Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2261 results about "Rolling angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coming to your question, ROLL ANGLE is the angle between the aircraft wings and the Y-axis. Greater the Roll angle, more quicker the plane turns to the intended direction.
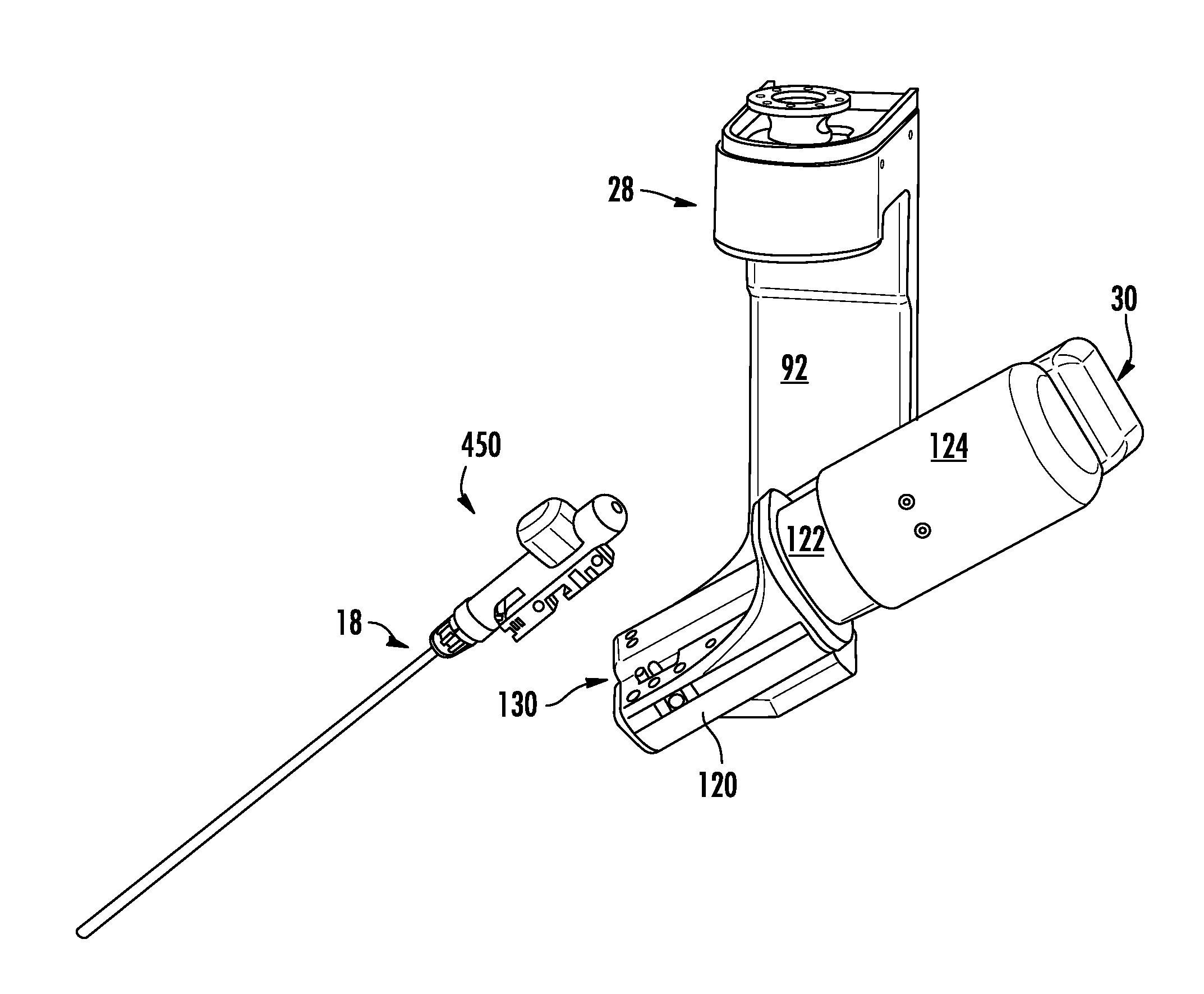
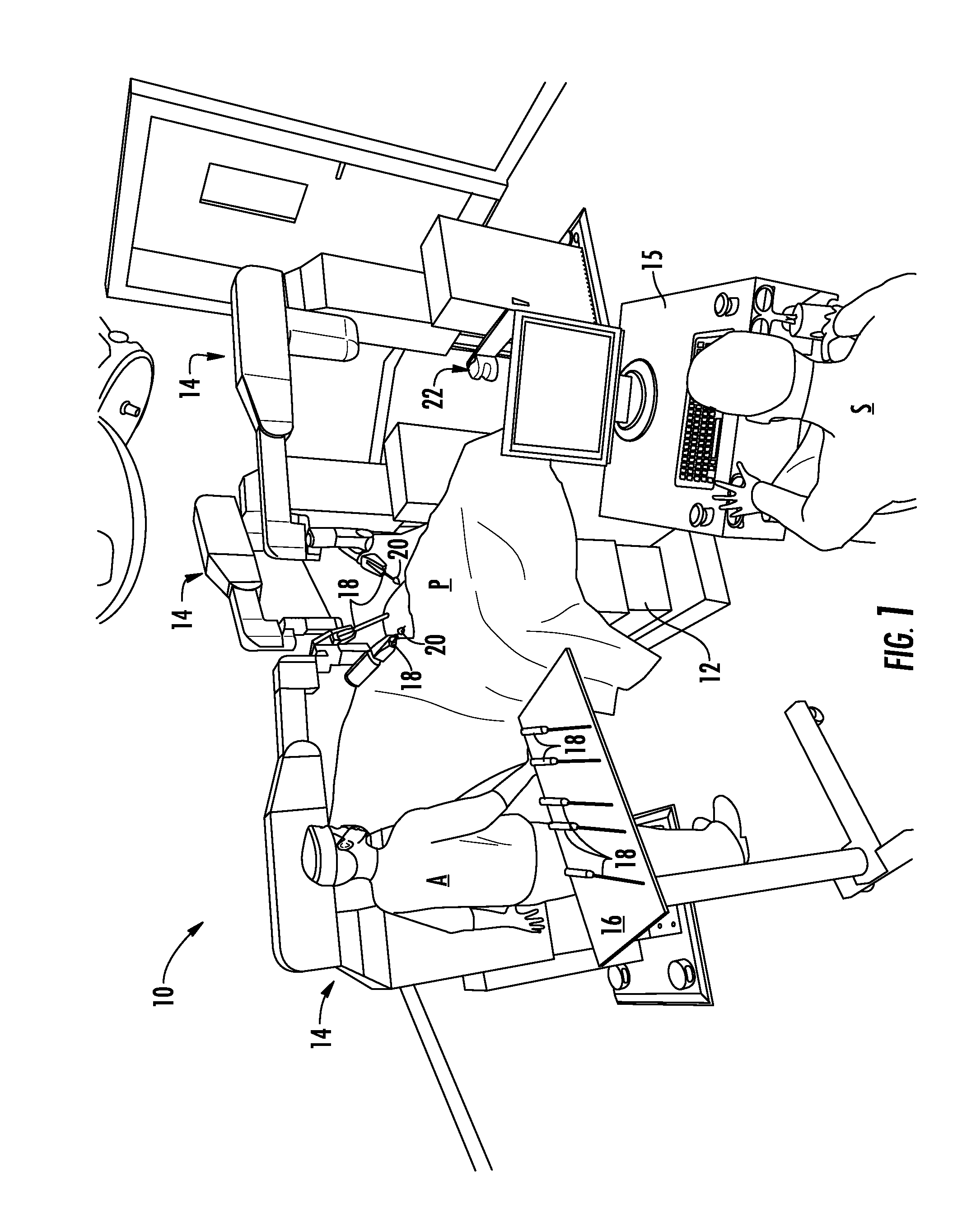
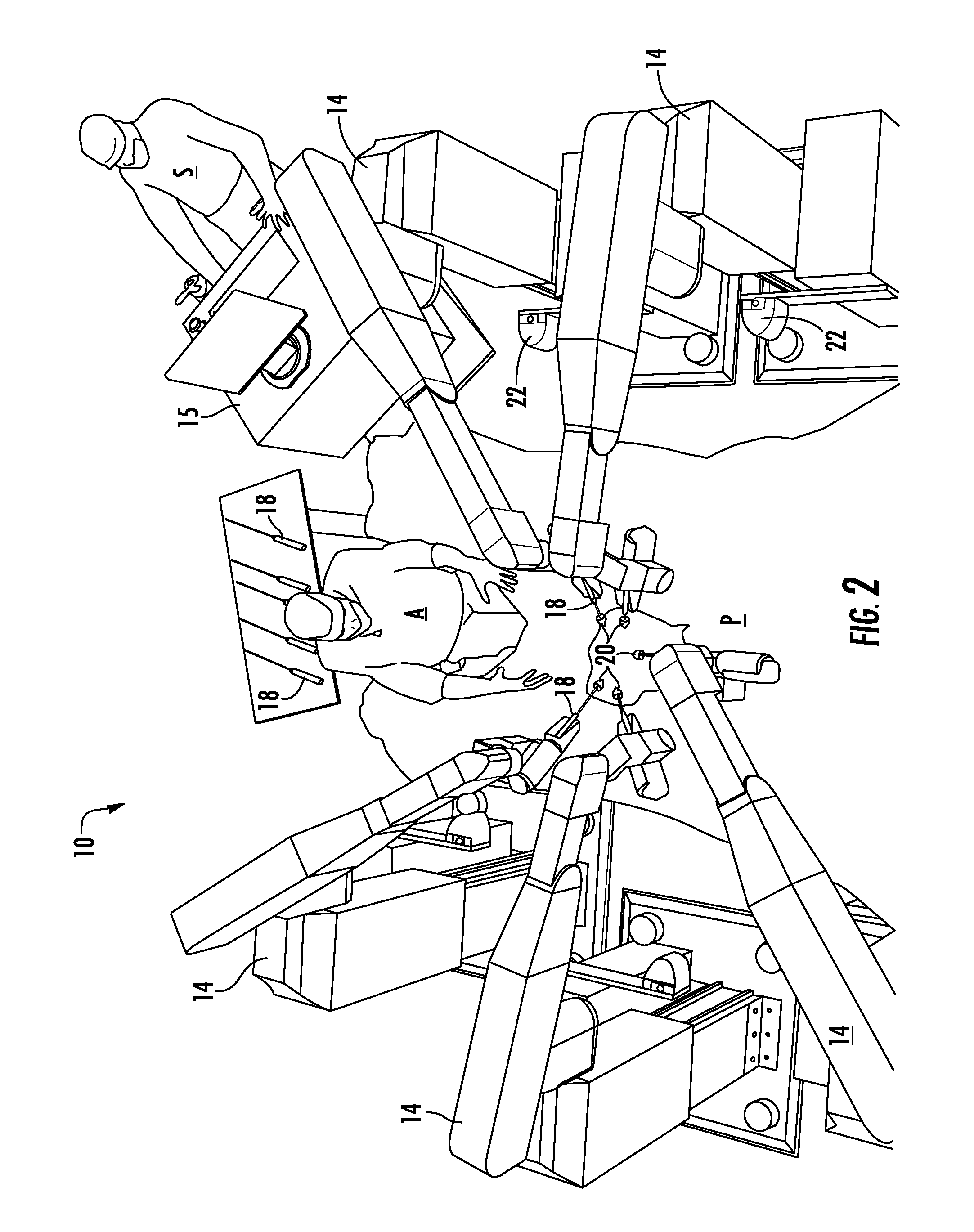
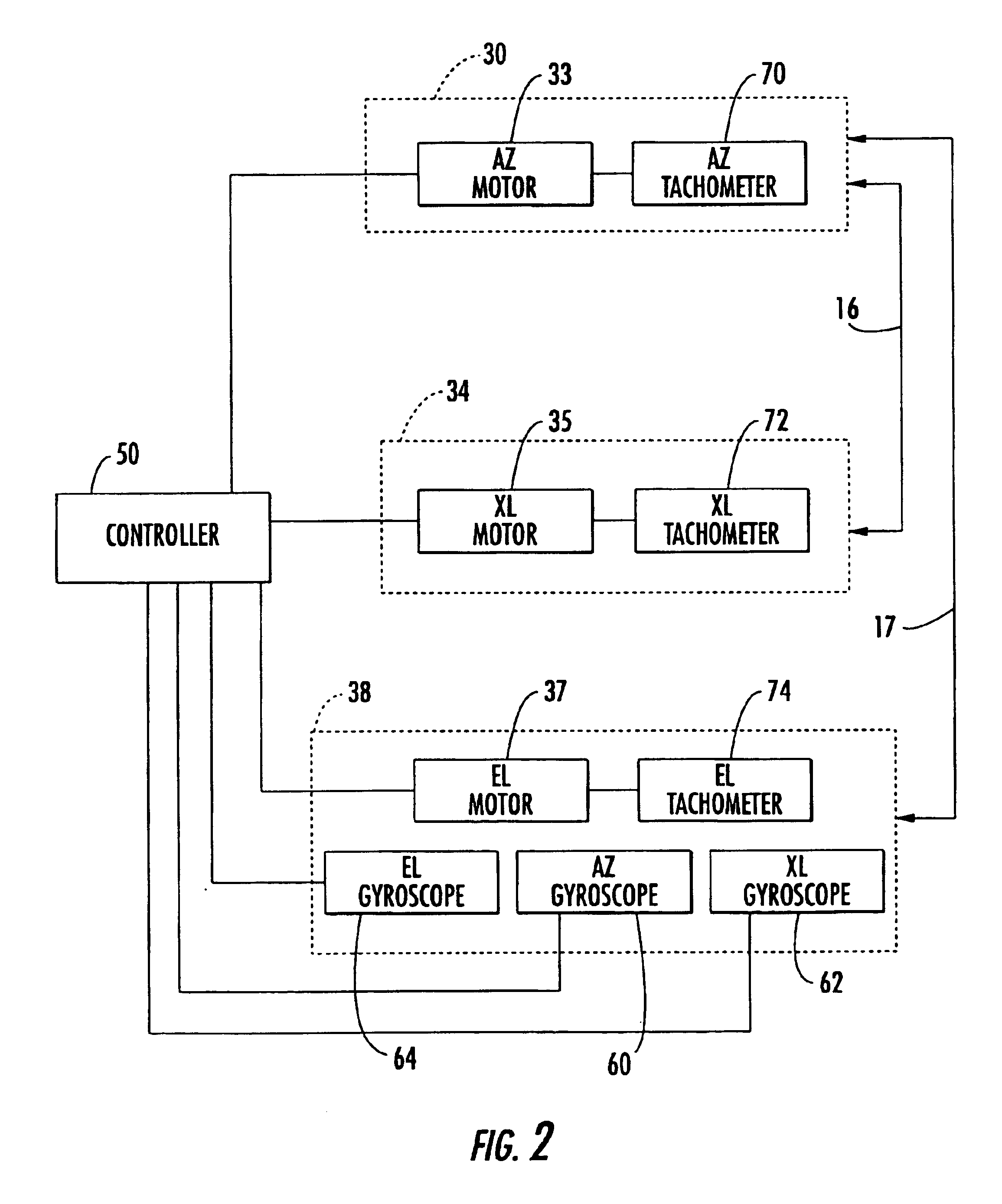
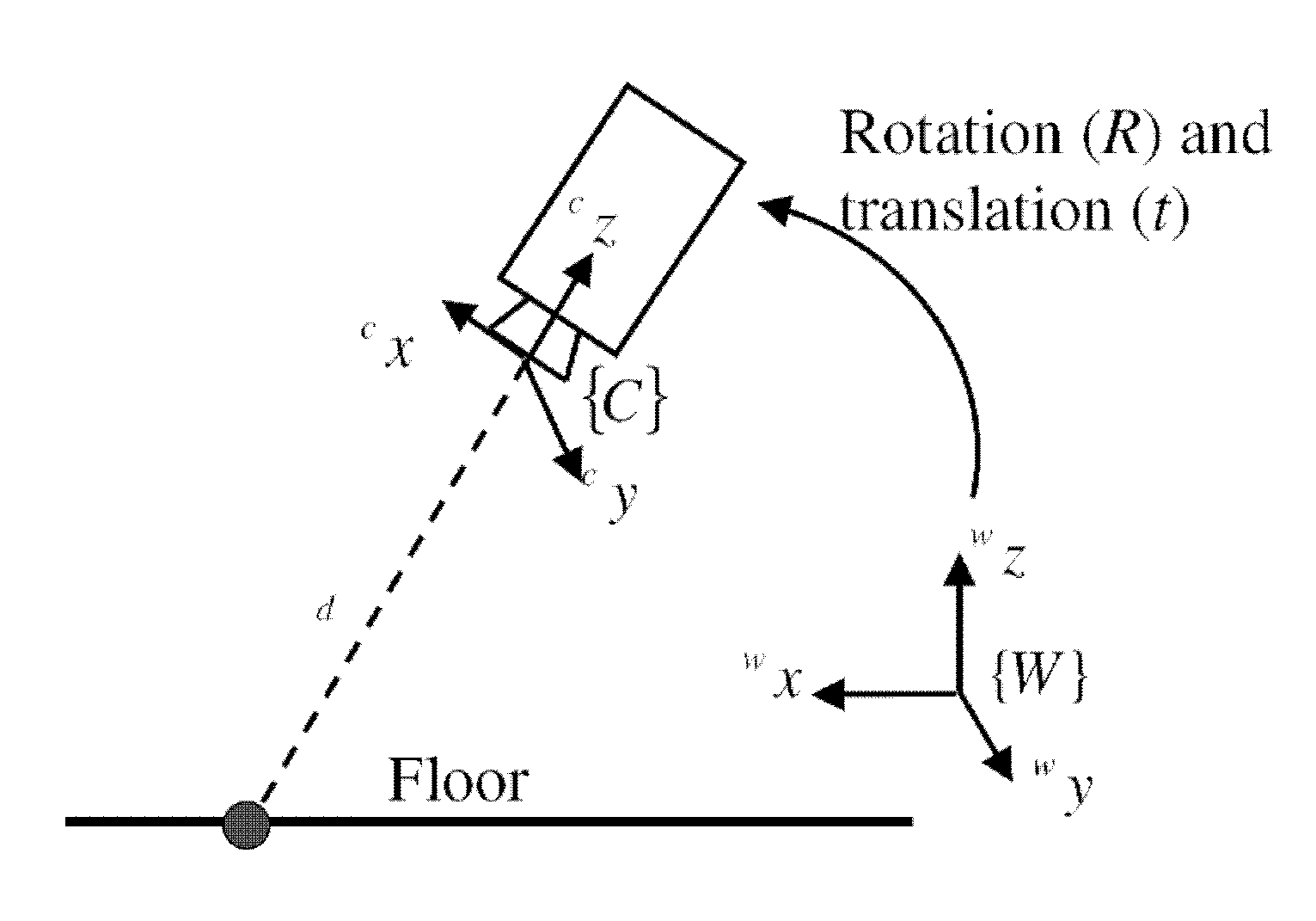
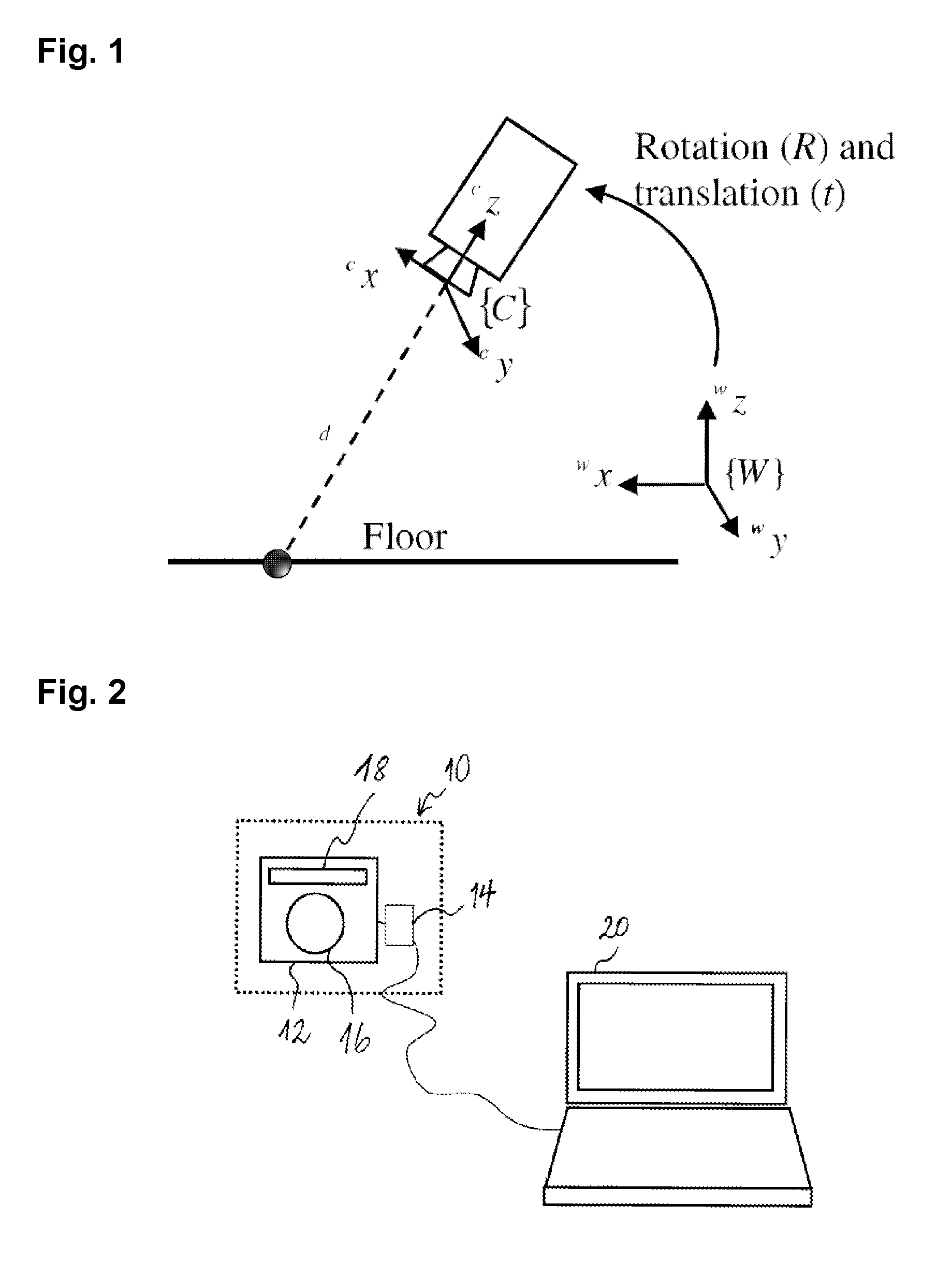
Robotic surgical system for performing minimally invasive medical procedures
ActiveUS8506555B2Level of manoeuvrabilityAccurate feedbackProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsAccelerometerWrist support
Owner:EURO ATOMIC ENERGY COMMUNITY (EURATOM)
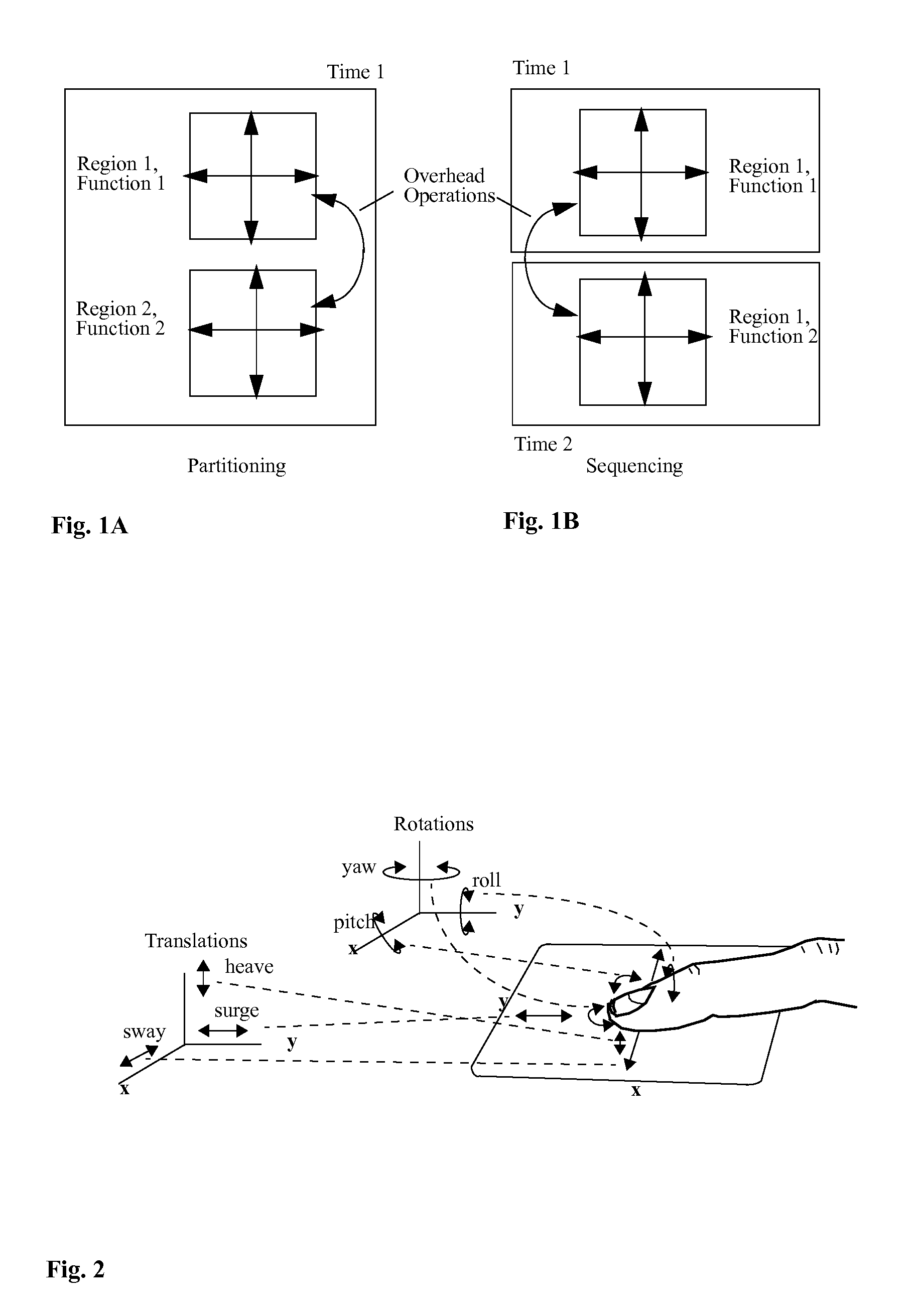
Sensors, algorithms and applications for a high dimensional touchpad
A high dimensional touchpad (HDTP) controls a variety of computer windows systems and applications by detecting a user's finger movement in the left-right, forward-backward, roll, pitch, yaw, and downward pressure directions. Measurements obtained from the touchpad of at least two attributes of finger movement at two different time intervals are used to provide a first and a second finger position attribute used to control an application on an electronic device. The finger roll angle is determined by detecting the edge and the peak region of a finger contact area. Also, a visual color displayed in an application operating on an electronic device is controlled by a measured-angle value of a finger in contact with a touchpad.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
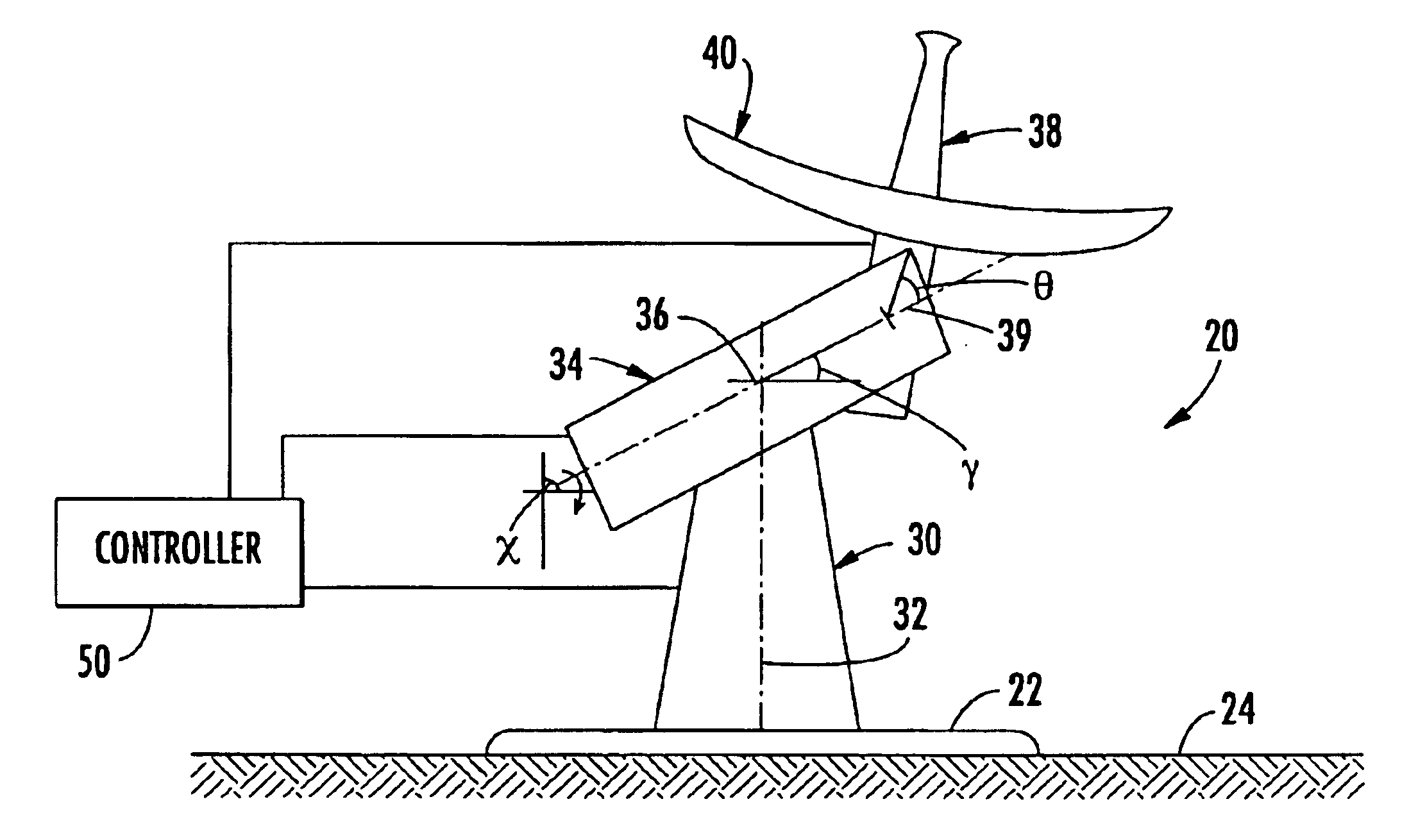
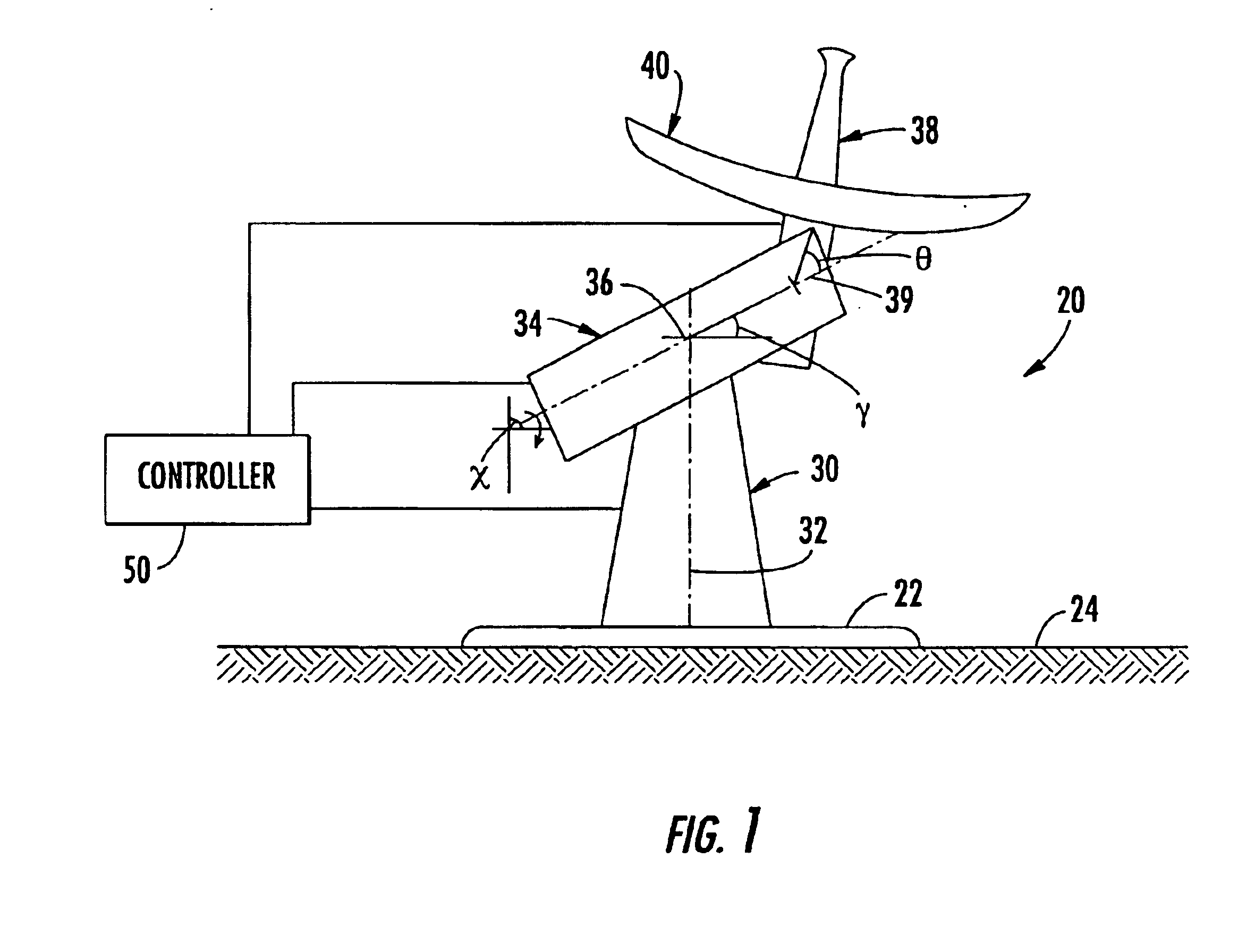
Antenna assembly decoupling positioners and associated methods
An antenna assembly for operation on a moving platform includes a base to be mounted on the moving platform, an azimuthal positioner extending upwardly from the base, and a canted cross-level positioner extending from the azimuthal positioner at a cross-level cant angle canted from perpendicular. The canted cross-level positioner may be rotatable about a cross-level axis to define a roll angle resulting in coupling between the azimuthal and canted cross-level positioners. The antenna assembly may also include an elevational positioner connected to the canted cross-level positioner resulting in coupling between the elevational and the azimuthal positioners because of the roll angle. An antenna may be connected to the elevational positioner. A controller operates the azimuthal, canted cross-level, and elevational positioners to aim the antenna along a desired line-of-sight and while decoupling at least one of the azimuthal and canted cross-level positioners, and the azimuthal and elevational positioners.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
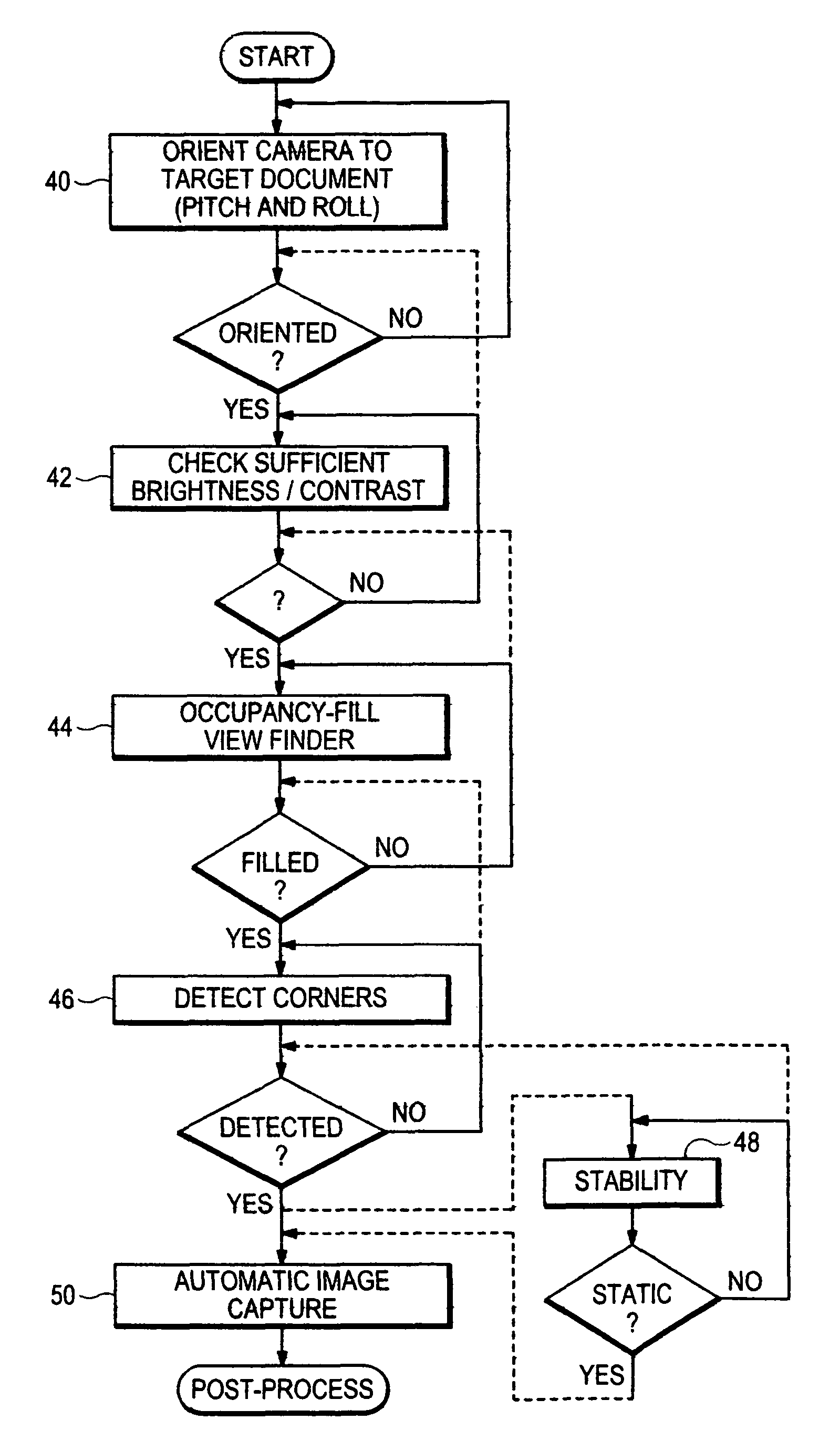
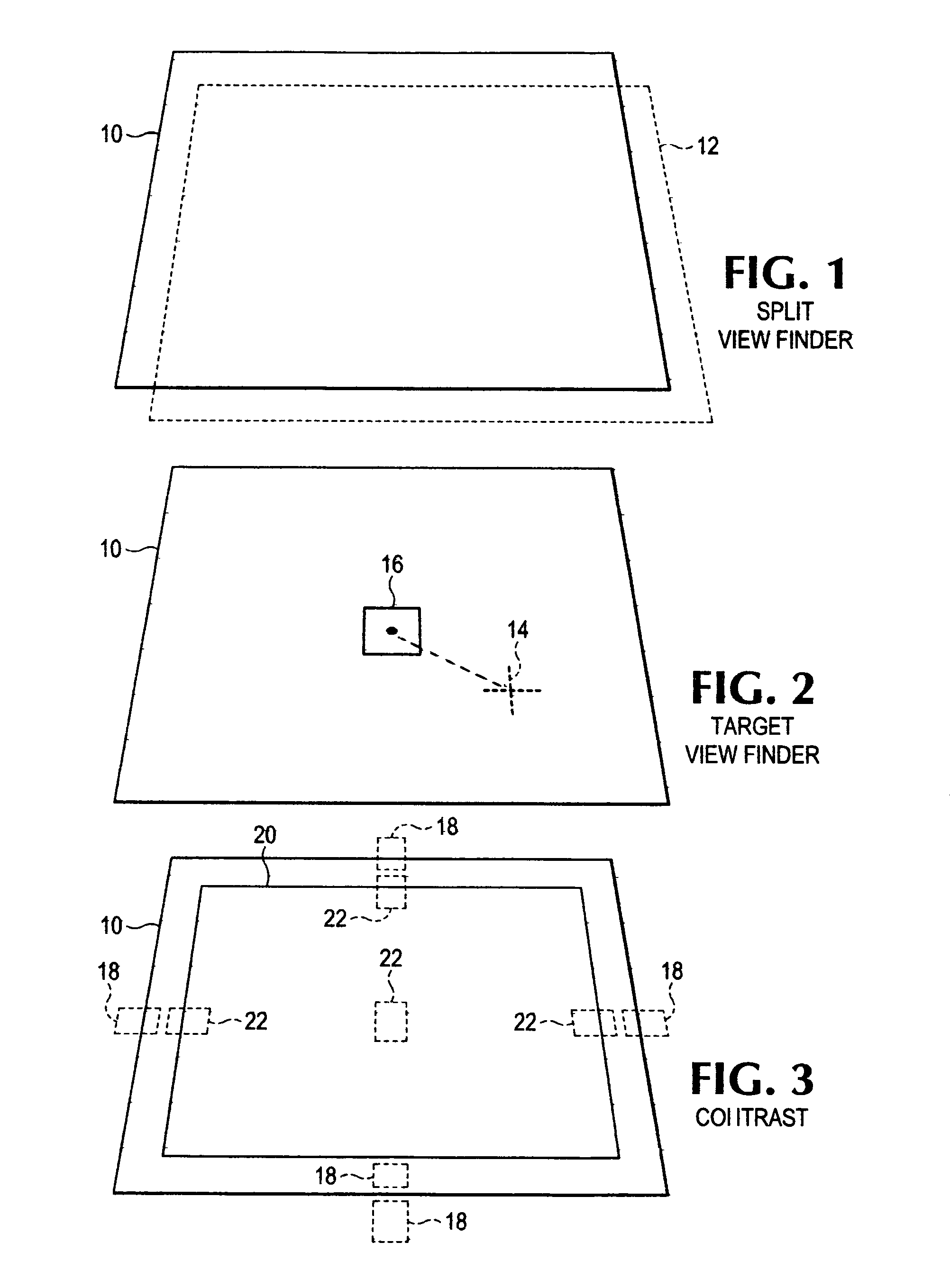
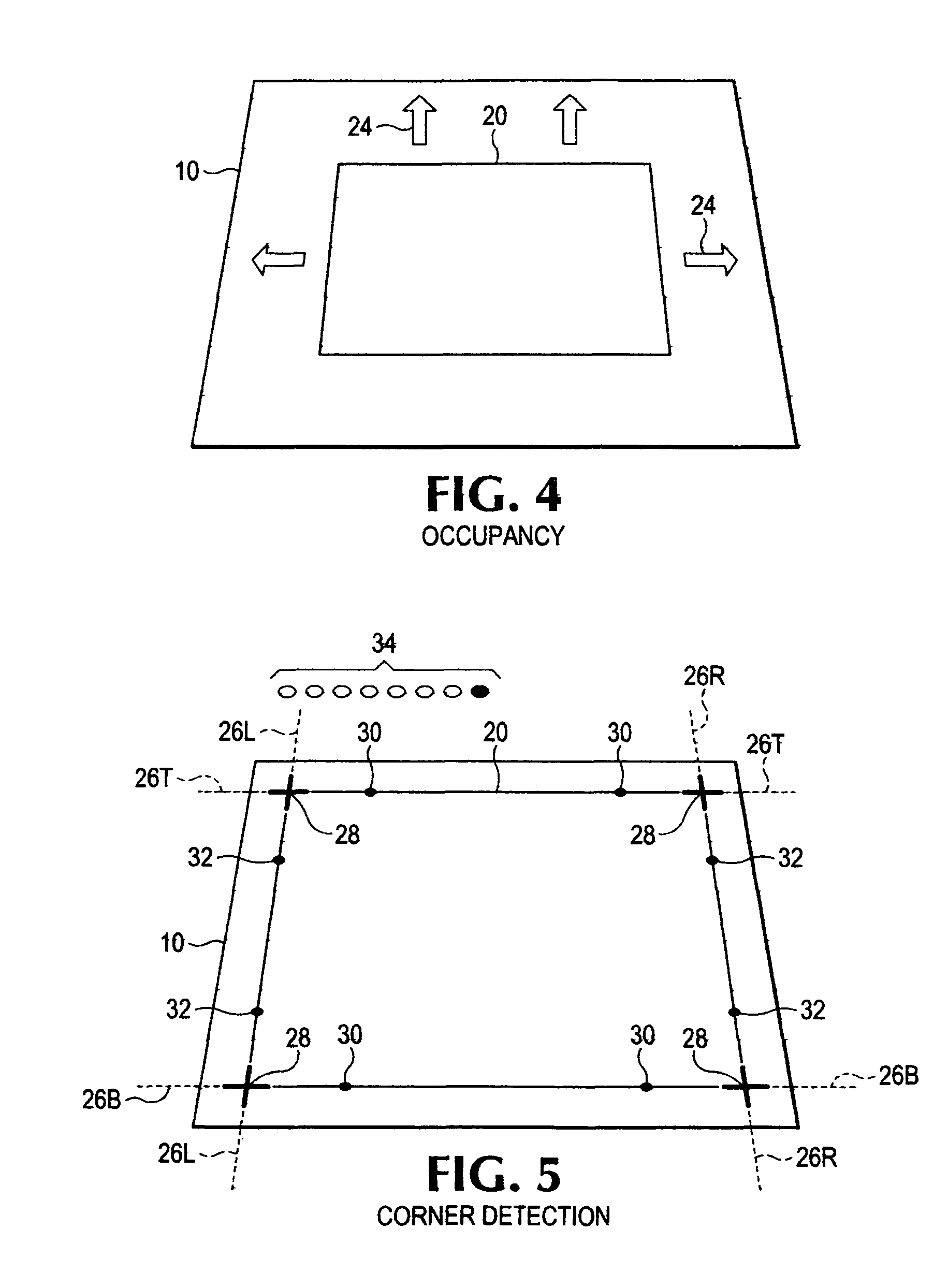
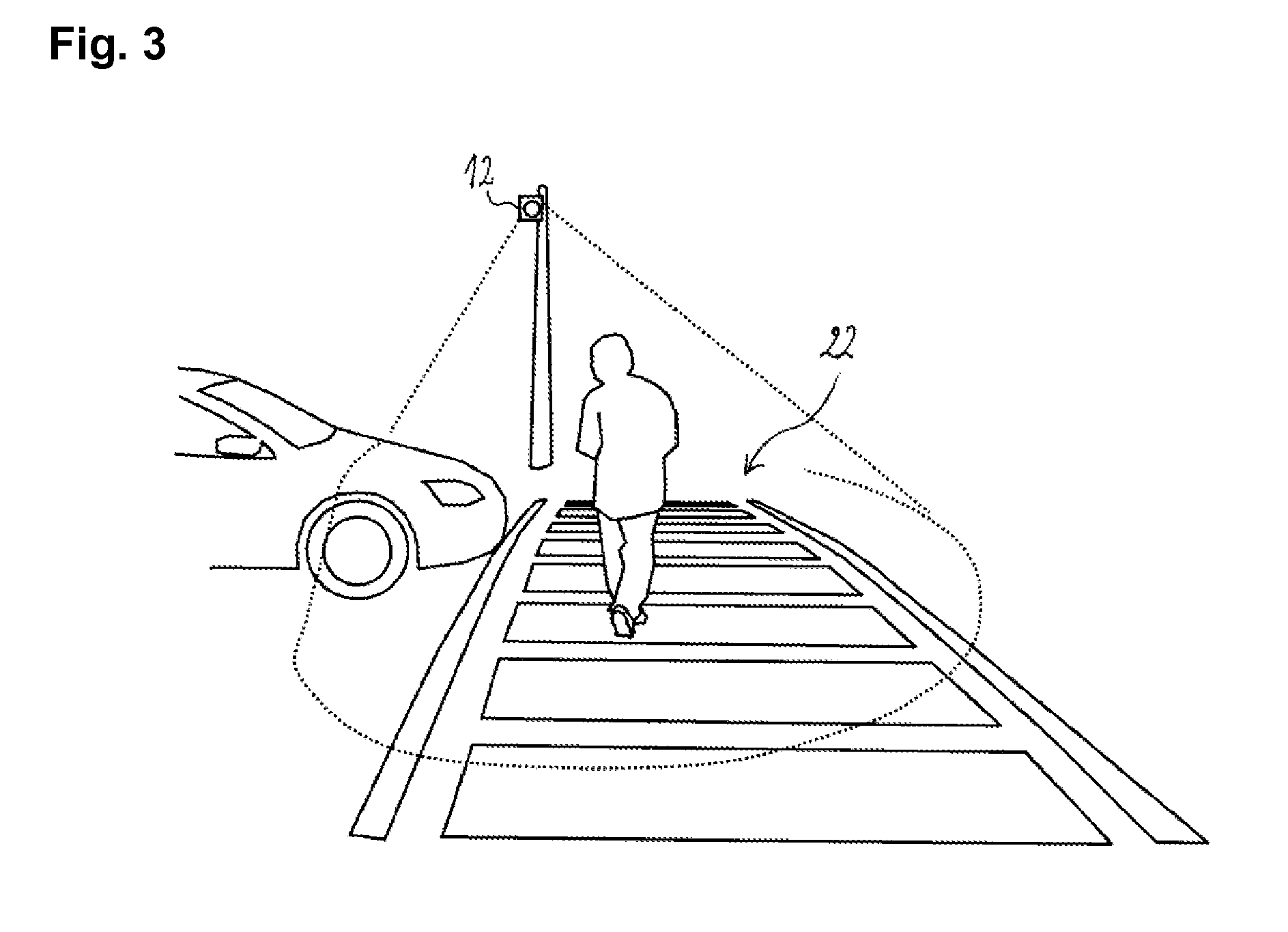
Automatic image capture
ActiveUS8559766B2Solve the lack of brightnessSolve lack of contrastTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceSingle image
