docked interface under loads induced by thrusting maneuvers of the combined spacecraft or loads induced by on-orbit servicing operations.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
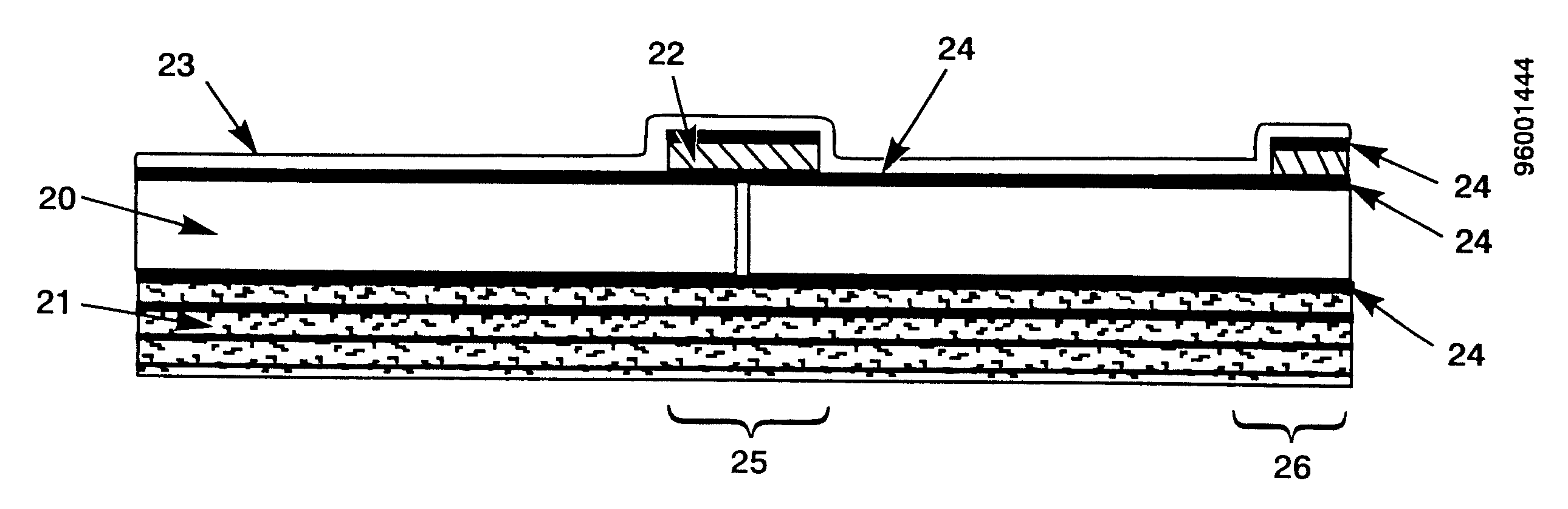
Structurally embedded intelligent power unit
InactiveUS7150938B2Increase capacityImprove power performanceBatteries circuit arrangementsCell temperature controlElectric power systemEngineering
An electrical power system for a spacecraft or other vehicle or structure comprising a structural member containing an integrated solid-state power source is disclosed. The power source includes a solar cell system and an energy storage system that are combined into a single unit or package, and in certain embodiments, are configured into the shape of a flexible aerobot balloon or a rigid nanosat surface panel. The power components of a preferred lightweight power unit, include thinly layered photovoltaic cells, a rechargeable lithium solid polymer electrolyte battery, a capacitor, electronics and thermal management capability.
Owner:LITHIUM POWER TECH
Spacecraft capture and docking system
InactiveUS6299107B1Robust, fail-safe and reliableReduces risk of collision and damageCosmonautic vehiclesSystems for re-entry to earthRotary stageUnderwater vehicle
A system for capturing and docking an active craft to a passive craft has a first docking assembly on the active craft with a first contact member and a spike projecting outwardly, a second docking assembly on the passive craft having a second contact member and a flexible net deployed over a target area with an open mesh for capturing the end of the spike of the active craft, and a motorized net drive for reeling in the net and active craft to mate with the passive craft's docking assembly. The spike has extendable tabs to allow it to become engaged with the net. The net's center is coupled to a net spool for reeling in. An alignment funnel has inclined walls to guide the net and captured spike towards the net spool. The passive craft's docking assembly includes circumferentially spaced preload wedges which are driven to lock the wedges against the contact member of the active craft. The active craft's docking assembly includes a rotary table and drive for rotating it to a predetermined angular alignment position, and mating connectors are then engaged with each other. The system may be used for docking spacecraft in zero or low-gravity environments, as well as for docking underwater vehicles, docking of ancillary craft to a mother craft in subsonic flight, in-flight refueling systems, etc.
Owner:HONEYBEE ROBOTICS
Structurally embedded intelligent power unit
InactiveUS20030038610A1Batteries circuit arrangementsCell temperature controlElectric power systemEngineering
An electrical power system for a spacecraft or other vehicle or structure comprising a structural member containing an integrated solid-state power source is disclosed. The power source includes a solar cell system and an energy storage system that are combined into a single unit or package, and in certain embodiments, are configured into the shape of a flexible aerobot balloon or a rigid nanosat surface panel. The power components of a preferred lightweight power unit, include thinly layered photovoltaic cells, a rechargeable lithium solid polymer electrolyte battery, a capacitor, electronics and thermal management capability.
Owner:LITHIUM POWER TECH
Moment-resistant structure, sustainer and method of resisting episodic loads
The present invention relates to a moment-resistant structure, sustainer, and method of construction for deformably resisting episodic loads, particularly those of high intensity. The episodic loads may be due to earthquake, impact, or other intense episodic sources. The structure and sustainer may be in buildings, bridges, or other civil works, land vehicles, watercraft, aircraft, spacecraft, machinery, or other structural systems or apparati. Deformation capacity is enhanced by the use of multiple dissipative zones. Dissipative zones that function in a manner similar to plastic hinges are determined by one or more voids that are located in the web of a sustainer. The one or more voids are of a size, shape, and configuration to assure that the dissipative zones deform inelastically when a critical stress, i.e., a maximum allowable demand, is reached, thereby developing the action of a structural fuse, preventing the occurrence of stress and strain demands sufficient to cause fracture of the connection welds or adjacent heat-affected zones, i.e., preventing the stress and strain demands from exceeding the strength capacity of the connection welds or adjacent heat-affected zones. The sustainers may be removably connected to the remainder of the structure, facilitating their replacement after inelastic deformation. The structure, sustainer, and method of construction may be utilized in new construction and in the rehabilitation of existing construction. Mechanical equipment and utilities may pass through the voids.
Owner:ASCHHEIM MARK AMOS
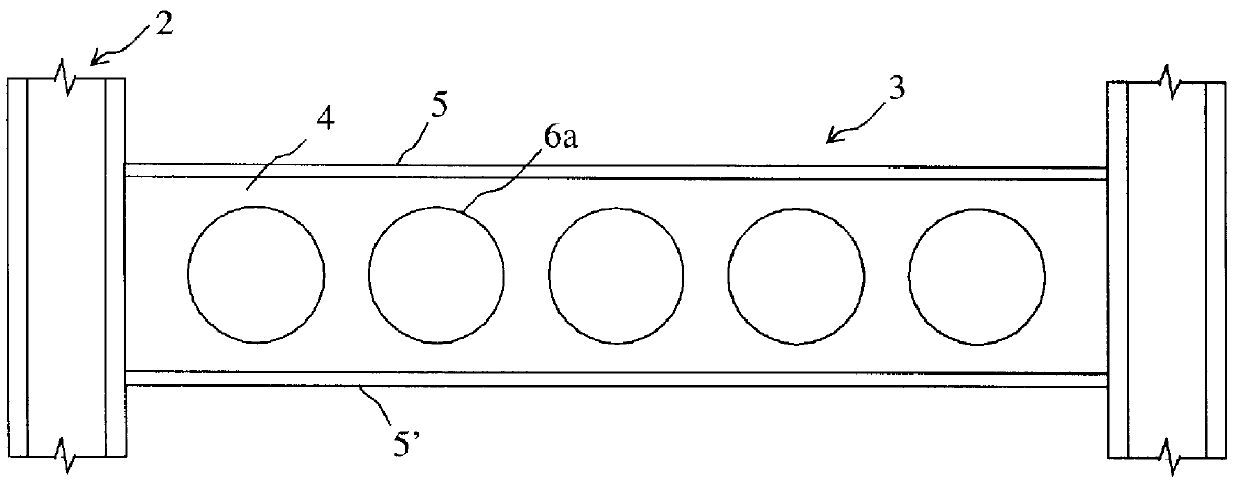
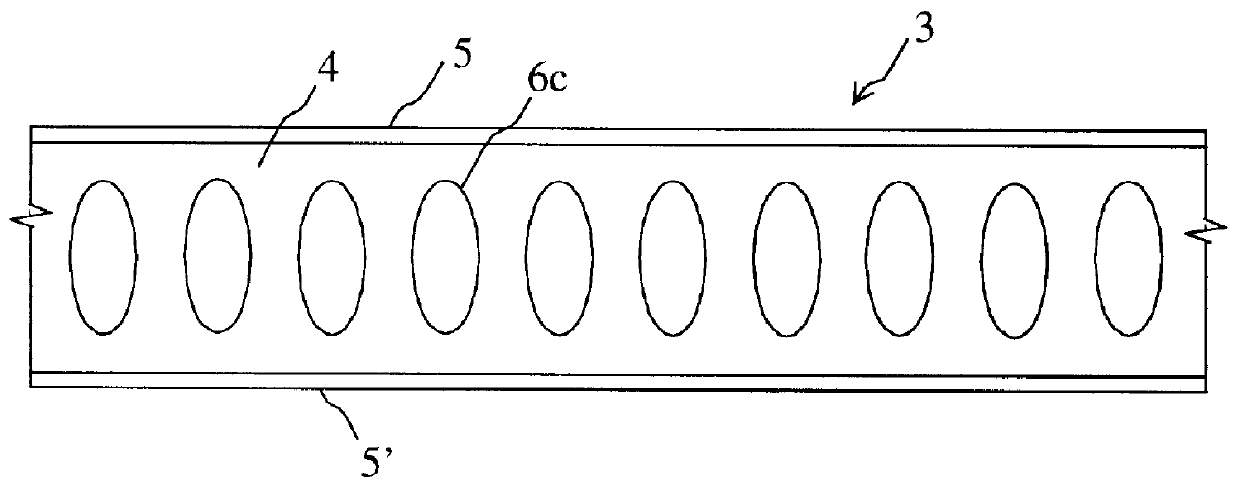
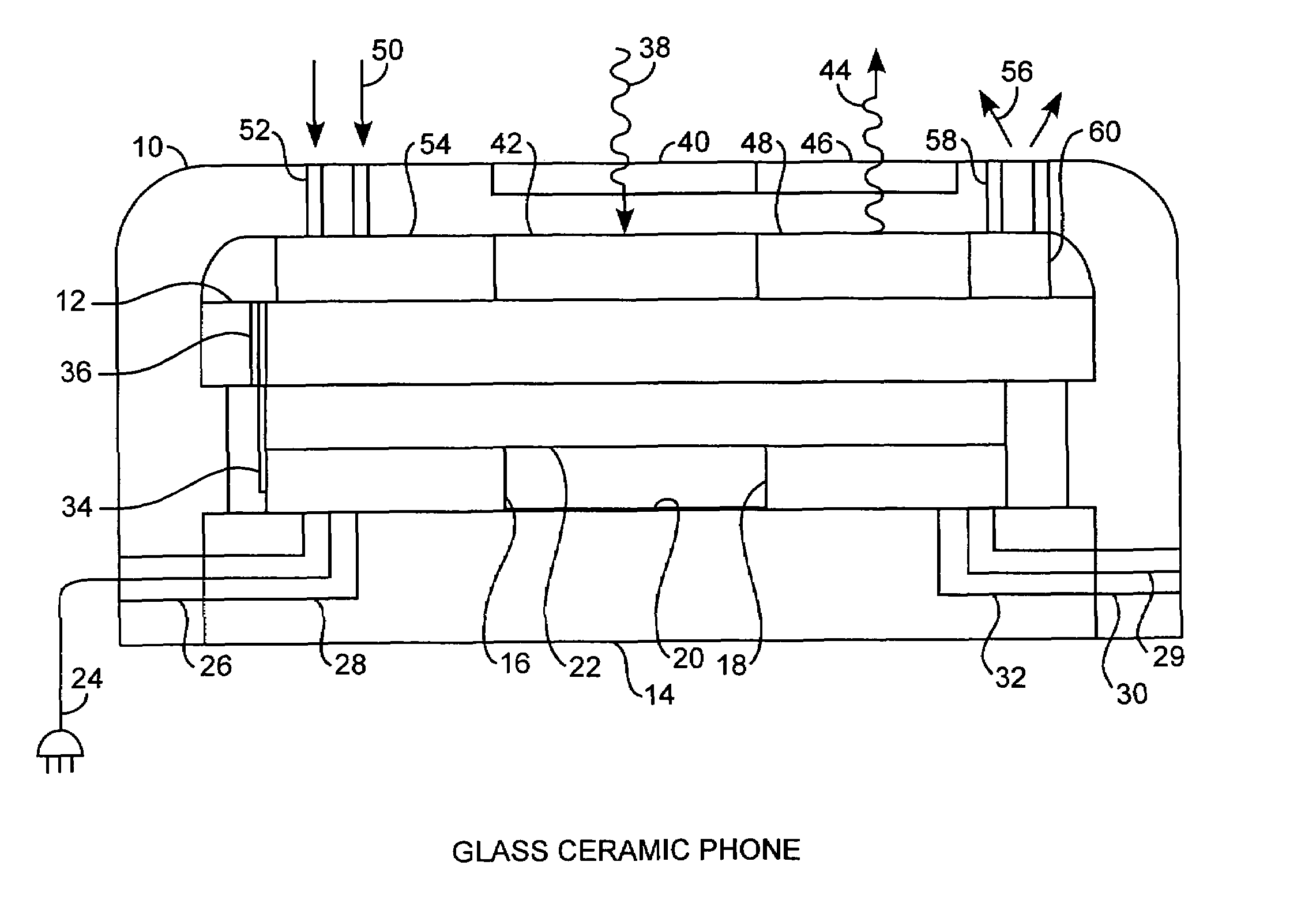
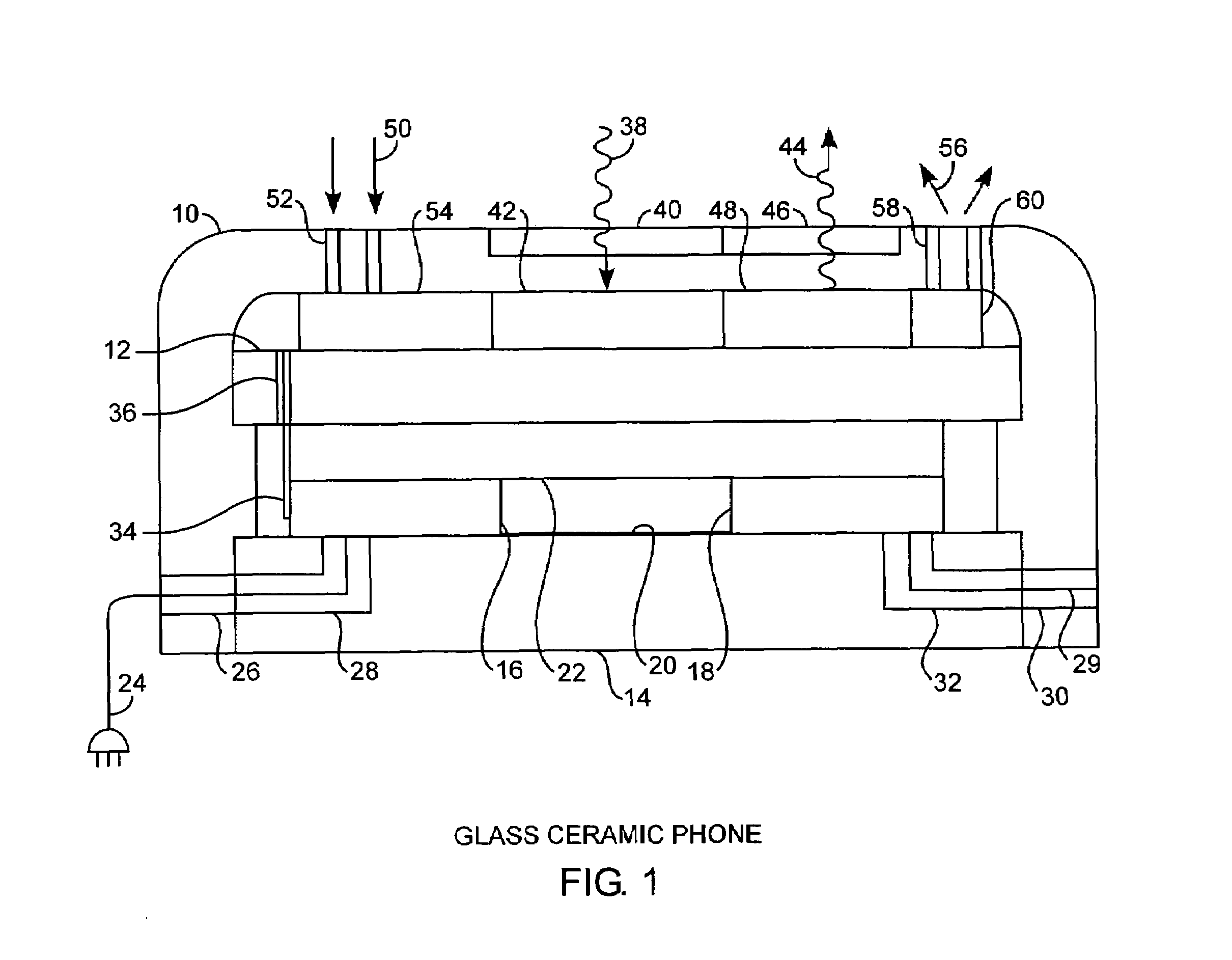
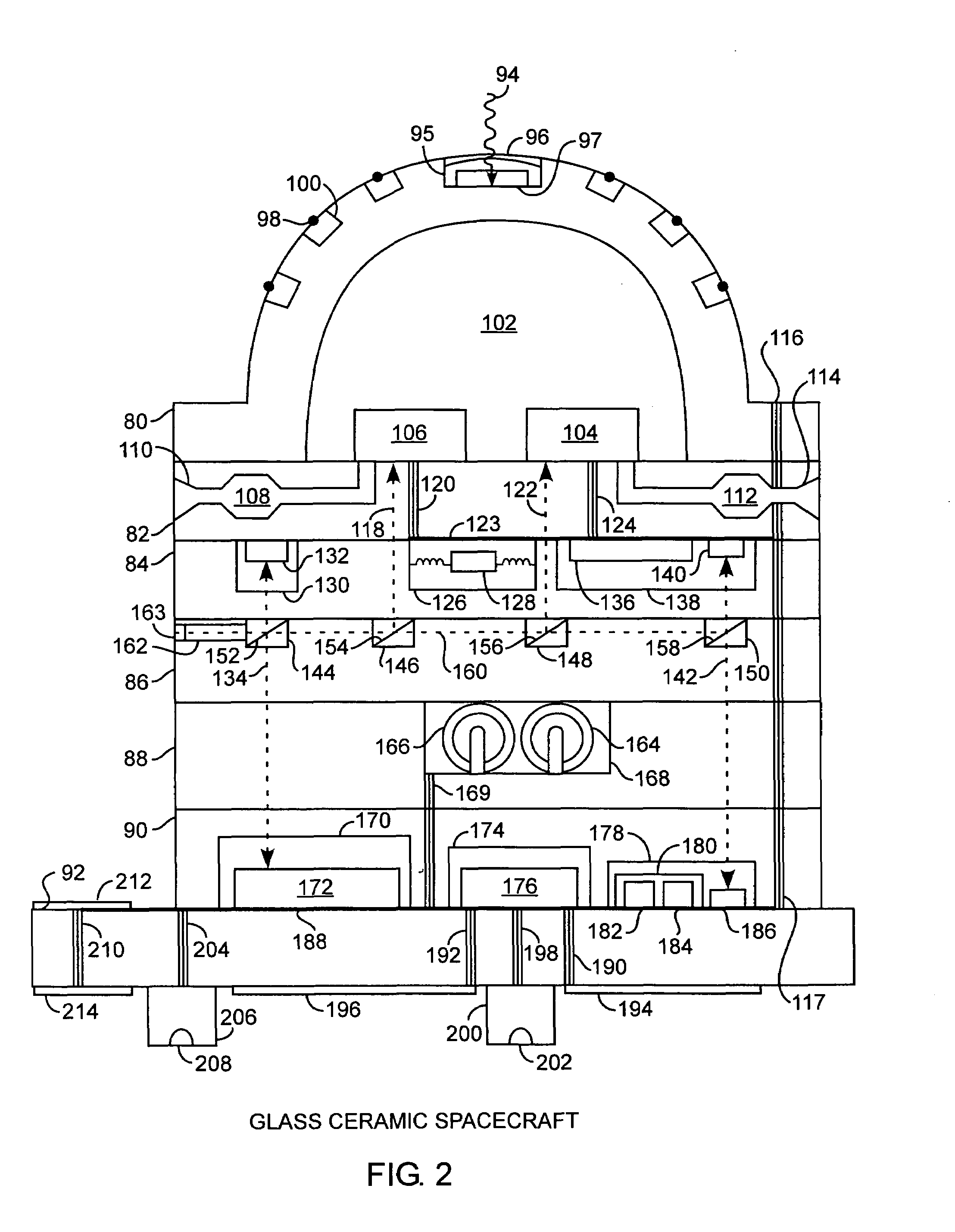
Integrated glass ceramic systems
ActiveUS6952530B2Improve structural strengthLow thermal conductivityCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCosmonautic power supply systemsElectricityOptical communication
Integrated glass ceramic spacecraft include a plurality of glass ceramic components including molded, tempered, annealed, and patterned glass ceramic components coupled together for forming a support structure or frame or housing through which is communicated optical signals through an optical communications grid and electrical signals through an electrical communications grid, with the optical communications grid and electrical communication grid forming a composite electrooptical communications grid for spacecraft wide intercommunications. The support structure multifunctions as a frame, a housing, a support, a thermal control system, and as part of an electrooptical communications grid while encapsulating a plurality of optical, electronic, electrical, and MEMS devices between which is communicated the electrical and optical signals over the electrooptical communication grid.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
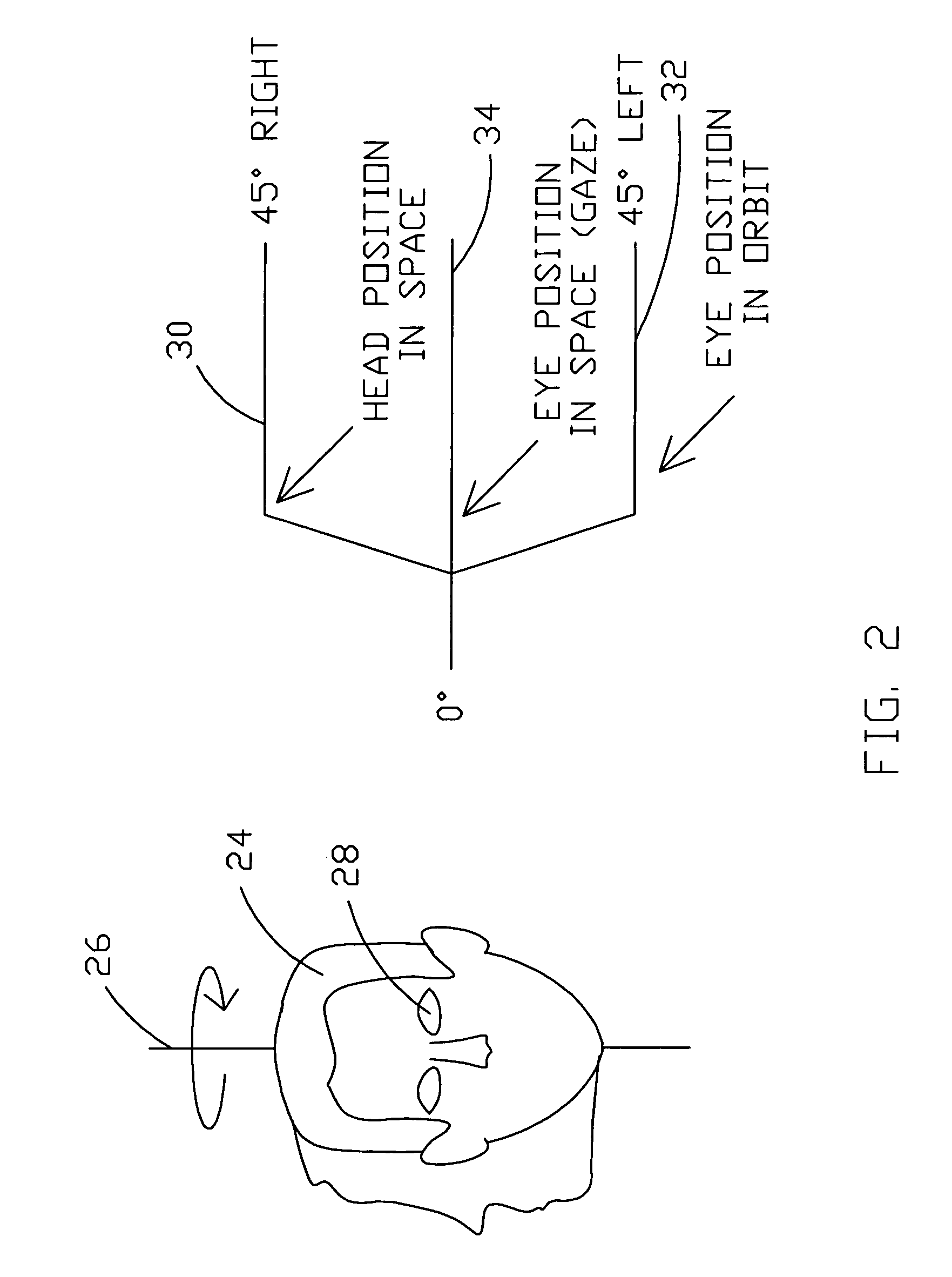
Motion sickness treatment apparatus and method
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for treating motion sickness. In a preferred embodiment a method of the invention comprises operating eyewear having shutter lenses to open said shutter lenses at a selected operating frequency ranging from within about 3 Hz to about 50 Hz. The shutter lenses are opened for a short duration at the selected operating frequency wherein the duration is selected to prevent retinal slip. The shutter lenses may be operated at a relatively slow frequency of about 4 Hz when the user is in passive activity such as riding in a boat or car or in limited motion situations in a spacecraft. The shutter lenses may be operated at faster frequencies related to motion of the user's head when the user is active.
