Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
565 results about "Real Time Kinematic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
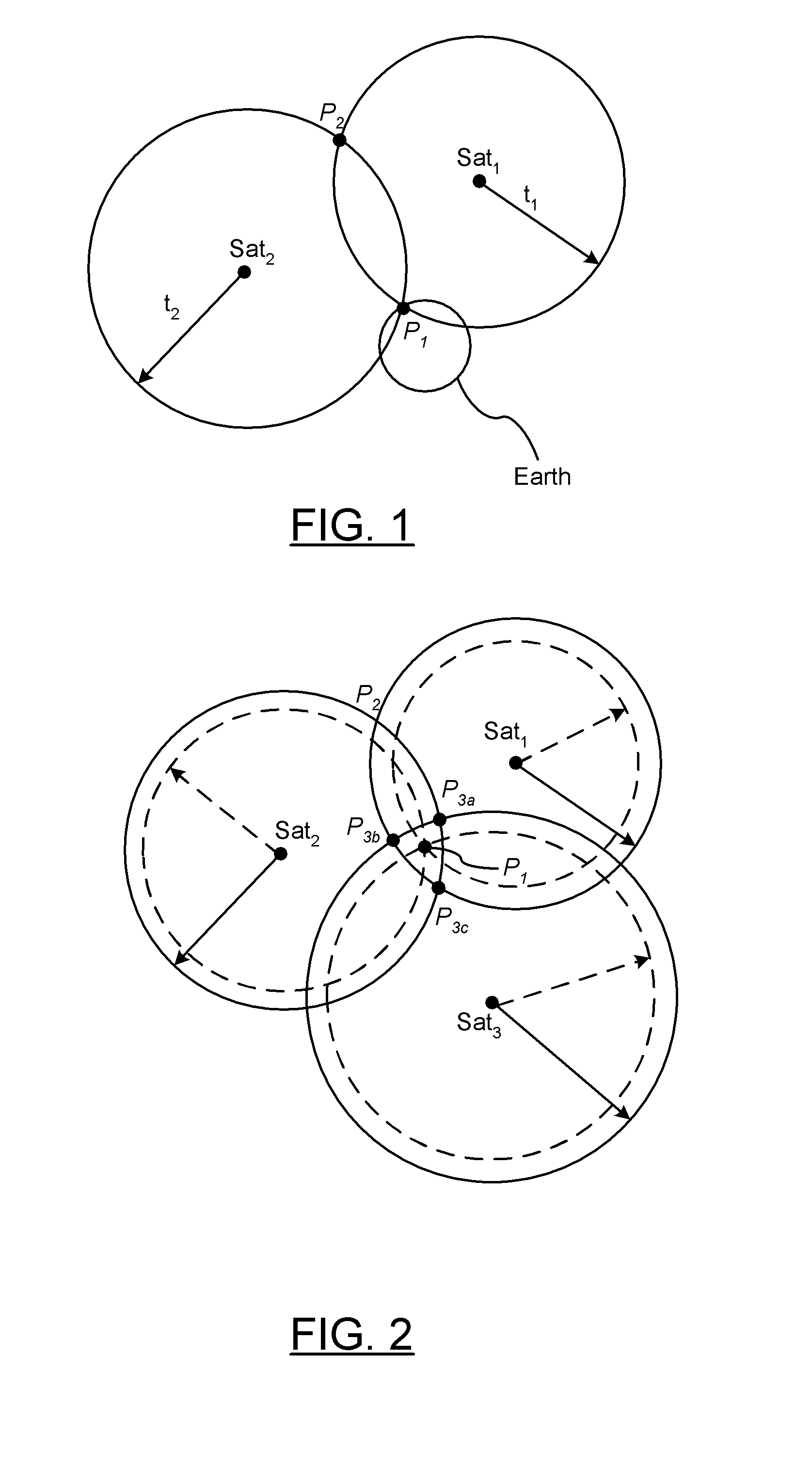
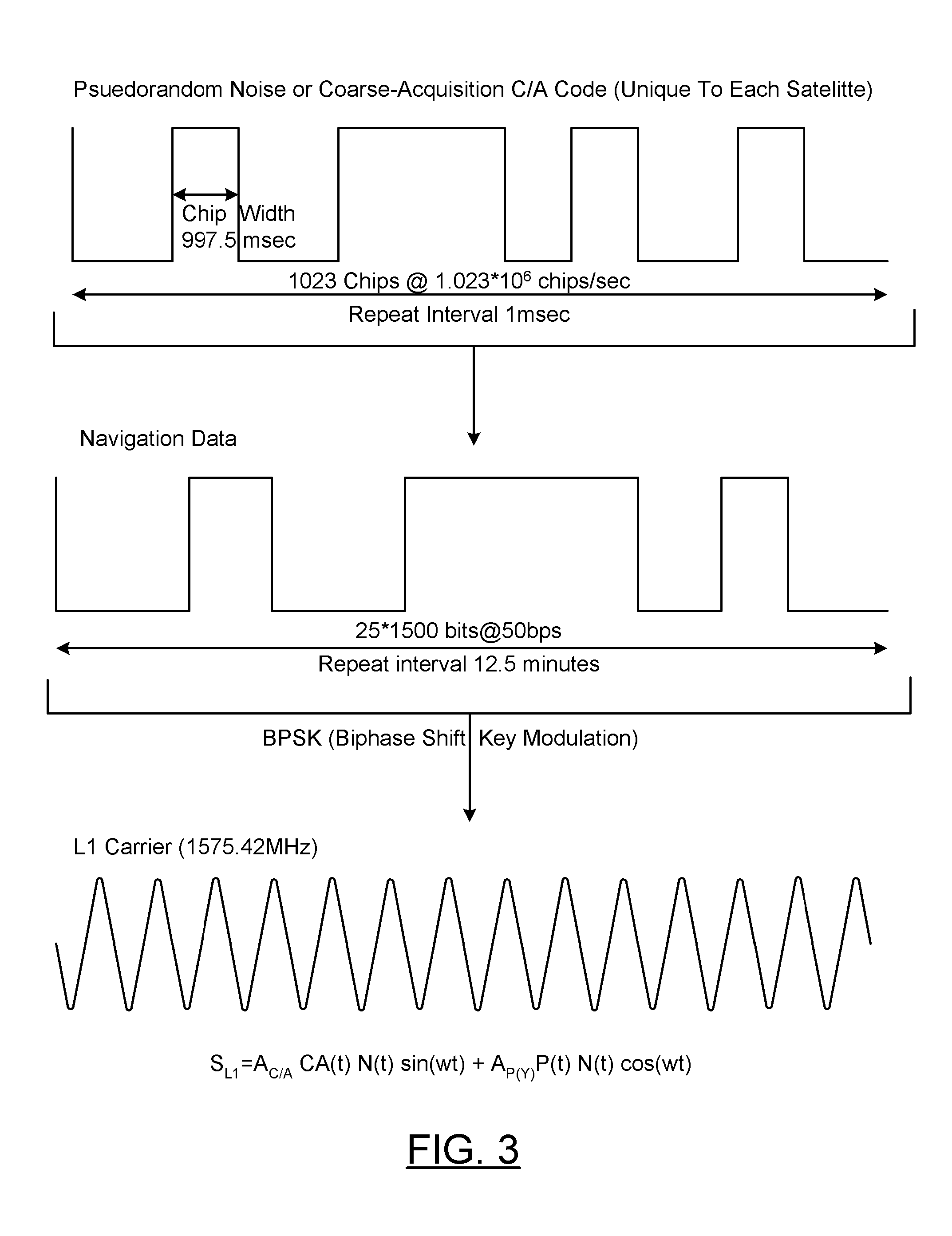
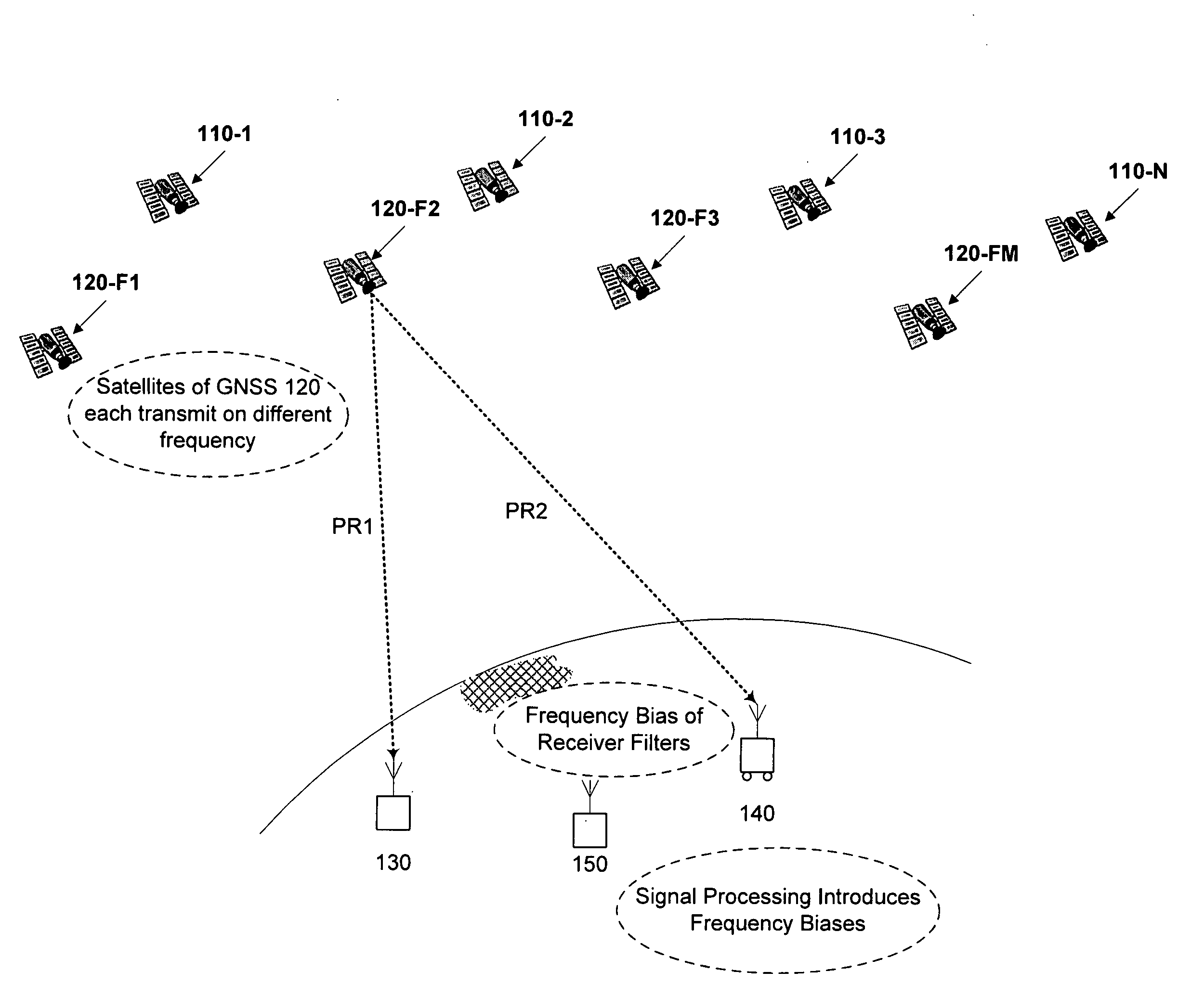
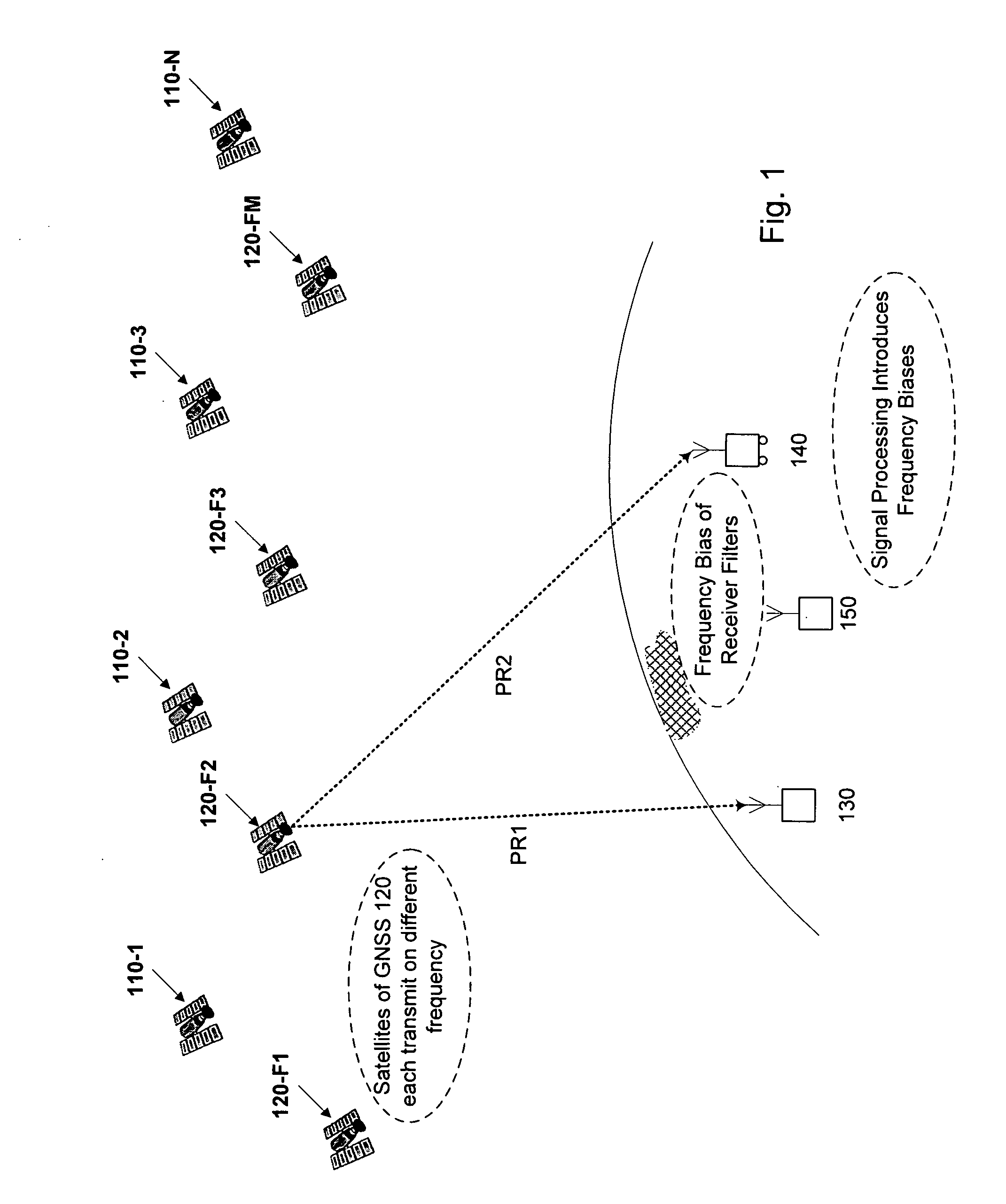
Real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning is a satellite navigation technique used to enhance the precision of position data derived from satellite-based positioning systems (global navigation satellite systems, GNSS) such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou. It uses measurements of the phase of the signal's carrier wave in addition to the information content of the signal and relies on a single reference station or interpolated virtual station to provide real-time corrections, providing up to centimetre-level accuracy. With reference to GPS in particular, the system is commonly referred to as carrier-phase enhancement, or CPGPS. It has applications in land survey, hydrographic survey, and in unmanned aerial vehicle navigation.
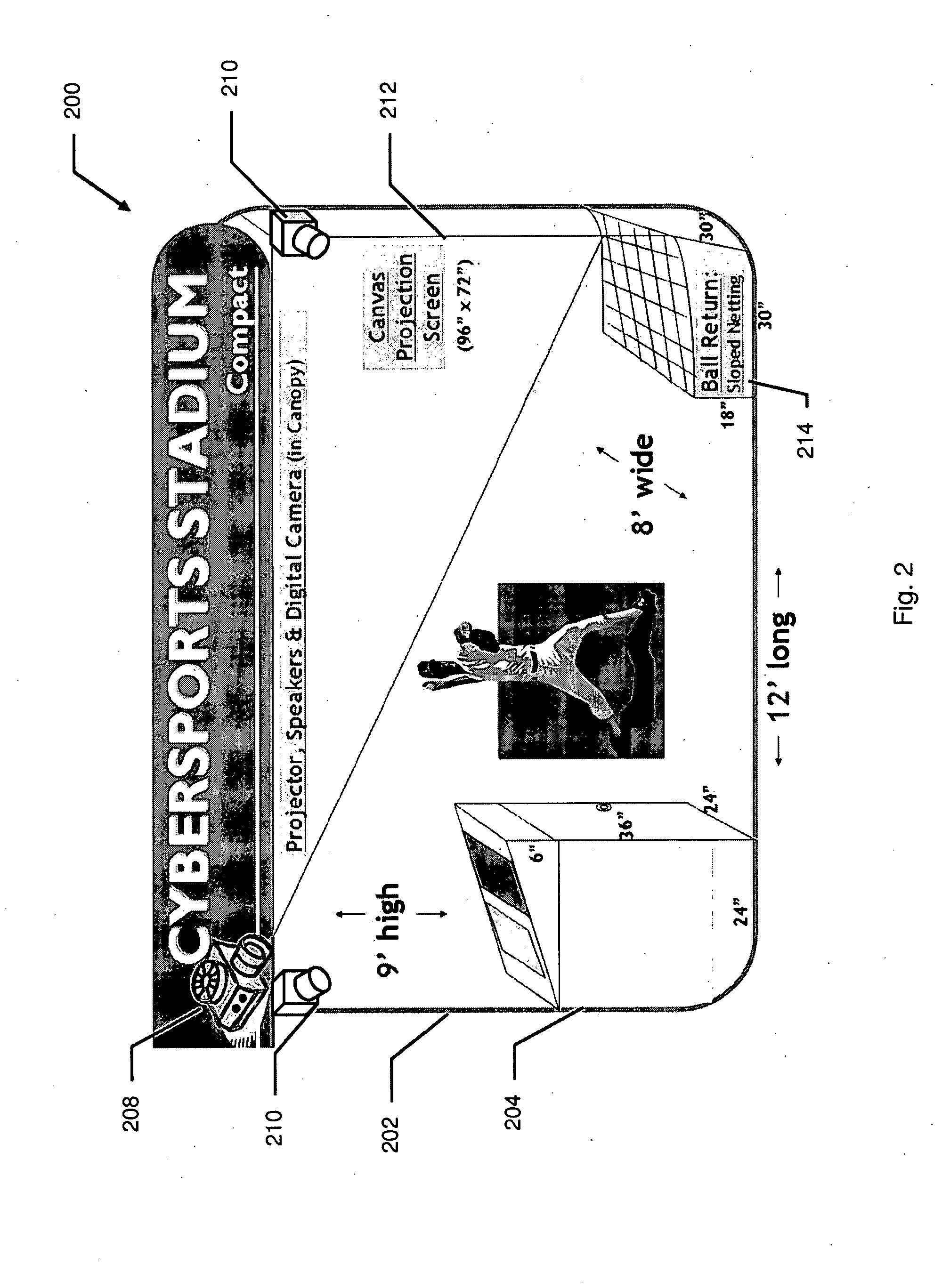
Method for representing real-time motion
InactiveUS6707487B1Accurate game reconstructionReduce data flowImage enhancementTelevision system detailsGraphicsContinuation
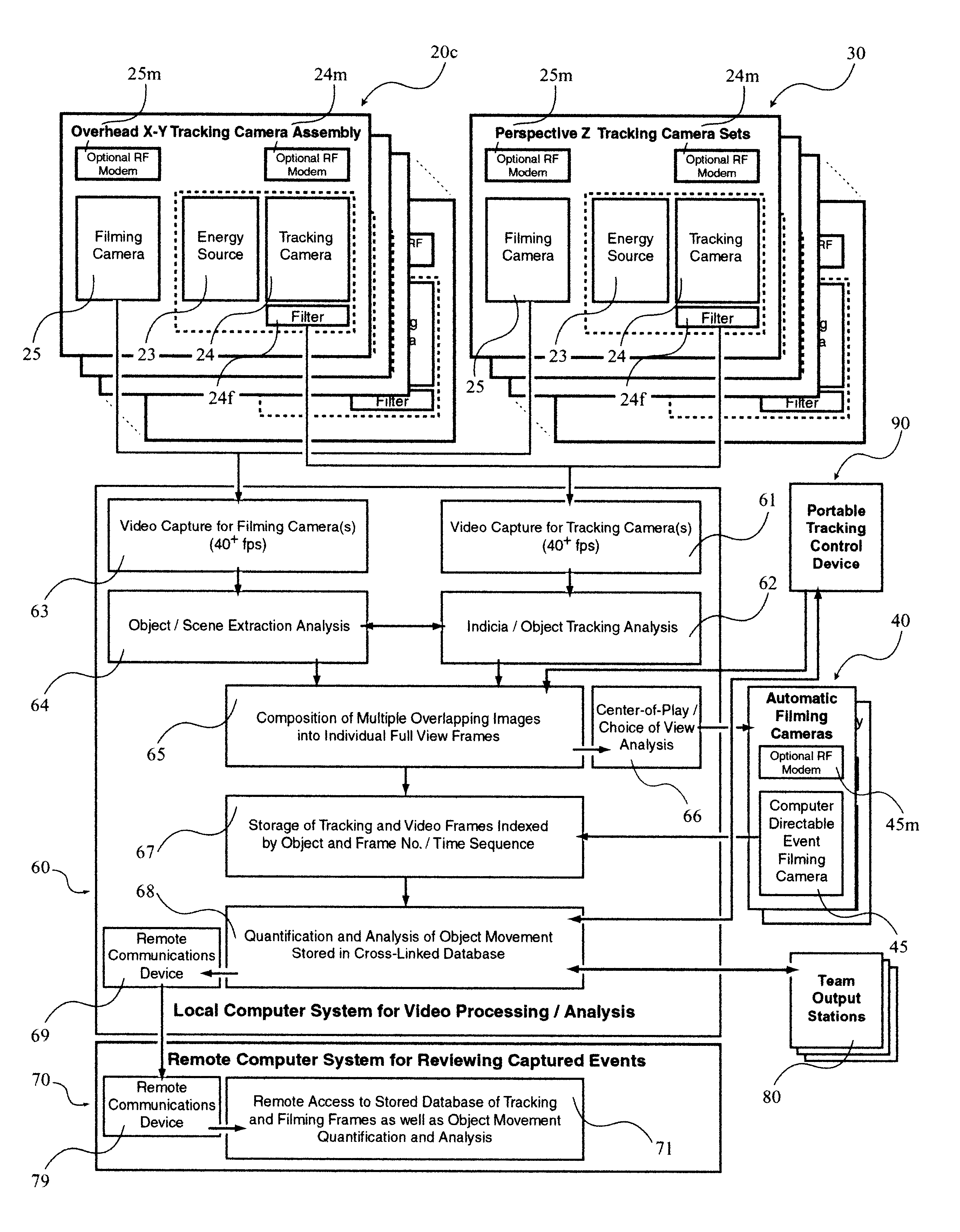
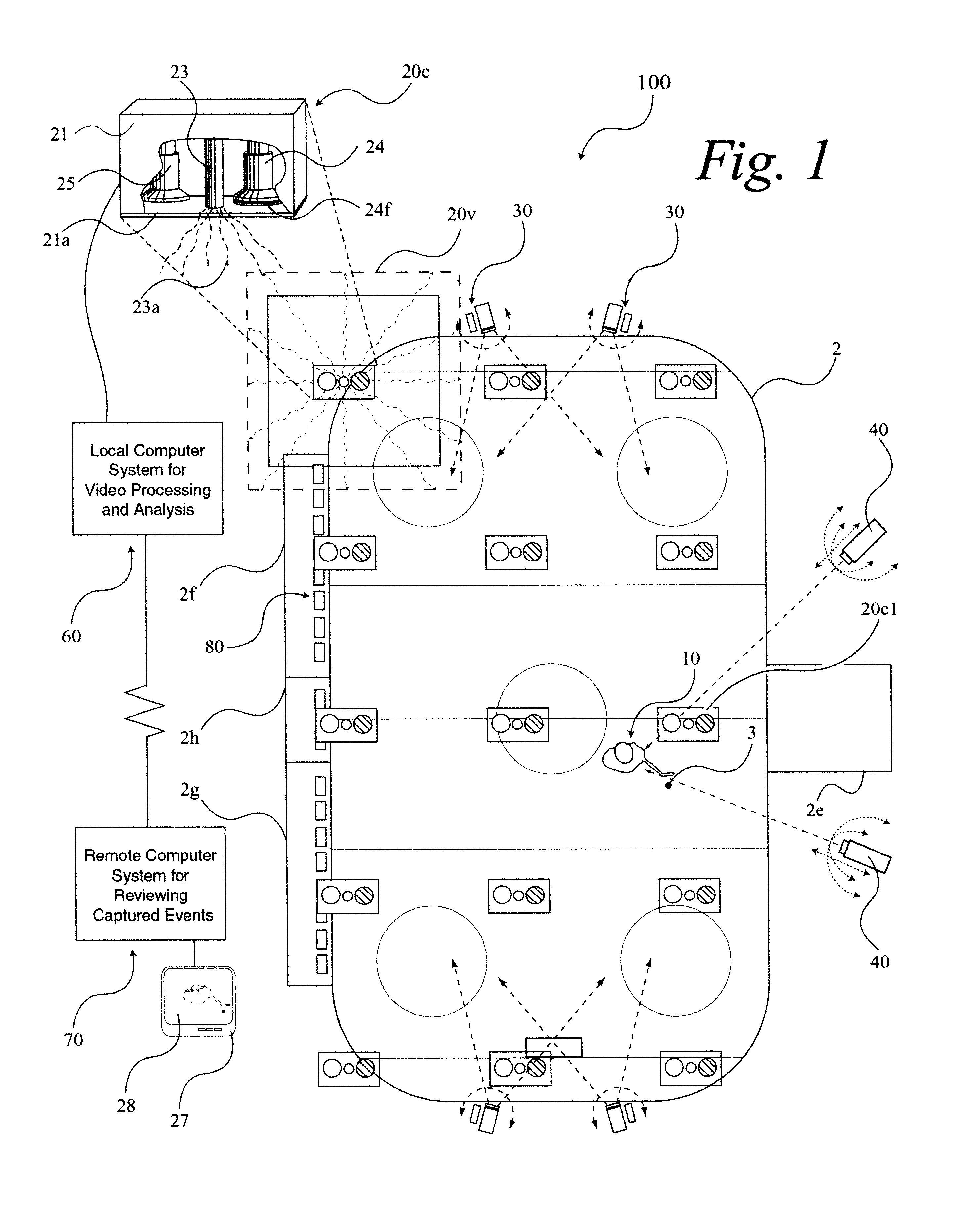
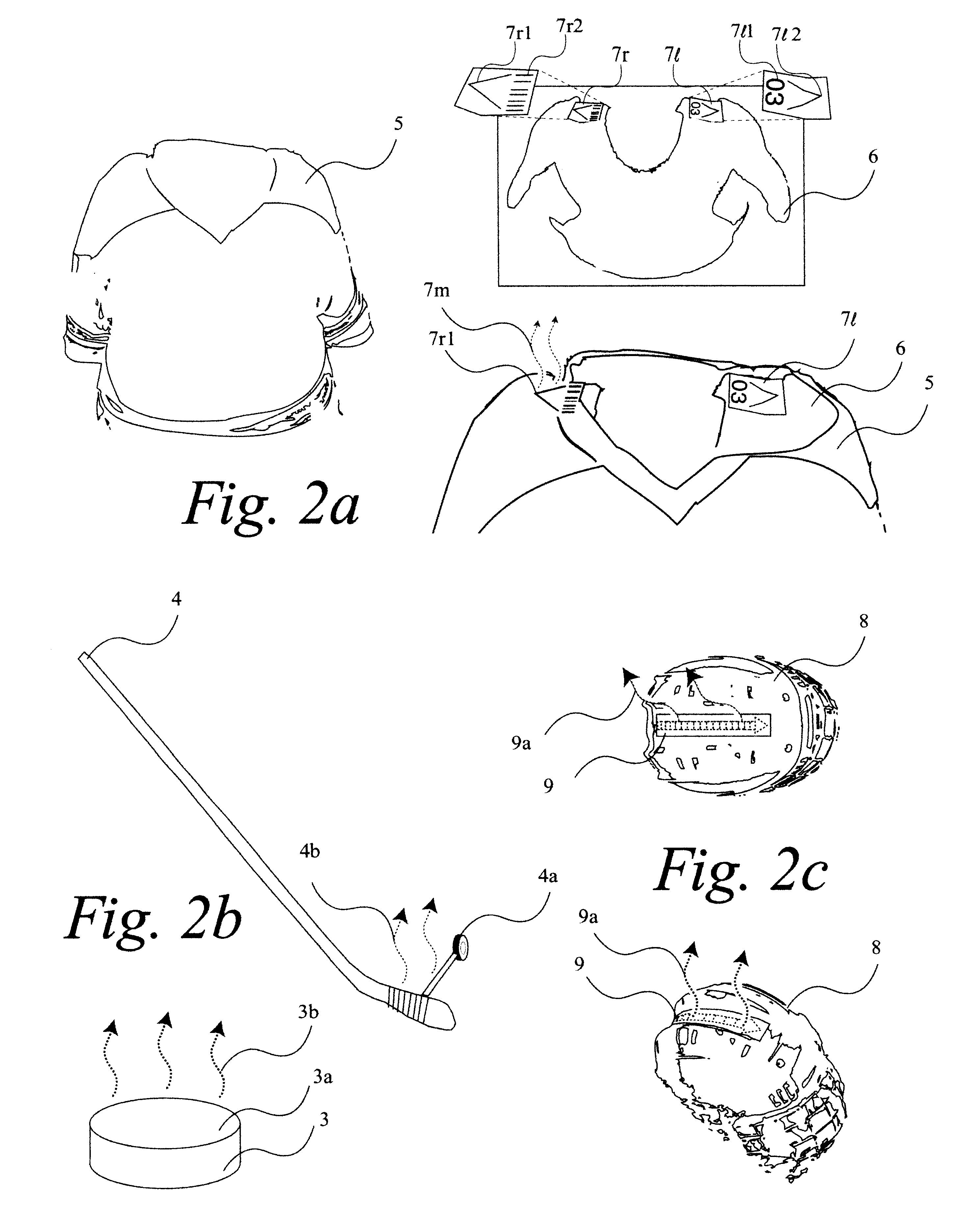
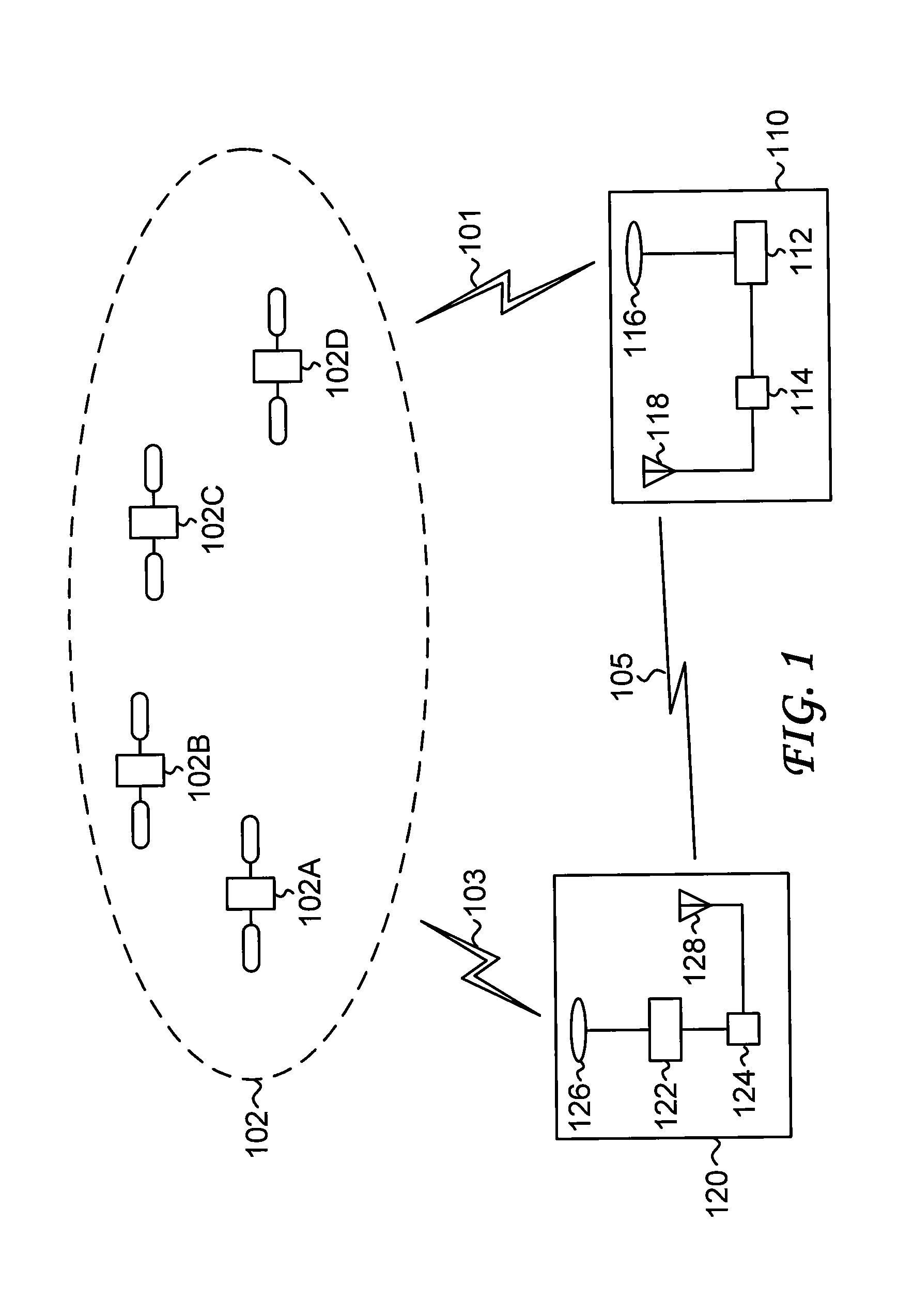
A system 100 for tracking the movement of multiple objects within a predefined area using a continuation of overhead X-Y tracking cameras 24 with attached frequency selective filter 24f. Also employed are perspective Z filming cameras sets 30. Objects to be tracked, such as player 17, have been marked to include some form of frequency selective reflective material such as an ink. Typical markers include patches 7r and 7l, sticker 9 and tape 4a as well as additional body joint markers 17af through 17l. System 100 radiates selected energy 23a throughout the predefined area of tracking that is specifically chosen to reflect off said reflective materials used to mark for instance player 17. The reflected energy is then received by tracking cameras 24 while all other ambient light is blocked by filter 24f. Local Computer System 60 continuously captures images from said tracking cameras 24 which include only the minimum information created by said reflected energy. System 60 efficiently locates said markings on said multiple objects and uses this location information to determine for each marking its angle of rotation, angle of azimuth and distance from a designated origin 17o local to player 17. Local origin 17o is then expressed as a three-dimensional coordinate with respect to the origin of the playing venue 2a. The continuous stream of tracked three-dimensional coordinates, defining the body joints on players such as 17, is then transmitted to a remote computer where it can be used to drive a graphic re-animation of the object movement. Along with this re-animation, additional performance measurements may be derived from the continuous stream and automatically made available in real-time.