An improved automatic image capture system for an intelligent mobile device having a camera guides a user to position the camera so only a single image needs to be automatically captured. A trapezoidal view finder on a display of the intelligent mobile device may be used to orient the camera with respect to a target document so there is an appropriate pitch and roll angle between the camera and the target document to avoid shadows caused by the camera or user. Further the user is guided to maximize the occupancy of the view finder with the document so that the document is maximized within the view finder. When all requisite conditions are satisfied, the camera automatically captures the image of the document for post-processing.
Owner:NORTHWEST IP LLC
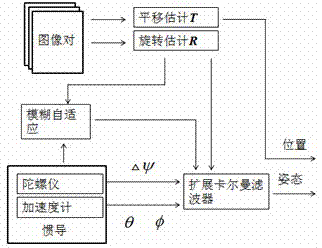
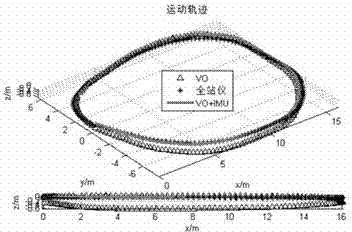
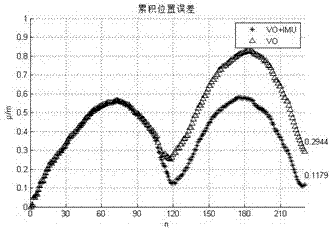
Machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method
InactiveCN102538781AReduce cumulative errorHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVisual perceptionInertial navigation system
The invention discloses a machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method which comprises the following steps of: synchronously acquiring a mobile robot binocular camera image and triaxial inertial navigation data; distilling front / back frame image characteristics and matching estimation motion attitude; computing a pitch angle and a roll angle by inertial navigation; building a kalman filter model to estimate to fuse vision and inertial navigation attitude; adaptively adjusting a filter parameter according to estimation variance; and carrying out accumulated dead reckoning of attitude correction. According to the method, a real-time expanding kalman filter attitude estimation model is provided, the combination of inertial navigation and gravity acceleration direction is taken as supplement, three-direction attitude estimation of a visual speedometer is decoupled, and the accumulated error of the attitude estimation is corrected; and the filter parameter is adjusted by fuzzy logic according to motion state, the self-adaptive filtering estimation is realized, the influence of acceleration noise is reduced, and the positioning precision and robustness of the visual speedometer is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
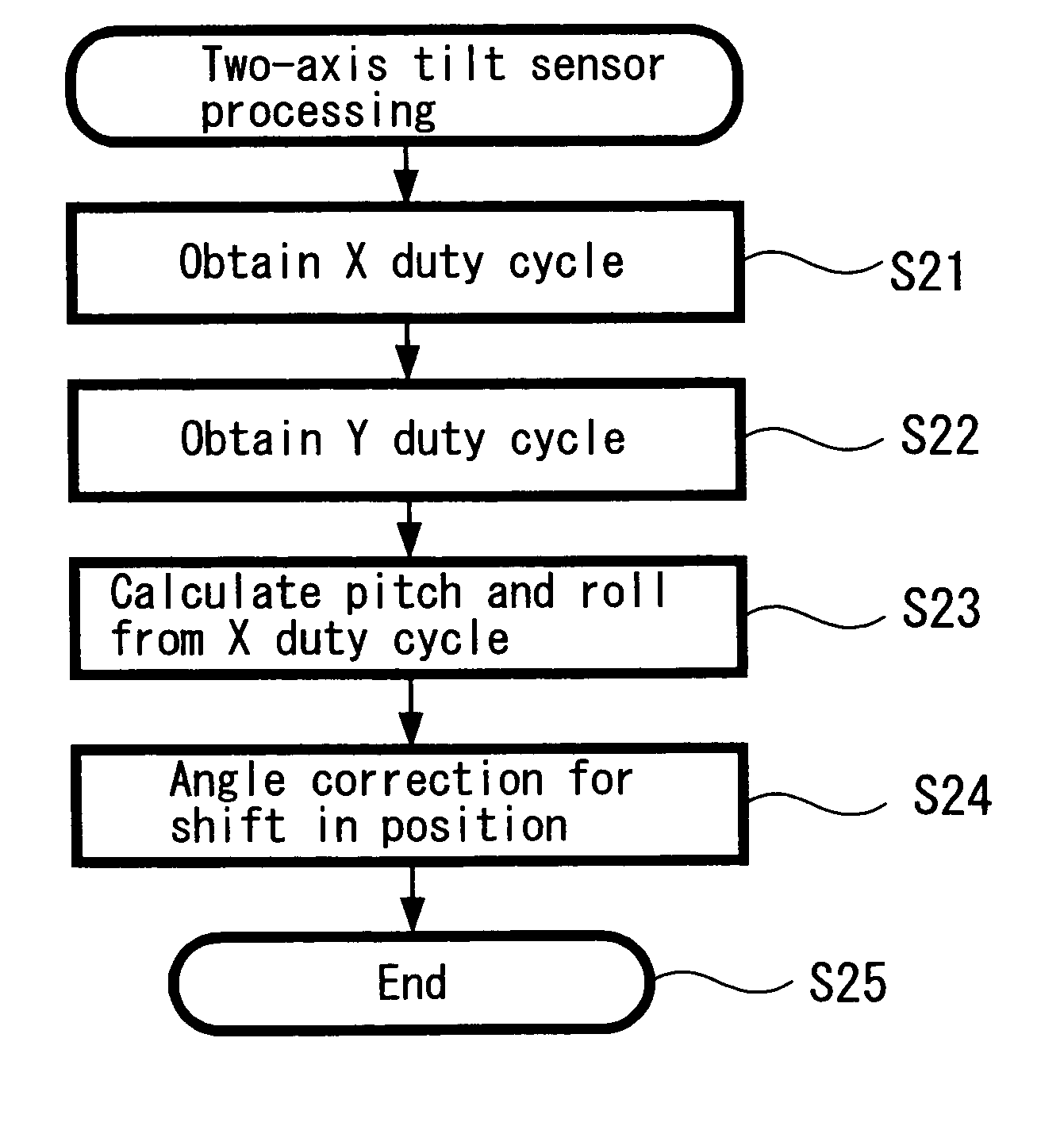
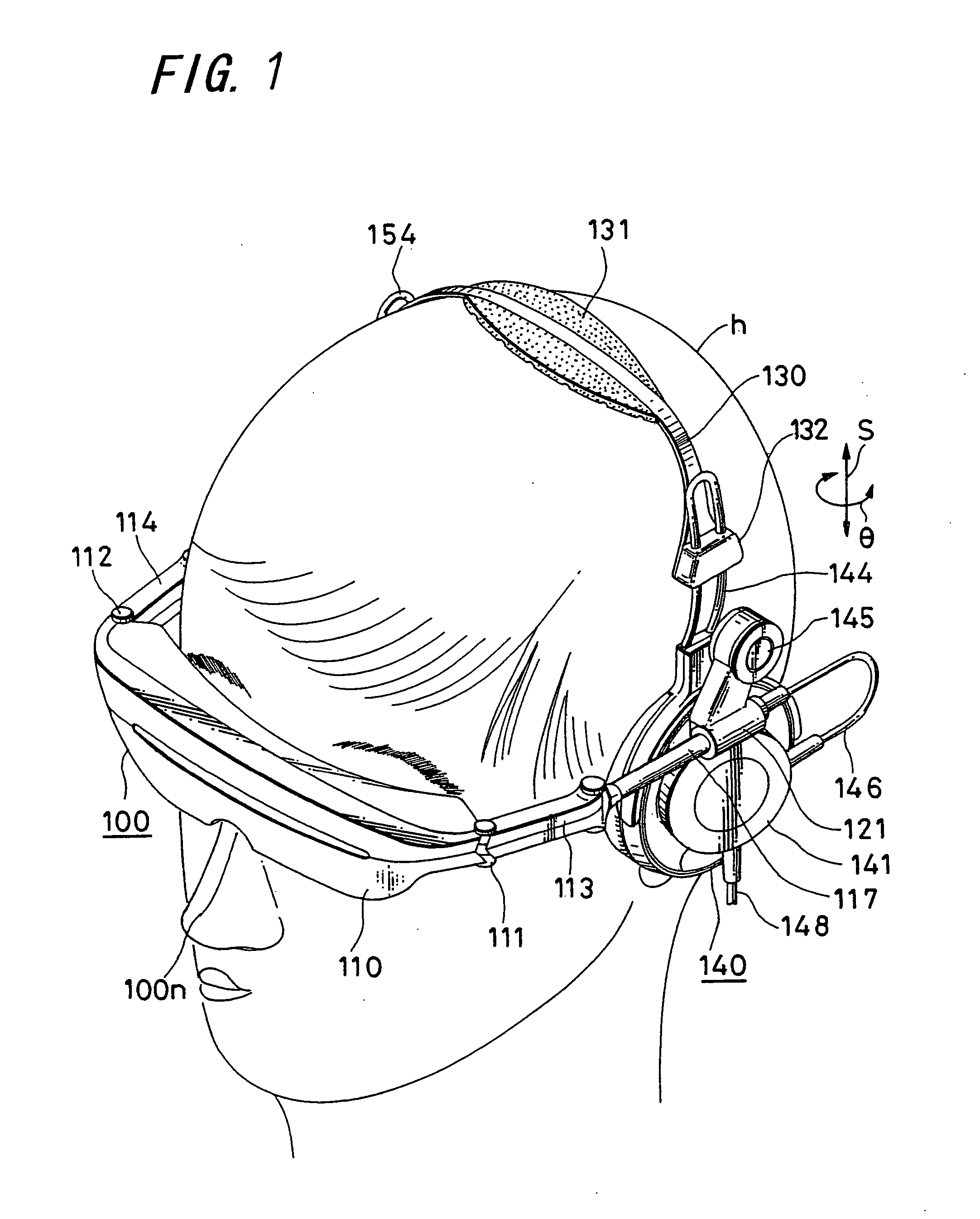
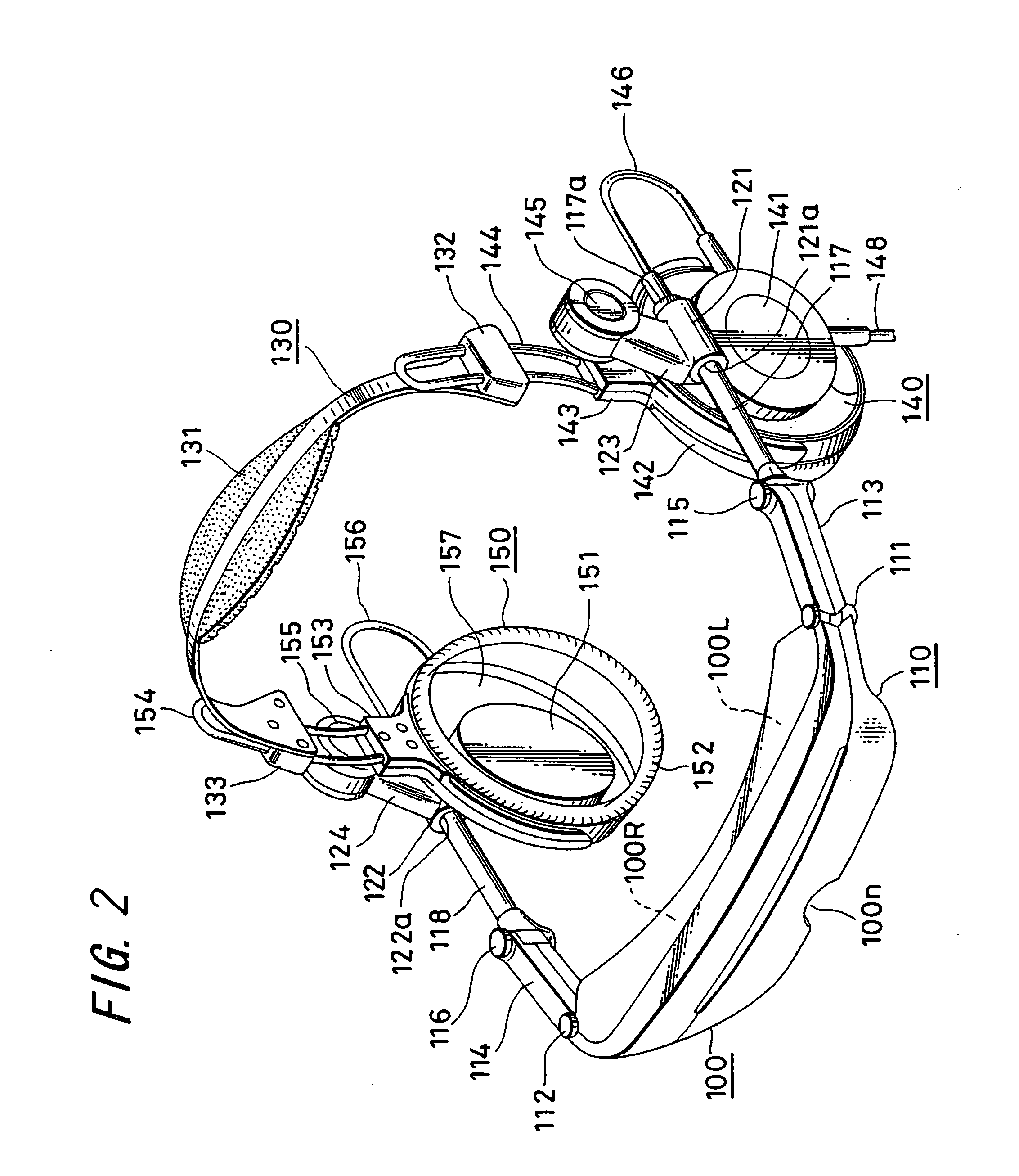
Method and device for head tracking
InactiveUS20050256675A1Accurate judgmentEasy accessInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsClassical mechanicsDisplay device
When the three-dimensional direction the head faces is detected by three axes, that is, a yaw angle that is an angle turning around an erect axis erected on the horizontal surface of the head, and a pitch angle and a roll angle that are angles formed by the above erect axis and two axes perpendicular thereto, a gyro sensor 11 which detects the yaw angle from the integral value of the acceleration, a tilt sensor 12 which detects the inclination of a plane that intersects the direction of the erect axis at right angles, and calculation element 14 which calculates the pitch angle and the roll angle from the output of a tilt sensor are provided, so that the direction that the head faces can be detected with a simple detecting structure including the two sensors, in a head mounted display or the like.