Owner:ADMINISTATOR OF NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE +1
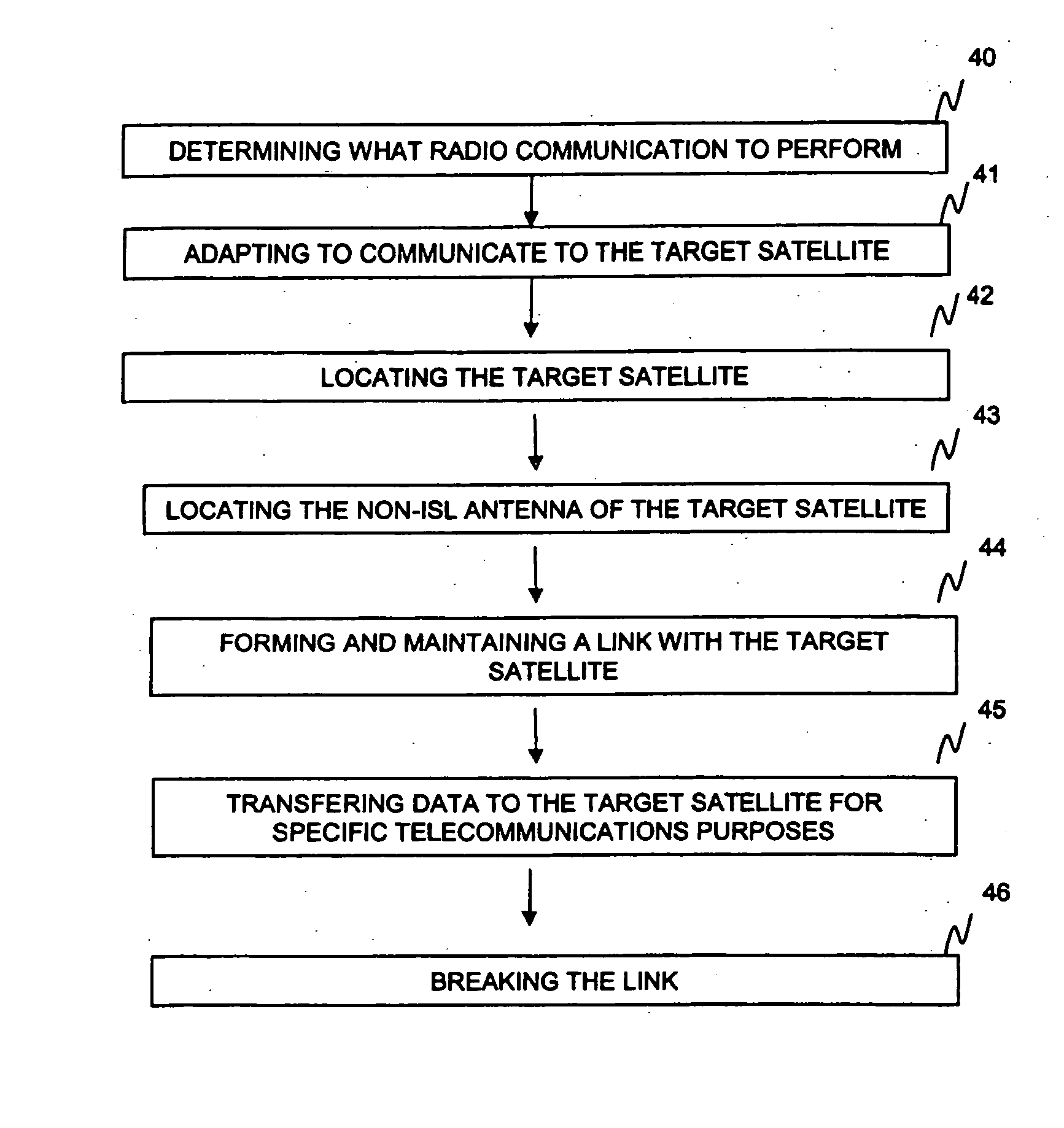
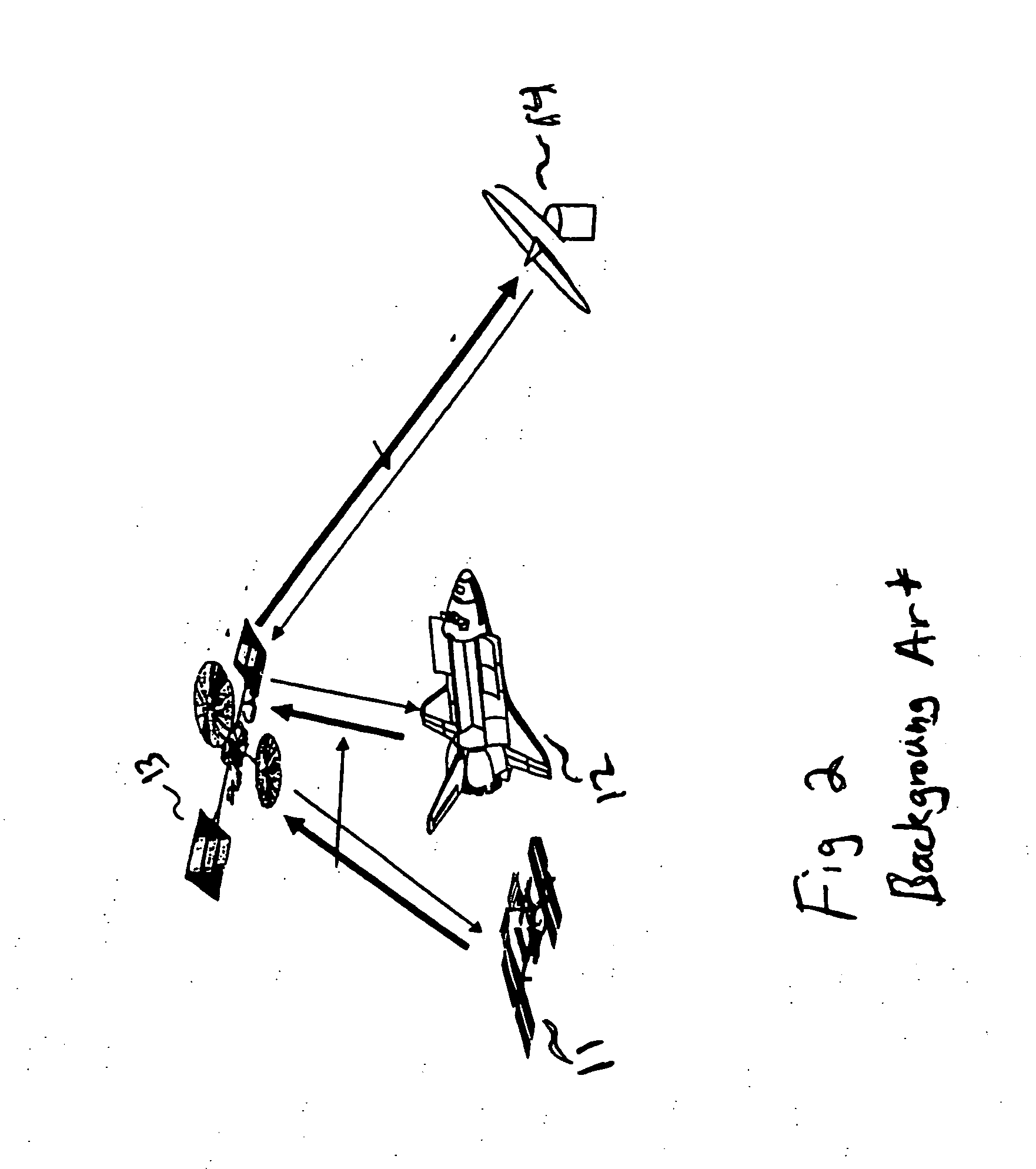
Inter-satellite crosslink communications system, apparatus, method and computer program product
InactiveUS20050143005A1Adapt quicklyAvoid wasting energyActive radio relay systemsWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemEngineering
A communications system, apparatus, method, and computer program product for inter-satellite and inter-spacecraft crosslinks (ISL) with non-ISL optimized antennas on spacecraft. The system includes a mobile communications platform that includes an ISL antenna configured to transmit information to a target satellite through a non-ISL antenna of the target satellite. The mobile communications platform is configured to relay transmissions through the non-ISL antenna of the target satellite to another communications platform. The mobile communications platform includes a controller configured to determine a location of the mobile platform; determine whether the target satellite is within communications range; and prepare a signal for relayed transmissions through a non-ISL antenna of the target satellite to another communications platform in a signal format that is decipherable by this other communications platform.
Owner:PEERSAT
Ceramic tile armor with enhanced joint and edge protection
InactiveUS6009789AMinimal increase in weightImprove reliabilityArmoured vehiclesPersonal protection gearCeramic compositeGround vehicles
A ceramic composite tile armor which is reinforced at the more vulnerable joint and free edge areas, using glass or ceramic strips or overlays bonded with an adhesive to the outer surface of the tile joints and free edges. This reinforcement provides improved ballistic threat protection for ground vehicle, aircraft, watercraft, spacecraft, and body (personnel) ceramic tile armor applications. Glass or ceramic overlay strips assist in fracturing impacting projectiles that strike the tile joints or free edges. The substrate laminate backing can then capture fragments of the projectile and broken ceramic and prevent penetration. The invention provides improved protection over conventional joint and edge enhancements with higher reliability of accurate positioning over joint and free-edge areas, with less added weight, and at lower associated production costs.
Owner:SIMULA
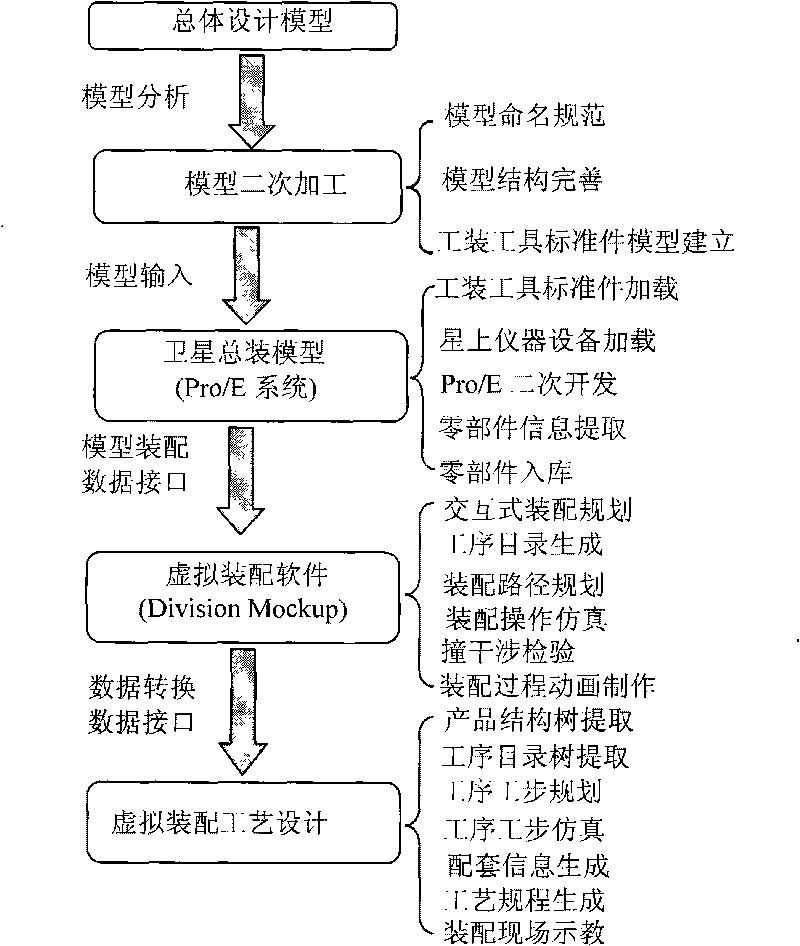
Spacecraft assembly simulation technique-based virtual assembly system and virtual assembly method
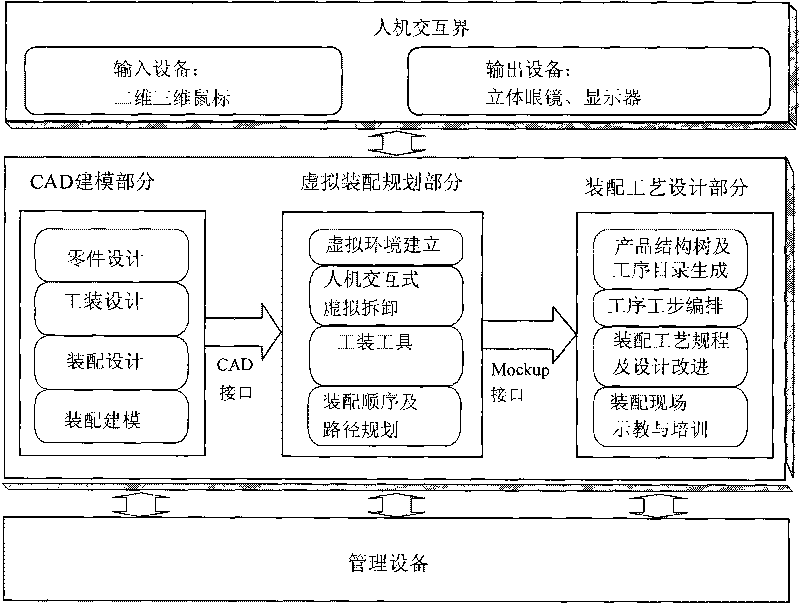
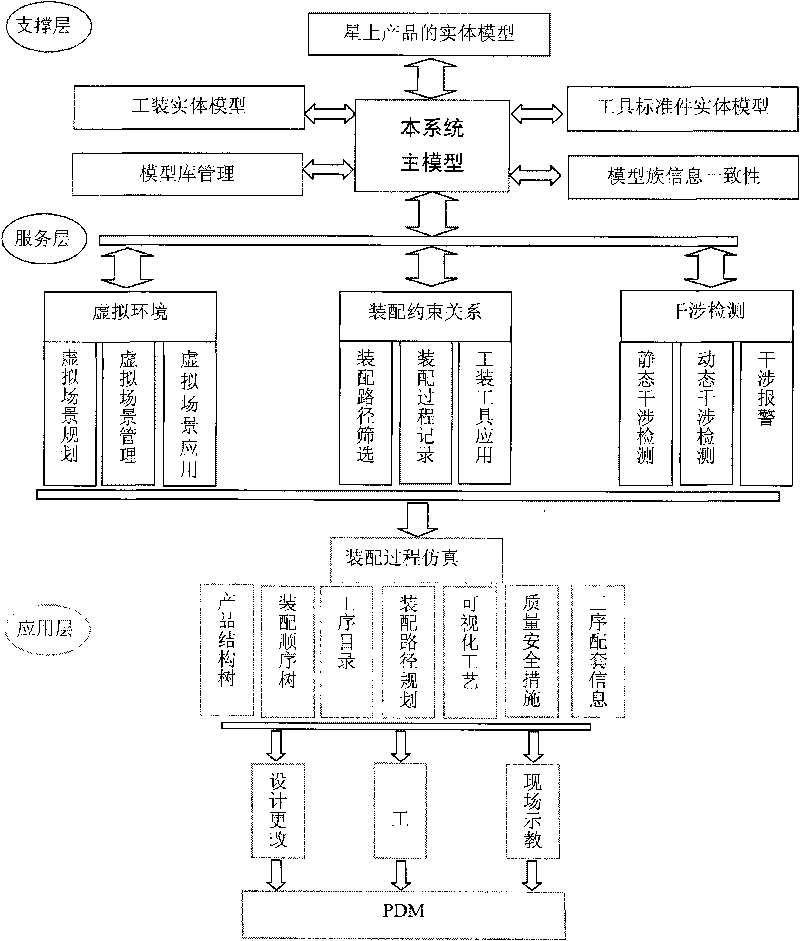
The invention relates to a spacecraft assembly simulation technique-based virtual assembly system. The virtual assembly system comprises a CAD modeling module, a virtual assembly planning module and an assembly process design module, wherein the CAD modeling module is used for designing components and tooling tools, and assembling the components together by defining a series of matching constraint relations so as to obtain an assembling model of products; the virtual assembly planning module is used for establishing a geometrical constraint-based virtual environment, planning an optimized assembly sequence according to disassembly directions, disassembly tools and precedence constraint information recorded in the virtual environment for execution, verifying the optimized assembly sequence, and performing simulation evaluation in the virtual environment; and the assembly process design module is used for designing a product structure tree and a process step catalog, editing process steps and assembling a technological process. The CAD modeling module is connected with the virtual assembly planning module through a CAD modeling interface so that models generated in the CAD modeling module are guided into the virtual assembly planning module; and the process planning result in the virtual assembly planning module is guided into the assembly process design module through a Mockup interface.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