Owner:MAXX HLDG
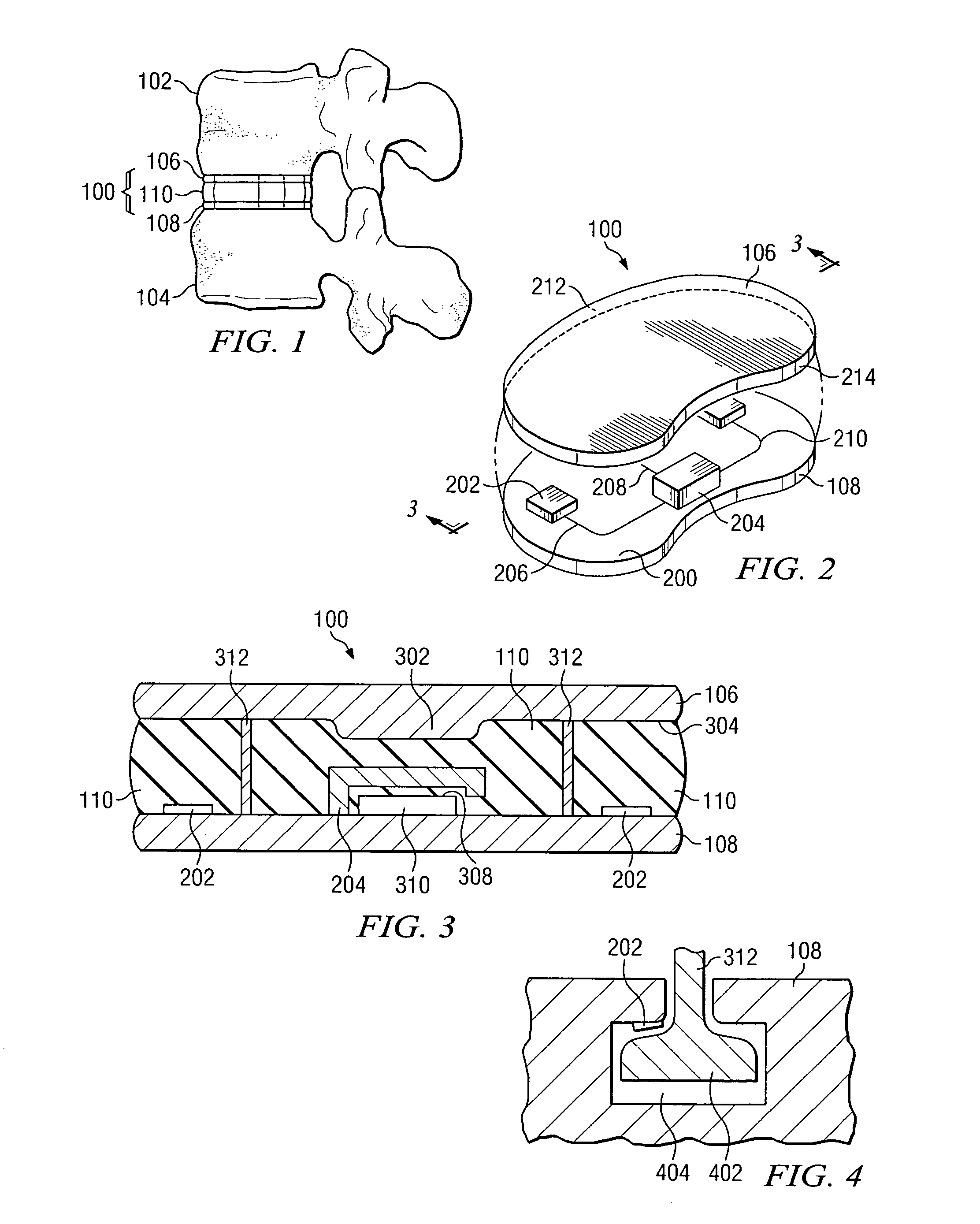
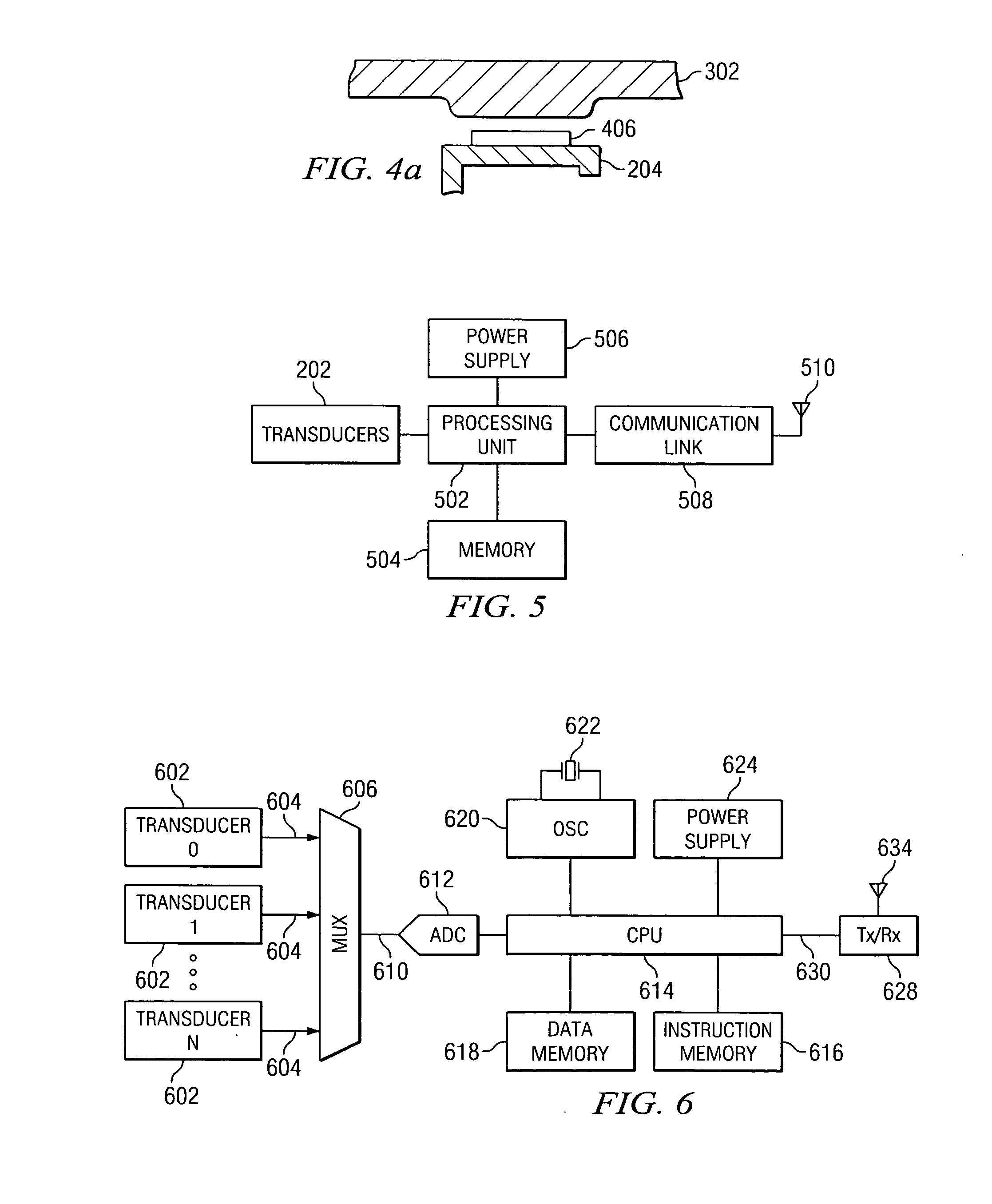
Prosthetic intervertebral spinal disc with integral microprocessor
A device for storing data related to movement of a prosthetic implant includes at least one transducer for generating at least one real time movement signal responsive to movement within the prosthetic implant. A processor generates movement data parameters and associated time stamps in response to the real time movement signal. The generated data parameters and time stamps are stored within a memory associated with the processor. A communications link may be used to selectively access the movement data parameters and the time stamps in the memory from an external source.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
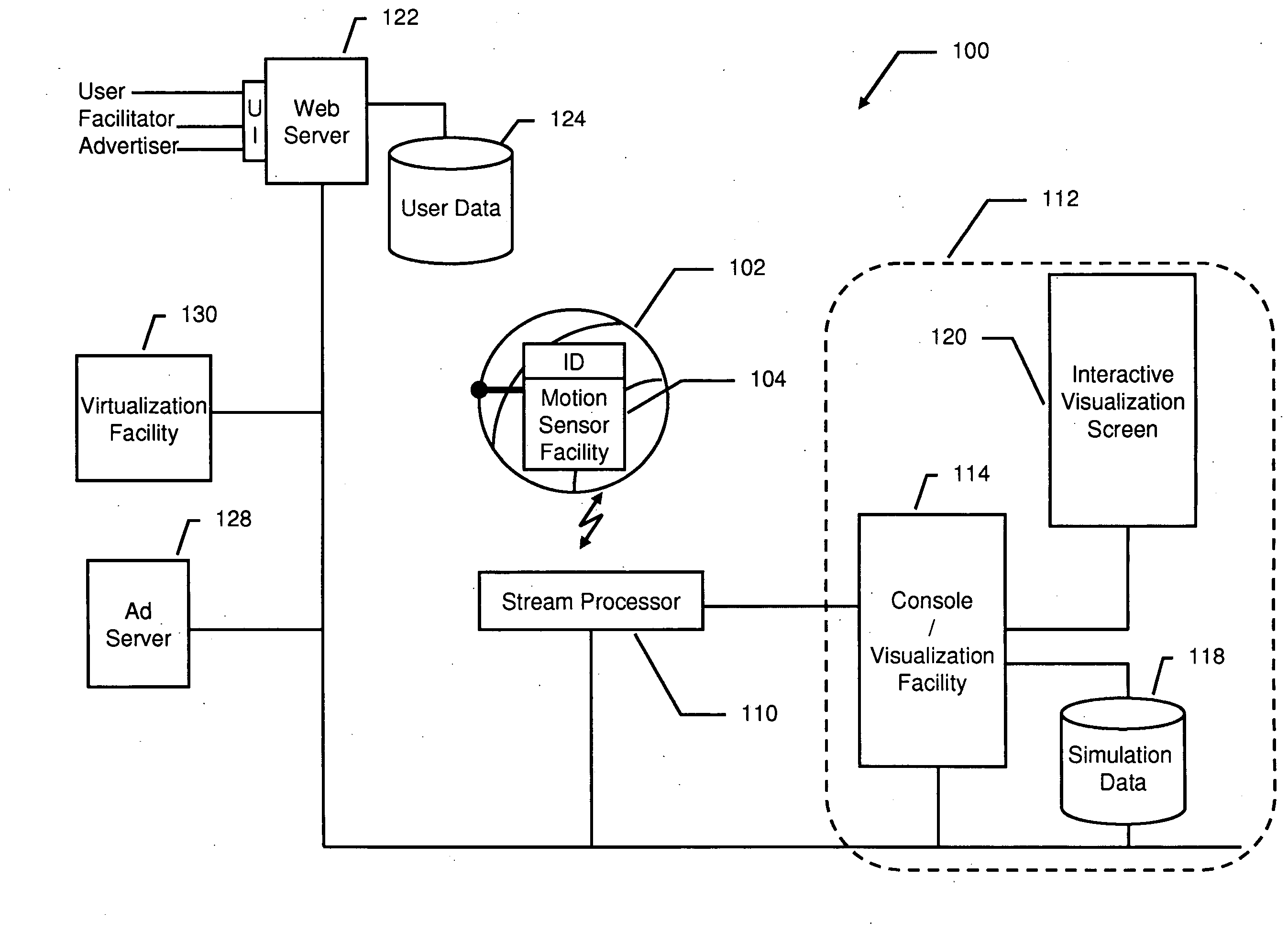
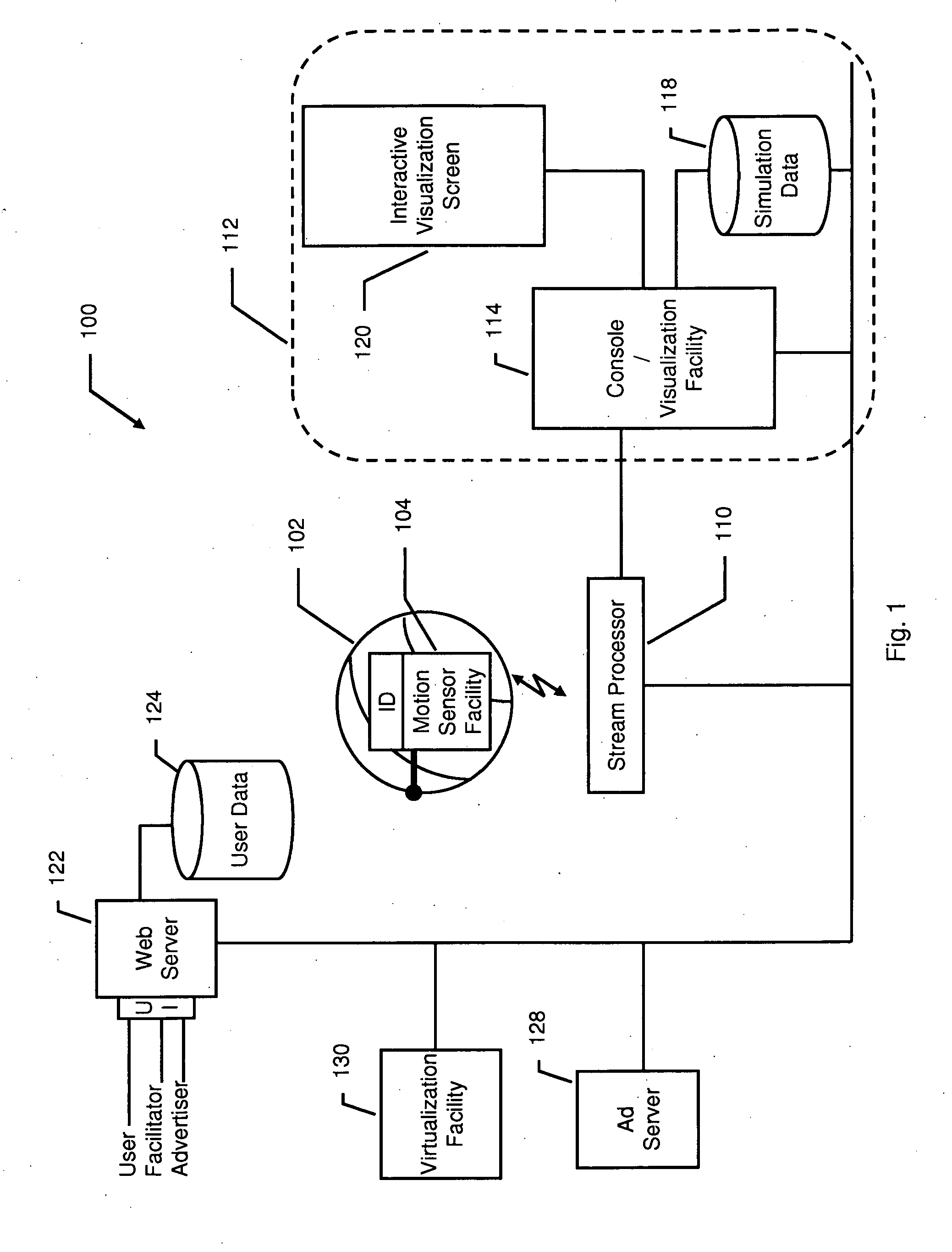
Tracking and Interactive Simulation of Real Sports Equipment
InactiveUS20090029754A1Enhanced interactionGymnastic exercisingBall sportsData streamSports equipment
A real-ball interactive sports entertainment and training system combines real-time motion sensing of real world sports equipment to create simulated interactions with amateur or professional sports figures on-screen, optionally including in-game advertising. The interactive sports entertainment and training experience extends to the internet, where users can view their statistics and highlights and compare notes and simulated sports stories with other users, or “cyberjocks.” The system implements methods that include embedding a plurality of three-axis motion sensors within a single piece of user sports equipment, wherein each of the plurality of sensors provides a continuous stream of relative motion data for each axis; disposing the plurality of three-axis motion sensors so that none of the axes are aligned; connecting the disposed motion sensors to a processor, and powering the sensors and the processor so that the processor receives the relative motion data; converting the relative motion data into a six or more axis representation of the motion of the single piece of sports equipment; and communicating the six or more axis representation to a multimedia facility.
Owner:CYBERSPORTS
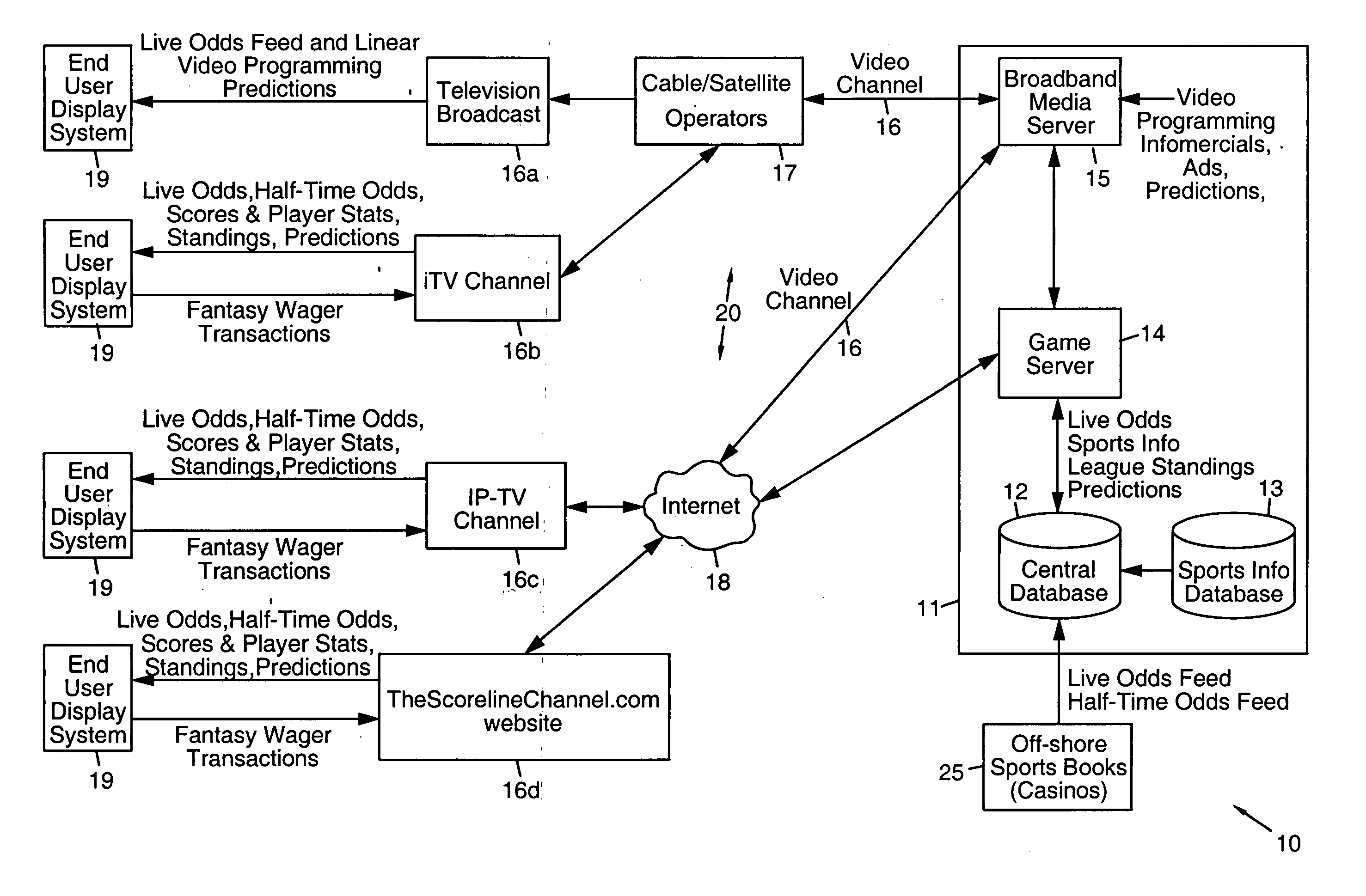
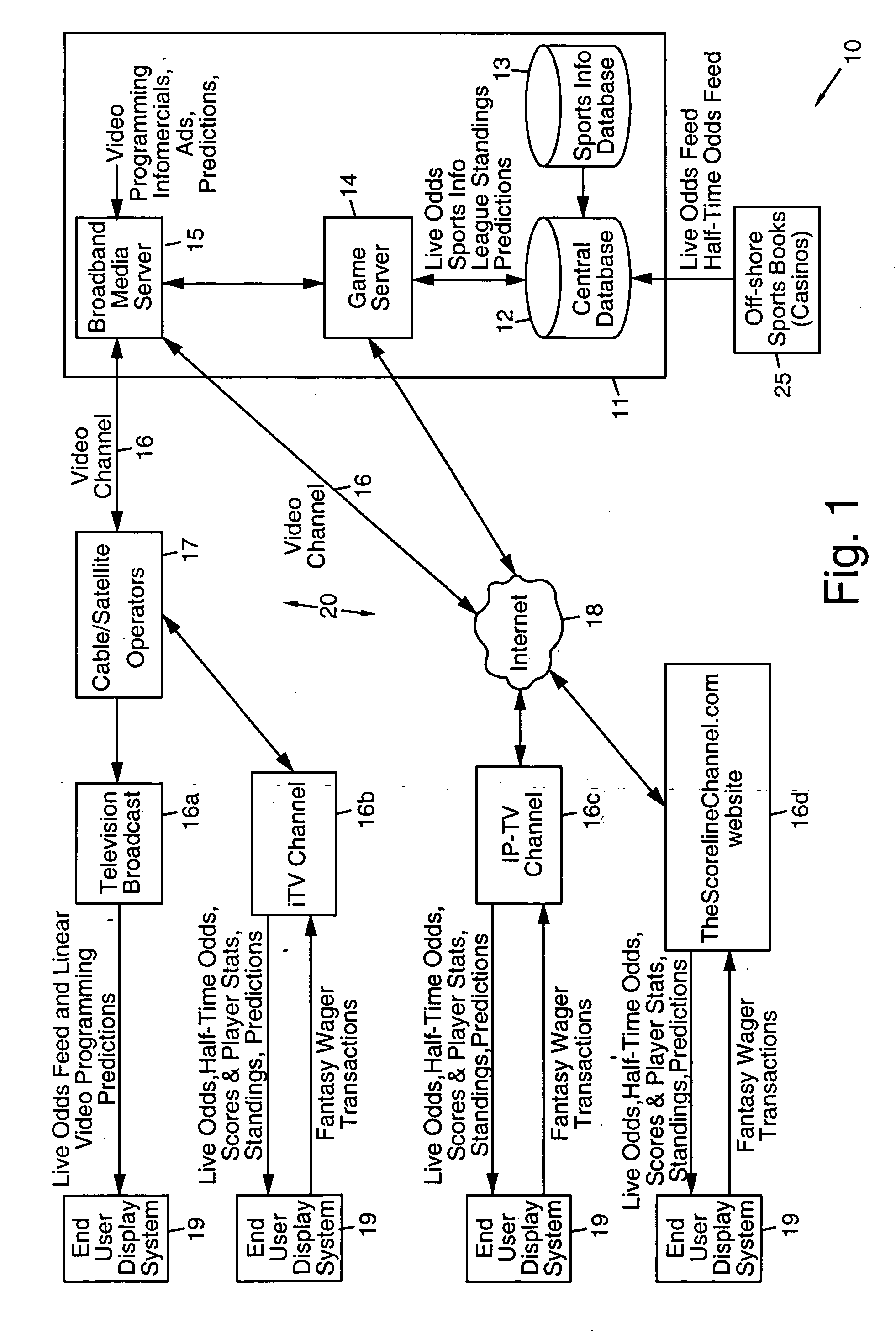
Fantasy sports television programming systems and methods
InactiveUS20060183547A1Gaming experience moreWithout providing any negative financial consequencesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesTelecommunications linkCommunication link
Systems and methods are disclosed that include display systems located at player sites, a server system for generating a television channel comprising real-time live off-shore odds, fantasy betting sports games, standard fantasy sports games, and sports prognosticator predictions, and a communication link for transmitting the television channel to the display systems. The television channel may comprise standard and enhanced fantasy sports games and standard and enhanced fantasy betting sports games with real-time live off-shore odds derived from the one or more off-shore sports books, and sports predictions from sports prognosticators using real-time live off-shore odds from one or more off-shore sports books. Exemplary communication links include cable and satellite providers, telephones, other wireless and wired devices and the Internet. Content may be transmitted by way of cable and satellite providers, telephones, other wired and wireless devices and the Internet. Exemplary display systems include digital non-interactive television systems, digital interactive television systems and web-enabled computer devices. Exemplary programming formats include a linear video channel, a linear interactive television (iTV) channel, an Internet protocol television (IP-TV) channel, and a website channel. The present invention permits interactive fantasy betting on and playing of fantasy betting sports games and fantasy sports games using real-time off-shore betting odds displayed on a television or computer device. The present invention delivers real-time off-shore odds, fantasy betting sports games, fantasy sports games, sports prognosticator predictions, fantasy betting casino games and fantasy casino games for display on television systems and computer devices that implement interactive TV, IP-TV and non-interactive TV.