Owner:SONY CORP
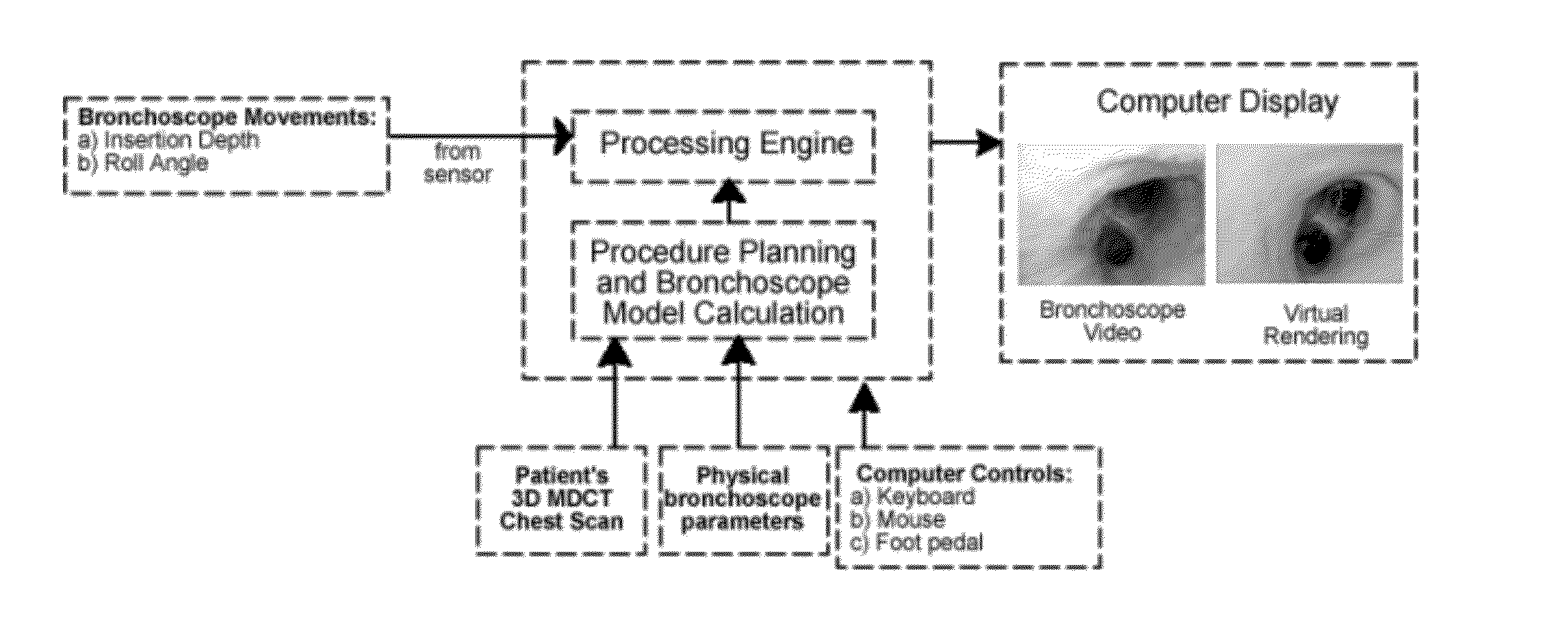
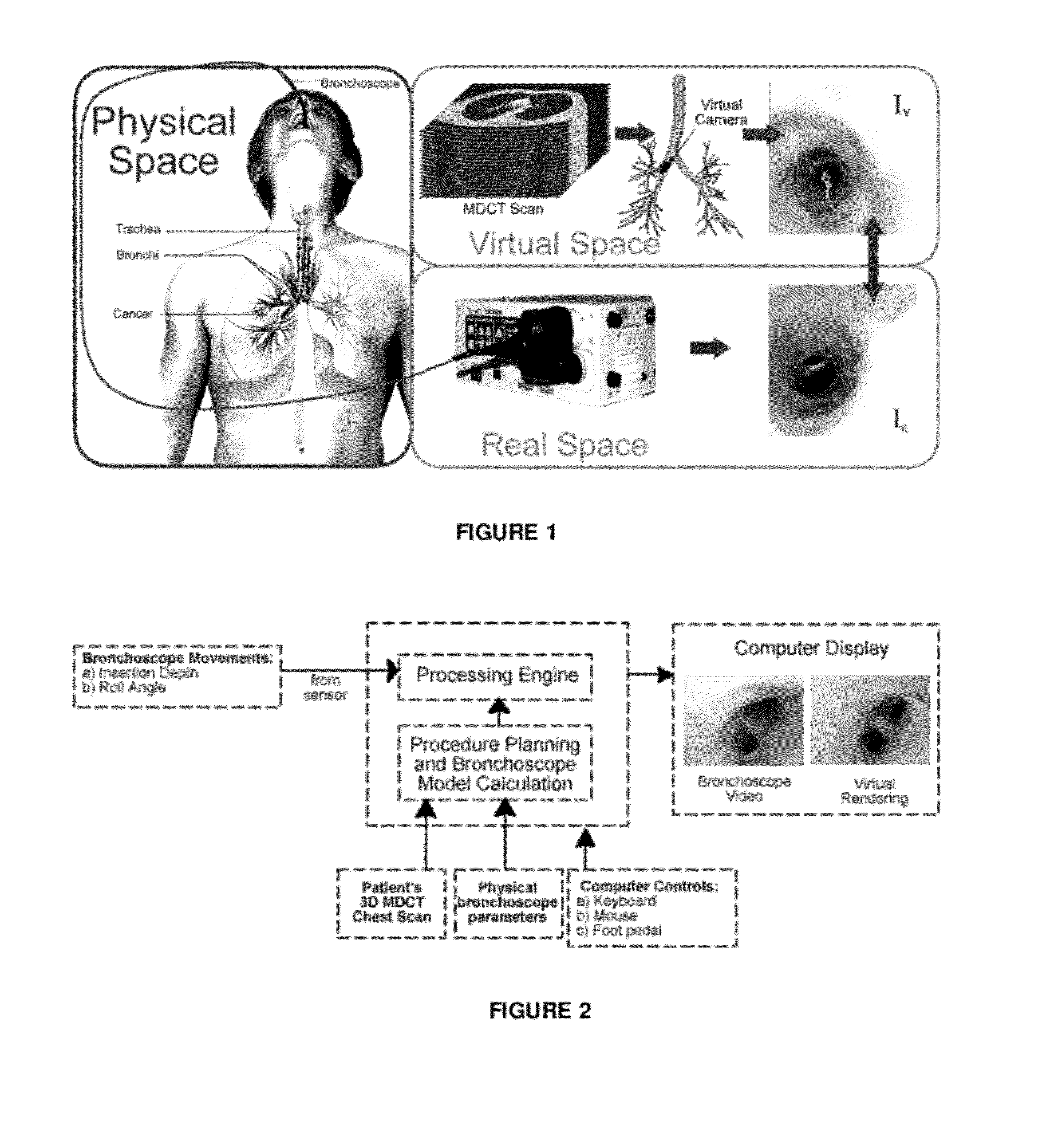
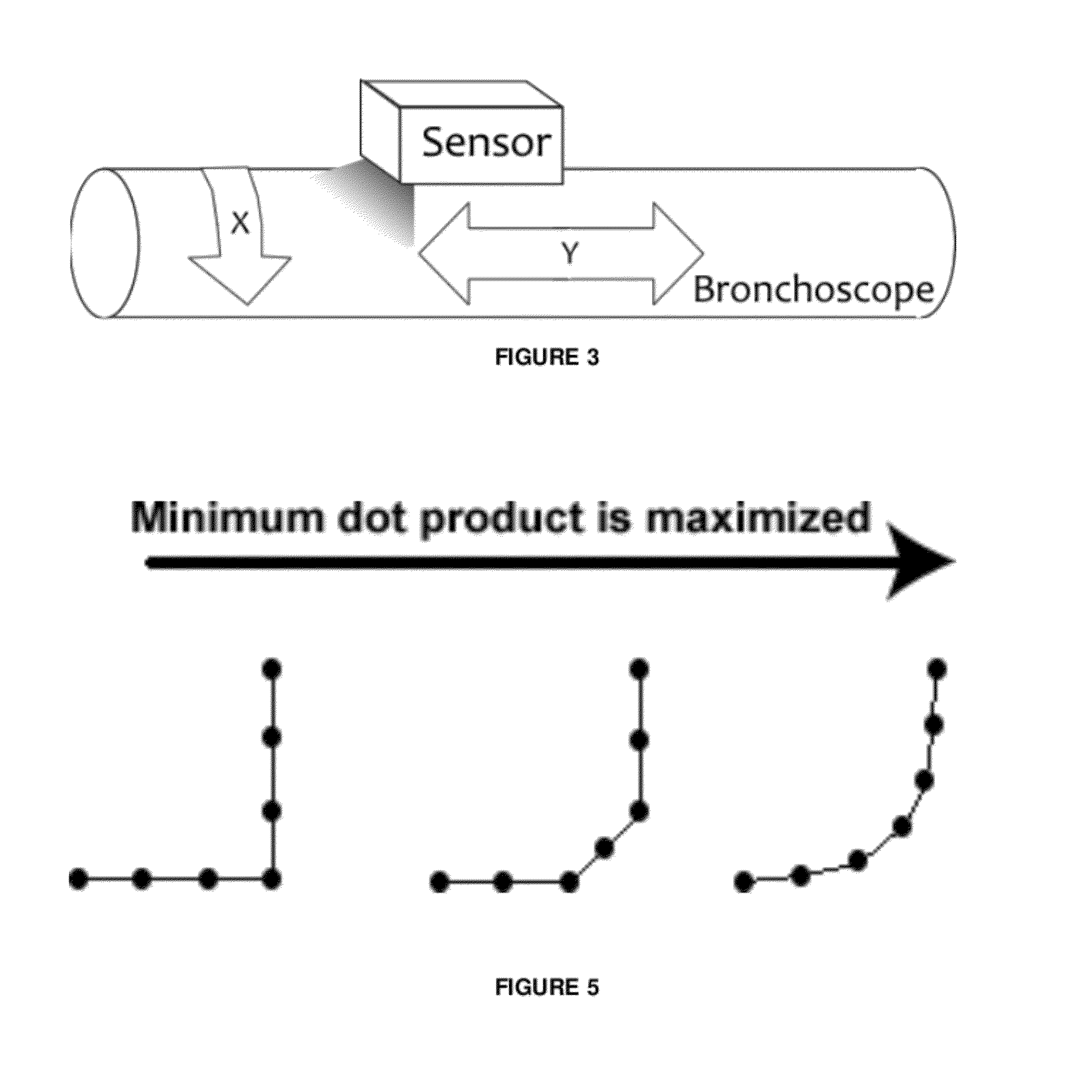
Method and device for determining the location of an endoscope
A technician-free strategy enables real-time guidance of bronchoscopy. The approach uses measurements of the bronchoscope's movement to predict its position in 3D virtual space. To achieve this, a bronchoscope model, defining the device's shape in the airway tree to a given point p, provides an insertion depth to p. In real time, the invention compares an observed bronchoscope insertion depth and roll angle, measured by an optical sensor, to precalculated insertion depths along a predefined route in the virtual airway tree to predict a bronchoscope's location and orientation.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