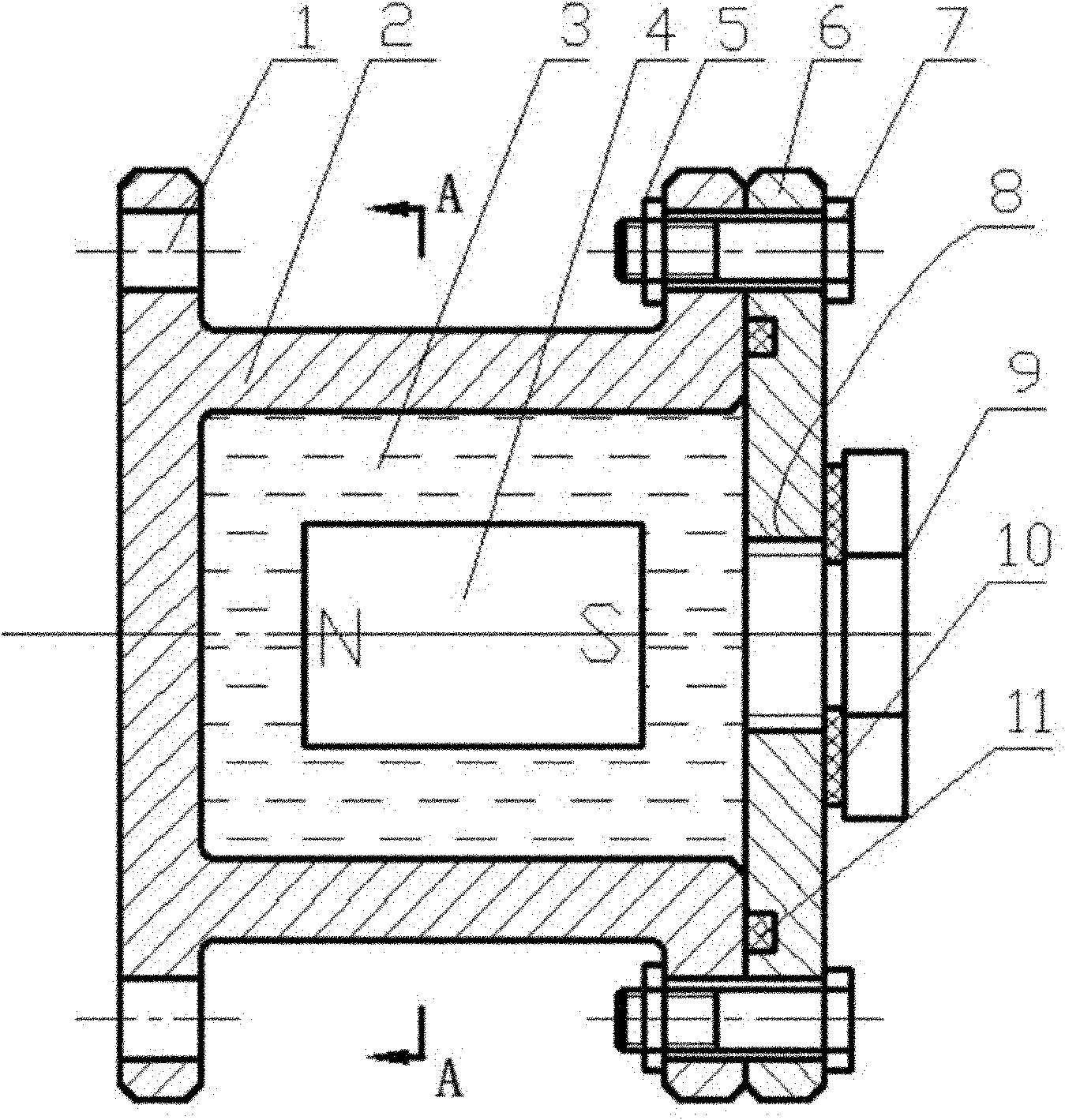
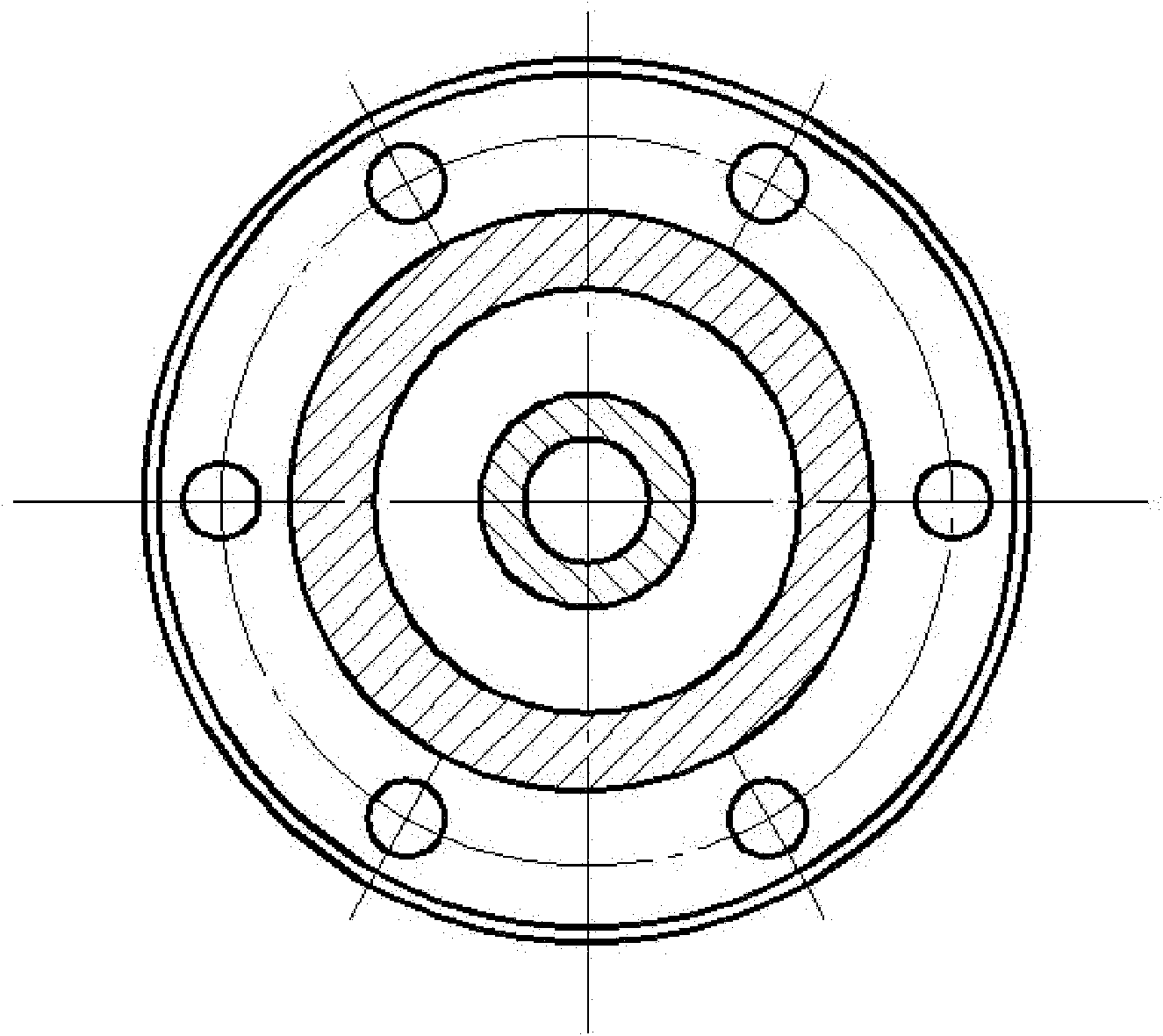
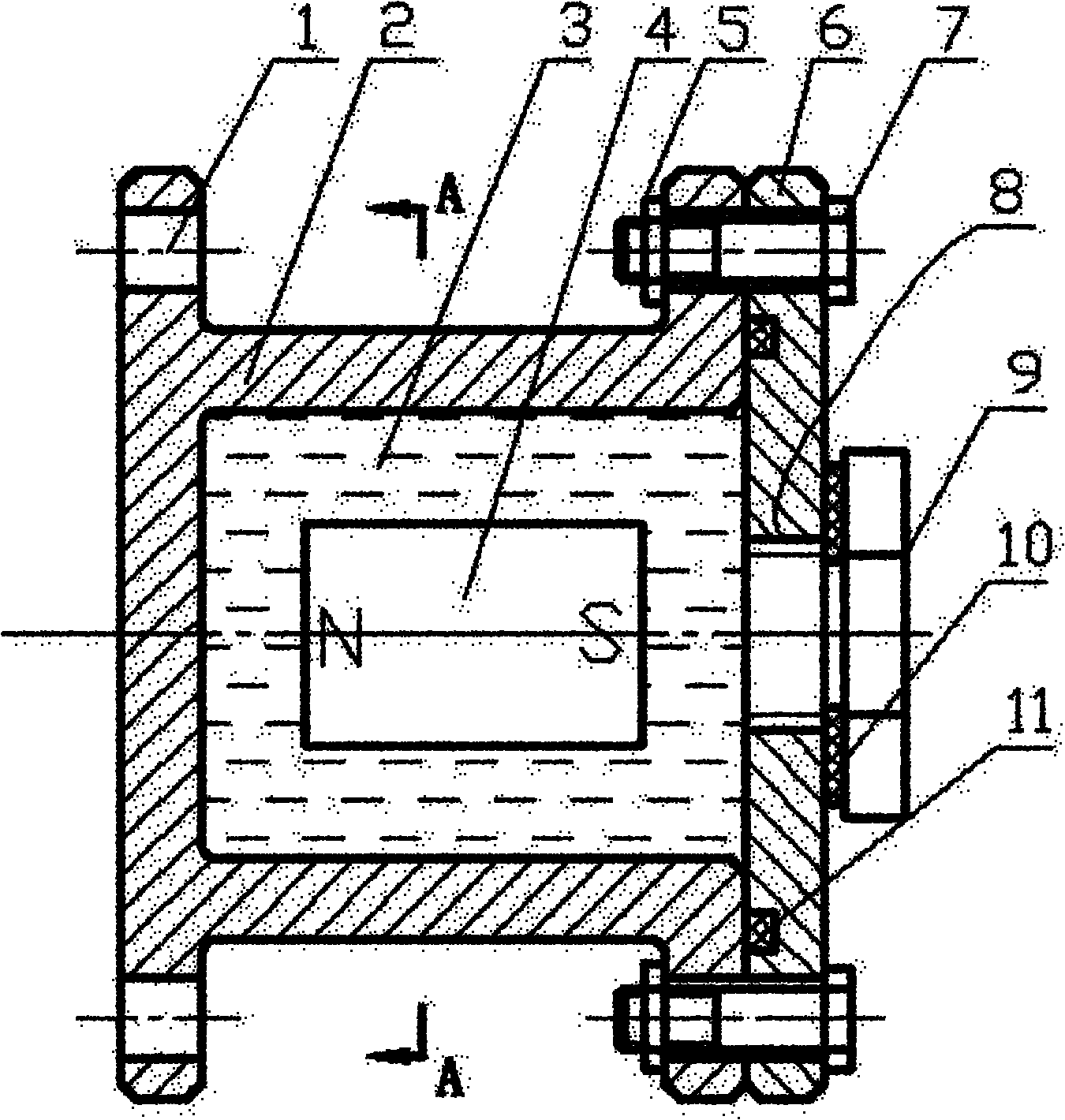
Magnetic fluid damping device
InactiveCN102032304ASolution to short lifeReduce frequencyMagnetic springsEngineeringMagnetic liquids
The invention relates to a magnetic fluid damping device, which is suitable for damping long objects in spacecrafts and solves the problem of the damping of the long objects in the spacecrafts. The device comprises a non-magnetic shell (2), magnetic liquid (3), a permanent magnet (4), a nut (5), an end cover (6), a bolt (7), a screw (9), a sealing gasket (10) and an O-shaped seal ring (11). The parts are connected in a way that: the permanent magnet (4) is arranged in the non-magnetic shell (2); the end cover (6) with the O-shaped seal ring (11) is fixed to one end of the non-magnetic shell (2) by the bolt (7) and the nut (5); the magnetic liquid (3) is filled into the non-magnetic shell (2) by a threaded hole (8); and the non-magnetic shell (2) is sealed by the screw (9) and the sealing gasket (10). The device is sensitive to inertia force, can perform damping on the vibration with the characteristics of low frequency, small displacement and low accelerated speed, and has long service life and simple assembly method.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
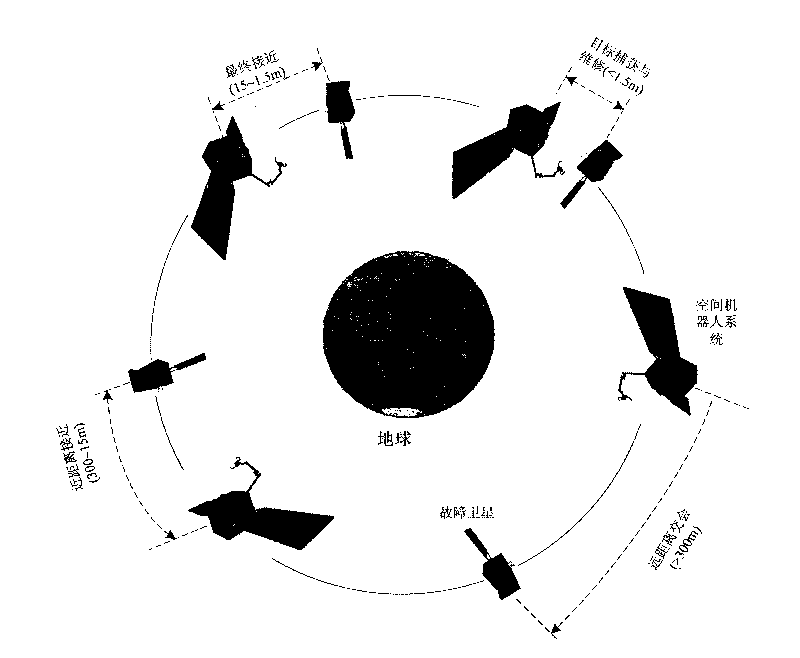
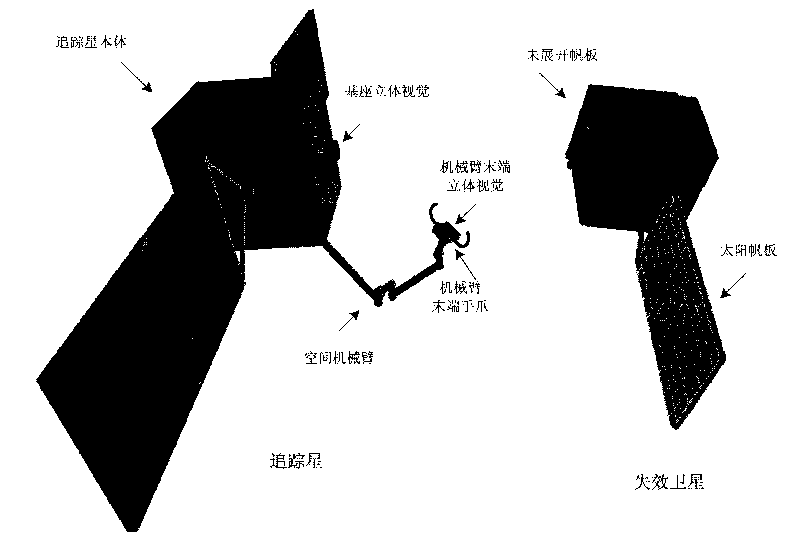
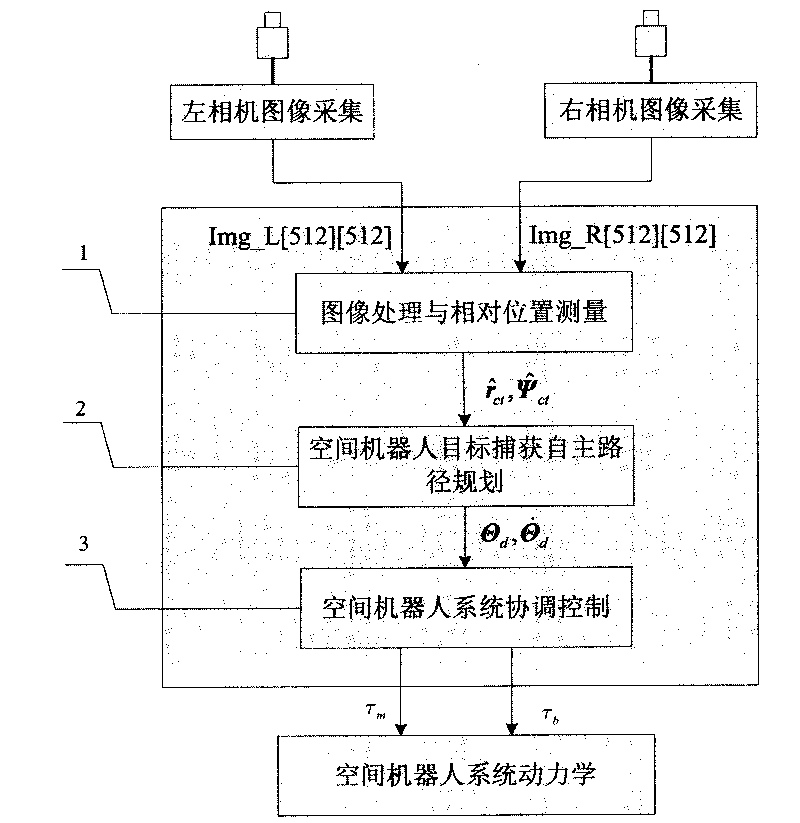
Autonomously identifying and capturing method of non-cooperative target of space robot
InactiveCN101733746AReal-time prediction of motion statusPredict interference in real timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorToolsKinematicsTarget capture
The invention relates to an autonomously identifying and capturing method of a non-cooperative target of a space robot, comprising the main steps of (1) pose measurement based on stereoscopic vision, (2) autonomous path planning of the target capture of the space robot and (3) coordinative control of a space robot system, and the like. The pose measurement based on the stereoscopic vision is realized by processing images of a left camera and a right camera in real time, and computing the pose of a non-cooperative target star relative to a base and a tail end, wherein the processing comprises smoothing filtering, edge detection, linear extraction, and the like. The autonomous path planning of the target capture of the space robot comprises is realized by planning the motion tracks of joints in real time according to the pose measurement results. The coordinative control of the space robot system is realized by coordinately controlling mechanical arms and the base to realize the optimal control property of the whole system. In the autonomously identifying and capturing method, a self part of a spacecraft is directly used as an identifying and capturing object without installing a marker or a comer reflector on the target star or knowing the geometric dimension of the object, and the planned path can effectively avoid the singular point of dynamics and kinematics.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
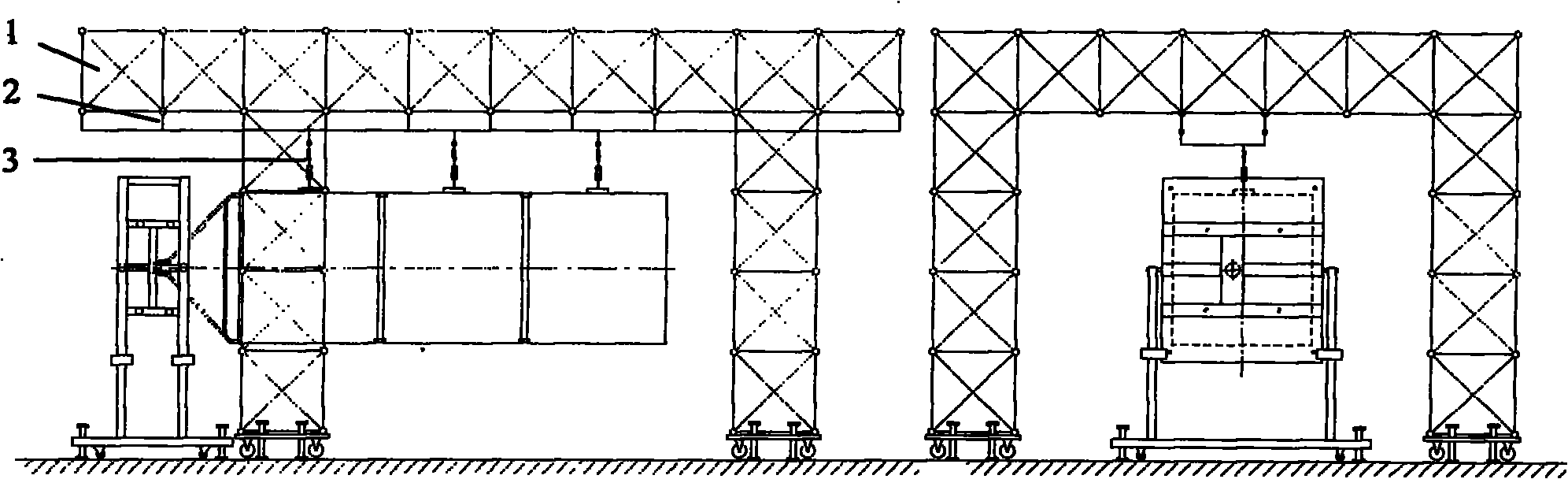
Zero-gravity suspension type deployment test device
ActiveCN102145755AThe overall structure is simple and reliableFlexible moving processCosmonautic condition simulationsSupporting systemEngineering
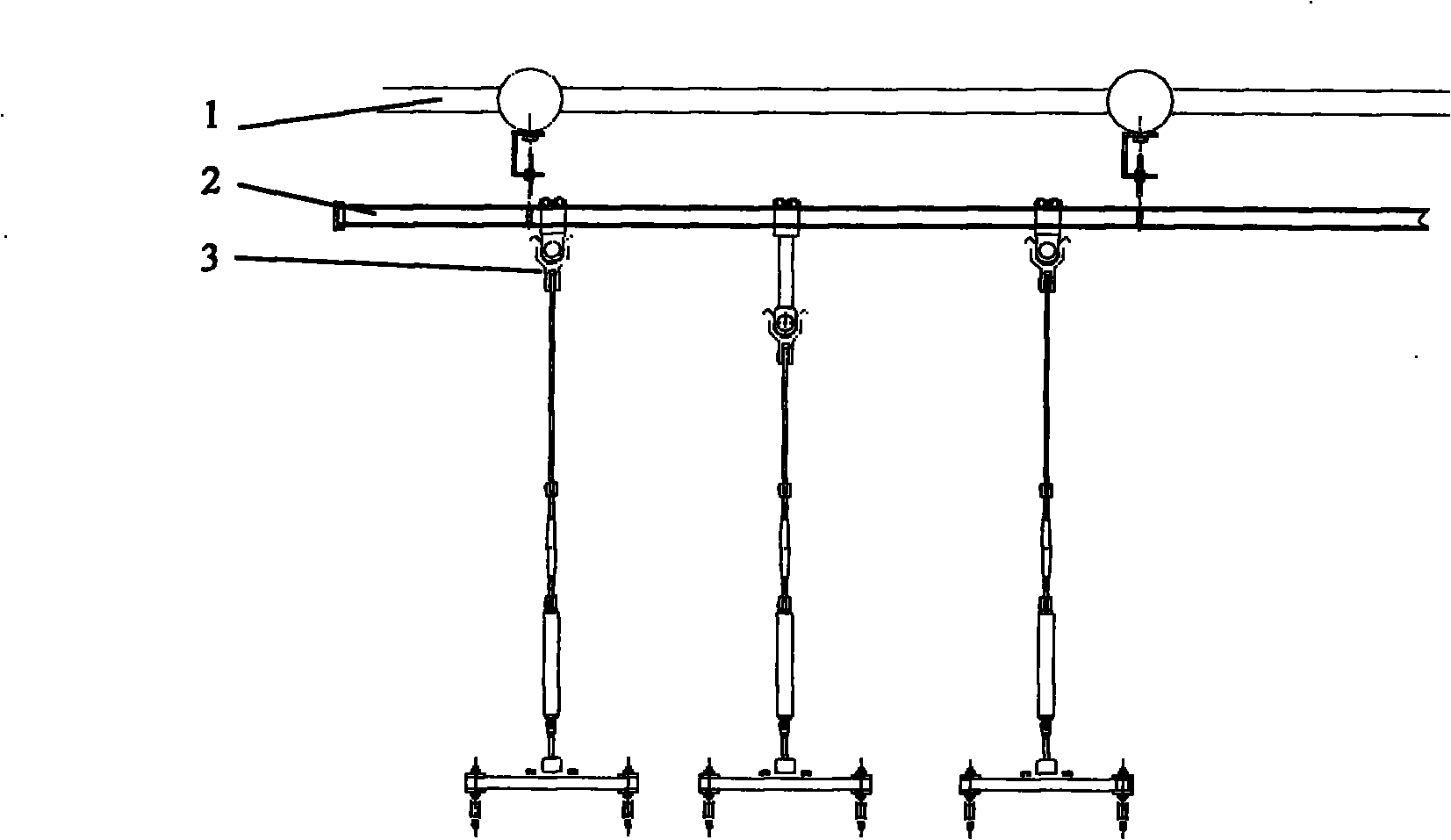
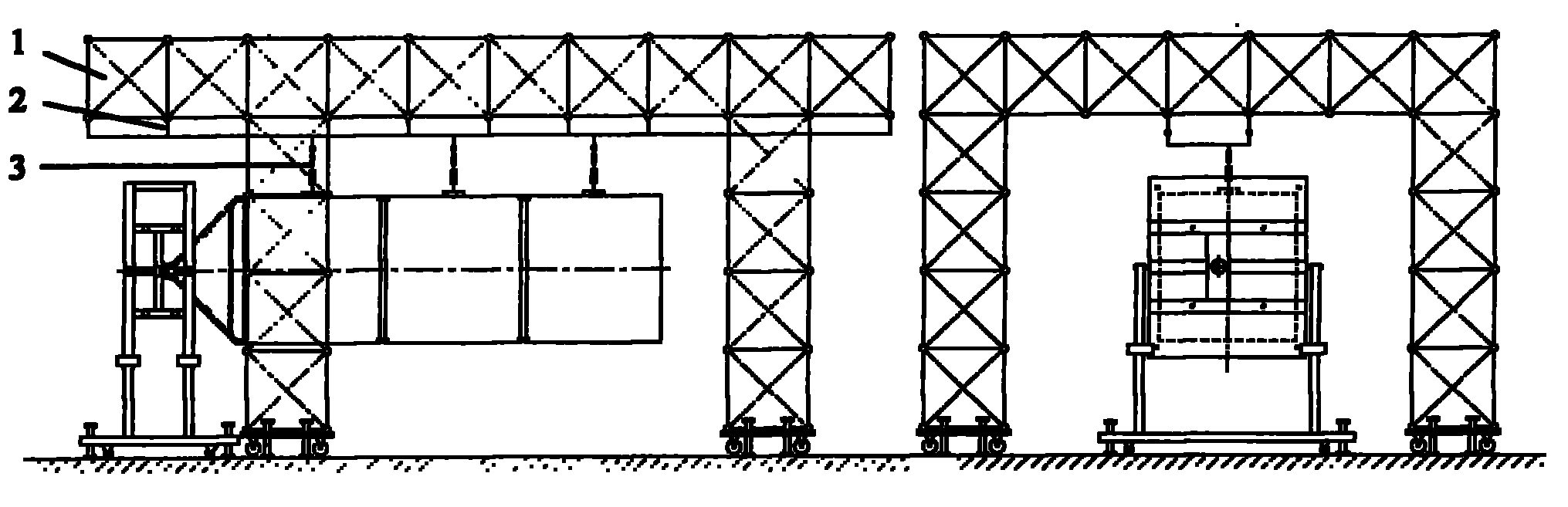