Owner:MCMONIGLE MACE
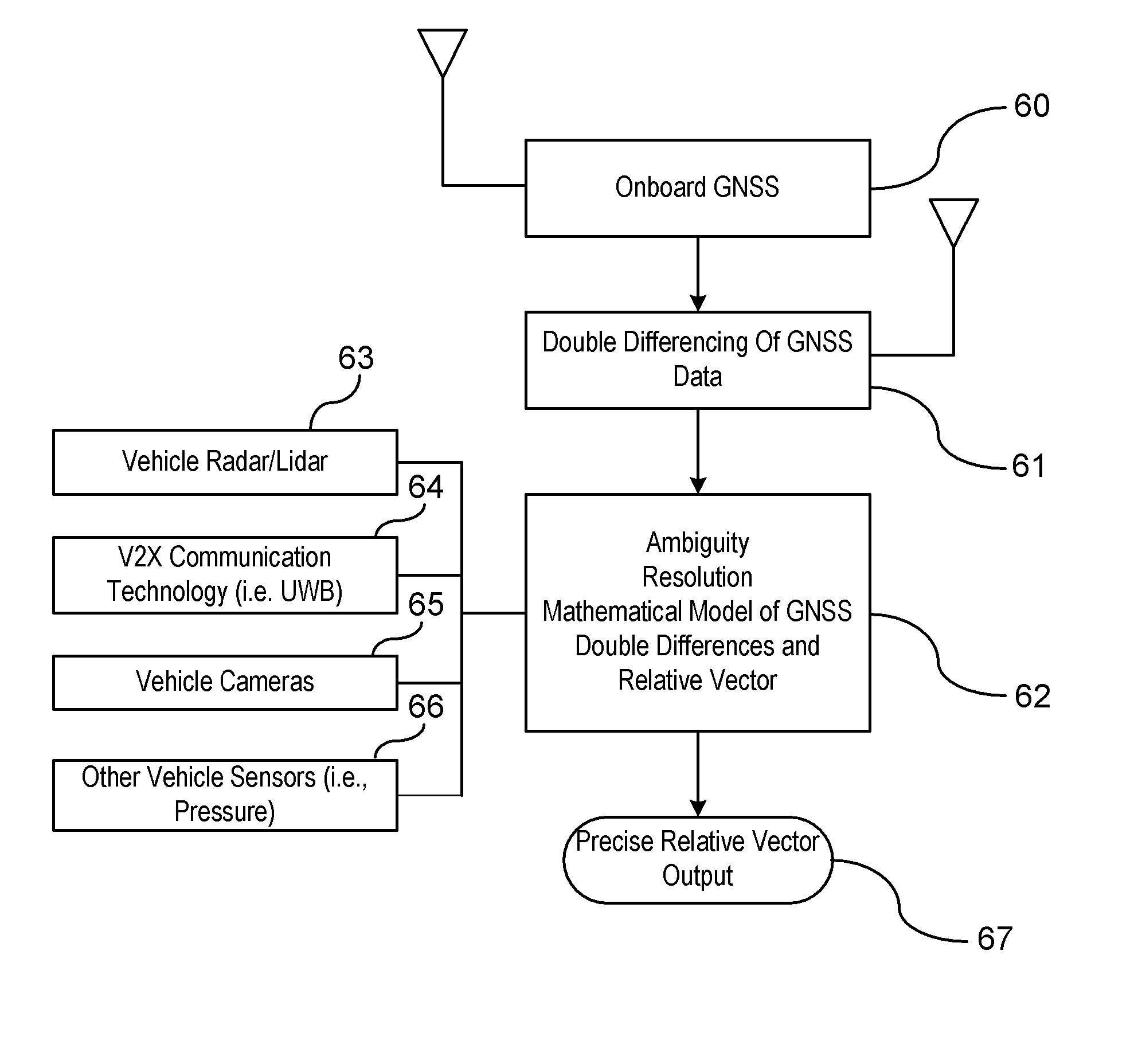
Measurement Level Integration of GPS and Other Range and Bearing Measurement-Capable Sensors for Ubiquitous Positioning Capability
A system and method are provided for determining a position of a host vehicle using a real time kinematics positioning technique when less than an optimal number of satellites are available for determining the position of the host vehicle. GPS data is retrieved from the host vehicle. GPS data is retrieved from vehicles remote from the host vehicle. Alternative vehicle position related data is retrieved. The position of the host vehicle is determined utilizing the real time kinematics positioning technique as a function of the retrieved GPS data of the host and remote vehicles and the alternative vehicle position data. The position of the host vehicle is utilized in a vehicle application.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus and method for real-time motion-compensated magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20090209846A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonanceReal Time Kinematic
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for real-time motion compensated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a human or animal. The apparatus includes one or more magnetic-resonance compatible cameras mounted on a coil of the MRI device, a calculation and storage device, and an interface operably connected to the MRI device and the calculation and storage device. The apparatus may also include a set of magnetic resonance compatible markers, where the markers are positioned on the human or animal. Alternatively, the apparatus may use a facial recognition algorithm to identify features of the human or animal. For the present invention, the frame of reference is defined by the animal or human being imaged, instead of the typical magnetic resonance coordinate system. Based on continuous positional information, the apparatus controls the magnetic resonance scanner so that it follows the human or animal's motion.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
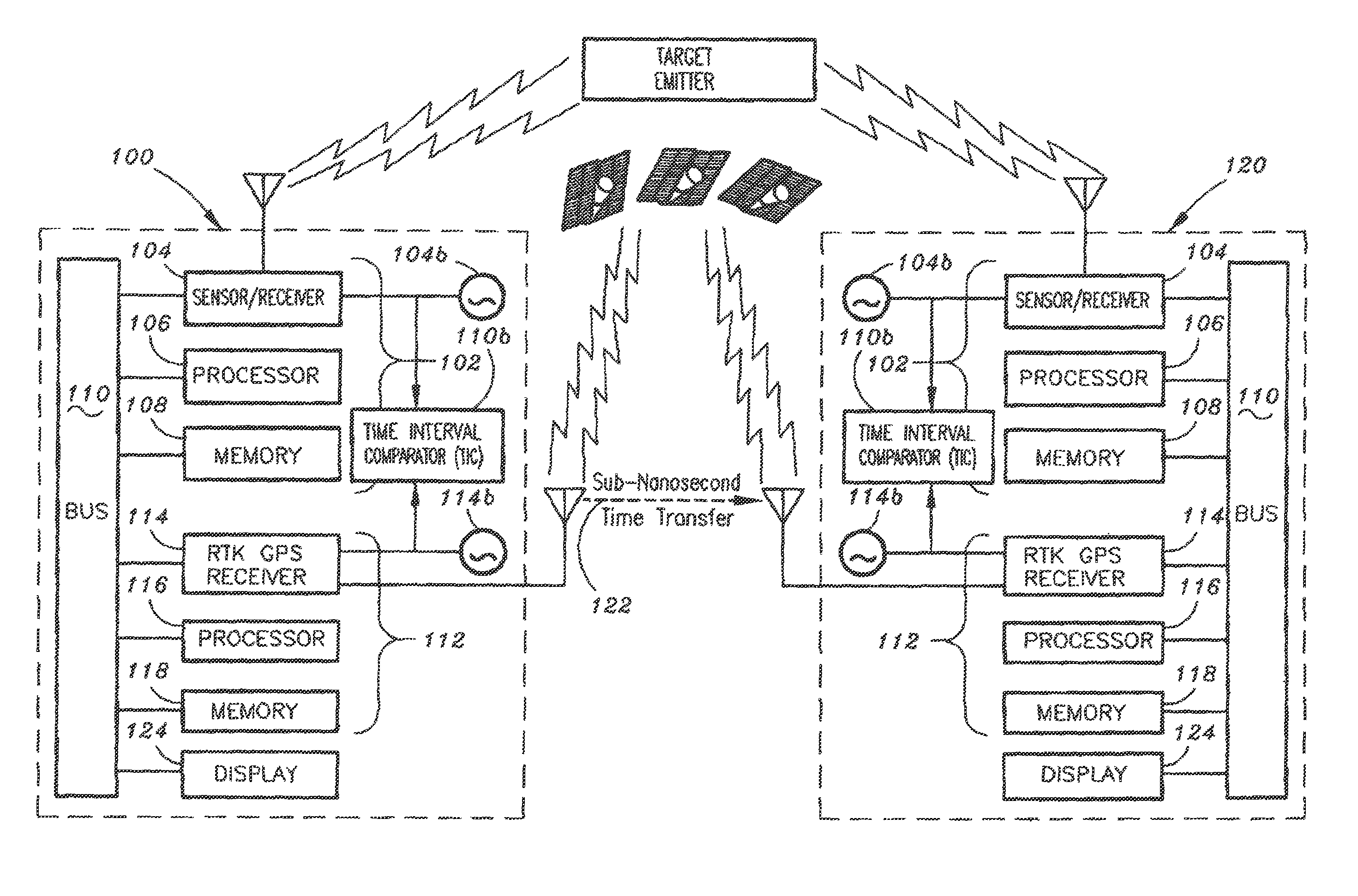