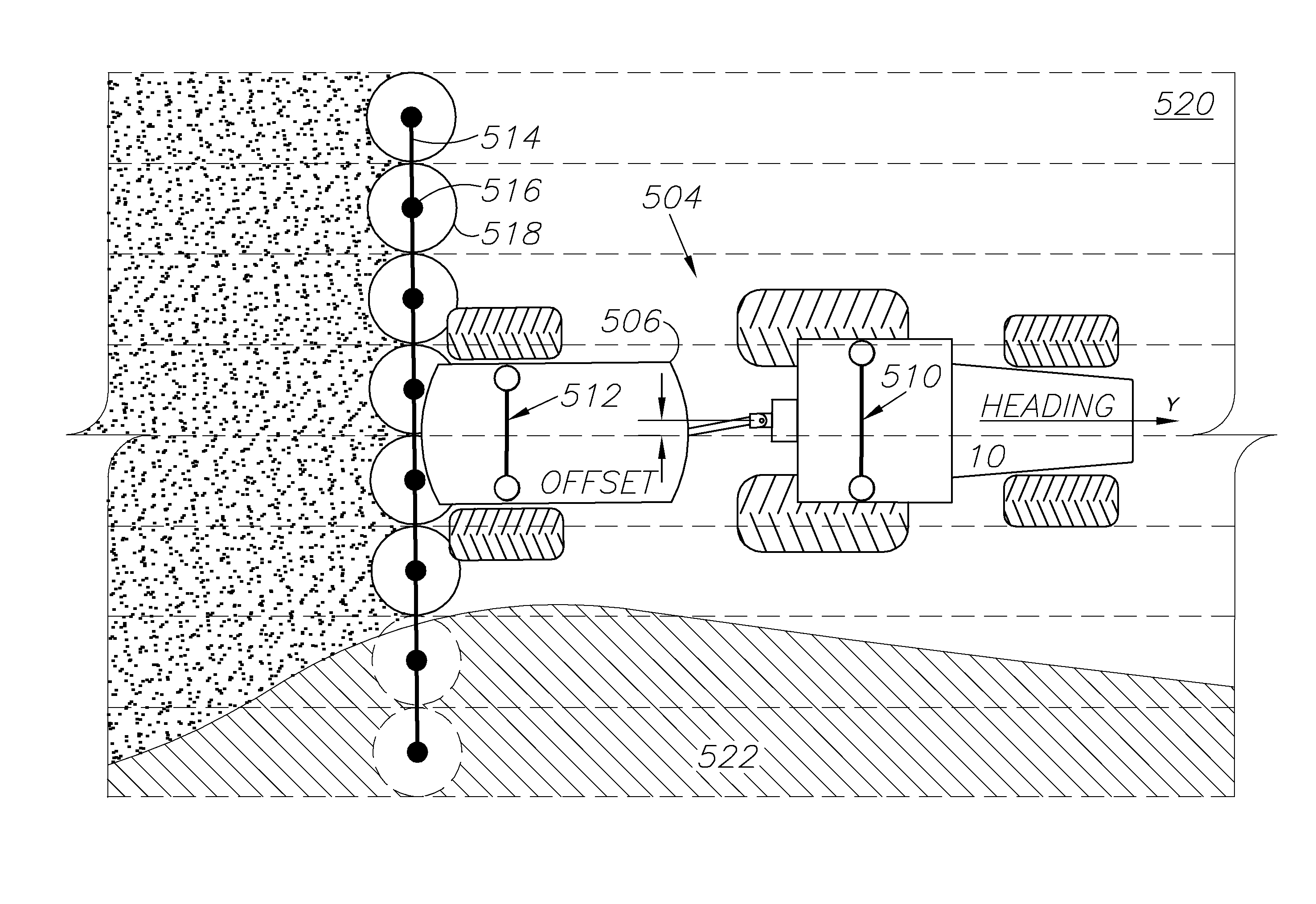
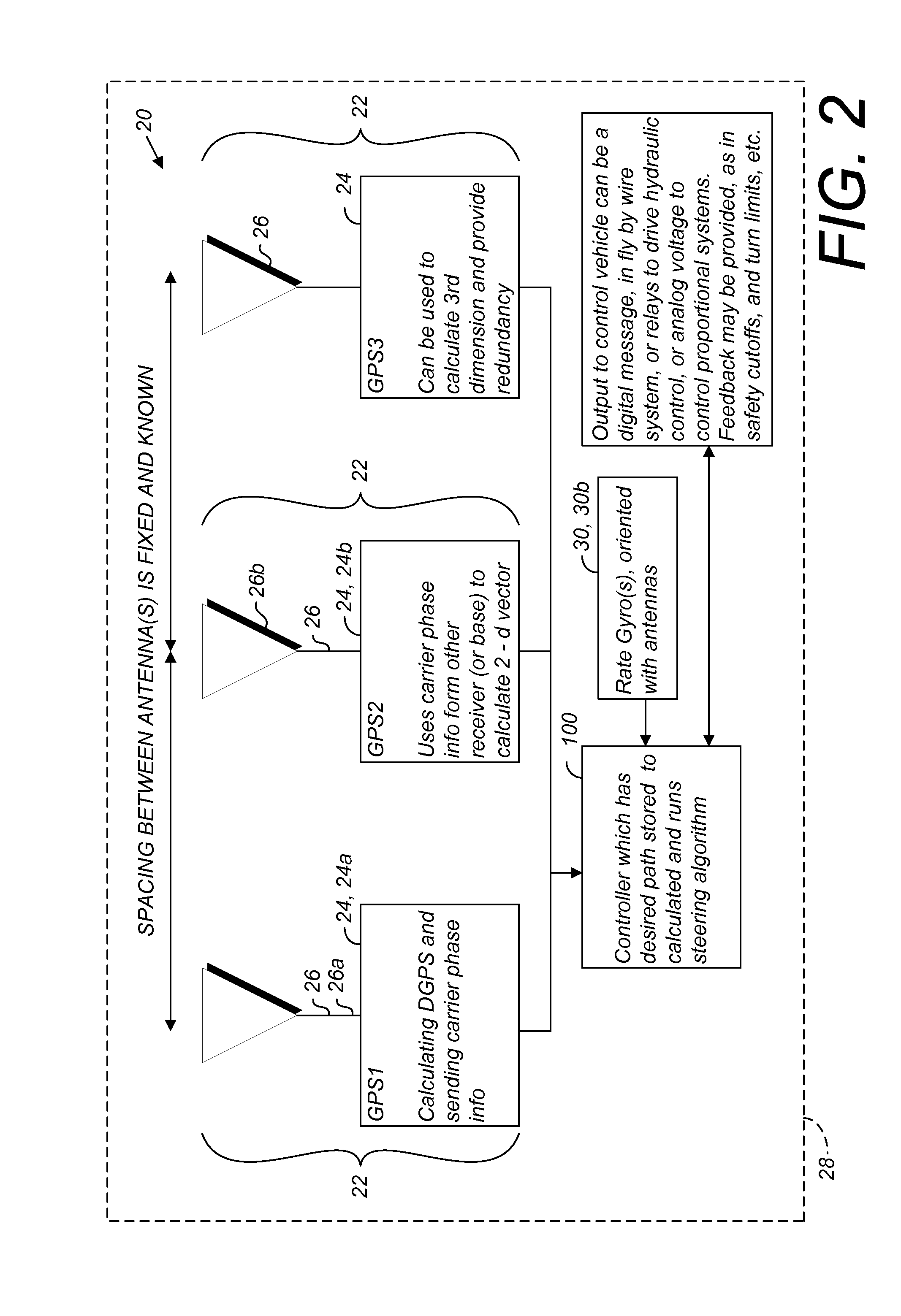
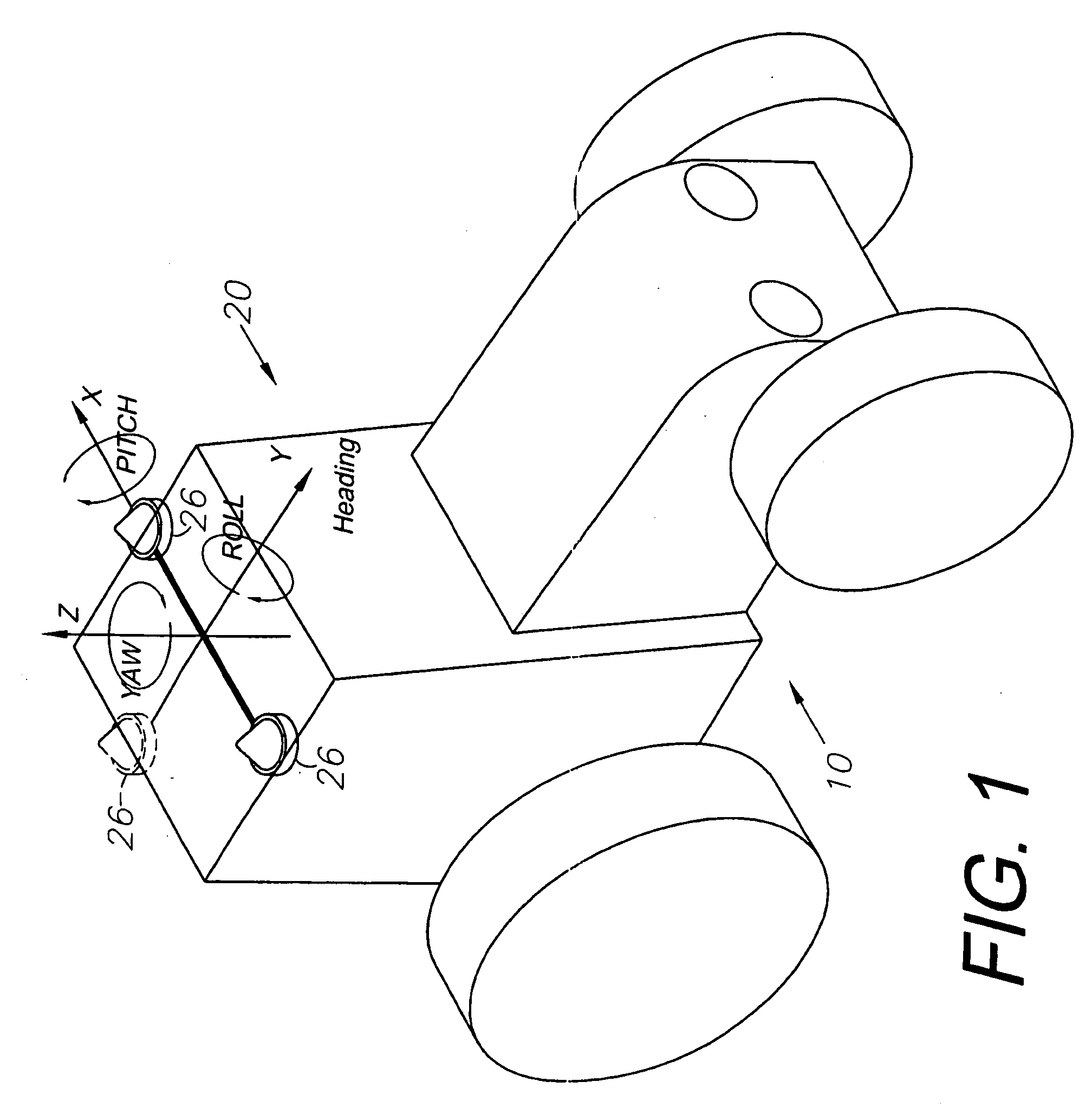
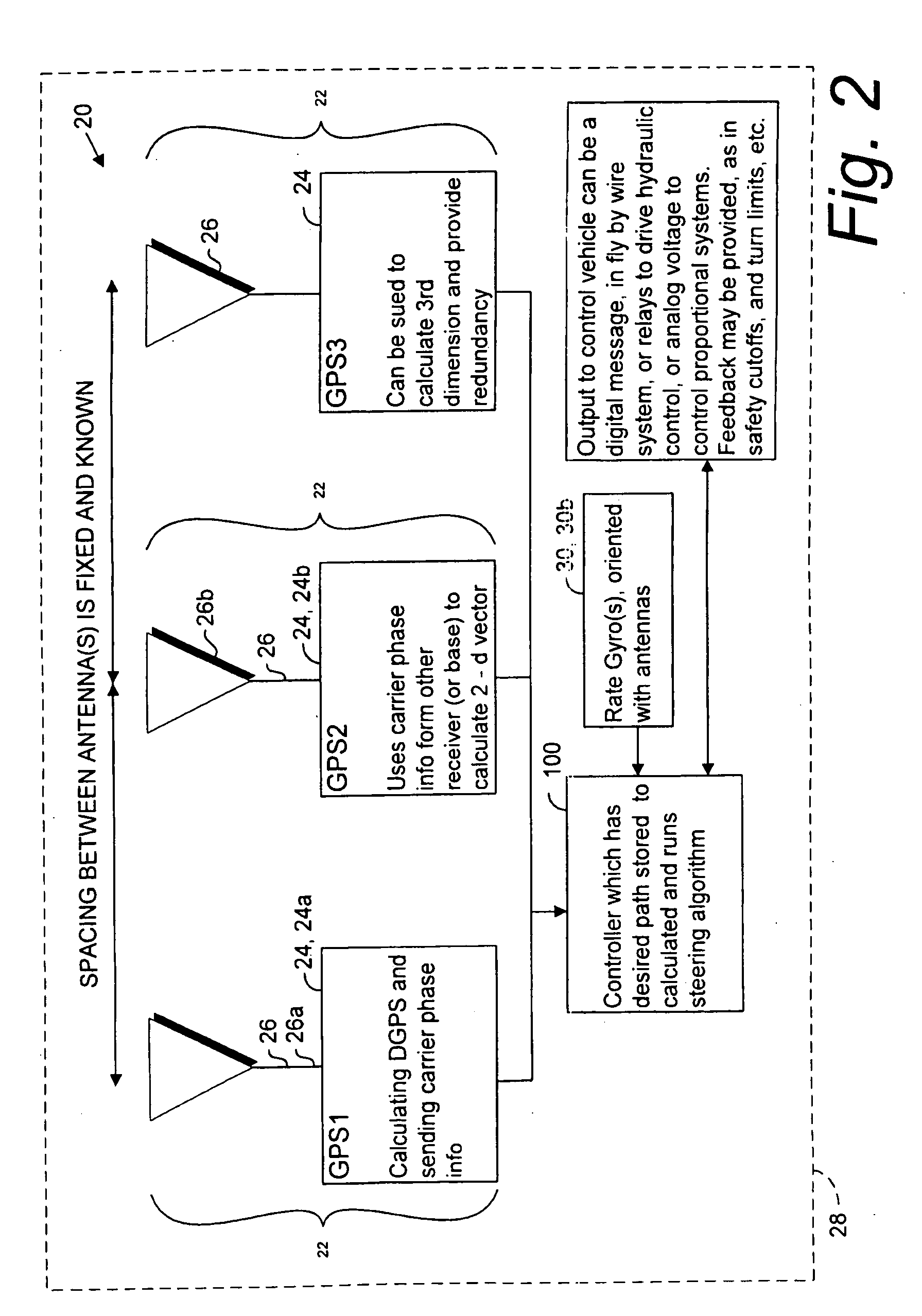
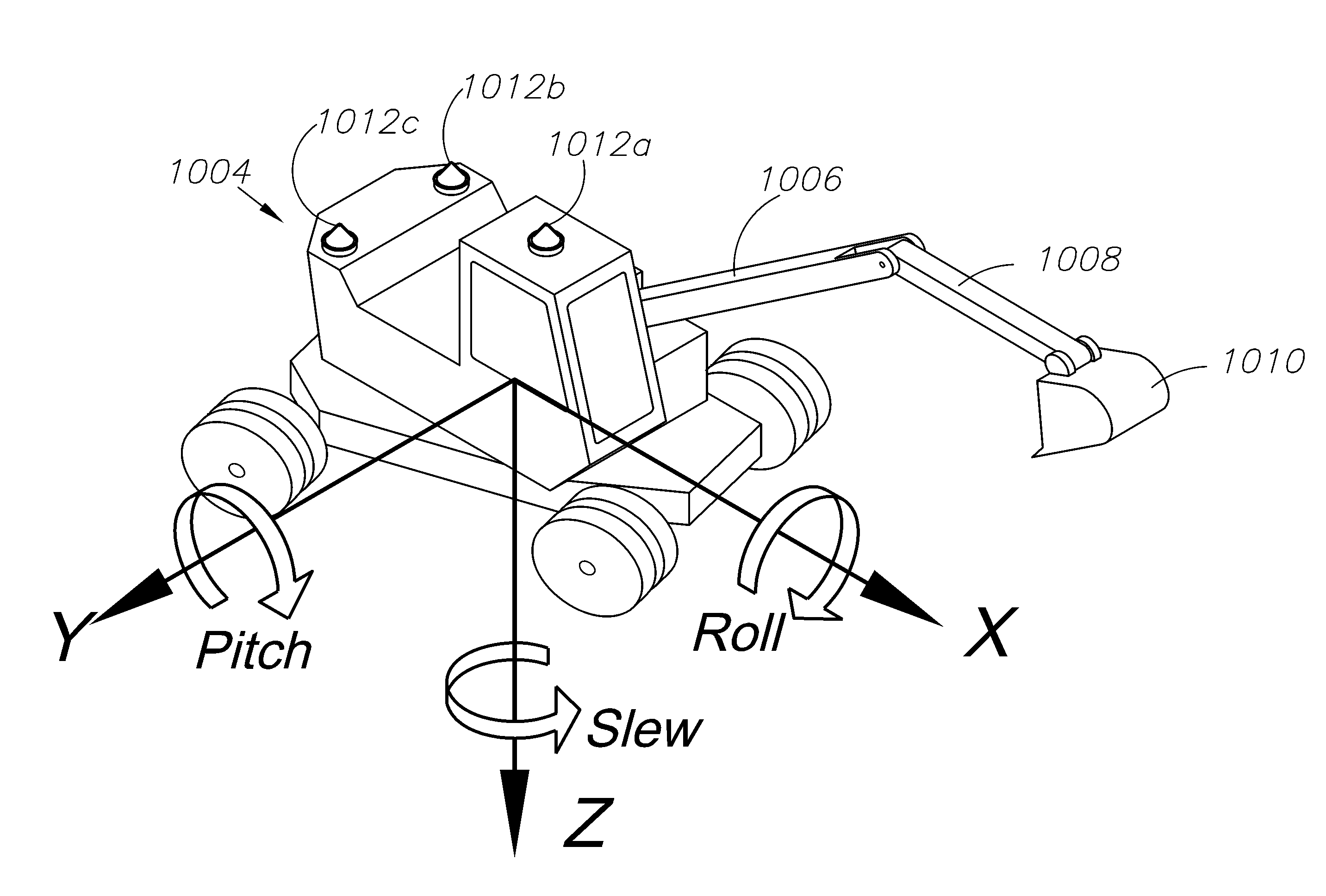
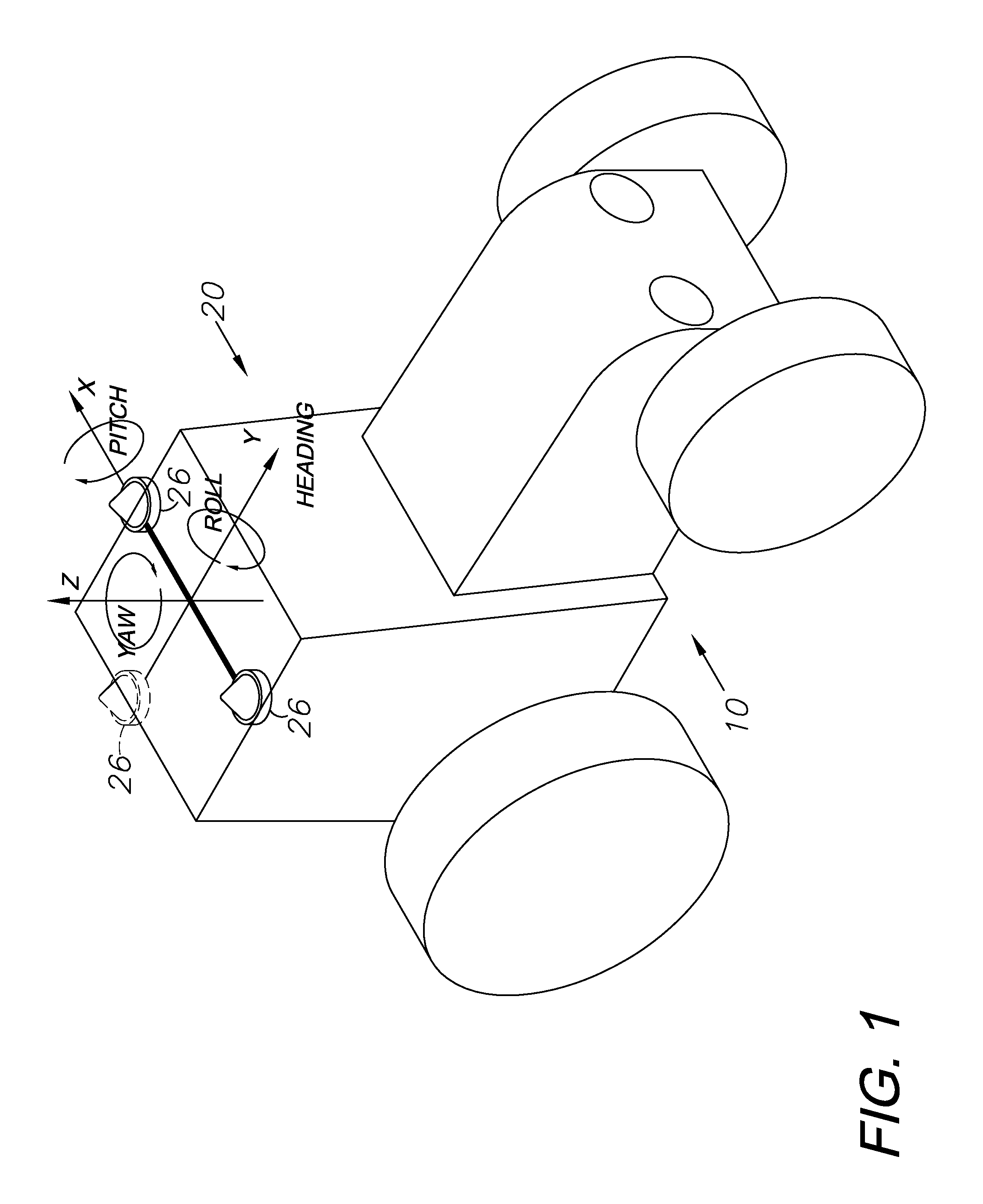
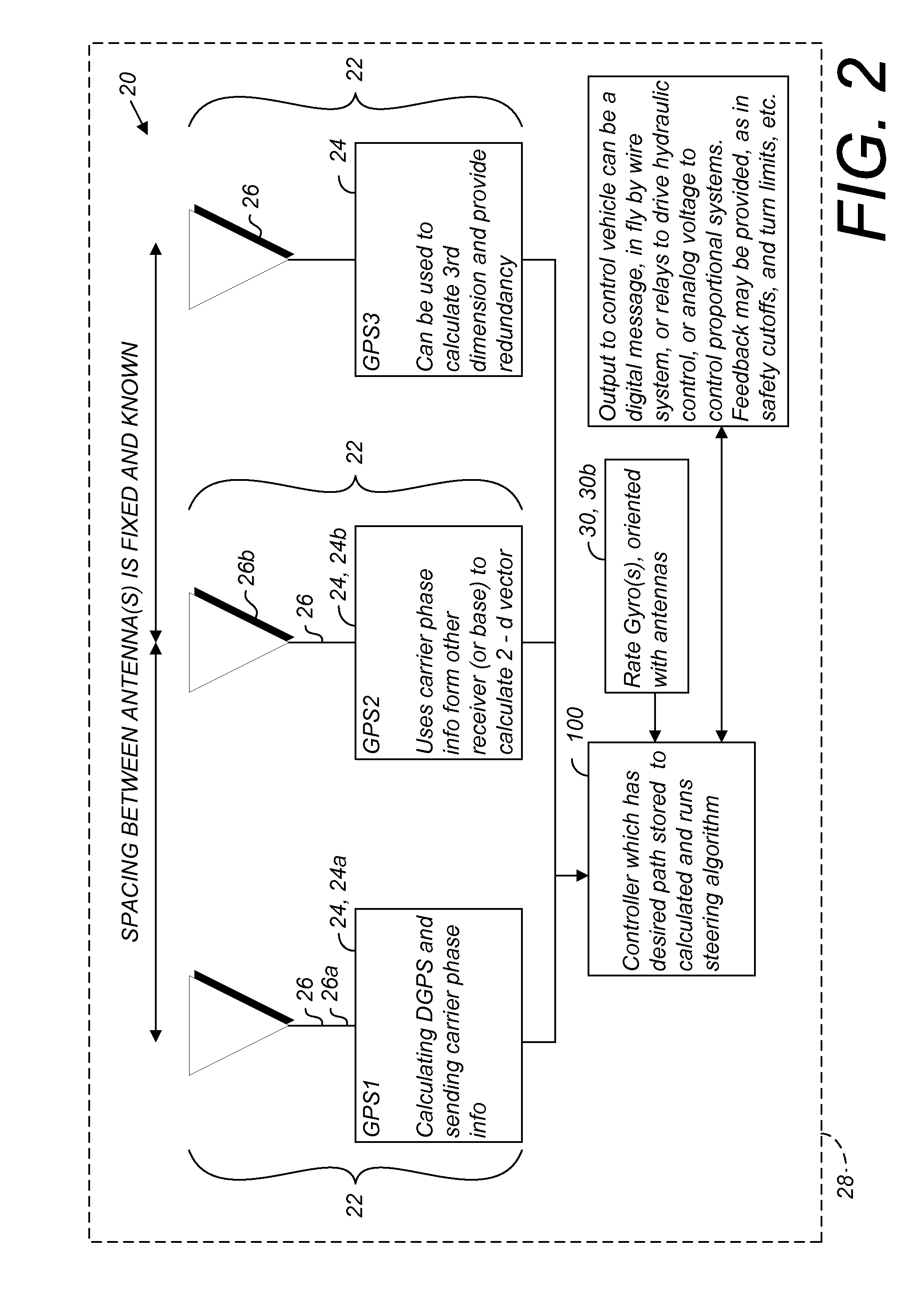
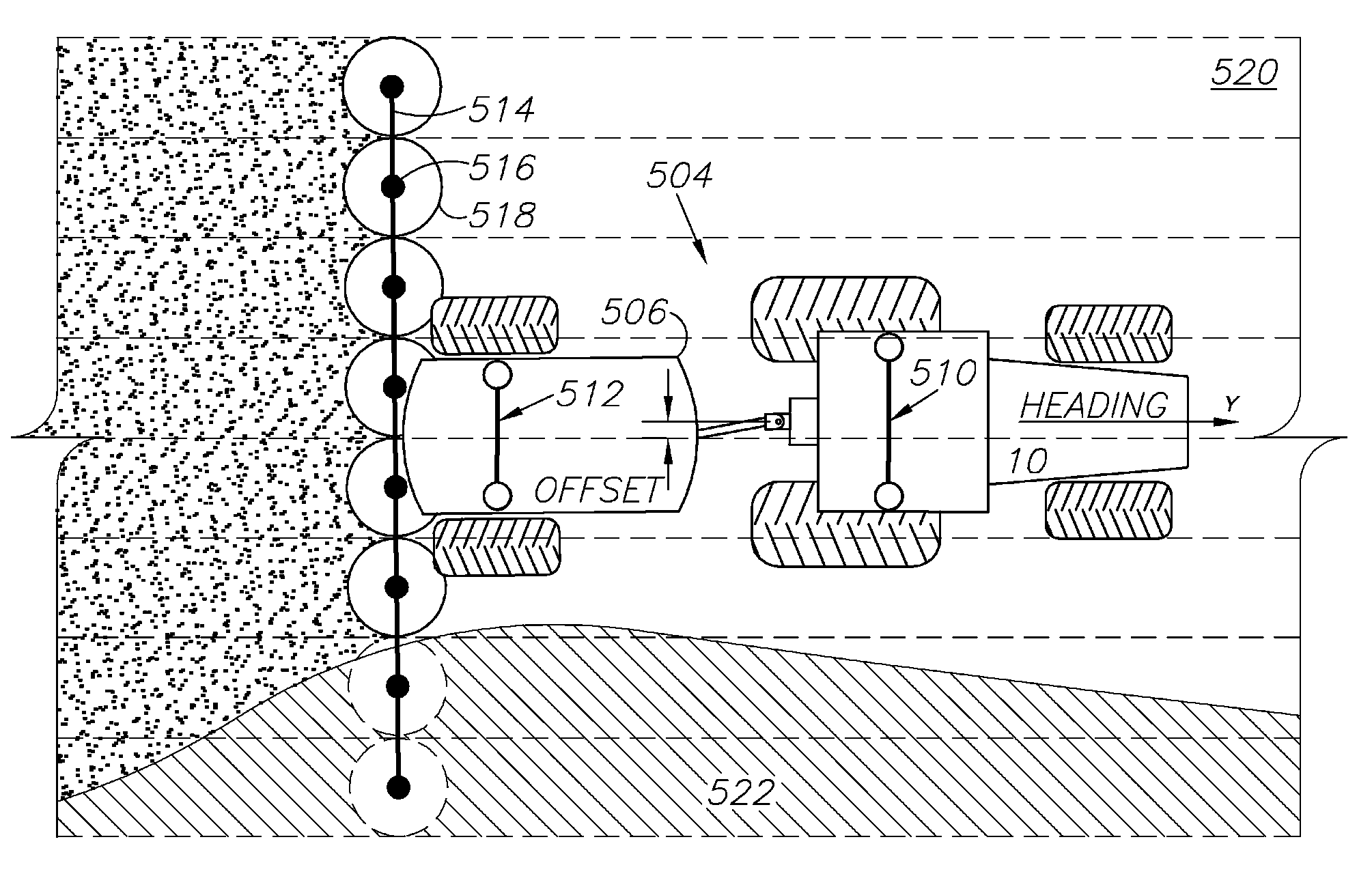
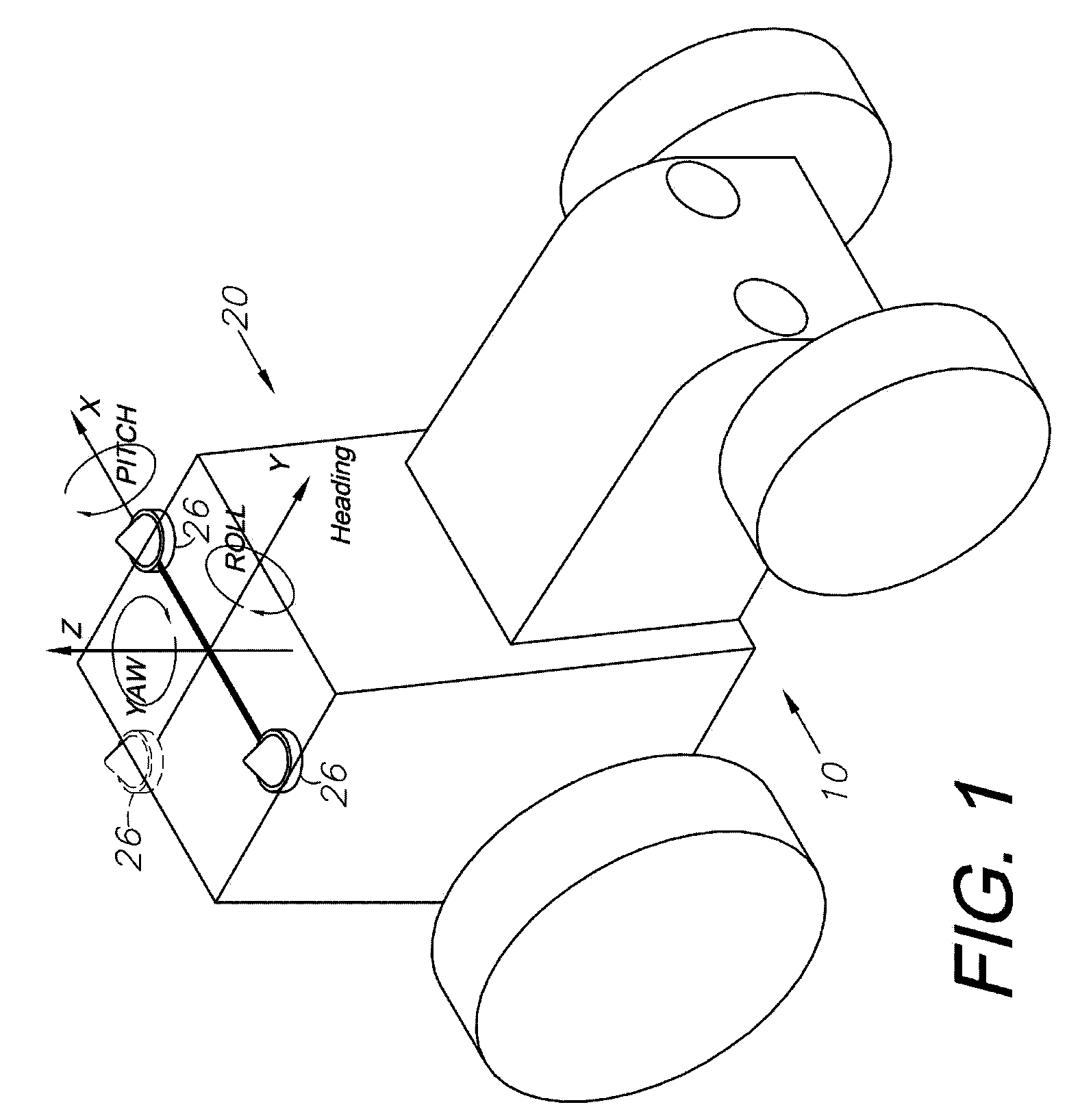
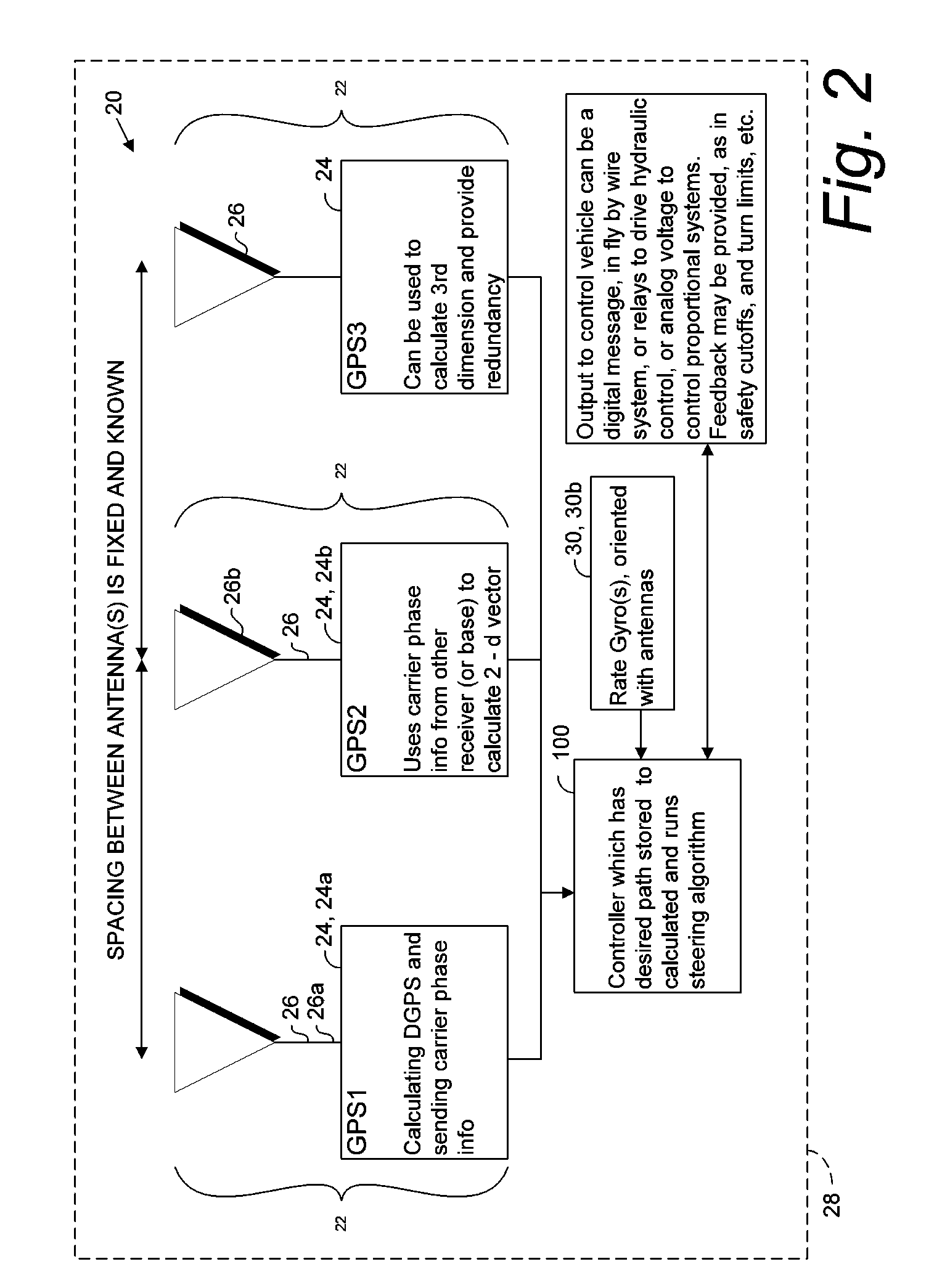
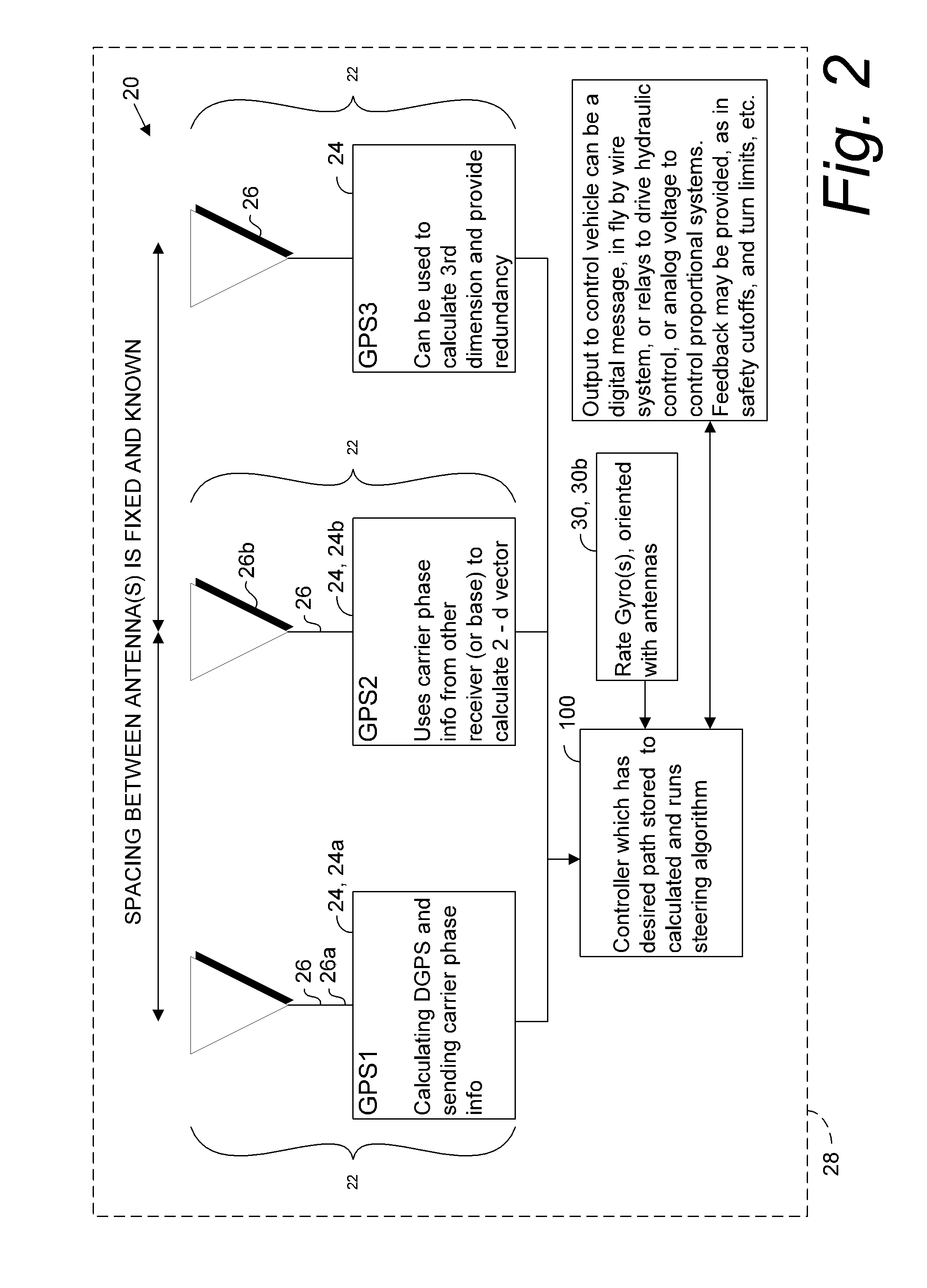
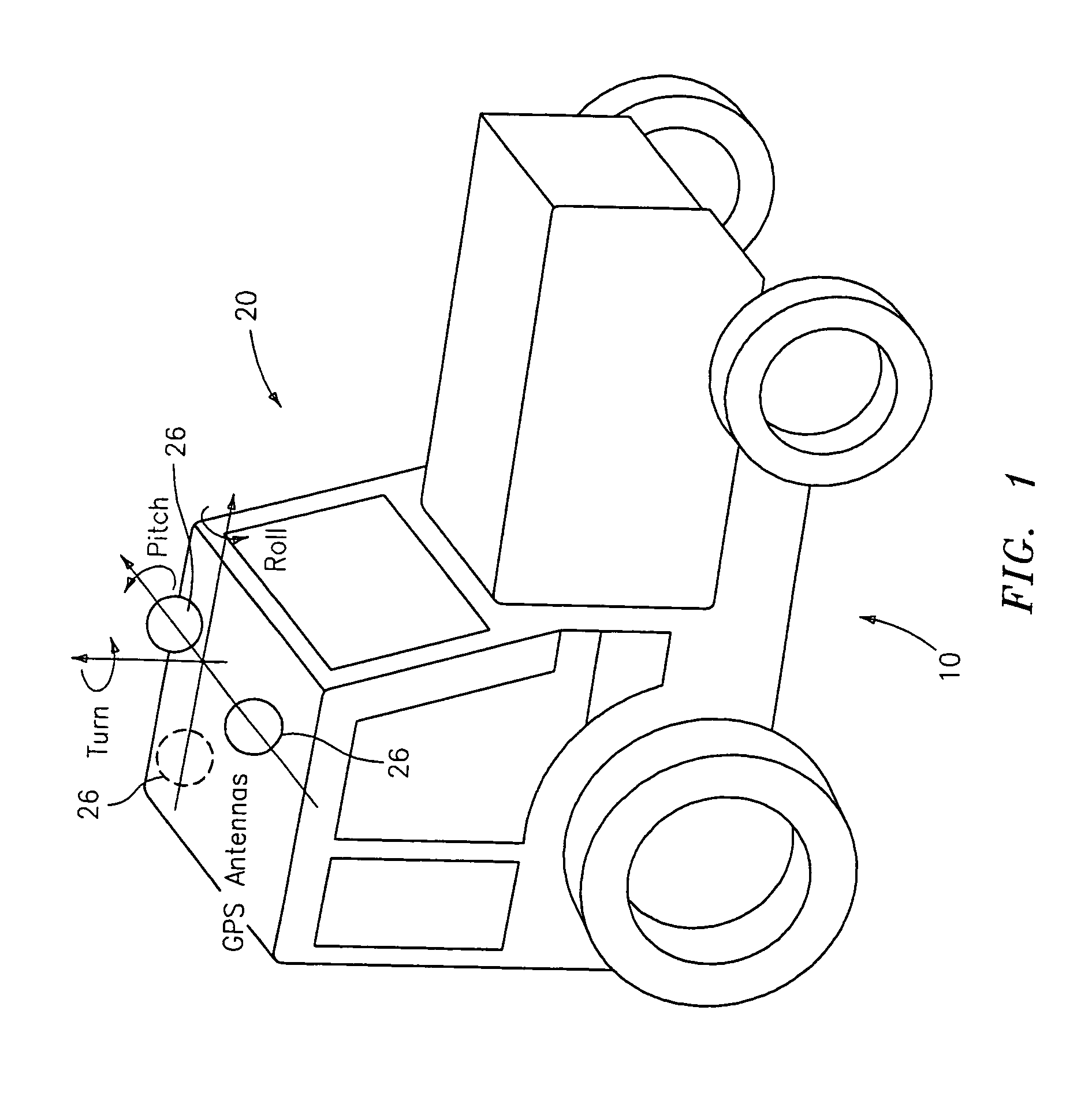
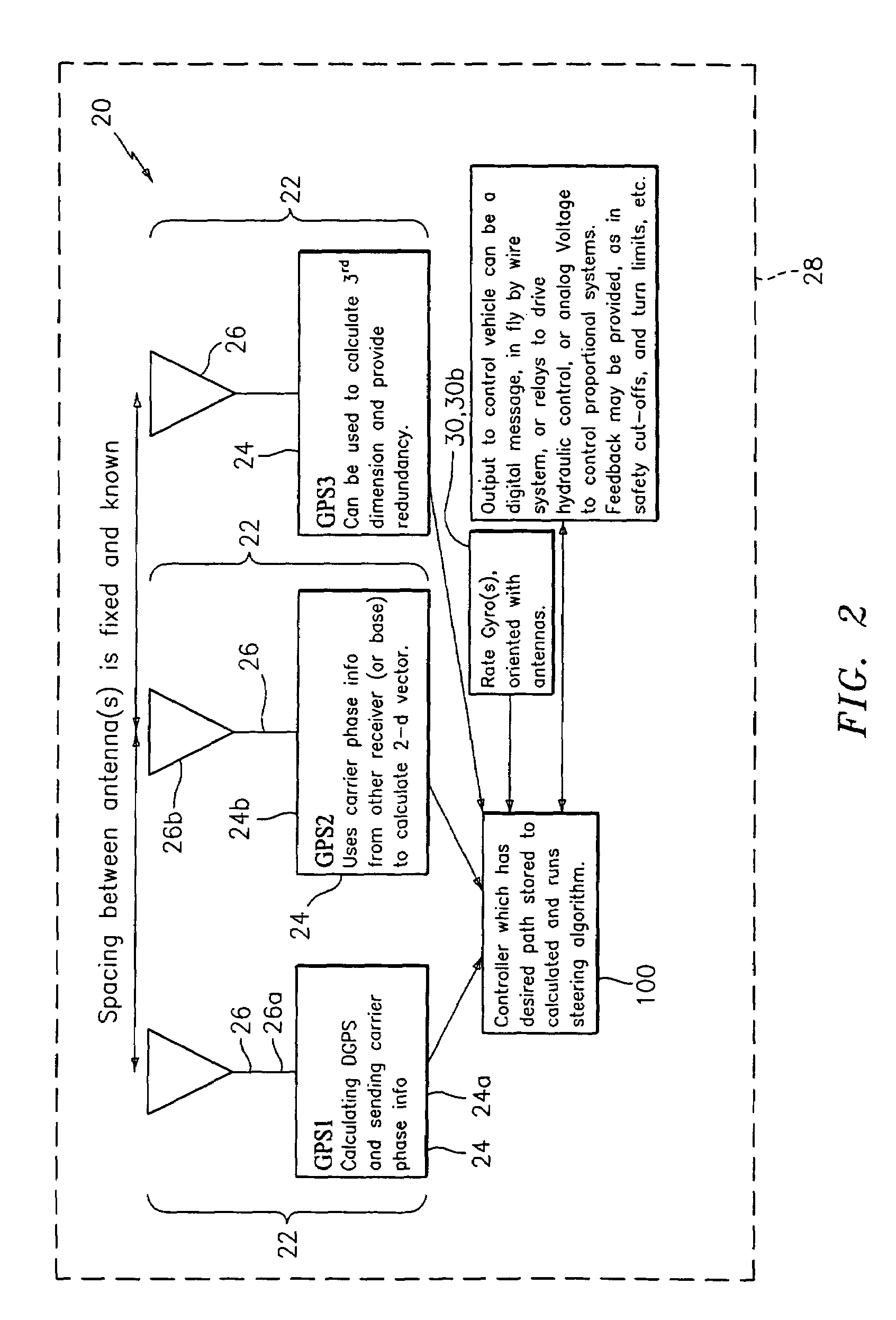
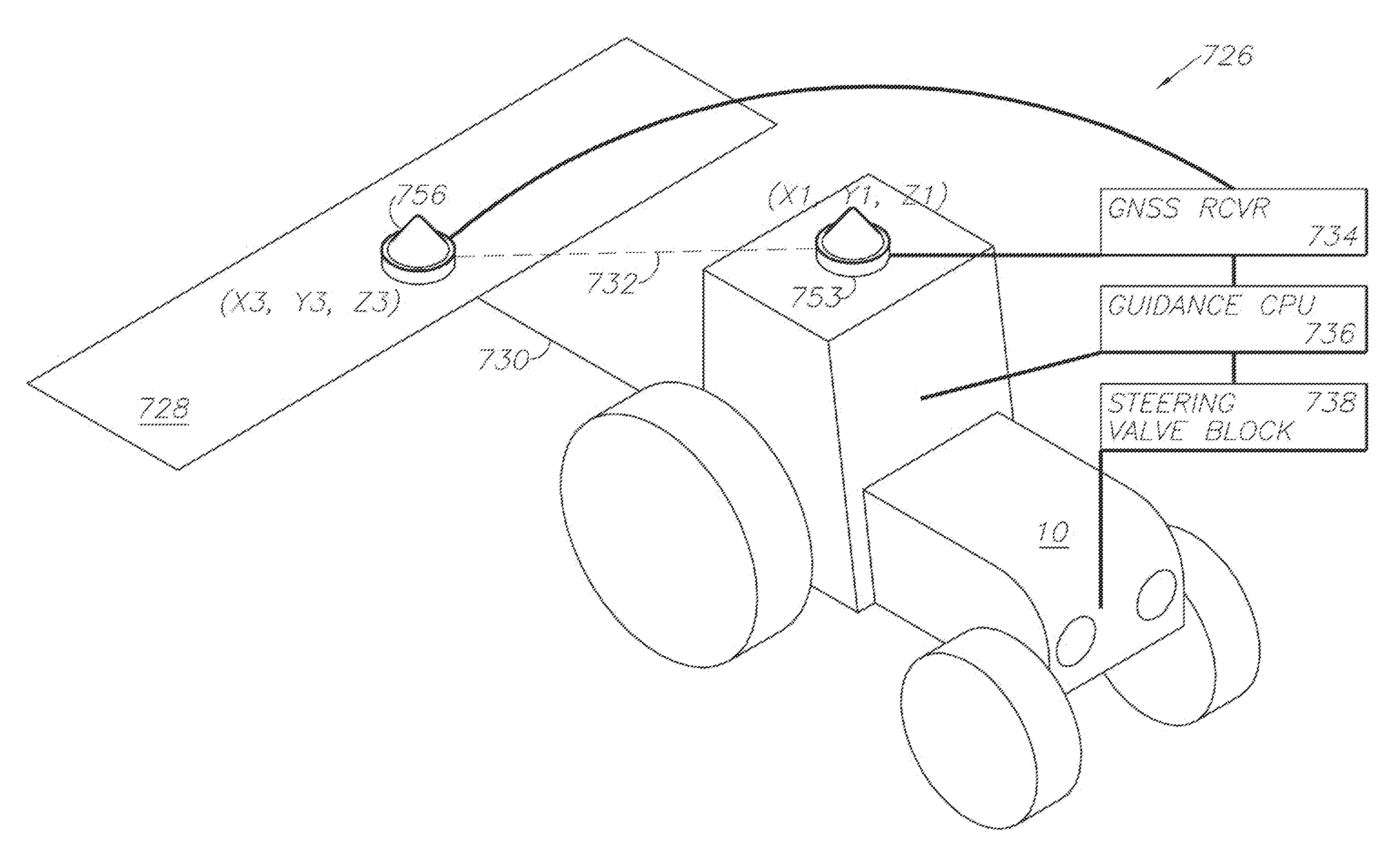
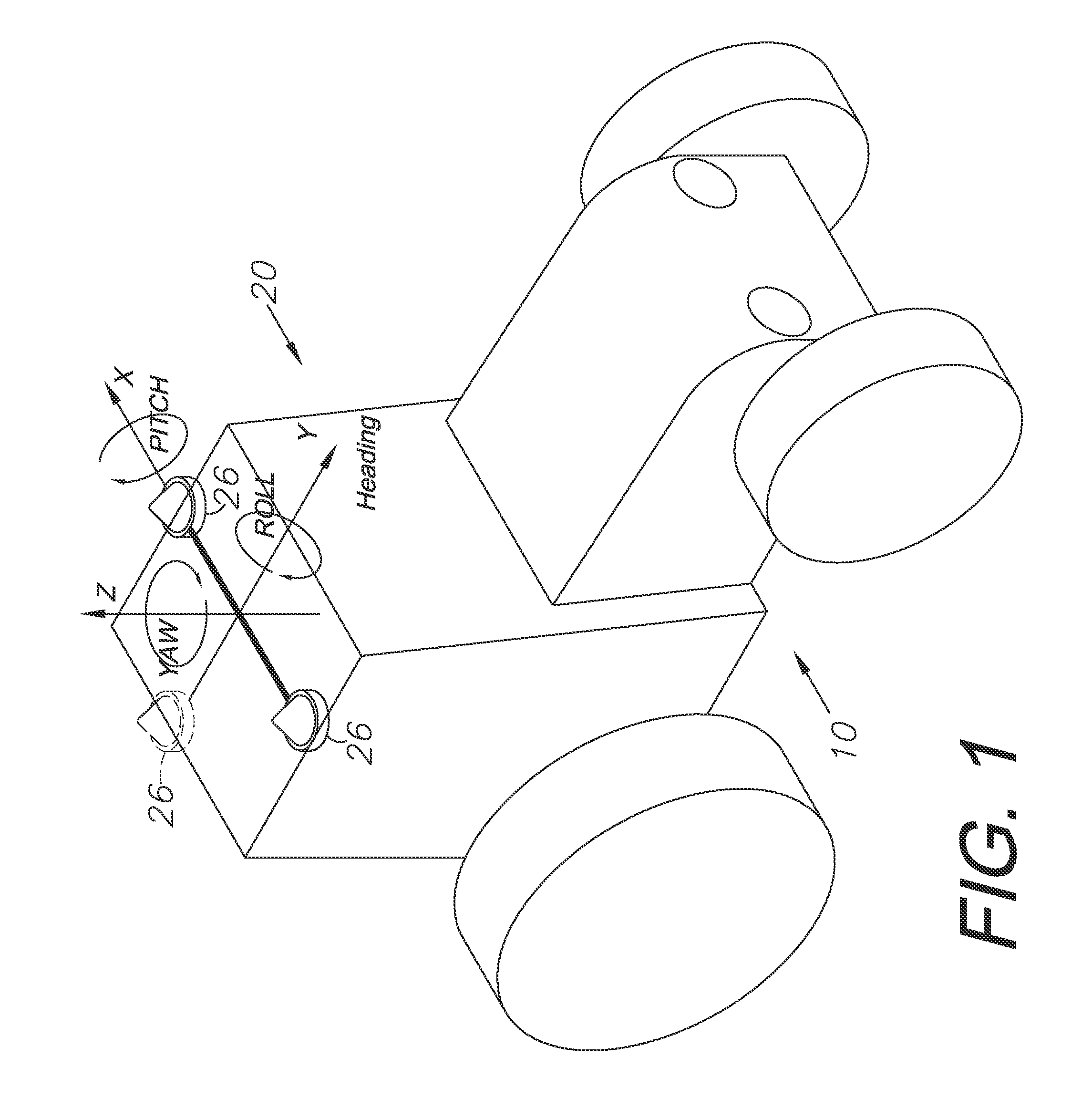
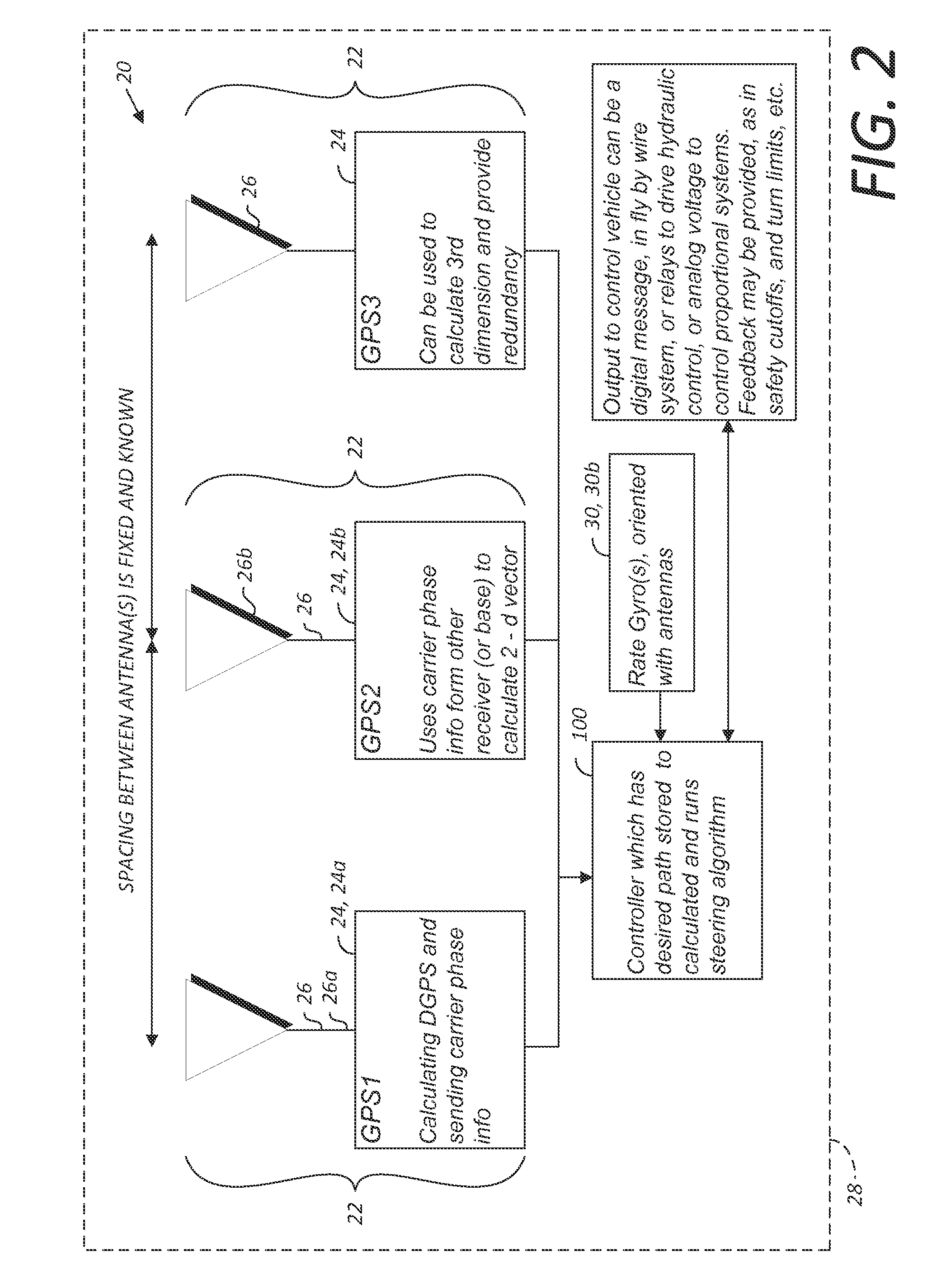
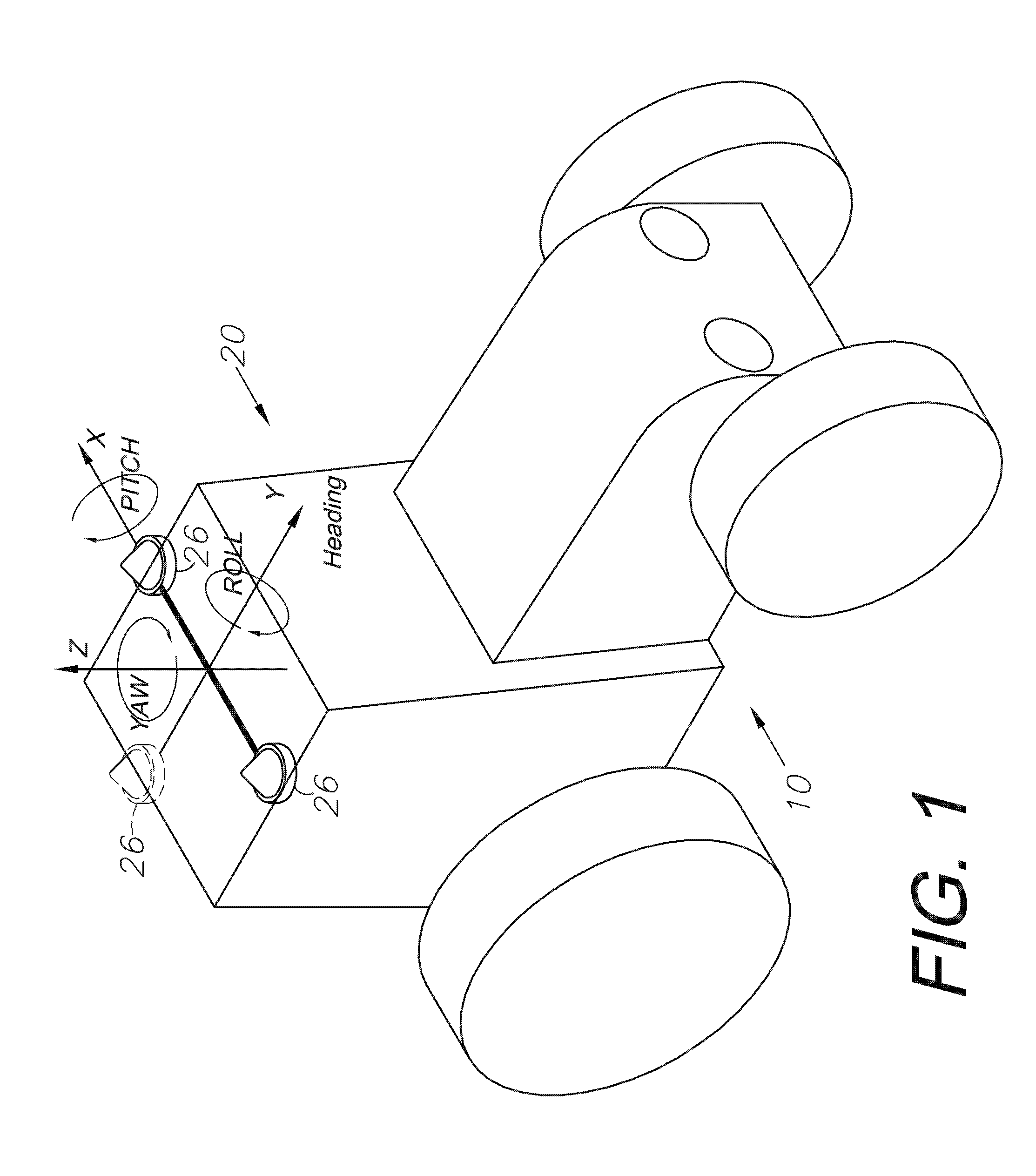
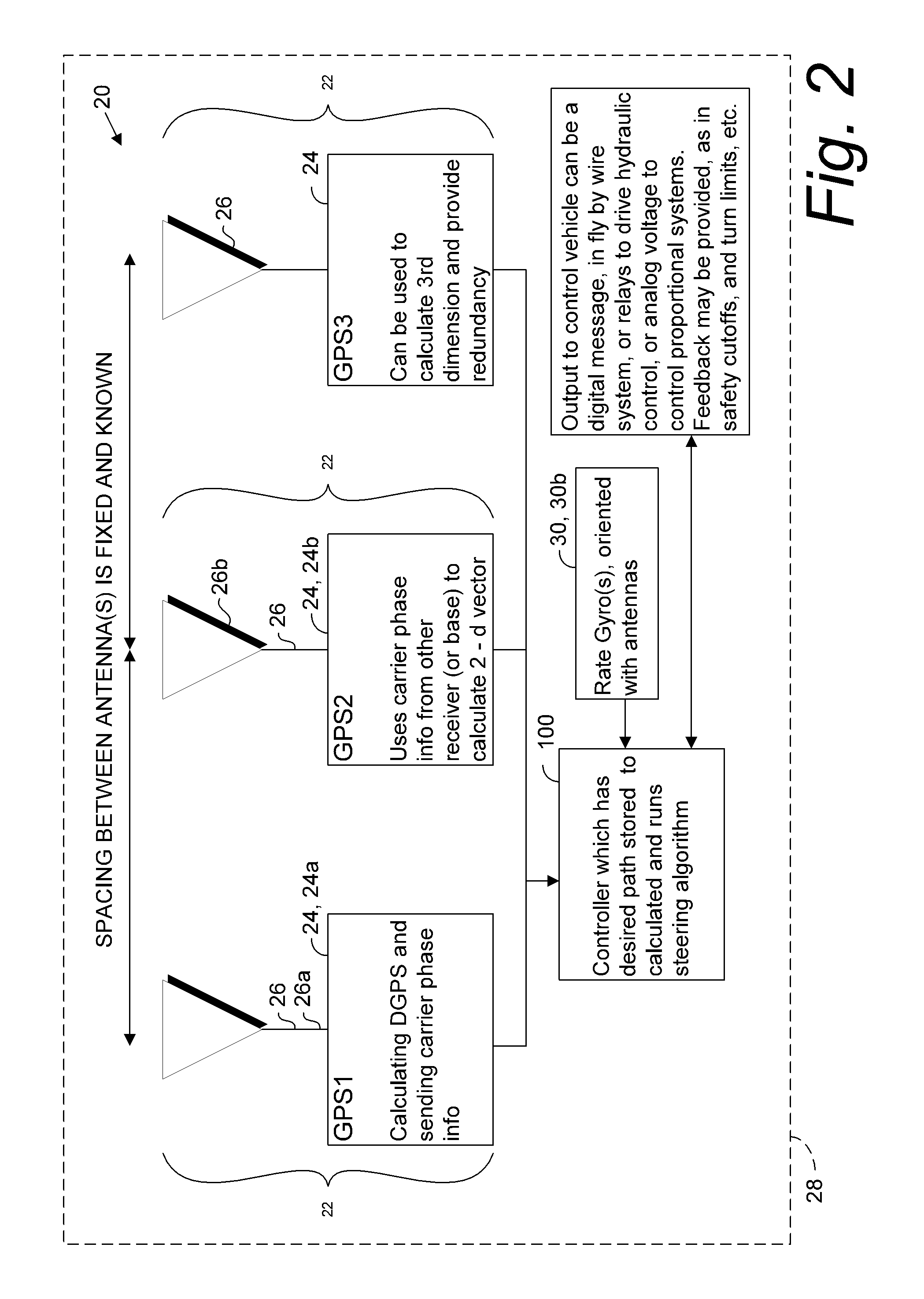
GNSS and optical guidance and machine control