The invention relates to a solar cell array and antenna deployment test device for spacecraft such as a satellite and the like, and provides a zero-gravity suspension type deployment test device which overcomes the shortcomings of the air-floating deployment test device in the prior art and solves the problem existing in simulation of the zero-gravity state of the environment orbit of the solar cell array and antenna of the satellite in the ground gravity environment. The zero-gravity suspension type deployment test device is characterized by comprising a support system [1], a guide rail system [2] and a hanging system [3]. The support system [1] comprises four upright frames and a horizontal frame. The guide rail system [2] comprises two longitudinal guide rails, multiple transverse guide rails and a guide rail hanger. The guide rail system [2] is mounted below the horizontal frame. The hanging system [3] comprises a rolling bearing frame, a tubular dynamometer and a connecting piece. Through the invention, the problems existing in simulation of the zero-gravity state of the environment orbit of the solar cell array and antenna of the satellite in the ground gravity environment and the like are solved, and beneficial effects of simple structure, convenience in use, strong adaptability and the like are obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
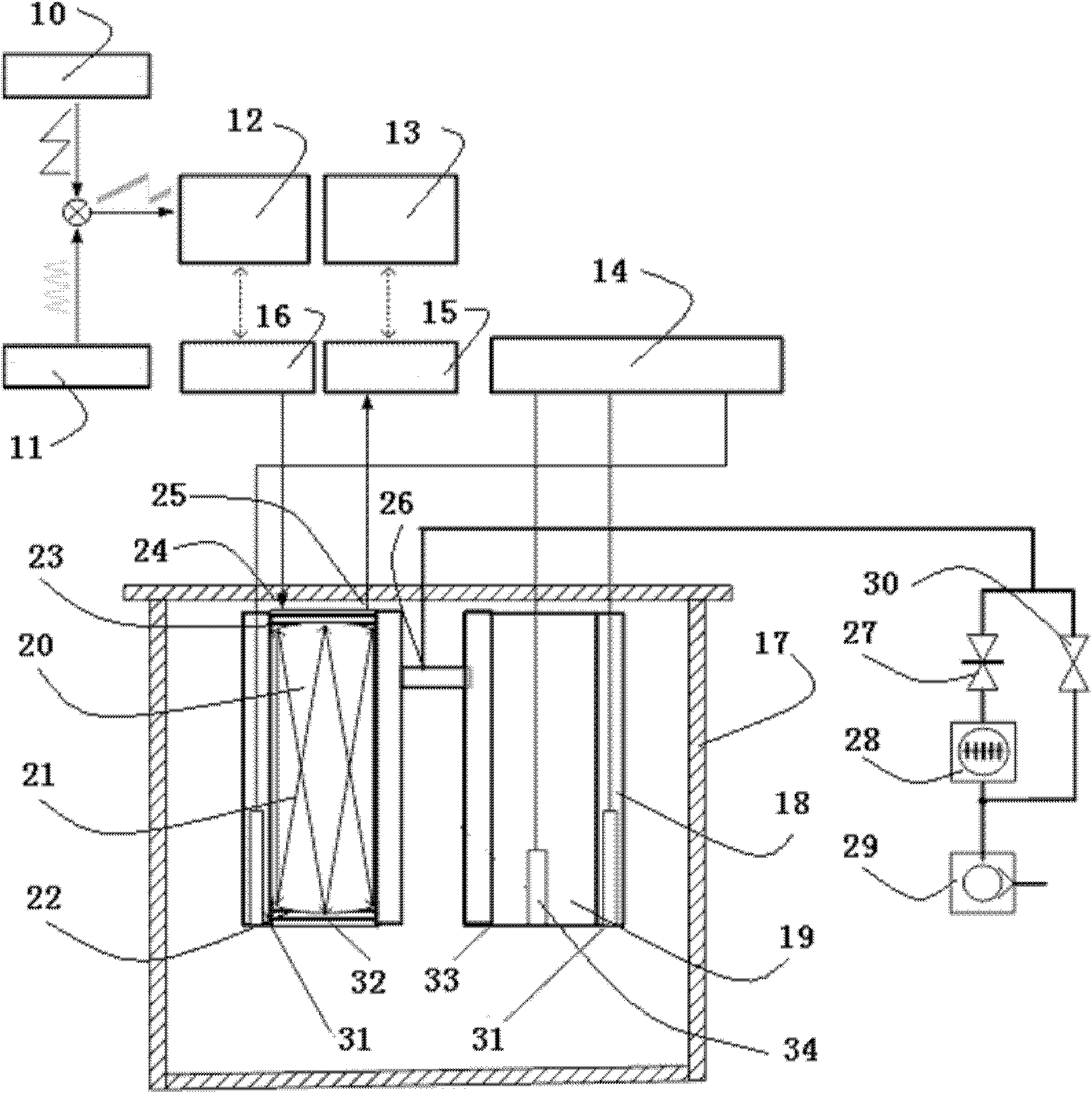
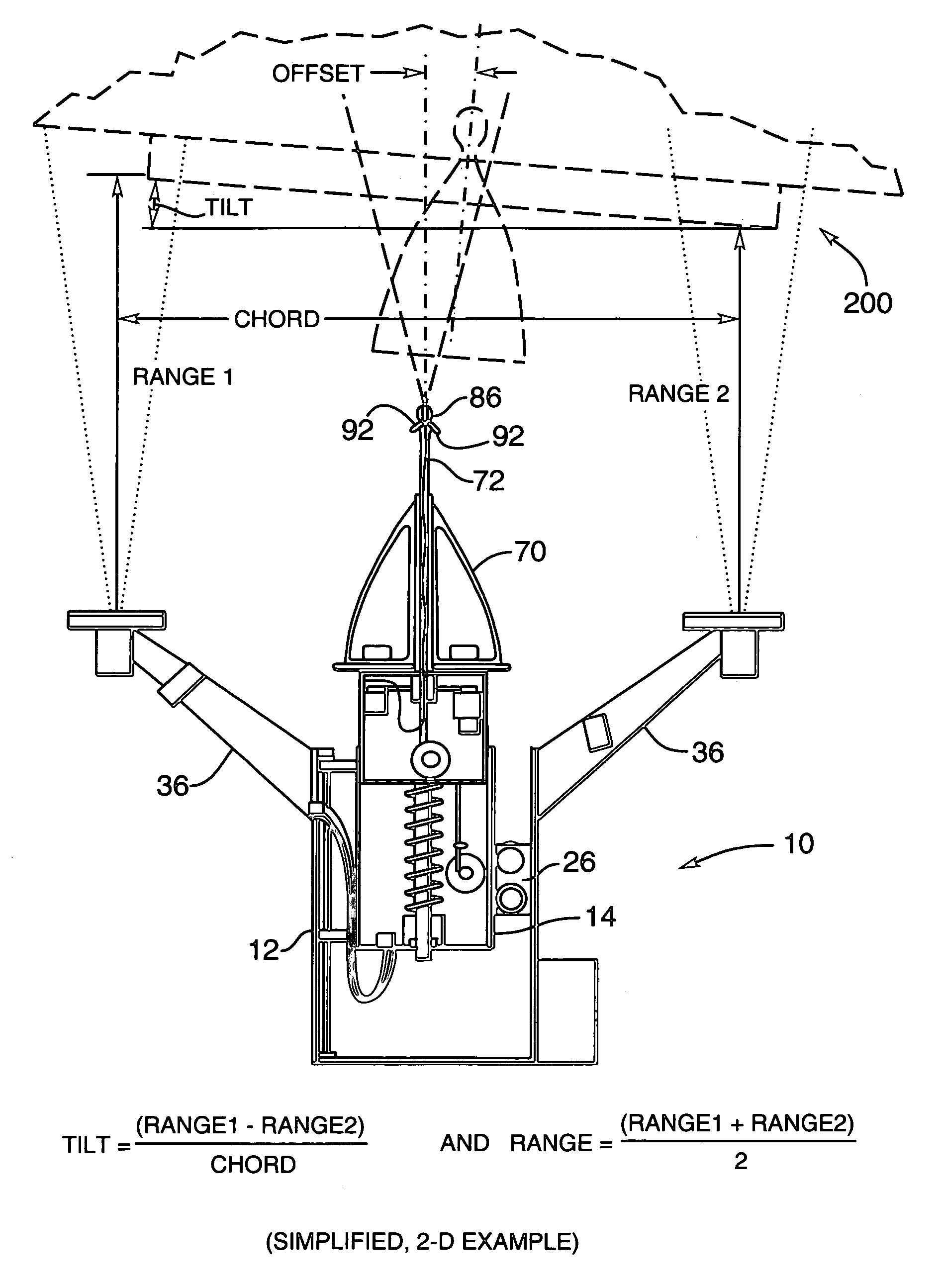
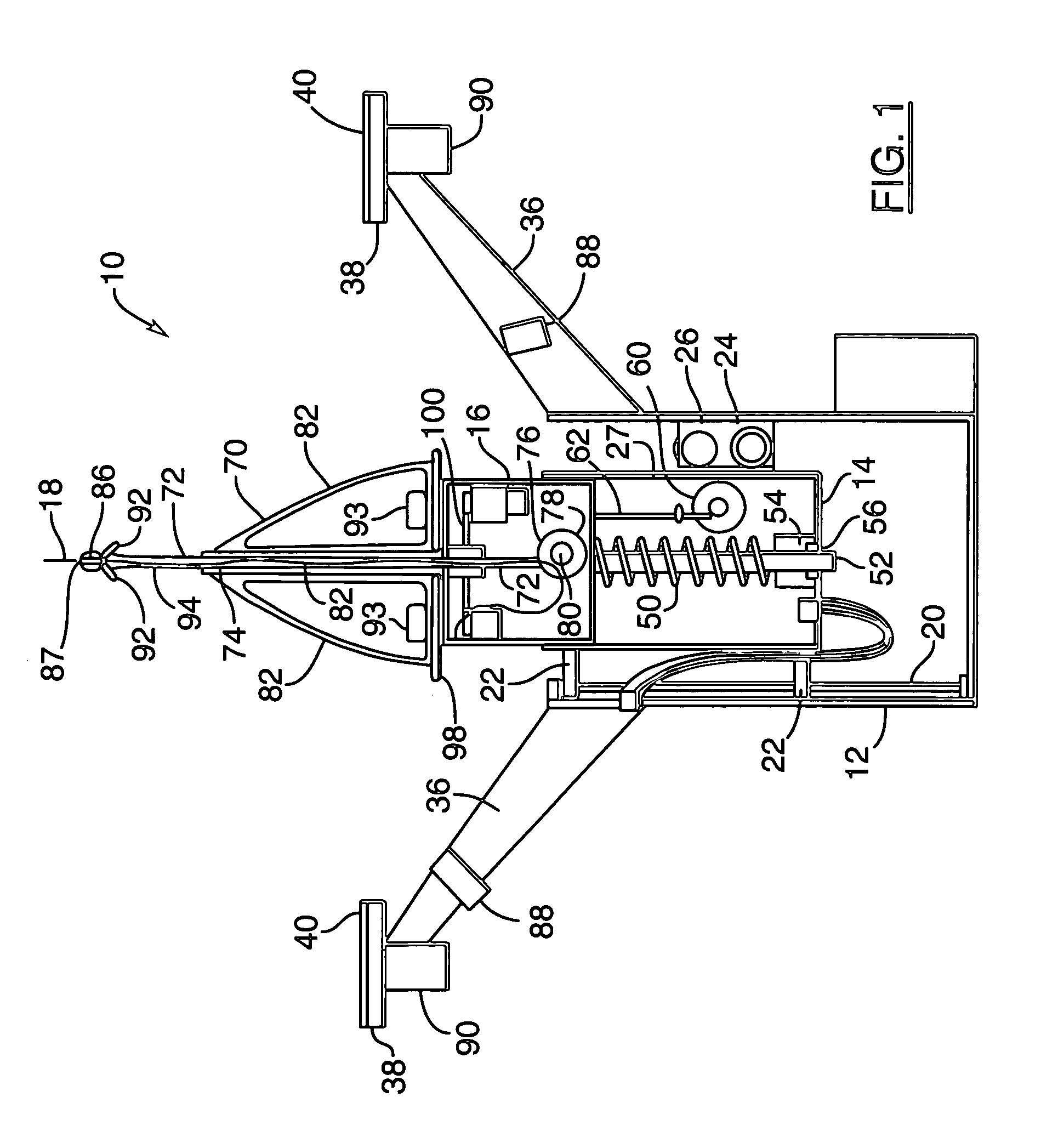
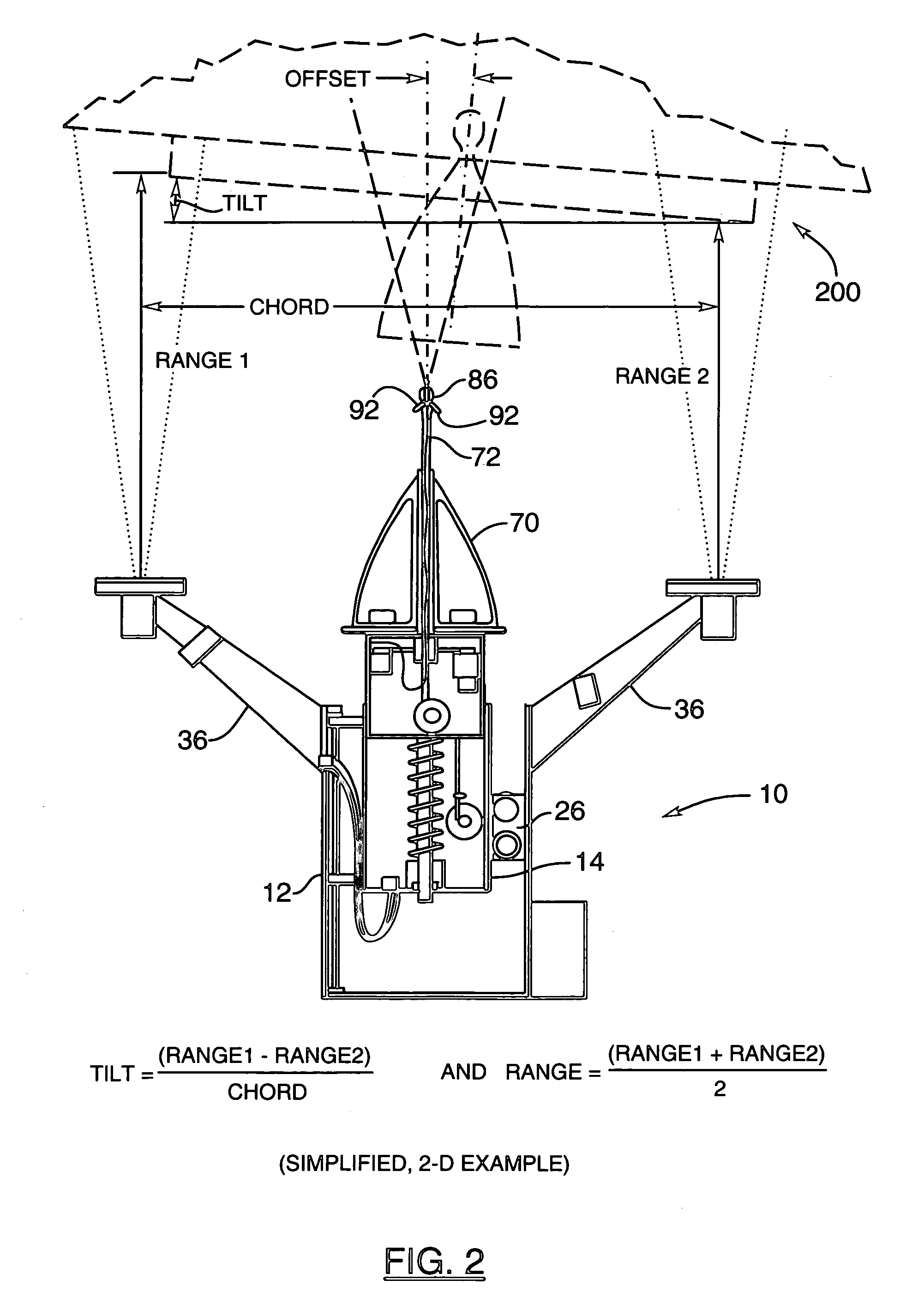
Arrangement for recovering spacecraft
A recovery craft with a coupling arrangement captures, engages, and transports a defective or expended non-maneuverable spacecraft. The coupling arrangement includes a coupling mast (e.g. a telescoping pipe), a releasable rigid mount that secures one end of the coupling mast to the recovery craft, and spreader arms that are radially spreadable from the other end of the coupling mast. The spreader arms are initially radially inwardly retracted, and are inserted into an interface ring of the spacecraft. Then the spreader arms are radially outwardly extended to engage behind a protruding rim of the interface ring. A spring braces against the spacecraft. Next, the rigid mount is released and the coupling mast remains connected to the recovery craft only by a tension-transmitting cable. Thrusters of the recovery craft are activated to tow the spacecraft to a new target position, orbit, or trajectory.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
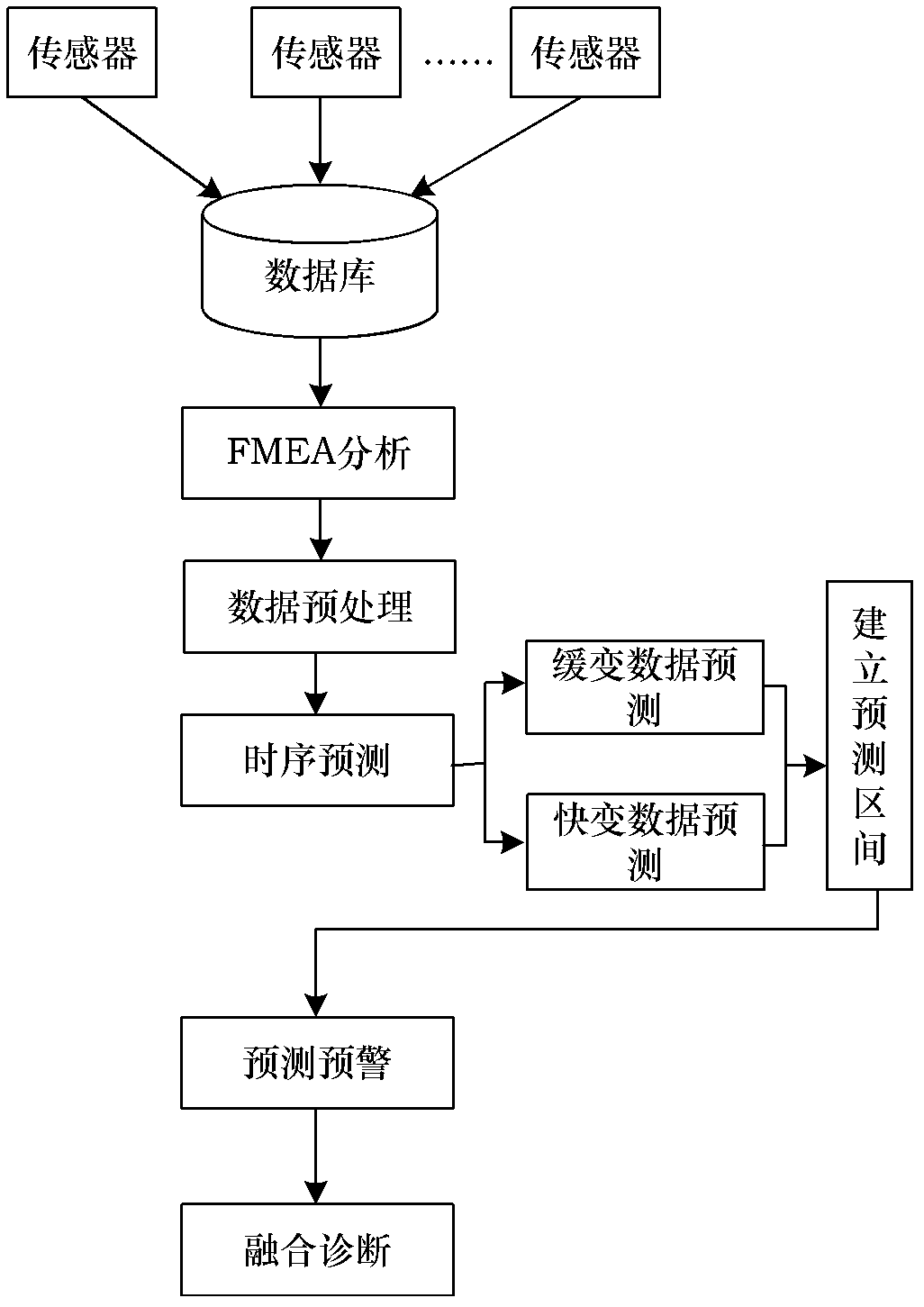
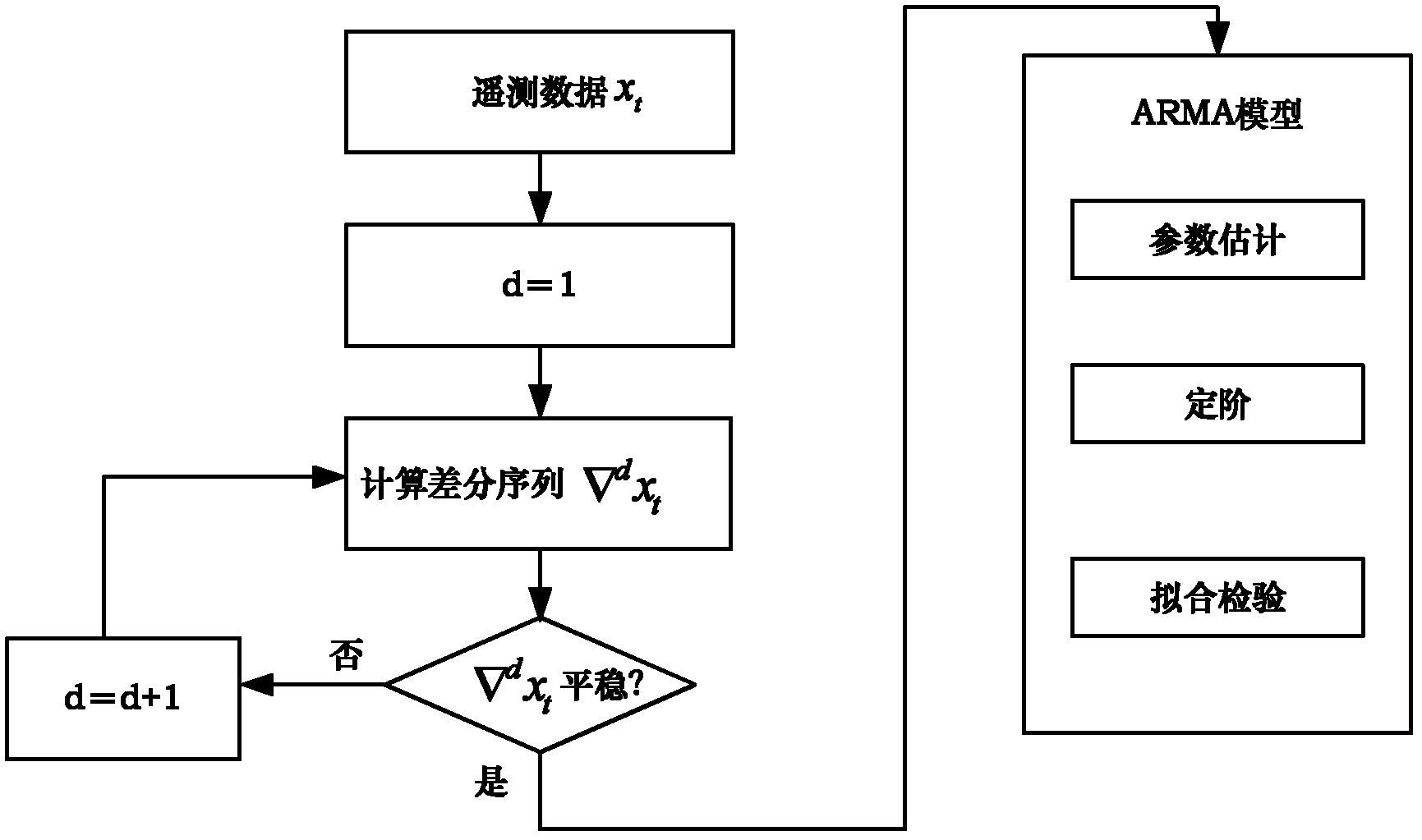
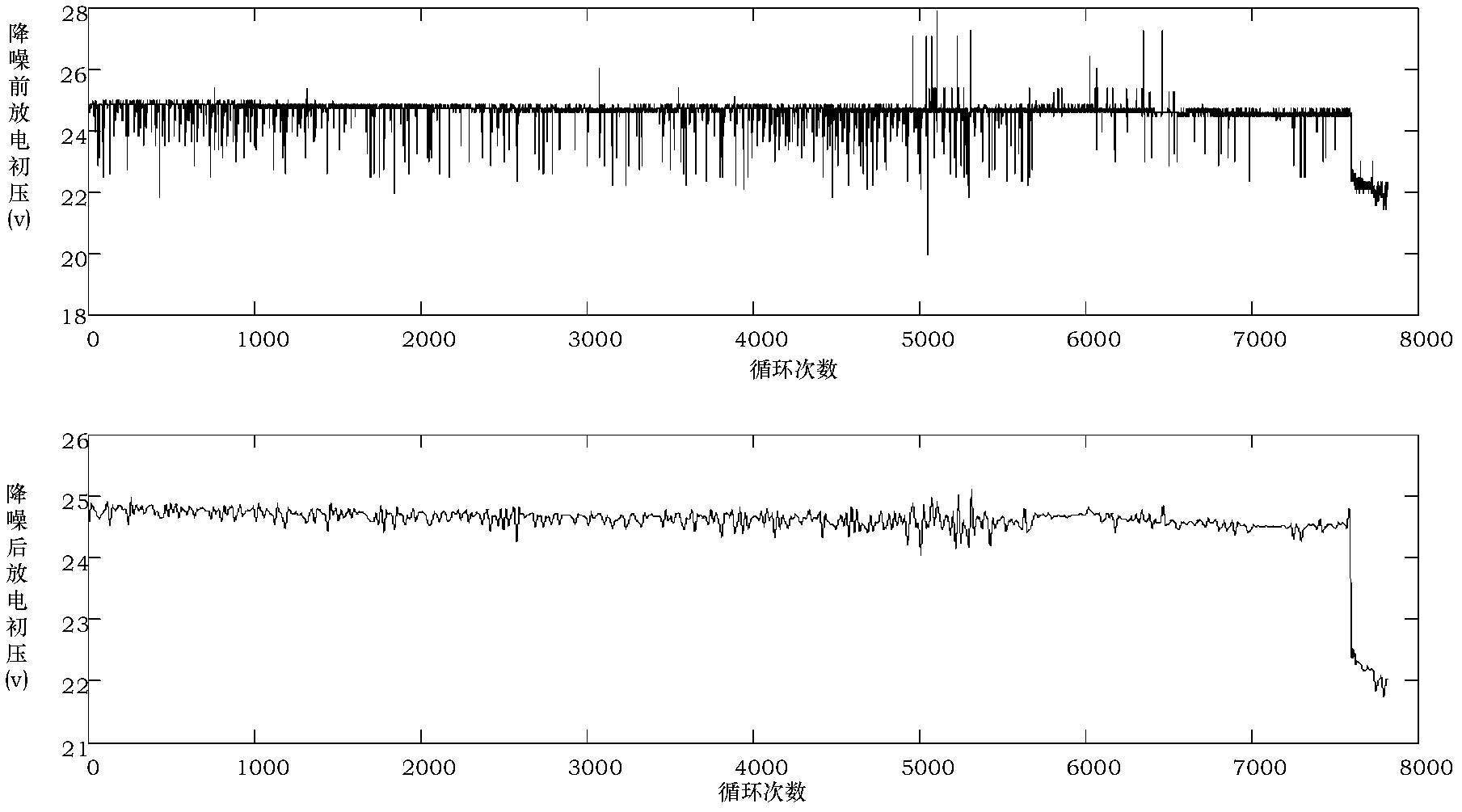
Fault predicting and diagnosing method suitable for dynamic complex system
InactiveCN102208028AOvercome the drawbacks of harsh restrictionsImprove general performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionPrediction intervalSystem failure
The invention provides a fault predicting and diagnosing method suitable for a dynamic complex system. The method can be applied in the field of fault prediction and diagnosis of dynamic complex systems of spacecrafts and the like. The method comprises the following steps of: performing failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) on the dynamic complex system to obtain a main fault mode and corresponding performance detection parameters, dividing the performance detection parameters into slowly variable data and fast variable data, pre-processing the performance detection parameters, establishingan autoregressive moving average model (ARMA) aiming at the slowly variable data to perform time sequence prediction, establishing a multi-resolution wavelet neural network aiming at the fast variable data to perform time sequence prediction, performing fault early warning on the time sequence prediction results by establishing a prediction interval model, and performing fault diagnosis by establishing a D-S (Dempster-Shafer) evidence theory-based multi-signal fusion model. The method can be used for predicting and diagnosing the faults of the dynamic complex system with high precision, and has strong universality.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
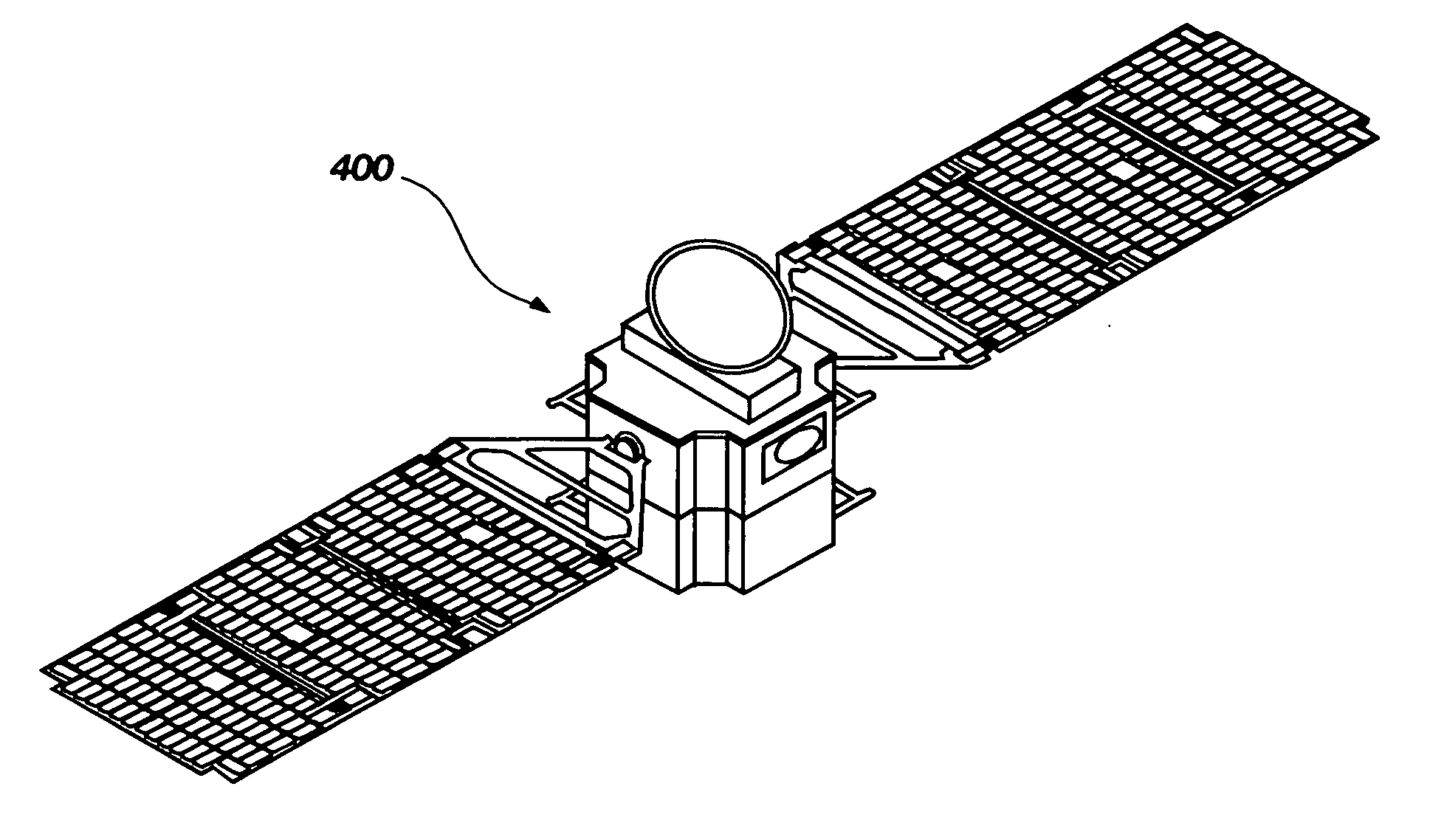
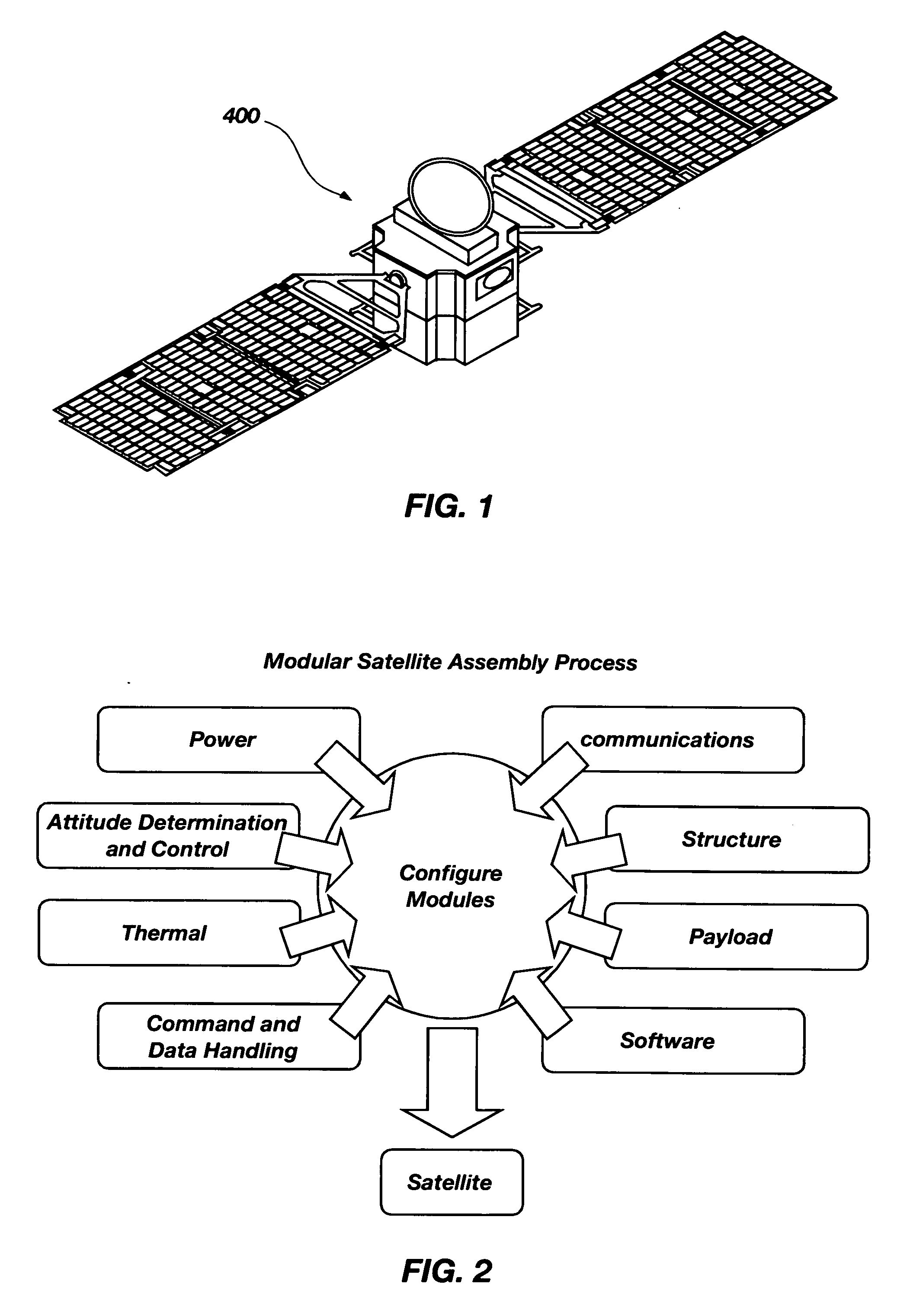
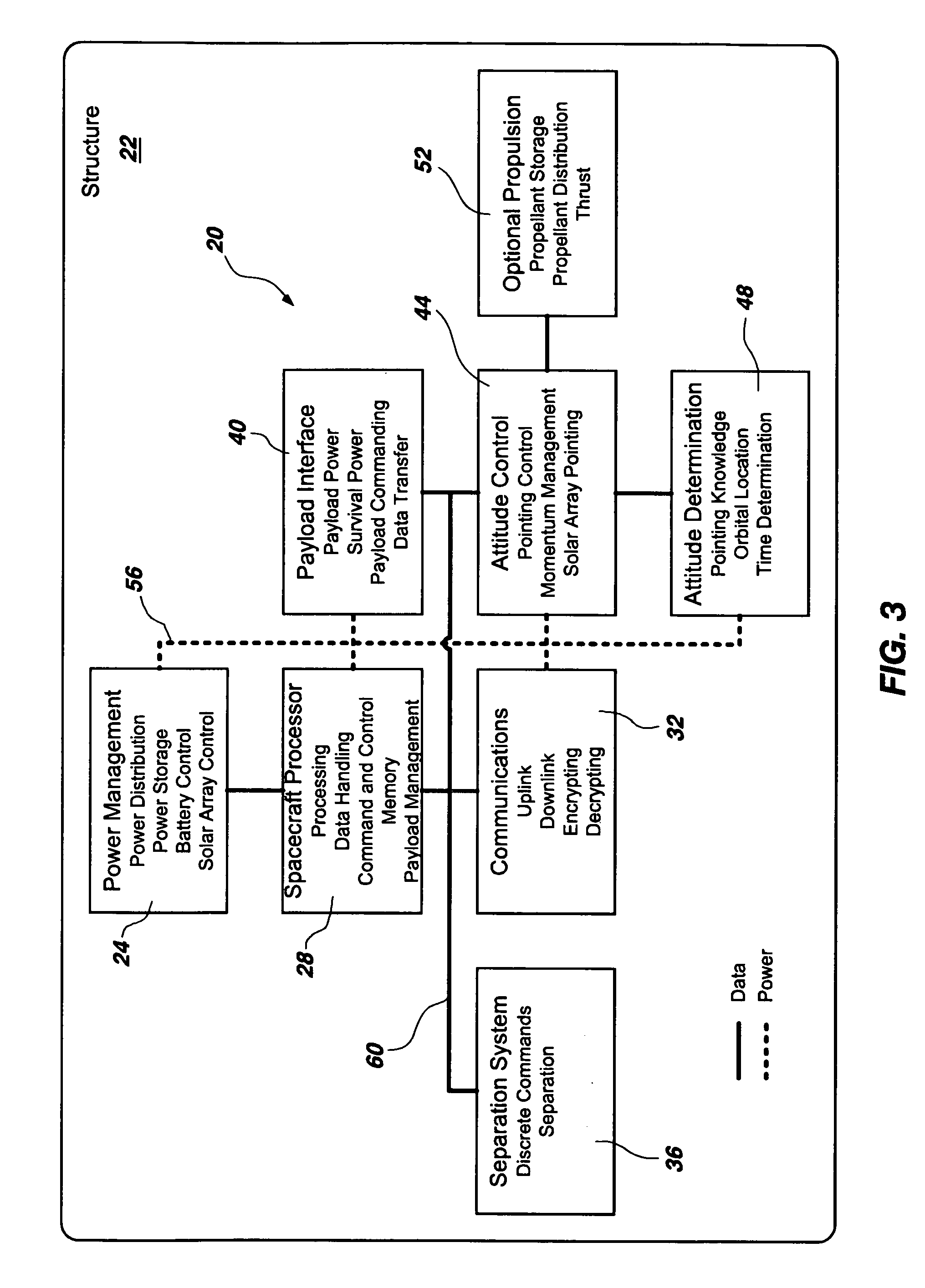
Modular platform architecture for satellites
InactiveUS20070029446A1Improve performanceCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesModularityEngineering