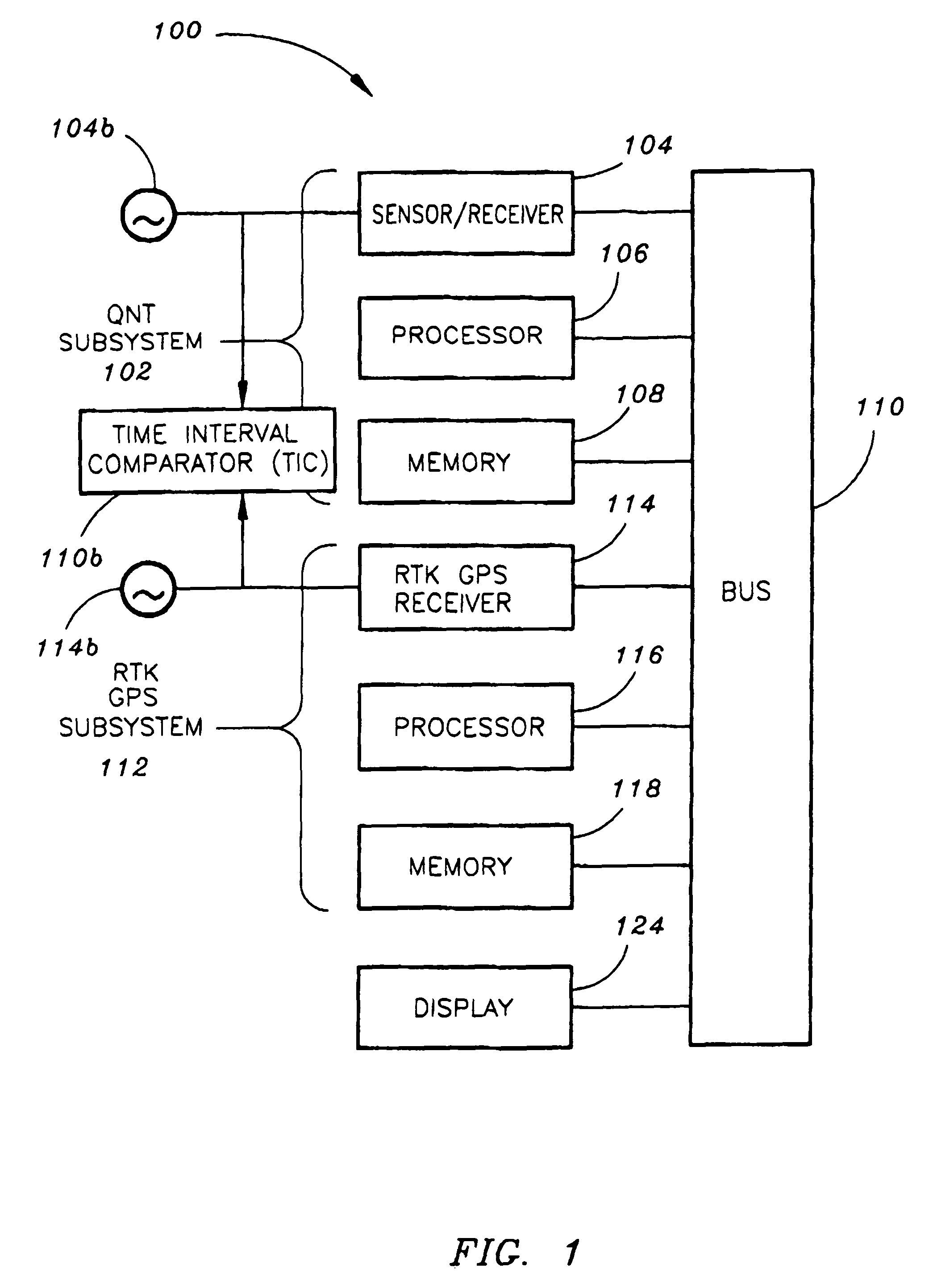
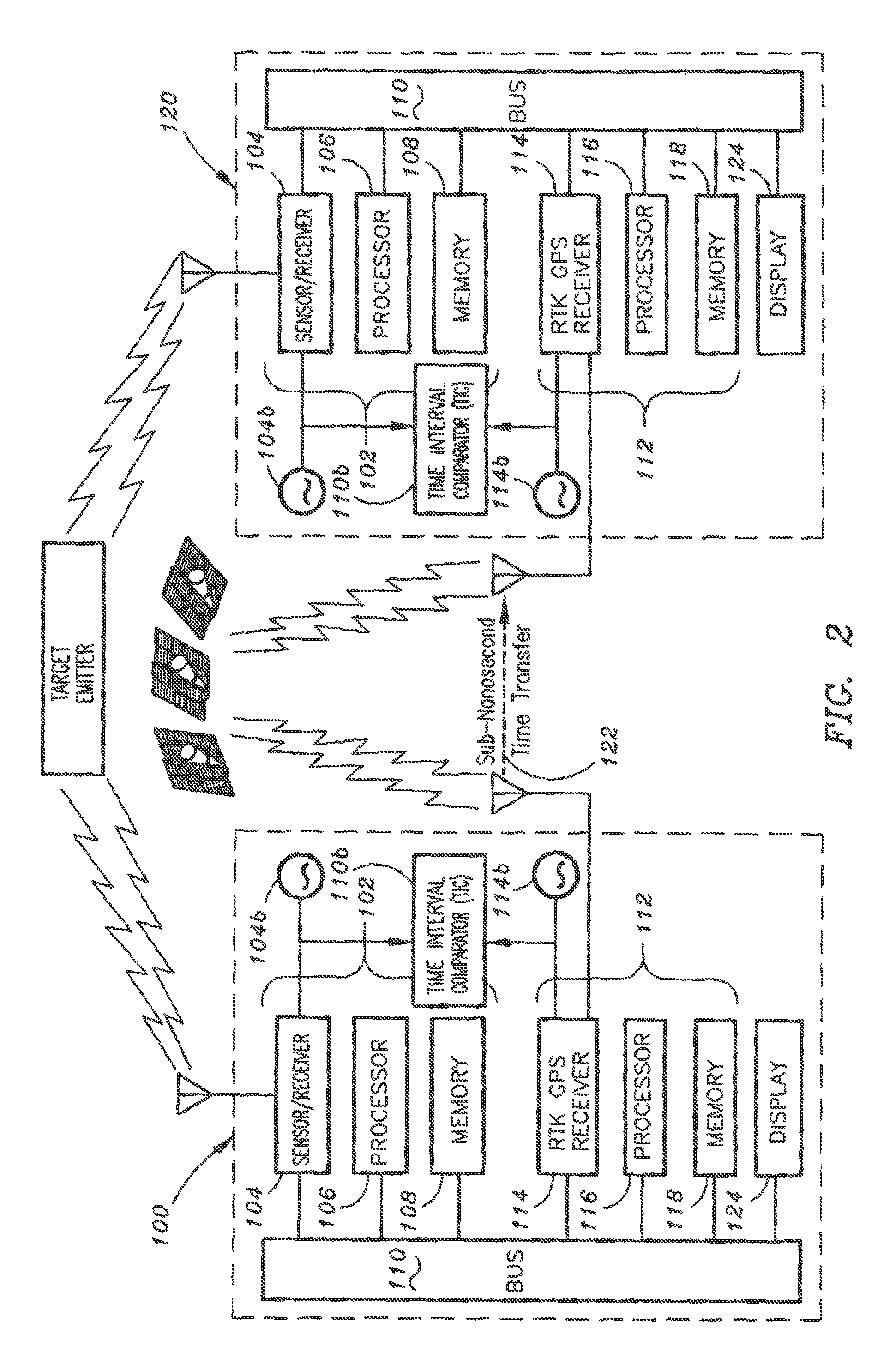
Coordinated sensing and precision geolocation of target emitter
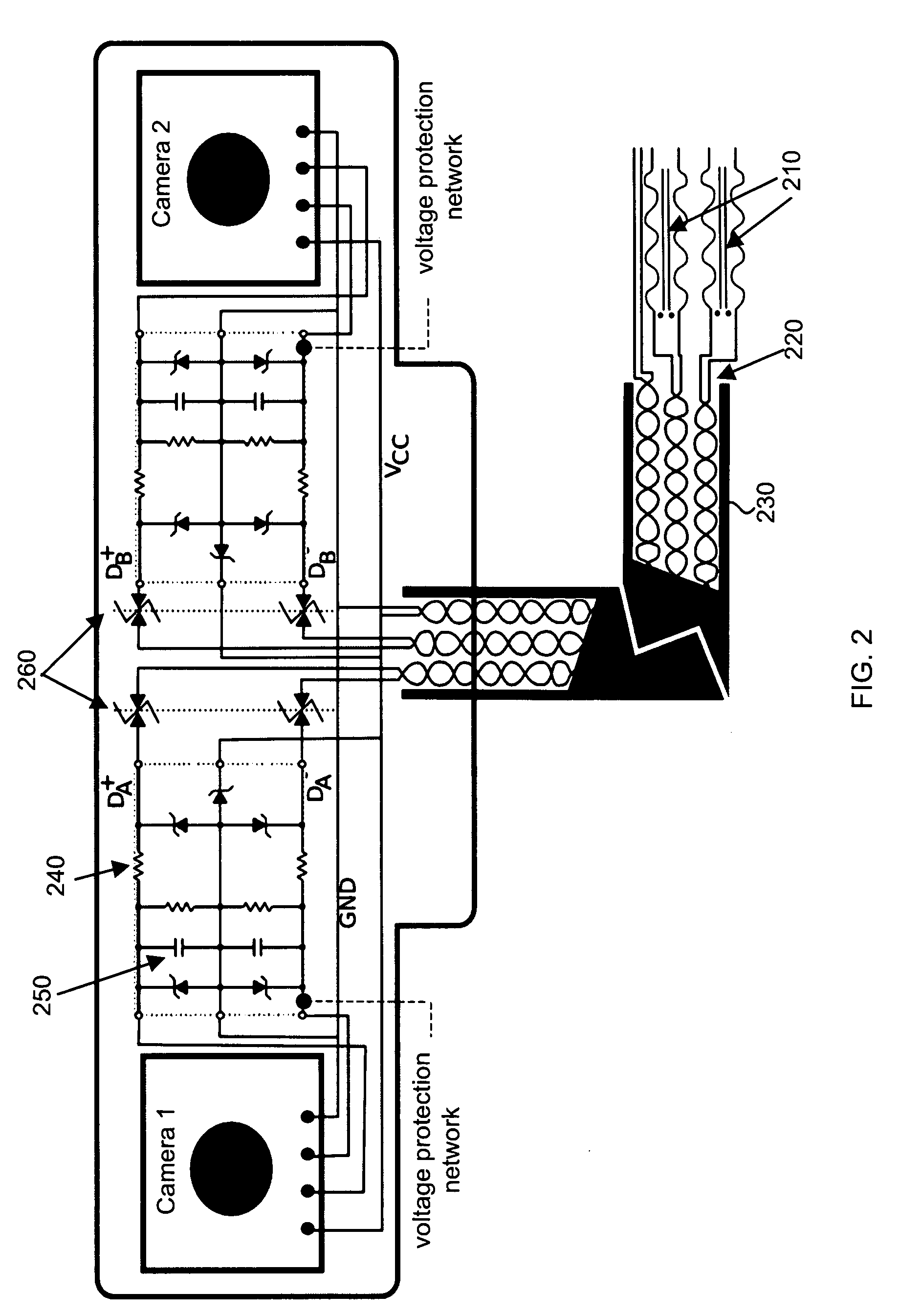
The present invention is a geolocation system for providing coordinated sensing and precision geolocation of a target emitter. The system may include a Quint Networking Technology (QNT) subsystem which may be configured receiving, detecting and identifying a target emitter signal. The QNT subsystem may be further configured for extracting a carrier phase of the signal. The system may further include a Real Time Kinematic Global Positioning System (RTK GPS) subsystem for determining a position of the geolocation system relative to a position of a second geolocation system. Further, the system may be configured for communicating with the second geolocation system via a QNT communication data link for: determining a QNT time difference via signal carrier phase differencing for calculating a time difference between the geolocation systems and geolocating the target emitter based on both the relative position information of the geolocation systems and the calculated time difference between the geolocation systems.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
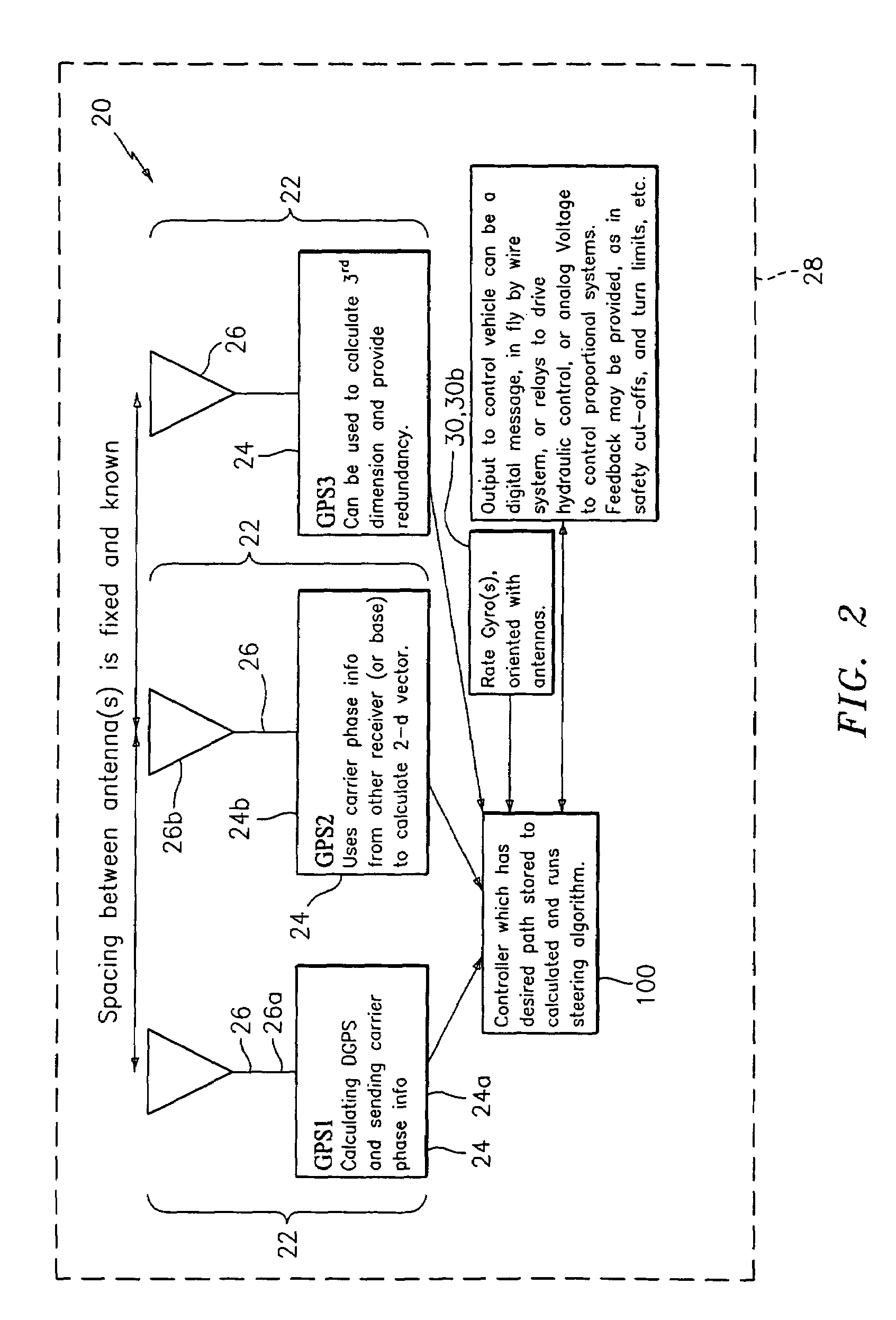
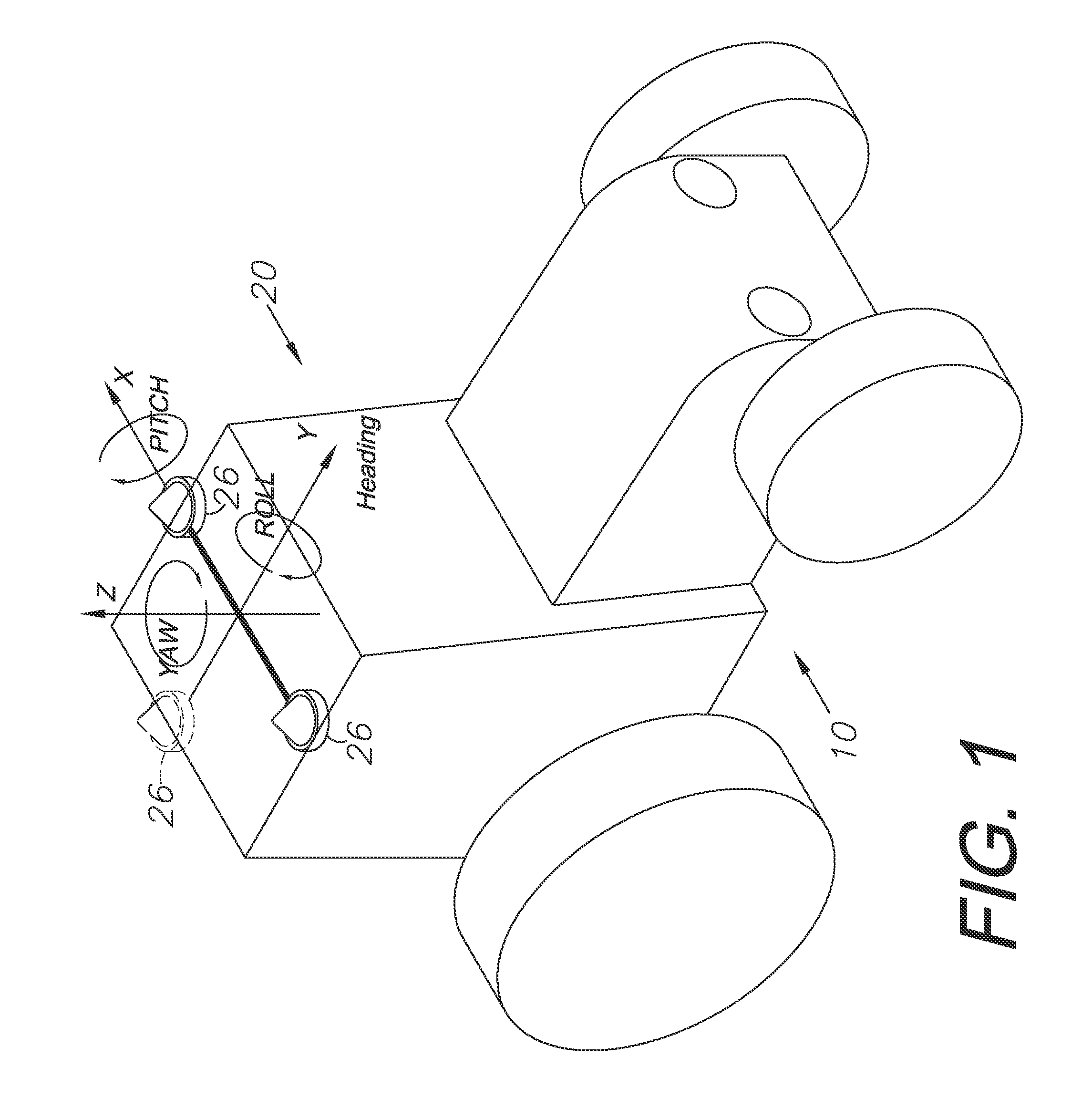
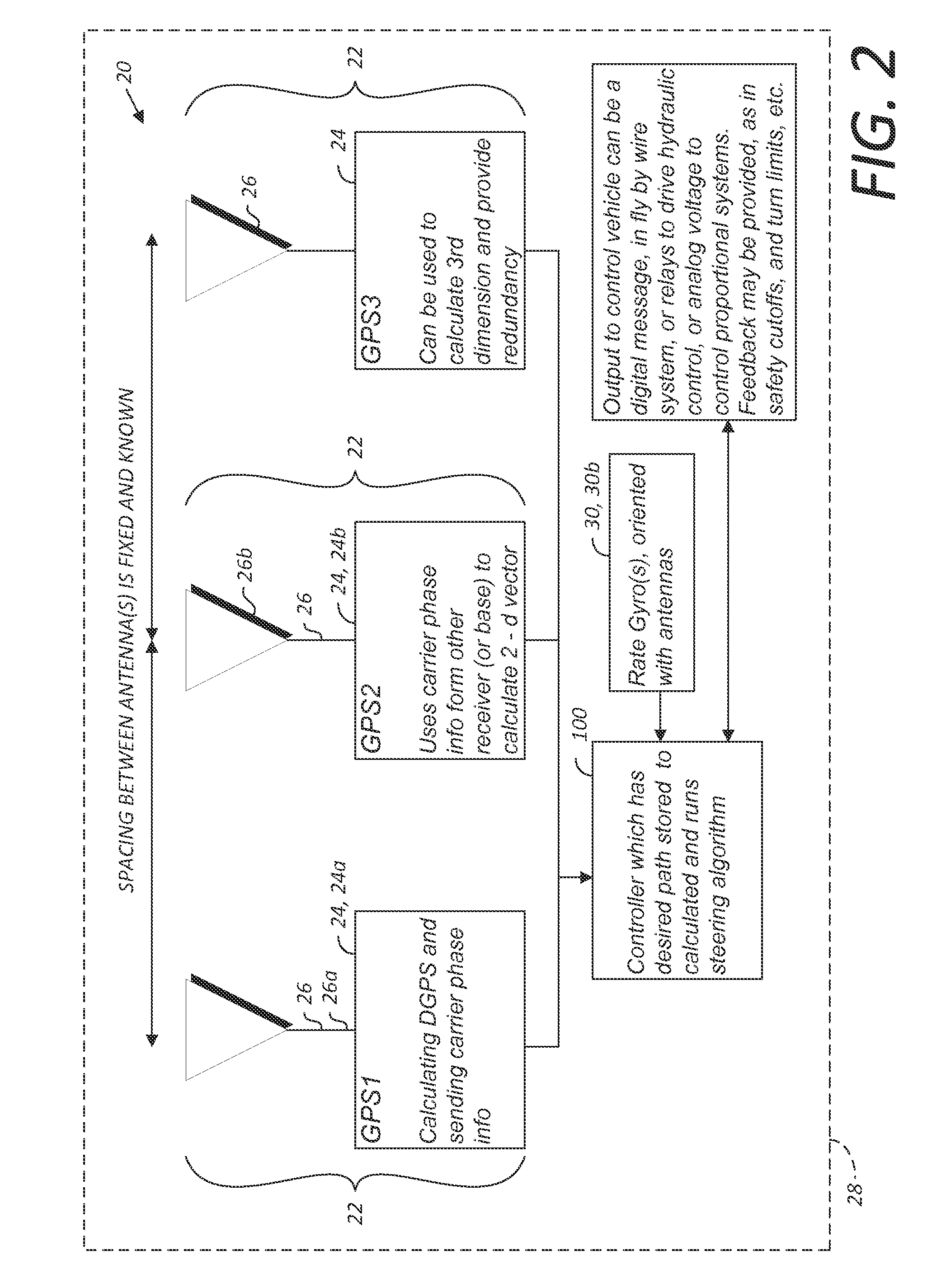
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS8639416B2Easy to correctAnalogue computers for trafficSteering initiationsGyroscopeMachine control
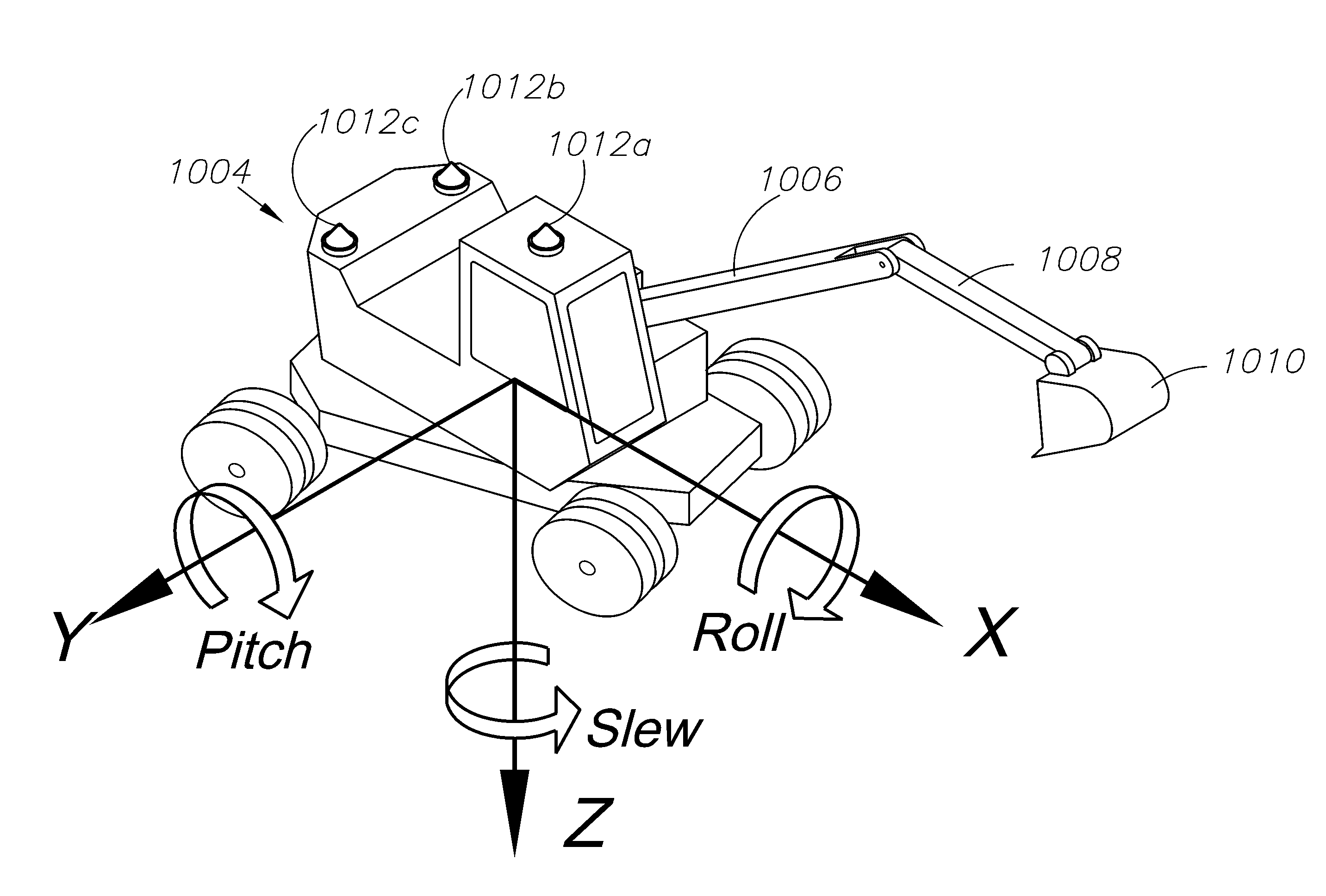
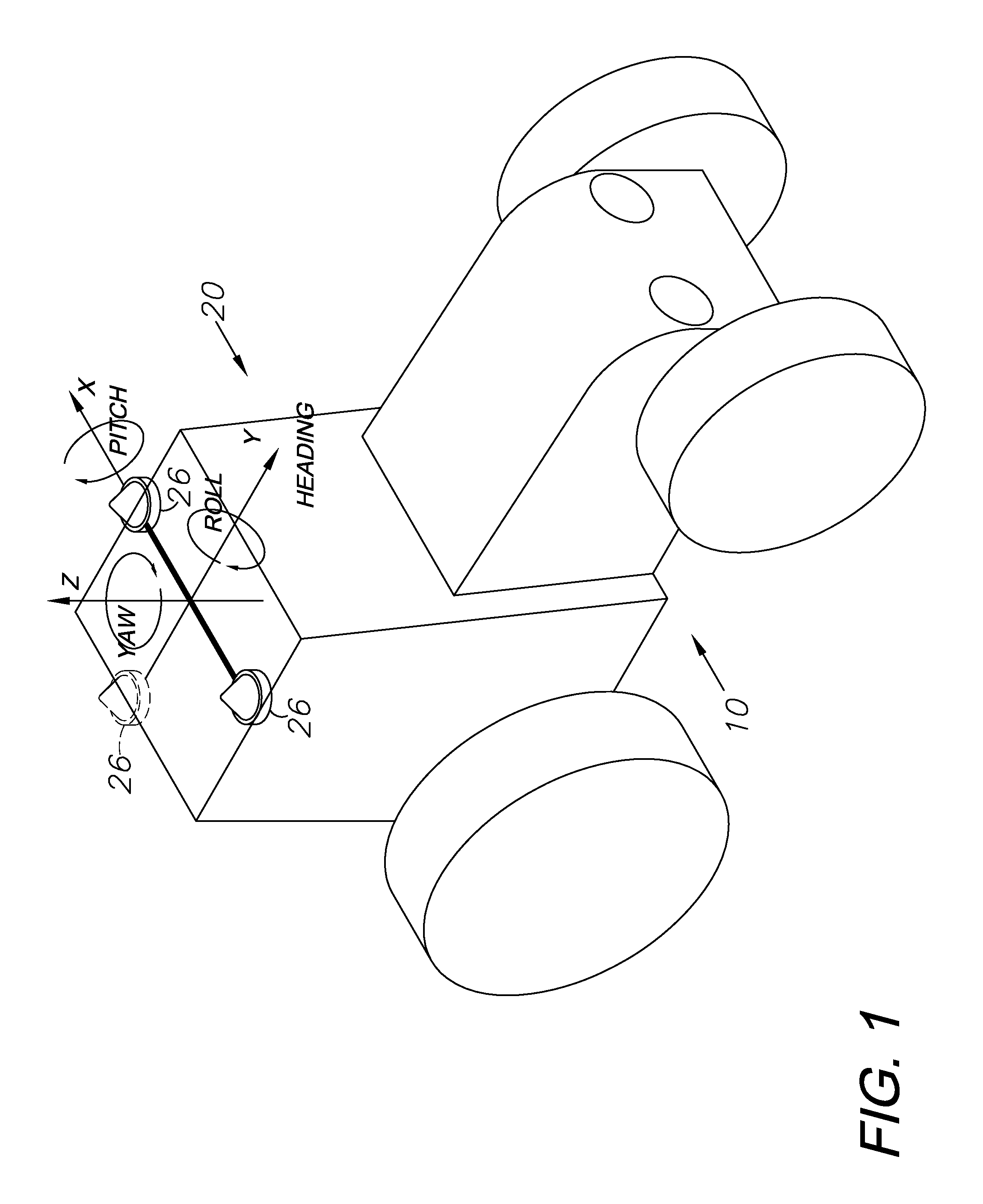
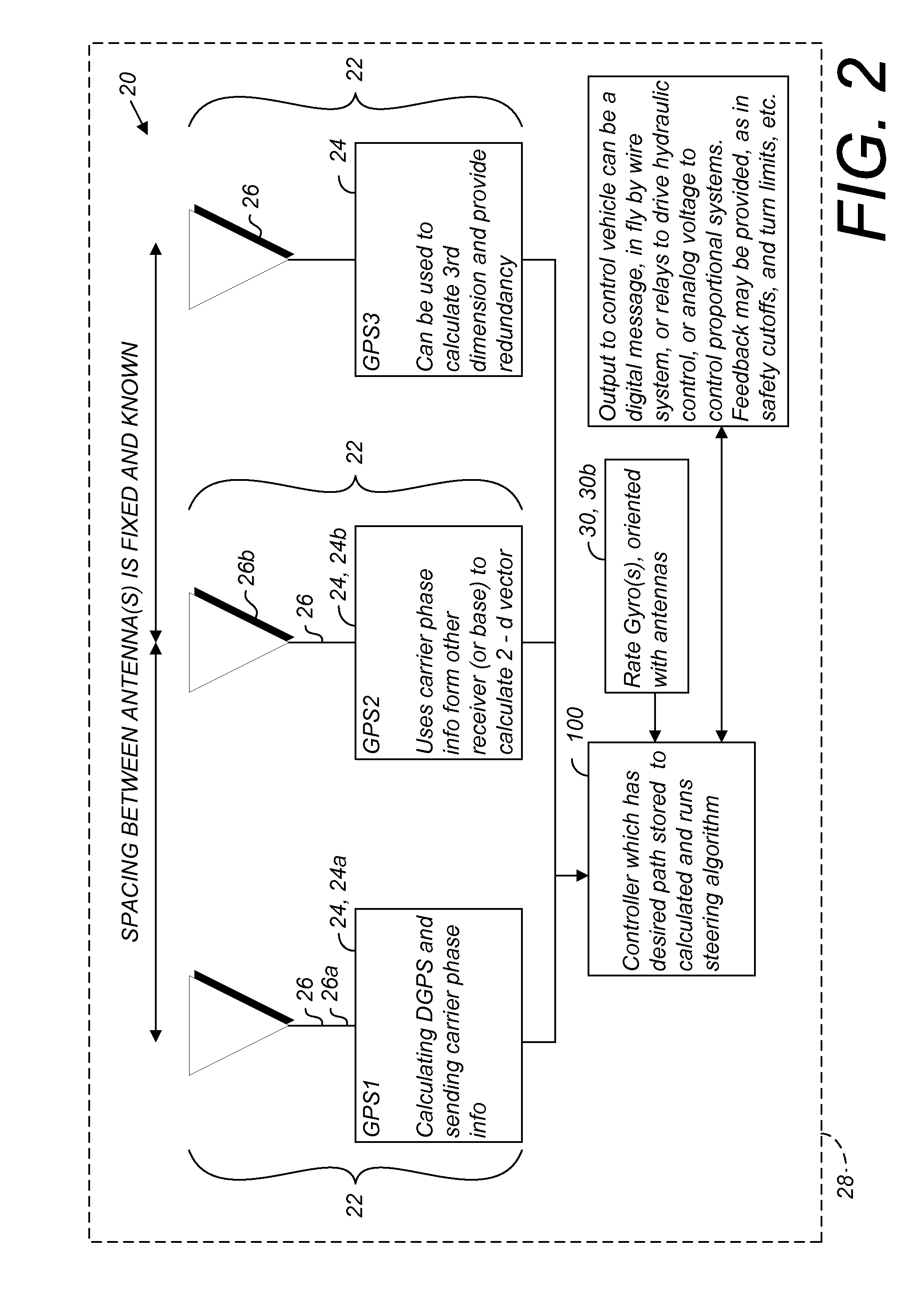
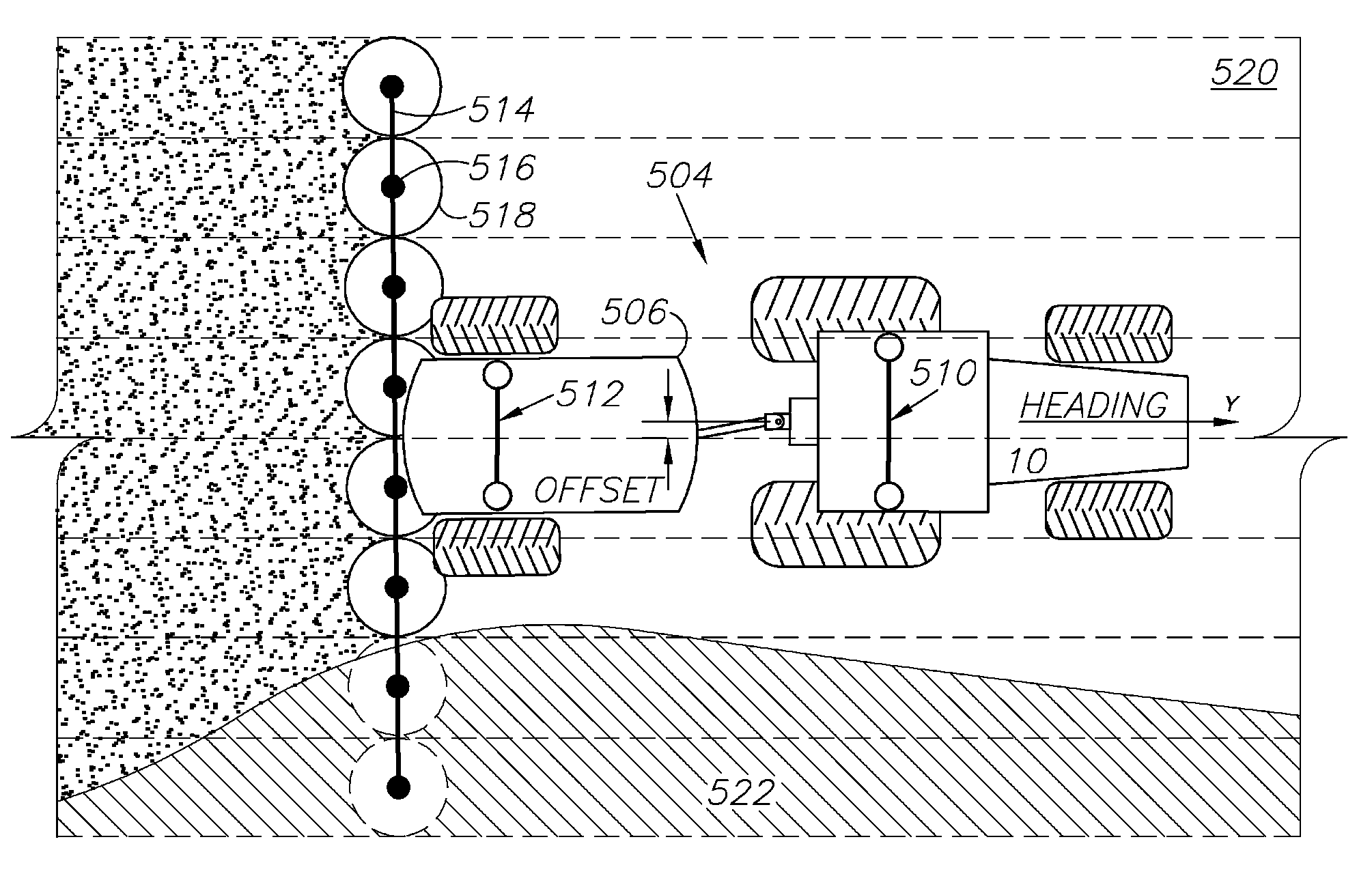
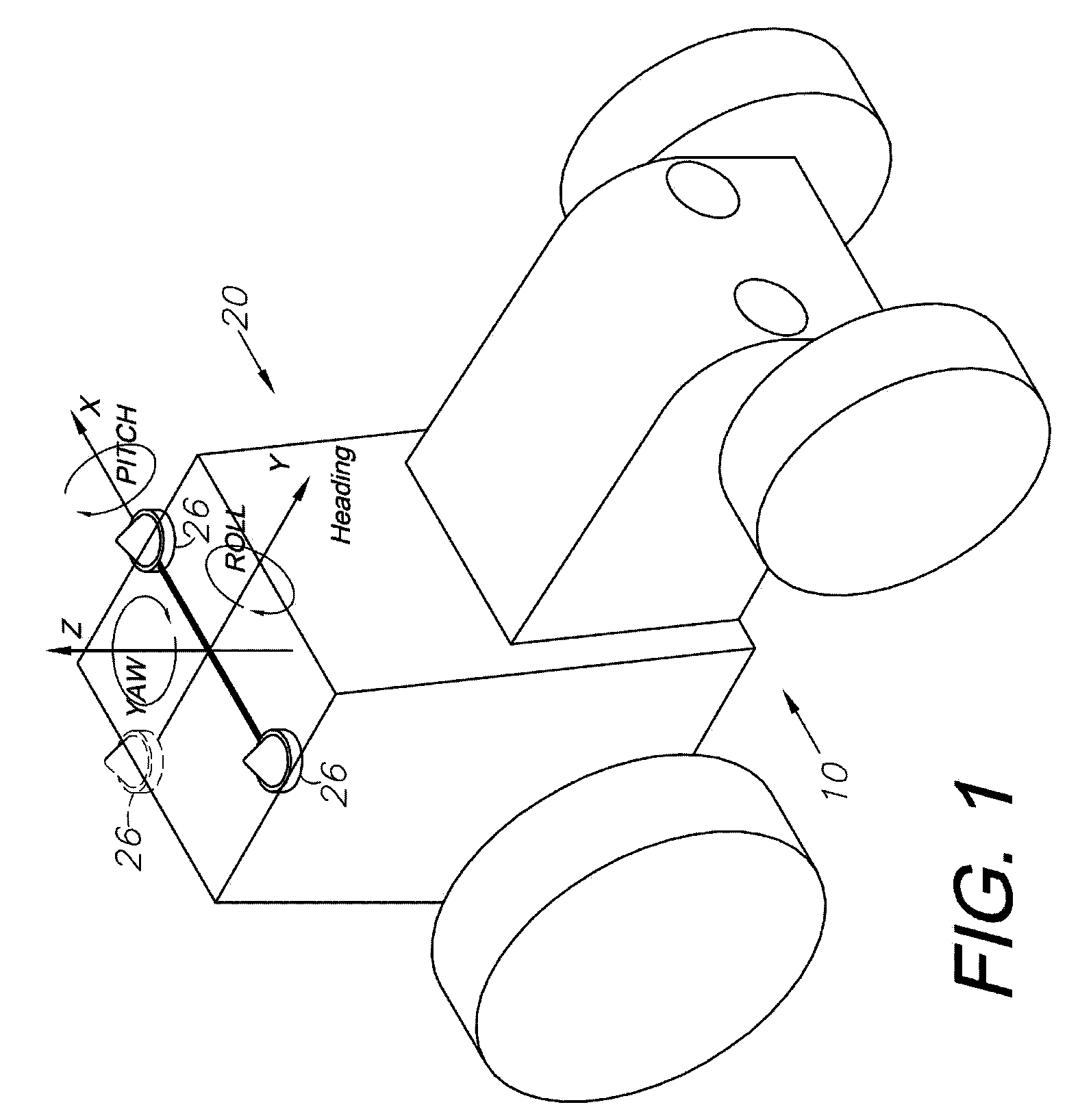
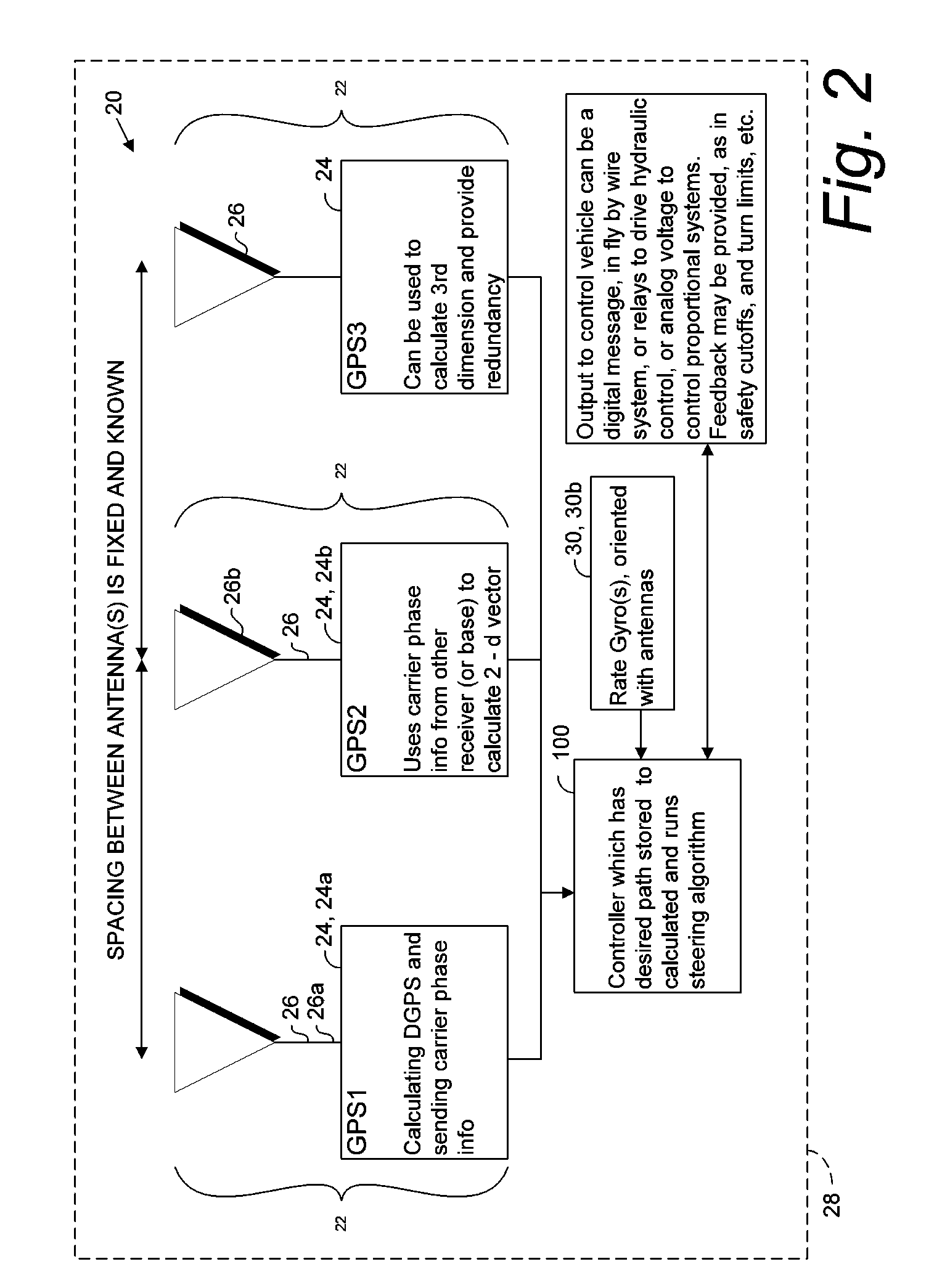
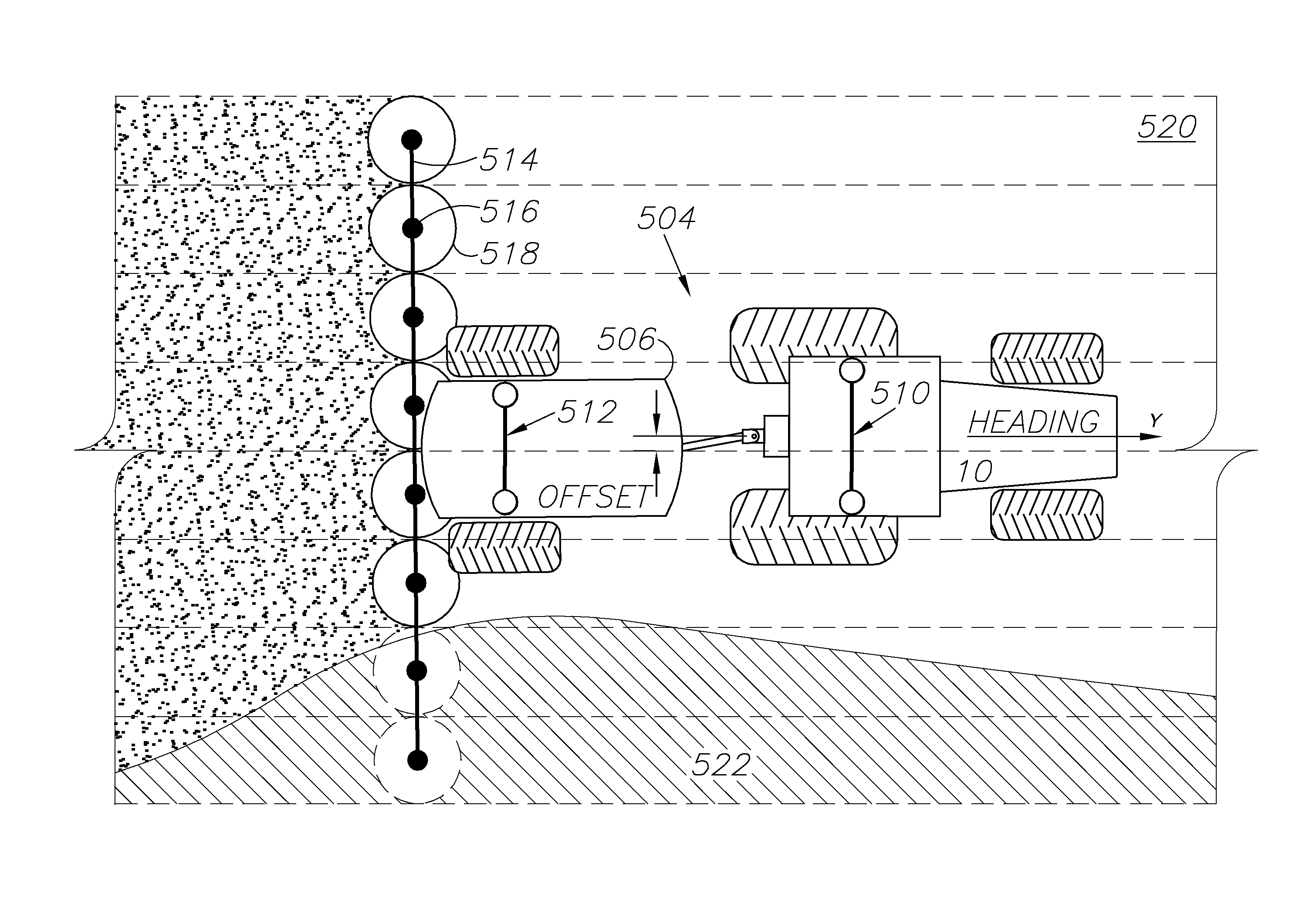
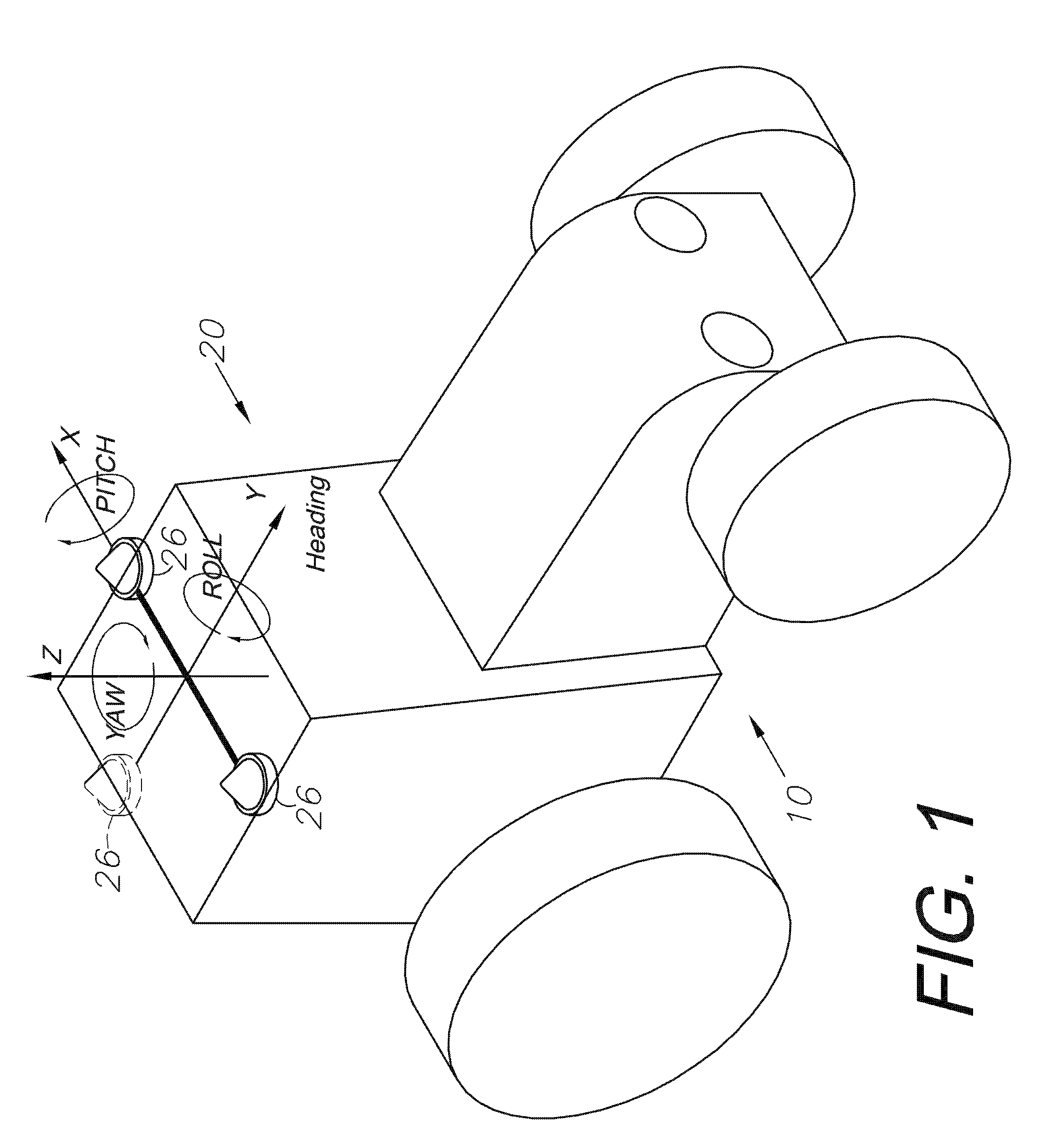
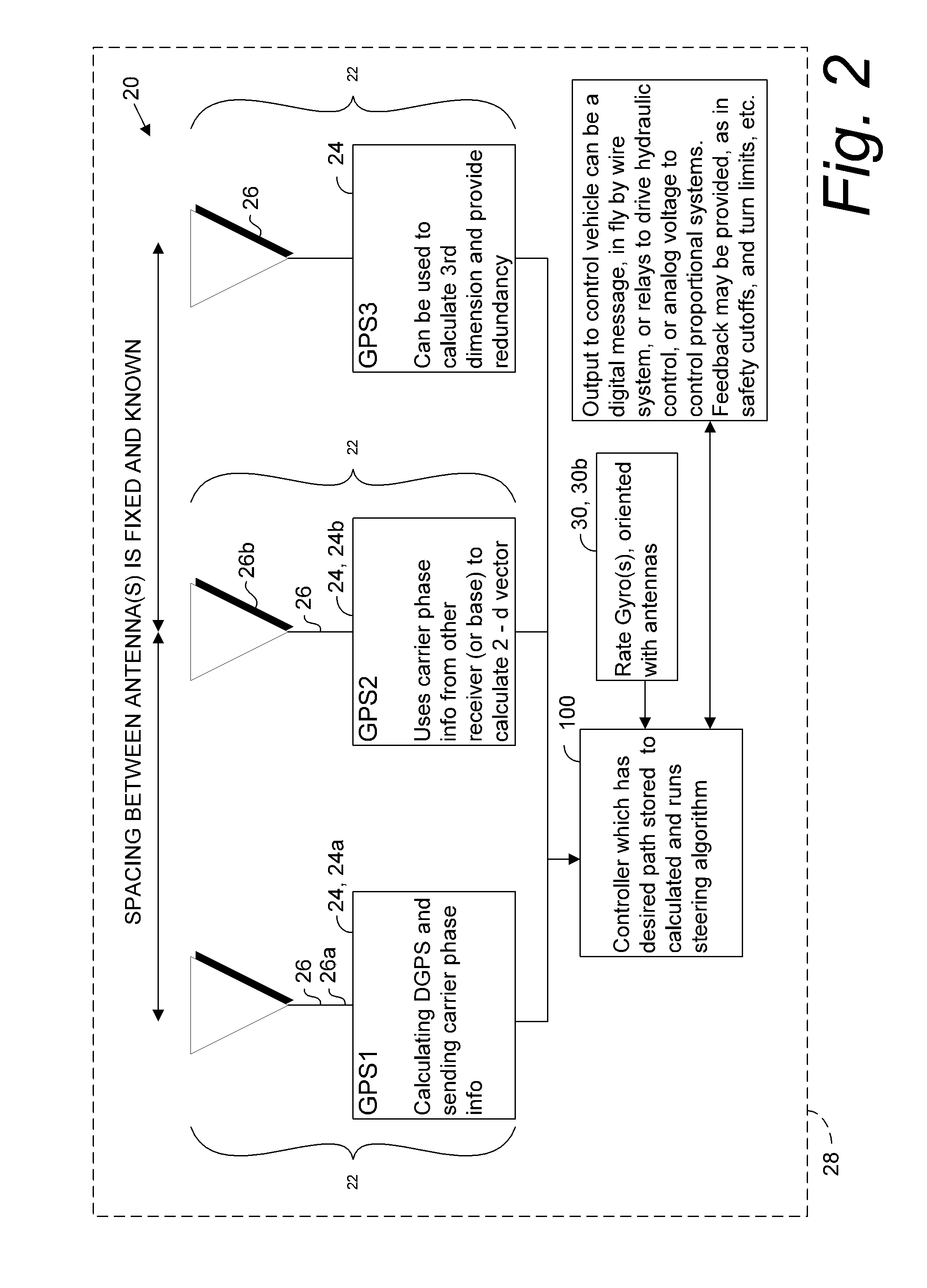
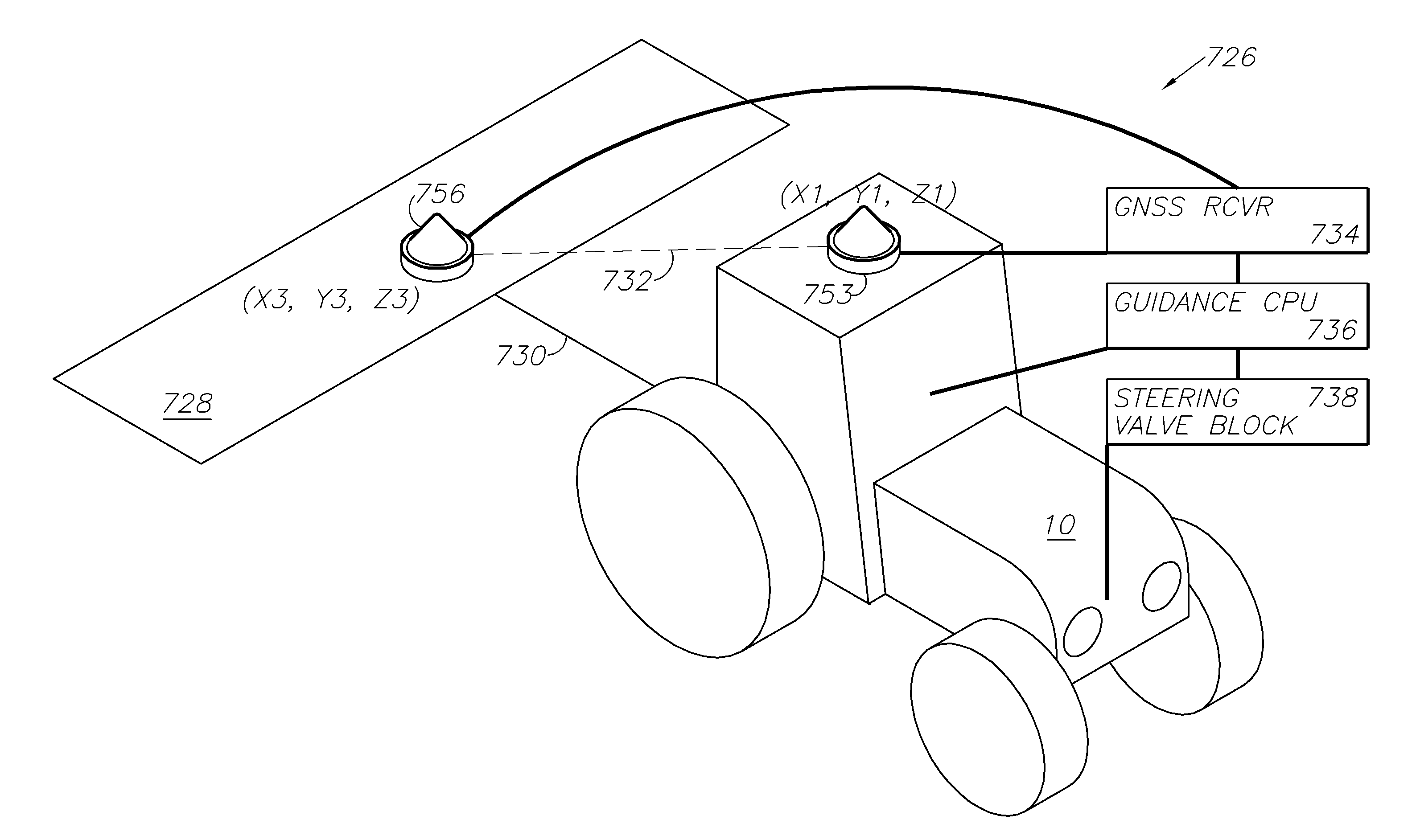
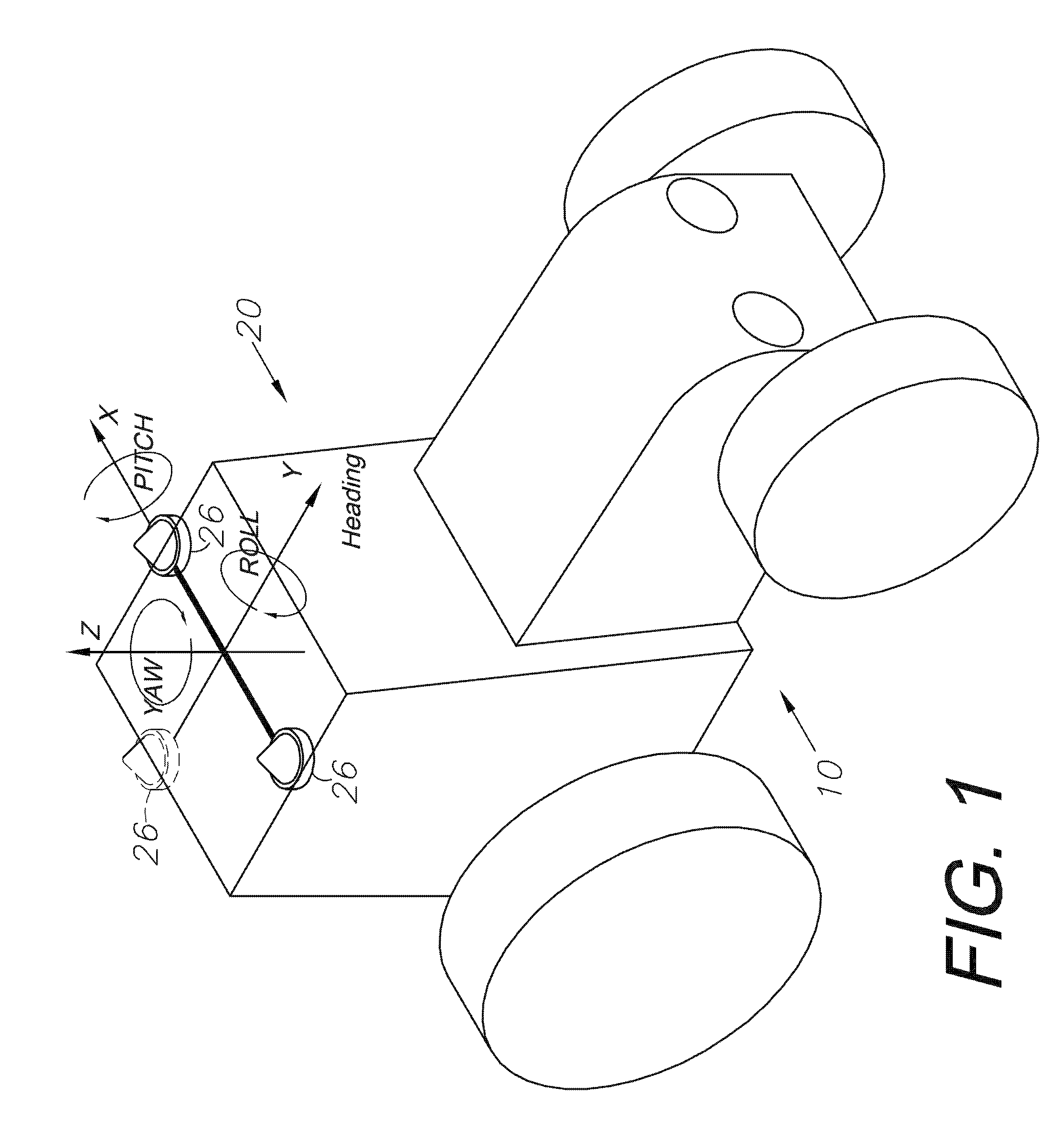
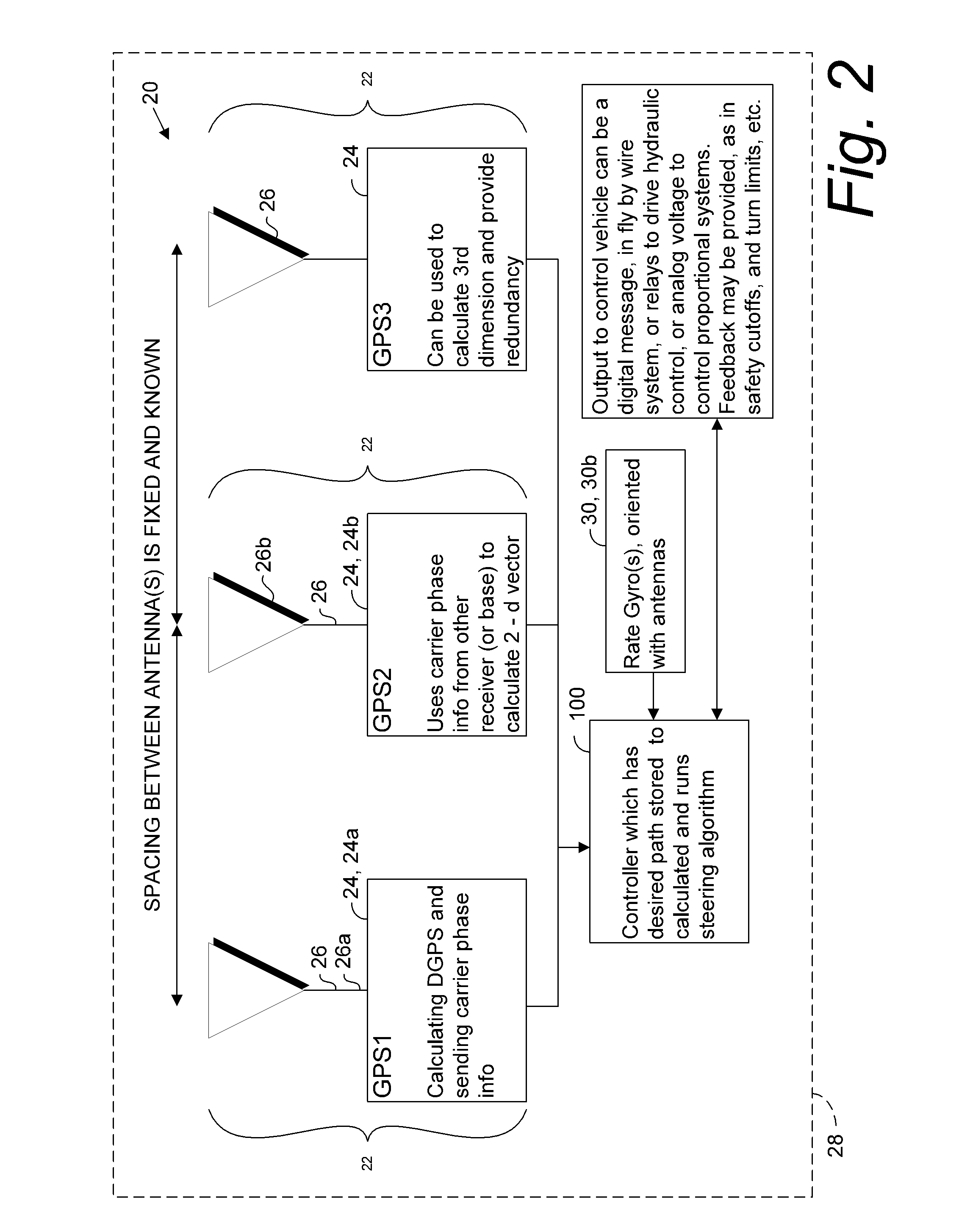
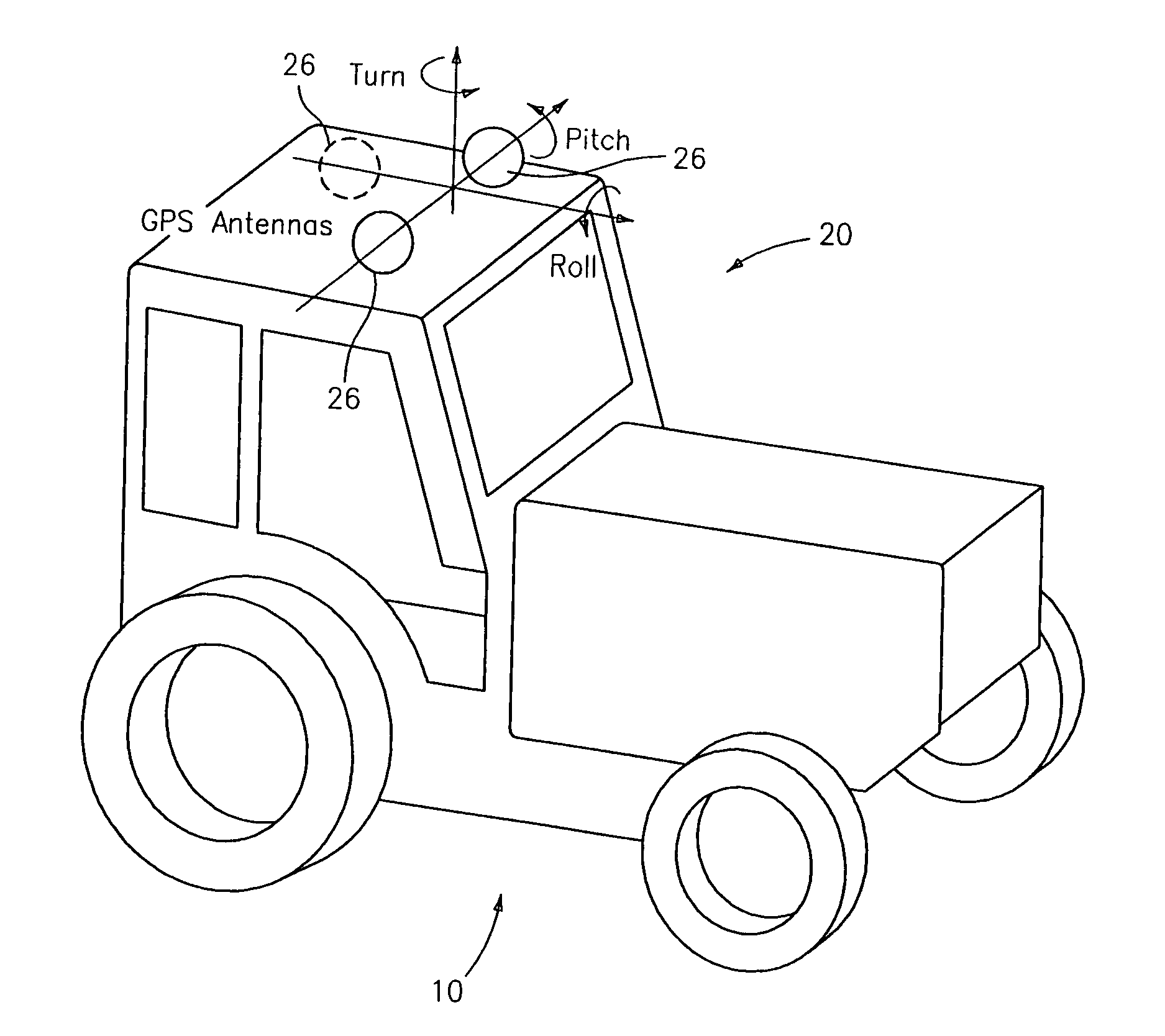
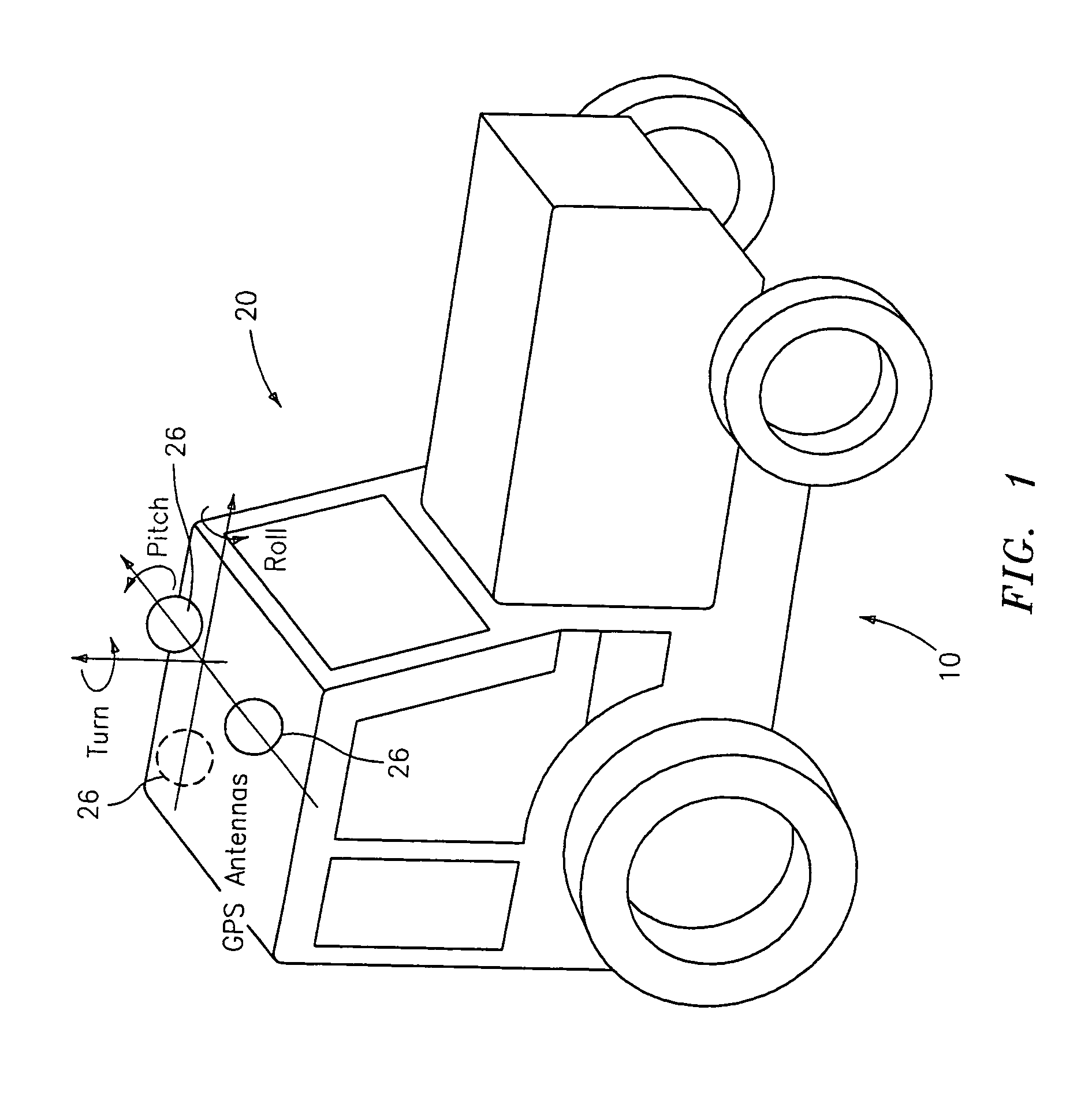
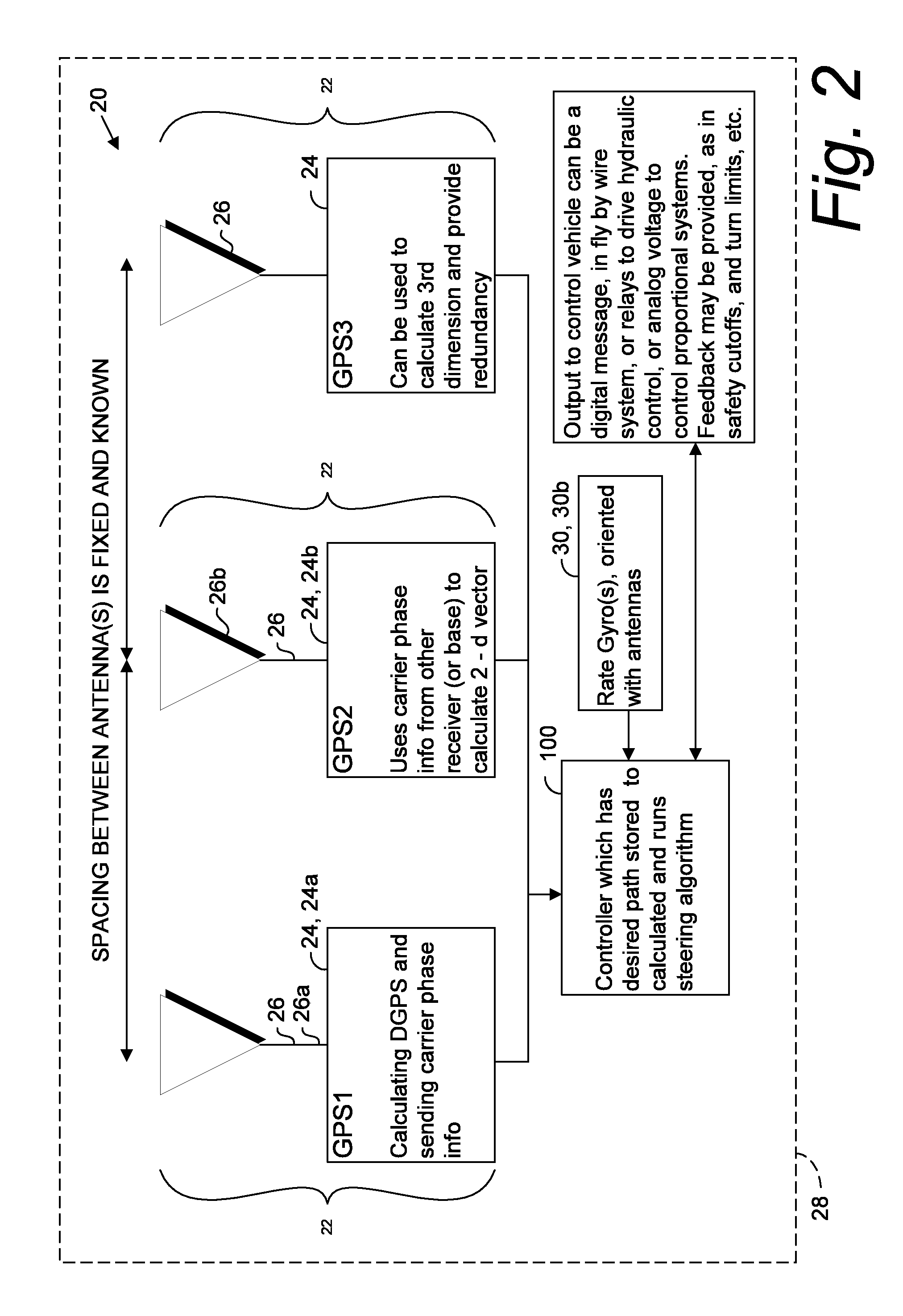
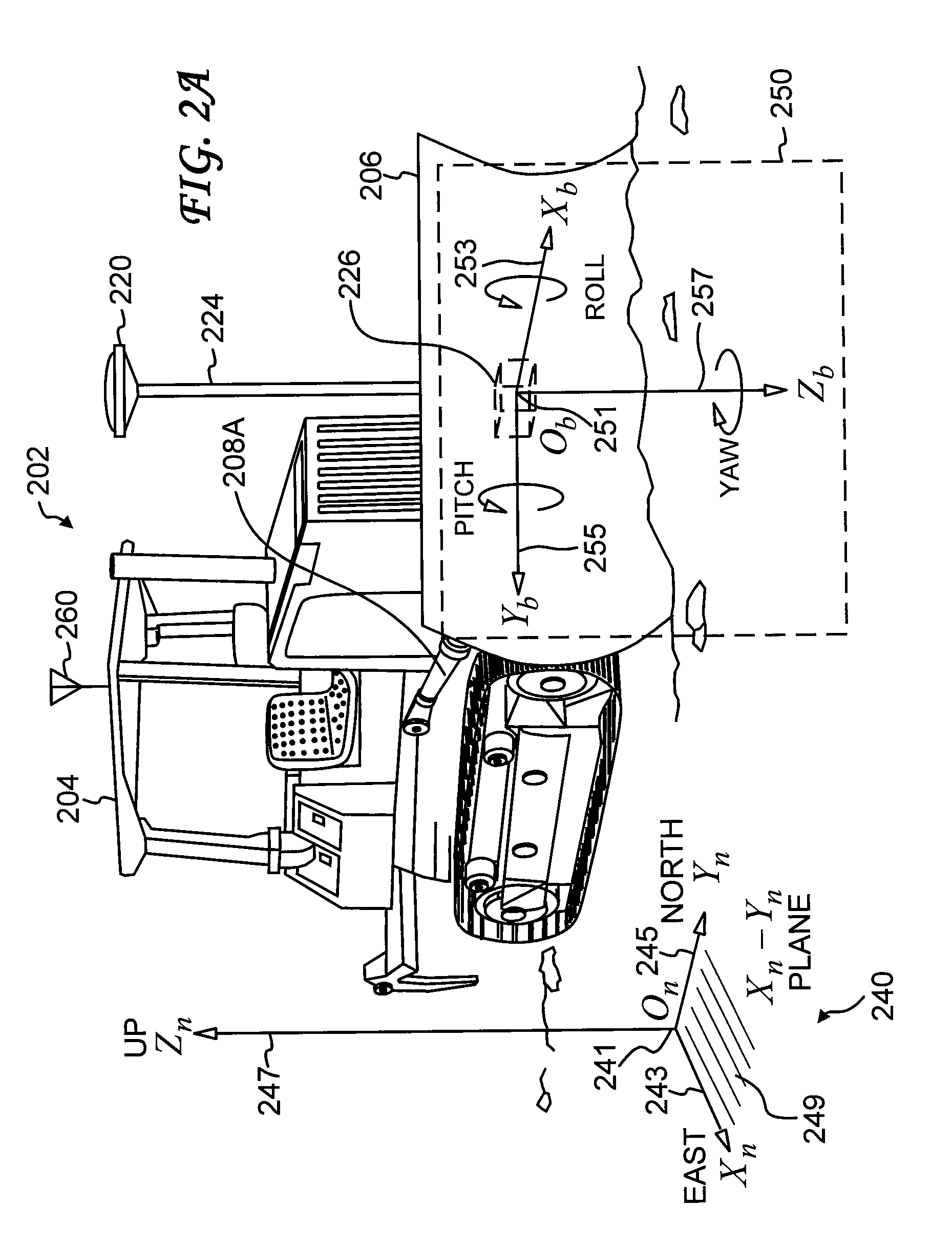