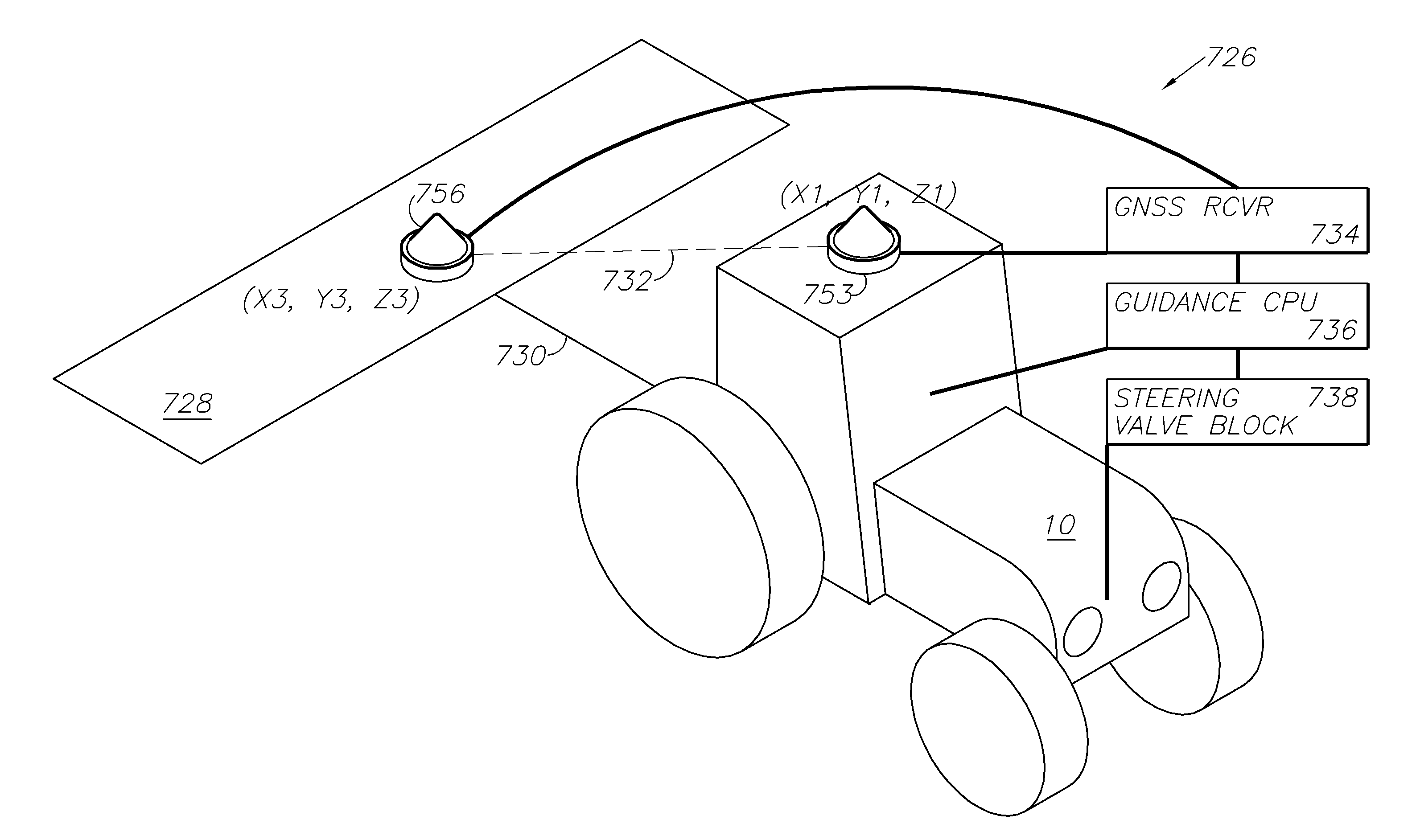
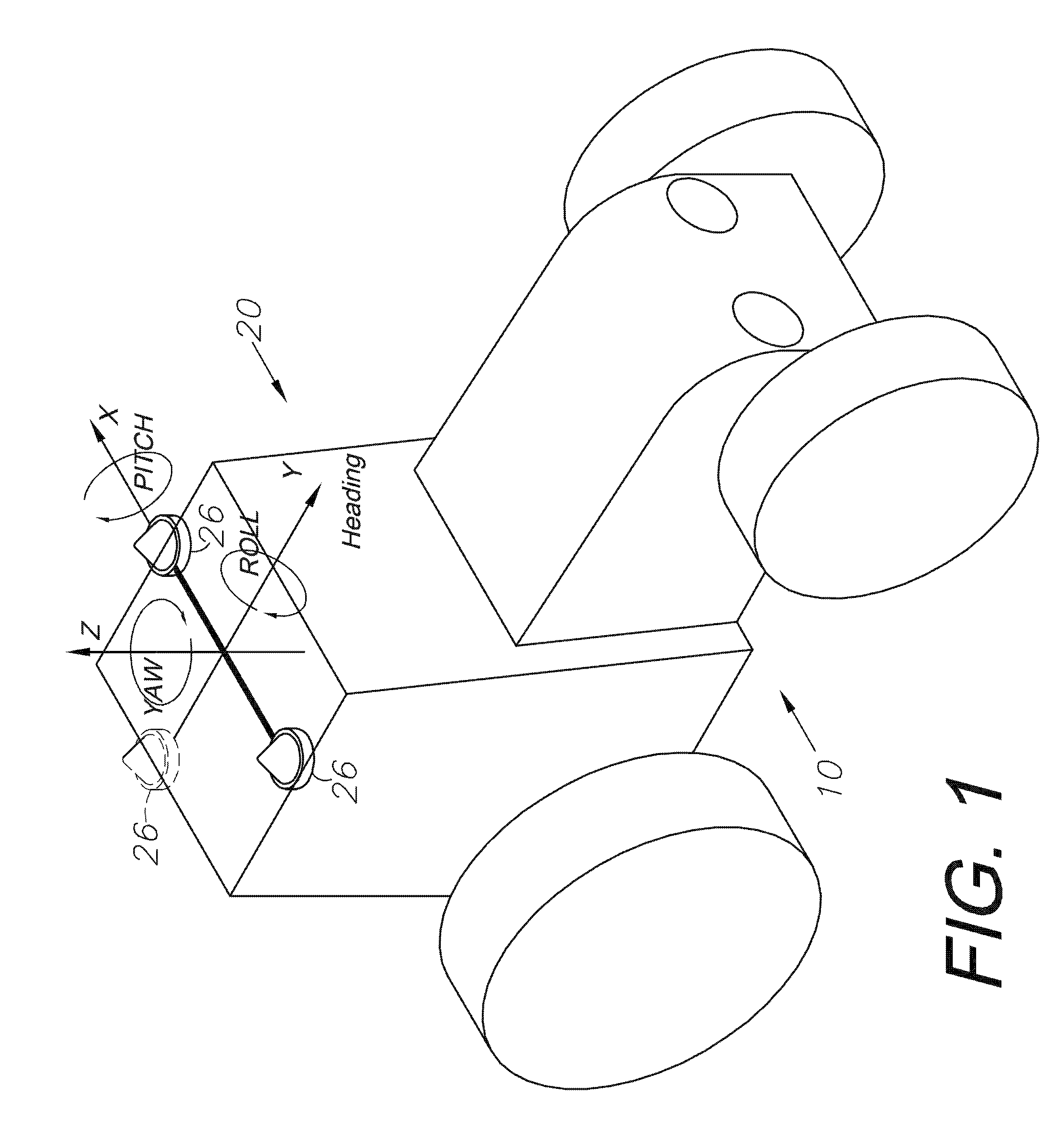
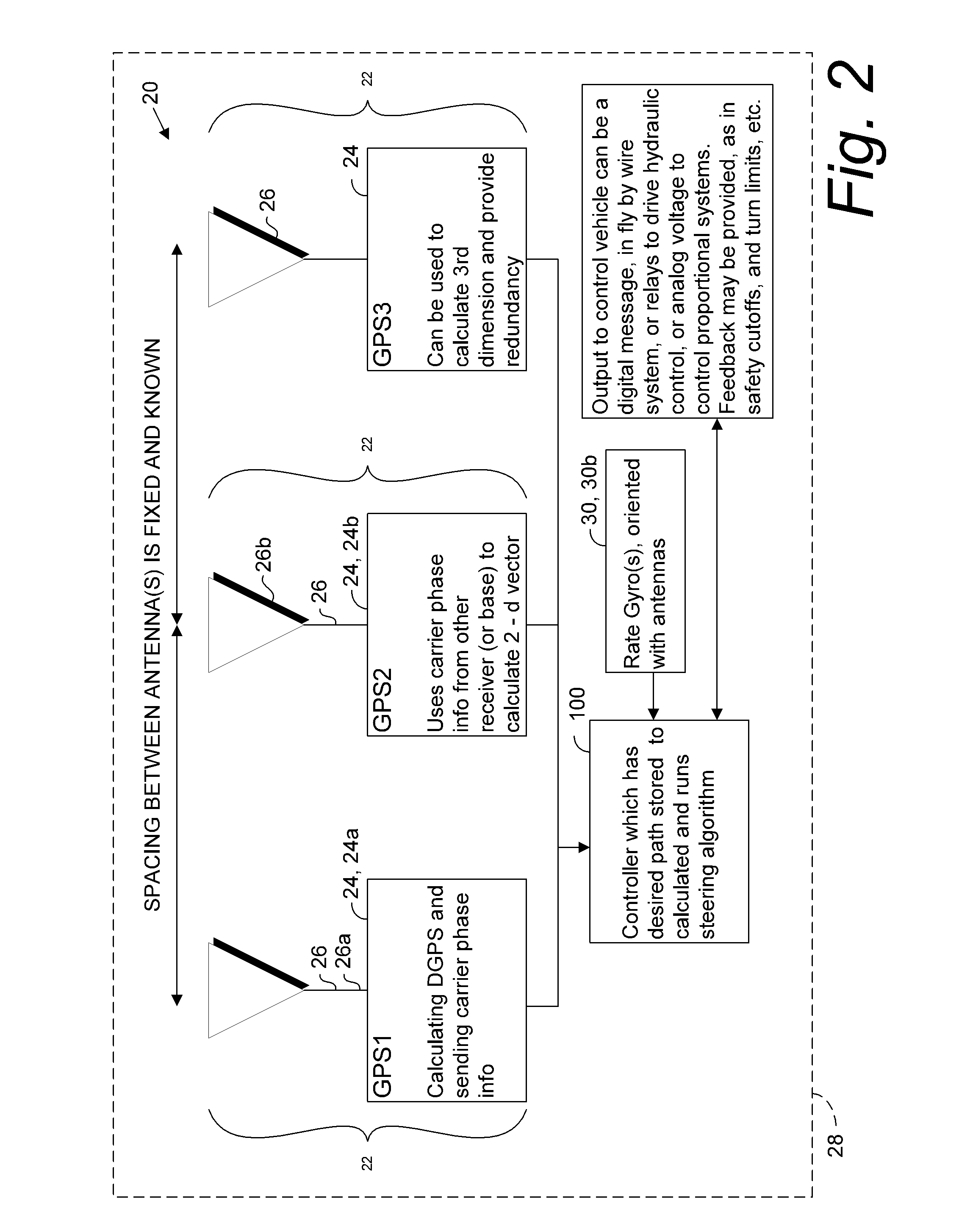
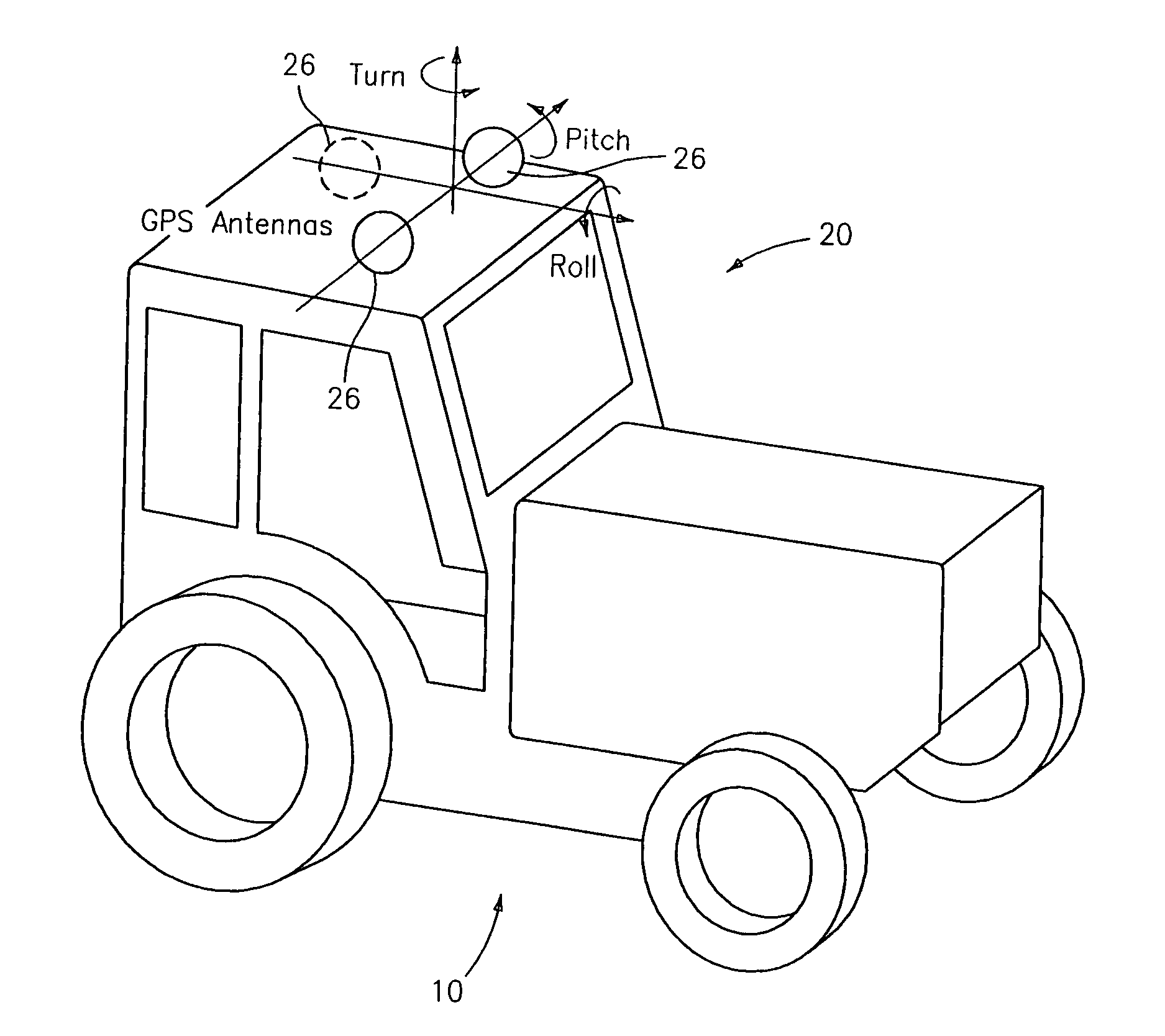
ActiveUS20140324291A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCarrier signalSteering control
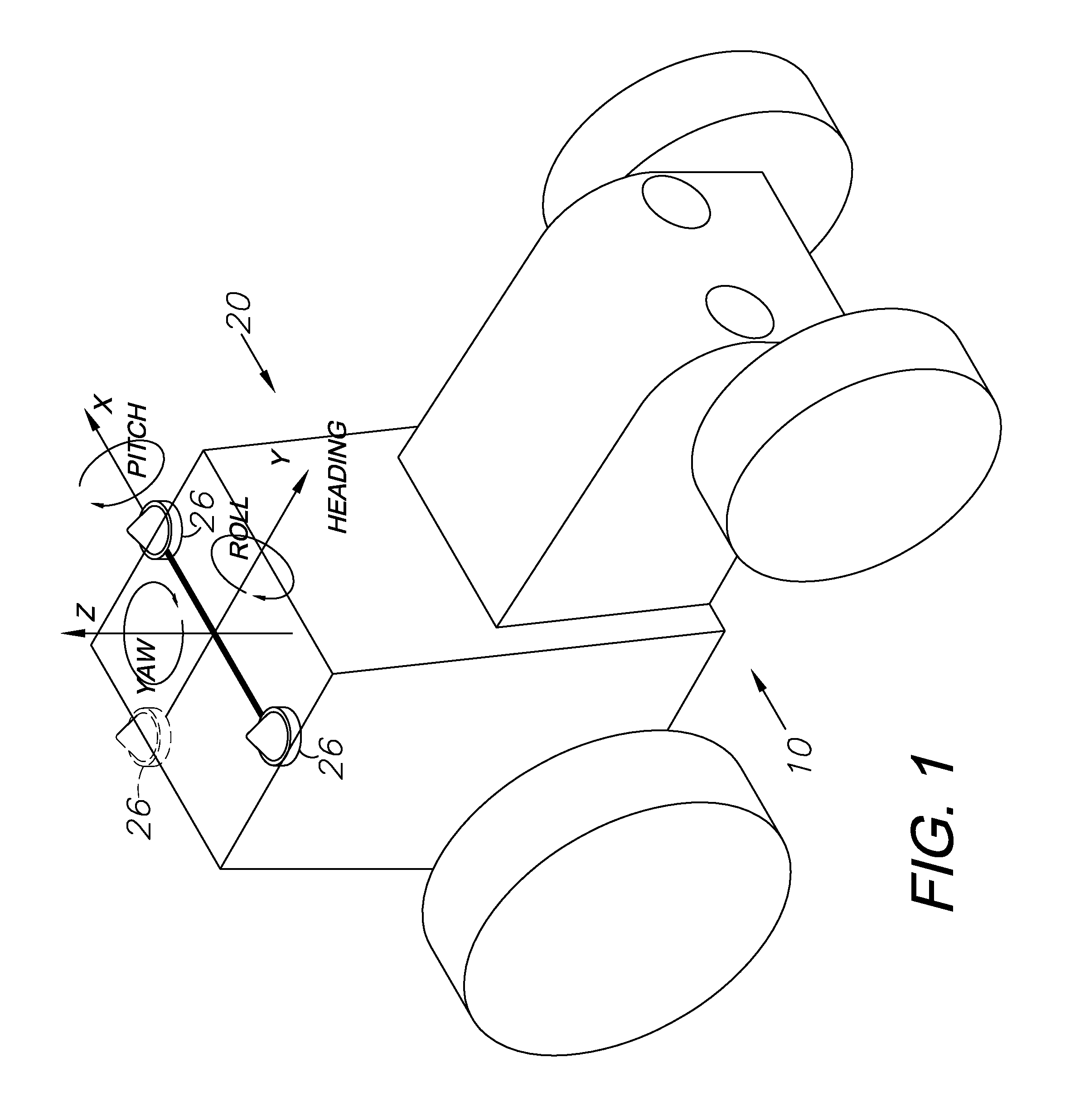
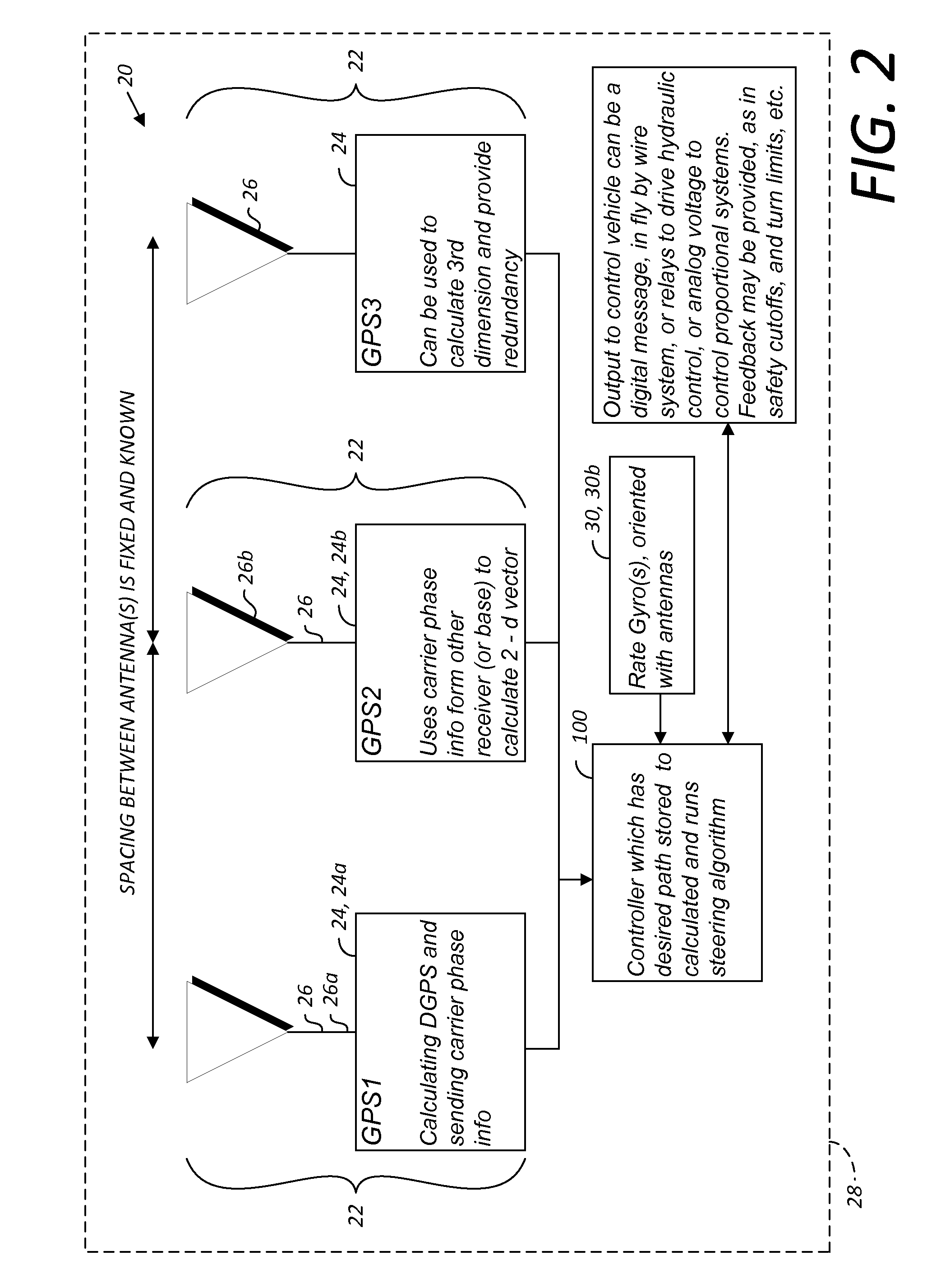
A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Relative orientations and attitudes between tractors and implements can be determined using optical sensors and cameras. Laser detectors and rangefinders can also be used.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
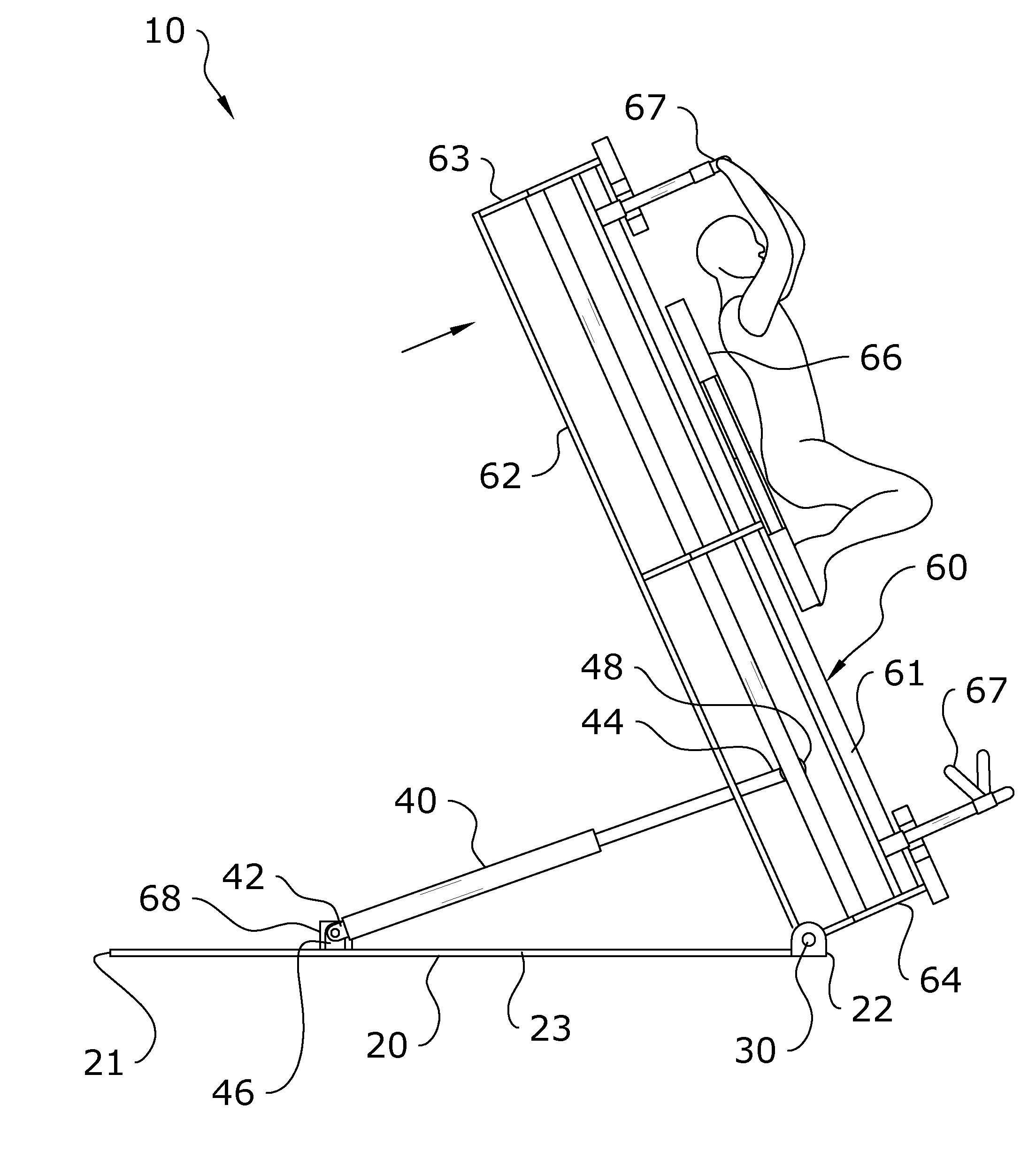
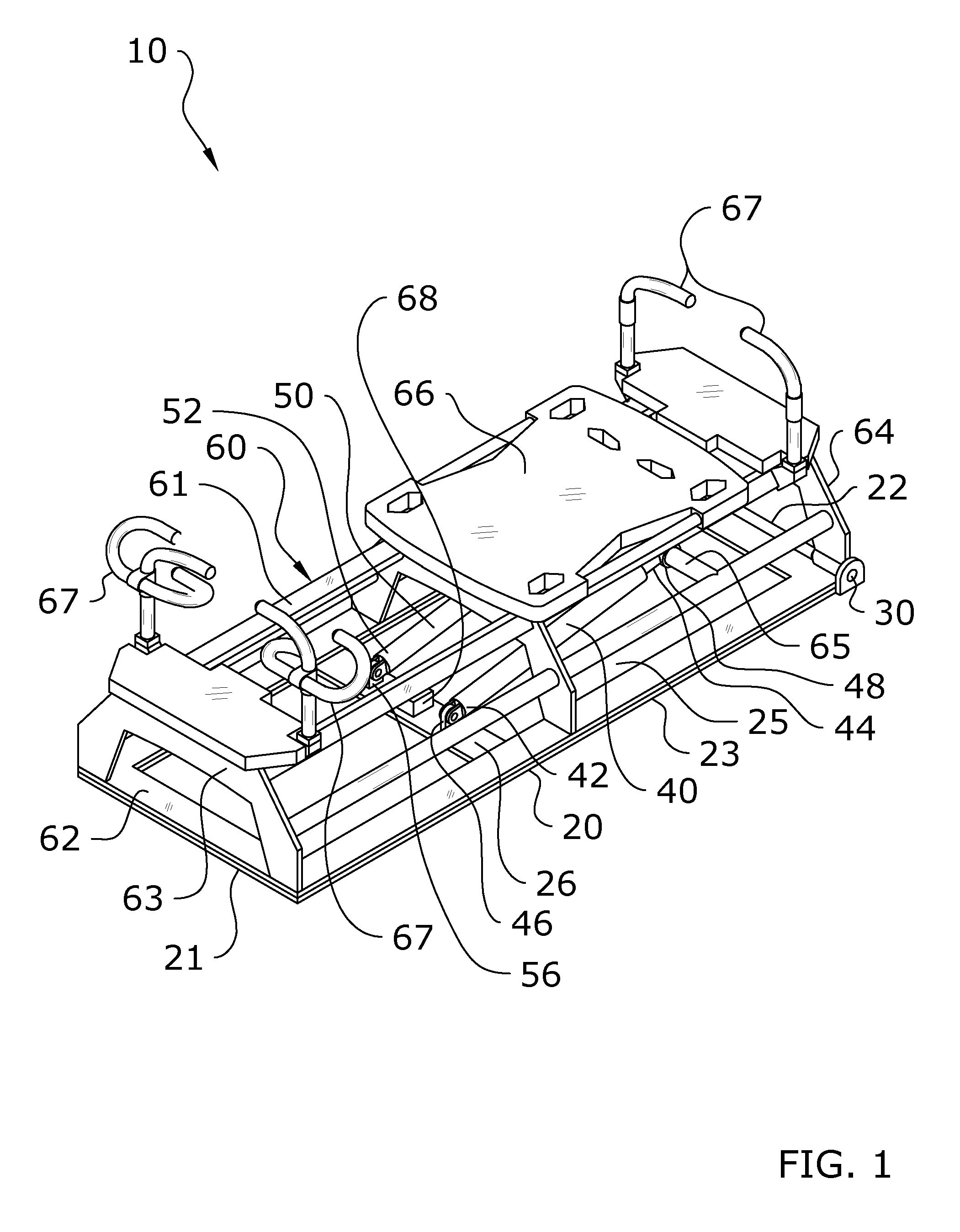
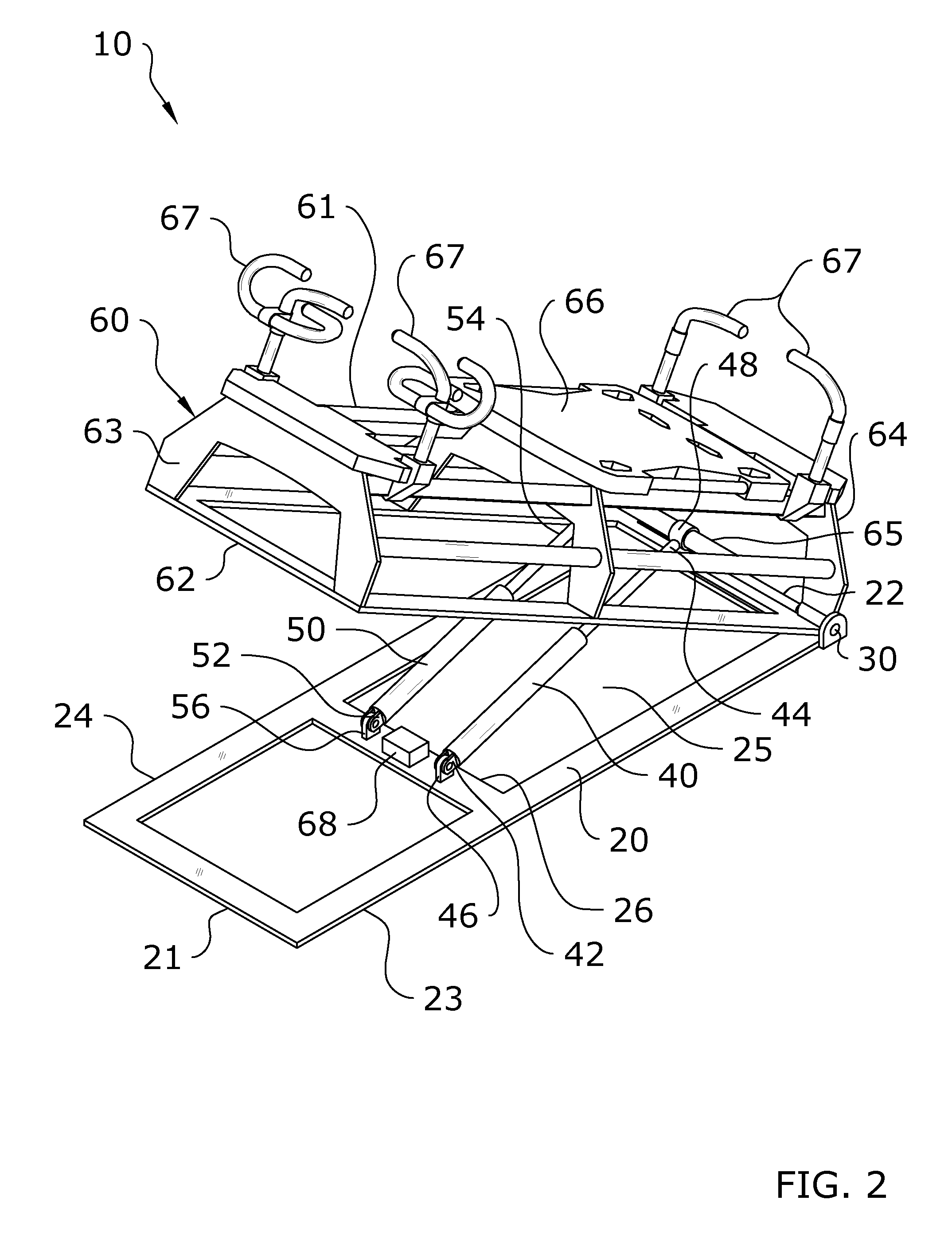
Multi-axis Adjustable Exercise Machine
ActiveUS20150343250A1Increases level stimulationImprove energy consumptionStiltsMovement coordination devicesEngineeringMulti axis
A multi-axis adjustable exercise machine which is pivotable about both a pitch axis and a roll axis with respect to a base for allowing an exerciser to perform a wide range of exercises on a pitched or rolled exercise machine. The multi-axis adjustable exercise machine generally includes an exercise machine which is adjustable with respect to a base. The exercise machine may be pivoted about a roll axis to adjust the roll angle of the exercise machine or may be pivoted about a pitch axis to adjust the pitch angle of the exercise machine. One or more actuators may be connected between the base and the exercise machine to effectuate the pivoting of the exercise machine about either or both axes with respect to the base.