A method for implementing a modular platform for the construction of satellites and other spacecraft based on modular platform architecture, the method comprising: (a) identifying a plurality of functional elements and their associated functional routines that may be operable within at least one satellite; (b) associating the functional routines with one another in a strategic manner; (c) dividing the functional routines to define a plurality of subsystems; and (d) deriving a plurality of modules from the plurality of subsystems, each of the modules being configured to operably interface with at least one other module to construct a working satellite capable of carrying out a pre-determined number of the functional routines.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Ceramic tile armor with enhanced joint and edge protection
InactiveUS6332390B1Minimal increase in weightImprove reliabilityArmoured vehiclesPersonal protection gearCeramic compositeGround vehicles
A ceramic composite tile armor which is reinforced at the more vulnerable joint and free edge areas, using glass or ceramic strips or overlays bonded with an adhesive to the outer surface of the tile joints and free edges. This reinforcement provides improved ballistic threat protection for ground vehicle, aircraft, watercraft, spacecraft, and body (personnel) ceramic tile armor applications. Glass or ceramic overlay strips assist in fracturing impacting projectiles that strike the tile joints or free edges. The substrate laminate backing can then capture fragments of the projectile and broken ceramic and prevent penetration. The invention provides improved protection over conventional joint and edge enhancements with higher reliability of accurate positioning over joint and free-edge areas, with less added weight, and at lower associated production costs.
Owner:SIMULA
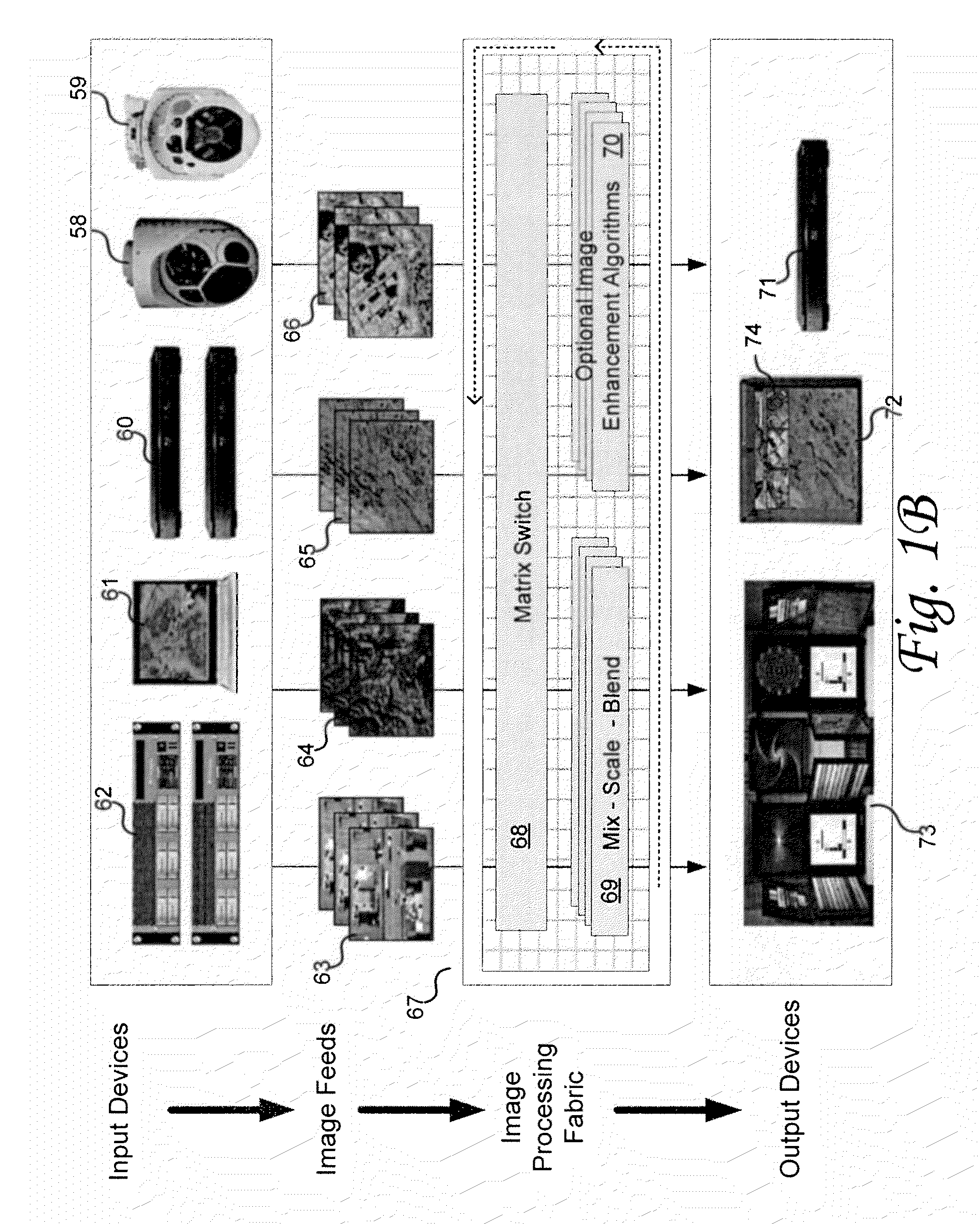
Systems and methods for image stream processing
ActiveUS20130073775A1Eliminate and reduce frame latencyIncrease heightTelevision systemsElectric digital data processingImaging processingIn vehicle
Various embodiments relate to systems and methods for simultaneously switching input image streams to output devices, while providing optional image processing functions on the image streams. Certain embodiments may provide vision systems and methods suitable for use in vehicles, particularly windowless vehicles, such as armored ground vehicles, submerged watercraft, and spacecraft. Some embodiments may enable sharing of image streams (e.g., with one or more other vehicles), generation of panoramic views (e.g., from various camera feeds), intelligent encoding of image streams, and implementation of security features based on image streams.
Owner:Z MICROSYST
Scanner/optical system for three-dimensional lidar imaging and polarimetry
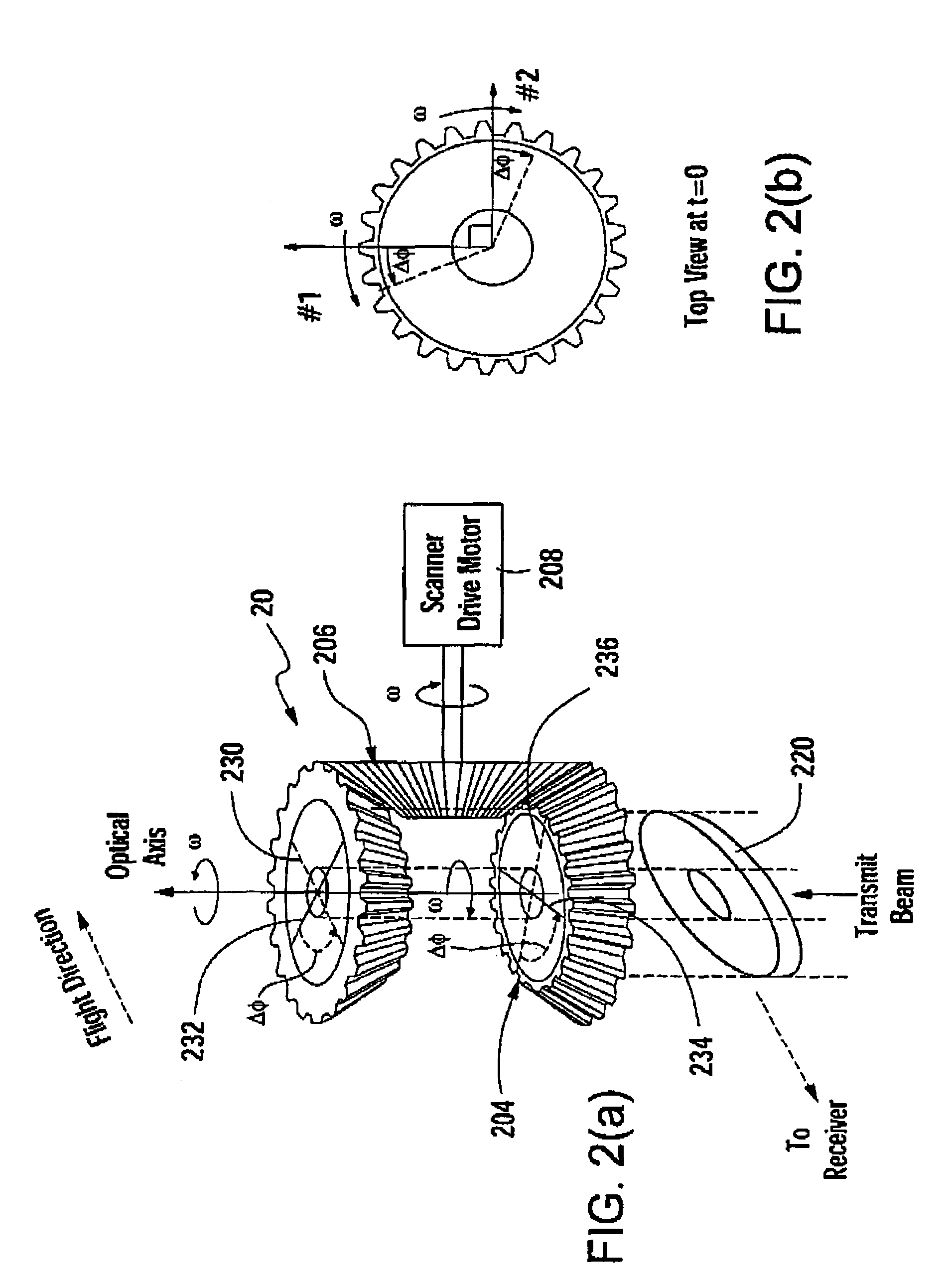
ActiveUS20070279615A1High repetition rateReduce solar background noiseOptical rangefindersColor television detailsOptical scannersLaser beams
An optical scanner system for contiguous three-dimensional topographic or volumetric imaging of a surface from an aircraft or spacecraft is disclosed. A servo controller synchronizes the rotation rates of a pair of wedge scanners with high precision to the multi-kilohertz laser fire rate producing an infinite variety of well-controlled scan patterns. This causes the beam pattern to be laid down in precisely the same way on each scan cycle, eliminating the need to record the orientations of the wedges accurately on every laser fire, thereby reducing ancillary data storage or transmission requirements by two to three orders of magnitude and greatly simplifying data preprocessing and analysis. The described system also uses a holographic element to split the laser beam into an array that is then scanned in an arbitrary pattern. This provides more uniform signal strength to the various imaging detector channels and reduces the level of optical crosstalk between channels, resulting in a higher fidelity three-dimensional image.