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other, and snow grooming equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Multi-antenna GNSS control system and method
ActiveUS20110054729A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficSteering controlEngineering
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, articulated implements with multiple antennas on each implement section, video input and guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20120174445A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctNavigation instrumentsGuiding agricultural machinesGyroscopeMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other, and snow grooming equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
A test method for a remotely piloted vehicle (PRV)
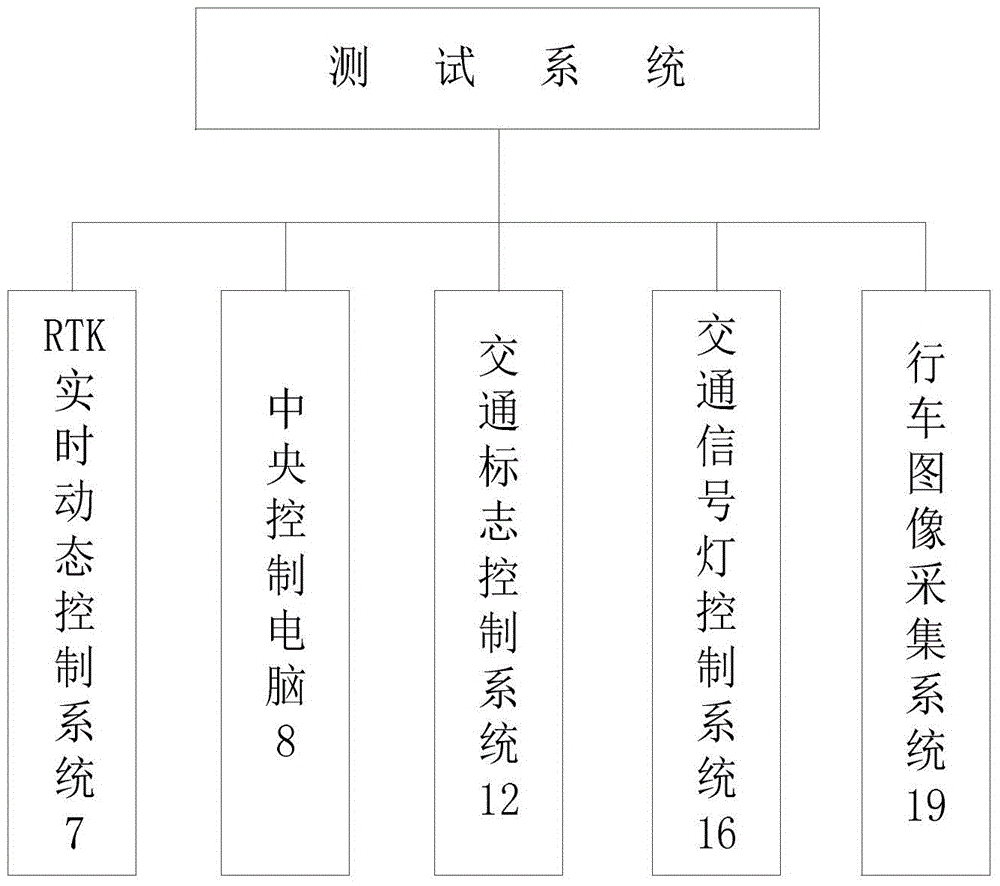
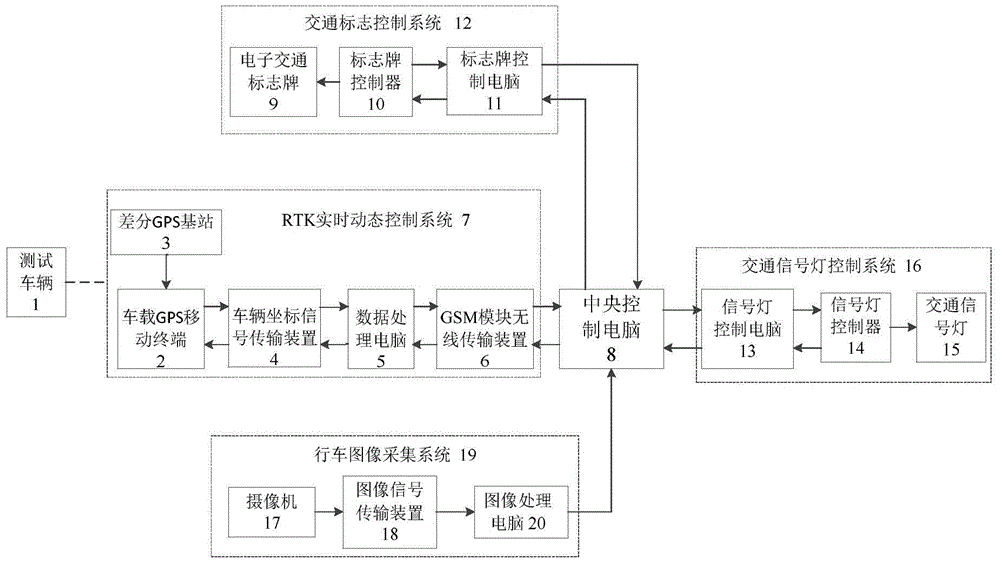
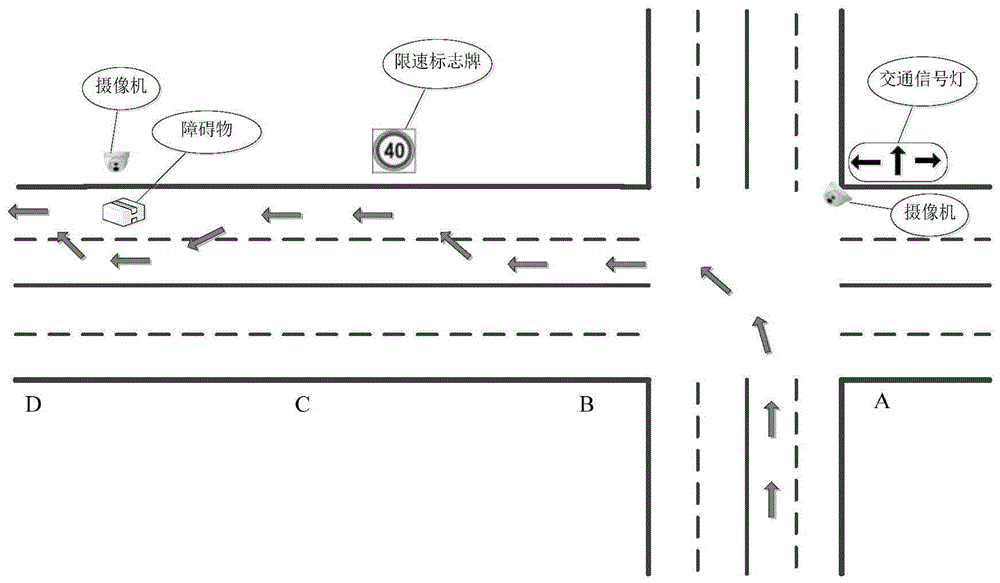
The invention discloses a test method for a remotely piloted vehicle (PRV). Constitution of a remotely piloted vehicle test field, a test system apparatus and a test method are comprised. The test field comprises a super highway, an urban road, a rural road and a special road. The test system apparatus comprises a RTK (real time kinematic) control system, a vehicle driving image acquisition system, a data processing device, etc. According to the test method, the RTK (real time kinematic) control system is utilized to record three-dimensional coordinates of the tested vehicle in real time, and the coordinates of the tested vehicle are compared with coordinates of a digitized three-dimensional test field to draft a tested vehicle running path diagram; data such as a deviation value and driving speed between the tested vehicle running path and a predicted path and vehicle running speed are calculated; and through vehicle running image acquisition systems installed at test points, external vehicle running states and operation behaviors of the tested vehicle in different traffic environments are recorded; and finally, results tested at each test point is compared with a test standard to determine whether the test result is qualified and thus a test report forms.