Owner:LAGREE TECH INC
Combined GNSS gyroscope control system and method
ActiveUS20080269988A1Avoid crossingEasy to correctSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering controlLateral movement
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS8639416B2Easy to correctAnalogue computers for trafficSteering initiationsGyroscopeMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other, and snow grooming equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Multi-antenna GNSS control system and method
ActiveUS20110054729A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficSteering controlEngineering
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, articulated implements with multiple antennas on each implement section, video input and guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
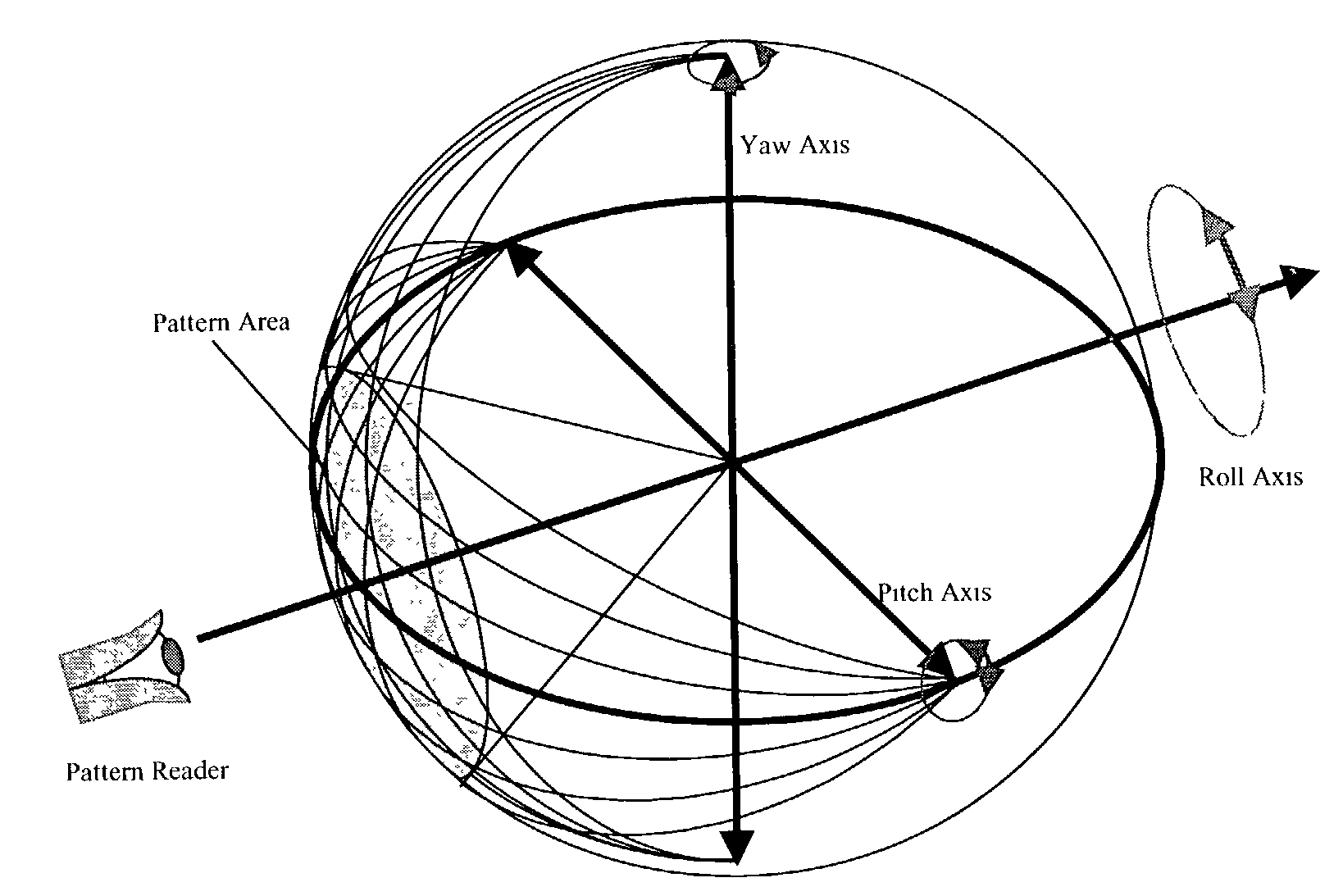
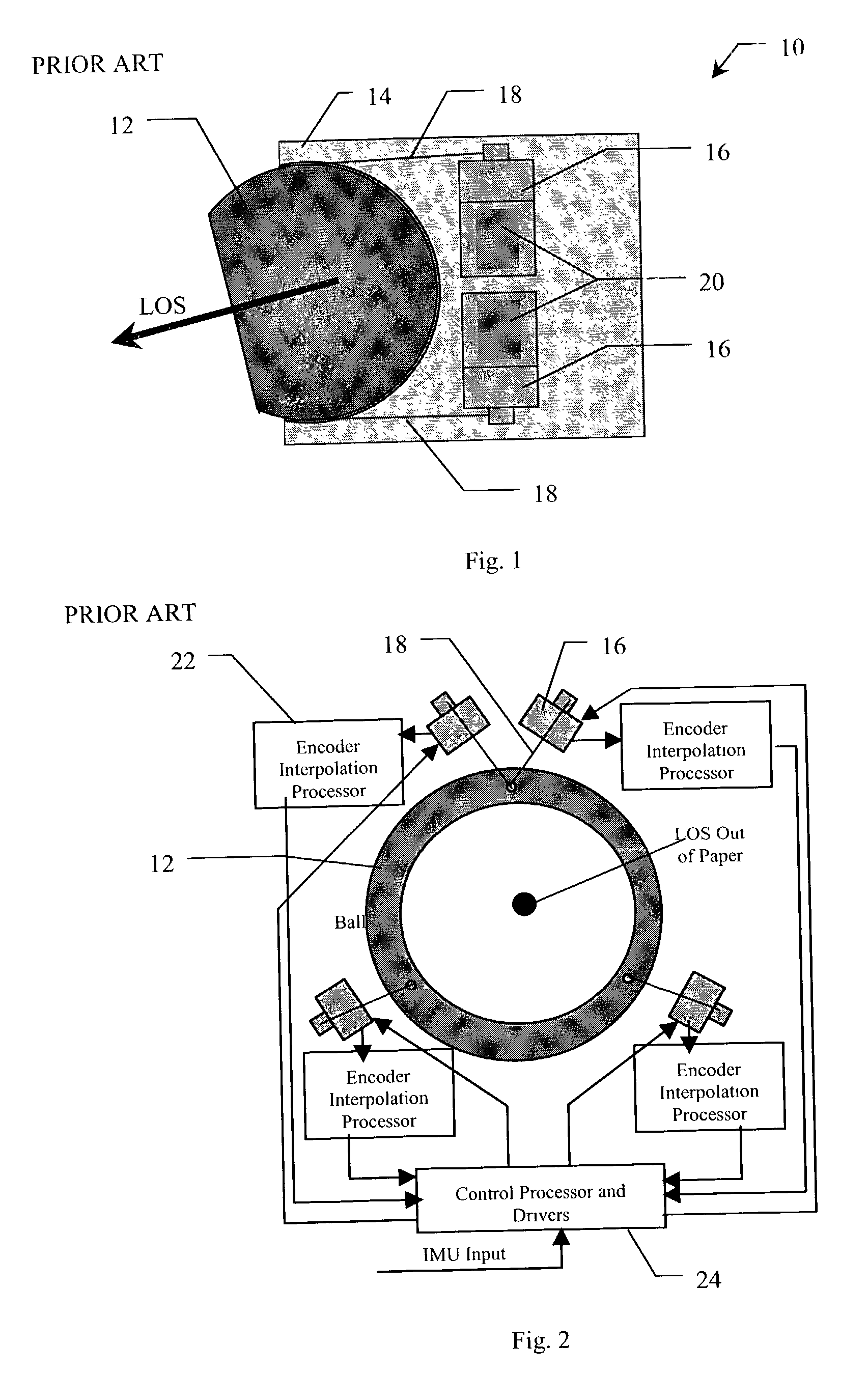
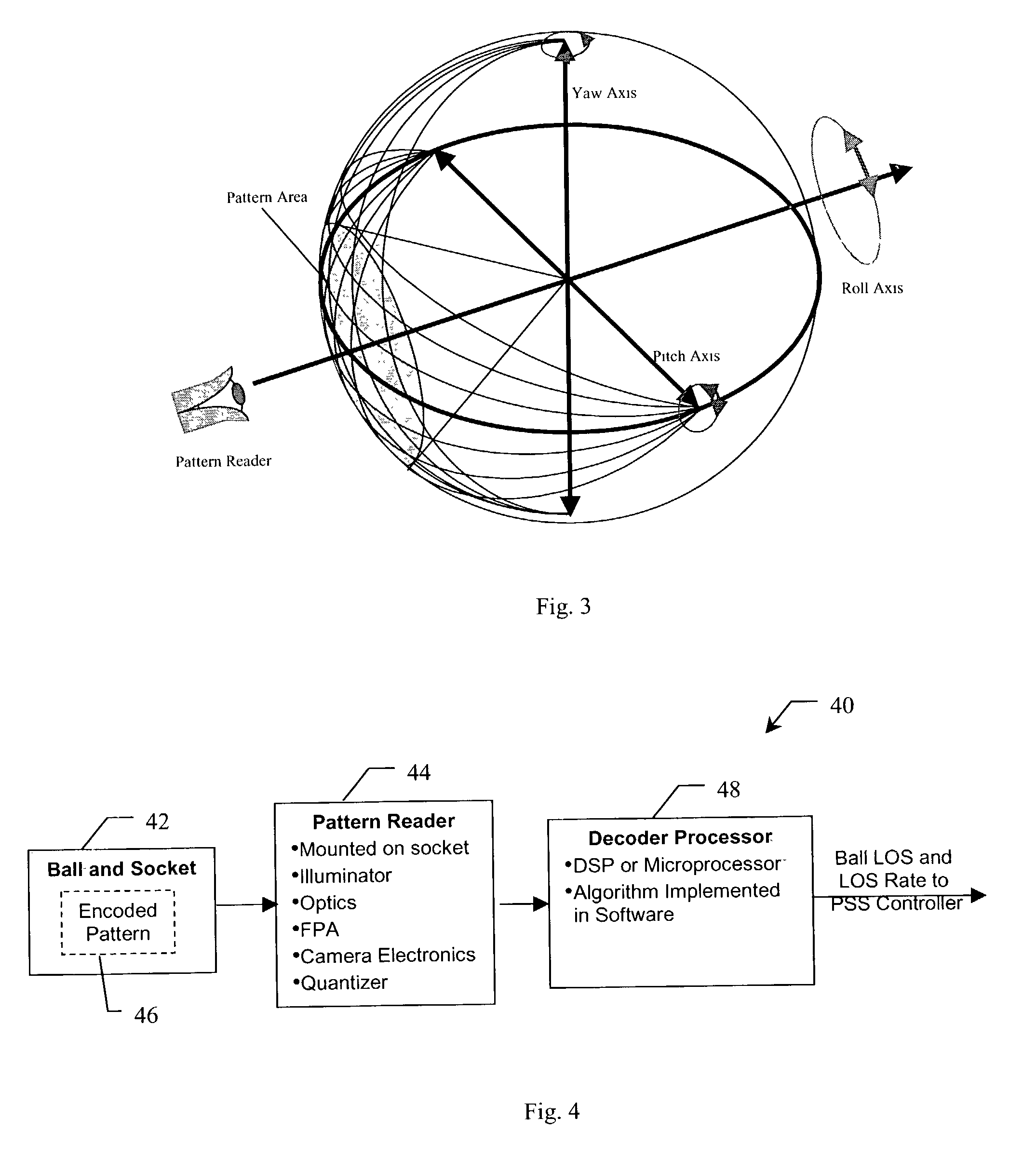
Three axes line-of-sight transducer
A system and method for measuring orientation of an object. In the illustrative embodiment, the object is a ball (42) in a ball and socket type pointing and stabilization system. The novel system (40) includes an encoded pattern (46) applied to a portion of the surface of the ball (42), a pattern reader (44) which reads the pattern (46) off the ball (42) and outputs data representative of the pattern (46), and a processor (48) which decodes the data into orientation information. In the preferred embodiment, the pattern reader (44) is an electro-optical sensor, and the encoded pattern (46) includes a grid of dots (52) arranged in a first predetermined number of dot code cycles (58) wherein each dot code cycle (58) includes a second predetermined number of dots. The processor (48) includes an algorithm (100) which computes pitch, yaw, and roll angles from the pattern reader data.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20120174445A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctNavigation instrumentsGuiding agricultural machinesGyroscopeMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other, and snow grooming equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
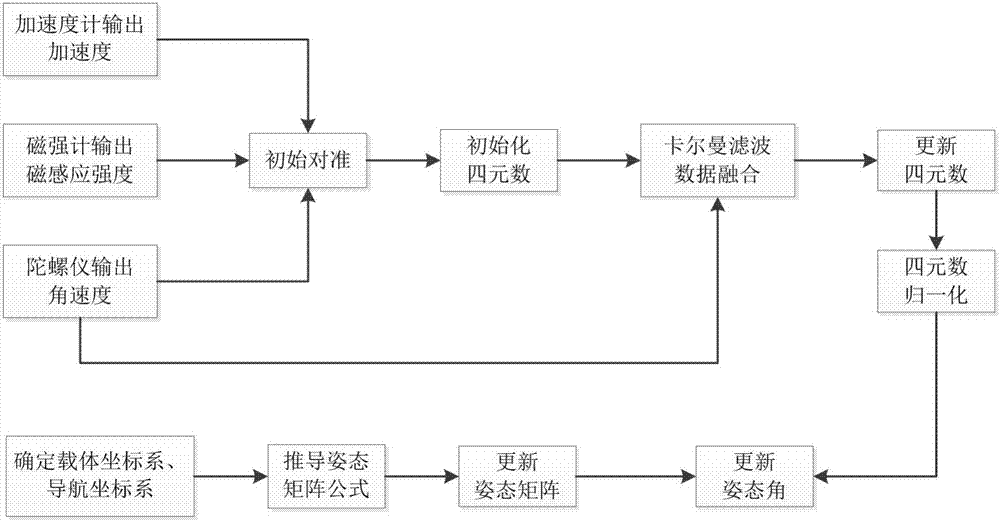
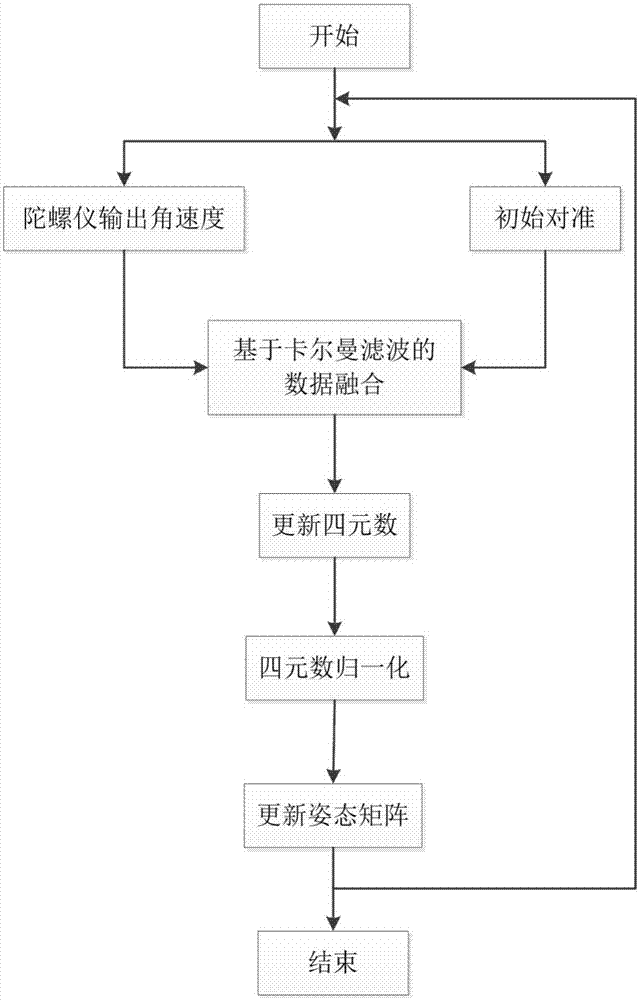
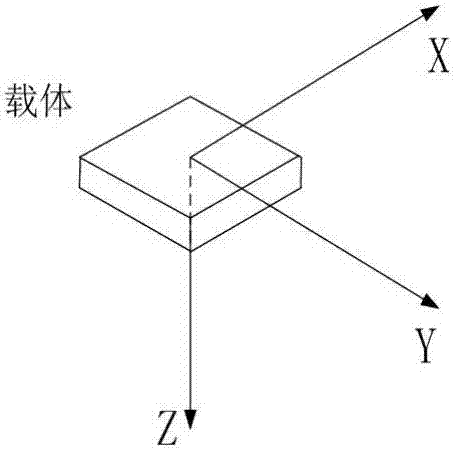
Human body attitude calculation method based on quaternion and Kalman filtering
InactiveCN107478223AEffective Data FusionHigh precisionNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention discloses a human body attitude calculation method based on quaternion and Kalman filtering. The method comprises determining a vector coordinate system and a navigation coordinate system, determining an attitude matrix, respectively acquiring accelerated speed, angular velocity and magnetic induction intensity signals through an accelerometer, a gyroscope and a magnetometer, carrying out initial alignment on a human body attitude detection system, calculating initial attitude angles such as a pitching angle, a rolling angle and a heading angle, transforming the initial attitude angles into initial quaternion, carrying out system modeling according to a quaternion differential equation, inputting the initial quaternion as a measured value, carrying out data fusion on the attitude data through a Kalman filtering algorithm, outputting an estimated value which is updated quaternion, carrying out normalization processing on the updated quaternion to obtain final posture information, updating the attitude matrix and acquiring updated attitude angles. The human body attitude estimation method effectively improves the accuracy of human posture detection, has a fast response speed, has good stability and instantaneity and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20100312428A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctGuiding agricultural machinesSatellite radio beaconingSteering controlFixed interval
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other and earth-moving equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Satellite position and heading sensor for vehicle steering control
ActiveUS7400956B1Avoid crossingEasy to correctInstruments for road network navigationGuiding agricultural machinesControl systemCarrier signal
A sensor system for vehicle steering control comprising: a plurality of global navigation satellite sensor systems (GNSS) including receivers and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase corrected real time kinematic (RTK) position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system.
Owner:AGJUNCTION INC
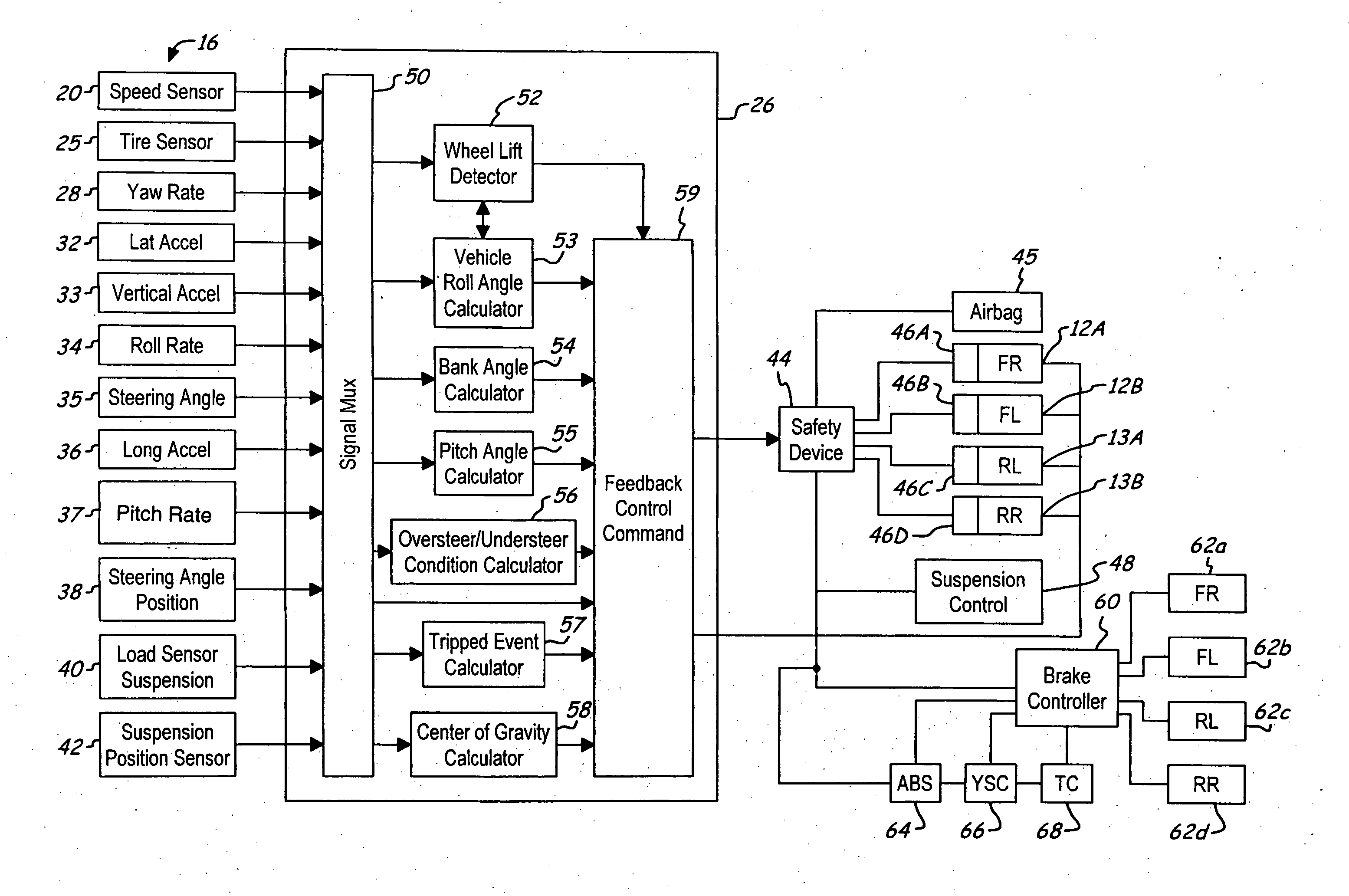
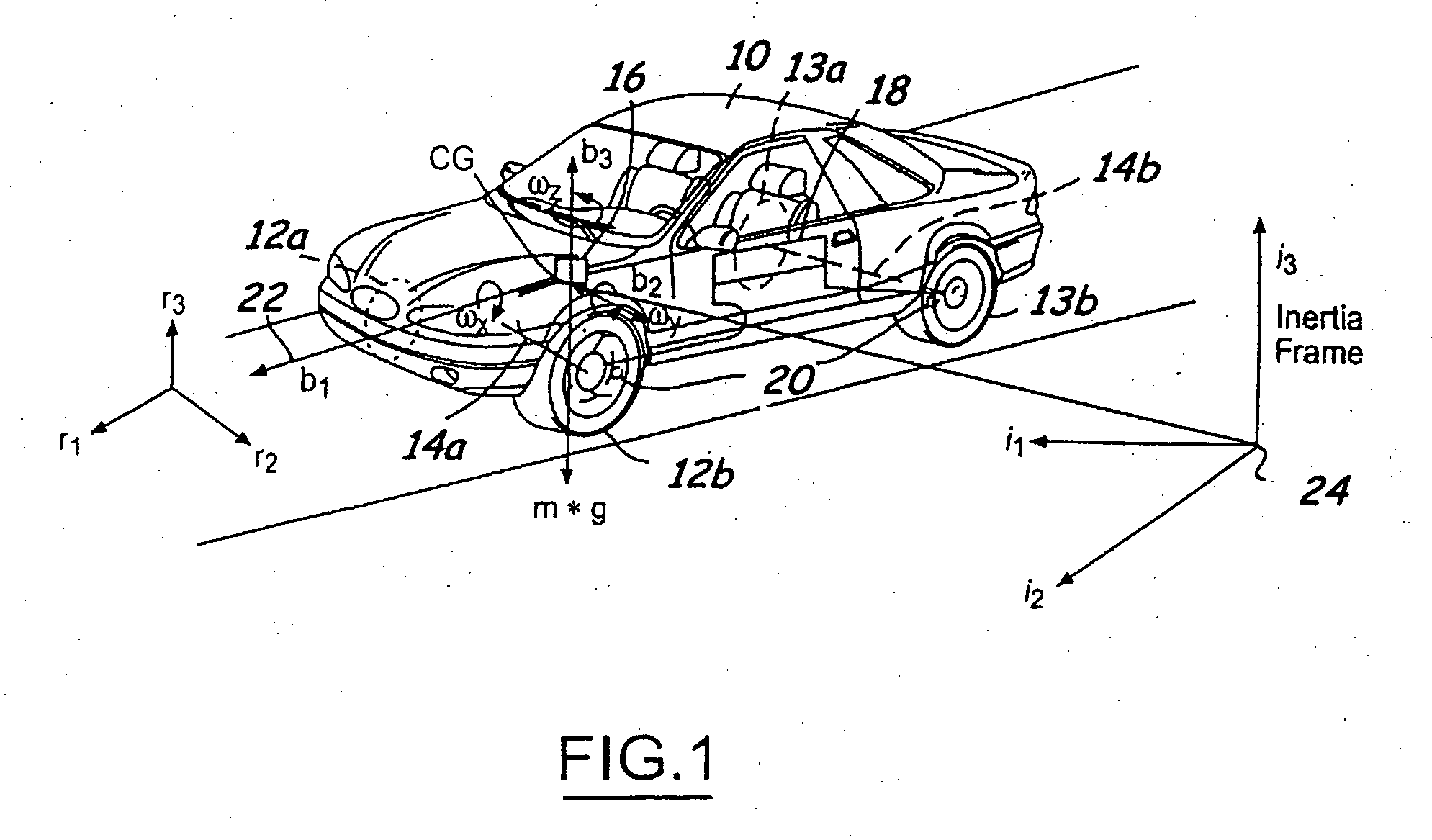
System and method for controlling a safety system of a vehicle in response to conditions sensed by tire sensors related applications
InactiveUS20050033486A1Low costDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemForce sensor
A control system for a vehicle (10) is described for use in conjunction with the safety system (44) of the vehicle (10). A tire sensor or plurality of tire sensors generates tire force signals. The tire force signals may include lateral tire forces, longitudinal (or torque) tire forces, and normal tire forces. Based upon the tire force signals, a safety system (44) may be activated. The tire force sensors may be used to monitor various conditions including but not limited to sensing a roll condition, wheel lift detection, a trip event, oversteering and understeering conditions, pitch angle, bank angle, roll angle, and the position of the center of gravity of the vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS8594879B2Easy to correctGuiding agricultural machinesSatellite radio beaconingSteering controlMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other and earth-moving equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
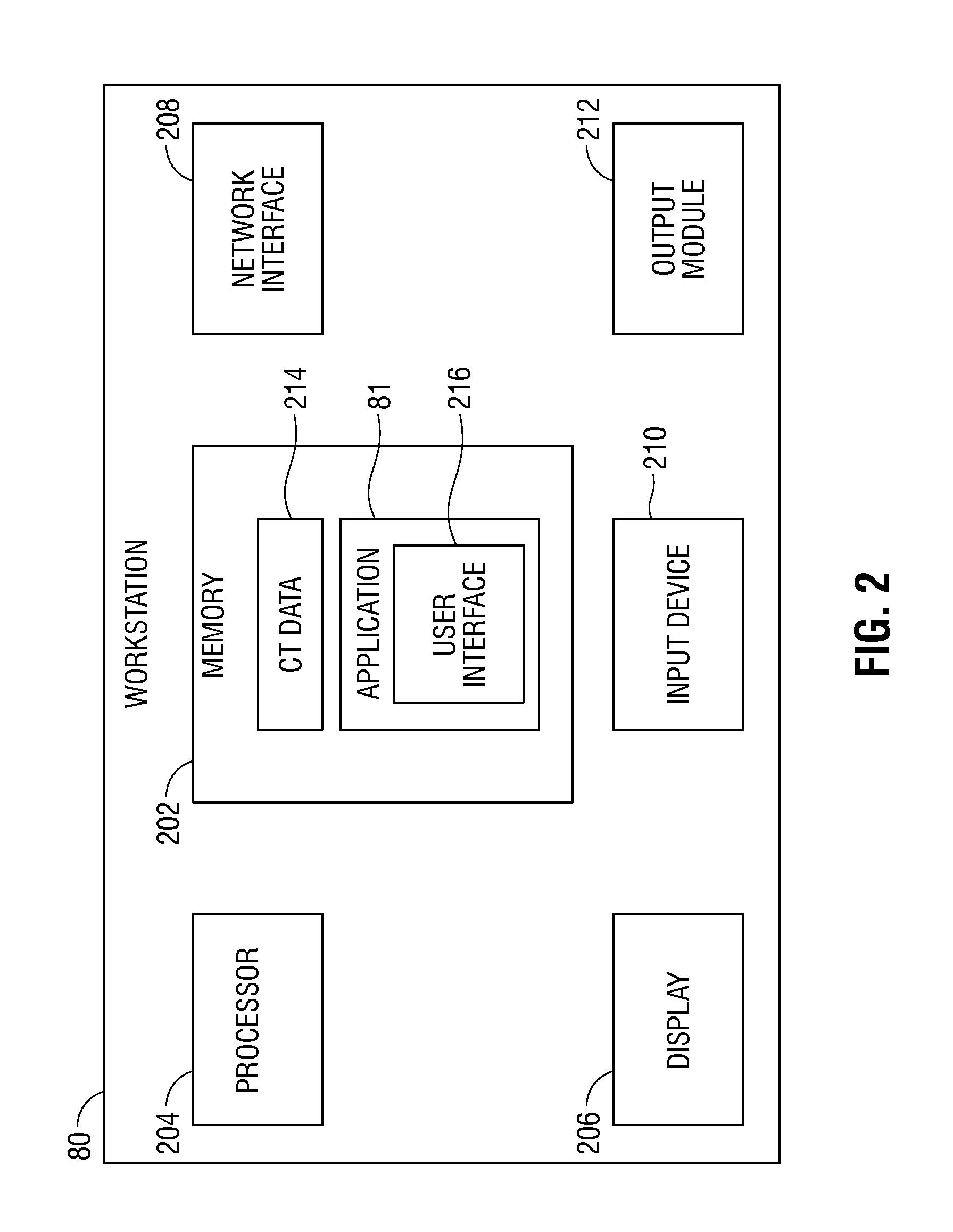
Fluoroscopic pose estimation
Methods and systems for registering three-dimensional (3D) CT image data with two-dimensional (2D) fluoroscopic image data using a plurality of markers are disclosed. In the methods and systems, a lateral angle and a cranial angle are searched for and a roll angle is computed. 3D translation coordinates are also computed. The calculated roll angle and 3D translation coordinates are computed for a predetermined number of times successively. After performing the calculations, the 3D CT image data is overlaid on the 2D fluoroscopic image data based on the lateral angle, the cranial angle, the roll angle, and the 3D translation coordinates.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Super-hydrophobic nanometer transparent coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104987520AExcellent superhydrophobic propertiesHigh transparencyCoatings with pigmentsFibre treatmentOrganic solventUltrasonic dispersion
The invention provides a super-hydrophobic nanometer transparent coating and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of super-hydrophobic paint. The method includes the steps that firstly, a first category of inorganic nanometer particles are added into an organic solution, and ultrasonic dispersion is performed; secondly, dispersing agents and a second category of inorganic nanometer particles are added, and ultrasonic dispersion is performed so that a dispersion solution can be obtained; crosslinking agents and additives are added in the dispersion solution, ultrasonic dispersion is performed, finally, low-surface energy polymers are added, mixtures are evenly mixed, and transparent and clear super-hydrophobic paint is obtained; the surface of a solid base materials is coated with the transparent and clear super-hydrophobic paint, and the super-hydrophobic nanometer transparent coating is obtained through low-temperature thermal drying and curing. The super-hydrophobic performance of the super-hydrophobic nanometer transparent coating prepared through the method is excellent, the contact angle can be 160 degrees, the rolling angle is 1-7 degrees, the super-hydrophobic nanometer transparent coating can be sprayed to the surfaces of most of common materials, the morphology of the surfaces of the materials are not changed, and the application prospects and the application potency are very wide.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
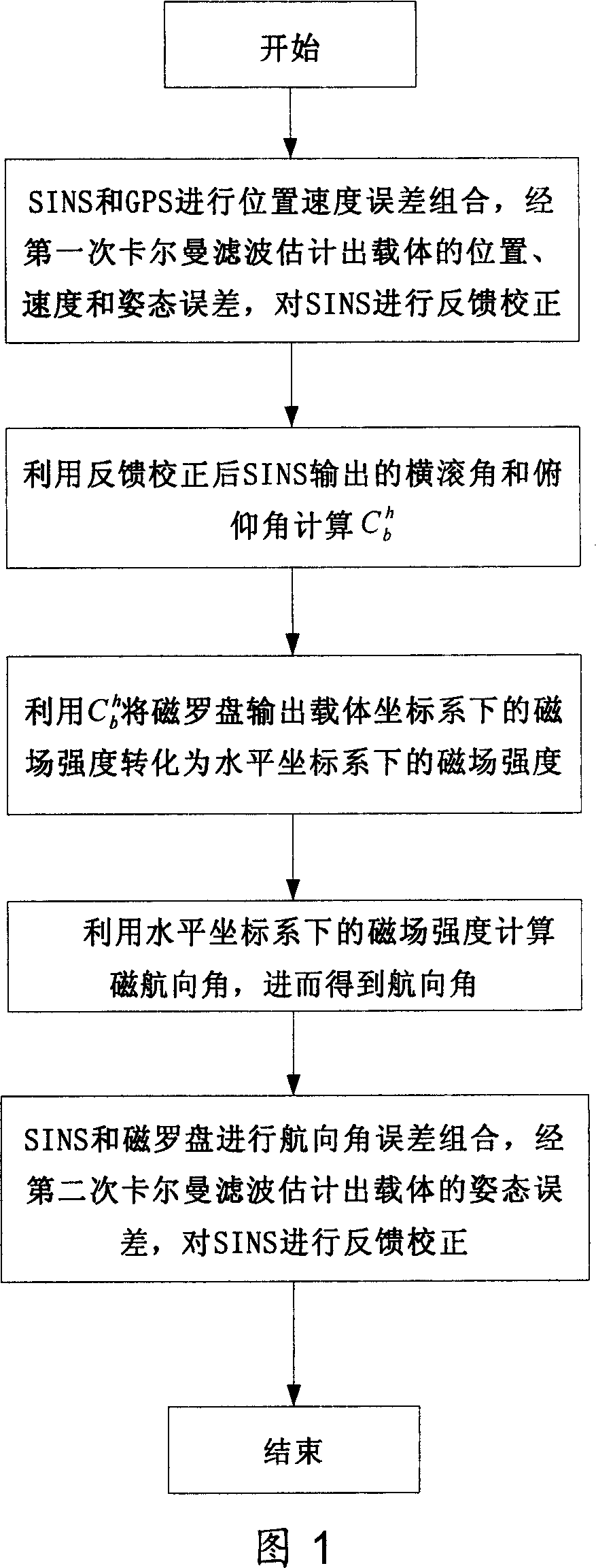
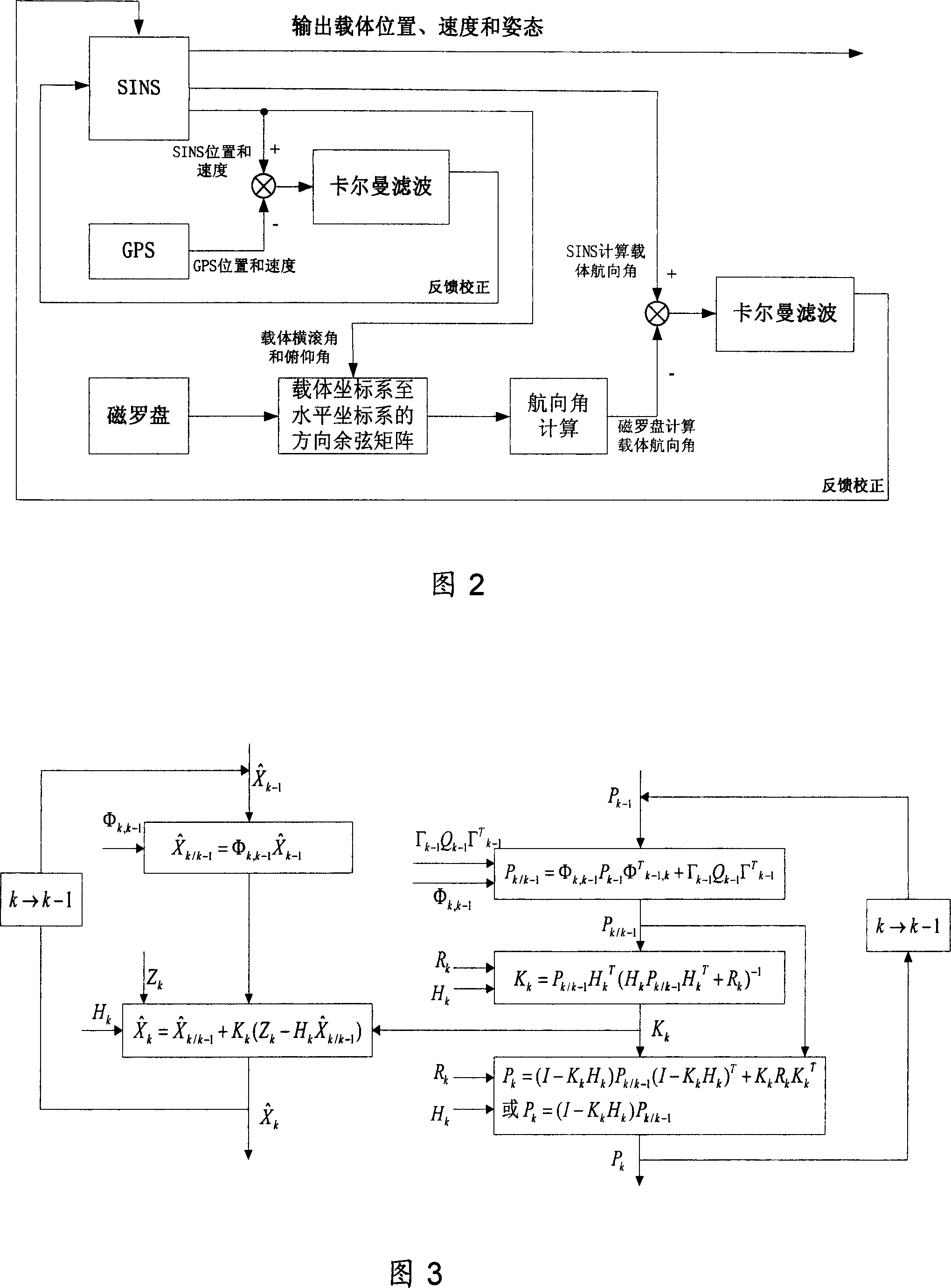
Data blending method of navigation system combined by SINS/GPS micromagnetic compass
InactiveCN101000245AHigh precisionImprove fault toleranceInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsRolling angleSpacecraft
The invention relates to SINS / GPS magnetic compass integrated navigation system data fusion method. It includes the following steps: processing position speed error combination for the SINS and GPS; estimating carrier position, speed, and altitude error by the first Kalman filtering to feed back and rectify SINS; calculating direction cosine matrix from carrier coordinate system to level coordinate system by outputted roll angle and pitch angle to assist magnetic compass to gain carrier magnetic course angle, and course angle; processing course angle error combination for the SINS and magnetic compass; estimating carrier altitude error by the second Kalman filtering to feed back and rectify SINS; outputting carrier position, speed, and altitude information from SINS to user. The invention has the advantages of simple computing, high precision, strong fault tolerant ability and wide application. Thus it can be used to increase magnetic compass altitude fixing precision, navigation precision of the SINS / GPS magnetic compass integrated navigation system used in space craft, aircraft, shipping, or surface car.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Super-hydrophobic and super-oleophobic surface preparation technology
The invention discloses super-hydrophobic and super-oleophobic surface preparation technology. In the preparation technology, aluminum or aluminum alloy sheets are subjected to two-step electrochemical treatment, and then are modified by using perfluorinated octadecyl trichlorosilane or perfluorinated polymethacrylate to prepare the super-hydrophobic and super-oleophobic surface. The surface has super-hydrophobic property on aqueous solution of which the pH value is between 1 and 14 and super-oleophobic property on various oil drops, wherein a contact angle of the surface on water is 171 degrees, and a rolling angle is less than 1 degree; the surface expresses the super-oleophobic property on various oil drops except for perfluorinated polymer liquid, and all contact angles between the oil drops and the surface are more than 150 degrees, and rolling angles are generally less than 10 degrees; and the surface can also be put in air for a long time and can still maintain the super-hydrophobic property and super-oleophobic property.