Owner:INTERGRAPH
Attitude control system for space vehicle and method thereof
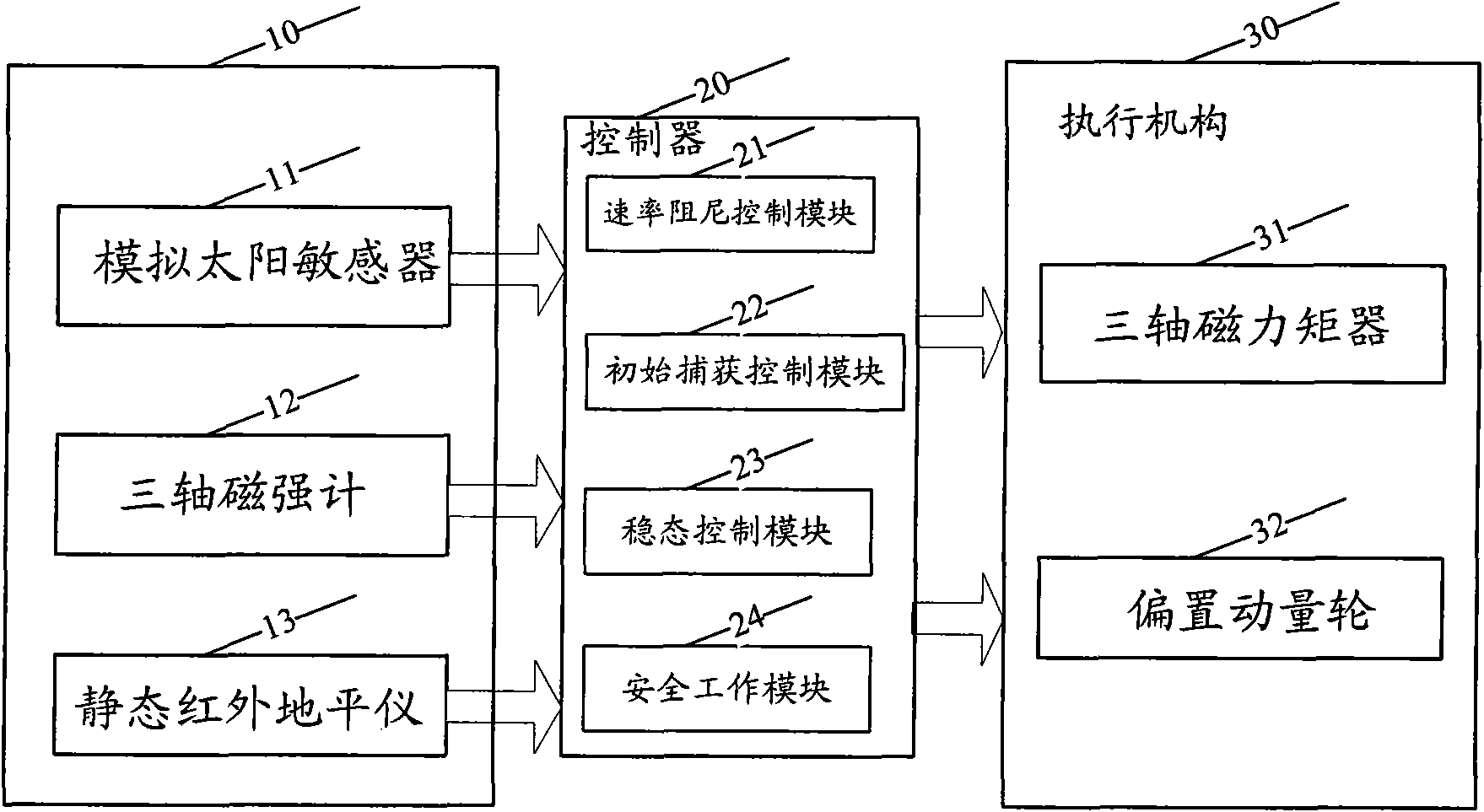
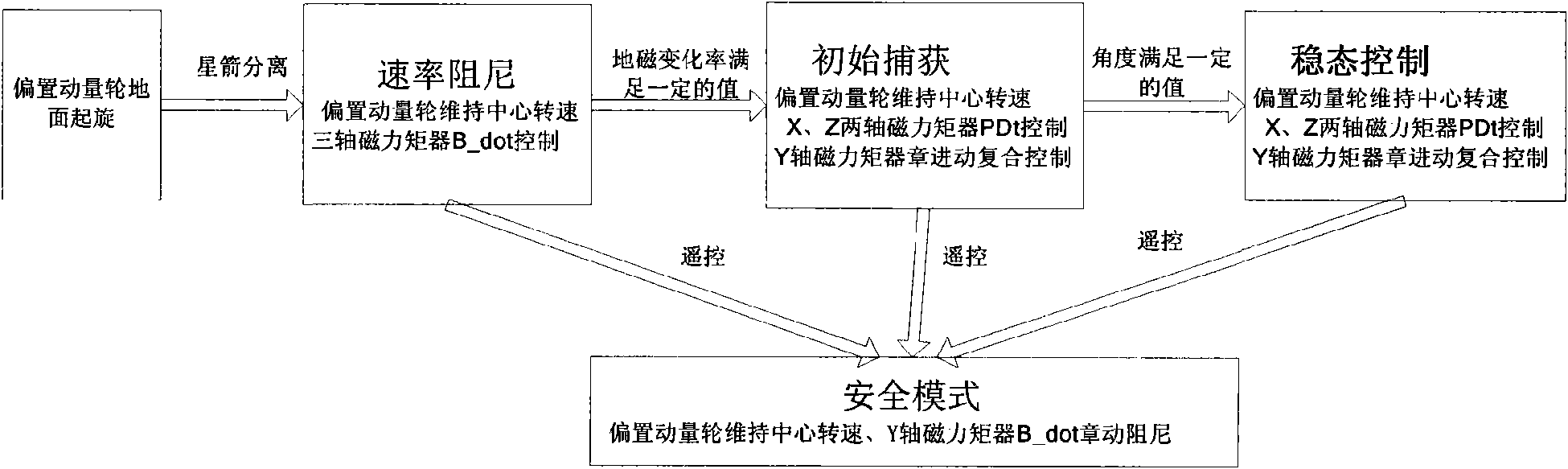
InactiveCN101554926AStable separationStable Initial Rate DampingSpacecraft guiding apparatusMagnetic tension forceNutation
The invention discloses an attitude control system for space vehicle and a method thereof. The control system has only one biased momentum wheel, one set of tri-axial magnetic torquer and one attitude controller loaded with algorithm. The method comprises a step of rate damping controlling, a step of initially capturing controlling and a step of stationarity controlling. At the rate damping stage, geomagnetism change is used to control the magnetic control of three passages of a satellite by B-dot; at the initially capturing stage, the magnetic control is realized, PD control is performed by pitching and the passages are rolled and yawed to carry out nutation and precession composite control; at the stationarity controlling stage, the magnetic control is realized, PD control is performed by pitching and the passages are rolled and yawed to carry out nutation and precession composite control. The capturing stage and the stationarity controlling stage fully depend on magnetic torquer to perform positive magnetic control, thereby changing which a satellite only uses a magnetic torquer to carry out unload of the momentum wheel or auxiliary magnetic control, so as to refine system configuration to further improve reliability of the system. Momentum of a satellite is biased to rotate on the ground, so as to ensure stable separation of the satellite without performing air injection control. Therefore, the magnetic torquer can be used for realizing fast and stable initial rate damping.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
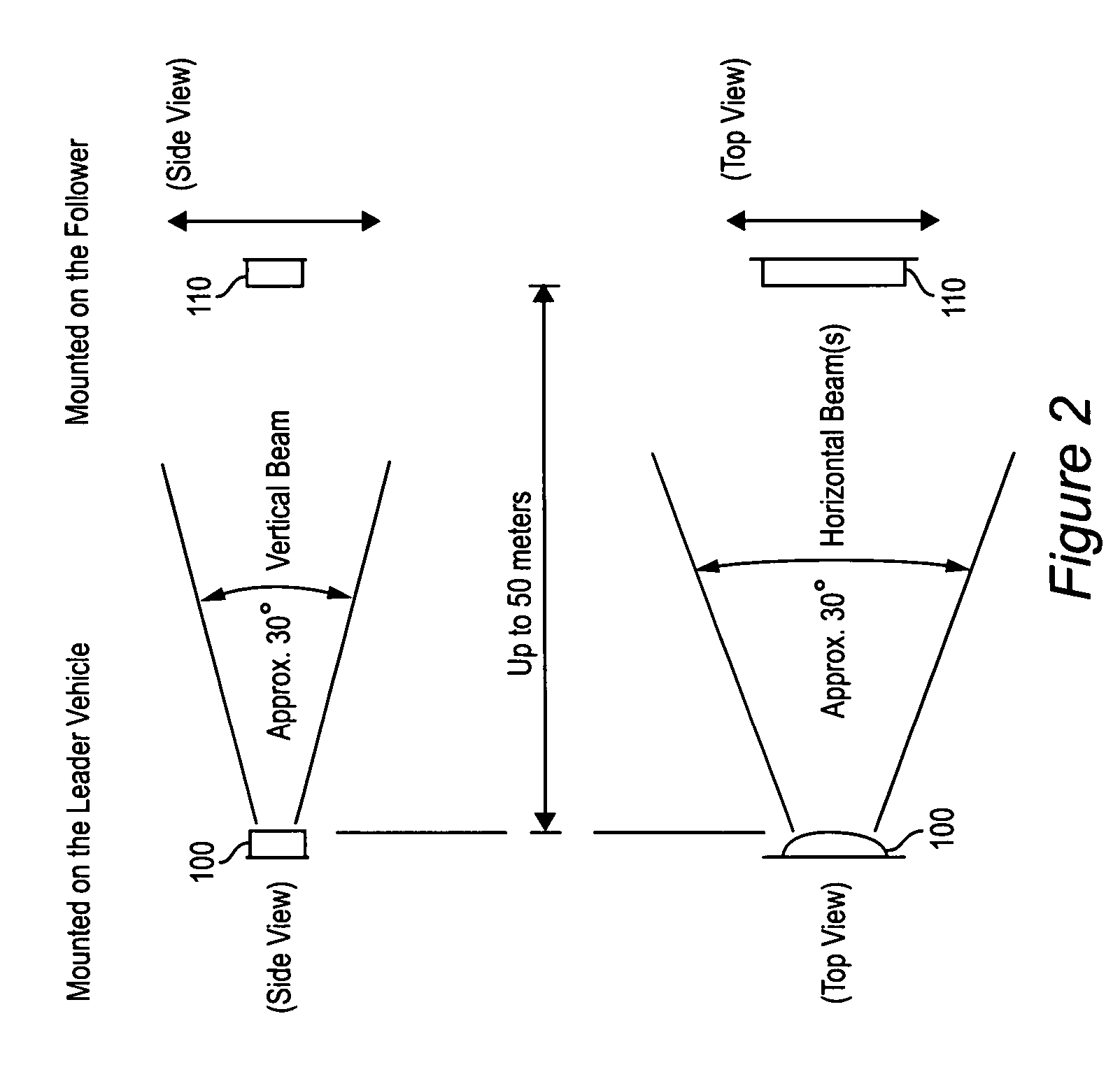
Automatic homing systems and other sensor systems
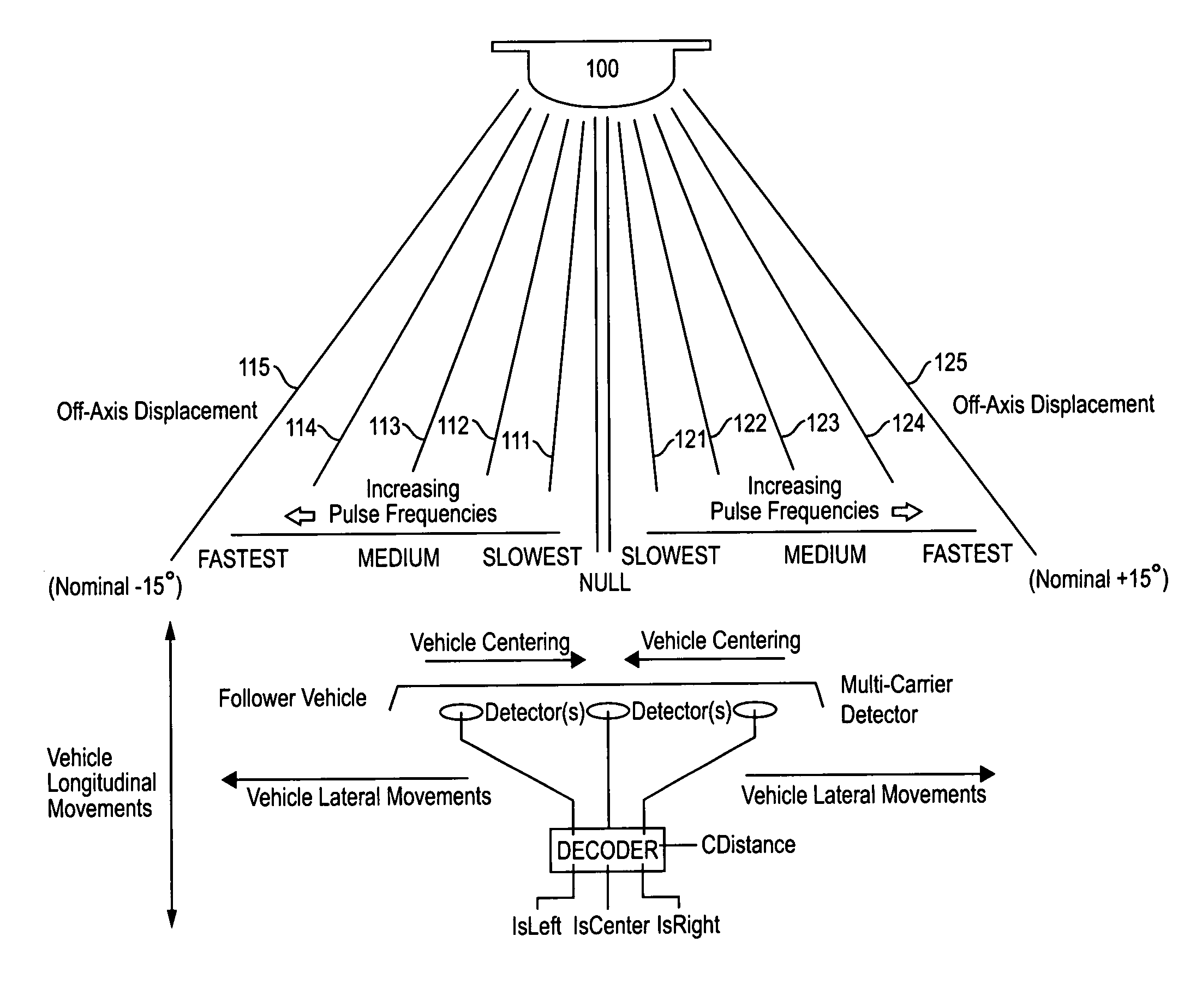
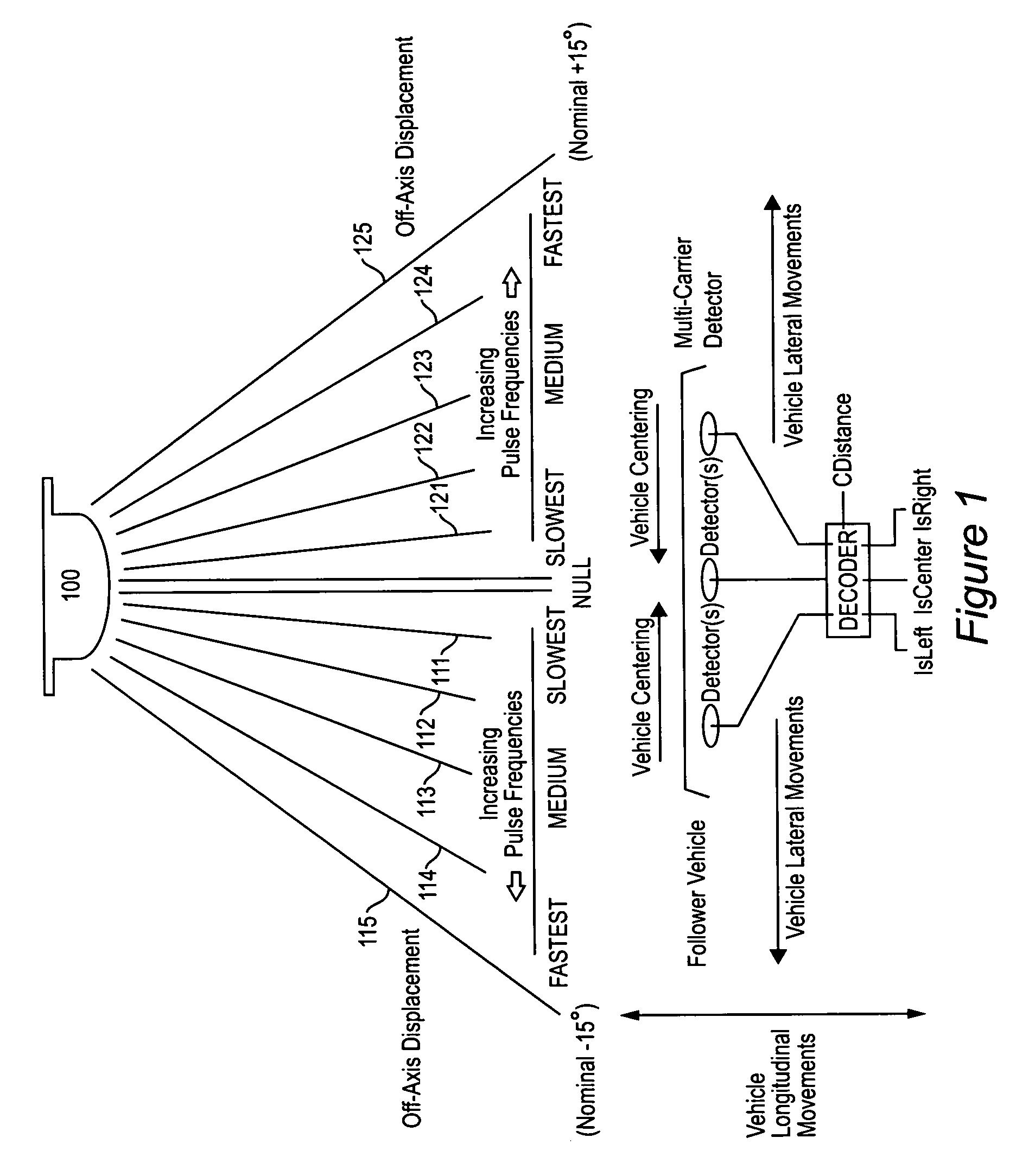
Automatic homing systems are disclosed, operable between pairs of objects. One or both of the objects in the pair may be moving and / or unmanned. Examples of a pair of objects between which the inventive automatic homing systems may be operated are ground vehicles in leader-follower configuration, as well as aircraft, spacecraft, watercraft. The automatic homing systems are based on a relatively simple, elegant concept of rightness / leftness and a line-of-sight link between a respective leader vehicle and follower vehicle. Complex EO / IR cameras, LIDAR, RADAR, and / or SONAR-based sensor systems can be avoided. Convoys of vehicles in leader-follower configuration advantageously may be operated without needing human operators in the follower vehicles.