Owner:CHANGZHOU JIAMEI TECH CO LTD
Processing Multi-GNSS data from mixed-type receivers
Computer-implemented methods and apparatus are presented for processing data collected by at least two receivers from multiple satellites of multiple GNSS, where at least one GNSS is FDMA. Data sets are obtained which comprise a first data set from a first receiver and a second data set from a second receiver. The first data set comprises a first FDMA data set and the second data set comprises a second FDMA data set. At least one of a code bias and a phase bias may exist between the first FDMA data set and the second FDMA data set. At least one receiver-type bias is determined, to be applied when the data sets are obtained from receivers of different types. The data sets are processed, based on the at least one receiver-type bias, to estimate carrier floating-point ambiguities. Carrier integer ambiguities are determined from the floating-point ambiguities. The scheme enables GLONASS carrier phase ambiguities to be resolved and used in a combined FDMA / CDMA (e.g., GLONASS / GPS) centimeter-level solution. It is applicable to real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning, high-precision post-processing of positions and network RTK positioning.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20100312428A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctGuiding agricultural machinesSatellite radio beaconingSteering controlFixed interval
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other and earth-moving equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
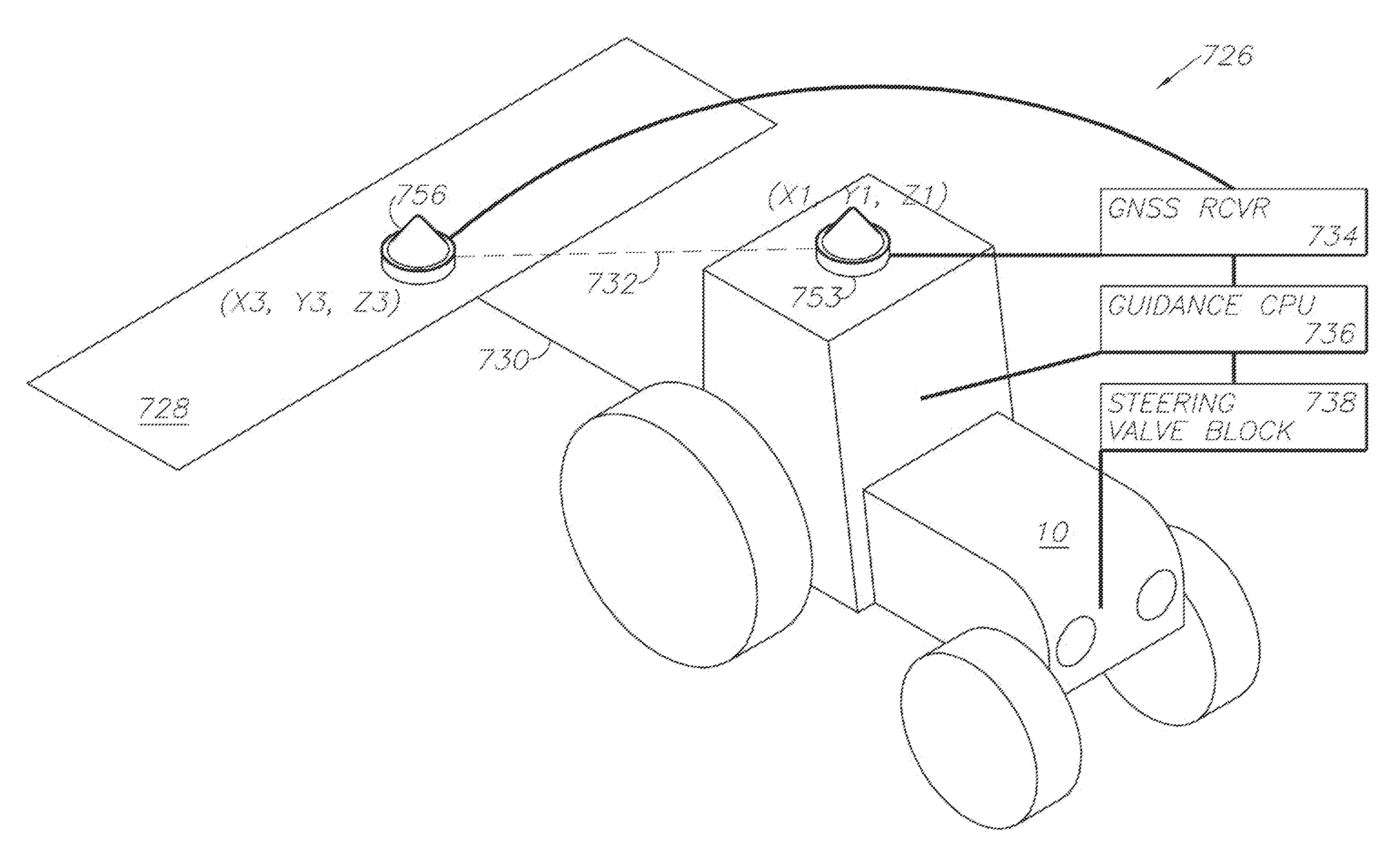
Satellite position and heading sensor for vehicle steering control
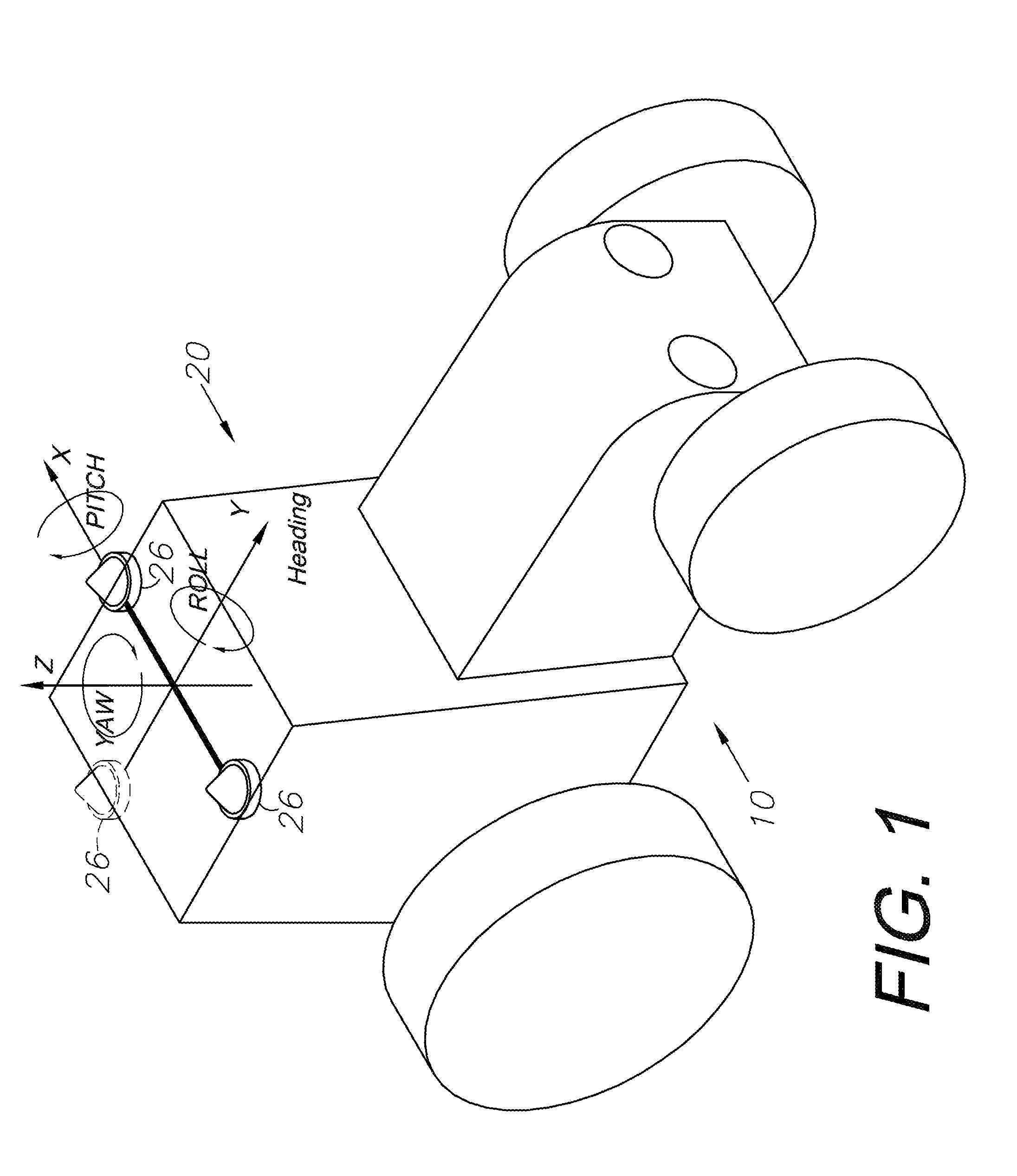
ActiveUS7400956B1Avoid crossingEasy to correctInstruments for road network navigationGuiding agricultural machinesControl systemCarrier signal
A sensor system for vehicle steering control comprising: a plurality of global navigation satellite sensor systems (GNSS) including receivers and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase corrected real time kinematic (RTK) position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system.
Owner:AGJUNCTION INC
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS8594879B2Easy to correctGuiding agricultural machinesSatellite radio beaconingSteering controlMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other and earth-moving equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Light stream based vehicle motion state estimating method
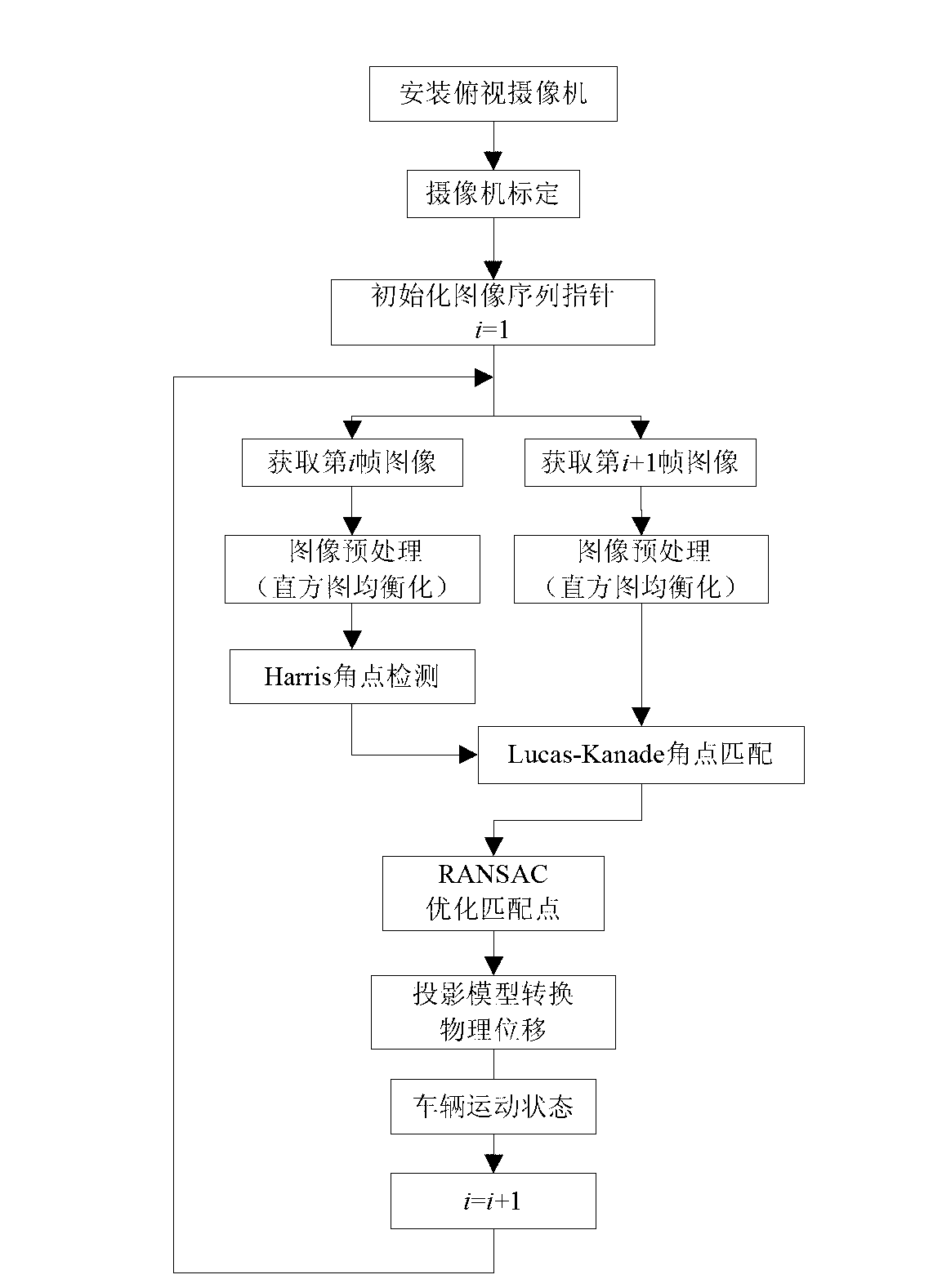
InactiveCN102999759AHigh measurement accuracyImprove real-time performanceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRoad surfaceHistogram equalization
The invention discloses a light stream based vehicle motion state estimating method which is applicable to estimating motion of vehicles running of flat bituminous pavement at low speed in the road traffic environment. The light stream based vehicle motion state estimating method includes mounting a high-precision overlook monocular video camera at the center of a rear axle of a vehicle, and acquiring video camera parameters by means of calibration algorithm; preprocessing acquired image sequence by histogram equalization so as to highlight angular point characteristics of the bituminous pavement, and reducing adverse affection caused by pavement conditions and light variation; detecting the angular point characteristics of the pavement in real time by adopting efficient Harris angular point detection algorithm; performing angular point matching tracking of a front frame and a rear frame according to the Lucas-Kanade light stream algorithm, further optimizing matched angular points by RANSAC (random sample consensus) algorithm and acquiring more accurate light stream information; and finally, restructuring real-time motion parameters of the vehicle such as longitudinal velocity, transverse velocity and side slip angle under a vehicle carrier coordinate system, and accordingly, realizing high-precision vehicle ground motion state estimation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
An Error Correction Method in GNSS Network Differential Positioning System
InactiveCN102298151AImprove reliabilityImprove correction accuracySatellite radio beaconingDifferential correctionReal Time Kinematic
In a virtual reference station, systematic biases existing in troposphere error corrections can be caused by elevation biases between a mobile station and reference stations, thus, the troposphere correction precision is reduced, and the positioning effect of the mobile station is influenced. The invention discloses an error correction method in a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) network differential positioning system. When comprehensive error corrections between the mobile station and the reference stations are obtained through an interpolation computation model, under the condition of considering the influences of elevations, a three-dimensional linear combination interpolation method is adopted to improve the accuracy and the reliability of network real time kinematic (RTK) differential correction information, and the real-time effective differential correction information of the mobile station is interpolated by utilizing spatially-correlated errors resolved by the reference station, including an ionosphere error and a troposphere error, according to the spatial and positional relations between the mobile station and the surrounding reference stations. By adopting the method, the troposphere correction precision can be increased to centimeter level from decimeter level in interpolation computation corrections, and the network RTK positioning accuracy is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Configuring antenna arrays of mobile wireless devices using motion sensors
A device and method for the real-time motion detection and reconfiguration of an antenna array of a mobile wireless device is described. The mobile wireless device includes an antenna array for receiving and transmitting wireless signals, a motion sensor coupled to the antenna array, and a first circuitry coupled to the antenna array and the motion sensor. A change in orientation of the antenna array is detected by the motion sensor in real time and recognized by the first circuitry. The antenna array is reconfigured by the first circuitry in response to the detected change in orientation in an expeditious manner.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
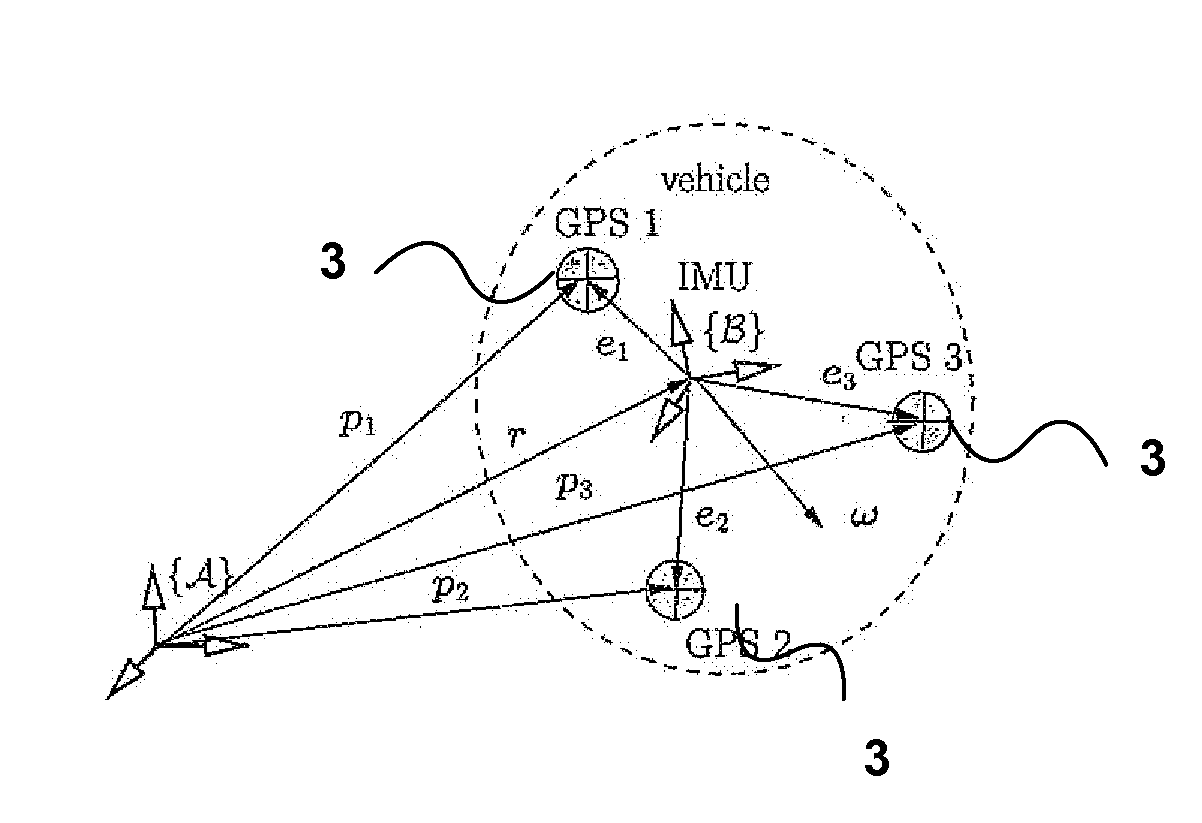
Apparatus and methods for driftless attitude determination and reliable localization of vehicles