Owner:中科润泉(烟台)工业科技有限公司
Super-hydrophobic ice-covering-proof coating having slowly-releasing function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102382536AExtensive sources of raw materialsWide variety of sourcesCoatingsNanoparticleWater contact
The invention discloses preparation of a super-hydrophobic ice-covering-proof coating having a slowly-releasing function. The ice-covering-proof coating consists of the following substances in parts by mass: 1.5-5 parts of inorganic hollow or porous nanoparticles for adsorbing small molecular anti-icing substances, 2-5 parts of fluorine-containing polymer and 1-15 parts of solvent. The super-hydrophobic ice-covering-proof coating having the slowly-releasing function can be obtained by uniformly mixing the three substances and coating the mixture onto the surface of a substrate. At the normal temperature, the water contact angle of the coating is greater than 150 degrees, and the rolling angle is smaller than 7 degrees. At 10 DEG C below zero, the low-temperature contact angle of water is greater than 140 degrees, and the rolling angle is smaller than 12 degrees. During testing of the ice cover at 10 DEG C below zero, the ice cover is lowered by over 70 percent, and is still higher than 50 percent after testing is performed circularly for ten times in comparison to a blank sample.
Owner:天津渤化讯创科技有限公司
Combined GNSS gyroscope control system and method
ActiveUS8265826B2Easy to correctDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationControl systemEngineering
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
Multi-antenna GNSS control system and method
ActiveUS8583315B2Easy to correctEconomical and accurateVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficControl systemSteering control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Preparation method for super-hydrophobic surface with bionic micro-nano composite structure
InactiveCN105413994AExcellent surface superhydrophobicityLow costPretreated surfacesSpecial surfacesMicro nanoElectrochemical response
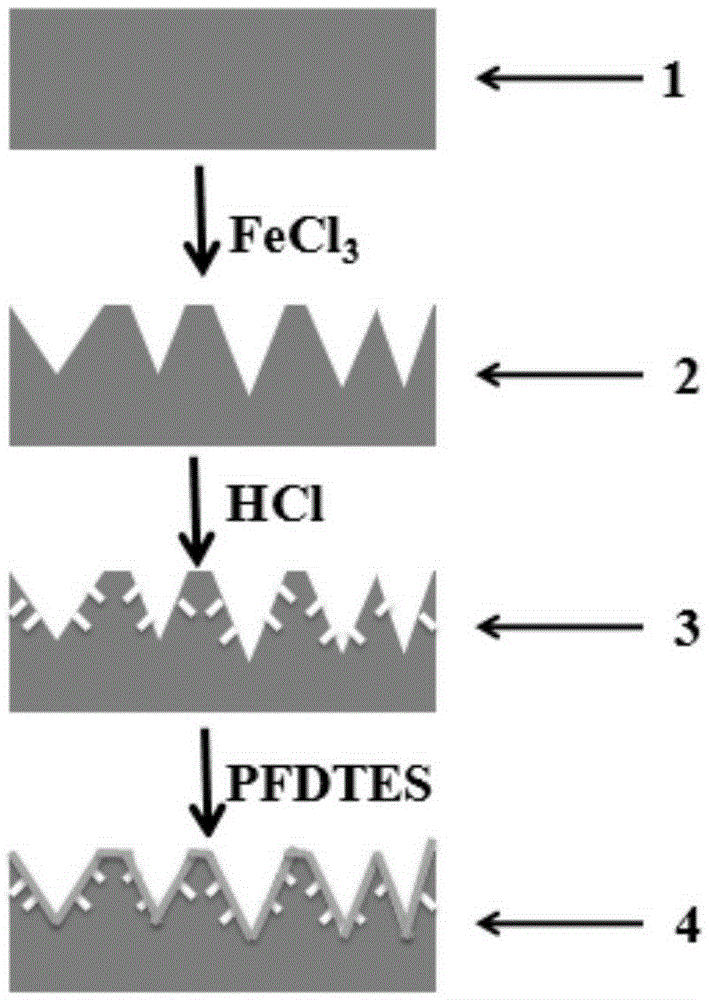
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of super-hydrophobic surfaces, and relates to a preparation method for a super-hydrophobic surface with a bionic micro-nano composite structure. From the angle of the super-hydrophobic surface, the super-hydrophobic surface is prepared by virtue of a mesoscale two-step etching method; etching treatment is carried out on a substrate surface twice; a micro-nano composite structure similar to a lotus leaf surface is constructed by utilizing a chemical or an electrochemical reaction etching substrate, and surface modification is carried out by virtue of a surface modifier to reduce surface free energy. The size of the micro-nano structure can be controlled by virtue of reaction time, a reaction temperature and concentration. A contact angle, on the surface of the micro-nano composite structure, of water drops is as high as 170 degrees while a rolling angle of the water drops is smaller than 5 degrees. According to electrochemical test results, corrosion resistance of a super-hydrophobic stainless steel sheet is 22 times that of common stainless steel. The method provided by the invention does not need special equipment, is low in cost, good in stability, excellent in super-hydrophobic property, good in corrosion resistance and can be applied to metal corrosion-resistant protection.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
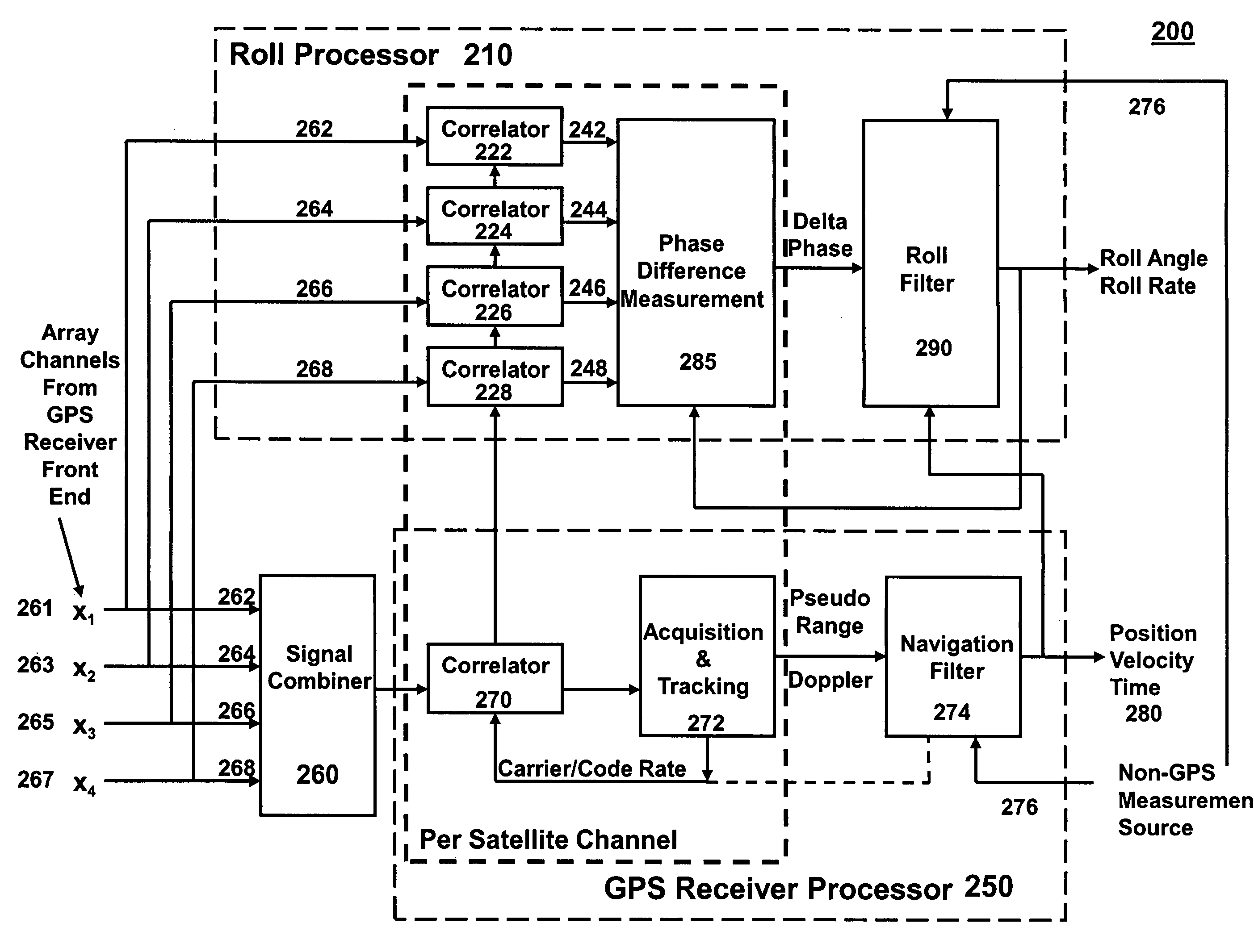
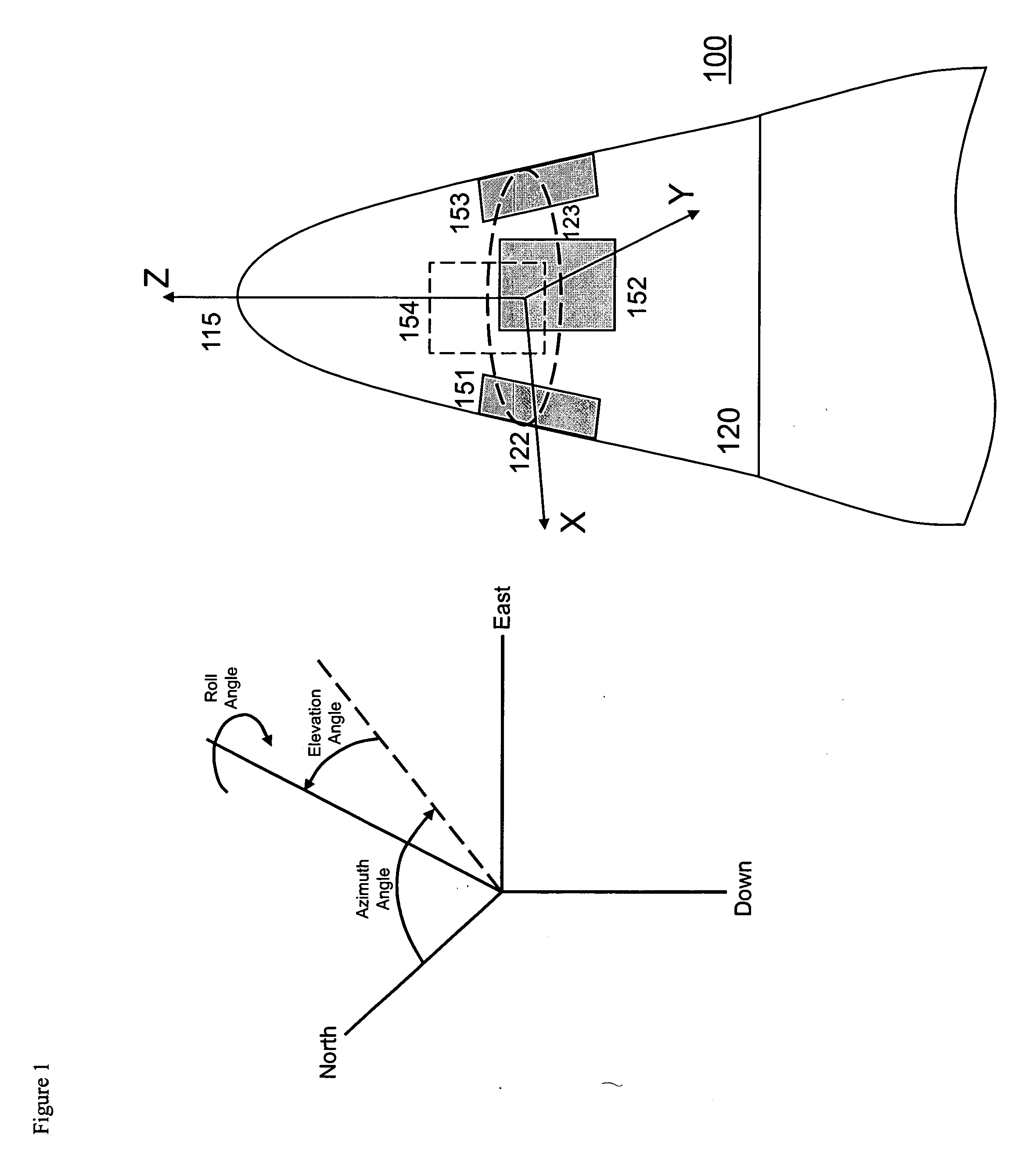
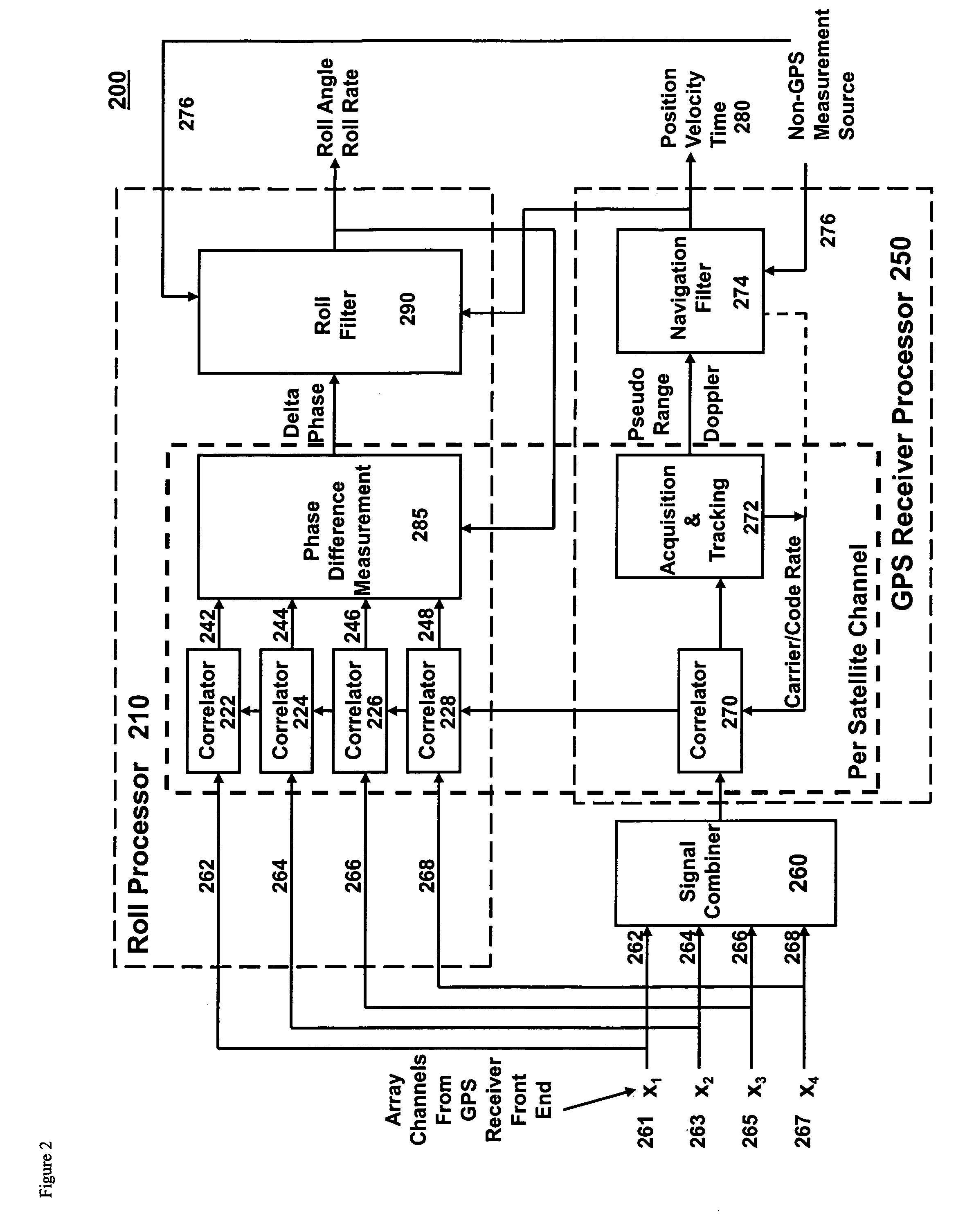
Gps-based measurement of roll rate and roll angle of spinning platforms
A system and method for determining the roll rate and roll angle of a spinning platform, using the measured phase differences between the GPS satellite signals received on two or more antennas. The measured phase differences and the navigation solution from a GPS receiver are processed in a Kalman filter to obtain the desired information. Data from non-GPS measurement sources is optionally provided to update the navigation solution. Although of wide applicability, the invention is uniquely suited to the measurement of roll rates and roll angles of fast spinning platforms with small baselines, in which the antennas are separated from each other by distances that are a fraction of the GPS signal wavelength.
Owner:MAYFLOWER COMM CO INC
3D time-of-flight camera system and position/orientation calibration method therefor
ActiveUS20110205340A1Easy to installImage enhancementImage analysisTime-of-flight cameraAngle of view
A camera system comprises a 3D TOF camera for acquiring a camera-perspective range image of a scene and an image processor for processing the range image. The image processor contains a position and orientation calibration routine implemented therein in hardware and / or software, which position and orientation calibration routine, when executed by the image processor, detects one or more planes within a range image acquired by the 3D TOF camera, selects a reference plane among the at least one or more planes detected and computes position and orientation parameters of the 3D TOF camera with respect to the reference plane, such as, e.g., elevation above the reference plane and / or camera roll angle and / or camera pitch angle.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Position and attitude parameter measurement system of machine body of boring machine and method thereof
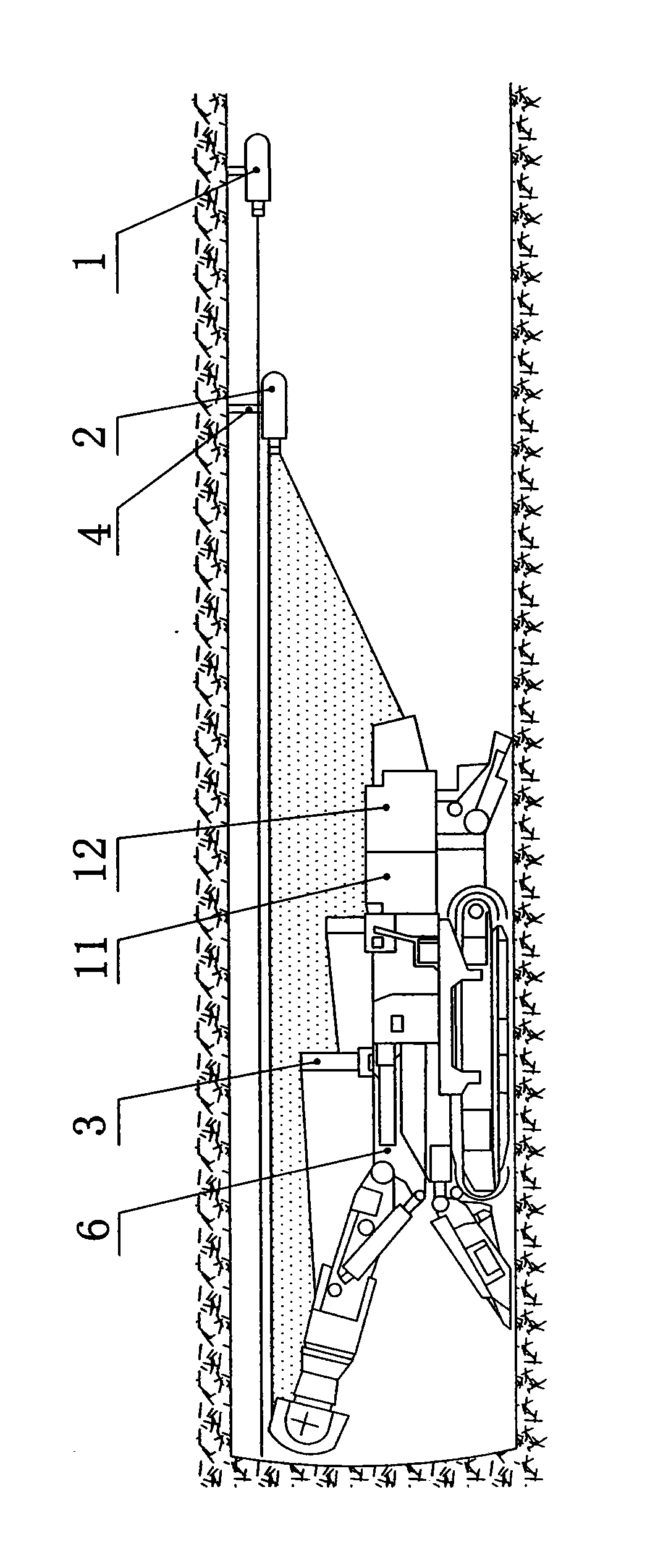
InactiveCN101629807AReal-time detectionIncrease the level of automationAngle measurementSurveying instrumentsLaser transmitterLaser target
The invention relates to a position and attitude parameter measurement system of a machine body of a boring machine and a method thereof, and the position and attitude parameter measurement system consists of a line laser transmitter, a rack of the line laser transmitter, laser targets, a programmable computer controller, an A / D conversion module and two inclination sensors. The line laser transmitter is positioned by a laser direction indicator and the rack of the line laser, emits a fan-shaped laser beam and forms linear spots on the machine body of the boring machine. An photosensitive element in one position on one of the two laser targets consisting of the photosensitive elements senses the laser beam and generates a current signal at any time, and the current signals are processed and calculated by an internal circuit of the laser targets and the programmable computer controller, thereby determining the positions of the laser beam on the laser targets; furthermore, the mounting positions of the laser targets on the boring machine are known, thereby obtaining a deflection angle and deflection displacement of the boring machine. Two inclination sensors measure a pitch angle and a roll angle of the boring machine, thereby completing the measurement of position and attitude parameters of the machine body of the boring machine. The system has the advantages of low cost, high precision, good real-time property and convenient operation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com