Owner:SRS TECH
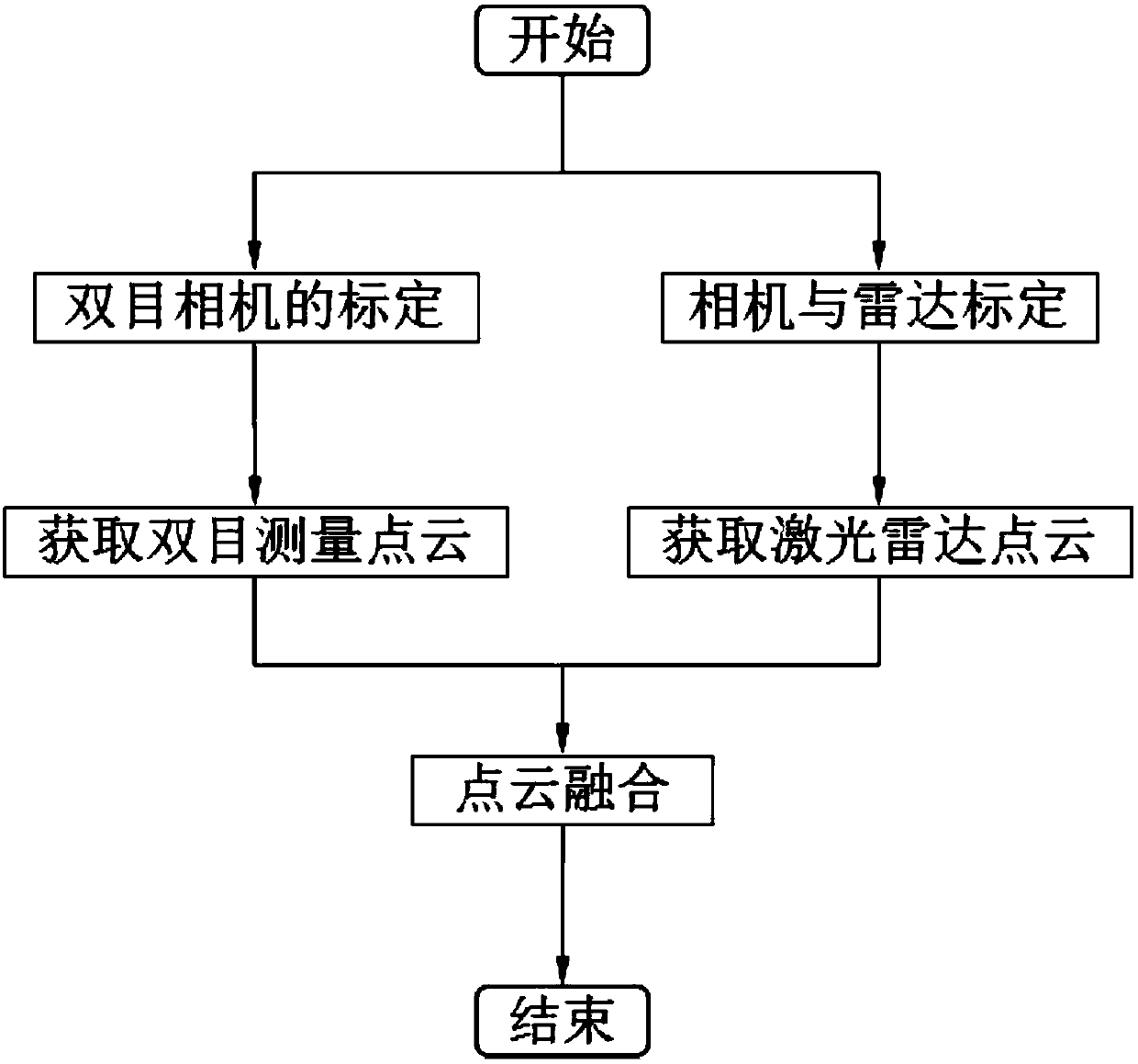
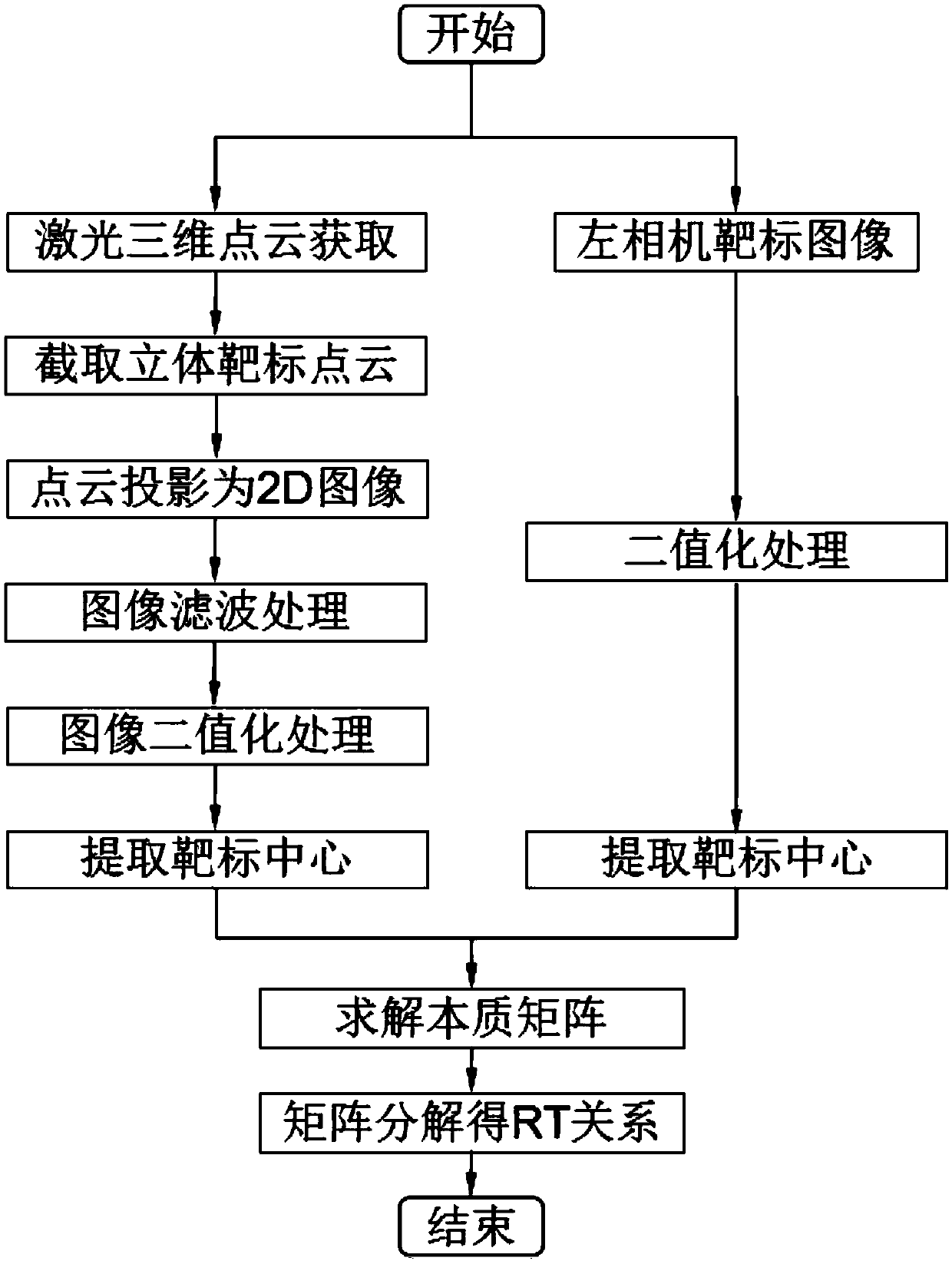
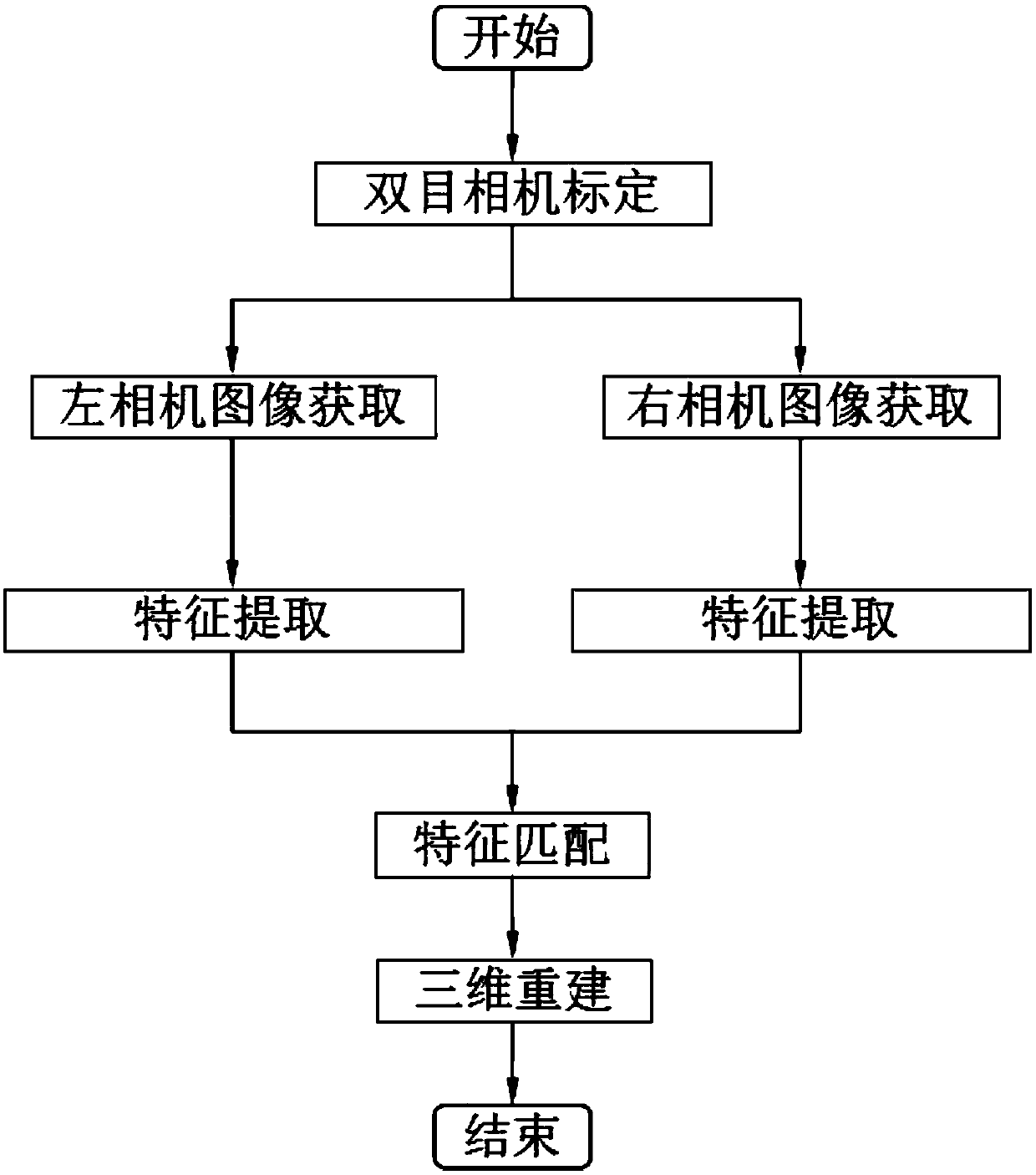
Joint measurement method based on laser radar and binocular visible light camera
ActiveCN108828606AAccurate locationIncrease workloadPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryElectromagnetic wave reradiationBinocular stereoVisual perception
The invention provides a joint measurement method based on a laser radar and a binocular visible light camera to obtain accurate and dense three-dimensional information simply and efficiently. The joint measurement method comprises assuming that the laser radar is a camera device with a fixed internal reference; directly projecting three-dimensional point cloud data into a two-dimensional image, calculating rotation and translation relationships between the laser radar device and the binocular camera by using an image processing method and the matching between the two-dimensional images; creatively introducing an idea for obtaining a matrix norm and a matrix trace to solve a rotation matrix; finally fusing laser radar and binocular stereo vision point cloud data. The method not only can obtain an accurate position and attitude information, but also can reconstruct the special texture and feature information of a target surface, which has a high application value for spacecraft dockingand hostile satellite capture in the military field and workpiece measurement and unmanned driving in the civilian field.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
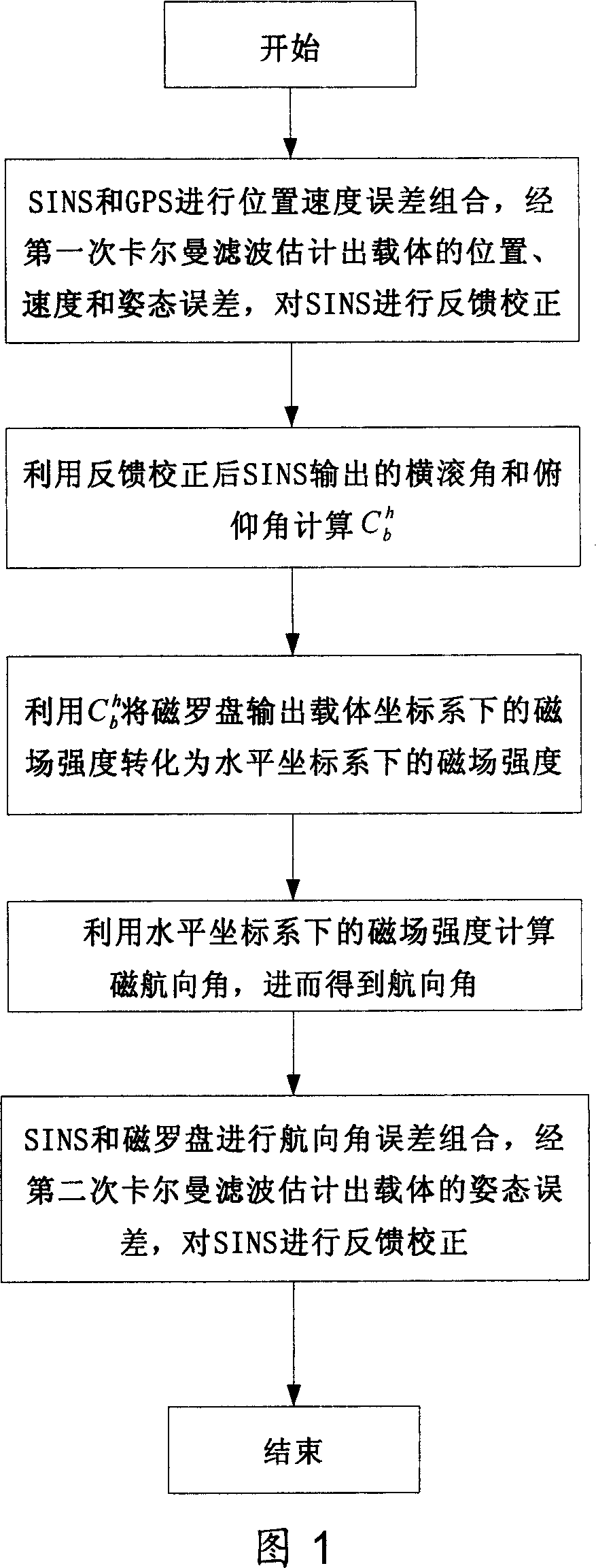
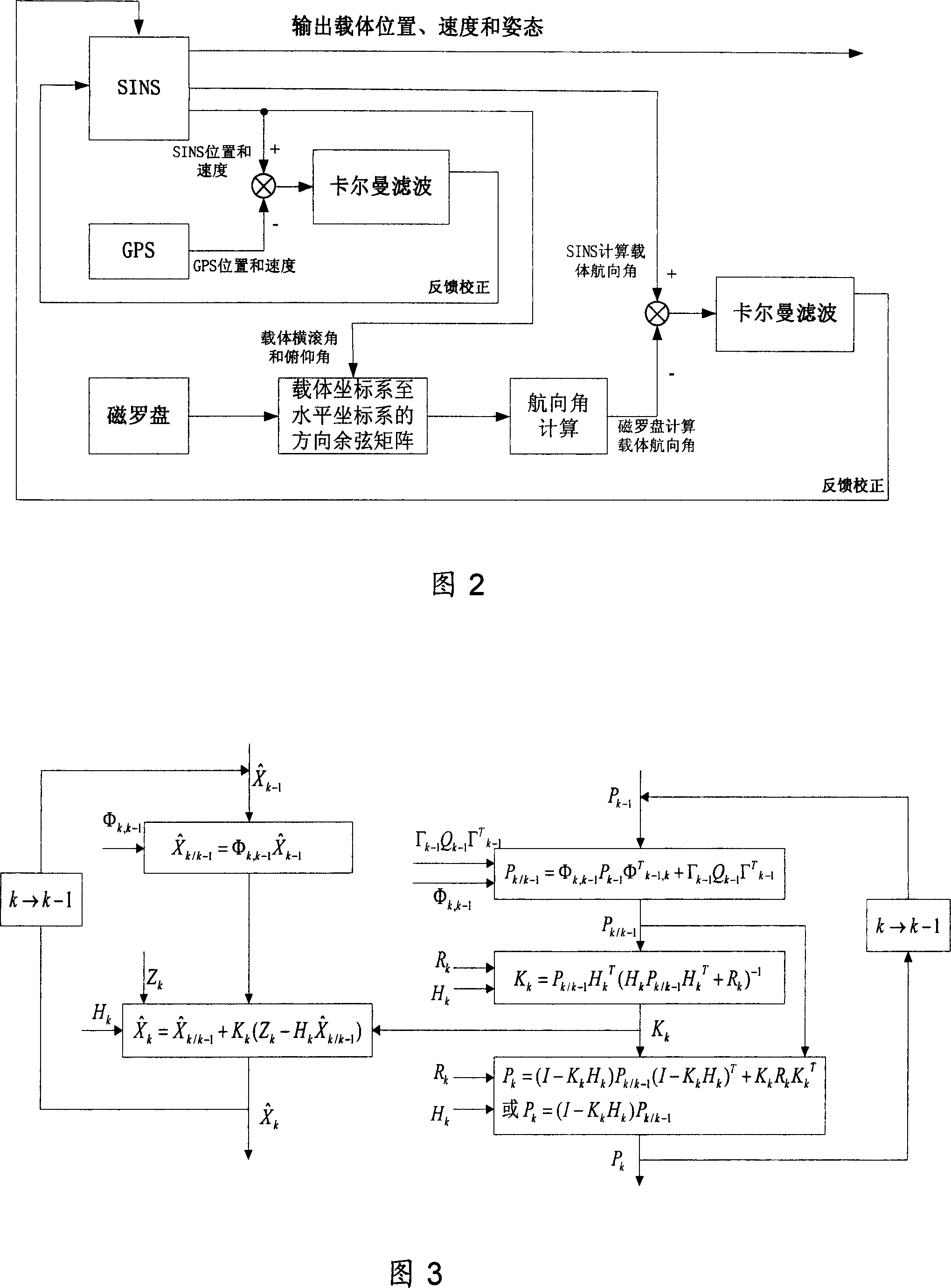
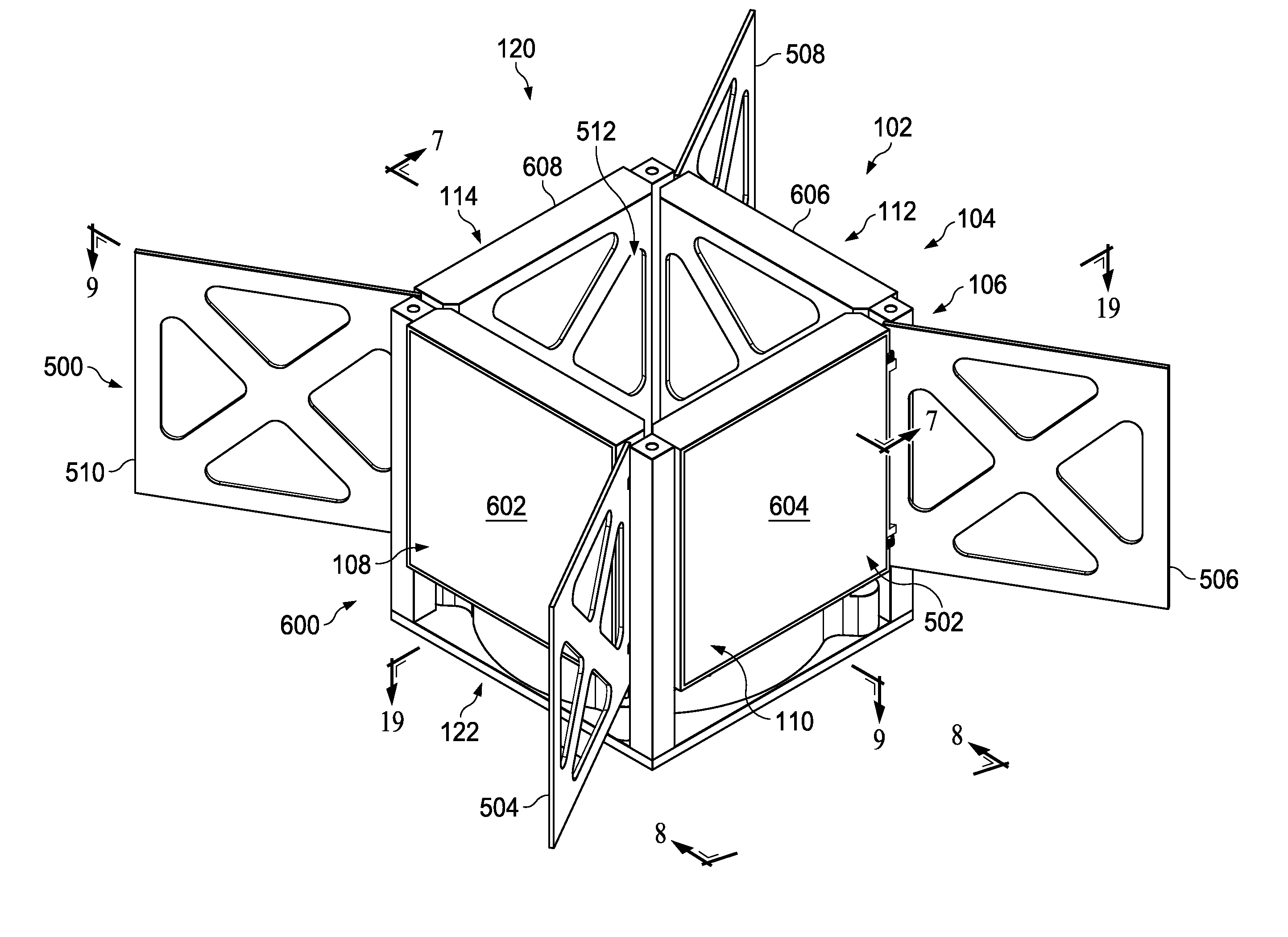
Data blending method of navigation system combined by SINS/GPS micromagnetic compass
InactiveCN101000245AHigh precisionImprove fault toleranceInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsRolling angleSpacecraft
The invention relates to SINS / GPS magnetic compass integrated navigation system data fusion method. It includes the following steps: processing position speed error combination for the SINS and GPS; estimating carrier position, speed, and altitude error by the first Kalman filtering to feed back and rectify SINS; calculating direction cosine matrix from carrier coordinate system to level coordinate system by outputted roll angle and pitch angle to assist magnetic compass to gain carrier magnetic course angle, and course angle; processing course angle error combination for the SINS and magnetic compass; estimating carrier altitude error by the second Kalman filtering to feed back and rectify SINS; outputting carrier position, speed, and altitude information from SINS to user. The invention has the advantages of simple computing, high precision, strong fault tolerant ability and wide application. Thus it can be used to increase magnetic compass altitude fixing precision, navigation precision of the SINS / GPS magnetic compass integrated navigation system used in space craft, aircraft, shipping, or surface car.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
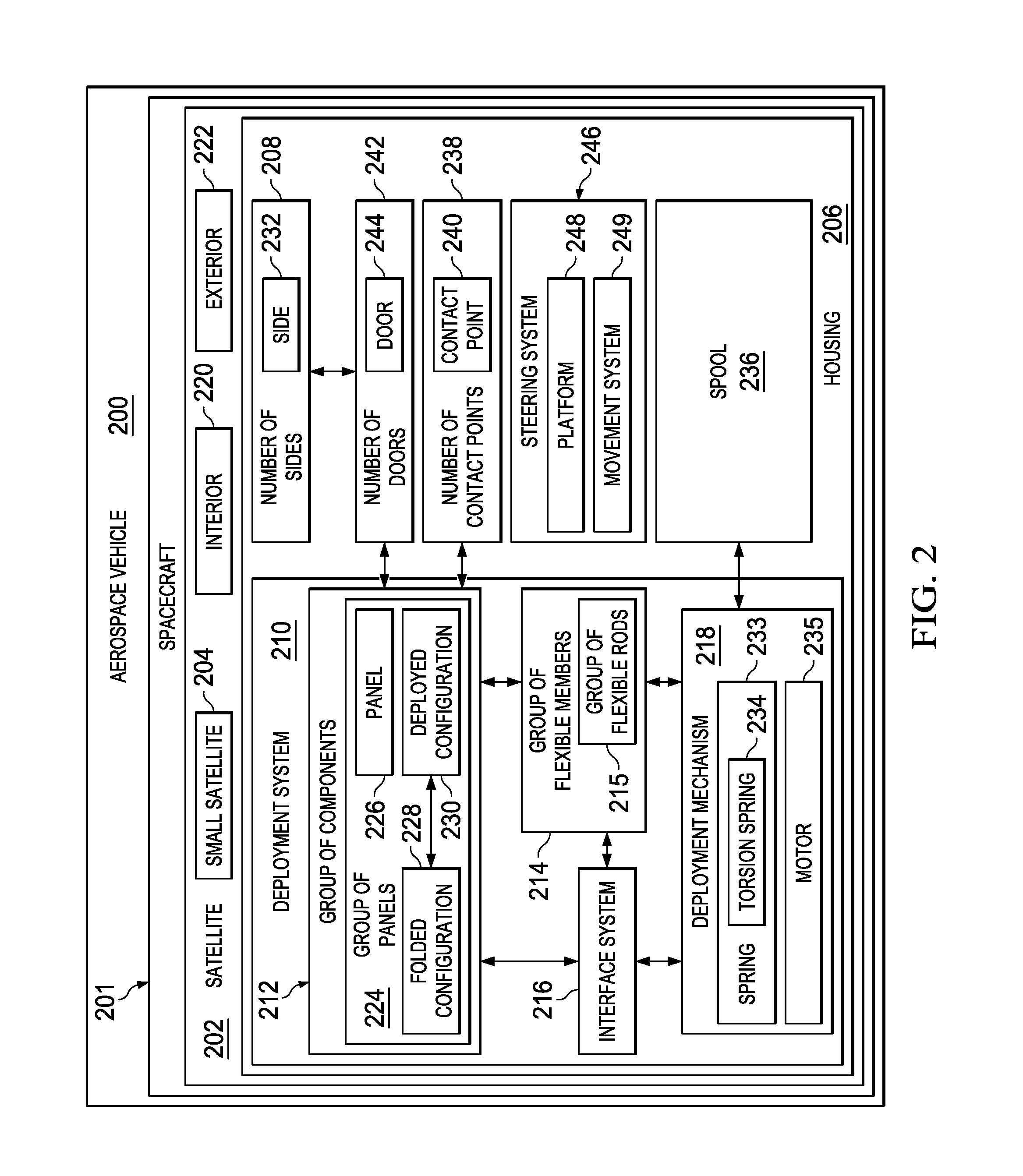
Component Deployment System
A method and apparatus for deploying a group of panels. An apparatus comprises a group of panels in a folded configuration against a side of a spacecraft, a group of flexible members connected to the group of panels, and an interface system associated with the group of panels and the group of flexible members. The interface system is configured to move the group of panels from the folded configuration to a deployed configuration when the group of flexible members is extended from the spacecraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
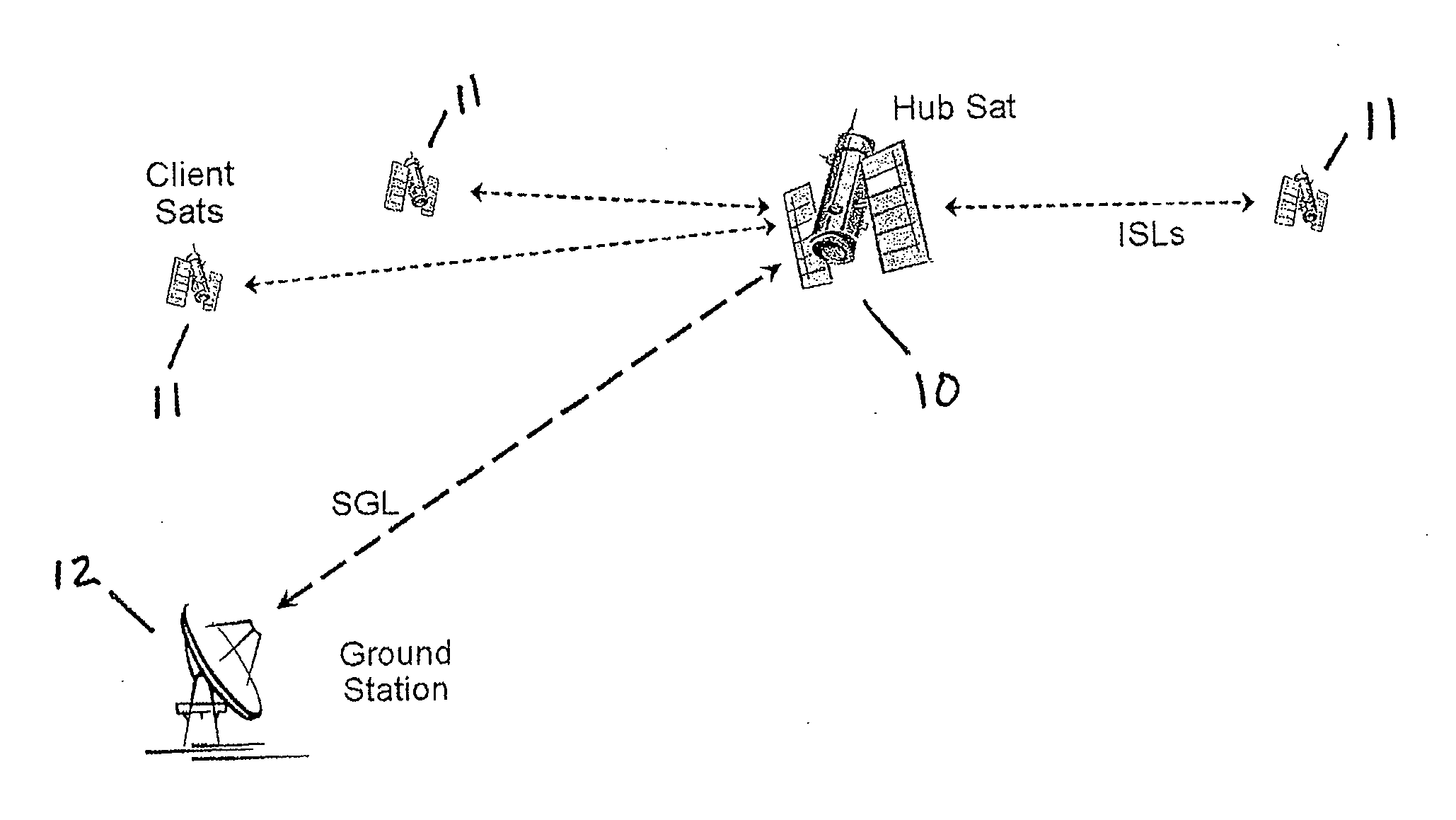
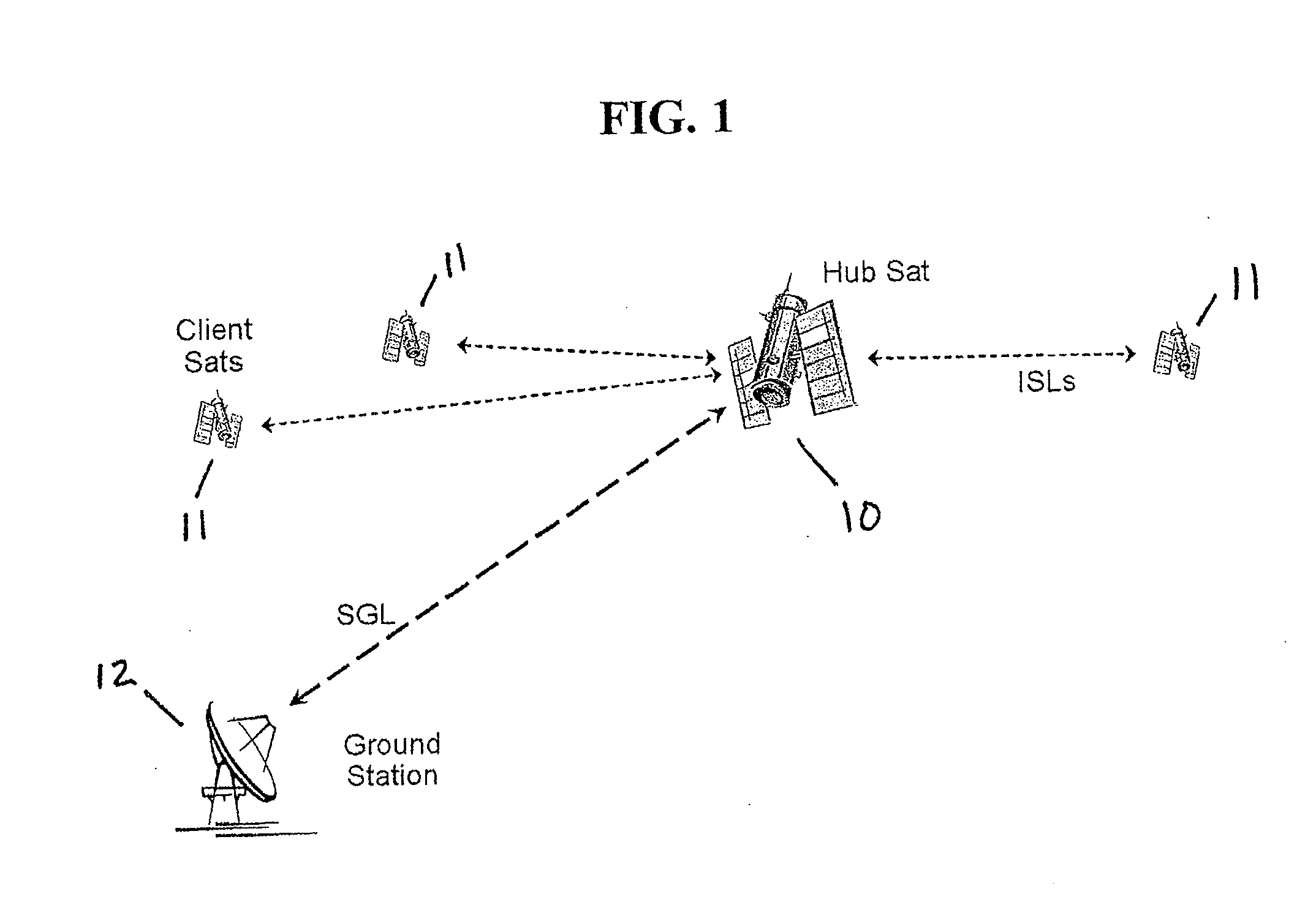
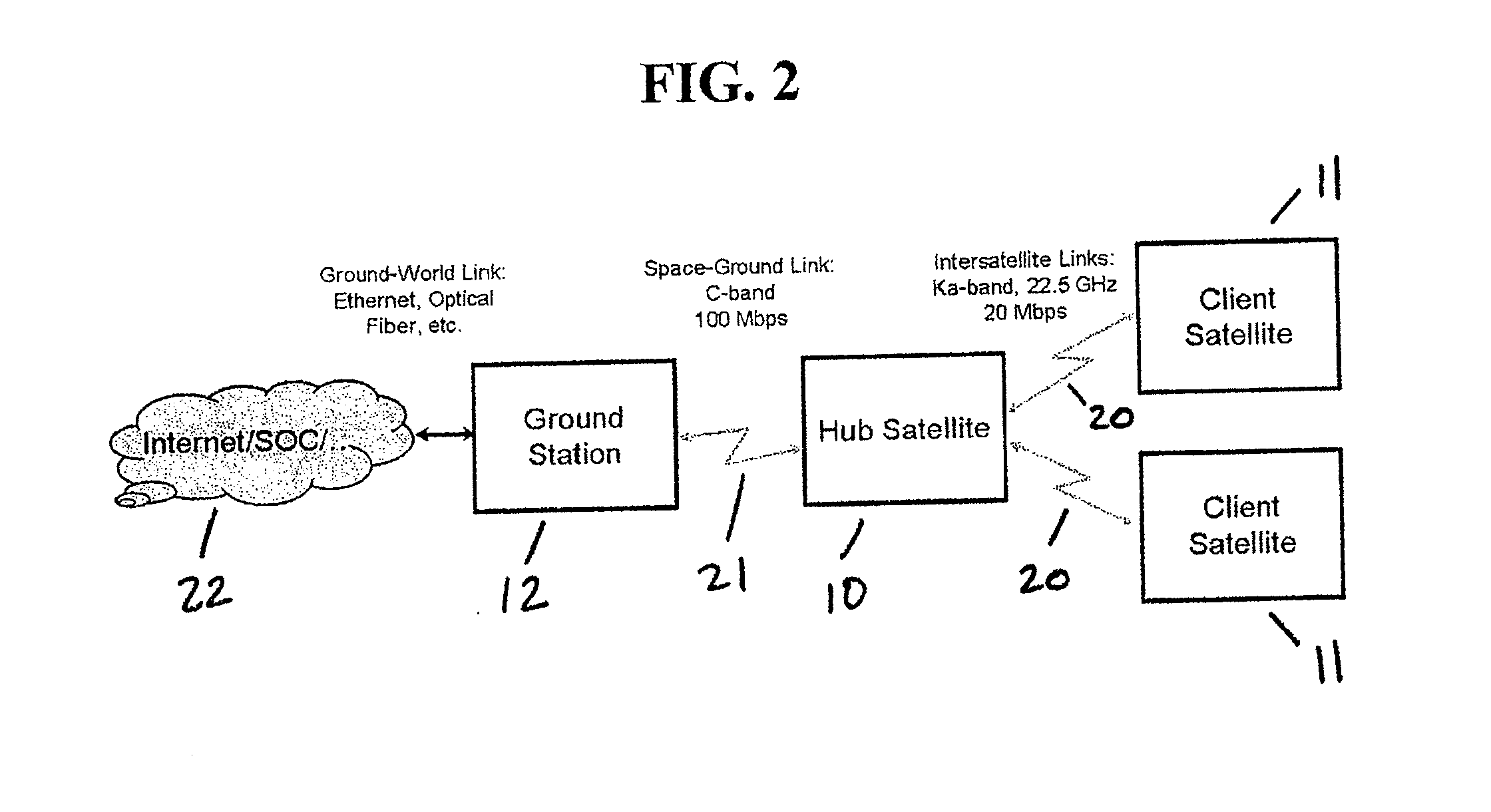
Space based local area network (SBLAN)
A spaced based local area network system for providing dynamically allocated downlink services for spacecraft in Geosynchronous Earth Orbit. The system includes at least two client satellites which host an inter-satellite communications payload; a hub satellite which hosts an inter-satellite communications payload, a downlink communications payload, and an aggregator payload; and a ground station which transmits data to and receives data from the hub satellite. The hub satellite, using the aggregator payload, aggregates at least two data flows received from the at least two client satellites over an inter-satellite link, by the inter-satellite communications payload, into a data stream that is downlinked to the ground station, using the downlink communications payload, over a space-to-ground link.
Owner:INTELSAT GLOBAL SERVICE
Robot system and method of operating a robot system