InactiveUS20120086598A1Enhanced positional informationImprove accuracySatellite radio beaconingReal Time KinematicAttitude determination
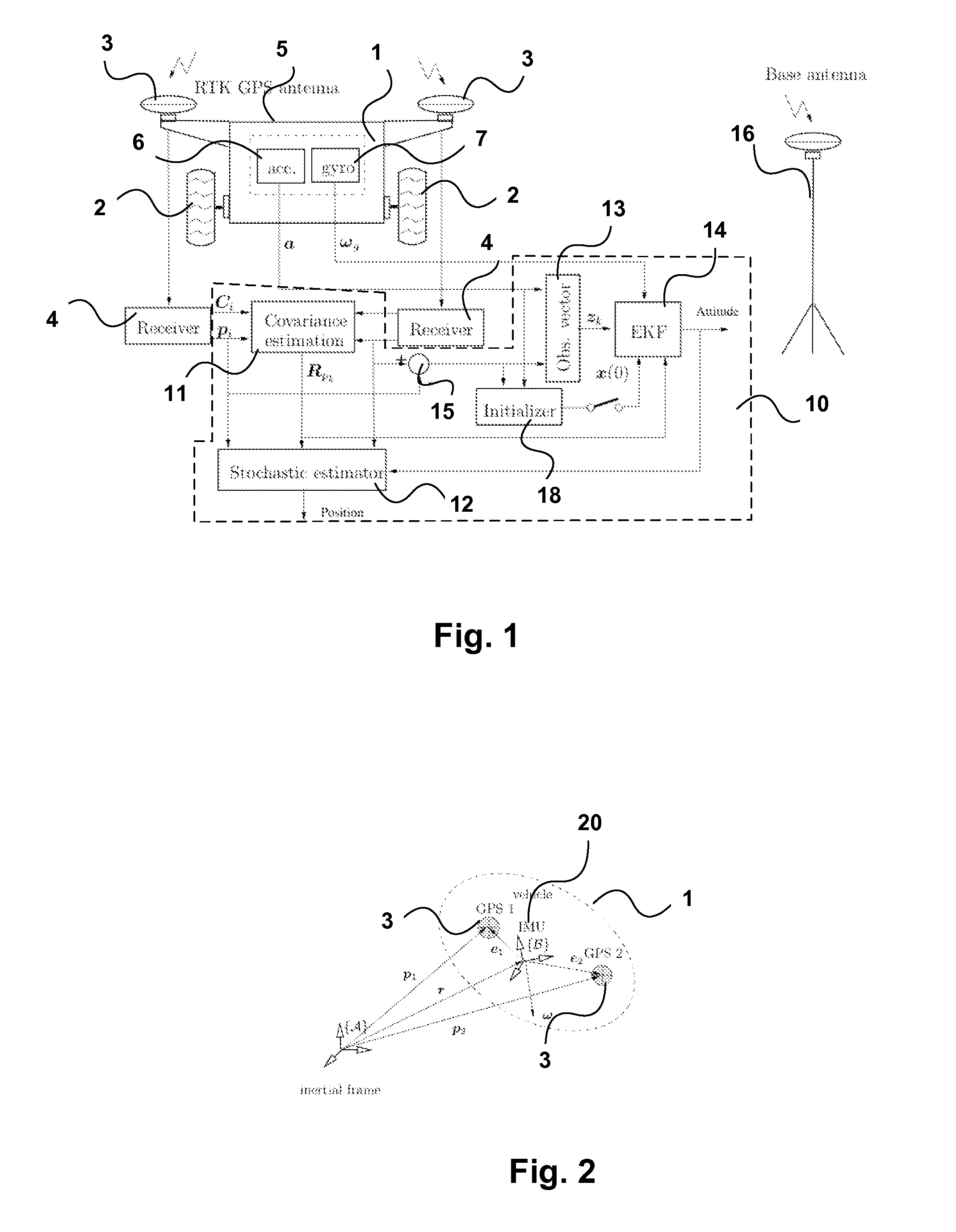
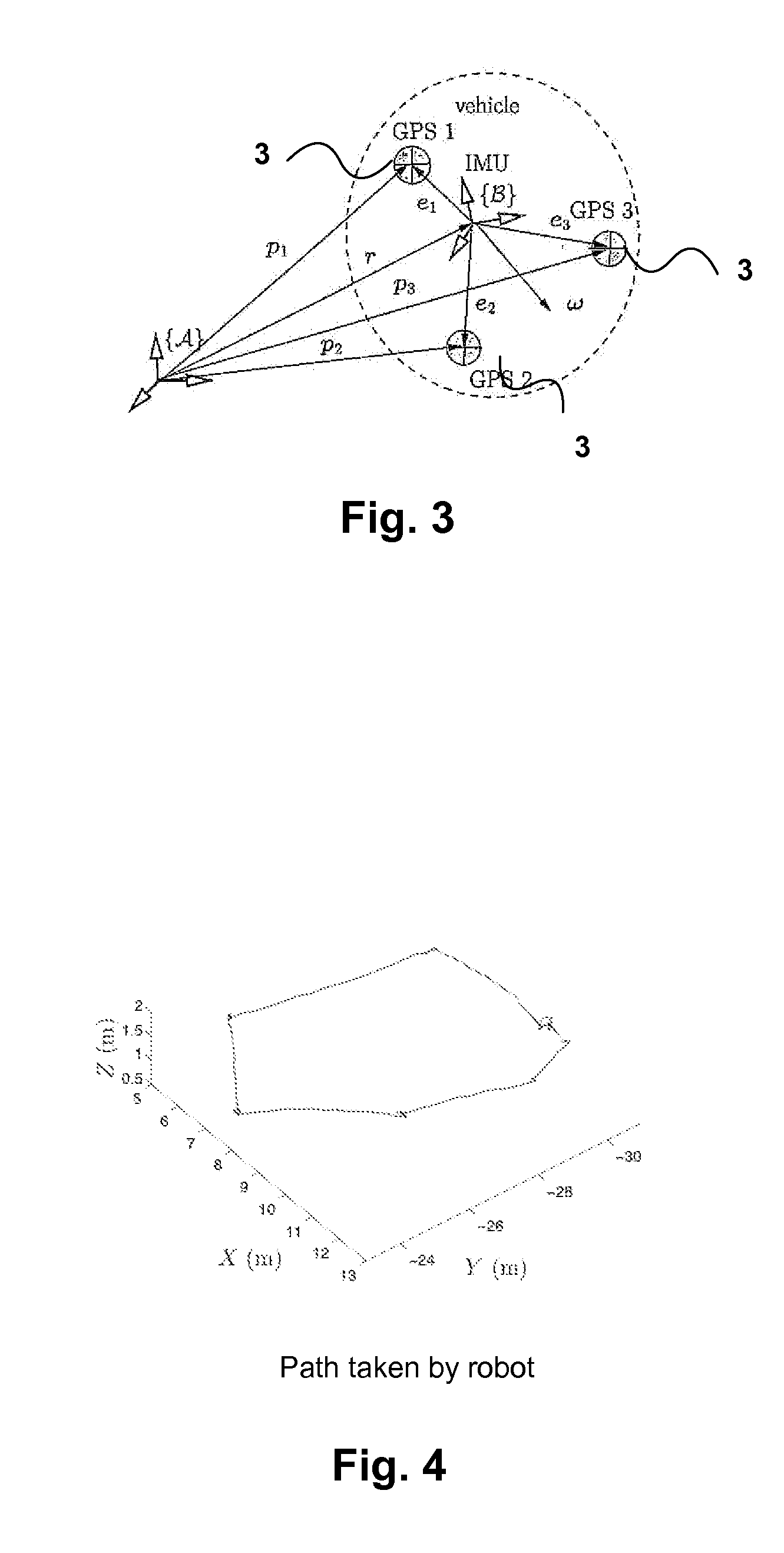
In order to determine positional information, about a mobile robot, Real Time Kinematic (RTK) Global Satellite Navigation System (GNSS) measurement data are obtained by at least two GNSS receivers mounted on the mobile robot. Estimates of the covariance matrices of the measurement data are computed. The RTK GNSS measurement data are combined according to the covariance matrices to obtain enhanced positional information. The results may be fused with data from an IMU to obtain driftless attitude and / or localization information.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
Multiple-antenna GNSS control system and method
ActiveUS8140223B2Easy to correctDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationSteering controlControl system
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction and guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
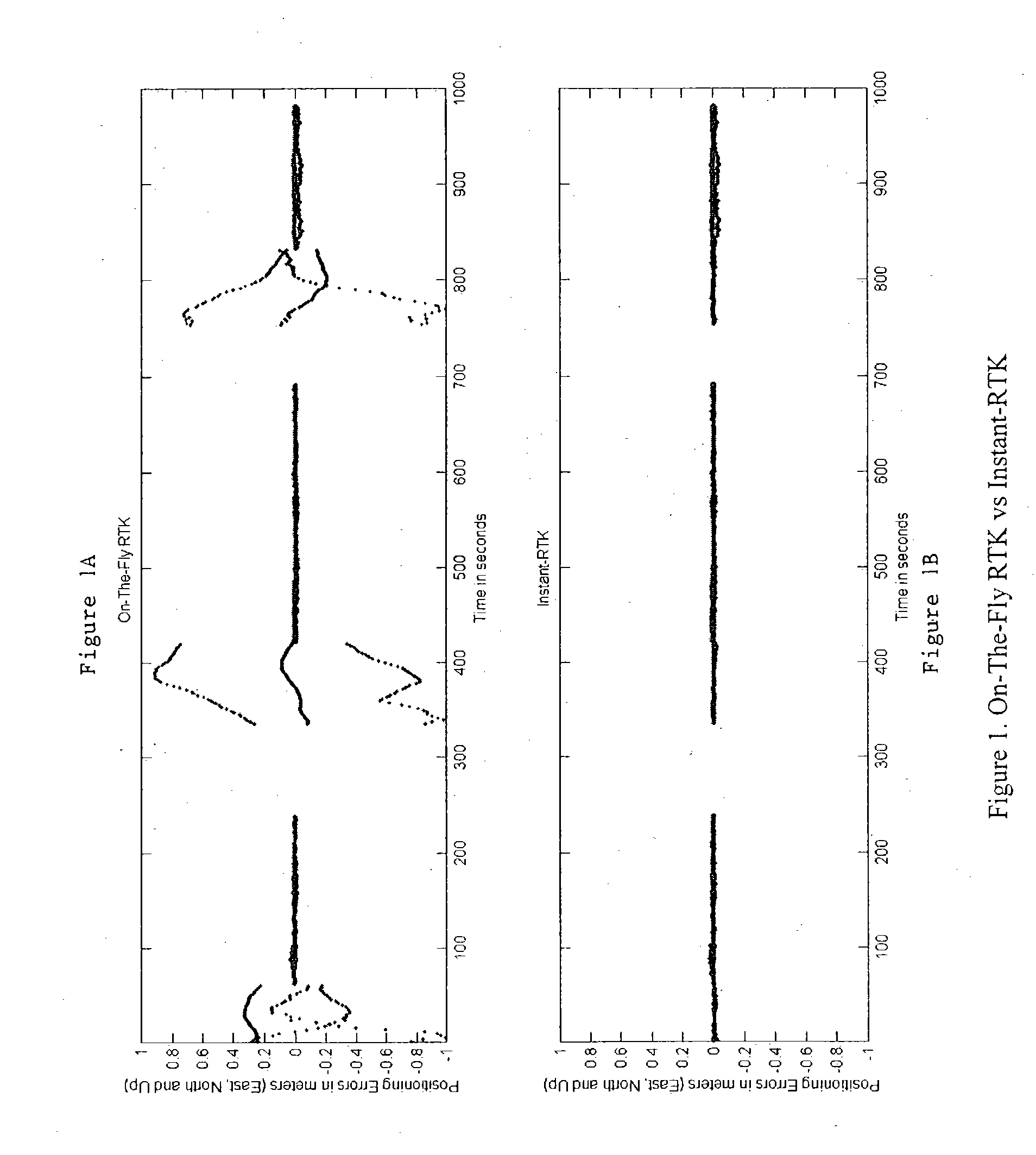
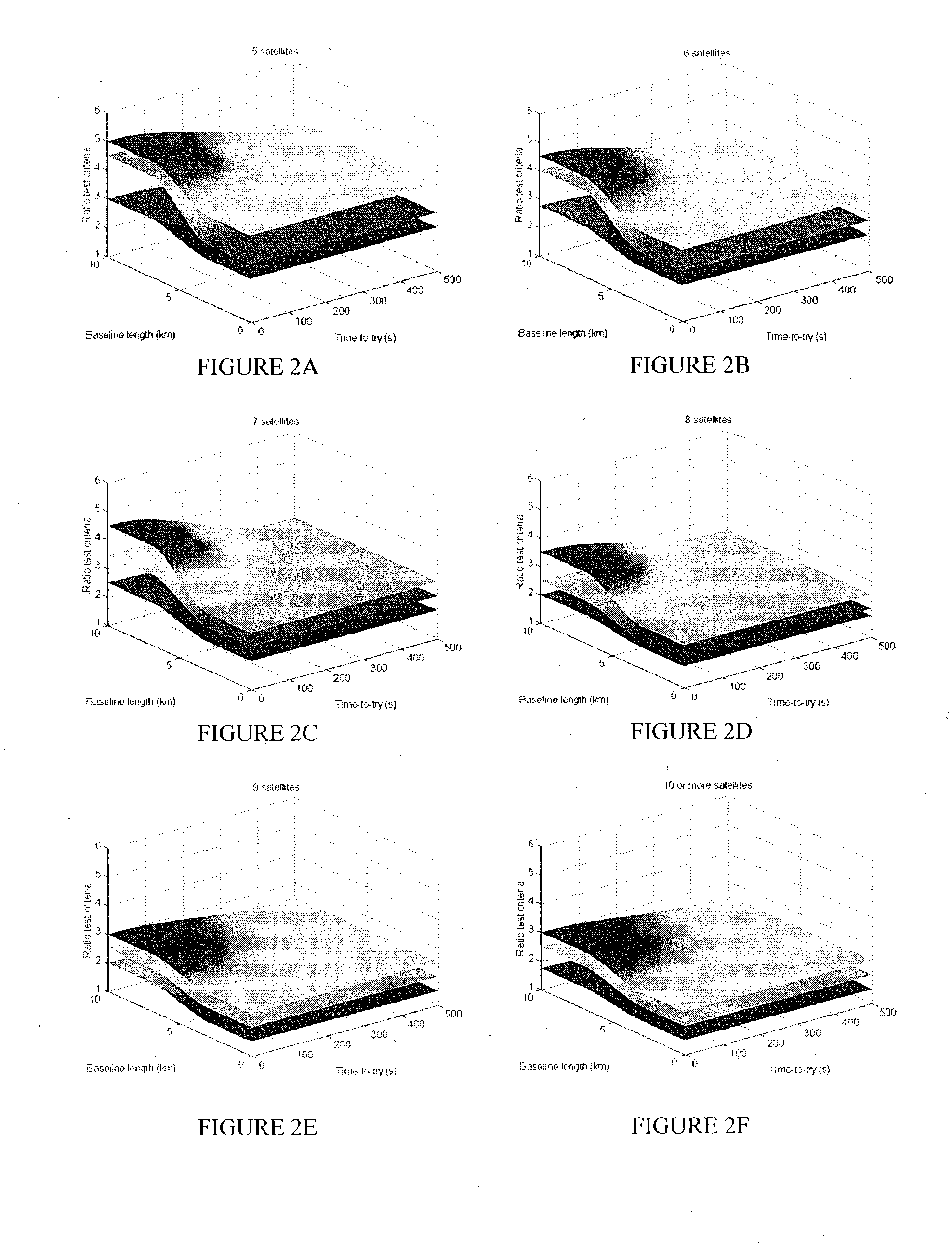
Enhanced real time kinematics determination method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050001762A1Improve accuracyPrecise positioningPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingSystems designKinematics
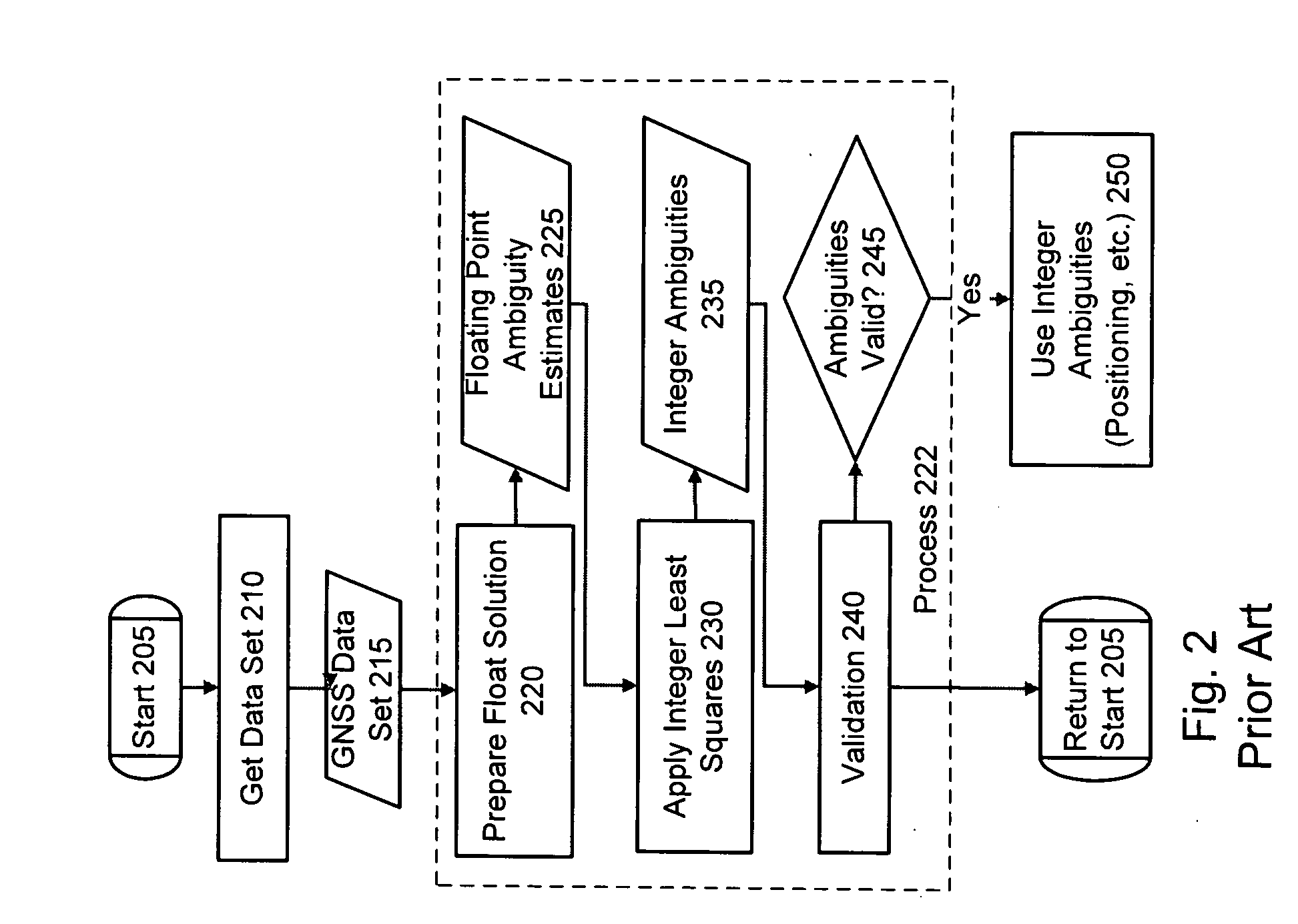
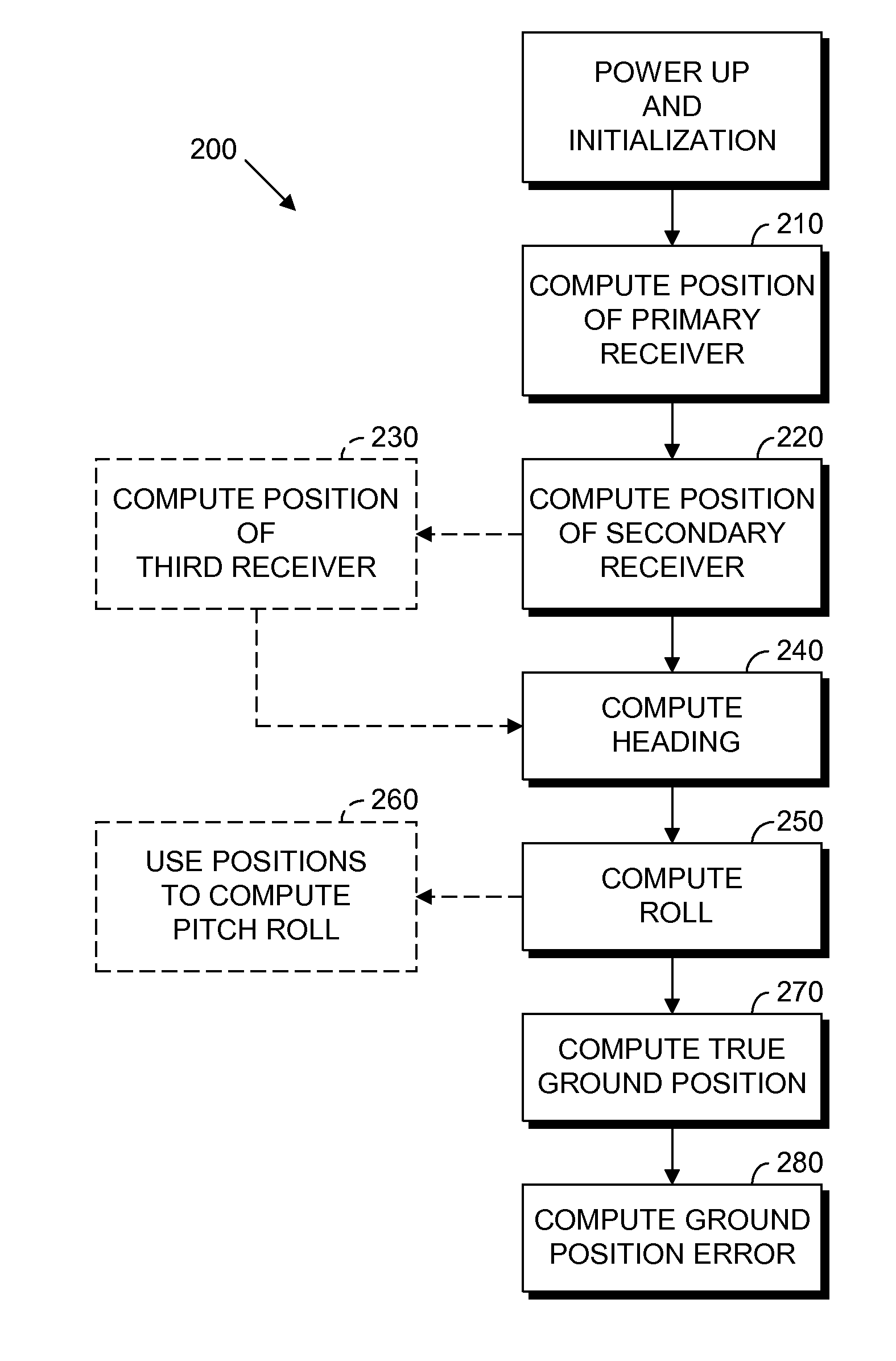
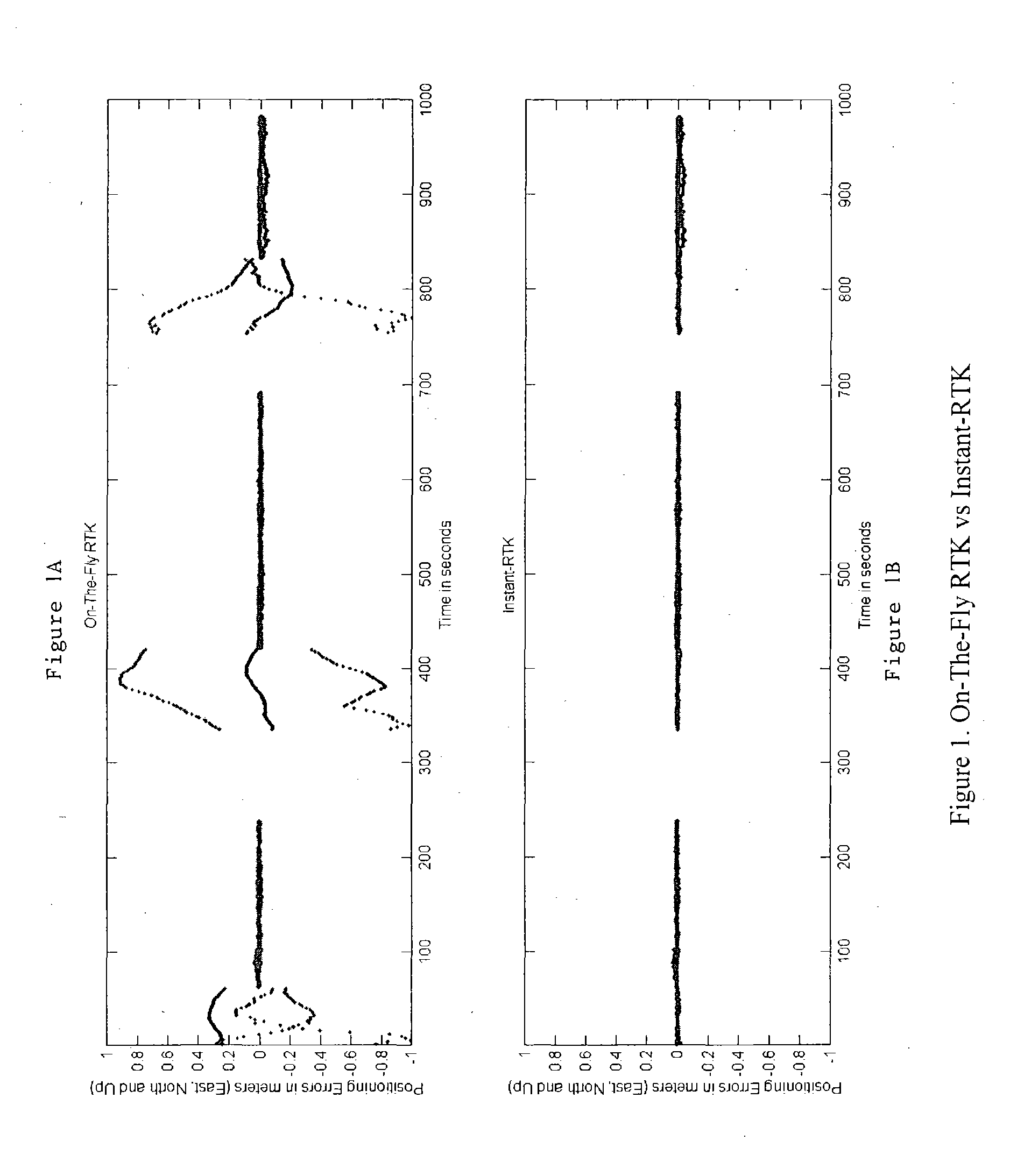
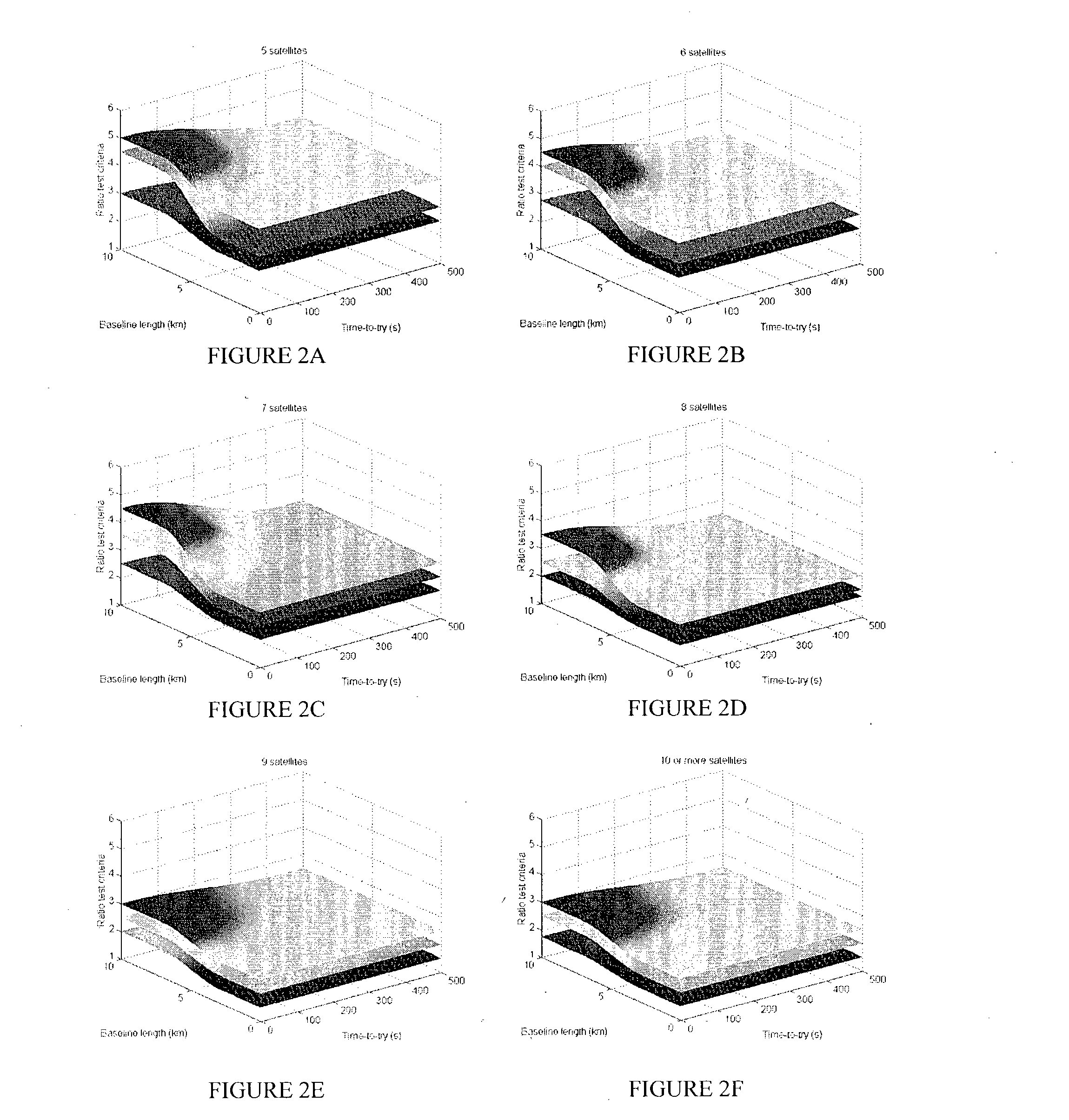
A method of and computer-readable medium containing instructions for high accuracy, reliable position determination. A high precision GPS-RTK system using the present novel techniques is initialized instantaneously or near instantaneously. To improve the computational efficiency and to improve the reliability of the procedure, advances in data functional and stochastic modeling, validation criteria, adaptation and system design were achieved. A position estimate using an integrated method is determined. Ambiguity resolution of the position estinate is enhanced by applying a quality control procedure using derived validation criteria. A second position estimate based on the enhanced ambiguity resolution is derived.
Owner:MAGELLAN NAVIGATION +1
Targeted Marketing System and Method
A system and method are provided for targeting marketing content to a user. A user's photographic likeness, in some embodiments as a still image, live moving image, or animated moving image, are altered to simulate the application of selected marketing content onto the photographic likeness. The marketing content is selected from a set of marketing content comprising input color, marketing content associated with an advertisement, or marketing content associated with a set of search results. The marketing content is selected based on a comparison of a user profile to target profiles of the set of marketing content.
Owner:FACECAKE MARKETING TECH
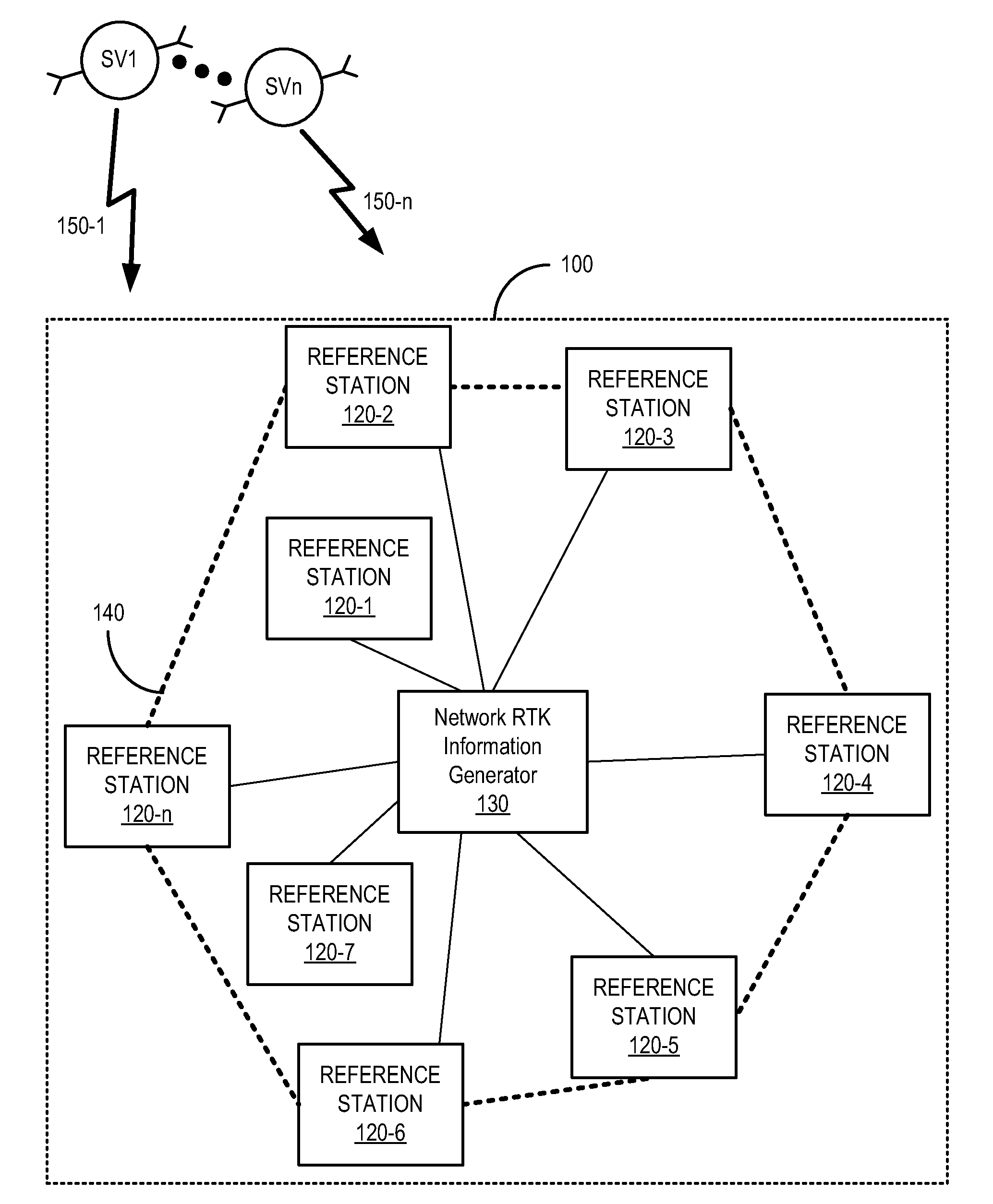
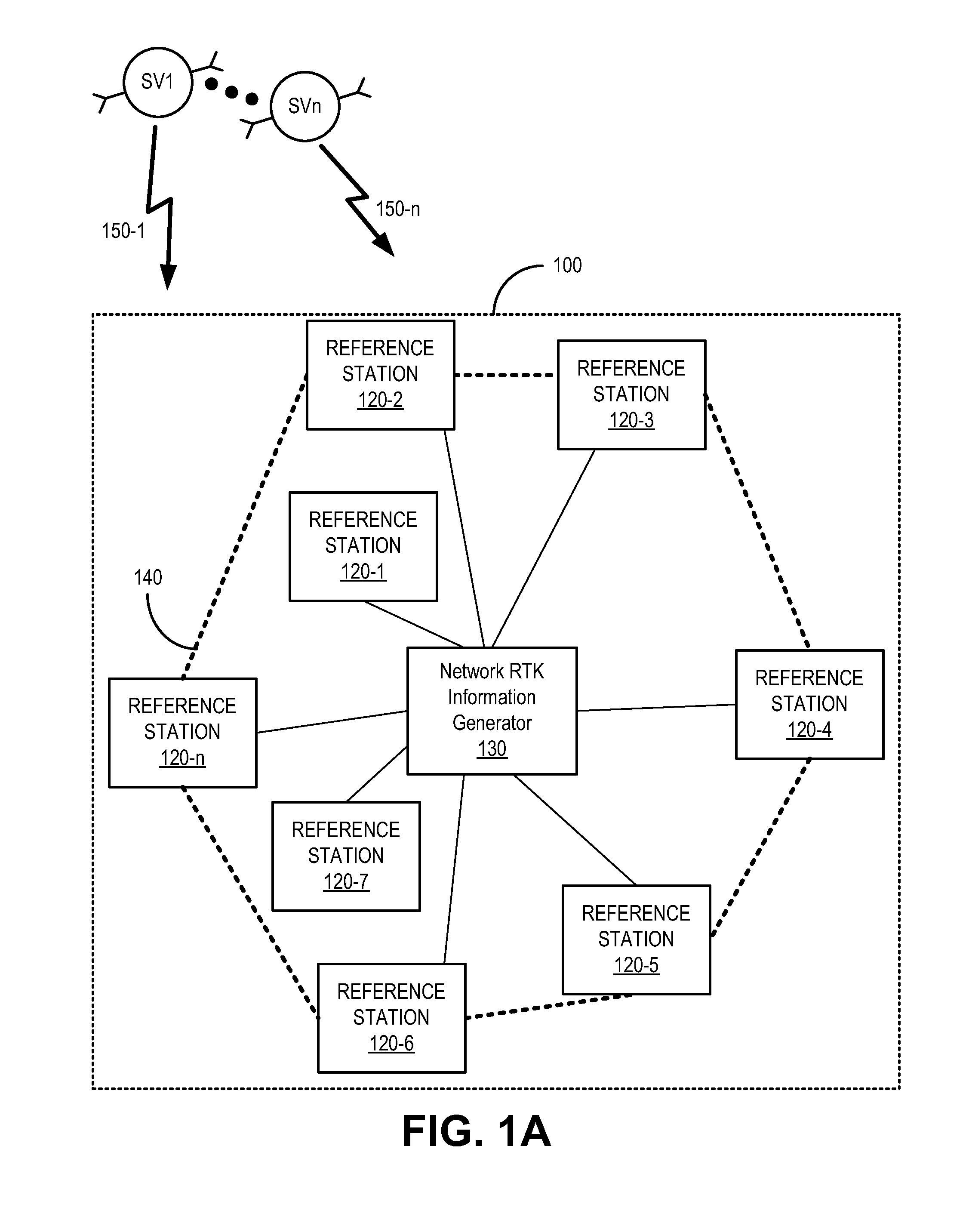
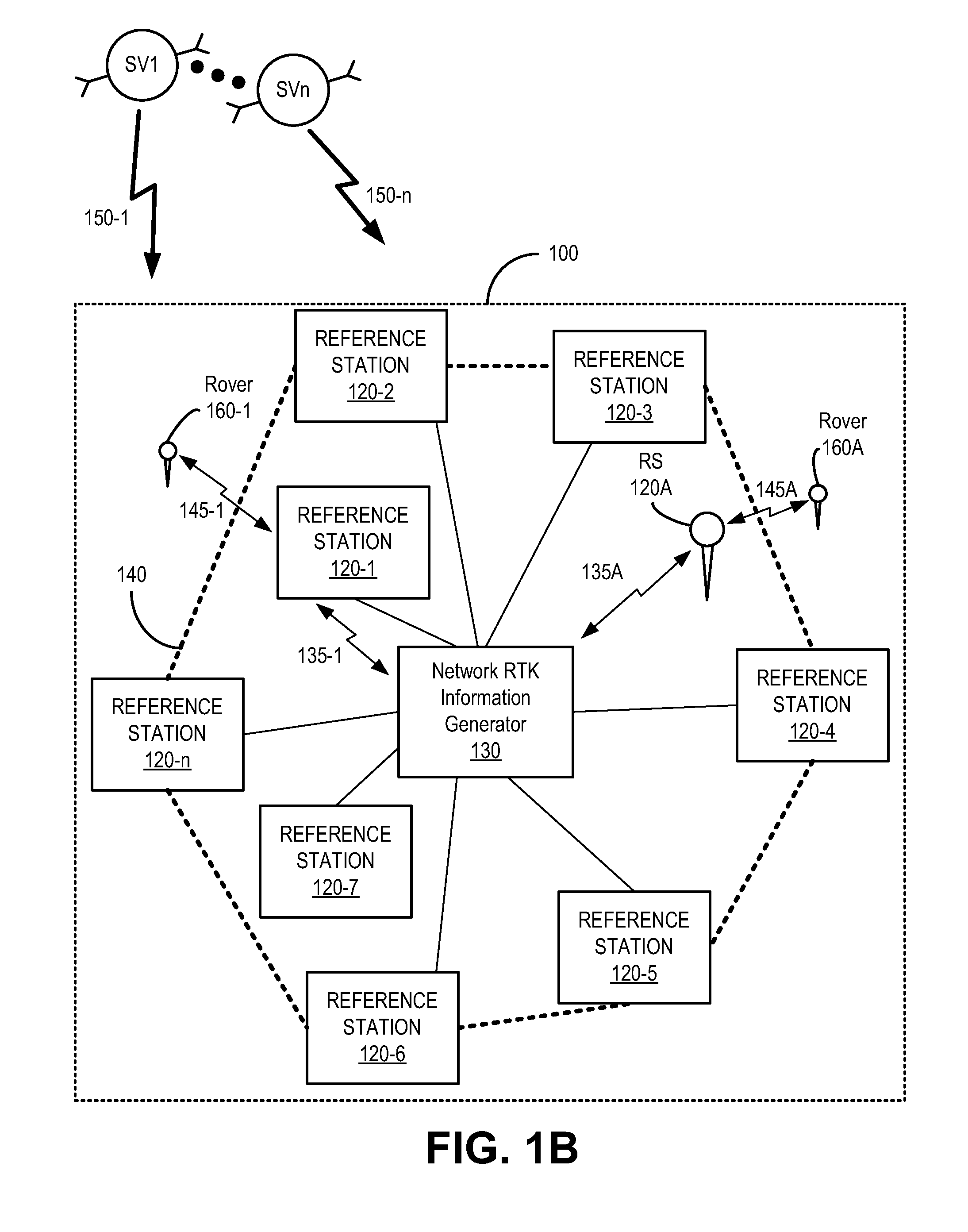
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) reference station integrity monitoring and assurance
In a method of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) reference station integrity monitoring, network Real Time Kinematic (RTK) information is accessed for a location associated with a GNSS reference station. At least one aspect of GNSS information local to the location of the GNSS reference station is compared with a corresponding aspect of the network RTK information. The results of the comparing are monitored for indication of occurrence of compromise to operational integrity of the GNSS reference station.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
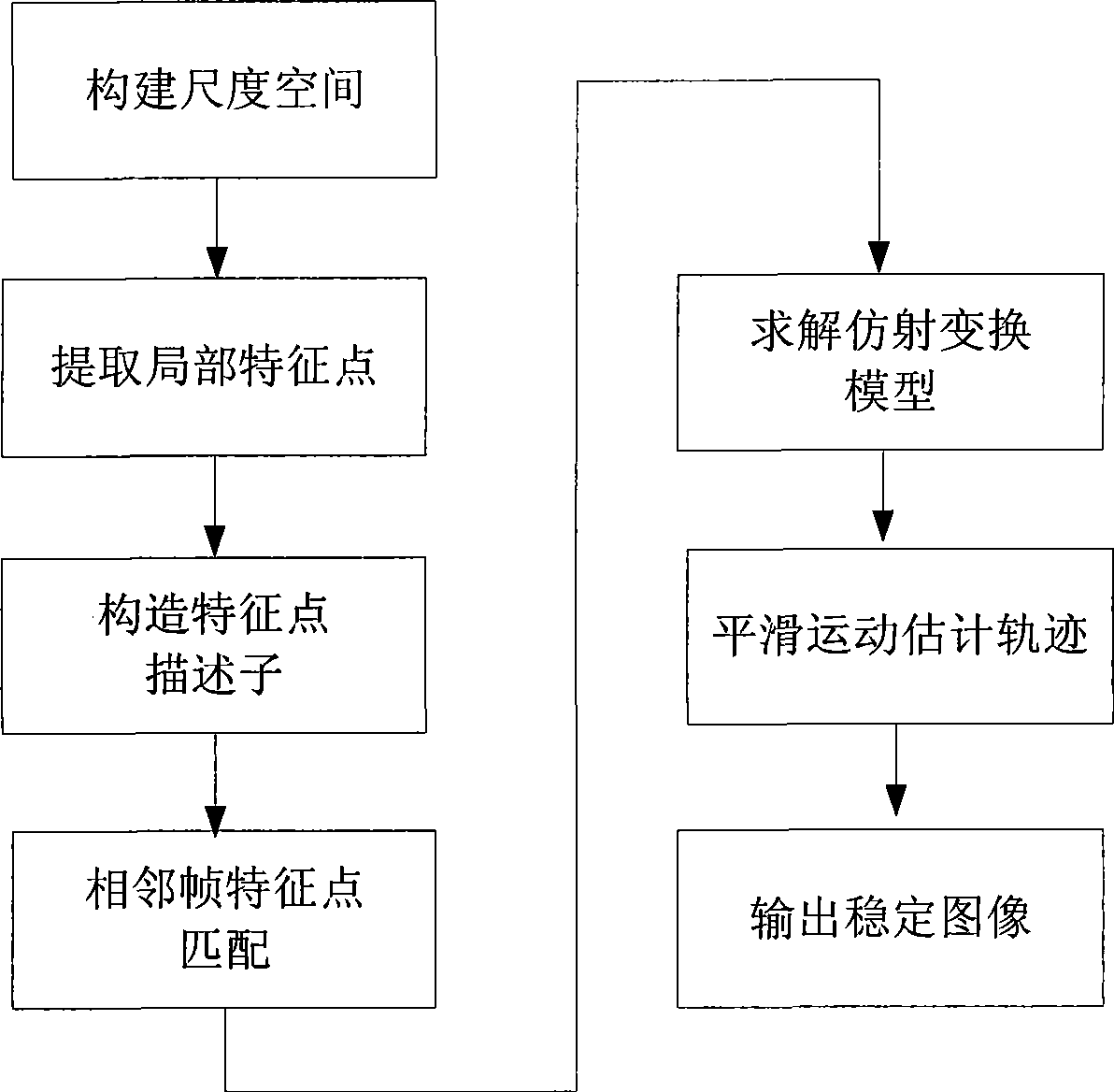
Real-time athletic estimating method based on multiple dimensioned unchanged characteristic
InactiveCN101521740AImprove estimation accuracyImprove matching accuracyTelevision system detailsImage analysisElectrical polarityReal Time Kinematic
The invention relates to a real-time athletic estimating method based on a multiple dimensioned unchanged characteristic, which comprises the steps: (1) a gauss scale space is constructed and a local characteristic point is extracted; (2) a characteristic descriptor of the polar distribution of a rectangular window is constructed; (3) the characteristic point is used for matching and establishing an interframe motion model; and (4) the offset of a current frame output position which corresponds to a window center is calculated. The athletic estimating method has a size, visual angle and rotation adaptive characteristic, can accurately match images with complicated athletic relation, such as translation, rotation, dimension, a certain visual angle change, and the like and has higher real-time performance. The estimating method has better robustness for common phenomena, such as mistiness, noise, and the like in a video, has higher estimated accuracy for arbitrary ruleless complicated athletic parameters and is combined with a motion compensating method based on motion state identification, thus, the image stabilizing requirement of a video image sequence which can be arbitrarily and randomly shot under complex environment can be realized, and the purposes of real-time output and video stabilization can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
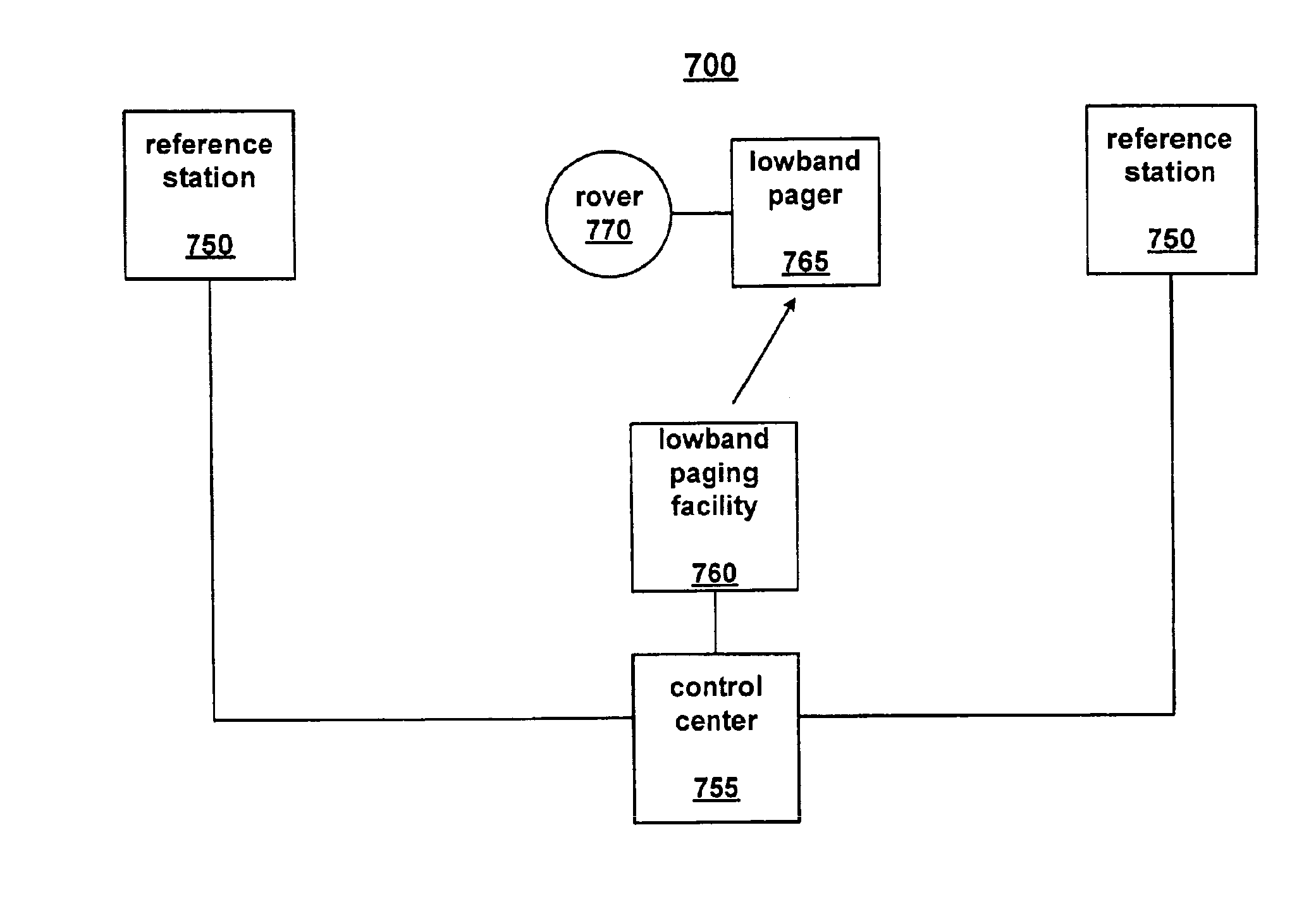
Method and system for transmission of real-time kinematic satellite positioning system data
InactiveUS6879283B1Precise positioningPosition fixationRadio transmission for post communicationReal Time KinematicData transmission
A method and system for communication in a real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning system by paging. An RTK positioning system having a reference station and a rover utilizes a paging system for data transfer. A single satellite positioning system (SATPS) reference station may be coupled to the paging system to provide RTK correction data, or multiple networked reference stations may be coupled to the paging system to provide data. Paging systems using allocated paging bands having fixed width channels (e.g. 20 kHz) such as those between 35 MHz and 36 MHz or 43 MHz and 44 MHz may be used.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Augmented communication and positioning using unmanned aerial vehicles
InactiveUS20170146990A1Convenient wireless communicationEnhanced signalUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftMachine visionReal Time Kinematic