ActiveUS10144126B2Safe and efficient to useProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsCoupling
A robot system for carrying out a plurality of operations during assembly or maintenance of an aircraft or spacecraft includes a first robot having a base portion, a movable robot arm having a first coupling portion, and a first control means for controlling the robot arm, a plurality of second robots having movement means, a drive portion operable to drive the movement means, a tool portion having a tool for carrying out a specific one of the operations, a second coupling portion adapted to be selectively and releasably coupled with the first coupling portion in a predetermined positional relationship, and a second control means for controlling the respective second robot. The first and second control means are adapted to control the drive portion of one of the second robots and the robot arm to couple the first coupling portion and the respective second coupling portion in the predetermined positional relationship.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
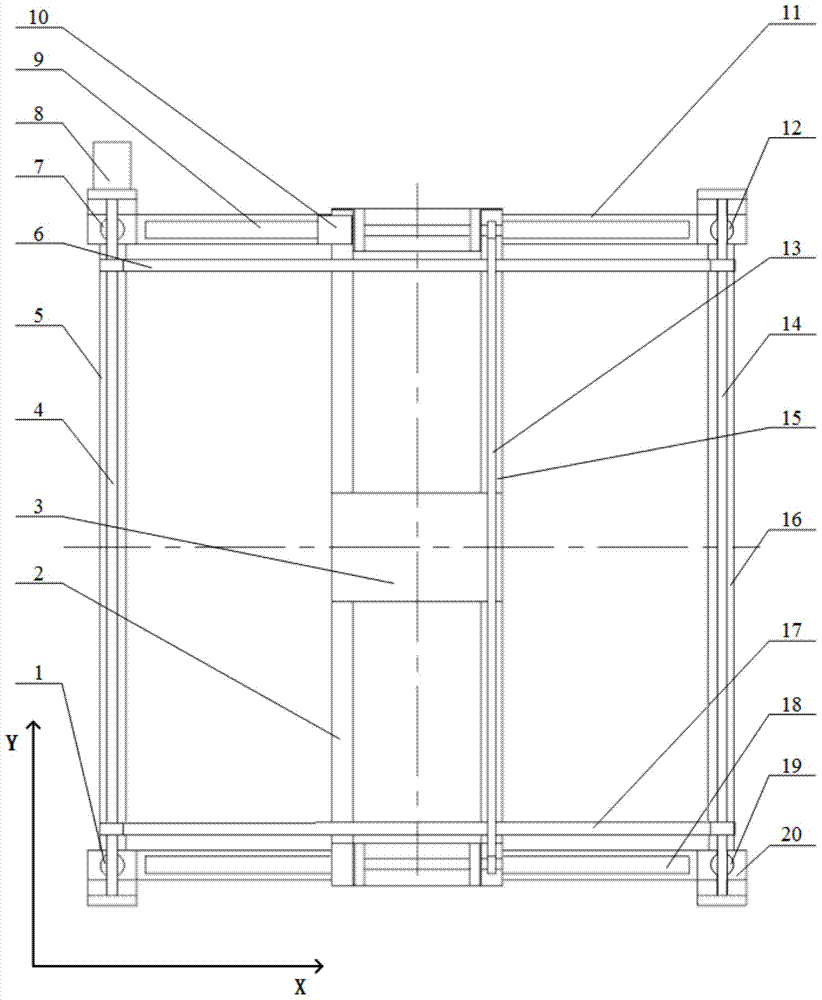
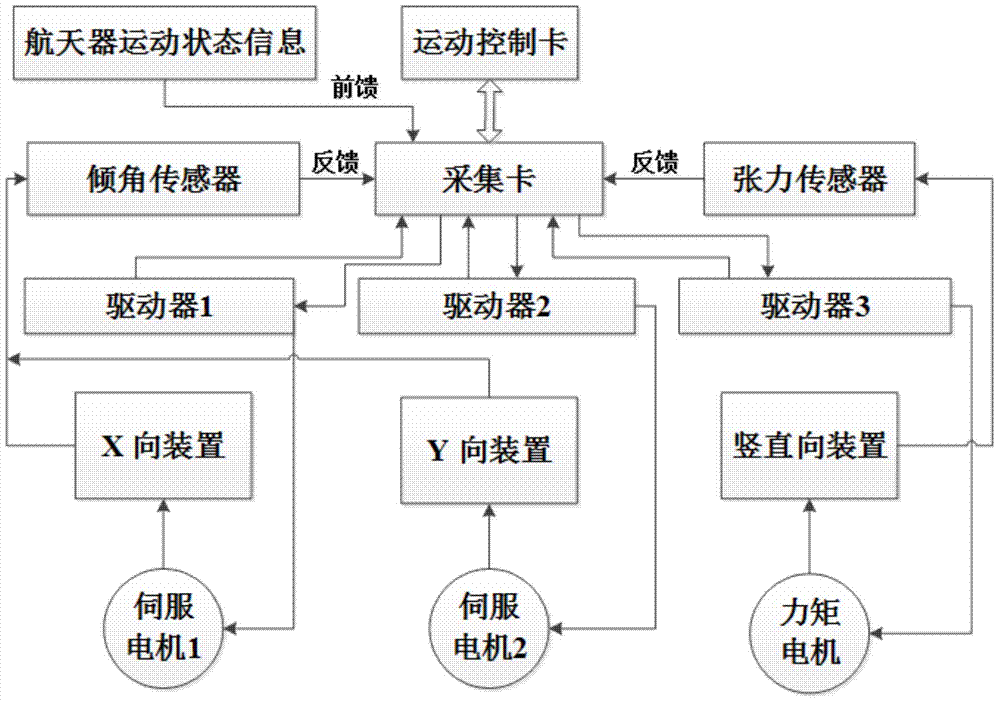
Design method of unrestricted suspension type initiative gravity compensation system
ActiveCN103482089AOvercome the influence of microgravity horizontal directionHigh compensation accuracyCosmonautic condition simulationsTorque motorEngineering
Provided is an unrestricted suspension type initiative gravity compensation system. The system is composed of an unrestricted connecting module, a vertical constant tension suspension module, a horizontal follow-up module and a control module. The unrestricted connecting module comprises a connecting sleeve, an outer mounting frame, a force applying piece and a low friction bearing, and enables a spacecraft to carry out approximate unrestricted rotation round a center of mass. The vertical constant tension suspension module comprises a torque motor, a pinion and rack, a suspension hanging spring and a tension sensor, and enable the tensile force borne by the spacecraft in movement is equal to gravity. The horizontal follow-up module comprises a servo motor, a guide rail, a synchronous belt and a tilt angle sensor, and the suspension module is made to carry out horizontal movement along with the spacecraft to guarantee that the hanging spring is in a vertical state. The control module comprises an acquisition card, a driver and a motion control card. The design method of the unrestricted suspension type initiative gravity compensation system can compensate the gravity of the spacecraft in a ground test environment, further is used for reproducing the real movement of the spacecraft in the interspace microgravity environment, has the advantages of being stable in running, through in compensation and the like, and can provide the approximate unrestricted microgravity environment for movements with six degrees of freedom.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
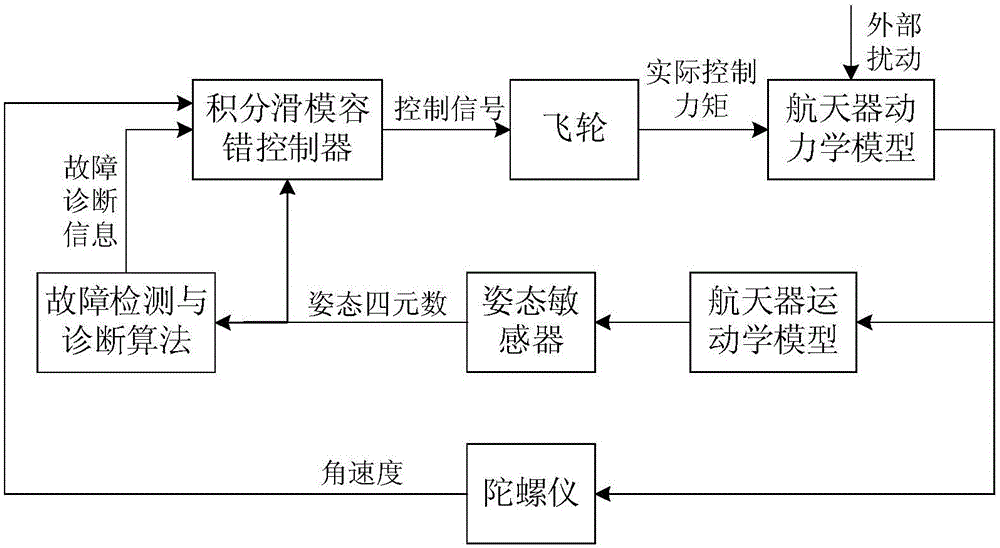
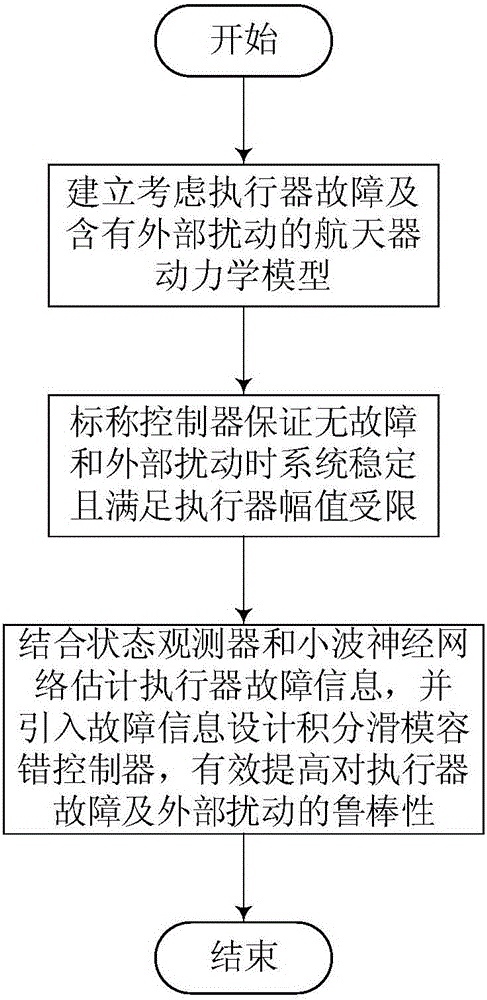
Spacecraft attitude integral sliding mode fault tolerance control method taking consideration of performer fault
ActiveCN105843240AEasy to satisfy control torque limited constraintsSatisfy the control torque limited constraintCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsActive faultDynamic models
The invention relates to a spacecraft attitude integral sliding mode fault tolerance control method taking consideration of a performer fault and provides a robustness attitude active fault tolerance control method based on an integral sliding mode surface for problems of the performer fault, external disturbance and control moment amplitude limits in a spacecraft attitude control process. The method comprises steps that firstly, a spacecraft attitude dynamics model taking consideration of the performer fault and containing external disturbance is established; secondly, on the condition that a performer is not in fault, a designed nominal controller can guarantee system stability, and input saturation amplitude limits can be easily satisfied through adjusting controller parameters; lastly, the fault information is introduced to design an integral sliding mode controller, robustness of external disturbance and the performer fault can be effectively improved, system stability is analyzed on the basis of an Lyapunov method. The method is advantaged in that stability of the attitude control system is guaranteed when a spacecraft operating on orbit generates the performer fault, and relatively strong fault tolerance capability and external disturbance robustness are realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com