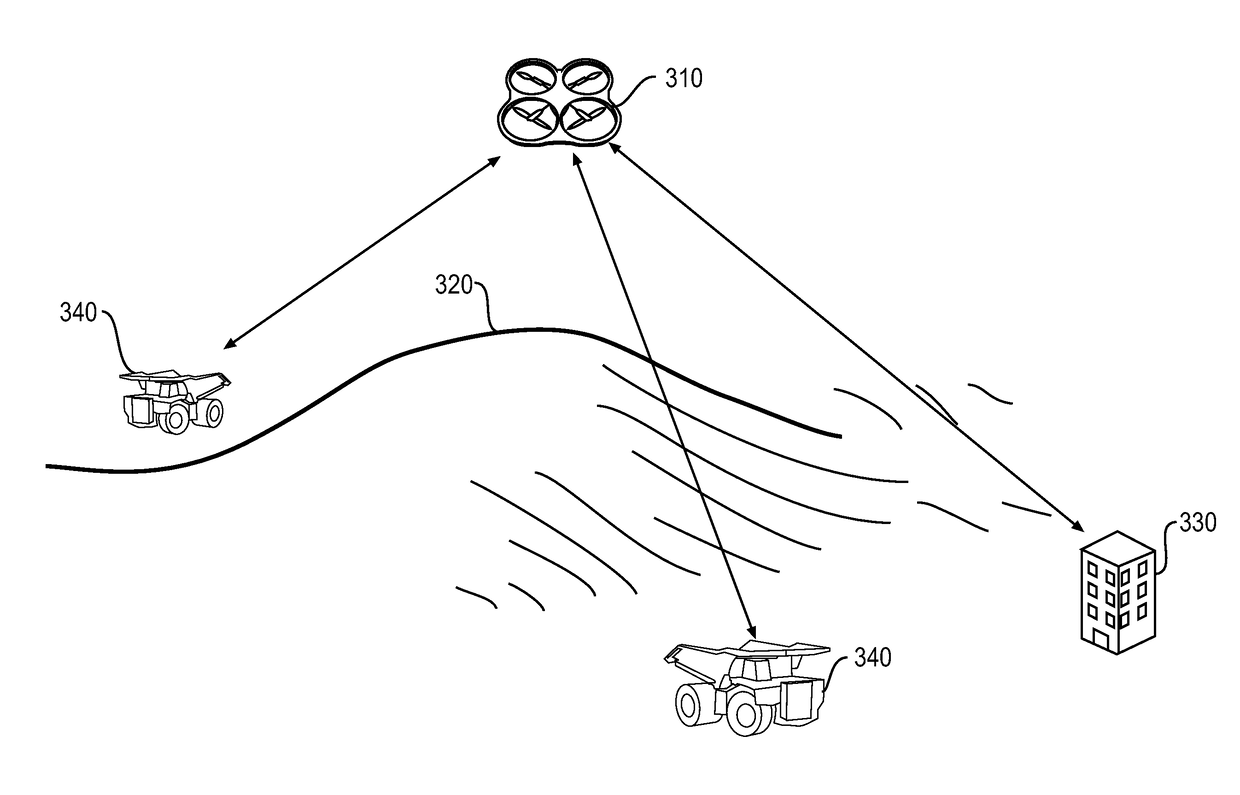
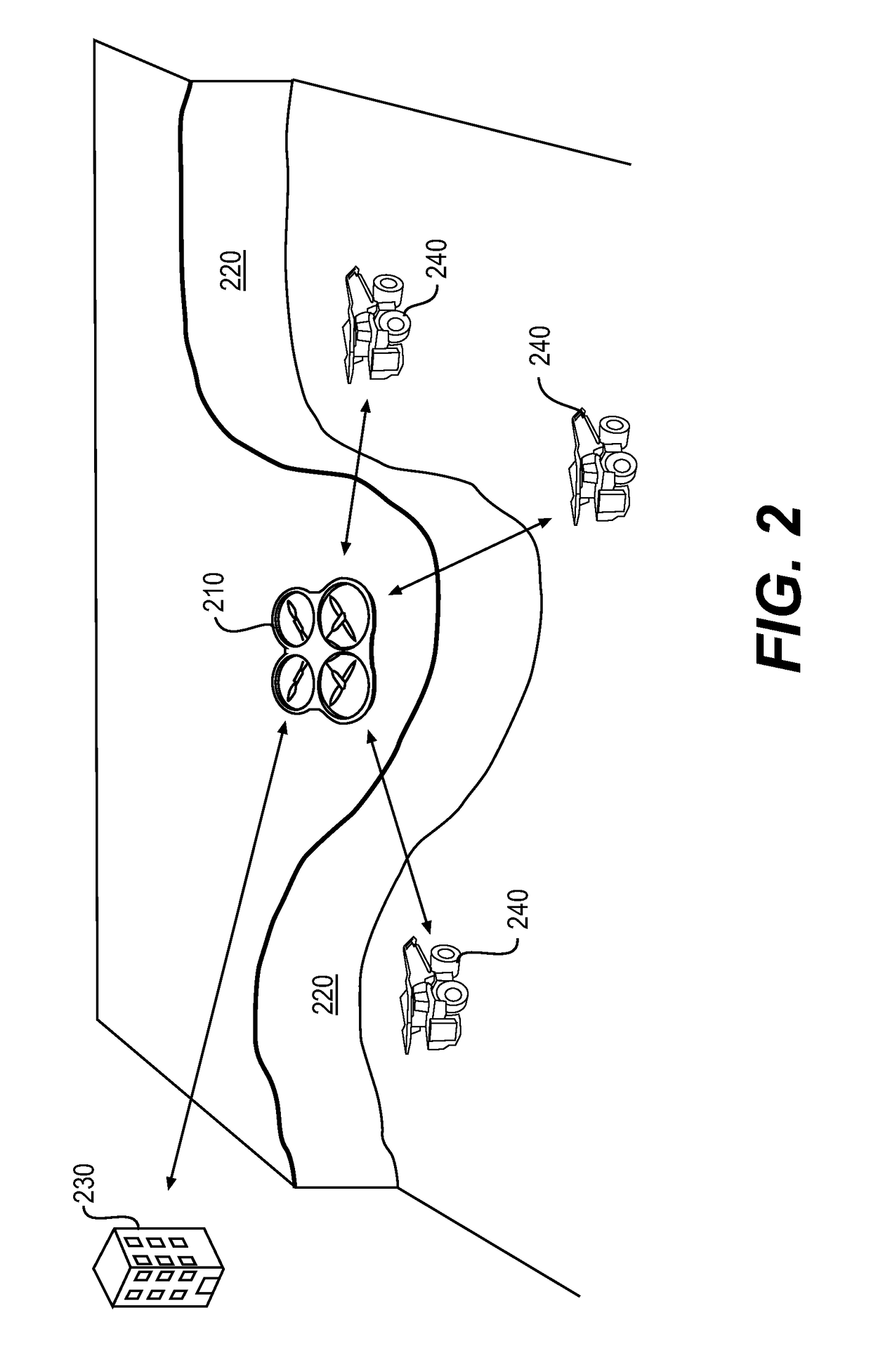
A system for augmenting wireless communication and satellite positioning for machines at a worksite includes one or more unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) configured to be remotely operated above an area encompassing the worksite. Each of the UAV includes a real time kinematic (RTK) global positioning system (GPS) onboard the UAV for determining the position of the UAV relative to a base station located at a known location, and a machine vision module for detecting an object on the ground at the worksite. The RTK GPS onboard each UAV determines the global coordinates of the detected object in 3D space using the position of the UAV. A flight control module receives information on current position of one or more machines operating at the worksite, and machine wireless communication and satellite positioning requirements in real-time from the one or more machines, and controls flight of at least one UAV to a position where the at least one UAV can augment wireless communication signal and GPS satellite signal connectivity to meet the machine wireless communication and satellite positioning requirements.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
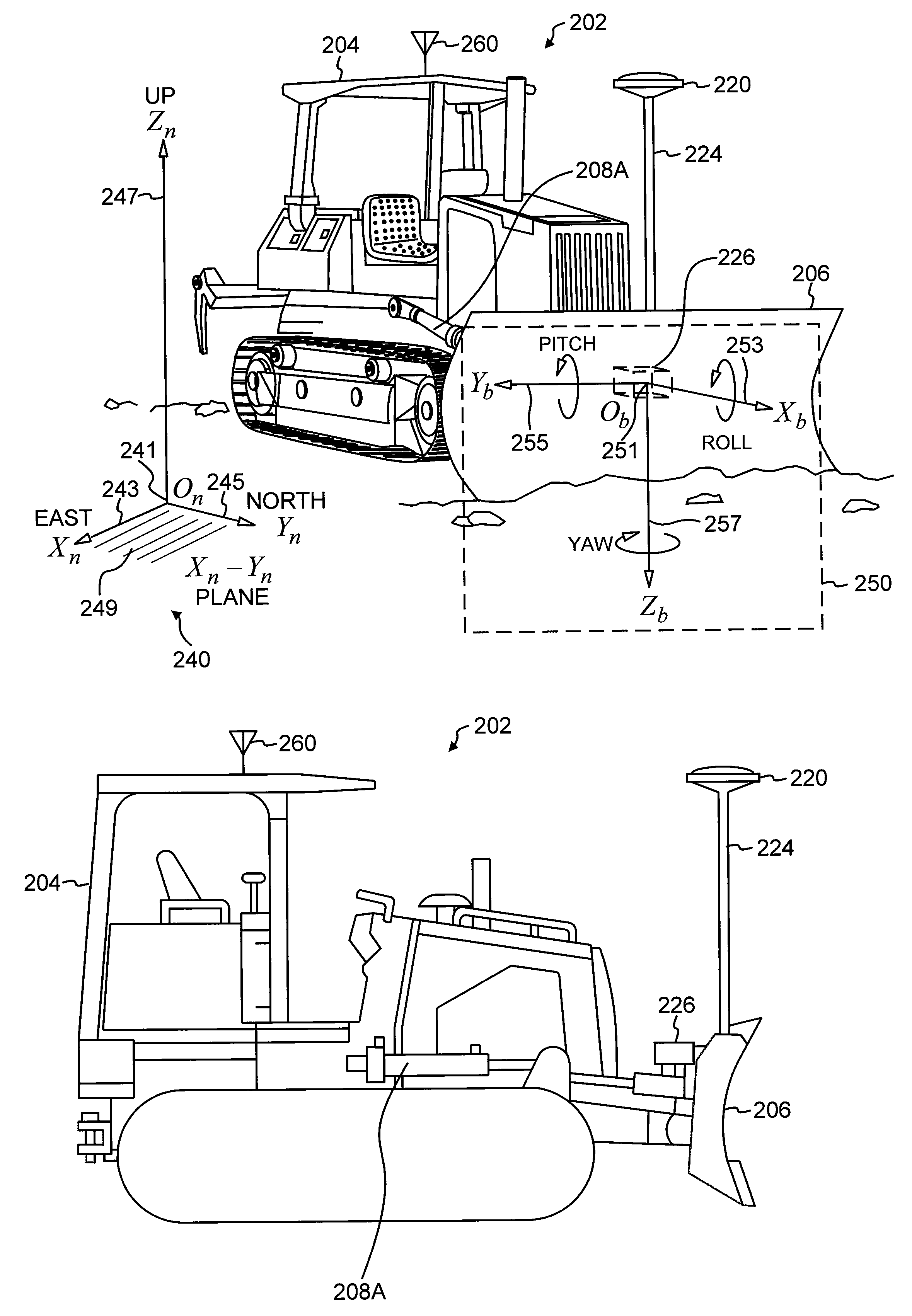
Automatic Blade Control System during a Period of a Global Navigation Satellite System ...
InactiveUS20120059554A1Easy to controlMachines/dredgers working methodsAnalogue computers for trafficTerrainAutomatic control
For precision grading of terrain by a dozer, the dozer blade can be automatically controlled based on measurements from a combination of a global navigation satellite system real-time kinematic mode (GNSS RTK) system and inertial sensors. At least one GNSS sensor and at least one inertial sensor are mounted on the dozer. Control algorithms are based on blade elevation and blade slope angle. During a period of GNSS RTK system outage, control of blade elevation is not available. Blade control is maintained by switching to control algorithms based on blade slope angle and blade pitch angle. Blade slope angle and blade pitch angle are controlled based on extrapolated target values of blade slope angle and blade pitch angle. The extrapolated target values of the angles are extrapolated from target values of the angles prior to the GNSS RTK system outage with the use of a distance travelled by the dozer.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
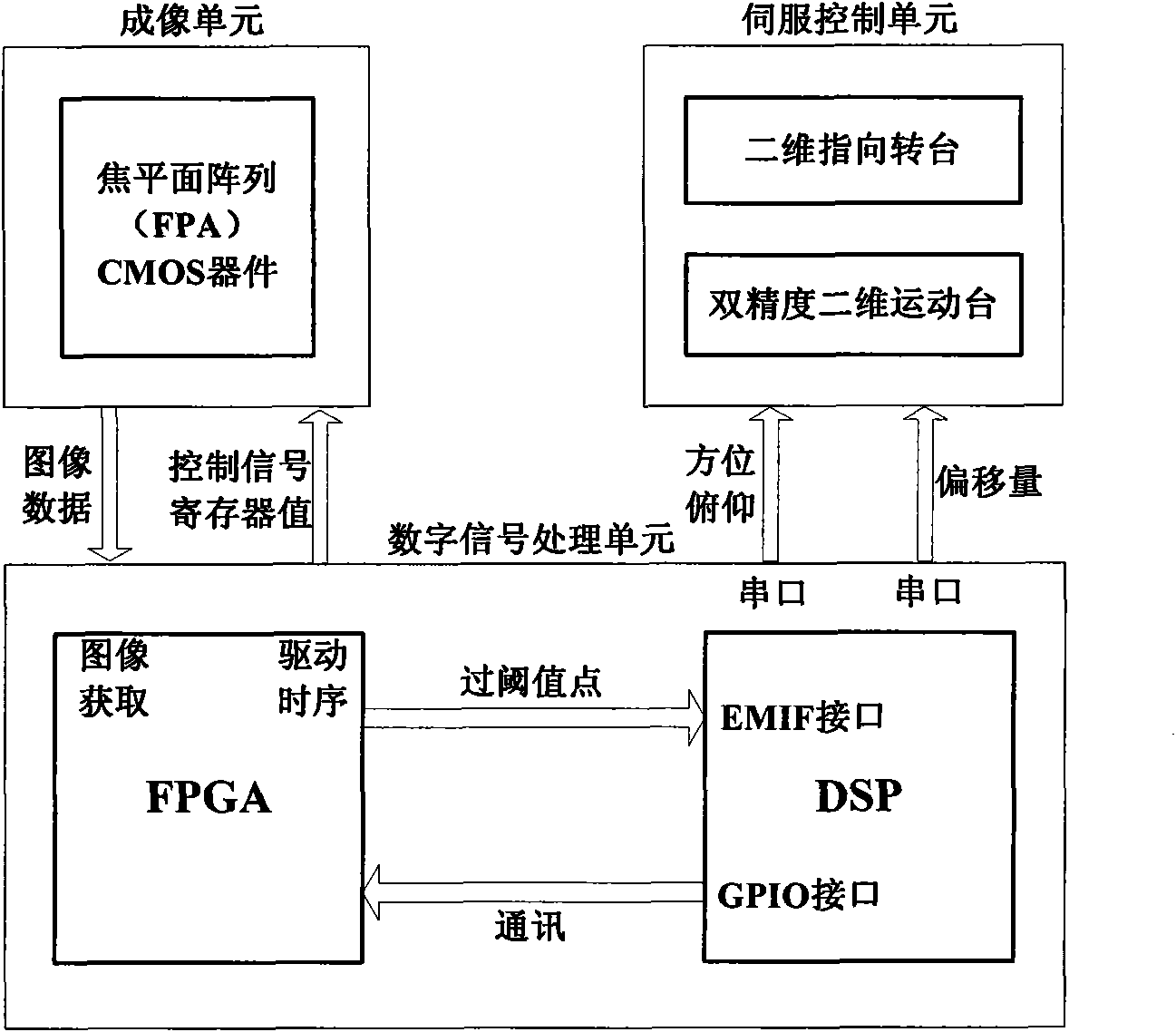
Real-time closed loop predictive tracking method of maneuvering target
InactiveCN102096925AReliable trackingContinuous and stable trackingImage analysisPrediction algorithmsClosed loop
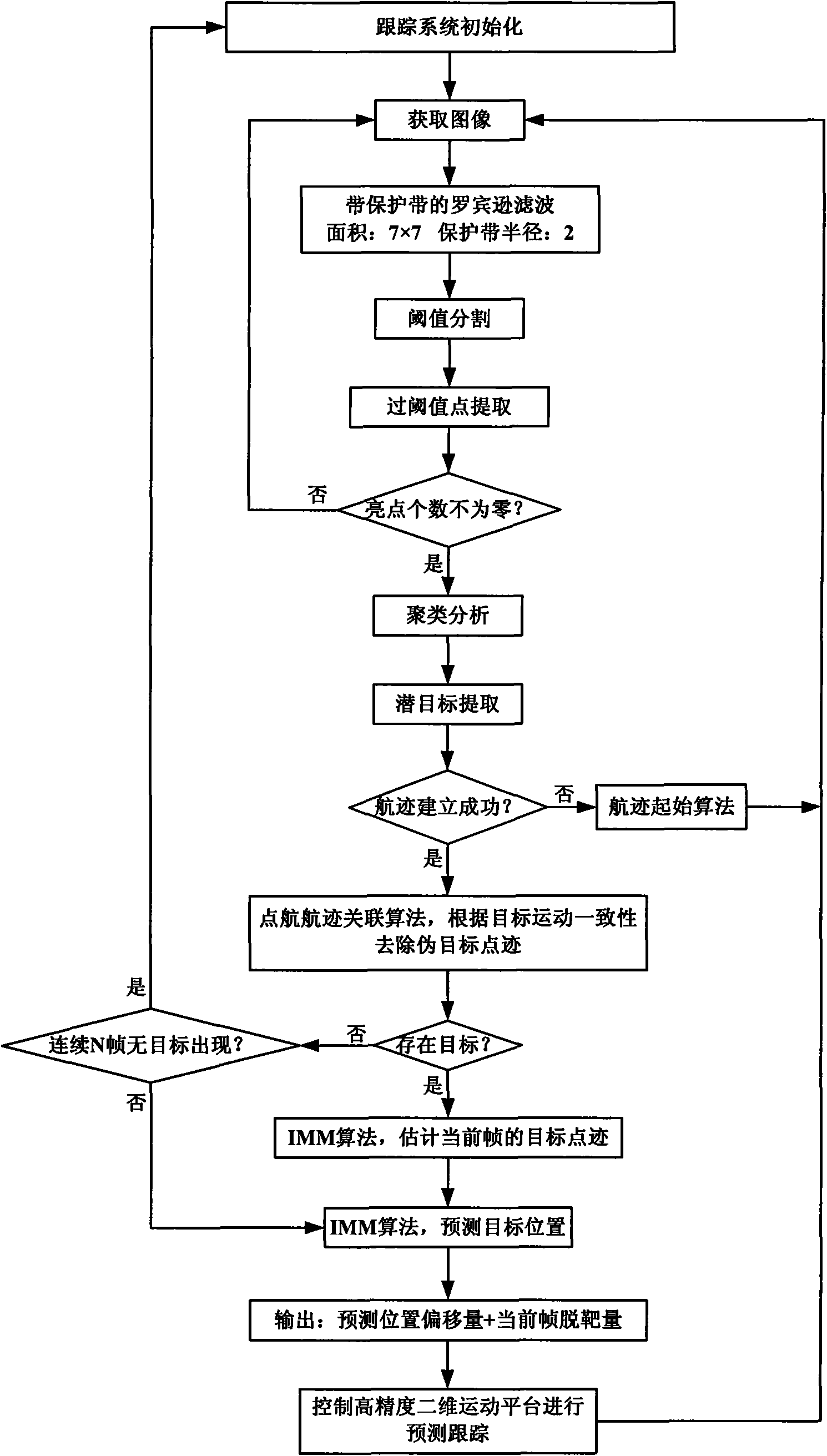
The invention discloses a real-time closed loop predictive tracking method of a maneuvering target, which is a closed loop real-time self-adaptive processing method of on-line predictive immediate tracking in a maneuvering small target imaging tracking system and is mainly used for fields of photoelectric imaging tracking, robot vision, intelligent traffic control and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, a captured target can be extracted to to establish a flight track, the target flight track is filtered, the position of a target at a next collection time is predicted, a platform is processed in real time on line with high performance of a DSP main processor and a FPGA coprocessor, a prediction algorithm which can cope with target maneuver with higher accuracy is adopted to predict the motion state of the target in real time and a prediction result is utilized to drive a piezoelectric ceramic motor two-dimensional motion station to carry out overcompensation, thereby the self-adaptive predictive tracking is realized. The invention has the advantages that the method can overcome the defect of a largened tracking error caused by system delay and can still carry out continuous and stable tracking when the target maneuvers or is temporarily sheltered.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
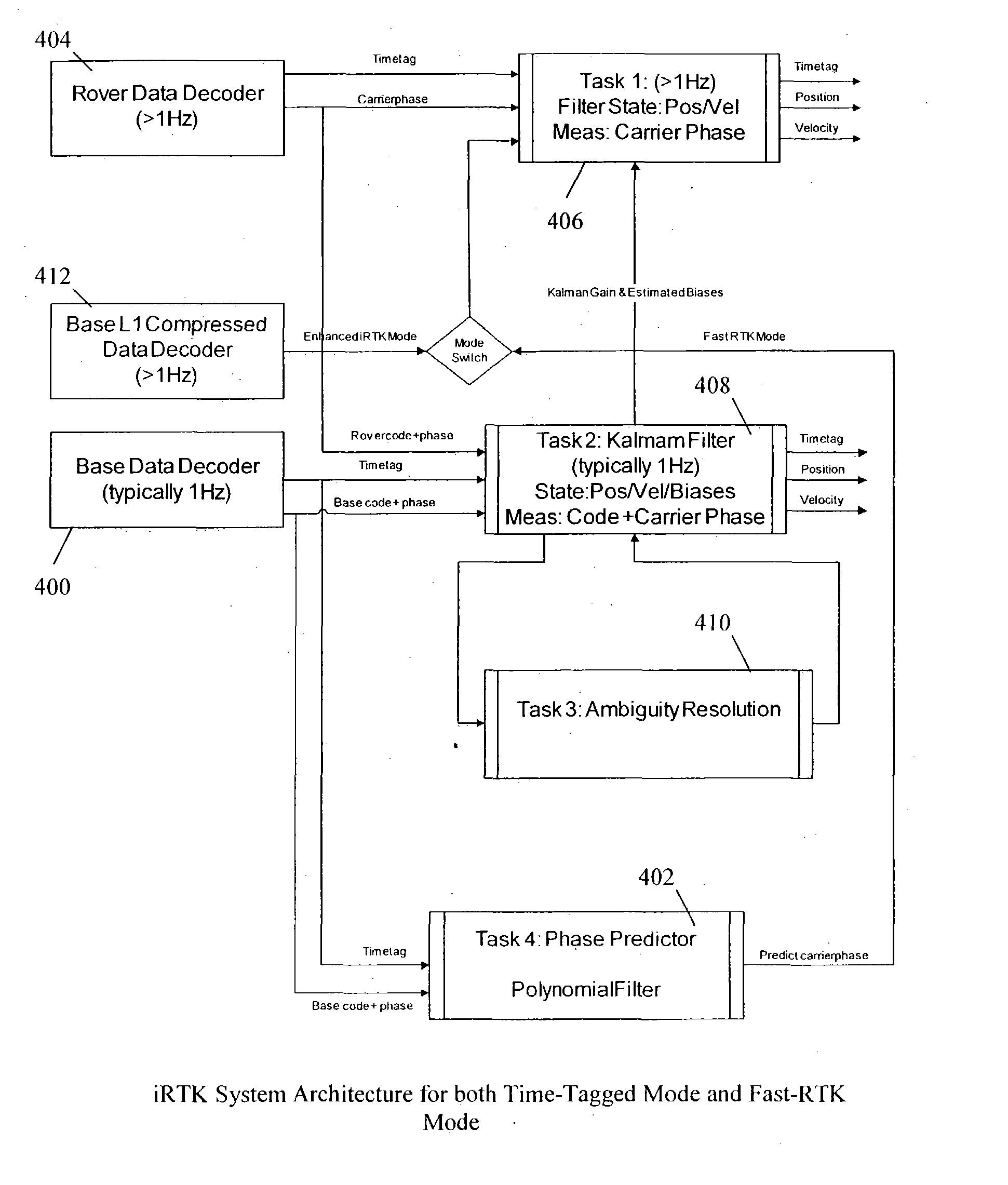
Enhanced rapid real time kinematics determination method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050001763A1Little informationThe process is fast and accuratePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingKinematicsInformation transmission
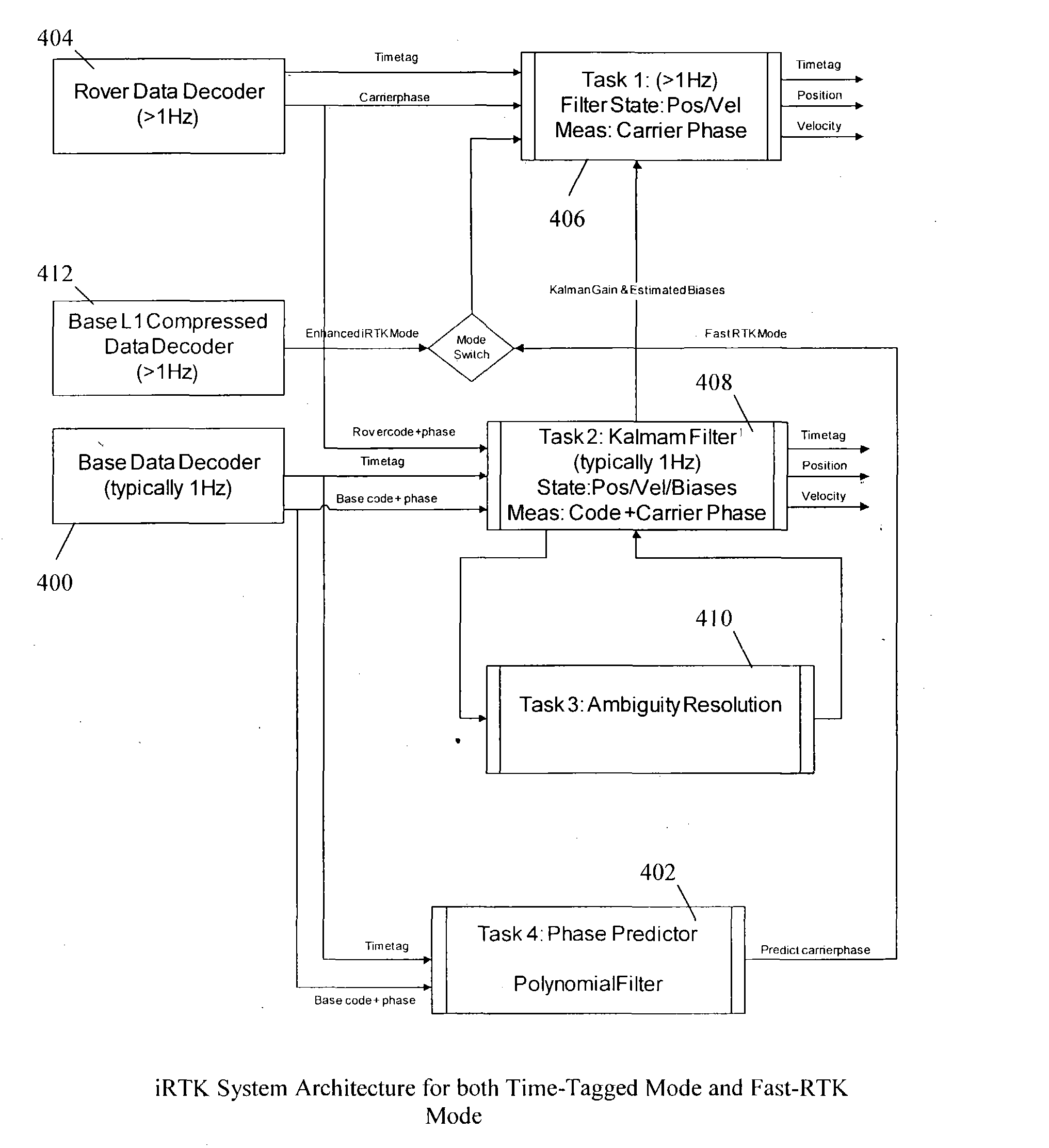
A method of, apparatus for, and computer-readable medium for rapid, real time kinematics determination requiring lowered information transmission for position updates than traditional RTK systems. Position signals are received from a base station and roving system and a compressed position signal is received from the base station. A position estimate using an integrated method is determined using the received position signals from the base station and the roving system and the compressed position signal from the base station. Ambiguity resolution of the position estimate is enhanced by applying a quality control procedure using derived validation criteria. A second position estimate is derived based on the enhanced ambiguity resolution. Because of the use of the compressed position signal smaller transmissions may be performed at a more rapid rate providing a higher position update rate.
Owner:MITAC INT CORP +1
Interactive exercise method and head-mounted intelligent device
ActiveCN106502388AHigh degree of reductionReal immersionInput/output for user-computer interactionGymnastic exercisingVirtual locomotionMixed reality
The invention discloses an interactive exercise method and a head-mounted intelligent device. The interactive exercise method comprises the following steps: receiving body exercise data and body image data; analyzing the body exercise data, and establishing a real-time exercise model; integrating the real-time exercise model and a virtual character image, thus generating a three-dimensional exercise virtual character; integrating the three-dimensional exercise virtual character and the body image data, thus generating mixed reality exercise image data; constructing a virtual exercise environment, wherein the virtual exercise environment at least comprises a virtual background environment; integrating the mixed reality exercise image data and the virtual exercise environment, thus generating a virtual exercise scene; outputting the virtual exercise scene. Through the mode, the reduction degree of a real character can be improved, and the beautiful virtual exercise environment can be constructed to provide a more real sense of immersion.
Owner:HUIZHOU TCL MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com